Patents
Literature
64 results about "Anisotropic crystal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
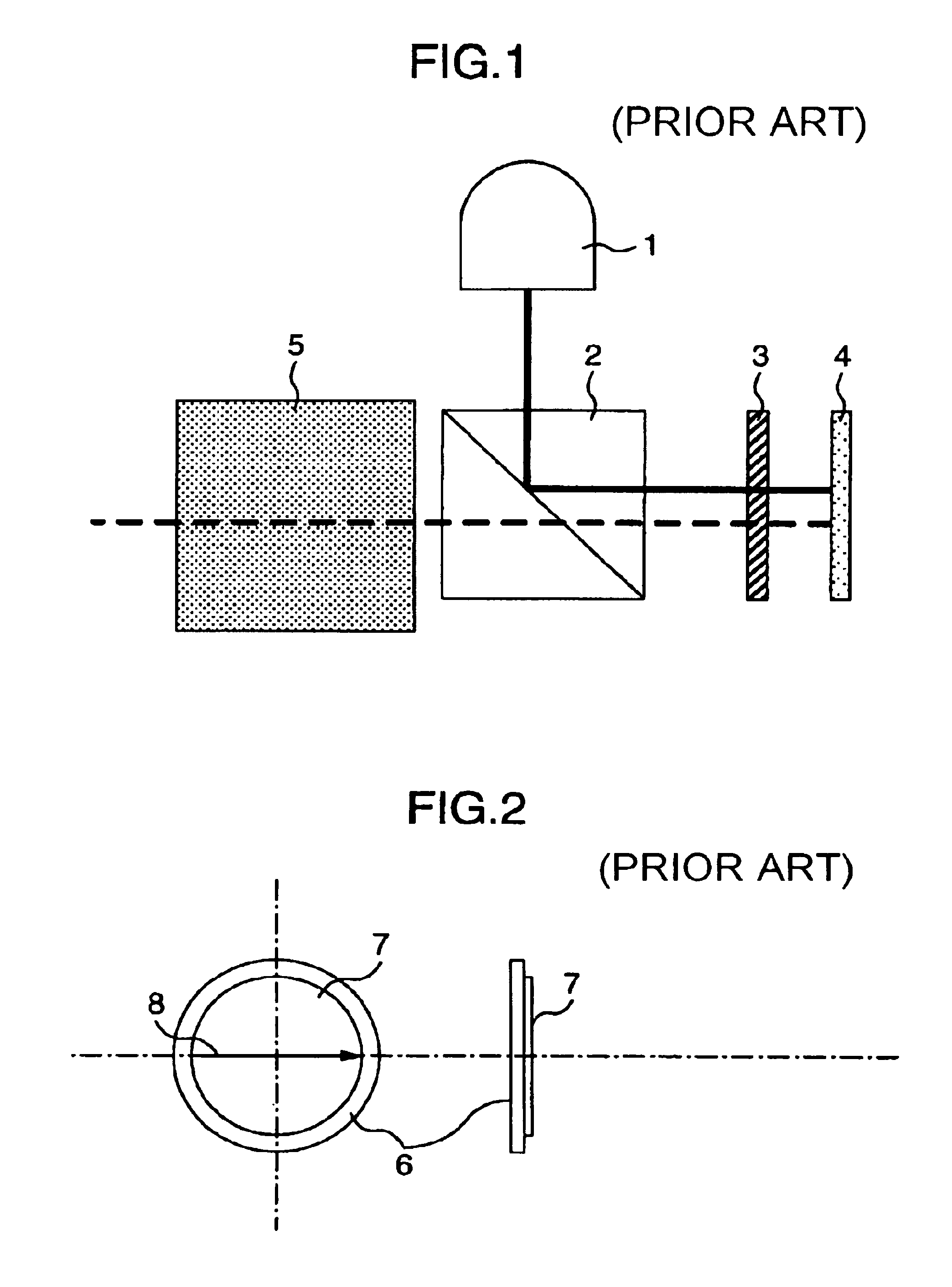
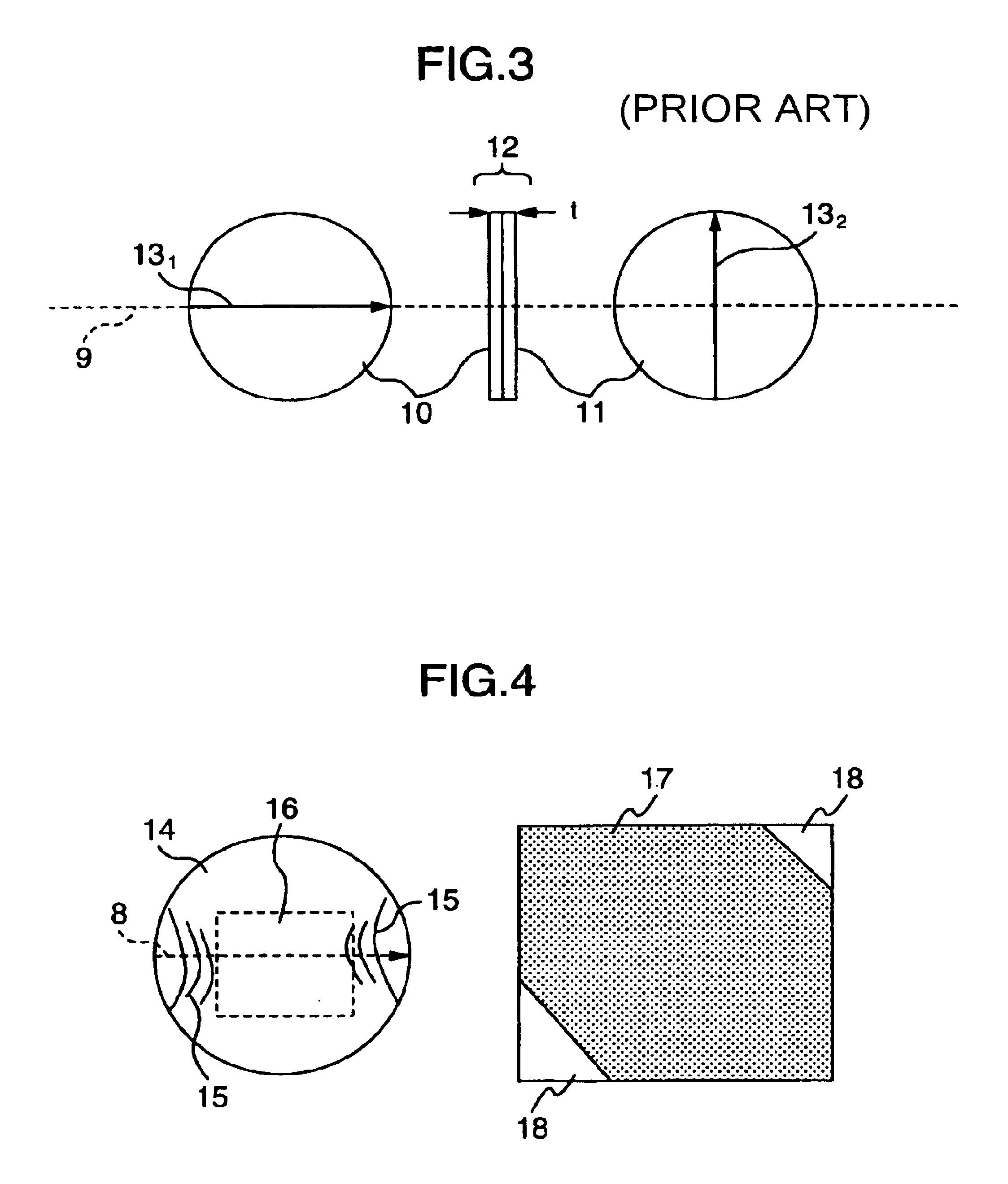
Anisotropy is most easily observed in single crystals of solid elements or compounds, in which atoms, ions, or molecules are arranged in regular lattices. In contrast, the random distribution of particles in liquids, and especially in gases, causes them rarely, if ever, to be anisotropic.
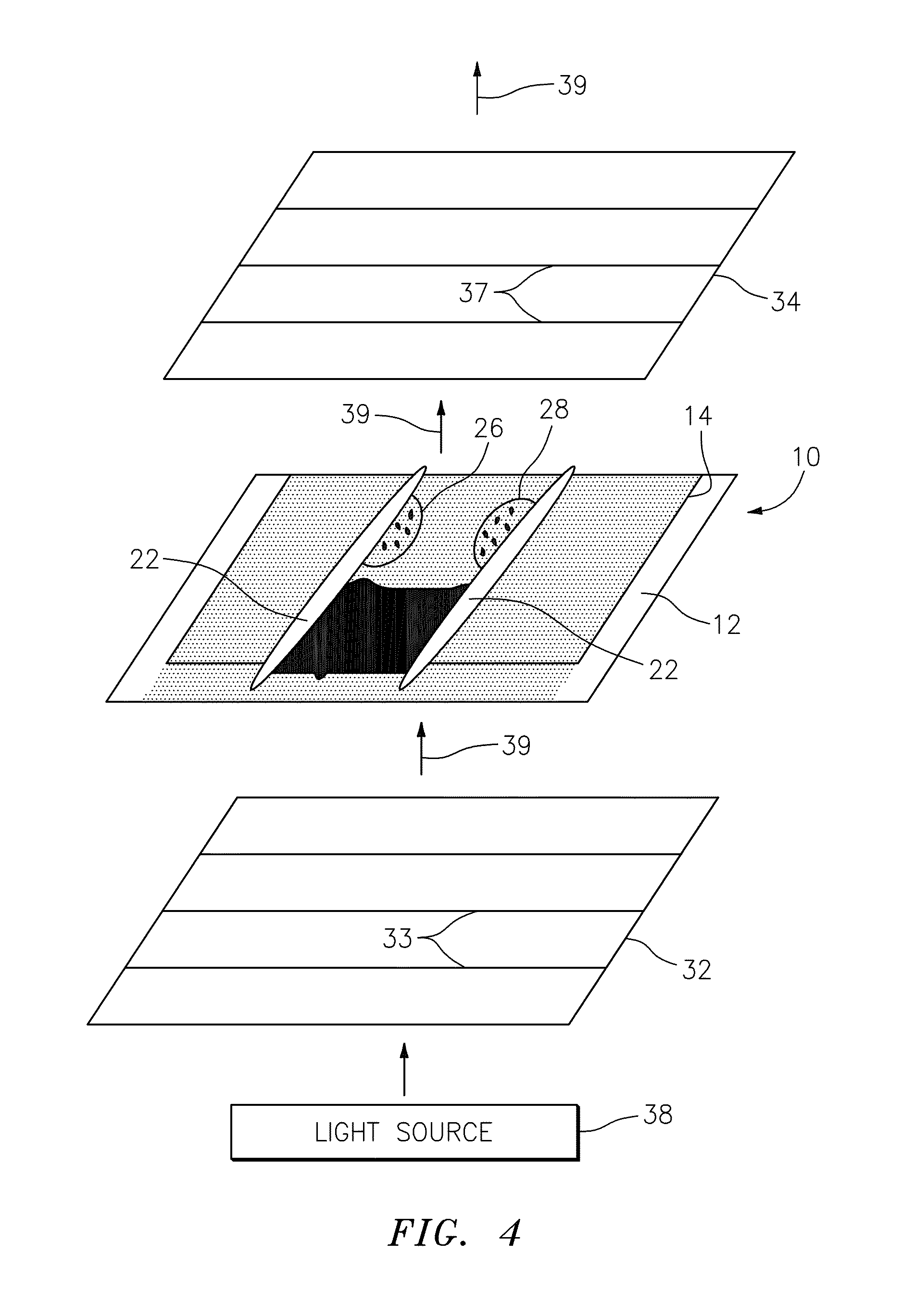
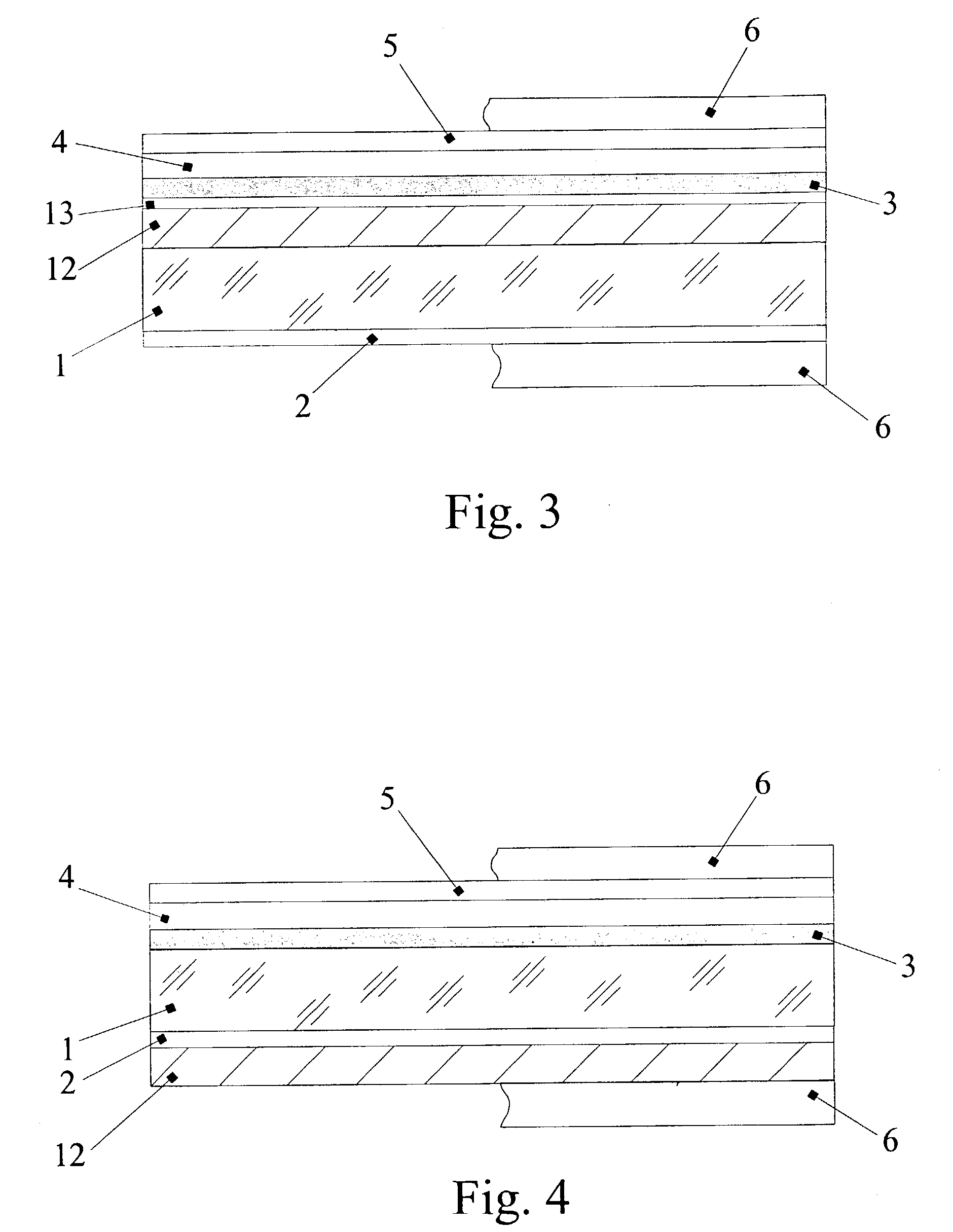
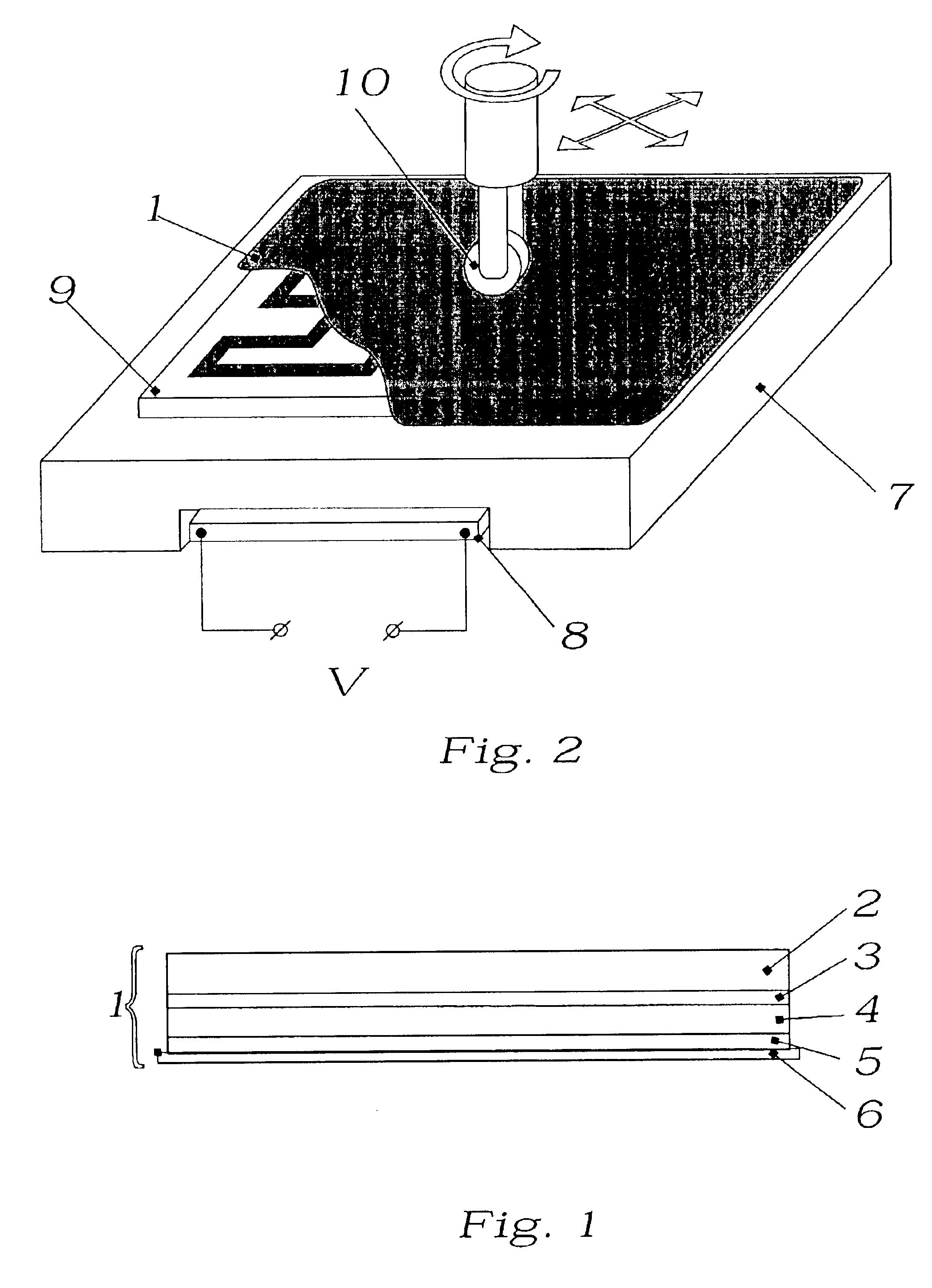
Segmented thermal barrier coating
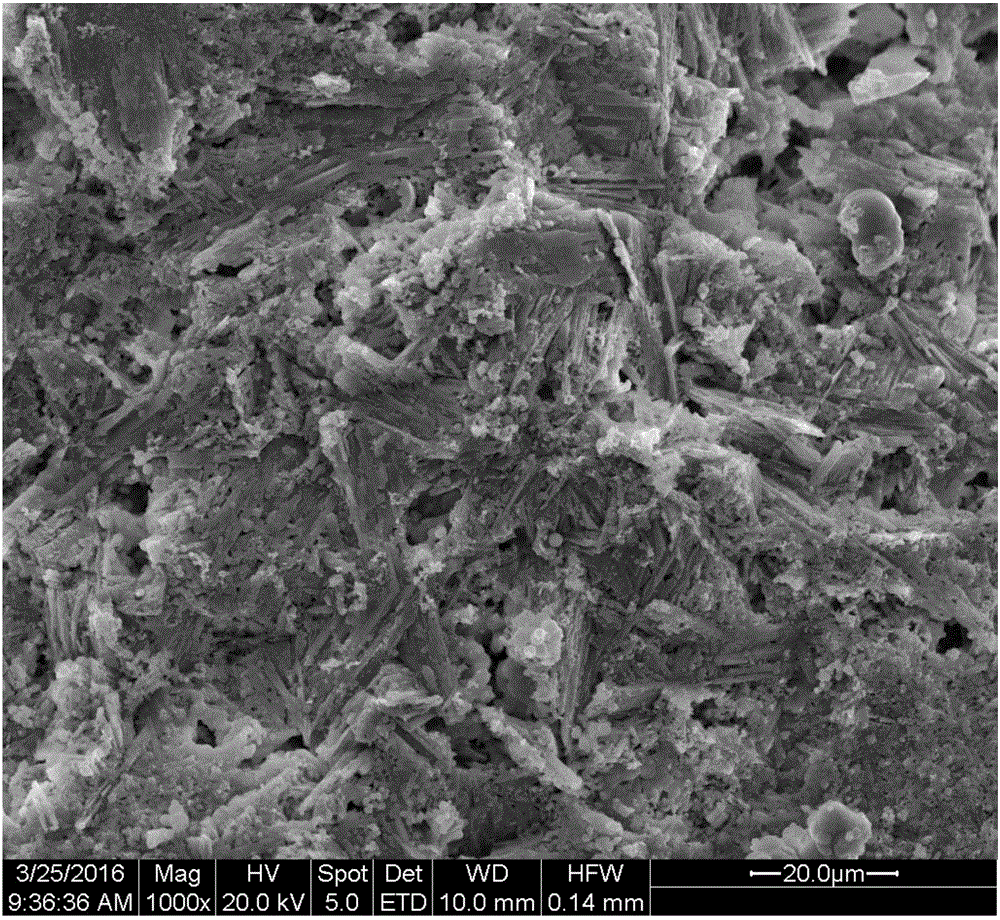
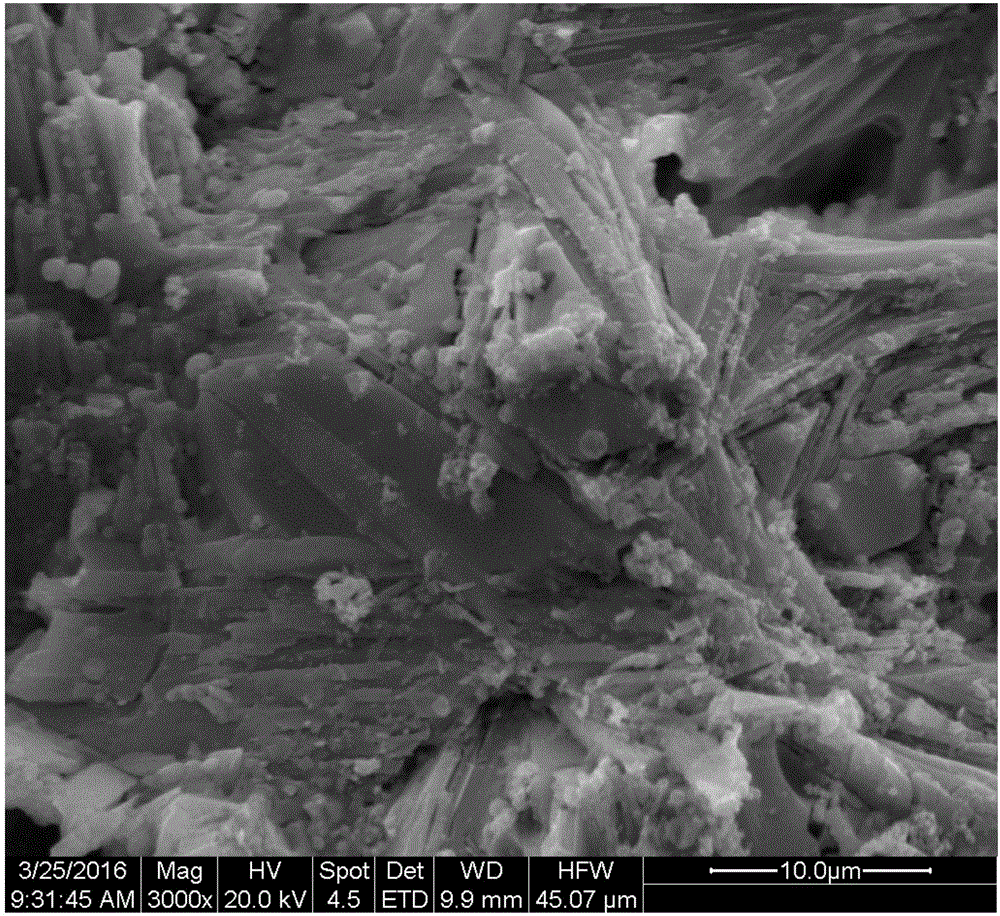
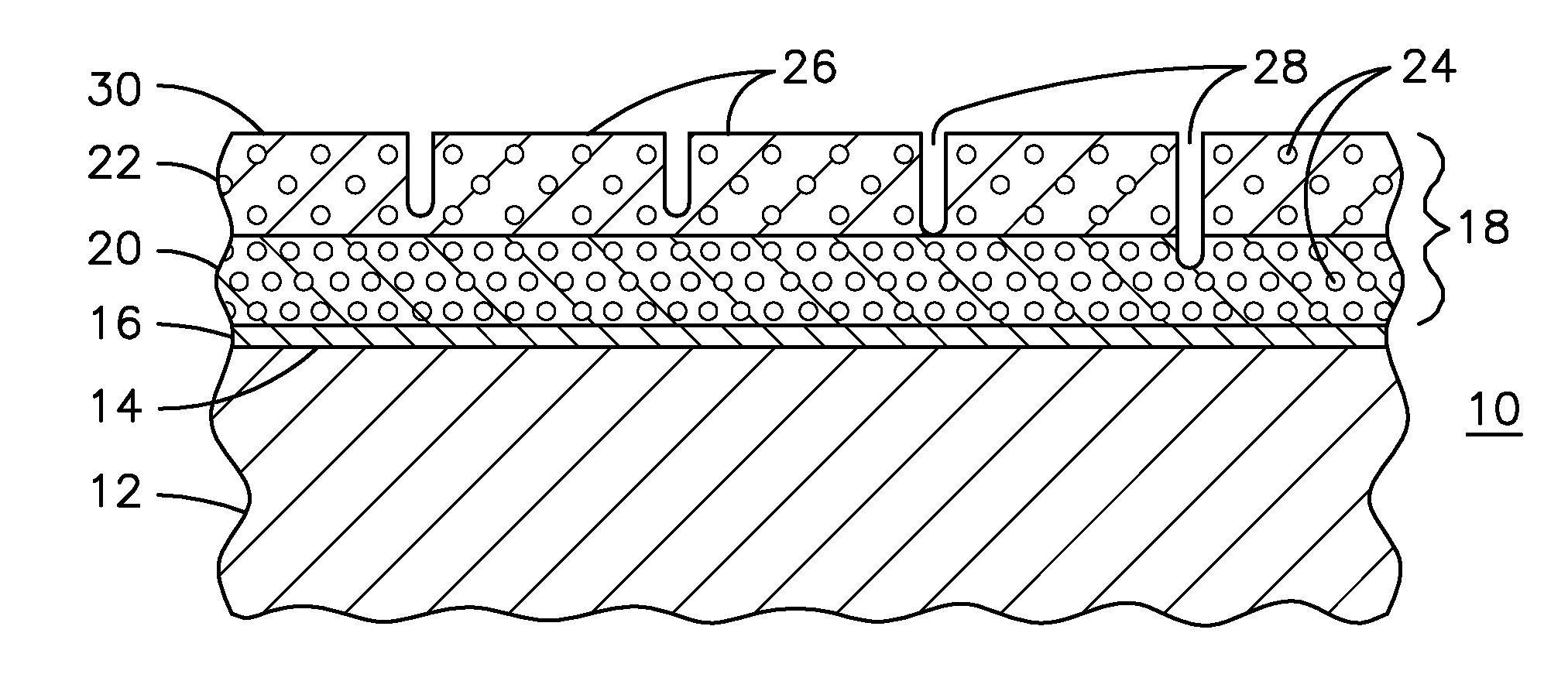
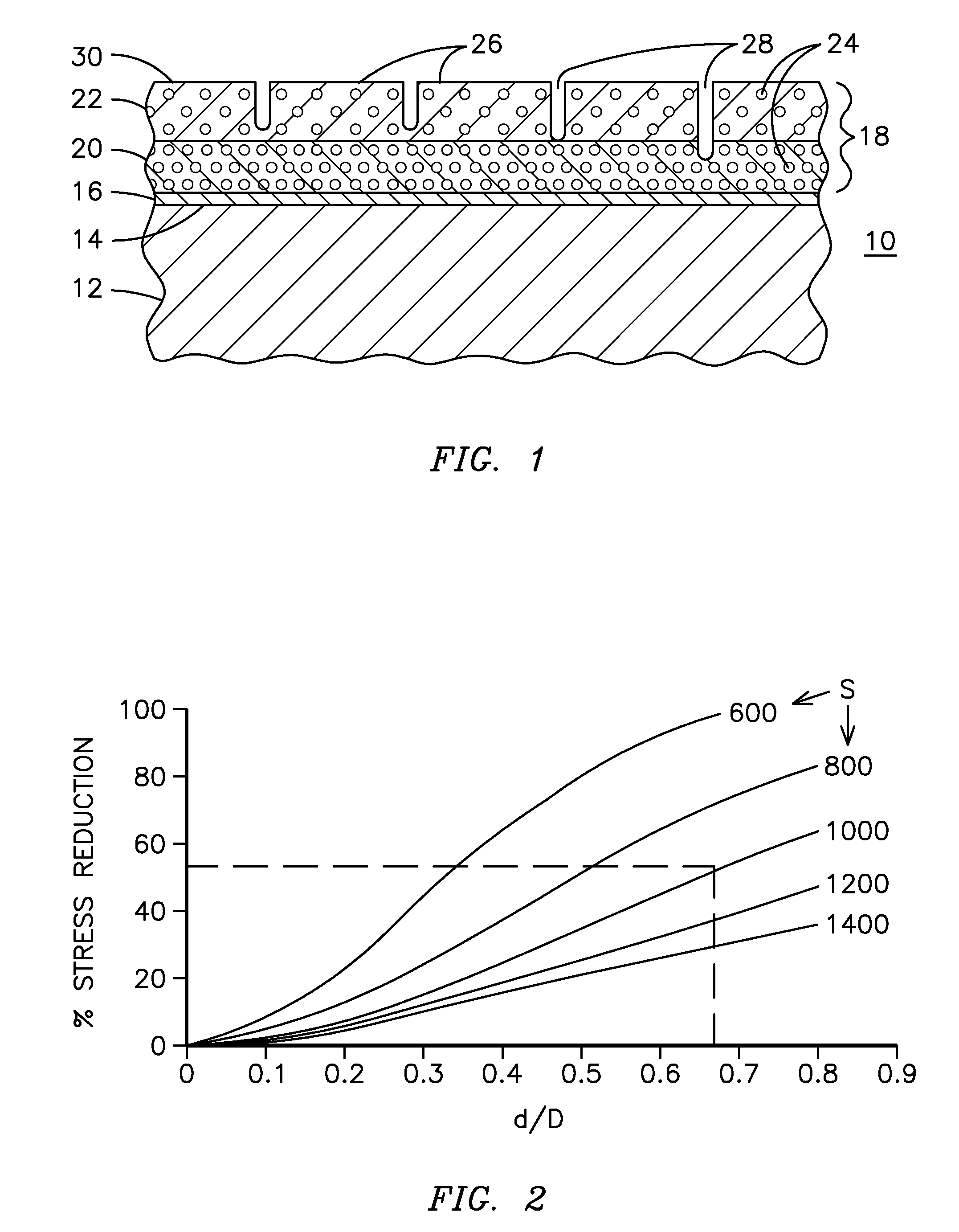
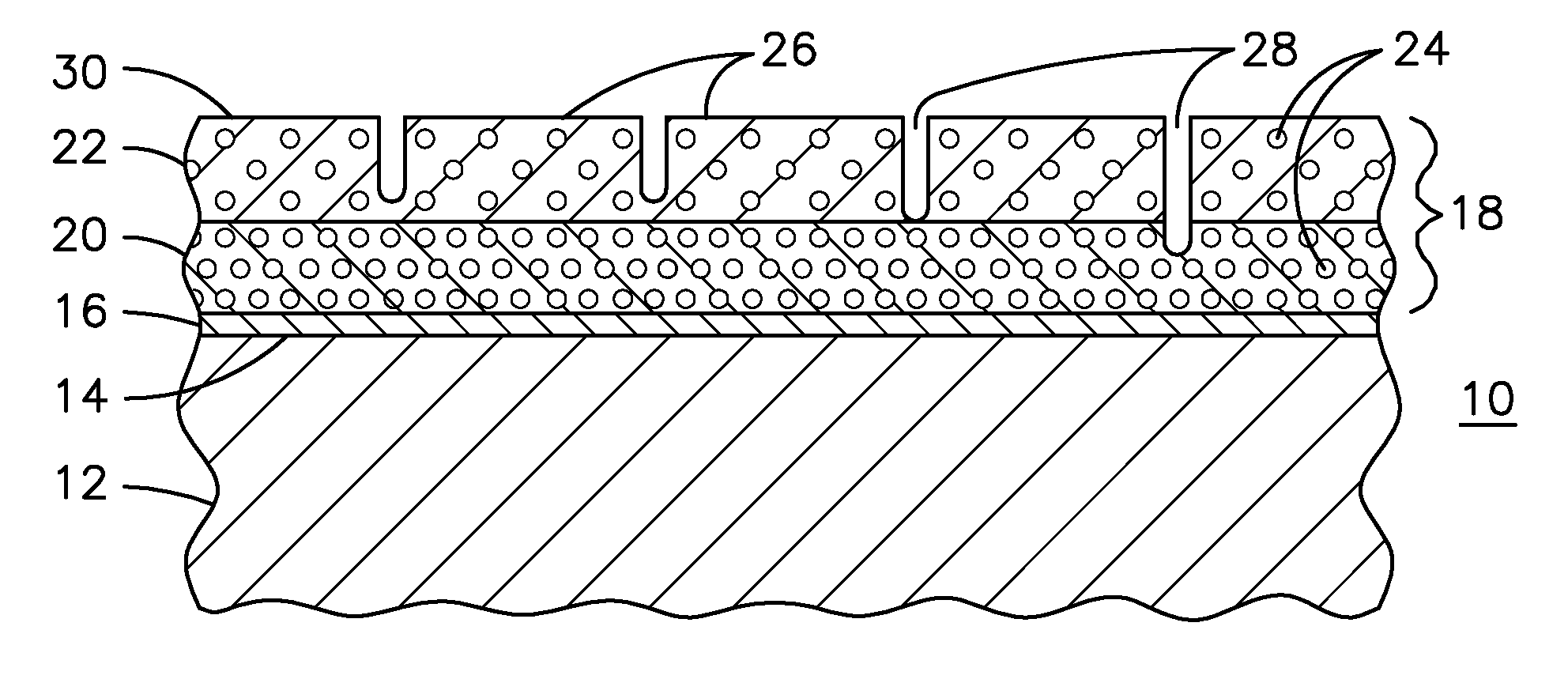
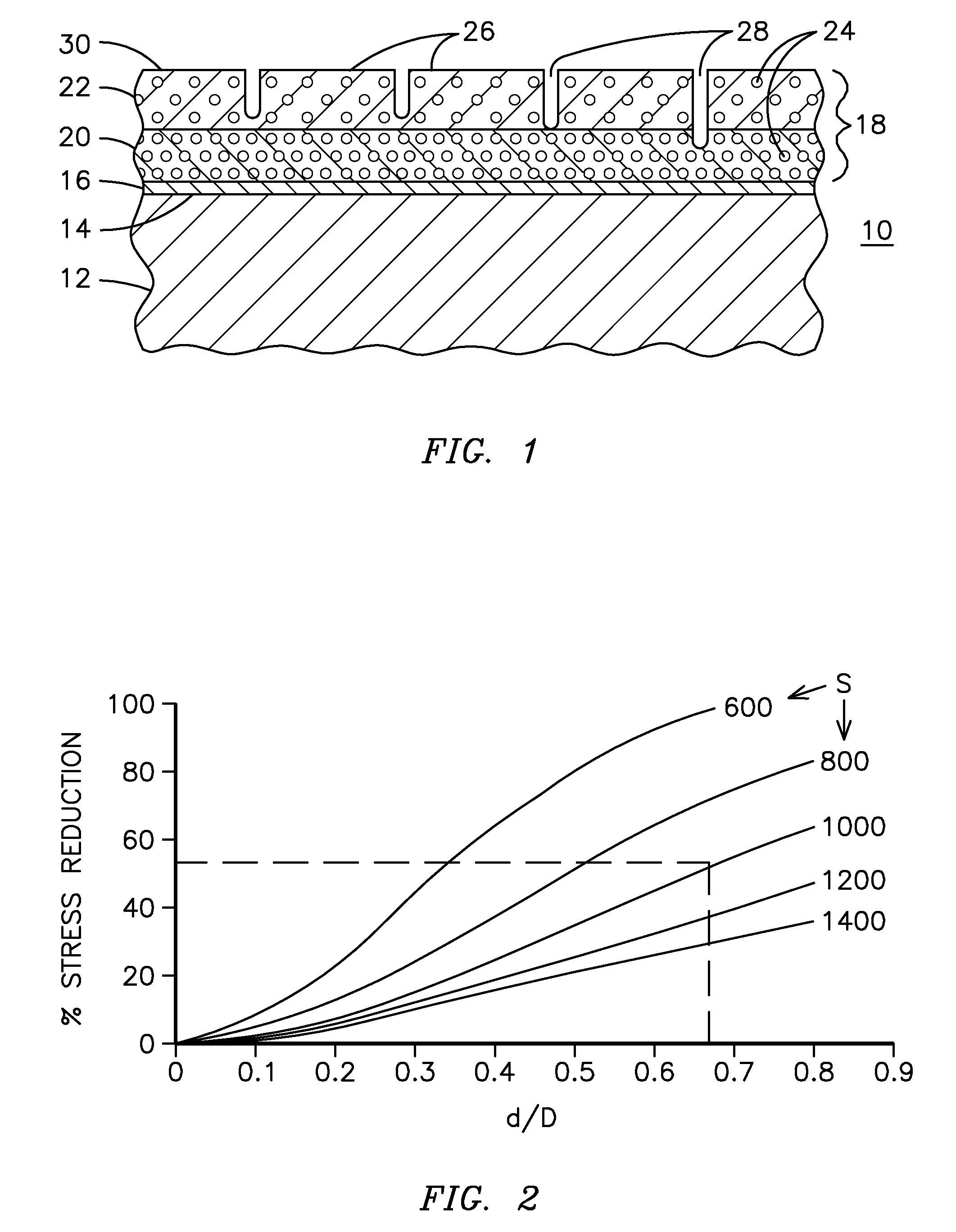
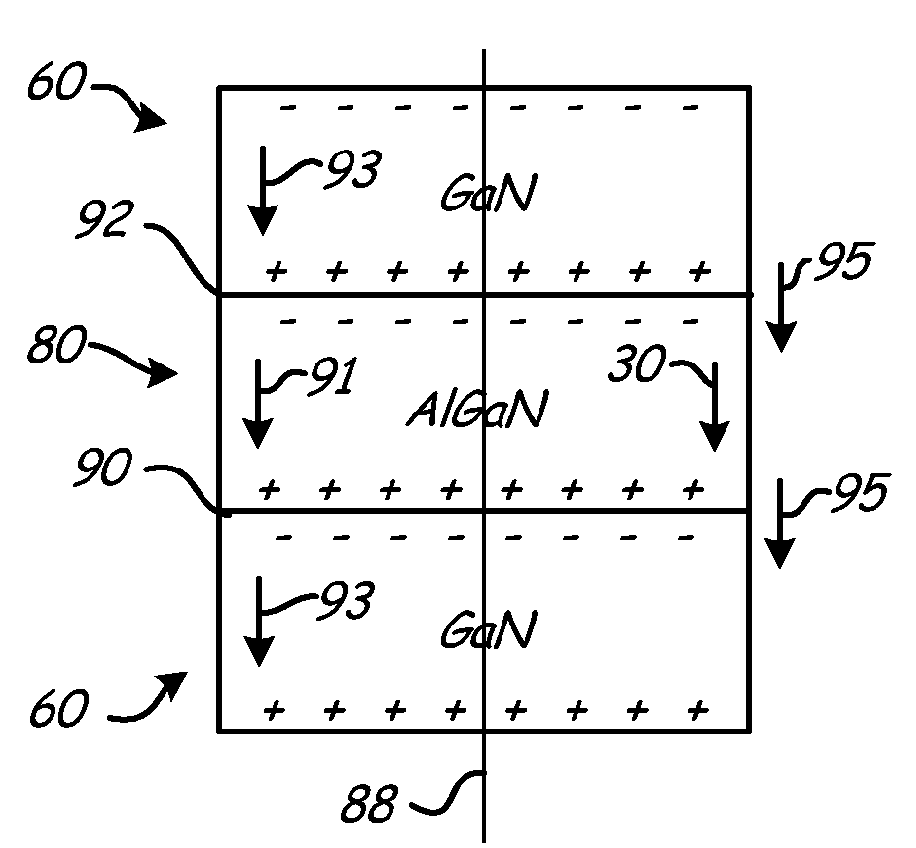
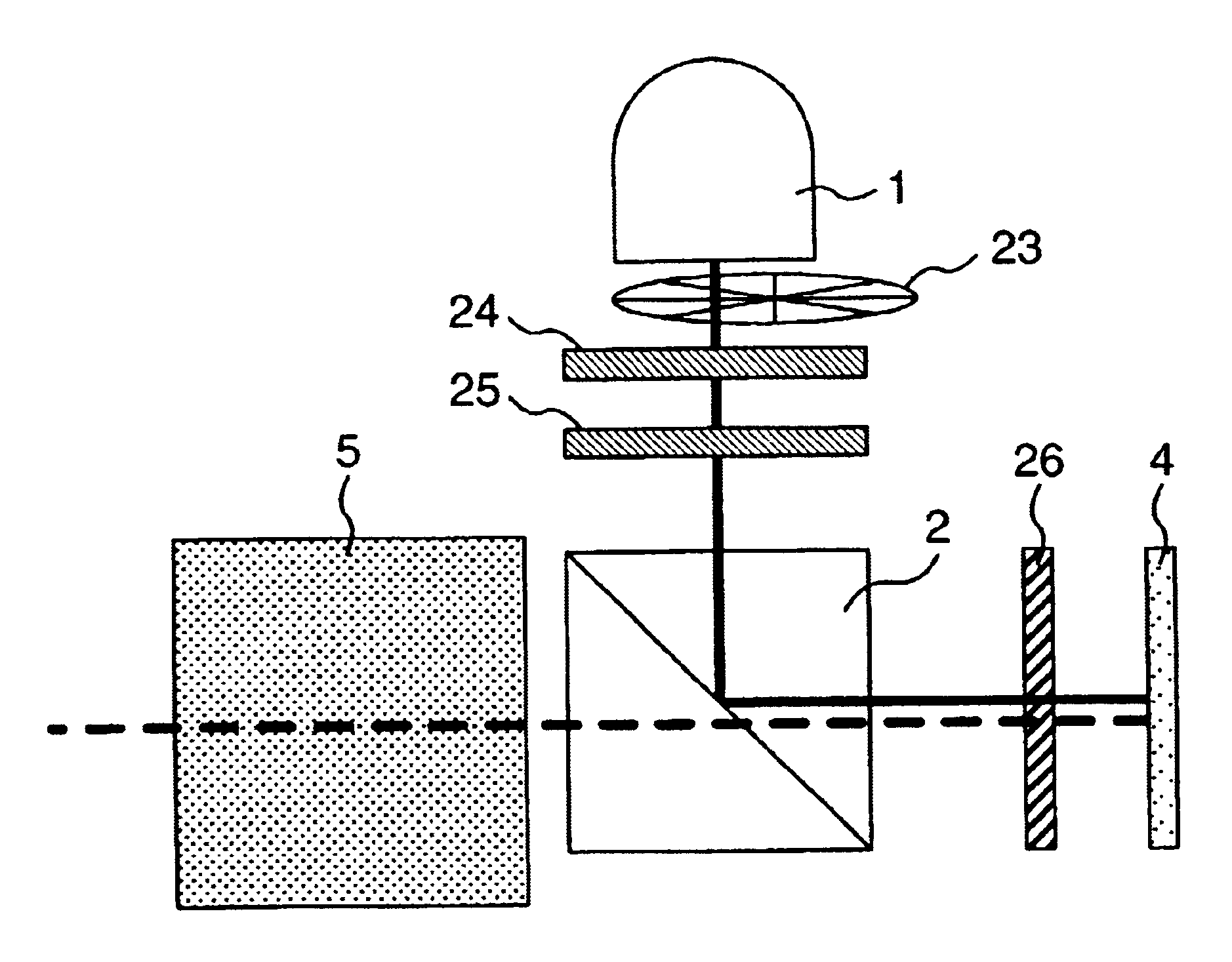
A ceramic thermal barrier coating (TBC) (18) having first and second layers (20, 22), the second layer (22) having a lower thermal conductivity than the first layer for a given density. The second layer may be formed of a material with anisotropic crystal lattice structure. Voids (24) in at least the first layer (20) make the first layer less dense than the second layer. Grooves (28) are formed in the TBC (18) for thermal strain relief. The grooves may align with fluid streamlines over the TBC. Multiple layers (84, 86,88) may have respective sets of grooves (90), Preferred failure planes parallel to the coating surface (30) may be formed at different depths (A1, A2, A3) in the thickness of the TBC to stimulate generation of a fresh surface when a portion of the coating fails by spalling. A dense top layer (92) may provide environmental and erosion resistance.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
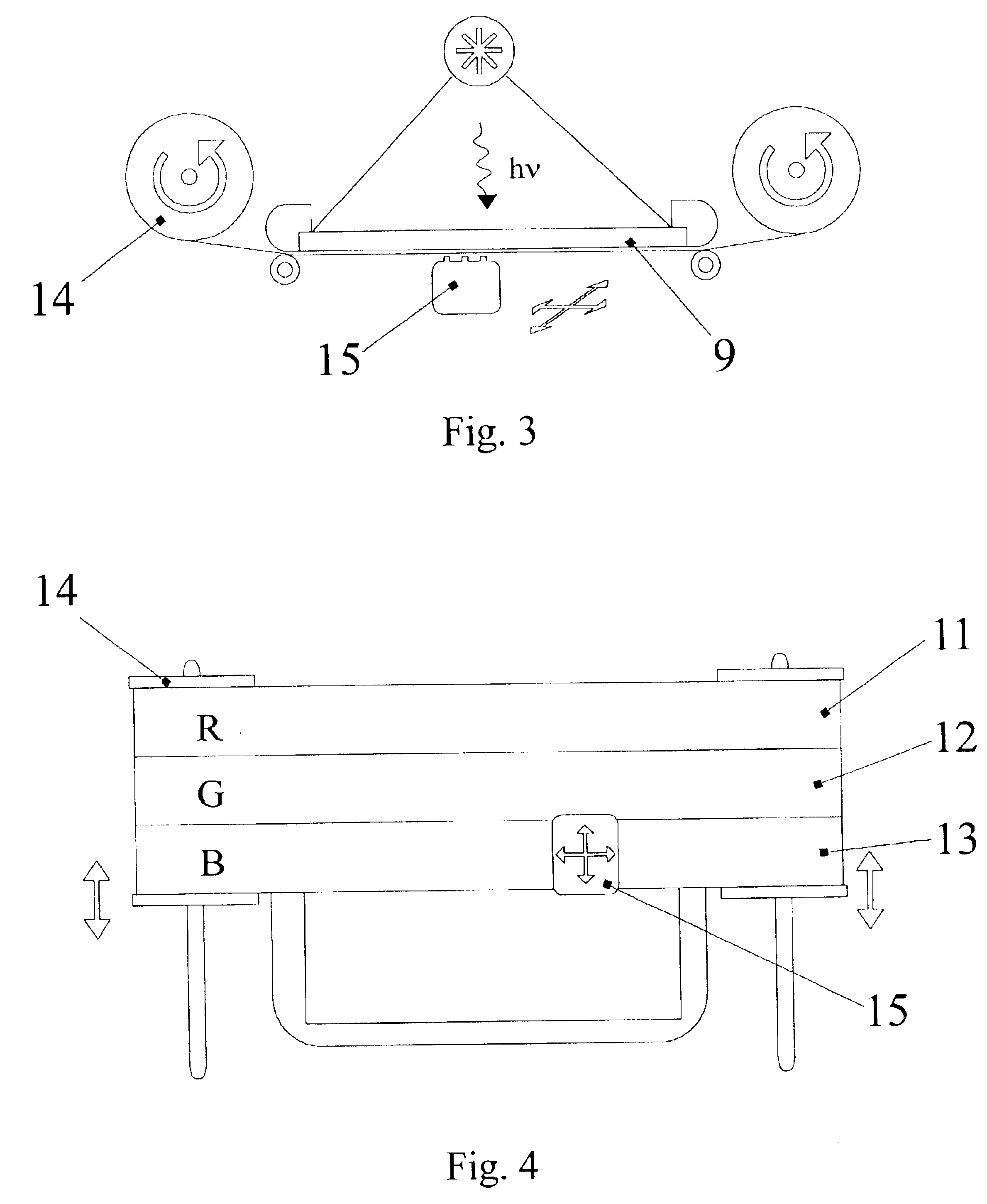
Method and apparatus for detecting the presence of anisotropic crystals and hemozoin producing parasites in liquid blood
InactiveUS20120021456A1Efficient detectionNo impact with respect to affecting the polarizationMicrobiological testing/measurementPolarisation-affecting propertiesLight filterOptical polarization
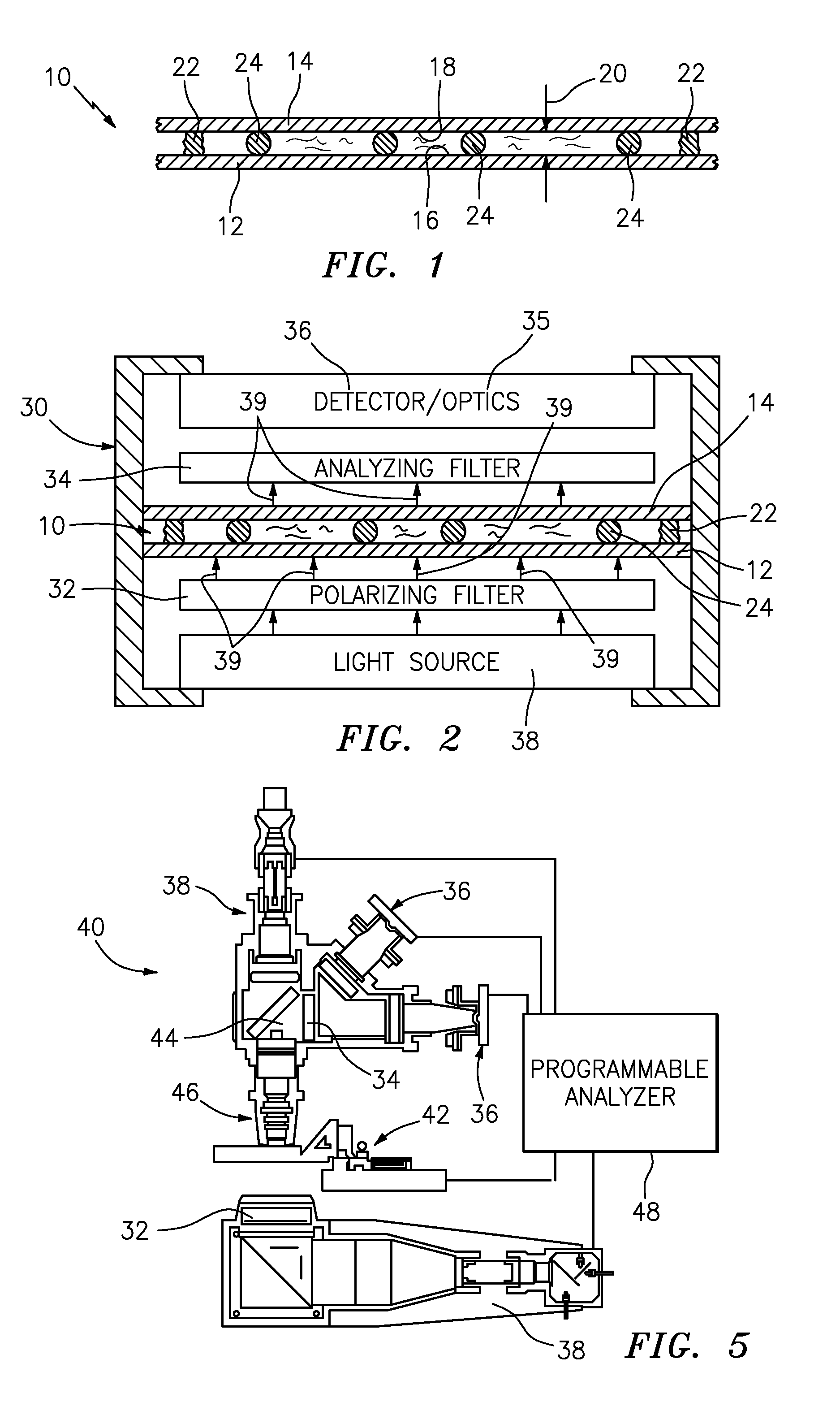
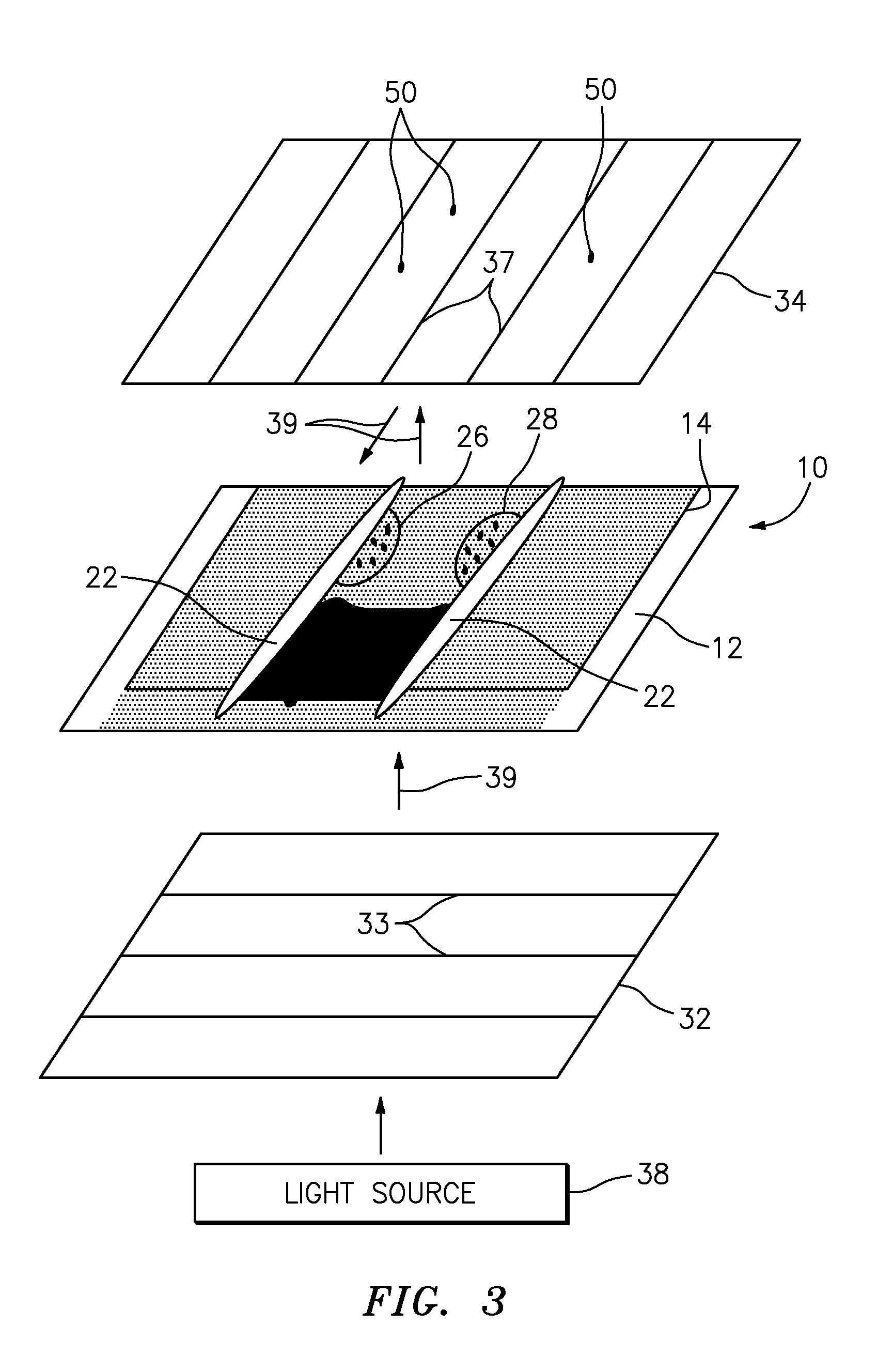
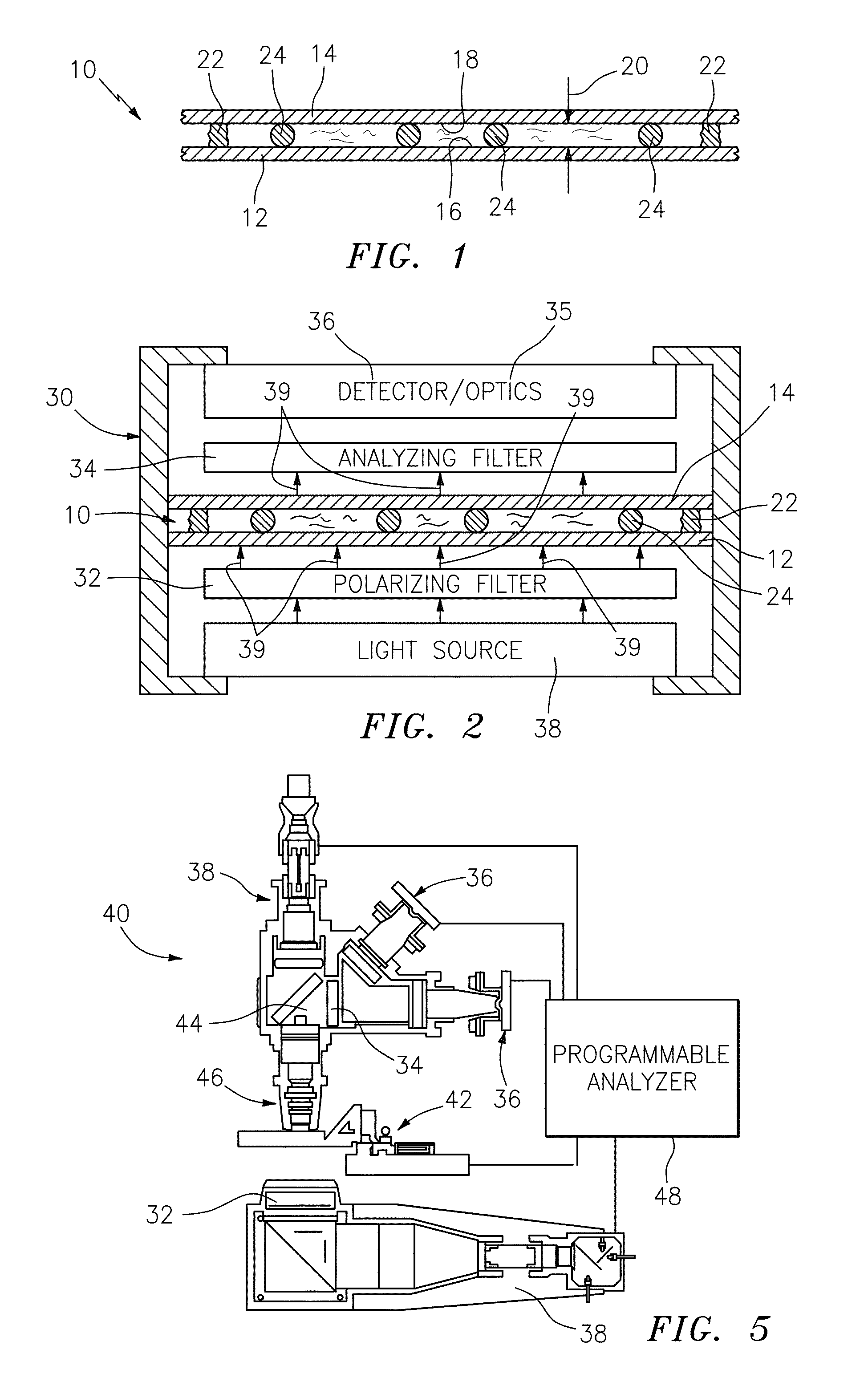
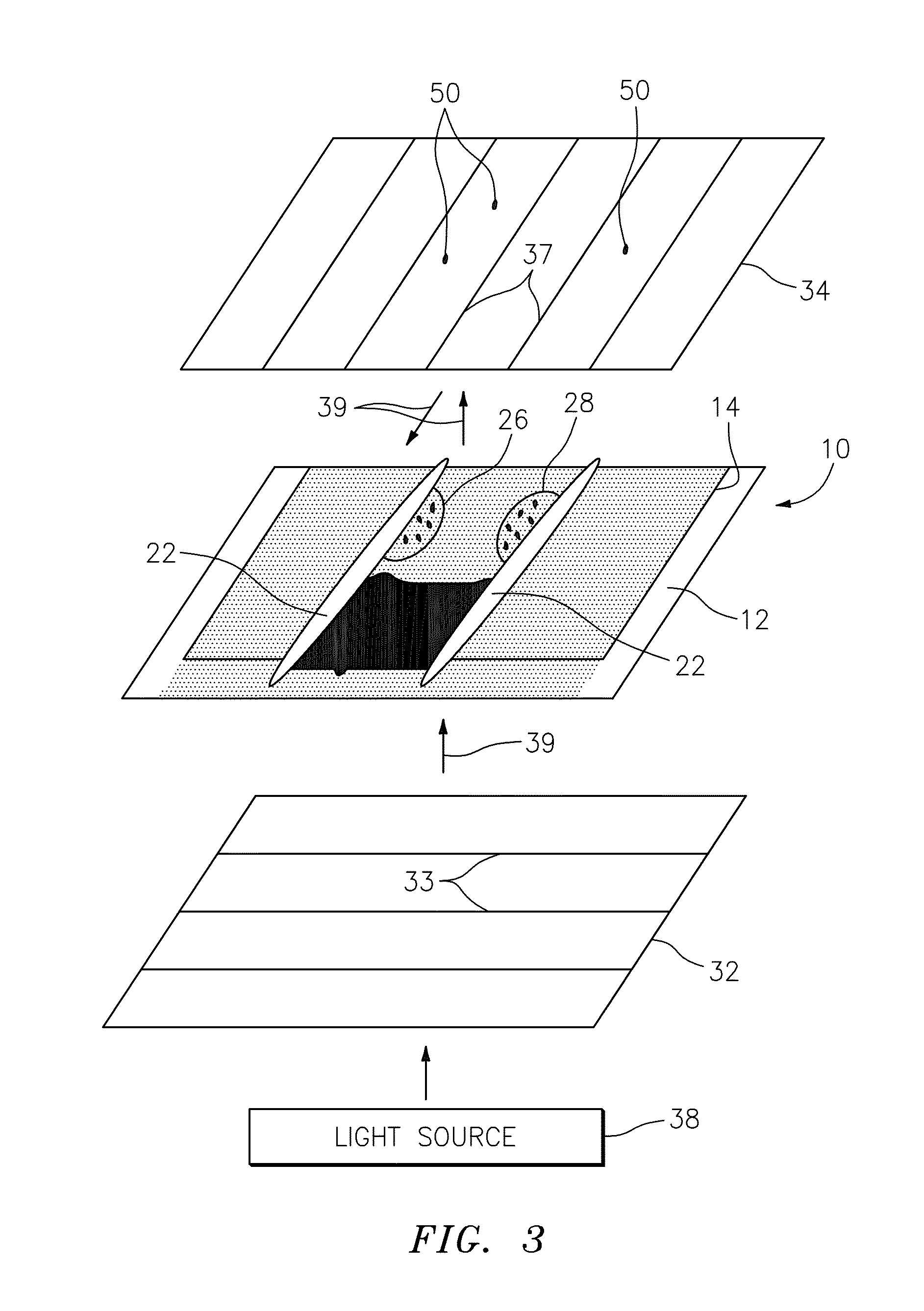
