Patents
Literature
292 results about "Tissue Part" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Any component of the anatomical structure consisting of similarly specialized cells and intercellular matrix, aggregated according to genetically determined spatial relationships, performing a specific function.
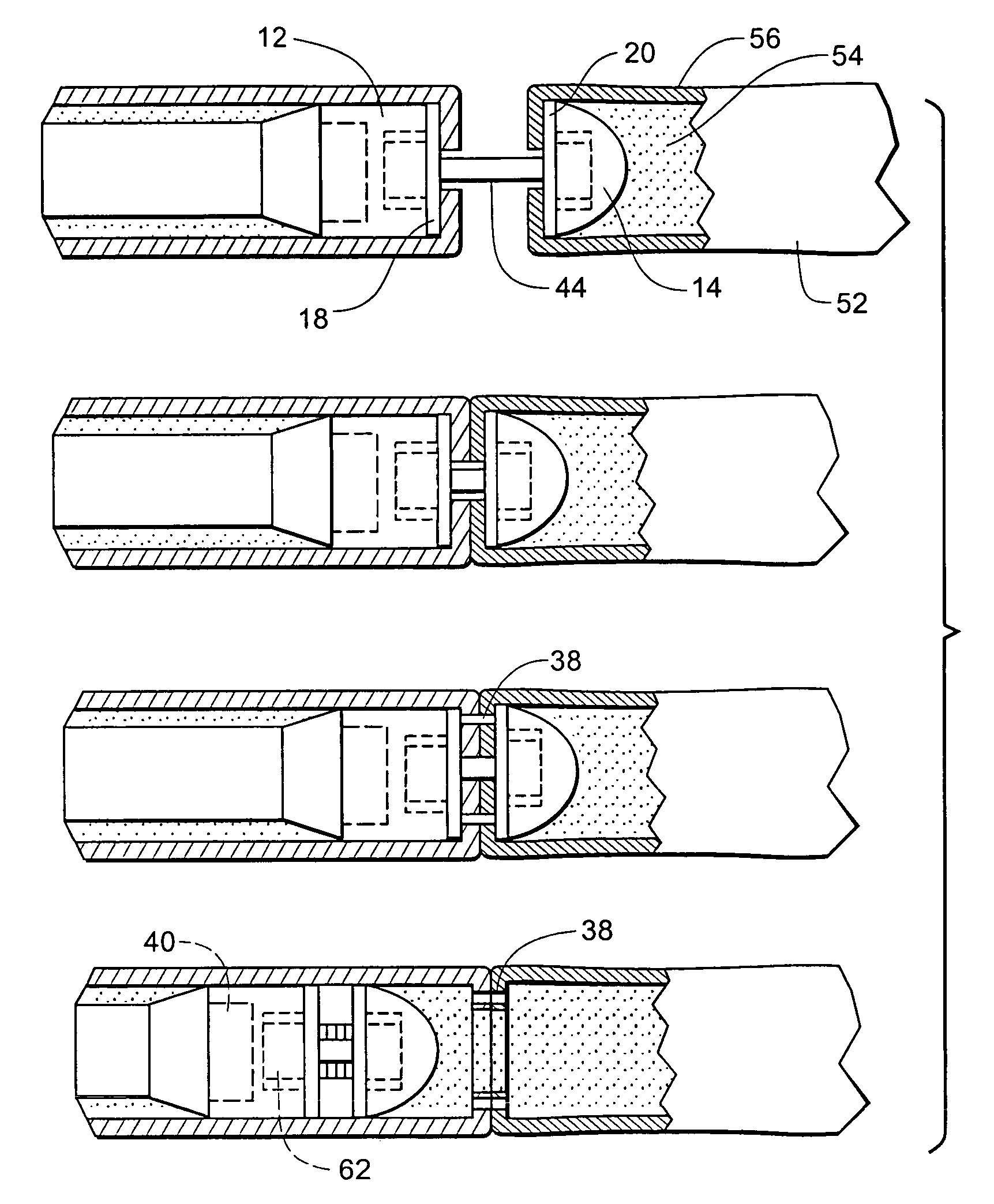
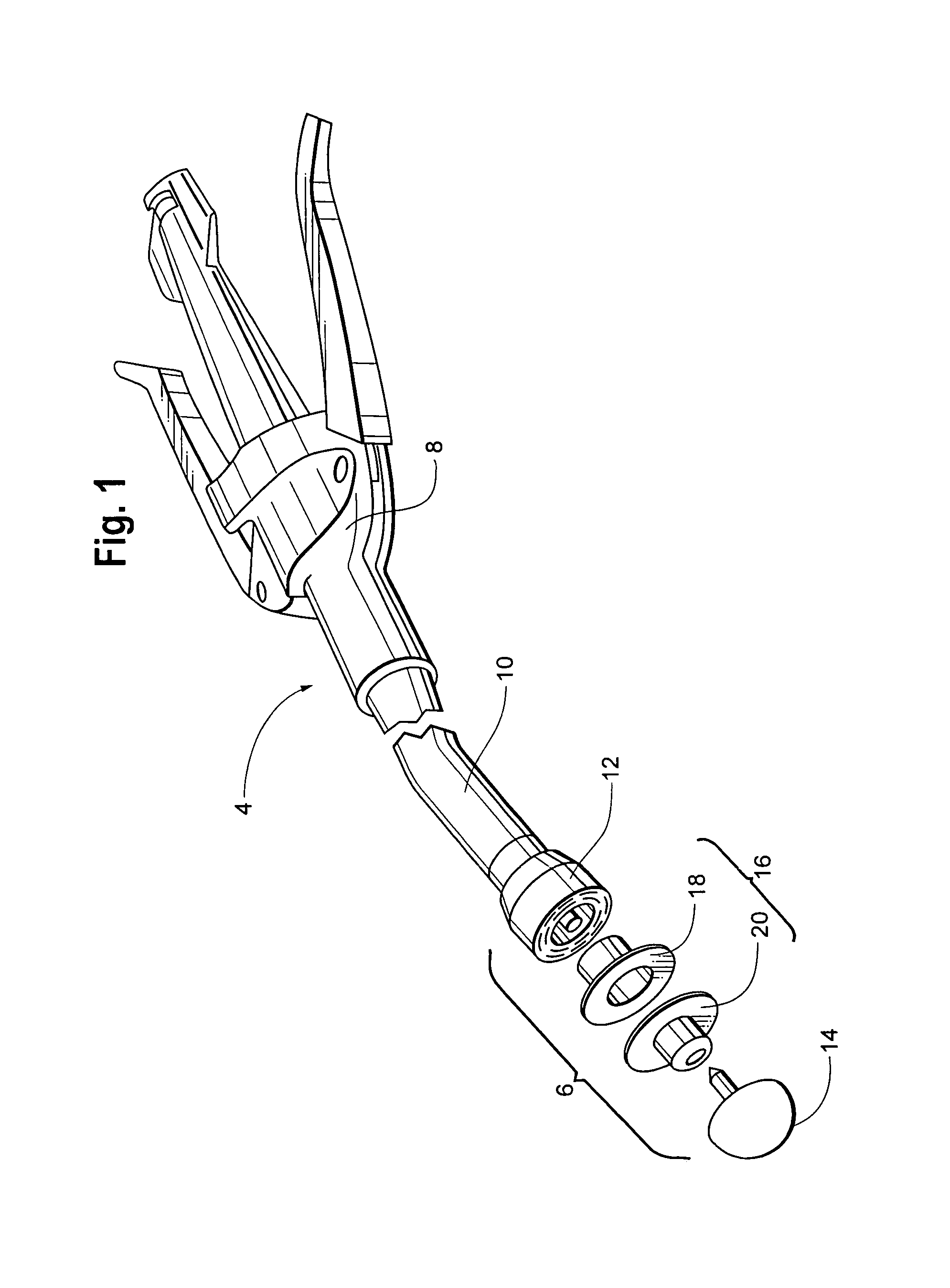
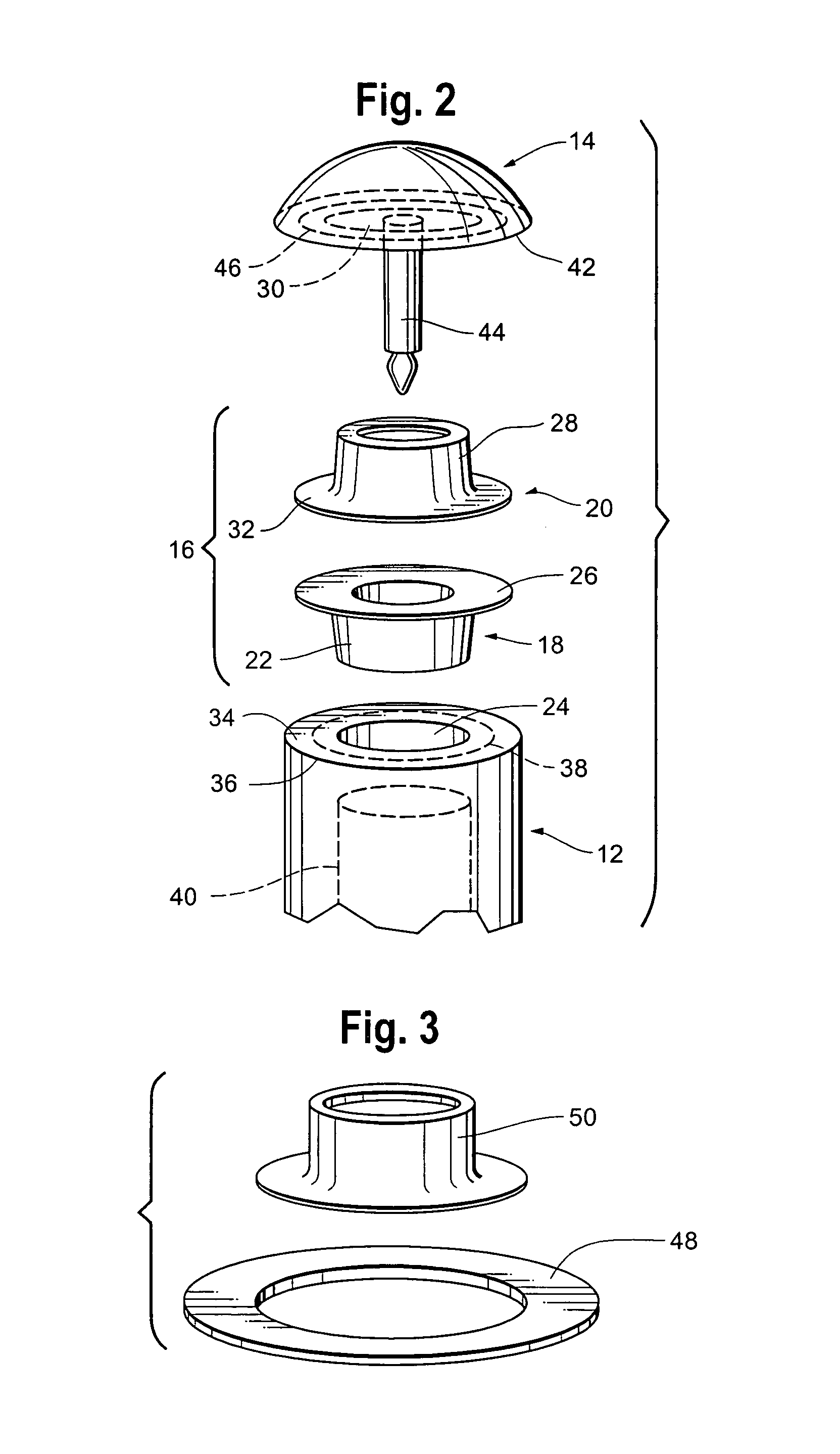
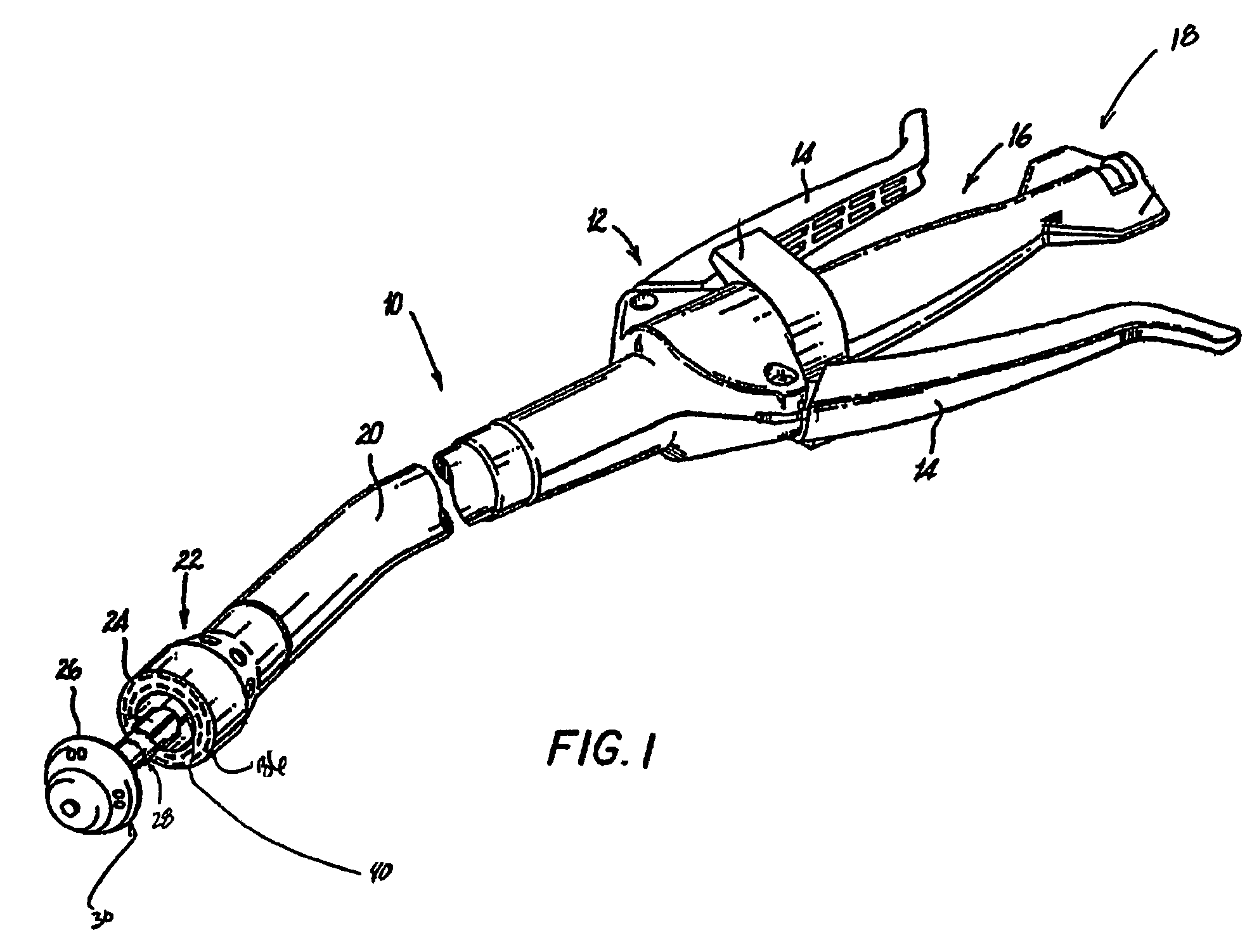
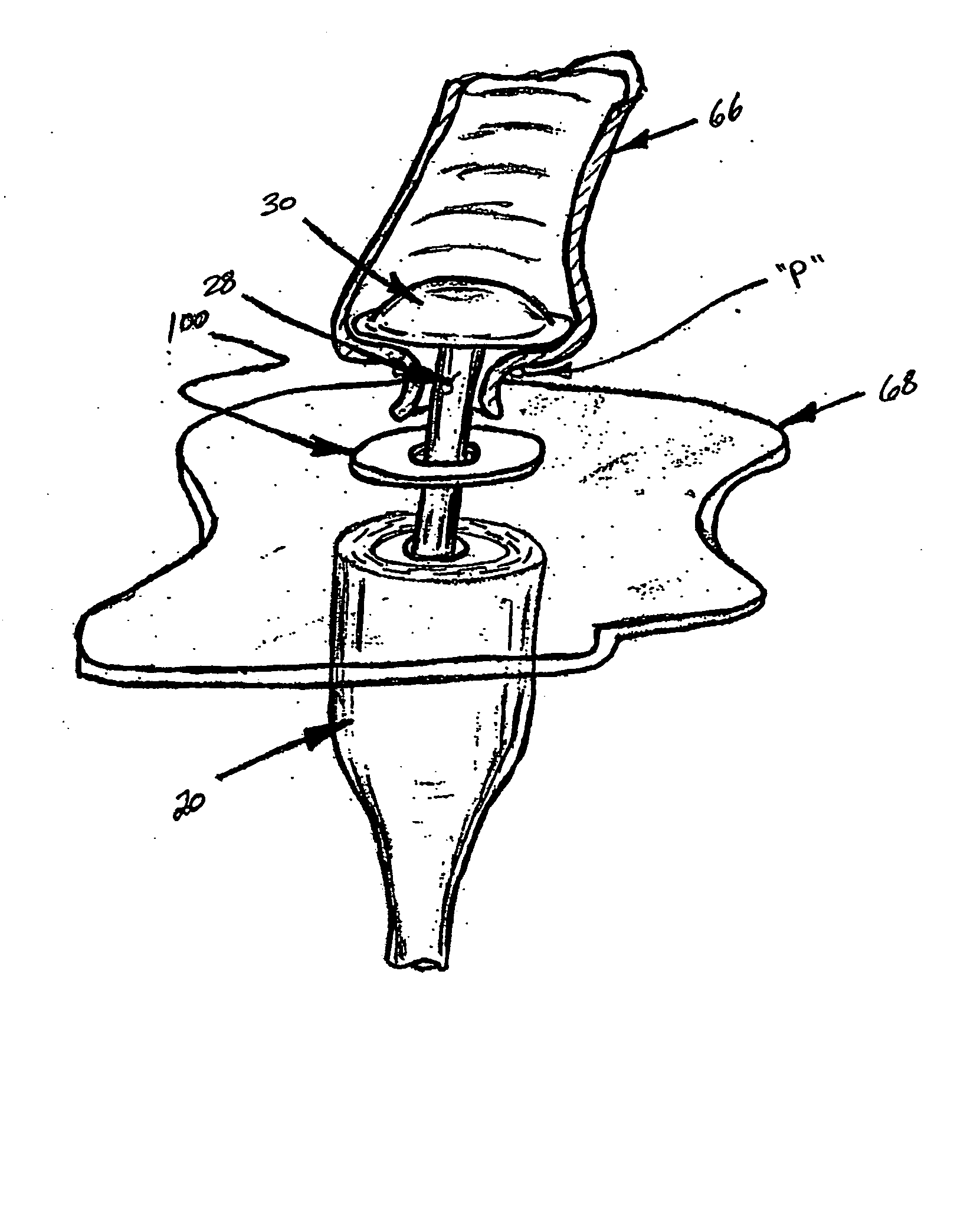
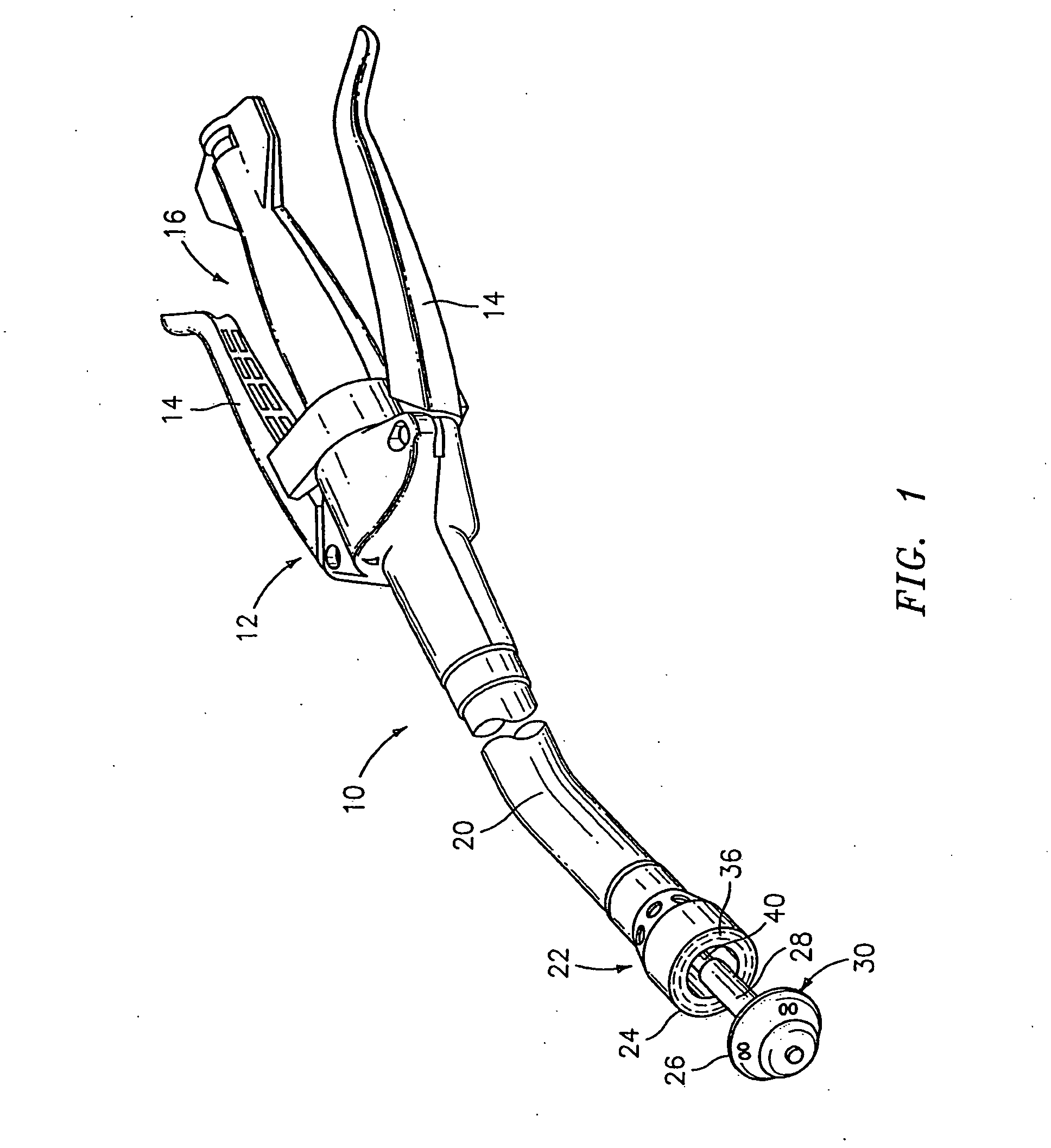
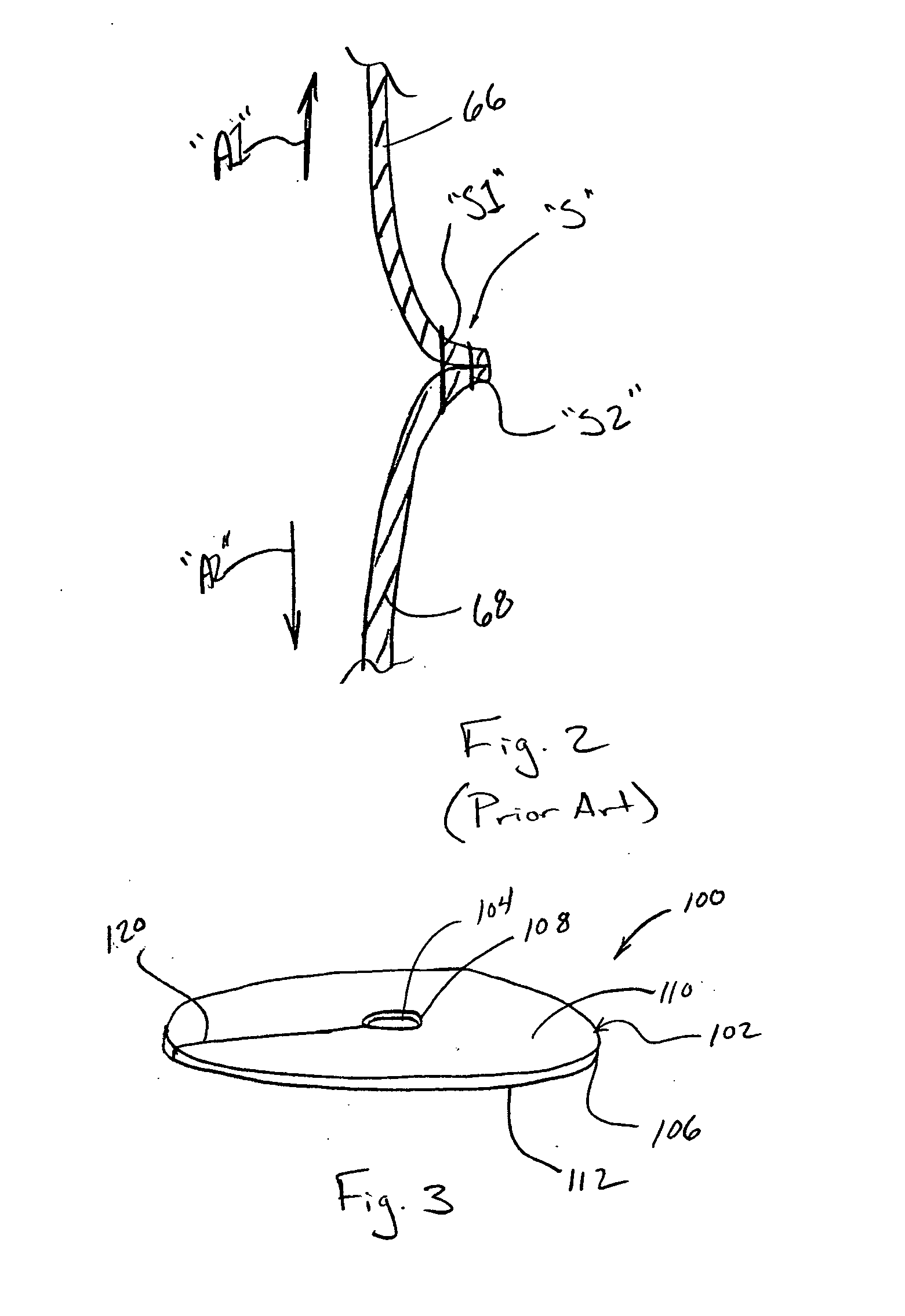
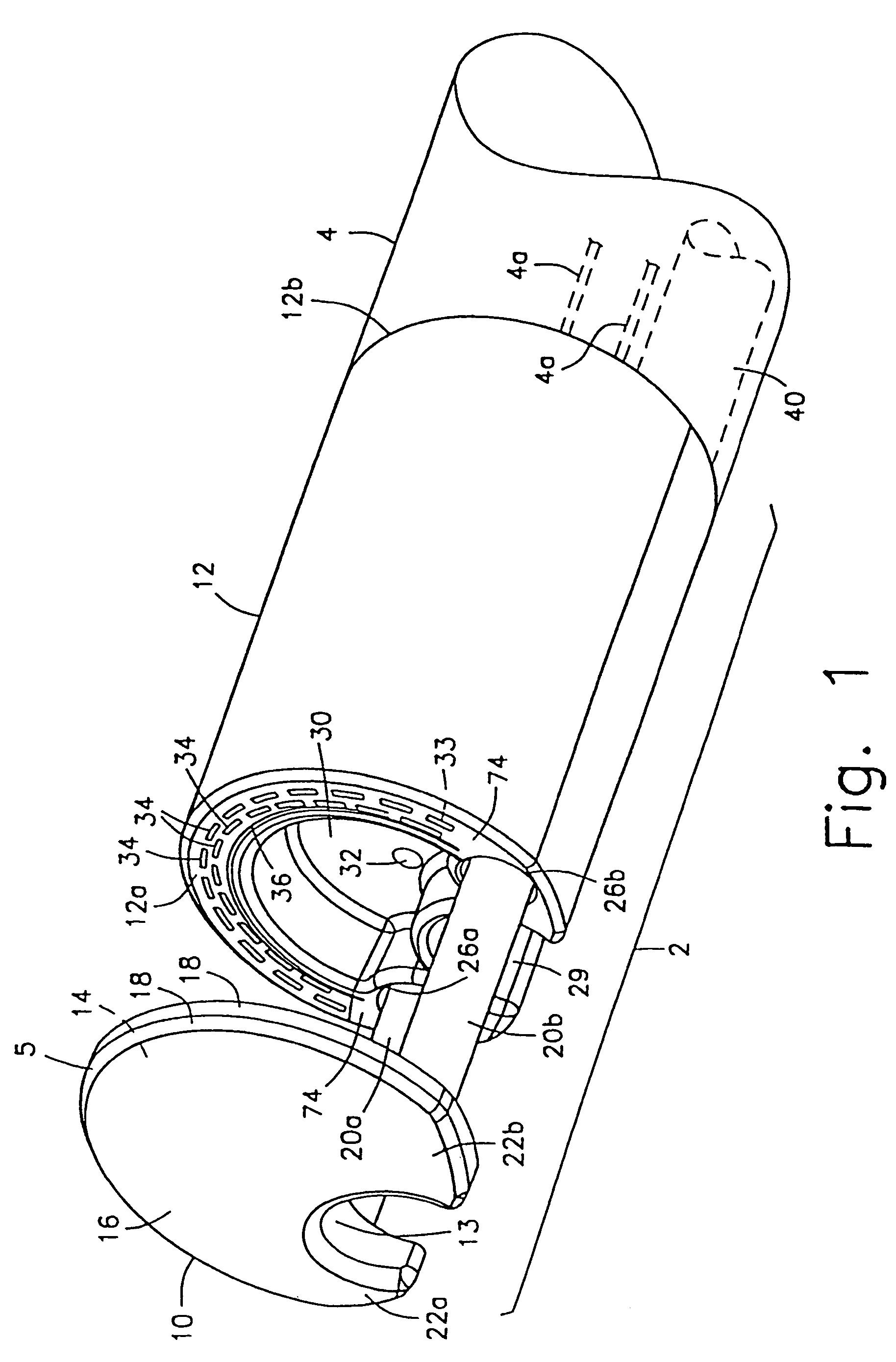
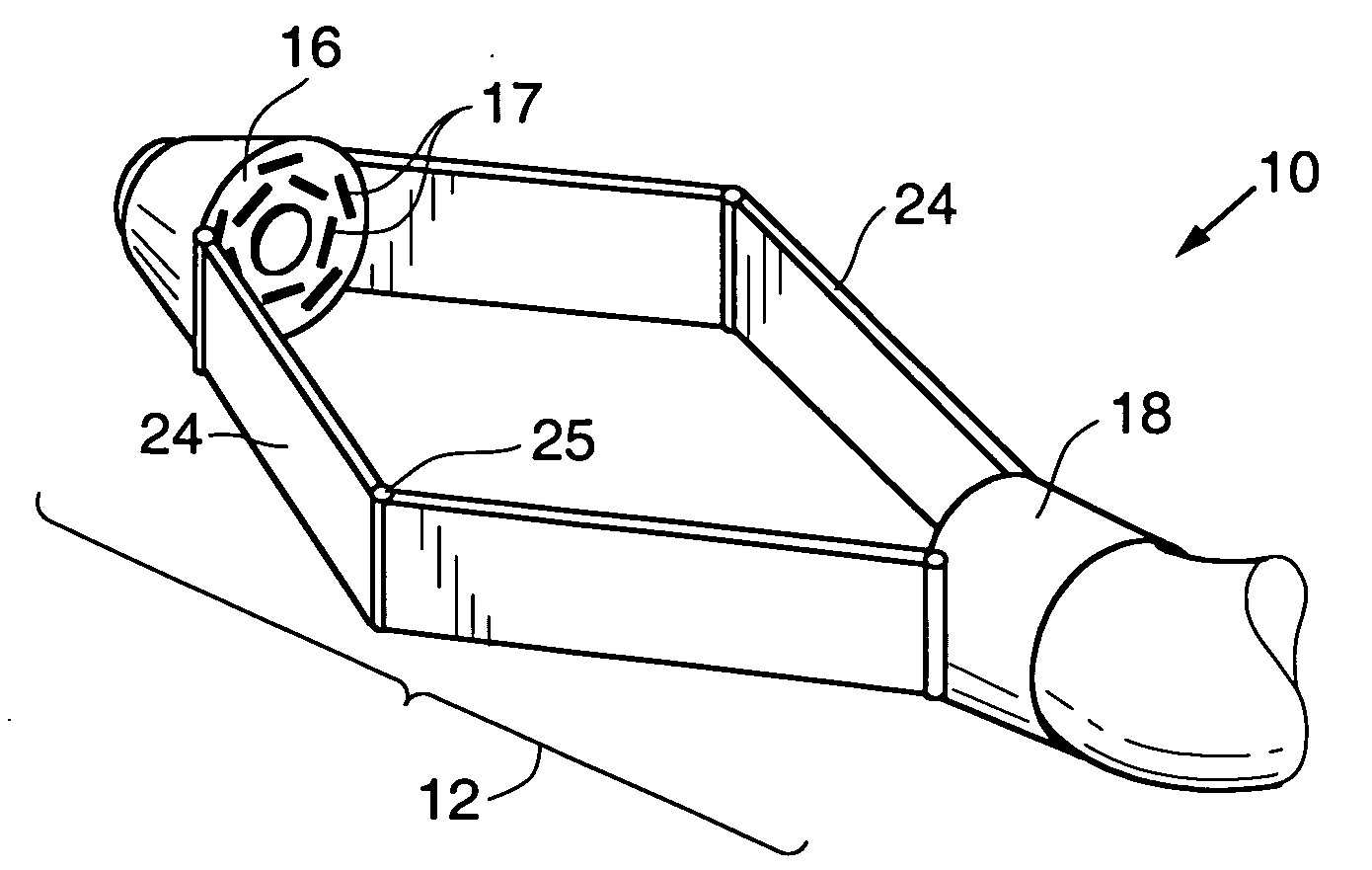
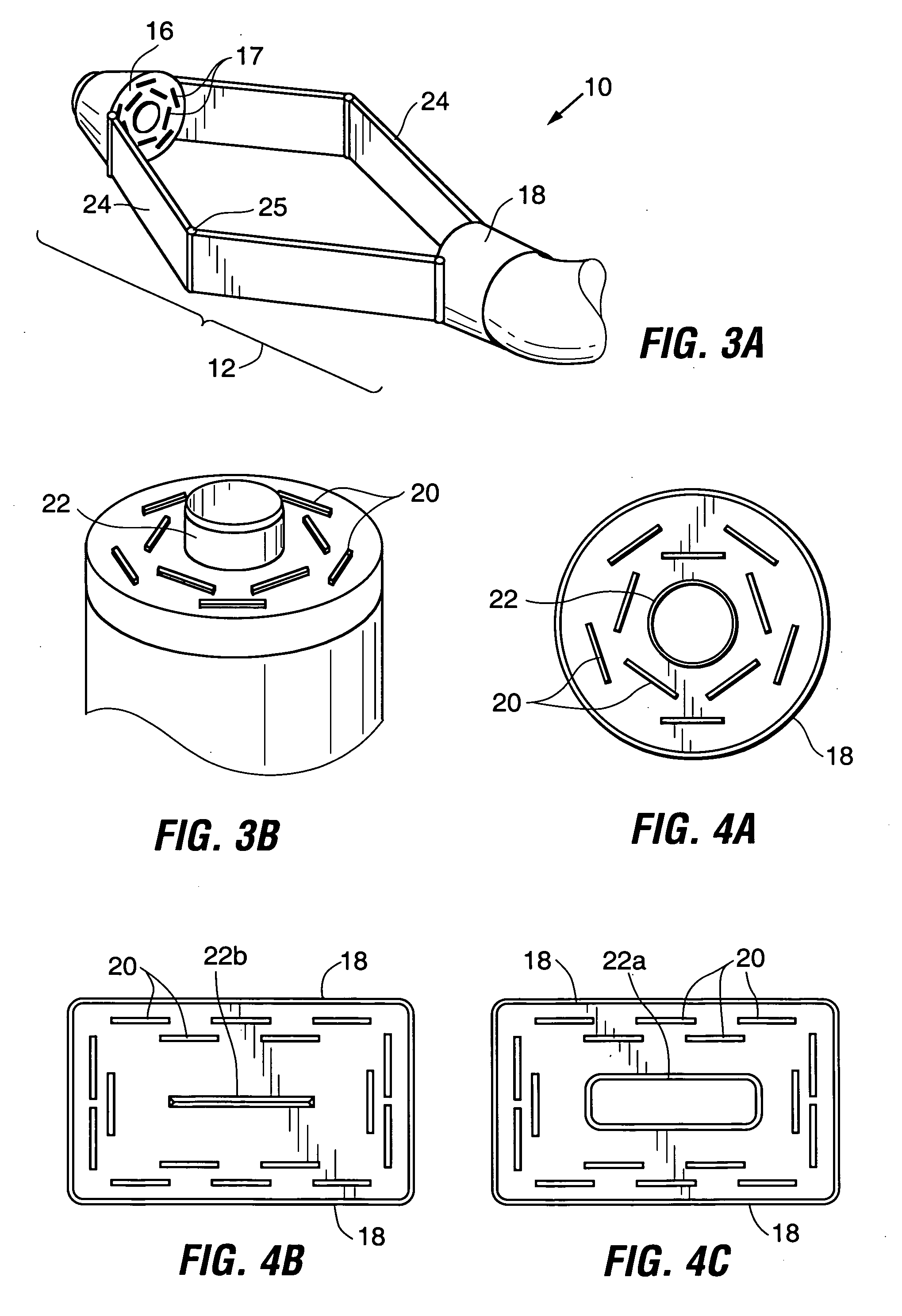
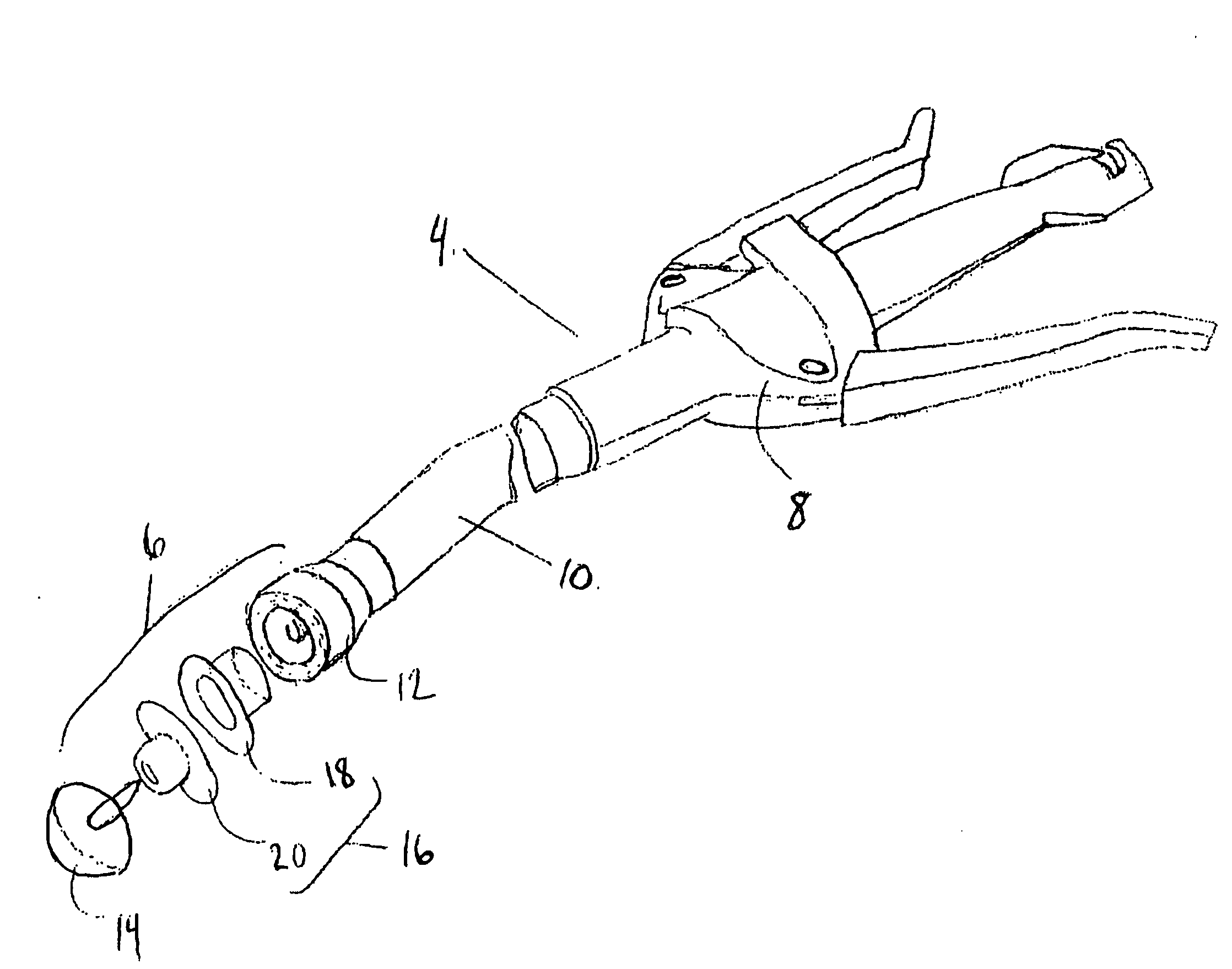
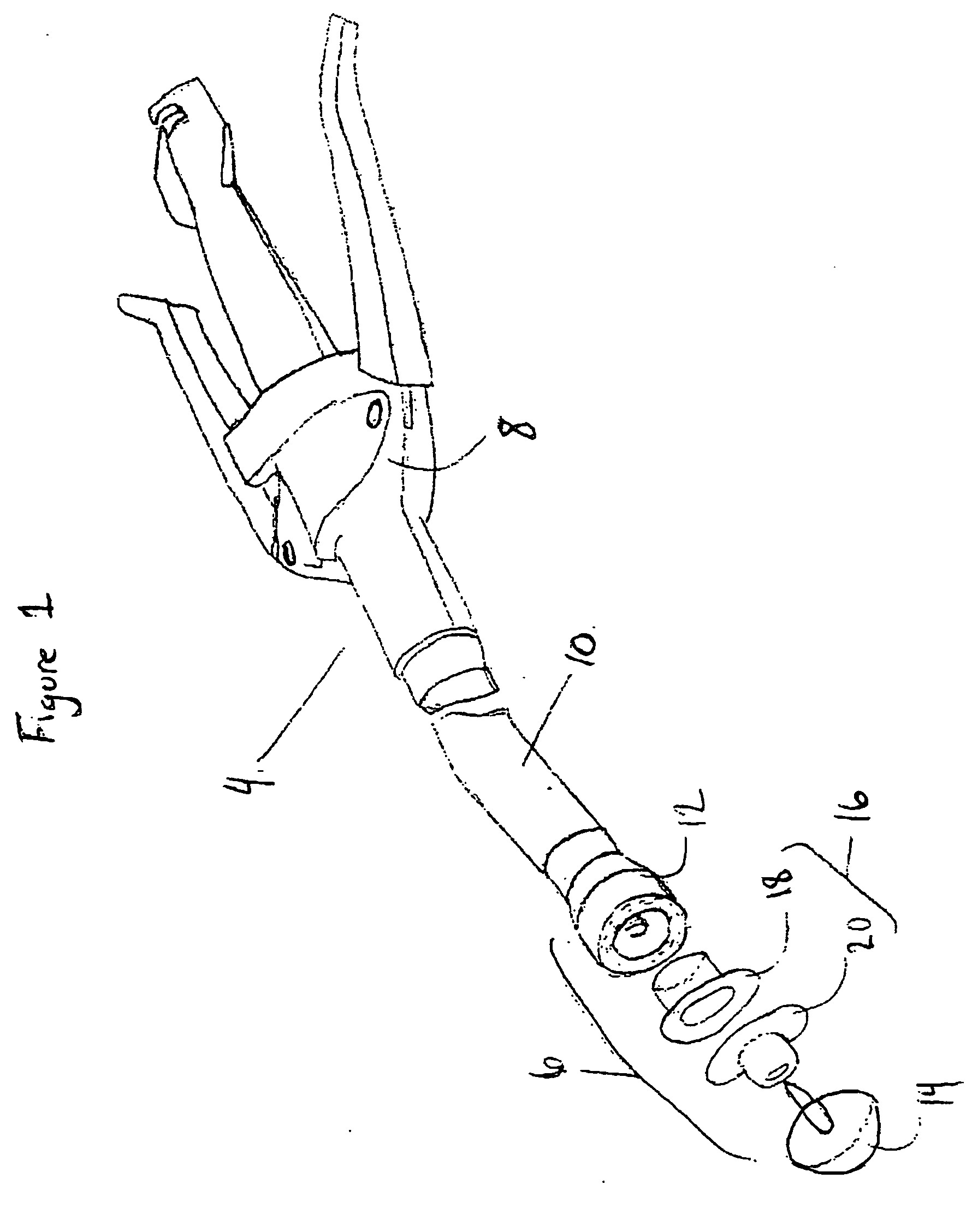
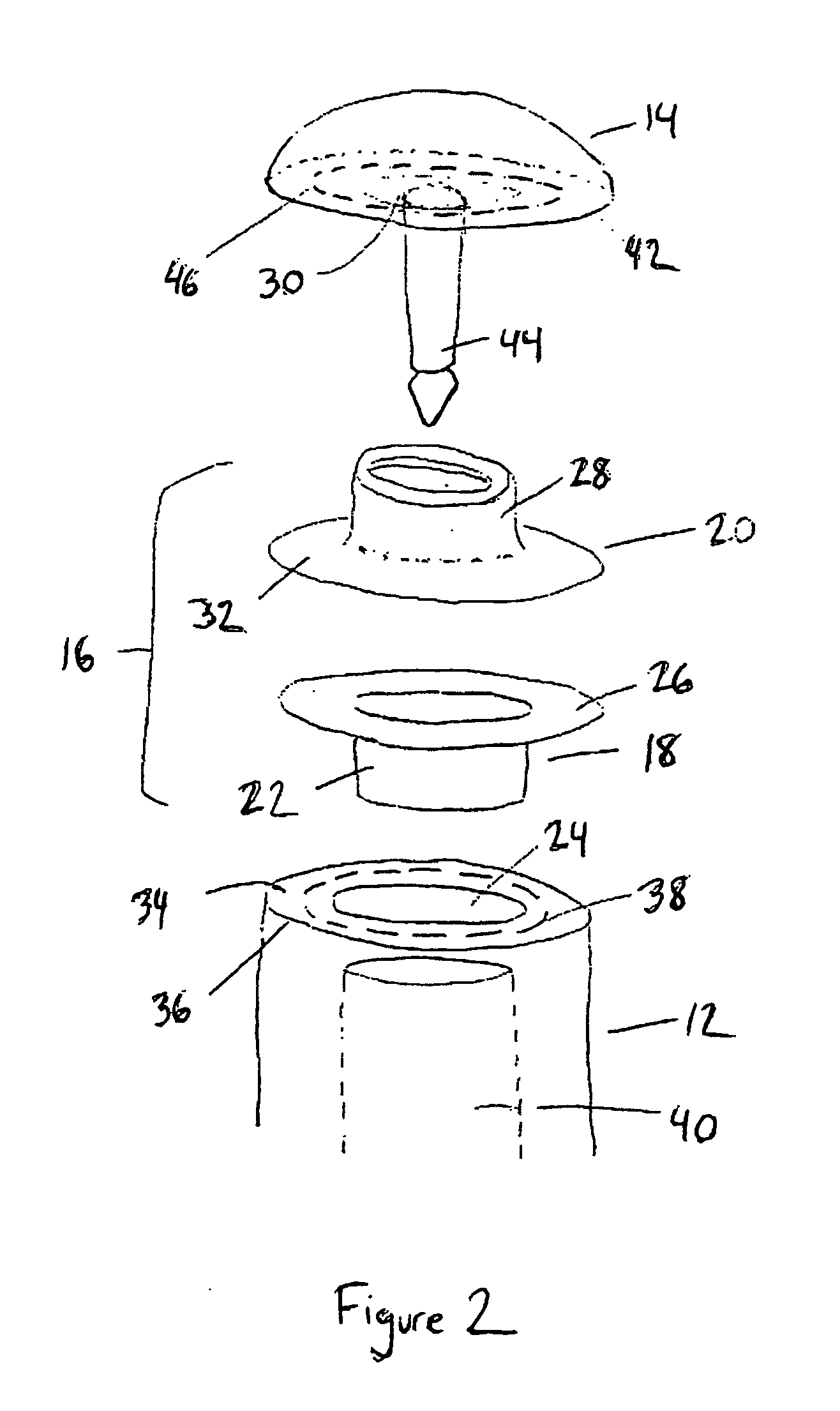
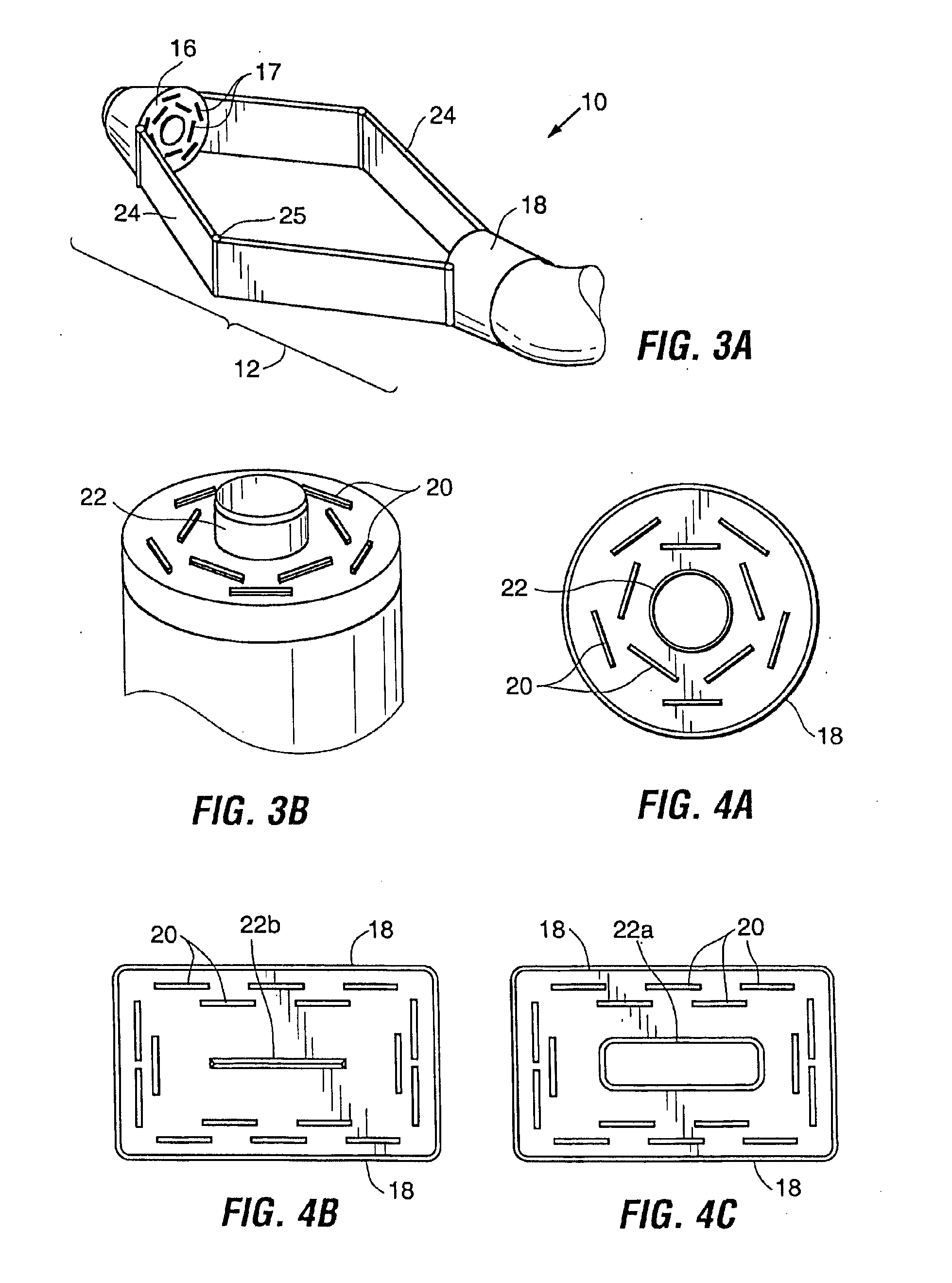
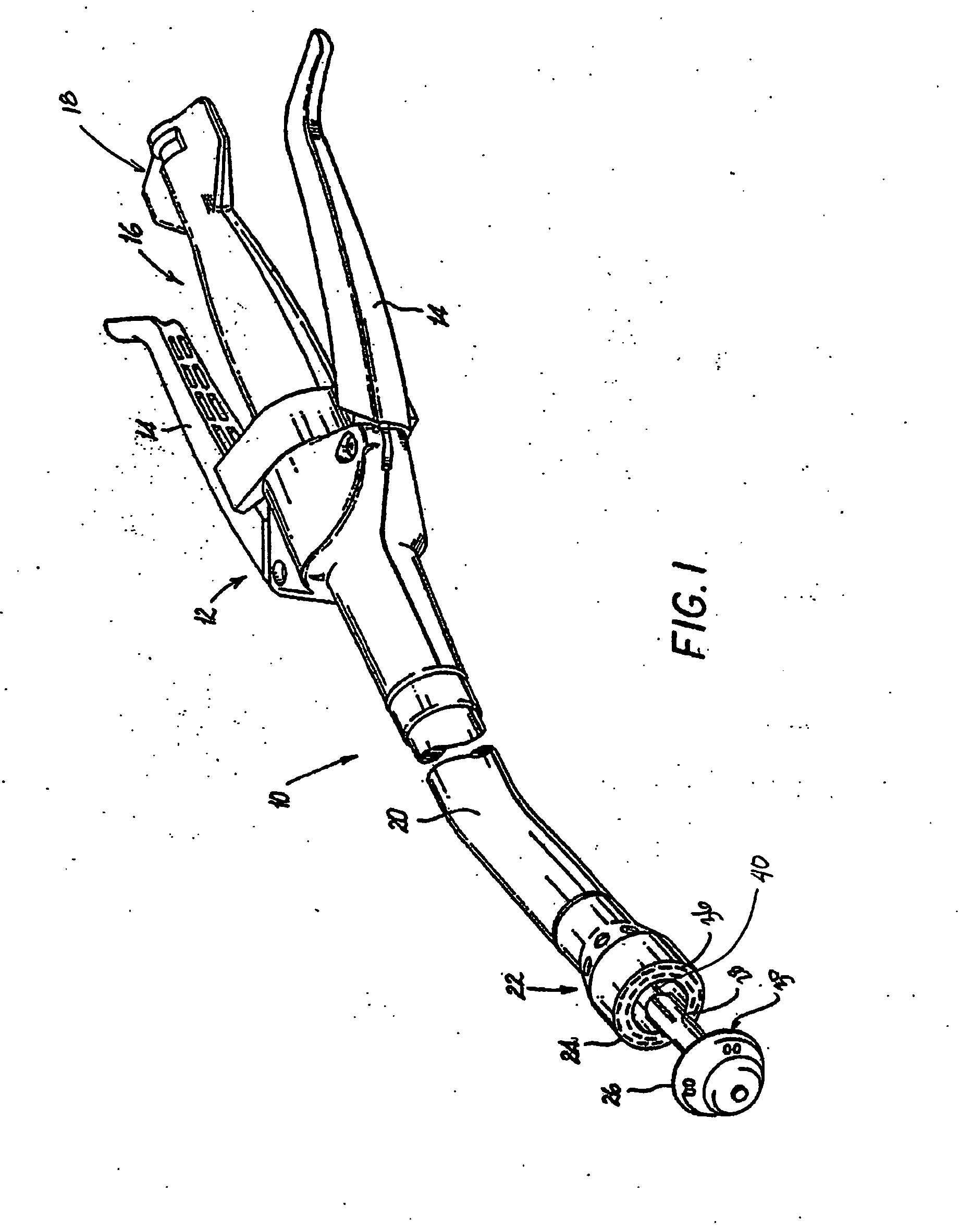
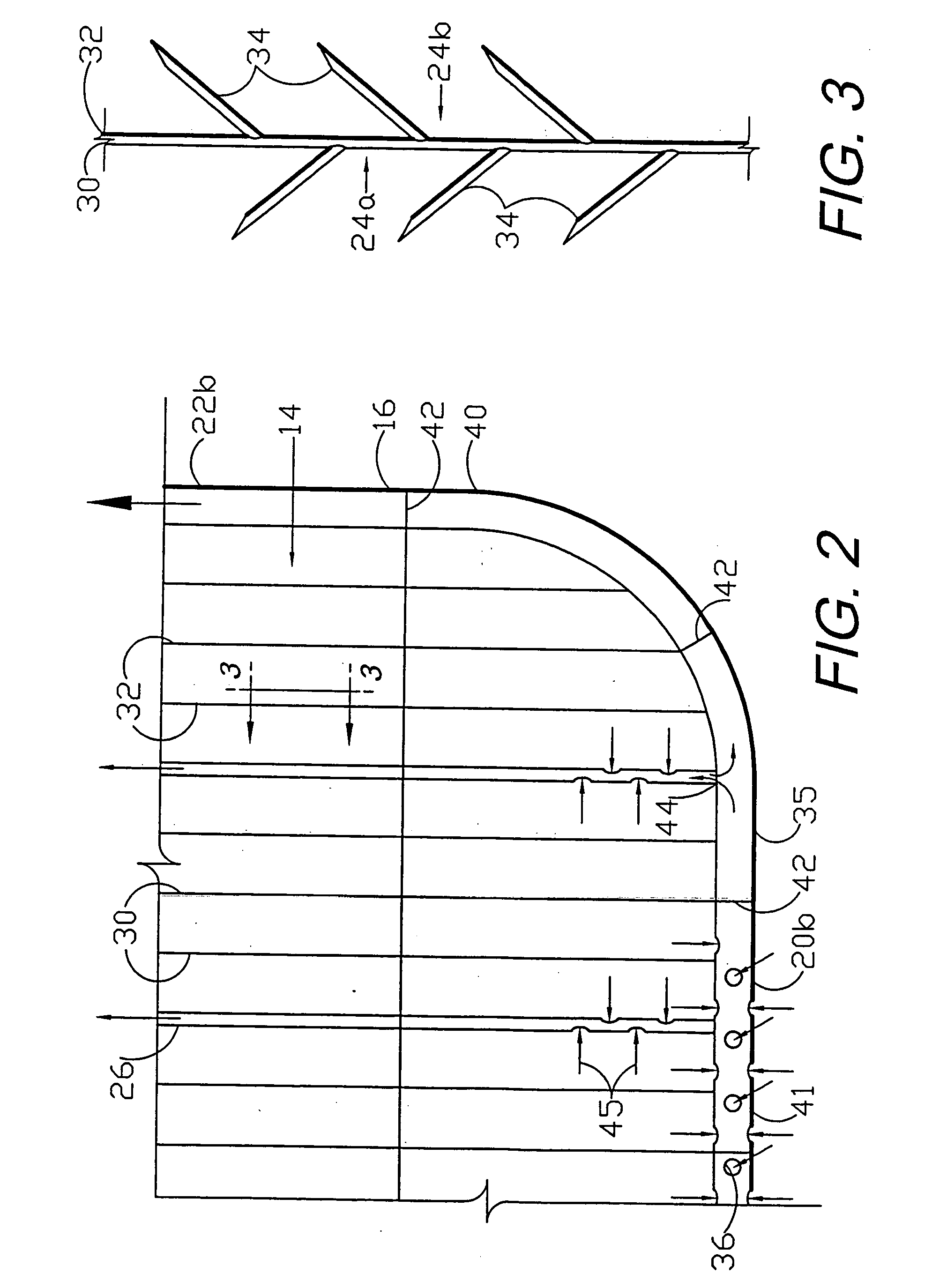
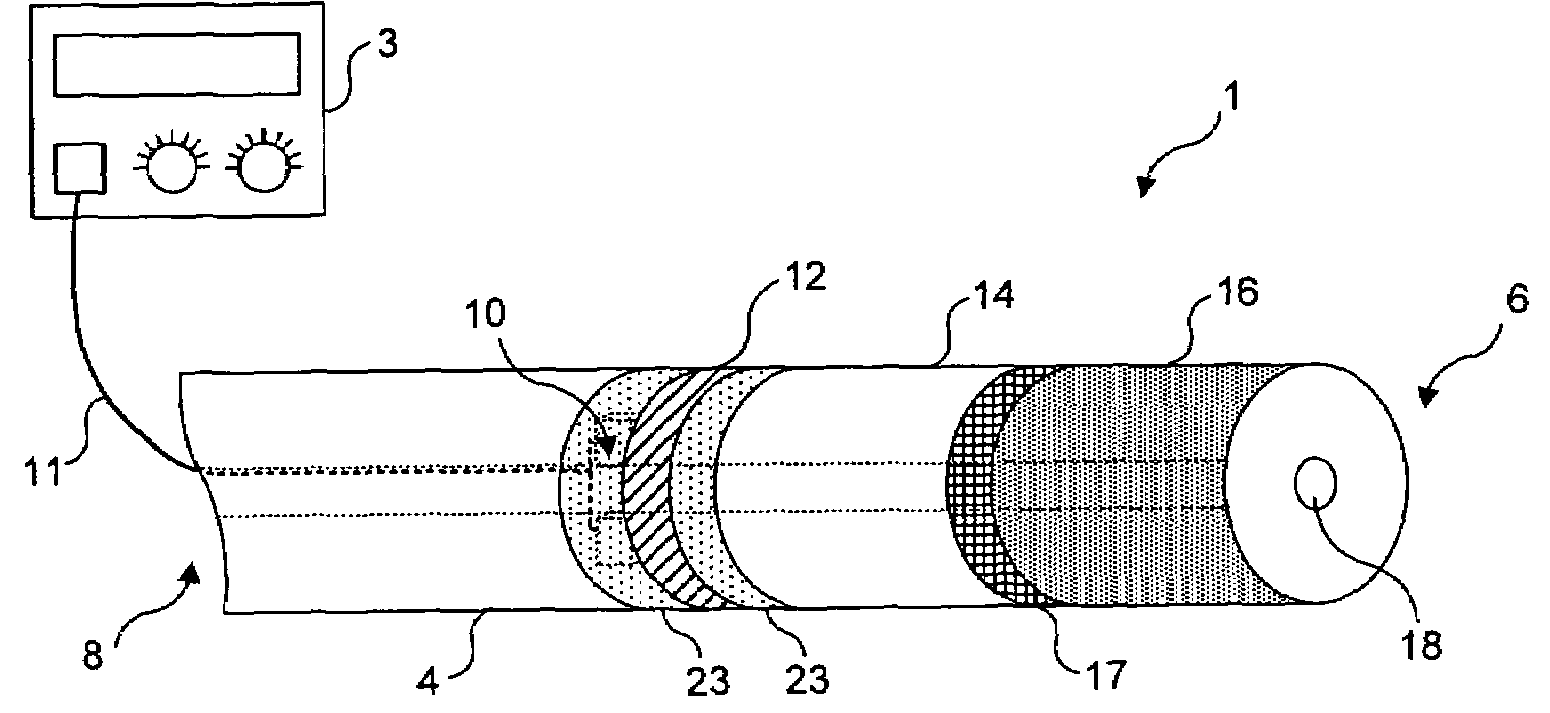
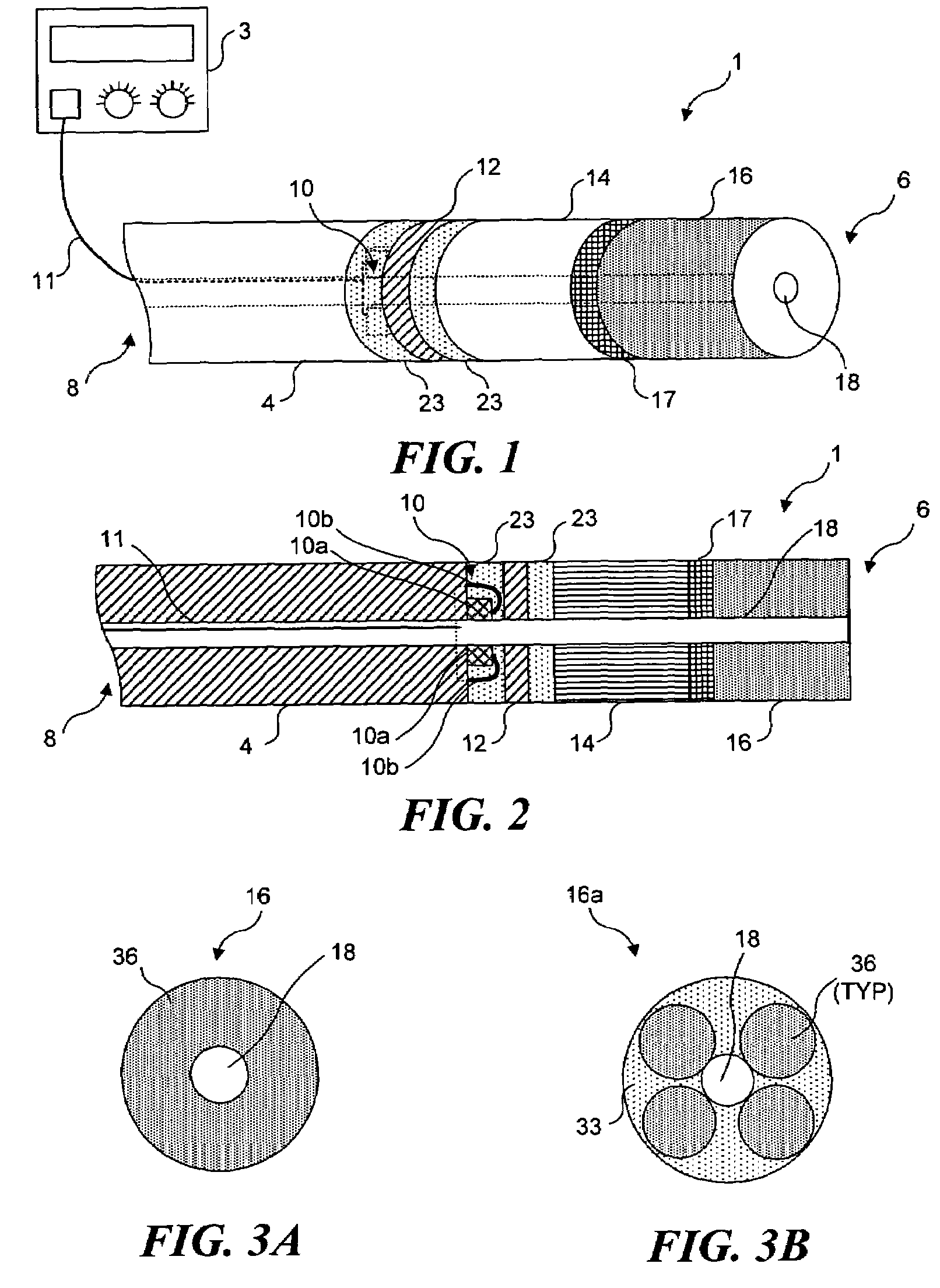
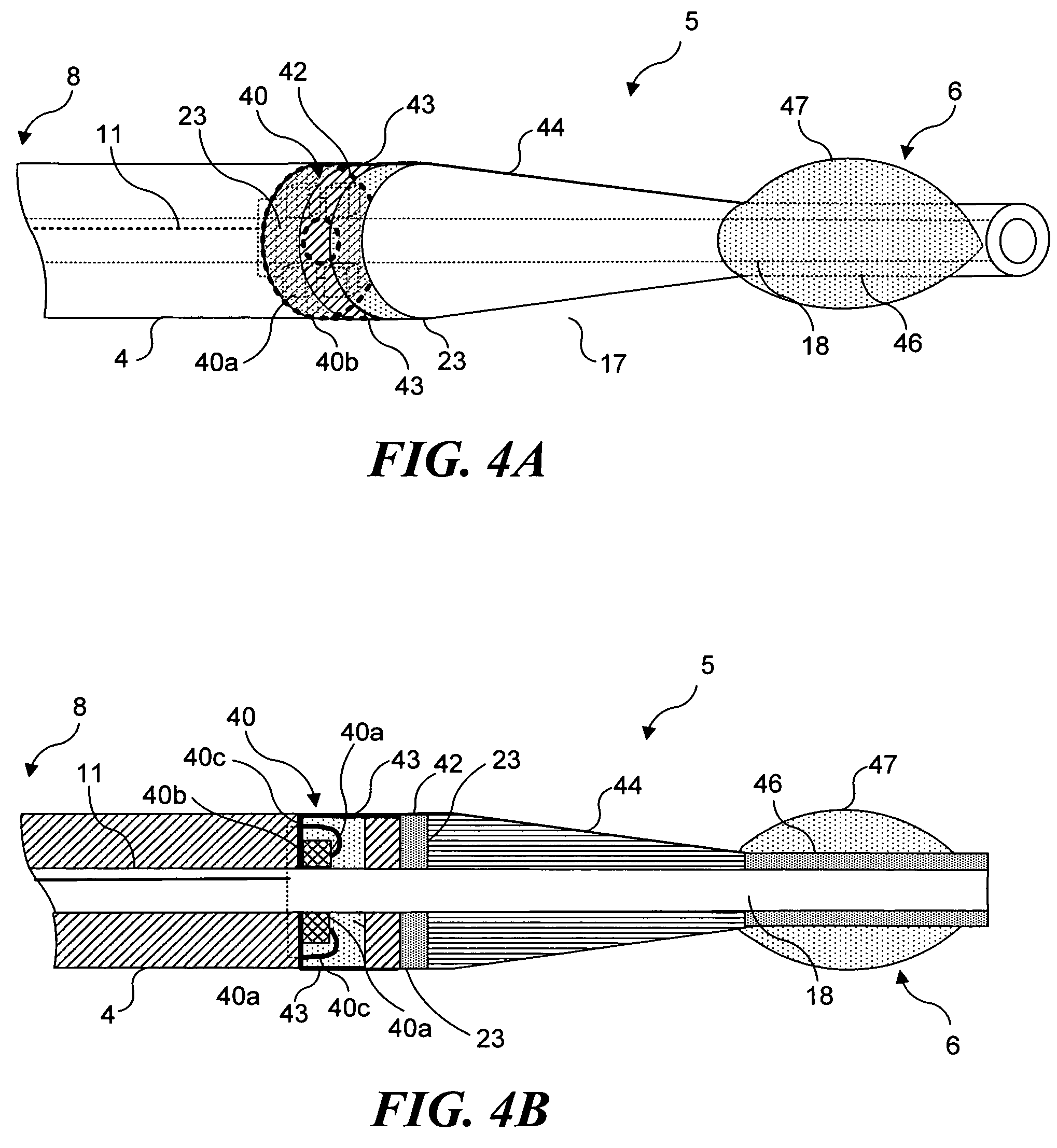
