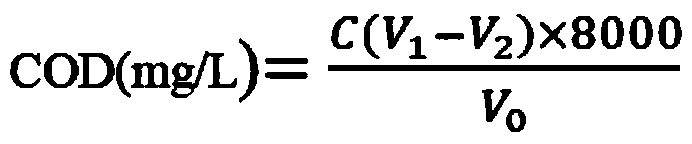Patents
Literature
57results about How to "No solid waste generated" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
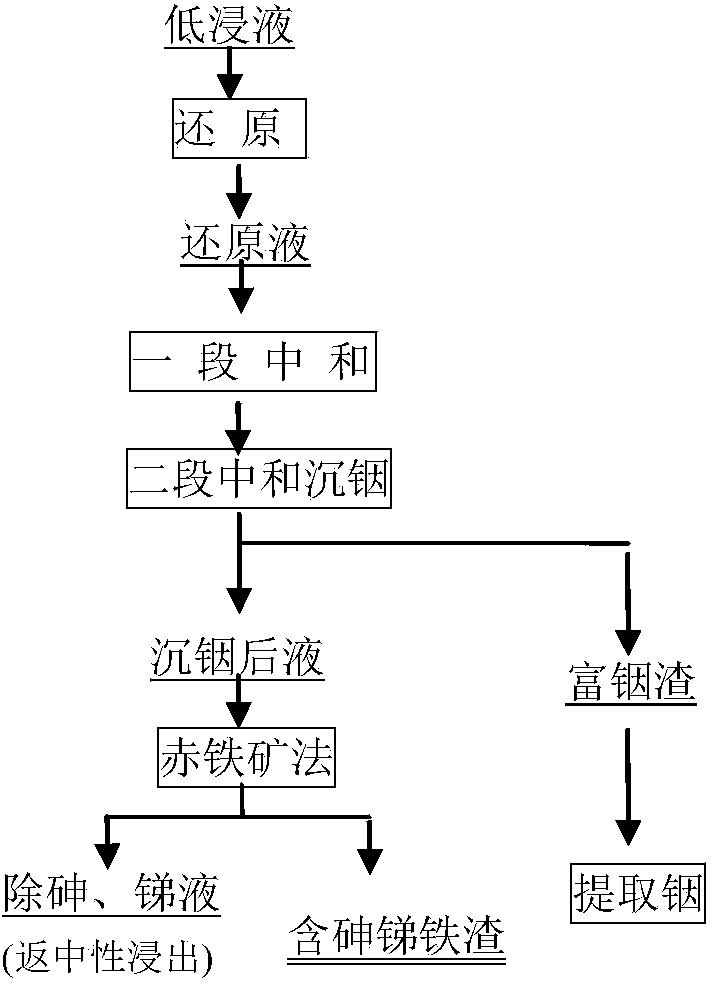
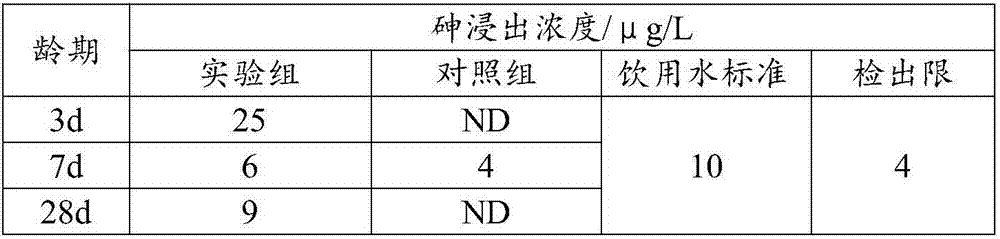
Method for removing arsenic and antimony from zinc smelting leach liquor
InactiveCN103911512AEfficient use ofStable physical and chemical propertiesProcess efficiency improvementIndium metalPregnant leach solution
The invention discloses a method for removing arsenic and antimony from zinc smelting leach liquor, and relates to a method for removing arsenic and antimony from a solution produced during zinc smelting by purifying. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: comprehensively recovering valuable components of zinc, indium, iron and the like by purifying in an arsenic and antimony removing process consisting of pre-reduction, neutralization of precipitated indium and a hematite process under the condition that zinc smelting low-acid leach liquor is taken as a raw material; turning high-valence iron into low-valence iron by taking zinc concentrate, zinc sulfite, sulfur dioxide and the like as reducing agents in the low-acid leach liquor, wherein the content of high-valence iron (Fe<3+>) in the reduced liquor is lower than 2g / L; performing two-stage neutralization by using lime, limestone, secondary zinc oxide, calcined sand and zinc oxide to regulate the pH value of reduced liquor to 4.0-5.4 in order to enrich indium precipitate; and removing arsenic and antimony from indium-precipitated liquor to fulfill the aim of efficiently cleaning and purifying the solution. The method has the advantages of high indium metal recovery rate, high arsenic and antimony removing rates, small residue amount, stable performance and environmental friendliness.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
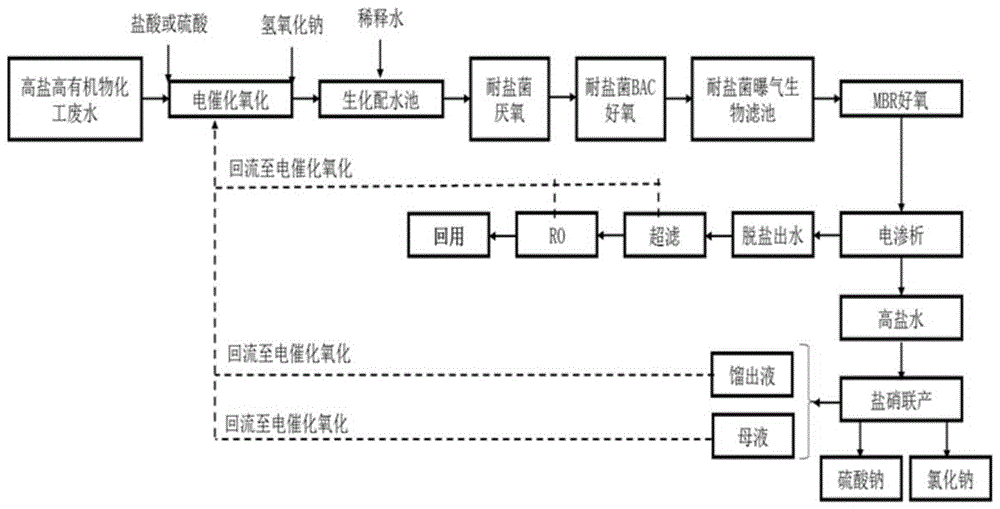
Recycling treatment system and treatment method of high-salinity high-organic-matter chemical wastewater
ActiveCN106495396ARealize resourcesReduce SS contentWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesElectricityUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a recycling treatment system of high-salinity high-organic-matter chemical wastewater. The recycling treatment system comprises an electrocatalytic oxidation device, a halotolerant bacteria biochemical system, an MBR aerobic device, an electroosmosis unit, an ultrafilter and an RO unit, the halotolerant bacteria biochemical system comprises a halotolerant bacteria anaerobic device, a halotolerant bacteria aerobic device and a halotolerant biological aerated filter. The invention further discloses a treatment method of the high-salinity high-organic-matter chemical wastewater. By the recycling treatment system and the treatment method, the problem of recycling treatment of the high-salinity high-organic-matter chemical wastewater is solved effectively, recycling rate of water and salt is high, no wastewater is discharged basically, no solid waste is generated, generated water is high in quality, generated salt is high in purity, and water resources and salt in the high-salinity high-organic-matter chemical wastewater are recycled to greatest extent; zero discharging of wastewater in the process of enterprise production is realized, and the recycling treatment system and the treatment method have important environment benefit.
Owner:JIANGSU LASON CHEM ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Method for extracting aluminum, silicon oxide and rare earth from waste rare earth polishing powder
ActiveCN109207737ANo solid waste generatedHigh priceSilicaProcess efficiency improvementStrong acidsRare earth
The invention discloses a method for extracting aluminum, silicon oxide and rare earth from waste rare earth polishing powder. The method comprises the following steps that (1) strong acid is added into the pretreated waste rare earth polishing powder, the aluminum and the rare earth are dissolved, and silicon oxide powder is left in leaching residues; (2) the leaching residues containing the silicon oxide powder are washed and purified so as to obtain the silicon oxide powder; (3) a precipitant is added into a leachate so as to precipitate the rare earth, and filtering is carried out so as toobtain a rare earth salt and an aluminum salt solution; (4) after the aluminum salt solution is neutralized, standing and settling are carried out for 2-12 hours so as to obtain an aluminum-containing product; and (5) the rare-earth salt is subjected to fluorination and is burnt so as to prepare rare earth polishing powder. According to the method, silicon, aluminum and the rare earth in the waste rare earth polishing powder are comprehensively recovered to form the superfine silicon oxide powder, the aluminum salt and the rare earth polishing powder, no solid waste is generated, and all valuable elements are utilized.
Owner:湖南景翌湘台环保高新技术开发有限公司 +1
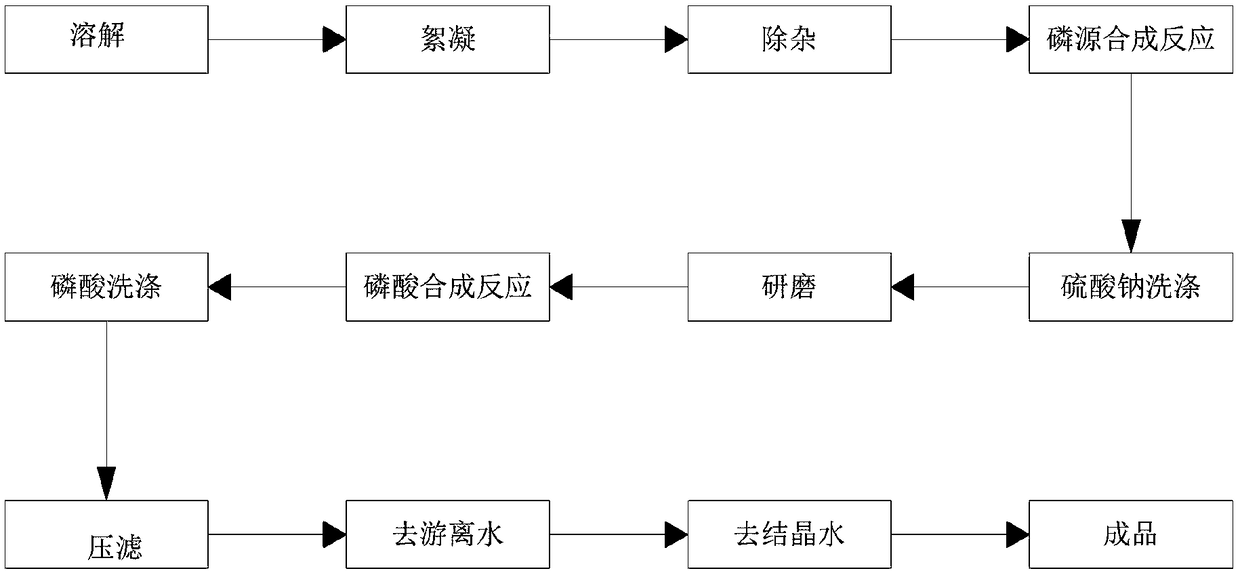
Method for producing battery-grade ferric orthophosphate from titanium dioxide solid waste
The invention belongs to the field of new energy battery materials, and comprises a method for producing battery-grade ferric orthophosphate from titanium dioxide solid waste. The method comprises thefollowing effective steps: adding water for thoroughly dissolving the titanium dioxide solid waste, adding a flocculant, and then performing multi-stage sedimentation filtration to obtain a high-purity ferrous sulfate solution; thoroughly mixing the prepared ferrous sulfate solution and a phosphorus source solution according to a molar ratio of 1:1 in a reaction kettle, then controlling the pH ofthe solution to be 5-7, controlling the temperature at 25-35 DEG C, reacting for about 2 hours while stirring to obtain a ferrous phosphate slurry and sodium sulfate; filtering and washing the ferrous phosphate slurry and the sodium sulfate after a reaction to remove sodium sulfate, slurrying a filter cake after washing, and dispersing and sanding the ferrous phosphate slurry; mixing the sanded ferrous phosphate slurry and phosphoric acid according to a molar ratio of 1:1 to 1:2 in the reaction kettle, adding an oxidizing agent, thoroughly reacting, heating the slurry to 80-100 DEG C, and aging for 2-3 hours; cooling a ferric phosphate slurry after the reaction, washing and performing tympanic membrane suction filtration, then conveying and drying to remove free water, and then removing crystal water through calcination to obtain the battery-grade ferric orthophosphate.
