Patents
Literature
120 results about "Asynchronous system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
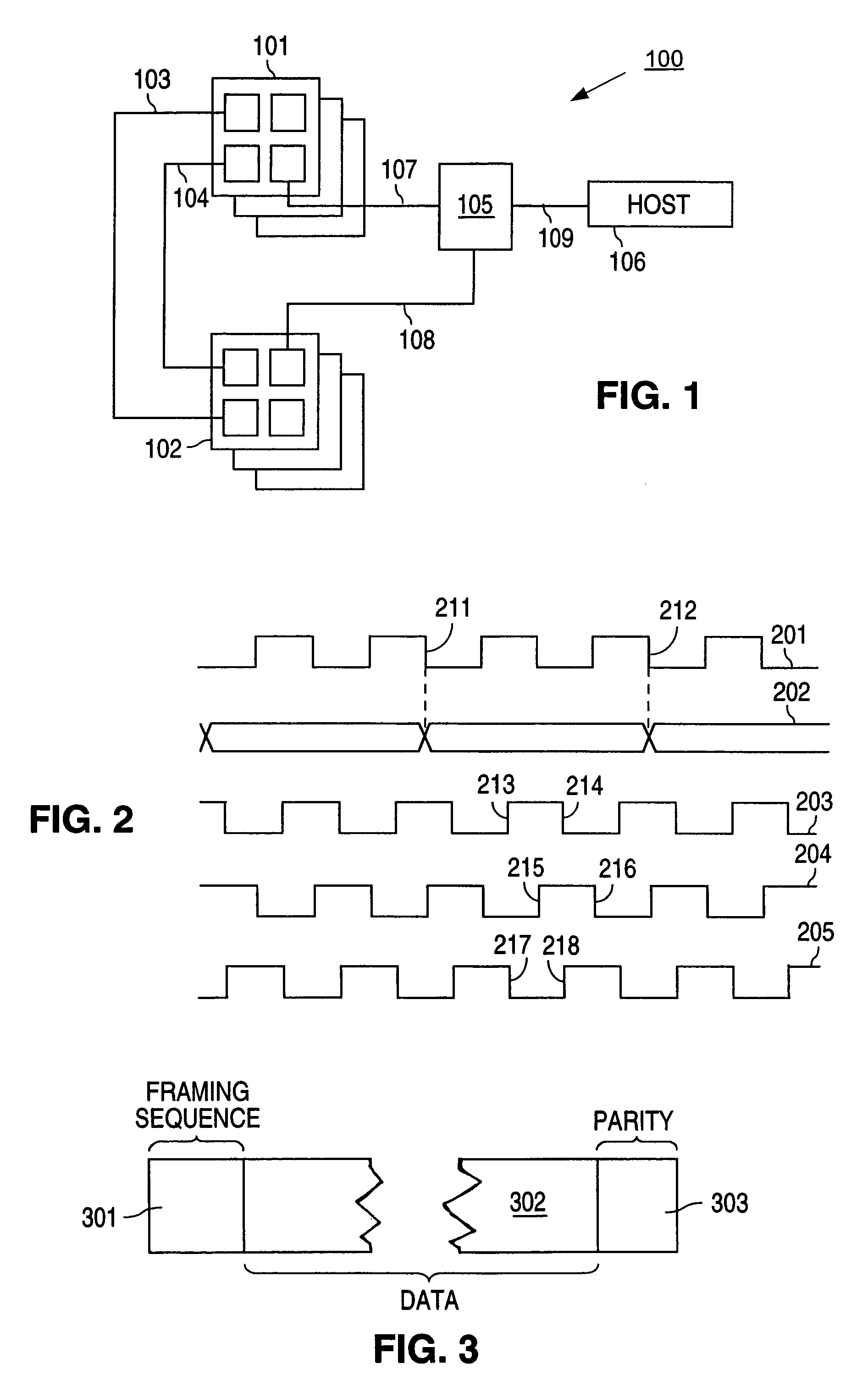
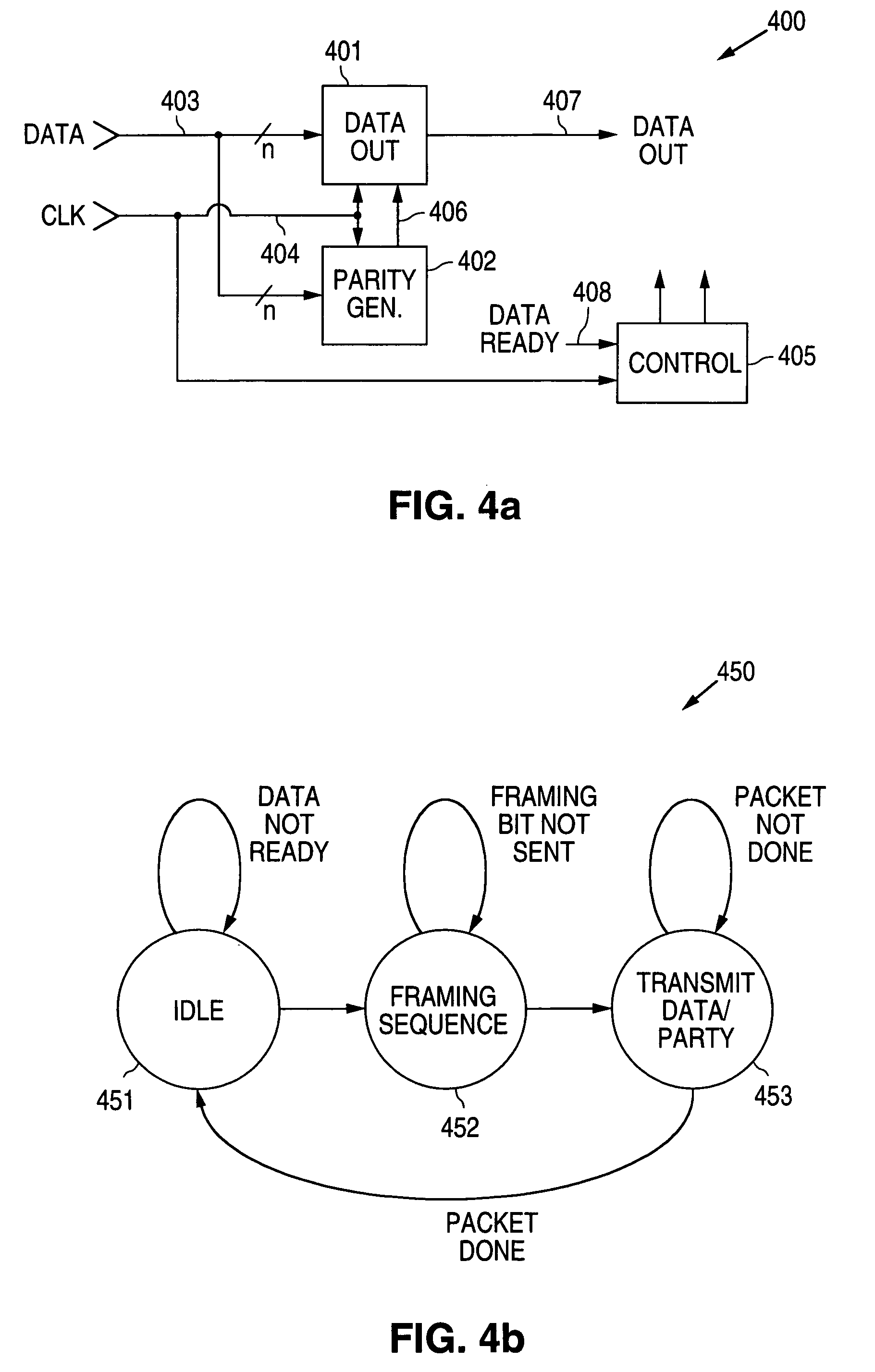
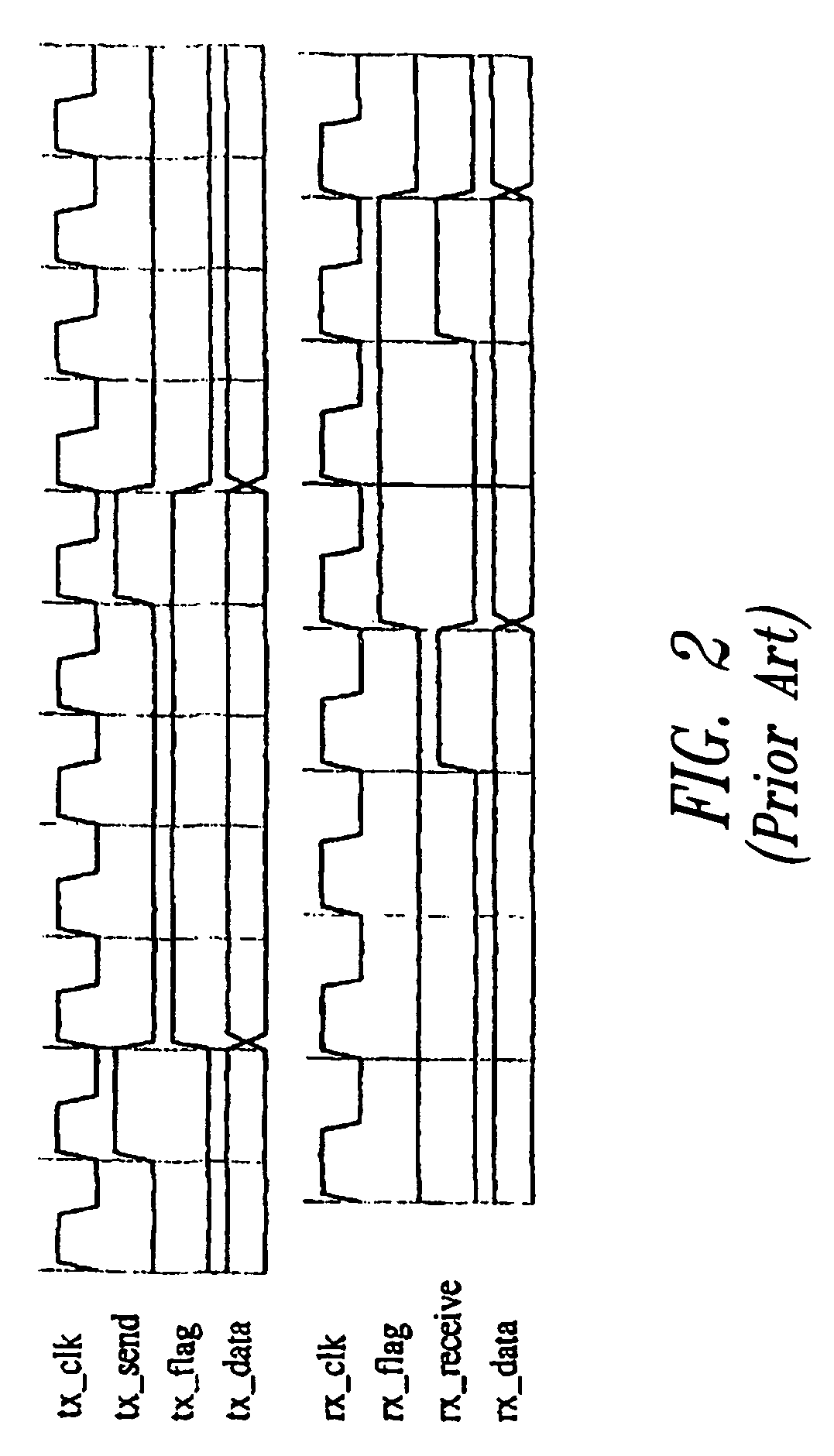
The primary focus of this article is asynchronous control in digital electronic systems. In a synchronous system, operations (instructions, calculations, logic, etc.) are coordinated by one, or more, centralized clock signals. An asynchronous digital system, in contrast, has no global clock. Asynchronous systems do not depend on strict arrival times of signals or messages for reliable operation. Coordination is achieved via events such as: packet arrival, changes (transitions) of signals, handshake protocols, and other methods.
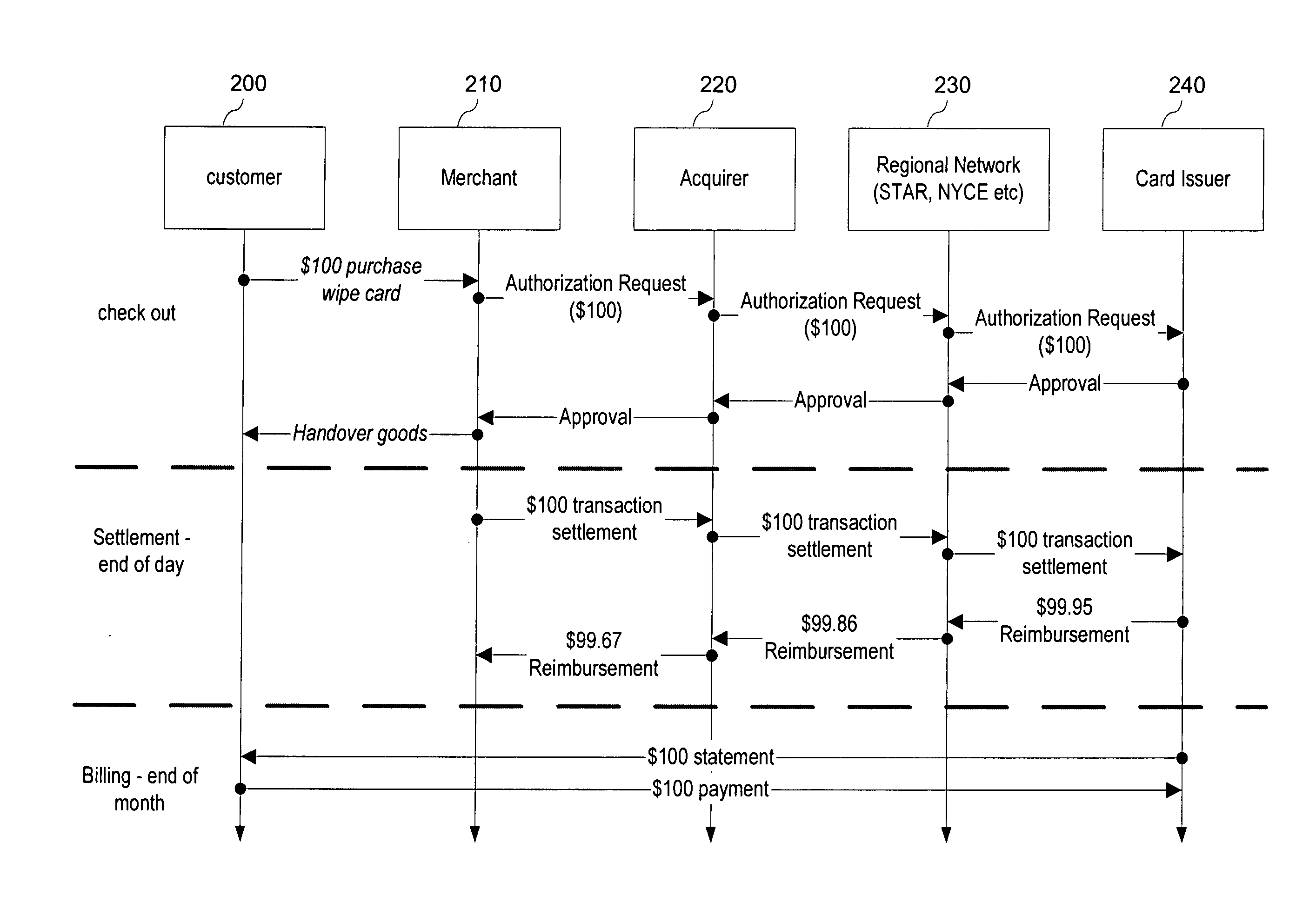
System and method for securely making payments and deposits
A system and method for securely making payments and deposits is disclosed. A method for securely and synchronously making a payment includes the steps of submitting a transaction request to a transaction center, the transaction request including details of a transaction between a customer and a third party, confirming the transaction request with the customer by communicating with a customer securely identifiable device, submitting the transaction request for approval, and paying the third party. A method of securely and synchronously making a deposit includes the steps of submitting a deposit request from a depositor to a transaction center, confirming an authorization request with the depositor by communicating with a customer securely identifiable device, receiving an authorization from the depositor, and depositing a deposit amount in a third party receiver account. Secure and asynchronous systems and methods are also disclosed.
Owner:CHEN YAOFEI +1
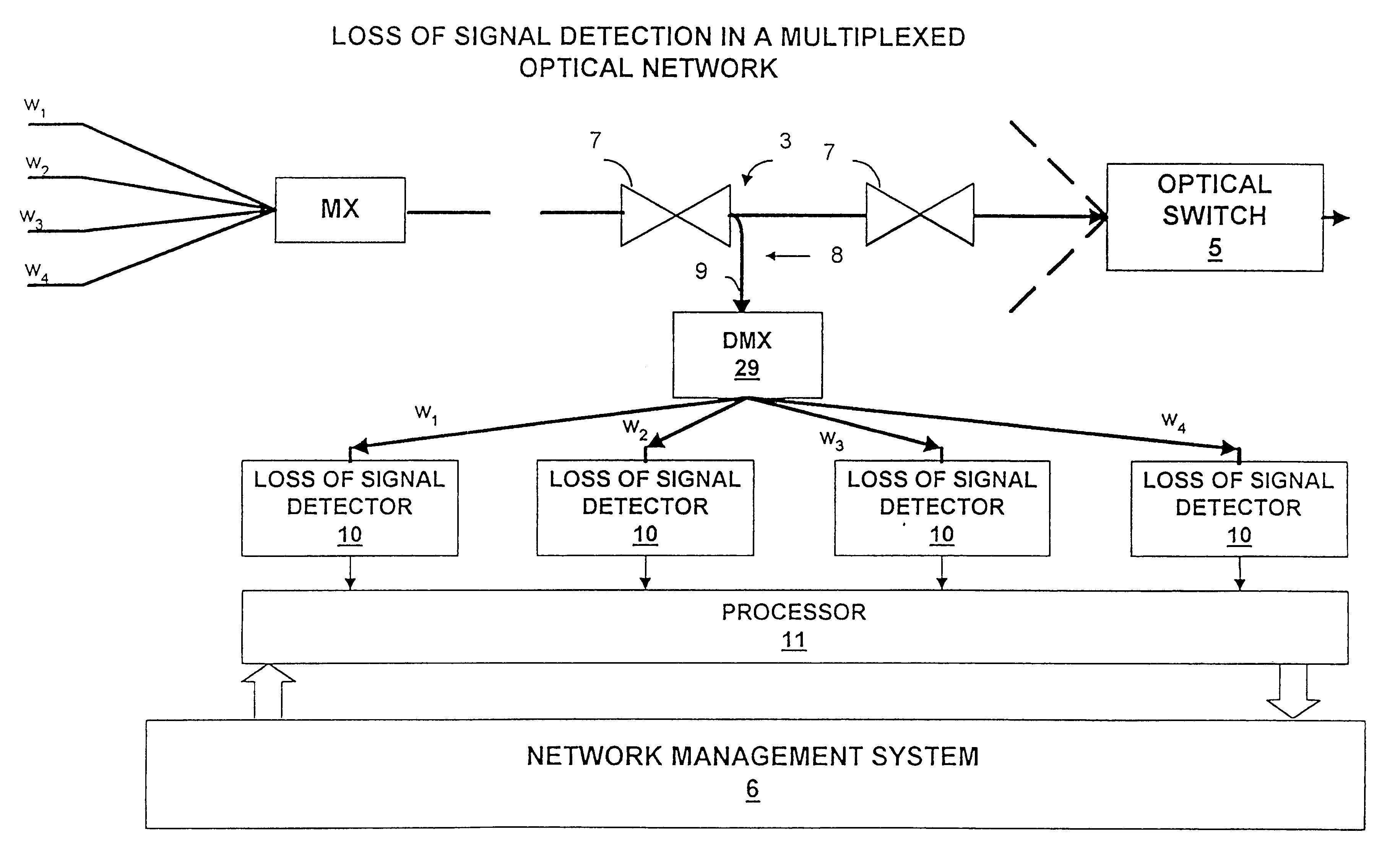
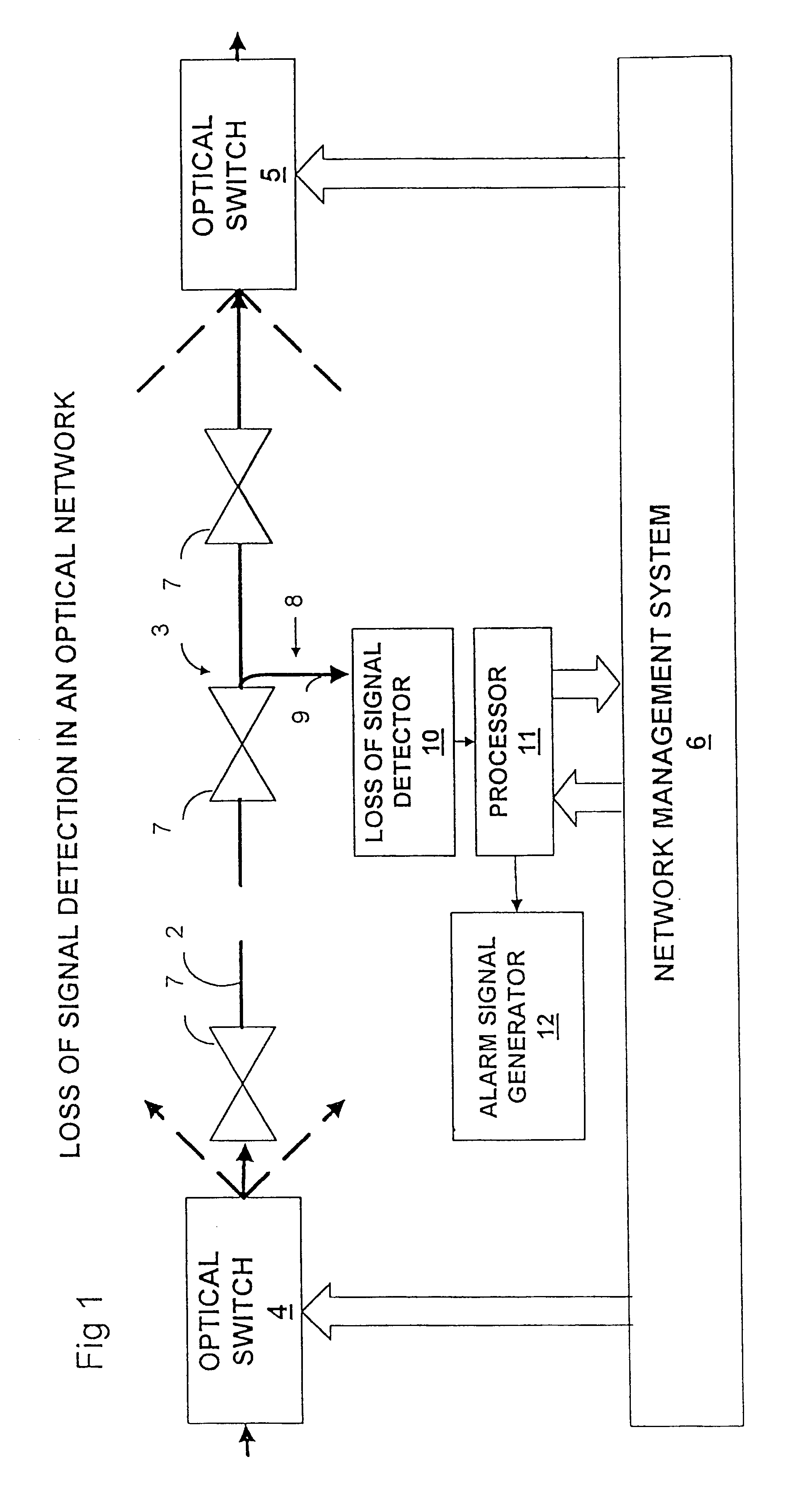
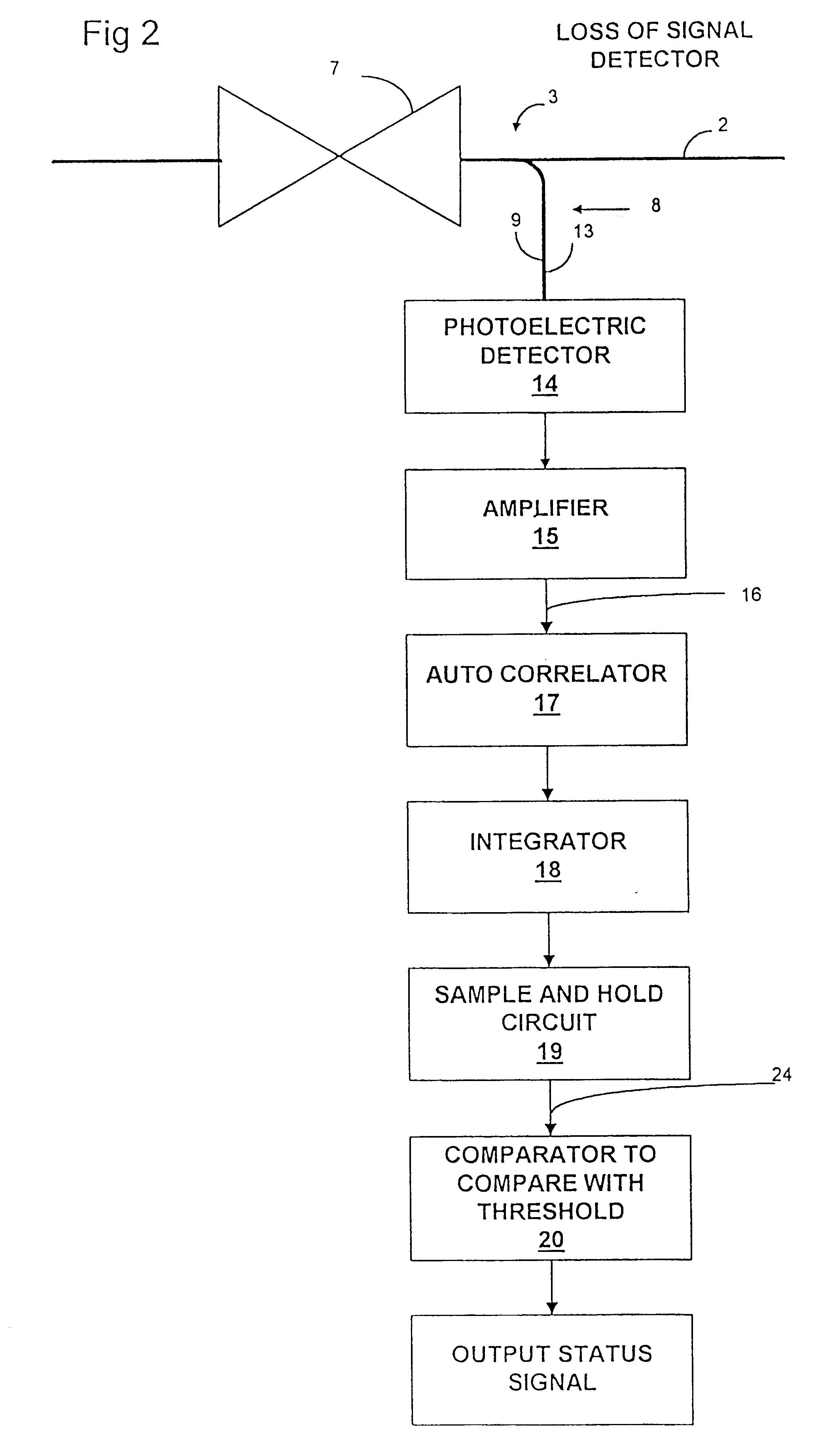
Optical network loss-of-signal detection
Loss of optical signal is detected in a synchronous communications system by detecting features of a monitor signal occurring at a detection frequency corresponding to the frame rate. Since the frame rate is substantially less than the bit rate, monitoring and detection can be performed at a lower bandwidth than the bit rate. An auto-correlation circuit utilises delays which are an integral multiple of the frame rate and produces a detection value which is compared with a threshold value. Alternatively, detection may be based on a power measurement of a band pass filtered monitor signal by setting the lower bandwidth limit above zero frequency and normalizing the measurement of power relative to an average power measurement. A loss of signal may then be detected by a change in power measurement relative to a threshold and can be used for asynchronous systems as well as synchronous systems. Loss of signal detection may be utilised to control an optical switch to re-route optical signals and generate alarm signals. The use of such detection in all optical networks avoids the requirement for electronic processing at the bit rate as a means of detection of loss of signal.
