Patents
Literature
713 results about "Packet reception" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
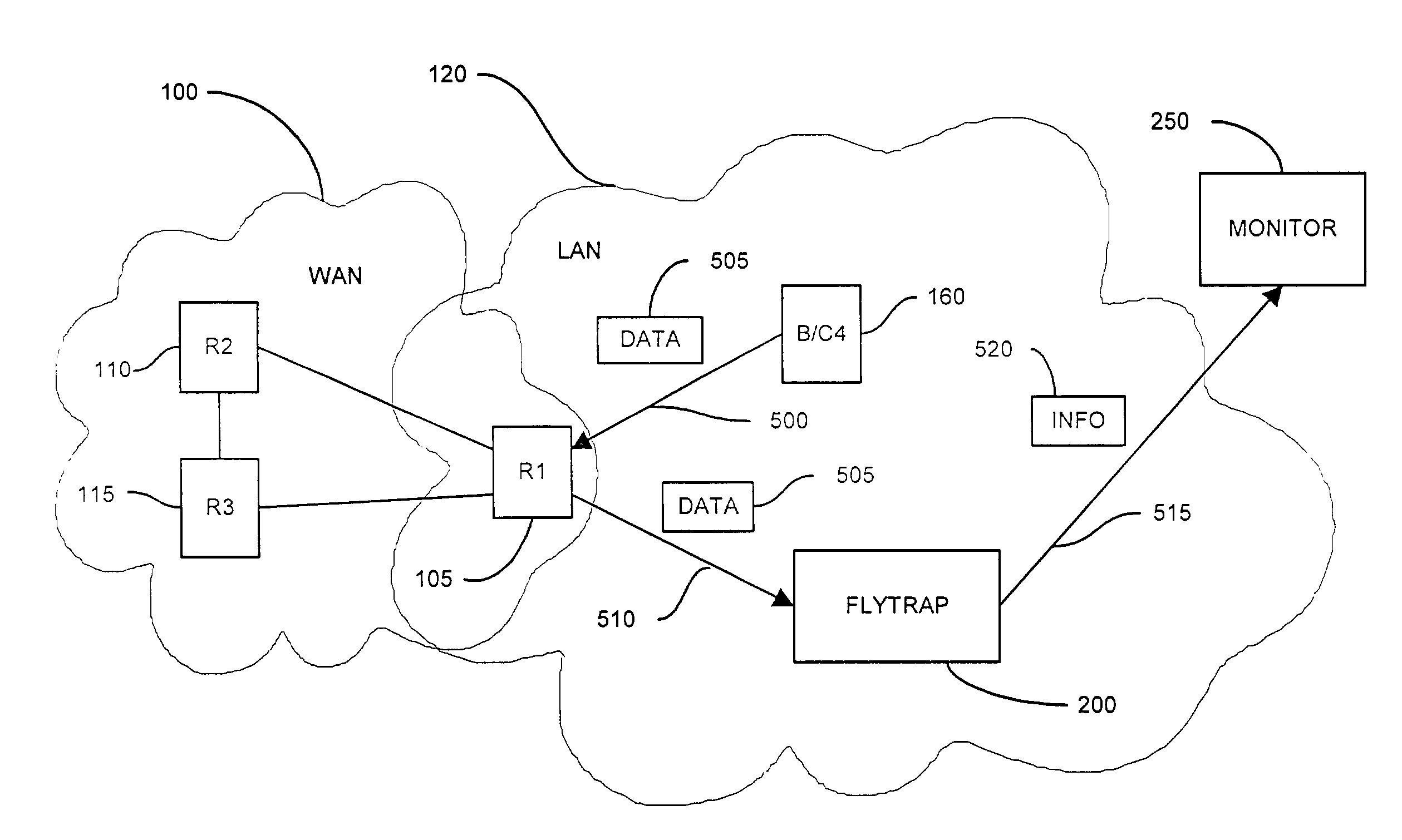
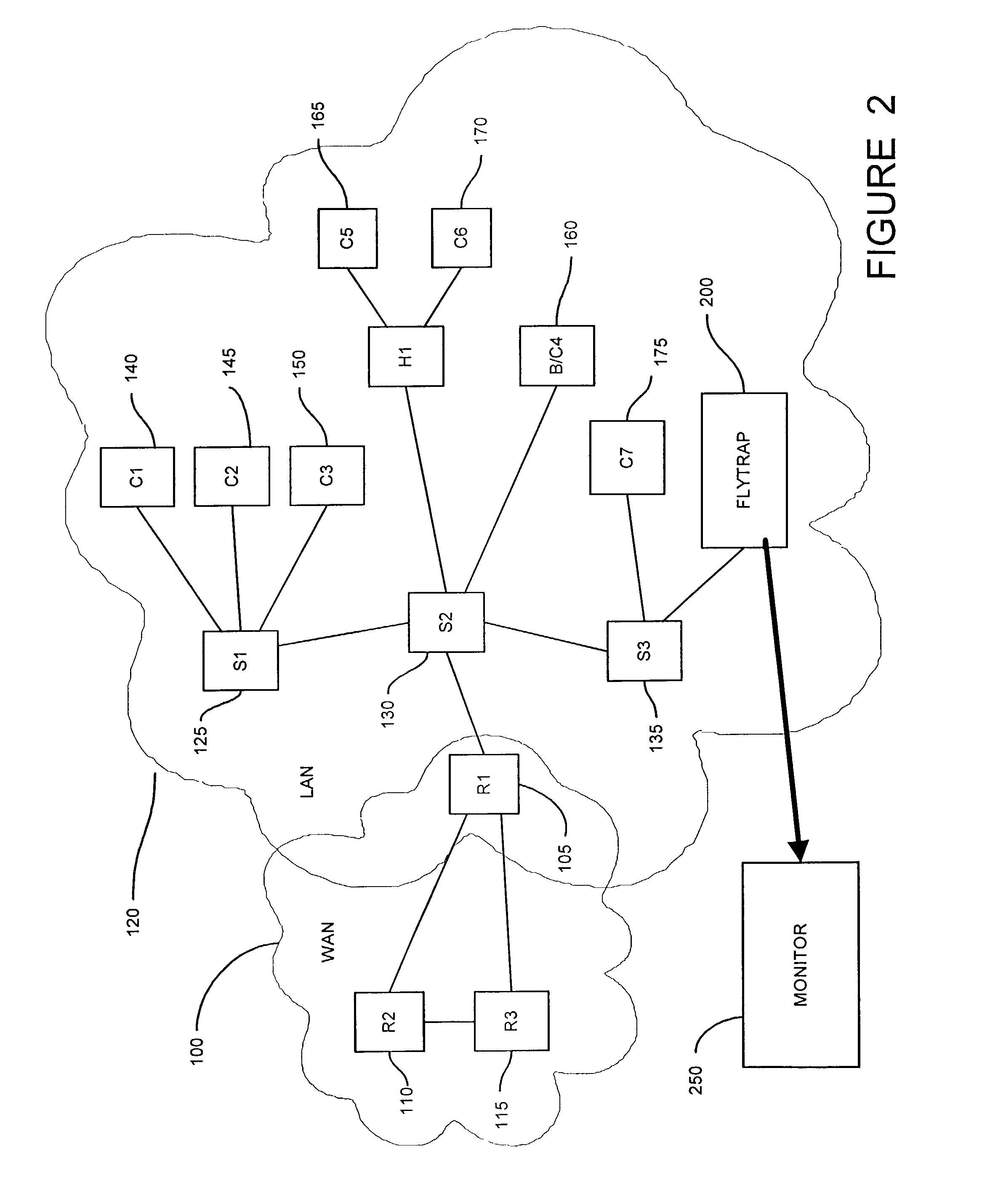
Method and apparatus for capturing and filtering datagrams for network security monitoring
ActiveUS7467408B1Improve network securityReduce network trafficMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionTraffic capacitySecurity monitoring
A method and system for security monitoring in a computer network has a packet sink with filtering and data analysis capabilities. The packet sink is a default destination for data packets having an address unrecognized by the network routers. At the packet sink, the packets are filtered and statistical summaries about the data traffic are created. The packet sink then forwards the data to a monitor, the information content depending on the level of traffic in the network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
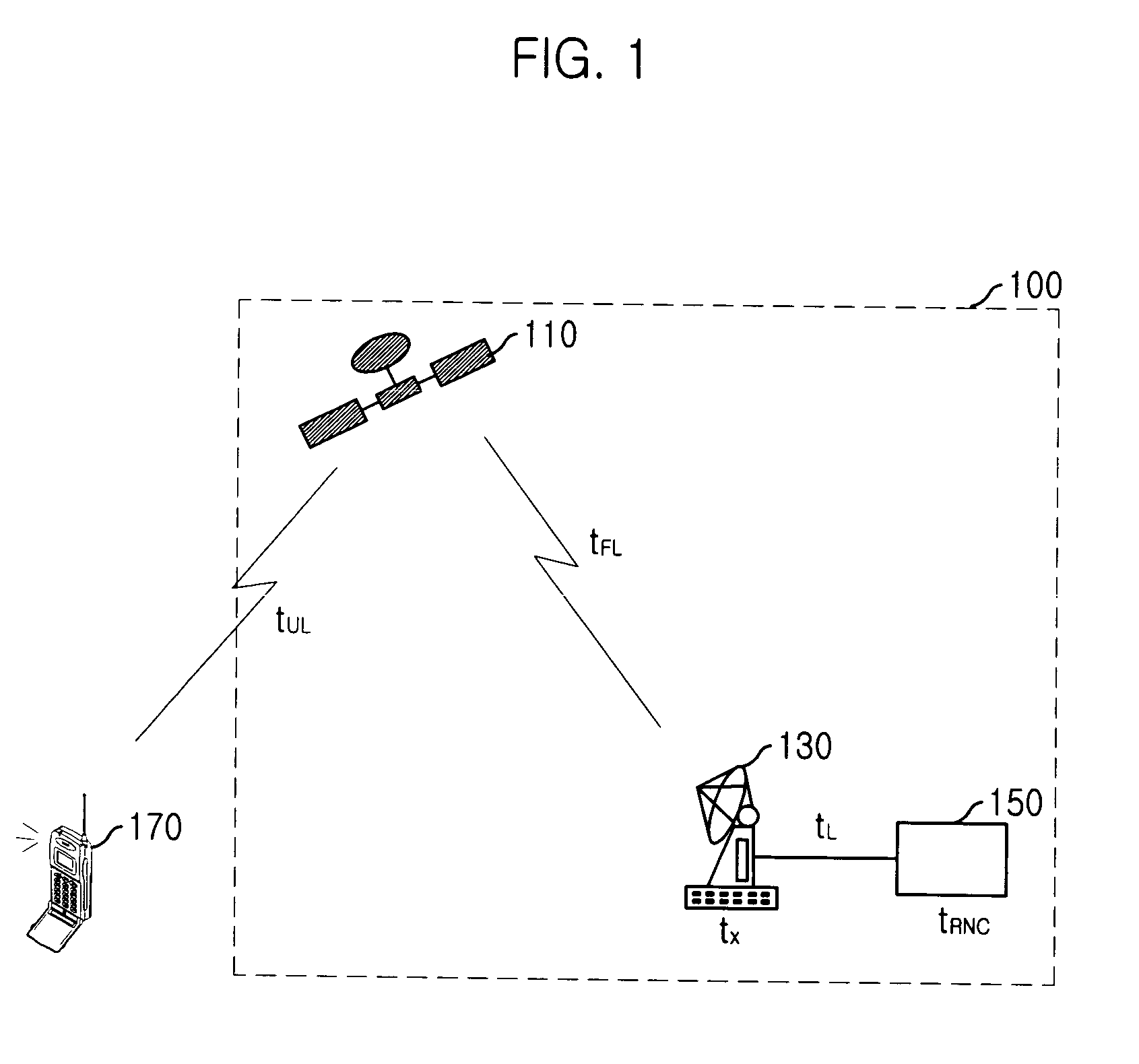
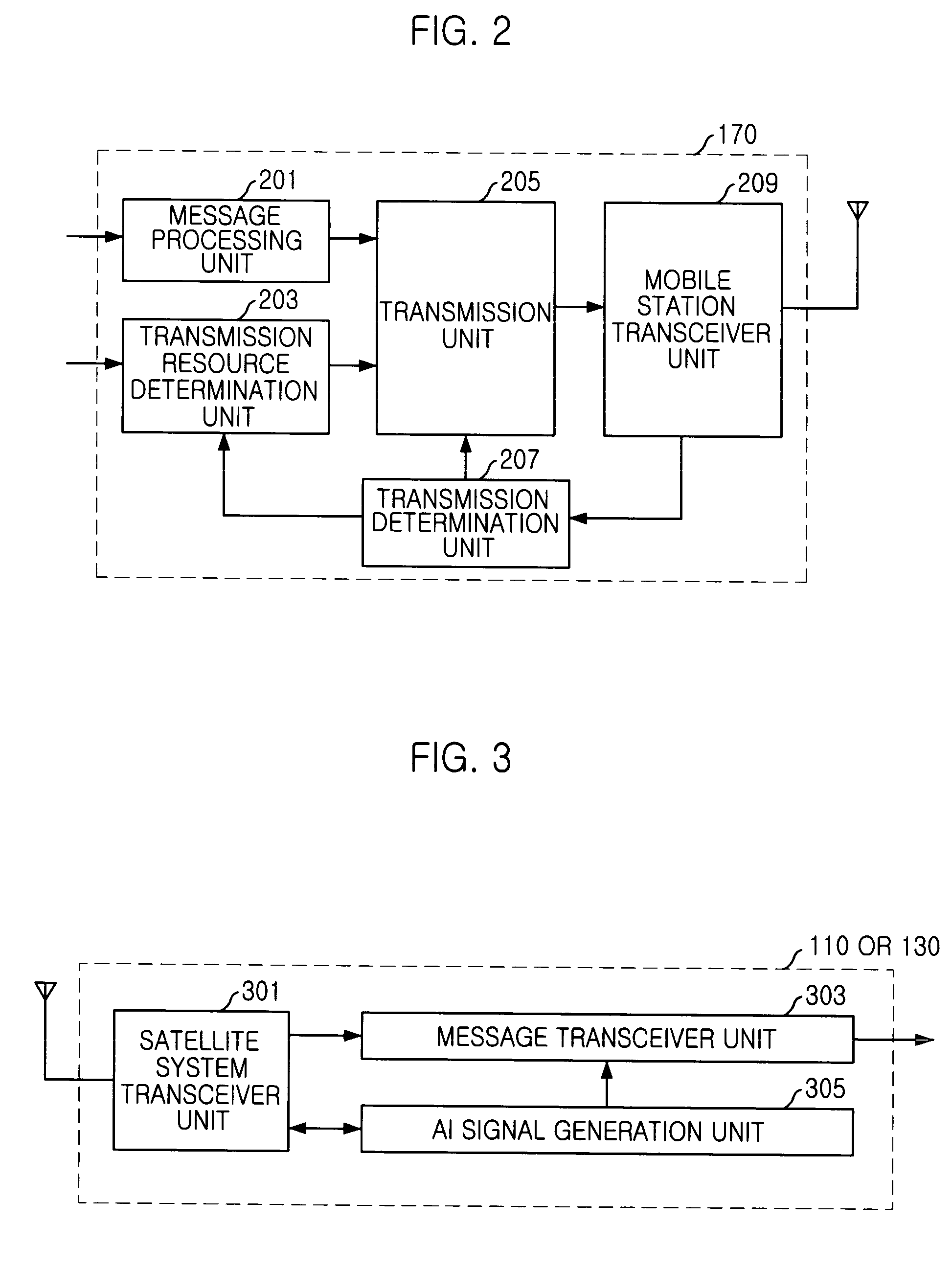
Random access channal access apparatus for mobile satellite communication system and method therefor
ActiveUS20040014452A1Reduce transmission delay timeIncrease probabilityTransmission control/equalisingNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsRandom-access channel
The present invention relates to Random Access Channel (RACH) access apparatus for mobile satellite communication system and method therefor. The method for accessing random access channel (RACH) on satellite system, random access channel (RACH) carrying message from a plurality of mobile stations to the satellite system, the method includes the steps of: receiving preamble and the message, the message successively transmitted with the preamble from the plurality of mobile stations; and transmitting acquisition response signal corresponding to the preamble or the message to the plurality of mobile stations. Accordingly, success of packet reception of satellite system is improved and transmission delay is reduced.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
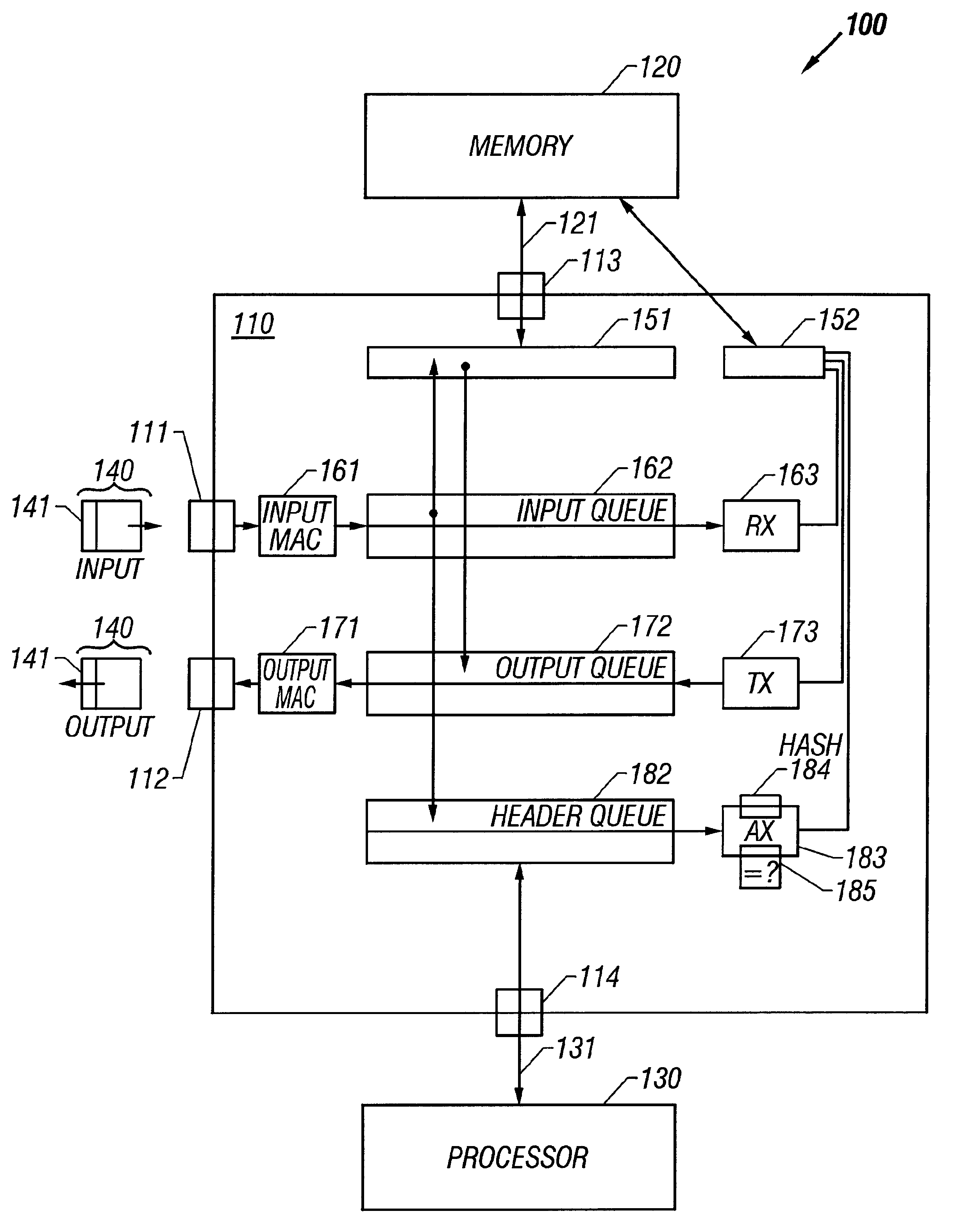
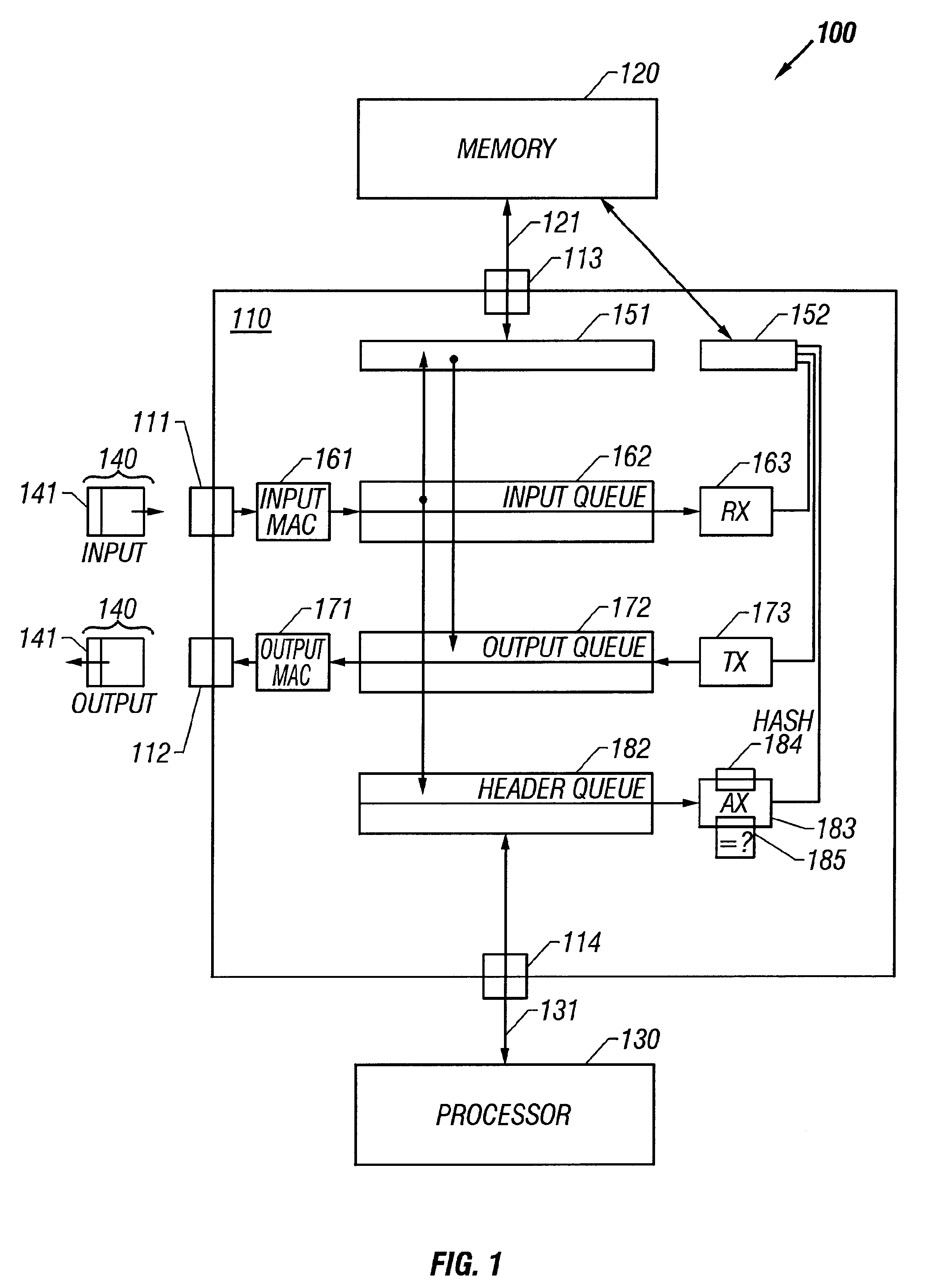
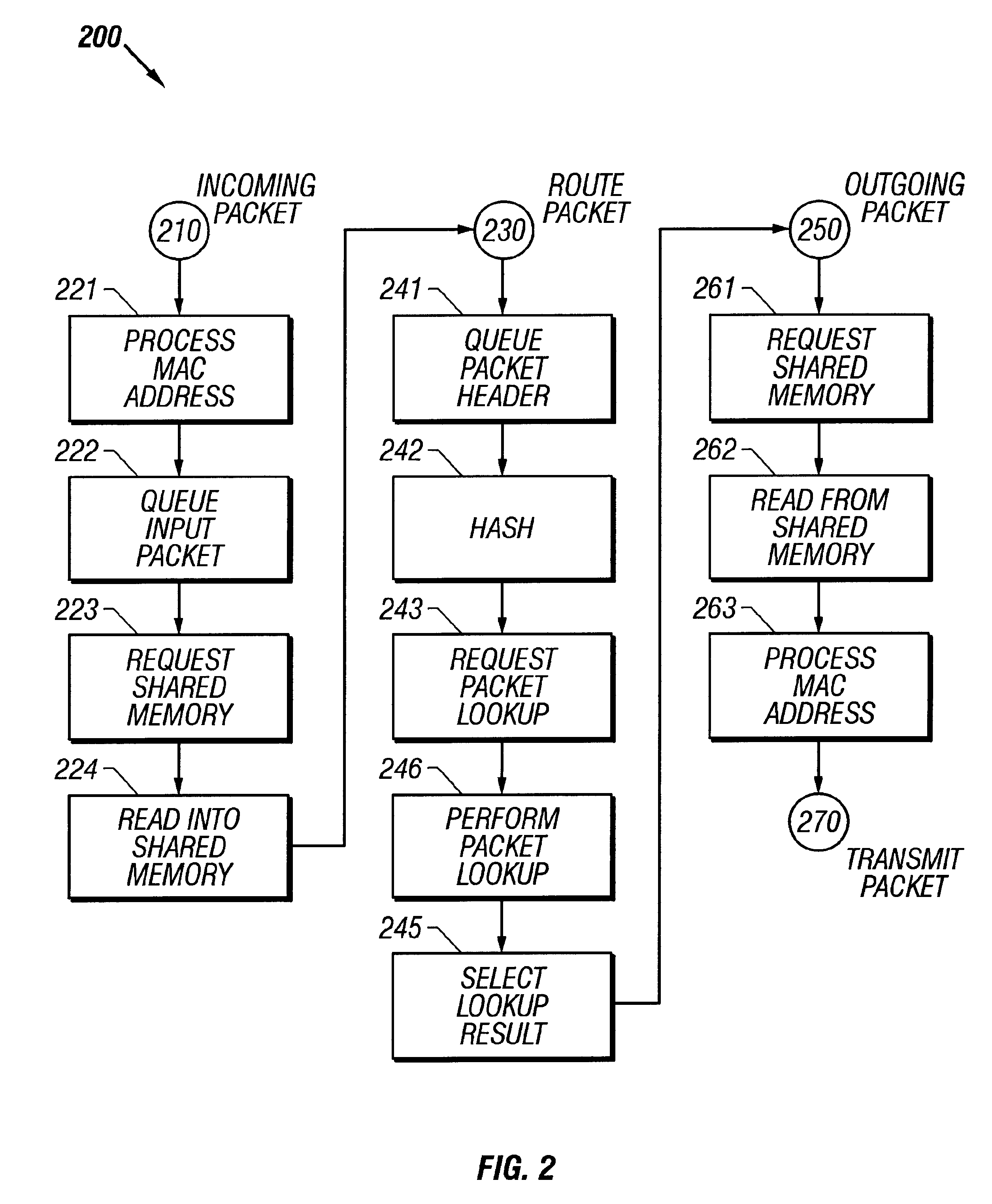
Single-chip architecture for shared-memory router
InactiveUS6343072B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsDigital computer detailsData bufferChip architecture
The invention provides a single-chip method. The method includes a memory shared among packet buffers for receiving packets, packet buffers for transmitting packets, and packet header buffers for packet forwarding lookup. Accesses to that shared memory are multiplexed and prioritized. Packet reception is performed with relatively high priority, packet transmission is performed with medium priority, and packet forwarding lookup is performed with relatively low priority. The single-chip method includes circuits for serially receiving packet header information, converting that information into a parallel format for transmission to an SRAM for lookup, and queuing input packets for later forwarding at an output port. Similarly, the single-chip method includes circuits for queuing output packets for transmission at an output port, receiving packet forwarding information from the SRAM in a parallel format, and converting packet header information from output packets into a serial format for transmission. The single-chip method also includes a region in its shared memory for a packet forwarding table, and circuits for performing forwarding lookup responsive to packet header information.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for transporting ethernet data packets via radio frames in a wireless metropolitan area network
InactiveUS6907048B1Improve efficiencyElectric/magnetic signal storageRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransceiverWireless transceiver
Method and apparatus for transporting Ethernet data packets via radio frames in a wireless metropolitan area network. A terminal includes a data packet receiver for receiving data packets for communication over a wireless link wherein not every data packet has a same length; a data packet formatting apparatus for formatting the data packets according to radio frames wherein the radio frames each have a same length and wherein the data packets are formatted into the radio frames such that boundaries for the data packets are not necessarily aligned with boundaries for the radio frames; and a wireless transceiver for communicating the radio frames over the wireless link. The packets can be Fast Ethernet packets. The terminal does not convert the Ethernet data packets into a telephony communication protocol or into an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) protocol prior to communication of the radio frames over the wireless link. The terminal can include a data packet synchronizer for synchronizing the data packets to a clock signal associated with the radio frames. The data packets can be time-division multiplexed into the radio frames. According to another aspect, a method of transporting Ethernet data packets via radio frames includes steps of receiving Ethernet data packets wherein each data packet includes a preamble and a start-of-frame delimiter, stripping off the preamble and start-of-frame delimiter, formatting the packet data according to radio frames, including appending a synch field to the packet data, and appending a length field to the packet data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
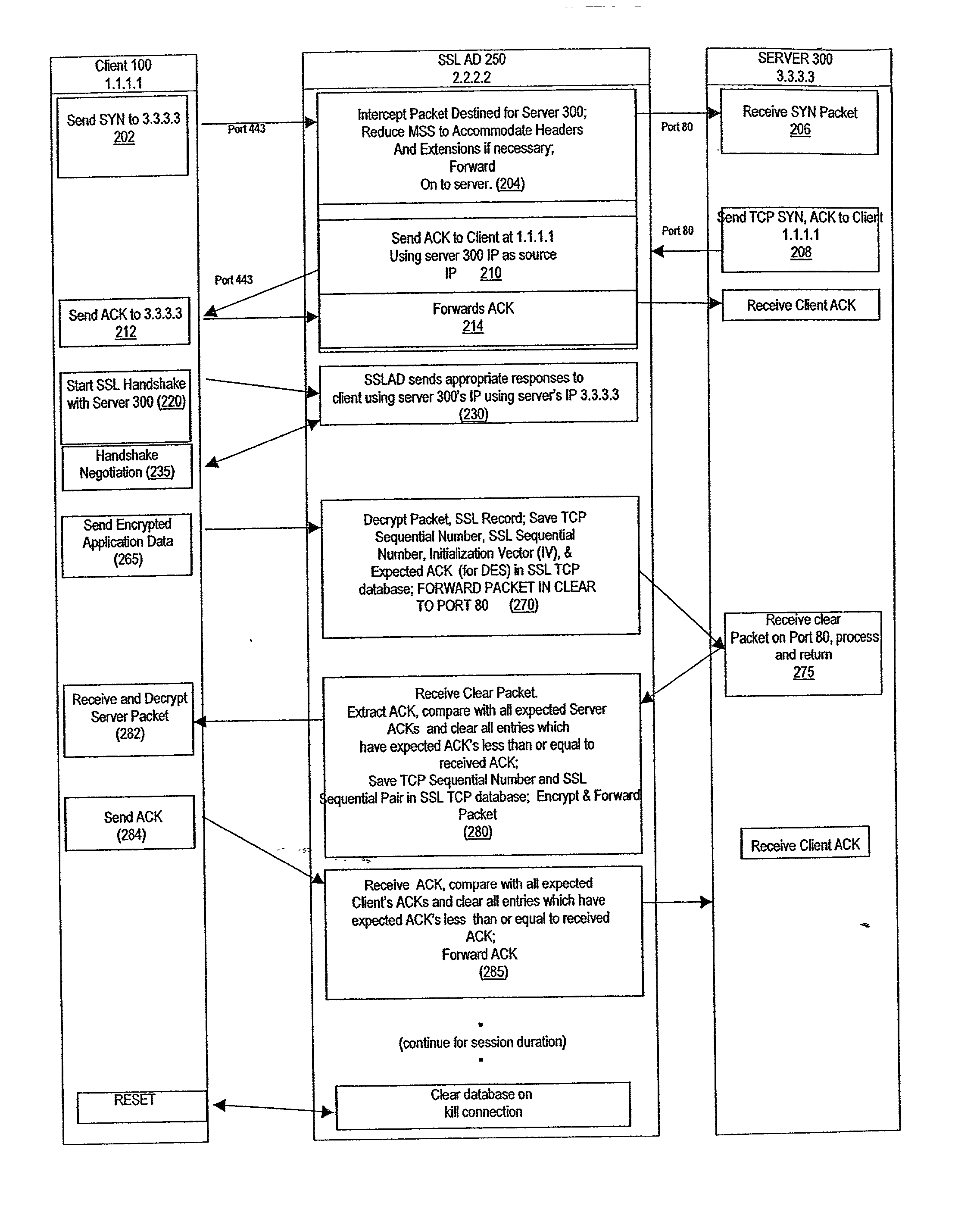
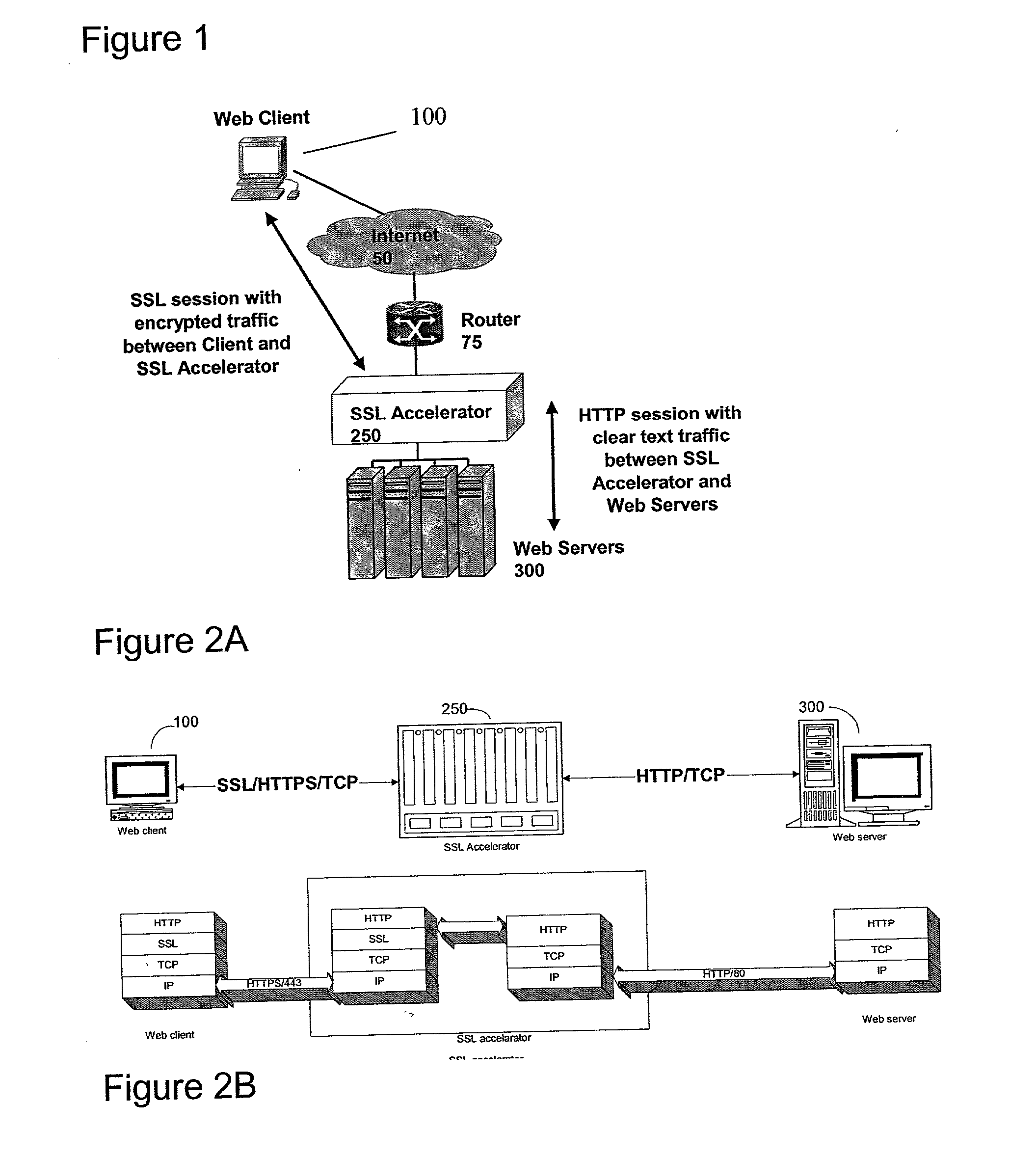
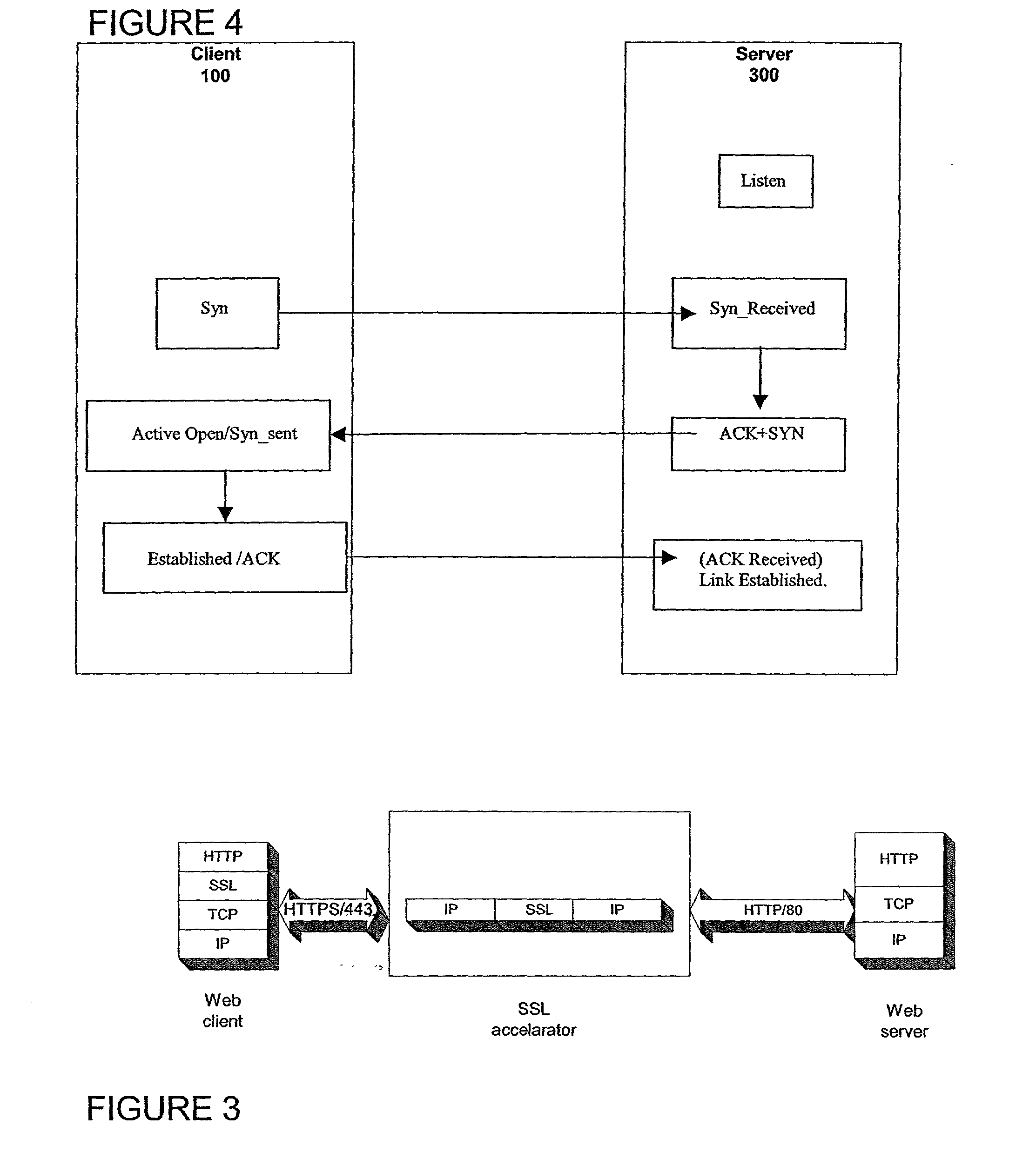
Bufferless secure sockets layer architecture
InactiveUS20030014625A1Minimization requirementsMore buffer memoryUser identity/authority verificationMultiple digital computer combinationsSecure communicationClient-side
A method for enabling secure communication between a client on an open network and a server apparatus on a secure network. The method is generally performed on a intermediary apparatus coupled to the secure network and the open network. The method includes the steps of negotiating a secure communications session with the client apparatus via the open network; negotiating an open communications session with the server via the secure network; receiving encrypted packet application data having a length greater than a packet length via multiple data packets; decrypting the encrypted packet application data in each data packet; forwarding decrypted, unauthenticated application data to the server via the secure network; and authenticating the decrypted packet data on receipt of a final packet of the segment.
