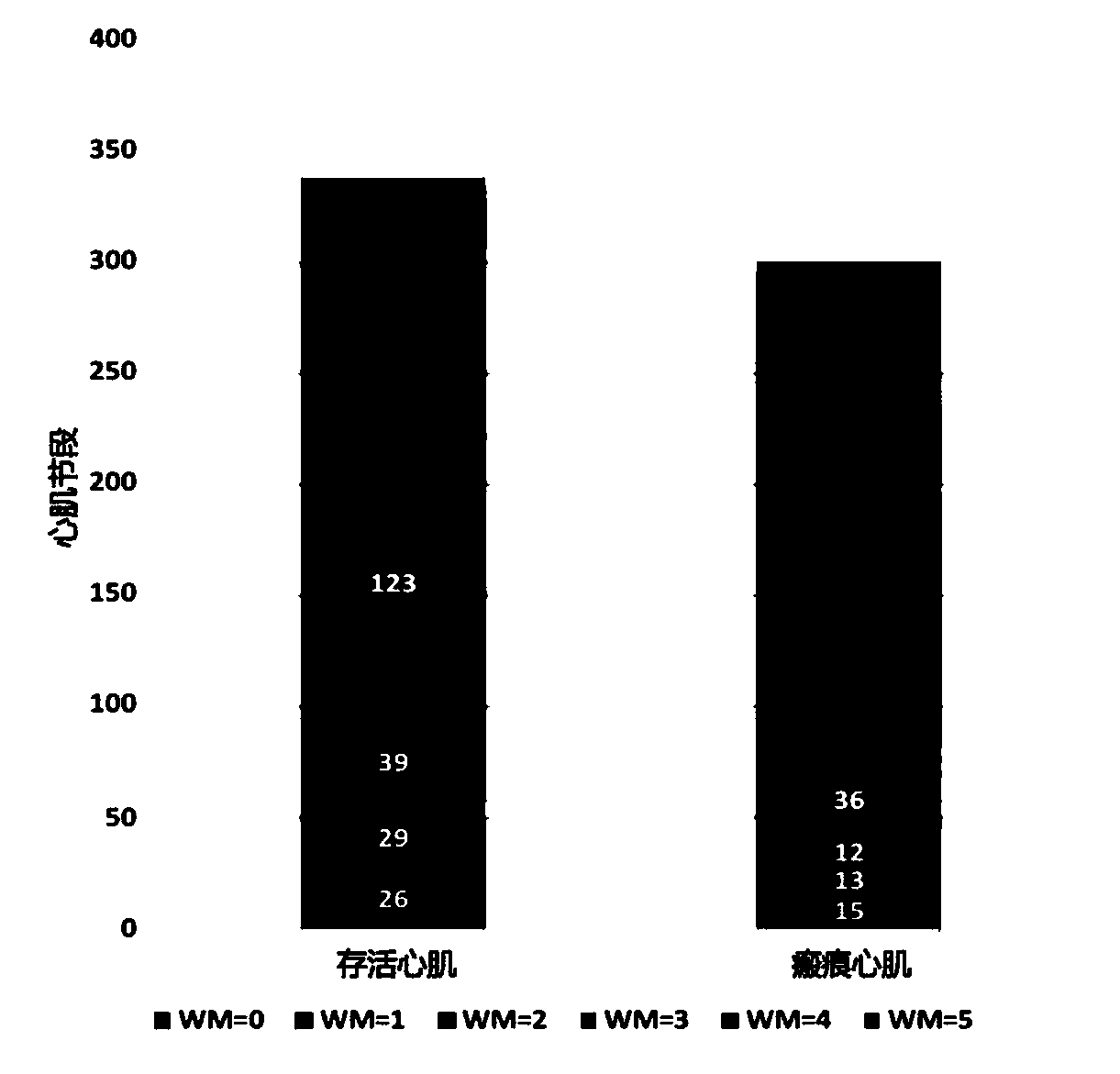
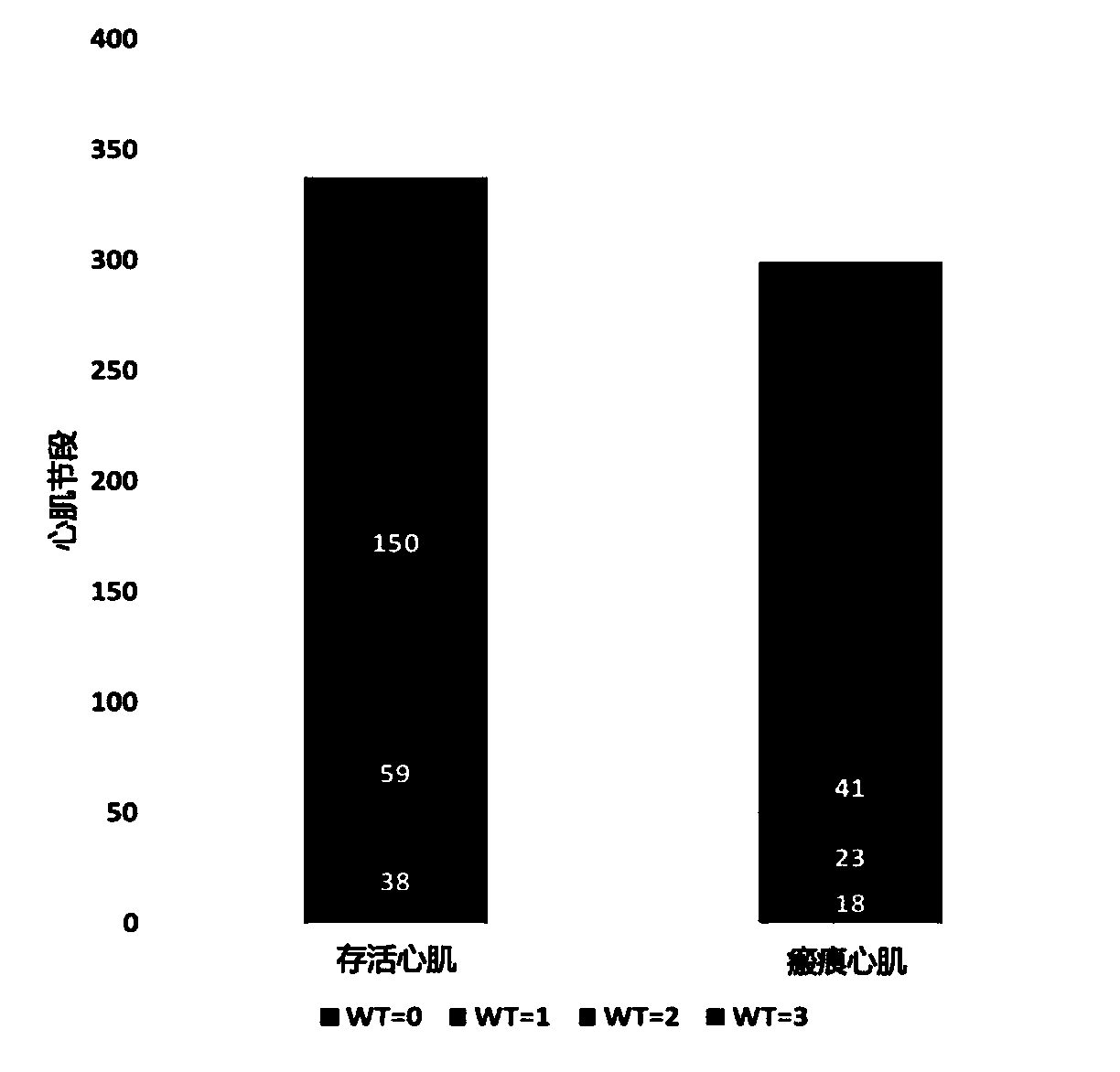
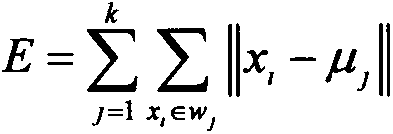Patents
Literature
41 results about "Left ventricular myocardium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Non-compaction of the myocardium is gaining prominence as a rare, distinct cardiomyopathy characterised by the presence of numerous, excessive prominent trabeculations and deep intertrabecular recesses which communicate with the left ventricular cavity.
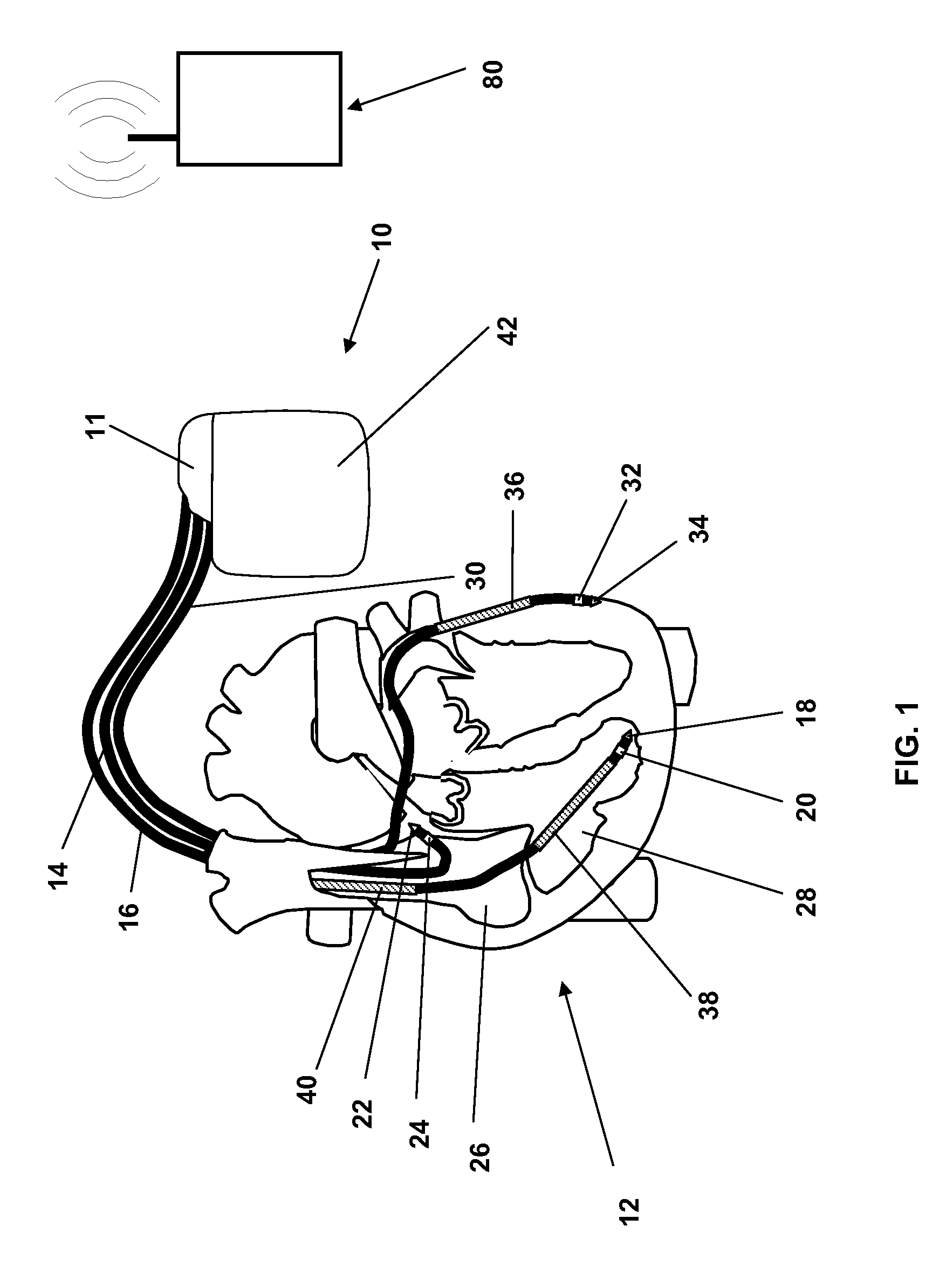
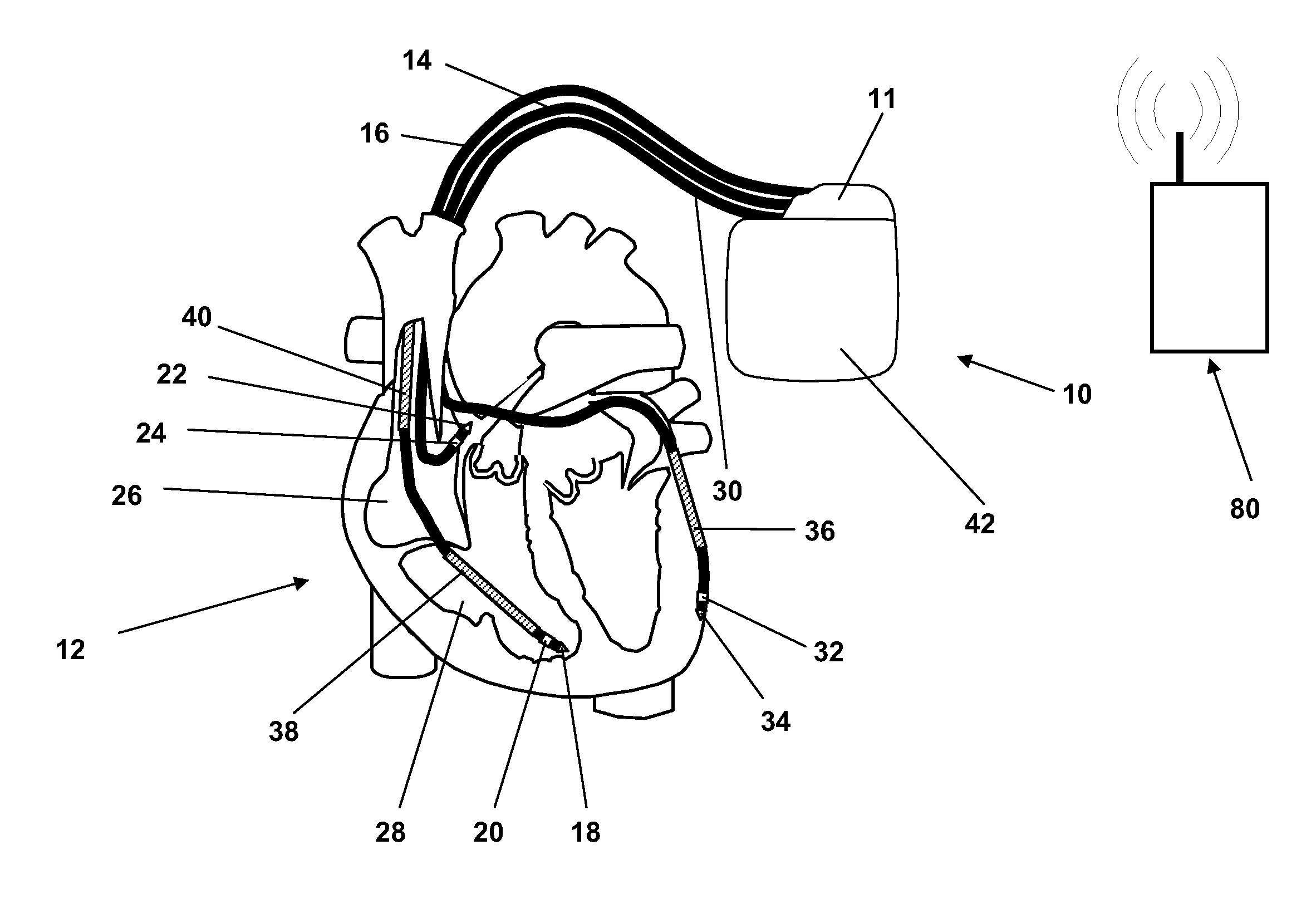
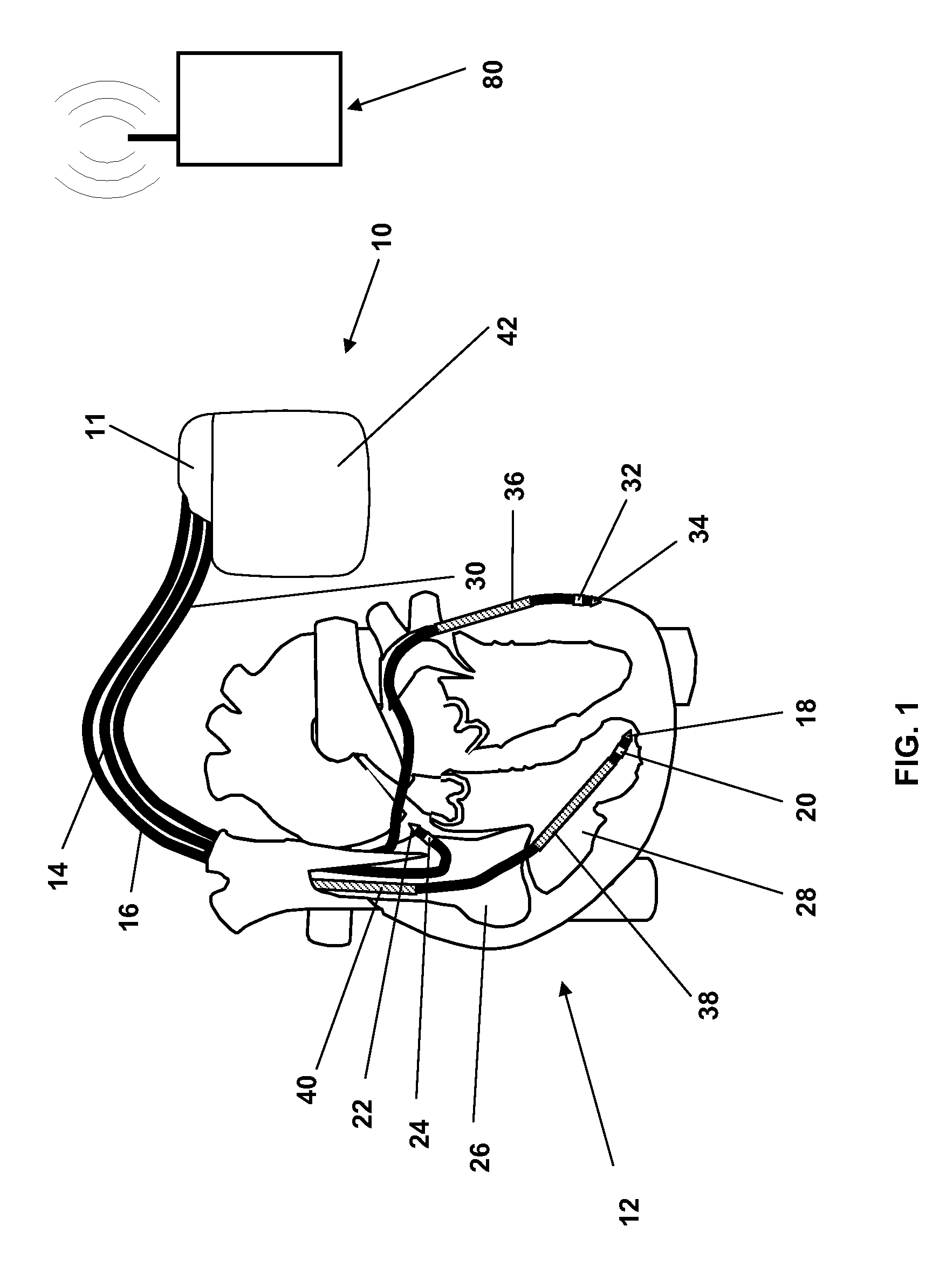
Systems and Methods for Heart and Activity Monitoring
InactiveUS20120165684A1ElectrocardiographyLocal control/monitoringTransplant rejectionCardiac muscle
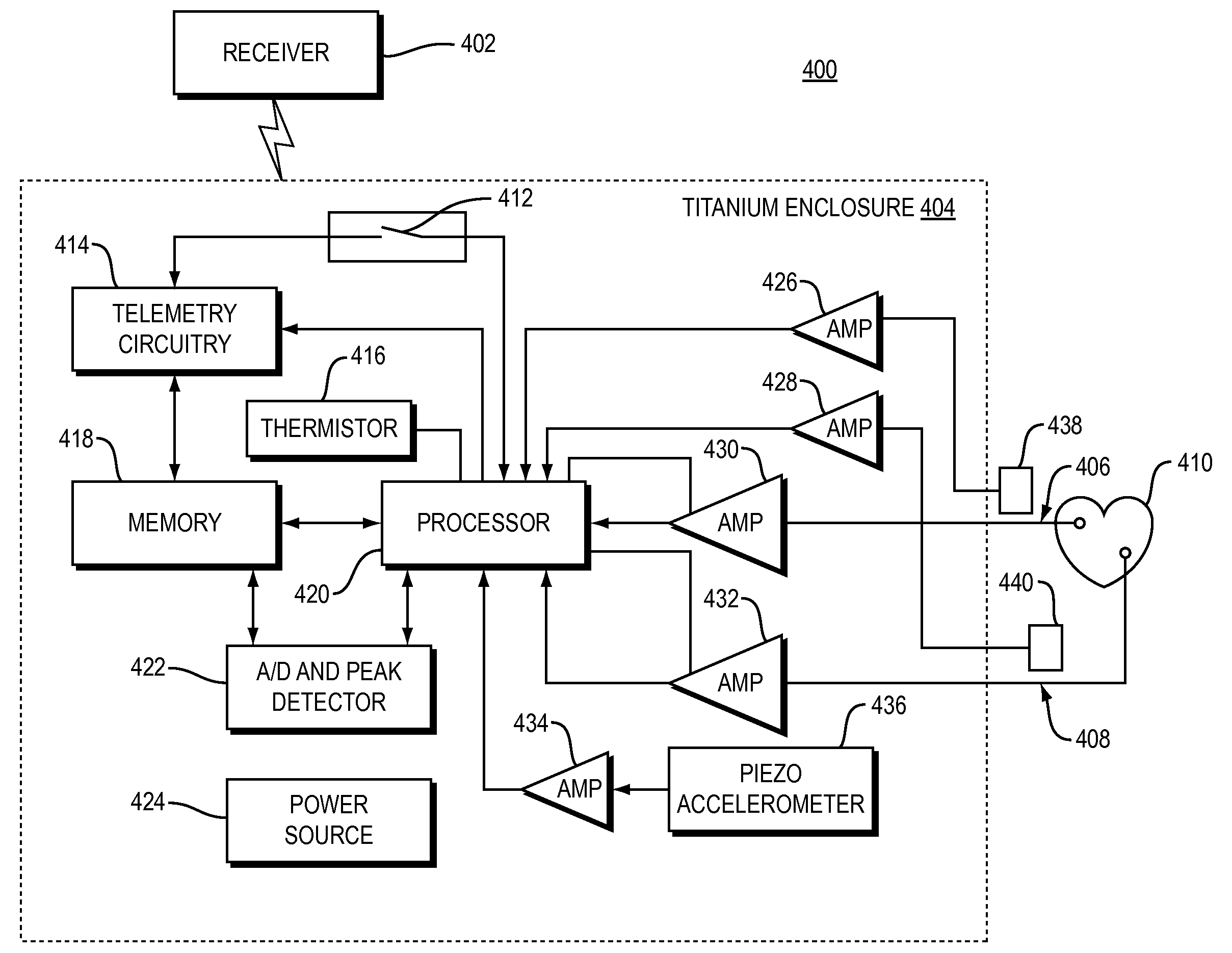
Methods and systems for monitoring a heart failure or transplant rejection status of a patient including use of a device or system to collect intramyocardial electrogram (IMEG) signals from the patient at different times automatically when a detected activity level of the patient is below a preset threshold level for a predetermined amount of time, and use of a device or system to generate a status indicator value proportional to a combination of parameters extracted from at least a portion of the collected IMEG signals. Methods and systems can also include measuring time delay values between IMEG signals collected from different locations in the patient. The IMEG signals can be collected from the right ventricular septum and the right ventricular apex of the patient or from the right and left ventricular myocardium of the patient.
