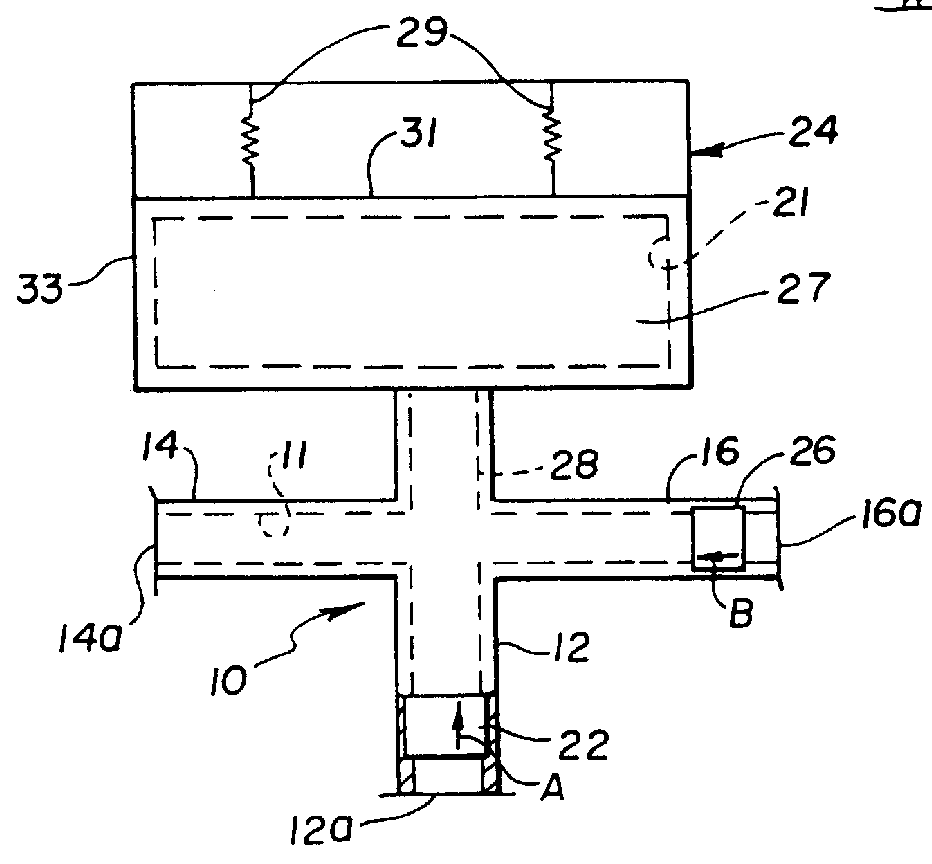
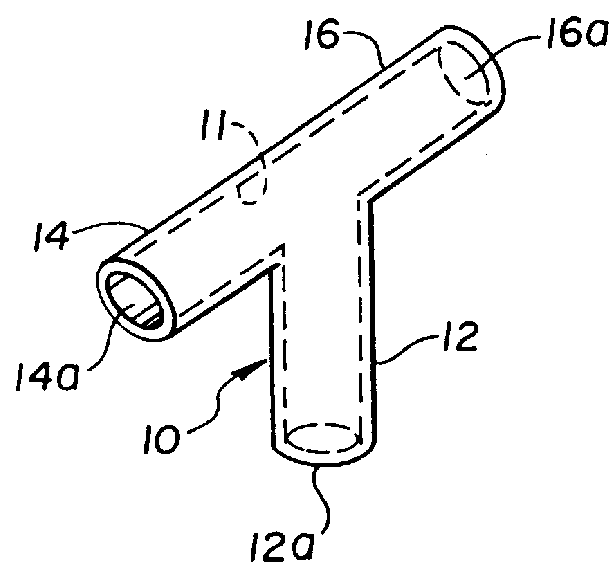
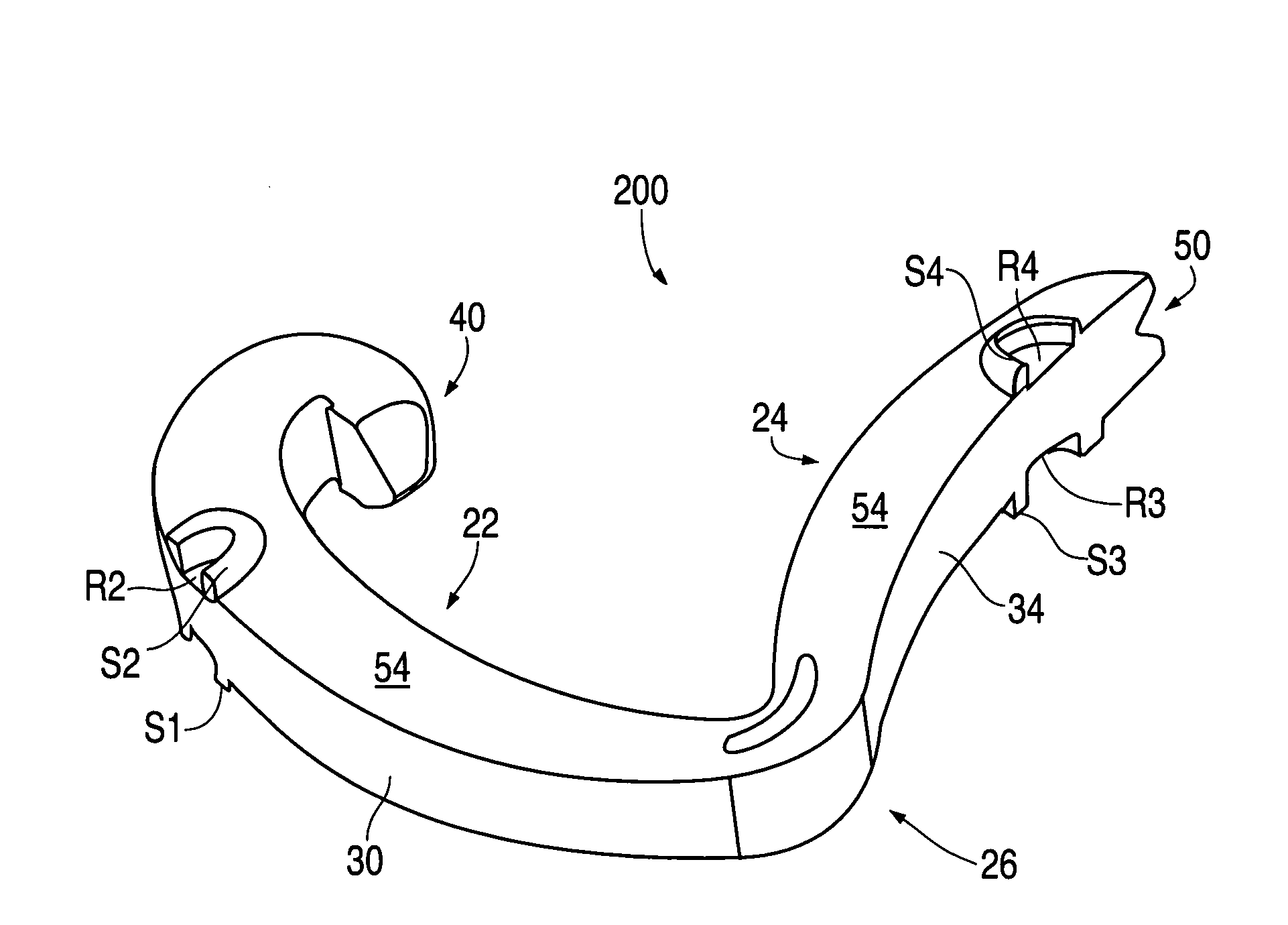
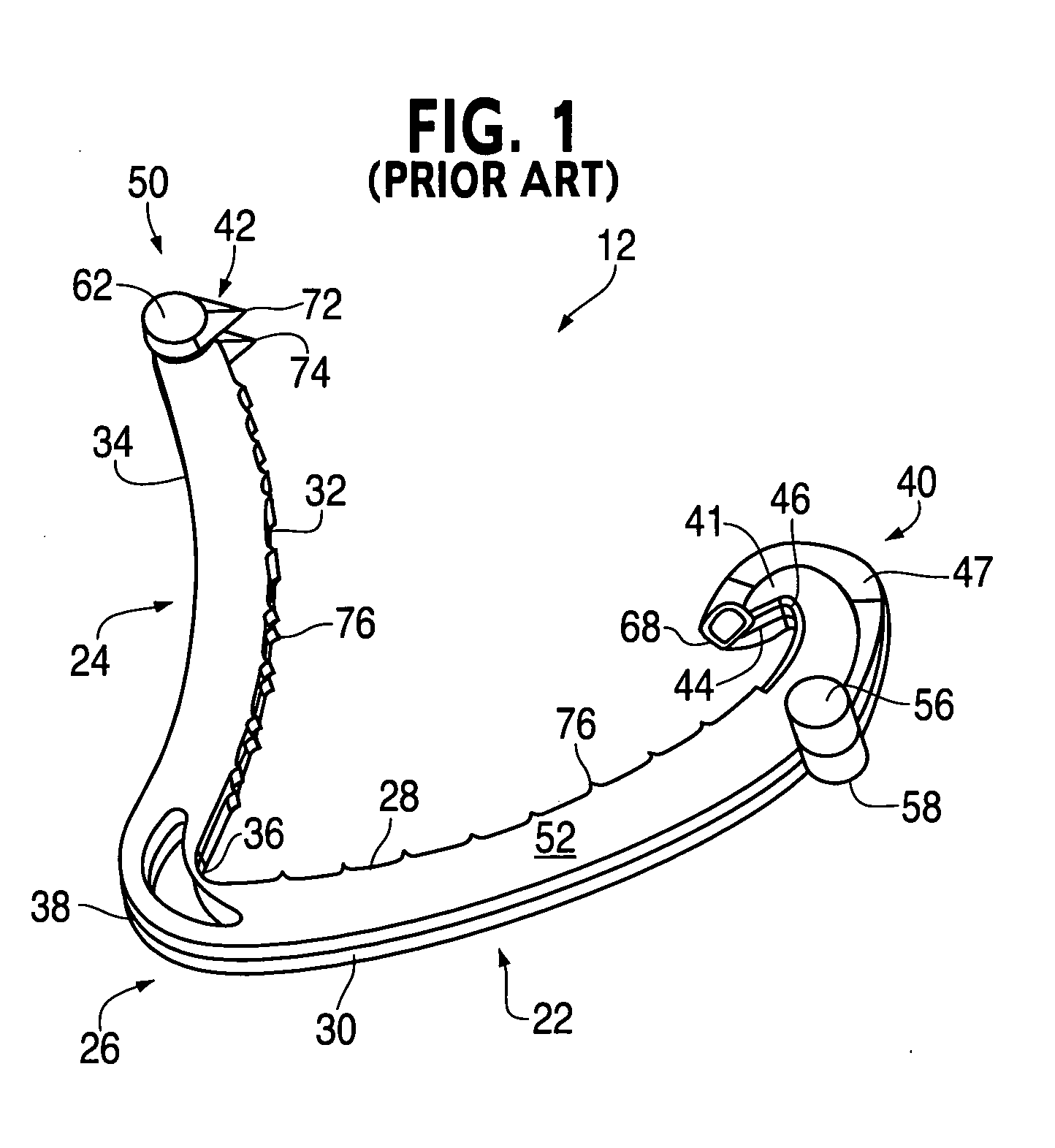
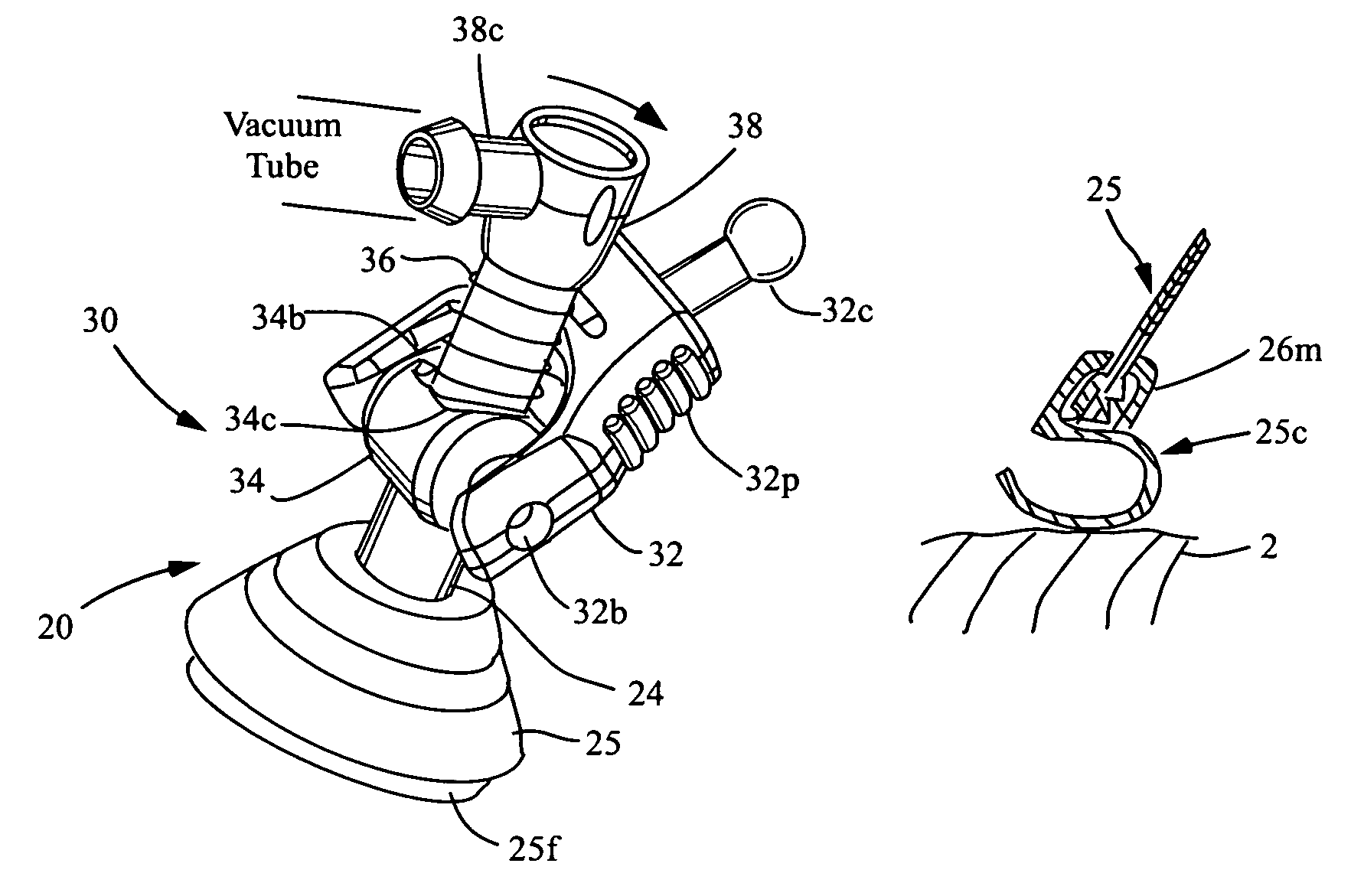
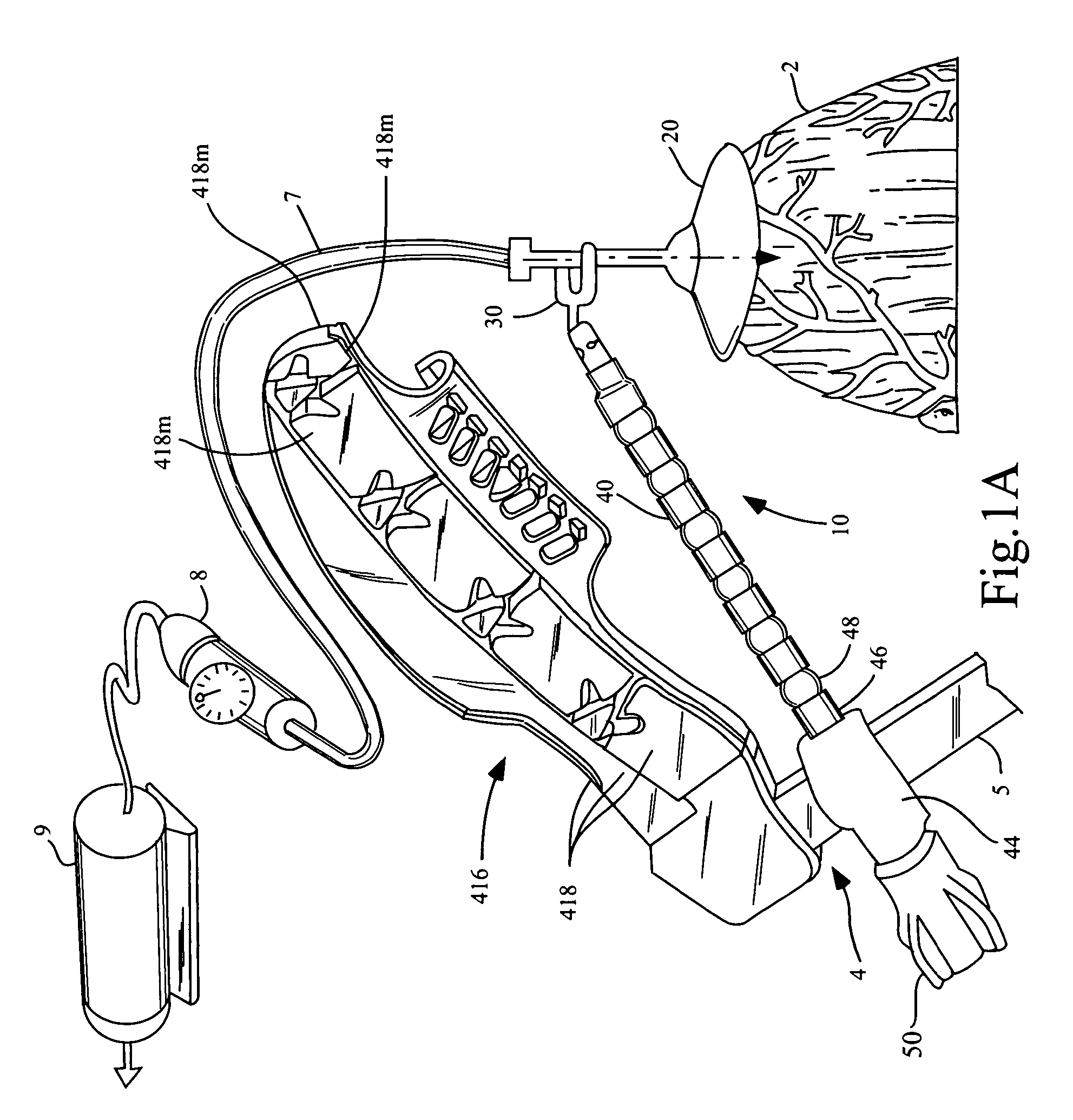
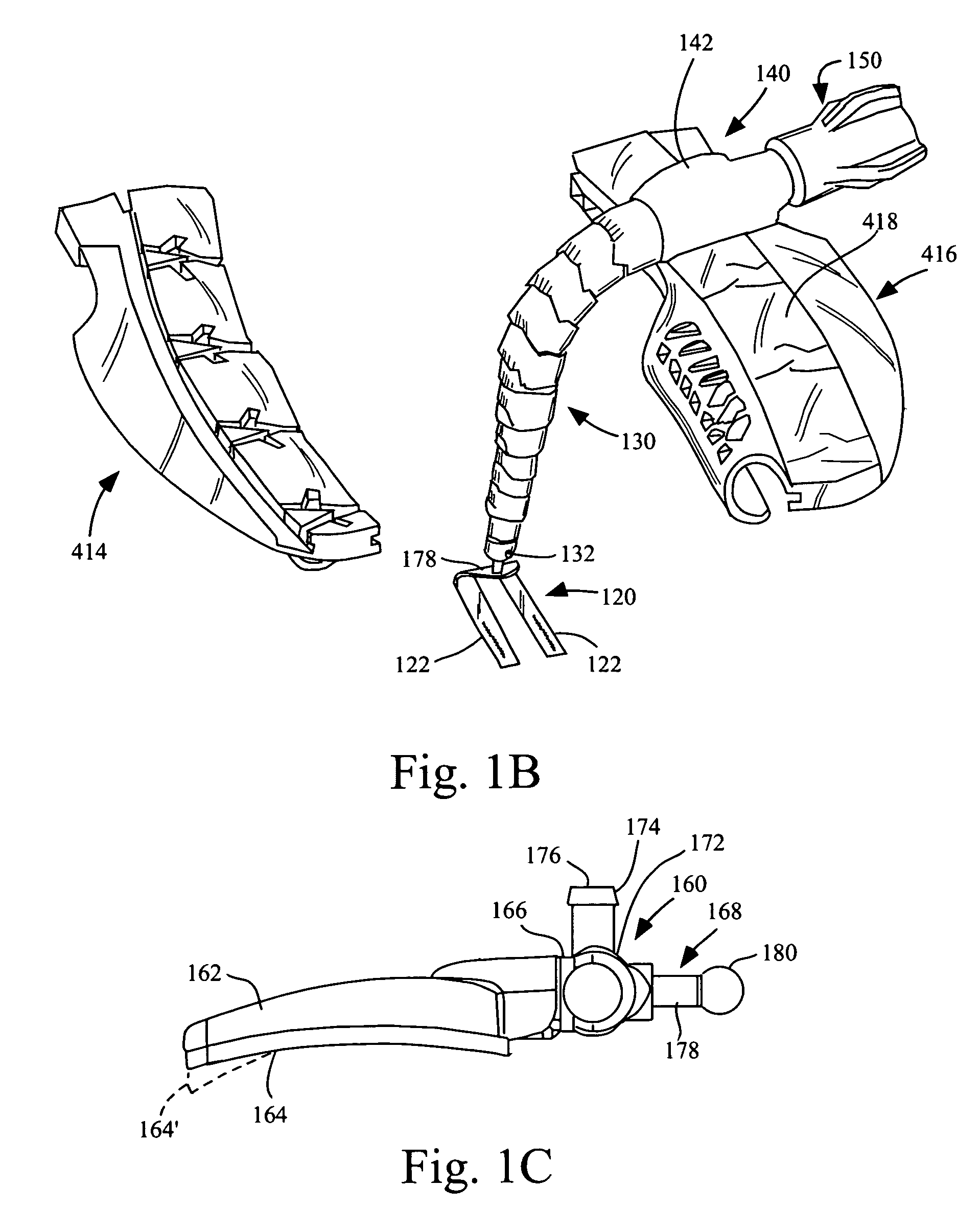
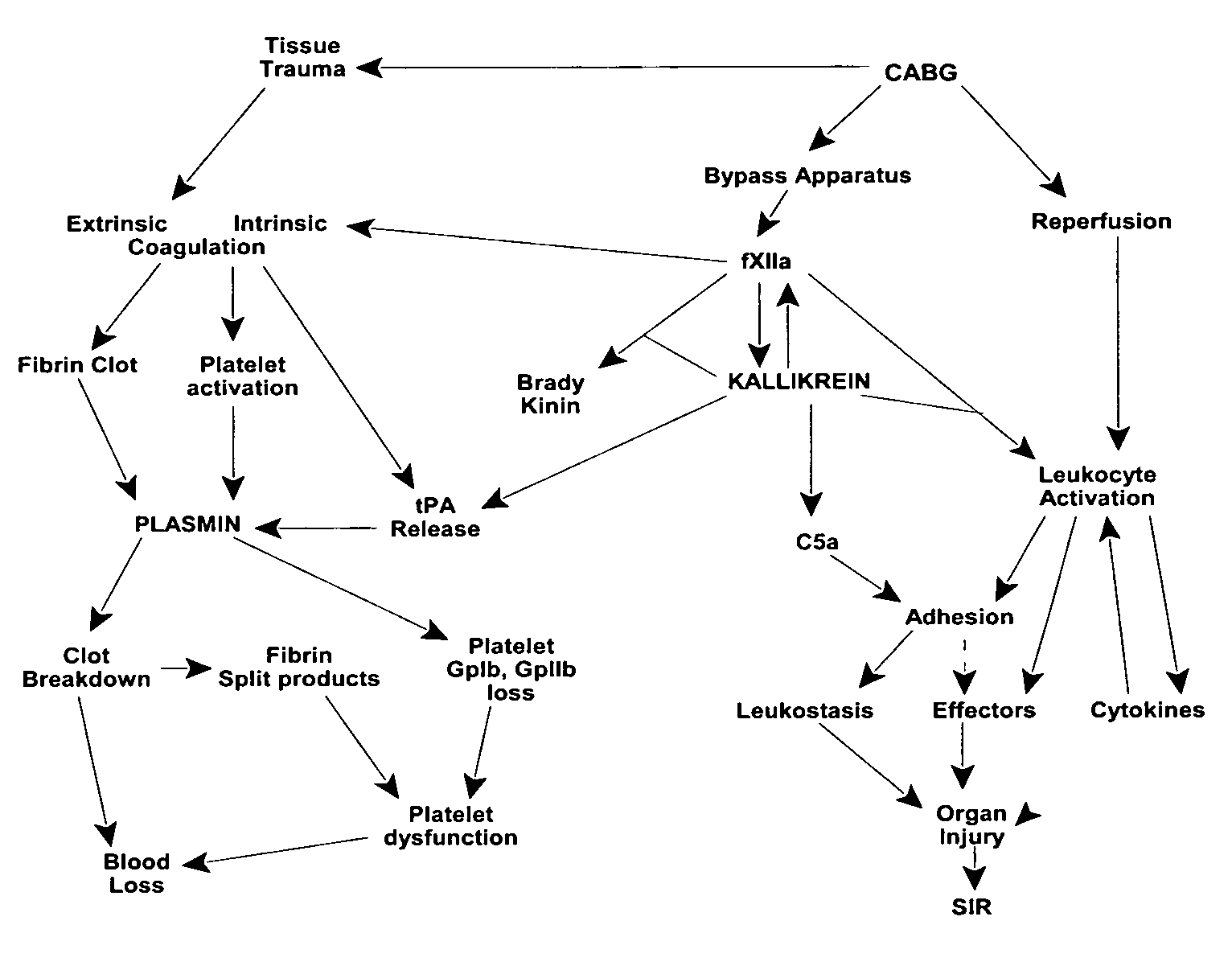
Patents
Literature
171 results about "Coronary Artery Bypasses" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Coronary artery bypass surgery is a procedure that detours (or bypasses) blood around a blocked section of one or more coronary arteries. It is also called coronary artery bypass grafting or CABG (pronounced "cabbage"). Coronary arteries are the blood vessels that supply the heart with oxygen and nutrients. You have several coronary arteries.