Owner:SHANDONG LUBEI ENTERPRISE GROUP
Cement filling material for co-solidifying arsenic and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a mine cement filling material for co-solidifying arsenious hazardous wastes and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the environment protection fields, such as the mine cement filling, solid waste resource utilization and the co-processing of the arsenious hazardous wastes. The preparation method comprises the following steps: milling the needed raw materials, such as mine slag, steel slag and desulfurization gypsum, with 0.01%-1% of the water content according to the dry basis weight percentage of 45%-50% of the mine slag, 10%-30% of the steel slag and 10-15% of the desulfurization gypsum, milling independently or milling by mixed powder until the specific surface area is 200-600 m<2> / Kg, adding 10%-35% of calcium hydroxide, uniformly mixing to obtain a cementing agent, and drying the arsenious hazardous wastes until the water content is 0.01%-1%, according to the weight proportion of the cementing agent / aggregate material of 1 / 4-1 / 8, the weight proportion of the arsenious hazardous wastes / (cementing agent + aggregate material) of 1 / 1000-1 / 100, adding 0%-1% of a water reducer, until the mass fraction of slurry is 65%-86%, and uniformly stirring to obtain the qualified mine cement filling material. The preparation method has the characteristics of simple and easy operation, low energy consumption, low cost, no new solid waste generation, small environmental pollution, and environmental protection.
Owner:BEIJING BEIKE FANGXING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
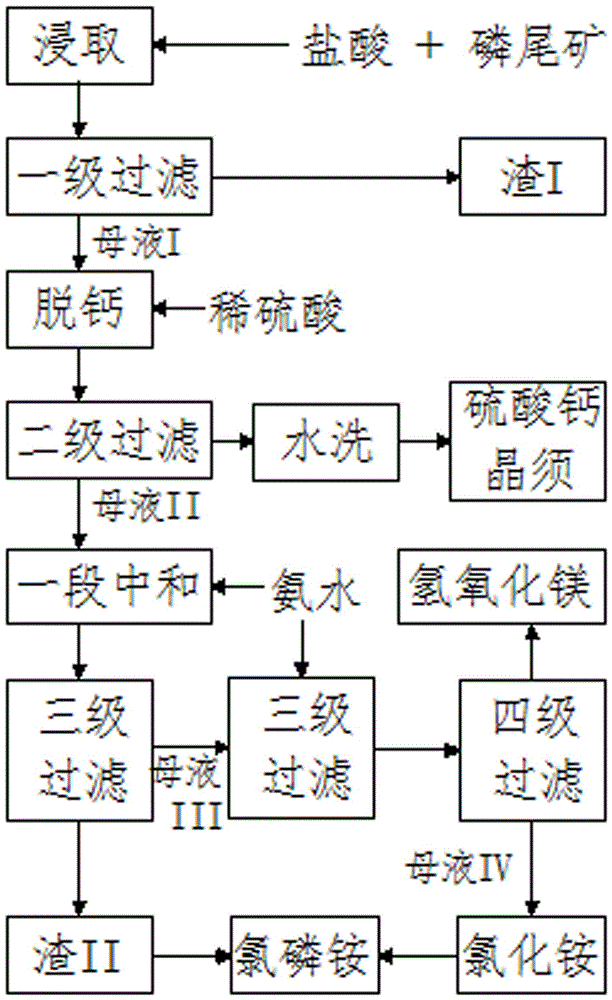
Method of decomposing phosphate tailings by hydrochloric acid to produce Mg(OH)2 and CaSO4
ActiveCN106495191ASolve unhandled problemsReduce pressure on environmental protectionCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesAmmonium salt fertilisersPhosphateRaw material
The invention belongs to the field of chemical engineering and particularly relates to a method of decomposing phosphate tailings by hydrochloric acid to produce Mg(OH)2 and CaSO4. The method includes the steps of: soaking the phosphate tailings in hydrochloric acid and water to perform a complete mixing reaction, and performing primary filtration to obtain a mother liquid (I); adding diluted sulfuric acid to the mother liquid (I) and performing secondary filtration to obtain a mother liquid (II) and filter cake, water-washing and crystallizing the filter cake to generate CaSO4 crystal whiskers; adding ammonia water to the mother liquid (II) to perform primary and secondary neutralization to obtain a Mg(OH)2 product and a mother liquid (IV); and mixing the mother liquid (IV) with residue (II), which is generated in primary neutralization, to produce ammonium chloride-phosphate. With the phosphate tailings and hydrochloric acid as raw materials, the method can produce the Mg(OH)2 and CaSO4 and can by-produce the ammonium chloride-phosphate. The whole process is simple and is in a total-closed circulating manner. The method can turn waste into resources and achieves clean production.
Owner:HUBEI SANNING CHEM
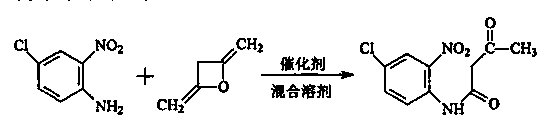
Green synthesis process for p-chloro-o-nitroacetoanilide
InactiveCN103408452AImprove solubilityNo need to crystallize againOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationSolubilityDiketene
The invention discloses a green synthesis process for p-chloro-o-nitroacetoanilide. The process comprises the following steps of mixing a novel mixed catalyst system and p-chloro-o-nitroaniline, and enabling the novel mixed catalyst system and the p-chloro-o-nitroaniline to dissolve, wherein the mole ratio of the p-chloro-o-nitroaniline to diketene is 1: (1.05-1.5); finishing the dropwise adding operation of the diketene within 3h; and continuing to react at the temperature of 90 DEG C for 4h to obtain the p-chloro-o-nitroacetoanilide. The solubility of the p-chloro-o-nitroaniline in a solvent is improved, the yield of products is high, the reaction time is shortened, the solvent dosage is reduced, and no solid wastes are generated.
Owner:JIANGSU LONGCHANG CHEM
Combined degradation treatment method of high-concentration high-polymerization-degree polyvinyl alcohol wastewater
ActiveCN111018081AEfficient degradationReduce difficultyWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by oxidationPolyvinyl alcoholHigh concentration
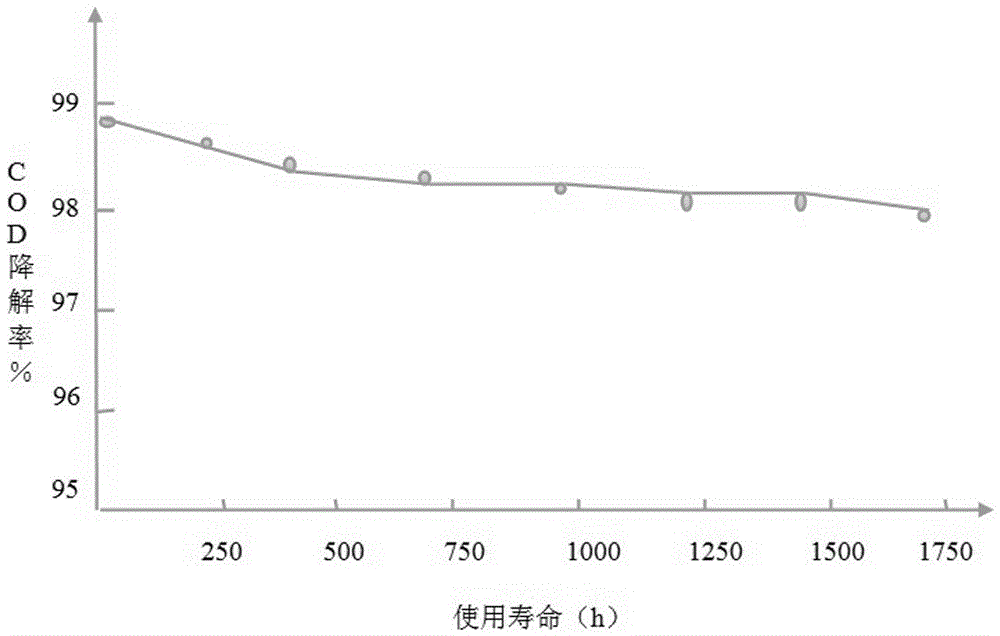
