Patents
Literature
418 results about "Laparoscopes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
ENDOSCOPES for examining the abdominal and pelvic organs in the peritoneal cavity.
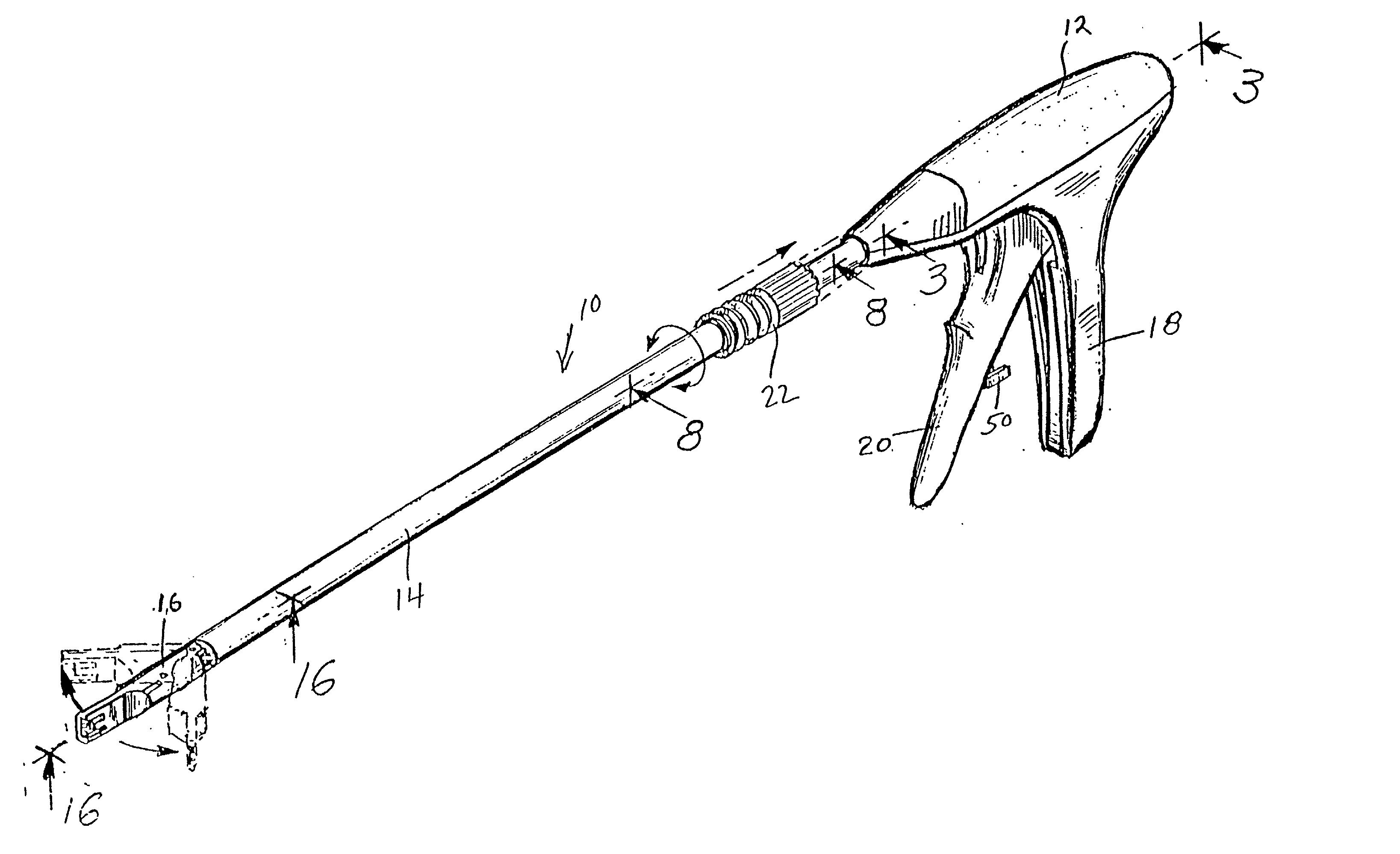
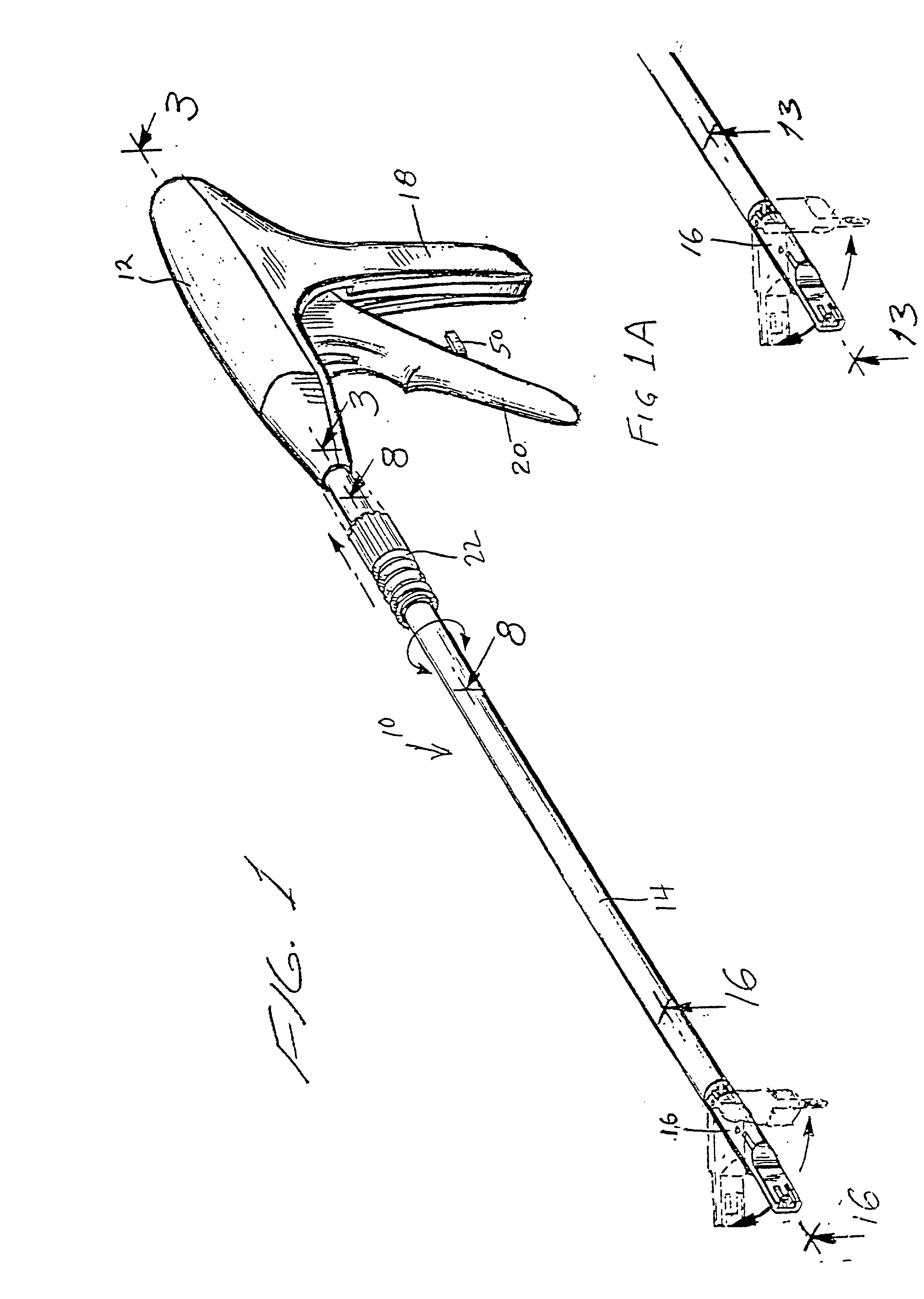
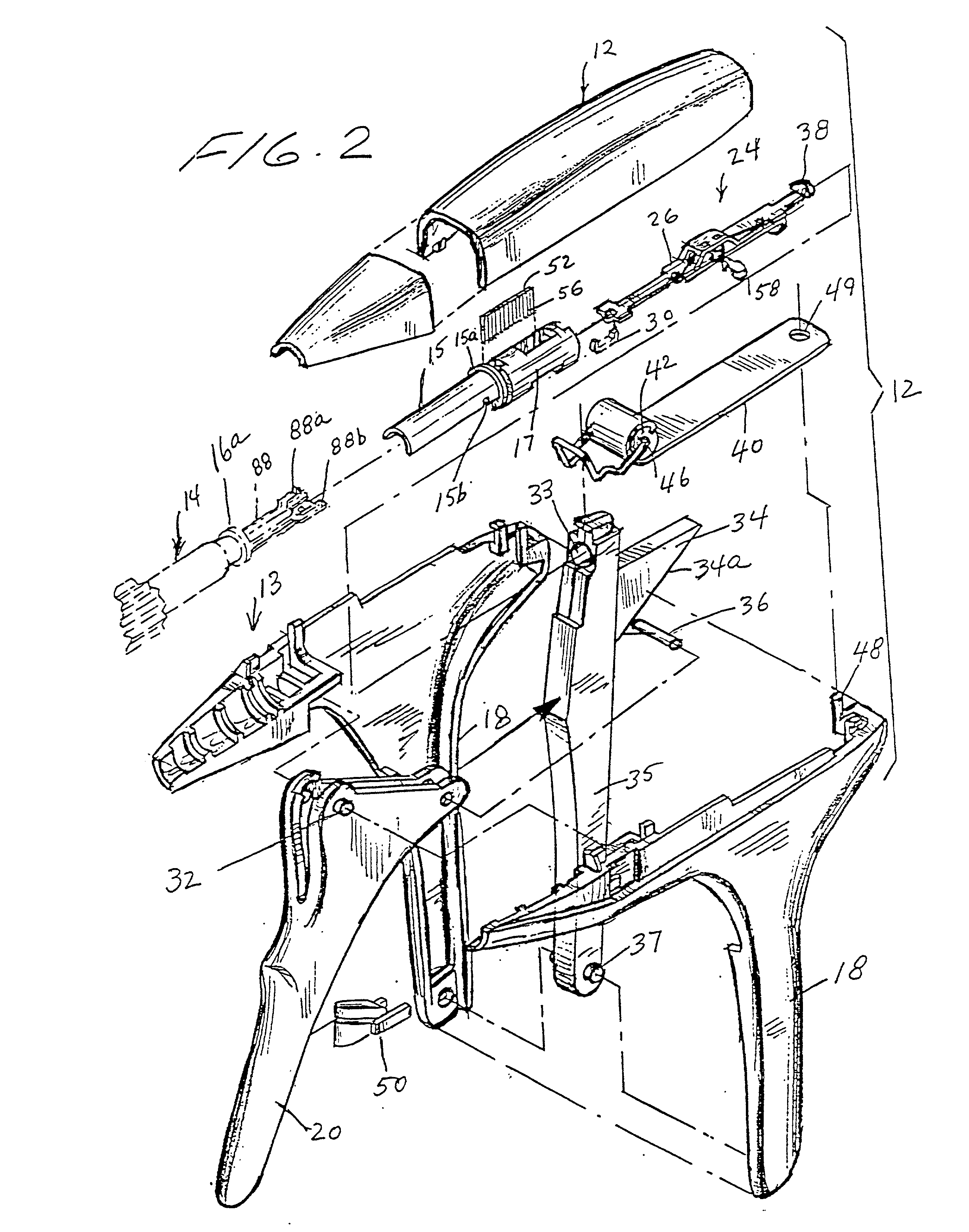
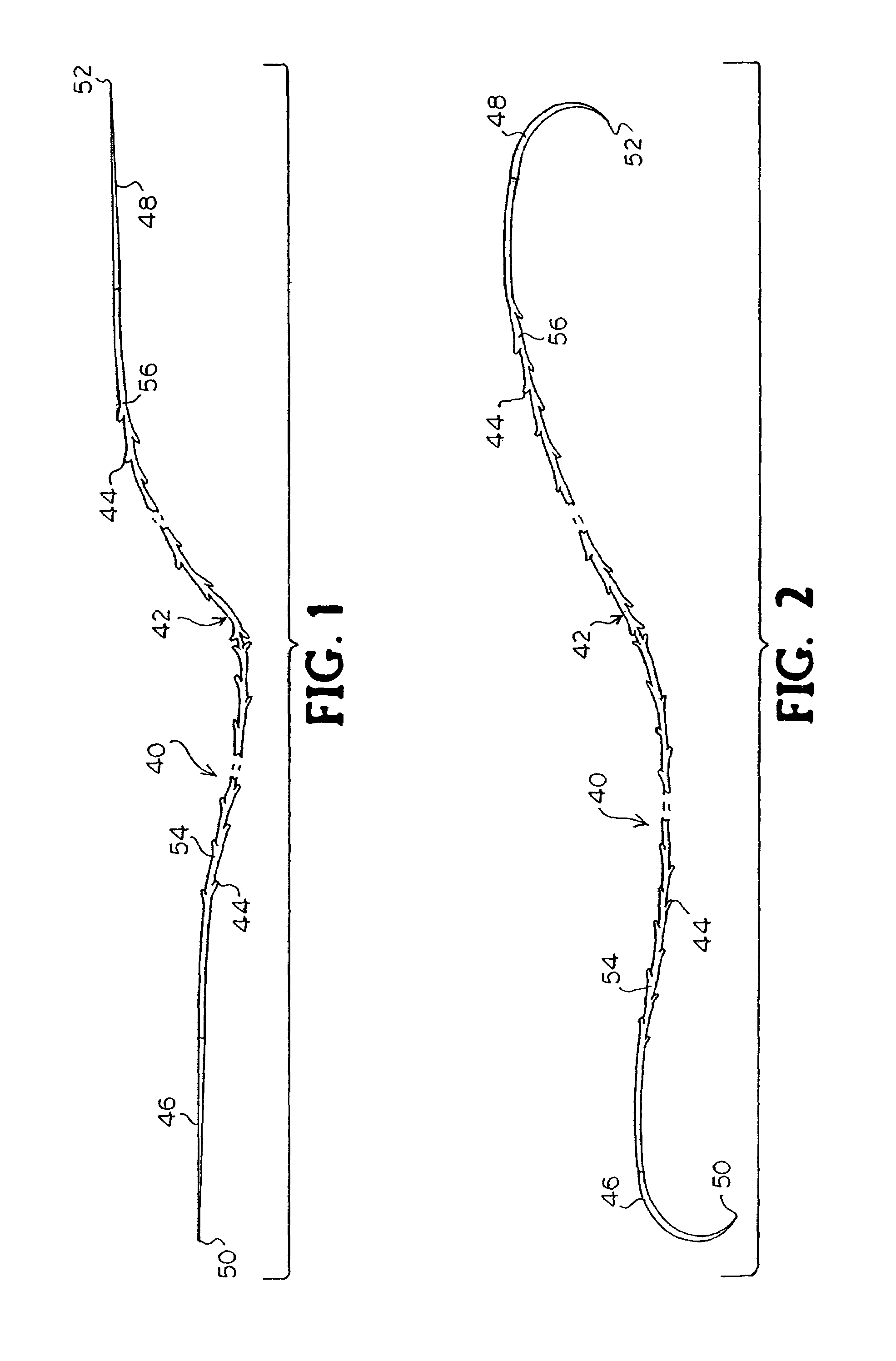
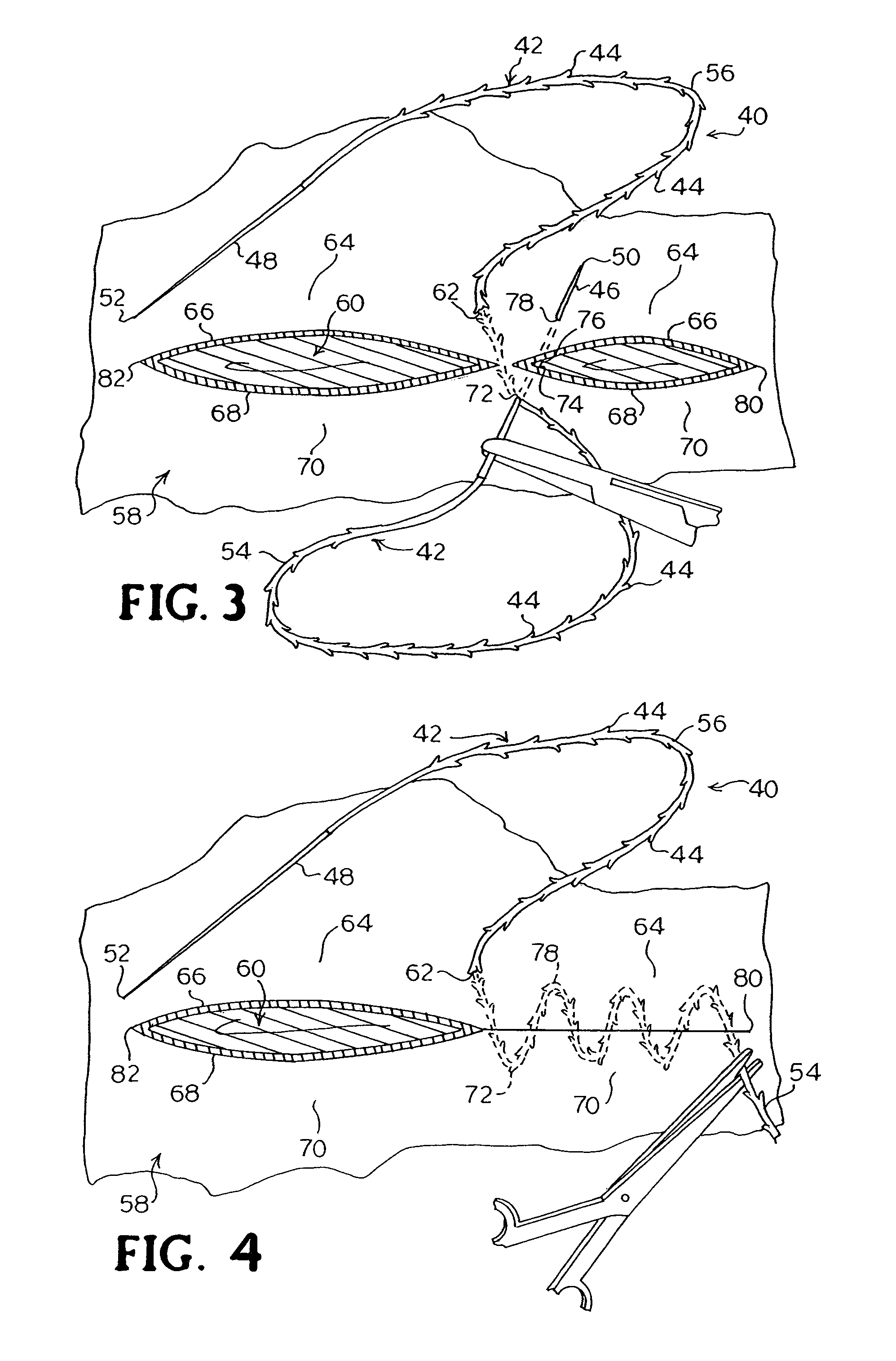
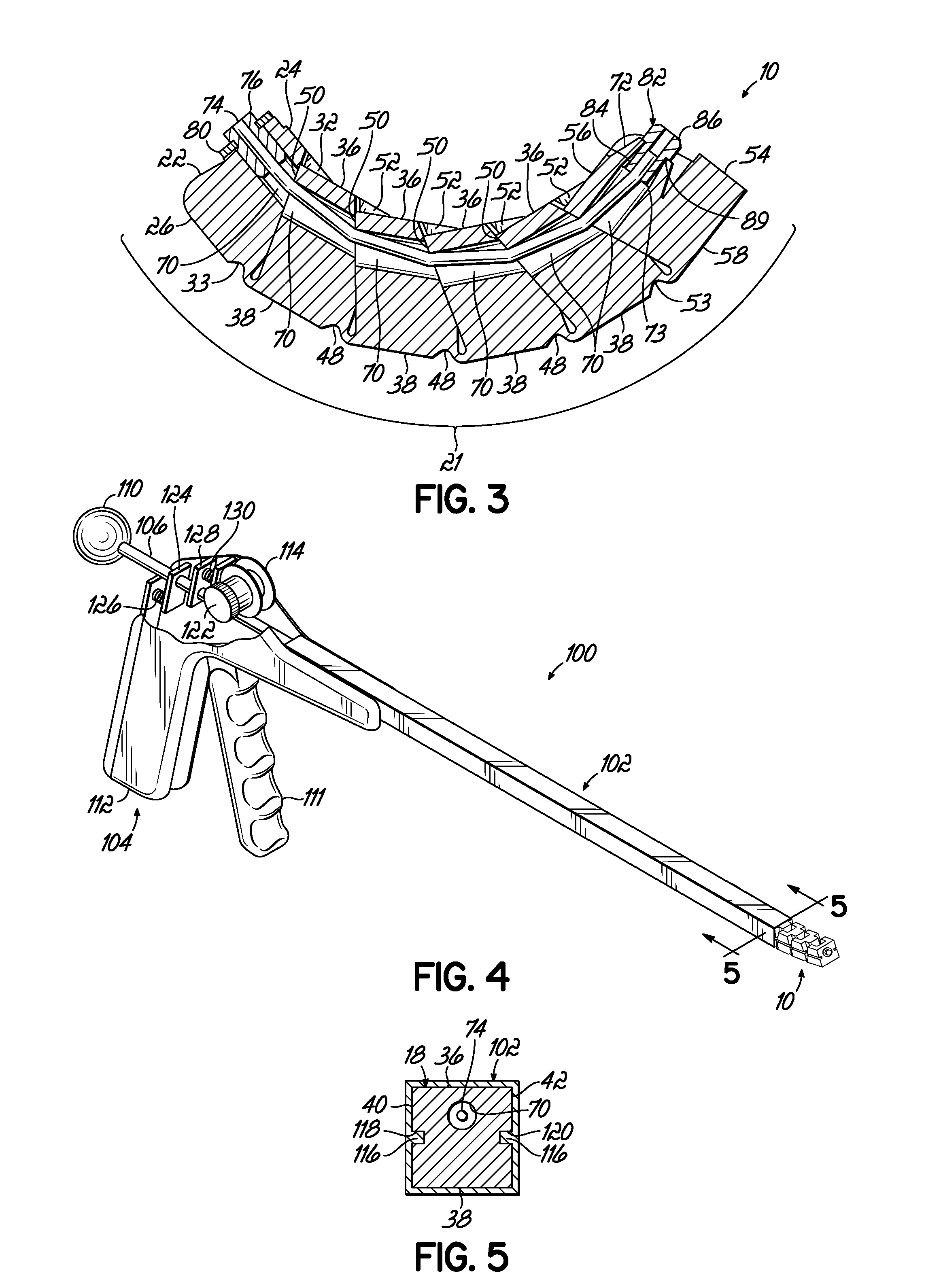
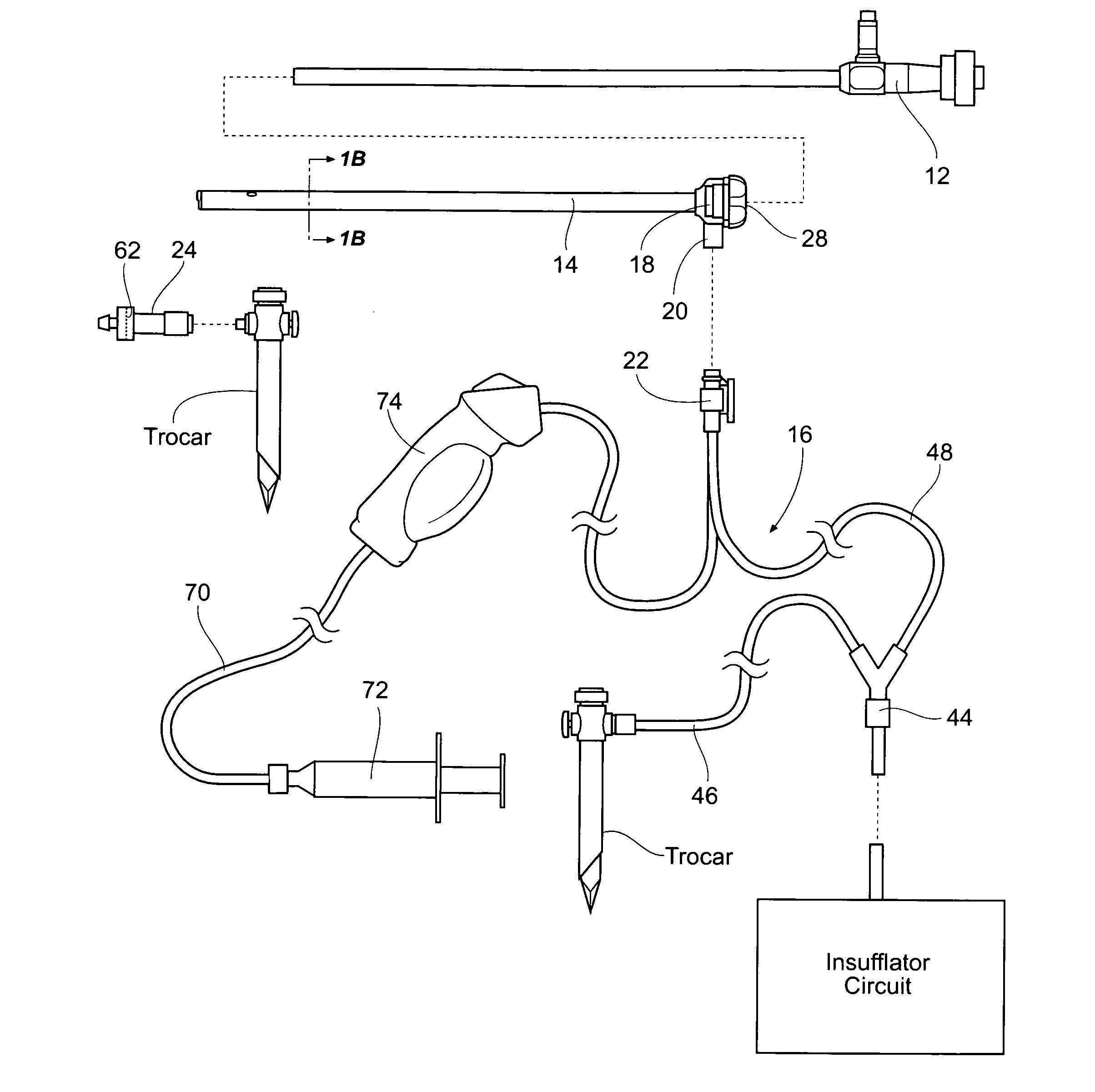
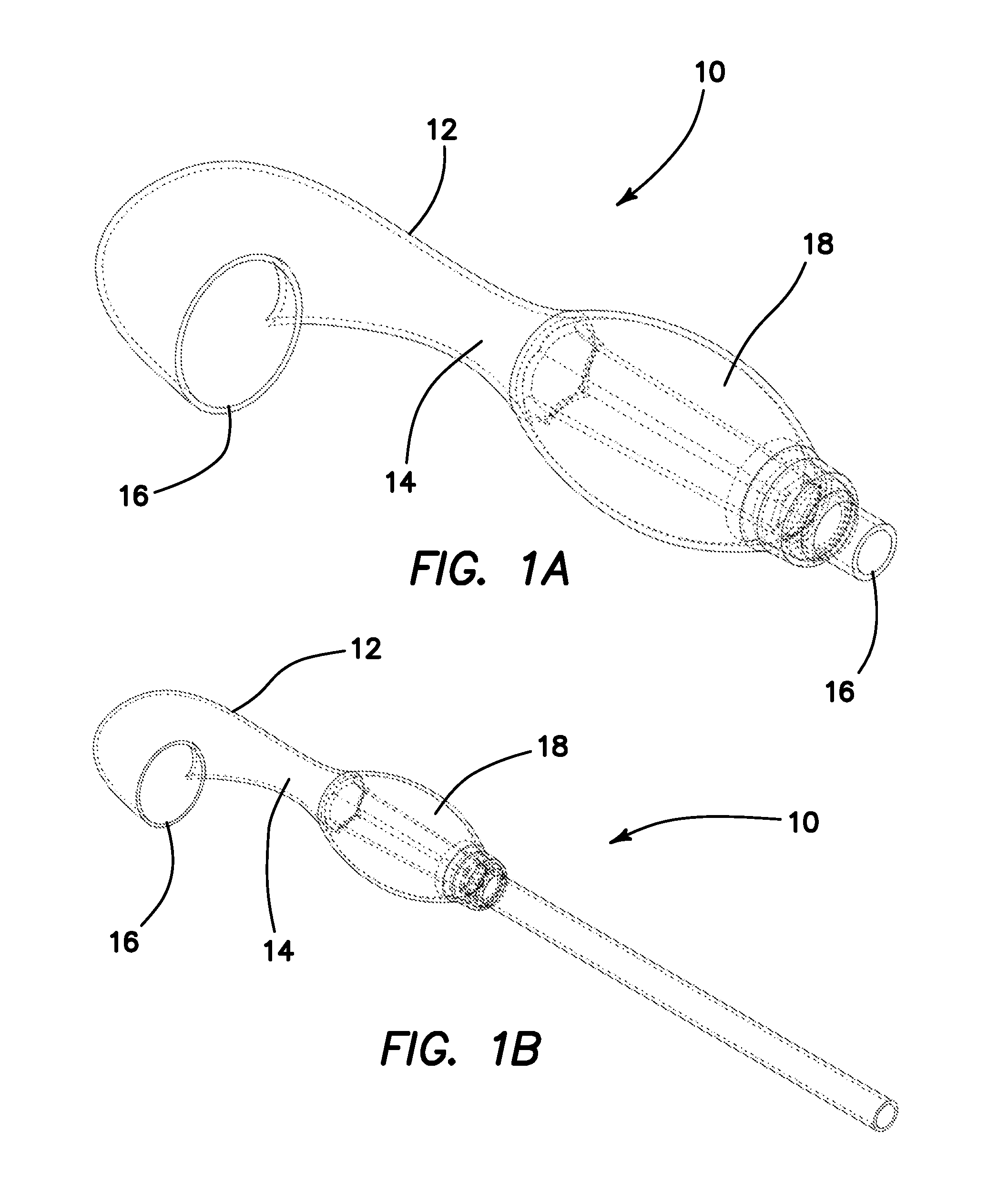
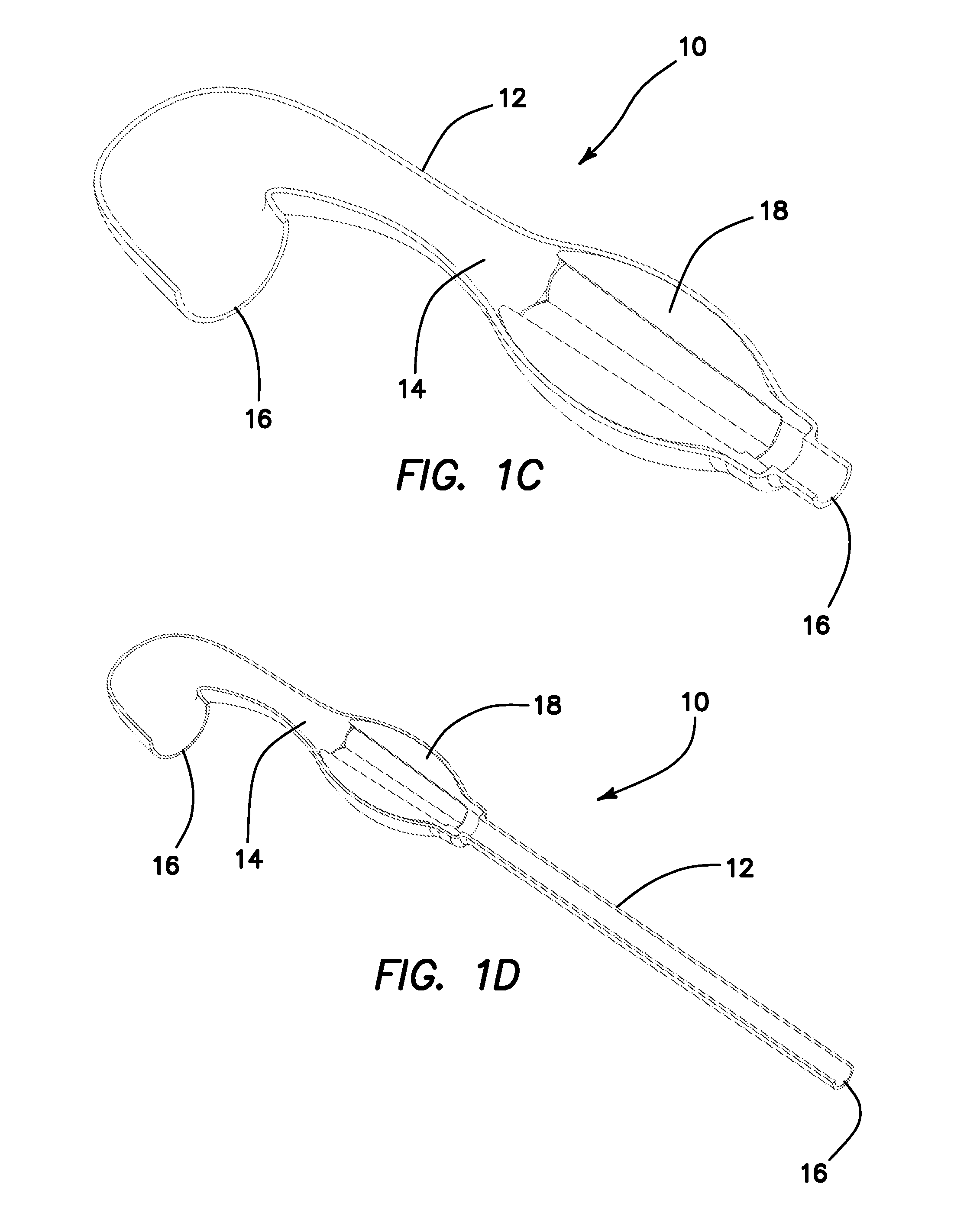
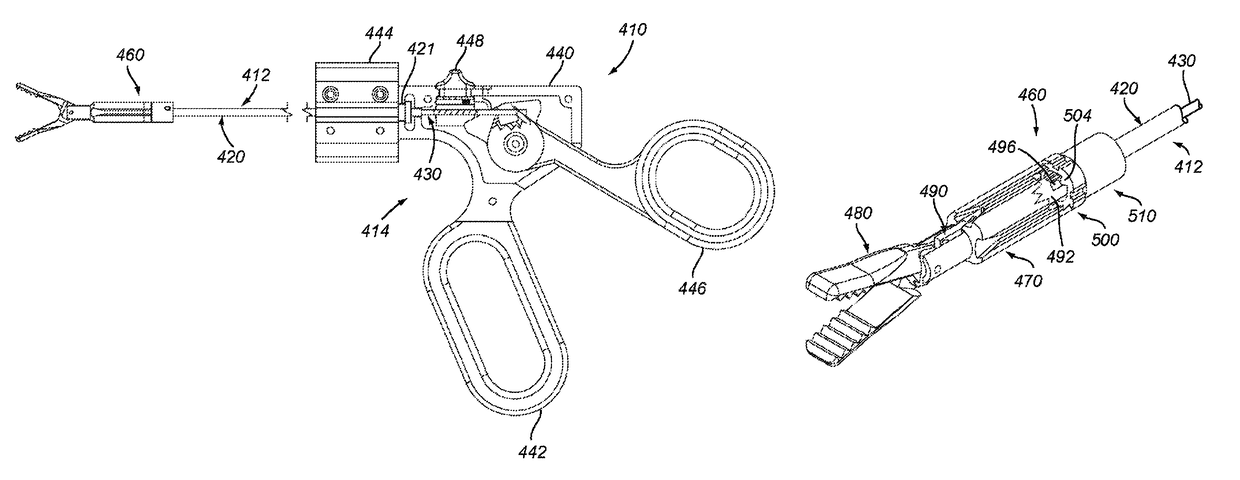
Apparatus and method for applying surgical staples to attach an object to body tissue
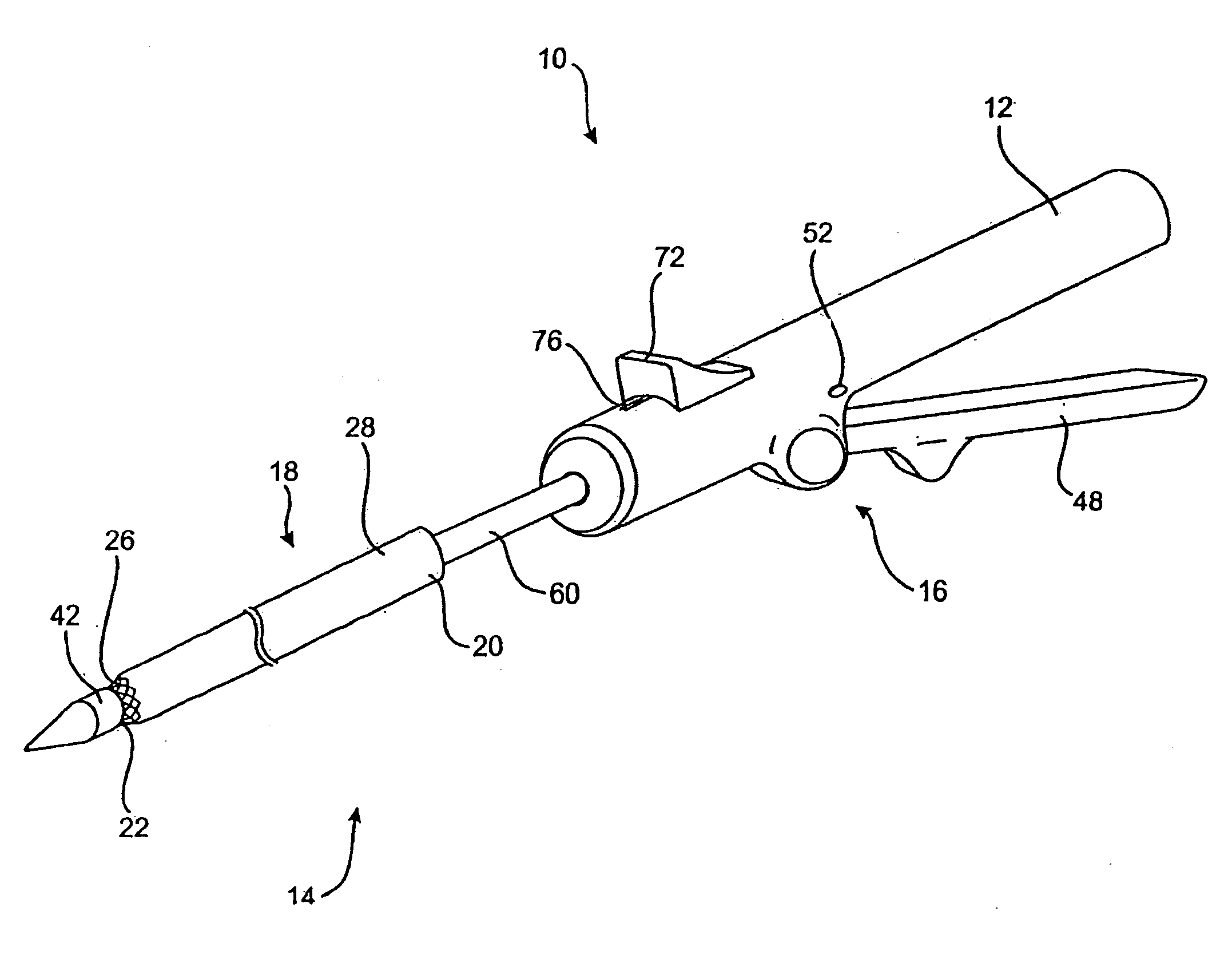
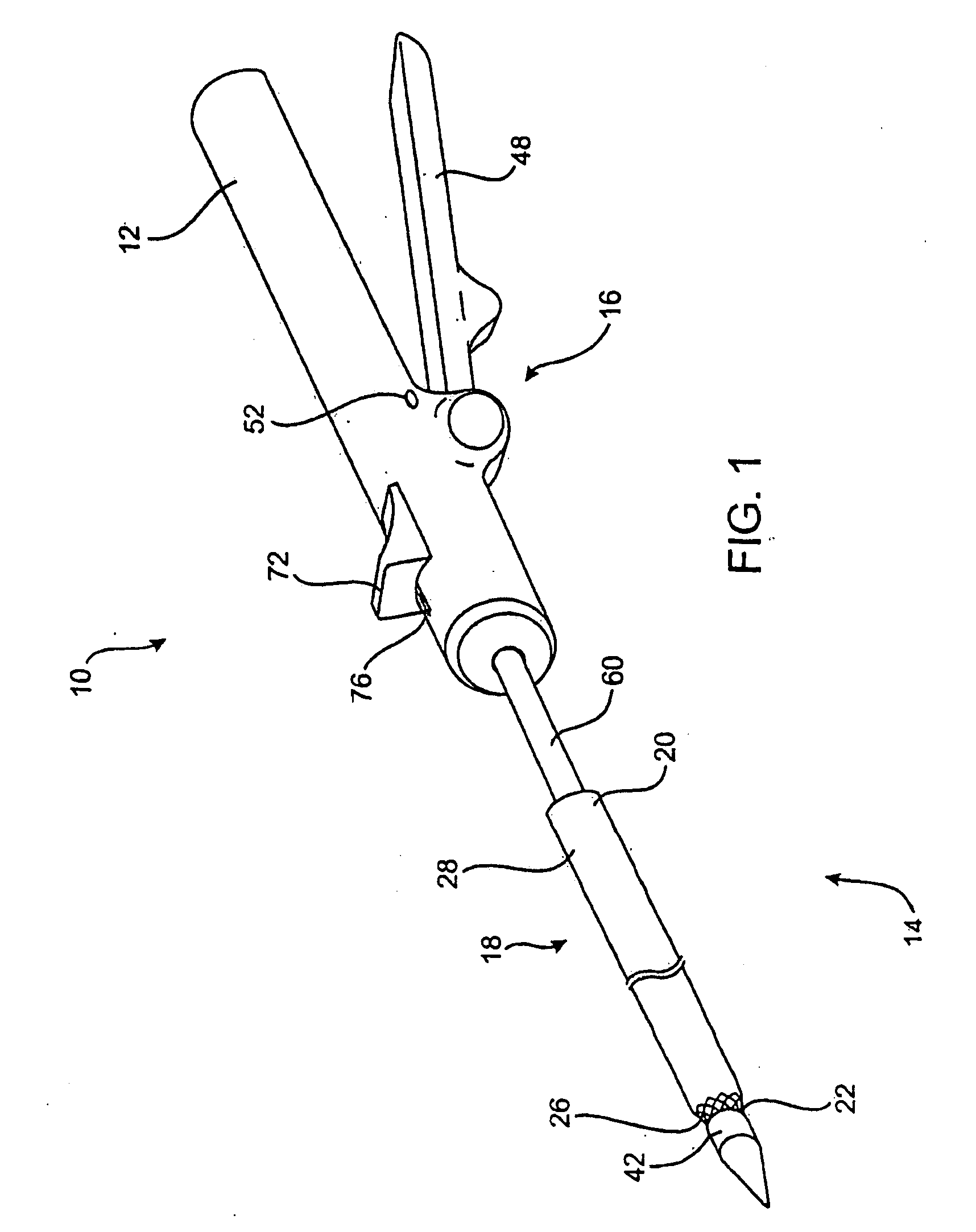
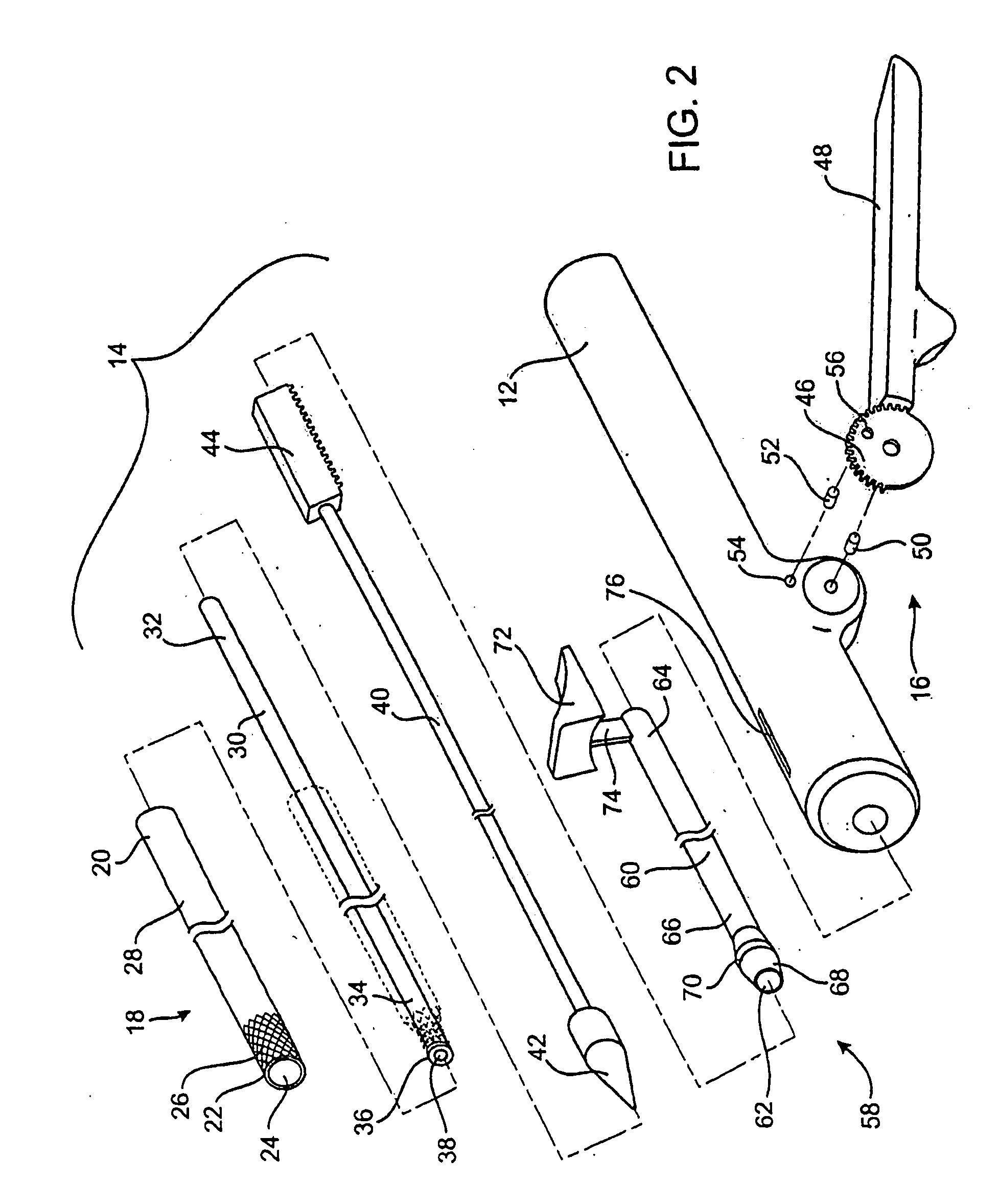
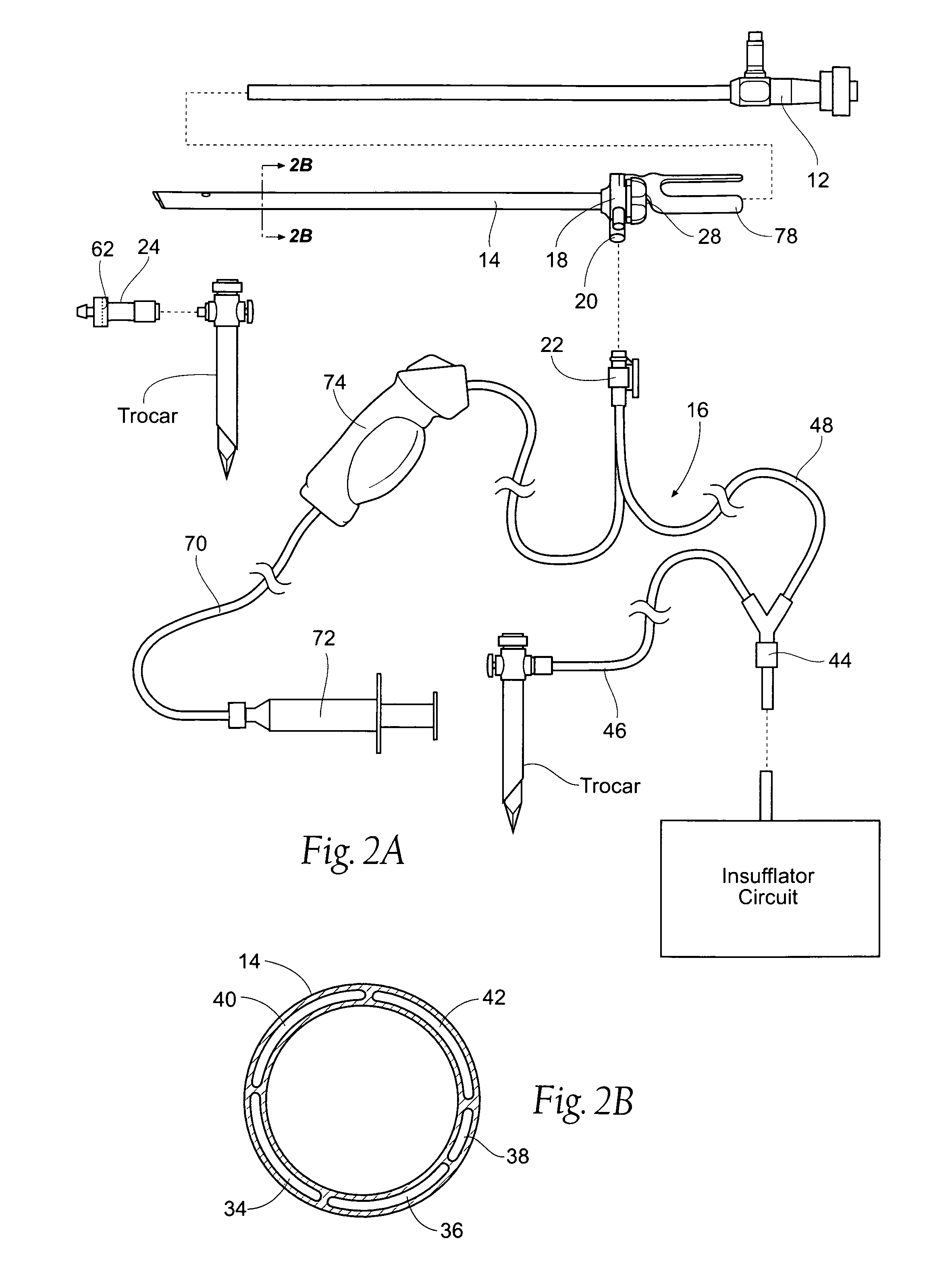
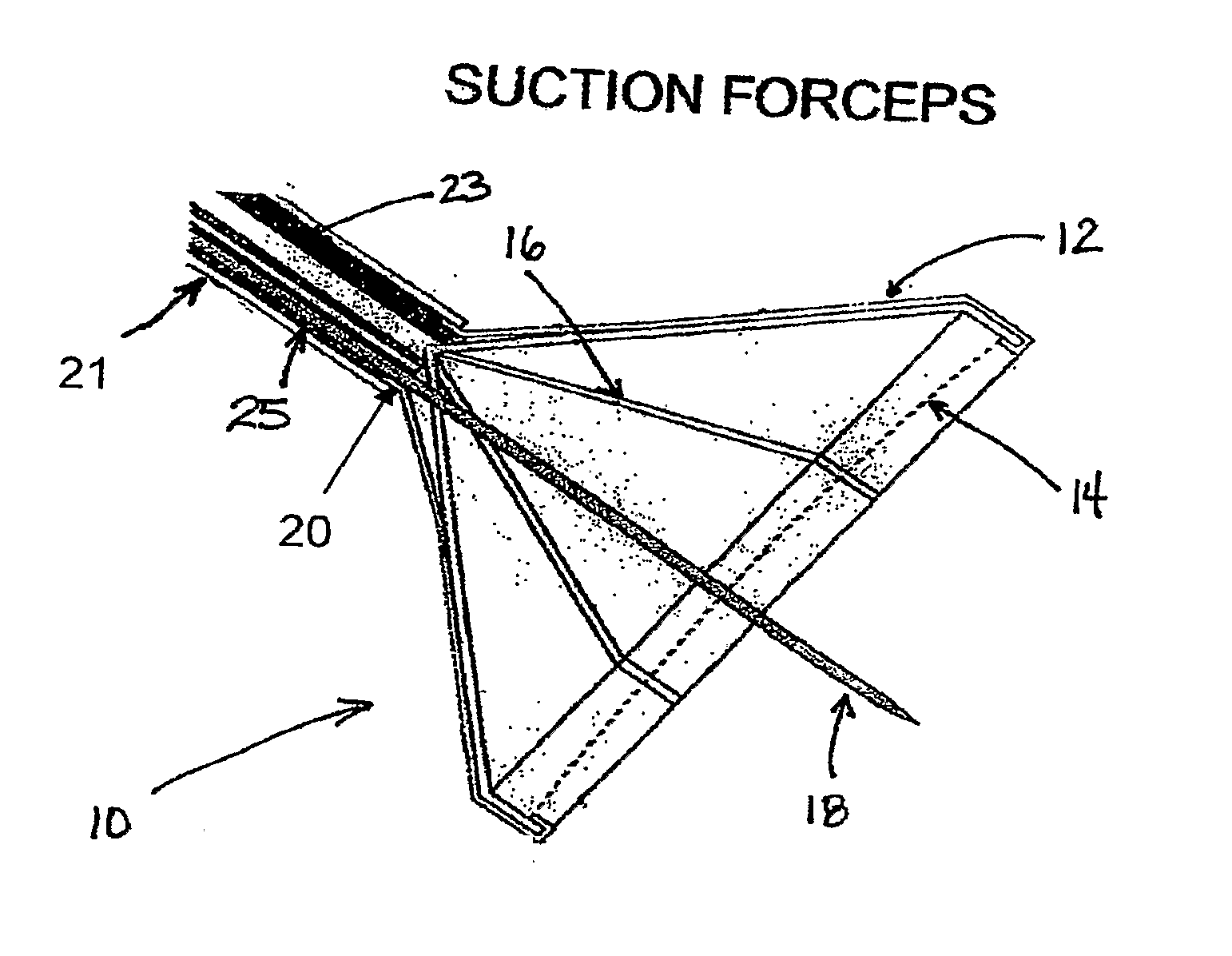
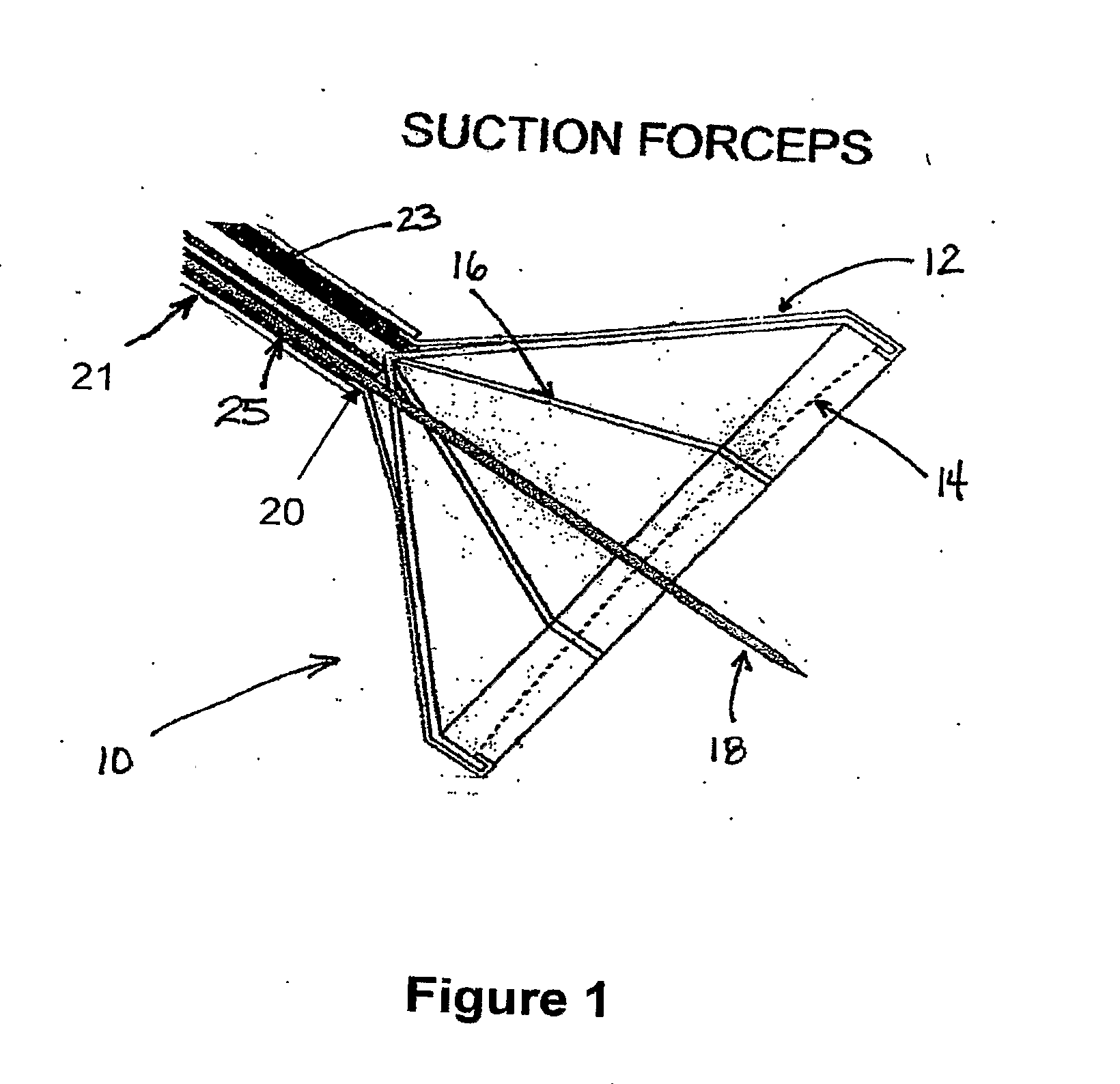
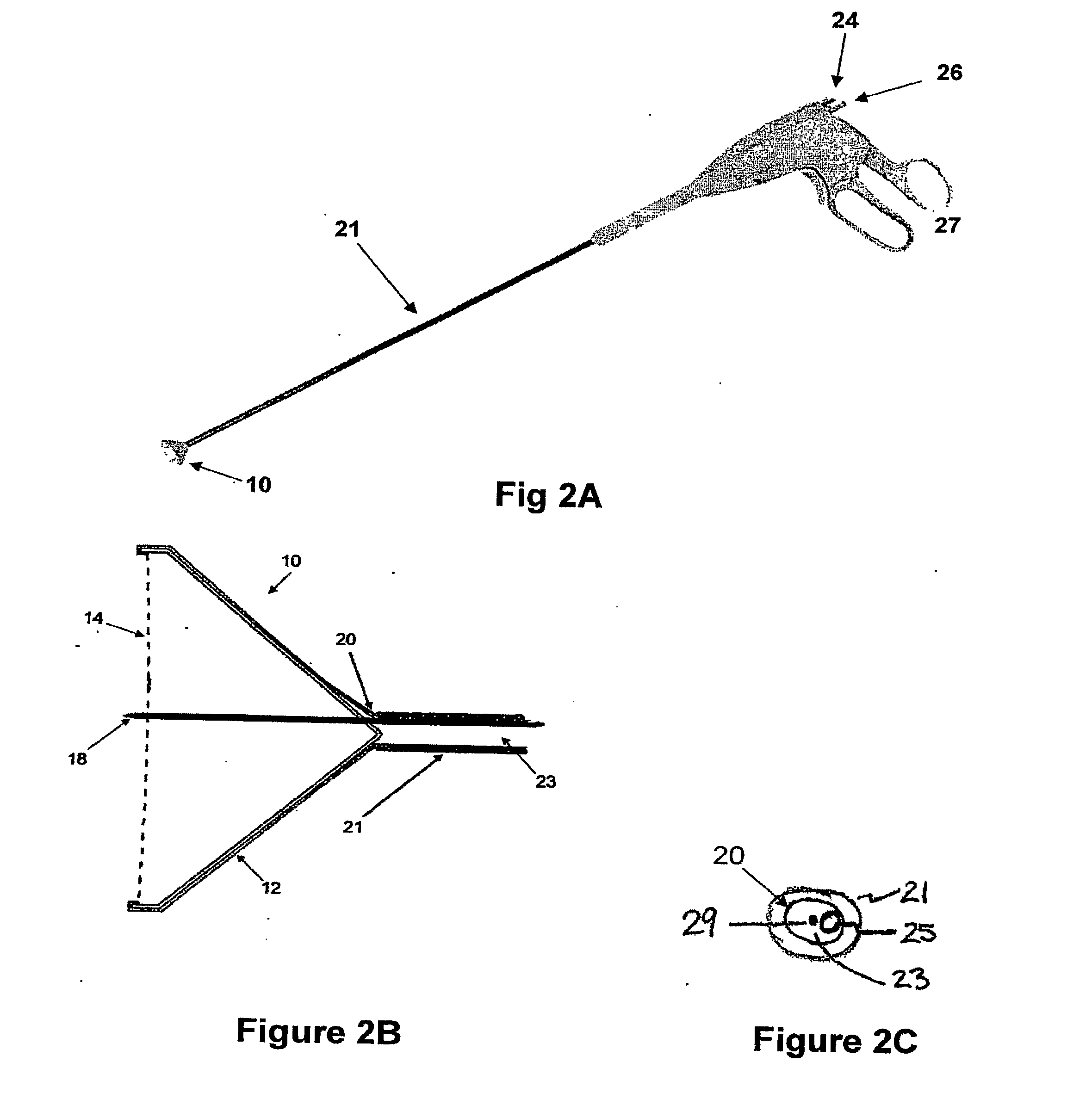
InactiveUS20020117534A1Avoid deformationSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSupporting systemSurgical staple
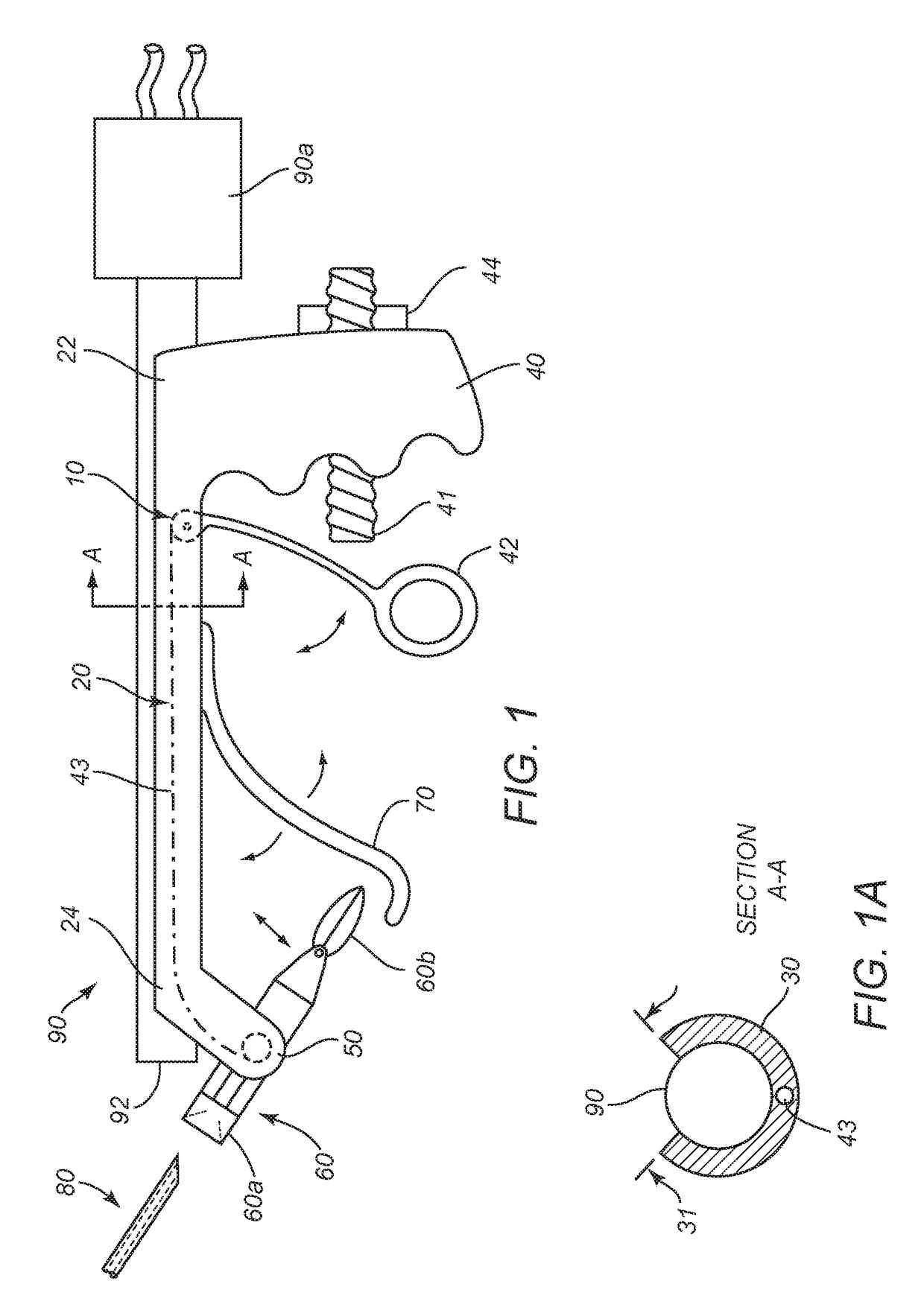
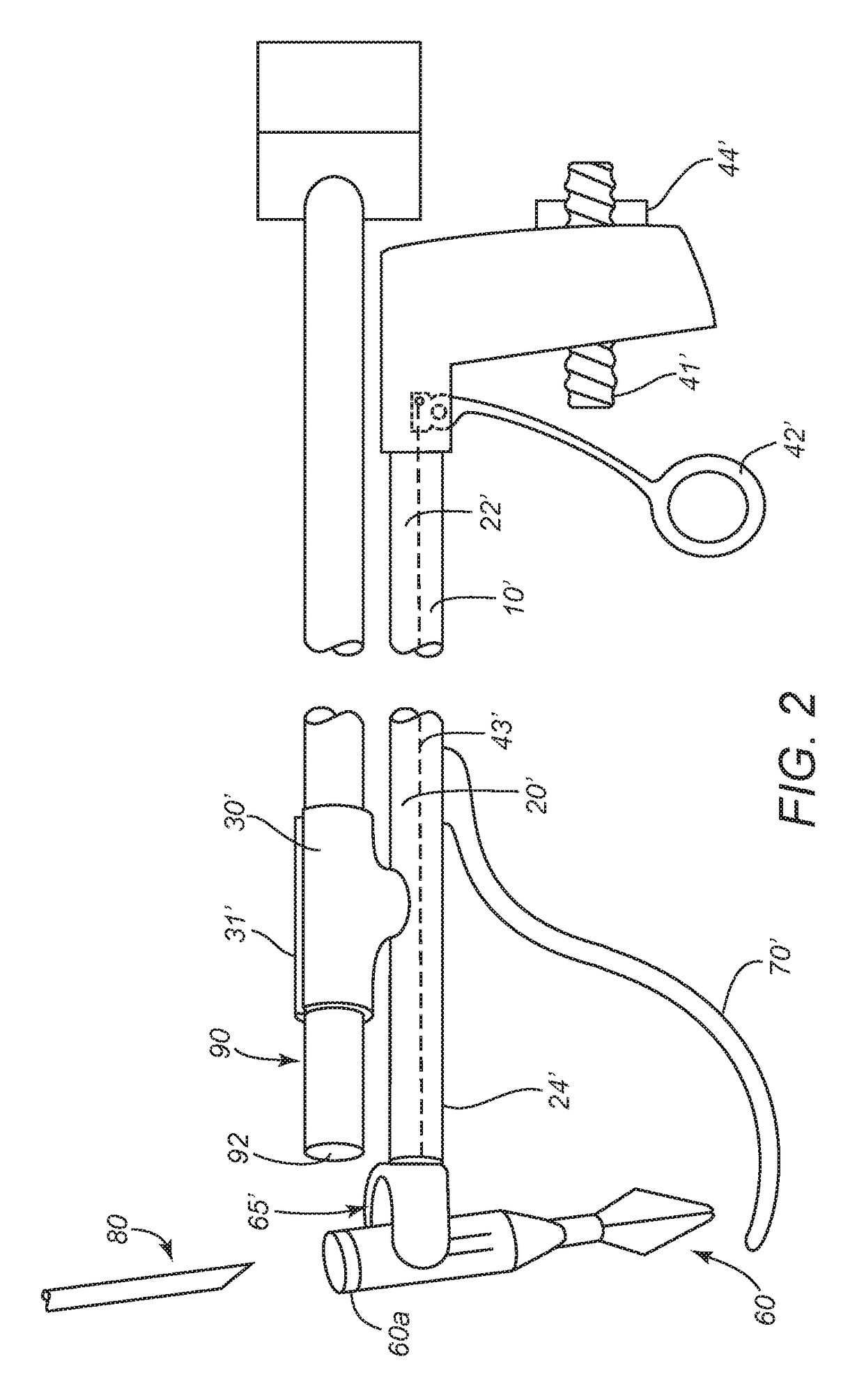
An apparatus is disclosed for endoscopic application of surgical staples adapted to attach surgical mesh to body tissue in laparoscopic hernia surgery. The apparatus includes a frame, and a generally elongated endoscopic section connected to the frame and extending distally therefrom. A staple storage cartridge is removably supported on a pivotal support system at the distal end portion of the endoscopic section with each staple being configured and adapted to attach the mesh to the body tissue. An elongated pusher system formed of several assembled components and extending from the frame to the endoscopic section is provided for individually advancing at least one staple at a time distally for positioning adjacent the surgical mesh and the body tissue. The pusher system also includes a trigger system to actuate the pusher. The trigger system is provided with perceptible tactile sensing means to indicate when the legs of the staple being advanced are exposed so as to be visible to the user for positioning and orientation purposes. Anvil means provides for individually