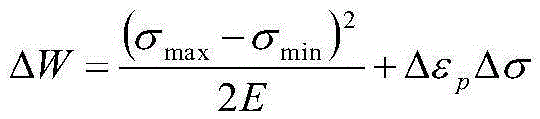Patents
Literature
230 results about "Thermal strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mechanics of solids: Thermal strains Temperature change can also cause strain. In an isotropic material the thermally induced extensional strains are equal in all directions, and there are no shear strains. In the simplest cases, these thermal strains can be treated as being linear in the temperature change….
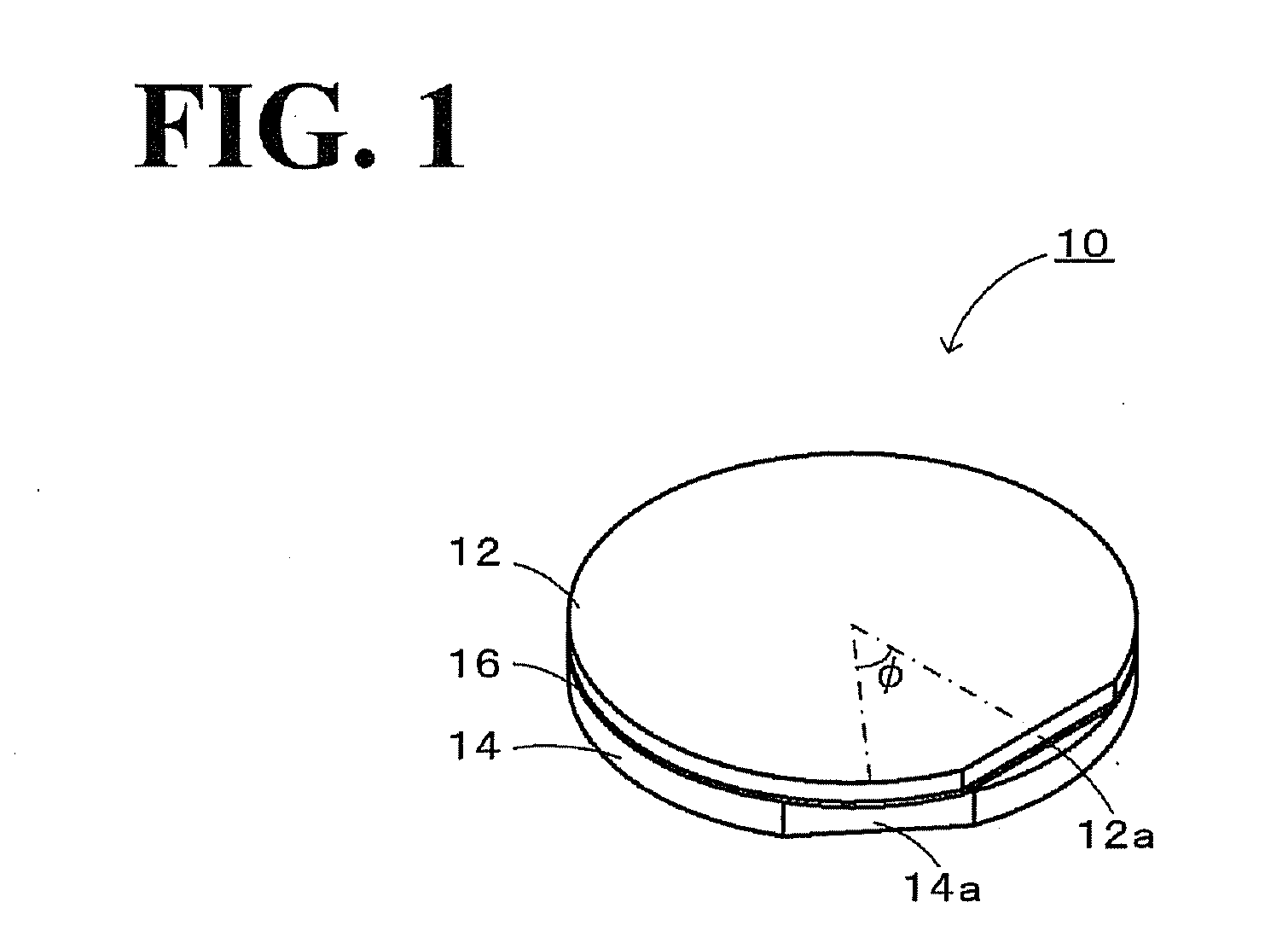
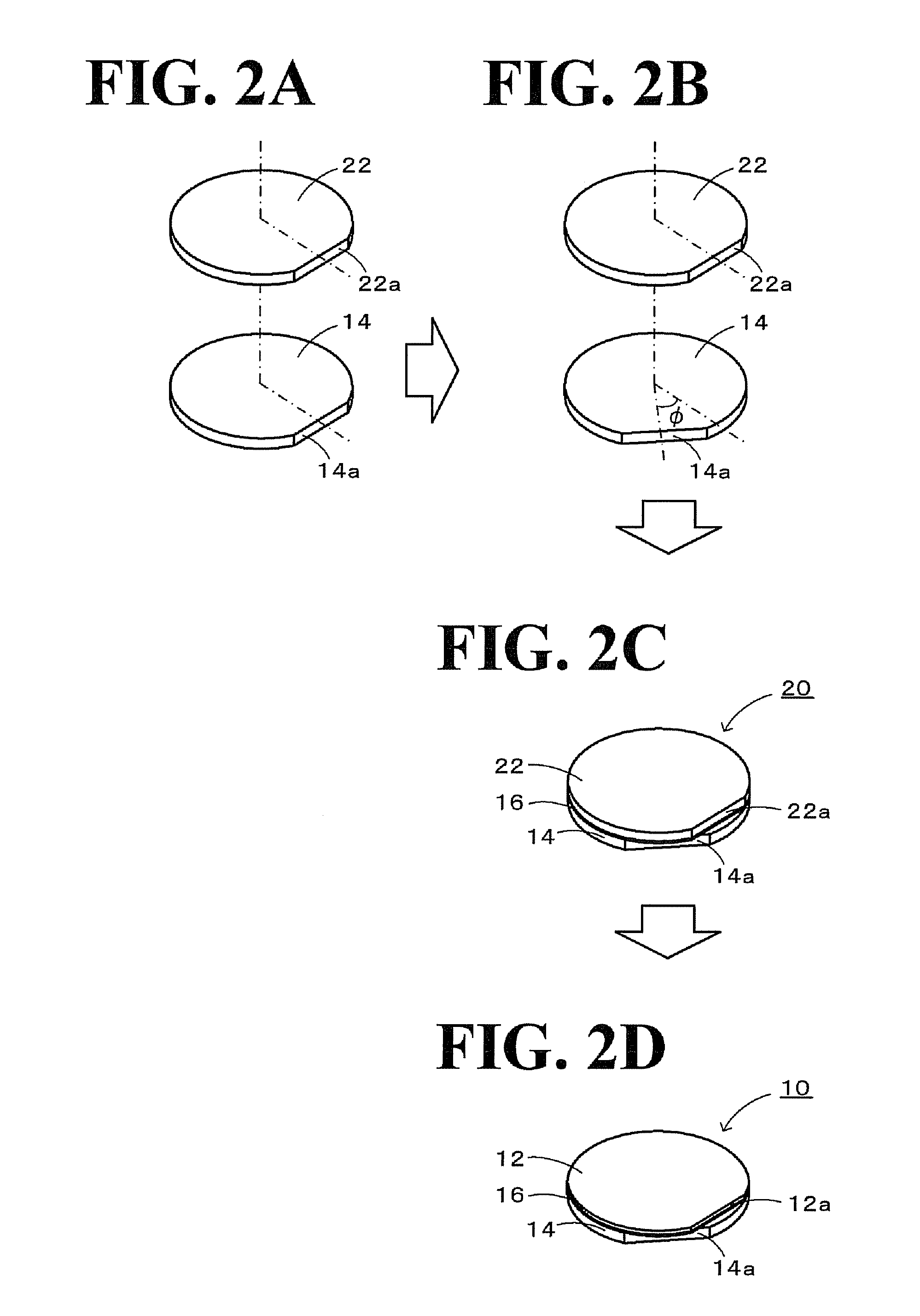
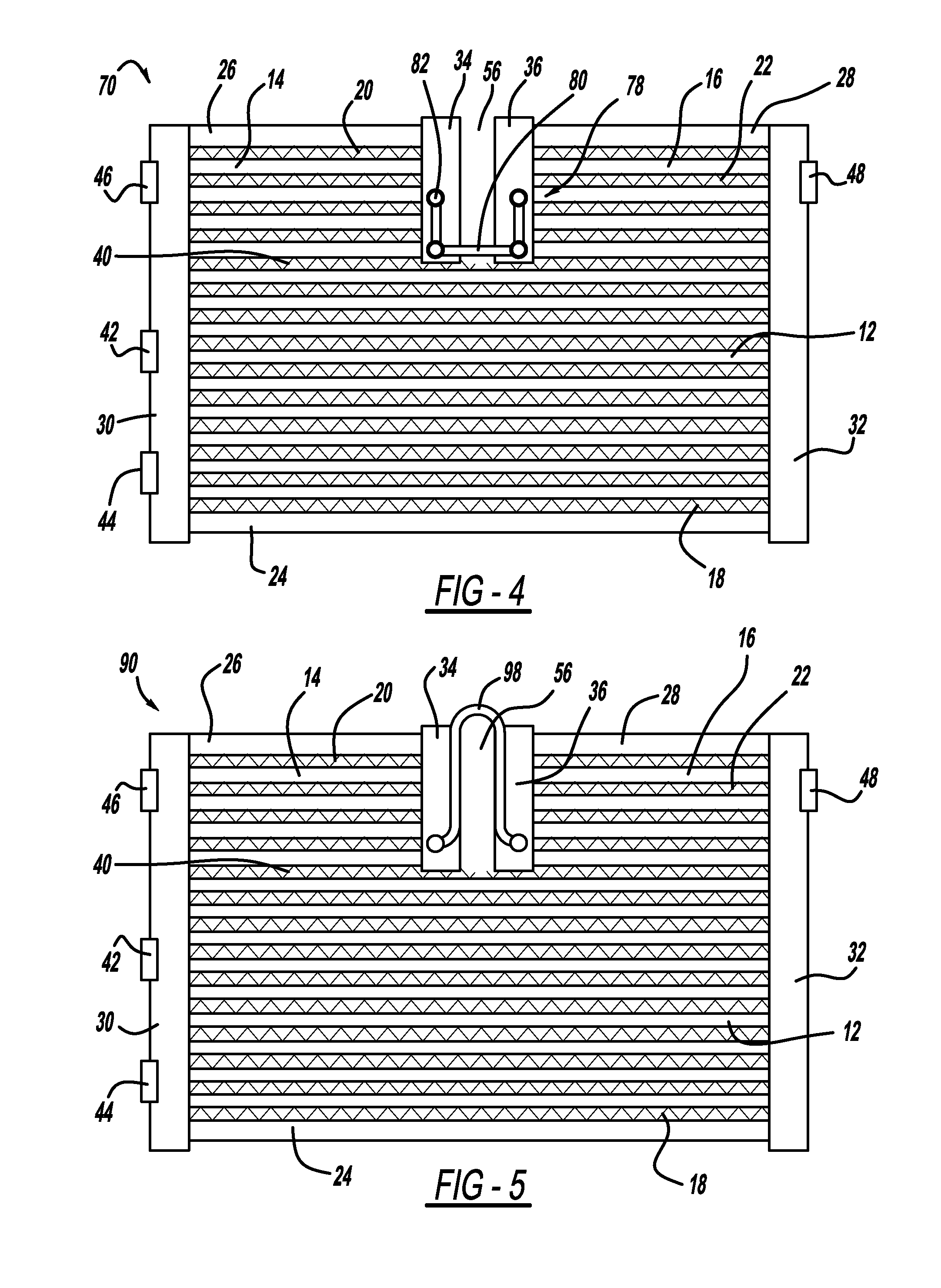
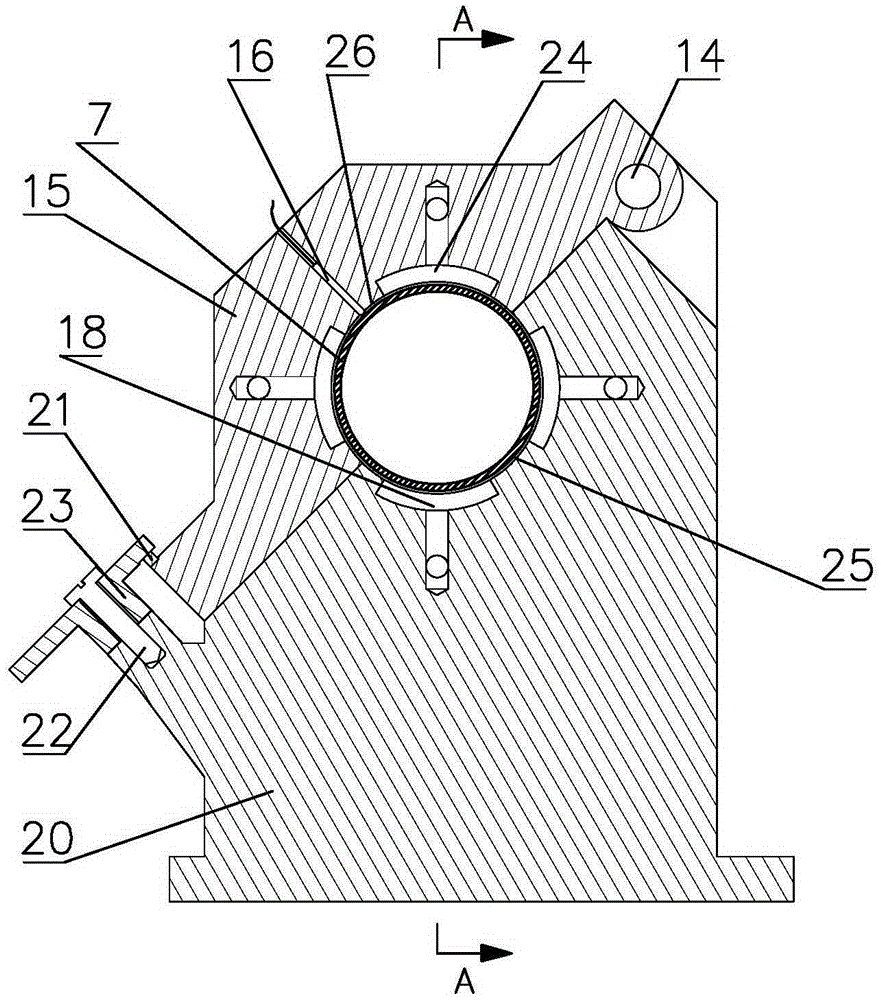
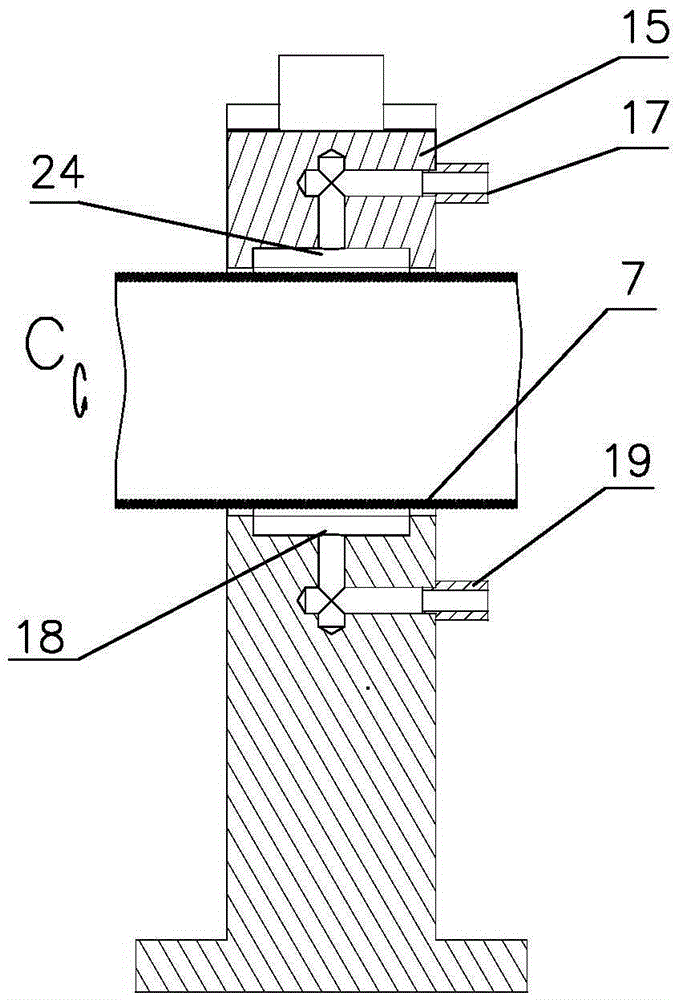
Segmented thermal barrier coating
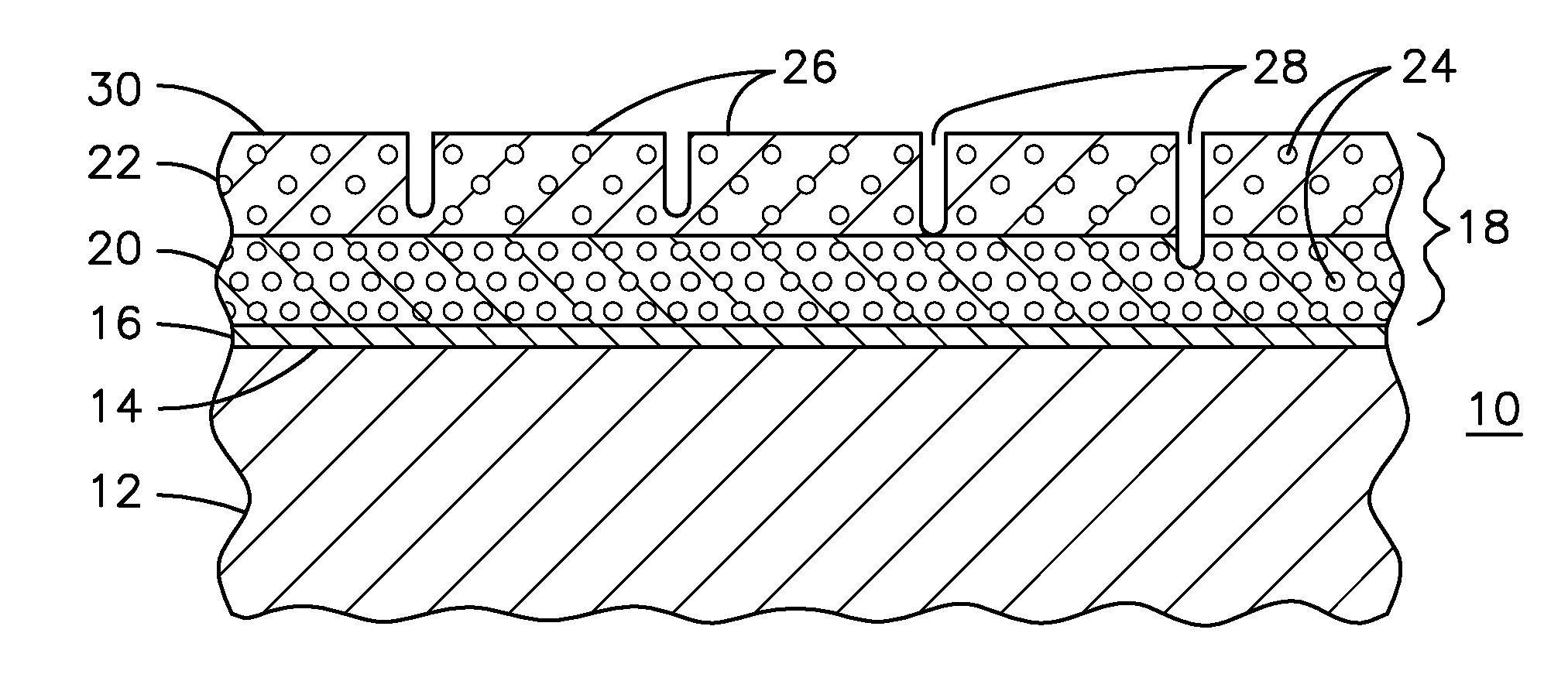
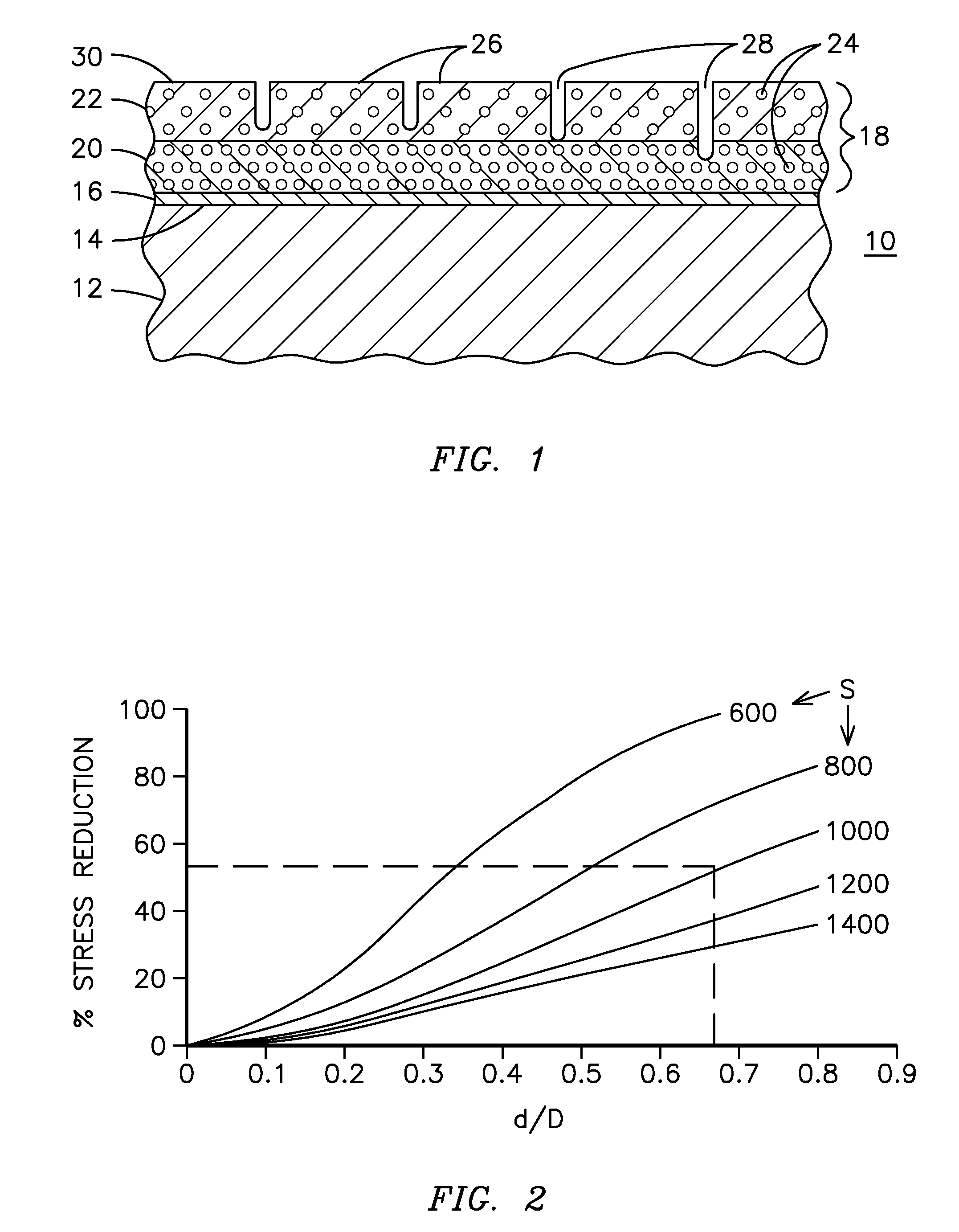
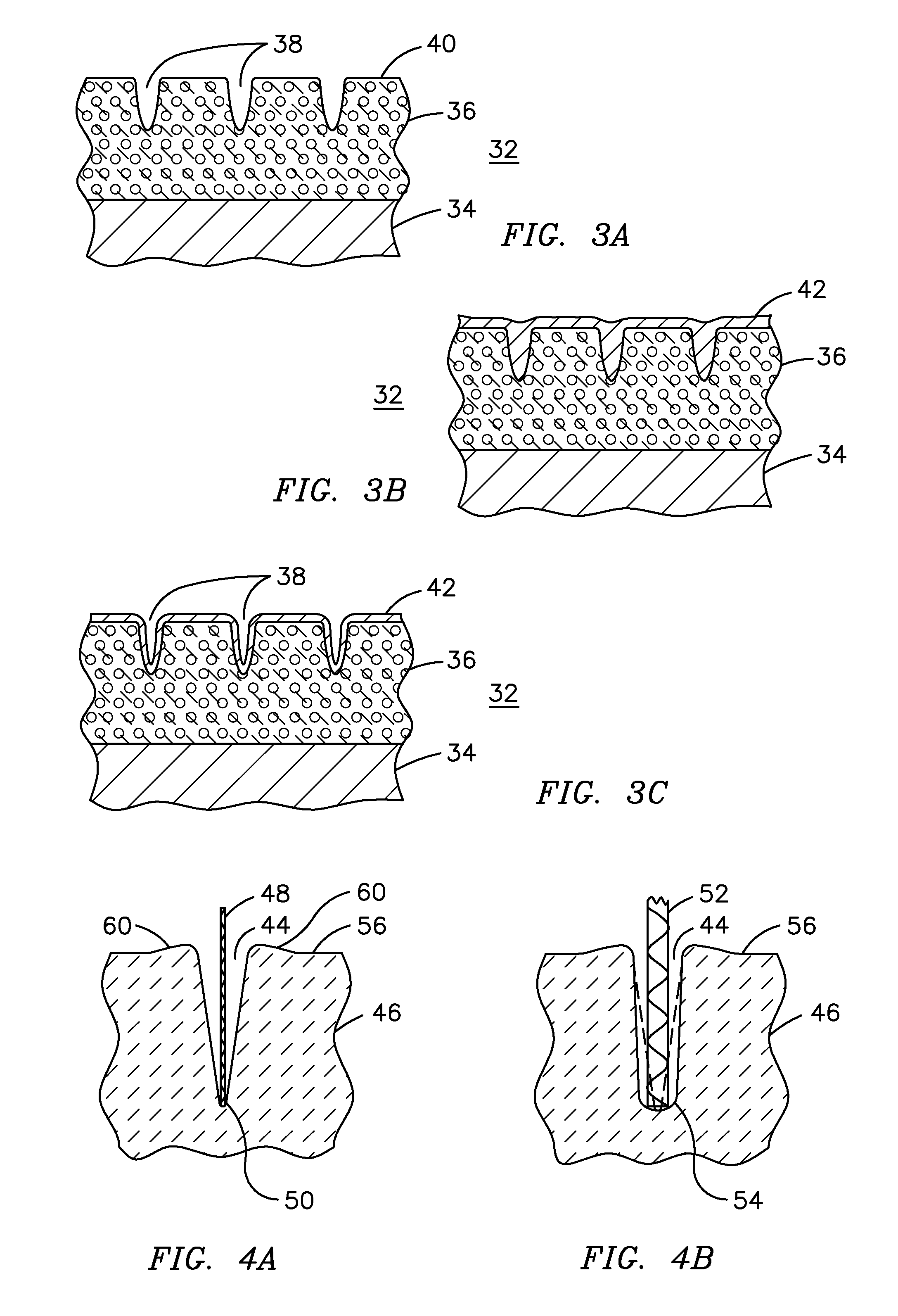
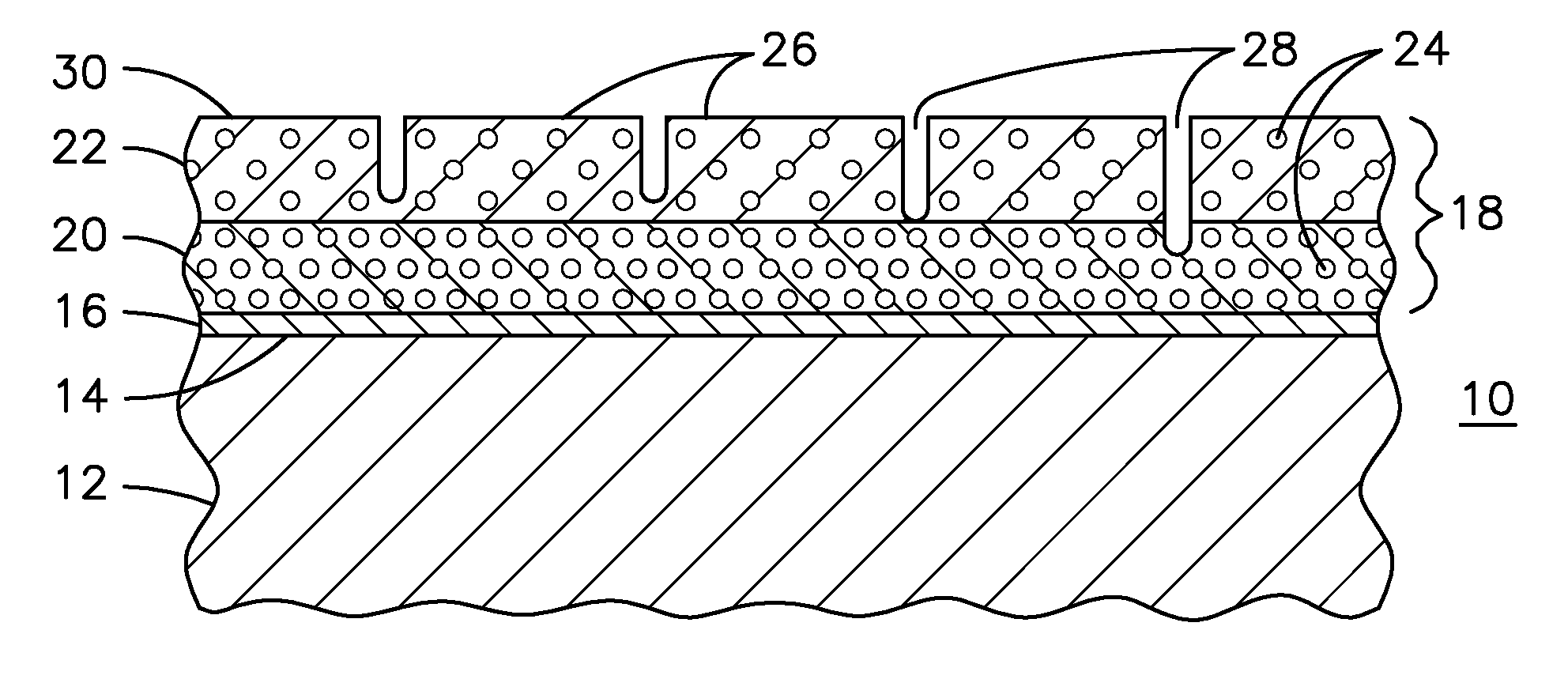
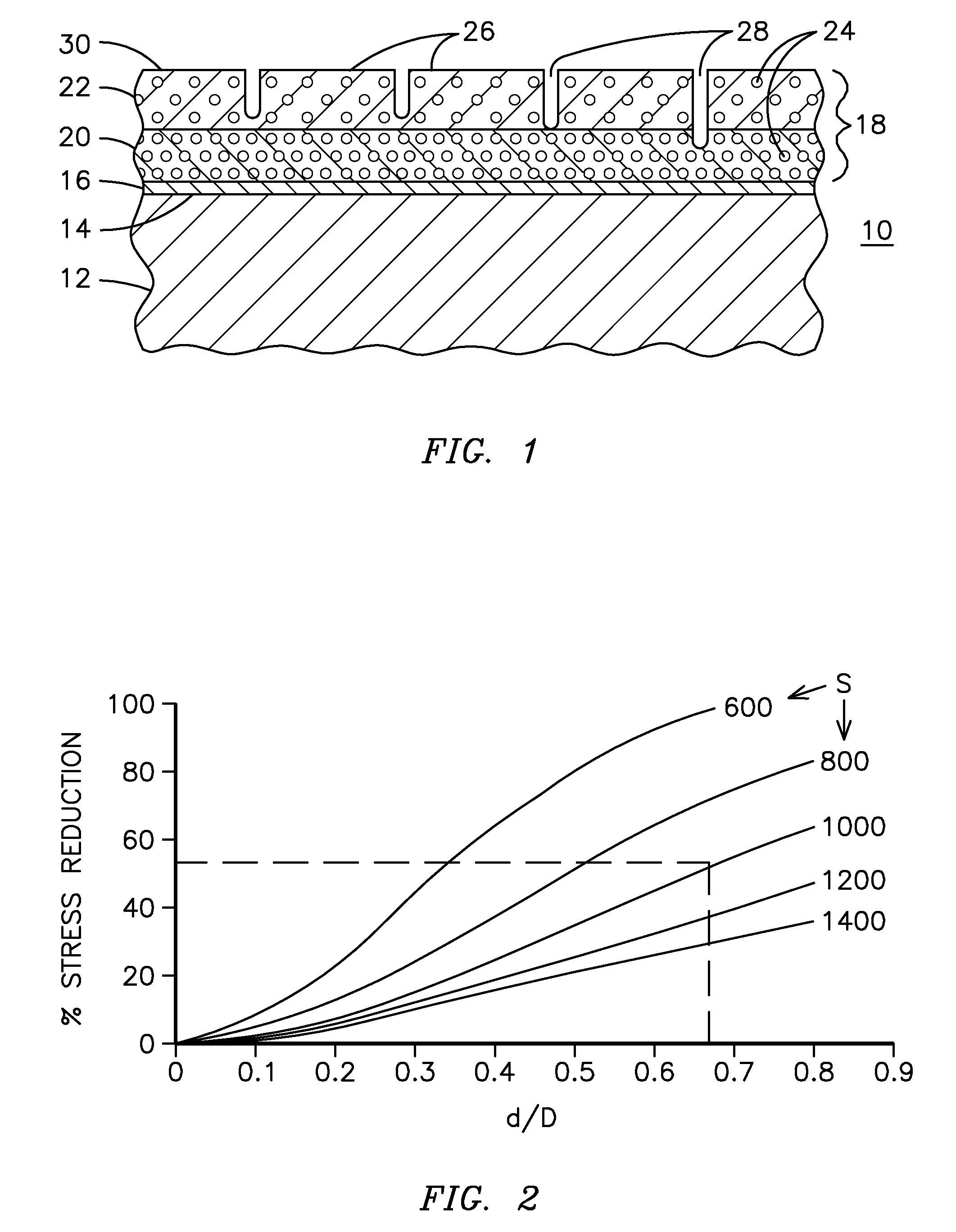
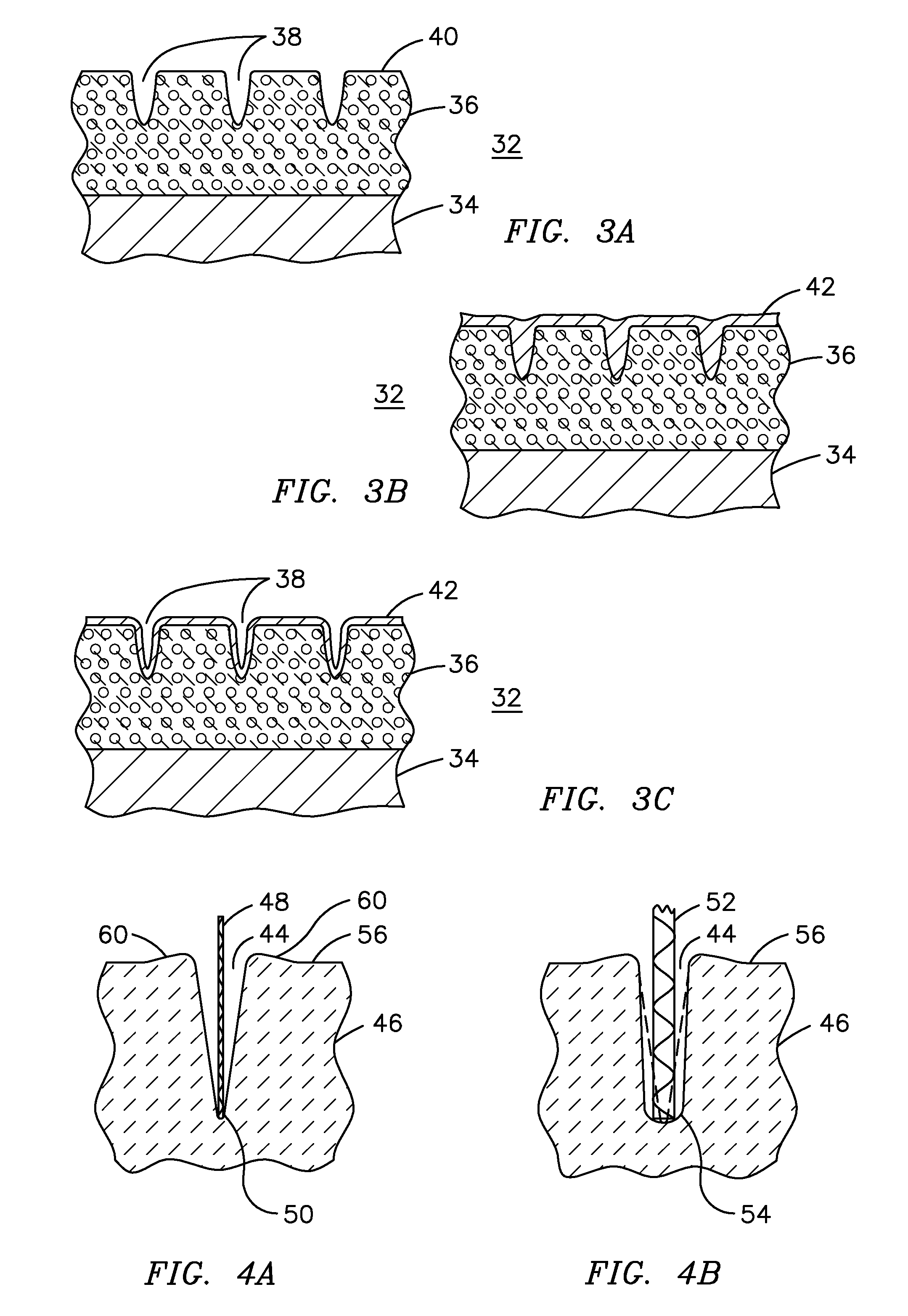
A ceramic thermal barrier coating (TBC) (18) having first and second layers (20, 22), the second layer (22) having a lower thermal conductivity than the first layer for a given density. The second layer may be formed of a material with anisotropic crystal lattice structure. Voids (24) in at least the first layer (20) make the first layer less dense than the second layer. Grooves (28) are formed in the TBC (18) for thermal strain relief. The grooves may align with fluid streamlines over the TBC. Multiple layers (84, 86,88) may have respective sets of grooves (90), Preferred failure planes parallel to the coating surface (30) may be formed at different depths (A1, A2, A3) in the thickness of the TBC to stimulate generation of a fresh surface when a portion of the coating fails by spalling. A dense top layer (92) may provide environmental and erosion resistance.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Soi substrate and method for manufacturing soi substrate
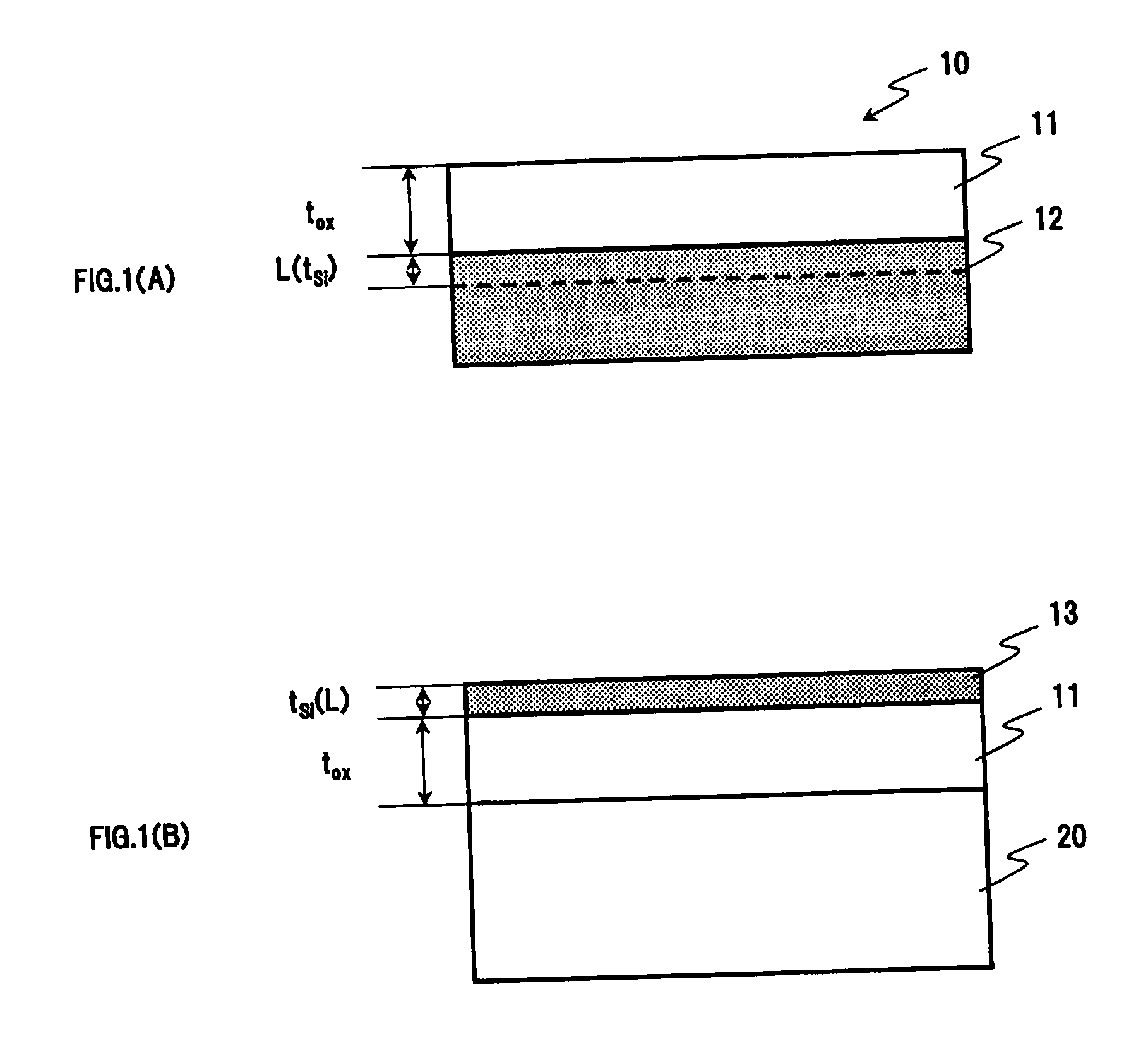
InactiveUS20100289115A1Prevent transfer defectIncrease productionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermal expansionSoi substrate
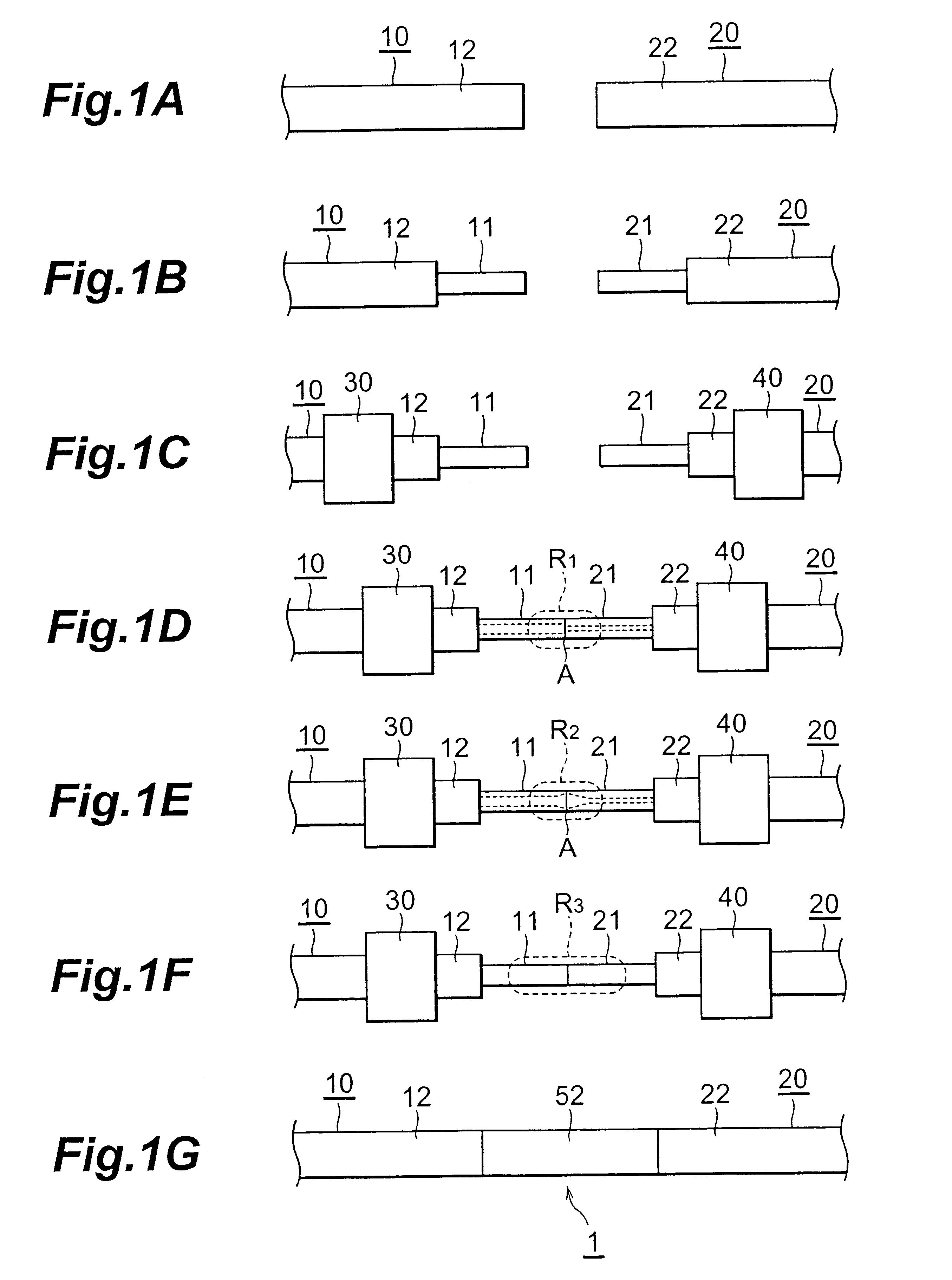
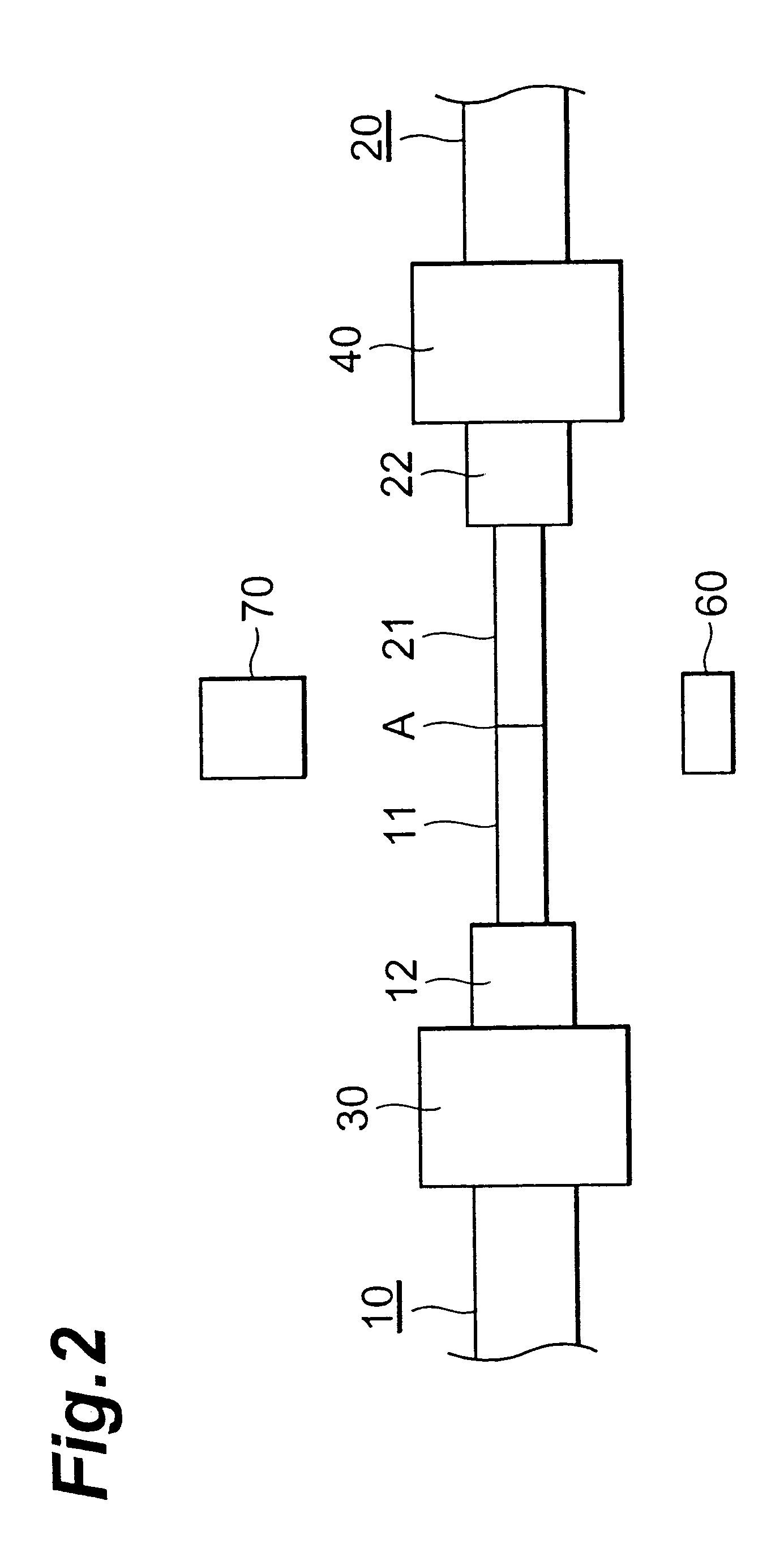
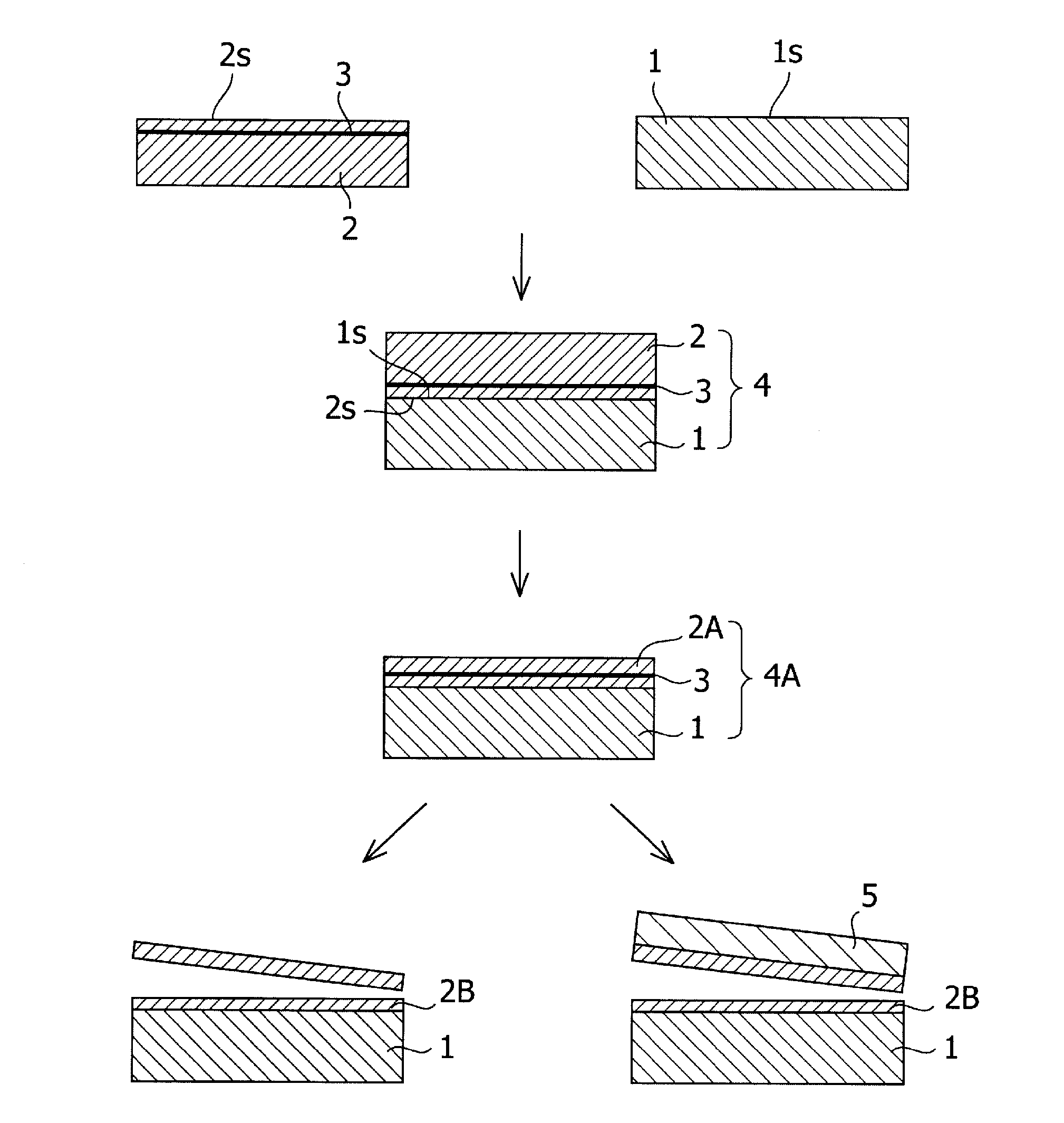
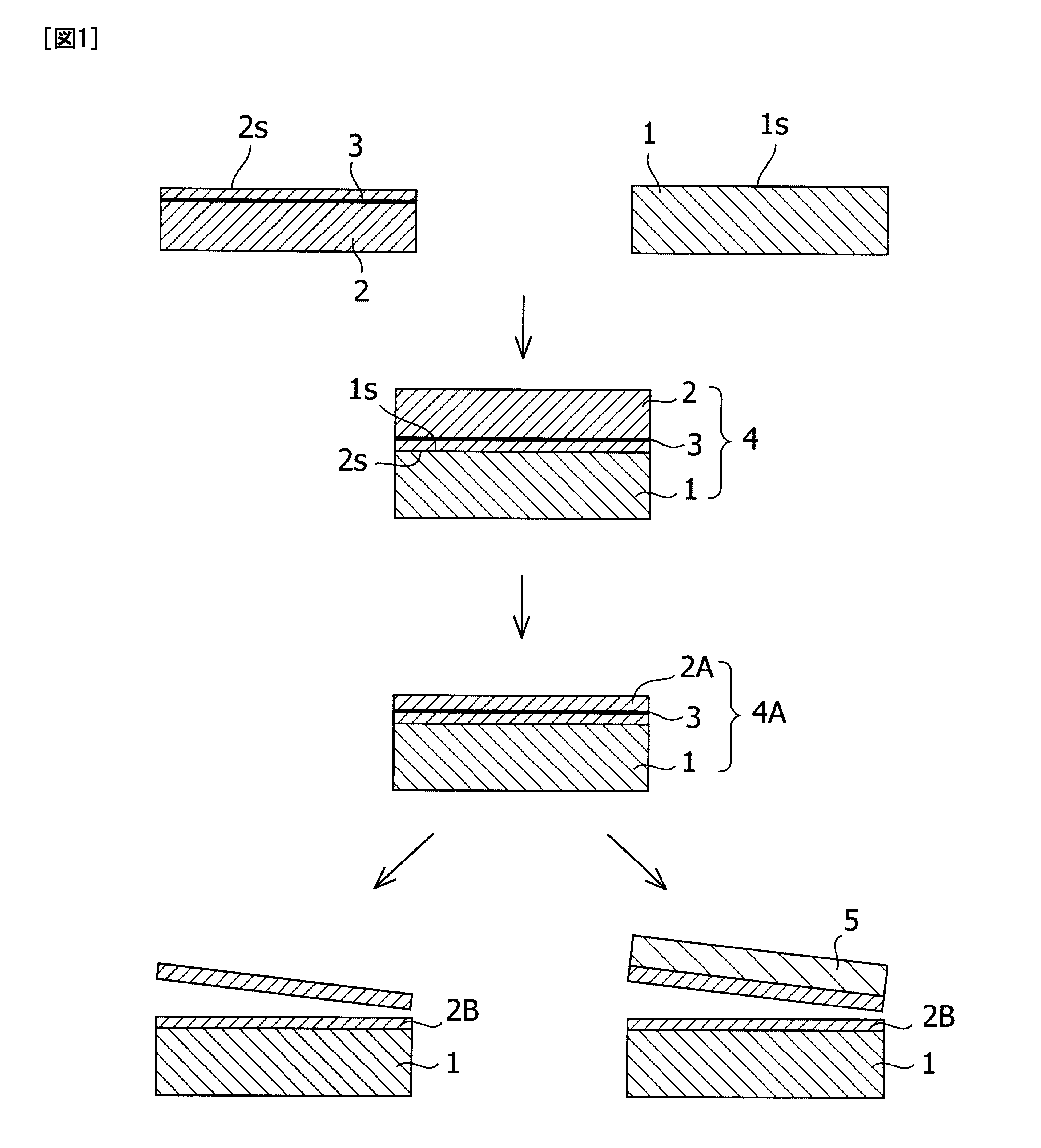
An oxide film having a thickness “tox” of not less than 0.2 μm is provided on the bonding surface of a single-crystal silicon substrate. In a method for manufacturing an SOI substrate according to the present invention, a low-temperature process is employed to suppress the occurrence of thermal strain attributable to a difference in the coefficient of thermal expansion between the silicon substrate and a quartz substrate. To this end, the thickness “tox” of the oxide film is set to a large value of not less than 0.2 μm to provide sufficient mechanical strength to the thin film to be separated and, at the same time, to allow strain to be absorbed in and relaxed by the relatively thick oxide film to suppress the occurrence of transfer defects during the step of separation.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