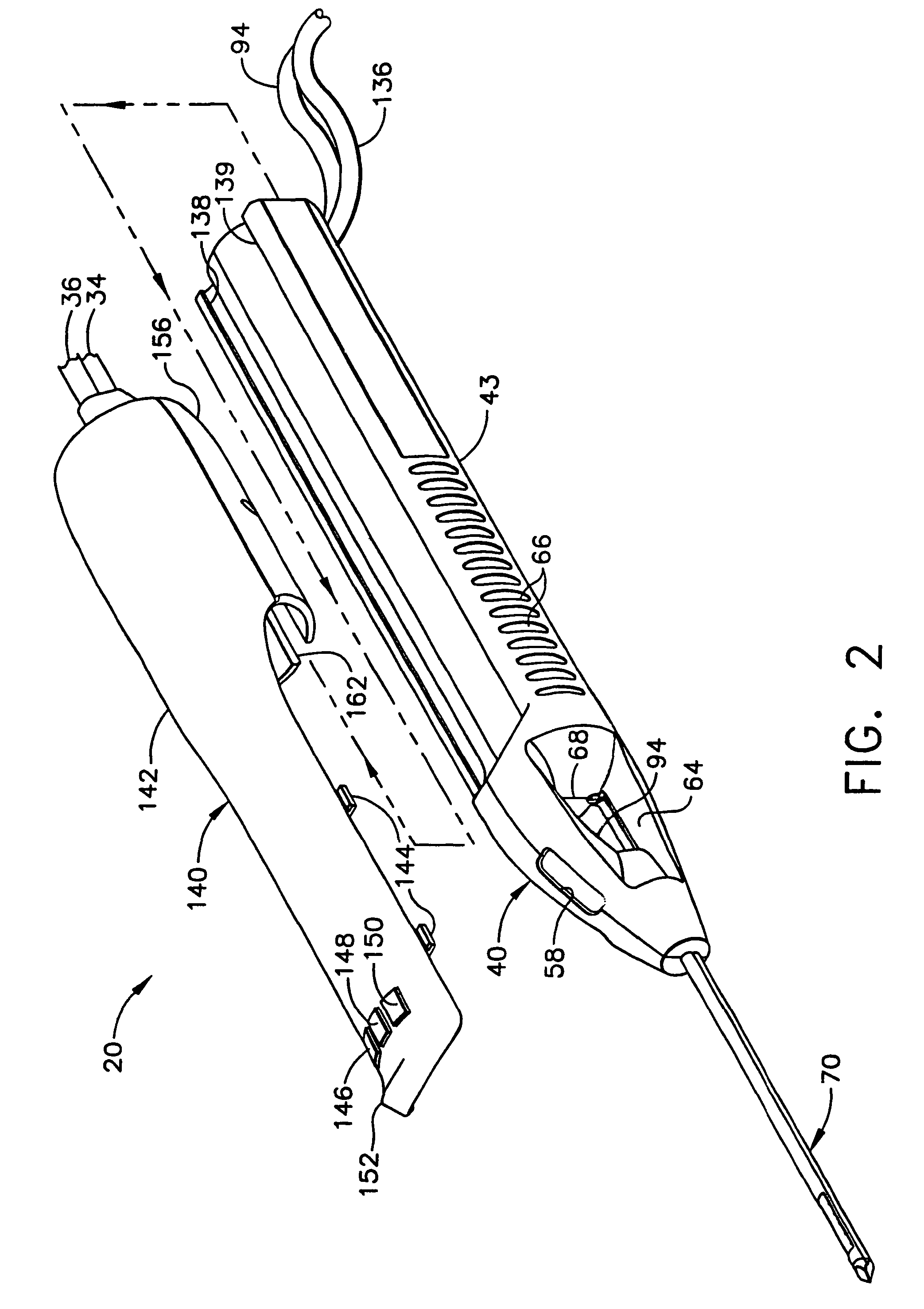
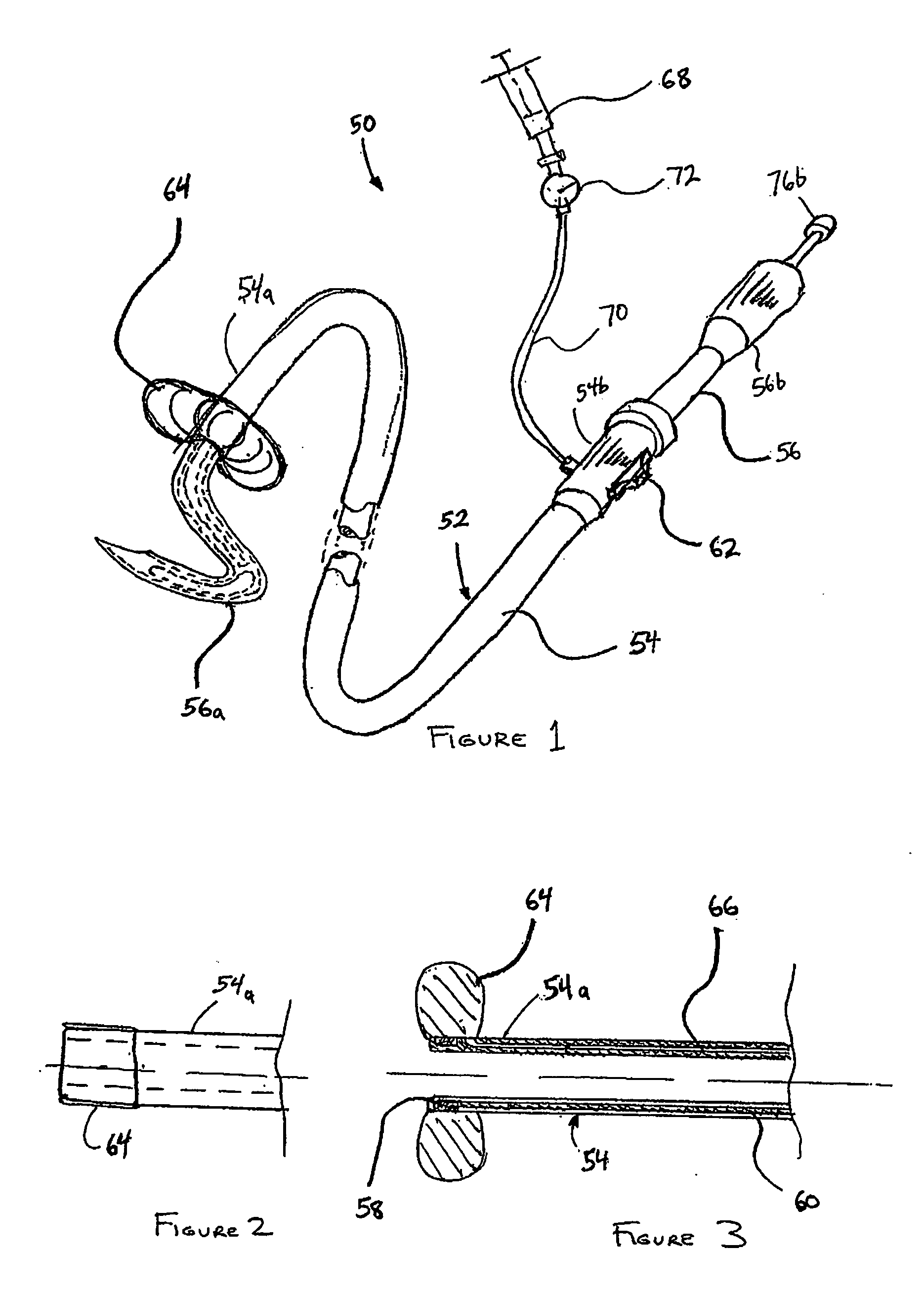
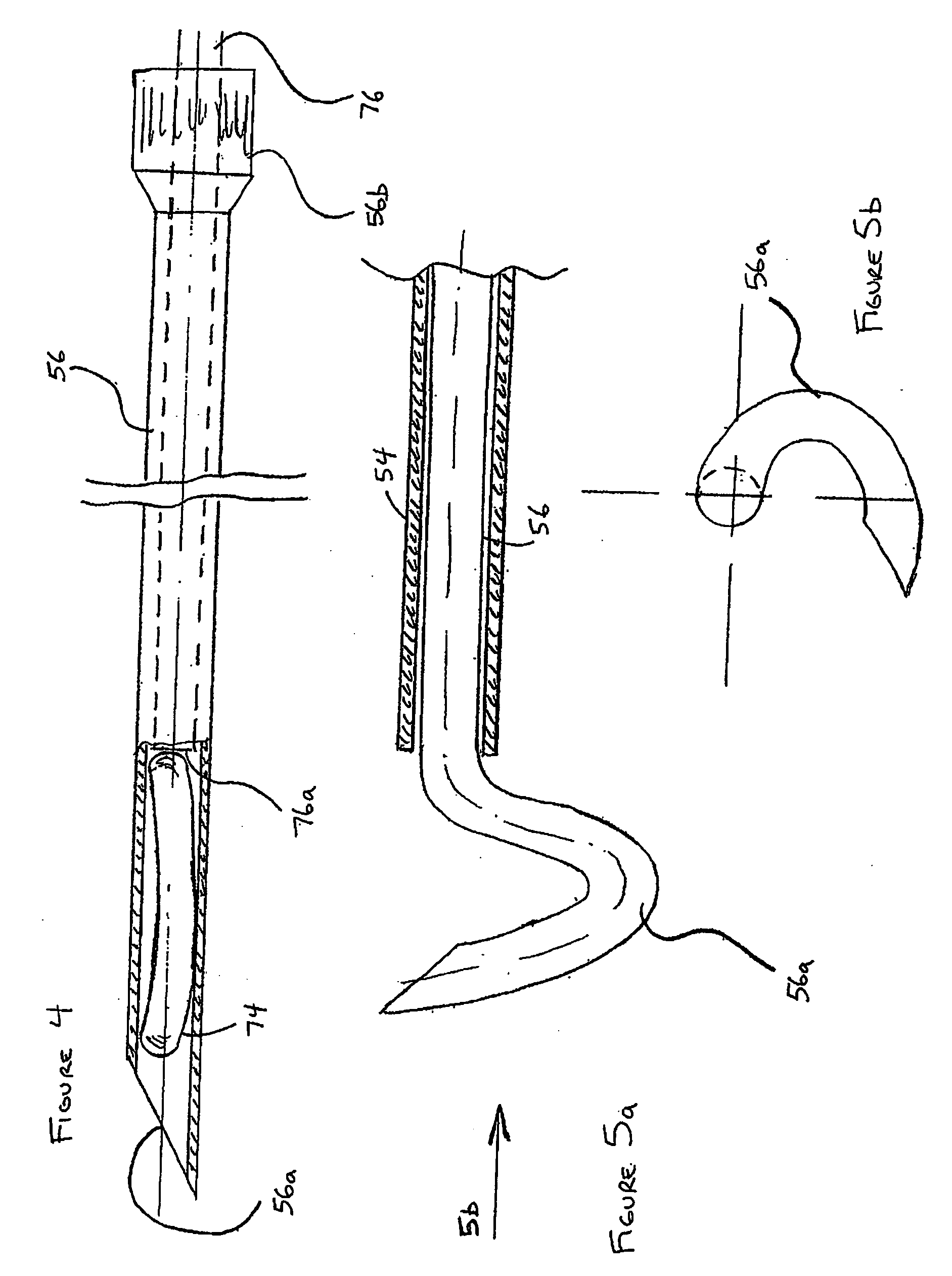
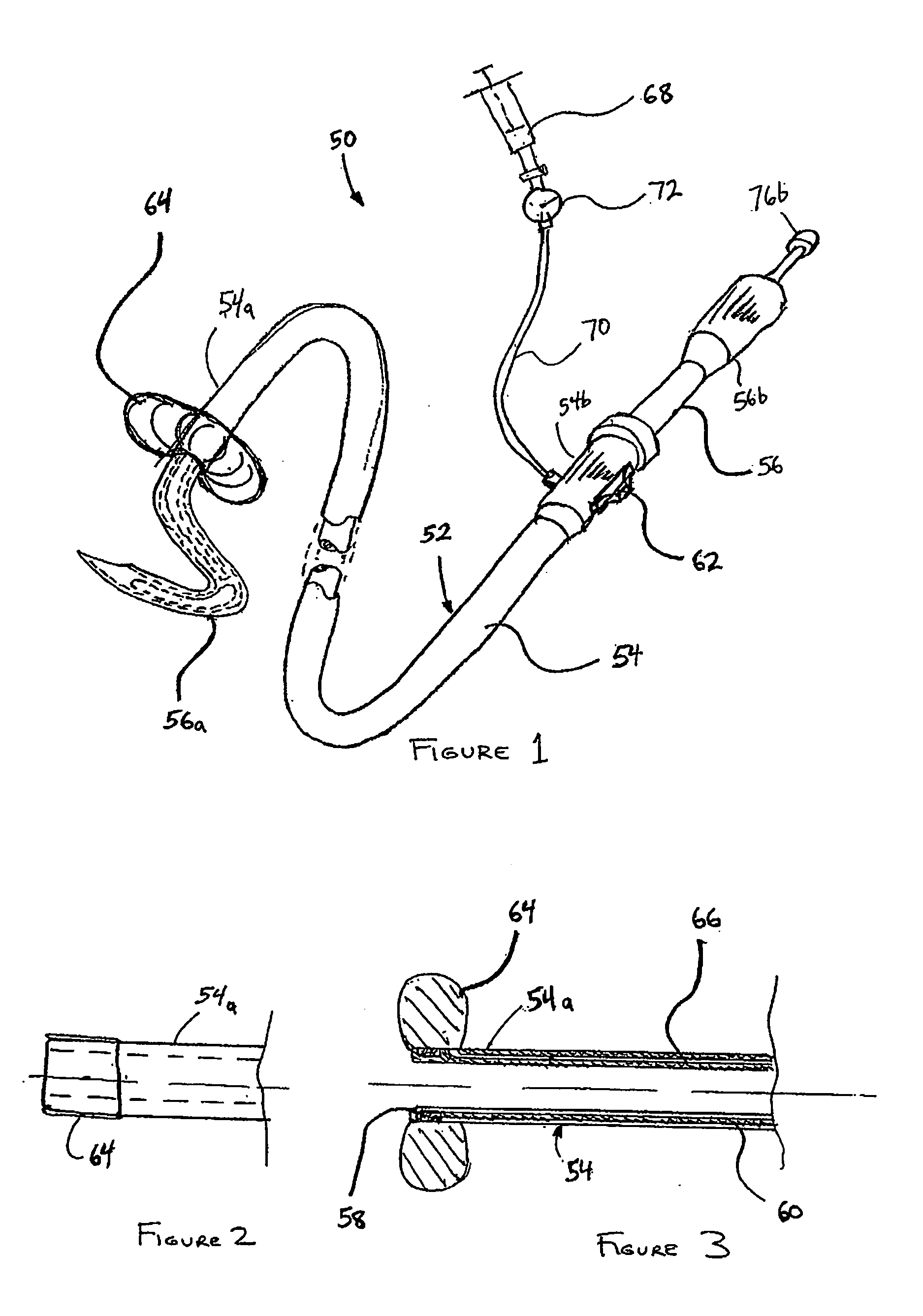
Circular stapler buttress combination
A combination medical device comprising a circular stapler instrument and one or more portions of preformed buttress material adapted to be stably positioned upon the staple cartridge and / or anvil components of the stapler prior or at the time of use. Positioned buttress material(s) are delivered to a tissue site where the circular stapler is actuated to connect previously severed tissue portions. The buttress material is retained and provides an improved seal between the joined tissue sections. The buttress material is made up of two regions, one of which serves primarily to secure the buttress material to the stapler prior to actuation, and one of which serves primarily to form the improved seal. The former region is severed and discarded upon activation of the circular stapler to form an anastomoses. Methods of use and preparation of the buttress material are also described.
