Method for establishing recovery type path of different faults in one communication network
A technology of communication network and establishment method, which is applied in the field of fault recovery, and can solve the problem that segmented time-slots cannot be considered, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
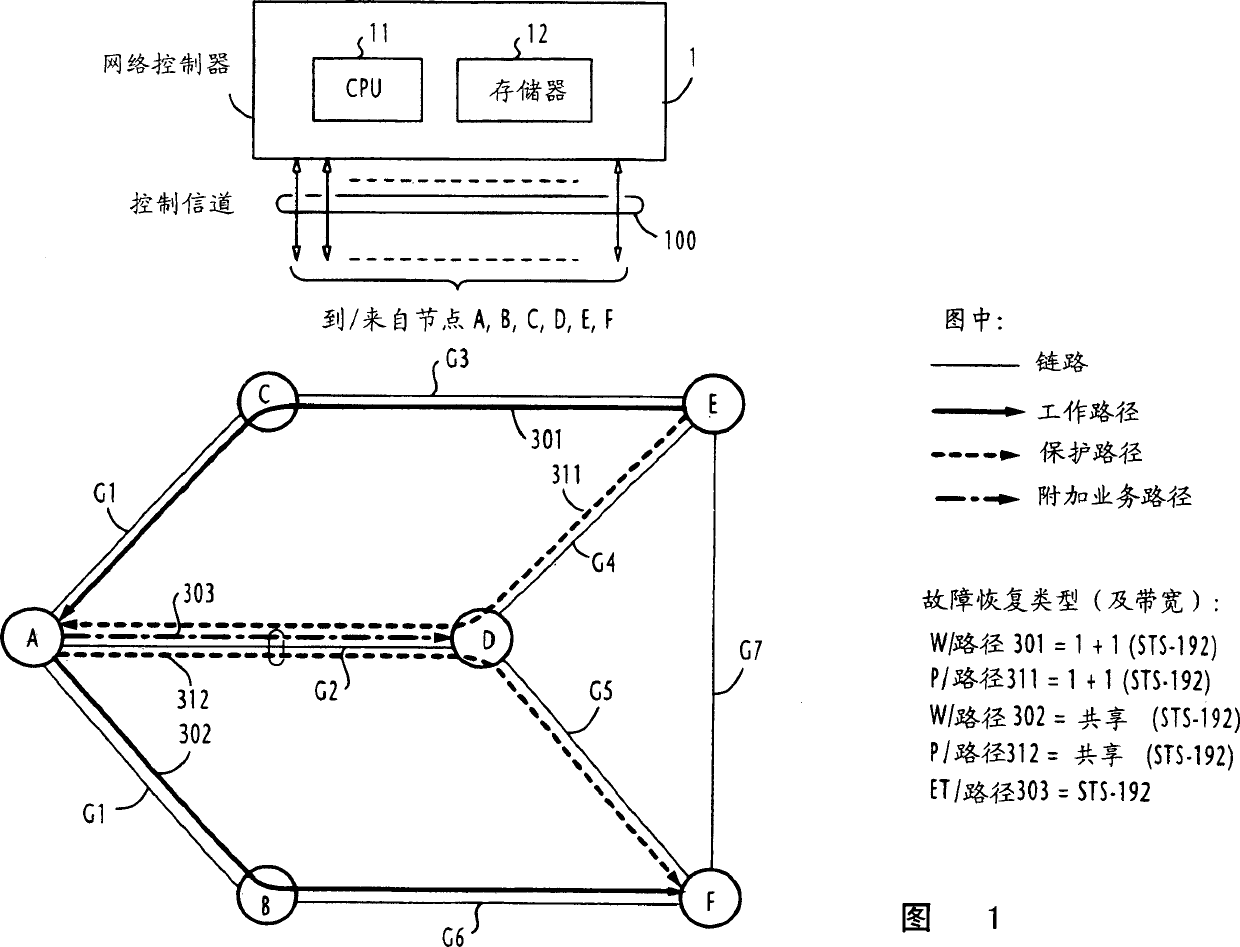
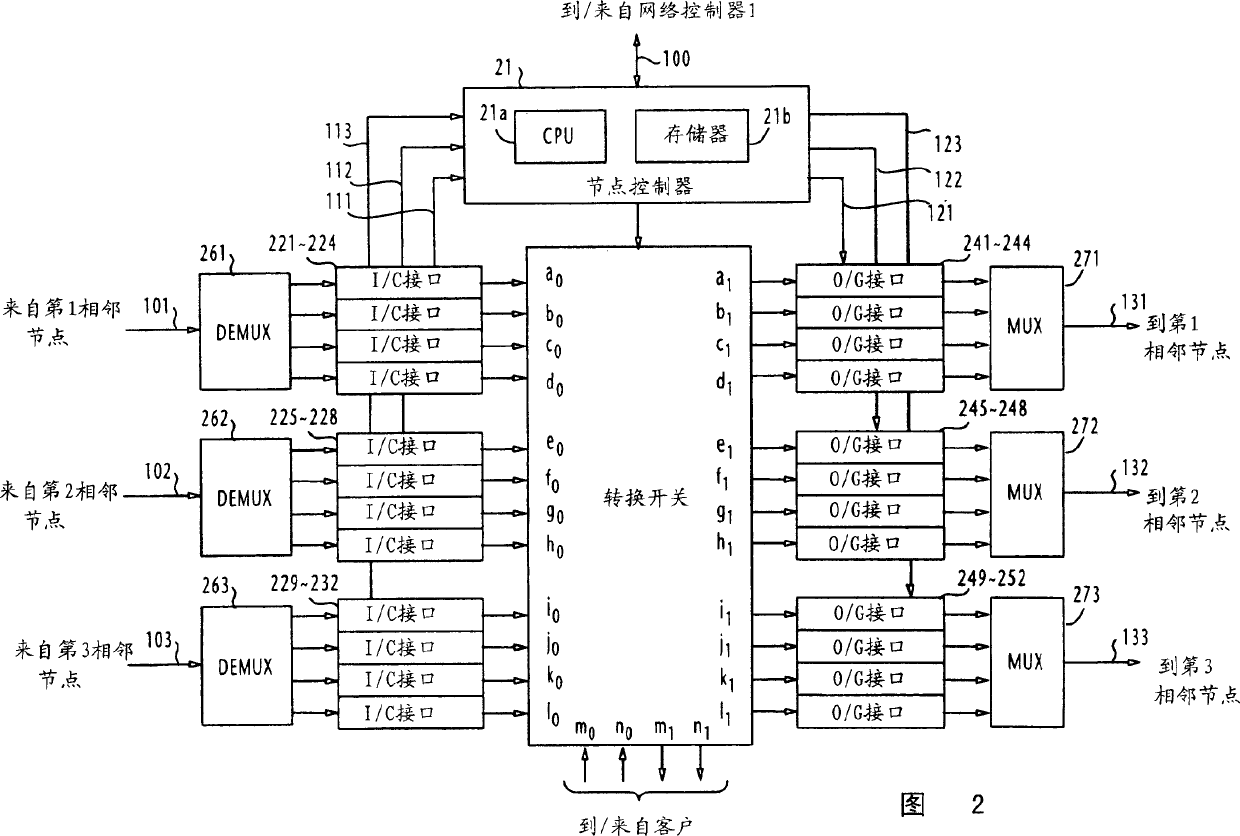
[0049] Referring to FIG. 1, there is shown an optical communication network of a first embodiment of the present invention comprising a network controller 1 and a plurality of nodes A to F interconnected by links in a mesh structure. For example, nodes A and B are interconnected by a link AB in the direction from node A to node B and by a link BA in the direction from node B to node A. In this embodiment, it is assumed that a path is established in a single direction from a start node to a terminal node. All links are denoted by SRLG (Shared Risk Link Group) identifiers G1 to G7. A bundle of links grouped under the same G1 includes, for example, the links AB, BA, AC and CA. All nodes are connected to a network controller 1 including a CPU 11 and a memory 12 via a control channel 100 .