Owner:QRS HEART
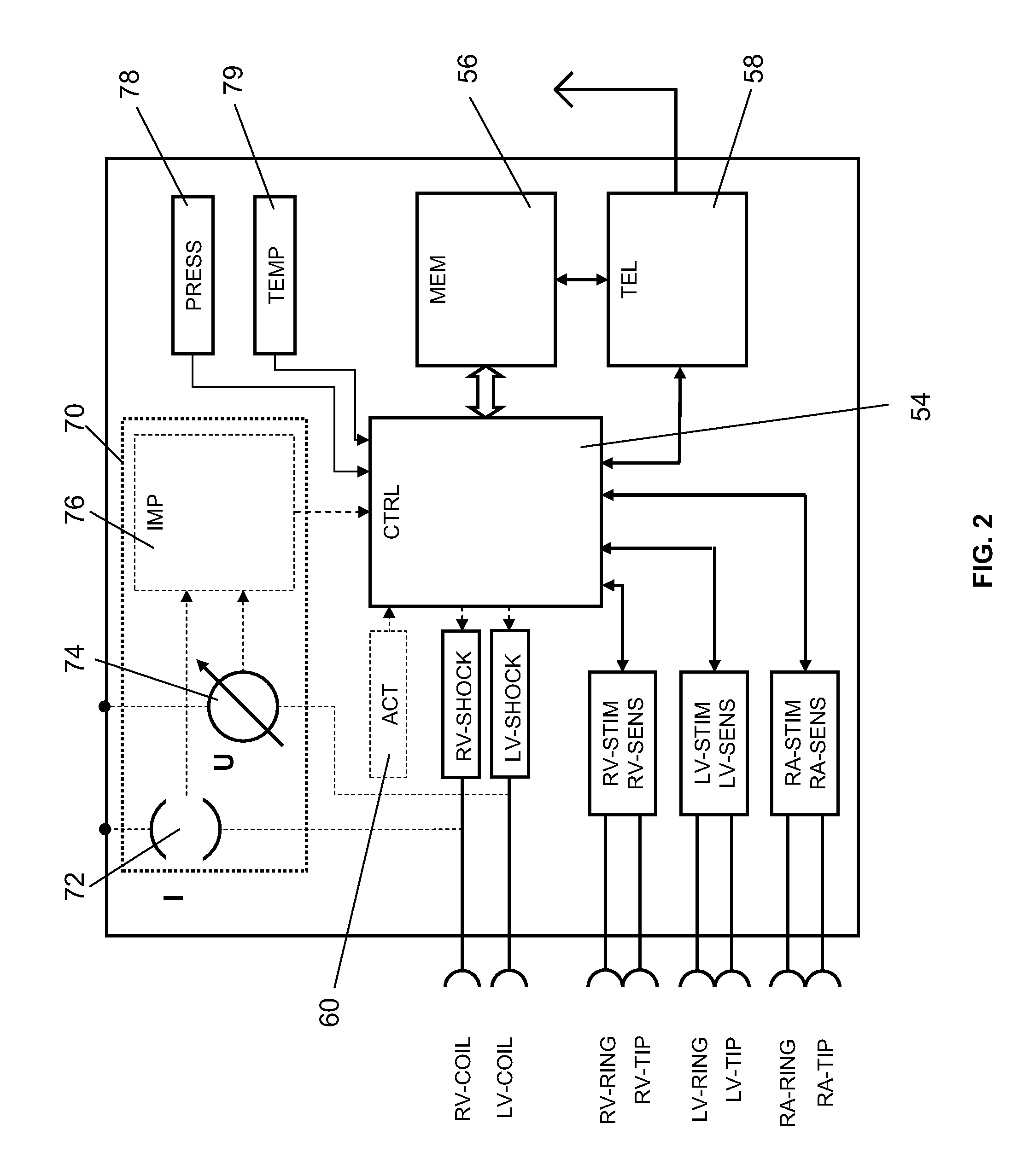
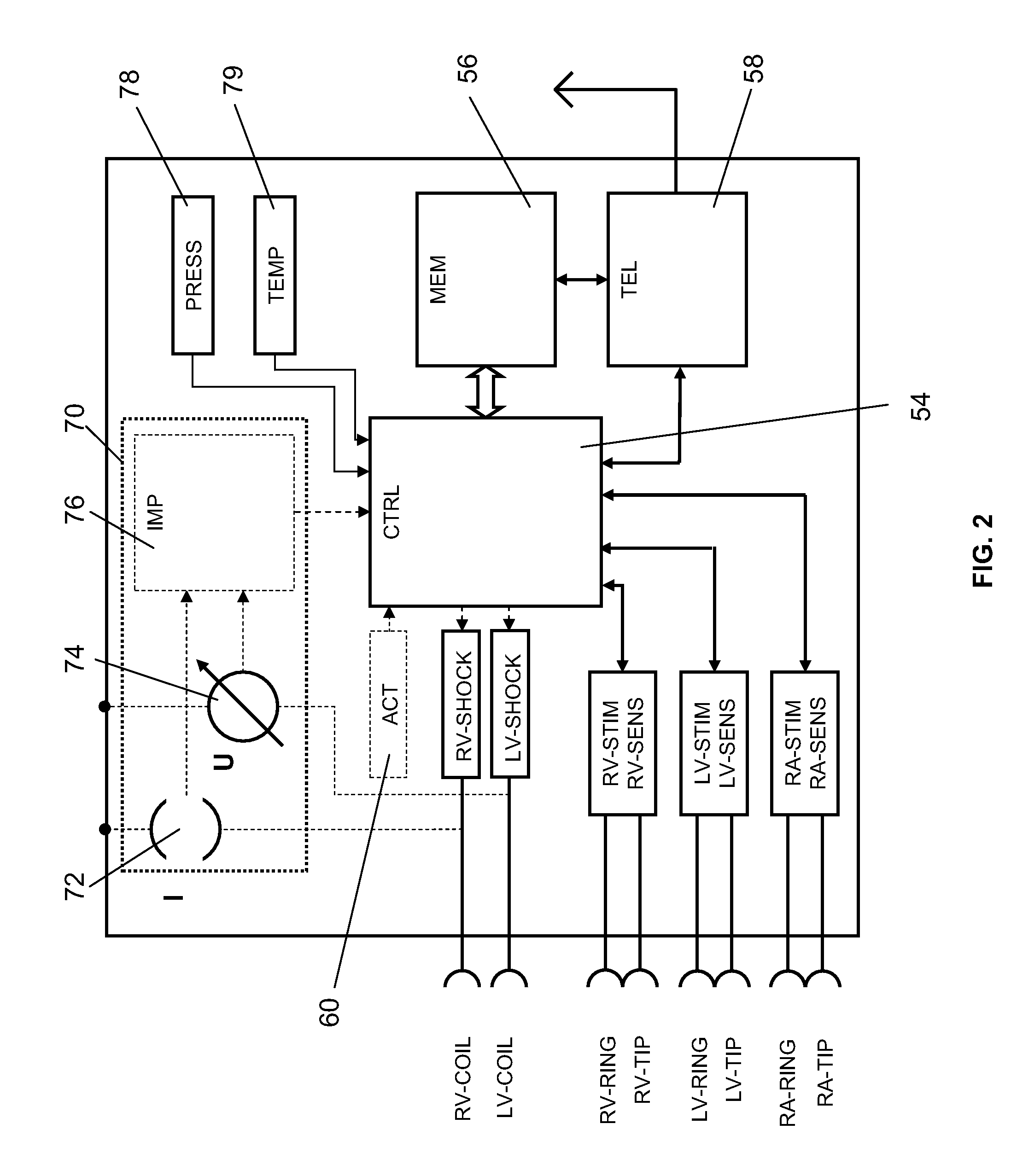
Switch polarity pacing to improve cardiac resynchronization therapy
InactiveUS20090240298A1Maximal improvement of cardiac functionSize is still affectedHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsLeft ventricular sizeCardiac muscle
The invention is directed to a heart stimulator for left-ventricular pacing comprising a left ventricular stimulation pulse generator connected or connectable to a single electrode lead for left ventricular stimulation having one or more electrodes for delivery of stimulation pulses to left ventricular myocardial heart tissue, said stimulation pulse generator being adapted to generate and deliver stimulation pulses of switchable polarity. The heart stimulator further comprises a control unit connected to the stimulation pulse generator for controlling the stimulation pulse generator and to trigger generation and delivery of stimulation pulses having a polarity controlled by said control unit, wherein the control unit is adapted to control said left ventricular stimulation pulse generator so as to deliver at least a pair of suprathreshold stimulation pulses of opposite polarity.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Non-invasive systems and methods for the determination of cardiac injury using a characterizing portion of a voxel histogram
Methods, systems and circuits predict cardiotoxicity induced cardiac injury prior to an irreversible state by electronically generating at least one histogram of mean intensities of voxels / pixels in an MRI image of a left ventricle myocardium and electronically determining a likelihood of cardiac injury due to cardiotoxicity based on data from the at least one histogram.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Non-invasive systems and methods for the determination of cardiac injury using a characterizing portion of a voxel histogram
Methods, systems and circuits predict cardiotoxicity induced cardiac injury prior to an irreversible state by electronically generating at least one histogram of mean intensities of voxels / pixels in an MRI image of a left ventricle myocardium and electronically determining a likelihood of cardiac injury due to cardiotoxicity based on data from the at least one histogram.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
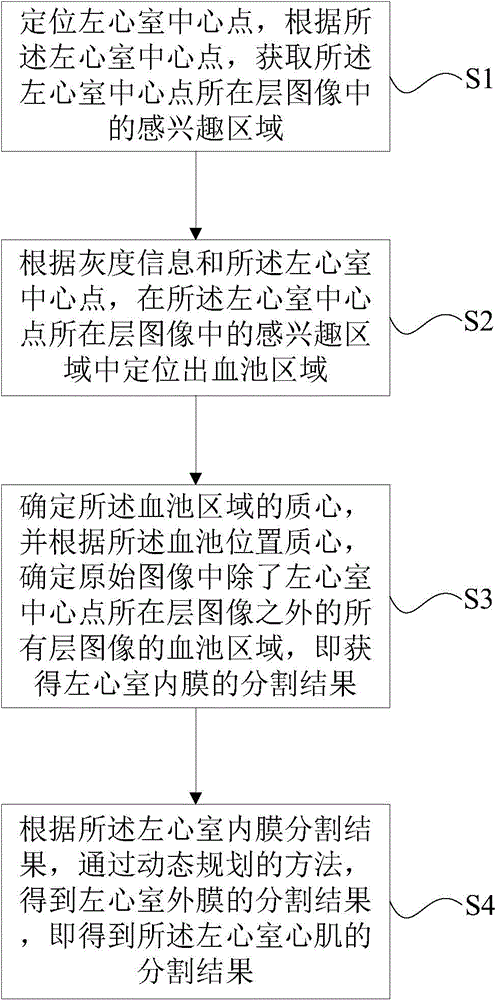
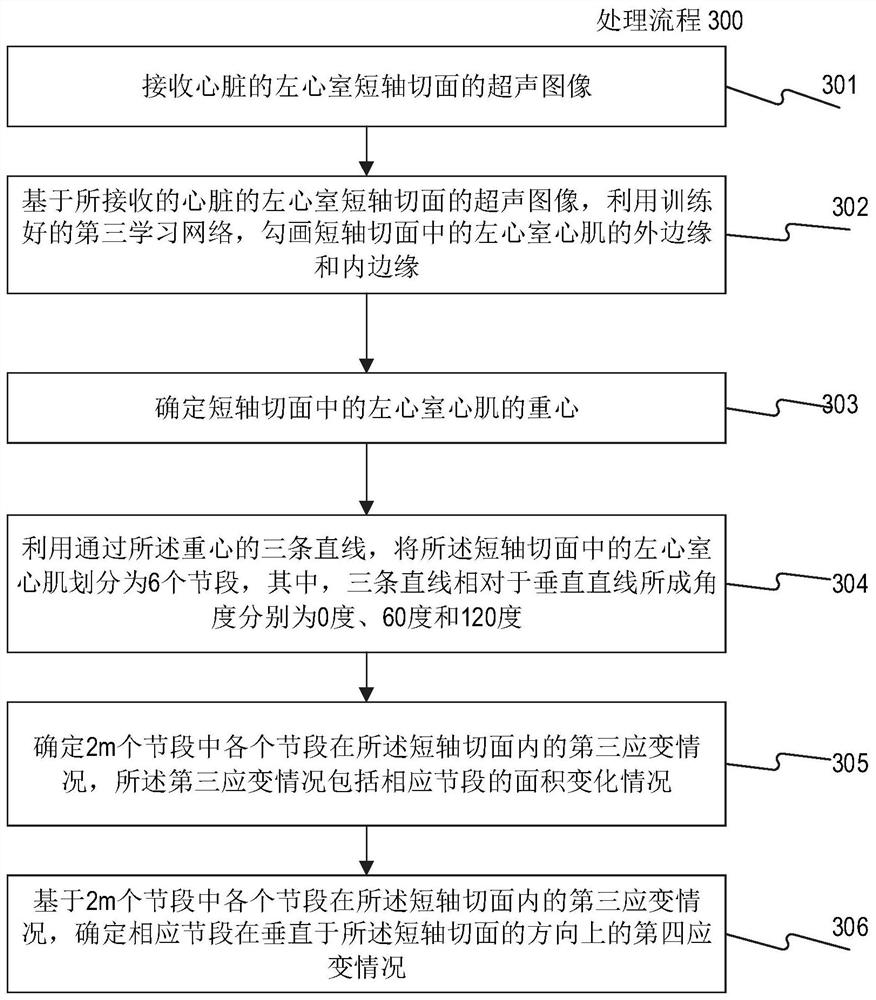
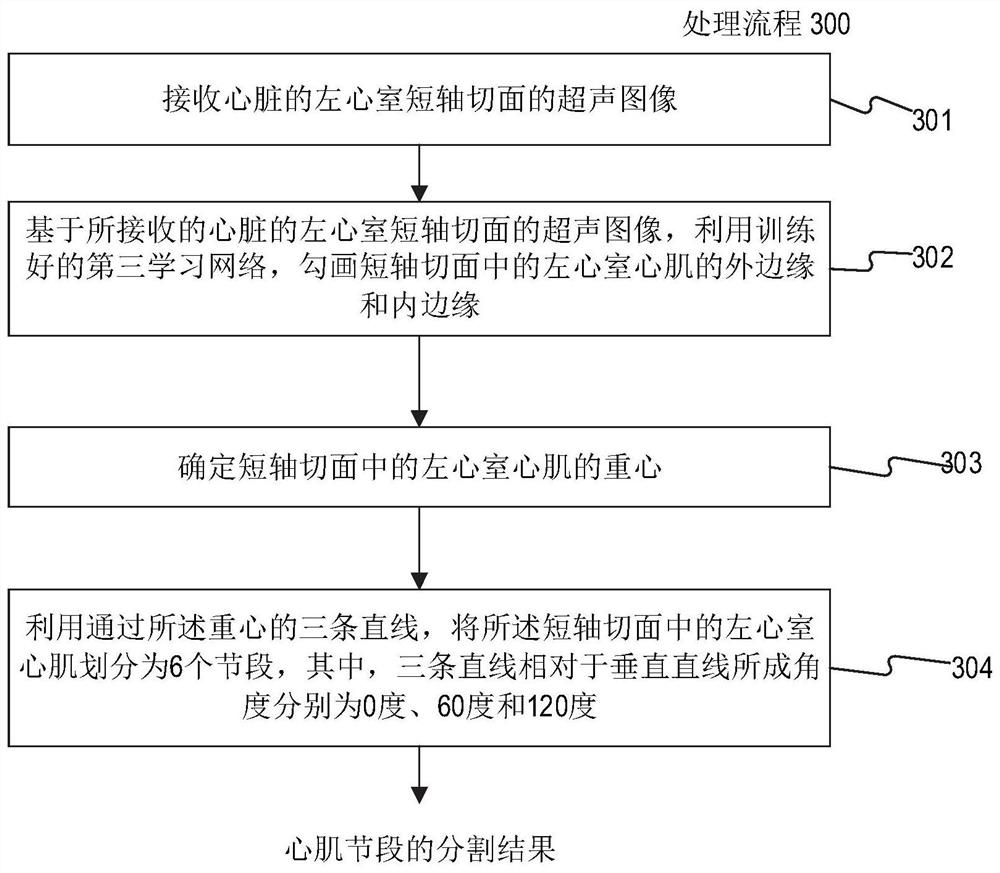
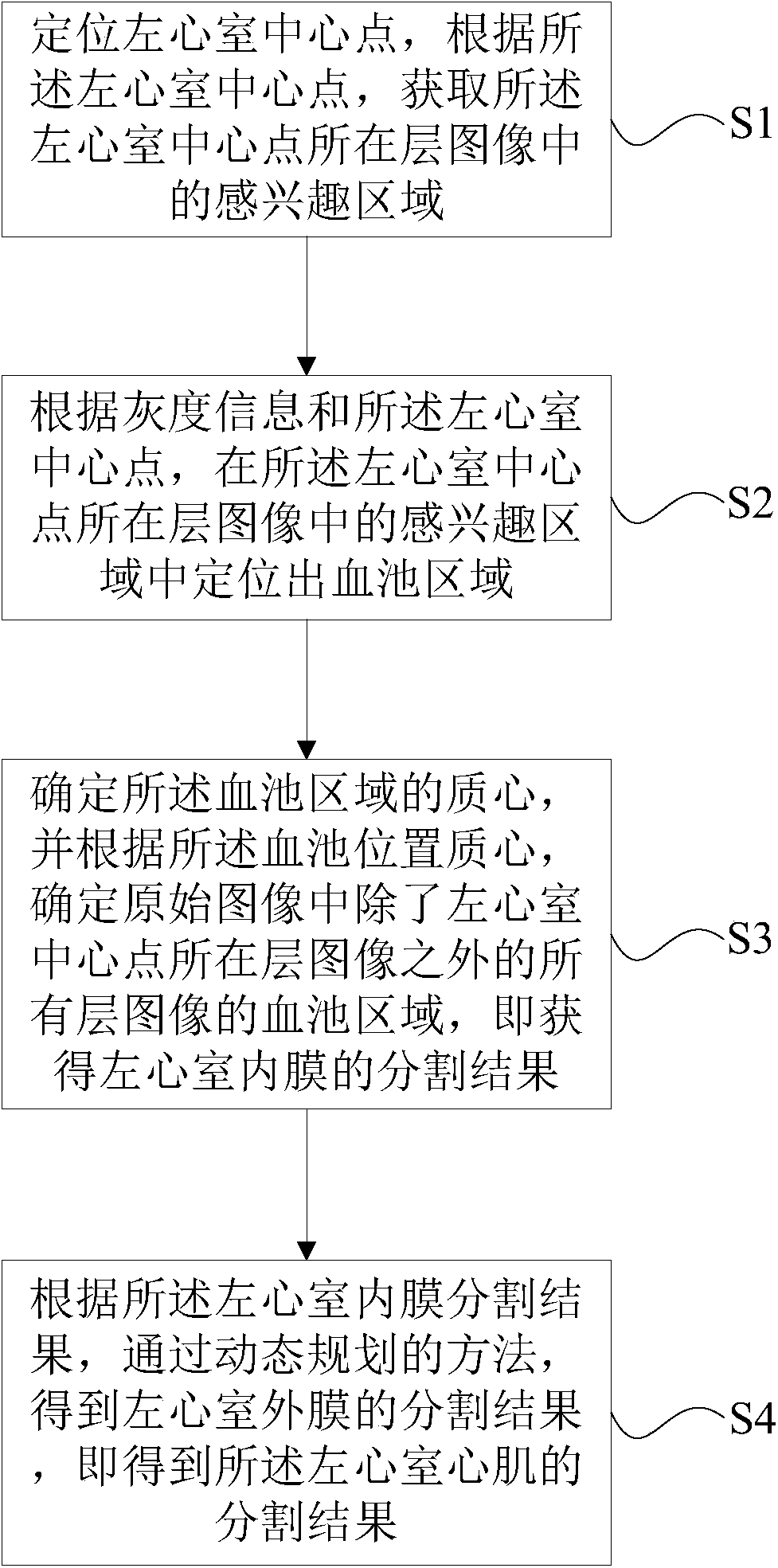
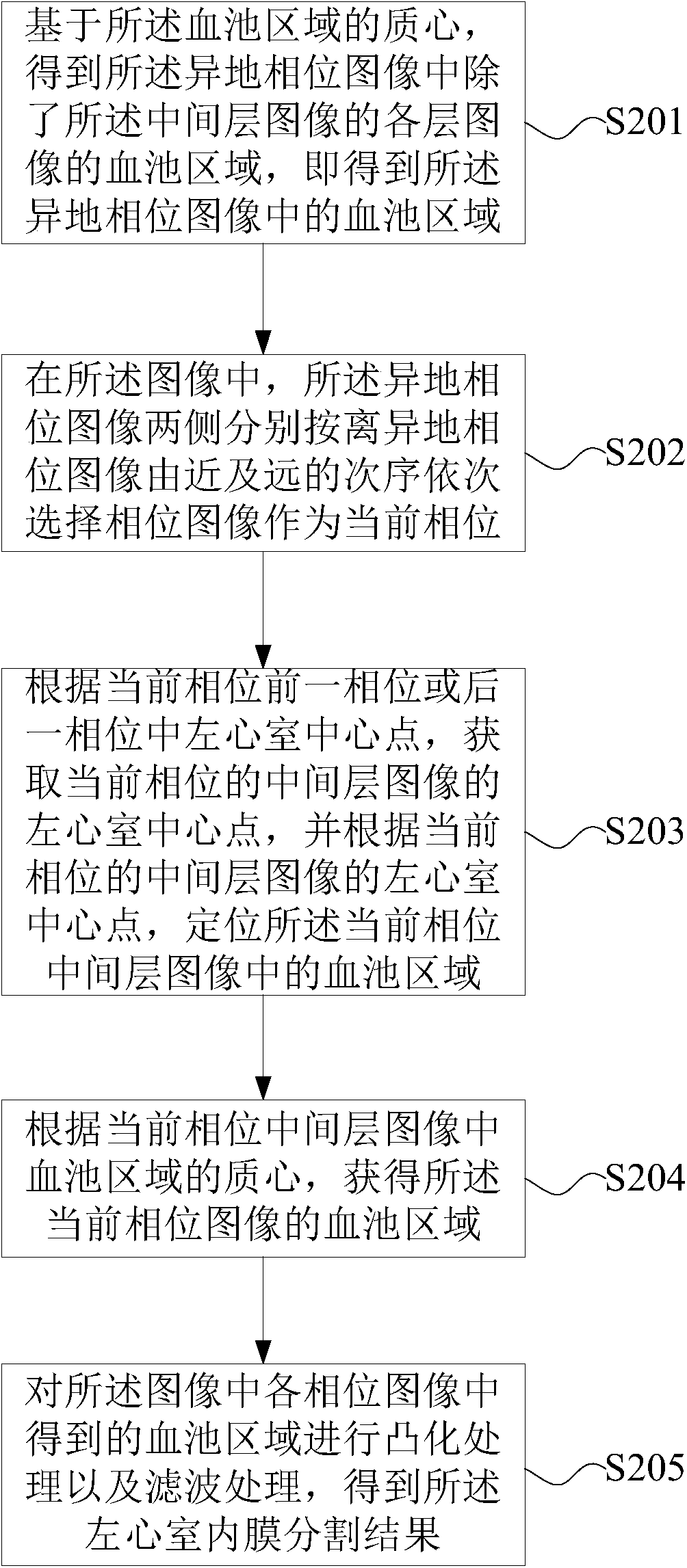
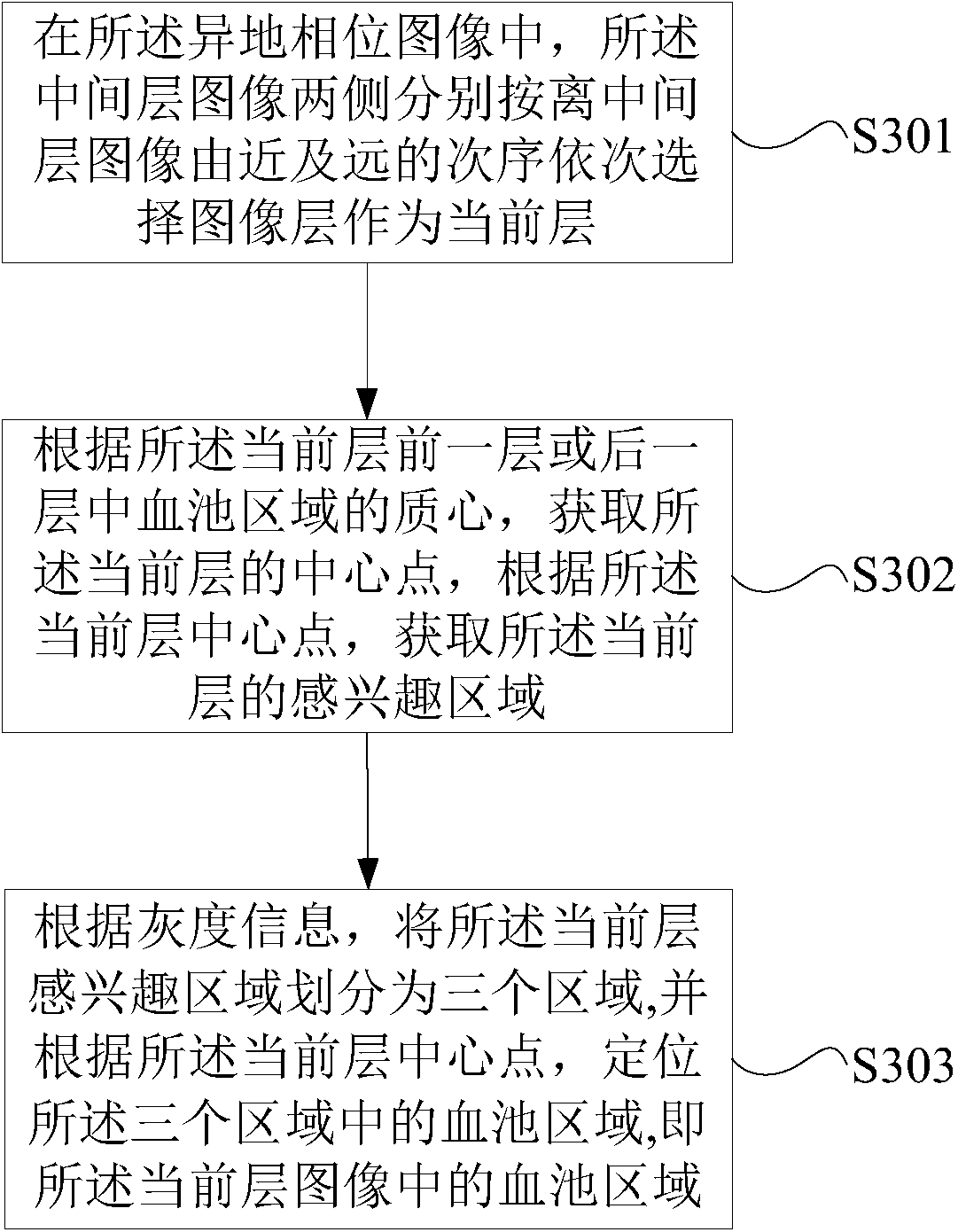
Division method and device of left ventricular myocardium
ActiveCN104978730AAutomatic segmentationSplit evenlyImage analysisDynamic planningLeft ventricular size
The invention provides a division method and device of left ventricular myocardium. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) positioning a left ventricular central point, and acquiring a region of interest in an image at a layer where the left ventricular central point is located; (2) positioning a blood pool region in the region of interest in the image at the layer where the left ventricular central point is located according to grey scale information and the left ventricular central point; (3) determining a mass center of the blood pool region, determining blood pool regions in an original image in all layers except the layer where the left ventricular central point is located, thereby obtaining a division result of left ventricular endocardium; and (4) obtaining a division result of left ventricular adventitia by a dynamic planning method according to the division result of the left ventricular endocardium, and thus obtaining a division result of the left ventricular myocardium. By the technical scheme provided by the invention, the left ventricular myocardium can be fully, uniformly and stably divided.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Fusion method for coronary artery CT image and cardiac ultrasonic strain image
ActiveCN108805913AClearly definedEasy to understandImage enhancementImage analysisThree dimensional ctDiagnostic Radiology Modality
The invention relates to a fusion method for a coronary artery CT image and a cardiac ultrasonic strain image. The invention provides a multi-mode image fusion technology method for fusing and mappinga two-dimensional UCG image and a three-dimensional CT image to stereoscopically display coronary artery lesions and myocardial damage conditions. According to the method, The cardiac ultrasonic image and the CT image are fused for the first time; the ultrasonic cardiogram and the coronary artery CT image are fused (figure 1) through a one-point one-surface three-section positioning method; and athree-dimensional pattern diagram is displayed. Then, on the basis of a three-dimensional ultrasonic volume image, two-dimensional images (figure 2) of 20 sections and 480 grid segments of a left ventricular myocardium are obtained by adopting a central axis rotation method and a refined segmentation method; based on this, the strain values of 480 segments are obtained; and myocardial perfusion ischemia information obtained by three-dimensional strain is superimposed into the three-dimensional coronary artery vascular pattern diagram (figure 3), thereby accurately reflecting a relation between a myocardial ischemia area and an actual coronary artery stenosis.