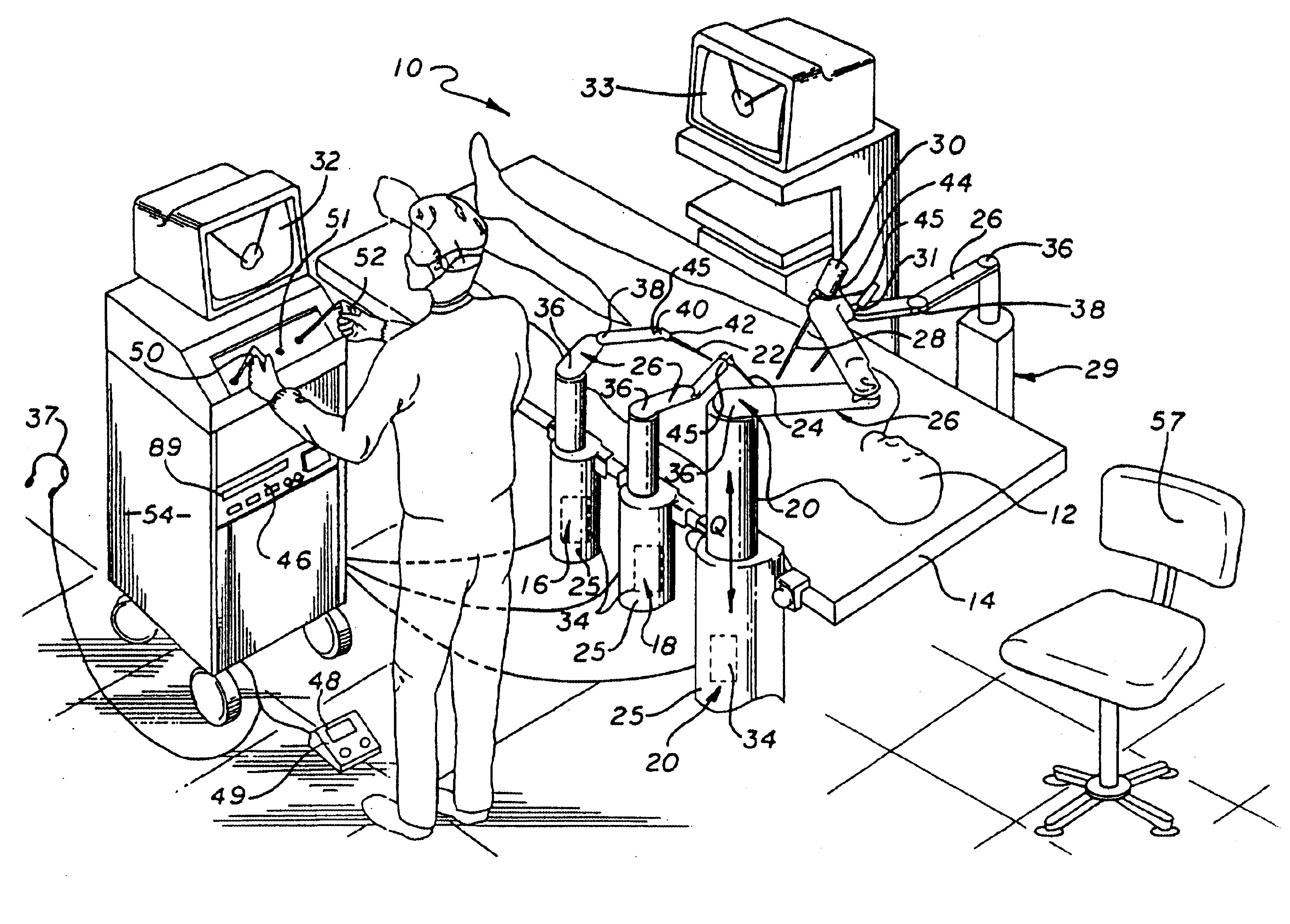
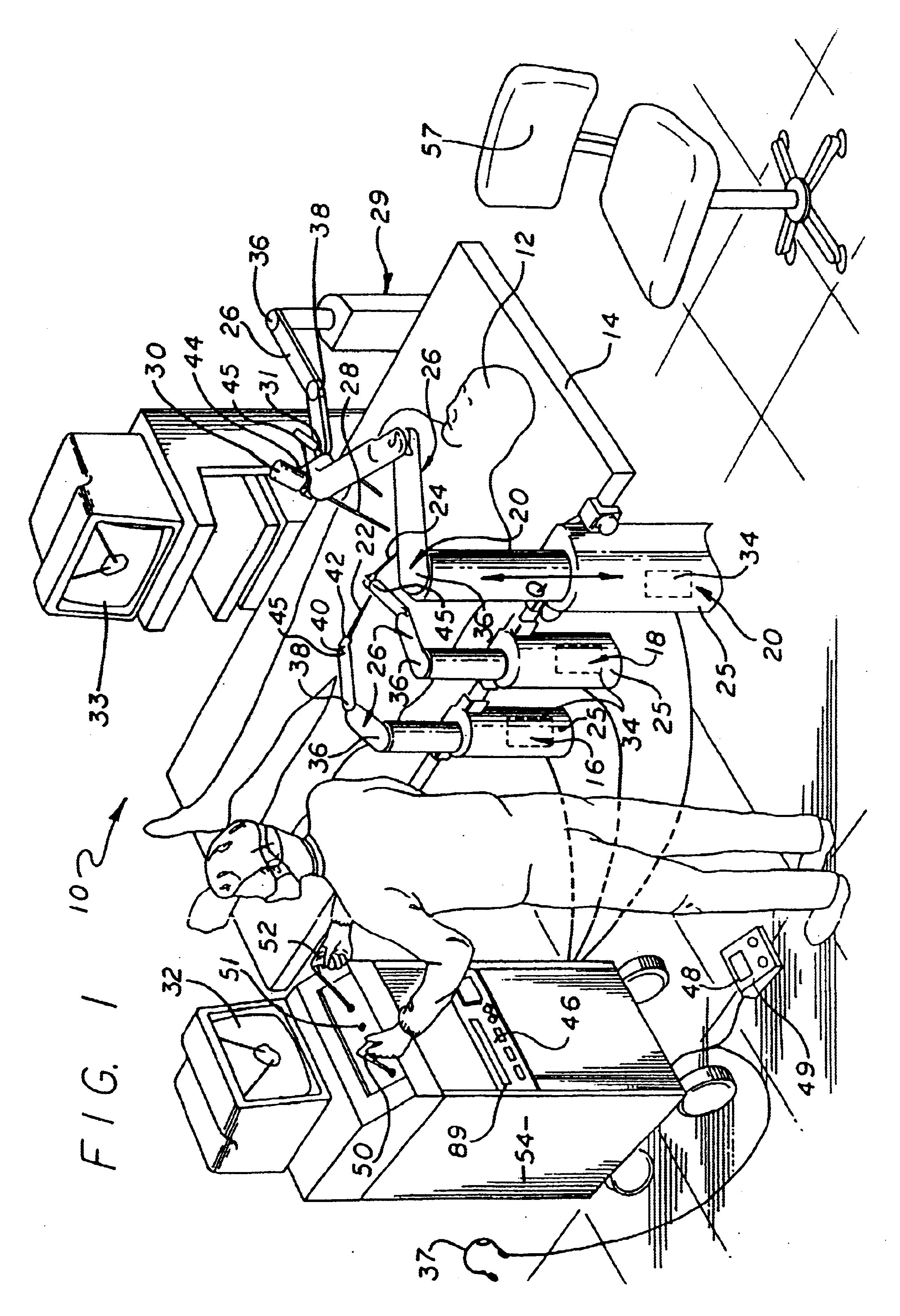
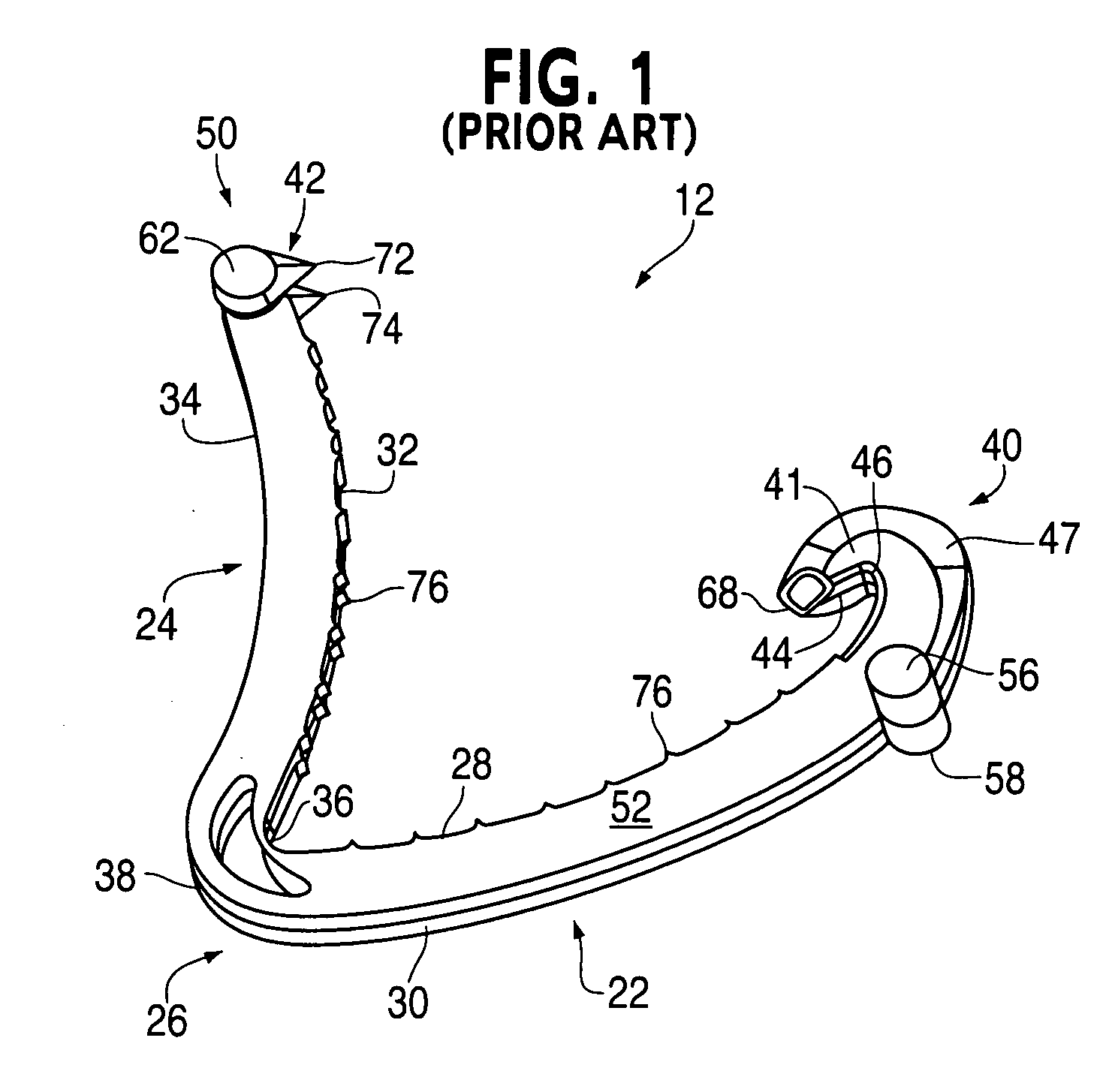
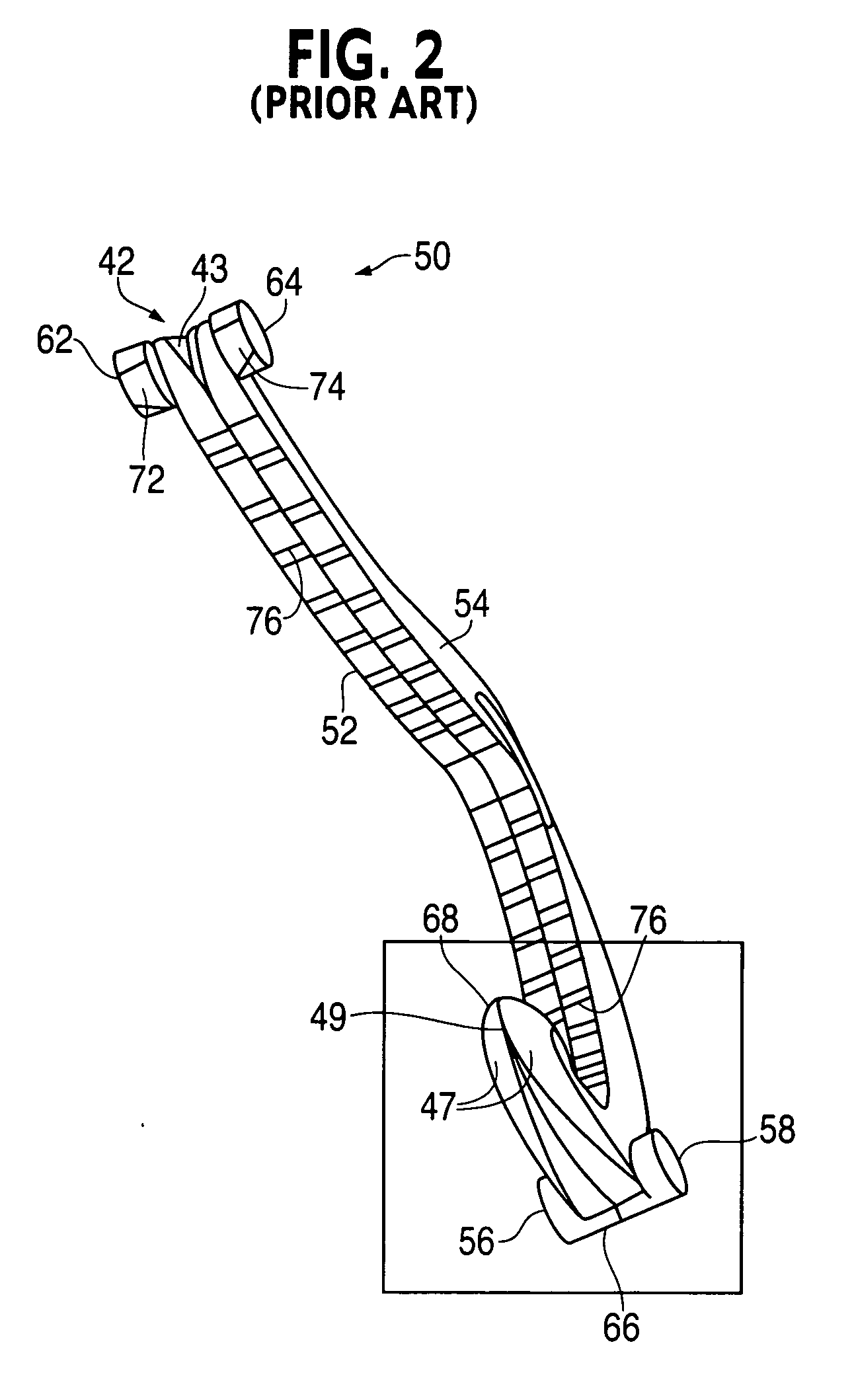
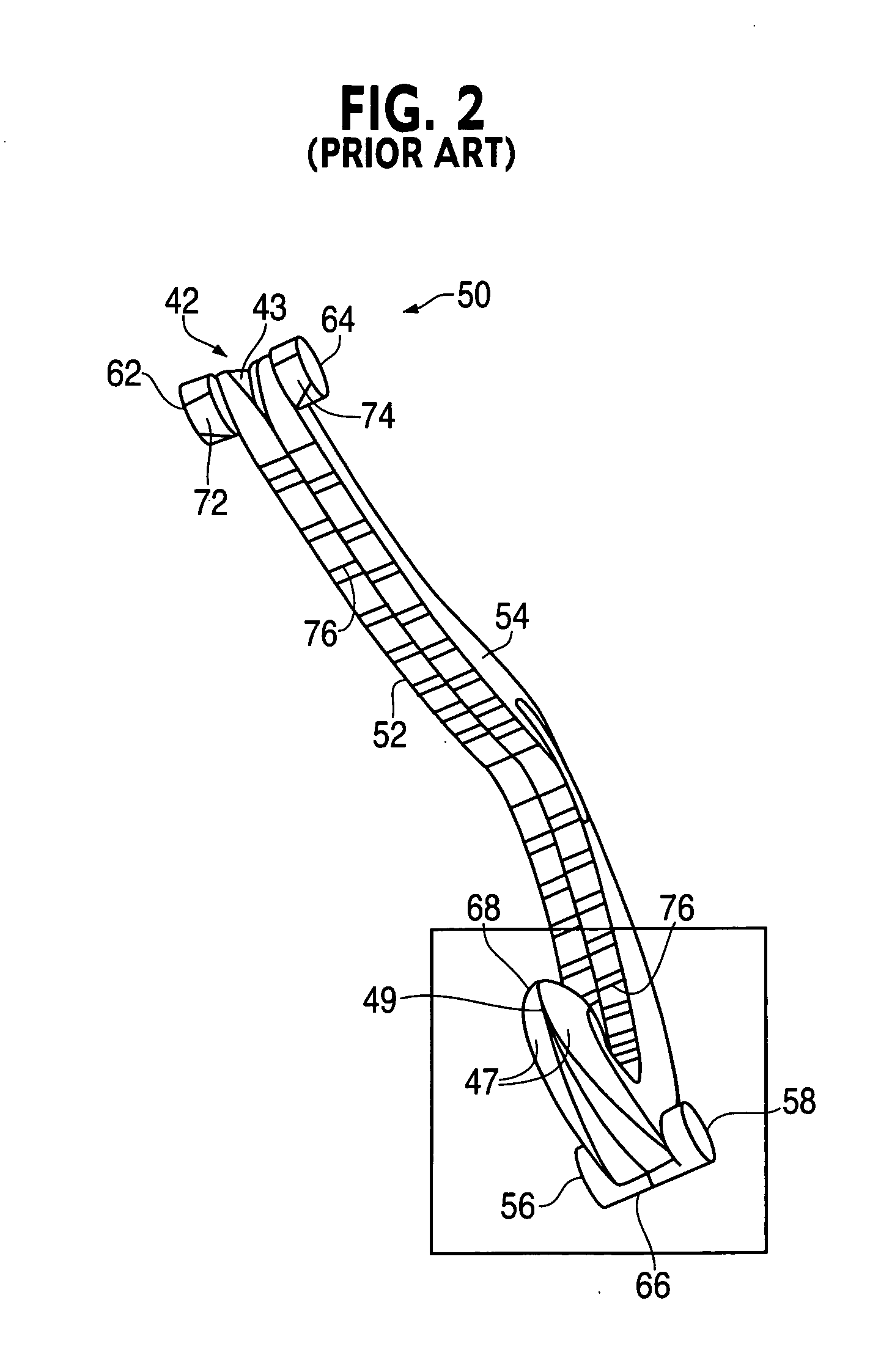
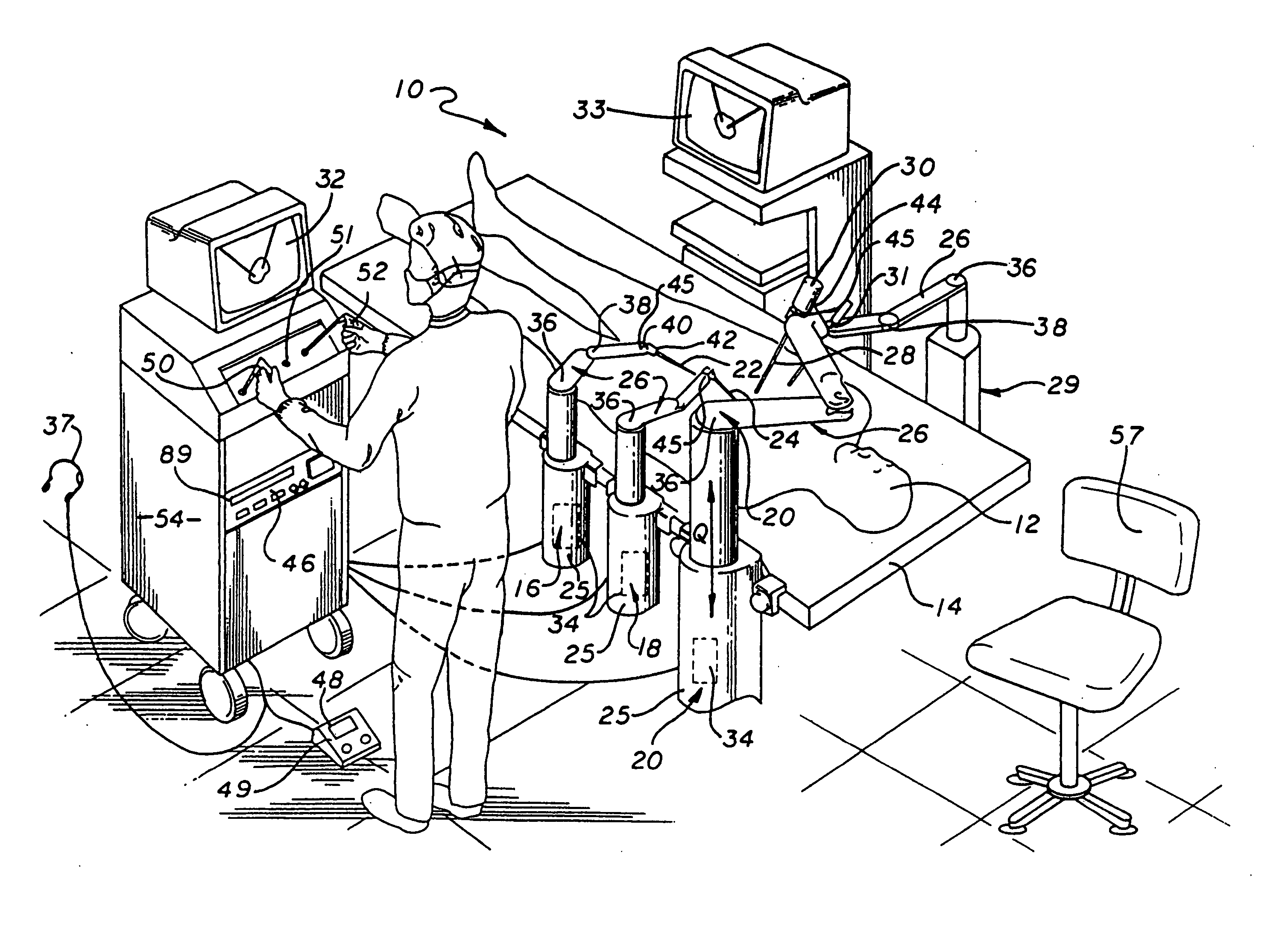
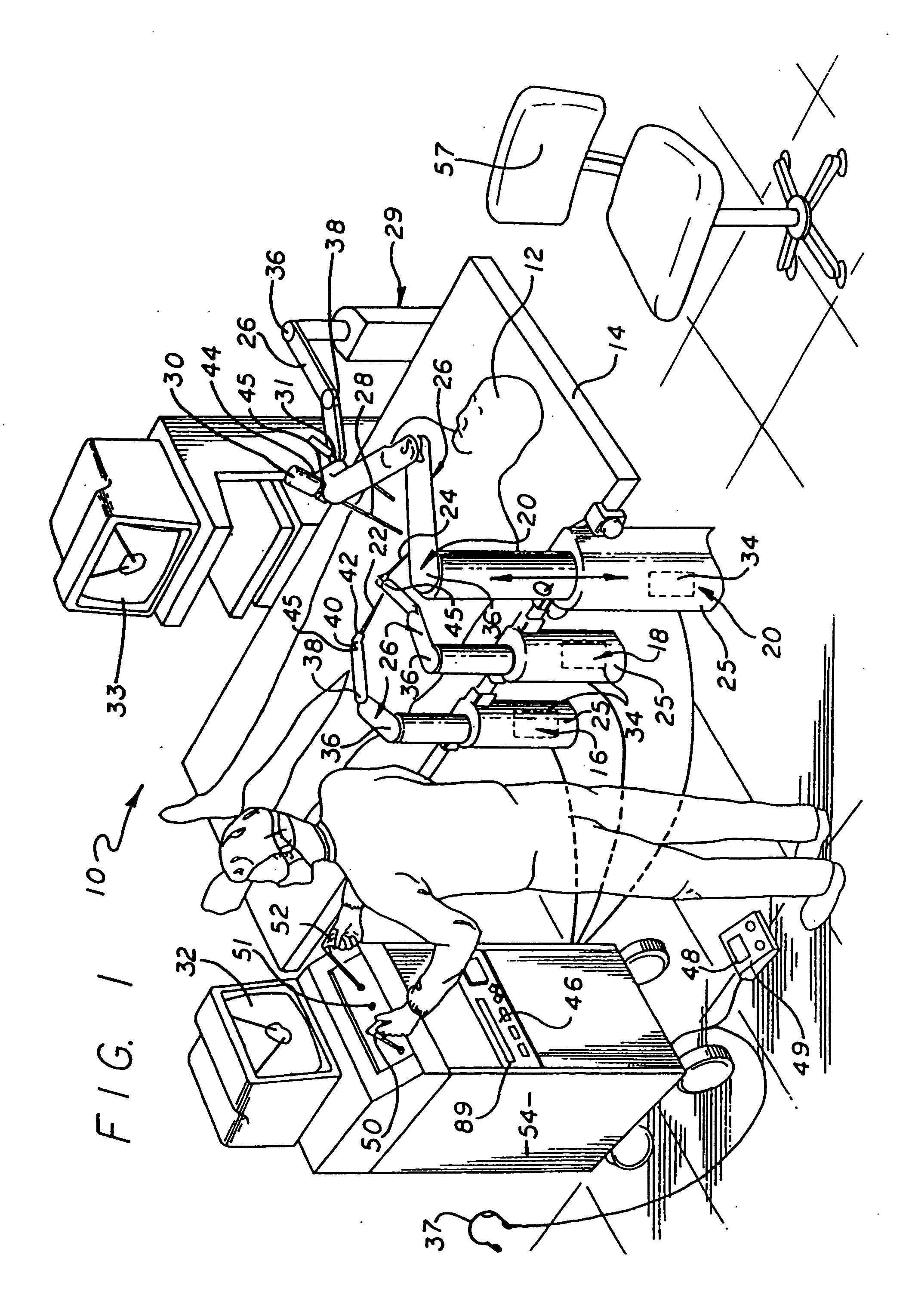
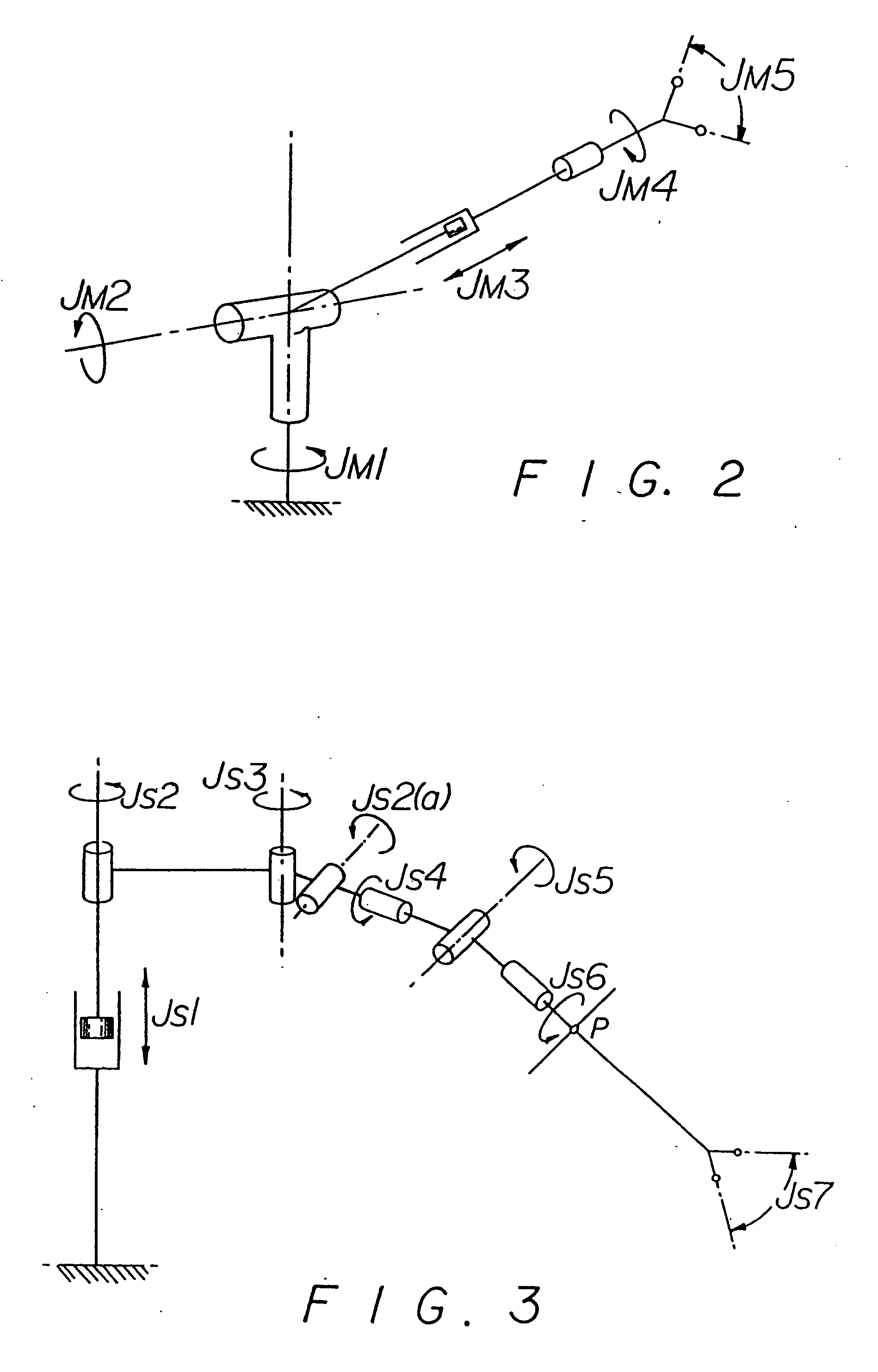
Method and apparatus for performing minimally invasive surgical procedures
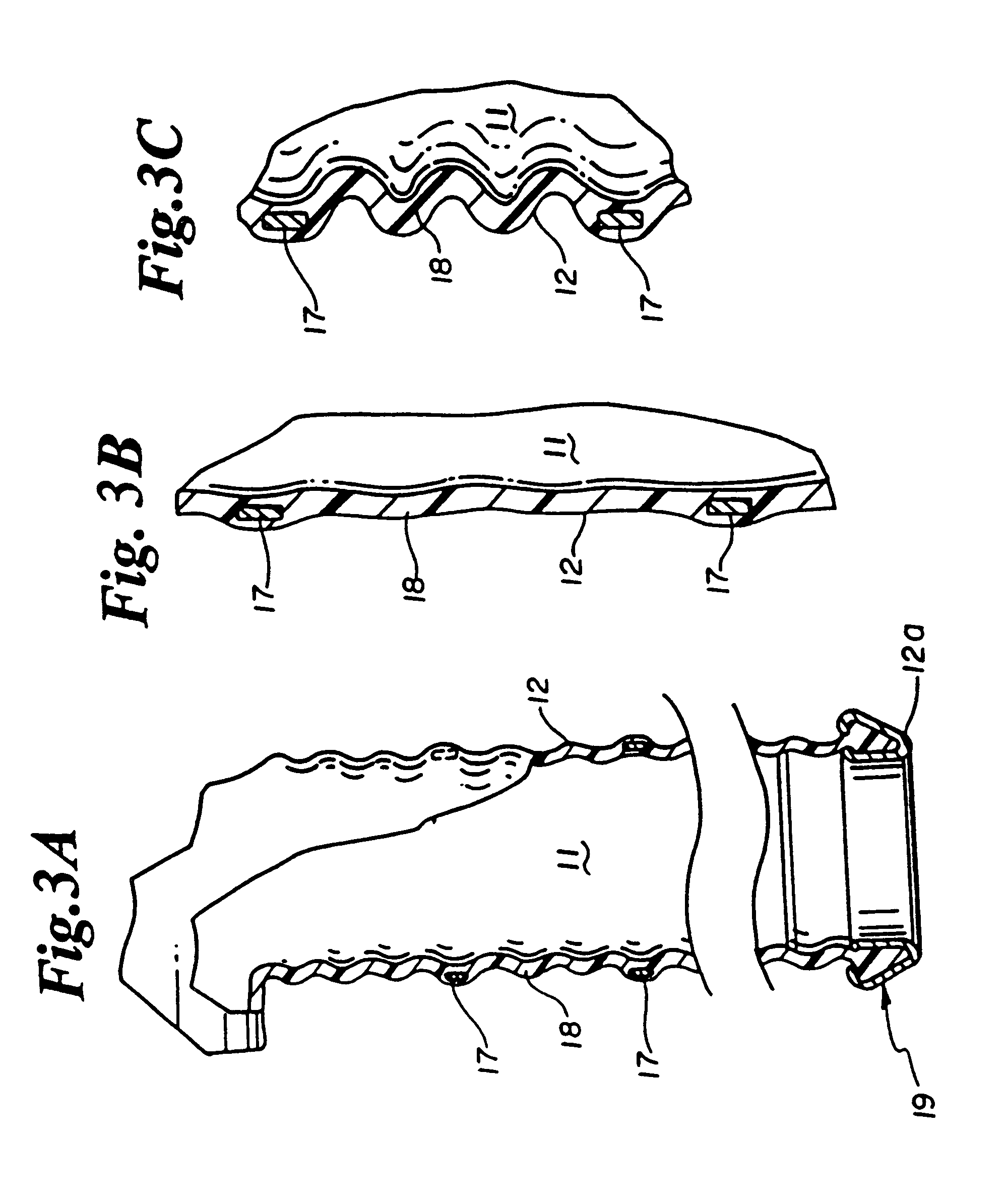
InactiveUS6905460B2Reserved functionHigh precisionProgramme controlSuture equipmentsRobotic armSurgical site
A system for performing minimally invasive cardiac procedures. The system includes a pair of surgical instruments that are coupled to a pair of robotic arms. The instruments have end effectors that can be manipulated to hold and suture tissue. The robotic arms are coupled to a pair of master handles by a controller. The handles can be moved by the surgeon to produce a corresponding movement of the end effectors. The movement of the handles is scaled so that the end effectors have a corresponding movement that is different, typically smaller, than the movement performed by the hands of the surgeon. The scale factor is adjustable so that the surgeon can control the resolution of the end effector movement. The movement of the end effector can be controlled by an input button, so that the end effector only moves when the button is depressed by the surgeon. The input button allows the surgeon to adjust the position of the handles without moving the end effector, so that the handles can be moved to a more comfortable position. The system may also have a robotically controlled endoscope which allows the surgeon to remotely view the surgical site. A cardiac procedure can be performed by making small incisions in the patient's skin and inserting the instruments and endoscope into the patient. The surgeon manipulates the handles and moves the end effectors to perform a cardiac procedure such as a coronary artery bypass graft.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Non-snag polymer ligating clip
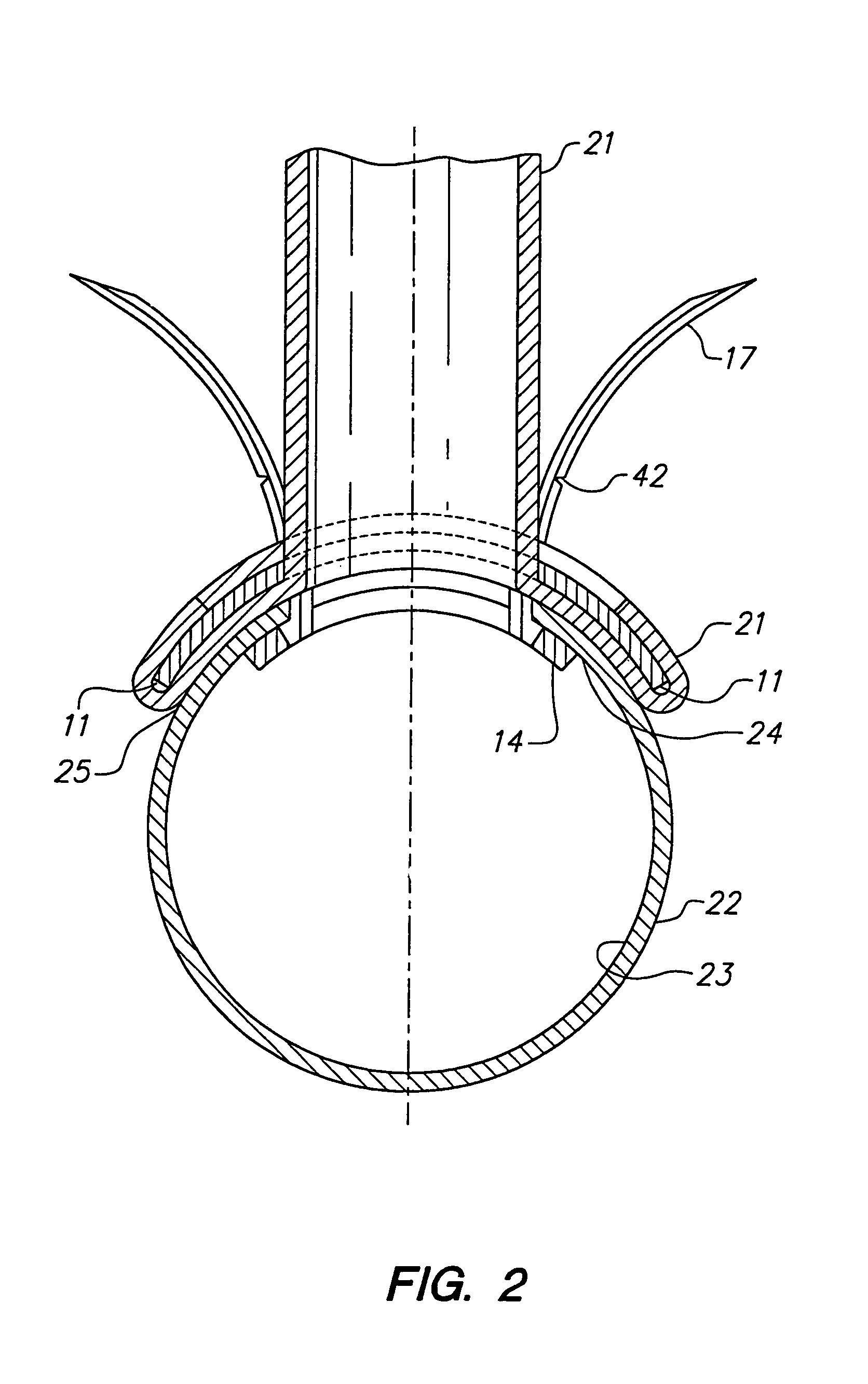
InactiveUS20070118161A1Removably lock the clipInterference minimizationWound clampsCoronary Artery BypassesLigating clips
A polymeric, surgical clip having first and second curved legs with each having a pair of opposing side surfaces joined at their proximal ends by a flexible hinge section and movable from an open position to a closed position for clamping a vessel between curved opposing inner surfaces. The first leg terminates at its distal end in a female locking member, and the second leg member terminates in a male locking member complimentary to the female locking member such that when the first and second leg members are moved from an open position to a closed position about the hinge section the male member is lockingly engaged in the female locking member. The clip is provided with low profile boss-like elements on the legs thereof to reduce the risk of snagging a suture during coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
Owner:TELEFLEX MEDICAL INC
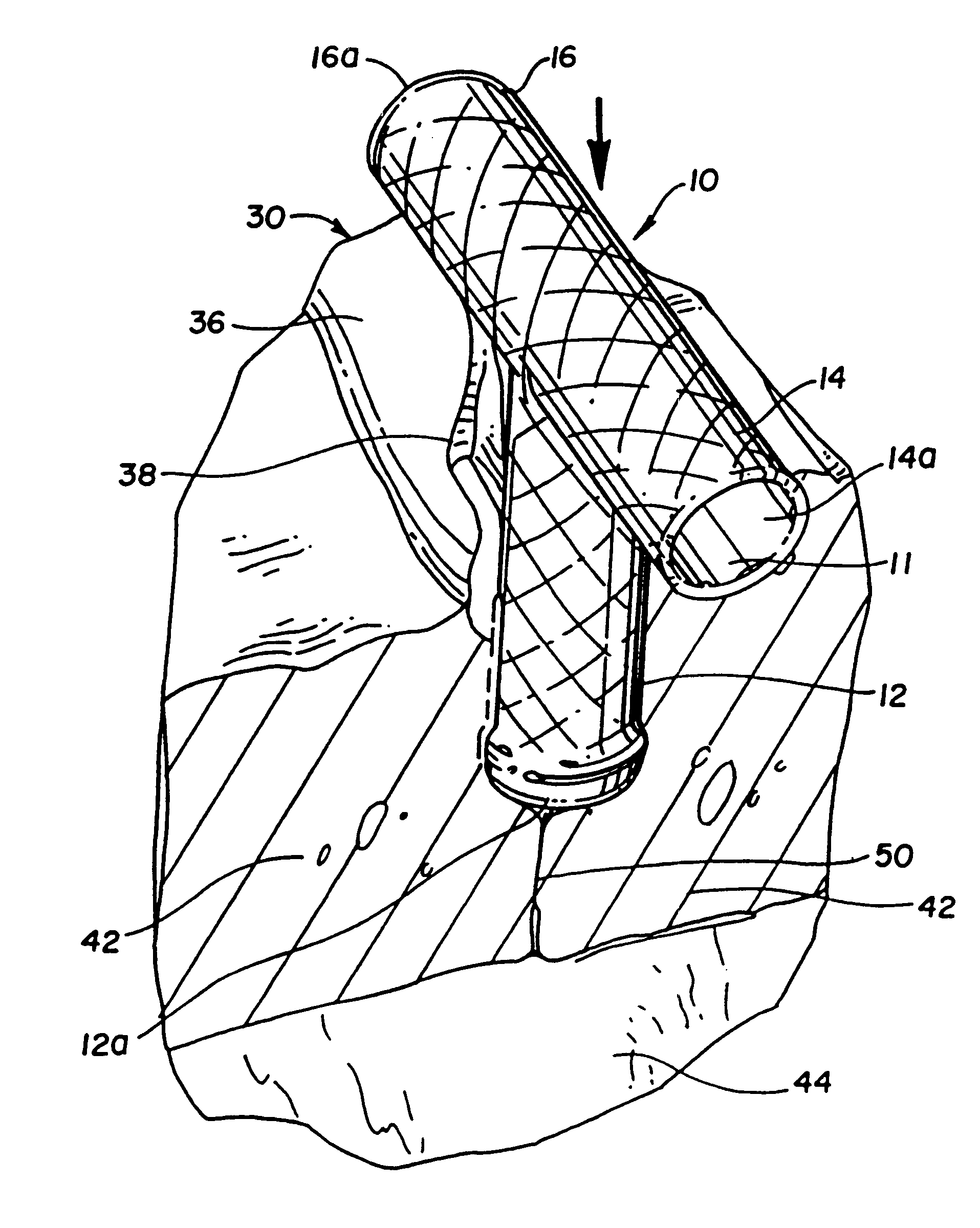
Expandable myocardial implant
InactiveUS6350248B1Improve visualizationReduce oxygen requirementStentsDiagnosticsCoronary arteriesHeart chamber
A method and apparatus for performing coronary artery bypass surgery establishes a channel leading directly from a chamber of a heart into a coronary artery. The coronary artery bypass procedure may be performed with or without cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:HORIZON TECH FUNDING CO LLC
Endoscopic beating-heart stabilizer and vessel occlusion fastener
InactiveUS7250028B2Physiological motion of stabilizedAvoid relative motionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsSurgical operationSurgical department
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Closed chest coronary bypass
