Method for segmenting blood pool in diastasis image in heart cardiac function magnetic resonance image
A magnetic resonance image, end-diastolic technology, applied in the field of medical images, can solve the problems of complexity and low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
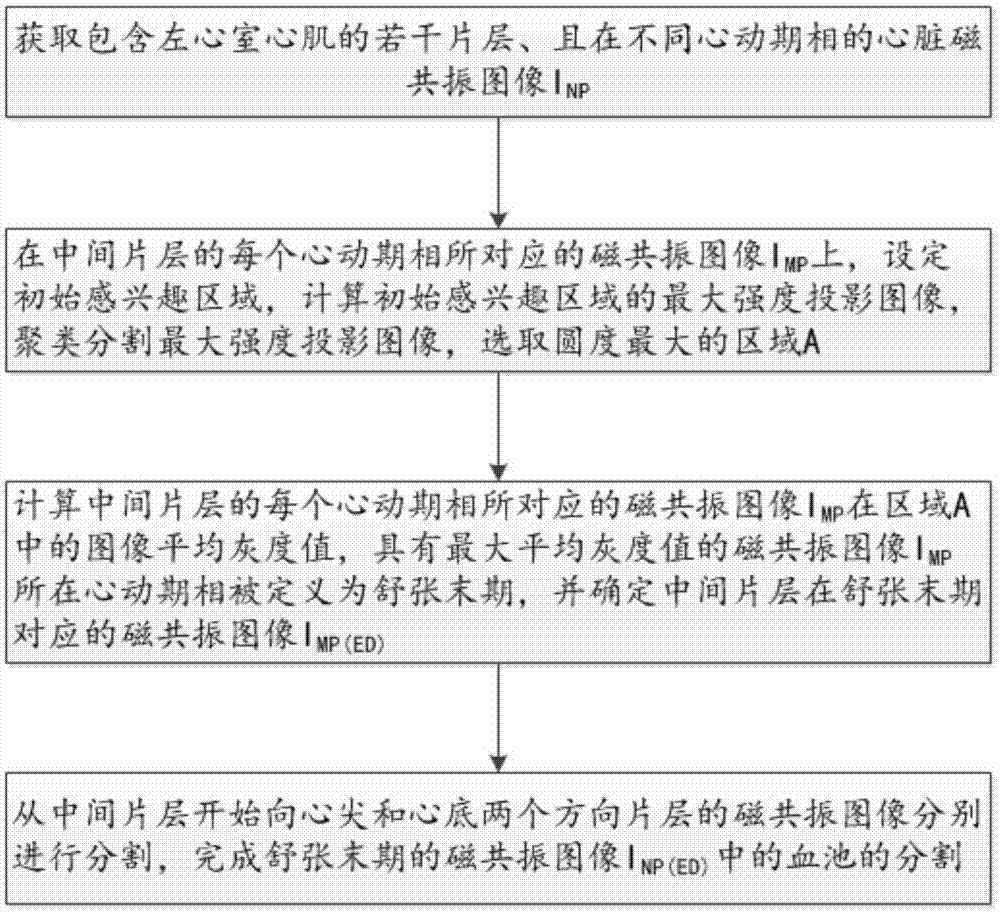
[0041] see figure 1 -3, a method for segmenting the blood pool in the end-diastolic image of cardiac functional magnetic resonance image in the embodiment of the present invention, comprising the following steps:
[0042] Acquire cardiac magnetic resonance images containing several slices of left ventricular myocardium at different cardiac phases I NP , where N represents the sequence number