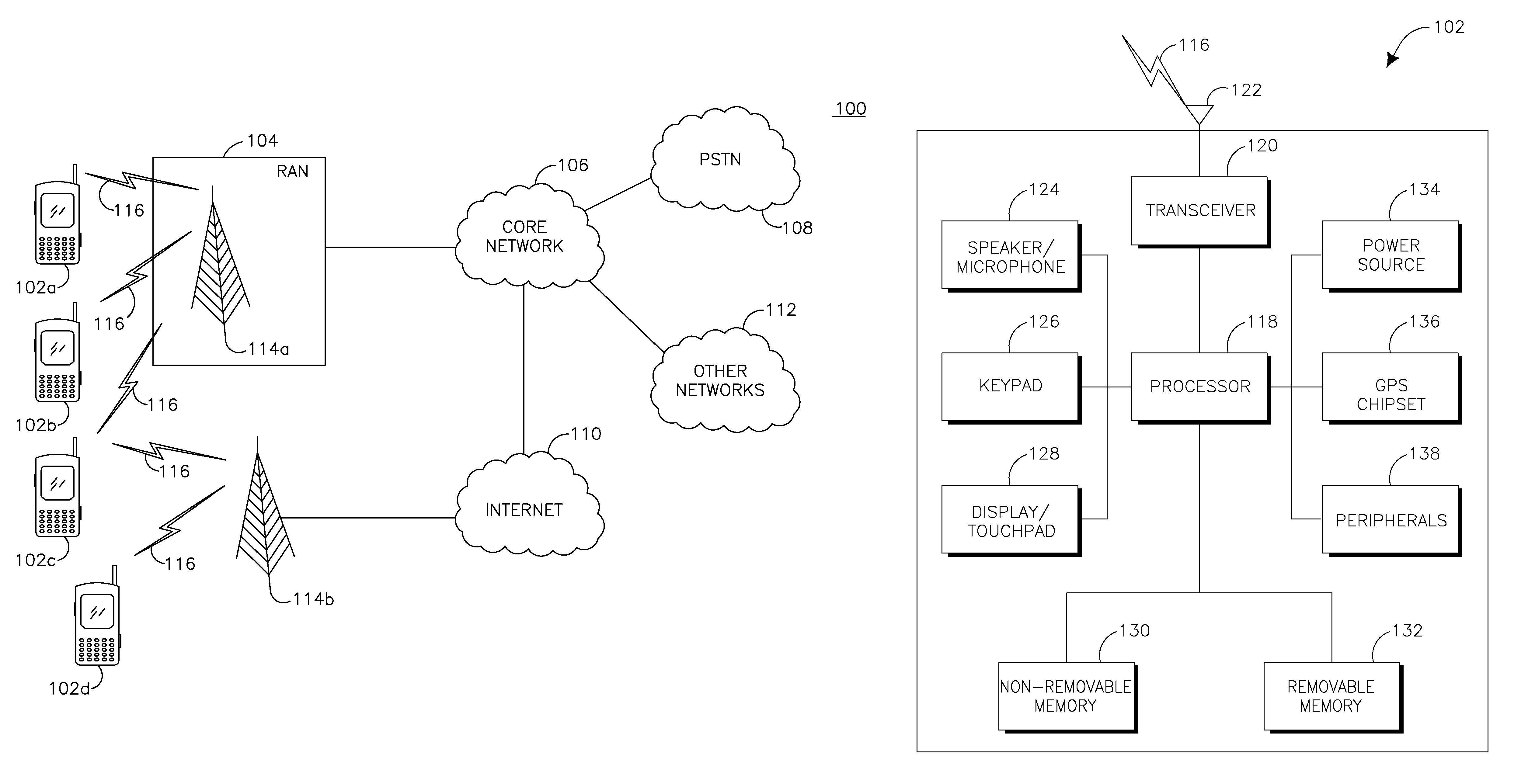
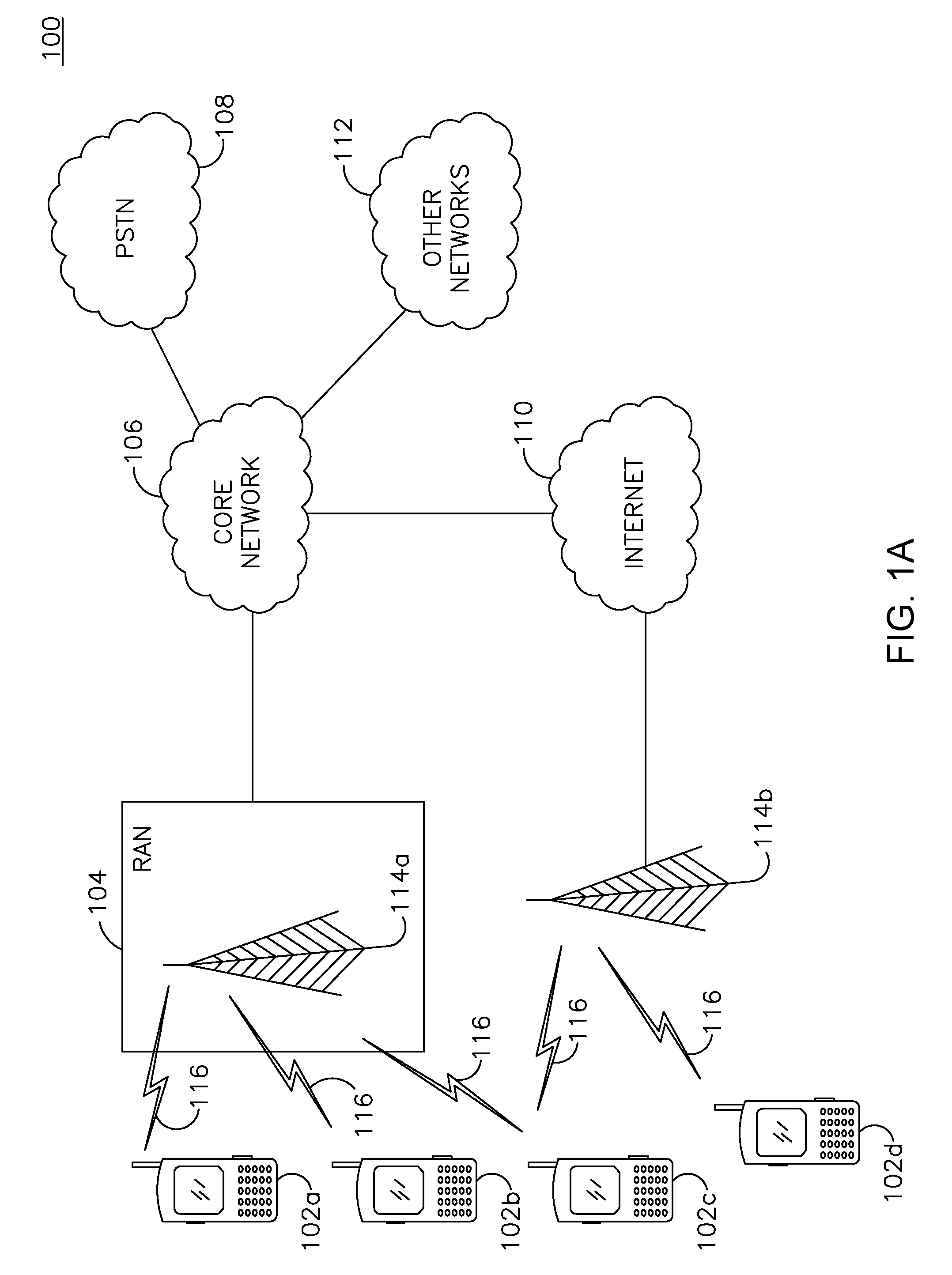
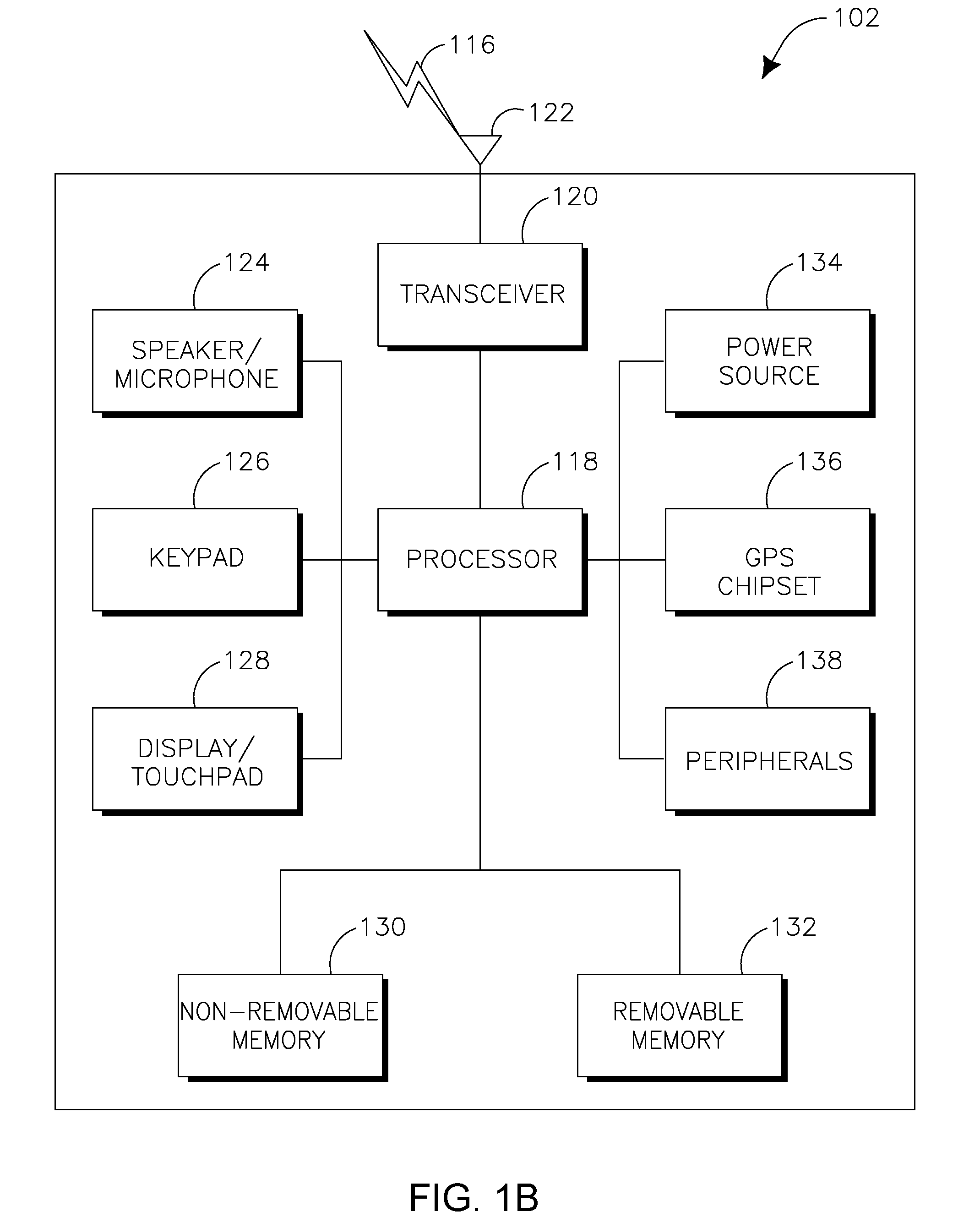
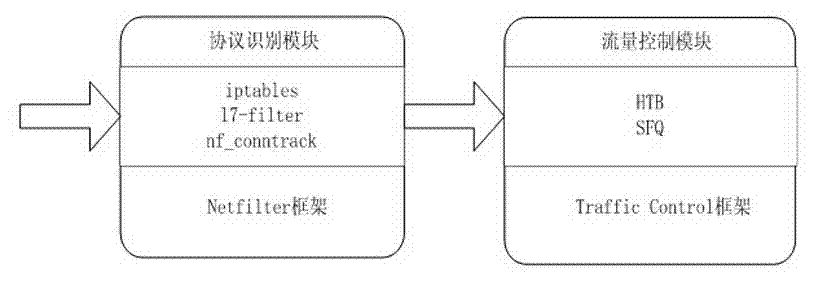
Patents
Literature
88 results about "Bandwidth provisioning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bandwidth provisioning is an important issue for Internet service providers (ISPs) and ensuring quality of service (QoS) is a major concern. QoS is closely related to the available bandwidth which itself is subject to financial constraints.
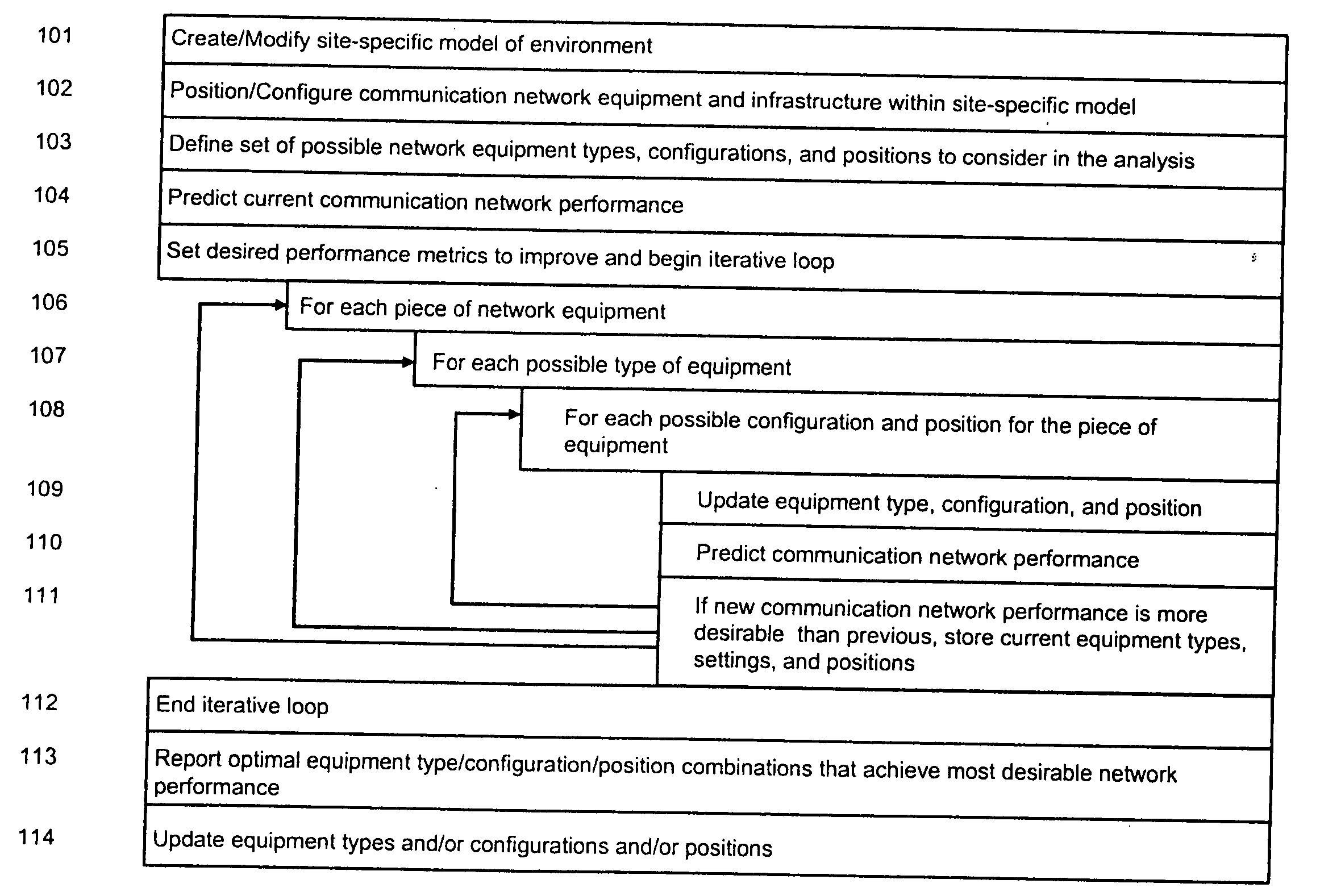
System and method for automated placement or configuration of equipment for obtaining desired network performance objectives and for security, RF tags, and bandwidth provisioning
ActiveUS20040236547A1Significant valueEasy to explainGeometric CADData taking preventionHard disc driveThe Internet
A method is presented for determining optimal or preferred configuration settings for wireless or wired network equipment in order to obtain a desirable level of network performance. A site-specific network model is used with adaptive processing to perform efficient design and on-going management of network performance. The invention iteratively determines overall network performance and cost, and further iterates equipment settings, locations and orientations. Real time control is between a site-specific Computer Aided Design (CAD) software application and the physical components of the network allows the invention to display, store, and iteratively adapt any network to constantly varying traffic and interference conditions. Alarms provide rapid adaptation of network parameters, and alerts and preprogrammed network shutdown actions may be taken autonomously. A wireless post-it note device and network allows massive data such as book contents or hard drive memory to be accessed within a room by a wide bandwidth reader device, and this can further be interconnected to the internet or Ethernet backbone in order to provide worldwide access and remote retrieval to wireless post-it devices.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
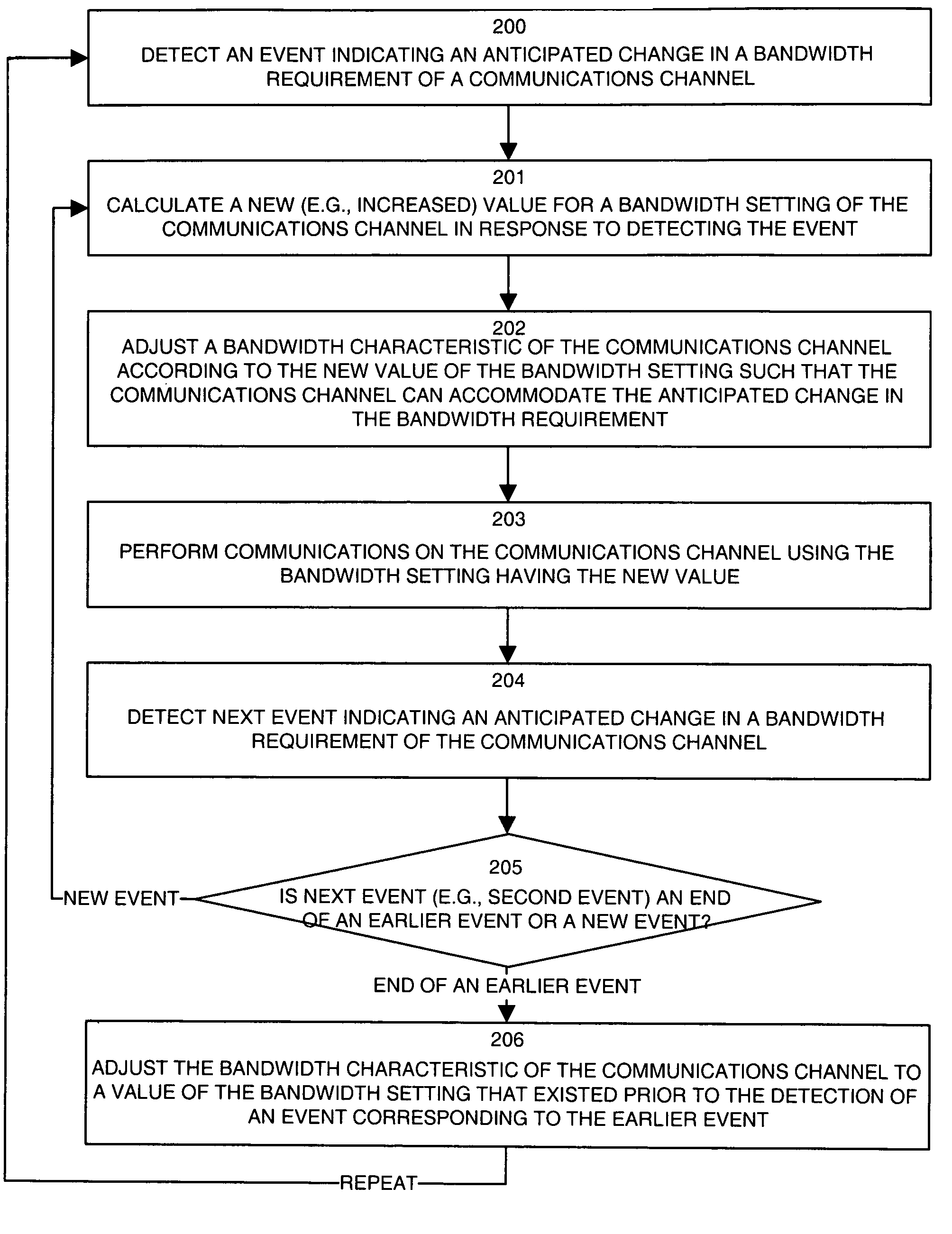
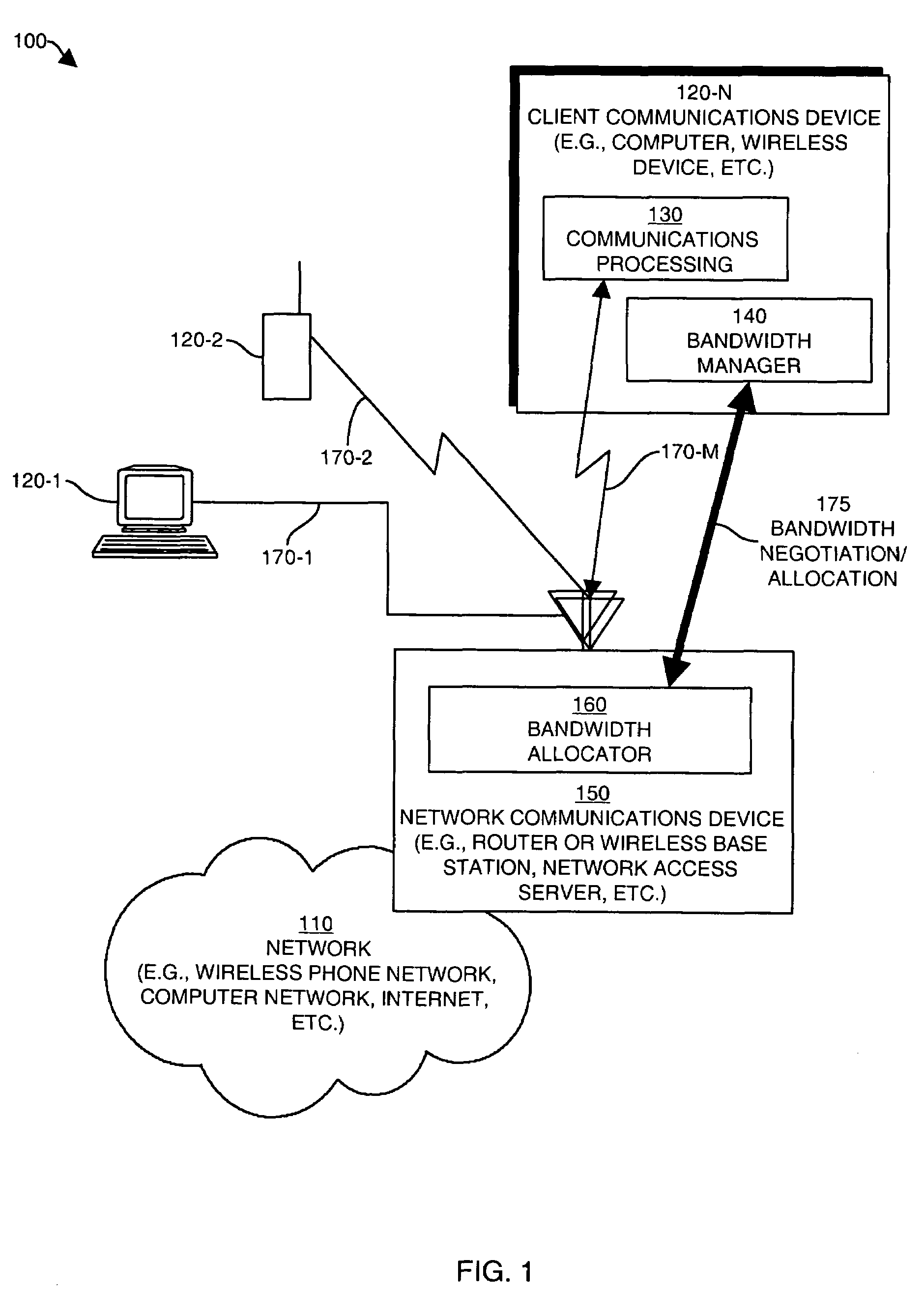
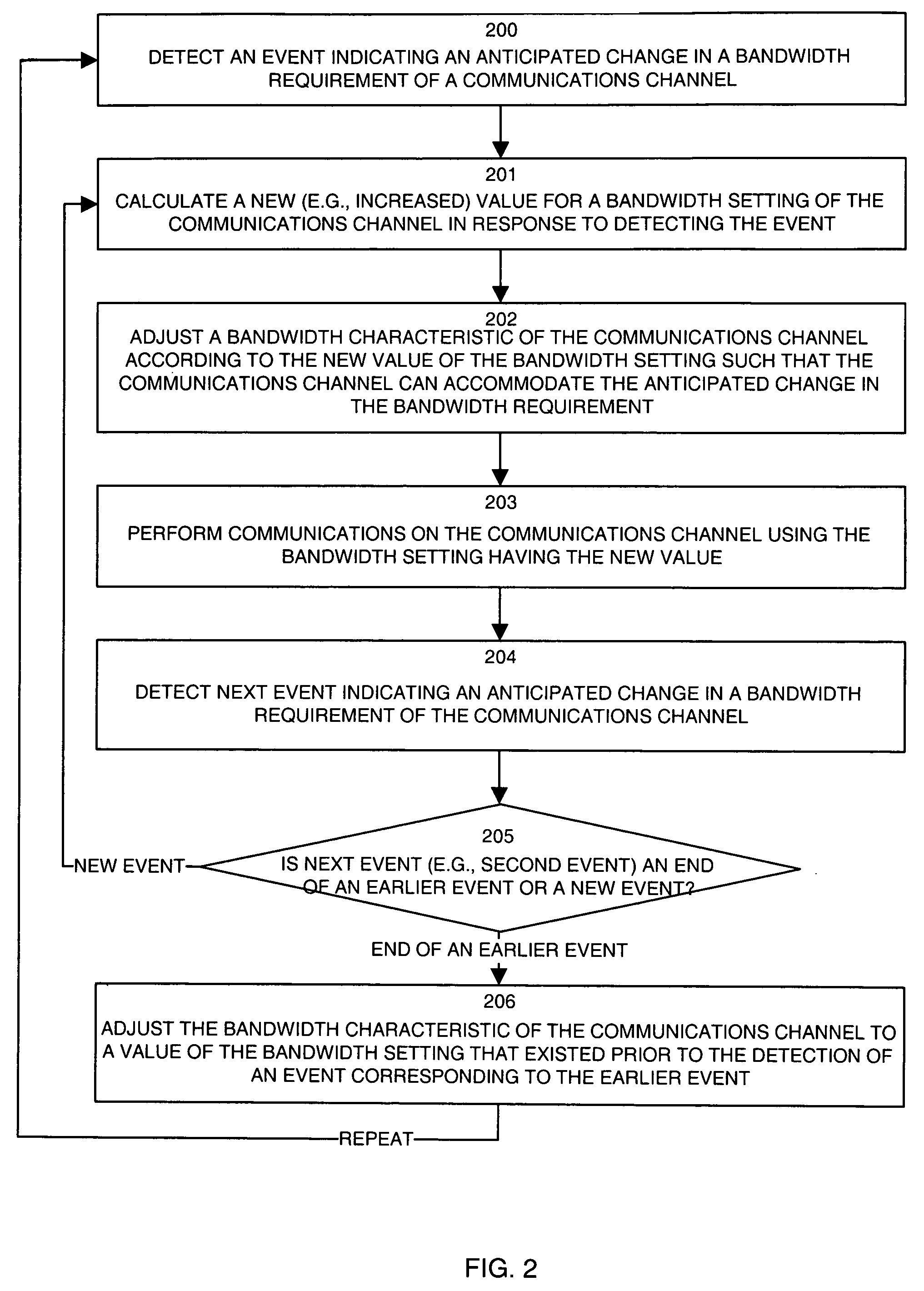
Methods and apparatus for dynamic bandwidth adjustment
ActiveUS7116682B1High bandwidthLow communication bandwidthNetwork traffic/resource managementDigital computer detailsCommunications systemBandwidth requirement
A configuration of a communications device, and a method for its operation are provided for automatically and dynamically adjusting bandwidth of a communications channel. The device and method operate to detect events indicating anticipated changes in bandwidth requirements of the communications channel. Such events may be browser or bandwidth related events, for example, that indicate a forthcoming requirement for increased or decreased bandwidth. The device and method then can extract a bandwidth determination factor if available and then calculate a new value for a bandwidth setting of the communications channel in response to detecting such an event and can adjust a bandwidth characteristic of the communications channel according to the new value of the bandwidth setting such that communications channel can accommodate the anticipated change(s) in the bandwidth requirement. The invention can operate in wireless and non-wireless communications systems to cause bandwidth to be adjusted to closely track usage requirements of the communications channel.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods of implementing dynamic QoS and/or bandwidth provisioning and related data networks, data service providers, routing gateways, and computer program products
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I LP
Methods of implementing dynamic QoS and/or bandwidth provisioning and related data networks, data service providers, routing gateways, and computer program products
A method of operating a data network may include establishing a data path through the data network between a routing gateway for a subscriber of the data network and a service provider providing a data service. Moreover, the data service may be provided for use at the routing gateway over the data path during a data session. A request may be received from the service provider wherein the request defines a data flow characteristic for the data path between the routing gateway and the service provider providing the data service during the data session. The data flow characteristic may then be transmitted to a node along the data path between the routing gateway and the service provider for enforcement of the data flow characteristic for the data path at the node. More particularly, the data session may be a point-to-point protocol data session. Related methods, data networks, data service providers, routing gateways, and computer program products are also discussed.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
System and method for dynamic bandwidth provisioning
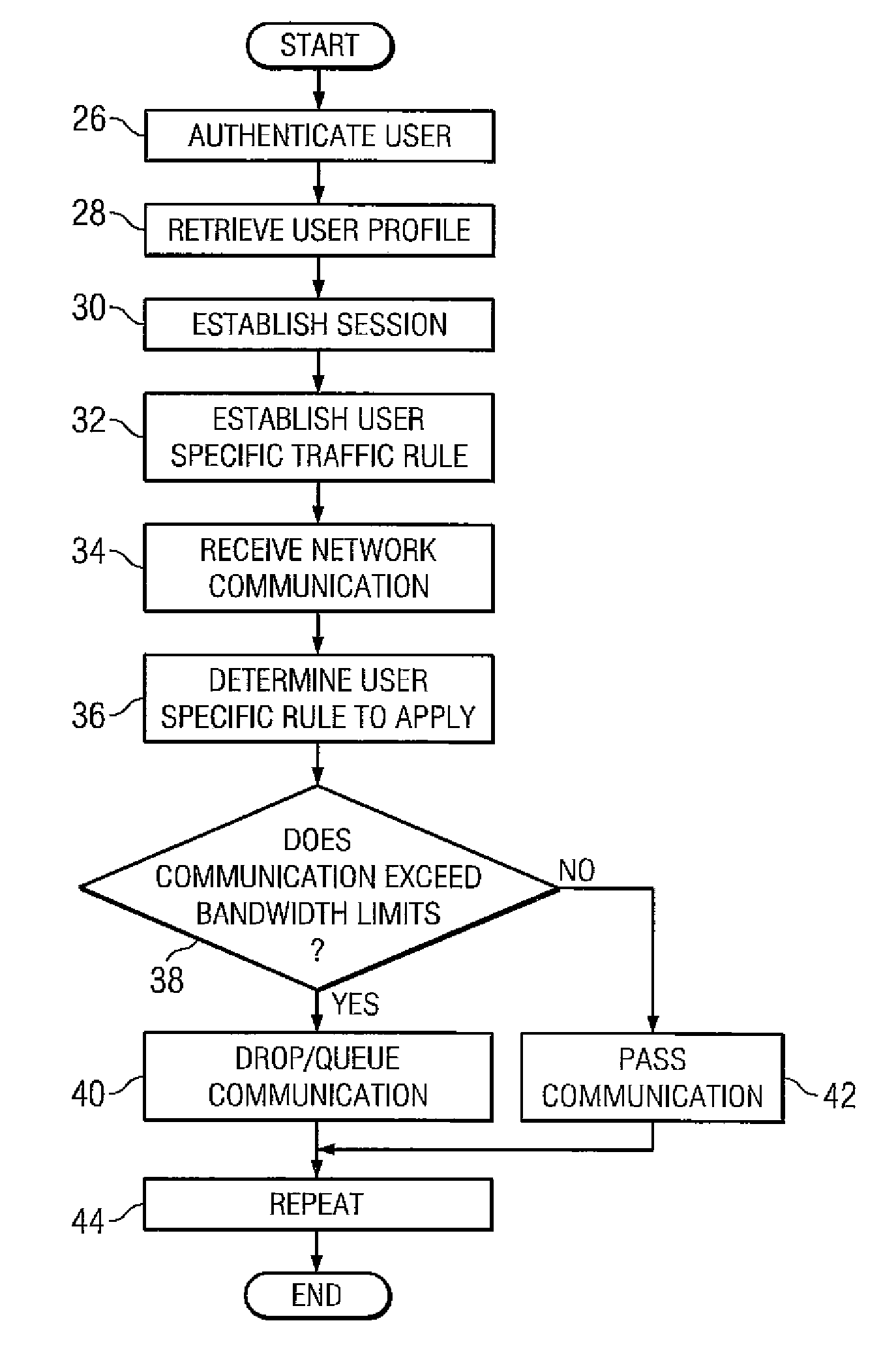
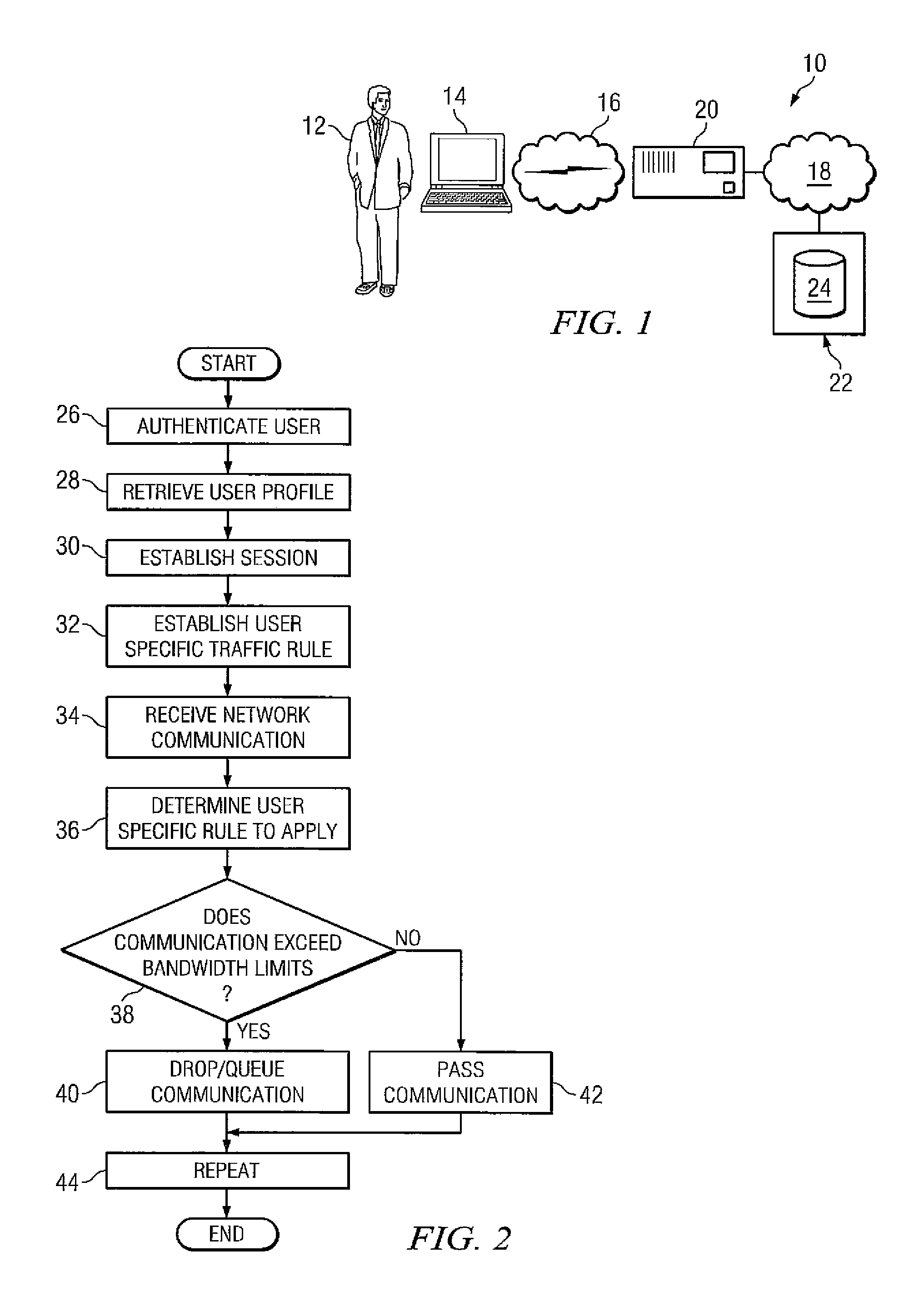
InactiveUS7587512B2Network traffic/resource managementMultiple digital computer combinationsUser profileDistributed computing
One embodiment of the present invention provides a device for allocating bandwidth on a per user basis. The device can be a computing device that comprises a processor, a first network interface coupled to the processor, a second network interface coupled to the processor, and a storage medium accessible by the processor that contains a set of computer instructions. The computer instructions can be executable by the processor to retrieve a set of user profiles. Based on the user profile for each user, the computer instructions can be executable to establish at least one bandwidth limit for each user. For each user, the computer instructions can be further executable to regulate bandwidth usage associated with that user based on the at least one bandwidth limit established for that user. The computer instructions can also be executable to update the at least one bandwidth limit.
