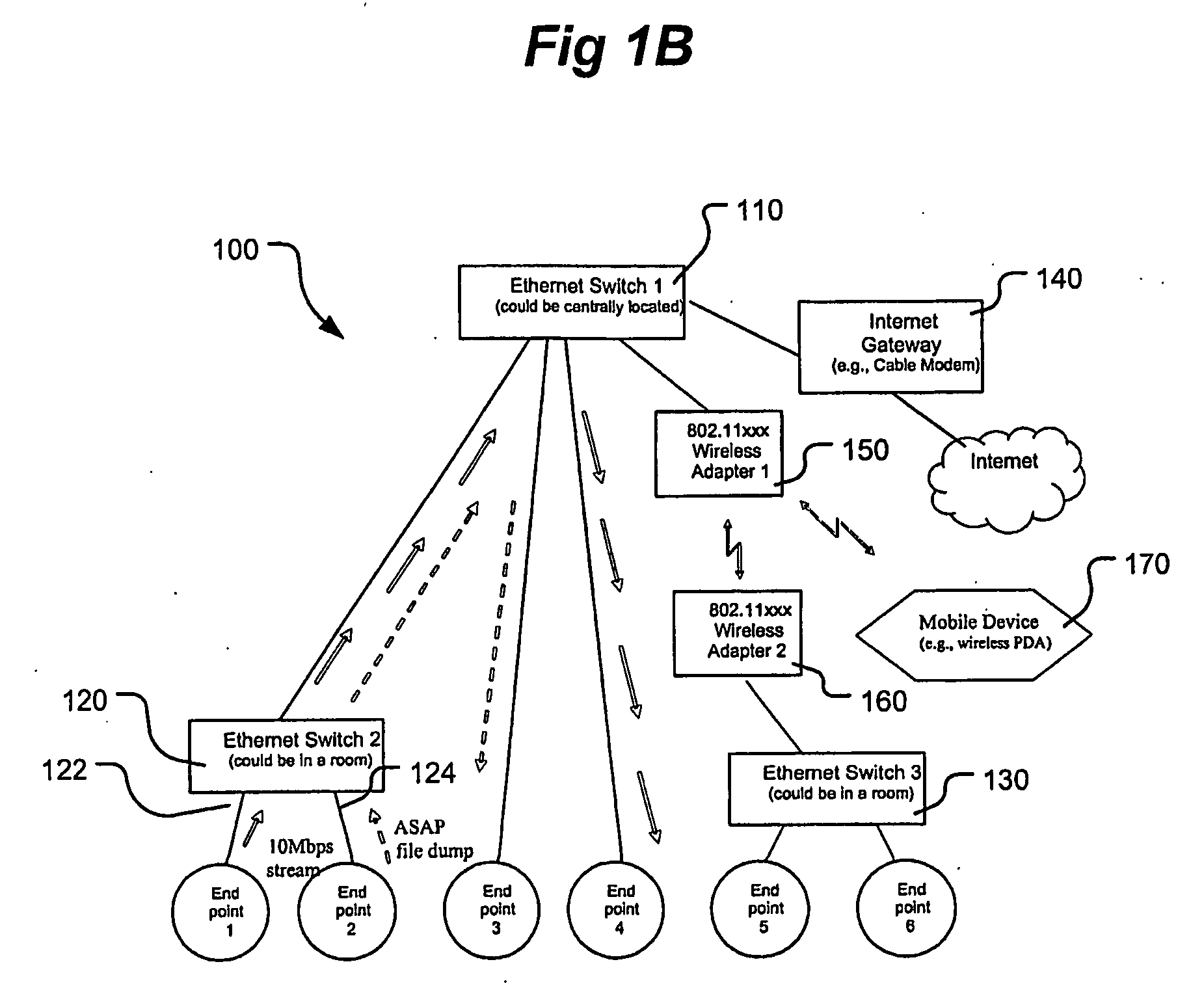
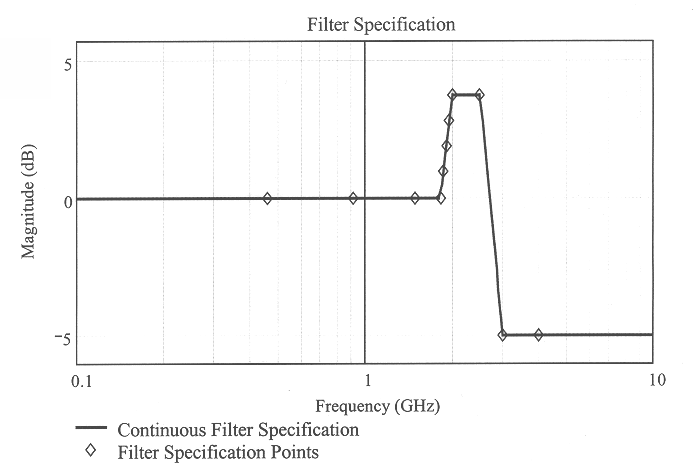
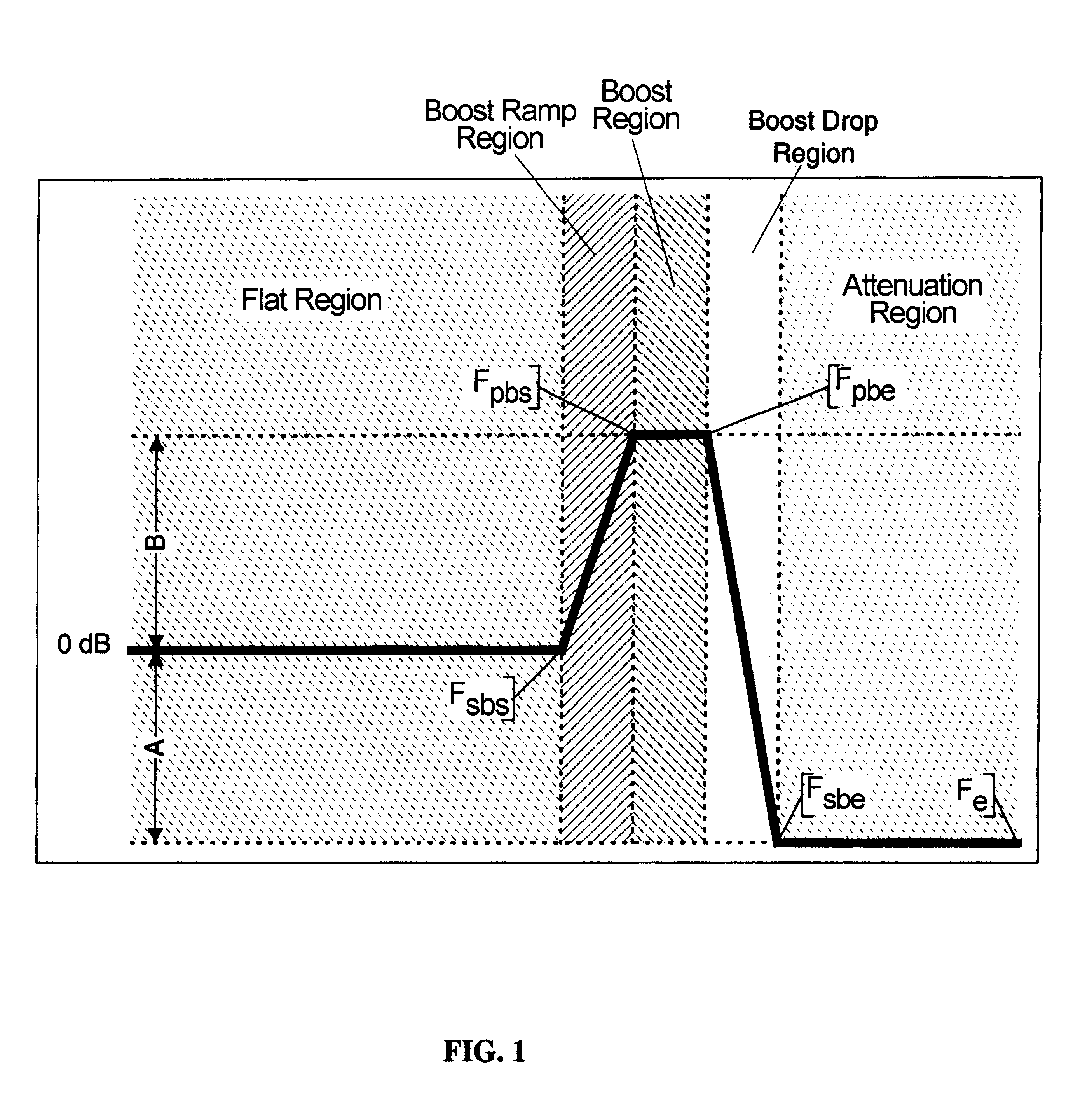
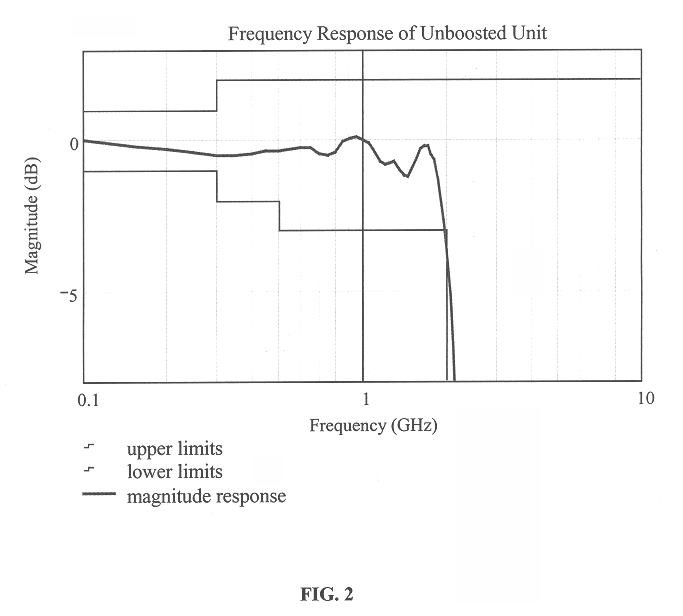
Patents
Literature
360 results about "Bandwidth throttling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bandwidth throttling is the intentional slowing or speeding of an internet service by an Internet service provider (ISP). It is a reactive measure employed in communication networks to regulate network traffic and minimize bandwidth congestion. Bandwidth throttling can occur at different locations on the network. On a local area network (LAN), a system administrator ("sysadmin") may employ bandwidth throttling to help limit network congestion and server crashes. On a broader level, the Internet service provider may use bandwidth throttling to help reduce a user's usage of bandwidth that is supplied to the local network. Bandwidth throttling is also used to speed up the Internet on speed test websites.
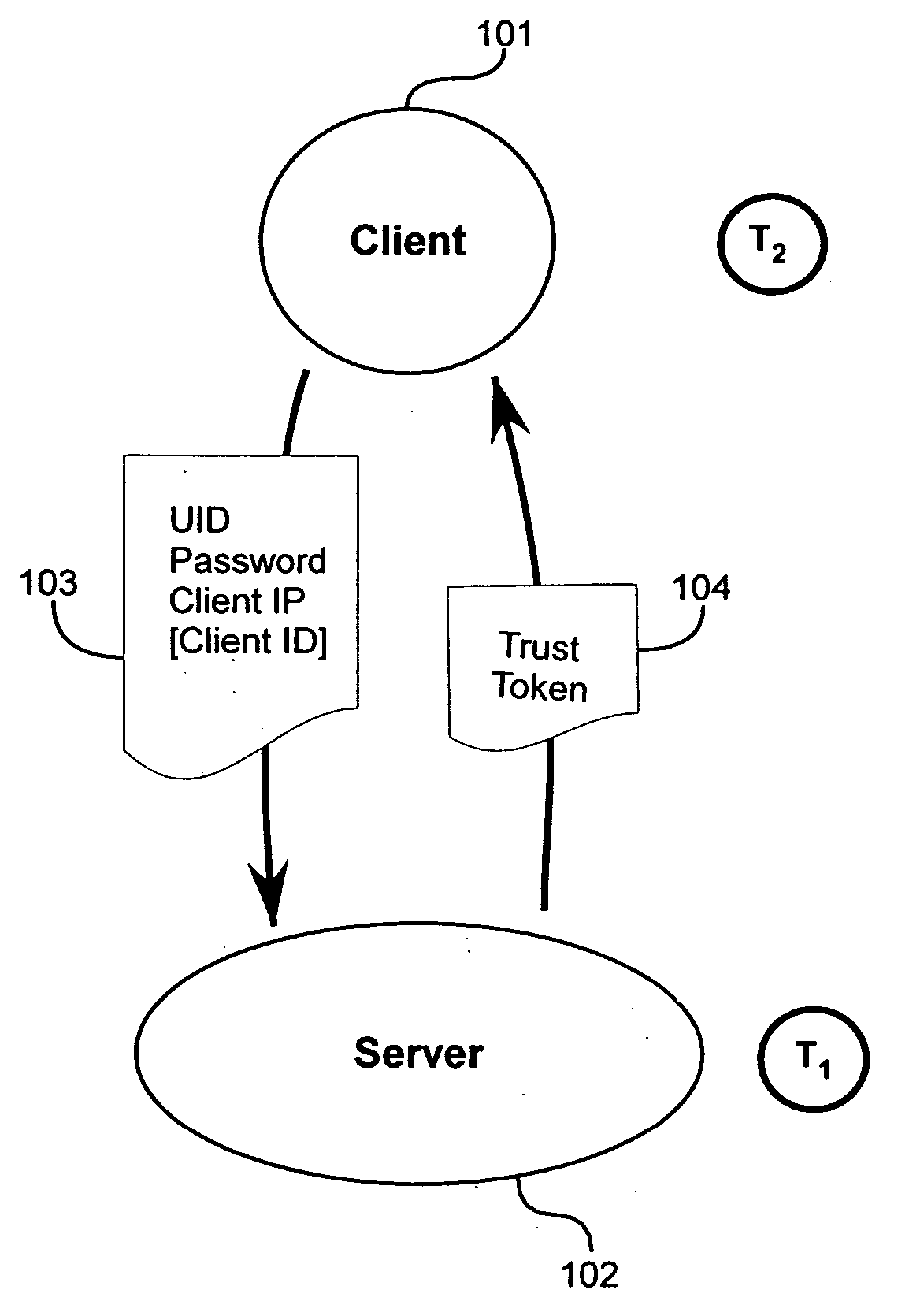
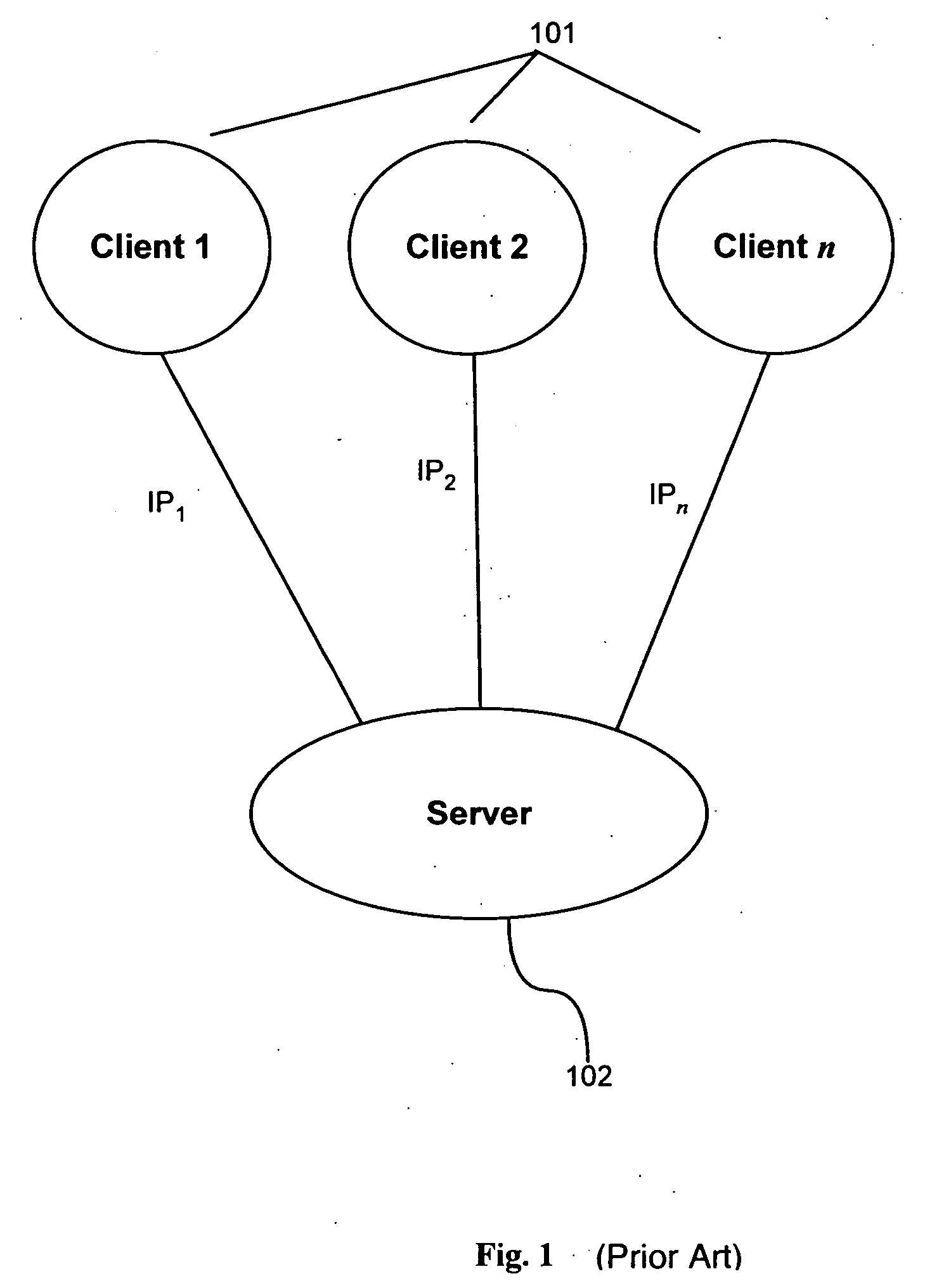
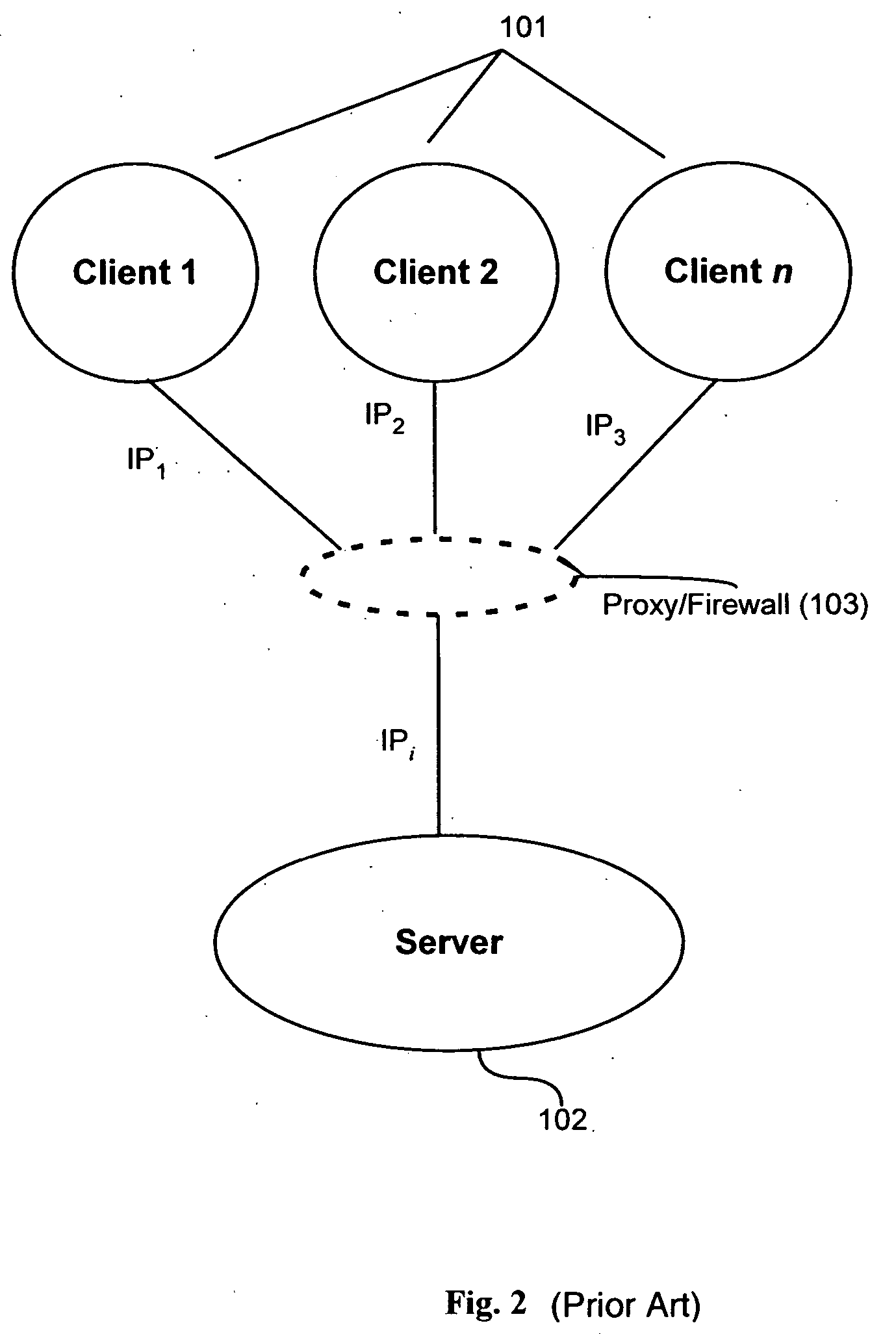
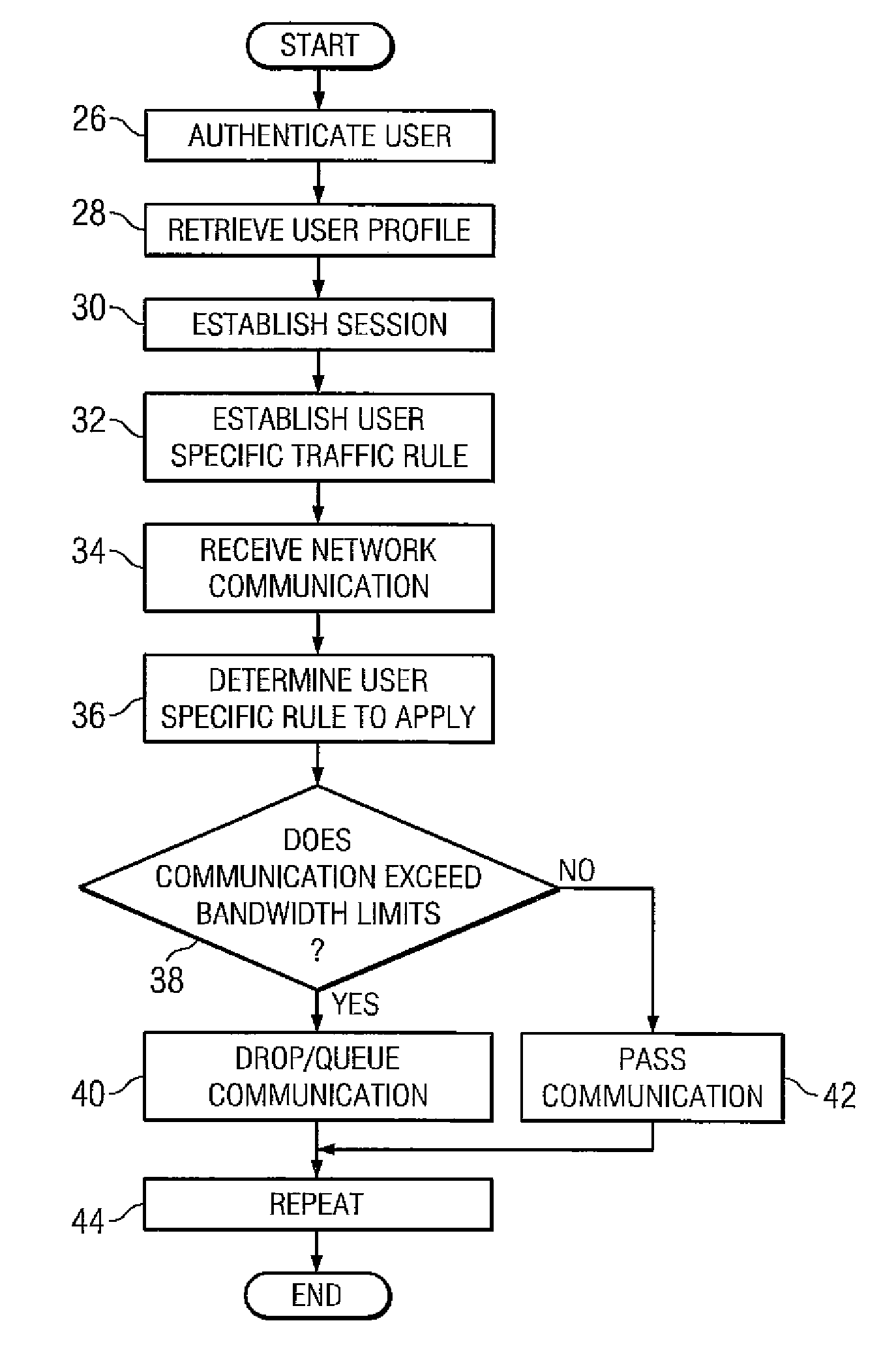
Method and apparatus for trust-based, fine-grained rate limiting of network requests
ActiveUS20050108551A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationRate limitingInternet traffic
A method and apparatus for fine-grained, trust-based rate limiting of network requests distinguishes trusted network traffic from untrusted network traffic at the granularity of an individual user / machine combination, so that network traffic policing measures are readily implemented against untrusted and potentially hostile traffic without compromising service to trusted users. A server establishes a user / client pair as trusted by issuing a trust token to the client when successfully authenticating to the server for the first time. Subsequently, the client provides the trust token at login. At the server, rate policies apportion bandwidth according to type of traffic: network requests that include a valid trust token are granted highest priority. Rate policies further specify bandwidth restrictions imposed for untrusted network traffic. This scheme enables the server to throttle untrusted password-guessing requests from crackers without penalizing most friendly logins and only slightly penalizing the relatively few untrusted friendly logins.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
System and method for dynamic bandwidth provisioning
InactiveUS7587512B2Network traffic/resource managementMultiple digital computer combinationsUser profileDistributed computing
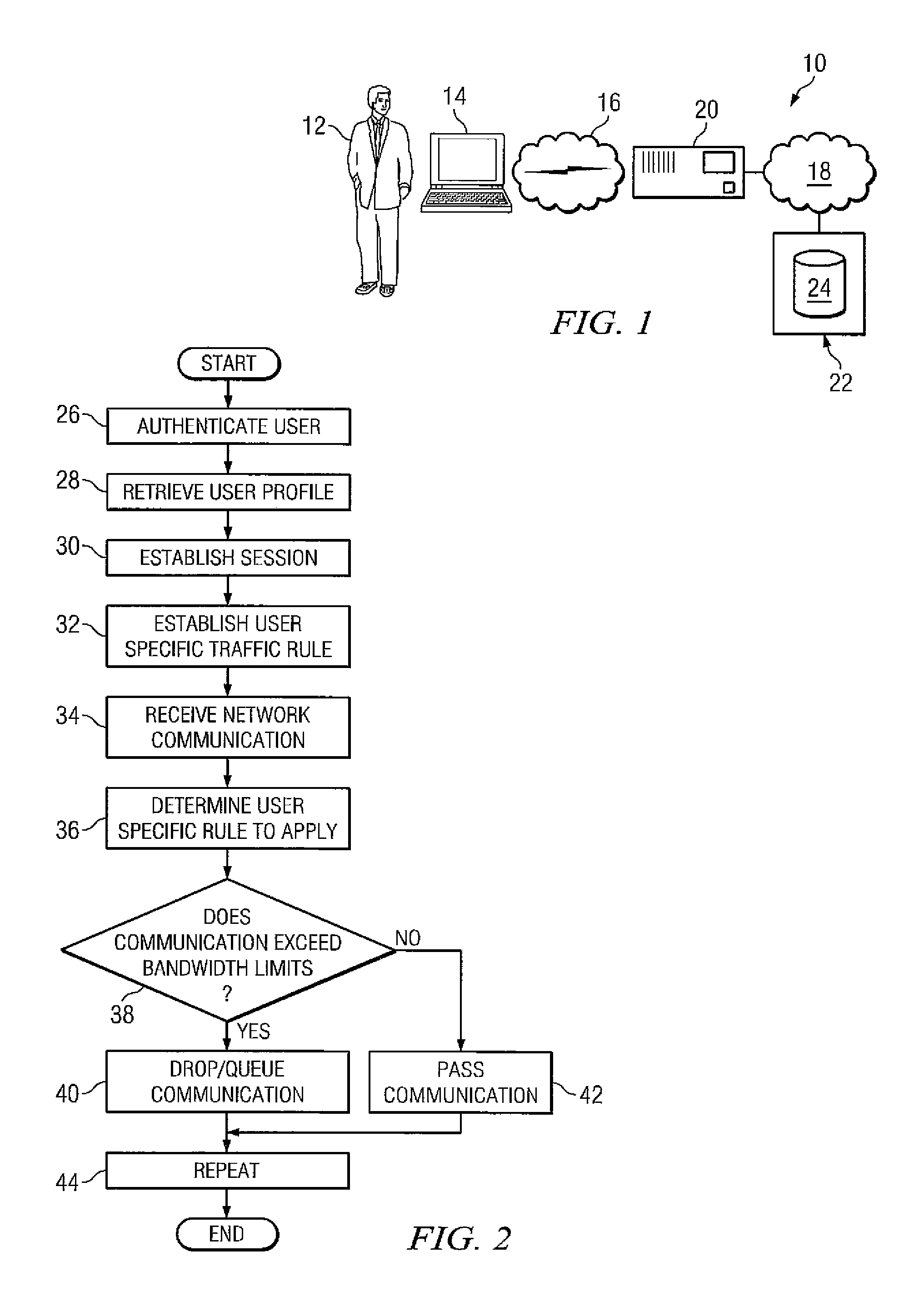
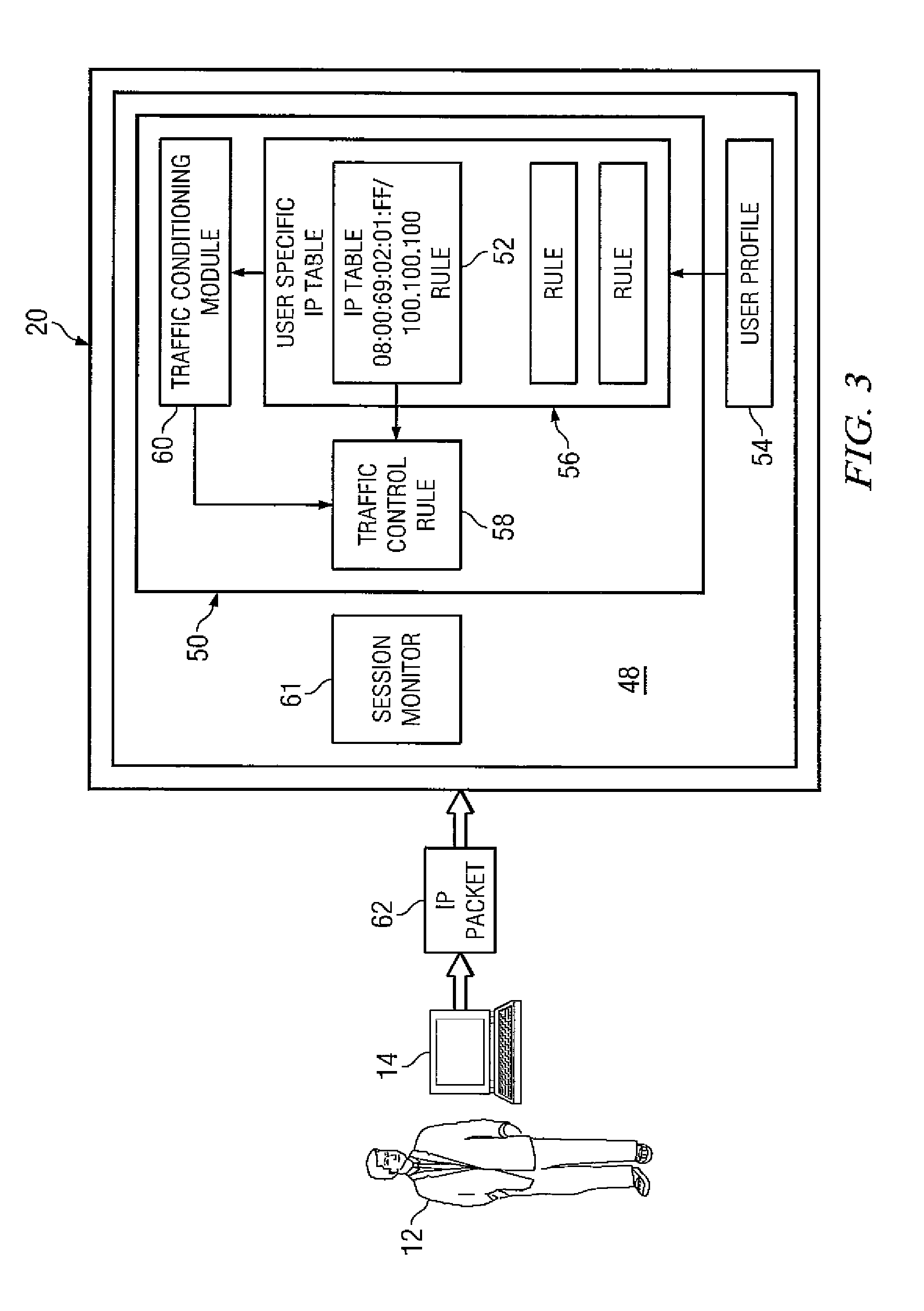
One embodiment of the present invention provides a device for allocating bandwidth on a per user basis. The device can be a computing device that comprises a processor, a first network interface coupled to the processor, a second network interface coupled to the processor, and a storage medium accessible by the processor that contains a set of computer instructions. The computer instructions can be executable by the processor to retrieve a set of user profiles. Based on the user profile for each user, the computer instructions can be executable to establish at least one bandwidth limit for each user. For each user, the computer instructions can be further executable to regulate bandwidth usage associated with that user based on the at least one bandwidth limit established for that user. The computer instructions can also be executable to update the at least one bandwidth limit.
Owner:RPX CORP
Packet scheduling system and method for multimedia data
InactiveUS6988144B1Time-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsPacket schedulingClient-side
A method for scheduling the delivery of multimedia data packets over a communications medium with a limited bandwidth. The packets may contain data representing images, sounds, or other media which are to be delivered from a source or server to a recipient or client. The 6 method described here minimizes the delay between the point in time when a client requests the multimedia data and the point in time when the client may start presenting the data without risk of interruption, for a given communications bandwidth. This method also determines the minimum buffer sizes needed by the client in order to present this multimedia data subject to the specified bandwidth limit.
Owner:IBM CORP
Admission control for aggregate data flows based on a threshold adjusted according to the frequency of traffic congestion notification
InactiveUS6839767B1Guaranteed bandwidthExacerbating congestion condition is avoidedError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityData stream
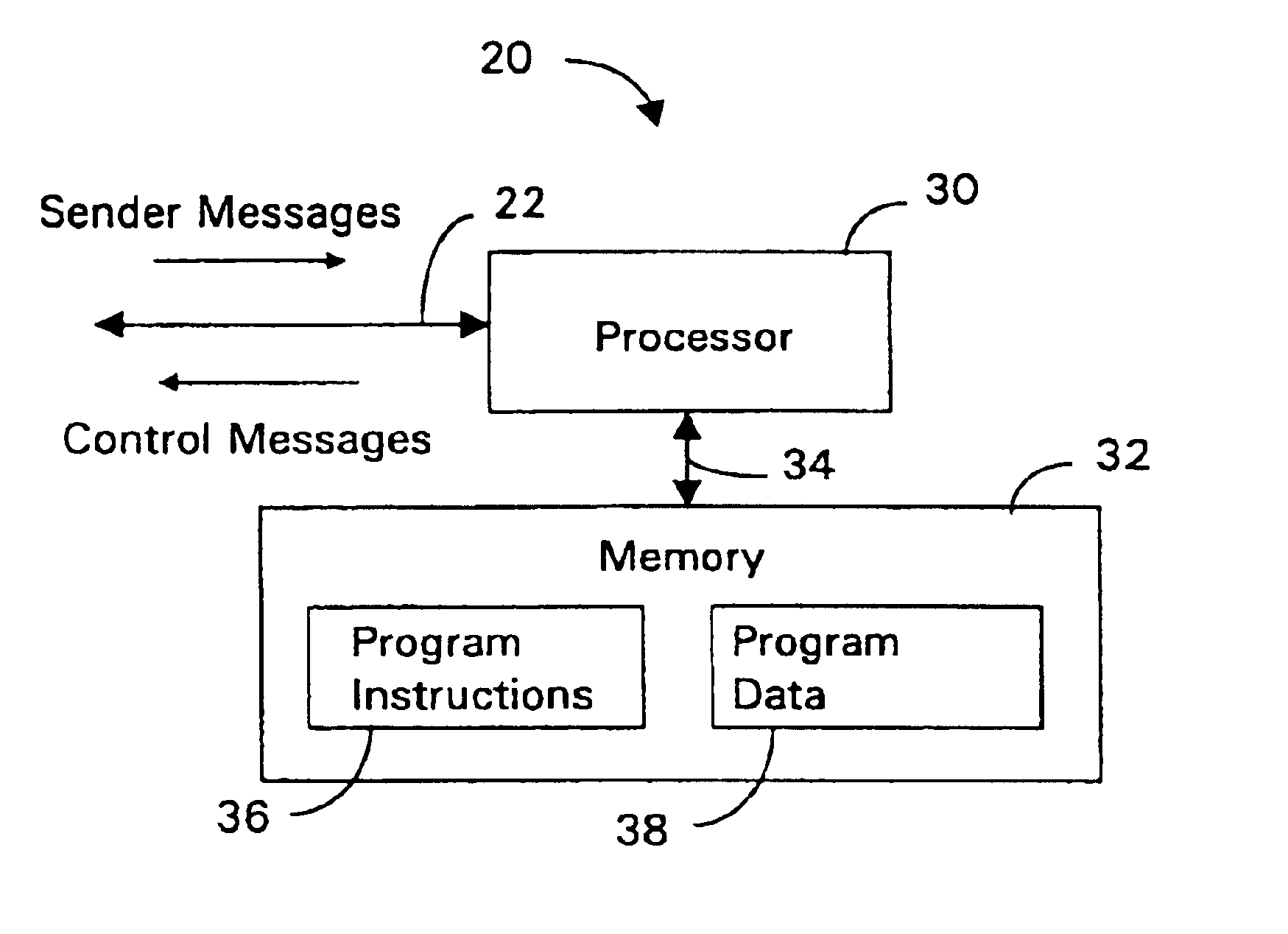
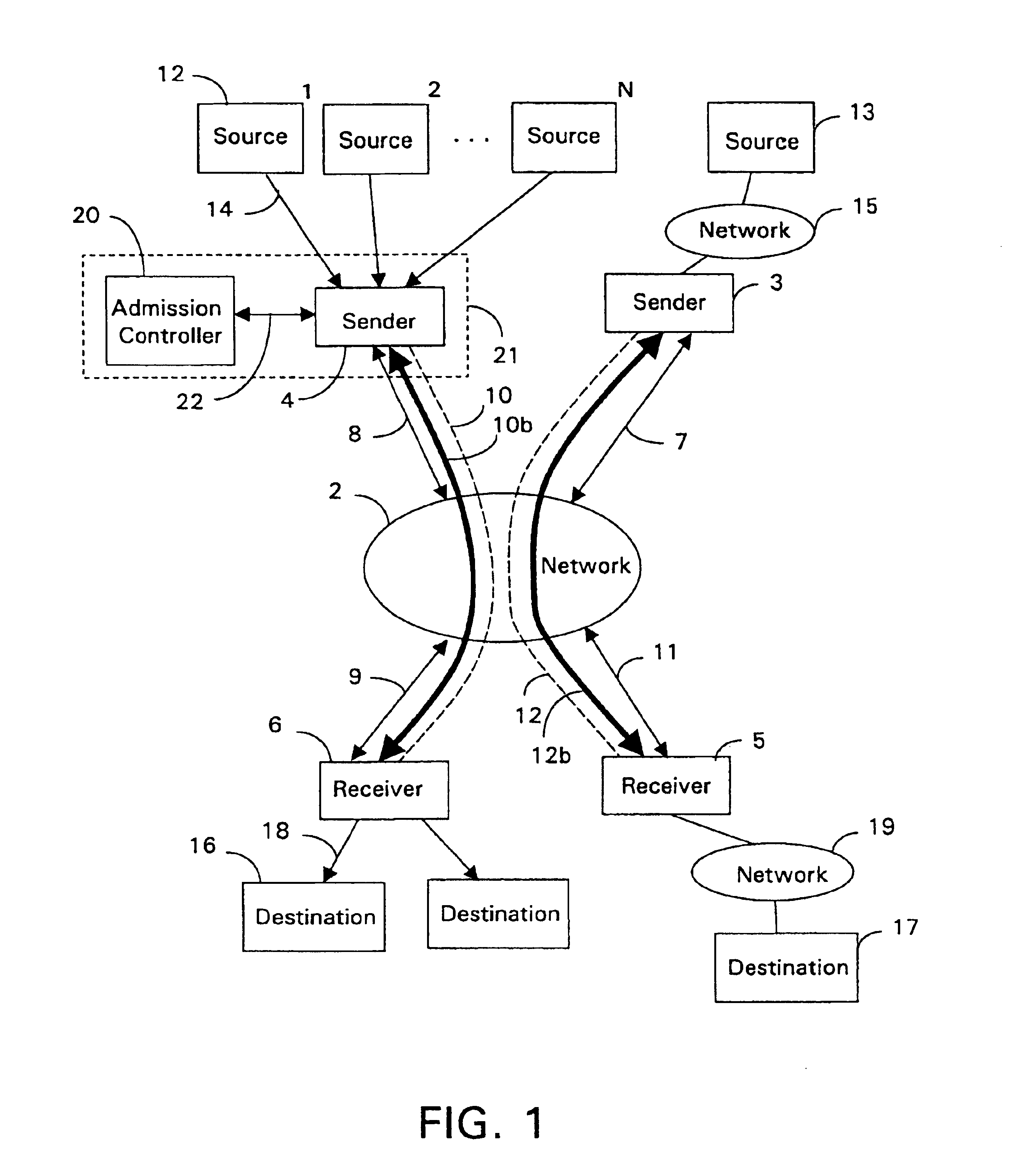
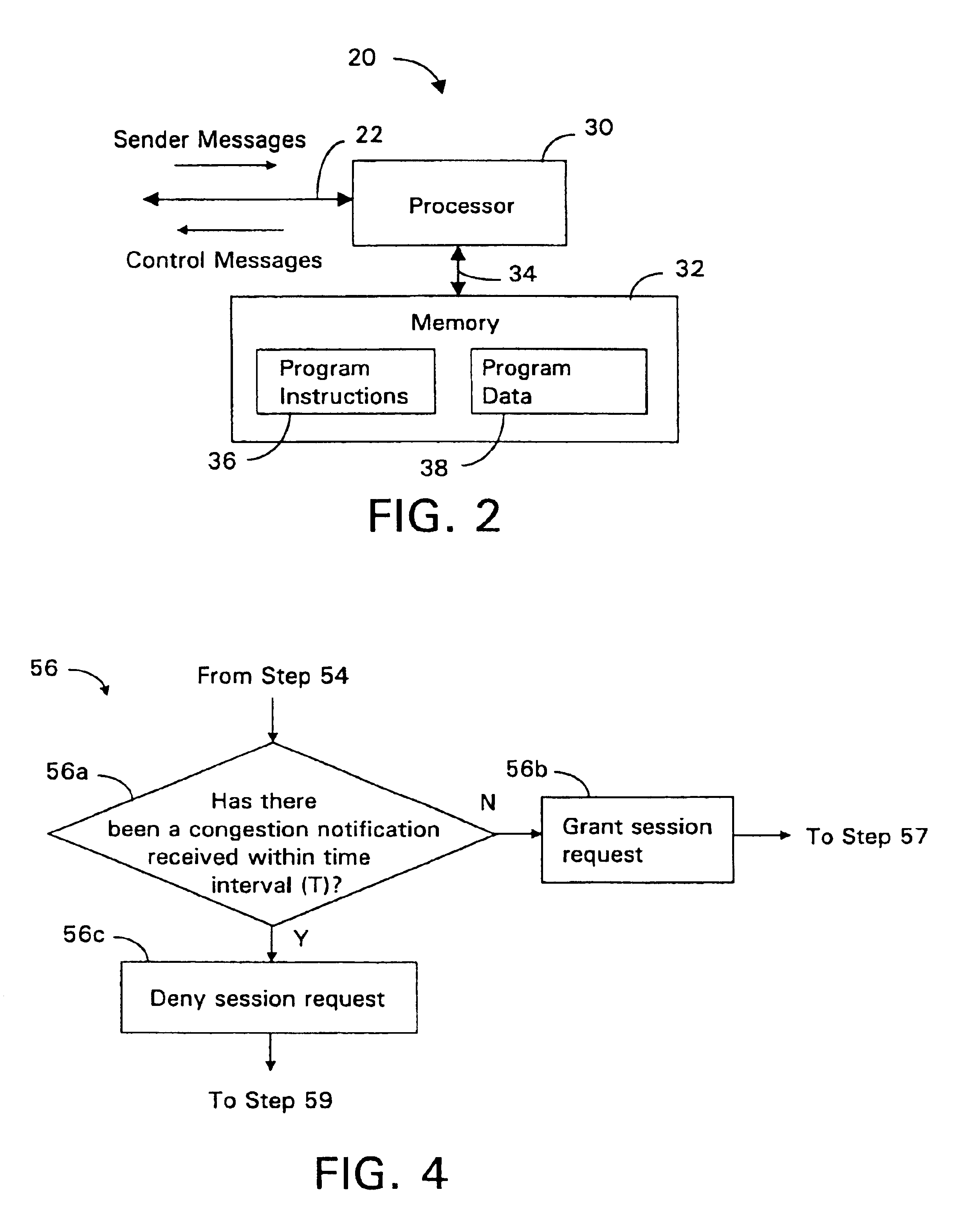