Owner:NEXSI SYST
Method and apparatus for compensating for mismatched delays in signals of a mobile display interface (MDDI) system
ActiveUS8812706B1Reduce complexityImprove reliabilityEnergy efficient ICTCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital interfaceData signal
A method, apparatus, and computer program product embodied on a hardware computer readable storage medium for compensating mismatched delays in at least two signals of a mobile display digital interface (MDDI) system. The method, apparatus, and computer program product embodied on a hardware computer readable storage medium sends a skew calibration packet from a host to a client. The host begins a calibration pattern; then toggling a data signal and a strobe signal at a substantially similar time which strobe signal is used by the client as a clock source. The method, apparatus, and computer program product embodied on a hardware computer readable storage medium also aligns a timing of the strobe signal and the data signal by providing varying delays and resetting the client to an original clock source before a next packet reception.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Network traffic analyzer
InactiveUS7562134B1Easily gleanedFacilitate trend analysisError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityExchange network
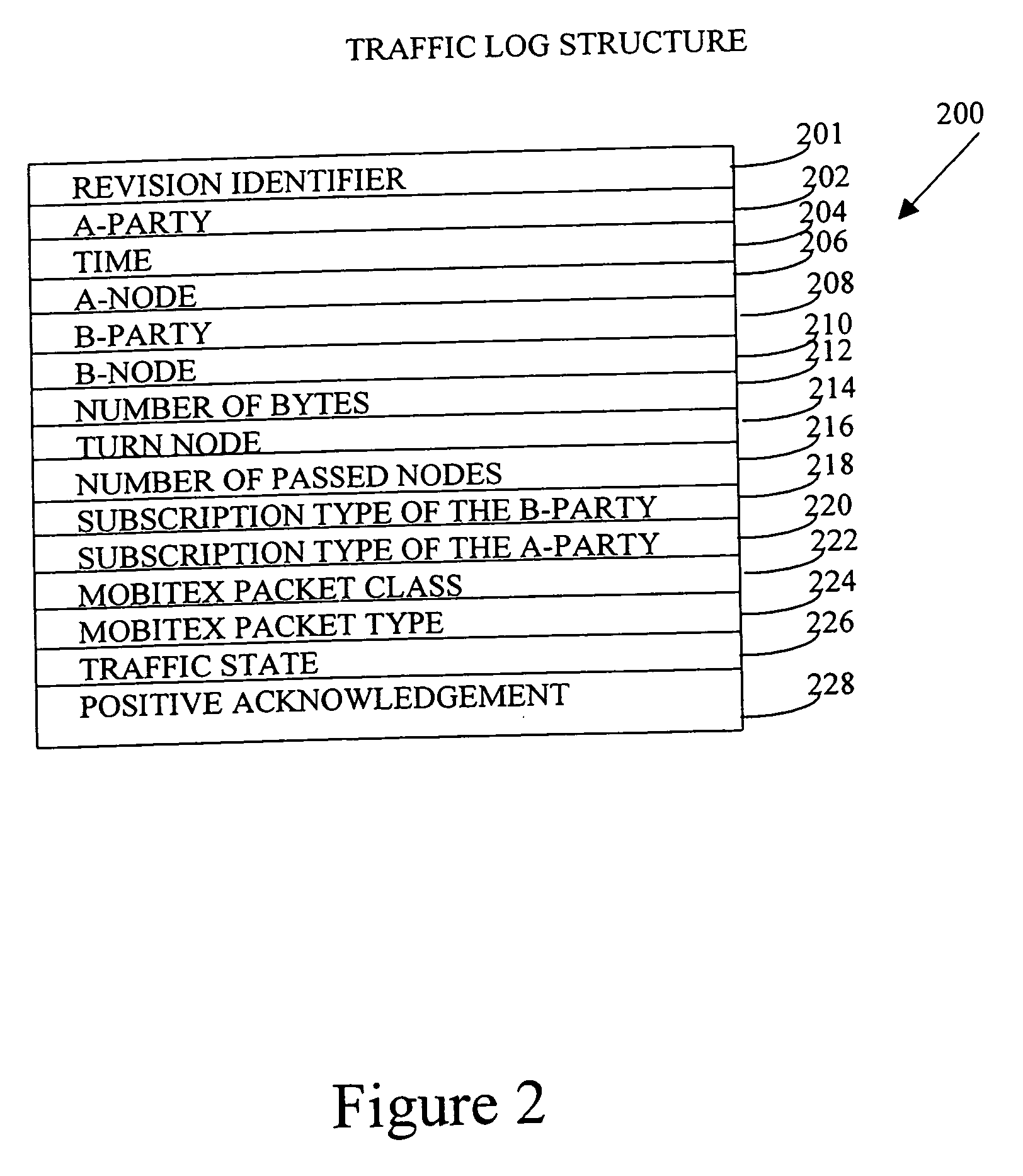
A system for and method of analyzing the performance of a packet-switched network, the network automatically generating a traffic log each time a packet enters or exits the network and each traffic log including at least the time the traffic log was created, the addresses of the packet sender and packet recipient, and the entry and exit network nodes. A server collects a plurality of traffic logs, parses the available information therein and generates a plurality of histograms, each histogram being based on information gleaned from the plurality of traffic logs. The histograms may be representative of packet traffic passing through a host connected to the network, packet traffic passing through a node in the network or the amount of data that travels over a link between two nodes of the network. To increase the delivery speed of the histogram data from the server to a client, the histograms are preferably stored as flat files to achieve direct and rapid access to stored data.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
Packet retransmission system, packet transmission device, packet reception device, packet retransmission method, packet transmission method and packet reception method
InactiveUS7114002B1Increase valueError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching by path configurationPacket communicationPacket reception
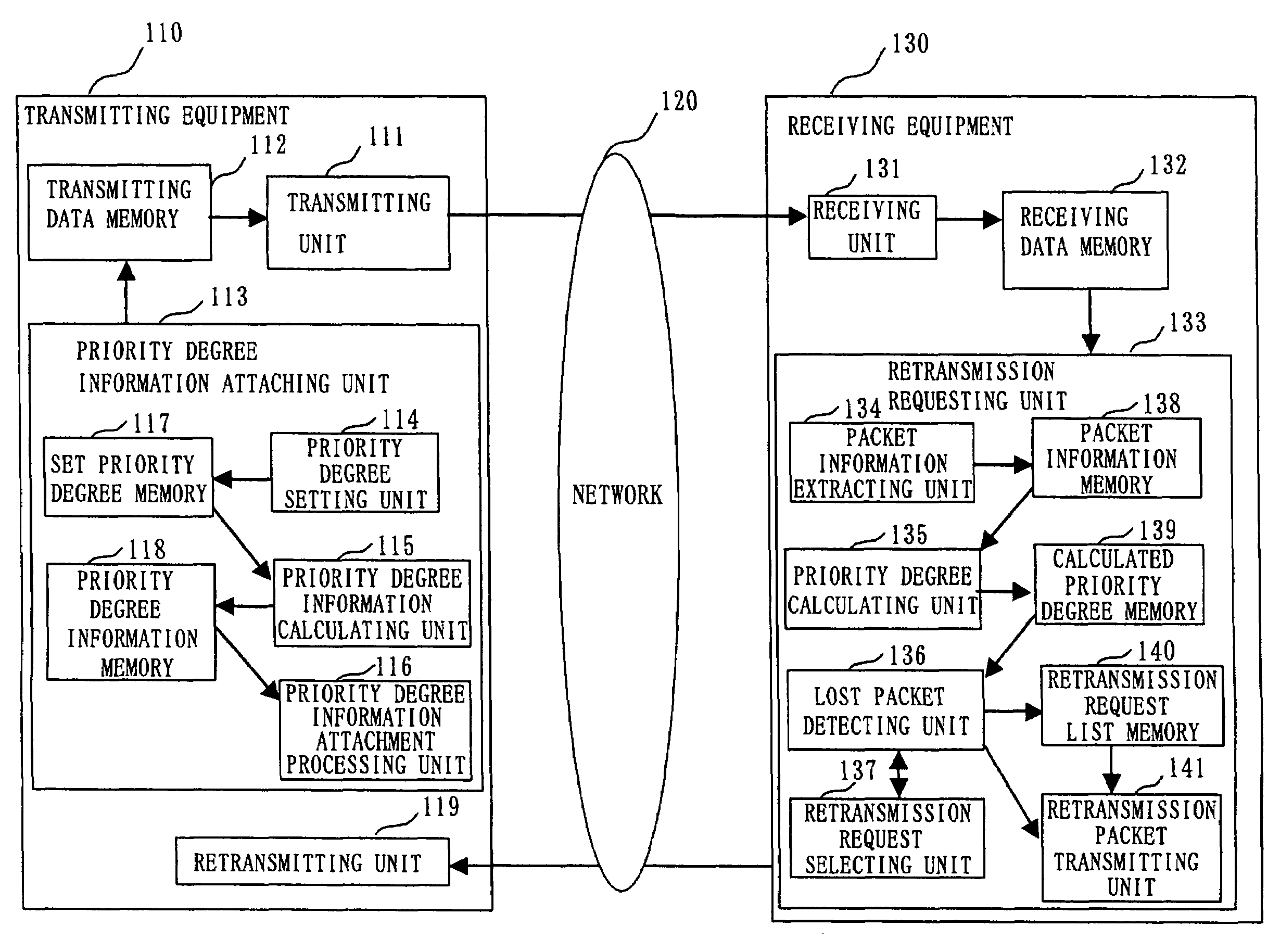
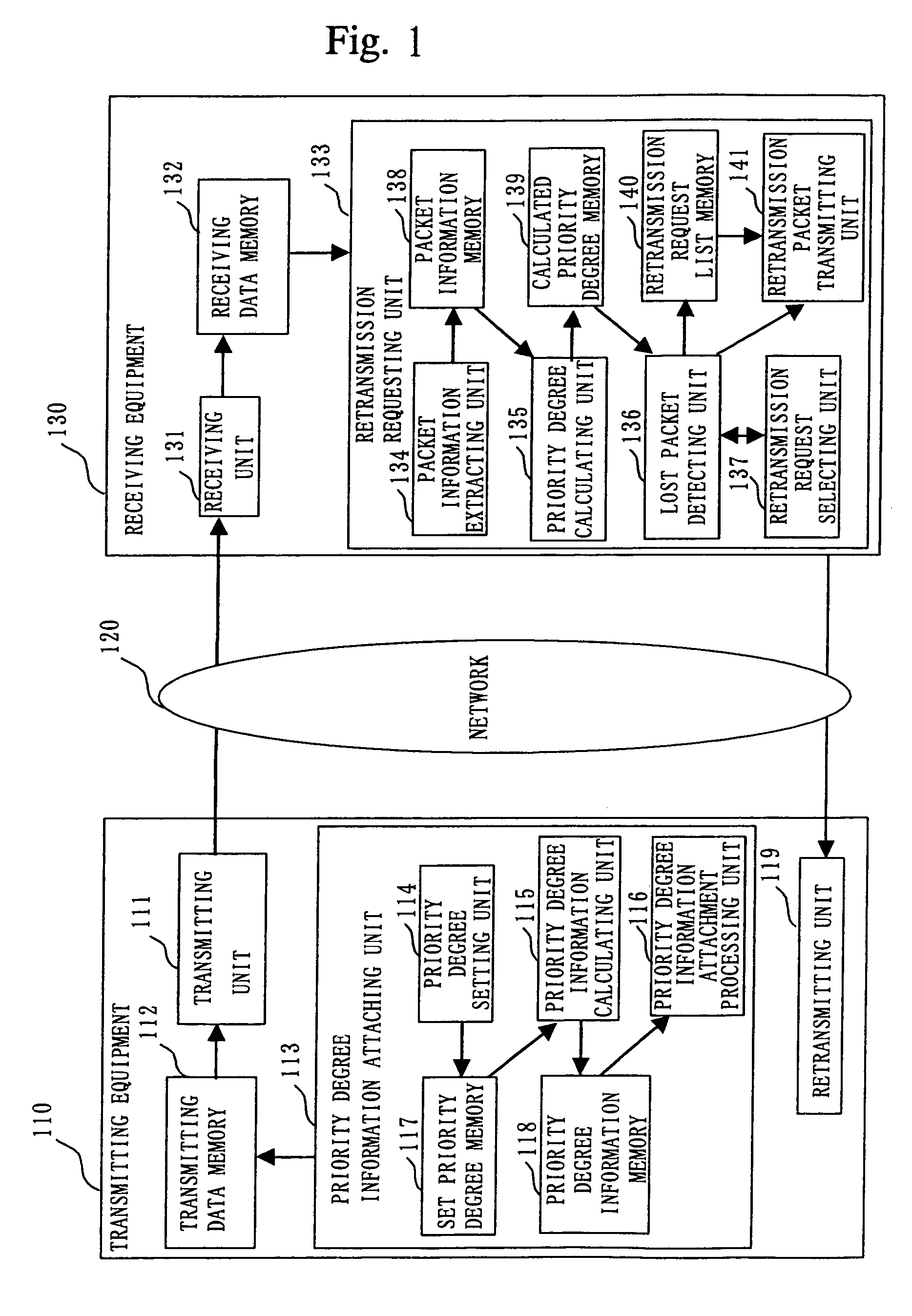
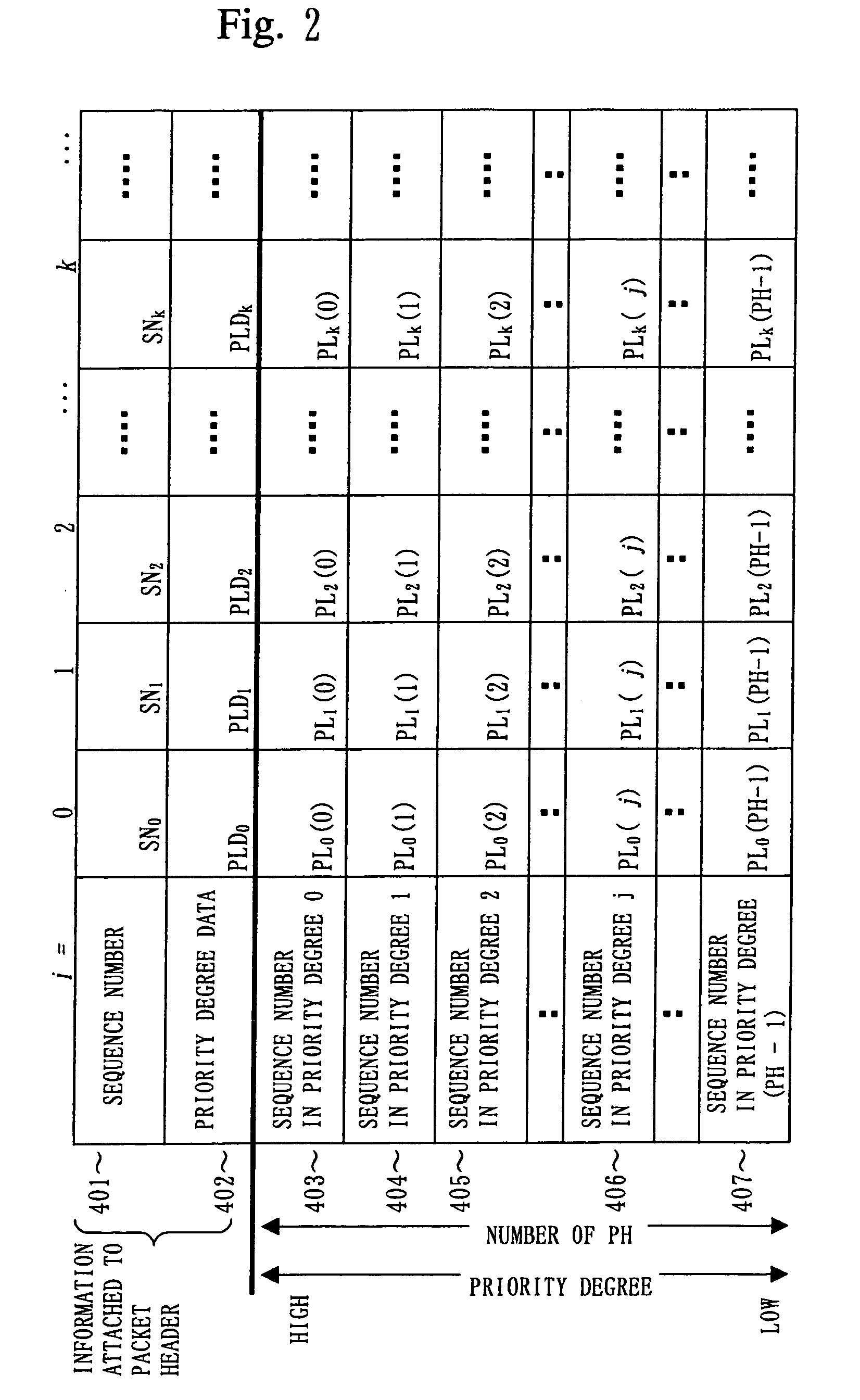
In a packet retransmitting system for retransmitting a packet including a sequence number in a packet header, which is lost during packet communication, a transmitting equipment (110) includes a priority degree information attaching unit (113) for defining a plurality of priority degrees, setting an importance degree of each of the plurality of priority degrees for a packet, producing priority degree information by using the plurality of priority degrees, and attaching the priority degree information to the packet header included in the packet repeatedly for each of the plurality of packets, a transmitter (111) for transmitting the plurality of packets, and a retransmitting unit (119) for receiving a retransmission request packet and retransmitting a packet of which retransmission is requested in the retransmission request packet received. A receiving equipment (130) includes a receiving unit (131) for receiving the plurality of packets and a retransmission requesting unit (133) for extracting a plurality of sequence numbers and a plurality of priority degree information from the packet header, detecting lost packets based on the plurality of sequence numbers and the plurality of priority degree information extracted, detecting an important packet among the lost packets, and requesting retransmission of the packet.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Packet transmission/reception device