An apparatus and method for detecting the presence of anisotropic crystals within a biologic fluid sample is provided. The method includes the steps of: a) disposing the sample within a sample chamber in a sample layer having a height riot greater than about fifteen microns (15μ); b) disposing the sample layer within the sample chamber between a polarizing filter and an analyzing filter; a) disposing the polarizing filter, sample chamber, and analyzing filter in a configuration relative to a light source such that polarized light passes through the sample, and subsequently impinges on the analyzing filter; and d) wherein polar orientations of the polarizing filter and the analyzing filter are such that the polarized light will not pass through the analyzing filter, and light passing through an anisotropic crystal disposed within the sample will pass through the analyzing filter and appear as a point of light.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Ion-conducting composite electrolyte comprising path-engineered particles
ActiveUS20140065513A1Made practicalLimit ionic conductivityFrom normal temperature solutionsLiquid separation by electricityPath lengthComposite electrolyte
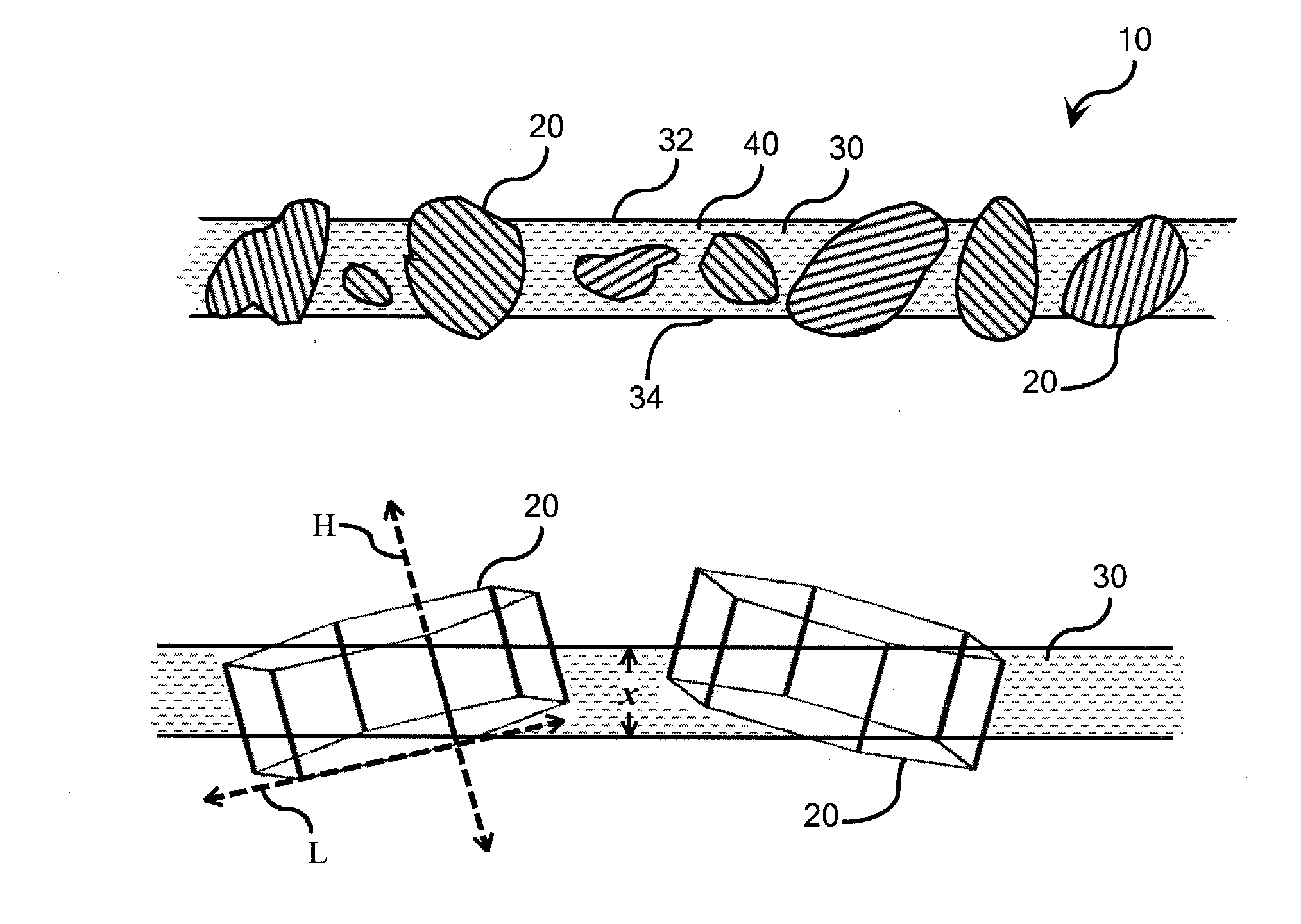
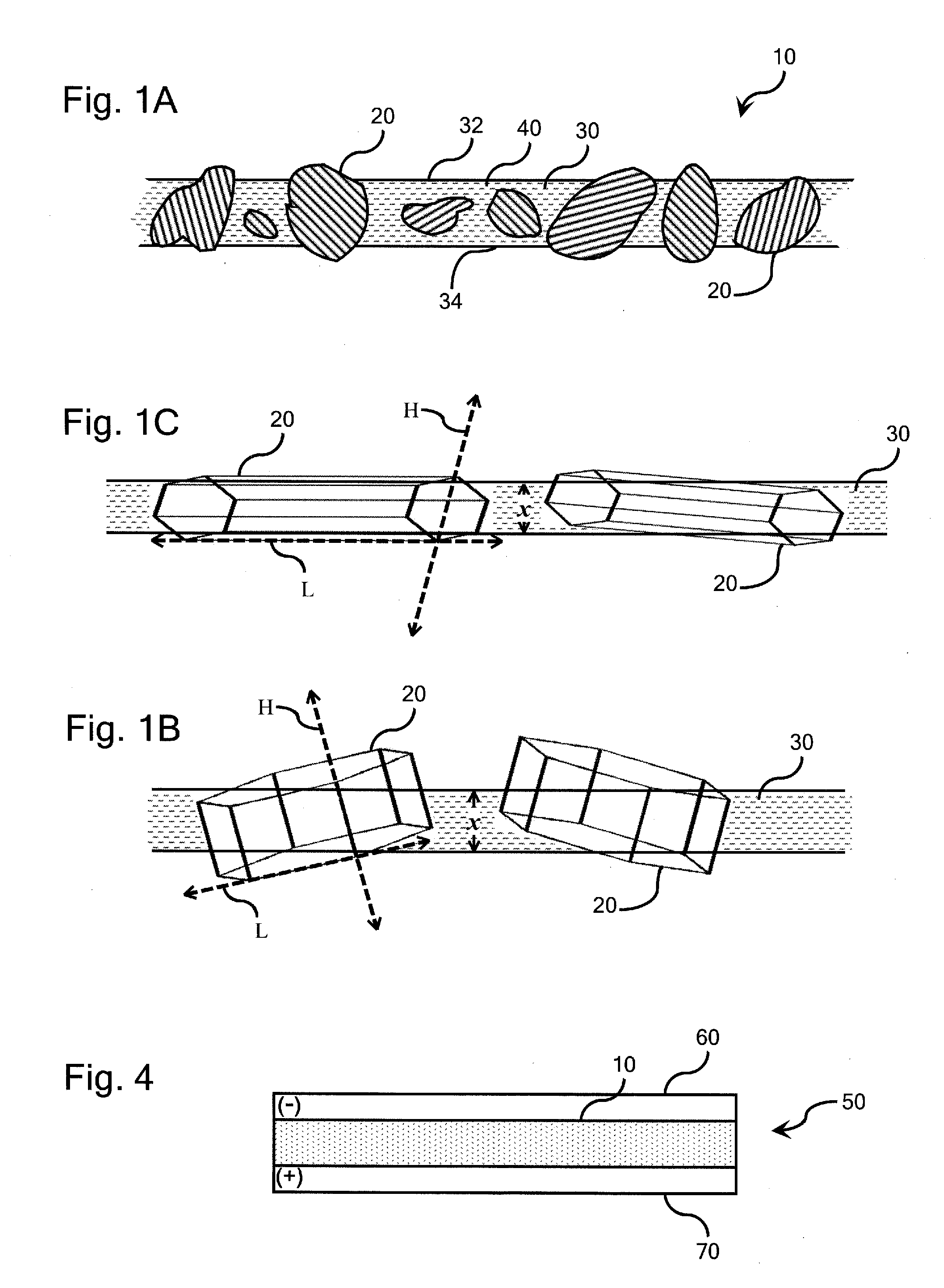
An ion-conducting composite electrolyte is provided comprising path-engineered ion-conducting ceramic electrolyte particles and a solid polymeric matrix. The path-engineered particles are characterized by an anisotropic crystalline structure and the ionic conductivity of the crystalline structure in a preferred conductivity direction H associated with one of the crystal planes of the path-engineered particle is larger than the ionic conductivity of the crystalline structure in a reduced conductivity direction L associated with another of the crystal planes of the path-engineered particle. The path-engineered particles are sized and positioned in the polymeric matrix such that a majority of the path-engineered particles breach both of the opposite major faces of the matrix body and are oriented in the polymeric matrix such that the preferred conductivity direction H is more closely aligned with a minimum path length spanning a thickness of the matrix body than is the reduced conductivity direction L.
Owner:CORNING INC
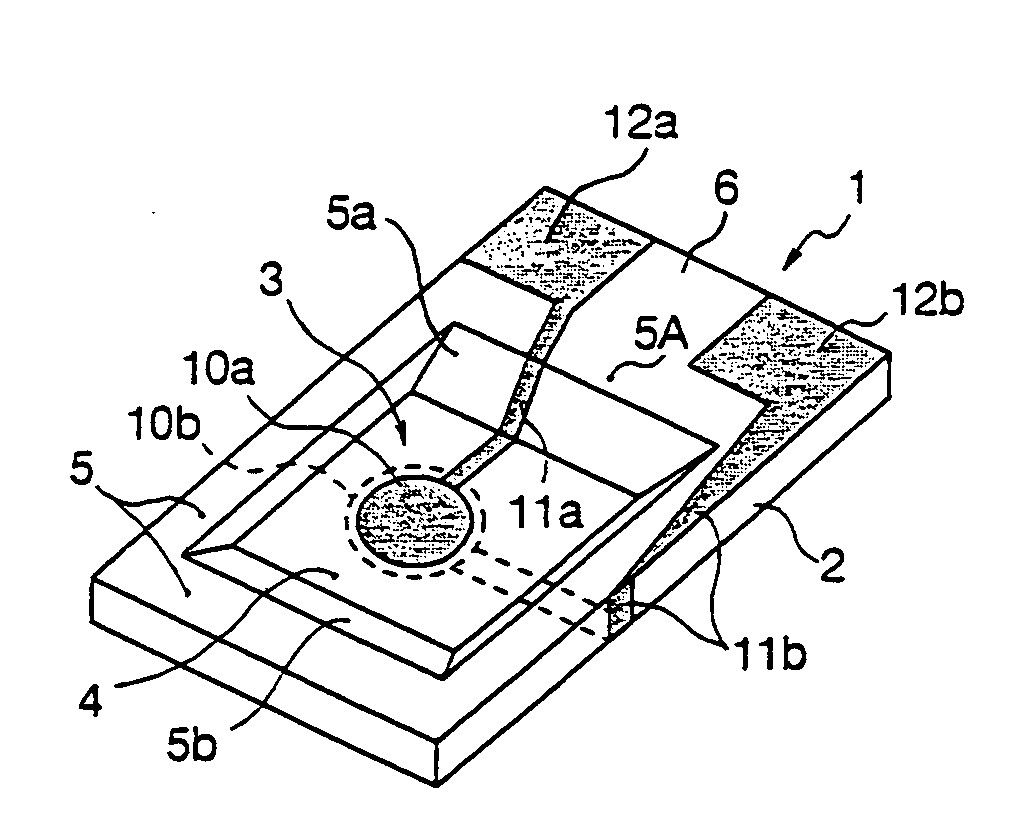
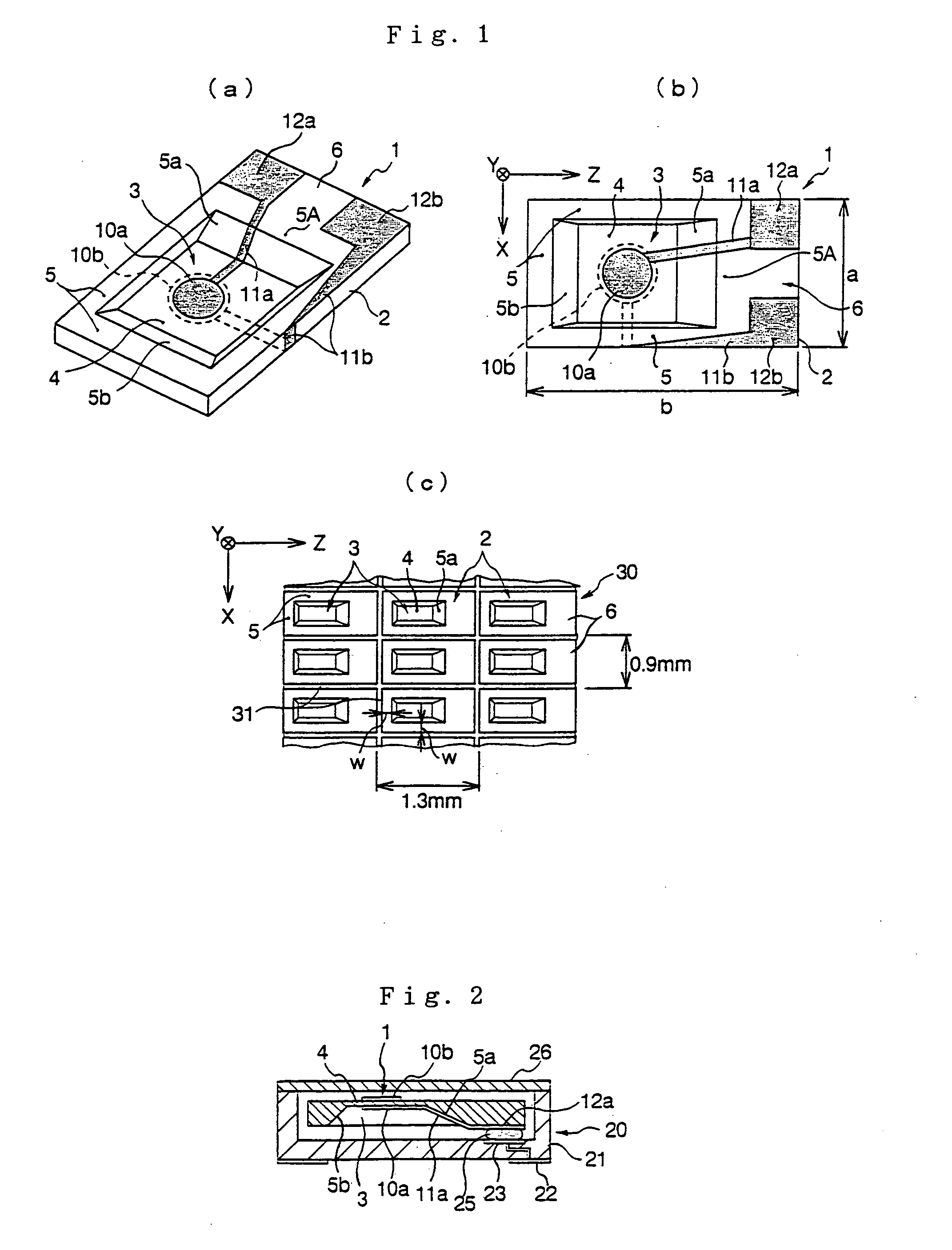
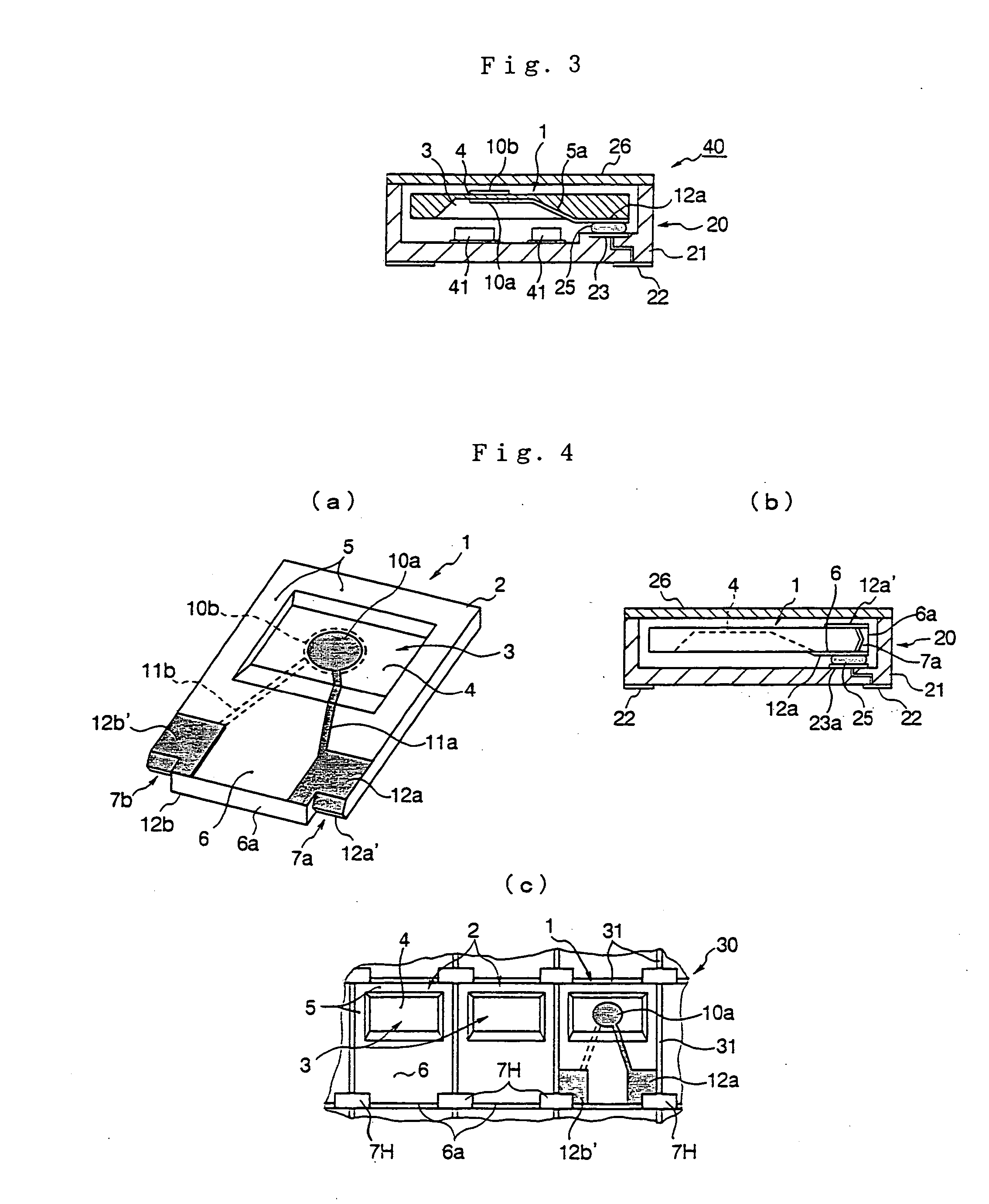
Piezoelectric resonator and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7098574B2Improve reliabilityArea maximizationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksCrystal orientationBatch operation
In the case where an ultraminiature piezoelectric substrate, which has a resonating portion formed by making a concavity by etching in the surface of the piezoelectric substrate made of an anisotropic crystal material, is mass-produced by batch operation using a large-area piezoelectric substrate wafer, an annular portion surrounding each concavity is formed sufficiently thick to prevent cracking from occurring when the wafer is severed. A piezoelectric substrate 2 of an anisotropic piezoelectric crystal material has a thin resonating portion 4 and