Owner:RPX CORP
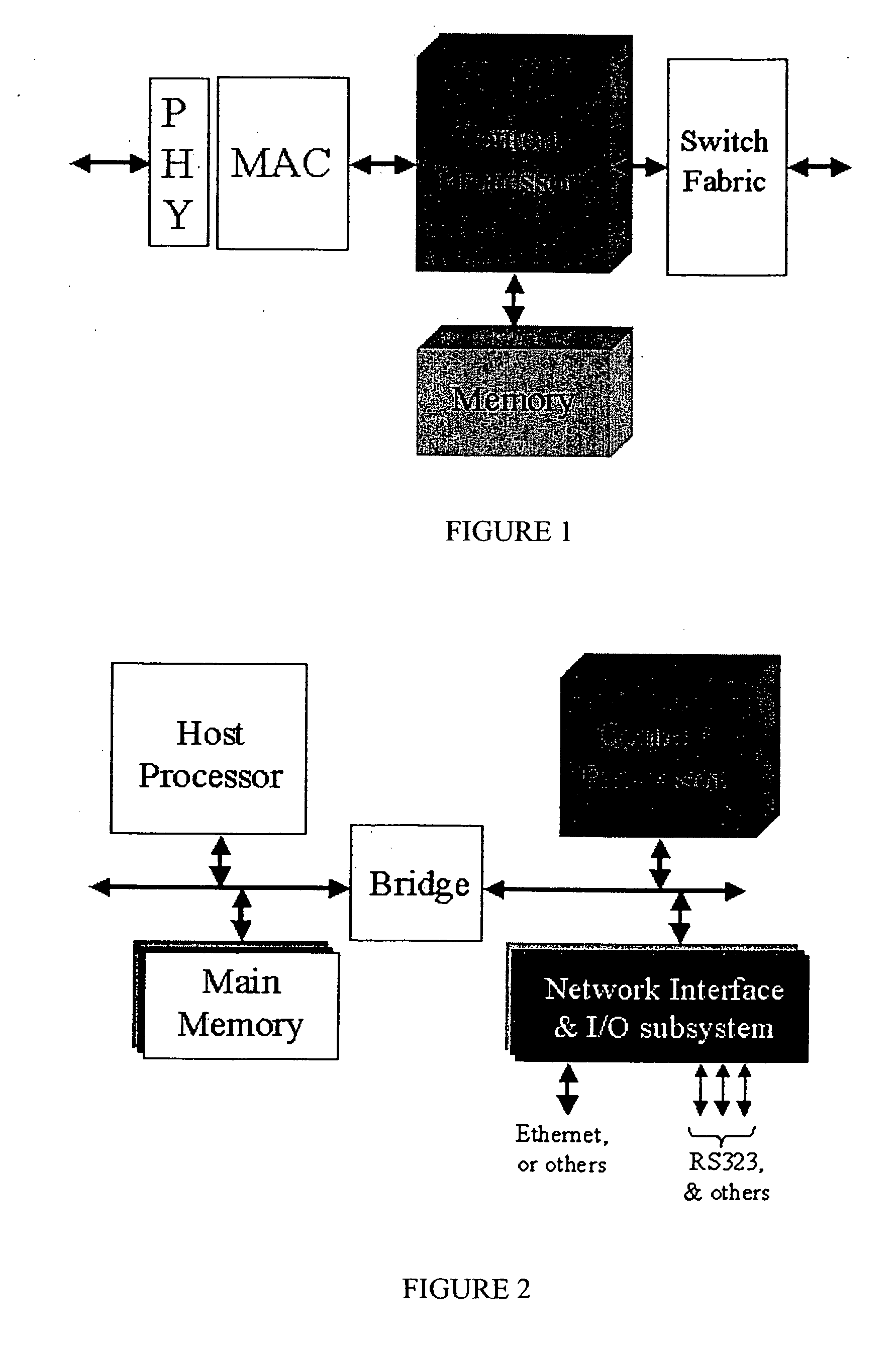
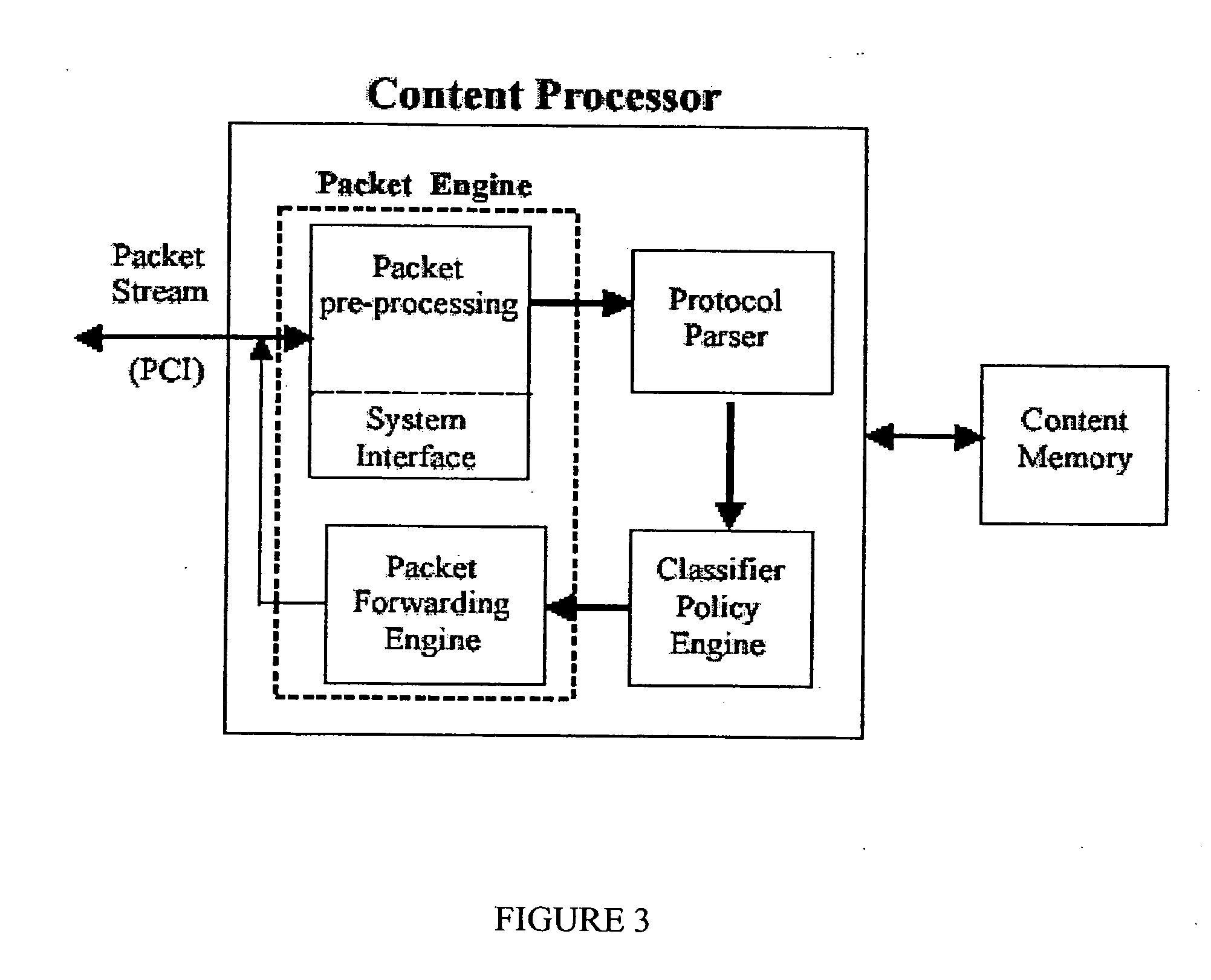
Network content processor including packet engine
InactiveUS20060242313A1Performance maximizationMaximize reliabilityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionQuality of serviceNetwork packet
Packets received over a network are routed using a packet engine of the invention based on information contained in layer 4 or above. The information for switching is contained in the header information of the packet. Based on this higher level information, the packet engine may drop the packet, redirect the packet, load balance the packet, perform bandwidth provisioning (e.g., limit the speed of a connection), or adjust quality of service (e.g., change priority or rearrange a queue of packets to be handled), or combinations of these.
Owner:LEWIZ COMM
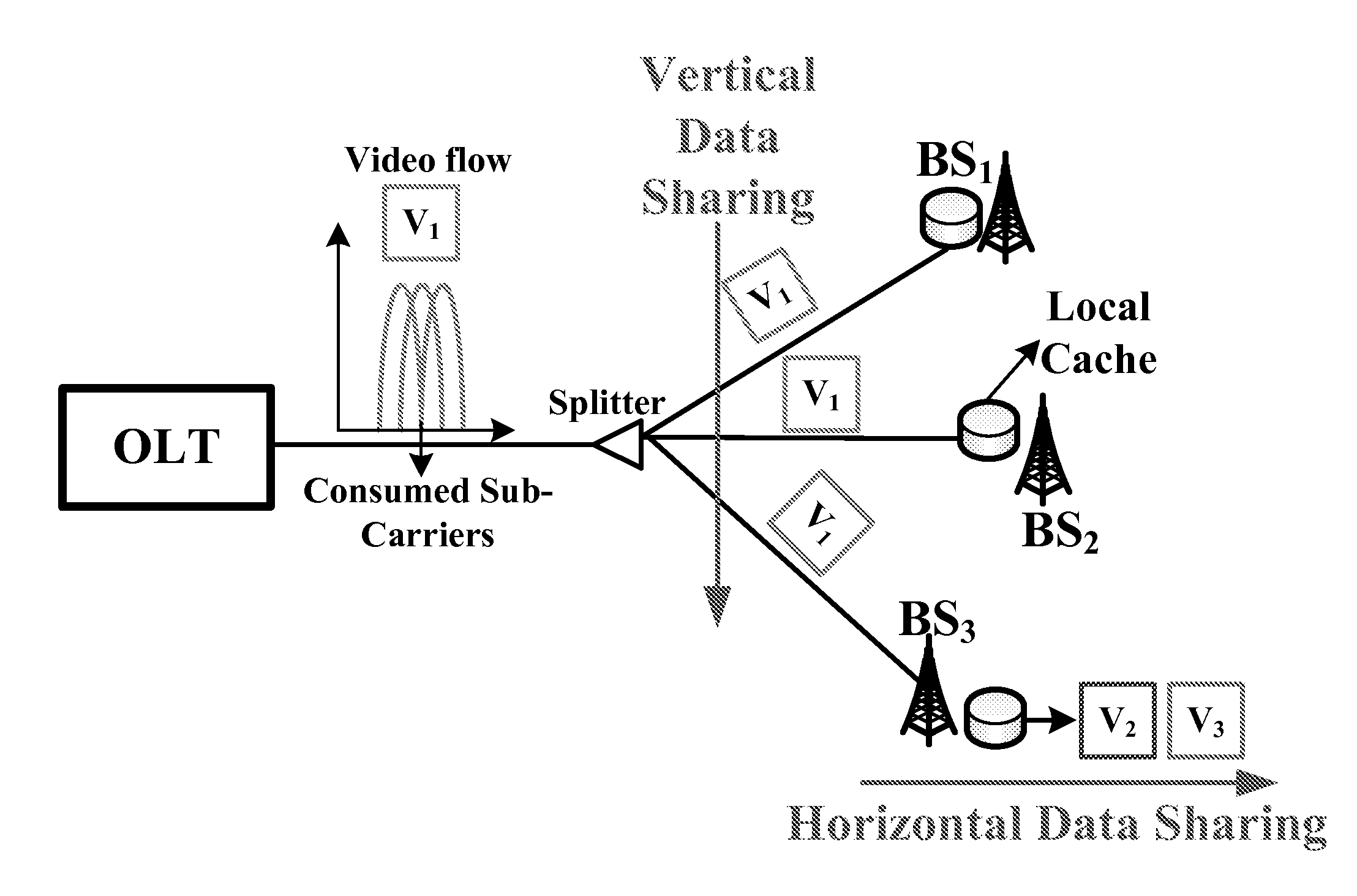
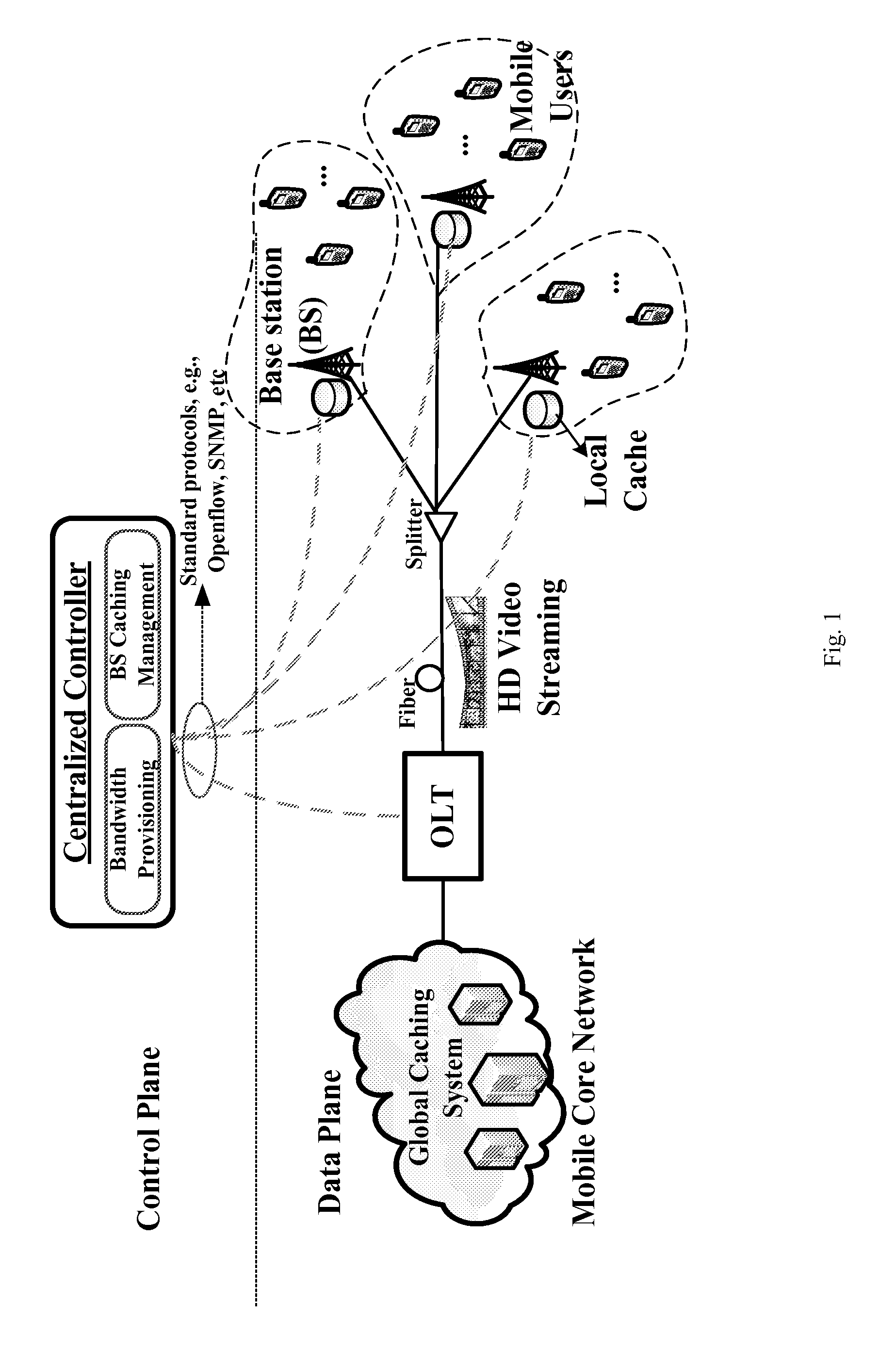
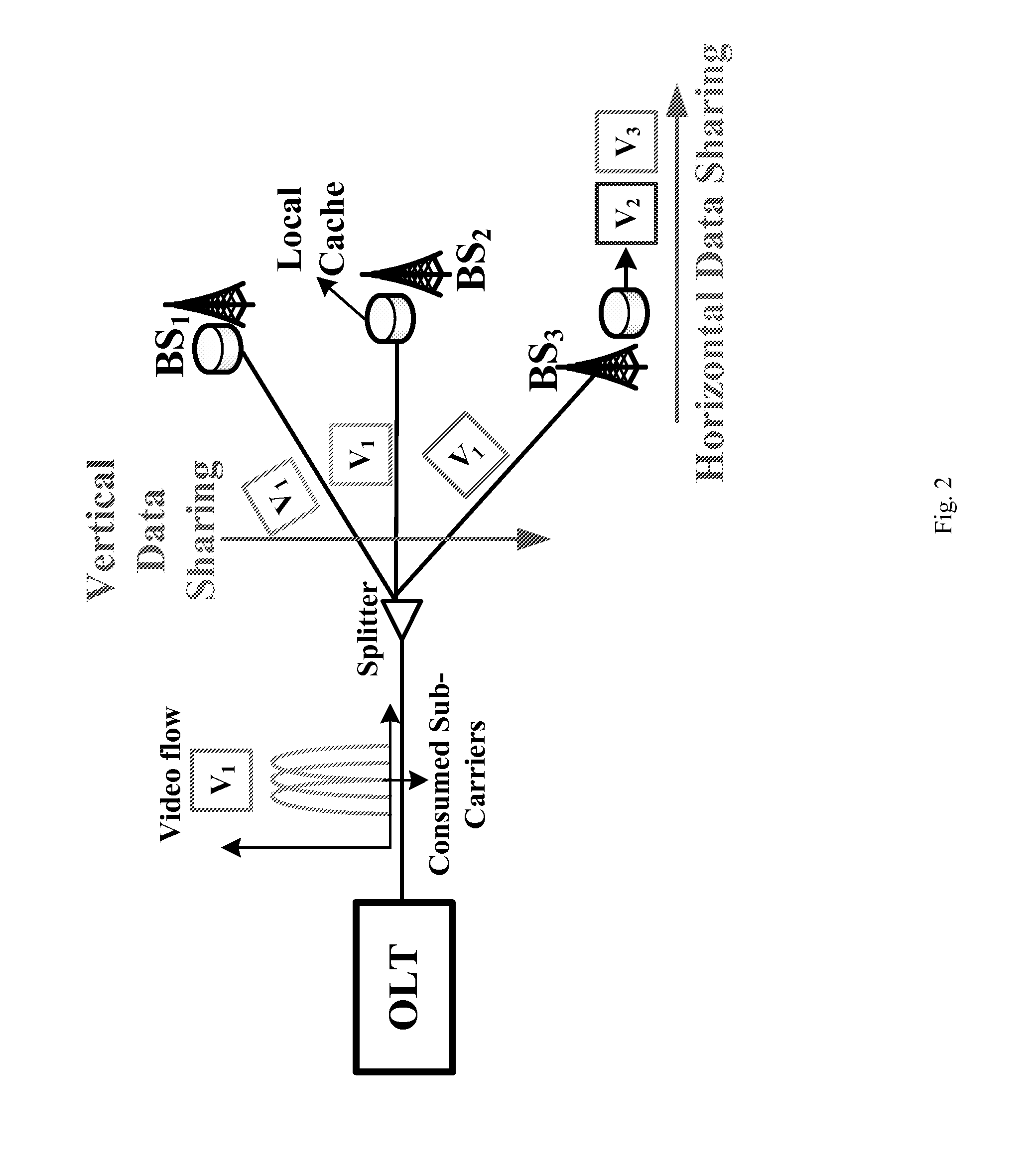
Software defined joint bandwidth provisioning and cache management for mbh video traffic optimization
ActiveUS20150106864A1Raise priorityTwo-way working systemsRadio-over-fibreVideo deliveryTraffic optimization
A method includes provisioning joint bandwidth in a software defined passive optical network PON based mobile backhaul MBH and cache management on base stations for video delivery across the network, the provisioning in each time unit includes grouping bandwidth utilization in the network into a first category used to support video requests which cannot directly be served by caches on base stations, the first category video requests being high priority, and if bandwidth remains after the high priority requests remaining bandwidth being used to deliver some videos that are low priority to caches.