The invention provides a combined degradation treatment method of high-concentration high-polymerization-degree polyvinyl alcohol wastewater. According to the combined degradation method, a pre-oxidation-catalytic oxidation two-stage oxidation method is combined, firstly, the polymerization degree of polyvinyl alcohol in the wastewater is reduced to 200 or below through a pre-oxidation stage, andthen the polyvinyl alcohol with ultralow polymerization degree and high concentration in the wastewater is further subjected to catalytic oxidation degradation, so that the optimal degradation treatment effect is achieved. The combined degradation treatment method is mainly used for carrying out degradation treatment on wastewater with the polymerization degree of at least 500, the concentration of 10-45wt.% and completely dissolved polyvinyl alcohol, the COD value of the wastewater is reduced to be below 100mg / L in a short time, and the COD value removal rate is as high as 99.95%; and the combined degradation treatment method is relatively low in cost and suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:HUNAN TAOHUAJIANG NUCLEAR POWER +1
Preparation method of biodiesel
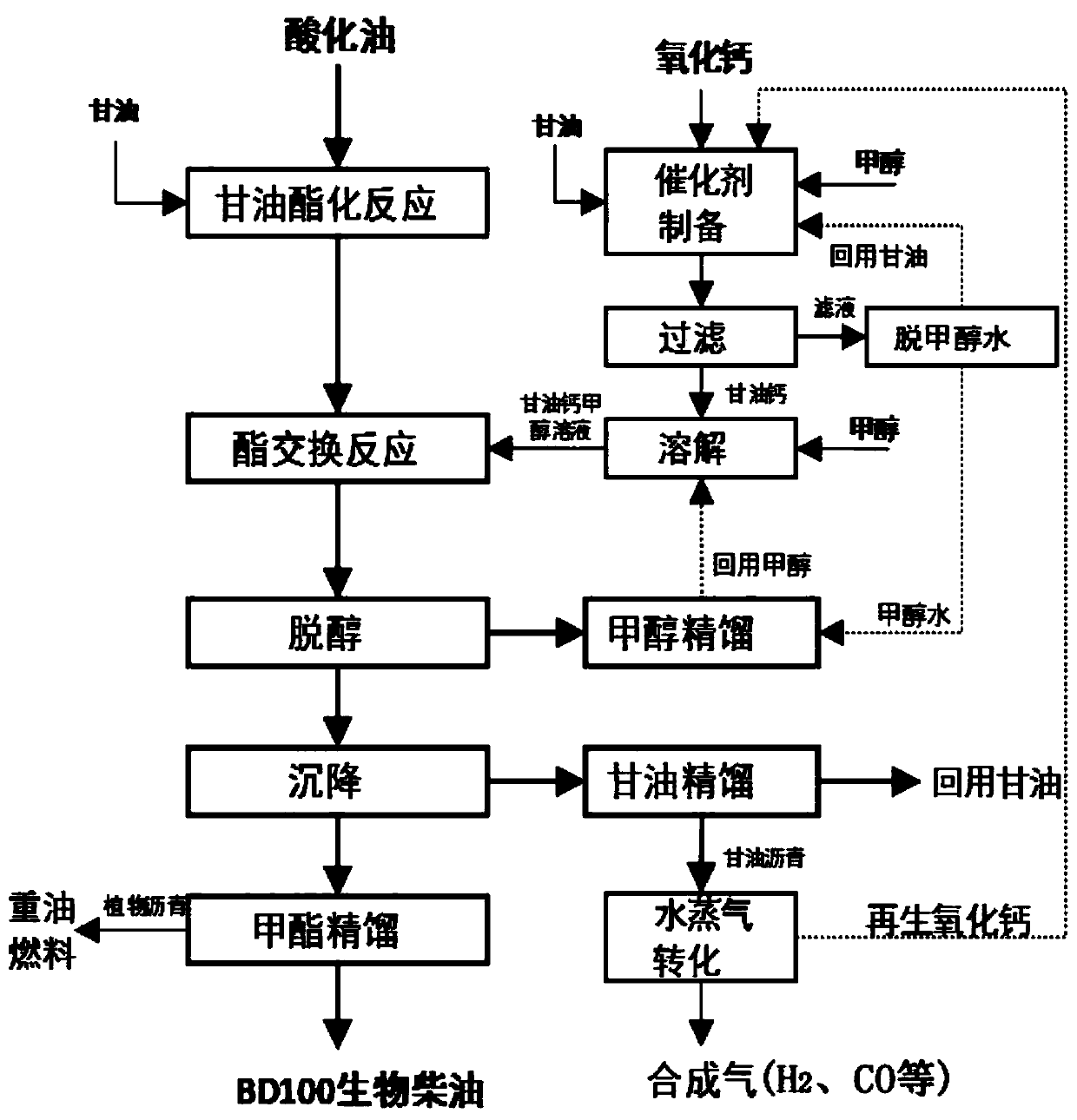
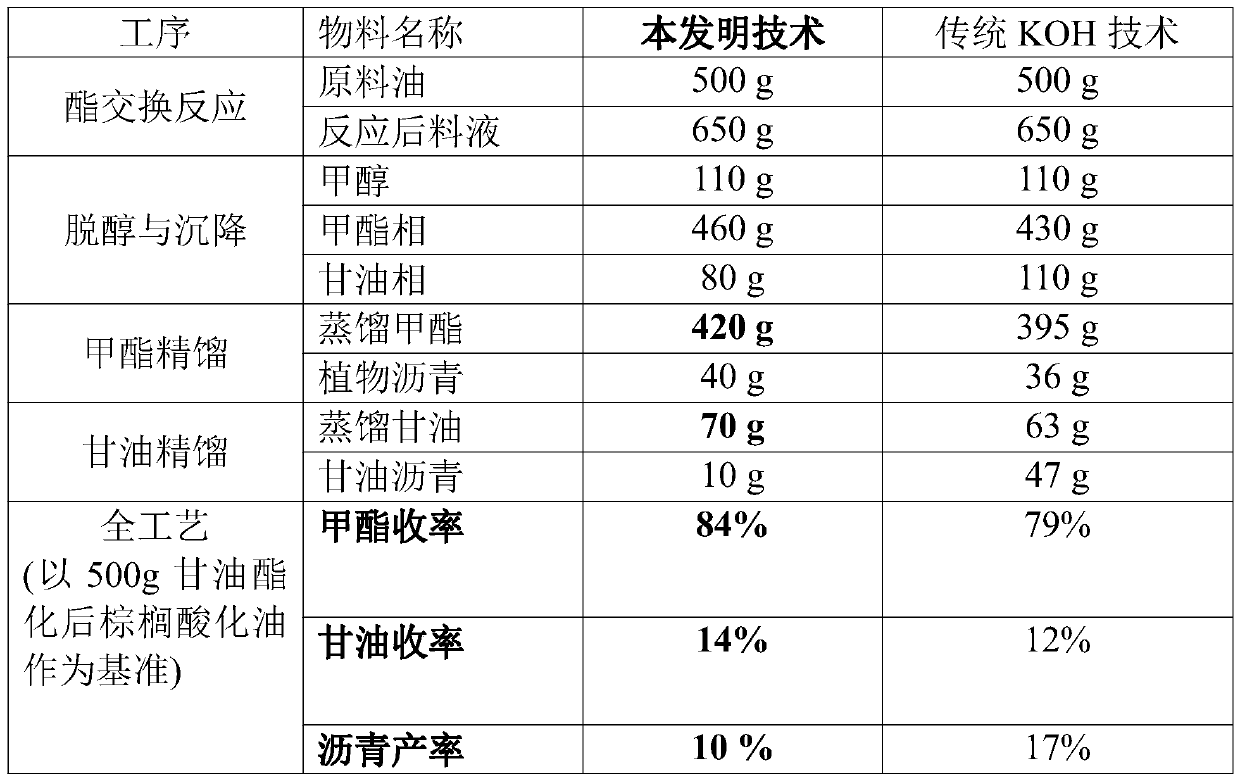
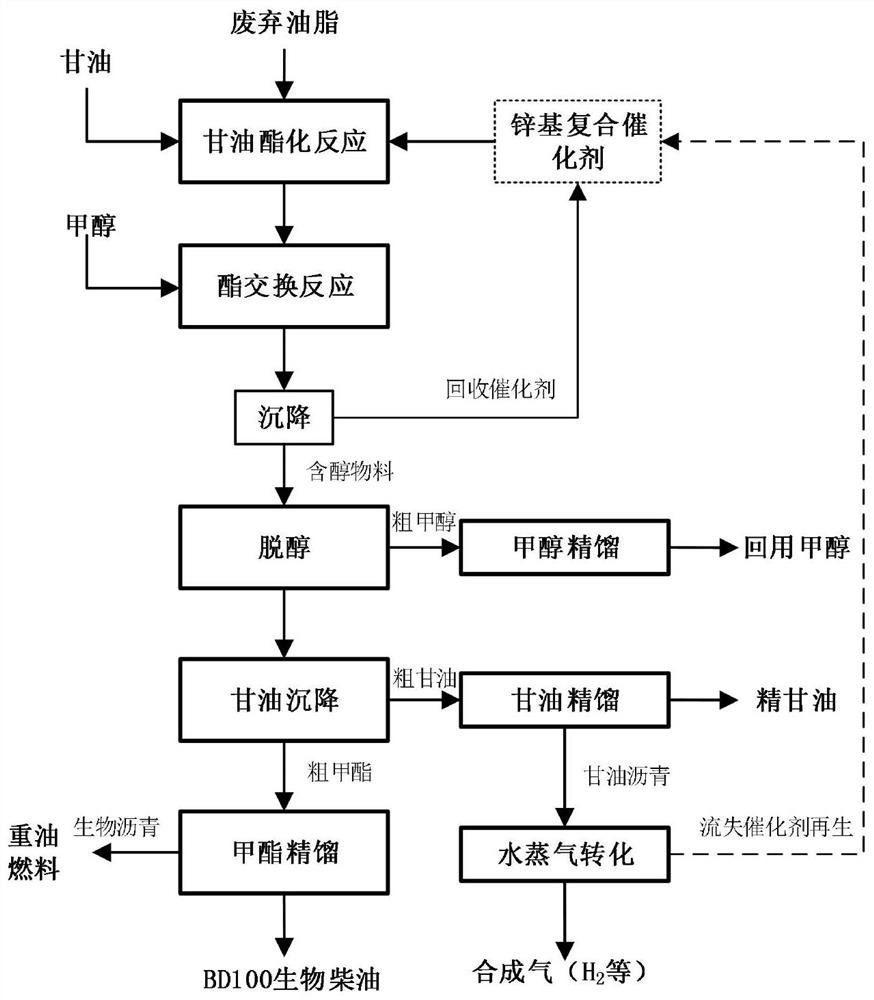
ActiveCN111500373AWide variety of sourcesHigh yieldFatty acid esterificationBiofuelsTrans esterificationPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of biodiesel. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out a glyceridation reaction, a transesterification reaction, dealcoholization, sedimentation and methyl ester rectification on raw material acid oil to obtain BD100 biodiesel, wherein calcium glyceroxide is used as a catalyst in the transesterification process; a calcium oxide solid formsa glycerol-calcium methanol solution through processes of catalyst preparation, filtration and dissolution, the glycerol-calcium methanol solution is used for catalyzing the transesterification reaction process of the acid oil, regeneration of calcium oxide is further realized through processes of dealcoholization, sedimentation, glycerol rectification and water vapor conversion, and the regenerated calcium oxide is reused for a catalyst preparation process. The method has the characteristics of low raw material requirement, wide application range, high product yield, no solid waste, wide catalyst raw material source, recyclability and the like, and is suitable for industrial production. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the BD100 biodiesel can be economically, greenly, efficiently and stably produced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
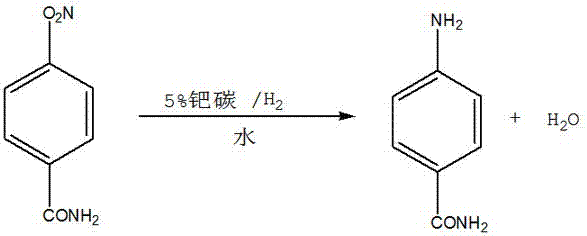
Synthesis method of 4-aminobenzamide
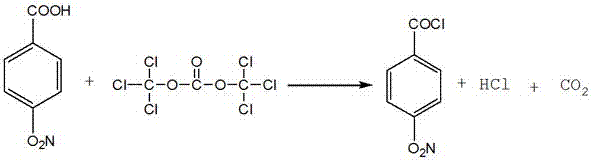
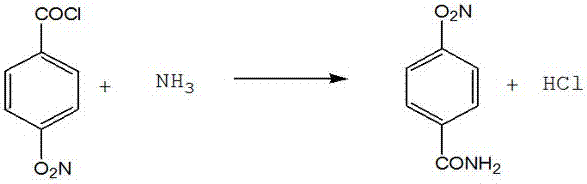
InactiveCN106946726AReasonable settingHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationSynthesis methodsPhosgene
The invention provides a method for synthesizing p-aminobenzamide, comprising the steps of: 1) taking a container, adding p-nitrobenzoic acid, triphosgene and a solvent, after the reaction is completed, collecting the solvent to obtain p-nitrobenzoyl chloride; ) take another reaction vessel, add ammonia and phase transfer catalyst, drop p-nitrobenzoyl chloride toluene solution to obtain p-nitrobenzamide; 3) take the reaction kettle, add p-nitrobenzamide, and add water, Catalyst, obtains described p-aminobenzamide. In the method, the amount of raw materials used is small and the reaction speed is fast. After the hydrogen chloride gas produced by the reaction is absorbed into hydrochloric acid by water, it can be used for other purposes, which effectively reduces the production cost. In the reduction reaction, the iron powder method is replaced by the hydrogenation method, so that the production The cost is reduced, no solid waste is generated, the labor load is greatly reduced, the process is environmentally friendly, and the economic benefit is good.
Owner:连云港恒贸化工有限公司
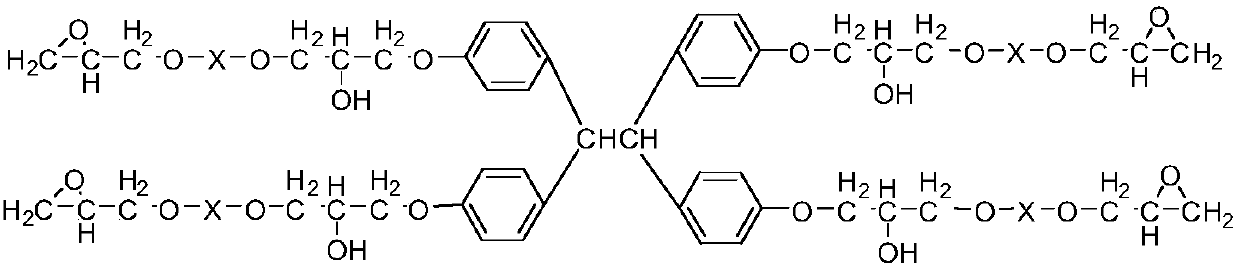
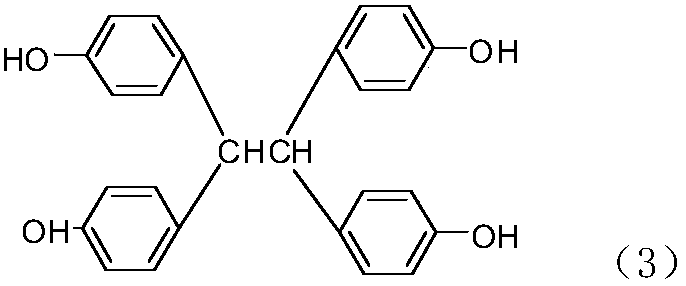
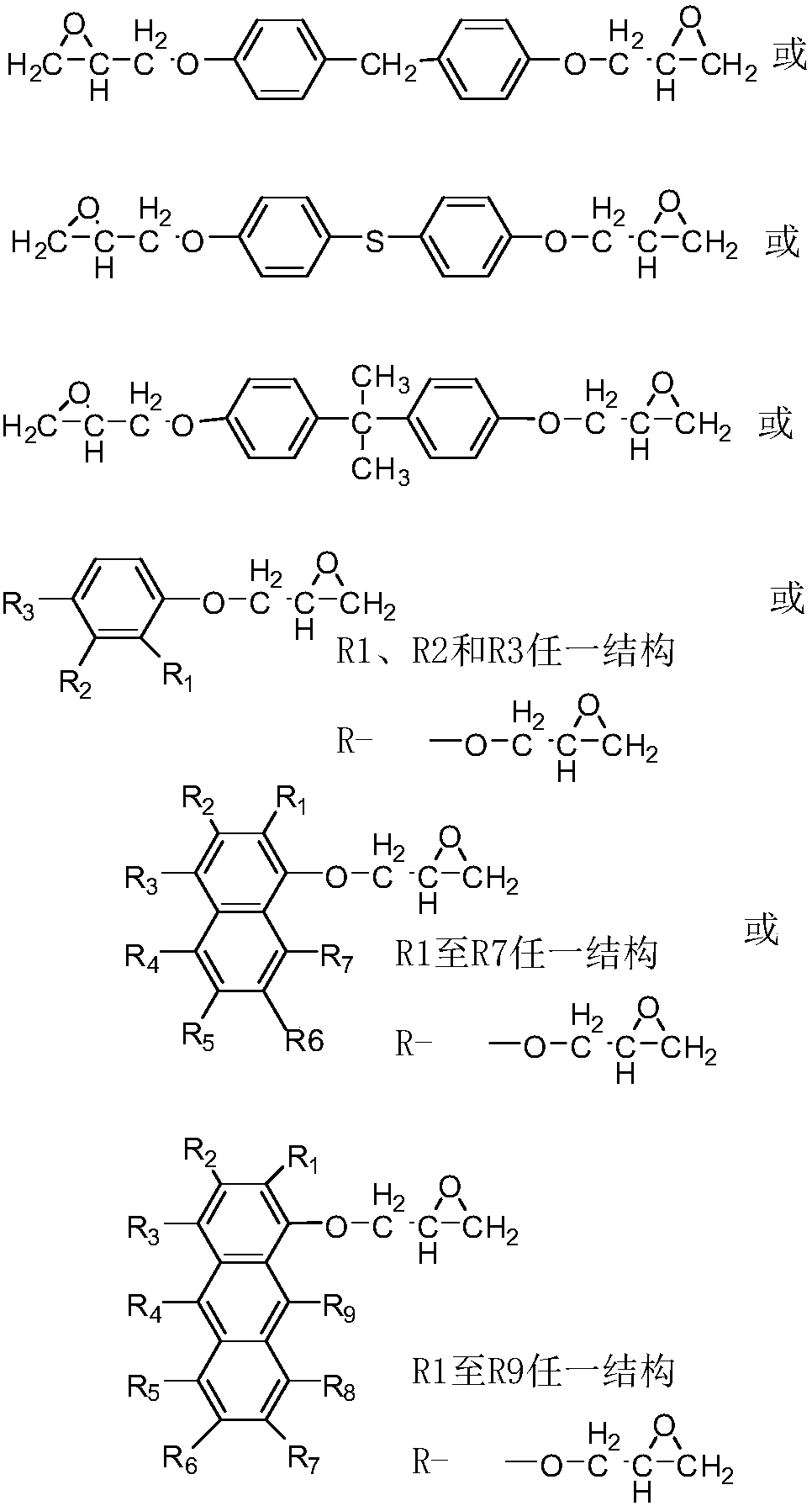
Tetrafunctional epoxy resin, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107935969ABlock ultraviolet light (UV)Block fluorescence propertiesOrganic chemistryEpoxyFluorescence
The invention relates to a novel tetrafunctional epoxy resin. The novel tetrafunctional epoxy resin has an ultraviolet light (UV) and fluorescence blocking function, and also has the advantages of short process route, small device investment, low energy consumption, low safety management difficulty and easy environmental protection based on the UV and fluorescence blocking function. The tetrafunctional epoxy resin can be compounded with any one or more epoxy resins to obtain epoxy resin with the UV and fluorescence blocking function, and also can be compounded with a curing agent to obtain a hardener.