a thick annular portion 5 integrally surrounding the outer marginal edge of the resonating portion to form a concavity 3 in at least one of major surfaces of the substrate; the inner wall 5a of the annular portion in the one crystal orientation slopes gently more than the inner wall in the other crystal orientation perpendicular to said one crystal orientation, and the piezoelectric substrate is longer in said one crystal orientation than in the other crystal orientation.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Multi-pass optical power amplifier
InactiveUS20090245304A1Quality improvementEffect of depolarization is negligibleOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical devices for laserOptical powerAnisotropic crystal
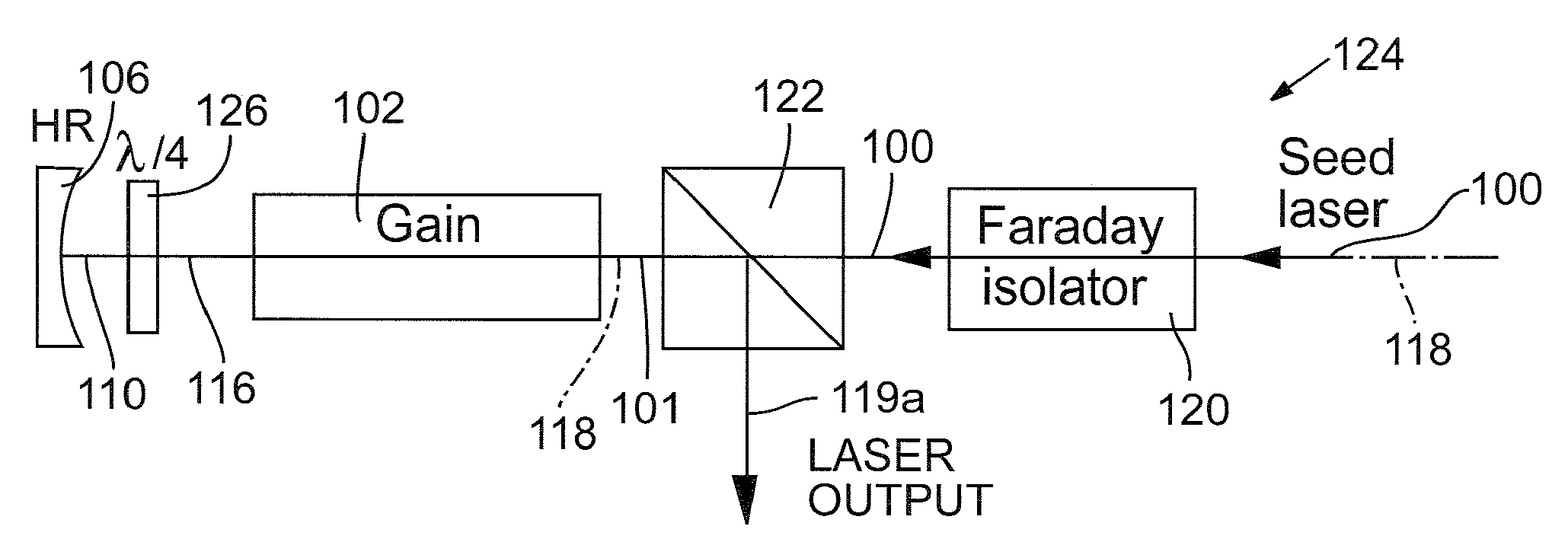
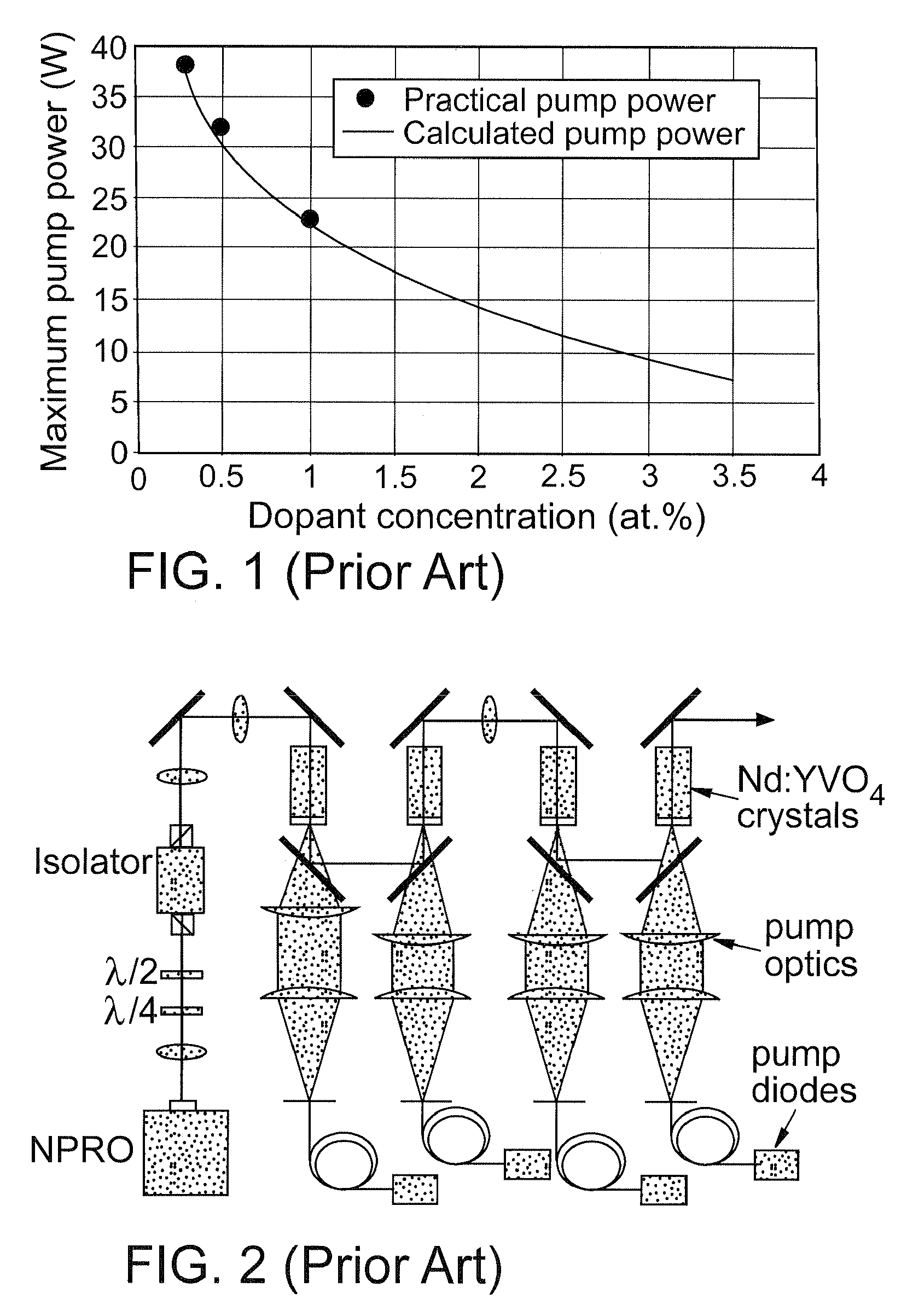
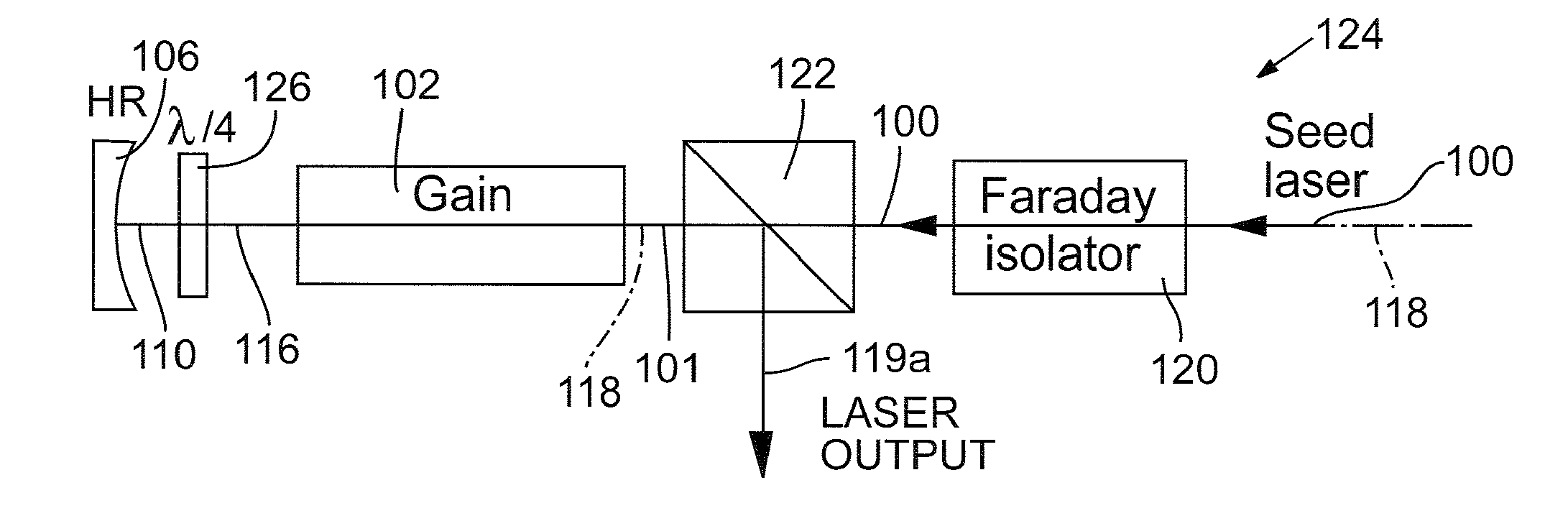
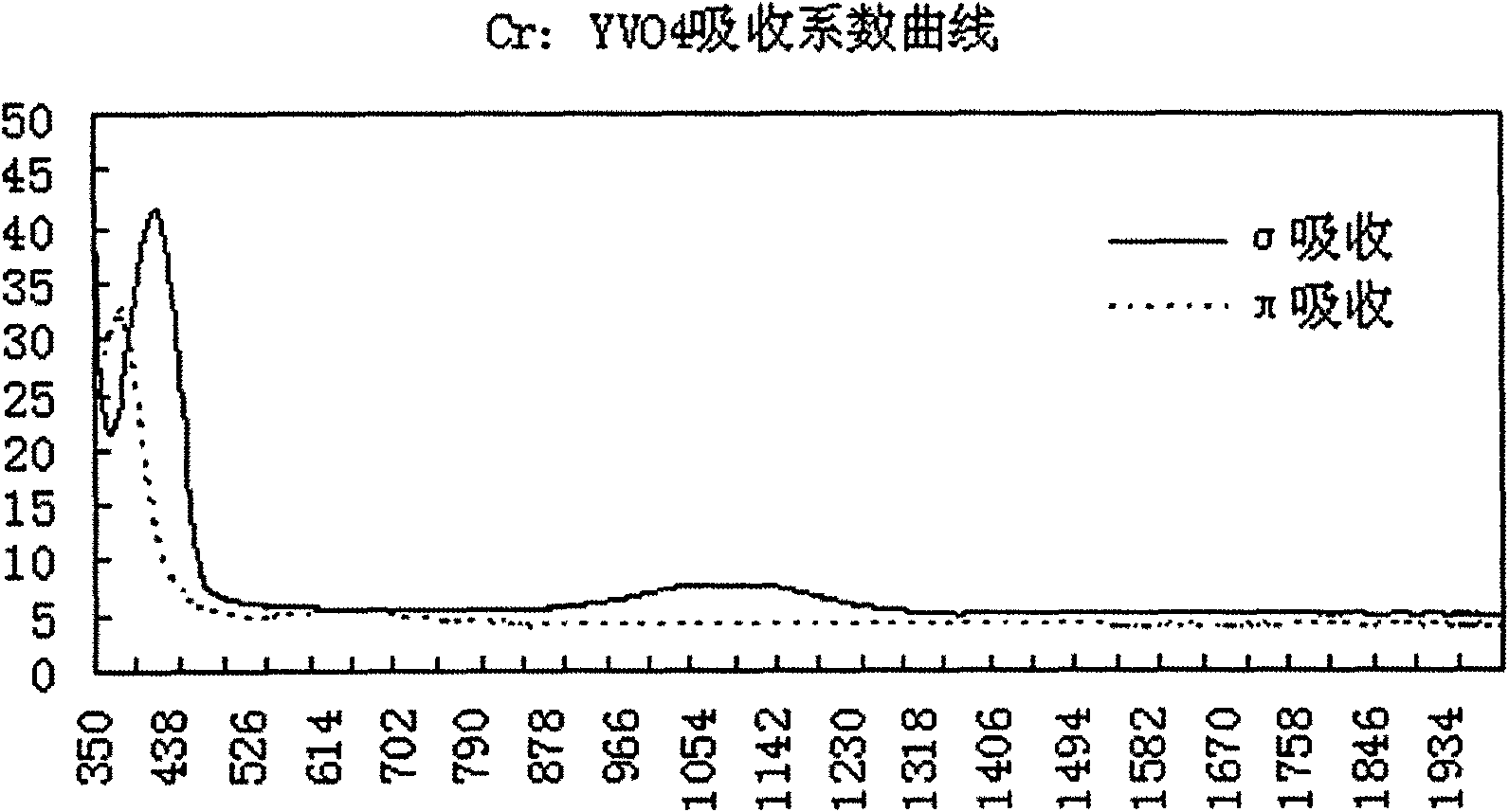
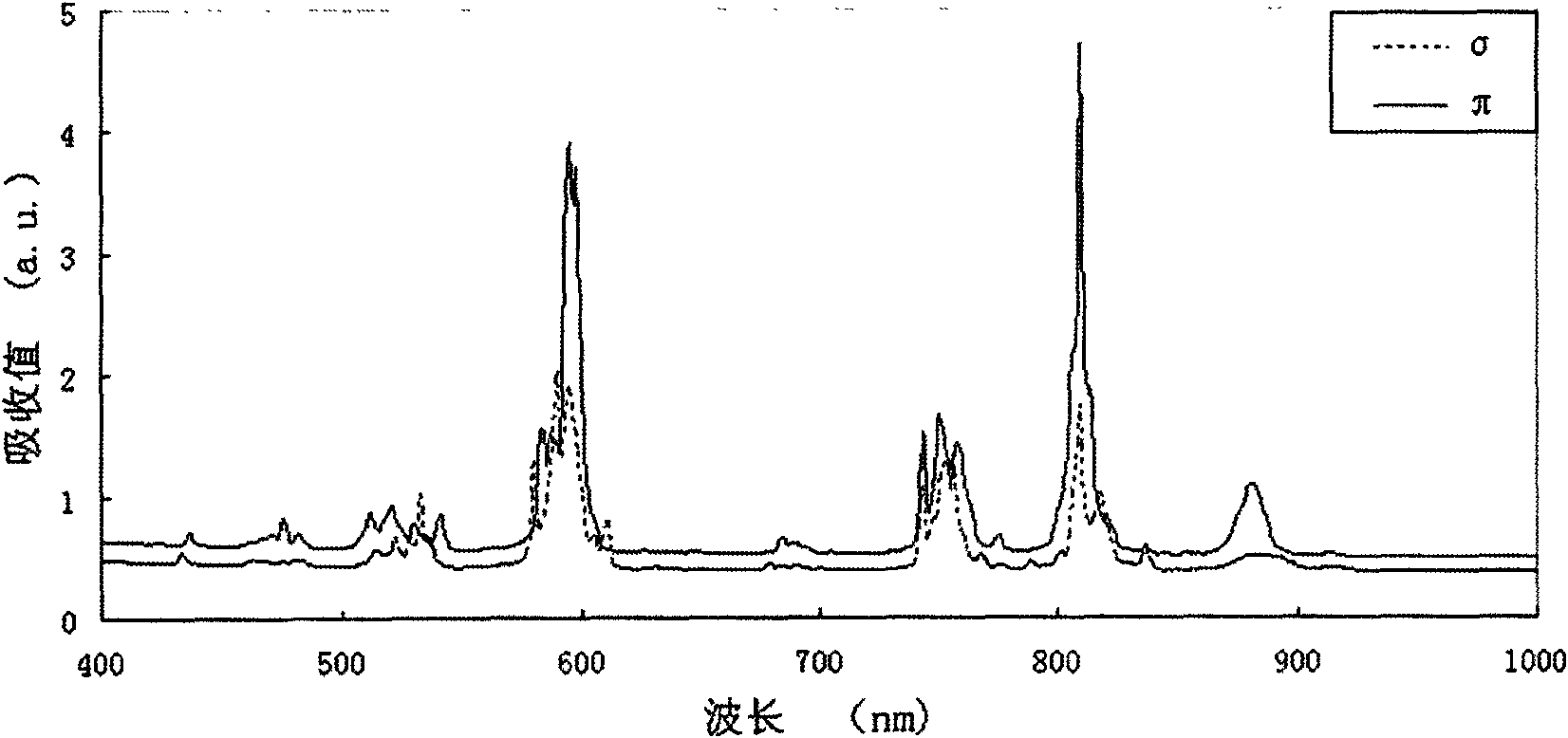
Anisotropic crystals such as Nd:YVO4, Nd:YLF, and Nd:GdVO4 have become preferred gain materials for many laser applications. The anisotropic gain medium without ancillary compensation ensures there is no degradation of laser modes when passing through the gain medium. An optical power amplifier that incorporates an anisotropic gain medium achieves power scaling with multiple passes while also maintaining good mode matching between the laser and the pump during each pass. Preferred embodiments implement for multiple passes of a seed laser beam through an anisotropic gain medium with substantially zero angular beam displacement during each pass. The multi-pass system provides an economical, reliable method of achieving high TEM00 power to meet the demands of micromachining, via drilling, and harmonic conversion applications.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Segmented thermal barrier coating
A ceramic thermal barrier coating (TBC) (18) having first and second layers (20, 22), the second layer (22) having a lower thermal conductivity than the first layer for a given density. The second layer may be formed of a material with anisotropic crystal lattice structure. Voids (24) in at least the first layer (20) make the first layer less dense than the second layer. Grooves (28) are formed in the TBC (18) for thermal strain relief. The grooves may align with fluid streamlines over the TBC. Multiple layers (84, 86, 88) may have respective sets of grooves (90), Preferred failure planes parallel to the coating surface (30) may be formed at different depths (A1, A2, A3) in the thickness of the TBC to stimulate generation of a fresh surface when a portion of the coating fails by spalling. A dense top layer (92) may provide environmental and erosion resistance.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Method for detecting the presence of anisotropic crystals in undiluted whole blood