Owner:CIENA
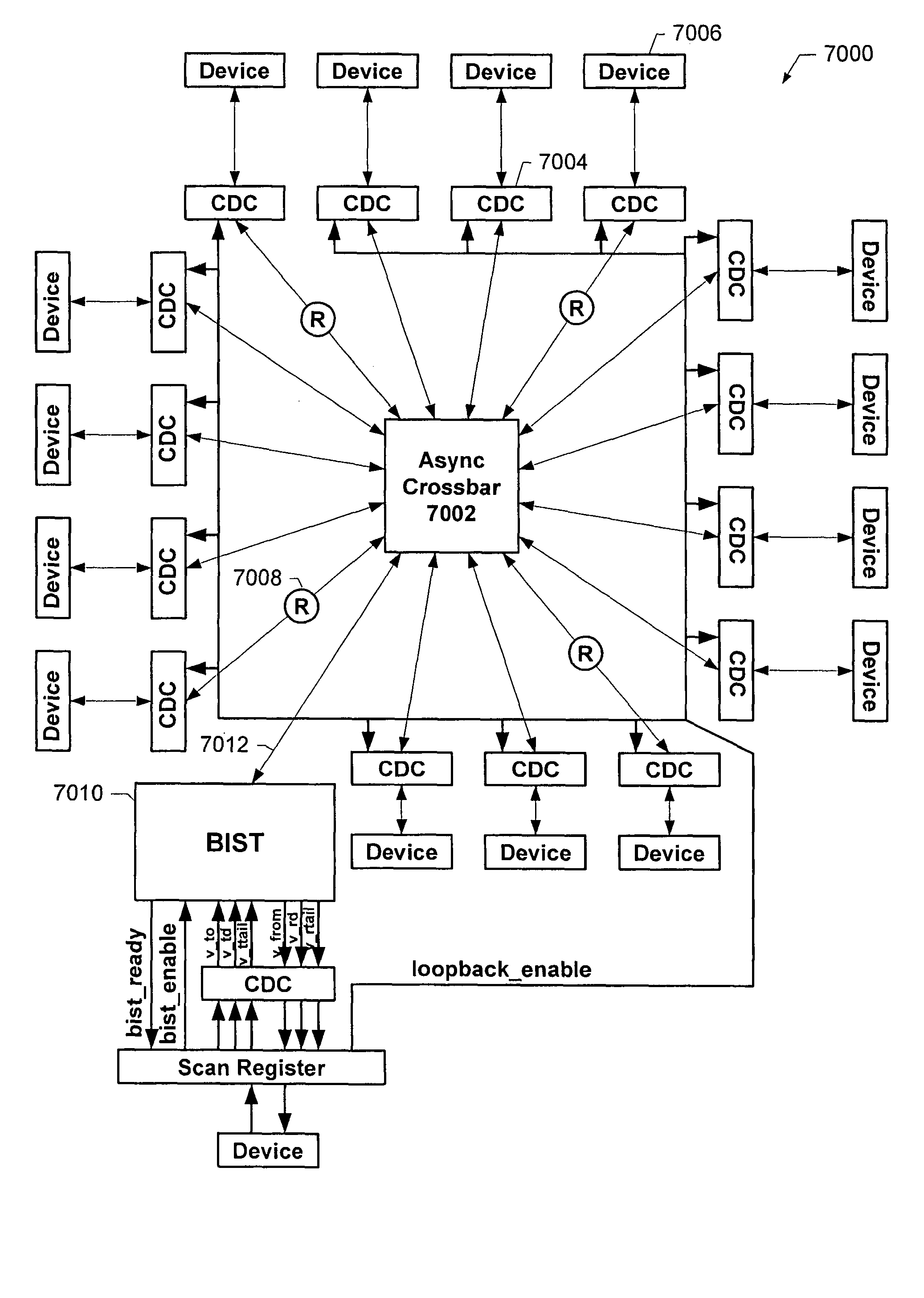
Asynchronous system-on-a-chip interconnect
InactiveUS7239669B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsSolid-state devicesComputer moduleData rate
Methods and apparatus are described relating to a system-on-a-chip which includes a plurality of synchronous modules, each synchronous module having an associated clock domain characterized by a data rate, the data rates comprising a plurality of different data rates. The system-on-a-chip also includes a plurality of clock domain converters. Each clock domain converter is coupled to a corresponding one of the synchronous modules, and is operable to convert data between the clock domain of the corresponding synchronous module and an asynchronous domain characterized by transmission of data according to an asynchronous handshake protocol. An asynchronous crossbar is coupled to the plurality of clock domain converters, and is operable in the asynchronous domain to implement a first-in-first-out (FIFO) channel between any two of the clock domain converters, thereby facilitating communication between any two of the synchronous modules.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Media flow method for transferring real-time data between asynchronous and synchronous networks
InactiveUS7126957B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationReal-time dataSynchronous motor
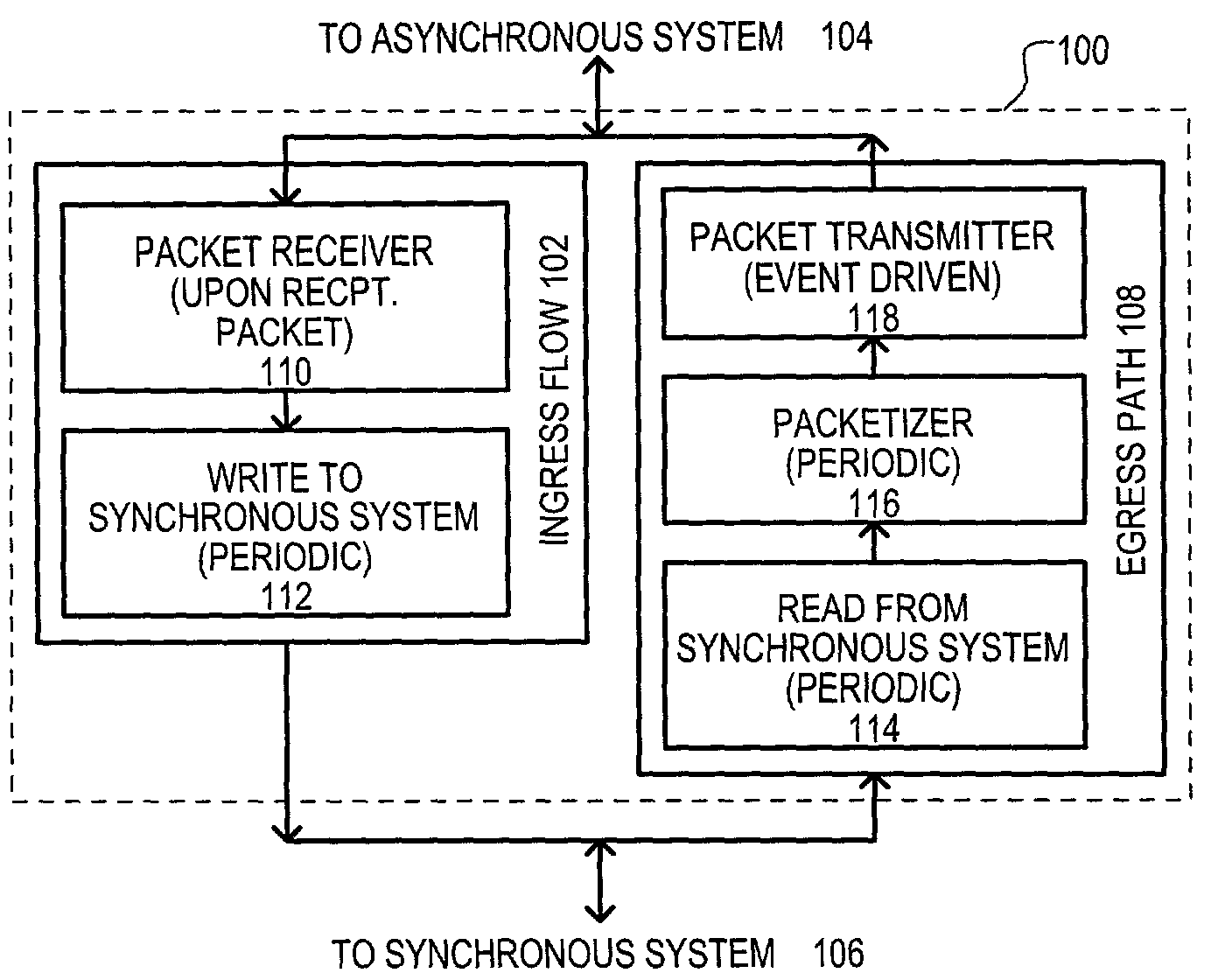
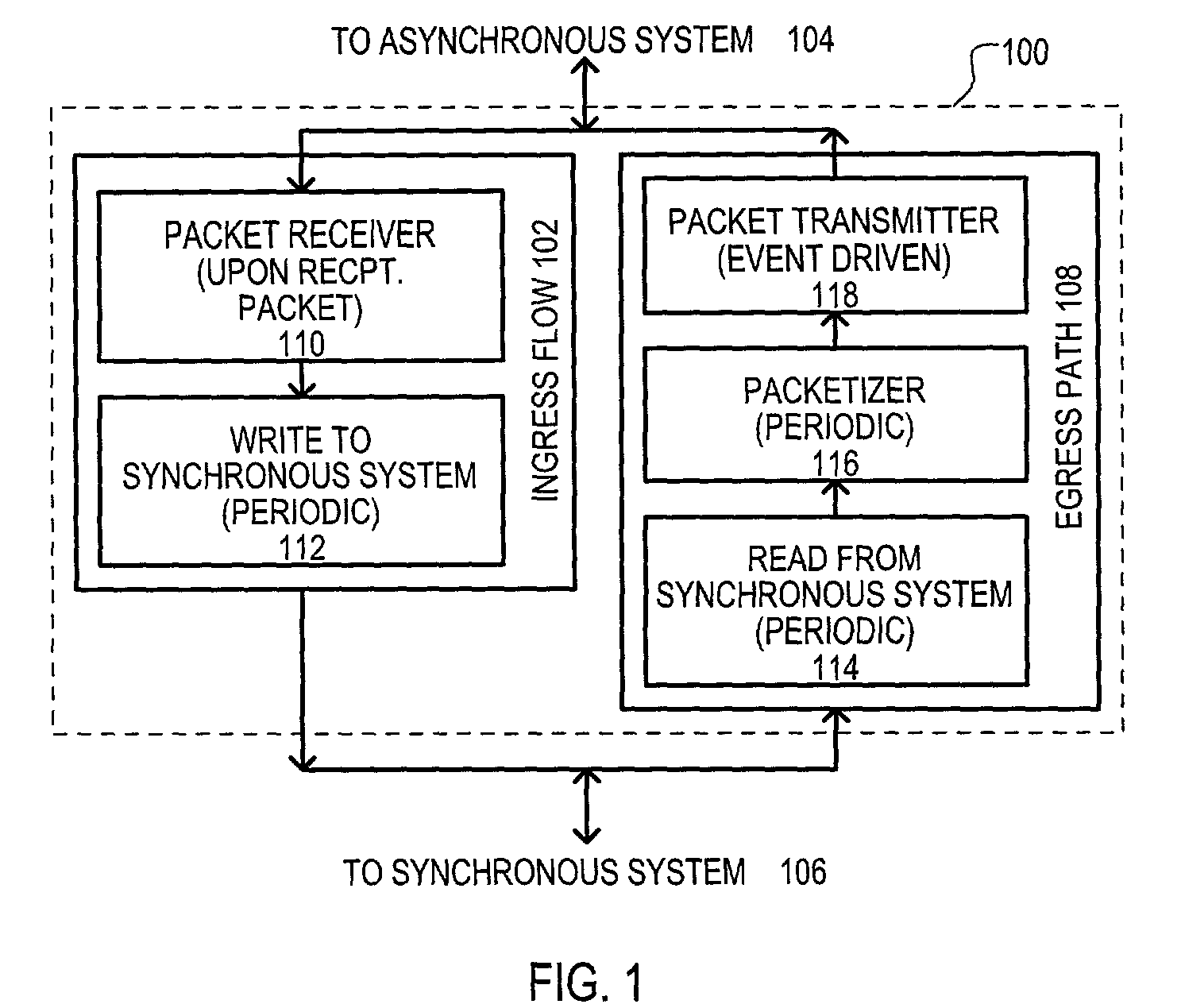
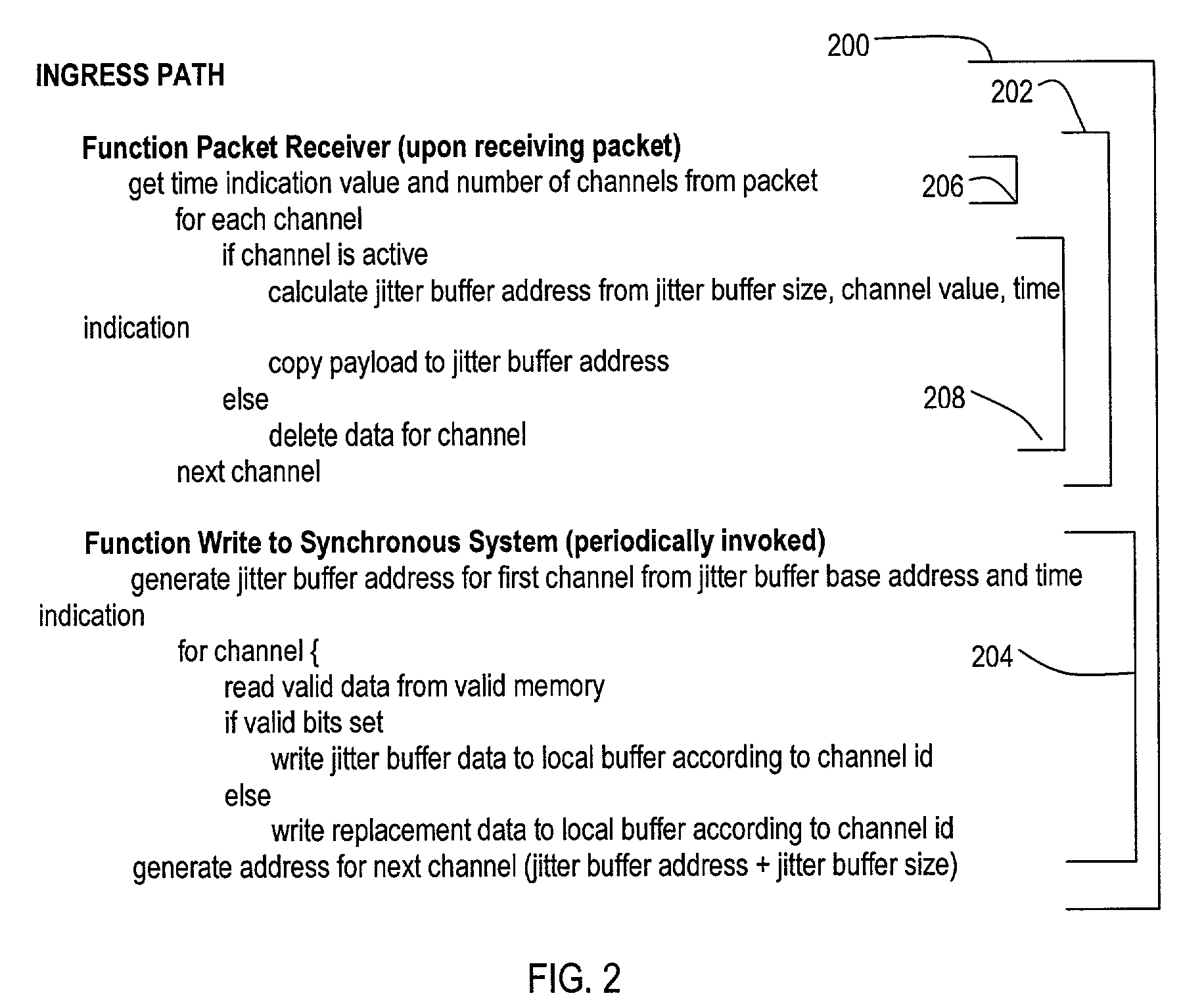
A system for transmitting real-time data between an asynchronous network (104) and a synchronous network (106) is disclosed. A method (100) may include an ingress path (102) for transmitting data from an asynchronous system (104) to a synchronous system (106), and an egress path (108) for transmitting data from a synchronous system (106) to an asynchronous system (104). An ingress path (102) may include a packet receiver (110) and write to synchronous system (112) steps. An egress path (108) may include read from synchronous system (114), packetizer (116), and packet transmitter (118) steps.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
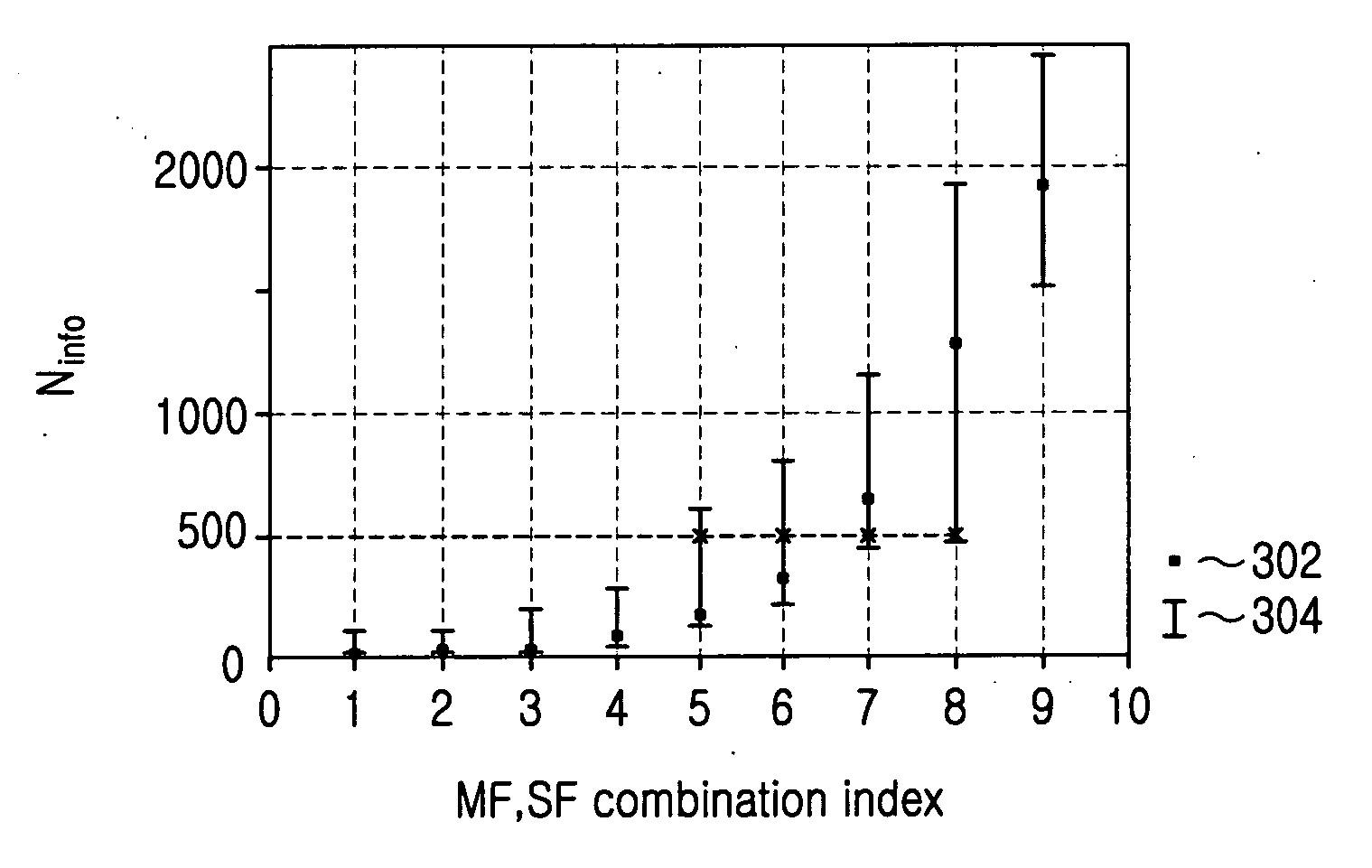
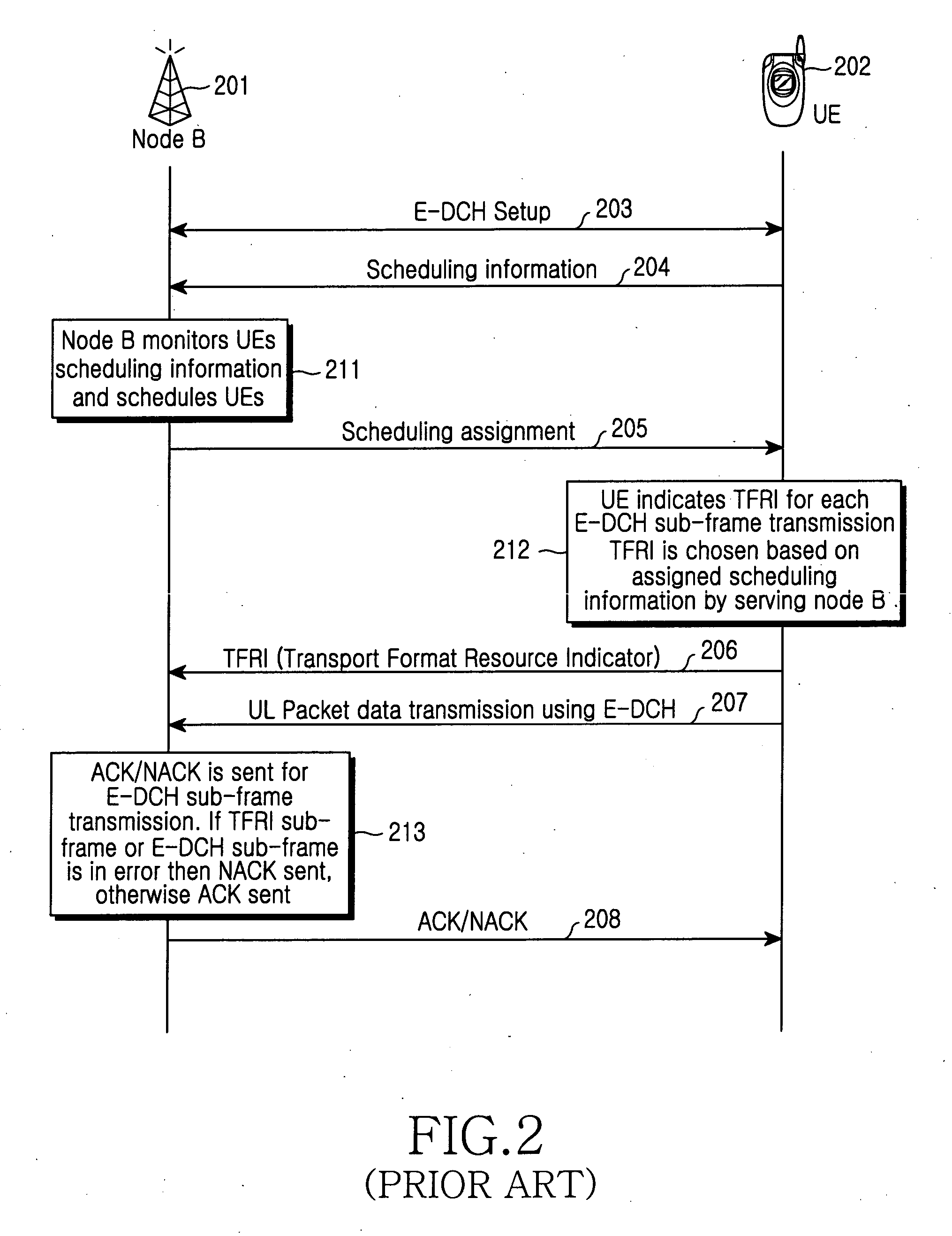
Method and apparatus for providing uplink packet data service in asynchronous WCDMA system
ActiveUS20050157687A1Efficiently determiningGuaranteed normal transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementChannel dataUplink transmission
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for providing uplink packet data services through an E-DCH in an asynchronous WCDMA system. A transport block size (TBS) for transmitting uplink transport channel data is determined. A combination of a spreading factor and a modulation scheme for uplink channel data transmission, corresponding to the determined TBS, is selected according to transmittable physical channel data bit sizes and puncturing limit values. The TBS is transmitted by incorporating it into control information of the uplink transport channel data. The modulation scheme and spreading factor combination is determined based on a physical channel data bit size that maximizes transmission efficiency and minimizes the number of punctured bits, without requiring an additional physical channel in transmitting the uplink data having the TBS. This method maximizes uplink transmission efficiency to save transmission resources and reduces signaling overhead required to transmit E-DCH control information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Asynchronous system-on-a-chip interconnect
InactiveUS20060239392A1Insensitive to variationMultiplex system selection arrangementsSolid-state devicesData rateAsynchronous system
Methods and apparatus are described relating to a system-on-a-chip which includes a plurality of synchronous modules, each synchronous module having an associated clock domain characterized by a data rate, the data rates comprising a plurality of different data rates. The system-on-a-chip also includes a plurality of clock domain converters. Each clock domain converter is coupled to a corresponding one of the synchronous modules, and is operable to convert data between the clock domain of the corresponding synchronous module and an asynchronous domain characterized by transmission of data according to an asynchronous handshake protocol. An asynchronous crossbar is coupled to the plurality of clock domain converters, and is operable in the asynchronous domain to implement a first-in-first-out (FIFO) channel between any two of the clock domain converters, thereby facilitating communication between any two of the synchronous modules.
Owner:FULCRUM MICROSYST