Owner:NEC CORP
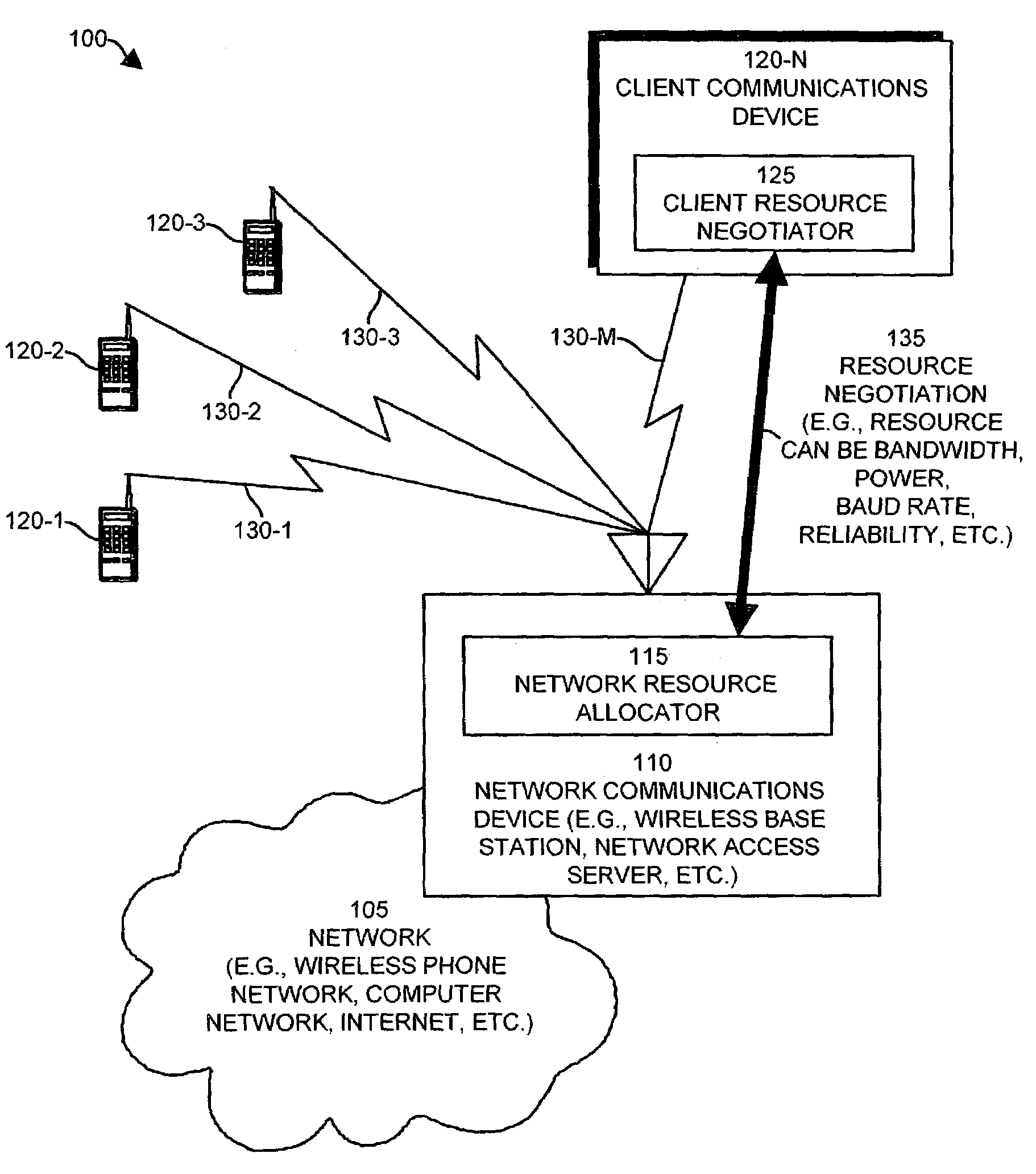
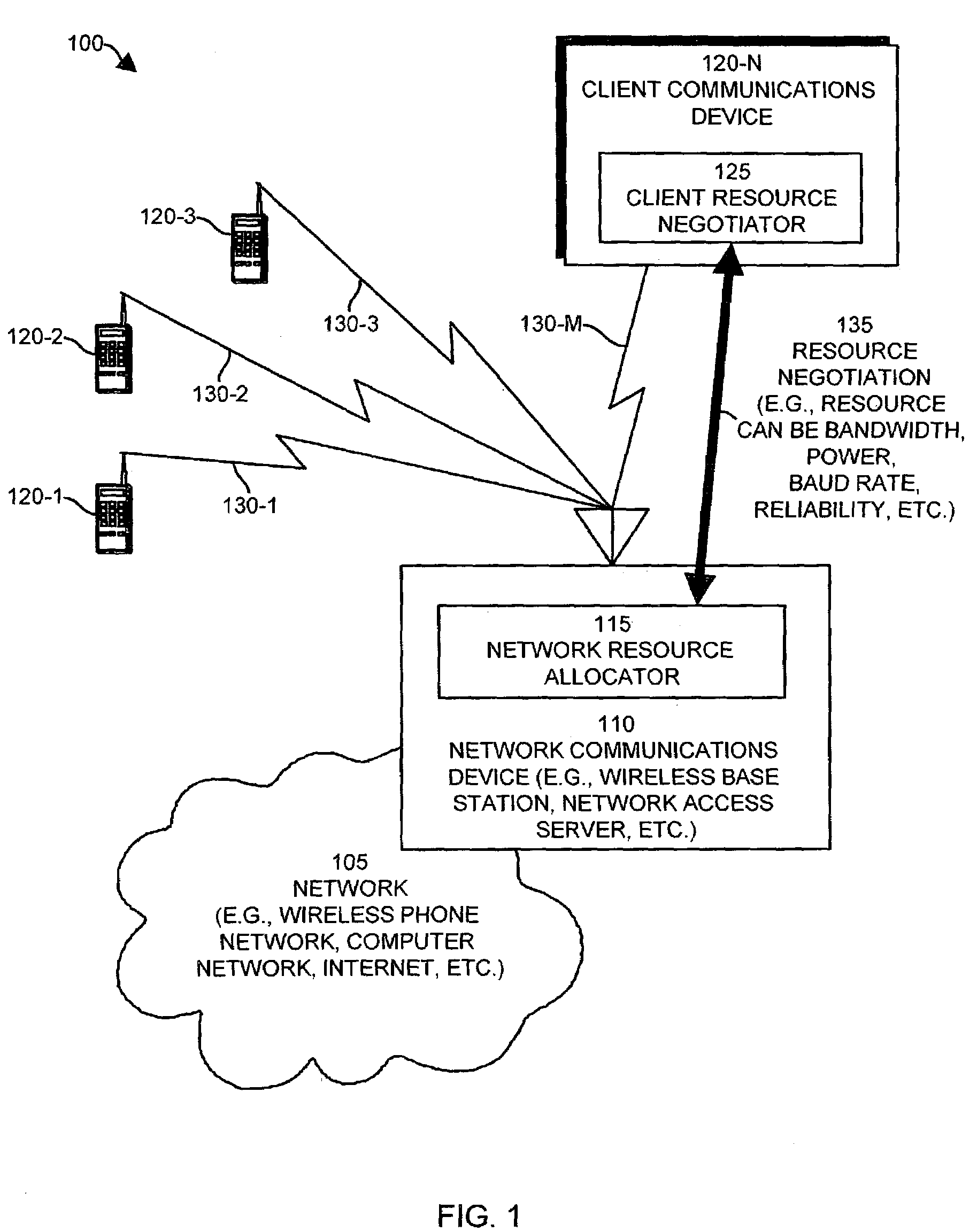
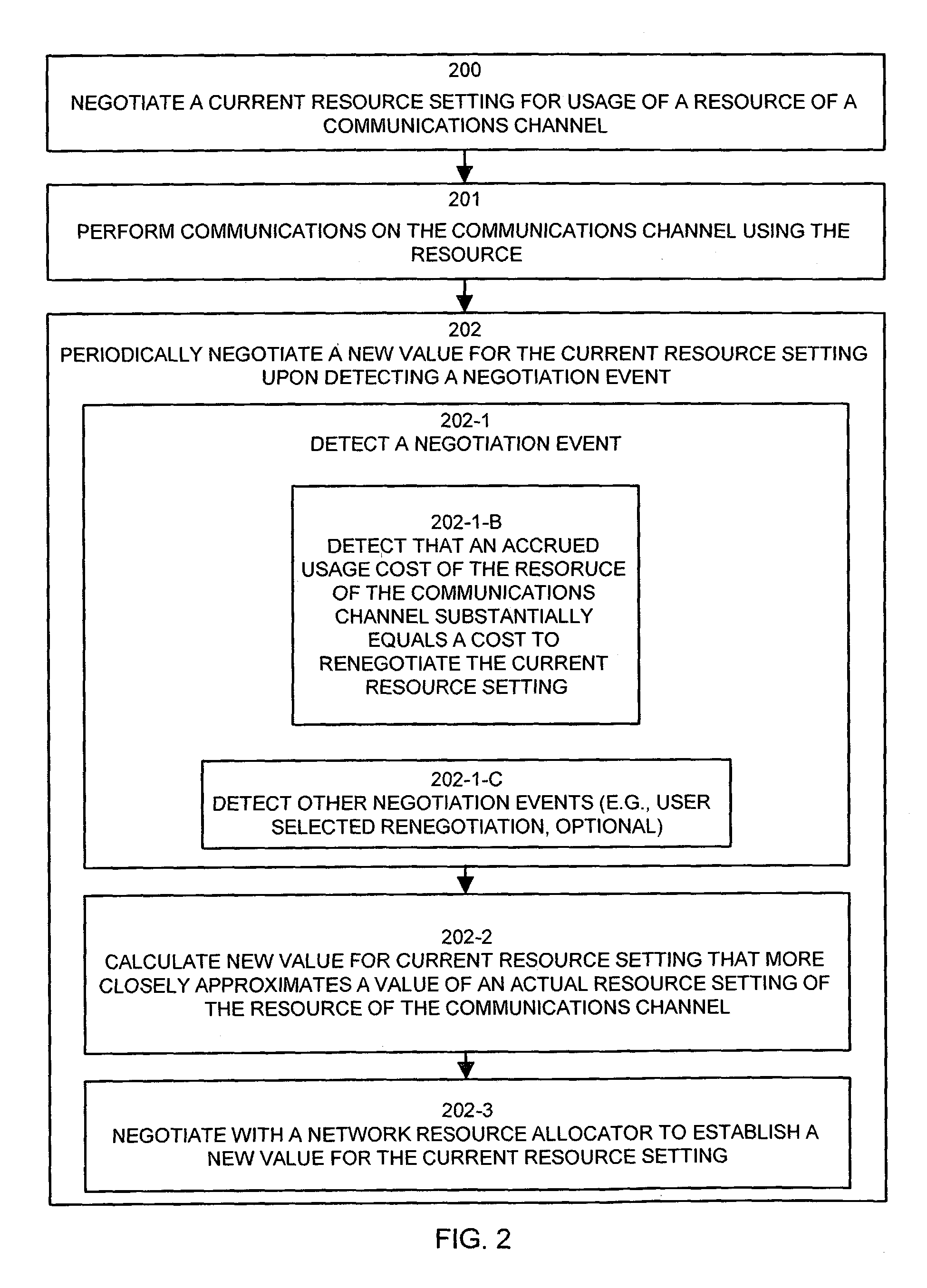
Methods and apparatus for allocating resources in a communications system
InactiveUS7433311B1Incurring costError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemComputer science
The invention provides a system including methods and apparatus that adjust usage of one or more resources of a data communications channel. The system can negotiate a current resource setting for usage of the resource of the communications channel and can perform communications on the communications channel using the resource. The resource can be, for example, a bandwidth setting of the communications channel. Periodically, the system can renegotiate a new value for the current resource setting upon detecting a negotiation event during performance of communications on the communications channel using the resource. One such negotiation event is an indication that an accrued usage cost of the resource of the communications channel substantially equals or exceeds a cost to renegotiate the current resource setting. Another negotiation event indicates that an actual resource setting of the communications channel substantially equals or exceeds the current resource setting for the communications channel. Another negotiation event indicates that a data communications device using the bandwidth setting of the communications channel has requested to negotiate a new value for the current resource setting of the communications channel.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
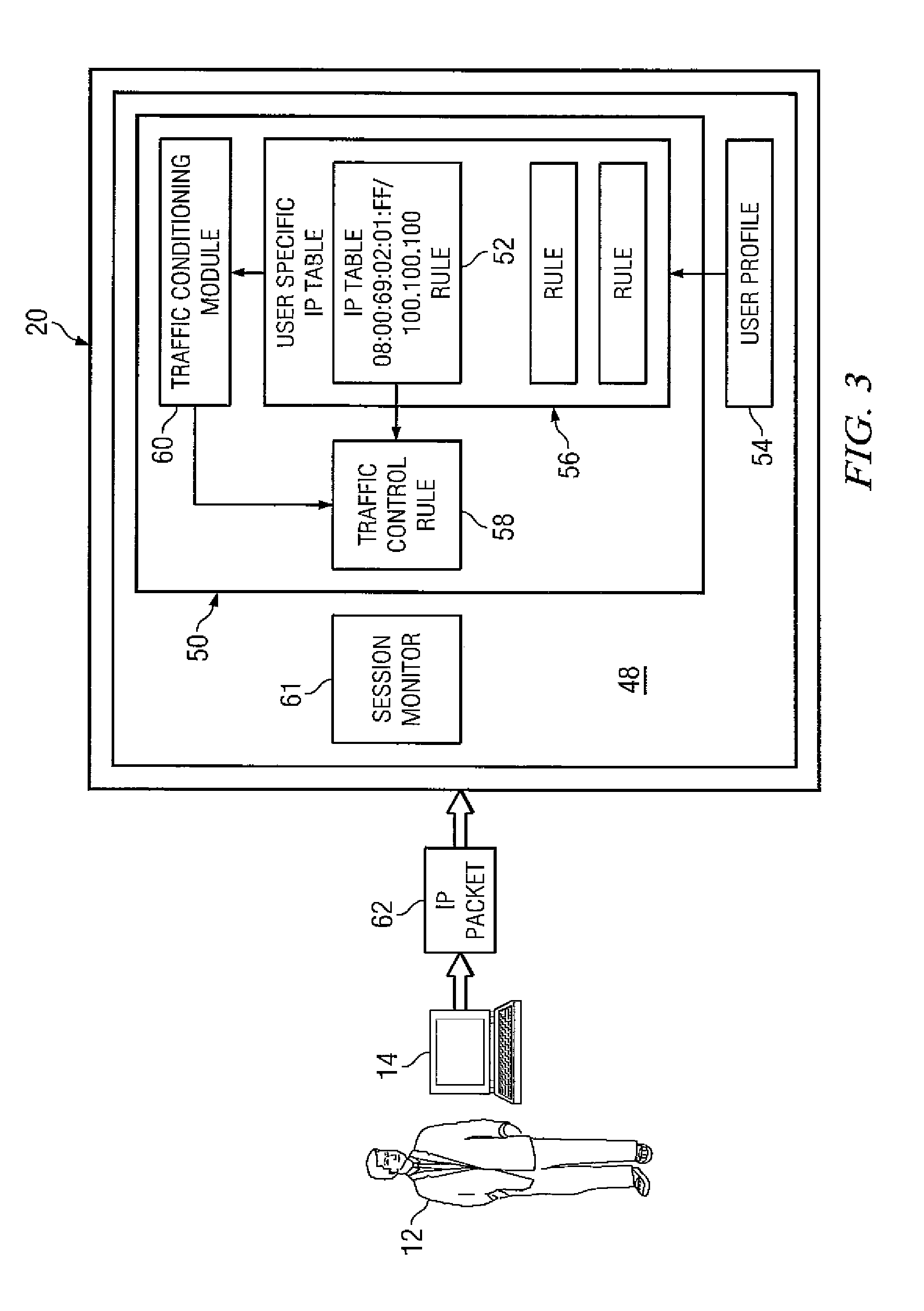
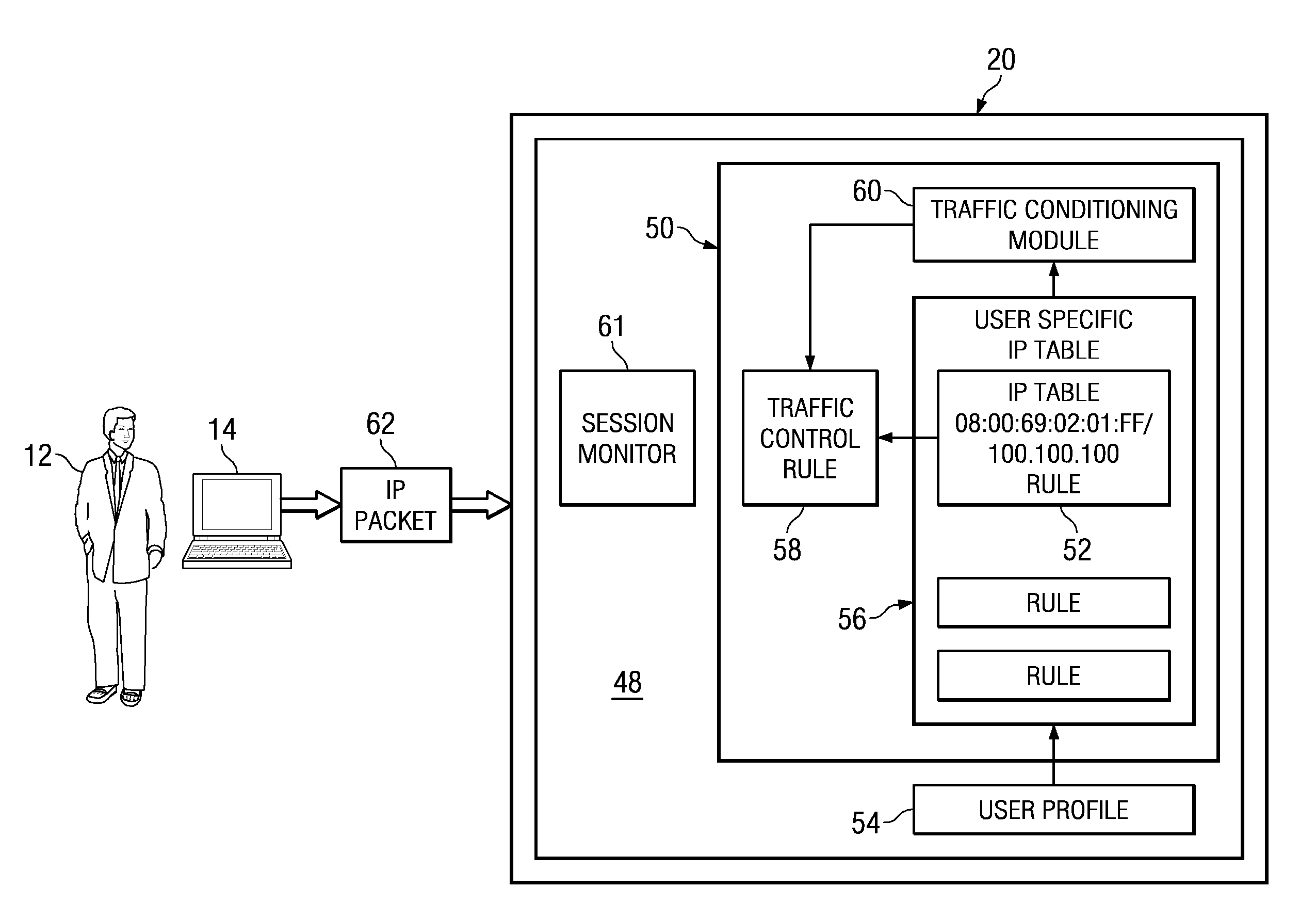
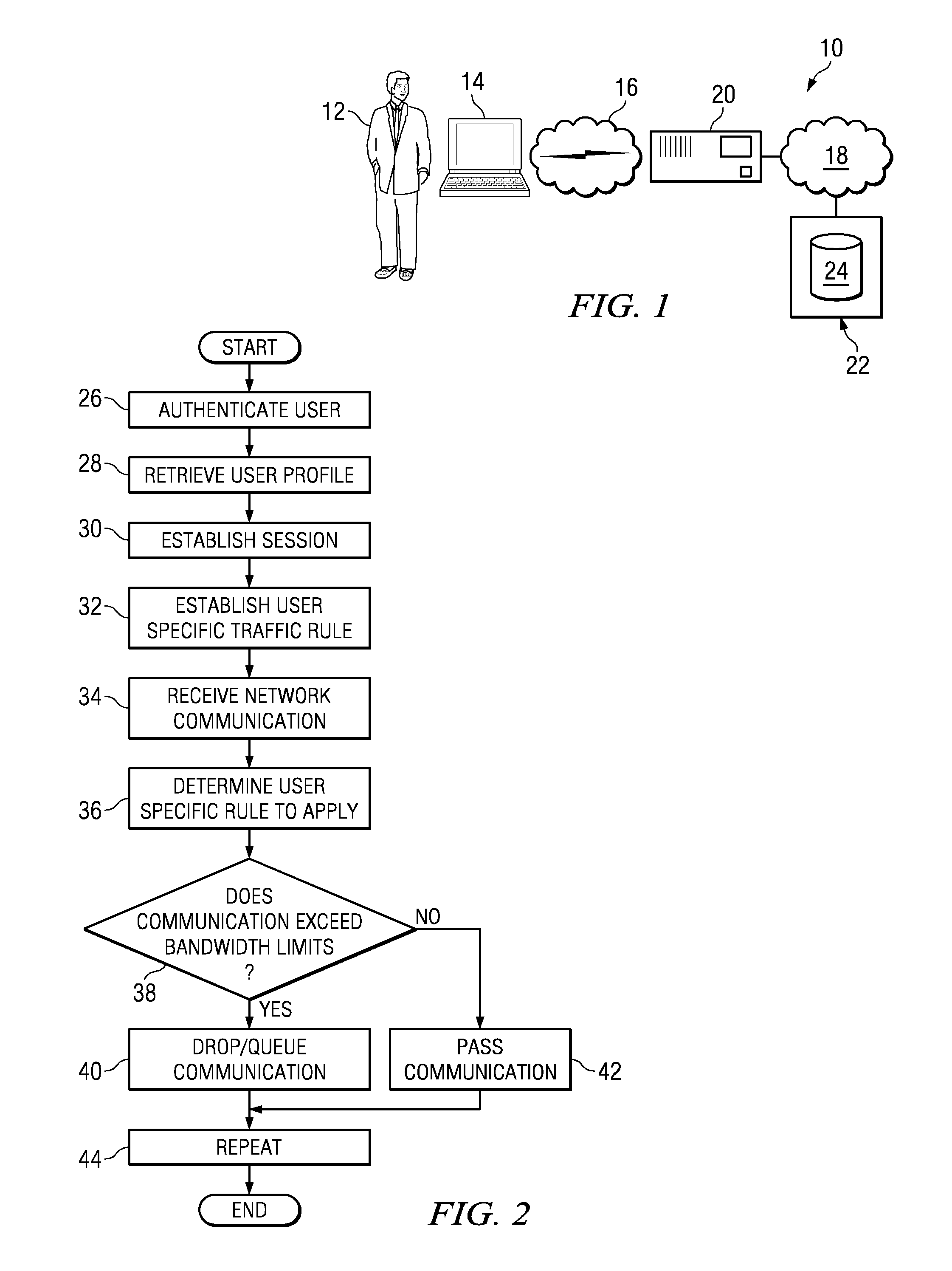
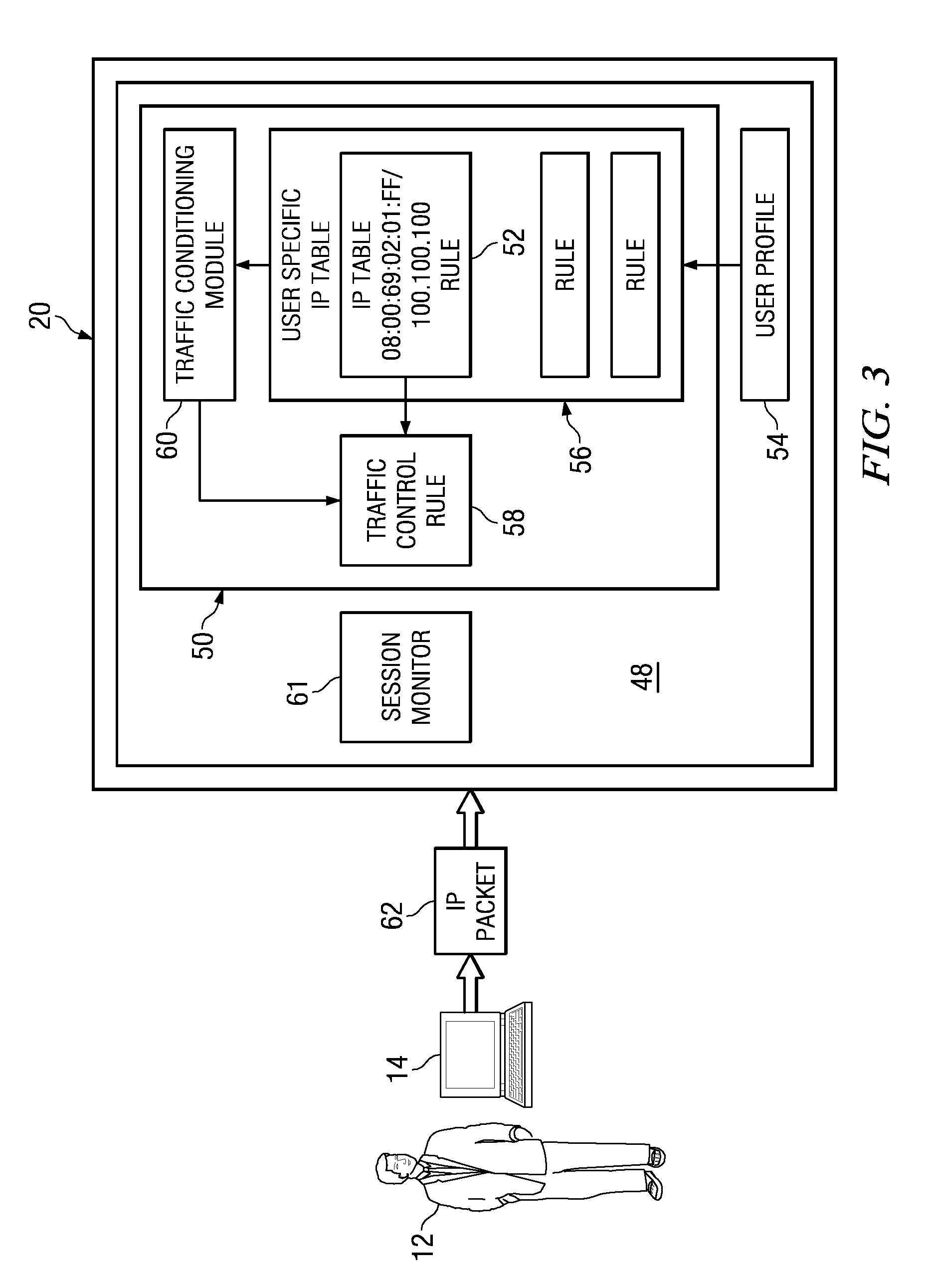
System and method for dynamic bandwidth provisioning
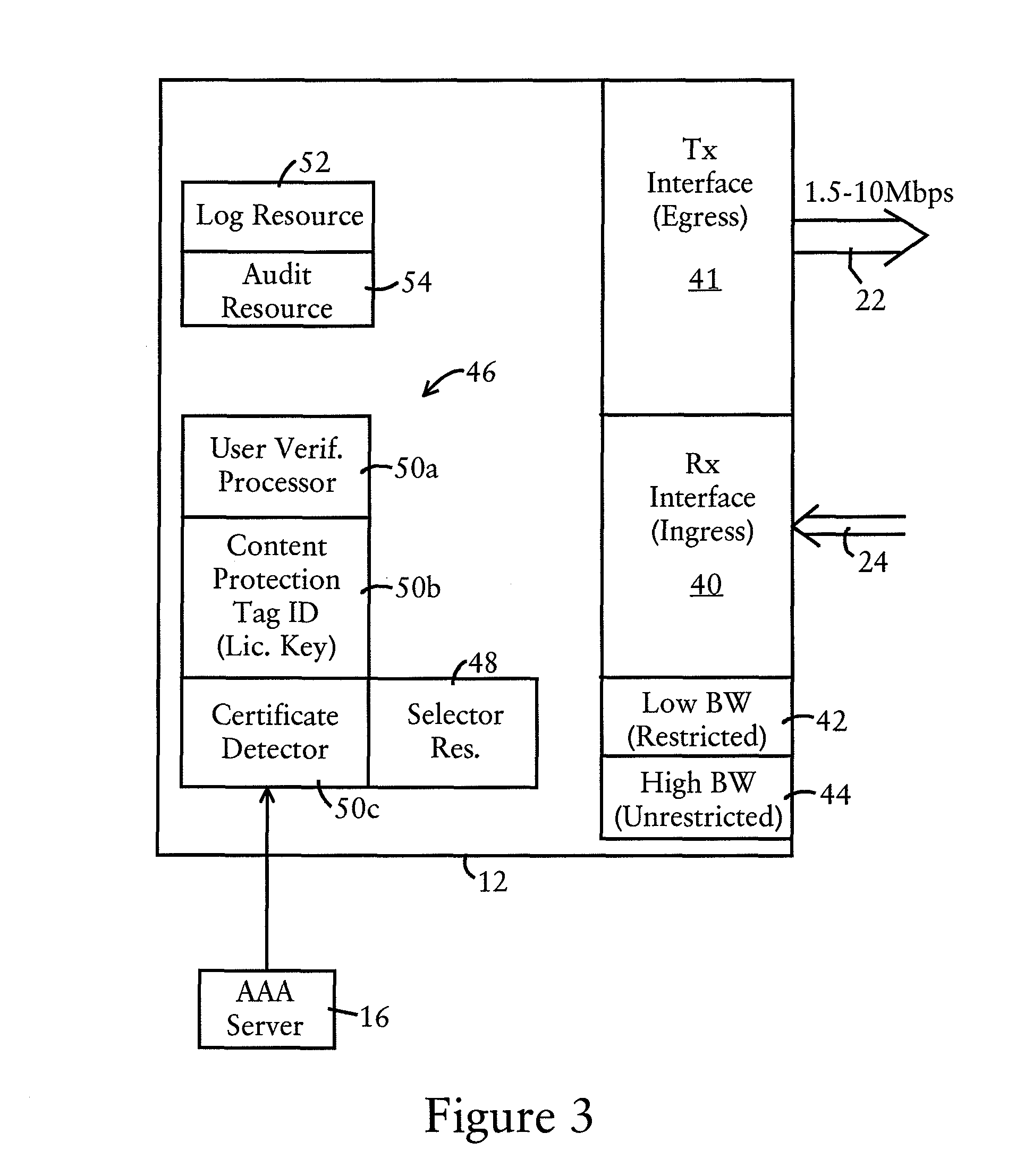
ActiveUS20090279567A1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexTraffic capacityUser device
Embodiments disclosed herein provide a control device and a method executing thereon for allocating network bandwidth to users accessing a controlled network. In response to a user connecting to the control device using a user device, the control device obtains a user bandwidth allocation profile for that user based on user credentials. The user bandwidth allocation profile may be stored local or remote to the control device. A provisioning module running on the control device can map attributes in the user bandwidth allocation profile to a traffic control rule and associate the traffic control rule with the user based on the user credentials and considering information identifying the user device used by the user to connect to the control device. A traffic conditioning module running on the control device can regulate the network bandwidth usage by the user utilizing the traffic control rule associated with the user.