An admission controller and its method of operation for controlling admission of data flows into an aggregate data flow are described. Admitted data flows are aggregated into an aggregate data flow for transmission by a router, for example, over a data network. The aggregate data flow typically follows a pre-established path through the network; for example a multi-protocol label switched (MPLS) path. The path has minimum and maximum bandwidth limits assigned to it. The admission controller controls admission of new data flows into the aggregate data flow by granting or denying new session requests for the new data flows. Congestion notifications received from the network and bandwidth limits of the path are considered in determining whether to grant or deny a new session request. In this way, the admission controller provides elastic sharing of network bandwidth among data flows without exacerbating network congestion and while remaining within the path's bandwidth limits. The data flows may include transaction oriented traffic.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Content delivery for client-server protocols with user affinities using connection end-point proxies
ActiveUS20050125553A1Services signallingMultiple digital computer combinationsBandwidth limitationIndependent data
In a network supporting transactions between clients and servers over a network path having operating characteristics to overcome, data is transported to overcome the operating characteristics using user affinities and dynamic user location information to selectively preload data, or representations, signatures, segments, etc. of data, in order to overcome the one or more operating characteristic. Examples of operating characteristics to overcome include bandwidth limitations, errors and latency. The dynamic location information can be stored in data structures accessible by agents of a data server and the data structures are populated based on user activities with respect to proxies associated with user locations, or the dynamic location information can be obtained implicitly as proxies maintain connections after termination by clients and the use of those maintained connections for preloading of data for the users associated with those clients. The data being preloaded can be protocol-specific data or protocol-independent data.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
Reducing perceived latency in servicing user requests on low-bandwidth communication channels
InactiveUS6243739B1Lower latencyService degradationDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsThe InternetApplication software
Access to hypermedia servers connected to networks such as the Internet can be provided through mobile devices such as wireless telephones. Unfortunately, limitations in processing power and memory space of the mobile device and limitations bandwidth of the communication channels connecting the mobile devices to the rest of the network cause long wait times for many types of requests to be serviced. In one application, a user is notified that unsolicited electronic mail has arrived in the user's mail box on a computer connected directly a network and, in response, the user requests the mail to be sent to the mobile device. The perceived latency in servicing such a request can be reduced by delivering at least a portion of the unsolicited electronic mail to mobile device before notifying the user that the mail has arrived in the mail box. In this manner, at least a portion of that mail can be presented to the user in response to a request with little delay.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Systems and methods of providing proxy-based quality of service
ActiveUS7706266B2Low transfer rateEnergy efficient ICTTransmission systemsQuality of serviceTransport layer
Systems and methods for dynamically controlling bandwidth of connections are described. In some embodiments, a proxy for one or more connections may allocate, distribute, or generate indications of network congestion via one or more connections in order to induce the senders of the connections to reduce their rates of transmission. The proxy may allocate, distribute, or generate these indications in such a way as to provide quality of service to one or more connections, or to ensure that a number of connections transmit within an accepted bandwidth limit. In other embodiments, a sender of a transport layer connection may have a method for determining a response to congestion indications which accounts for a priority of the connection. In these embodiments, a sender may reduce or increase parameters related to transmission rate at different rates according to a priority of the connection.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
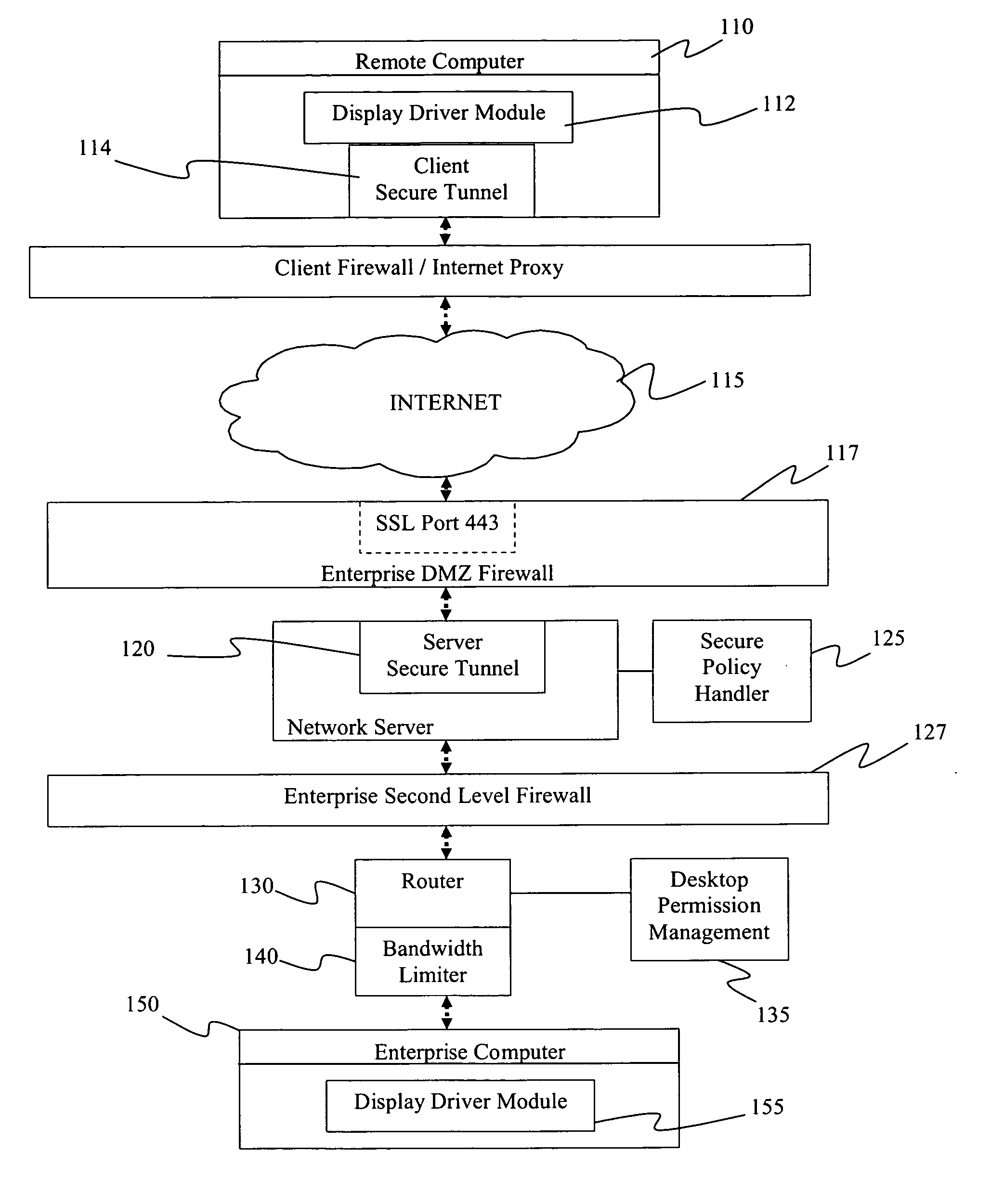
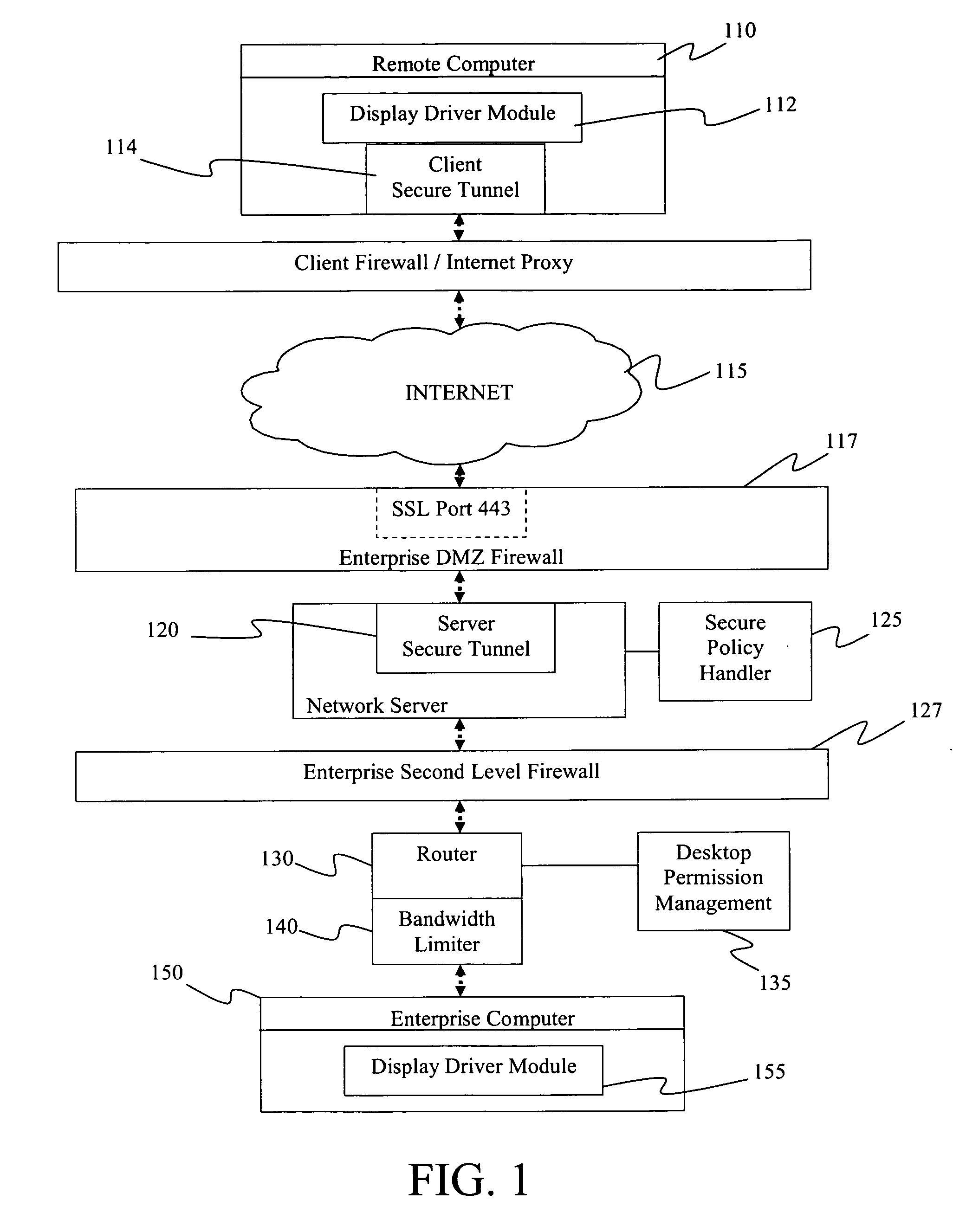
System and method for secure remote desktop access
InactiveUS20070143837A1User identity/authority verificationMultiple digital computer combinationsRemote desktopClient-side
A secure remote access system includes client software installed on a portable computer that establishes a remote session with a counterpart server software installed on a server in a DMZ of the company's internal network through a secure tunnel. The DMZ server is connected to a router behind an enterprise second level firewall. The router routes the session to the appropriate desktop computer if the desktop is permitted remote access. A bandwidth limiter may be provided to balance the load through the router.