InactiveUS8481282B2Efficient detectionNo impact with respect to affecting the polarizationMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmaceutical containersElectrical polarityBiological fluids
An apparatus and method for detecting the presence of anisotropic crystals within a biologic fluid sample is provided. The method includes the steps of: a) disposing the sample within a sample chamber in a sample layer having a height not greater than about fifteen microns (15μ); b) disposing the sample layer within the sample chamber between a polarizing filter and an analyzing filter; c) disposing the polarizing filter, sample chamber, and analyzing filter in a configuration relative to a light source such that polarized light passes through the sample, and subsequently impinges on the analyzing filter; and d) wherein polar orientations of the polarizing filter and the analyzing filter are such that the polarized light will not pass through the analyzing filter, and light passing through an anisotropic crystal disposed within the sample will pass through the analyzing filter and appear as a point of light.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
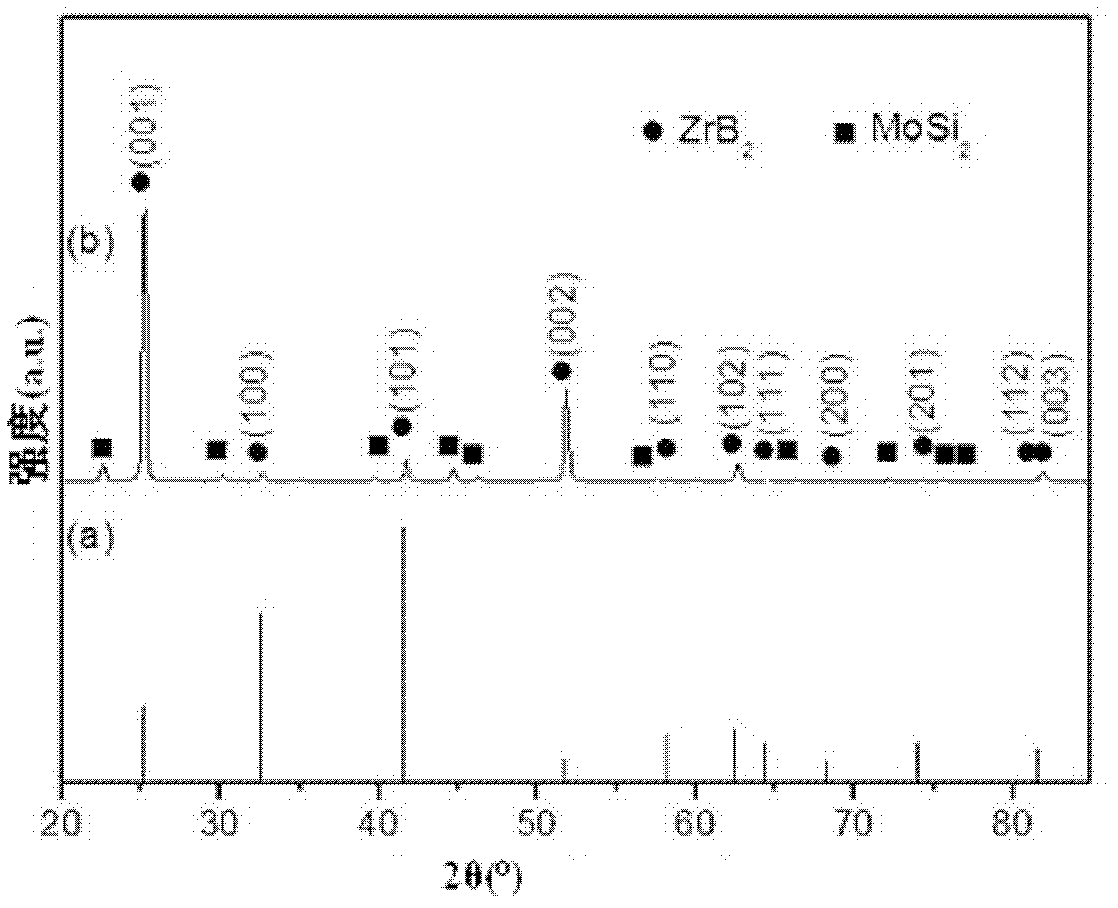
Method for preparing texturing boride super-high-temperature ceramic
The invention discloses a method for preparing texturing boride super-high-temperature ceramic. The method for preparing the texturing boride super-high-temperature ceramic comprises the steps that IVB group metal simple substance, amorphous boron powder, silica powder, and transition metal are adopted as raw materials, and complex-phase powder containing boride seed crystal and silicide particles is prepared; and slurry is prepared by mixing the complex-phase powder and boride ceramic powder, a ceramic body is prepared by means of the casting process technology or high-intensity magnetic field orientation process technology, and then hot pressed sintering is carried out on the ceramic body. According to the method for preparing the texturing boride super-high-temperature ceramic, the boride seed crystal is enabled to grow in the ceramic body in a orientation-arrangement mode due to the preparation of boride seed crystal with anisotropic microstructure and the adoption of the casting process technology or high-intensity magnetic field orientation process technology for preparation of the ceramic body, and then the texturing boride super-high-temperature ceramic with anisotropic crystal particle morphology is prepared. According to the ceramic prepared with the method, relative density is more than 98%, material Lotgering orientation factor f (001) can reach to 0.95, and obvious anisotropism can be represented by each performance.