Owner:建滔电子材料(江阴)有限公司
Method for treating washing wastewater of coal chemical industry
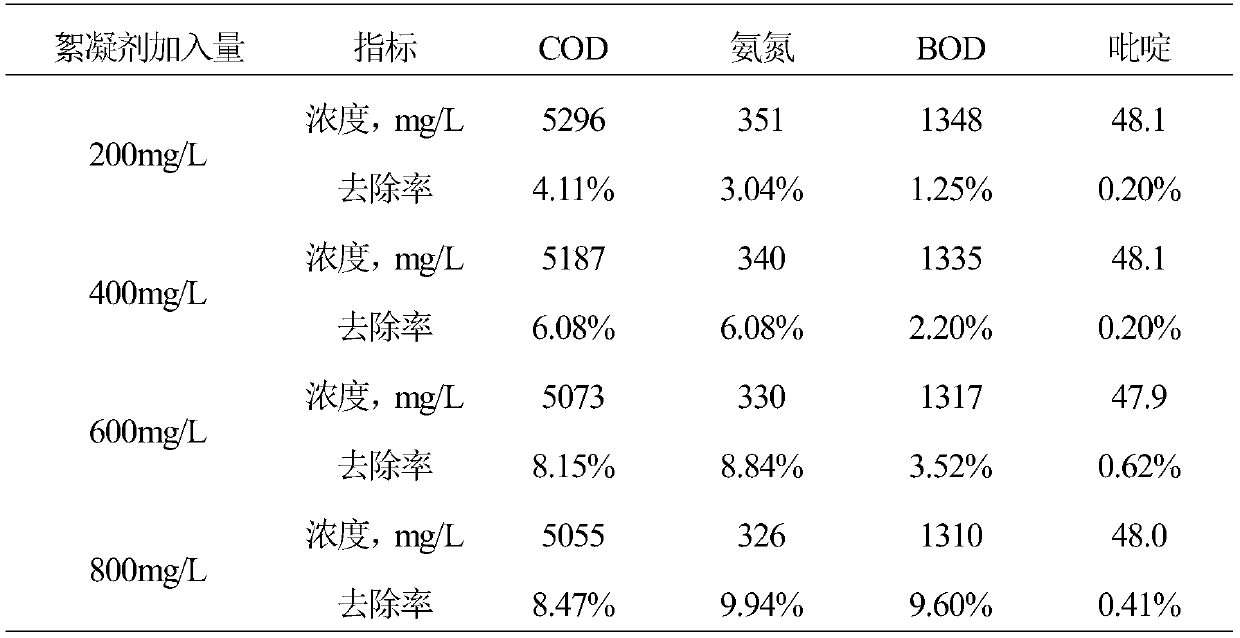
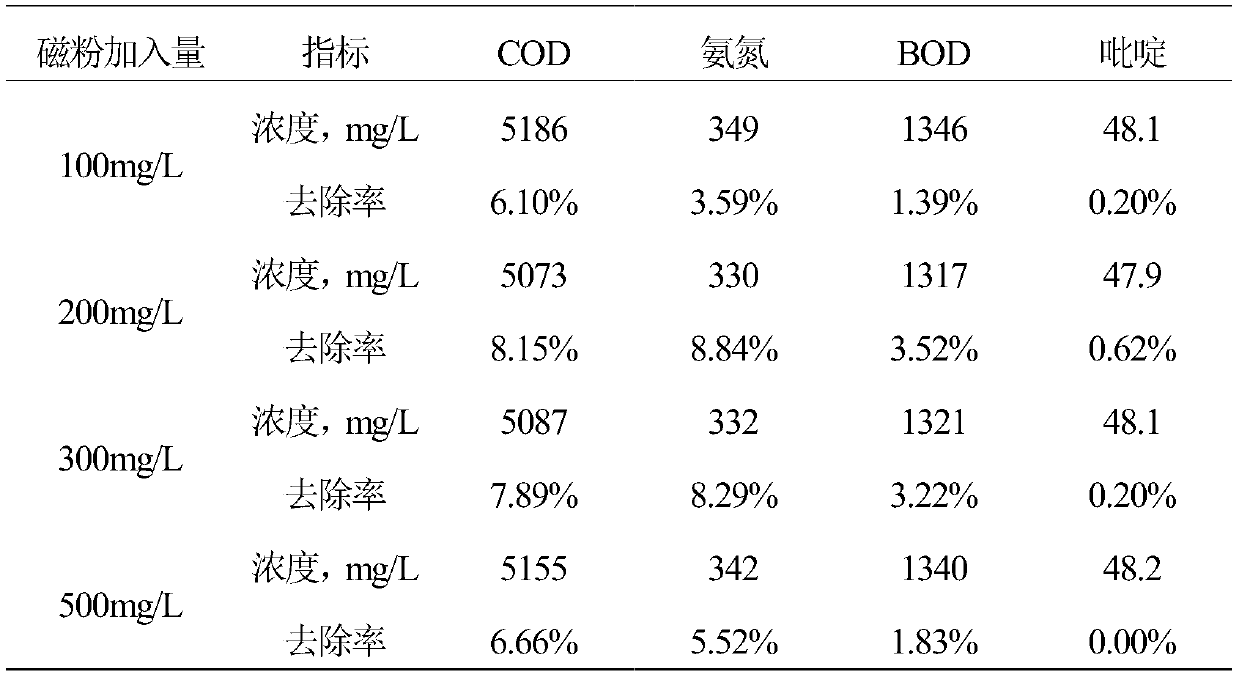
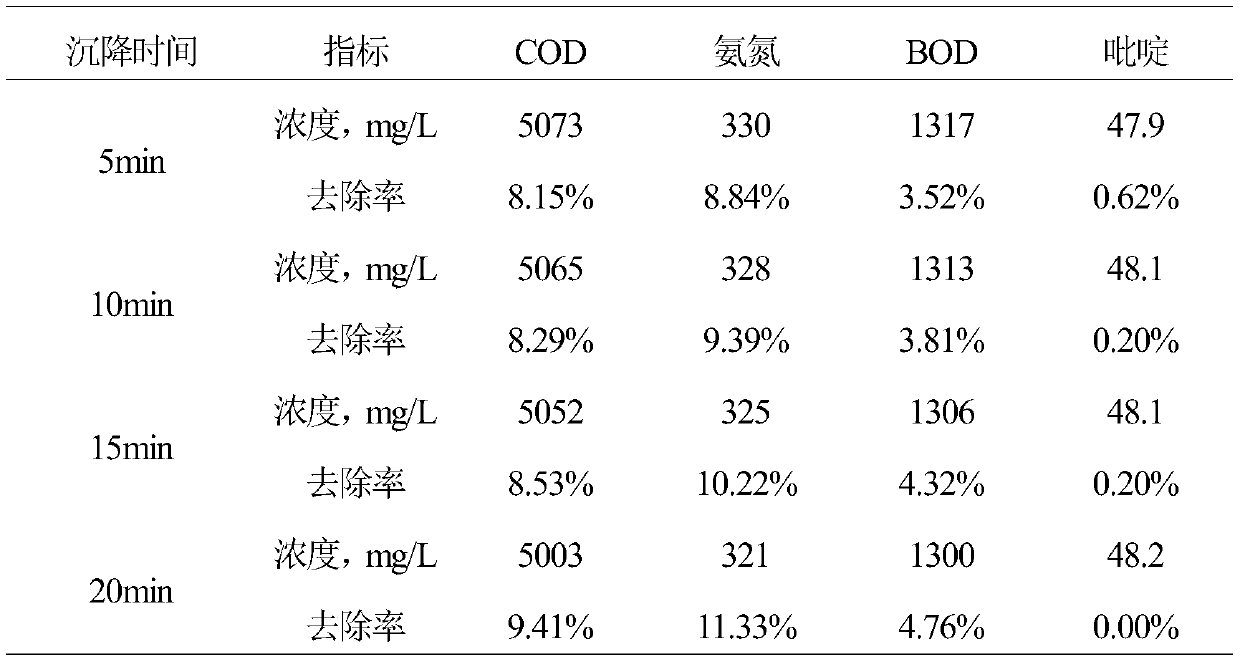
ActiveCN110759578AHigh densityIncrease settling velocityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsOrganic matter mineralizationSulfate radicals
The invention discloses a method for treating washing wastewater of coal chemical industry. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out partial removal on tar, suspended impuritiesand other macromolecular substances in the wastewater through a magnetic flocculation precipitation strengthening flocculation effect, then carrying out ultraviolet activated persulfate oxidation toexcite generation of sulfate radicals, effectively carrying out ring opening on refractory organic matters such as pyridine and quinoline to be decomposed into easily degradable substances such as allyl alcohol and acetamide, and thus improving the removal rate of the refractory organic matters and improving the biodegradability of the wastewater; reusing an photoelectric-Fenton oxidation method,producing a Fenton reagent by using an electrochemical method to treat the wastewater, and meanwhile, introducing ultraviolet light, wherein the ultraviolet light and Fe<2+> have a synergistic effecton the catalytic decomposition of H2O2, so that the decomposition rate is greatly improved, the refractory organic matters can be effectively treated, the degree of mineralization is high, secondary pollution cannot be generated, the operation is simple, the control parameters are only voltage and current, and the automatic control can be conveniently realized.
Owner:神美科技有限公司
Processing method of explosive wastewater
ActiveCN105936561AEnergy savingChemically stableWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsChemistryTitanium dioxide
The invention provides a processing method of explosive wastewater. The processing method comprises the following steps: (1) adjusting the pH value of explosive wastewater to 1-4 by acid, adding 0.05 to 0.5 M of persulfate, wherein persulfate accounts for 1 to 10 wt% of explosive wastewater, and evenly mixing; (2) placing an UV lamp in the explosive wastewater or on the surface of explosive wastewater, adding a copper-cerium modified titanium dioxide catalyst accounting for 5 to 30 wt% of explosive wastewater, carrying out aeration at the same time, and carrying out reactions for 2 to 12 hours; wherein the copper-cerium modified titanium dioxide catalyst is prepared by doping titanium dioxide by copper and cerium, and copper and cerium respectively account for 5 to 10 wt% and 10 to 20 wt% of titanium dioxide. The processing technology is simple, the cost is low, the maintenance is convenient, and the explosive wastewater can be recycled only through one step. Moreover, persulfate is taken as the oxidant, no secondary pollution or solid waste is generated; the service life of catalyst is long, and the catalyst can be continuously used and does not need regeneration.