InactiveUS6123682AImprove visualizationReduce oxygen requirementStentsDiagnosticsCoronary arteriesHeart chamber
A method and apparatus for performing coronary artery bypass surgery establishes a channel leading directly from a chamber of a heart into a coronary artery. The coronary artery bypass procedure may be performed with or without cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:HORIZON TECH FUNDING CO LLC
Non-snag polymer ligating clip
Owner:KENNEDY DANIEL L +2
Methods and systems for performing thoracoscopic coronary bypass and other procedures
InactiveUS6027476AImprove isolationReduce complicationsSuture equipmentsCannulasThoracoscopeHeart operations
A method for closed-chest cardiac surgical intervention relies on viewing the cardiac region through a thoracoscope or other viewing scope and endovascularly partitioning the patient's arterial system at a location within the ascending aorta. The cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia can be induced, and a variety of surgical procedures performed on the stopped heart using percutaneously introduced tools. The method of the present invention will be particularly suitable for forming coronary artery bypass grafts, where an arterial blood source is created using least invasive surgical techniques, and the arterial source is connected to a target location within a coronary artery while the patient is under cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Coronary bypass implant
InactiveUS6093166AImprove visualizationReduce oxygen requirementStentsDiagnosticsCoronary arteriesHeart chamber
A method and apparatus for performing coronary artery bypass surgery establishes a channel leading directly from a chamber of a heart into a coronary artery. The coronary artery bypass procedure may be performed with or without cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:HORIZON TECH FUNDING CO LLC
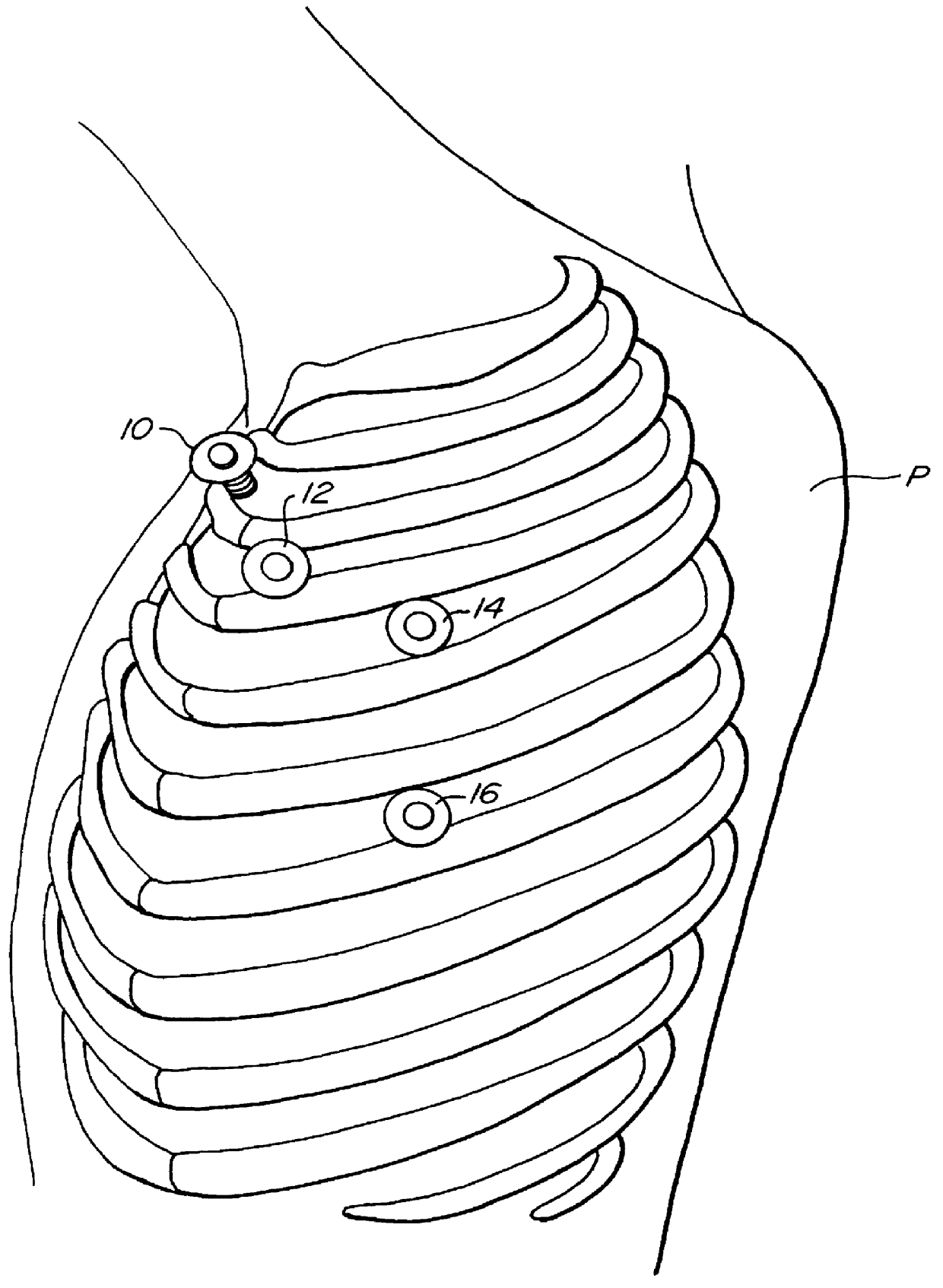
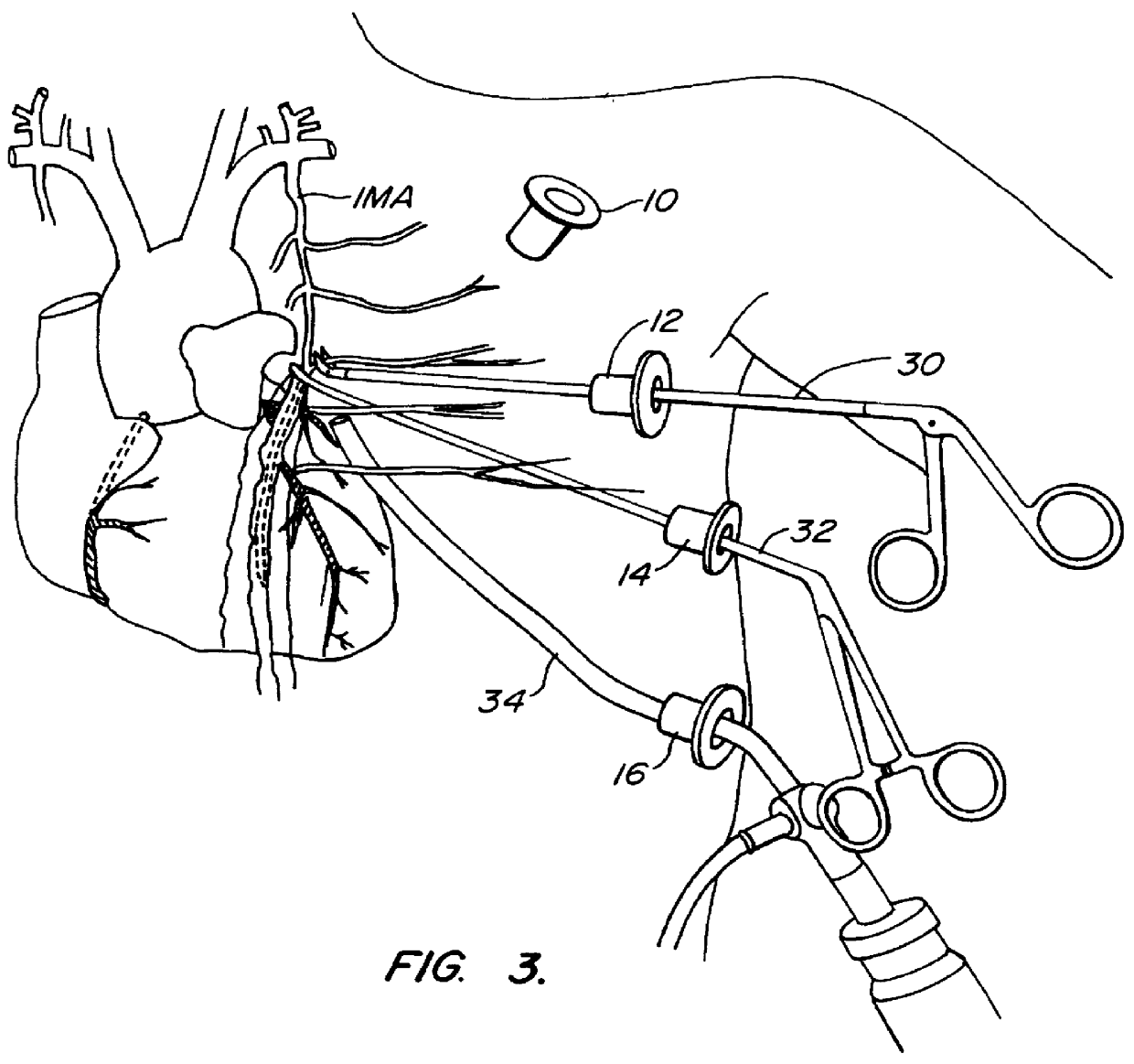
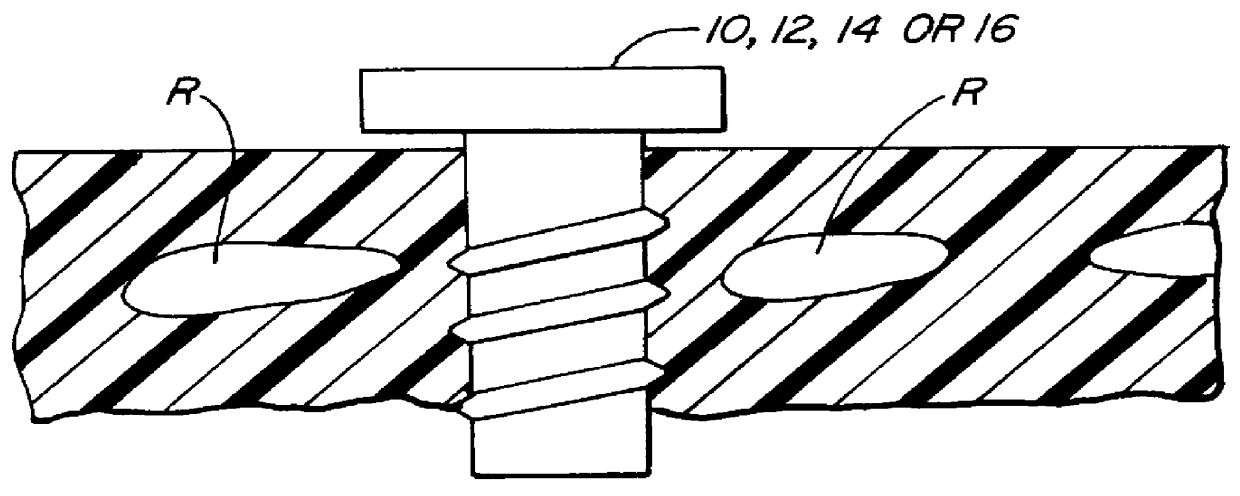
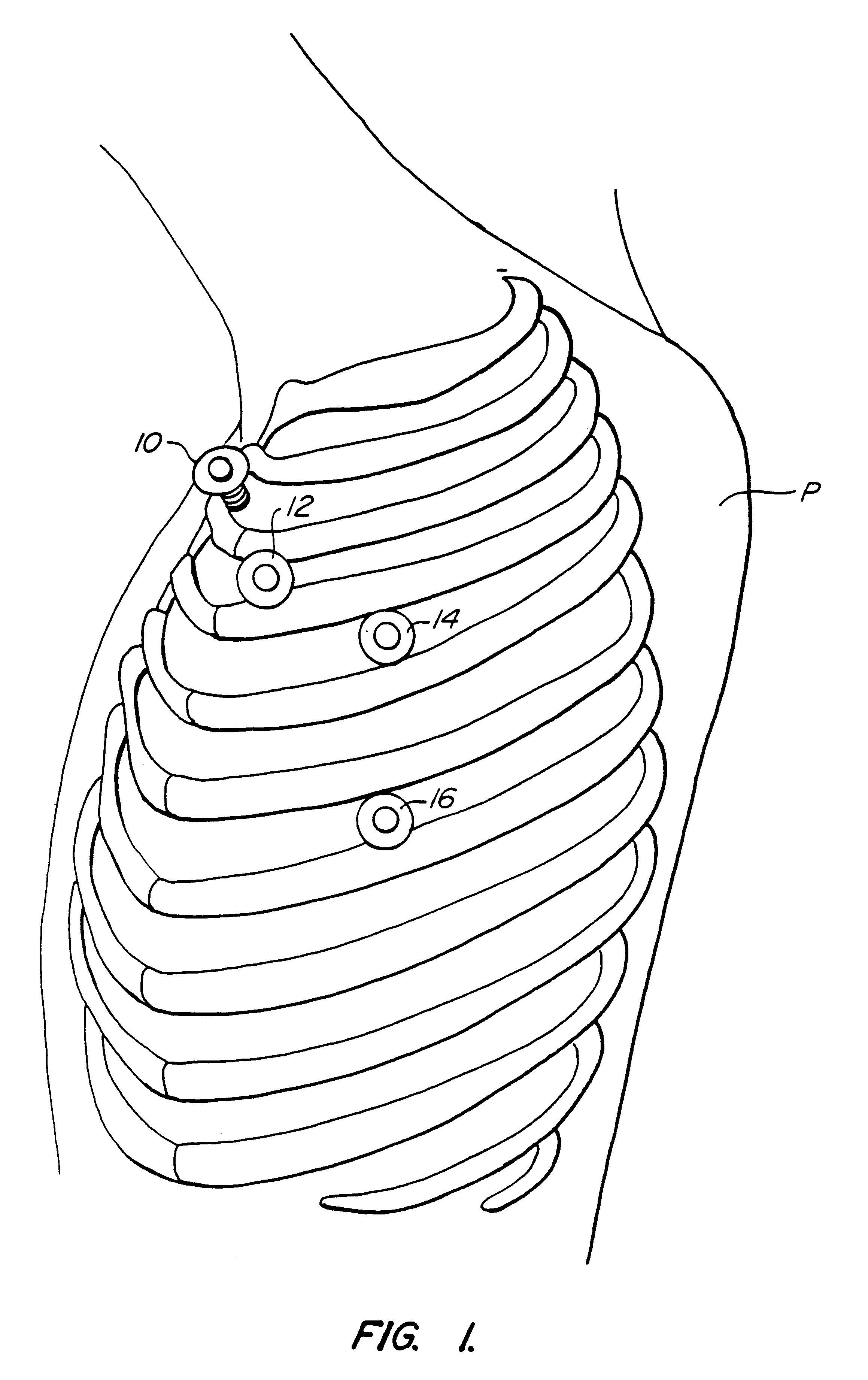
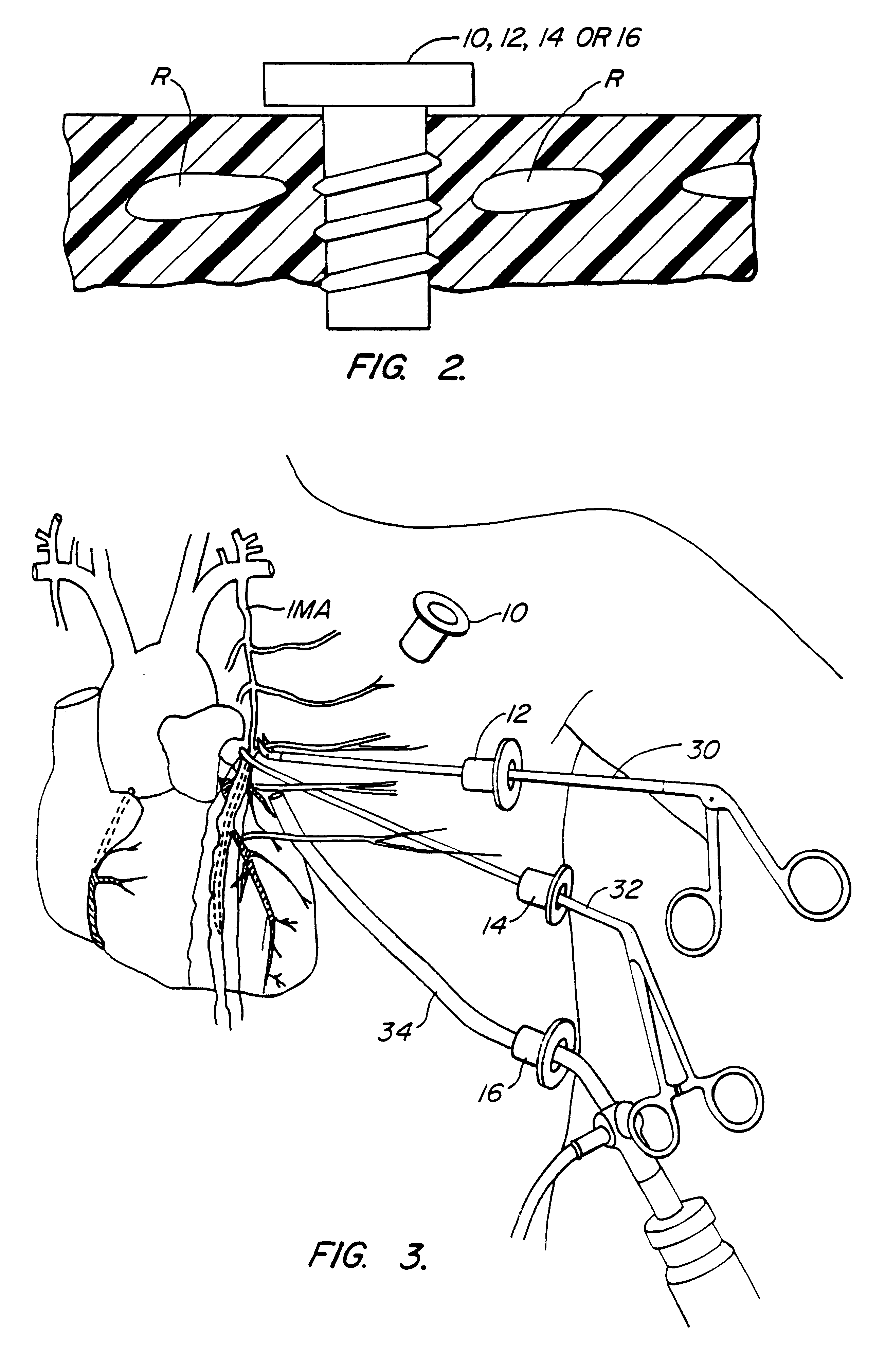
Devices and methods for port-access multivessel coronary artery bypass surgery
InactiveUS6478029B1Reduce oxygen demandReduce the temperatureSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsDiseaseSurgical approach
Surgical methods and instruments are disclosed for performing port-access or closed-chest coronary artery bypass (CABG) surgery in multivessel coronary artery disease. In contrast to standard open-chest CABG surgery, which requires a median sternotomy or other gross thoracotomy to expose the patient's heart, post-access CABG surgery is performed through small incisions or access ports made through the intercostal spaces between the patient's ribs, resulting in greatly reduced pain and morbidity to the patient. In situ arterial bypass grafts, such as the internal mammary arteries and / or the right gastroepiploic artery, are prepared for grafting by thoracoscopic or laparoscopic takedown techniques. Free grafts, such as a saphenous vein graft or a free arterial graft, can be used to augment the in situ arterial grafts. The graft vessels are anastomosed to the coronary arteries under direct visualization through a cardioscopic microscope inserted through an intercostal access port. Retraction instruments are provided to manipulate the heart within the closed chest of the patient to expose each of the coronary arteries for visualization and anastomosis. Disclosed are a tunneler and an articulated tunneling grasper for rerouting the graft vessels, and a finger-like retractor, a suction cup retractor, a snare retractor and a loop retractor for manipulating the heart. Also disclosed is a port-access topical cooling device for improving myocardial protection during the port-access CABG procedure. An alternate surgical approach using an anterior mediastinotomy is also described.