Owner:BARCLAYS CAPITAL INC
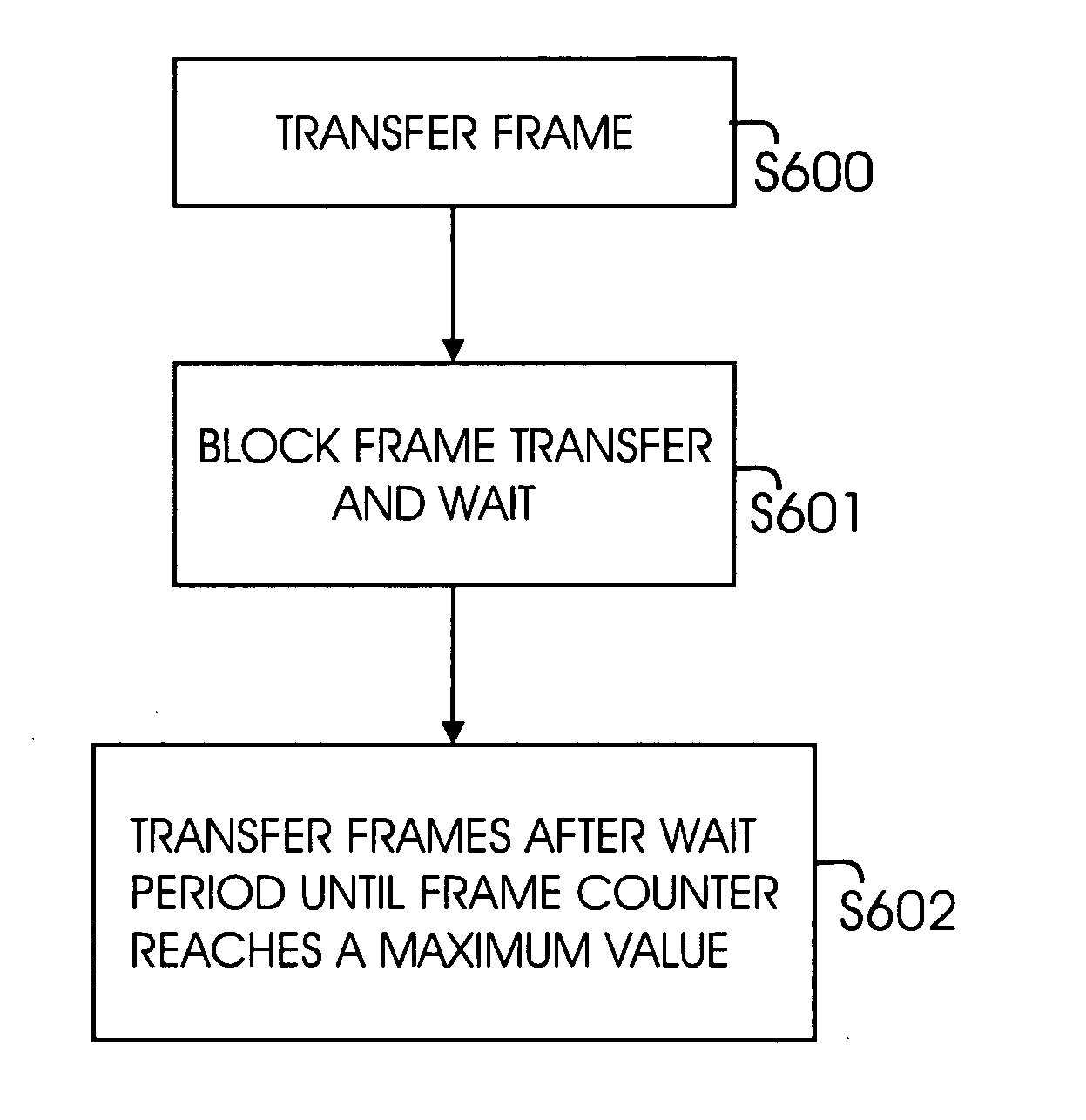
Method and system for congestion control based on optimum bandwidth allocation in a fibre channel switch
InactiveUS20050018606A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionFibre Channel switchReal-time computing
A method and system for optimizing bandwidth allocation in a fibre channel network having a fibre channel switch element, is provided. The switch element includes, a port control module having a receive and transmit segment, wherein the transmit segment is programmed to block frame transmission from a particular frame source port for a certain duration based on a programmable threshold value. The method includes, enabling a bandwidth limitation counter; and programming the threshold value for blocking frame transmission from a frame source port for a certain duration and during this duration, other source ports may be chosen for frame transmission. After a frame is transmitted from a source port, a tag valid blocking from the same source port is used to block frame transmission. A quality of service register is used to store the threshold value and the threshold value is programmable.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
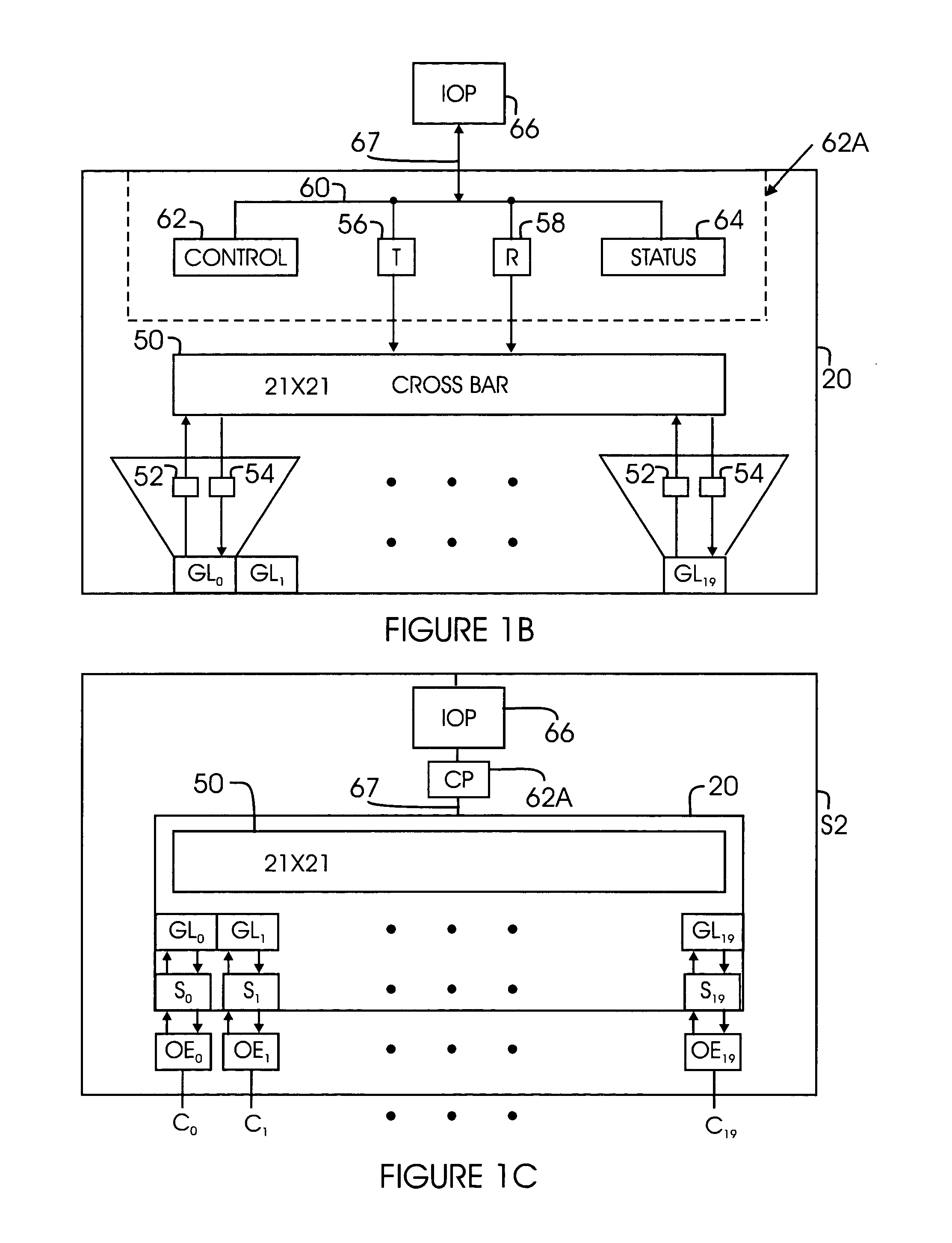
Allocating access across a shared communications medium of a DOCSIS 1.0 compliant cable network
InactiveUS6917628B2Energy efficient ICTBroadband local area networksModem deviceCommunications media
A method of incorporating allocations of network access in a DOCSIS 1.0 compliant cable network, wherein users compete for bandwidth, includes limiting bandwidth consumed by a cable modem of a user to a value representative of that user's bandwidth allocation for a time interval. Preferably, the method includes the steps of: (a) generating cable modem configuration files, each of which limits bandwidth consumption by a cable modem of a user to a bandwidth allowance of that user equaling to the respective bandwidth allocation; (b) sending the configuration files to a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) Server of the DOC Network; and (c) sending a command either to each user's cable modem, or to a cable modem termination system to which each user's cable modem is connected, to cause the cable modem to implement the respective new configuration file.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
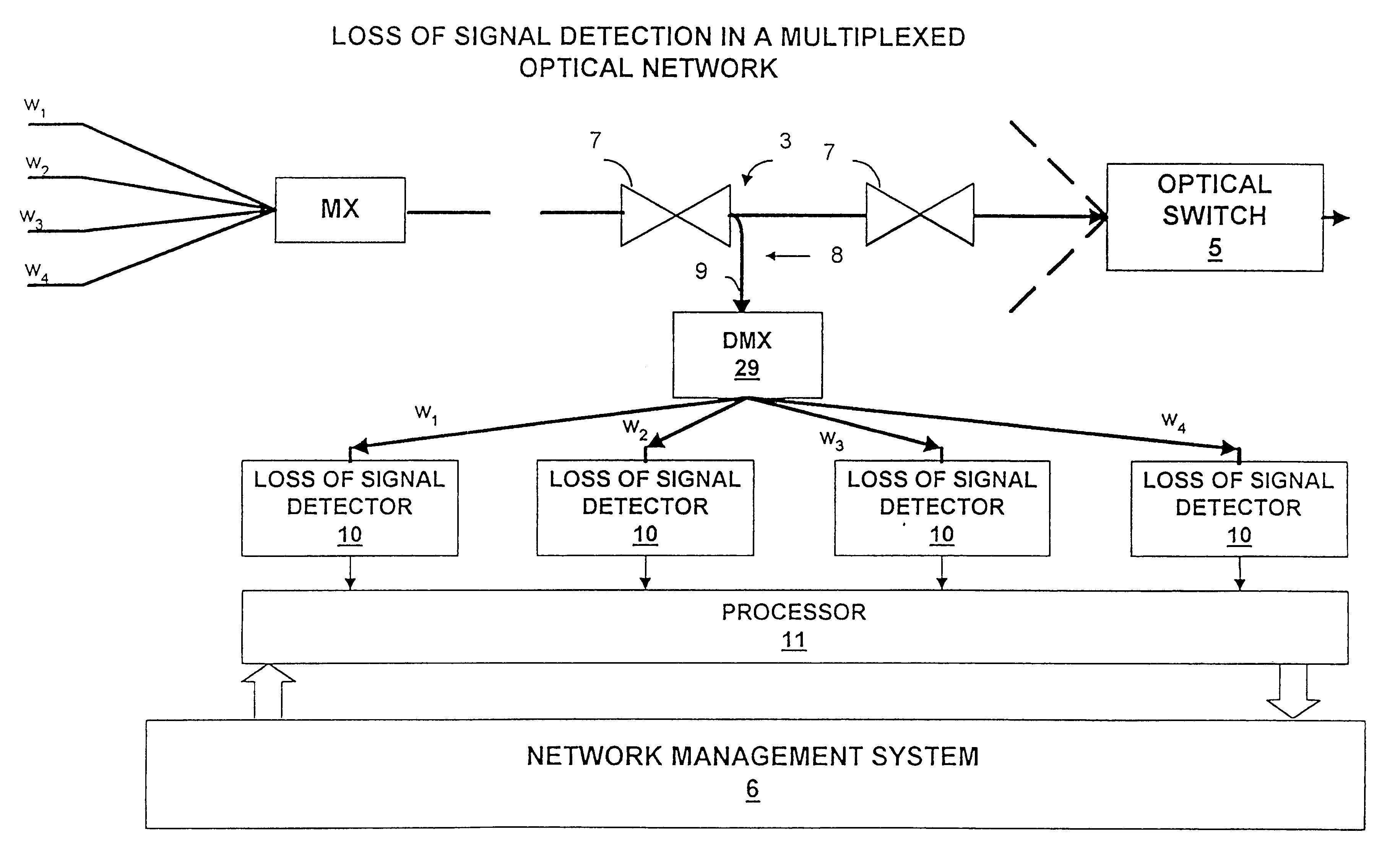
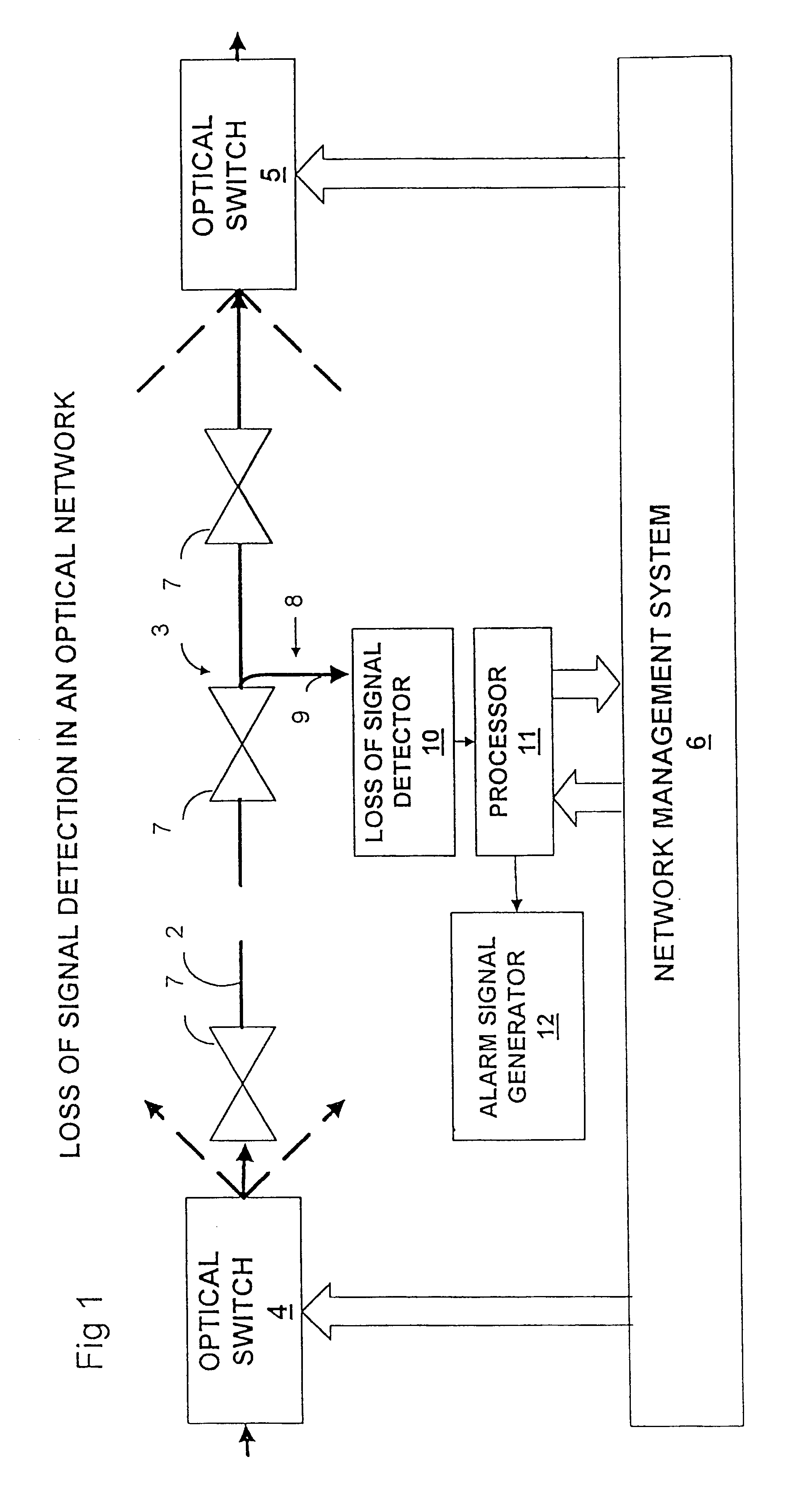
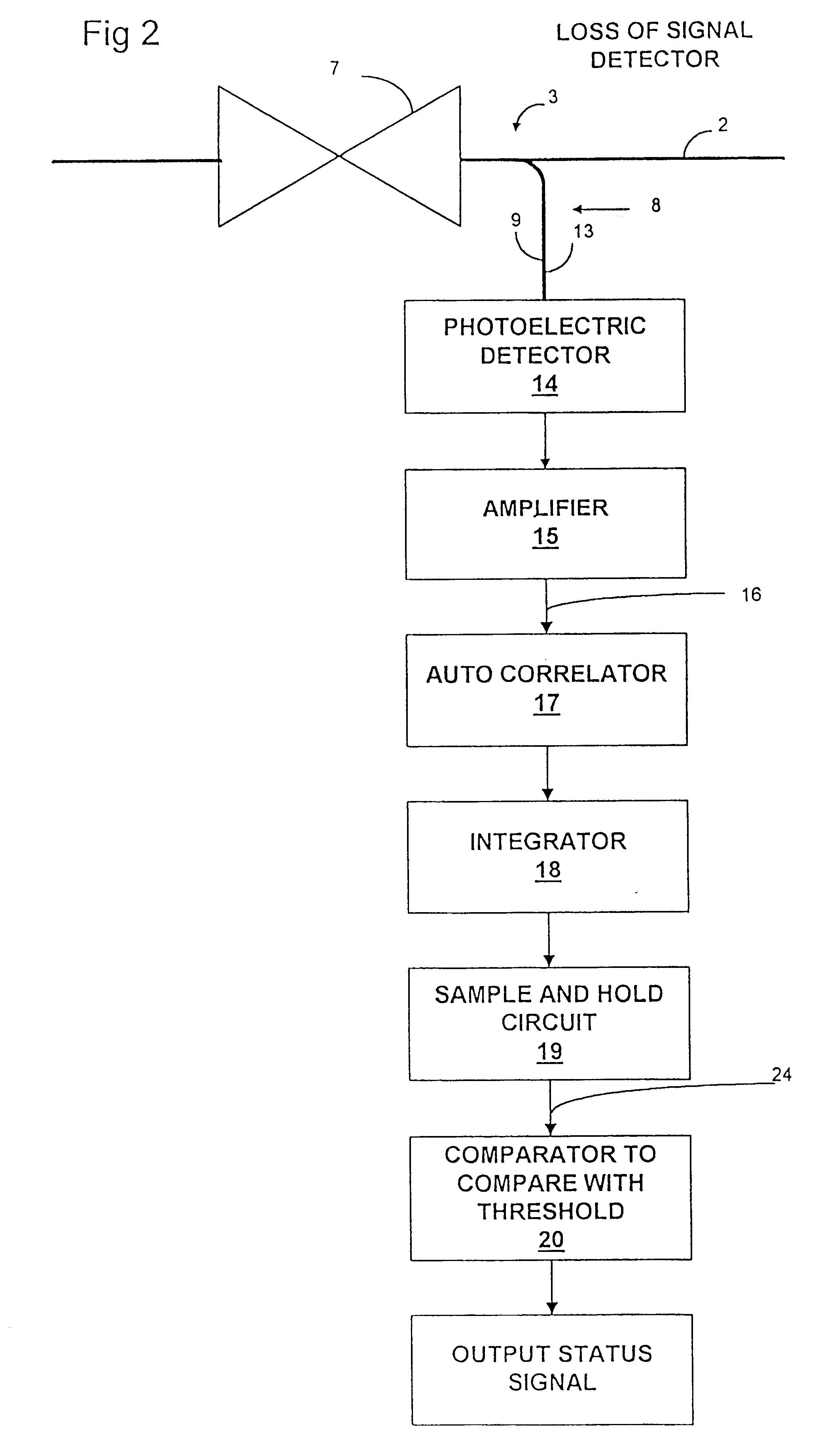
Optical network loss-of-signal detection
Loss of optical signal is detected in a synchronous communications system by detecting features of a monitor signal occurring at a detection frequency corresponding to the frame rate. Since the frame rate is substantially less than the bit rate, monitoring and detection can be performed at a lower bandwidth than the bit rate. An auto-correlation circuit utilises delays which are an integral multiple of the frame rate and produces a detection value which is compared with a threshold value. Alternatively, detection may be based on a power measurement of a band pass filtered monitor signal by setting the lower bandwidth limit above zero frequency and normalizing the measurement of power relative to an average power measurement. A loss of signal may then be detected by a change in power measurement relative to a threshold and can be used for asynchronous systems as well as synchronous systems. Loss of signal detection may be utilised to control an optical switch to re-route optical signals and generate alarm signals. The use of such detection in all optical networks avoids the requirement for electronic processing at the bit rate as a means of detection of loss of signal.