Owner:RPX CORP
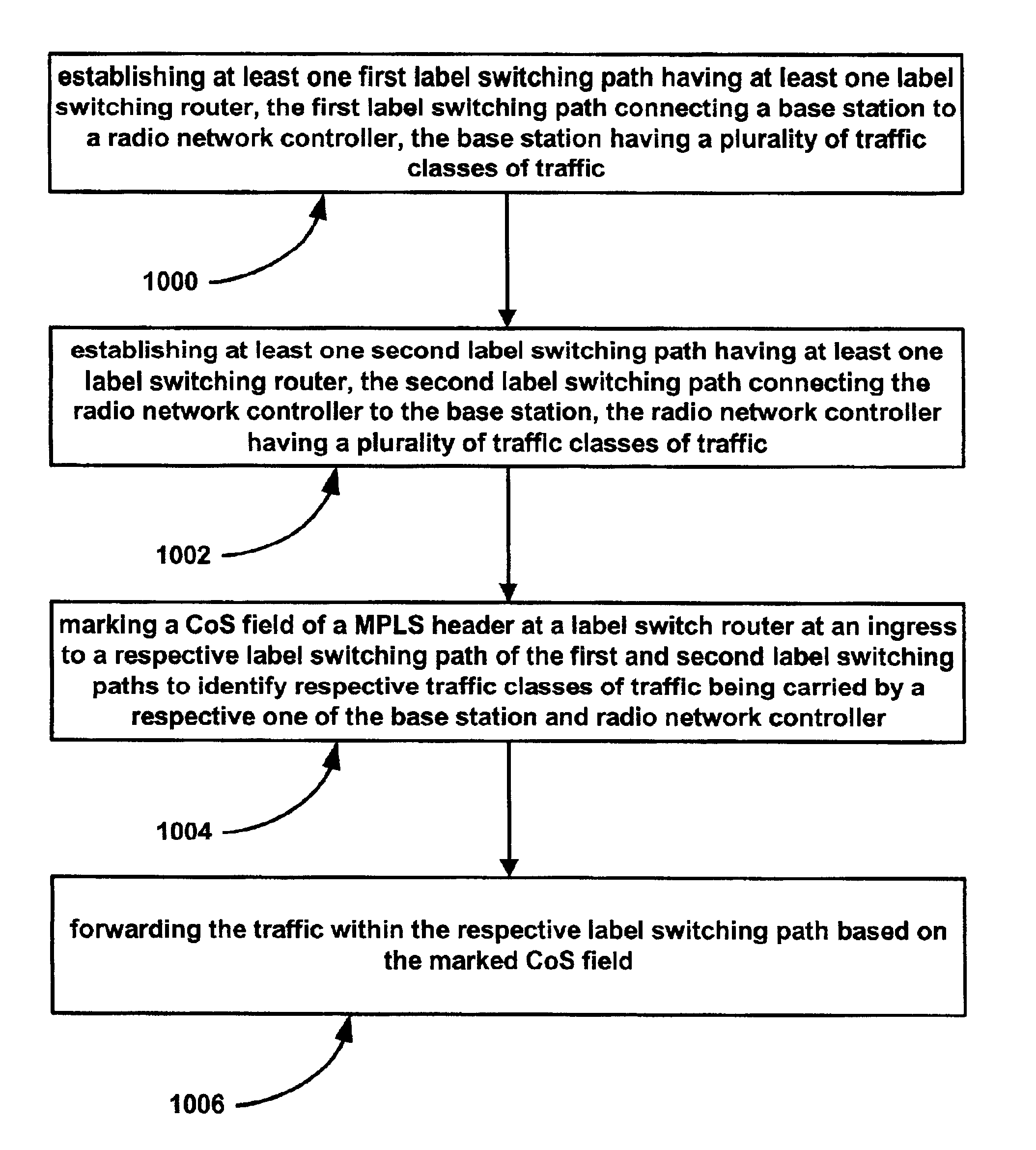
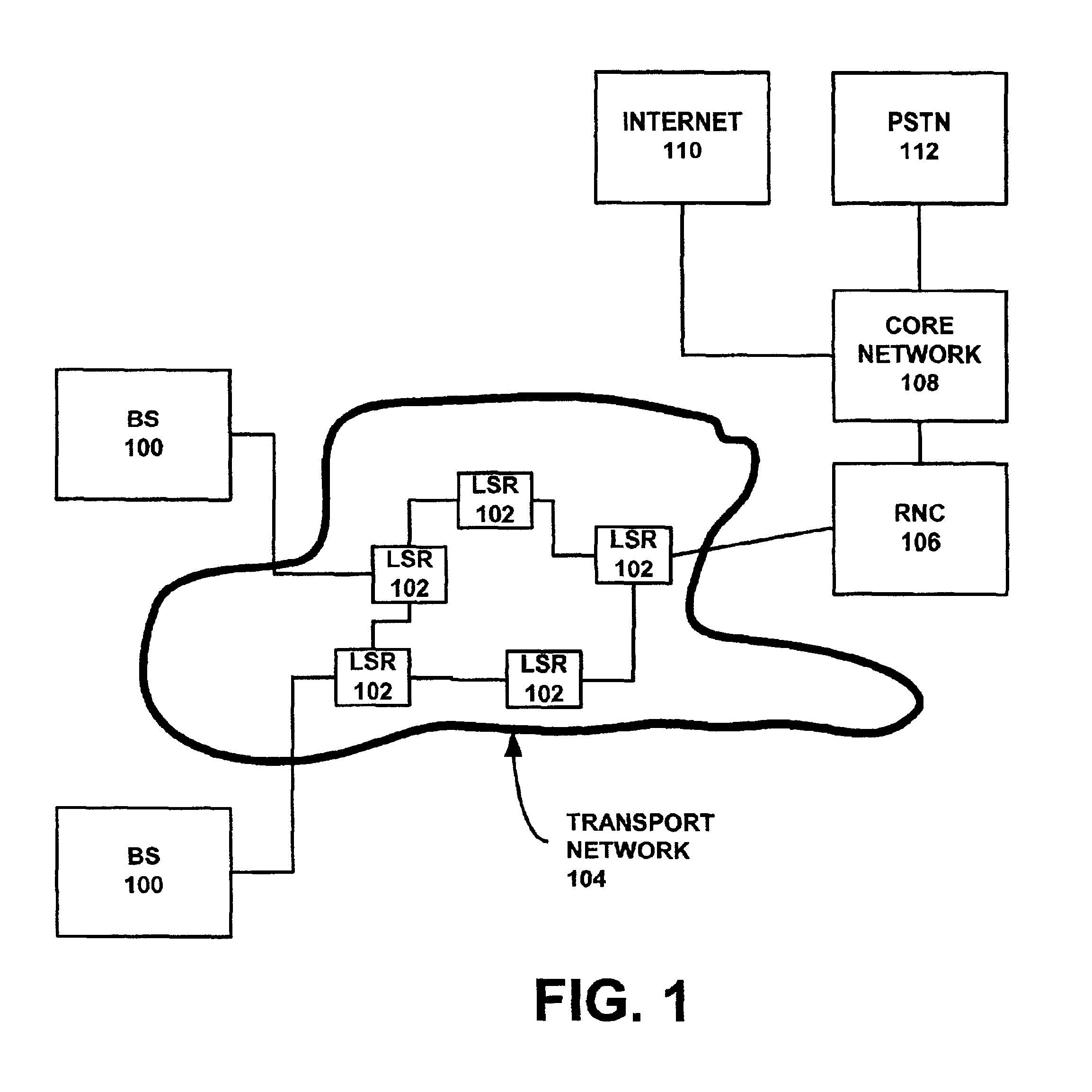
IP/MPLS-based transport scheme in 3G radio access networks
ActiveUS6950398B2Reduce protocol overheadError preventionTransmission systemsRadio networksThird generation
A transport scheme is provided based on Internet protocol (IP) and multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) technology for third generation (3G) radio access networks (RAN). Label switched paths are established and managed for interconnecting base stations and radio network controllers. The process incorporates constraint-based routing and Diffserv to provide transport bearers that can support bandwidth provisioning and a variety of QoS requirements in the RAN.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Method and apparatus for bandwidth provisioning in a wlan
InactiveUS20060153117A1Eliminate requirementsReduce distractionsNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesTime informationBroadcasting
The invention provides for a receiver transmitter comprising: a plurality of logical access points; for downloading a duration into a mobile terminal in accordance with an access point determination of the maximum amount of time information linked with a downlink broadcast traffic to deliver all the broadcast / multicast information in a single communication stream. The invention also provides for a method of broadcast / multicast frames “Duration” are set to values in order to deliver all the broadcast / multicast information in a single communication stream eliminating the requirement for contending for the medium for each broadcast / multicast frame transmission. This pseudo-reservation of the wireless medium can also be made periodic for enabling broadcast / multicast services.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
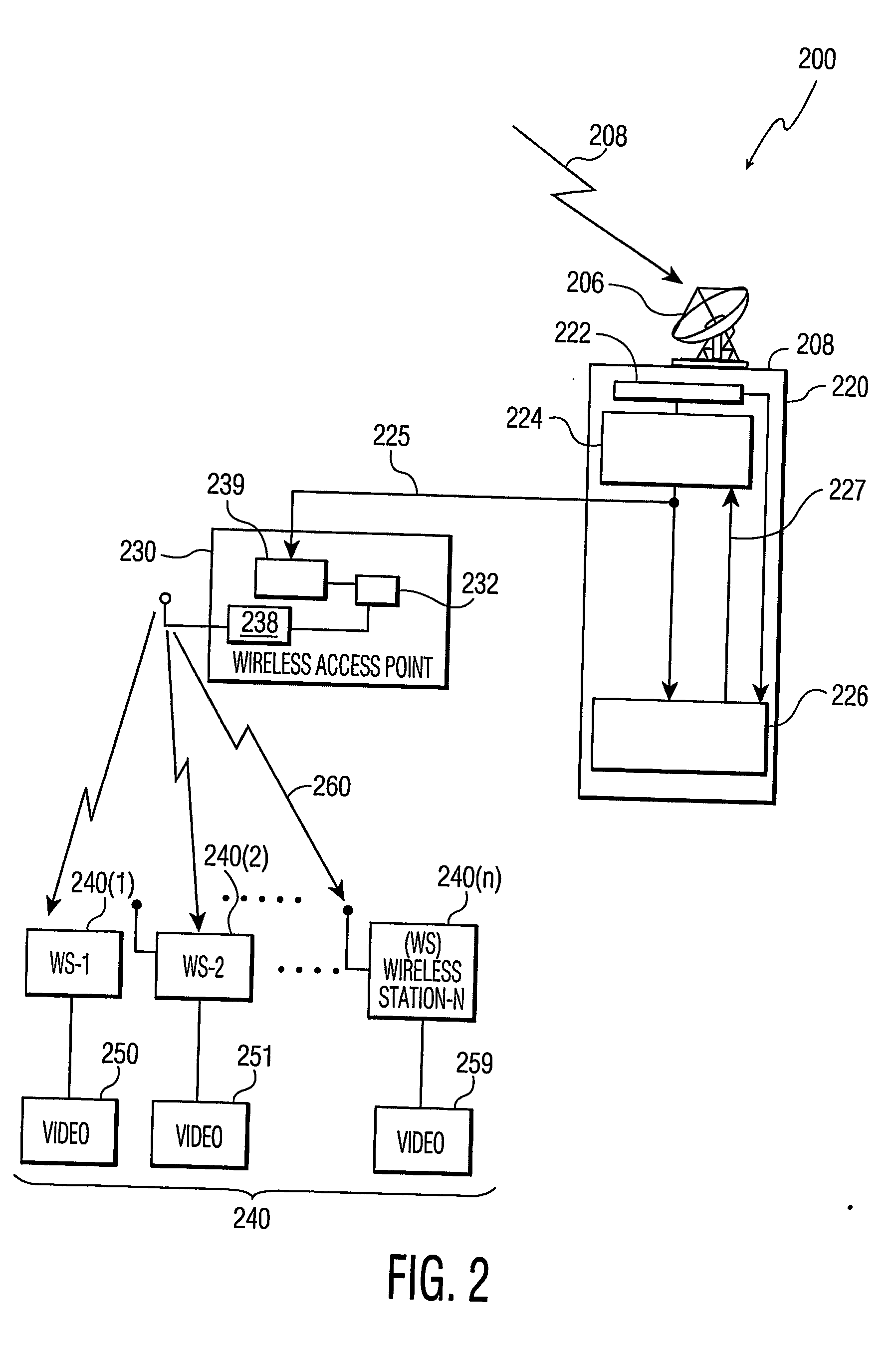
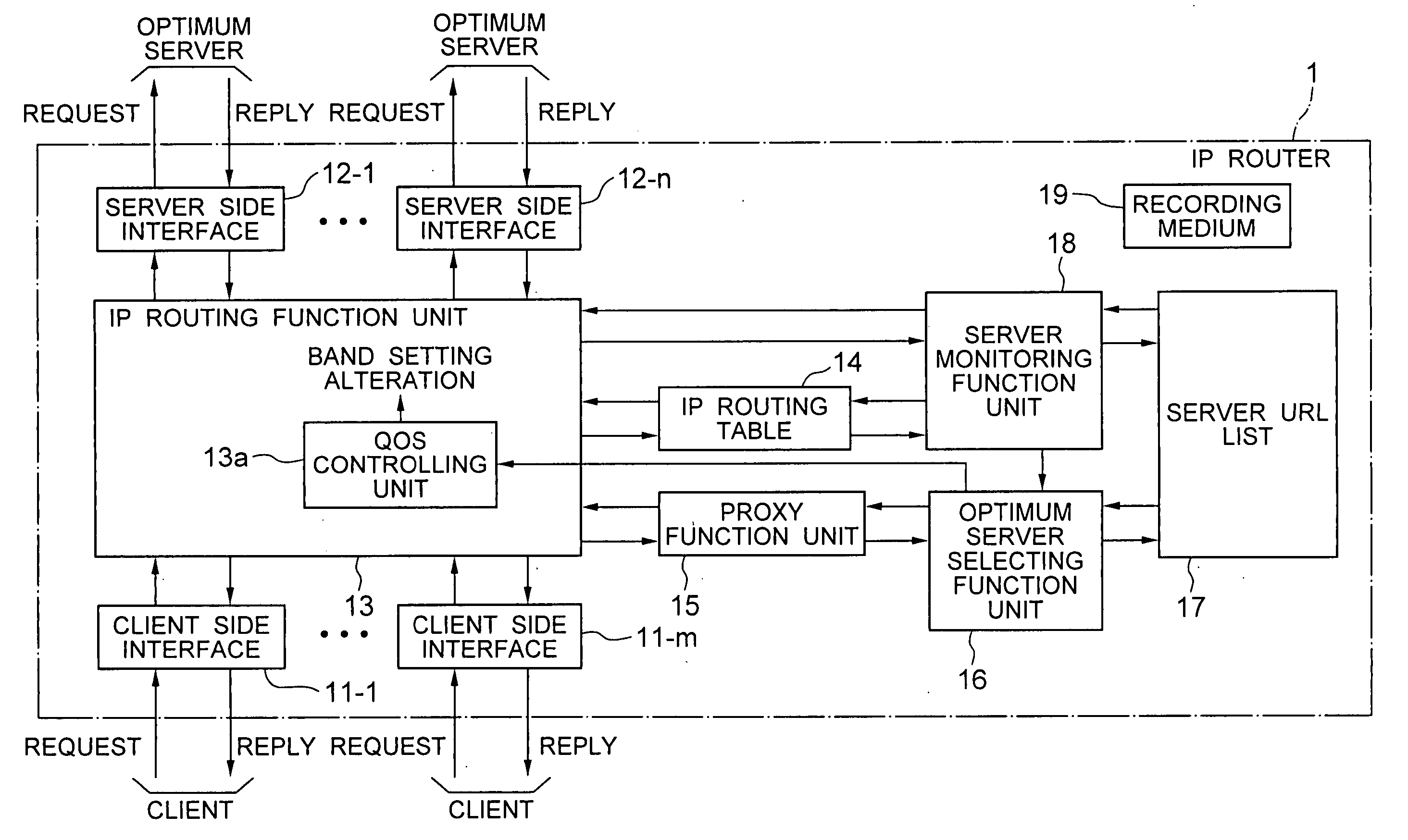
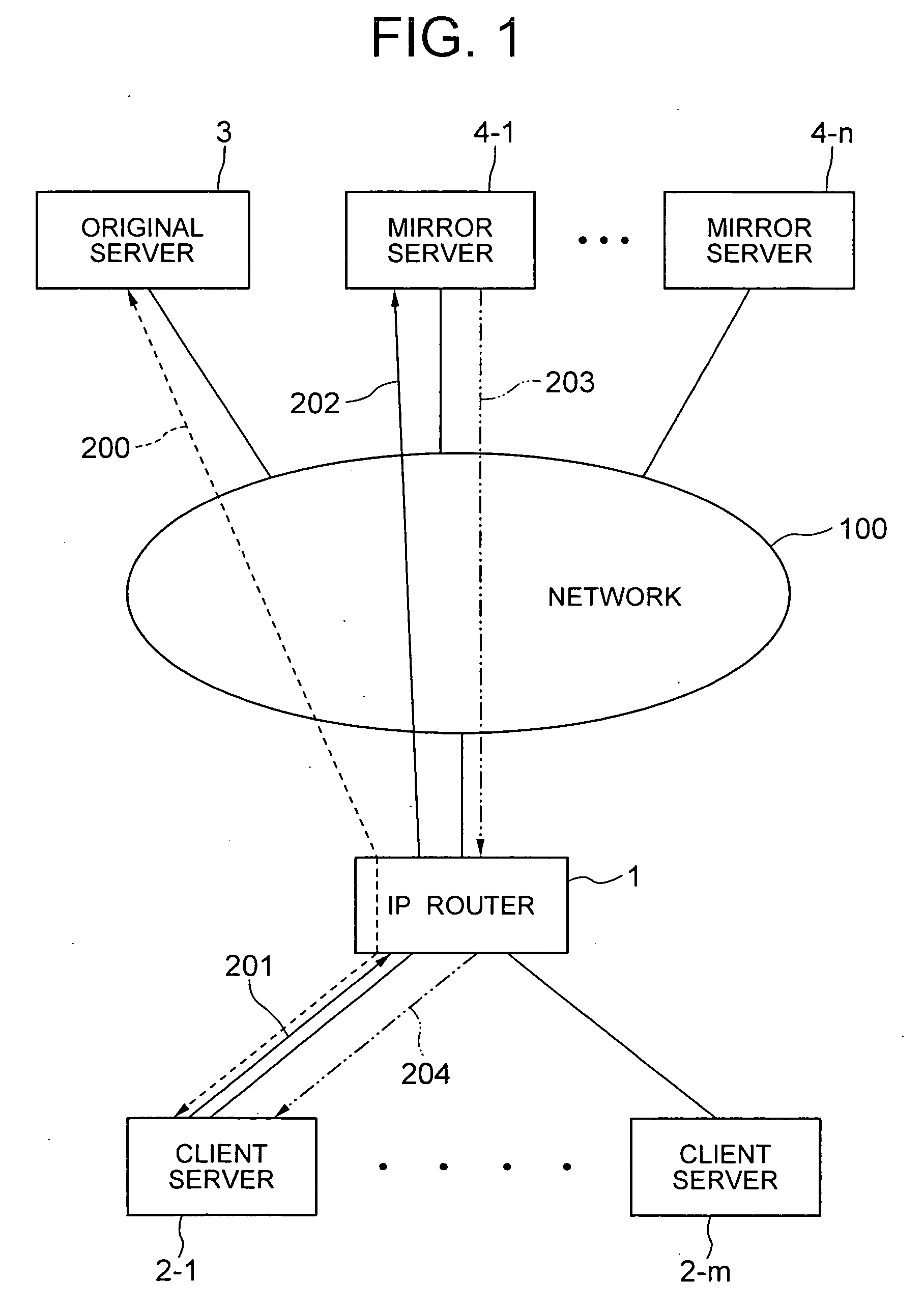
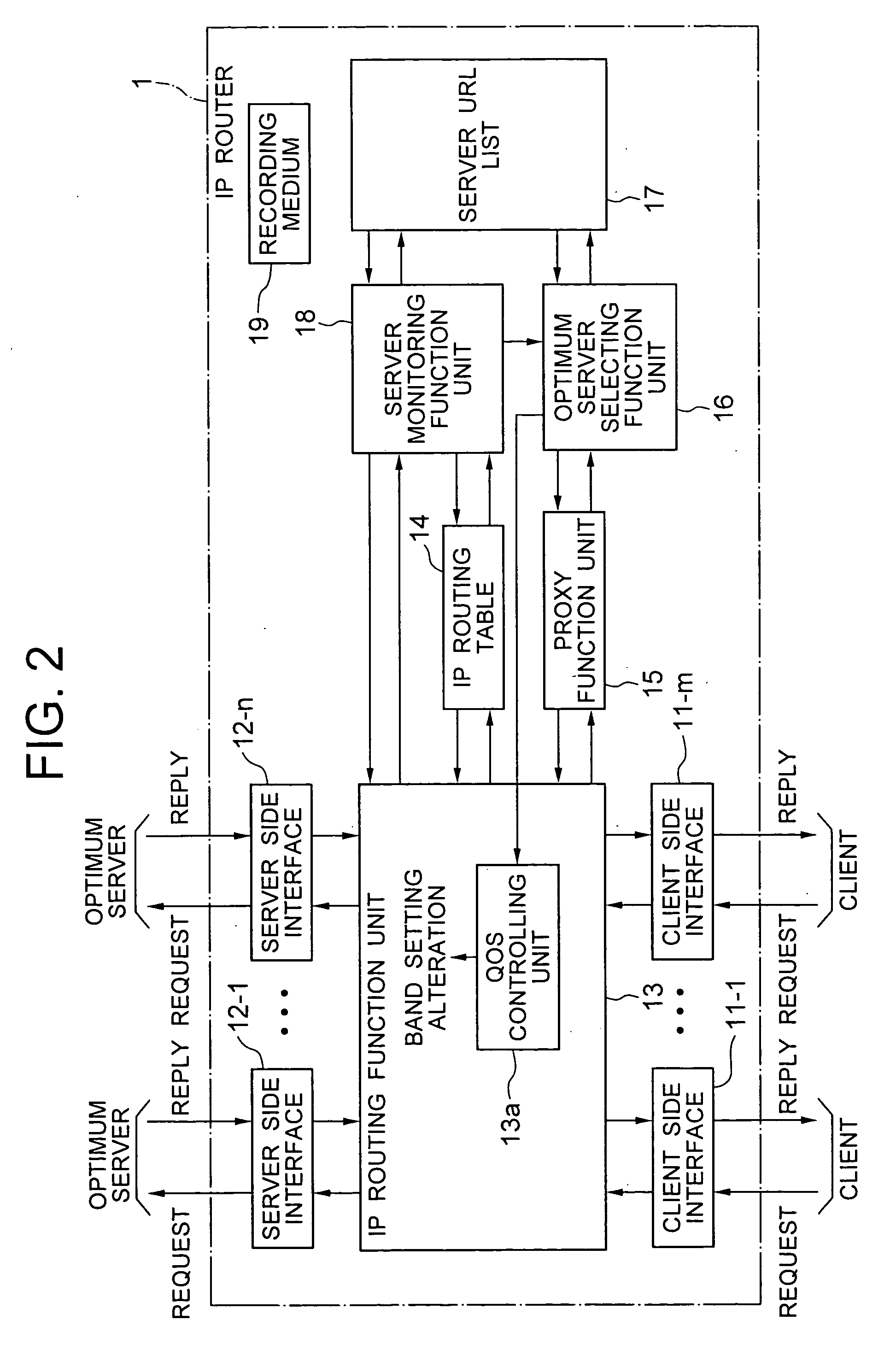
IP router, communication system and band setting method used therein and its program
ActiveUS20040172470A1Digital computer detailsNetworks interconnectionTraffic capacityCommunications system
A server monitoring function unit recognizes a running / stopping state of each server, throughput and the like by performing a health check based on obtained positioning information of an original server and mirror servers, informs an optimum server selecting function unit of the information, and updates a server URL list based on the positioning information. When the server monitoring function unit detects a change in the network topology from a change in an IP routing table, the optimum server selecting function unit alters the selection criteria of the optimum server and informs a QoS controlling unit of a traffic change. The QoS controlling unit alters a band setting for each service class according to the traffic change informed.
Owner:NEC PLATFORMS LTD
Method and apparatus for dynamic bandwidth provisioning in frequency division duplex systems
InactiveUS9413500B2Spectral gaps assessmentTransmission path divisionFrequency spectrumLicensed spectrum
A method and apparatus are described that provides flexible spectrum usage by using a paired frequency division duplex (FDD) spectrum to enable dynamic access in television white space (TVWS), sub-leased spectrum or unlicensed spectrum, (e.g., industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) bands), in a femto cell environment or the like. Elastic FDD (E-FDD) enables femto cell operation in TVWS, sub-leased spectrum and / or unlicensed spectrum, either simultaneously with licensed spectrum or as an alternate channel to licensed spectrum. E-FDD enables dynamic asymmetric bandwidth allocation for uplink (UL) and downlink (DL) in FDD, and enables variable duplex spacing, (i.e., using FDD with minimum duplex spacing between DL and UL spectrum, or, using hybrid-FDD, (FDD in a time duplexed fashion), when a spectrum gap between the UL and DL spectrum is below a certain minimum threshold. Additionally, the signaling enhancements to implement E-FDD are also provided.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
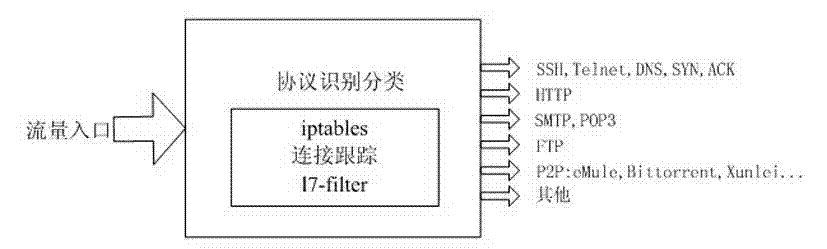
Flow control method based on application layer detection
InactiveCN103036803AImprove service qualitySuppress trafficData switching networksWeb serviceThe Internet
The invention relates to a flow control method based on application layer detection .The flow control method based on the application layer detection is a systematic method of identification and control for the flow of a variety of web services. Bandwidth management is carried out for different user groups. Different bandwidths are distributed to different user groups according to difference of businesses of departments in enterprises. The bandwidths of some users are limited. Each group of users can obtain the minimum guaranteed bandwidth whenever the users surf the internet and network congestion can be avoided. Maximum bandwidth which can be borrowed and borrowing priority of each group are set at the same time. Therefore, waste of resources caused by excess bandwidths of sub-networks can be avoided and users of high priority can borrow more remaining bandwidths. Bandwidth management is carried out for different application protocols. Different bandwidths are distributed to different application protocols according to criticality of businesses. Different priority levels are set, and non-critical business flow of peer-to-peer (P2P) and the like are restrained. Therefore, service quality of critical businesses is guaranteed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
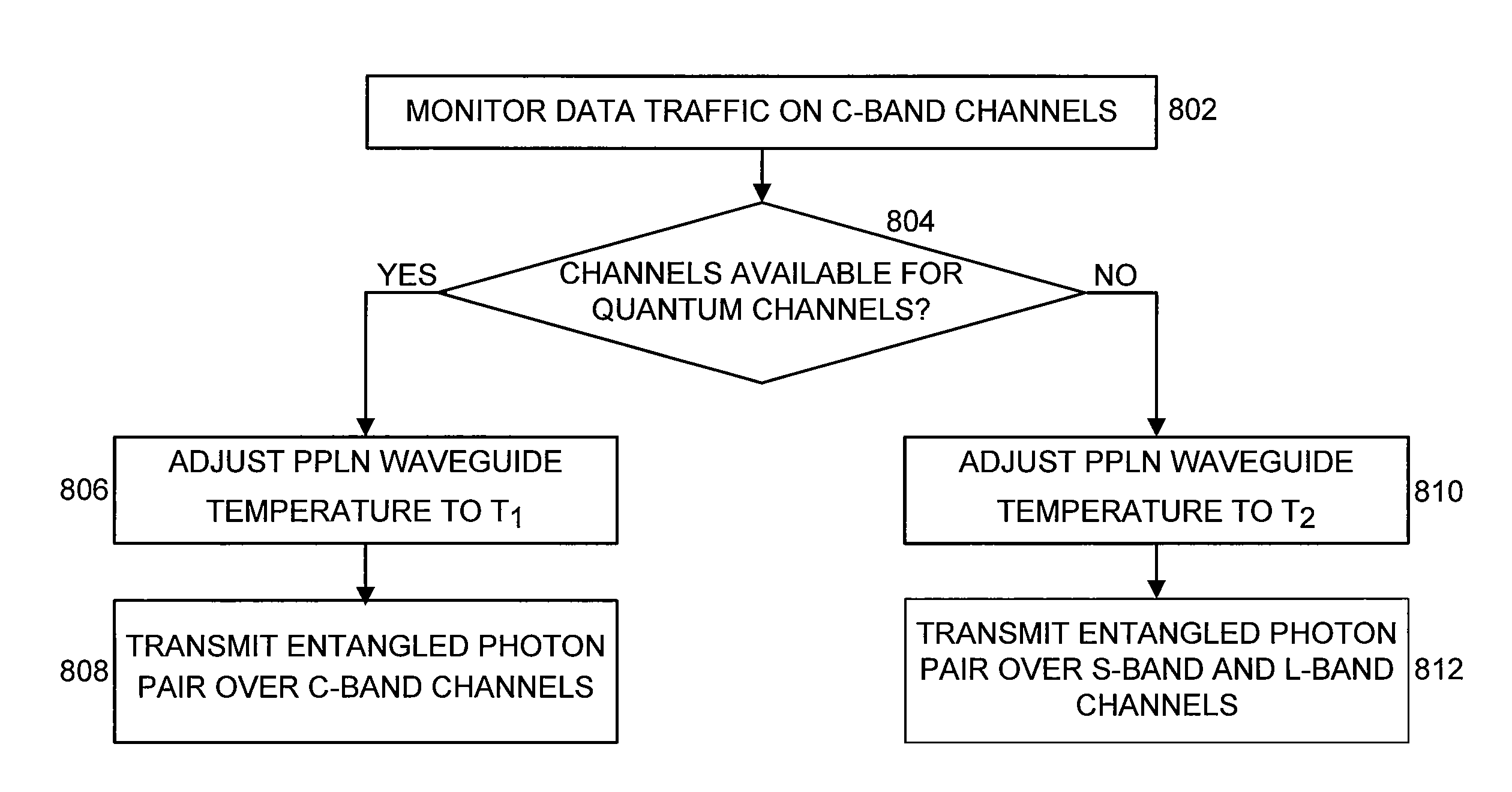
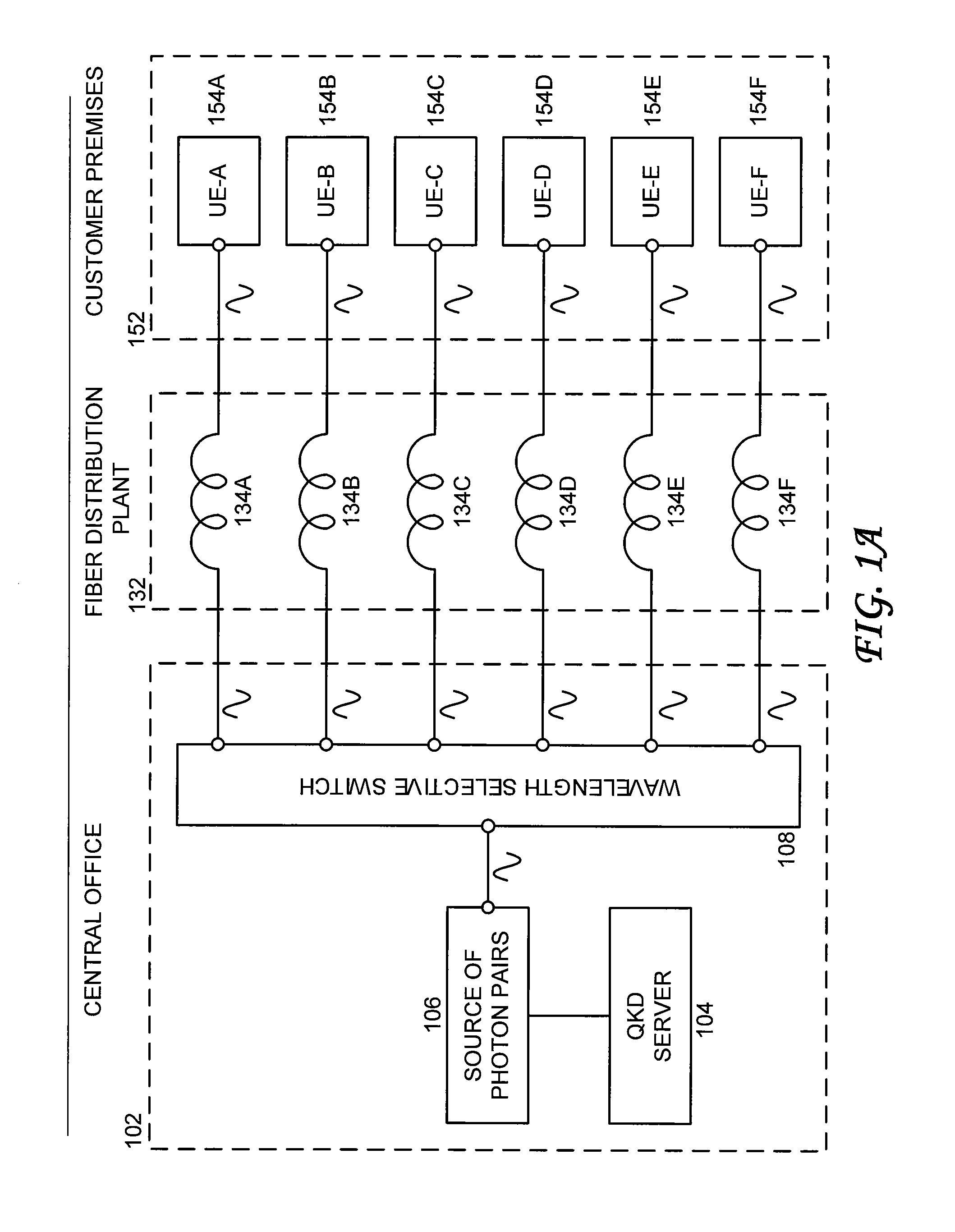
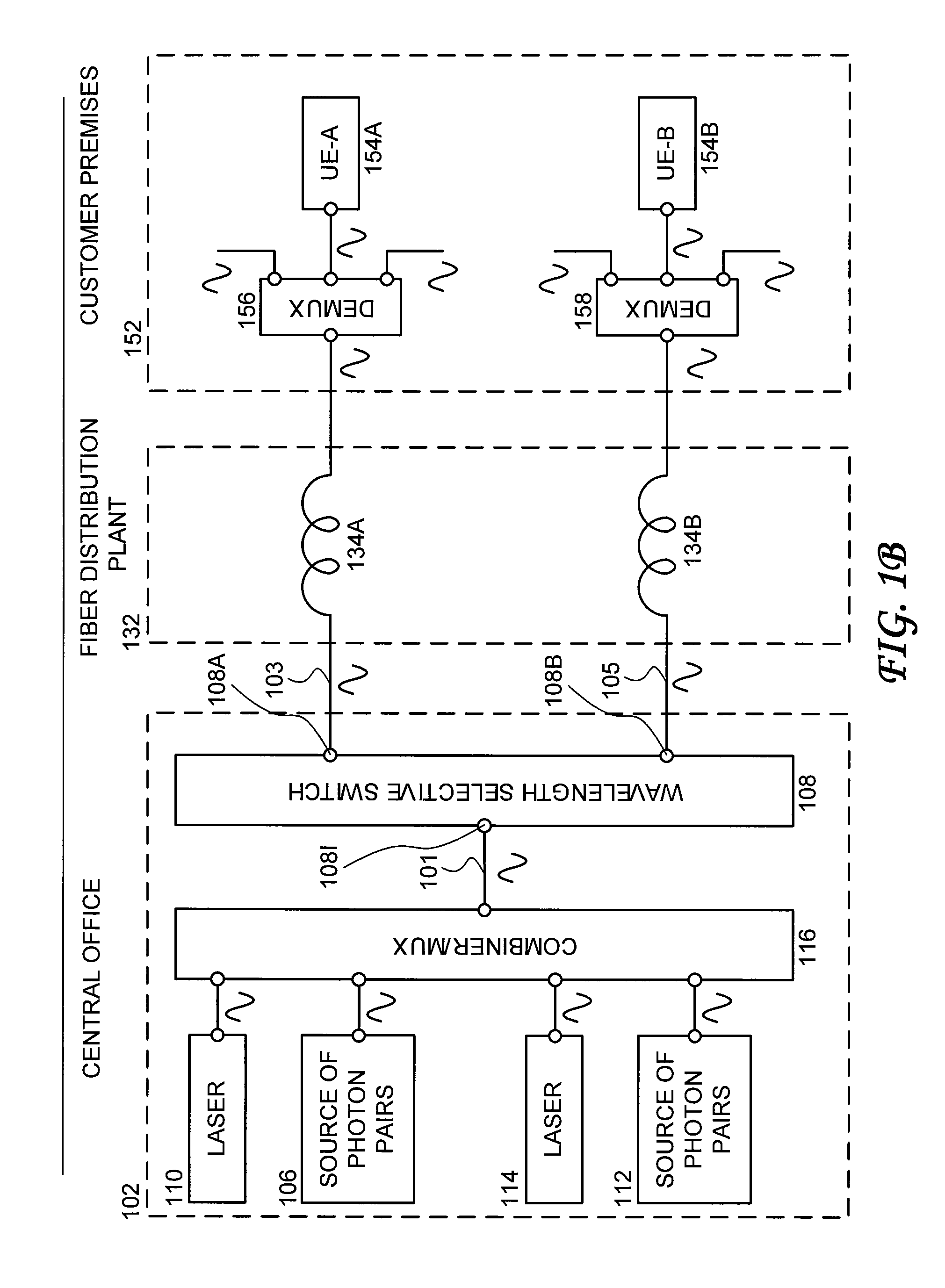
Bandwidth provisioning for an entangled photon system
ActiveUS8280250B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsC bandingFiber network
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
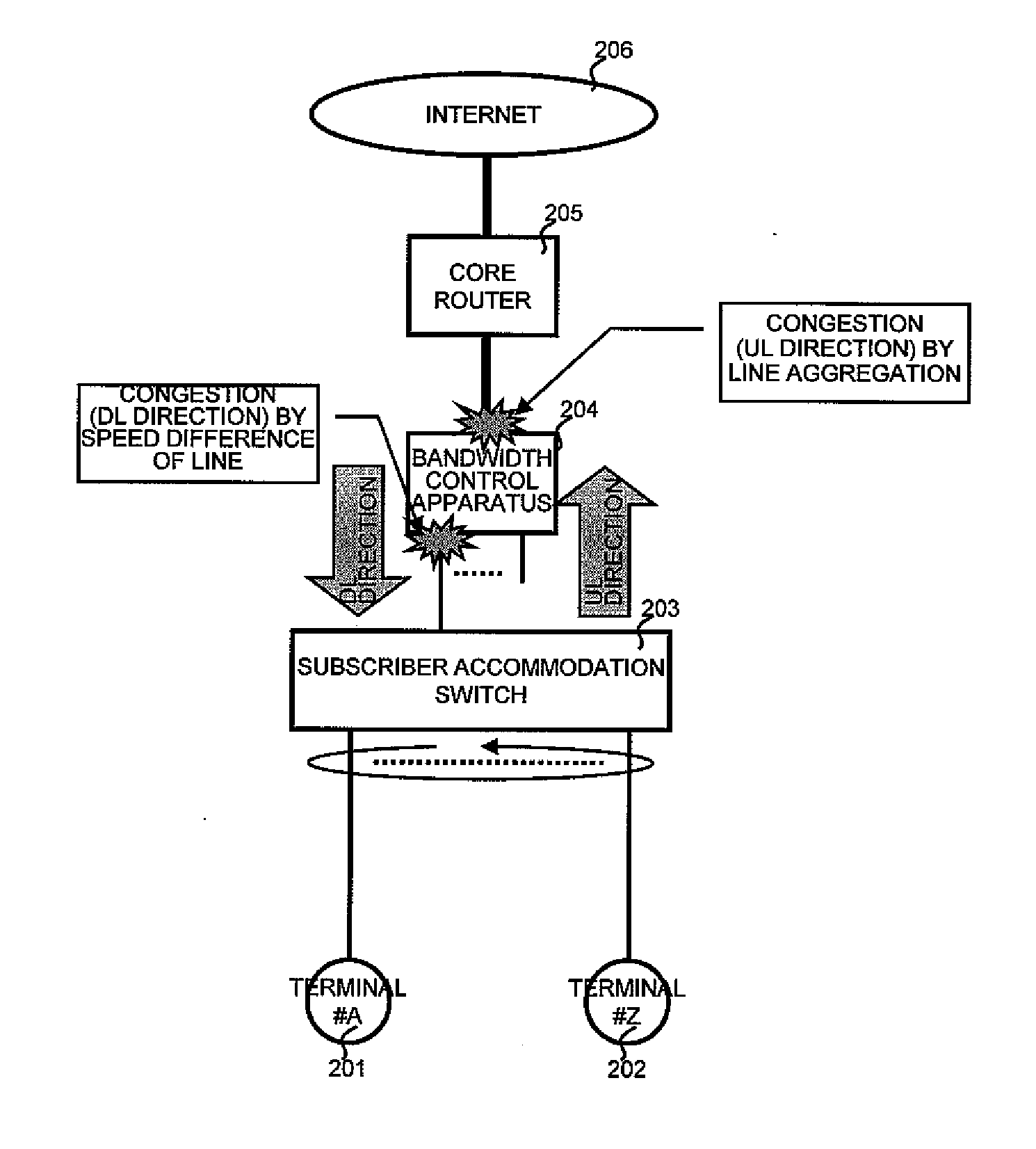
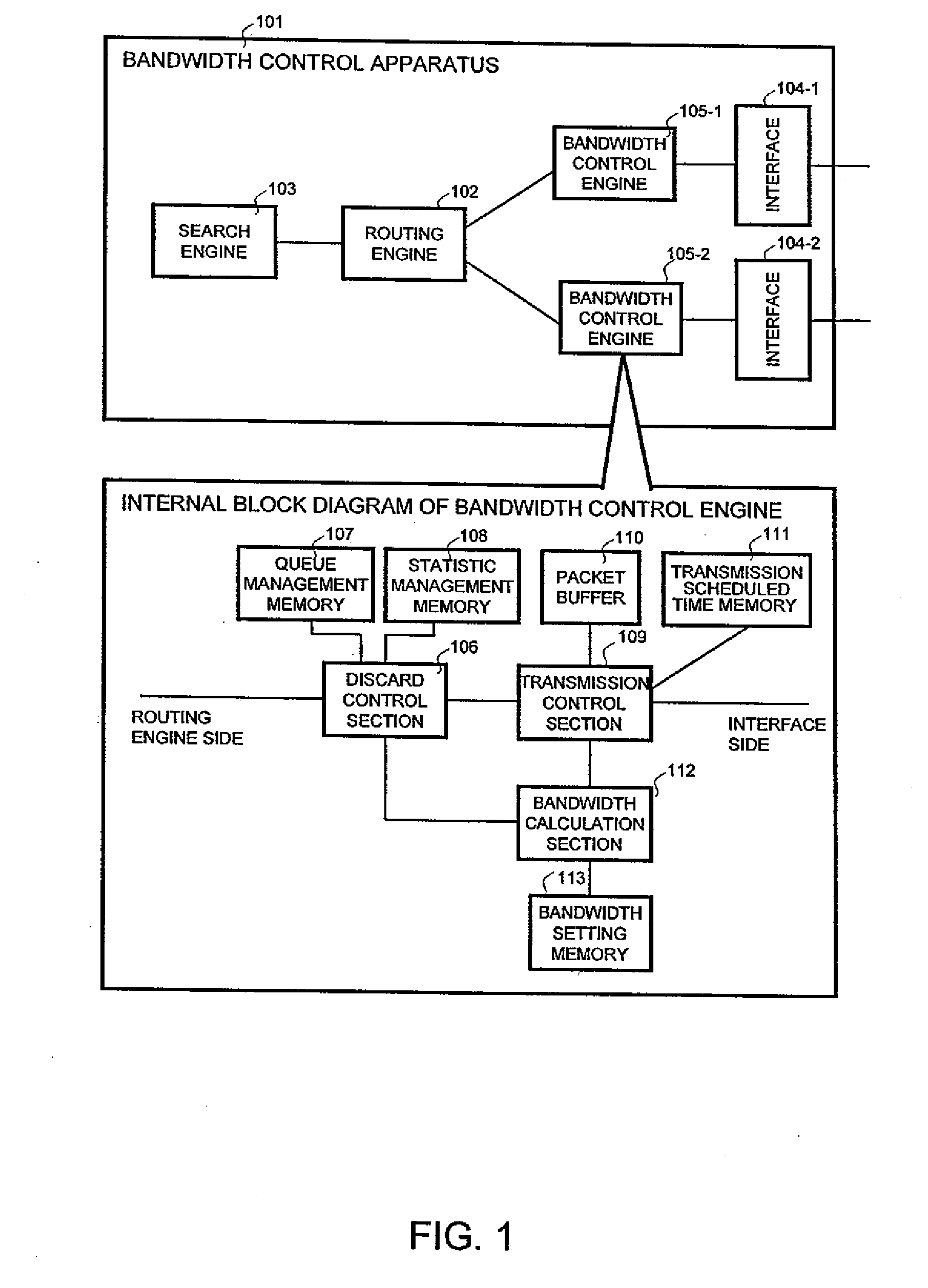
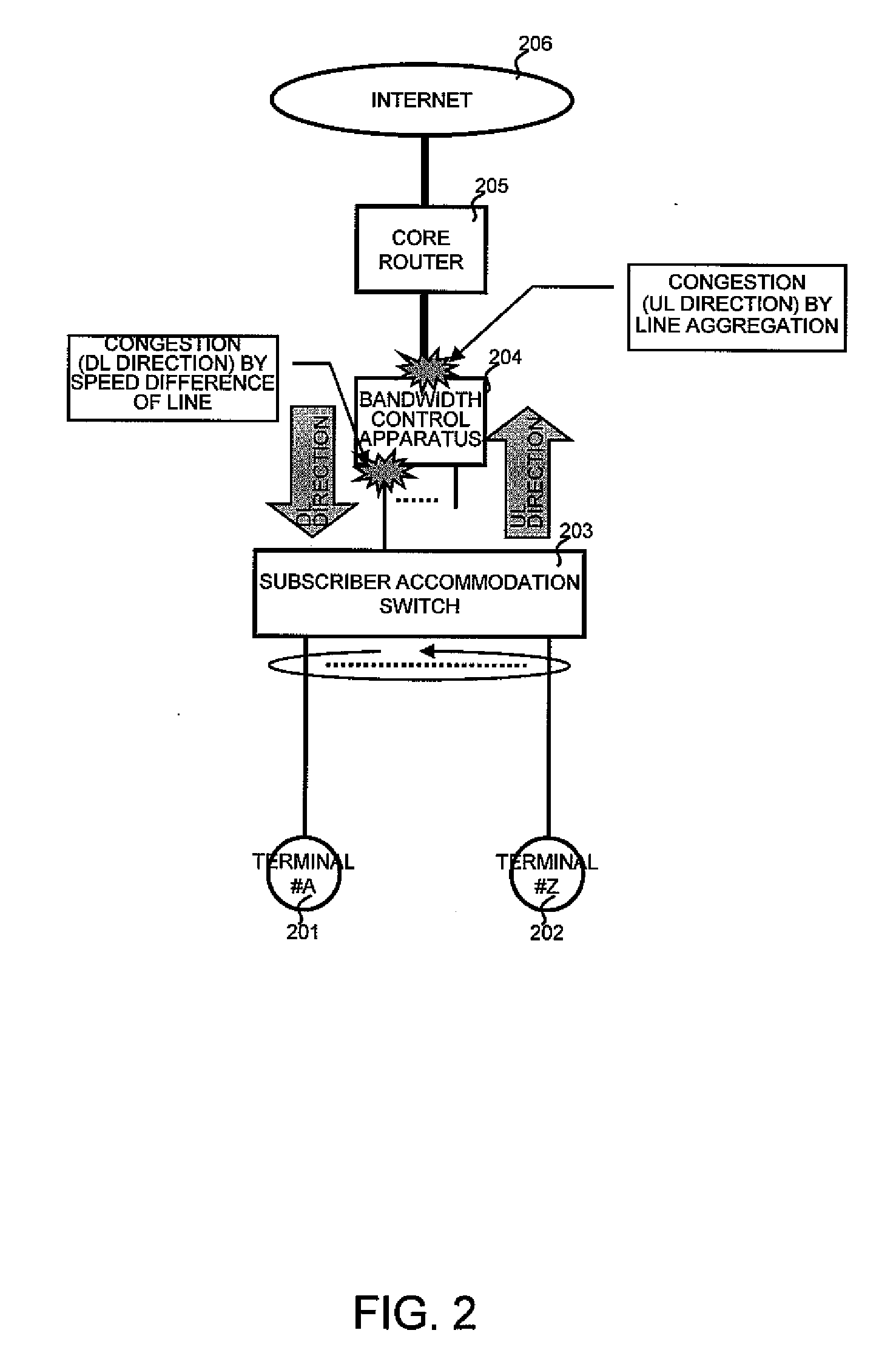
Bandwidth control apparatus
ActiveUS20100189129A1Correction biasTime-division multiplexTransmissionTransmission scheduleConnection time
A bandwidth calculation section calculates a usable bandwidth from a communication amount of each user or a session connection time stored in a statistic management memory and minimum bandwidth information and maximum bandwidth information recorded in a bandwidth setting memory. The bandwidth calculation section allocates a large usable bandwidth to a user with a small communication amount or a short session connection time. A transmission control section performs transmission scheduling of packet information stored in a packet buffer based on a transmission scheduled time calculated from the usable bandwidth stored in a transmission scheduled time memory.