closing each staple to encompass at least a portion of the surgical mesh and to penetrate the body tissue in a manner to attach the portion of the mesh to the body tissue. Projecting distally of the cartridge support system is a pair of legs which are dimensioned and configured to engage the staple during closure to prevent unwanted roll or deformation outside of the plane of the staple.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Suture method
A method for joining and holding closed a wound in bodily tissue, fastening junctions of wounds, tying off wounds, joining a foreign element to tissue, and altering the position of tissue using a barbed suture including sharp pointed ends. Each end of the suture includes barbs on that permit movement in an opposing direction to the barbs on the other end of the suture. This two-way barbed suture is used by the method of the present invention in applications including abdominal surgeries such as a Nissen fundoplication, laparoscopic uses such as stabilizing a bowel structure and performing a closure of a cystostomy, liver to bowel anastomosis, closure of an orifice of a Zenker's Diverticulum, endoscopic uses such as closure of ulcerative lesions or and post-procedural tissue defects, bladder wound closure, valve replacement surgery, device attachment, cosmetic surgery, and blood vessel wound closure.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Deployable segmented tlif device
A segmented intervertebral body fusion support includes a plurality of segments, the segments including an initial segment, a final segment and at least one intermediate segment. The intermediate segment has a generally trapezoidal configuration and the initial and final segments include tapered side walls providing triangular gaps between adjacent segments. A draw wire is fixed to the first segment and passes through the remaining segments. By pulling the draw wire relative to the segments, the segments are drawn together in a generally arcuate configuration. The draw wire includes an enlargement that passes through the final segment and engages a plurality of fingers on the final segment, which prevents the draw wire from retracting, maintaining the arcuate configuration. The segmented device can be inserted through a laparoscopic device into the intervertebral space and can be subsequently drawn into the arcuate configuration to establish the desired intervertebral spacing.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