Owner:HEARTPORT
Method and apparatus for performing minimally invasive surgical procedures
InactiveUS20050228365A1Reserved functionHigh precisionProgramme controlSuture equipmentsRobotic armSurgical site
The system includes a pair of surgical instruments that are coupled to a pair of robotic arms. The instruments have end effectors that can be manipulated to hold and suture tissue. The robotic arms are coupled to a pair of master handles by a controller. The handles can be moved by the surgeon to produce a corresponding movement of the end effectors. The movement of the handles is scaled so that the end effectors have a corresponding movement that is different, typically smaller, than the movement performed by the hands of the surgeon. The scale factor is adjustable so that the surgeon can control the resolution of the end effector movement. The movement of the end effector can be controlled by an input button, so that the end effector only moves when the button is depressed by the surgeon. The input button allows the surgeon to adjust the position of the handles without moving the end effector, so that the handles can be moved to a more comfortable position. The system may also have a robotically controlled endoscope which allows the surgeon to remotely view the surgical site. A cardiac procedure can be performed by making small incisions in the patient's skin and inserting the instruments and endoscope into the patient. The surgeon manipulates the handles and moves the end effectors to perform a cardiac procedure such as a coronary artery bypass graft.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
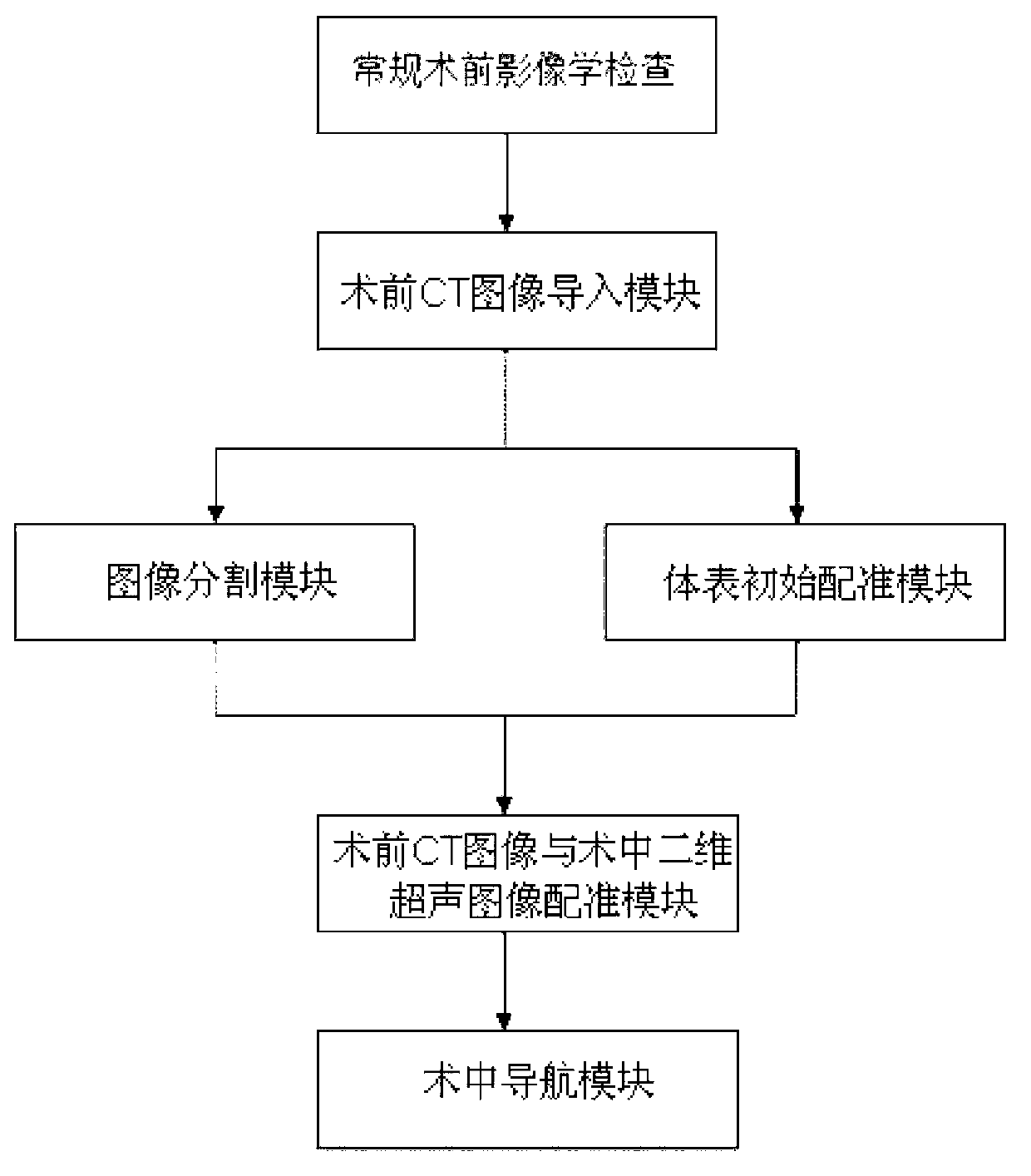
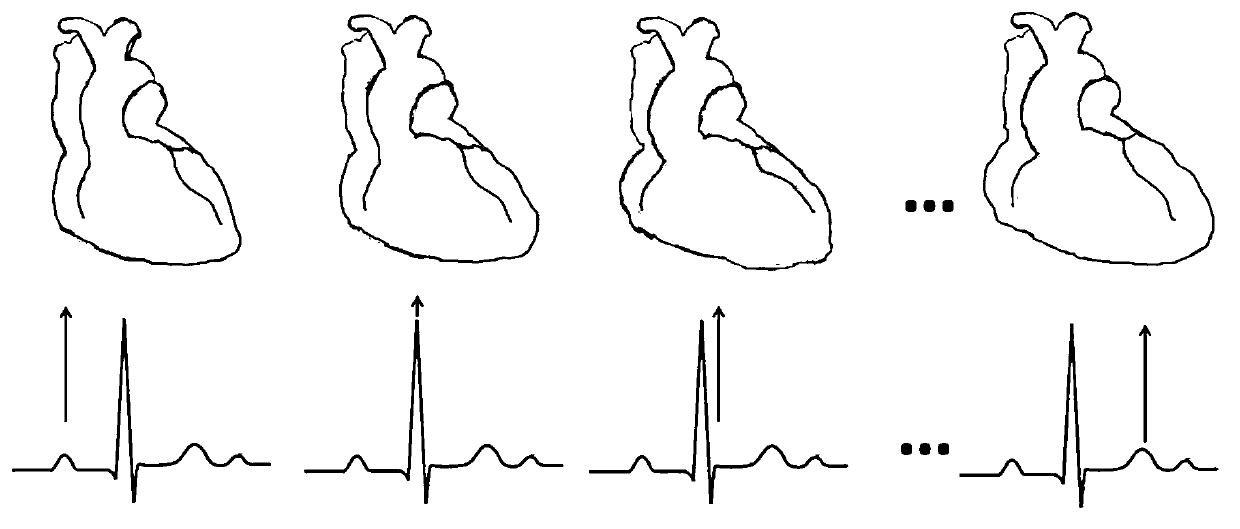
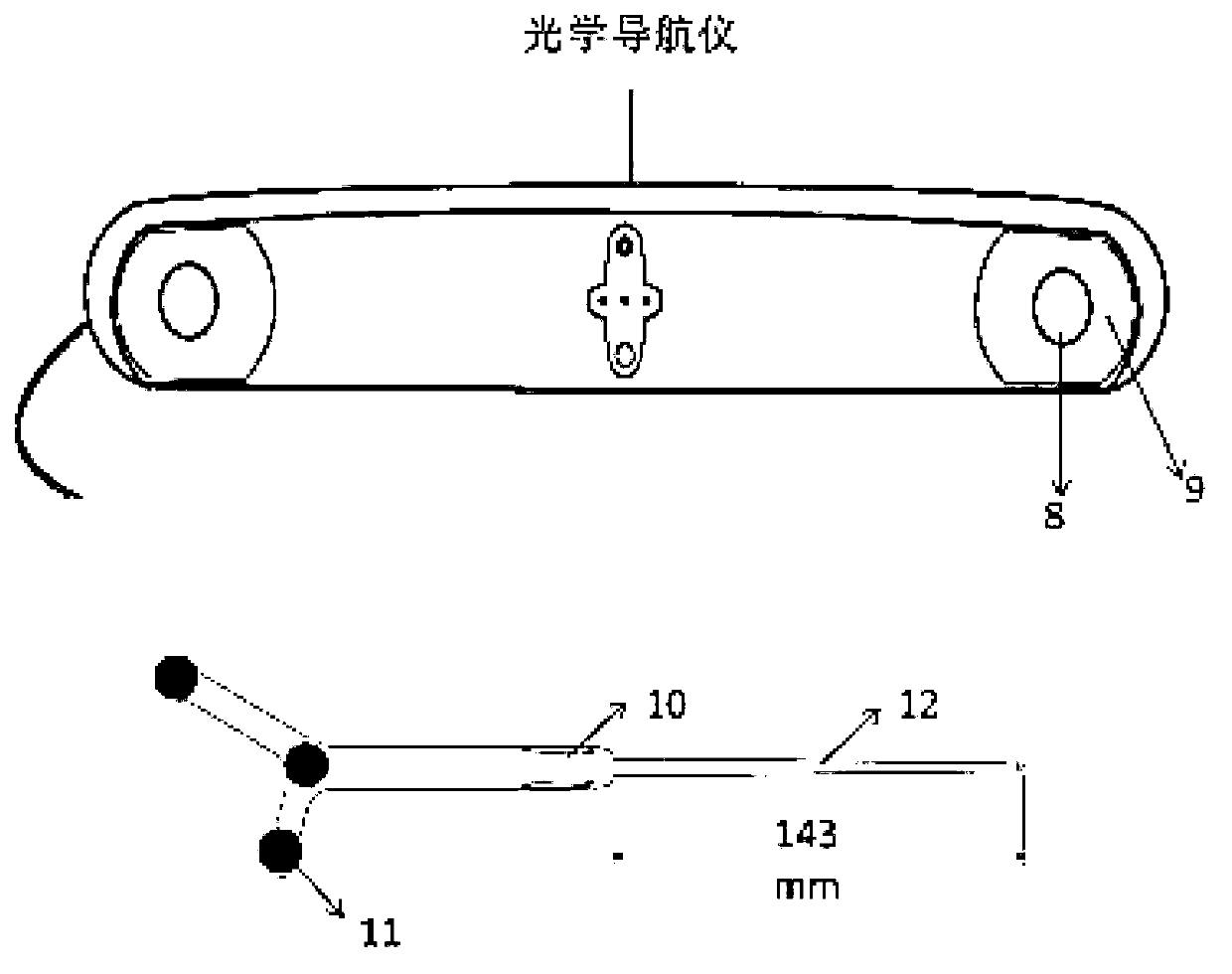
Optical navigation positioning system based on CT (computed tomography) registration results and navigation method thereby
ActiveCN102999902AResolve uncertaintyImage analysisDiagnosticsImage segmentationIntraoperative ultrasound
Disclosed are an optical navigation positioning system based on CT (computed tomography) registration results and a navigation method thereby. The system comprises a preoperative CT image guide input module, an image segmentation module, a body surface initial-registration module, a preoperative CT image and intraoperative two-dimensional ultrasound image module and an intraoperative navigation module. By combining virtual reality and intraoperative ultrasound, intraoperative positioning errors caused by factors such as breathing are compensated, and accordingly a target point for coronary artery bypass grafting is accurately positioned and navigated. Cardiac and coronary vessel tree in preoperative cardiac CT image data is manually segmented and reconstructed, an augmented virtual reality environment integrating endoscope and virtual endoscope is built by the aid of optical navigation apparatus and CT-ultrasound-based intraoperative registration error correction, and accordingly the target point of coronary artery bypass grafting is accurately positioned and navigated.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
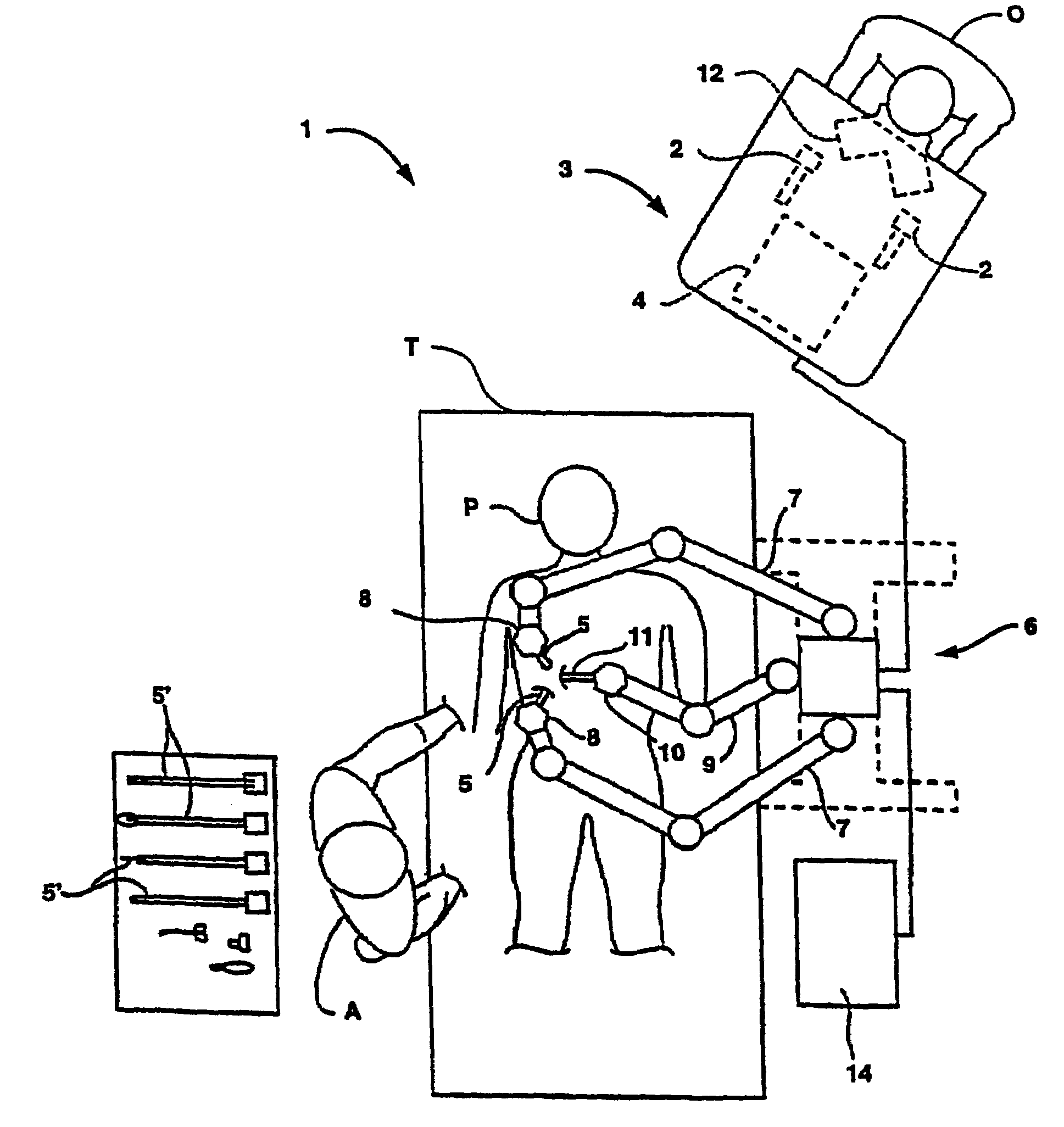
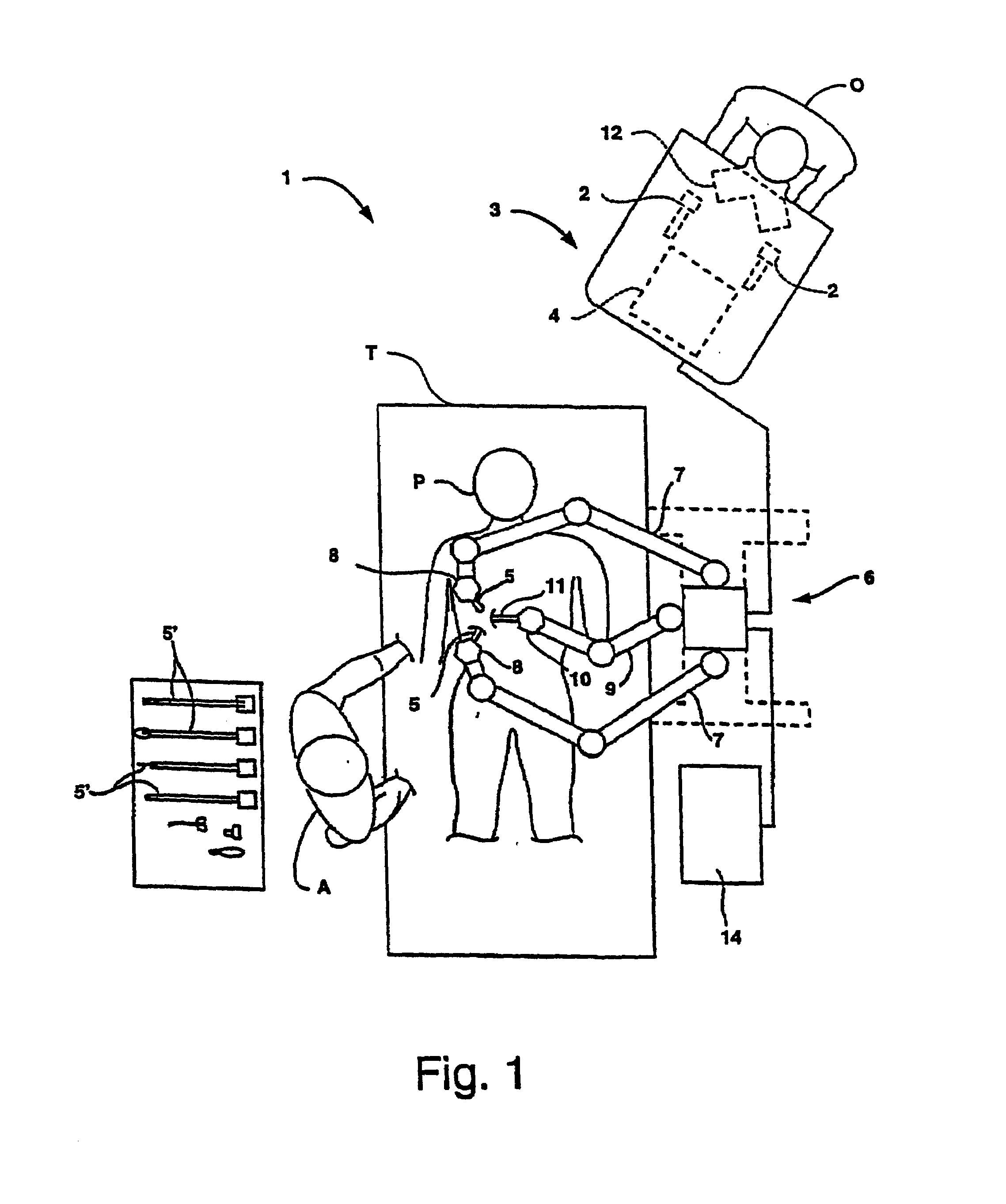
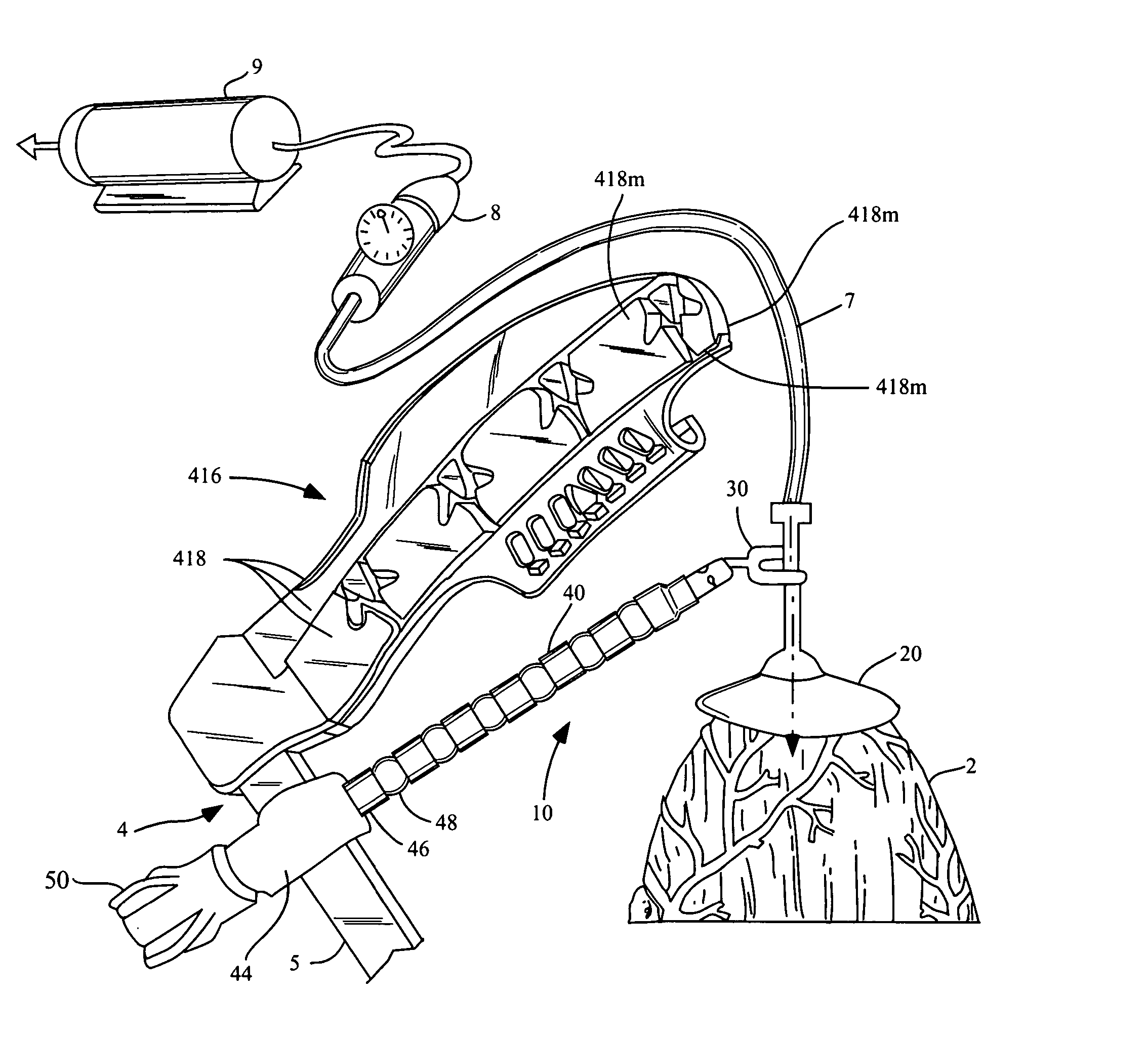
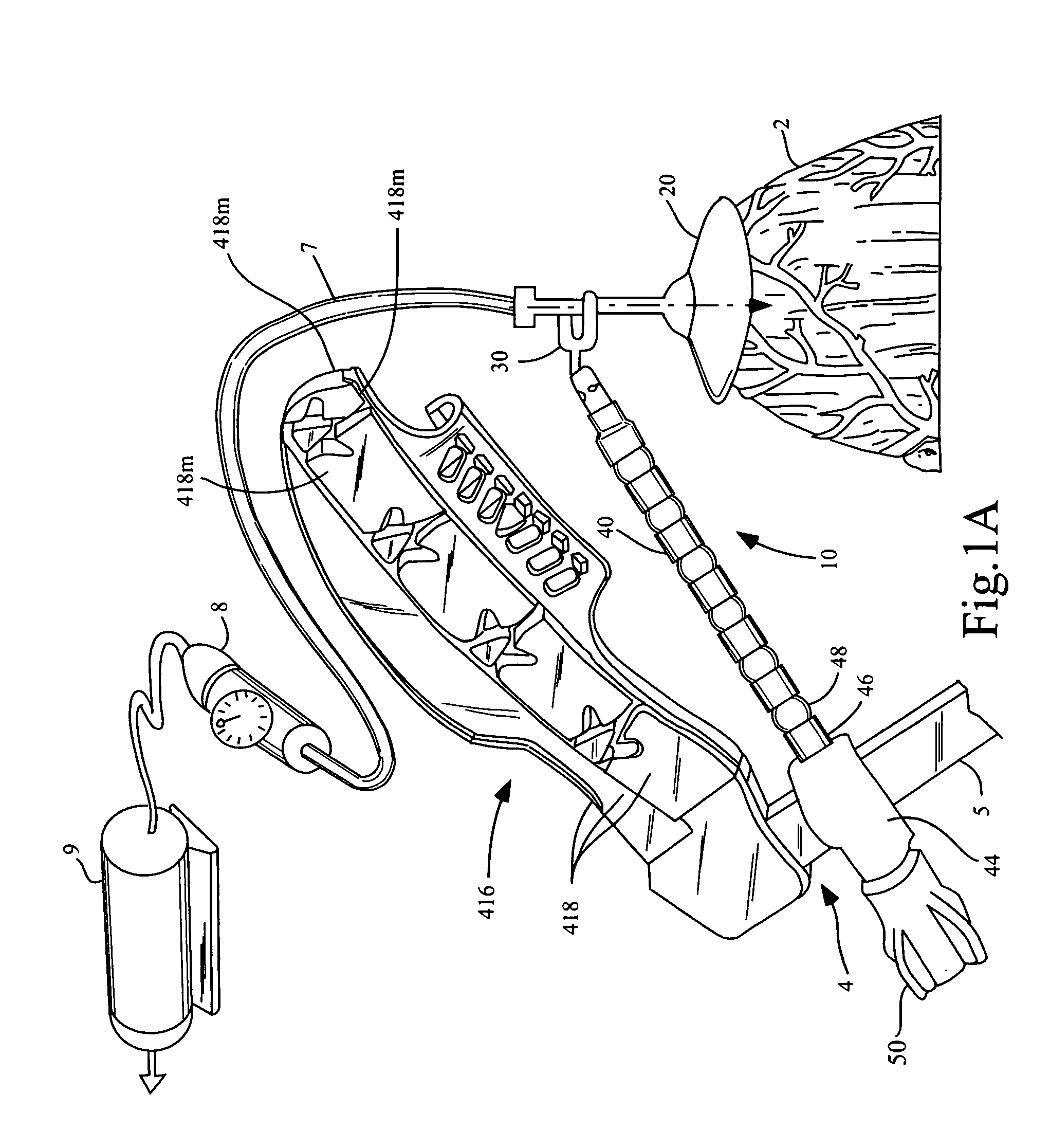
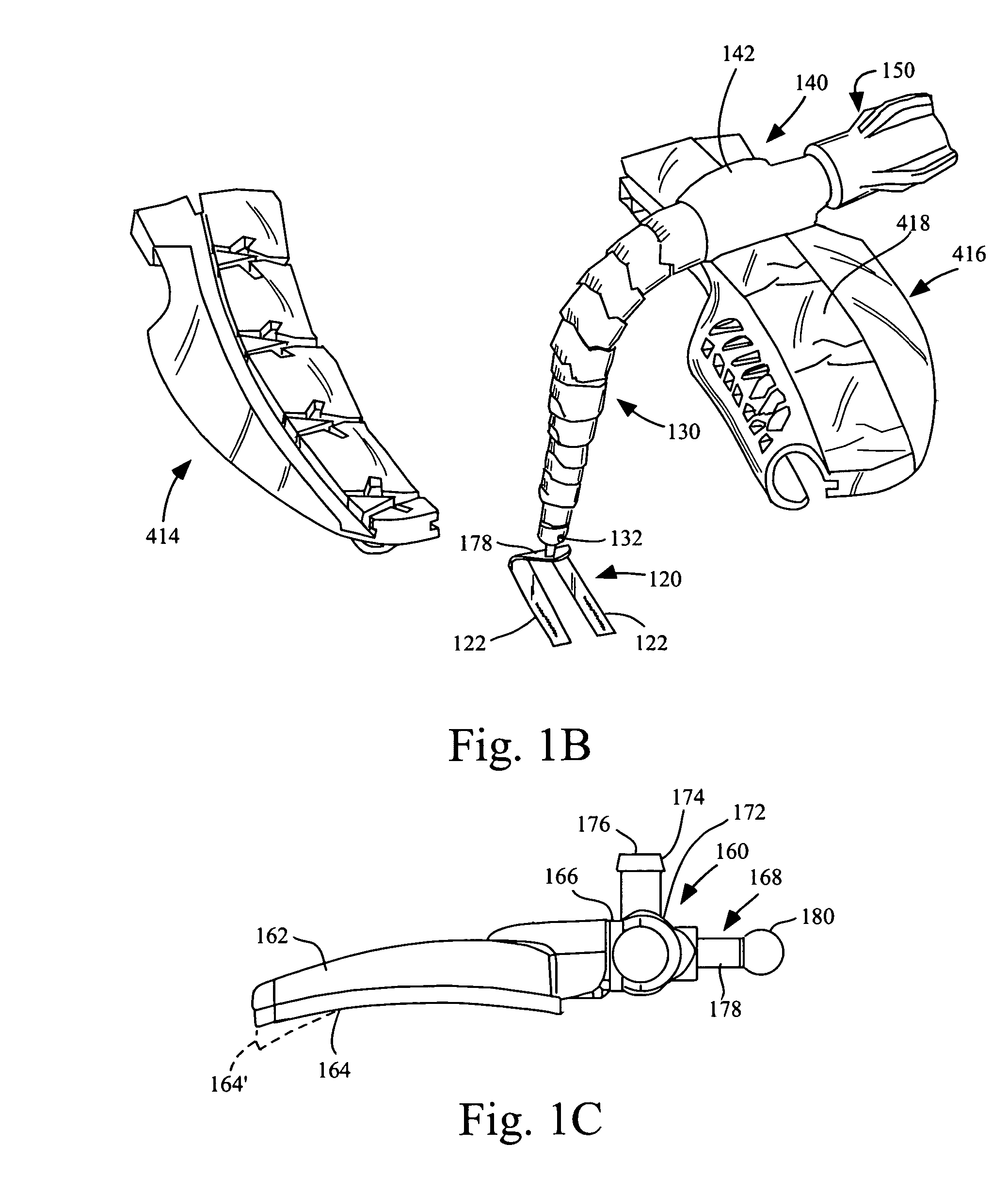
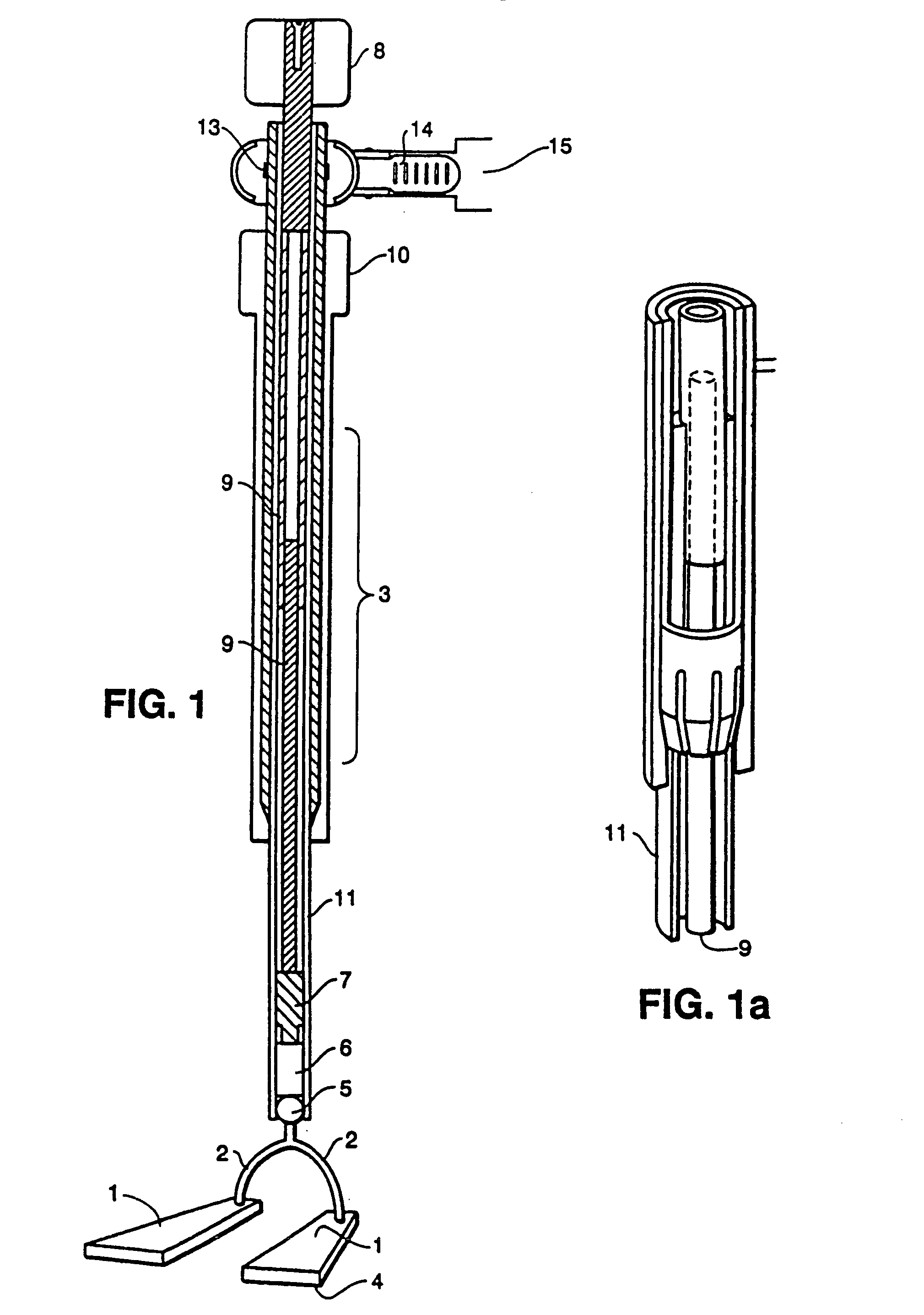
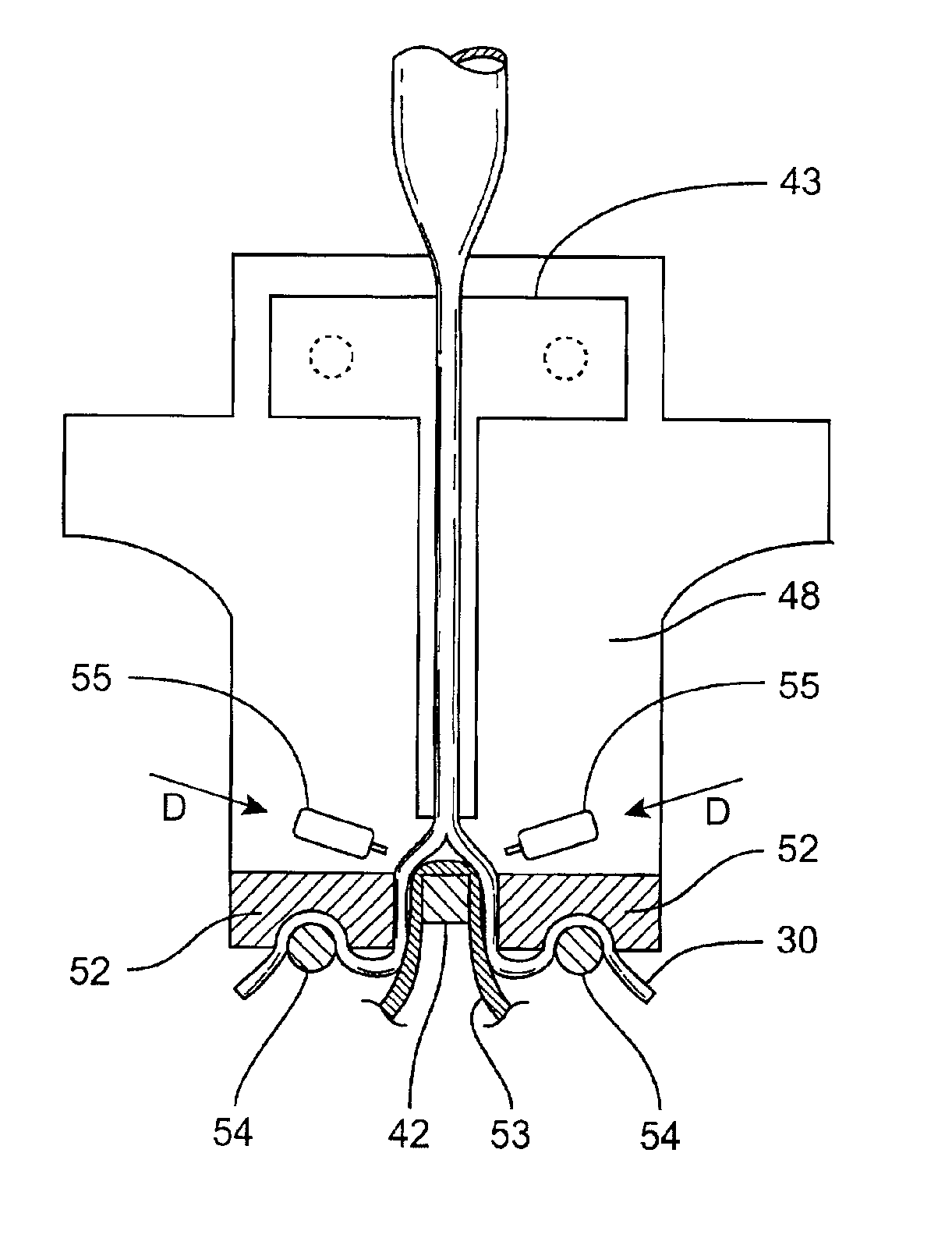
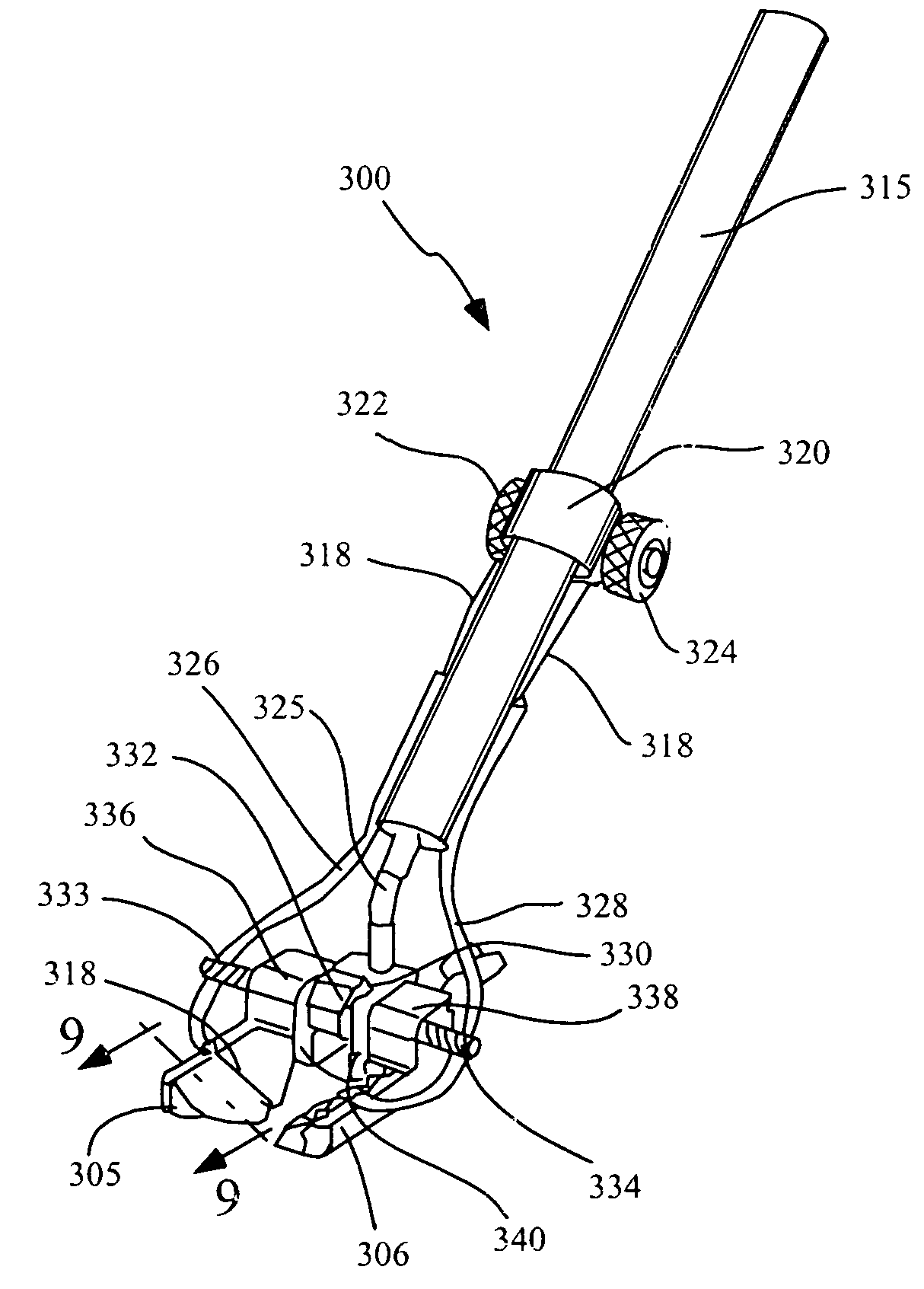
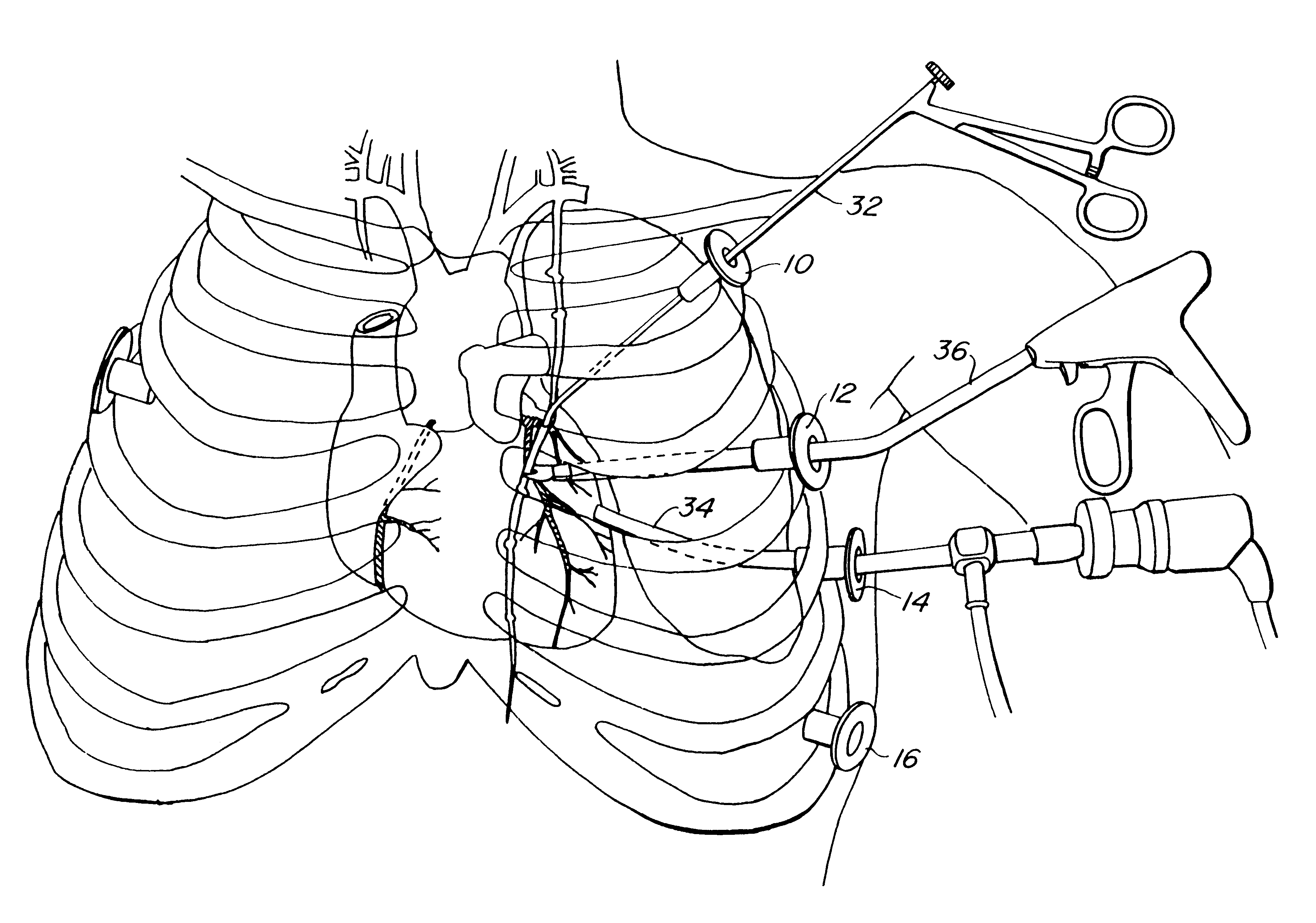
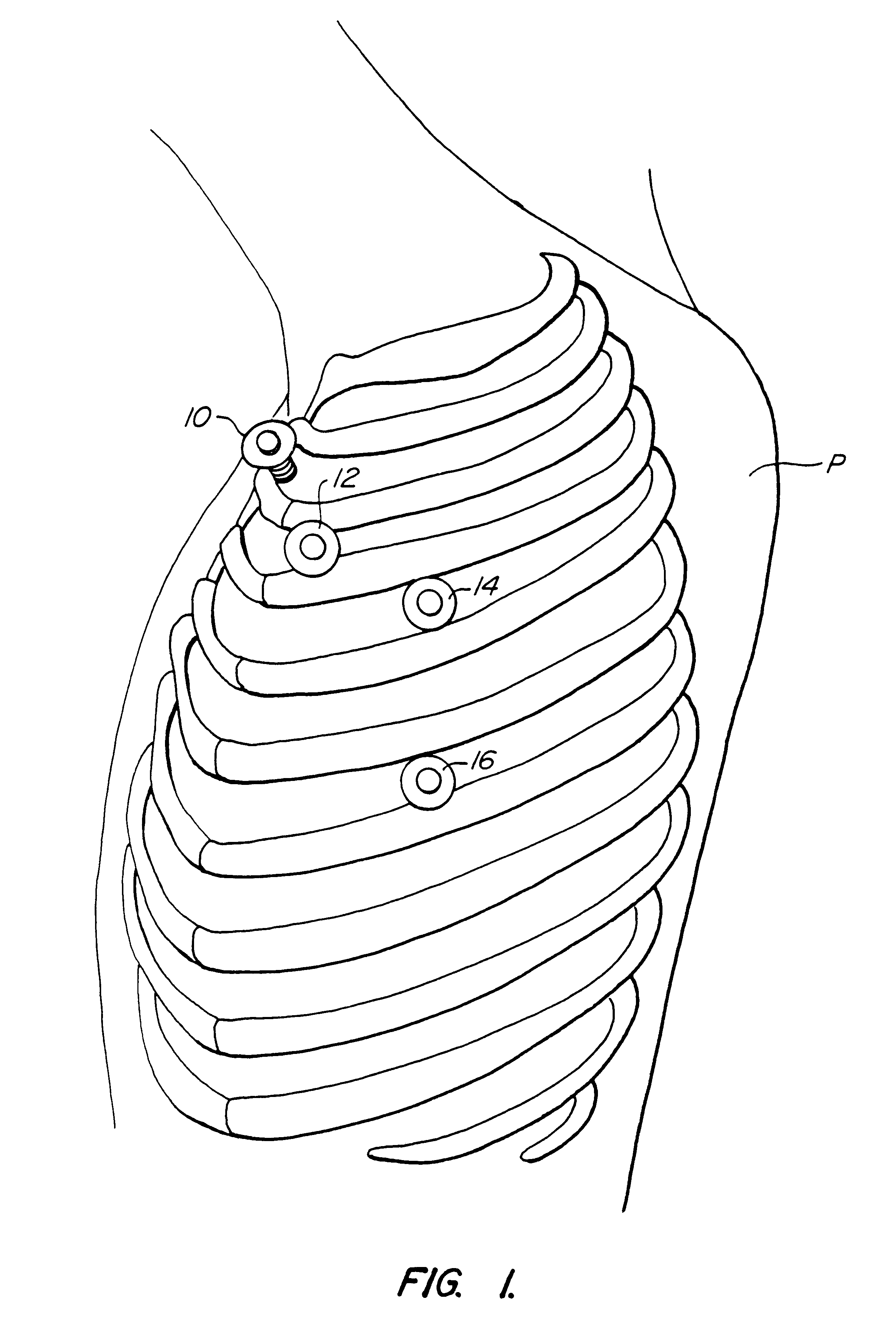
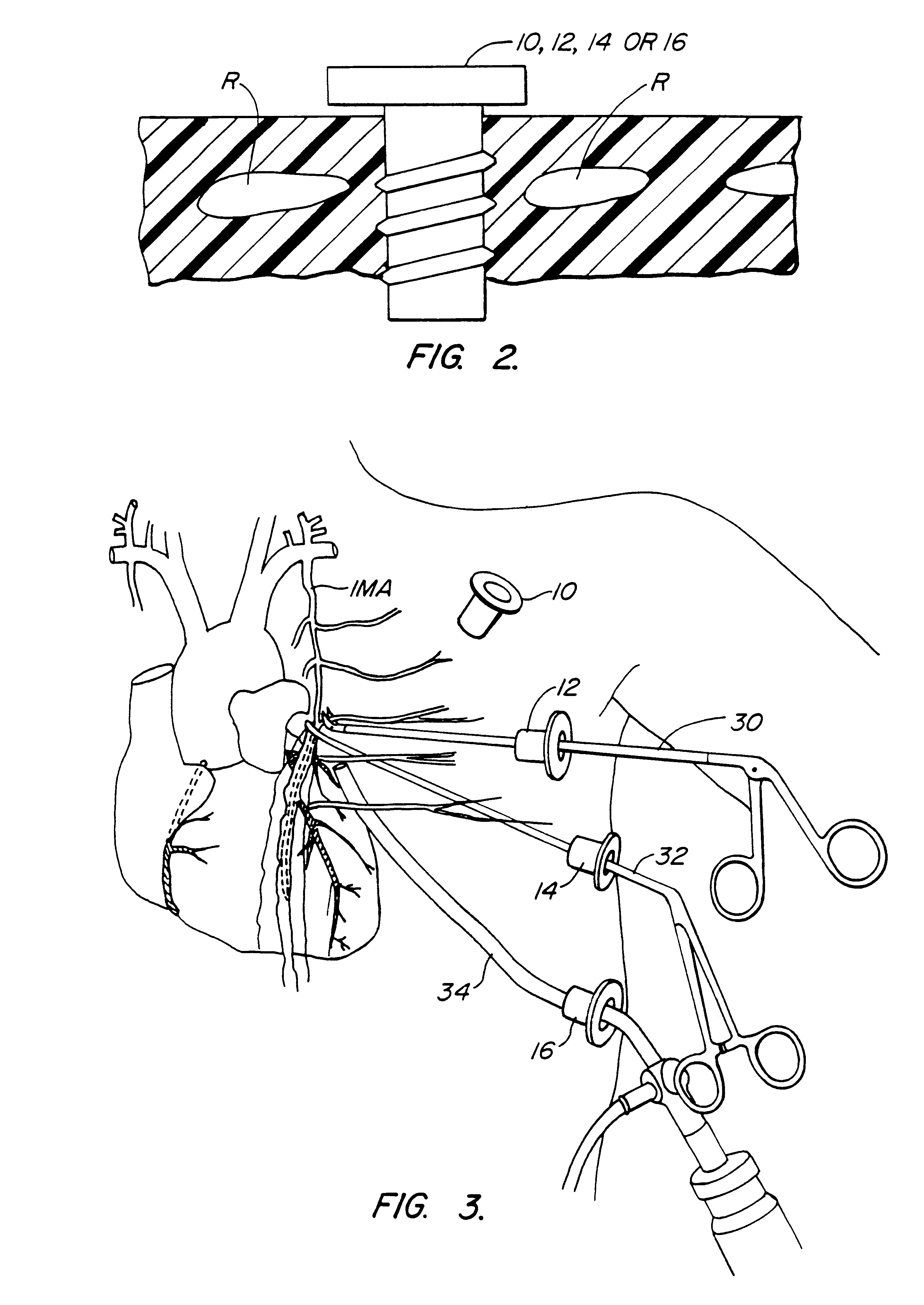
Organ manipulator apparatus
InactiveUS20050010197A1Prevent kinkingReduce creationDiagnosticsIntravenous devicesCoronary arteriesThoracic bone
Organ manipulation devices for atraumatically grasping the surface of an organ and repositioning the organ to allow access to a location on the organ that would otherwise be substantially inaccessible. Methods of accessing a beating heart, retracting the heart using an organ manipulation apparatus, and stabilizing a surgical target area with a stabilizer. Both the organ manipulator and stabilizer are fixed to a stationary object which may be a sternal retractor. A system for performing beating heart coronary artery bypass grafting includes a sternal retractor, organ manipulator and stabilizer.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Organ manipulator apparatus
InactiveUS7479104B2Reduce creationDiagnosticsIntravenous devicesThoracic boneCoronary Artery Bypasses