Owner:SYNOVIS LIFE TECH
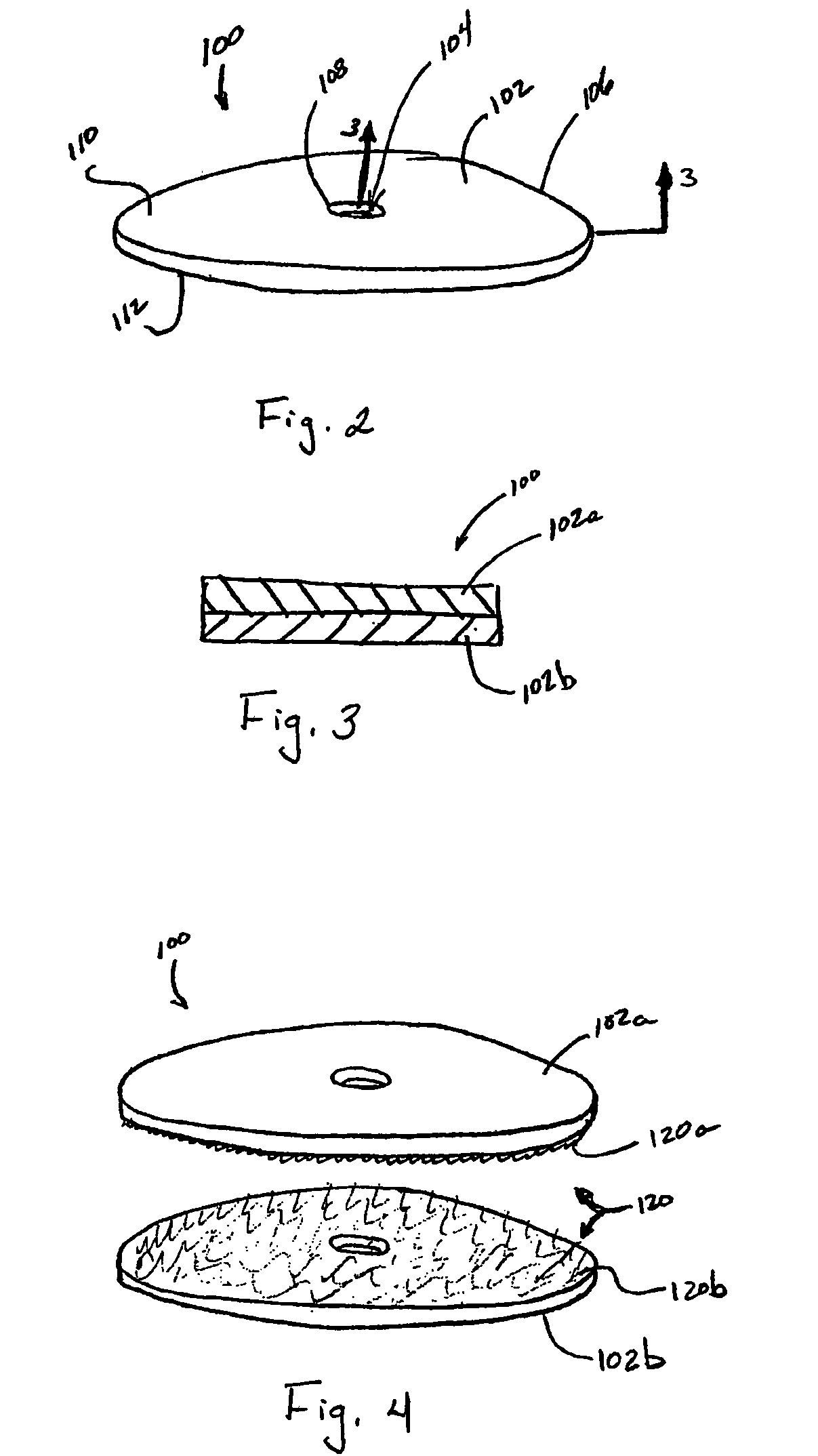
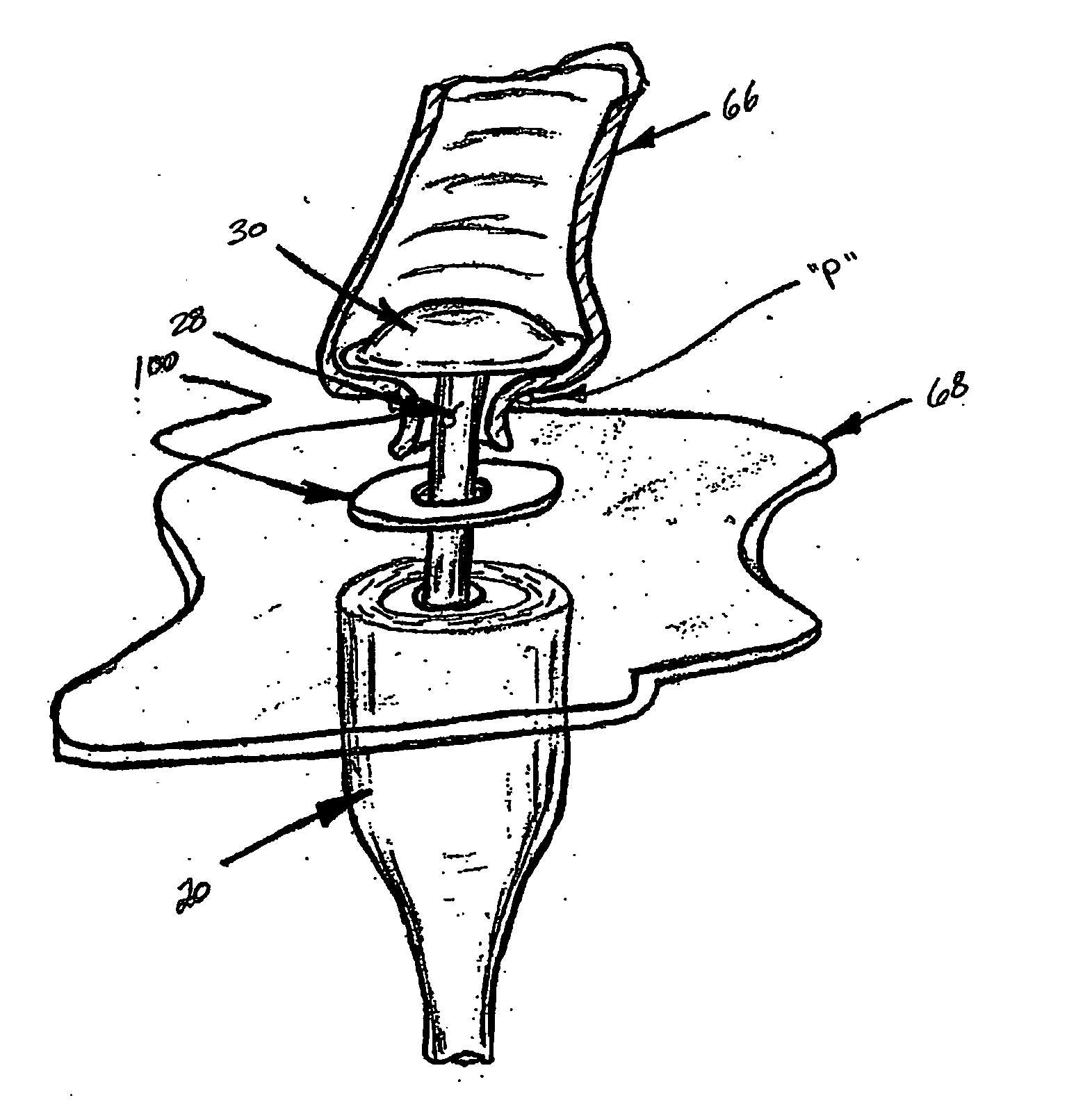
Annular adhesive structure
An assembly for joining tissue is provided and includes an anvil assembly and a body portion juxtaposed with respect to one another along a shaft and arranged so as to be approximated with respect to one another; and an applicator supported on the anvil assembly and configured for retaining a wound treatment material therein and for dispensing the wound treatment material therefrom. A method for joining tissue is provided and includes the steps of dispensing the wound treatment material from the applicator so as to distribute wound treatment material onto at least one of a first tissue section and a second tissue section; and approximating the anvil assembly and the body portion to one another so that the first tissue section and the second tissue section are in contact with one another with the dispensed wound treatment material interposed there between.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Annular disk for reduction of anastomotic tension and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20070203510A1Reduce generationReduce tensionSurgical staplesWound clampsEngineeringMechanical engineering
An apparatus for forming an anastomosis between adjacent tissue sections is provided. The apparatus includes an anastomosis device including an anvil assembly having a shaft which is selectively attachable to a tubular body portion, wherein the tubular body portion includes at least one annular row of staples operatively disposed therein. The apparatus further includes a disk having an outer terminal portion and a substantially centrally located aperture. The disk includes an adhesive material at the outer terminal portion. Wherein the outer terminal portion of the disk extends radially outward beyond the outer-most row of the at least one annular row of staples to adhesively attach the tissue sections together radially outward of the at least one annular row of staples.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method and device for full thickness resectioning of an organ
Described is a full-thickness resection system which includes a control unit coupled to a proximal end of a flexible endoscope. The control unit remains outside of a body when the stapling head is in an operative position within a body lumen. The control unit includes (i) an anvil actuator coupled to an anvil in the stapling head, actuation of the anvil actuator moves the anvil axially relative to a stapling mechanism in the stapling head to compress a folded full-thickness portion of lumenal tissue between the anvil and the stapling mechanism. In addition, the control unit includes (ii) a stapler actuator coupled to the stapling mechanism in the stapling head, actuation of the stapler actuator causing the stapling mechanism to drive staples through the folded lumenal tissue against the anvil. Also, the control unit includes (iii) a tissue cutter actuator coupled to a tissue cutter in the stapling head, actuation of the tissue cutter actuator causing the tissue cutter to resect portions of the folded lumenal tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
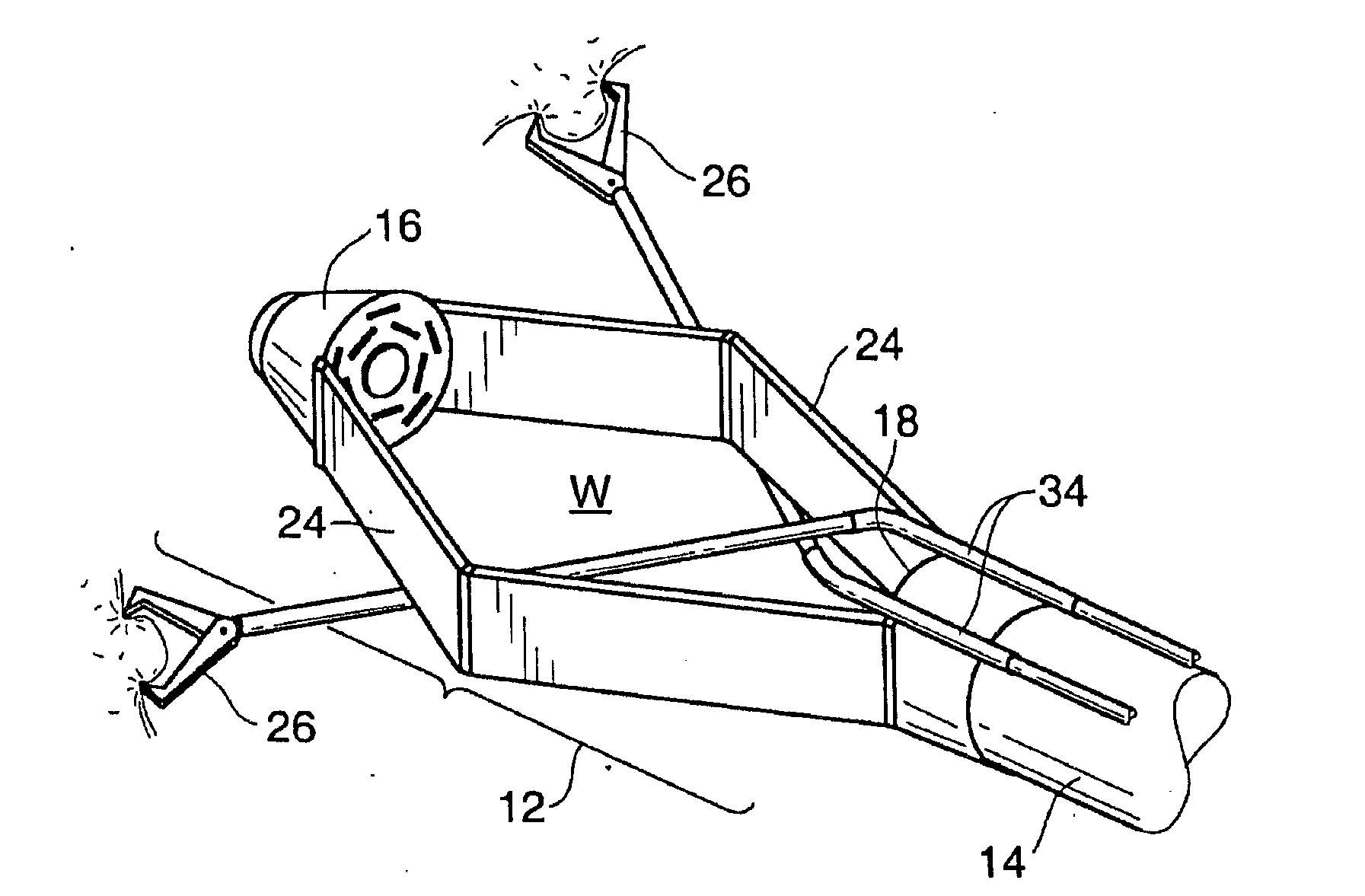
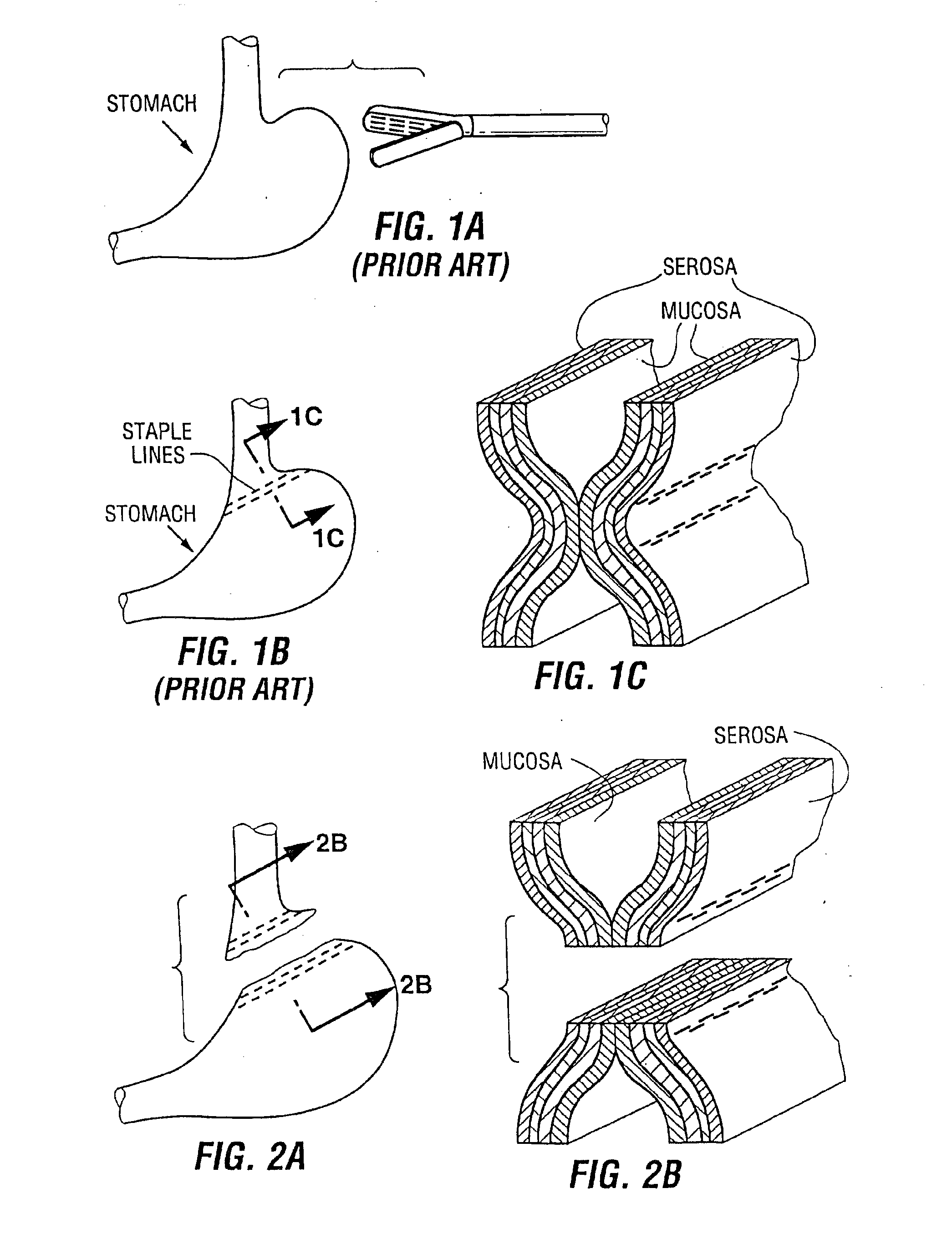
Devices and methods for stomach partitioning
A device and method for remodeling or partitioning a body cavity, hollow organ or tissue tract includes graspers operable to engage two or more sections of tissue within a body cavity and to draw the engaged tissue between a first and second members of a tissue remodeling tool. The two or more pinches of tissue are held in complete or partial alignment with one another as staples or other fasteners are driven through the pinches, thus forming a four-layer tissue plication. Over time, adhesions formed between the opposed serosal layers create strong bonds that can facilitate retention of the plication over extended durations, despite the forces imparted on them by stomach movement. A cut or cut-out may be formed in the plication during or separate from the stapling step to promote edge-to-edge healing effects that will enhance tissue knitting / adhesion.
Owner:BAROSENSE
Circular stapler buttress combination
ActiveUS20050228446A1Less-expensive to manufactureMore rigidSuture equipmentsStapling toolsButtressBiological activation
A combination medical device comprising a circular stapler instrument (4) and one or more portions of preformed buttress material (16) adapted to be stably positioned upon the staple cartridge (12) and / or anvil (14) components of the stapler (4) prior or at the time of use. Positioned buttress material(s) (16) are delivered to a tissue site where the circular stapler (4) is actuated to connect previously severed tissue portions. An embodiment of the invention allows tissue portions to be joined without the use of sutures. The buttress material (16) is made up of two regions, one of which serves primarily to secure the buttress material (16) to the stapler (4) prior to acuation, and one of which serves primarily to form the improved seal. The former region is severed and discarded upon activation of the circular stapler (4) to form anastomoses, while the remaining material secures and seals the newly connected tissue. Methods of use and preparation of the buttress material (16) are also described.
Owner:SYNOVIS LIFE TECH
Devices and methods for stomach partitioning
A device and method for remodeling or partitioning a body cavity, hollow organ or tissue tract includes graspers operable to engage two or more sections of tissue within a body cavity and to draw the engaged tissue between a first and second members of a tissue remodeling tool. The two or more pinches of tissue are held in complete or partial alignment with one another as staples or other fasteners are driven t9hrough the pinches, thus forming a four-layer tissue plication. Over time, adhesions formed between the opposed serosal layers create strong bonds that can facilitate retention of the plication over extended durations, despite the forces imparted on them by stomach movement. A cut or cut-out may be formed in the plication during or separate from the stapling step to promote edge-to-edge healing effects that will enhance tissue knitting / adhesion.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
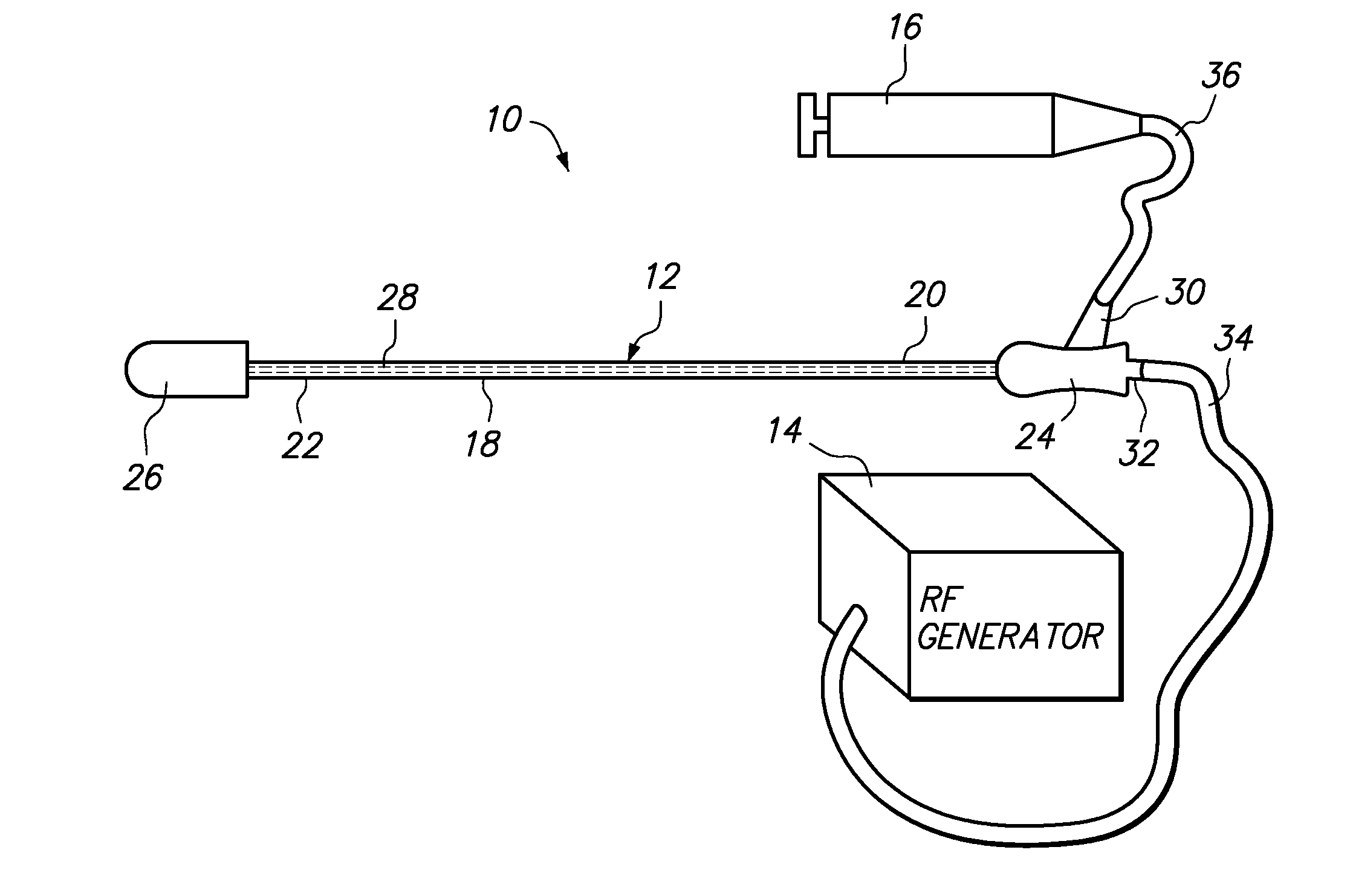
Method and apparatus for applying thermal energy to tissue asymmetrically
Systems and methods are described for treating tissue with thermal energy while minimizing the amount of thermal energy to which adjacent tissue is exposed. A surgical instrument for delivering thermal energy to a section of tissue during percutaneous surgery, includes: an elongated shaft having a proximal end and a distal end; and a split tip electrode coupled to the distal end, the split tip electrode i) including a first component and a second component coupled to the first component, and ii) defining a principle axis. The thermal energy is delivered to the section of tissue so as to heat the section of tissue asymmetrically with regard to the principle axis of the split tip electrode. The systems and methods provide advantages in that thermal energy can be directed to one side of the split tip so that a first of two juxtaposed areas of a surgical site can be heated while a second of the two juxtaposed layers is substantially not heated. In alternate embodiments a portion of the site may be actively cooled while an adjacent portion of the site may be actively cooled.