Owner:CIENA
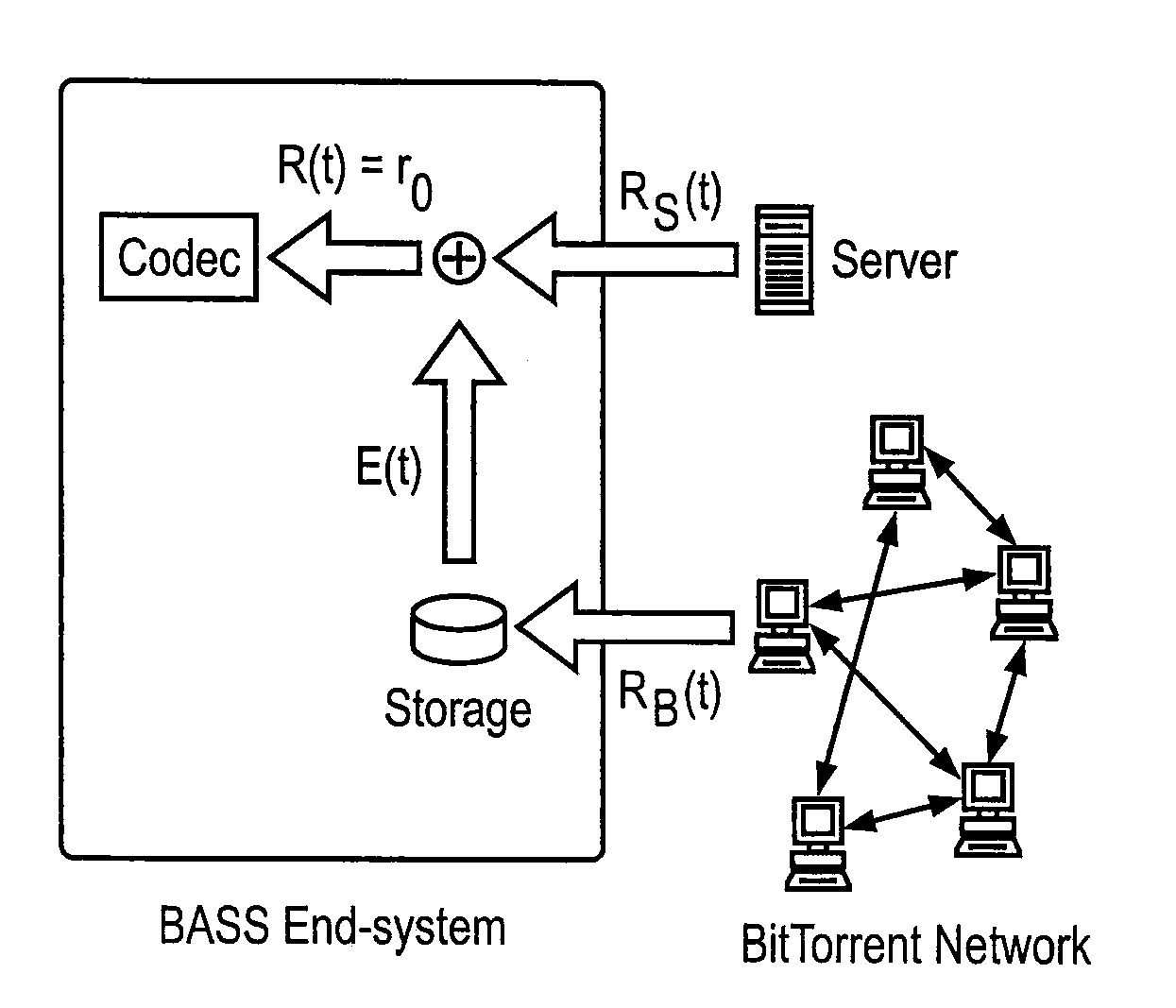
Peer-to-Peer Streaming Of Non-Live Content
ActiveUS20080140853A1Minimal impactEasy to scaleMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionPoint-to-Point ProtocolEnd system
A Peer-to-Peer protocol such as BitTorrent is used to assist streaming. Peers download streaming content from the P2P network while simultaneously playing the downloaded content. As the stream plays, an end system downloads any missing pieces directly from a server or other infrastructure node. This method roughly squares server capacity and can be refined to require on average 0(1) servers regardless of the number of concurrent users. Thus BitTorrent assisted streaming scales better than traditional server-client and other infrastructure-only solutions, each of which requires a number of infrastructure nodes that scale linearly as a function of the number of users. Unlike End-System-Multicast, BitTorrent assisted streaming does not subject users to the vagaries of intermediate unreliable, potentially bandwidth-constrained end-systems; the departure of any single end-system has minimal impact on overall performance; and BitTorrent has a well-crafted incentive mechanism for encouraging users to contribute their upstream capacity.
Owner:BITTORRENT
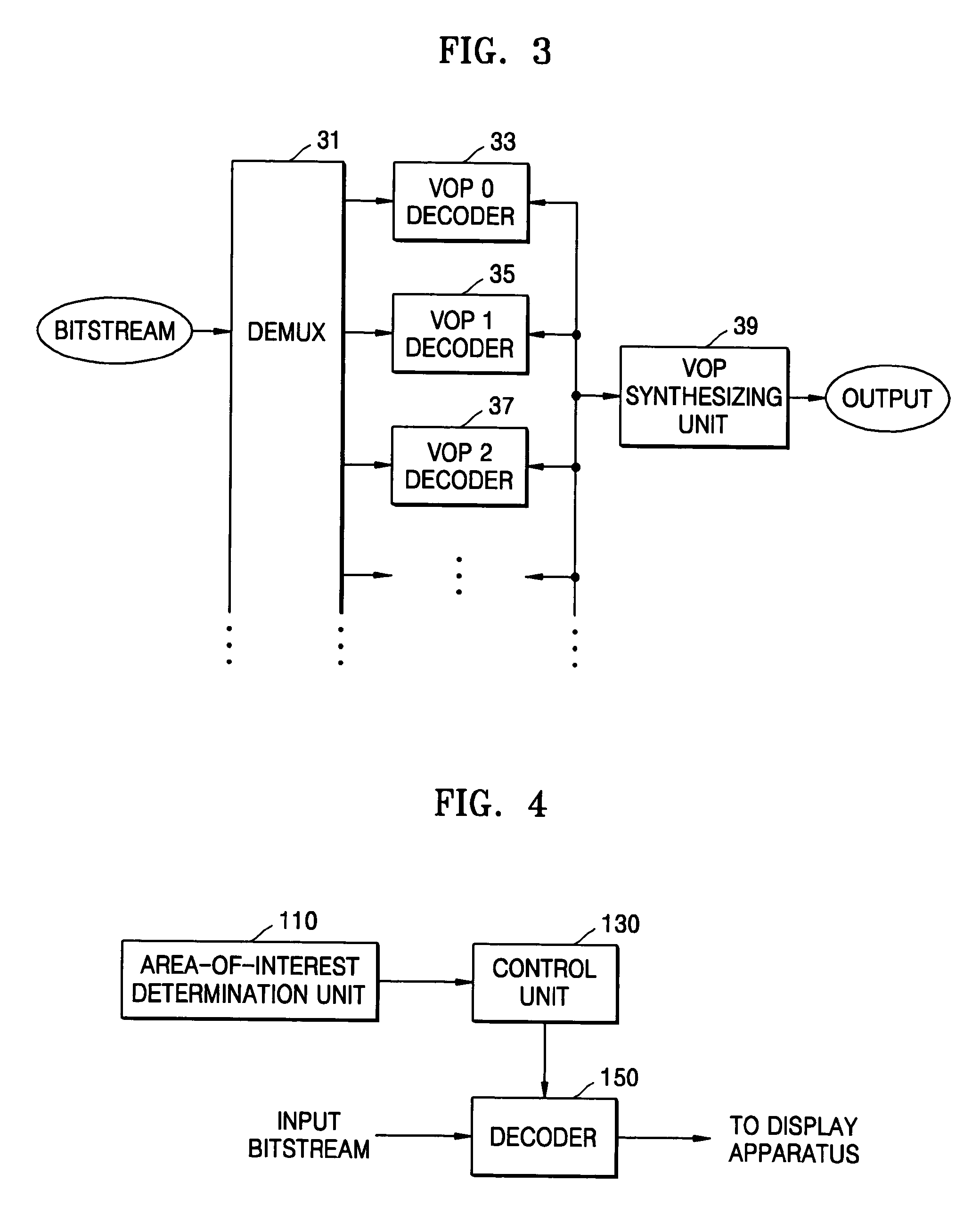
Apparatus and method for processing video data using gaze detection
InactiveUS20070162922A1Improve picture qualityWork lessTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionWorkloadRegion of interest
An apparatus and method for processing video data using gaze detection are provided. According to the apparatus and method, the position of an area-of-interest which a user gazes at in a current image being displayed is detected and the area-of-interest is scalably decoded to enhance the picture quality such that the work load to the decoder can be reduced and the bandwidth limit of a data communication channel can be overcome.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
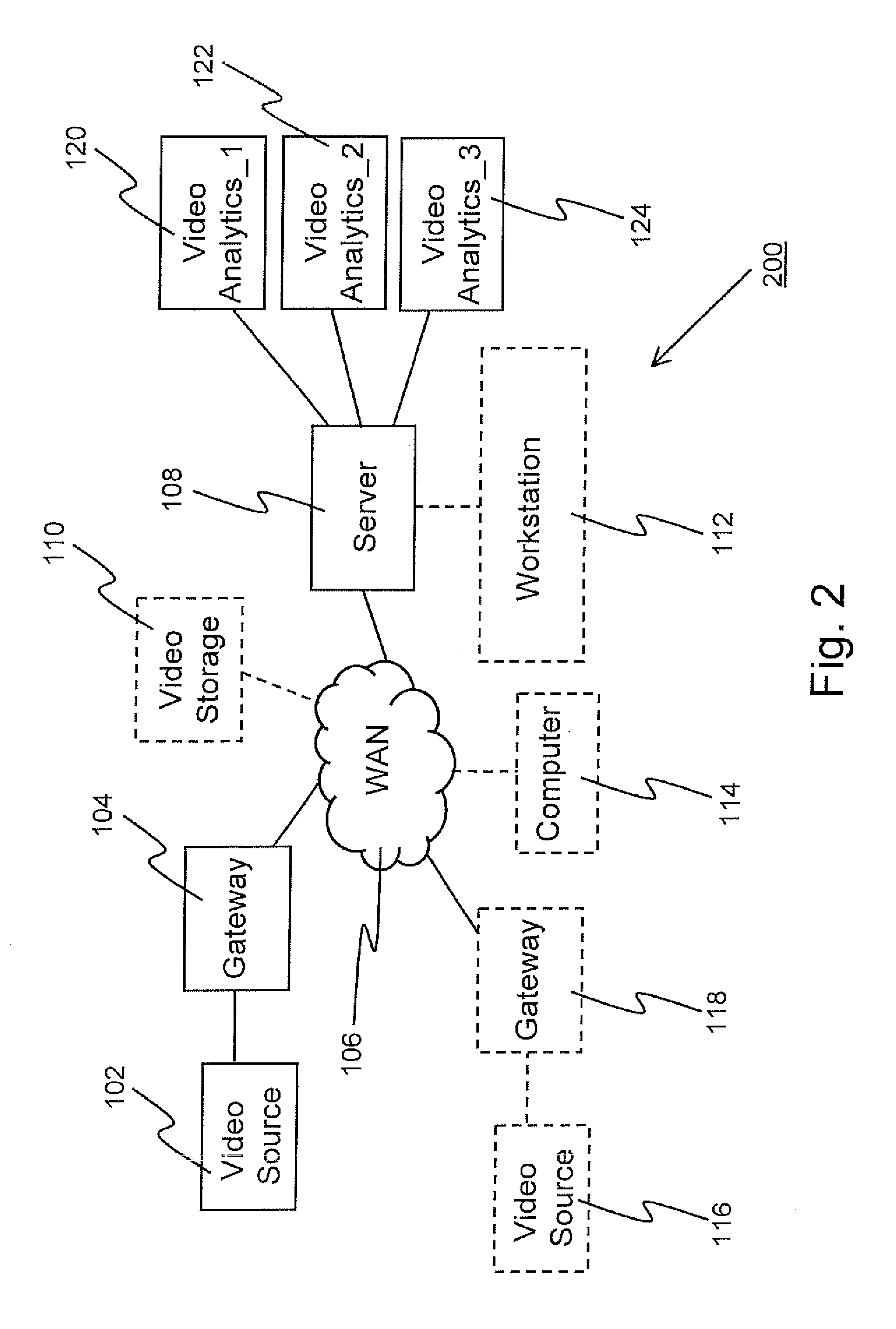
Video analytics with pre-processing at the source end
ActiveUS20120195363A1Reduce bandwidth requirementsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningData compressionComputer graphics (images)
A method for performing video analytics includes receiving at a source end video data including first video data relating to an event of interest. Using video analytics, other than a data compression process, pre-processing of the video data is performed at the source end to reduce the bandwidth requirement for transmitting the video data to below a bandwidth limit of a Wide Area Network (WAN) over which the video data is to be transmitted. The pre-processed video data is transmitted to a central server via the WAN, where other video analytics processing of the pre-processed video data is performed. Based on a result of the other video analytics processing, a signal is generated for performing a predetermined action, in response to an occurrence of the event of interest at the source end.
Owner:HANWHA VISION CO LTD
Secure covert combat identification friend-or-foe (IFF) system for the dismounted soldier
ActiveUS7308202B2Minimize opportunityReduce usageAiming meansElectromagnetic transmissionInfraredAnti spoofing
A combat IFF system, for use in a combat exercise or on the battlefield, including a helmet-mounted passive IFF response unit and a weapon-mounted IFF interrogatory unit for each soldier. Infrared (IR) signals are employed for both challenge and response. The IR response signal is a very narrowly-targeted reflection of the relatively narrow IR transmit signal, thereby minimizing interception opportunities. The transmit and response signals are encoded in a transaction that cannot be compromised even when either or both signals are intercepted and decoded by the enemy. The combat IFF system includes biometric anti-spoofing features that prevent any use by an enemy in possession of captured units. Military radio-frequency (RF) spectrum is not required so there are no bandwidth limitations on simultaneous IFF transactions in the battlefield. A combat IFF transaction is completed in milliseconds.
Owner:CUBIC DEFENSE SYST
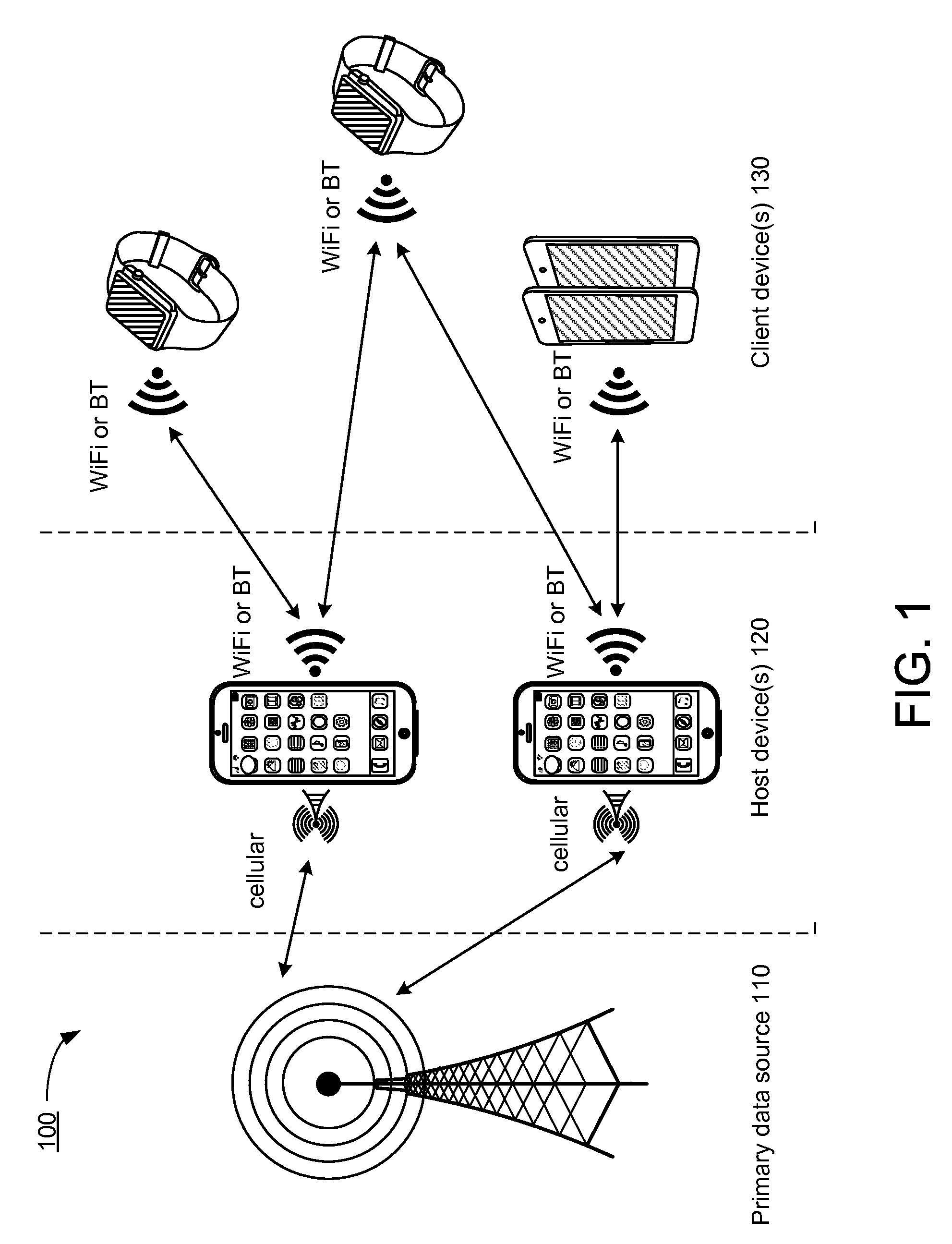
Network bandwidth sharing for small mobile devices
ActiveUS20160095017A1Monitor amountService provisioningAccounting/billing servicesFile area networkClient-side
Client devices with wireless functionality, but without wide area network or cellular network functionality, can obtain network access via a host device, where the host device has network access. Such network access can be obtained when a client device of a user is in local range of a host device, e.g., of a different user. The host device may enable network bandwidth sharing with settings that specify a threshold of resource usage (e.g., battery or bandwidth limit). An authentication process can confirm that either one or both of a client device and a host device are registered for the network bandwidth sharing. A server can monitor the amount of resources shared by the host device, and manage incentives to the user of the host device.
Owner:APPLE INC
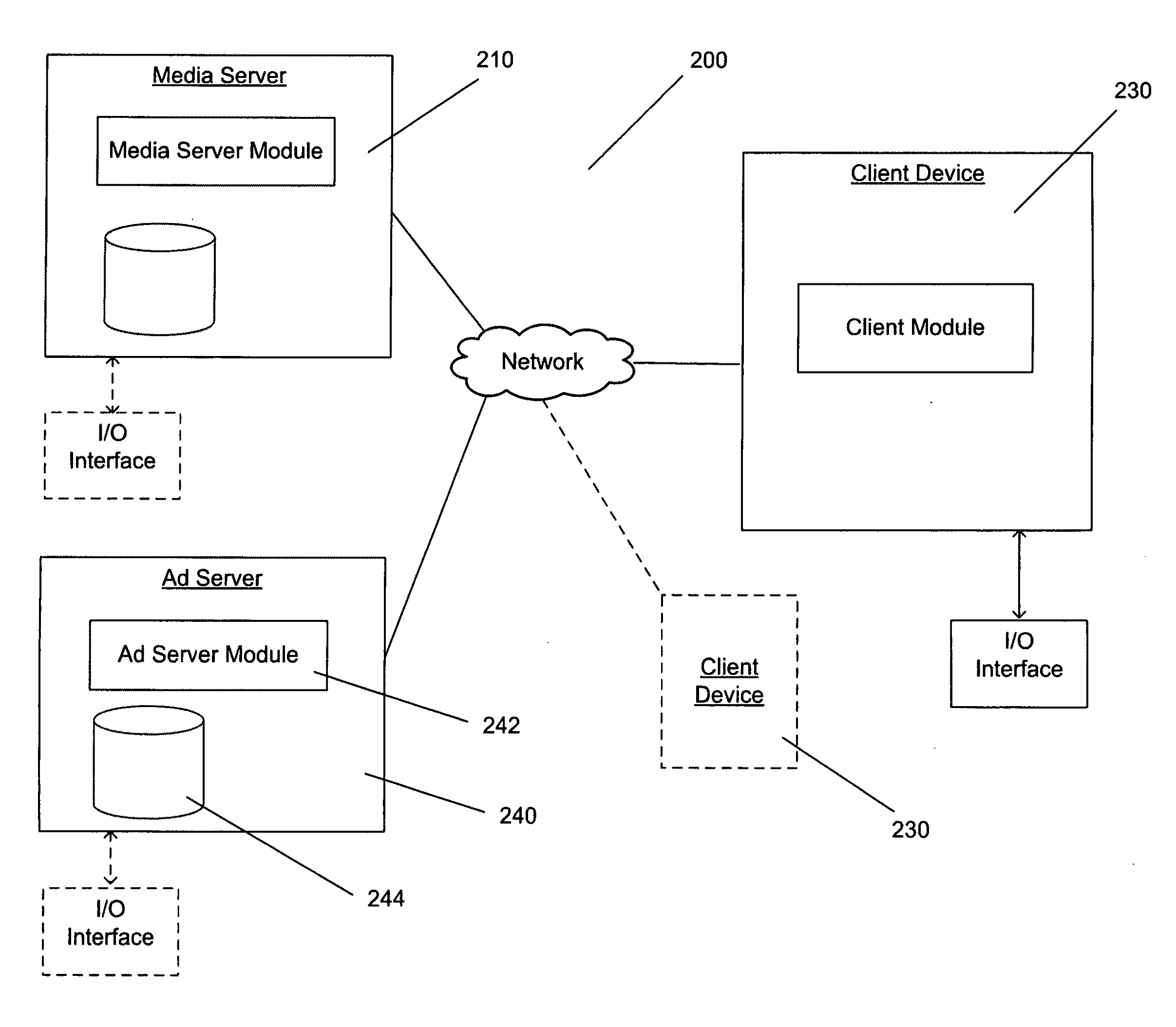
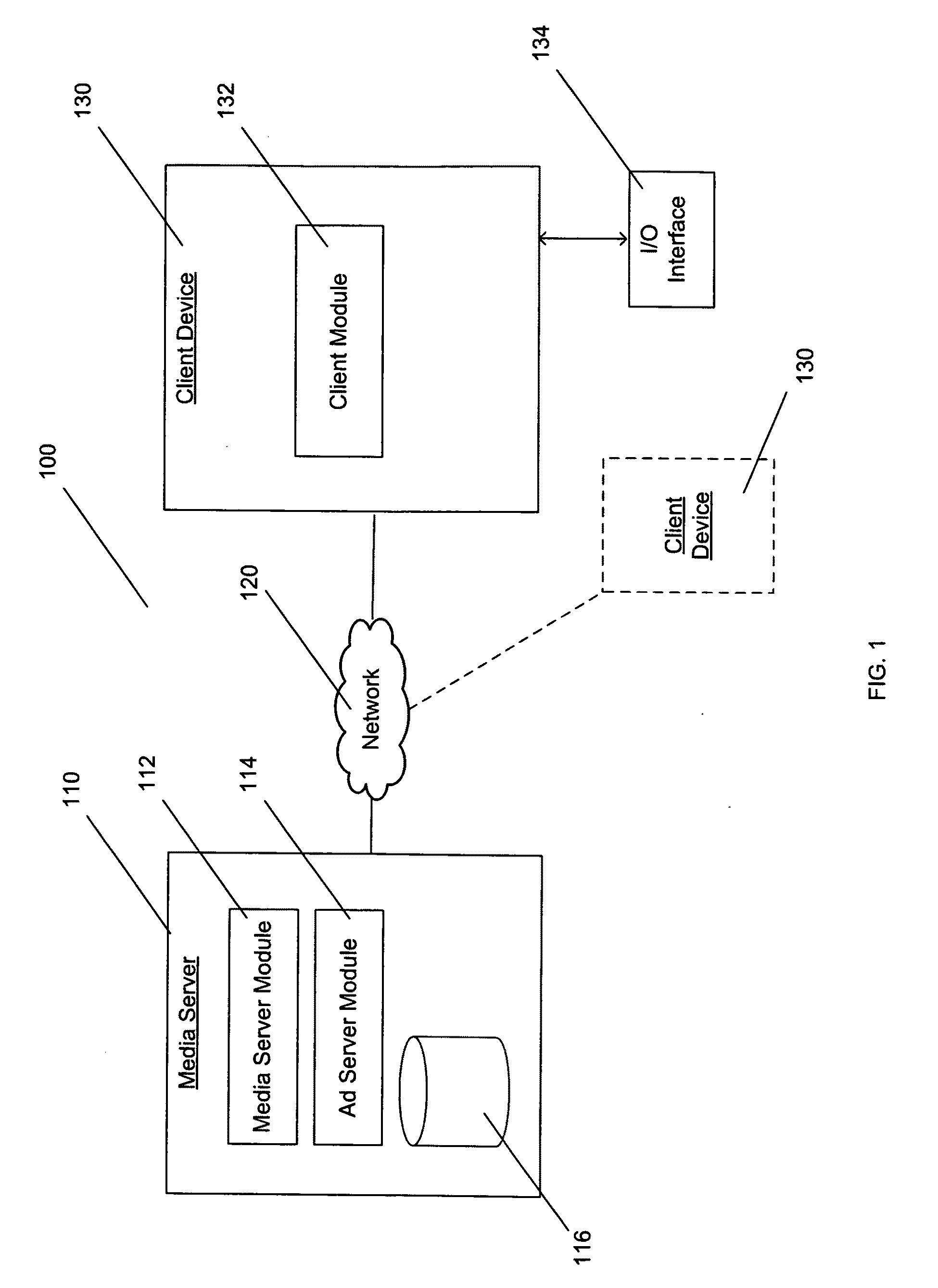
Interactive advertising System
InactiveUS20110295667A1Draw in and maintain a user's attentionImprove transfer rateDiscounts/incentivesInteractive displaysData transmission
A system and computerized process for interactive display of advertisements is contemplated. The computerized process is embodied by online software that enables end users to voluntarily view and interact with an advertisement. Incentives may be offered for interacting with the advertisement. The incentives may relate to data transmission parameters such as data transmission rate. The incentives may be based on a monitored level of interaction by a user with the advertisement. Upon acceptance and / or interaction with the advertisement the transmission rate of the file may be increased up to the limit of the bandwidth otherwise available to the user.