InactiveUS20060112272A1Simple structurePrevent eavesdroppingUser identity/authority verificationTelevision systemsComputer hardwareKey exchange
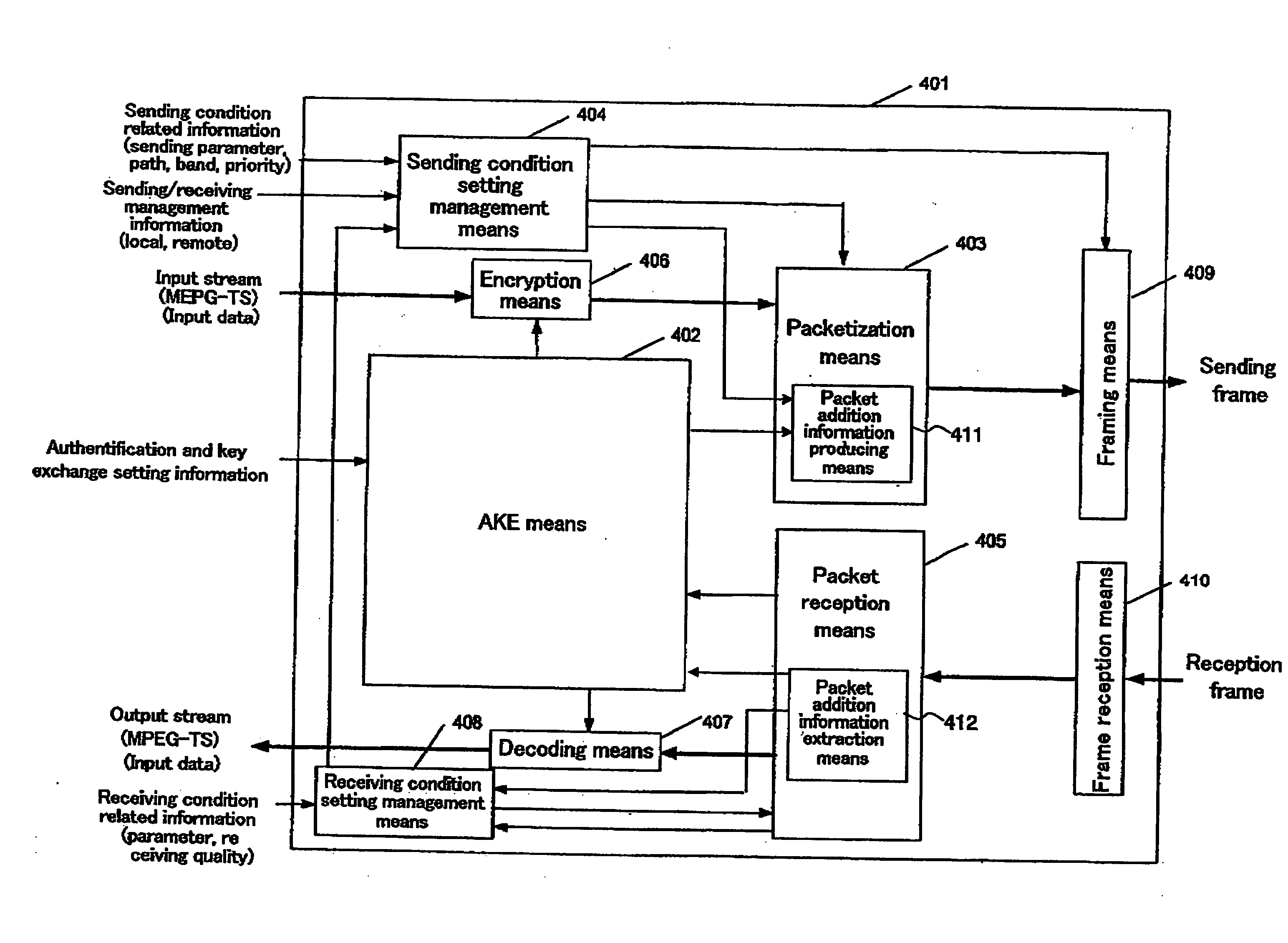
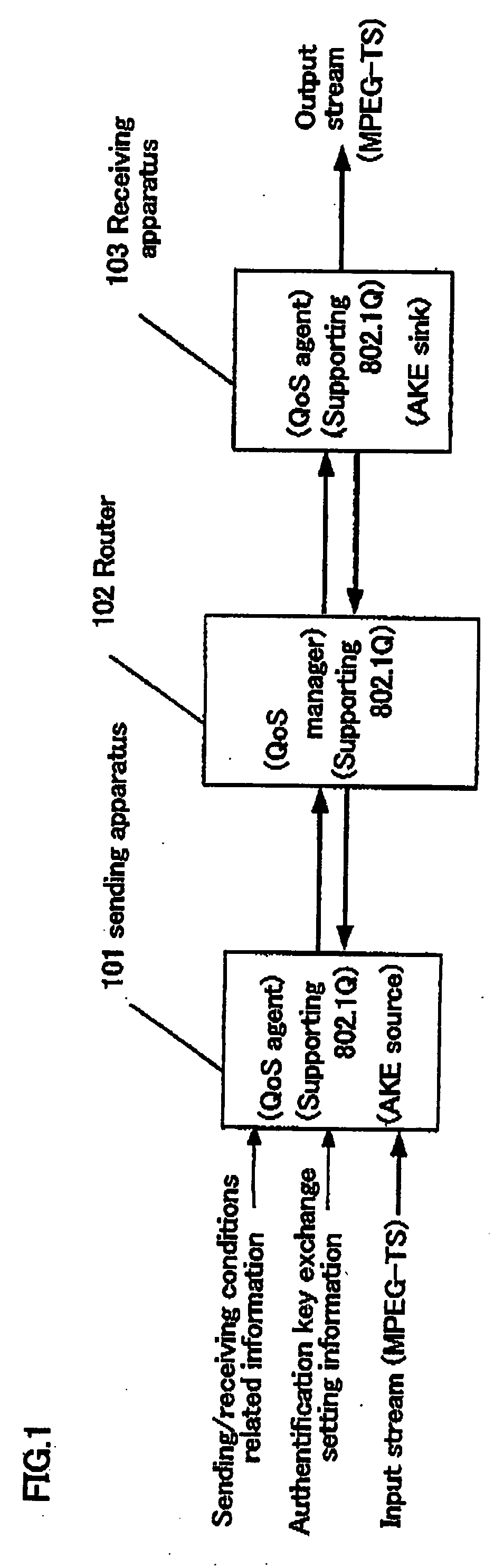
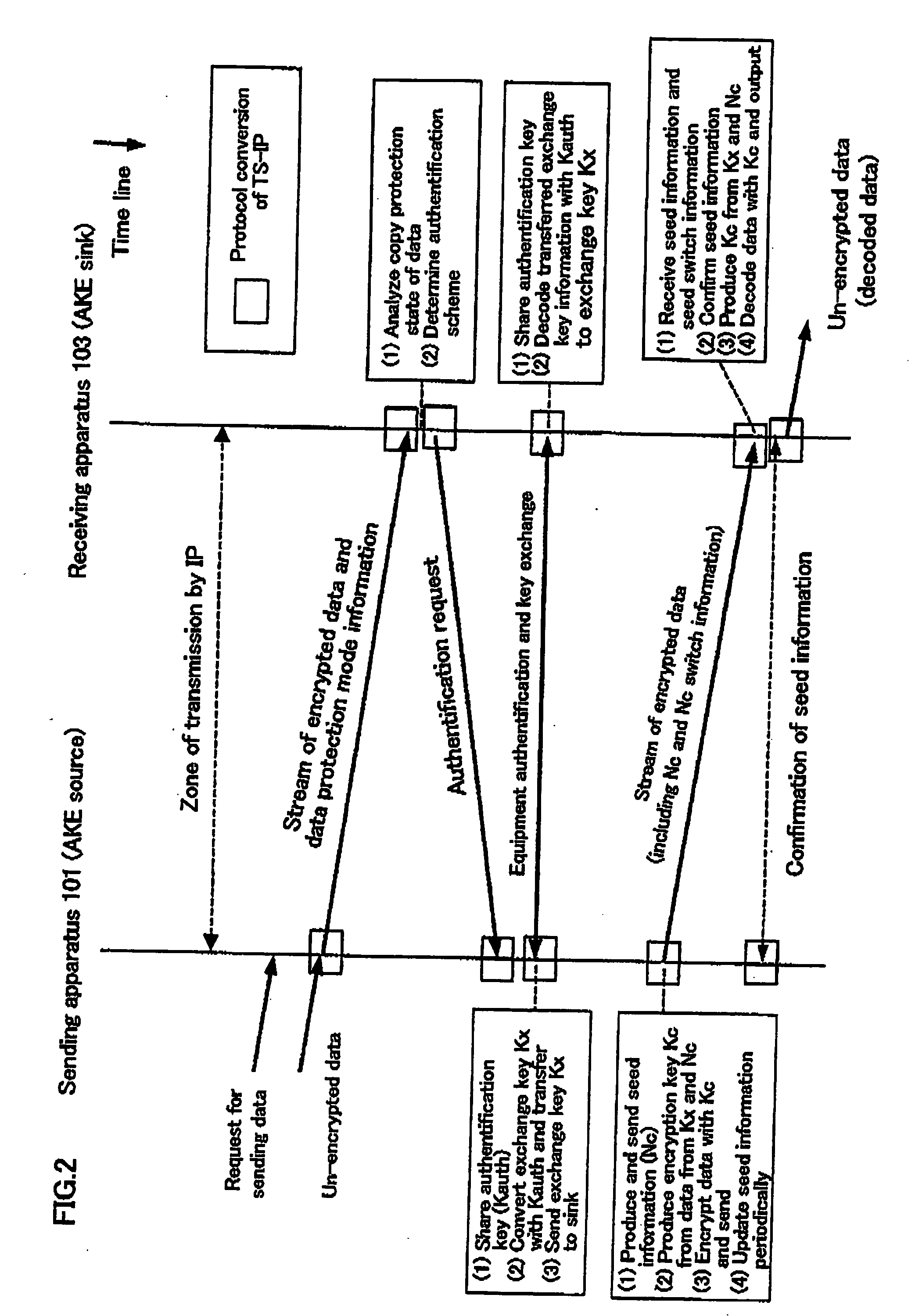
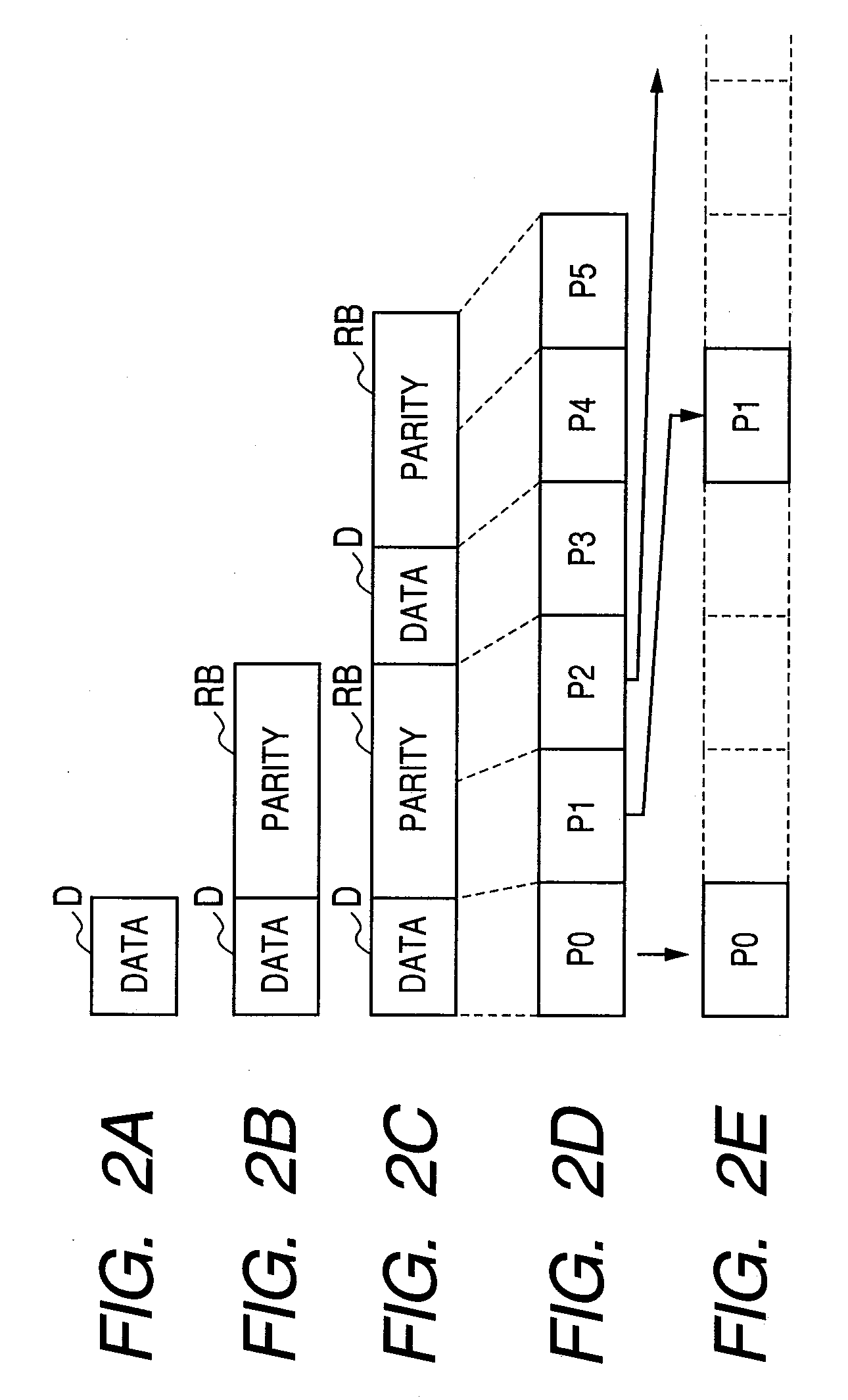
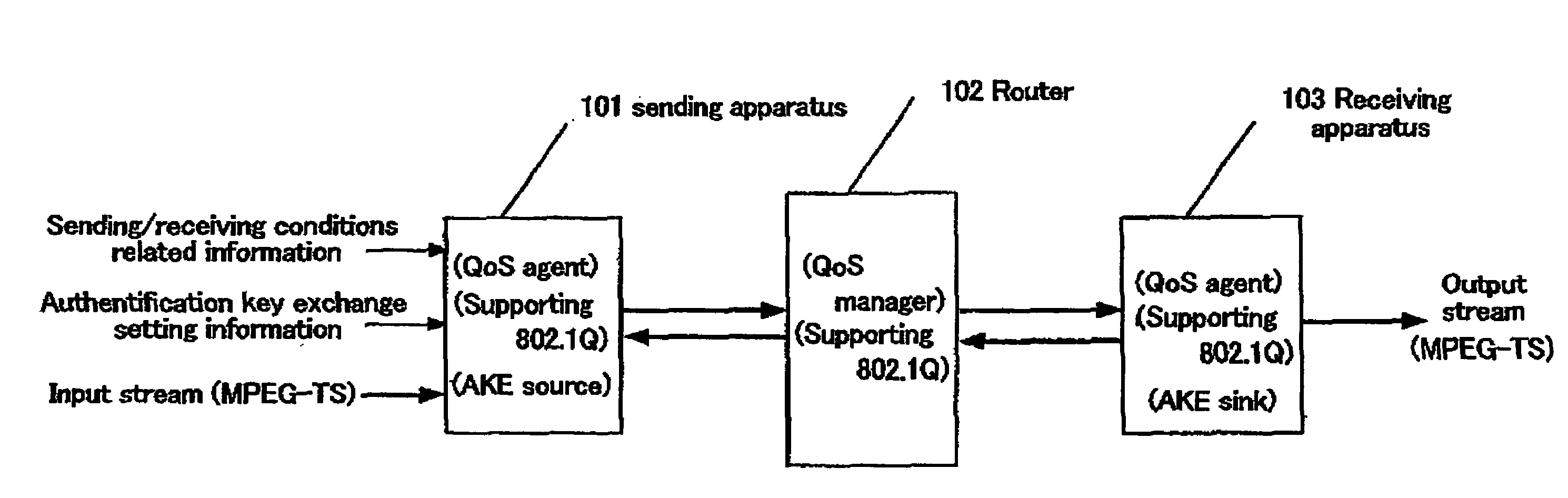
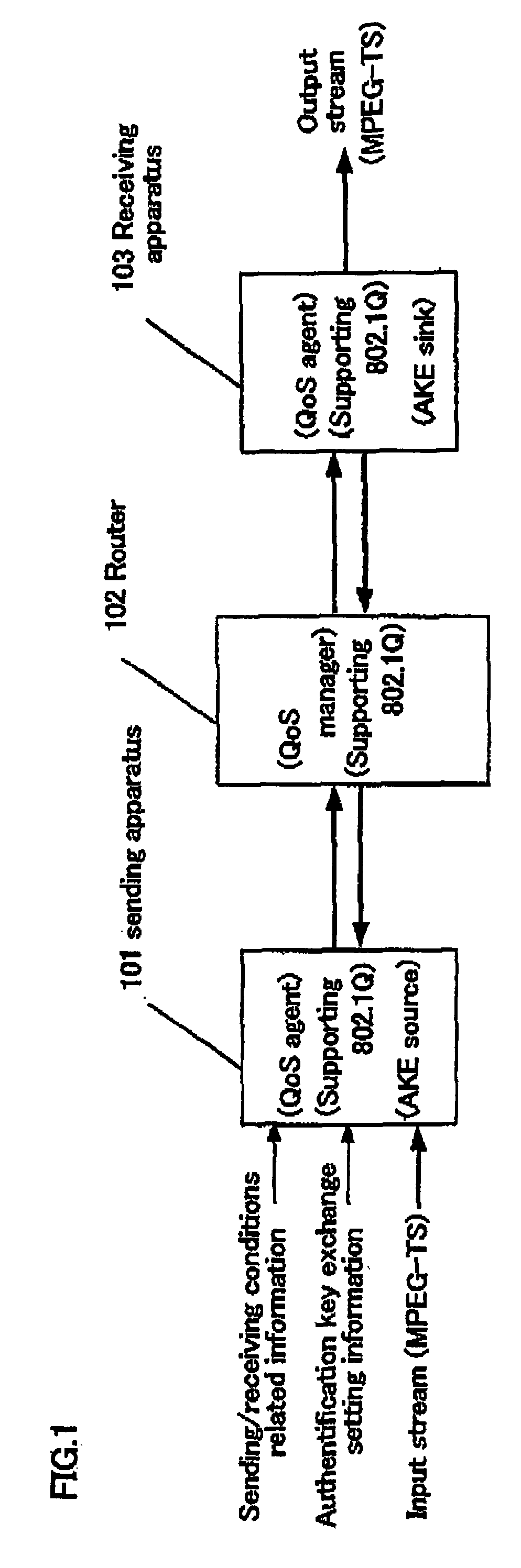
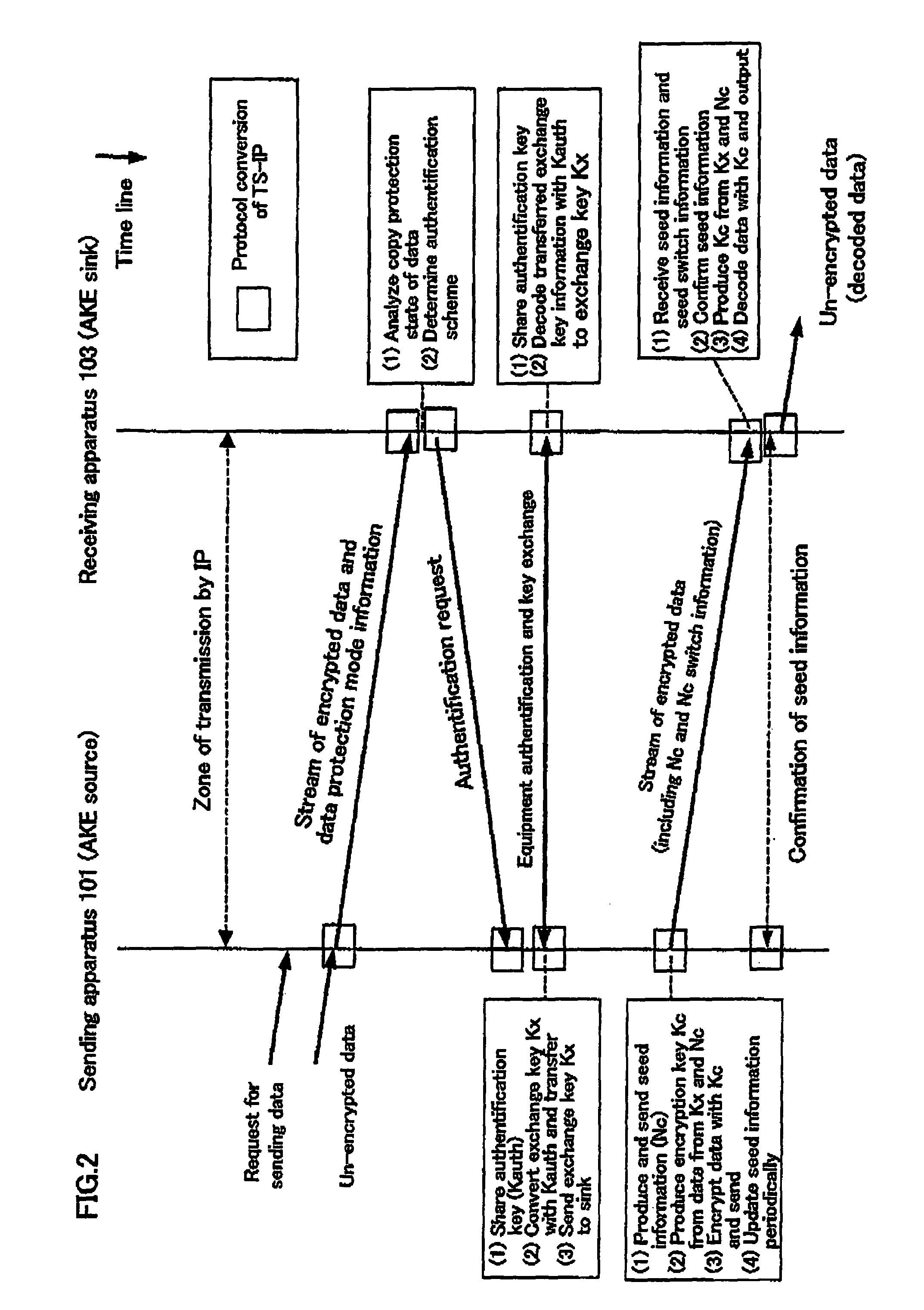
A packets sending / receiving apparatus, comprising: authentication and key exchange means; encryption means for producing an encryption sending data; sending condition setting management means for producing sending condition setting information for setting sending condition of the sending packets; packetization means for producing the sending packets using the encryption sending data; receiving condition setting management means for producing receiving condition setting information for setting receiving condition of the receiving packets; packets reception means for receiving the reception packets; and decoding means for decoding the reception data using the decoding key.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Cellular system, base station, mobile station, and communication control method
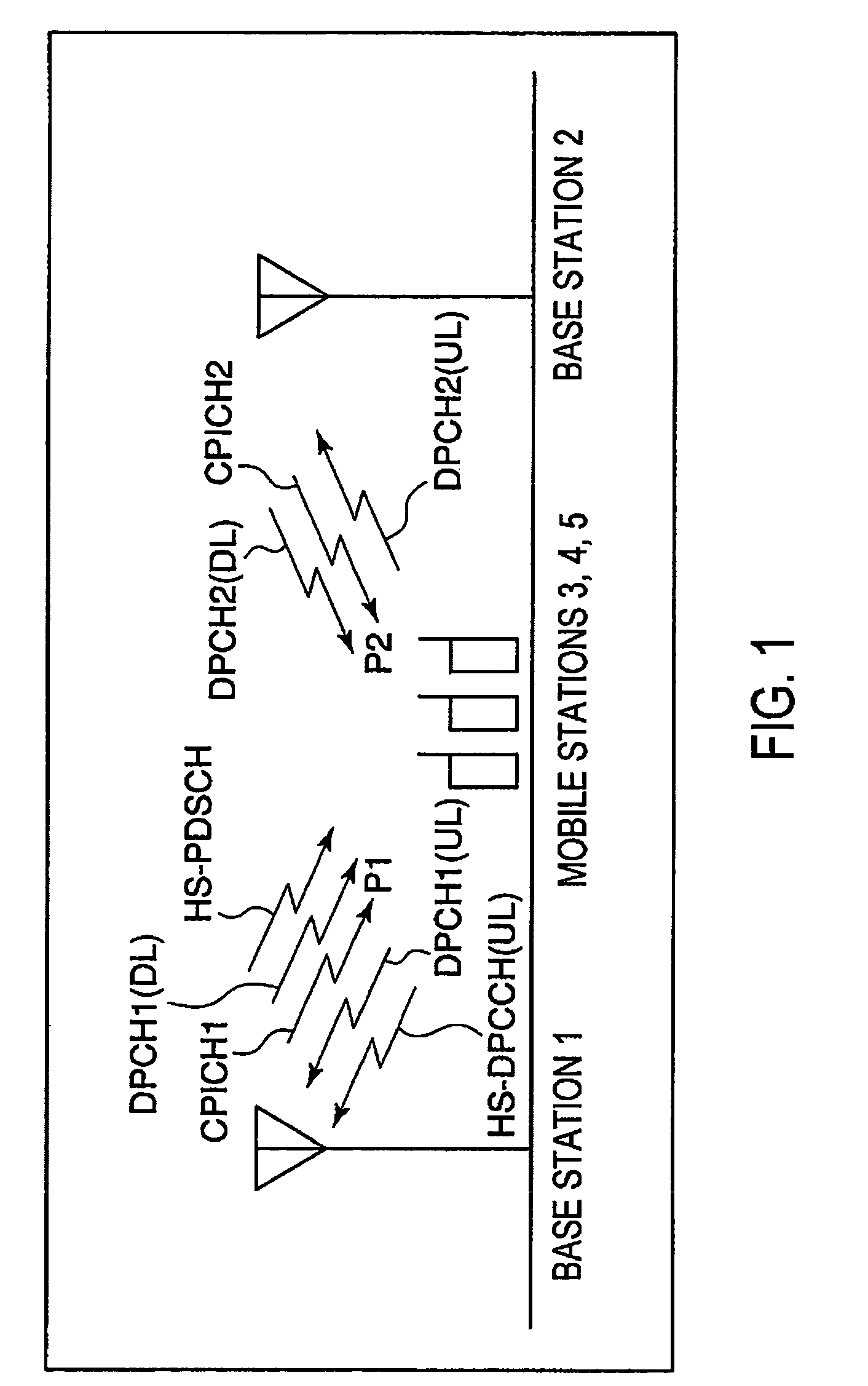
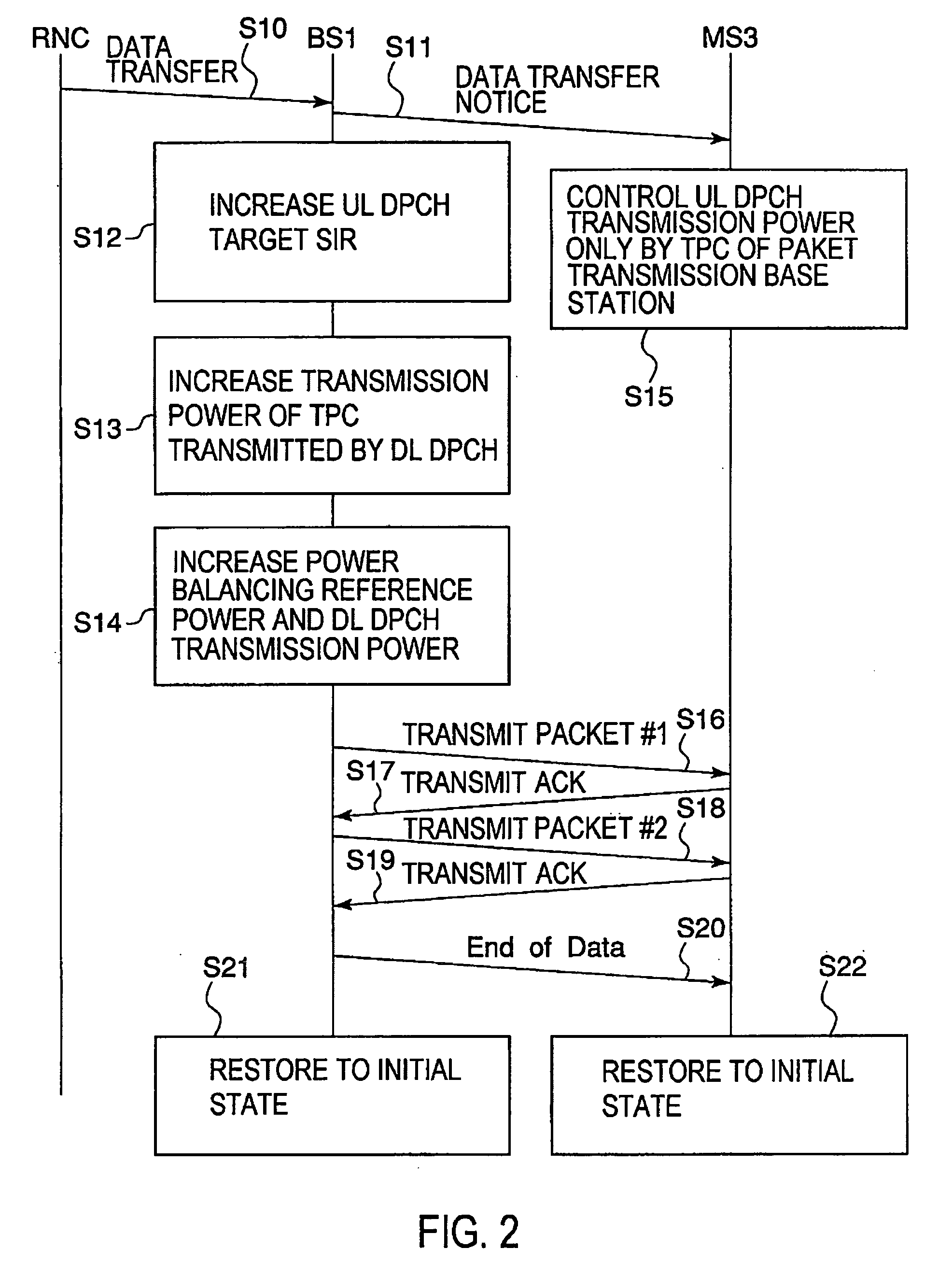
ActiveUS20050277419A1Increase valueIncrease transmit powerPower managementError prevention/detection by using return channelDPCCHPower balancing
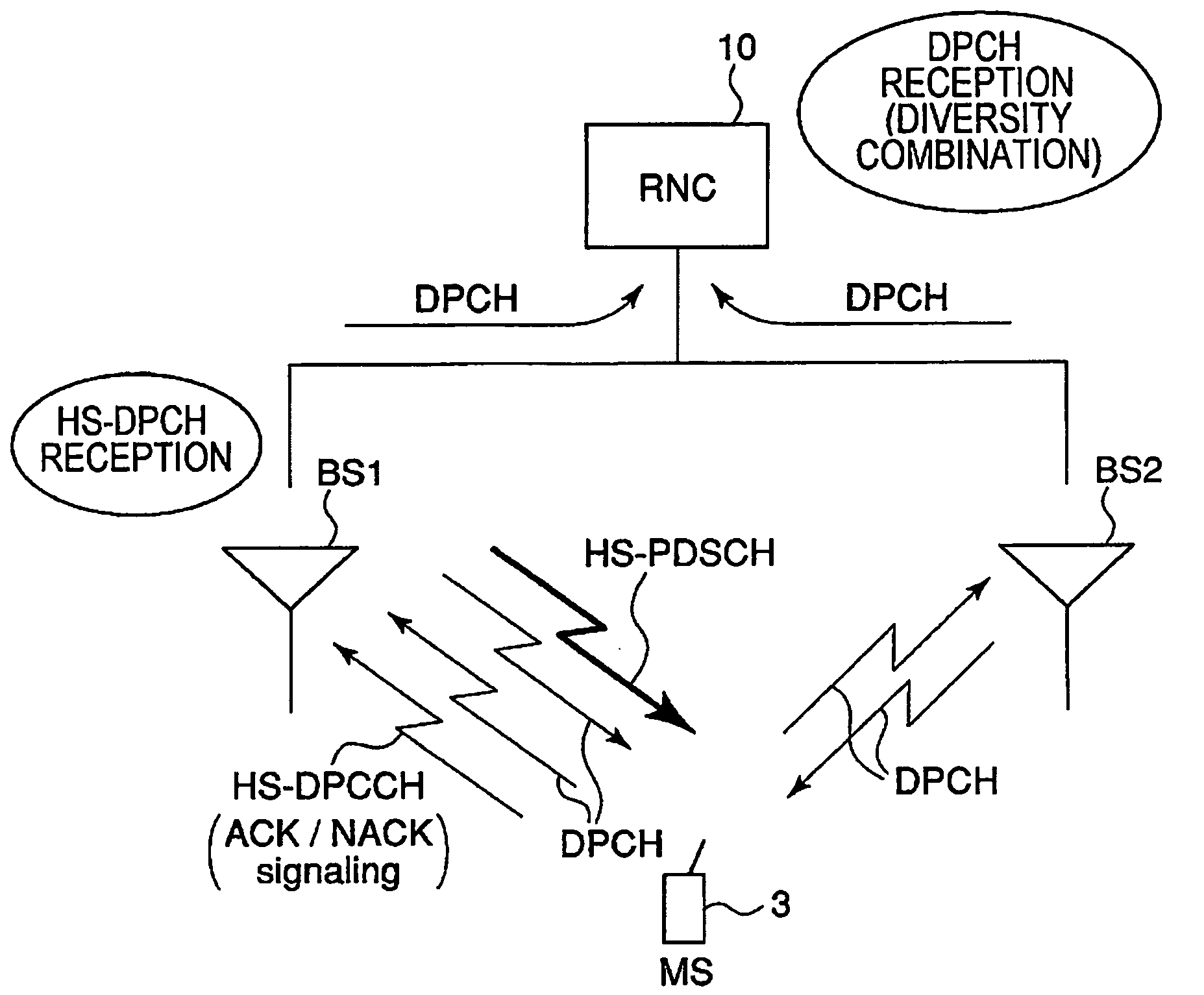
Immediately before transmitting a packet signal, a packet transmission base station (BS1) increases a target ISR of UL DPCH (S12), increases the TPC transmission power transmitted by the DPCH (S13), increases a power balancing reference power, and increases a DL DPCH transmission power (S14). In a mobile station (MS3), during packet reception, only a packet transmission base station (1) controls the UL DPCH transmission power (S15). This improves the reception quality at the base station (1) of HS-DPCCH including ACK / NACK and reduces the error ratio of the ACK / NACK signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
Radio communication system, mobile station, and radio base station
InactiveUS20090016265A1Shorten transmission intervalReduce transmission delayError preventionSecret communicationPacket communicationCommunications system
A radio communication system of an HARQ method that makes an HARQ transmission interval of subpackets appropriate and reduces data transmission delay resulting from subpacket retransmission. In the radio communication system in which a packet is transmitted and receives with the HARQ method between a base station and multiple radio mobile stations, each of the base station and the multiple radio mobile stations has: a packet transmission circuit for transmitting subpackets in predetermined intervals; a packet reception circuit for repeating decoding processing by combining a newly received subpacket and a previously received former subpacket until an original packet is successfully decoded; and a HARQ control equipped with a function of, for packet communication whose data length is short, transmitting a subpacket or response from the packet transmission circuit in an HARQ transmission interval that is shortened from the HARQ transmission interval of the normal mode.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Packet transmission/reception device
InactiveUS7228422B2Easy to processUser identity/authority verificationTelevision systemsComputer hardwareKey exchange