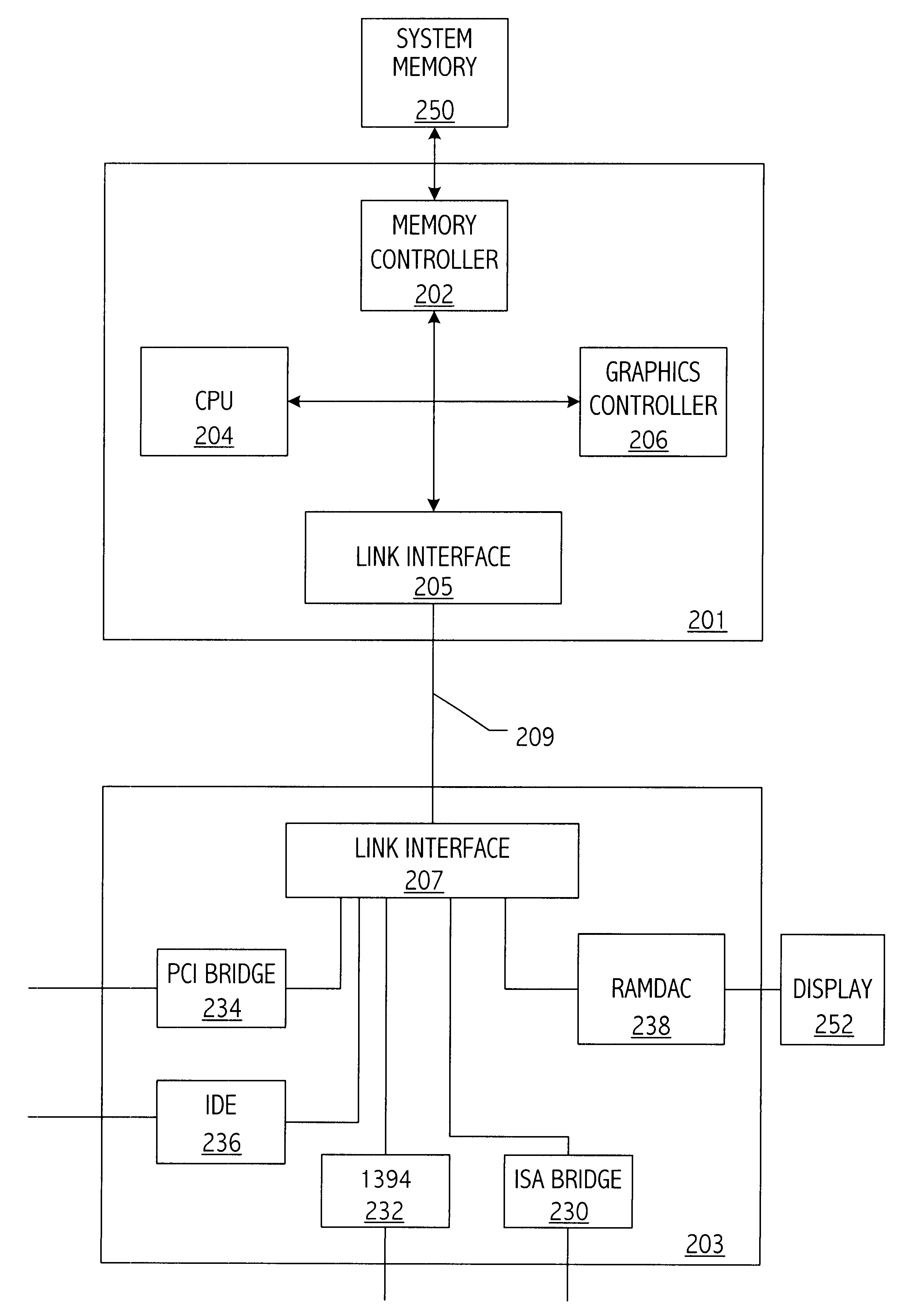
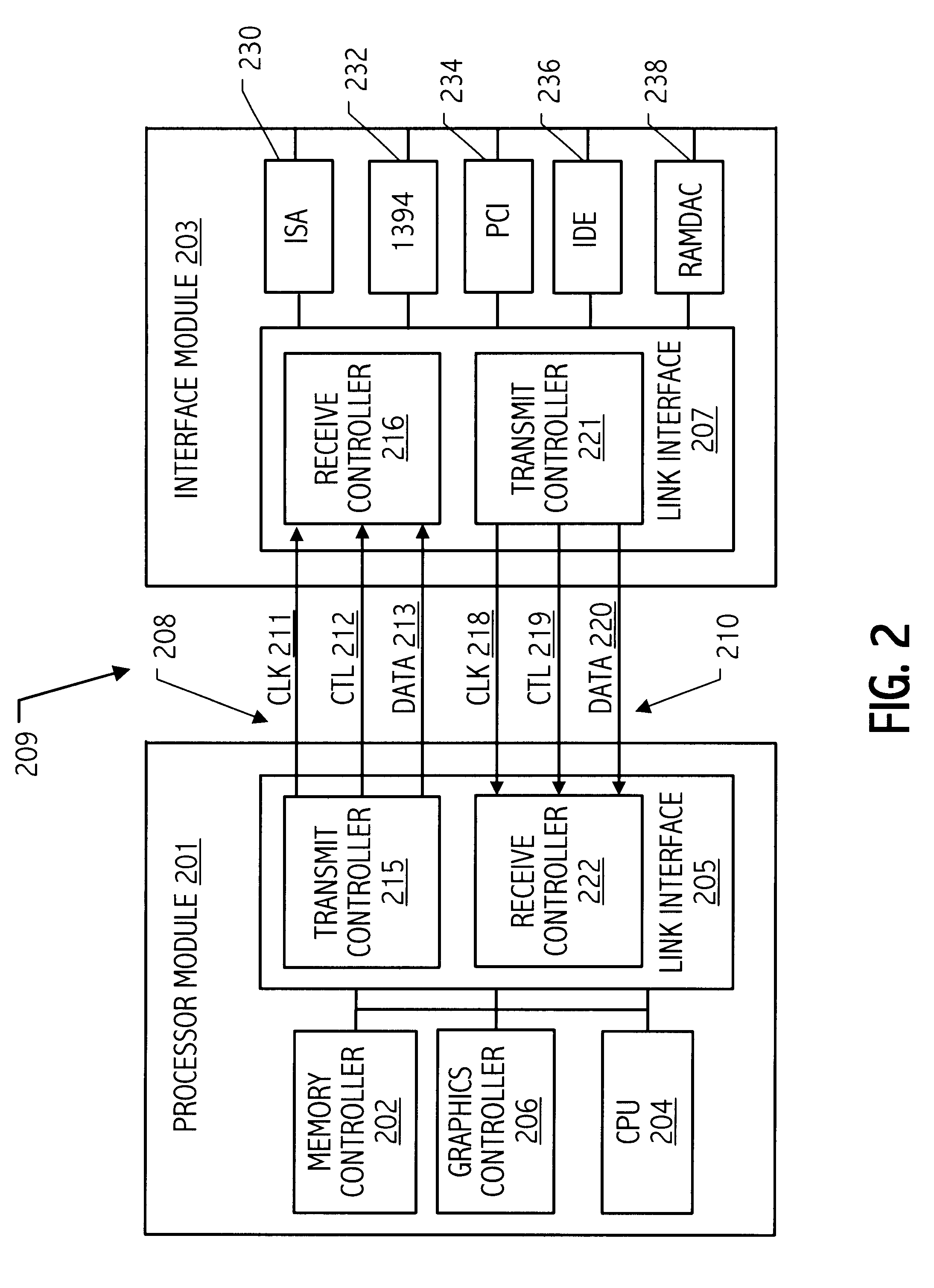
Input/output integrated circuit hub incorporating a RAMDAC
InactiveUS6532019B1Energy efficient ICTGeneral purpose stored program computerComputerized systemAsynchronous system
A computer system includes a first integrated circuit that has a central processing unit (CPU) and a graphics controller. An I / O hub, which is coupled to a plurality of input / output buses, includes a RAMDAC. An interconnect bus couples the first integrated circuit and the I / O hub and carries both graphics data to or from a frame buffer and also carries asynchronous system data between the processor and the input / output integrated circuit. The frame buffer may be located in the I / O hub to reduce graphics traffic over the interconnect bus.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
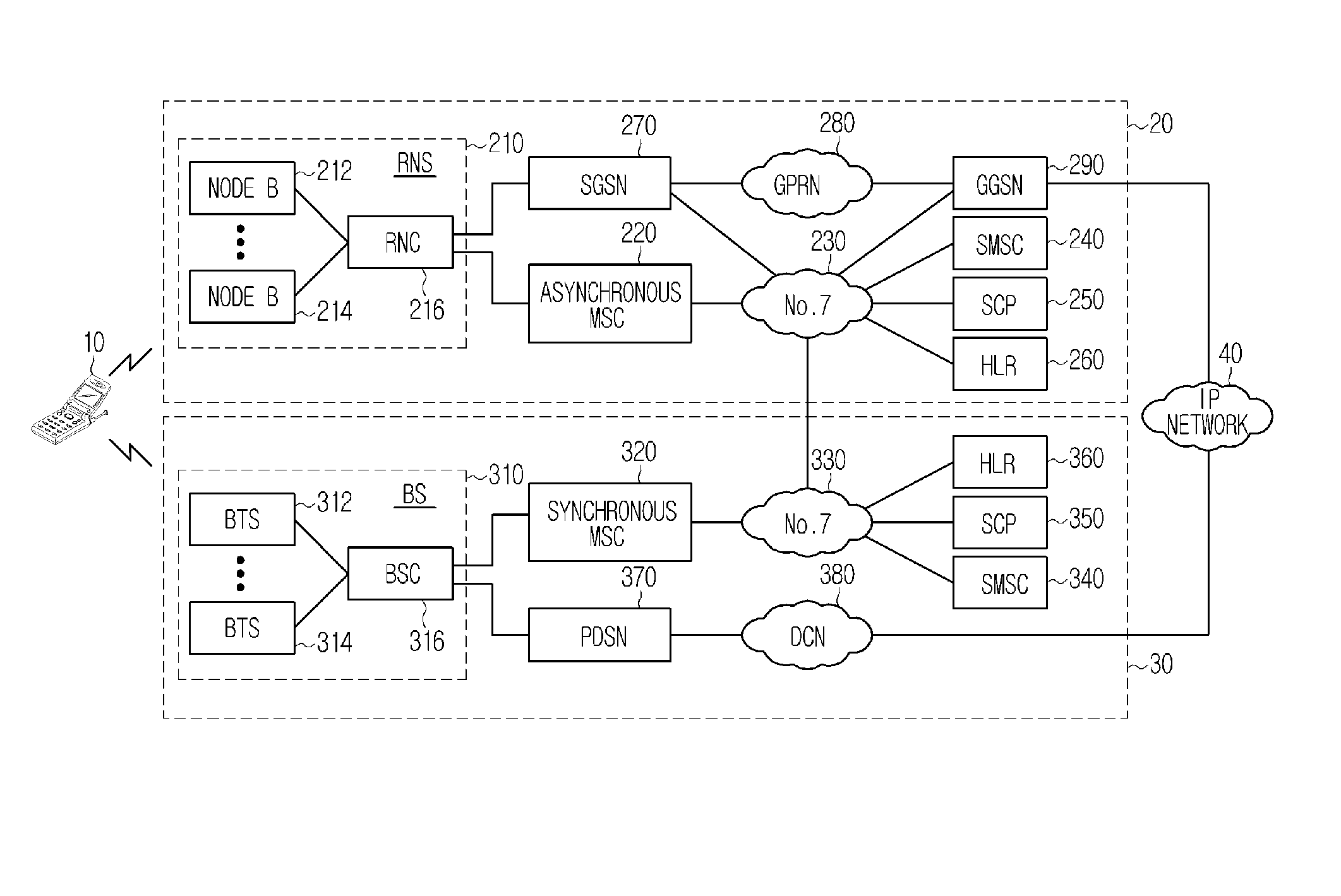
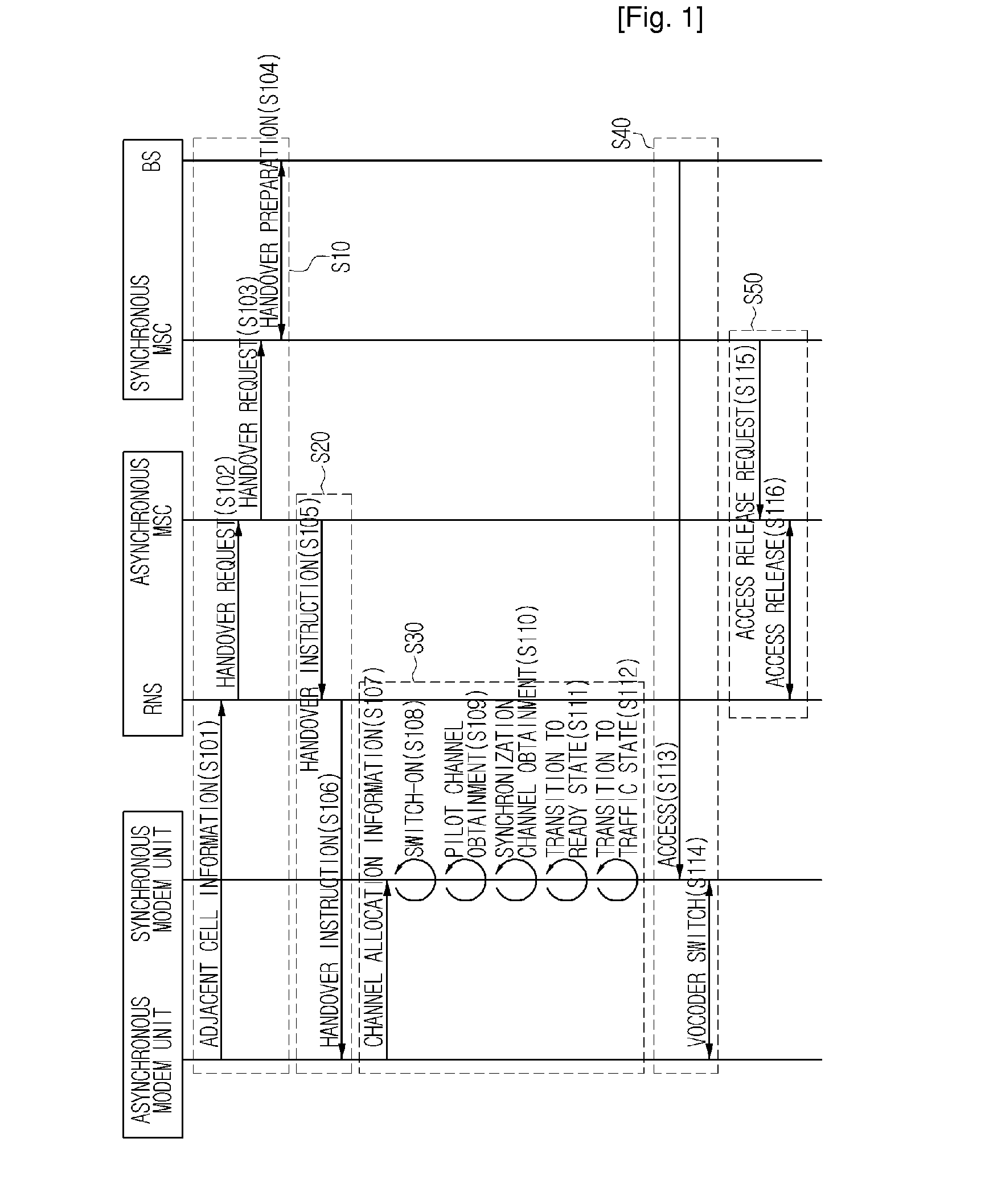
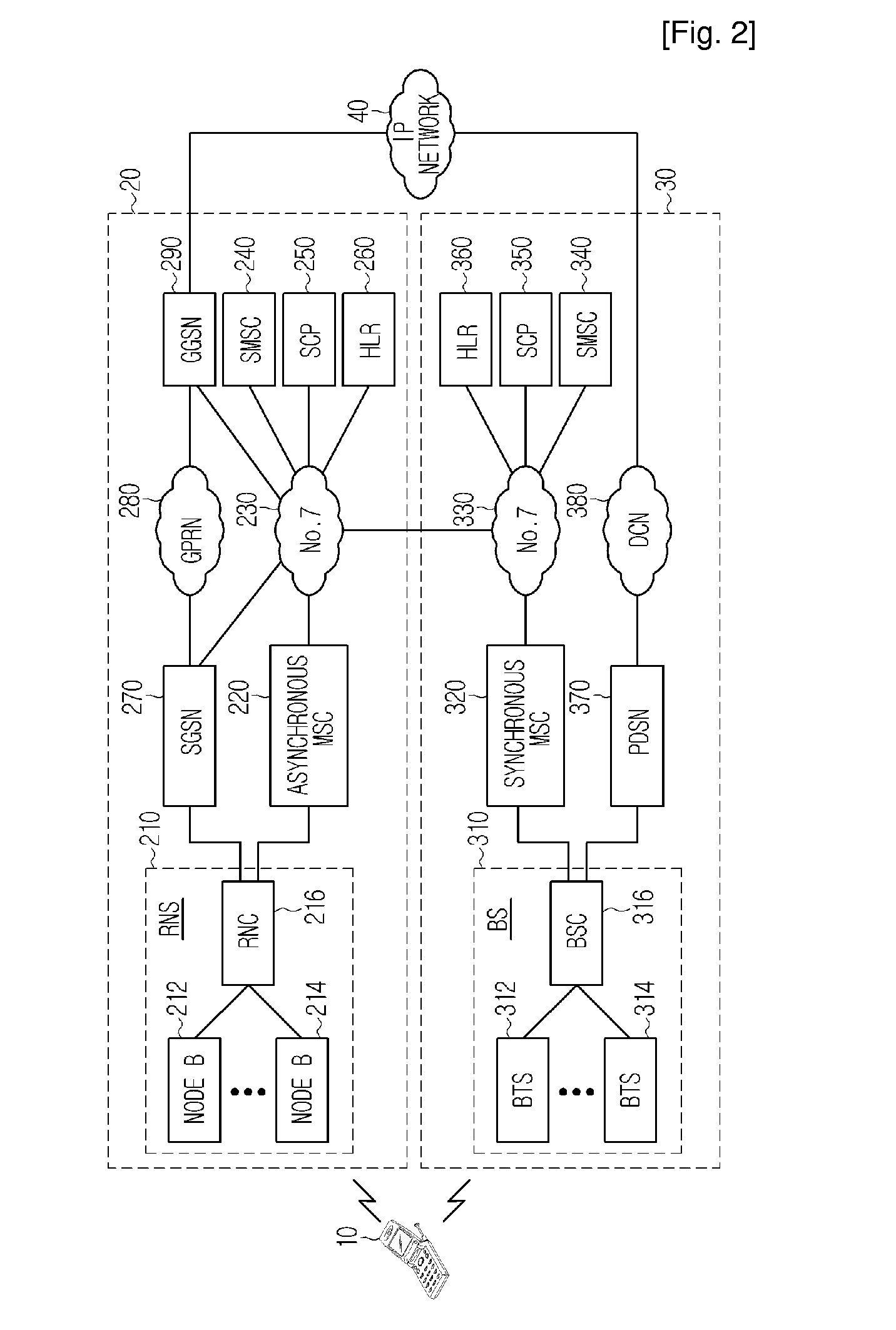
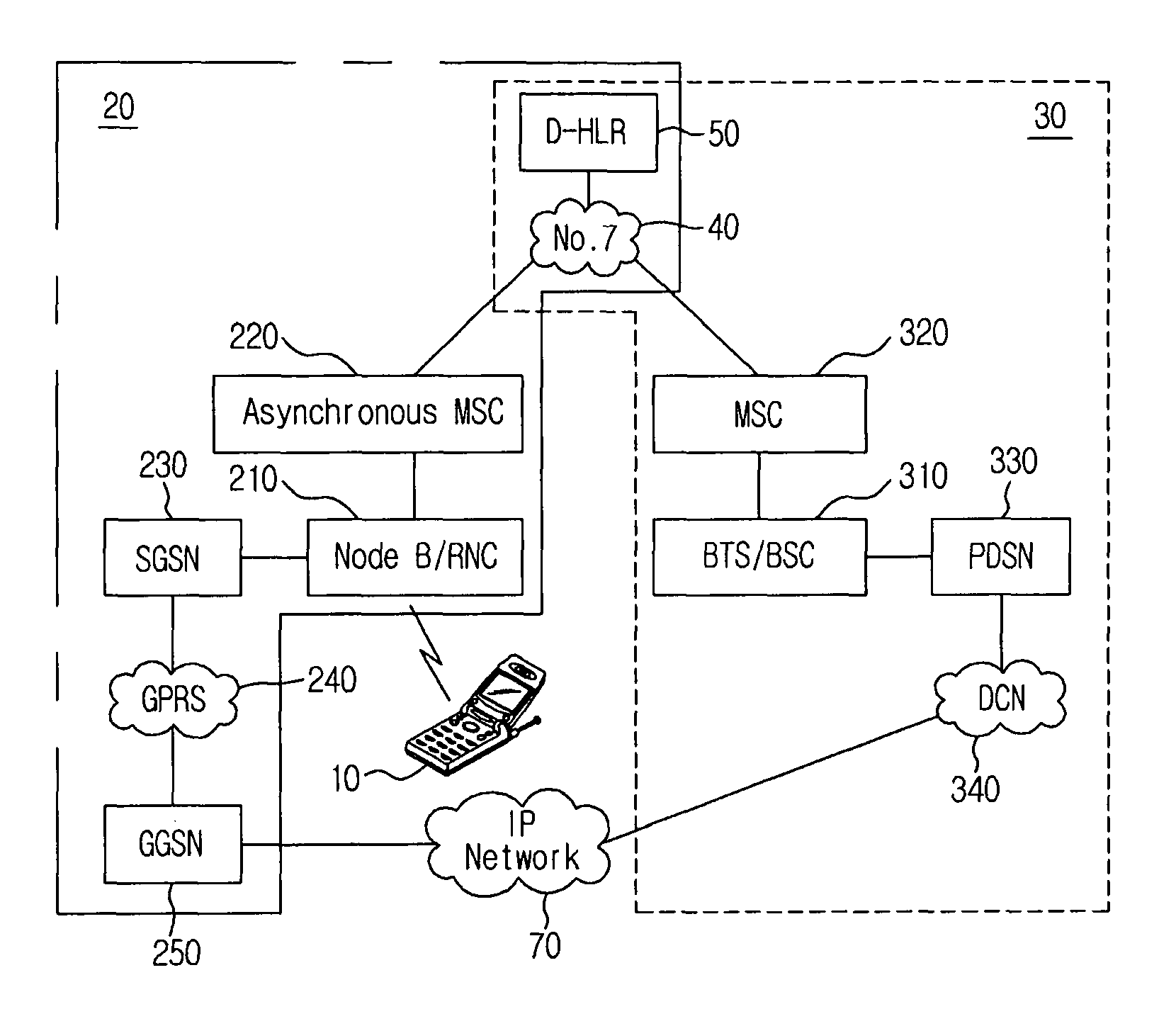
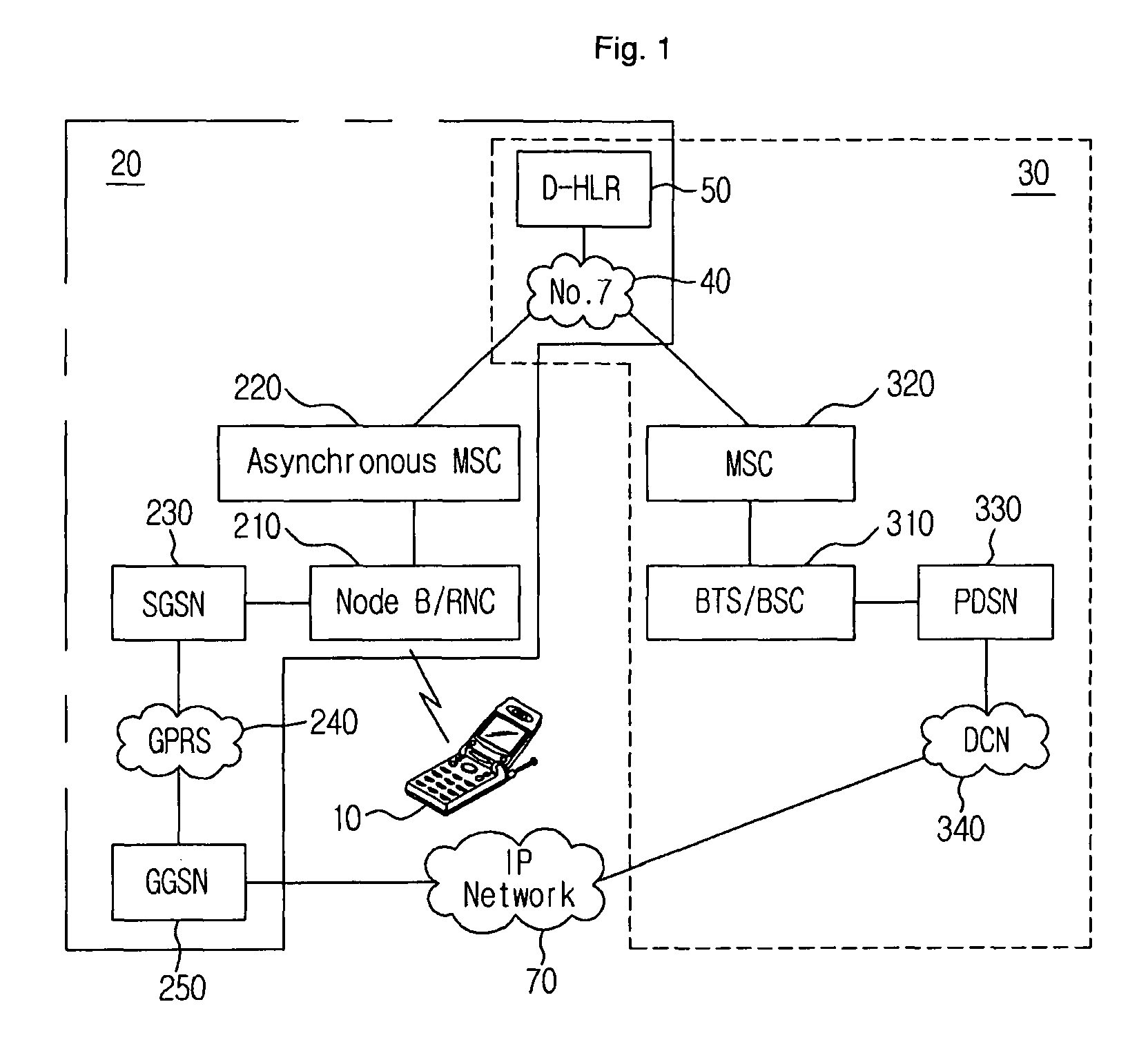
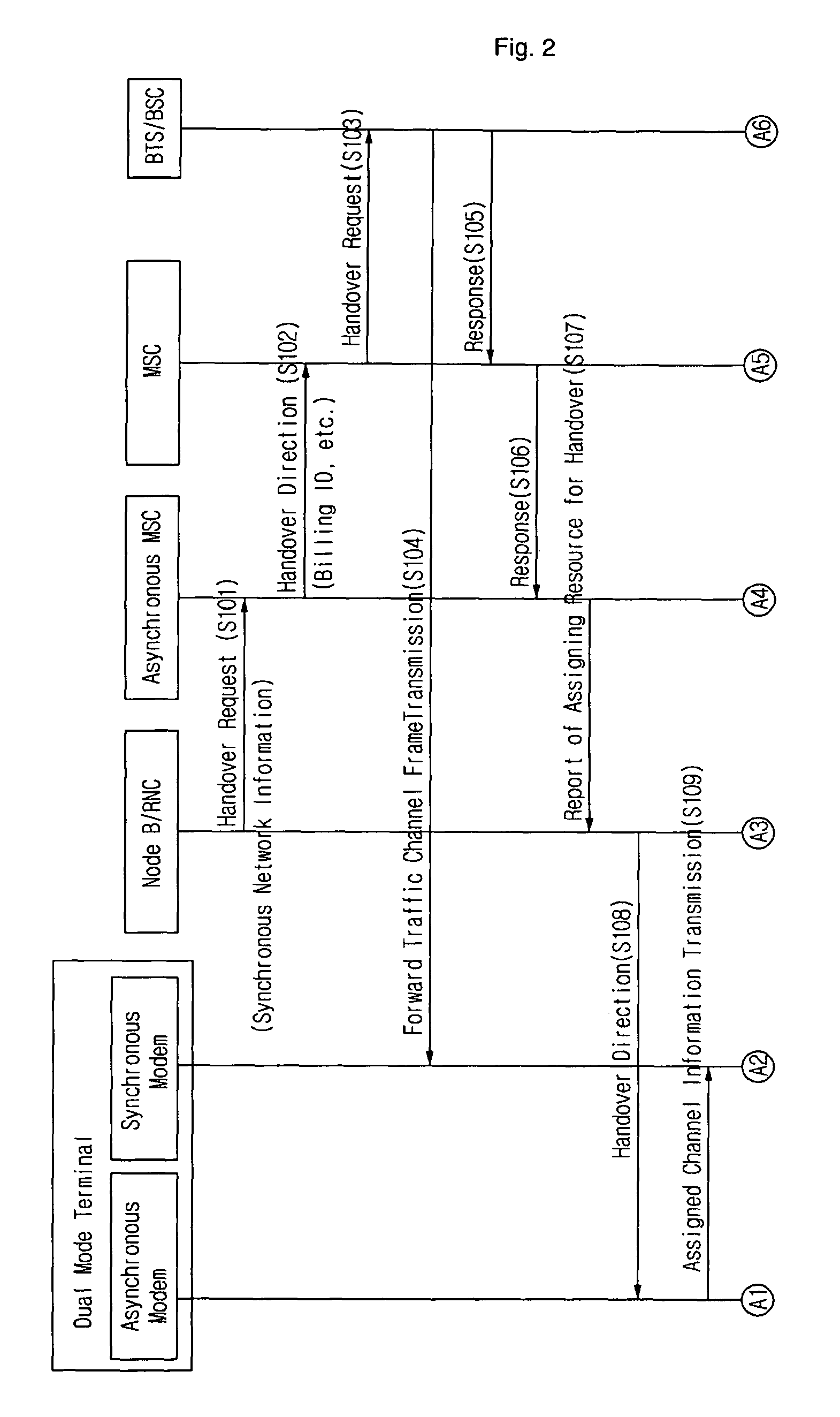
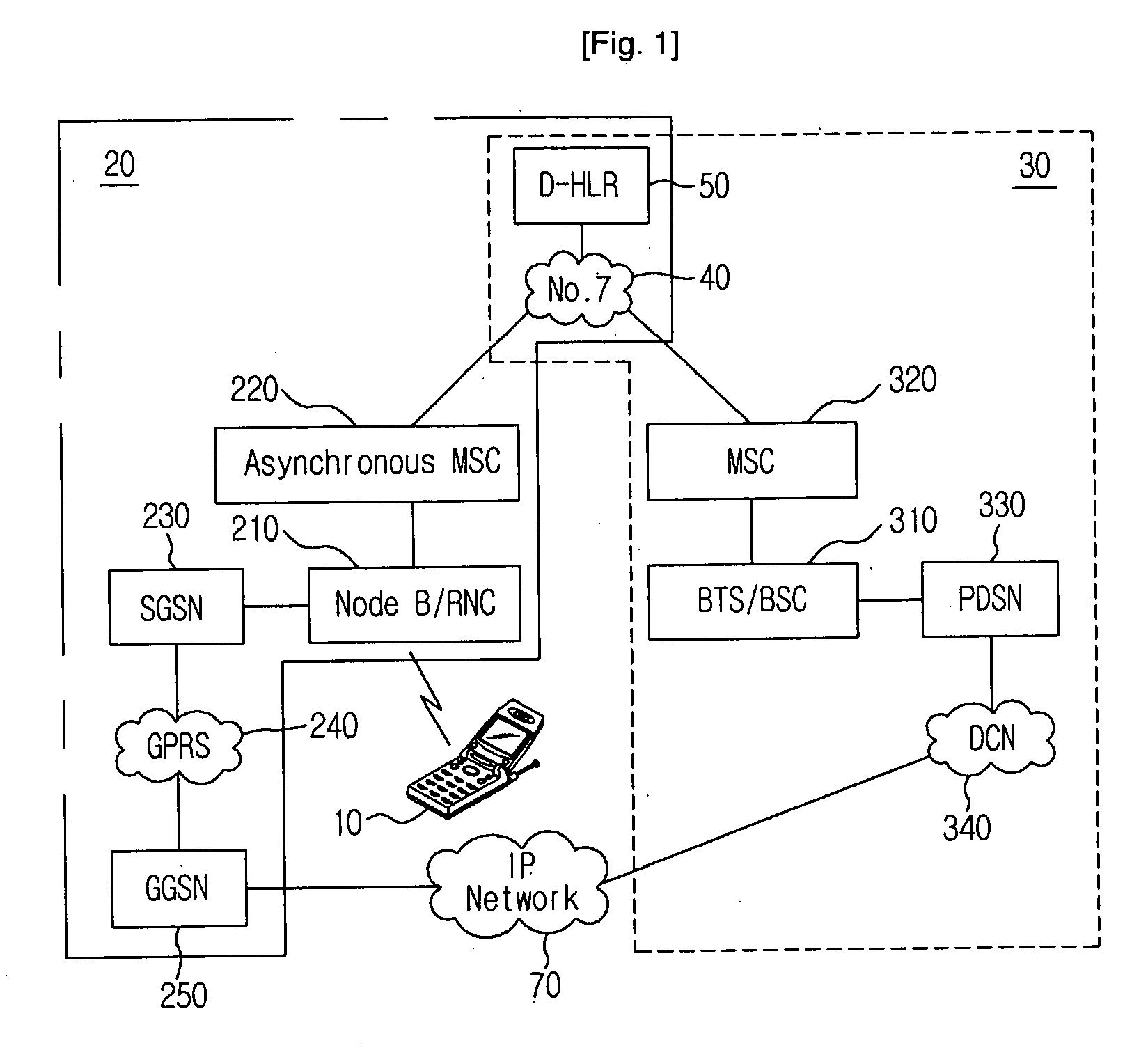
Handover Method for Mixed Mobile Communication System of Asynchronous Network and Synchronous Network
InactiveUS20080219212A1Increase success rateReduce power consumptionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationModem deviceAsynchronous network
A method for improving a success rate of handover in a mobile communication system in which an asynchronous network and a synchronous network are mixed is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of: an asynchronous system instructing an asynchronous modem of a mobile station to initiate a synchronous modem according to a handover request, the handover request that is generated from the mobile station when intensions of a forwarding and receiving signals between the mobile station and a node B of the asynchronous system are less than a predetermined intension; the asynchronous system determining a cell for the handover and instructing the mobile station to handover a synchronous system; the asynchronous modem requesting the synchronous modem to receiving a current communication according to a handover request of the asynchronous system to the asynchronous modem; the mobile station accessing the synchronous system; and the asynchronous releasing the communication with the mobile station.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
Spreading code synchronization method, receiver, and mobile station
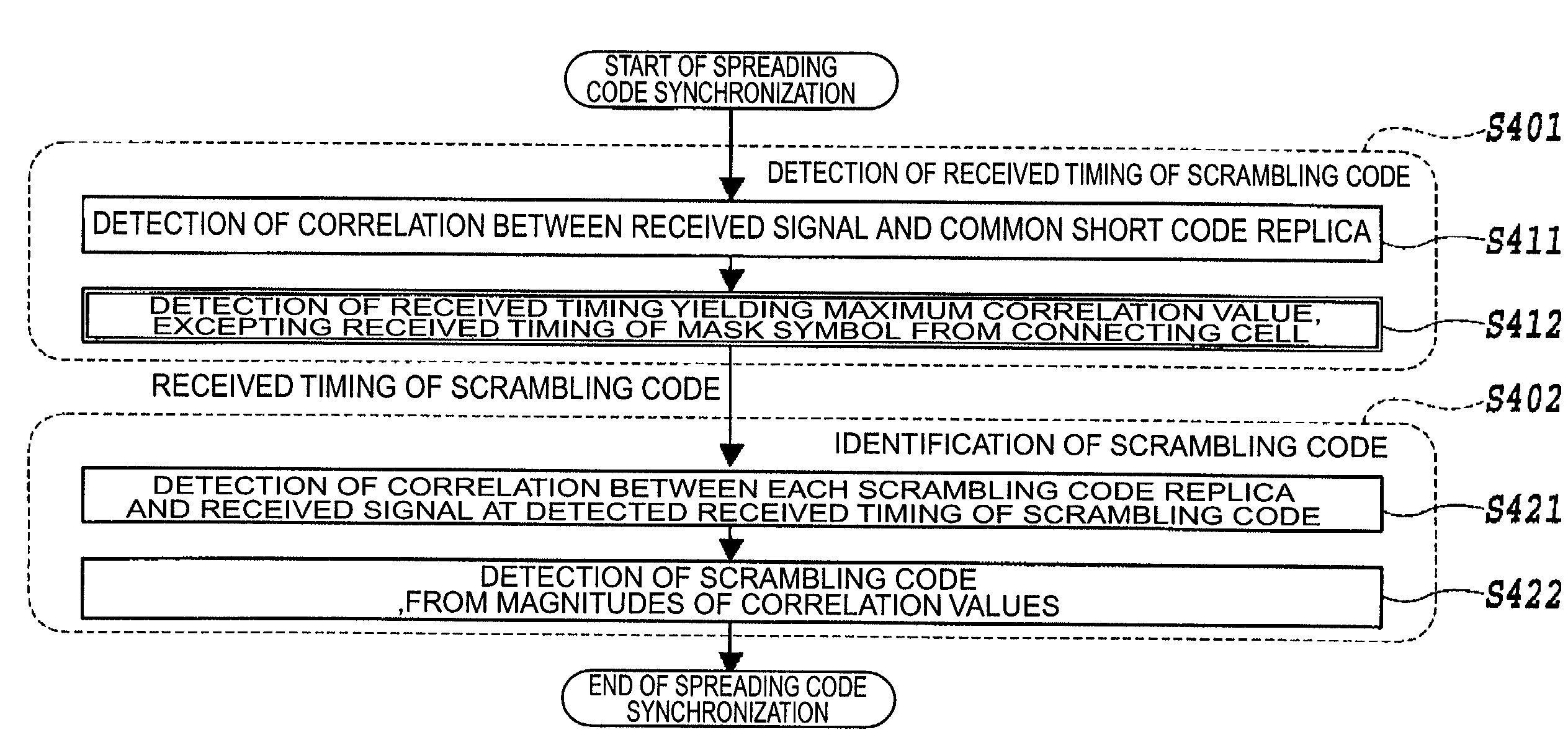
ActiveUS7154973B2Shorten the timeQuick checkRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationCell searchAsynchronous system
The present invention relates to a spreading code synchronization method and others for implementing fast cell search during entry of a mobile station into a soft handover mode in an intercell asynchronous system. In the spreading code synchronization method according to the present invention, a correlation is first detected between a received signal and a common short code, and a received timing of a scrambling code mask of a handover destination cell is detected based thereon. At this time, in order to avoid reception of a signal transmitted from a connecting cell, a received timing of a mask symbol from the connecting cell is excepted from a search range for the received timing of the scrambling code mask of the handover destination cell. The spreading code synchronization method further includes steps of detecting for each of scrambling code candidates a correlation between the received signal and a code of a product of a scrambling code and a common short code at the received timing of the scrambling code mask of the handover destination cell detected, and identifying the scrambling code of the signal transmitted from the handover destination cell, from magnitudes of correlation values.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Non-synchronized multiplex data transport across synchronous systems
InactiveUS6961691B1Reliable transmissionComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLogic emulationAsynchronous system
A method allows two substantially asynchronous system components of a logic emulation system to exchange data packets with reference to a clock signal of predetermined frequency. In one example, each bit is transmitted across the system components over two or more cycles of the clock signal. The reference clock signal can be distributed to the two system components from a common clock signal generator, or can be generated locally independently.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
Synchronizing clocks in an asynchronous distributed system