Owner:ALAXALA NETWORKS
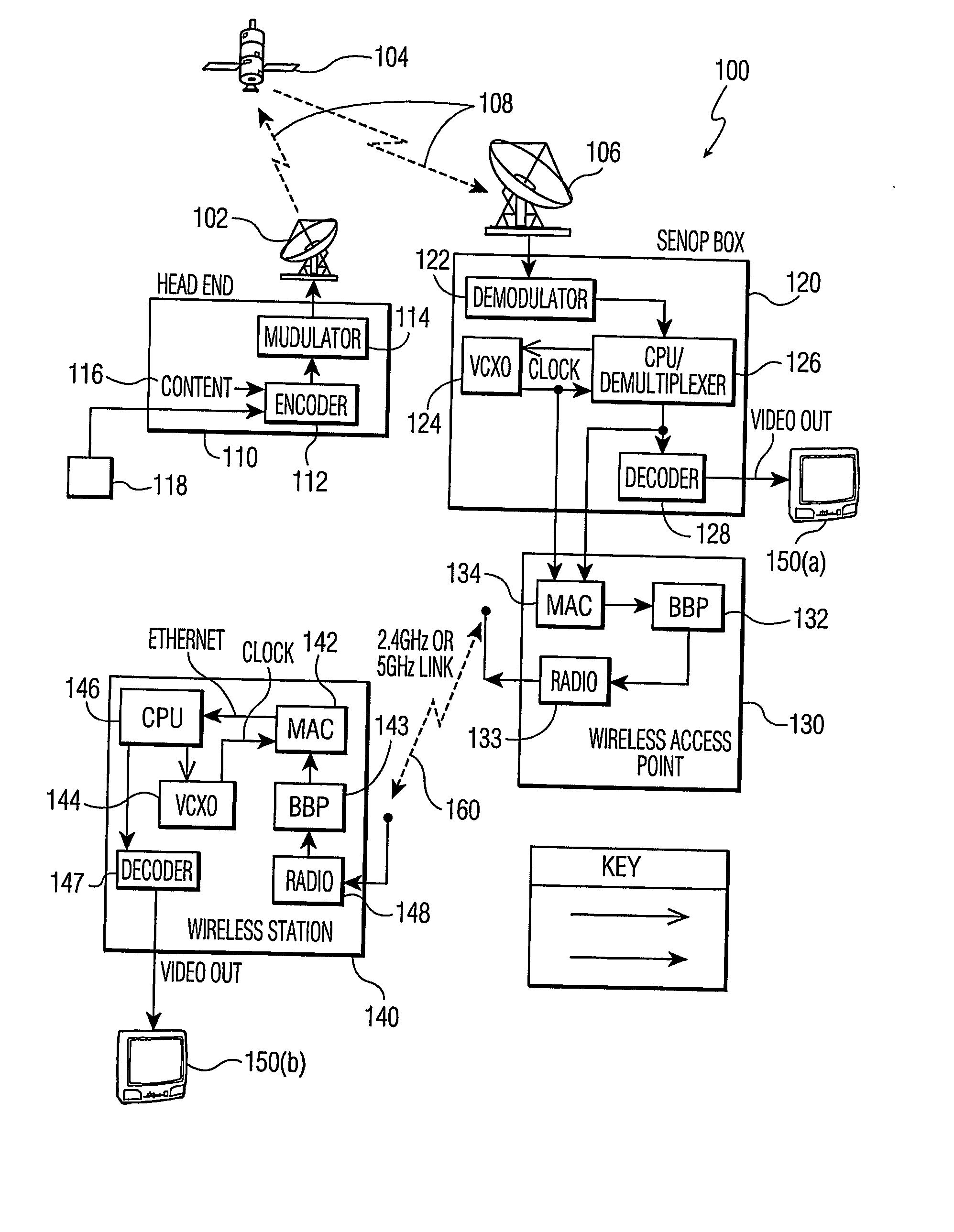
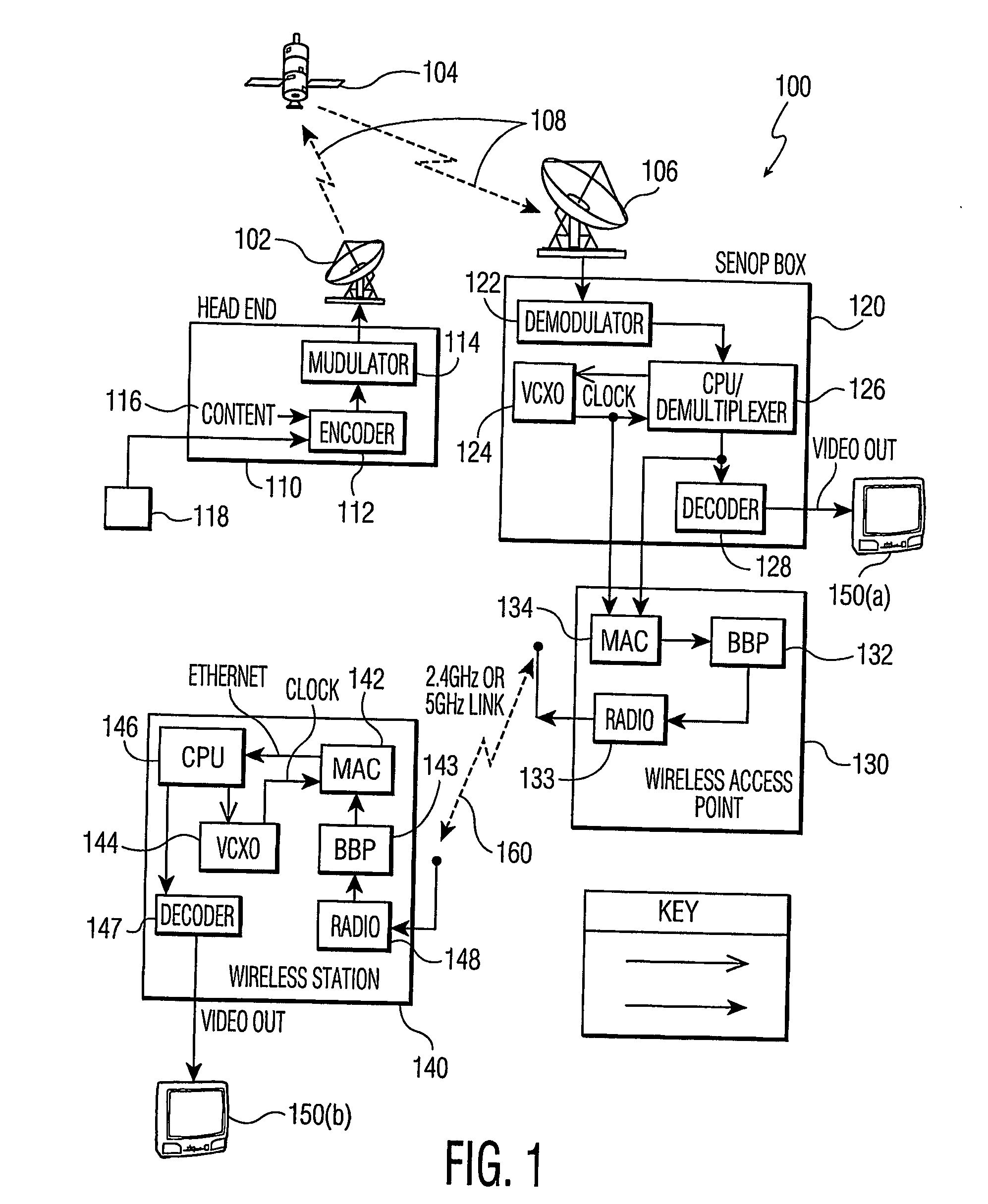
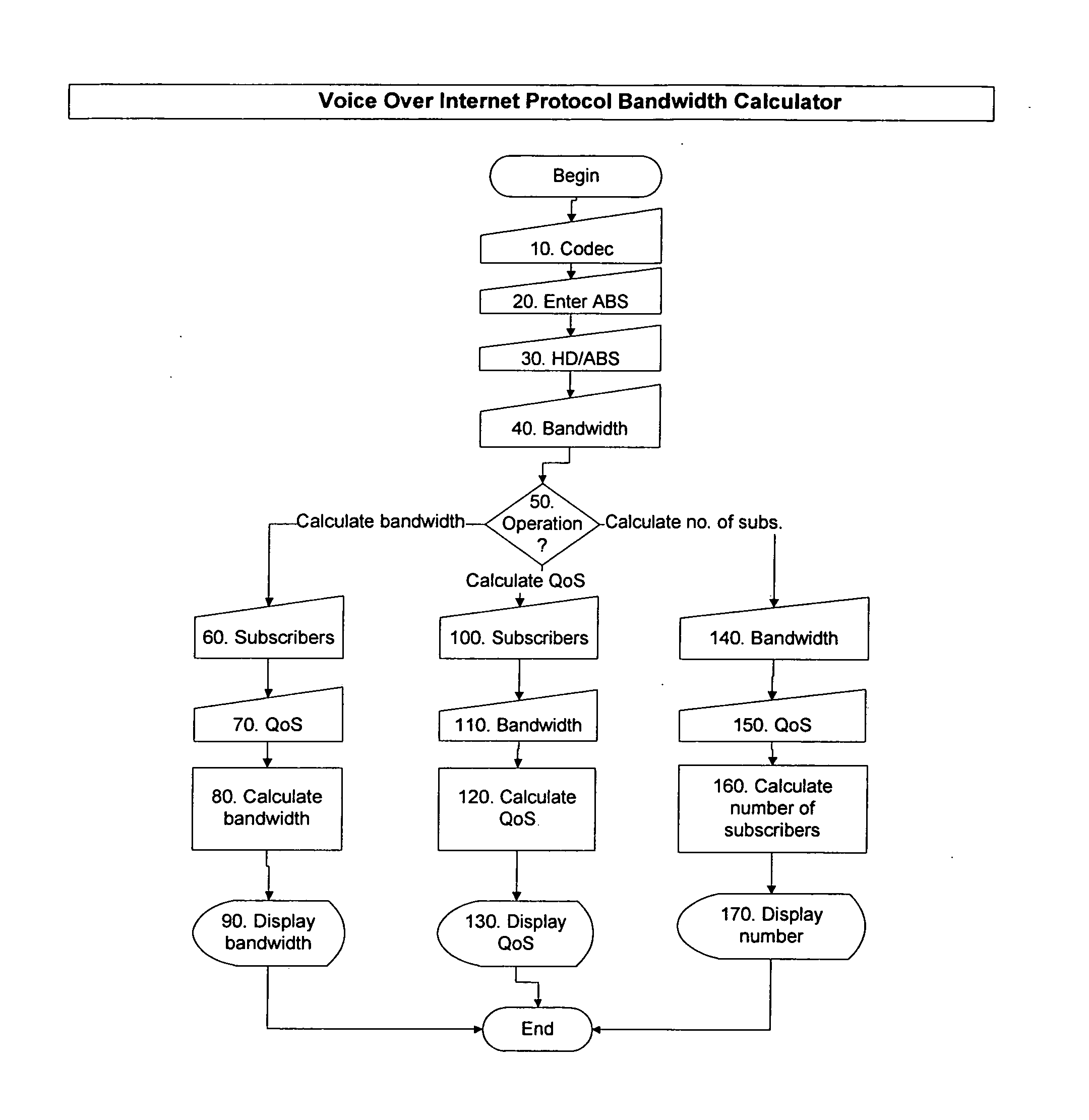
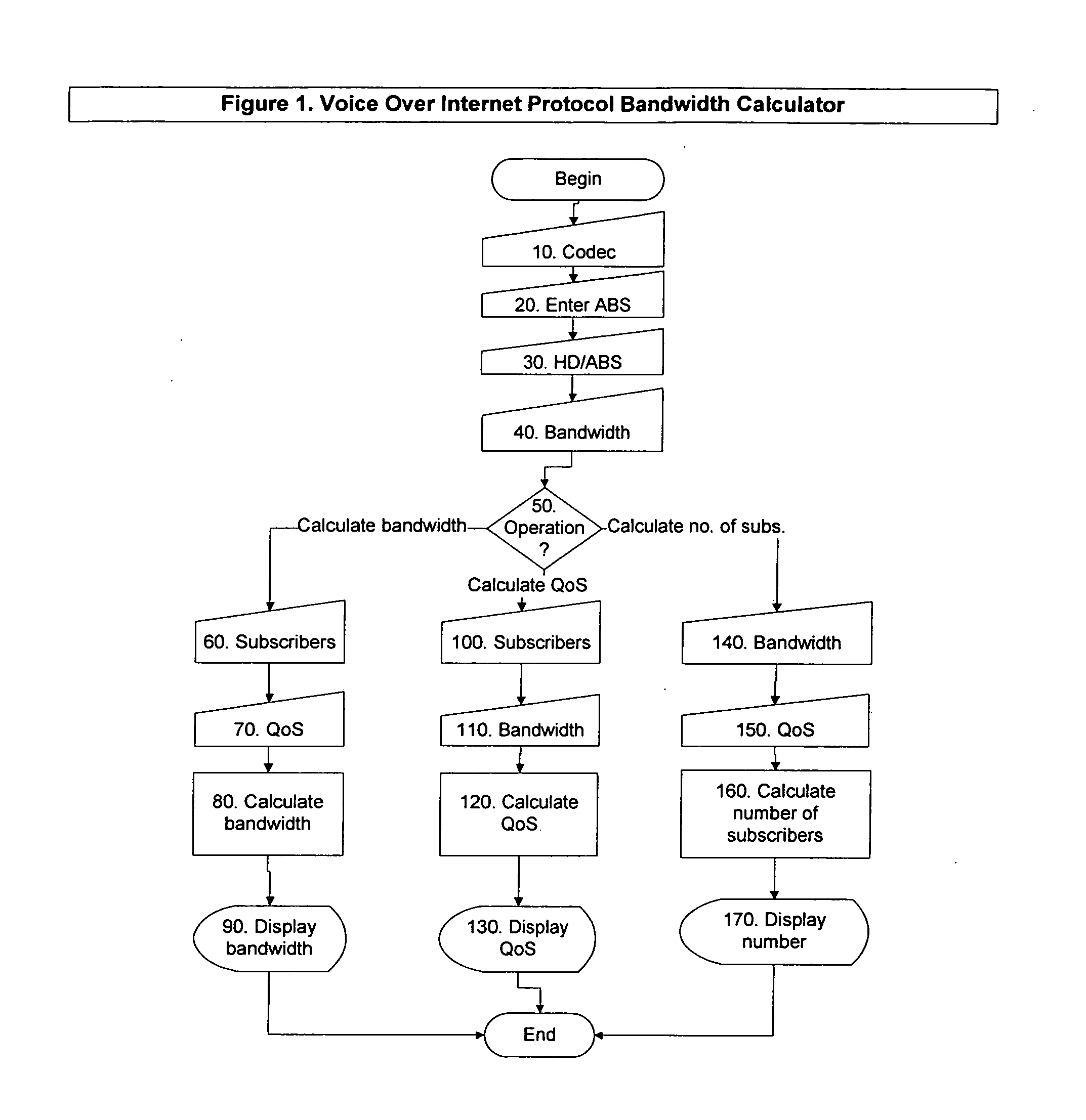
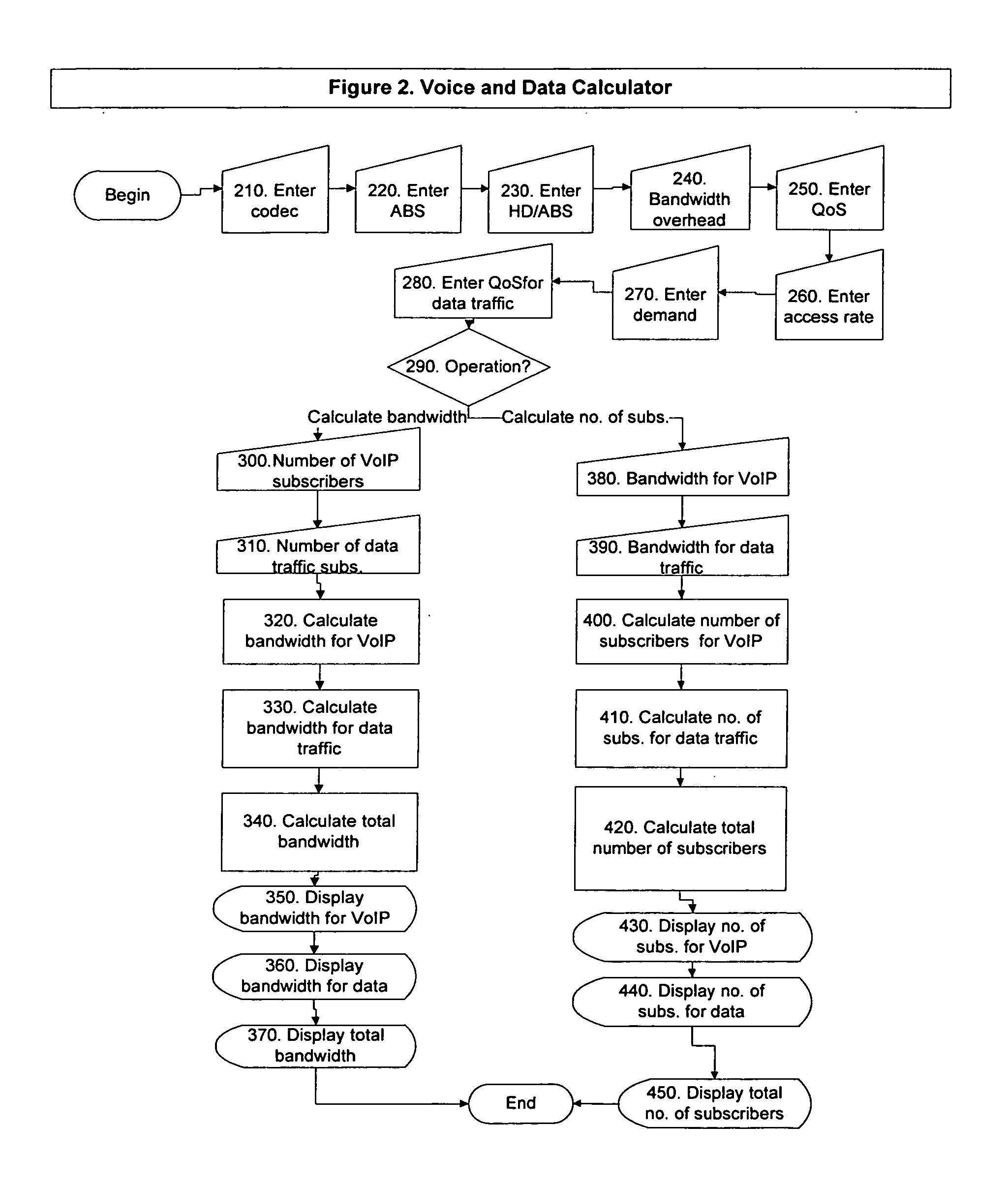
Bandwidth provisioning tools for internet service providers
An accurate bandwidth provisioning tool for Internet Service Providers, for both Voice over IP and data traffic, which is able to predict the demand for network resources based on the network traffic characteristics and the number of subscribers after taking into account subscriber growth and other relevant factors. To predict the demand, the tool uses a Gaussian model for Voice traffic, and a Gamma model, or alternatively, a dimensioning formula, for data traffic. The tool also discloses a method of planning Cable television network capacity when converting analog channels to digital channels.