Organ manipulation devices for atraumatically grasping the surface of an organ and repositioning the organ to allow access to a location on the organ that would otherwise be substantially inaccessible. Methods of accessing a beating heart, retracting the heart using an organ manipulation apparatus, and stabilizing a surgical target area with a stabilizer. Both the organ manipulator and stabilizer are fixed to a stationary object which may be a sternal retractor. A system for performing beating heart coronary artery bypass grafting includes a sternal retractor, organ manipulator and stabilizer.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
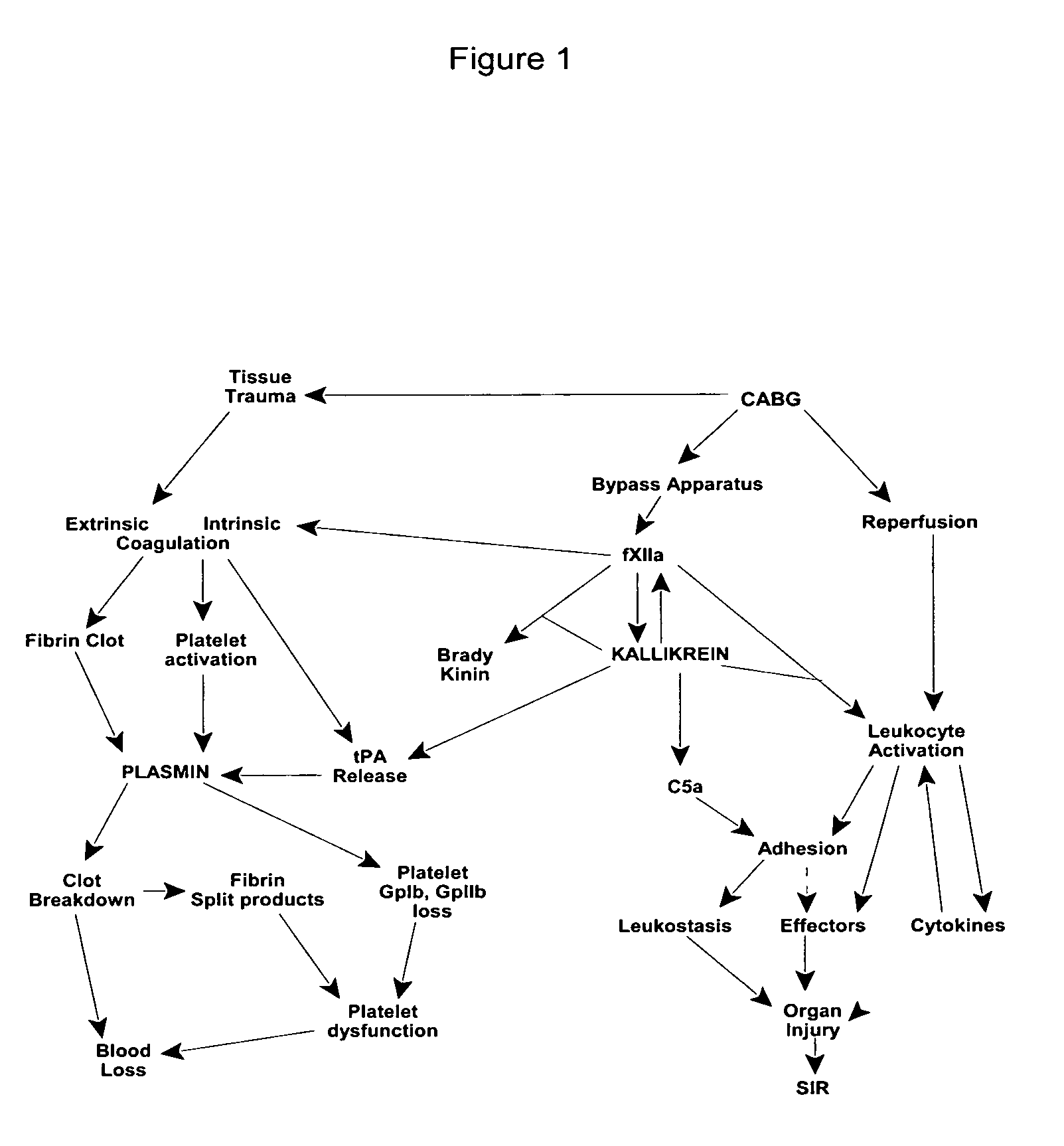
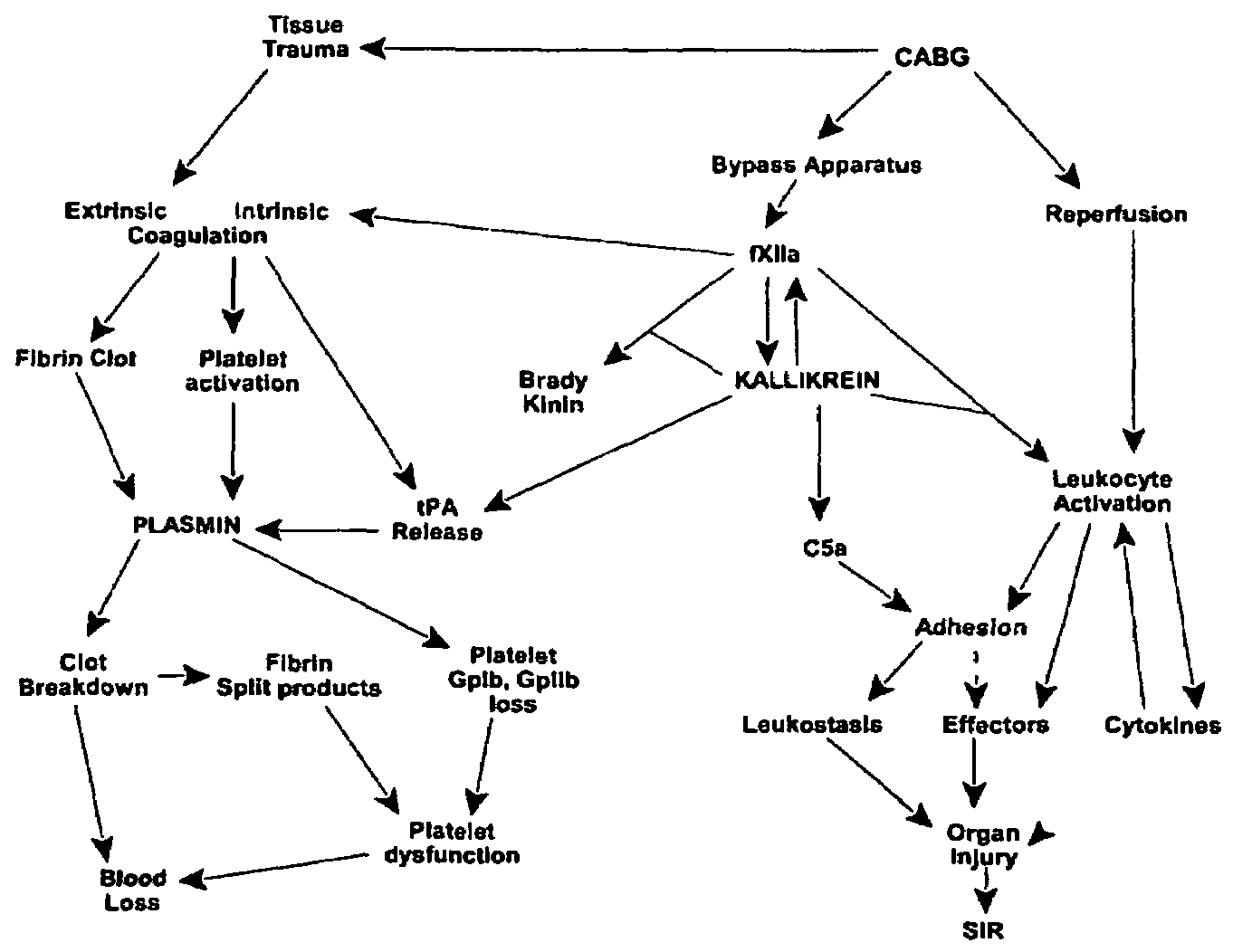
Prevention and reduction of blood loss
InactiveUS7064107B2Preventing and reducing onsetReduce and preventNervous disorderHydrolasesWhole bodySurgical department
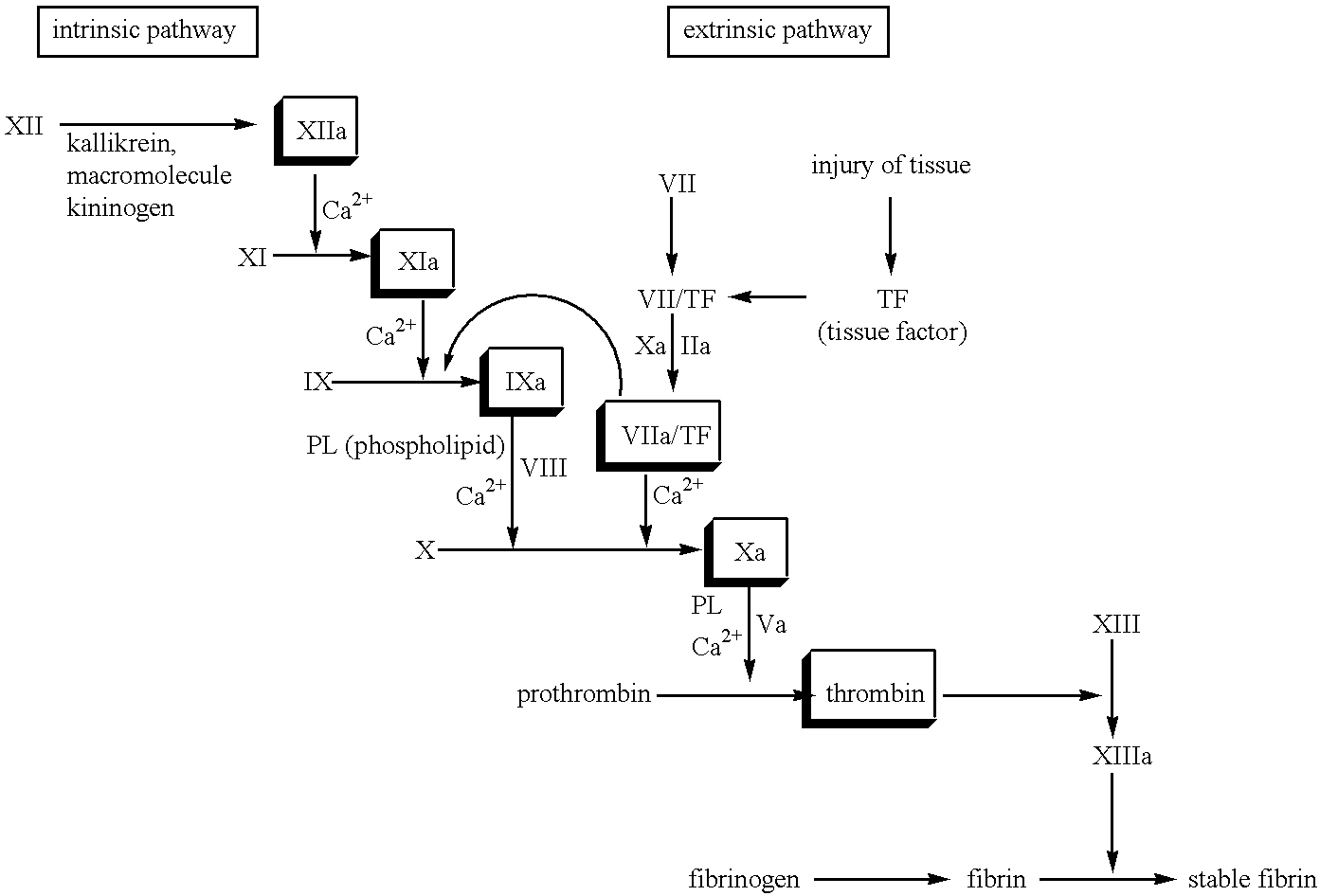
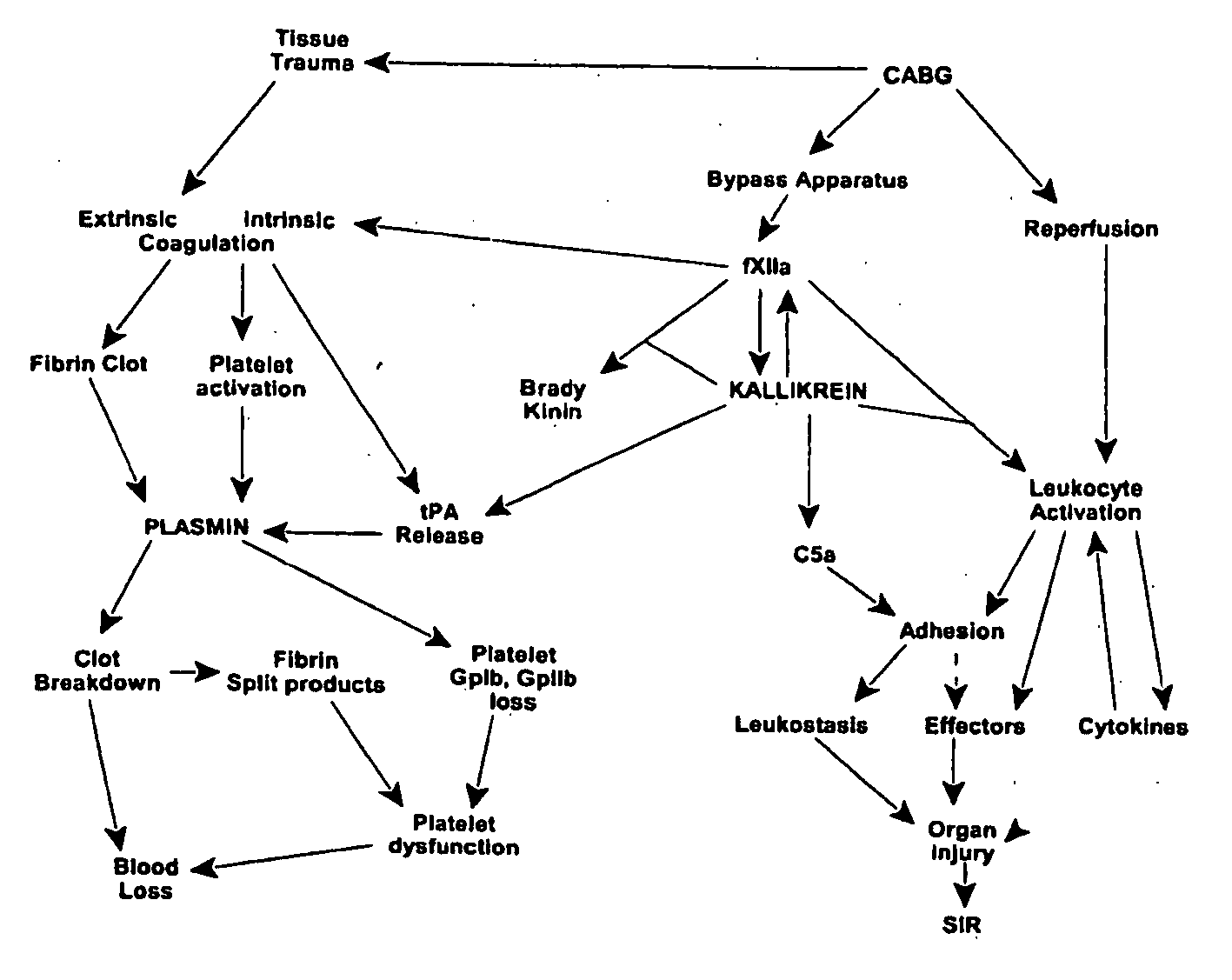
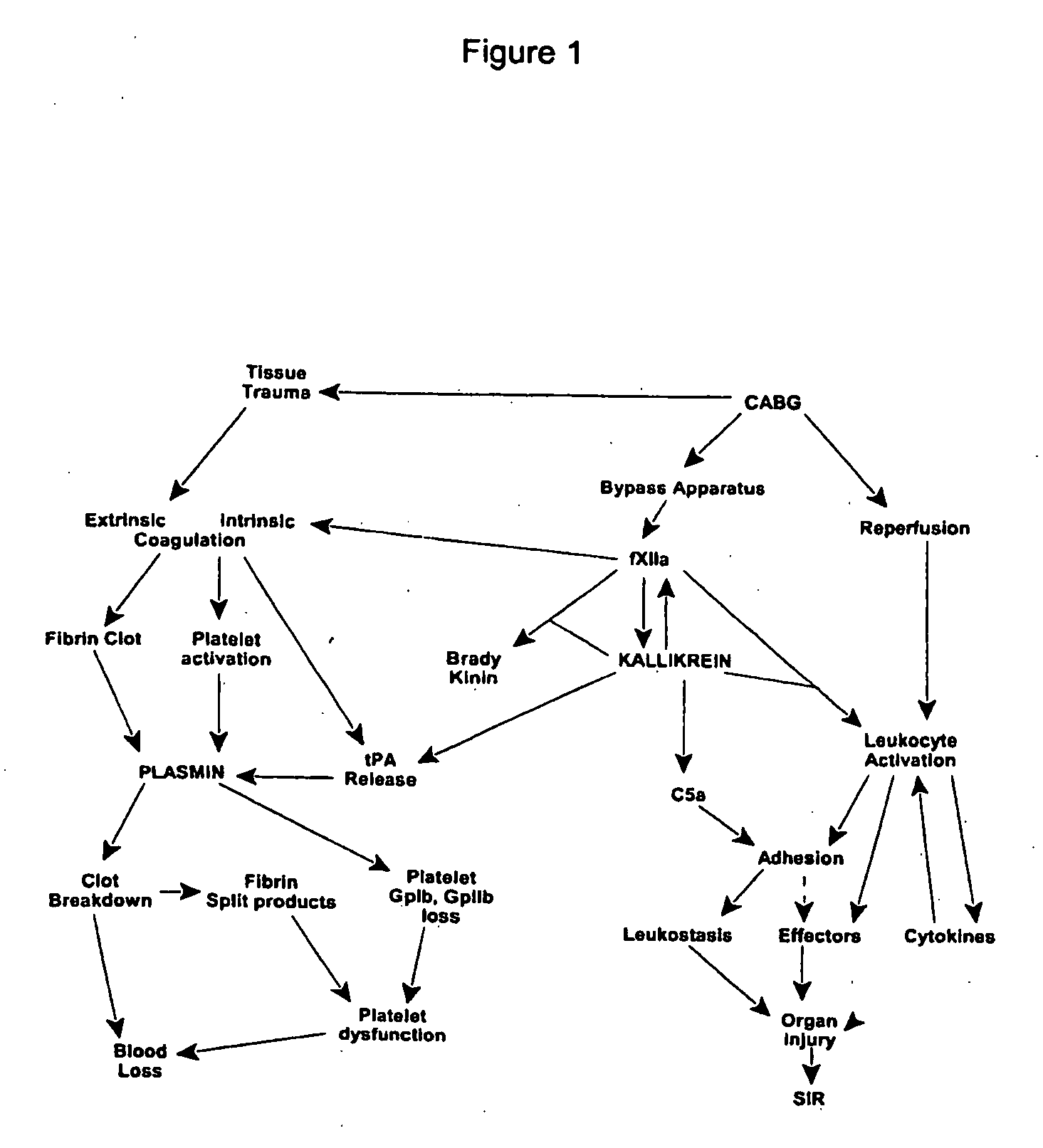
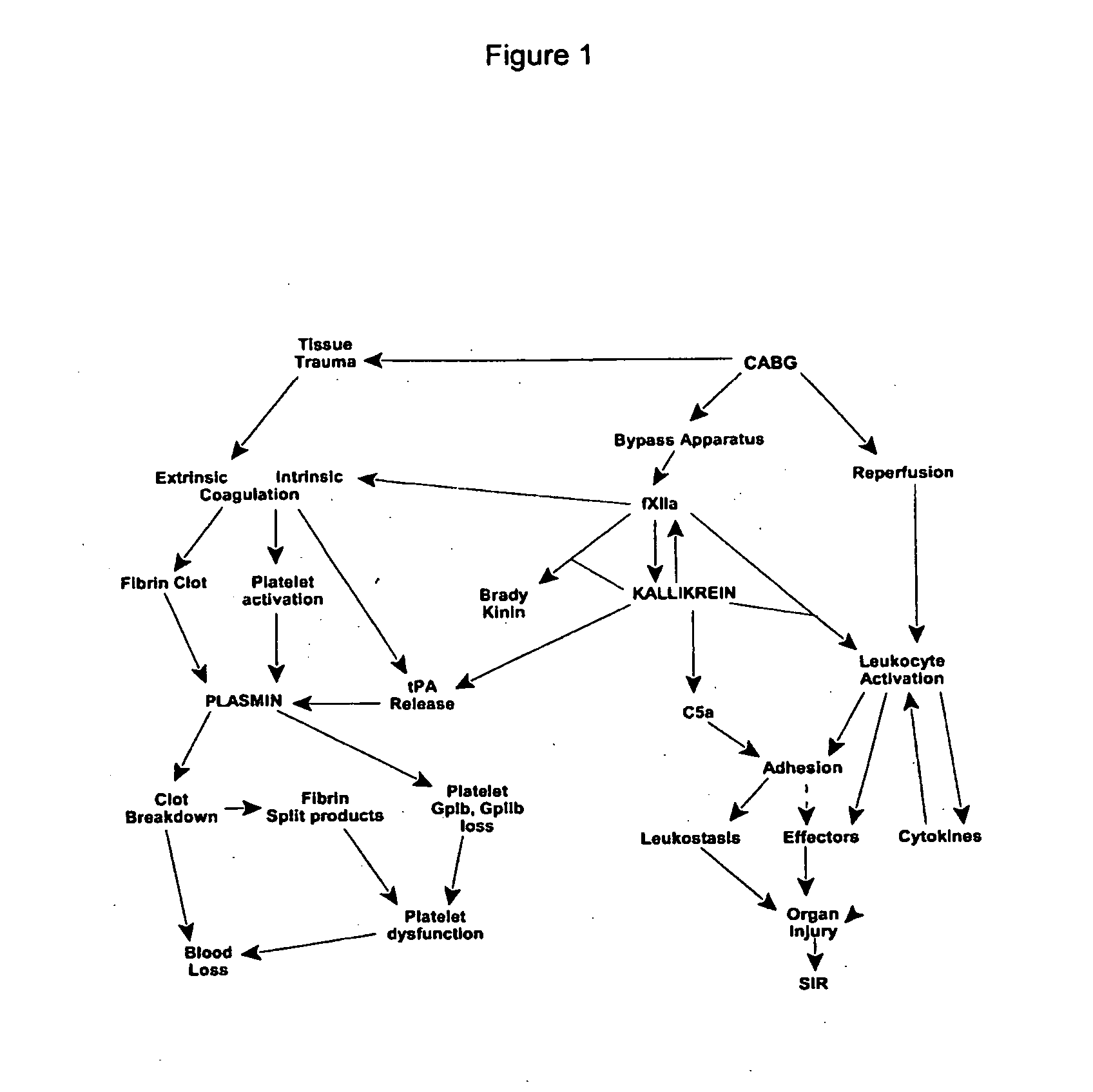
Methods are described for preventing or reducing ischemia and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient such as perioperative blood loss and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient subjected to cardiothoracic surgery, e.g., coronary artery bypass grafting and other surgical procedures, especially when such procedures involve extra-corporeal circulation, such as cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Surgical instruments and procedures for stabilizing the beating heart during coronary artery bypass graft surgery
InactiveUS7056287B2Less traumaMiniaturization exerciseCannulasDiagnosticsSurgical siteCardiac muscle
Devices for stabilizing tissue during a surgical procedure. The beating heart may be stabilized during a surgical procedure on the heart, using a described stabilizing device. In one example, a stabilizing device is introduced through an opening in the chest and brought into contact with the beating heart. By contacting the heart with the device and by exerting a stabilizing force on the device, the motion of the heart caused by the contraction of the heart muscles id effectively eliminated such that the heart is stabilized and the site of the surgery moves only minimally if at all.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Prevention and reduction of blood loss
Methods are described for preventing or reducing ischemia and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient such as perioperative blood loss and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient subjected to cardiothoracic surgery, e.g. coronary artery bypass grafting and other surgical procedures, especially when such procedures involve extra-corporeal circulation, such as cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
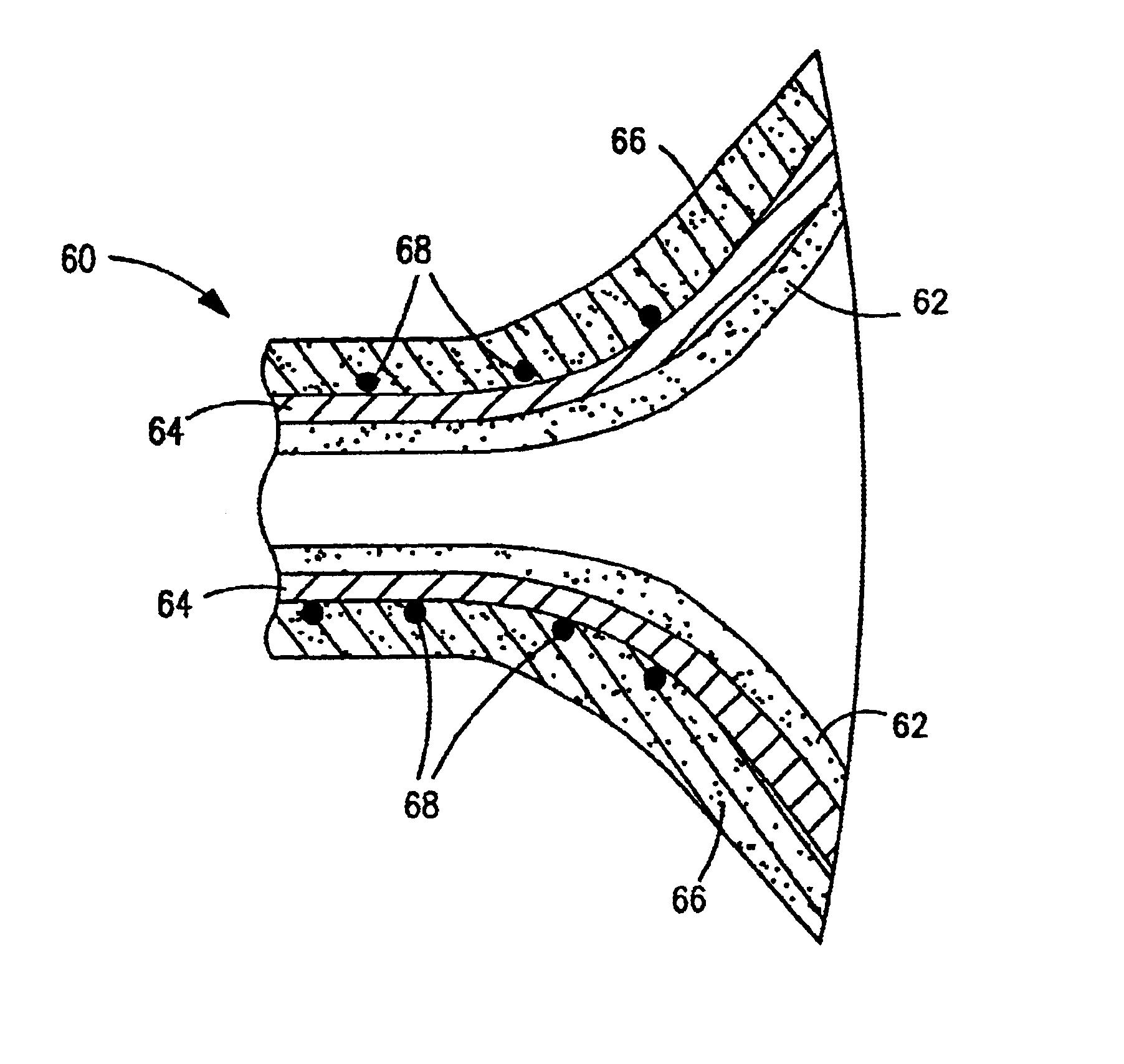
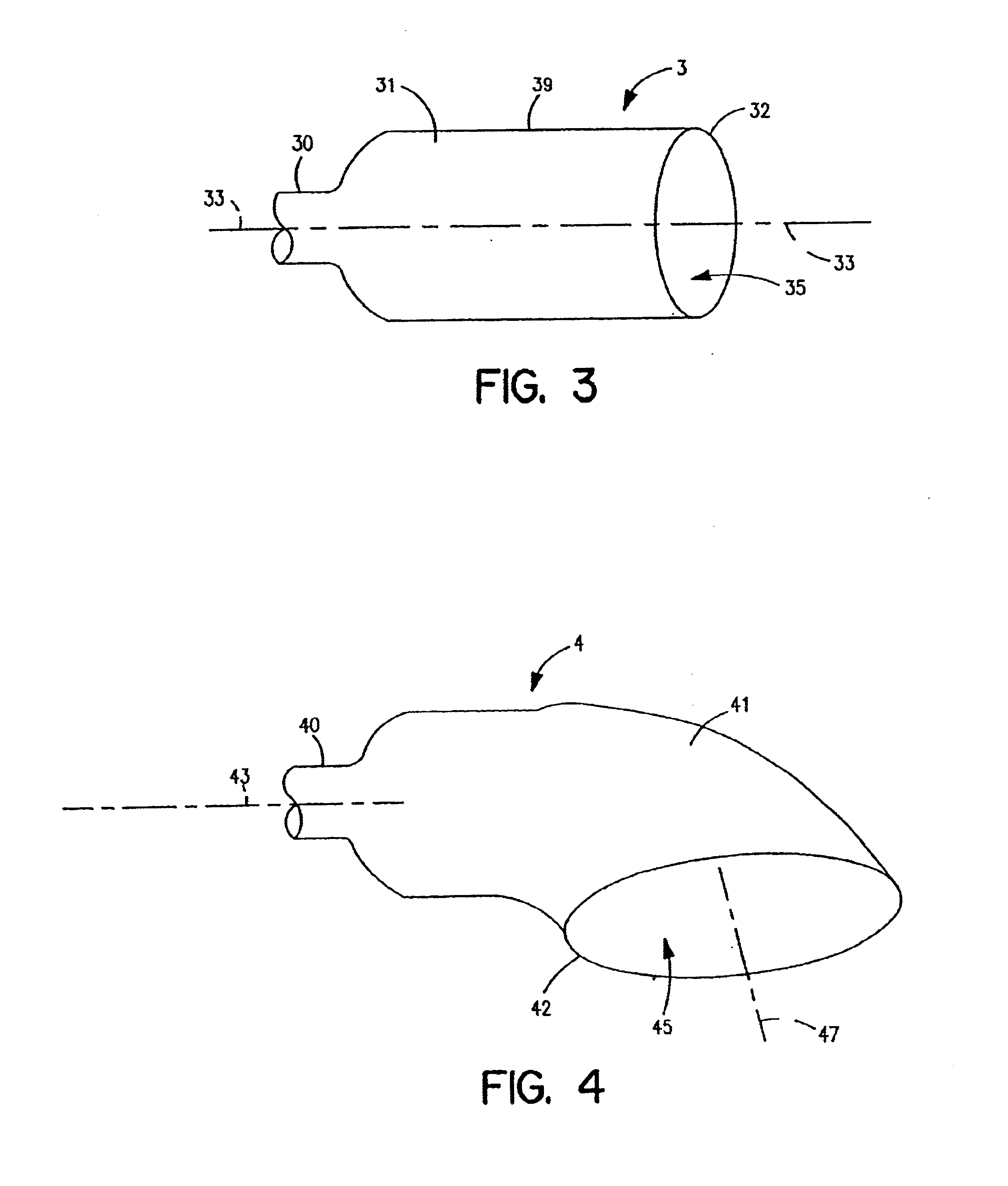
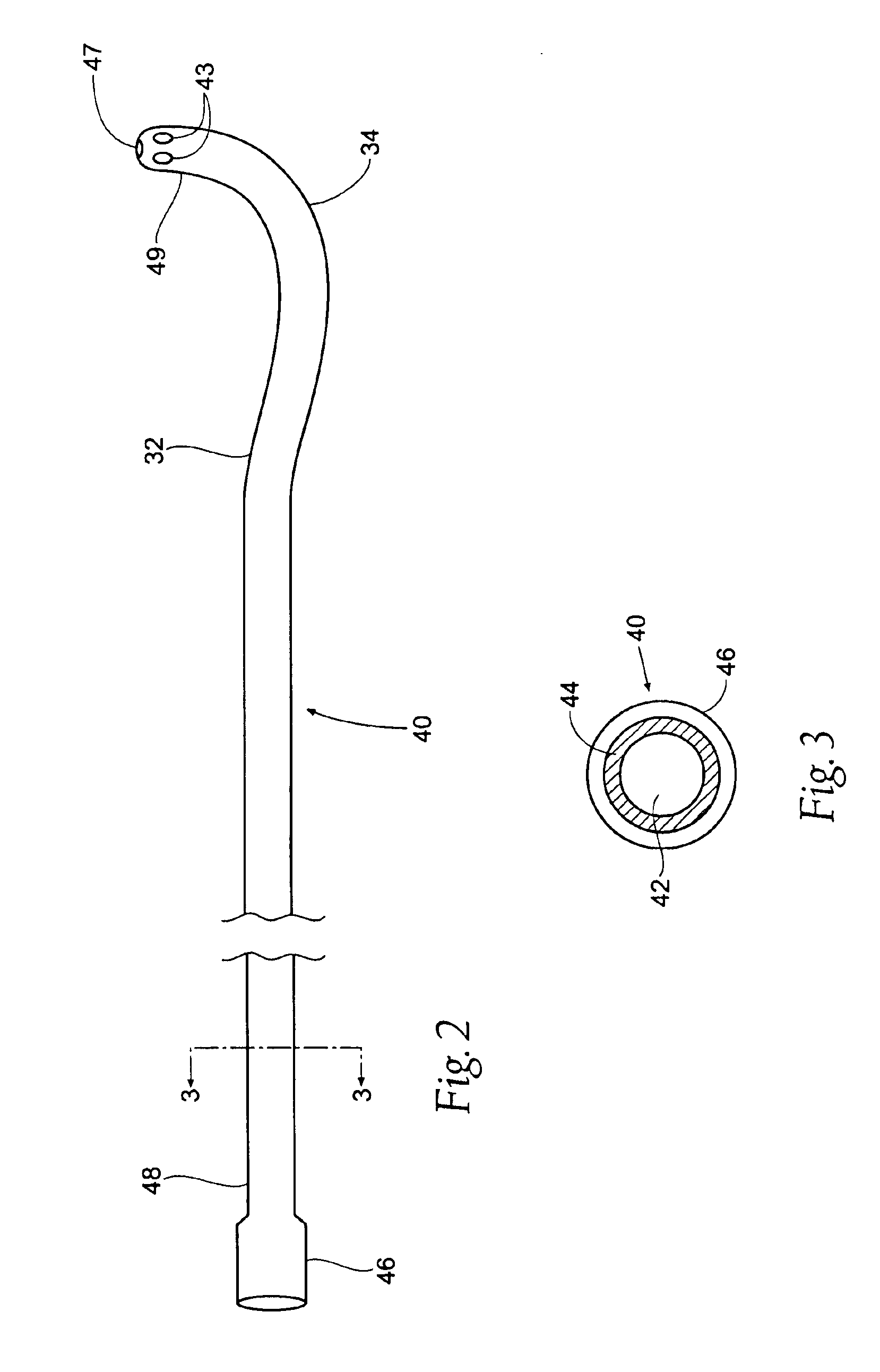
Flared coronary artery bypass grafts
InactiveUS6821295B1Increase resistanceHigh strengthLigamentsMusclesBypass graftsCoronary Artery Bypasses
A bypass graft includes a tubular portion having an internal tubular diameter and a first end and a second end. The tubular portion has a central axis. A flared portion has an adjoining end, wherein the adjoining end of the flared portion is integrally formed on and is substantially concentric with the second end of the tubular portion, and a flared end, wherein the flared end has a flared end internal diameter, such that the internal flared end diameter is greater than the internal tubular diameter. The flared portion includes a circumferential skirt for surgical attachment of the graft to a patient's blood vessel. A method for manufacturing a bypass graft, includes the steps of providing a mandrel having a tubular portion and a flared end with a flared end central axis; forming a layer of polyurethane over the mandrel; drying the layer of polyurethane on the mandrel; forming a skirt edge around the flared end of the mandrel to form an opening at a predetermined angle to the flared end central axis; forming a second edge around the tubular portion of the mandrel, and removing the graft from the mandrel.
Owner:THORATEC CORPORTION
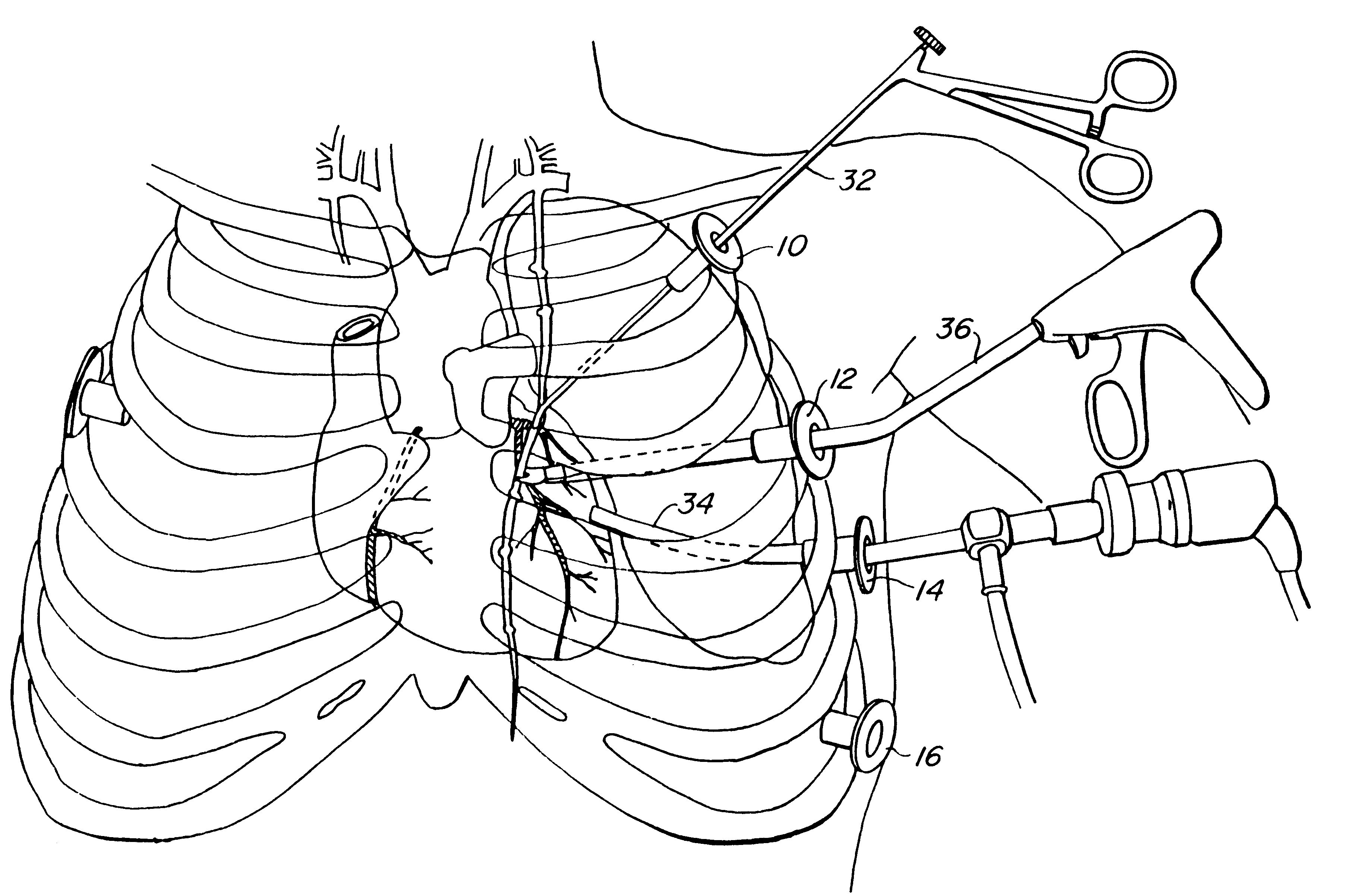
Method and system for performing closed-chest bypass
InactiveUS6869437B1Addressing slow performancePromote recoverySurgical staplesWound clampsMeasurement deviceThoracic cavity
A coronary artery bypass graft procedure is performed through one or more openings made in the patient to create a point of entry to the thoracic cavity. A vein measurement device measures the distance between the proximal and distal anastomotic sites for each graft. A proximal anastomosis tool splits to release a graft vessel after deploying an anastomosis device at the proximal anastomosis site. The tool may be articulated. An integrated stabilizer stabilizes one or more tools relative to the surface of the beating heart at a distal anastomotic site. A distal anastomotic tool may be provided as part of the integrated stabilizer, and connects one end of the graft vessel to a target vessel. An epicardial dissector may be provided as part of the integrated stabilizer, and dissects the epicardium from the target vessel at a distal anastomotic site, as needed.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