Owner:HUNAN YONKER ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION RES INST +1
Preparation method of battery-grade iron phosphate
The invention provides a preparation method of battery-grade iron phosphate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding high-purity iron powder into hydrochloric acid with a proper concentration, and carrying out a reaction until the iron powder is not dissolved any more; filtering, adding a proper amount of hydrogen peroxide, and reacting until no ferrous ions exist in the reaction solution; adding phosphoric acid, uniformly stirring, and carrying out spray drying to obtain iron phosphate dihydrate; and sintering at a high temperature to remove crystal water to obtain anhydrous iron phosphate. According to the invention, the method comprises the steps of ferrous solution synthesis, oxidation, ferric phosphate dihydrate synthesis and high-temperature sintering, so that the procedures of ferric phosphate precipitation, aging, filtering, washing and the like are reduced, the procedures are reduced, the flow is shortened, the production period is shortened, the production efficiency is improved, water resources are saved, and the cost is low; the raw materials are recycled, no solid waste is generated, and the cost is reduced; and a neutralizer is not needed, the useof raw materials is reduced, the opportunity of impurity introduction is reduced, the obtained product is high in purity and low in impurity content, and the market requirements of battery-grade rawmaterials can be well met.
Owner:博创宏远新材料有限公司
Trimming-free novel flexible foam rubber and plastic heat insulation product and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a trimming-free novel flexible foam rubber and plastic heat insulation product and a preparation method thereof. By adopting a multi-roll calender and additionally arranging an excess material recovery device in an extrusion and trimming process, the surface of a product is smooth, and the side surface of the product is not trimmed and has no broken holes. The interior of the novel flexible foam rubber and plastic heat insulation product is uniform in foaming, the surface of the product is smooth and has no die lines, the novel flexible foam rubber and plastic heat insulation product has high tear strength, the edges are comfortable, and the transverse thickness is uniform. The product is not trimmed and has no broken holes, a broken hole heat dissipation channel is plugged, so that vacuum water absorption and heat conductivity coefficient are lowered and the heat insulation effect is improved. Furthermore, the product is not trimmed, thus improving the raw material use efficiency, lowering the cost, generating no solid waste, and being beneficial to environment conservation, energy conservation and emission reduction.
Owner:HEBEI HUAMEI CHEM & BUILDING MATERIALS GRP
Method for preparing long-chain fatty diacid monobenzyl ester and application of long-chain fatty diacid monobenzyl ester
ActiveCN111333505ASimple and fast operationEasy to purifyPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganic compound preparationEngineeringEnvironmental engineering
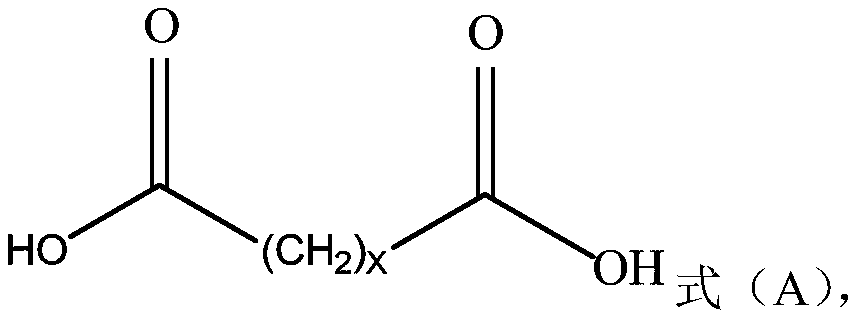
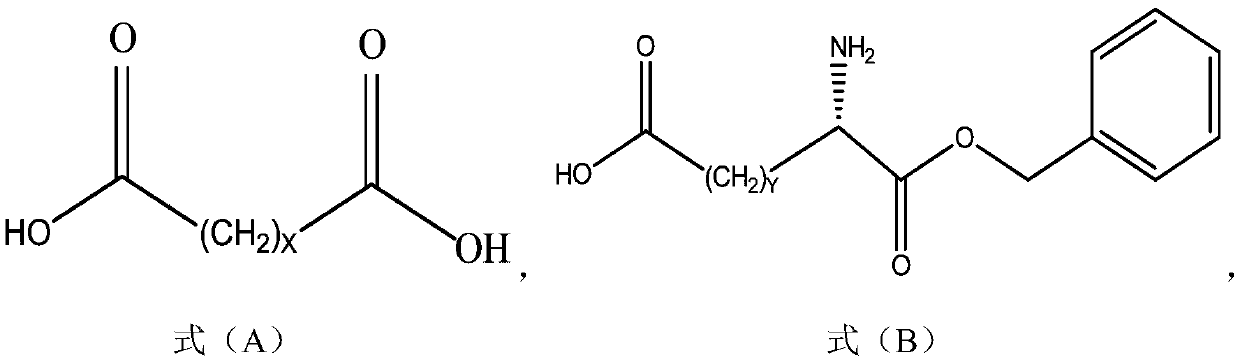
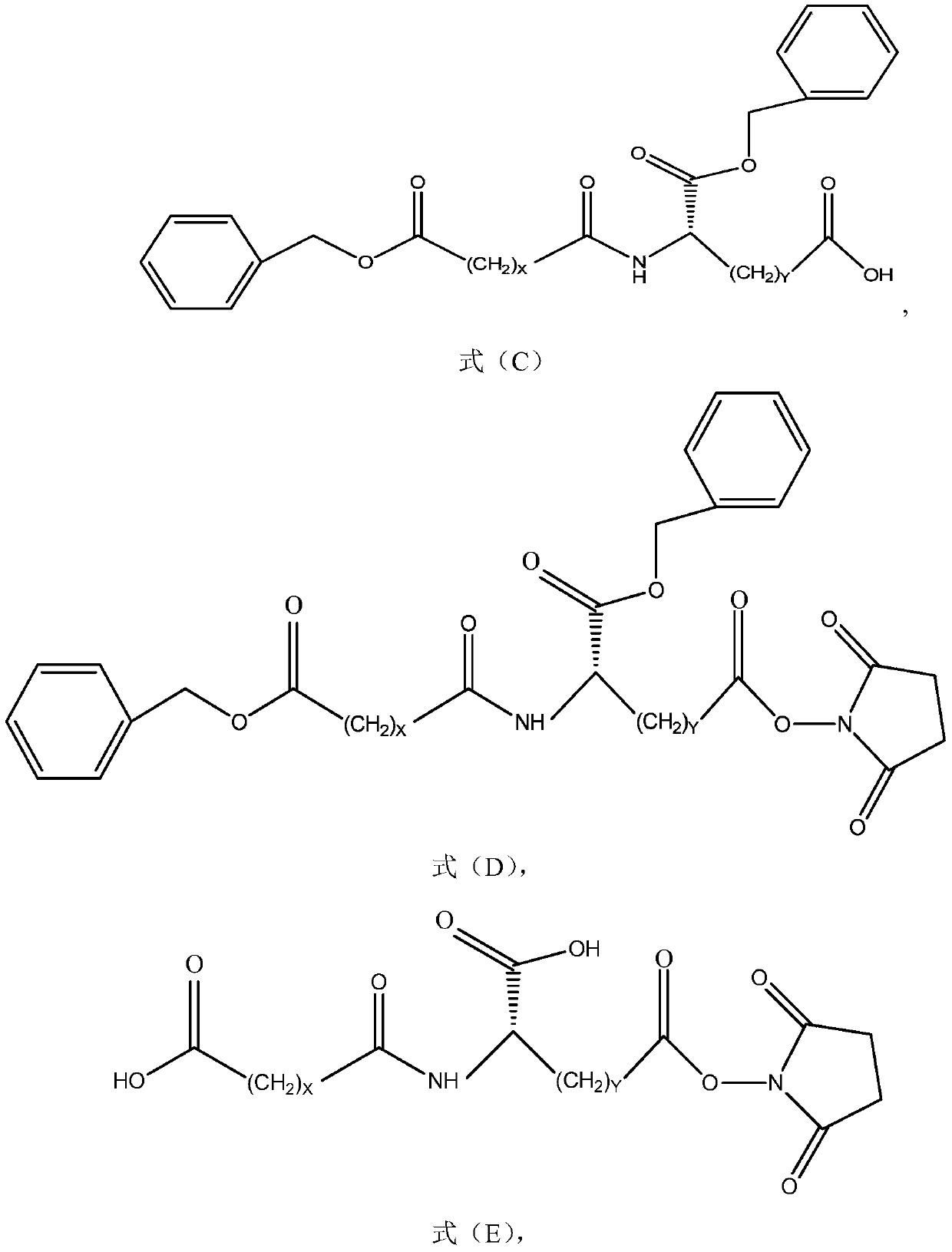
The invention provides a method for preparing long-chain fatty acid monobenzyl ester. The method comprises the following steps: 1) carrying out esterification reaction on long-chain fatty diacid to obtain long-aliphatic chain dibenzyl ester; and 2) carrying out hydrolysis reaction on the long-aliphatic chain dibenzyl ester to obtain long-chain fatty diacid monobenzyl ester; wherein the long-chainfatty diacid has a structure shown as formula (A), and X is an integer of 6-32. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of cheap and easily available reaction reagent, simple operation, low product related impurity content, simple intermediate purification, short production period, high yield, low cost, little generated waste liquid, no generation of solid waste and low environmental protection pressure.
Owner:DONGGUAN HEC BIOPHARMACEUTICAL R&D CO LTD +1
Method for producing intensive bus ducts
InactiveCN104354002AReduce temperature riseGuaranteed work efficiencyOther manufacturing equipments/toolsBusbarEngineering
The invention discloses a method for producing intensive bus ducts. According to the method for producing the intensive bus ducts, disclosed by the invention, the intensive bus ducts are riveted into a whole through dedicated riveting equipment, a riveting technology of the dedicated riveting equipment is verified through a tension test, 4000-N tension force can be borne by riveting bodies of shells of the intensive bus ducts, the riveting bodies can be separated by a tension force which is greater than 4000N, and the riveting strength is reliable; riveting contact surfaces are in close contact while the riveting strength is reliable, the effect of heat transfer during load operation of the intensive bus ducts is enhanced, the temperature rise of the intensive bus ducts during normal use is effectively reduced, the electric conductivity of a busbar of the intensive bus ducts is increased, the working efficiency of the intensive bus ducts is ensured, and looseness due to vibration during transit cannot be generated.
Owner:JIANGSU HUAPENG INTELLIGENT ELECTRICAL
Treatment method of spray washing water in activated carbon production process
InactiveCN109205916AEfficient removalTo achieve the purpose of secondary useWater/sewage treatmentMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationPersulfate
The invention discloses a treatment method of spray washing water in an activated carbon production process, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment, and the method includes: 1, chemical precipitation, to be more specific, adding magnesium ions to form a precipitate, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain a liquid phase entering the next step for treatment; 2, magneticflocculation and sedimentation, to be more specific, adding a flocculant and magnetic powder for flocculation and sedimentation, and performing magnetic separation to obtain a liquid phase entering the next step for treatment; and 3, persulfate oxidative degradation, to be more specific, adding a persulfate for reaction, wherein after the reaction is sufficient, macromolecular organic matters arebasically removed, and ammonia nitrogen and total phosphorus contents are low, and residual organic matters are small molecular components. The treatment method is used for treating the spray washingwater containing a large amount of tar and phosphoric acid and a relatively high concentration of the ammonia nitrogen in the activated carbon production process, can effectively remove the higher concentration of the ammonia nitrogen and total phosphorus in wastewater, and has high efficiency, simple process and reaction, mild and easy-to-control conditions and other characteristics.
Owner:ZHEJIANG QICAI ECO TECH CO LTD
Continuous preparation method of alicyclic epoxy compound
ActiveCN113444058AHigh reaction conversion rateHigh reaction yieldOrganic chemistryChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsMicroreactorEmulsion
The invention provides a continuous preparation method of an alicyclic epoxy compound. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, continuously introducing alicyclic olefin and a hydrogen peroxide aqueous solution into a micro-emulsifier for emulsification to form an emulsion, the concentration of the hydrogen peroxide aqueous solution being greater than or equal to 8wt%; s2, continuously introducing the emulsified liquid into a microreactor for oxidation reaction to obtain a crude product mother solution; and S3, purifying the crude product mother liquor to obtain the alicyclic epoxy compound. According to the preparation method, the dynamic micro-channel reactor is adopted, the homogeneity of the reaction system is ensured through the combination of the micro-emulsifier and the micro-reactor, and the problem of poor mixing effect is avoided, so that relatively high reaction conversion rate and yield of alicyclic epoxy compound preparation can be realized by adopting the low-concentration hydrogen peroxide aqueous solution as the oxidizing agent. Besides, a continuous operation process is adopted, so that the process is small in danger, safe and controllable.