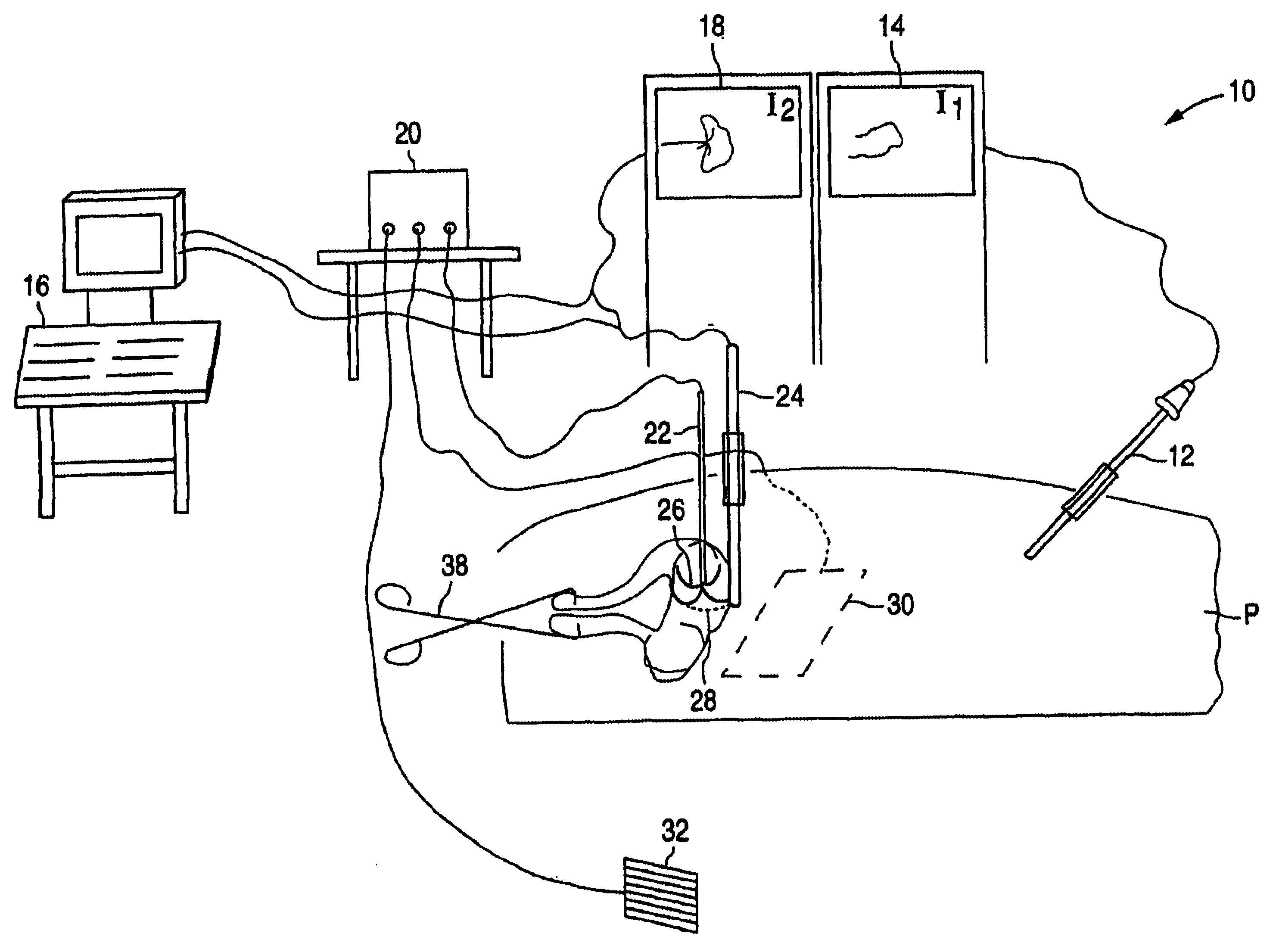
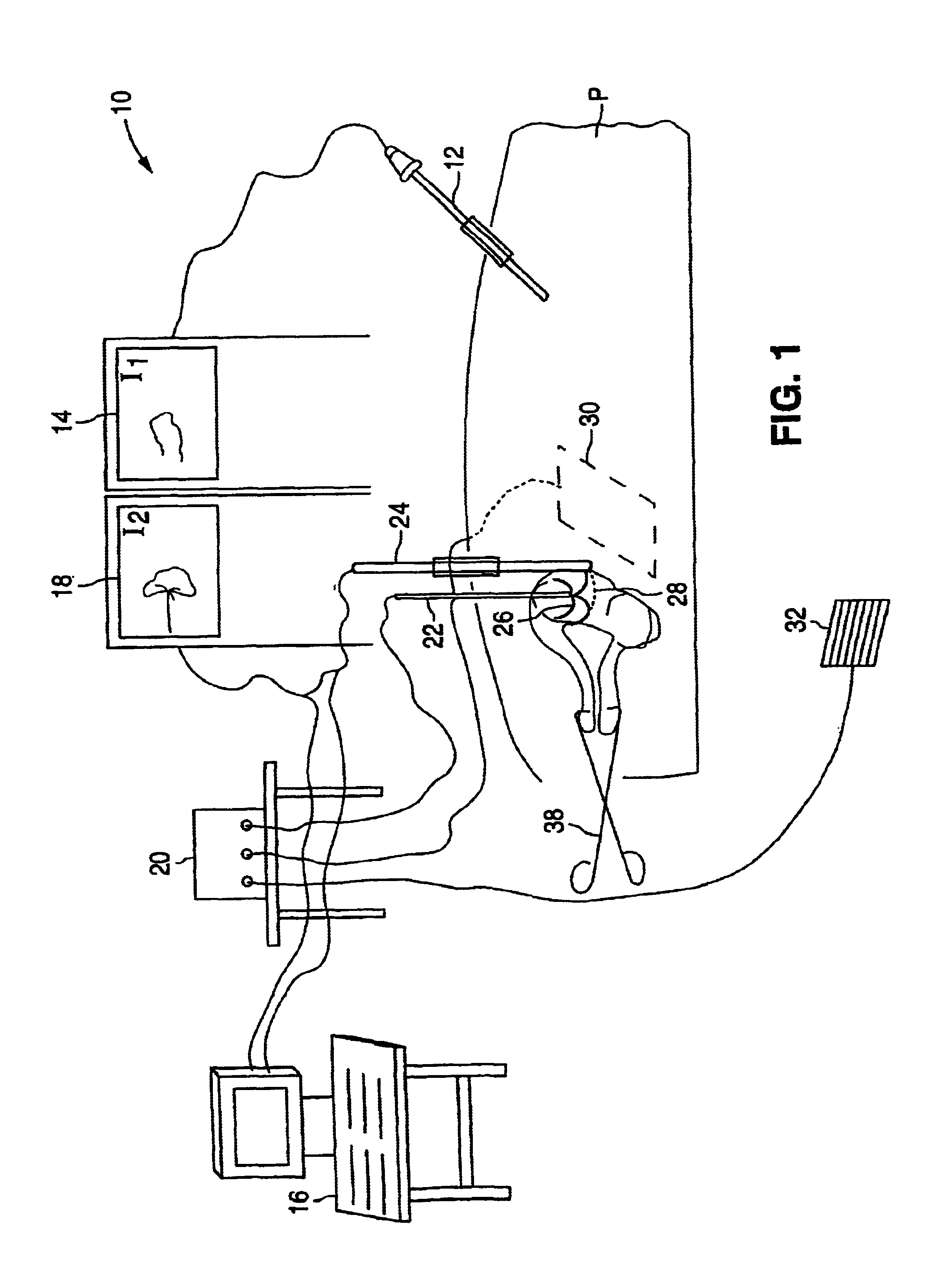
Gynecological ablation procedure and system using an ablation needle
InactiveUS6840935B2Efficient ablationFast recovery timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesProximateMedicine
A method for treating pelvic tumors, such as uterine leiomyomata, includes inserting an ablation apparatus into a pelvic region and positioning the ablation apparatus either proximate or into a pelvic tumor. The method further includes using a laparoscope and an imaging device, such as an ultrasound machine, to confirm the location of the pelvic tumor and placement of the ablation apparatus. Various ablation apparatuses may be used, including those with multiple needles or deployable arms that are inserted into the pelvic tumor and those without arms. The method further includes delivering electromagnetic energy or other energy through the ablation apparatus to the pelvic tumor to ablate the tumor. A surgical system for ablating pelvic tumors is also provided.
Owner:ACESSA HEALTH INC +1
Surgical access port with embedded imaging device
Disclosed is a disposable access port for use in endoscopic procedures, including laparoscopic procedures. The access port includes a cannula with an embedded camera in communication with an external control box. In operation, a trocar is combined with the access port to facilitate insertion of the access port into an anatomical site. Prior to insertion, the camera is pushed inside the cannula, where it remains during insertion. The trocar is removed after the access port has been inserted to allow surgical instruments to access the anatomical site. During removal of the trocar, a portion of the trocar urges the camera out of the cannula, thereby allowing visualization of the anatomical site. The camera can be fixedly or adjustably mounted on the port. A camera may also be mounted on the trocar. The trocar may include irrigation and suction channels to facilitate a clear view of the anatomical site.