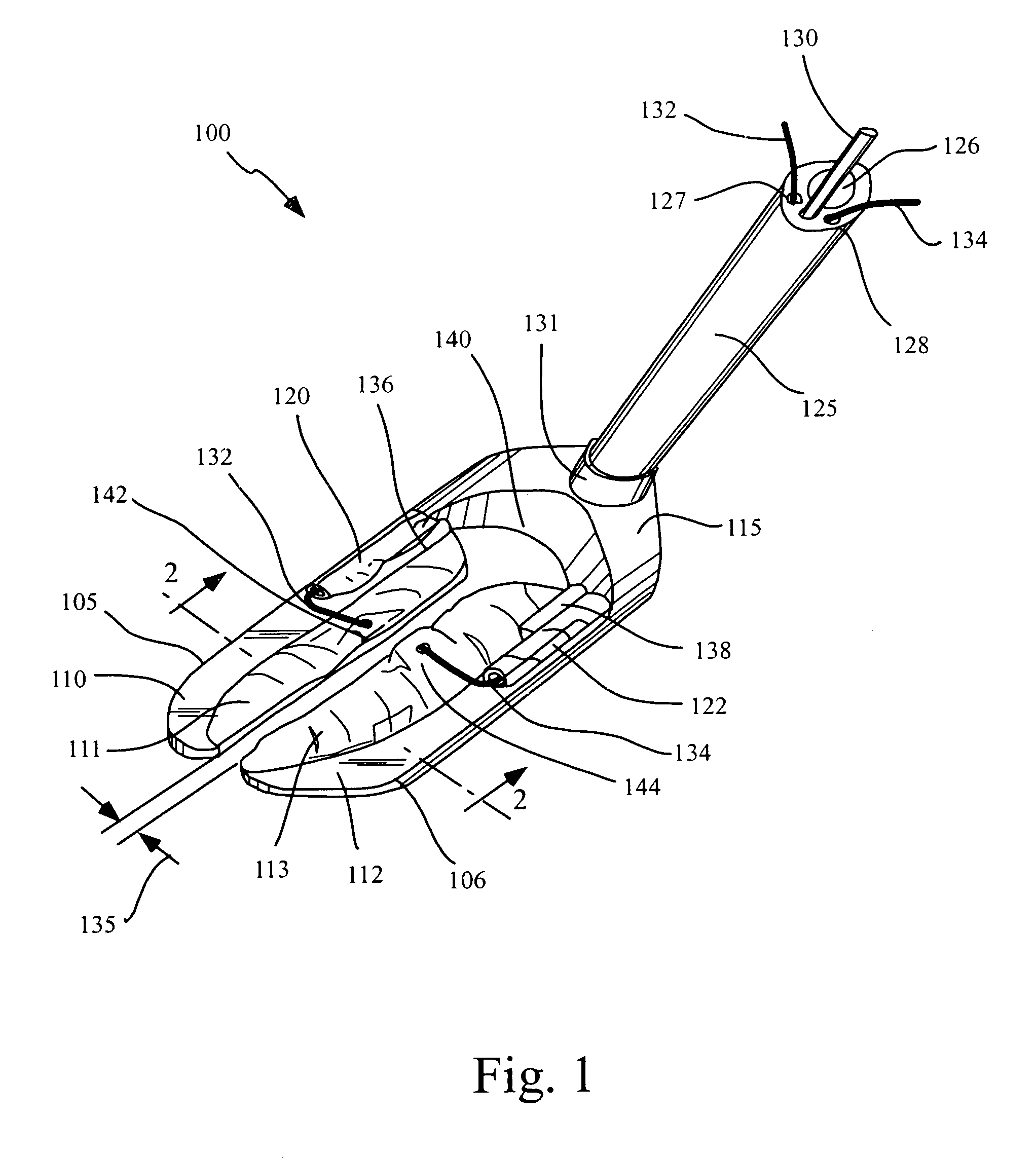
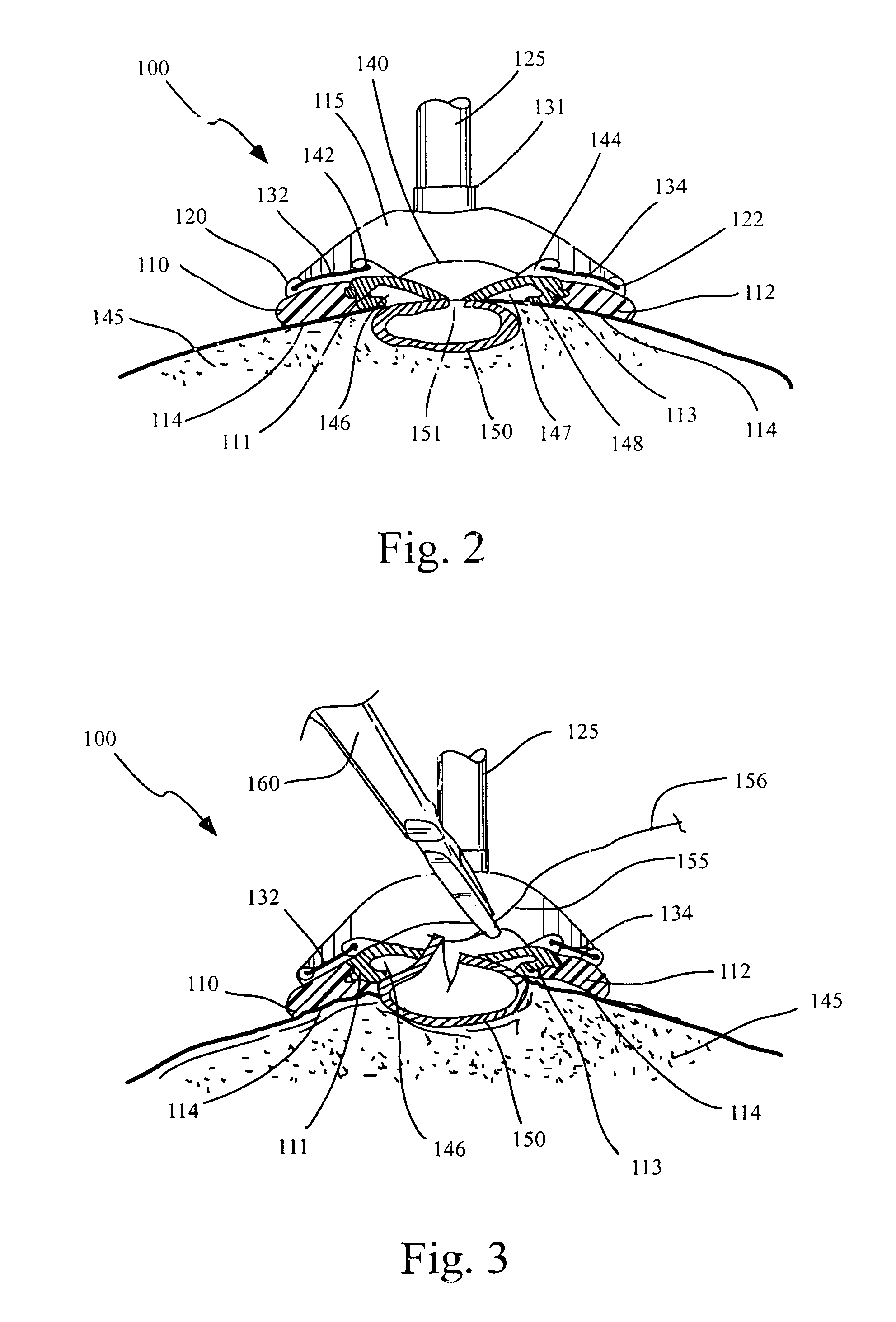
Tissue stabilizer having an articulating lift element
InactiveUS7326177B2Easy to operateEasy to demonstrateSurgical pincettesProsthesisSurgical operationCoronary Artery Bypasses
Devices and methods are disclosed for stabilizing tissue within a patient's body during a surgical operation to provide a relatively motionless surgical field, such as during a coronary artery bypass graft procedure. The devices include tissue stabilizers which engage and provide stabilization to a targeted area of tissue and further have the ability to engage and manipulate some portion of tissue within or adjacent the targeted area to improve the surgical presentation of that portion of tissue. The tissue stabilizer typically has one or more stabilizer feet which have a first foot portion configured to provide stabilization to the targeted tissue and a second foot portion moveable relative to the first foot portion for manipulating a portion of tissue to improve the surgical presentation.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Method and systems for performing thoracoscopic cardiac bypass and other procedures
InactiveUS6311693B1Promote healingEqual efficacySuture equipmentsCannulasHeart operationsThoracoscopes
A method for closed-chest cardiac surgical intervention relies on viewing the cardiac region through a thoracoscope or other viewing scope and endovascularly partitioning the patient's arterial system at a location within the ascending aorta. The cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia can be induced, and a variety of surgical procedures performed on the stopped heart using percutaneously introduced tools. The method of the present invention will be particularly suitable for forming coronary artery bypass grafts, where an arterial blood source is created using least invasive surgical techniques, and the arterial source is connected to a target location within a coronary artery while the patient is under cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
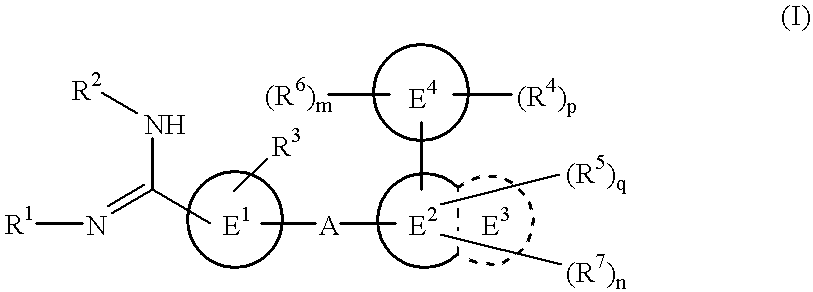
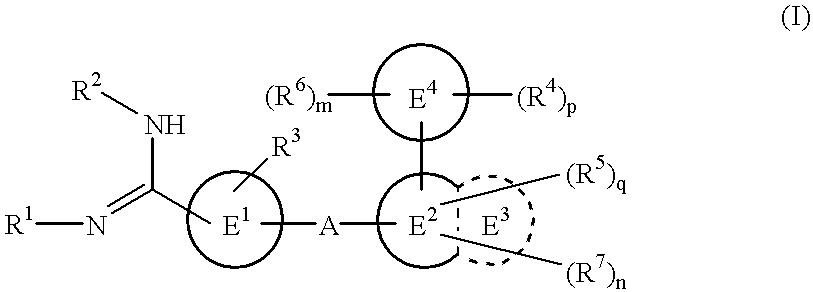
Amidino derivatives and drugs containing the same as the active ingredient
InactiveUS6358960B1BiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsExtracorporeal circulationDisseminated coagulopathy
The novel amidino derivatives of the formula (I):wherein all the symbols are as in specification defined;have an inhibitory activity of a blood coagulation factor VIIa and are useful for treatment and / or prevention of several angiopathy caused by enhancing a coagulation activity, such as disseminated intravascular coagulation, coronary thrombosis, cerebral infarction, cerebral embolism, transient ischemic attack, cerebrovascular disorders, pulmonary vascular diseases, deep venous thrombosis, peripheral arterial obstruction, thrombosis after artificial vascular transplantation and artificial valve transplantation, post-operative thrombosis, reobstruction and restenosis after coronary artery bypass operation, reobstruction and restenosis after PTCA or PTCR, thrombosis by extracorporeal circulation and procoagulative diseases such as glomerlonephriitis.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
Prevention and reduction of blood loss
InactiveUS20080064637A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsWhole bodyCardiopulmonary bypass time
Methods are described for preventing or reducing ischemia and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient such as perioperative blood loss and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient subjected to cardiothoracic surgery, e.g. coronary artery bypass grafting and other surgical procedures, especially when such procedures involve extra-corporeal circulation, such as cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:DYAX CORP
Prevention and reduction of blood loss
InactiveUS20070249807A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass time
Methods are described for preventing or reducing ischemia and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient such as perioperative blood loss and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient subjected to cardiothoracic surgery, e.g. coronary artery bypass grafting and other surgical procedures, especially when such procedures involve extra-corporeal circulation, such as cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Methods and systems for performing thoracoscopic coronary bypass and other procedures