Owner:ORATEC INTERVENTIONS
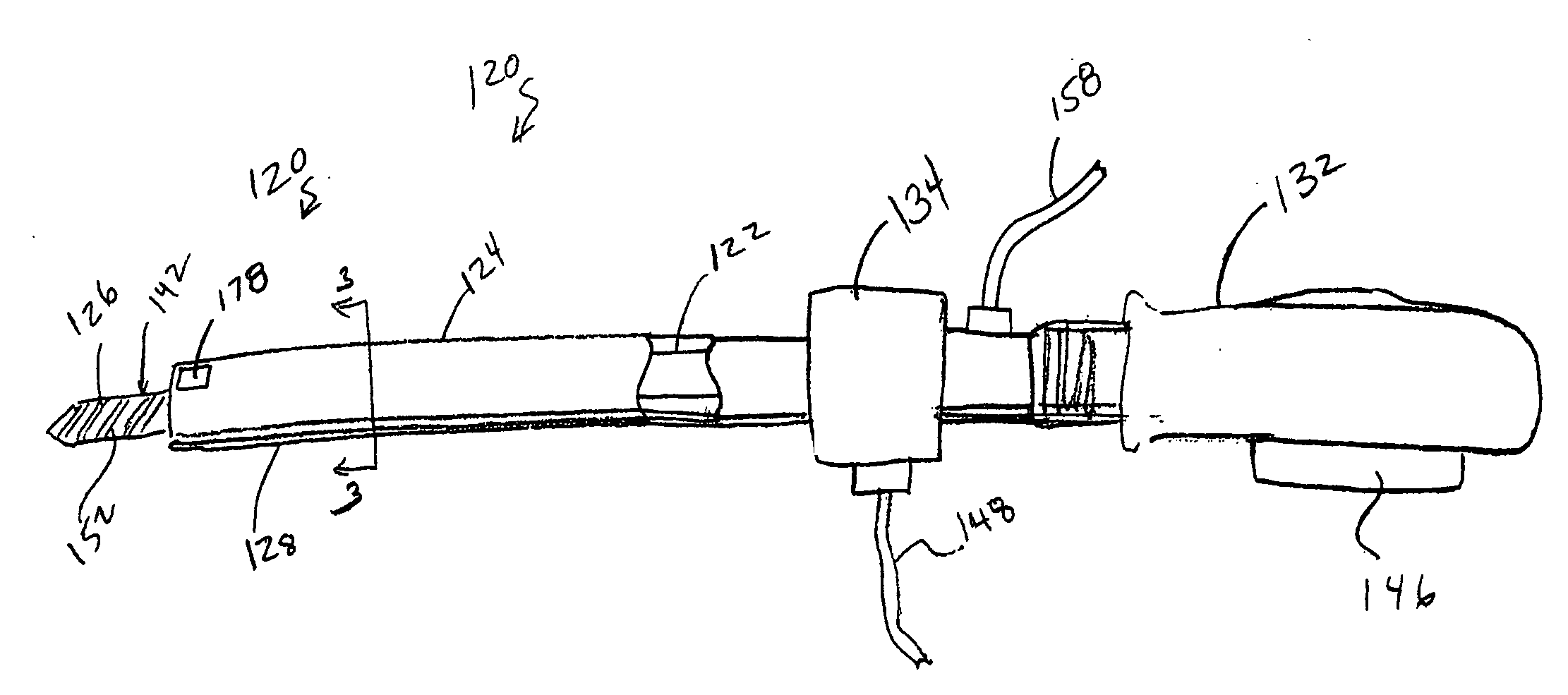
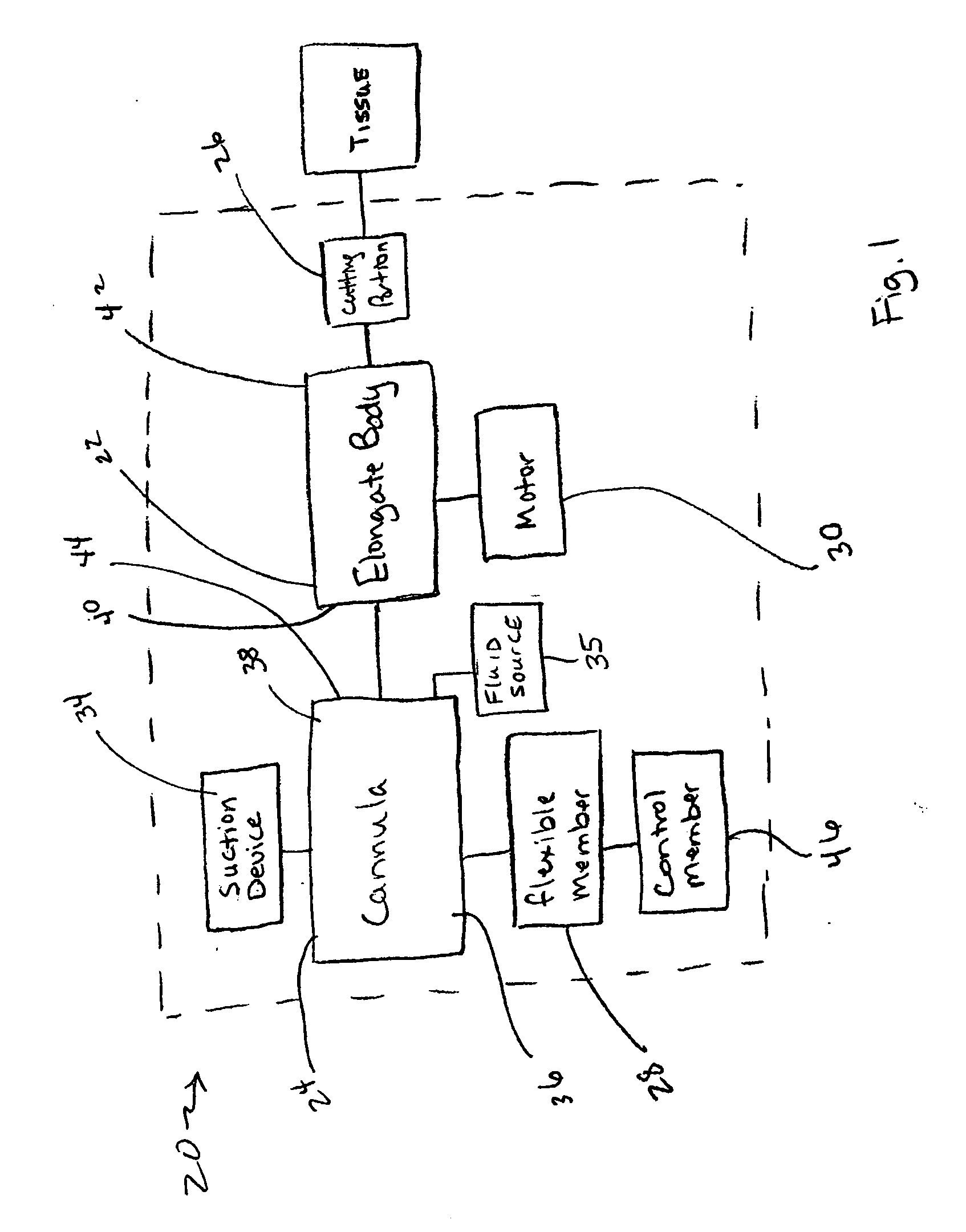
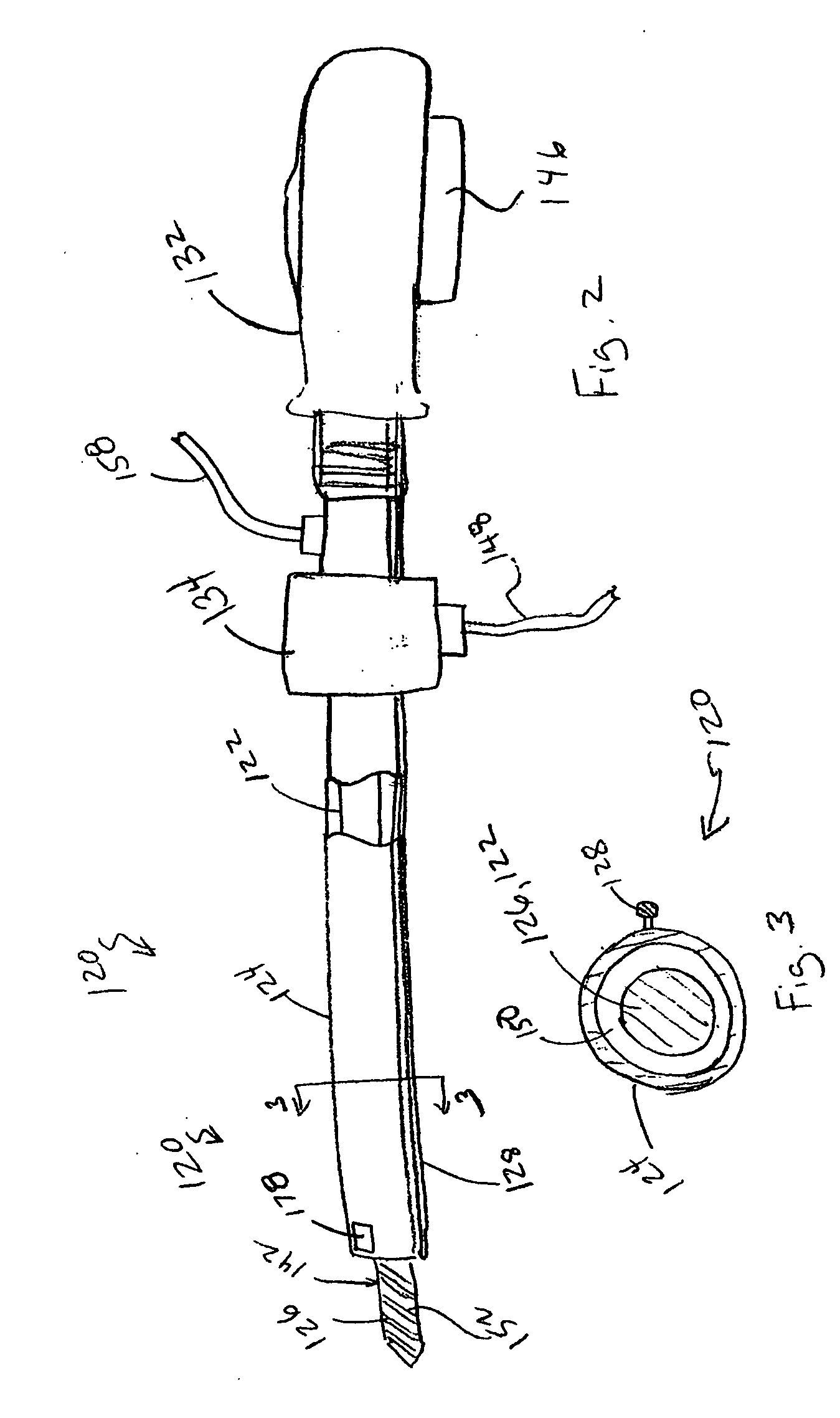
Tissue debulking device and method of using the same
InactiveUS20070287933A1Surgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDistal portionGeneral surgery
Apparatuses and methods for debulking a tissue in a patient's body are disclosed herein. In one variation, an apparatus includes a cannula configured to provide percutaneous access to an interior portion of a tissue. The cannula has a distal portion, a proximal portion, and a lumen defined between the distal portion and the proximal portion. A flexible member is coupled to the cannula and configured to steer the distal portion of the cannula within the tissue. An elongate body has a distal portion and is configured to be movably disposed within the lumen of the cannula. The distal portion of the elongate body defines a cutting portion configured to disrupt at least a portion of the tissue when the cutting portion is moved, for example, rotated and / or shuttled. In one variation, the disrupted portion of tissue includes a portion of a tumor.
Owner:KYPHON
Annular adhesive structure
An assembly for joining tissue is provided and includes an anvil assembly and a body portion juxtaposed with respect to one another along a shaft and arranged so as to be approximated with respect to one another; and an applicator supported on the anvil assembly and configured for retaining a wound treatment material therein and for dispensing the wound treatment material therefrom. A method for joining tissue is provided and includes the steps of dispensing the wound treatment material from the applicator so as to distribute wound treatment material onto at least one of a first tissue section and a second tissue section; and approximating the anvil assembly and the body portion to one another so that the first tissue section and the second tissue section are in contact with one another with the dispensed wound treatment material interposed there between.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method and apparatus for applying thermal energy to tissue asymmetrically
Systems and methods are described for treating tissue with thermal energy while minimizing the amount of thermal energy to which adjacent tissue is exposed. A surgical instrument for delivering thermal energy to a section of tissue during percutaneous surgery, includes: an elongated shaft having a proximal end and a distal end; and a split tip electrode coupled to said distal end, said split tip electrode i) including a first component and a second component coupled to said first component, and ii) defining a principle axis. The thermal energy is delivered to said section of tissue so as to heat said section of tissue asymmetrically with regard to said principle axis of said split tip electrode. The systems and methods provide advantages in that thermal energy can be directed to one side of the split tip so that a first of two juxtaposed areas of a surgical site can be heated while a second of the two juxtaposed layers is substantially not heated. In alternate embodiments a portion of the site may be actively cooled while an adjacent portion of the site may be actively cooled.
Owner:ORATEC INTERVENTIONS
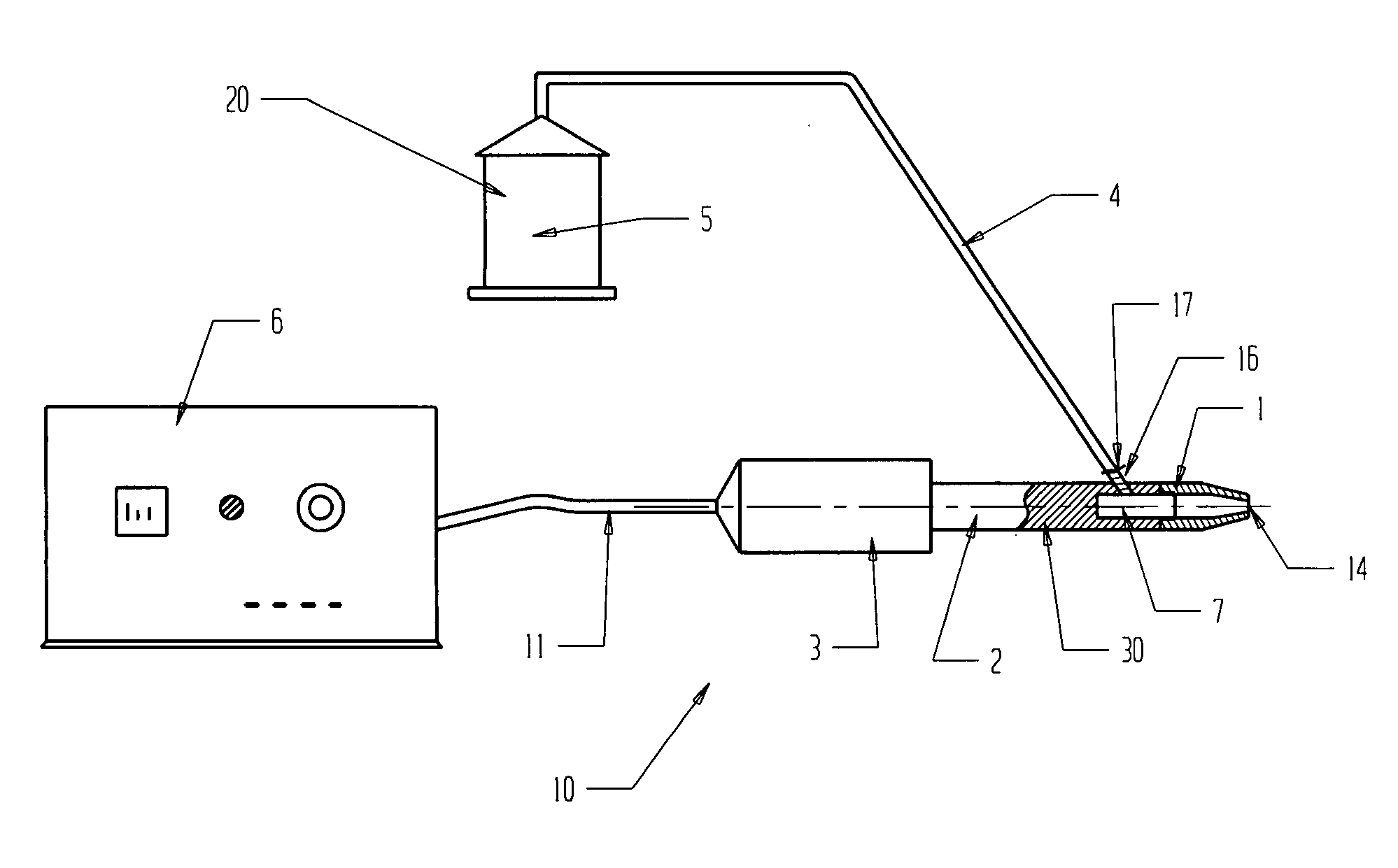
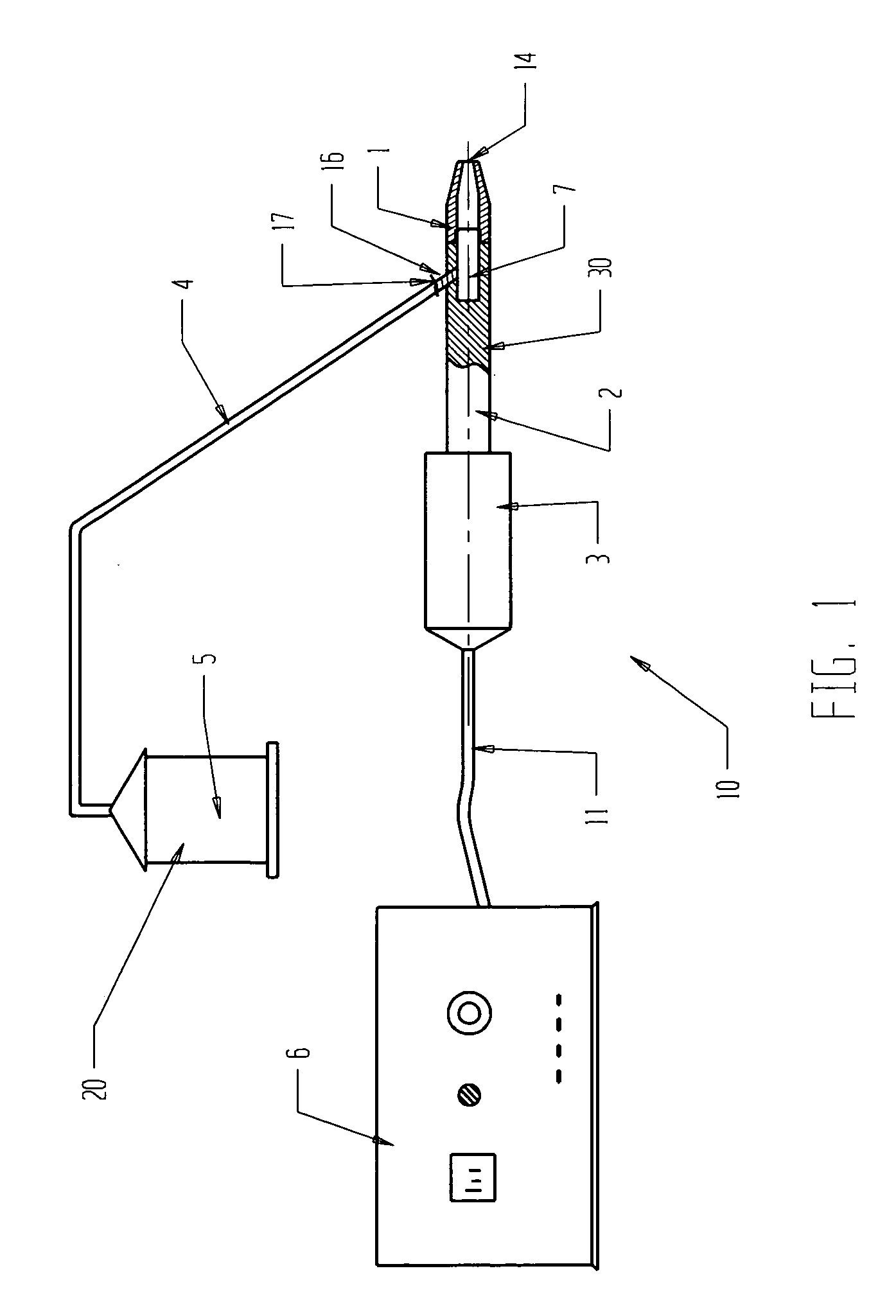
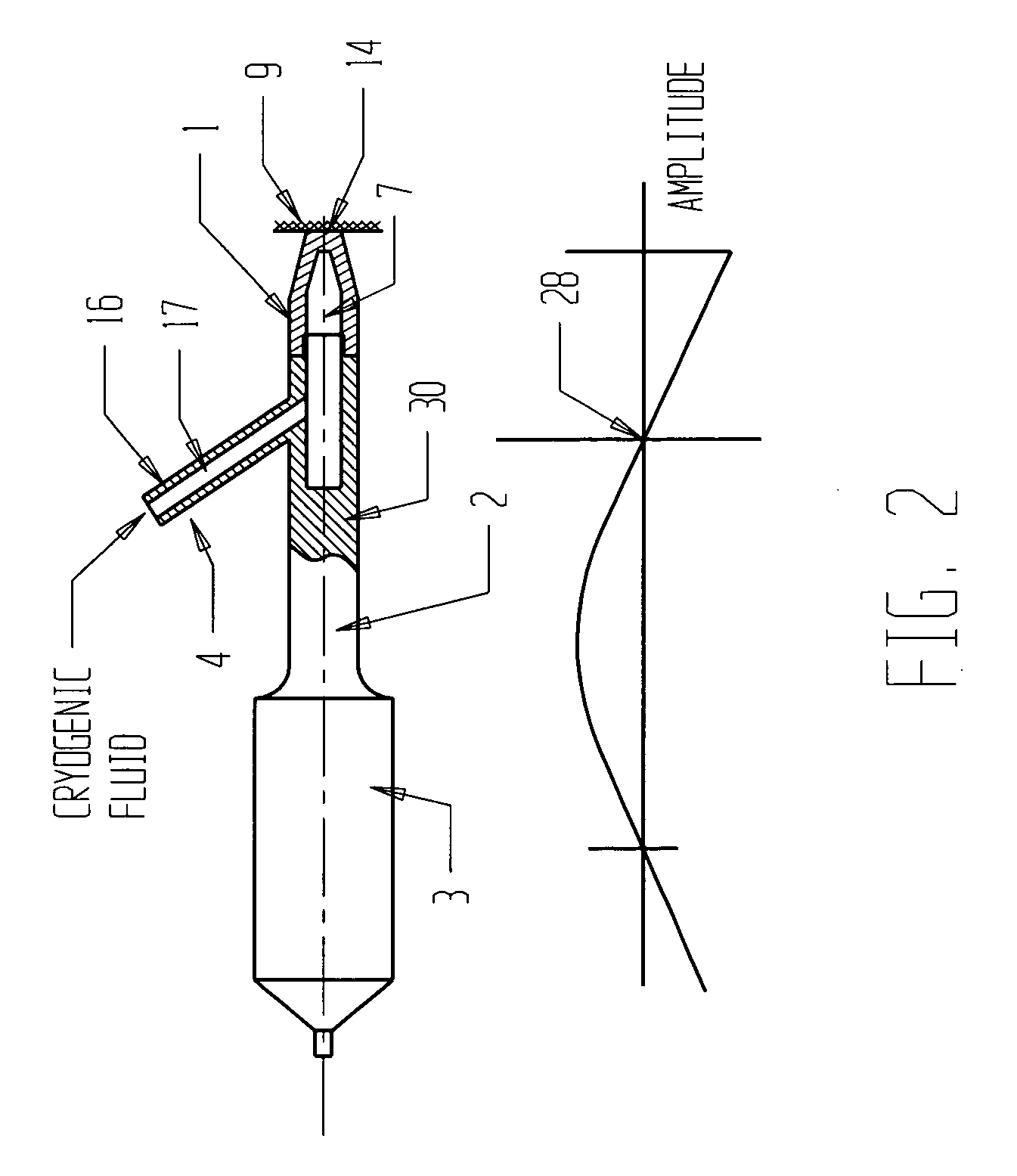
Apparatus and methods for the selective removal of tissue using combinations of ultrasonic energy and cryogenic energy
InactiveUS7572268B2Improve cooling effectAvoid stickingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasound deviceUltrasound energy
An ultrasonic apparatus and method is provided for the selective and targeted removal of unwanted tissues. The apparatus and methods may utilize combinations of ultrasonic and cryogenic energy for the selective removal tissue. The apparatus generates and delivers to the tissue cryogenic and ultrasonic energy either in combination or in sequence, provides resize ablation of unwanted tissue parts, and may be used on various body tissues including internal organs.
Owner:BACOUSTICS LLC
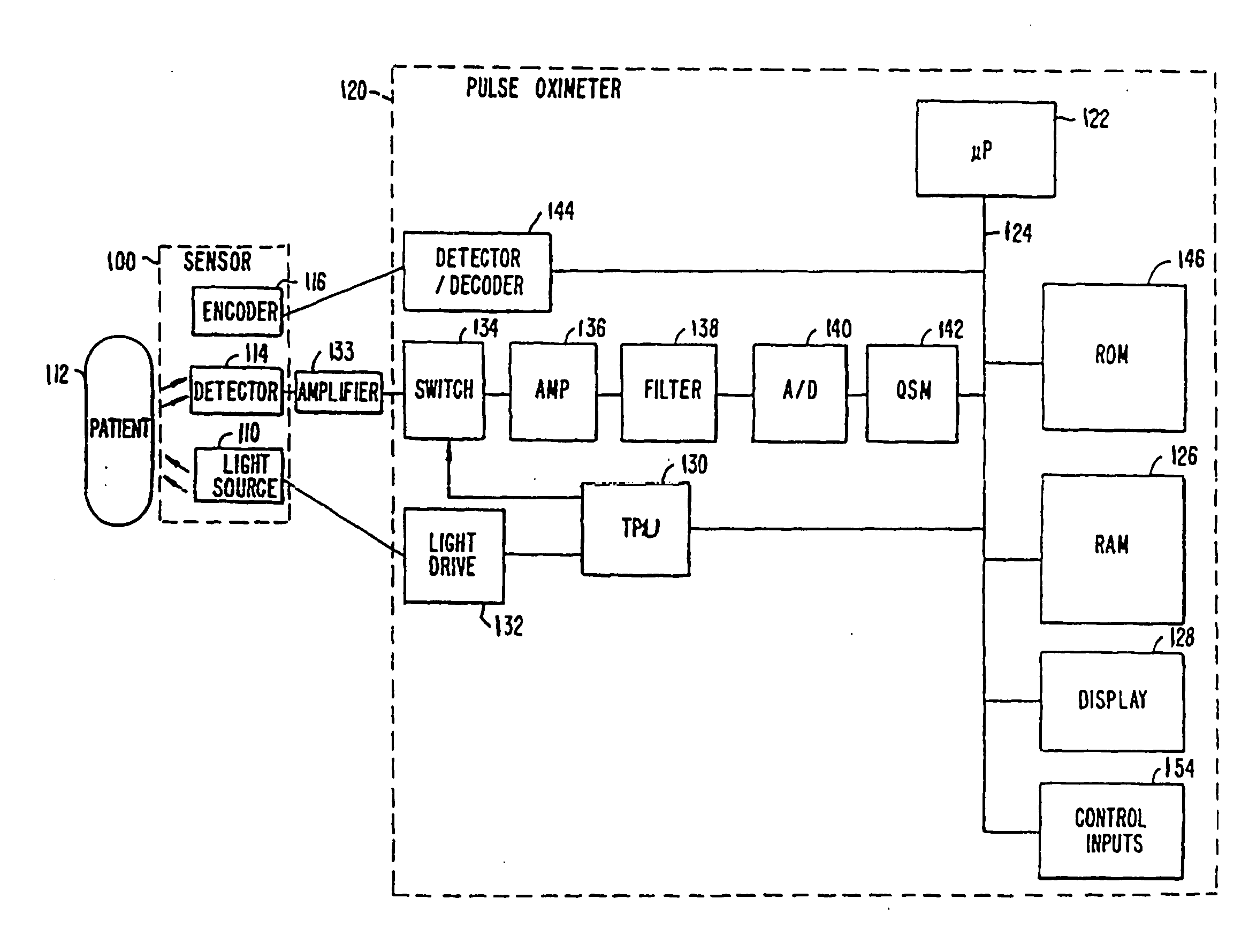
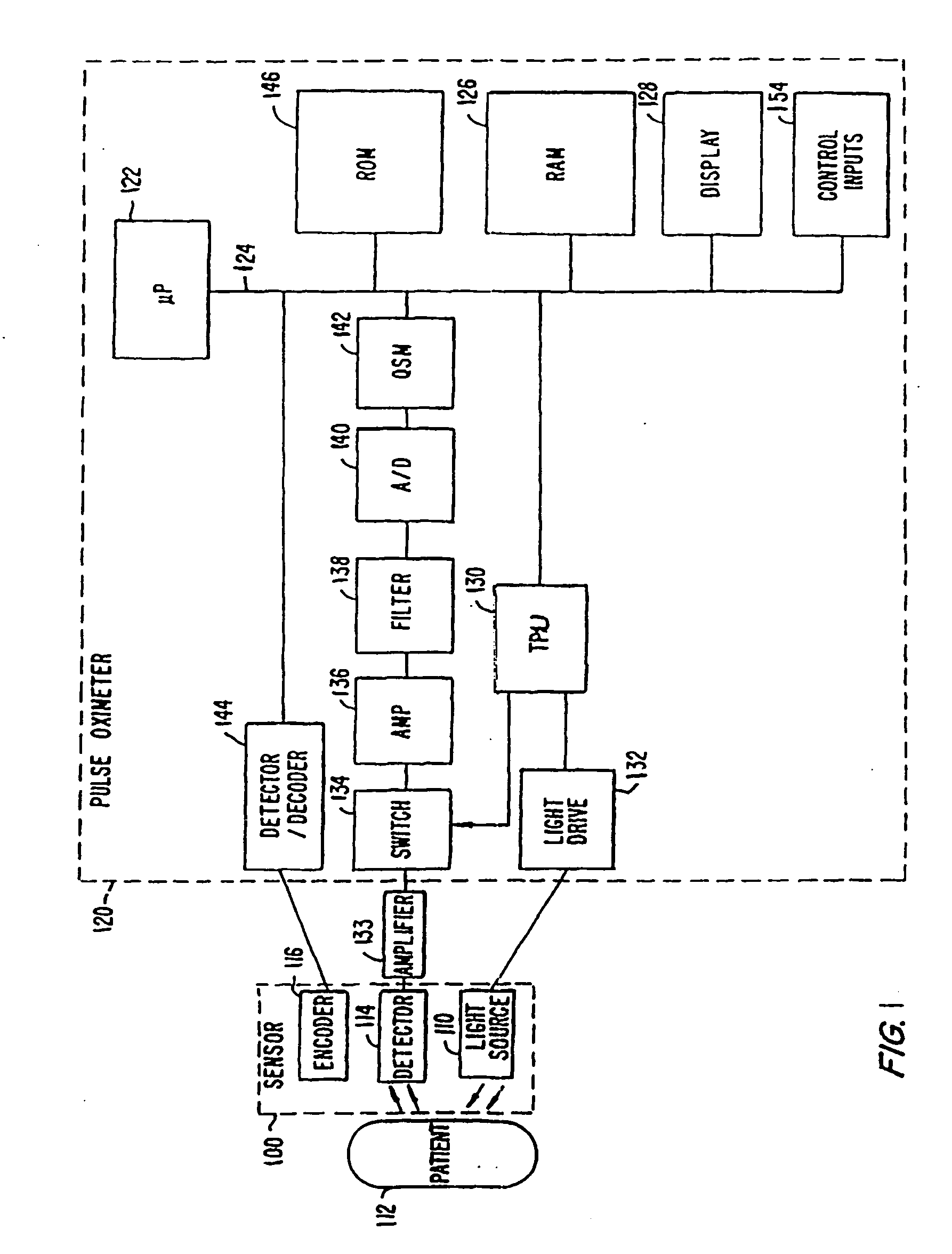
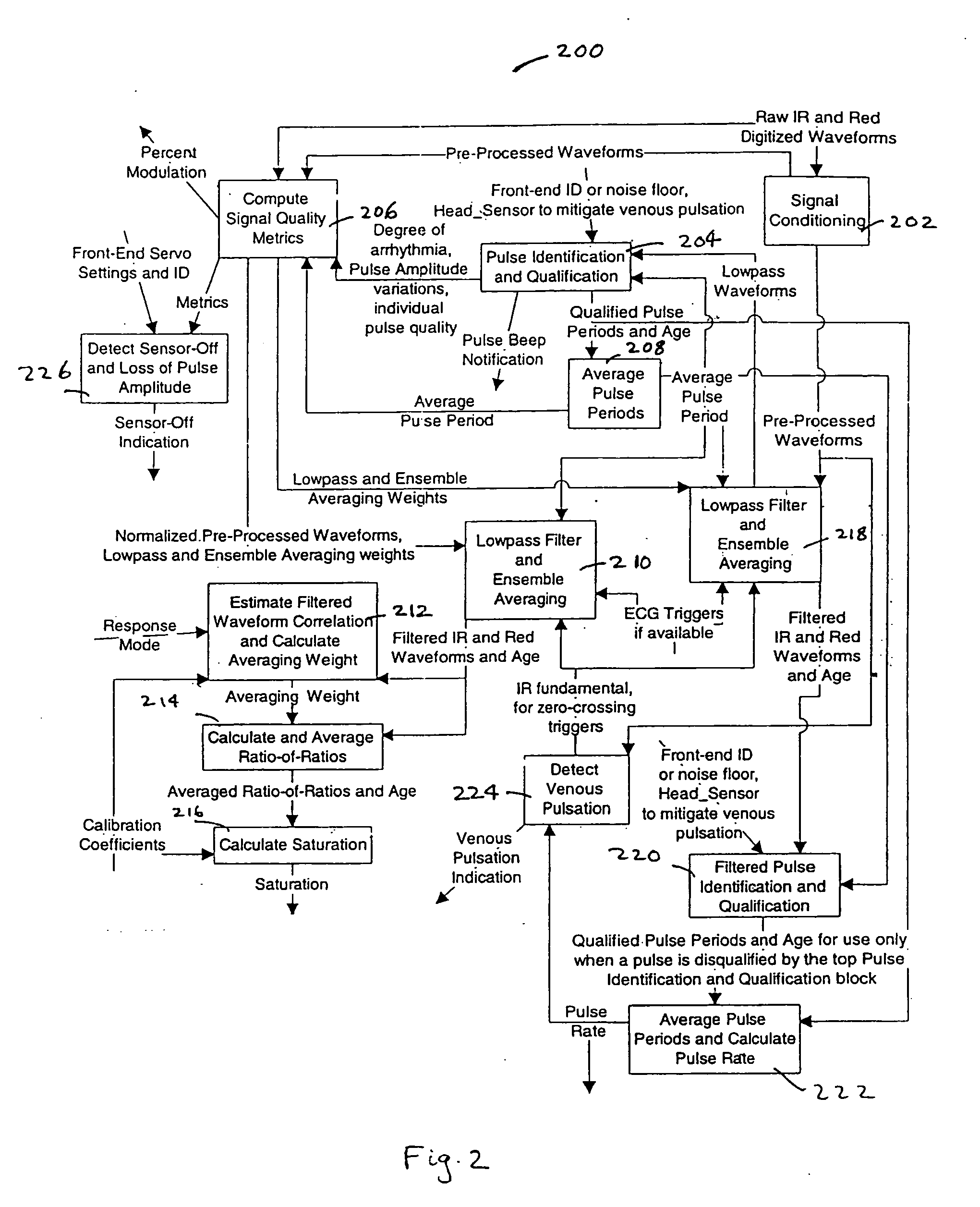
Pulse oximetry motion artifact rejection using near infrared absorption by water
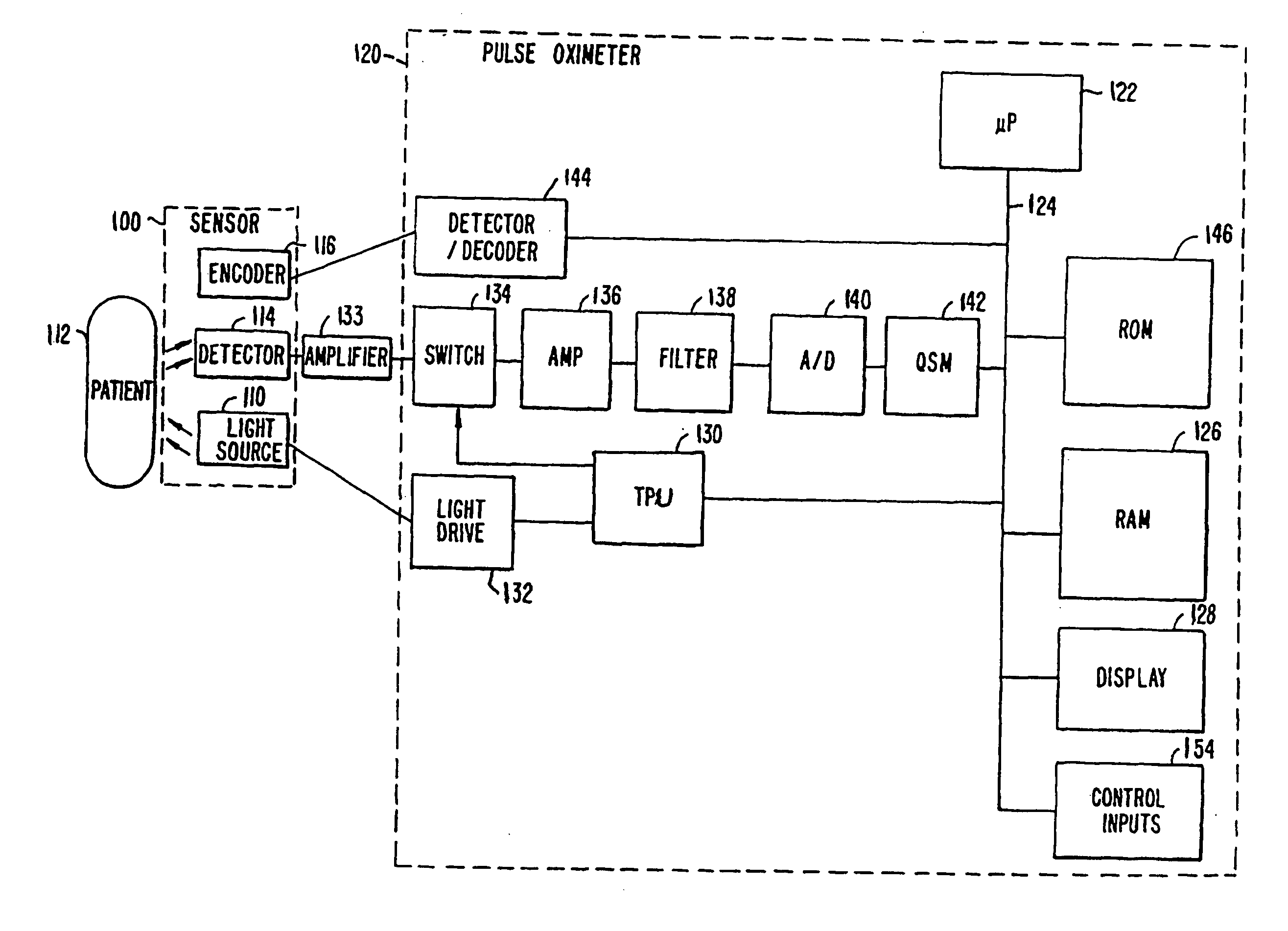
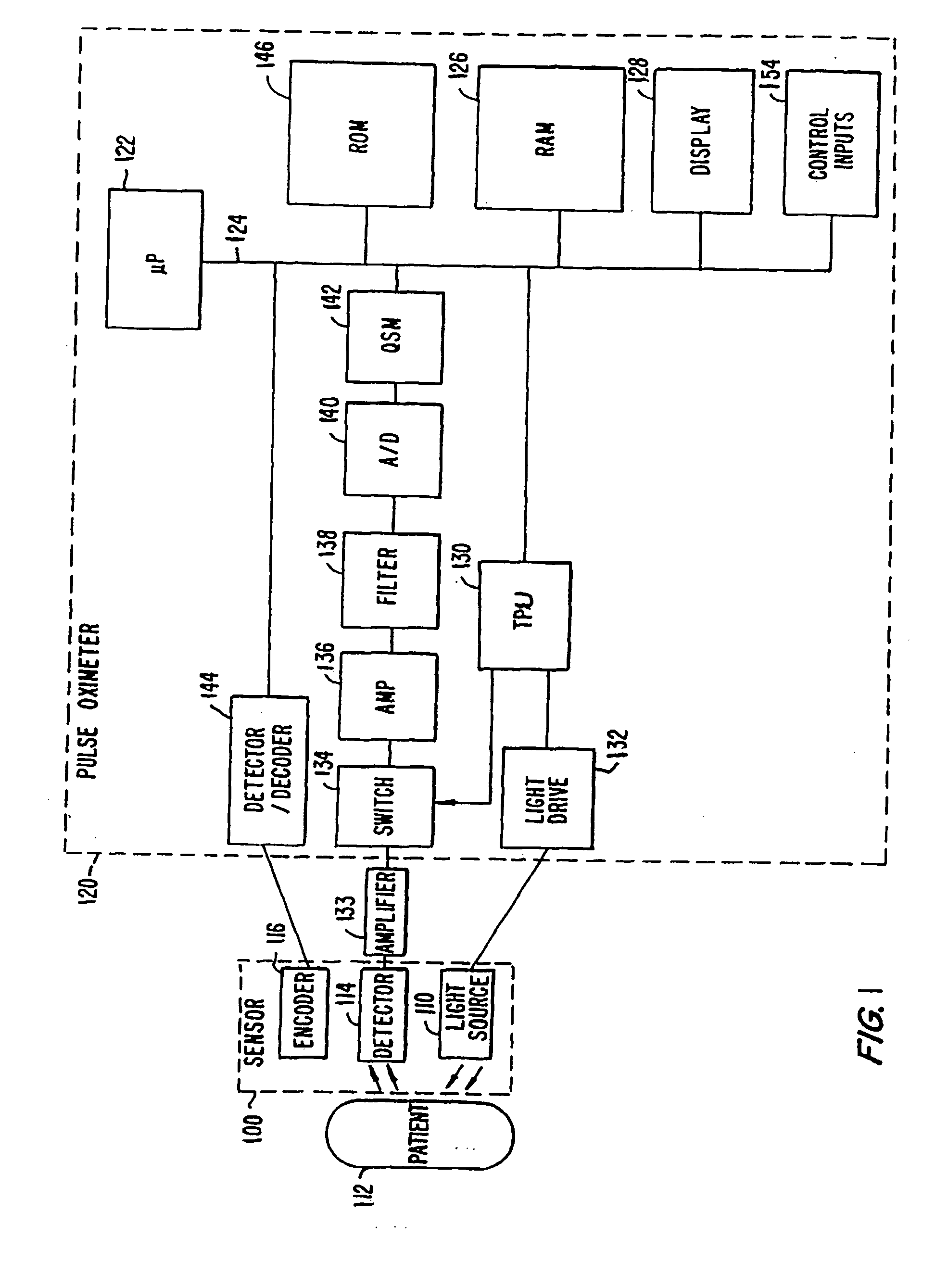
ActiveUS20050203357A1Signals is relatively smallSeparating signalCatheterSensorsNear infrared absorptionPulse oximetry