Owner:BEIJING ANZHEN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Medical MR image segmentation method based on Hough transform and geometric active contour
InactiveCN105243666AEffective segmentationActs as a shape constraintImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentationCURE data clustering algorithm
The present invention discloses a medical MR image segmentation method based on Hough transform and a geometric active contour and belongs to the technical field of image processing. According to the method, firstly, the prior shape knowledge that inner and outer contours of a left ventricle myocardium on a short axis image are of a round-like shaped is utilized, Hough transform is adopted to estimate an initial contour of a left ventricle and the reason of adopting Hough transform is that Hough transform has strong robustness, is not quite sensitive for the incompleteness of data or noise and can recognize partially deformed or partially shielded objects; the reason of using a K-means clustering algorithm is that as a square error based clustering method, the K-means clustering algorithm is simple and has a high clustering speed; and by using the method provided by the present invention, the inner and outer contours of the left ventricle can be segmented effectively, relative positions of evolving curves of the inner and outer contours of the left ventricle can be controlled and a function of shape constraint can be realized.
Owner:NANNING BOCHUANG INFORMATION TECH DEV CO LTD
Method for quantitatively evaluating myocardial infarction on basis of nuclide image and CT (computed tomography) coronary angiography fusion
InactiveCN109498046AAvoid interferenceImprove registration efficiencyComputerised tomographsTomographyLeft ventricular sizeCompanion animal
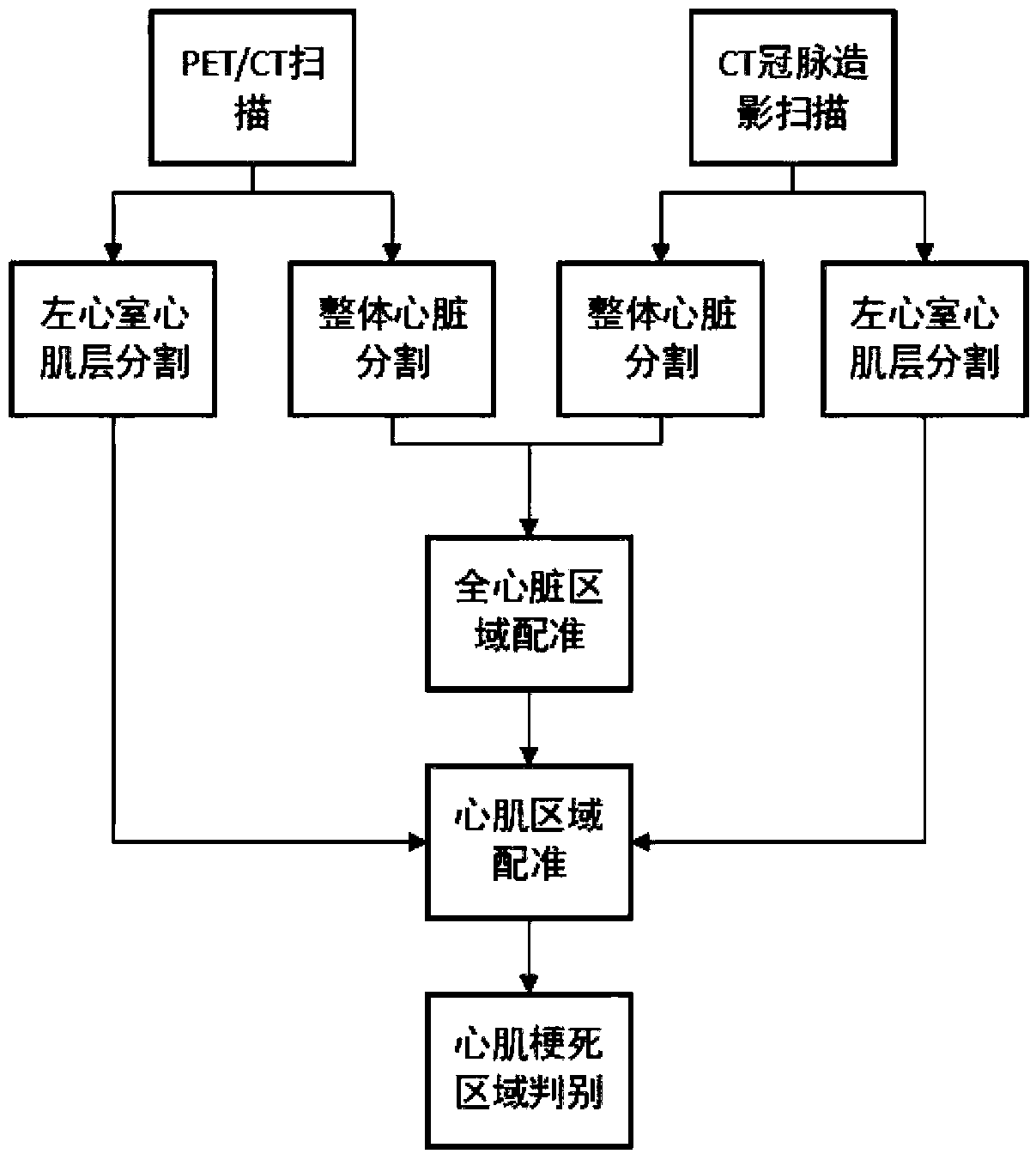
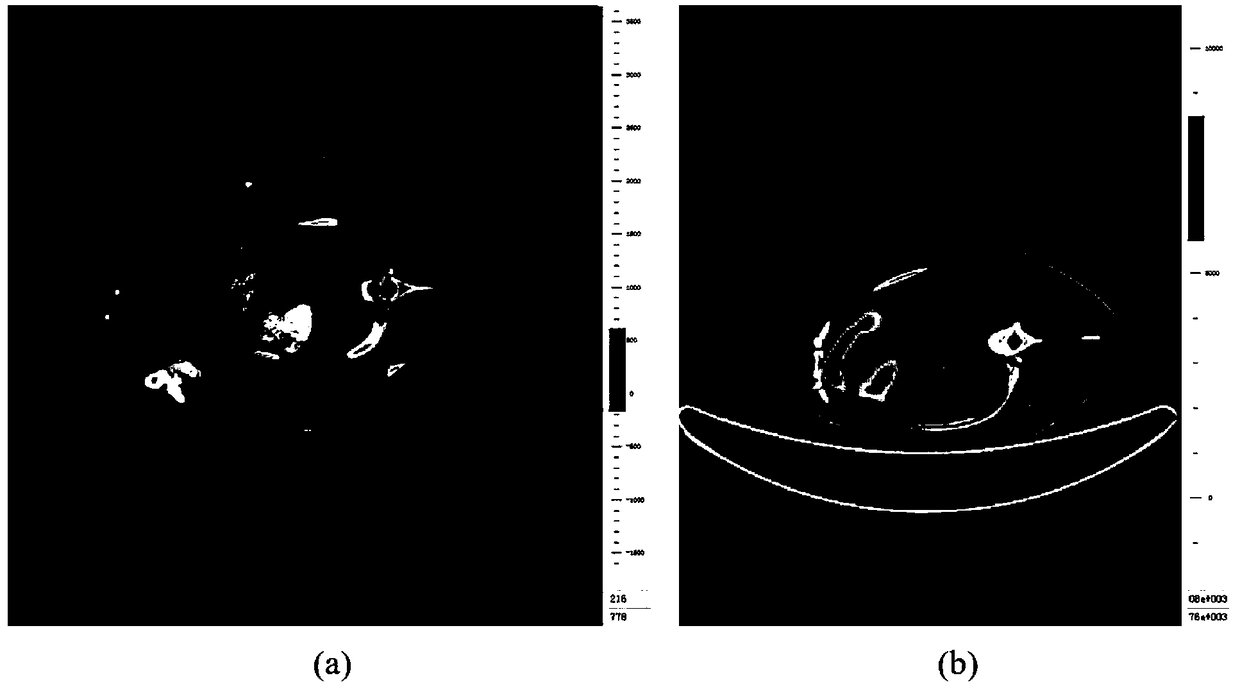
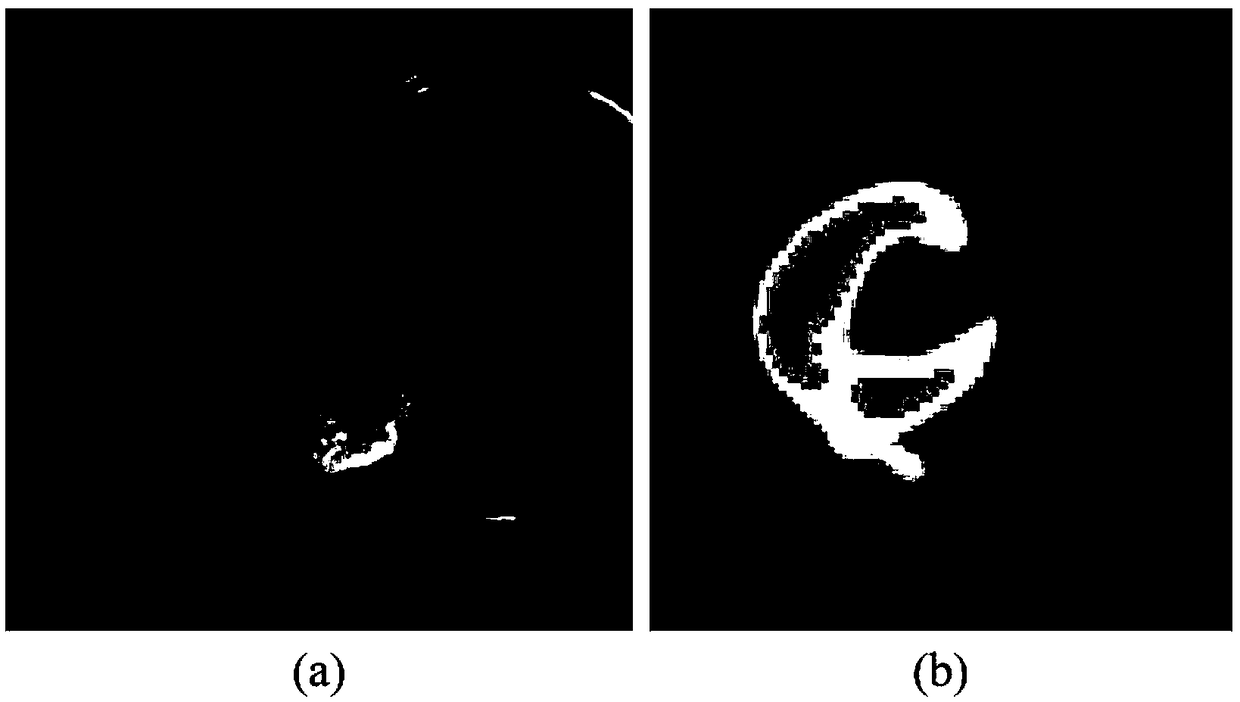
The invention belongs to the field of medical image processing, and discloses a method and a system for quantitatively evaluating myocardial infarction on the basis of nuclide image and CT (computed tomography) coronary angiography fusion. The method includes acquiring heart PET (positron emission tomography) / CT and CTA (computed tomography angiography) data; carrying out three-dimensional DCT (discrete cosine transformation) frequency-domain interpolation on PET / CT images; acquiring heart regions in the PET / CT images and CTA images by the aid of multi-spectrum segmentation processes; acquiring left ventricular cardiac muscle regions in PET images by the aid of threshold processes; manually segmenting left ventricular cardiac muscle regions in the CTA images layer by layer; registering images; classifying pixel points according to the locations of pixel points on the registered images and tracer uptake values; inversely transforming infarction regions into original CTA spaces and dividing the volumes of left ventricular cardiac muscles from the volumes of the transformed infarction regions; three-dimensionally displaying fused images in volume rendering manners. The method and thesystem have the advantages that integral registration procedures can be fully automated, the method and the system are good in objectivity, intuitive results can be obtained, and analysis can be facilitated for clinical doctors.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for processing cardiac perfusion magnetic resonance image
ActiveCN106709919ARealize visualizationImage enhancementImage analysisInner membraneLeft ventricular cavity
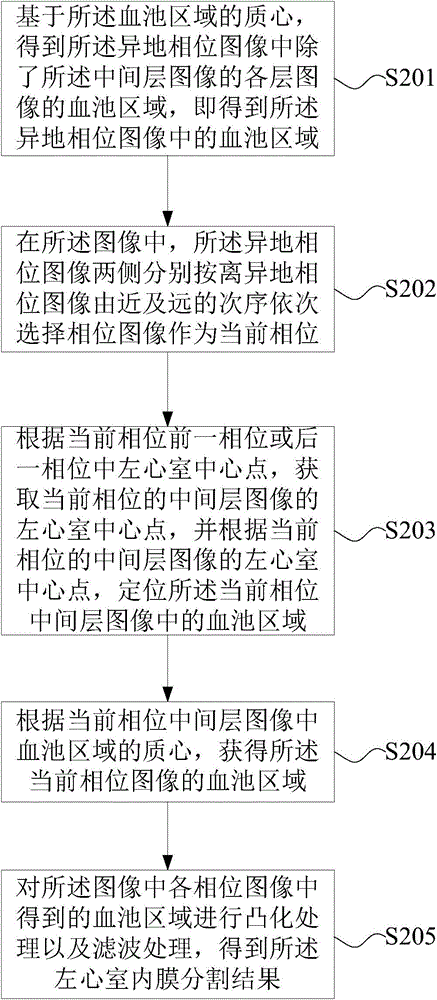