A packets sending / receiving apparatus, comprising: authentication and key exchange means; encryption means for producing an encryption sending data; sending condition setting management means for producing sending condition setting information for setting sending condition of the sending packets; packetization means for producing the sending packets using the encryption sending data; receiving condition setting management means for producing receiving condition setting information for setting receiving condition of the receiving packets; packets reception means for receiving the reception packets; and decoding means for decoding the reception data using the decoding key.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
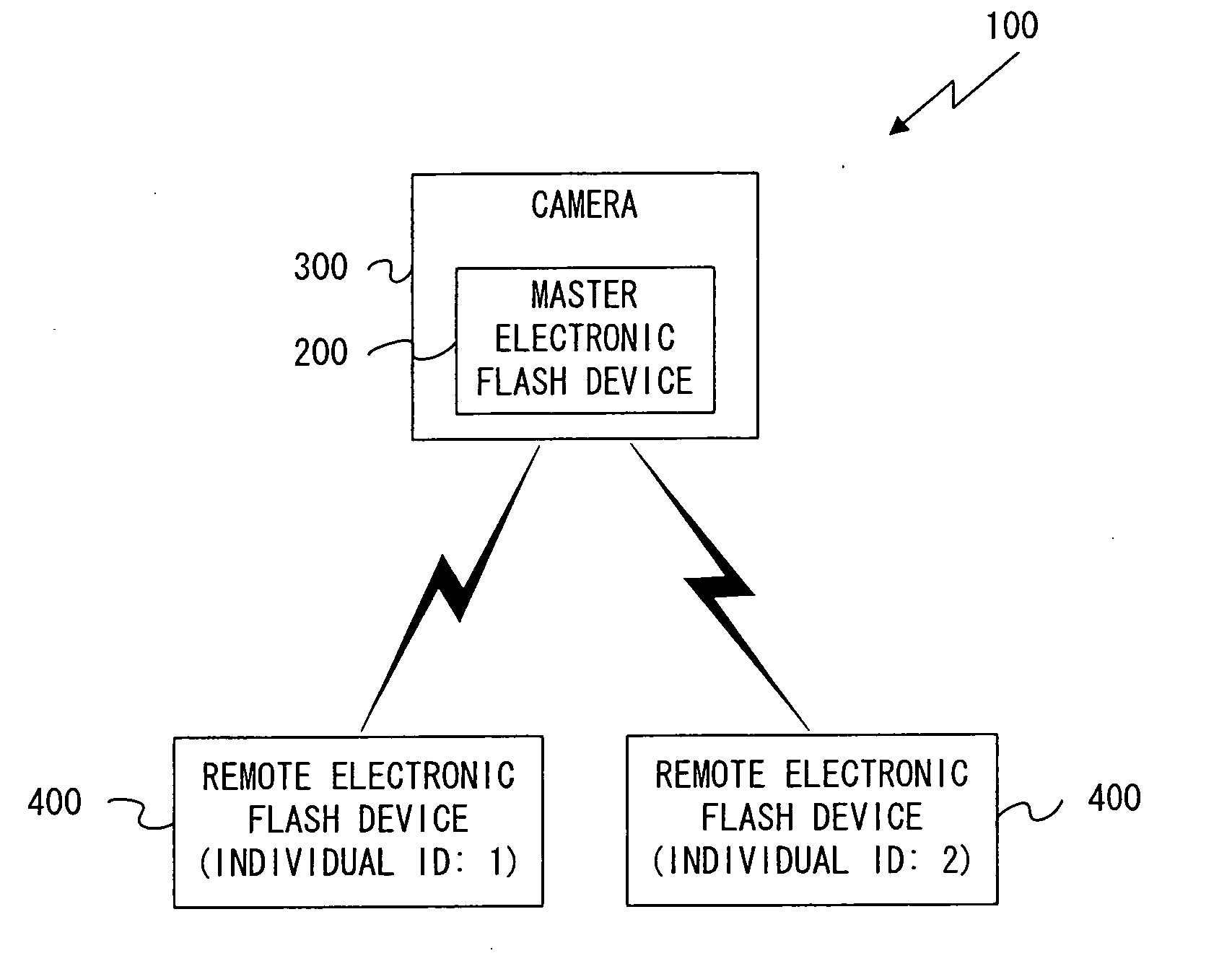
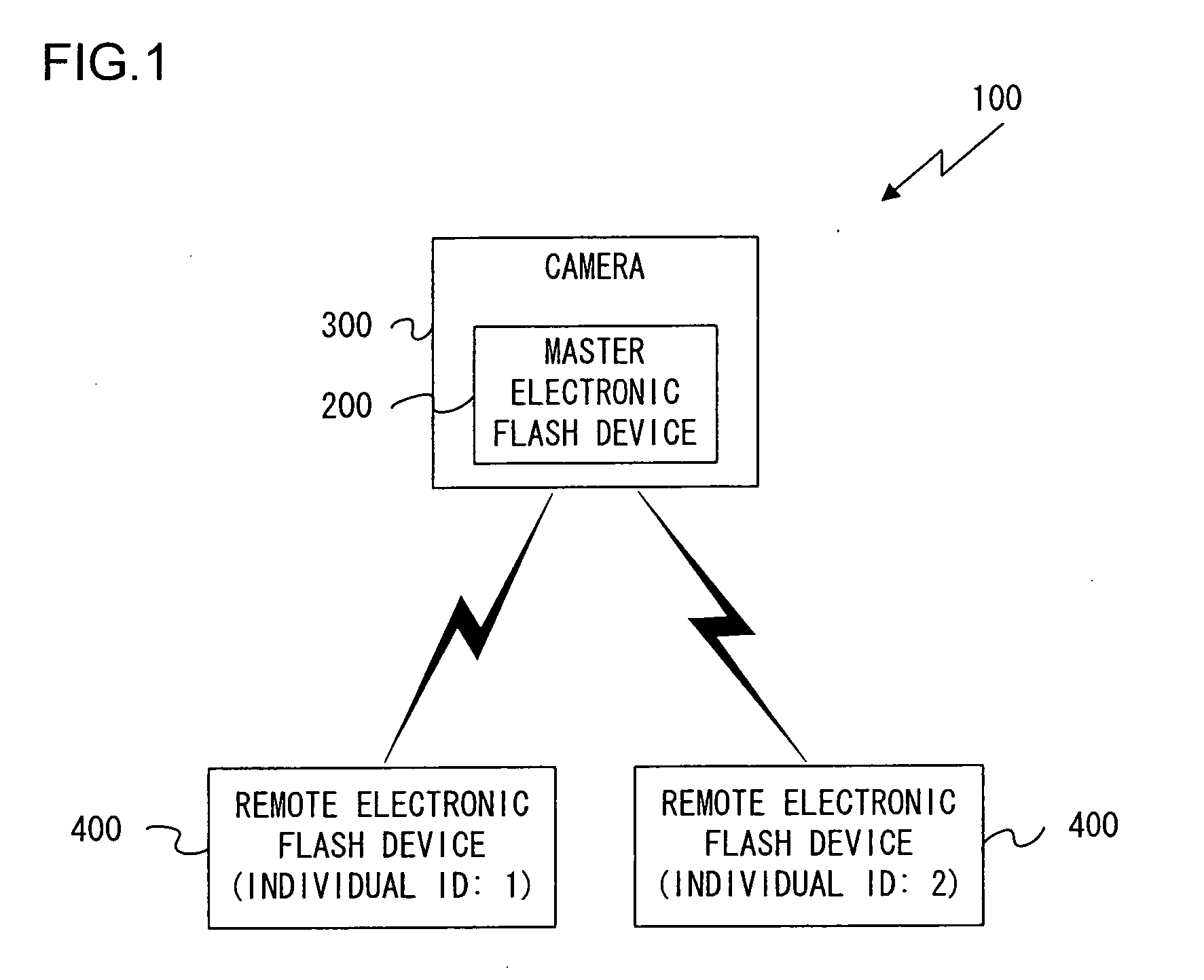
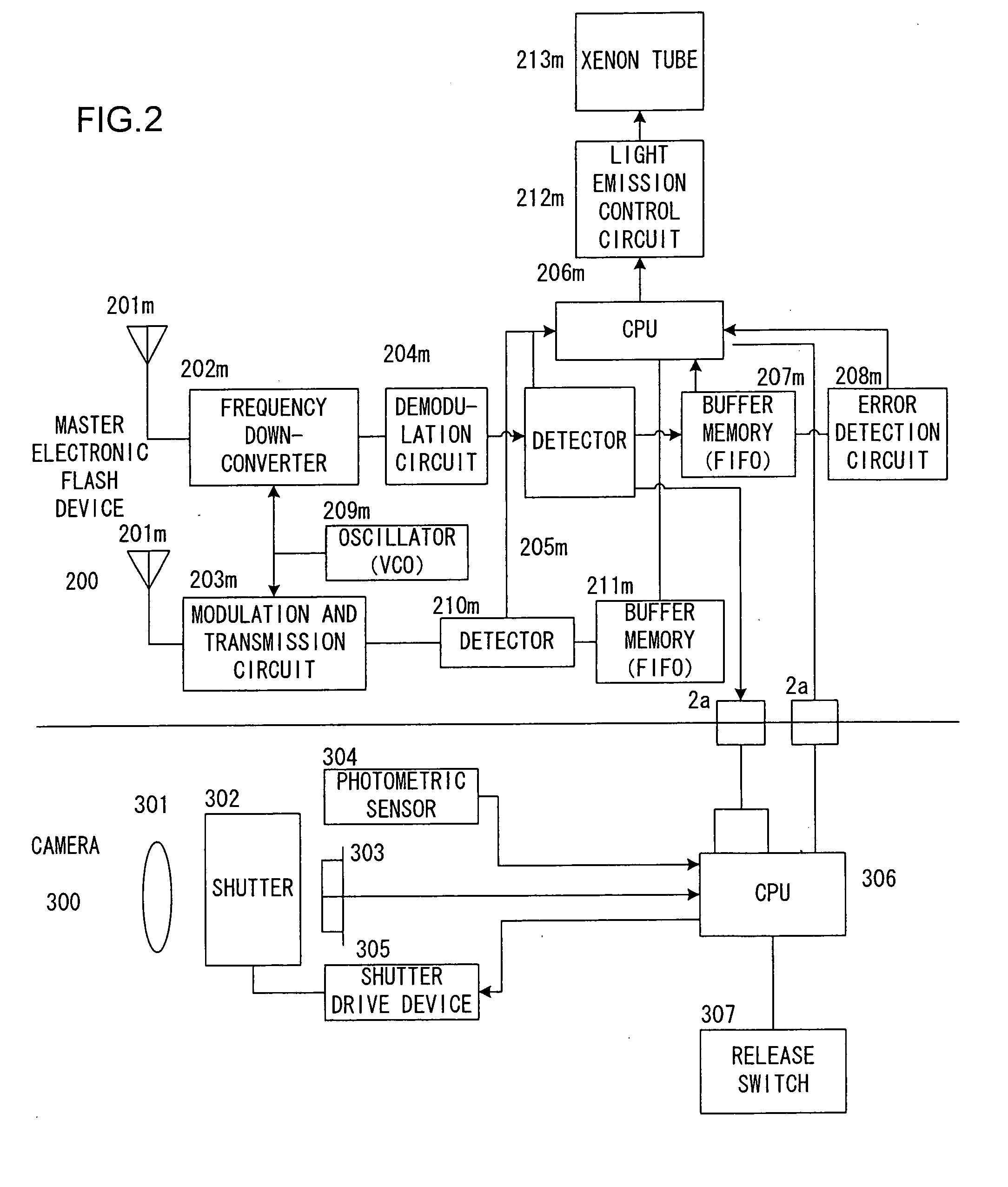
External device, electronic flash device, and camera
ActiveUS20090135262A1High synchronization accuracyTelevision system detailsTime-division multiplexWireless connectivityCommunication device
The external device, for example, an electronic flash device, is wirelessly connectable to an information communication device, for example, a camera. The external device includes: a synchronization data creation unit that outputs synchronization data for synchronization of timing of processing related to photography; a packet creation unit that creates a communication packet including control information; and a packet output unit that outputs the communication packet to the exterior by wireless communication. The packet creation unit includes a packet reception unit that receives the communication packet; a detection unit that detects the synchronization data before all of the received communication packets received by the packet reception unit has been read in; and a signal output unit that outputs a synchronization signal used for establishing synchronization of the timing of the processing related to photography on the basis of detection by the detection unit of the synchronization data.
Owner:NIKON CORP
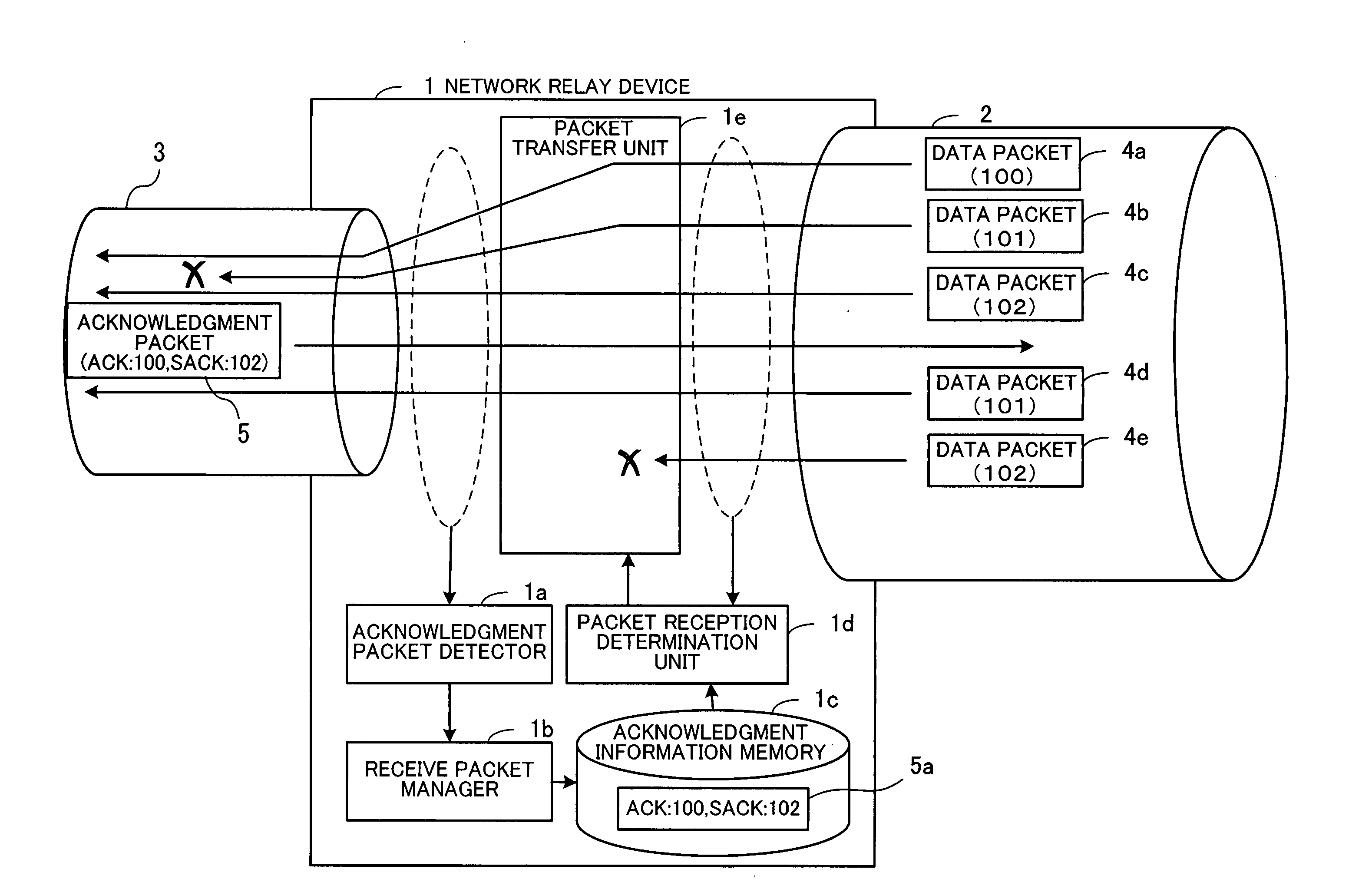
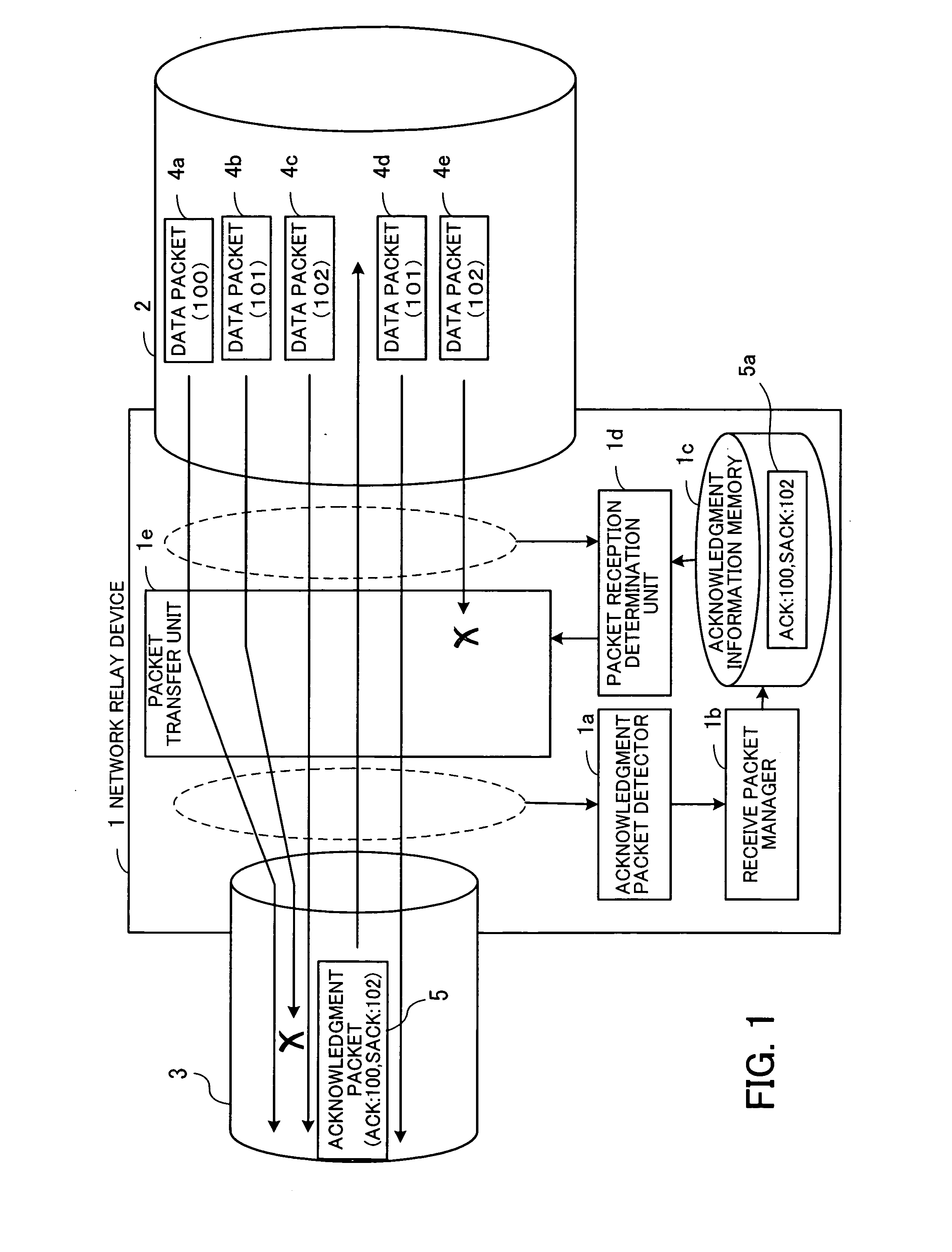
Congestion control network relay device and method
InactiveUS20060221825A1Transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer sciencePacket reception
A congestion control network relay device capable of preventing redundant retransmission of packets which are already delivered to a receiving-side device. When an acknowledgment packet is detected by an acknowledgment packet detector, a receive packet manager stores acknowledgment information in an acknowledgment information memory. If first and second data packets are retransmitted thereafter from a transmitting-side device and input to the congestion control network relay device, a packet reception determination unit judges, for example, that the first data packet has not yet been received by the receiving-side device while the second data packet has already been received by the receiving-side device. In this case, a packet transfer unit transfers the first data packet to the receiving-side device and discards the second data packet.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
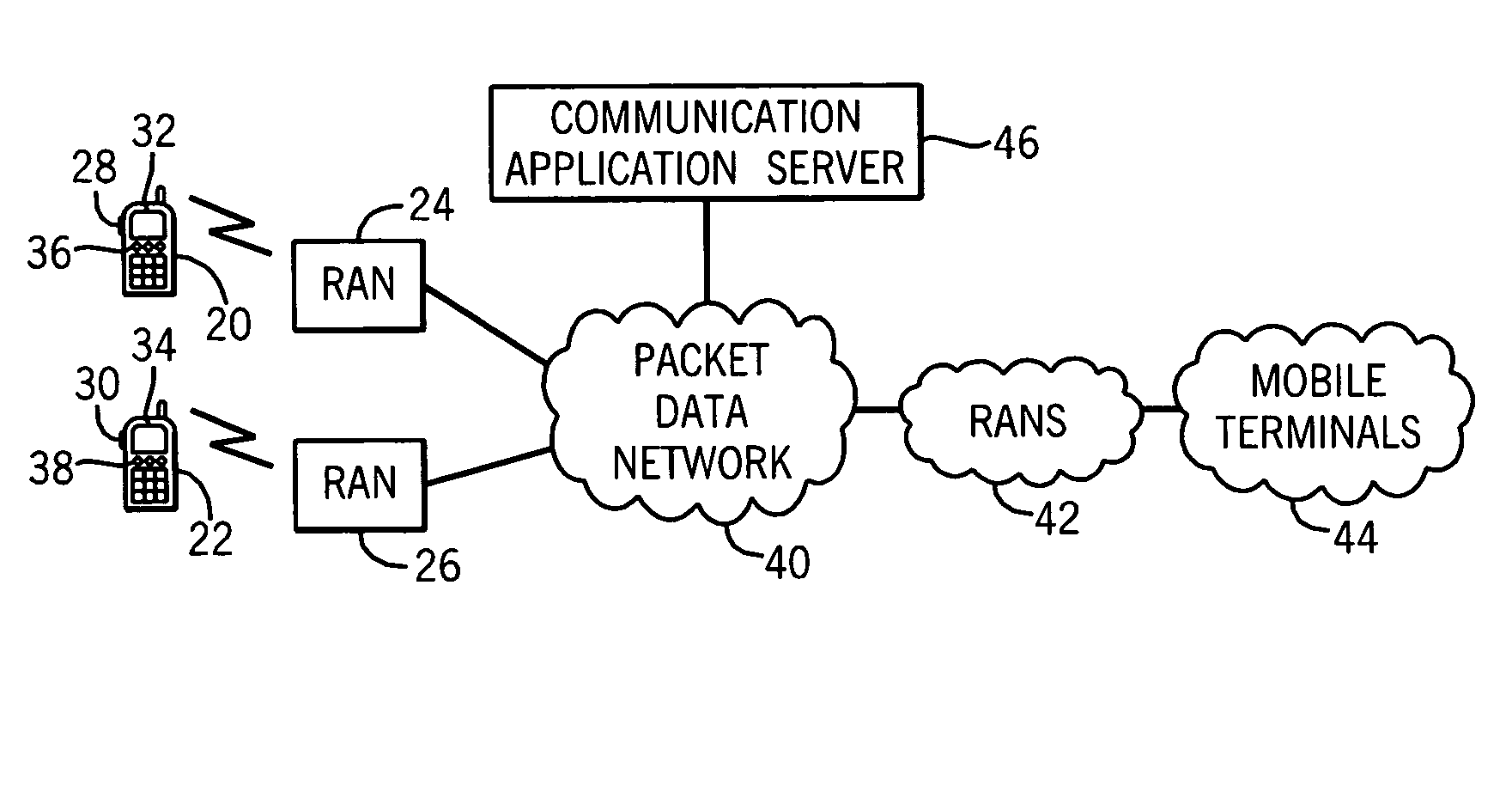
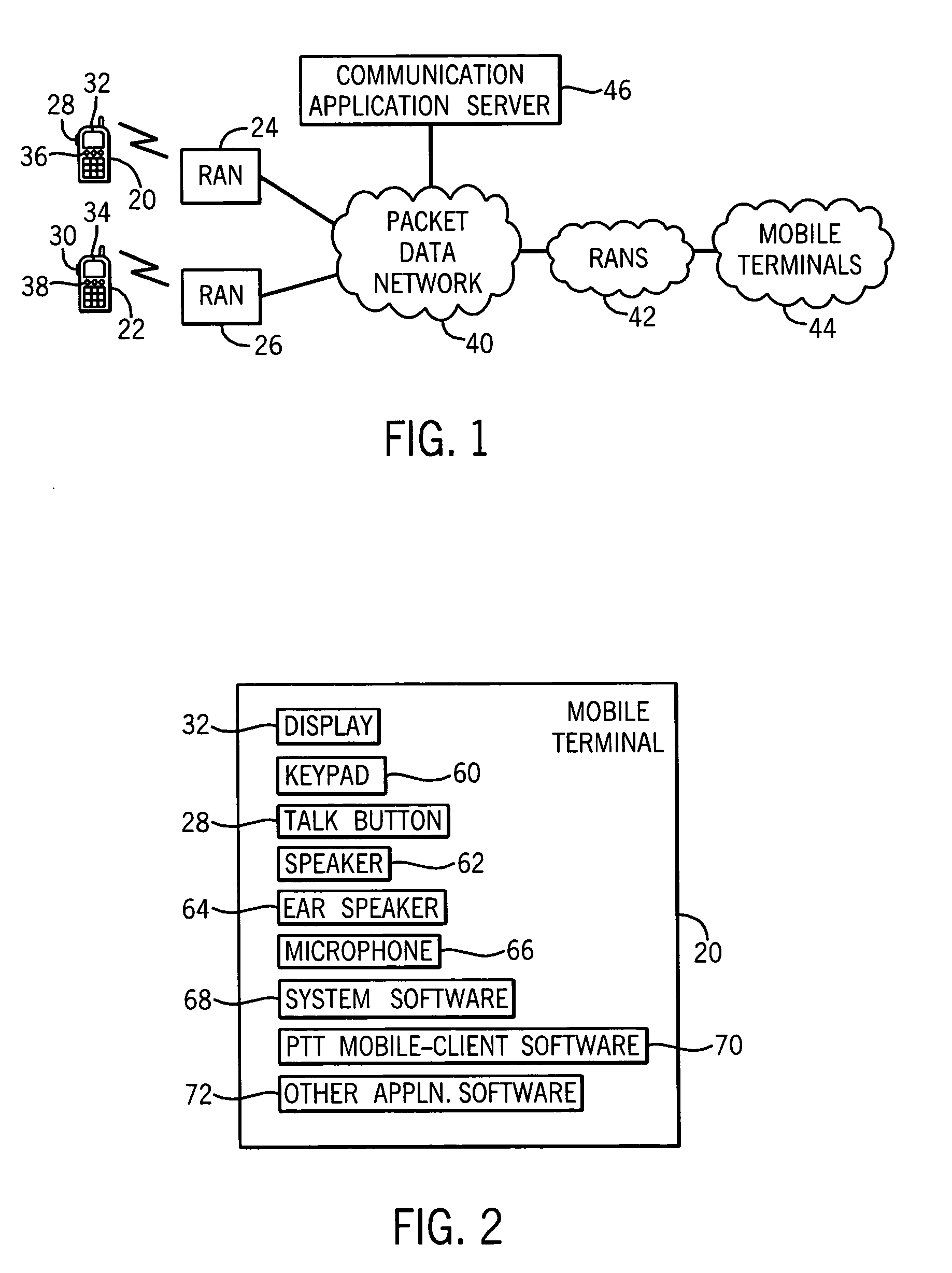
Voice message storage in a push-to-talk communication system
InactiveUS20050164681A1Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingConnection managementData packCommunications system
A method permits an originating PTT subscriber to be able to elect to transmit a voice message that will be stored by the PTT system for a later delivery to the designated recipient. A communication application server receives the voice message via packets and upon recognizing a predetermined code stores the voice message for later delivery to the designated recipient. The server then transmits a status update message to the mobile terminals of the originating subscriber and the designated recipient causing the respective status of each to be modified with indicia indicating that a voice message from the originating subscriber awaits delivery to the designated recipient. Upon the election of the designated recipient, the stored voice message from the originating subscriber is requested to be played.
