Patents
Literature
74results about How to "Avoid a lot of time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
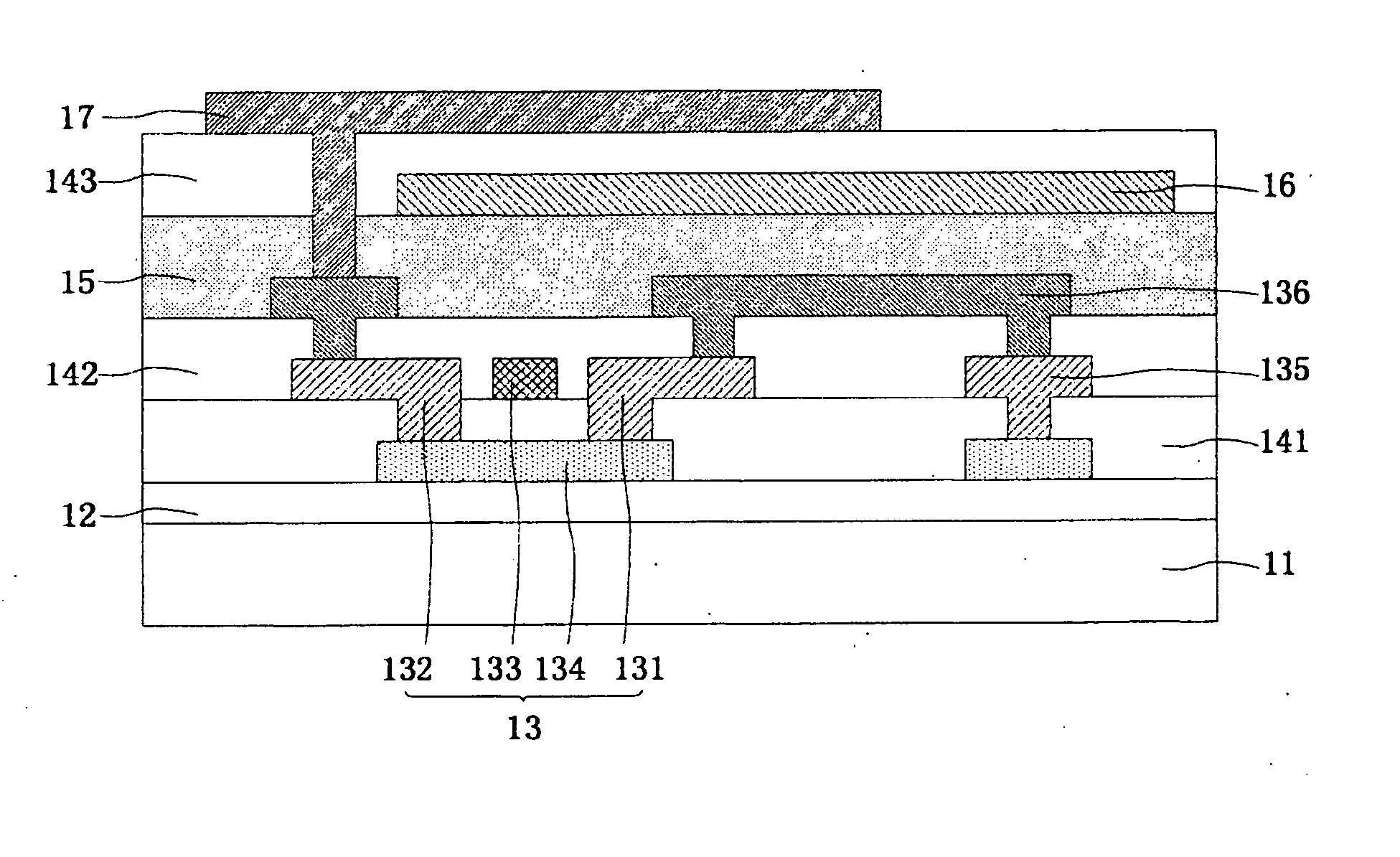
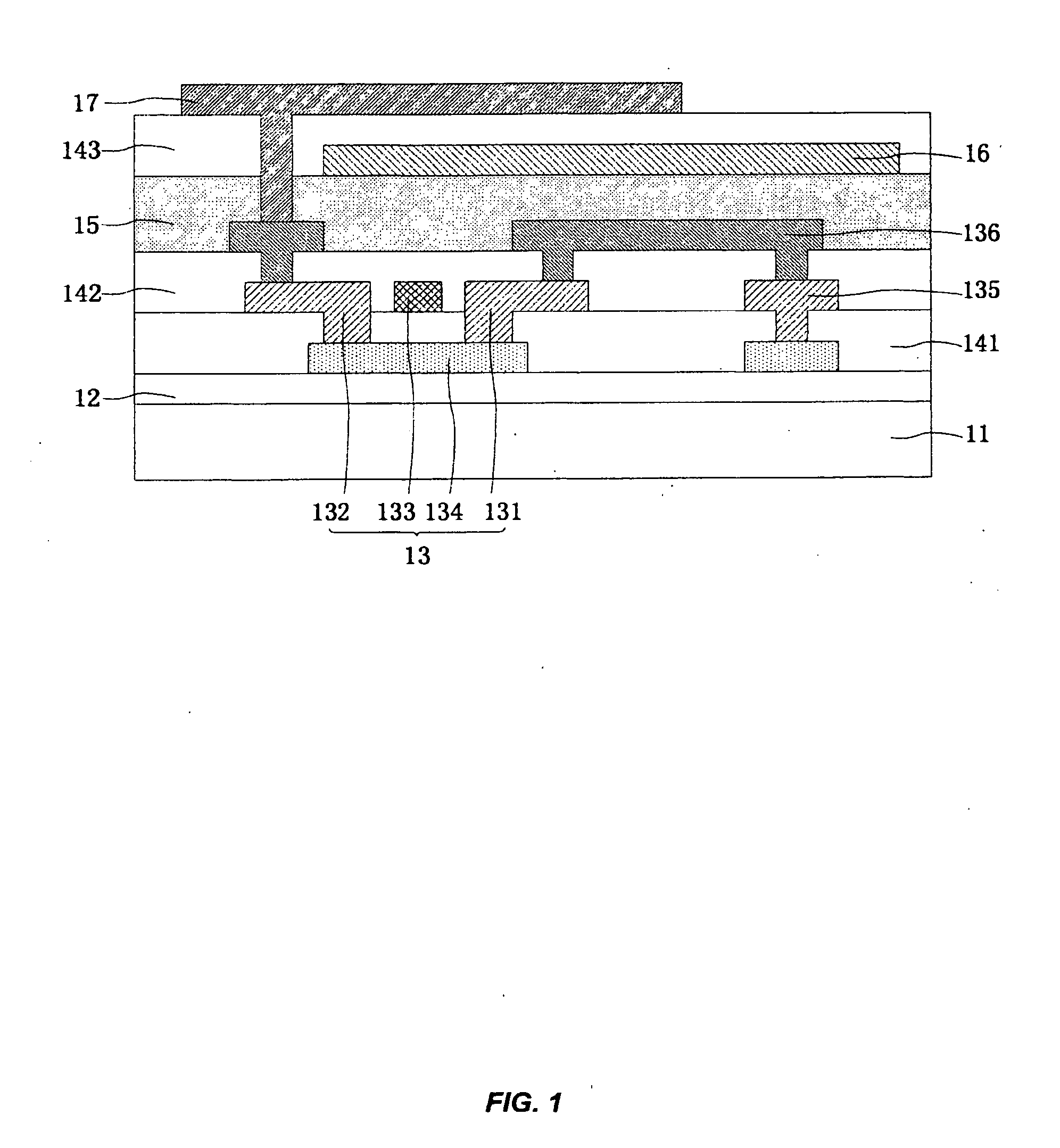
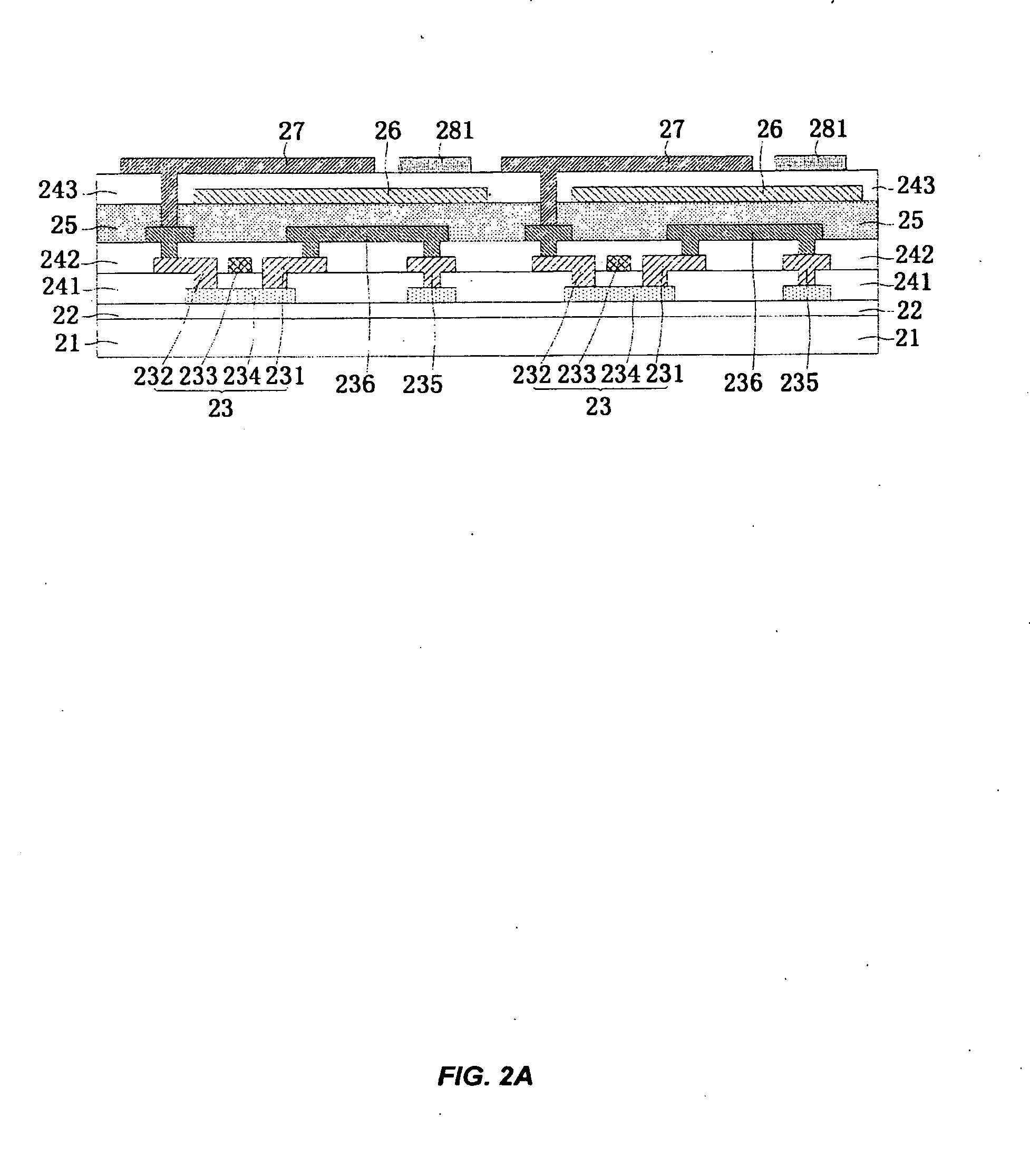
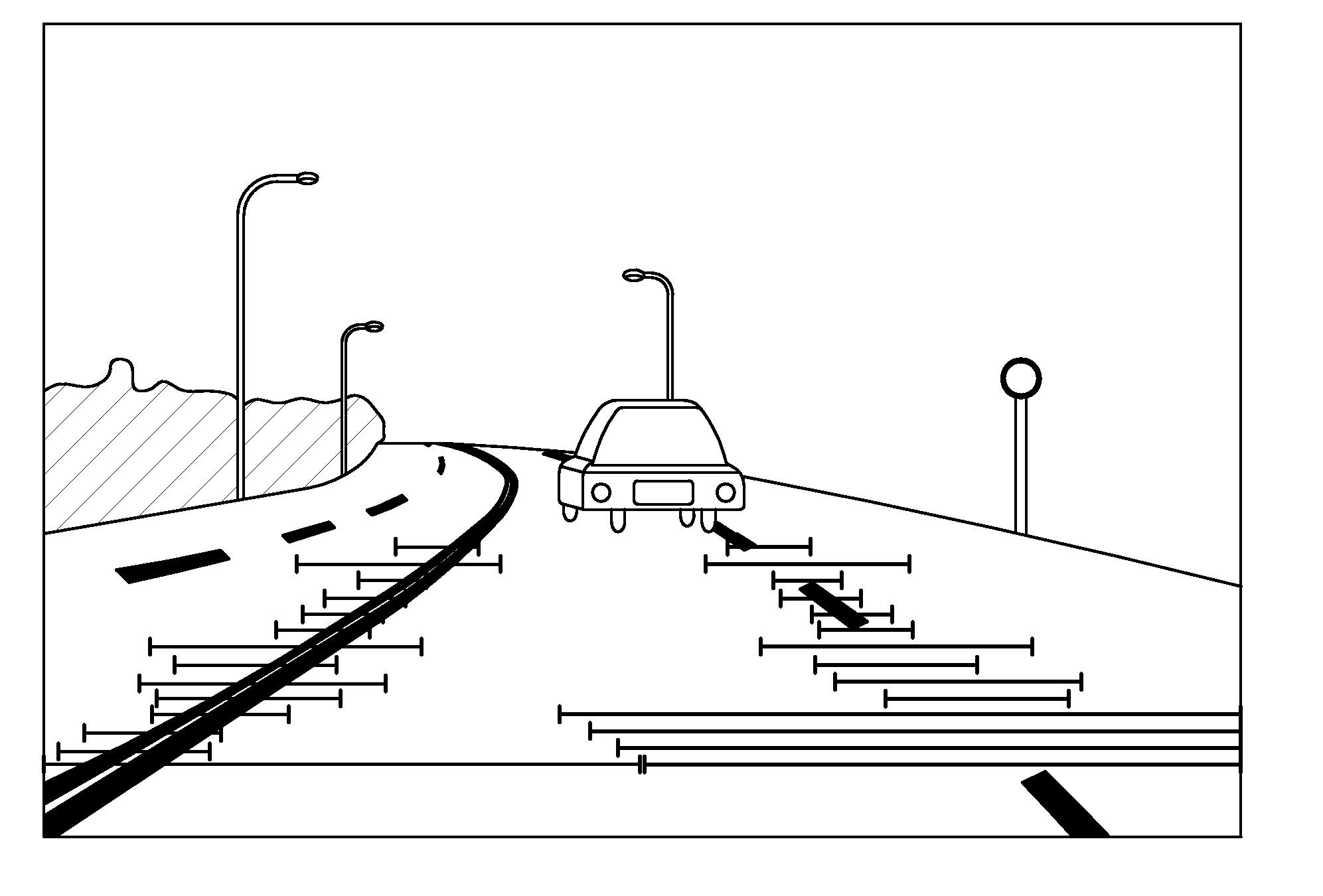
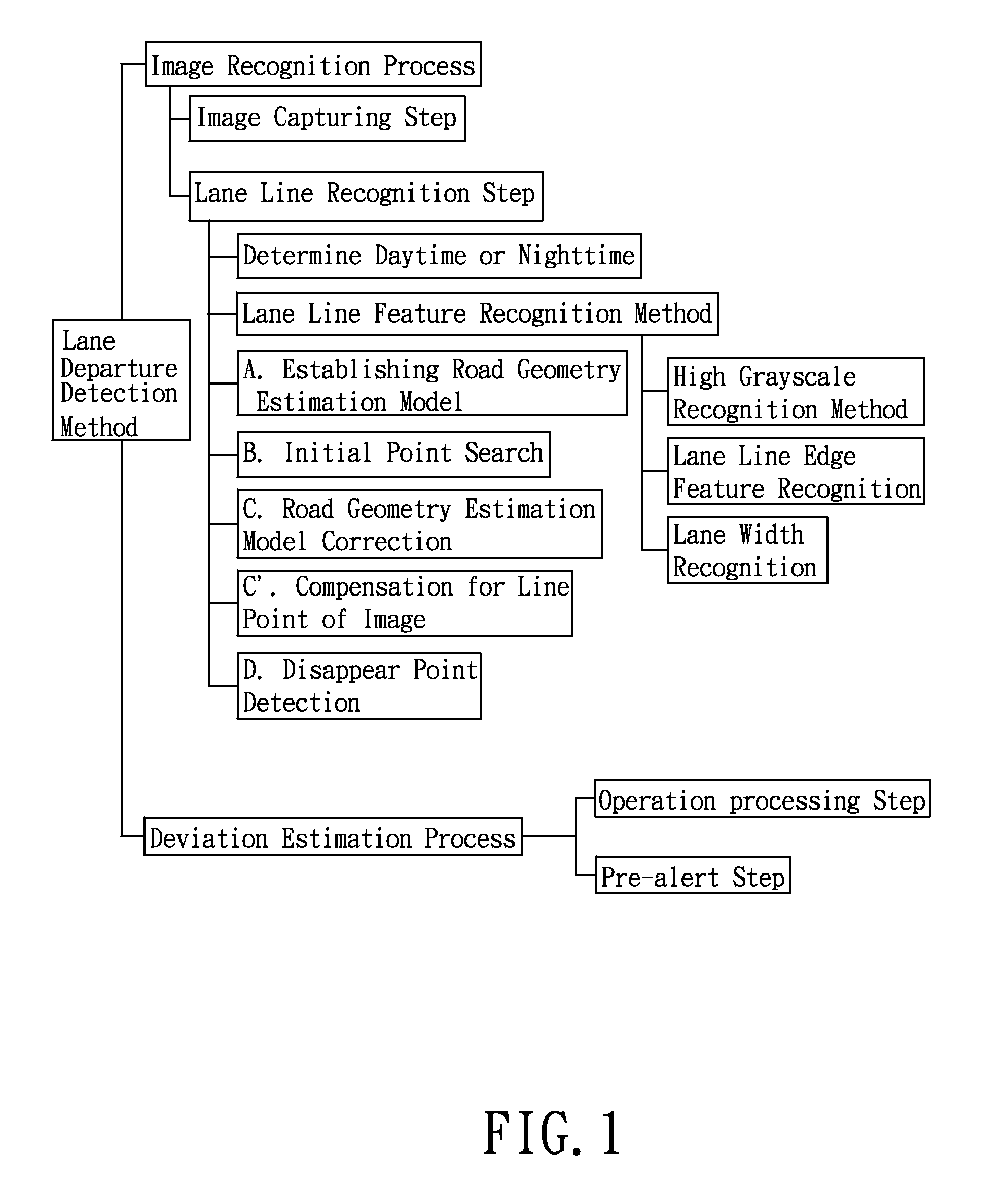
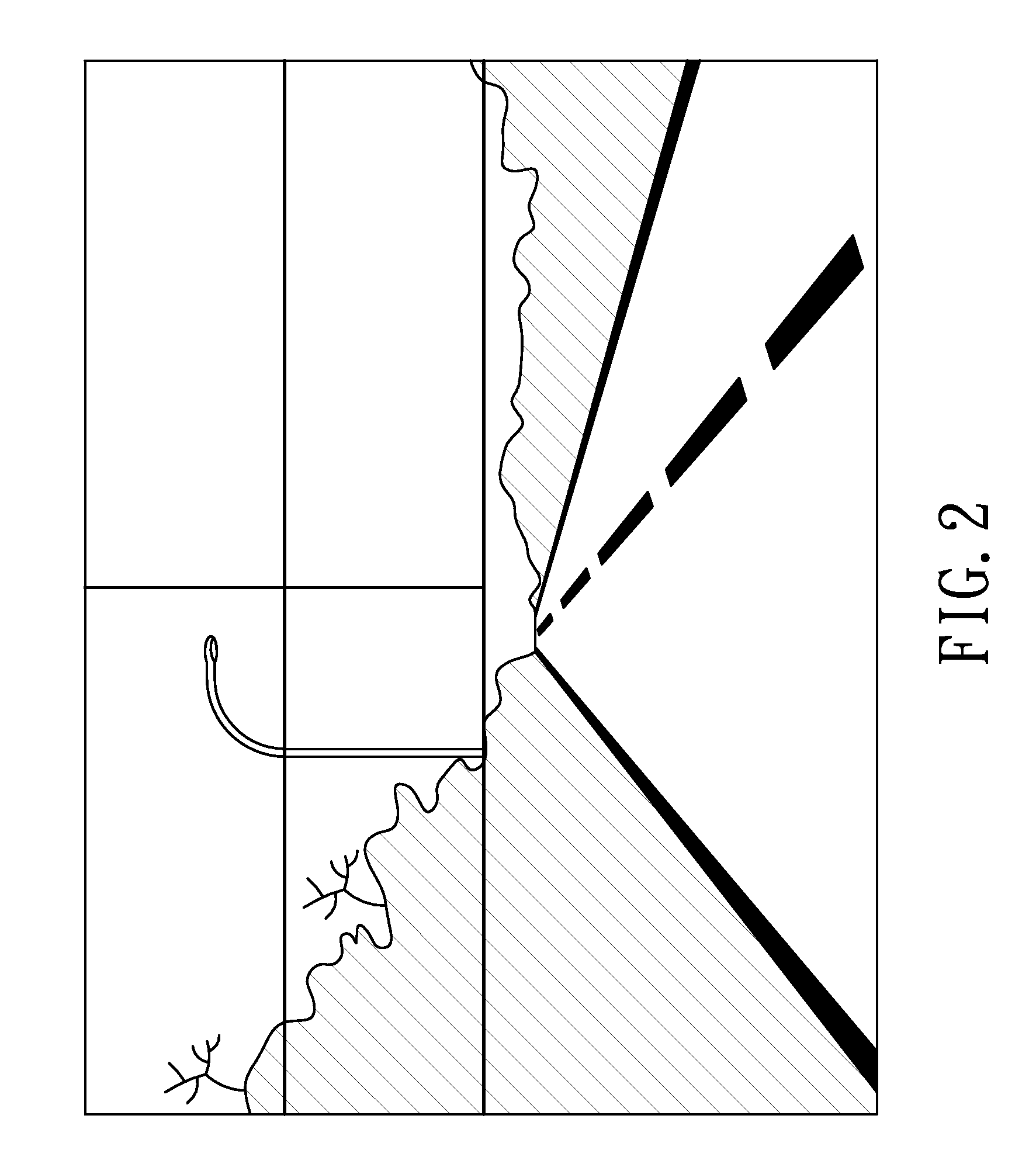
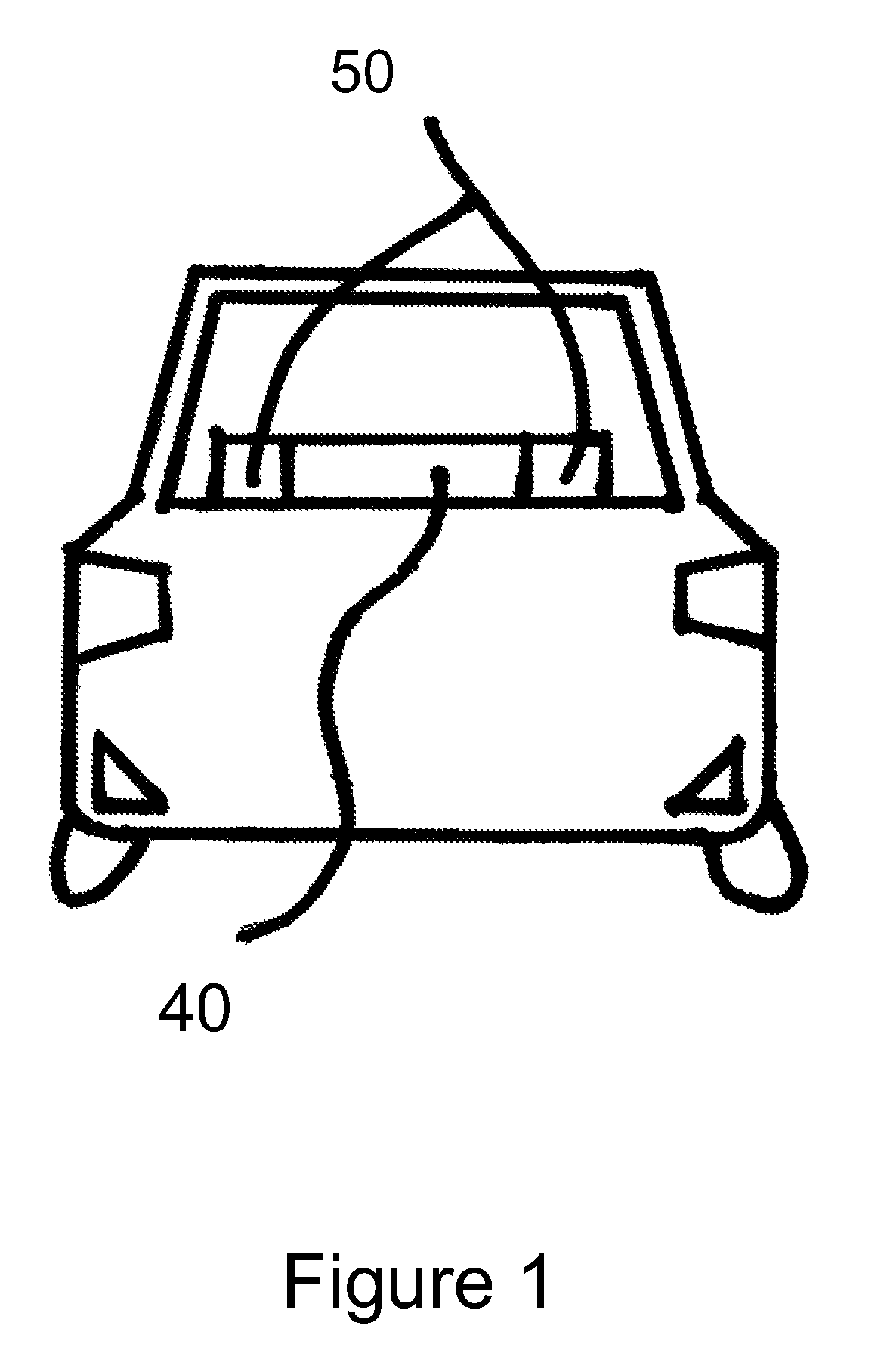
Method for detecting lane departure and apparatus thereof
ActiveUS20100002911A1Improve shortcomingsResponse time is insufficientCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsDriver/operatorComputer graphics (images)
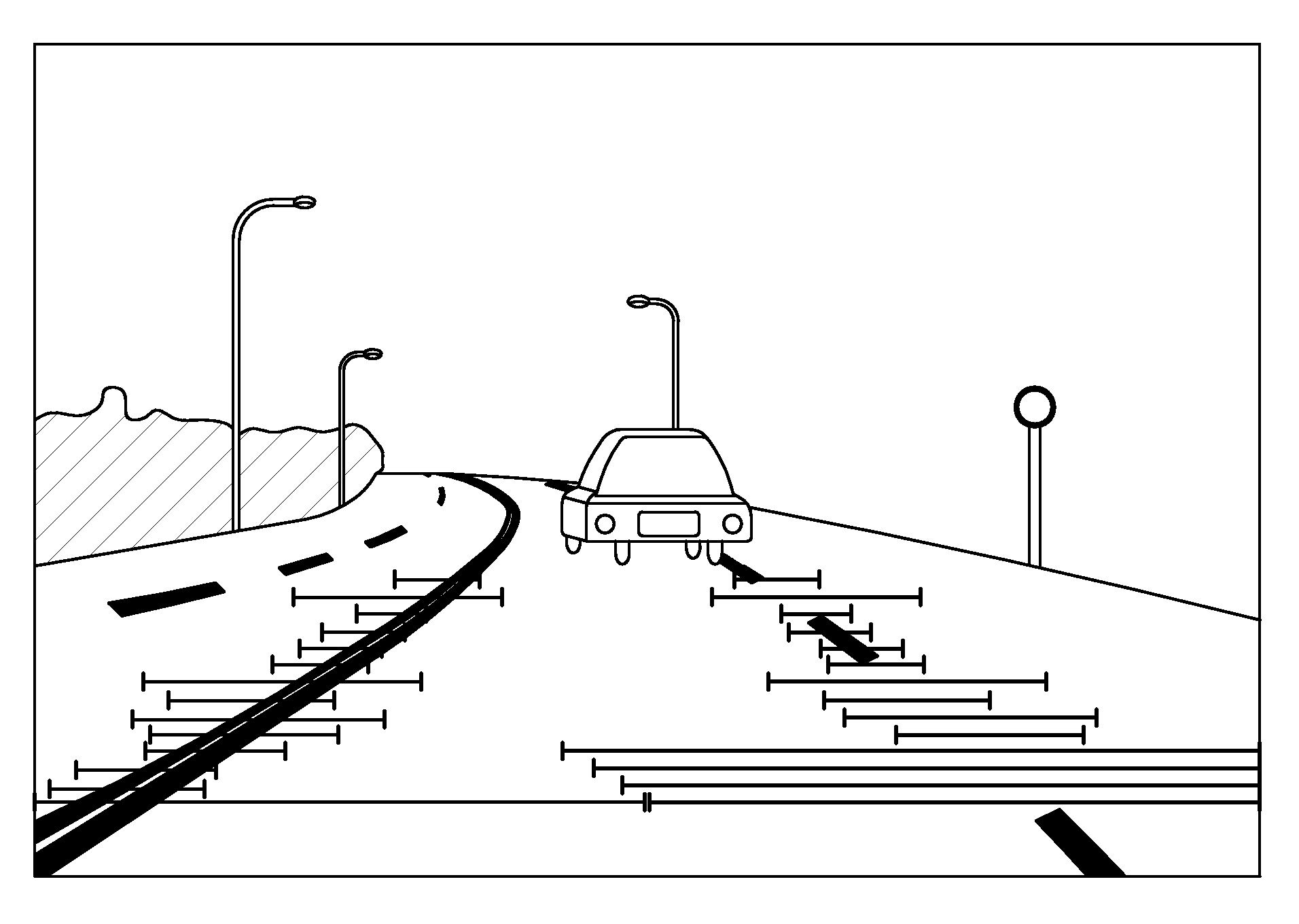
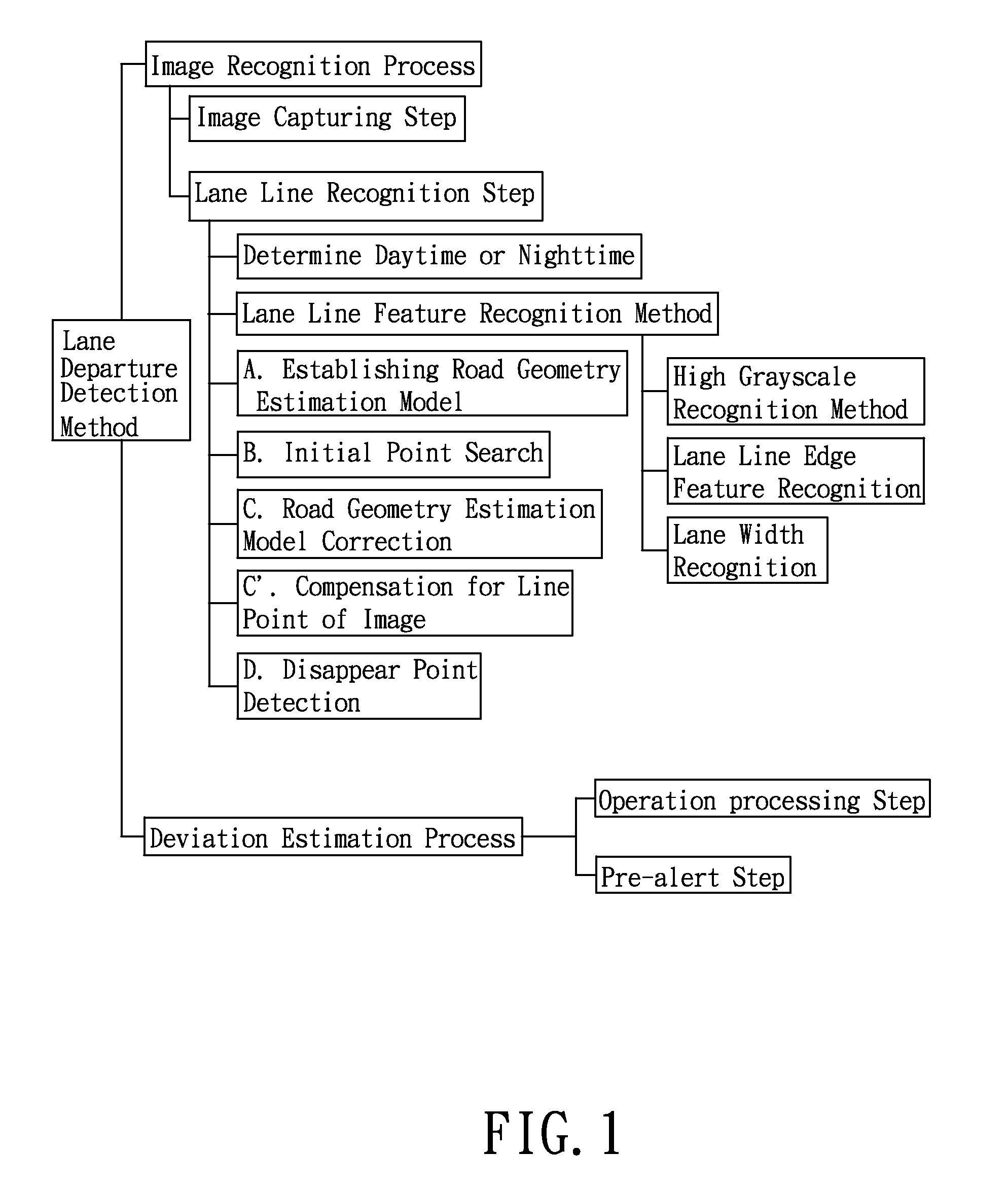
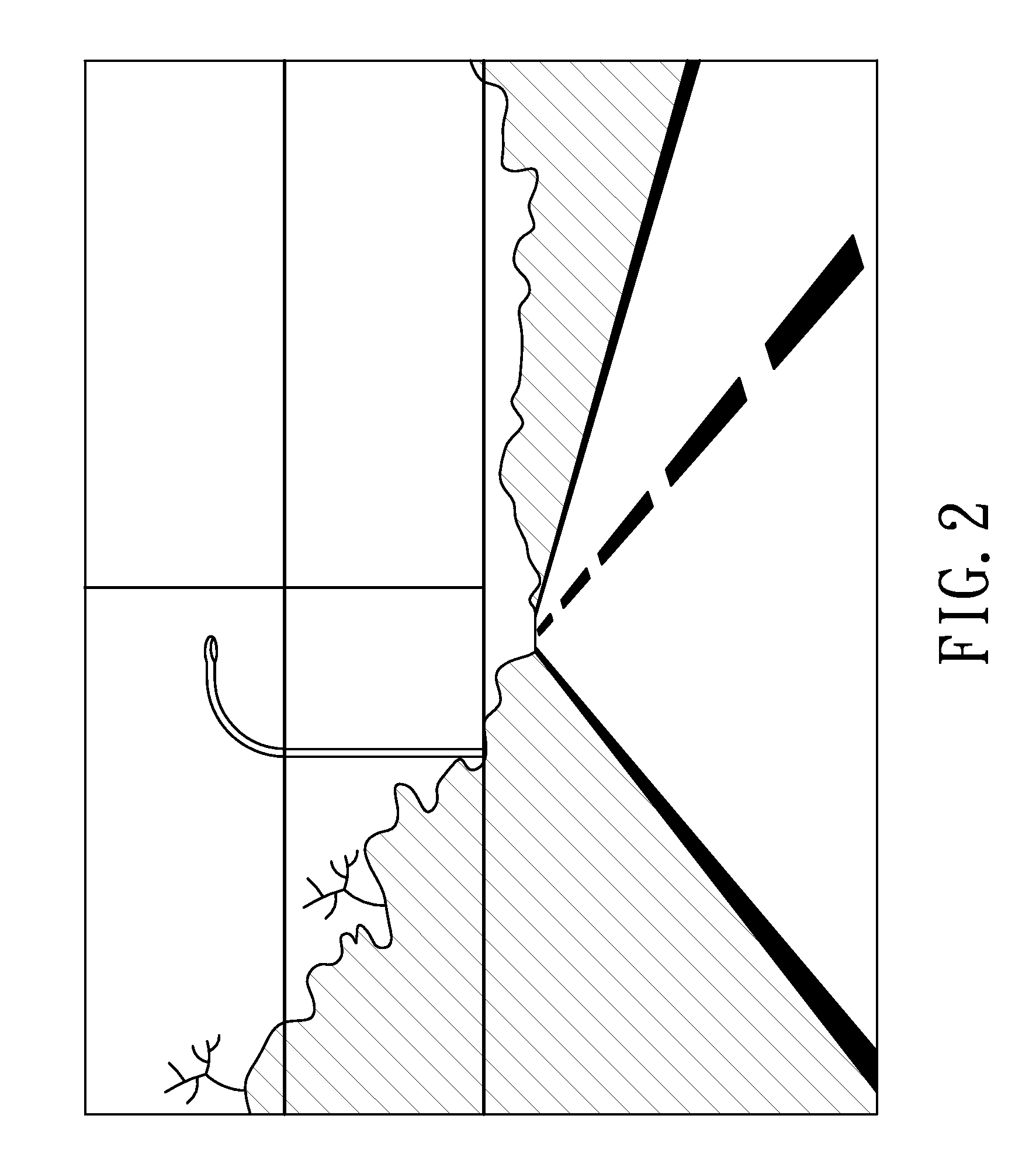
A method for detecting the lane departure of a vehicle includes an image recognition process and a deviation estimation process. The image recognition process includes the following steps: an image capturing step for capturing image frame data by using an image capturing unit; and a lane line recognition for analyzing the image frame data for determining the lane lines. By using a quadratic curve fitting equation, a plurality of lane line being detected so as to establish a road geometry estimation model. The road geometry estimation model is inputted into the deviation estimation process to detect the lane departure of the vehicle so as to alert the driver. Furthermore, an apparatus for detecting the deviation of the vehicle, comprising: an image capturing unit, a processing unit and a signal output unit.