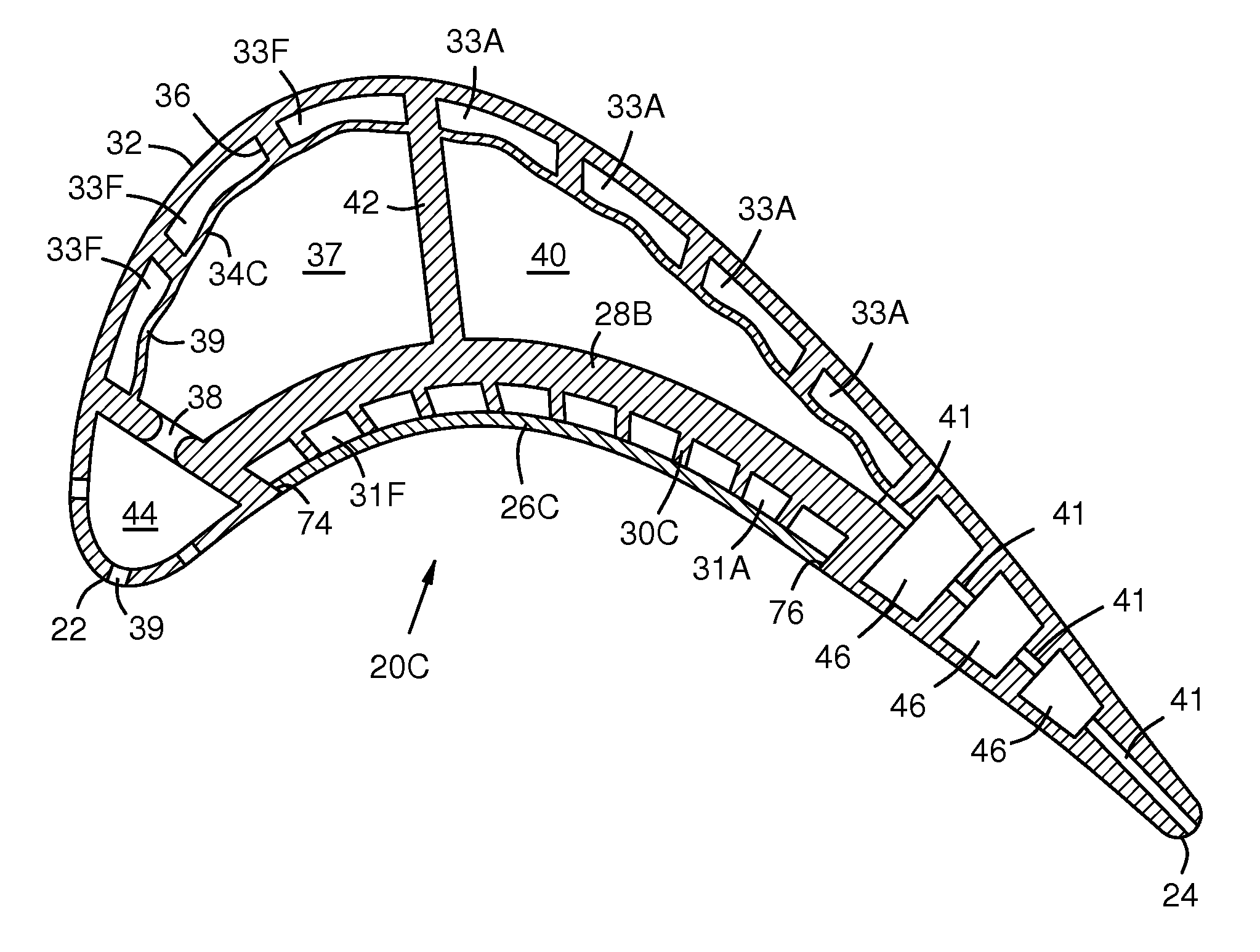
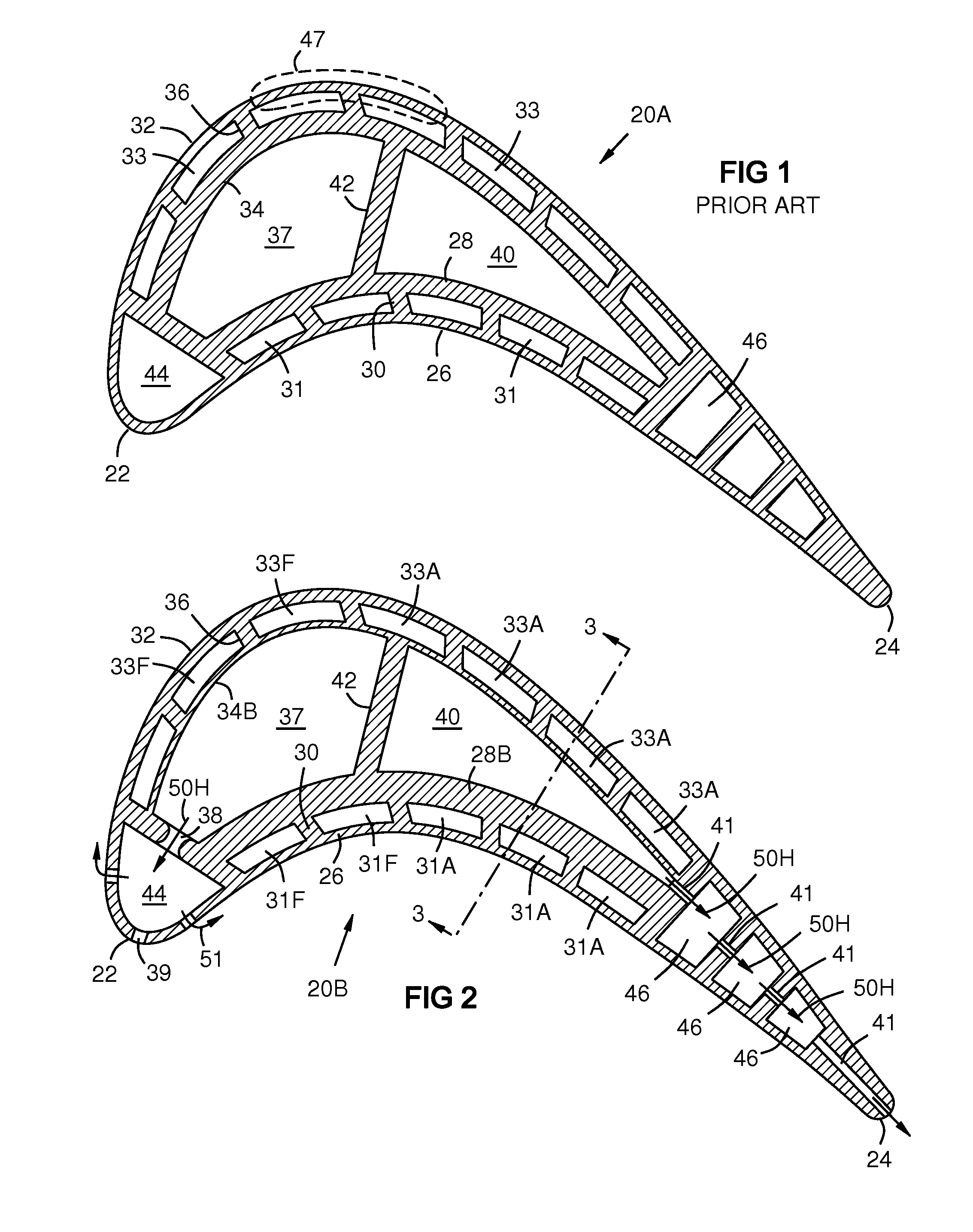
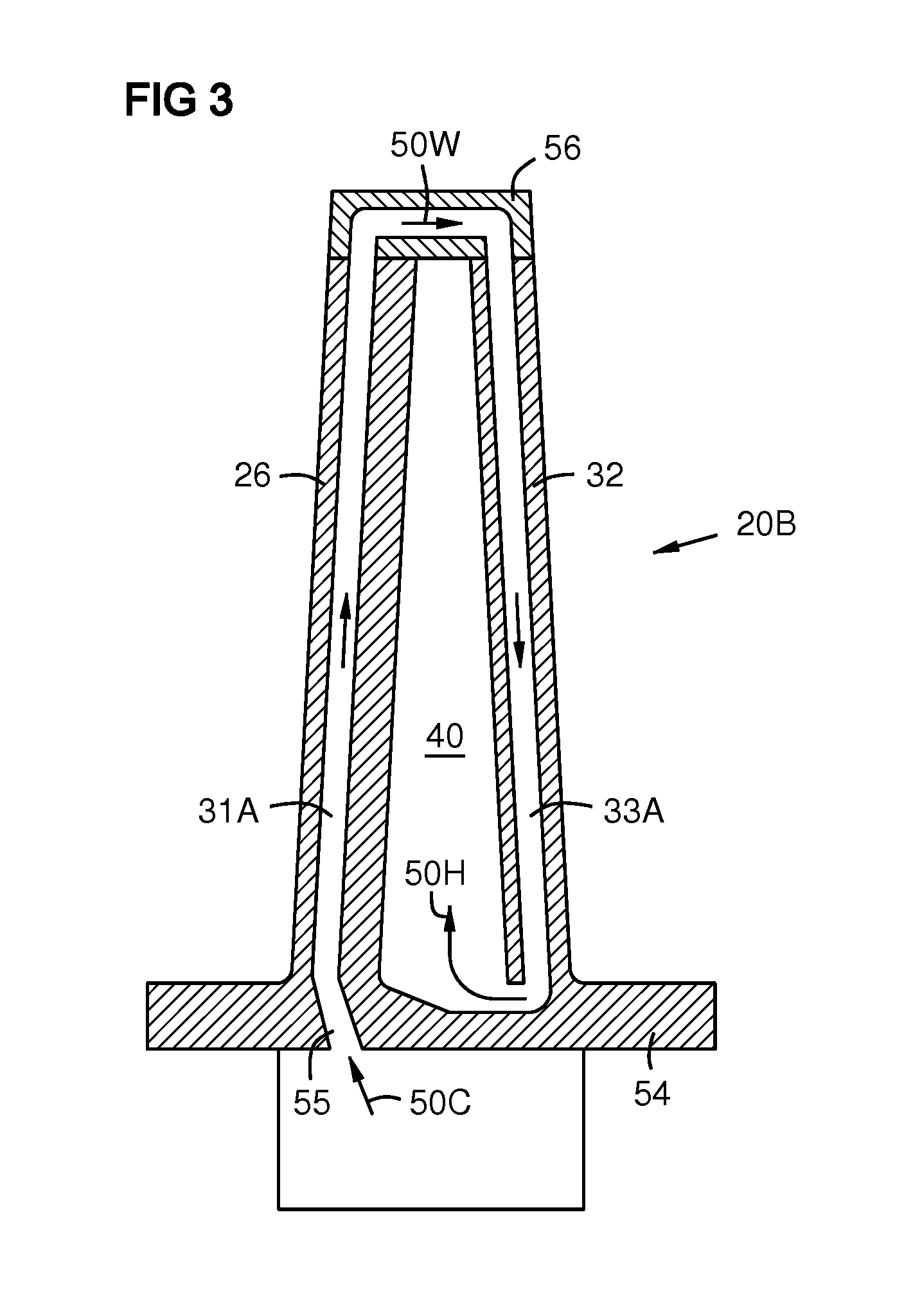
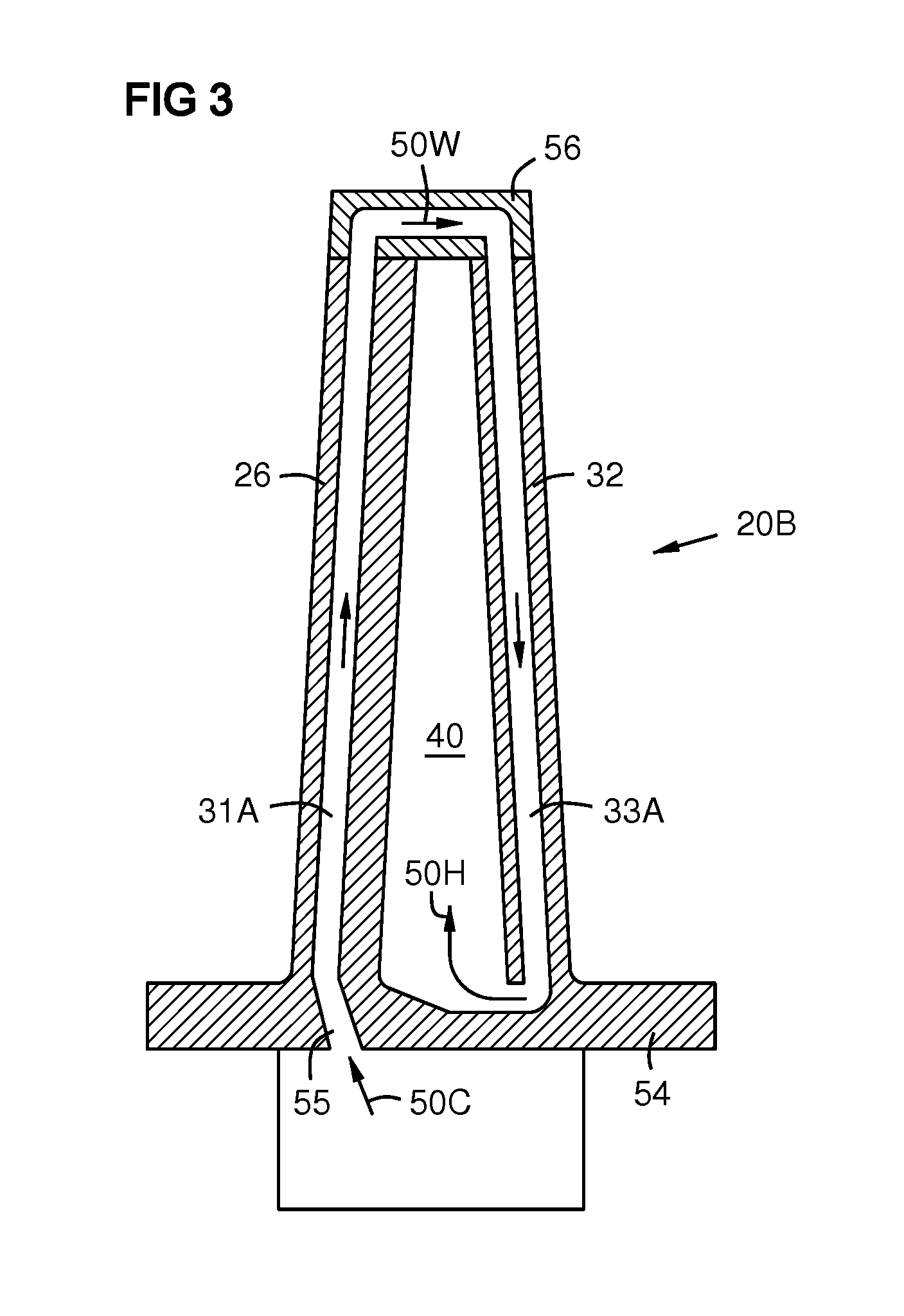
Four-Wall Turbine Airfoil with Thermal Strain Control for Reduced Cycle Fatigue
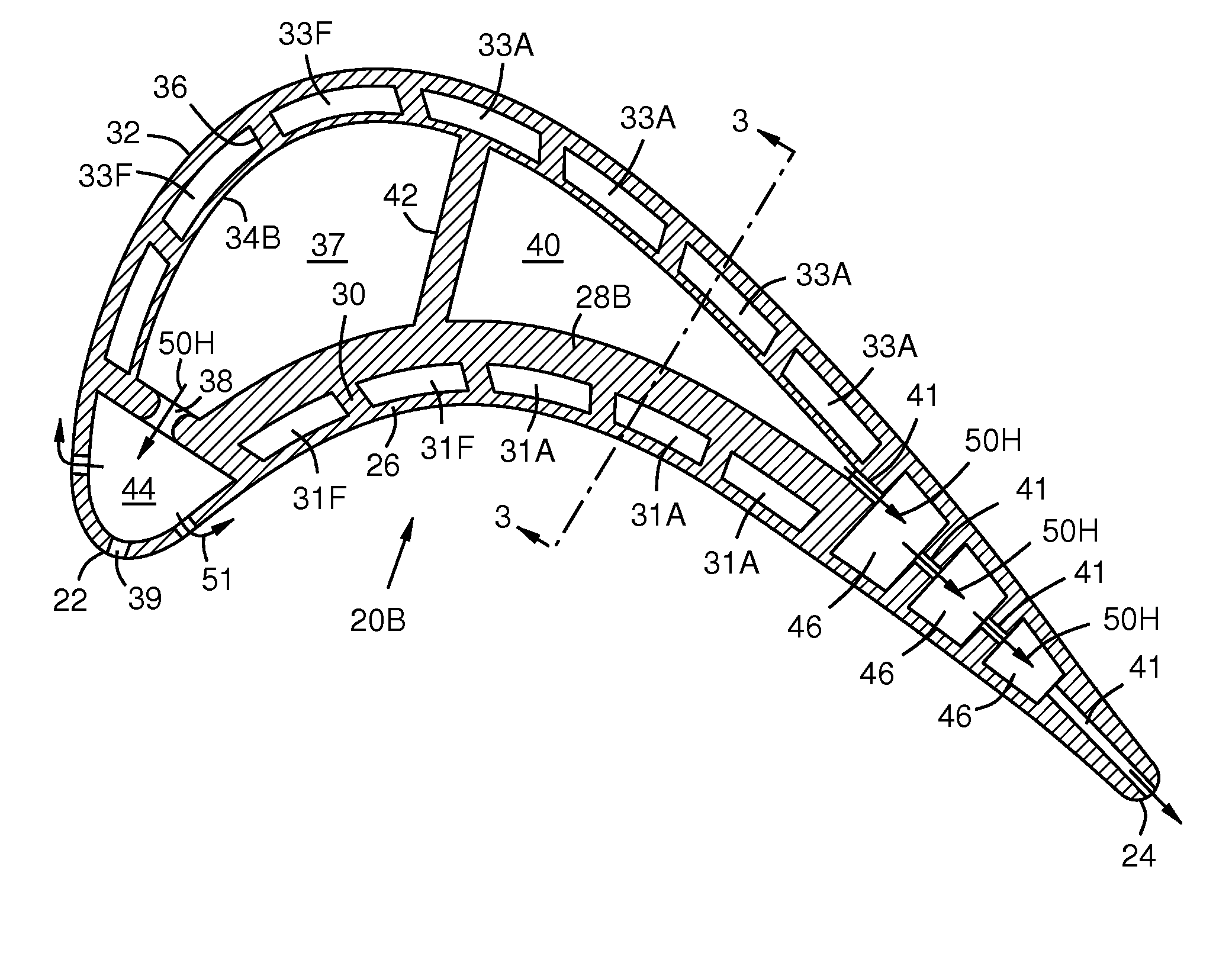
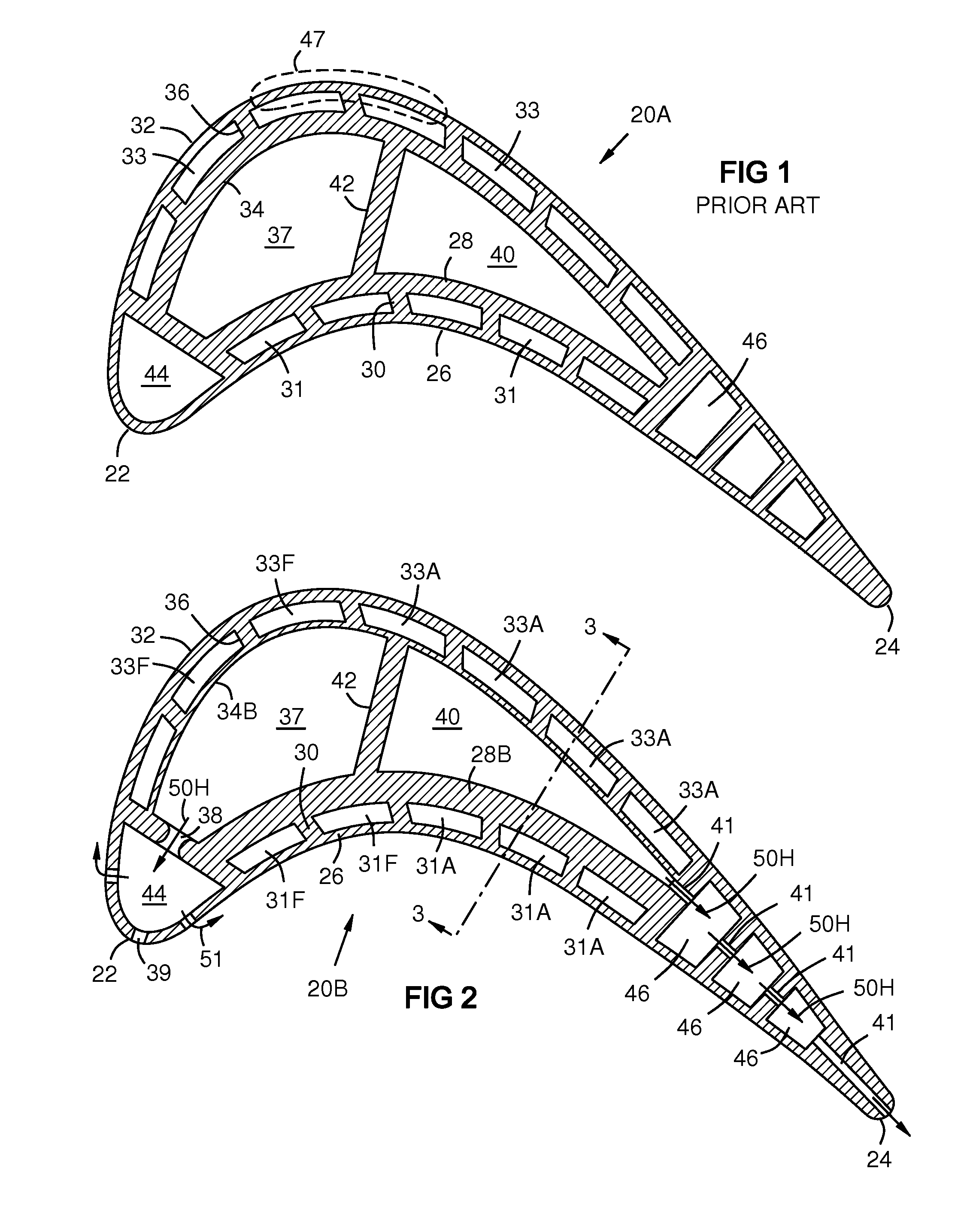
A turbine airfoil (20B) with a thermal expansion control mechanism that increases the airfoil camber (60, 61) under operational heating. The airfoil has four-wall geometry, including pressure side outer and inner walls (26, 28B), and suction side outer and inner walls (32, 34B). It has near-wall cooling channels (31F, 31A, 33F, 33A) between the outer and inner walls. A cooling fluid flow pattern (50C, 50W, 50H) in the airfoil causes the pressure side inner wall (28B) to increase in curvature under operational heating. The pressure side inner wall (28B) is thicker than walls (26, 34B) that oppose it in camber deformation, so it dominates them in collaboration with the suction side outer wall (32), and the airfoil camber increases. This reduces and relocates a maximum stress area (47) from the suction side outer wall (32) to the suction side inner wall (34B, 72) and the pressure side outer wall (26).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Simulation test method of thermal fatigue failure of blade with thermal barrier coating
ActiveCN101776645AMonitor temperature in real timeReal-time monitoring of temperature gradientsMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsAviationCeramic coating
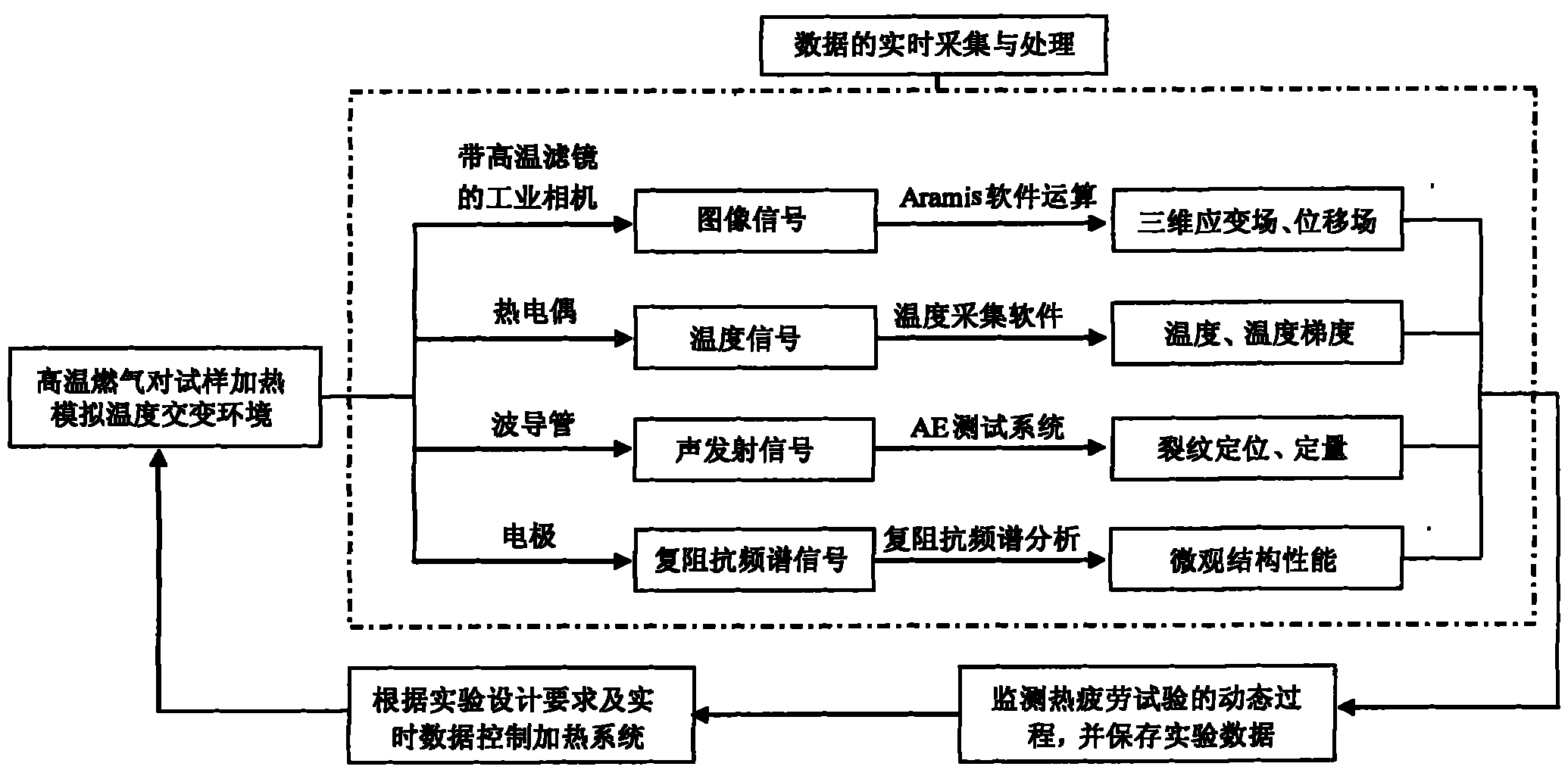
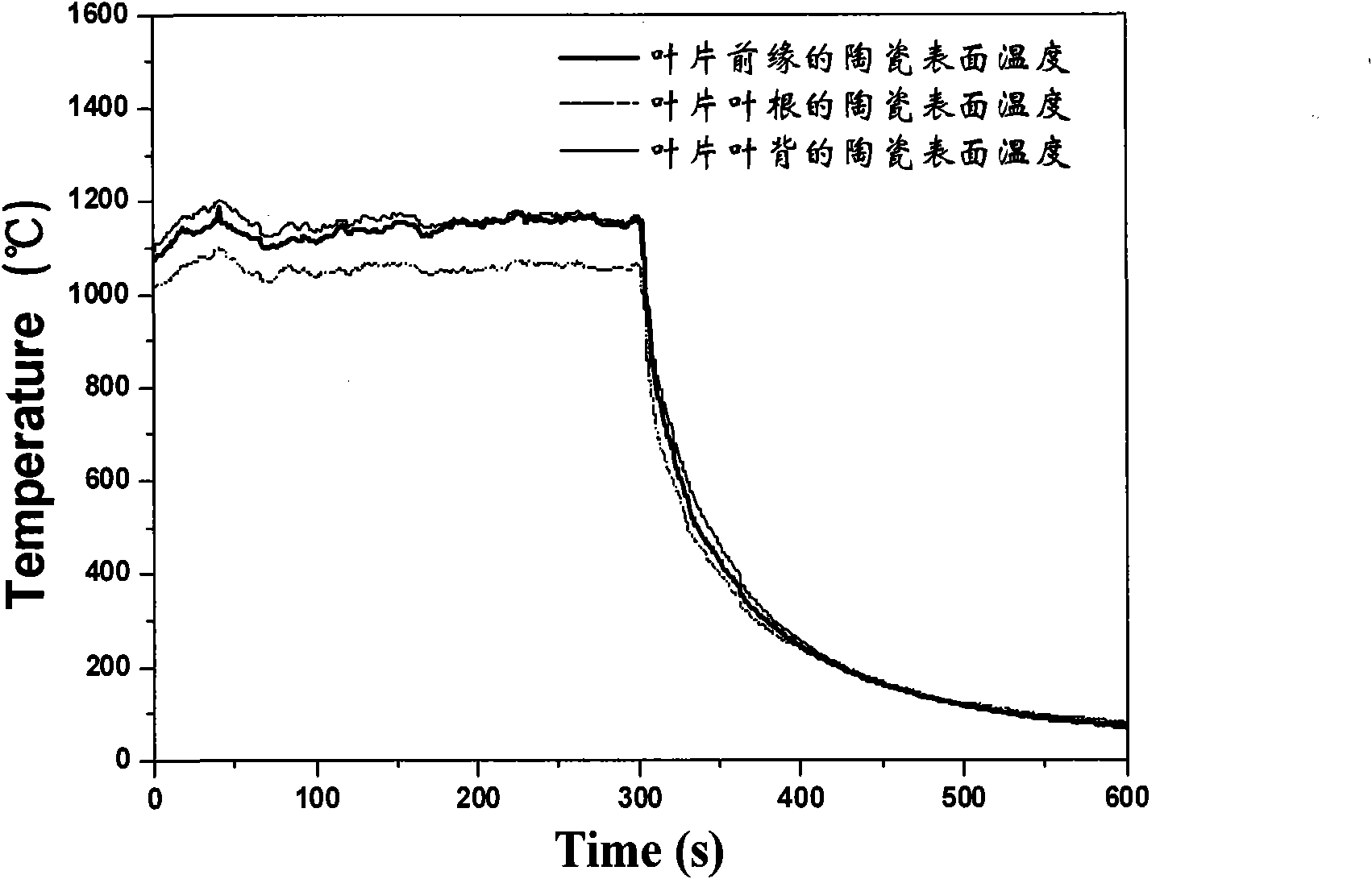
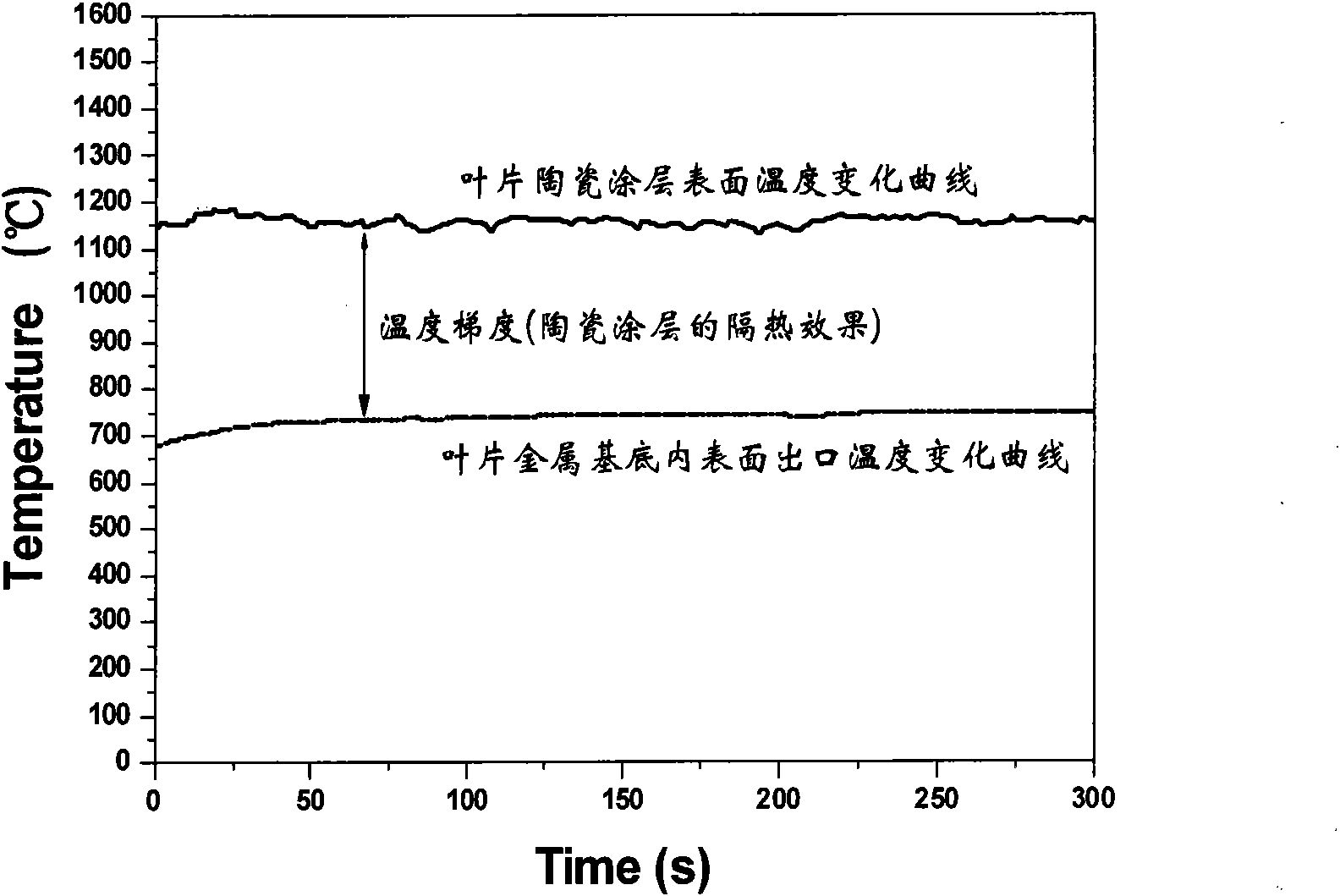
The invention belongs to the technical field of turbine blade performance detection in the aviation industry, in particular to a simulation test method of thermal fatigue failure of a blade with thermal barrier coating. The method can simulate the thermal fatigue work environment of temperature alternating circulation of various blades in an aircraft engine with high performance, and simultaneously tests and analyzes data, such as temperature, temperature gradient, surface topography image evolution, three dimensional deformation field, three dimensional displacement field, interface oxidation layer and thickening rule