InactiveUS6325067B1Reduce complicationsAllows can be cooledSuture equipmentsCannulasHeart operationsThoracoscopes
A method for closed-chest cardiac surgical intervention relies on viewing the cardiac region through a thoracoscope or other viewing scope and endovascularly partitioning the patient's arterial system at a location within the ascending aorta. The cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia can be induced, and a variety of surgical procedures performed on the stopped heart using percutaneously introduced tools. The method of the present invention will be particularly suitable for forming coronary artery bypass grafts, where an arterial blood source is created using least invasive surgical techniques, and the arterial source is connected to a target location within a coronary artery while the patient is under cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Method and system for attaching a graft to a blood vessel
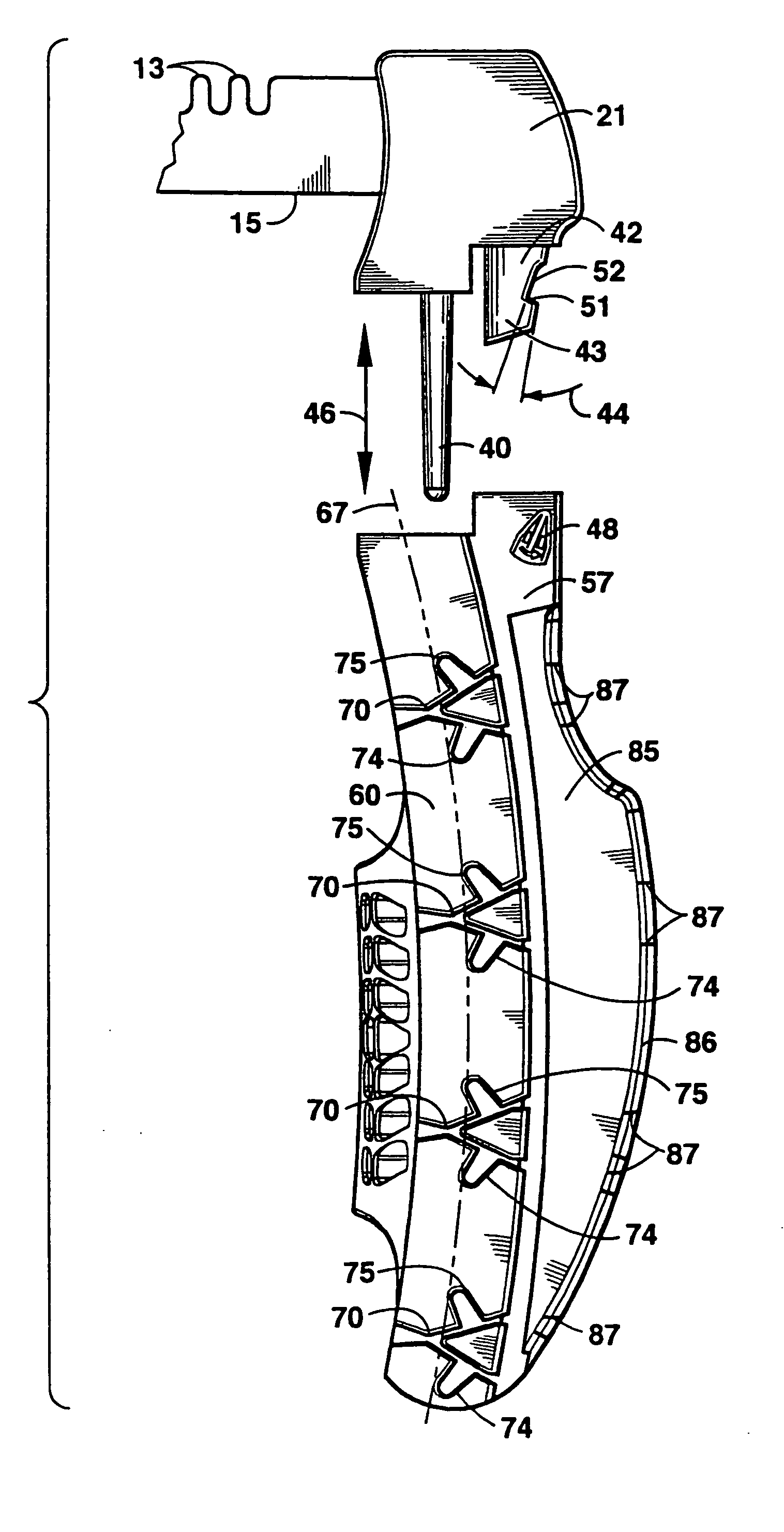
InactiveUS7018388B2Minimizing restenosisMinimizing thrombosisDiagnosticsStaplesCoronary arteriesInsertion stent
Anastomotic stents for connecting a graft vessel to a target vessel, and methods of use thereof. The anastomotic stents of the invention are suitable for use in a variety of anastomosis procedures, including coronary artery bypass grafting. One embodiment of the invention comprises a large vessel anastomotic stent for use with large diameter target vessels such as the aorta or its major side branches. Another embodiment of the invention comprises a small vessel anastomotic stent for use on a target vessel which has a small diameter such as a coronary artery. Another aspect of the invention involves applicators for use with the stents of the invention.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
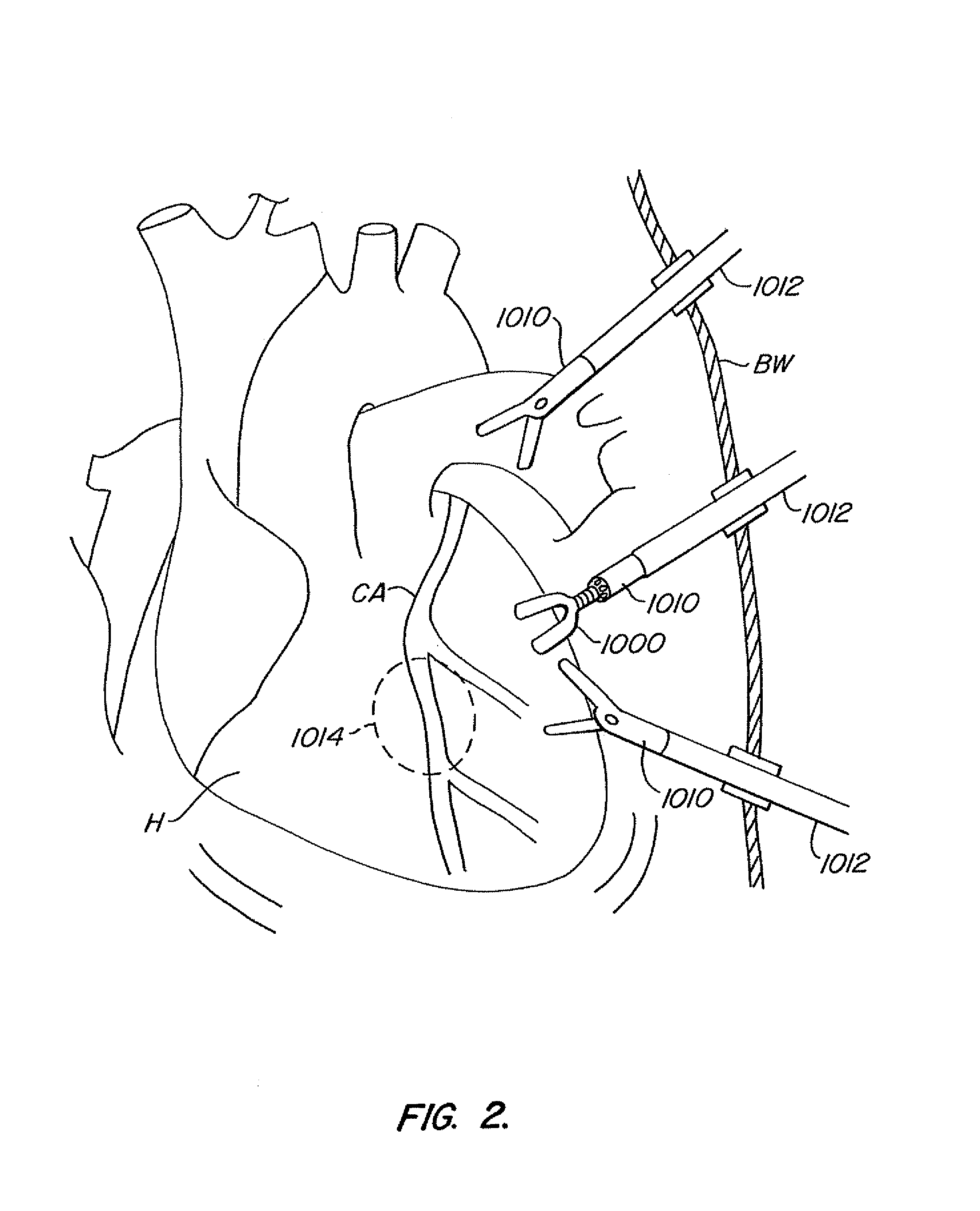
Intravascular cannulation apparatus and methods of use
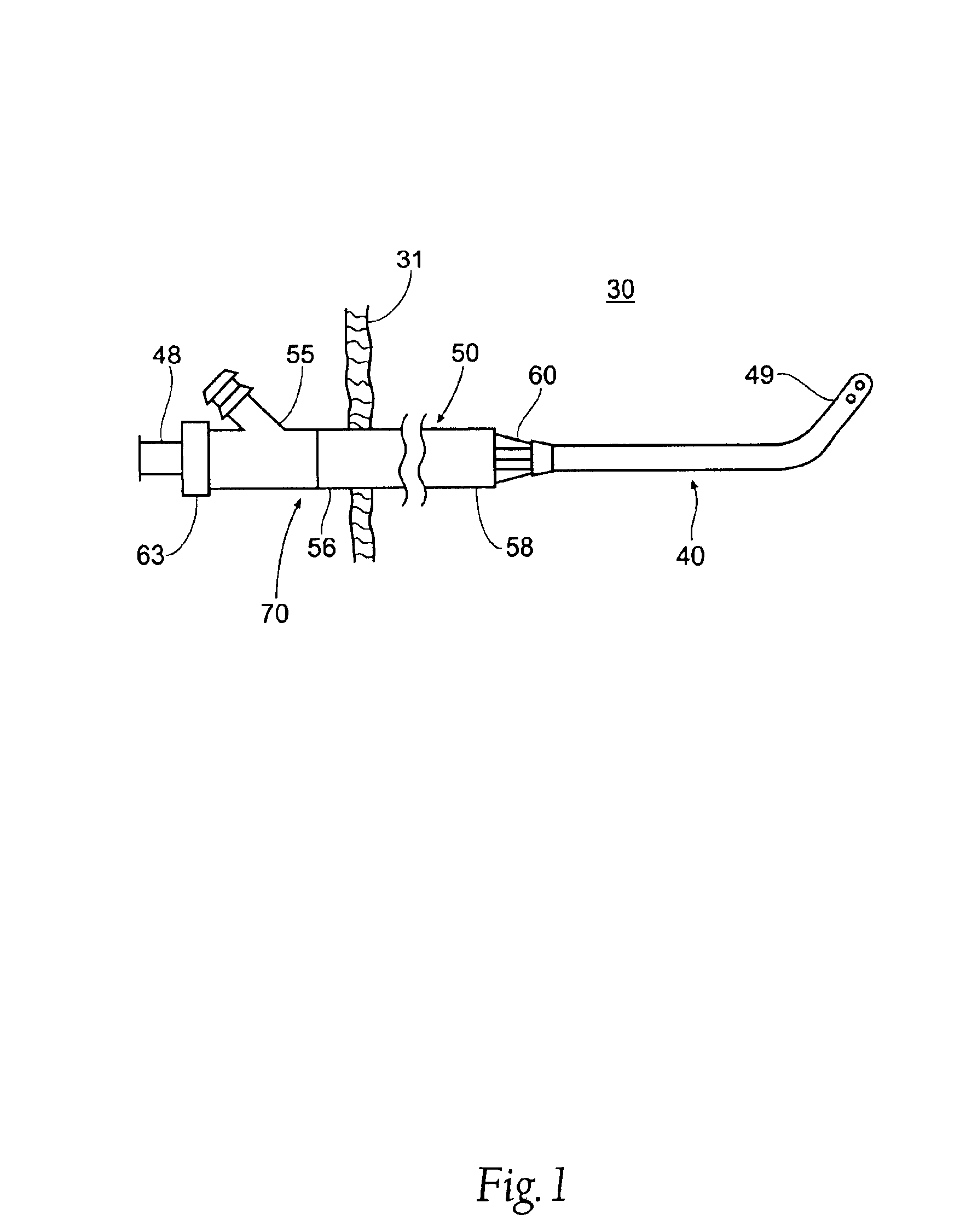
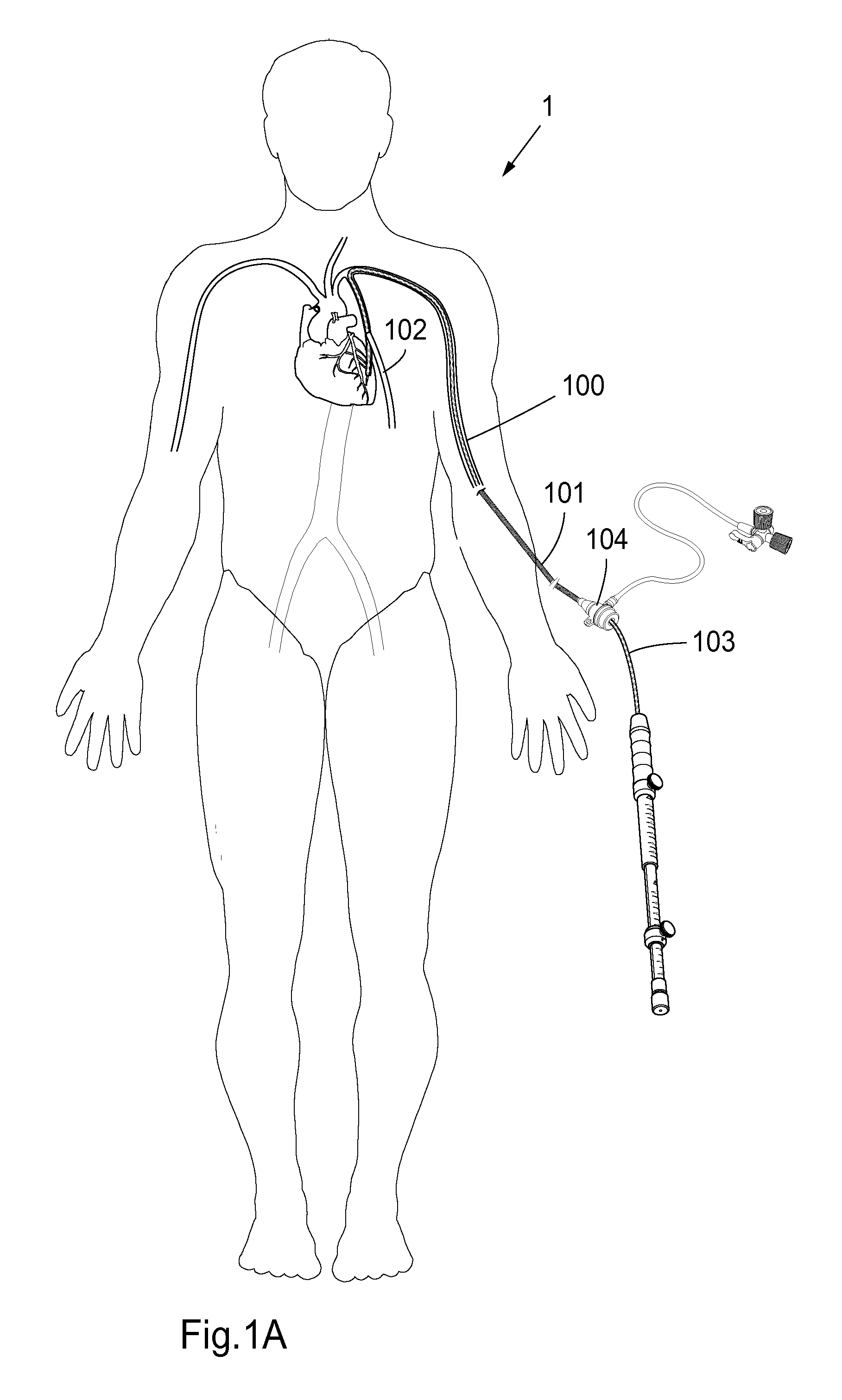
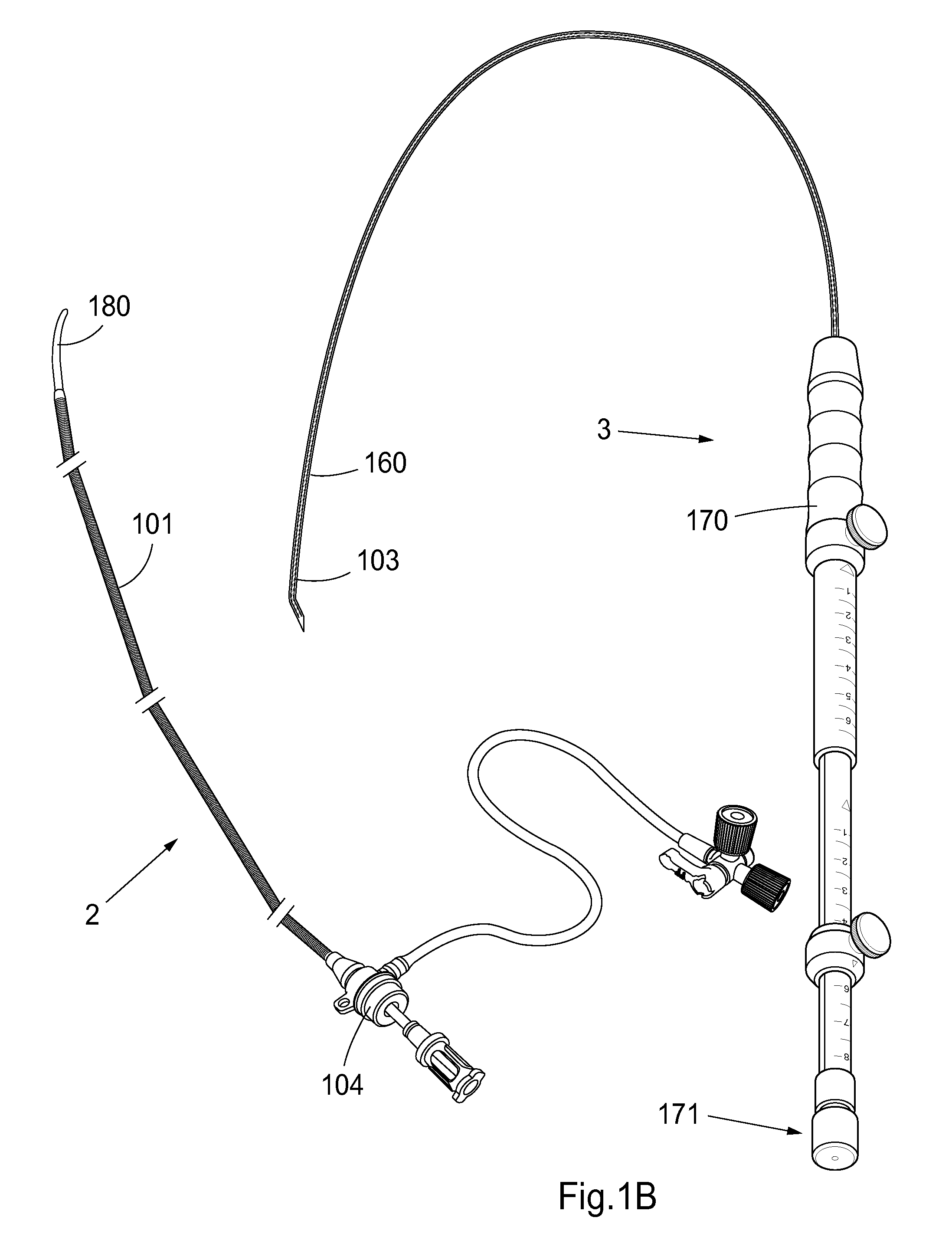
This invention is a cannulation apparatus, and related methods for providing indirect access to a surgical site within a patient. The cannulation apparatus includes at least two fluid flow paths that are slidable coupled (40) (50) to one another, and selectively positional within the patient. The first, the second flow path s may be advanced through a single incision disposed remotely from the surgical field to first, and second predetermined locations within the patient. Exemplary sites for the incision include the groin region or in the neck region of the patient. The cannulation apparatus, and method of the present invention are particularly suited for use in providing cardiopulmonary support during cardiac surgery, including coronary artery bypass graft surgery. The cannulation apparatus of the present invention also provides an entry site for one or more support devices used in the surgical procedure.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC +1
Method and system for attaching a graft to a blood vessel
InactiveUS7041110B2Prevent movementMinimizing restenosisStaplesNailsCoronary arteriesInsertion stent
Owner:AESCULAP AG
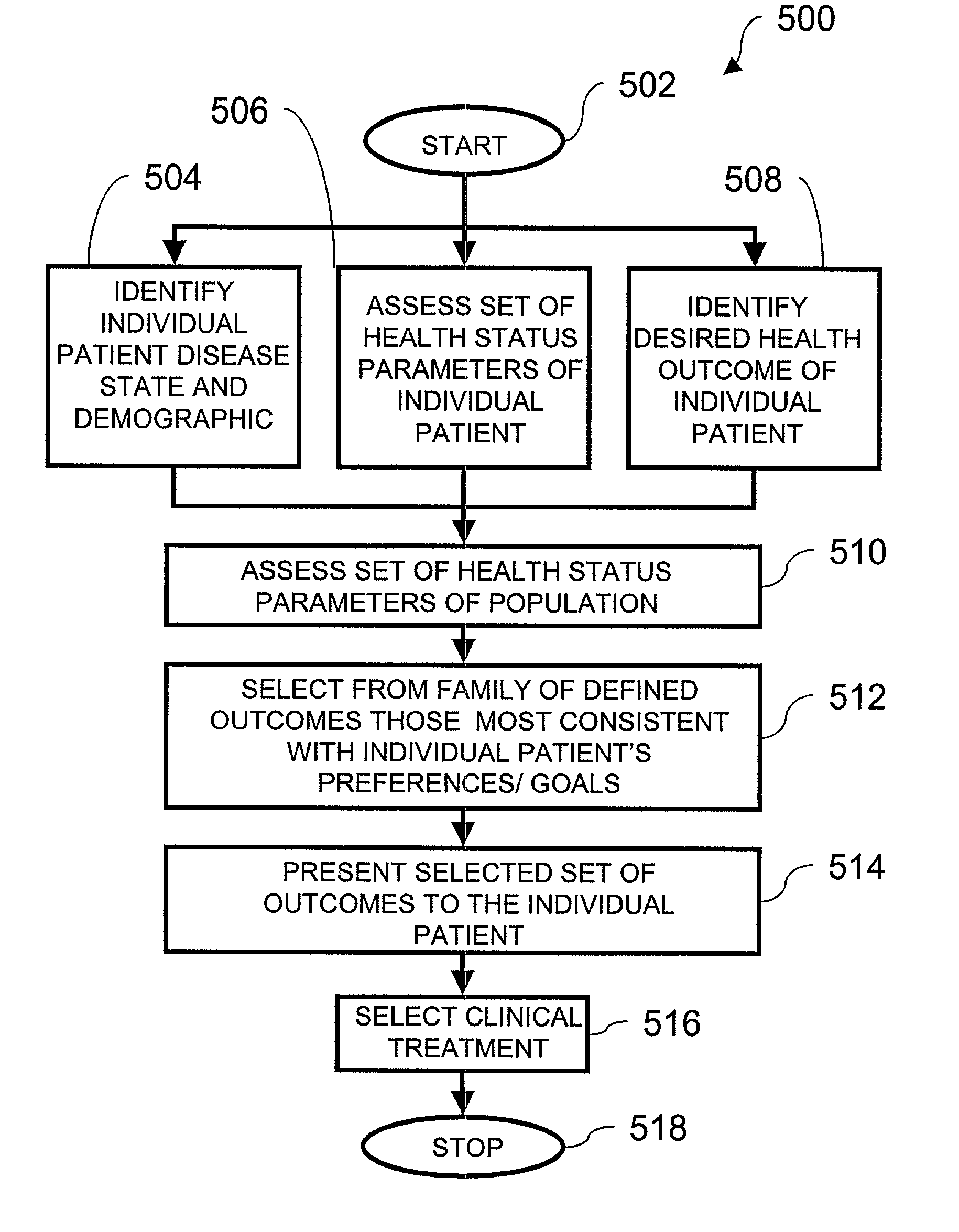
Method for selecting a clinical treatment plan tailored to patient defined health goals
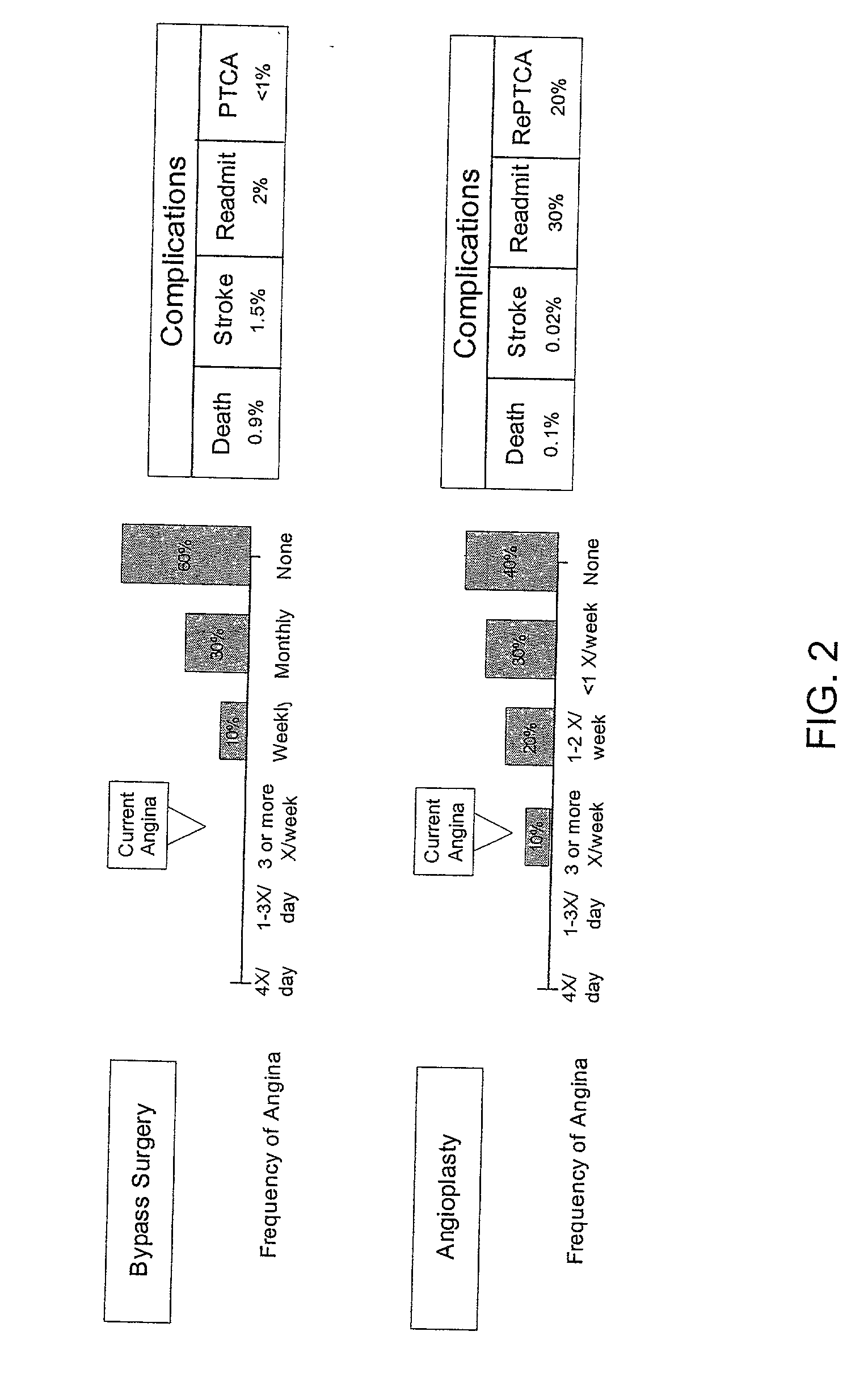
ActiveUS20030229513A1TherapiesHealth-index calculationHer DiseaseCoronary Revascularization Procedure
The invention discloses a method by which the health care professional or patient may draw upon historical medical data concerning patients similarly situated in medical condition, to assist him / her in deciding on a clinical intervention procedure to select. This method is specifically tailored to the patient, as data is provided and evaluated from only similarly situated patients, and provides an expectation of potential outcome of the patient should one or the other of the options be selected. The invention further provides a database that may be used in order to provide this comparison based evaluation method. A computer based software system is further disclosed that implements the method. The invention more speiocifically provides a method by which a post-coronary event patient may make an informed decision of which post-coronary revascularization procedure to undergo in the future management of his disease. This method employs the patient's health status date (symptoms, function and quality of life), and provides projections of the patient's expected survival, risk, and 1-year health status outcome from the selection of revascularization procedure, such as Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) or Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI).