Owner:AUTOMOTIVE RES & TESTING CENT
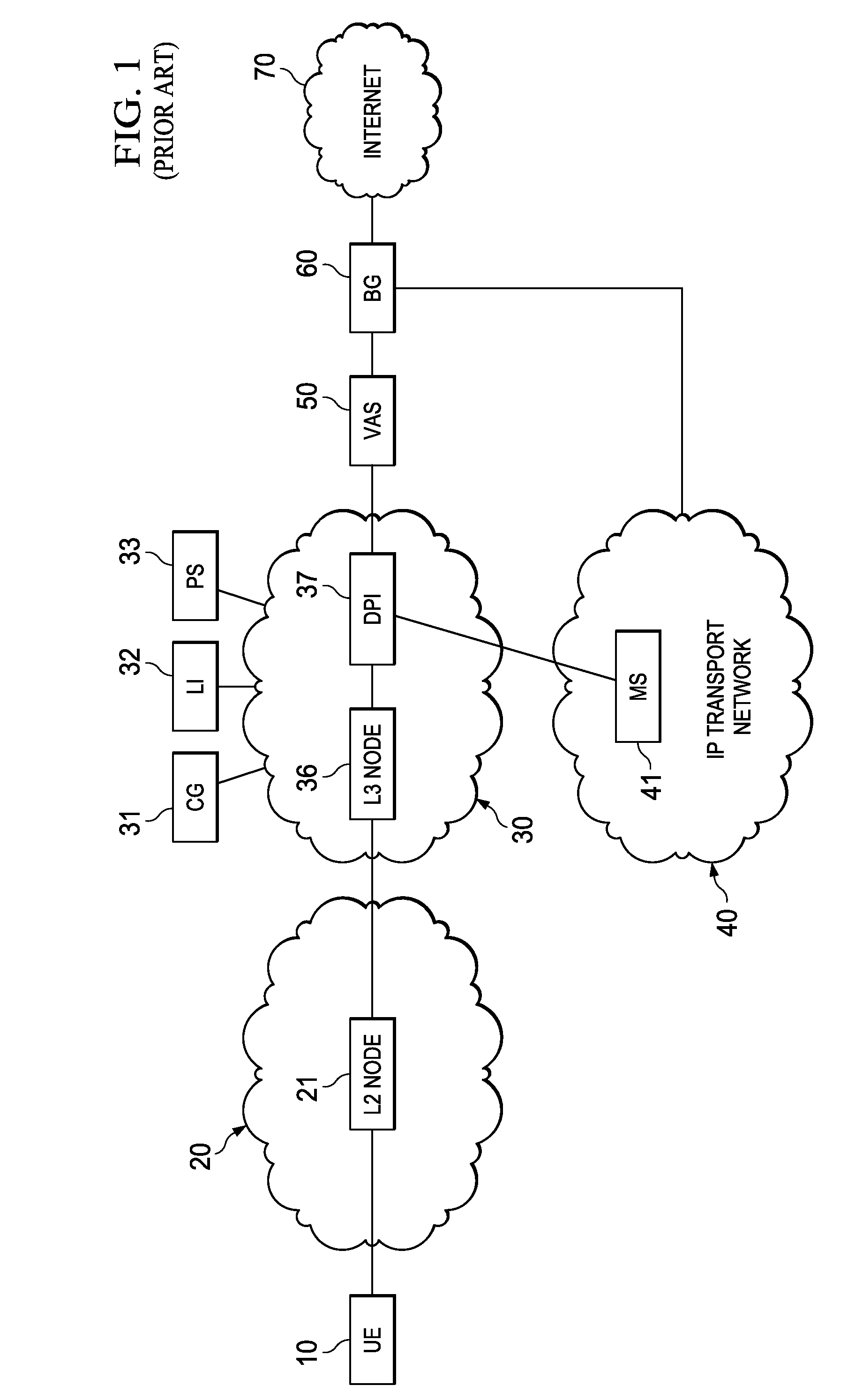
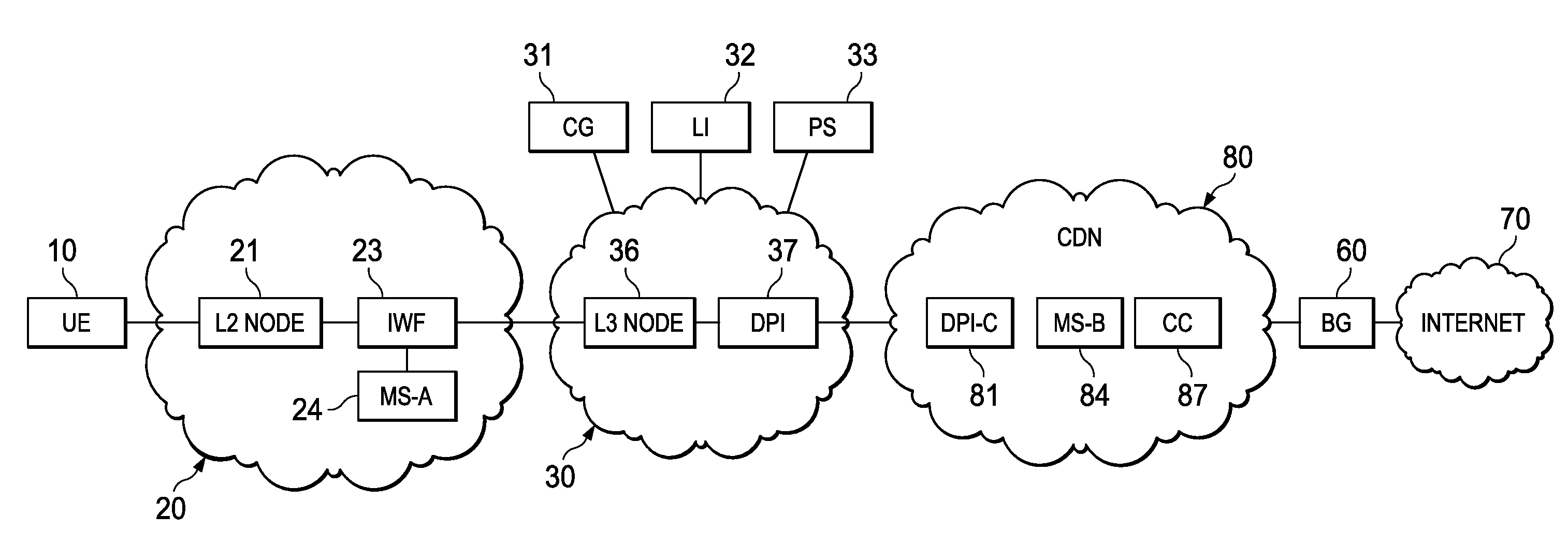
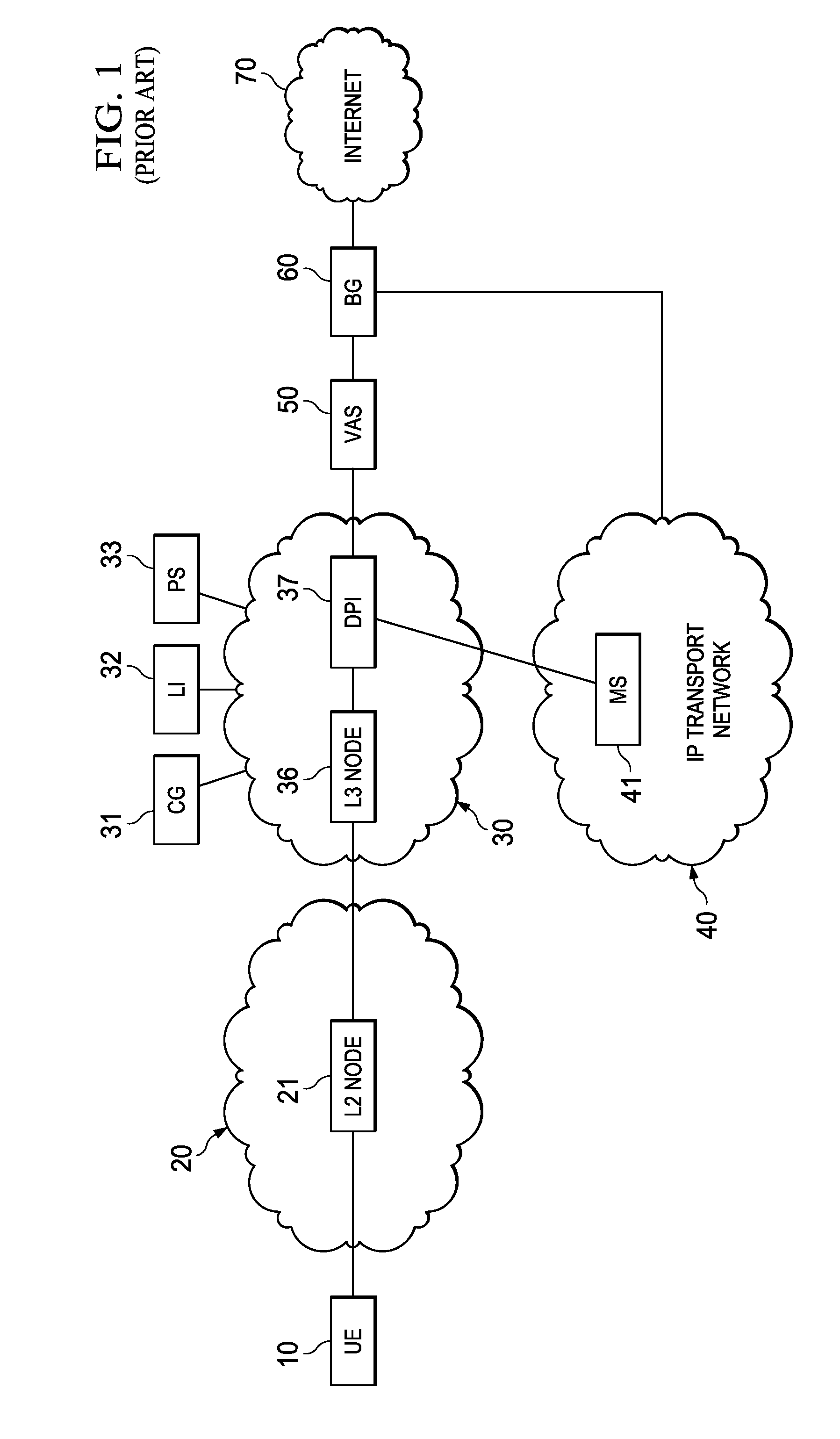
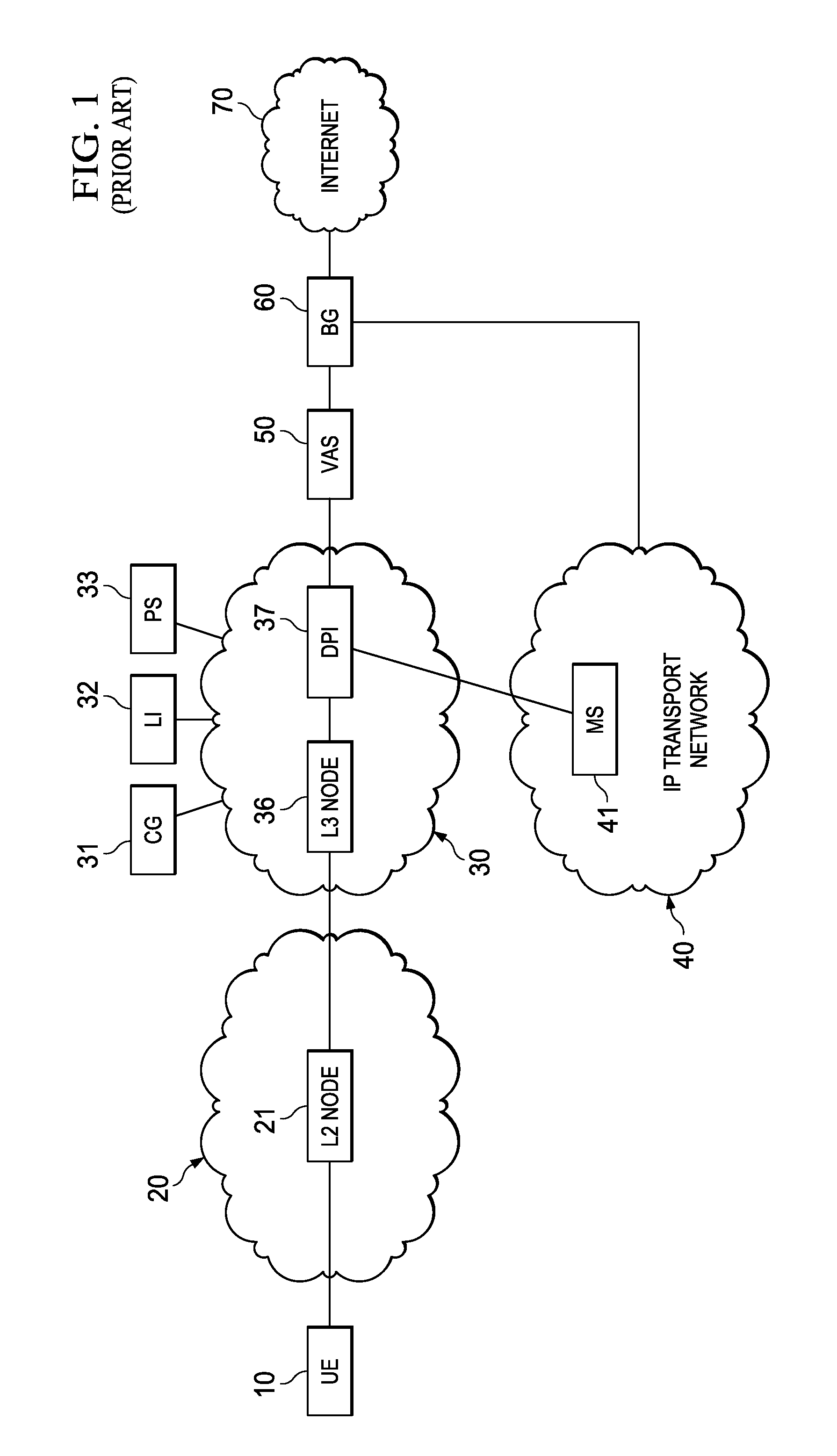
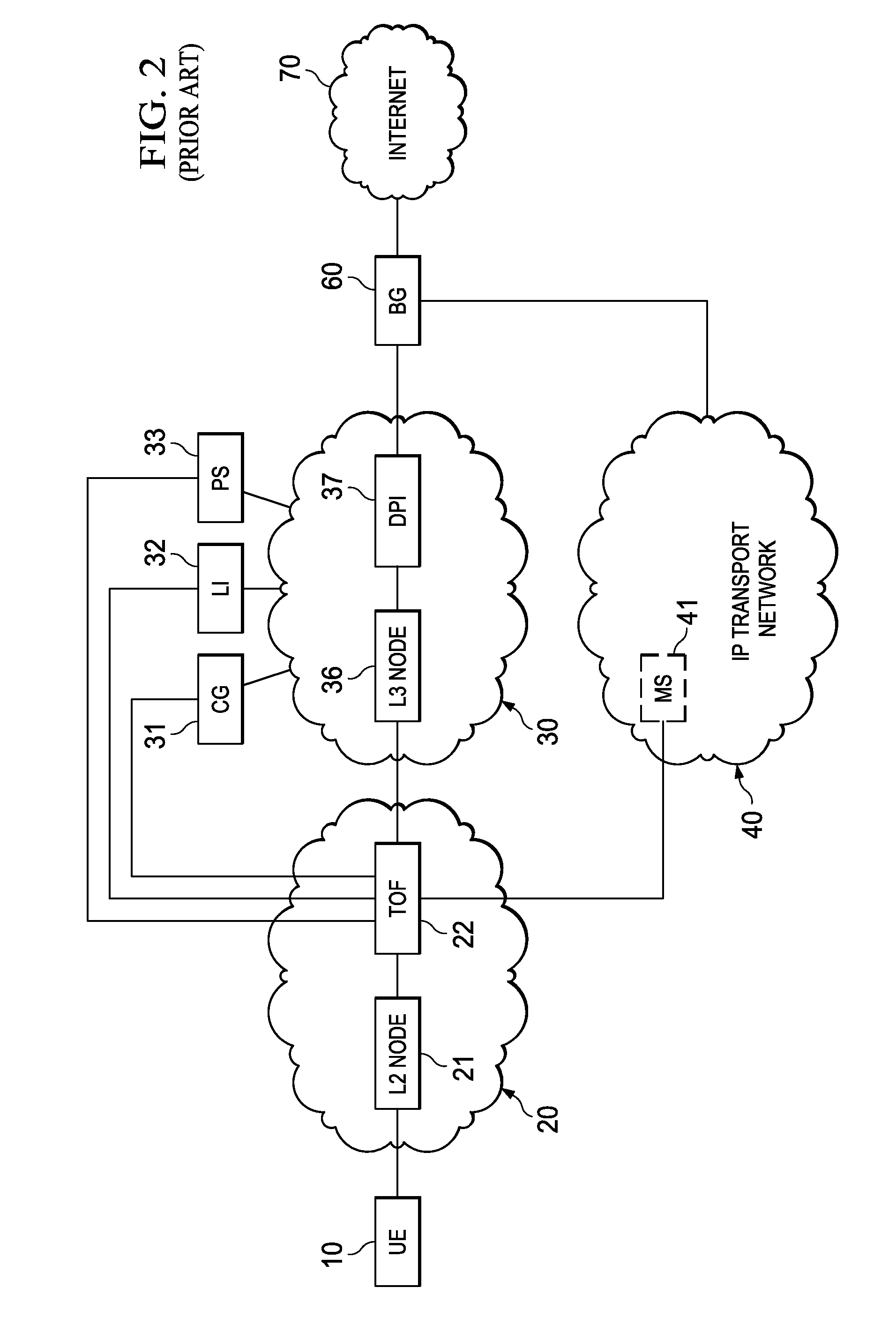
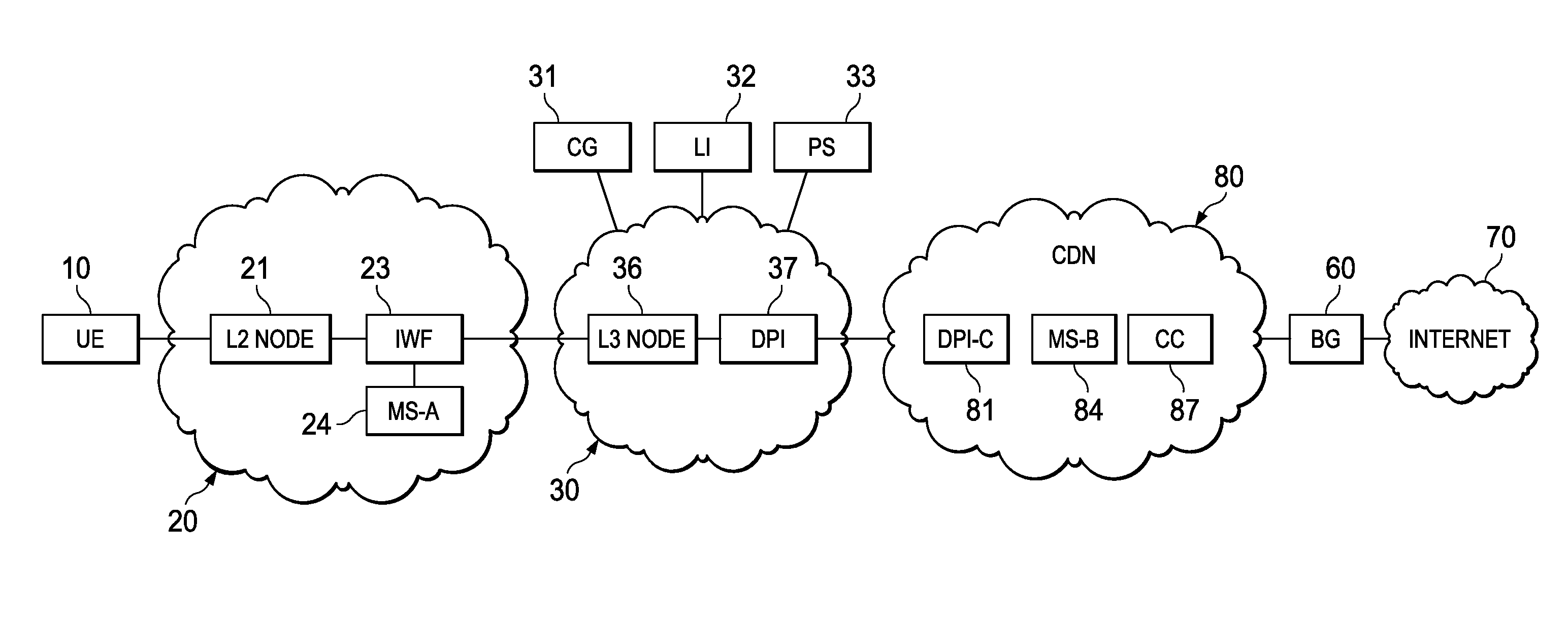
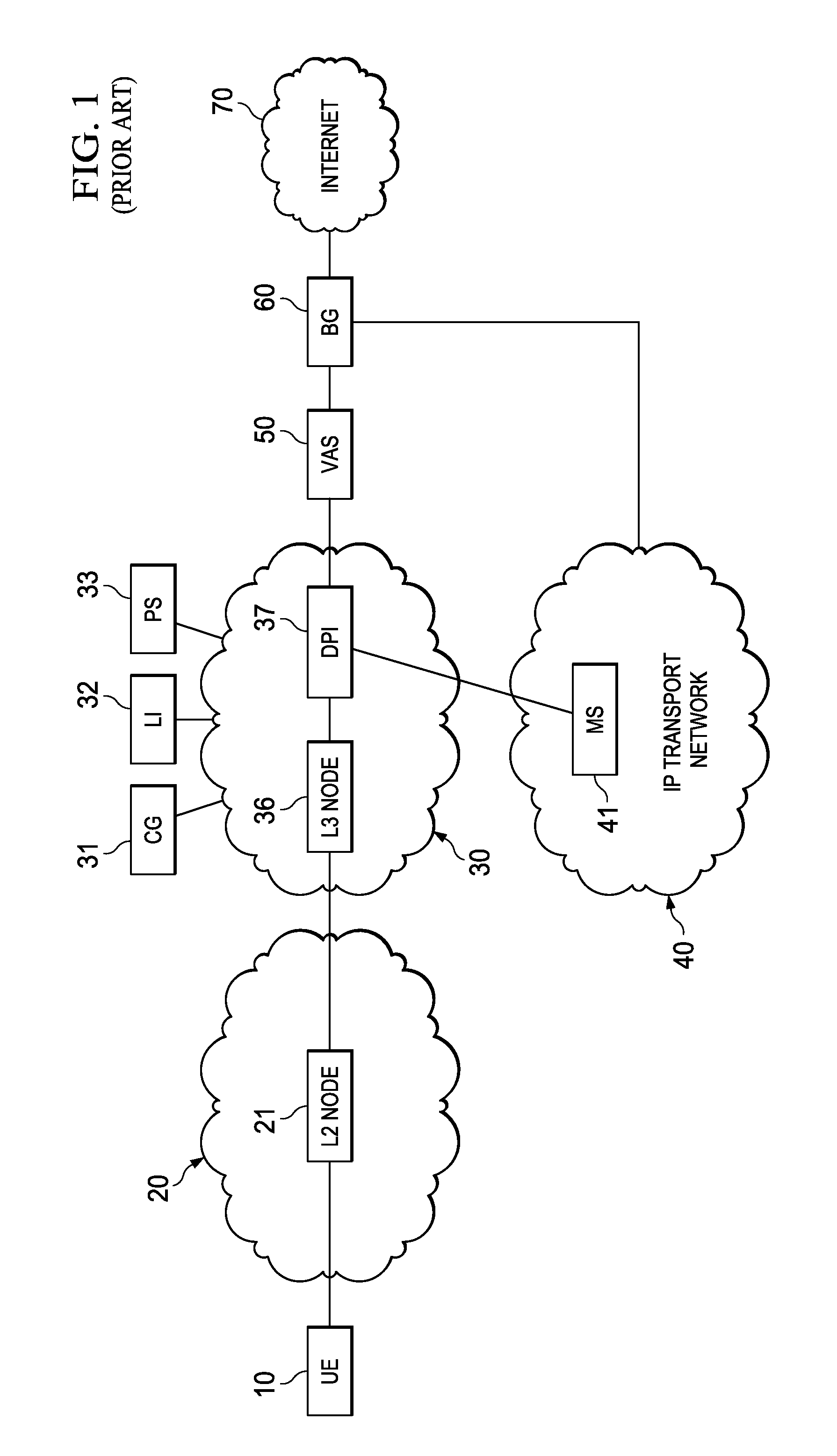
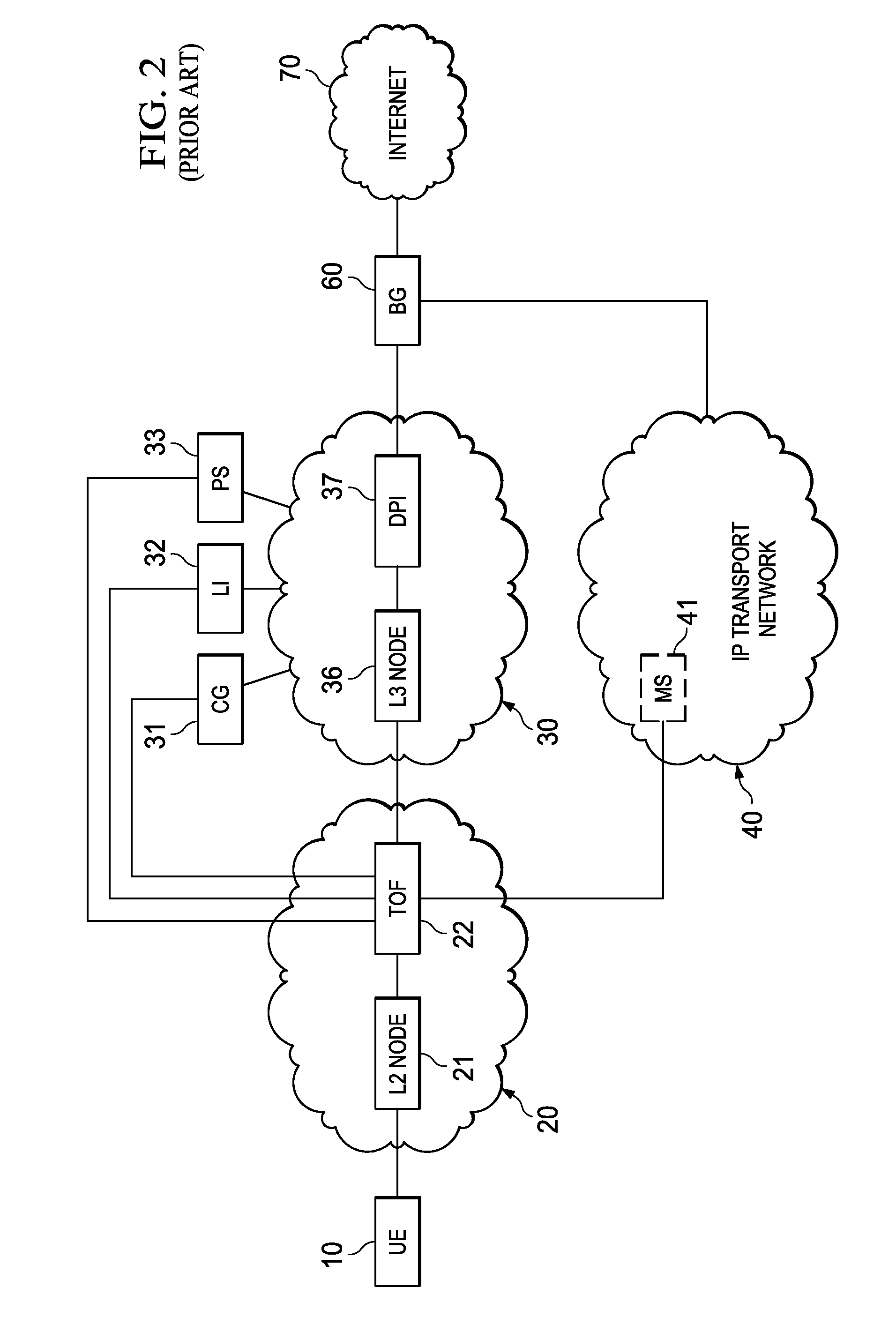
System, Apparatus for Content Delivery for Internet Traffic and Methods Thereof
ActiveUS20110280143A1Effective decouplingImprove cache hit ratioDigital data information retrievalMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccess networkInternet traffic
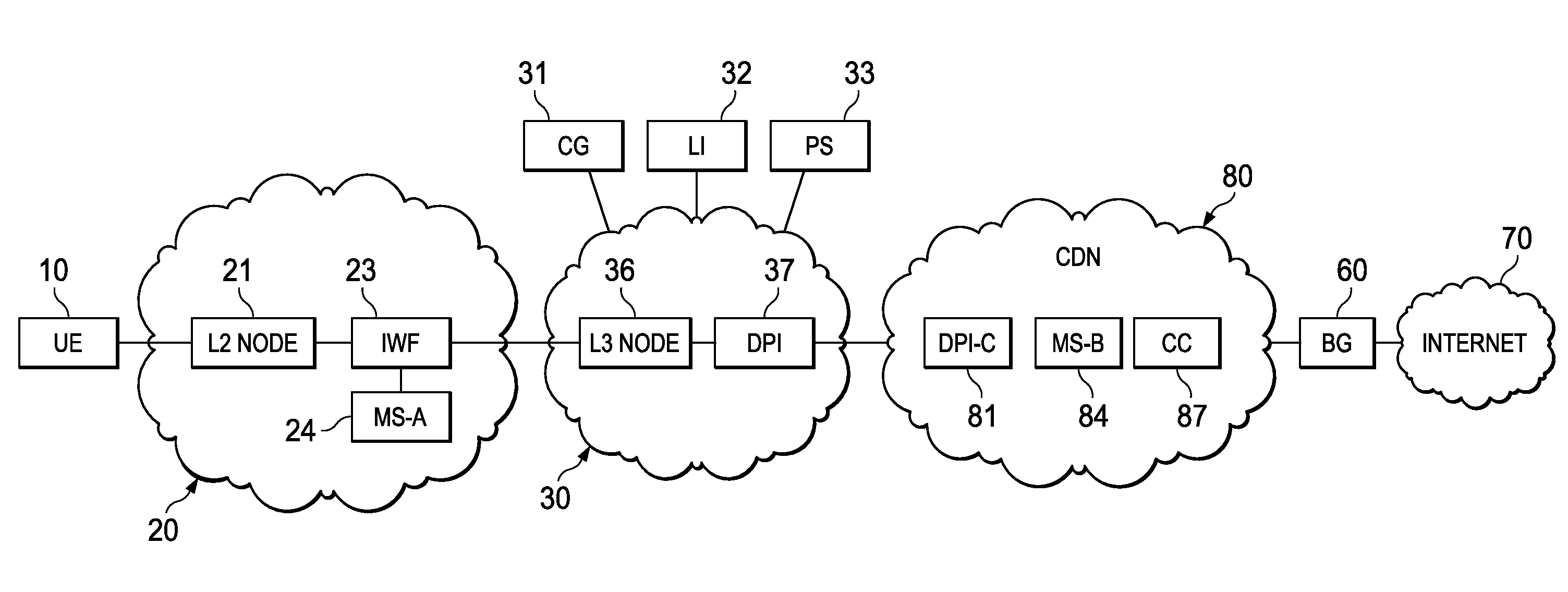
In one embodiment, a method of serving media includes receiving a delivery log of traffic use after every first time interval for an user equipment. The user equipment is part of a hot billing class of users. The traffic use comprises data usage by the user equipment during communication with a media server in a layer2 access network. A user traffic information computed from the delivery log is transmitted to a billing center. A account status information is received from the billing center. The account status information is received if the user equipment exceeds a user account metric. A session termination information based on the account status information is transmitted.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
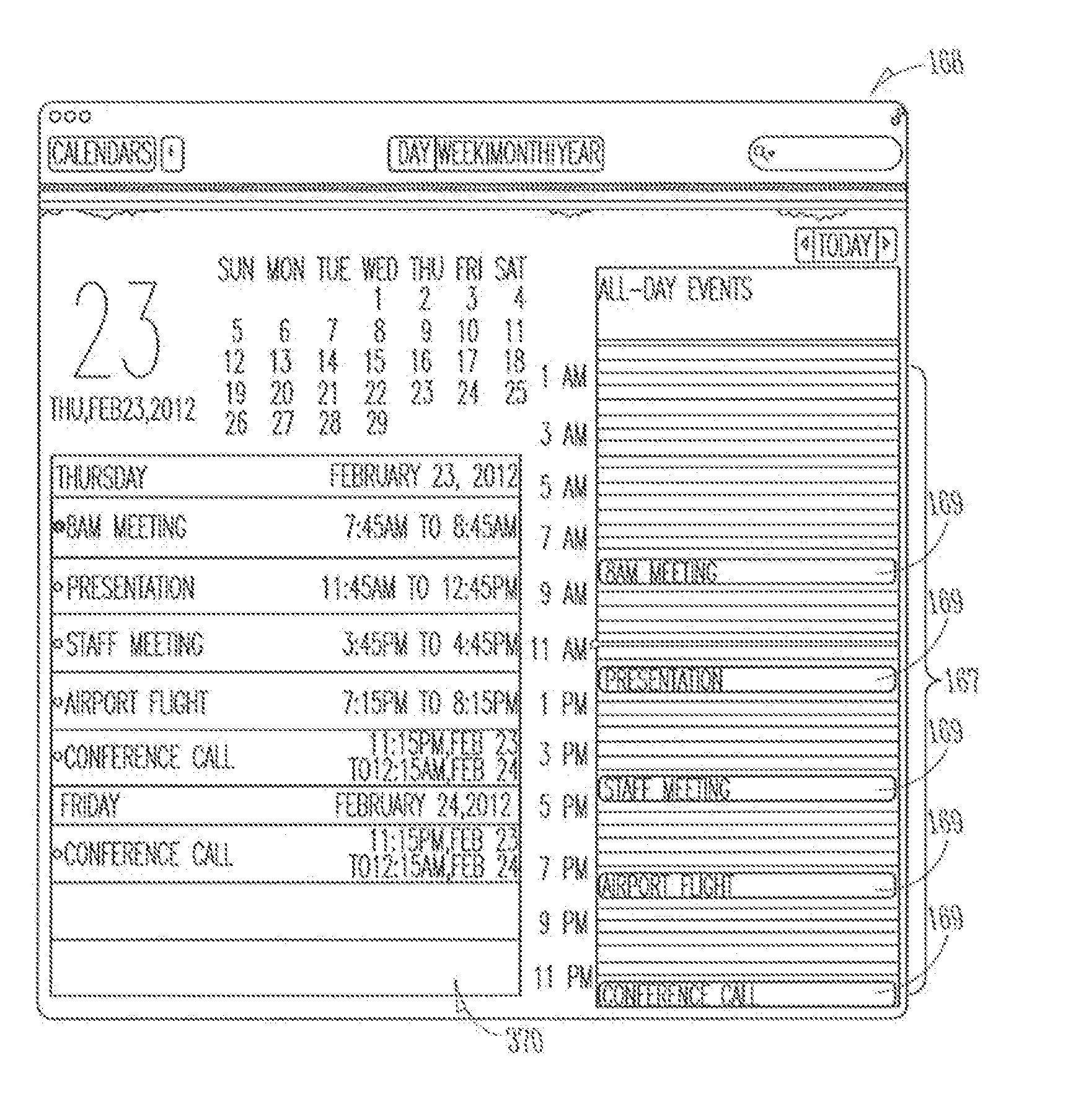
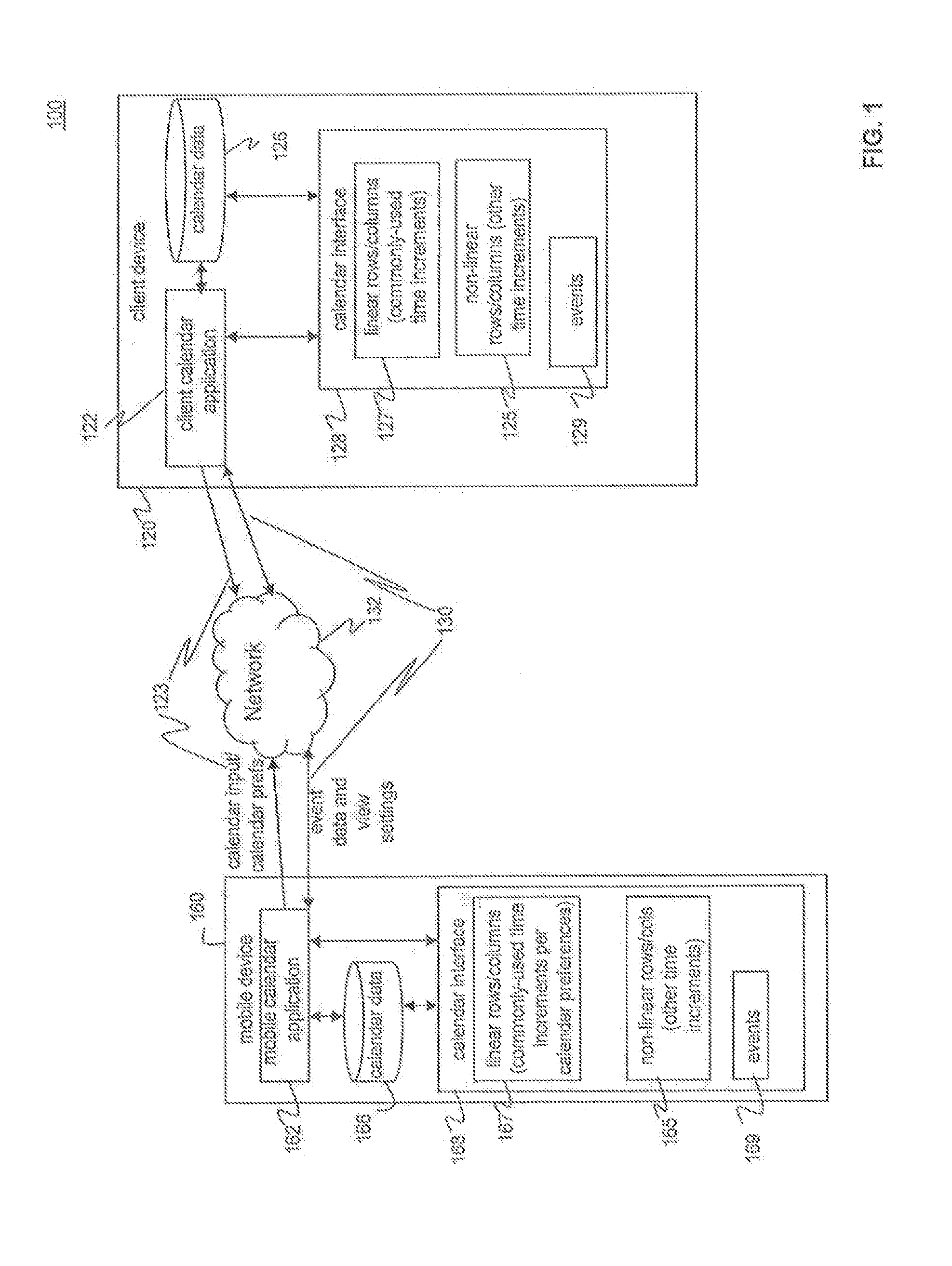
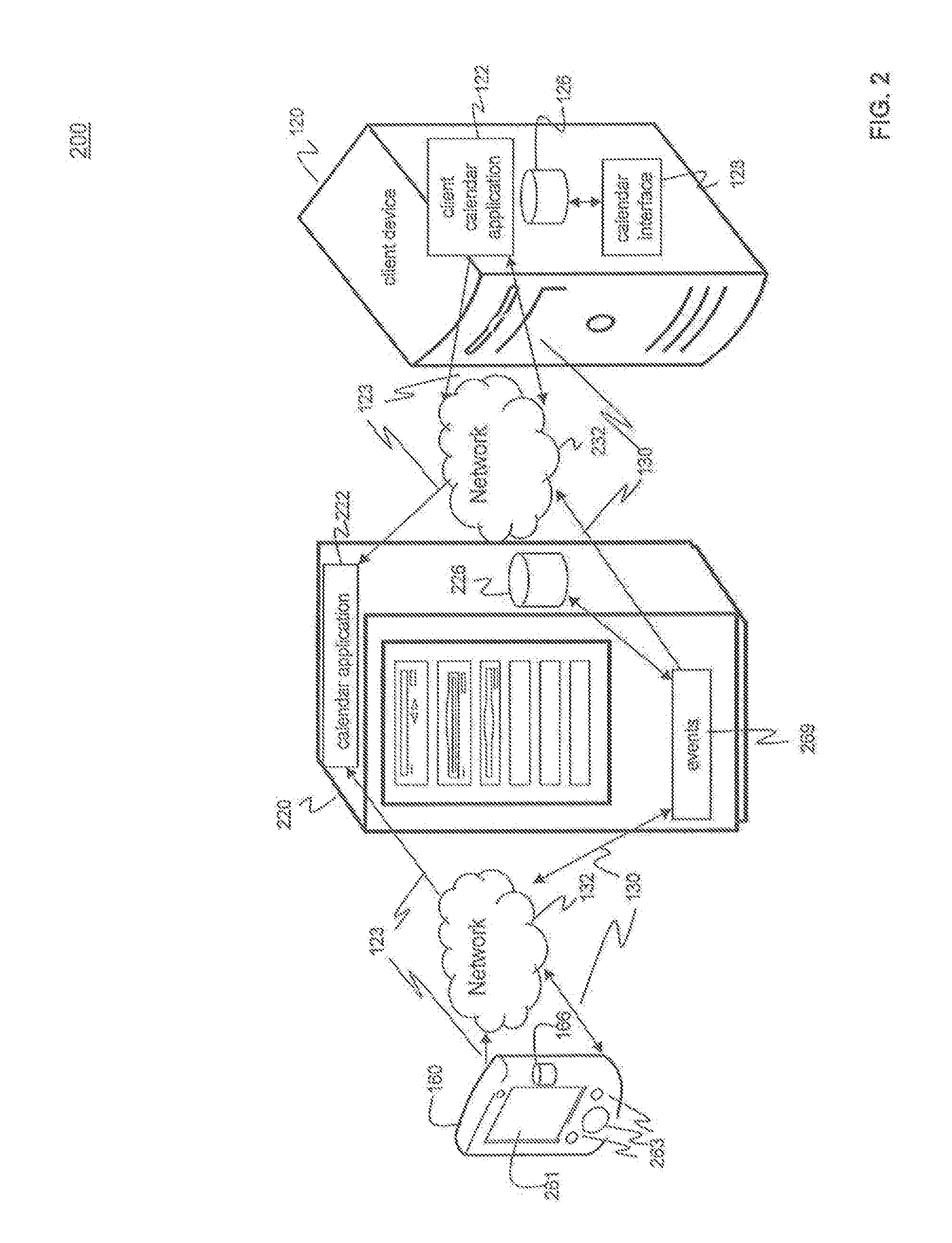
Methods and systems for non-linear representation of time in calendar applications
ActiveUS20140059487A1Avoid a lot of timeEffective displayInput/output processes for data processingSimulationIndustrial engineering
Methods and systems for displaying increments of time in a calendar view are disclosed. In an embodiment, a method receives a selection of commonly-used increments of time for the calendar and allots equal amounts of display space in the calendar view for each commonly-used increment. The method allots less display space for other increments of time that are not commonly-used as compared to space allotted for the commonly-used increments. In another embodiment, a system presents a calendar view having a plurality of increments of time and events in a display. The system includes an input device for receiving a selection of commonly-used increments of time and a processor configured to alter the calendar view by displaying the commonly-used increments of time linearly with equal amounts of display size for commonly-used increments of time and decreasing the size of other increments of time in proportion to their proximity to commonly-used increments.
Owner:APPLE INC
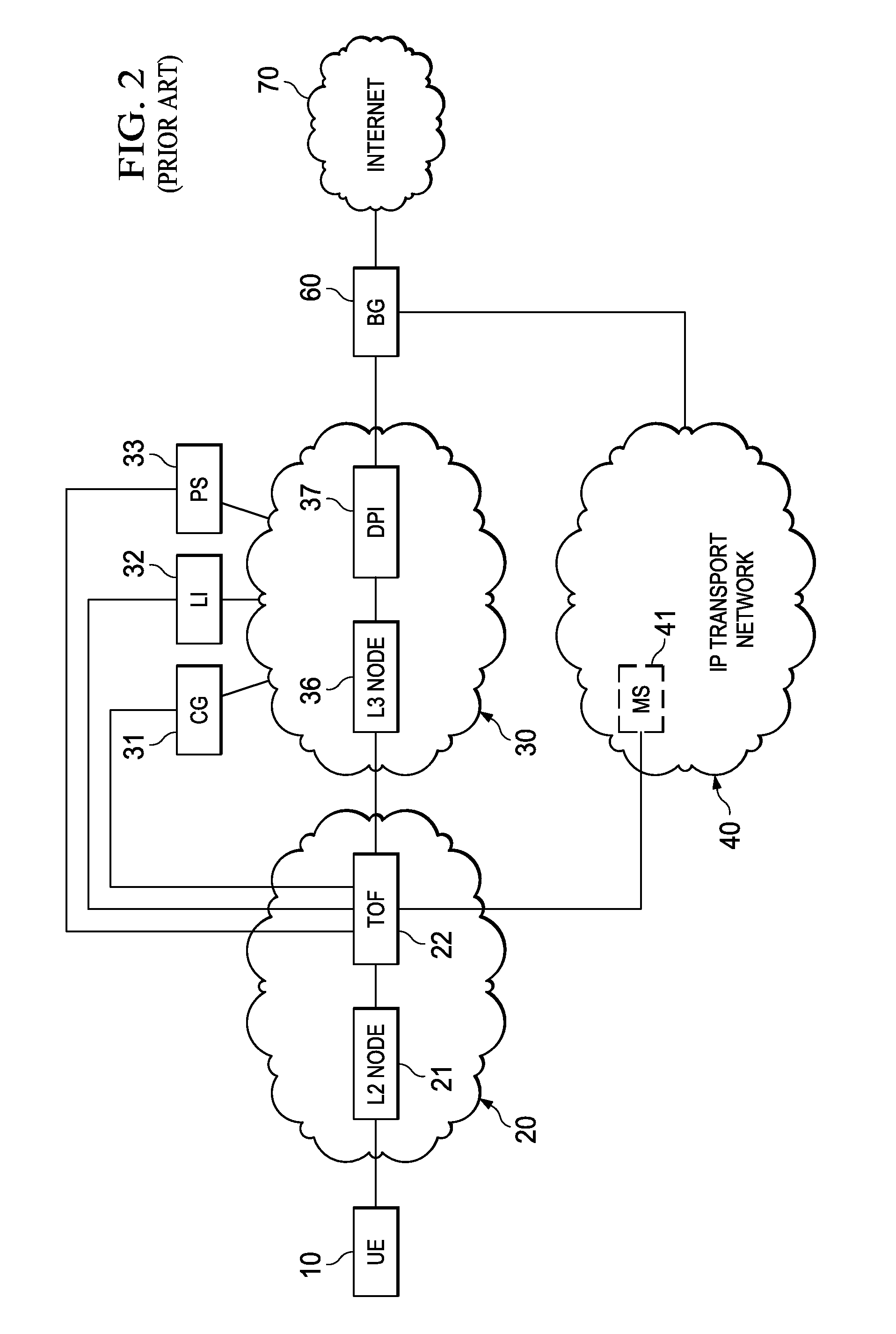
System, Apparatus for Content Delivery for Internet Traffic and Methods Thereof
ActiveUS20110280216A1Effective decouplingImprove cache hit ratioDigital data information retrievalMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccess networkInternet traffic
In one embodiment, a method of serving media includes receiving a request to serve a cacheable media content to a user equipment at a second media server deployed in a second layer2 access network. The request is received around when the user equipment is handed-off from a first layer2 node in a first layer2 access network to a second layer2 node in the second layer2 access network and when a streaming session of the cacheable media content to the user equipment from a first media server is terminated. The method further includes determining if the cacheable media content is stored in a cache of the second media server, and serving the cacheable media content from the cache of the second media server to the user equipment if the media content is stored in the cache of the second media server.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
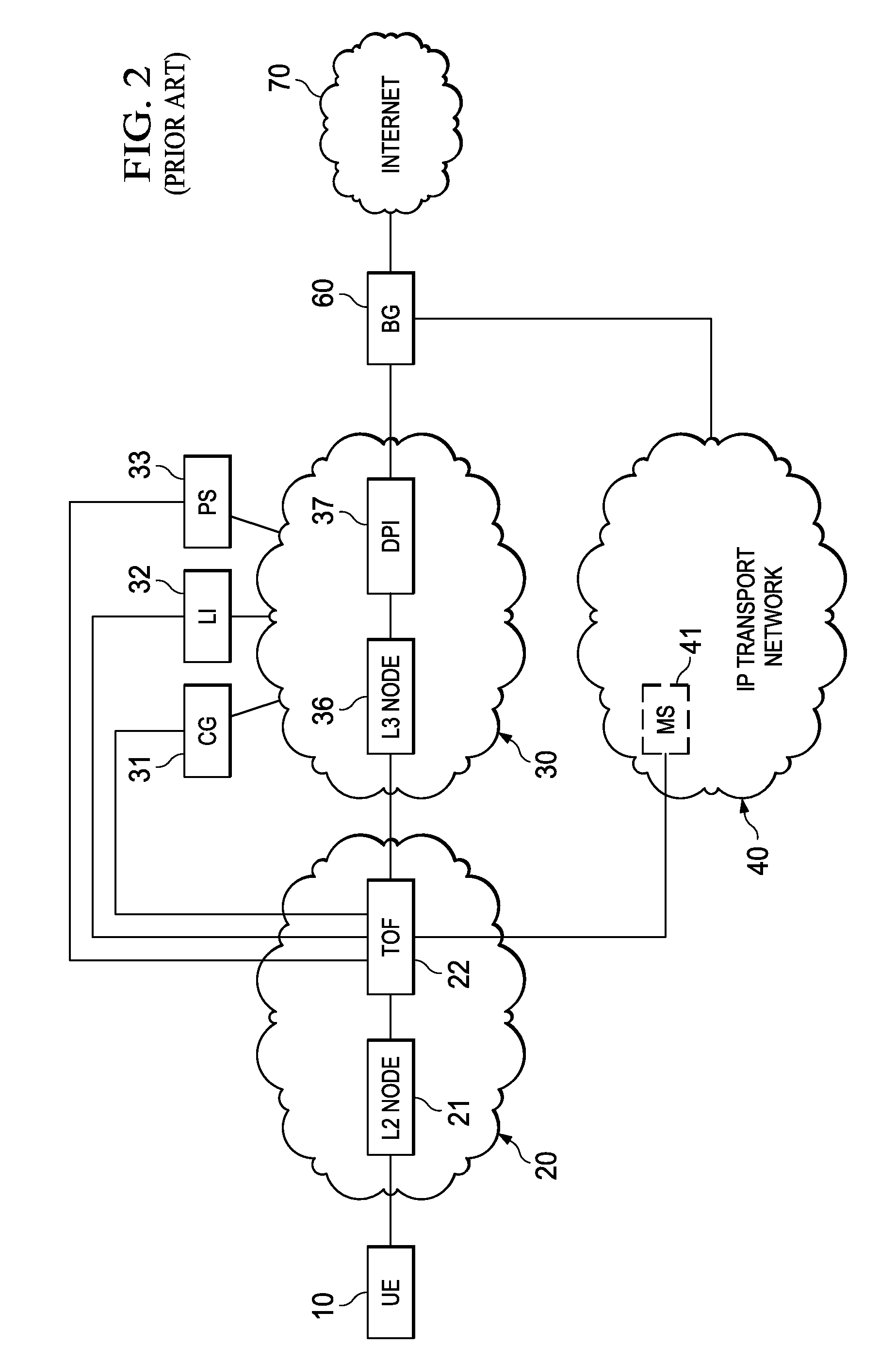
System, Apparatus for Content Delivery for Internet Traffic and Methods Thereof