thereof, thermal fatigue flaw initiation and expansion, cooling airflow and the like of a blade sample with a thermal barrier coating, thus realizing real-time monitoring of three dimensional thermal strain and stress of the blade in the process of thermal fatigue experiments, and providing an important means for predicting thermal fatigue damaging position and invalidation time of the blade. The experimental data obtained by the method can provide important experiment basis for effectively evaluating the failure mechanism of the aircraft engine blade in the environment of high-temperature gas and predicting ceramic coating dropping position, dropping time and service life.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
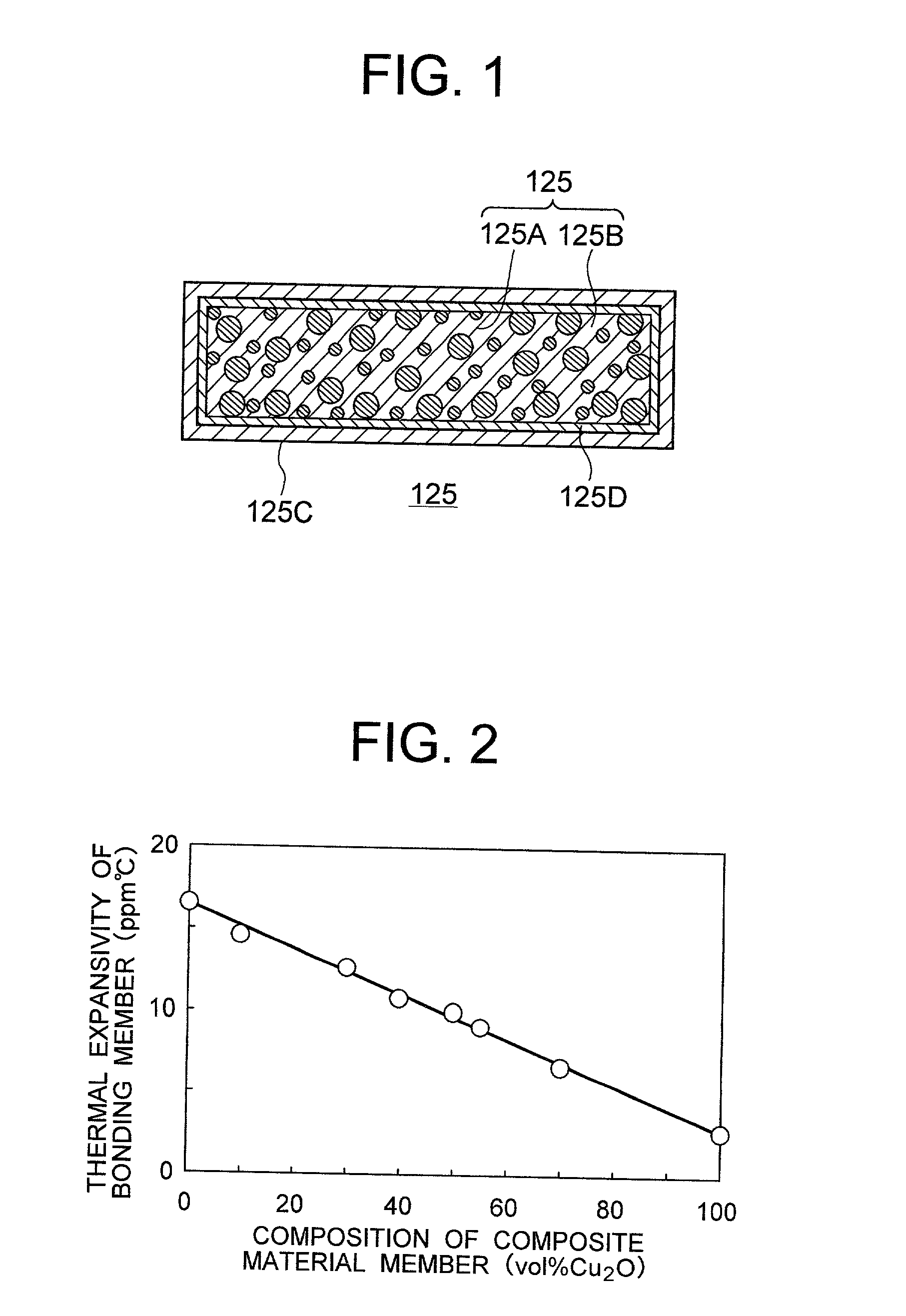
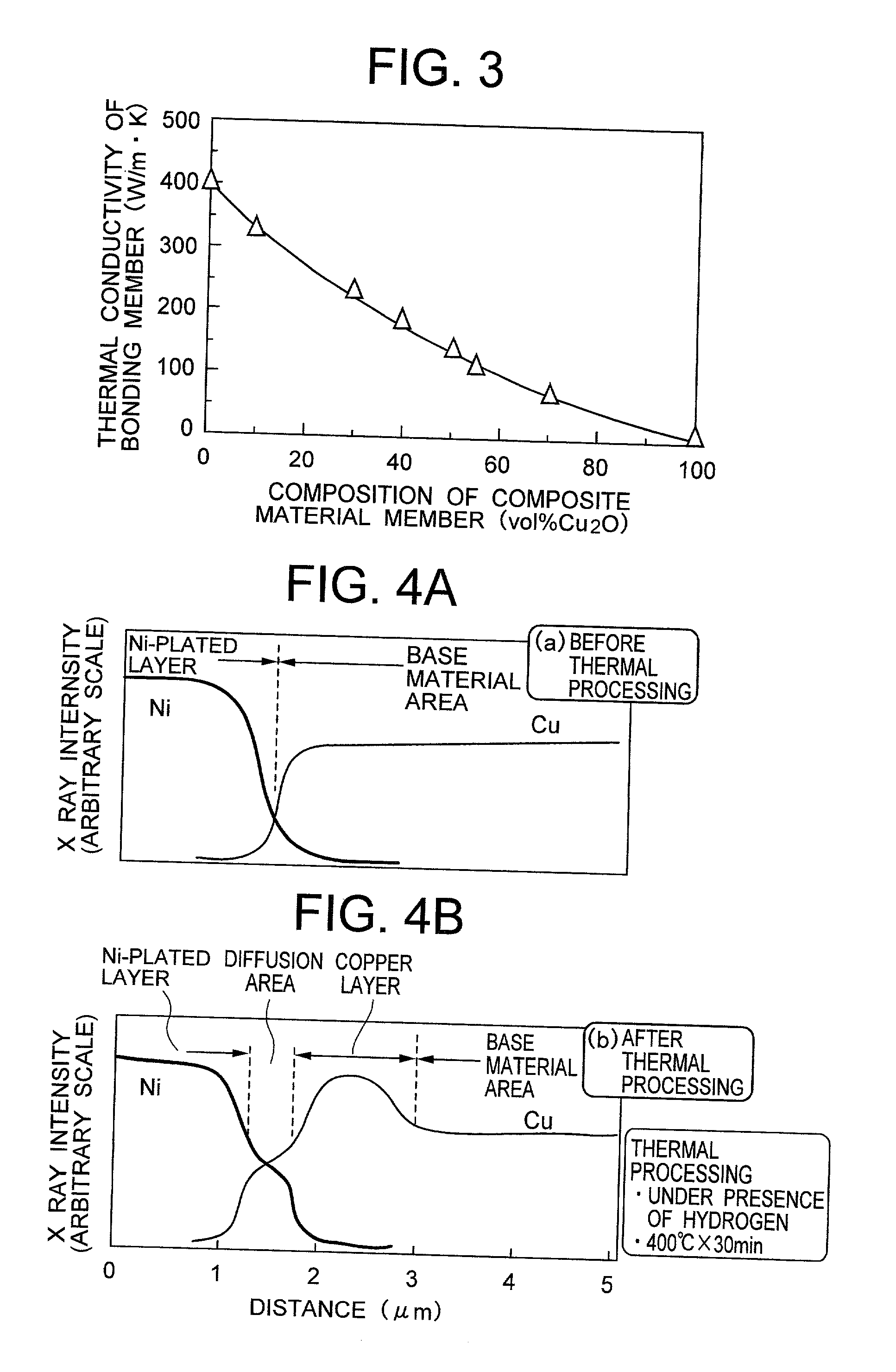
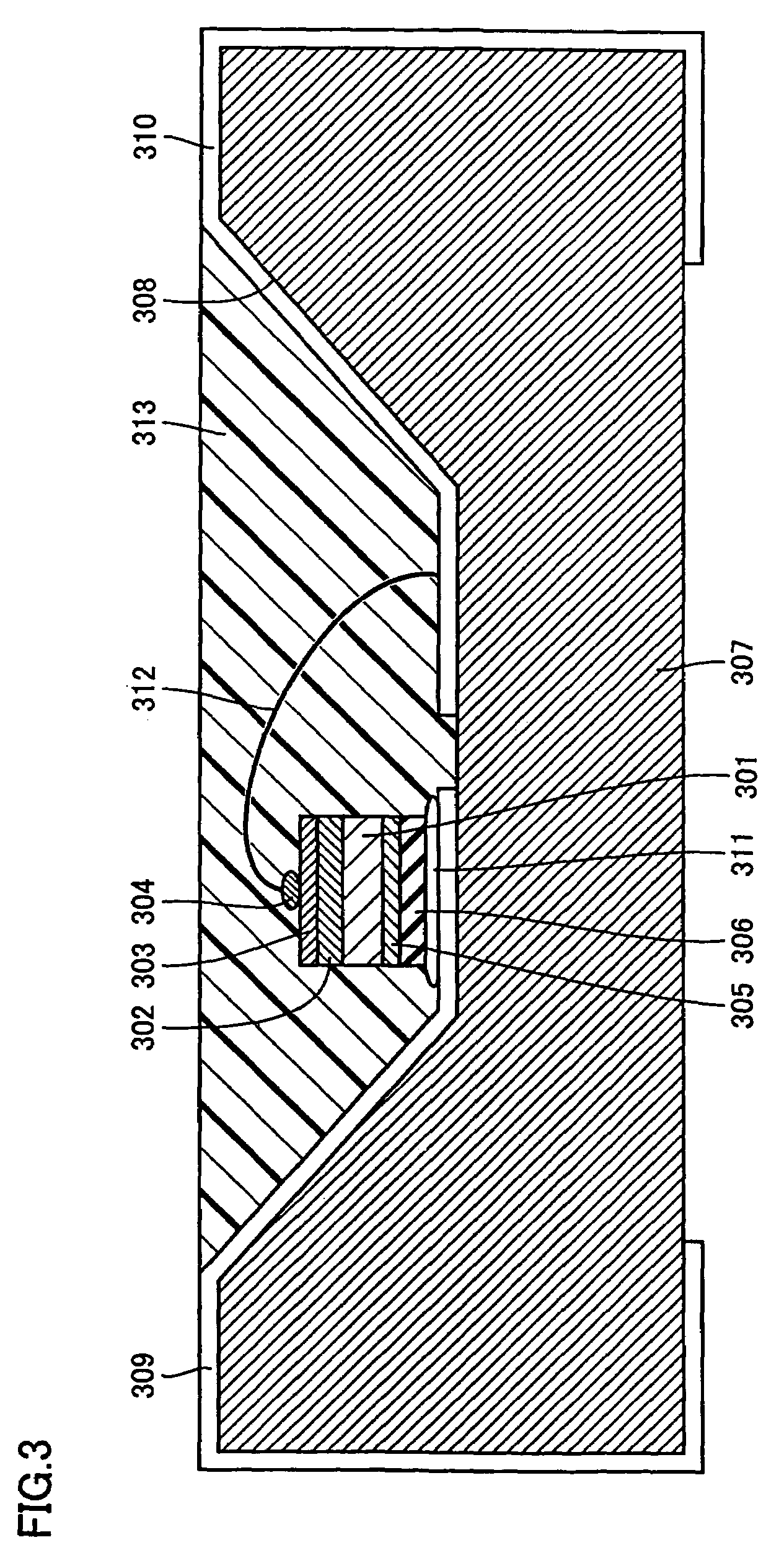
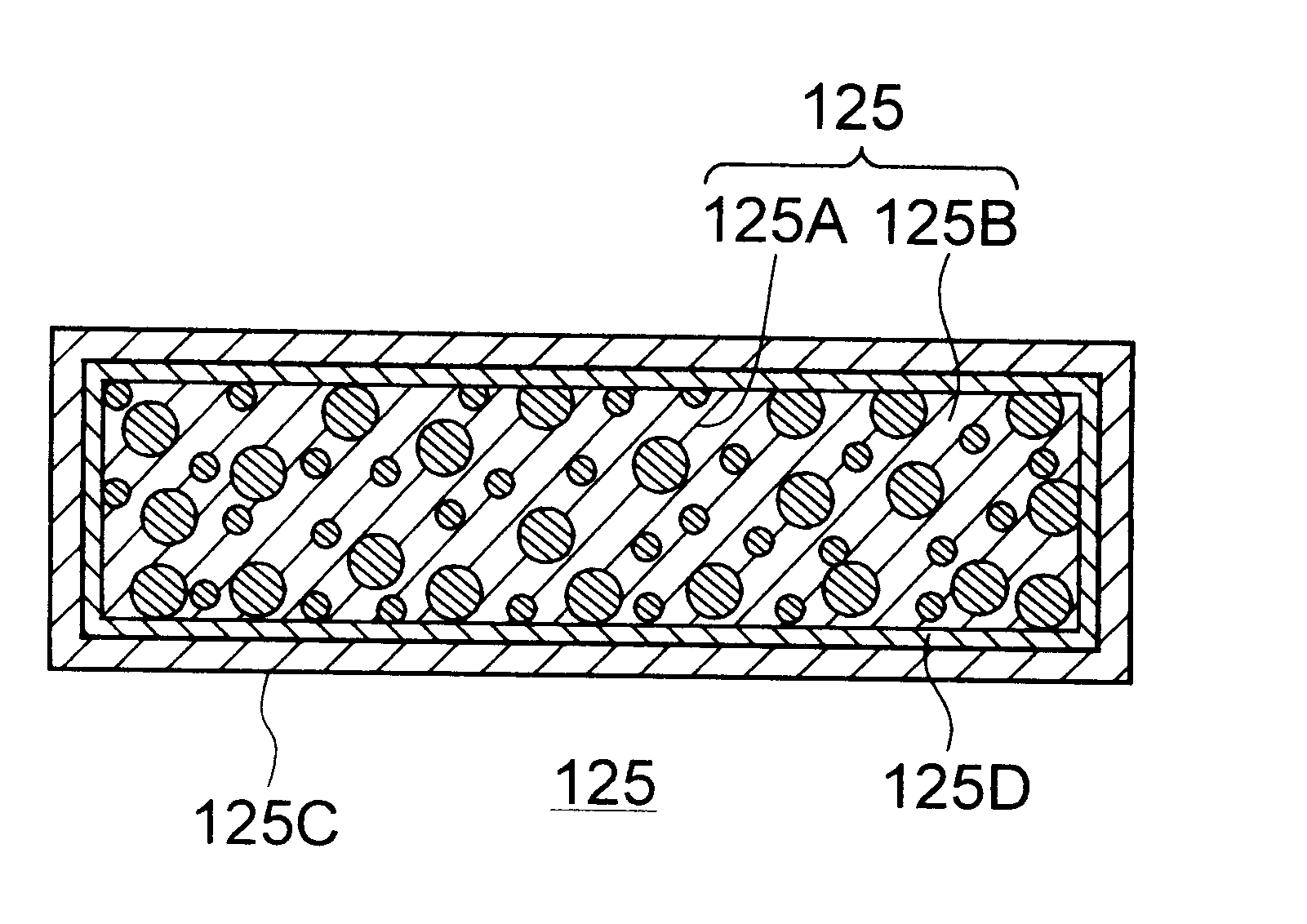
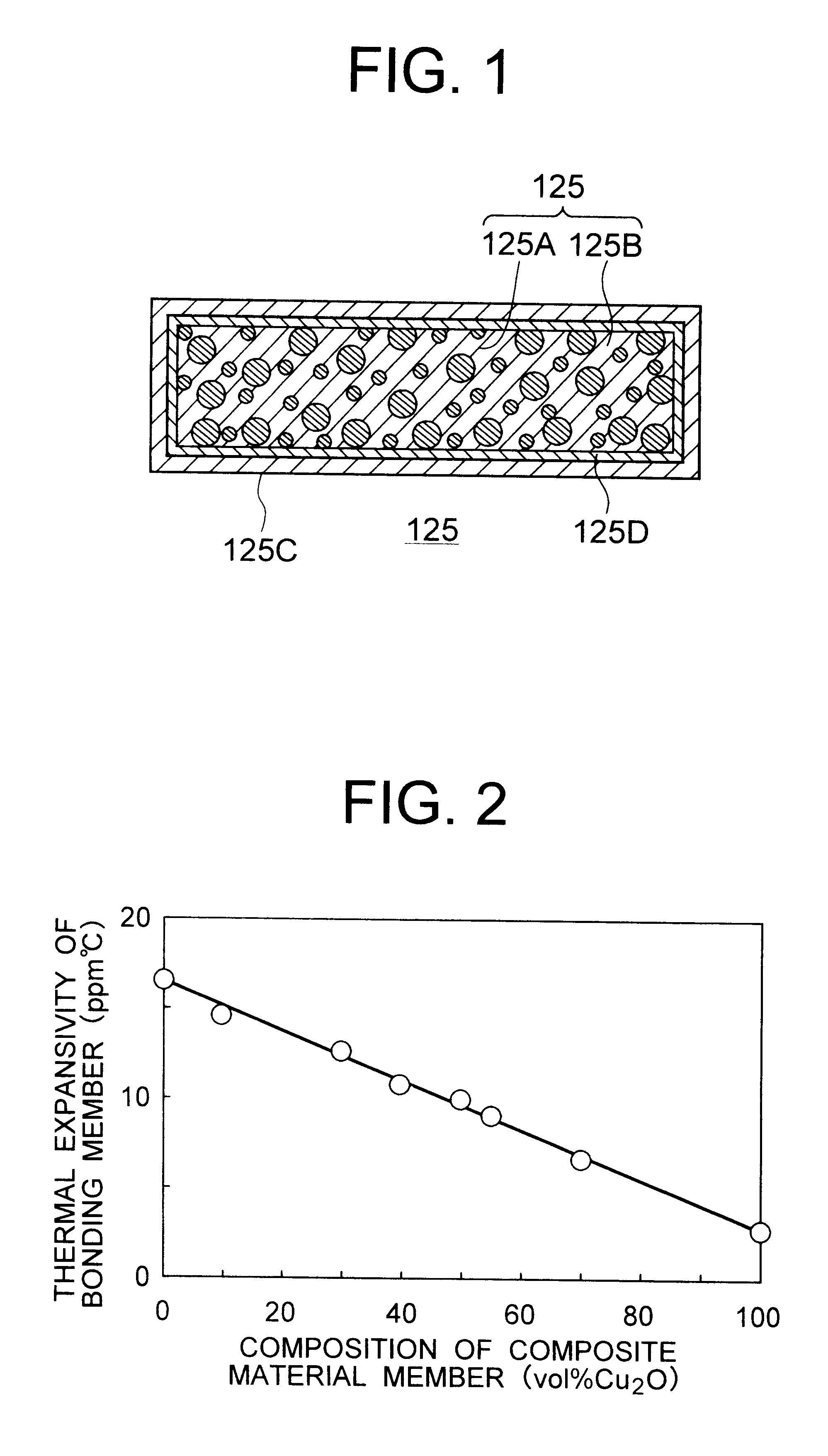
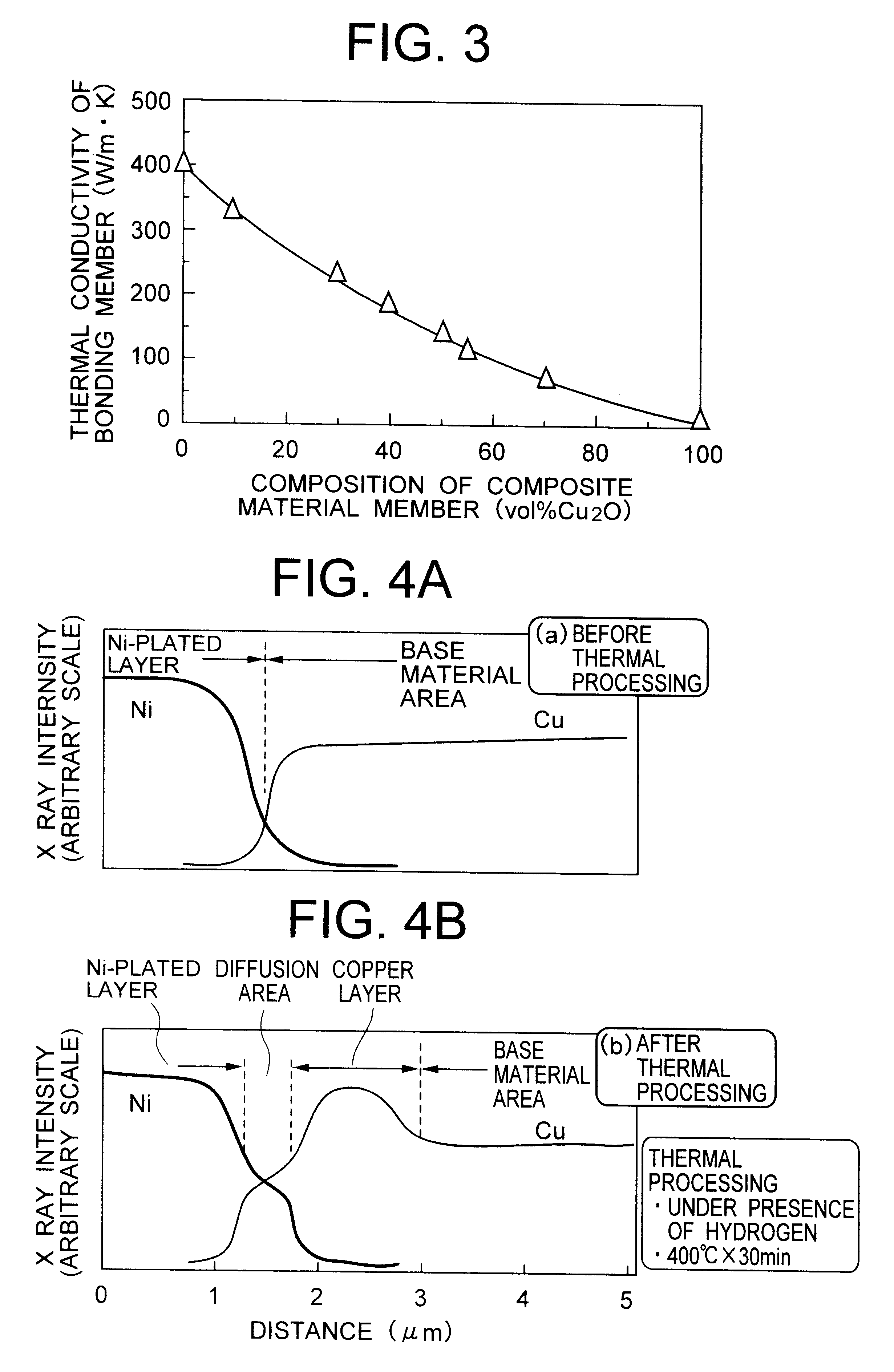
Composite material member for semiconductor device and insulated and non-insulated semiconductor devices using composite material member
InactiveUS20030201530A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductorSurface cover
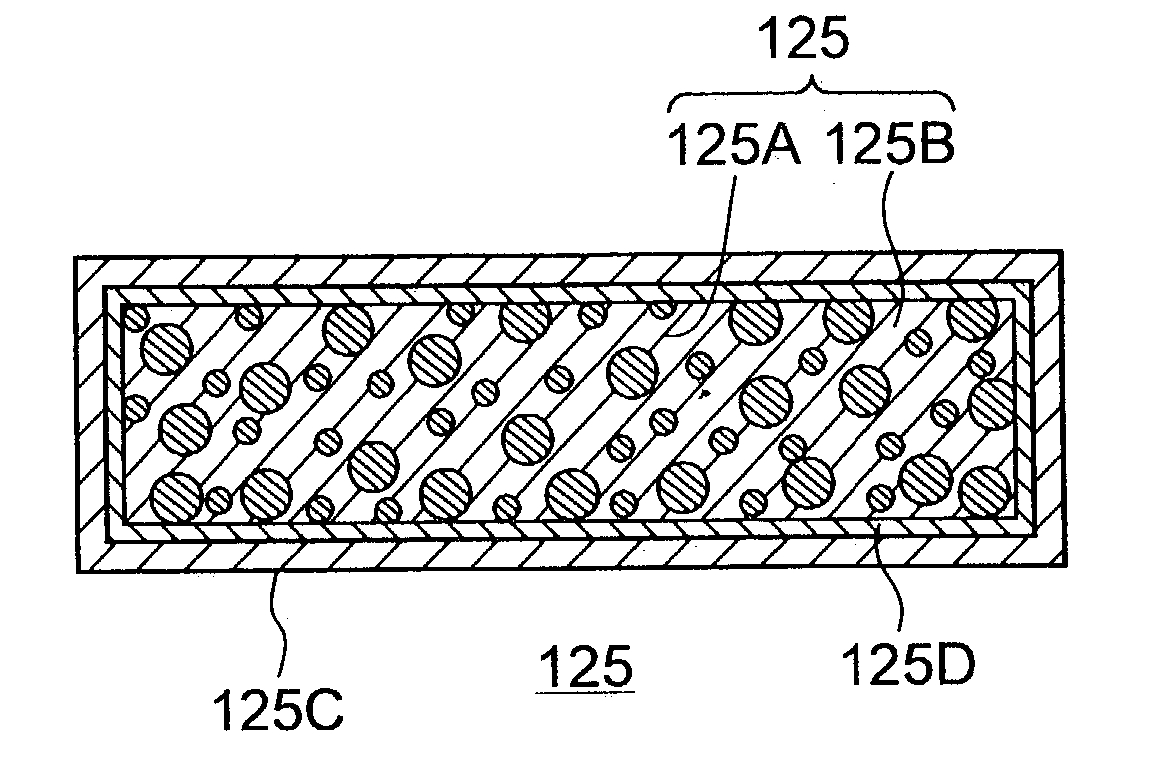
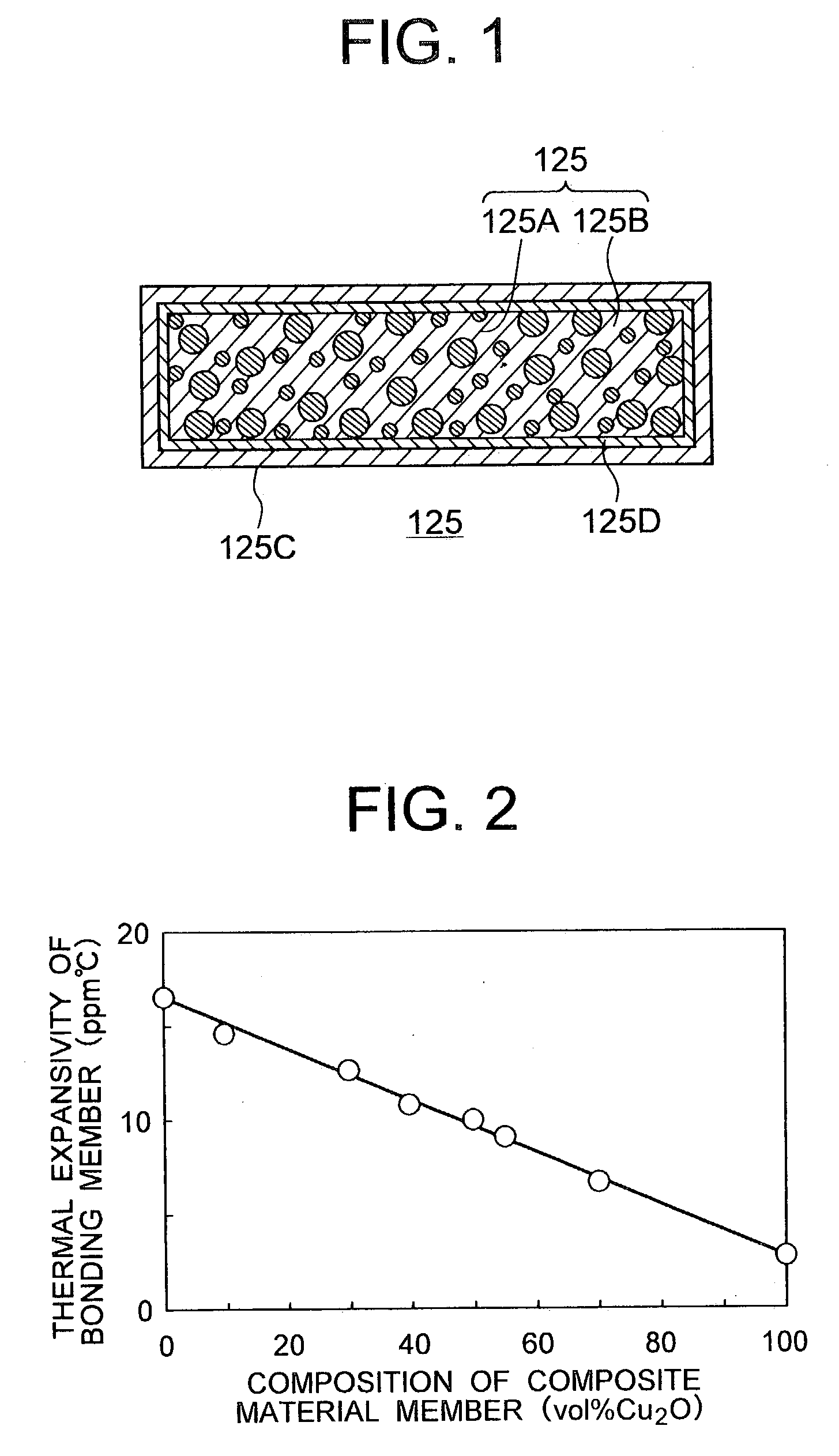
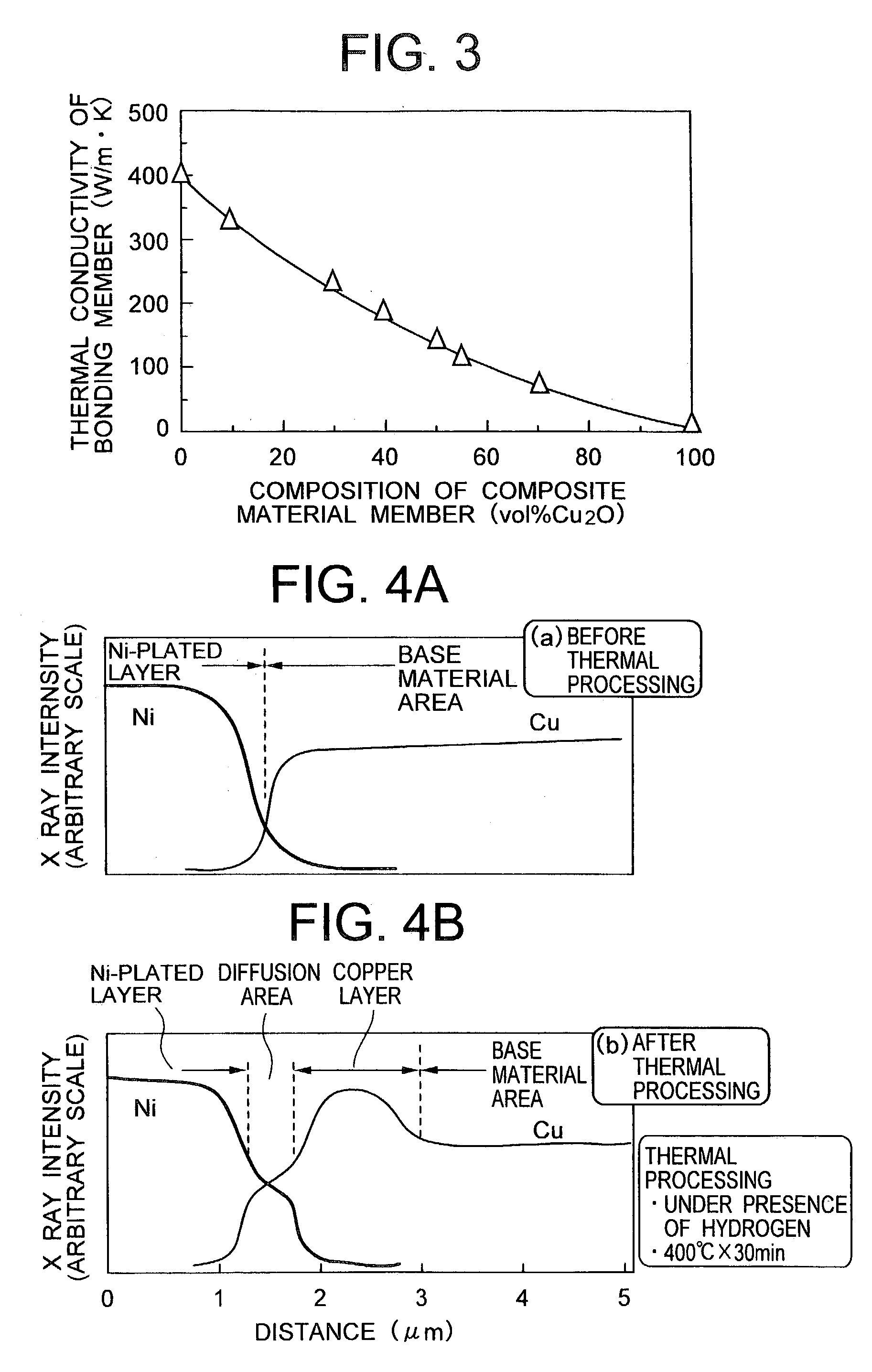
To provide a composite material member for semiconductor device, an insulated semiconductor device and non-insulated semiconductor device using the composite material member, which are effective for obtaining a semiconductor device that alleviates thermal stress or thermal strain occurring during production or operation, has no possibilities of deformation, degeneration and rupture of each member, and is highly reliably and inexpensive. The composite material member for semiconductor device is characterized by being a composite metal plate with particles composed of cuprous oxide dispersed in a copper matrix, in which a surface of the composite metal plate is covered with a metal layer, and a copper layer with thickness of 0.5 mum or larger exists in an interface formed by the composite metal plate and the metal layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and apparatus for separating sheet glass
InactiveUS20060191970A1Heating evenlyQuality improvementWood compressionGlass severing apparatusFlat glassInitiation point
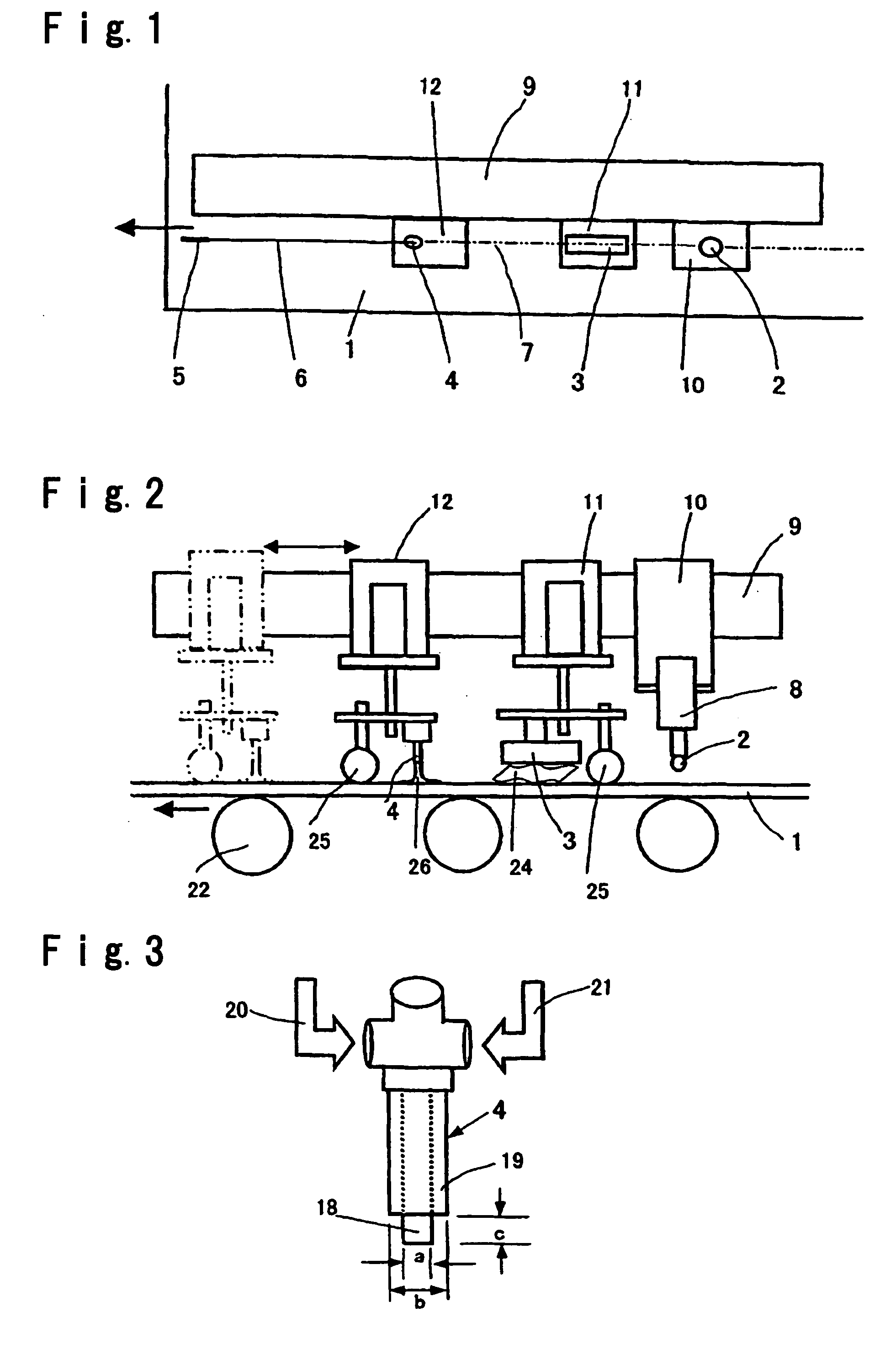