Owner:BUTLER DAVID
Flexible spectrum support in cellular wireless communications
ActiveUS20140126498A1Pilot signal allocationWireless commuication servicesFrequency spectrumCommunications system
Systems and methods for flexible spectrum, or bandwidth, support in a cellular communications network are disclosed. In one embodiment, a base station for a cellular communications network is configured to transmit a non-standardized bandwidth carrier and information that identifies a standardized bandwidth and additional information that, together with the information that identifies the standardized bandwidth, defines a non-standardized bandwidth of the non-standardized bandwidth carrier. In one embodiment, the additional information defines a bandwidth adjustment for the standardized bandwidth that defines the non-standardized bandwidth. In one embodiment, the bandwidth adjustment is a symmetric bandwidth restriction. In another embodiment, the bandwidth adjustment is an asymmetric bandwidth restriction. In yet another embodiment, the bandwidth adjustment is a symmetric bandwidth expansion. In yet another embodiment, the bandwidth adjustment is an asymmetric bandwidth expansion.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
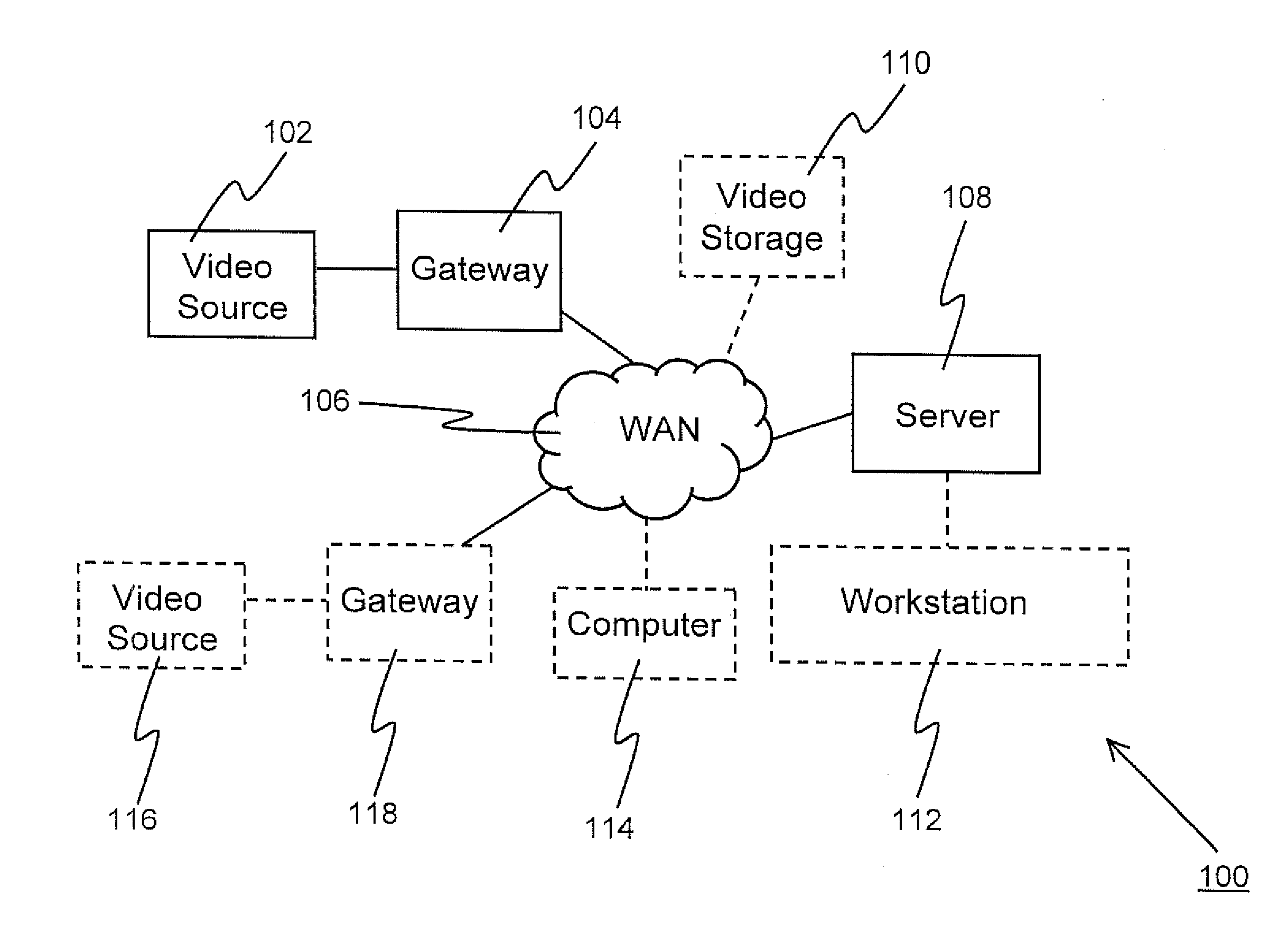
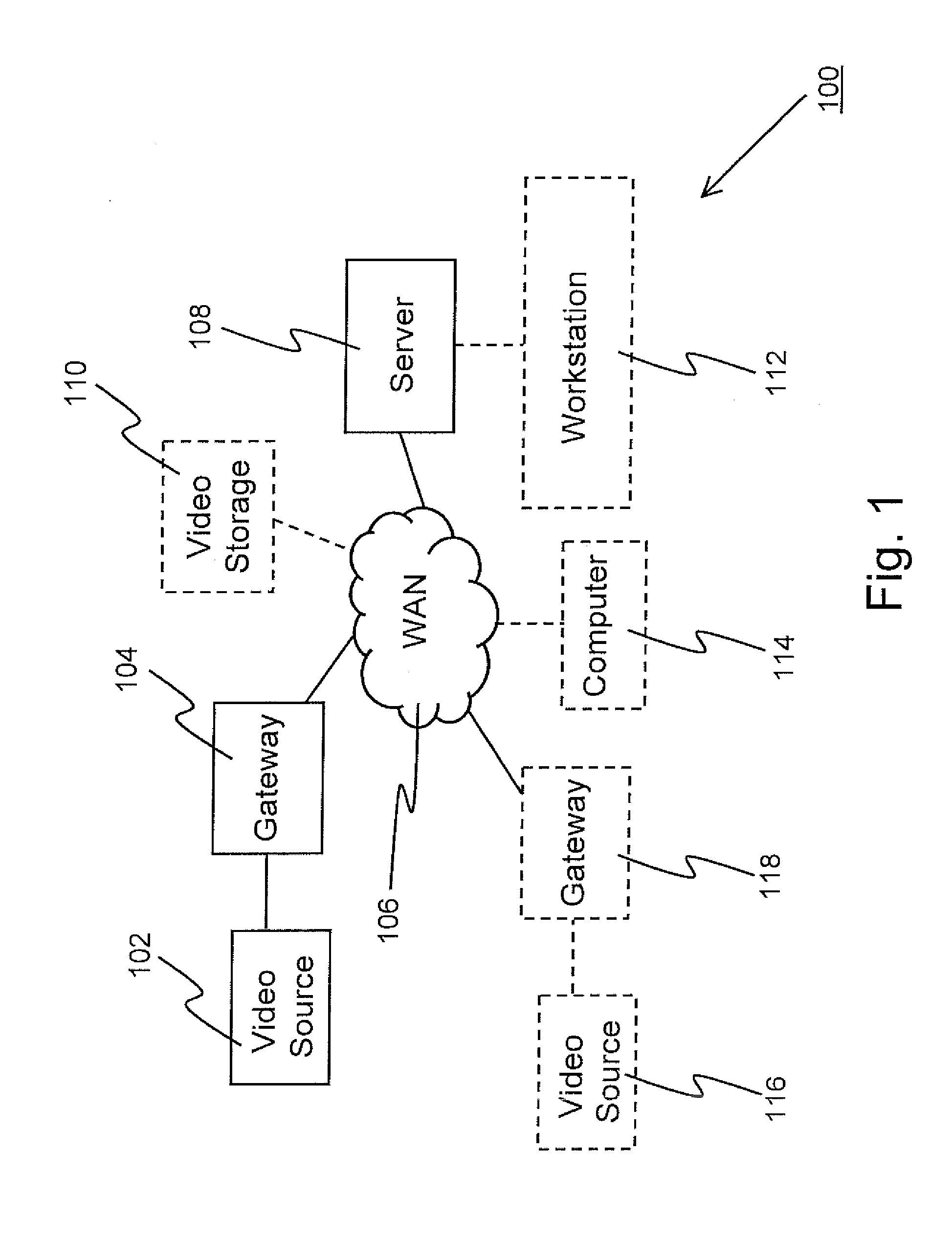
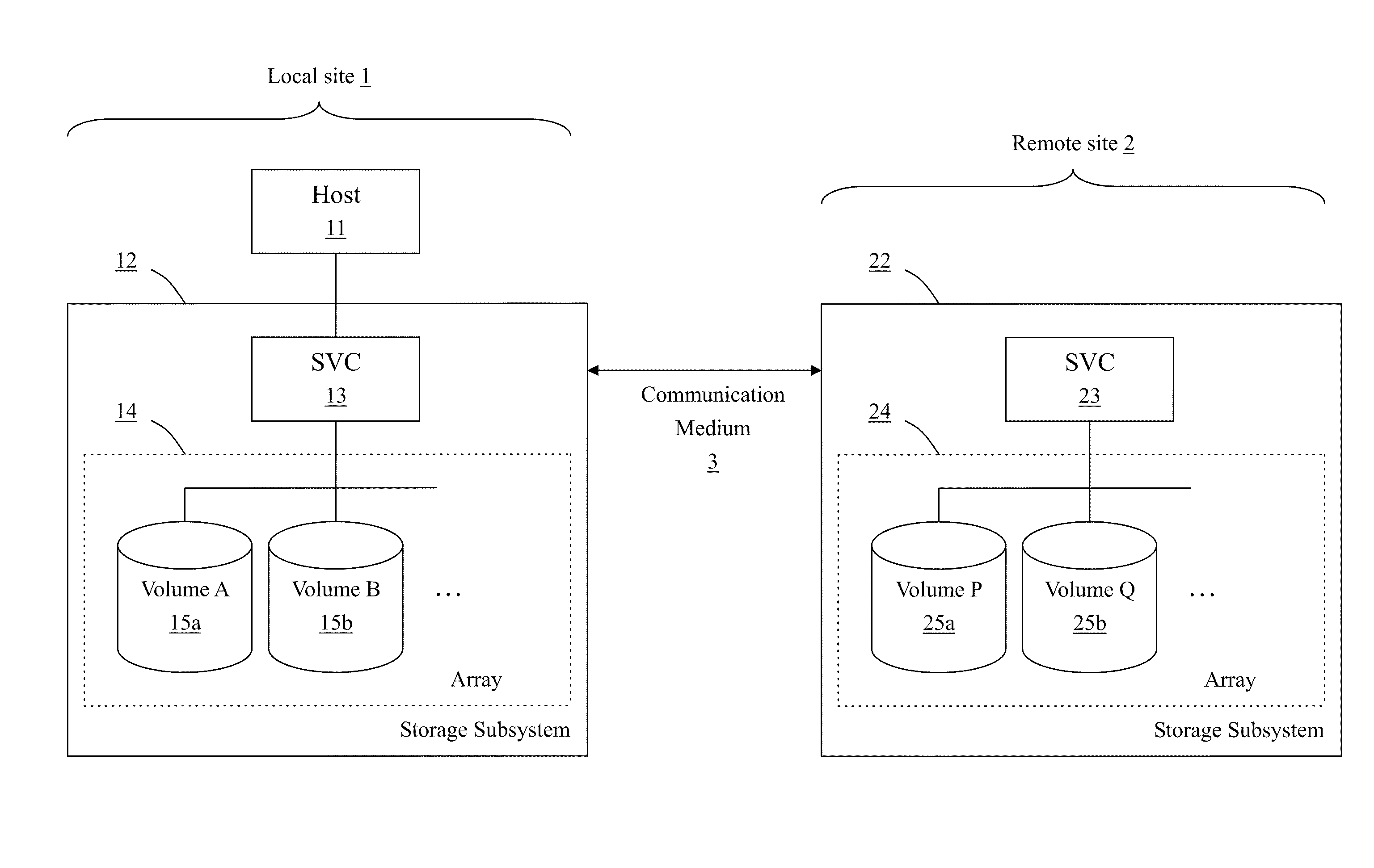
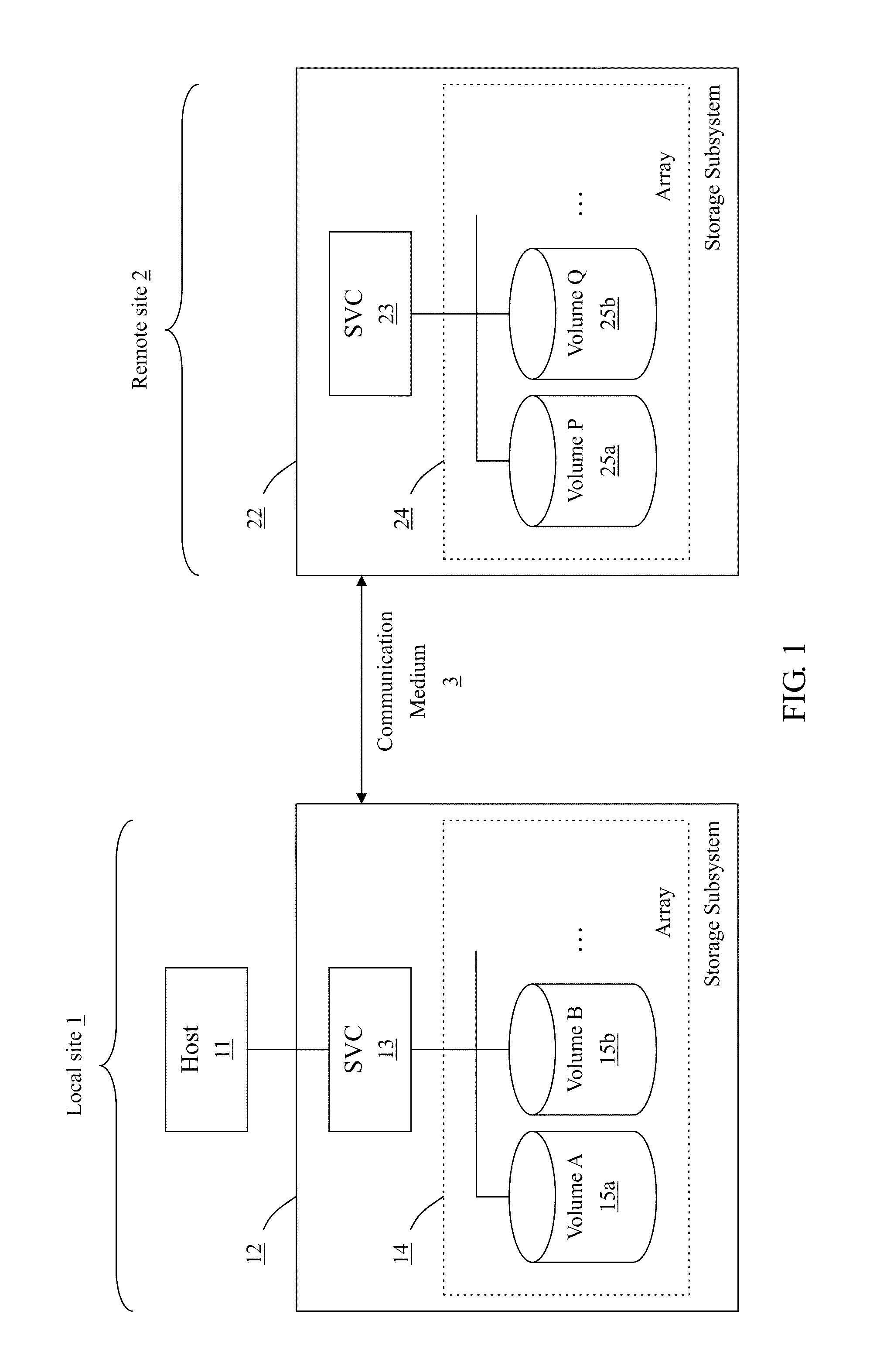
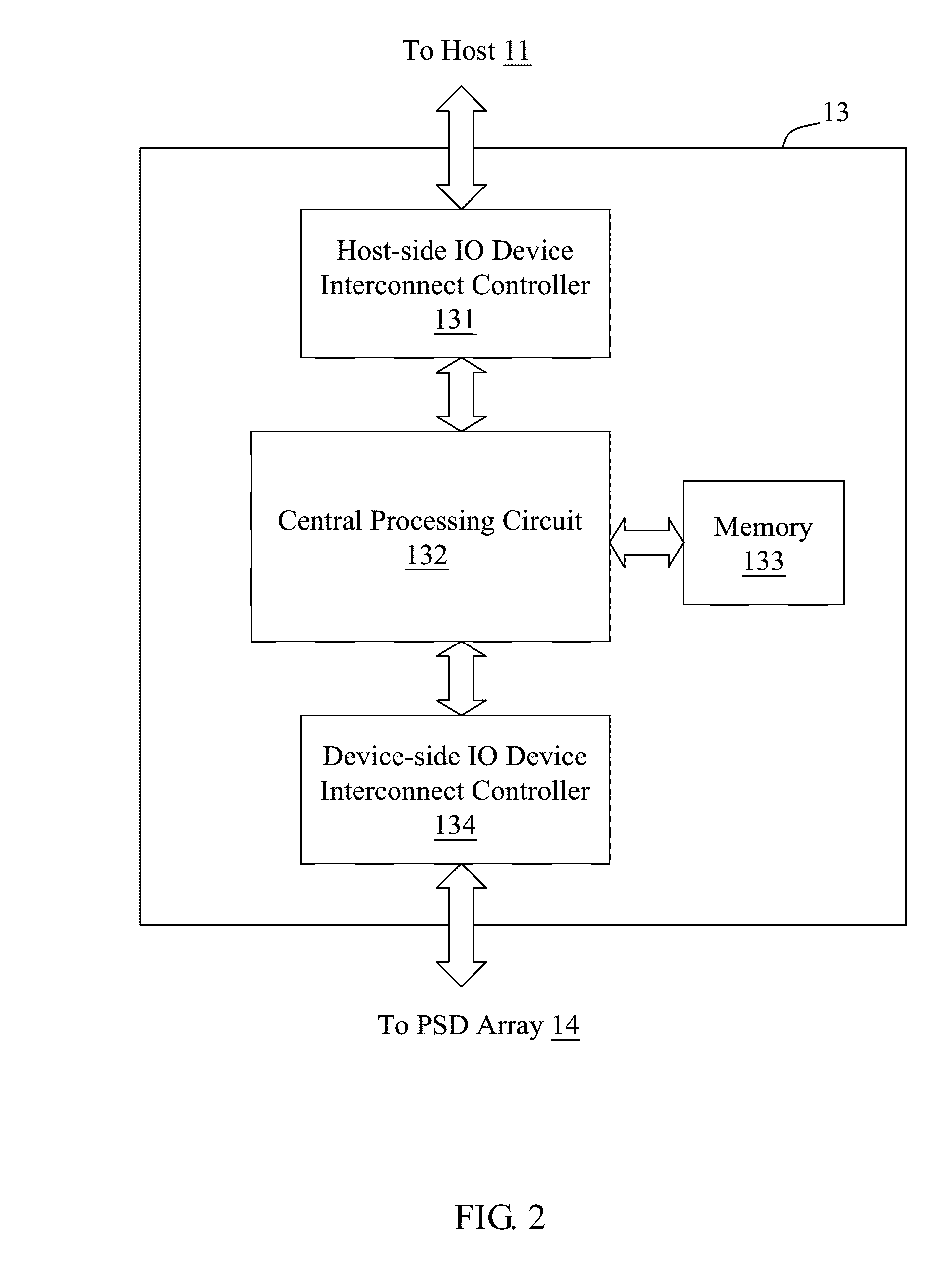
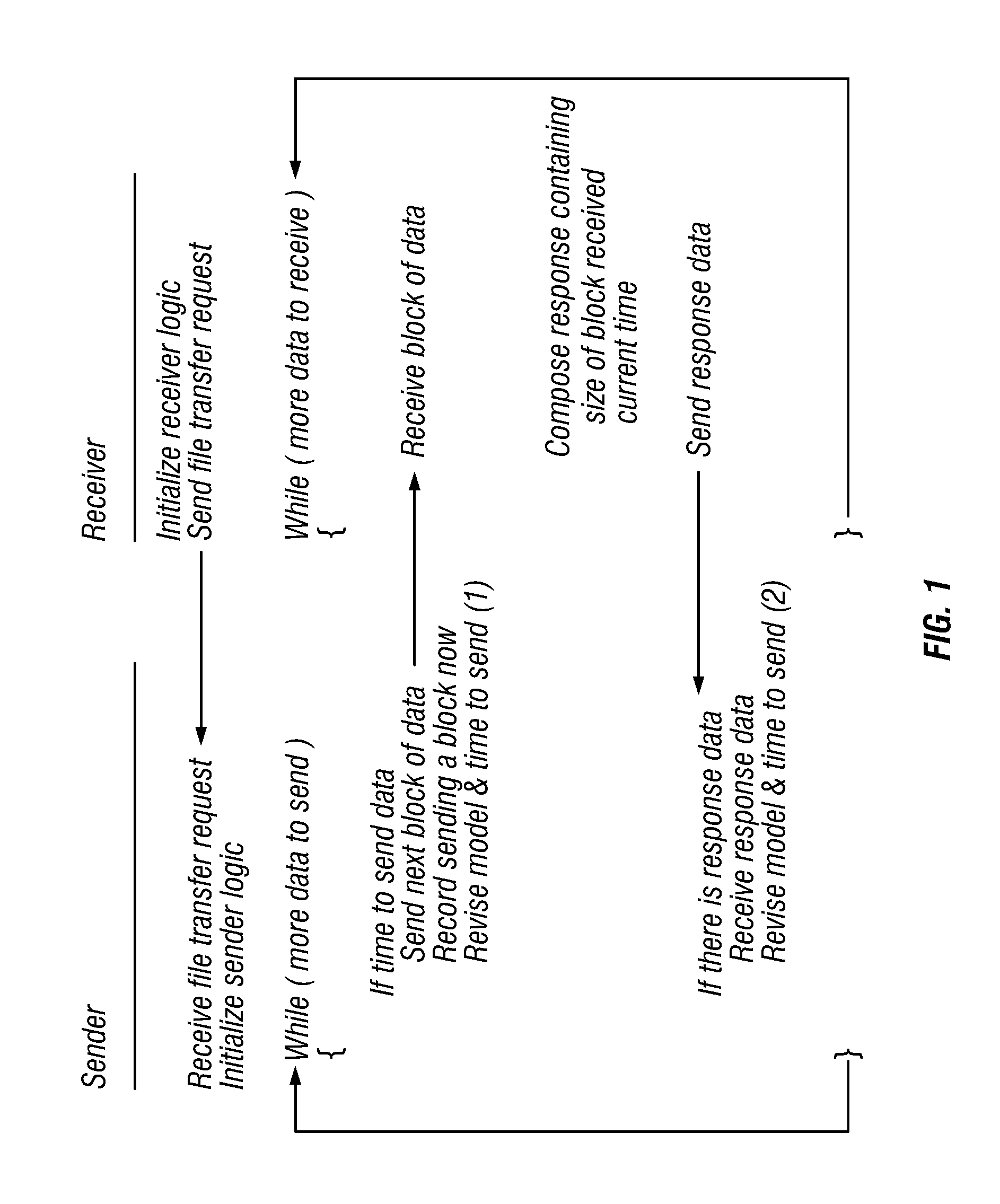
Method for Remote Asynchronous Replication of Volumes and Apparatus Therefor
ActiveUS20100205392A1Enhanced data transmissionGuaranteed uptimeMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionOriginal dataRemote data transmission
A method for remote asynchronous volume replication and apparatus therefore are disclosed. Asynchronous replication is applied to deal with data changes on the source volume on the local site incurred by Host IO requests. In coordination with the “point-in-time differential backup” technology, the data is subjected to be backuped to Source BAS on the local site (backup-on-write operation) only when the original data being written into the block of the source volume is different from the data of the corresponding block of the destination volume on the remote site. As a result, once a new data is written into the source volume completely, the host will be responded that its Host IO request is completed. Therefore, the data necessarily transmitted to the destination volume on the remote site can be minimized, and the problem of remote data transmission limited by network bandwidth can be prevented effectively, thereby keeping the operation performance of the storage system at a better level.