Owner:CHANGZHOU TRONLY ADVANCED ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CO LTD +1
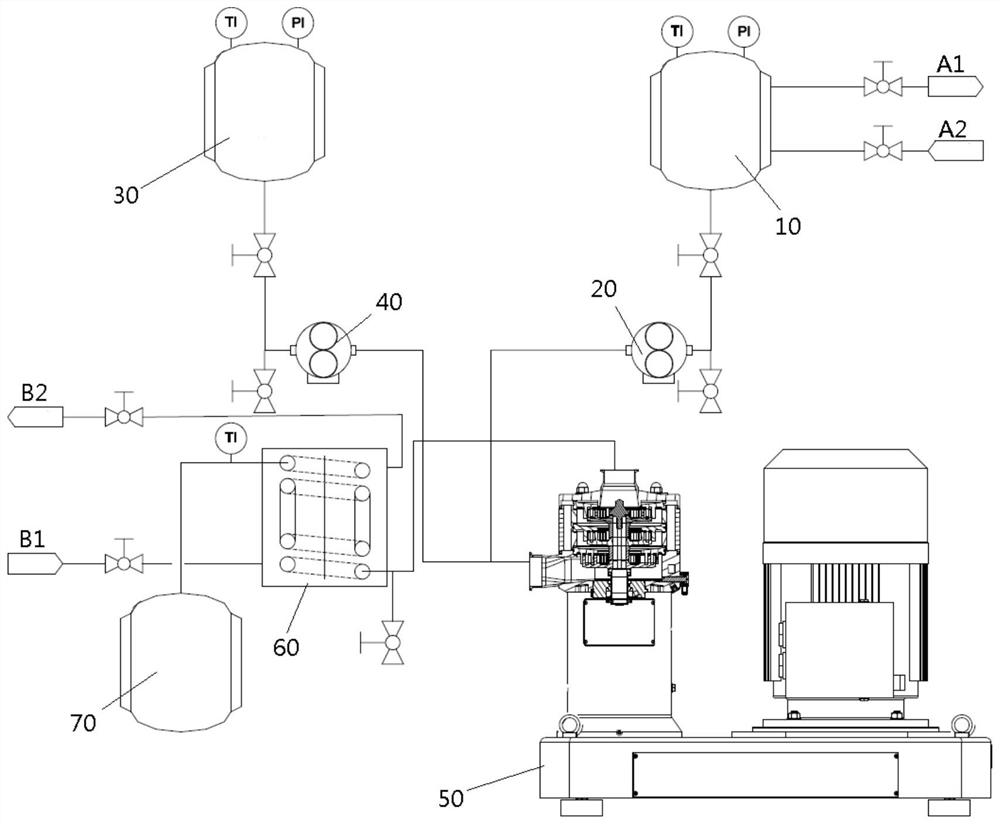
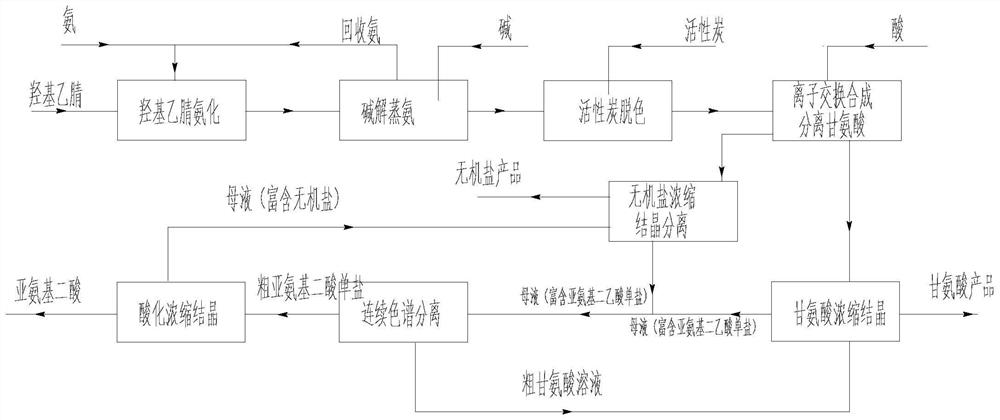
Production process of glycine
PendingCN113563215ASuitable for industrial productionReduced unevenness coefficientOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationIminodiacetic acidInorganic salts
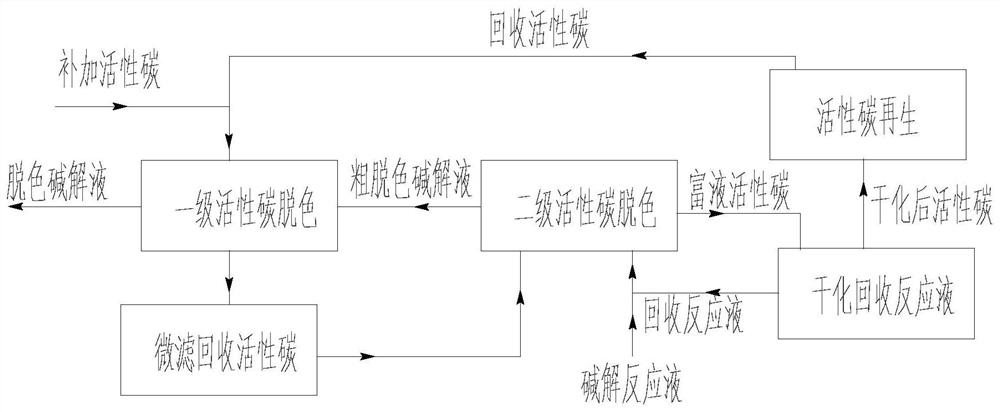
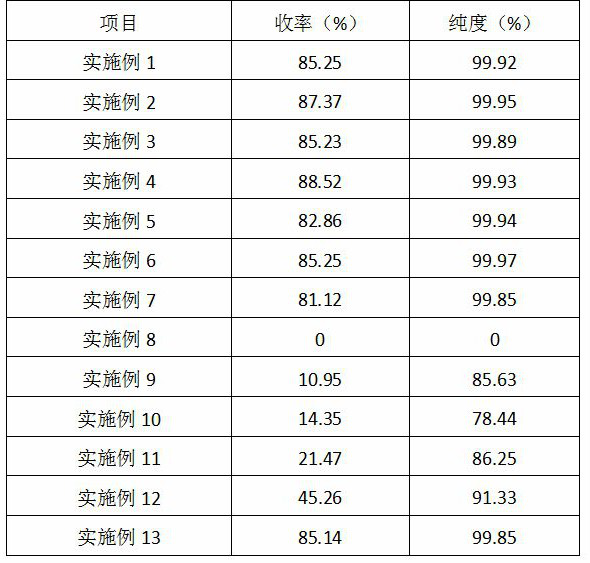
The invention discloses a production process of glycine. The production process comprises the following steps of: S1, performing ammonification; S2, performing alkaline hydrolysis ammonia distillation; S3, performing decolorizing with activated carbon; S4, performing ion exchange acidification separation, specifically, performing ion exchange reaction on metal ions of discolored glycinate and H < + > on ion exchange resin to generate glycine, discharging the glycine out of a system along with an aqueous solution, performing ion exchange reaction on iminodiacetic acid disalt and the H < + > to generate iminodiacetic acid monosalt, adsorbing the iminodiacetic acid monosalt on the resin, discharging the iminodiacetic acid monosalt and an inorganic salt solution generated in a resin regeneration process out of the system; S5, concentrating and crystallizing glycine, and when the iminodiacetic acid monosalt in circulating mother liquor is accumulated to 10% or above of the total solute, pumping out the mother liquor, concentrating and crystallizing the inorganic salt, and when iminodiacetic acid monosalt in the solute of the circulating mother liquor is accumulated to 15% or above of the total solute, extracting the mother liquor; S6, mixing the extracted mother liquor, and carrying out continuous chromatographic separation; and S7, recycling the iminodiacetic acid. The production process of the glycine provided by the invention has good glycine synthesis and separation effects.
Owner:SHANGHAI LANKE PETROCHEM ENG & TECH
Preparation method of 2, 3-dipicolinic acid
InactiveCN112794816AHigh yieldImprove adsorption capacityOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesActivated carbonSorbent
The invention relates to the field of fine chemical synthesis, in particular to a preparation method of 2, 3-dipicolinic acid. According to the method, oxygen is adopted to oxidize quinoline under the reaction pressure of 2-4 MPa in the presence of sulfuric acid and copper sulfate, the finished product of 2, 3-dipicolinic acid is obtained through filtration, alkali fusion, decoloration, acid pickling and drying, waste liquid generated in the reaction can be directly applied to the production process of 2, 3-dipicolinic acid, and the yield is increased to 83% or above. According to the method, the magnetic activated carbon prepared from the cotton straw is adopted as the adsorbent to perform decoloration and impurity removal on the 2, 3-dipicolinic acid crude product, the adsorption effect is good, the 2, 3-dipicolinic acid product is a white crystal, and the product purity is as high as 99.97%.
Owner:SINOCHEM HEBEI FUHENG CO LTD
Method for producing zinc oxide for ceramic glaze by using hot-dip galvanized ash
The invention discloses a method for producing zinc oxide for ceramic glaze by using hot-dip galvanizing ash, which comprises the following steps: wet ball milling, filtering to remove iron, wet dechlorination, drying and calcining, wherein zinc in the hot-dip galvanizing ash is recovered in the form of zinc oxide which can be directly applied to the ceramic glaze. According to the method, the dechlorinated zinc ash is directly dried and calcined to prepare a zinc oxide product, high-temperature reduction volatilization and reoxidation are not needed, the recovery rate of zinc is increased and can reach 99%, meanwhile, a large amount of energy materials such as high-quality anthracite (or coke powder) are saved, the production cost is reduced, and good economic benefits are achieved; and the production process is clean and environment-friendly, no solid waste is generated in the whole process, no smoke is discharged, zero wastewater is discharged, good environment-friendly benefits are achieved, and the prepared zinc oxide is large in specific gravity, good in flowability, low in volatile matter and capable of being directly applied to the ceramic glaze industry.
Owner:李发武
Device and method for removing organic sulfur and inorganic sulfur in coal gas by wet process
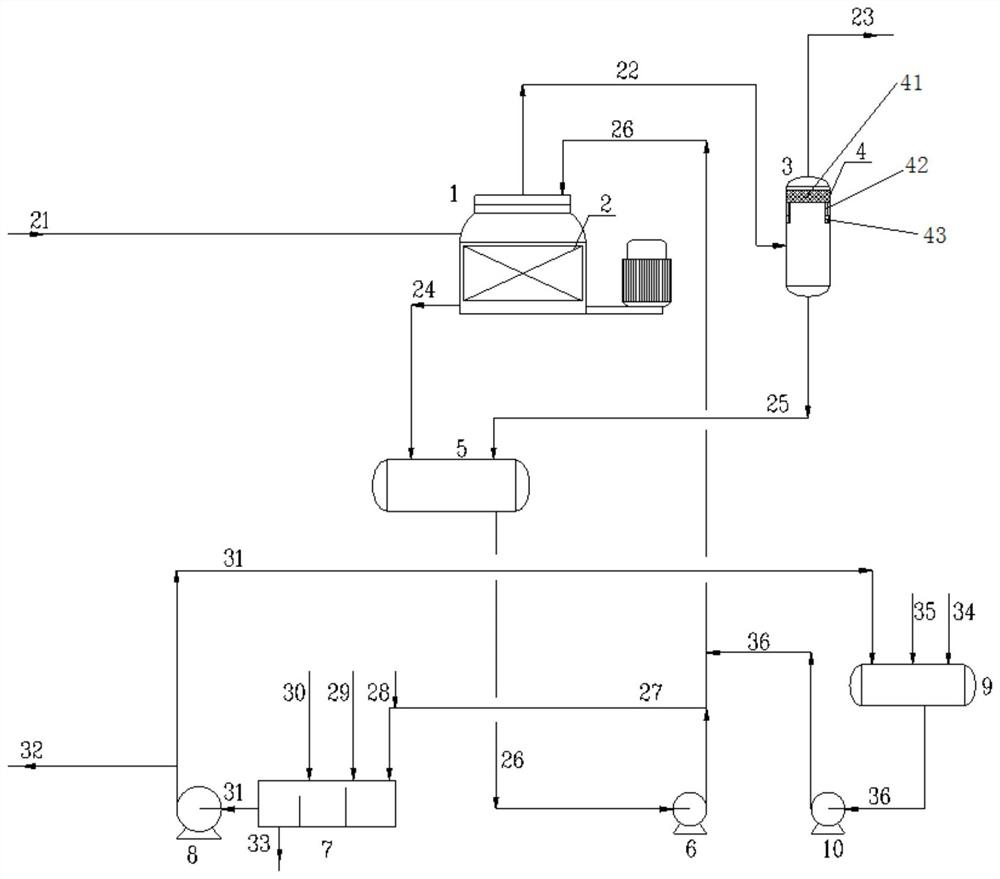
PendingCN114456850AAvoid pressure lossSolve the pressure lossGas contaminants removalGas dust removalPtru catalystExhaust fumes
The invention discloses a device and a method for removing organic sulfur and inorganic sulfur in coal gas by a wet method. The device comprises a supergravity rotating bed, a coal gas liquid removal tank, a blade separator, a desulfurizing agent buffer tank, a desulfurizing agent sedimentation tank and a fresh desulfurizing agent preparation tank, the method comprises the following steps: S1, removing organic sulfur and inorganic sulfur in sulfur-containing coal gas; s2, treating and utilizing the desulfurized rich desulfurizer; and S3, removing liquid drops entrained in the desulfurized coal gas, and recovering the desulfurizer. The device and the method can solve the problems of large gas pressure loss, high energy consumption, high desulfurization cost and difficulty in solid waste treatment in a dry desulfurization process, and the problems of short service life of a solid hydrolysis catalyst, high desulfurization cost and difficulty in waste liquid treatment in a semi-dry desulfurization process, so that the effects of short process route, small equipment quantity, low device investment, simplicity and convenience in operation and low cost are achieved. The treated coal gas has no pressure loss, the liquid desulfurizing agent is automatically and continuously replaced, no waste gas or solid waste is generated, and the desulfurization cost is low.