Owner:CLARITY COMM SYST
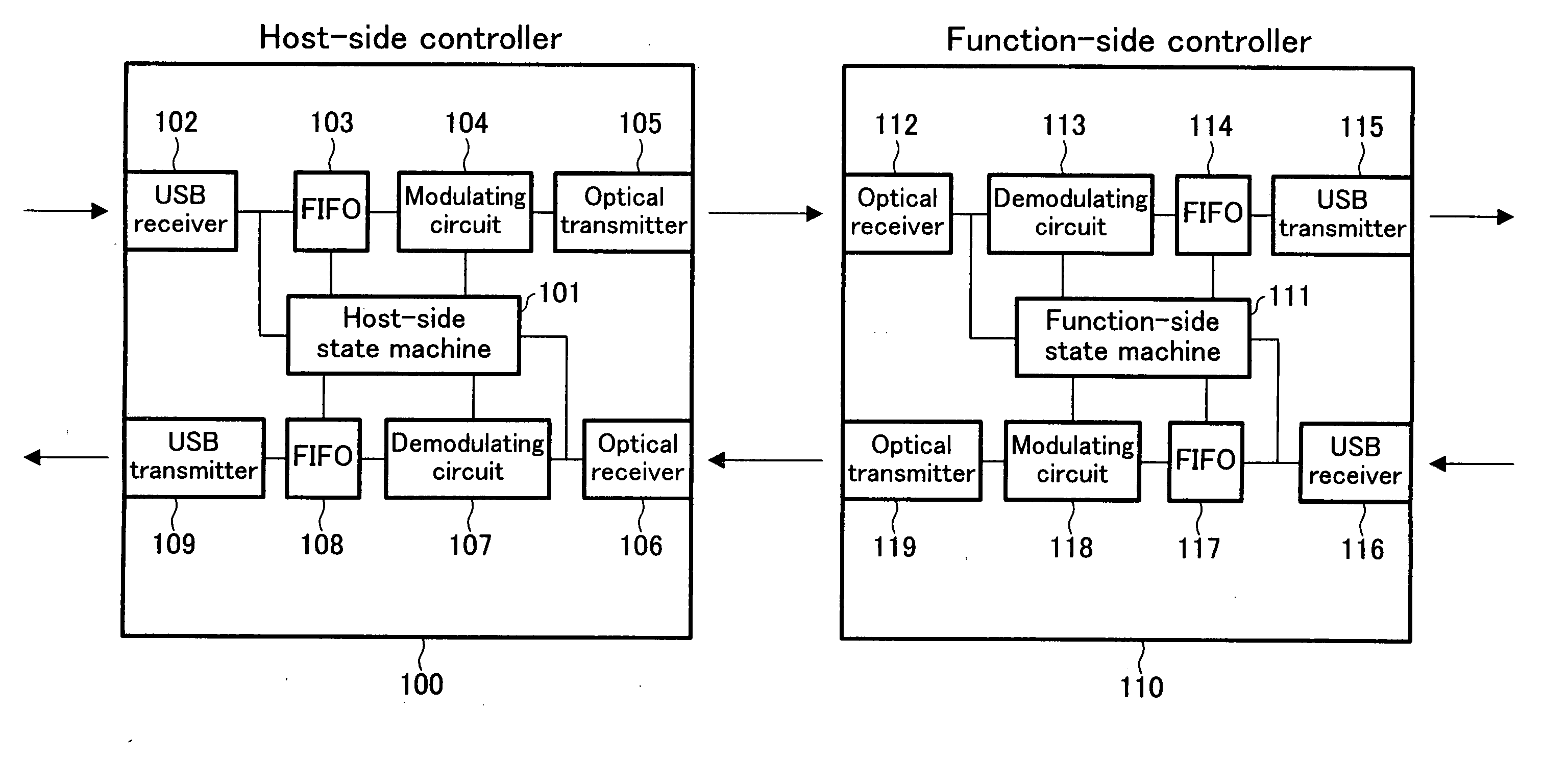
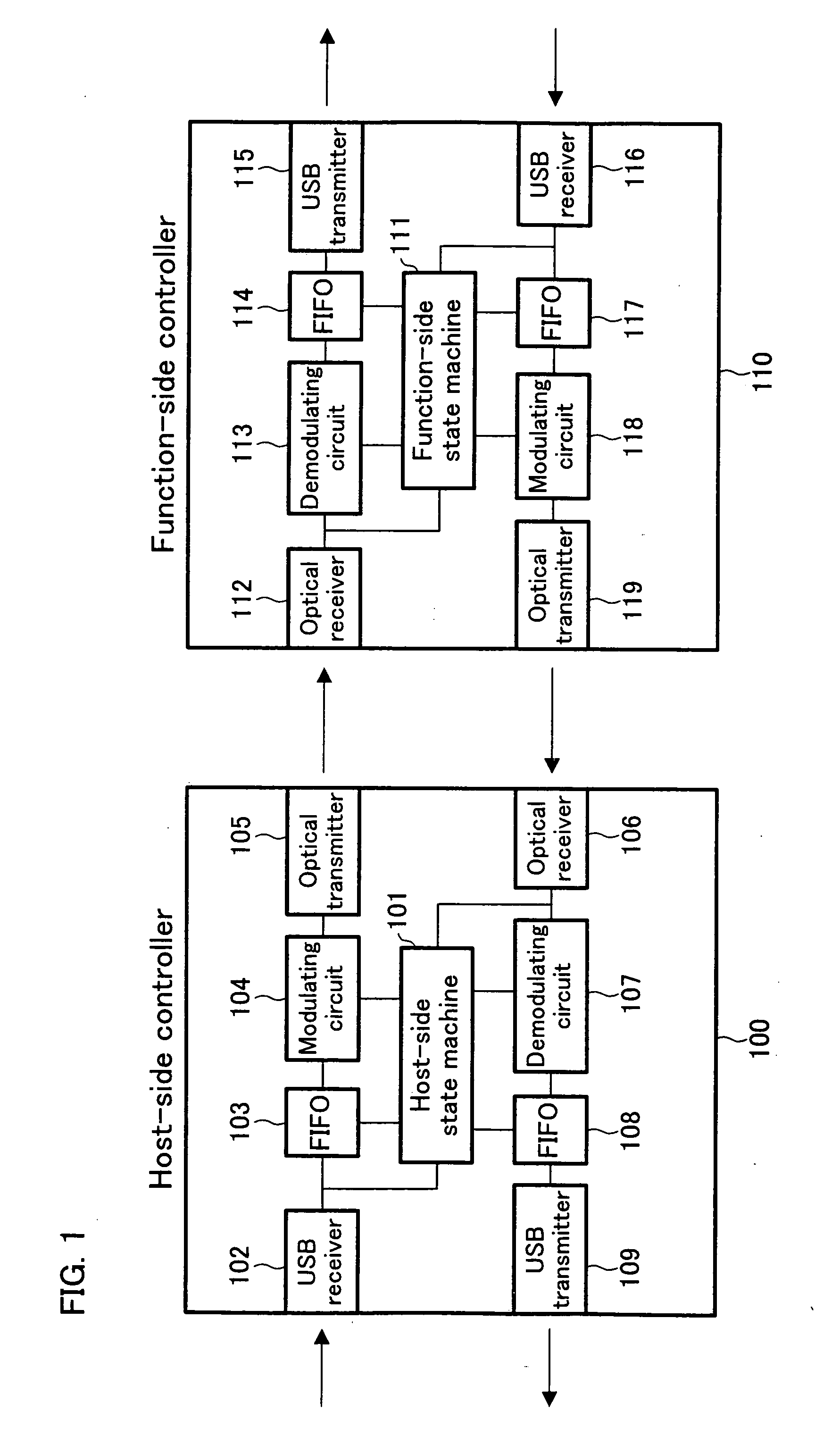
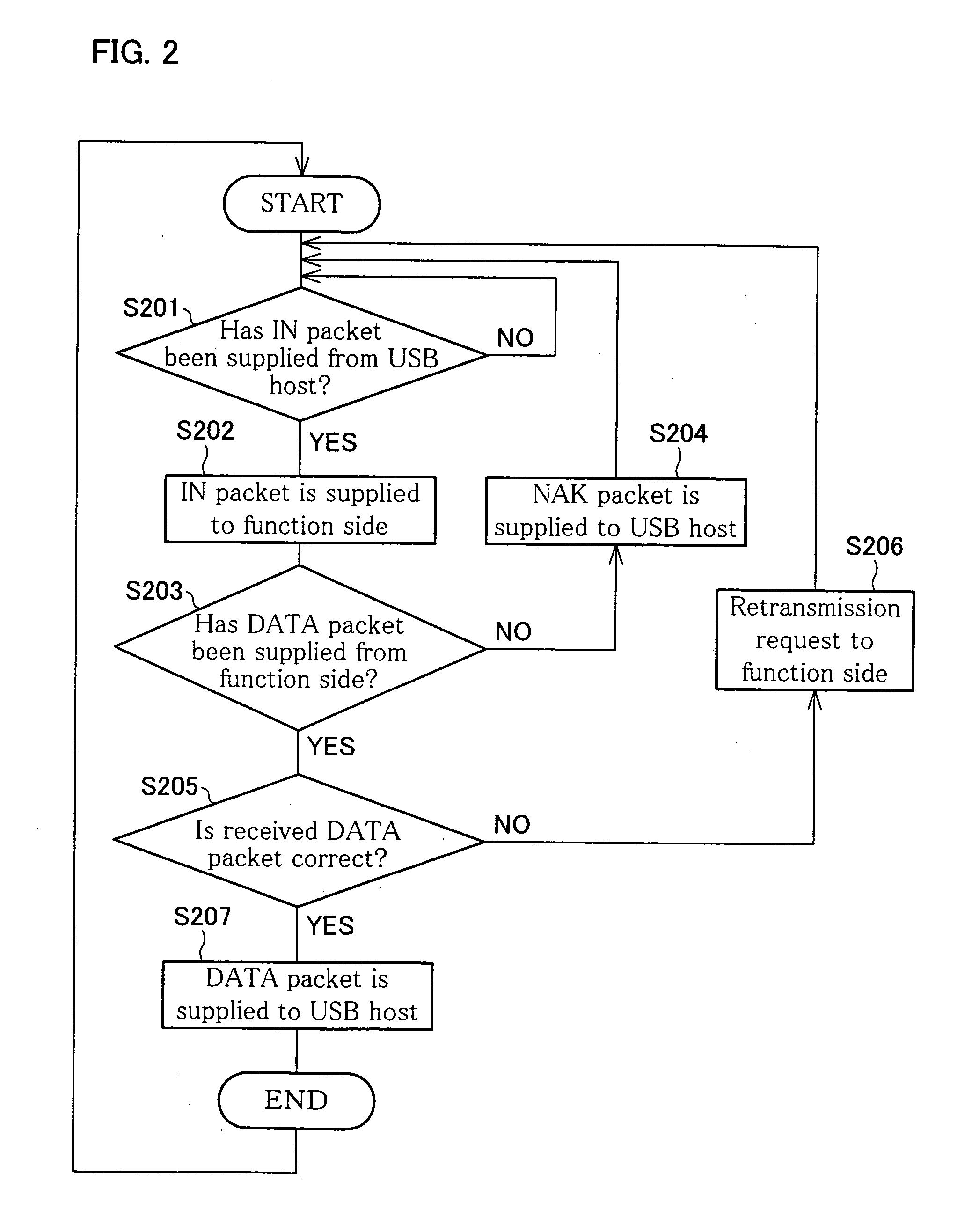
Communication controller, host-side controller, communication system, USB system, communication equipment, communication method, packet-based communication method, packet-based communication program, and storage medium
ActiveUS20050071733A1Easily preserve and distributeError prevention/detection by using return channelCorrect operation testingData packCommunications system
A two-way transmission system of the present invention is arranged in such a manner that, when a host-side controller confirms the receipt of an IN packet from a USB host, the host-side controller transfers the IN packet to a function-side controller, and receives a DATA packet from the function side. The received DATA packet is temporarily stored in a FIFO. At the time of the receipt of the IN packet again, the host-side controller supplies, to the USB host, the DATA packet stored in the FIFO.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
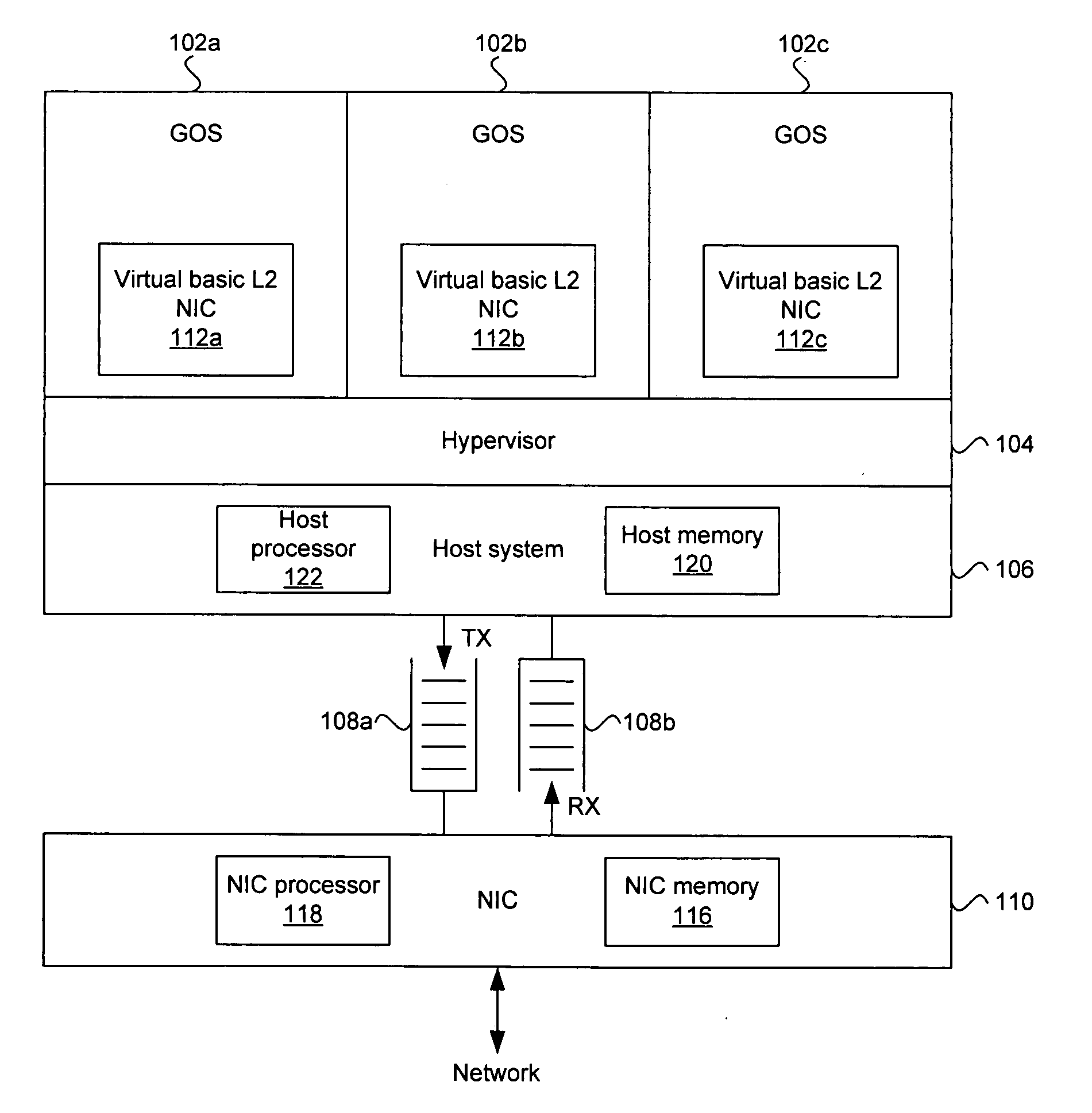
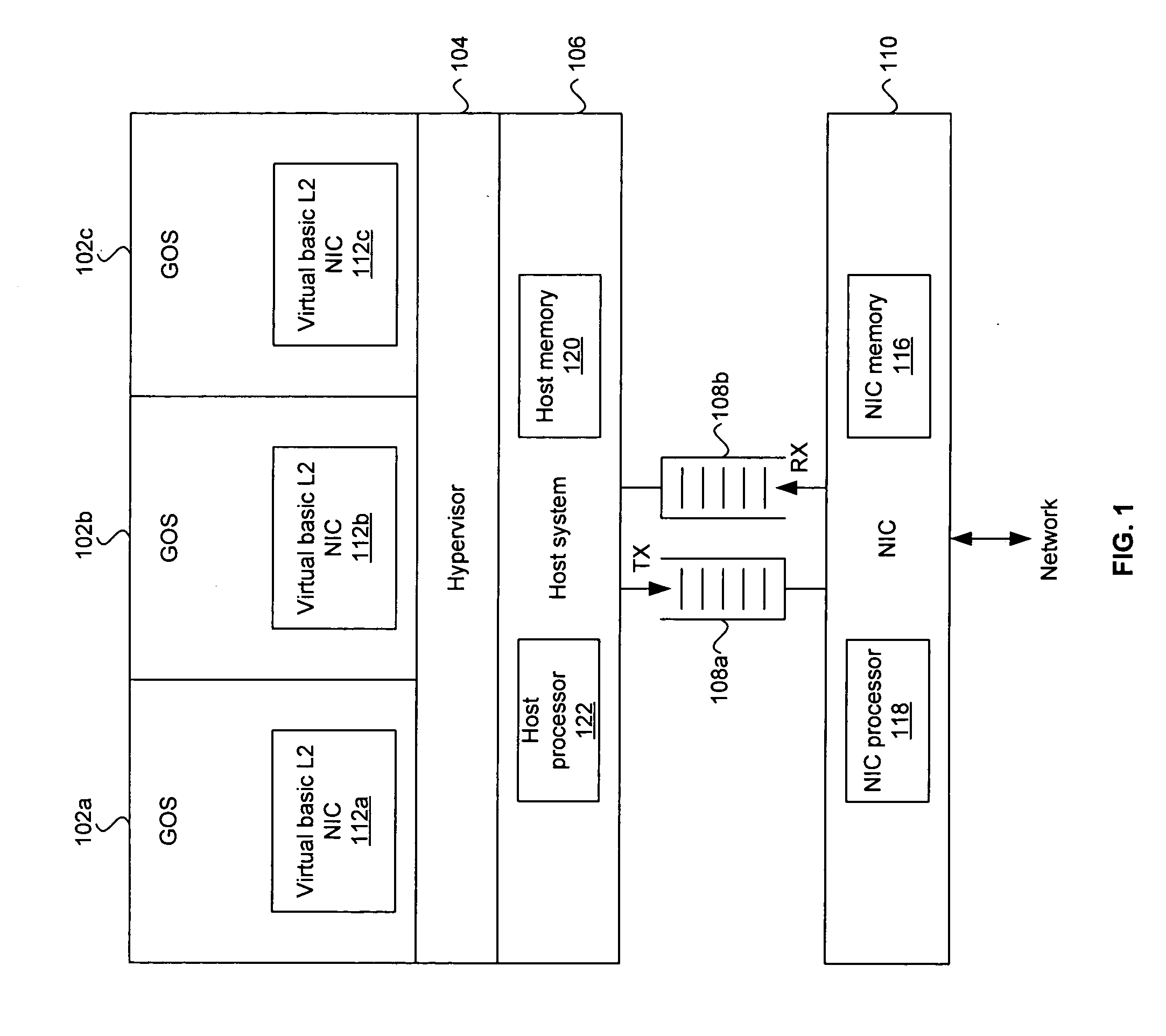
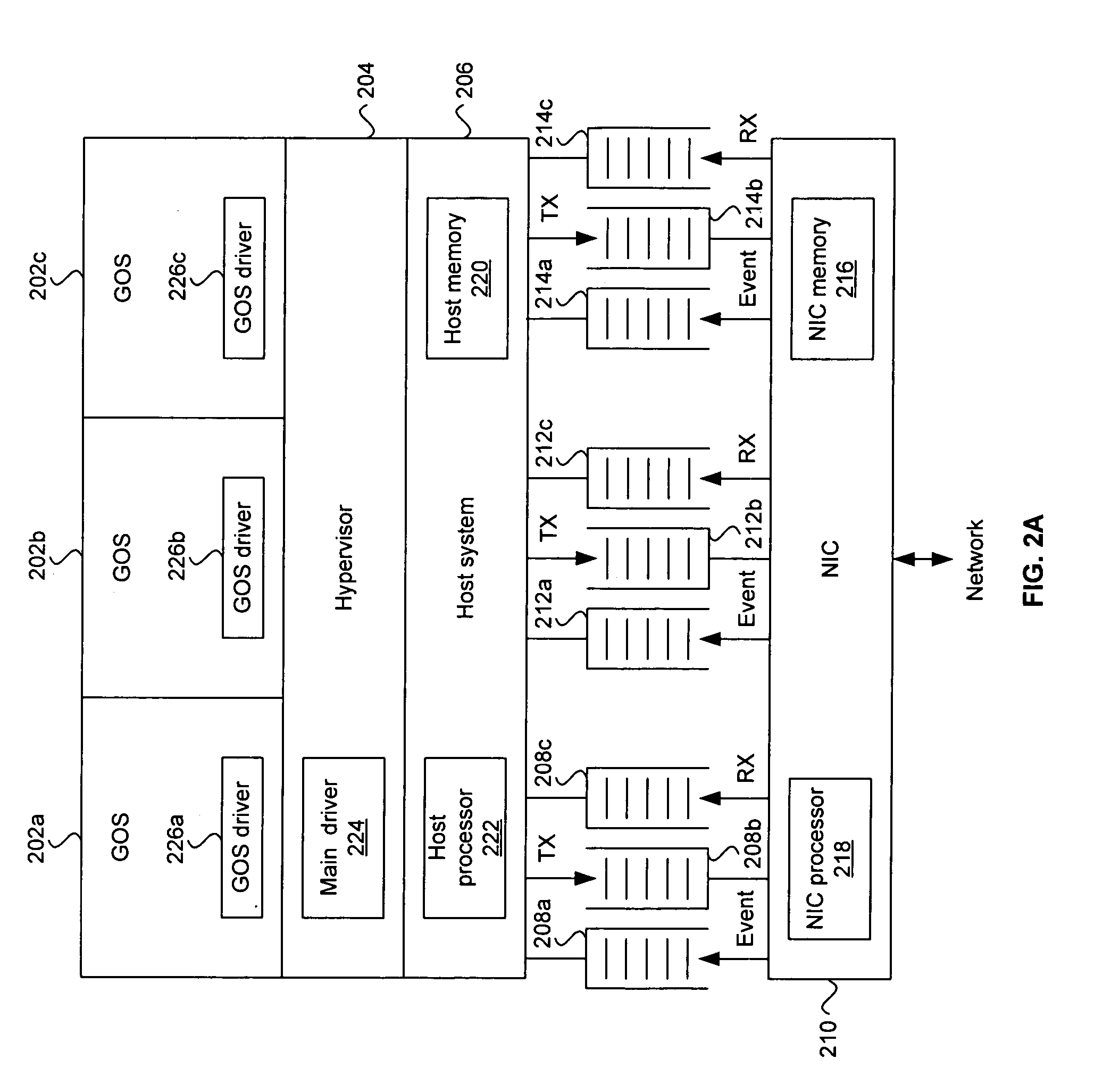
Method and system for an OS virtualization-aware network interface card
Aspects of a method and system for an operating system (OS) virtualization-aware network interface card (NIC) are provided. A NIC may provide direct I / O capabilities for each of a plurality of concurrent guest operating systems (GOSs) in a host system. The NIC may comprise a GOS queue for each of the GOSs, where each GOS queue may comprise a transmit (TX) queue, a receive (RX) queue, and an event queue. The NIC may communicate data with a GOS via a corresponding TX queue and RX queue. The NIC may notify a GOS of events such as down link, up link, packet transmission, and packet reception via the corresponding event queue. The NIC may also support unicast, broadcast, and / or multicast communication between GOSs. The NIC may also validate a buffered address when the address corresponds to one of the GOSs operating in the host system.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
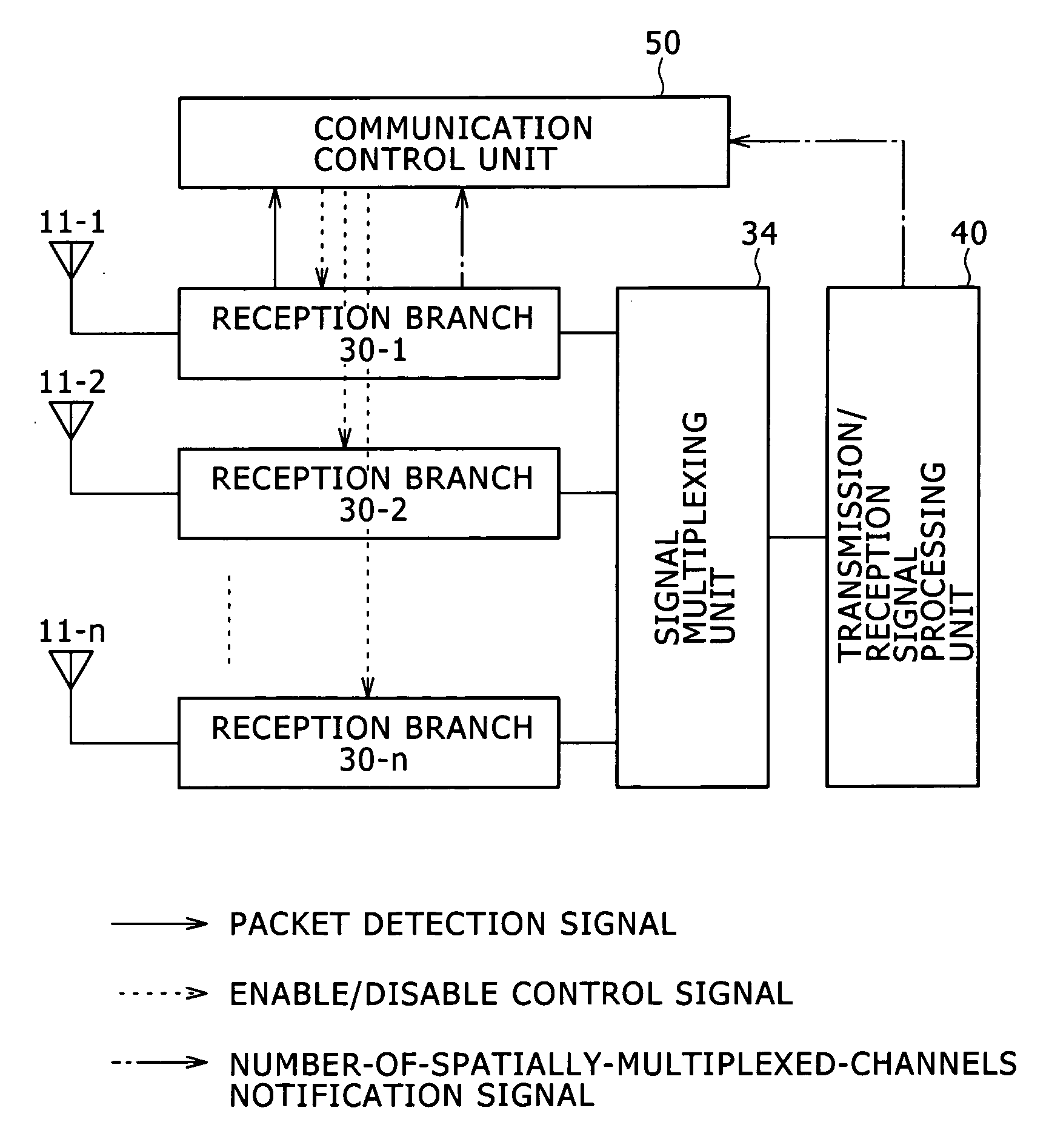
Wireless communication apparatus, wireless communication method, and computer program
ActiveUS20060023669A1Improve transmission performanceReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTError preventionTelecommunicationsMimo transmission
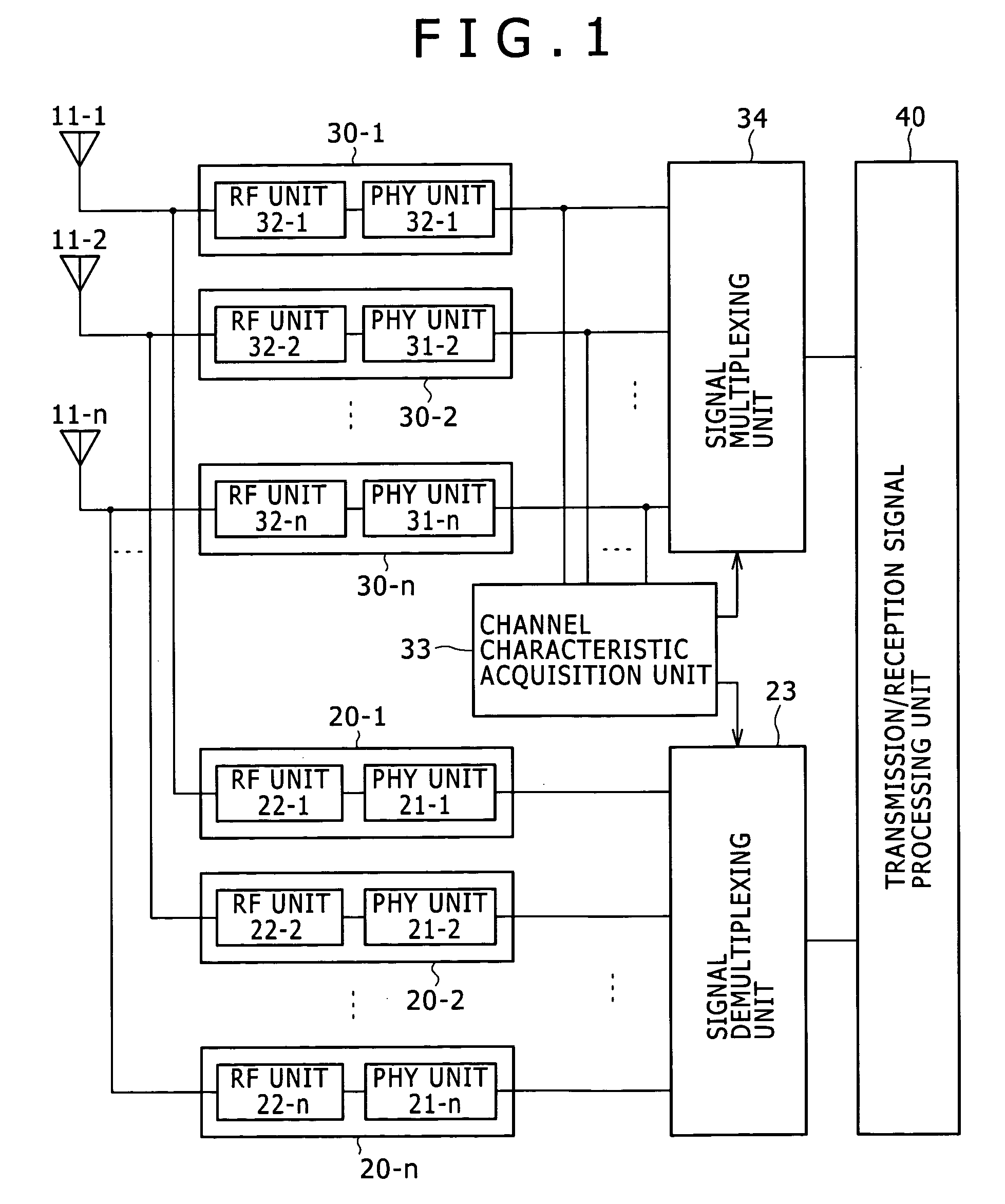
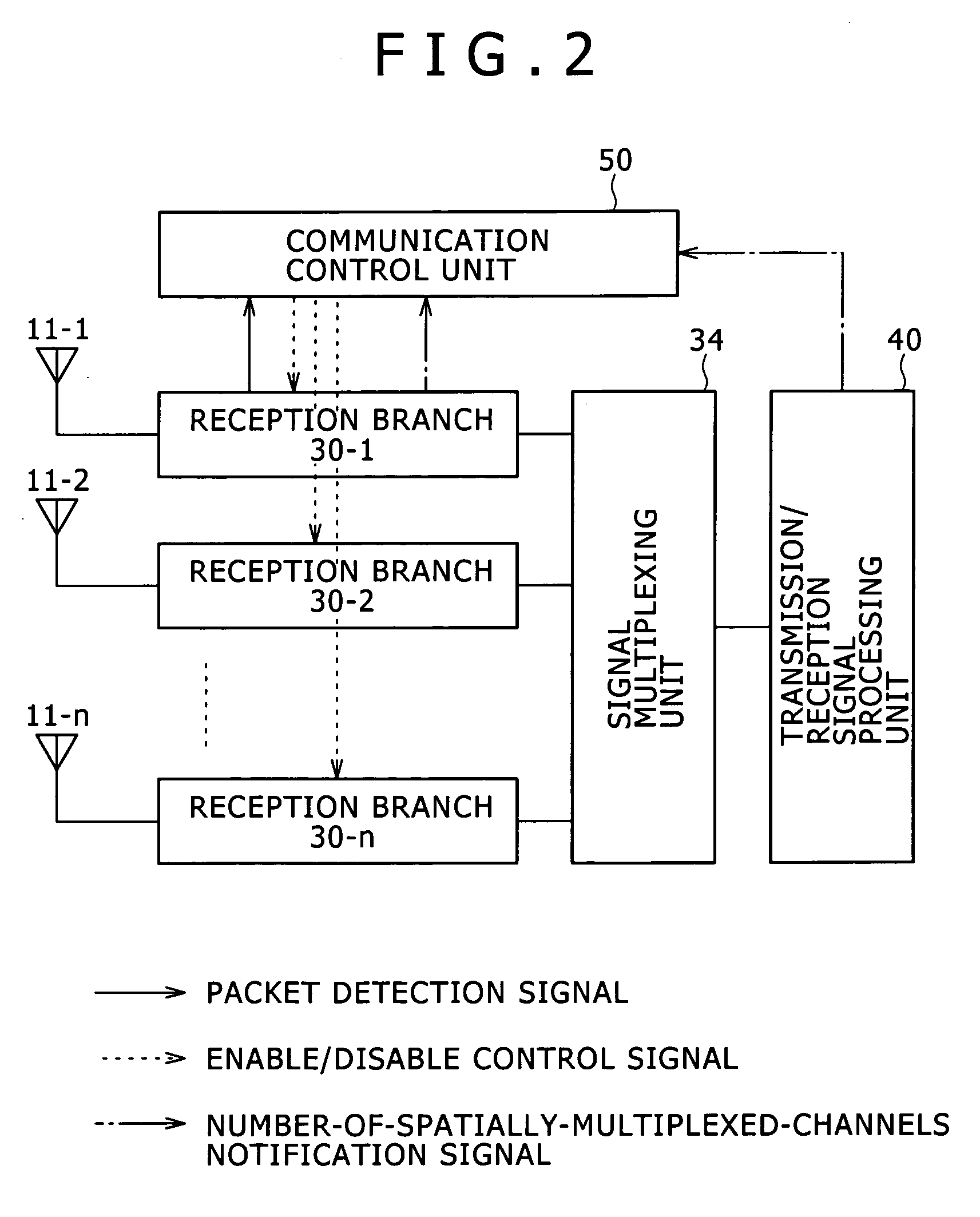
Disclosed are a wireless communication apparatus, a wireless communication method, and a computer program for intercommunication between a plurality of wireless stations. In a reception standby state, packet detection is performed by using a part of the plurality of reception branches to disable the reception operation of the remaining reception branches that do not perform packet detection, and thereby reducing the power consumption during packet detection standby. Further, in a packet reception state, only the minimum necessary number of reception branches for receiving signal that is spatially multiplexed is enabled by MIMO transmission, and thereby reducing the power consumption also during reception of MIMO signals.