The invention discloses a method for processing a cardiac perfusion magnetic resonance image. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring magnetic resonance images INT of a plurality of layers of slices including left ventricular myocardium; from the start layer, respectively segmenting the myocardial inner membrane of the magnetic resonance images of the N layers of slices within T heartbeat cycles to obtain a reference image Imr corresponding to each layer of slice; based on the reference image Imr, registering the magnetic resonance image of the current layer of slice within the T heartbeat cycles; based on the segmentation result of the myocardial inner membrane of the magnetic resonance image of each layer of slice, segmenting a myocardial outer membrane; calculating and smoothing a mean gray-time curve of a left ventricular cavity zone and a right ventricular cavity zone; and taking the connecting line of the centroid point of a blood pool zone defined by the myocardial inner membrane and the center point of a right ventricular boundary as a base line, blocking the myocardium according to a bovine eye graph partitioning method. The method can realize visual and full-automatic quantitative analysis on the signal intensity change curve of the left ventricular myocardium with time.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
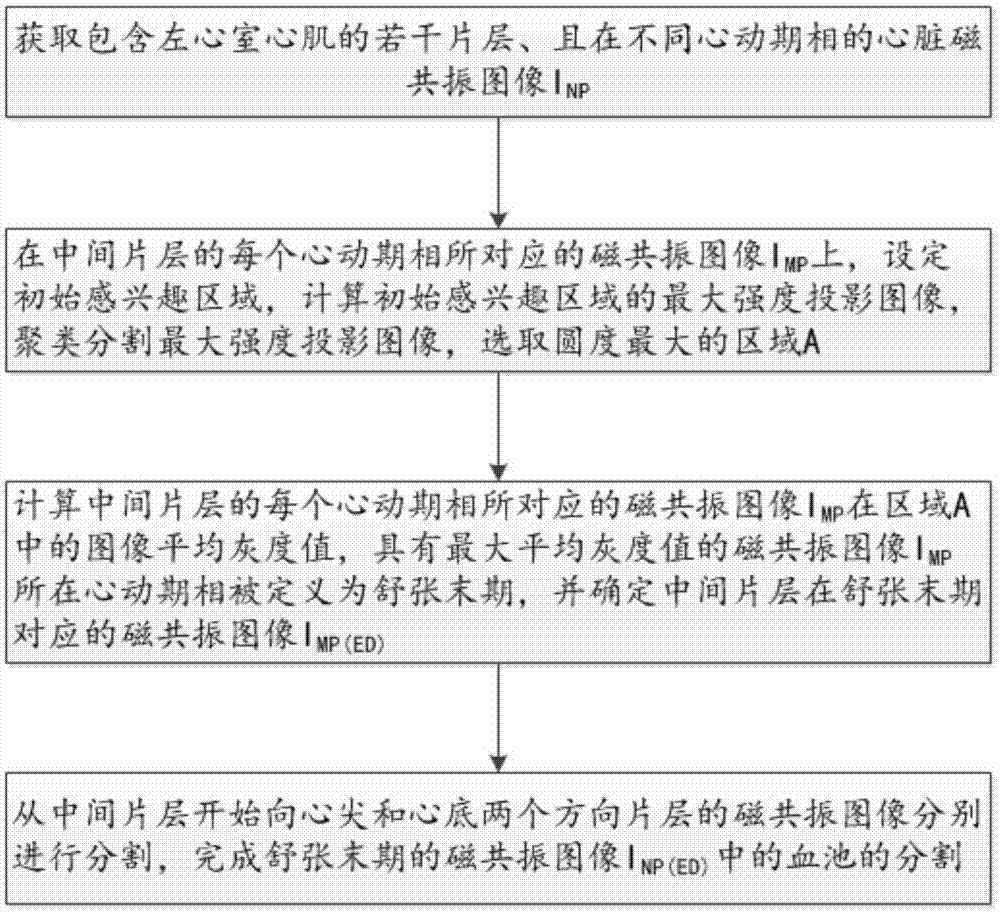
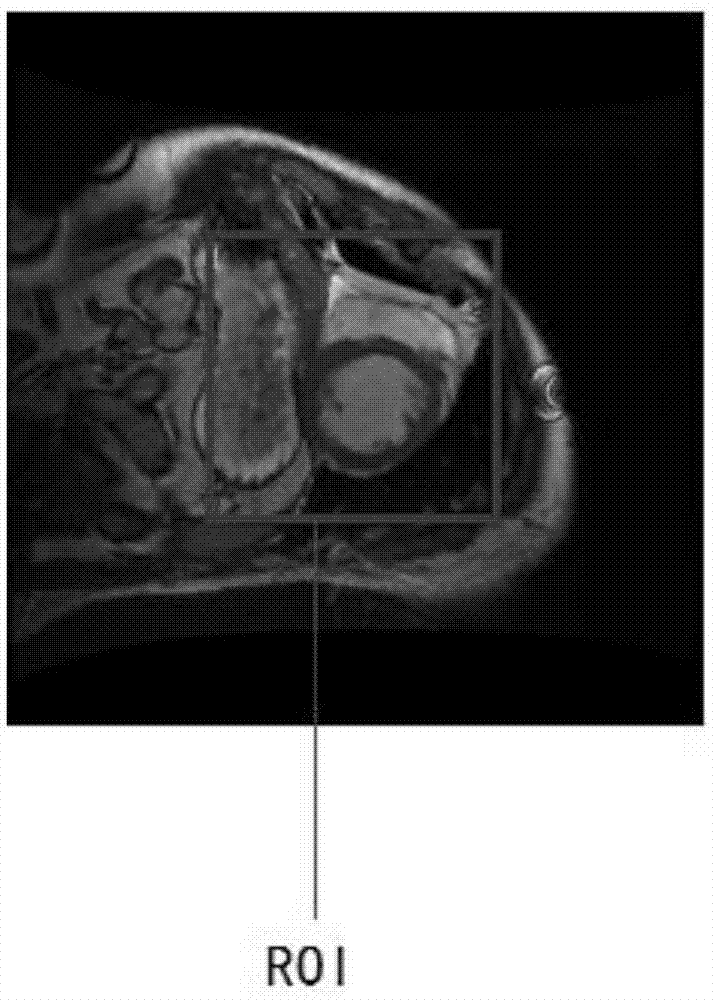
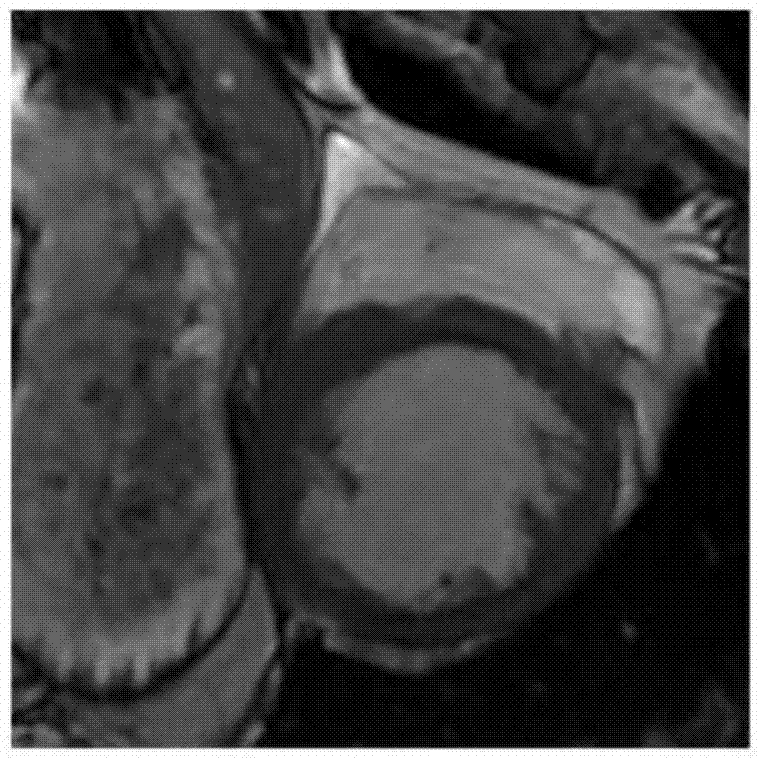
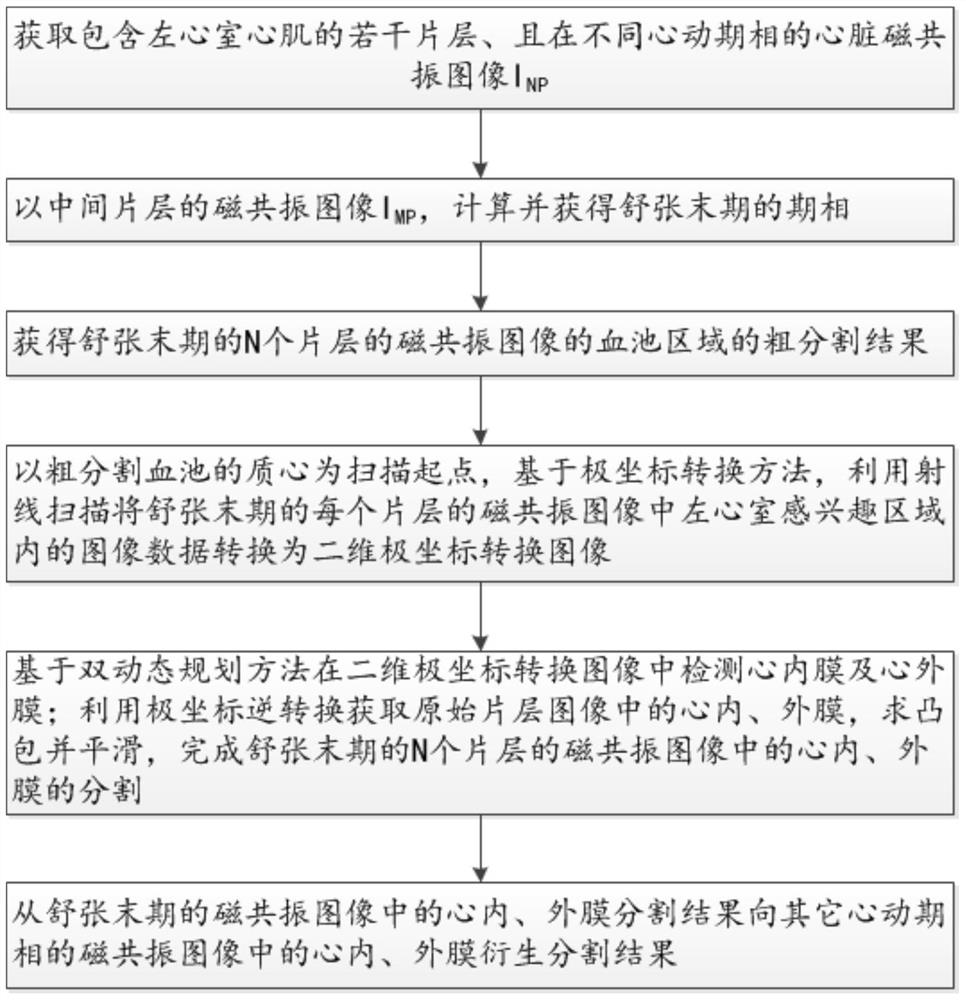
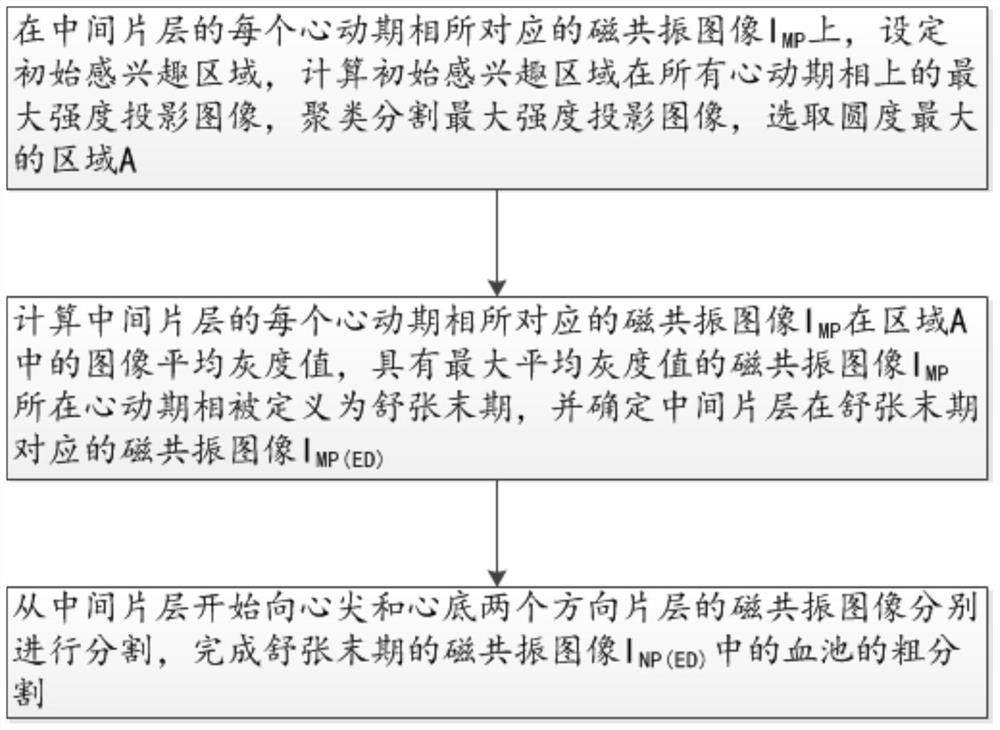
Method for segmenting endocardium and epicardium in heart cardiac function magnetic resonance image
ActiveCN106910194ARealize detectionAccurate and effective detectionImage enhancementImage analysisCardiac cycleLeft ventricle wall
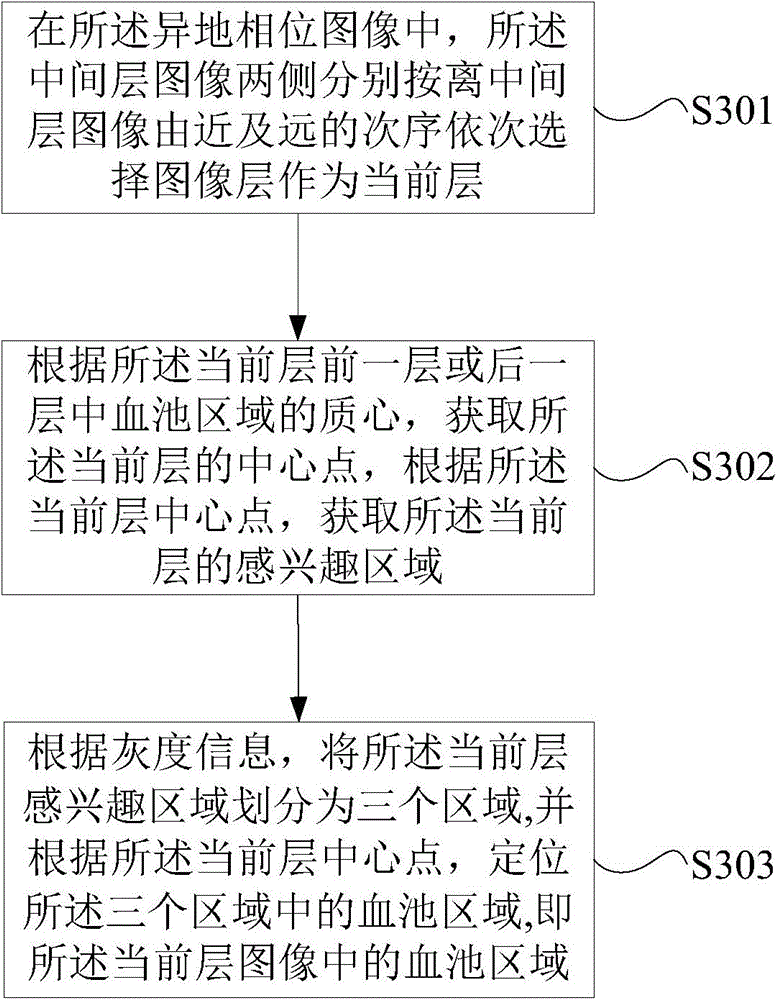
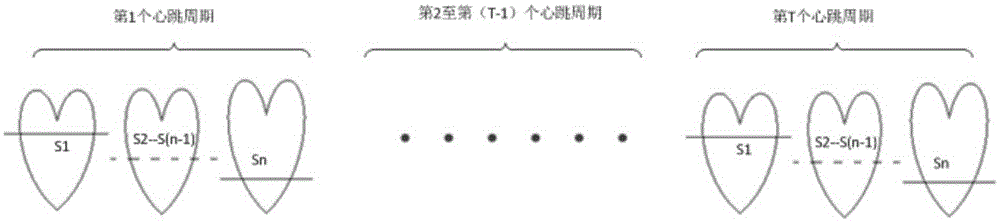
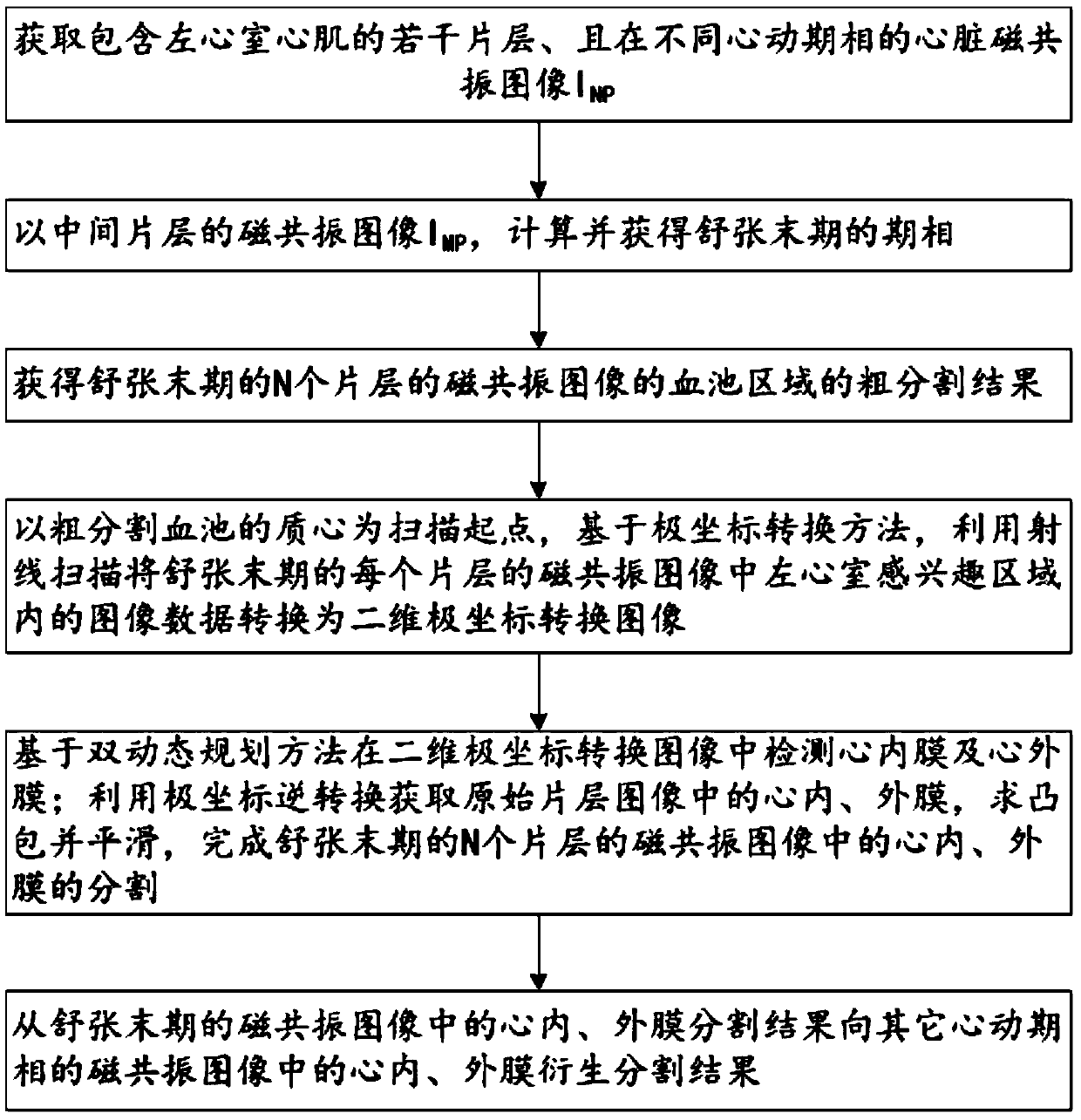
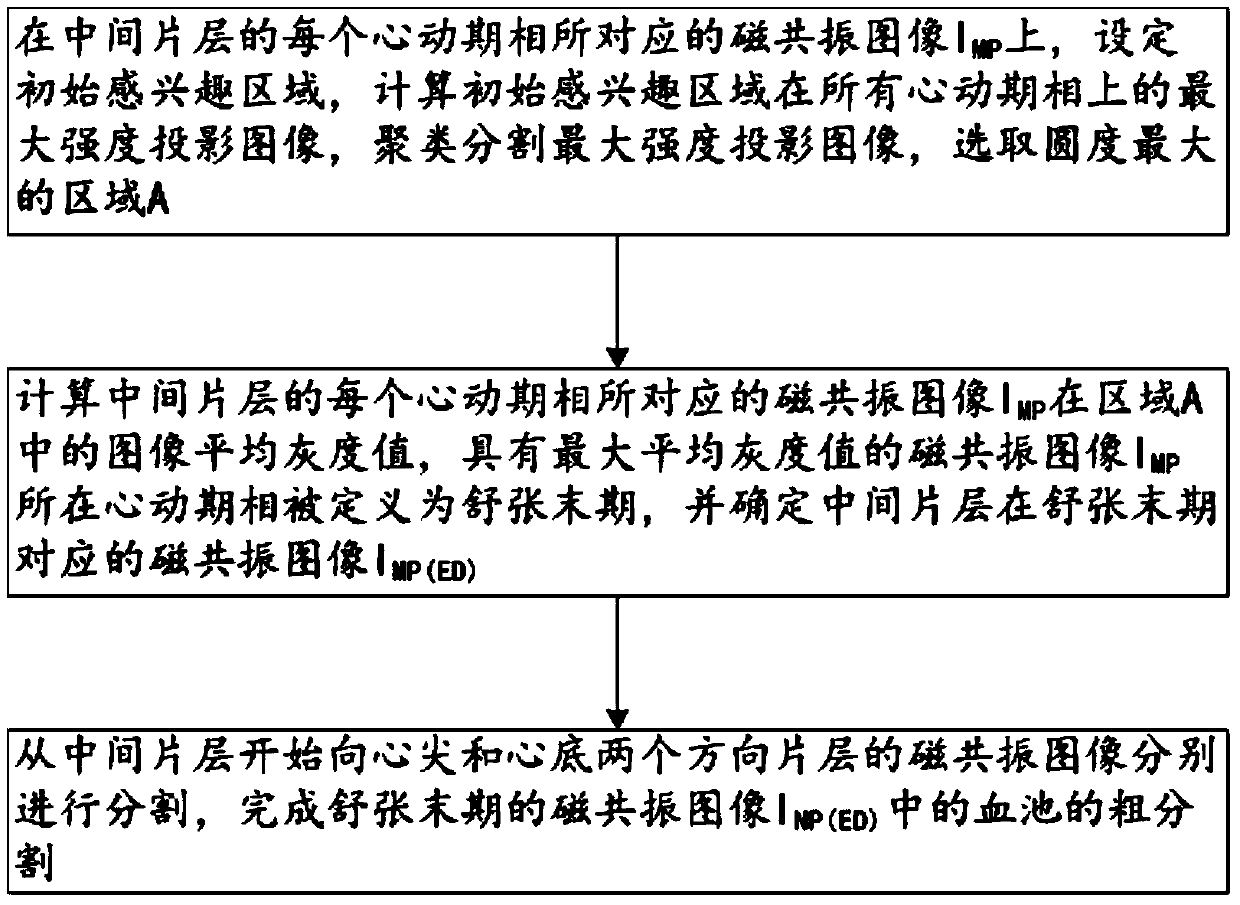
The invention discloses a method for segmenting the endocardium and the epicardium in a heart cardiac function magnetic resonance image. The method comprises positioning the diastasis in heart magnetic resonance images I<NP> including several lamellas of the left ventricular myocardium and in different cardiac cycle phases, and obtaining a coarse segmentation result of blood pools of magnetic resonance images of N lamellas in the diastasis; converting image data in the left ventricle region-of-interest in the magnetic resonance image of each lamella in the diastasis into a two-dimension polar coordinate conversion image by means of ray scanning based on a polar coordinate conversion method; detecting the endocardium and the epicardium in the two-dimension polar coordinate conversion image based on a bidynamic programming method; obtaining the endocardium and the epicardium in an original lamella image by means of polar coordinate inverse conversion, calculating the convex hull and smoothing the convex hull, and completing segmentation of the endocardium and the epicardium in the magnetic resonance images of the N lamellas in the diastasis; and deriving the segmentation result of the in the endocardium and the epicardium in the magnetic resonance images in the diastasis to the endocardium and the epicardium in the magnetic resonance images in other cardiac cycle phases.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Left ventricular myocardial segmentation method, device, and computer-readable storage medium
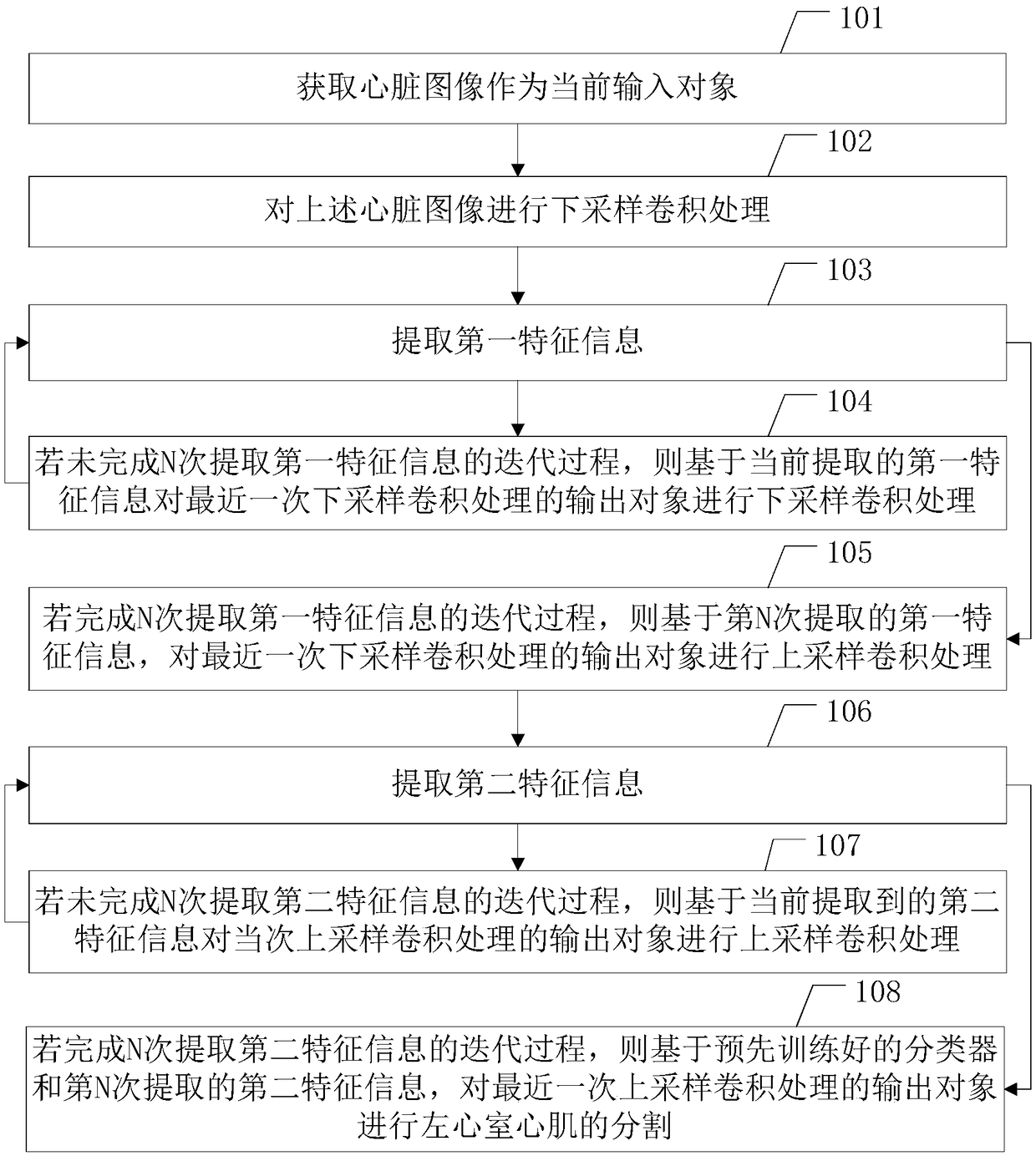
InactiveCN109285157ARealize automatic segmentationImprove segmentation efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisLeft ventricular sizeLeft ventricular myocardium
A left ventricular myocardial segmentation method, device and compute readable storage medium are disclosed, wherein, that left ventricular myocardial segmentation method comprises the follow steps of: obtaining a heart image; for the heart image, N times of down-sampling convolution processing and extraction of the first feature information are performed iteratively; if the iterative process of extracting the first feature information is completed for N times, performing N times of up-sampling convolution processing and extracting the second feature information for the output object of the Nth down-sampling convolution processing based on the first feature information extracted for the Nth time; if the iterative process of extracting the second feature N times is completed, the left ventricular myocardium is automatically segmented based on the pre-trained classifier. The technical proposal provided by the present application can effectively improve the efficiency of left ventricularmyocardial segmentation.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Heart segmentation model and pathological classification model training, heart segmentation and pathological classification method and device based on heart MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