Owner:TERUMO MEDICAL CORP
Device, system, kit, and method for epicardial access
ActiveUS20100069820A1Minimizes immunologicalMinimizes rejection complicationRespiratorsStentsExtracorporeal circulationWhole body
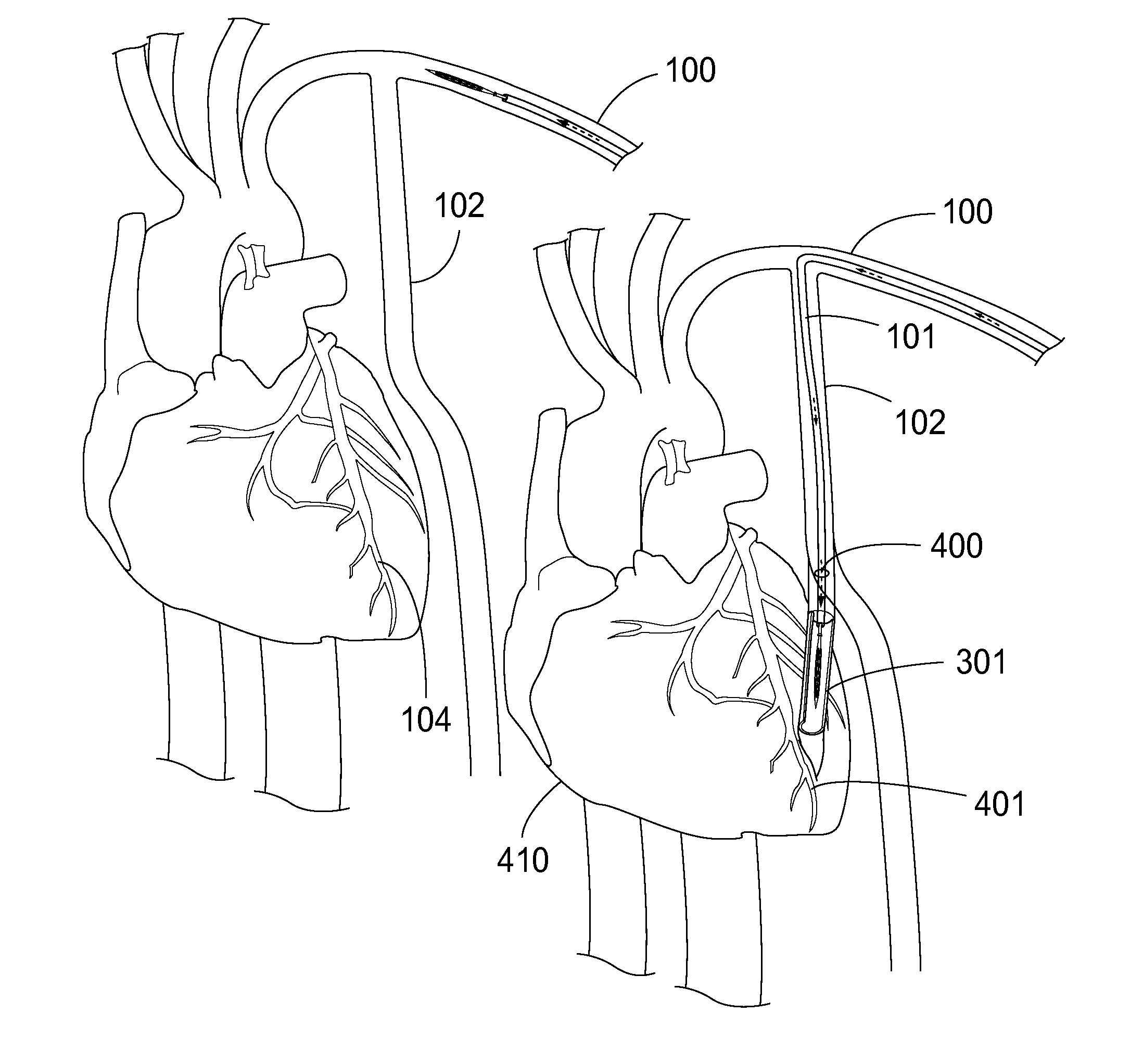
Described are equipment, a system, a kit and a method for the performance of a minimally-intensive body access, such as cardiac access. Epicardial Access Surgery (EAS) is disclosed. EAS does not need general anesthesia or extracorporeal circulation nor does it need a chest opening, which is very advantageous for various aspects. For instance an operation of a coronary artery bypass is created by creating a direct path of flow from one body artery into a coronary artery with the aid of catheter-based minimally-invasive EAS based bypass surgery. In addition, various medical devices are used, such as a special partially flexible needle, a special partially covered stent, and a special partially flexible port.
Owner:CARAG AG
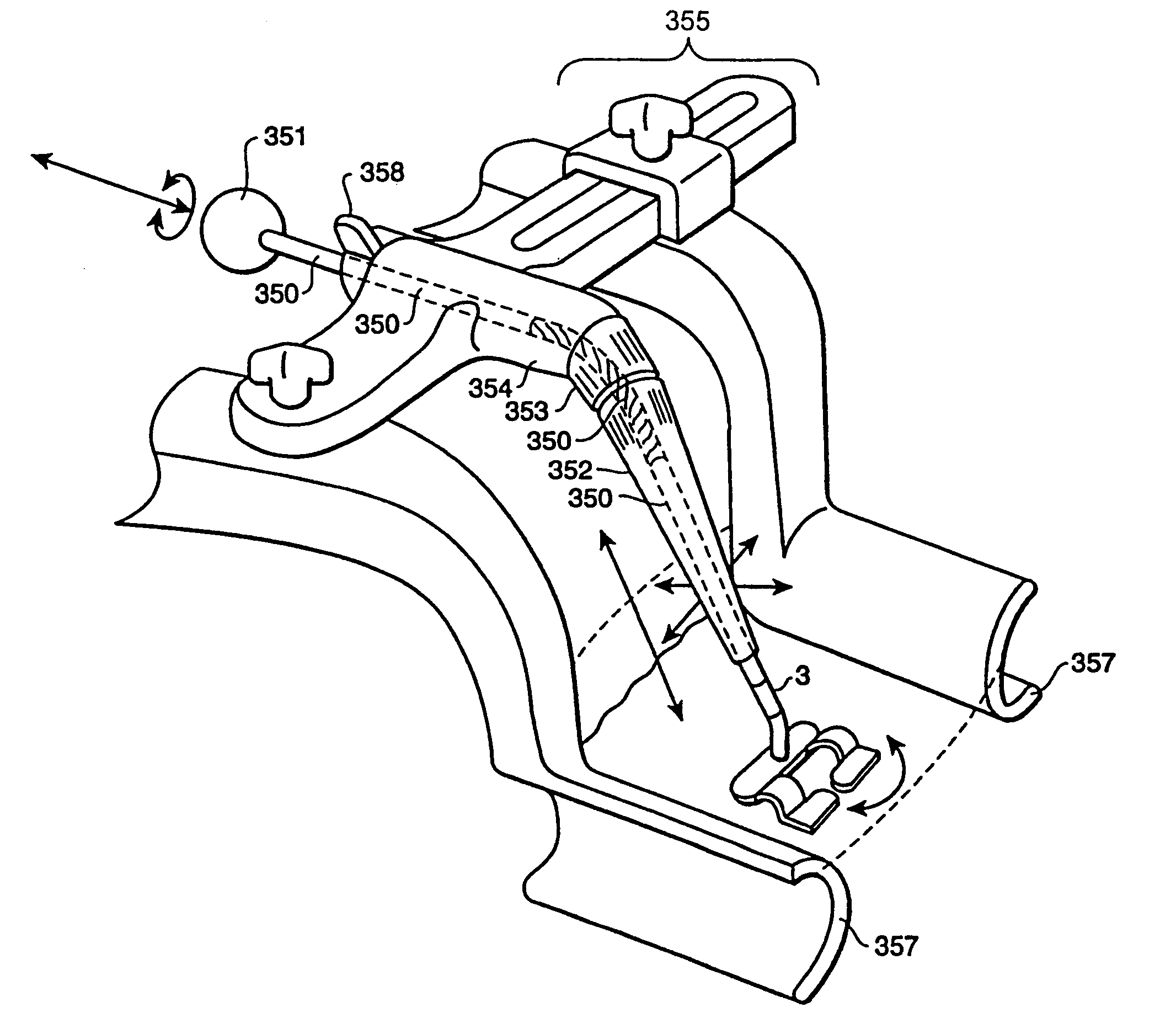
Surgical retractor blade and system
InactiveUS7220228B2Easy to createEasy to installSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsSurgical approachCoronary Artery Bypasses
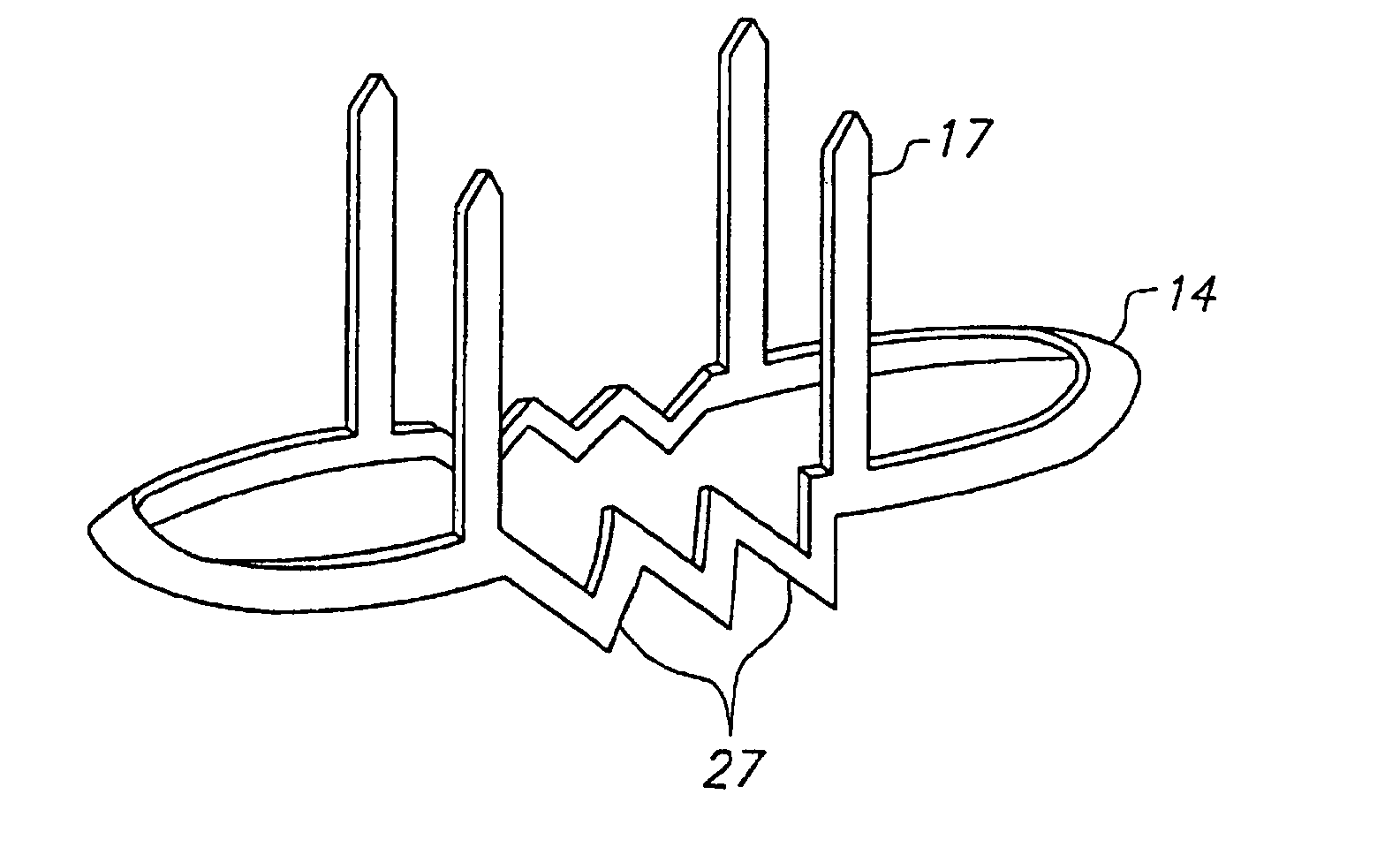
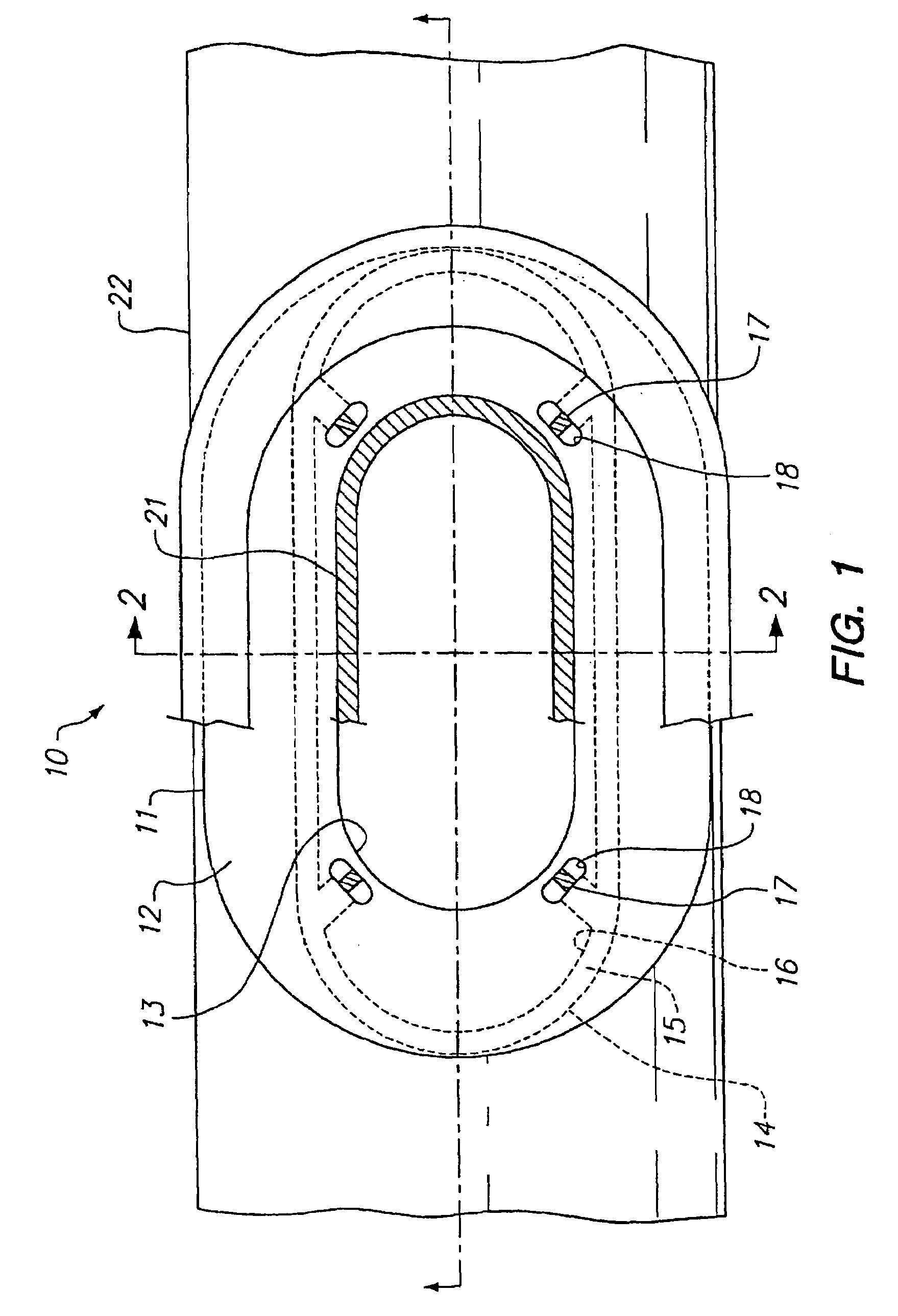
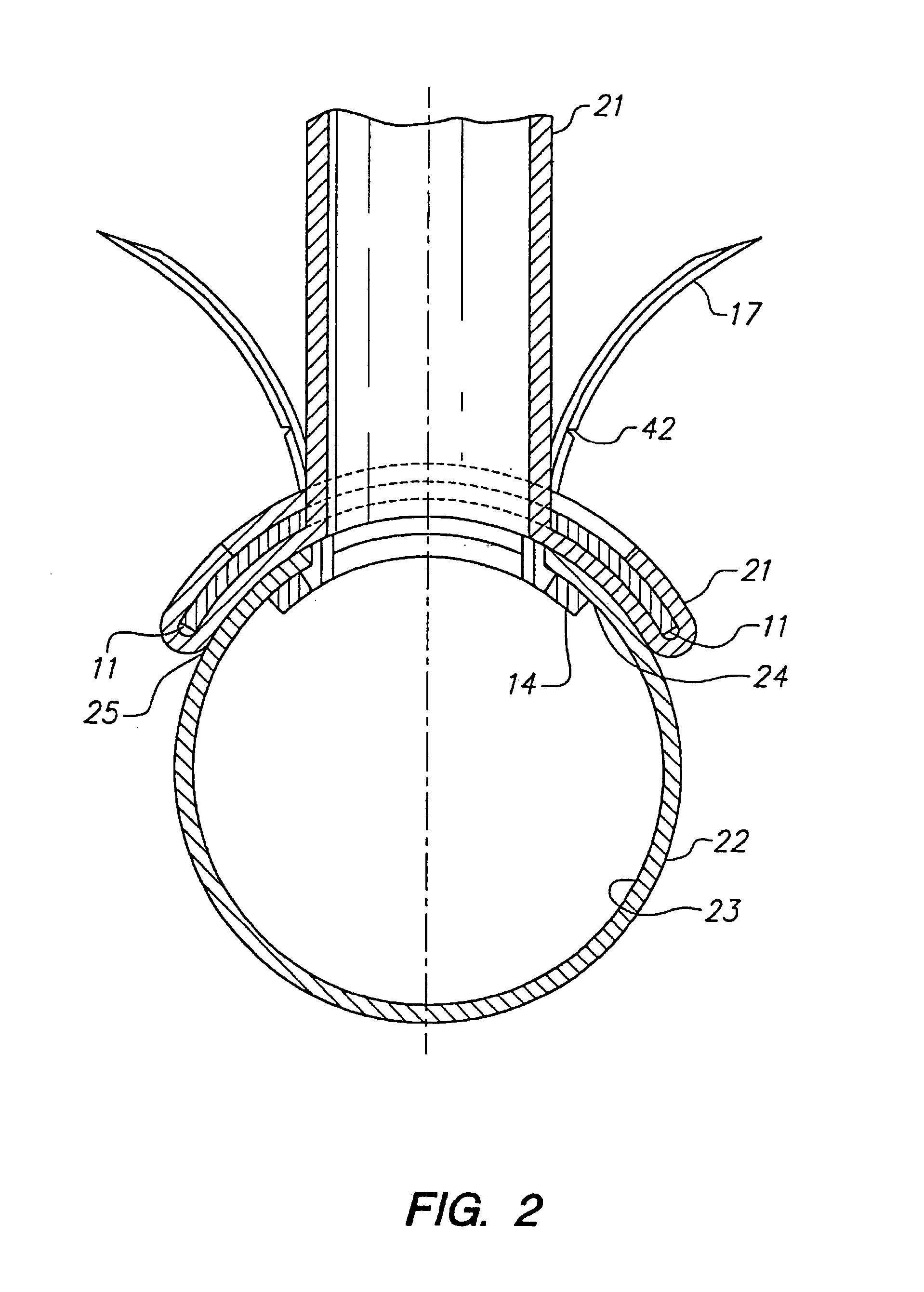
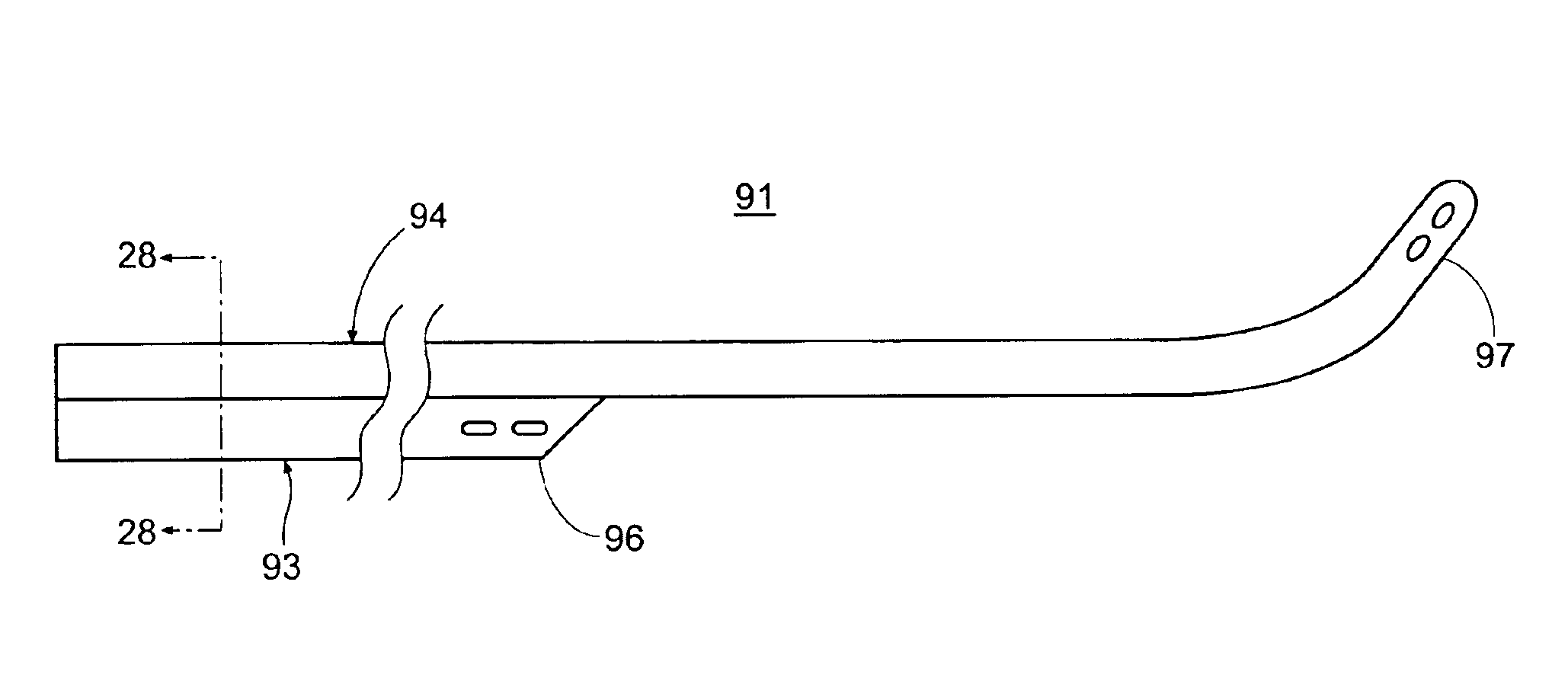
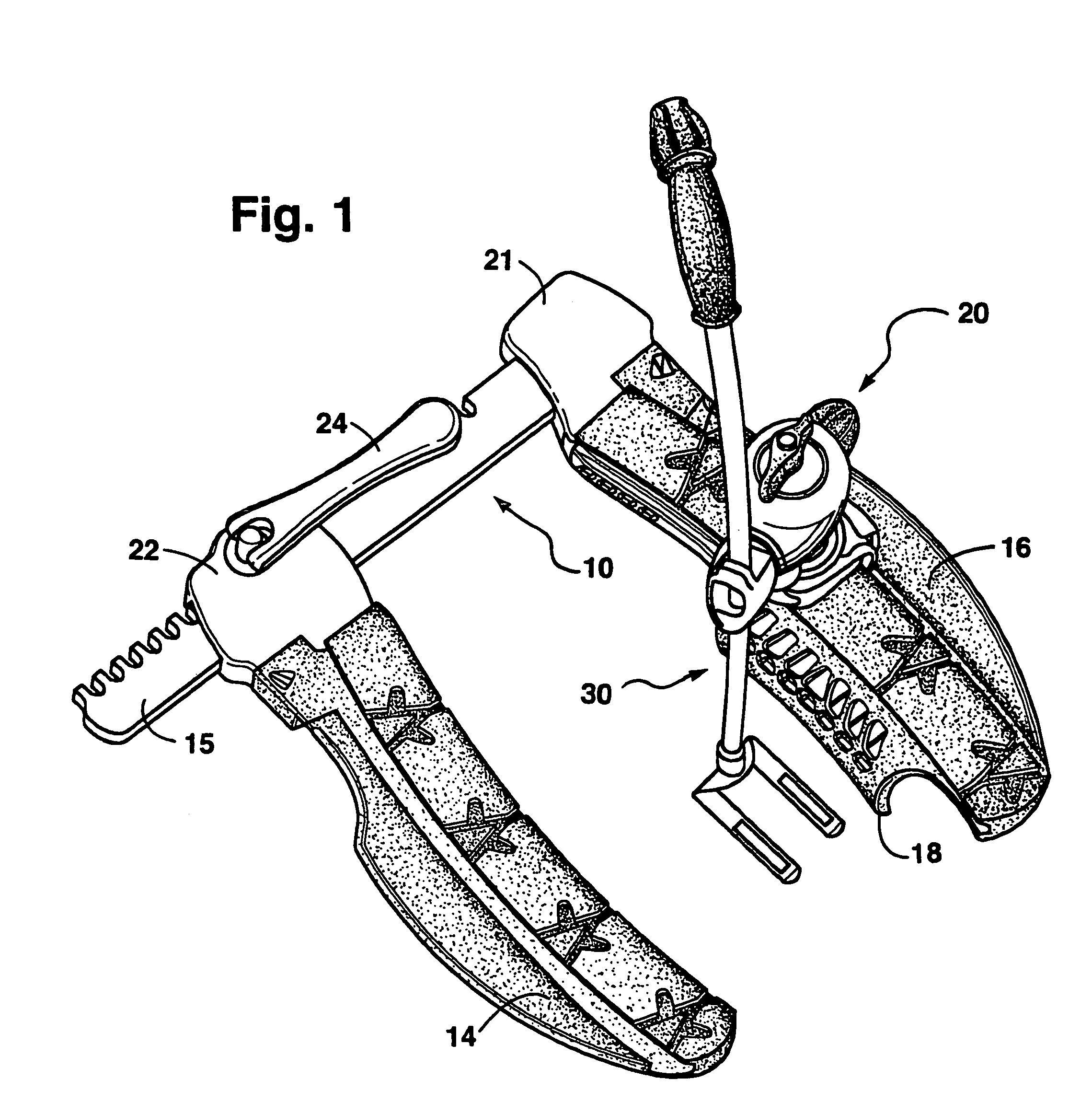
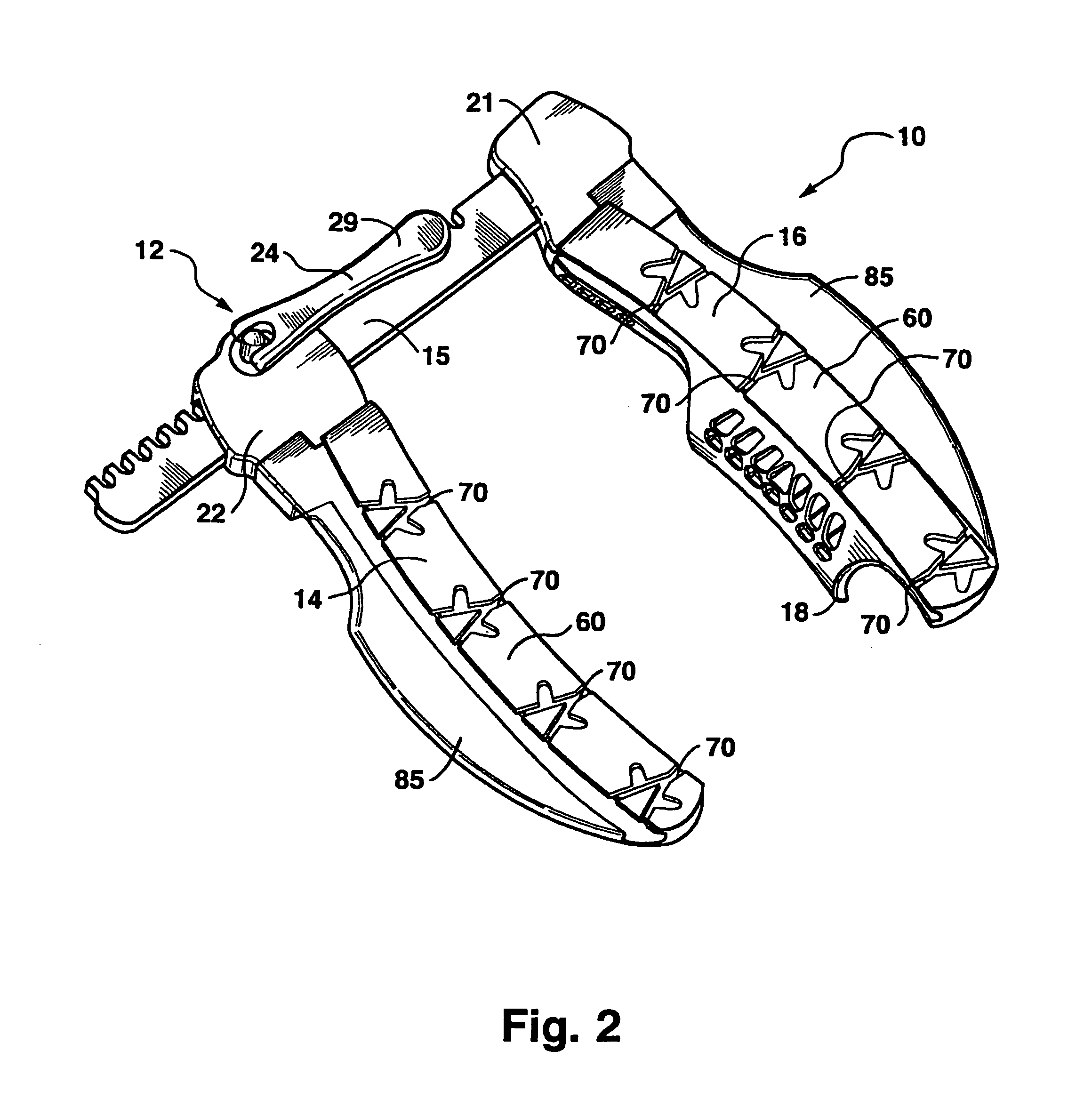
In accordance with the present invention, there is disclosed surgical methods and apparatus for accessing and stabilizing the heart. The methods and apparatus facilitate access to an anastomosis site, allows various instruments or devices to be maneuvered and secured in place, and provide stabilization of the heart. In particular, the apparatus involves a retractor apparatus having one or more opposing blades having a channel adapted to engage an incision in a patient. The retractor blades may have features to cooperatively engage an instrument mount. The instrument mount preferably is configured to hold an instrument, such as a tissue stabilizer, and allows the instrument to be easily maneuvered. The retractor blades may have a number of suture locks for securing sutures used during surgery. The retractor system is particularly useful in accessing, positioning and stabilizing the beating heart for coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com