Respiration separation type strain imaging method based on ultrasonic images of living body
A technology of ultrasonic images and imaging methods, applied in the field of medical image processing, which can solve problems such as errors, increased errors in displacement and strain calculations, and gate failure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
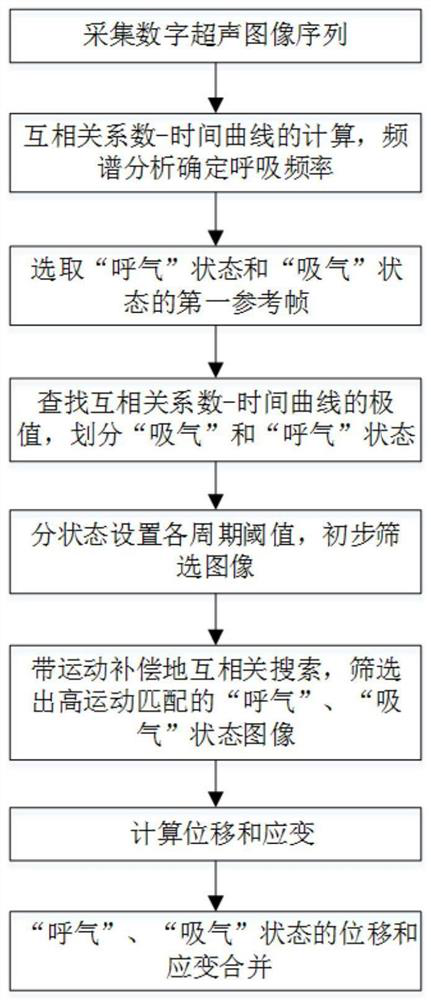
[0049] combine figure 1 Shown, a kind of respiratory separation type strain imaging method based on in vivo ultrasonic image of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0050] 1) Acquisition of digital ultrasound image sequences
[0051] Ultrasonic image acquisition is performed on the strain-concentrated area of the living body to obtain a digital ultrasonic image sequence; specifically, the target area of the living body is heated or an external force is applied to form concentrated strain in the target area; it should be noted that the present invention is applicable to a variety of Application scenario requirements, such as tissue local temperature rise monitoring, elastic imaging, tissue scatterer motion tracking, etc. It is further worth noting that when an external action is applied to biological tissue, the specific form of the action is not limited, and it can be microwave ablation, radiofrequency ablation, ultrasonic ablation, laser ablation, and i...
Embodiment 2
[0091] In this example, the method of Example 1 is used to heat the adipose tissue of live pigs by microwave ablation, and the thermal strain is calculated. The specific steps of the method are as follows:
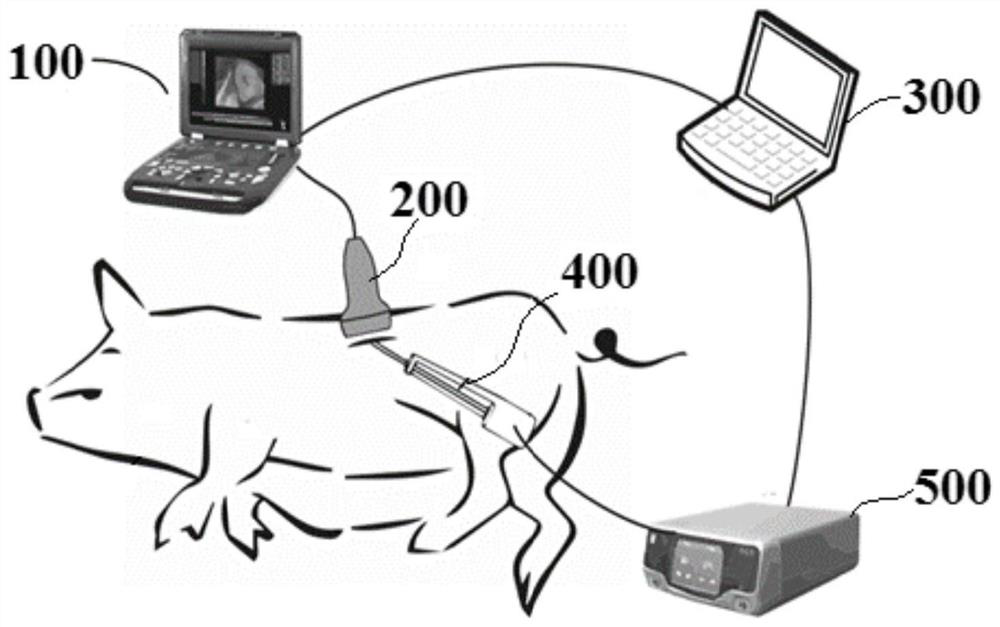
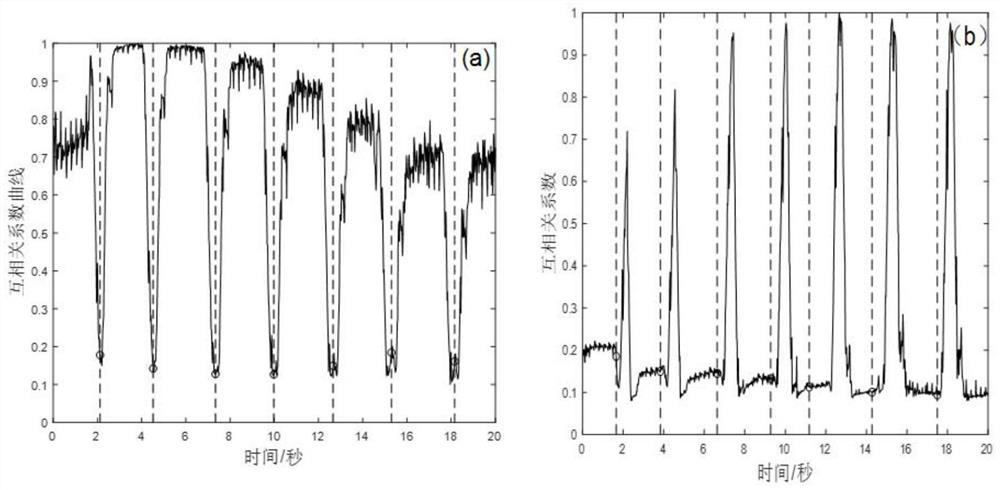
[0092] Step 1, such as figure 2 As shown, the ultrasonic imaging system 100 of the present embodiment adopts a B-ultrasound imager with a sampling rate of 40 MHz, and the imaging probe 200 is a linear array probe with 128 elements and a center frequency of 10.5 MHz to image live pig adipose tissue, with an imaging depth of 4 cm, microwave The power emission area of the ablation needle 400 is on the imaging plane; the B-ultrasound imager outputs RF images with a size of 128 pixels*2048 pixels per frame at an average frame rate of 50 frames per second, and each experiment uses a microwave heater 500 from the microwave An image sequence with a length of 20 seconds was acquired from the start of heating. The computer 300 controls the ultrasonic instrument and the microwave...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com