A method and an apparatus for measuring a physiological parameter, functioning based on obtaining a first signal derived from electromagnetic energy transmitted through a tissue portion at a first wavelength, the first signal including a signal portion corresponding with motion-related events and a signal portion corresponding with arterial pulsation events, where at the first wavelength water is a dominant absorber of electromagnetic energy in the tissue portion; obtaining a second signal derived from electromagnetic energy transmitted through a tissue portion at a second wavelength, the second signal including a signal portion corresponding with motion-related events and a signal portion corresponding with arterial pulsation events, where at the second wavelength hemoglobin is a dominant absorber of electromagnetic energy in the tissue portion; and combining the first signal and the second signal to generate a combined plethysmograph signal, such that the combined signal has a signal portion corresponding with motion-related events that is smaller than that present in the first signal or the second signal.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
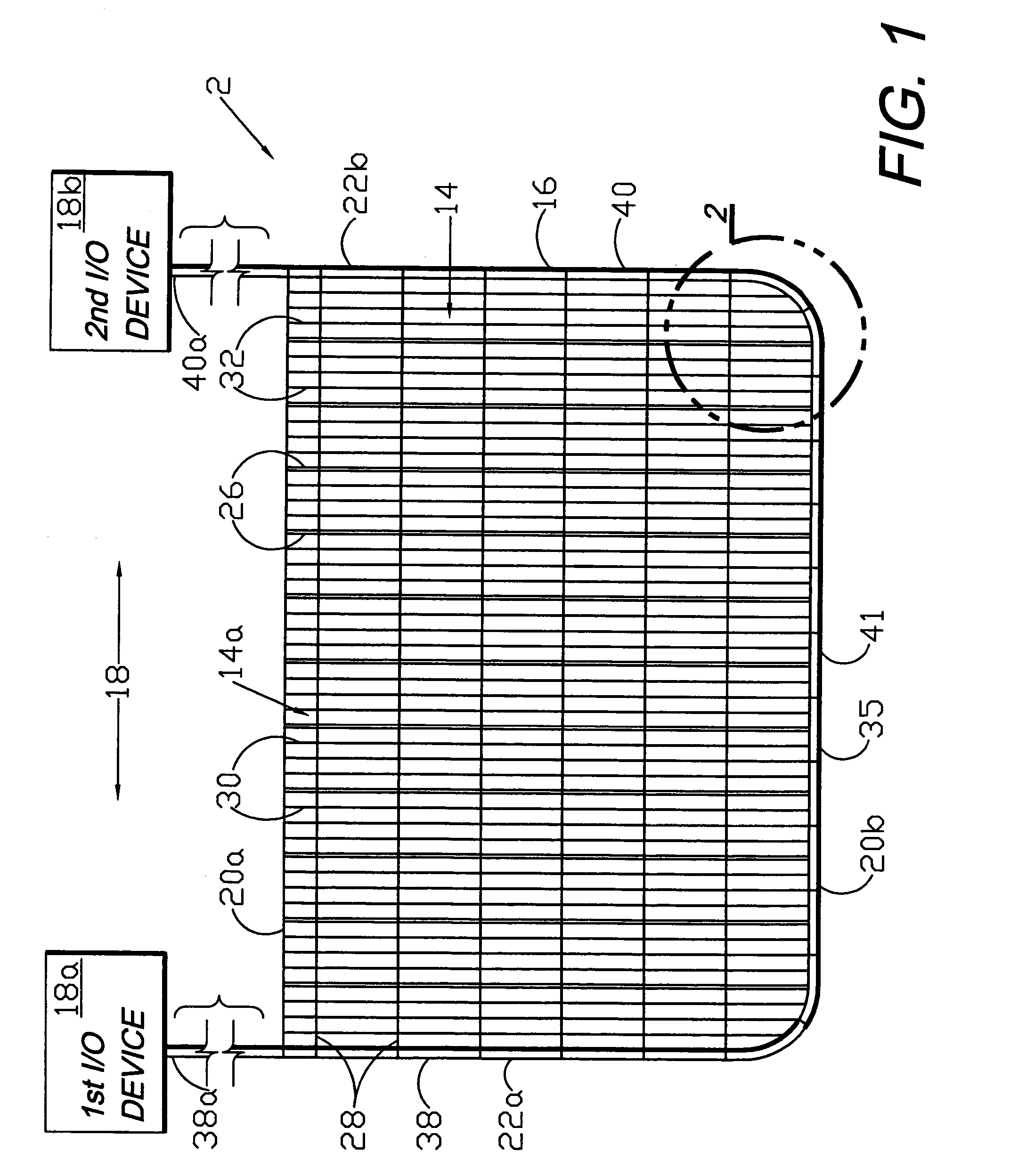
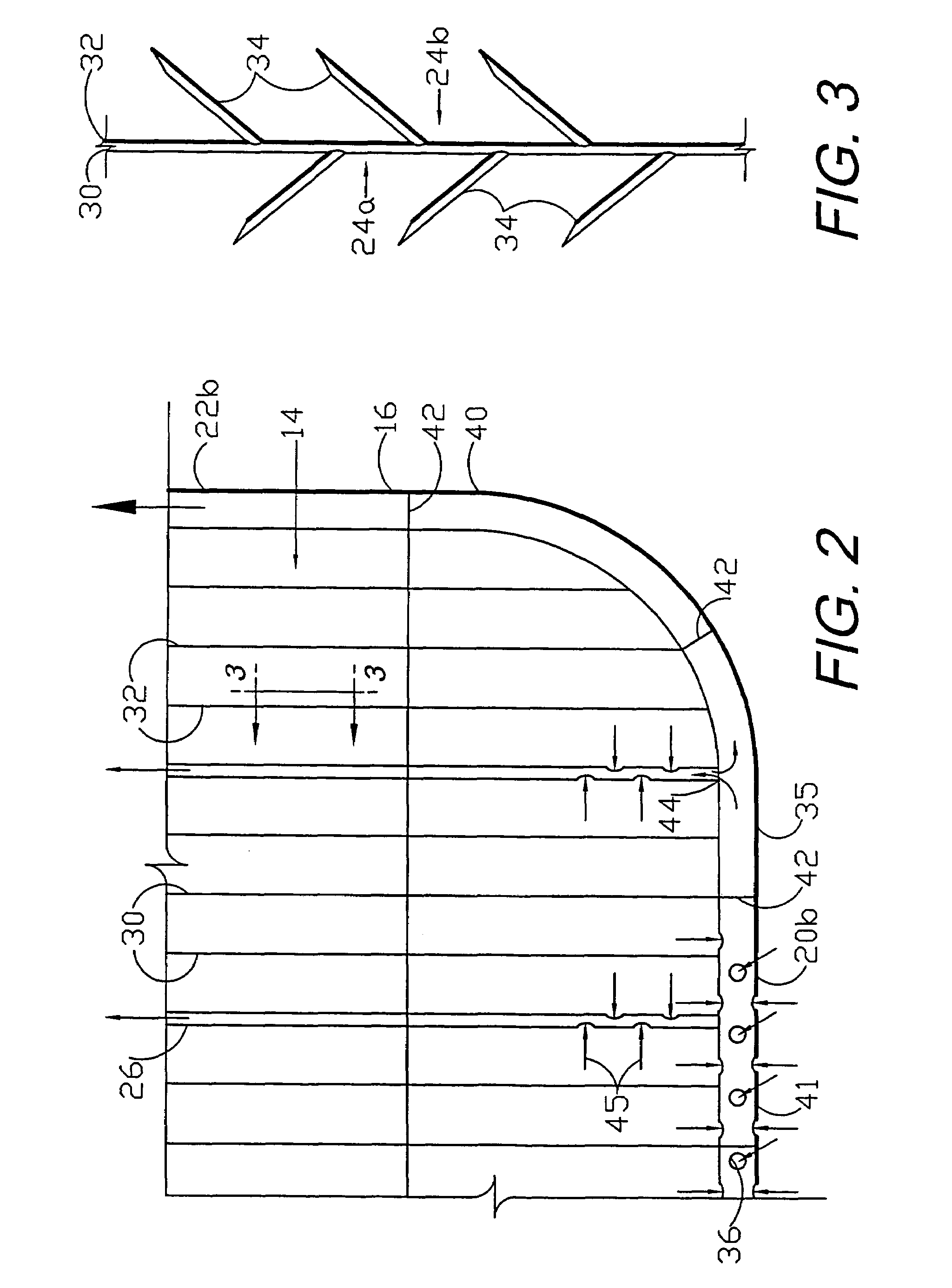
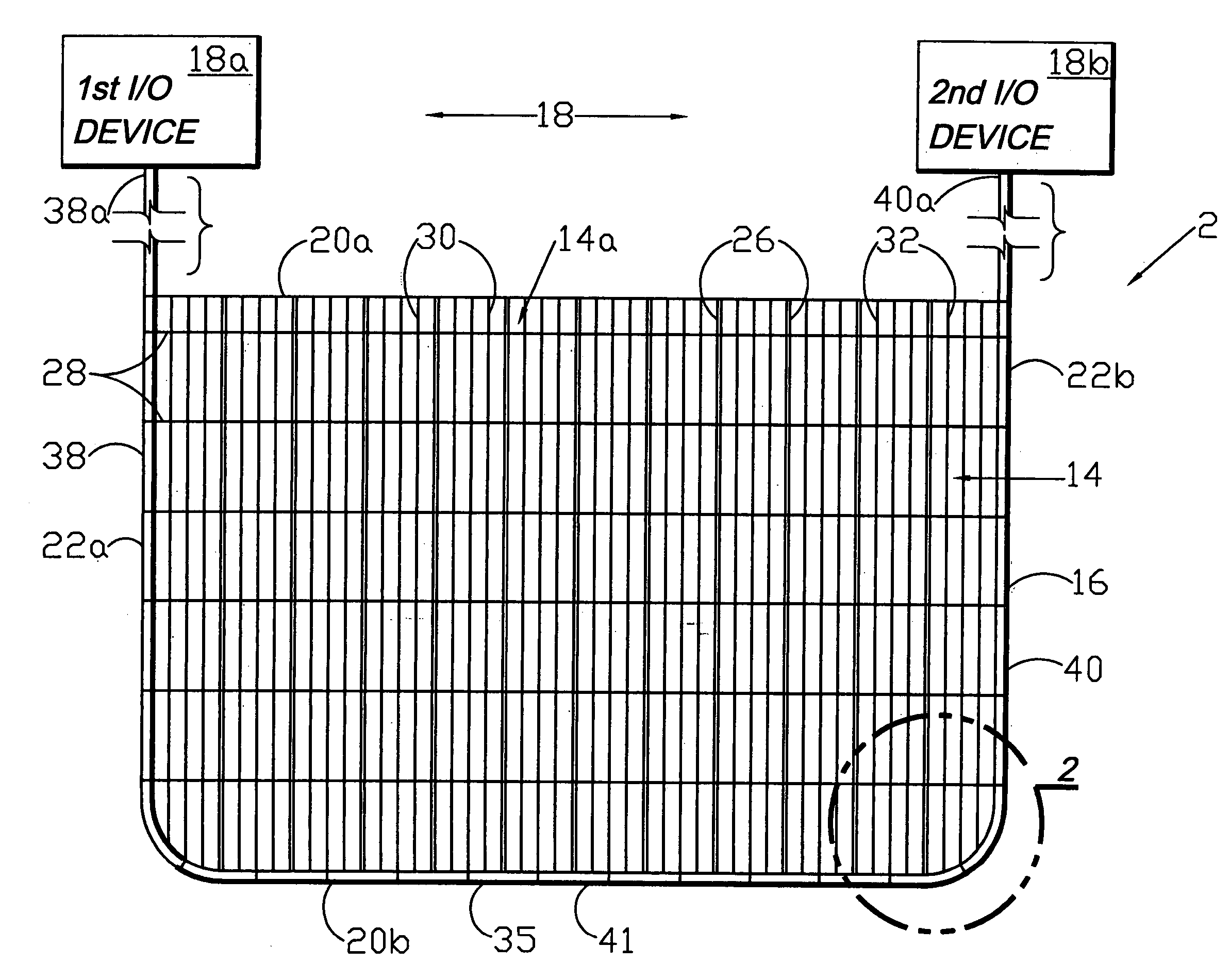
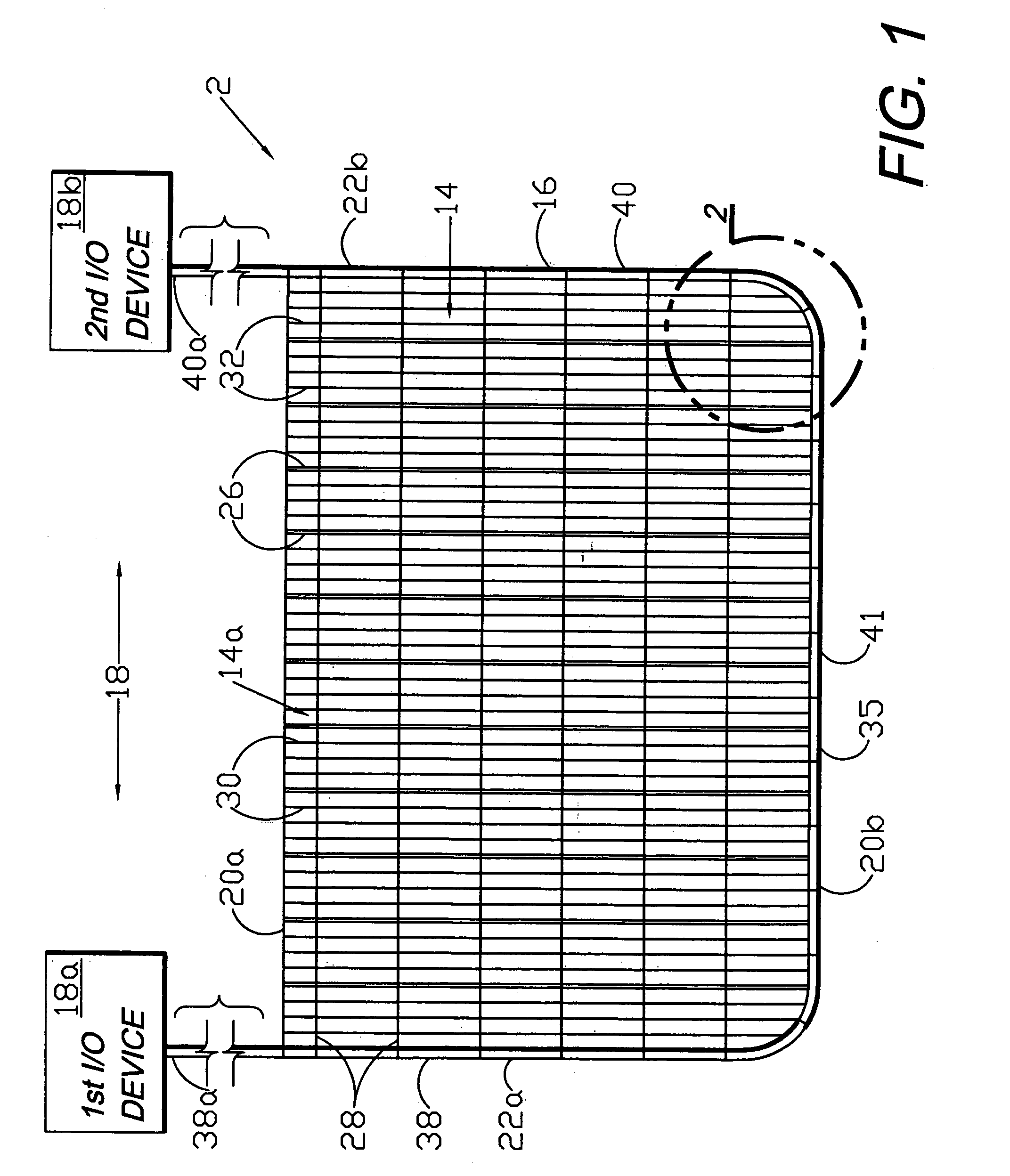
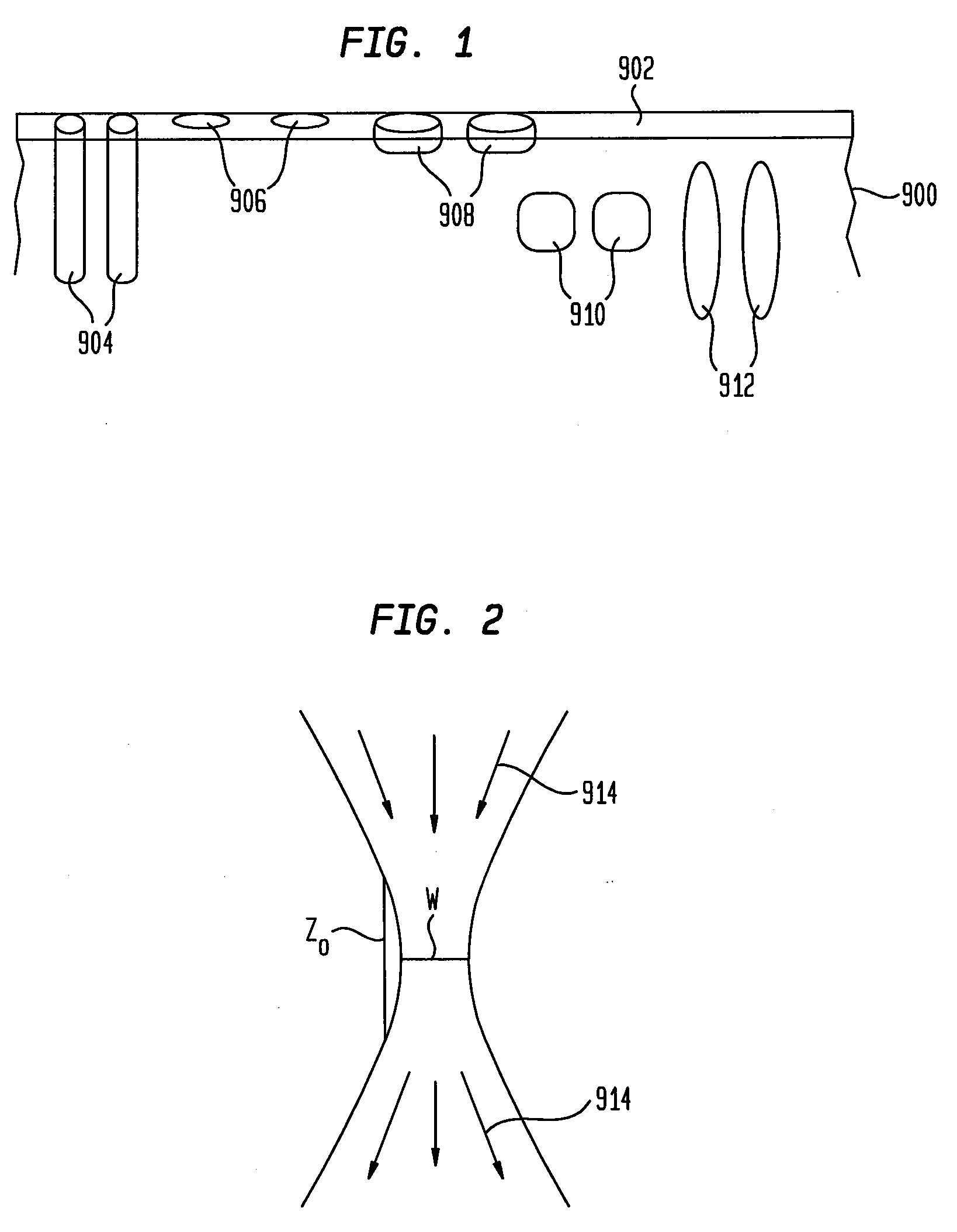
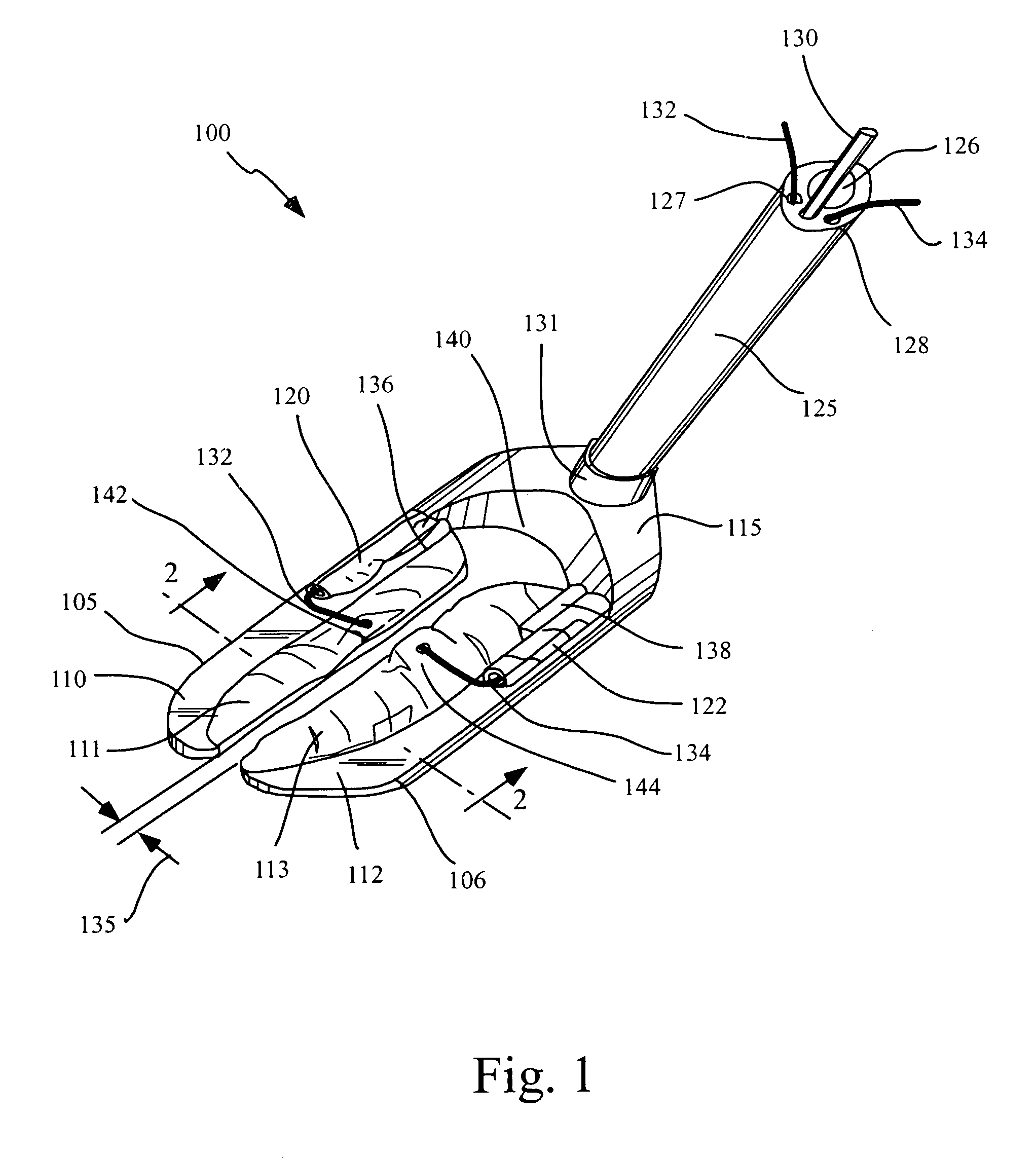
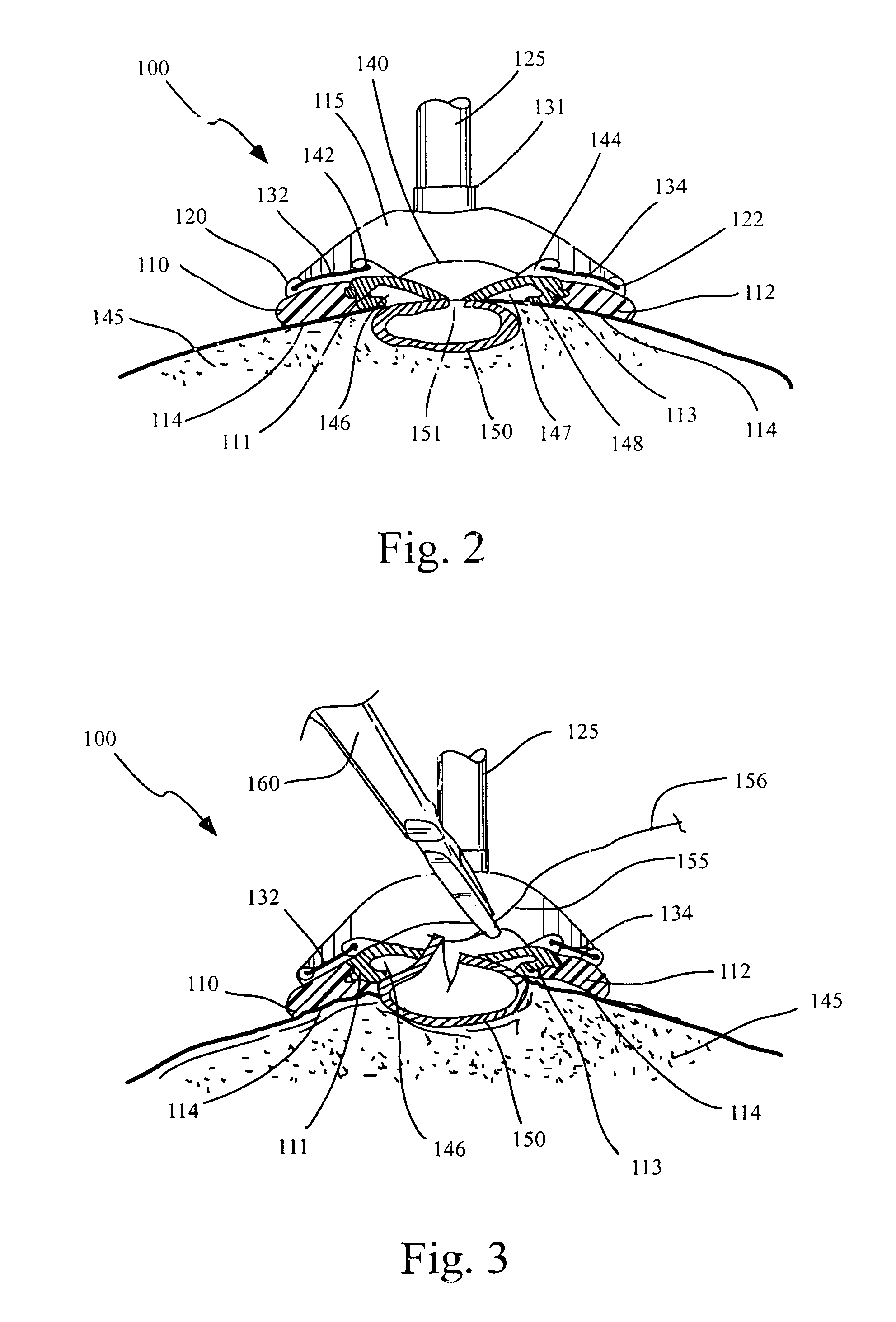
Circumferential medical closure device and method
A flexible medical closure screen device for a separation of first and second tissue portions is provided, which includes a mesh screen comprising tubular vertical risers, vertical strands with barbed filaments, and horizontal spacers connecting the risers and strands in a grid-like configuration. An optional perimeter member partly surrounds the screen and can comprise a perimeter tube fluidically coupled with the vertical risers to form a tubing assembly. Various input / output devices can optionally be connected to the perimeter tube ends for irrigating and / or draining the separation according to methodologies of the present invention. Separation closure, irrigation and drainage methodologies are disclosed utilizing various combinations of closure screens, tubing, sutures, fluid transfer elements and gradient force sources. The use of mechanical forces associated with barbed strands for repositionably securing separated tissues together is disclosed. The use of same for eliminating or reducing the formation of subcutaneous voids or pockets, which can potentially form hematoma and seroma effects, is also disclosed. Alternative embodiments of the invention have circumferential configurations for approximating and closing separated tissue portions such as tendons, nerves and blood vessels. Tissue closure methods include the steps of circumferentially applying a screen to separated tissue portions and penetrating the tissue portions with prongs.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Circumferential medical closure device and method
A flexible medical closure screen device for a separation of first and second tissue portions is provided, which includes a mesh screen comprising tubular vertical risers, vertical strands with barbed filaments, and horizontal spacers connecting the risers and strands in a grid-like configuration. An optional perimeter member partly surrounds the screen and can comprise a perimeter tube fluidically coupled with the vertical risers to form a tubing assembly. Various input / output devices can optionally be connected to the perimeter tube ends for irrigating and / or draining the separation according to methodologies of the present invention. Separation closure, irrigation and drainage methodologies are disclosed utilizing various combinations of closure screens, tubing, sutures, fluid transfer elements and gradient force sources. The use of mechanical forces associated with barbed strands for repositionably securing separated tissues together is disclosed. The use of same for eliminating or reducing the formation of subcutaneous voids or pockets, which can potentially form hematoma and seroma effects, is also disclosed. Alternative embodiments of the invention have circumferential configurations for approximating and closing separated tissue portions such as tendons, nerves and blood vessels. Tissue closure methods include the steps of circumferentially applying a screen to separated tissue portions and penetrating the tissue portions with prongs.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Light generating device to intravascular use
InactiveUS7252677B2High light transmittanceFacilitated DiffusionElectrotherapySurgical instrument detailsPhotodynamic therapyMedicine
Light generating devices for illuminating portions of vascular tissue, to render photodynamic therapy. In one embodiment, a light source array preferably including a plurality of light emitting diodes, a focusing lens, and a light diffusing element are included in a distal end of a catheter. A balloon is optionally provided to interrupt blood flow that can block the transmission of light, and to center the apparatus in a blood vessel. Optical fibers optionally direct light from the light source to the diffusing element. The light source array can have a radial or linear configuration and can produce more than one wavelength of light for activating different photoreactive agents. Linear light source elements are particularly useful to treat elongate portions of tissue in a vessel. One embodiment intended for use with a conventional balloon catheter integrates light sources into a guidewire.