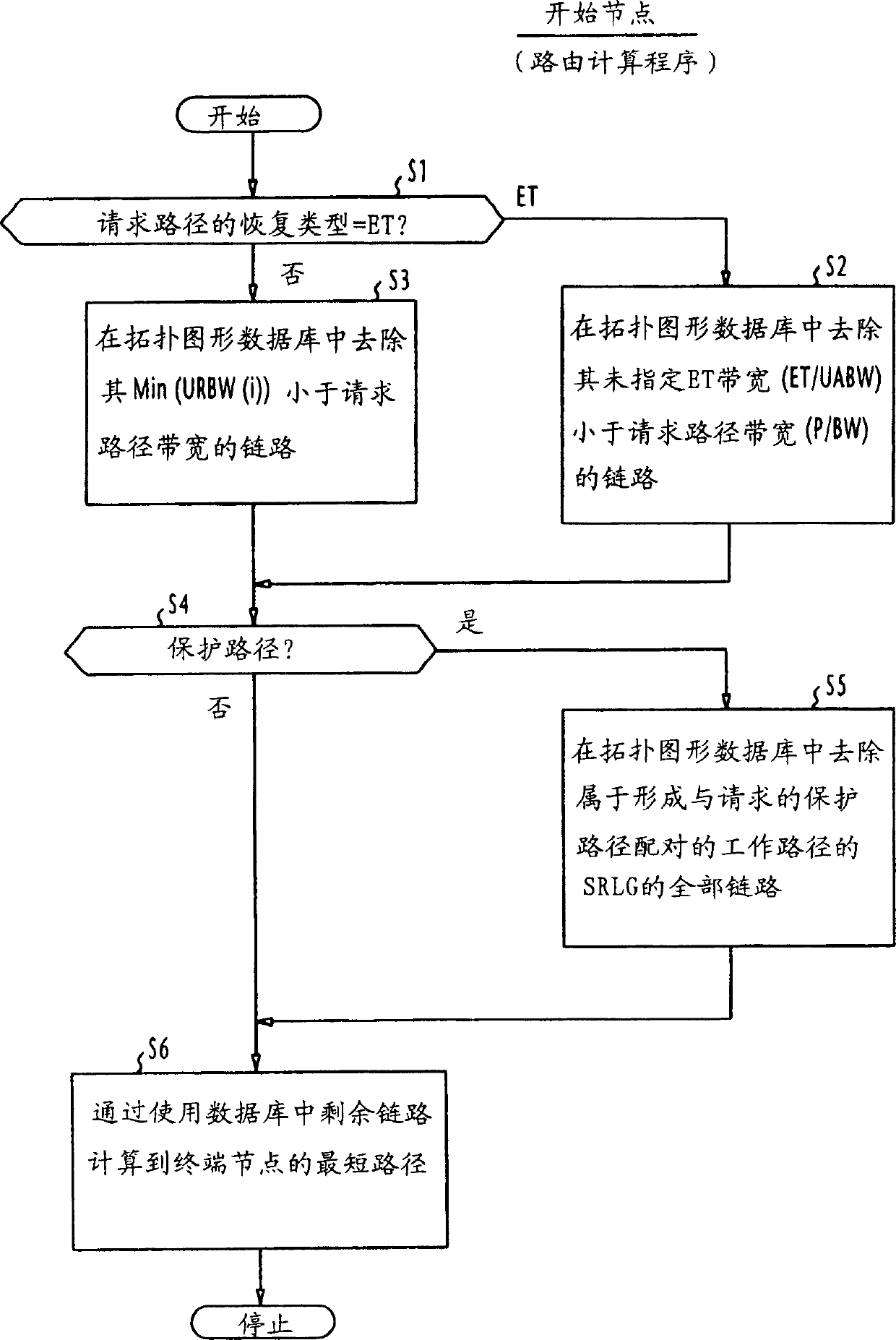
[0050] A typical example of a structure of working paths and protection paths is established in the network of FIG. 1 . Assume that a working path 301 of restoration type "1+1" is establishe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com