ActiveUS20090248900A1Time-division multiplexComputer security arrangementsTime deviationAsynchronous distributed systems
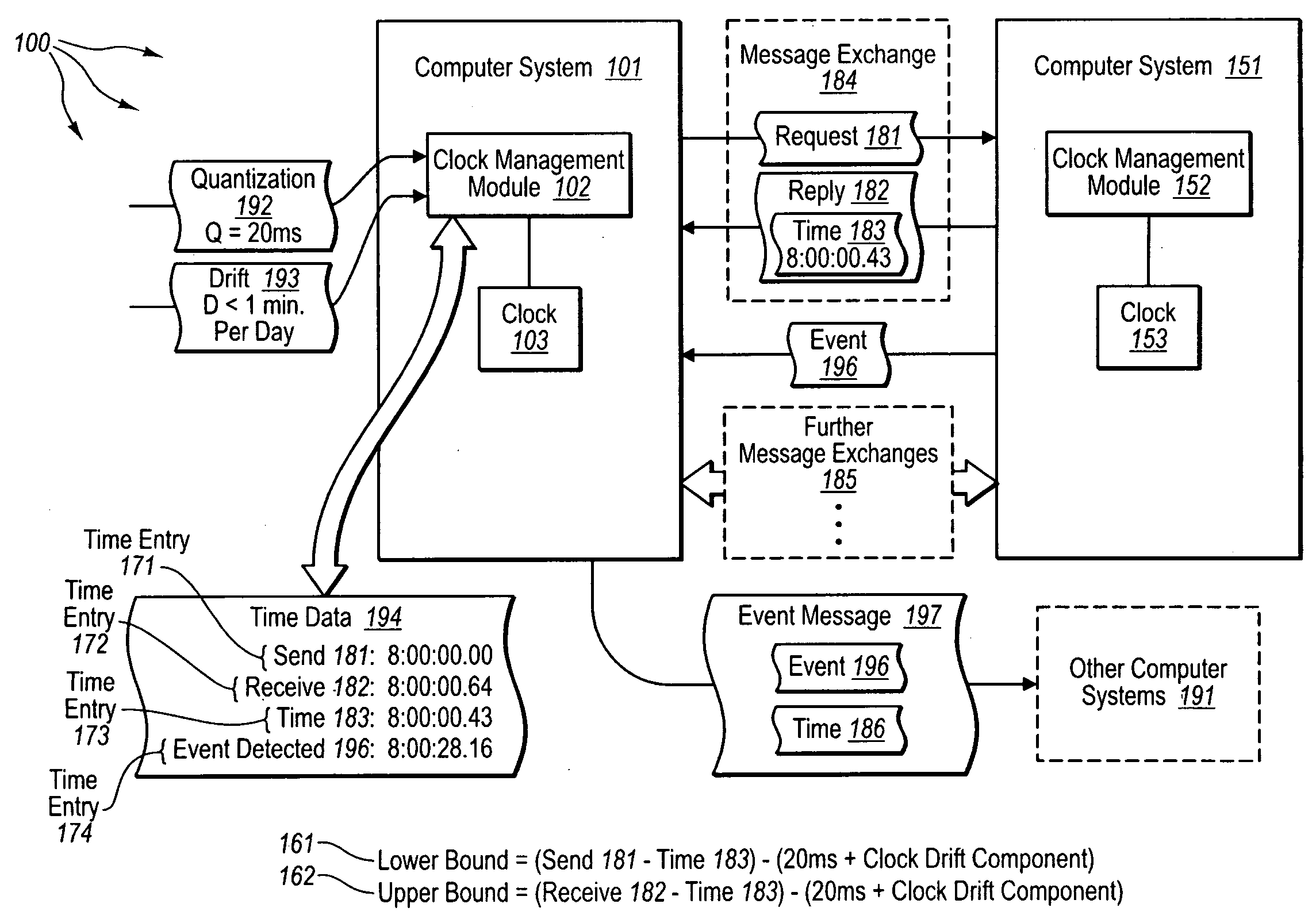
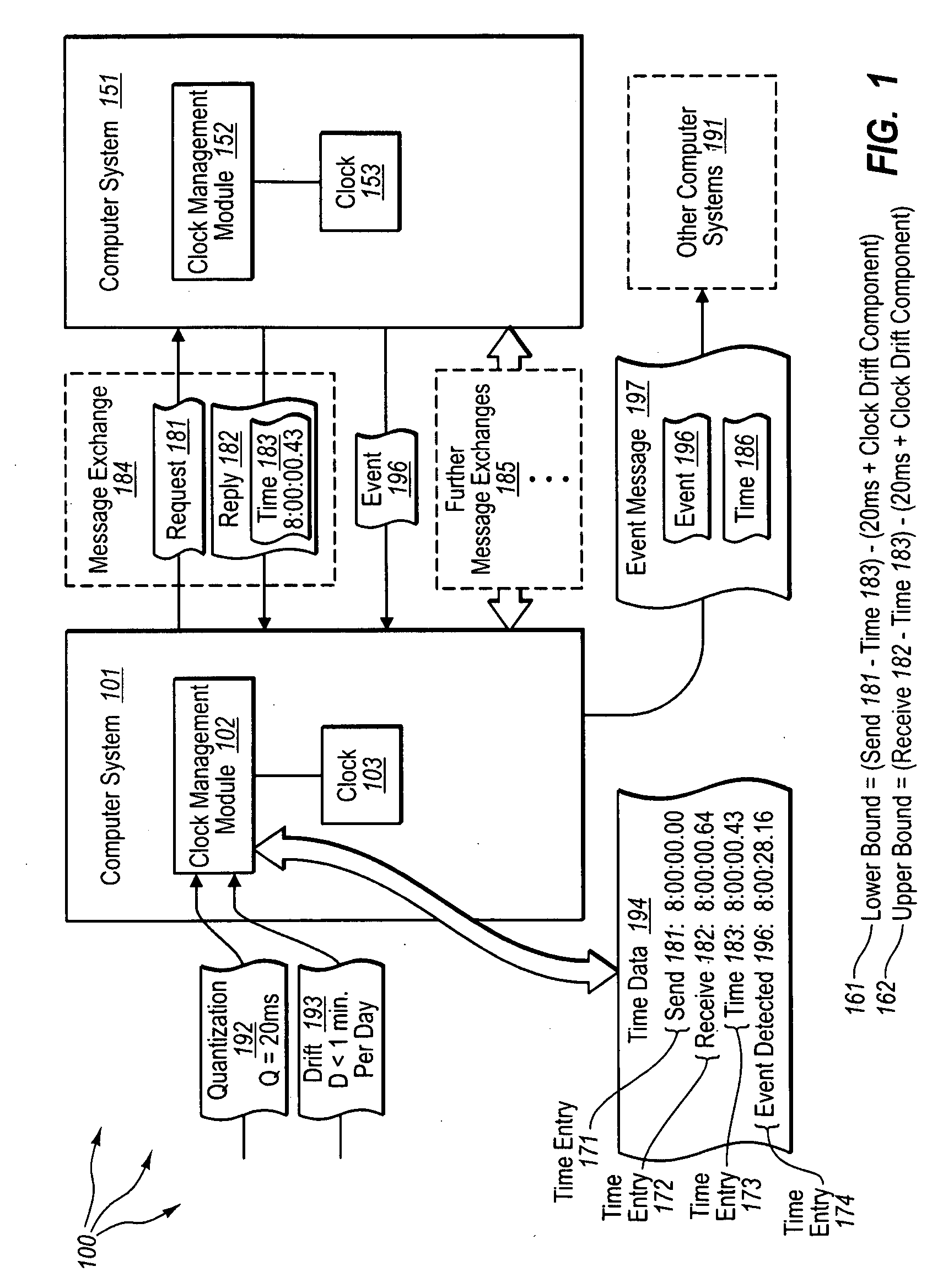
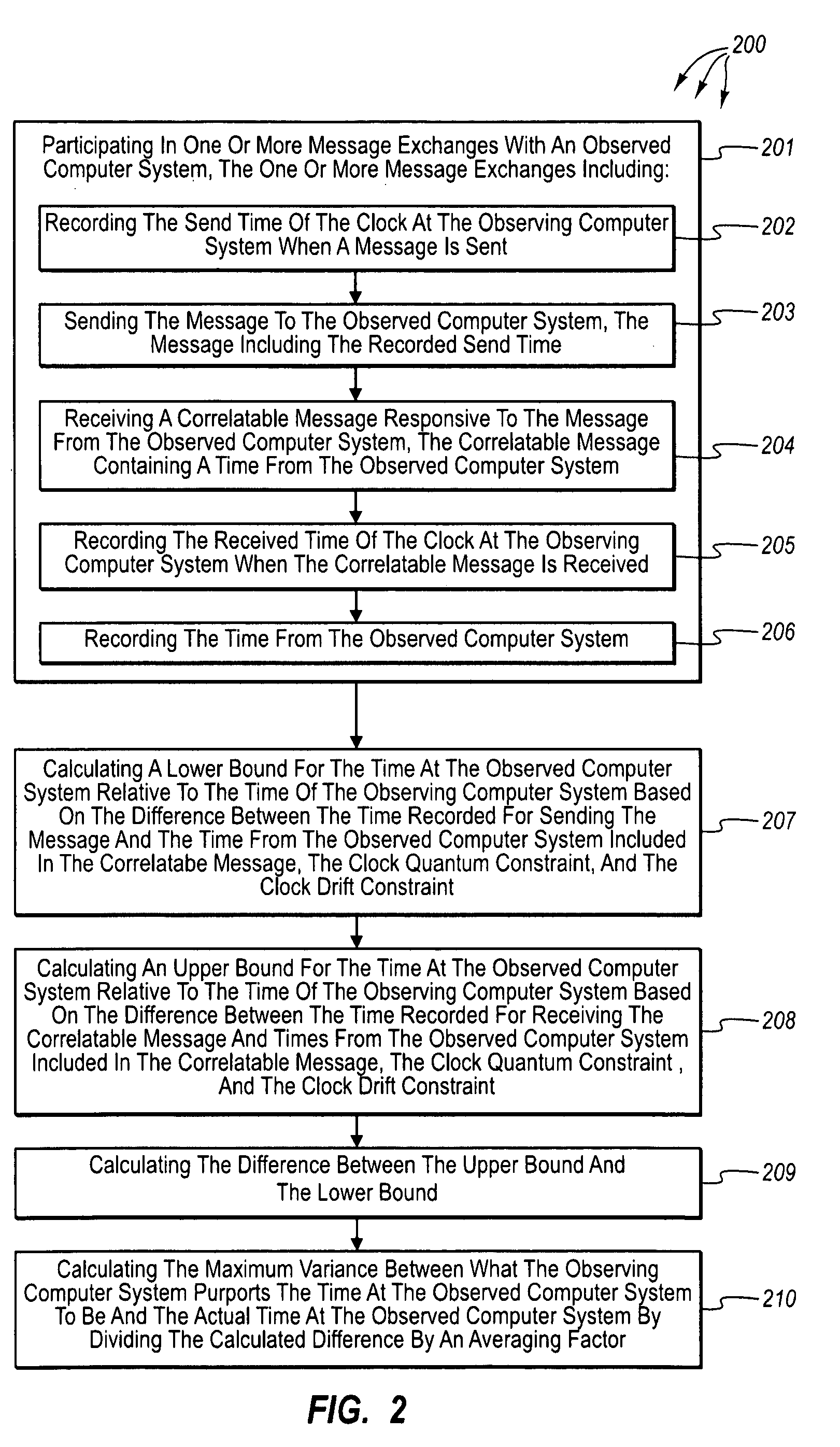
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for synchronizing clocks in an asynchronous distributed system. Embodiments of the invention facilitate creation of a trustable and practical common time (time of day) reference across a set of peer nodes (observers), such as, for example, members within a common asynchronous (distributed) system. A class of pseudo synchronous system can be created via tracking and accumulating worst case relativistic time skews amongst pairs of nodes (observers), without reference to a common master. As such, cooperating nodes can essentially guarantee a lower bound on the time-of-day that one node will observe, given an observation on another node. Accordingly, embodiments of the invention can be applied to provide a consistent (essentially safe) view of the worst case (i.e., greatest variance in) current time across such an asynchronous system—without a common external time-of-day clock entity being used.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
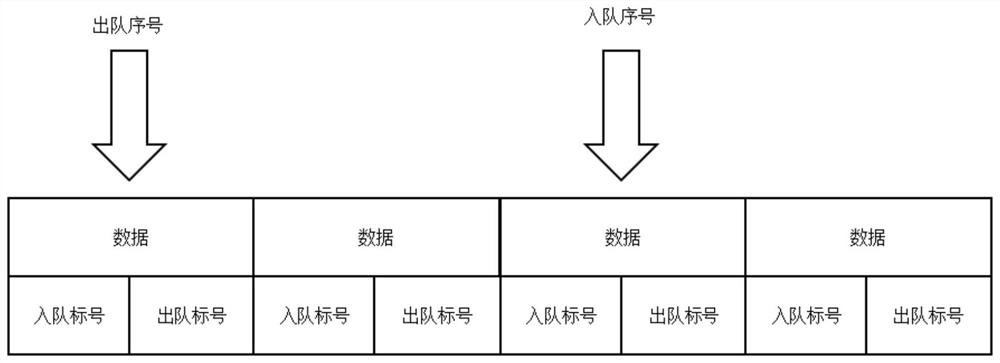
Method, apparatus and system for reading and writing data of asynchronous FIFO memory
InactiveCN101373424ASave memoryMemory space and address reductionData conversionGray codeClock synchronization
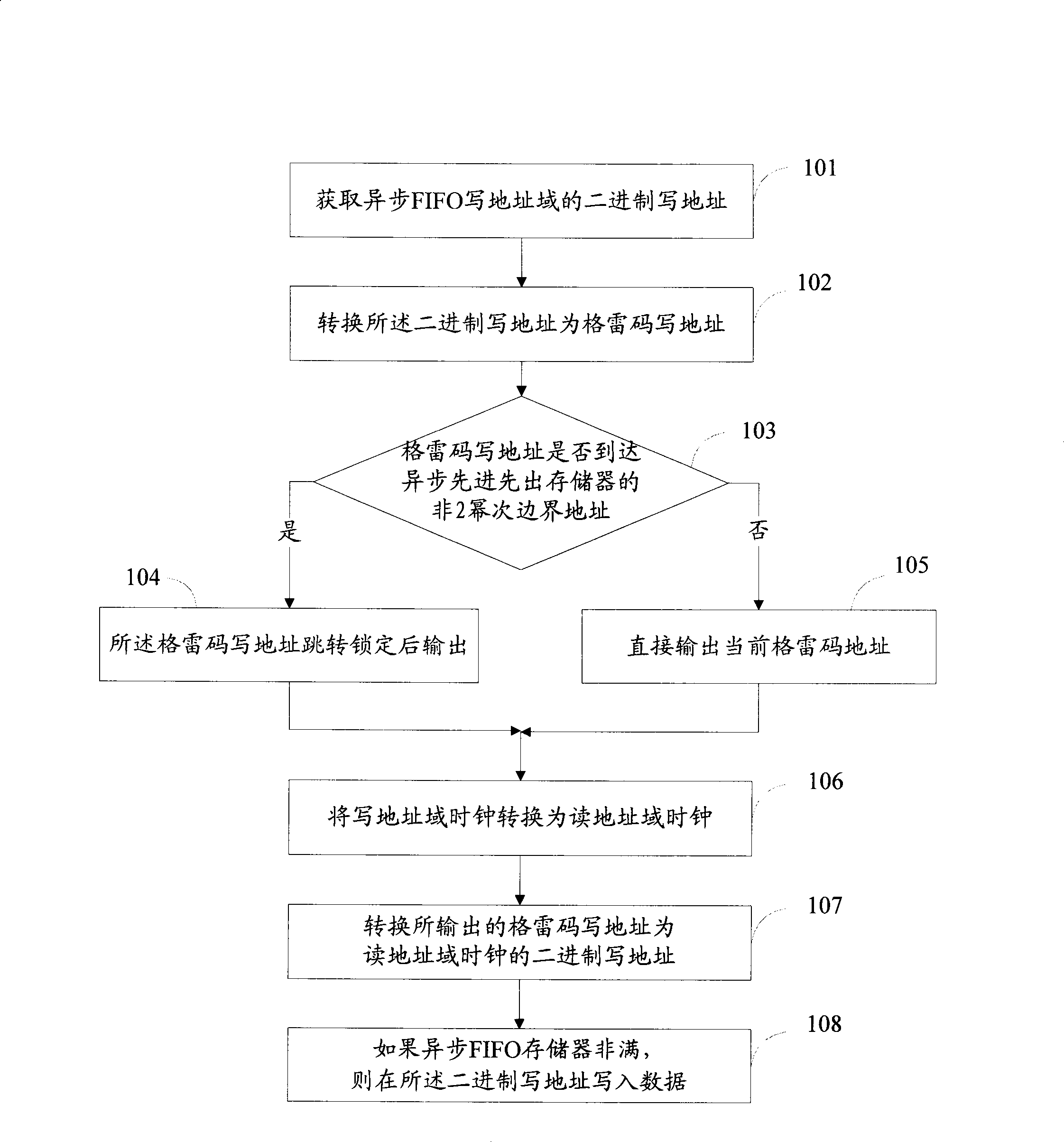
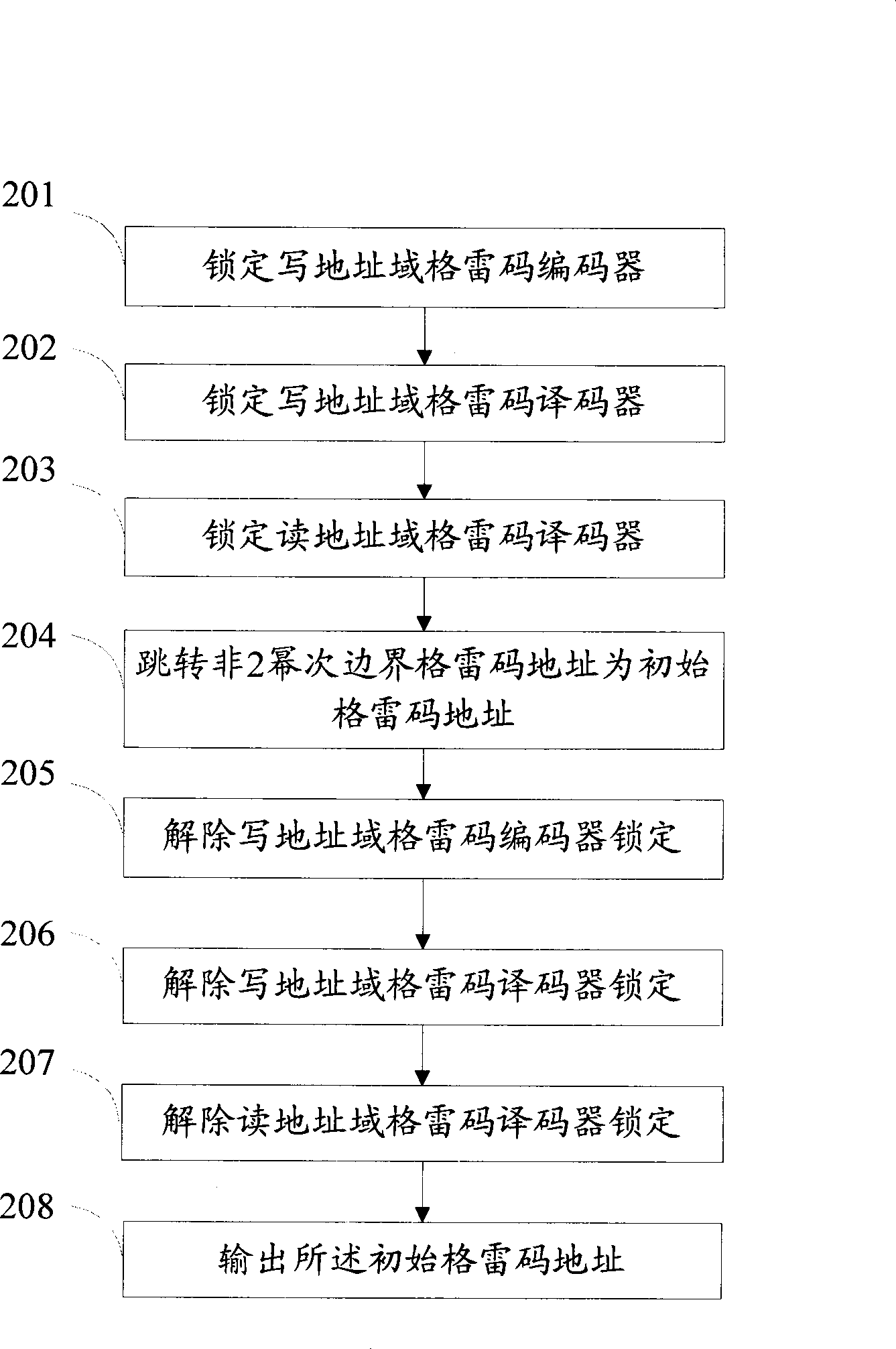
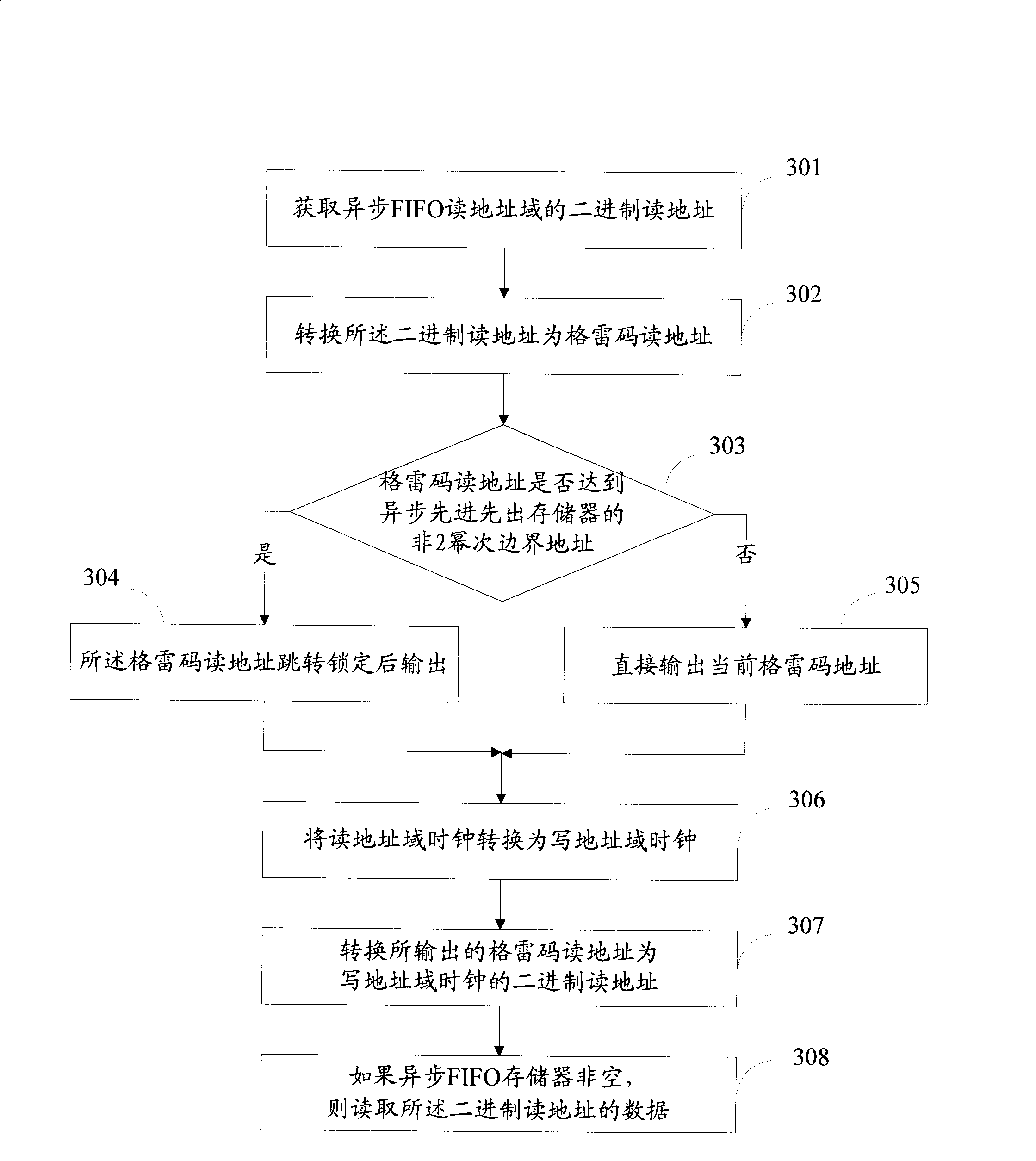
The invention provides a data reading / writing method, a device and a system for an asynchronous first-in first-out memorizer. The asynchronous FIFO system comprises a first-in first-out memorizer, an address writing subsystem and an address reading subsystem, wherein the address writing subsystem is composed of an address writing domain gray-code coder, an address writing domain address jumping and locking unit, an address writing domain trans-clock synchronous register, an address writing domain gray-code decoder and an address writing unit; and the reading address domain subsystem is composed of an address reading domain gray-code coder, an address reading domain address jumping and locking unit, an address reading domain trans-clock synchronous register, an address reading domain gray-code decoder and an address reading unit. When the asynchronous FIFO memorizer address jumps to an initial address from a non-two-power boundary, the gray-code output is locked so as to realize stable jumping of the address, so that the asynchronous FIFO can be realized through the gray-code when the depth of the asynchronous FIFO address is not the power of two, thereby saving memory, hardware and power consumption.
Owner:VIMICRO CORP
Inter-system handover
InactiveUS7983676B2Minimize periodRadio transmission for post communicationWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemComputer terminal
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
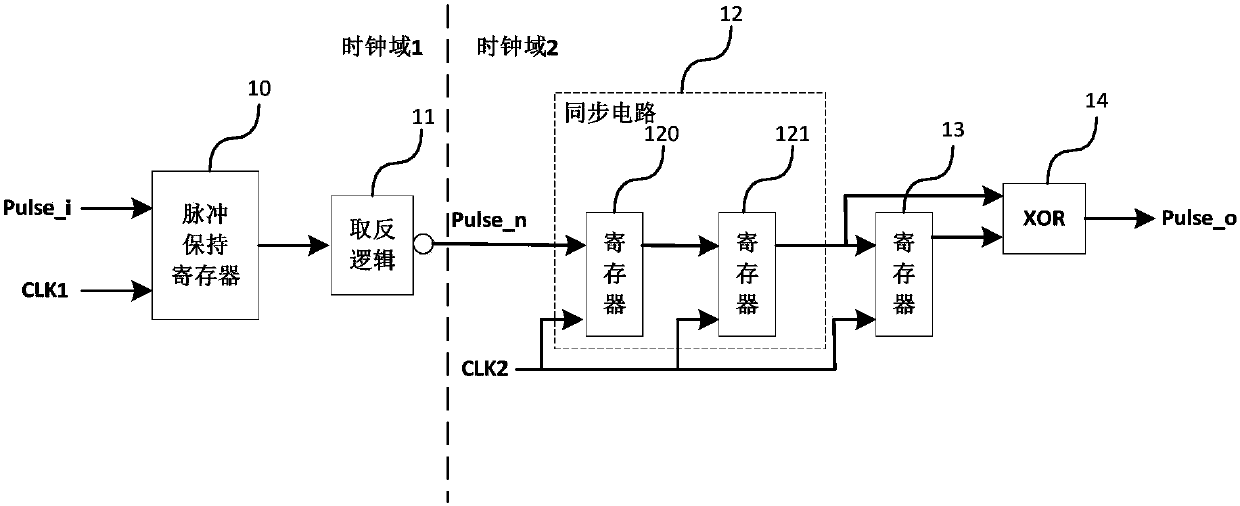
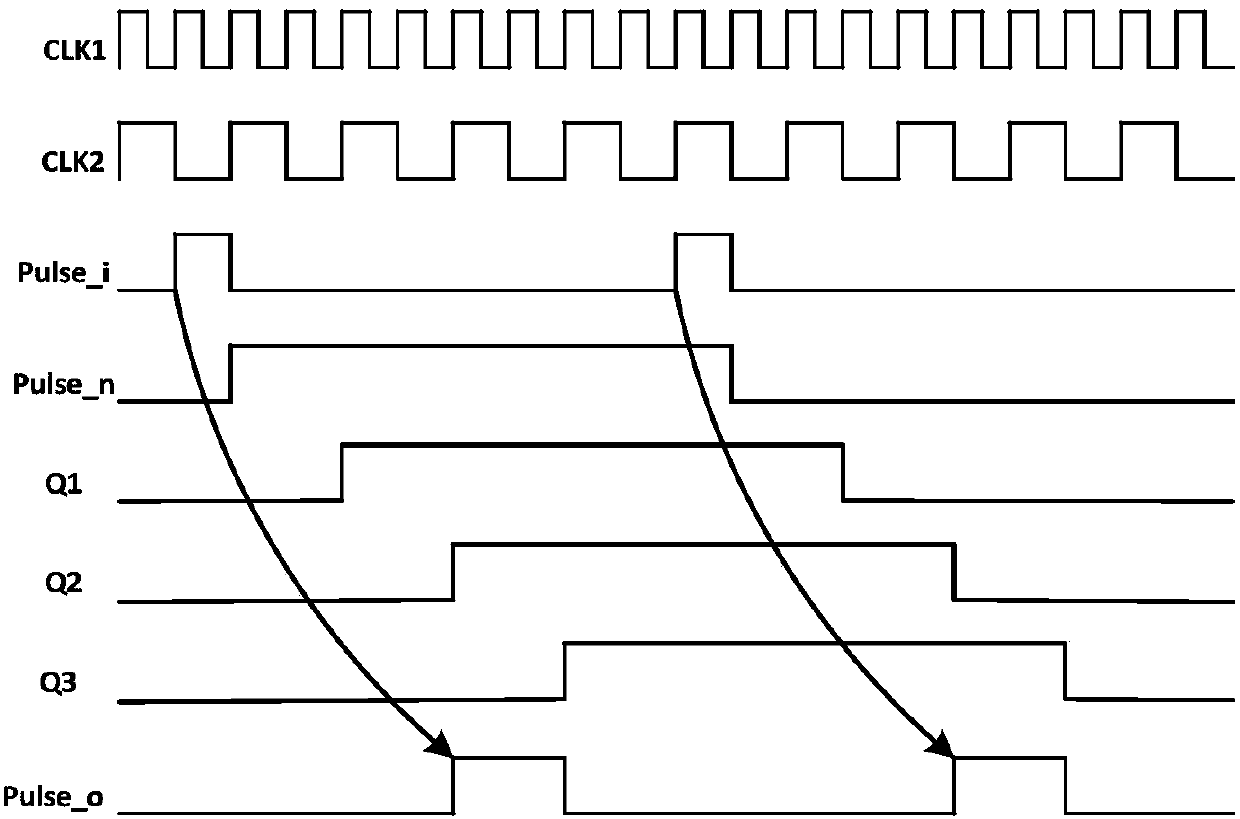
Device and method for processing clock-domain-crossing asynchronous data, chip and operating method of chip
InactiveCN102510281AGood precisionGood synchronizationPrintingLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsLogical operationsData signal
The invention provides a device and a method for processing clock-domain-crossing asynchronous data, a chip and an operating method of the chip. The device comprises a first data sampling unit, a second data sampling unit, a logical operation unit and a clock signal synchronization unit, wherein the first data sampling unit acquires data and obtains a first data signal in a first clock domain; the second data sampling unit acquires the data and obtains a second data signal in a second clock domain; the logical operation unit receives the first data signal and the second data signal and performs logical operation; the clock signal synchronization unit samples a first clock signal in the first clock domain and / or a second clock signal in the second clock domain to obtain a first synchronous clock signal and / or a second synchronous clock signal; and at least one of the first data sampling unit and the second data sampling unit acquires the data under the first synchronous clock signal and / or the second synchronous clock signal. The method comprises the following steps of: synchronizing clock signals in other clock domains by using a reference clock signal; and sampling the data. By the invention, data synchronism can be ensured, and the processing accuracy of the data is improved.