Owner:江苏先进无机材料研究院
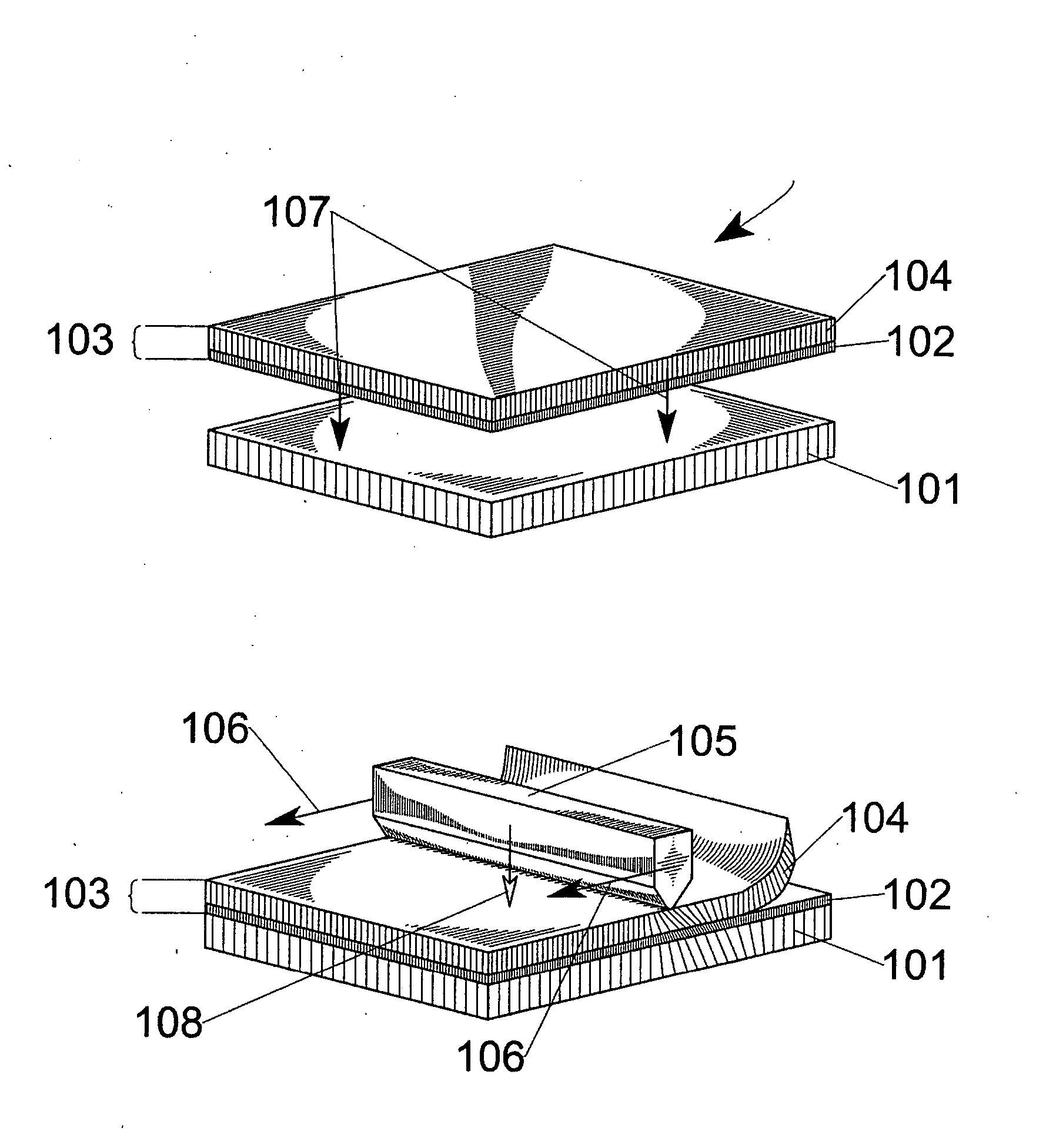
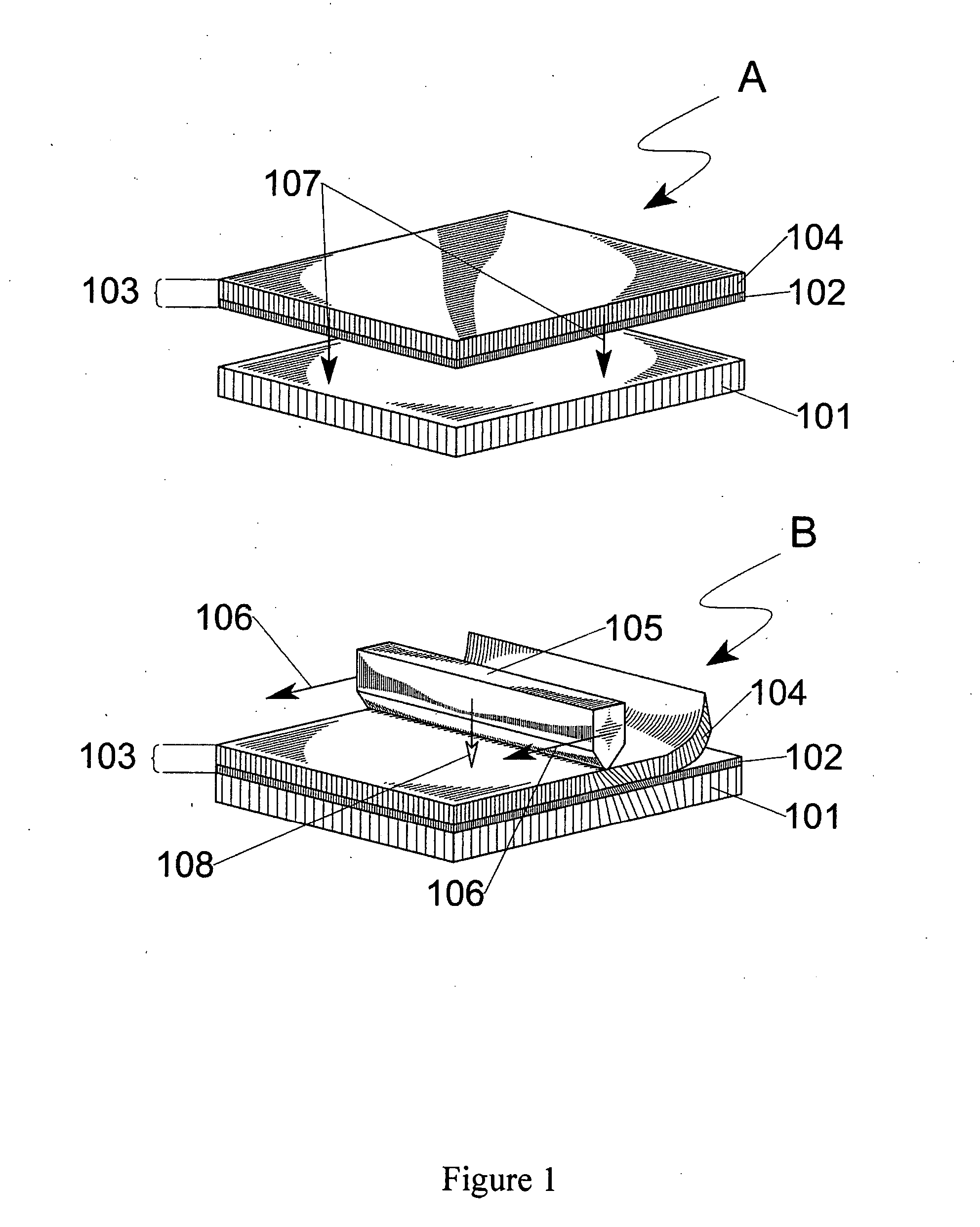
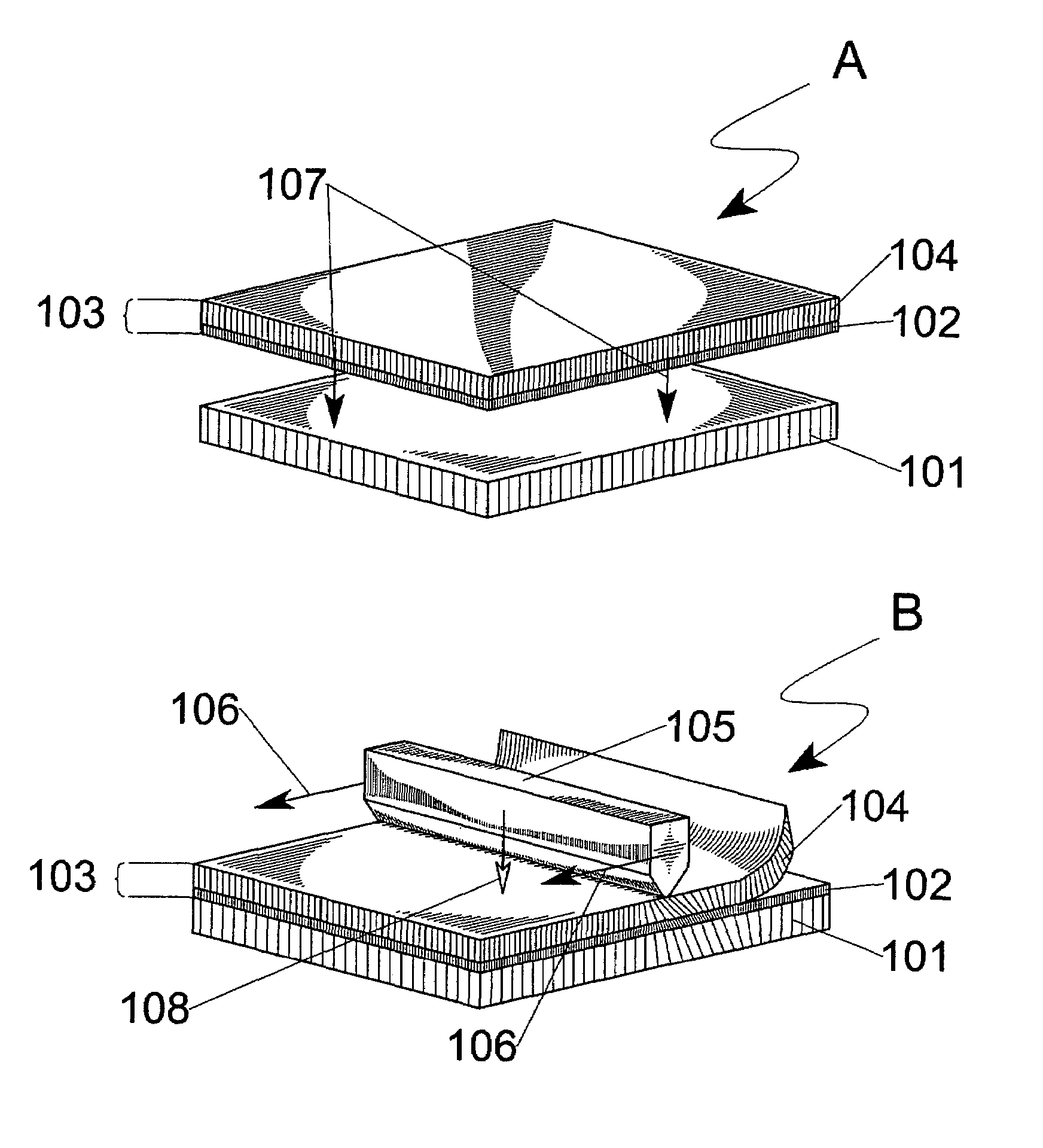
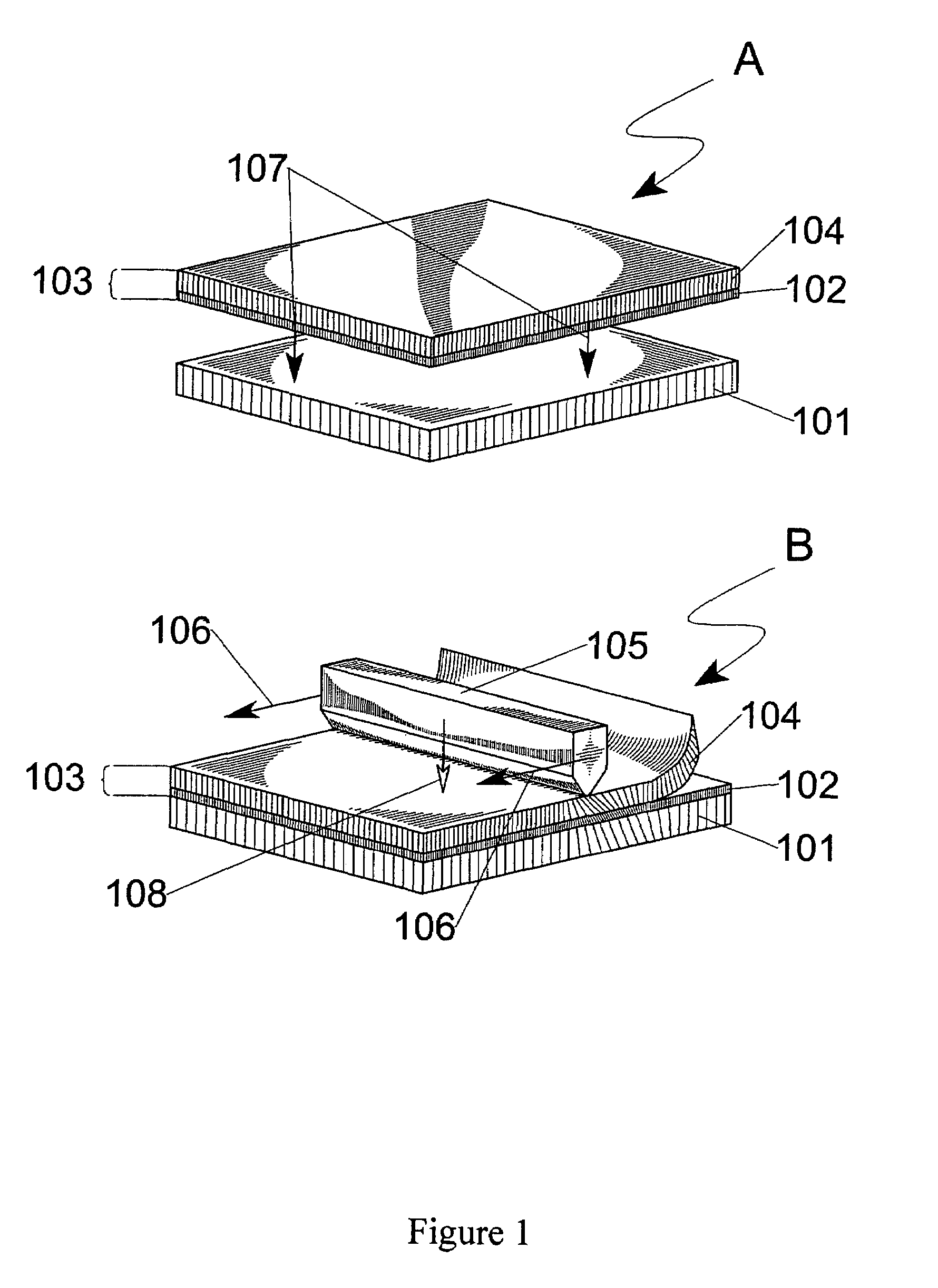
Method and device for transferring anisotropic crystal film from donor to receptor, and the donor
ActiveUS20050136345A1Maintain alignmentLiquid crystal compositionsAfter-treatment detailsCrystallographyAnisotropic crystal
A method of forming an anisotropic crystal film, comprising providing a donor which comprises a base and an anisotropic crystal film bounded to the base, and a receptor. At least a portion of the anisotropic crystal film is placed in contact with the receptor. A loading is applied to at least a portion of the base, whereby providing shear and compressive stresses onto the donor and receptor, and transferring at least a portion of the anisotropic crystal film onto the receptor and delaminating the at least portion of the anisotropic crystal film from the base.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Piezoelectric substrate, piezoelectric resonating element and surface-mount piezoelectric oscillator
InactiveUS20060244346A1Reduction in productivityHighly reliable piezoelectric substratesImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSurface mountingCrystal orientation
In the case where an ultraminiature piezoelectric substrate, which has a resonating portion formed by making a concavity by etching in the surface of the piezoelectric substrate made of an anisotropic crystal material, is mass-produced by batch operation using a large-area piezoelectric substrate wafer, an annular portion surrounding each concavity is formed sufficiently thick to prevent cracking from occurring when the wafer is severed. A piezoelectric substrate 2 of an anisotropic piezoelectric crystal material has a thin resonating portion 4 and a thick annular portion 5 integrally surrounding the outer marginal edge of the resonating portion to form a concavity 3 in at least one of major surfaces of the substrate; the inner wall 5a of the annular portion in the one crystal orientation slopes gently more than the inner wall in the other crystal orientation perpendicular to said one crystal orientation, and the piezoelectric substrate is longer in said one crystal orientation than in the other crystal orientation.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Multi-pass optical power amplifier
InactiveUS7796671B2Quality improvementEffect of depolarization is negligibleExcitation process/apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionAudio power amplifierHarmonic
Anisotropic crystals such as Nd:YVO4, Nd:YLF, and Nd:GdVO4 have become preferred gain materials for many laser applications. The anisotropic gain medium without ancillary compensation ensures there is no degradation of laser modes when passing through the gain medium. An optical power amplifier that incorporates an anisotropic gain medium achieves power scaling with multiple passes while also maintaining good mode matching between the laser and the pump during each pass. Preferred embodiments implement for multiple passes of a seed laser beam through an anisotropic gain medium with substantially zero angular beam displacement during each pass. The multi-pass system provides an economical, reliable method of achieving high TEM00 power to meet the demands of micromachining, via drilling, and harmonic conversion applications.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
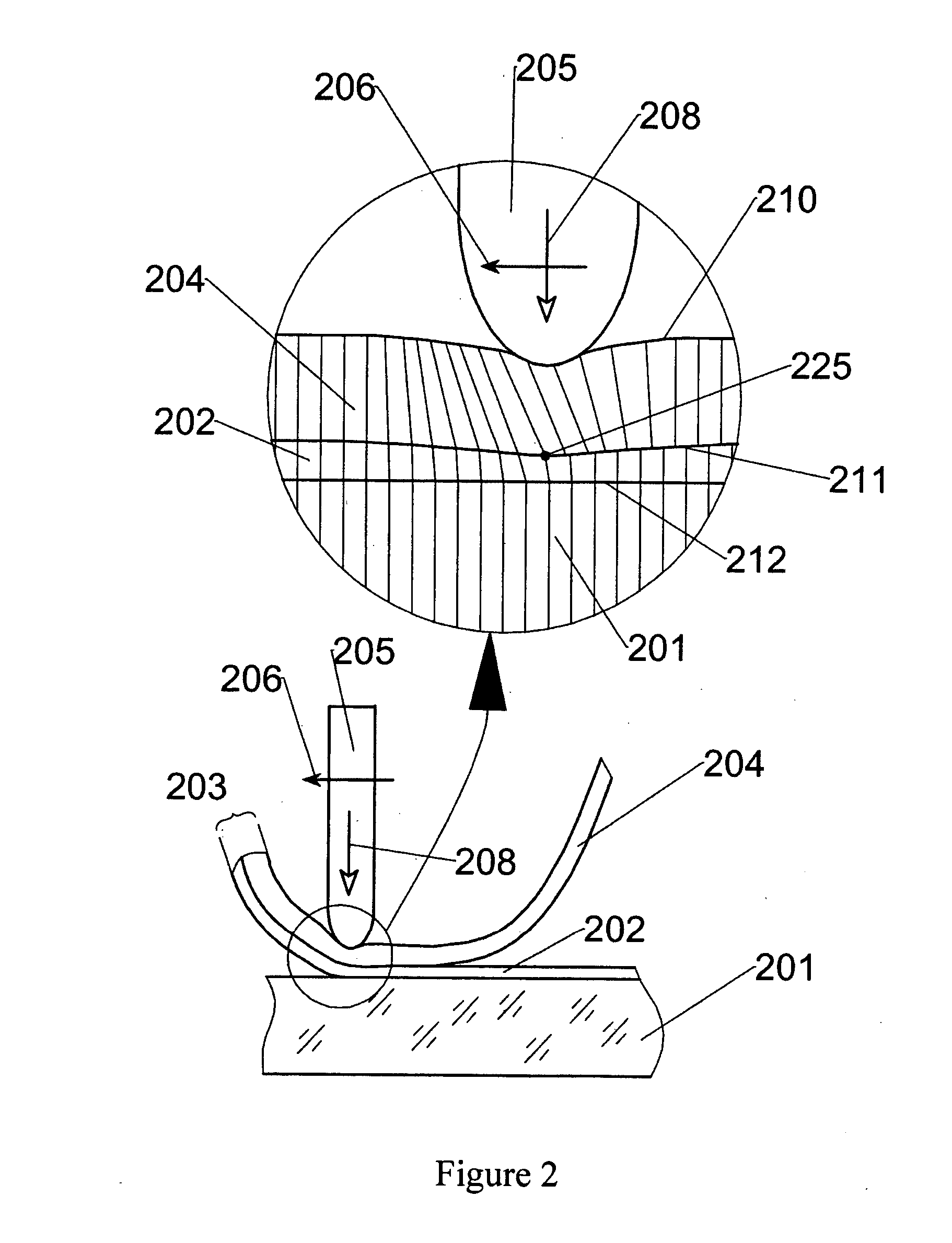
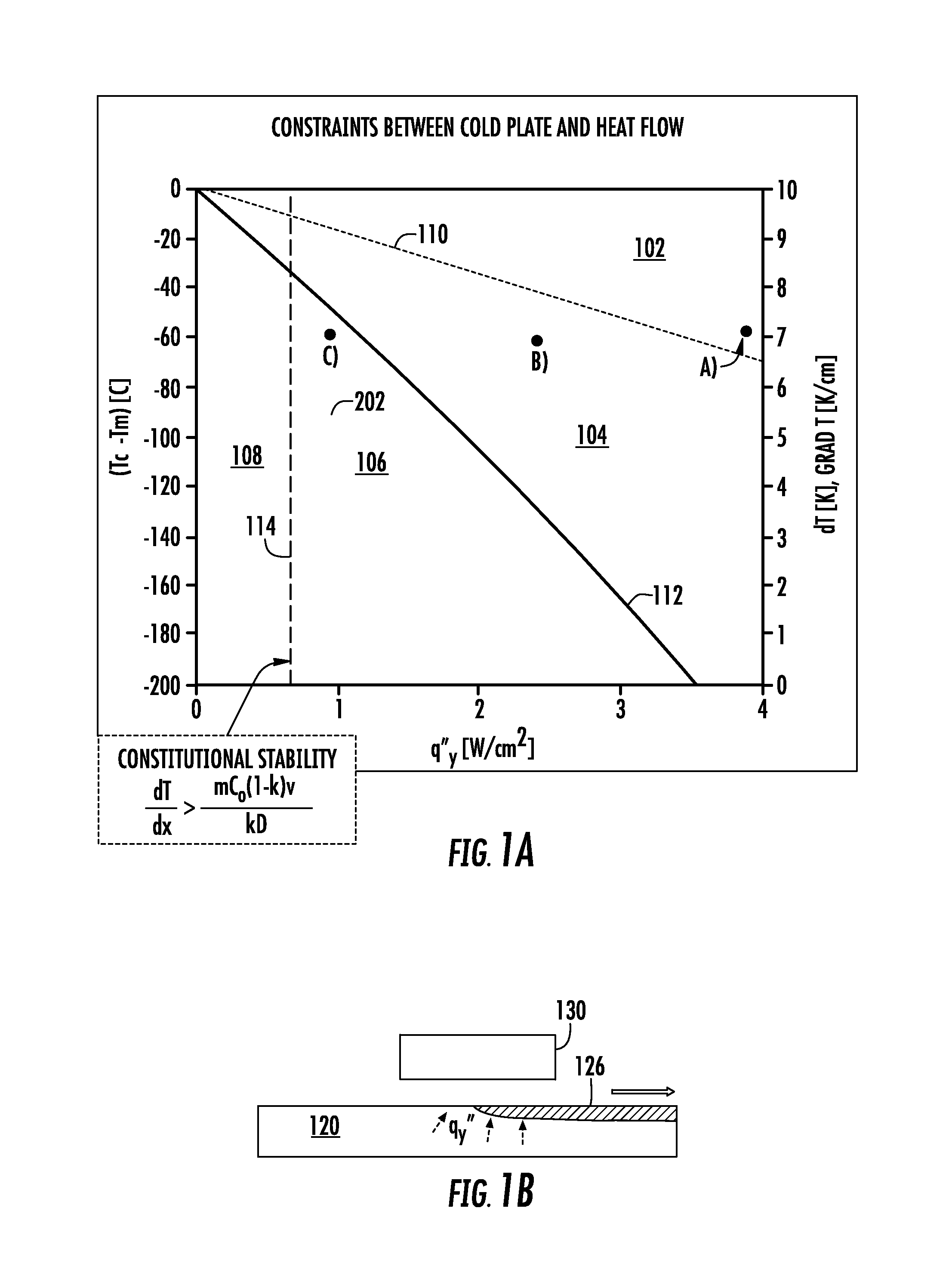
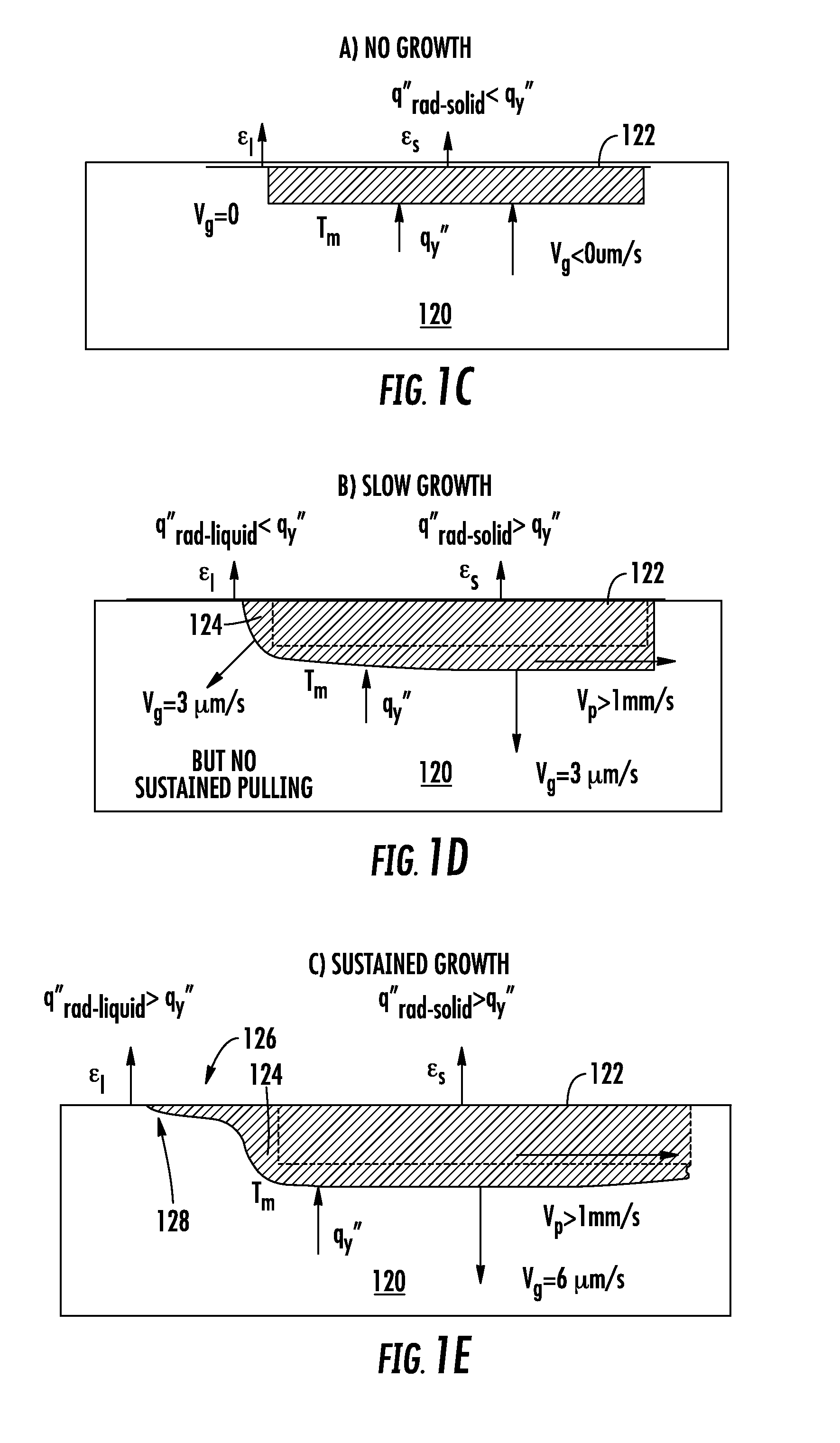
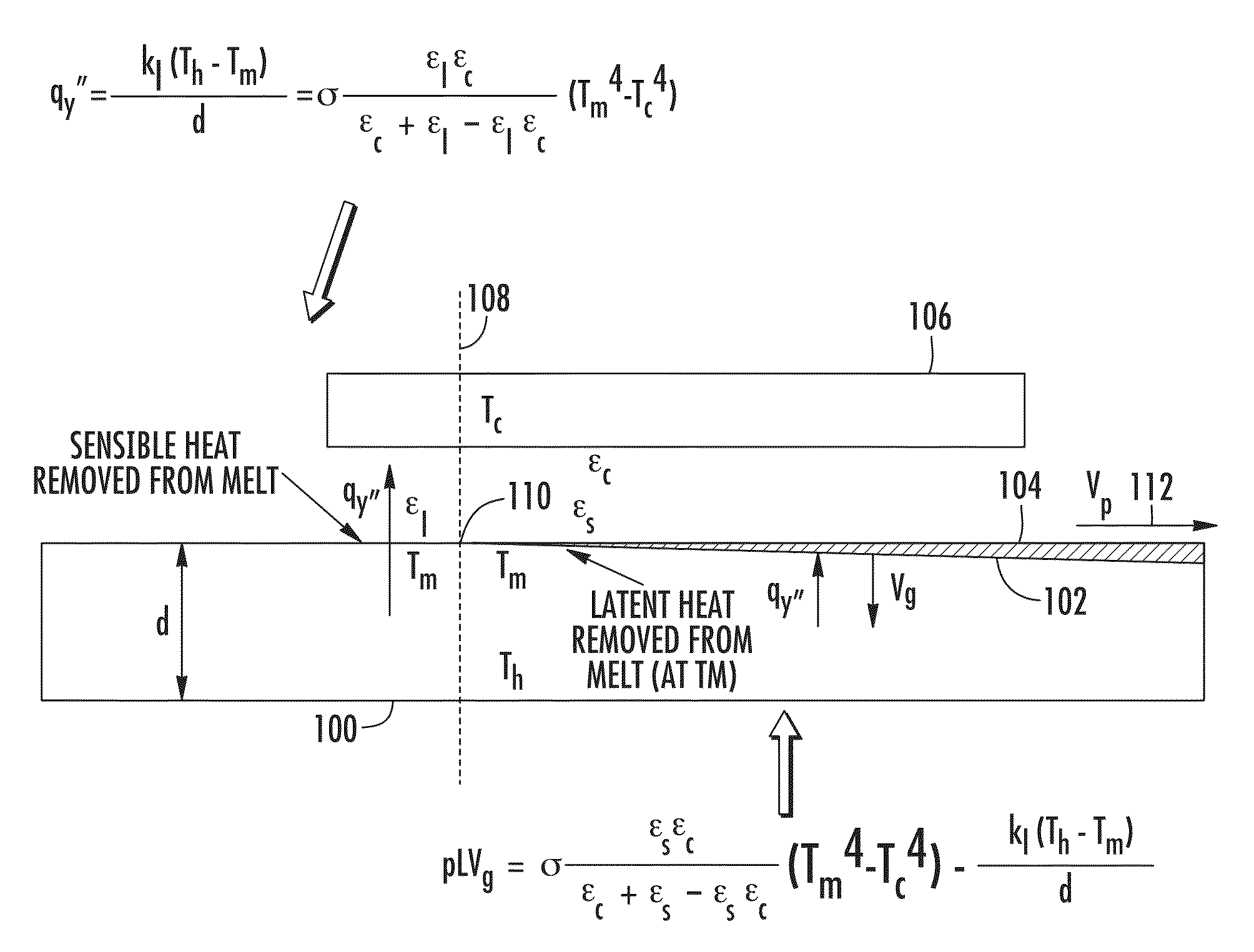
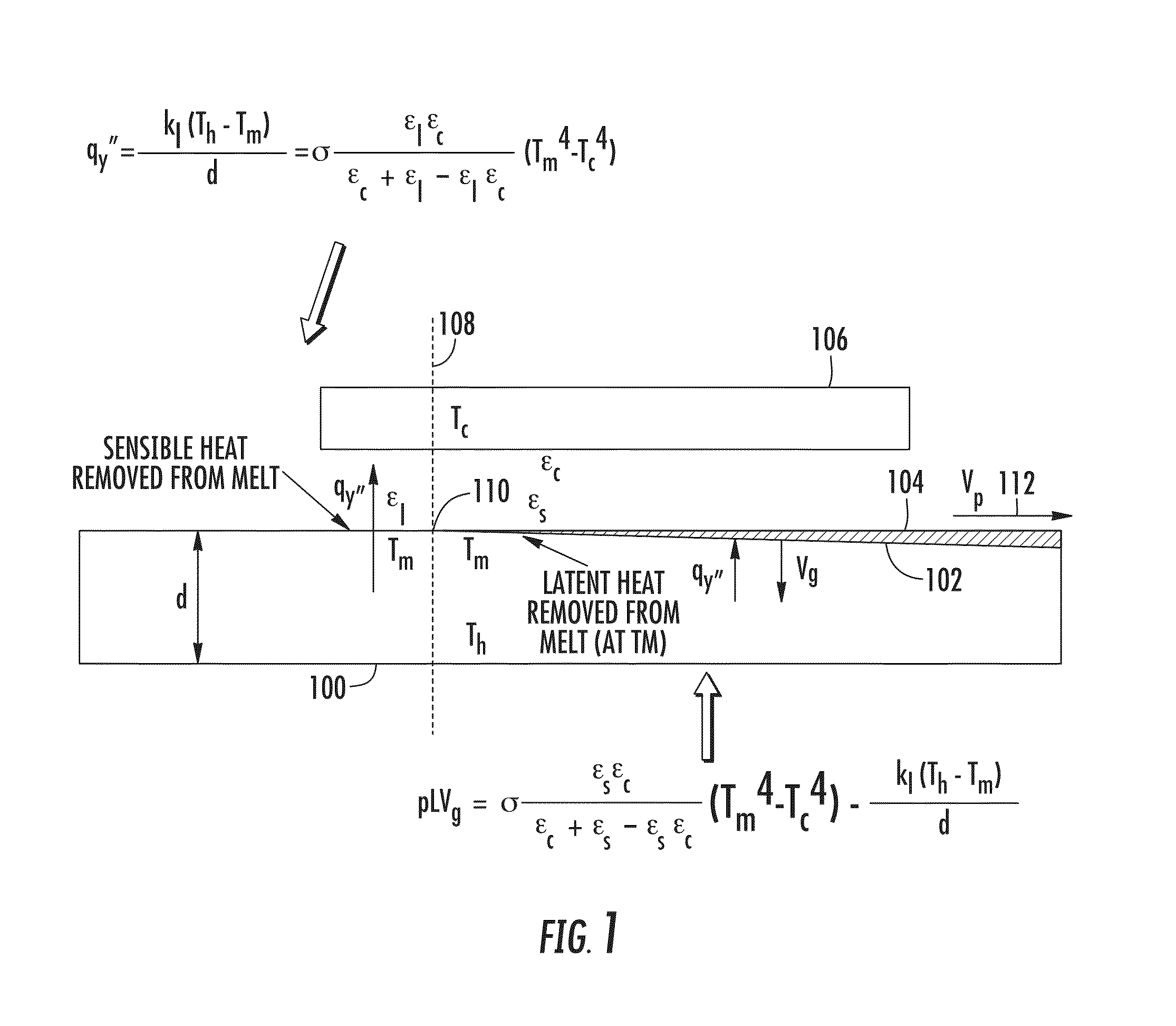
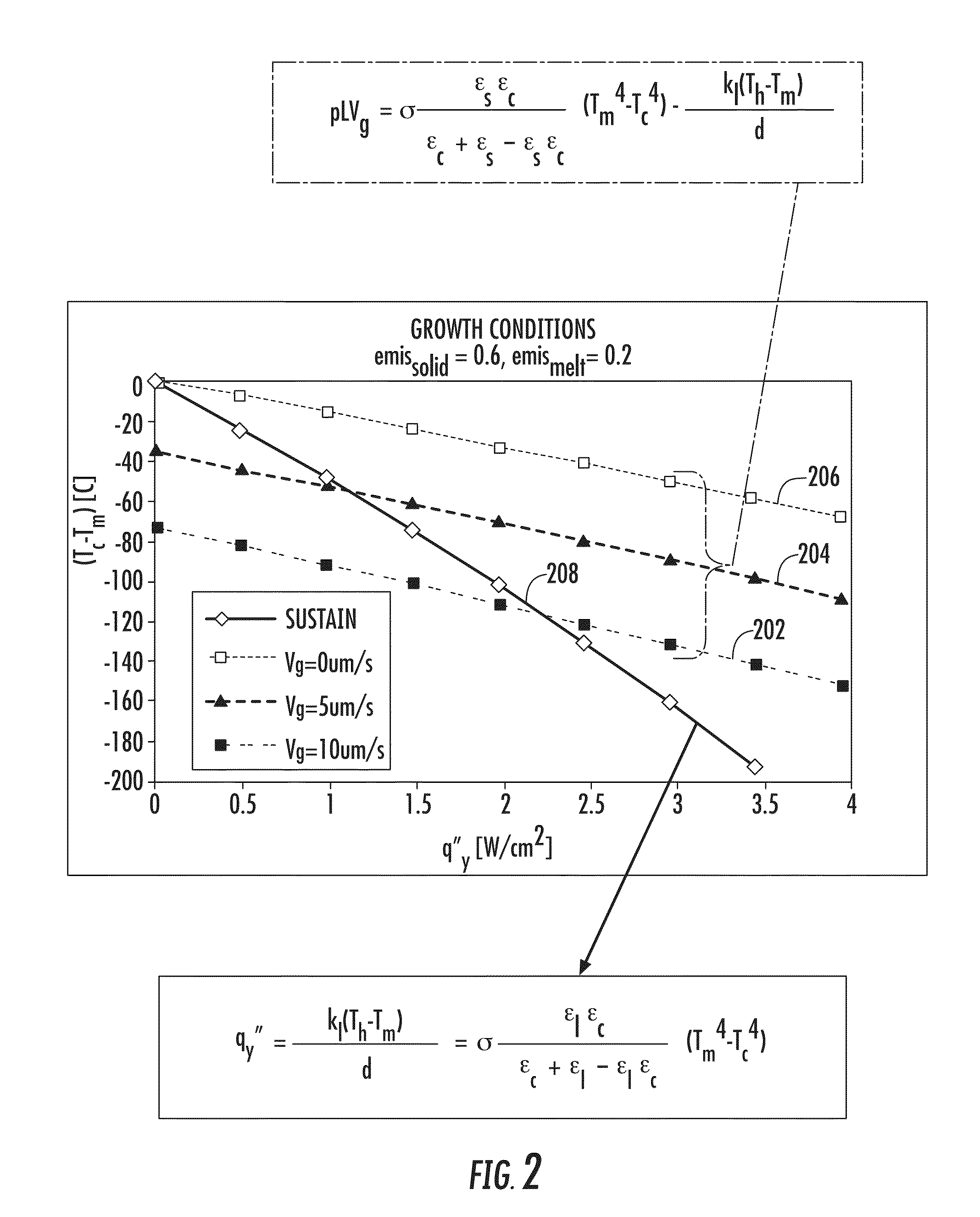
Method for achieving sustained anisotropic crystal growth on the surface of a silicon melt
An apparatus for growing a crystalline sheet from a melt includes a cold block assembly. The cold block assembly may include a cold block and a shield surrounding the cold block and being at an elevated temperature with respect to that of the cold block, the shield defining an opening disposed along a surface of the cold block proximate a melt surface that defines a cold area comprising a width along a first direction of the cold block, the cold area operable to provide localized cooling of a region of the melt surface proximate the cold block. The apparatus may further include a crystal puller arranged to draw a crystalline seed in a direction perpendicular to the first direction when the cold block assembly is disposed proximate the melt surface.
Owner:LEADING EDGE CRYSTAL TECH INC
Multilayer plate and display panel with anisotropic crystal film and conducting protective layer
InactiveUS7317499B2Reduce thicknessImprove reliabilityLiquid crystal compositionsSynthetic resin layered productsOptical axisTransmittance
A multilayer plate is provided comprising an optically transparent substrate, a protective layer, a conducting layer, and at least one anisotropic thin crystal film. The anisotropic thin crystal film is made of a substance containing aromatic rings and possessing a structure with an interplanar spacing of 3.4±0.2 Å along one of optical axes. The thin crystal film is situated between the substrate and the conducting layer and is separated from the conducting layer by the protective layer. The transmission of the multilayer plate for UV radiation does not exceed 1% at any wavelength below 380 nm.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