In separation of sheet glass by making use of thermal strain, separated surfaces can be obtained to avoid the occurrence of glass chips and to have excellent linearity even in relatively thick sheet glass. After a score, which serves as a crack initiation point is engraved at a separation initiation point in sheet glass, the sheet glass is heated along an imaginary line of by a heating burner; the heated portion of the sheet glass with the imaginary line of separation set therein is locally cooled by a mist, which is produced by a cooling nozzle comprising a liquid-ejecting port disposed at a central portion thereof and a gas-ejecting port disposed around an outer periphery of the liquid-ejecting port, the liquid-ejecting port projecting farther than the gas-ejecting port; and a minute crack of the score is caused to propagate along the imaginary line of separation to form a crack required for separation of the sheet glass.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Four-wall turbine airfoil with thermal strain control for reduced cycle fatigue
A turbine airfoil (20B) with a thermal expansion control mechanism that increases the airfoil camber (60, 61) under operational heating. The airfoil has four-wall geometry, including pressure side outer and inner walls (26, 28B), and suction side outer and inner walls (32, 34B). It has near-wall cooling channels (31F, 31A, 33F, 33A) between the outer and inner walls. A cooling fluid flow pattern (50C, 50W, 50H) in the airfoil causes the pressure side inner wall (28B) to increase in curvature under operational heating. The pressure side inner wall (28B) is thicker than walls (26, 34B) that oppose it in camber deformation, so it dominates them in collaboration with the suction side outer wall (32), and the airfoil camber increases. This reduces and relocates a maximum stress area (47) from the suction side outer wall (32) to the suction side inner wall (34B, 72) and the pressure side outer wall (26).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Method for preparing thin film heterostructure
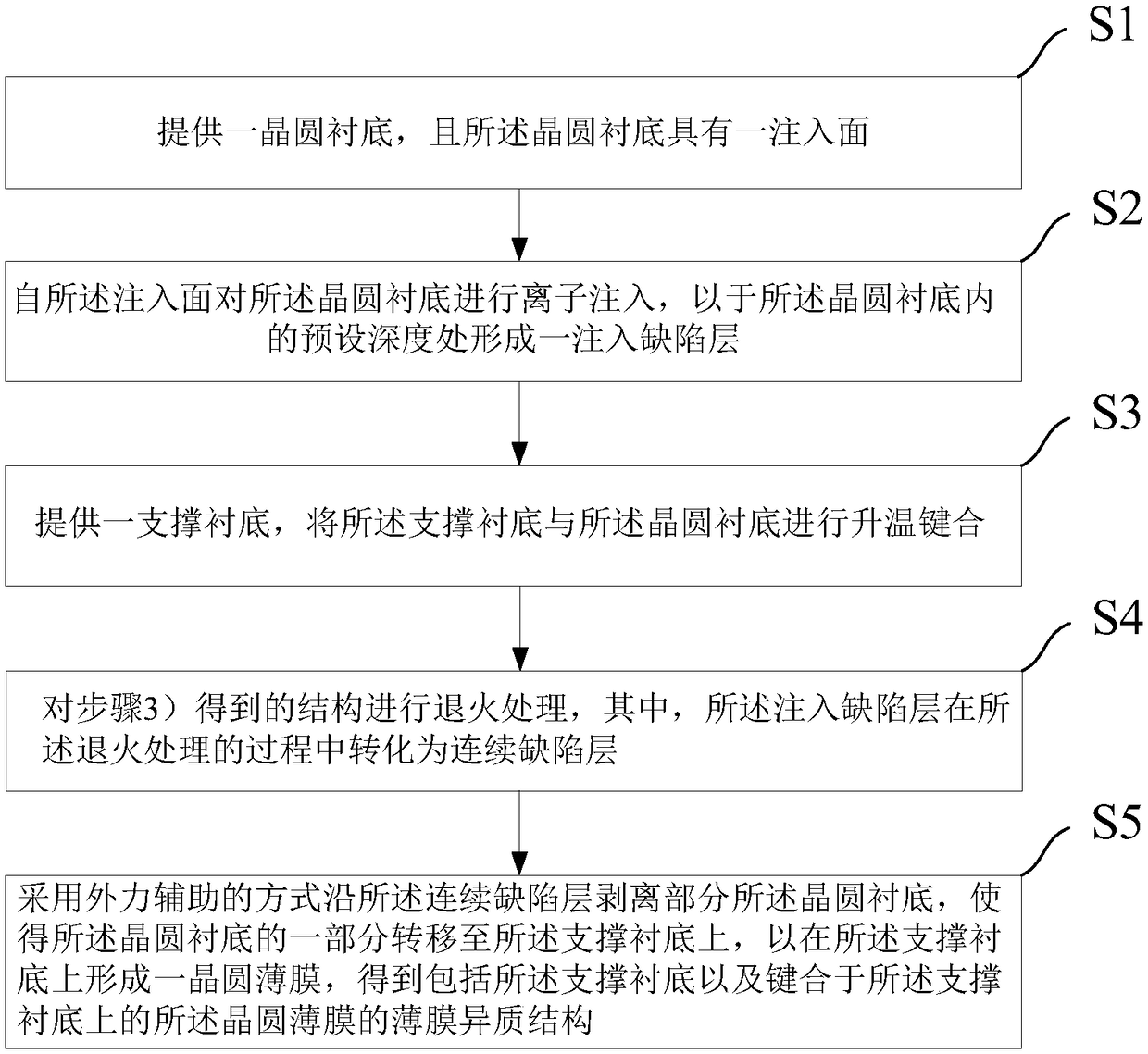
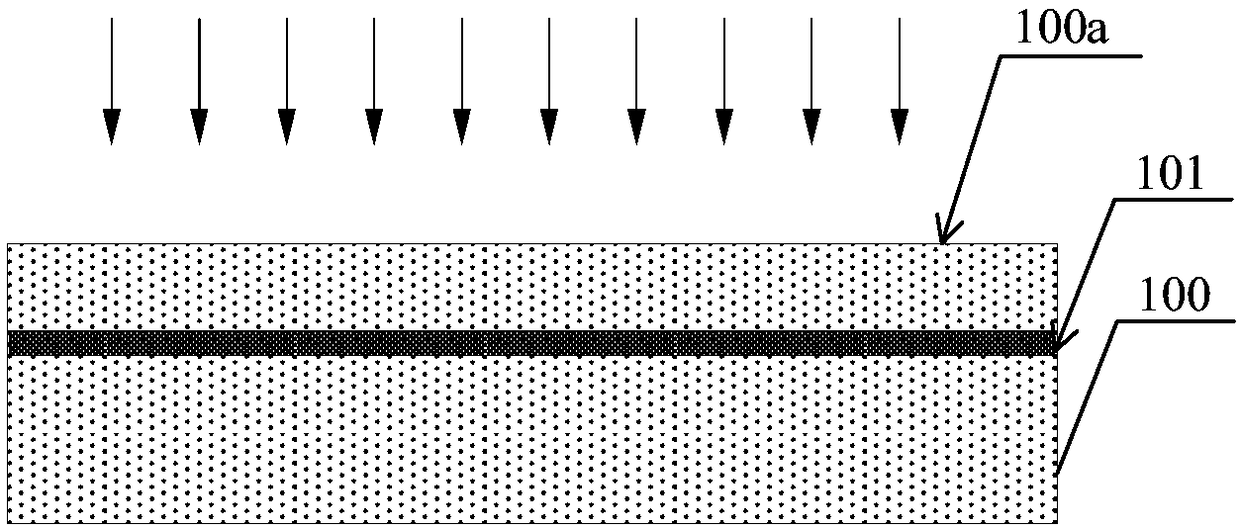
InactiveCN108336219AReduce thermal strainAvoid chippingPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesOptoelectronicsIon implantation
The invention provides a method for preparing a thin film heterostructure. The method comprises the steps of providing a wafer substrate with an injection surface; conducting ion injection from the injection surface on the wafer substrate to form an injection defect layer at the predetermined depth of the wafer substrate; providing a support substrate, and performing temperature rising bonding onthe support substrate and the wafer substrate; annealing a obtained structure to form a continuous defect layer; stripping part of the wafer substrate through external force assisting, and forming wafer film on the wafer substrate to obtain a thin film heterostructure including the support