Owner:NINGBO ZHANGFU ENERGY TECH CO LTD
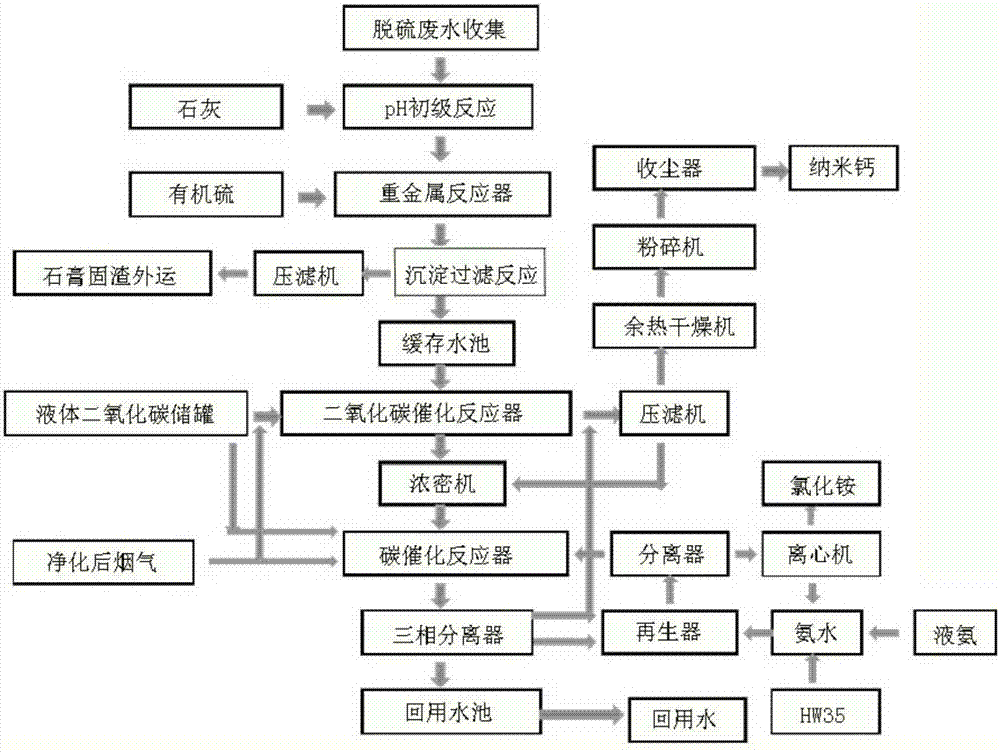
Desulfurization wastewater zero discharging process with carbon dioxide method
InactiveCN107459054ASolution can not be recycledSolve the high concentration of chloride ionsCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesNanotechnologyWastewaterFluoride
The invention provides a desulfurization wastewater zero discharging process with a carbon dioxide method. The process comprises the following steps: collecting desulfurization wastewater; performing a pH primary reaction; adjusting the pH value to an alkaline condition by adding lime, so as to precipitate magnesium ions, fluoride ions, sulfate ions and heavy metal ions; finally, enabling chlorine ions and ammonia gas to react through an organic substance catalytic reaction, so as to obtain an ammonium chloride product. According to the process, the problem that the wastewater cannot be recycled as the desulfurization wastewater is high in the content of chlorine ions is solved.
Owner:WUHAN HAOPUNENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION EQUIP ENG
Method for reducing dehydrolincomycin in lincomycin hydrochloride
InactiveCN108409812AEasy to recycleNo solid waste generatedSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationHydrogenation reactionLincomycin Hydrochloride
The invention discloses a method for reducing dehydrolincomycin in lincomycin hydrochloride, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, dissolving lincomycin hydrochloride in purified water with the weight of 2 to 4 times of the weight of the lincomycin hydrochloride to obtain an aqueous solution; S2, adding a Raney nickel catalyst with the weight of 1 / 10 of the weight of the lincomycin hydrochloride to the aqueous solution of the step S1; S3, introducing hydrogen into the aqueous solution of the step S2 for reaction for 6-8h to obtain a reaction liquid; S4, filtering the reaction liquid to filter out the Raney nickel catalyst to obtain a filtrate; S5, using purified water to wash the reaction liquid attached to the surface of the Raney nickel catalyst away to obtain a washing liquid; and S6, combining the filtrate and the washing liquid, and crystallizing to obtain the lincomycin hydrochloride; the method adopts the Raney nickel catalyst for hydrogenation reaction, the cost issuccessfully reduced, and the method is suitable for industrial production; the hydrogenation reaction is carried out under normal pressure, and the safety production coefficient is improved.
Owner:XINYU PHARM CO LTD
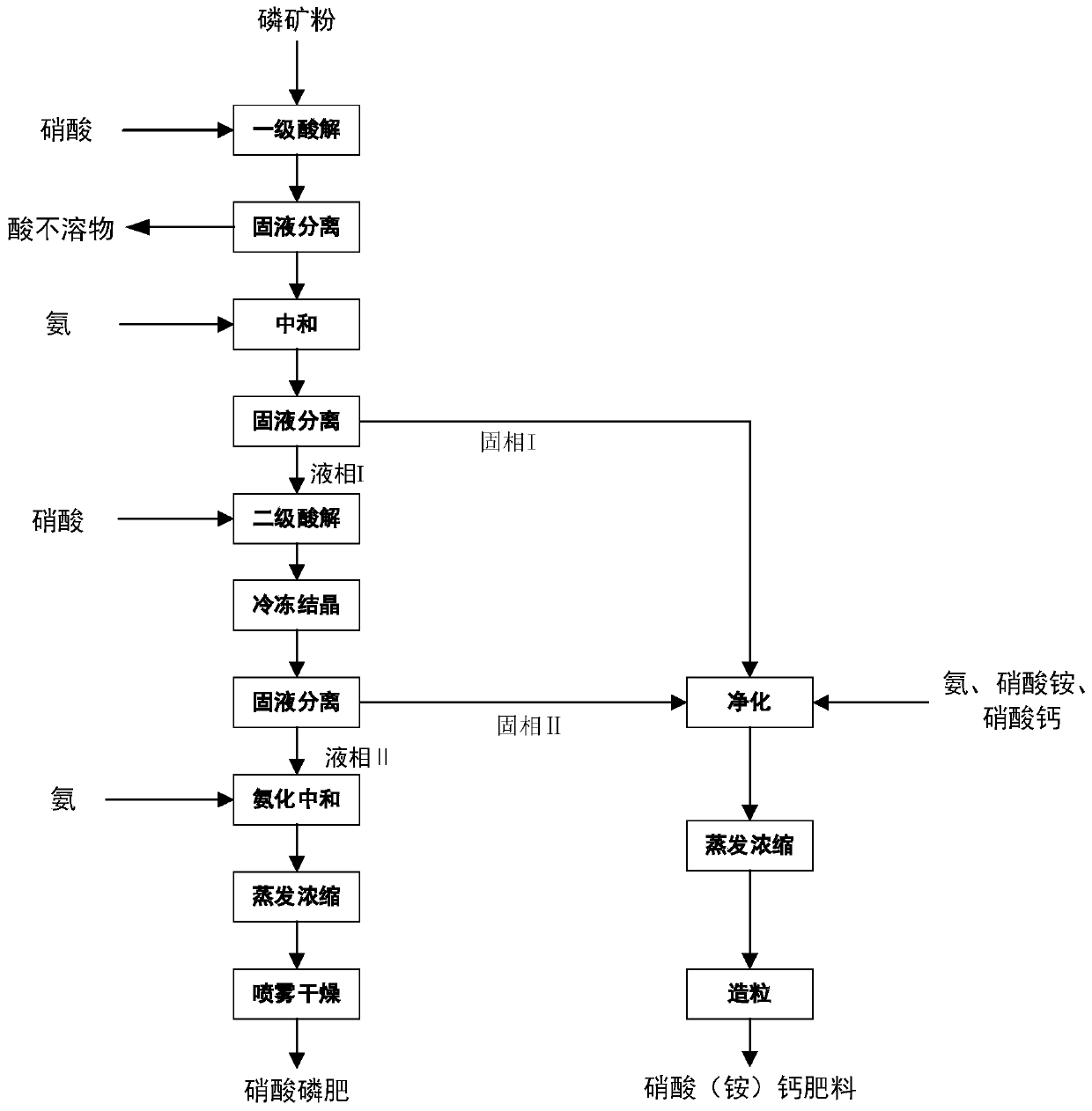
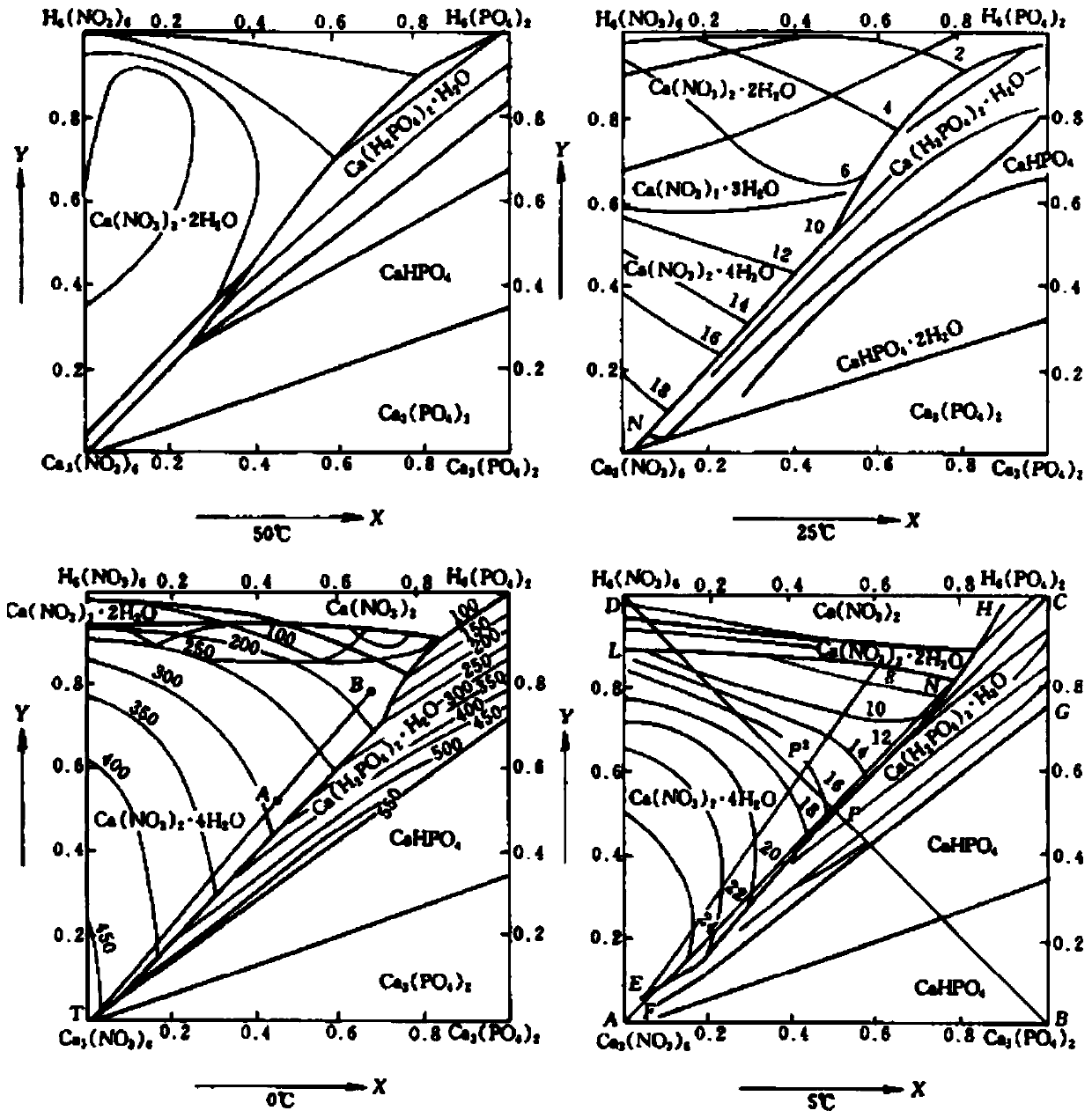
Separation method of P and Ca in medium-low-grade phosphorite and method for producing fertilizer
ActiveCN111517832AHigh element utilizationGood economic benefitsAmmonium nitrate fertilisersNitrate fertilisersFertilizerAgricultural engineering
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
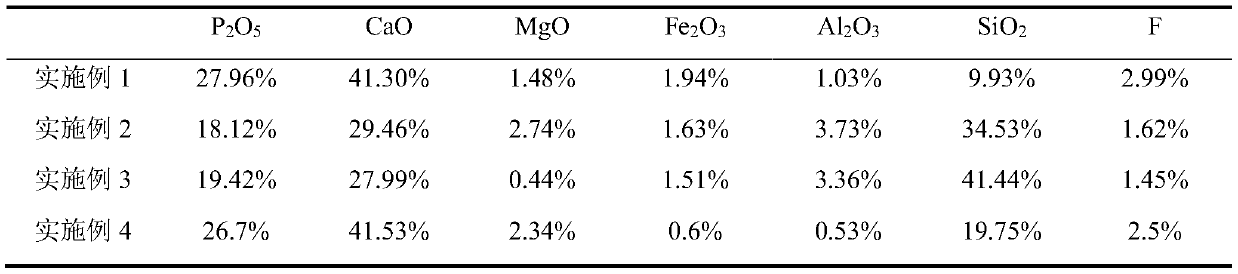
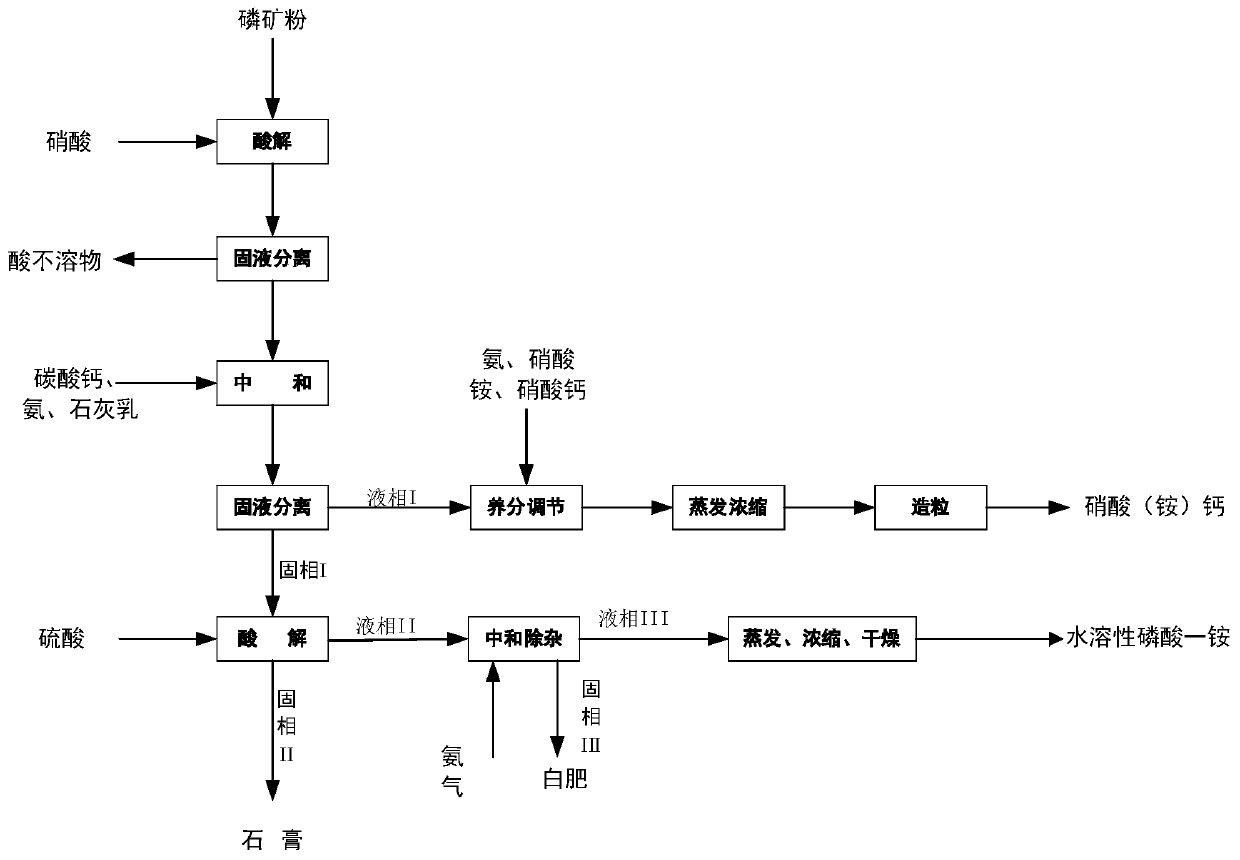
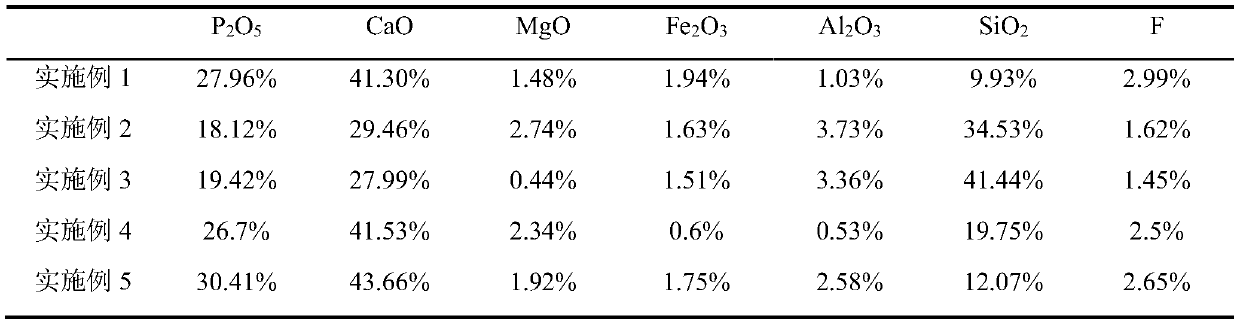
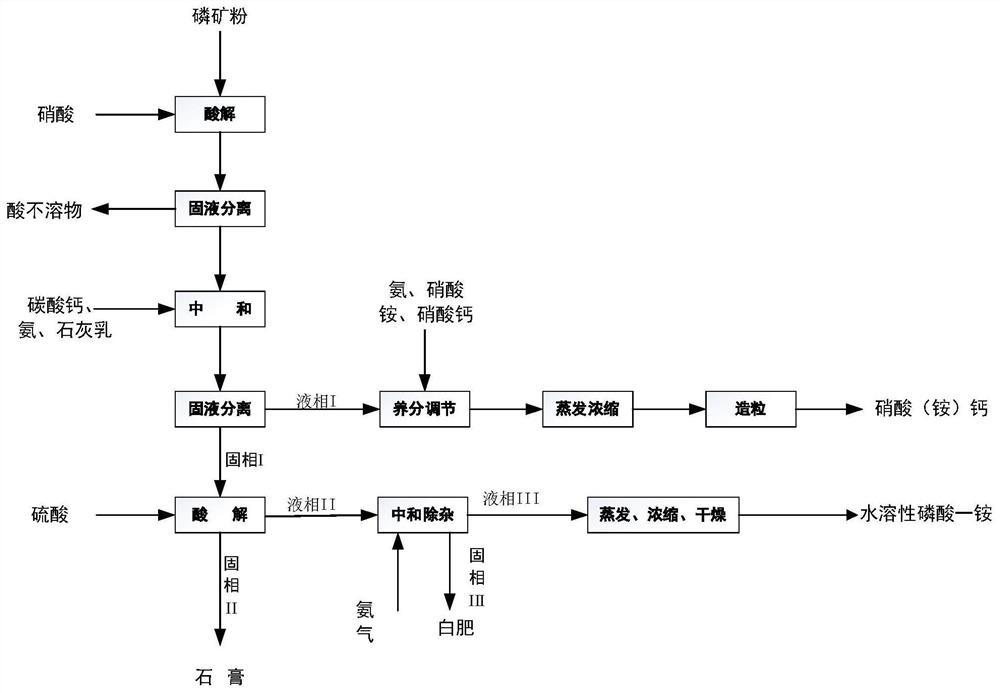
Production method of water-soluble monoammonium phosphate
ActiveCN111533099AIncrease profitHigh purityPhosphatesAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserFluid phasePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a production method of water-soluble monoammonium phosphate, and belongs to the technical field of phosphorite clean processing and utilization. The method comprises the following steps: a. mixing nitric acid and phosphorite, reacting at 30-70 DEG C for 0.5-2 hours, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain an acidolysis solution; b, neutralizing the acidolysis solution until the pH value is 6.5-8, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain a solid phase I and a liquid phase I; c, mixing the solid phase I with a sulfuric acid solution, reacting at 30-70 DEG C for 0.3-2 hours, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain a solid phase II and a liquid phase II; neutralizing the liquid phase II until the pH value is 4.0-4.5, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain a solid phase III and a liquid phase III, wherein the liquid phase III is processed to obtain the water-soluble monoammonium phosphate. According to the method, phosphorusand calcium in phosphorite are completely separated, the utilization rate of calcium, phosphorus and other elements is greatly increased, and water-soluble monoammonium phosphate can be directly produced.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for preparing biodiesel from waste oil