ActiveUS20110283011A1Quality of experience for equipmentEffective decouplingMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsDigital data information retrievalAccess networkInternet traffic
In one embodiment, a method of serving media includes receiving user profiles from a layer3 node in an access network, and receiving a request to serve media content to a user equipment. The user profiles include information relating to user account and / or network characteristics of the user equipment. The method further includes using an user equipment information from the user profiles, assigning a first media server from a hierarchical set of media servers to serve the user equipment if the media content to be served is cacheable. The hierarchical set of media servers include a plurality of first type of media servers deployed in a plurality of layer2 (L2) access networks. The user equipment is coupled to a content delivery network through a layer2 access network of the plurality of layer2 access networks.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
System, Apparatus for Content Delivery for Internet Traffic and Methods Thereof
ActiveUS20110280153A1Effective decouplingImprove cache hit ratioDigital data information retrievalMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccess networkInternet traffic
In one embodiment, a method of serving media includes receiving a request to serve media content to an user equipment, and receiving caching information regarding the media content. The caching information includes information regarding whether the media content requested by the user equipment is cacheable. A first media server is assigned from a hierarchical set of media servers to serve the user equipment if the media content to be served is cacheable. The hierarchical set of media servers includes a plurality of first type of media servers deployed in a plurality of layer2 (L2) access networks. The user equipment is coupled to the content delivery network through a layer2 access network of the plurality of L2 access networks.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Array substrate, display panel and display device
ActiveUS20160103547A1Solve the real problemShorten charging timeNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
An array substrate includes a plurality of data lines; a plurality of scanning lines intersecting the data lines to define pixel units; a plurality of pixel electrodes within the pixel units; and a plurality of touch electrodes having a grid shape and formed by a plurality of first sub-electrodes and a plurality of second sub-electrodes intersecting each other. Projections of the first sub-electrodes and the second sub-electrodes onto a layer containing the pixel electrodes are respectively located between adjacent pixel electrodes, or the first sub-electrodes and the second sub-electrodes are respectively located between adjacent pixel electrodes. The product of the resistance of the touch electrode and the load capacitance between the touch electrode, the source electrode and the first metal is reduced, which reduces the charging time of the touch driving signal and enables the touch state and the display state to operate in a time division manner.
Owner:SHANGHAI TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
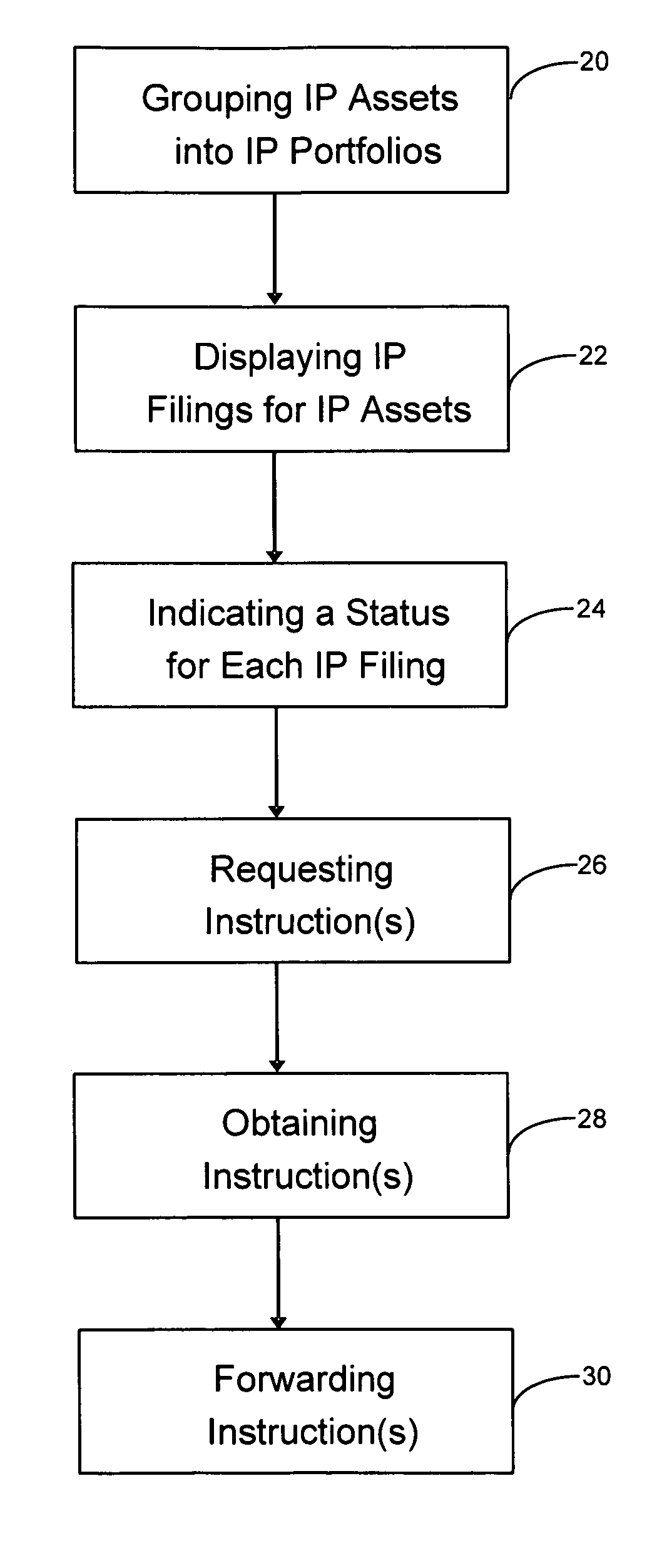
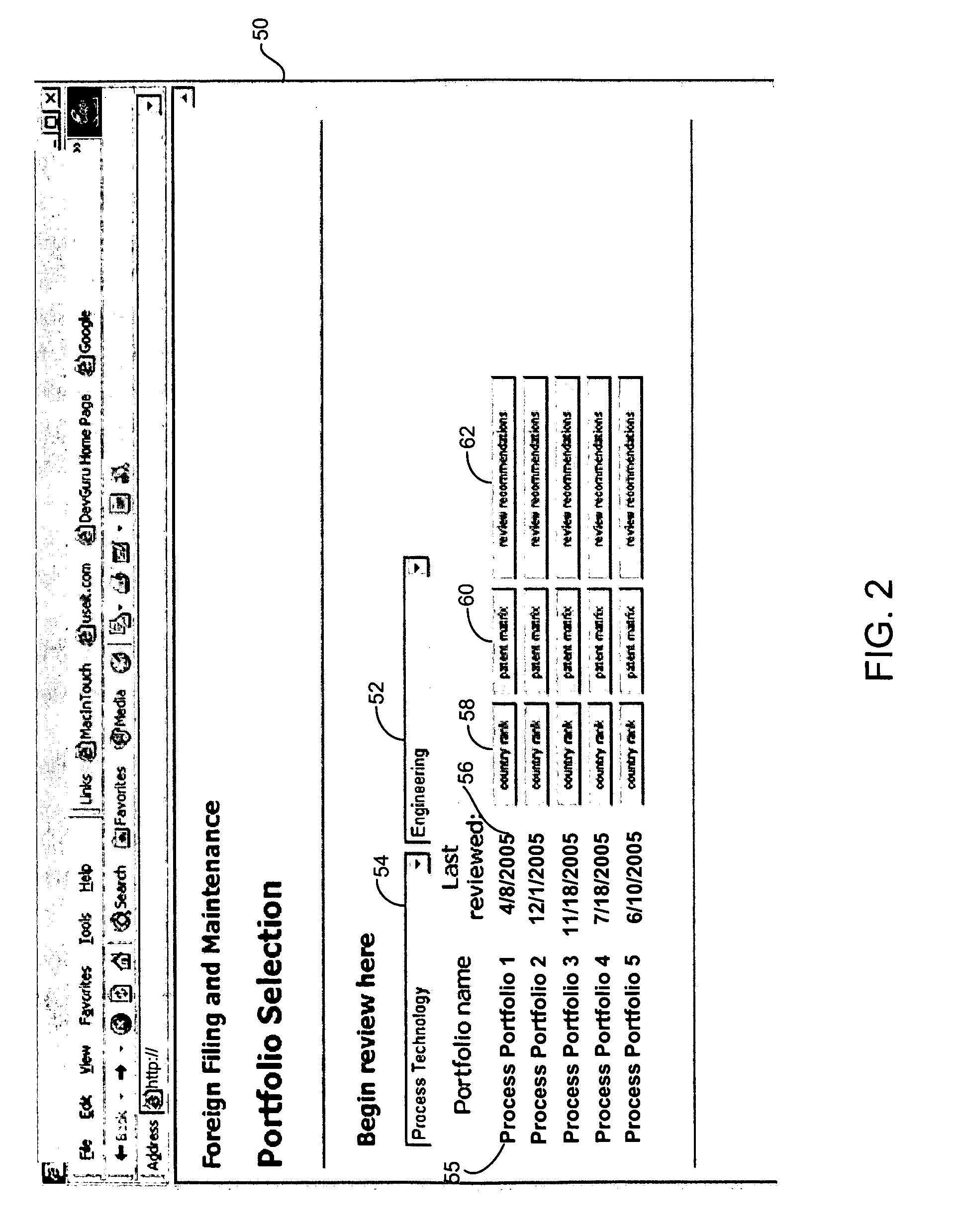
Intellectual property portfolio management method and system
InactiveUS20070136373A1Avoid a lot of timeNot easy to detectOffice automationSpecial data processing applicationsIntellectual propertyWorld Wide Web
A method and system for managing intellectual property (IP). An IP filing for an IP asset is displayed in a display matrix on a computer screen. A status for the IP filing is indicated through the display matrix. A filing instruction or a prosecution instruction for the IP filing is obtained through the display matrix.