Owner:LIGHT SCI ONCOLOGY
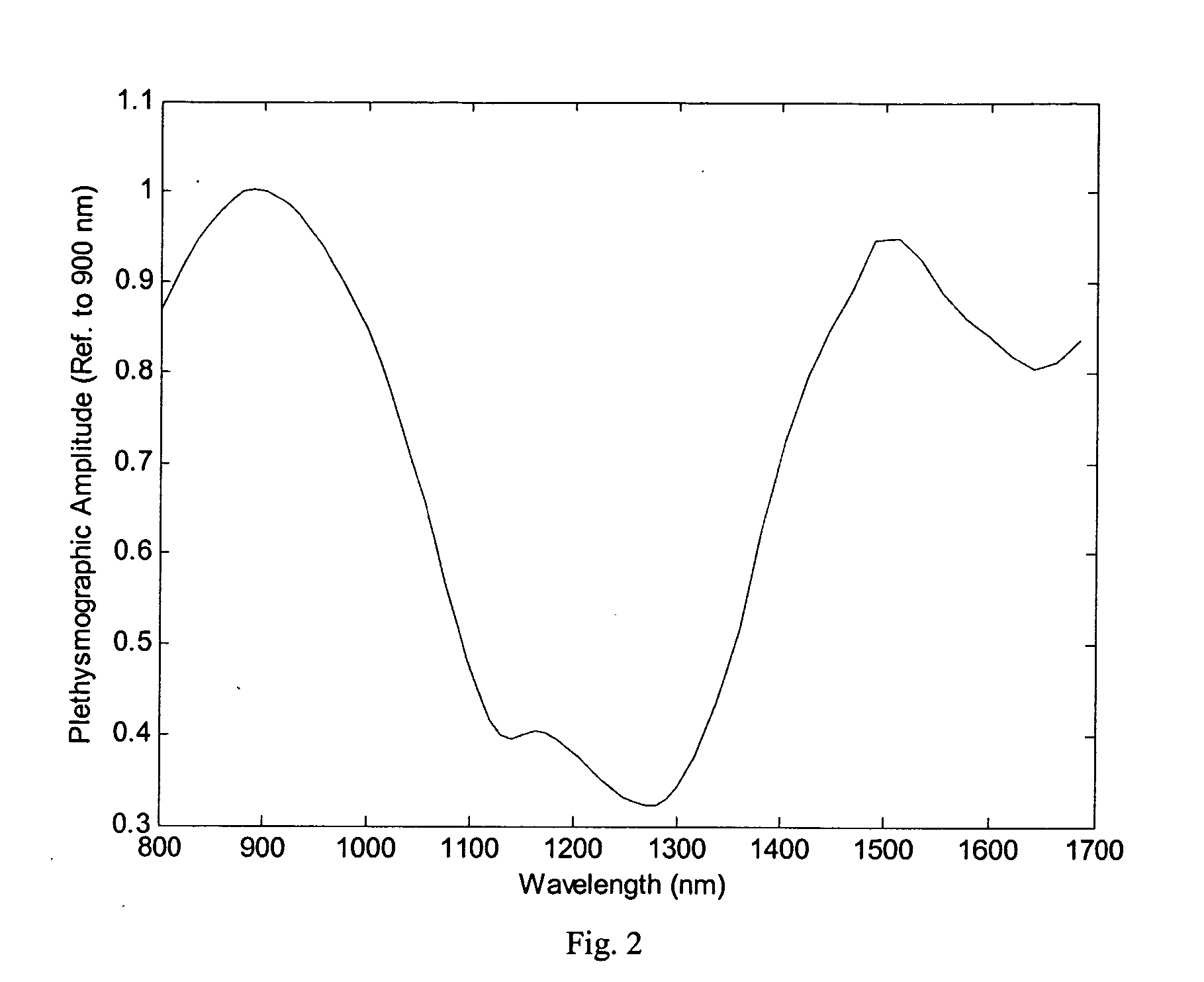
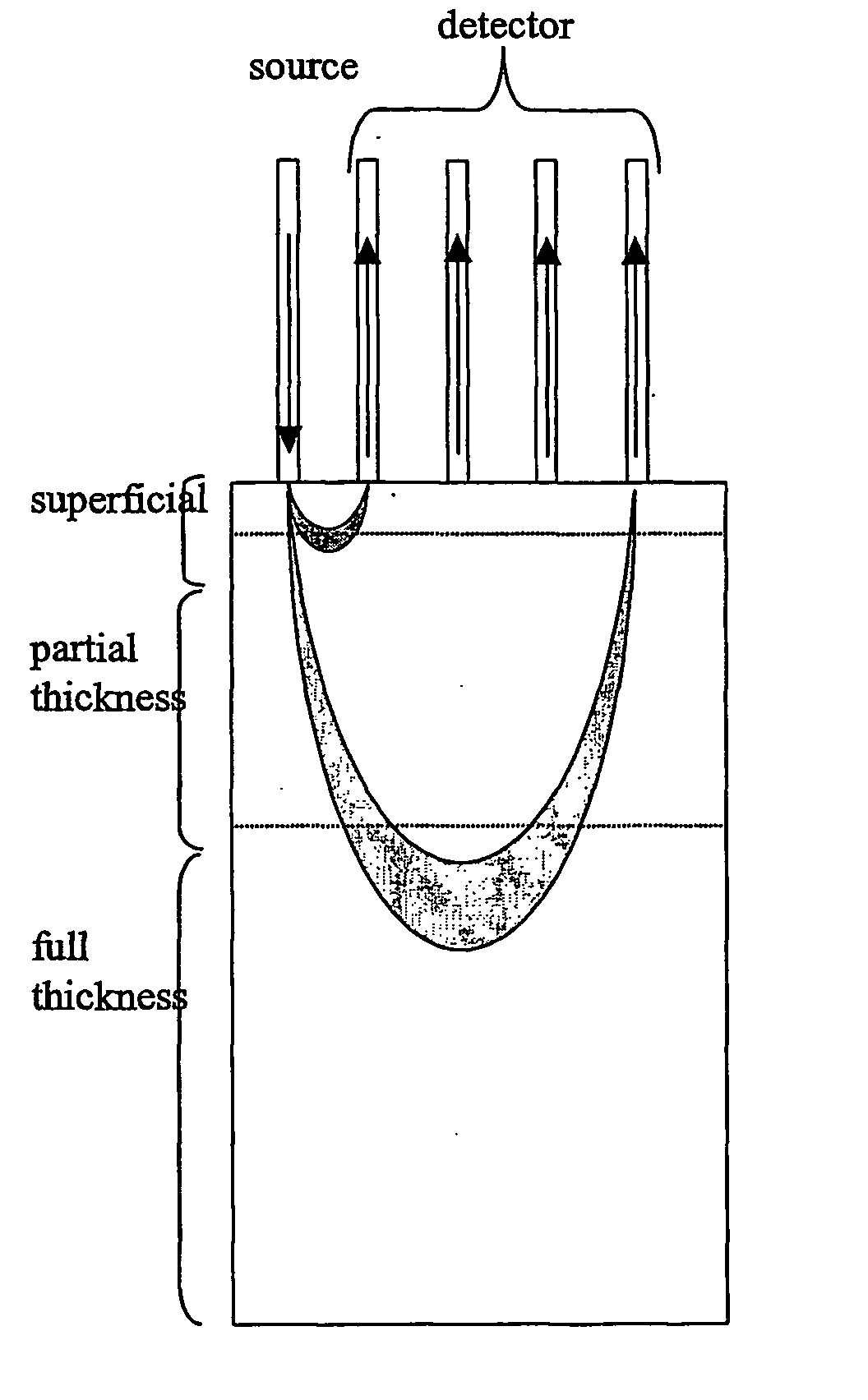
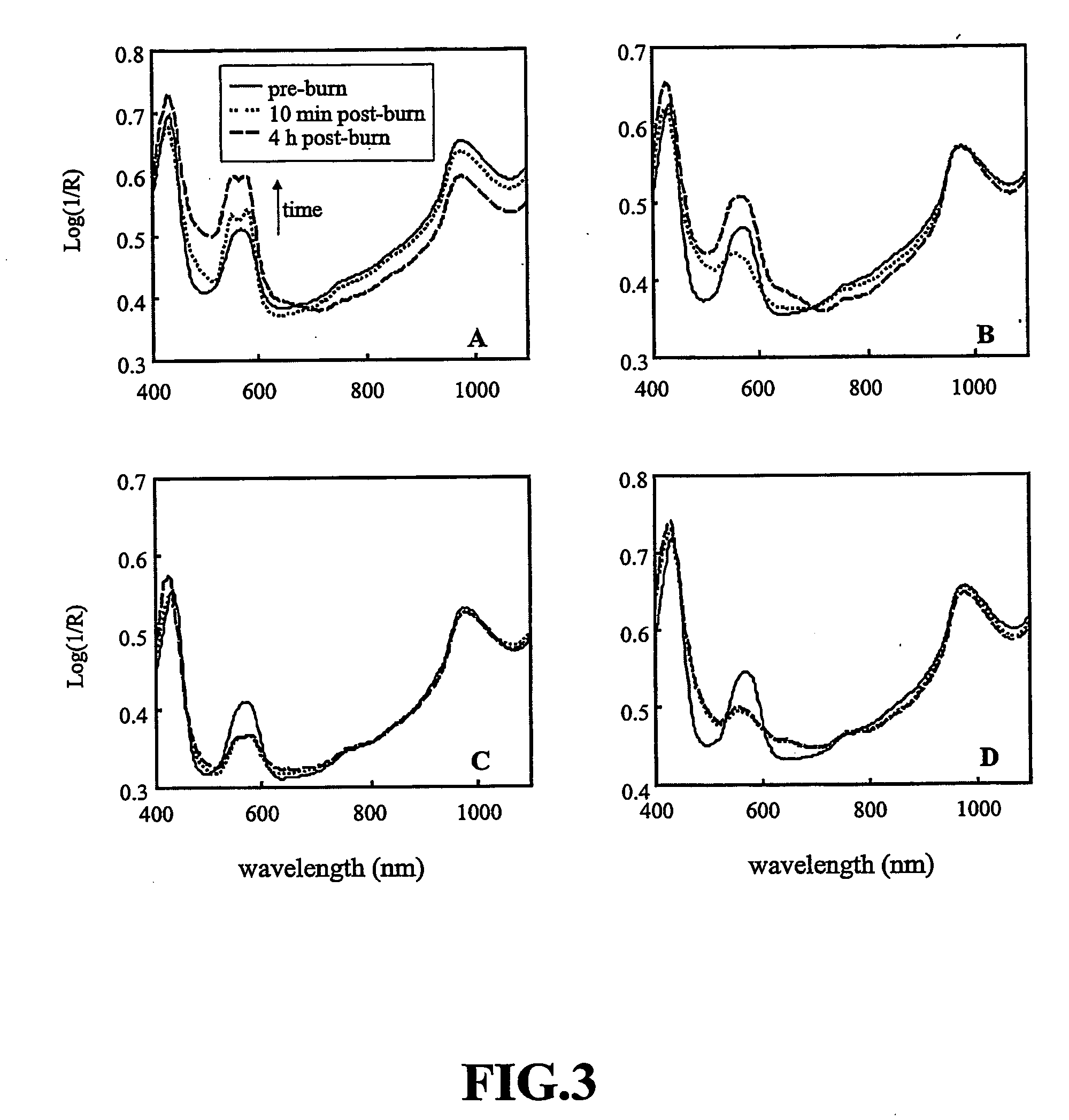
Visible-near infrared spectroscopy in burn injury assessment
ActiveUS20060155193A1Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyBurning tissueFull thickness burn
A non-invasive method of characterizing burn injuries using near infrared spectroscopy is described. In the method, a beam of light is emitted into the burnt tissue portion at two or more different tissue depths. The spectra are then compared using multivariate analysis to determine diagnostic regions of the spectra. This information is used to categorize the burn. In some cases, the diagnostic regions correspond to wavelengths related to the hemodynamics of the tissue portion. The spectra can also be repeated over time, thereby allowing trends and changes in the spectra to be measured. This data is in turn used to categorize the burn as either a superficial burn, partial thickness burn, deep partial burn or a full thickness burn. Once the burn has been categorized, the clinician can intervene as needed to treat the burn.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Methods And Devices For Fractional Ablation Of Tissue For Substance Delivery
InactiveUS20090069741A1Broaden applicationSignificant tissue damageUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyExAblatePharmaceutical drug
Methods and devices for ablating portions of a tissue volume with electromagnetic radiation (EMR) to produce lattices of EMR-treated ablation islets in the tissue are disclosed, including lattices of micro-holes, micro-grooves, and other structures. Also, methods and devices for using the ablated islets are disclosed, including to deliver chromophores, filler, drugs and other substances to the tissue volume.
Owner:PALOMAR MEDICAL TECH
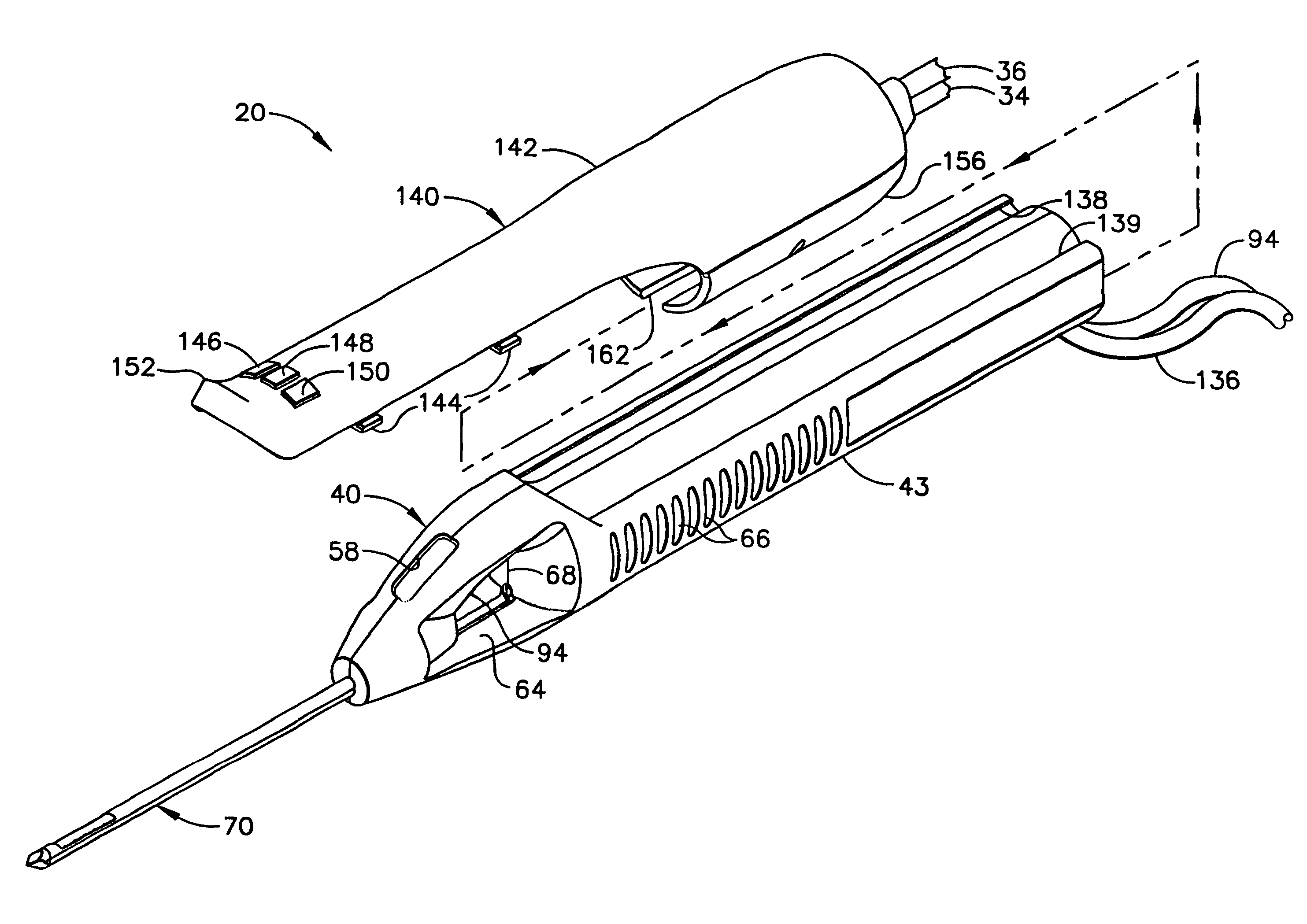
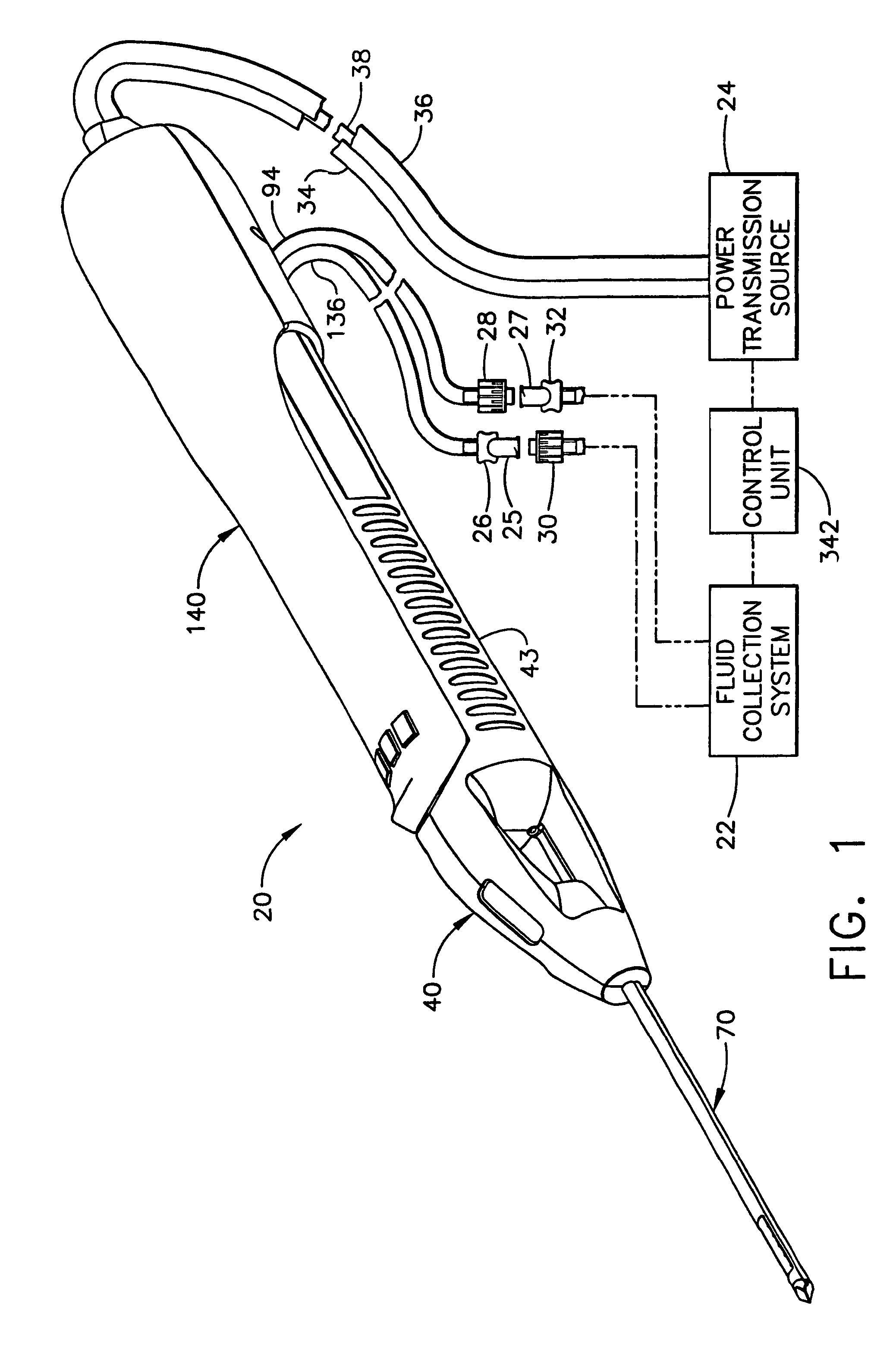
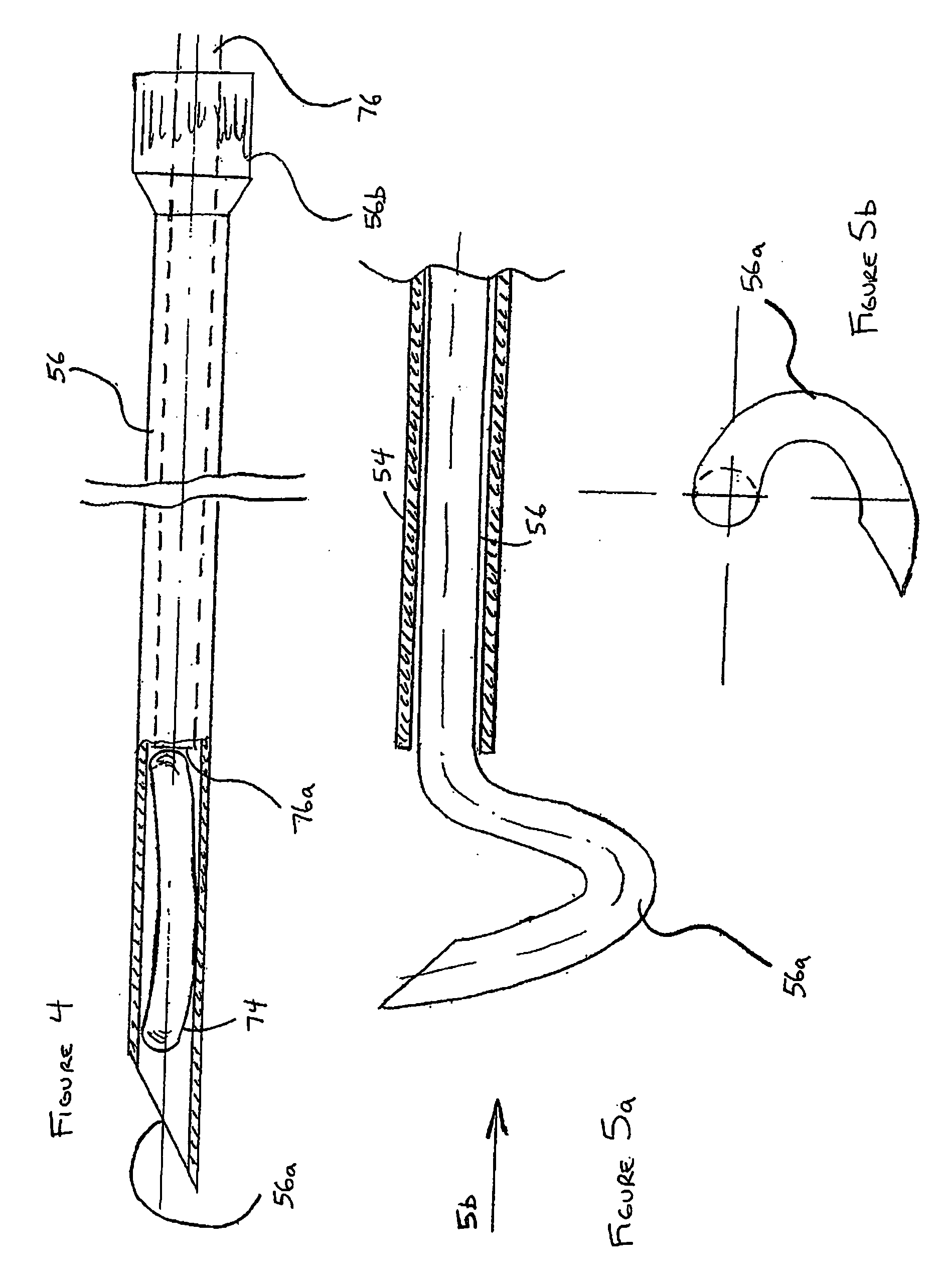
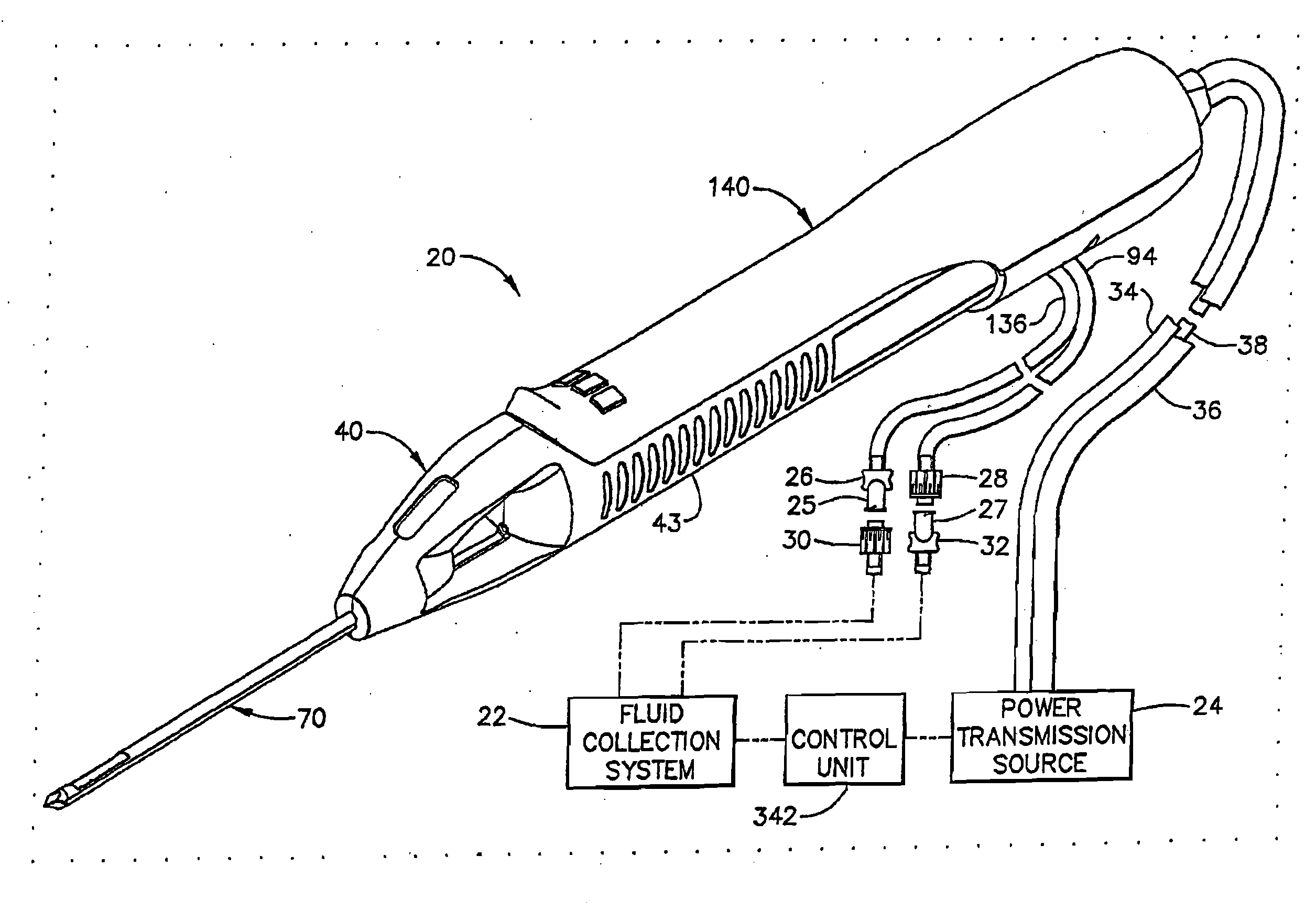
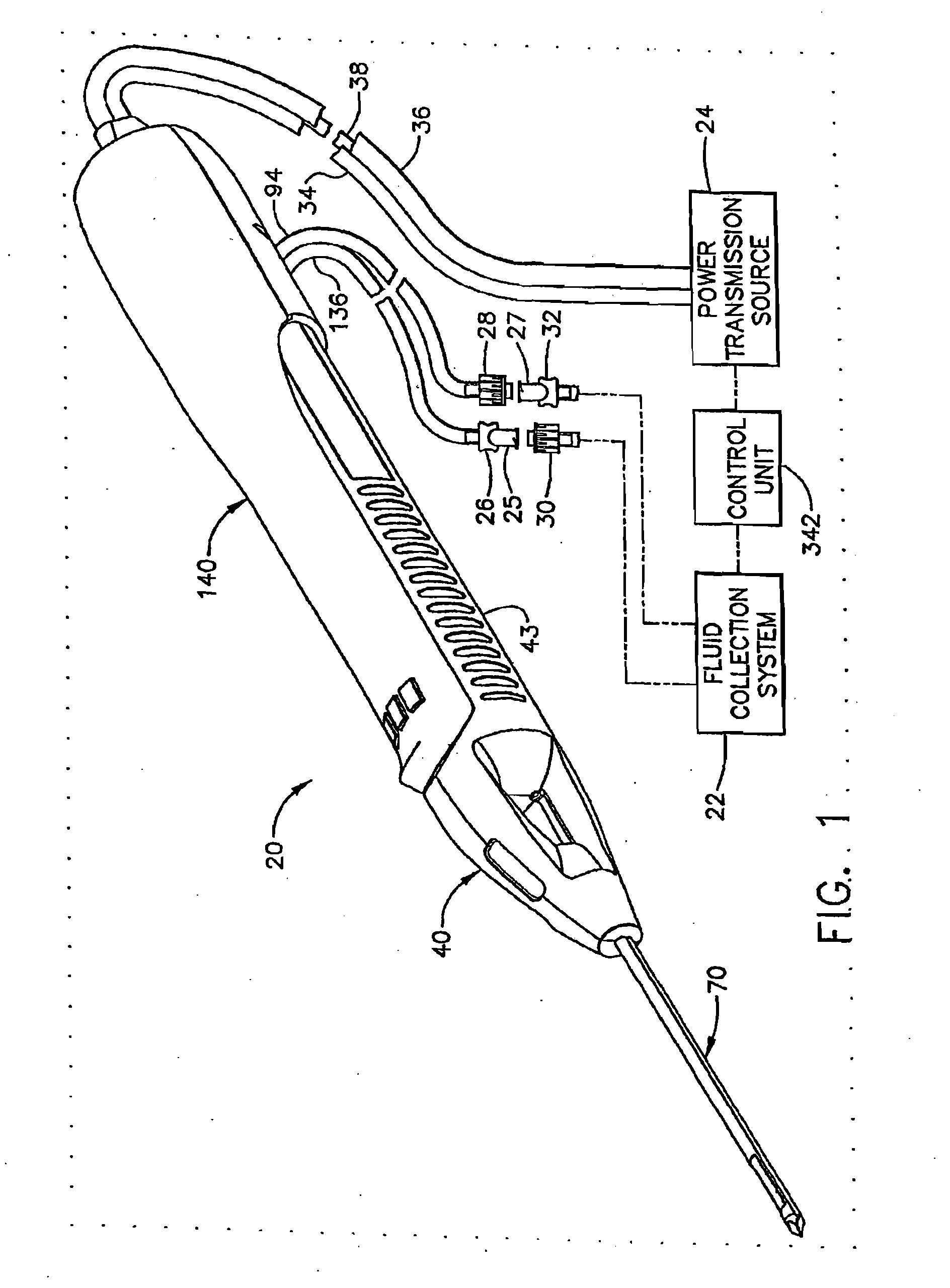
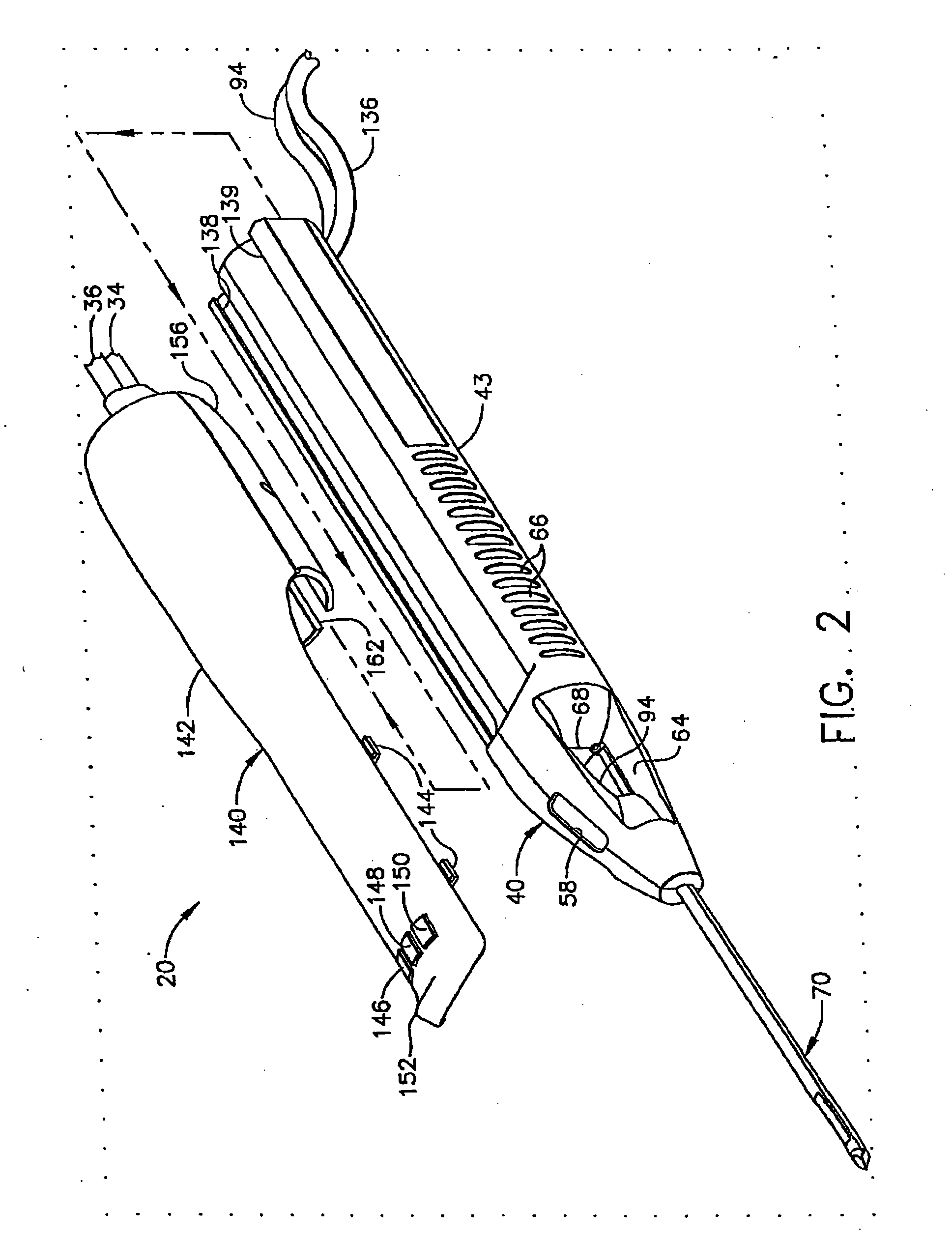
Surgical device for the collection of soft tissue
A handheld biopsy device is provided for the collection of soft tissue samples from a surgical patient. In a preferred embodiment, the biopsy device comprises a handpiece, a fluid collection system, and a power transmission source. The handpiece is configured for grasping by a single hand, and being independently manipulatable by hand for movement of the instrument toward and away from the patient. An elongated piercer extends from the distal end of the handpiece. The piercer has a sharpened distal end for entering the tissue and a port located proximal to the sharpened distal end for receiving a portion of tissue mass. An elongated cutter is disposed coaxially relative to a piercer lumen of the piercer. A distal blade of the cutter slides distally past the port of the piercer to severe the tissue portion drawn into the port by vacuum. The cutter is retracted to a most proximal position for removal of the tissue portion from a cutter lumen of the cutter. The handpiece further comprises a holster for detachably connecting a cutter rotational transmission and a cutter axial transmission to the power transmission source.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Bonding of soft biological tissues by passing high frequency electric current therethrough
InactiveUS7025764B2Avoid stickingAvoid burnsDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingForcepsEngineering
Technique for bonding soft biological tissue having an incision therein with forceps adapted to grip a portion of tissue on both sides of incision. Electrodes are secured to forceps for contracting the tissue portion. An electrical power source provides a high frequency electrical signal to electrodes to be passed through the tissue portion. The electrical power source is controlled to provide electrodes with one voltage signal during a first of two stages, wherein the voltage rises linearly, and another voltage signal during a second of the two stages, wherein the voltage is stabilized and modulated with a low frequency rectangular signal. A clamping means applies force with the forceps to compress the tissue at one or different levels during two time periods while the high frequency voltage is passed through the electrodes. The tissue impedance is measured as a function of time, with its minimal value being determined and stored.