Owner:PSIP LLC
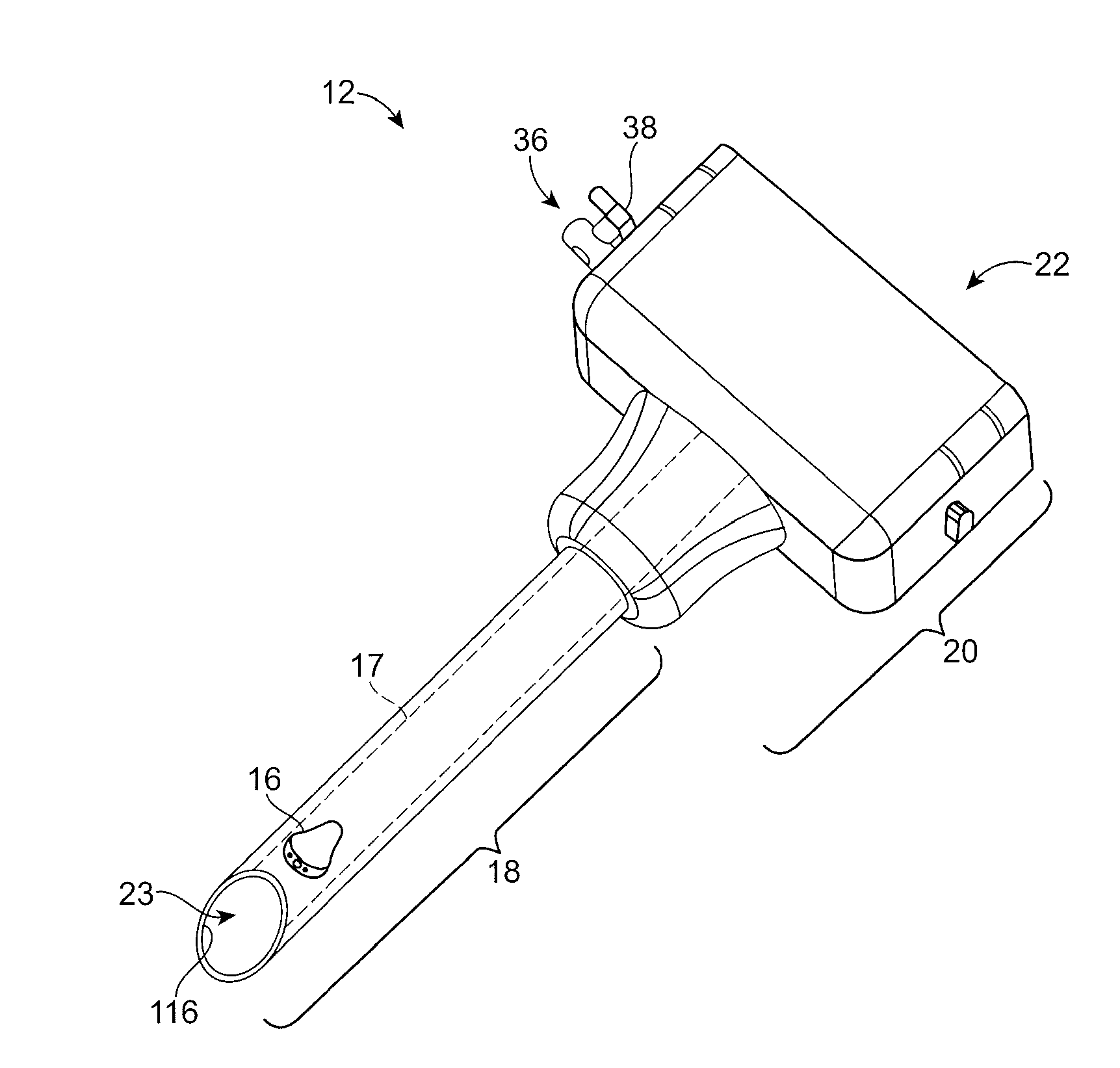
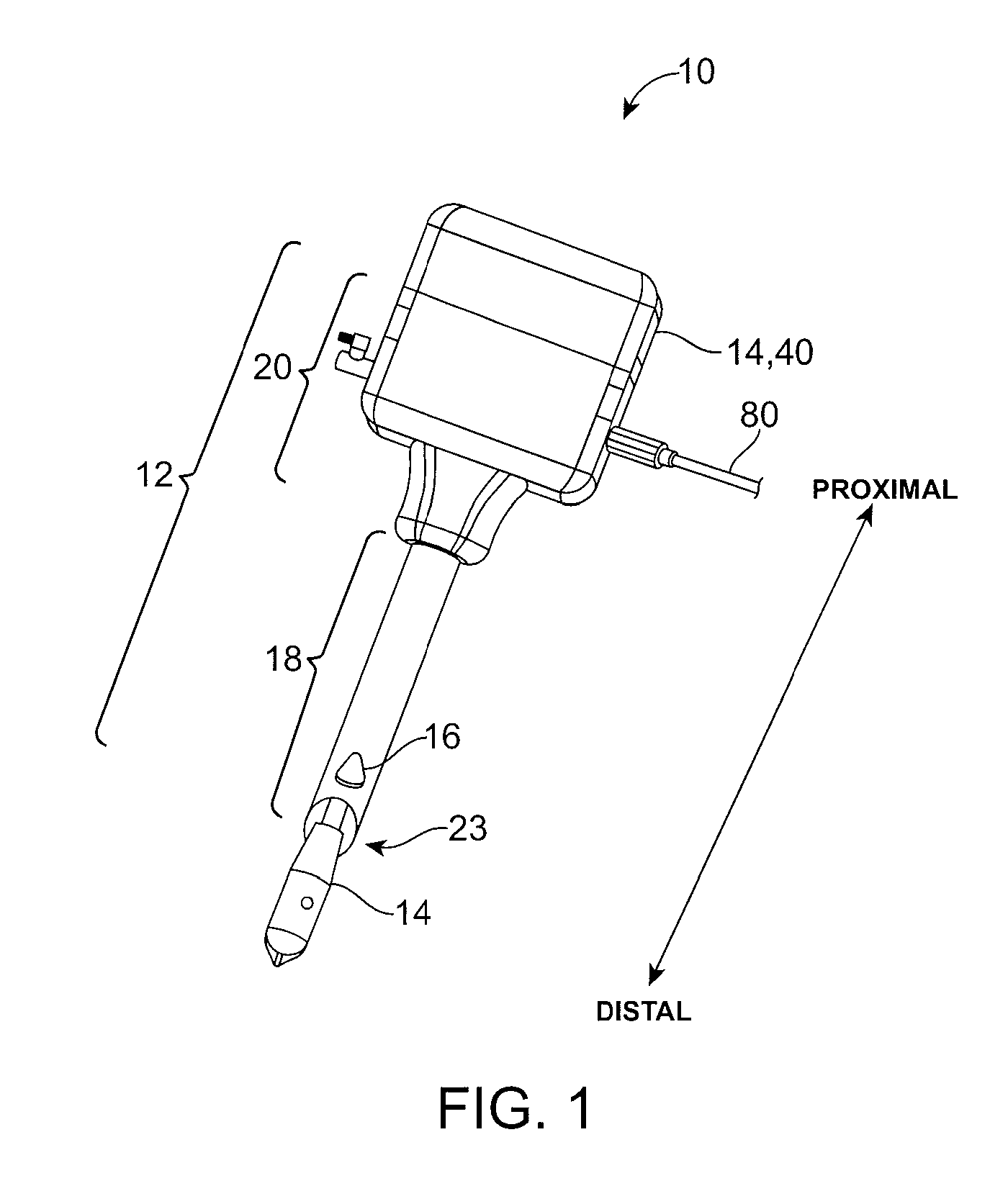
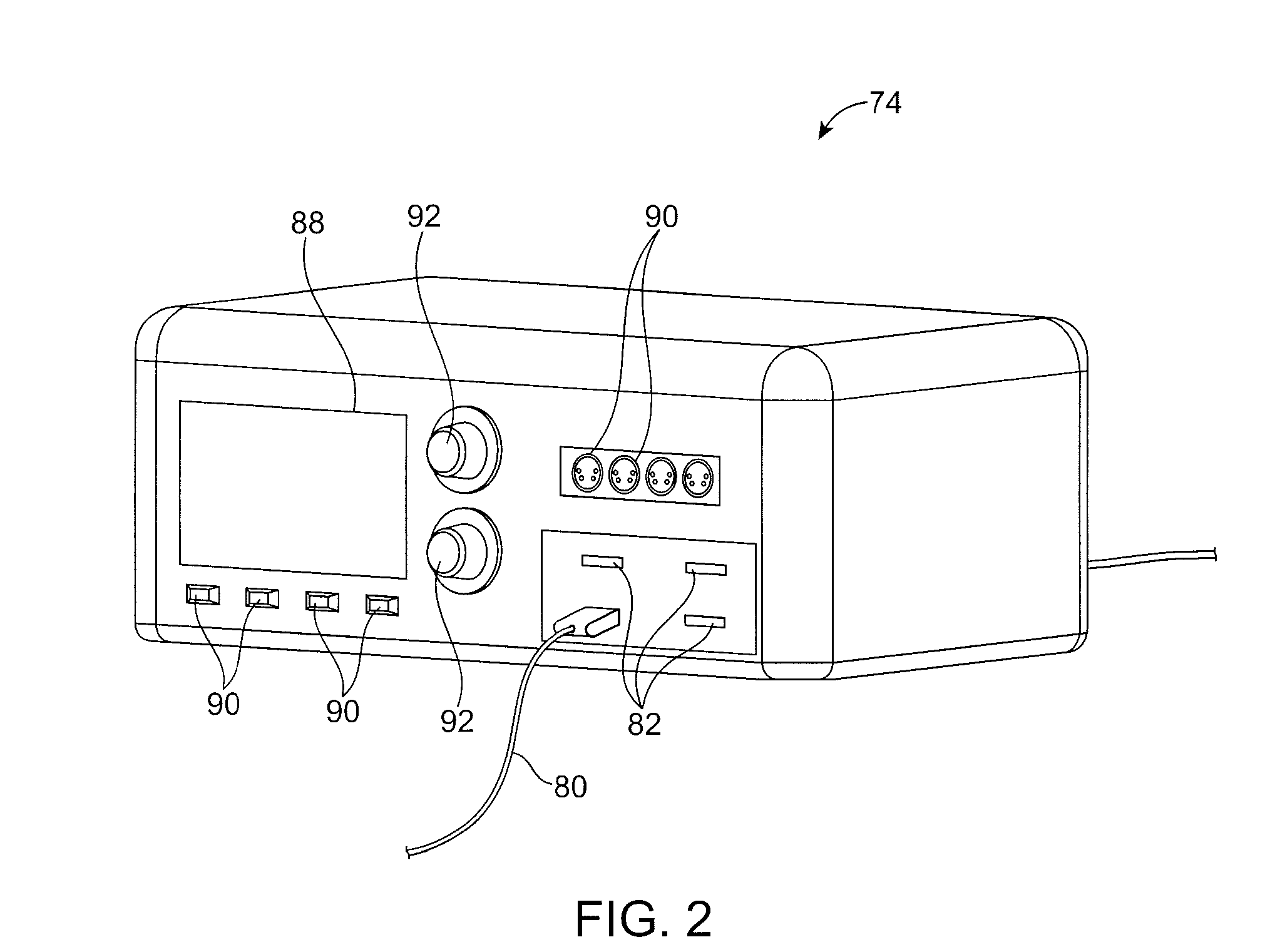
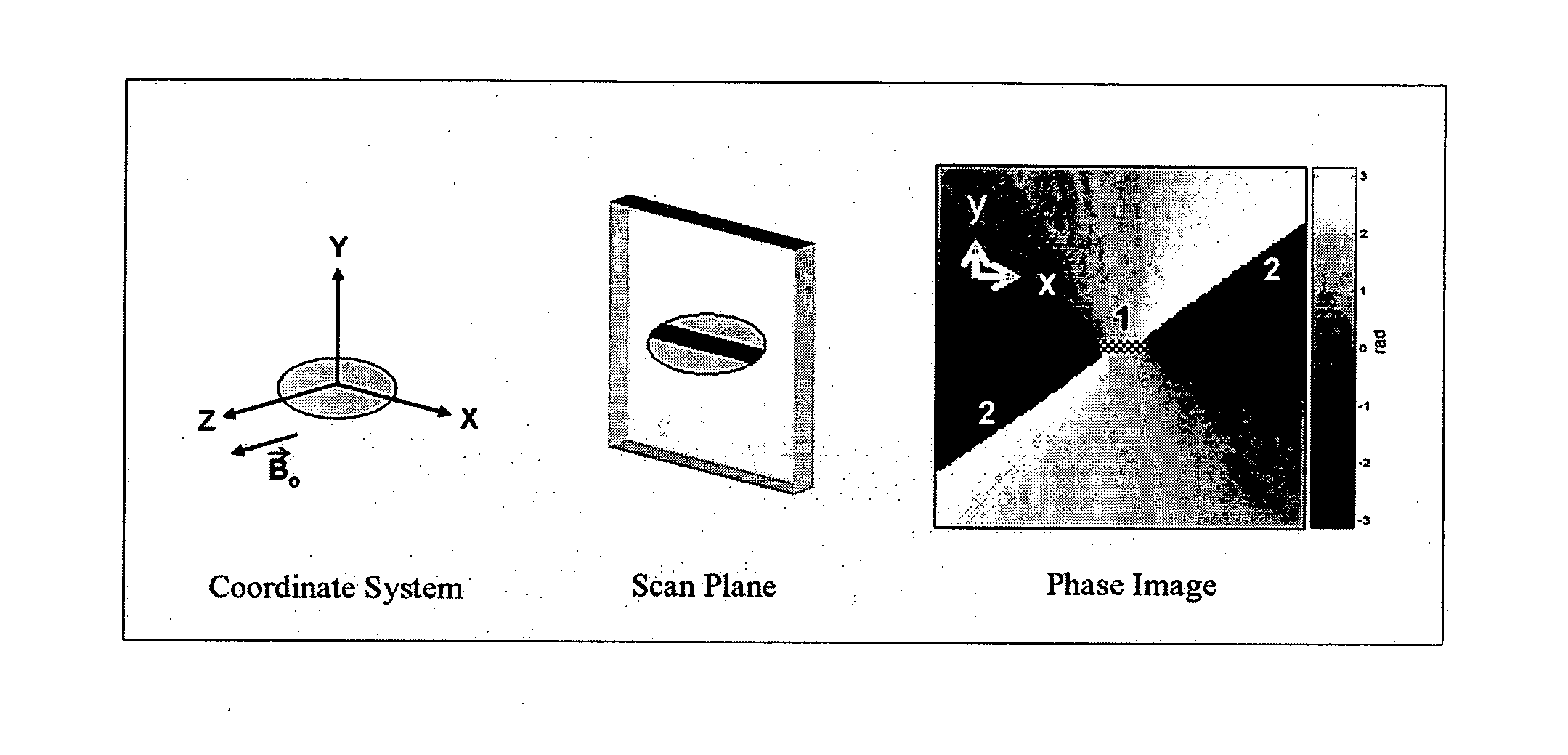
Catheter tracking with phase information
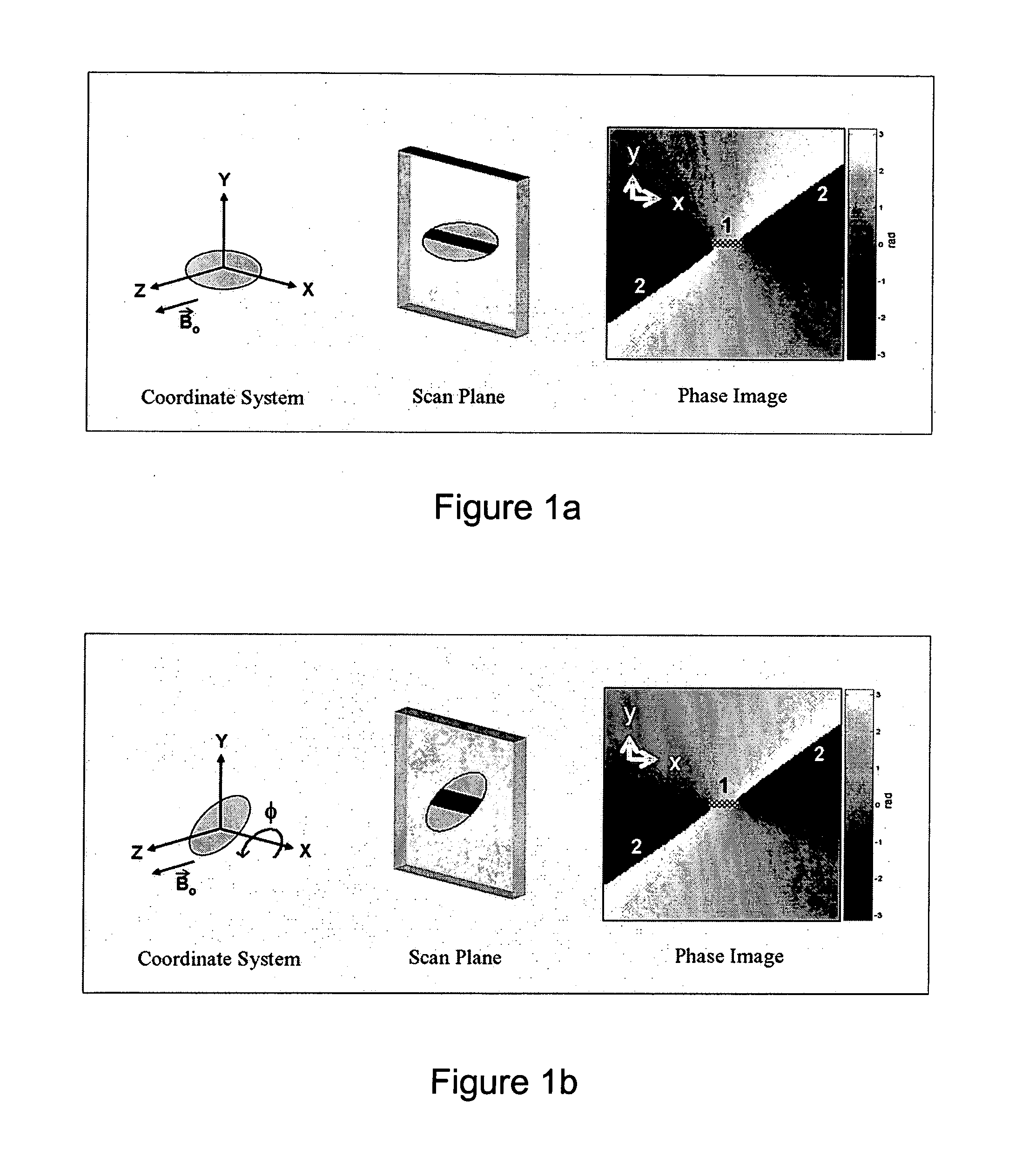
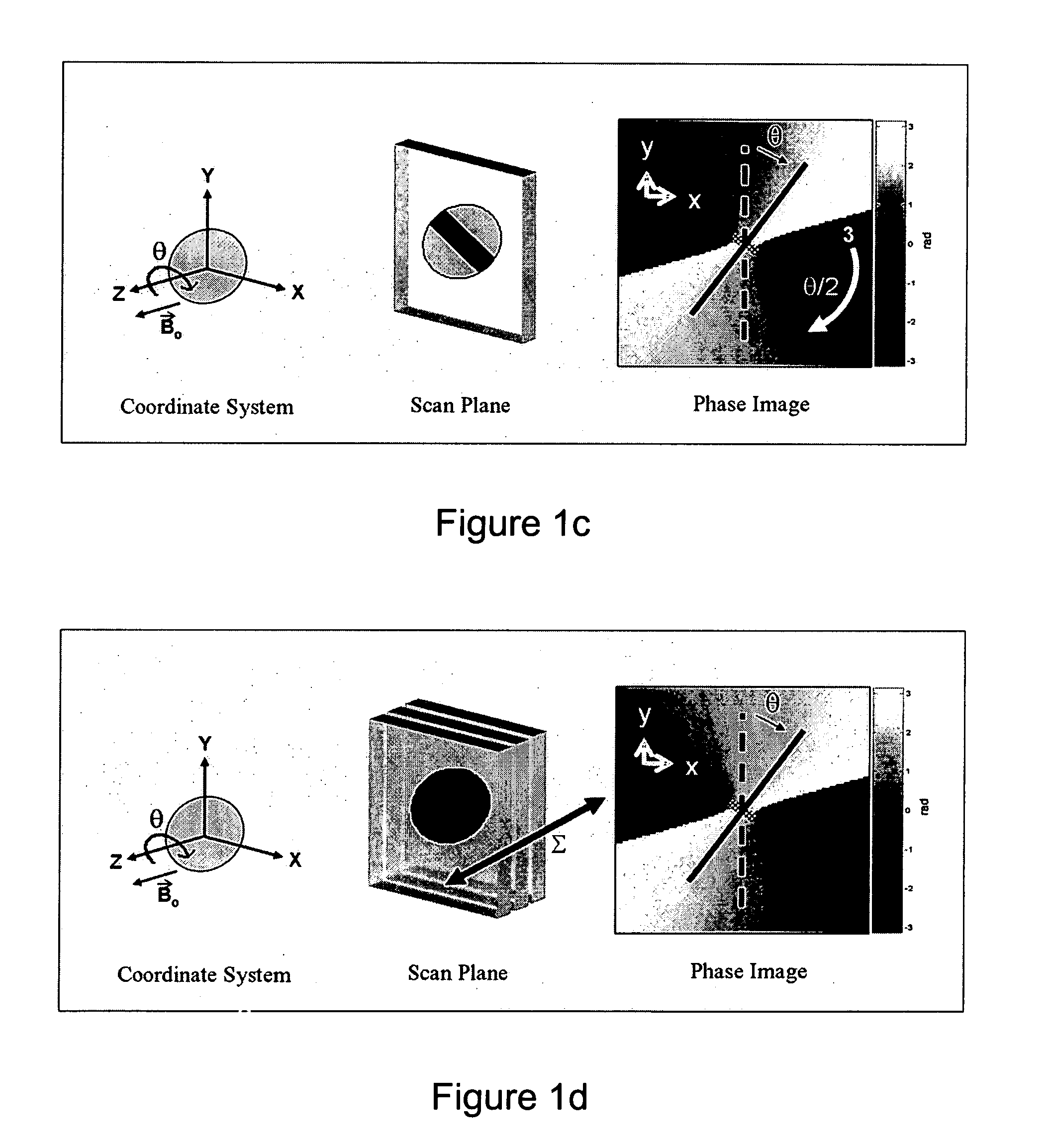
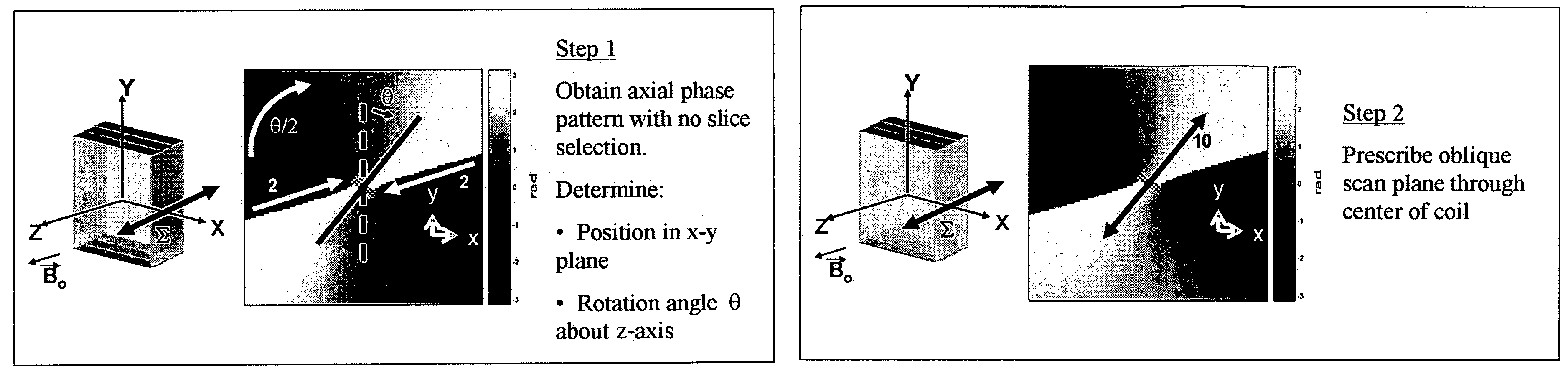
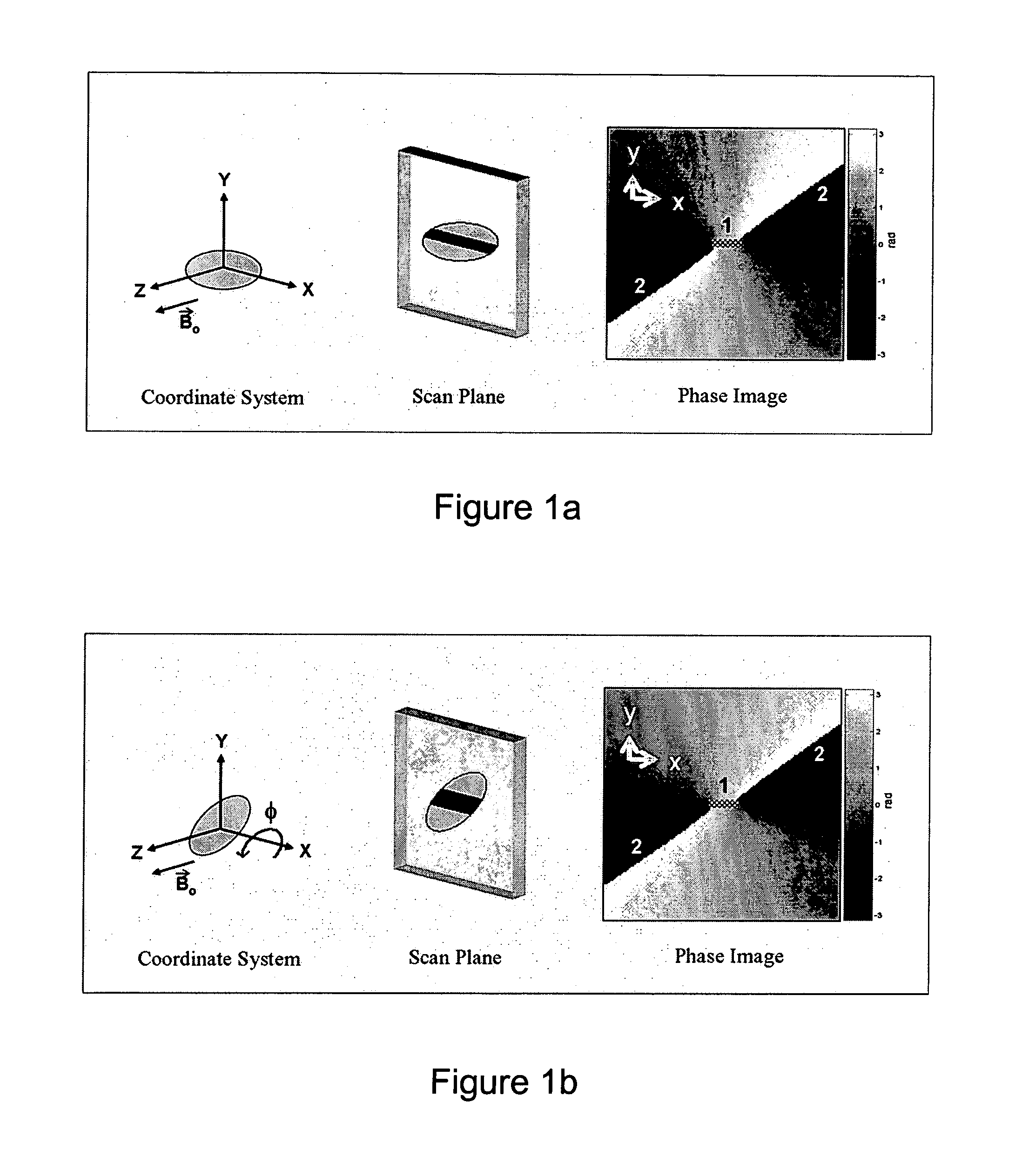
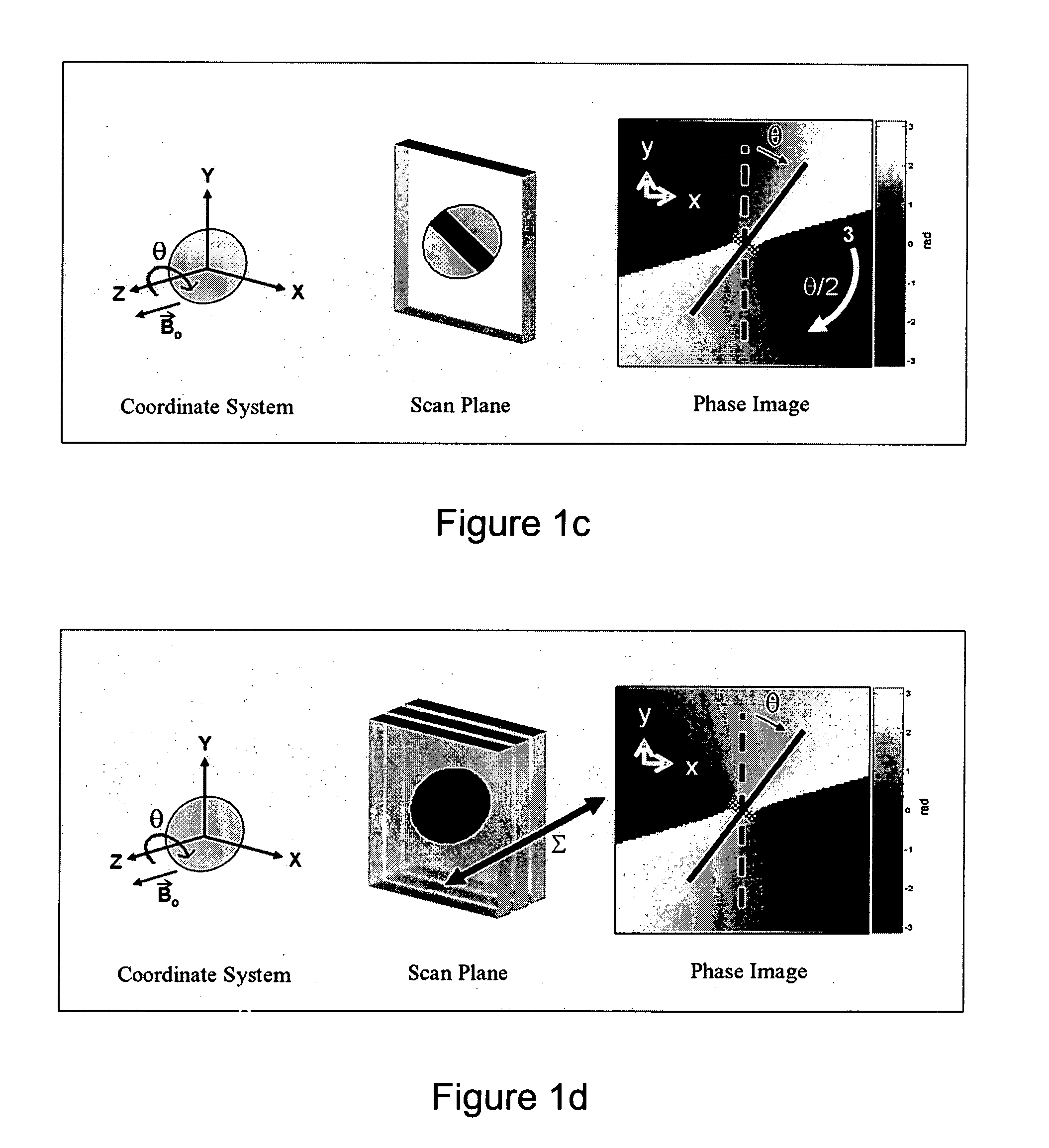
ActiveUS20050245814A1Precise positioningTrack positionCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringLaparoscopesBiopsy
The present invention discloses a method for determining the position and / or orientation of a catheter or other interventional access device or surgical probe using phase patterns in a magnetic resonance (MR) signal. In the method of the invention, global two-dimensional correlations are used to identify the phase pattern and orientation of individual microcoils, which is unique for each microcoil's position and orientation. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, tracking of interventional devices is performed by one integrated phase image projected onto the axial plane and a second image in an oblique plane through the center of the coil and normal to the coil plane. In another preferred embodiment, the position and orientation of a catheter tip can be reliably tracked using low resolution MR scans clinically useful for real-time interventional MRI applications. In a further preferred embodiment, the invention provides real-time computer control to track the position of endovascular access devices and interventional treatment systems, including surgical tools and tissue manipulators, devices for in vivo delivery of drugs, angioplasty devices, biopsy and sampling devices, devices for delivery of RF, thermal, microwave or laser energy or ionizing radiation, and internal illumination and imaging devices, such as catheters, endoscopes, laparoscopes, and related instruments.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT +1
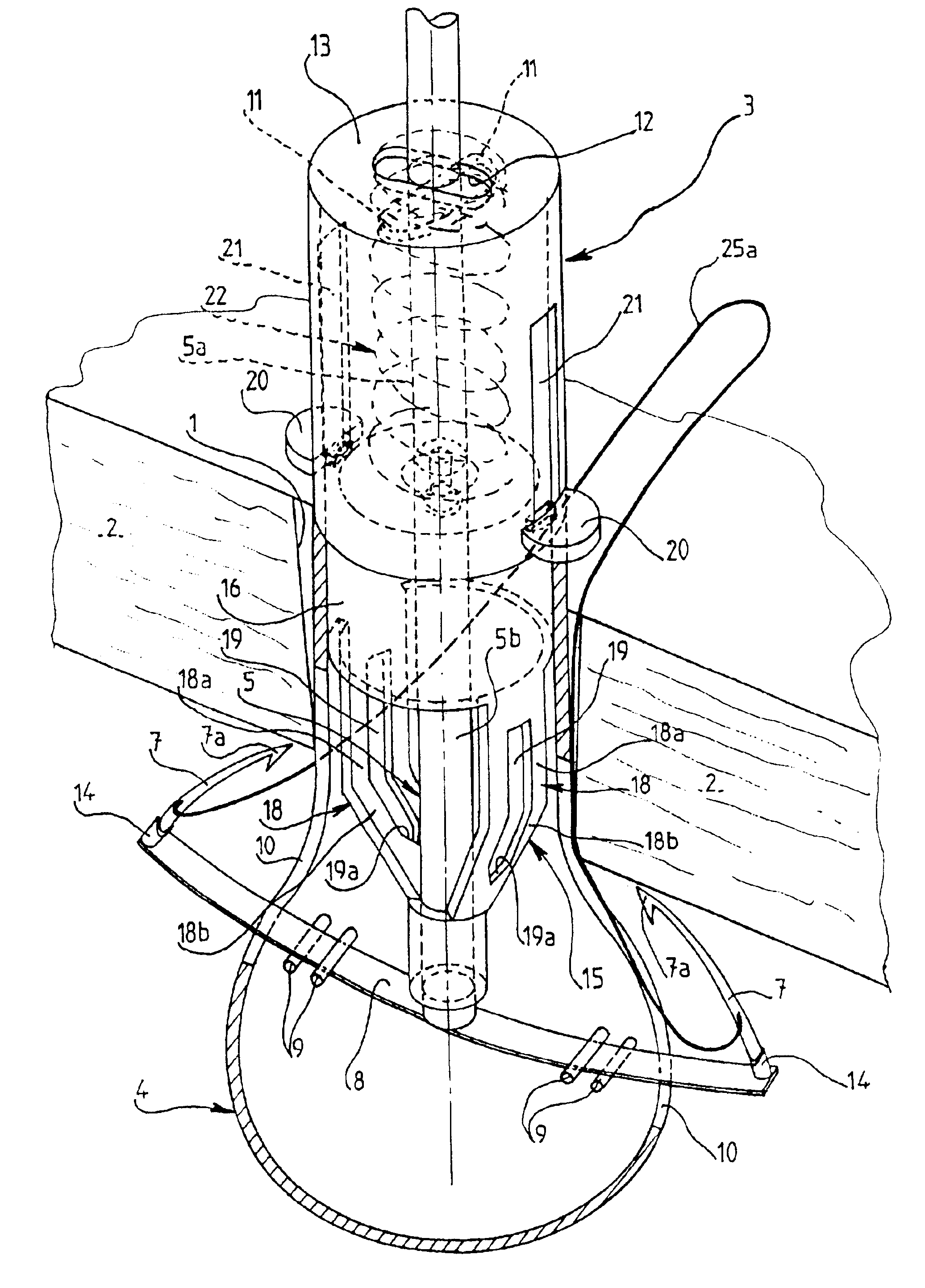
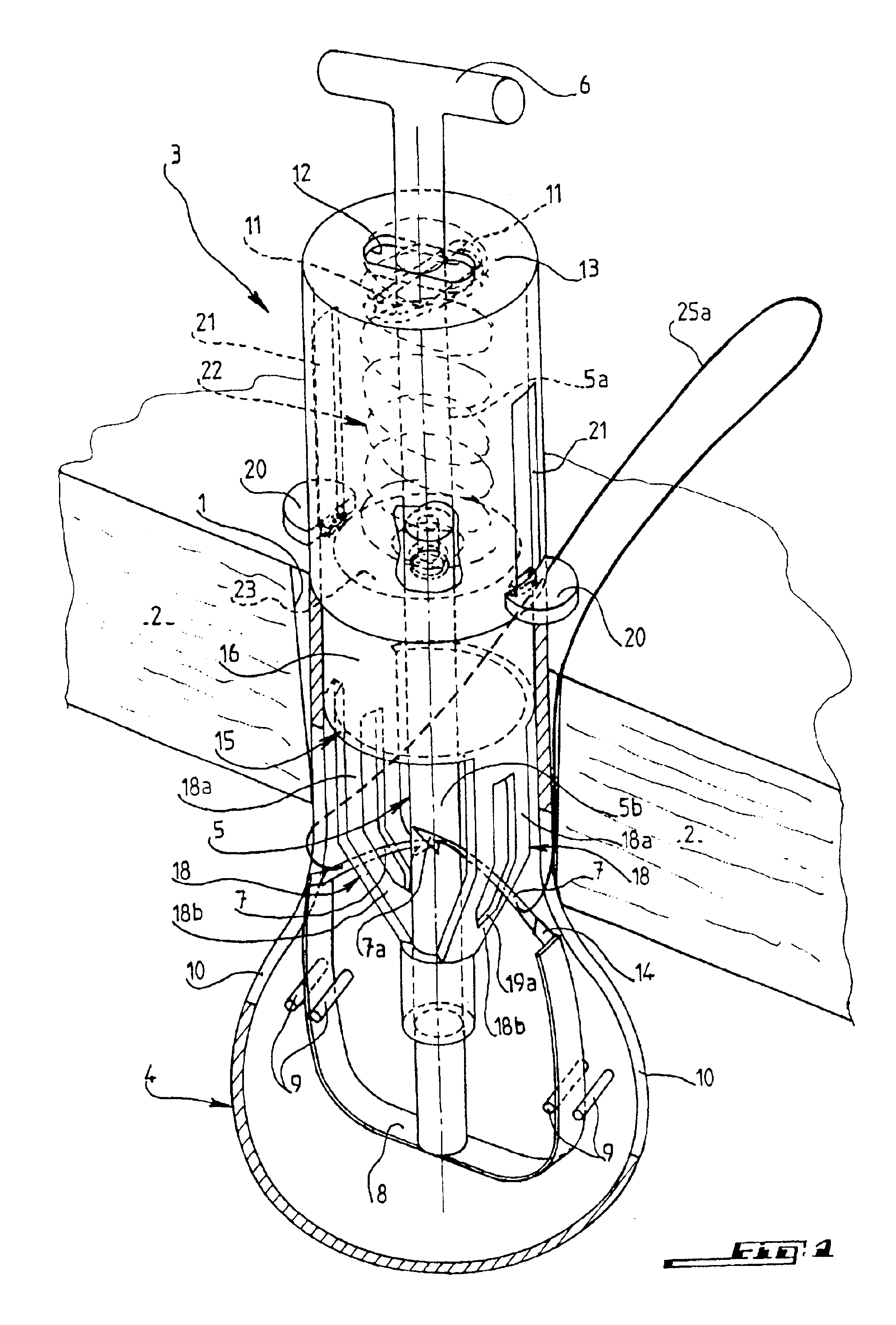
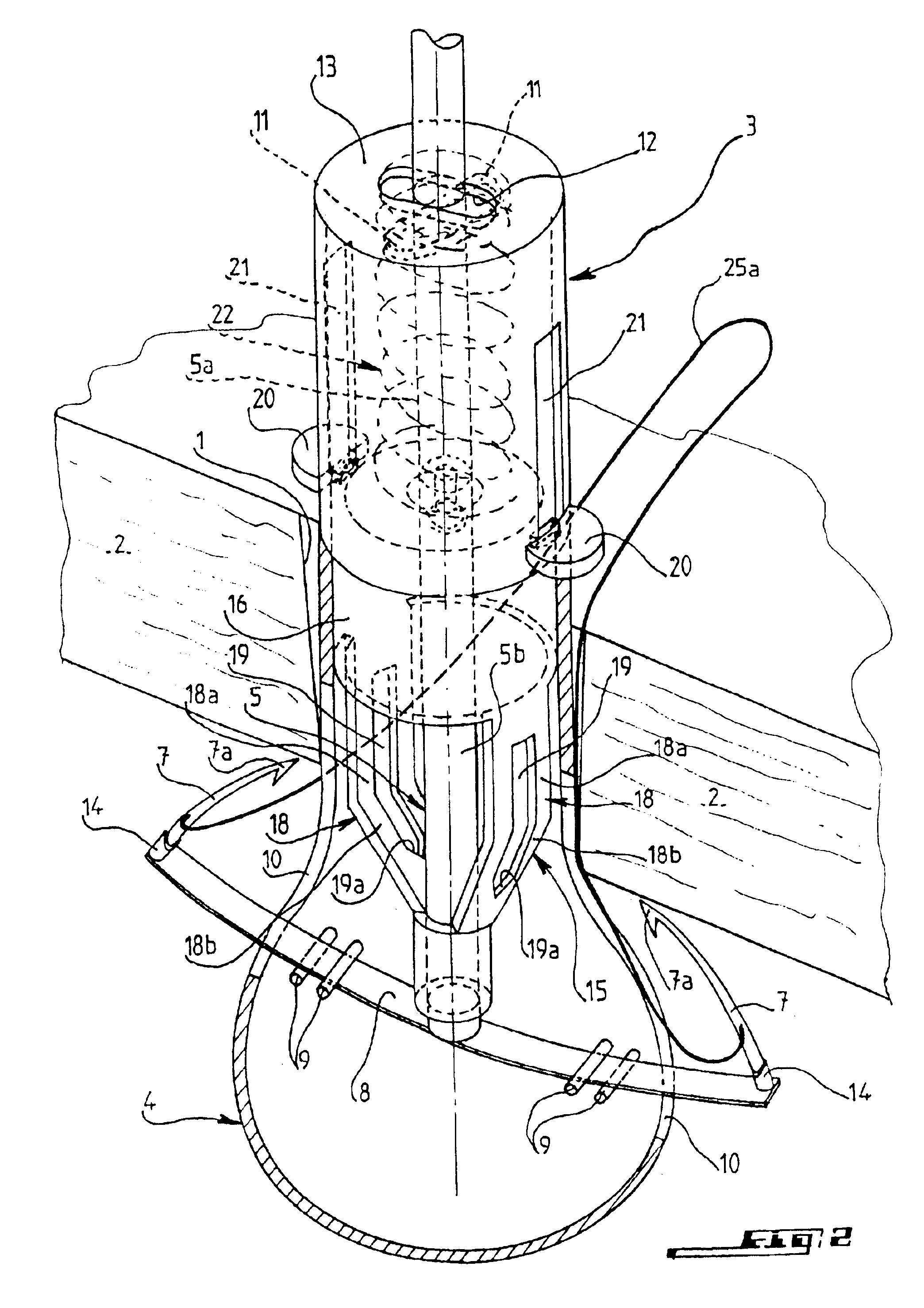
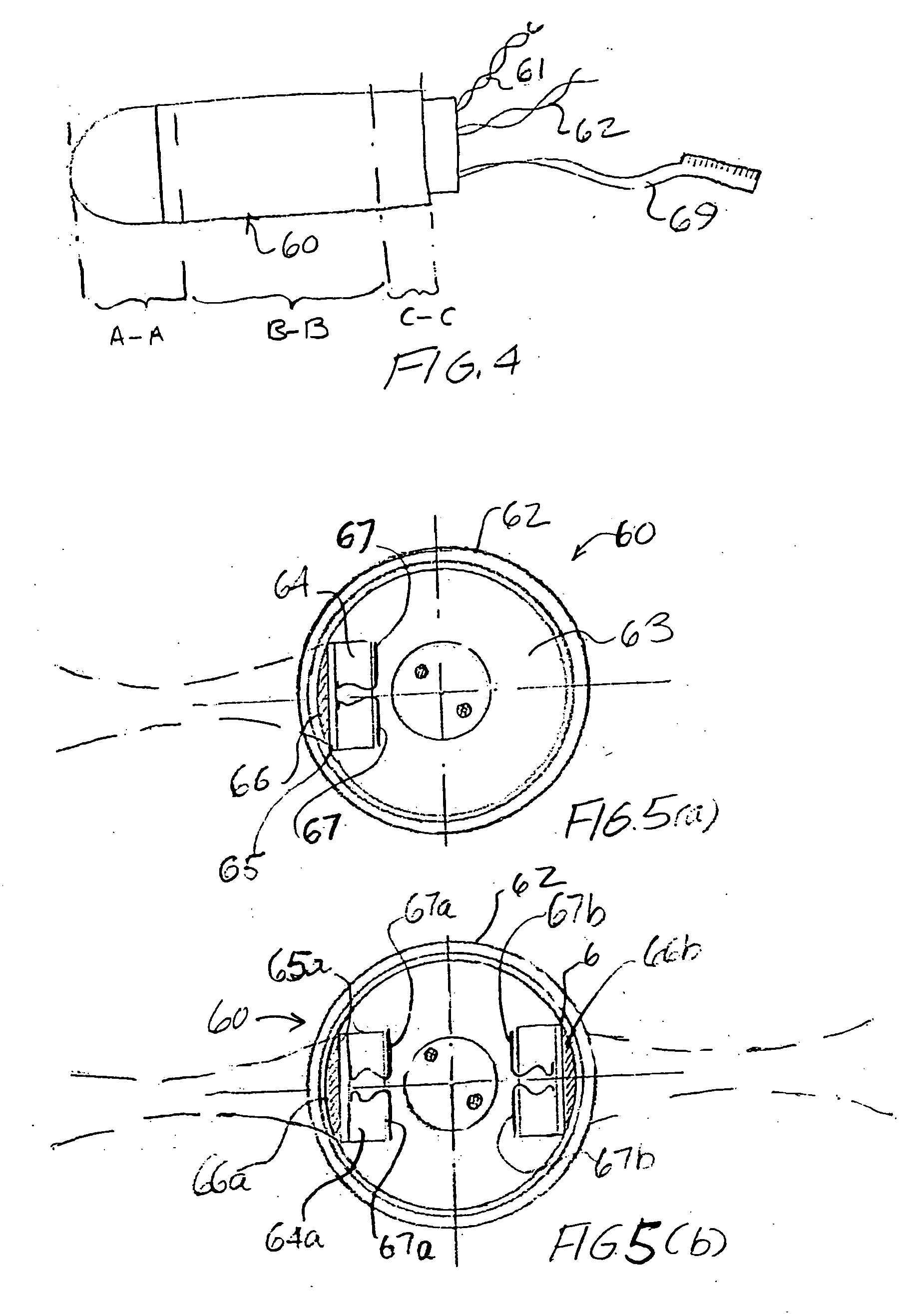
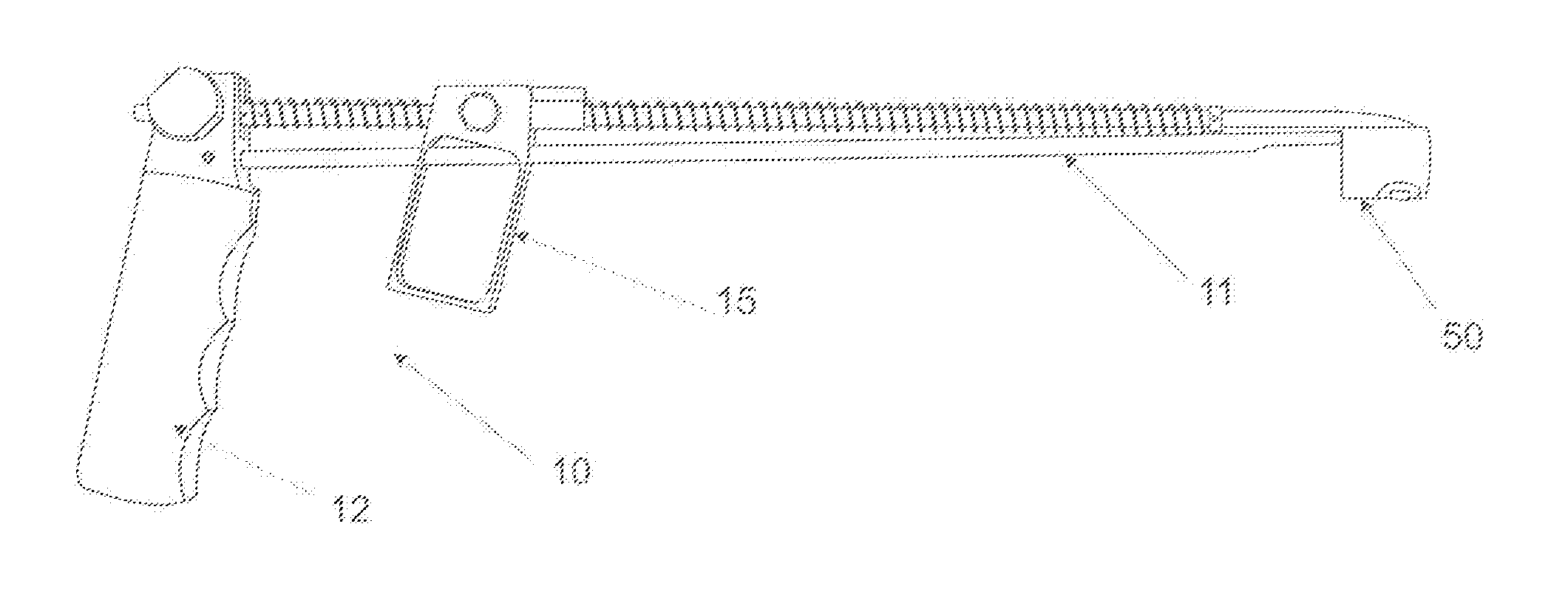
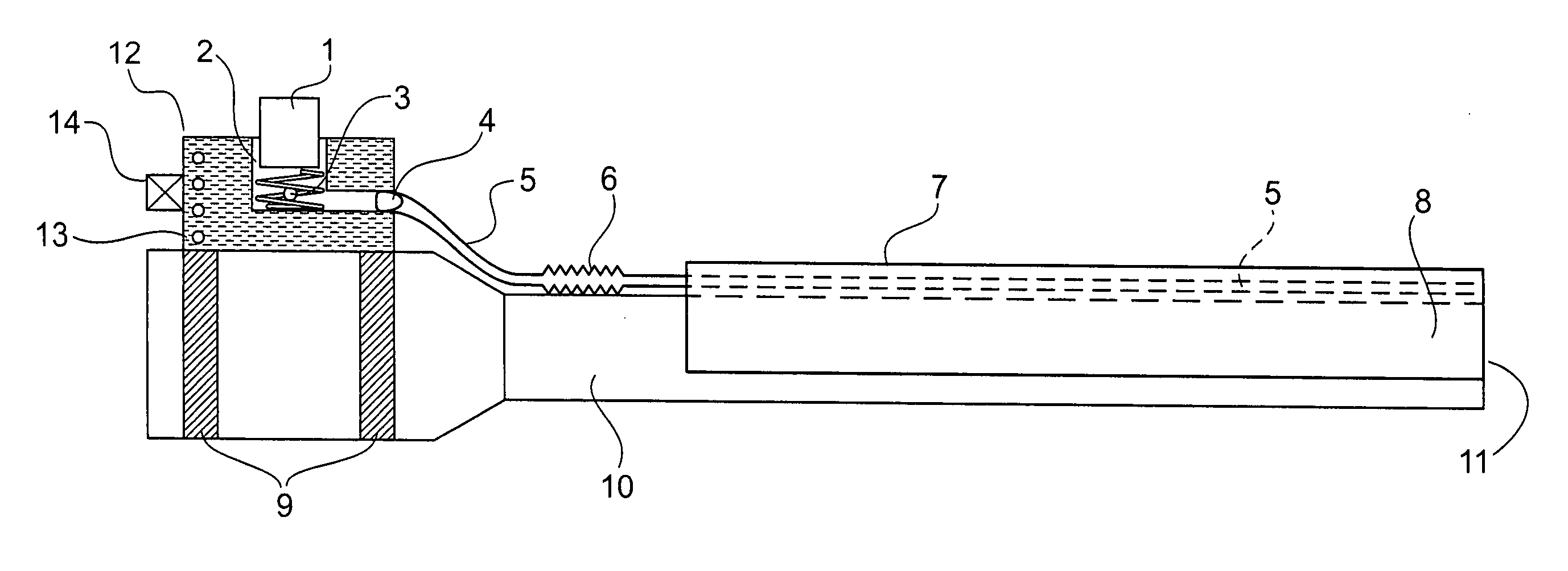
Instrument for closing, by subcutaneous suturing, an orifice made in the abdominal wall of a patient
InactiveUS6939357B2Effectively closedSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSurgical operationLaparoscopes
An instrument for closing, by subcutaneous suturing, an orifice made in the abdominal wall of a patient. The instrument has a piston rod (5) whose end acts on a flexible support strip (8) for needles (7), thus causing them to emerge at an exterior of the lower part (4) of a cannula (3) of the instrument underneath the abdominal wall (2), so that the needle can then penetrate into a thick part of this wall. Also, a method for suturing of orifices after a surgical operation by laparoscopy.
Owner:NAVARRO FRANCIS +1
Improved interface for laparoscopic surgeries - movement gestures
The present invention discloses a surgical maneuvering system, in which movement of a moving element is used to control a surgical device such as a surgical tool or an endoscope. The moving element can be a tool or a portion of an operator's body. The relationship between the moving element and the surgical device can be any of: motion of a moving element controlling motion of a surgical device, motion of a moving element controlling an action of a surgical device, a command of a moving element controlling motion of a surgical device, or a command of a moving element controlling an action of the device. Commands are typically arbitrary movements such as shaking a tool. Actions are changes in a surgical device that do not change its overall position, such as closing a grasper.