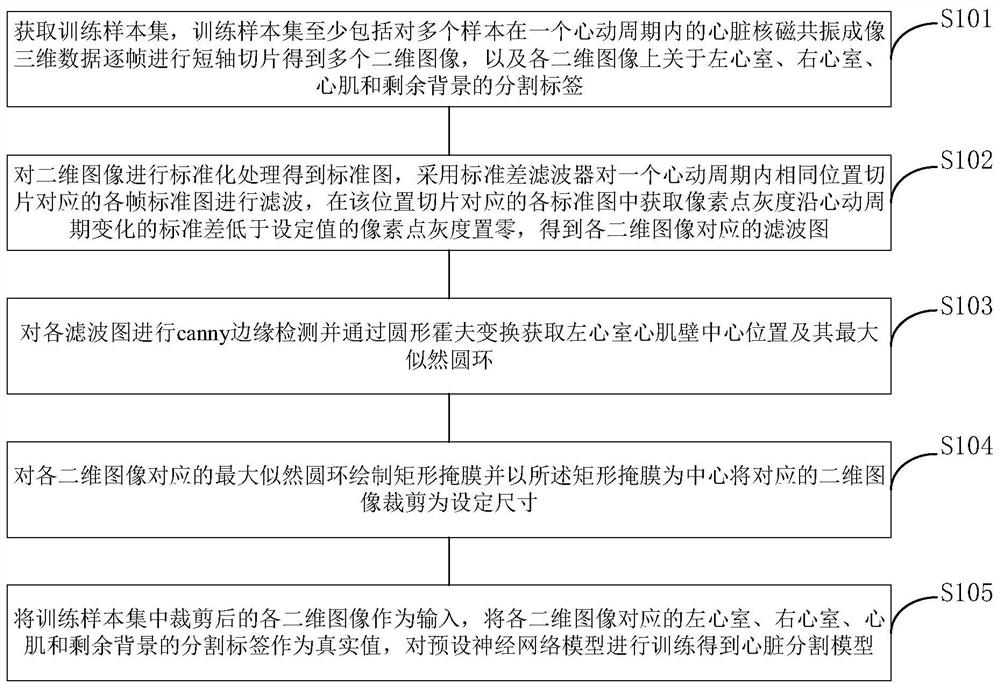
PendingCN113012173AFast convergenceSuppress background distractionsImage enhancementImage analysisLeft ventricular sizeCardiac cycle
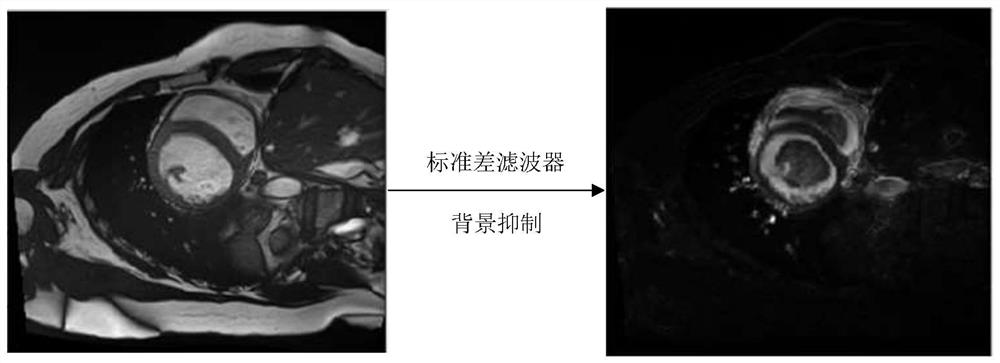
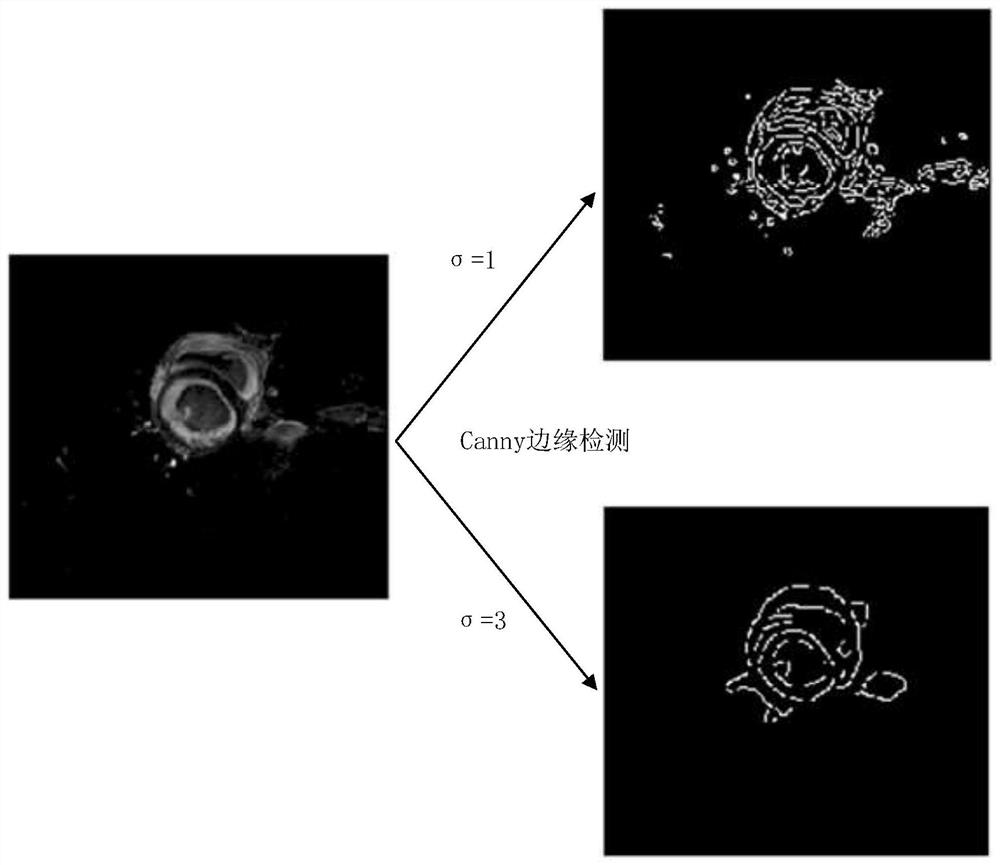
The invention provides a heart segmentation model and pathology classification model training, heart segmentation and pathology classification method and device based on heart MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), and the method comprises the steps: suppressing a residual background part with a small pixel gray level change through a standard deviation filter, highlighting a left ventricle, a right ventricle and a myocardial ,the central position of the left ventricular myocardial wall being further obtained through canny edge detection and circular Hough transform, drawing a rectangular mask, the two-dimensional image being cut based on the rectangular mask to serve as input for training a preset neural network model for training. Background interference can be greatly inhibited, and fast convergence of neural network training is promoted. The pathology classification model training method comprises the following steps: segmenting a two-dimensional image obtained by segmenting each frame of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging short axis in a cardiac cycle based on a cardiac segmentation model, calculating classification feature values, and constructing a random forest based on the classification feature values of a plurality of samples and pathology classification to obtain a cardiac pathology classification model; and realizing automatic pathological classification.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
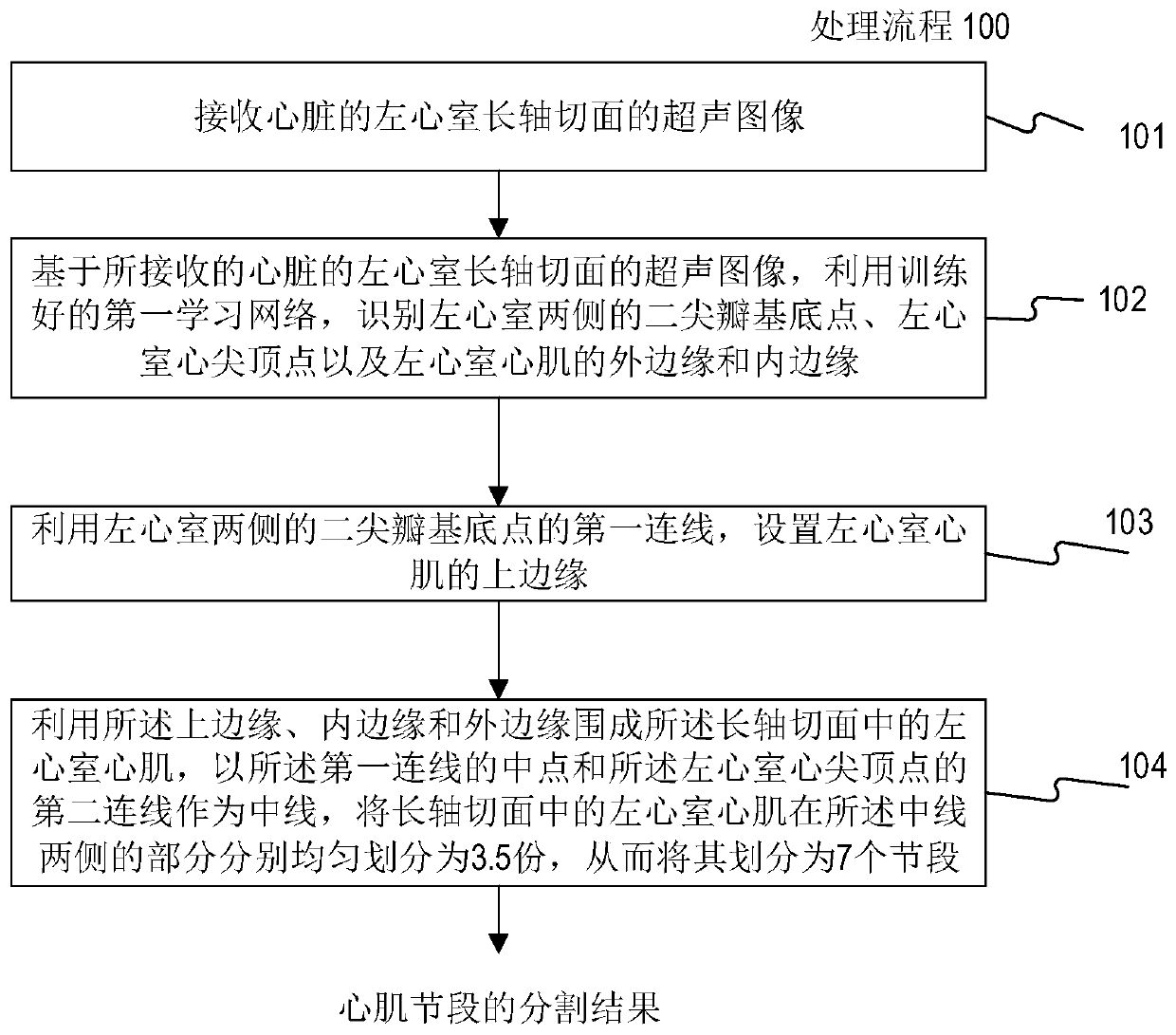
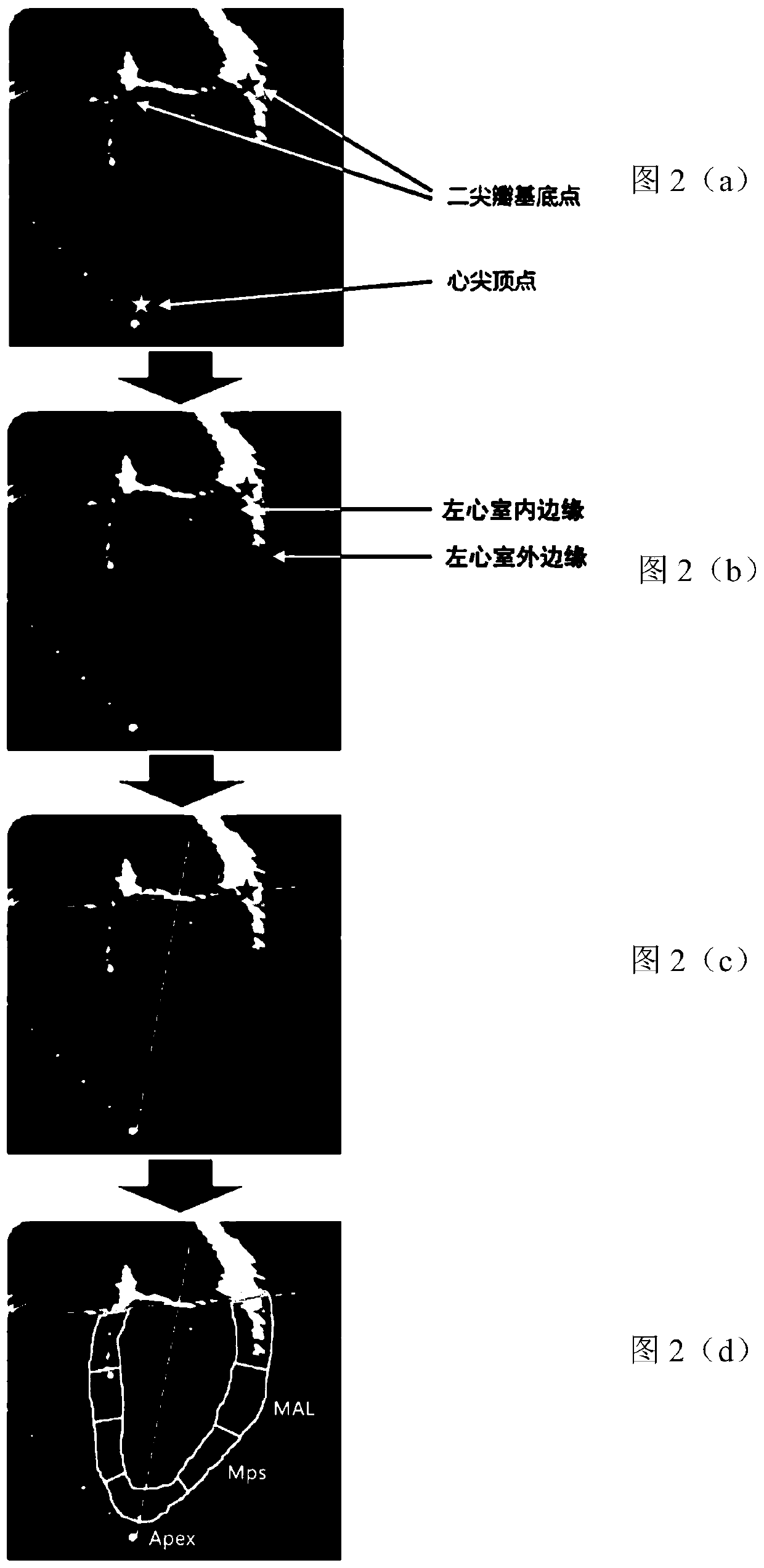
Cardiac medical image processing device, processing system and medium
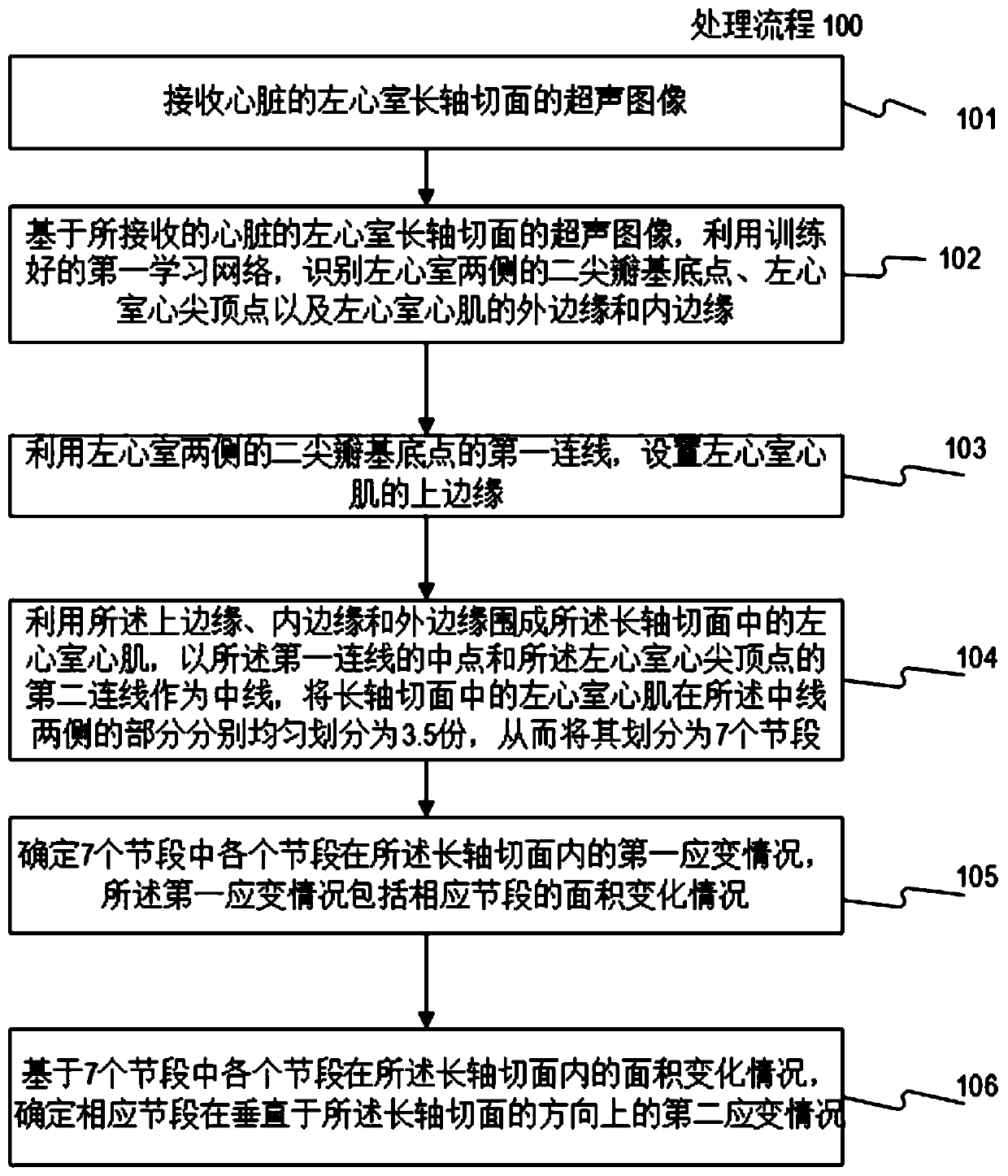
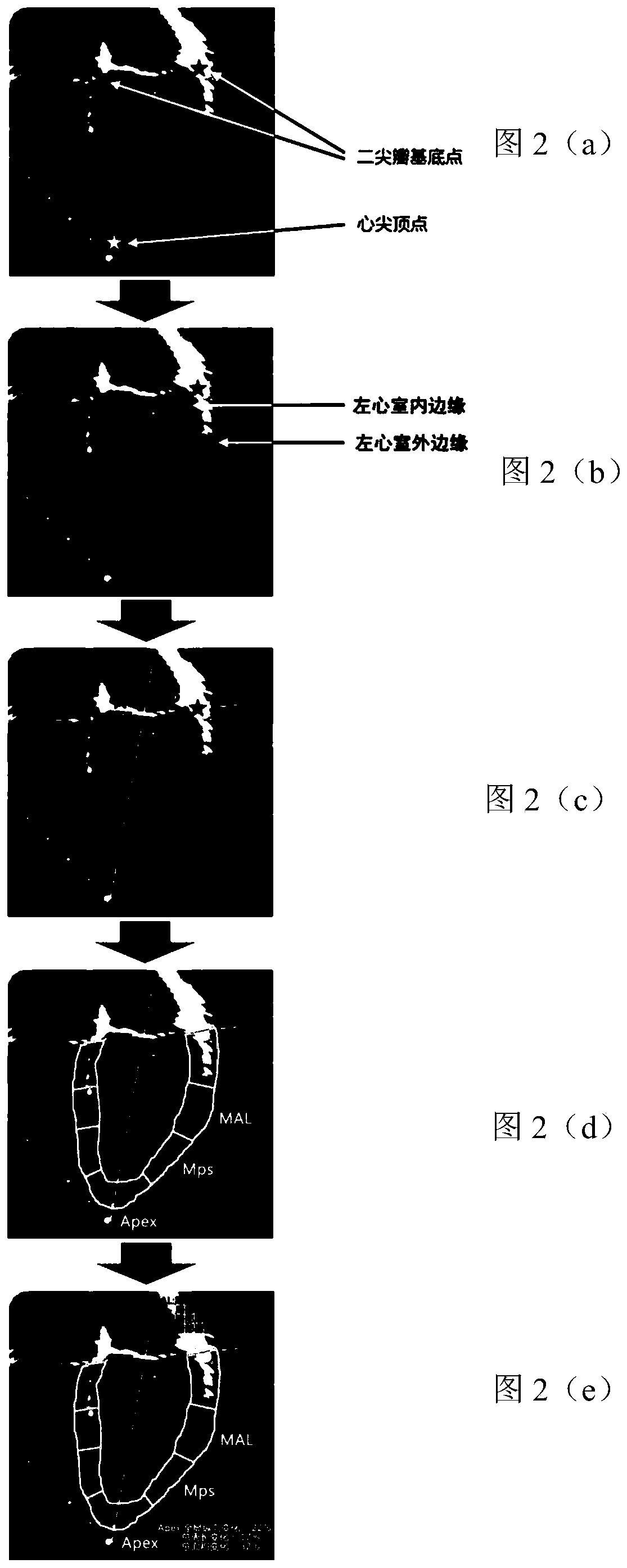
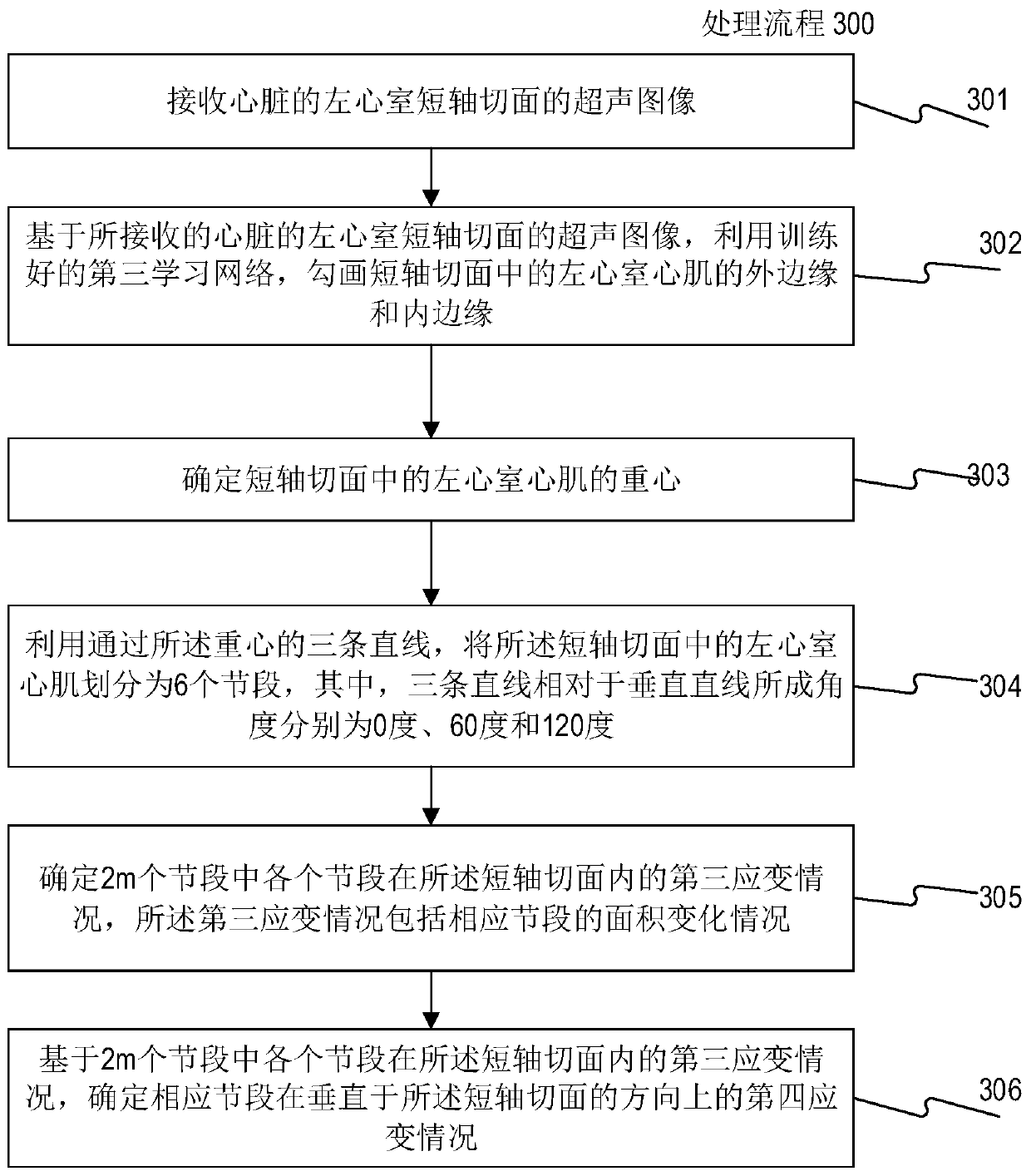
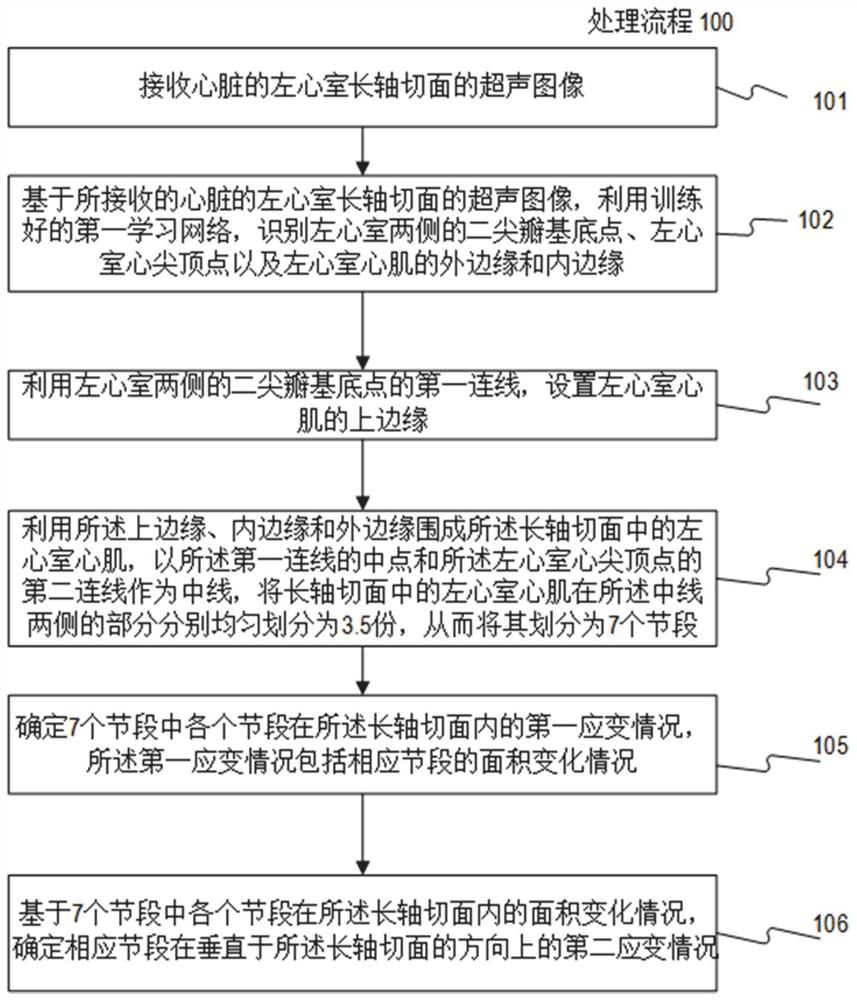
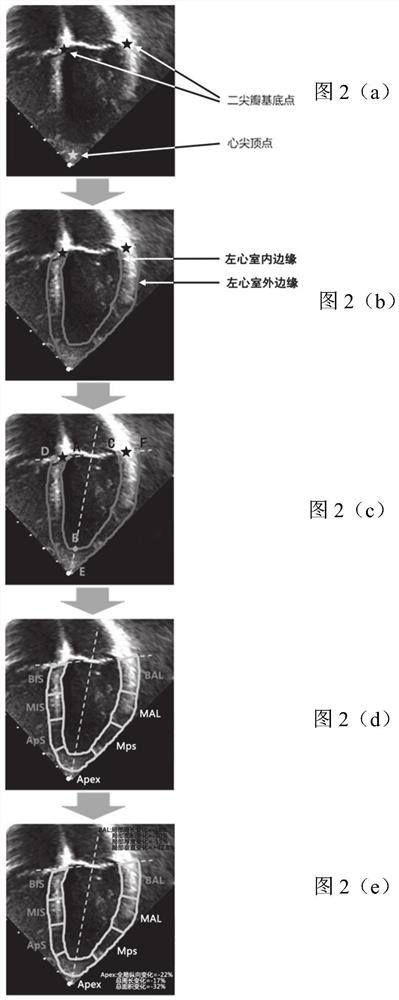
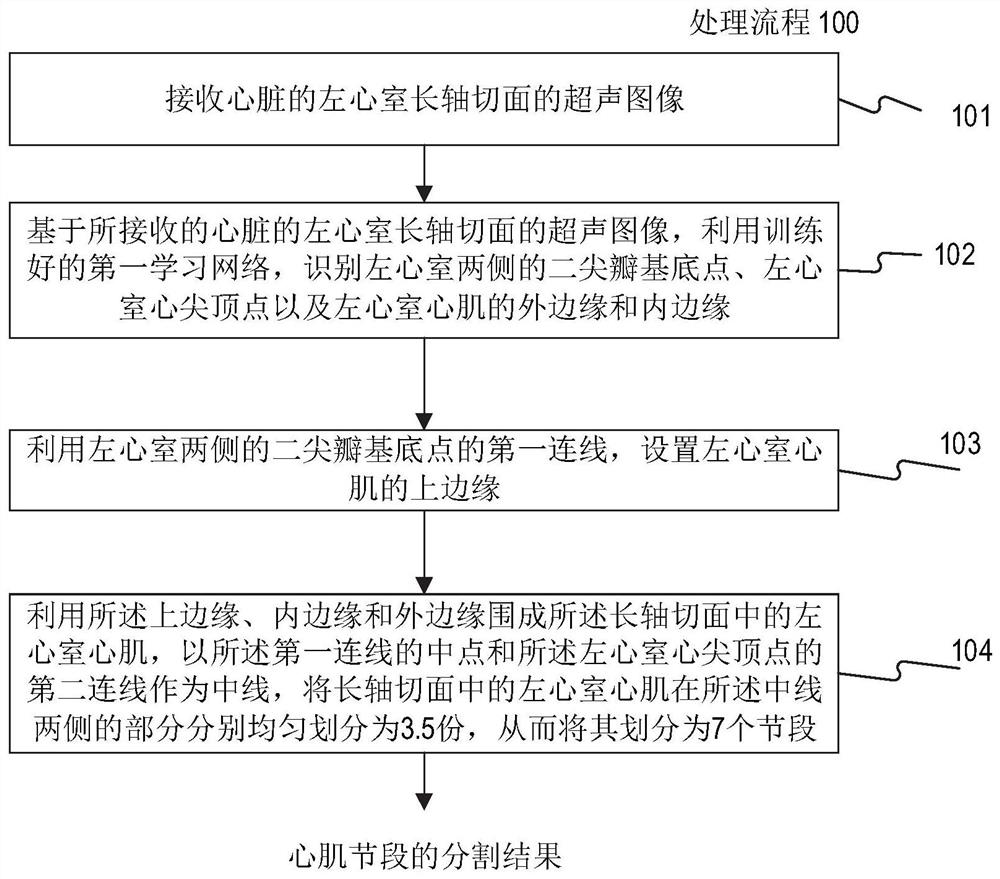
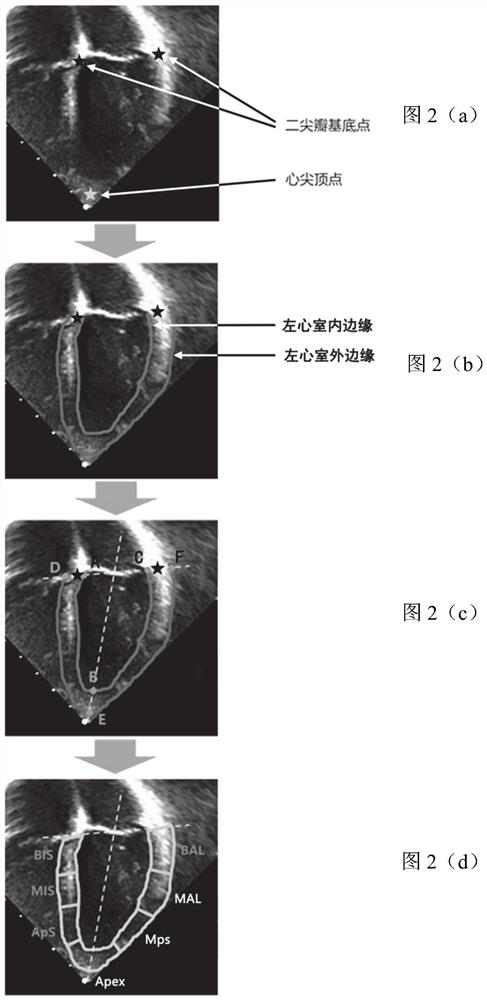
ActiveCN110335235AAccurate and rapid identificationDraw accurately and quicklyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementImaging processingLong axis
The invention relates to a cardiac medical image processing device, a processing system and a medium. The processing device comprises a processor, configured to identify a mitral valve basal point, acardiac apex vertex and outer and inner edges of a left ventricular myocardium by using a first learning network based on a heart image of a long-axis section; arrange an upper edge by utilizing a first connecting line of the mitral valve base point; define the left ventricular myocardium by the upper edge, the inner edge and the outer edge, the second connecting line of the midpoint of the firstconnecting line and the apex serves as the midline, evenly divide the left ventricular myocardium on the two sides, and achieve segment division; determine a first strain condition of each section inthe long-axis section, wherein the first strain condition comprises an area change condition of the corresponding section; and determining a second strain condition of the corresponding segment in thevertical direction based on the area change condition of each segment. All myocardial segments can be automatically, accurately and rapidly recognized, the global or local three-dimensional strain condition of the left ventricle can be determined, and myocardial strain and functional conditions can be conveniently and comprehensively evaluated.