of the slice, P represents the sequence number of the cardiac phase (phase), and N and P are integers greater than or equal to 1;
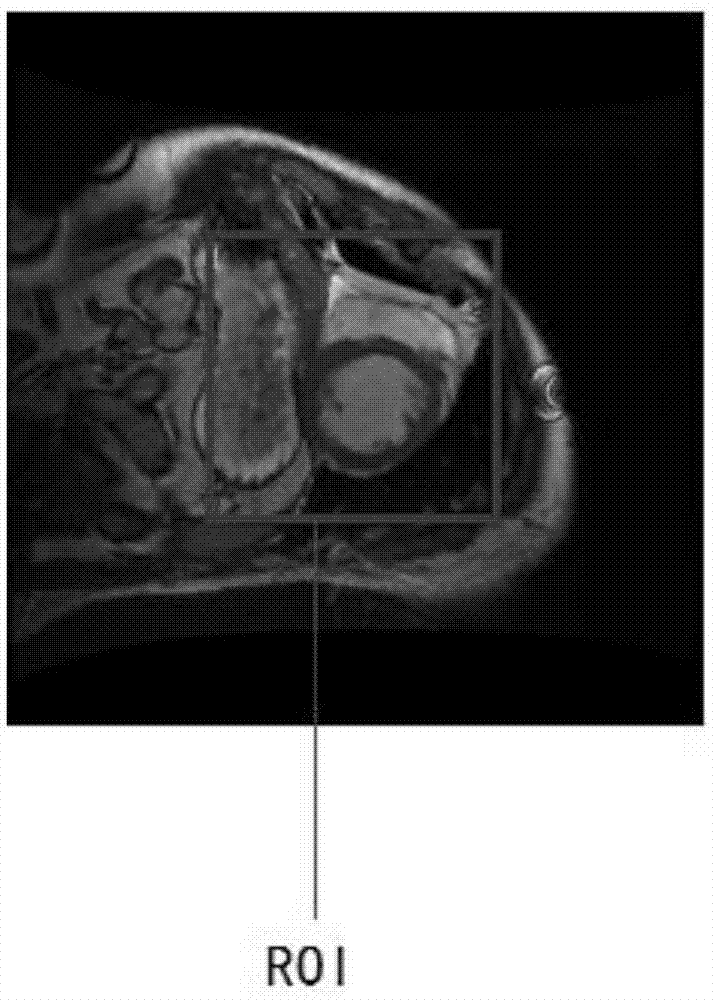
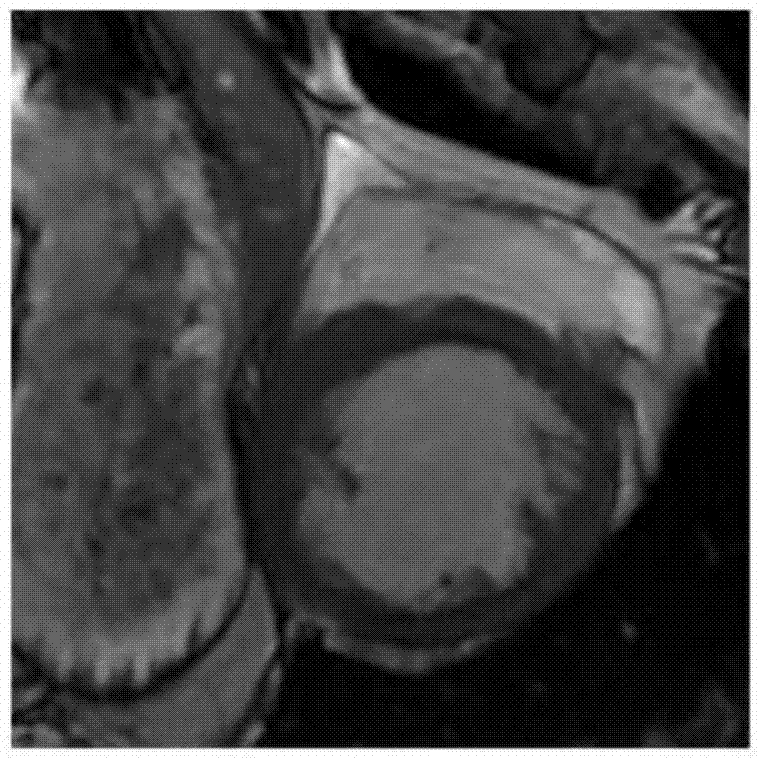
[0043] MRI images corresponding to each cardiac phase in the middle slice I MP Above, set the initial region of interest, calculate the maximum intensity projection image (MIP) of the initial region of interest on all cardiac phases (P cardiac phases), cluster and segment the maximum intensity projection image (MIP), and select the roundness The largest area A; the preferred clustering and segmentation method is the fuzzy C-means clustering method;
[0044]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com