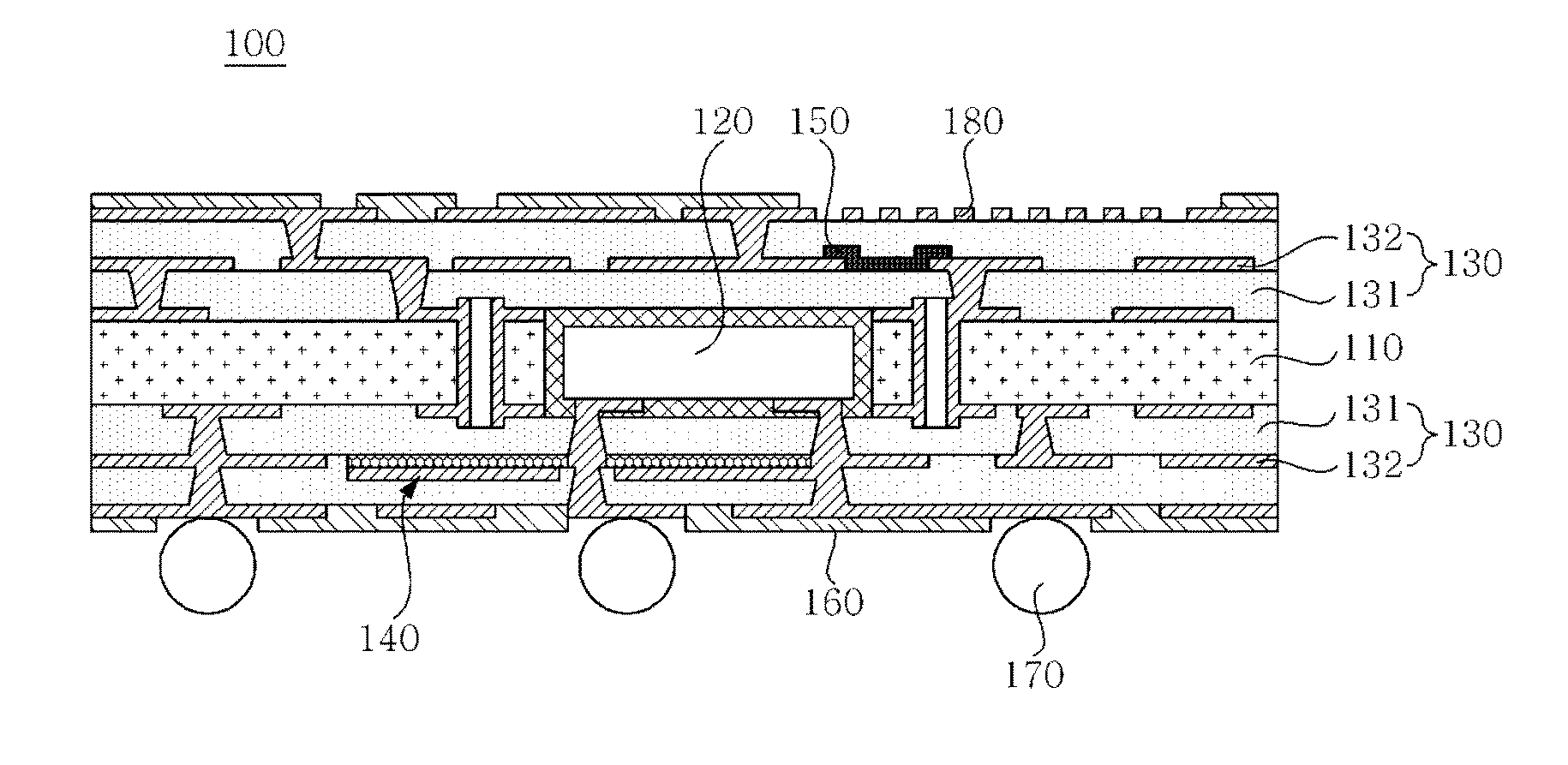
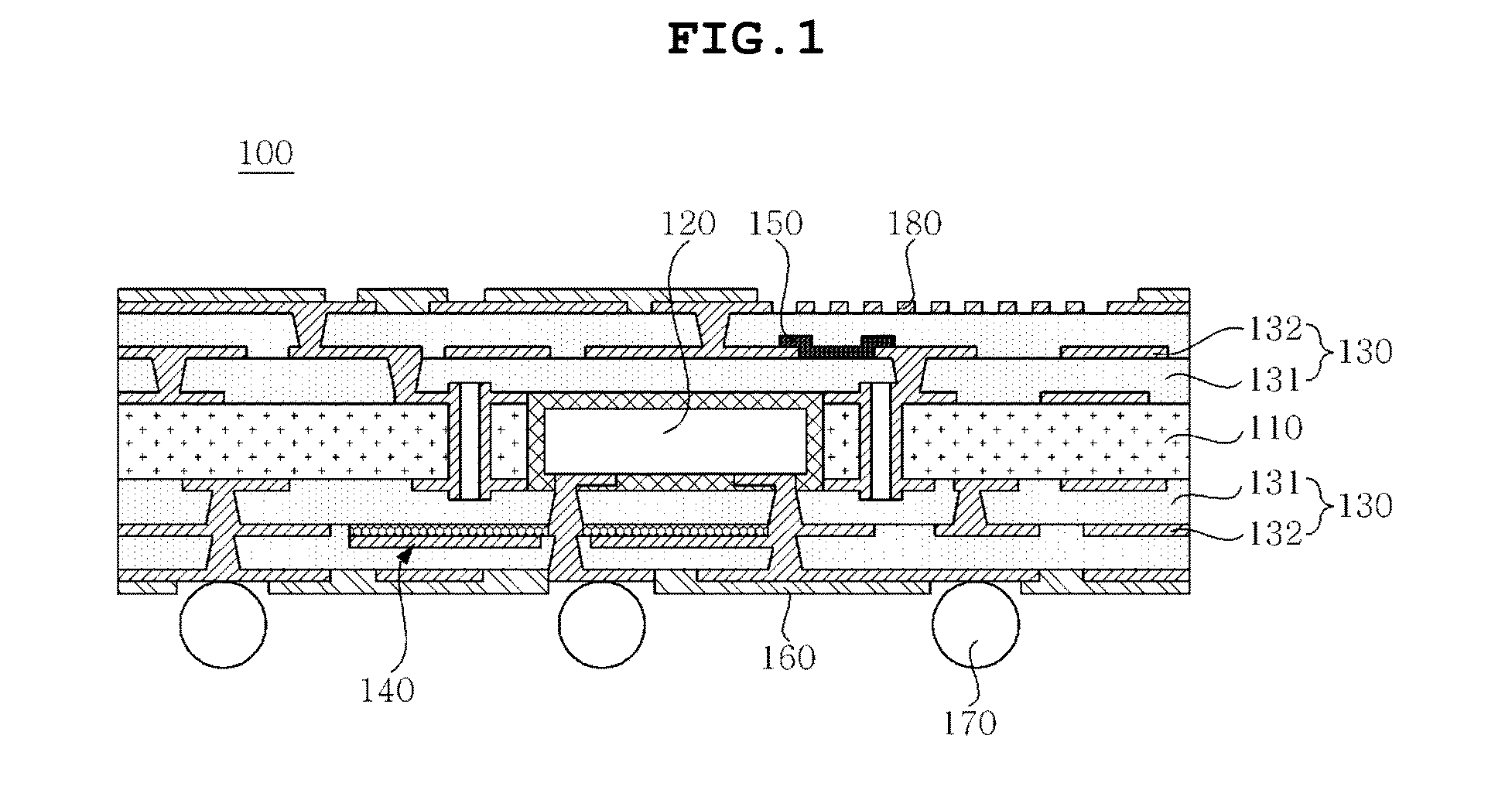
Printed circuit board having copper plated layer with roughness and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20140186651A1Economical and simple methodImprove adhesionInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementPhotomechanical apparatusCopper platingGas plasma
Disclosed herein are a printed circuit board having a copper plated layer with an anchor shaped surface and roughness by forming the copper plated layer having an anisotropic crystalline orientation structure using a plating inhibitor at the time of forming the copper plated layer serving as a circuit wiring and using composite gas plasma and a dilute acid solution, and a method of manufacturing the same.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Method for achieving sustained anisotropic crystal growth on the surface of a melt
InactiveUS20130213296A1Well formedPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsLeading edgeHeat flow
A method of horizontal ribbon growth from a melt includes forming a leading edge of the ribbon using radiative cooling on a surface of the melt, drawing the ribbon in a first direction along the surface of the melt, and removing heat radiated from the melt in a region adjacent the leading edge of the ribbon at a heat removal rate that is greater than a heat flow through the melt into the ribbon.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Method of fabricating anisotropic crystal film on a receptor plate via transfer from the donor plate, the donor plate and the method of its fabrication
InactiveUS6841320B2Increased anisotropyReduce adhesionLiquid crystal compositionsDiffusion transfer processesColor imagePolarizer
The invention pertains to the field of fabrication of devices of various purposes, which use anisotropic films: polarizers, retarders, etc., as well as technology of obtaining coatings with anisotropy of electric conductivity, magnetic properties, thermal conduction and other physical properties.The invention includes the method of forming anisotropic crystal film on a receptor plate via transferring it from the donor plateImplementing the disclosed invention preserves the high degree of anisotropy and optical parameters of crystal films after the transfer. Additionally, it is possible to form anisotropic coatings on the surface of any configuration (including curved) and different degree of roughness; also, it is possible to transfer films of various sizes and configurations as well as multilayer coatings containing anisotropic film and form color images.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Method and device for transferring anisotropic crystal film from donor to receptor, and the donor
ActiveUS7297209B2Maintain alignmentLiquid crystal compositionsAfter-treatment detailsCrystallographyAnisotropic crystal
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Optical filter
InactiveUS7567382B2Improve performanceReduce decreasePolarising elementsNon-linear opticsLight filterPhysics
Owner:DAISHINKU CORP
Microcrystalline glass binder, preparation method thereof, superhard material grinding tool and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106514499ASimple ingredientsReduce manufacturing costAbrasion apparatusGrinding devicesSuperhard materialMetallurgy
Owner:FUNIK ULTRAHARD MATERIAL
Far-field sub-diffraction optical lenses (fasdol)
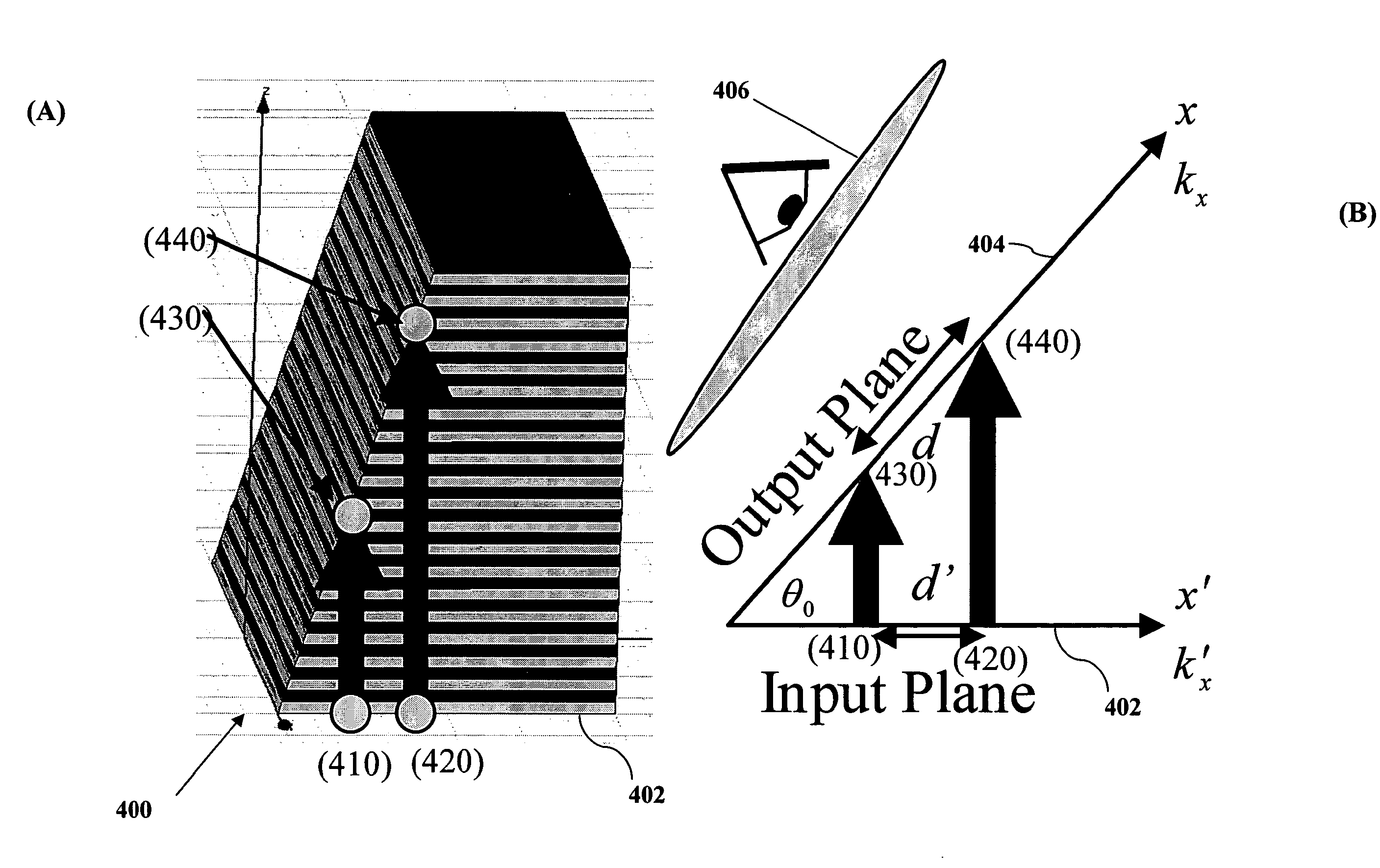
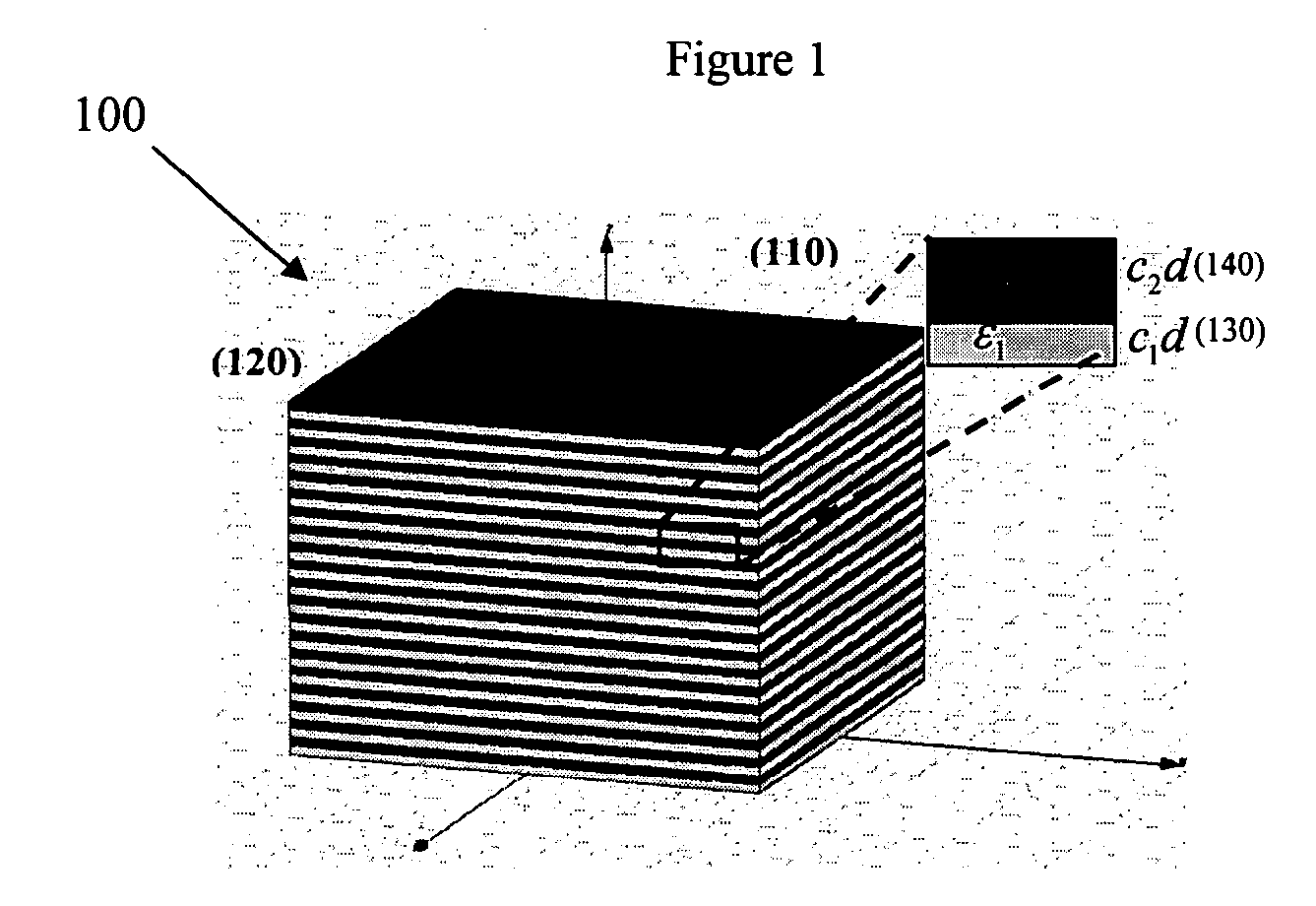
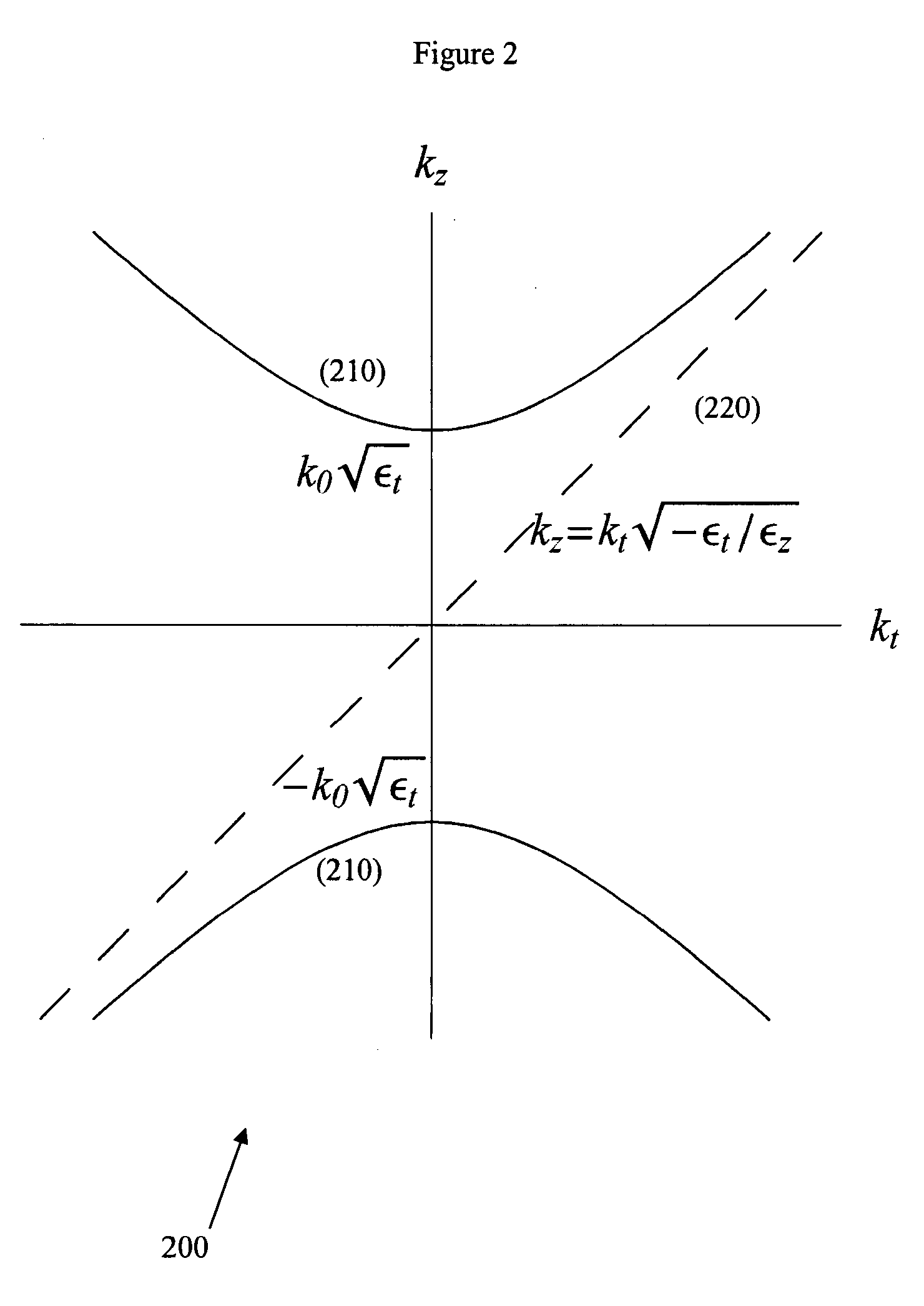
Far-field sub-diffraction optical lenses “FaSDOLs” comprise an anisotropic crystal having special dispersion characteristics such that it supports diffraction free propagation. An image with subwavelength features on the input surface is transferred through a propagation function to the output surface with effectively no, or minimal, loss in information. These special properties may be exploited in several ways, including but not limited to, magnification of an image at the input surface through the use an oblique cut at the output surface, magnification of an image at the input surface through use of a curved crystalline structure, and more generally near-field optical processing.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method and device for controlling crystal orientation in steady-state magnetic field through directional solidification
InactiveCN104862777ASimple methodEasy to operatePolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsHeat fluxCrystal orientation
The invention discloses a method and a device for controlling crystal orientation in a steady-state magnetic field through directional solidification. Metal containing anisotropic crystals and alloys are put in a directional solidification device in the steady-state magnetic field; for a certain crystal with a difference in easy growth direction and easy magnetization direction, the steady-state magnetic field and direction solidification are adopted, so that textures can be formed in the easy growth direction and easy magnetization direction respectively, that is, when the easy growth direction of the crystal is orientated in the direction opposite to heat flux in the directional solidification process, the steady-state magnetic field is applied at a certain angle in the directional solidification process according to characteristics of crystallography, accordingly, the easy magnetization direction can turn to a magnetic field direction, and the purpose that multiple crystals form multi-crystal-orientation textures is achieved. The method is simple and convenient to operate.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Diode pumped solid-state laser with improved pump light absorption