Owner:TRANSENTERIX EURO SARL
Methods and Devices for Placing a Conduit in Fluid Communication with a Target Vessel
Methods and devices for placing a conduit in fluid communication with a target vessel and a source of blood, such as the aorta or a heart chamber. The device may be actuated using one hand to place the conduit. The invention allows air in the conduit to be removed prior to placement of the conduit. The invention deploys the conduit in the target vessel by moving a sheath in a distal direction and then in a proximal direction. A conduit is provided with a reinforcing member to prevent kinking of the conduit, and a structure for preventing blockage of the conduit by tissue. A vessel coupling may be used to secure a conduit to a target vessel so as to preserve native blood flow through the vessel, and the conduit may be placed in fluid communication with a target vessel via a laparoscopic or endoscopic procedure.
Owner:GITTINGS DARIN C +3
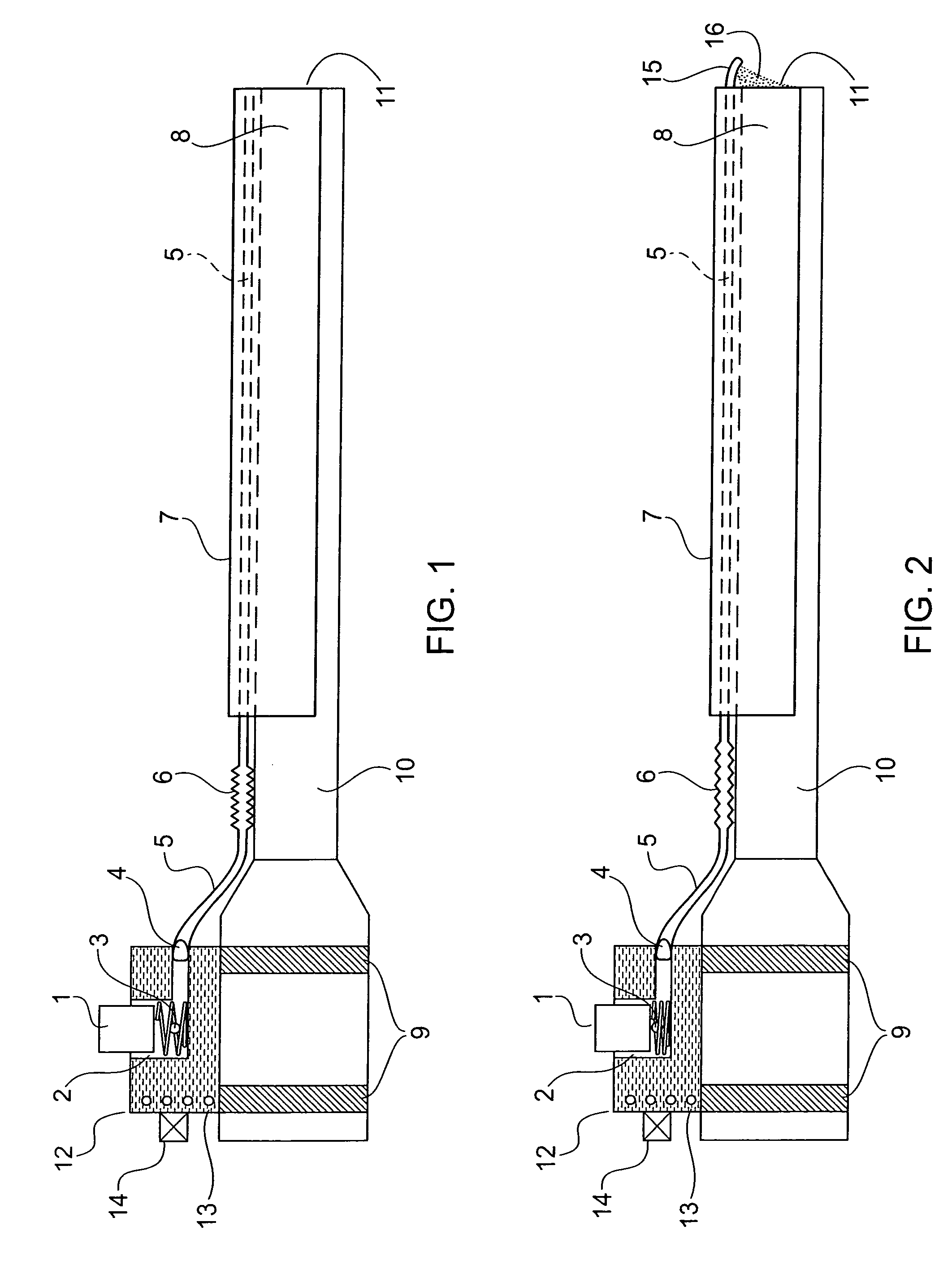
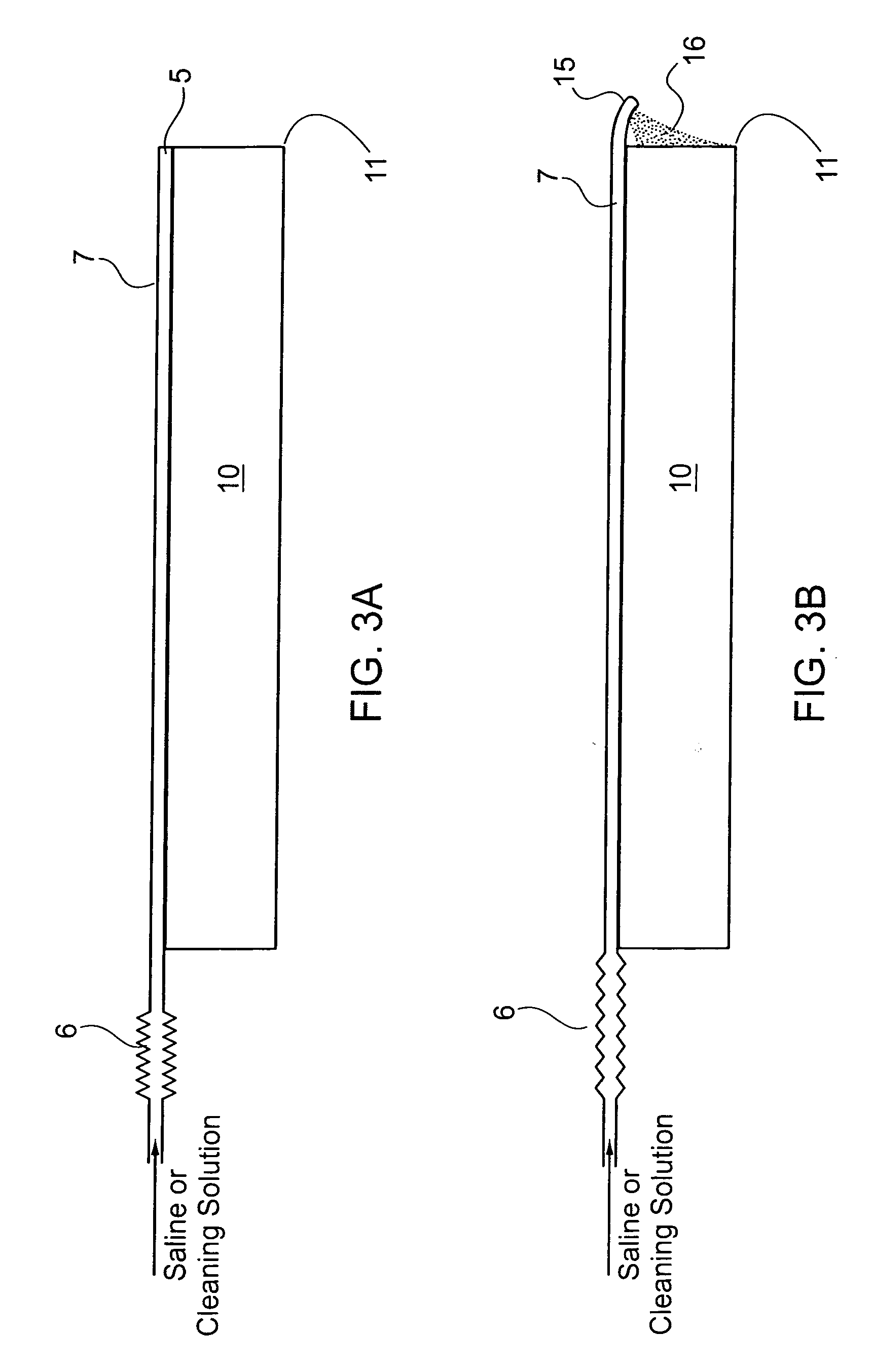
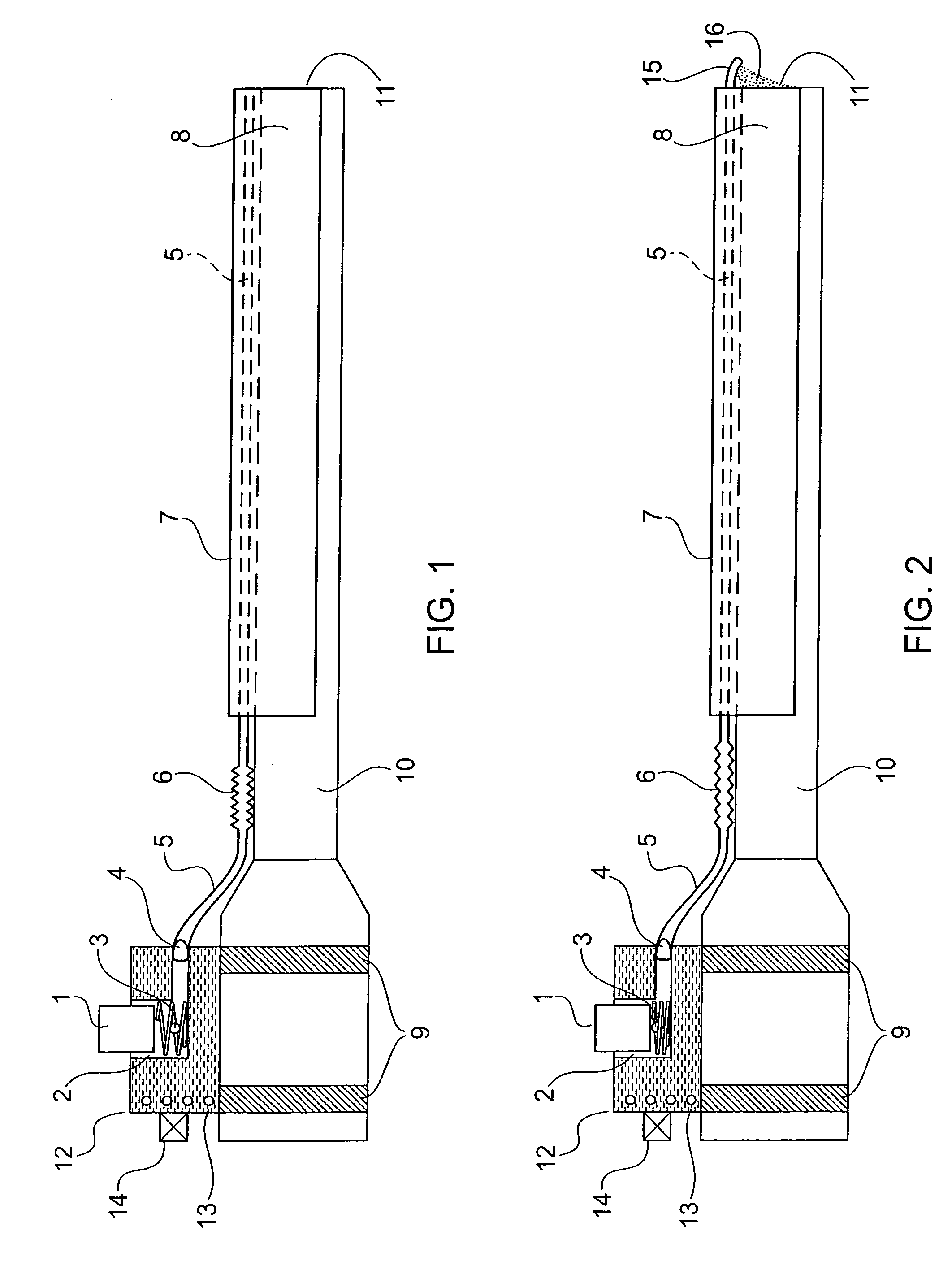
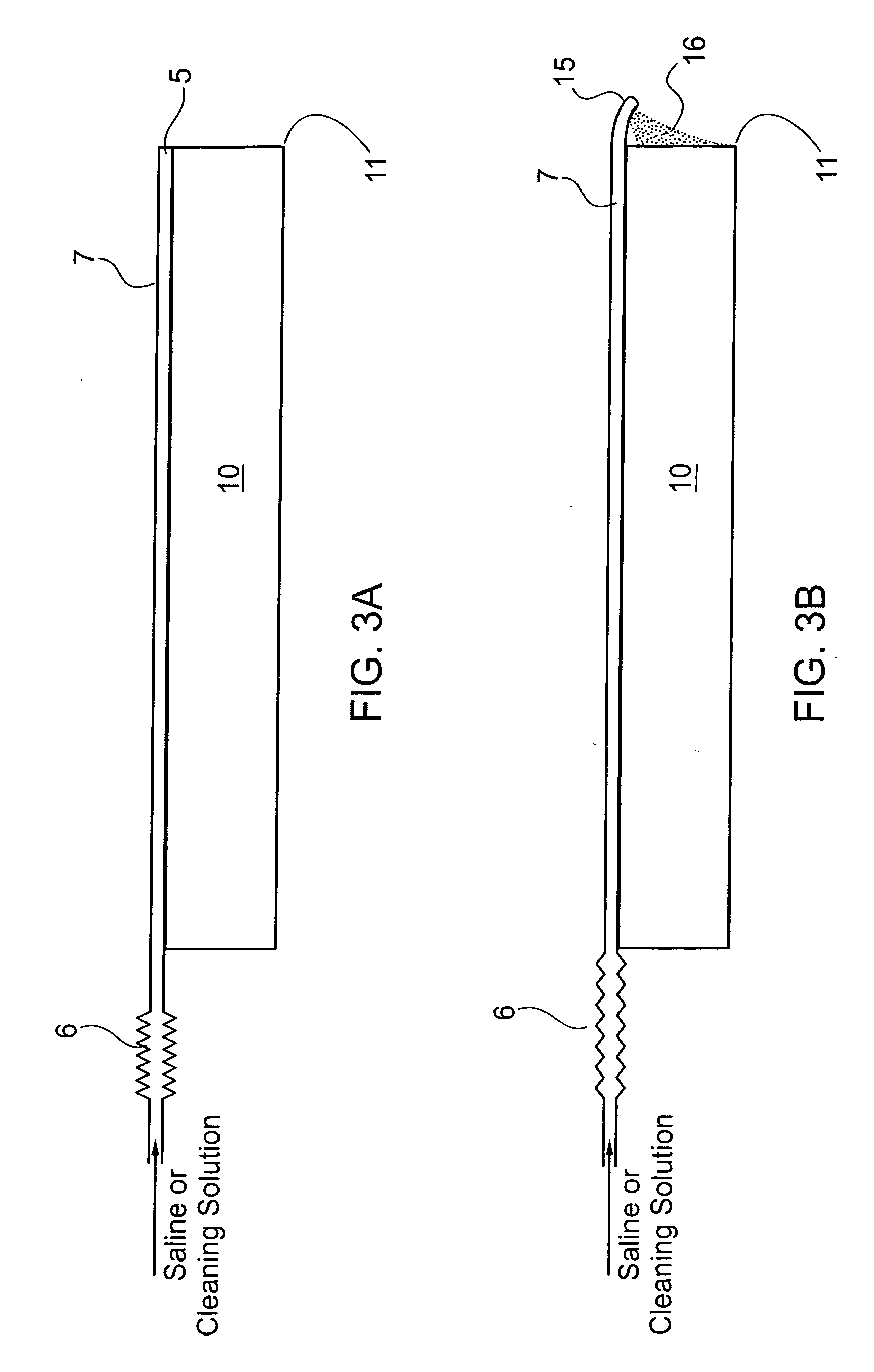
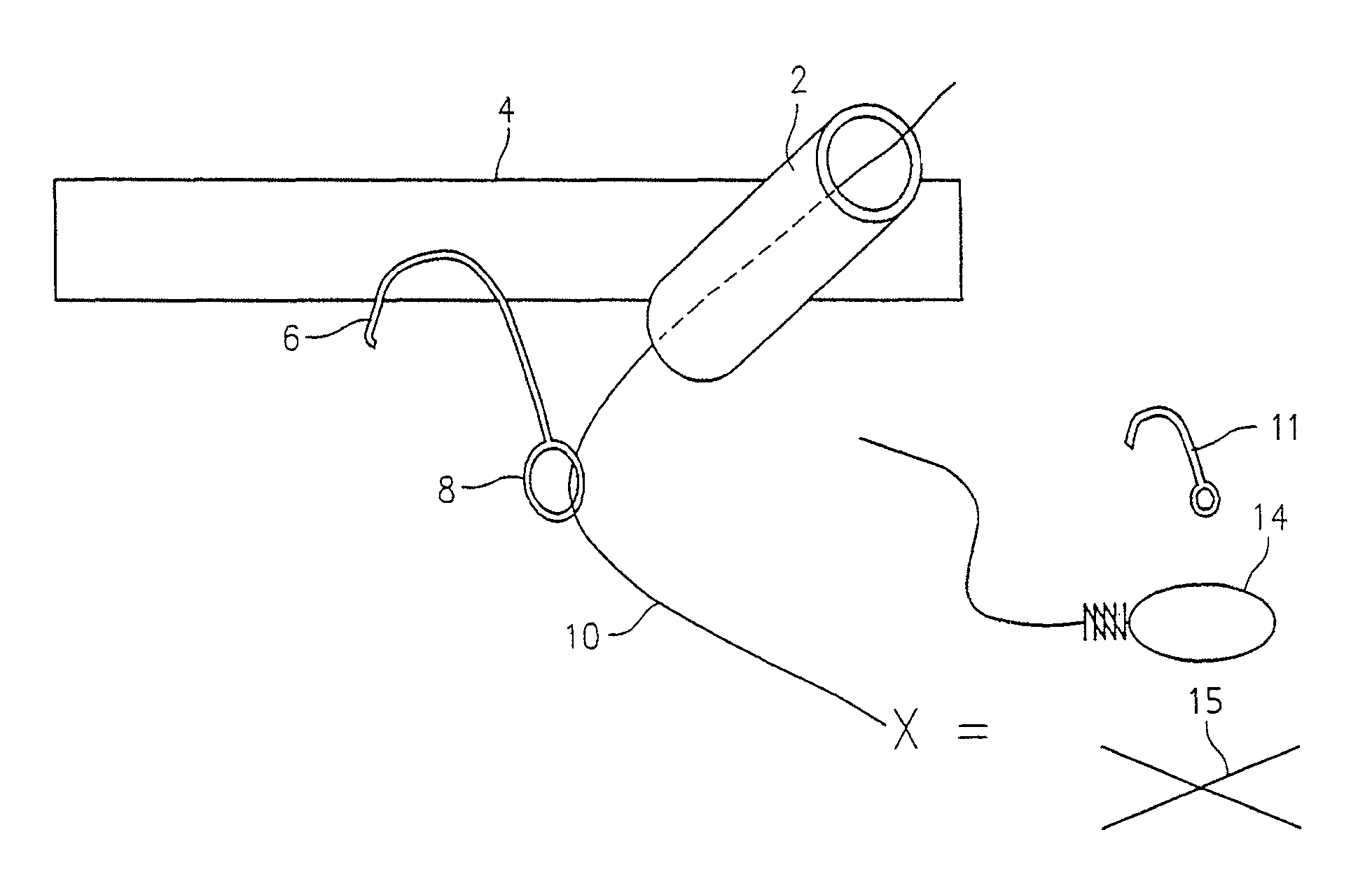
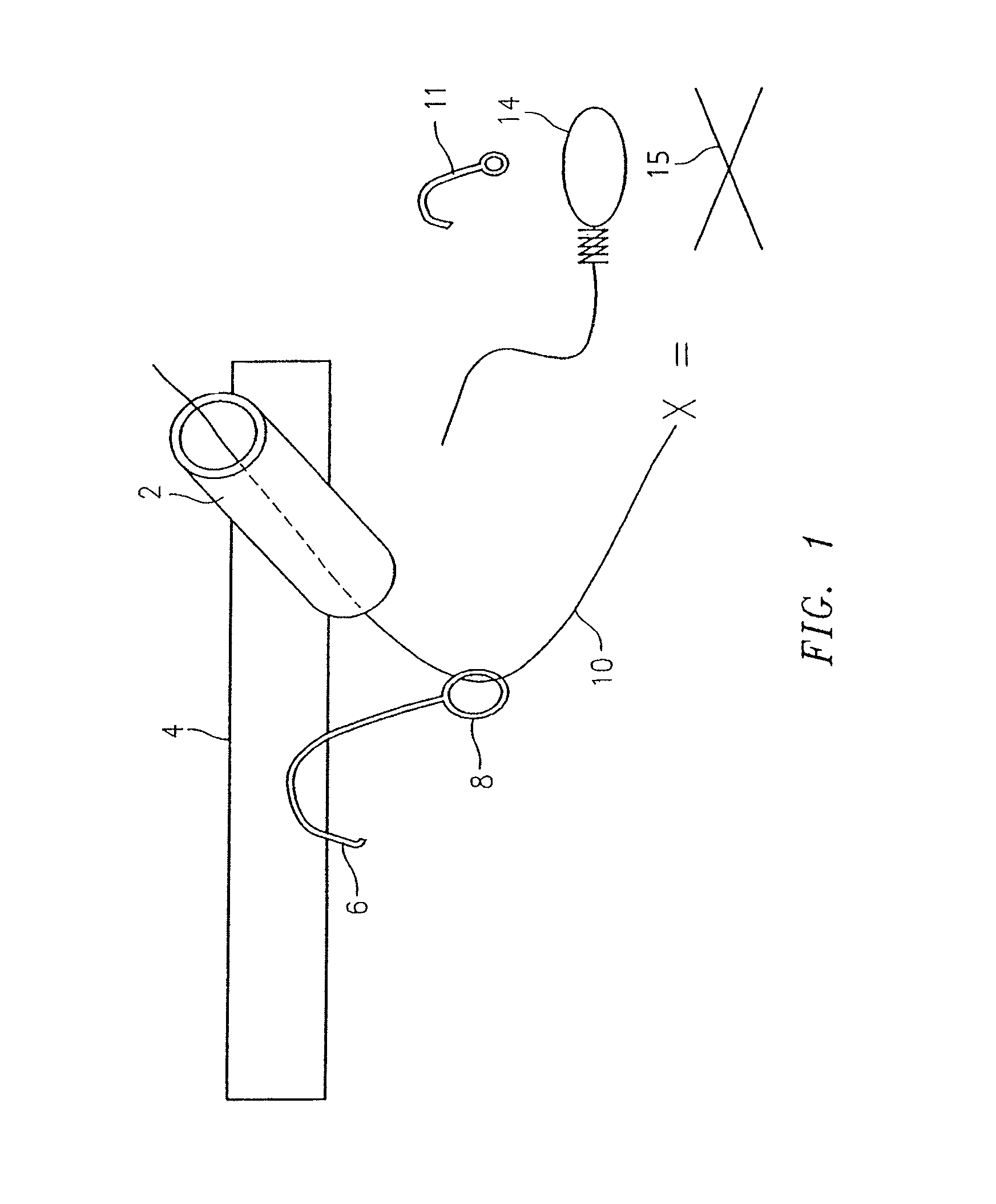
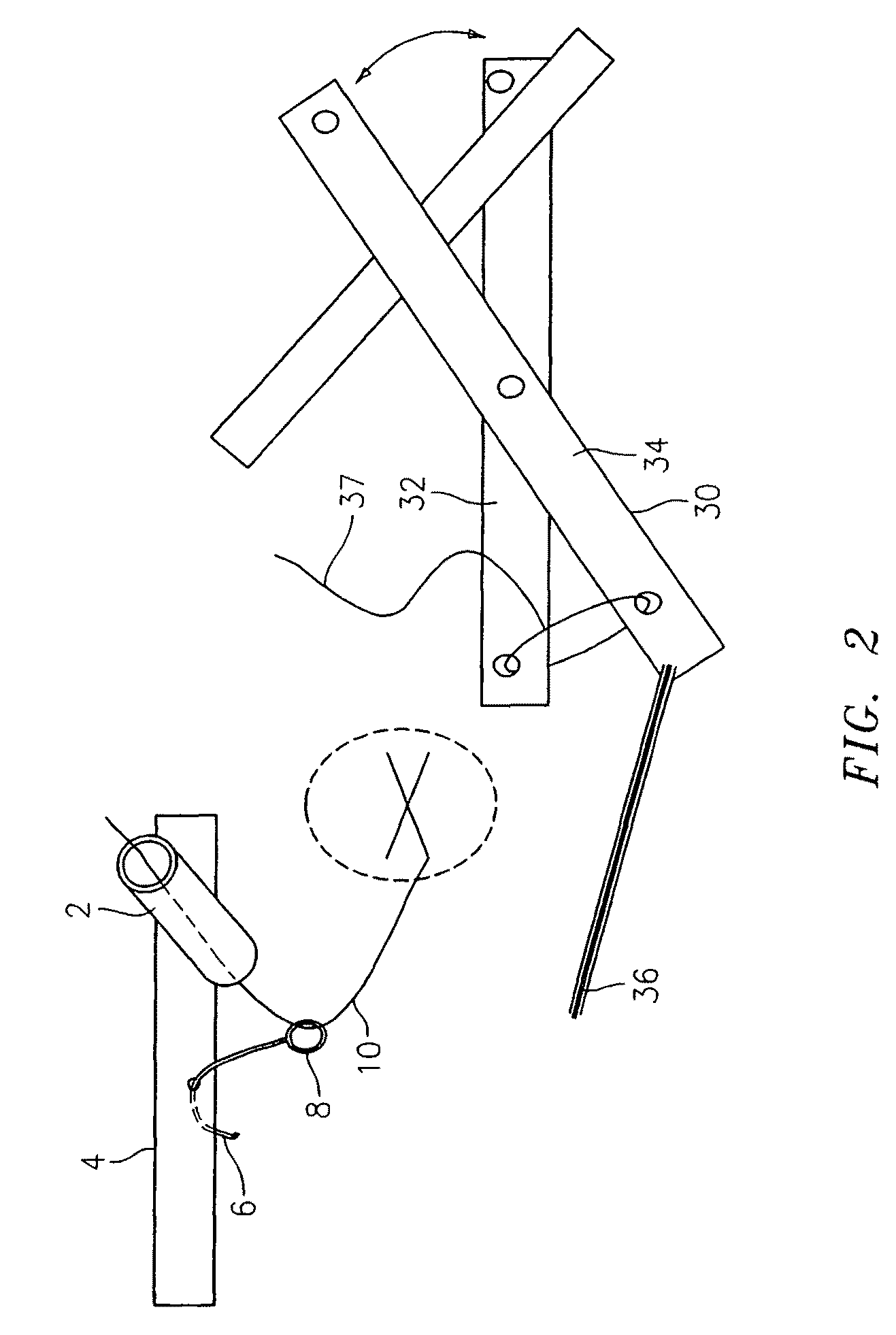
Laparoscope cleaning system
Owner:MONDSCHEIN ROBERT
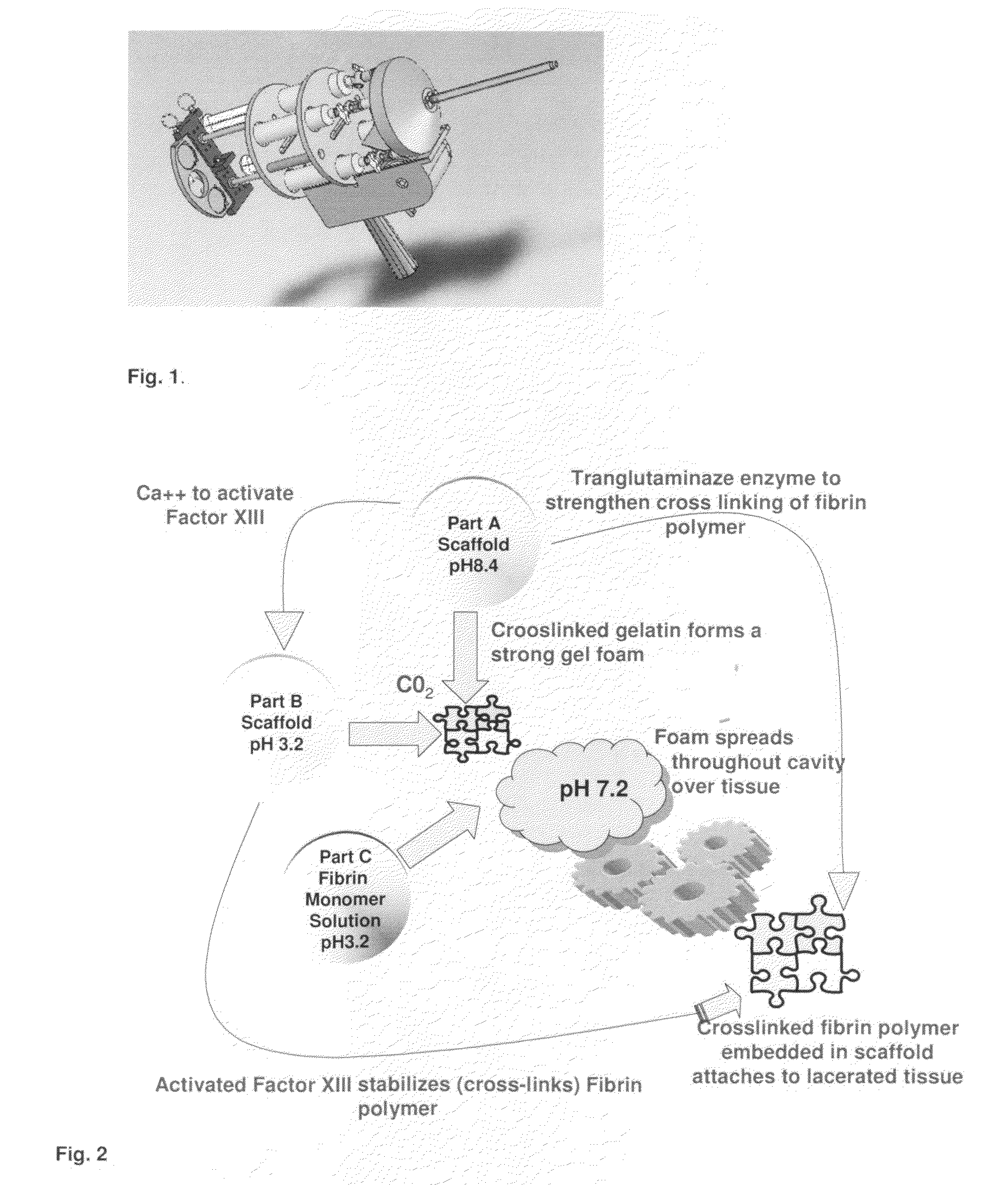
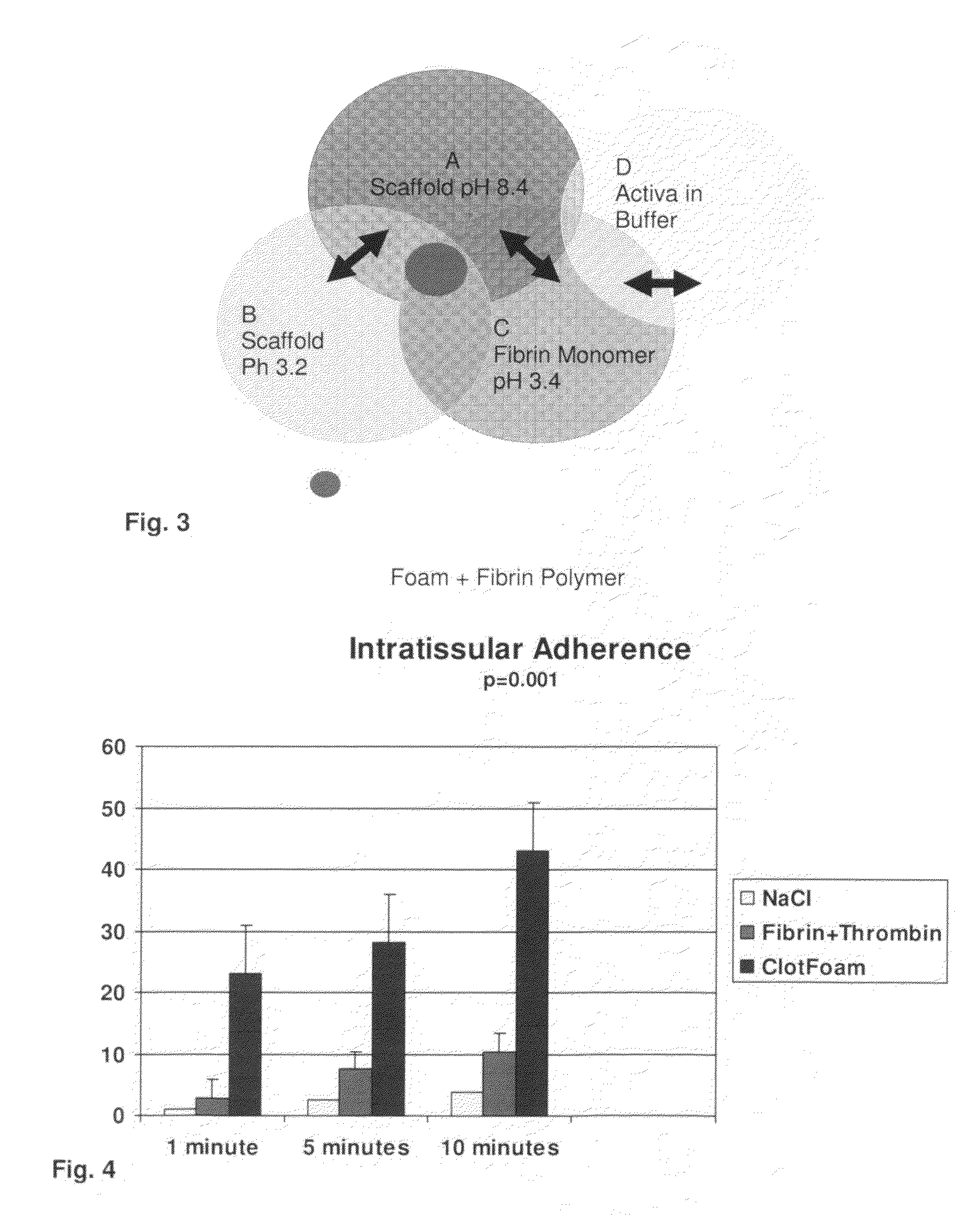
Tissue Sealant for Use in Non Compressible Hemorrhage
InactiveUS20110066182A1Excellent hemostatic agent candidateLeast riskSuture equipmentsPowder deliveryTissue sealantThoracic cavity
ClotFoam is a surgical sealant and hemostatic agent designed to be used in cases of non-compressible hemorrhage. It can be applied in the operating room through laparoscopic ports, or directly over lacerated tissue in laparotomy procedures or outside the operating room through a mixing needle and / or a spray injection method following abdominal, chest, extremities or other intracavitary severe trauma to promote hemostasis. Its crosslinking technology generates an adhesive three-dimensional polymeric network or scaffold that carries a fibrin sealant required for hemostasis. When mixed, Clotfoam produces a foam that spreads throughout a body cavity reaching the lacerated tissue to seal tissue and promote the coagulation cascade.The viscoelastic attachment properties of the foam as well as the rapid formation of a fibrin clot that ensure that the sealant remains at the site of application without being washed away by blood or displaced by movement of the target tissue .
Owner:FALUS GEORGE D PHD
Apparatus and method for performing a bypass procedure in a digestive system
InactiveUS20060229643A1Increase contactSurgical staplesWound clampsSurgical instrumentationLaparoscopes
Surgical instrumentation and methods for performing a bypass procedure in a digestive system incorporate laparoscopic techniques to minimize surgical trauma to the patient. The instrumentation includes an outer guide member dimensioned for insertion and passage through an esophagus of a patient and defining an opening therein extending at least along a portion of the length of the outer guide member, an elongate anvil delivery member at least partially disposed within the opening of the outer guide member and being adapted for longitudinal movement within the outer guide member between an initial position and an actuated position and an anvil operatively engageable with the delivery member. The anvil includes an anvil rod defining a longitudinal axis and an anvil head connected to the anvil rod. The anvil head is at least partially disposed within the opening of the outer guide member when in the initial position of the delivery member and is fully exposed from the distal end of the outer guide member upon movement of the delivery member to the actuated position.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Catheter tracking with phase information