Owner:BIOFUSE MEDICAL TECH +1
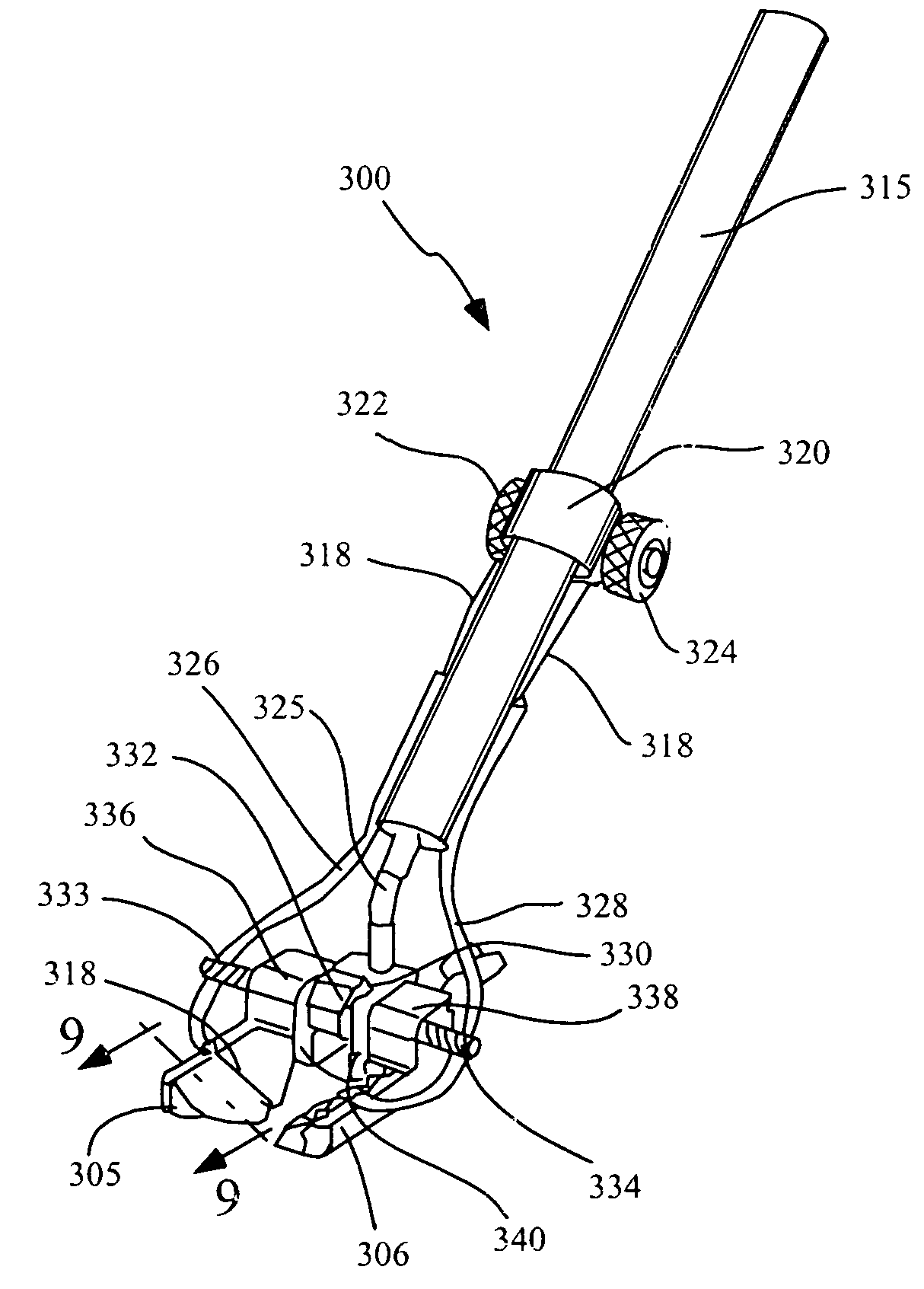
Implantation of repair chords in the heart
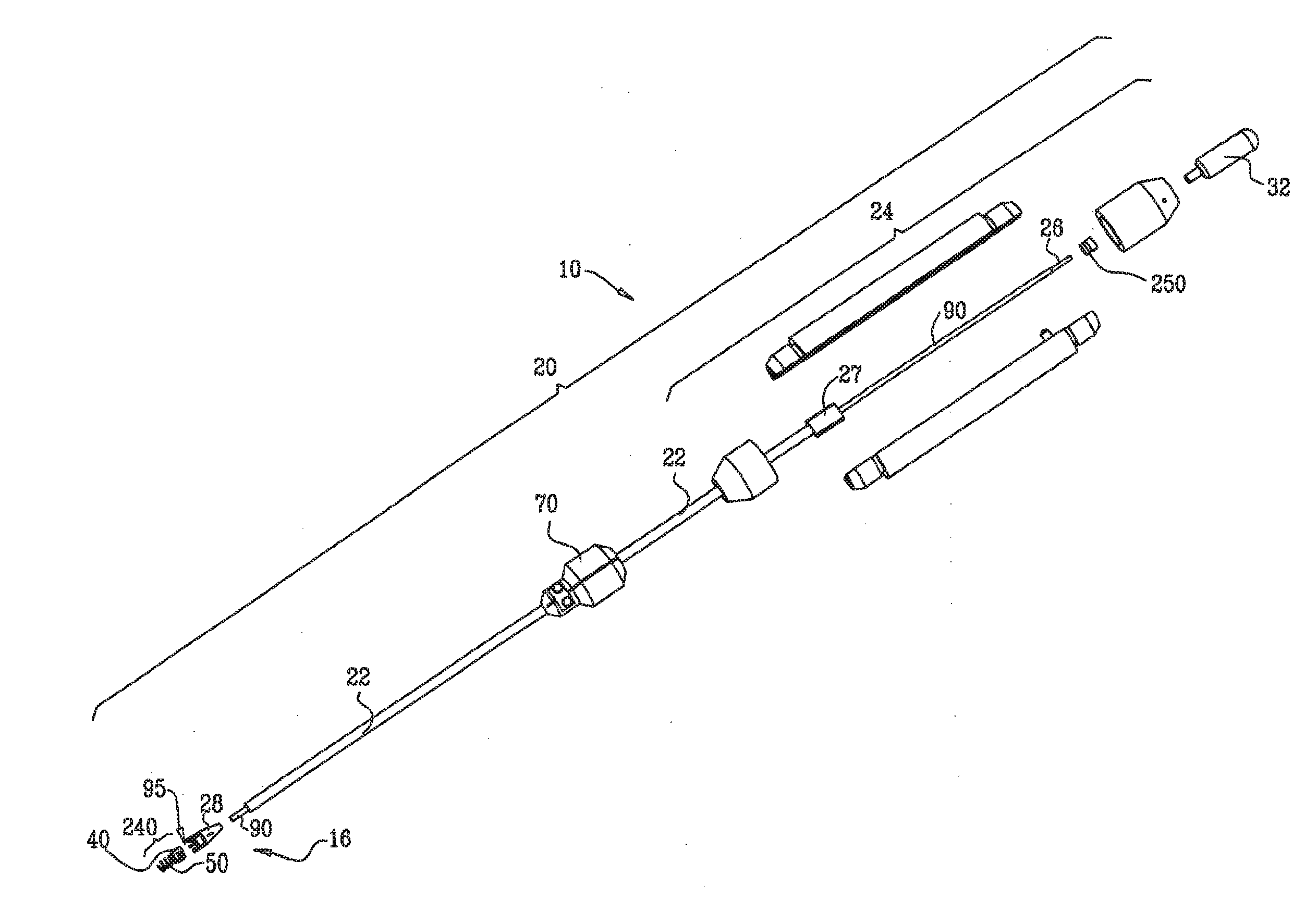
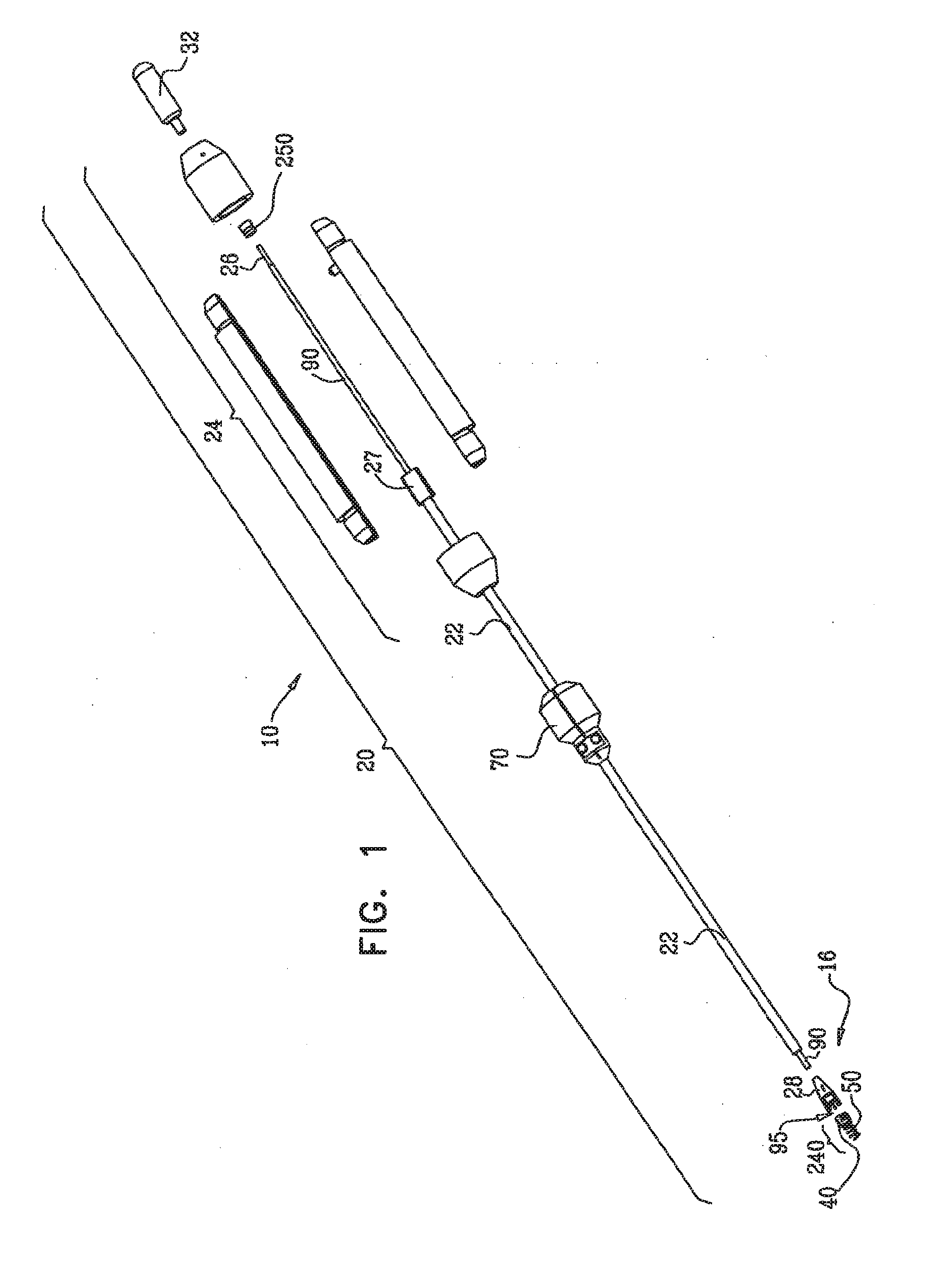
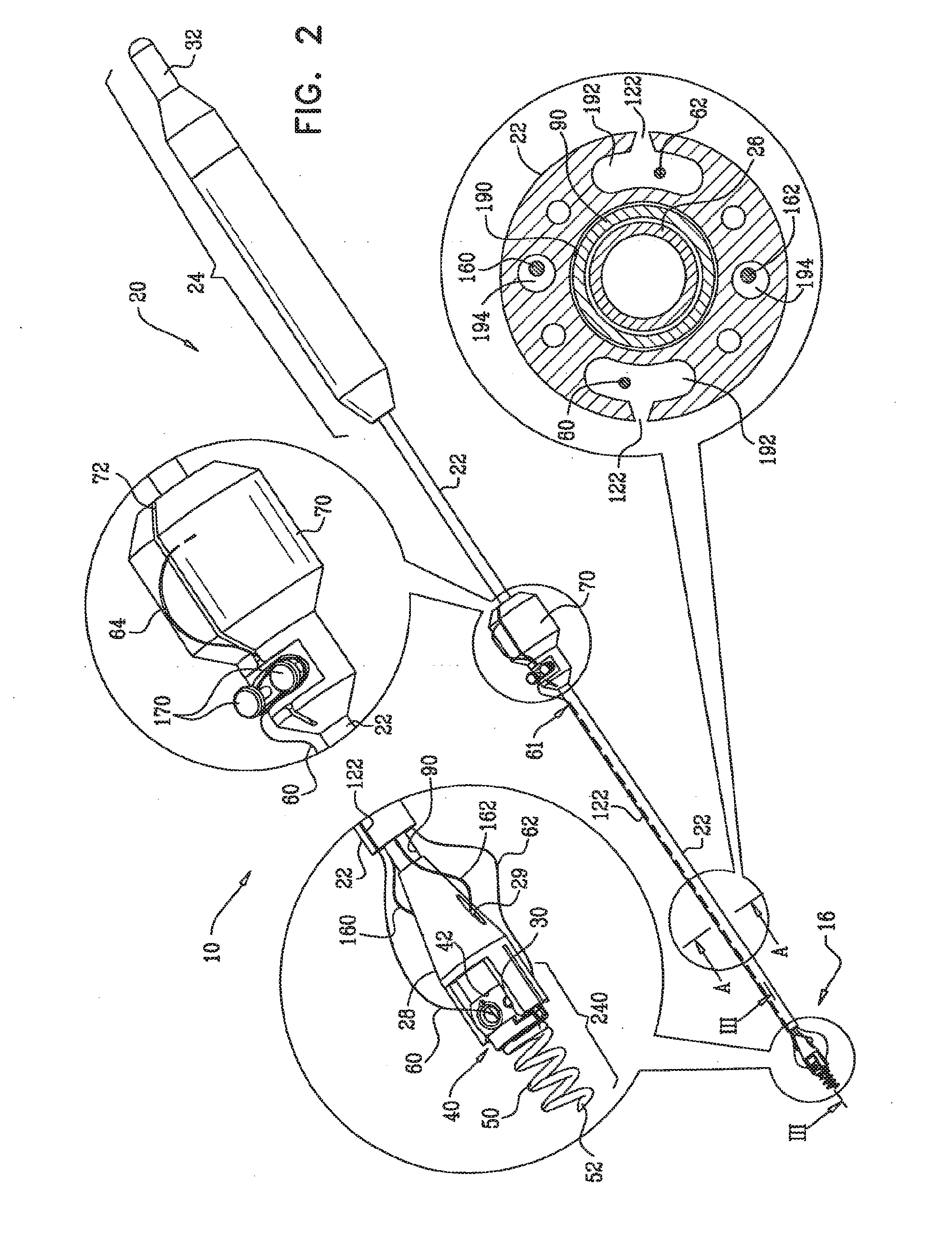
ActiveUS20160158008A1Reduce the overall diameterEasy to implantSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCardiac VentricleTissue Part
Apparatus is provided, including first and second longitudinal members coupled at respective first portions thereof to tissue surrounding the ventricle. The first portion of at least the first longitudinal member is coupled to a tissue anchor, and respective second portions of the first and second longitudinal members are coupled to respective first and second leaflets of a cardiac valve. The longitudinal members are arranged with respect to the tissue anchor and the portion of tissue surrounding the ventricle in a manner which facilitates adjustment of a degree of tension of the first and second longitudinal members to draw the first and second leaflets together. A longitudinal-member-coupling device is coupled to the first and second longitudinal members, and is advanceable toward a ventricular surface of the first and second leaflets, and responsively to draw together the first and second longitudinal members. Other applications are also described.
Owner:VALTECH CARDIO LTD
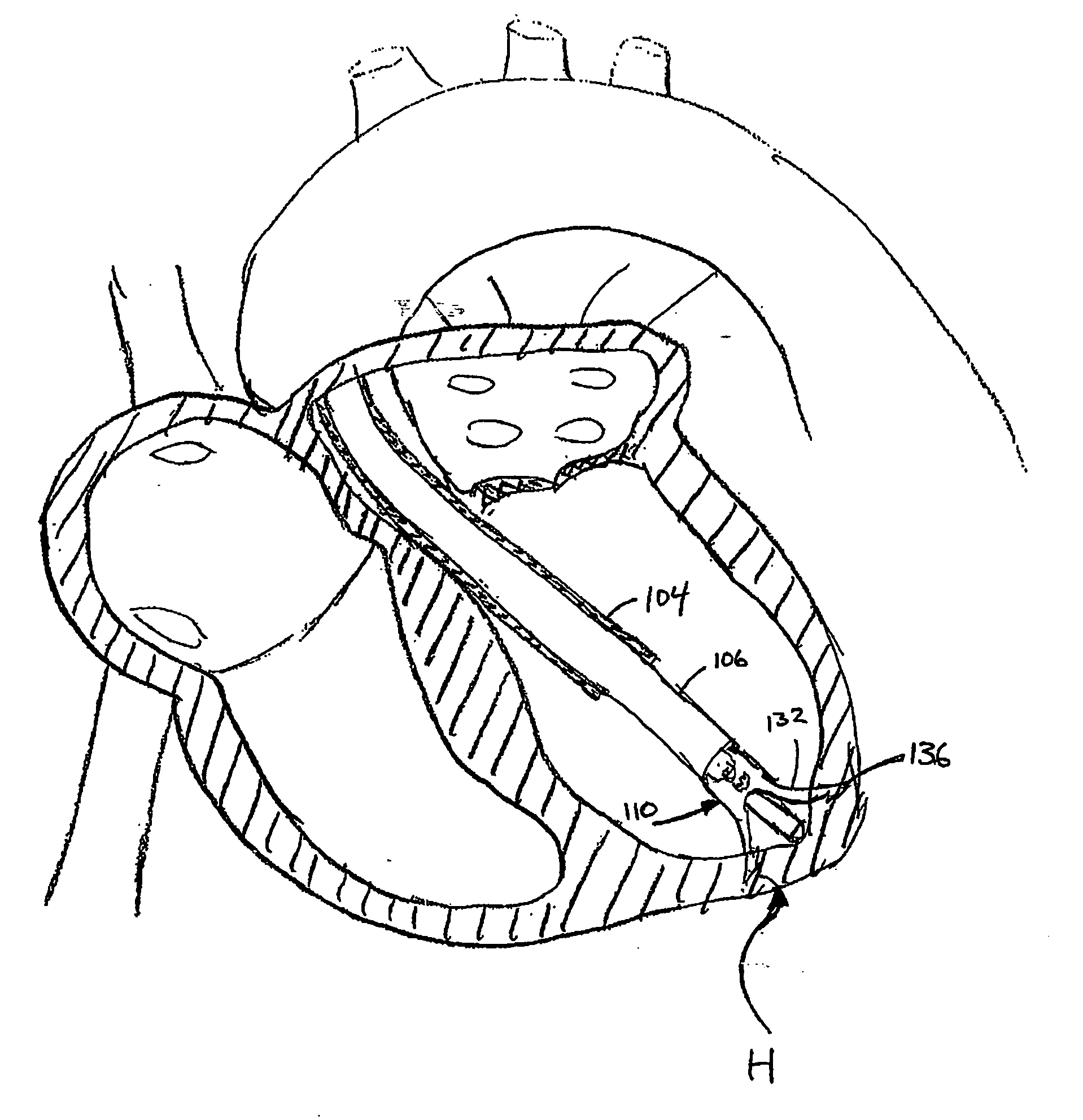
Catheter-based tissue remodeling devices and methods
InactiveUS20060135970A1Reduce volumeLower the volumeSuture equipmentsSurgical instrument detailsTissue remodelingLeft ventricle wall
Devices and methods utilizing a catheter to remodel soft tissue of a patient and, in a preferred embodiment, to reduce the volume of the left ventricle of a heart. In one embodiment, one or more sutures are passed through a wall of the ventricle. The ends of the one suture and, more preferably, the multiples sutures are drawn together to draw tissue portions towards one another. In another embodiment, tissue remodeling clip is implanted into a wall of the ventricle. Ends of the clip are resiliently biased to move relative to one another to draw tissue portions towards one another. In yet another embodiment, a tissue remodeling anchor includes a base and a plurality of legs attached to the base. The legs of the tissue anchor are implanted into a wall of the ventricle and moved toward one another to draw tissue portions toward one another. A retaining member is positioned on the tissue anchor to prevent the legs from moving apart.
Owner:BENVENUE MEDICAL
Catheter-based tissue remodeling devices and methods
InactiveUS20060135968A1Reduce volumeLower the volumeSuture equipmentsSurgical instrument detailsTissue remodelingLeft ventricle wall
Devices and methods utilizing a catheter to remodel soft tissue of a patient and, in a preferred embodiment, to reduce the volume of the left ventricle of a heart. In one embodiment, one or more sutures are passed through a wall of the ventricle. The ends of the one suture and, more preferably, the multiples sutures are drawn together to draw tissue portions towards one another. In another embodiment, tissue remodeling clip is implanted into a wall of the ventricle. Ends of the clip are resiliently biased to move relative to one another to draw tissue portions towards one another. In yet another embodiment, a tissue remodeling anchor includes a base and a plurality of legs attached to the base. The legs of the tissue anchor are implanted into a wall of the ventricle and moved toward one another to draw tissue portions toward one another. A retaining member is positioned on the tissue anchor to prevent the legs from moving apart.
Owner:BENVENUE MEDICAL
Surgical Device for The Collection of Soft Tissue
A handheld biopsy device is provided for the collection of soft tissue samples from a surgical patient. In a preferred embodiment, the biopsy device comprises a handpiece, a fluid collection system, and a power transmission source. The handpiece is configured for grasping by a single hand, and being independently manipulatable by hand for movement of the instrument toward and away from the patient. An elongated piercer extends from the distal end of the handpiece. The piercer has a sharpened distal end for entering the tissue and a port located proximal to the sharpened distal end for receiving a portion of tissue mass. An elongated cutter is disposed coaxially relative to a piercer lumen of the piercer. A distal blade of the cutter slides distally past the port of the piercer to severe the tissue portion drawn into the port by vacuum. The cutter is retracted to a most proximal position for removal of the tissue portion from a cutter lumen of the cutter. The handpiece further comprises a holster for detachably connecting a cutter rotation transmission and a cutter axial transmission to the power transmission source.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Method and apparatus for optical detection of mixed venous and arterial blood pulsation in tissue
A method and device for detecting the presence of mixed venous and arterial blood pulsation in tissue, including receiving first and second electromagnetic radiation signals from a blood perfused tissue portion corresponding to infrared and red wavelengths of light, obtaining a measure of a phase difference between the first and second electromagnetic radiation signals, comparing the measure with a threshold value to form a comparison, and detecting the presence or absence of venous pulsation using the comparison.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
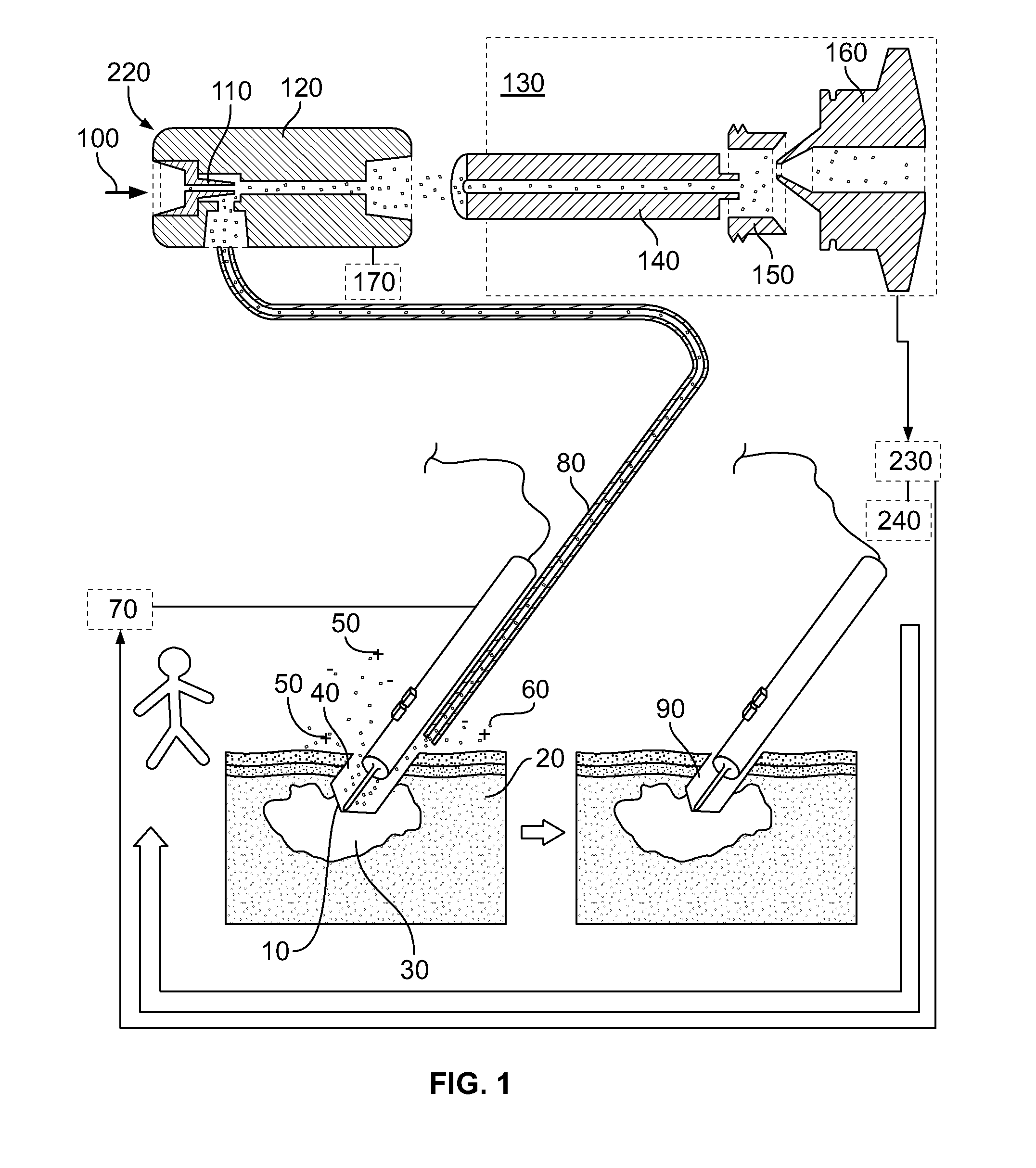