Owner:SHANGHAI YIZHI HEALTHCARE TECH CO LTD
Method for Assessing The Functional Condition Of Cardiovascular System
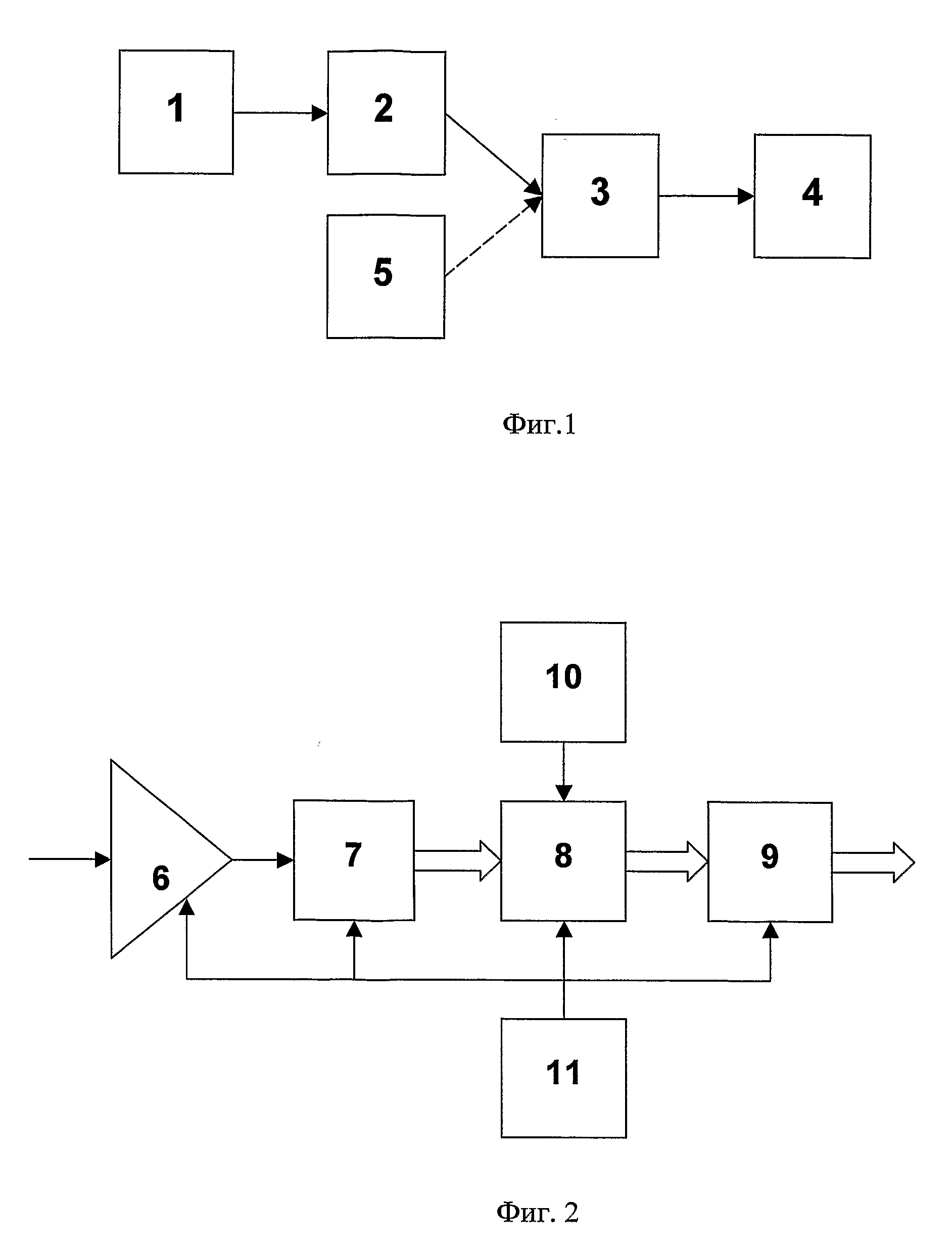
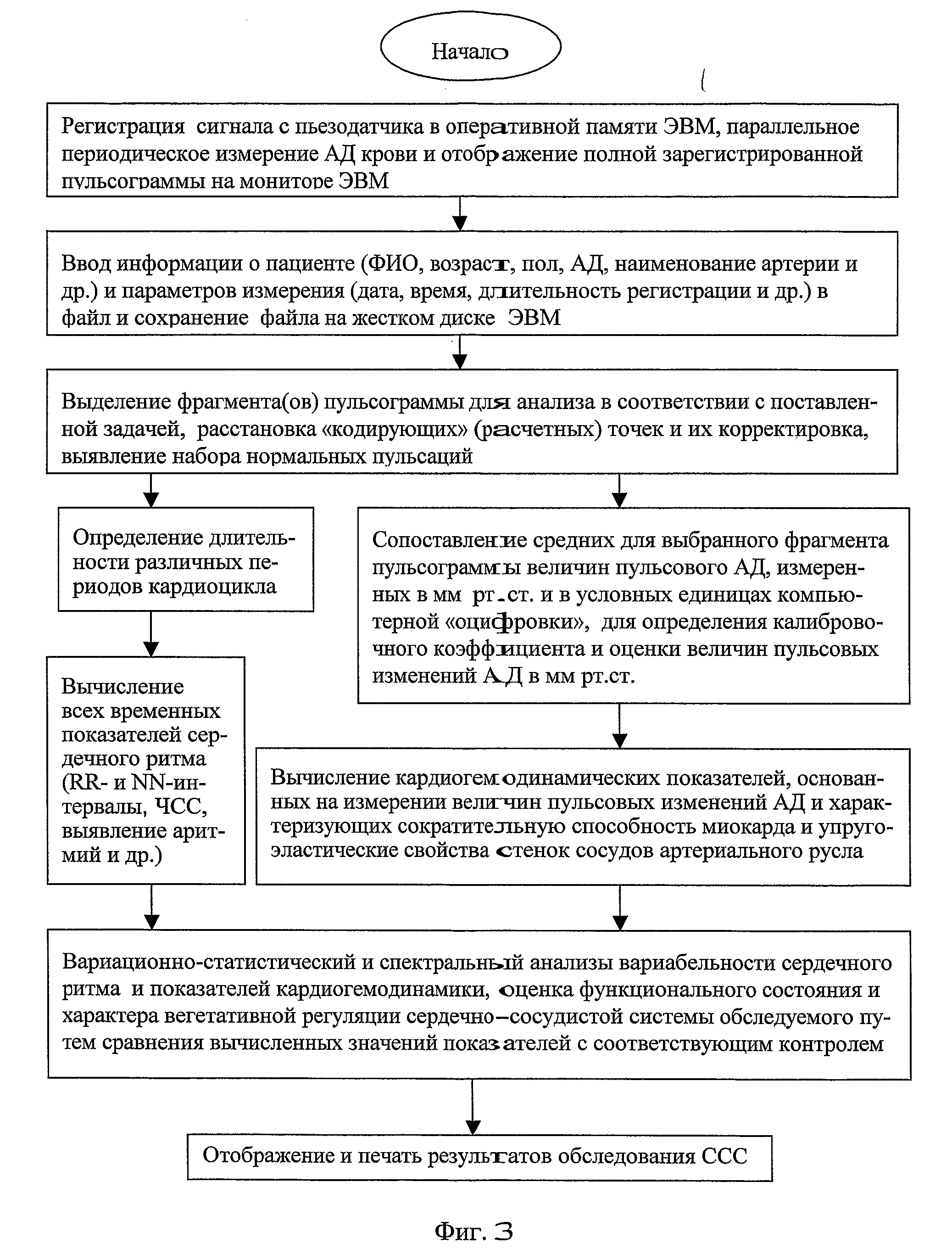
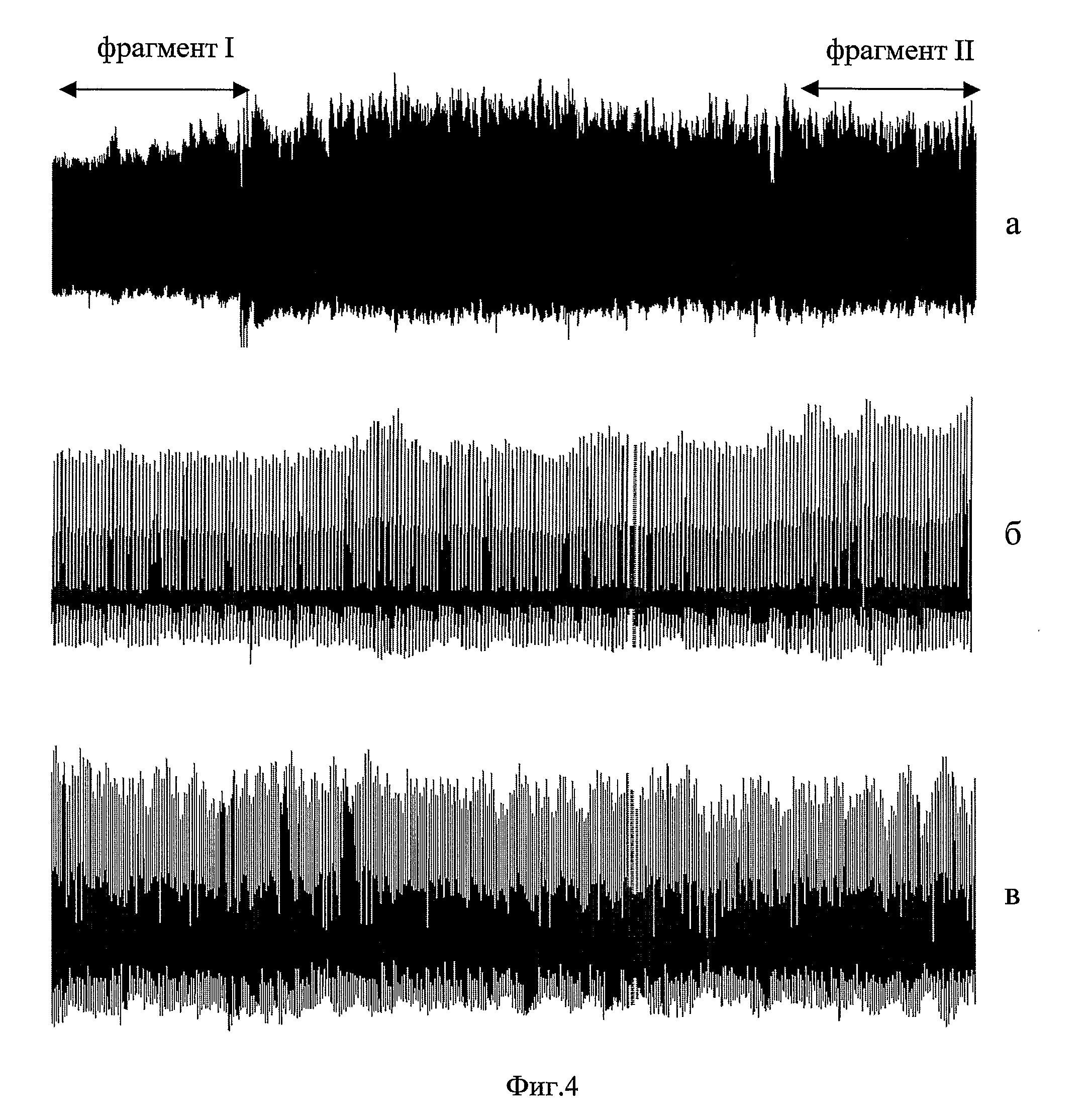
InactiveUS20080287811A1Easy to optimizeEasy to operateEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterNervous systemCardiac cycle
The invention relates to medicine, namely: to cardiology, and may be used for assessment of functional condition of the human cardiovascular system (CVS) and the character of its control by the autonomic nervous system and other regulatory systems of the homeostasis. A method of non-invasive examination of the human CVS was developed, the method enabling to continuously, during a necessary period of time and quite simply with the aid of a computer and a piezoceramic tranducer (FIG. 3), record differential sphygmograms (FIG. 4) and by these sphygmograms using the method of determining the “coding” points to perform express-analysis simultaneously of two main pulse characteristics: a) rhythmicity and b) pulse oscillation of the arterial pressure (AP). The automatic disposition of the “coding” points in the averaged graph of the cardiocycle and their additional visual correction (FIG. 5) guarantee precision of determining the amplitude-temporal parameters at each recognised normal pulsation of a selected pulsogram fragment. By this fragment, the cardiac rhythm and all the amplitude-temporal cardiohemodynamic parameters will be measured and analysed, the parameters characterising the left ventricle myocardium contractile capacity as well as the resilient-elastic properties of the arterial bed vessel walls. For this purpose, the conventional units of the computer “digitizing” will be calibrated and transformed into accepted units of the blood AP measurement (mm Hg) and then, by means of integrating by respective areas of the cardiocycle graphs, the values of the blood AP pulse increment will be determined for different stages of the cardiac cycle. The continuous monitoring of the pulsogram parameter changes provides fulfillment of spectral analysis of the cardiac rhythm variability as well as of the selected cardiohemodynamic parameters. By results of the statistical and spectral analyses of the measured parameters' variability, the functional condition and the character of the subject's CVS vegetative regulation will be assessed by comparing the obtained values with the average statistical numerical values of these same parameters established for the CVS of groups of people who were selected as control subjects. The results may be used for resolving the problems of differential diagnosis of the cardiovascular diseases under clinical conditions, for individual examination of patients as well as for performing an operative medical checkup of health condition in various groups of population.
Owner:NESTEROV VLADIMIR PETROVICH +2
Method for segmenting blood pool in diastasis image in heart cardiac function magnetic resonance image
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Switch polarity pacing to improve cardiac resynchronization therapy
InactiveUS8380307B2Maximum functionSize is still affectedElectrotherapyLeft ventricular sizeCardiac muscle
The invention is directed to a heart stimulator for left-ventricular pacing comprising a left ventricular stimulation pulse generator connected or connectable to a single electrode lead for left ventricular stimulation having one or more electrodes for delivery of stimulation pulses to left ventricular myocardial heart tissue, said stimulation pulse generator being adapted to generate and deliver stimulation pulses of switchable polarity. The heart stimulator further comprises a control unit connected to the stimulation pulse generator for controlling the stimulation pulse generator and to trigger generation and delivery of stimulation pulses having a polarity controlled by said control unit, wherein the control unit is adapted to control said left ventricular stimulation pulse generator so as to deliver at least a pair of suprathreshold stimulation pulses of opposite polarity.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Cardiac medical image processing method, processing device, processing system and medium
ActiveCN110335236AAutomatic IdentificationAccurate and rapid identificationImage enhancementImage analysisData setLeft ventricular size
The invention relates to a cardiac medical image processing method, a processing device, a processing system and a medium. The method comprises the following steps: receiving a cardiac medical image of a left ventricle long-axis section; utilizing the trained first learning network to identify mitral valve base points and apex apexes on two sides of the left ventricle and the outer edge and the inner edge of the left ventricle myocardium; arranging an upper edge by utilizing a first connecting line of a mitral valve base point; defining the left ventricular myocardium by the upper edge, the inner edge and the outer edge, using the midpoint of the first connecting line and the second connecting line of the apex of the left ventricular as the midline, evenly dividing the parts, on the two sides of the midline, of the left ventricular myocardium into n parts, and therefore the left ventricular myocardium is divided into 2n sections. According to the cardiac medical image processing method, the processing device, the processing system and the medium, each cardiac muscle area can be automatically, accurately and quickly drawn and identified, the workload of doctors is greatly reduced, and automatic identification of the cardiac medical image processing device can continuously benefit from a training data set marking the cardiac muscle areas through training.
Owner:SHANGHAI YIZHI HEALTHCARE TECH CO LTD
Medicine for resisting pressure overload myocardial hypertrophy and ventricular remodeling and application
InactiveCN112773784AInhibit hypertrophyImproved cardiac diastolic dysfunctionCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsStainingBlood flow
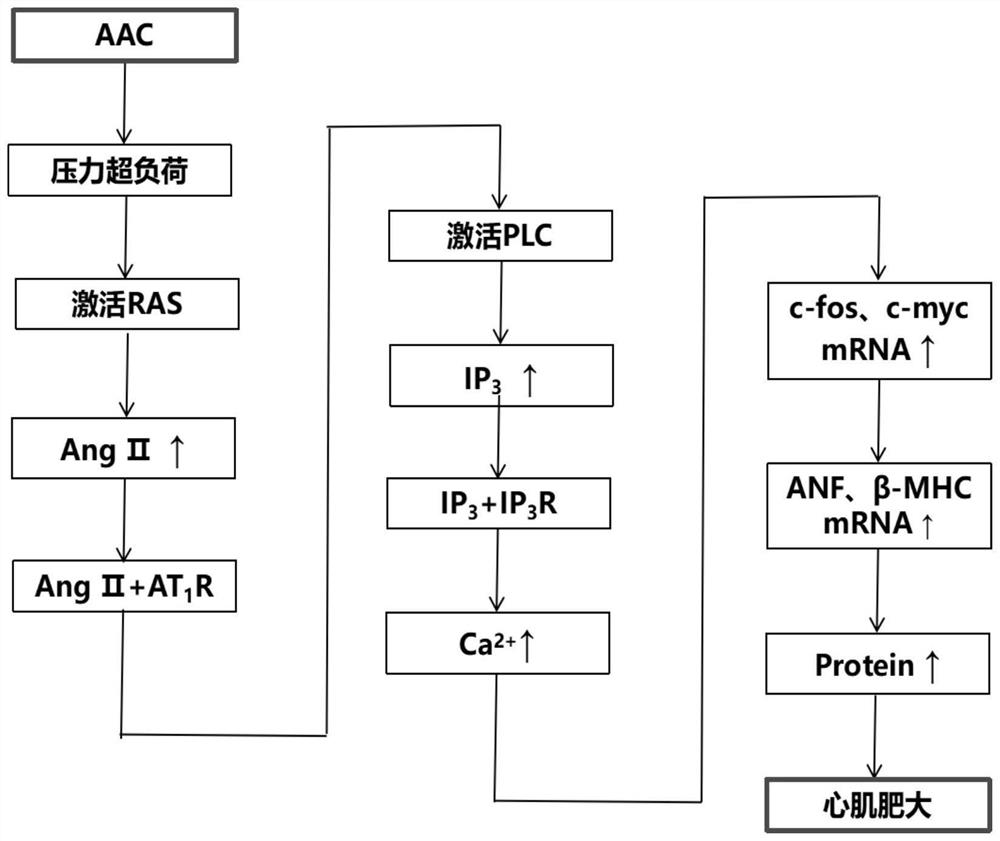
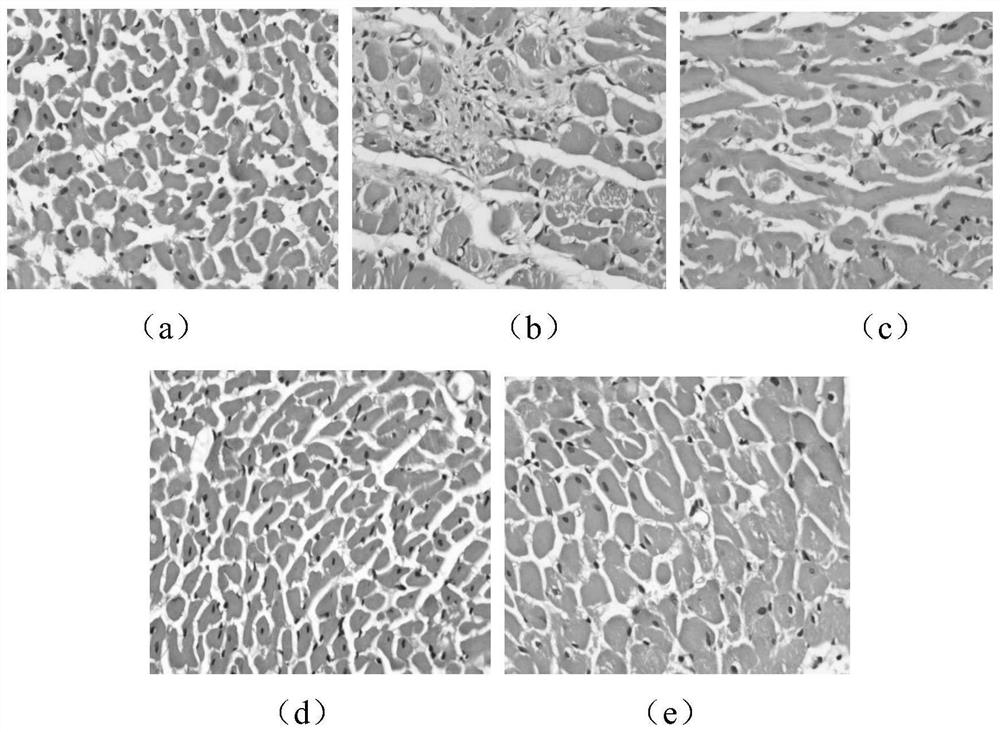
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological pharmacy, and discloses a medicine for resisting pressure overload myocardial hypertrophy and ventricular remodeling and application. The application comprises the following steps of: establishing a pressure overload rat myocardial hypertrophy and ventricular remodeling animal model by adopting abdominal aorta constriction; constricting the abdominal aorta for 28d, and sequentially detecting the change of a hemodynamic index and the diameter of a myocardial cell; and transecting the left ventricular myocardial tissue of a rat, observing the form of the myocardial cell under an optical microscope after conventional HE staining, and observing the change effect of leonurine on the pathological form of the left ventricular myocardial tissue of the rat. The invention proves that high and low dosage groups of leonurine have a certain improvement effect on cardiac diastolic and systolic dysfunction of a myocardial hypertrophy rat induced after abdominal aorta constriction; the high and low dosage groups of leonurine can reduce the left ventricular hypertrophy index of the rat after AAC operation; and the high and low dosage groups of leonurine and a positive group can inhibit myocardial cell hypertrophy of the rat after AAC operation and inhibit ventricular remodeling.
Owner:贵州中医药大学
Survival myocardial evaluation method
ActiveCN111311566AImprove consistencyImprove diagnostic accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisLeft ventricular sizeBlood flow
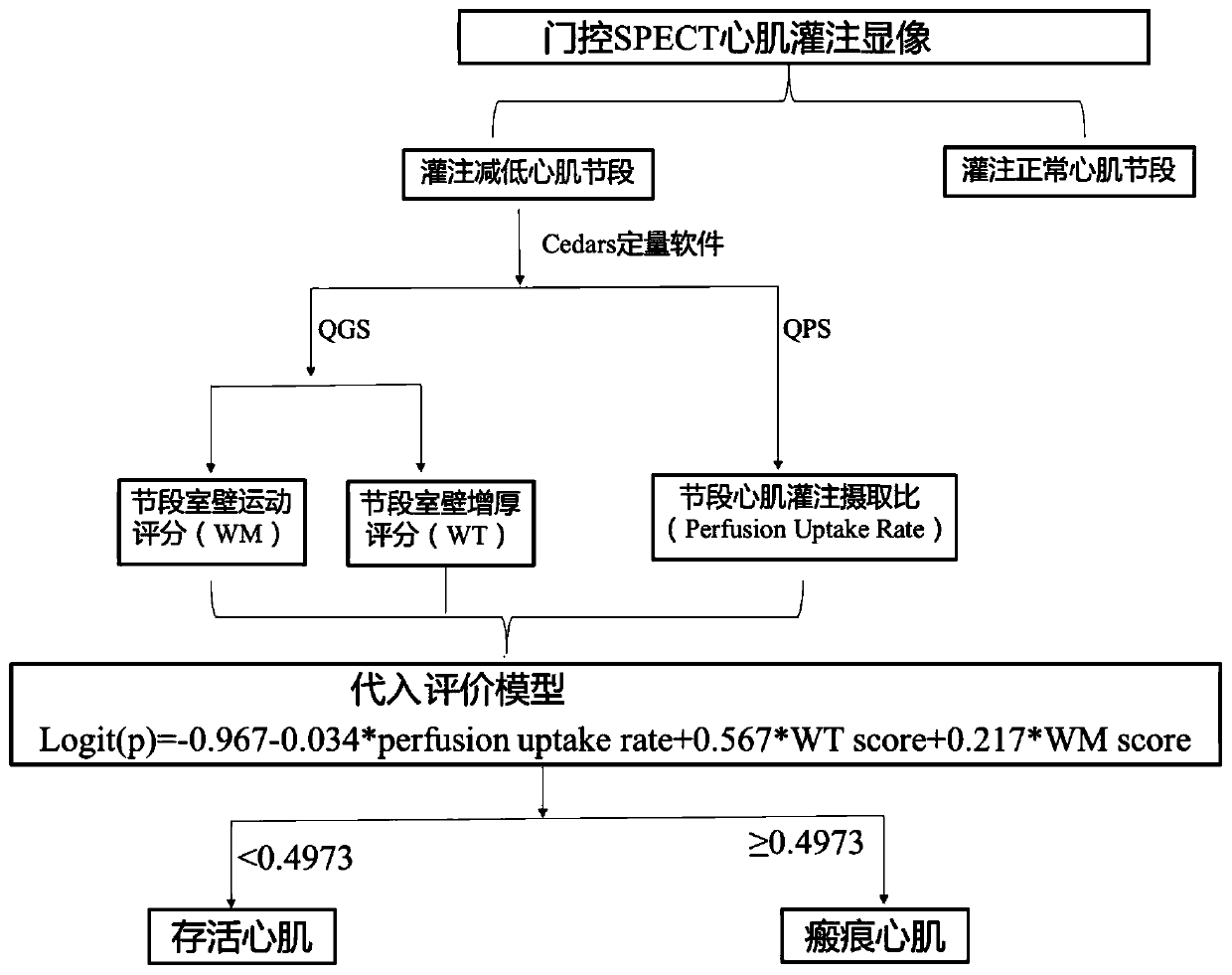
The invention relates to a survival myocardial evaluation method, which is used for evaluating based on gating SPECT myocardial perfusion development myocardial functions in combination with myocardial perfusion, and comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring an examination image by adopting gating SPECT myocardial perfusion development, and reconstructing to obtain a left ventricular minoraxis image, a left ventricular horizontal major axis image and a left ventricular vertical major axis image; then carrying out semi-quantitative scoring on blood perfusion uptake of the left ventricular myocardial segment, and judging a perfusion reduction segment; quantitatively evaluating to obtain the blood perfusion uptake ratio of each segment of the left ventricular myocardium; analyzing the reconstructed gated SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging, respectively obtaining a ventricular wall movement score and a thickening rate score of each myocardial segment, and finally substituting theparameters into an evaluation model for calculation. Evaluation is carried out based on gated SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging myocardial functions in combination with myocardial perfusion, and themethod is particularly suitable for evaluating survival myocardium of coronary heart disease heart failure patients before blood supply reconstruction and guiding clinical treatment decisions.