Owner:ALMHANA JALAL
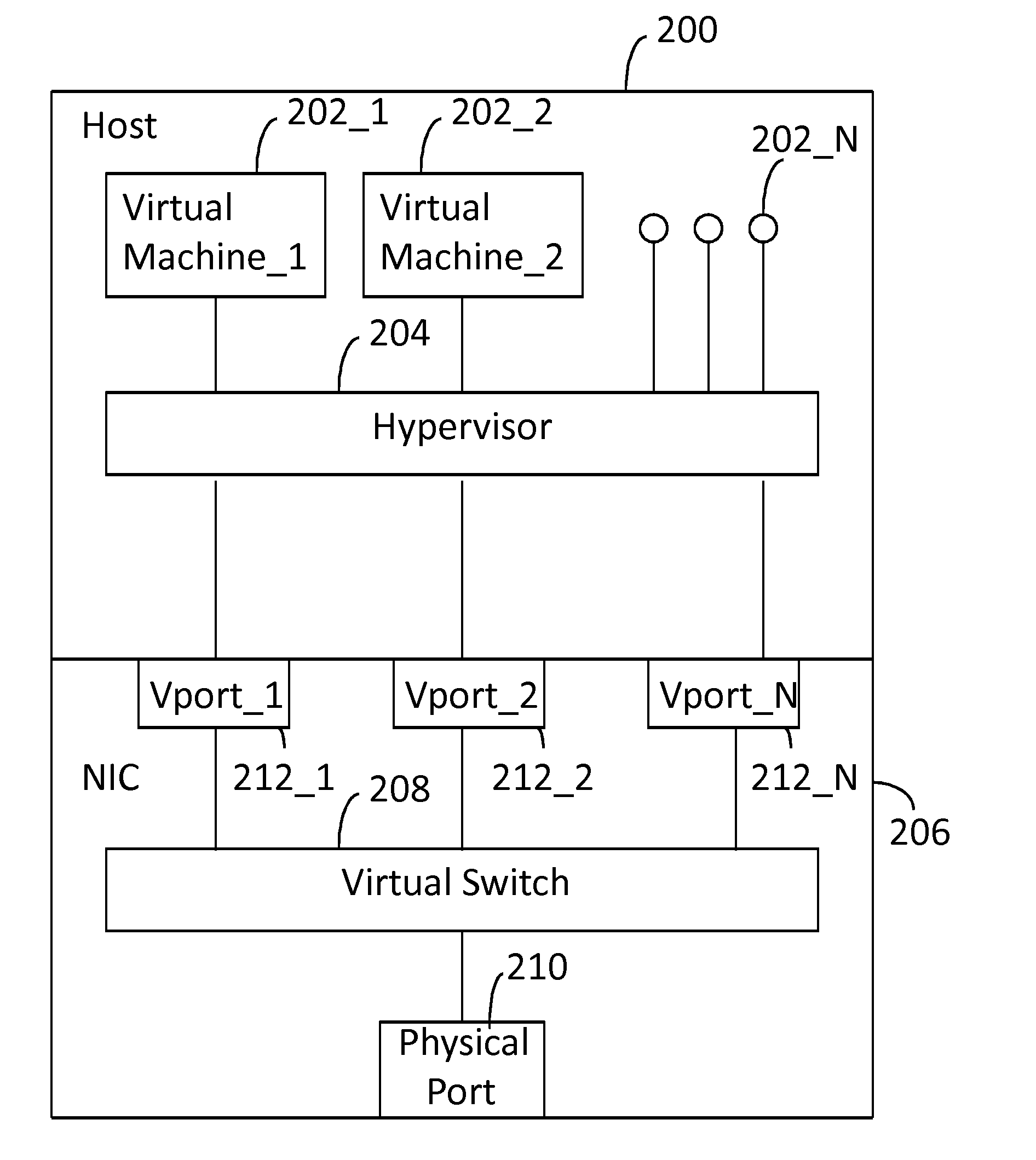
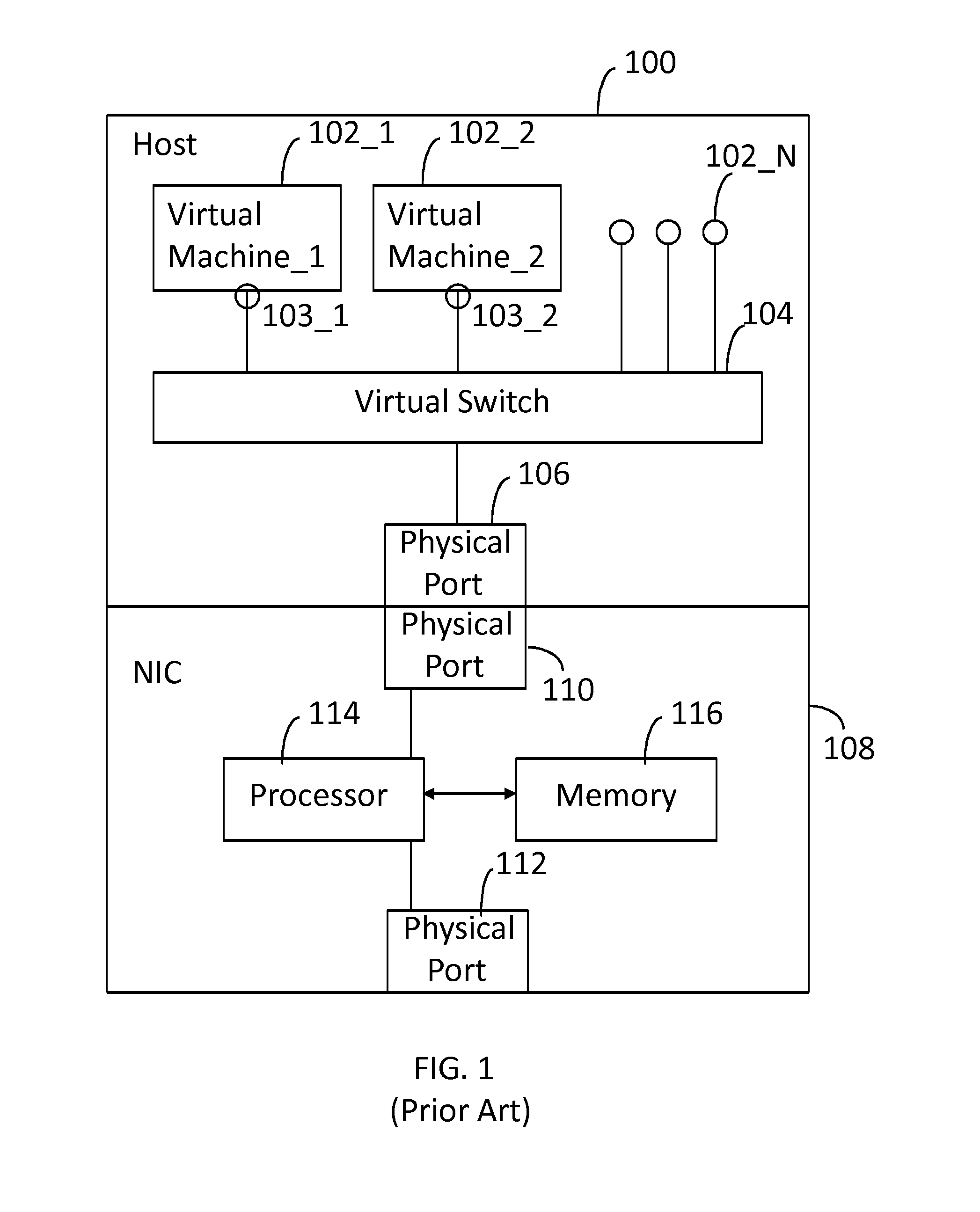
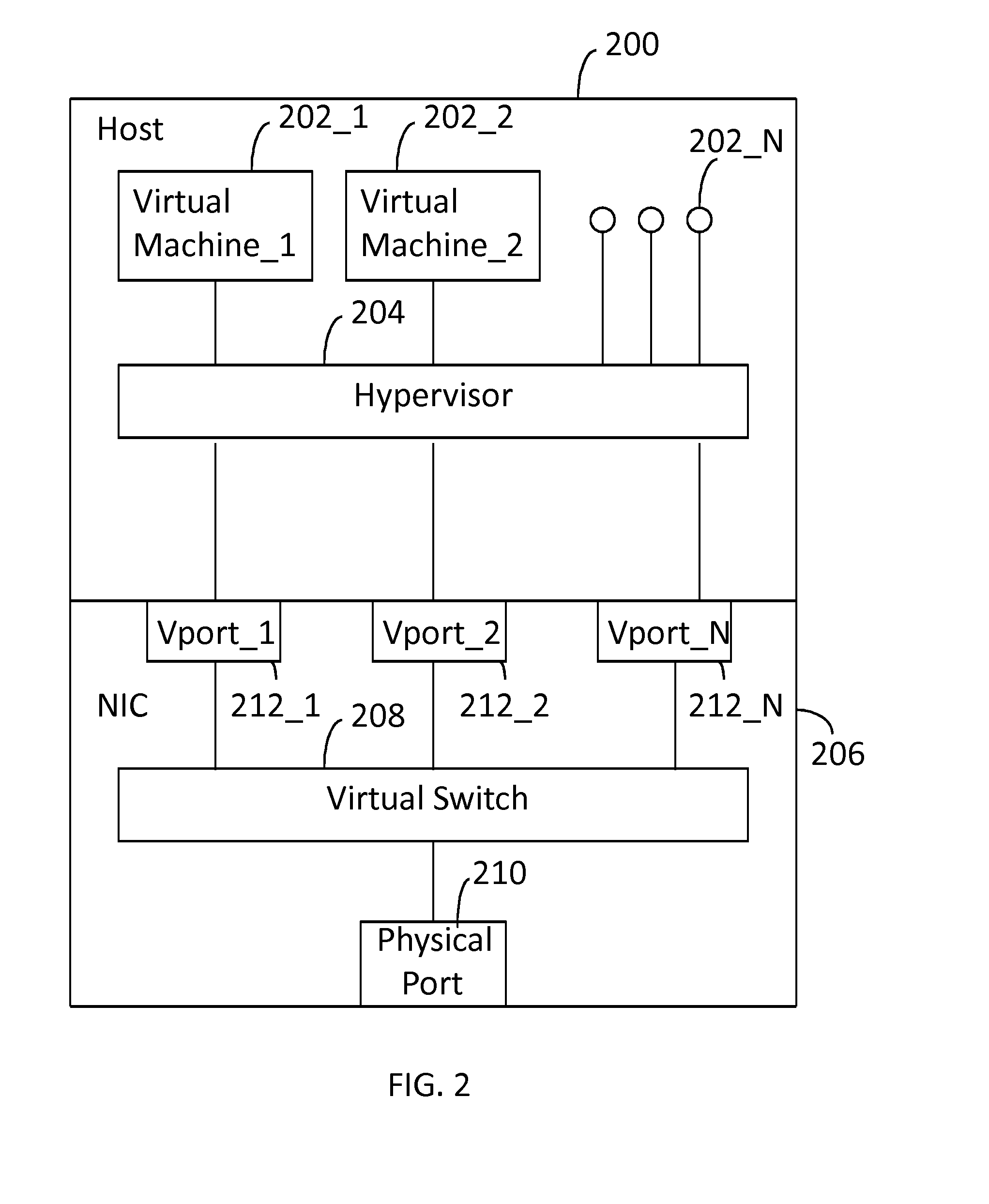
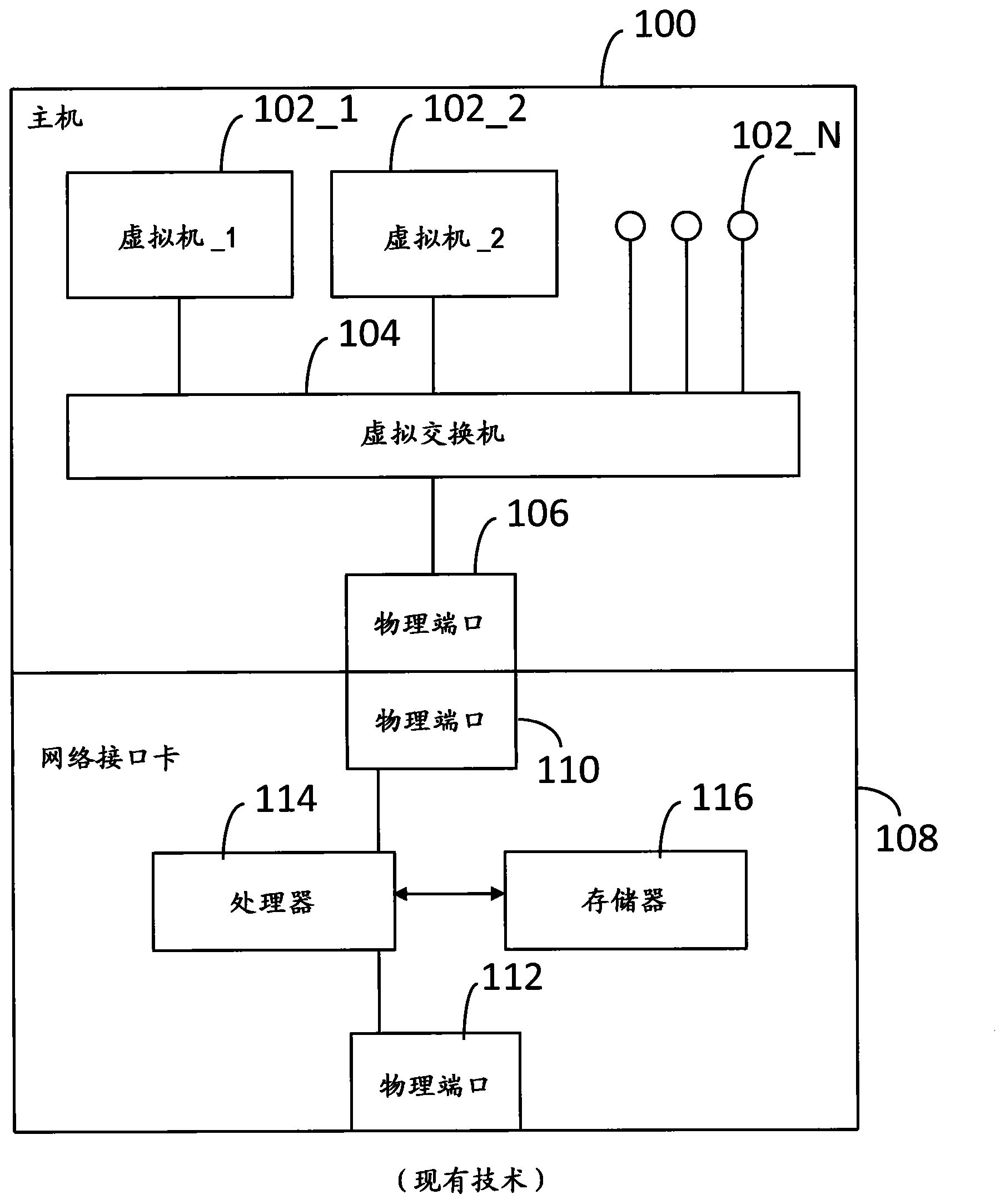
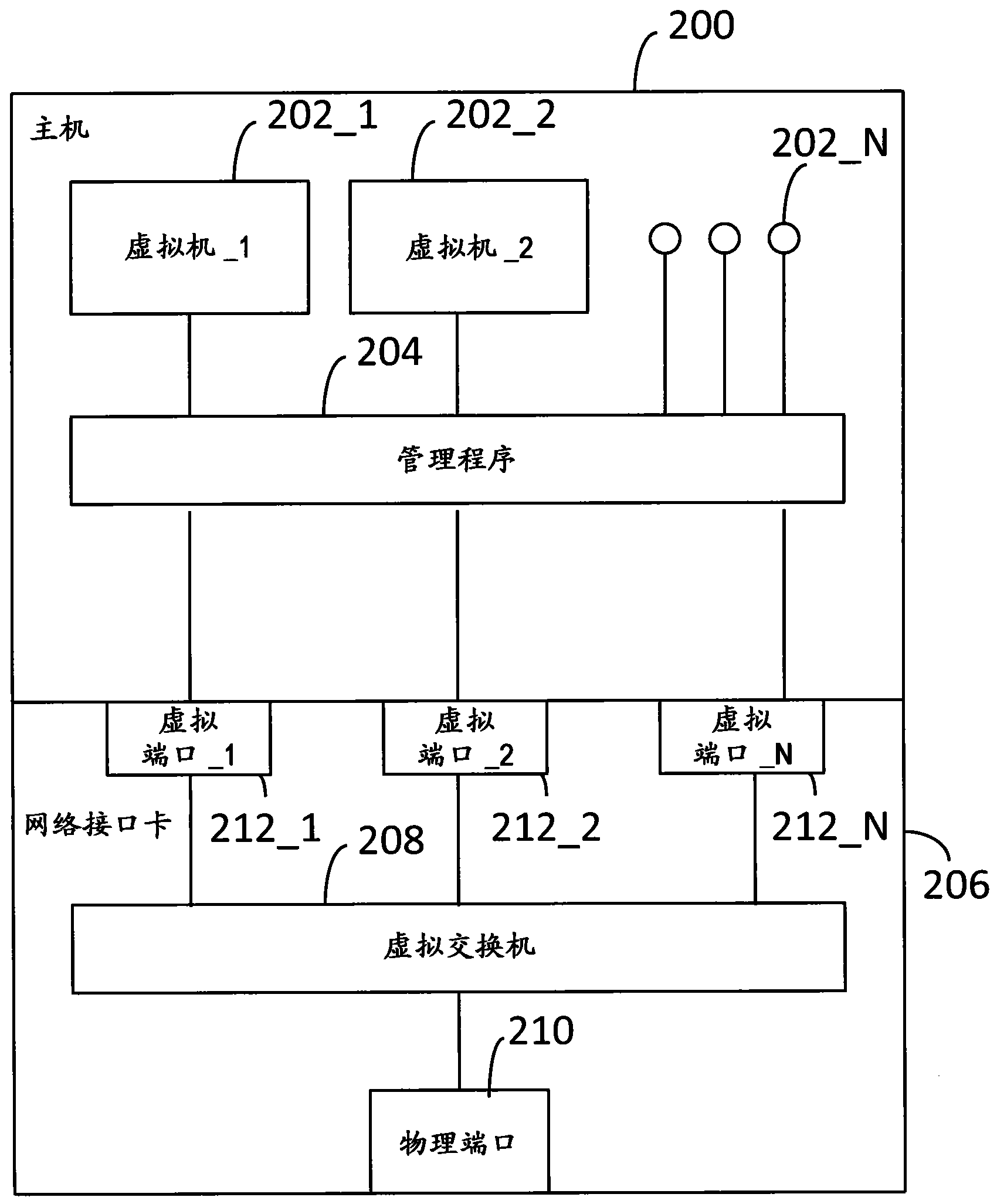
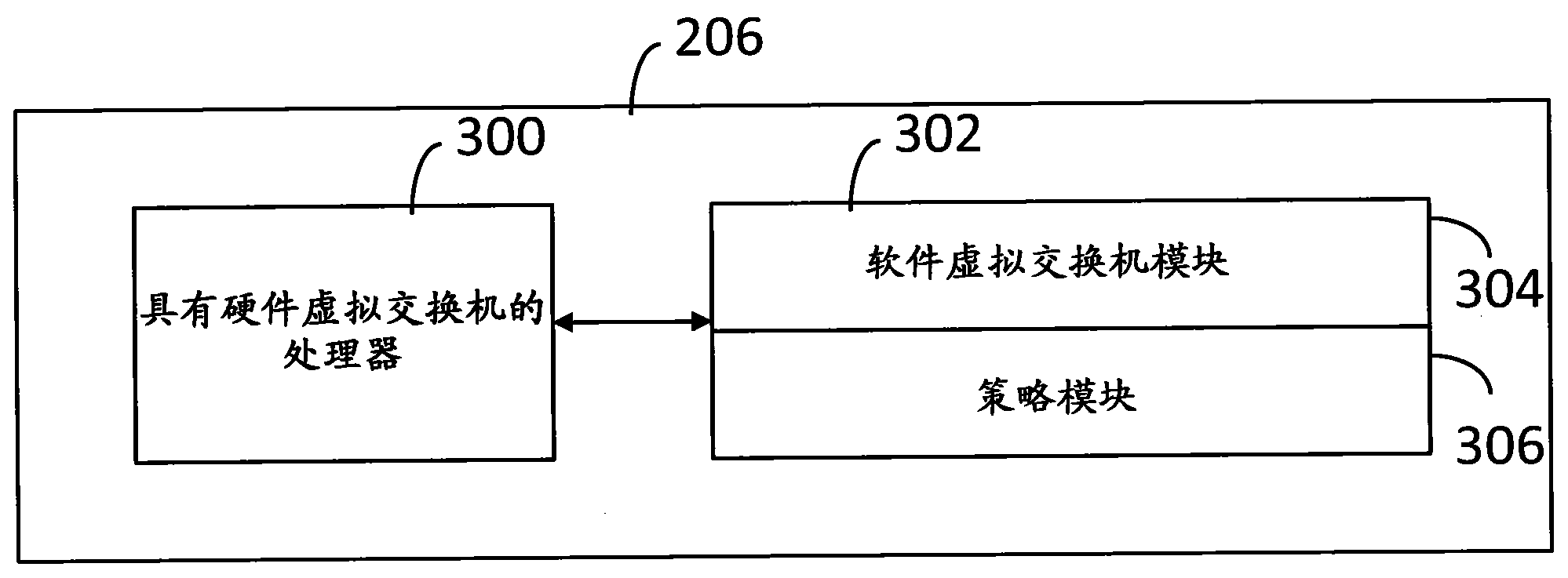
Network Interface Card with Virtual Switch and Traffic Flow Policy Enforcement
InactiveUS20150033222A1TransmissionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTraffic capacityVirtual switch
A system includes a host computer executing virtual machines under the control of a hypervisor. A network interface card is coupled to the host machine. The network interface card implements a virtual switch with virtual ports. Each (one or more) virtual port is associated with a virtual machine. The network interface card may operate as a co-processor for the host computer by managing selected traffic flow policies, such as QoS and bandwidth provisioning on a per virtual machine basis.
Owner:CAVIUM NETWORKS
Arrangement for controlling content distribution by dynamically controlling bandwidth for transfer of the content based on content authorization
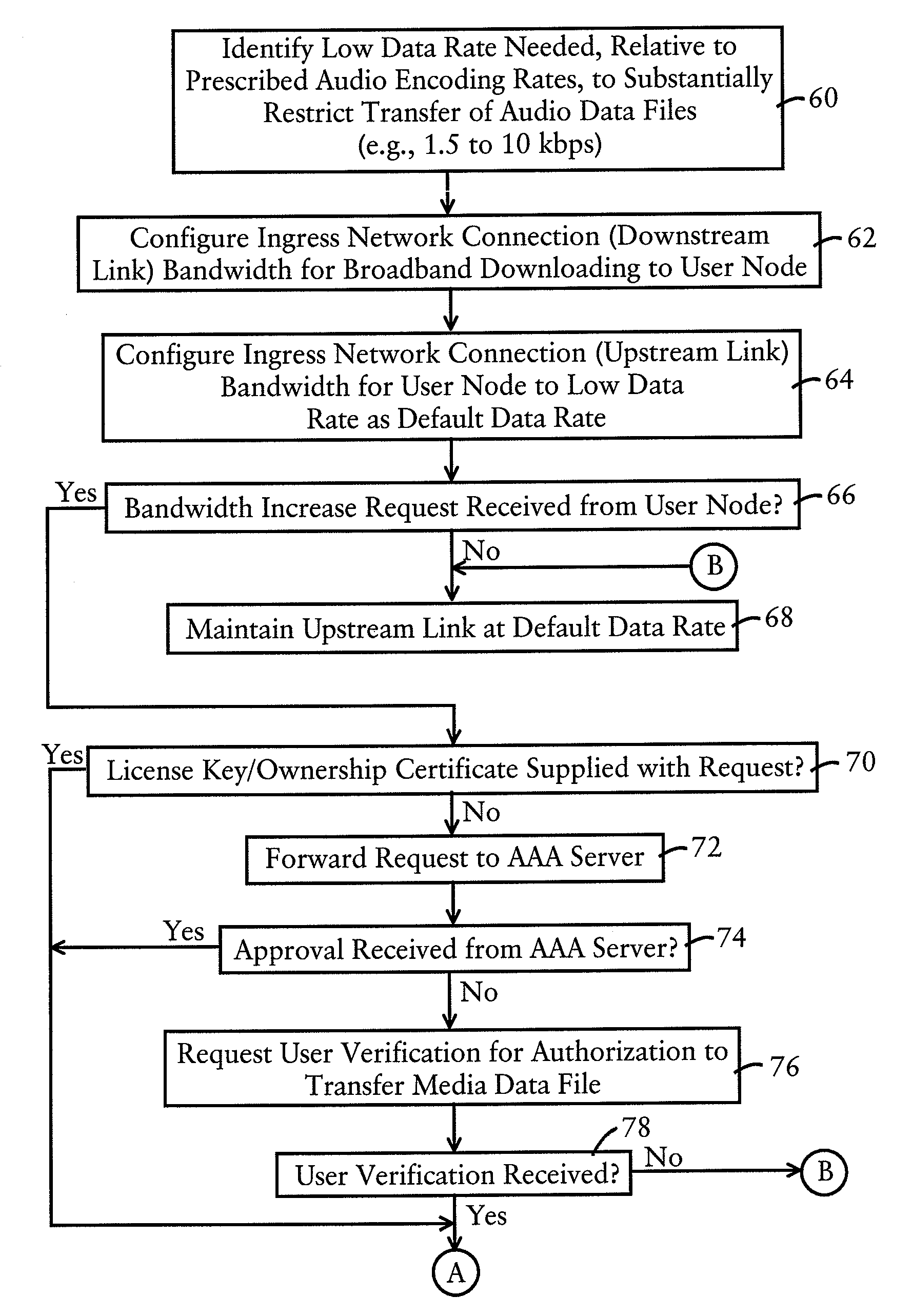
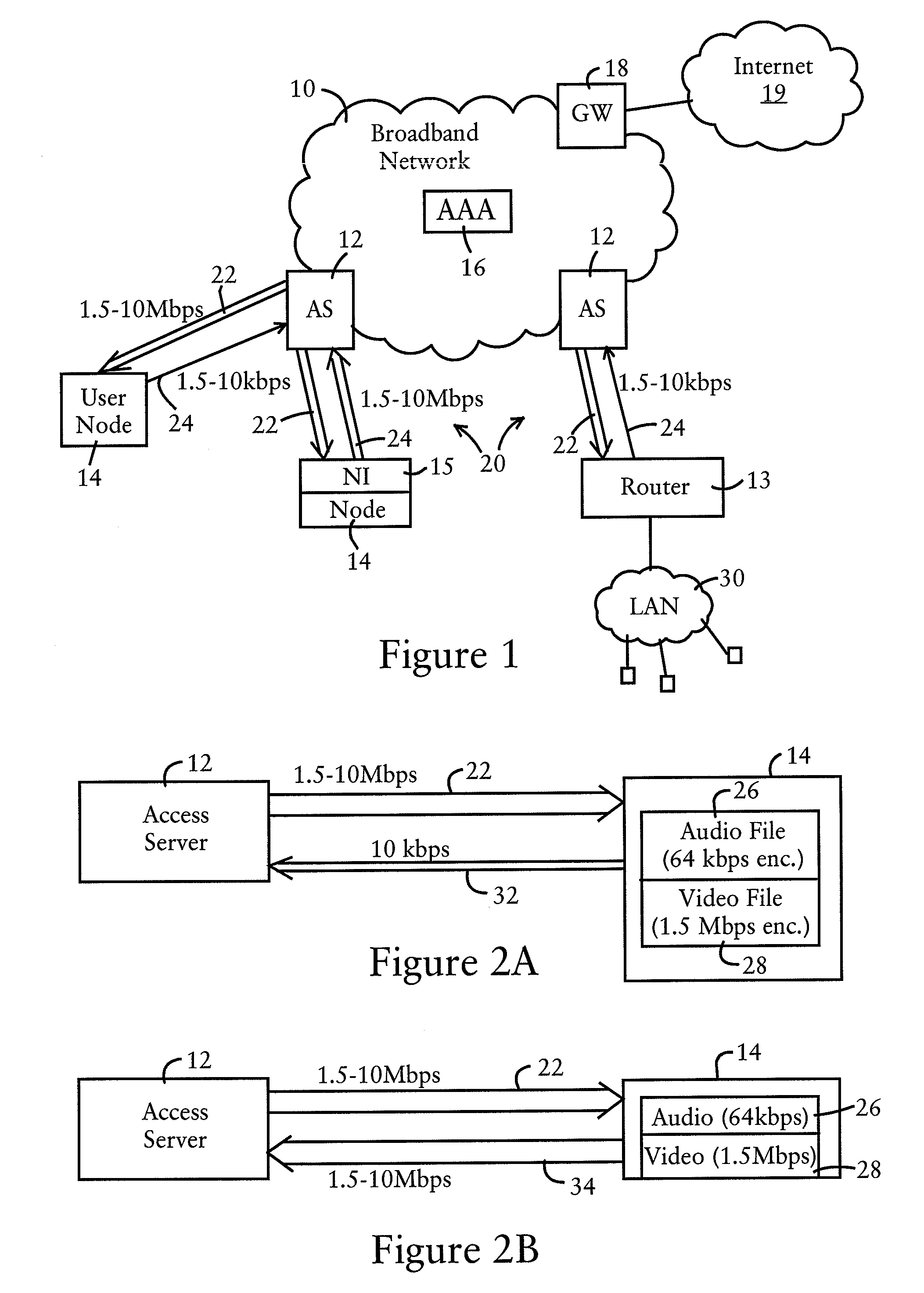
ActiveUS8024808B1Minimize occurrenceHigh bandwidthDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsContent distributionDigital video
A broadband network device is configured, in a broadband network, for dynamically controlling an upstream link bandwidth of a user node configured for downloading content via a downstream link having a prescribed bandwidth and uploading content through the broadband network via an upstream link according to the upstream link bandwidth. The broadband network device sets the upstream link bandwidth to a bandwidth value optimized for minimal-size data (e.g., message-based) transfers and that substantially restricts transfers of media-based (e.g., digital video or audio) data transfers to substantially long time intervals. The broadband network device is configured for dynamically increasing the upstream link bandwidth to an increased bandwidth value optimized for media-based data transfers, based on an identified authorization. The authorization may be supplied externally, for example, by a content provider, or based on a verification supplied by an authorization server that the user node is authorized to redistribute the content. Hence, content distribution can be controlled based on dynamically controlling the upstream link bandwidth according to content authorization, substantially minimizing the occurrences of unauthorized content redistribution.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
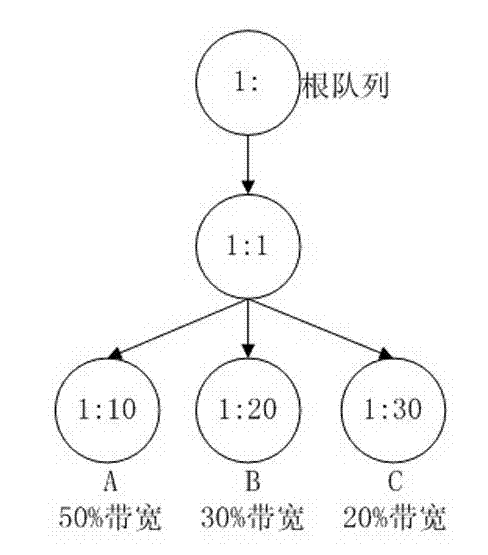
Multi-stage hierarchical bandwidth management method
The invention discloses a multi-stage hierarchical bandwidth management method, which comprises the following steps of: A10, configuring CIR (Committed Information Rate) and PIR (peak Information Rate) (or EIR (Excess Information Rate)) of each stage of scheduling node according to a business model, wherein the CIR of the node is set according to the bandwidth purchased by a user in the first stage, the bandwidth distribution principle of each node from the second stage of scheduling is shown in the description, EIRni=PIRni-CIRni, and n is not less than 2; and A20, respectively marking messages as green, yellow or red by using MEF (Managed Extensibility Framework), RFC2697 (Request for Comments 2697) or RFC2698 algorithms in the first stage, configuring each node into a color sensitive mode and a coupling mode from the second stage, and shaping the traffic according to the MEF algorithm. By using the invention, the multi-stage hierarchical bandwidth management is realized on an exchanging chip supporting the MEF Traffic Shaping algorithm without need of special ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuits) or hardware; and the requirements are satisfied through updating software under the situation of changing or updating the business so that considerable hardware cost is saved; and the bandwidth distribution algorithm of the hierarchical business model is simple and convenient for web masters to configure.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Data processor and communication system
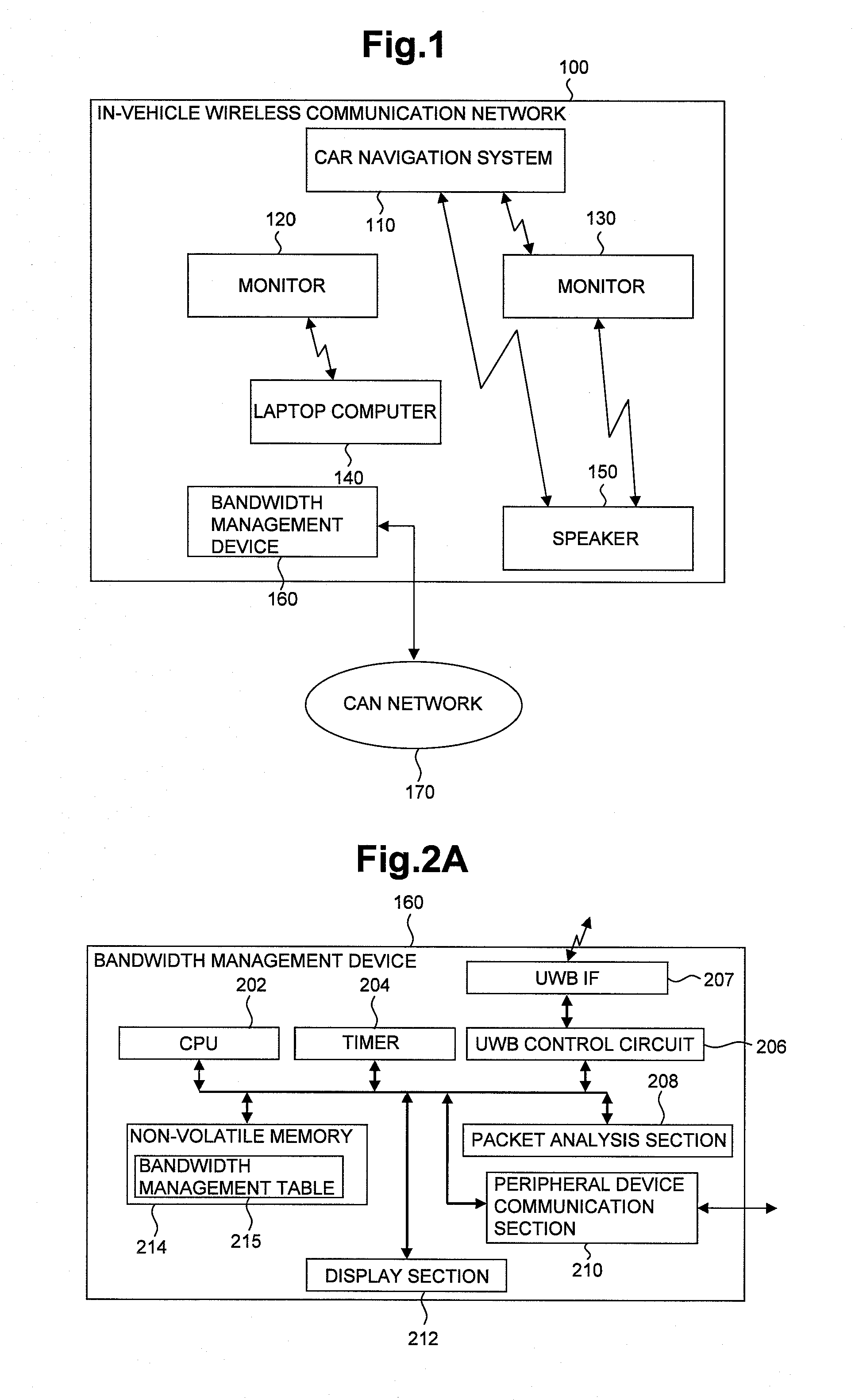
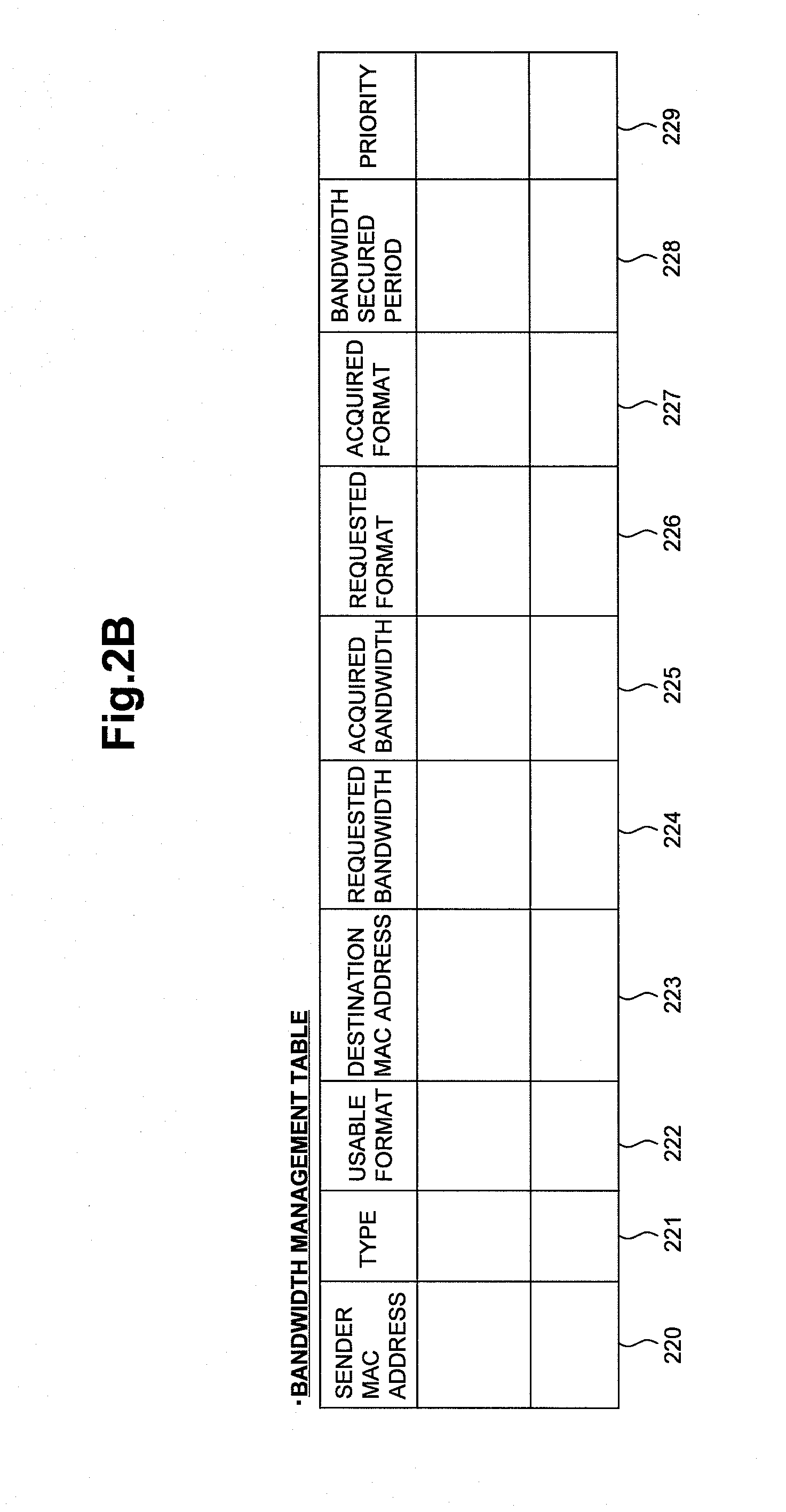
ActiveUS20110110397A1Set change settingFlexible controlError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemImage resolution