ActiveCN114410383ARealize integrated catalysisImprove universalityHydrogenFatty acid esterificationOil and greasePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for preparing biodiesel from waste grease. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out low-temperature glyceride esterification reaction, transesterification reaction, dealcoholization, glycerol sedimentation and methyl ester rectification on the raw material waste grease to obtain BD100 biodiesel; wherein the low-temperature glyceride esterification reaction procedure and the ester exchange reaction procedure both adopt a composite zinc catalyst, and the composite zinc catalyst can be directly recovered through settling separation; wherein the composite zinc catalyst is obtained by taking a zinc-containing compound, fatty acid and glycerol as reaction raw materials, reacting and then filtering. On the basis of the acid-base homologous active center of zinc, integrated catalysis of glycerol esterification and ester exchange reaction processes is realized, and the method has the characteristics of low raw material requirement, wide application range, high product yield, easiness in glycerol recovery, no generation of solid waste, recyclability and reusability of the catalyst and the like, and is suitable for industrial production. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the BD100 biodiesel can be economically, green, efficiently and stably produced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A kind of production method of water-soluble monoammonium phosphate
ActiveCN111533099BIncrease profitHigh purityPhosphatesAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserFluid phasePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a production method of water-soluble monoammonium phosphate, which belongs to the technical field of clean processing and utilization of phosphate rock. A method for producing water-soluble monoammonium phosphate, comprising the following steps: a. mixing nitric acid and rock phosphate, reacting at 30-70°C for 0.5-2 hours, and separating solid and liquid to obtain an acidolysis solution; b. and until the pH is 6.5-8, solid-liquid separation, solid phase I and liquid phase I are obtained; c, solid phase I and sulfuric acid solution are mixed, 30-70 ° C for 0.3-2h, solid-liquid separation, solid phase II and Liquid phase II; neutralize the liquid phase II until the pH is 4.0-4.5, and then separate the solid and liquid to obtain solid phase III and liquid phase III; wherein, the liquid phase III is water-soluble monoammonium phosphate after processing. The method of the invention completely separates phosphorus and calcium in the phosphate rock, greatly improves the utilization rate of elements such as calcium and phosphorus, and can directly produce water-soluble monoammonium phosphate.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Flue gas desulfurization system and flue gas desulfurization method
ActiveCN111298627ARealize resource utilizationReduce pollutionGas treatmentDispersed particle separationSodium metabisulfiteSulfite salt
The invention discloses a flue gas desulfurization system and a flue gas desulfurization method, and belongs to the field of chemical engineering. According to the method, sodium alkali is adopted asan absorbent to by-produce sulfates, the purity of a main product is controllable, the typical byproducts such as sodium sulfate, sodium sulfite, sodium metabisulfite and the like belong to a large number of commodities in the market and easily enter the commodity market, no solid waste or waste liquid is generated, and the environmental protection benefit is good. According to the invention, through reasonable process layout, sodium sulfite can be directly produced by intermittently bypassing the evaporative crystallization system, so that 20-50% of steam consumption can be saved under the same working medium; and the novel evaporative crystallizer is adopted, so that the operation flexibility of the evaporative crystallization system is improved, and the industrial problem that the evaporative crystallization system is frequently started and stopped and is high in energy consumption is solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com