Owner:ZHUHAI TIANWEI TECH DEV CO LTD
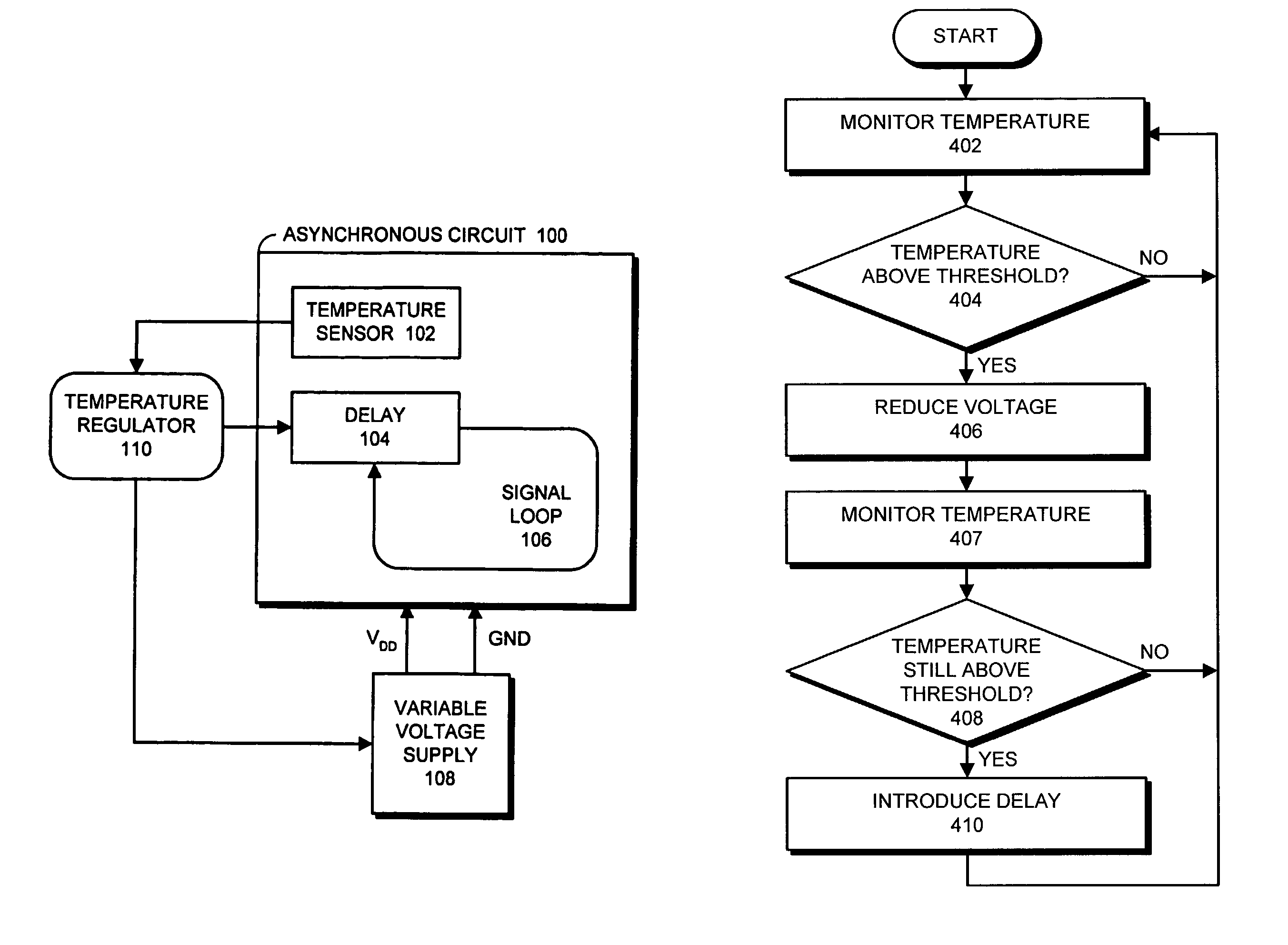
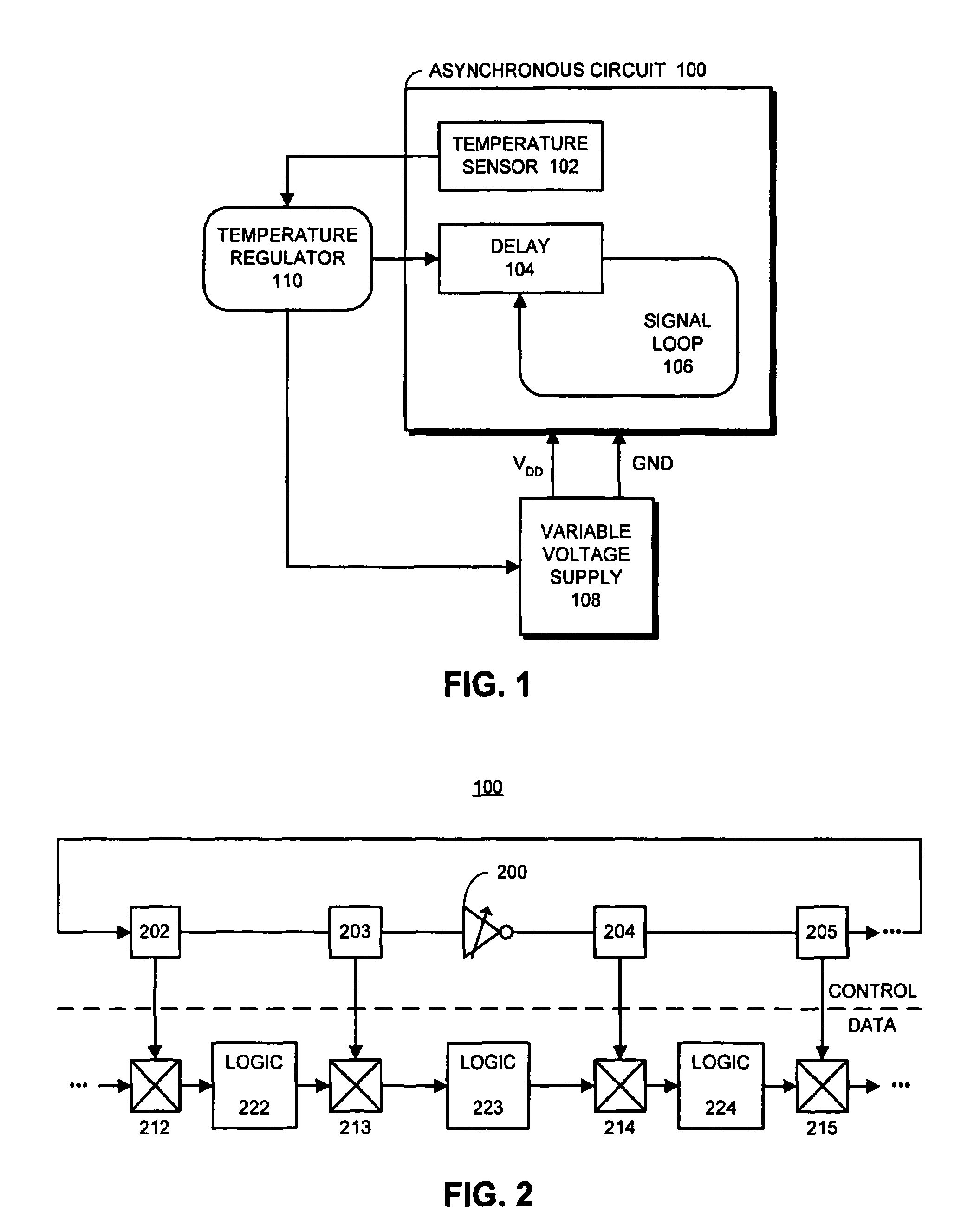
Method and apparatus for regulating heat in an asynchronous system
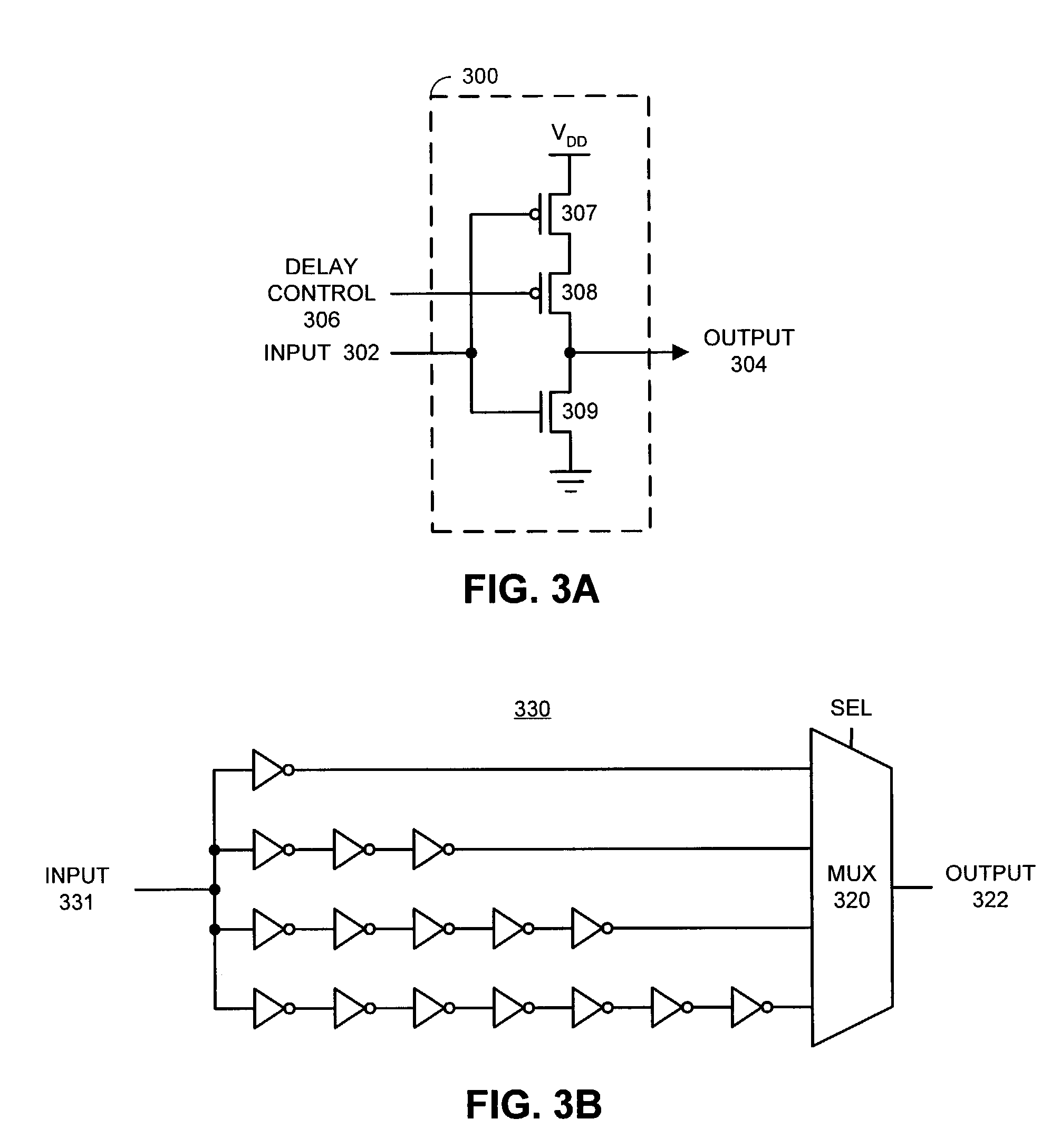
InactiveUS7012459B2Less heatReduce voltageThermometer detailsGenerator stabilizationAsynchronous systemEngineering
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that regulates heat within an asynchronous circuit. During operation, the system monitors a temperature within the asynchronous circuit. If the temperature exceeds a threshold value, the system introduces a delay into the asynchronous circuit that causes signals to propagate more slowly through the asynchronous circuit. This causes circuit elements within the asynchronous circuit to switch less frequently and consequently causes the circuit elements to generate less heat.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP +1
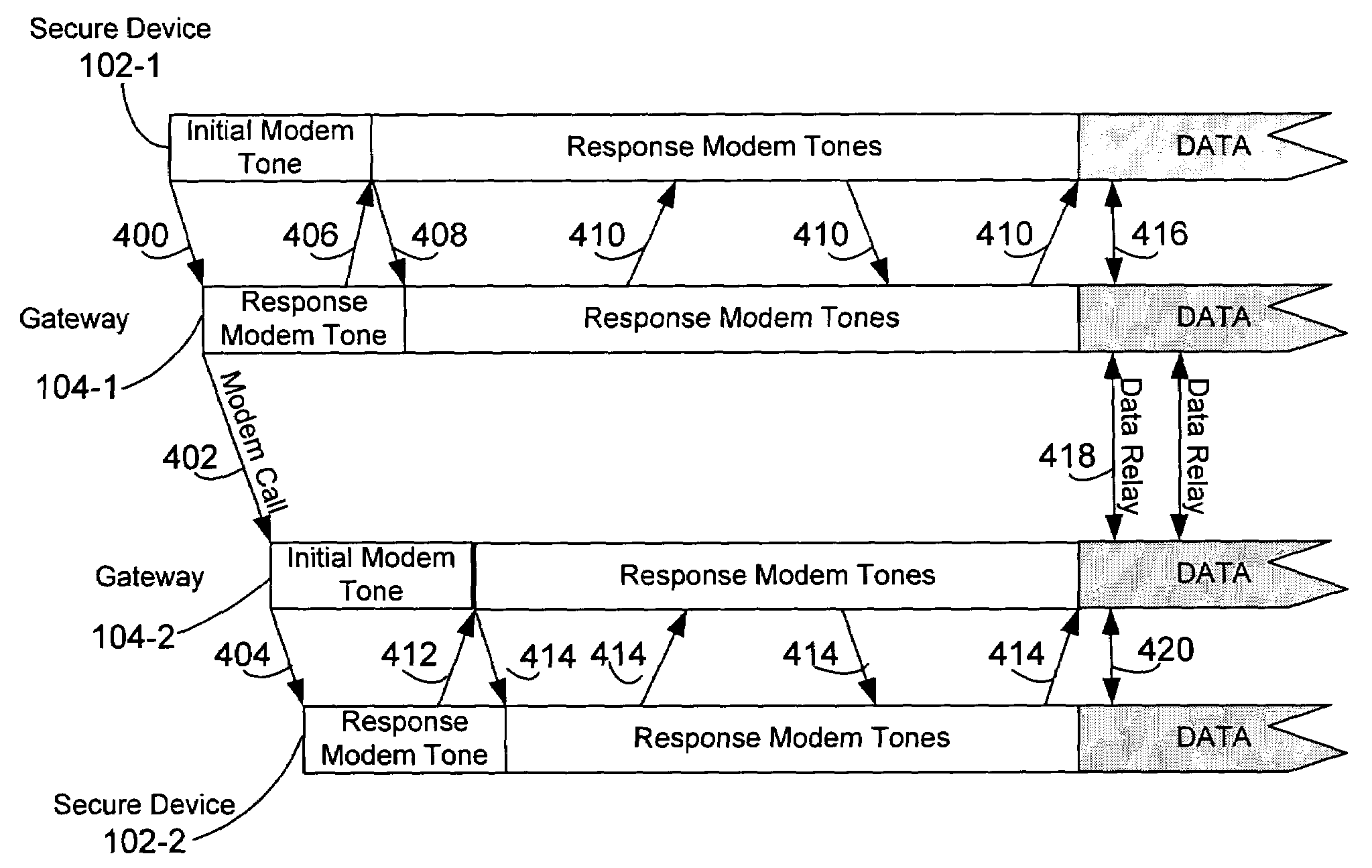
Techniques for asynchronous compensation for secure communications
Techniques for compensating for synchronous data stream transported over an asynchronous system are provided. The techniques include compensating for network jitter for an asynchronous connection over an asynchronous transport, using frame slip control for compensating for a synchronous connection over an asynchronous transport, and dropping filler frames for compensating for a synchronous connection over an asynchronous transport.
Owner:RIBBON COMM OPERATING CO INC
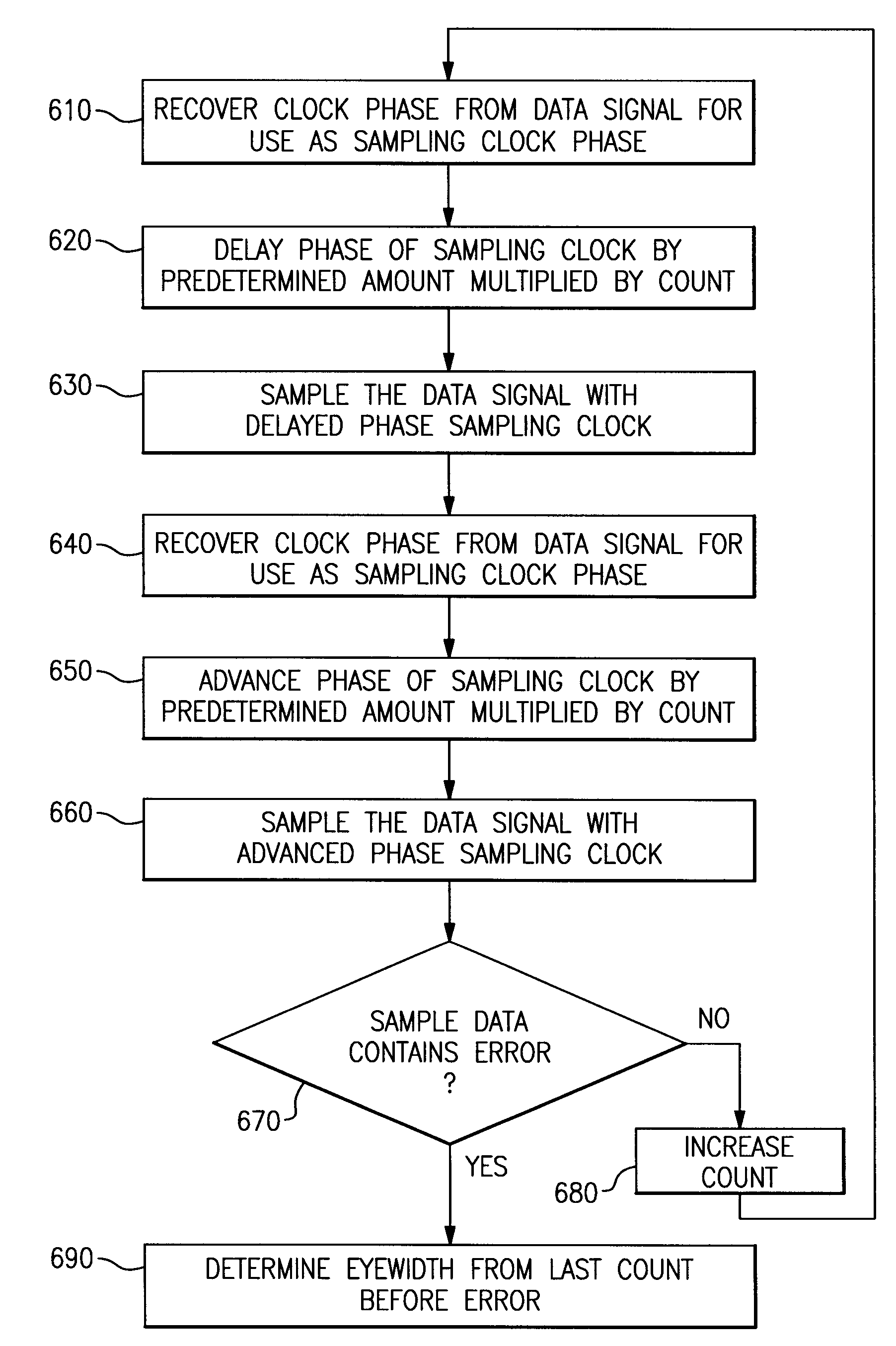
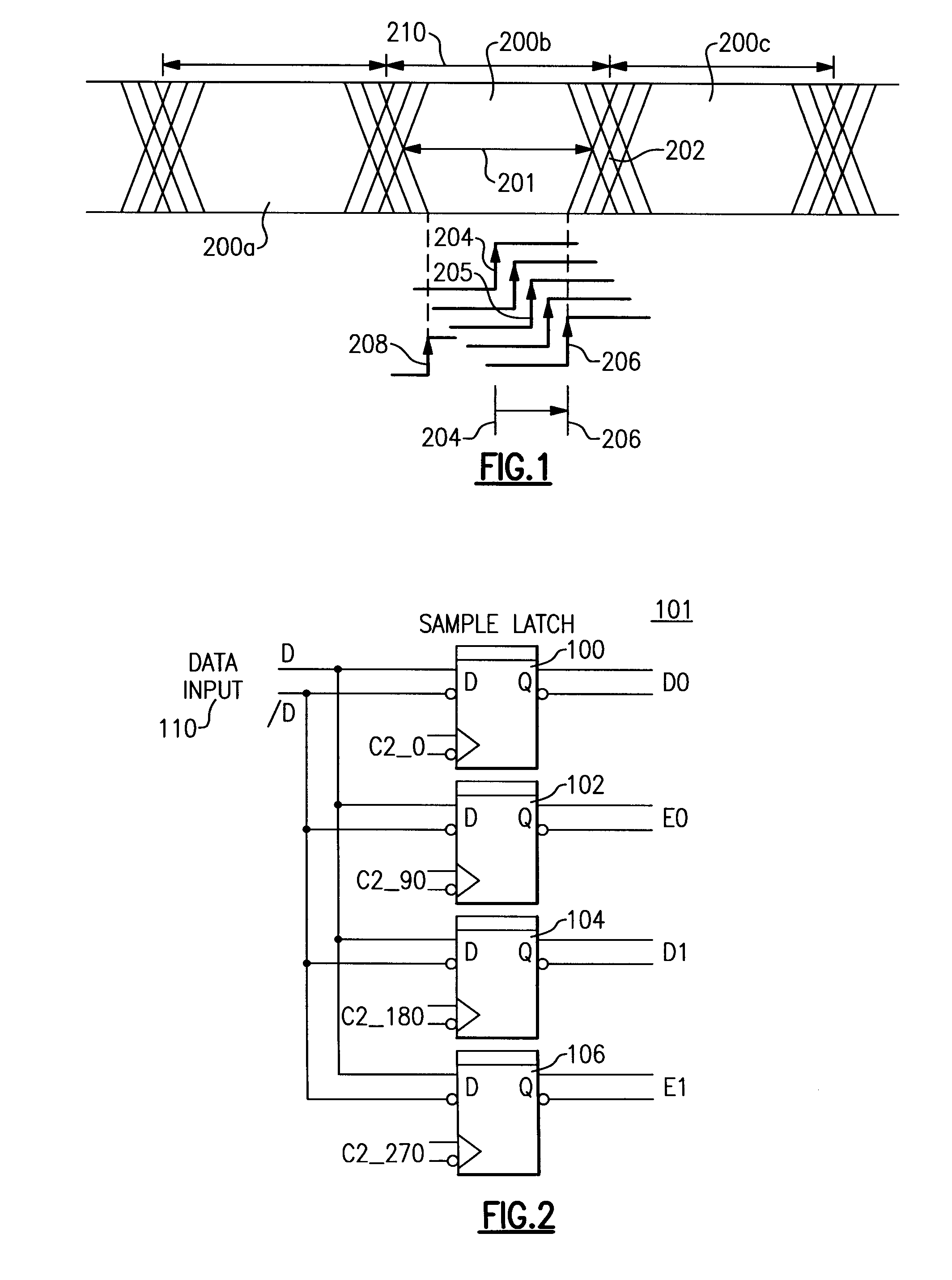
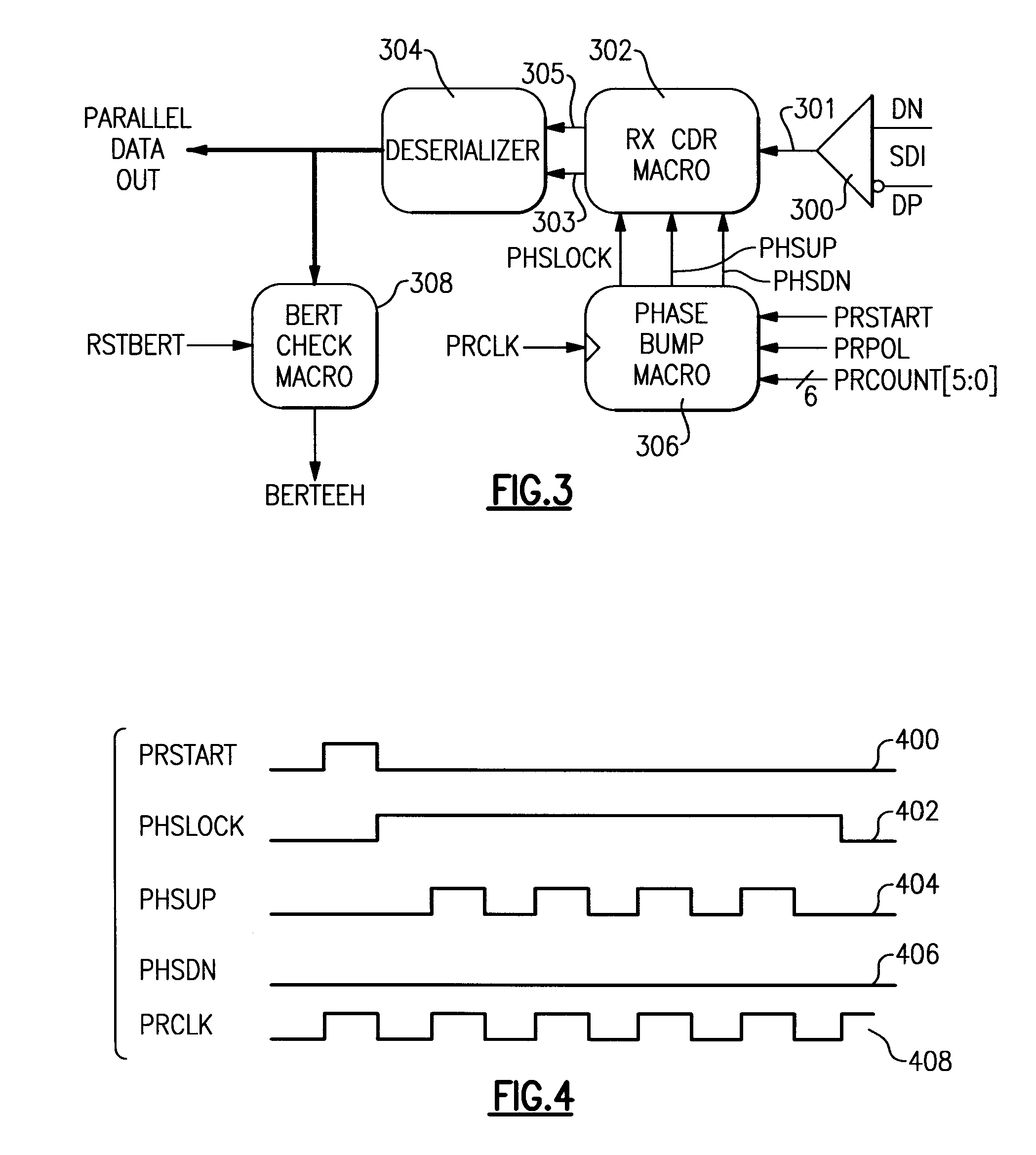
System for measuring an eyewidth of a data signal in an asynchronous system
An eyewidth of a data signal is determined by steps including: (a) recovering a phase of a clock from a data signal as a sampling clock; (b) shifting the phase of the sampling clock away from the first phase by a count multiplied by predetermined phase amount; (c) sampling the data signal with the shifted sampling clock phase to obtain sample data; d) determining whether the sample data contains error; (e) when the sample data does not contain error, recovering the phase of the clock from the data signal again for use as the first phase of the sampling clock, increasing the count value and repeating steps (b) through (e); and f) when the sample data contains error, determining the eyewidth based on the last shifted phase of the sampling clock prior to determining that the sample data contains error.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
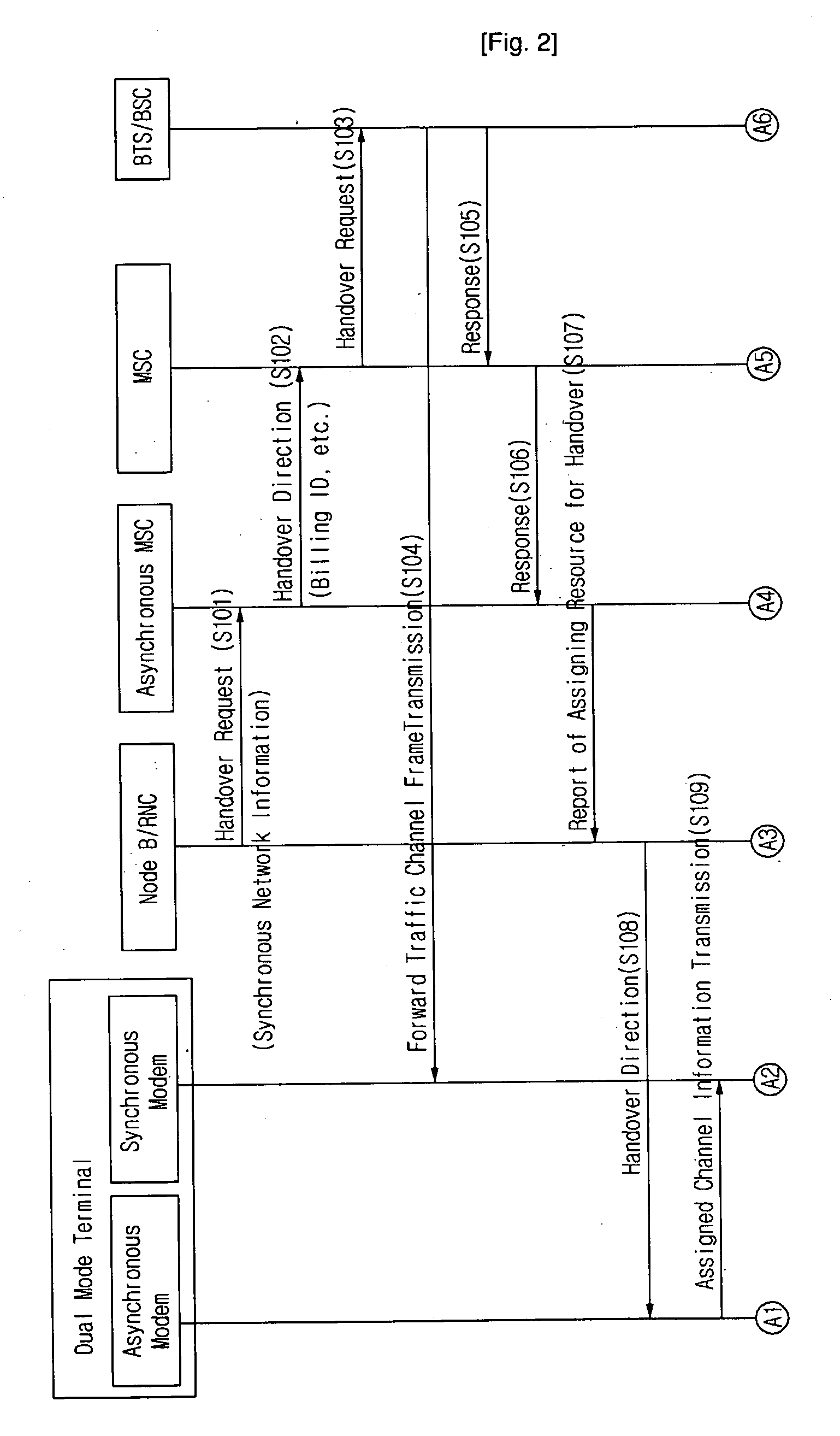
Inter-System Handover
InactiveUS20080242304A1Minimize silent periodMinimize periodRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationCommunications systemDual mode
A method of handover in a wireless communication system in which an asynchronous system and a synchronous system are mixed is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of: the asynchronous system ordering a dual mode mobile terminal to perform a handover from the asynchronous system to the synchronous system; when the handover order is received at the mobile terminal, the mobile terminal transmitting a frame or a preamble through a reverse traffic channel to the synchronous system, reporting to the synchronous system that the handover is completed and initiating a timer of the mobile terminal which is set according to a predetermined time; the mobile terminal switching from an asynchronous vocoder into a synchronous vocoder when the timer expires; and the wireless communication system switching vocoders of asynchronous and synchronous MSCs when the report is received.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
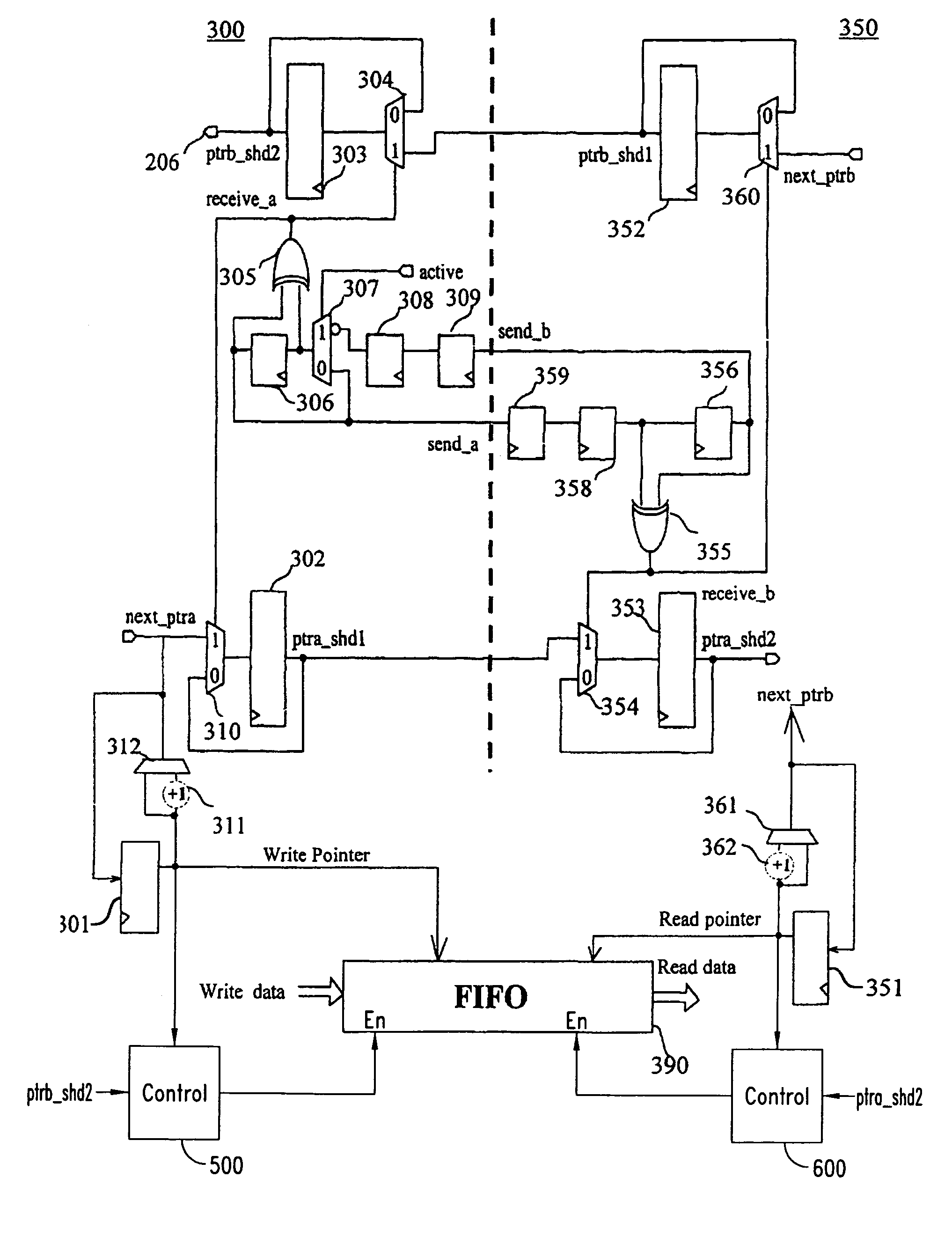
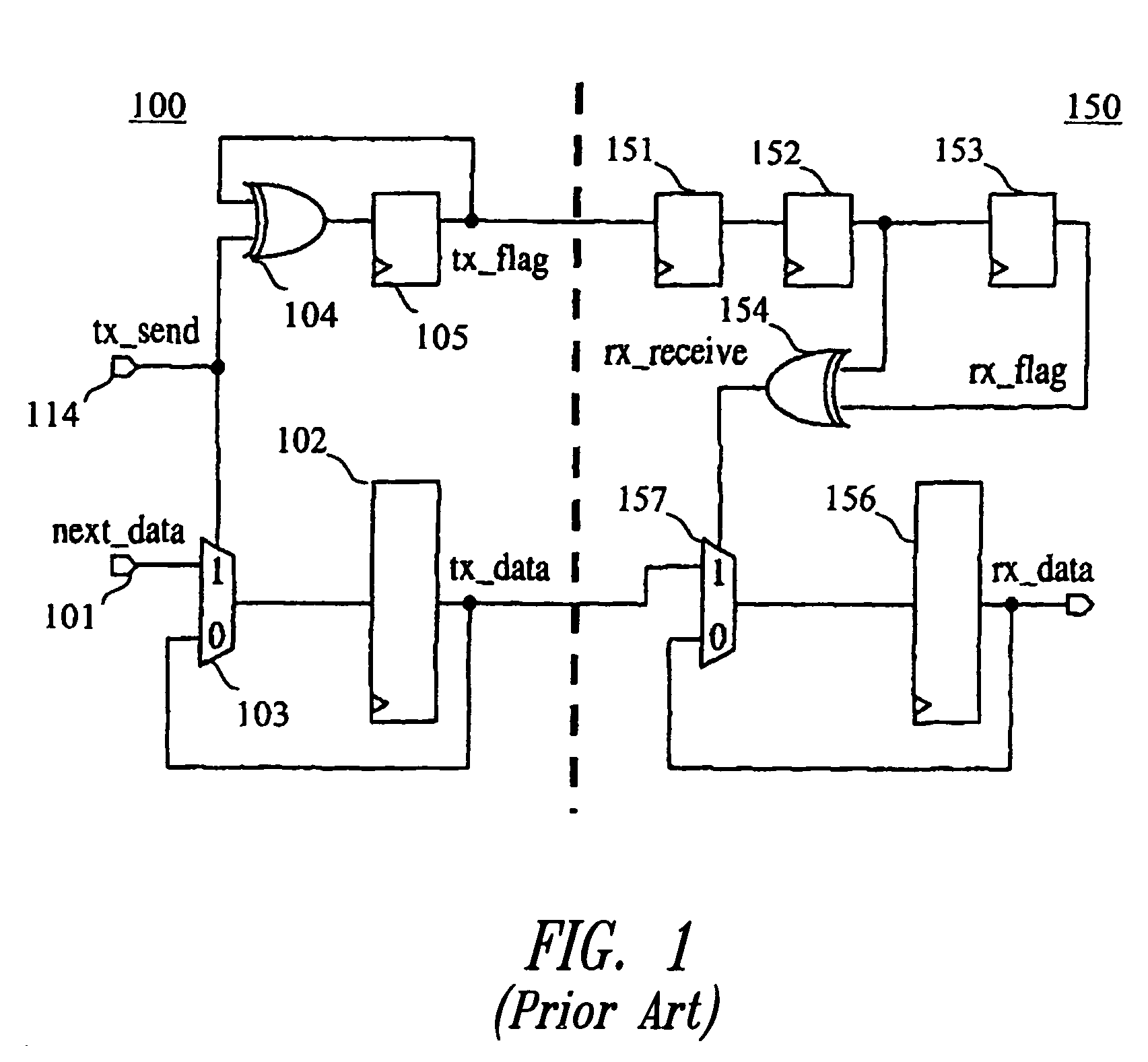
Device for transferring data via write or read pointers between two asynchronous subsystems having a buffer memory and plurality of shadow registers
ActiveUS7185125B2Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationProcessor registerParallel computing
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
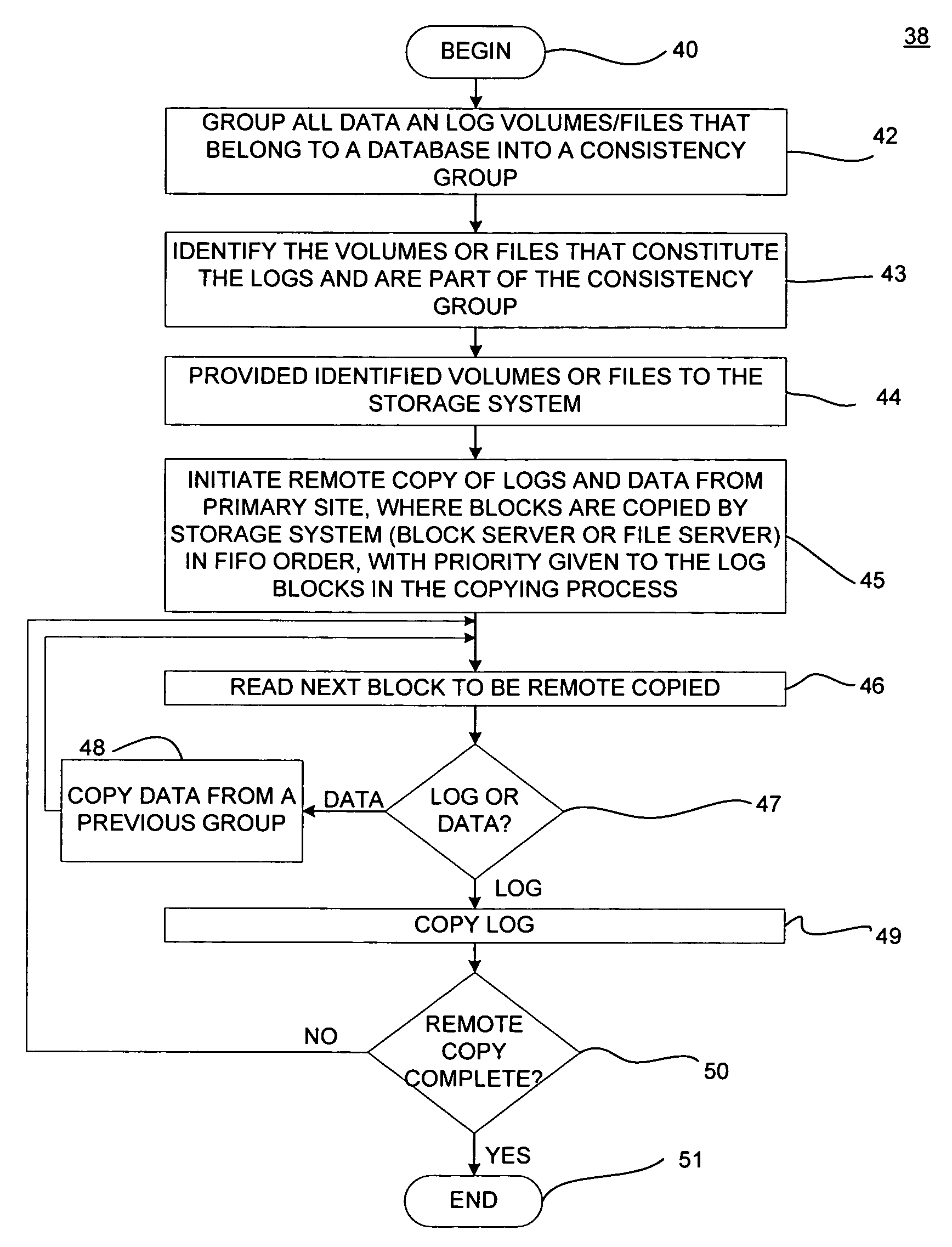