Owner:SONY CORP
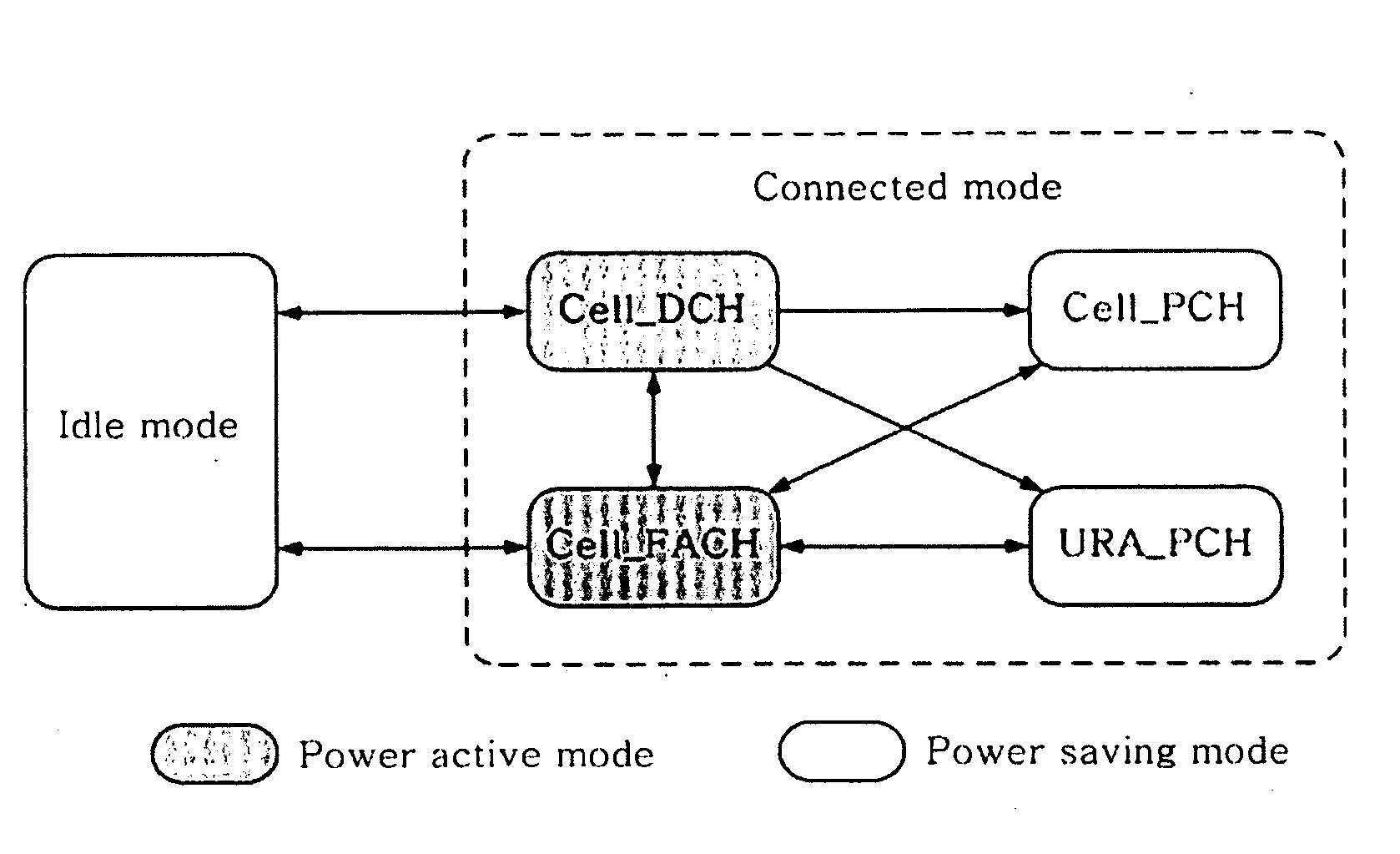
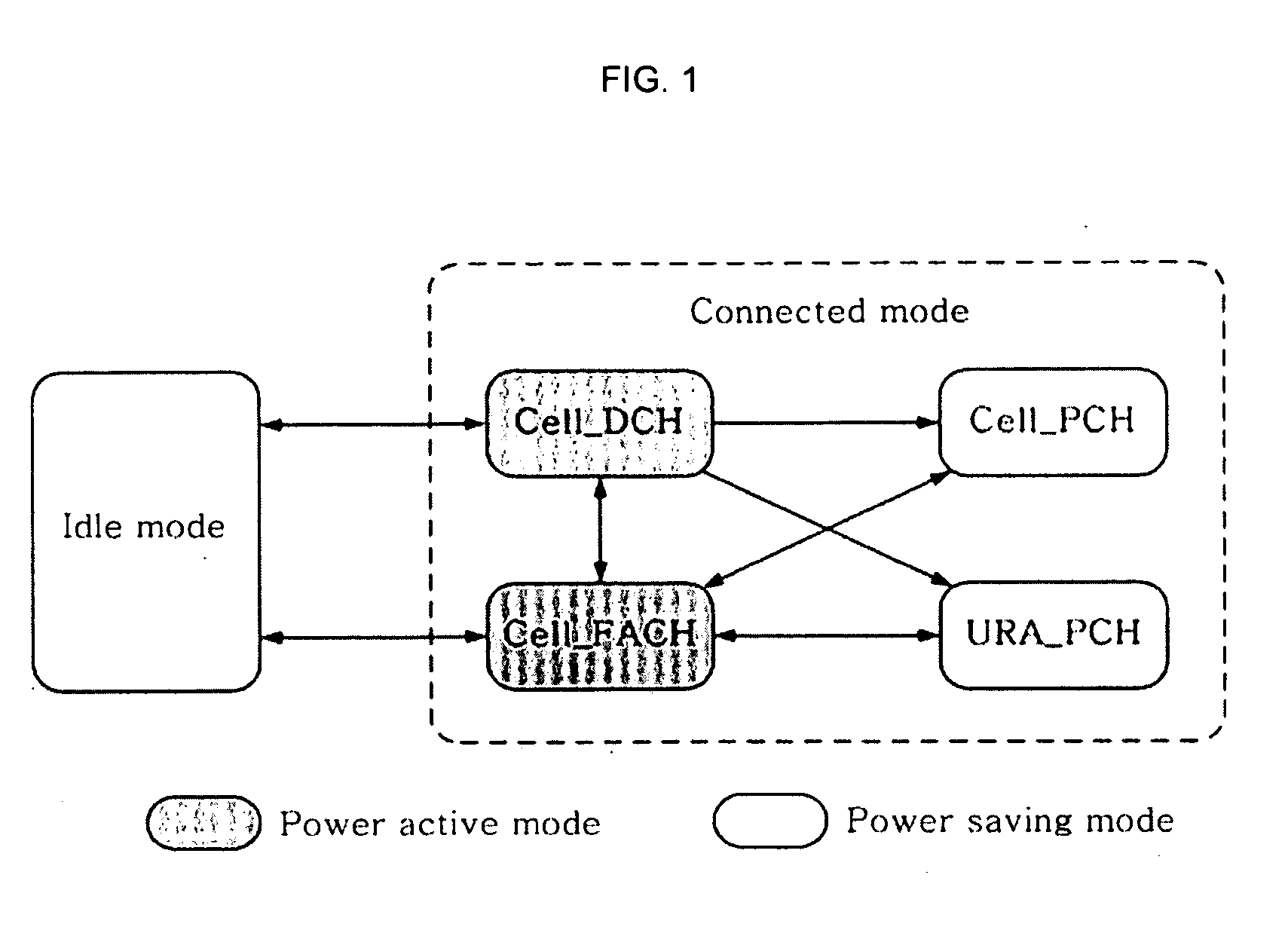
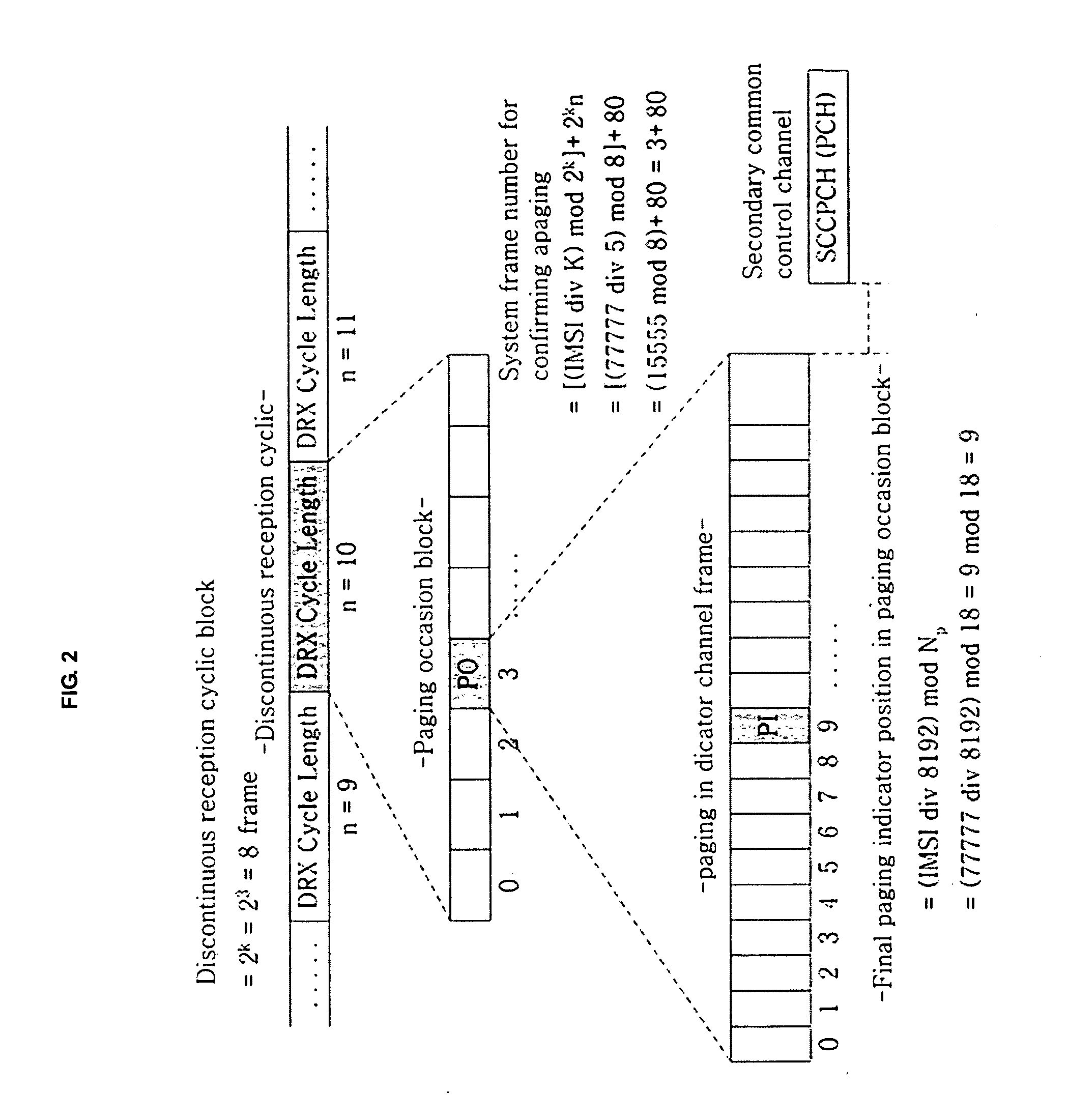
Method for Adaptive Discontinuous Reception Based On Extented Paging Indicator for Improvement of Power Effective Performance at Mobile Terminal on WCDMA
ActiveUS20090040955A1Significant power saving effectPower managementTransmission systemsCode division multiple accessDiscontinuous reception
An extended paging indicator-based adaptive discontinuous reception method is proposed so as to improve a power saving performance of a terminal in an asynchronous wideband code division multiple access schemes. To this end, a plurality of terminals for performing power saving receive an extended paging indicator for a discontinuous reception cycle, conform a type of a bit Run for configuring the extended paging indicator, and change the discontinuous reception period. In addition, the terminals set the discontinuous reception period update factor value to be varied according to the extended paging indicator as an initial value so as to determine a next paging occasion block, change the discontinuous reception period update factor value according to the paging indicator of the bit Run received from base station, and change the discontinuous reception period according to the variance of the discontinuous reception period update factor value. The extended paging indicator-based adaptive discontinuous reception method may improve transmission time delay and transmission failure probability performances for packet reception as well as a power saving performance in comparison with a conventional fixed discontinuous reception method.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
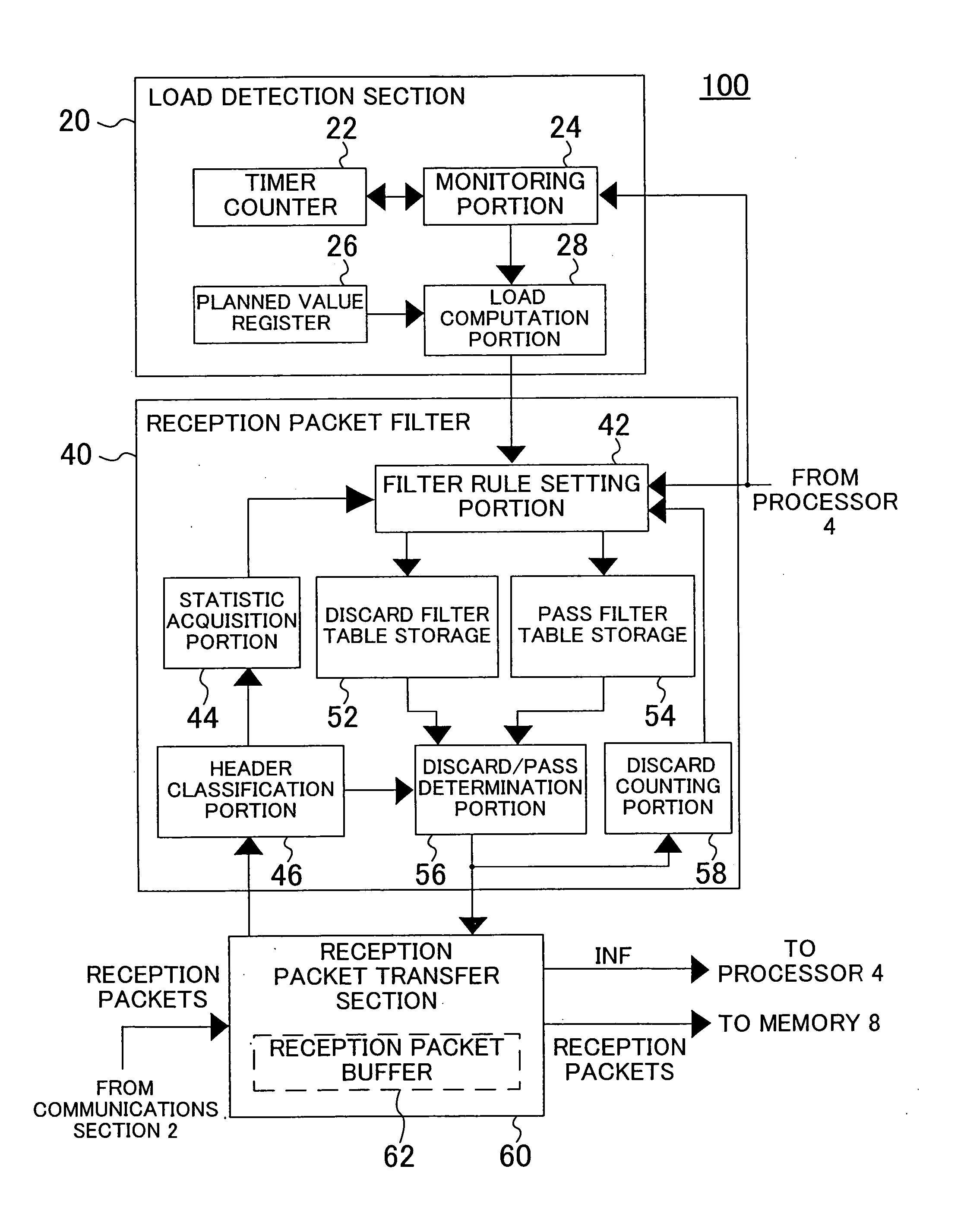
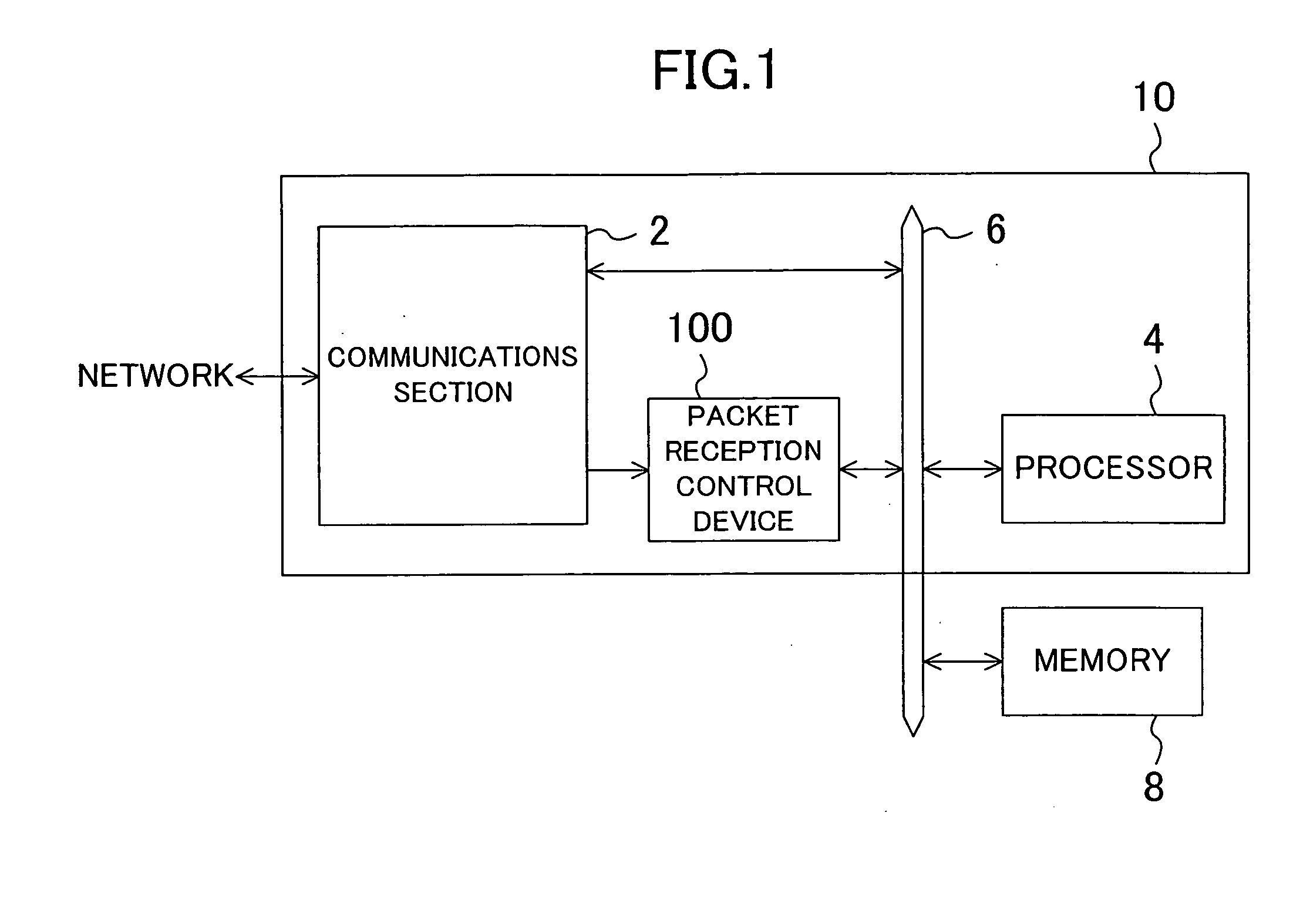
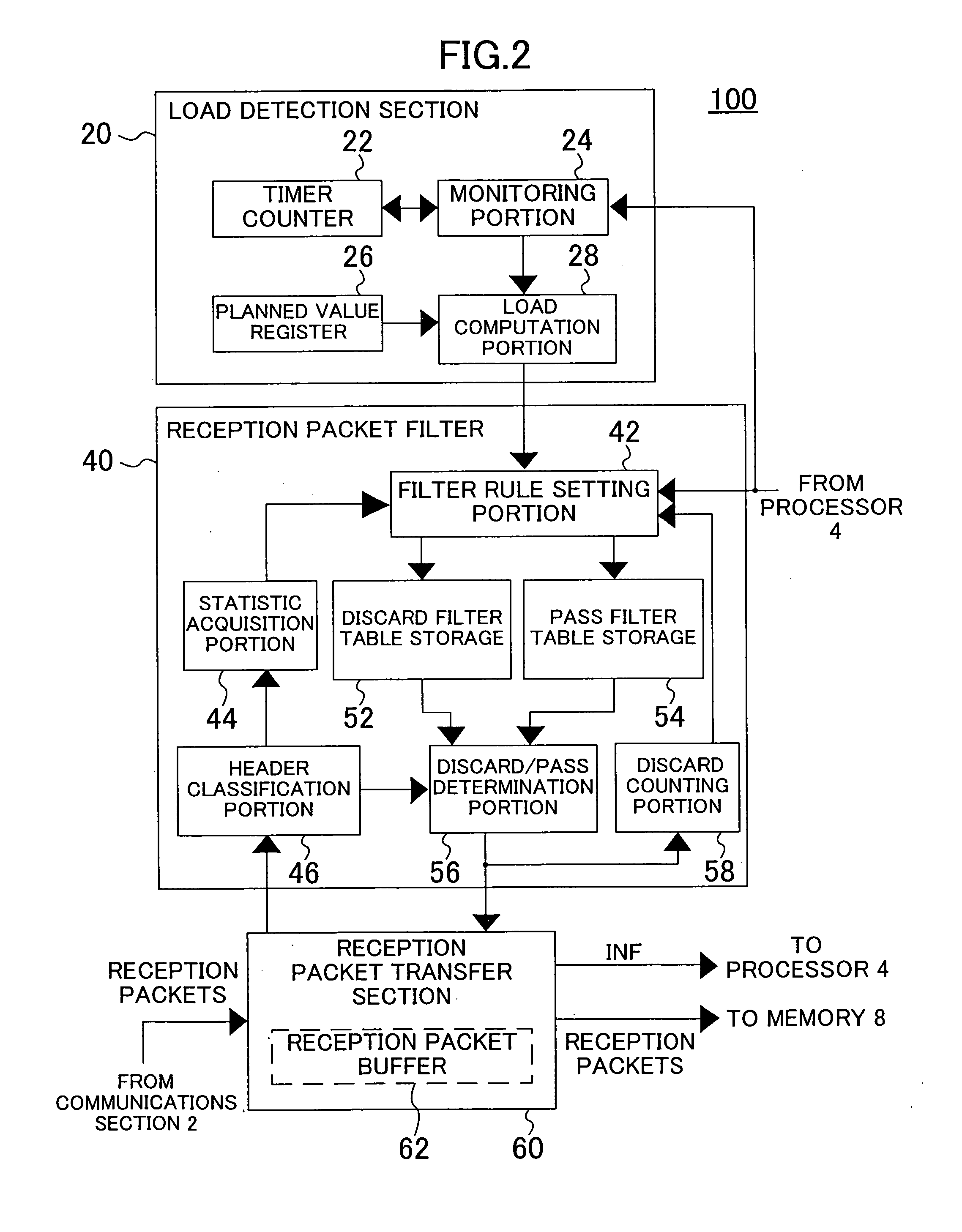
Packet reception control device and method
InactiveUS20060067231A1Overload state can be improvedGuaranteed functionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsControl equipmentPacket reception
The packet reception control device includes: a load detection section for detecting a load on a processor and outputting the detection result; and a reception control section for determining whether or not the processor should receive a reception packet based on the detection result output from the load detection section and outputting the determination result. The processor receives the reception packet according to the determination result output from the reception control section.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
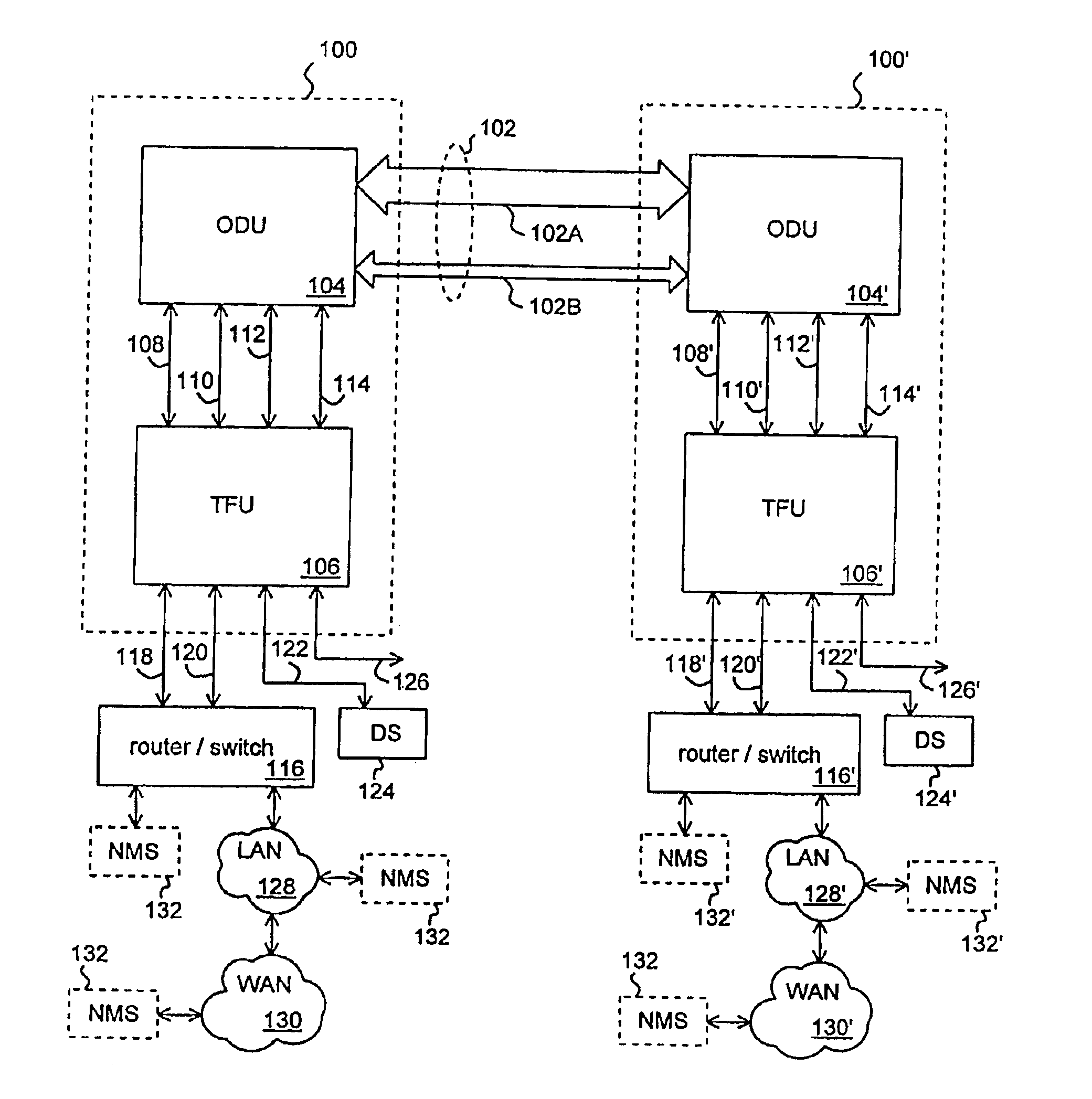
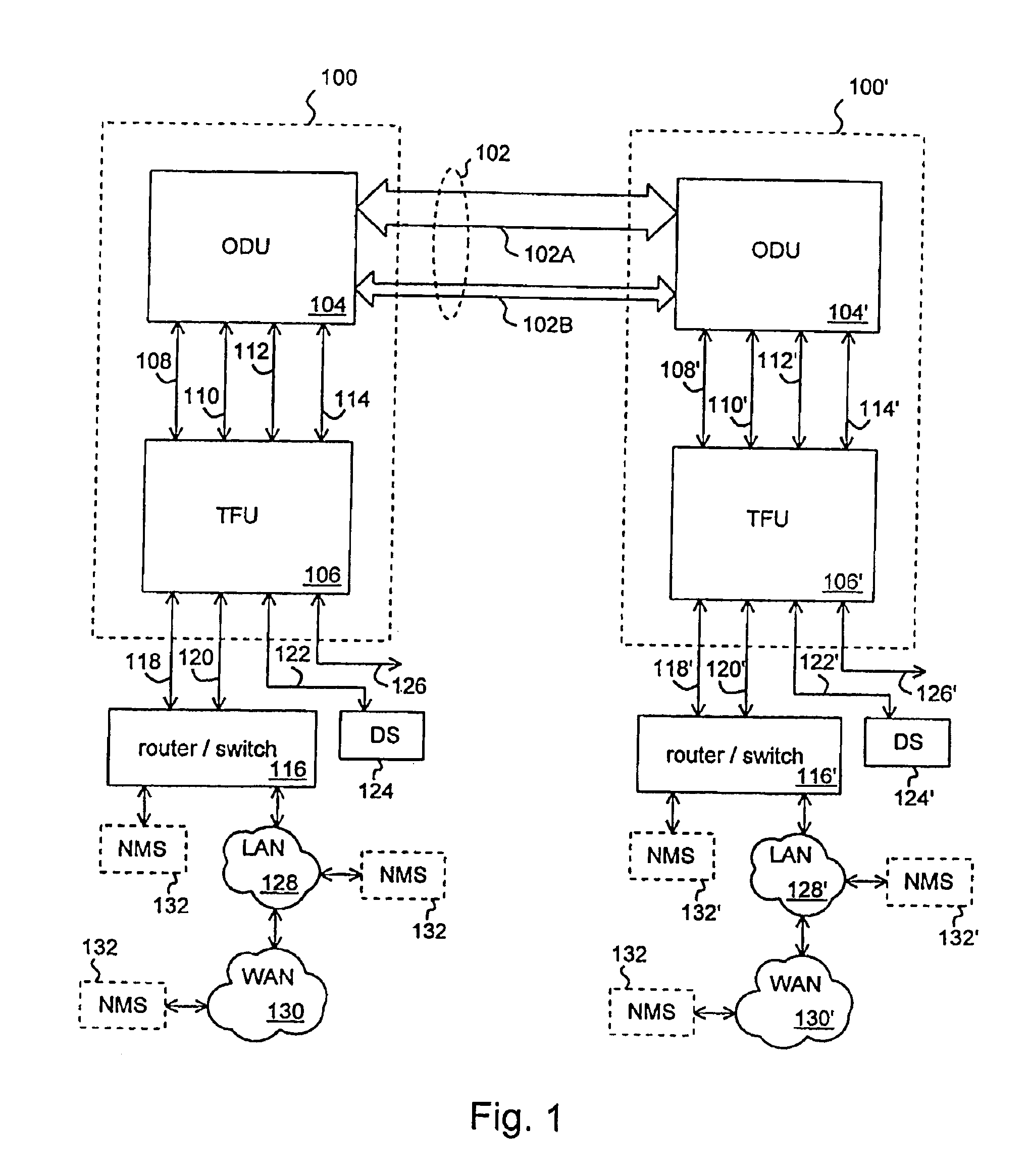
Media flow method for transferring real-time data between asynchronous and synchronous networks
InactiveUS7126957B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationReal-time dataSynchronous motor
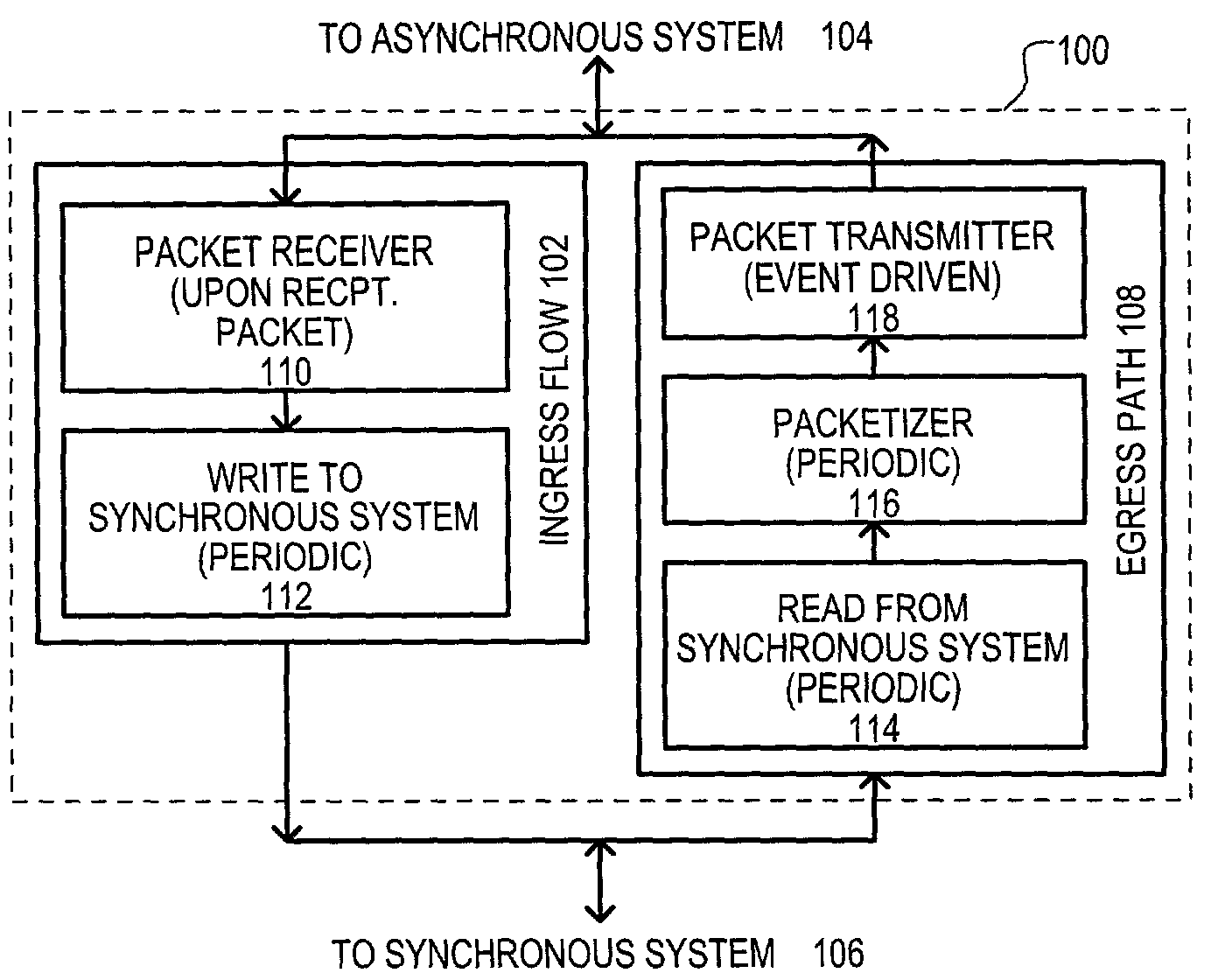
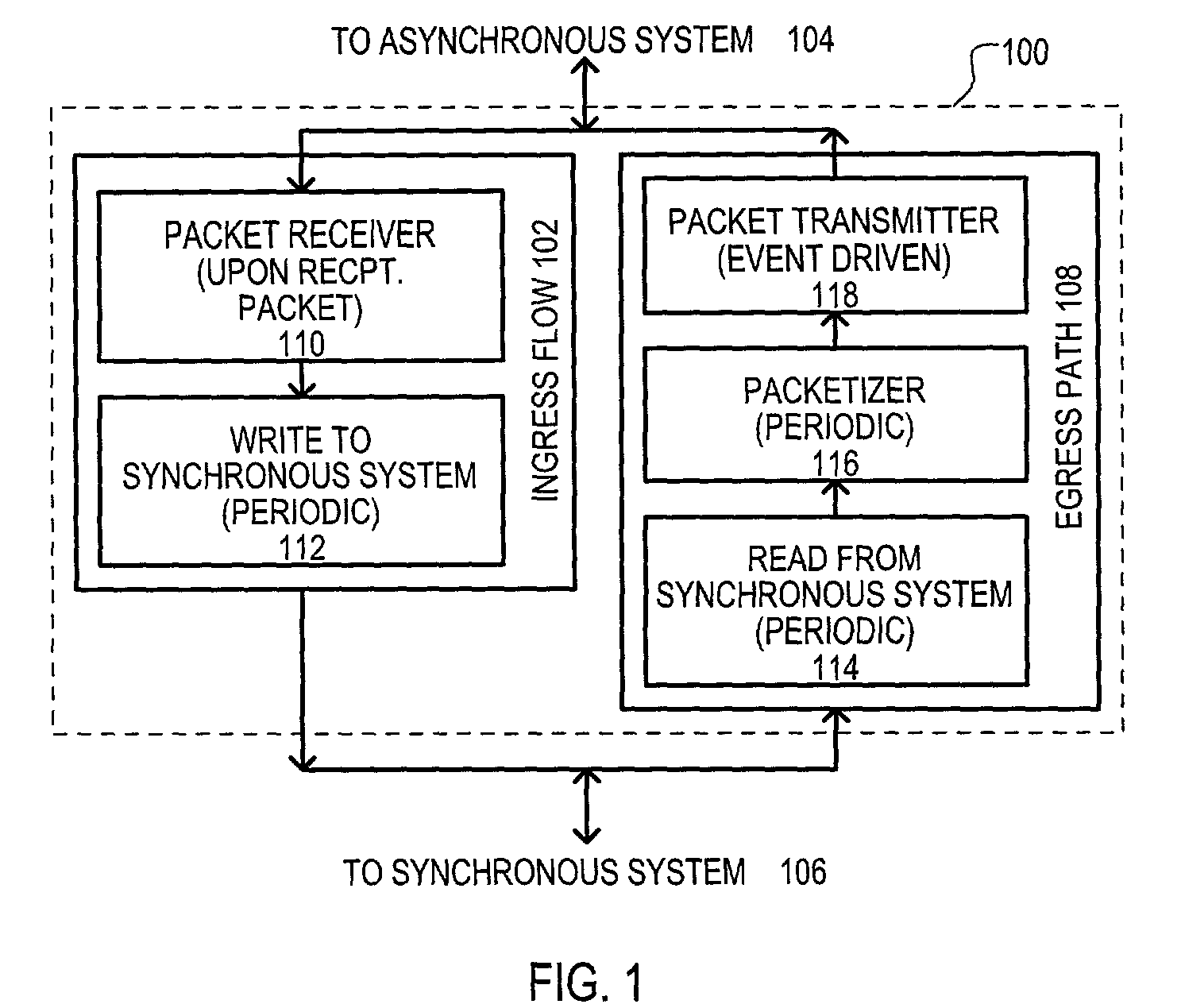
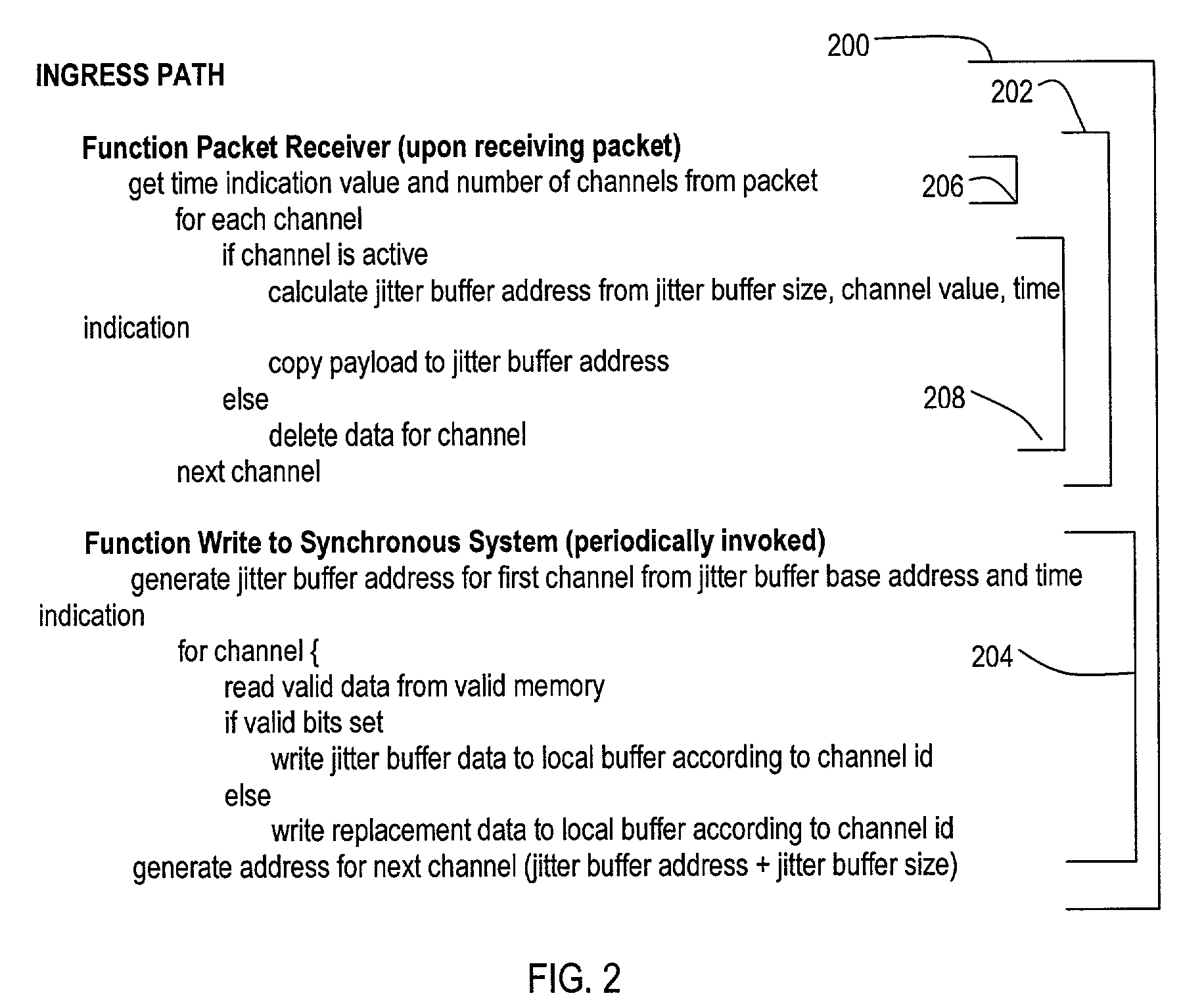
A system for transmitting real-time data between an asynchronous network (104) and a synchronous network (106) is disclosed. A method (100) may include an ingress path (102) for transmitting data from an asynchronous system (104) to a synchronous system (106), and an egress path (108) for transmitting data from a synchronous system (106) to an asynchronous system (104). An ingress path (102) may include a packet receiver (110) and write to synchronous system (112) steps. An egress path (108) may include read from synchronous system (114), packetizer (116), and packet transmitter (118) steps.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
Packet communication apparatus
InactiveUS20060176862A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket communicationTimer
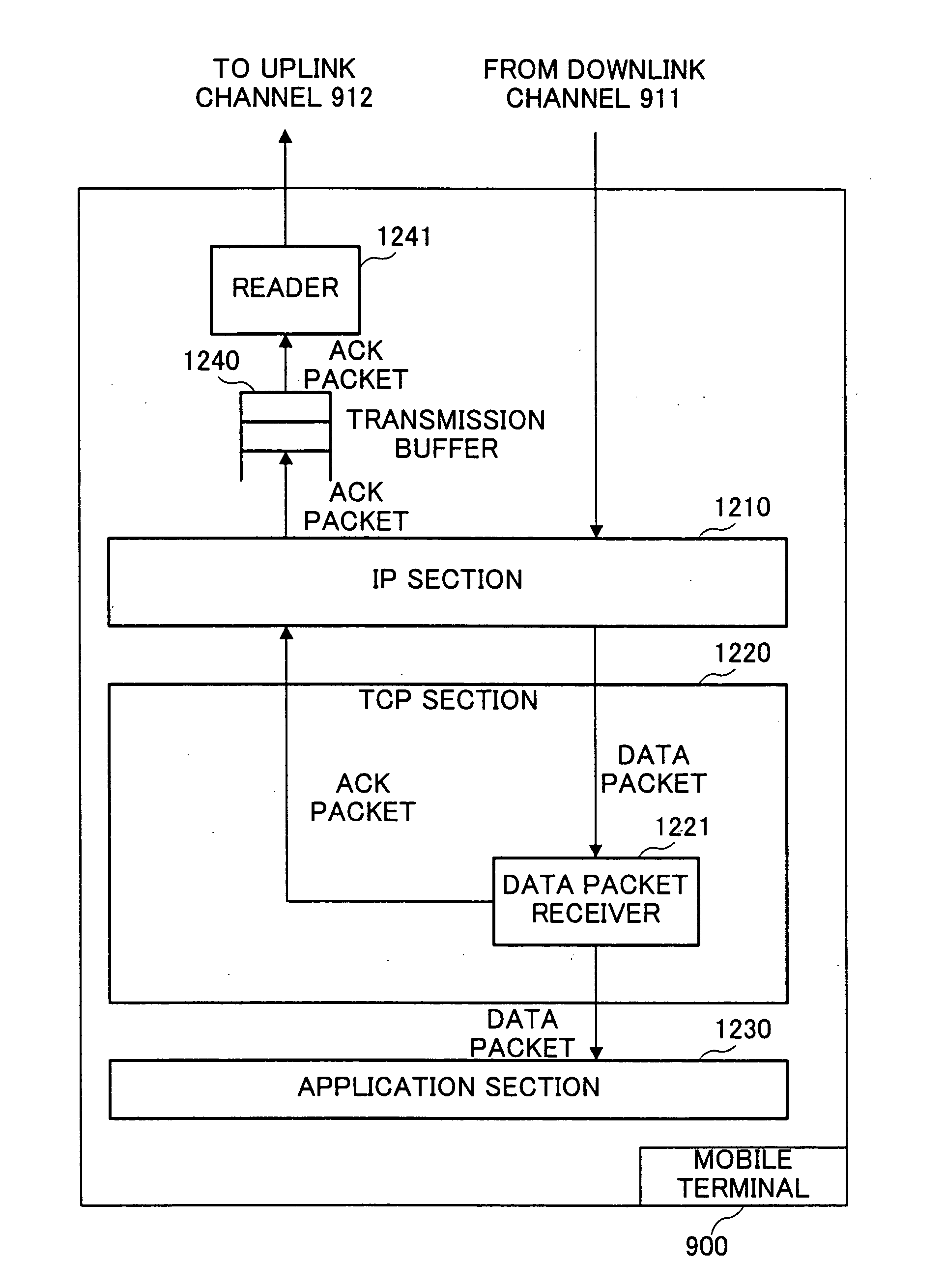