Owner:INFORTREND TECH INC
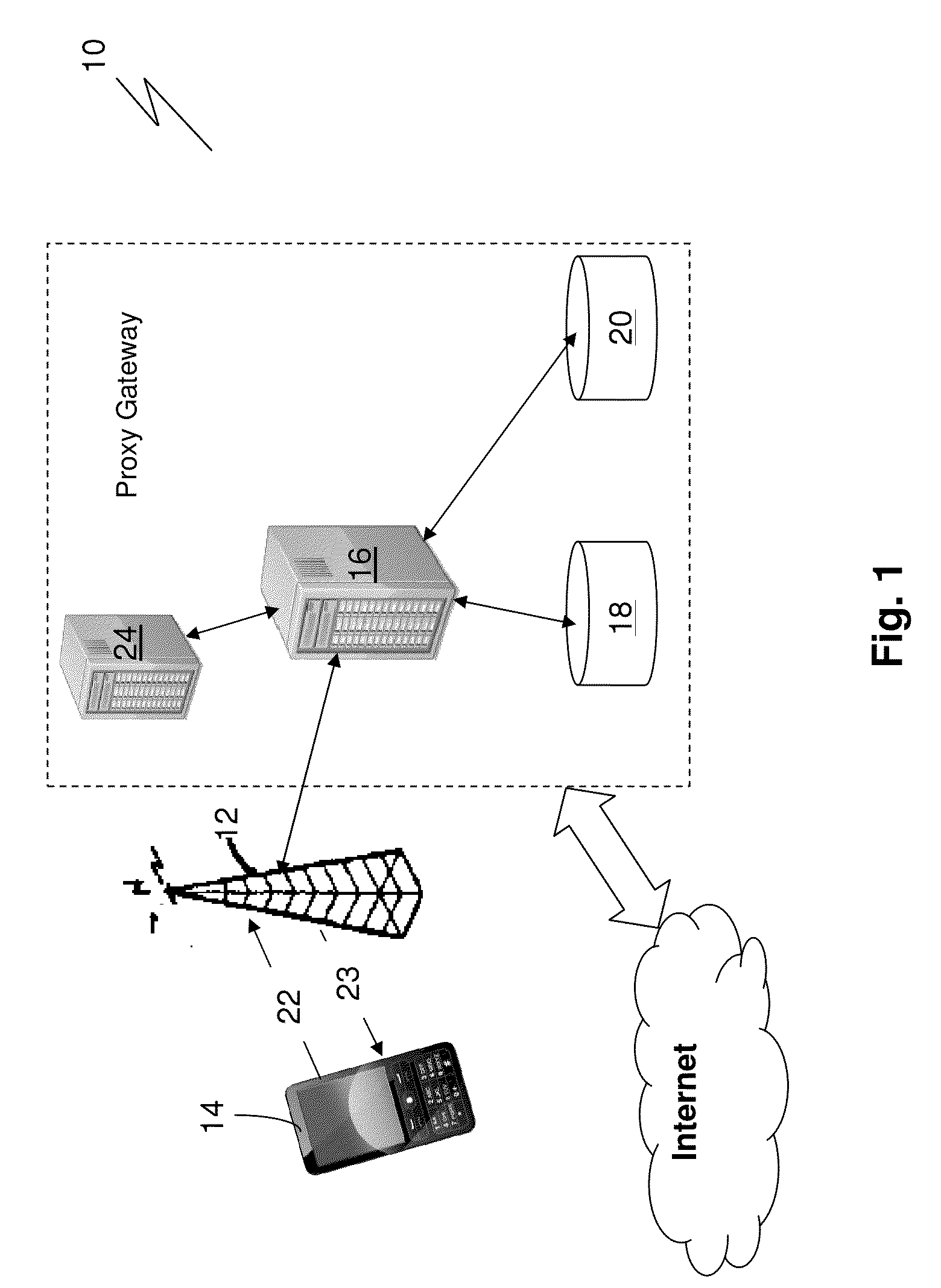
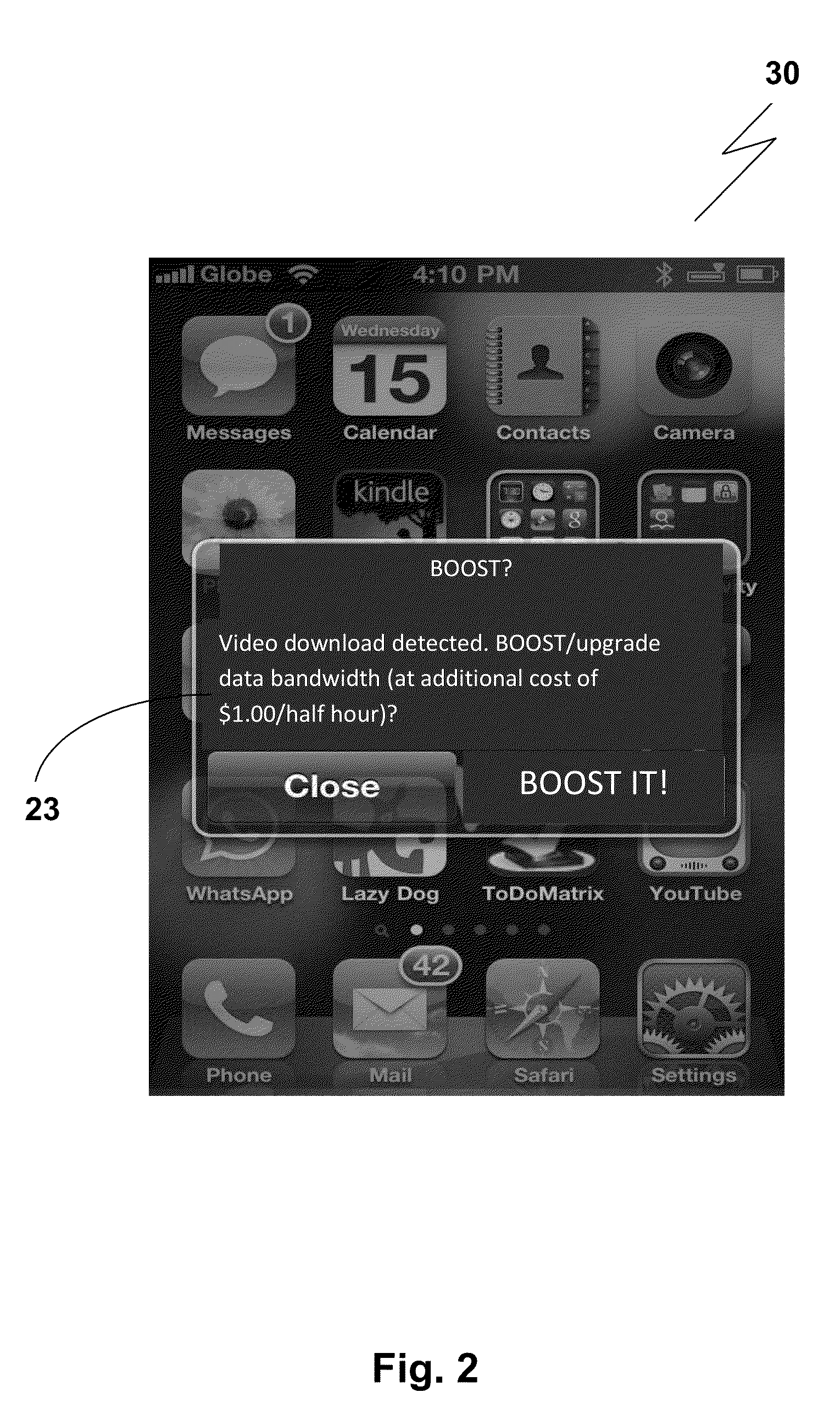
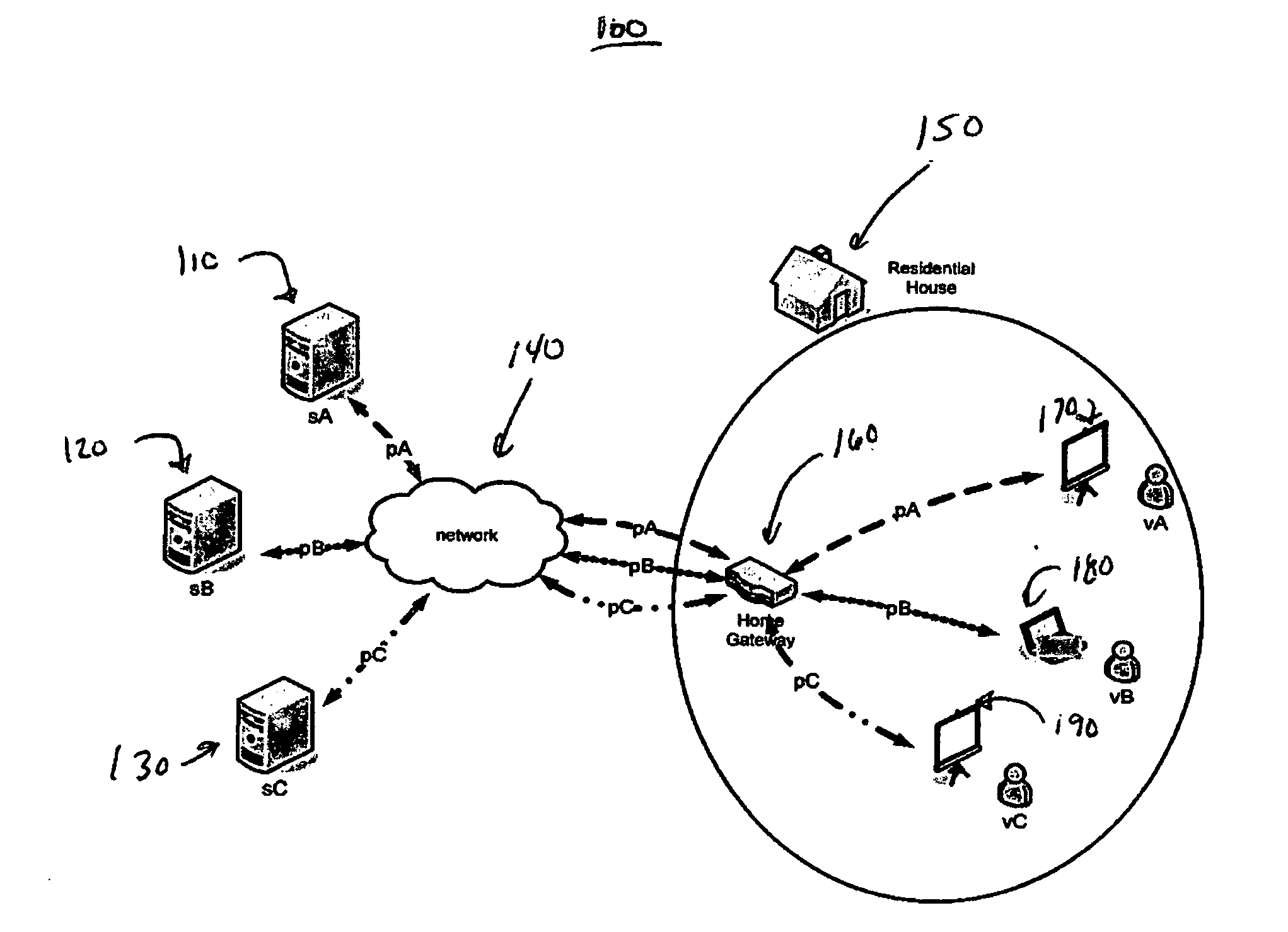
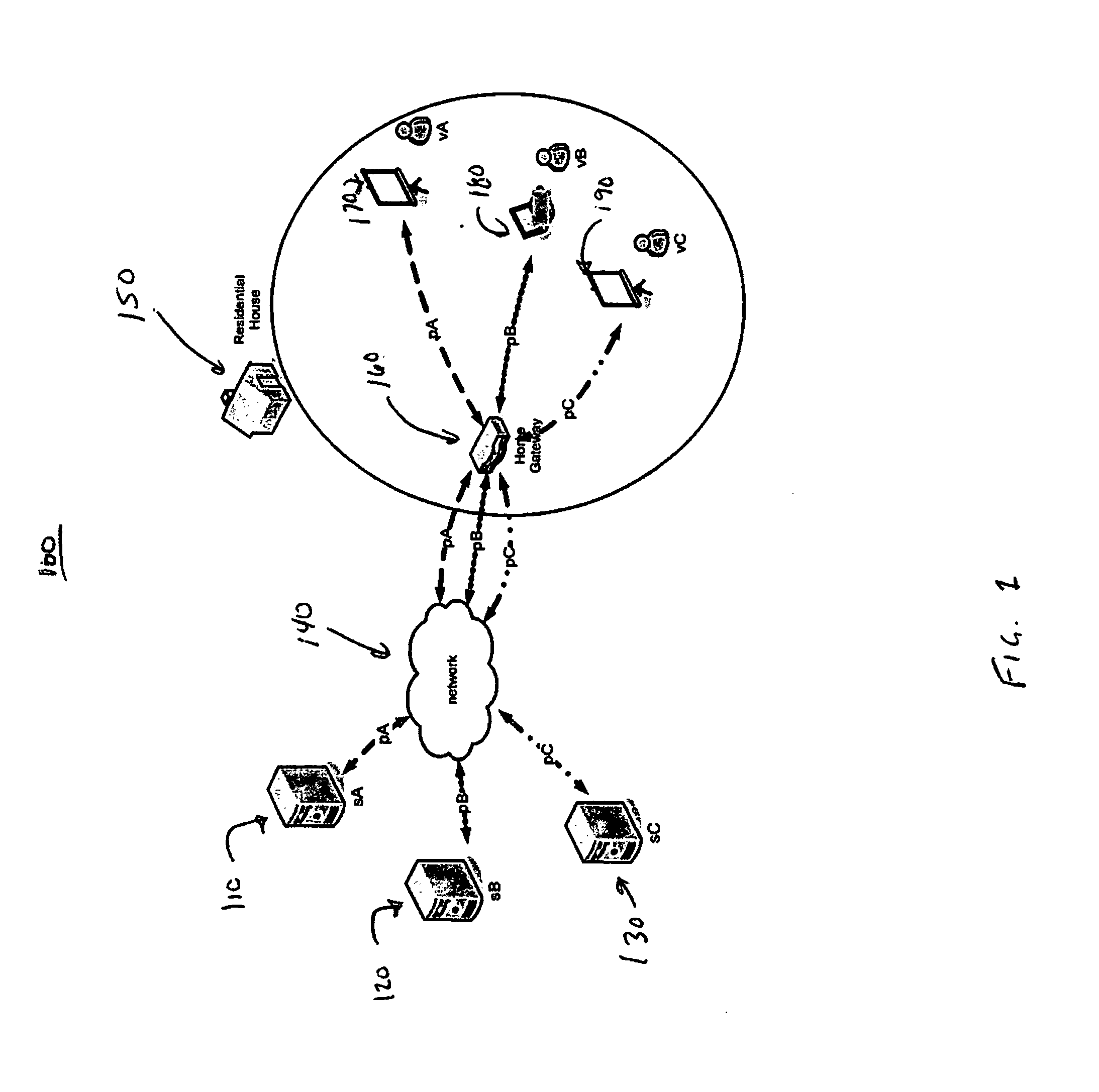
System and method for adjusting the amount of data bandwidth provided to a mobile device
ActiveUS20130023232A1Accounting/billing servicesNetwork traffic/resource managementAction modelMobile device
The invention provides a system for adjusting the amount of data bandwidth provided to a mobile device comprising a bandwidth adjustment facilitator arranged to receive a request from the mobile device for adjusting the amount of data bandwidth; a bandwidth throttler in communication with the bandwidth adjustment facilitator; the bandwidth throttler adapted to cap or allocate excess available data bandwidth to the mobile device; wherein on receipt of the request, the bandwidth adjustment facilitator process the request and if the request is successfully processed, adjusts the data bandwidth provided to the mobile device via the bandwidth throttler. The system may further be adapted for billing / charging based on either pay-per-specified-time model or pay per action model.The invention is conveniently suited for use in telecommunications system and does not require modifications to be made to existing telecommunications system.
Owner:CHIKKA PTE LTD
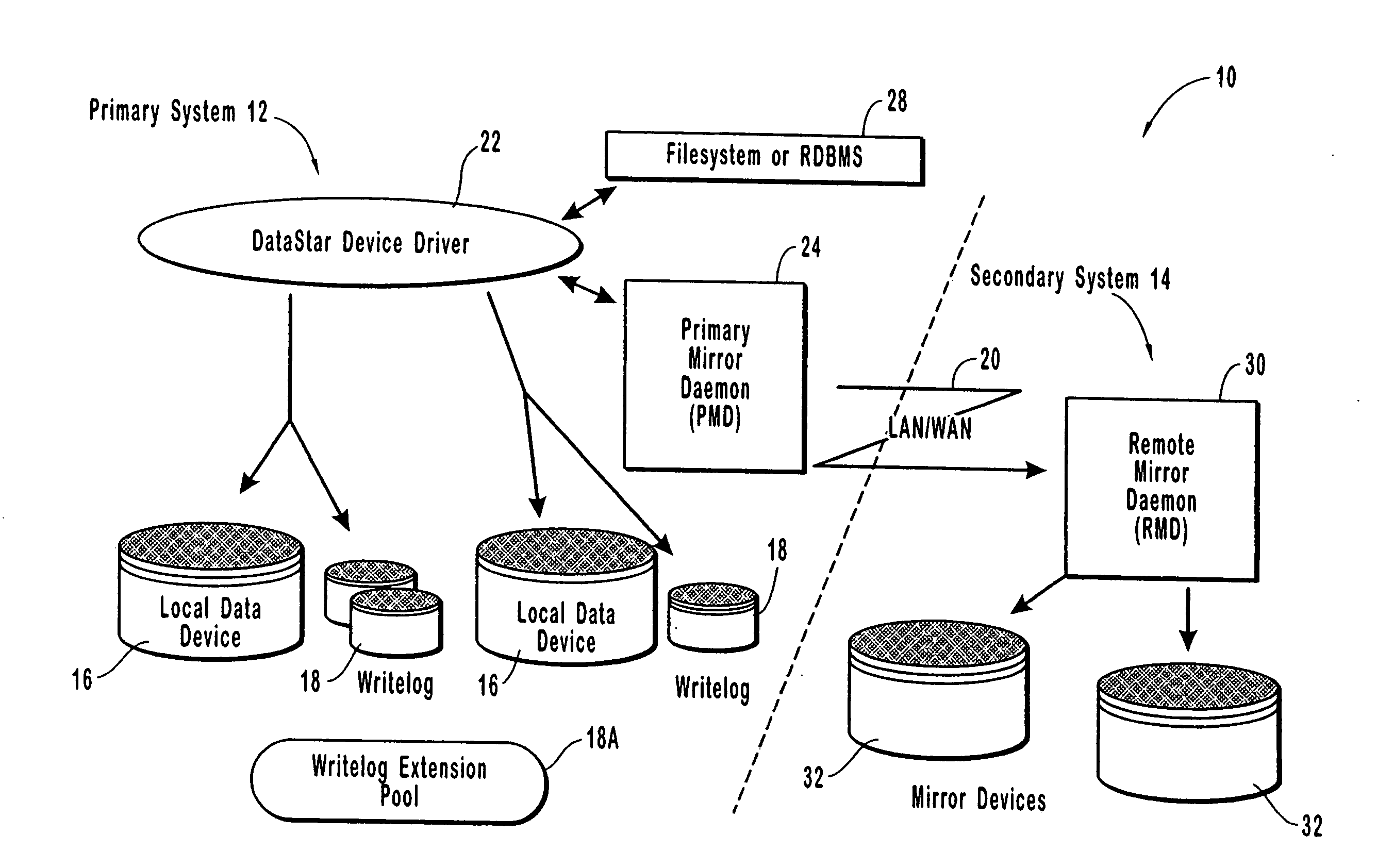
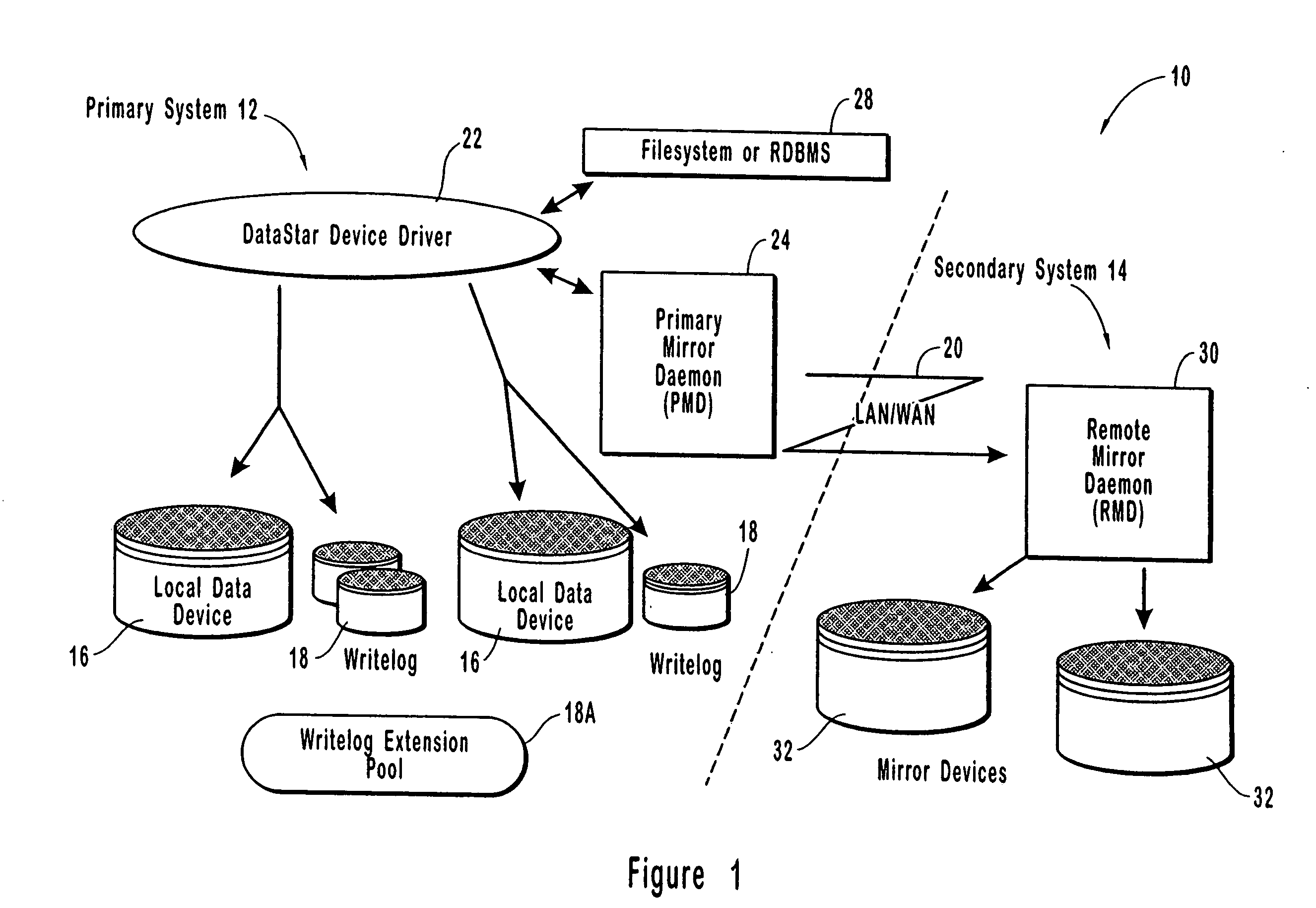
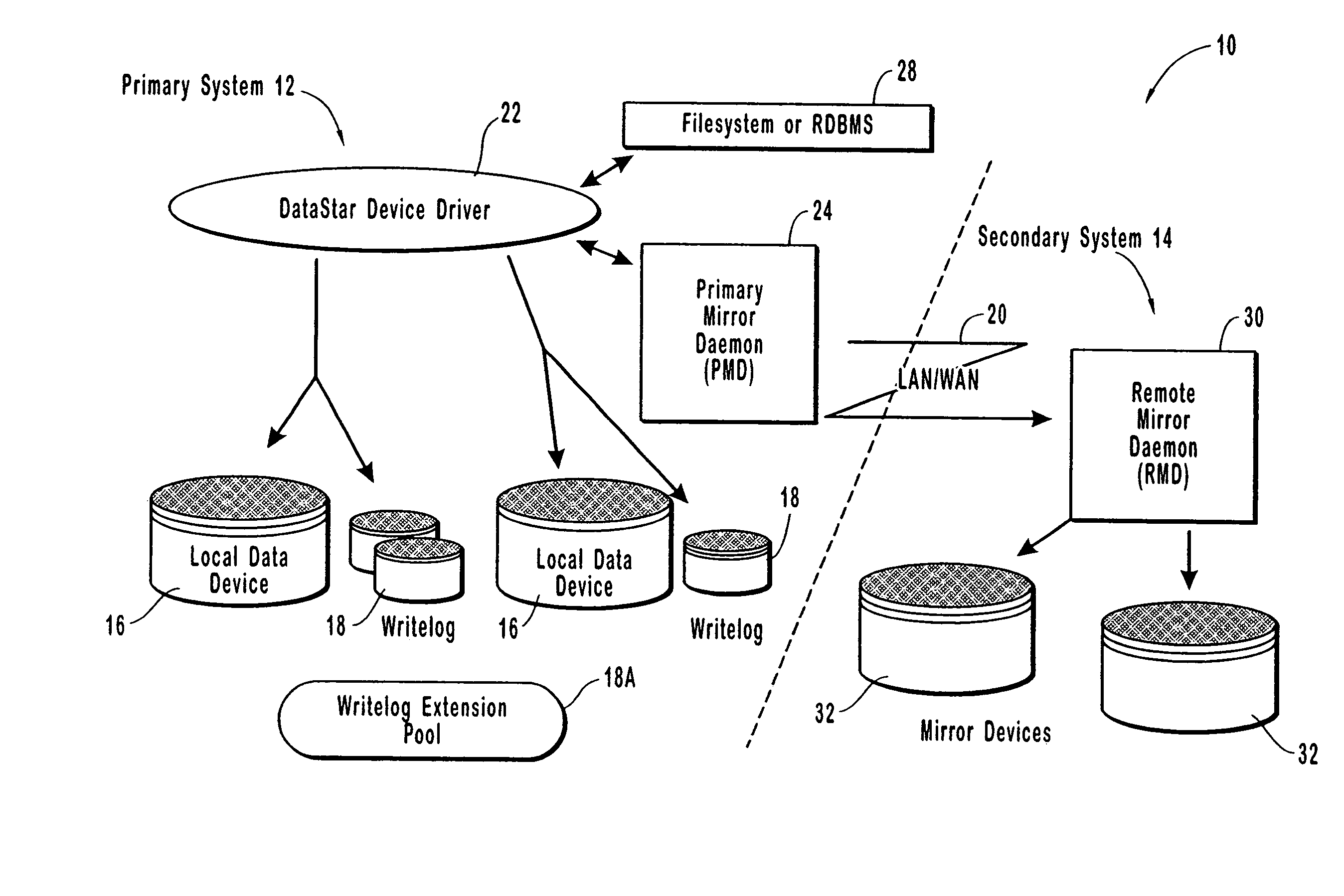
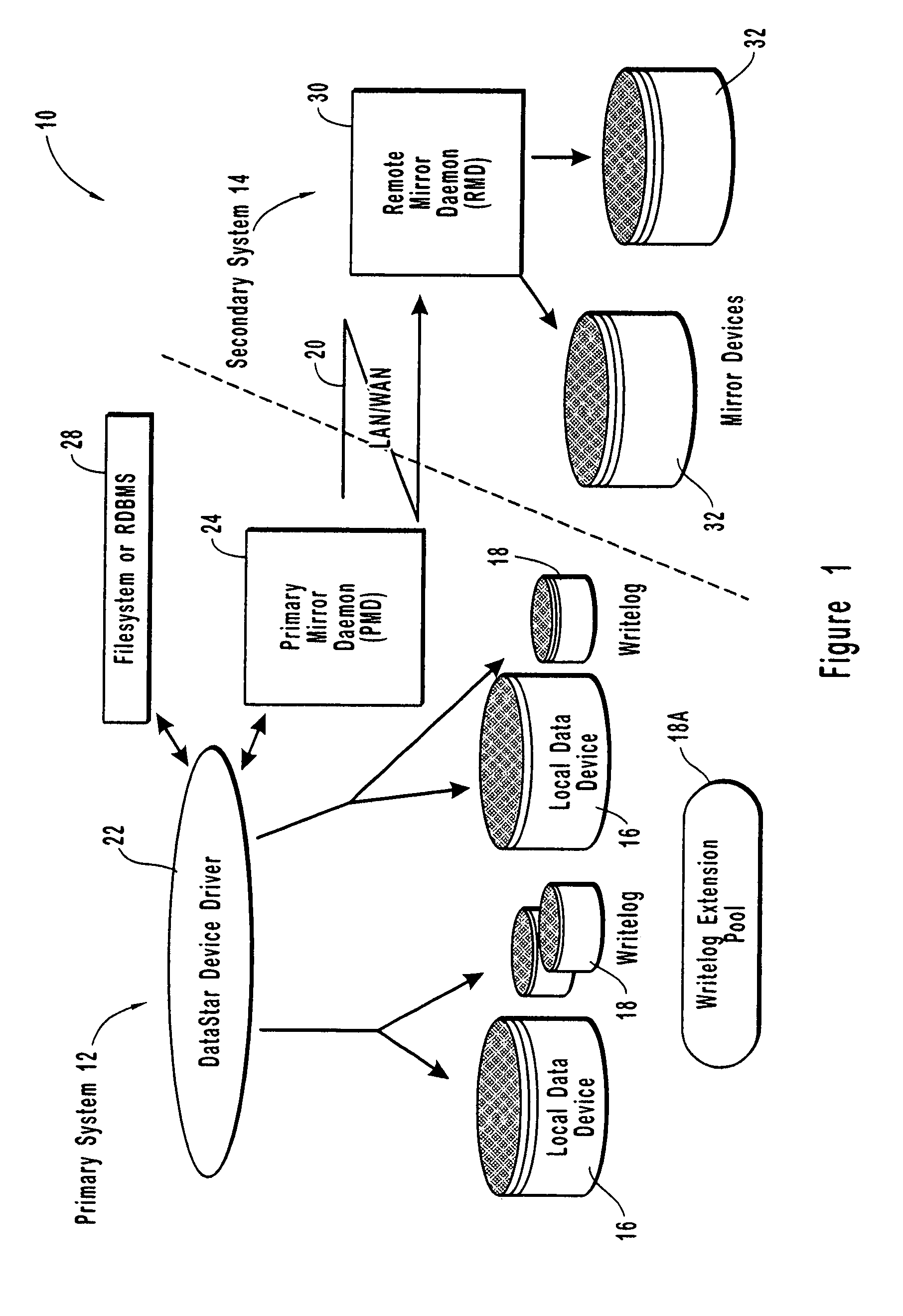
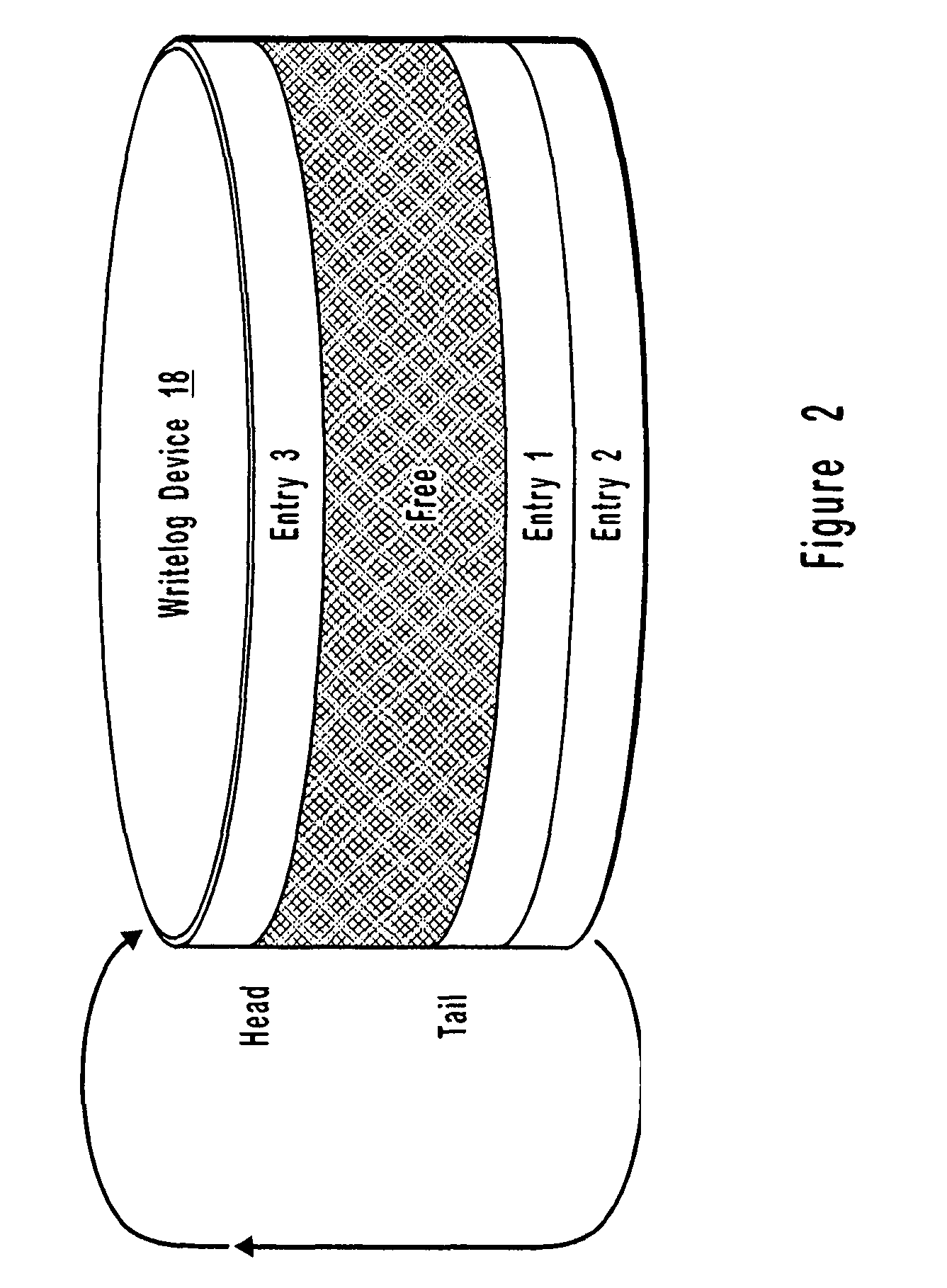
Resource allocation throttling in remote data mirroring system
InactiveUS20070028139A1Increase spaceImprove reliabilityResource allocationError detection/correctionGraphicsGraphical user interface
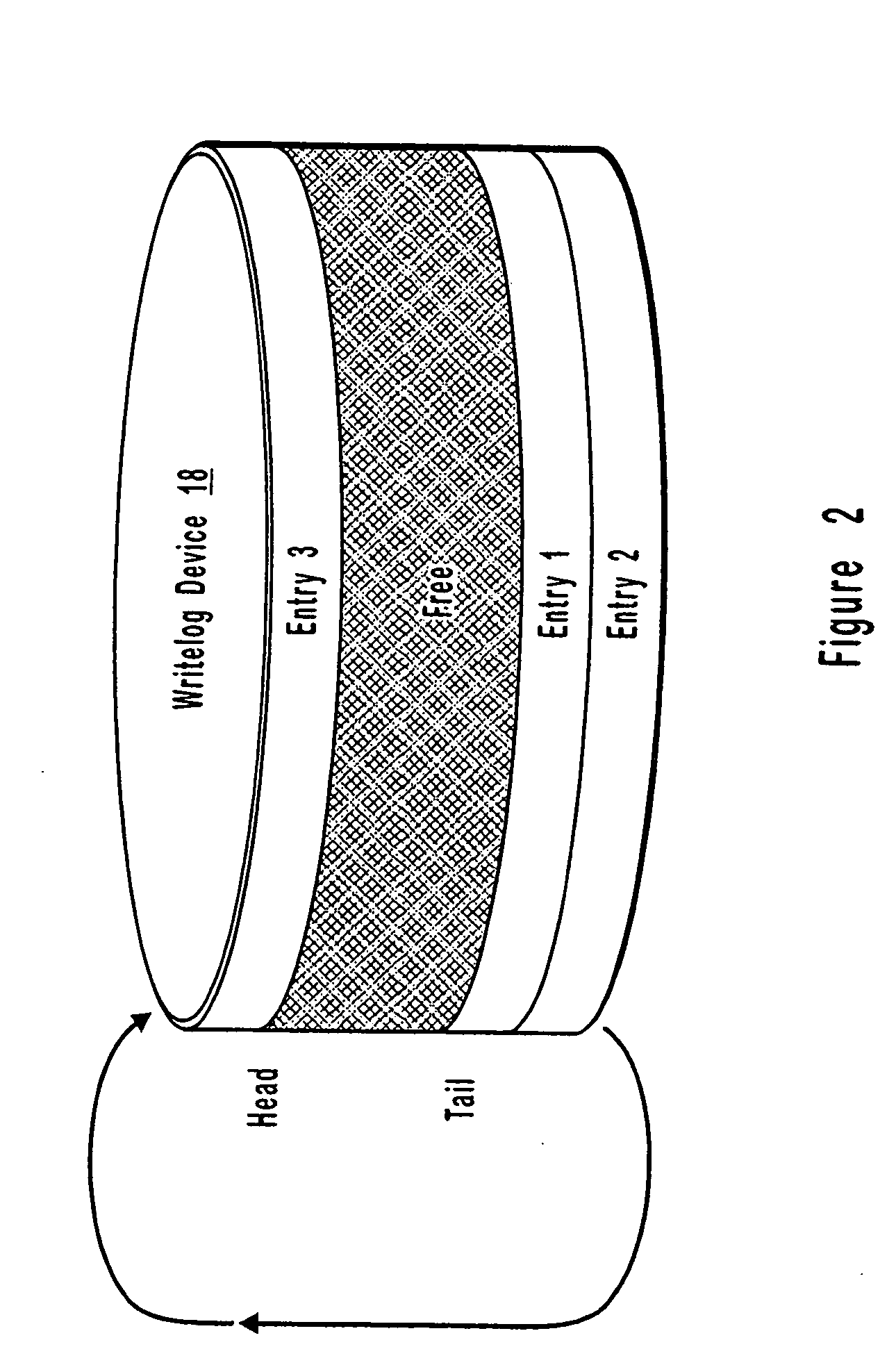
A computer network remote data mirroring system writes update data both to a local data device and to a local, chronologically sequenced journal storage area, or writelog device. A graphical user interface enables a user to create and configure throttles, which are user-defined tests and actions evaluated by the primary mirror daemon to regulate network bandwidth, CPU, and writelog device utilization during data update mirroring. Network bandwidth throttling enables a predetermined portion of the network bandwidth to be assigned to remote data mirroring based on user-selected criteria. CPU throttling enables a user to control the amount of time the local data storage unit will wait prior to returning control to applications after an update. Writelog device throttling prevents a memory overflow condition by dynamically assigning memory to the writelog device by chaining writelog device extensions to the writelog device.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Dynamic software control interface and method
InactiveUS20030169289A1Current generateSoftware engineeringDigital computer detailsElectricityControl signal
A software interface that is installable on a processor for interfacing with an electrically or electronically controllable device. The software comprises means for receiving input from a user remotely via a network and a means for translating the network communicated user input into at least one of a control signal and a configuration signal. The software interface further comprises means for communicating a control signal to control software. Such control software, which is already known in the art, is configured in controlling relation to at least one of an electrically or electronically controllable device through a hardware interface. Further, means are included for translating a configuration signal into a user interface application between the control software and an indicator displayable to the user; means rendering a dynamic user interface in response to changes in connected devices; and means for ensuring the reliable relay of command and configuration signals across unreliable networks susceptible to limited bandwidths and communication interruptions.
Owner:NEARMEDIA +1
Systems and methods for providing quality of service precedence in TCP congestion control
ActiveUS20080225721A1Low transfer rateError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceTransport layer