InactiveCN102449862ALarge toleranceReduce manufacturing costOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialPower flowDiode-pumped solid-state laser
For a diode pumped solid-state laser, measures to improve the pump light absorption in anisotropic crystals are proposed. The proposed measures reduce the dependency of the pump light absorption on the diode current and the diode temperature as well as on the detuning of the pump diode from the absorption line. These measures include sending the pump radiation twice through the crystal, placement of the laser crystal in an orientation that does not exhibit the optimum absorption and the use of a retarder.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
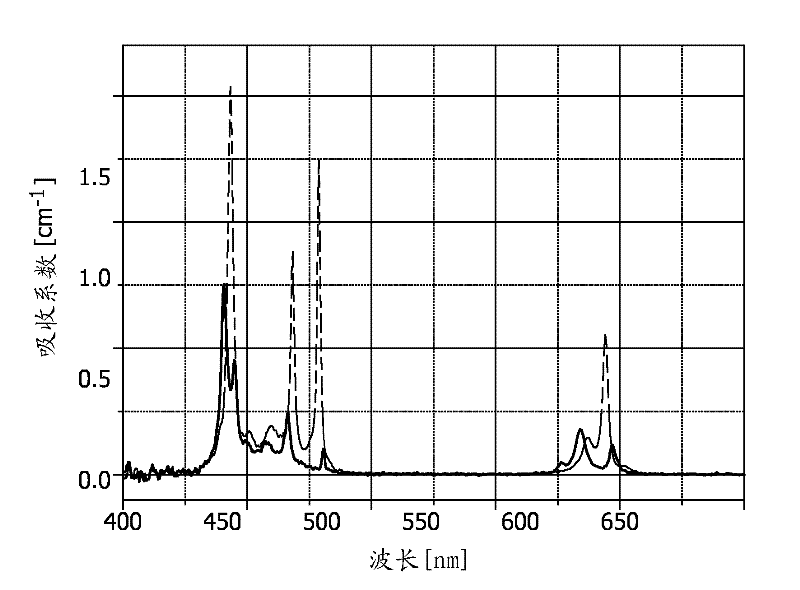
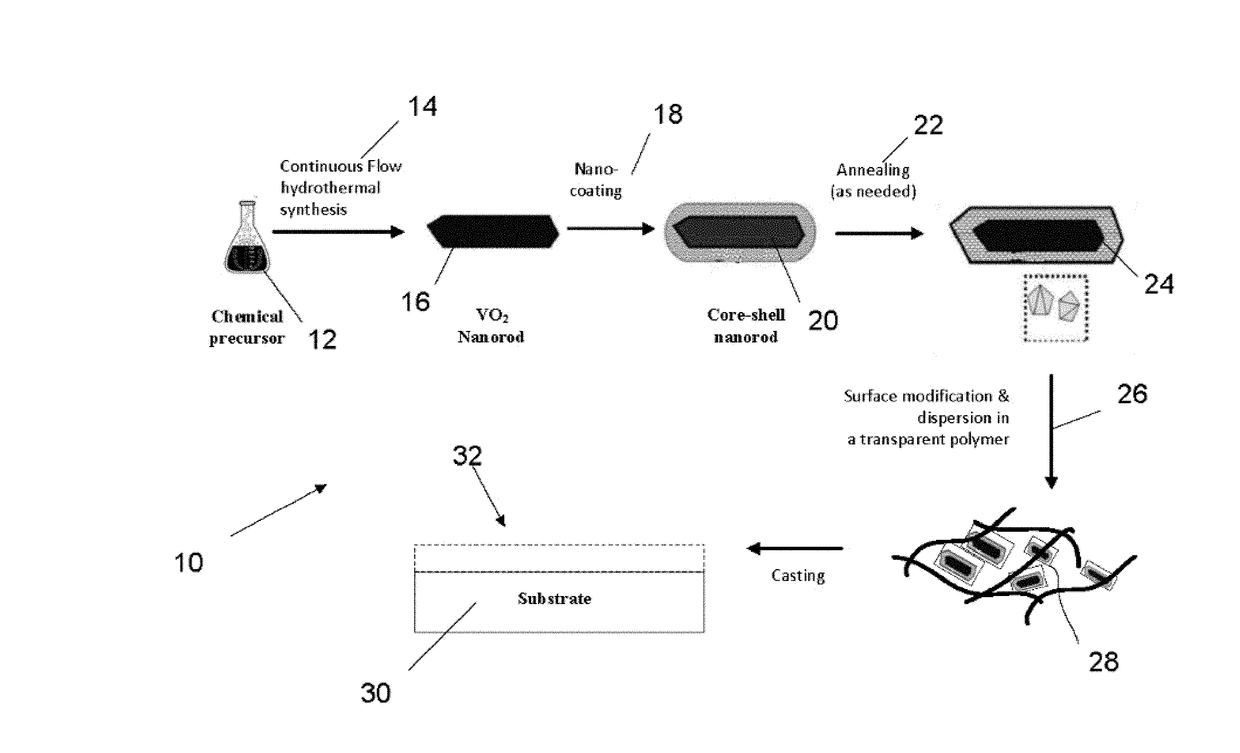
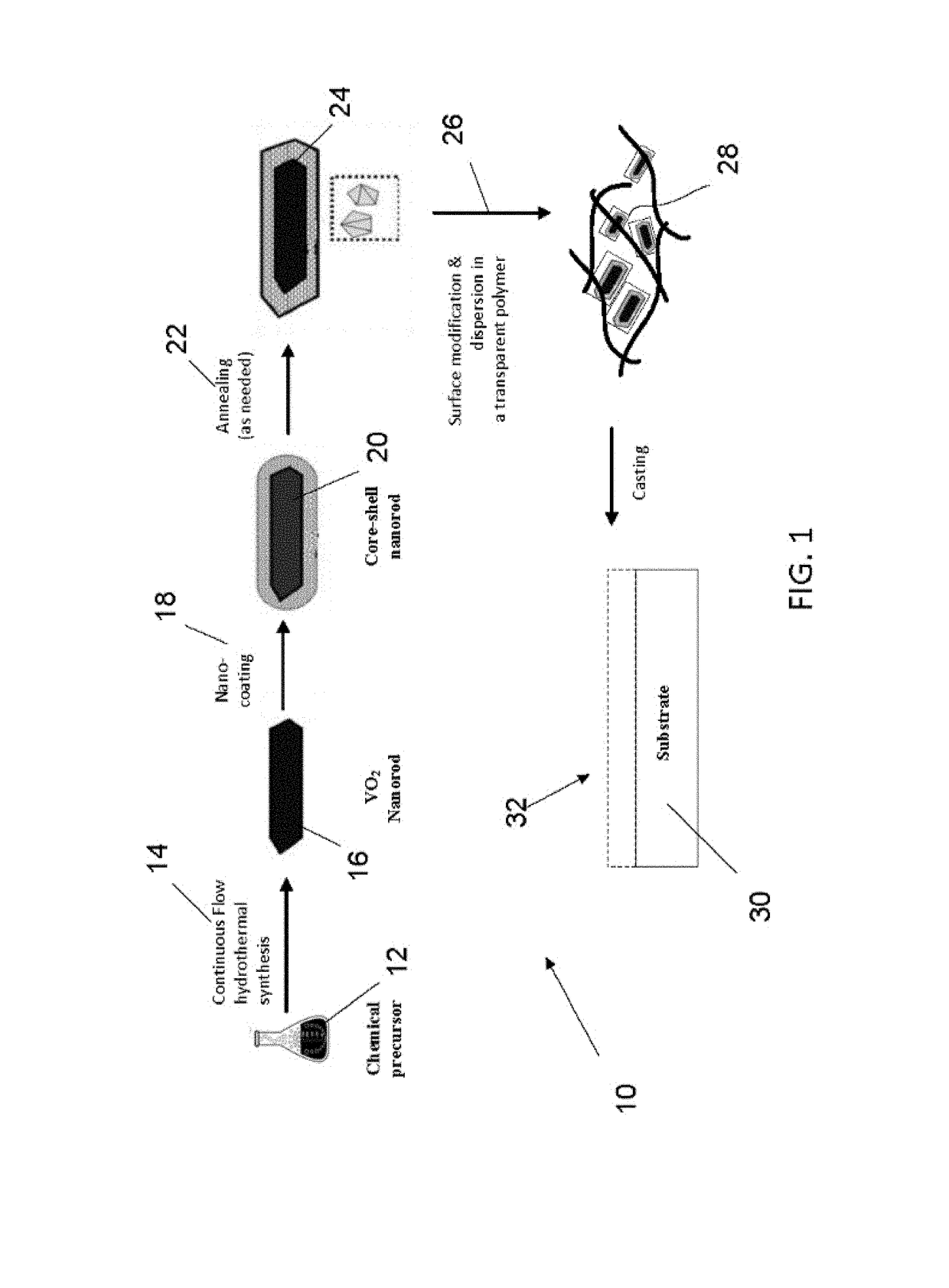
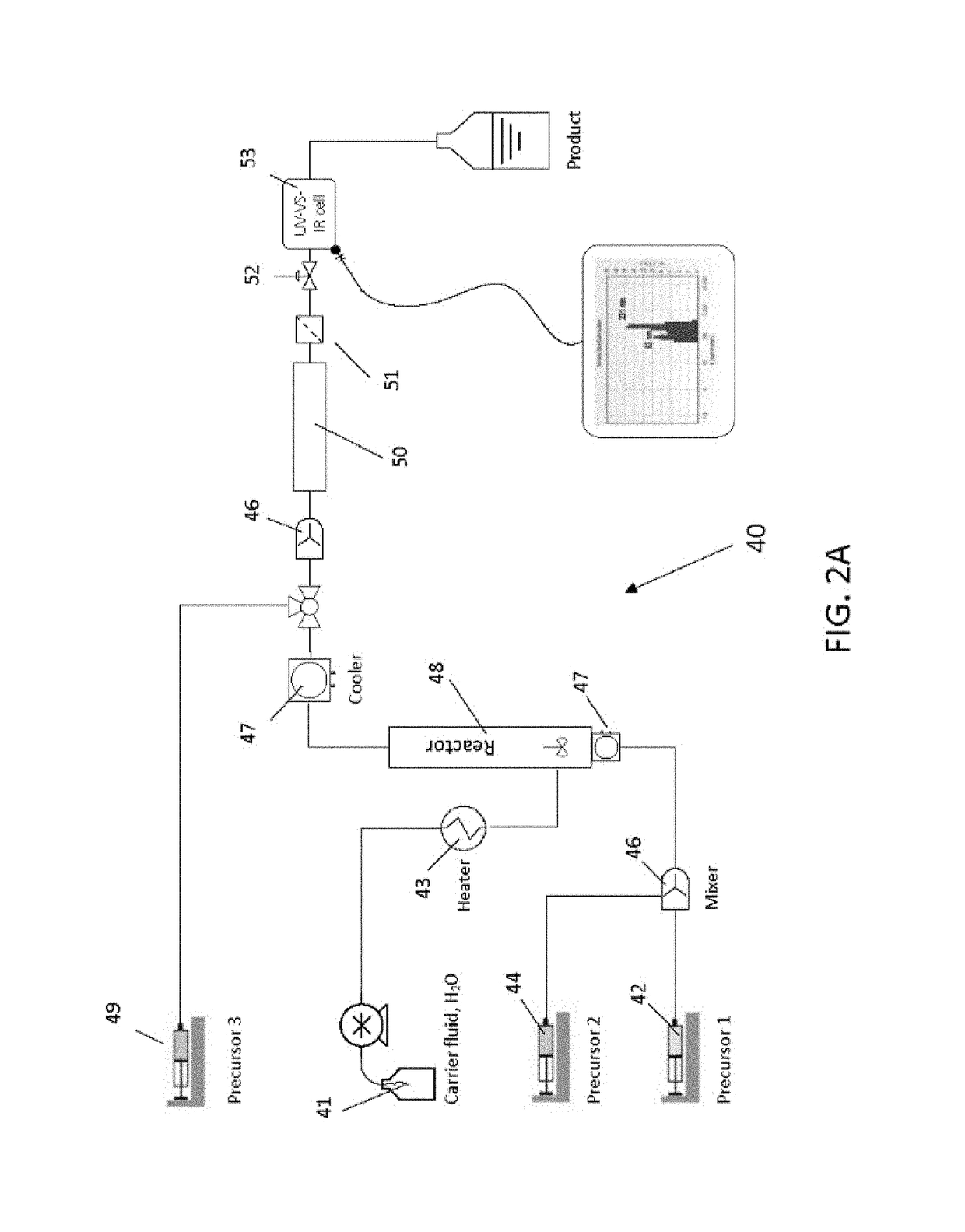
Continuous flow synthesis of vo2 nanoparticles or nanorods by using a microreactor
ActiveUS20170297949A1Delayed reaction timeEconomic treatmentGlass shaping apparatusVanadium oxidesContinuous flowComposite nanoparticles
The invention provides a method for producing composite nanoparticles, the method using a first compound capable of transitioning from a monoclinic to a tetragonal rutile crystal state upon heating, and having the steps of subjecting the first compound to a hydrothermal synthesis to create anisotropic crystals of the compound; encapsulating the first compound with a second compound to create a core-shell construct; and annealing the construct as needed. Also provided is a device for continuously synthesizing composite nanoparticles, the device having a first precursor supply and a second precursor supply; a mixer to homogeneously combine the first precursor and second precursor to create a liquor; a first microreactor to subject the liquor to hydrothermic conditions to create an\isotropic particles in a continuous operation mode; and a second microreactor for coating the particles with a third precursor to create a core-shell construct.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Optical filter
InactiveUS20070121042A1Improve performancePolarising elementsNon-linear opticsLight filterOptical anisotropy
This optical filter is constituted such that at least one optically anisotropic crystal plate and at least one substrate are stuck together in a state in which a principal face of the optically anisotropic crystal plate and a principal face of the substrate are perpendicular to the direction of transmission of the ray. Also, a substrate is used as the end face on the ray incident side, and another optically anisotropic crystal plate or another substrate that is thinner than the substrate that is the end face on the ray incident side is stuck onto the substrate.
Owner:DAISHINKU CORP
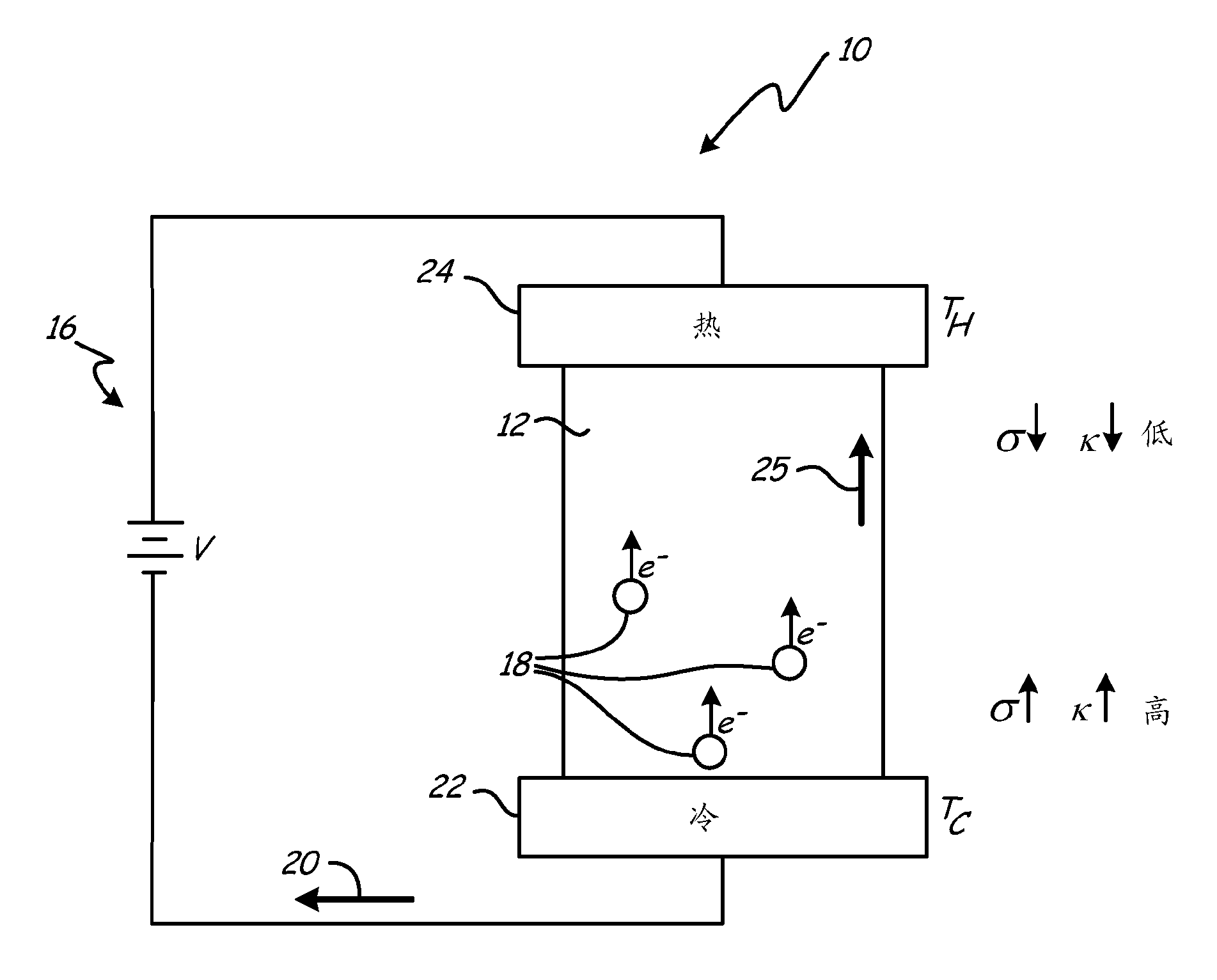
Polarization aligned and polarization graded thermoelectric materials and method of forming thereof
InactiveCN102210034AThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermoelectric materialsAtomic physics
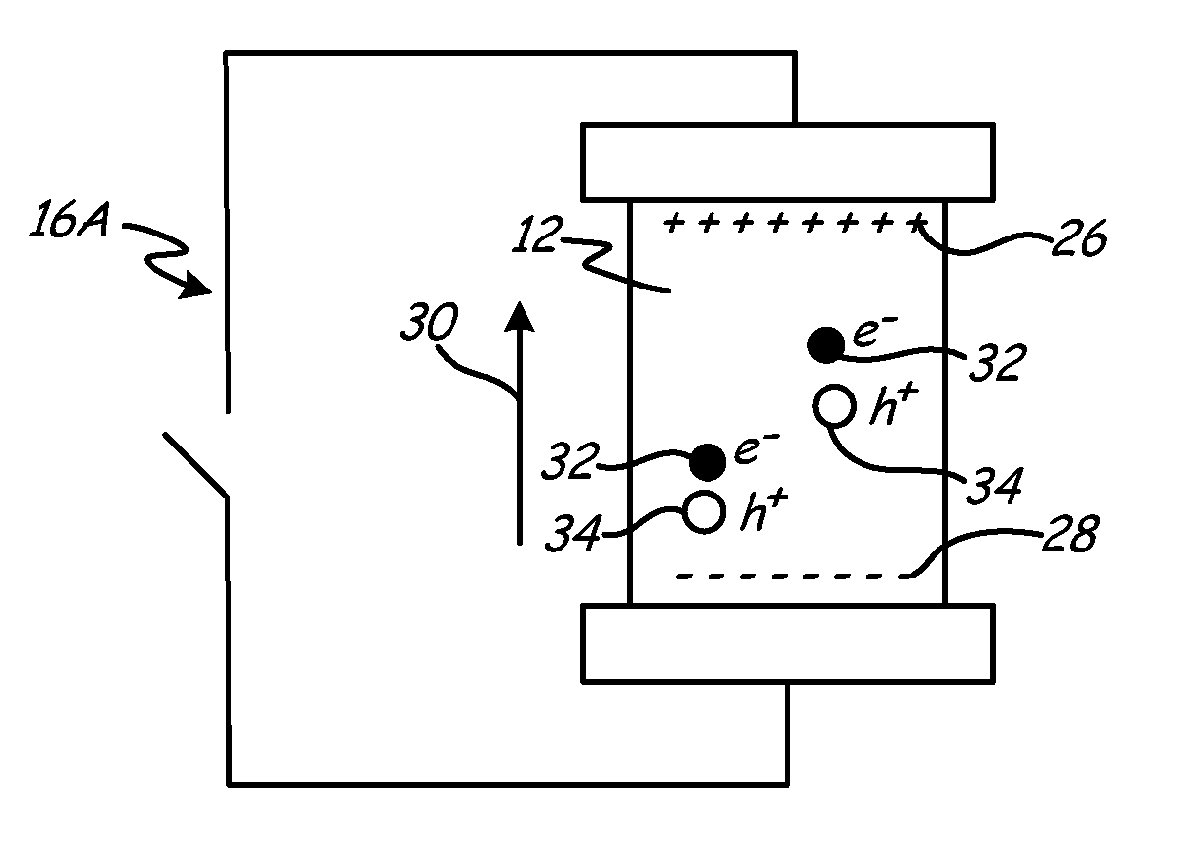
Exemplary embodiments of the invention include a thermoelectric material having an aligned polarization field along a central axis of the material. Along the axis are a first atomic plane and a second atomic plane of substantially similar area. The planes define a first volume and form a single anisotropic crystal. The first volume has a first outer surface and a second outer surface opposite the first outer surface, with the outer surfaces defining the central axis passing through a bulk. The bulk polarization field is formed from a first electrical sheet charge and a second opposing electrical sheet charge, one on each atomic plane. The opposing sheet charges define a bulk polarization field aligned with the central axis, and the bulk polarization field causes asymmetric thermal and electrical conductivity through the first volume along the central axis.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
High frequency acousto-optic frequency shifter having wide acceptance angle
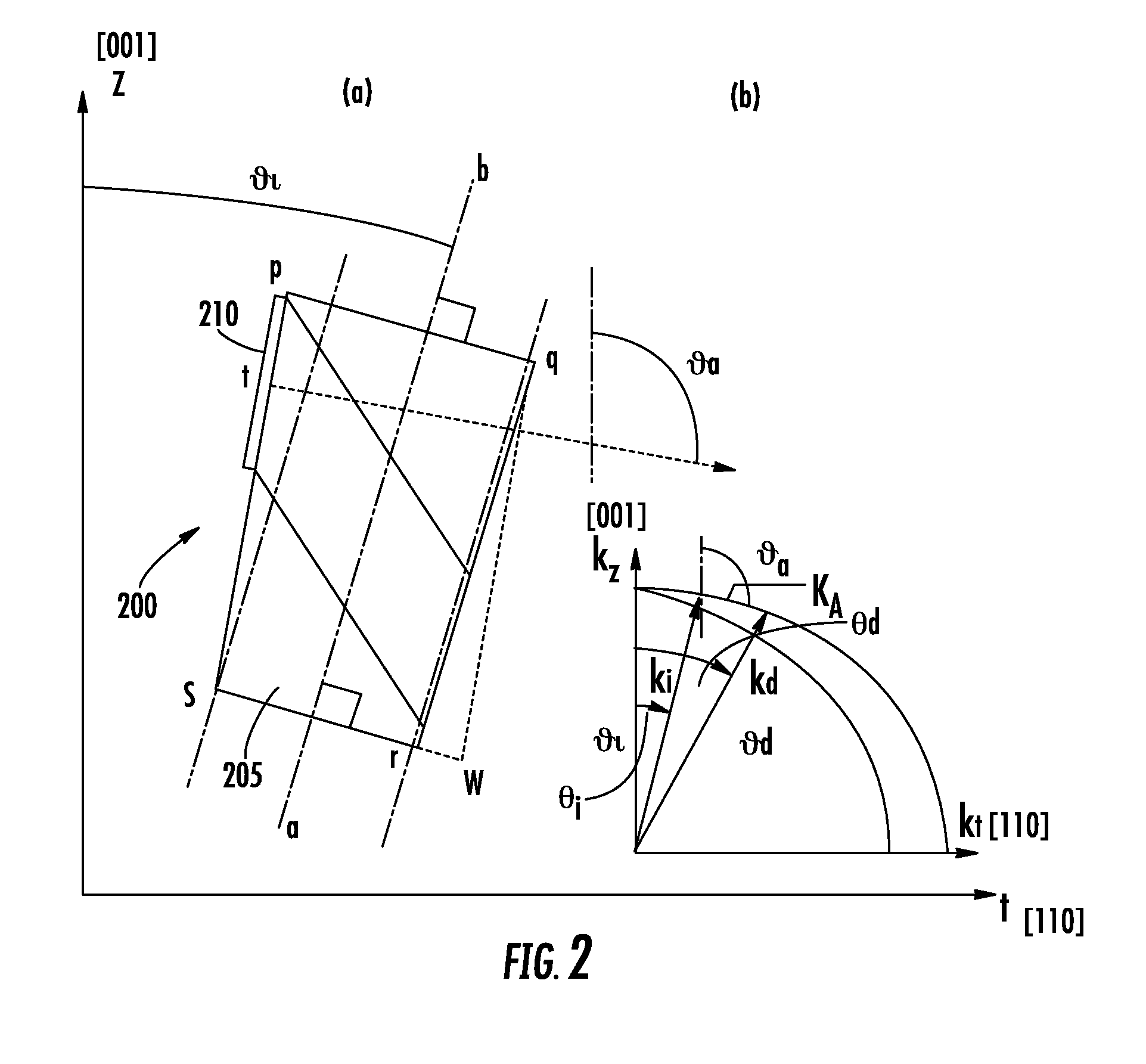
An acousto-optic (AO) frequency shifter includes an anisotropic crystal having an optical axis and an input face, and an acoustic transducer having electrodes affixed to the face for receiving an electrical signal and projecting an acoustic wave into the crystal. The anisotropic crystal is cut relative to the face so that the transducer is at an acoustic angle (θa) corresponding to a predetermined angle of incidence (θi) of an optical beam to be directed relative to the optic axis of the anisotropic crystal to substantially satisfy the parallel tangents phase matching condition.