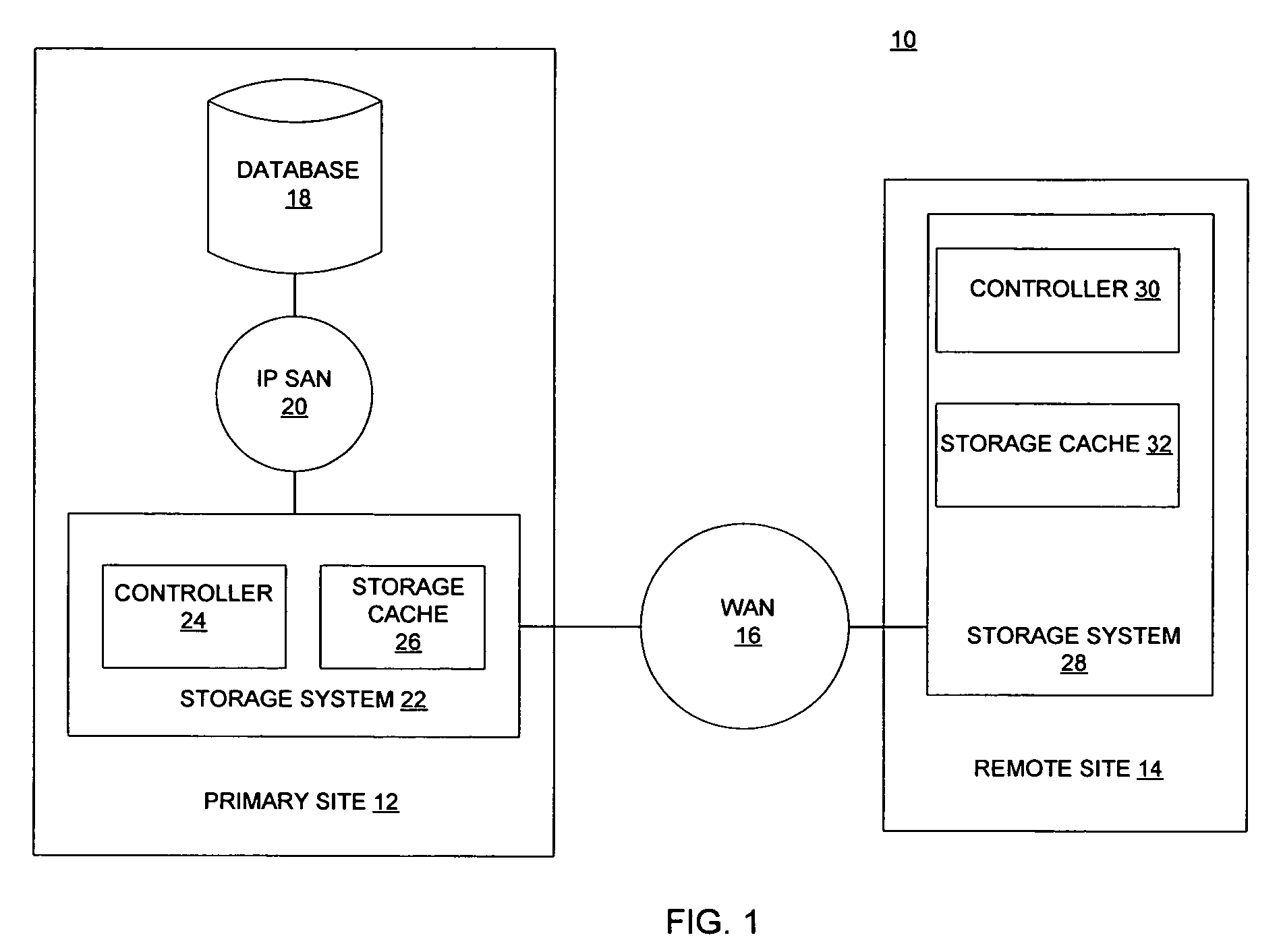
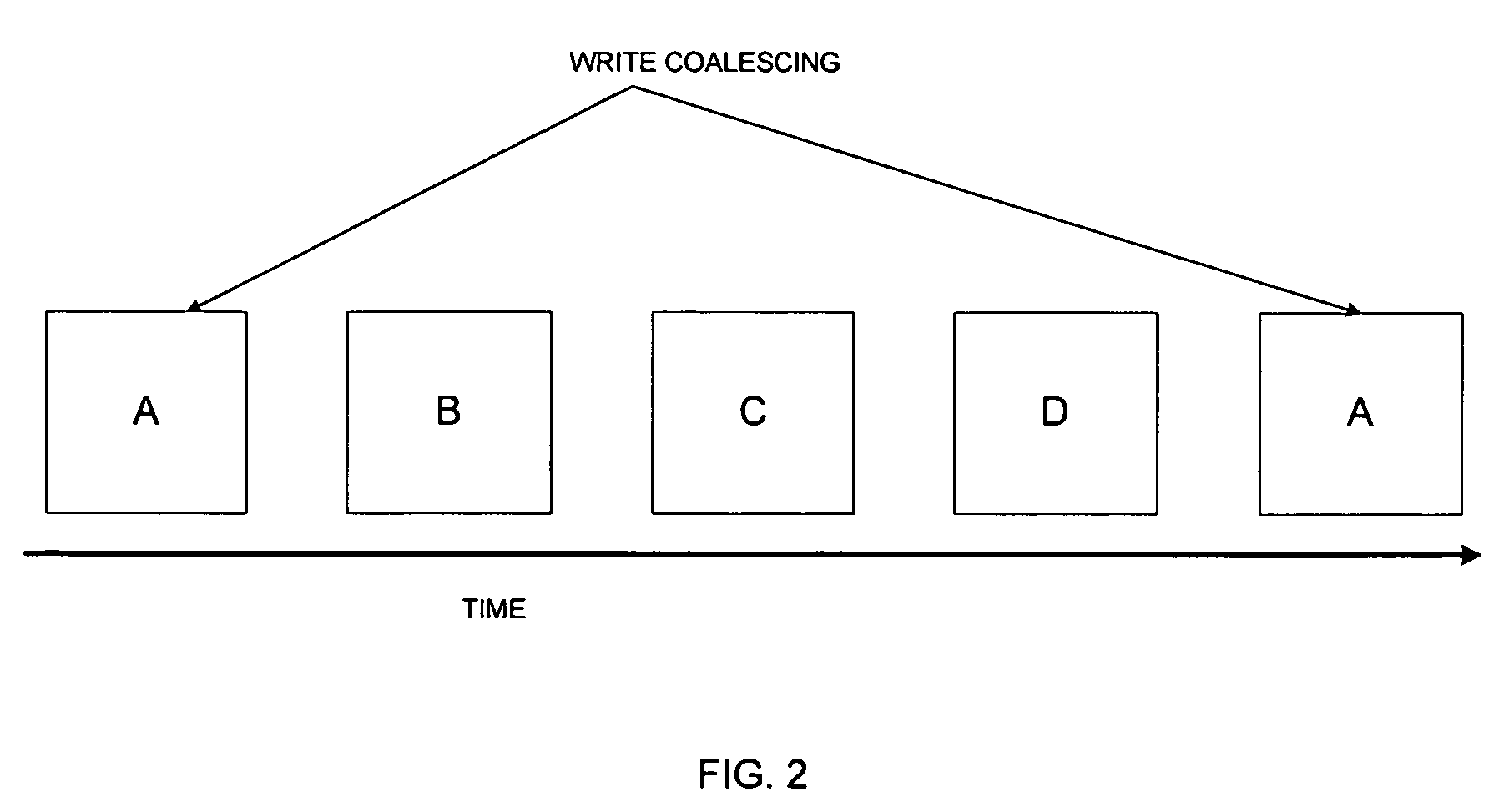
Asynchronous remote mirroring techniques for databases
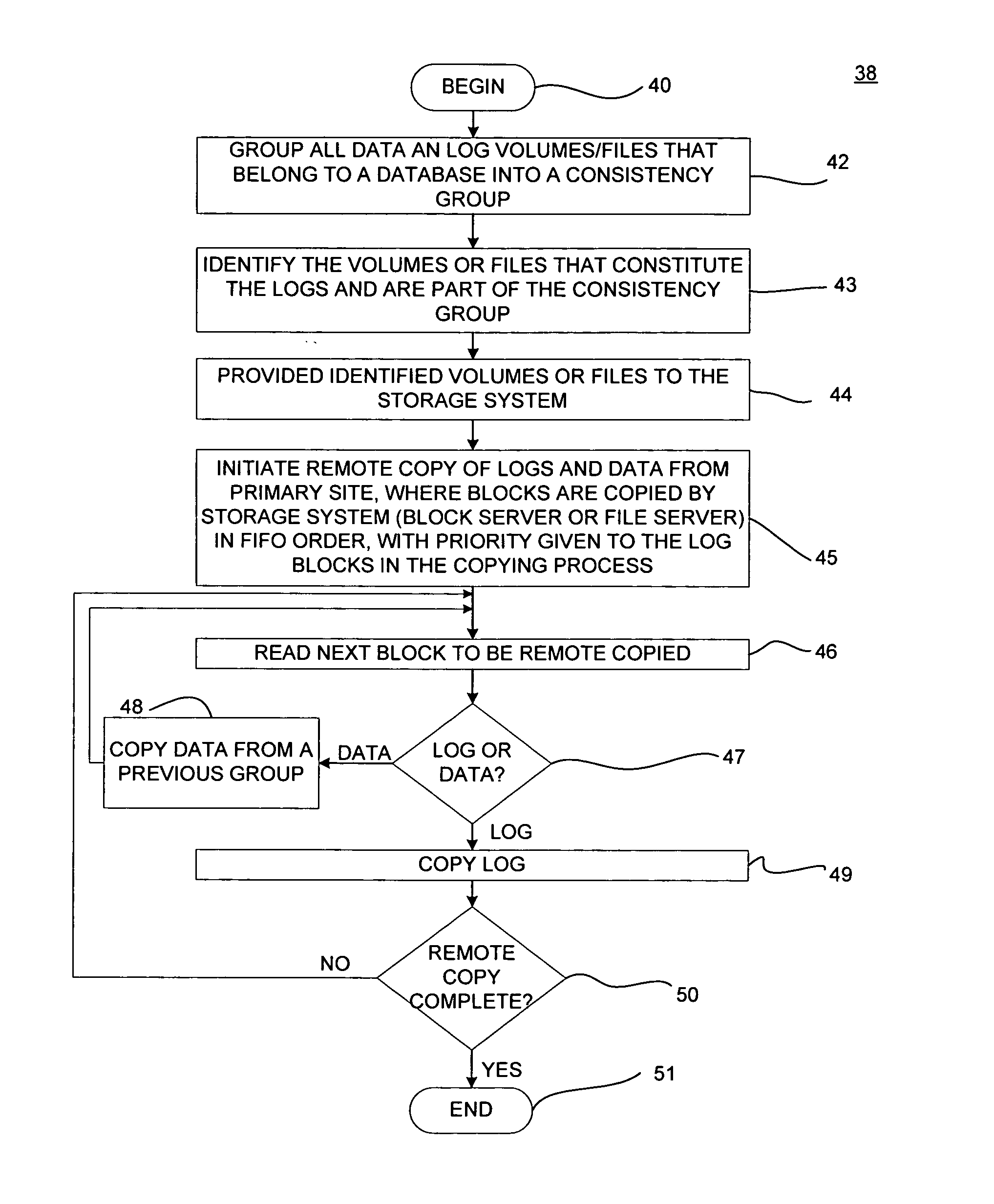
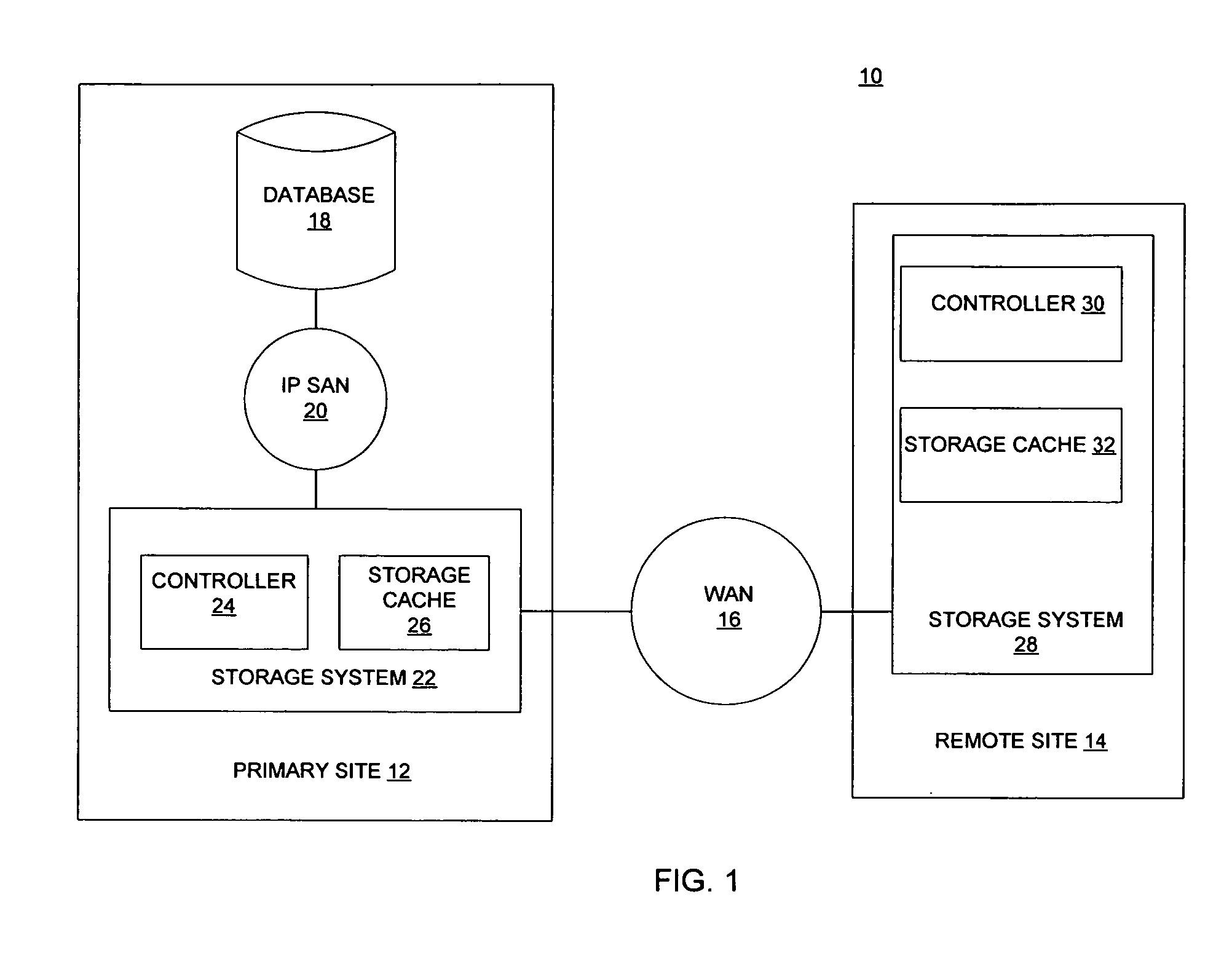
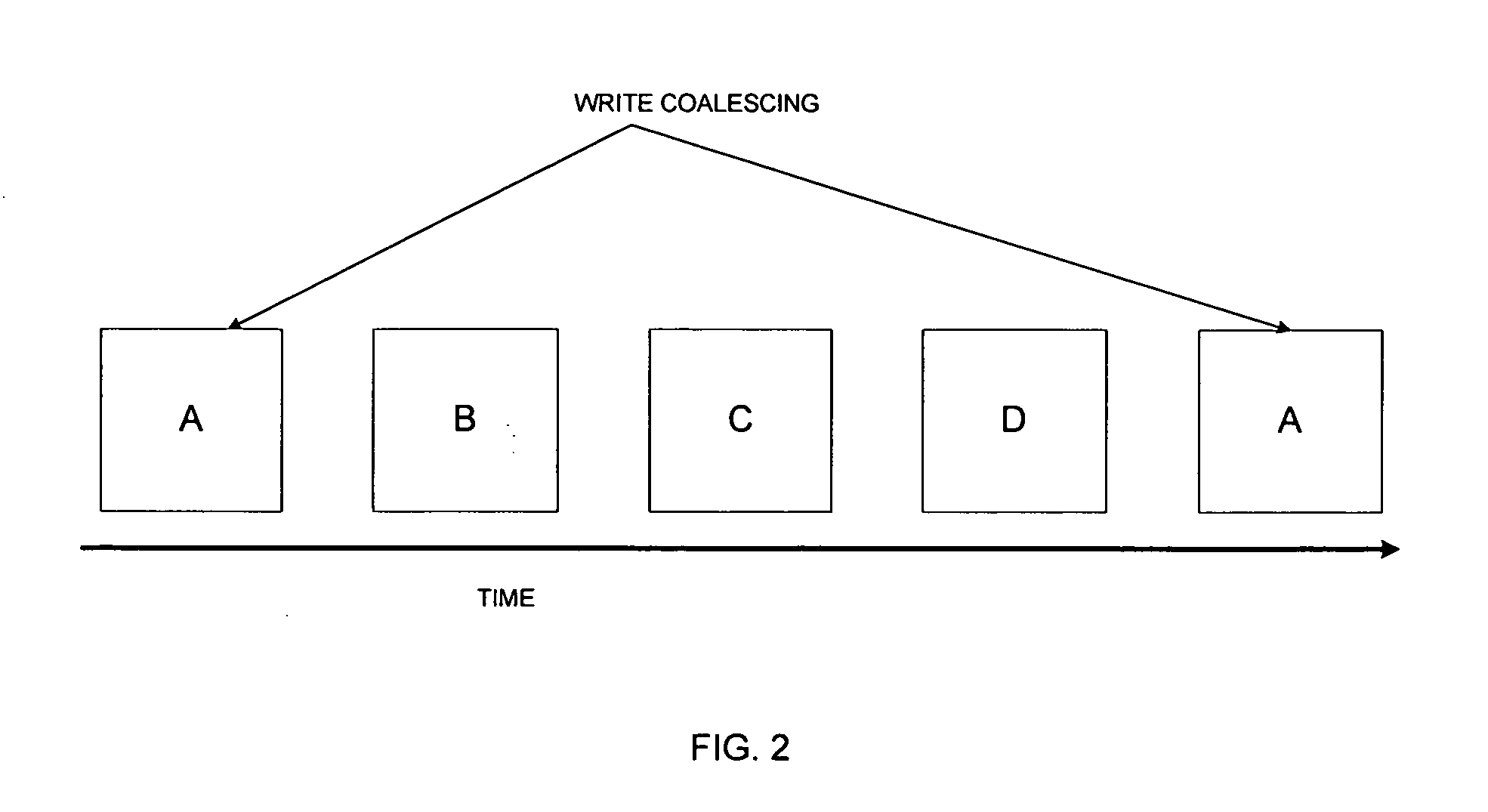
InactiveUS7337194B2Data processing applicationsError detection/correctionPrimary sitesAsynchronous system
There is provided a method and system to asynchronously remotely copy database content changes from a primary site to a remote site utilizing consistency groups. Log information and data are separated. When log information and data are copied to the remote site, the log information is given priority over data. Data is not copied for the current consistency group for which log information is in the process of being copied, until all log information in the current consistency group has been copied. Thus, only data included as part of the consistency groups for which all log information has been copied, is copied to the remote site. Because most logs are written sequentially, copying the log blocks immediately does not result in a larger amount of data being copied. In addition, since the log block has been copied over at the earliest instant possible, the extent of data loss has been reduced to the minimum possible in an asynchronous system.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Asynchronous remote mirroring techniques for databases
InactiveUS20050165851A1Data processing applicationsError detection/correctionPrimary sitesAsynchronous system
There is provided a method and system to asynchronously remotely copy database content changes from a primary site to a remote site utilizing consistency groups. Log information and data are separated. When log information and data are copied to the remote site, the log information is given priority over data. Data is not copied for the current consistency group for which log information is in the process of being copied, until all log information in the current consistency group has been copied. Thus, only data included as part of the consistency groups for which all log information has been copied, is copied to the remote site. Because most logs are written sequentially, copying the log blocks immediately does not result in a larger amount of data being copied. In addition, since the log block has been copied over at the earliest instant possible, the extent of data loss has been reduced to the minimum possible in an asynchronous system.
Owner:IBM CORP
Permanent magnet electric transmission system of urban trolley car
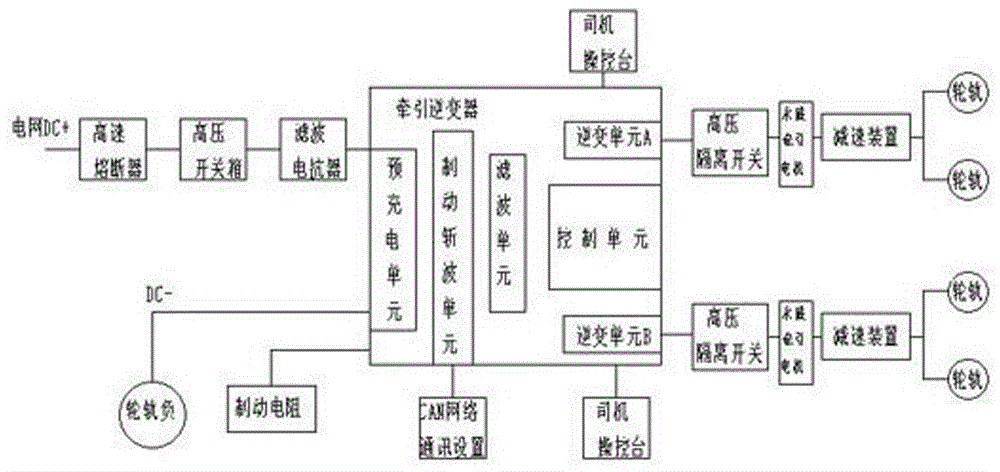
InactiveCN106494238AMeet operational reliabilityProtection securityPropulsion using ac induction motorsElectric locomotivesPre-chargeElectric cars
The invention particularly discloses a permanent magnet electric transmission system of an urban trolley car, and solves the problem that the operating data of the existing alternating current asynchronous system cannot be detected in real time because the electrical network capacity of an electric car direct current power station is limited. The input terminal of a traction invertor is respectively connected with a brake resistor, a CAN network communication device and one terminal of a filter reactor; the other terminal of the filter reactor is connected with a high-speed fuse; the traction invertor comprises a pre-charge unit, a braking chopping unit, a filtering unit, an inverter unit A, an inverter unit B and a control unit; the output terminal of the inverter unit A is connected with the input terminal of one permanent magnet traction motor; the output terminal of the inverter unit B is connected with the input terminal of the other permanent magnet traction motor; the output terminals of the permanent magnet traction motors are respectively connected with the input terminals of corresponding reduction gears; the output terminals of the reduction gears are connected with a wheel track. The permanent magnet electric transmission system improves the energy saving rate by 18 to 44 percent, is long in the service life of a winding, and improves the operability and the safety of the system.