Systems and methods for dynamically controlling bandwidth of connections are described. In some embodiments, a proxy for one or more connections may allocate, distribute, or generate indications of network congestion via one or more connections in order to induce the senders of the connections to reduce their rates of transmission. The proxy may allocate, distribute, or generate these indications in such a way as to provide quality of service to one or more connections, or to ensure that a number of connections transmit within an accepted bandwidth limit. In other embodiments, a sender of a transport layer connection may have a method for determining a response to congestion indications which accounts for a priority of the connection. In these embodiments, a sender may reduce or increase parameters related to transmission rate at different rates according to a priority of the connection.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
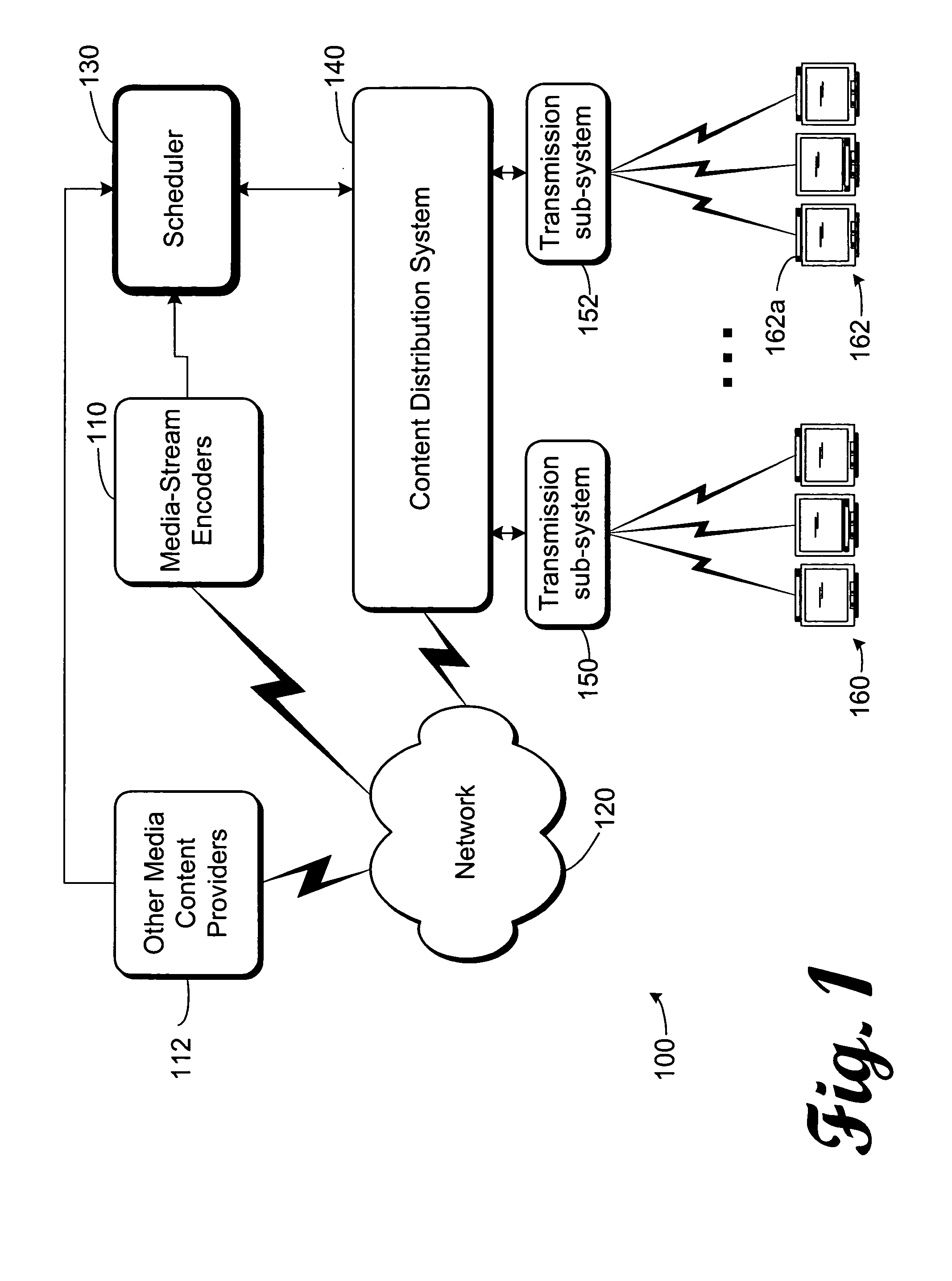
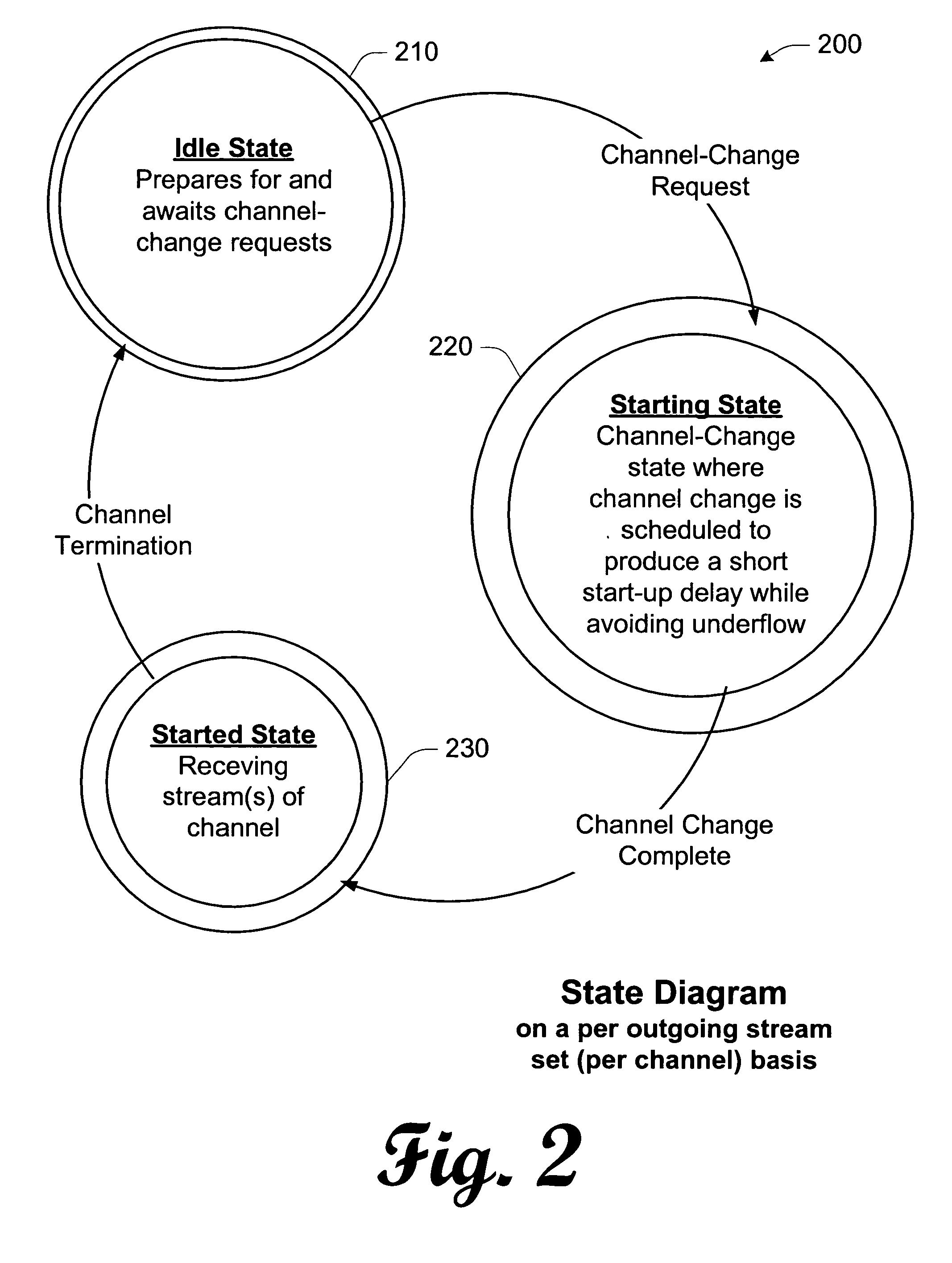
Media stream scheduling for hiccup-free fast-channel-change in the presence of network chokepoints
InactiveUS20050080904A1Facilitates fast start-up of a new media streamAvoid disturbanceTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionHiccupsNew media
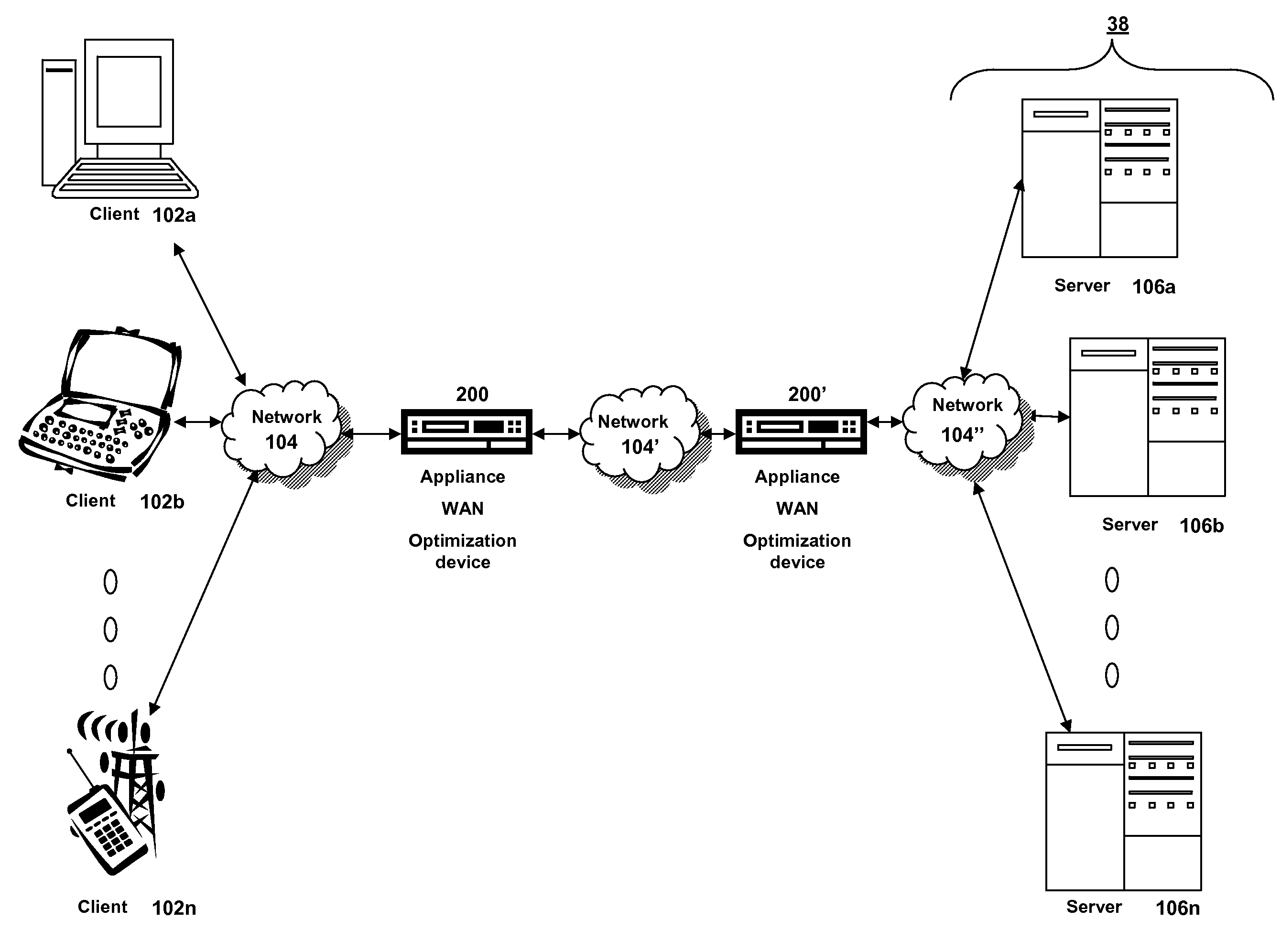
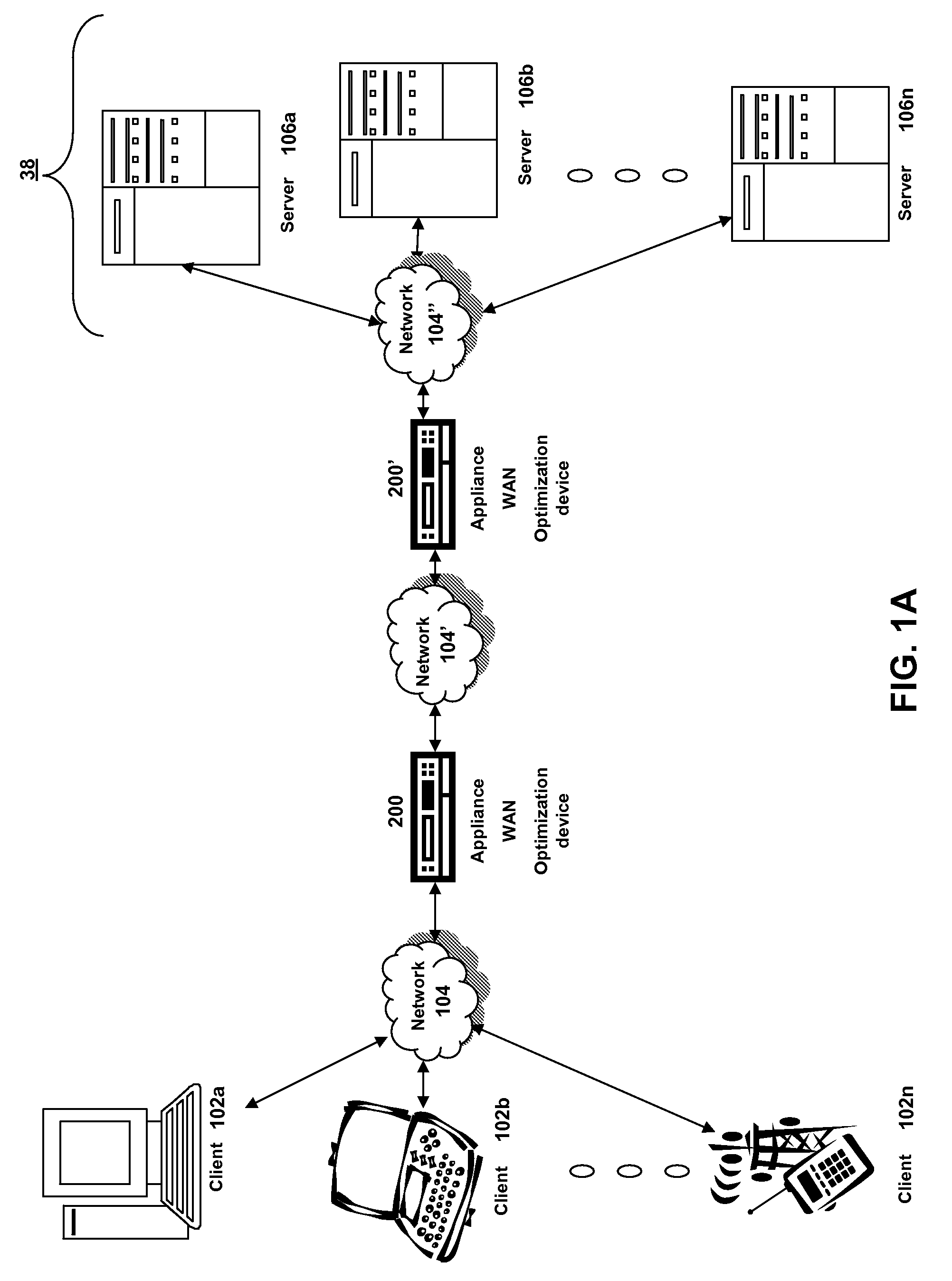
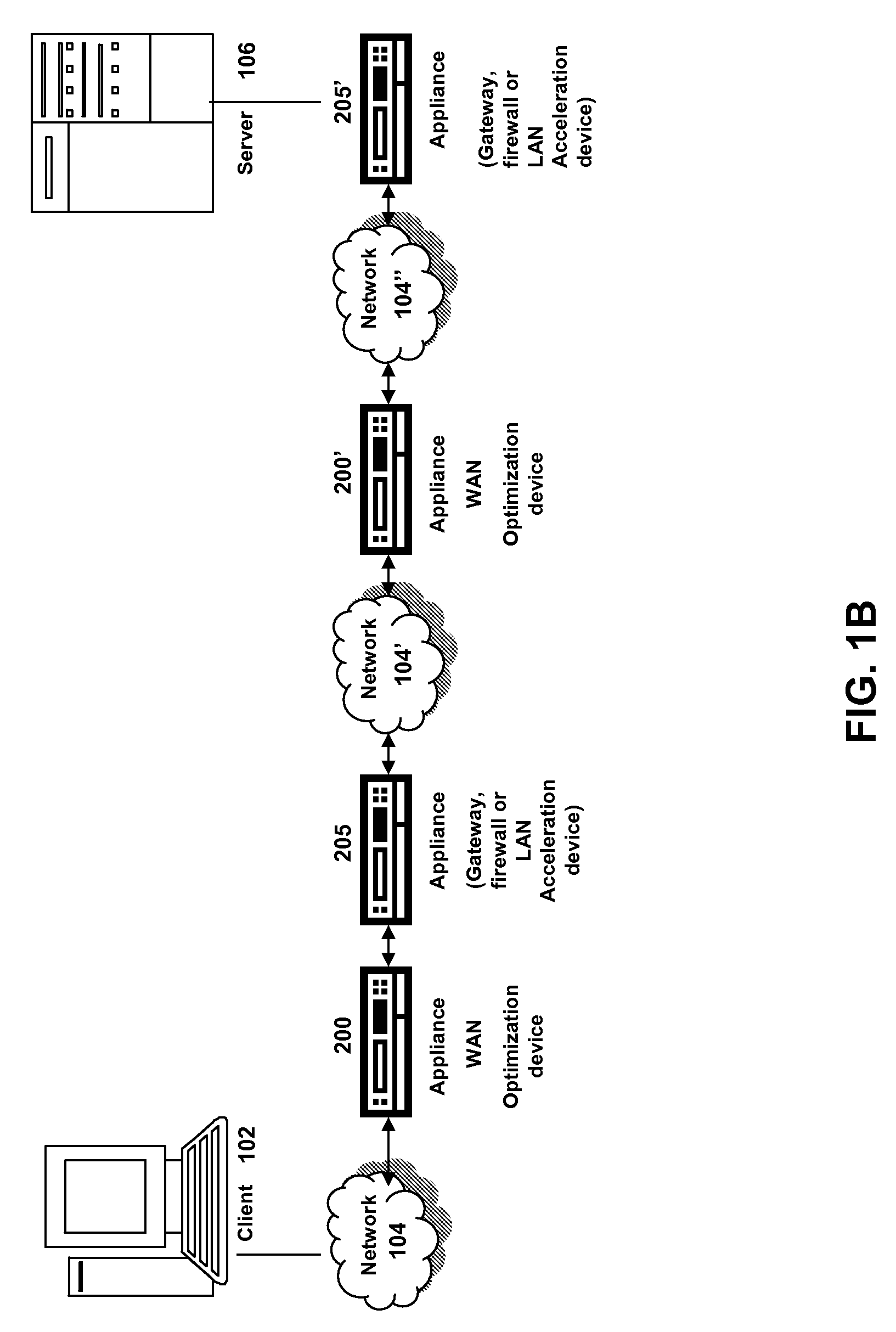
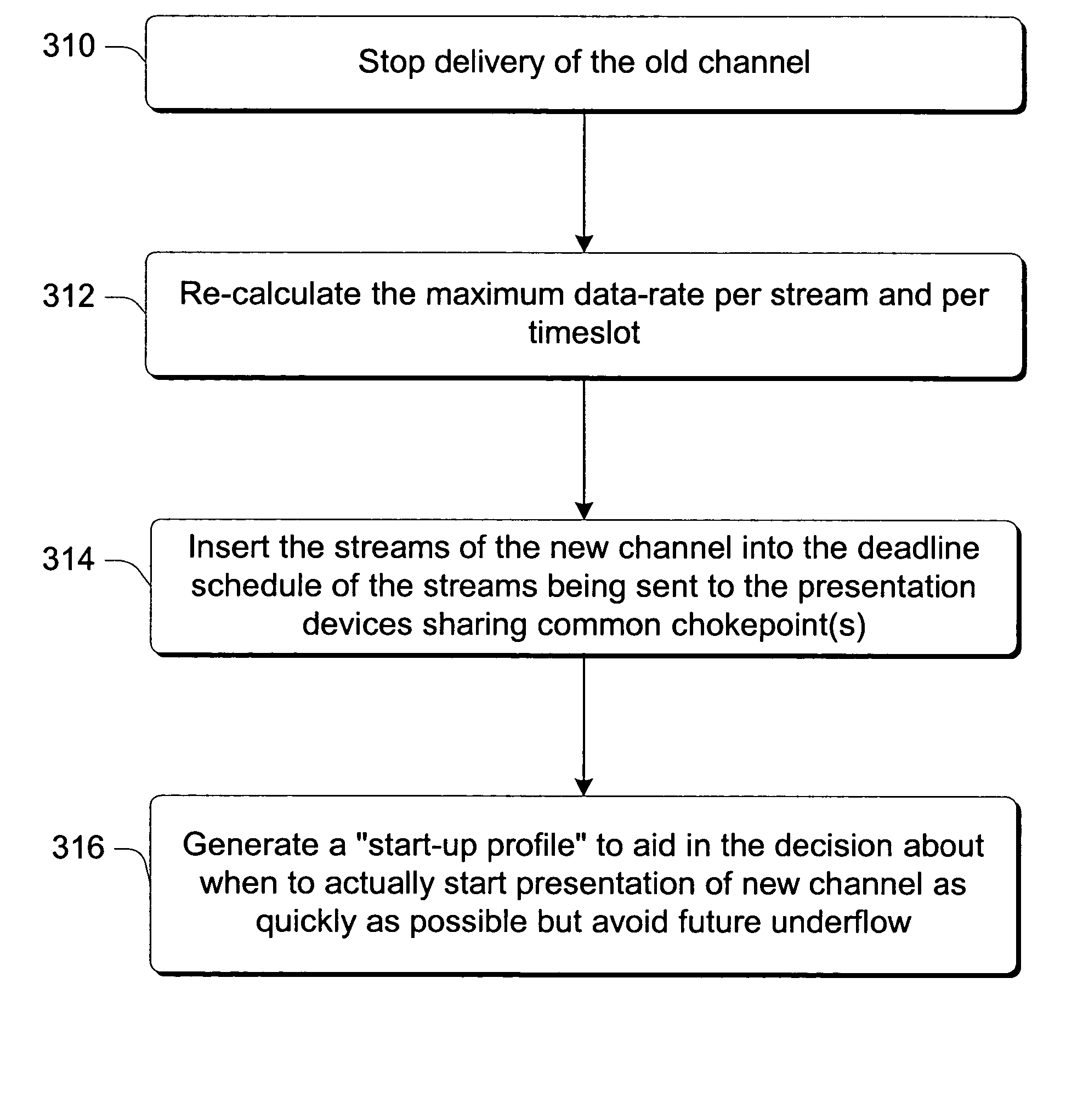
An implementation, as described herein, facilitates fast start-up of a new media stream while avoiding temporal interruption (i.e., “hiccups”) of the presentation of that new media stream. At least one implementation, described herein, coordinates the delivery of multiple simultaneous media streams on a media-stream network. Its coordination accounts for traversal of bandwidth-restricted chokepoints; quickly stopping delivery of one or more media streams from the set of streams; quickly initiating delivery and presentation of one or more new media streams not previously in the set (i.e., a “channel change”); and producing clean playback of all of the streams in the set, despite their different timelines. This abstract itself is not intended to limit the scope of this patent. The scope of the present invention is pointed out in the appending claims.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
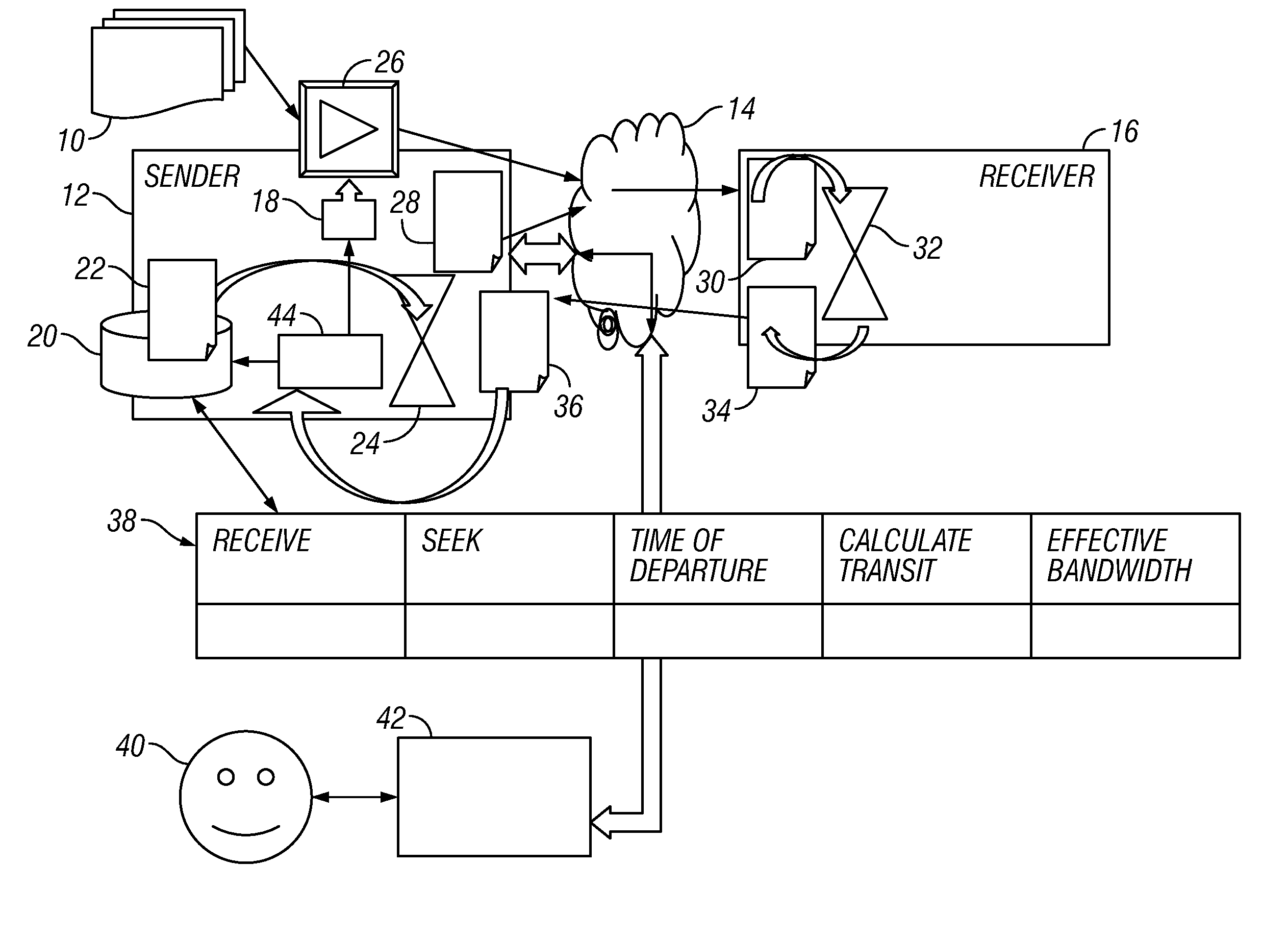
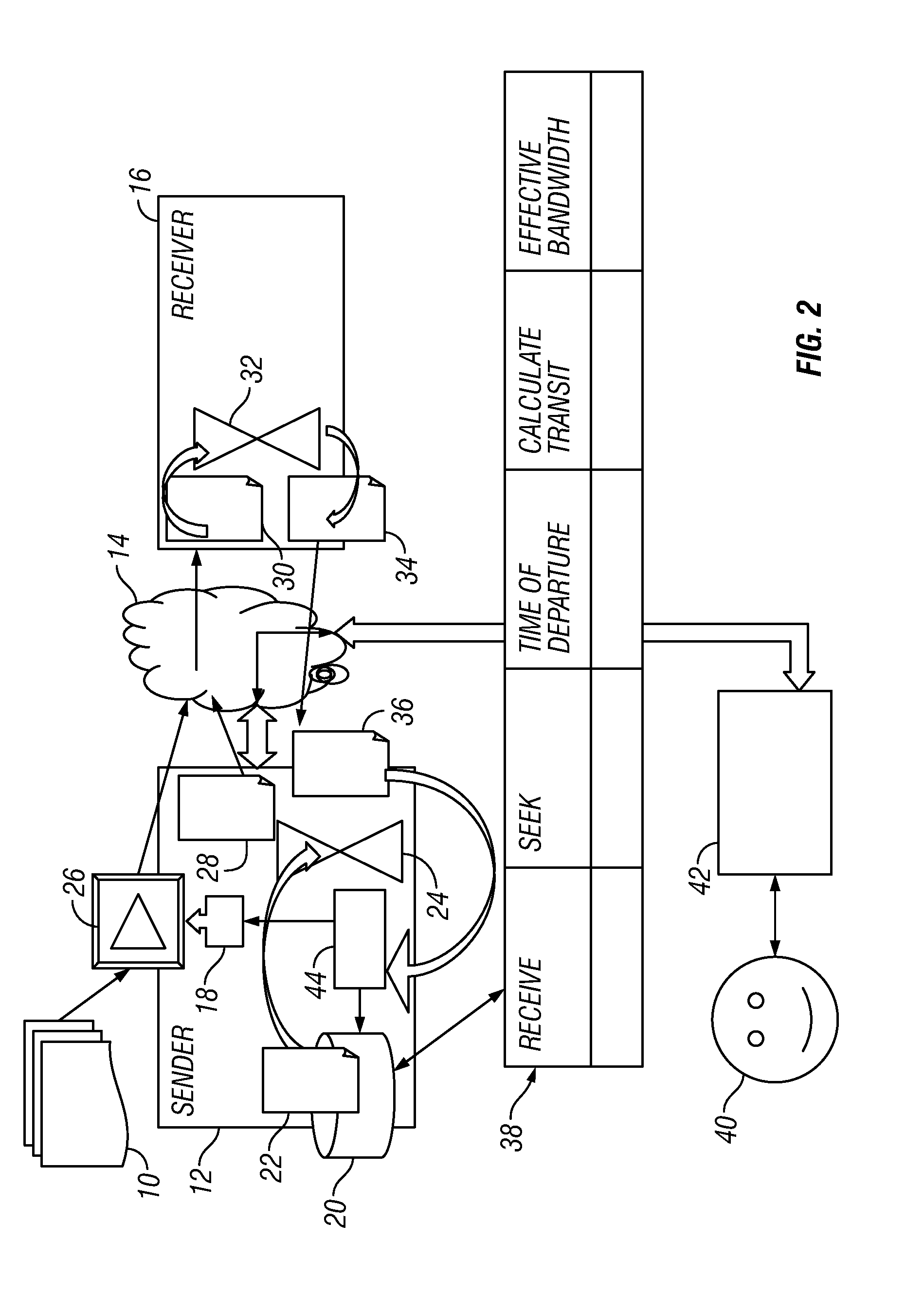
Dynamic bandwidth throttling
ActiveUS20110066752A1Data transmission rate is downSubstation remote connection/disconnectionMultiple digital computer combinationsObservation dataData transmission
An approximation of the bandwidth of the narrowest link in a network is determined by watching how fast data gets to the other end and then back again. The rate of data transmission is limited according to this approximation. Dynamic capacity of the link, i.e. the amount of data that can be in-flight at the same time, neglecting any buffers, is also tracked. The technique looks at how much data is in-flight and, if there is more data in flight than the dynamic capacity of the network, the data transmission rate is slowed down.
Owner:IBM CORP
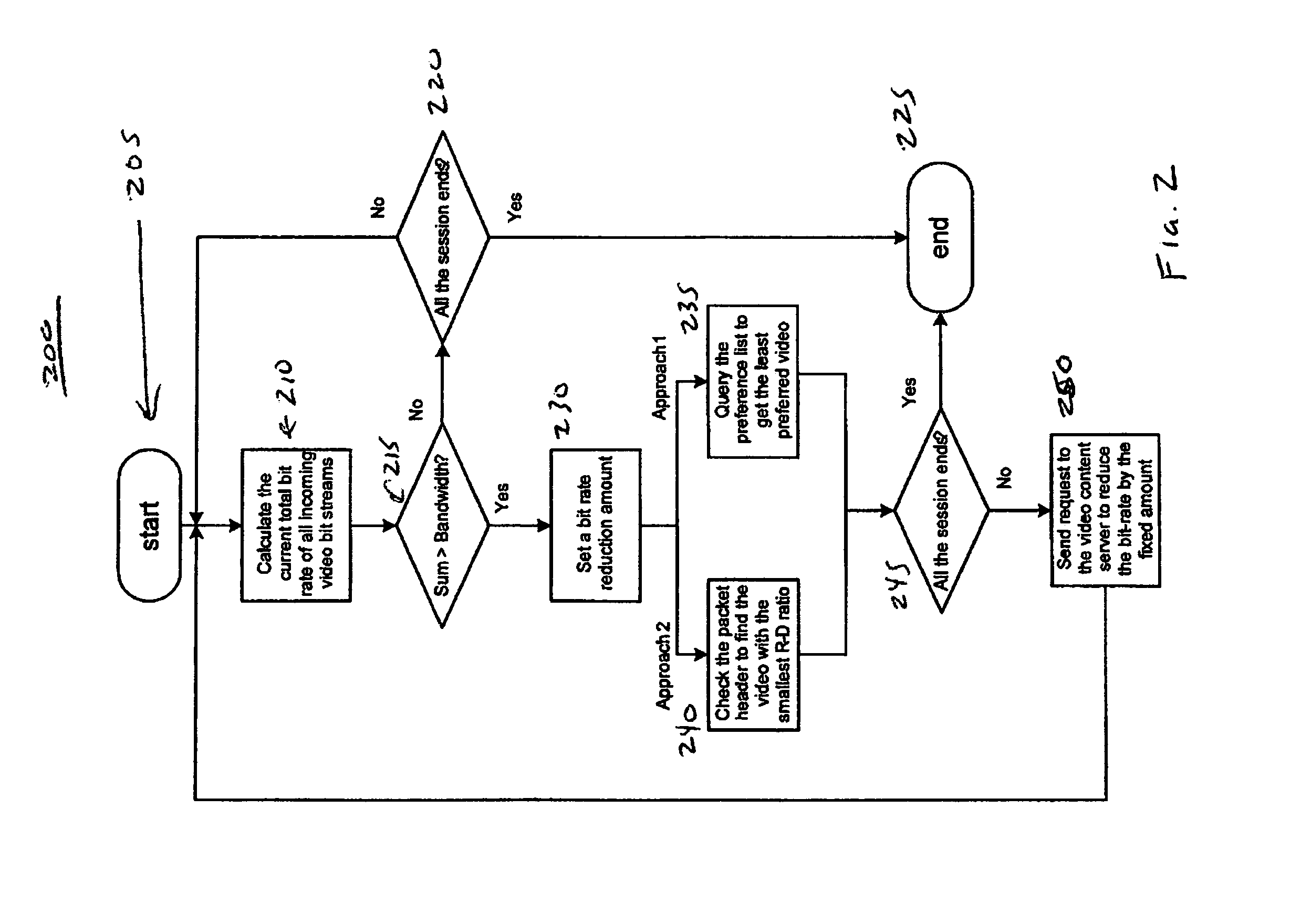
Bit rate adjustment in an adaptive streaming system
InactiveUS20130007831A1Improve video qualityHigh quality videoTwo-way working systemsTransmissionVideo bitstreamService provision
A method and apparatus for adaptively streaming multiple video bit streams through a network node is disclosed. In particular, a system is taught where at least one of the video bit streams is scaled in response to a bandwidth limitation or availability, where the selection of the bit stream selected for scaling in made in response to at least one of a user defined, service provider defined, and usage analysis defined priority list.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Resource allocation throttling in remote data mirroring system
InactiveUS7103797B1Assure data synchronicityExpense of applicationResource allocationError detection/correctionGraphicsGraphical user interface