Owner:UOP LLC
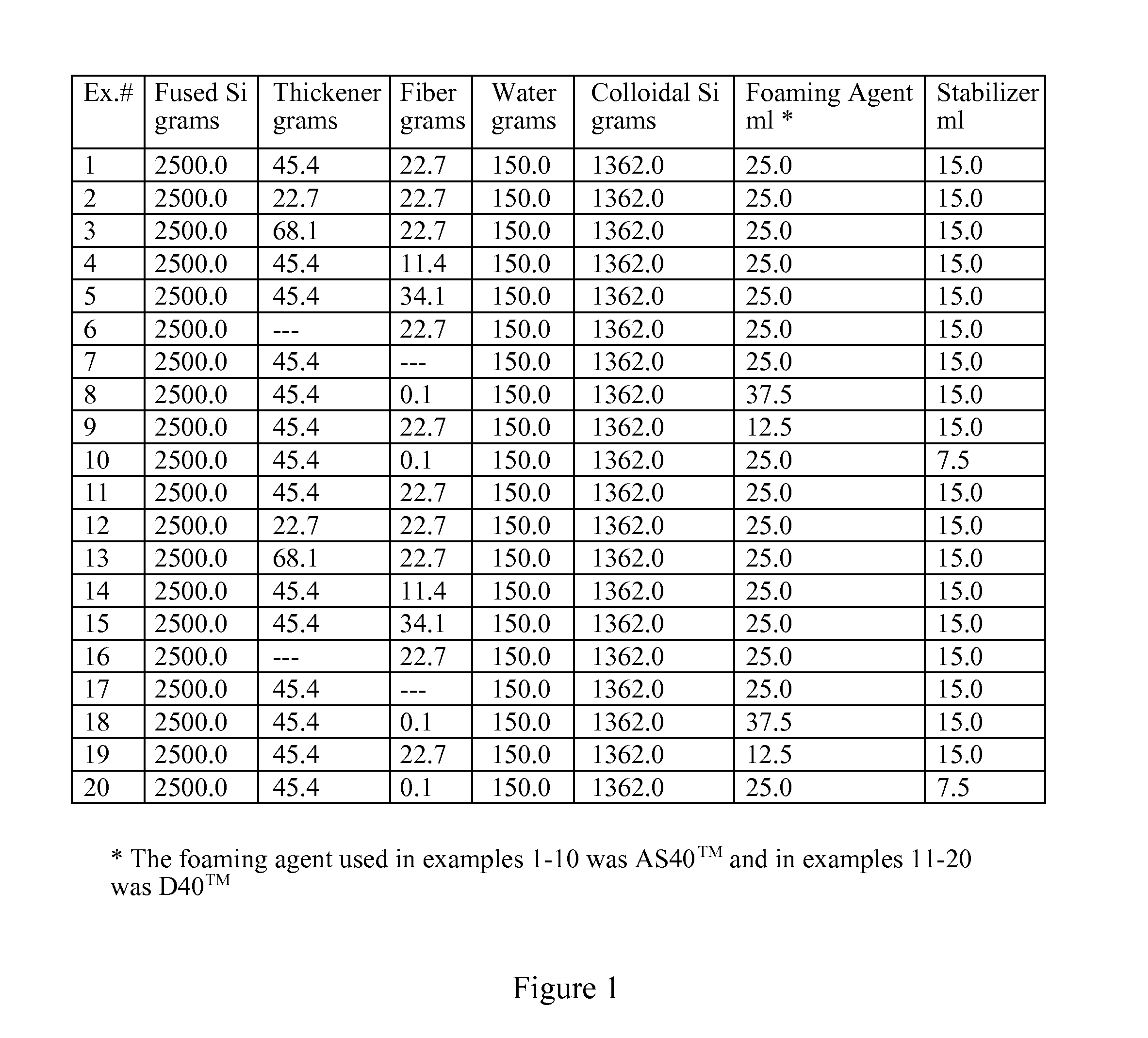
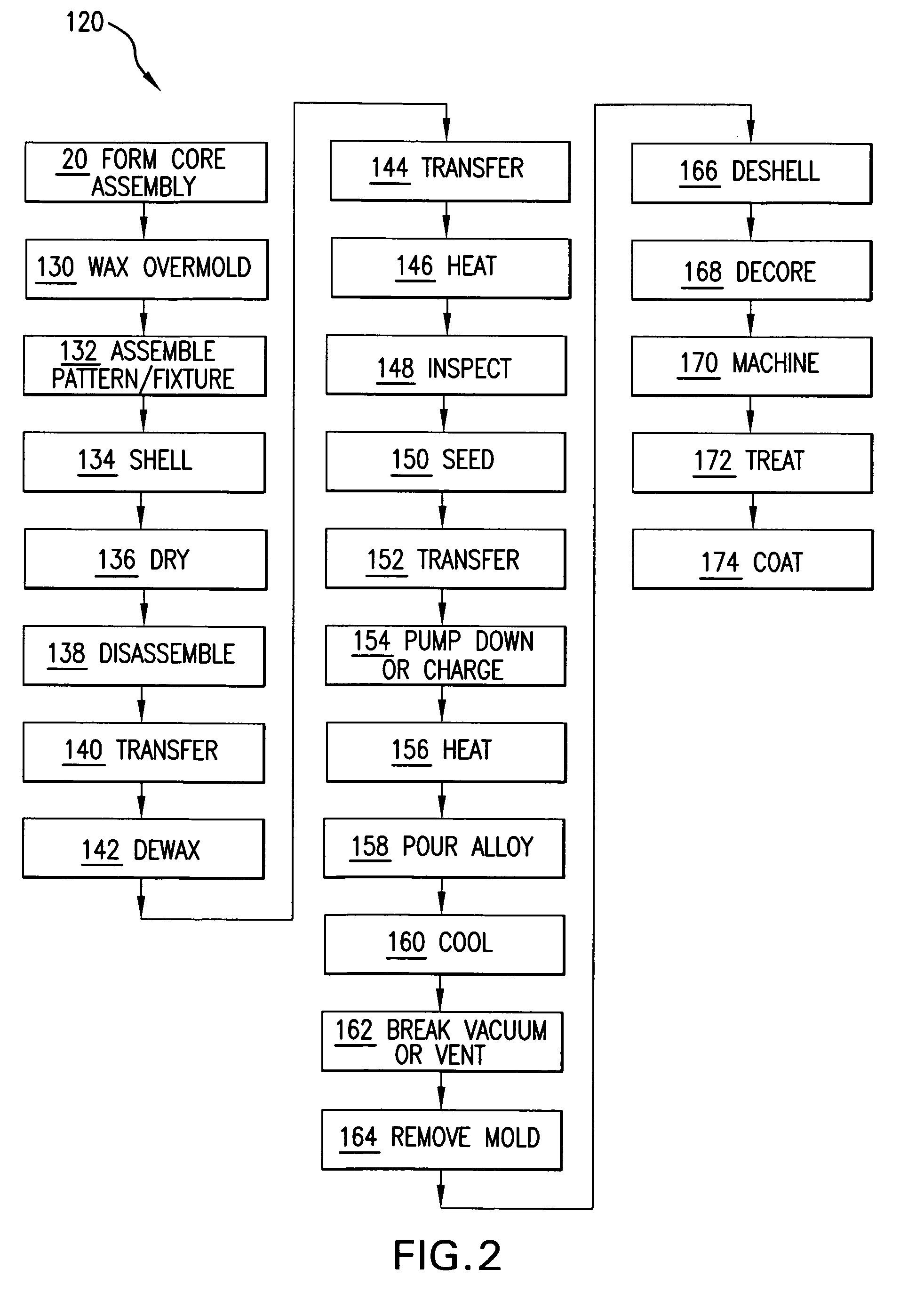
Insulated Investment Casting Mold and Method of Making
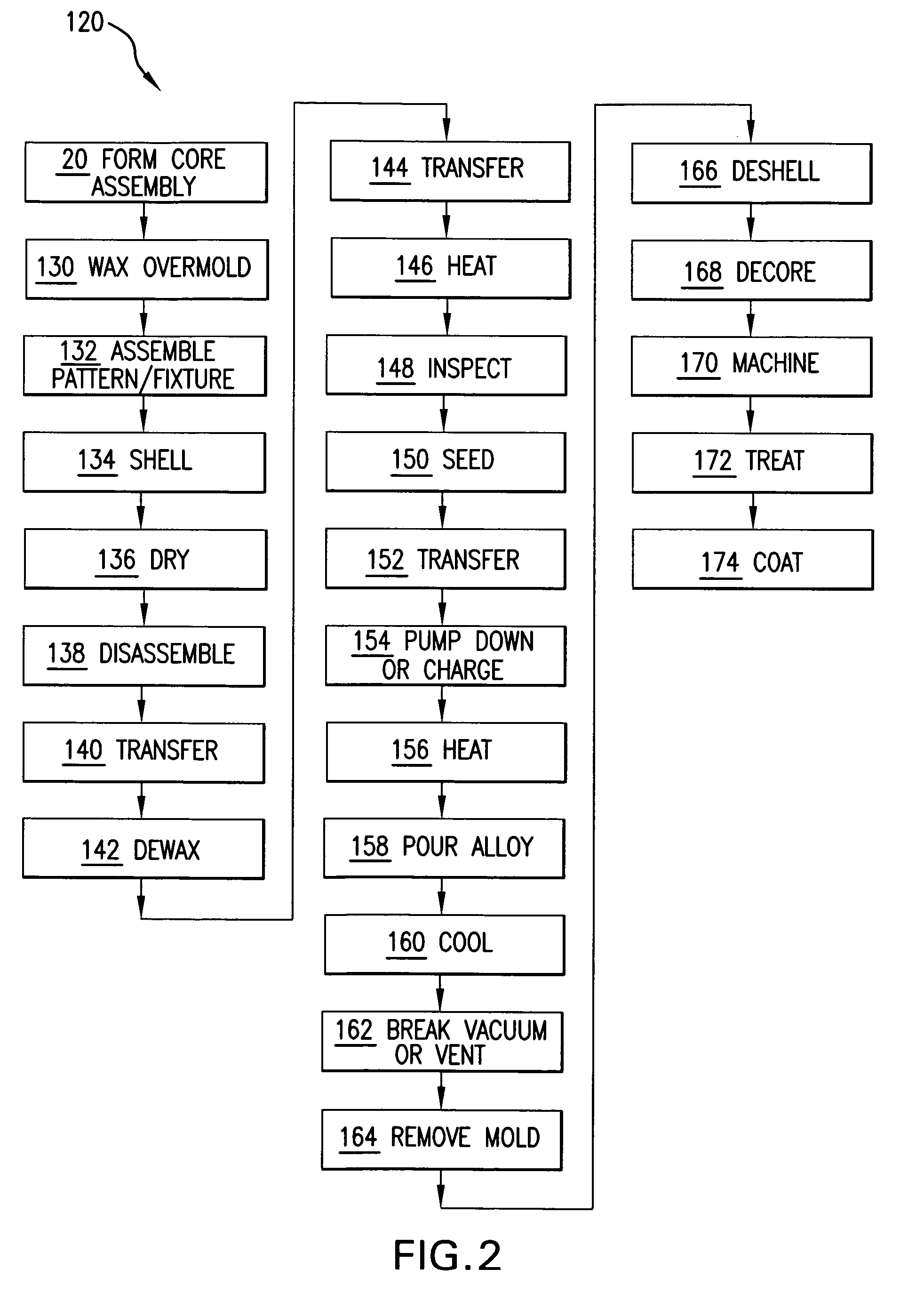
InactiveUS20110114279A1Loss of fluidityAvoid a lot of timeFoundry mouldsFoundry coresPorosityFoaming agent
An insulated investment casting shell mold is made by first mixing at least one refractory material with a slurry vehicle forming a prime coat slurry, and optionally mixing at least one refractory material with a slurry vehicle forming a backup slurry. The prime slurry is coated onto a fugitive pattern and optionally dried and / or stuccoed wherein the stucco has at least one refractory material. Optionally, at least one coat of the backup slurry is applied to the prime coated fugitive pattern and optionally dried and / or stuccoed after each coat of the backup slurry. The backup and stucco may be applied a plurality of times to obtain a desired shell wall thickness. An insulating slurry is formed by introducing gas into a slurry vehicle having at least one refractory material and containing a stabilizer and a foaming agent wherein gaseous bubbles become entrained therein forming an insulating slurry having closed porosity therein. The insulating slurry is coated onto at least one portion of the pattern after the prime coat and preferably at least a portion of the outermost layer of a backup coated pattern has the insulating slurry thereon.
Owner:CERADYNE
Radio frequency identification based exercise behavior management system
An RFID-based exercise behavior management system is disclosed. The system comprises an RFID tag, a front-end subsystem and a back-end subsystem. The RFID tag contains a unique identification for a participant and is carried by or implanted in the participant whose exercise behavior can be recorded automatically when he is engaging exercise in the field where the front-end subsystem is installed. The backend subsystem enables the recorded exercise behavior to be accessed ubiquitously and to be delivered to related personnel. Thus this invention helps any health promoting agent in realizing and developing trackable exercise programs.
Owner:TZU CHI UNIV
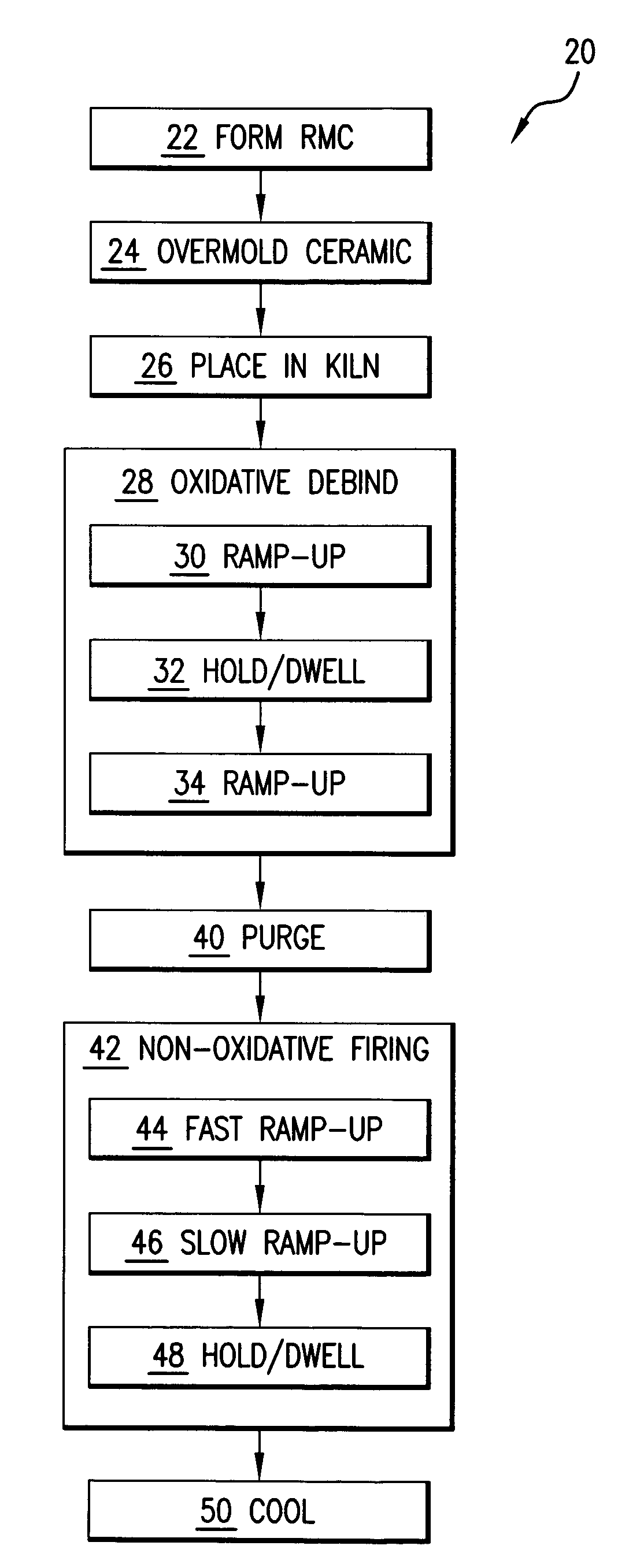
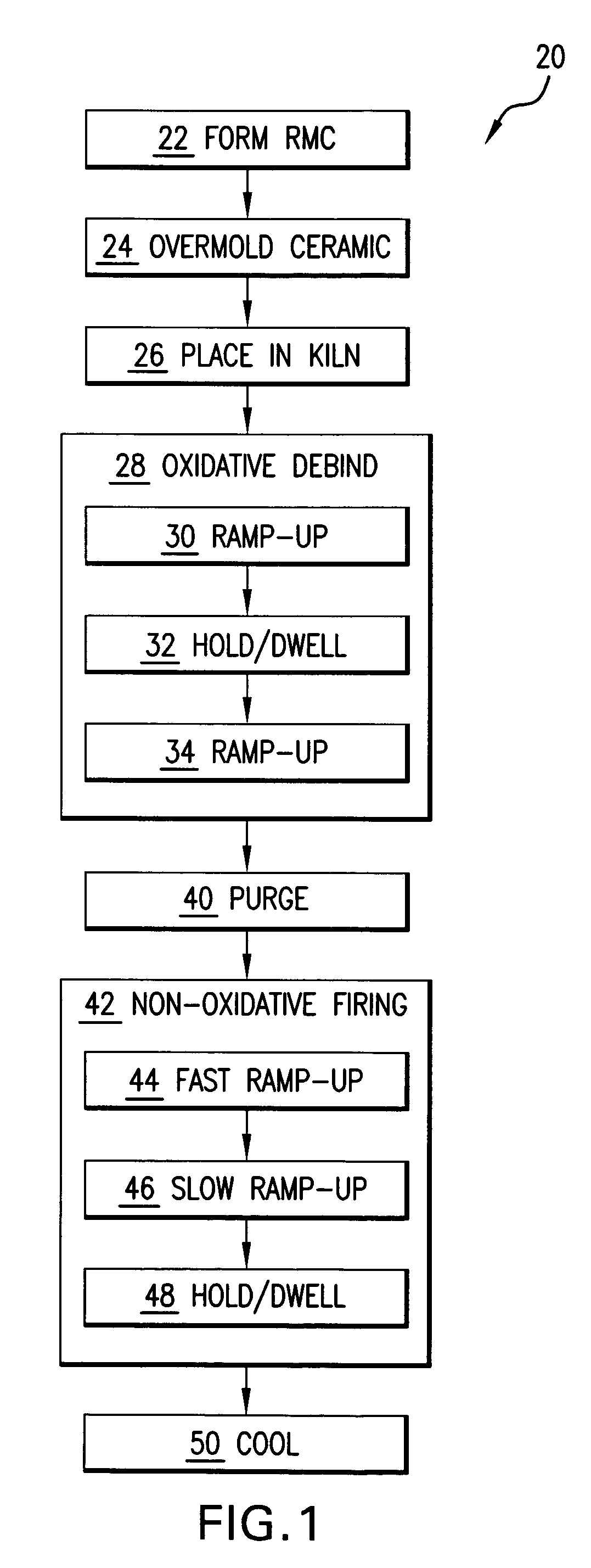
Method for firing a ceramic and refractory metal casting core
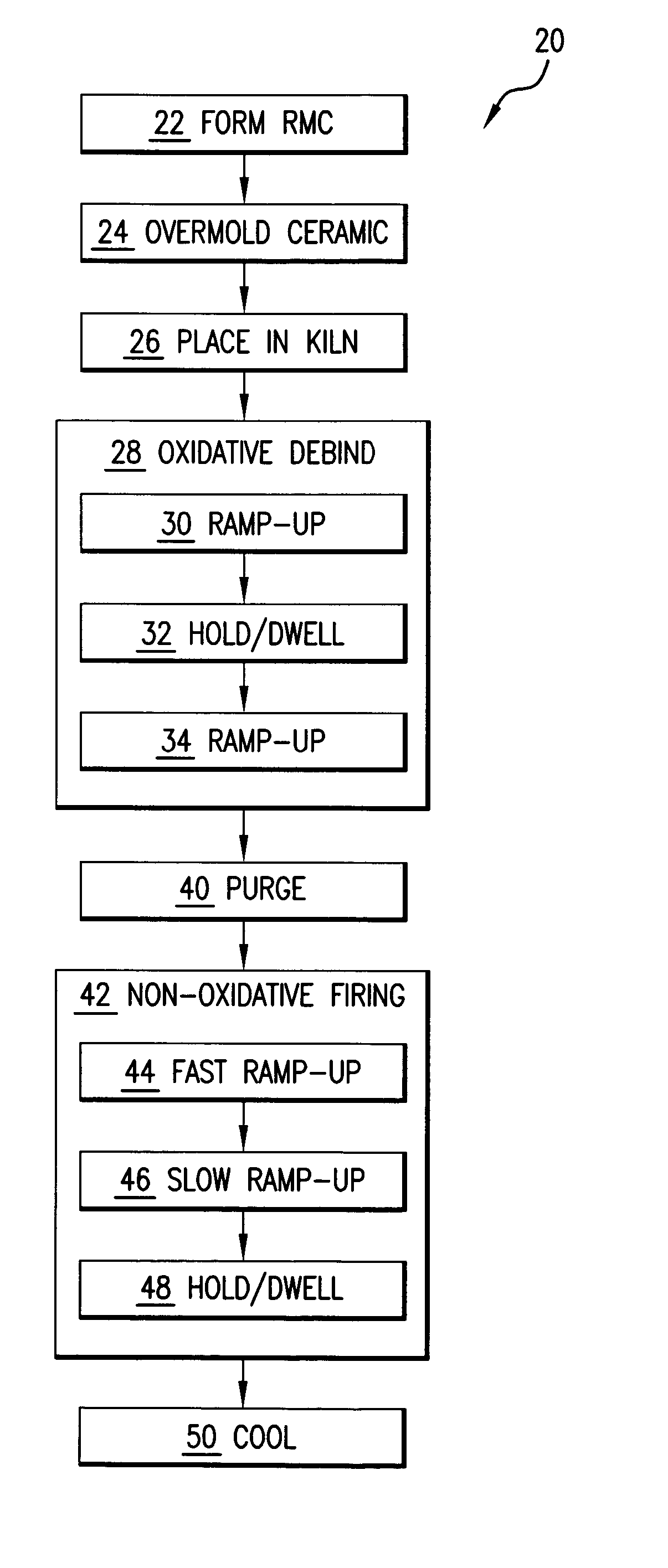
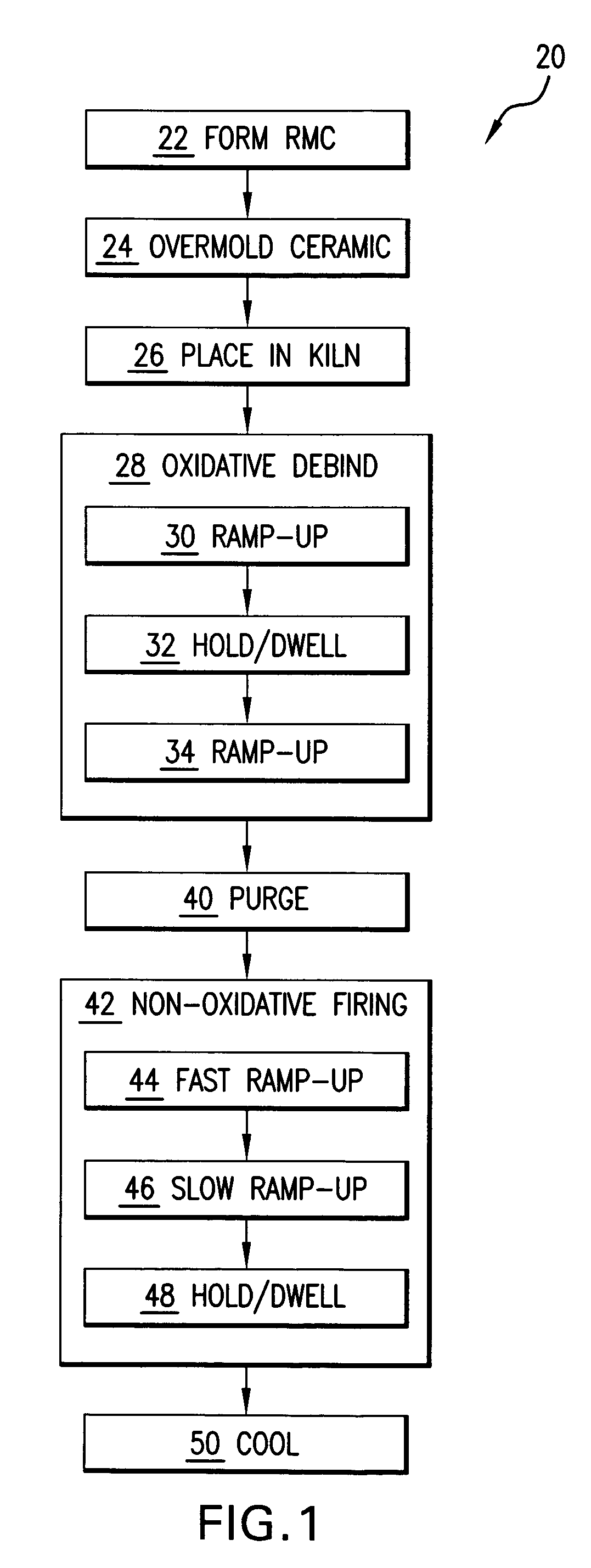
InactiveUS7861766B2Insufficient temperatureAvoid a lot of timeFoundry mouldsFoundry coresInvestment castingNon oxidative
In an investment casting process, a composite core is formed as a combination of ceramic casting core element and a non-ceramic casting core element. The core is heated in an oxidative atmosphere and then heated in a non-oxidative atmosphere.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
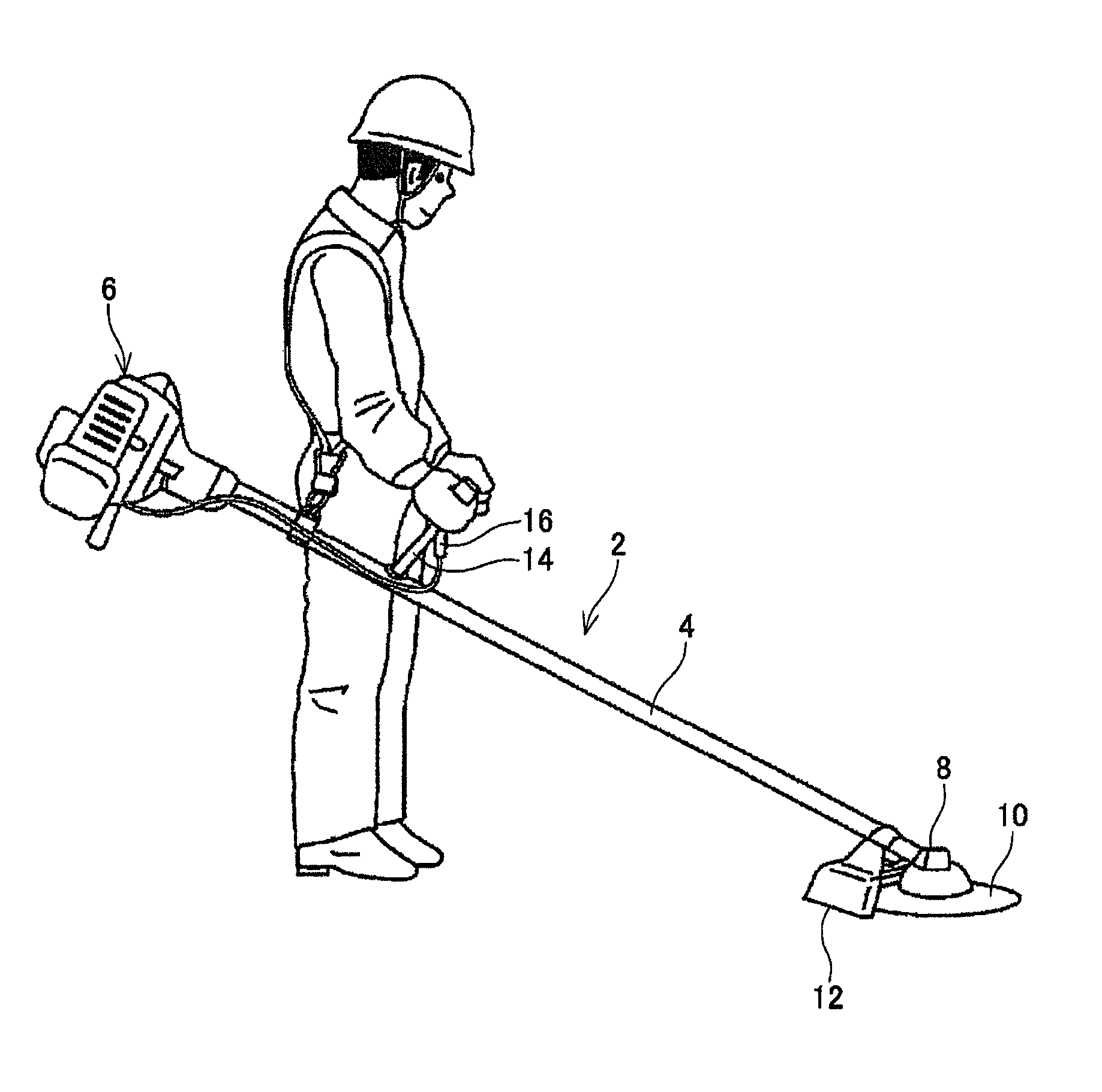
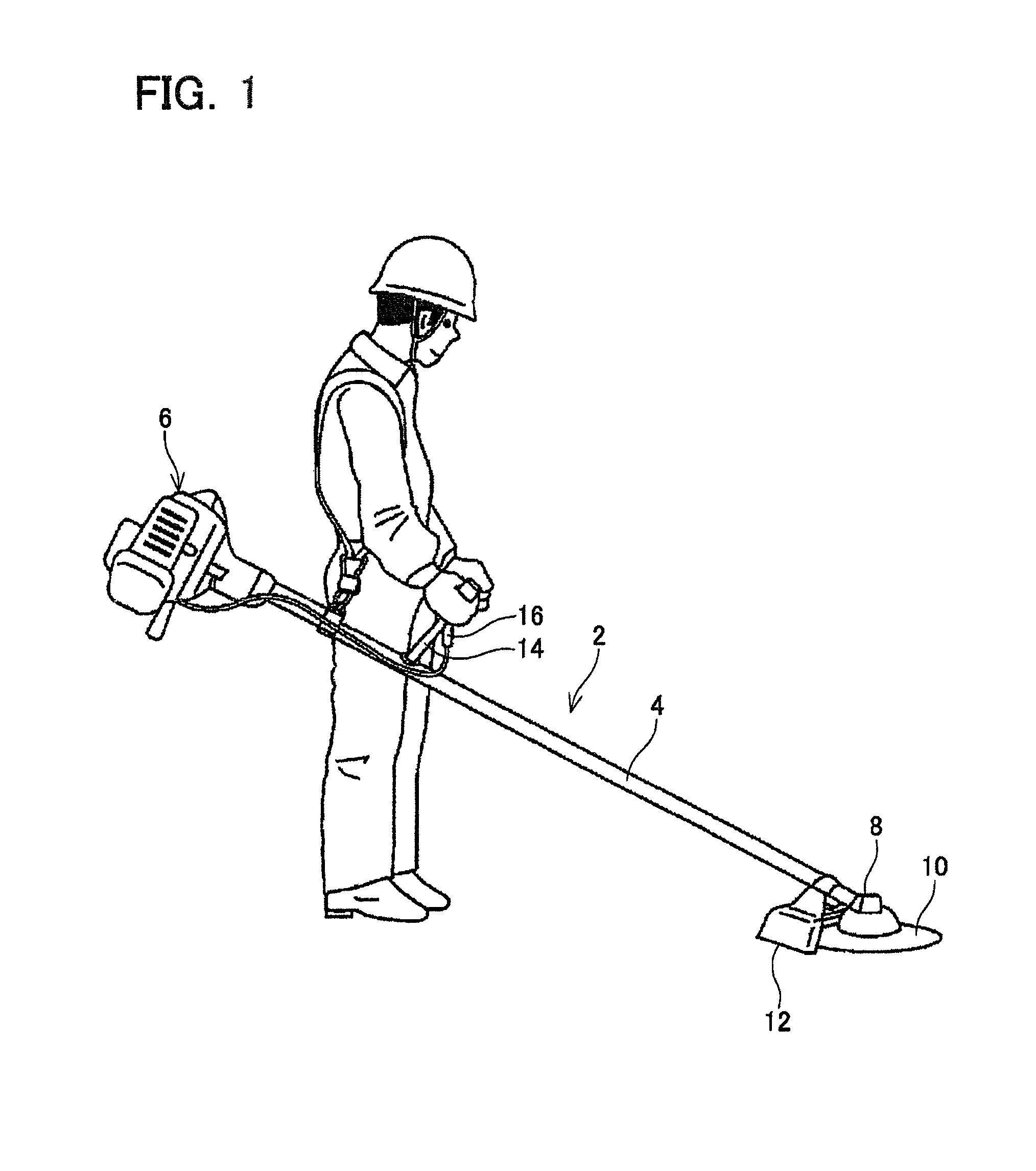
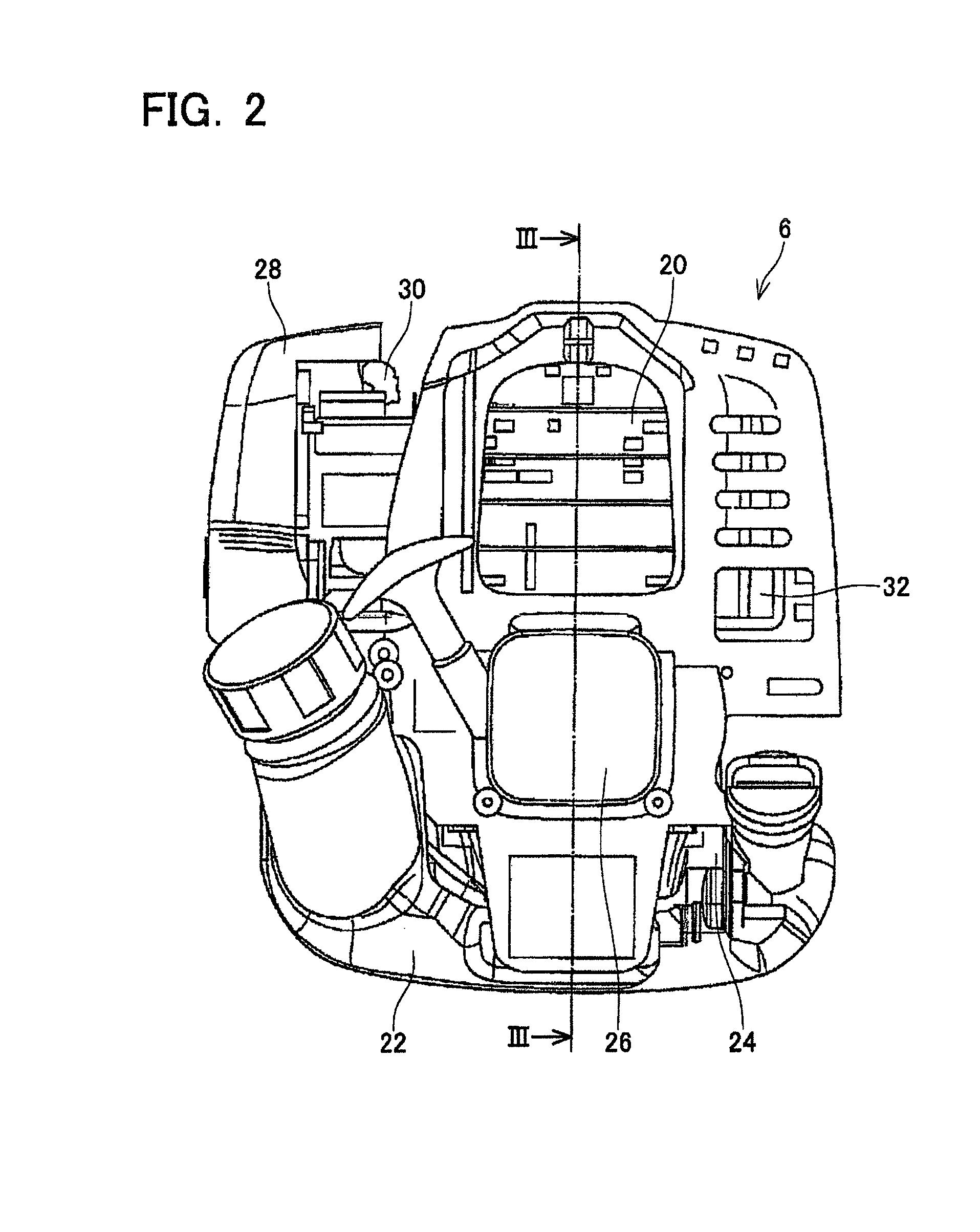
Human-carried work machine powered by hybrid drive system
InactiveUS20140008092A1Increase work outputIncrease powerDrilling rodsConstructionsBrushless motorsCrankcase
A human-carried work machine is provided with an engine and an electric motor as a prime mover for driving a tool. The engine includes an output shaft that is connected to the tool, and the electric motor is configured to apply torque to the output shaft of the engine. The electric motor is an outer rotor-type brushless motor and includes a rotor that is fixed to the output shaft of the engine and a stator core that is fixed to a crankcase of the engine. The rotor includes a peripheral wall that surrounds the stator core and a magnet is disposed on an inner surface of the peripheral wall.