Owner:THE FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF CHANGZHOU
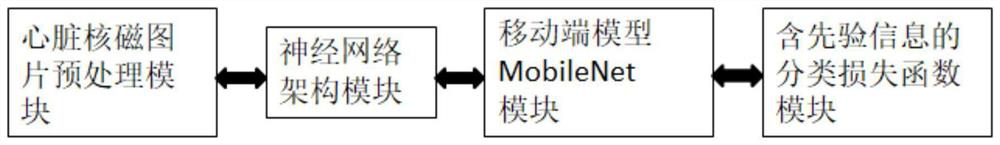
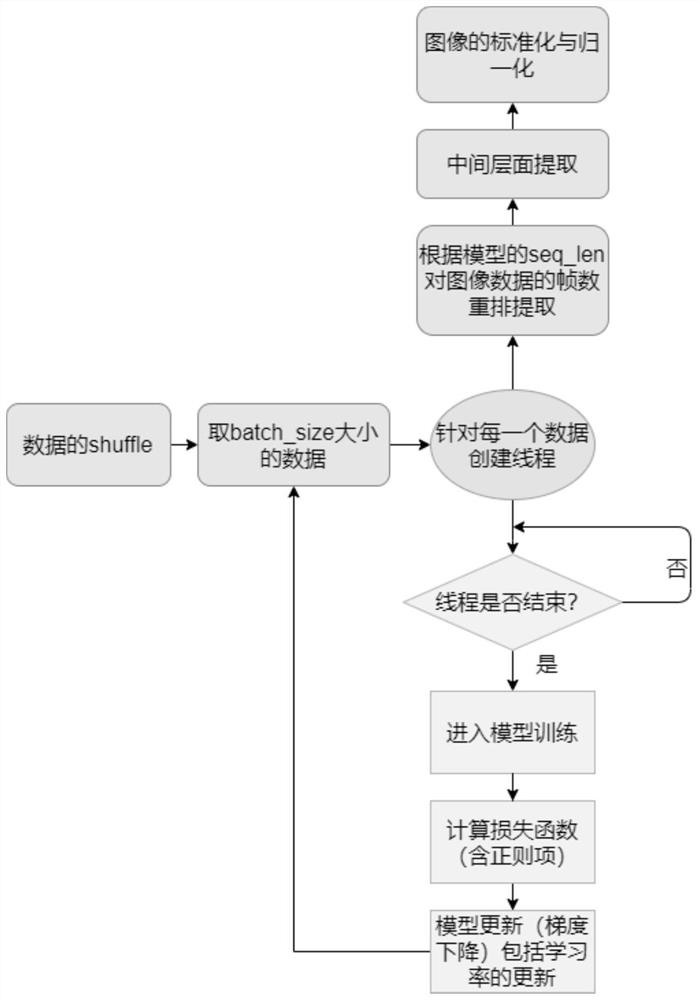
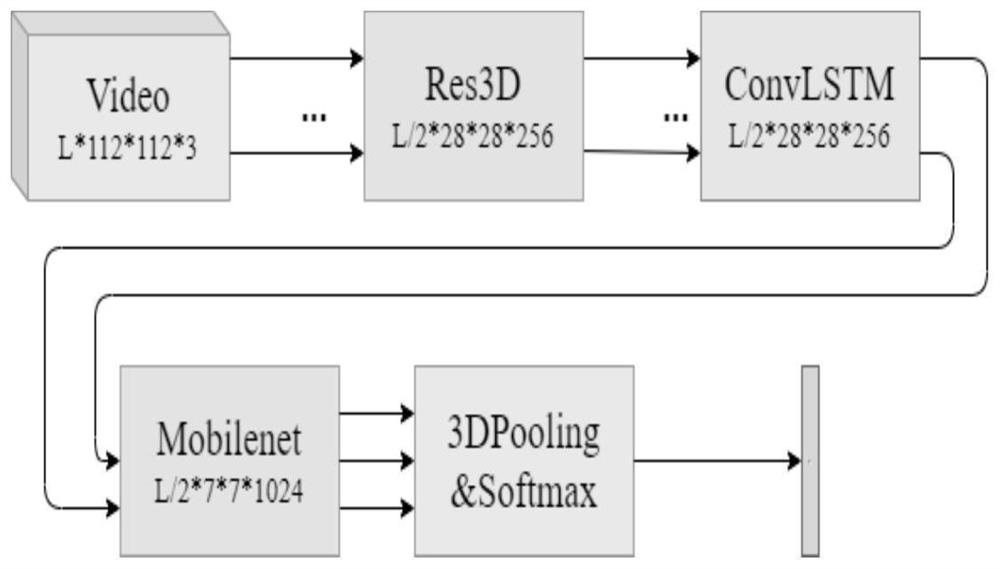
Cardiomyopathy recognition system based on convolution and long short-term memory neural network
InactiveCN112863650AImprove diagnostic efficiencyReduce mistakesMedical automated diagnosisCharacter and pattern recognitionAnatomical structuresData set
The invention relates to a cardiomyopathy recognition system based on a convolution and long short-term memory neural network, and belongs to the technical field of medical image analysis. The system comprises the following modules: 1, a heart nuclear magnetic picture preprocessing module; 2, a neural network architecture module; 3, a mobile terminal model MobileNet module; and 4, a classification loss function module containing prior information. According to the system, variants of a deep convolutional neural network and a convolutional long-short-term memory neural network are mainly combined, anatomical structures such as left ventricle myocardial internal and external membranes do not need to be manually segmented, classification training is performed by giving enough data sets based on certain priori knowledge, and finally, fitting determination of model parameters is realized; therefore, the heart nuclear magnetic data can be improved to complete the diagnosis accuracy of the fertile heart disease, the dilated heart disease and the normal cardiac muscle, and the processing and diagnosis time of the clinical heart magnetic resonance image can be shortened through the breakthrough of the technology.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
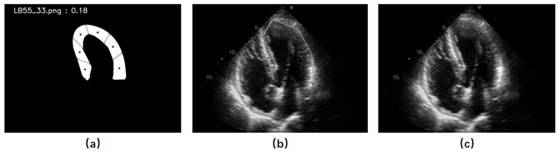
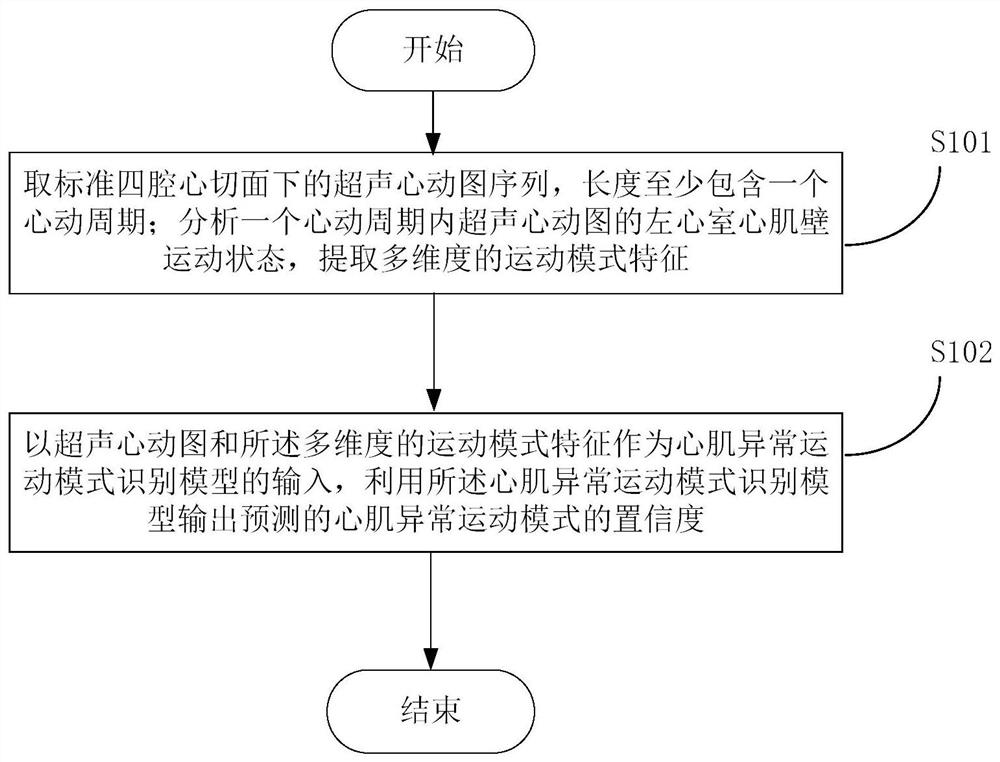
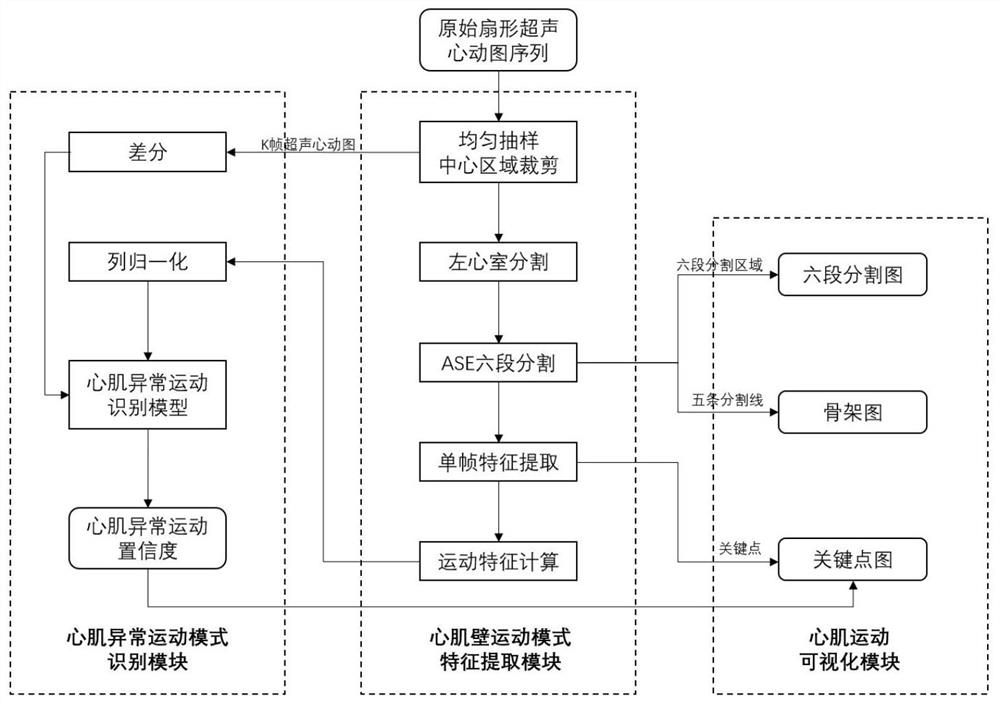
Ultrasonocardiogram myocardial abnormal motion mode analysis method and system, and storage medium
PendingCN112258476AThe recognition result is accurateFeatures fully reflectImage enhancementImage analysisLeft cardiac chamberImaging processing
The invention provides an ultrasonic cardiogram myocardial abnormal motion mode analysis method and system and a storage medium and relates to the technical field of medical image processing. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring an echocardiogram sequence under a standard four-cavity cardiac tangent plane, wherein the length at least comprises one cardiac cycle; analyzing the leftventricular myocardial wall motion state of the echocardiogram in one cardiac cycle, and extracting multi-dimensional motion mode characteristics; and taking the echocardiogram sequence and the motion mode characteristics as the input of a myocardial abnormal motion mode identification model, and outputting the predicted confidence coefficient of the myocardial abnormal motion mode by using the myocardial abnormal motion mode identification model. According to the method, by extracting the motion mode characteristics in the echocardiogram sequence in one cardiac cycle, the time sequence information and the local motion information in the echocardiogram are fully mined, so accurate myocardial abnormal motion mode analysis can be automatically carried out according to the characteristics, and the prediction result is returned.
Owner:东软教育科技集团有限公司
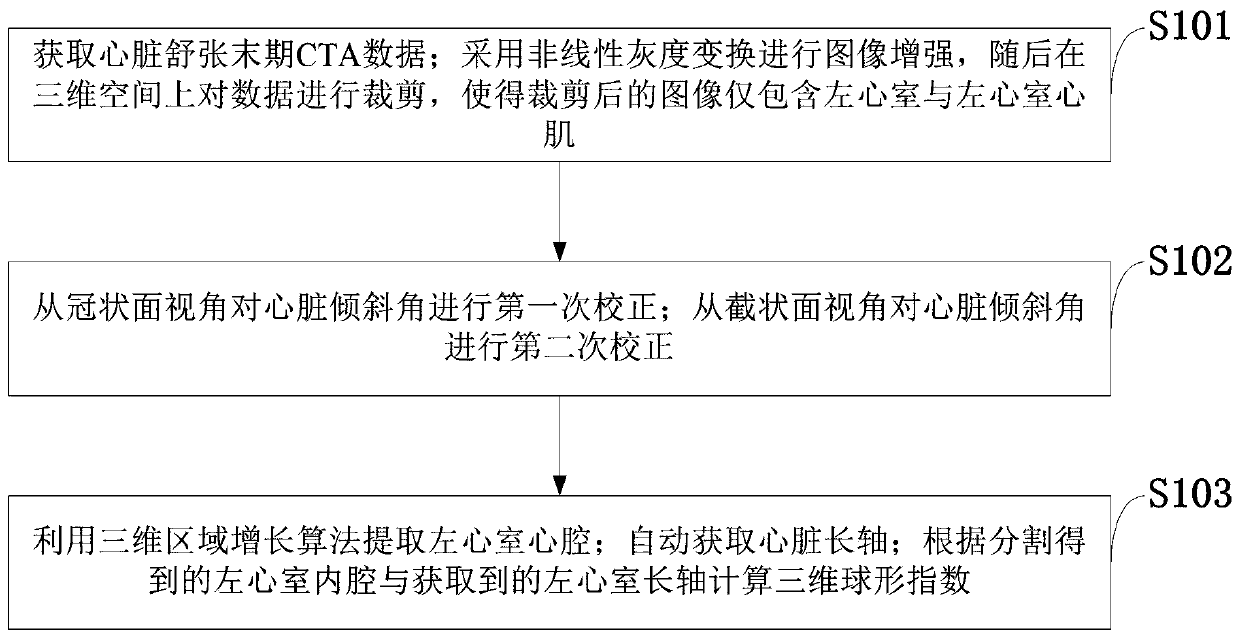
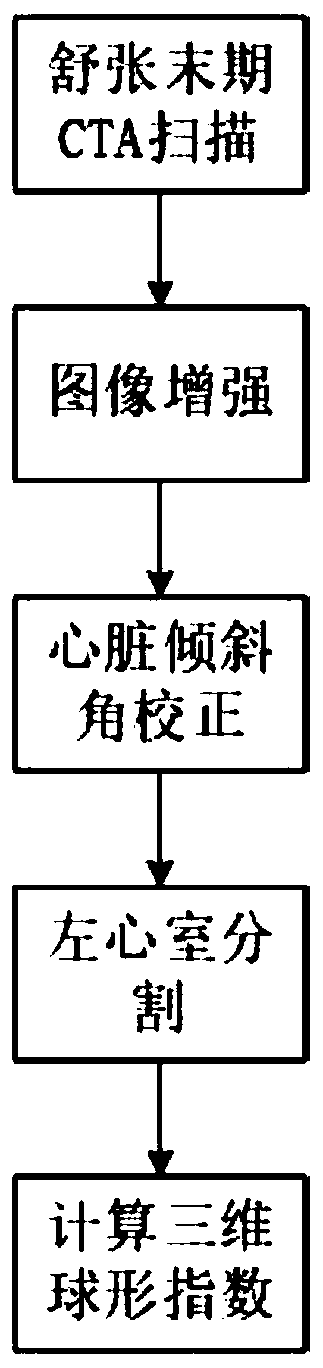
A three-dimensional spherical index determination method based on a CTA image
ActiveCN109785296AEasy to controlConvenient for clinical operationImage enhancementImage analysisCoronal planeShape change
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical image processing, and discloses a three-dimensional spherical index determination method based on a CTA image. The method includes: Obtaining CTA data at the final diastole stage; Carrying out image enhancement by adopting nonlinear gray scale transformation, and then clipping data in a three-dimensional space, so that the clipped image onlycomprises the left ventricle and the left ventricle myocardium; Correcting the heart inclination angle for the first time from the coronal plane view angle; Correcting the heart inclination angle forthe second time from the perspective of the section surface; Extracting a left ventricle heart cavity by using a three-dimensional region growing algorithm; Automatically obtaining a heart long axis;And calculating a three-dimensional spherical index according to the left ventricle inner cavity obtained through segmentation and the obtained left ventricle long axis. According to the method, an automatic measurement method is provided for evaluation of centrifugal reconstruction caused by overload or integral myocardial reconstruction caused by non-acute myocardial infarction, and an accurateand robust ventricular shape change degree quantification result is provided.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
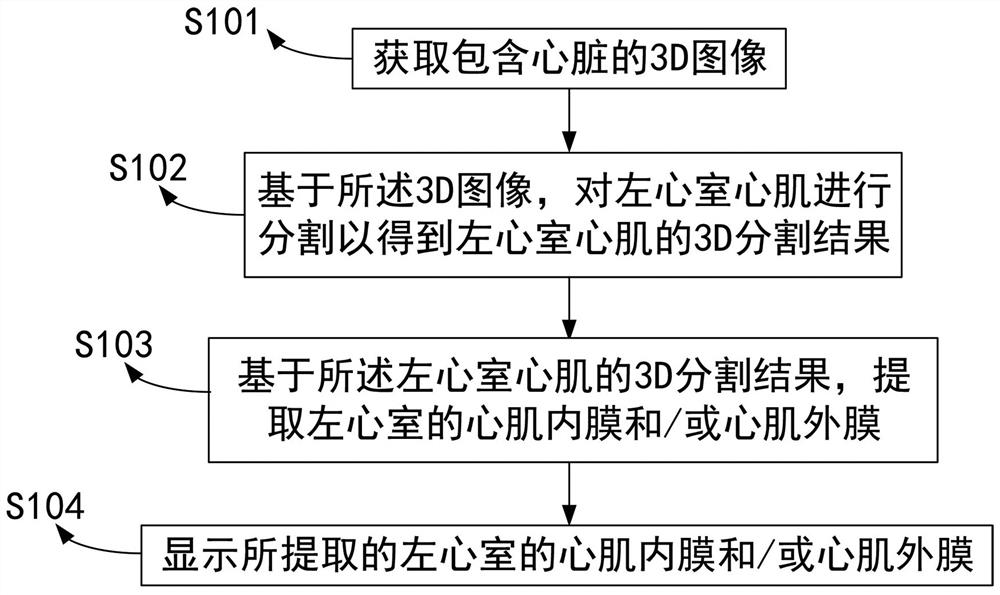
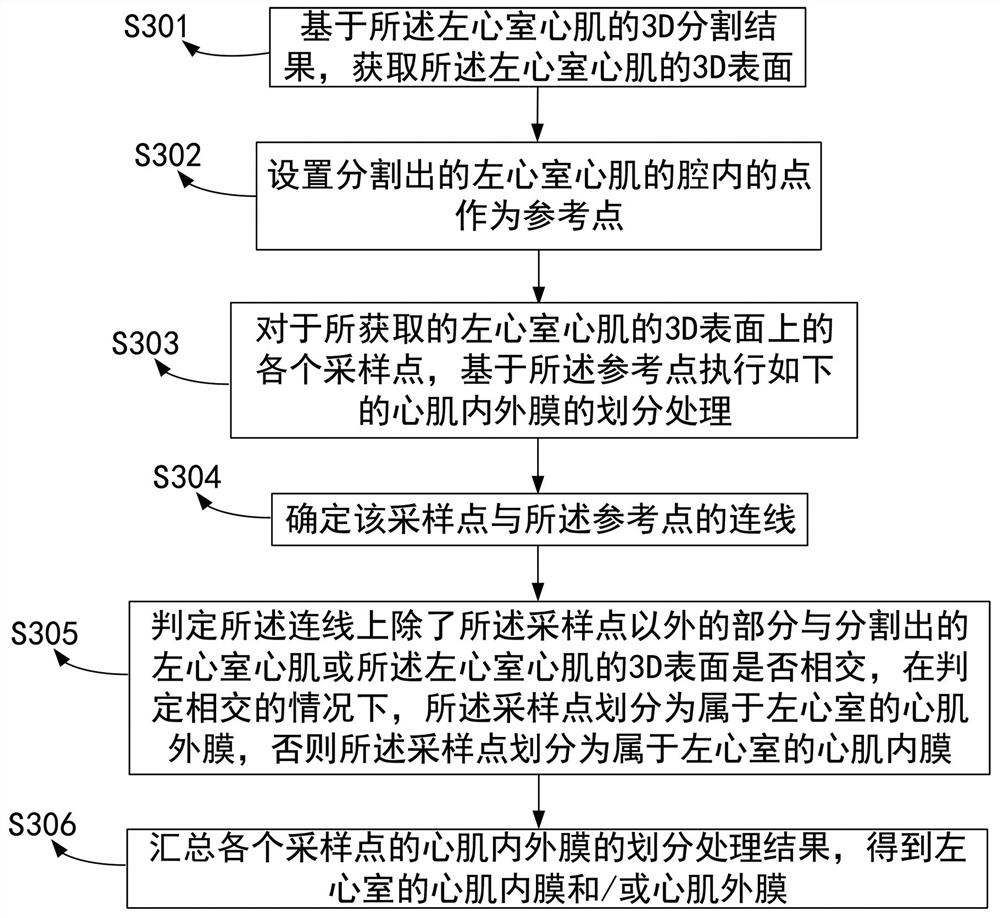
Segmentation method and device for inner myocardial membrane and/or outer myocardial membrane of left ventricle of heart
ActiveCN114419032AReduce adverse effectsReduce segmentation complexityImage enhancementImage analysisVentricular myocardium3d image
The invention provides a method for segmenting an inner myocardial membrane and / or an outer myocardial membrane of a left ventricle of a heart, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a 3D image containing the heart through a processor; based on the 3D image, segmenting the left ventricular myocardium to obtain a 3D segmentation result of the left ventricular myocardium; based on the 3D segmentation result of the left ventricular myocardium, extracting an inner myocardial membrane and / or an outer myocardial membrane of the left ventricle; and displaying the extracted inner and / or outer myocardial membranes of the left ventricle. The method can improve the segmentation efficiency, reduce the segmentation error and improve the segmentation accuracy.