substrate and the wafer film. The method can reduce the thermal strain of a bonding structure through the temperature rising bonding, so that the bonding structure remains stable and complete in the high-temperature process, and avoid the problem of film cracking caused by thermal mismatch in the stripping process, the bonding structure is separated from the continuous defect layer through the external force assisting method, so that no effect is caused on a bonding interface, and an external force assisting stripping method can reduce stripping temperature and stripping time, thereby reducing the cumulative effect of thermal stress in a piezoelectric crystal.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of mfg. GaN-base LED
InactiveCN1564331AImprove thermal stabilityExtend your lifeSemiconductor devicesLuminosityThermal expansion
Zone of luminosity in tube core is divided into more than two zones in smaller size through etching deep trough in order to raise luminous efficiency, thermal stability and service life of device. Or, using reverse welding technique welds tube core onto heat sink material with higher thermal conductivity and using laser lift-off technology peels off substrate material. Thermal strain between epitaxial layer and substrate material or between epitaxial layer and heat sink material caused by unmatched coefficients of thermal expansion is controlled in very low level in the invention. The invention raises luminous efficiency, thermal stability and service life of device, and does not generate unfavorable influence on characteristic of GaN substrate material.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Vacuum insulating glass unit with viscous edge seal
InactiveUS20130101759A1Provide structural strengthFit closelyClimate change adaptationWindows/door improvementViscous shearGlass sheet
Vacuum insulating glass (VIG) units and edge seals for VIG units are provided. The VIG units include an edge seal that includes a viscous material, and is configured to allow the glass sheets to move laterally relative to one another when the glass sheets experience differential thermal strain and further configured such that viscous shear occurs within at least a portion of the viscous material when there is relative lateral movement between the glass sheets. The edge seals comprise a cavity that contains at least a portion of the viscous material, wherein at least a portion of a boundary defining the cavity is reversibly expandable and collapsible such that the viscous material and the cavity are configured to maintain volume compatibility when one or both of the viscous material and the cavity undergo a temperature-induced volume change.