Owner:MAKITA CORP
Vehicle Warning System
An Abrupt Braking Indicator (ABI) that complements a vehicle's existing rear brake light by determining the difference between regular brake pedal usage and dangerous abrupt stops or abrupt-braking that often causes accidents. It is when, and only when, an abrupt stop or hard brake occurs at the differential gravitational value of 0.5 G or more that the present invention emits highly noticeable flashing lights that warn following drivers of the sudden hazard ahead.
Owner:MALIK MOHD B
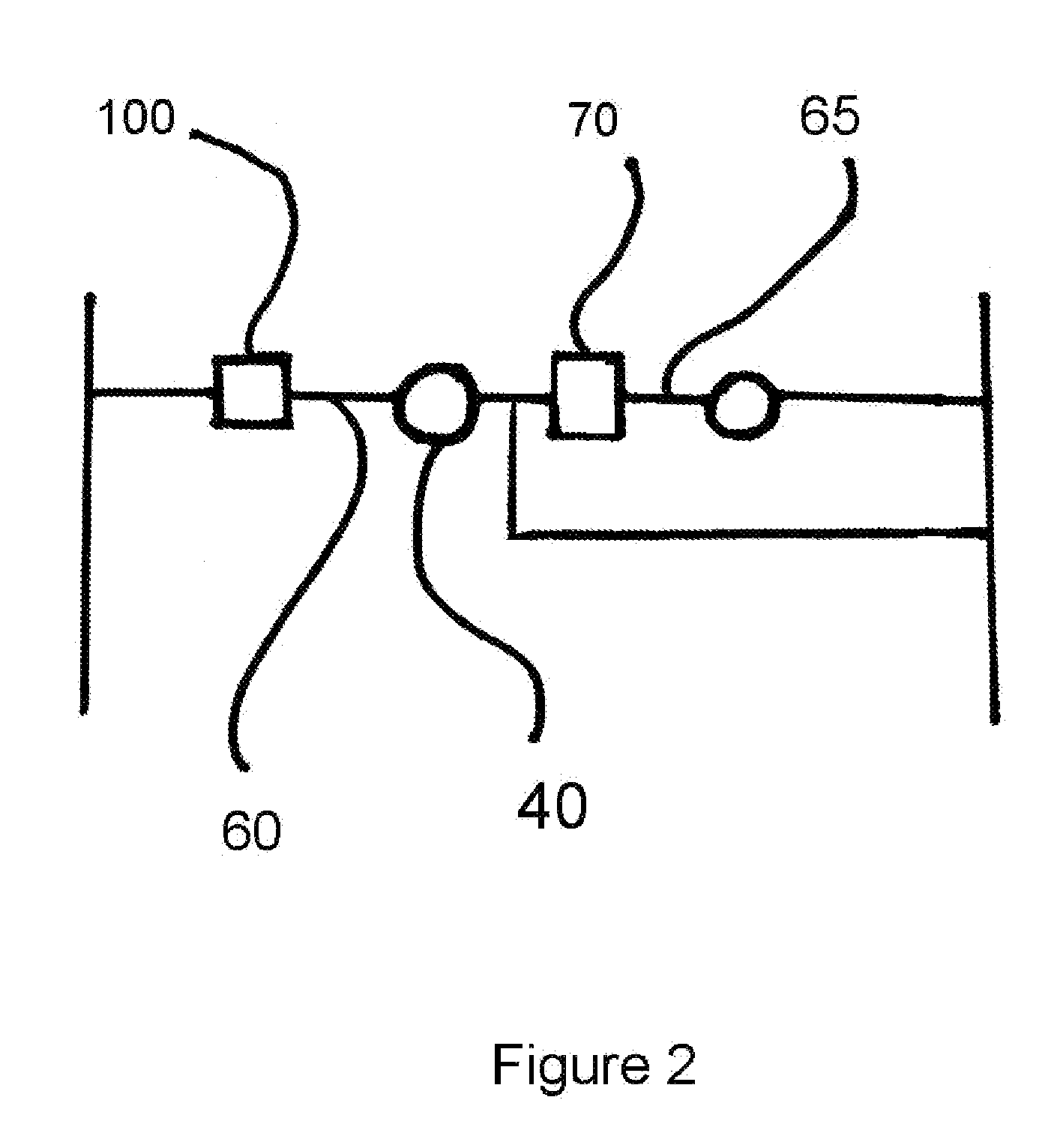
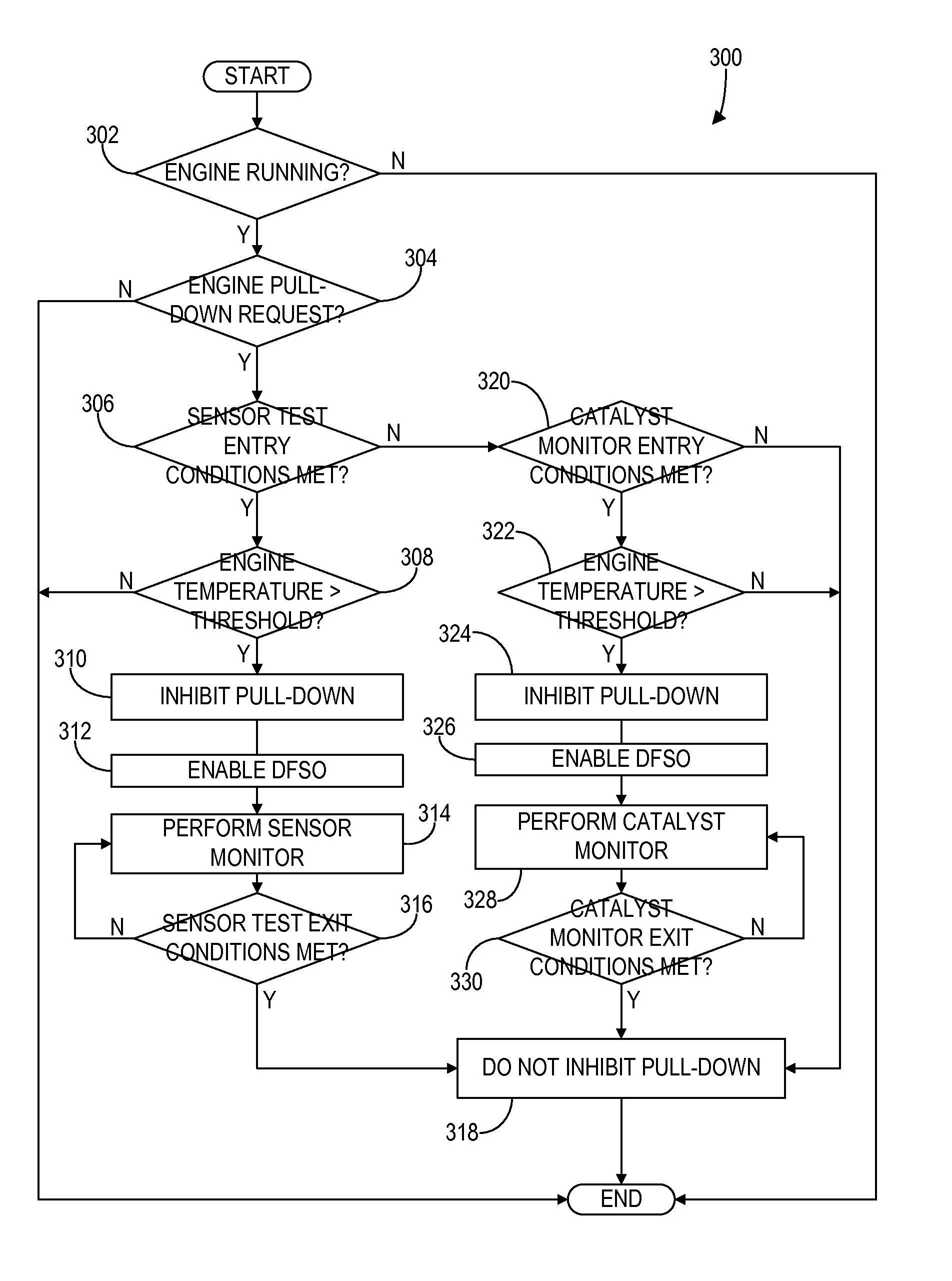
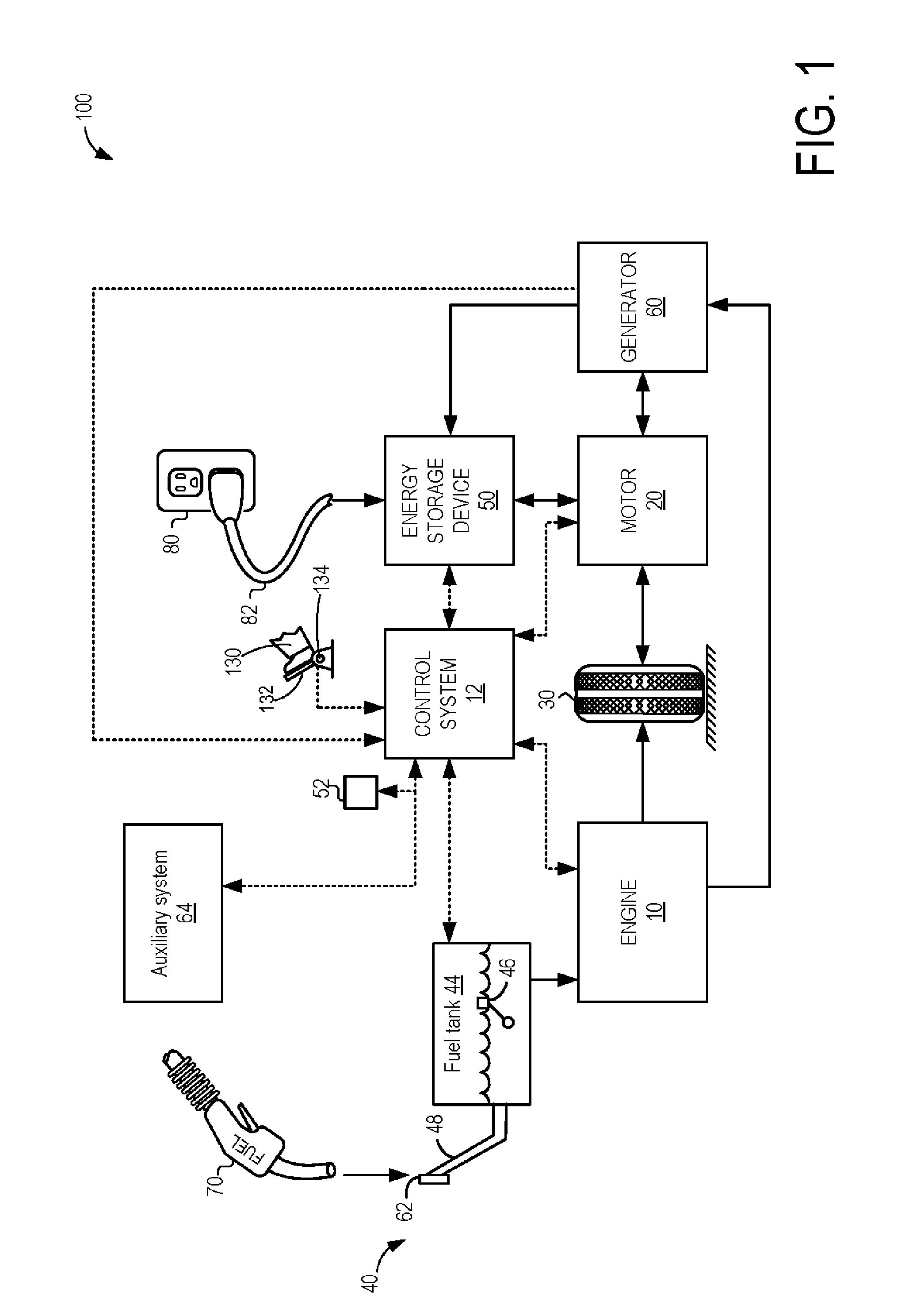
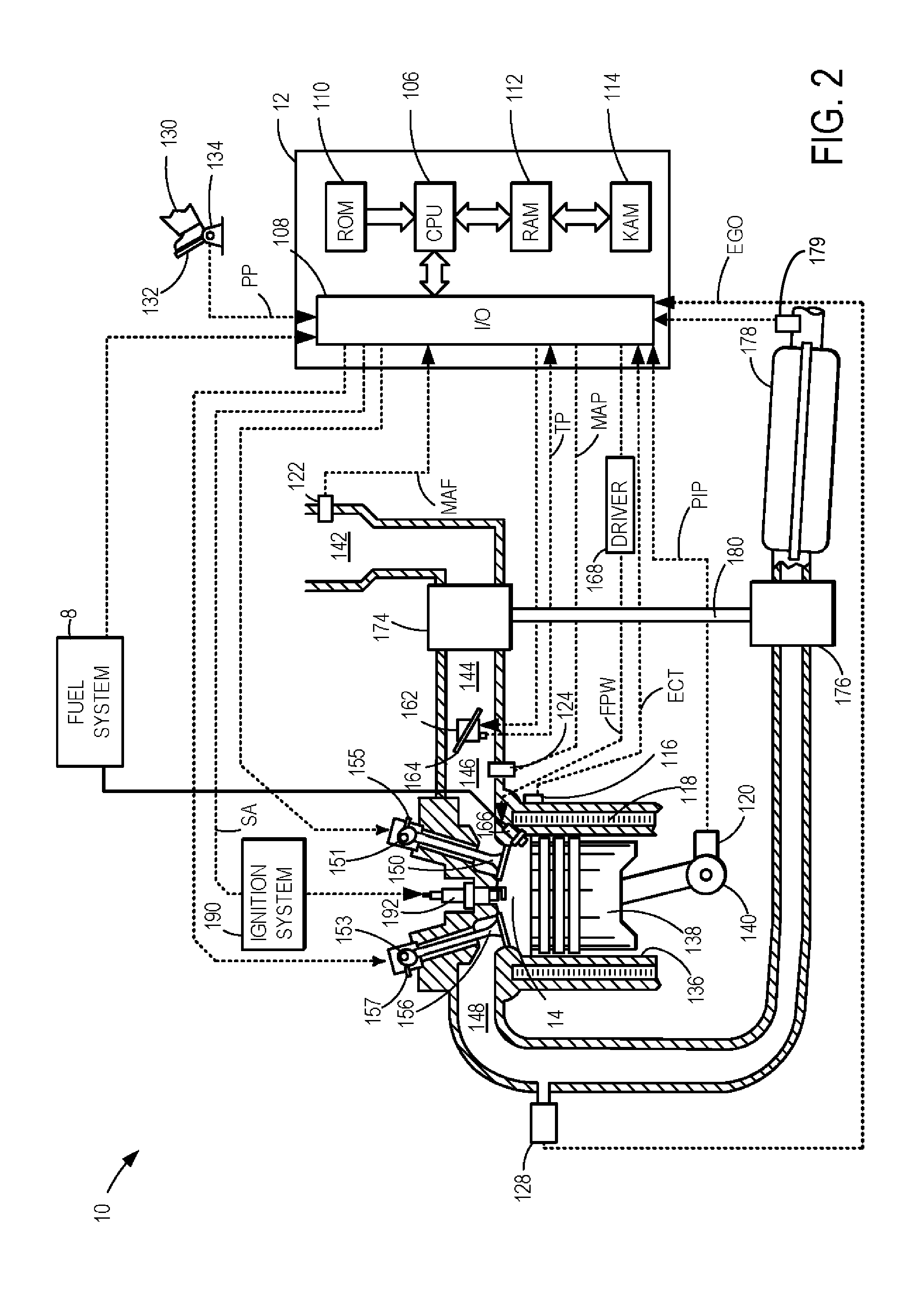
Hybrid vehicle exhaust diagnostics
ActiveUS20140277998A1Shorten operation timeShort engine operation timeHybrid vehiclesAnalogue computers for vehiclesDiagnostic programHybrid vehicle
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for detecting lane departure and apparatus thereof
ActiveUS8311283B2Improve shortcomingsLimit distanceCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsDriver/operatorComputer graphics (images)
A method for detecting the lane departure of a vehicle includes an image recognition process and a deviation estimation process. The image recognition process includes the following steps: an image capturing step for capturing image frame data by using an image capturing unit; and a lane line recognition for analyzing the image frame data for determining the lane lines. By using a quadratic curve fitting equation, a plurality of lane line being detected so as to establish a road geometry estimation model. The road geometry estimation model is inputted into the deviation estimation process to detect the lane departure of the vehicle so as to alert the driver. Furthermore, an apparatus for detecting the deviation of the vehicle, comprising: an image capturing unit, a processing unit and a signal output unit.
Owner:AUTOMOTIVE RES & TESTING CENT
Vehicle warning system
An Abrupt Braking Indicator (ABI) that complements a vehicle's existing rear brake light by determining the difference between regular brake pedal usage and dangerous abrupt stops or abrupt-braking that often causes accidents. It is when, and only when, an abrupt stop or hard brake occurs at the differential gravitational value of 0.5 G or more that the present invention emits highly noticeable flashing lights that warn following drivers of the sudden hazard ahead.
