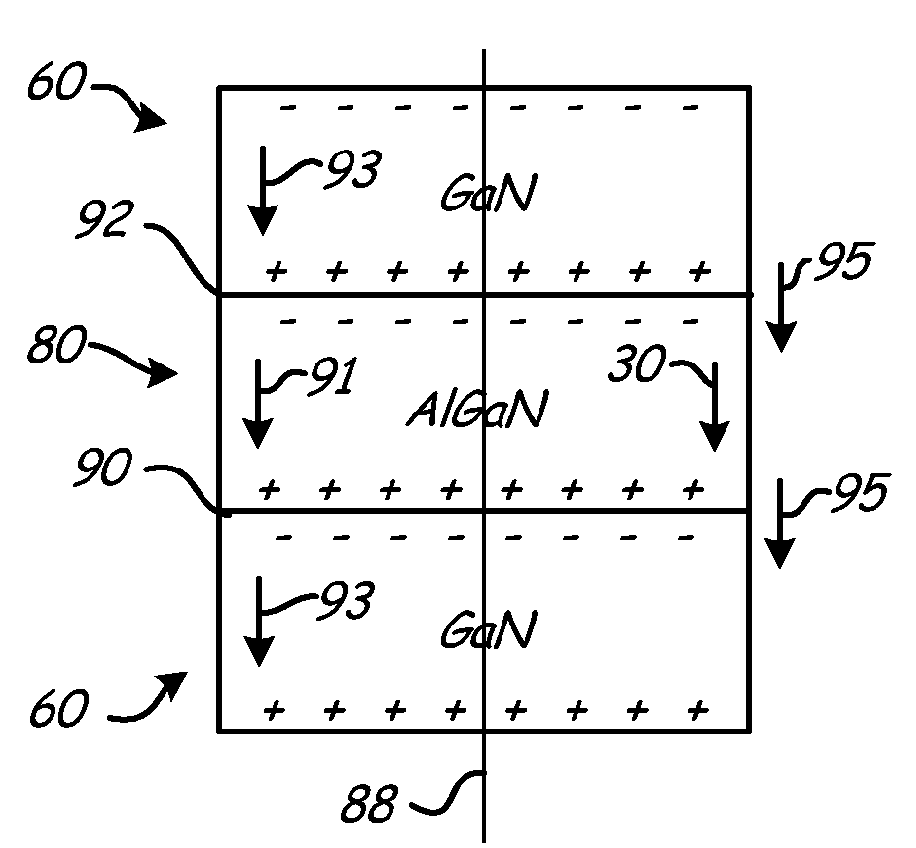
Polarization aligned and polarization graded thermoelectric materials and method of forming thereof
A technology of thermoelectric materials and polarization fields, which can be applied to thermoelectric device node lead-out materials, circuits, and thermoelectric devices that only use the Peltier or Seebeck effect, etc., and can solve the problem of no substantial increase in ZT
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
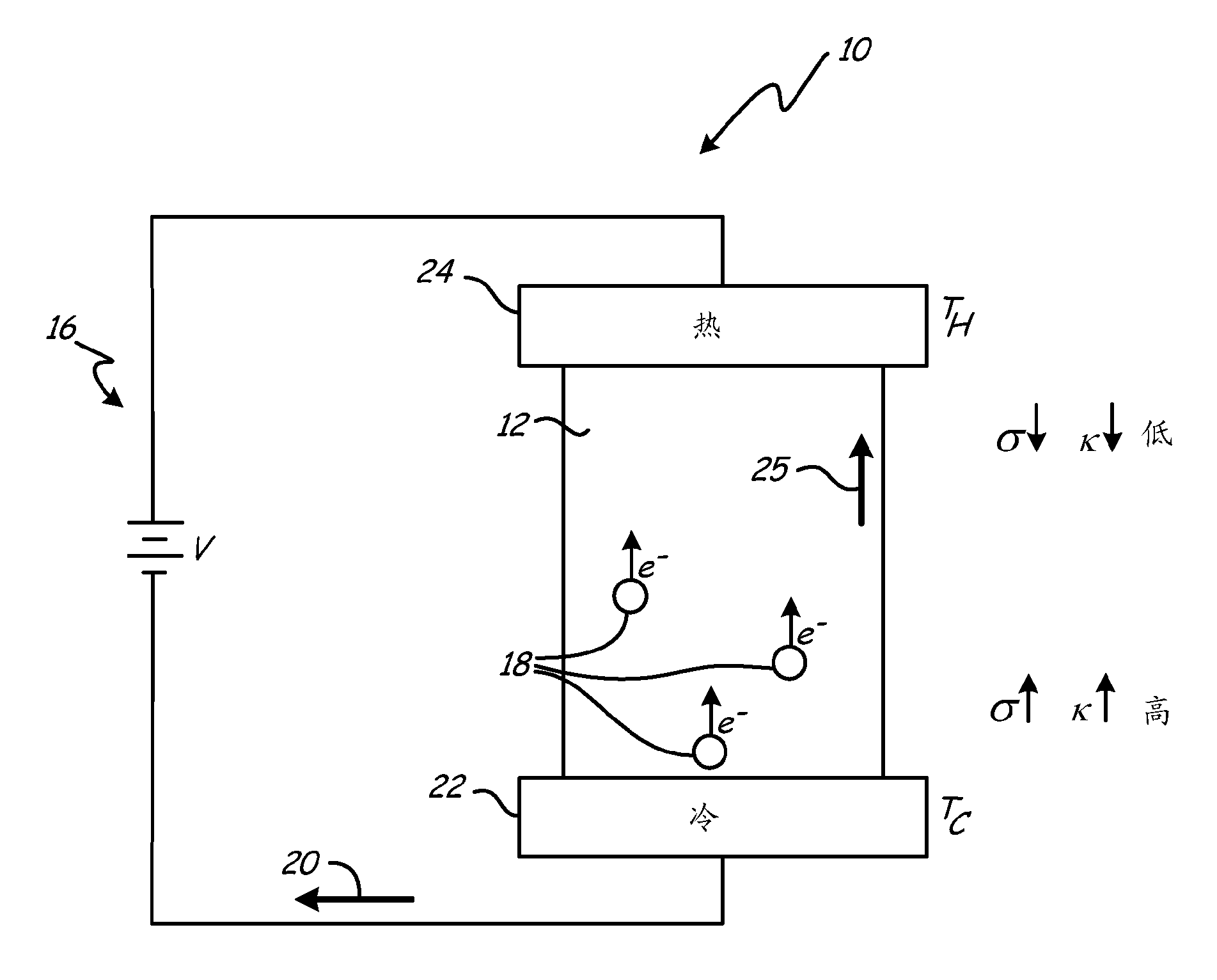
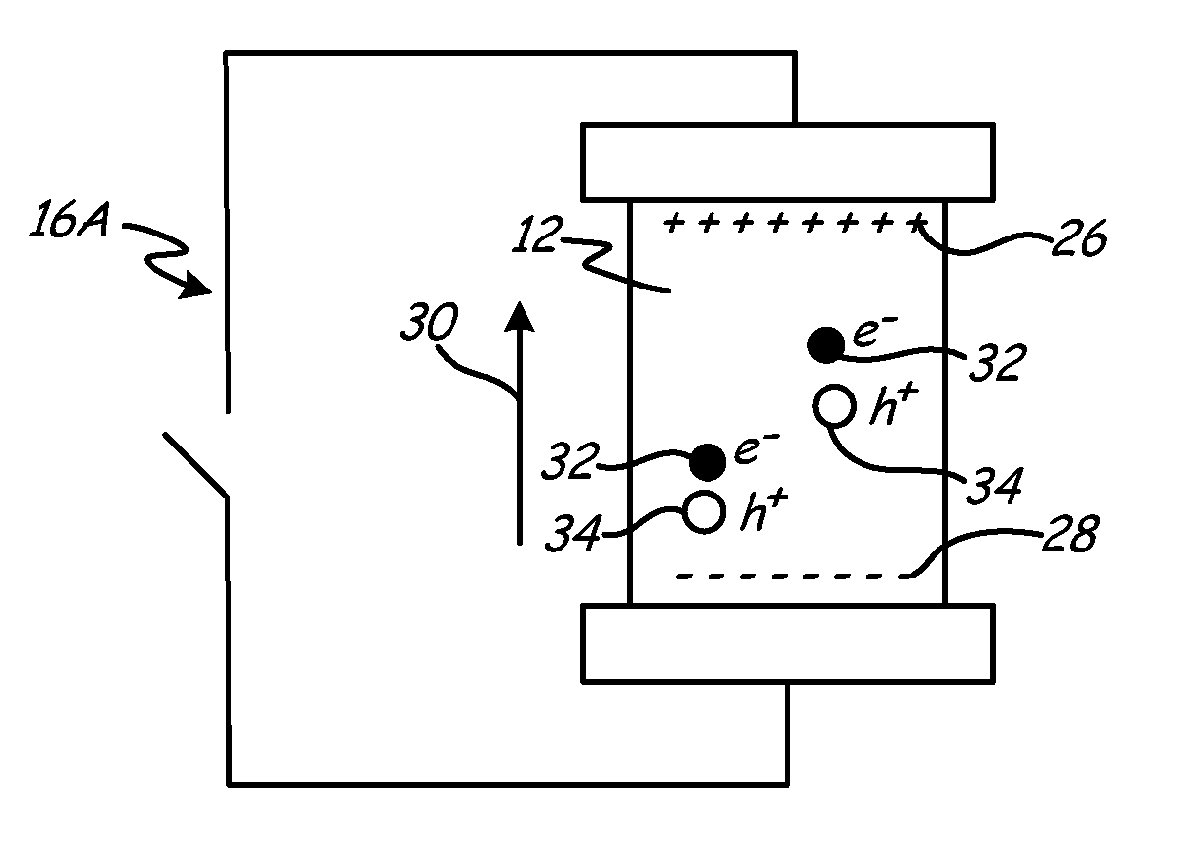
[0025] figure 1 A simplified schematic diagram of a thermoelectric cooling device 10 utilizing the Peltier effect in a thermoelectric material 12 to convert electrical energy into a thermal gradient ΔΤ is depicted. When an input voltage V is applied to circuit 16 , electrons 18 flow in material 12 , resulting in a current I in the direction indicated by arrow 20 . As electrons 18 pass through material 12, a thermal gradient ΔT=T is created due to heat Q flowing away from cold side 22 towards hot side 24 as indicated by arrow 25 H -T C . A thermal gradient ΔT is maintained by the current 20 across the material 12 as heat is removed from the hot side 24 via heat removal means such as a heat sink or heat exchanger (not shown), thereby inducing a continuous The temperature decreases until an equilibrium state is reached. The thermal gradient ΔT arises from the relative electrical and thermal energy flow due to the conductivity of charge carriers and acoustic phonons through t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com