Owner:CRRC YONGJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
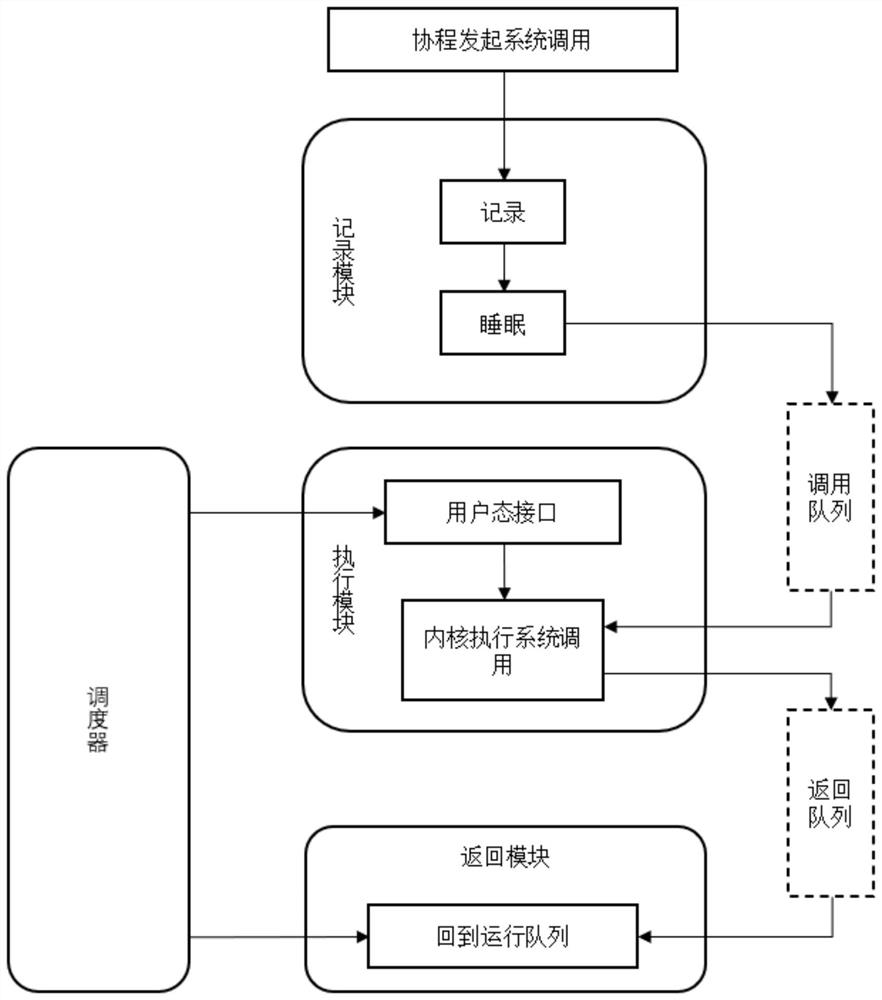
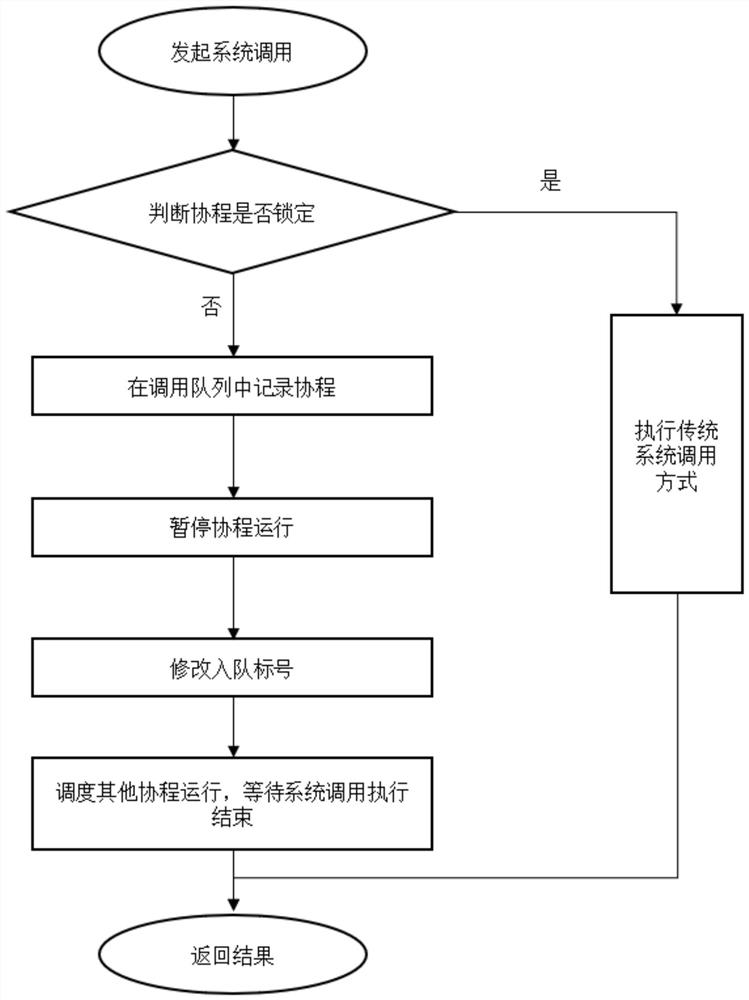
Coroutine-based asynchronous system calling system
PendingCN111767159AImprove performanceImprove kernel performanceInterprogram communicationEngineeringAsynchronous system
The invention discloses a coroutine-based asynchronous system calling system, which comprises a recording module, an execution module and a return module; a calling queue is arranged between the recording module and the execution module, and a return queue is arranged between the execution module and the return module; the recording module is used for receiving a system call request initiated by acoroutine, recording system call parameters and coroutine information contained in the system call request, storing the system call parameters and the coroutine information into a call alignment, pausing the coroutine initiating system call, and then judging whether to execute system call or not; the execution module is used for executing the system call transmitted by the call queue by adoptingan auxiliary thread, and storing a system call return value and cothread information into the return queue after the system call is executed; and the return module is used for reading the system callreturn value from the return queue and adding the coroutine to the running queue according to the coroutine information so as to recover coroutine running. The asynchronous execution problem of systemcalling based on the coroutine is solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
System and method for communicating between a plurality of asynchronous systems
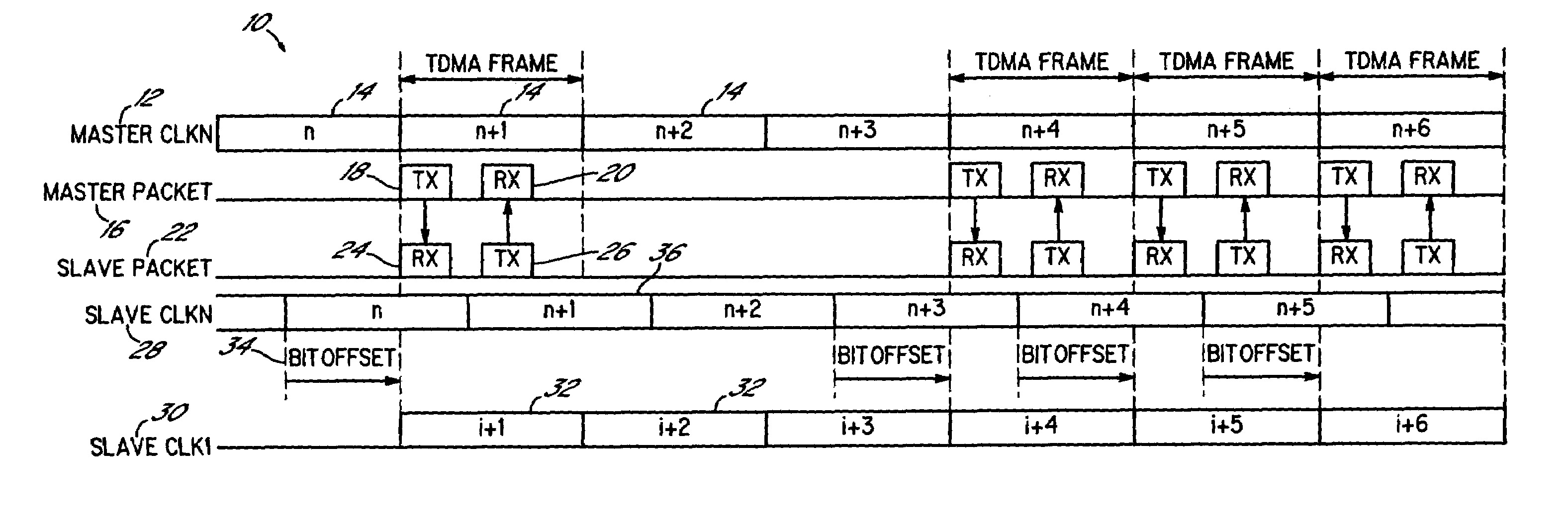
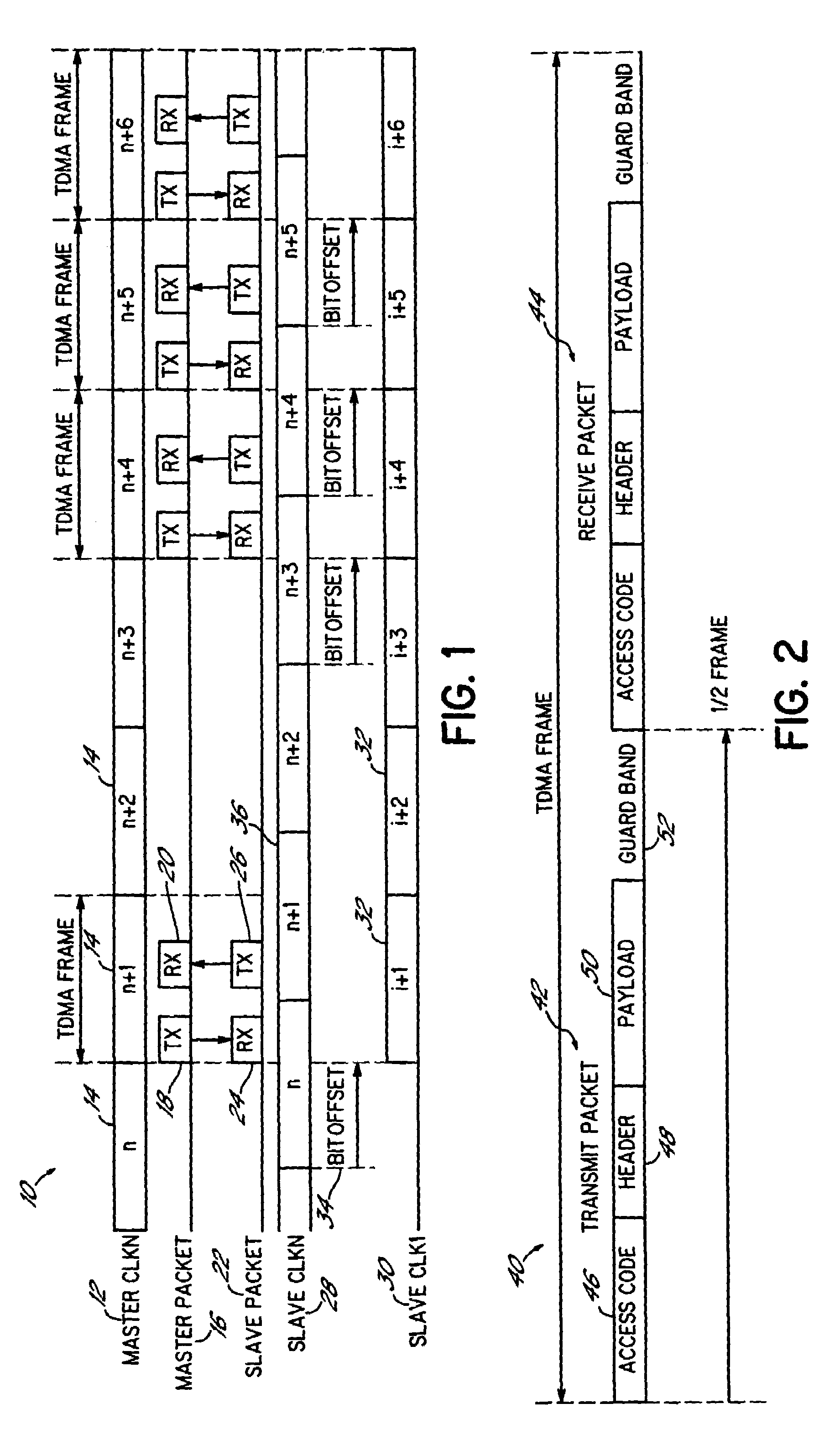
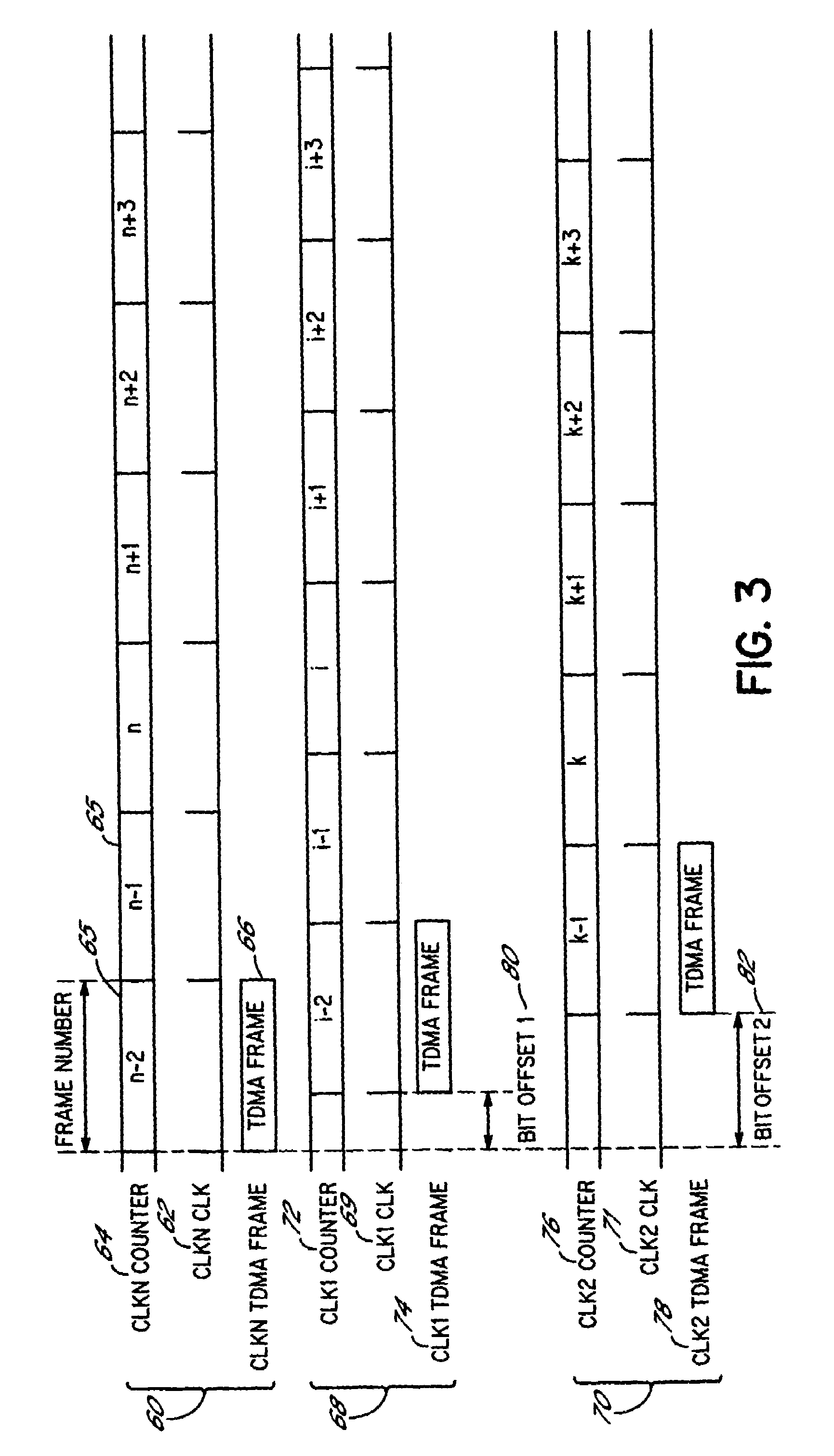
ActiveUS6975610B1Reduce hardware complexityReduce power consumptionTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationAsynchronous systemEmbedded system
A method and apparatus for communicating between a plurality of asynchronous transmitting and receiving systems using digital streams arranged in multiple access frames comprises a master system, which cycles a counter using a clock reference to generate a master count, and uses the master count to establish a master frame count. A slave system cycles a counter using a clock reference to generate a main count, and uses the main count to establish a main frame count. From a difference between the master frame count and the main frame count of the slave system, a frame count offset value is determined. A slave frame count for the slave system is then established by adding the offset value to the main frame count, and thereby aligning the slave frame count of the slave system with the master frame count and incrementing the slave frame count when the main count is incremented.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Method and apparatus to determine time and distance between transceivers using phase measurements
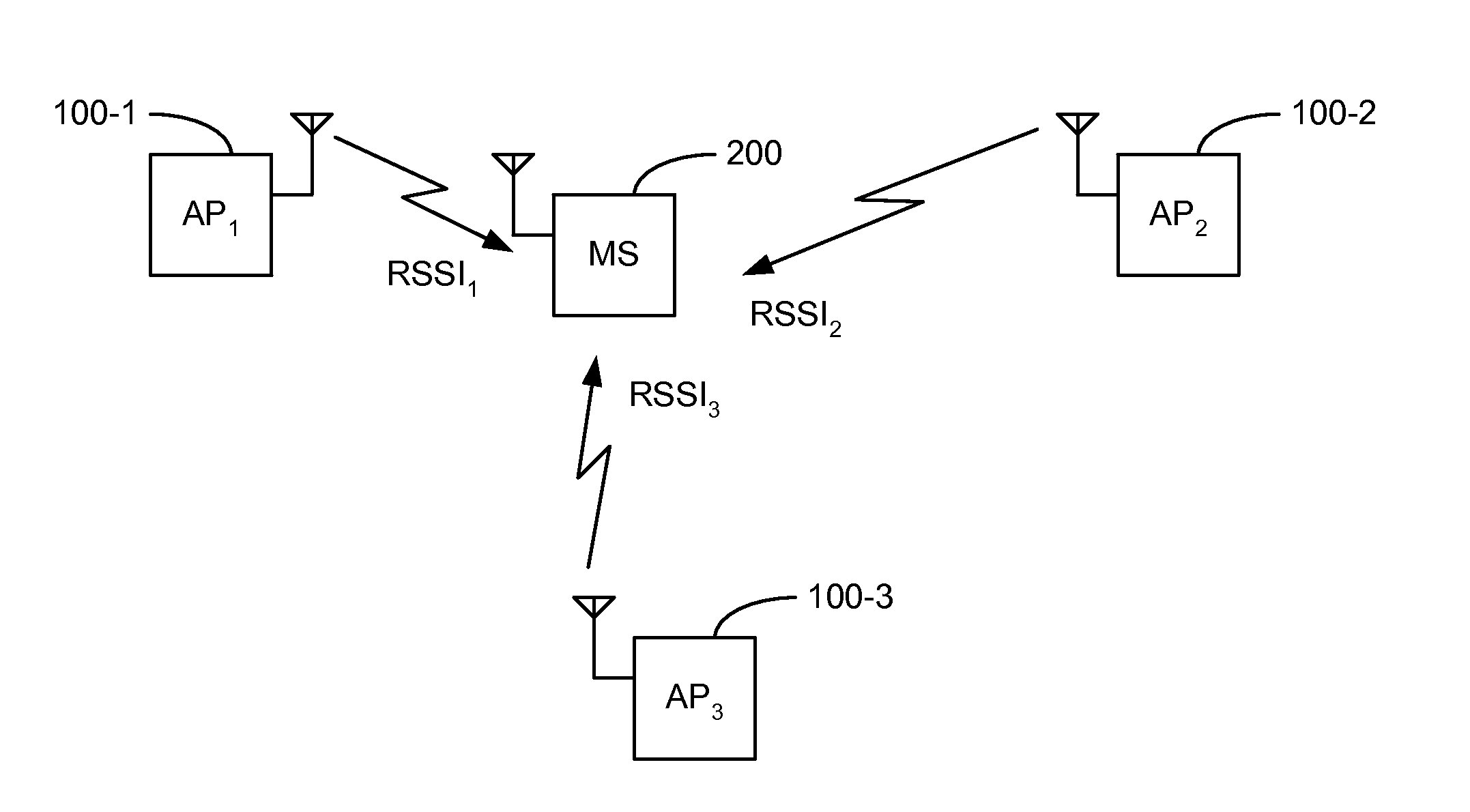
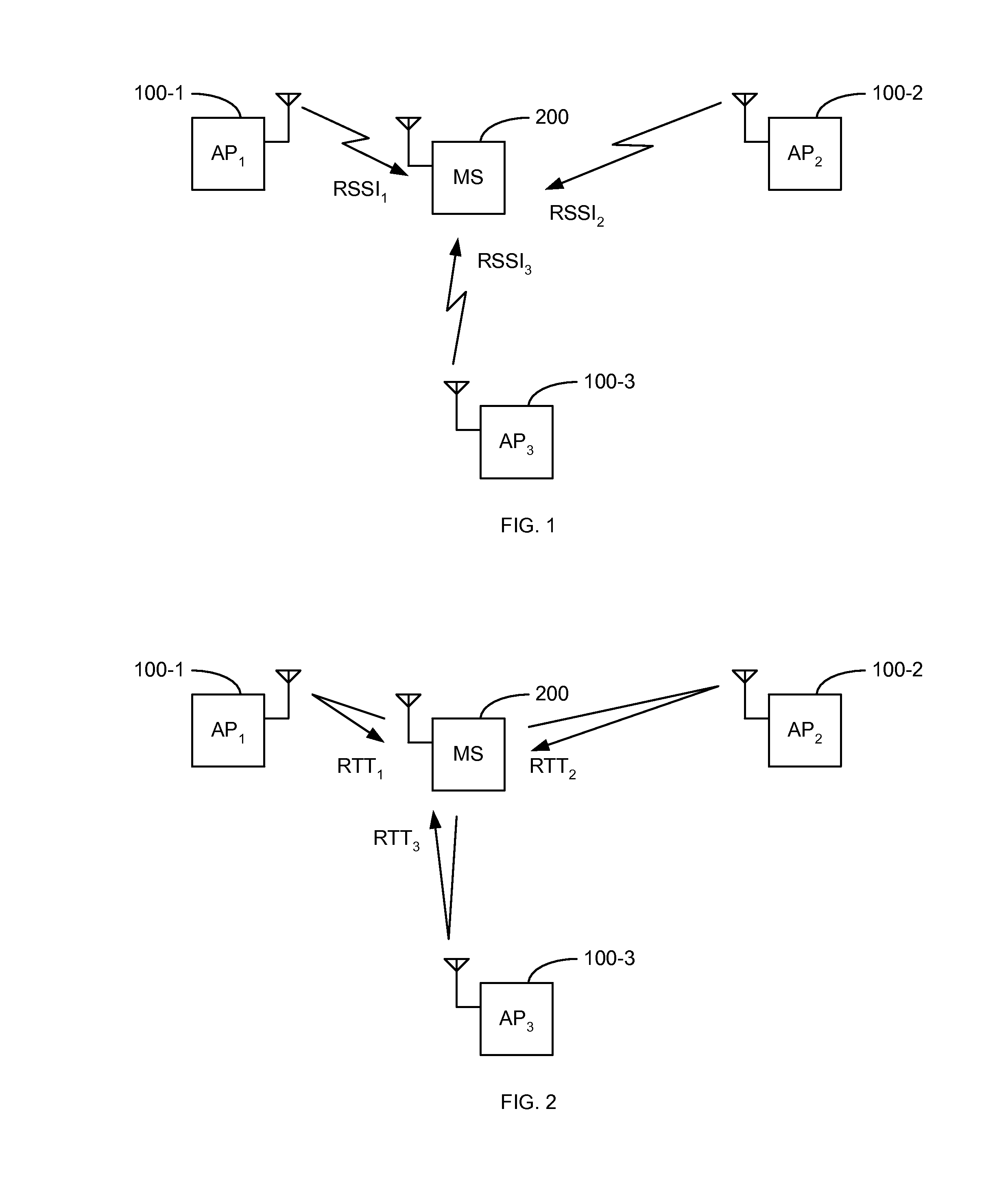
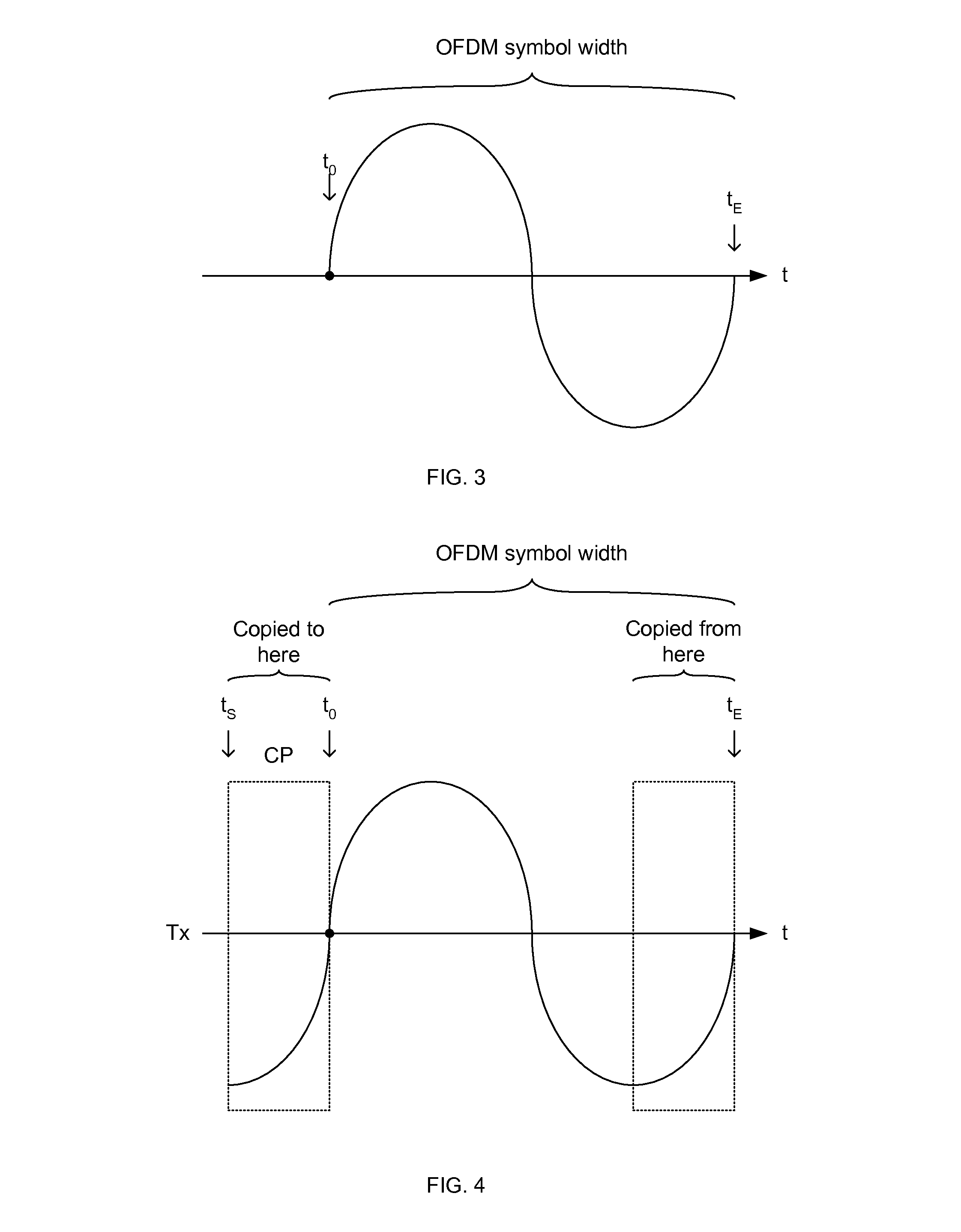
InactiveUS20140233624A1Synchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsTransceiverPropagation time
Systems, apparatuses and methods are disclosed for estimating a signal travel time, and thus distance between transceivers, in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system. The signal travel time is measured between a transmit time (tT) and a receive window time (twindow) adjusted by the phase delay (TΦ). The phase delay (TΦ) is determined as a difference between a receive time (tR) and the receive window time (twindow). The receive time (tR) may be determined based on either an amplitude of the received signal at the receive window time (twindow) or when the received signal crosses a positive-negative axis. In synchronous systems, either a one-way time (OWT) or round-trip time (RTT) may be used for estimation. In asynchronous systems, an RTT is used for estimation.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
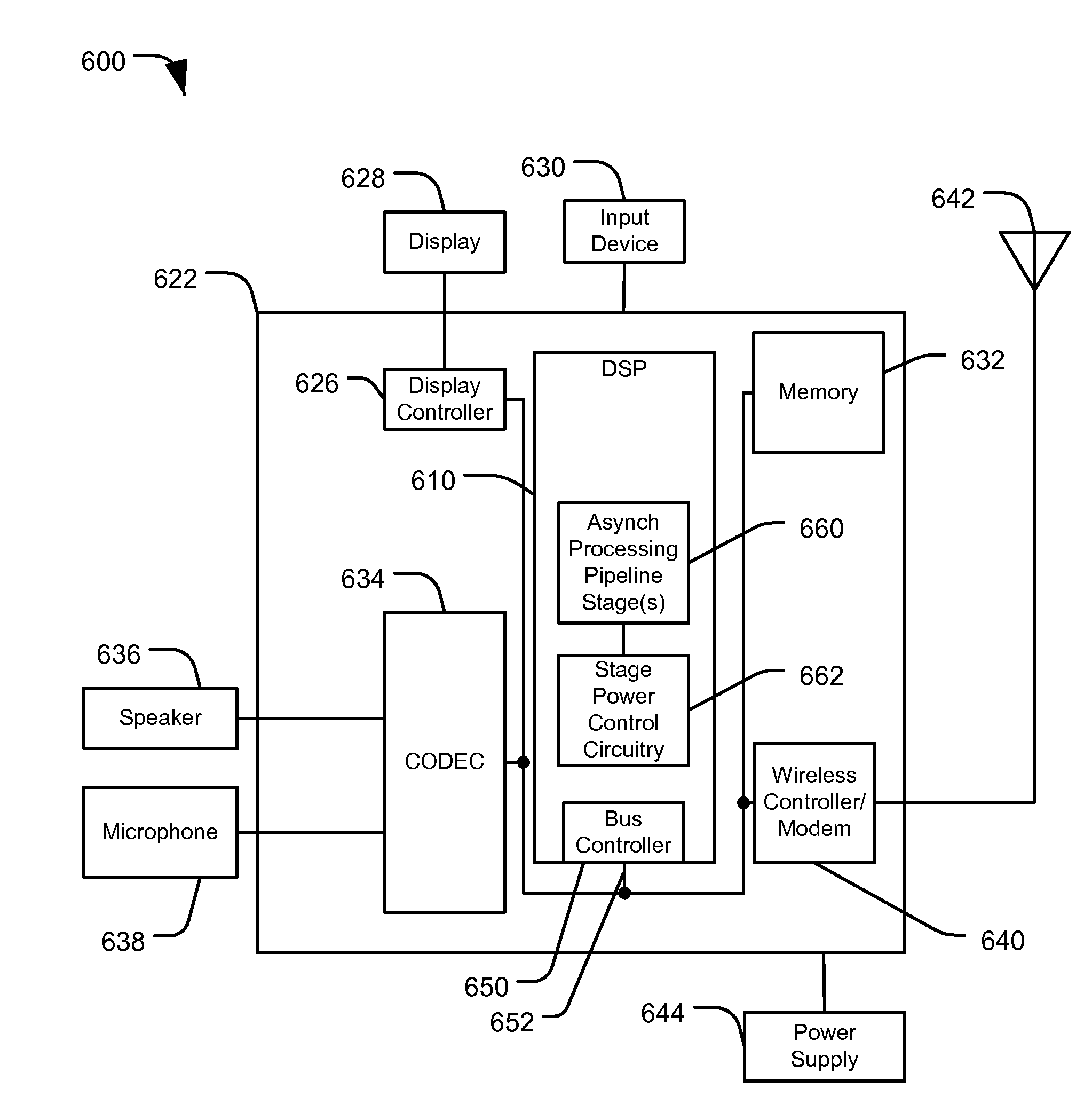
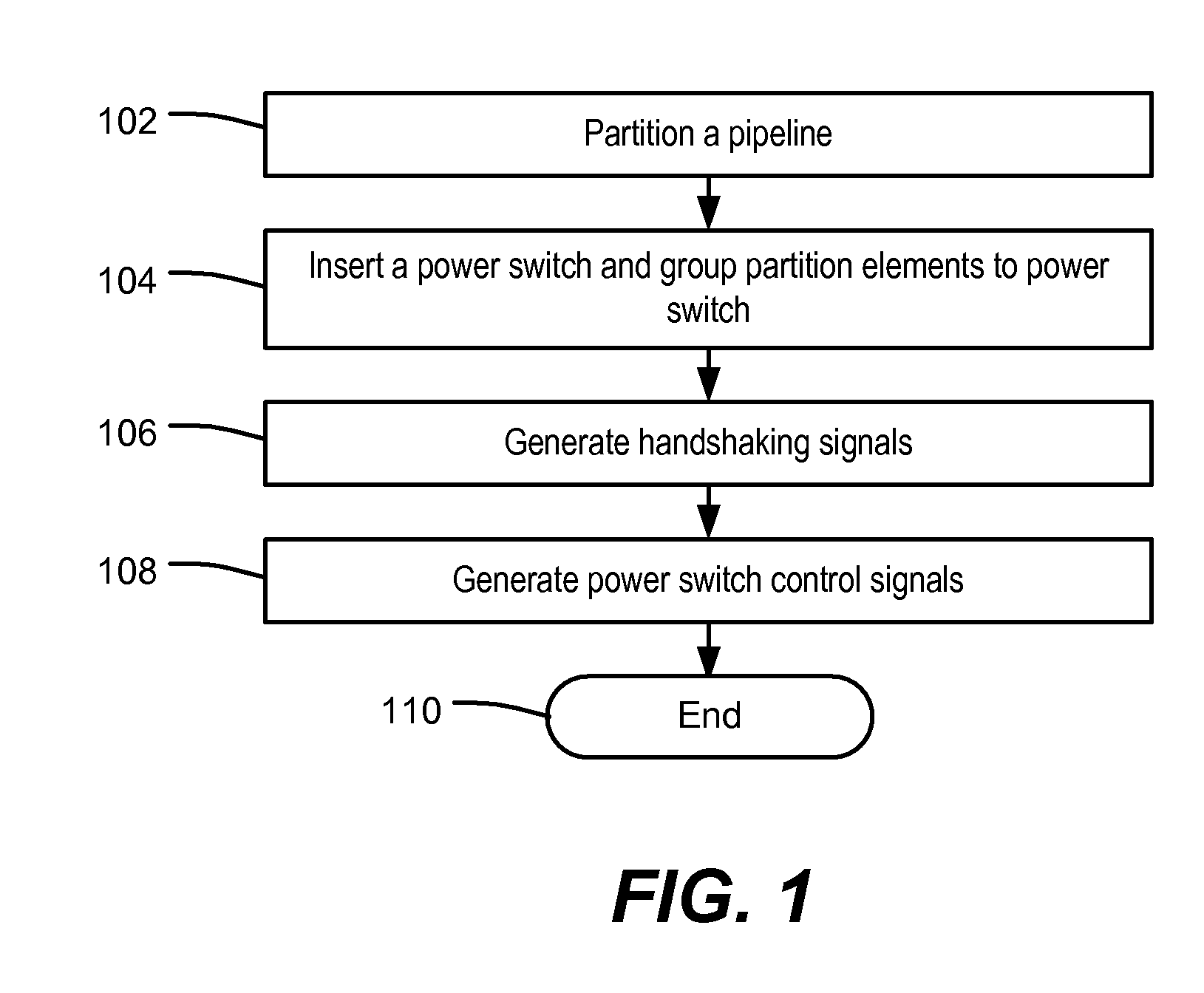
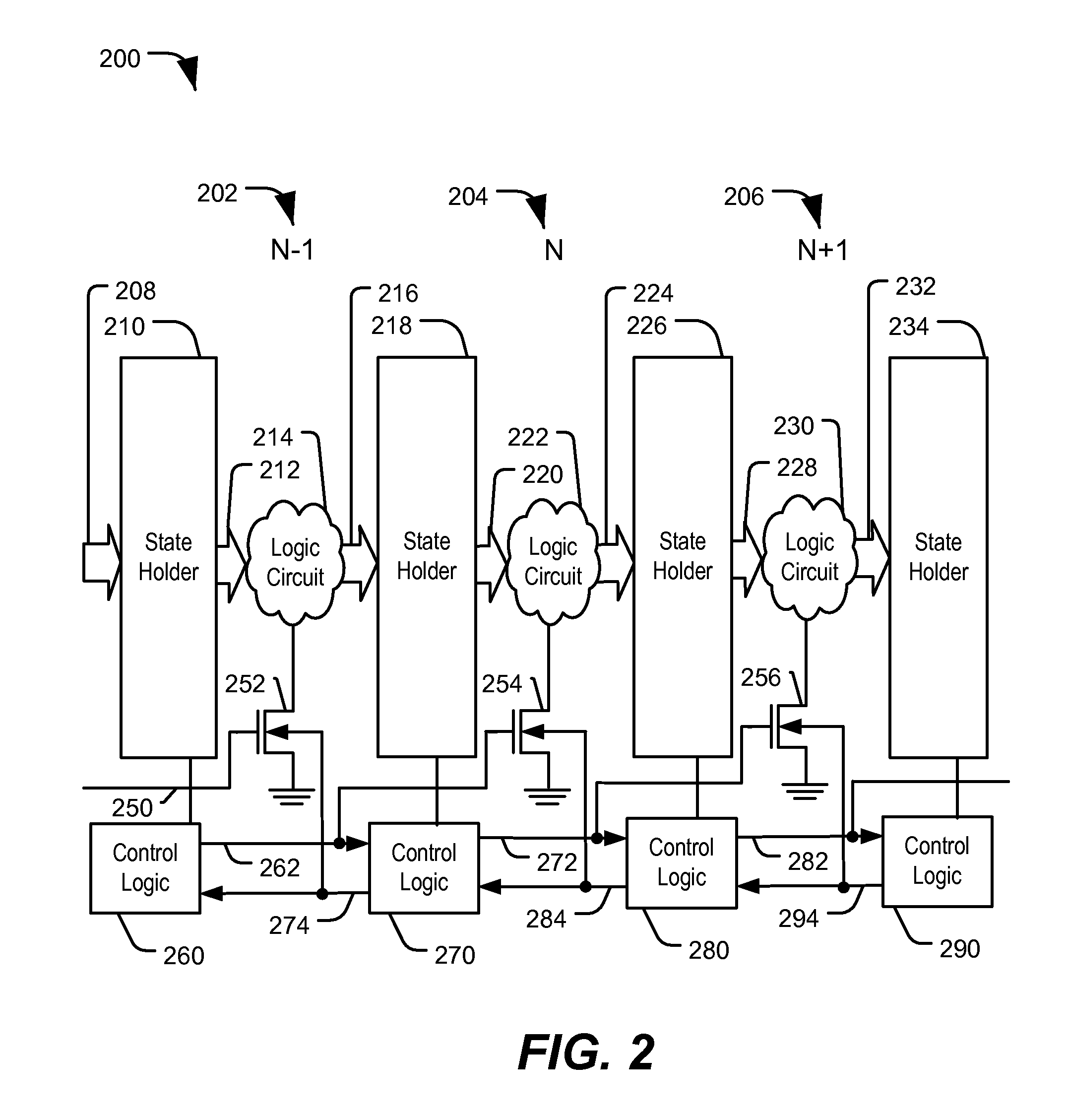
System and Method of Leakage Control in an Asynchronous System
ActiveUS20090172452A1Reduce power consumptionReduce leakage currentPower reduction by control/clock signalVolume/mass flow measurementControl signalControl system
Systems and methods of leakage control in an asynchronous pipeline are disclosed. In an embodiment, a signal is received from a preceding stage at an operative stage of an asynchronous circuit device, and a switch associated with the operative stage is activated in response to the control signal being sent to the operative stage to enable power to the operative stage.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for encoding and decoding asynchronous space-time code for collaborative multi-point transmission
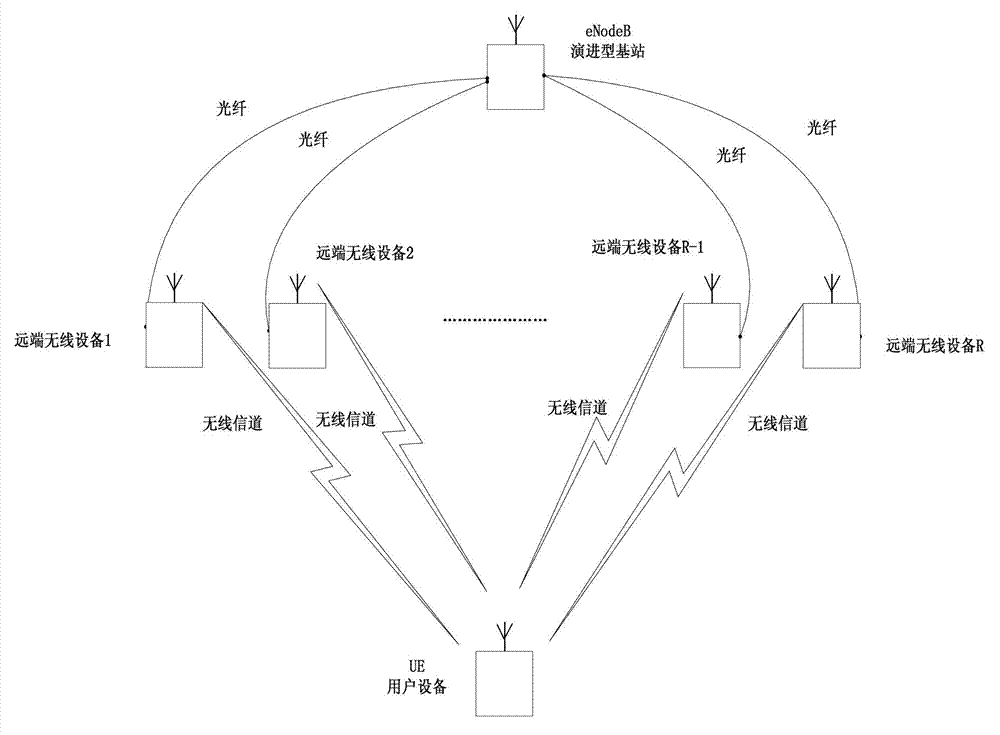
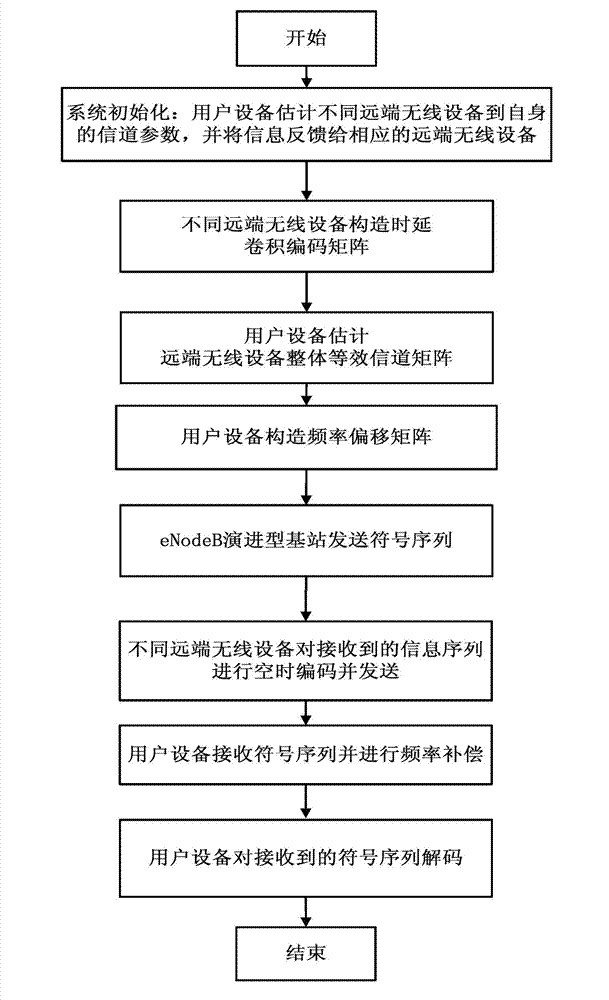
InactiveCN102932041AIncreased complexityReduce complexitySpatial transmit diversityFrequency compensationChannel parameter