Owner:GOOCH & HOUSEGO
Laser
ActiveUS20130094533A1Requirement for wavelength accuracy can be reducedImprove accuracyExcitation process/apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionVisible spectral rangeLaser light
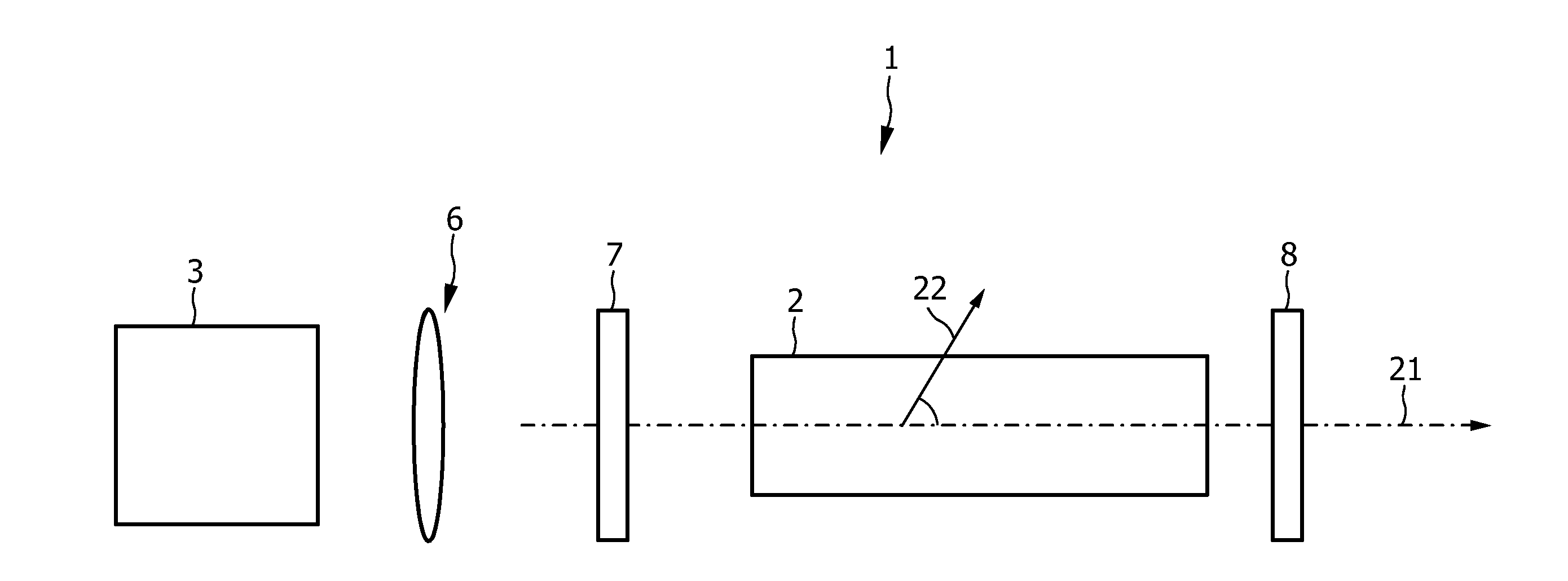
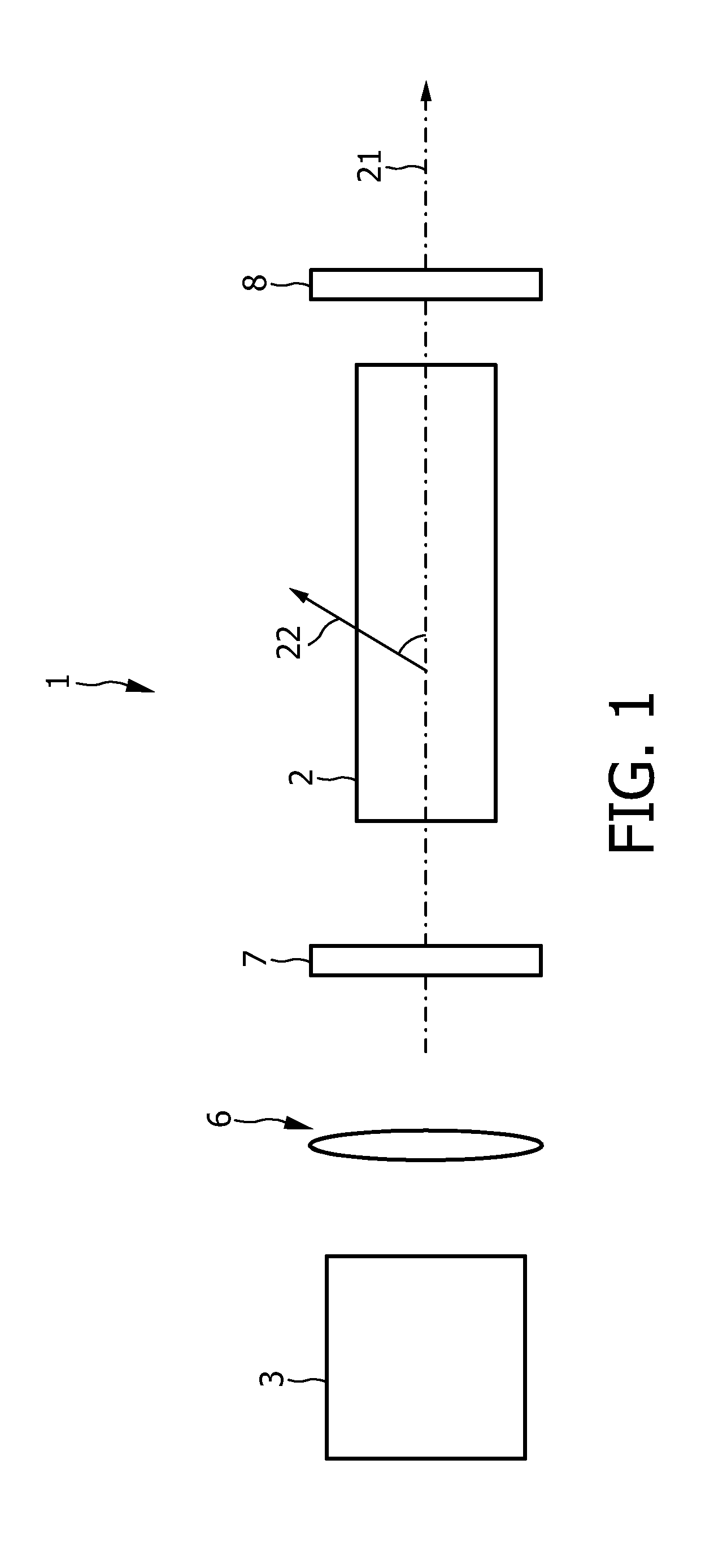
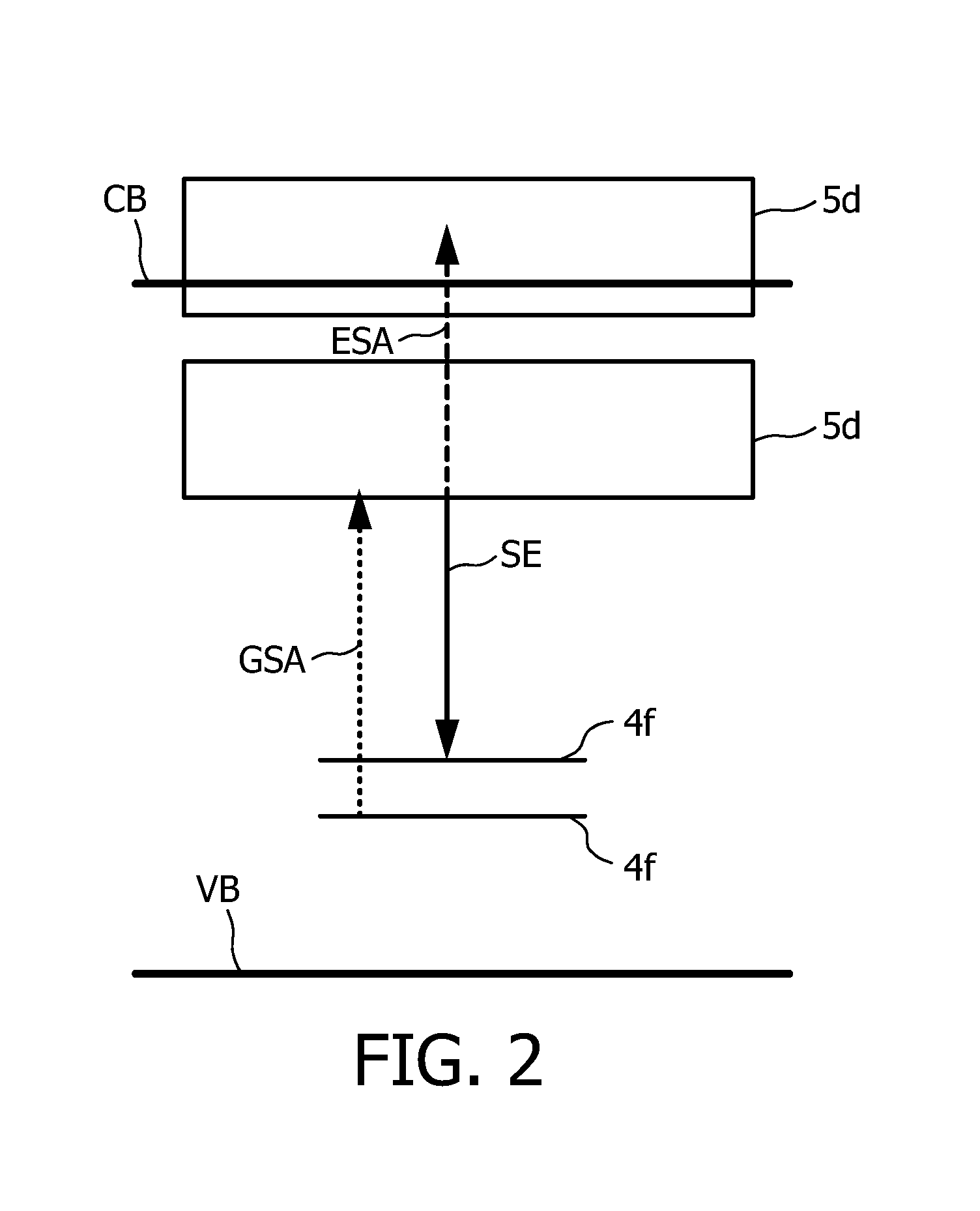
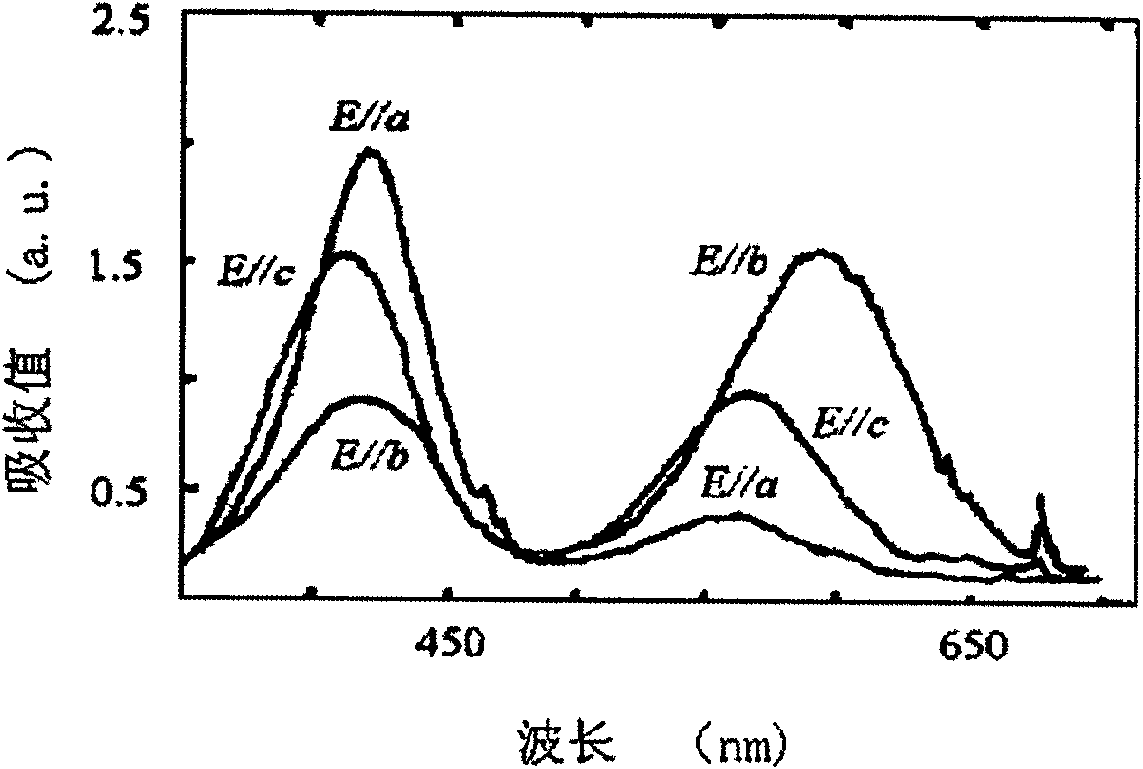
The invention relates to a laser (1) for emitting laser light in the visible spectral range. A rare earth doped anisotropic crystal (2) comprising a 5d-4f transition is arranged within a laser resonator (7, 8), and a pumping light source (3) pumps the crystal (2) for generating laser light in the visible spectral range by using the 5d-4f transition. The 5d-4f transition of the rare earth doped anisotropic crystal comprises an absorption band extending over several nm. Thus, pump light having a wavelength within a relatively broad wavelength range can be used. This reduces the requirements with respect to the wavelength accuracy of the pumping light source and, thus, more pumping light sources of an amount of produced pumping light sources can be used for assembling the laser, thereby reducing the amount of rejects.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Absorption type polarizer for polarization in cavity
InactiveCN101615753AReduce volumeIncreased Laser Damage ThresholdLaser detailsPolarising elementsHigh volume manufacturingOptoelectronics
The invention relates to the field of lasers, in particular to a polarizer in the field of lasers and application thereof, and discloses a polarizer and a partial polarizer formed by absorption inconsistency of two polarization directions of a doped anisotropic crystal in a partial spectral range. The polarizer can be applied to the polarization in the cavity of a laser. Compared with the conventional birefringent polarizing prism and other kinds of polarizers, the polarizer has the advantages of small volume, high laser damage threshold value, good heat dissipation performance, easiness for mass production and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI BRANCH FUZHOU GAOYI COMM CO LTD
Quarter wavelength plate and projection type video display device using same
InactiveUS6982772B2Reduce the impactIncrease brightnessProjectorsPolarising elementsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
A quarter wavelength plate for reducing the dependence of a retardation value on an incident beam angle in optically anisotropic crystals. The quarter wavelength plate is formed of optically anisotropic crystals in a thickness of 0.1 mm to 0.5 mm. The quarter wavelength plate can contribute to a reduction in the dependence of the retardation value on the angle at which a light beam impinges on the quarter wavelength plate, and to a reduction in color shading caused by a rise in temperature. A reflection type liquid crystal display device which employs the quarter wavelength plate can enhance the luminance and contrast.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
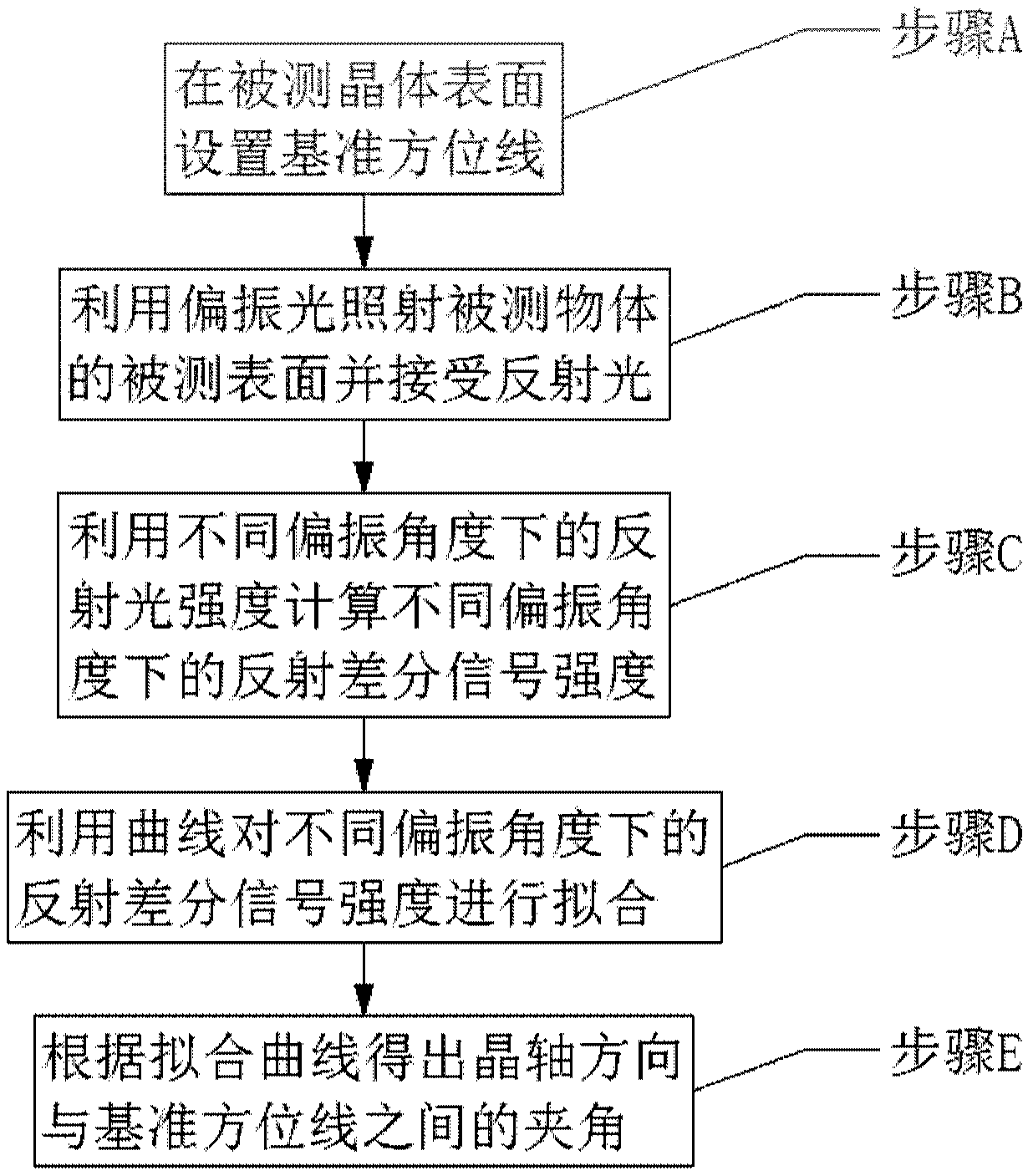
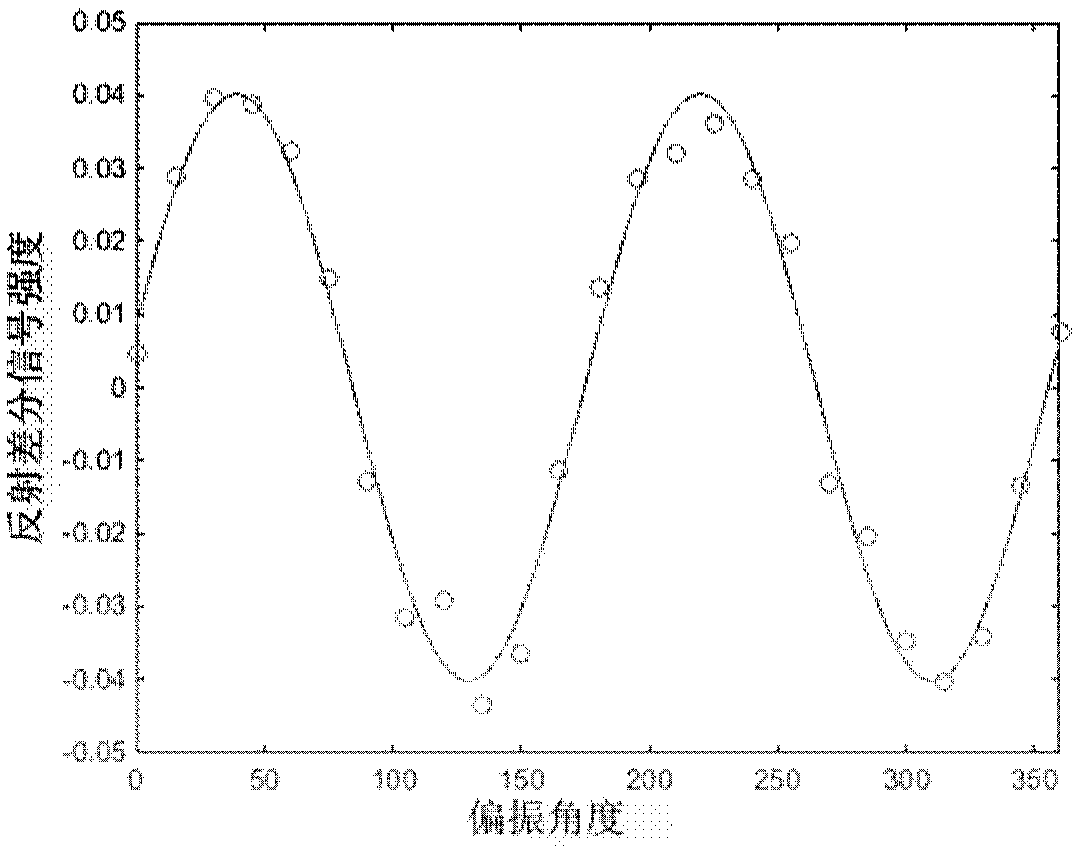
Method and equipment for orientating crystal axis of in-plane anisotropic crystal
ActiveCN108398386AEnough precisionReduce mistakesPolarisation-affecting propertiesOptical reflectionIn plane
The invention provides a method and equipment for orientating a crystal axis of an in-plane anisotropic crystal. The method comprises the following steps: A, setting a reference azimuth line on a to be tested surface of a to be tested crystal; B, irradiating the to be tested surface of the to be tested crystal by utilizing polarized light and receiving reflected light; C, changing a polarization angle of the polarized light, and calculating the intensity of reflection differential signals at different polarization angles by utilizing the intensity of the reflected light at the different polarization angles; D, fitting the intensity of the reflection differential signals at the different polarization angles by utilizing a curve; and E, obtaining an included angle between a crystal axis direction and the reference azimuth line according to a fitted curve. The method and the equipment for orientating the crystal axis of the in-plane anisotropic crystal, which are provided by the invention, apply an optical reflection differential technology to determine the direction of the crystal axis, so that the technical problems of complex test flow, low precision and strict use conditions of acrystal axis orientating method in the prior art can be effectively solved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com