ActiveUS7505808B2Precise positioningTrack positionCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringLaparoscopesIn vivo
A method for determining the position and / or orientation of a catheter or other interventional access device or surgical probe using phase patterns in a magnetic resonance (MR) signal. In the method of the invention, global two-dimensional correlations are used to identify the phase pattern around individual microcoils, which is unique for each microcoil's position and orientation. In one embodiment the position and orientation of a catheter tip can be reliably tracked using low resolution MR scans clinically useful for real-time interventional MRI applications. In a further embodiment, the invention provides real-time computer control to track the position of endovascular devices and interventional treatment systems, including surgical tools and tissue manipulators, devices for in vivo delivery of drugs, angioplasty devices, biopsy and sampling devices, devices for delivery of RF, thermal, microwave or laser energy or ionizing radiation, and internal illumination and imaging devices, such as catheters, endoscopes, laparoscopes, and related instruments.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT +1
Systems and methods for optimizing and maintaining visualization of a surgical field during the use of surgical scopes
InactiveUS20100198014A1Maintaining visualizationClear visualizationCannulasSurgical needlesSurgical operationLess invasive surgery
Systems and methods make use of a view optimizing assembly having a deflector assembly with critical physical, pneumatic, and optical characteristics that make possible intra-operative defogging, surgical debris deflection, and cleaning of a laparoscope lens during minimally invasive surgery, while also maintaining visualization of the surgical site. The view optimizing assembly can incorporate a quick exchange feature, which makes possible a surgical method for maintaining clear visualization that includes the ability to make a quick exchange of laparoscopes having different operating characteristics (e.g., laparoscopes with different tip angles, lengths, or diameters) entirely on the sterile operating field and without interference with the preexisting surgical set-up on the sterile operating field. The view optimizing assembly integrates with the existing suite of minimally invasive instrumentation. It does not interfere with the surgical set-up, and it requires minimal change in the process or practice of a surgical operating room (OR) team.
Owner:FLOSHIELD INC
Motorized ultrasonic scanhead
ActiveUS20070038110A1Improved EMI protectionImprove eyesightUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterContinuous scanningLaparoscopes
A motorized scanhead device is capable of rotating an array transducer through 360 degrees of angular rotation in a manner such as to provide acquisition of images in successive scanning planes arranged around the principal axis of the device. The device can be incorporated in endoscopes (e.g., transesophageal endoscopes), laparoscopes, endocavity or intracavity probes so as to provide an expanded angle of vision or to render 3D images, without the need for external movement of the device. The motorized scanhead device includes a motor that is isolated from the transducer signal interconnections in order to minimize electrical discharges associated with motor operation and to provide more room between an associated probe housing and the scanhead device.