Mobile terminal 100 has: operator 251 that calculates the generation interval of ACK packets based on the size of the ACK packet that is to be transmitted and the channel rate of the transmitting channel, held in controller 250; delay ACK timer 223 that repeats counting the calculated ACK packet generation interval as one period and outputs an expiration signal every time the one period expires; and data packet receiver 221 that, every time the expiration signal is input, generates an ACK packet containing the latest reception confirmation information relating to data packets received while the expiration signal was being received, and transmits the ACK packet to transmission buffer 240 via IP section 210.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Bufferless secure sockets layer architecture
InactiveUS7228412B2Reduce workloadEnhance layeringData taking preventionUser identity/authority verificationSecure communicationClient-side
A method for enabling secure communication between a client on an open network and a server apparatus on a secure network. The method is generally performed on a intermediary apparatus coupled to the secure network and the open network. The method includes the steps of negotiating a secure communications session with the client apparatus via the open network; negotiating an open communications session with the server via the secure network; receiving encrypted packet application data having a length greater than a packet length via multiple data packets; decrypting the encrypted packet application data in each data packet; forwarding decrypted, unauthenticated application data to the server via the secure network; and authenticating the decrypted packet data on receipt of a final packet of the segment.
Owner:NEXSI SYST
Packet transfer apparatus having network address translation circuit which enables high-speed address translation during packet reception processing
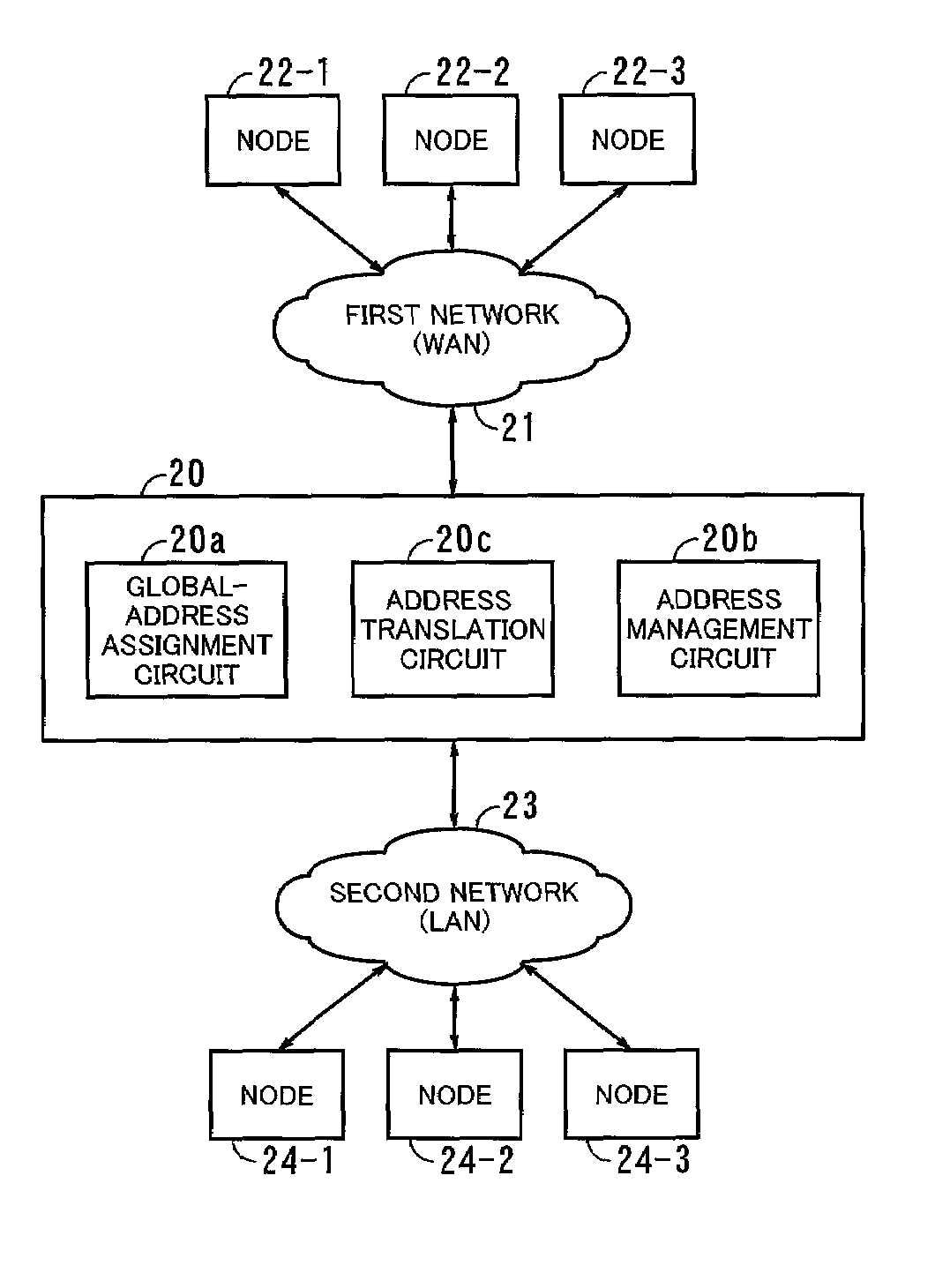
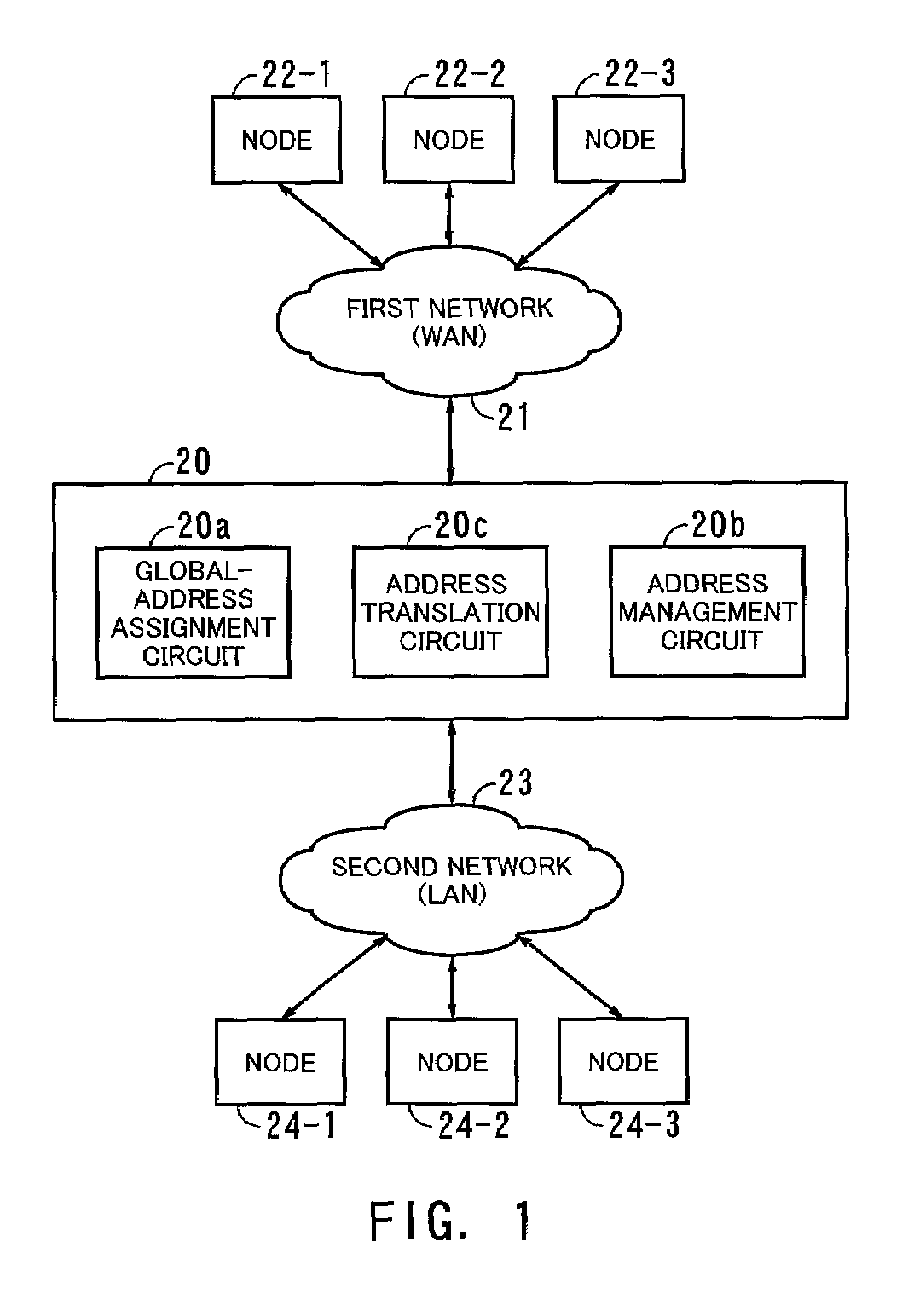
ActiveUS7197035B2Low costNo longer performedNetworks interconnectionElectric digital data processingPrivate networkNetwork addressing
In a packet transfer apparatus for transferring packets between first and second networks, a translated network address is assigned to a first node in the first network and having a first private network address when the first packet from the first node is transferred to a second node in the second network, and said translated network address is stored in an address management circuit associated with said first and second network addresses. Thereafter, address translation for realizing an NAT function is performed on subsequent packets transferred between the first and second nodes, by a dedicated hardware circuit and reference to the address management circuit, while performing processing for receiving the packets.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
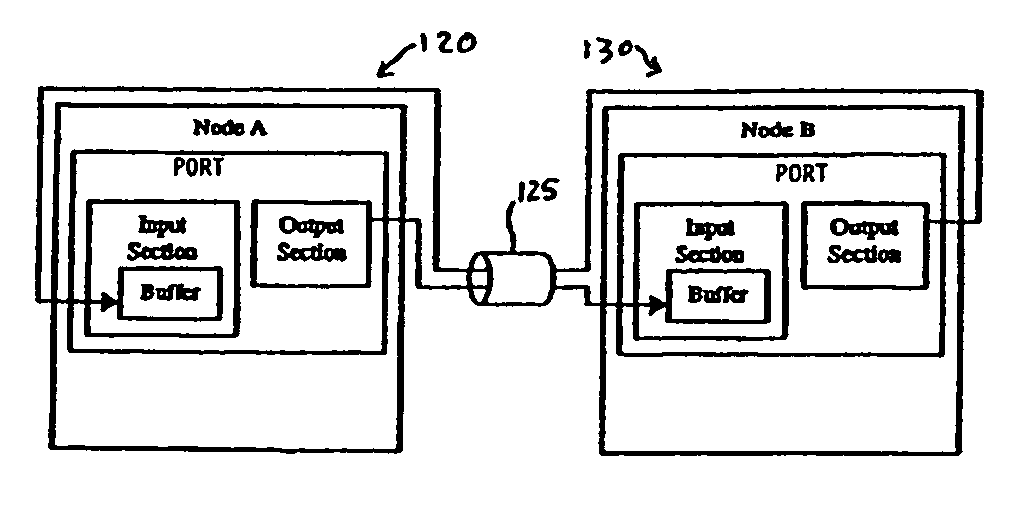
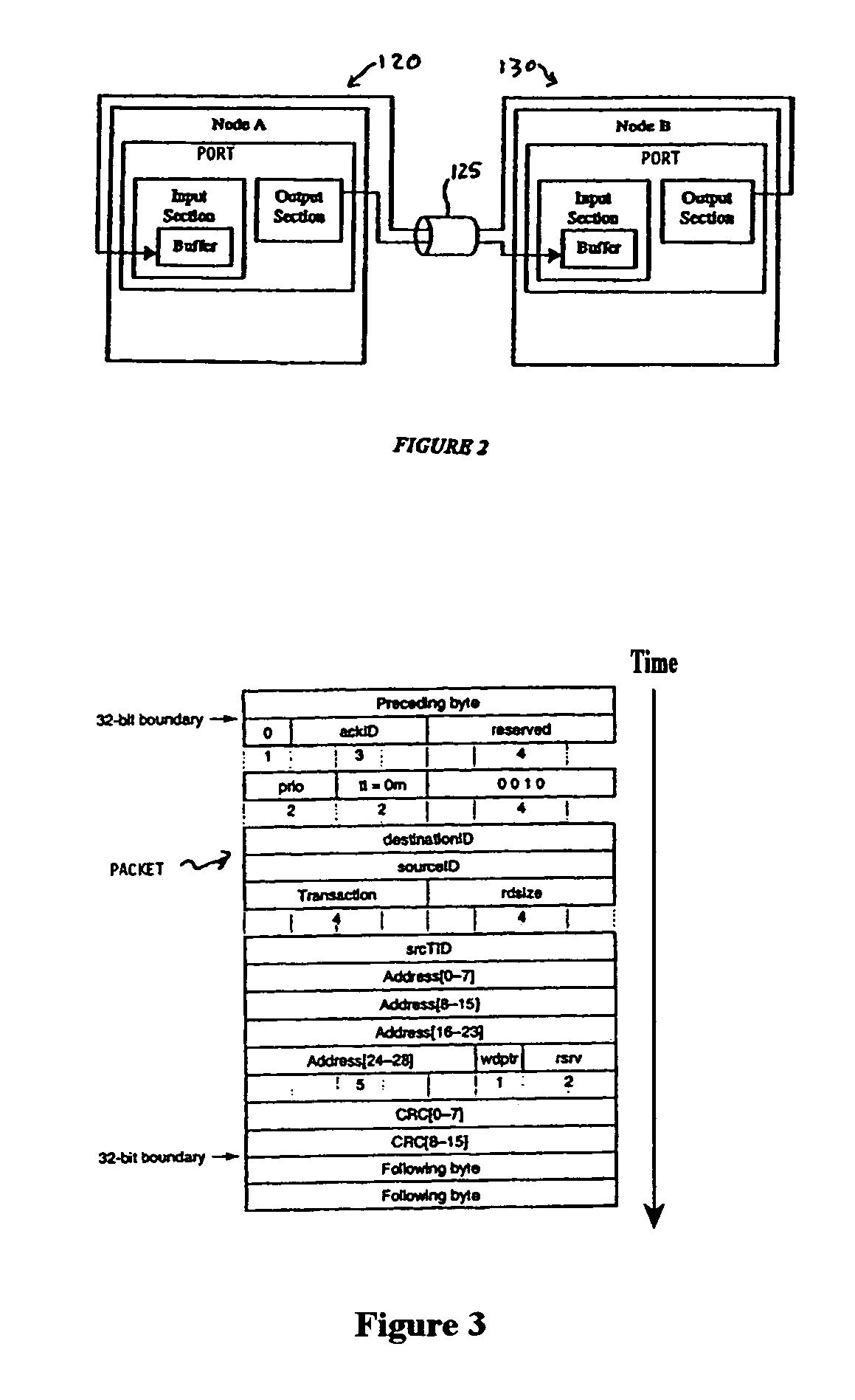
Method and system for link fabric error detection and message flow control
InactiveUS7106742B1Enhance accuracy and efficiencyRegulate transmission rateTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsData transmissionDigital data
A digital data system employs multiple error protection mechanisms on messages that pass along a link interconnect fabric from one node or device to another node or device. The nodes may be end points (such as processor or storage units), or may be intermediate devices or branch points (such as routers or switches in the interconnect fabric). The interconnect fabric comprises a set of one or more routers, switches, electrical, optical, electroptical or other links along which messages are passed. Messages are packets having a defined format including, e.g., a header portion, typically with source and target addresses, and codes indicating message-type or other information, followed by one or more data or other fields. A first node (“sending” node) of a digital data system as described sends a data transmission comprising one or more message packets to a second node (“receiving” node) over a link of a fabric as described above. The receiving node returns a control symbol to the sending node for each packet received on the link. The sender uses information in that symbol to control the further transmission of message packets to receiver over the link.