System and method for identification of biological tissues
ActiveUS20120156712A1Easy to detectOverall light weightBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCombined useTissue sample
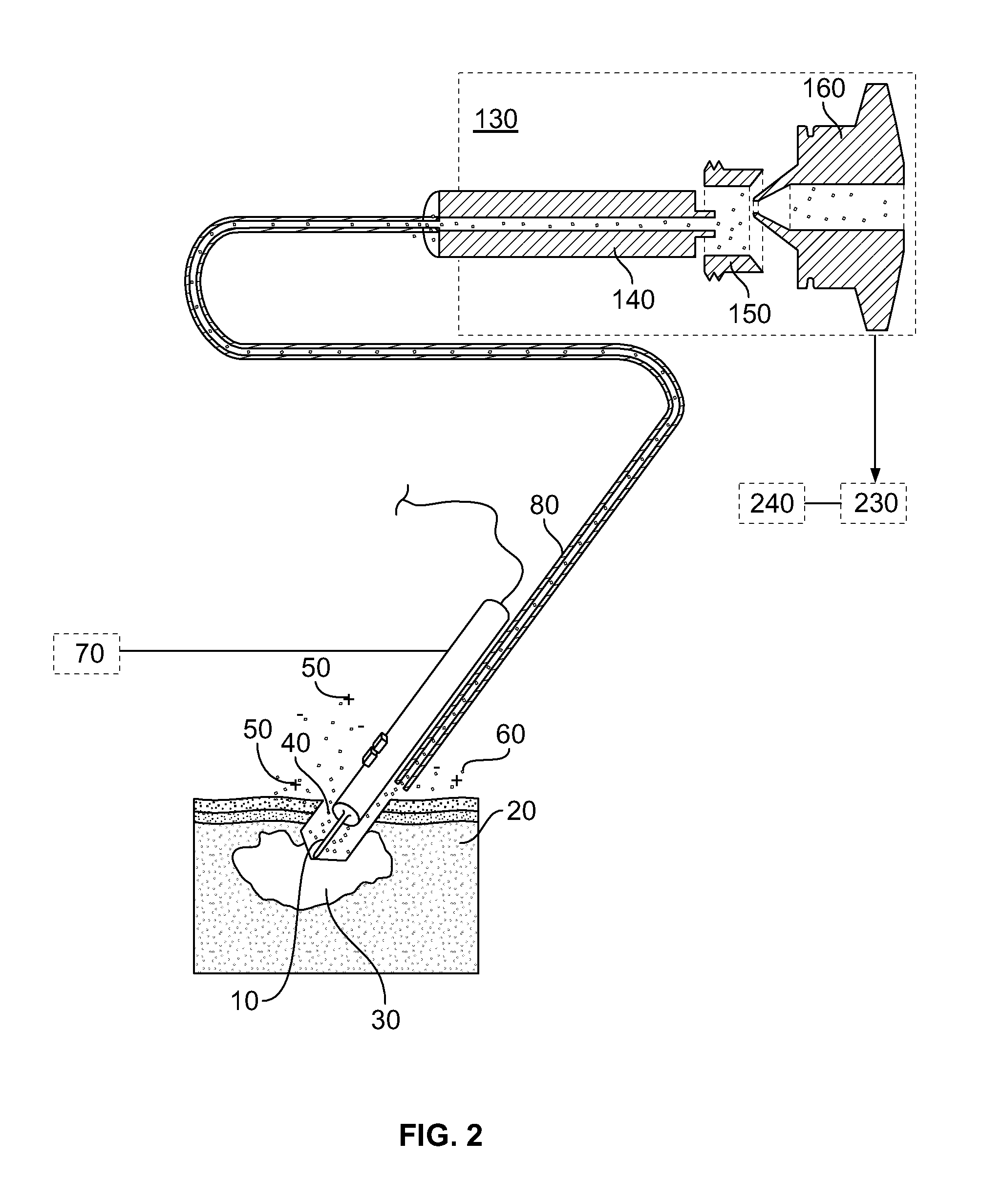
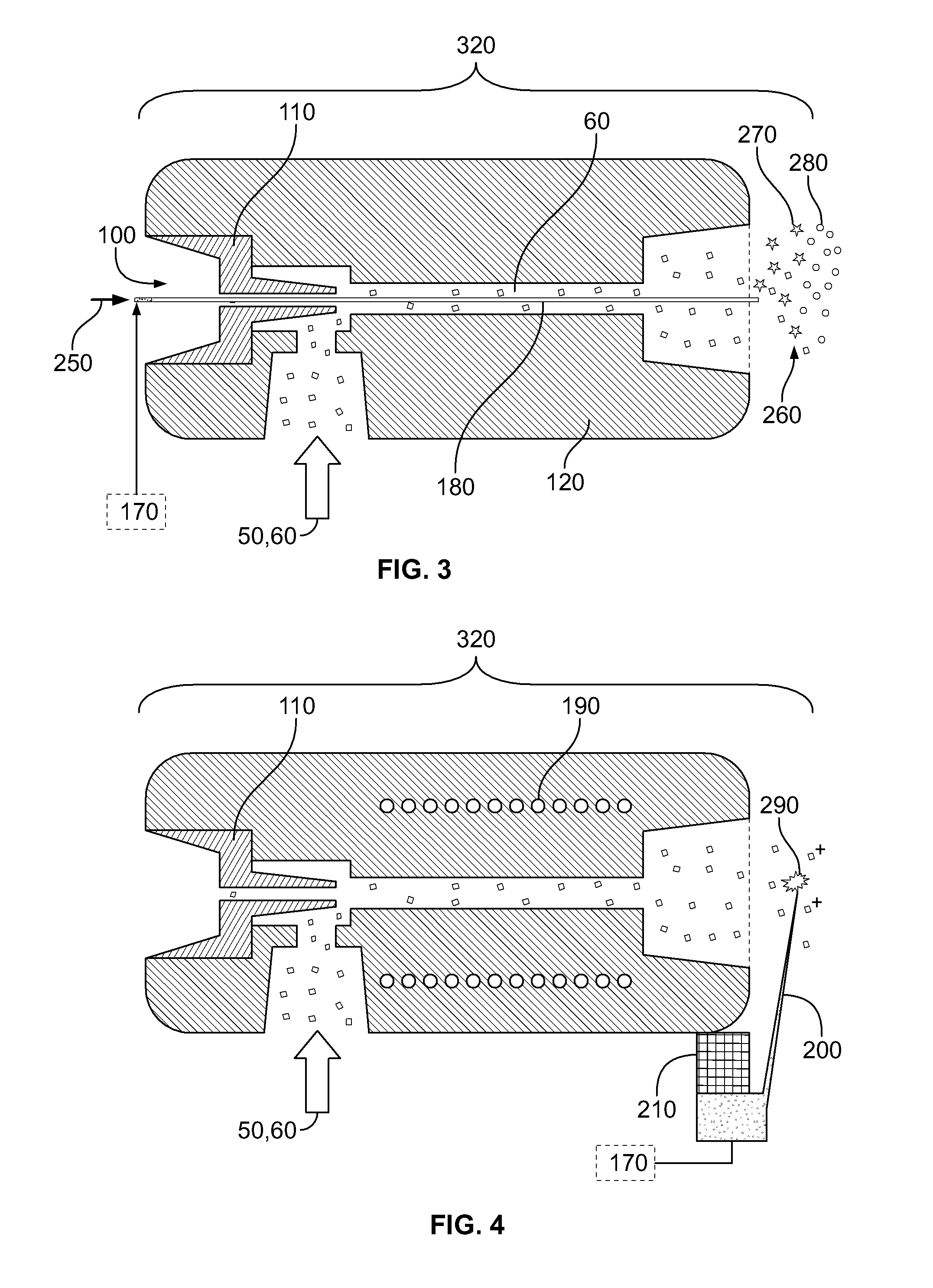
The present invention provides for a system, method, and device for analyzing, localizing and / or identifying tissue types. The method includes analyzing, localizing and / or identifying one or more tissue samples, characterized in that the method comprises: (a) generating gaseous tissue particles from a site in the one or more tissue samples, (b) transporting the gaseous tissue particles from the site to an analyser, (c) using the analyser for generating tissue-related data based on the gaseous tissue particles, and (d) analyzing, localizing and / or identifying the one or more tissue samples based on the tissue-related data. The invention can either be used in close conjunction with a surgical procedure, when one or more surgical tools are an integrated part of ionization, or as a separate mass spectrometric probe for the analysis of one or more tissue parts.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD +1
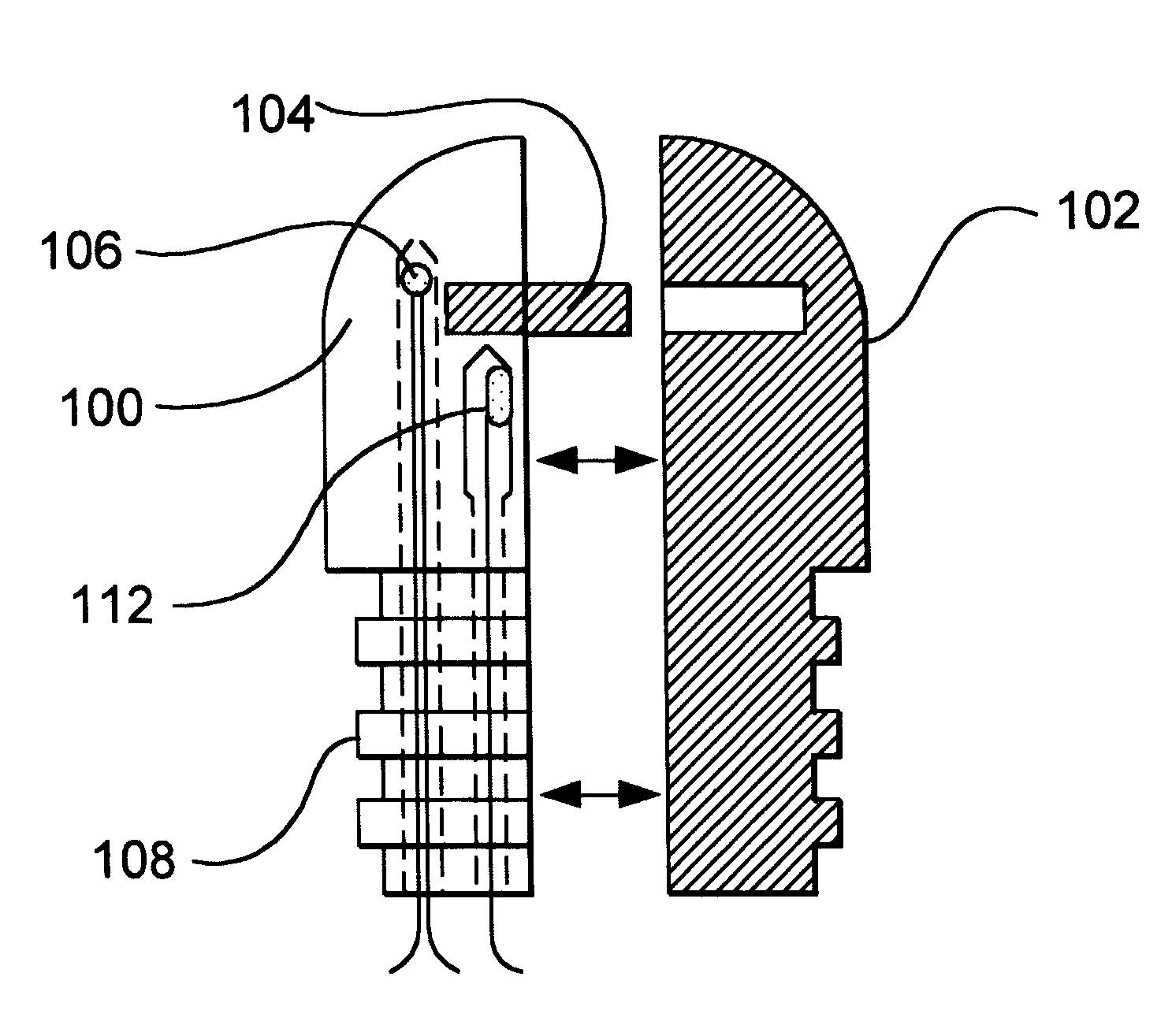
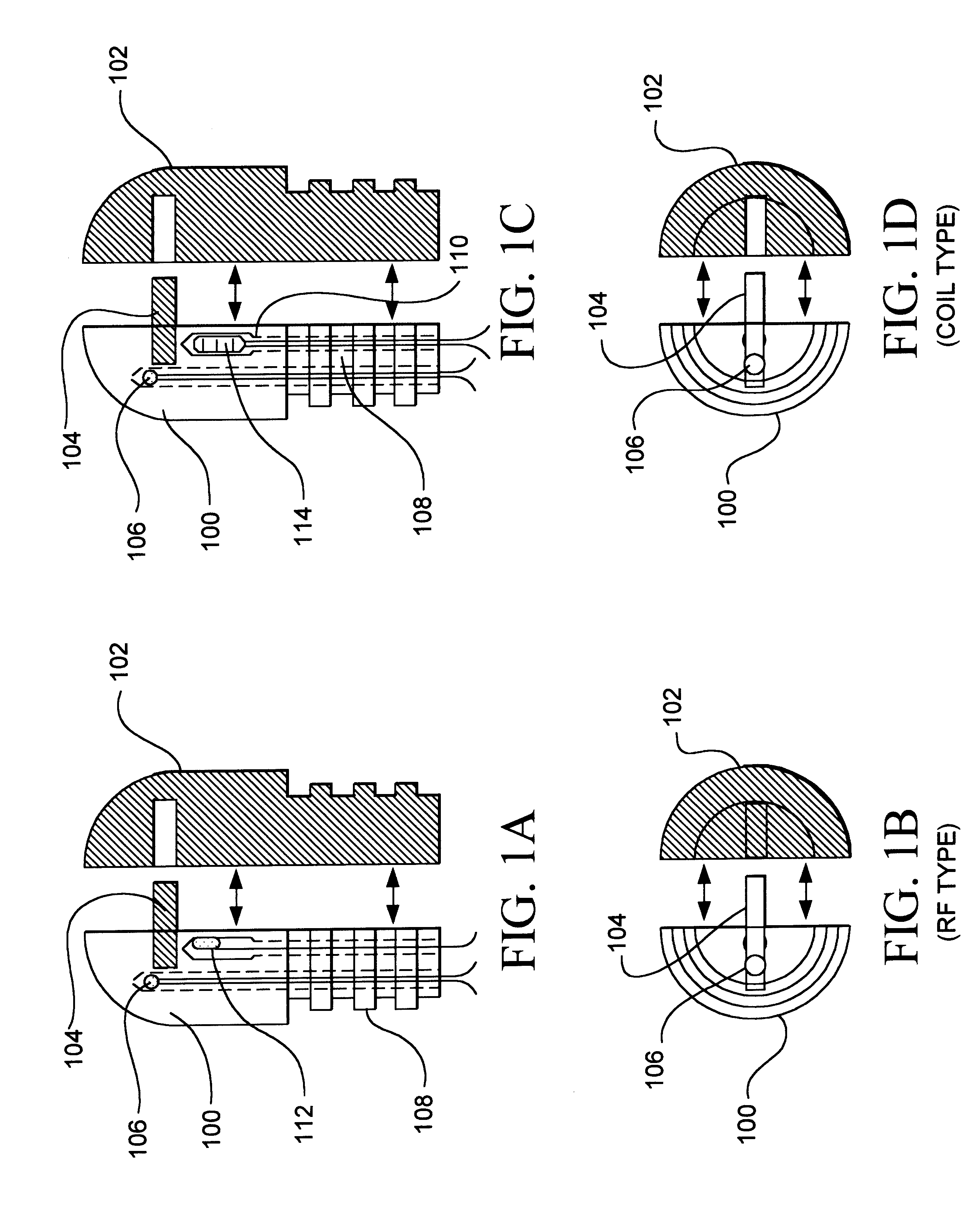
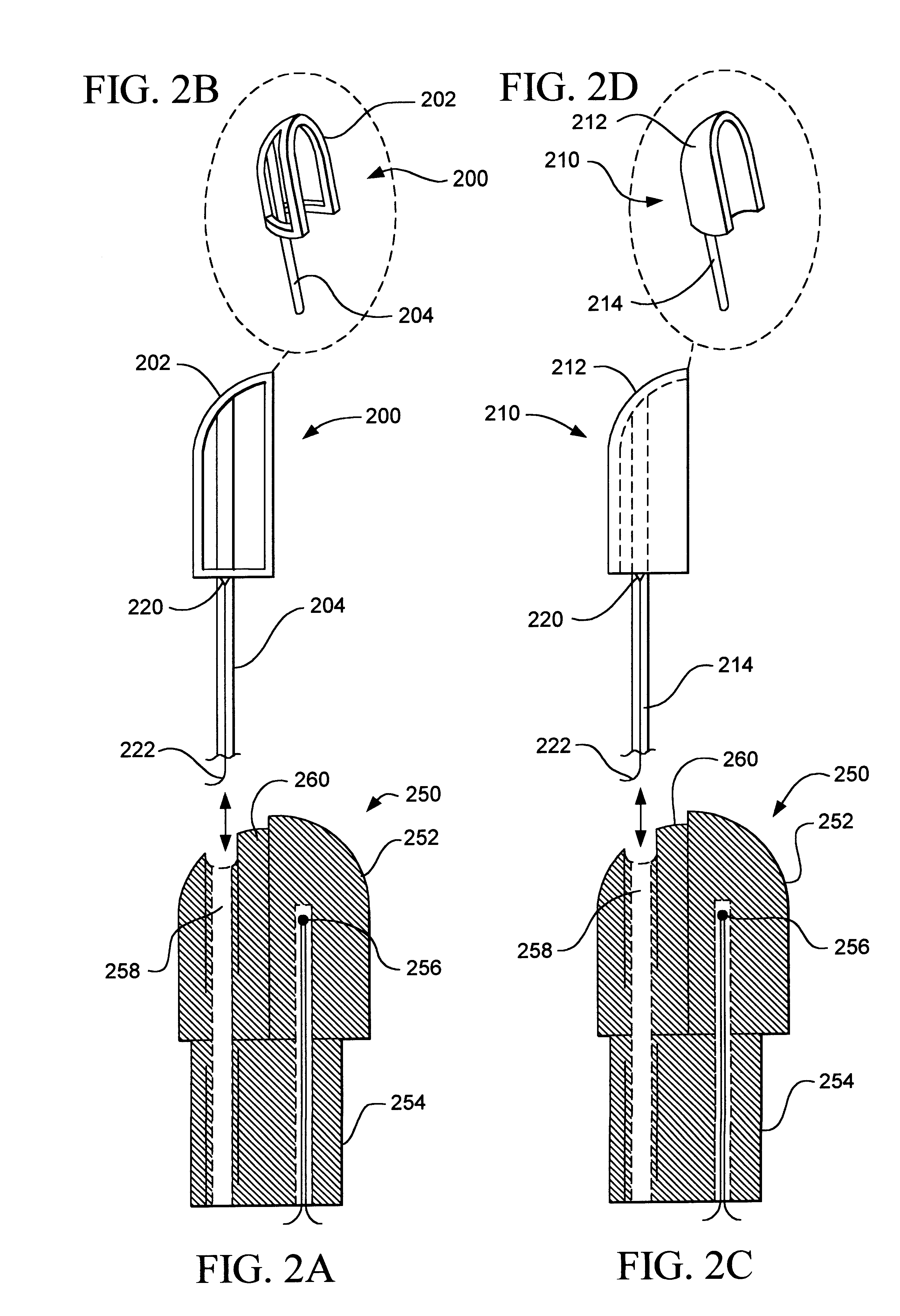
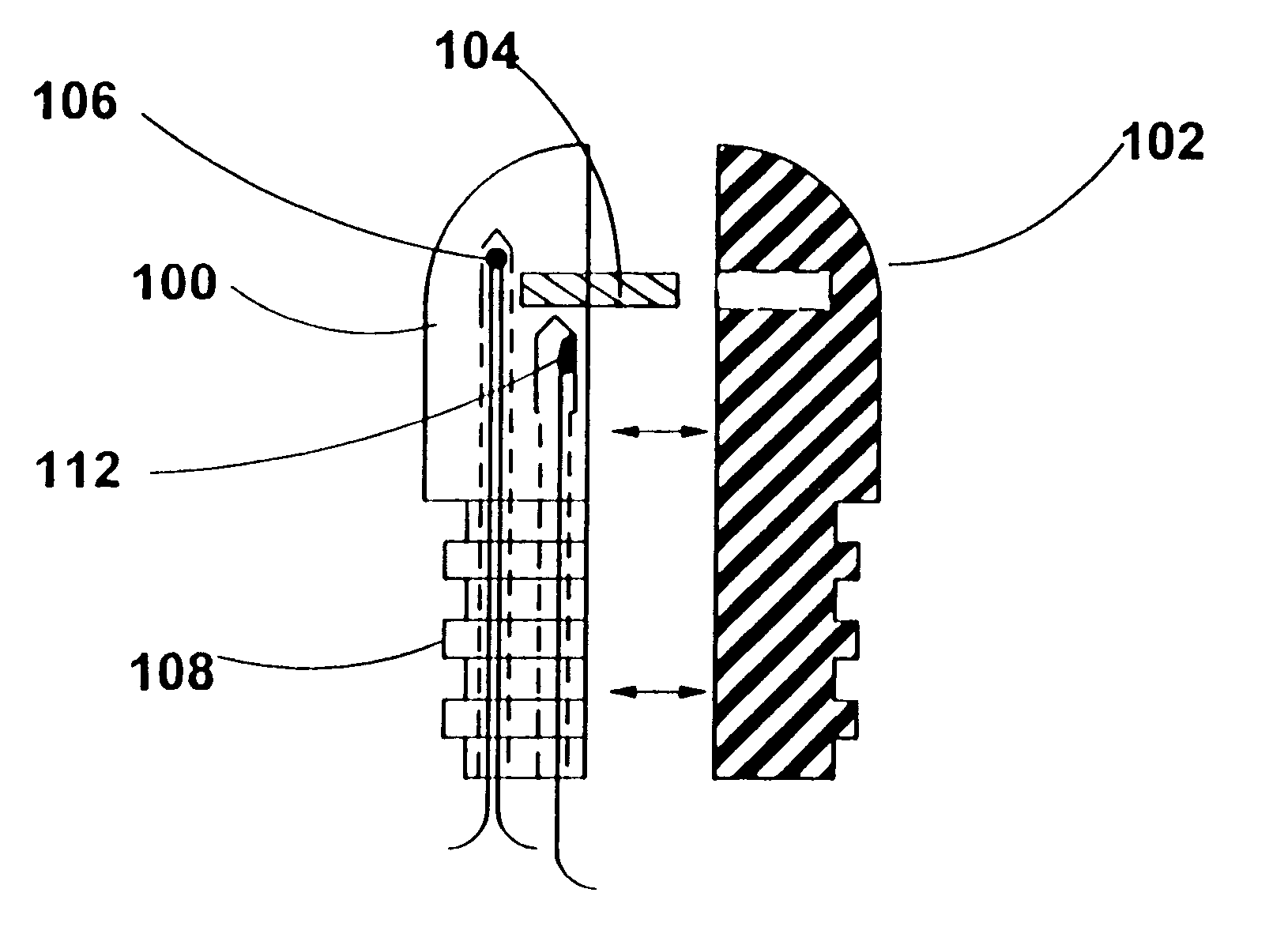
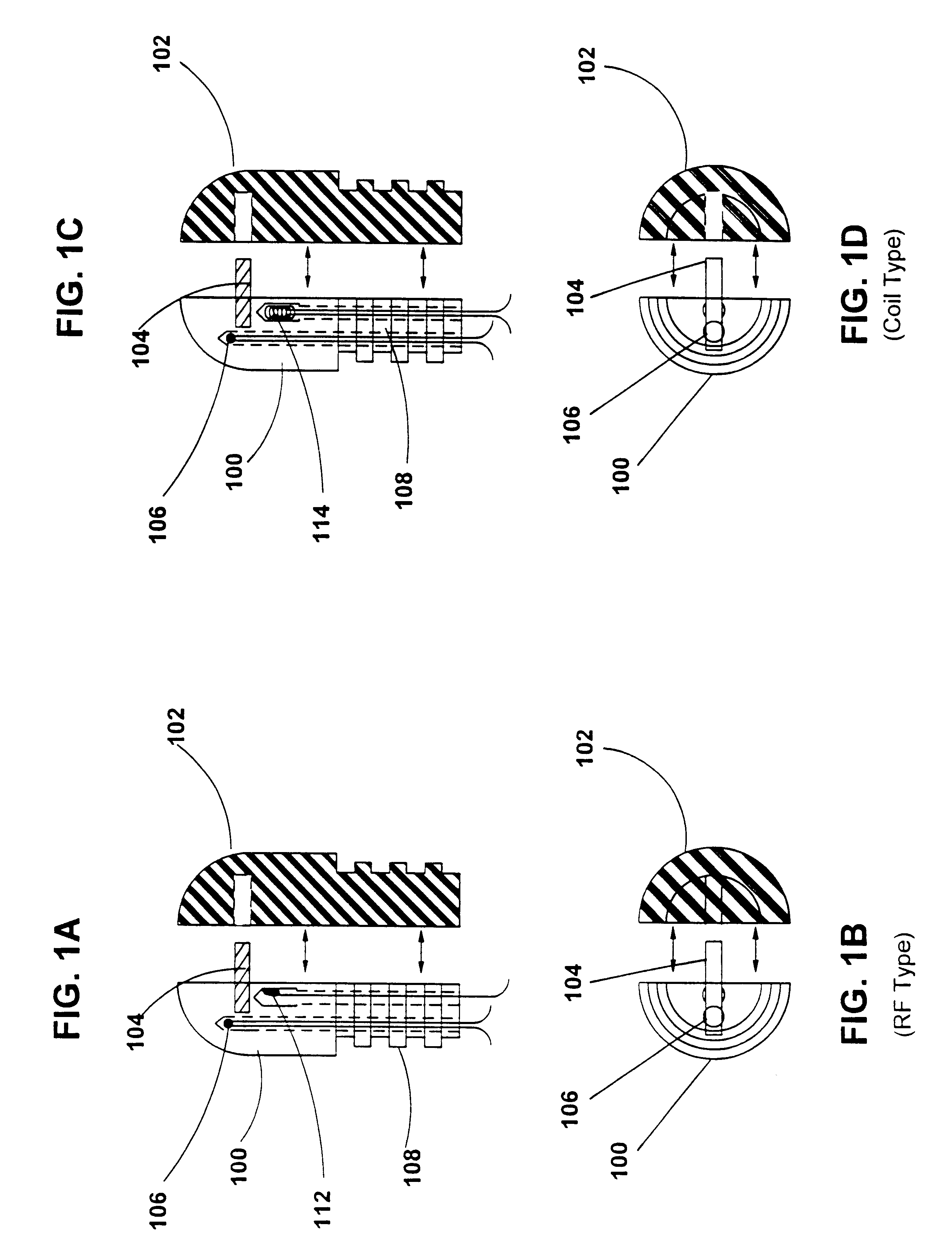
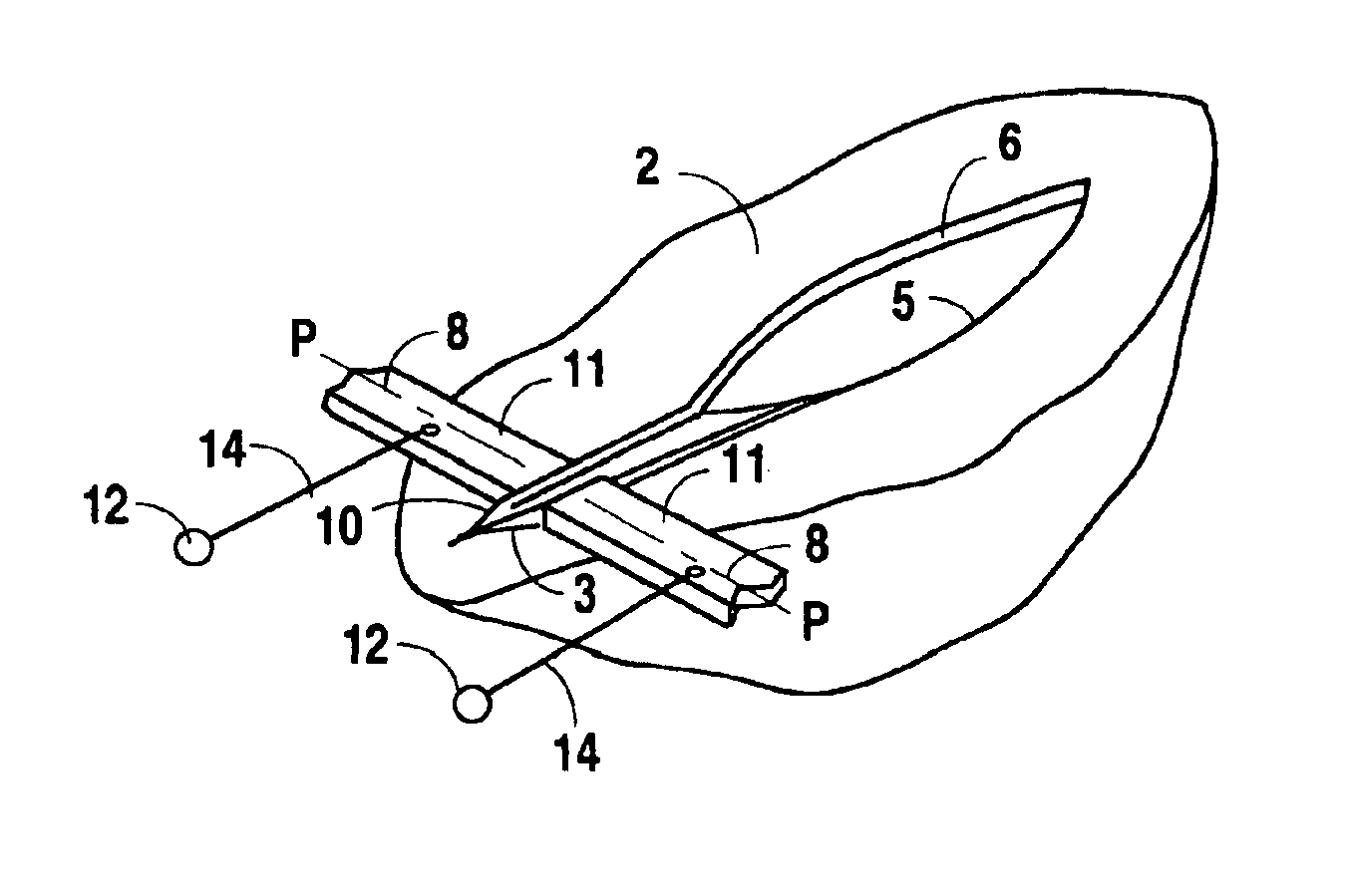
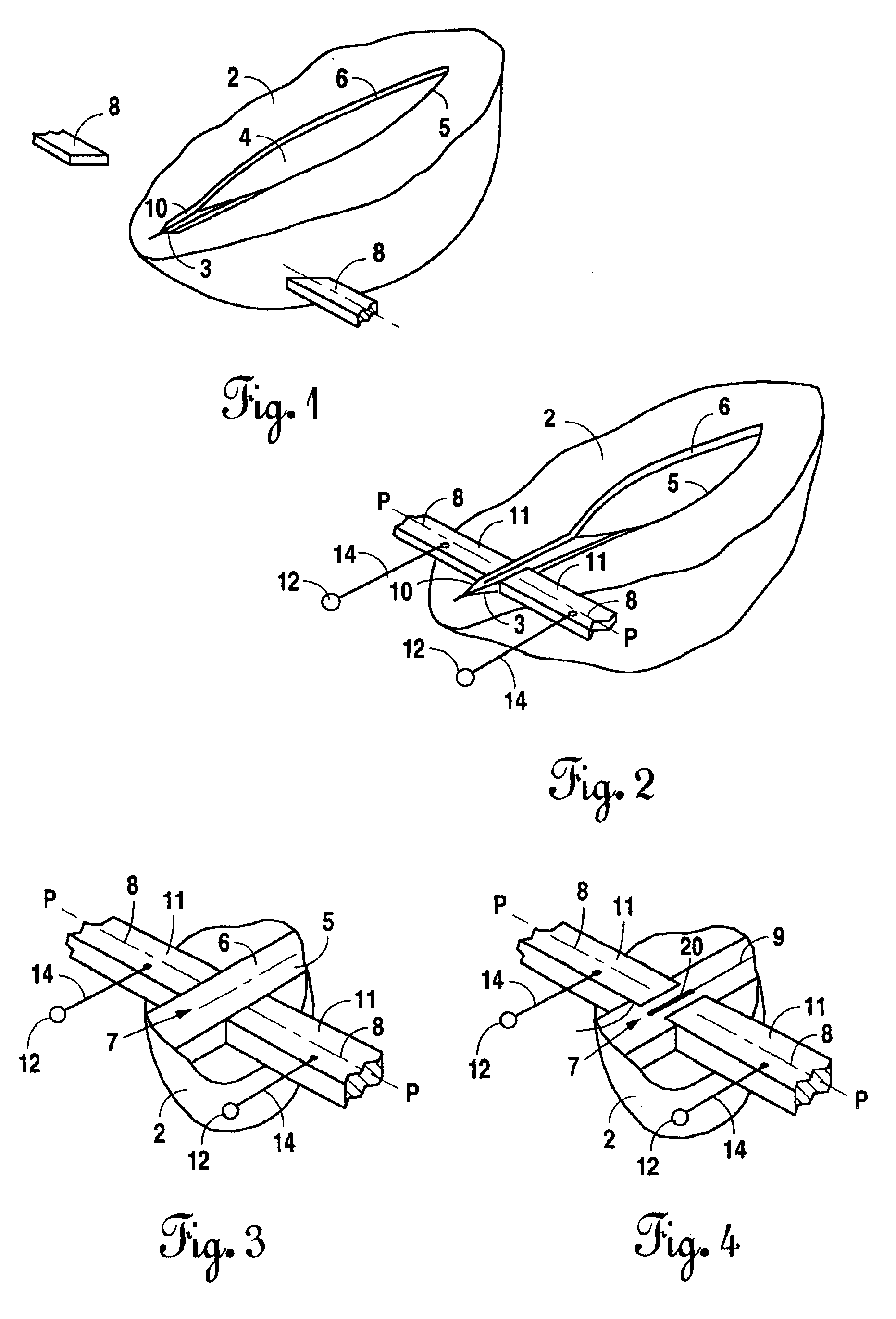
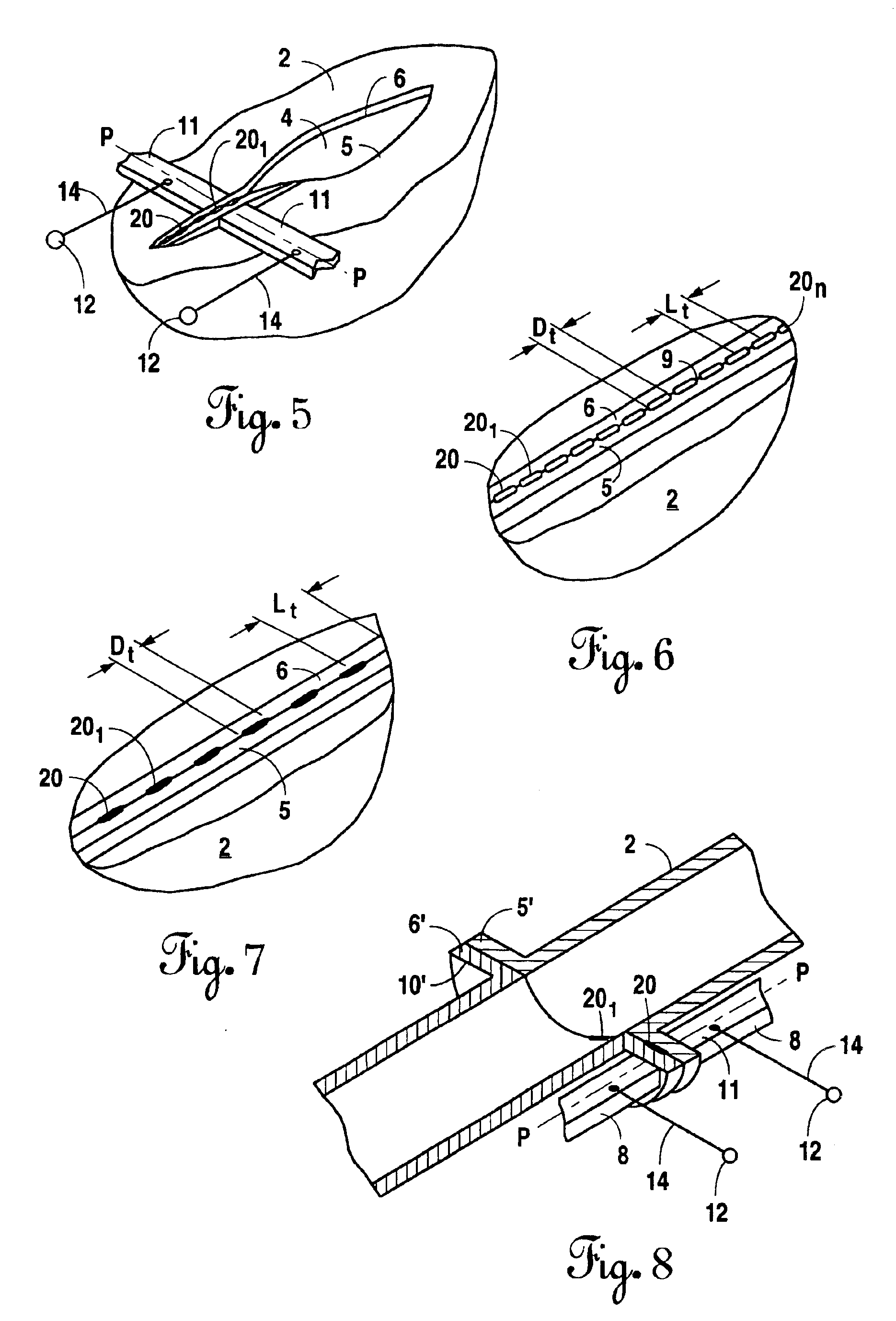
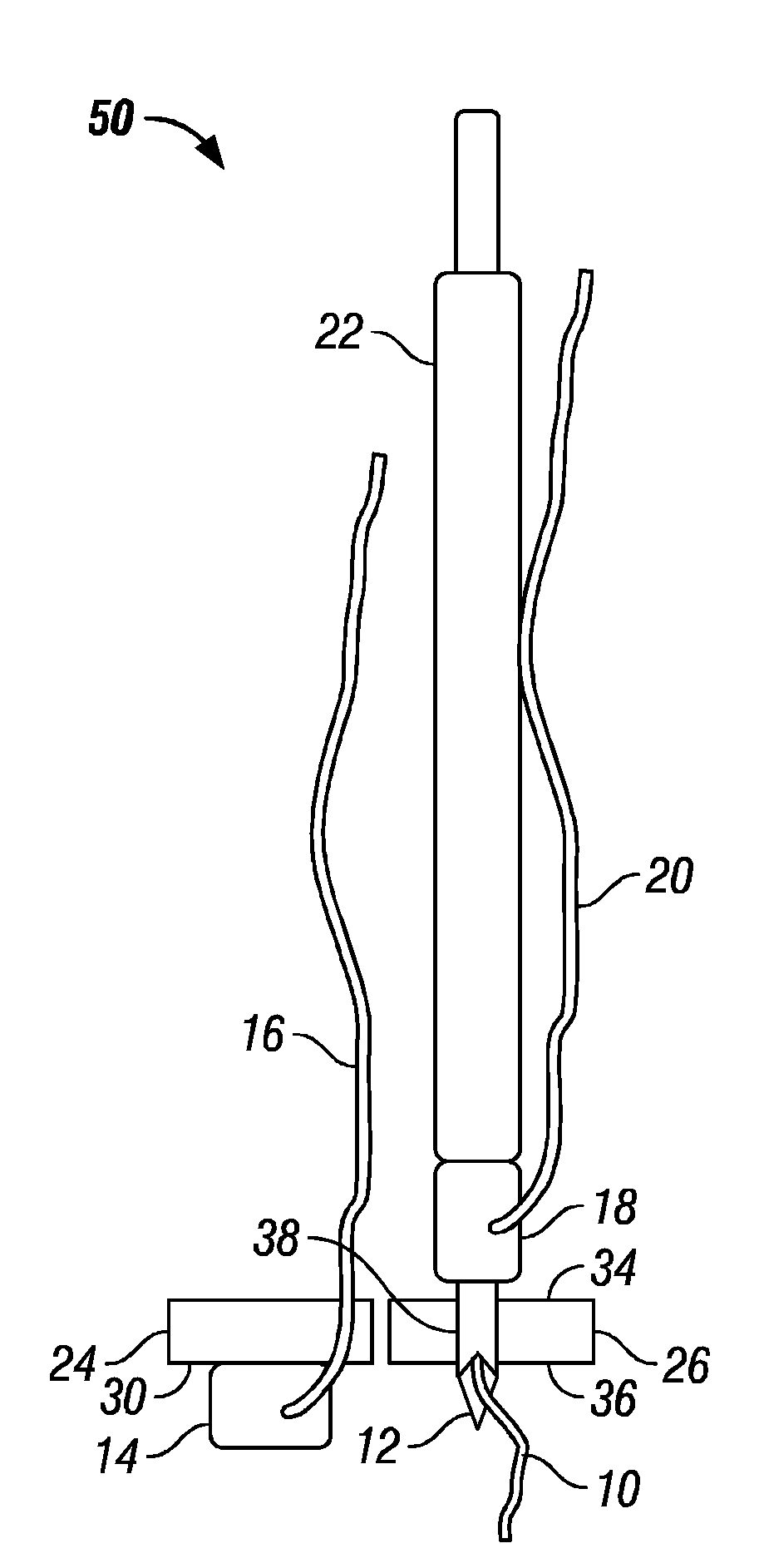
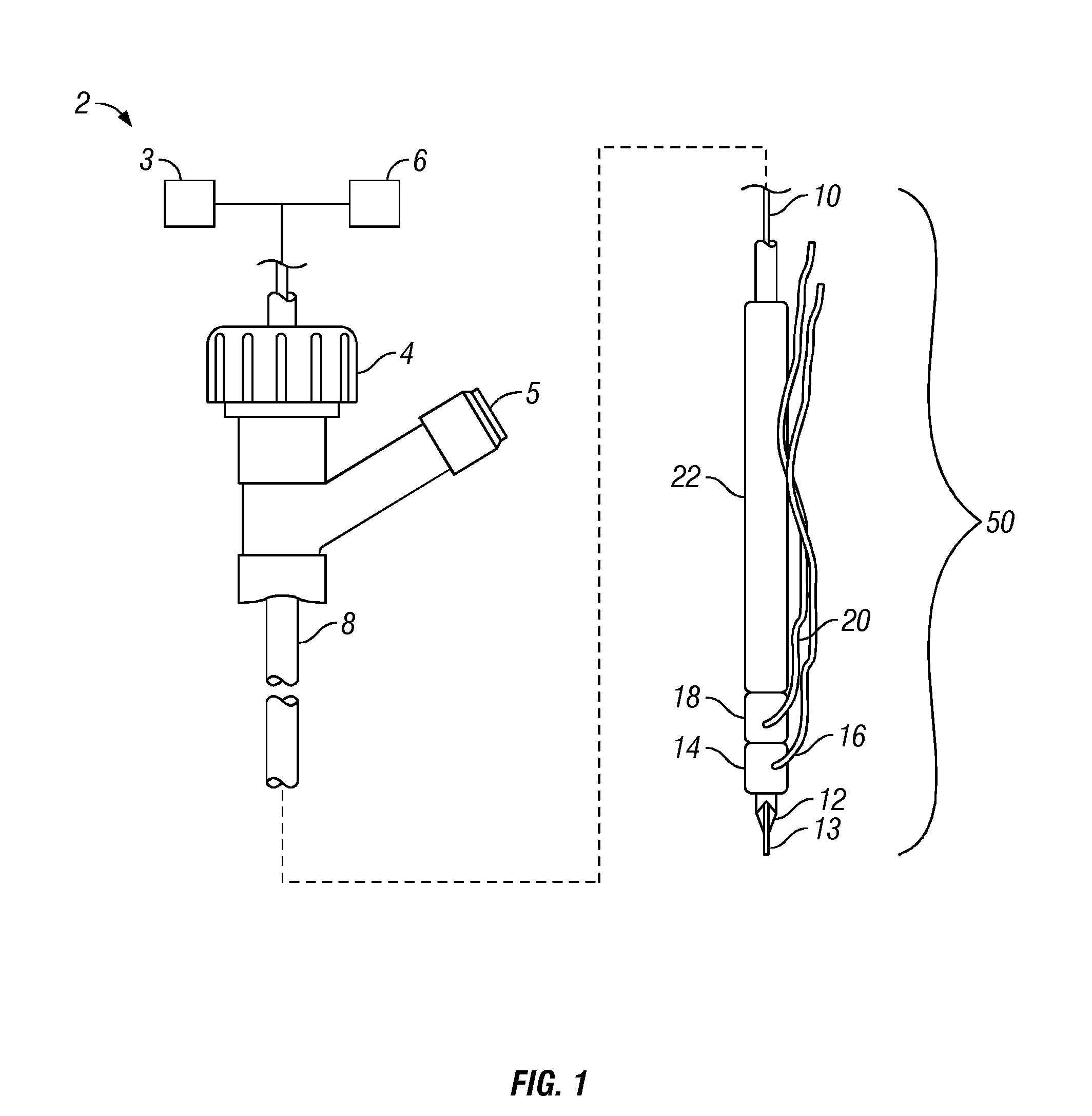
Needle-electrode and tissue anchor system
ActiveUS20100094341A1Improve abilitiesIncrease costSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsEngineeringTissue Part
The disclosure provides a needle-electrode anchor system having a needle and an optional electrode with one or more anchors. The system can provide an electrical cutting current to the needle-electrode to create an opening in a tissue portion. An anchor coupled to the needle-electrode can be pushed through the opening with a pusher and pulled into position to set the anchor on a distal surface of the opening. If the tissue portion is to be approximated to another tissue portion, the system can be relocated to another tissue portion and another opening created with the cutting current with another anchor pushed through the opening and secured on a distal surface. Lines coupled to the anchors can be pulled together, approximating the tissue portions. If the tissue portion is to be retracted, an anchor line can be grasped to retract the tissue portion from an adjacent tissue portion.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Apparatus and methods for the selective removal of tissue using combinations of ultrasonic energy and cryogenic energy
InactiveUS20070088217A1Avoid stickingLess painfulUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyBody tissueUltrasound energy
Ultrasonic apparatus and method for selective and targeted removal of unwanted tissues are disclosed. The apparatus and methods may utilize combinations of ultrasonic and cryogenic energy for the selective removal of tissue. The apparatus generates and delivers to the tissue both cryogenic and ultrasonic energy either in combination or in sequence and provides resize ablation of unwanted tissue parts and may be used on other body tissues including internal organs.
Owner:BACOUSTICS LLC
Tissue stabilizer having an articulating lift element
InactiveUS7326177B2Easy to operateEasy to demonstrateSurgical pincettesProsthesisSurgical operationCoronary Artery Bypasses
Devices and methods are disclosed for stabilizing tissue within a patient's body during a surgical operation to provide a relatively motionless surgical field, such as during a coronary artery bypass graft procedure. The devices include tissue stabilizers which engage and provide stabilization to a targeted area of tissue and further have the ability to engage and manipulate some portion of tissue within or adjacent the targeted area to improve the surgical presentation of that portion of tissue. The tissue stabilizer typically has one or more stabilizer feet which have a first foot portion configured to provide stabilization to the targeted tissue and a second foot portion moveable relative to the first foot portion for manipulating a portion of tissue to improve the surgical presentation.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
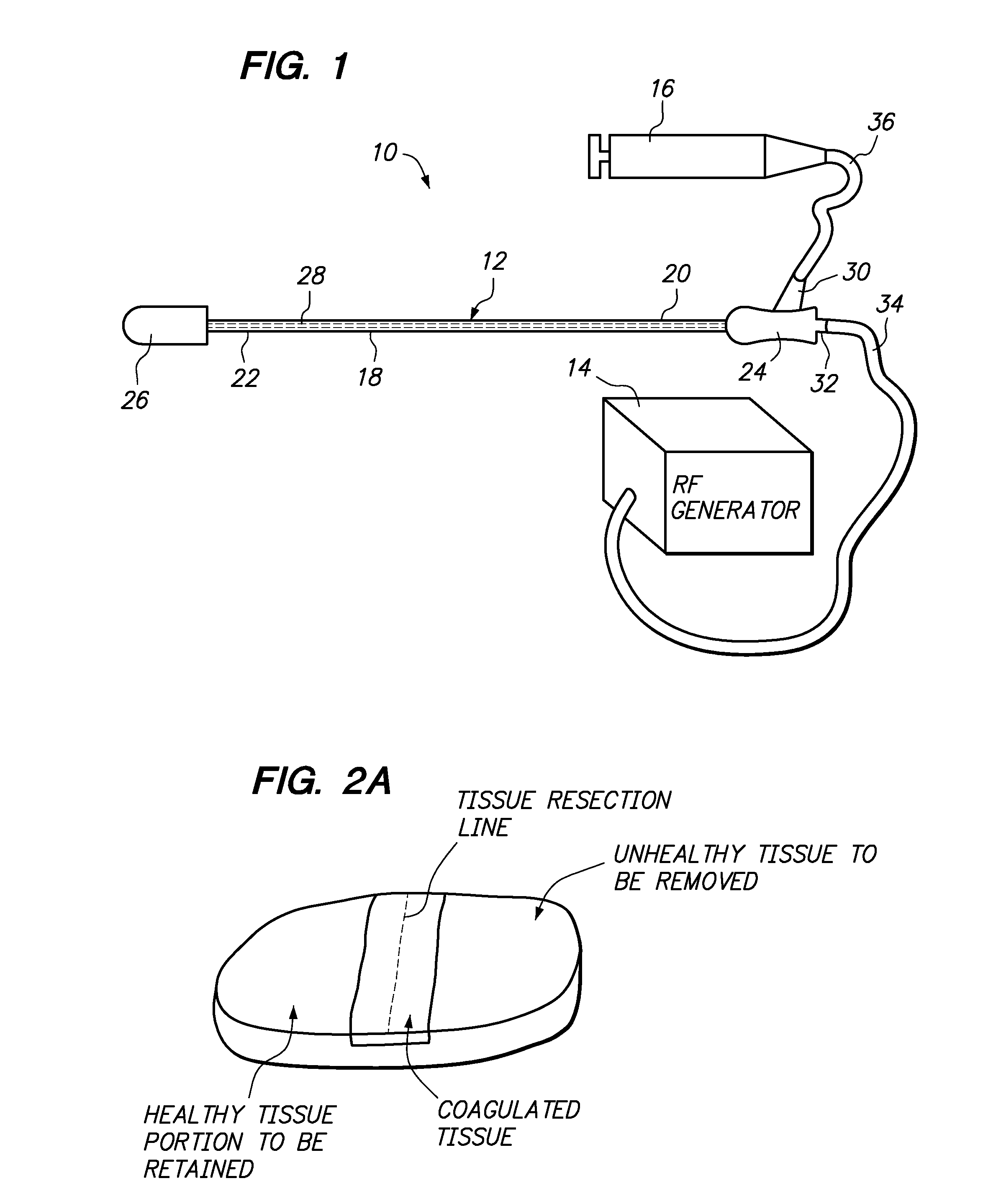
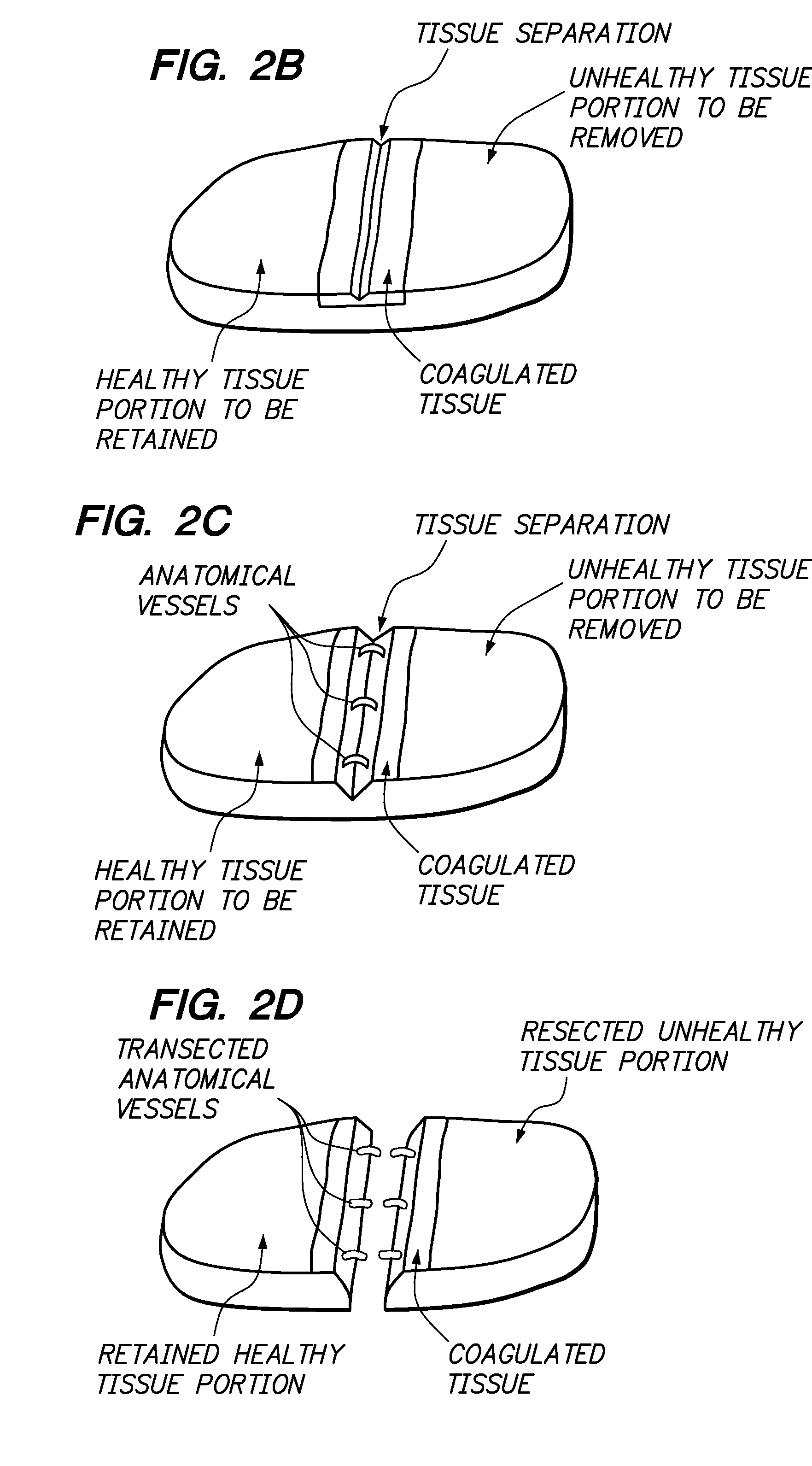
Foam electrode and method of use thereof during tissue resection
InactiveUS20070156127A1Conveniently mountedEasy to provideSurgical instruments for heatingRadio frequencyHealthy tissue
Assemblies and methods are provided for resecting a portion of tissue to be removed (e.g., unhealthy tissue, such as cancerous tissue) from a portion of the tissue to be retained (e.g., healthy tissue) within a patient is provided. An electrically conductive fluid, such as saline, may be absorbed into a hydrophilic electrode. Electrical energy (e.g., radio frequency (RF) energy) is conveyed to or from the hydrophilic electrode while being moved in proximity to the tissue along a resection line, whereby tissue adjacent to the resection line is coagulated. A resection member, such as a blunt resection member or a resection electrode, which may be on the same device as the hydrophilic electrode, is used to separate the tissue along the resection line to resect the tissue portion to be removed from the tissue portion to be retained.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com