The invention discloses a method for encoding and decoding an asynchronous space-time code for collaborative multi-point transmission, to solve the problem that the collaborative communication can not be carried out due to time asynchronization and frequency offset during collaborative multi-point joint processing. The method comprises the following specific steps that: (1) user equipment estimates the channel parameter and feeds back the channel parameter to remote wireless equipment; (2) different remote wireless equipment constructs delay convolutional encoding matrixes; (3) the user equipment estimates the overall equivalent channel matrix of the remote wireless equipment; (4) the user equipment constructs the frequency offset matrix; (5) an eNodeB evolutional base station transmits the symbol sequence; (6) the remote wireless equipment carries out space-time coding on the information sequence and sends the information sequence; (7) the user equipment carries out frequency compensation on the received symbol sequence; and (8) the user equipment judges the feedback decoding by using the minimum mean square error and decodes. Due to the adoption of the method, the full-mark set gain can be obtained without carrying out accurate time and frequency synchronization, and the decoding complexity is reduced.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
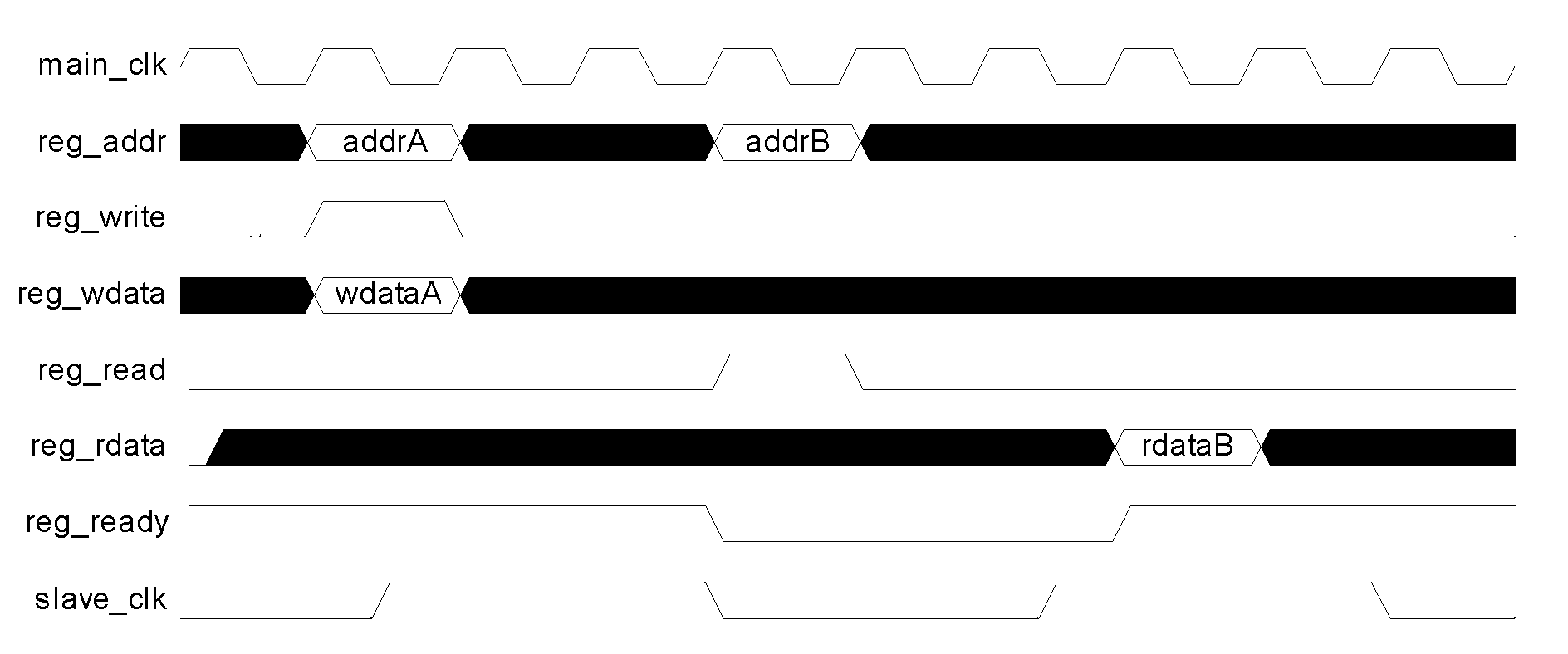
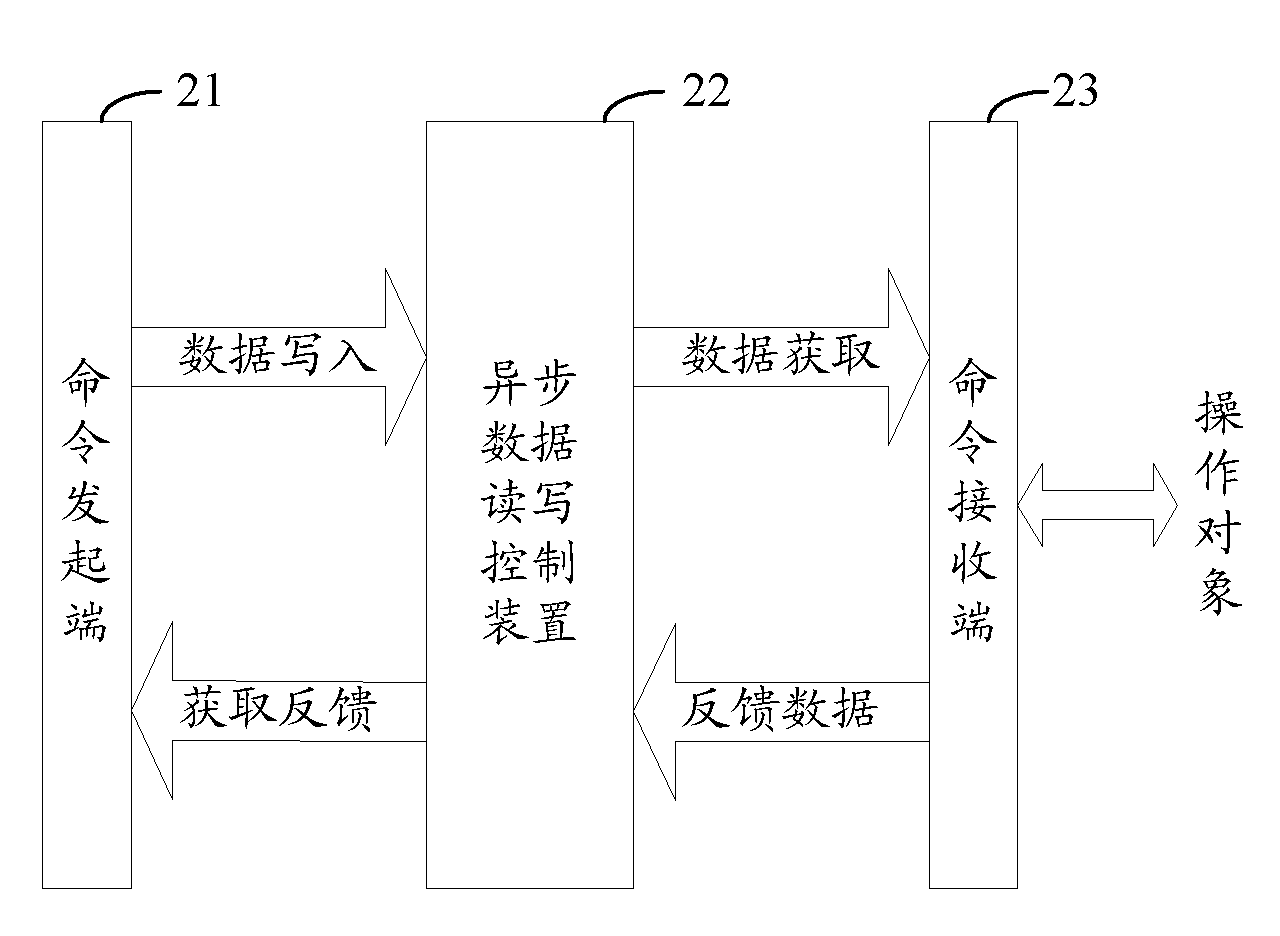
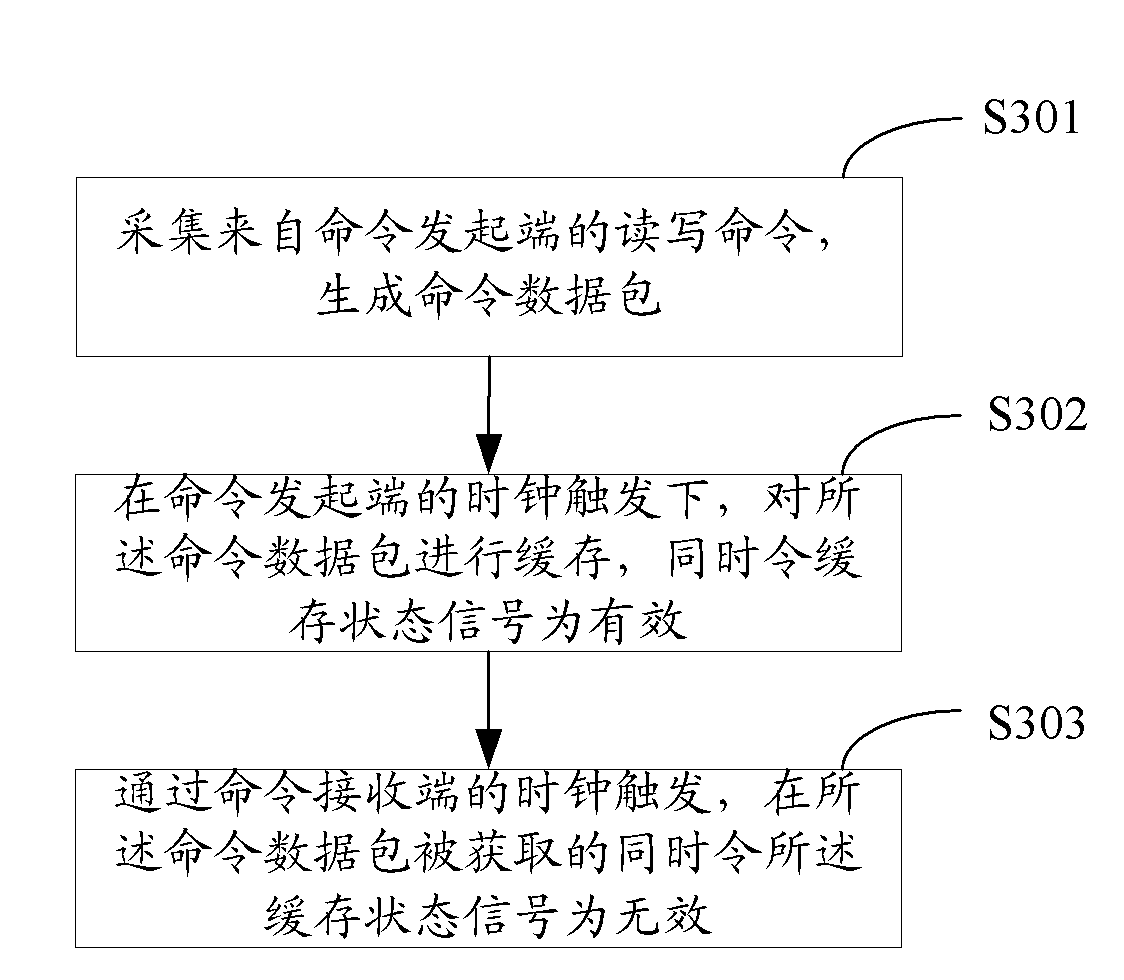
Asynchronous data reading/writing control method, device and system
InactiveCN102654852ARealize timely feedbackEffective isolationElectric digital data processingNetwork packetData signal
The invention is applicable to the field of chip design, and provides an asynchronous data reading / writing control method, device and system. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a reading / writing command from a command initiation end, and generating a command packet, wherein the command packet comprises an enable signal, an address signal and a data signal of the reading / writing command; caching the command packet through the clock trigger of the command initiation end, and setting a caching state signal to be effective at the same time; and setting the caching state signal to be ineffective at the time when the command packet is obtained by a command receiving end through the clock trigger of the command receiving end. In the invention, timely feedback of the caching state and effective isolation among different clock domains are realized by setting the caching state signal to be effective through the clock trigger of the command initiation end at the time when the reading / writing command of the command initiation end is encapsulated and cached and setting the caching state signal to be ineffective through the clock trigger of the command receiving end at the time when the command receiving end acquires the command.
Owner:ANYKA (GUANGZHOU) MICROELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
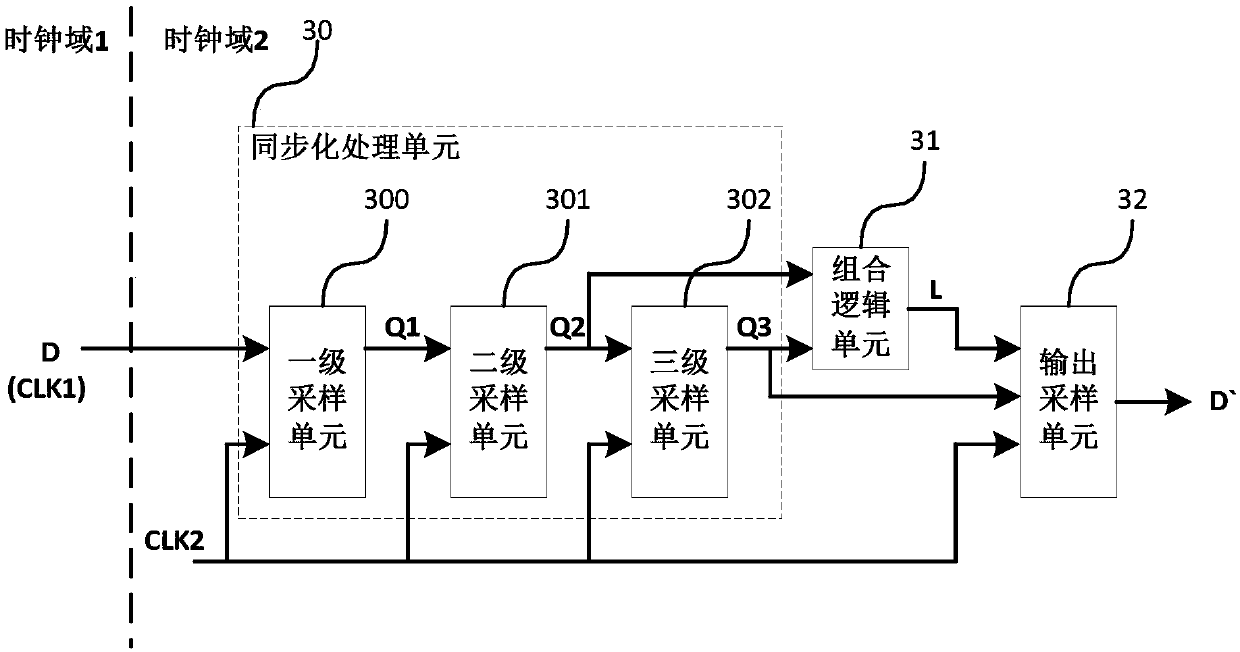
Synchronous filter and method for asynchronous data across clock domains
ActiveCN107911102ASolve Logical ConfusionImprove stabilitySingle output arrangementsSynchronous IdleData signal
The invention provides a synchronous filter and method for asynchronous data across clock domains. The synchronous filter comprises a synchronization processing unit (30), a combined logic unit (31) and an output sampling unit (32); the synchronization processing unit (30) carries out synchronization processing on a data signal of a clock domain 1, and obtains a data signal of a clock domain 2; the combined logic unit (31) carries out combined logic processing on the data signal of the clock domain 2, and obtains a combined logic processing result; and the output sampling unit (32) samples thecombined logic processing result and the data signal of the clock domain 2, and outputs the data signal of the clock domain 2. The synchronous filter for the asynchronous data across the clock domains provided by the invention effectively reduces the probability of the metastable state of the signals when the data signals are transmitted from the clock domain 1 to the clock domain 2, solves the problem of logic chaos in a post-stage circuit caused by the metastable state, and greatly improves the stability of the circuit.
Owner:长园深瑞继保自动化有限公司
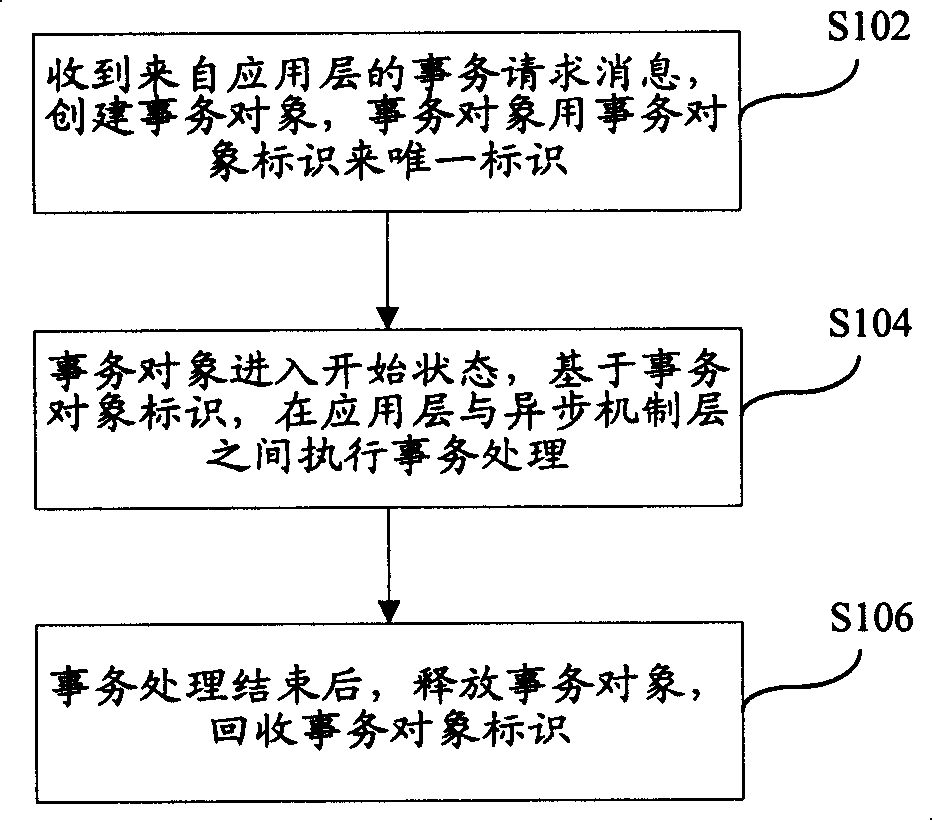
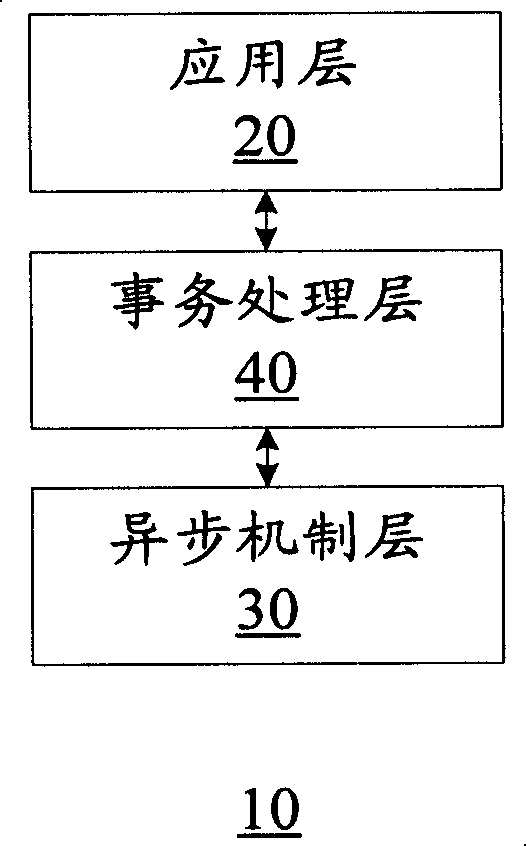
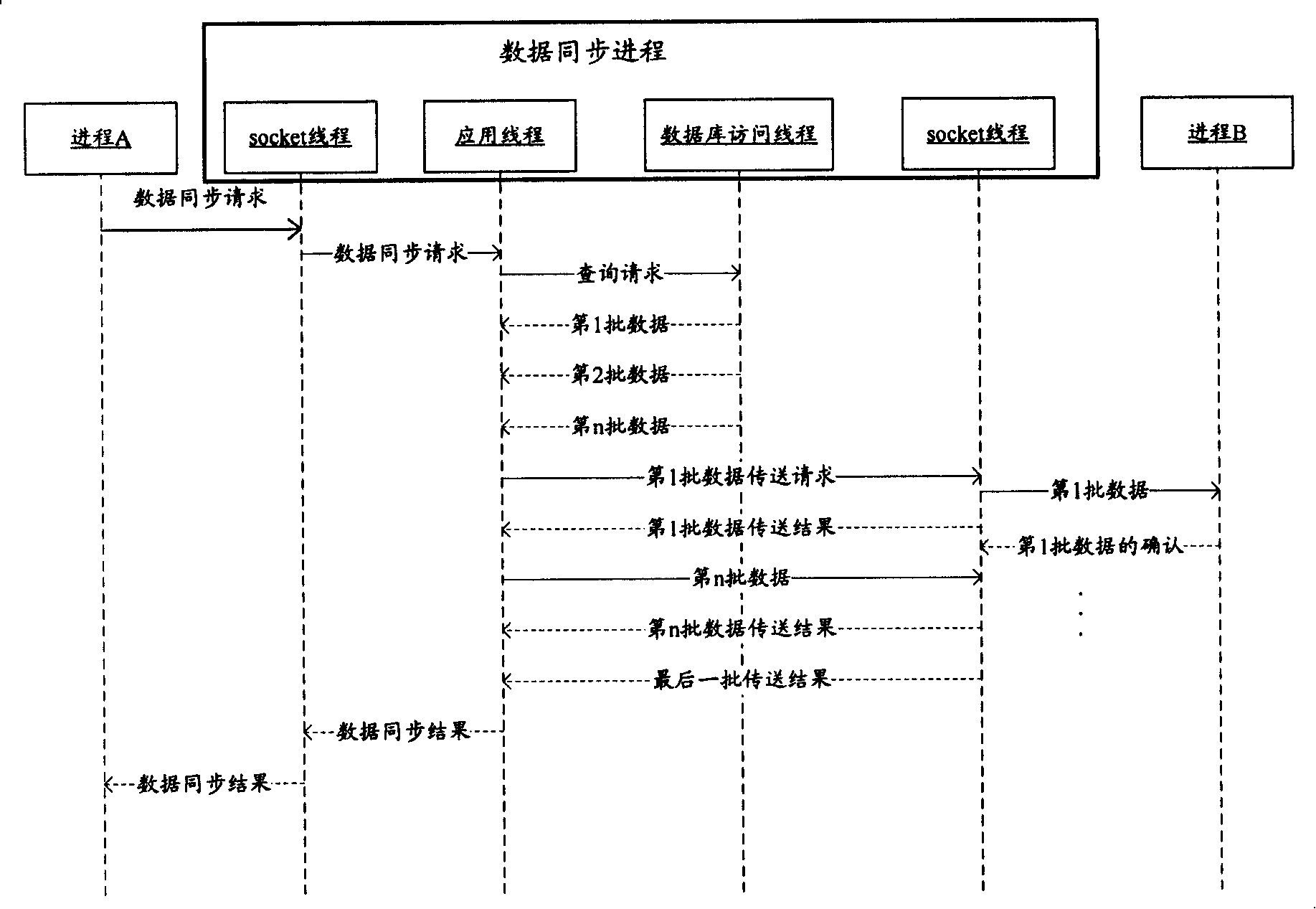
Parallel processing transaction asynchronous method
InactiveCN101192173AImprove developmentResolve mutual interferenceMultiprogramming arrangementsProgramming languageAsynchronous system
The invention discloses an asynchronous method for parallel processing of transaction, wherein, the method includes step S102: a transaction request message from an application layer is received and a transaction object which is marked by transaction object identification is created; step S104: the transaction object enters into an initial state and base on the transaction object identification, transaction processing is executed between the application layer and an asynchronous mechanism layer; step S106: after transaction processing is finished, the transaction object is released and the transaction object identification is recycled. The invention not only can solve the problem of mutual interference inside an asynchronous system during parallel execution of a plurality of transactions to increase system efficiency, but also can simplify the development of the asynchronous system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com