Owner:NXP USA INC +1
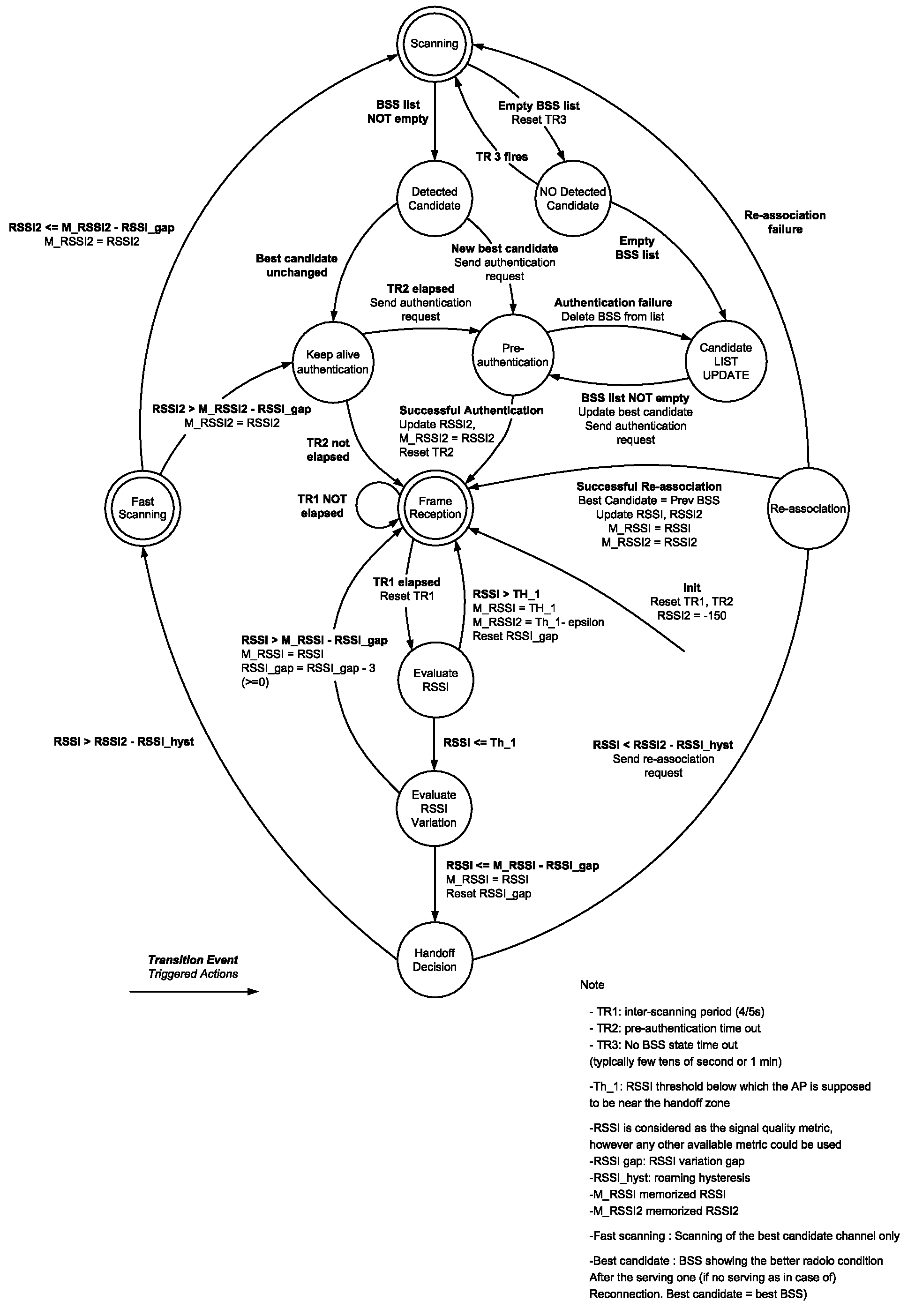
VoWLAN ROAMING CONTROLLER WITH STATION PRE-AUTHENTICATION
ActiveUS20090010222A1Increasing RSSIDecreasing RSSIRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesTelecommunicationsMobile station
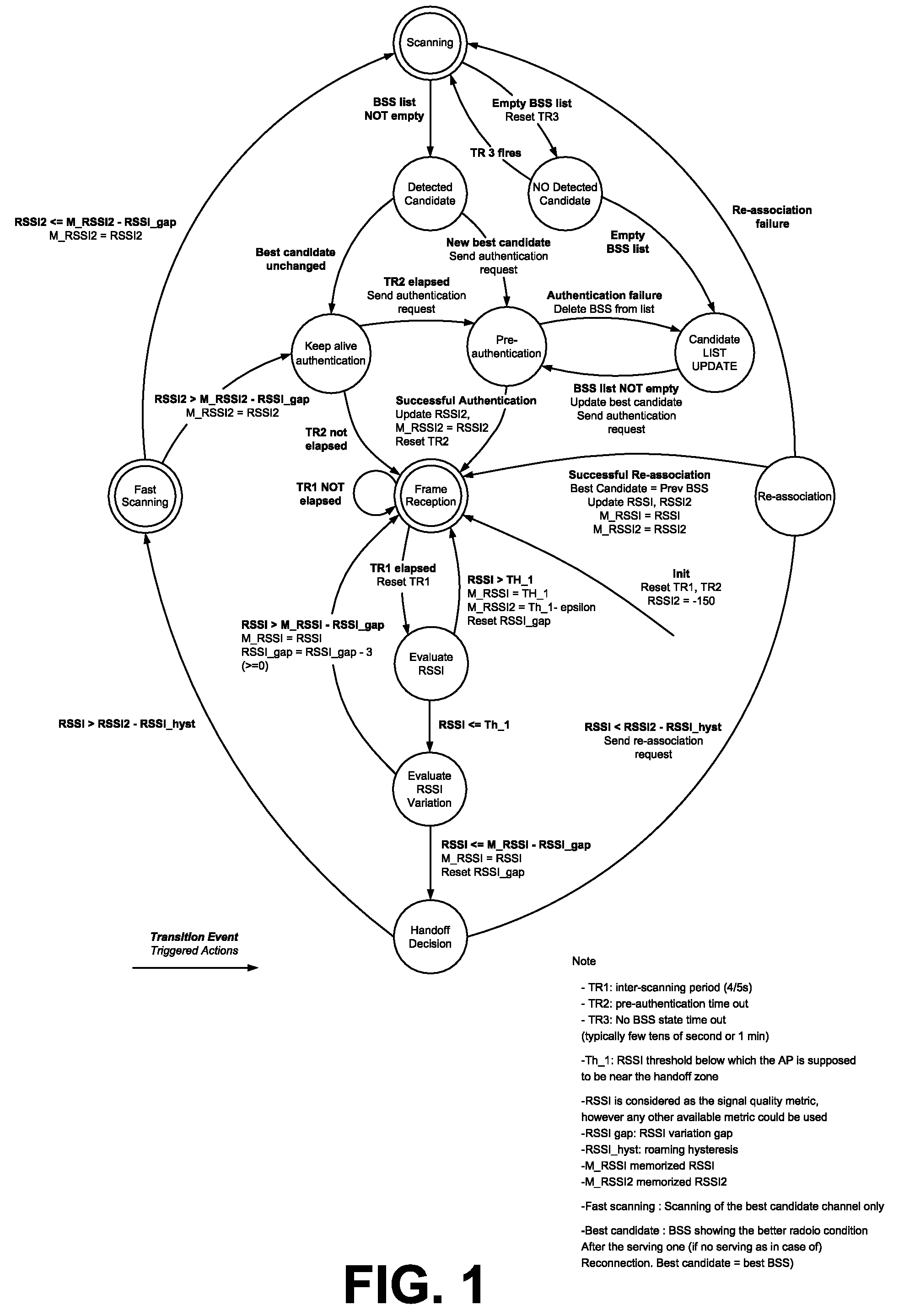
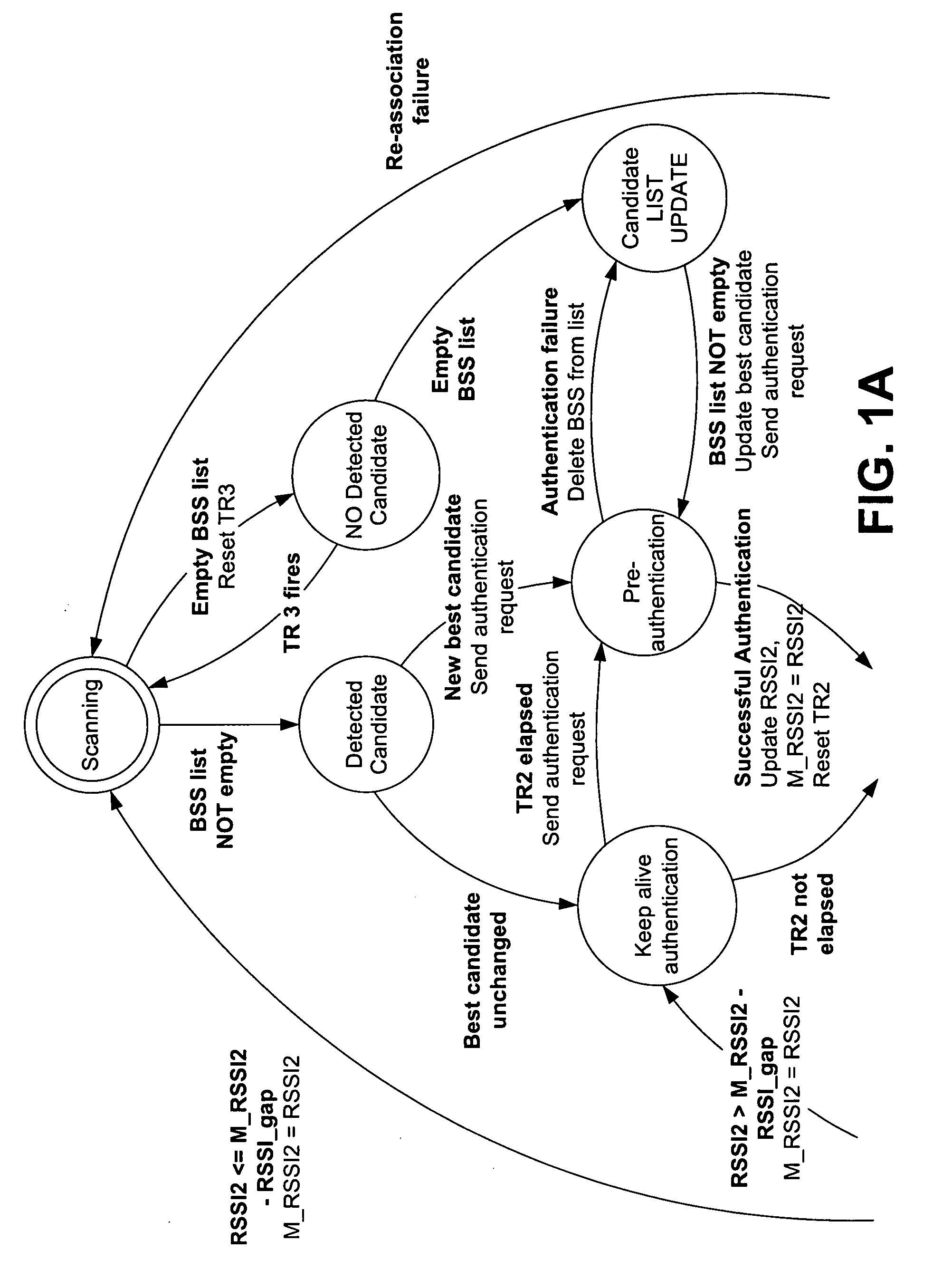
A method of triggering handoff of a mobile station to a candidate BSS, for VoWLAN communication, uses a roaming controller for monitoring link qualities of the serving and candidate BSS by selective / controlled fast scanning through RSSI screening at each packet reception. Using link qualities, a list of candidate BSSs for handoff is maintained. The controller selects a candidate BSS for handoff and completes pre-authentication of the mobile station with the selected best candidate BSS. When the link quality of the of the selected candidate BSS becomes better than that of the serving BSS, handoff is triggered. Link qualities may be monitored by screening a metric other than RSSI. When no candidate BSS is found, scanning is reduced / temporarily interrupted, to conserve power. When the serving BSS link quality is above a given threshold when the mobile station is in the serving BSS center, the functions of fast scanning and pre-authentication are interrupted.
Owner:WIPRO LTD
Method and system for partitioning and encoding of uncompressed video for transmission over wireless medium
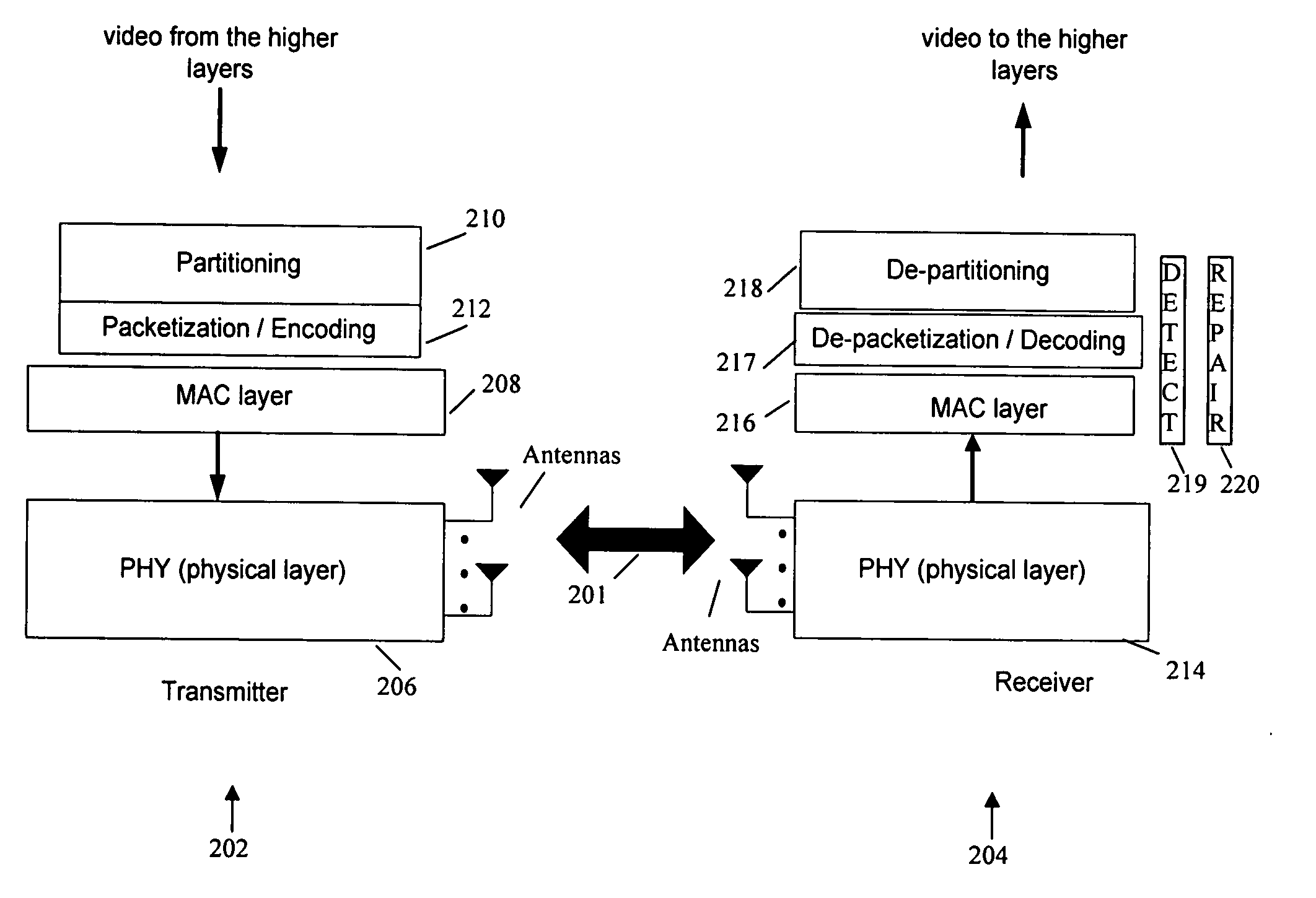
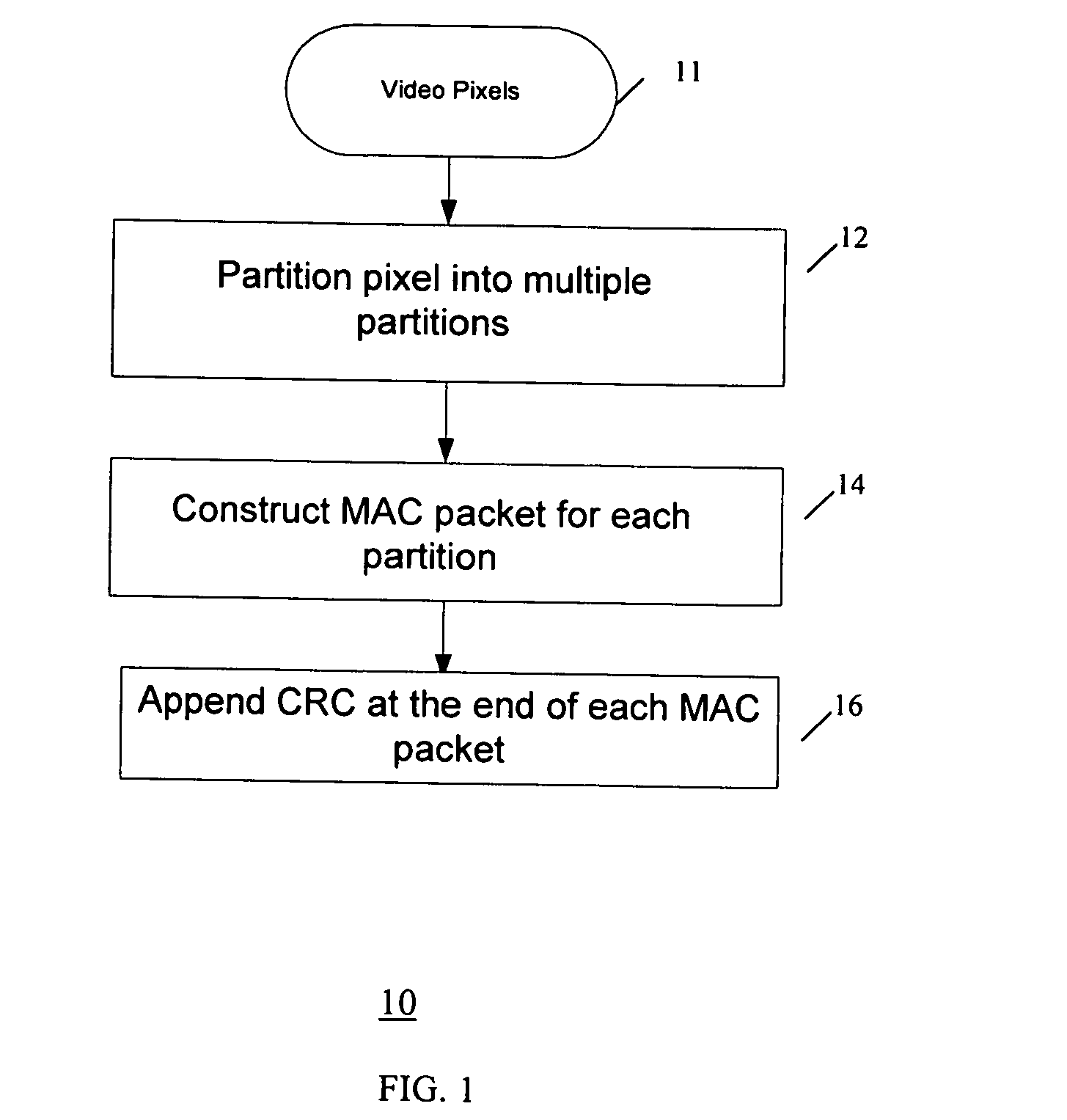
InactiveUS20070202842A1Improve transmission robustnessReduce bandwidth requirementsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningSpatial correlationSystems approaches
A method and system for transmitting uncompressed video over a wireless channel by inputting a frame of pixel information, partitioning spatially correlated pixels into different packets, and transmitting the packets separately over a wireless channel. For robust transmission, error detection data can be generated for each packet and appended to each packet before transmission. A receiver receives the transmitted packets and checks if a received packet is corrupt based on the appended error detection data. For a corrupt packet, the receiver corrects the corrupt pixels using pixel information in other received packets containing neighboring pixels to recover each corrupt pixel in the corrupt packet.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Digital data system with link level message flow control
InactiveUS7031258B1Keep openEnhance speed and accuracy and efficiencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDigital dataError checking
A digital data system comprises a plurality of links for passing messages between nodes, which may be end points such as memory or processing units, or intermediate or branch points such as routers or other devices in the system. A link level flow control is implemented by control symbols passed between adjacent nodes on a link to efficiently regulate message burden on the link. The control symbols may be embedded within in a message packet to quickly effect control on a link—such as reducing data flow, requesting retransmission of corrupted data, or other intervention—without disruption of the ongoing packet reception. A control symbol may be recognized within the packet by a flag bit, a marker such as a transition in a signal, or a combination of characteristics. The control symbol may be a short word, having a control action identifier code at defined bit positions to indicate the desired link-level control function. A node receiving the control symbol implements the designated control action while maintaining packet order data (such a bit positions and byte counts), and applying message housekeeping processing (such as error checking) as though the control symbol were absent. The control symbol is thus embedded in a manner such that a receiving node need not receive a complete message, or even a complete packet, before acting on the control symbol. The beginning and end of the interrupted packet, meanwhile, are handled as a single message packet, and are processed by the receiving node in properly-aligned bit positions, allowing message flow to continue along the link without interruption. Thus, retransmission of the affected packet or message is not required. The result is that control operations dictated by the embedded control symbol are effected immediately and without slowing down communications.
Owner:MERCURY SISTEMS INC +1
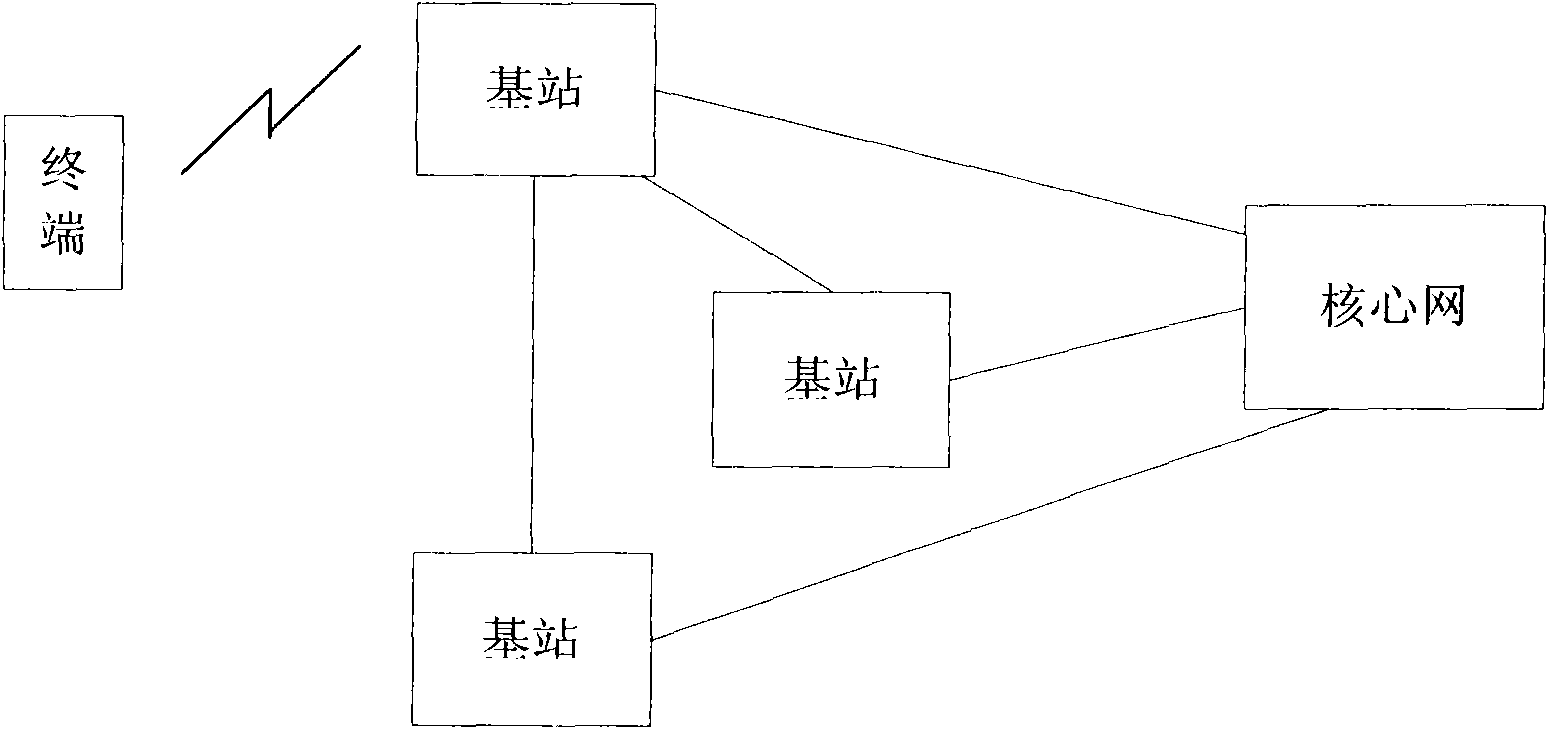
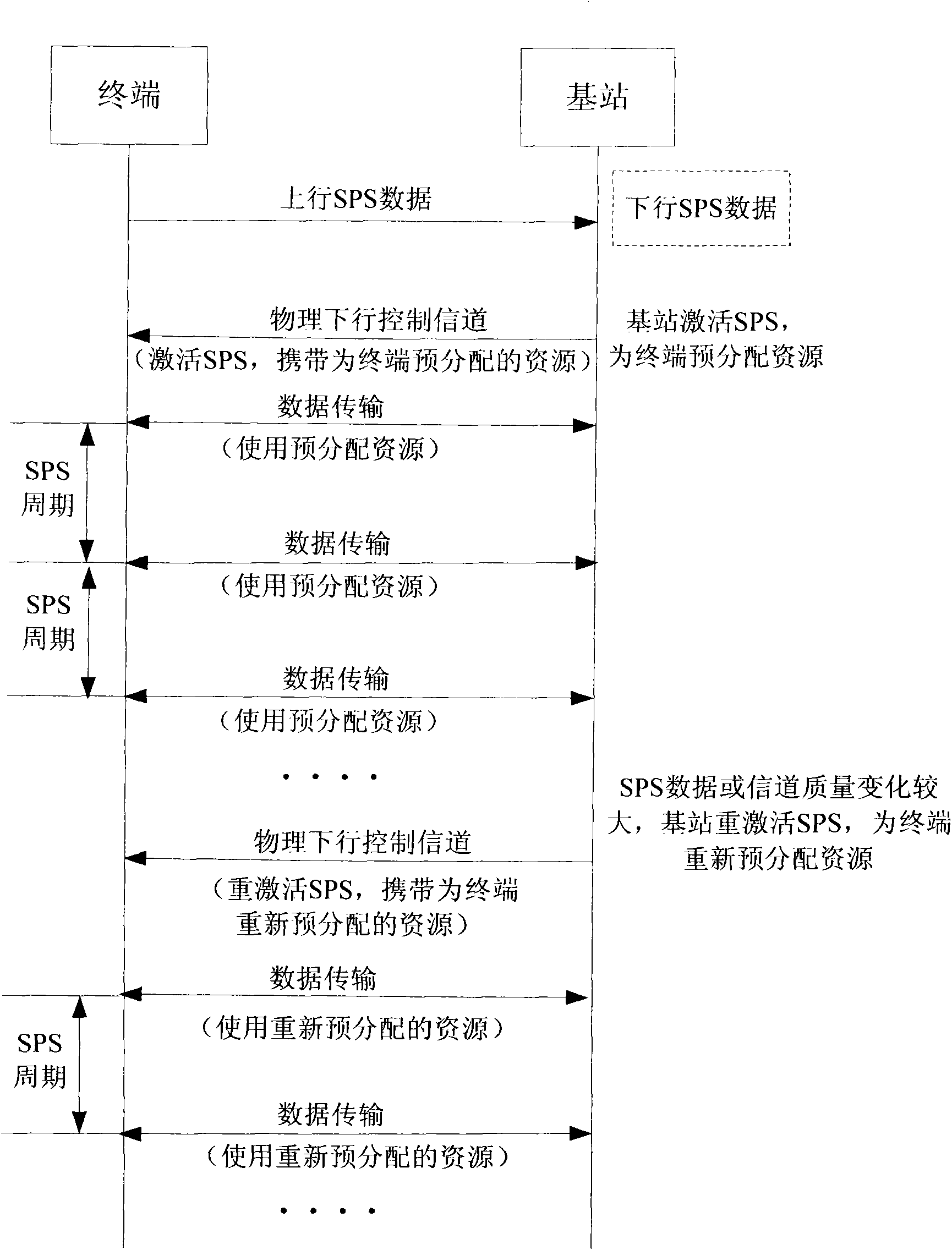
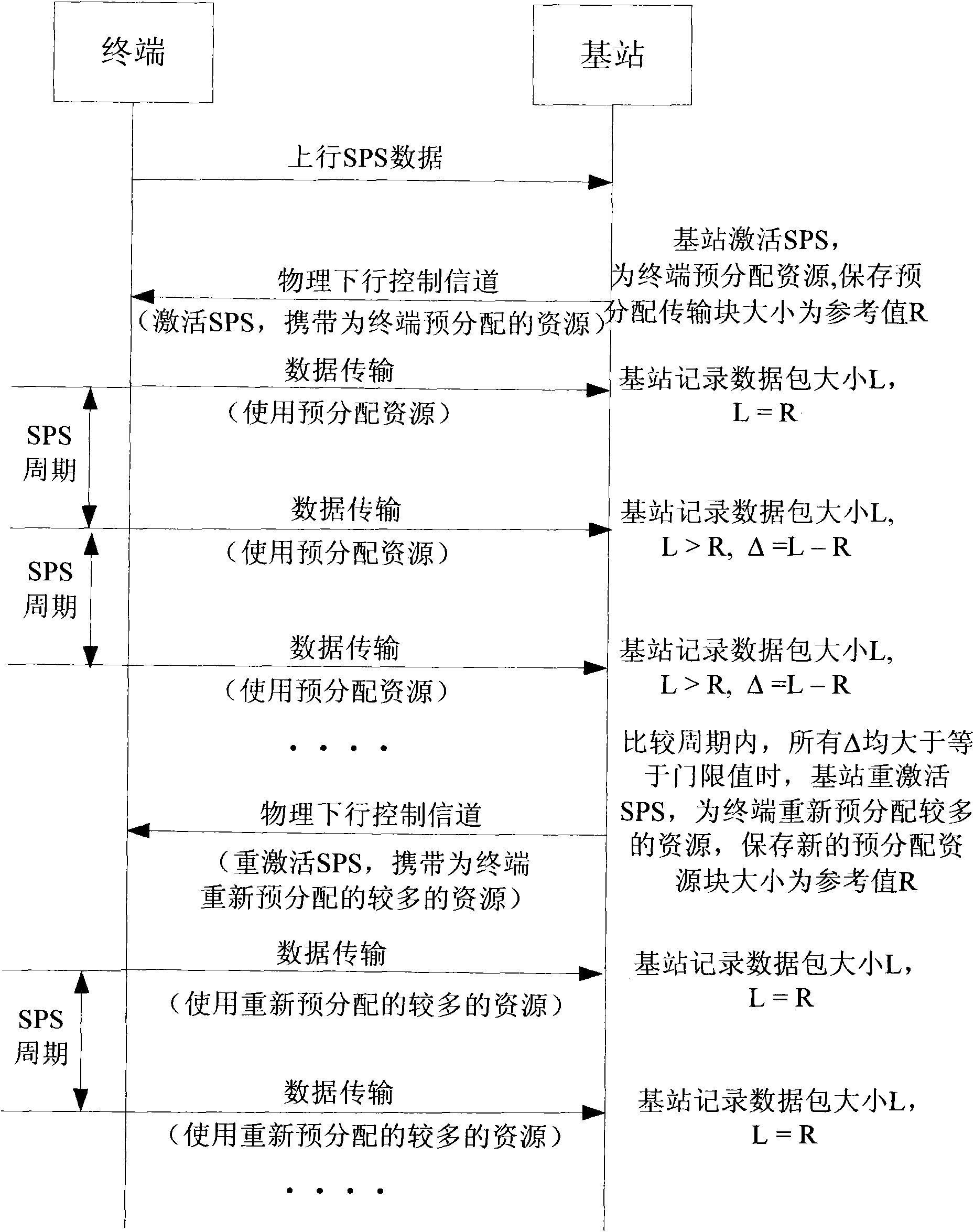
Method for reactivation of semi-static scheduling, and base station thereof
ActiveCN102014508AReasonable distributionSolve the problem that the upstream SPS cannot be reactivatedConnection managementResource assignmentAir interface
The present invention relates to a method and a base station for the reactivation of semi-static scheduling, wherein the base station comprises a storage module, a resource assignment module, a data packet reception module and a comparison module, besides, the method comprises the following steps: the base station of activated semi-static scheduling (eNB) preassigns resources to a terminal (UE), then stores the size information of the preassigned transmission block; the eNB receives complete semi-static scheduling data packet uploaded by the UE, then makes a comparison between the size of data packet and the size of preassigned transmission block stored in the eNB, and reactivates the semi-static scheduling in the case that the both are not of same size. The present invention solves the problem that the eNB can not reactivate the uplink SPS when the SPS data changes in a period of time, in the case that SPS business as well as dynamic scheduling business coexist and assigned to a UE in the same LCG. When in use, the invention makes the assignment of air interface resources more reasonable.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Predictive recommendation engine
ActiveUS20160127010A1Mathematical modelsPower distribution line transmissionUser deviceUser interface
Systems and methods for alerting a user device when an objective is mastered according to a piecewise Gaussian distribution updated according to a Bayesian method are disclosed herein. The system can include a user device having a network interface to exchange data with a server via a communication network, and an I / O subsystem to convert electrical signals to user interpretable outputs user interface. The system can include a server that can: receive a response from the user device; identify a user associated with the response; receive user attribute data; identify a next objective; provide a data packet from the aggregation of data packets to the user via the user device; receive a response from the user device; update the user attribute data according to a Bayesian method; and generate and provide an alert to the user device.
Owner:PEARSON EDUCATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com