Owner:JONES ROBERT S
Method of Preparing Metal Matrix Composite and Coating Layer and Bulk Prepared Thereby
InactiveUS20090120539A1High temperature strengthAvoid heat buildupMolten spray coatingEfficient propulsion technologiesCrazingHeat treated
This invention provides a method of preparing a metal matrix composite, and a coating layer and bulk prepared by using the same and in particular, it provides a method of preparing a metal matrix composite, which comprises the steps of providing a substrate; preparing a mixed powder comprising i) a first metal powder comprising a metal, alloy or mixture particle thereof, ii) a second metal powder comprising an intermetallic compound forming metal particle which forms an intermetallic compound along with the metal or the alloy element of the alloy, and iii) a ceramic powder comprising a ceramic or mixture particle thereof; injecting the mixed powder prepared above into a spray nozzle for coating; coating the mixed powder on the surface of the substrate by accelerating the mixed powder in the state of non-fusion at a speed of 300 to 1,200 m / s by the flow of transportation gas flowing in the spray nozzle; and forming the intermetallic compound by the thermal treatment of the coated coating layer, and a coating layer and bulk prepared by using the same, whereby the coating layer and bulk material with high wear resistance and excellent resistance against fatigue crack on the surface without causing damages such as heat strain to the substrate during the preparation of the coating layer can be provided.
Owner:SKC SOLMICS
Composite material member for semiconductor device and insulated and non-insulated semiconductor devices using composite material member
InactiveUS20020192488A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductorSurface cover
To provide a composite material member for semiconductor device, an insulated semiconductor device and non-insulated semiconductor device using the composite material member, which are effective for obtaining a semiconductor device that alleviates thermal stress or thermal strain occurring during production or operation, has no possibilities of deformation, degeneration and rupture of each member, and is highly reliably and inexpensive. The composite material member for semiconductor device is characterized by being a composite metal plate with particles composed of cuprous oxide dispersed in a copper matrix, in which a surface of the composite metal plate is covered with a metal layer, and a copper layer with thickness of 0.5 mum or larger exists in an interface formed by the composite metal plate and the metal layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Segmented thermal barrier coating
A ceramic thermal barrier coating (TBC) (18) having first and second layers (20, 22), the second layer (22) having a lower thermal conductivity than the first layer for a given density. The second layer may be formed of a material with anisotropic crystal lattice structure. Voids (24) in at least the first layer (20) make the first layer less dense than the second layer. Grooves (28) are formed in the TBC (18) for thermal strain relief. The grooves may align with fluid streamlines over the TBC. Multiple layers (84, 86, 88) may have respective sets of grooves (90), Preferred failure planes parallel to the coating surface (30) may be formed at different depths (A1, A2, A3) in the thickness of the TBC to stimulate generation of a fresh surface when a portion of the coating fails by spalling. A dense top layer (92) may provide environmental and erosion resistance.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Composite substrate, elastic wave device using the same, and method for manufacturing composite substrate
ActiveUS20100244631A1Easy to manufactureInhibit the generation of cracksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesIn planeComposite substrate
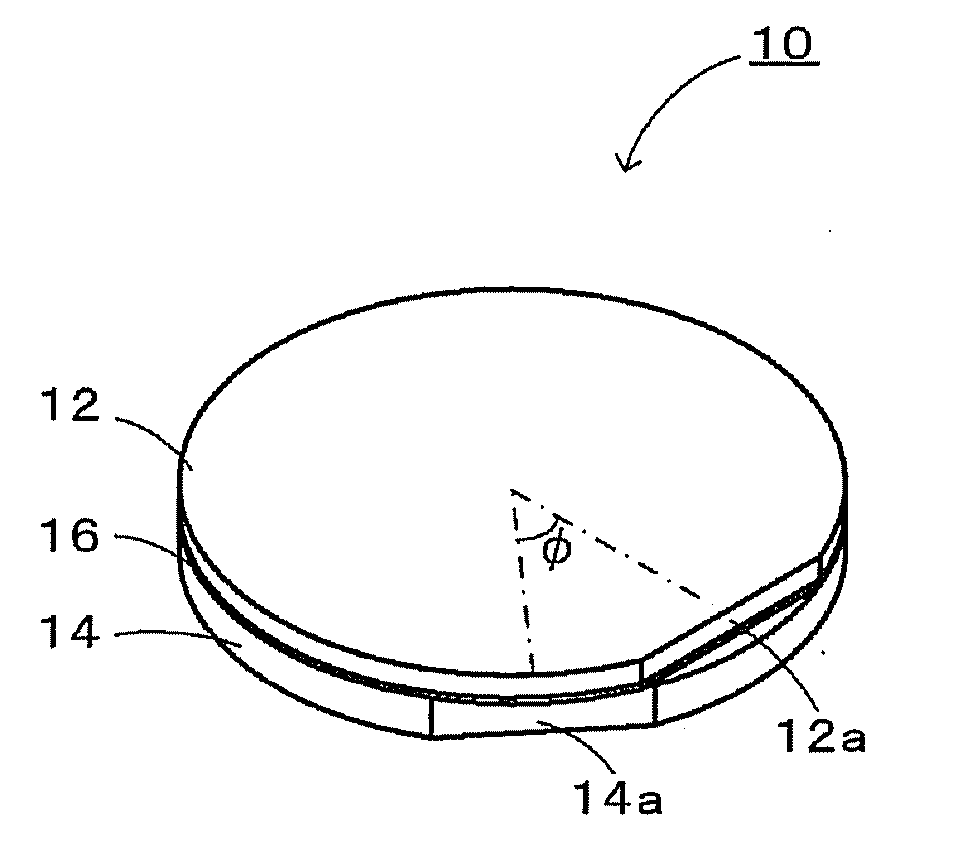
In a composite substrate 10, the piezoelectric substrate 12 which is capable of transmitting an elastic wave and a support substrate 14 which a smaller thermal expansion coefficient than the piezoelectric substrate 12 are bonded to each other. The in-plane maximum thermal strain amount which is the largest thermal strain amount in the plane of the composite substrate 10 has a minimum value and a maximum value when the piezoelectric substrate 12 and the support substrate 14 are relatively rotated 0° to 360°, and the piezoelectric substrate 12 and the support substrate 14 are bonded to each other so that the in-plane maximum thermal strain amount has the minimum value or a value in the vicinity thereof.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
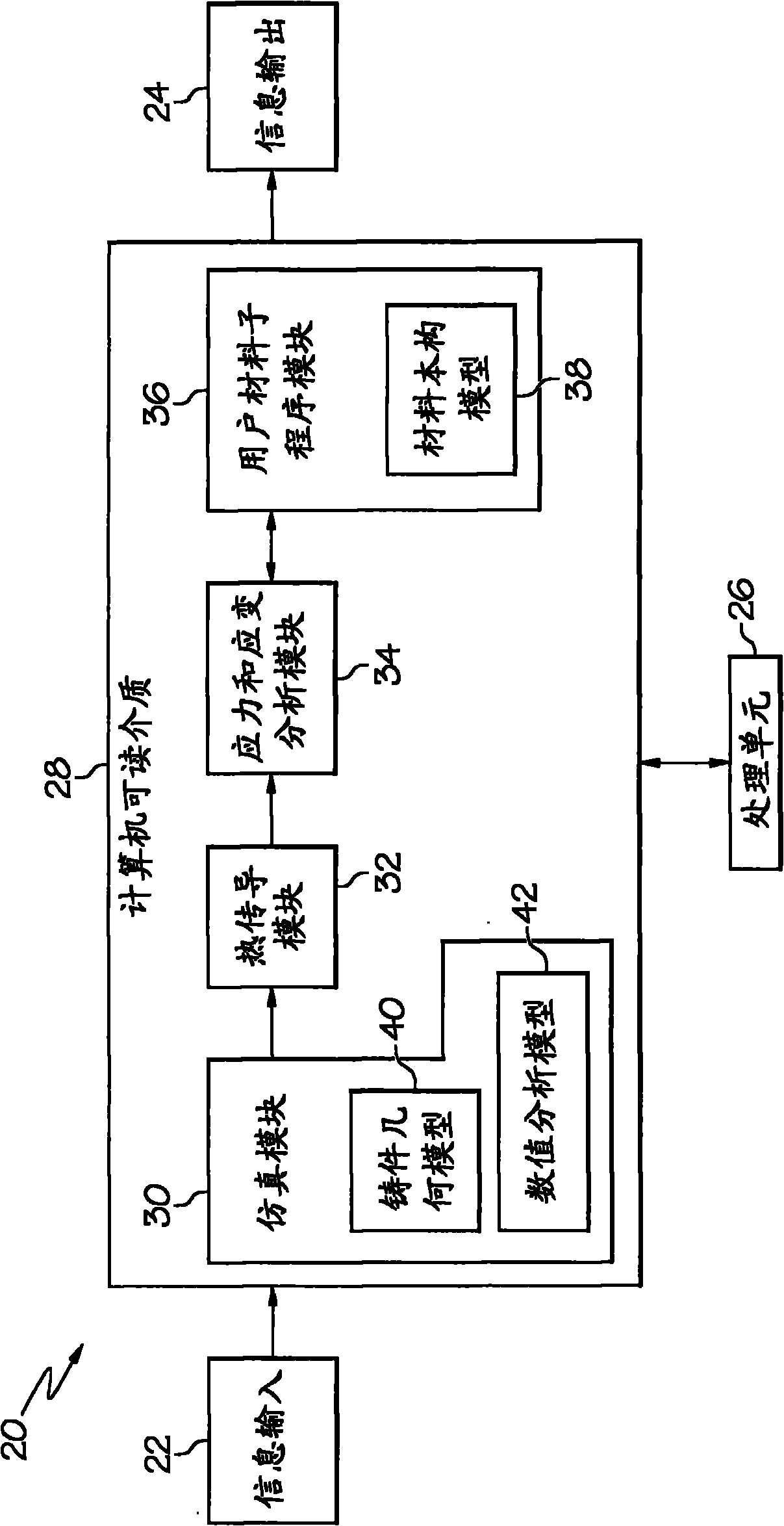
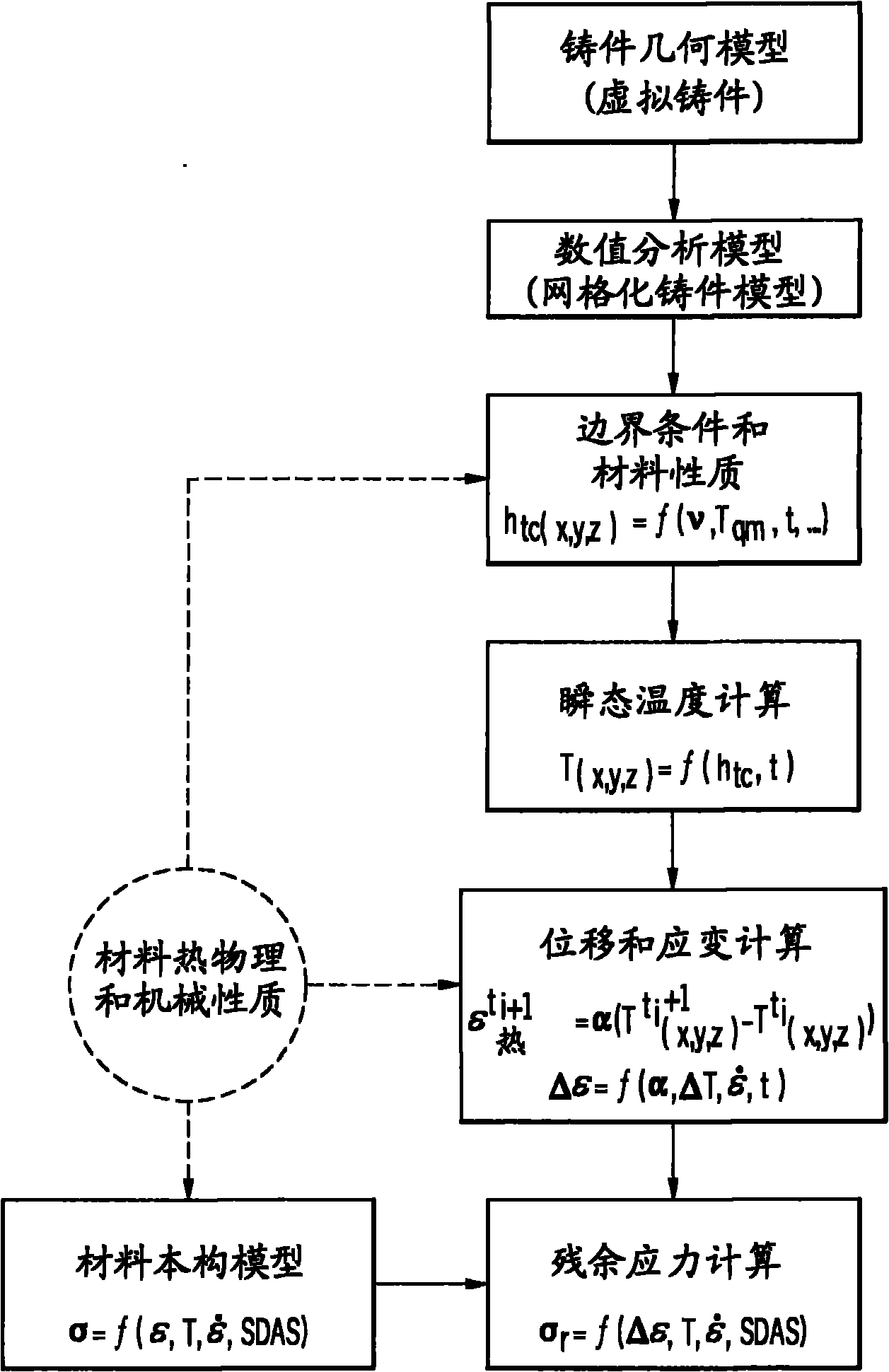
Methods of predicting residual stresses and distortion in quenched aluminum castings
ActiveCN101887472ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsQuenchingDistortion
Computational systems, methods, and articles of manufacture to predict at least one of residual stresses and distortion in quenched aluminum castings. Residual stresses and distortion may be predicted through incorporating thermal strains induced during quenching with the nonlinear constitutive behavior of quenched microstructures of a quenched aluminum casting, wherein thermal strains arise generally from non-uniform transient temperature distribution of the casting during quenching. The transient temperature distribution of the aluminum casting during quenching may be calculated based on heat transfer coefficients specific to one or more nodes, elements and / or zones on the surfaces of the aluminum casting. The nonlinear constitutive behavior of the quenched aluminum casting may be modeled as functions of temperatures, strain rates, and microstructure variations. A material constitutive model accounts for not only strain hardening and creep, but also precipitate hardening. Thereby, residual stresses and distortion in the quenched aluminum castings can be predicted using the embodiments.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
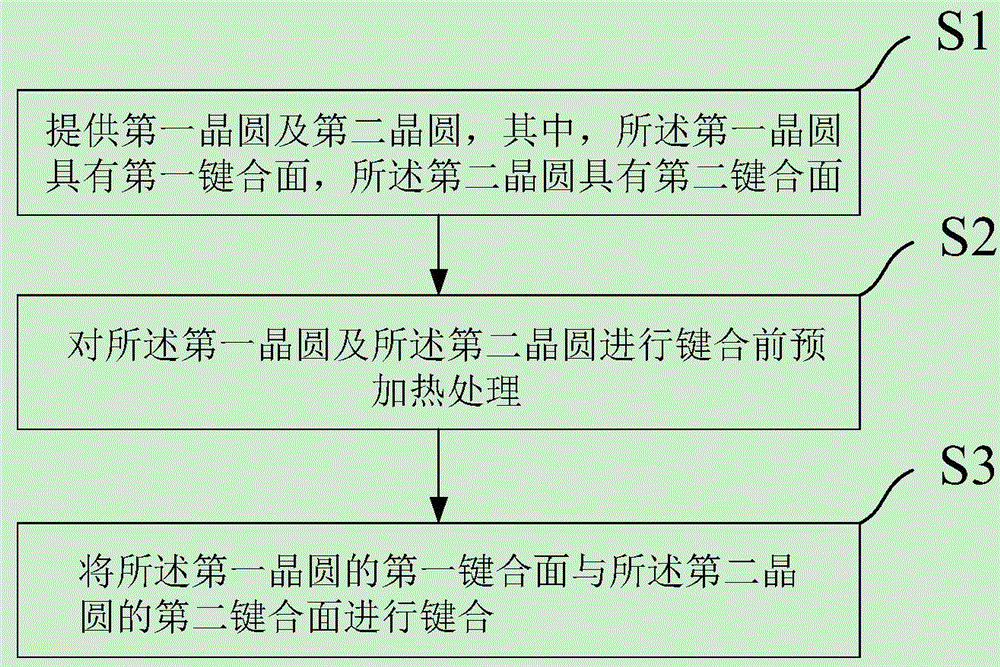
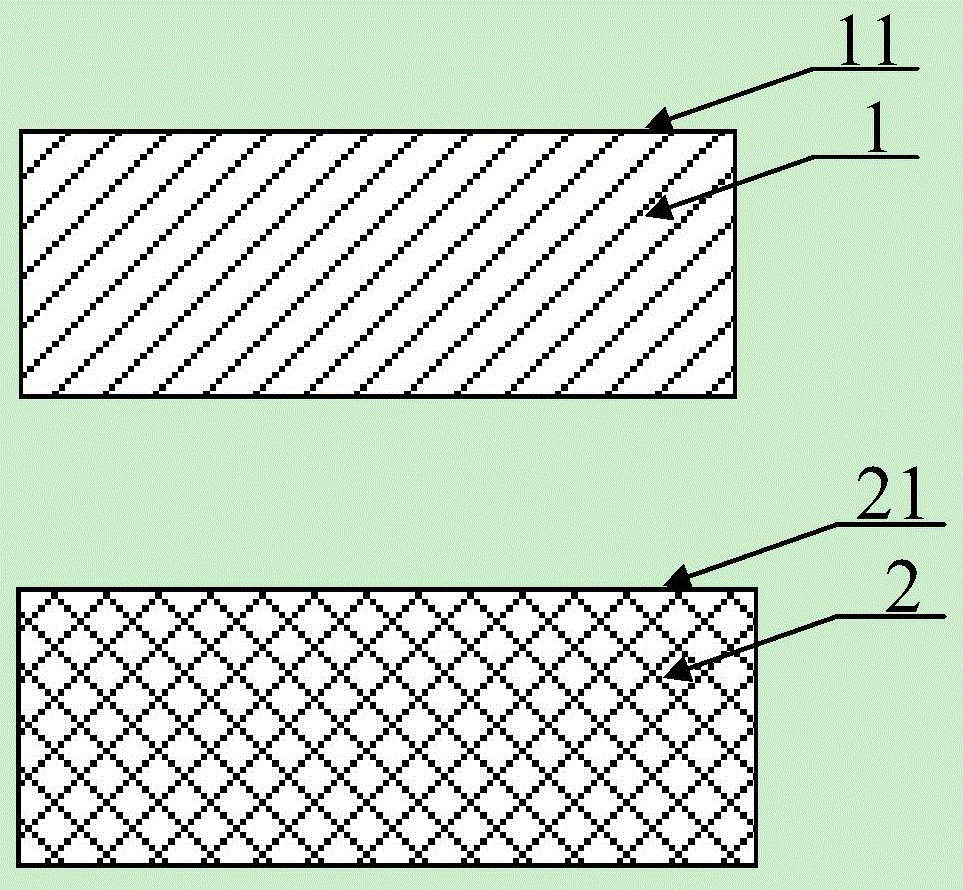
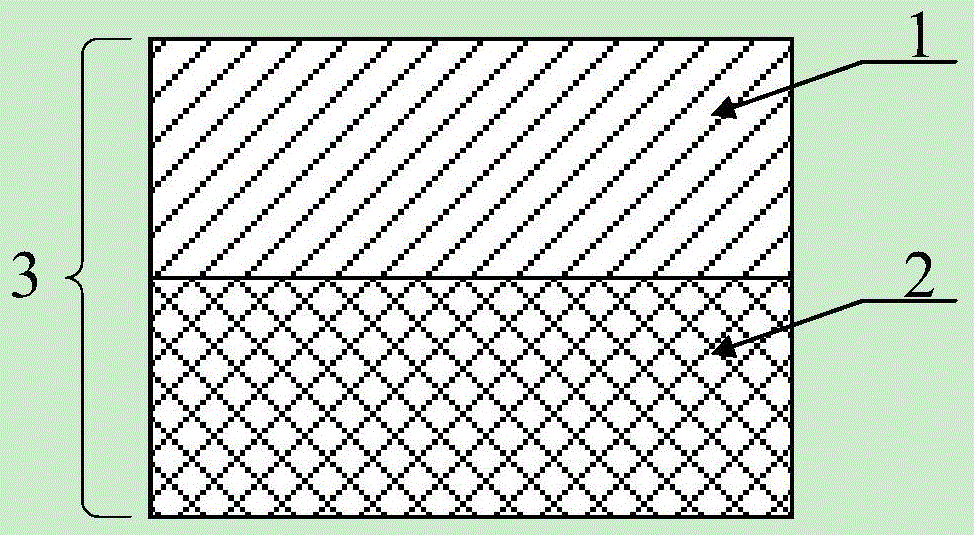
Wafer bonding method and preparation method for foreign substrate
ActiveCN106711027AReduce thermal strainImprove reliabilityPrecision positioning equipmentSoldering apparatusEngineeringWafer bonding
The invention provides a wafer bonding method and a preparation method for a foreign substrate. The wafer bonding method at least comprises the following steps: S1) supplying a first wafer and a second wafer, wherein the first wafer is equipped with a first bonding surface, and the second wafer is equipped with a second bonding surface; S2) preheating before bonding the first wafer and the second wafer; and S3) bonding the first bonding surface of the first wafer with the second bonding surface of the second wafer. According to the scheme, the preheating before the bonding for the wafers is capable of effectively reducing the thermal strain of the foreign bonding structure in a high-temperature post-annealing process, so that the use scope of the foreign bonding can be widened and the reliability of a foreign integrated material can be promoted. Meanwhile, the problems of de-bonding and broken bonding structure caused by thermal strain of the foreign bonding structure in the high-temperature post-annealing process can be solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI NOVEL SI INTEGRATION TECH CO LTD
High temperature elastomers with low hydrocarbon vapor permeability
InactiveUS20060229416A1Improve robustnessIncrease flexibilitySynthetic resin layered productsConductive materialParticulatesHigh stress
An elastomer blend is made by admixing fluoroelastomer and fluorinated silicone polymer (with optional filler and / or conductive particulate) into a polymeric admixture in weight ratios to provide a low vaporous hydrocarbon permeation rate and high thermal strain value in thermally robust elastomer cured from the blend. The blend is of especial use for making gaskets for use in high stress conditions at elevated operating temperatures.