A data processor which can flexibly control bandwidth settings and setting changes is provided. The data processor controls bandwidth allocation to electronic devices participating in a communication network. The data processor has a communication section used to communicate with the electronic devices and a bandwidth management section which performs control to variably allocate, based on requests from the electronic devices, bandwidths to be used for communication by the electronic devices. In cases where an additional device is added to the communication network and an adequate bandwidth cannot be allocated to the additional device, the bandwidth management section requests another electronic device transmitting video data of a resolution higher than corresponding to the user's intention to change its data format so as to allow an adequate bandwidth to be allocated to the additional device.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method, apparatus, and program for configuring networks with consistent route and bandwidth settings
ActiveUS20070189152A1Maintain qualityMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionDistributed computingMajor and minor
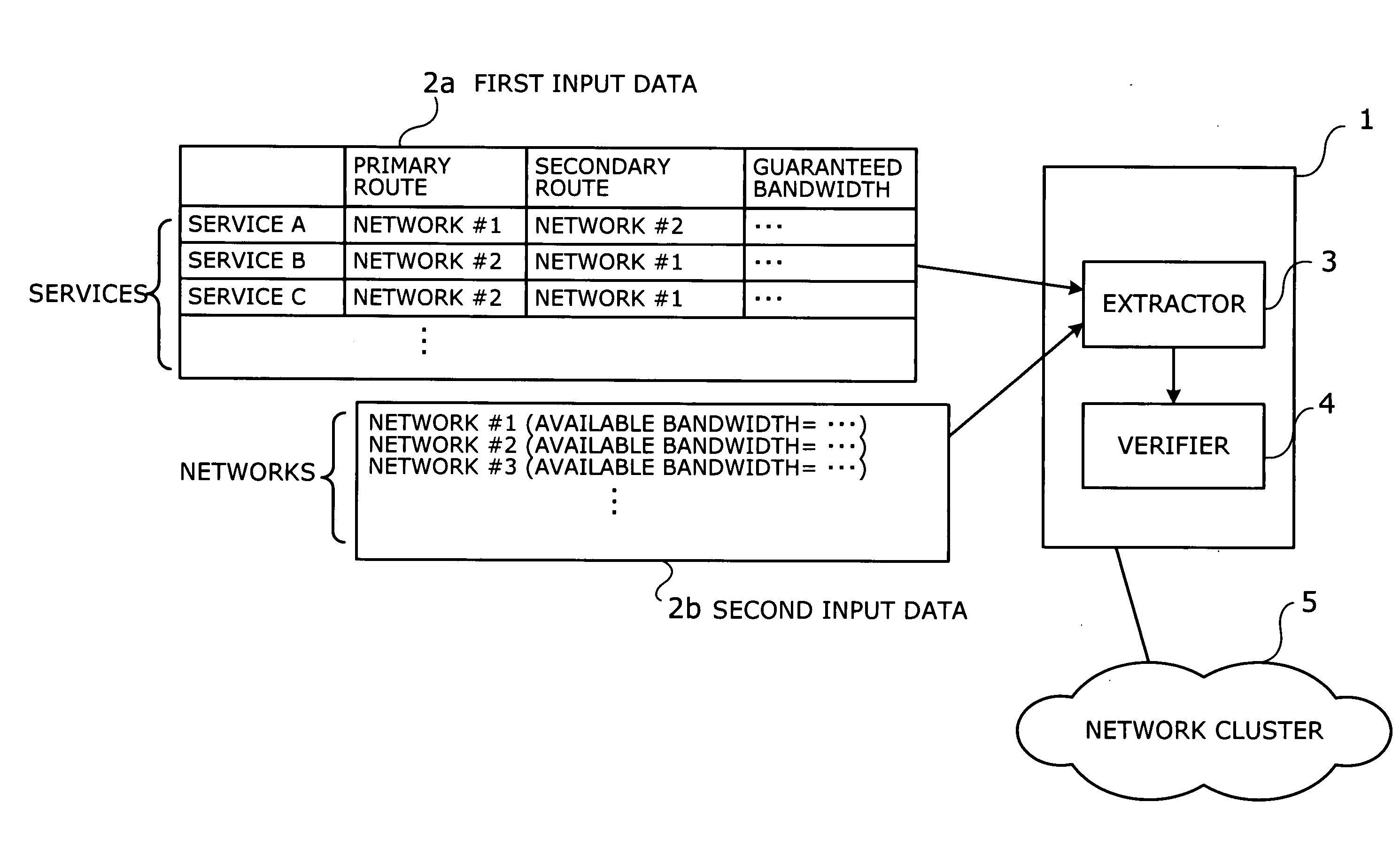
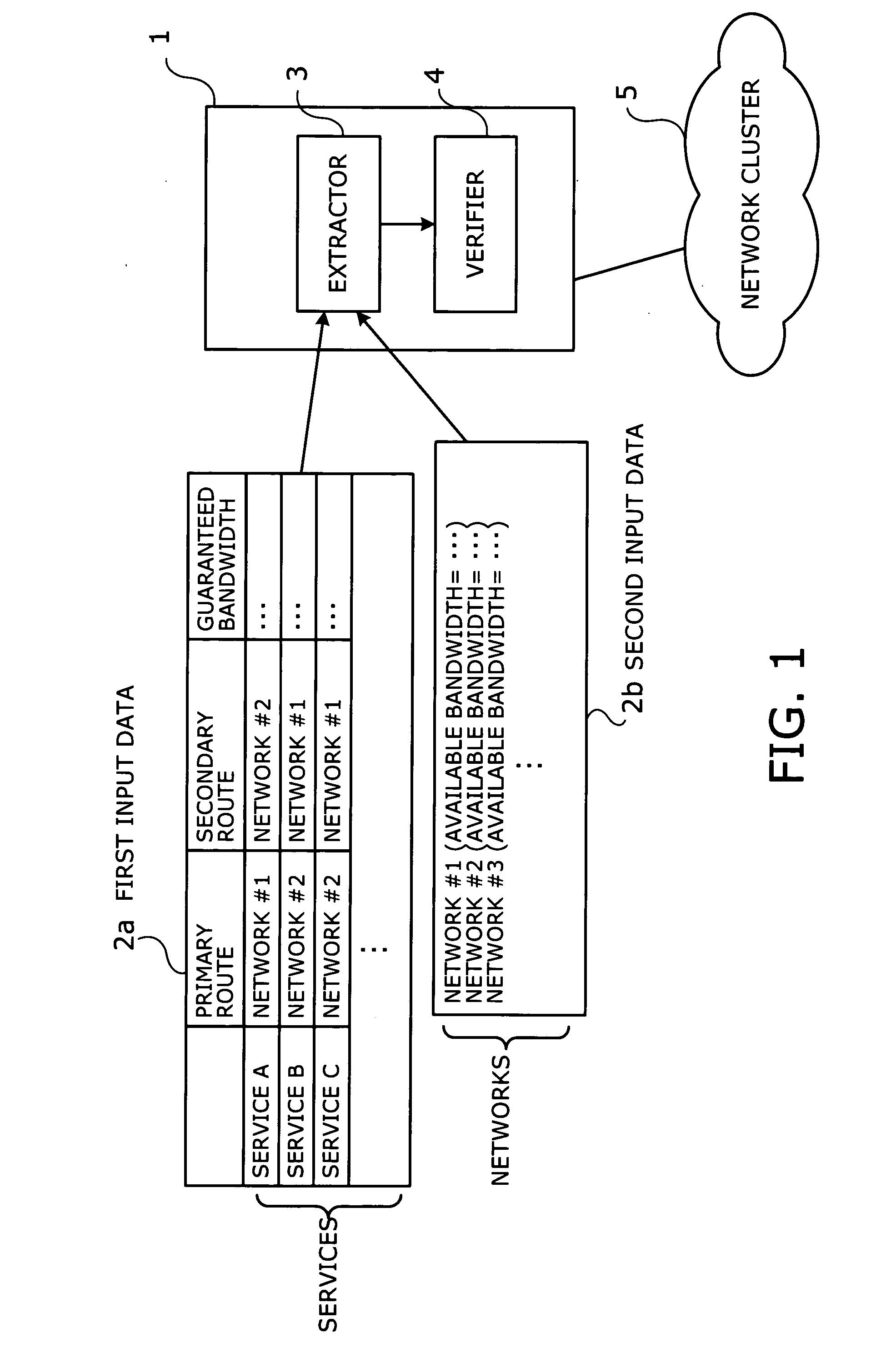
An apparatus and method for verifying route and bandwidth settings of multiple services provided over networks. The apparatus has an extractor and a verifier. Based on input data describing services each having primary and secondary routes between specific locations, an available bandwidth of each network, and a guaranteed bandwidth of each service, the extractor selects a first network to be verified and extracts first services that use the first network as their respective primary routes. The extractor then selects at least one second network from among the networks that the first services specify as their respective secondary routes. The extractor extracts second services that use the second network as their primary routes and specify the first network as their secondary routes. The verifier sums up guaranteed bandwidths that the first and second services should provide, and determines whether the sum is smaller than an available bandwidth of the first network.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Network interface card with virtual switch and traffic flow policy enforcement
A system includes a host computer executing virtual machines under the control of a hypervisor. A network interface card is coupled to the host machine. The network interface card implements a virtual switch with virtual ports. Each (one or more) virtual port is associated with a virtual machine. The network interface card may operate as a co-processor for the host computer by managing selected traffic flow policies, such as QoS and bandwidth provisioning on a per virtual machine basis.
Owner:CAVIUM NETWORKS
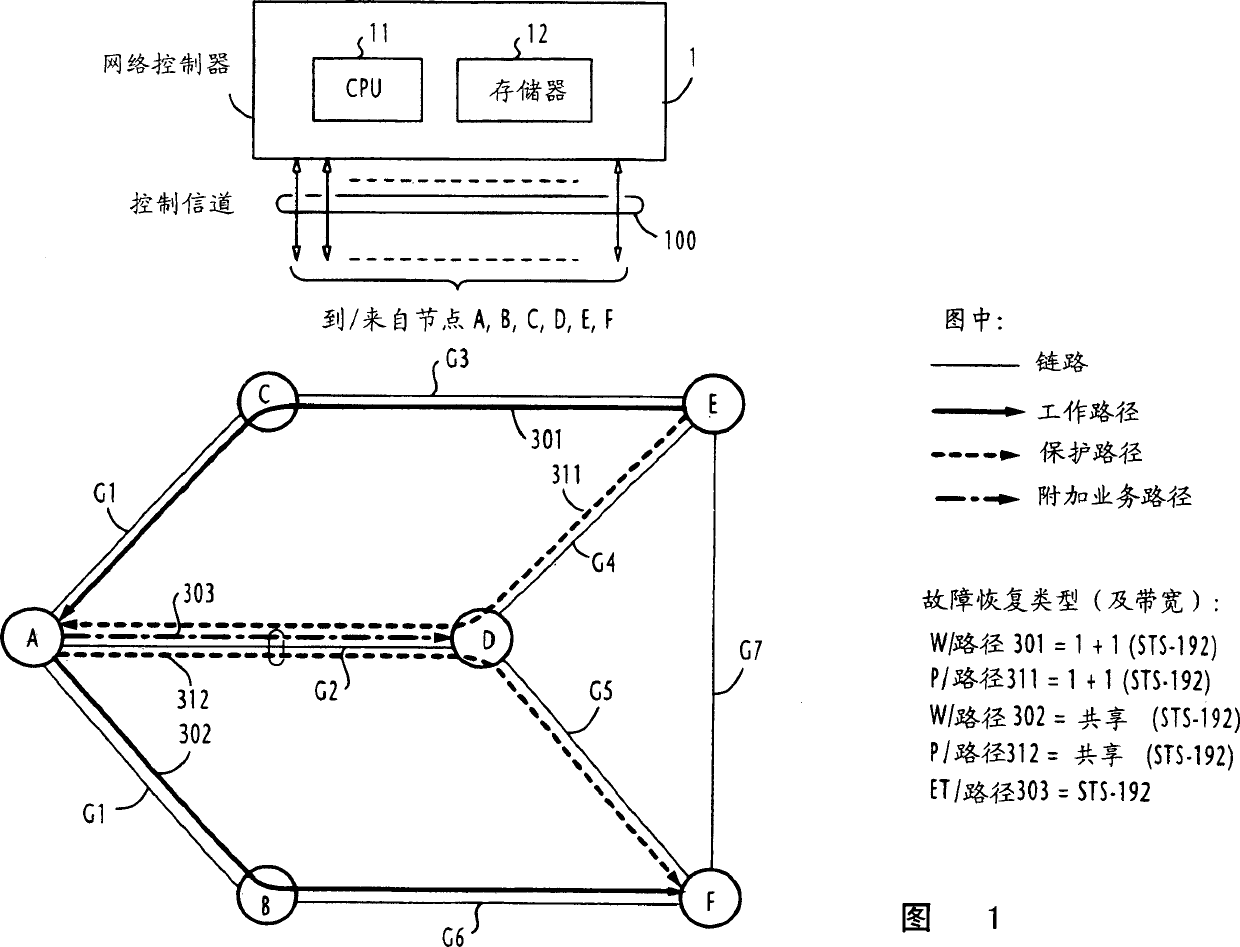
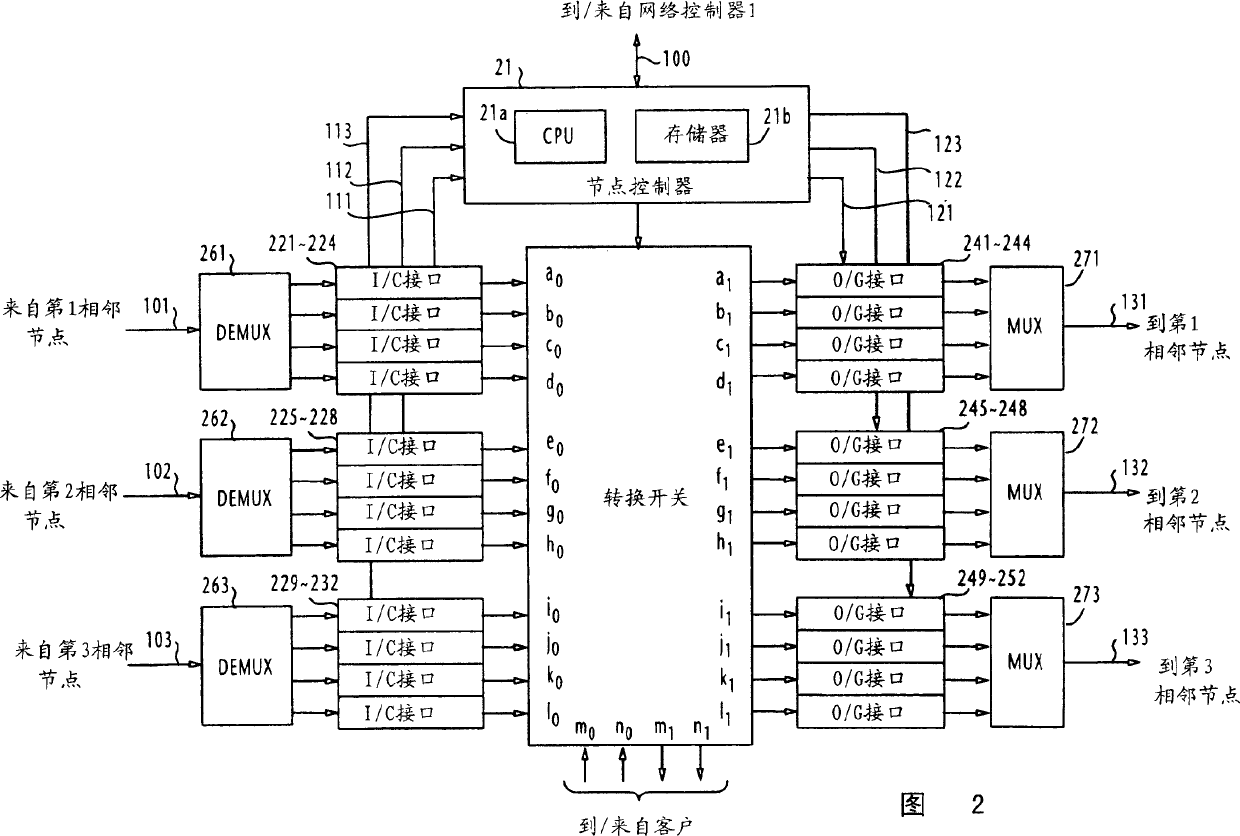
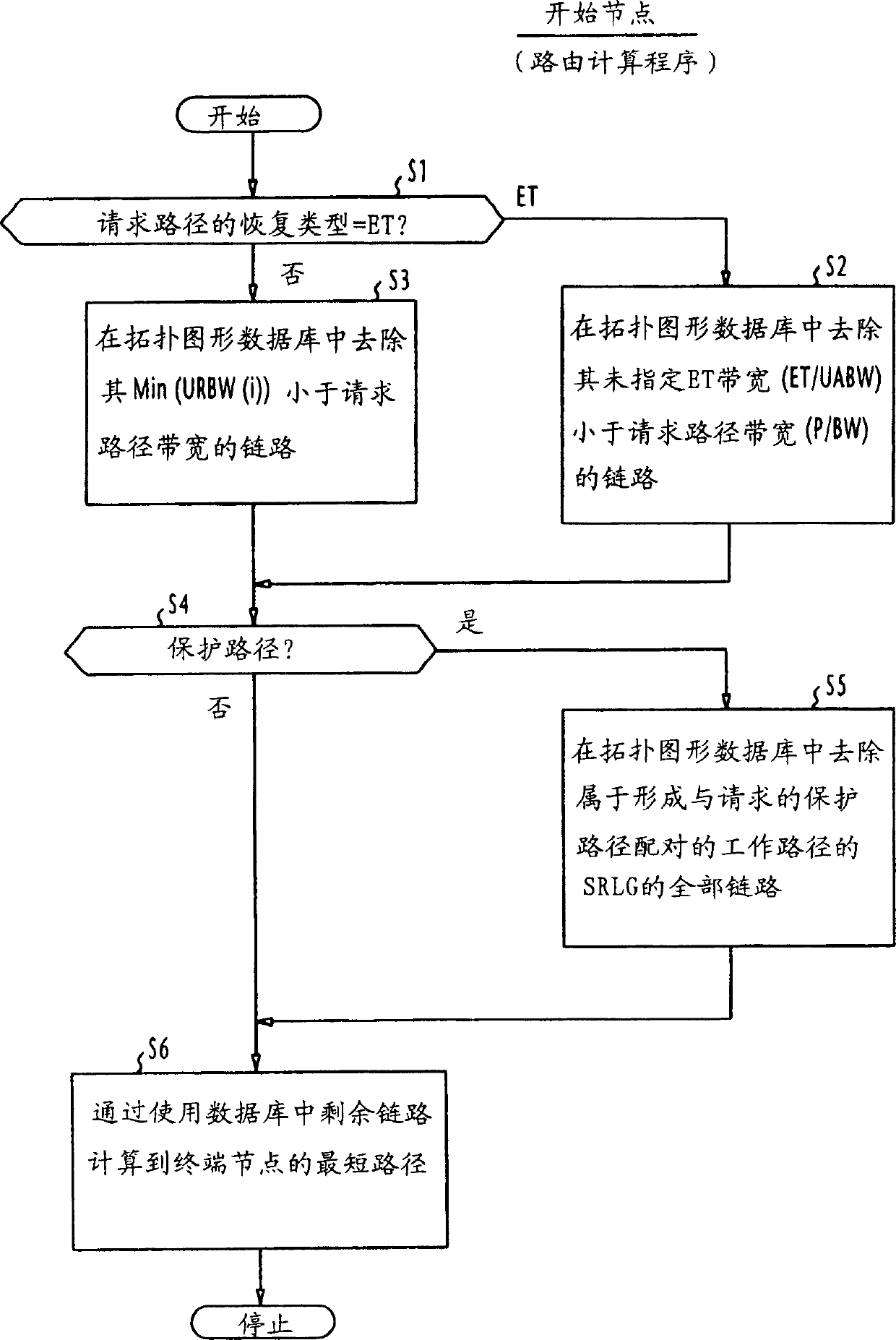
Method for establishing recovery type path of different faults in one communication network
InactiveCN1437356AMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionShared risk link groupDistributed computing
In a communications network where multiple shared risk link groups are formed by links having a common risk, unreserved bandwidths are defined corresponding to all SRLG's and a maximum bandwidth of each link is set as an initial value of each of the defined unreserved bandwidths when a working path or a protection path of "1+1" or "1:1" recovery type is requested. When a protection path of "shared" recovery type is requested, unreserved bandwidths are defined corresponding to the SRLG's to which the links of its corresponding working path belong and a maximum bandwidth of each link is set as an initial value to each of the defined unreserved bandwidths. The bandwidth of the working or protection path is subtracted from each of the unreserved bandwidths. The request is rejected if a minimum of the subtracted values is smaller than a threshold.
Owner:NEC CORP
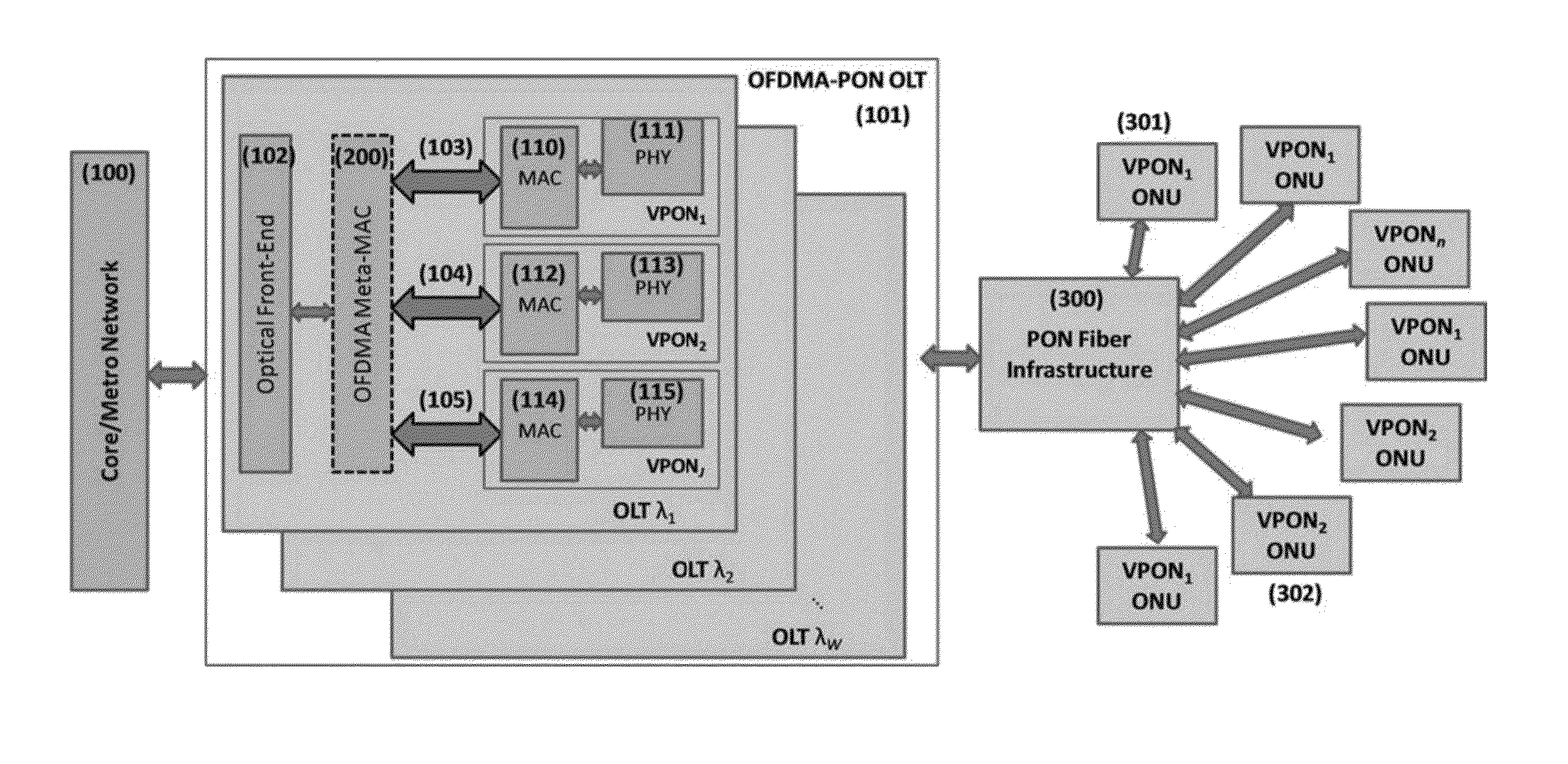
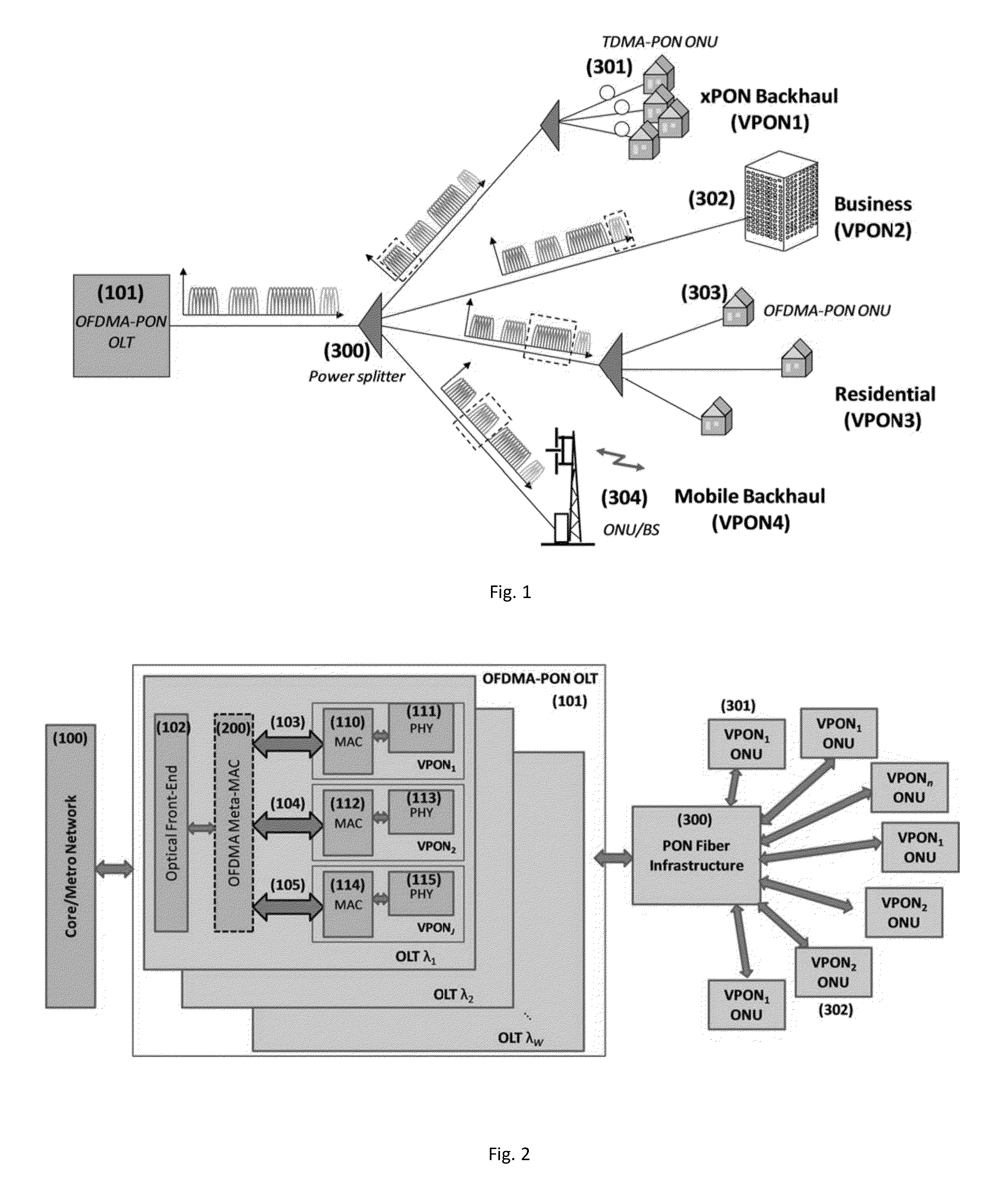
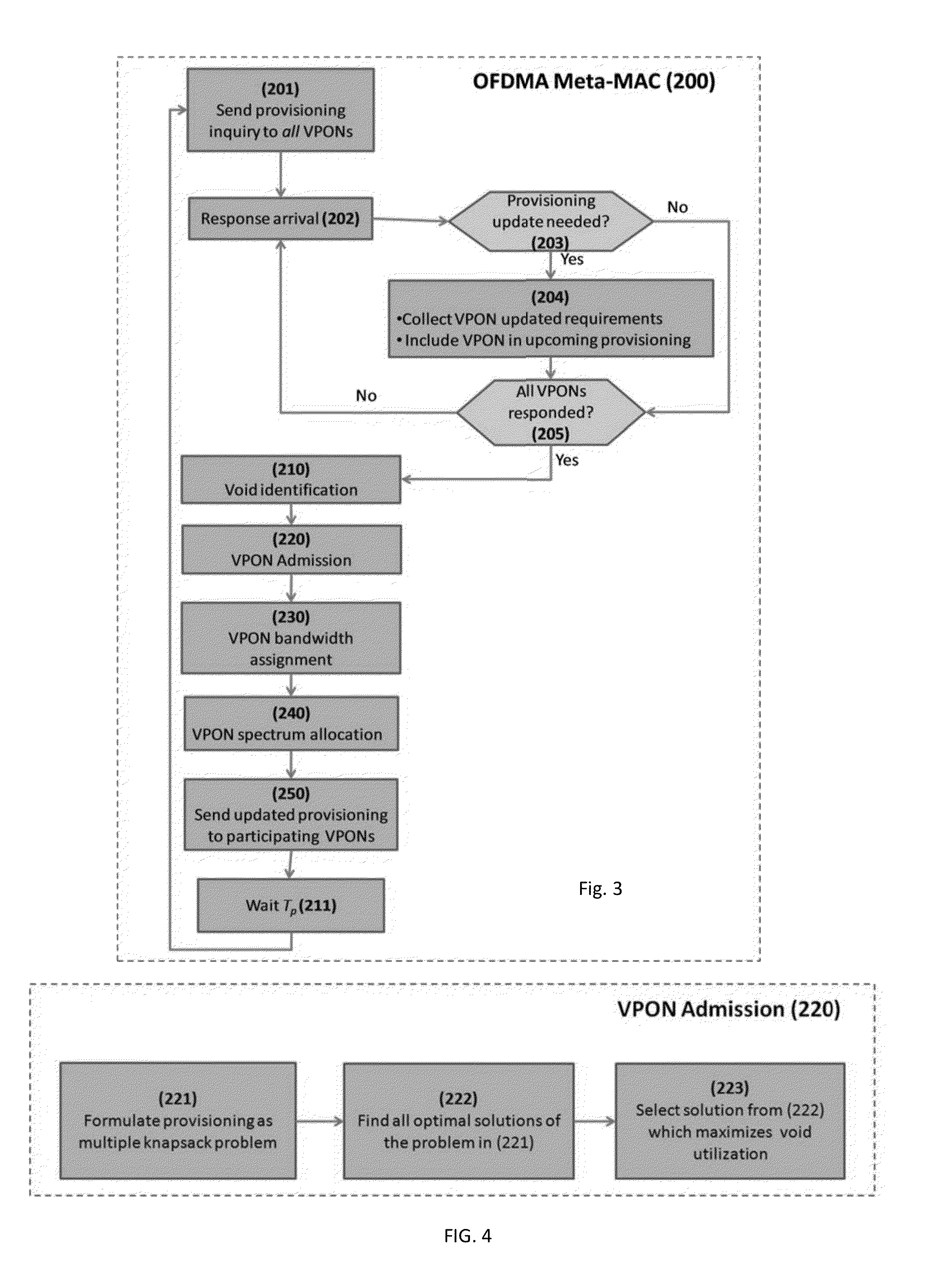
Multi-Service Provisioning in Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing-Passive Optical network OFDMA-PON
ActiveUS20130045012A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsLength waveDistributed computing
A method for multi-service provisioning in an OFDMA-PON that includes linking communicatively to a core network and bandwidth provisioning, dynamically within a single wavelength, traffic from the core network to a network of multiple virtual passive optical networks VPONs for multi-service provisioning to the VPONs.