Owner:MALIK MOHD B
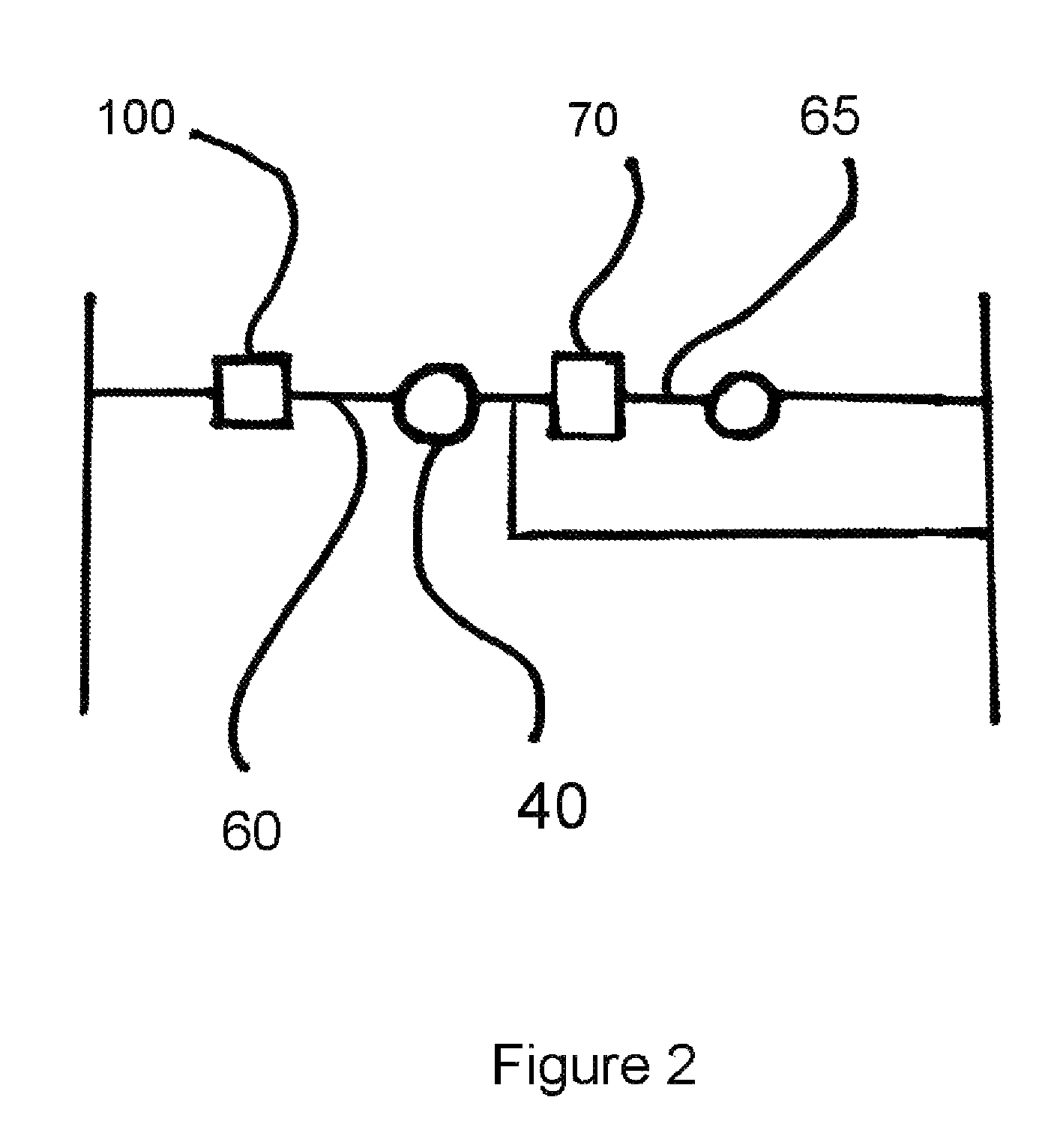
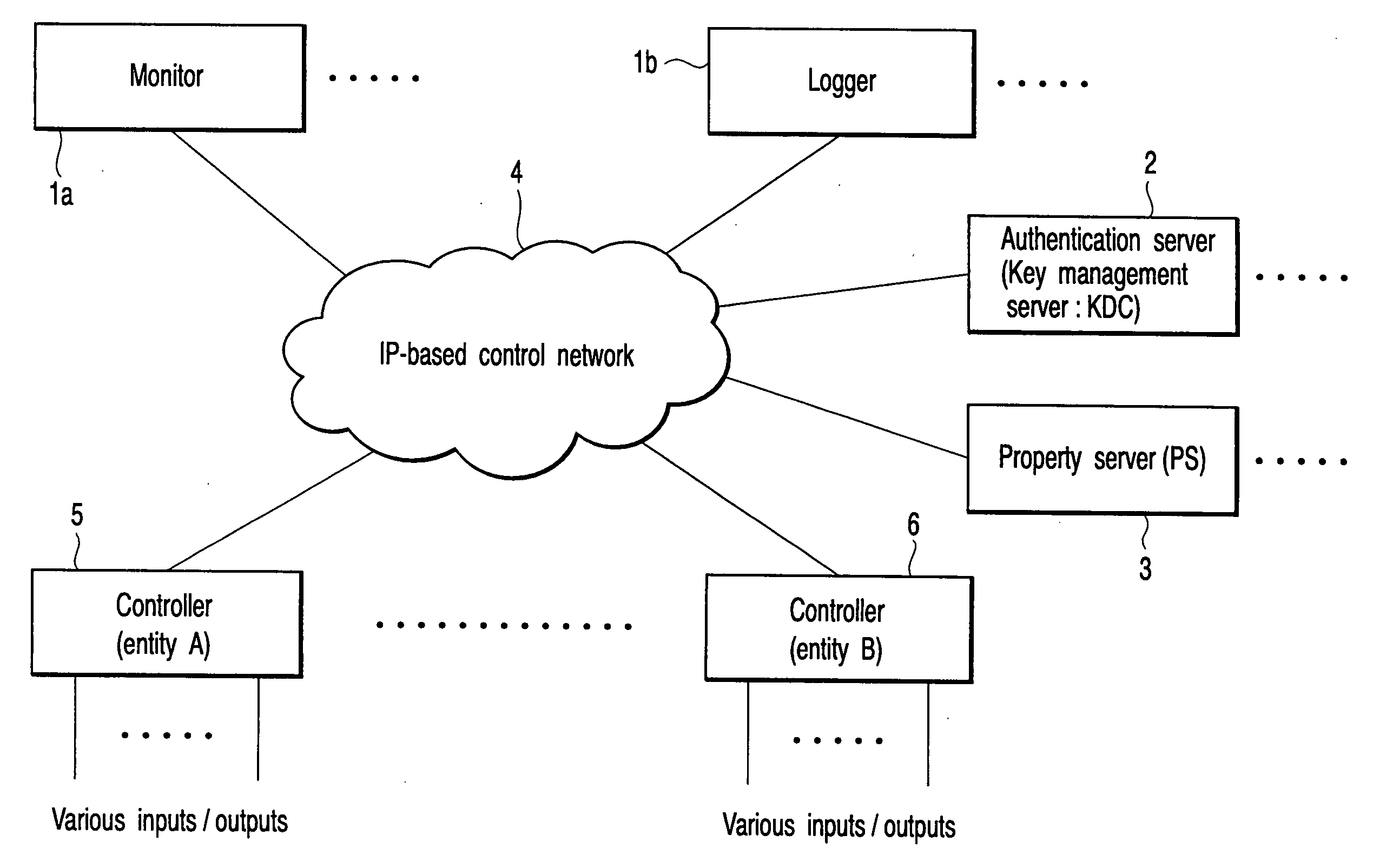
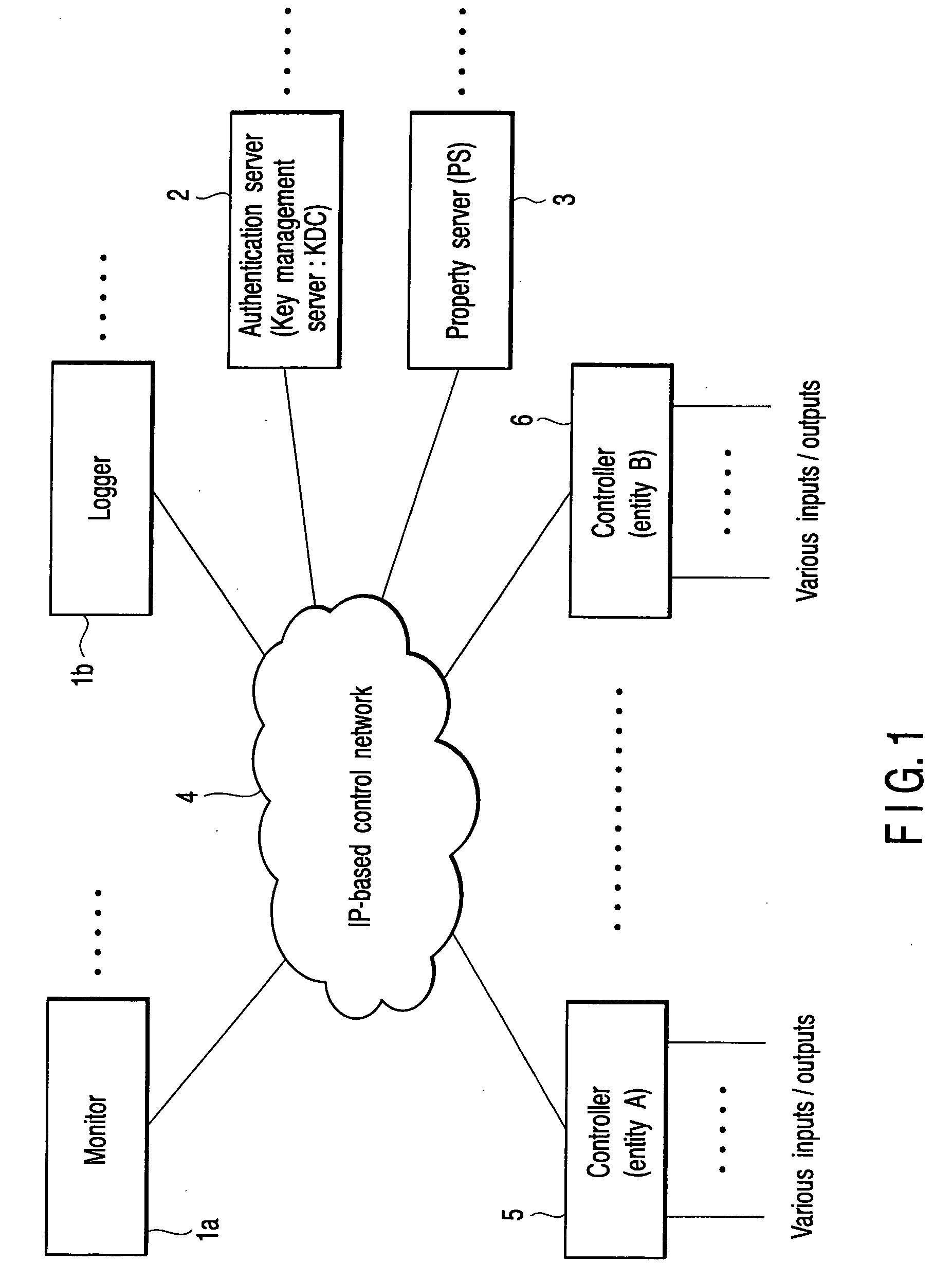
Network information setting method, network system and communication device
InactiveUS20050135271A1Avoid a lot of timeOptimizationKey distribution for secure communicationData switching by path configurationSecure communicationNetwork addressing
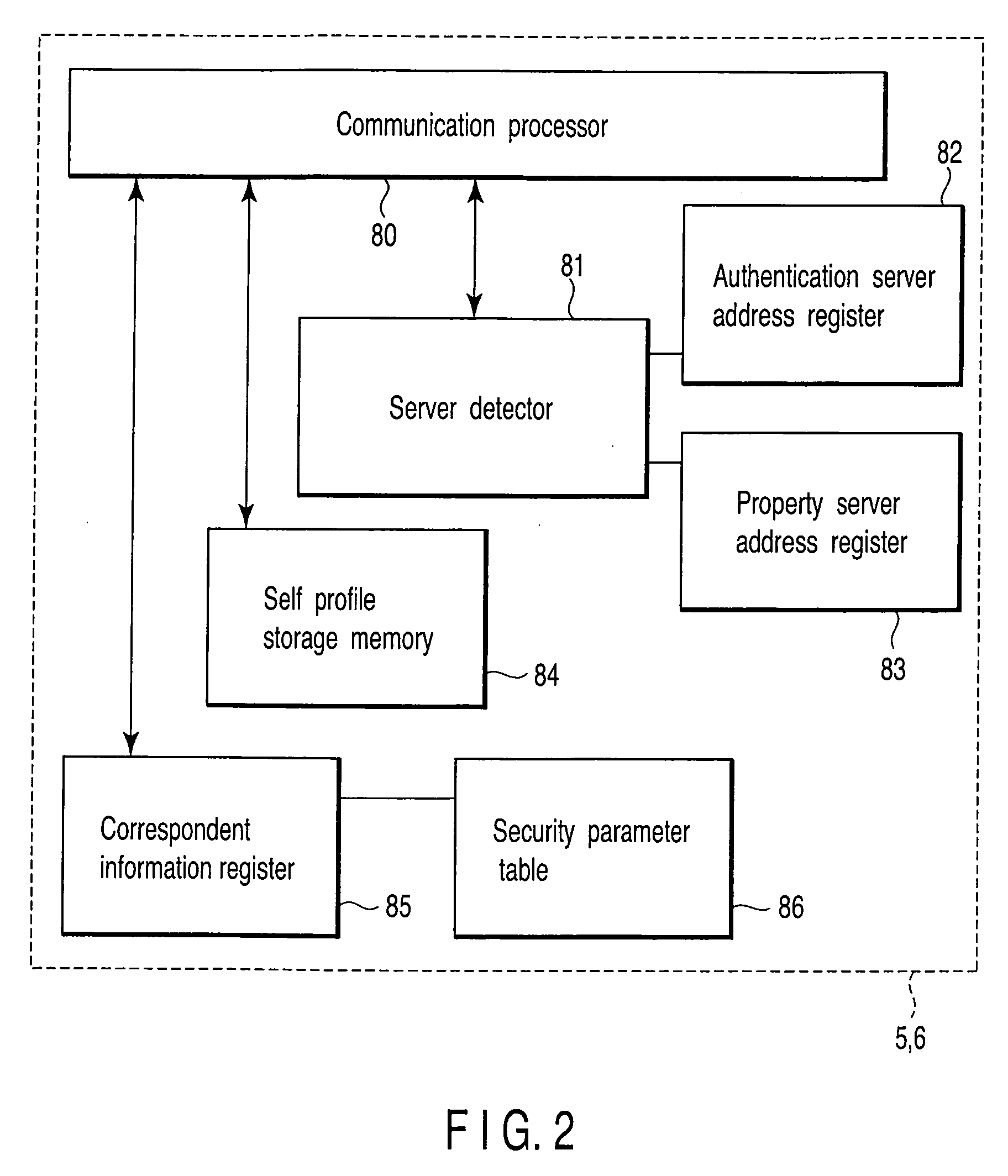
Property information of a communication device is initialized in a second server when the communication device is connected to a control network to which a first server for storing key information and a second server for storing property information are connected. Key information necessary for security communication with respect to the second server is acquired from the first server and property information containing at least an identifier and network address of the communication device is transmitted to the second server via security communication using the key information.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Method and device for decoding a scalable video signal utilizing an inter-layer prediction
InactiveUS20130028324A1Execution time missTime miss rateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionInter layerComputer architecture
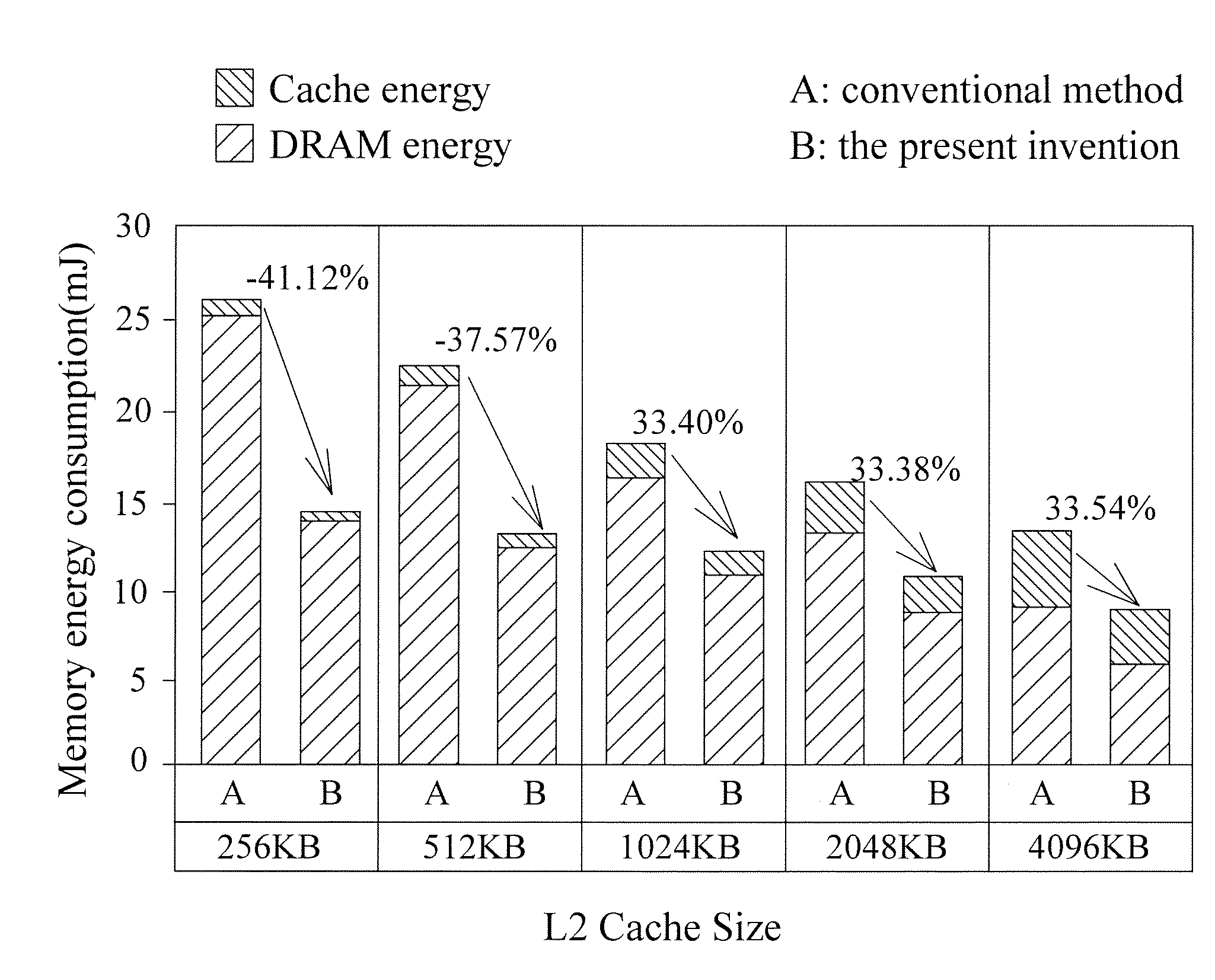
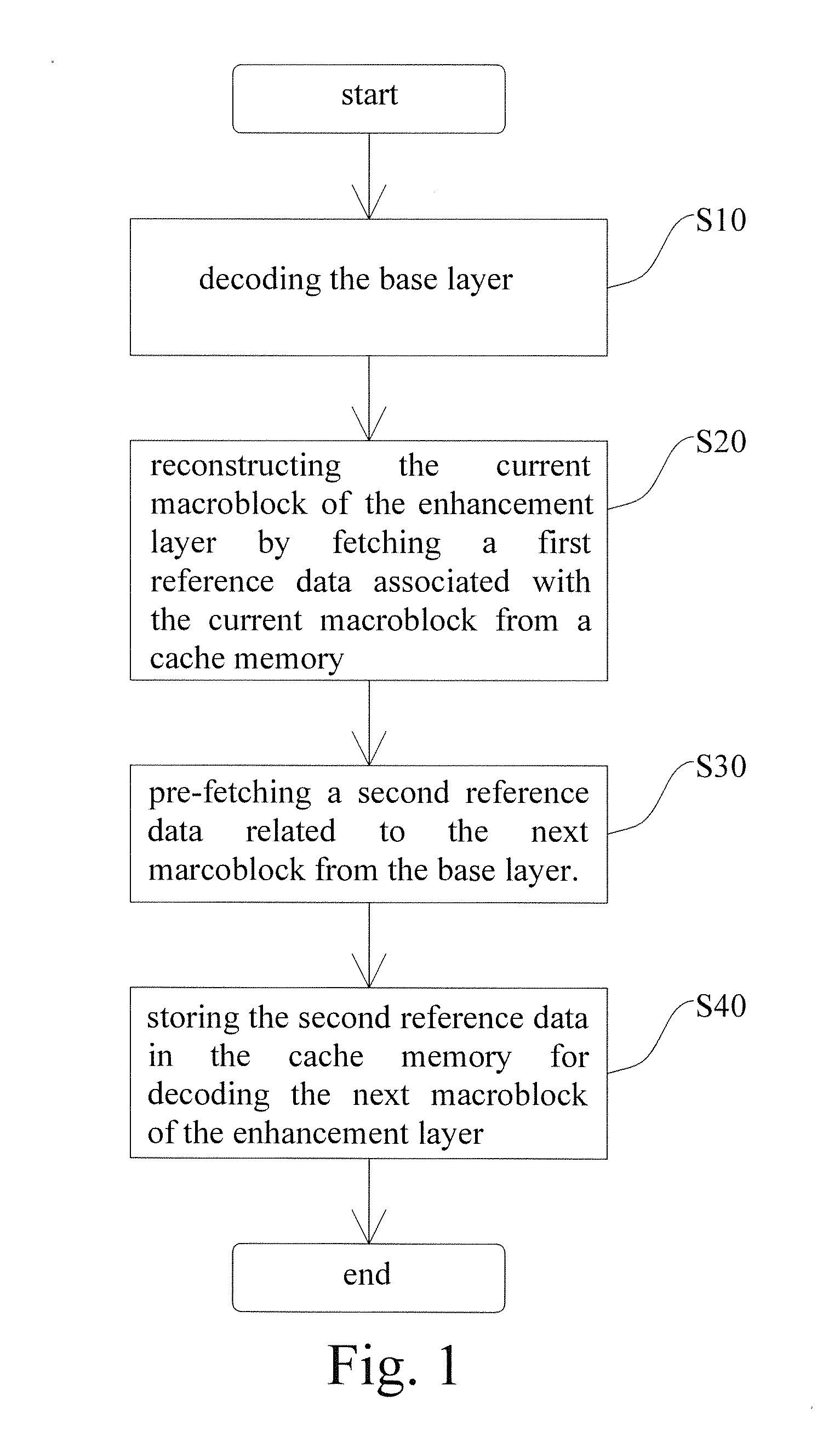
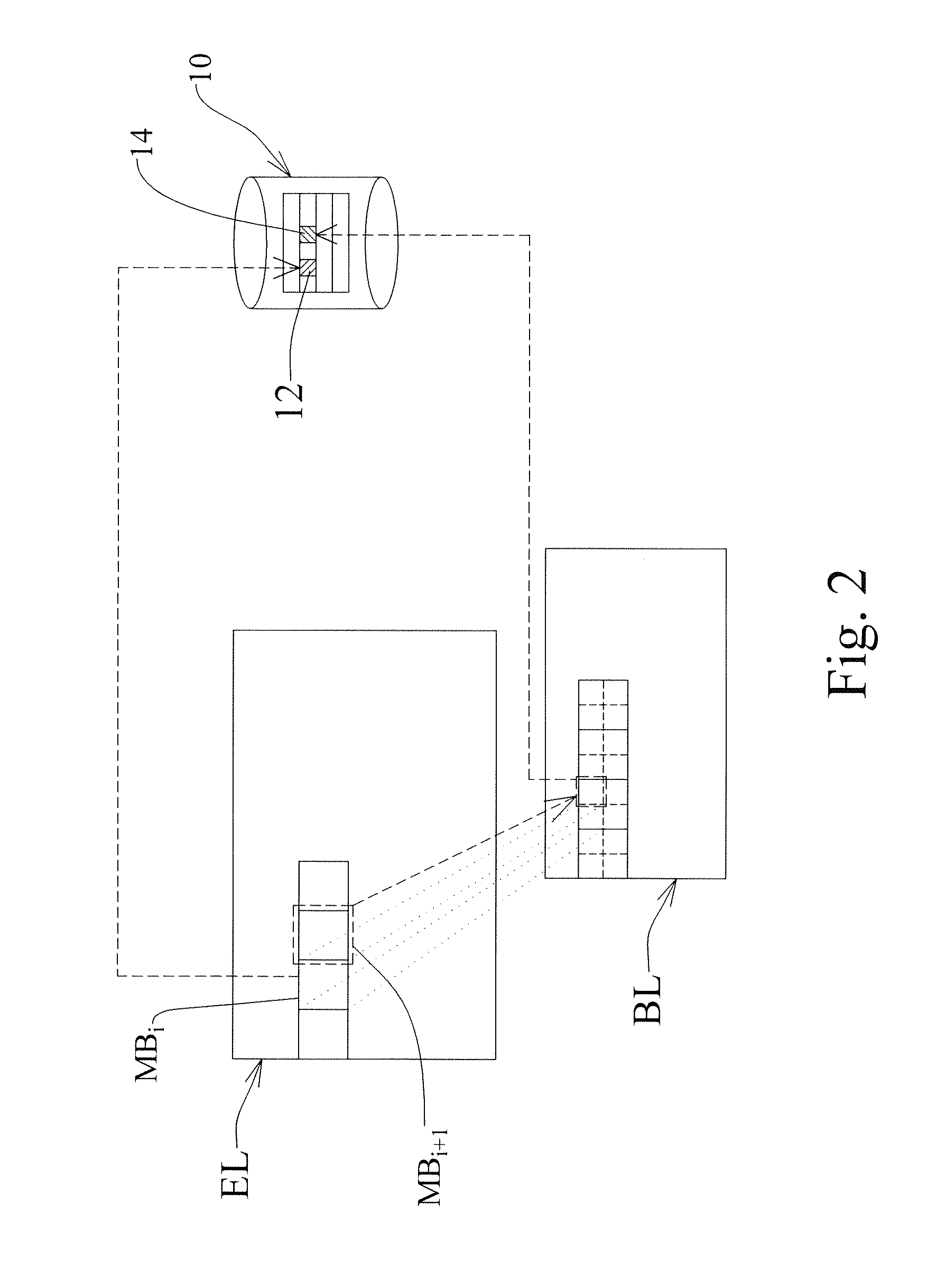
A method and device for decoding a scalable video signal utilizing an inter-layer prediction are provided herein. An inter-layer pre-fetch scheme (IPS) is presented to improve the performance for scalable video coding (SVC) decoder. With proposed invention, the required information for inter-layer prediction in SVC technique will be pre-fetched ahead when reconstructing the enhancement layer so that the cache miss rate can be reduced significantly. Accordingly, the execution time and memory energy consumptions can be improved.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
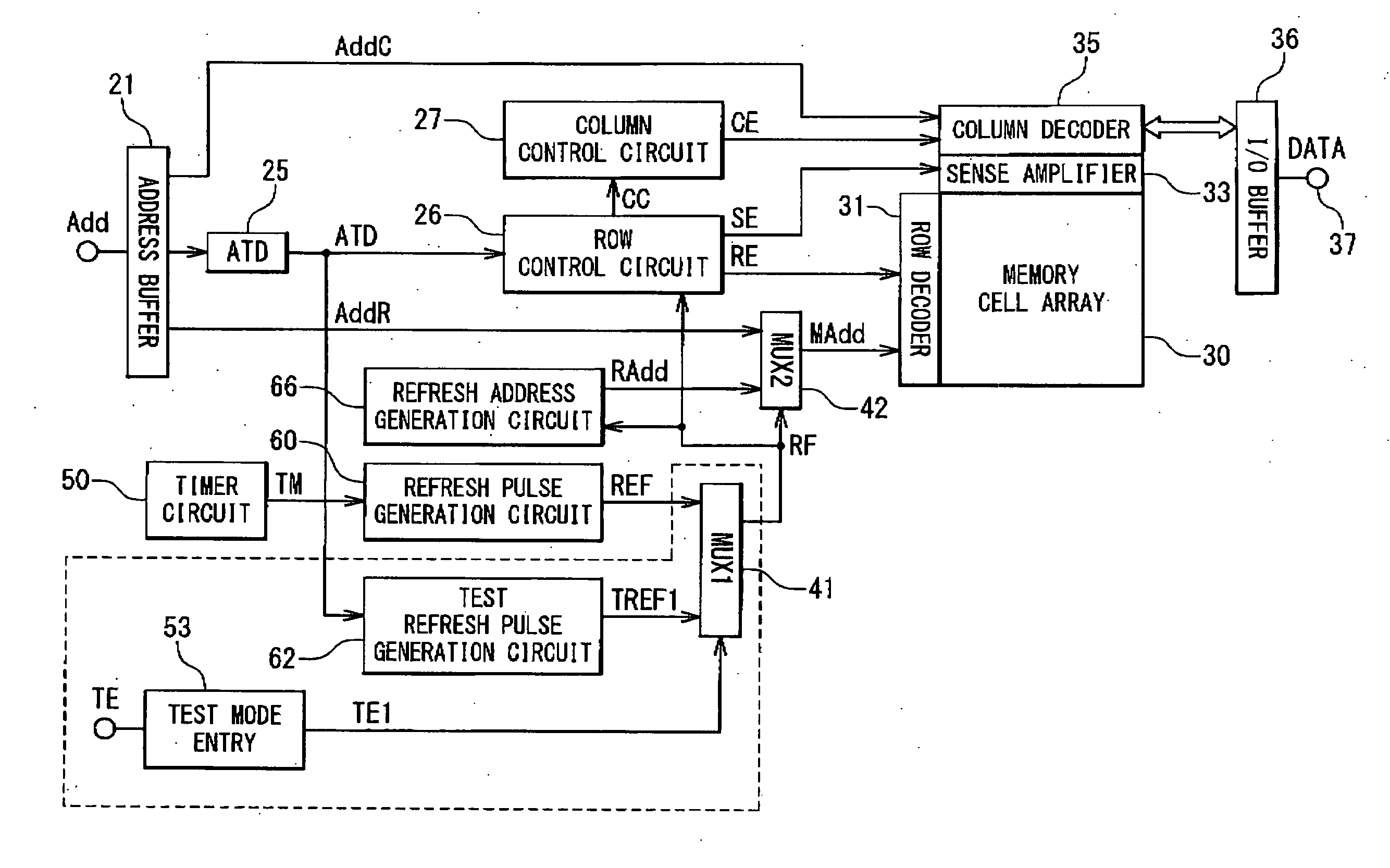
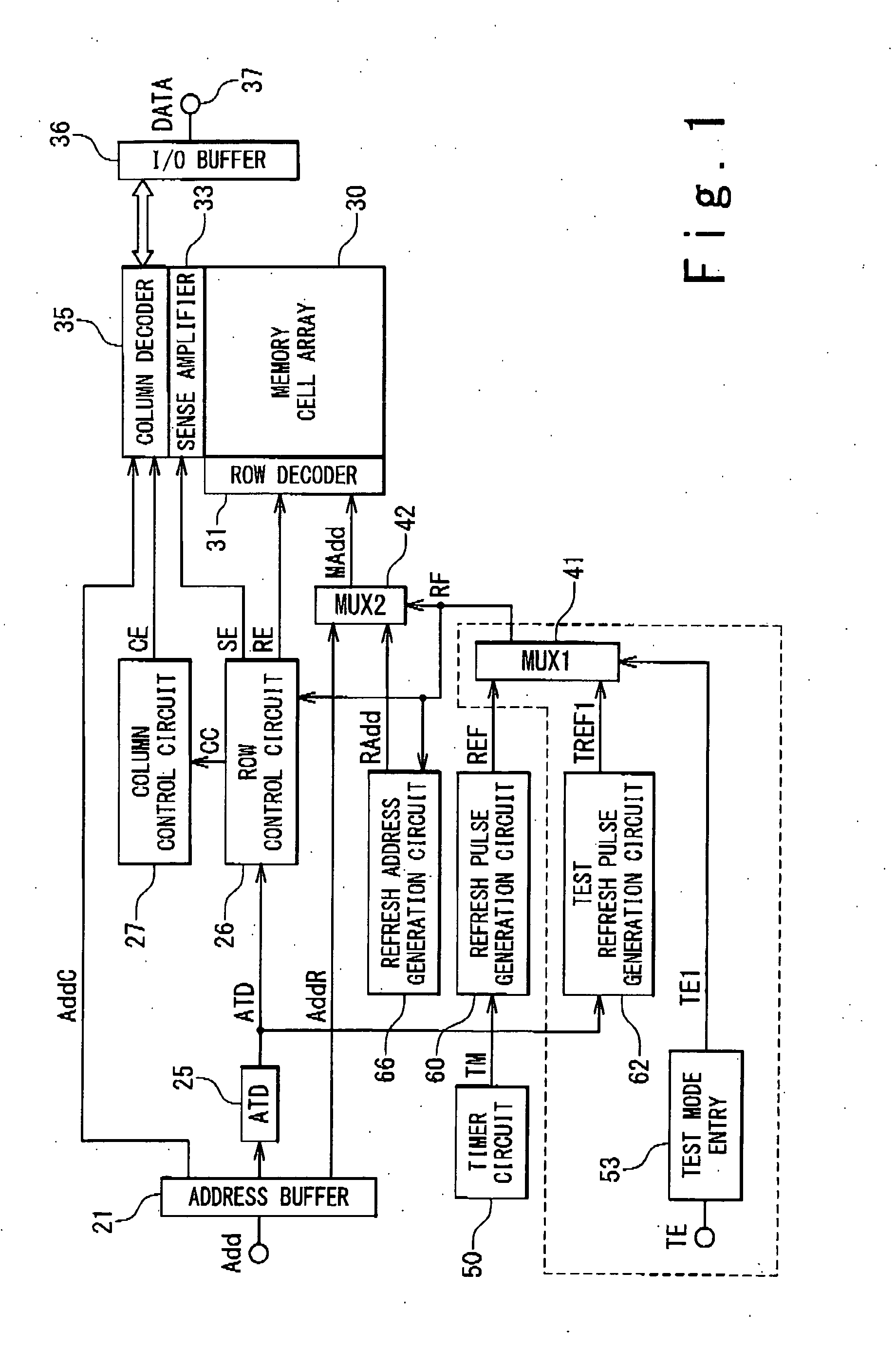
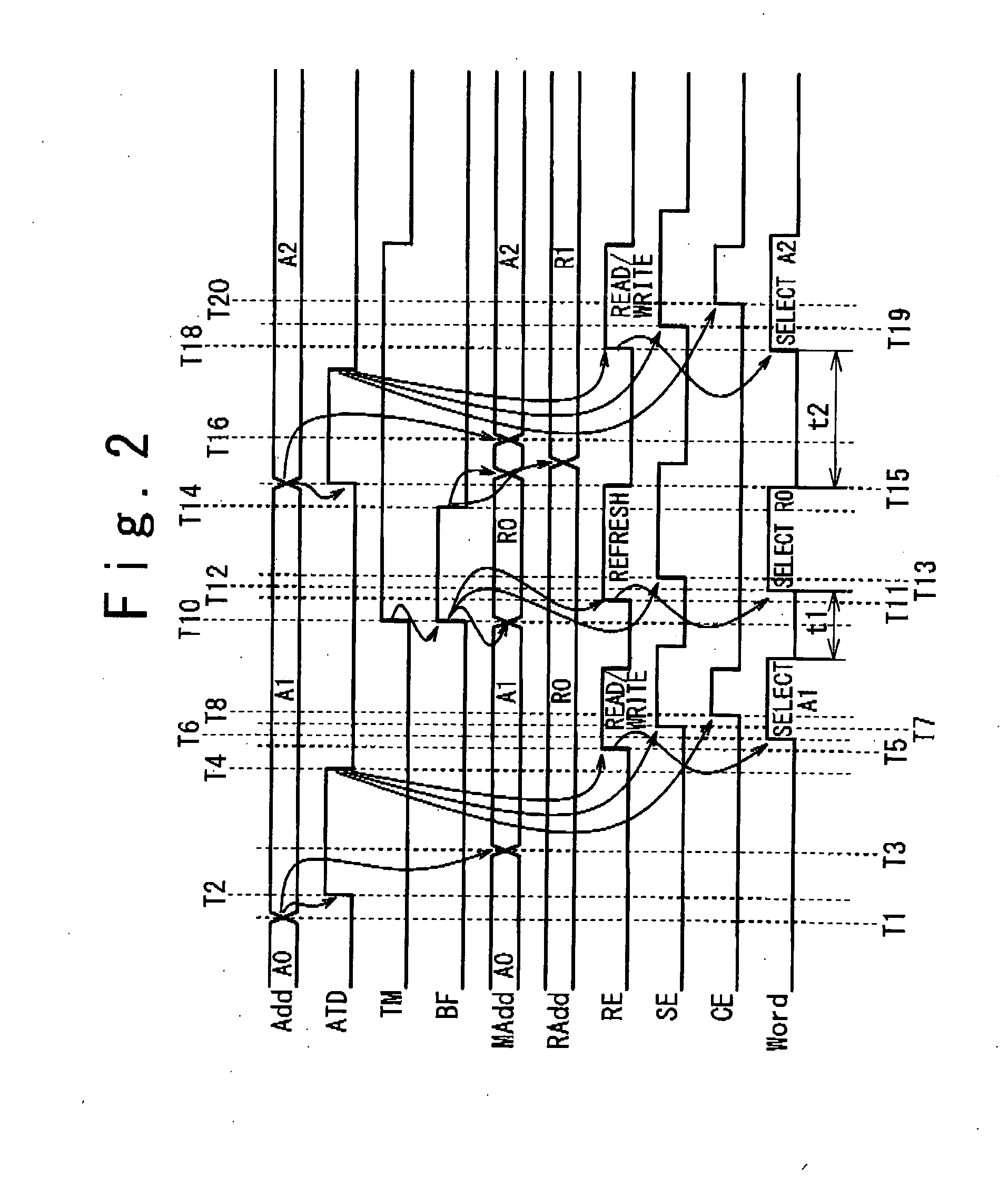
Semiconductor storage device and refresh control method thereof
In a large capacity semiconductor storage device having a multi-bank configuration, it is desired to reduce a peak current of one refresh operation, to avoid an interference between adjacent banks, and to prevent a data breaking of a memory cell caused by a lack of a data hold time. A semiconductor storage device includes: a memory cell array part including a plurality of banks; a refresh control circuit configured to output a refresh timing control signal periodically; and an access control circuit configured to perform a refresh operation on a group of banks which are not adjacent to one another in accordance with a preset combination of banks which are simultaneously activated and a preset activating order when the refresh timing control signal is supplied.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Conjugate roller drive
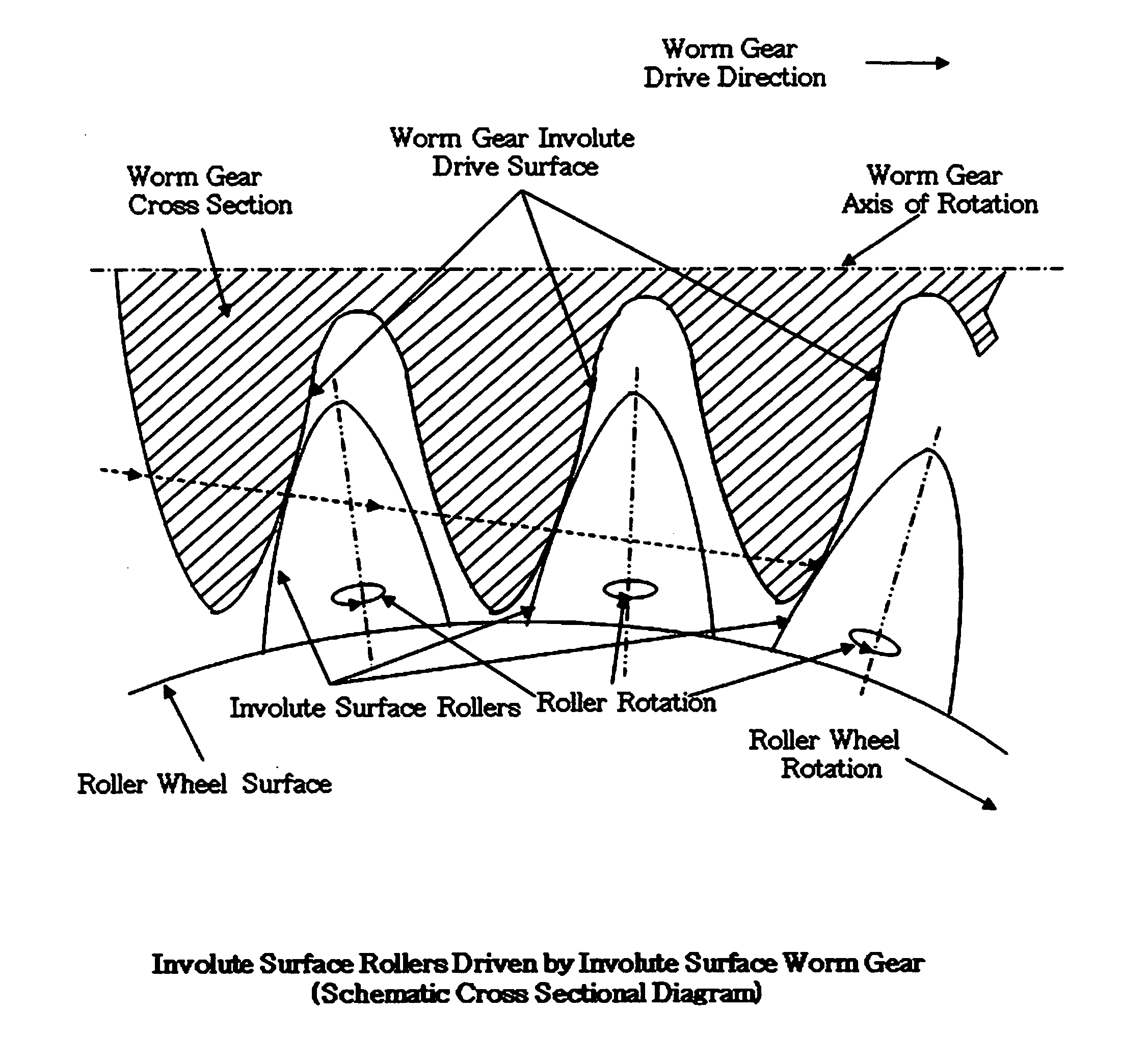
InactiveUS20100212444A1Readily apparentEfficient energy transferPortable liftingToothed gearingsEnergy lossWorm drive
This invention provides improvements to worm drives for mechanical power transmission and roller wheels and the worm screws for use in such drives. The principal innovation is utilizing conjugate mesh between the worm screw and the roller wheel by shaping both the surfaces of the threads of the worm screw and the driven surfaces of the roller tips so that they become conjugate surfaces that accomplish the most efficient energy transfer.Previous worm drive approaches have emphasized conforming shapes for the roller tips and the worm screw as well as certain other techniques in an attempt to compensate certain inherent limitations to energy transfer between driving and driven surfaces. This has caused greater energy losses in the gearing mechanism with corresponding decreased power transfer efficiency. The use of conjugate shapes for the roller tips and the driving worm gear surface represents a significant improvement to the concept.
