Method for removing arsenic and antimony from zinc smelting leach liquor
A technology for zinc smelting and leaching solution, applied in the field of zinc metallurgy, can solve problems such as comprehensive utilization of unfavorable valuable metals, low content of valuable elements, increase labor intensity, etc., and achieve high content of valuable metals, stable physical and chemical properties, and reduce acid consumption. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
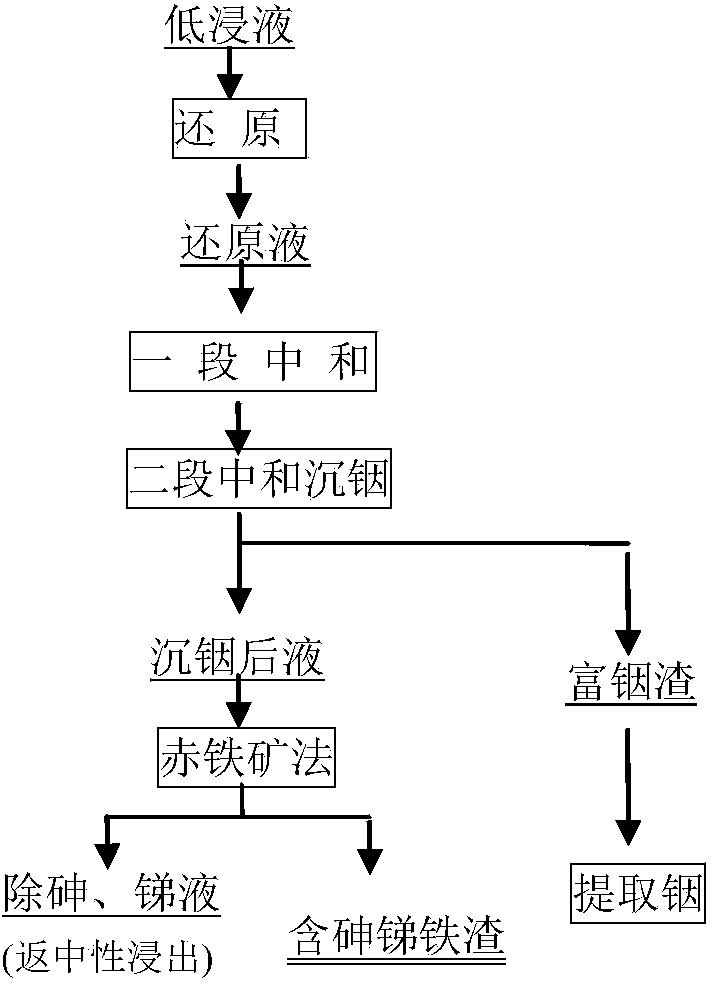
[0024] Add Zn104g / L, Fe21g / L, In0.15g / L, As0.10g / L, Sb0.05g / L low-acid leaching solution to pre-reduce zinc concentrate, the amount of concentrate added is 1.2 times the theoretical amount, React at 95°C for 3 hours, the ferric iron in the reduced solution is about 0.9g / L, the reduction rate is 95.7%, and the reduced liquid is obtained by solid-liquid separation; at 90°C, limestone is slowly added to the reduced liquid to adjust the pH value of the solution, and wait for When the pH value of the solution is stable at about 1.0, continue to react for 120 minutes, and separate the solid and liquid to obtain a section of neutralized liquid; neutralize the residual acid with sub-zinc oxide at 90°C, control the pH value of the end point to about 4.5, and separate the solid and liquid to obtain indium-rich liquid after 2 hours of reaction slag and indium-precipitated liquid (ie, neutralized liquid); the indium-precipitated liquid was reacted for 3 hours at a temperature of 170°C, an ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Add zinc sulfite to the low-acid leach solution of Zn104g / L, Fe21g / L, In0.15g / L, As0.15g / L, Sb0.1g / L for pre-reduction, and the amount of zinc sulfite added is 1.1 times of the theoretical amount , react at 95°C for 3 hours, the ferric iron in the reduced liquid is about 0.6g / L, the reduction rate is 97.1%, and the reduced liquid is obtained by solid-liquid separation; at 90°C, the calcined sand is slowly added to the reduced liquid to adjust the pH value of the solution , when the pH value of the solution is stabilized at about 1.0, continue to react for 120 minutes, and separate the solid and liquid to obtain a section of neutralized liquid; neutralize the residual acid with zinc oxide at 80 ° C, control the pH value of the end point to about 4.5, and separate the solid and liquid after 2 hours of reaction to obtain Indium-rich slag and indium-precipitated solution (neutralized solution); the indium-precipitated solution was reacted for 3 hours at a temperature of 120°...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Add zinc sulfite to the low-acid leach solution of Zn104g / L, Fe21g / L, In0.15g / L, As1g / L, and Sb1g / L for pre-reduction. The amount of zinc sulfite added is 1.1 times the theoretical amount, and the reaction is performed at 95°C After 3 hours, the ferric iron in the reduced liquid was about 0.6g / L, the reduction rate was 97.1%, and the reduced liquid was obtained by solid-liquid separation; at 90°C, zinc oxide was slowly added to the reduced liquid to adjust the pH value of the solution. When the value is stable at about 1.0, continue to react for 120 minutes, and obtain a section of neutralized liquid after solid-liquid separation; neutralize the residual acid with secondary zinc oxide at 90 ° C, control the pH value of the end point to about 4.5, and separate the solid-liquid after 2 hours to obtain indium-rich slag and The liquid after sinking indium (ie, the liquid after neutralization); react the liquid after sinking indium at a temperature of 170°C, an oxygen partial...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com