Owner:SHENZHEN KEYA MEDICAL TECH CORP
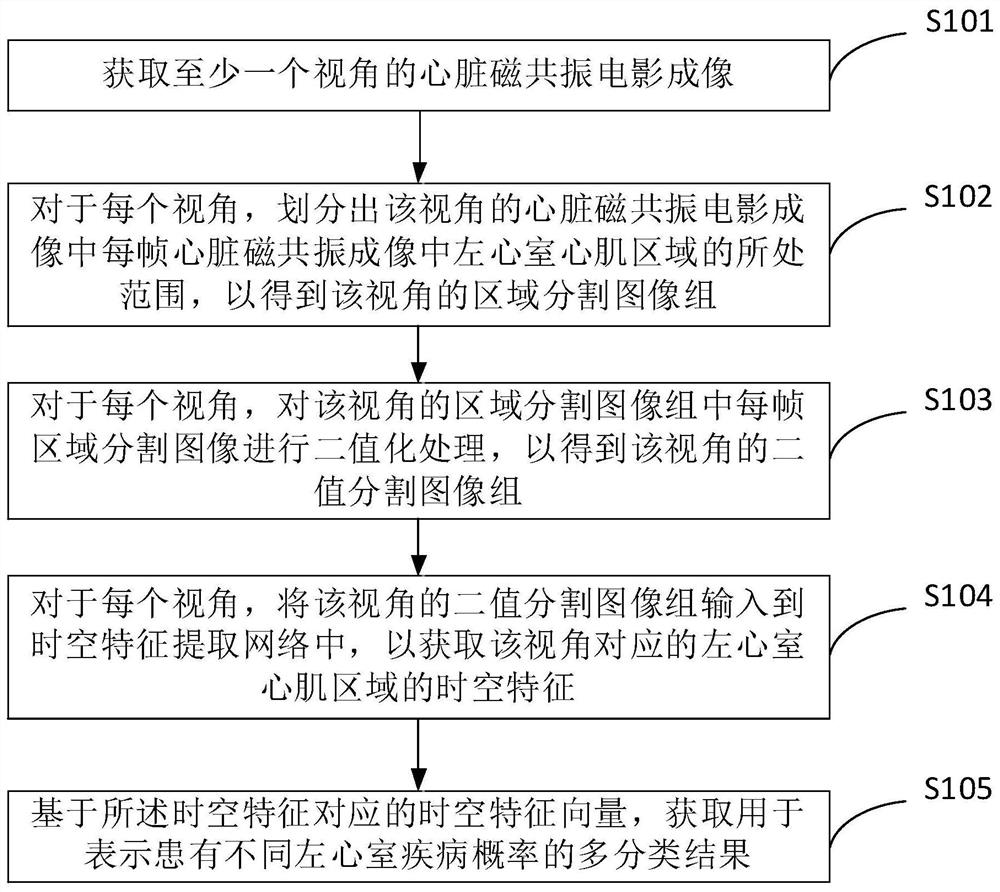
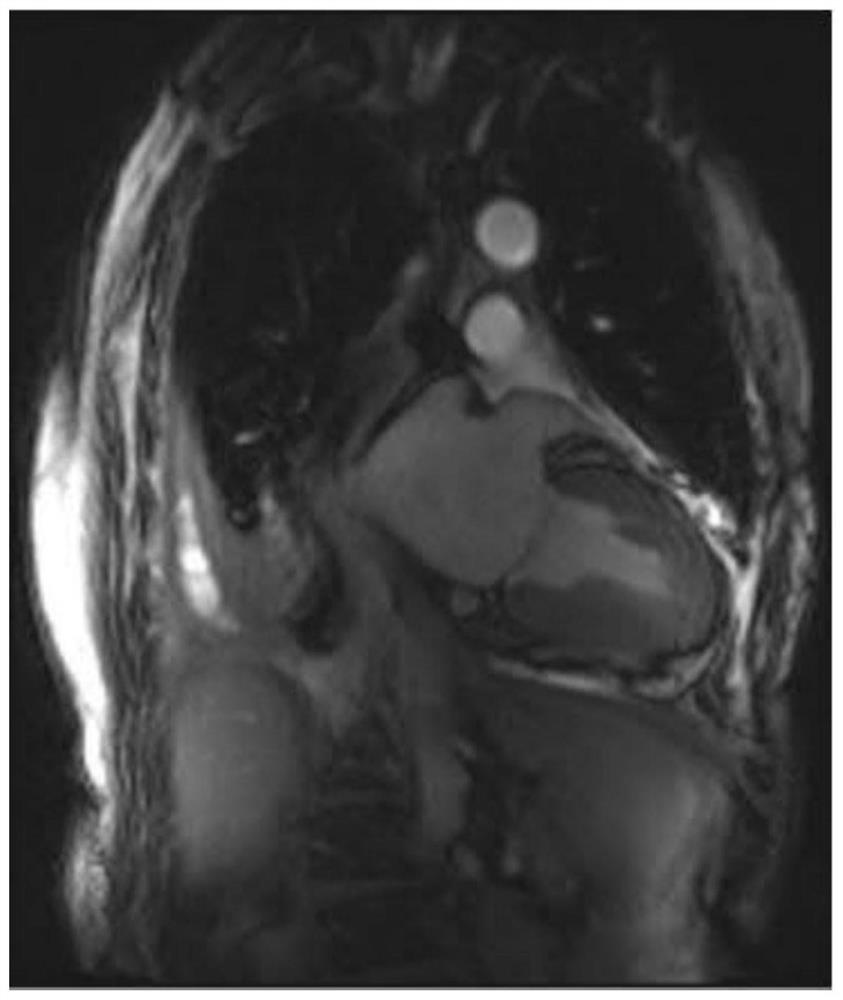
Image processing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN113744287AAvoid interferenceImprove judgment accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisLeft ventricular sizeBinary segmentation
The invention provides an image processing method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps: acquiring cardiac magnetic resonance film imaging of at least one view angle; for each view angle, marking off the range of a left ventricle myocardial region in each frame of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in the cardiac magnetic resonance film imaging of the view angle so as to obtain a region segmentation image group of the view angle; for each view angle, performing binarization processing on each frame of region segmentation image in the region segmentation image group of the view angle to obtain a binary segmentation image group of the view angle; for each view angle, inputting the binary segmentation image group of the view angle into a spatial-temporal feature extraction network to obtain spatial-temporal features of the left ventricular myocardial region corresponding to the view angle; and acquiring a multi-classification result based on the spatio-temporal feature vector corresponding to the spatio-temporal feature. According to the method and the device, the probability of suffering from different left ventricular diseases can be judged according to the motion morphological characteristics of the left ventricular myocardial region in the multi-frame image of at least one view angle.
Owner:INFERVISION MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
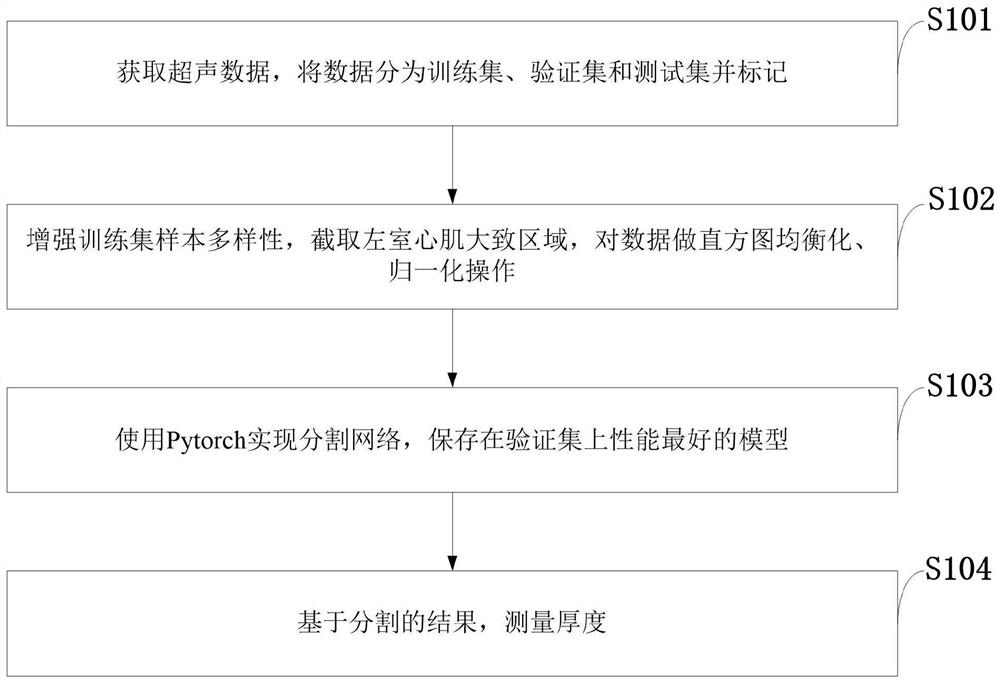
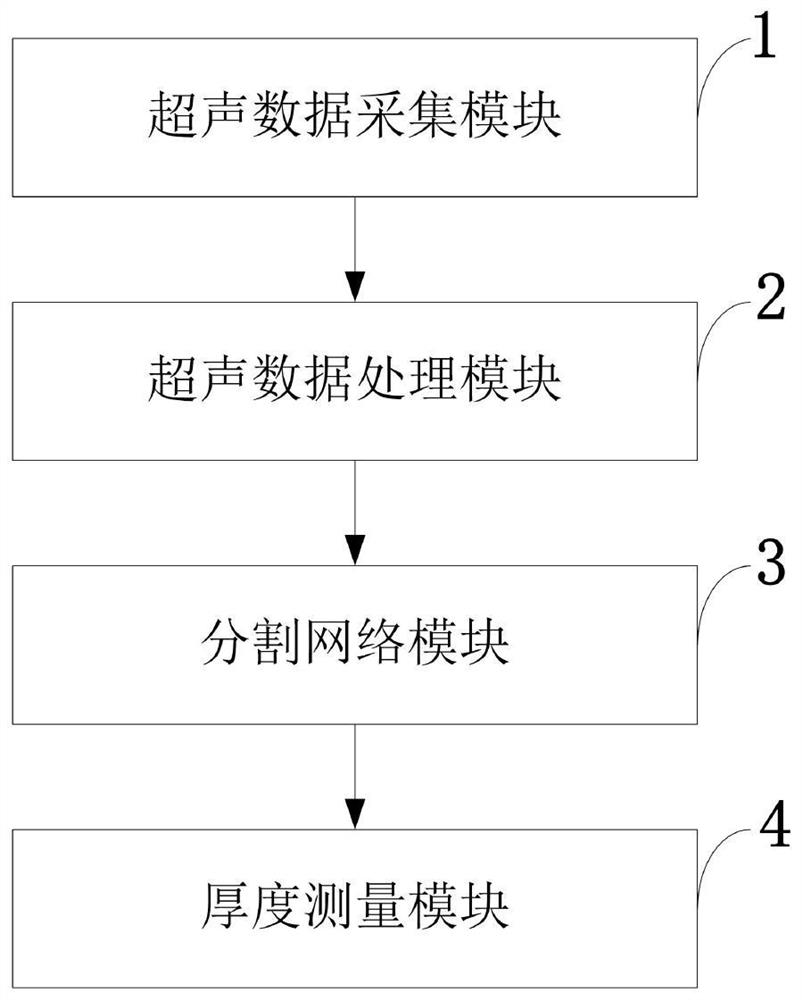
Ultrasonic image left ventricular myocardium segmentation method and system and application
ActiveCN111870279AReduce signal to noise ratioUndersegmentationImage enhancementImage analysisLeft ventricular sizeHistogram equalization
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing, and discloses an ultrasonic image left ventricular myocardium segmentation method and system and an application. The method comprisesthe steps of obtaining ultrasonic data, dividing the data into a training set, a verification set and a test set, and performing marking; enhancing the diversity of training set samples, interceptingan approximate left ventricular myocardium region, and performing histogram equalization and normalization operation on the data; using Pytorch to realize network segmentation, and storing a model having the best performance on the verification set; and measuring the thickness based on a segmentation result. According to the ultrasonic image left ventricular myocardium segmentation method based ona convolutional neural network, the left ventricular myocardium at the end of diastole can be automatically segmented, shape information of the left ventricular myocardium is added into the network to assist network learning, proposed mixed loss functions are optimized from three angles, and boundary information is further enhanced during learning; and the thickness can be automatically measuredbased on the segmentation result, and no post-processing is needed in the whole process.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
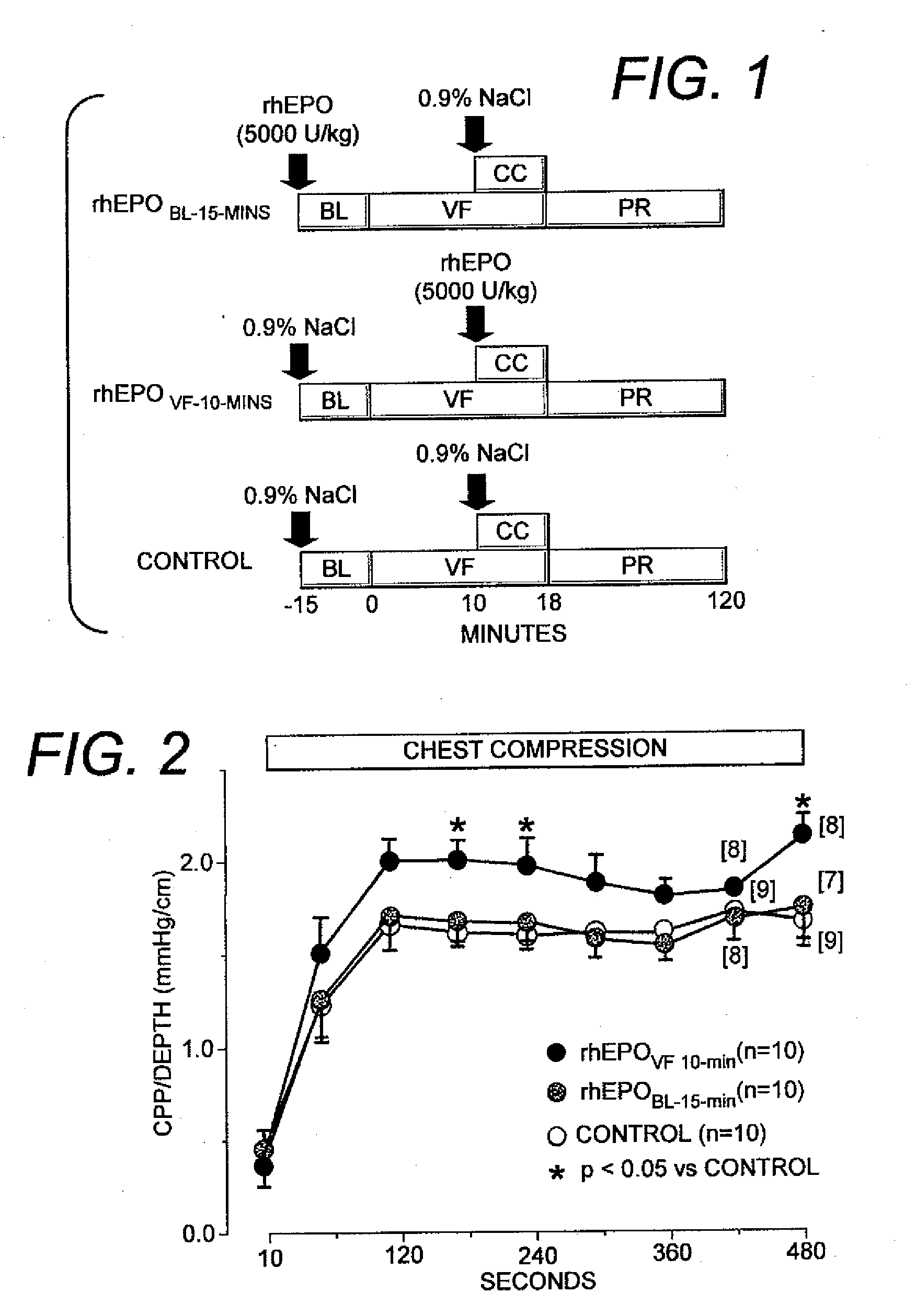
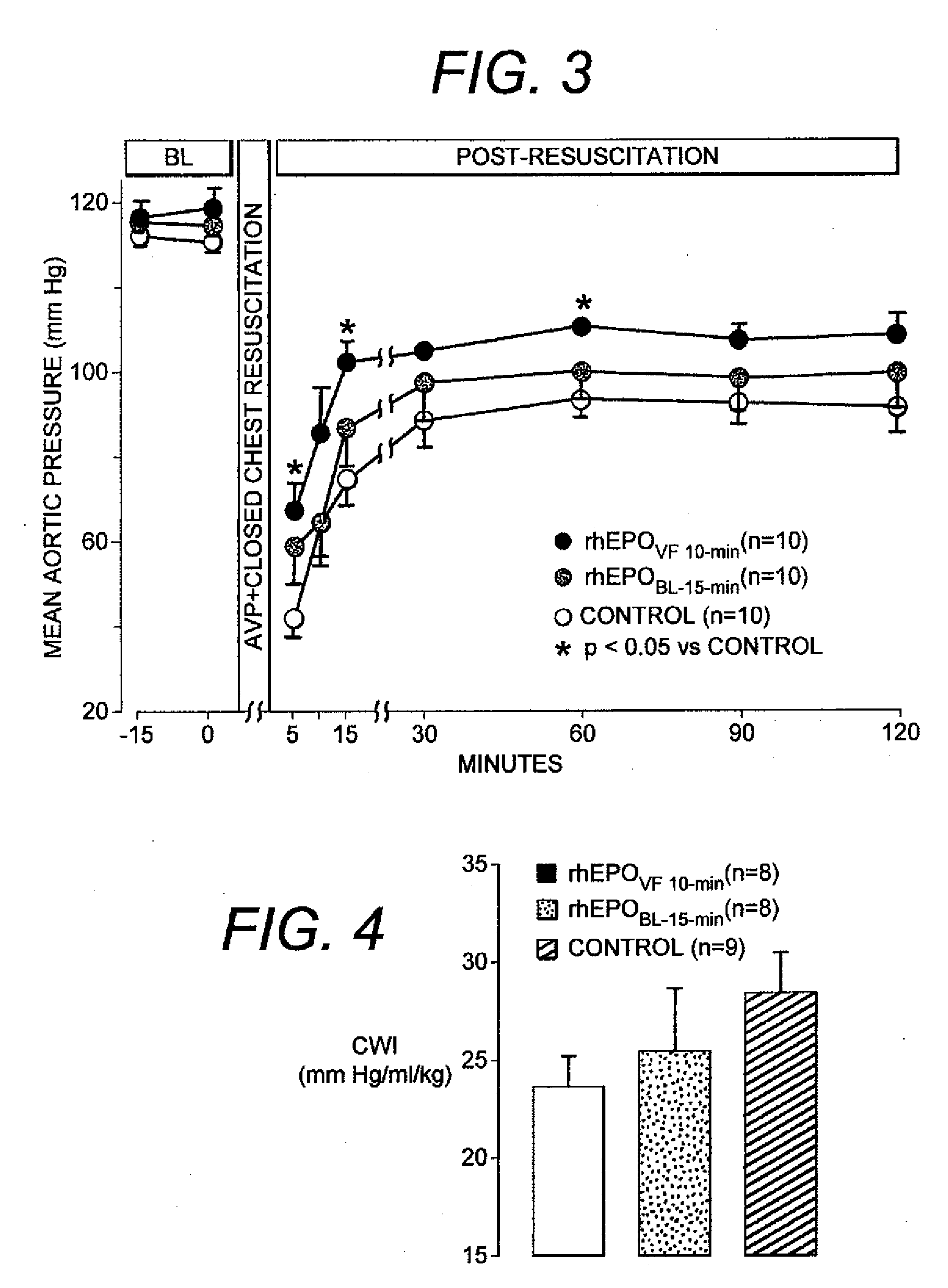
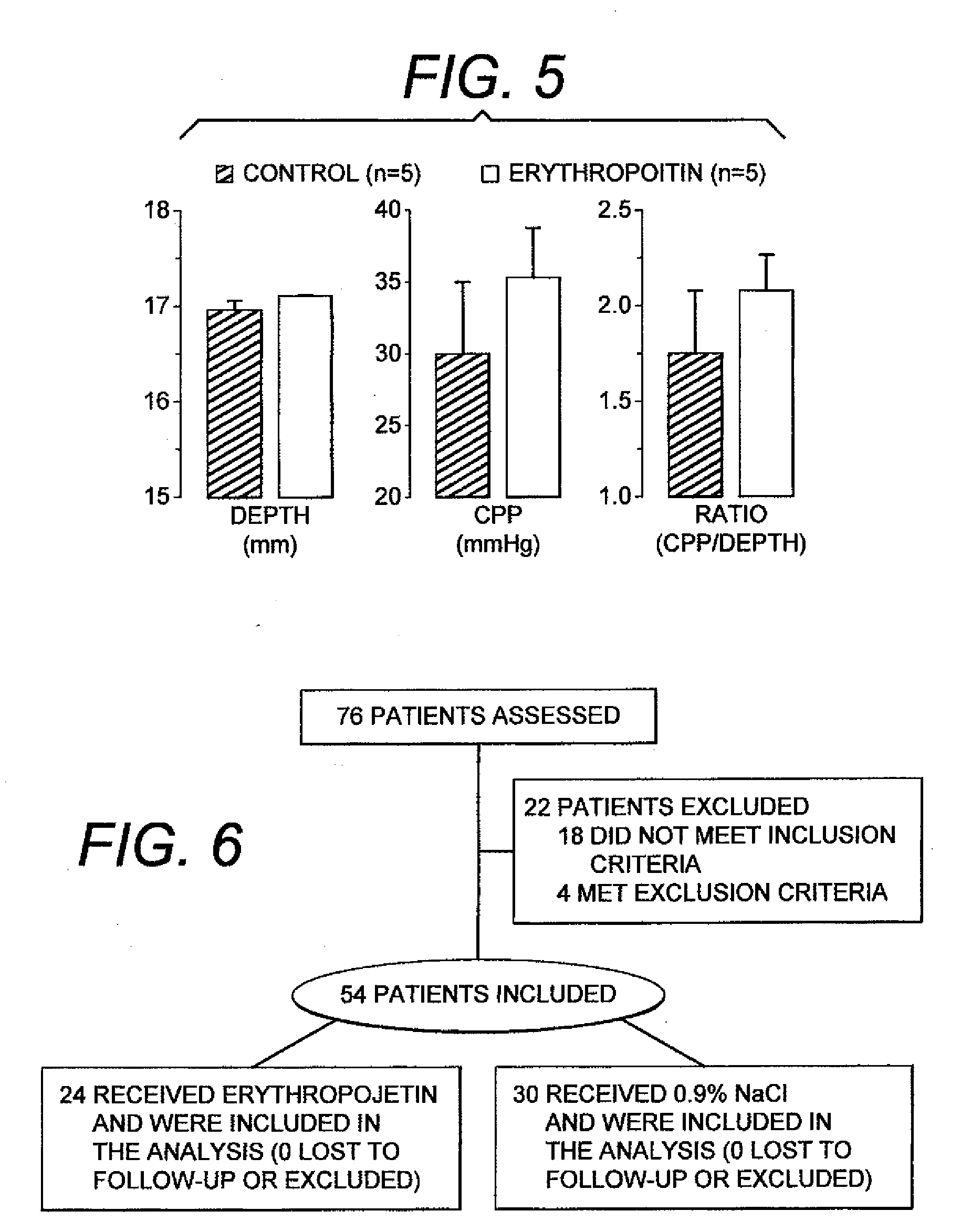
Facilitation of resuscitation from cardiac arrest by erythropoietin
ActiveUS20100130407A1Peptide/protein ingredientsHeart defibrillatorsHigh rateCardiorespiratory arrest
The present invention relates generally to the use of erythropoietin (EPO) to facilitate resuscitation from cardiac arrest. For a mammalian subject suffering from cardiac arrest, concurrent administration of EPO with resuscitation after the onset of ventricular fibrillation facilitates the resuscitation. Administration of EPO serves to attenuate myocardial abnormalities caused by cardiac arrest and the resuscitation efforts and favor improved resuscitation outcomes. The main effect of EPO that facilitates resuscitation is the preservation of left ventricular myocardial distensibility leading to improve left ventricular preload and the amount of blood ejected by chest compression. This effect enables higher coronary perfusion pressures to be generated resulting in a higher rate of return of spontaneous circulation and higher survival rates. The very same effect enables the return of spontaneous circulation to occur faster reducing the time a human subject is in cardiac arrest. These effects lead to a higher number of cardiac arrest victims to survive and to do so with intact neurological function in most of the survivors.
Owner:ROSALIND FRANKLIN UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND SCIENCE +1
Cardiac medical image processing device, processing system and medium
ActiveCN110335235BAccurate and rapid identificationReduce workloadUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementHeart apexImaging processing
Owner:SHANGHAI YIZHI HEALTHCARE TECH CO LTD
Cardiac medical image processing method, processing device, processing system and medium
ActiveCN110335236BAutomatic IdentificationAccurate and rapid identificationImage enhancementImage analysisHeart apexMyocardium region
The present disclosure relates to a processing method, a processing device, a processing system and a medium for cardiac medical images. The method includes: receiving a cardiac medical image of a long-axis view of the left ventricle; using a trained first learning network to identify the mitral valve base points on both sides of the left ventricle, the apex apex, and the outer edge and inner edge of the left ventricular myocardium; The first connecting line of the mitral valve base point, set the upper edge; use the upper edge, inner edge and outer edge to enclose the left ventricular myocardium, and use the midpoint of the first connecting line and the second connecting line of the apex of the left ventricle as the midline , the parts of the left ventricular myocardium on both sides of the midline are evenly divided into n parts, thereby dividing it into 2n segments. The processing method, processing device, processing system and medium of the cardiac medical image can automatically, accurately and quickly delineate and identify various myocardial regions, greatly reducing the workload of doctors, and its automatic identification can continue to benefit from the labeling of myocardial regions after training training data set.
Owner:SHANGHAI YIZHI HEALTHCARE TECH CO LTD
Method and device for segmenting left ventricular myocardium
ActiveCN104978730BAutomatic segmentationSplit evenlyImage analysisDynamic planningLeft ventricular size
The invention provides a division method and device of left ventricular myocardium. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) positioning a left ventricular central point, and acquiring a region of interest in an image at a layer where the left ventricular central point is located; (2) positioning a blood pool region in the region of interest in the image at the layer where the left ventricular central point is located according to grey scale information and the left ventricular central point; (3) determining a mass center of the blood pool region, determining blood pool regions in an original image in all layers except the layer where the left ventricular central point is located, thereby obtaining a division result of left ventricular endocardium; and (4) obtaining a division result of left ventricular adventitia by a dynamic planning method according to the division result of the left ventricular endocardium, and thus obtaining a division result of the left ventricular myocardium. By the technical scheme provided by the invention, the left ventricular myocardium can be fully, uniformly and stably divided.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Segmentation method of epicardium and epicardium in cardiac functional magnetic resonance images
ActiveCN106910194BRealize detectionAccurate and effective detectionImage enhancementImage analysisCardiac cycleDiastasis
The invention discloses a method for segmenting the endocardium and the epicardium in a heart cardiac function magnetic resonance image. The method comprises positioning the diastasis in heart magnetic resonance images I<NP> including several lamellas of the left ventricular myocardium and in different cardiac cycle phases, and obtaining a coarse segmentation result of blood pools of magnetic resonance images of N lamellas in the diastasis; converting image data in the left ventricle region-of-interest in the magnetic resonance image of each lamella in the diastasis into a two-dimension polar coordinate conversion image by means of ray scanning based on a polar coordinate conversion method; detecting the endocardium and the epicardium in the two-dimension polar coordinate conversion image based on a bidynamic programming method; obtaining the endocardium and the epicardium in an original lamella image by means of polar coordinate inverse conversion, calculating the convex hull and smoothing the convex hull, and completing segmentation of the endocardium and the epicardium in the magnetic resonance images of the N lamellas in the diastasis; and deriving the segmentation result of the in the endocardium and the epicardium in the magnetic resonance images in the diastasis to the endocardium and the epicardium in the magnetic resonance images in other cardiac cycle phases.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com