Owner:SMITH THOMAS DAVID
Circuit for compensating color shift of a color sequential display method and method thereof
InactiveUS20130027445A1Response time is insufficientAvoid a lot of timeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingPattern recognitionColor compensation
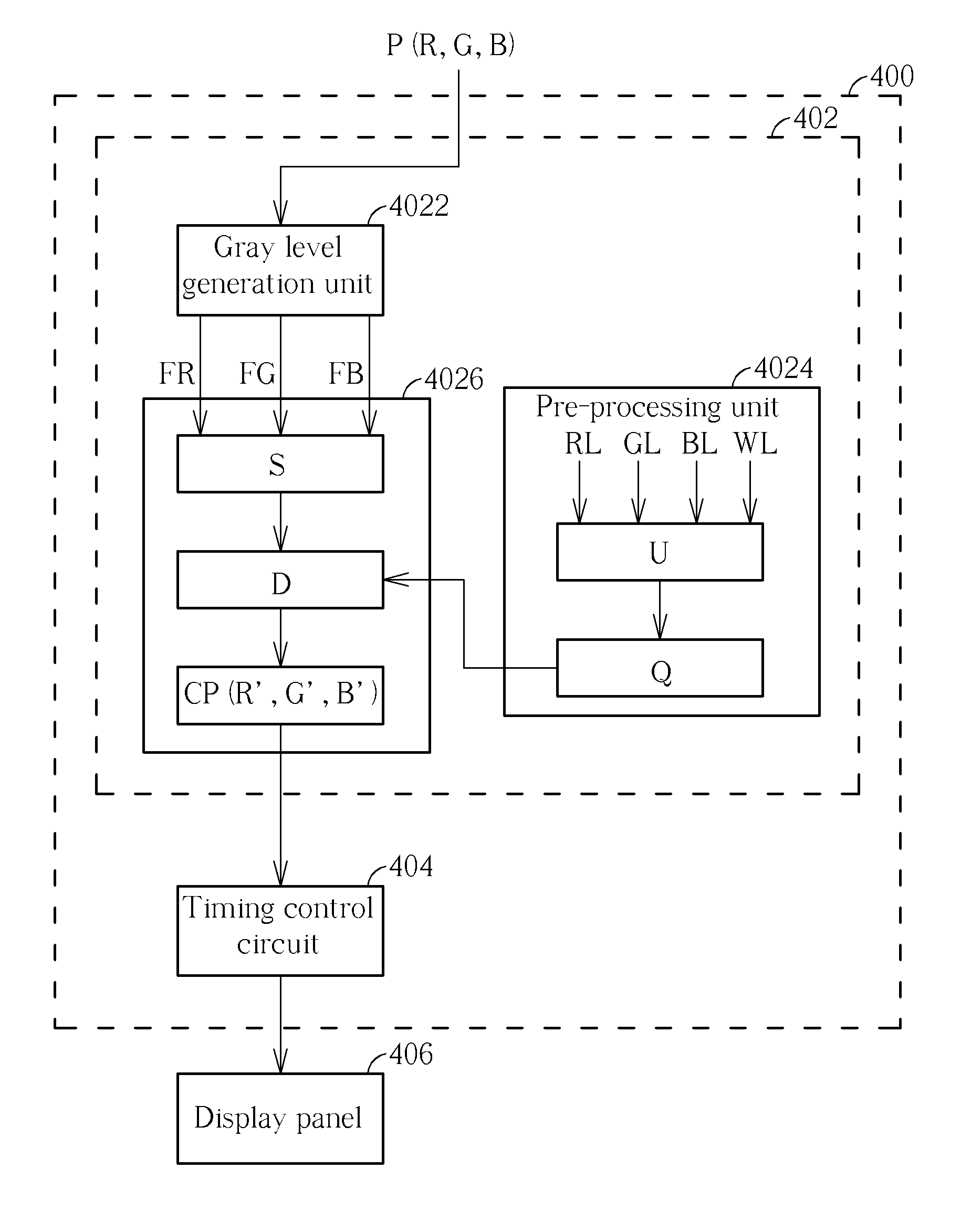
A circuit for compensating color shift of a color sequential display method includes an image processing unit and a timing control circuit. The image processing unit includes a gray level generation unit, a pre-processing unit, and a color compensation unit. The gray level generation generates first gray levels of red, green, and blue sub-pixels. The pre-processing unit generates a pure color uniformity of a display panel and a color compensation value. The color compensation unit generates a color saturation of a pixel, a compensation difference of the pixel, and gray levels of red, green, and blue sub-pixels of a compensated pixel. The timing control circuit sequences the gray levels of the red, green, and blue sub-pixels of the compensated pixel according to the color sequential display method, and outputs the gray levels of the red, green, and blue sub-pixels of the compensated pixel to the display panel.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
Plug-in connector
Owner:HUBERSUHNER AG
Compound probiotics for strawberry planting
InactiveCN103725635APromote photosynthesisGuaranteed to thriveBiocideAgriculture tools and machinesFragariaSoil treatment
The invention relates to compound probiotics for strawberry planting. The probiotics can be applied through soil treatment, manufacturing of bacterial manure, irrigation, foliage spray, ground spray and air atomization and bacteria removal. The yield, quality and disease resistance of strawberries are improved.
Owner:陕西万源生物农业科技有限公司
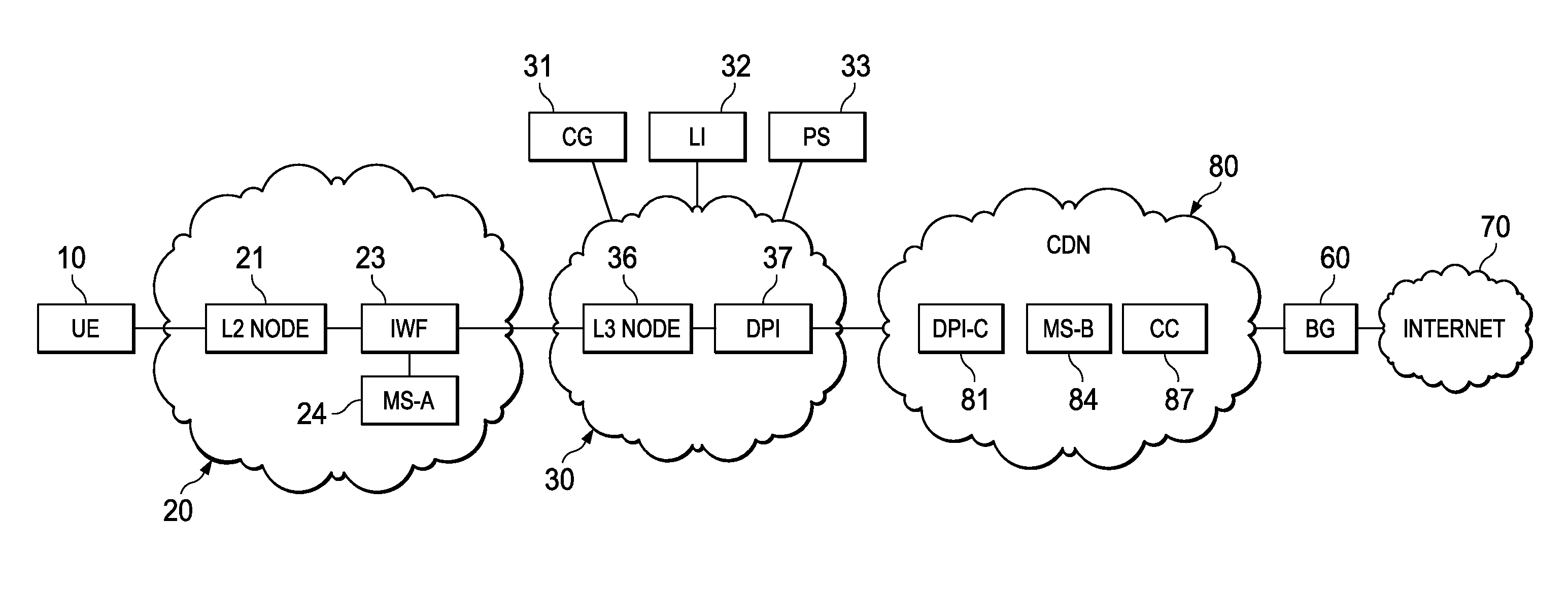
System, apparatus for content delivery for internet traffic and methods thereof
ActiveUS8982738B2Effective decouplingImprove cache hit ratioSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTraffic capacityAccess network
In one embodiment, a method of serving media includes receiving a request to serve media content to an user equipment, and receiving caching information regarding the media content. The caching information includes information regarding whether the media content requested by the user equipment is cacheable. A first media server is assigned from a hierarchical set of media servers to serve the user equipment if the media content to be served is cacheable. The hierarchical set of media servers includes a plurality of first type of media servers deployed in a plurality of layer2 (L2) access networks. The user equipment is coupled to the content delivery network through a layer2 access network of the plurality of L2 access networks.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Method for firing a ceramic and refractory metal casting core
InactiveUS20070235158A1Insufficient temperatureAvoid a lot of timeFoundry mouldsFoundry coresInvestment castingNon oxidative
In an investment casting process, a composite core is formed as a combination of ceramic casting core element and a non-ceramic casting core element. The core is heated in an oxidative atmosphere and then heated in a non-oxidative atmosphere.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
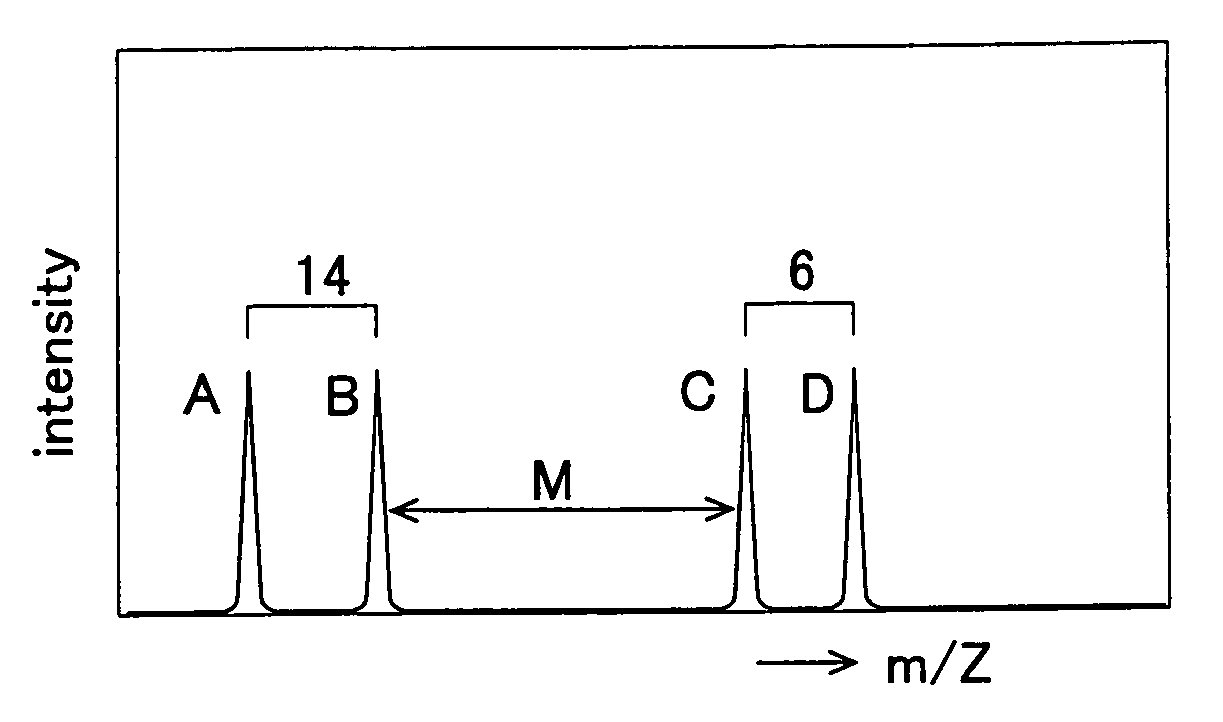
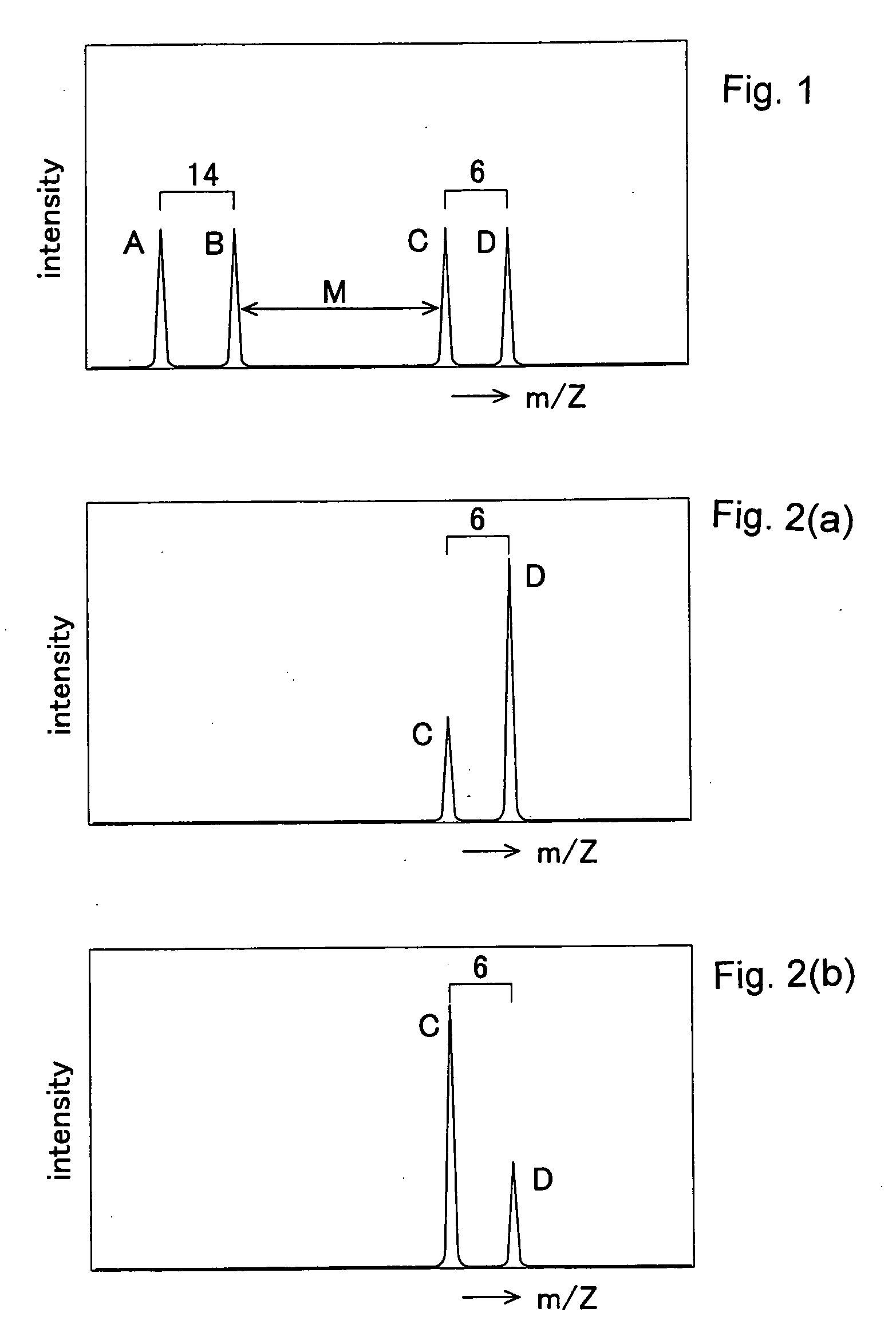
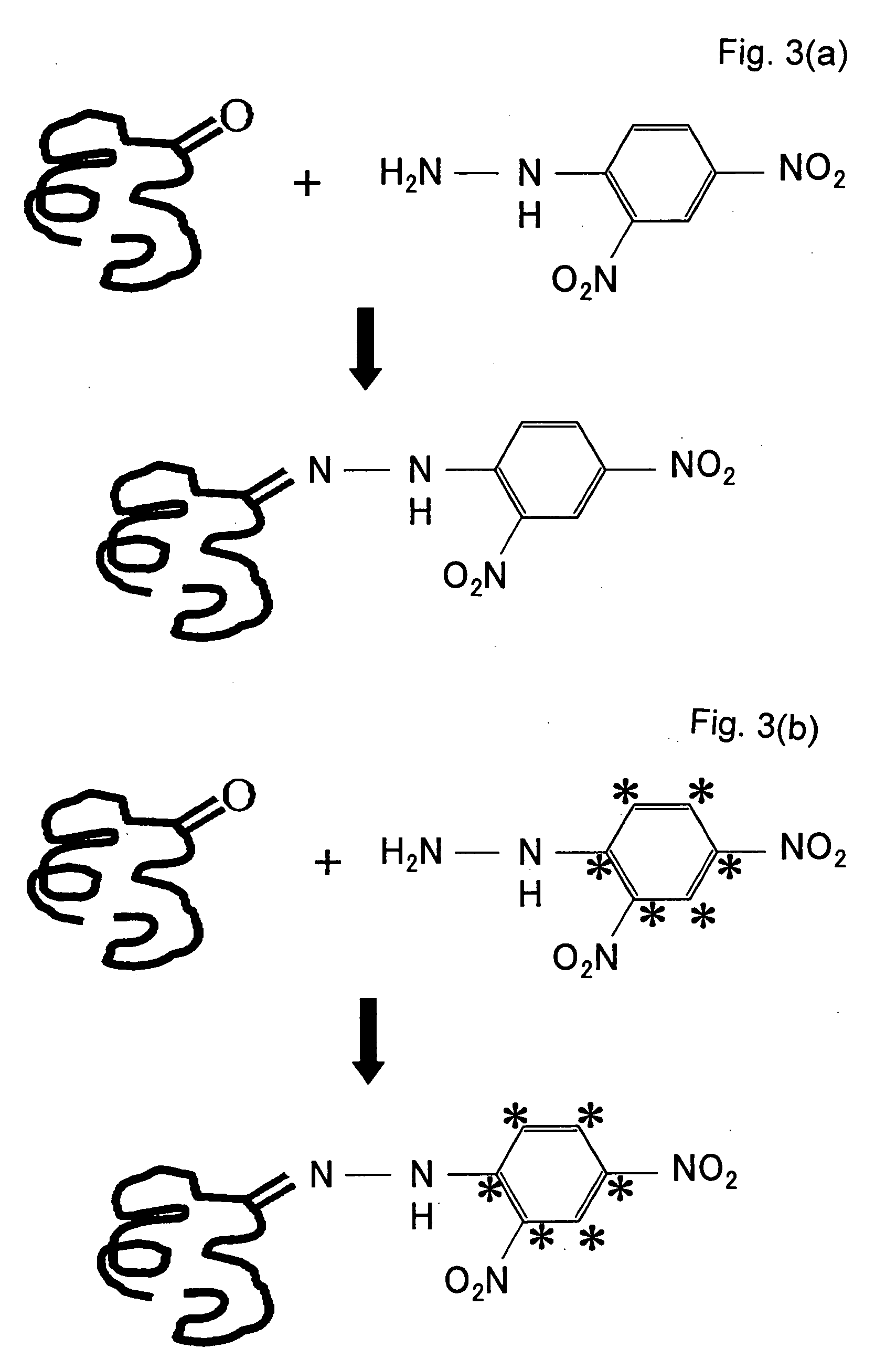
Method of Quantitative Analysis of Oxidized Protein, Labeling Reagents for Quantitative Analysis of Oxidized Protein and Labeling Reagent kit for Quantitative Analysis of Oxidized Protein
InactiveUS20090226884A1Rapid quantitationHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingChemical structureMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Oxidized proteins, which have undergone oxidative modifications, are labeled with labeling reagents and quantified by mass spectrometry. In this process, a first labeling reagent, which is capable of reacting with the oxidized proteins, and a second labeling reagent, which has the same chemical structure as the first labeling reagent and in which at least part of the component atoms is substituted by an isotope of the atom concerned, are employed as the labeling reagents. The oxidized proteins labeled with the first labeling reagent and the oxidized proteins labeled with the second labeling reagent are mixed together and subjected to mass spectrometry, with mixing ratios varied. As the labeling reagents, are raised here 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine and 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine in which a carbon atom on the phenyl group has been substituted by a stable isotope (13C), for example.
Owner:JAPAN ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
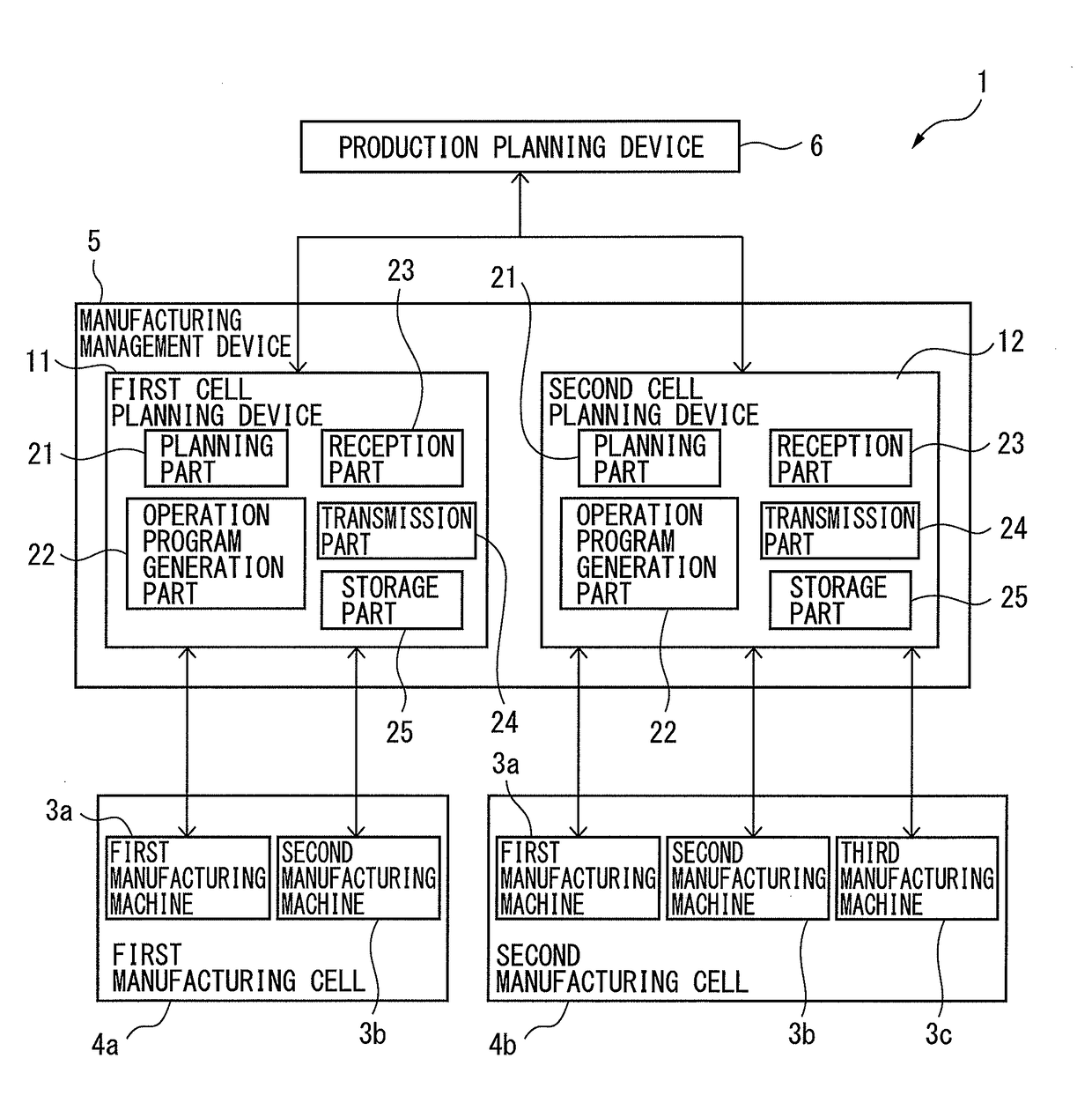
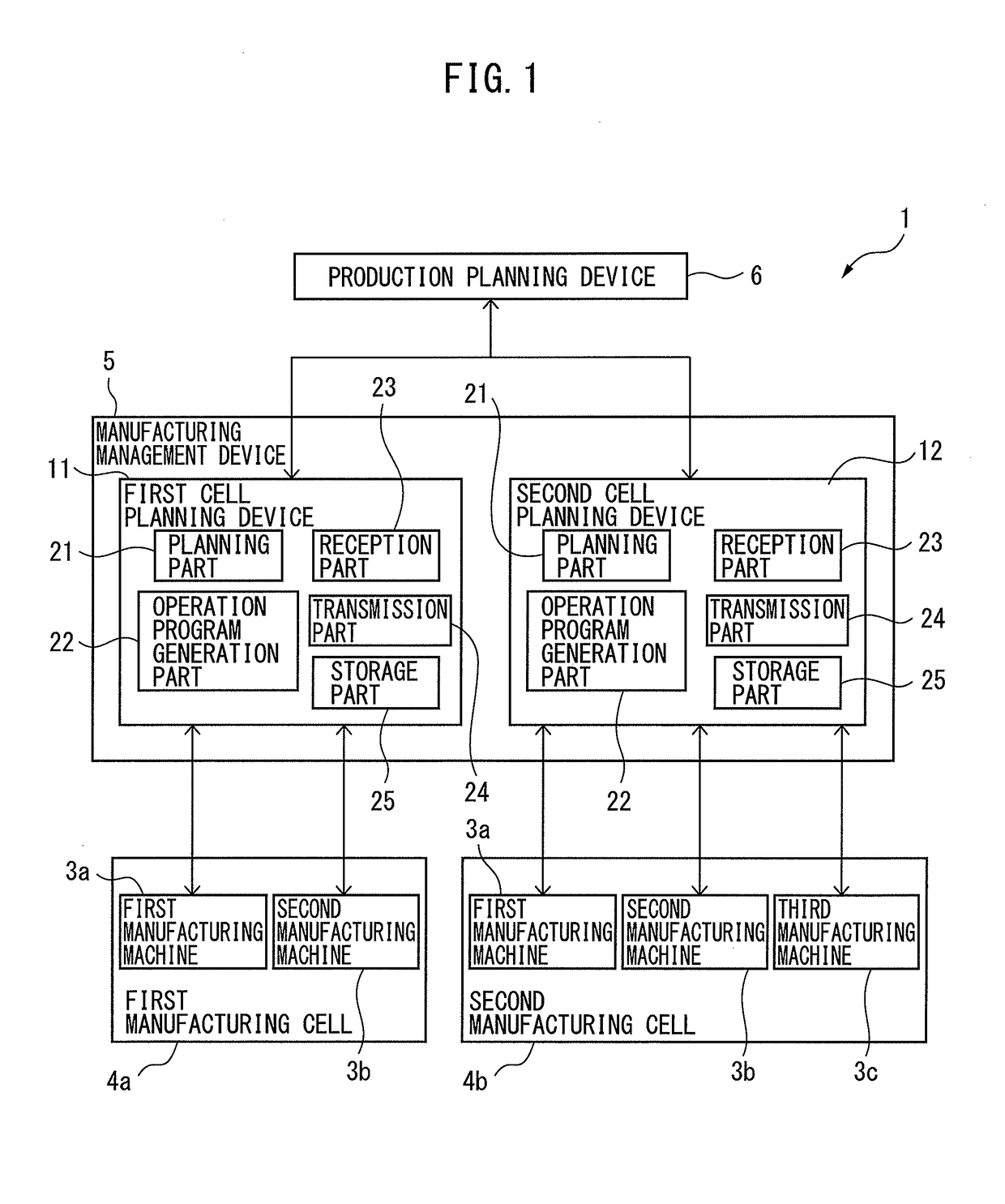
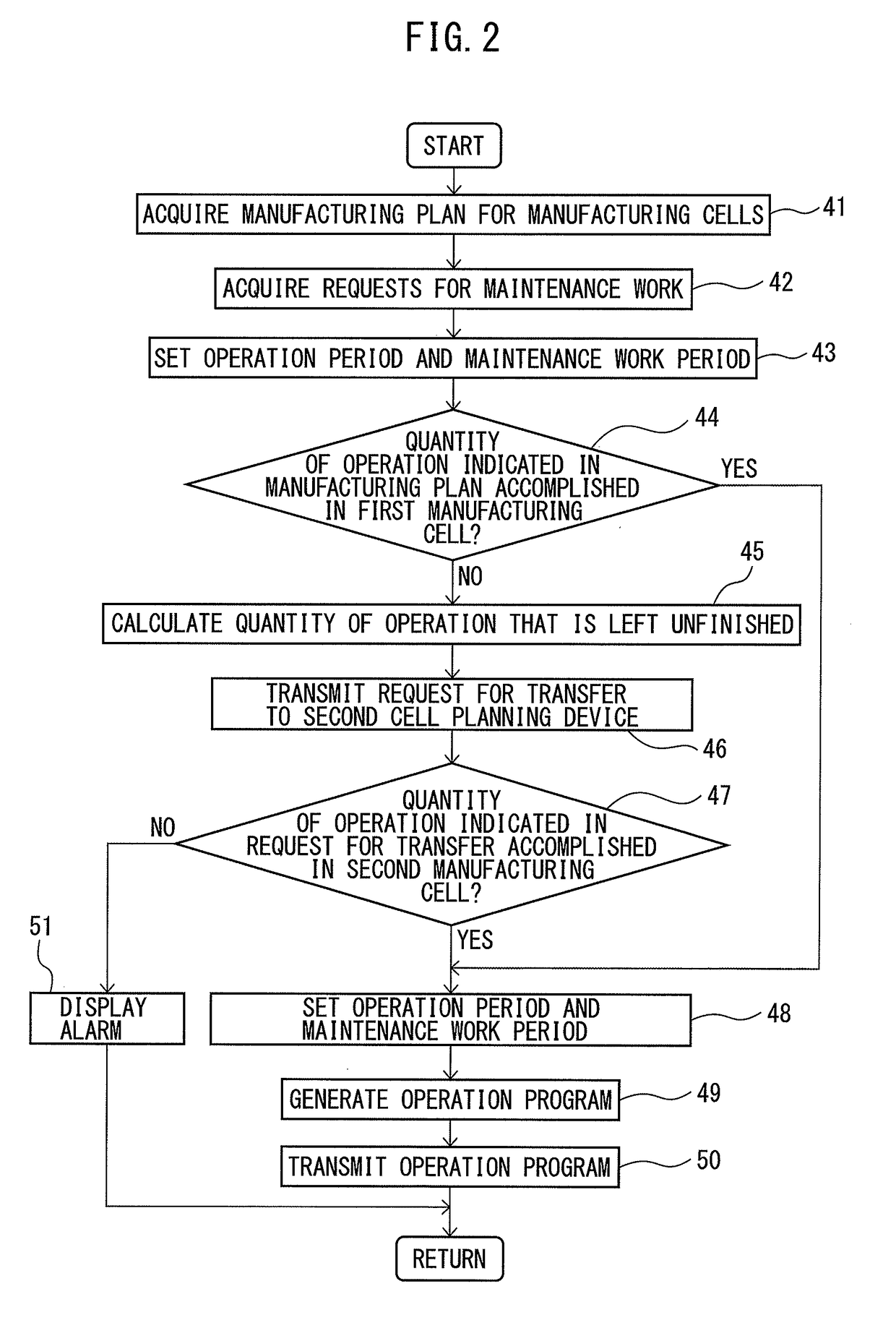
Manufacturing management device for controlling manufacturing cells in which maintenance work is conducted
InactiveUS20170343994A1Productivity is deterioratedDeterioration in operation rateTechnology managementResourcesManufacturing schedulingManufacturing management
A manufacturing management device includes first cell planning device connected to the manufacturing machine of first manufacturing cell, and second cell planning device connected to the manufacturing machine of second manufacturing cell. The planning part of the first cell planning device calculates quantity of operation that would be left unfinished with respect to the quantity stipulated in a manufacturing plan. The first cell planning device transmits a request for transfer including information on the quantity of operation that would be left unfinished to the second cell planning device. The second cell planning device modifies at least one of the operation period and the period of maintenance work of the manufacturing machine in the second manufacturing cell so as to increase the quantity of operation during the predetermined period.