Owner:VERMON
Suspension/retraction device for surgical manipulation
ActiveUS20100286473A1Faster healLess infectionSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSurgical ManipulationNatural orifice surgery
A device that can be delivered into a body cavity to manipulate tissue intracorporeally while being controlled extracorporeally and a method of using the device to perform a single-port laparoscopic or natural orifice surgery. The device is being capable of being passed through an interior diameter of a single port into the body cavity. The device comprises an anchor or suspension element that is attachable or mountable to the tissue intracorporeally, a guide element attached to the anchor or suspension element that allows for manipulation of at least one structure in at least one direction, and at least one structure attached to a suture or thread that is passable through the interior diameter of the port and positionable by the guide element. The structure is controllable extracorporeally by manipulating the suture or thread so that the structure moves in at least one direction intracorporeally.
Owner:YALE UNIV
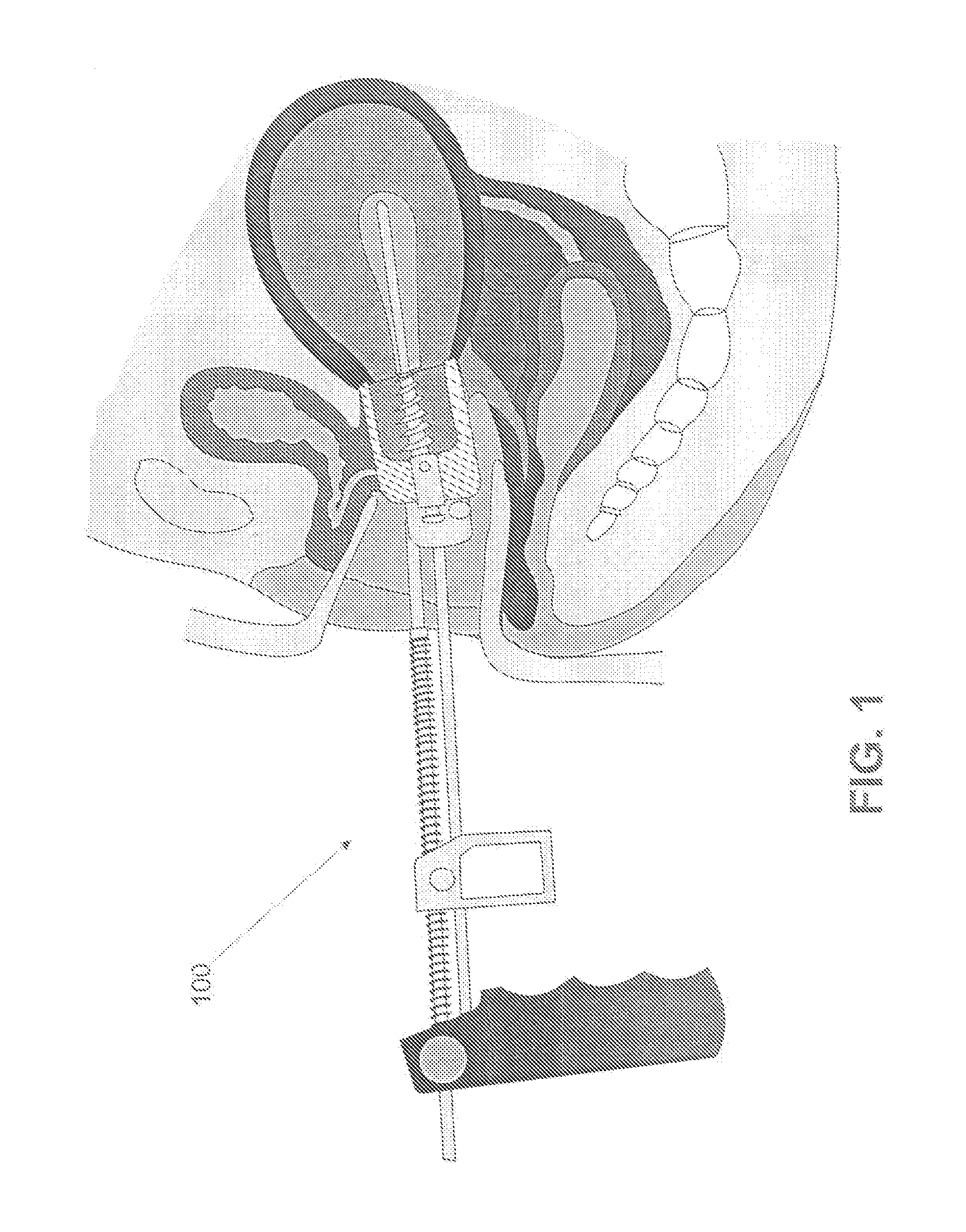
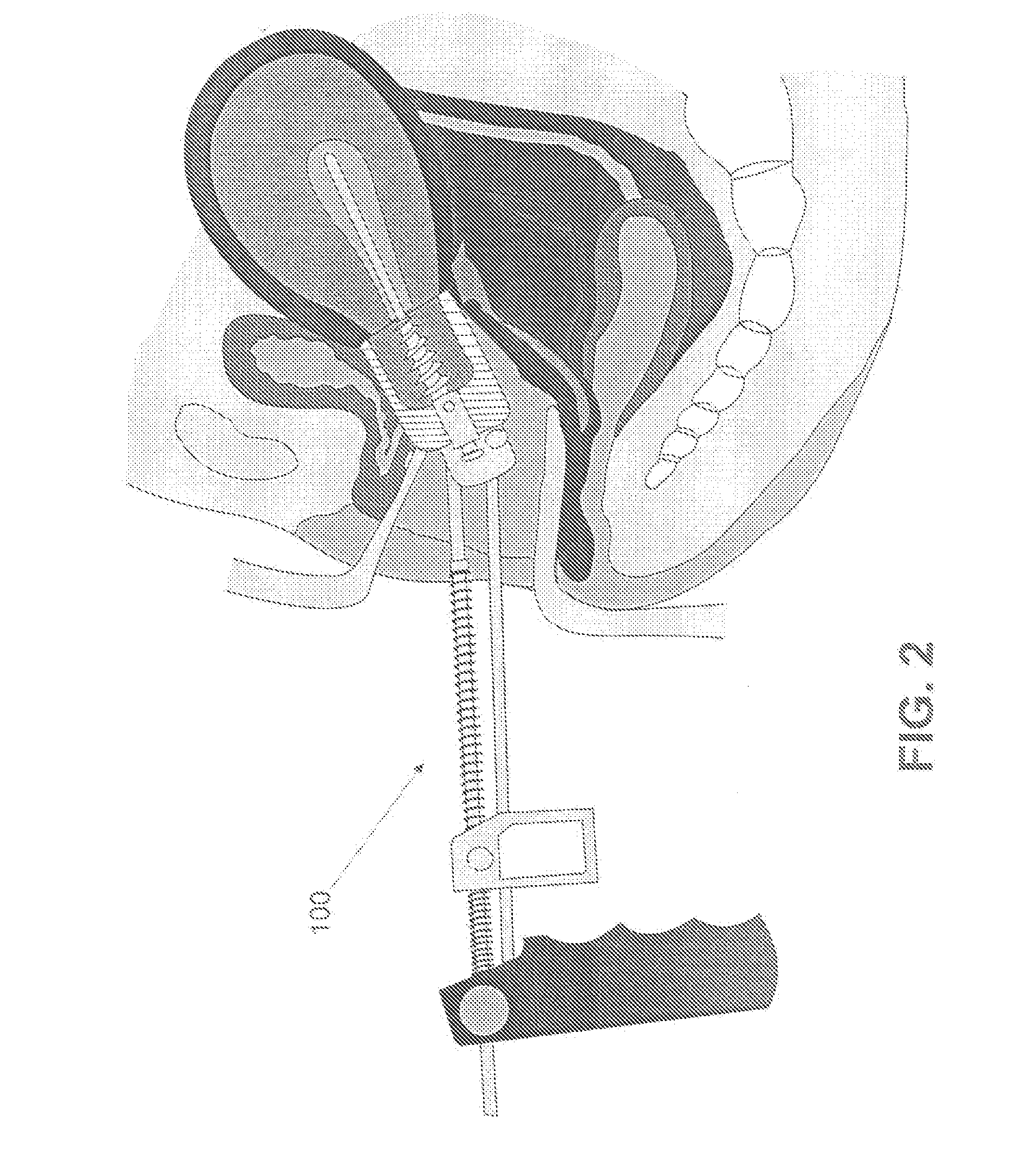
Uterine Manipulator for Complete Removal of Human Uteri
A uterine manipulator designed to perform a total laparoscopic hysterectomy in an easy, safe and effective manner, which simplifies the surgical procedure by improving the anatomical angle of access to round ligaments, salpinges, utero-ovarian ligaments, broad ligaments, uterine vessels, anterior endopelvic fascia, lateral endopelvic fascia, but very especially to the posterior endopelvic fascia due to innovative design of said manipulator that allows the anteversoflexion movement of uterus. In addition, the invention moves ureters away from the risk zone when tying the uterine vessels, and protects and prevents the mobilization of the bladder and rectum, as a result of improving the angle of access. Additionally, the manipulator has the advantage of being easily manageable because of the anatomical design of its handle and its strong design allows for total hysterectomy uterus, still too big and heavy uteri.
Owner:LOPEZ ZEPEDA MARCO ANTONIO
Simulated tissue structures and methods
Simulated tissue structures and methods of manufacturing are provided. The simulated tissue structures are particularly useful for placement inside abdominal simulators for practicing laparoscopic surgical techniques. One simulated tissue structure includes a combination of two materials that are attached together wherein one of the materials forms a hollow anatomical structure configured to contain the other material. The two materials are attached in an anatomically advantageous manner such that the inner surface of the outer material closely conforms to the outer surface of the inner material. Another simulated tissue structure includes a plurality of layers wherein at least one layer is applied by printing the layer with at least one stencil to impart one or more functional characteristic to the simulated tissue structure.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Systems and methods for optimizing and maintaining visualization of a surgical field during the use of surgical scopes
InactiveUS8888689B2Maintaining visualizationClear visualizationCannulasSurgical needlesLess invasive surgerySurgical operation
Systems and methods make use of a view optimizing assembly having a deflector assembly with critical physical, pneumatic, and optical characteristics that make possible intra-operative defogging, surgical debris deflection, and cleaning of a laparoscope lens during minimally invasive surgery, while also maintaining visualization of the surgical site. The view optimizing assembly can incorporate a quick exchange feature, which makes possible a surgical method for maintaining clear visualization that includes the ability to make a quick exchange of laparoscopes having different operating characteristics (e.g., laparoscopes with different tip angles, lengths, or diameters) entirely on the sterile operating field and without interference with the preexisting surgical set-up on the sterile operating field. The view optimizing assembly integrates with the existing suite of minimally invasive instrumentation. It does not interfere with the surgical set-up, and it requires minimal change in the process or practice of a surgical operating room (OR) team.
Owner:FLOSHIELD INC
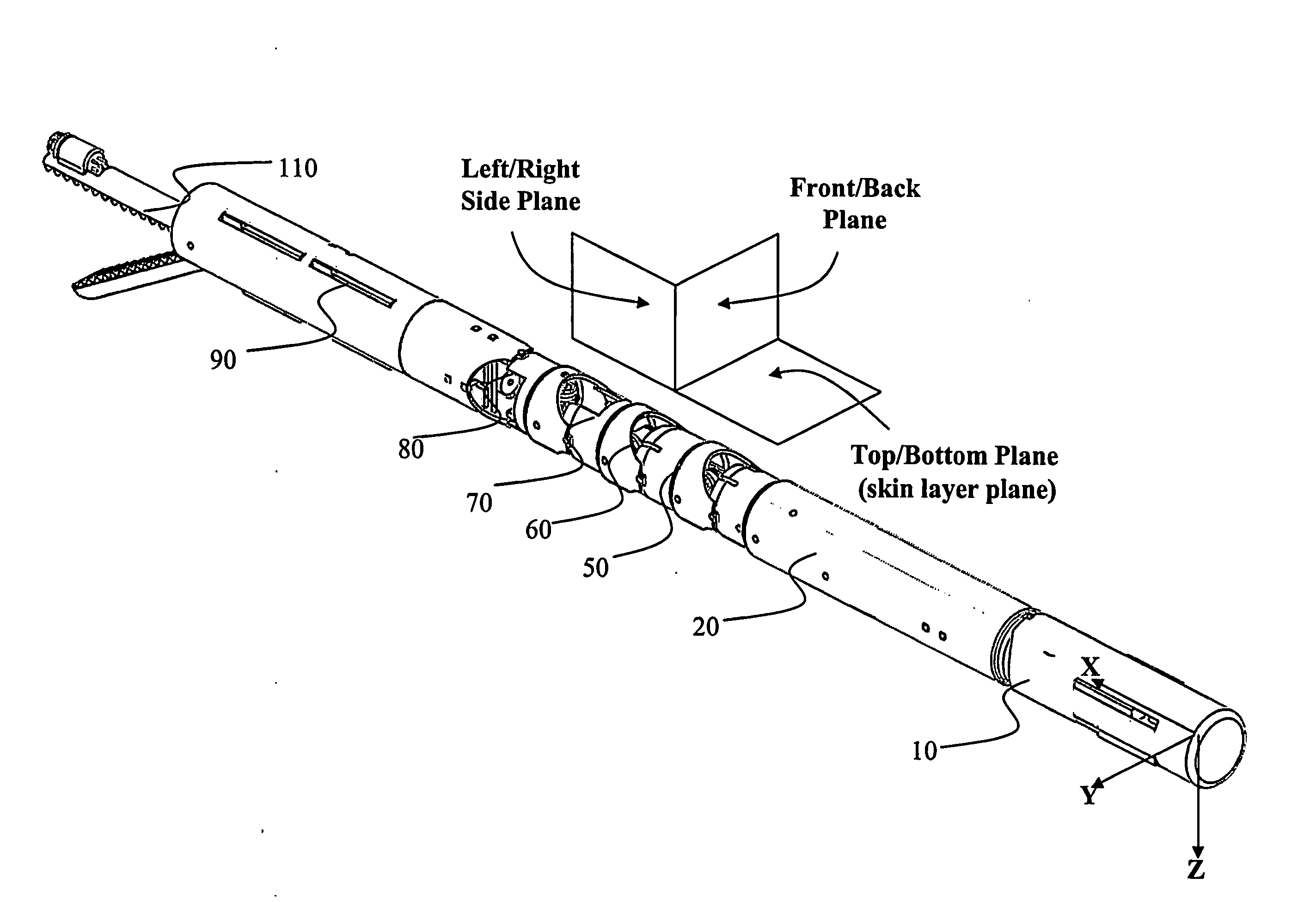
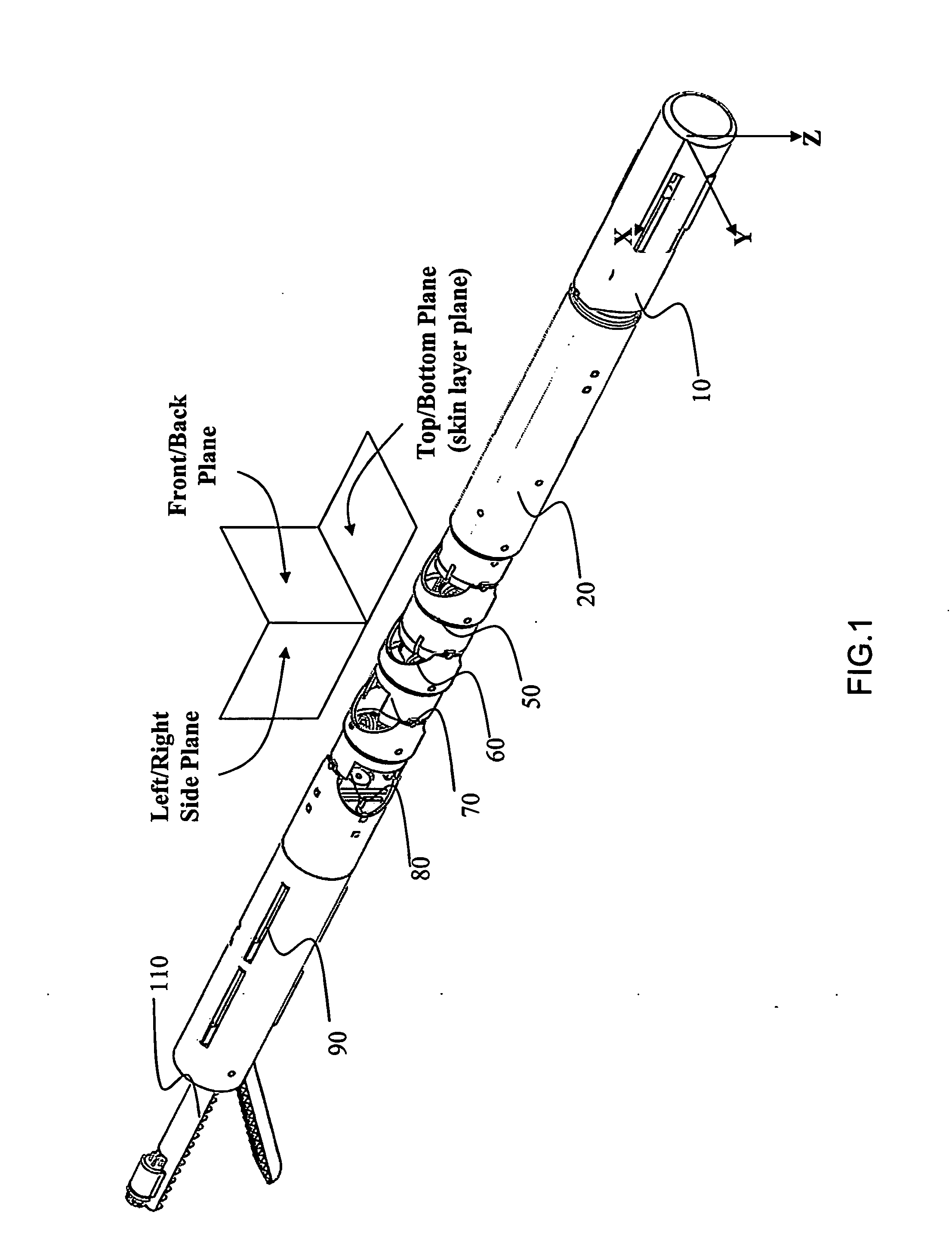
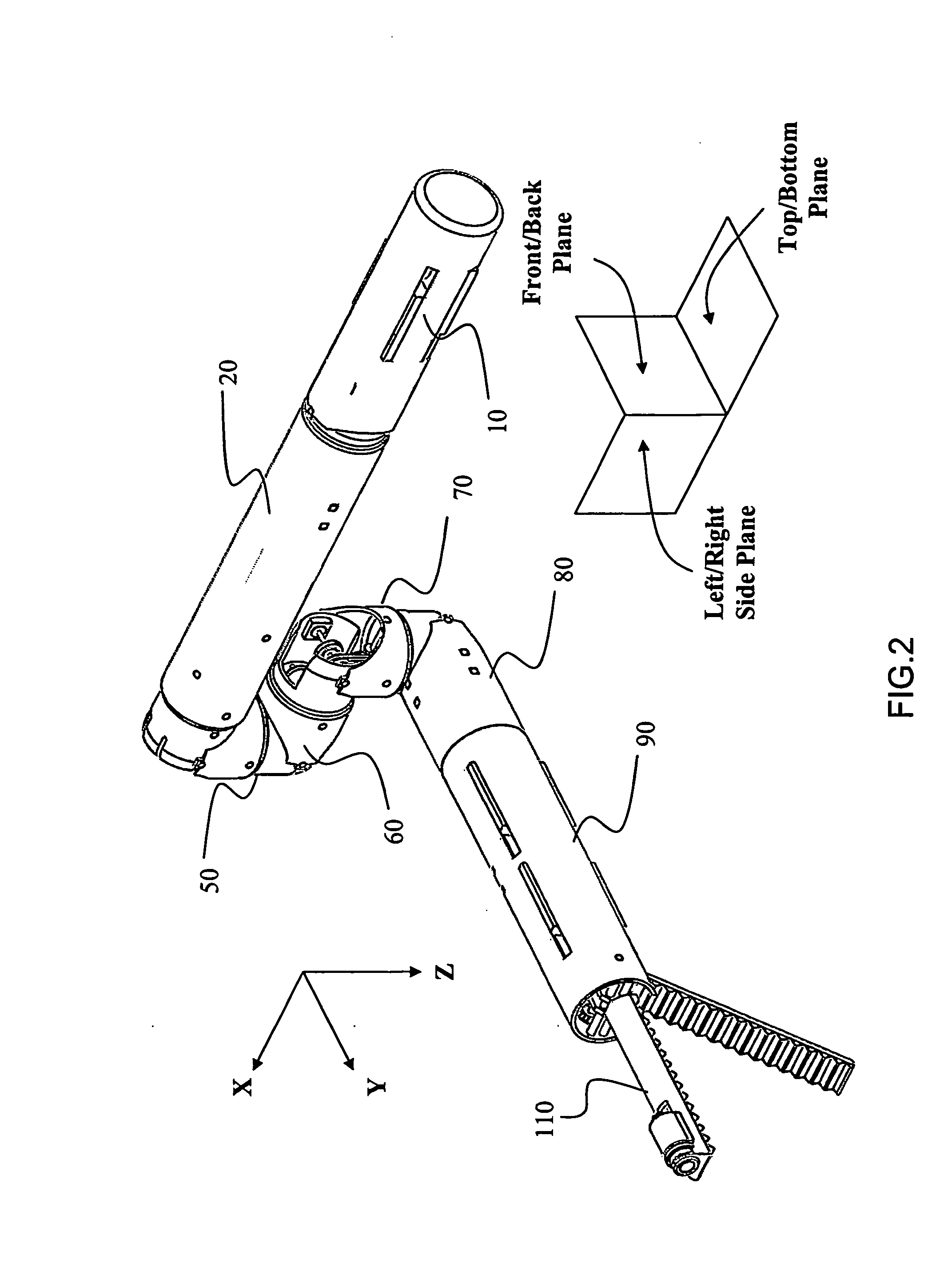
N degrees-of-freedom (DOF) laparoscope maneuverable system
A laparoscope including a cylindrical device of multiple degrees of freedom which can be inserted through a small surgical incision. This is accomplished by means of a series of coaxial members nested within the aforementioned cylinder, each can rotate independently and actuate a desired motion at the distal end. The laparoscope has multiple consecutive arm sections, each includes several coaxial input shafts adapted to be rotated around an input axis of rotation by multiple sources of torque. In addition, several constant velocity couplers connect the arm sections and are equipped with coaxial input transmission means, coaxial second transmission means and coaxial output transmission means to transfer the input torque to coaxial output shafts and facilitate the independent rotation and motion of the device distal end within the patient's body.
Owner:M S T MEDICAL SURGERY TECH LTD
Suction dome for atraumatically grasping or manipulating tissue
InactiveUS20090270789A1Sufficient supportImprove sealingSurgical needlesSurgical pincettesLaparoscopesForceps
The present invention provides a suction dome for atraumatically grasping, manipulating, and / or extracting tissues. The suction dome may be used with a surgical instrument having a suction channel. Such instruments include, for example: forceps, laparoscopes, endoscopes, bronchoscopes, and catheters. The suction dome comprises an outer wall non-permeable membrane and a tissue-engaging permeable membrane base. The non-permeable membrane may be supported by a plurality of expanding arms and defines a chamber in communication with the suction channel of the instrument.
Owner:CARILION BIOMEDICAL INST
Laparoscope cleaning system
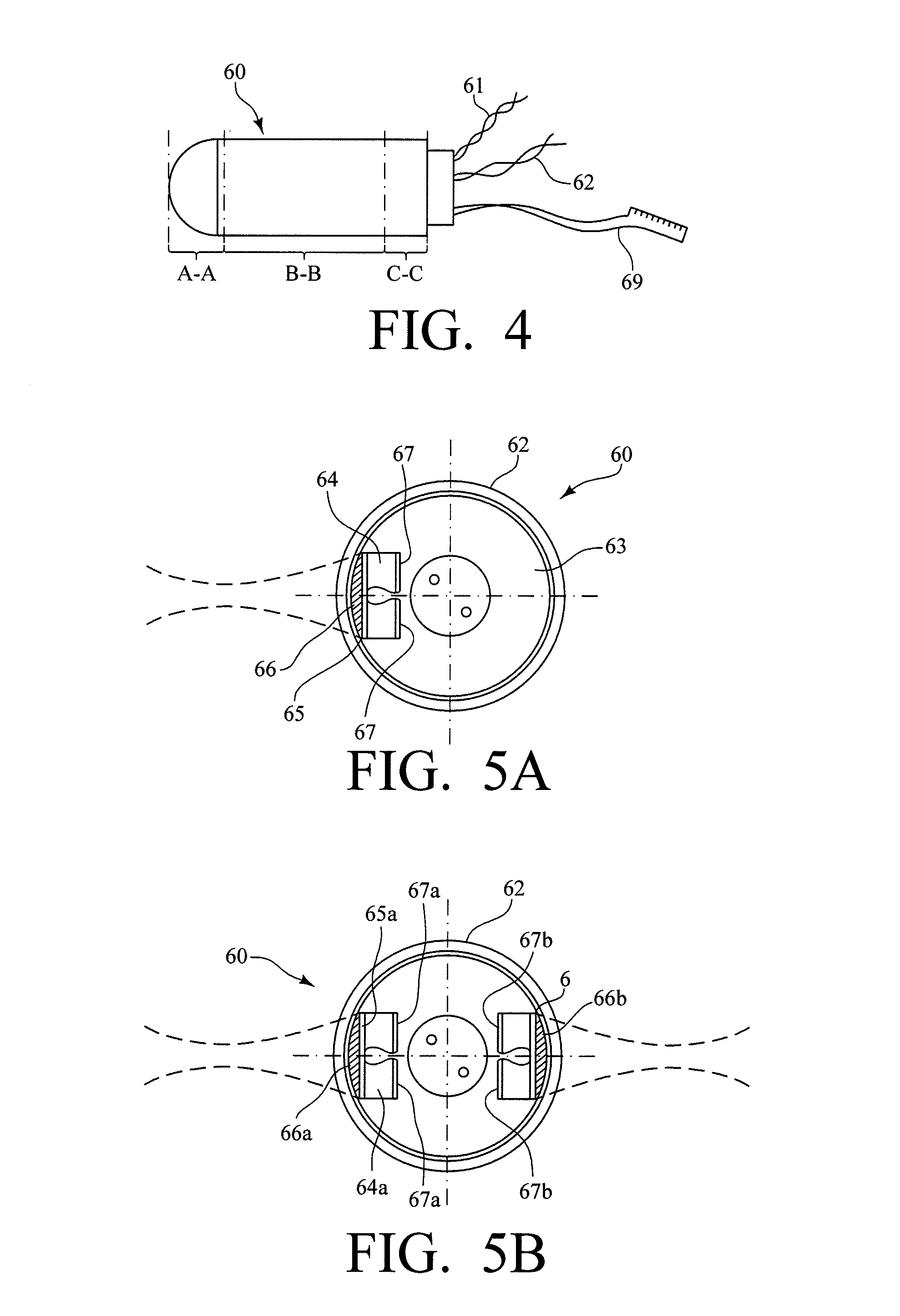
A laparoscope lens cleaning system includes a housing that is configured to be connected to existing laparoscopes. The housing forms a lumen which carries a tube for dispensing cleaning solution. An extension system enables the tubing to be extended beyond the end of the laparoscope such that a hole or a plurality of holes in the extended tube end enables the dispensing of cleaning solution on the lens without requiring removal of the laparoscope from the patient. A pumping system is connected to the other end of the tubing and provides a cleaning solution reservoir and means for selectively dispensing the cleaning solution when required by the surgeon.
Owner:MONDSCHEIN ROBERT
Device and methods of improving laparoscopic surgery
ActiveUS20130123804A1Electric signal transmission systemsEndoscopesLaparoscopic surgeryMedical assistant
Methods and devices for improving the interface between a surgeon and an operating medical assistant or between the surgeon and an endoscope system for laparoscopic surgery. A device is useful for controlling an endoscope system for laparoscopic surgery and includes a wearable interface for enhancing the control of an endoscope system during laparoscopic surgery.