Owner:FREUDENBERG NOK GEN PARTNERSHIP
Nitride-based semiconductor light-emitting device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7170101B2Improve responseImprove adhesionOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsNitrideLight emitting device
Owner:SHARP KK
Composite material member for semiconductor device and insulated and non-insulated semiconductor devices using composite material member
InactiveUS6579623B2Mosaic printer telegraph systemSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductorMetal
To provide a composite material member for semiconductor device, an insulated semiconductor device and non-insulated semiconductor device using the composite material member, which are effective for obtaining a semiconductor device that alleviates thermal stress or thermal strain occurring during production or operation, has no possibilities of deformation, degeneration and rupture of each member, and is highly reliably and inexpensive. The composite material member for semiconductor device is characterized by being a composite metal plate with particles composed of cuprous oxide dispersed in a copper matrix, in which a surface of the composite metal plate is covered with a metal layer, and a copper layer with thickness of 0.5 mum or larger exists in an interface formed by the composite metal plate and the metal layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
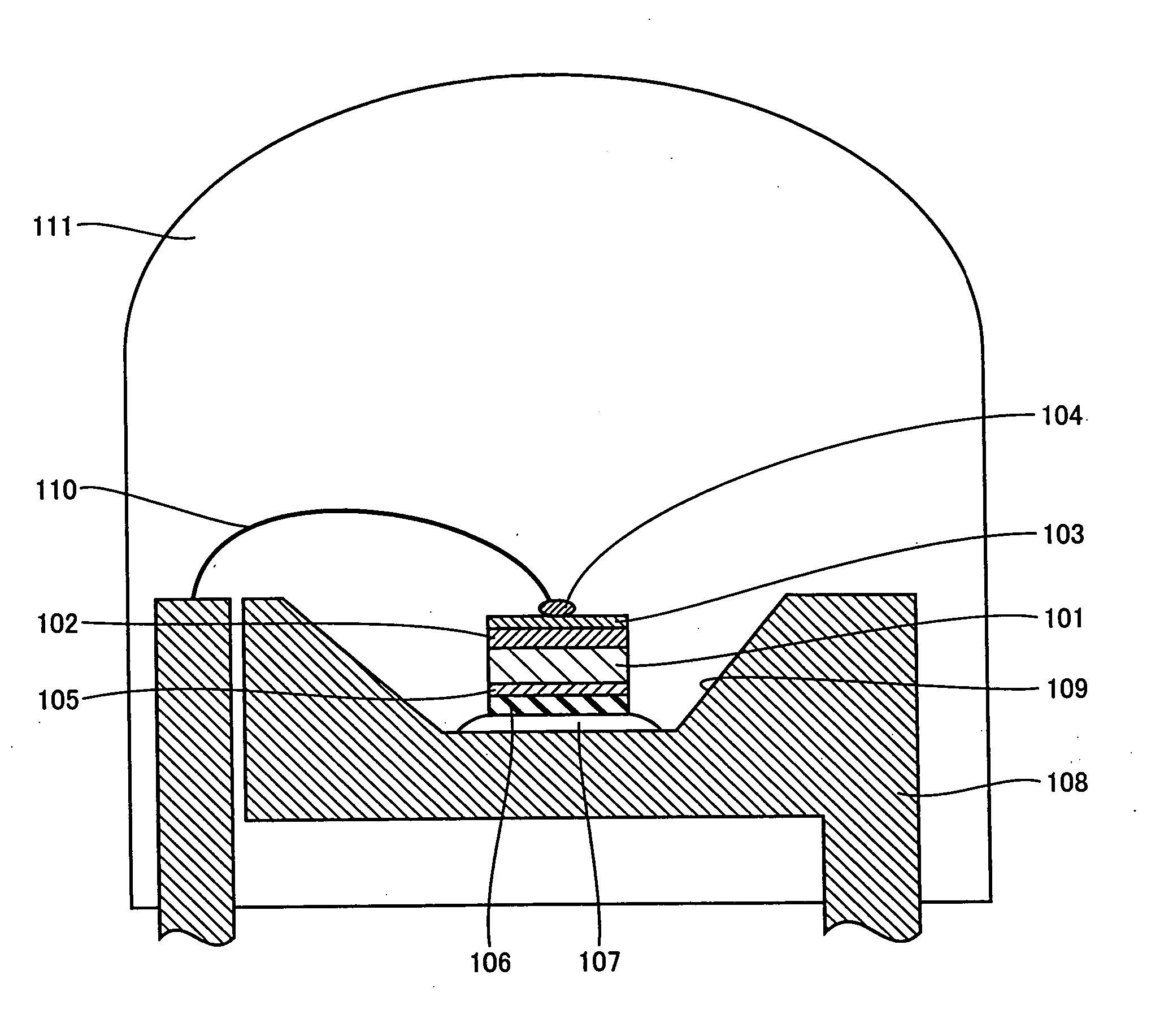
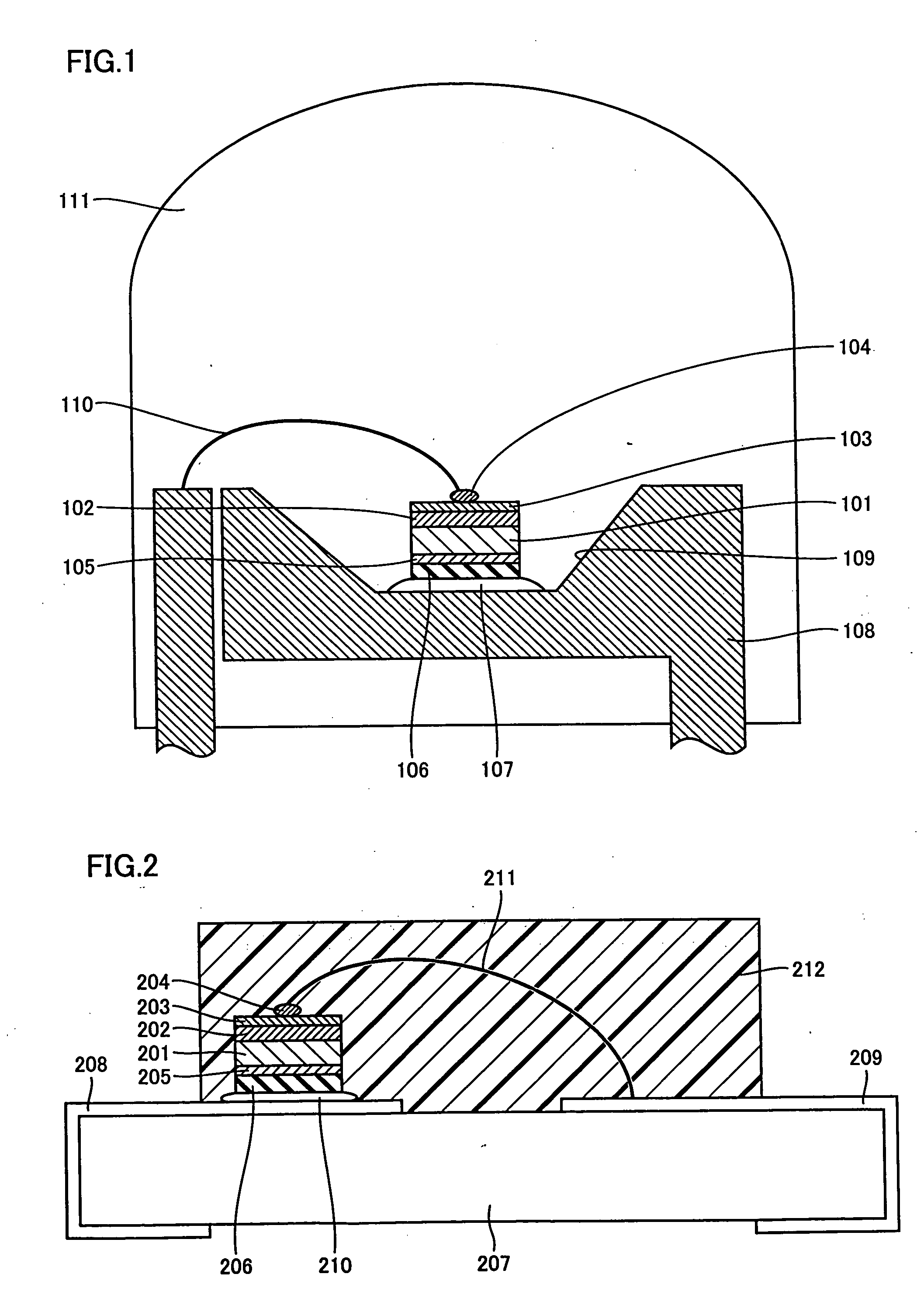
Extension of fatigue life for C4 solder ball to chip connection
InactiveUS20050224973A1Reduces thermally induced strainReduce strainPrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCouplingSolder ball
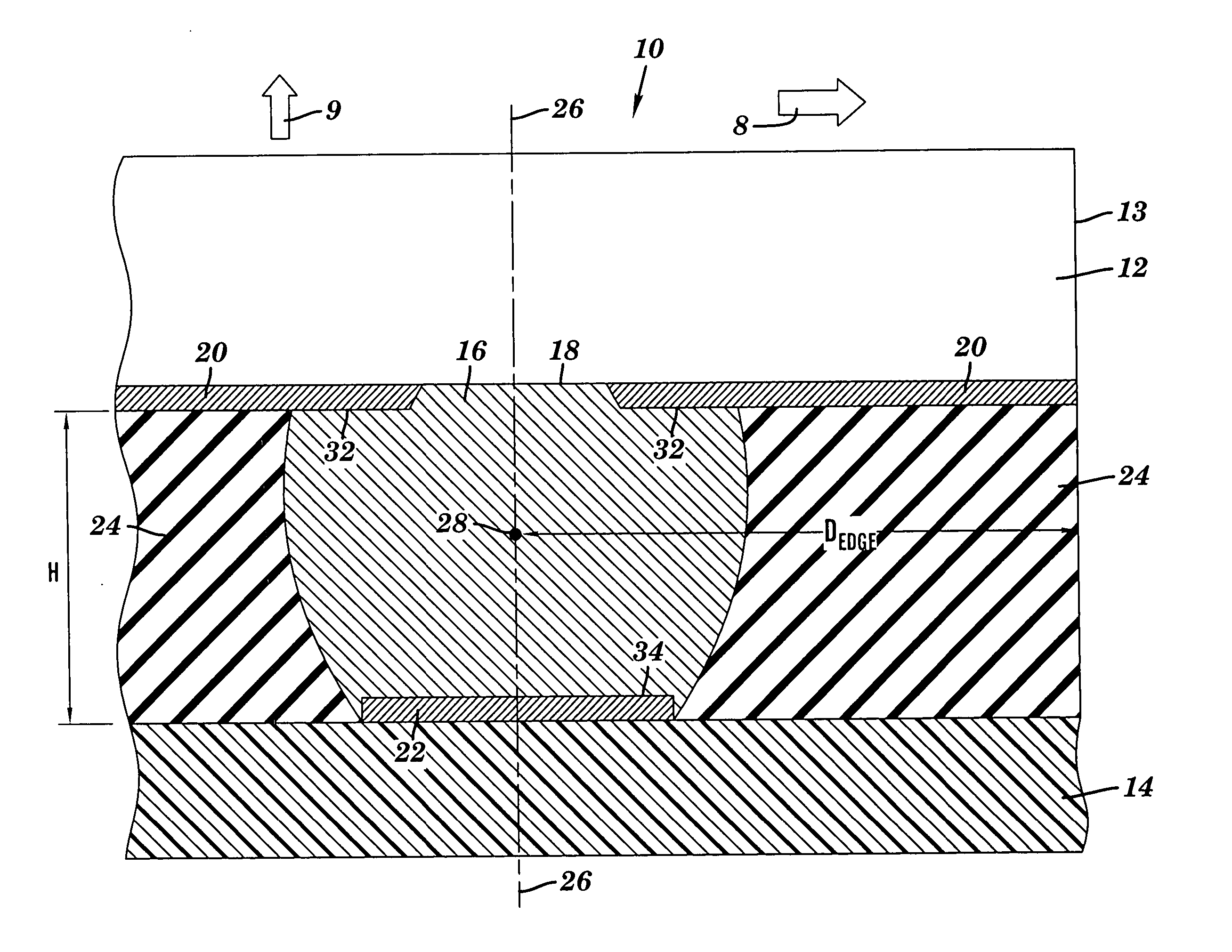
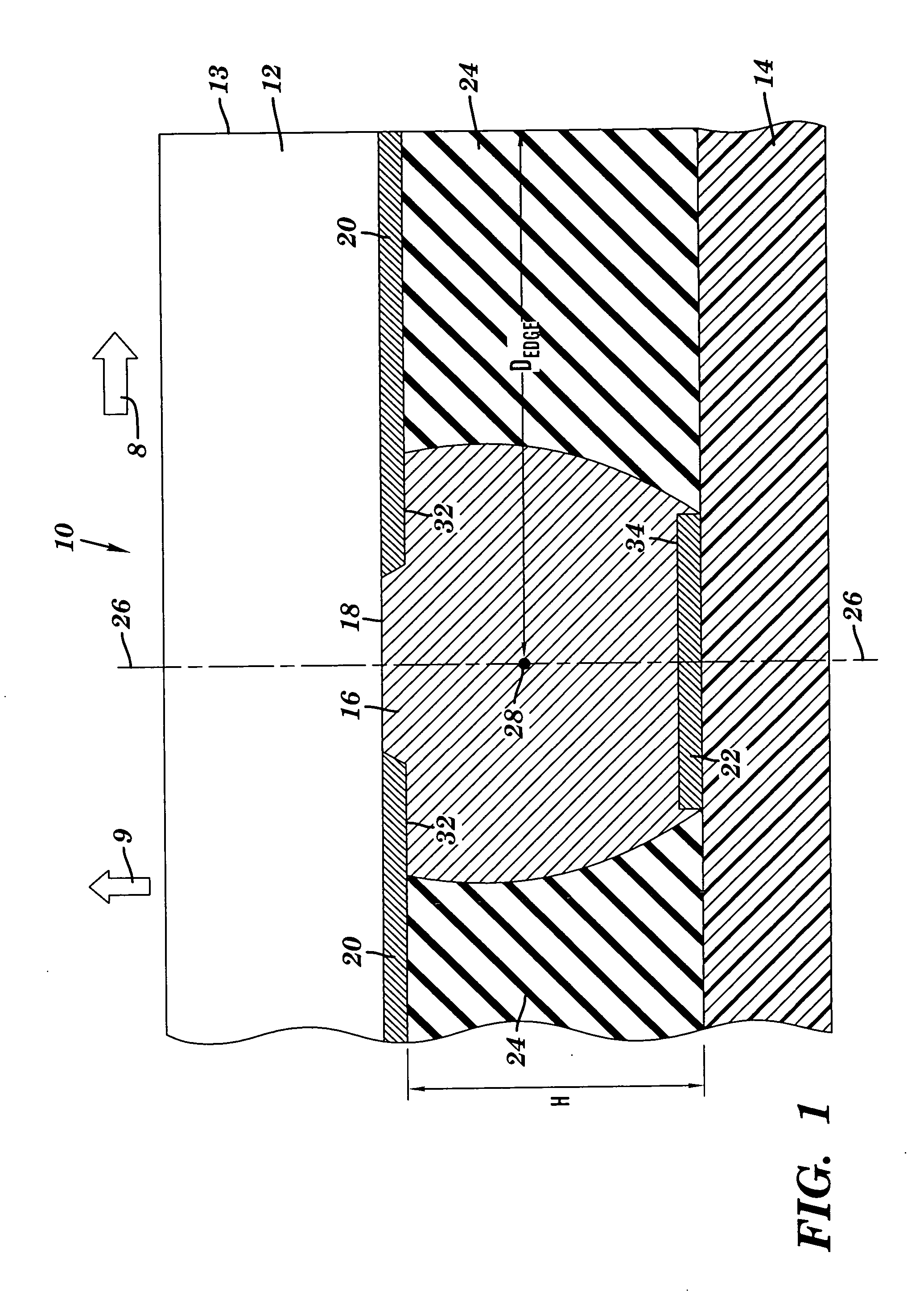
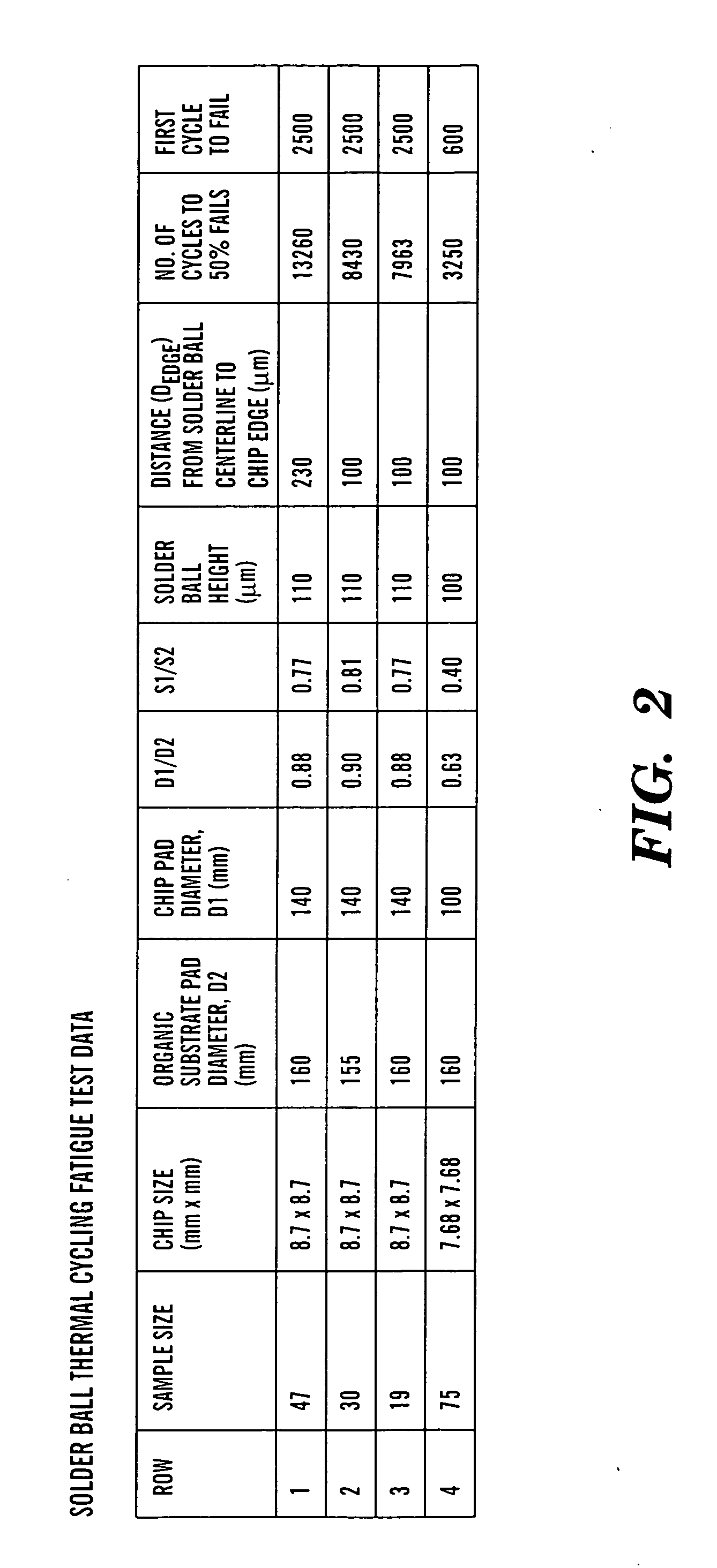
A method and structure for coupling a semiconductor substrate (e.g., a semiconductor chip) to an organic substrate (e.g., a chip carrier). The coupling interfaces a solder member (e.g., a solder ball) to both a conductive pad on the semiconductor substrate and a conductive pad on the organic substrate. Thermal strains on the solder member during thermal cycling may be reduced by having a surface area of the pad on the semiconductor substrate exceed a surface area of the pad on the organic substrate. Thermal strains on the solder member during thermal cycling may also be reduced by having a distance from a centerline of the solder member to a closest lateral edge of the semiconductor substrate exceed about 0.25 mm.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method of splicing two optical fibers
InactiveUS6550985B2Splice loss can be reducedHigh mechanical strengthCoupling light guidesGlass fiberOptical fiber cable
Two optical fibers to be spliced are prepared, coatings of resin are removed from end portions of the respective optical fibers to expose glass fibers, the glass fibers are aligned to each other, an a fusion step is carried out to heat the end faces of the glass fibers to cause fusion thereof to form a fusion-spliced portion. After that, an additive-diffusing step is carried out to diffuse an additive added in the glass fibers around the fusion-spiced portion, by a heat treatment around the fusion-spliced portion, by a heat treatment around the fusion-spliced portion at a first temperature of not less than 800° C. nor more than 1500° C. Further after the additive-diffusing step, a thermal-strain-removing step is carried out to remove thermal strain by a heat treatment of a wider region than heated regions in the fusion splice step and in the additive-diffusing step of the fusion-spliced portion, at a temperature of not less than 500° C. nor more than 1200° C.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Low thermal strain multi-cooler
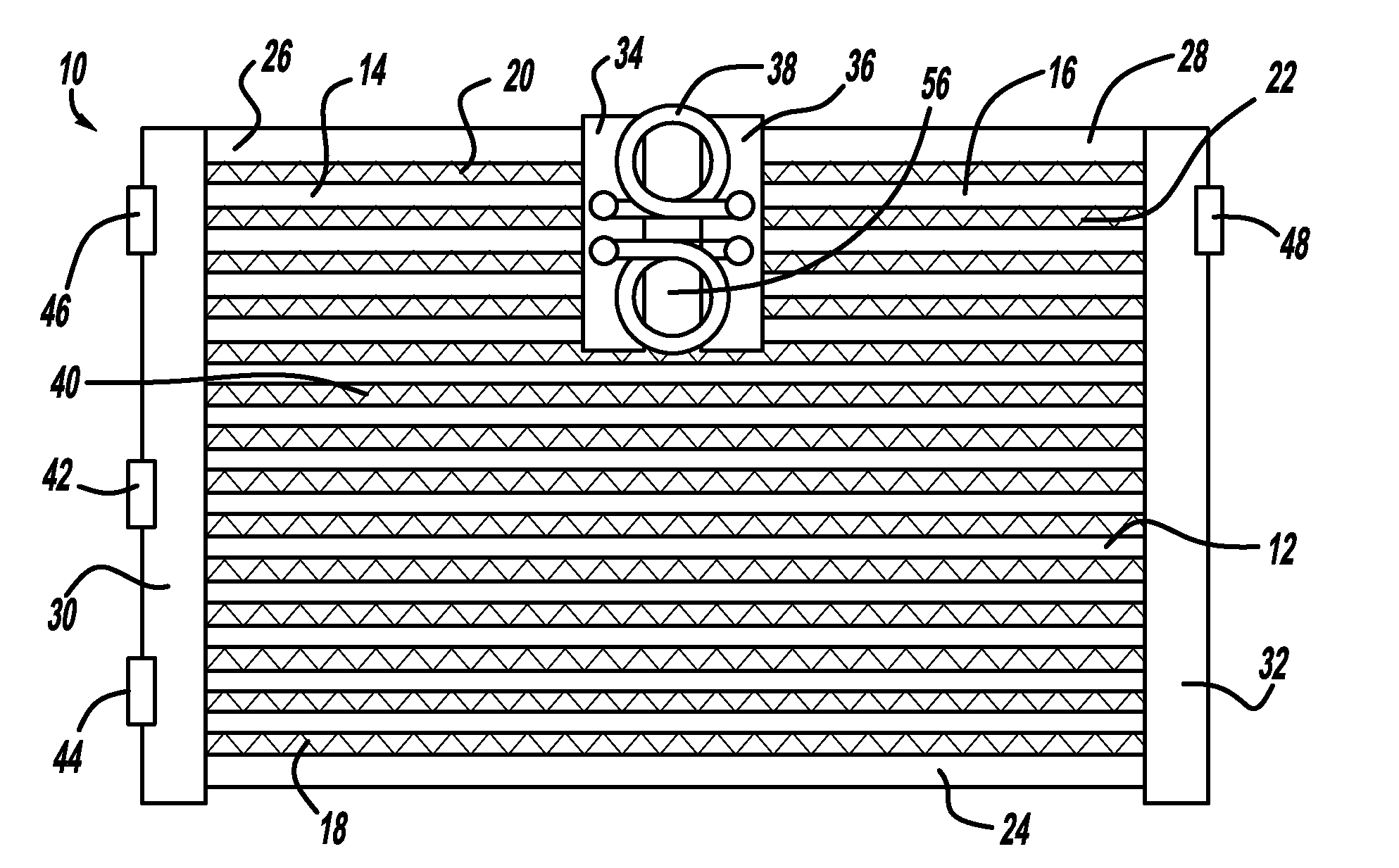
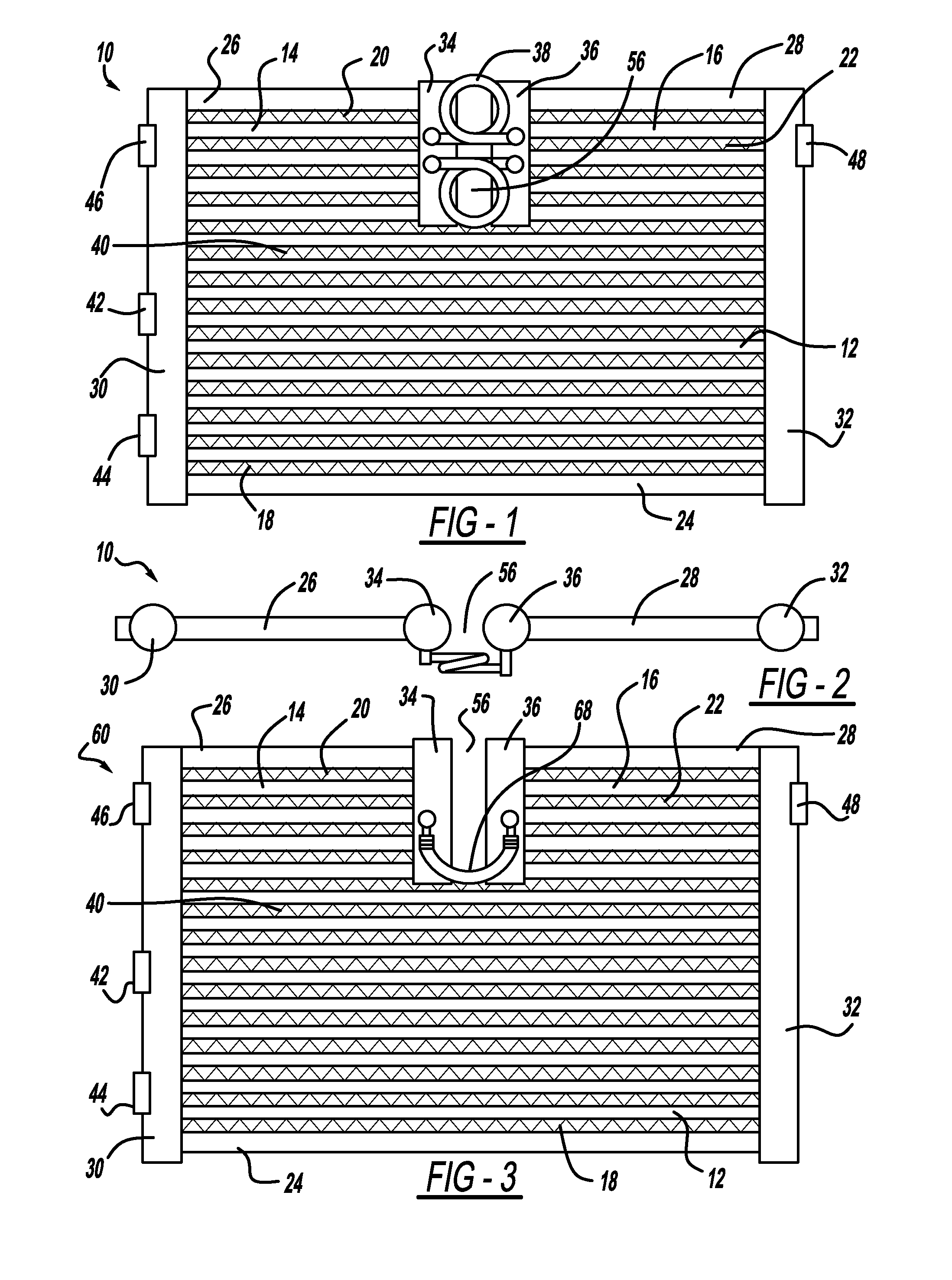
InactiveUS20110240275A1Reduce thermal strainSafety devices for heat exchange apparatusStationary conduit assembliesWaste managementHeat exchanger
A heat exchanger with multi-flow capabilities includes a pair of intermediate tanks located between a pair of header tanks. An open gap is provided between the two intermediate tanks. A first plurality of tubes extend between the header tanks. A second plurality of tubes extend between one of the header tanks and one of the intermediate tanks. A third plurality of tubes extend between the other header tank and the other intermediate tank. In a two flow system, the two intermediate tanks are in fluid communication through a flexible jumper tube. In a three flow system the two intermediate tanks are isolated from each other. The open gap between the intermediate tanks allows for the uneven heat expansion between the various fluid flows.