Owner:FANUC LTD
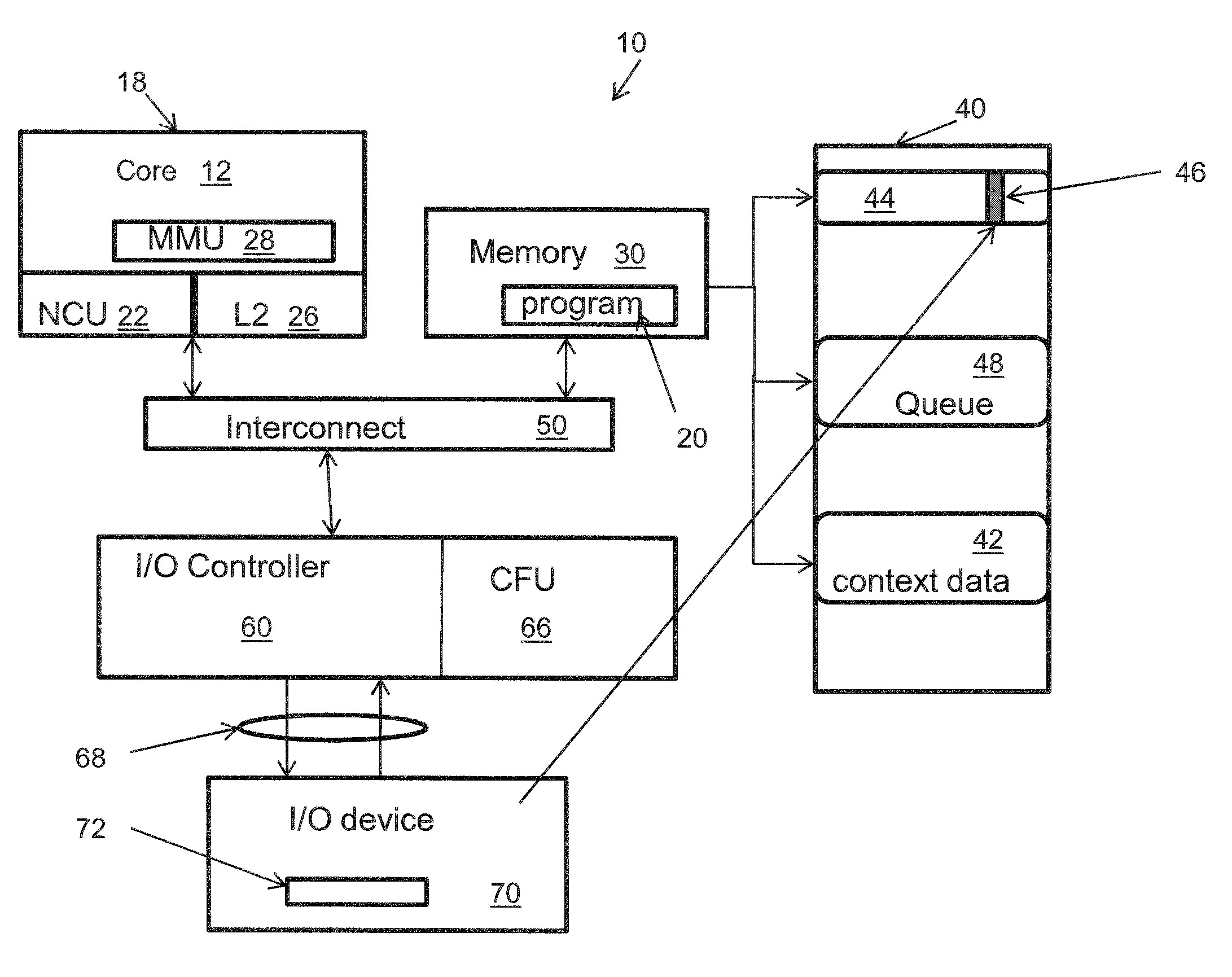
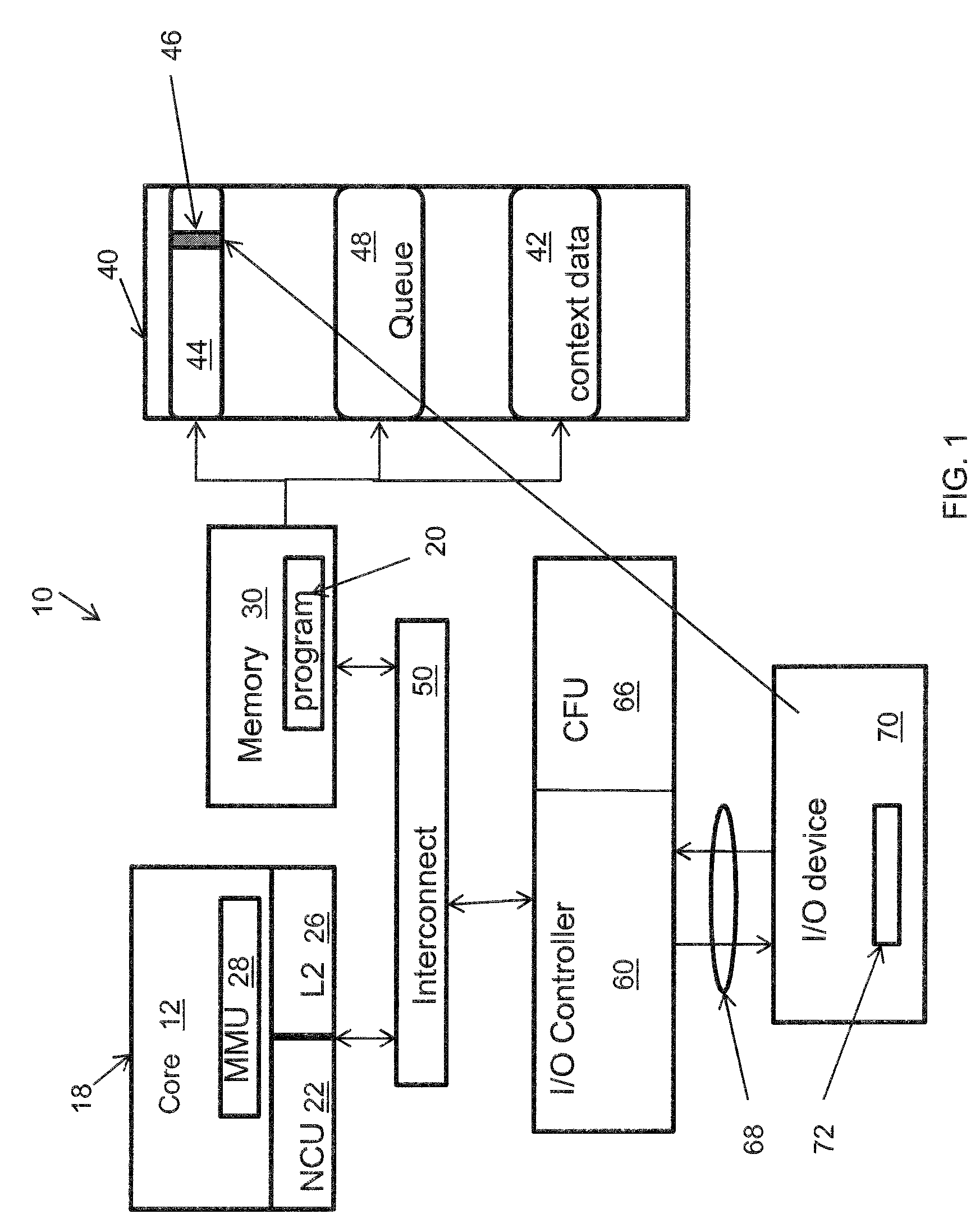
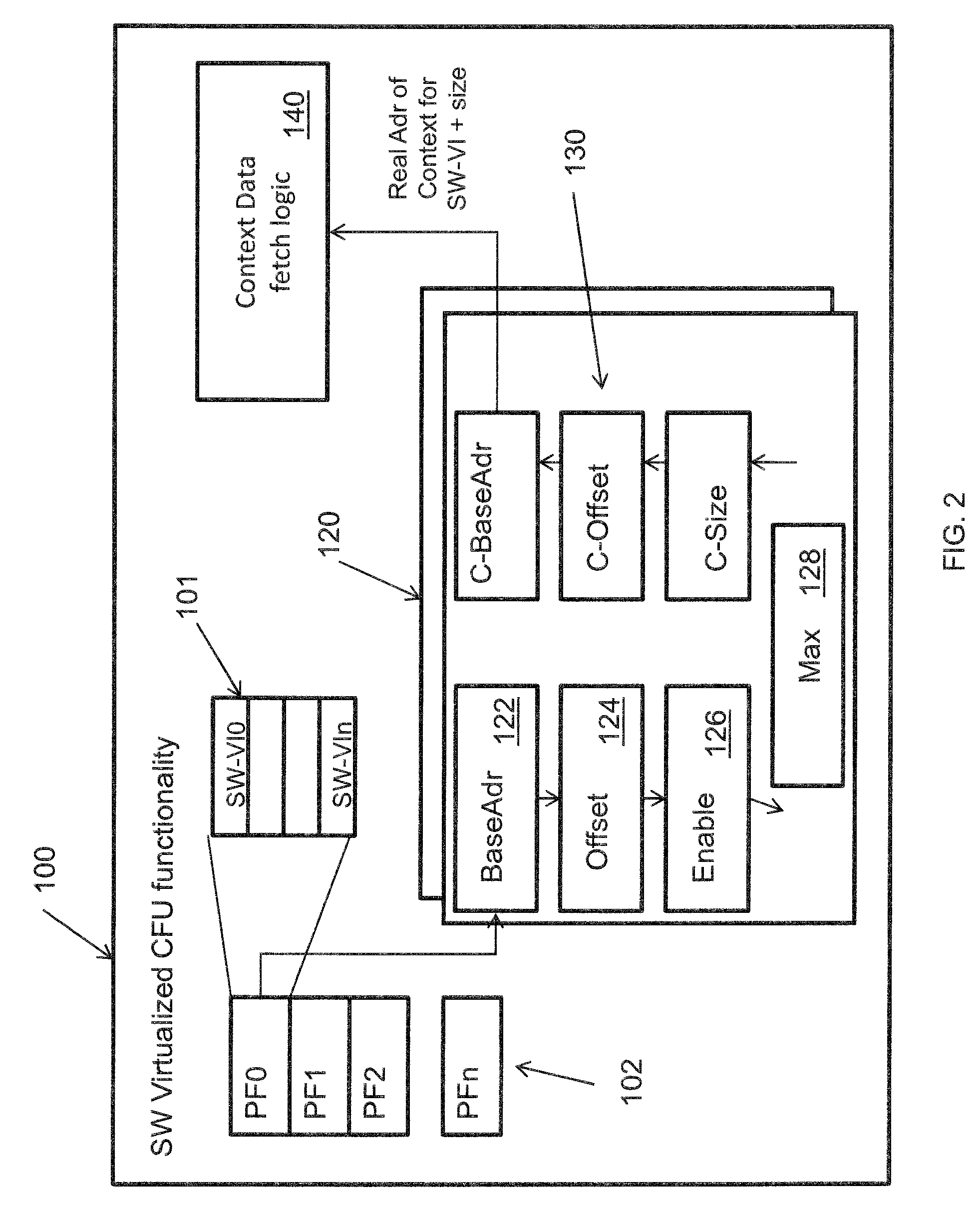
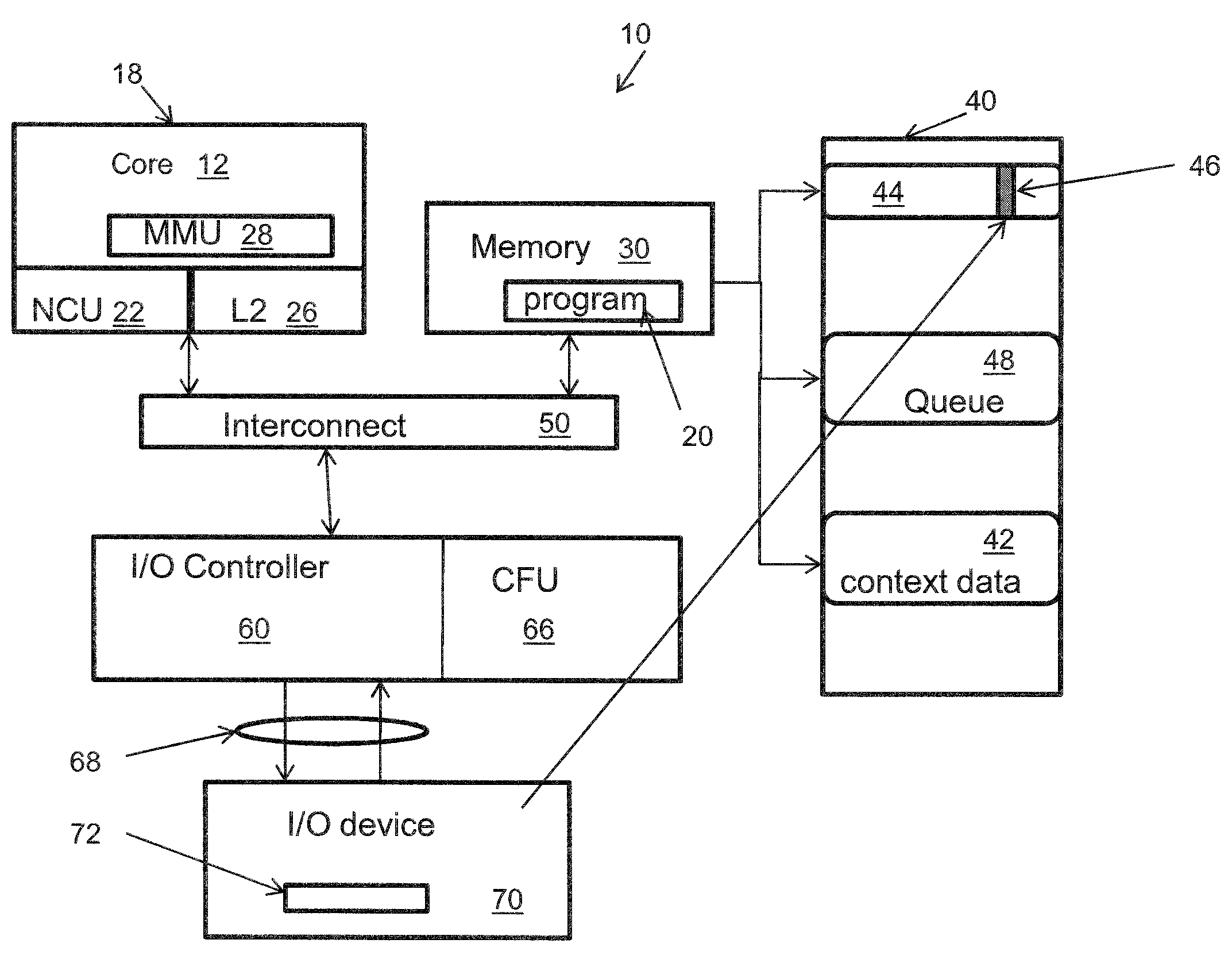
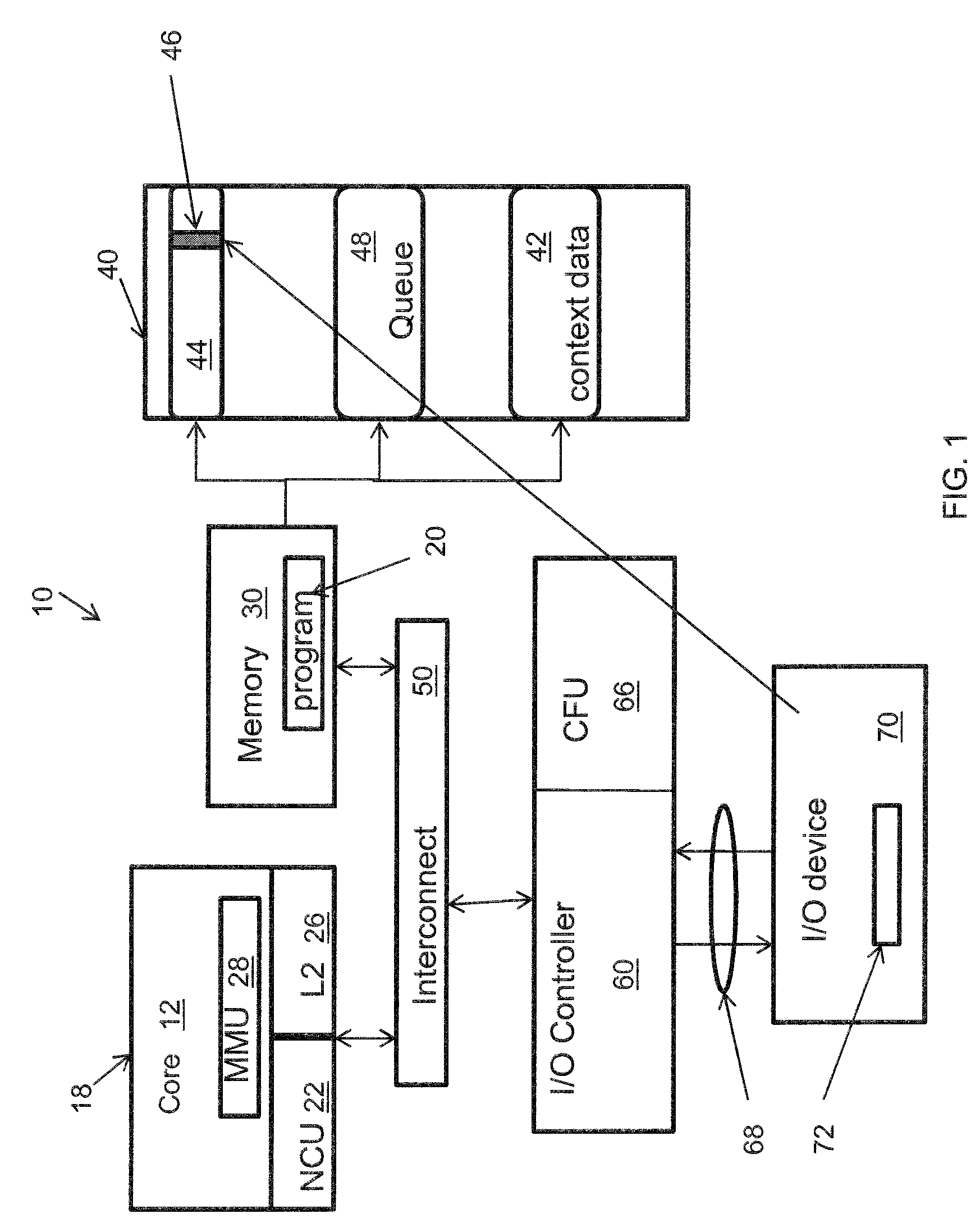
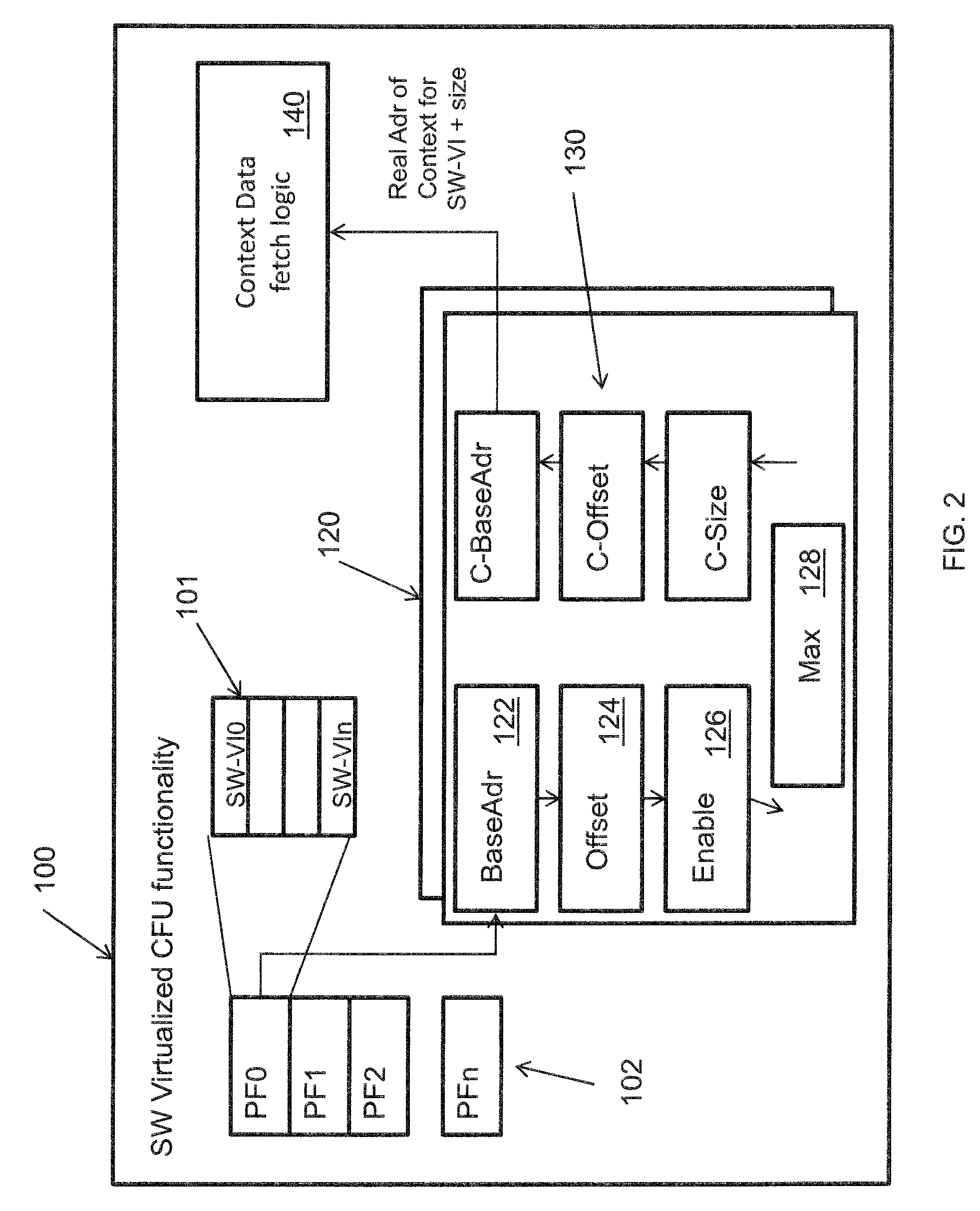
Method for pushing work request-associated contexts into an IO device
InactiveUS8424014B2Avoid a lot of timeDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsComputerized systemContext data
A system and method employing the system for pushing work request associated contexts into a computer device includes issuing a request to a device in a computer system. Context data is fetched from a data storage device for the device. Context is determined for specified data requests, and context misses in the device are predicted. The system and method then initiates a context push and pushes the context into the device using a controller when a context miss is detected. Thereby, reducing the context miss latency time or delay in retrieving context data.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
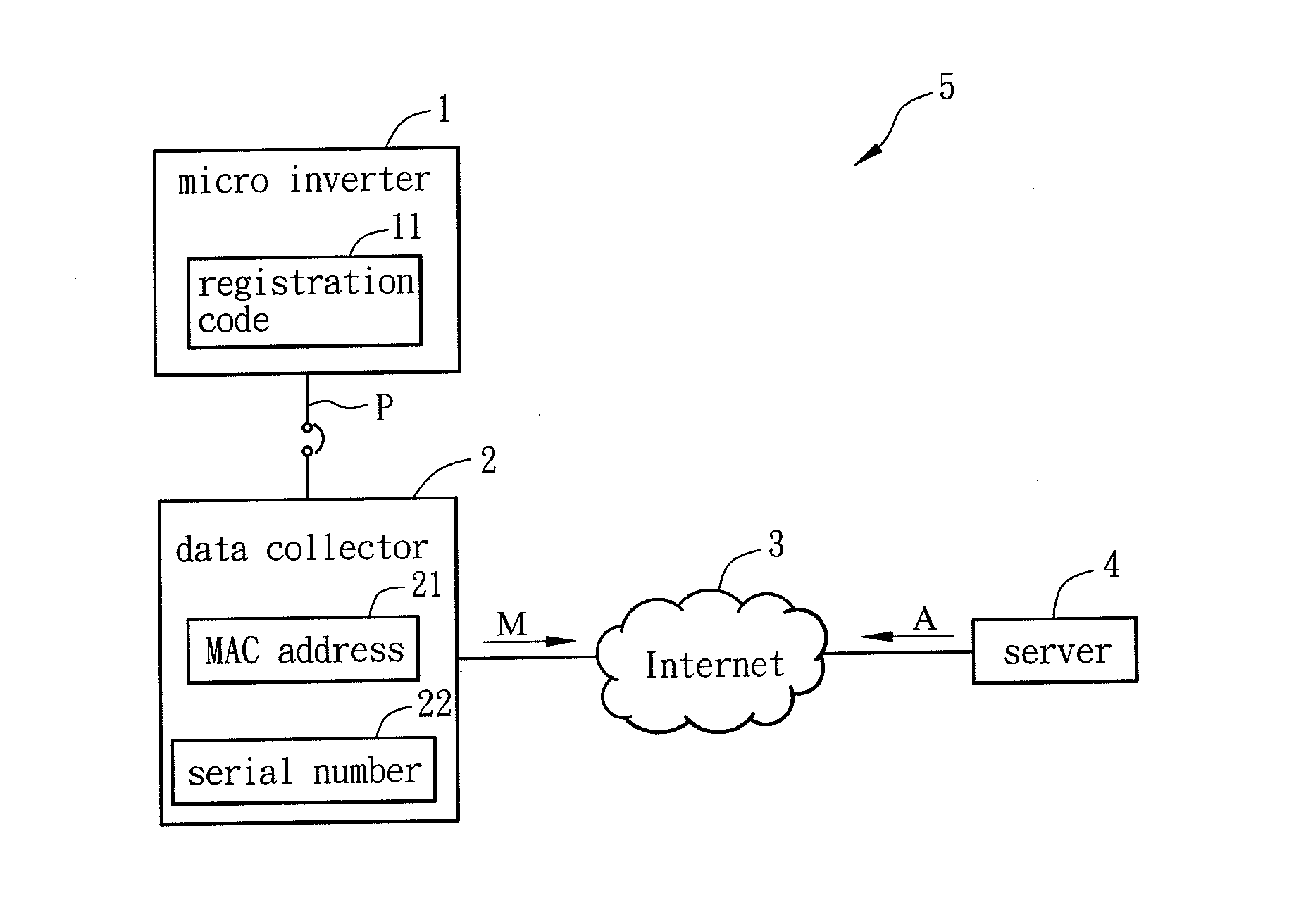
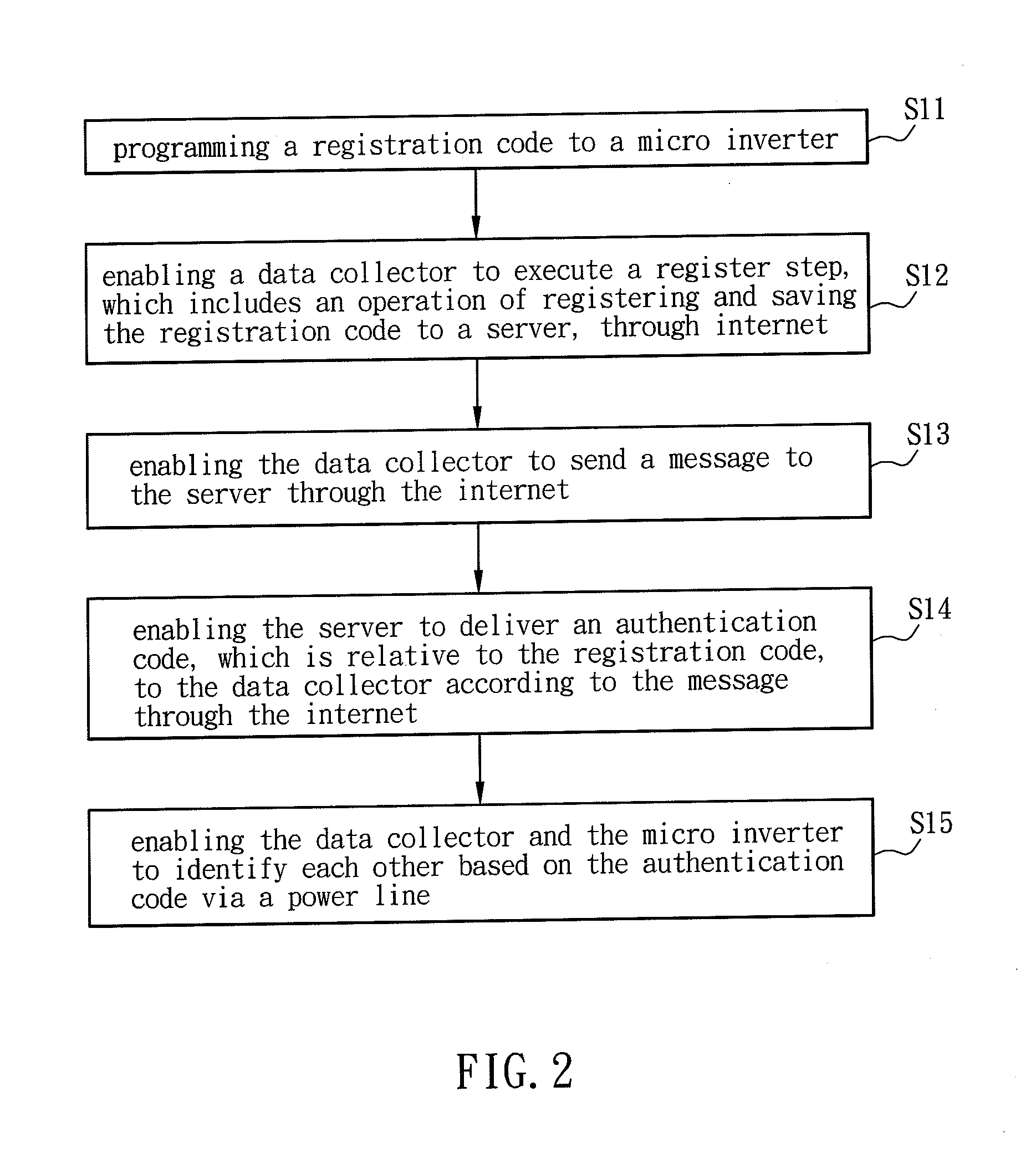
Power line communcation method and power line communication system
InactiveUS20130202018A1Improve convenienceAvoid a lot of timePower distribution line transmissionLock network applicationsComputer hardwareThe Internet
A power line communication (PLC) method includes the steps of: programming a registration code into a micro inverter; enabling a data collector to execute a register step, which includes an operation of registering and saving the registration code to a server, through internet; enabling the data collector to send a message to the server through the internet; enabling the server to deliver an authentication code, which is relative to the registration code, to the data collector through the internet according to the message; and enabling the data collector and the micro inverter to identify each other via a power line based on the authentication code.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Method for pushing work request-associated contexts into an io device
InactiveUS20100223624A1Reduce context miss latency timeAvoid a lot of timeDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsComputerized systemContext data
A system and method employing the system for pushing work request associated contexts into a computer device includes issuing a request to a device in a computer system. Context data is fetched from a data storage device for the device. Context is determined for specified data requests, and context misses in the device are predicted. The system and method then initiates a context push and pushes the context into the device using a controller when a context miss is detected. Thereby, reducing the context miss latency time or delay in retrieving context data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com