Owner:NEC CORP
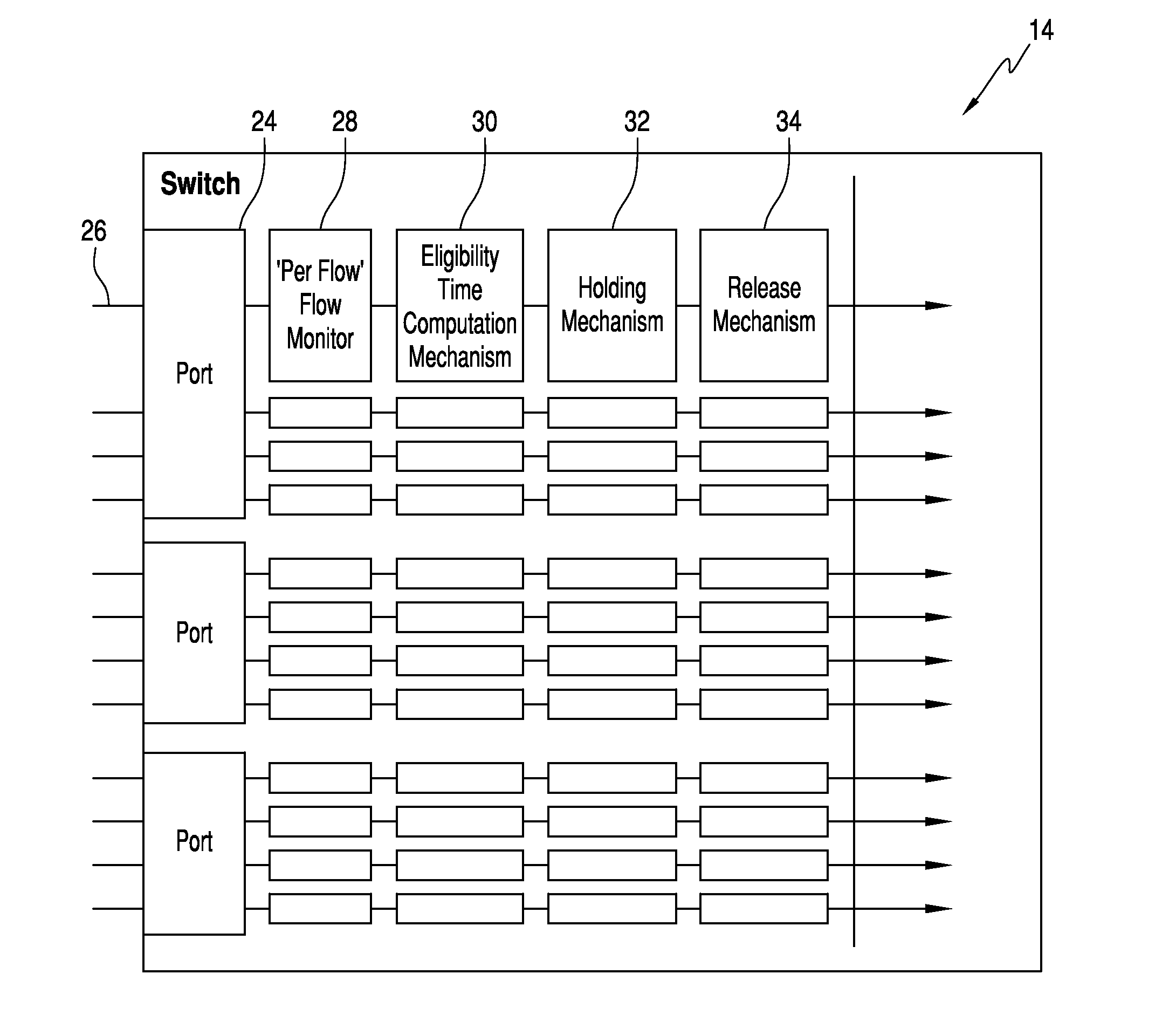
Data network with “per flow” flow monitoring
ActiveUS8958297B1Improve utilizationSimplifies and reduces costError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityTraffic shaping
A ‘per flow’ flow monitor is operatively associated with each ingress port of the switch of the data network, for monitoring the arrival data flow on each flow in defined traffic constraint envelopes containing frames. An eligibility time computation mechanism computes an eligibility time at which arriving frames on each flow will be conformant to the defined traffic envelope to the ingress port given past frame arrivals on that same flow. A holding mechanism holds the arriving frames on each flow until the eligibility time is reached. A release mechanism releases the arriving frames on a flow at the eligibility time. The flow monitor, computation mechanism, holding mechanism, and release mechanism cooperate to provide an ‘per flow’ traffic shaping function in conformance with delay and delay-jitter bound, frame loss probability, and bandwidth provisioning requirements, thus allowing the switch to enforce the traffic constraint envelope for each flow.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
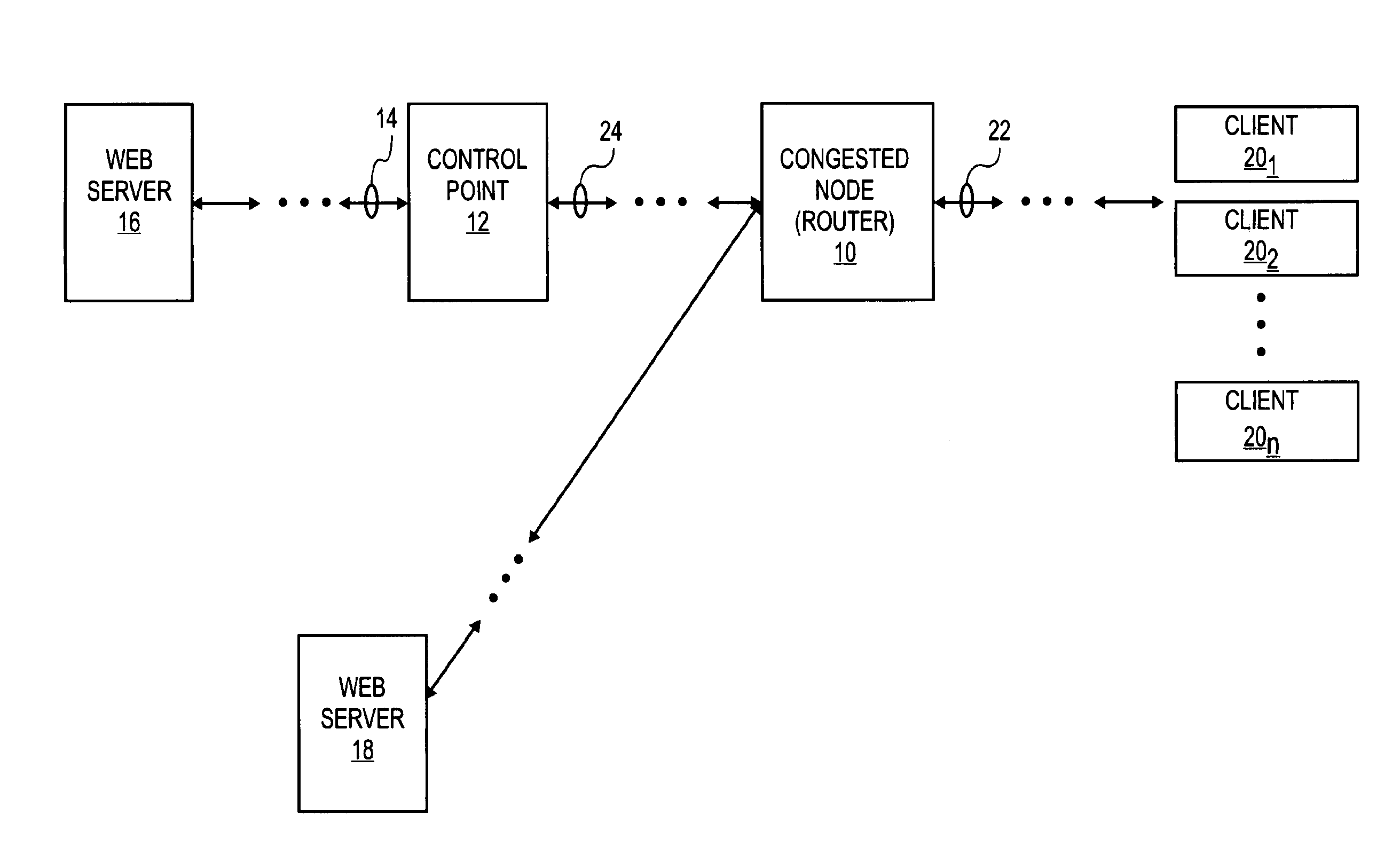
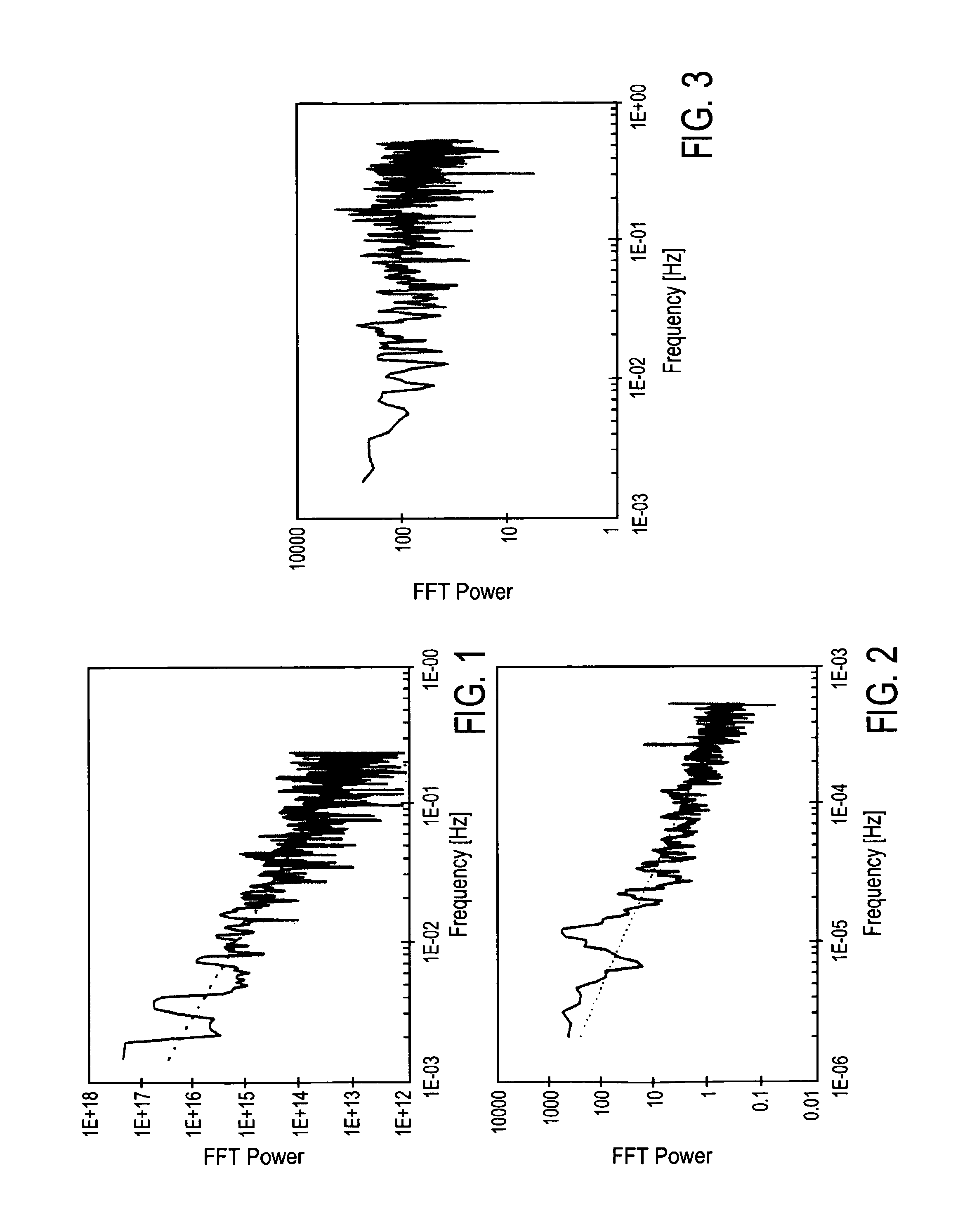
Method of reducing packet loss by resonance identification in communication networks
A control node of a communication network is operated at a packet bandwidth determined according to observations of performance metrics of the network at the control point. These performance metrics may be one or more of throughput, average fetch time and packet loss. The control node is operated so as to set a control bandwidth to corresponding resonance points of the performance metrics. The resonance points are determined by scanning across a range of control bandwidths, until one or more of the performance metrics is / are optimized. The packet bandwidth is set by varying an inter-packet delay time over selected communication links at the control node.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
Uplink bandwidth assignment method for Ethernet passive optical network system
InactiveCN101964756AReduce the allocation frequencySolve the problem of frequent repeated allocation of bandwidthMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksTelecommunicationsOptical network unit
The invention discloses an uplink bandwidth assignment method for an Ethernet passive optical network system, which is characterized by comprising the following steps that: firstly, an optical line terminal (OLT) automatically sets corresponding attributes for an uplink bandwidth of an optical network unit (ONU) when assigning the uplink bandwidth to the ONU; secondly, the OLT transmits the uplink bandwidth and the corresponding attributes to the ONU and informs the ONU of using the corresponding uplink bandwidth according to the attributes of the uplink bandwidth; and finally, the ONU transmits data by utilizing the uplink bandwidth according to the received attributes set by the OLT. In the method, the attributes are set for the assigned uplink bandwidth, so that the ONU can use the uplink bandwidth permanently or periodically for long and the OLT does not need to periodically assign the uplink bandwidth frequently. Therefore, the method can reduce interaction between the OLT and the ONU, reduce the assignment frequency of the uplink bandwidth and the occupation of downlink bandwidth resources and simultaneously bring convenience for the ONU to perform unified planning on the use of the uplink bandwidth.
Owner:南京扬舟信息科技有限公司
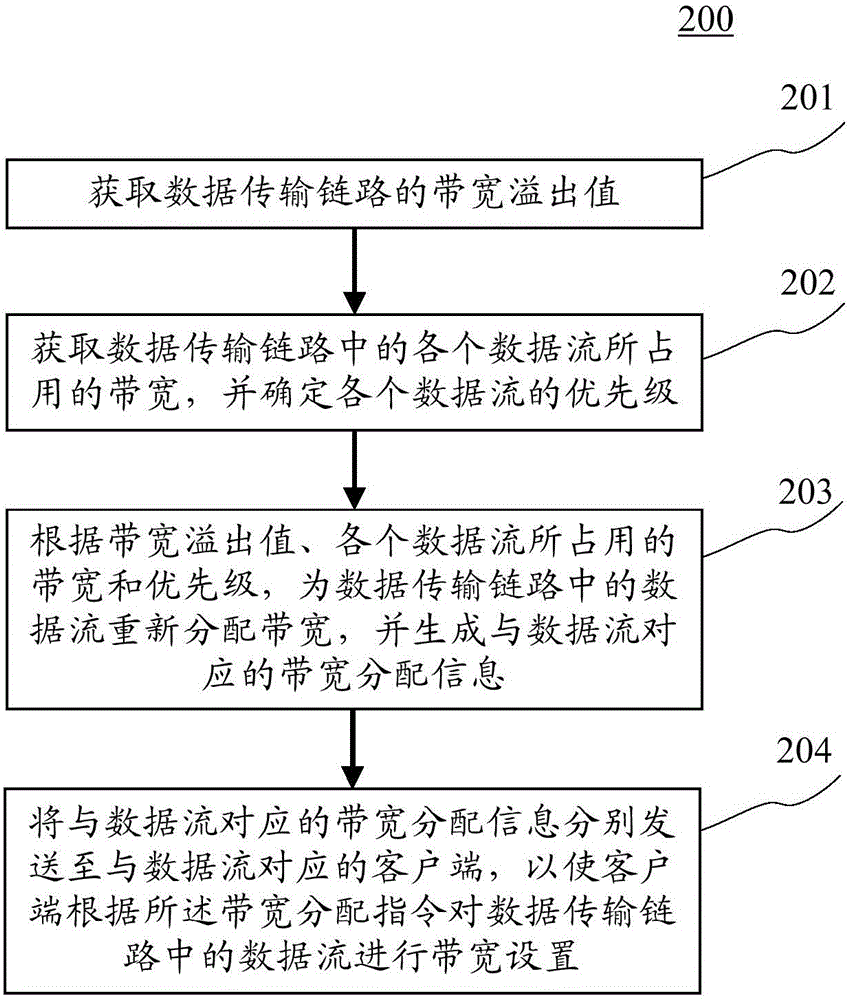
Bandwidth setting method, device and system
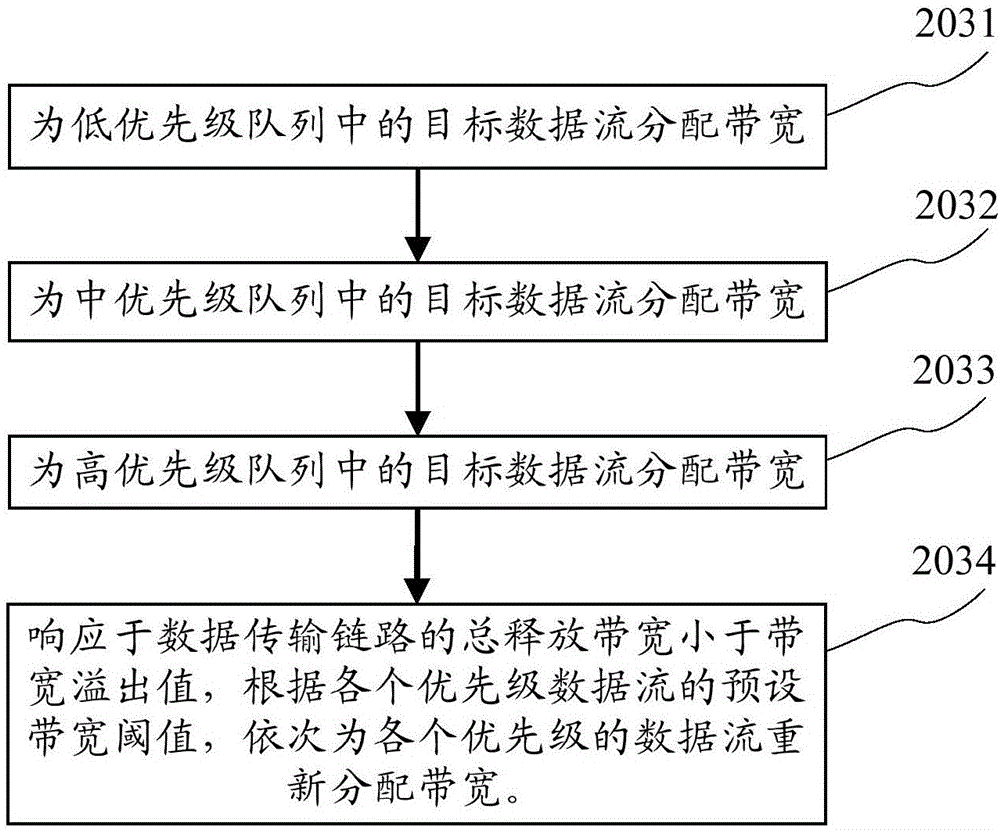
The application discloses a bandwidth setting method, device and system. A specific embodiment of the method comprises the following steps: acquiring a bandwidth overflow value of a data transmission link, wherein the bandwidth overflow value is the difference value between the bandwidth occupied by the data transmission link and a preset maximum allowable occupied bandwidth; acquiring the bandwidth occupied by each data flow in the data transmission link, and determining the priority of each data flow; re-distributing the bandwidth for the data flows in the data transmission link according to the bandwidth overflow value, the bandwidth occupied by each data flow and the priority of each data flow, and generating bandwidth distribution information corresponding to the data flows, wherein the bandwidth distribution information comprises a bandwidth distribution instruction; and respectively sending the bandwidth distribution information corresponding to the data flows to clients corresponding to the data flows so that the client can set the bandwidth for each data flow in the data transmission link according to the bandwidth distribution instruction. Through the adoption of the method, device and system disclosed by the embodiment, the effective and reasonable bandwidth distribution is realized.
Owner:BEIJING BAIDU NETCOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
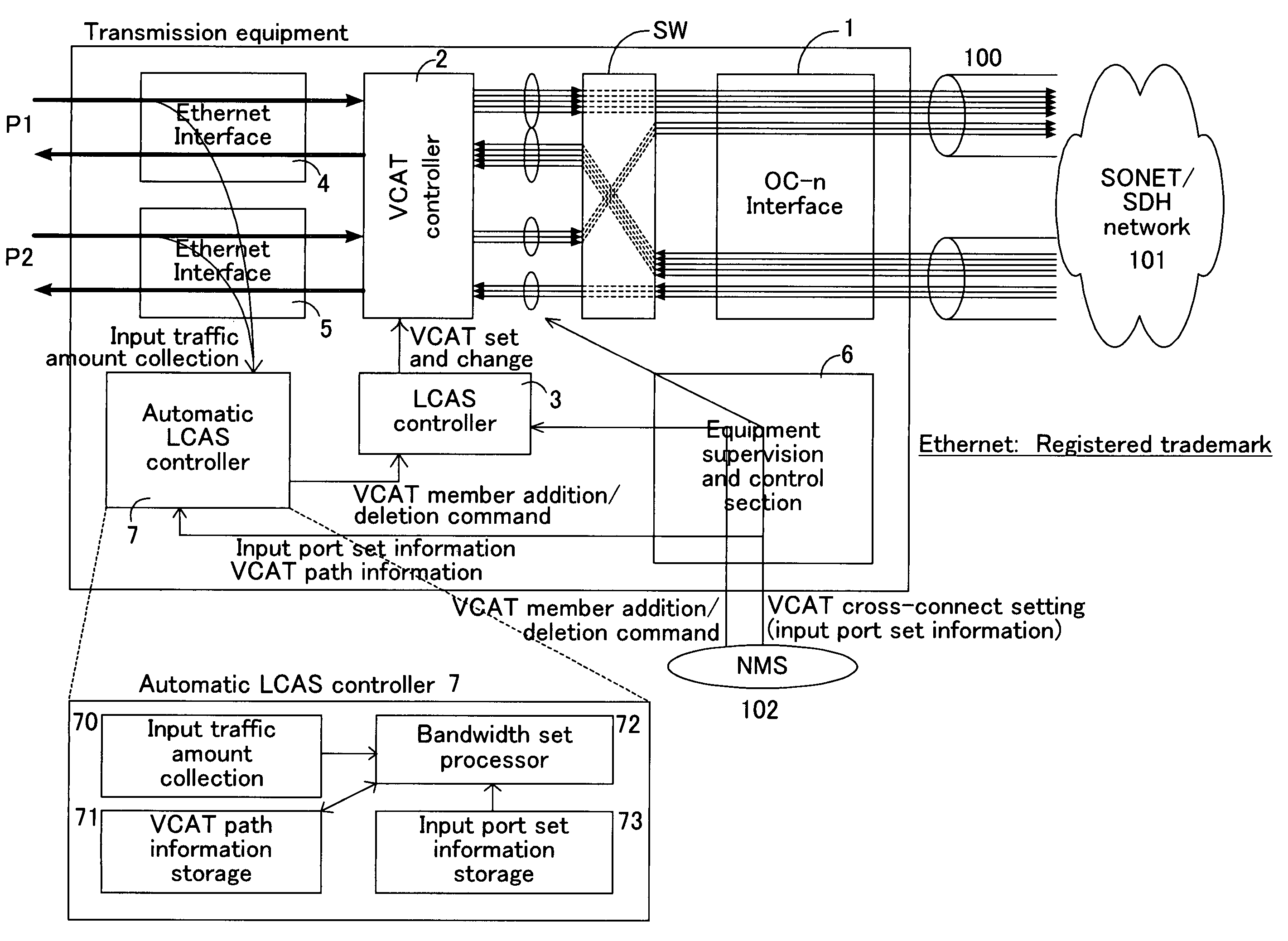
Automatic change method of virtual concatenation bandwidth
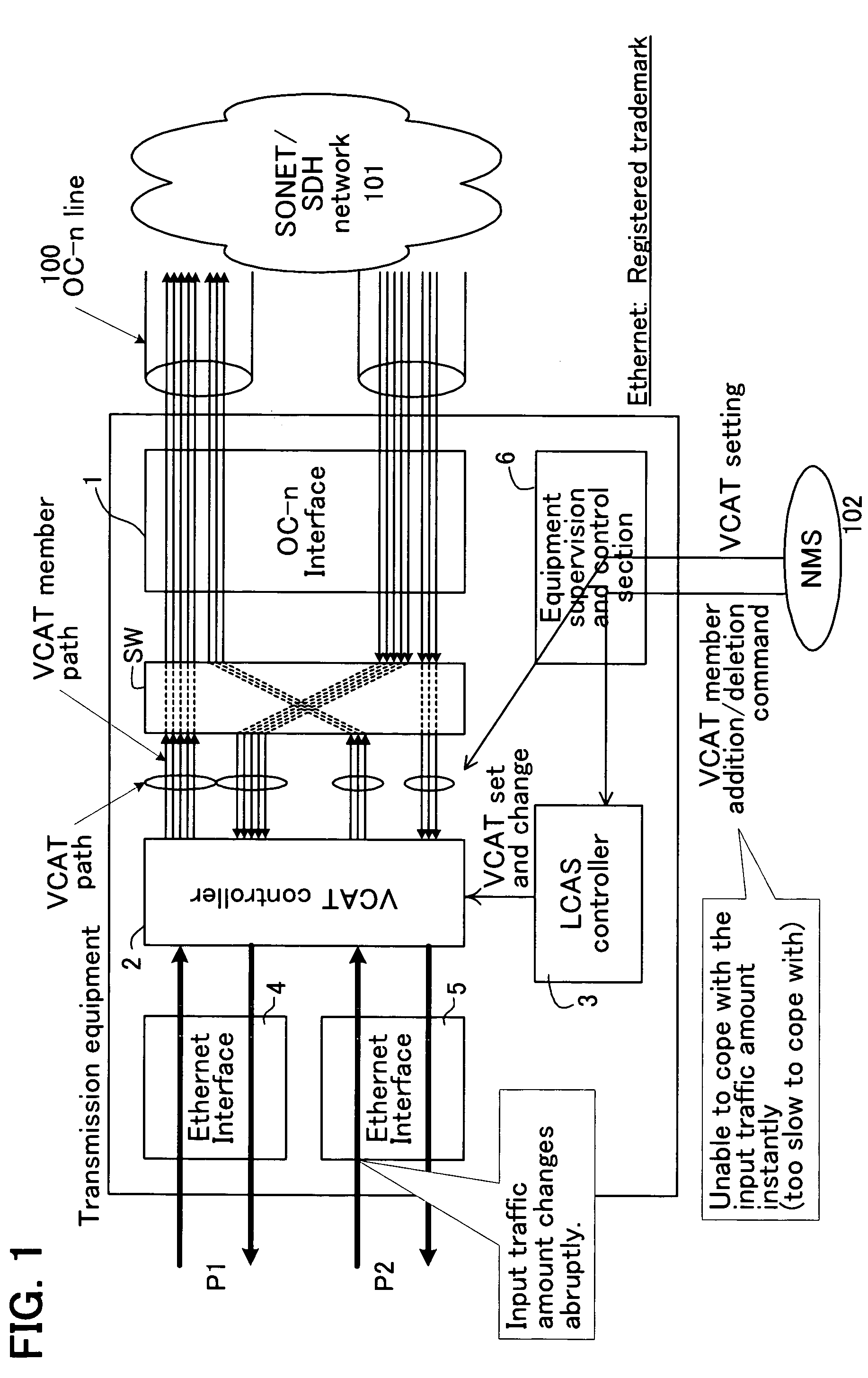
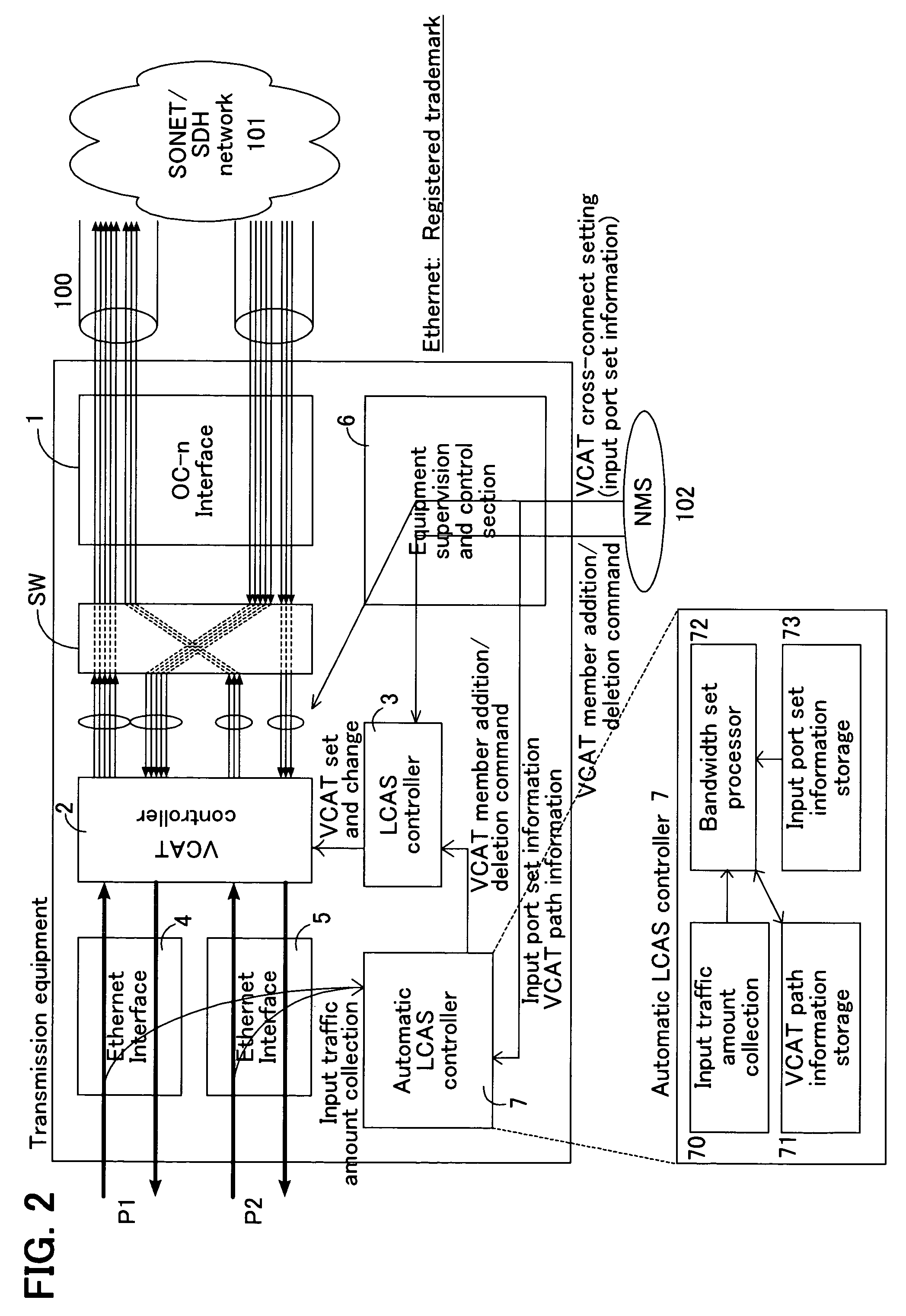
InactiveUS7567585B2Efficient networkingImprove throughputTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityLink Capacity Adjustment Scheme
Equipment enables an improved efficiency in network bandwidth usage, and an improved upper-layer throughput even when abrupt change occurs in input traffic. The equipment includes an input traffic collector which collects and retains an input traffic amount of each input port for one period at preset periods; a bandwidth set processor which calculates a bandwidth for use in each input port from the input traffic amount retained in the input traffic collector, and calculates the corresponding number of virtual concatenation member paths from the difference of the bandwidth in use and a virtual concatenation path bandwidth having been allocated to the input port, and issues an addition command or a deletion command for adding or deleting the virtual concatenation member paths for the calculated number; a virtual concatenation controller which sets a virtual concatenation path bandwidth against the traffic input from the plurality of ports; and a link capacity adjustment scheme controller which sets and changes the virtual concatenation to the virtual concatenation controller, based on the addition command or the deletion command of the virtual concatenation member paths issued by the bandwidth set processor.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com