Owner:DENSO INTERNATIONAL AMERICA
Method for producing silicon film transferred insulator wafter
ActiveUS20110014775A1Improve thickness uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMechanical impactSilicon membrane
[PROBLEM] Provided is a method for producing an SOI wafer which the method can prevent occurrence of thermal strain, detachment, crack and the like attributed to a difference in thermal expansion coefficients between the insulating substrate and the SOI layer and also improve the uniformity of film thickness of the SOI layer.[MEANS FOR SOLVING THE PROBLEM] Provided is a method for producing an SOI wafer comprising steps of: performing a surface activation treatment on at least one of a surface of an insulator wafer and a hydrogen ion-implanted surface of a single crystal silicon wafer having a hydrogen ion-implanted layer; bonding the hydrogen ion-implanted surface to the surface of the insulator wafer to obtain bonded wafers; heating the bonded wafers at a first temperature; grinding and / or etching a surface of a single crystal silicon wafer side of the bonded wafers thus heated so as to thin the single crystal silicon wafer of the bonded wafers; heating the bonded wafers thus ground and / or etched at a second temperature which is higher the first temperature; and performing detachment at the hydrogen ion-implanted layer by applying a mechanical impact to the hydrogen ion-implanted layer of the bonded wafers thus heated at the second temperature.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Wiring forming method of printed circuit board
InactiveUS20080282537A1Minimizes thermal thermal decompositionMinimizes thermal strain thermalPrinted circuit aspectsConductive pattern formationEngineeringPrinted circuit board
The present invention relates to a method for forming a wiring of a printed circuit board and more particularly, to a method including: preparing a base film; forming a wiring pattern with ink including metal nanoparticles on the base film by printing; and forming a wring by the induction heating of the base film on which the wiring pattern is formed. The method of the present invention which minimizes the thermal strain and thermal decomposition of a base film, provides an appropriate sintering process of wirings, shortens the manufacturing process, and exhibits excellent mechanical strength is provided by using the induction heating.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Strain measurement apparatus, linear expansion coefficient measurement method, and correction coefficient measurement method for temperature distribution detector
ActiveUS20130107004A1Easy to measureEasily strainedUsing optical meansSteroscopic systemsStereo cameraThermodynamics
A strain measurement apparatus includes: a stereo camera device that produces a first stereo image and a second stereo image of a measurement object; an actual strain calculation portion configured to find a three-dimensional configuration of the measurement object from the first stereo image and the second stereo image to find actual strain of the measurement object; a temperature distribution detector that detects a temperature distribution of the measurement object; a free thermal strain calculation portion configured to find free thermal strain of the measurement object from the temperature distribution detected by the temperature distribution detector; and a constraint strain calculation portion configured to find as constraint strain of the measurement object a difference obtained by subtracting the free thermal strain found by the free thermal strain calculation portion from the actual strain found by the actual strain calculation portion.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method and device for producing images of heating tines near a tissue part
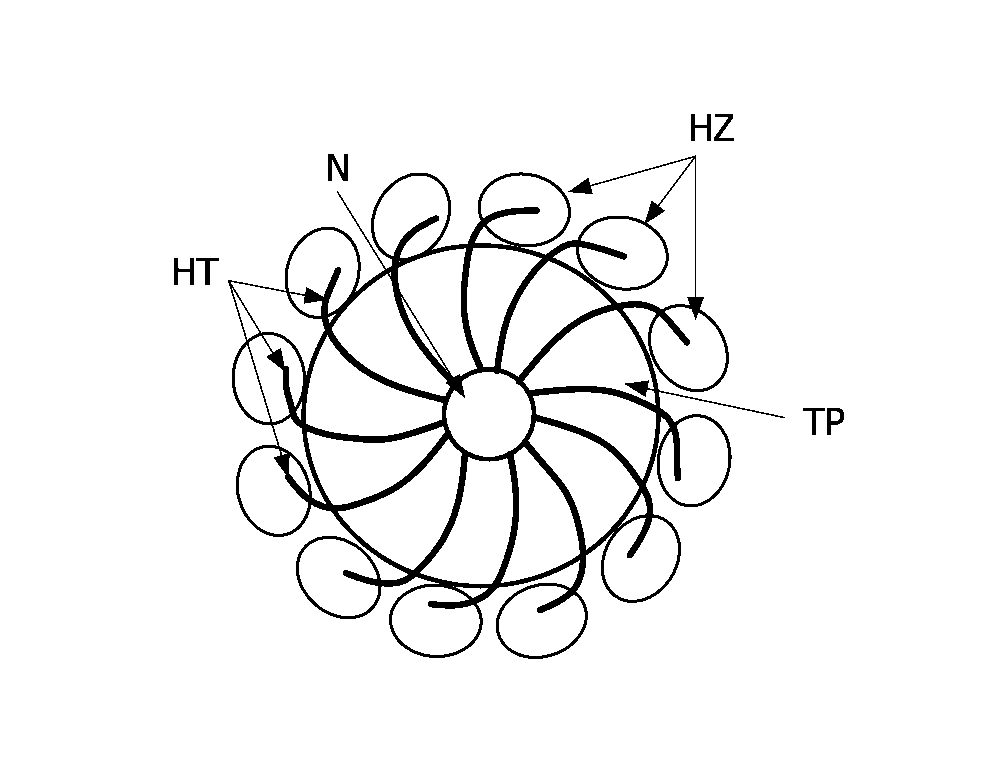
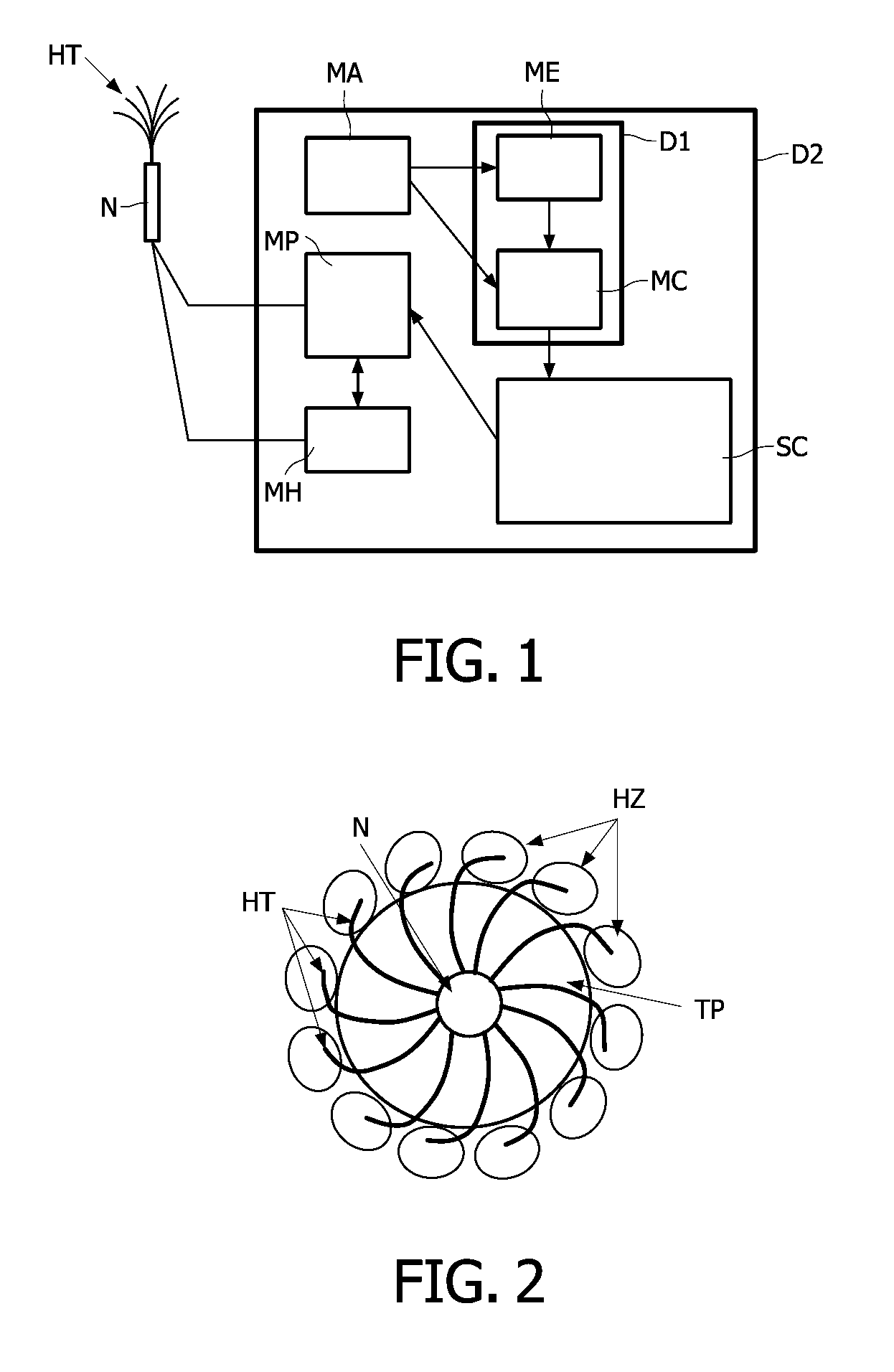
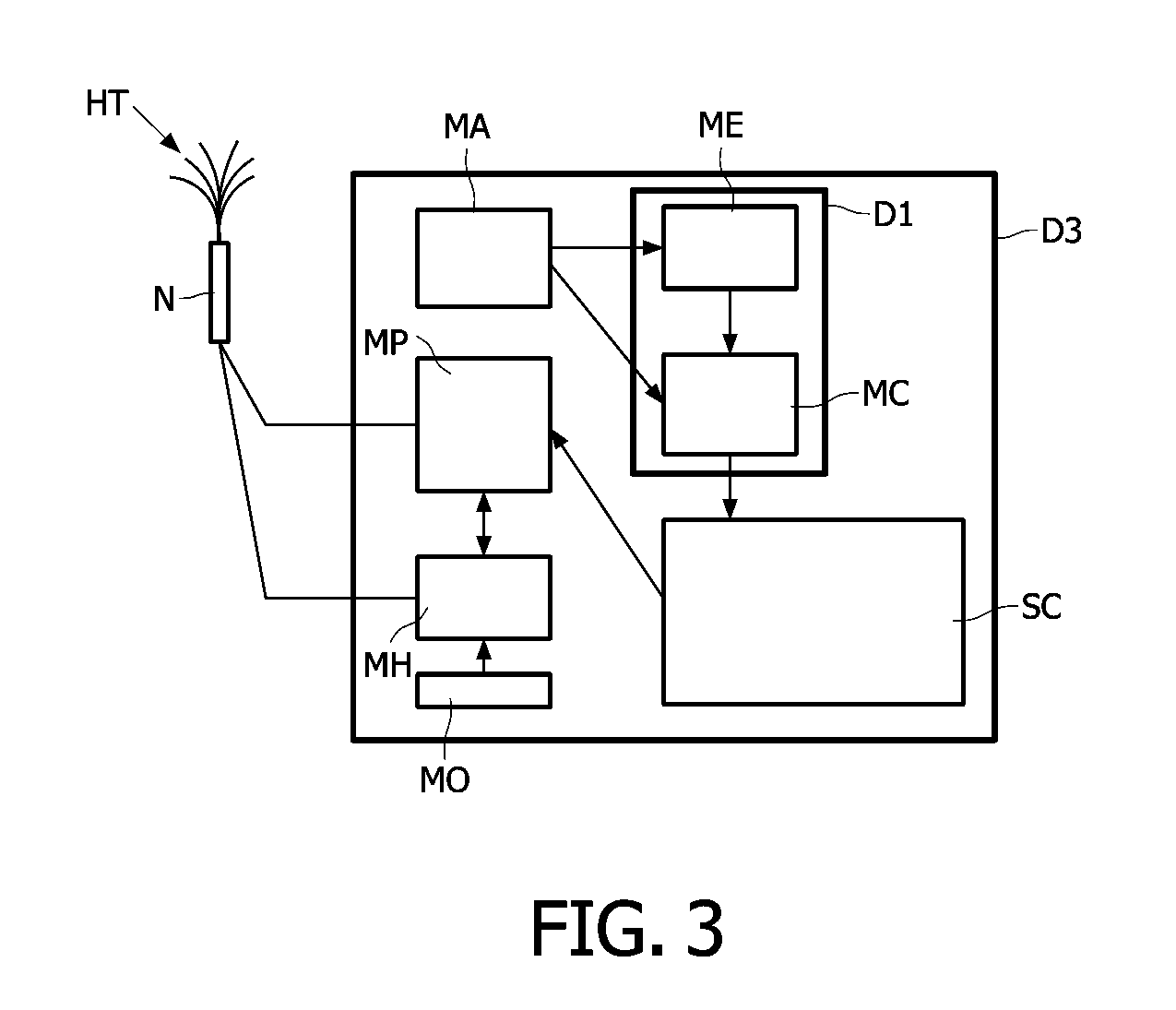
A device (D1) is intended for producing images of heating tines (HT) coupled to a needle (N) positioned near a chosen tissue part of tissues located in an area of a body. This device (D1) comprises i) a means (ME) for estimating tissue thermal strains, induced by means of the heating tines (HT) into the tissue surrounding the chosen tissue part, from received ultrasound image data, and for deducing relative positions of these heating tines (HT) to the chosen tissue part from the estimated tissue thermal strains, and ii) a means (MC) for combining the received ultrasound image data with position data representative of the deduced relative positions to produce images of the area with thermal strain information showing the relative positions of the heating tines (HT) to the chosen tissue part.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Radial locating unit and locating and clamping device for internal grinding of thin-walled cylinder workpieces
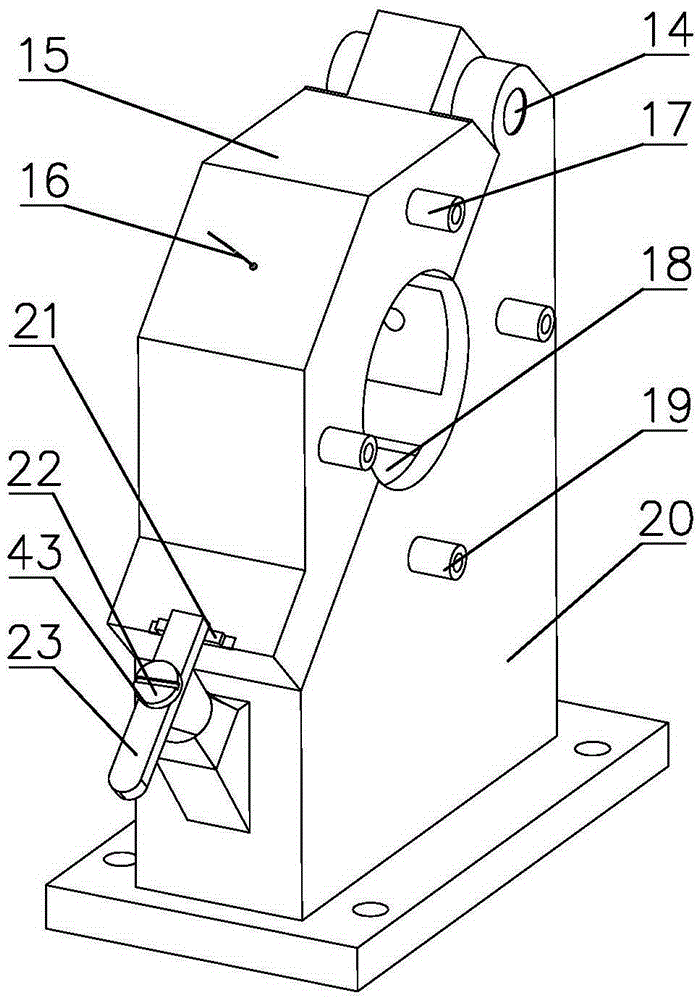
ActiveCN105397636AGuaranteed automaticImprove radial positioning accuracyRevolution surface grinding machinesGrinding work supportsEngineeringMachining process
The invention discloses a radial locating unit and locating and clamping device for internal grinding of thin-walled cylinder workpieces, belonging to the technical field of machining processes. The radial locating unit comprises a supporting base and a supporting cover, wherein one end of the supporting cover is pivoted to the supporting base; the supporting base is provided with a clamping curved surface I, and the supporting cover is provided with a clamping curved surface II, so that workpieces are clamped; the supporting base is provided with a fixing part capable of fixing the supporting cover when the supporting cover and the supporting base are buckled; the clamping curved surface I is provided with inward concave structures to form hydraulic chambers I; the clamping curved surface II is also provided with inward concave structures to form hydraulic chambers II; and the locating and clamping device also comprises a hydraulically-supported axial locating driving unit. The radial locating unit and the locating and clamping device are uniform in clamping force, difficult to deform, more suitable for internal grinding of workpieces with small diameters and capable of improving the locating rigidity and precision, avoiding damage of the surfaces of the workpieces, effectively cooling grinding wheels and the workpieces and reducing thermal strain.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Nitride-based semiconductor light-emitting device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050051788A1Improve responseImprove adhesionOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsNitrideLight emitting device
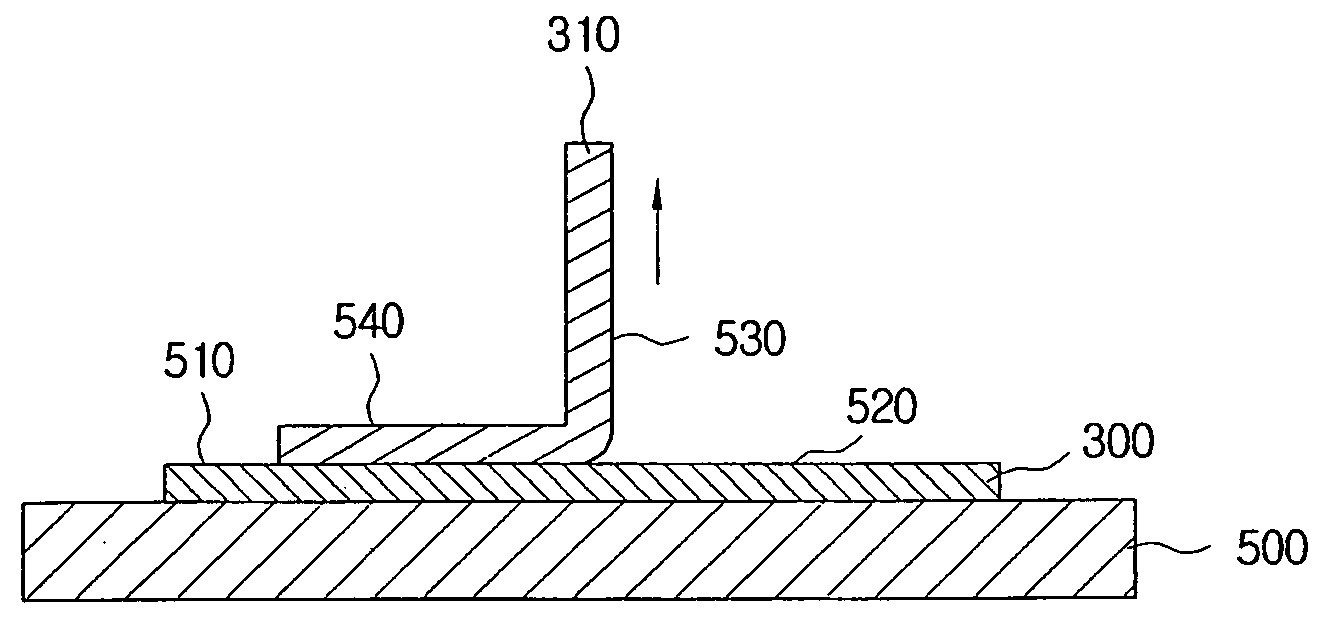
A nitride-based semiconductor light-emitting device includes a light-emitting element having an n-GaN substrate and a nitride-based semiconductor multilayer film formed on the n-GaN substrate. The n-GaN substrate of the light-emitting element is fixed to a mount surface. The n-GaN substrate has one surface with the nitride-based semiconductor multilayer film formed thereon and an opposite surface with a metal layer and an ohmic electrode formed thereon. The metal layer contains a first metal and a second metal and the ohmic electrode is formed of the second metal. The adhesion between the ohmic electrode and the n-GaN substrate is thus improved. Accordingly, the semiconductor light-emitting device which is highly reliable with respect to the thermal strain from the mount surface can be provided.
Owner:SHARP KK
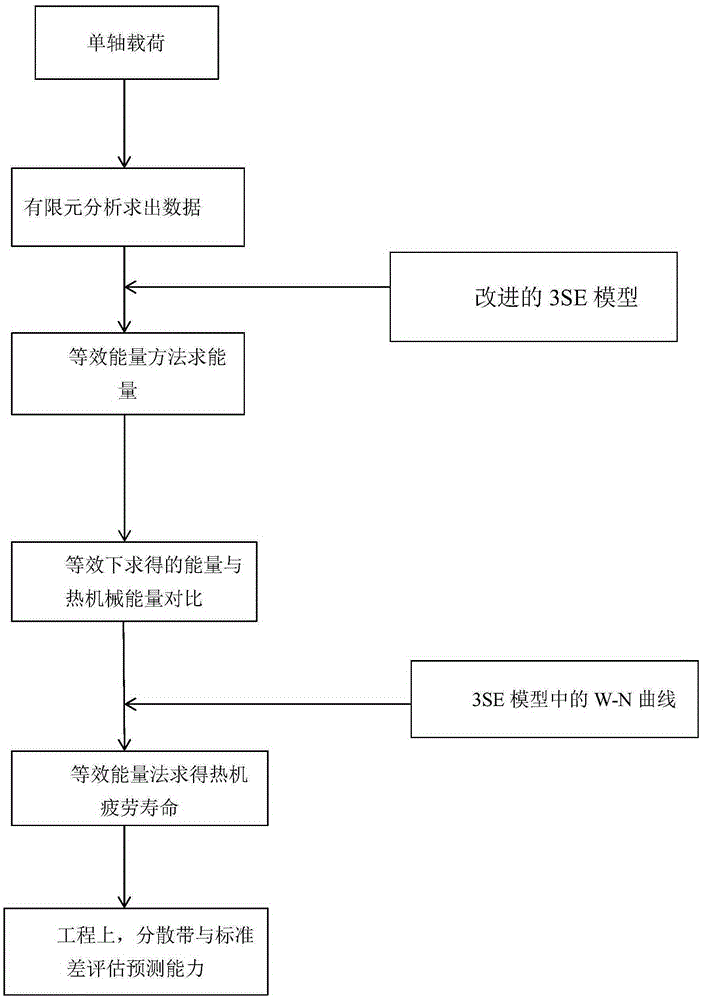
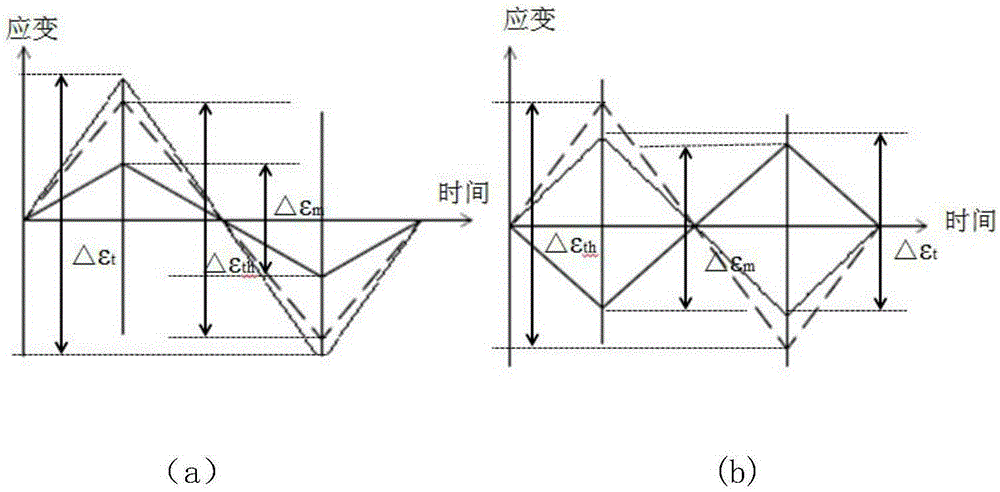
Equivalent method for predicting thermo-mechanical fatigue life
ActiveCN105302987AReduce testing costsGood forecastSpecial data processing applicationsUltimate tensile strengthEnergy method
The invention provides an equivalent method for predicting the thermo-mechanical fatigue life and relates to the field of fatigue strength. The method comprises the following steps: 1, using a finite element method for calculating out high temperature fatigue data of thermo-mechanical fatigue at the highest temperature and corresponding thermal strain data within a corresponding temperature range; 2, converting an original three-parameter power function energy method at the constant temperature into a three-parameter power function energy method containing thermal strain items by taking thermal strain into consideration; 3, comparing equivalent energy obtained by applying the improved three-parameter power function energy method to data obtained through finite element calculation with energy obtained by calculating data obtained through thermo-mechanical tests; 4, utilizing the improved three-parameter power function energy method for conducting prediction on the thermo-mechanical fatigue life; 5, in engineering, applying a dispersion band and standard deviation to the equivalent energy method and a stretching lagging energy model for measuring the capability of the model for predicting the life. A prediction result shows that the equivalent method can be used for better calculating the thermo-mechanical fatigue life.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Polyester film for capacitors
InactiveCN1397077AGood insulation propertiesNo reduction in processing characteristicsFixed capacitor dielectricDomestic articlesDielectricPolyester
A film which is a biaxially oriented film comprising polyethylene-2,6-naphthalenedicaboxylate as a principal component, having a thermal strain ratio RMD (150) in the machine direction of the film at a temperature of 150 DEG C is -1.5%< / =RMD (150)< / =0.0% when the thermal strain ratio RMD (T) in the machine direction of the film at a temperature T DEG C based on the length LMD (t) in the machine direction (MD) of the film at a temperature t DEG C is defined by <DF>RMD (T) = äÄLMD(T) - LMD (35)Ü / LMD (35)ü x 100 (%), < / DF> excellent in insulation characteristics without lowering processing characteristics, especially the characteristics during hot-pressing and suitable as a dielectric for capacitors.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com