Owner:TRANSENTERIX EURO SARL
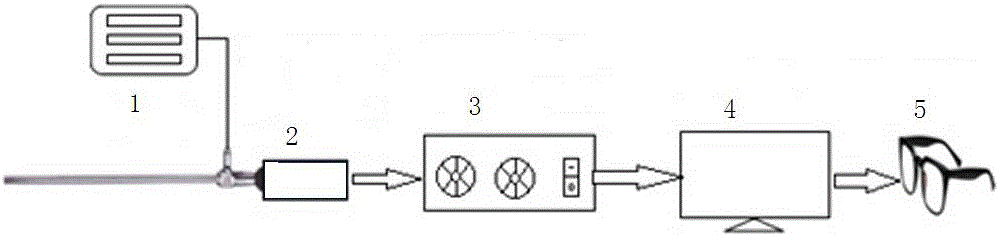
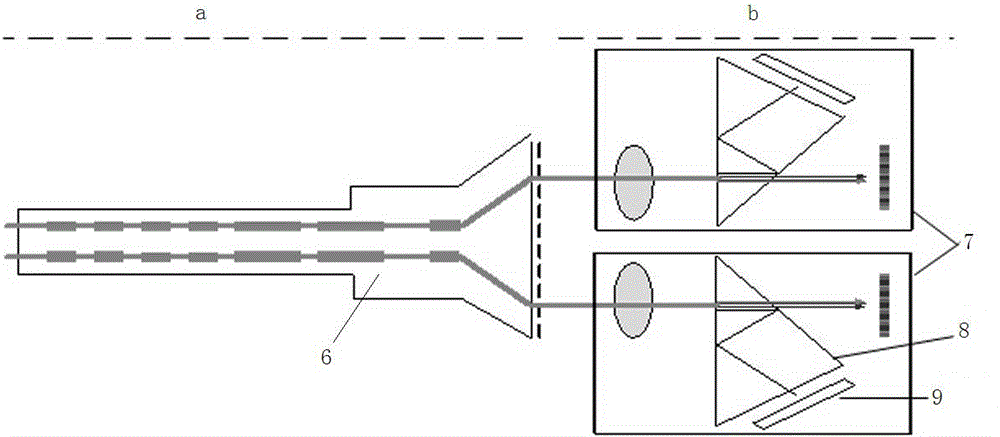
3D optical molecular imaging laparoscopic imaging system
ActiveCN106236006APrecision FusionAccurate display of three-dimensional structureDiagnostics using spectroscopySurgeryBeam splitterEyepiece
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical laparoscope, and particularly relates to a 3D optical molecular imaging laparoscopic imaging system, aiming at solving the problem in existing laparoscope technology and fluorescent laparoscopes. The system comprises a 3D laparoscope, wherein two output optical channels of the 3D laparoscope are parallel; a dual-channel charge coupled device (CCD) is respectively arranged outside the 3D laparoscope corresponding to two eye lenses, and a beam splitter prism is arranged in each dual-channel CCD; a cut-off filter is arranged at the near infrared channel behind the beam splitter prism, and a black-white near infrared CCD is arranged behind the cut-off filter; and a colored CCD is arranged at the visible light channel behind the beam splitter prism. According to the 3D optical molecular imaging laparoscopic imaging system, a target optical molecular image is precisely integrated with a visible light image, and is displayed in a 3D manner, so that the 3D structure of a target focus and the 3D anatomical relationship of the 3D structure and surrounding tissues can be displayed precisely, rich deep information is provided to doctors, and the accuracy of doctor operation and scientific researches can be greatly improved.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Suspension/retraction device for surgical manipulation
ActiveUS8827891B2Promotes faster healingRelieve painSuture equipmentsInfusion syringesSurgical ManipulationLaparoscopes
A device that can be delivered into a body cavity to manipulate tissue intracorporeally while being controlled extracorporeally and a method of using the device to perform a single-port laparoscopic or natural orifice surgery. The device is being capable of being passed through an interior diameter of a single port into the body cavity. The device comprises an anchor or suspension element that is attachable or mountable to the tissue intracorporeally, a guide element attached to the anchor or suspension element that allows for manipulation of at least one structure in at least one direction, and at least one structure attached to a suture or thread that is passable through the interior diameter of the port and positionable by the guide element. The structure is controllable extracorporeally by manipulating the suture or thread so that the structure moves in at least one direction intracorporeally.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Robotic module for natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES)
ActiveUS20130012821A1Little strengthSufficient forceSurgical manipulatorsSurgical robotsIn vivoActuator
A miniature in-vivo robotic module to be used for conducting dexterous manipulations on organs and other target entities in a patient's abdominal or peritoneal cavity as part of Natural Orifice Transluminal Endoscopic Surgery (NOTES) is disclosed in this invention. The robotic module is a serial manipulator consisting of seven cylindrical links and six actively controllable rotational degrees of freedom, thereby enabling an end effector equipped with a laparoscopic type instrument to assume a commanded position and orientation within the robot's workspace. After overtube navigation starting from a natural orifice or preexisting wound, the module must be anchored and guided to a designated location along the inner abdominal cavity wall. This is accomplished via magnetic coupling forces between internal embedded magnets and magnets fixed to the end of a different robotic manipulator located external to the patient.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
Motorized ultrasonic scanhead
ActiveUS7798971B2Improved EMI protectionImprove eyesightUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterContinuous scanningLaparoscopes
Owner:VERMON
Laparascope and Endoscope Cleaning and Defogging Device
ActiveUS20160135673A1Limited visualizationMaximize rangeBoard cleaning devicesCarpet cleanersSurgical mirrorSurgical site
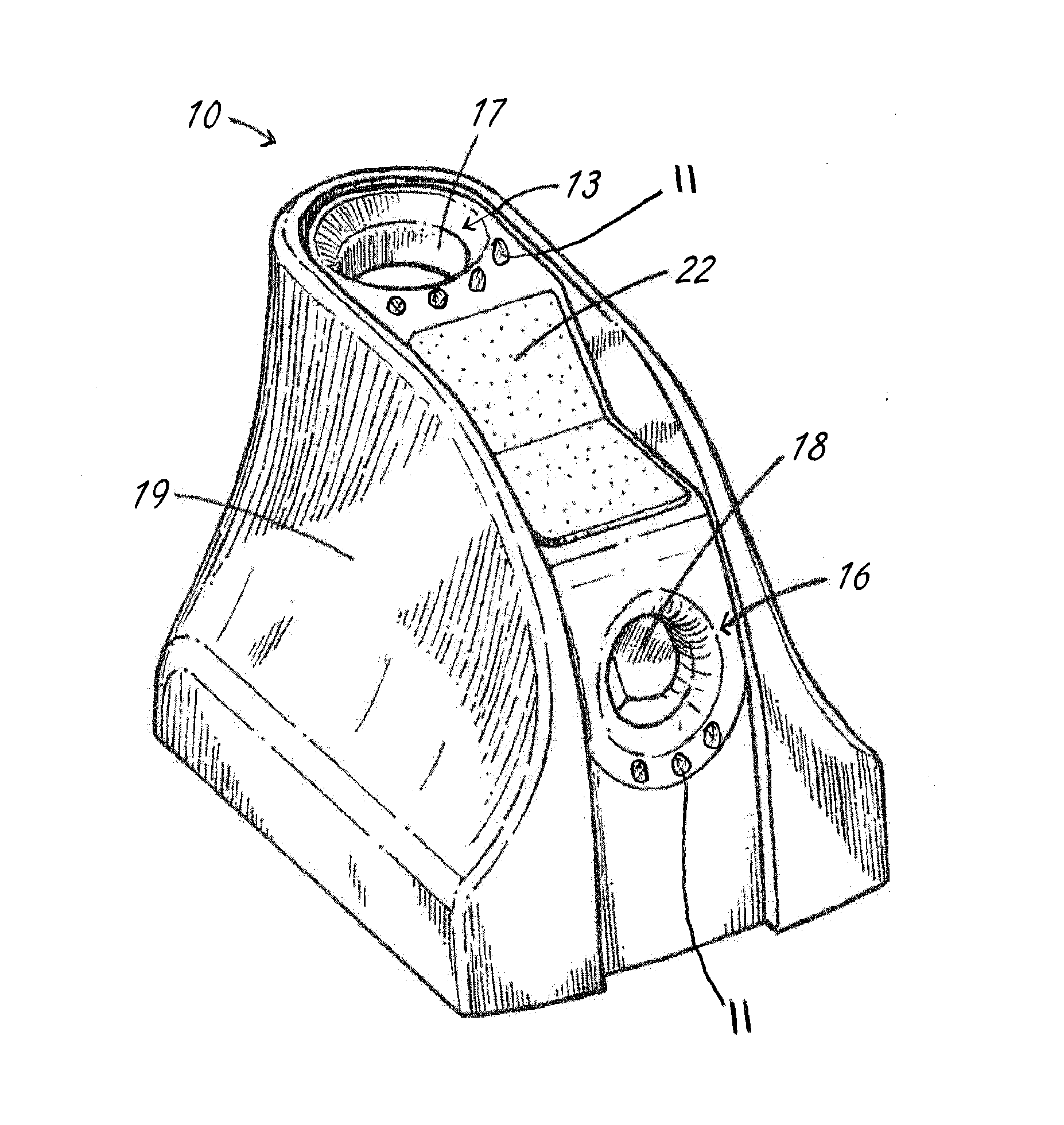
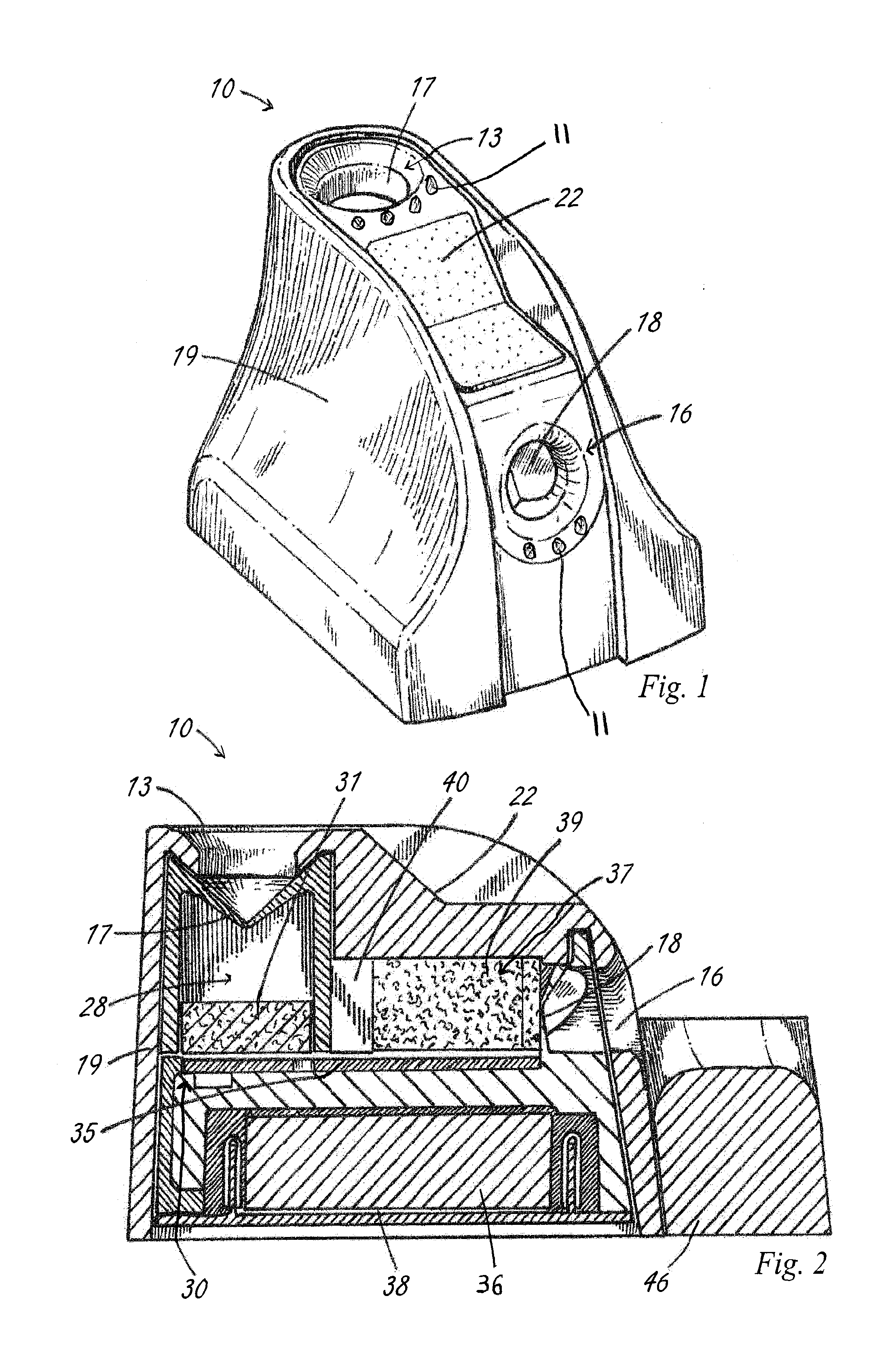
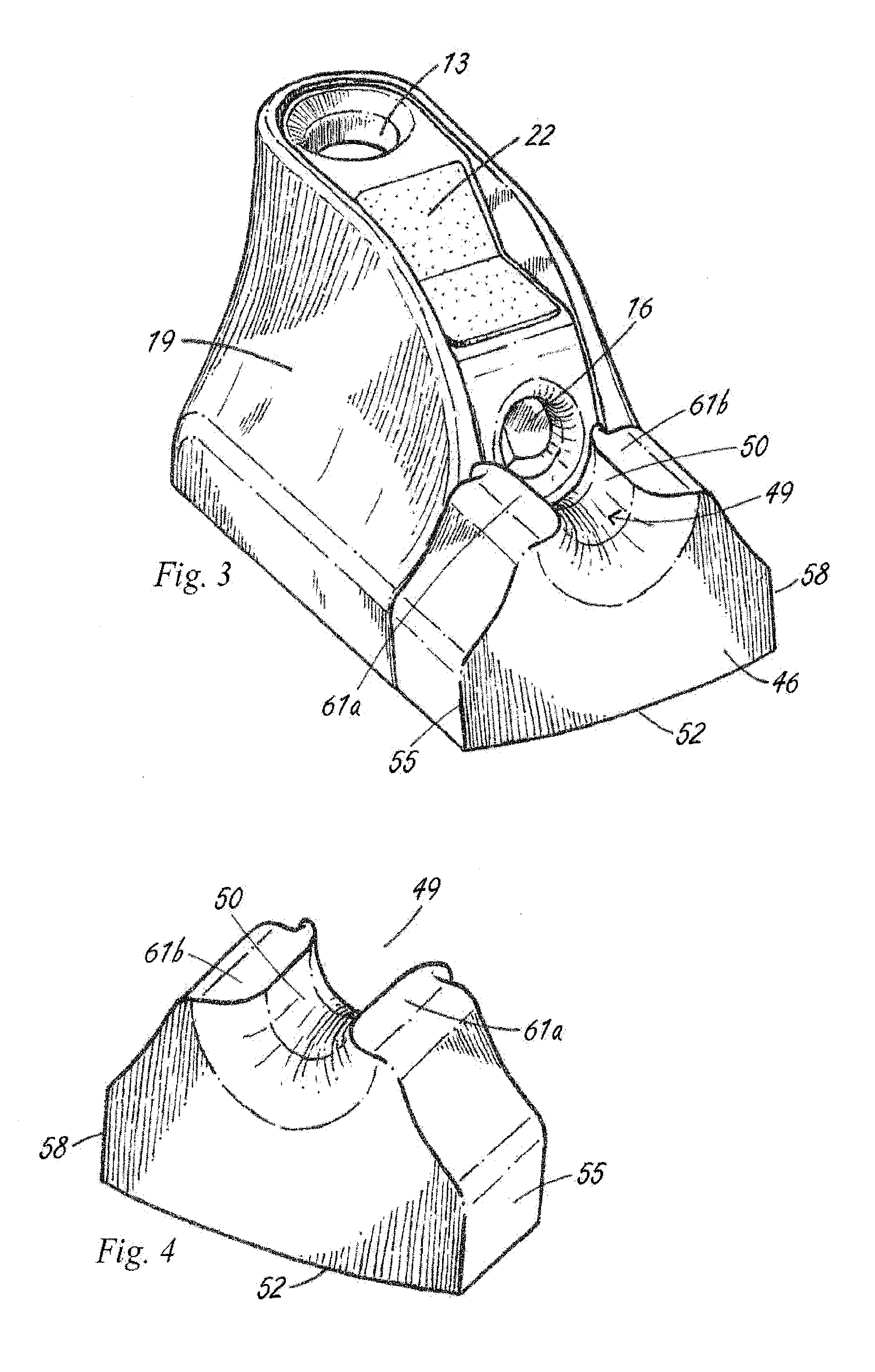
A laparascope and endoscope cleaning and de-fogging device with a port located horizontally that is used to warm the scope prior to insertion into the body cavity / surgical site. The scope punctures the initial membrane and enters the cavity between two bodies of absorbent material that contain fluid. The absorbent material is arranged such that the passage of a scope would be accommodated for different sizes of surgical scopes. A circuit board is located on the bottom of the chamber that has a design element used to warm the liquid to a temperature equal to or greater than the temperature of the proposed surgical environment. When the scope is located between the two absorbent bodies, the heat generated by the circuit board is transferred via the liquid and contacts the scope, warming it in preparation for surgery.
Owner:BUFFALO FILTER
Spindly non-pneumoperitoneum device for single-port laparoscopy
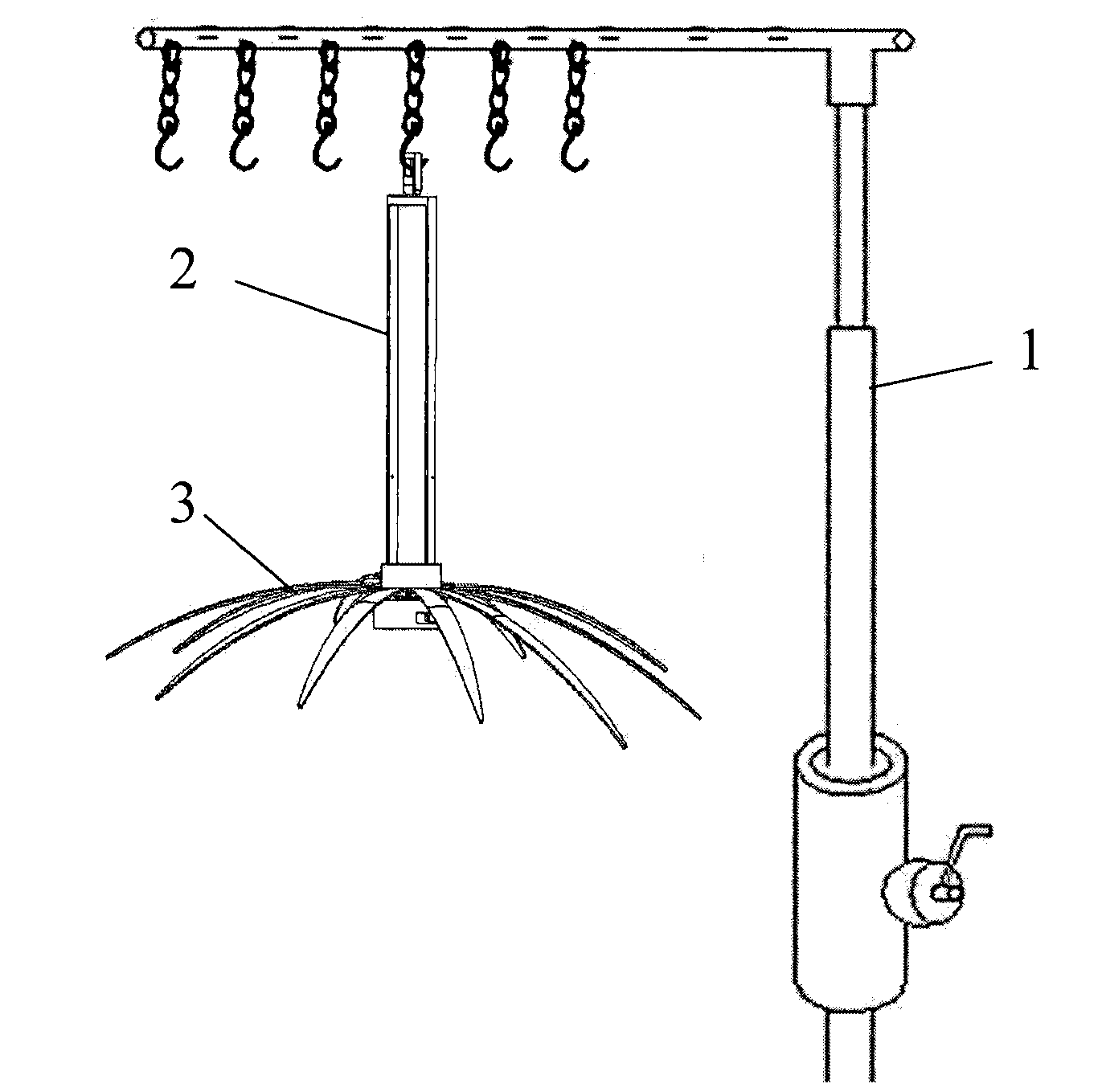
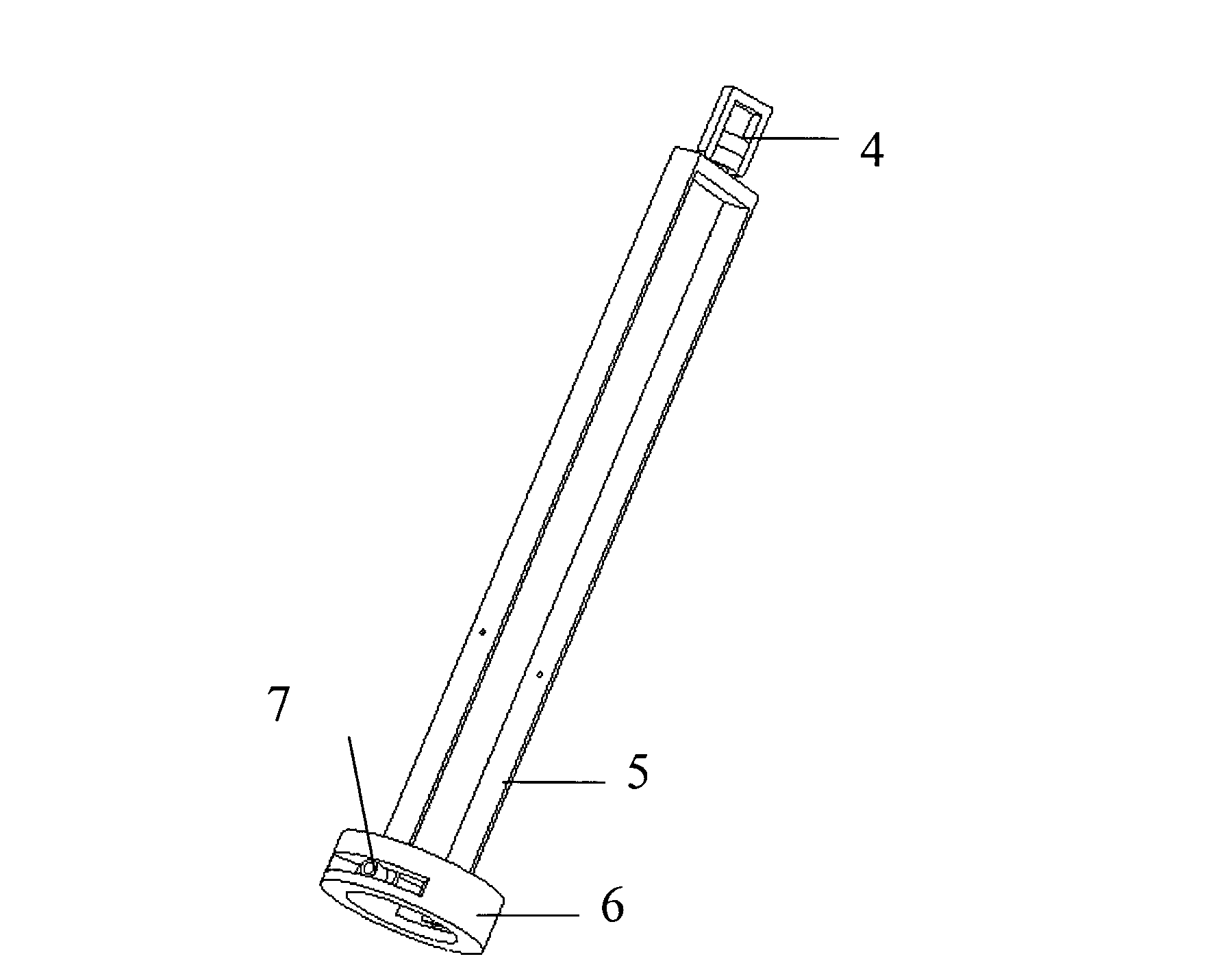
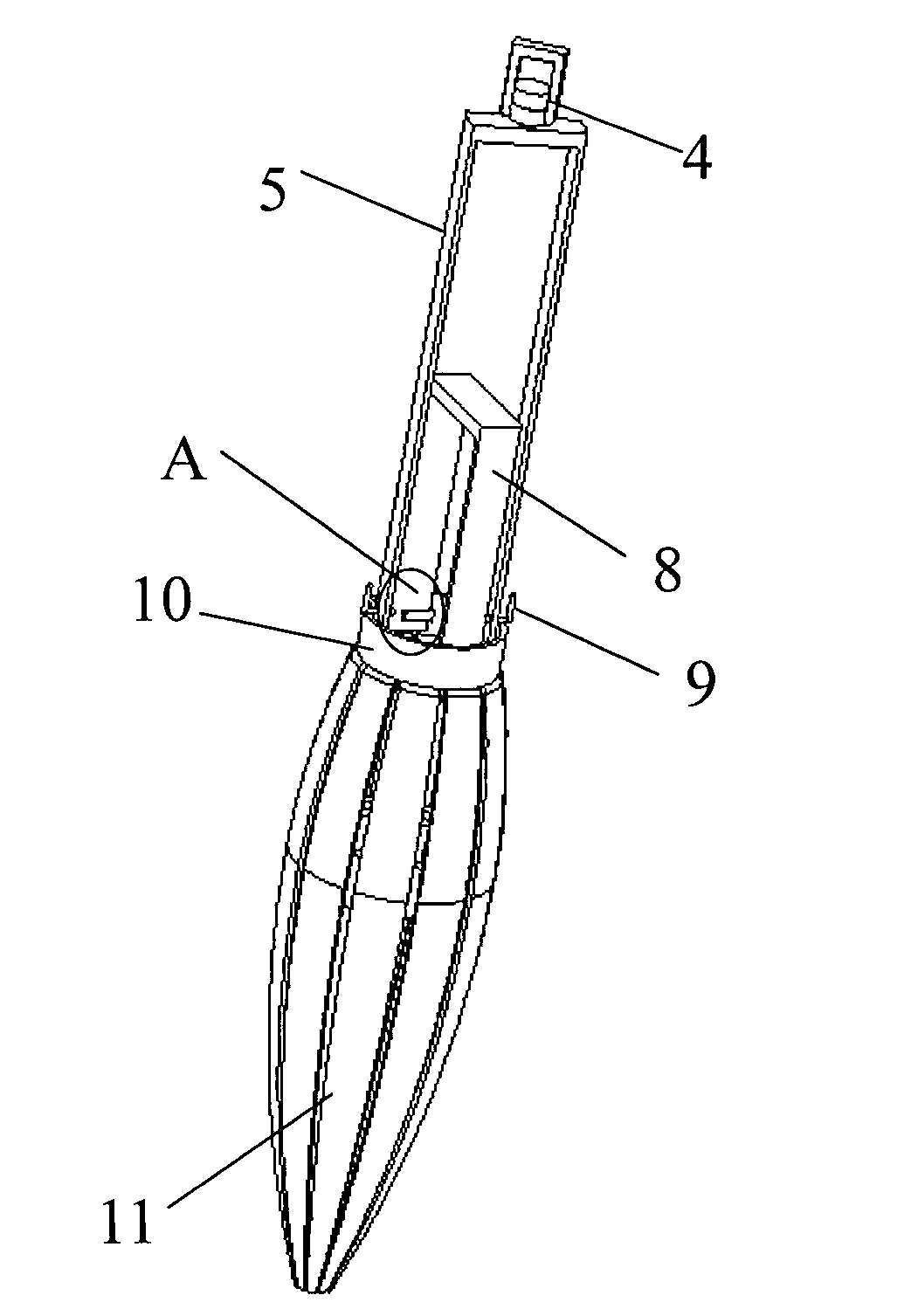
InactiveCN103202719ASolve the large number of incisionsSolve postoperative susceptibility to infectionSurgeryPneumoperitoneumUmbilical region
The invention relates to the field of laparoscopic micro-invasive surgery, in particular to a spindly non-pneumoperitoneum device for a single-port laparoscopy. According to the spindly non-pneumoperitoneum device, the defects of small surgery space, poor surgical field exposure and great quantity of abdominal incisions in a traditional non-pneumoperitoneum technology can be overcome. The spindly non-pneumoperitoneum device consists of a fixed frame, a suspension mechanism and a spindle mechanism. Due to the adoption of the technical scheme that a support ring enables spindly spokes to be stretched off and be arrayed in an umbrella shape by upwards lifting a suspender, an anterior abdominal wall is semi-spherically lifted and suspended by the spokes arrayed in an umbrella shape and the phenomenon that the surgery space becomes smaller and narrower due to the fact that abdominal walls on two sides gather towards the middle to extrude intestinal canal to be concentrated to the middle by a suspending pull force of the abdominal walls is avoided; due to adoption of single incision in umbilical region, an illuminating probe, surgical instruments and the like extend into an abdominal cavity for surgery by using a hollow structure of the device; and due to the adoption of a rotational suspension device, the surgical instruments obtain a more favorable operation angle and the problems of small surgery space, insufficient surgical field exposure and great quantity of abdominal incisions in the traditional non-pneumoperitoneum technology are better solved.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Apparatus, systems, and methods for performing laparoscopic surgery
ActiveUS9861272B2Facilitate surgeryMinimize the numberLaproscopesSurgical forcepsLaparoscopesEngineering
Apparatus, systems, and methods for laparoscopic abdominal surgery are disclosed. For example, a system or kit is provided for performing a procedure within a surgical space within a patient's body that includes a plurality of tool heads, and a tool head carrier including features for removably receiving one or more tool heads, the tool head carrier sized for introduction through a trocar or other port into a surgical space. The system or kit may also include a surgical tool including a tool shaft introduceable into the surgical space and including features for securing a tool head to the tool. Optionally, the tool head carrier may include a clip for securing the tool head carrier to an endoscope.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com