A computer network remote data mirroring system writes update data both to a local data device and to a local, chronologically sequenced journal storage area, or writelog device. A graphical user interface enables a user to create and configure throttles, which are user-defined tests and actions evaluated by the primary mirror daemon to regulate network bandwidth, CPU, and writelog device utilization during data update mirroring. Network bandwidth throttling enables a predetermined portion of the network bandwidth to be assigned to remote data mirroring based on user-selected criteria. CPU throttling enables a user to control the amount of time the local data storage unit will wait prior to returning control to applications after an update. Writelog device throttling prevents a memory overflow condition by dynamically assigning memory to the writelog device by chaining writelog device extensions to the writelog device.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Systems and methods of providing proxy-based quality of service
ActiveUS20080225715A1Low transfer rateEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceTransport layer
Systems and methods for dynamically controlling bandwidth of connections are described. In some embodiments, a proxy for one or more connections may allocate, distribute, or generate indications of network congestion via one or more connections in order to induce the senders of the connections to reduce their rates of transmission. The proxy may allocate, distribute, or generate these indications in such a way as to provide quality of service to one or more connections, or to ensure that a number of connections transmit within an accepted bandwidth limit. In other embodiments, a sender of a transport layer connection may have a method for determining a response to congestion indications which accounts for a priority of the connection. In these embodiments, a sender may reduce or increase parameters related to transmission rate at different rates according to a priority of the connection.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
System and Method for Enhancing Network Quality of Service
InactiveUS20070223470A1Reduce riskControl rateData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceNetwork on
A data transfer network infrastructure device having a plurality of ingress ports for accepting data from a domain of a data network; and, a user interface for enabling a user to limit a rate at which data is accepted from the data network on at least one of the ingress ports, wherein the data transfer rate between the at least one of the ingress ports and a device coupled to the at least one of the ports is limited, whereby a bandwidth limit is implemented by the limit at which the data is accepted into the ingress port.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Method and apparatus for increasing bandwidth in sampled systems
InactiveUS6542914B1Easy to controlReduce system noiseDigital variable displayDigital technique networkTime domainDigital filter
Systems that sample a continuous analog time-domain signal. The invention is particularly applicable to systems whose analog components have a bandwidth limit below that desired or specified. The invention has been created to address particular problems in the design of digital sampling oscilloscopes (DSOs) that require more bandwidth than that which is easily achievable through traditionally analog techniques. A method and apparatus are provided in the form of a digital filter that is capable of surgically increasing the bandwidth of the system beyond the bandwidth achievable in an analog system. Furthermore, it is demonstrated that this system can perform this bandwidth increase without degradation in the time-domain performance of the system such as pulse or step response. In some cases, the time-domain performance is improved by flattening of the frequency response. Additionally, the system, while boosting the bandwidth, is capable of simultaneously removing noise and therefore producing a digitized signal of higher fidelity than that obtained without the filter in place.
Owner:TELEDYNE LECROY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com