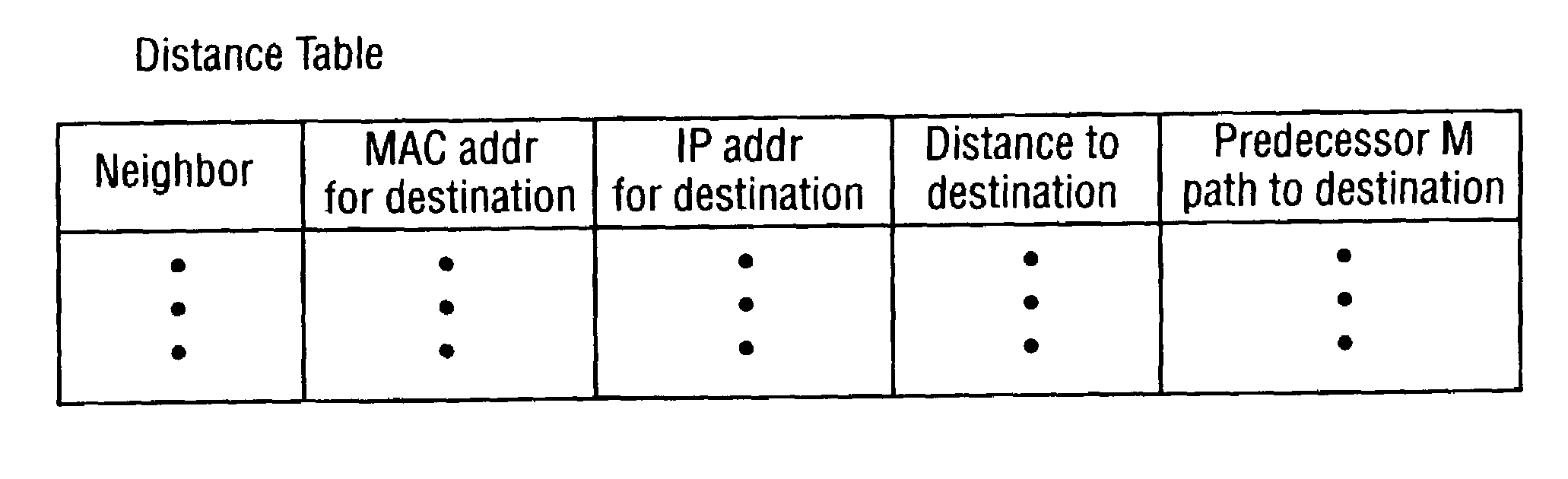
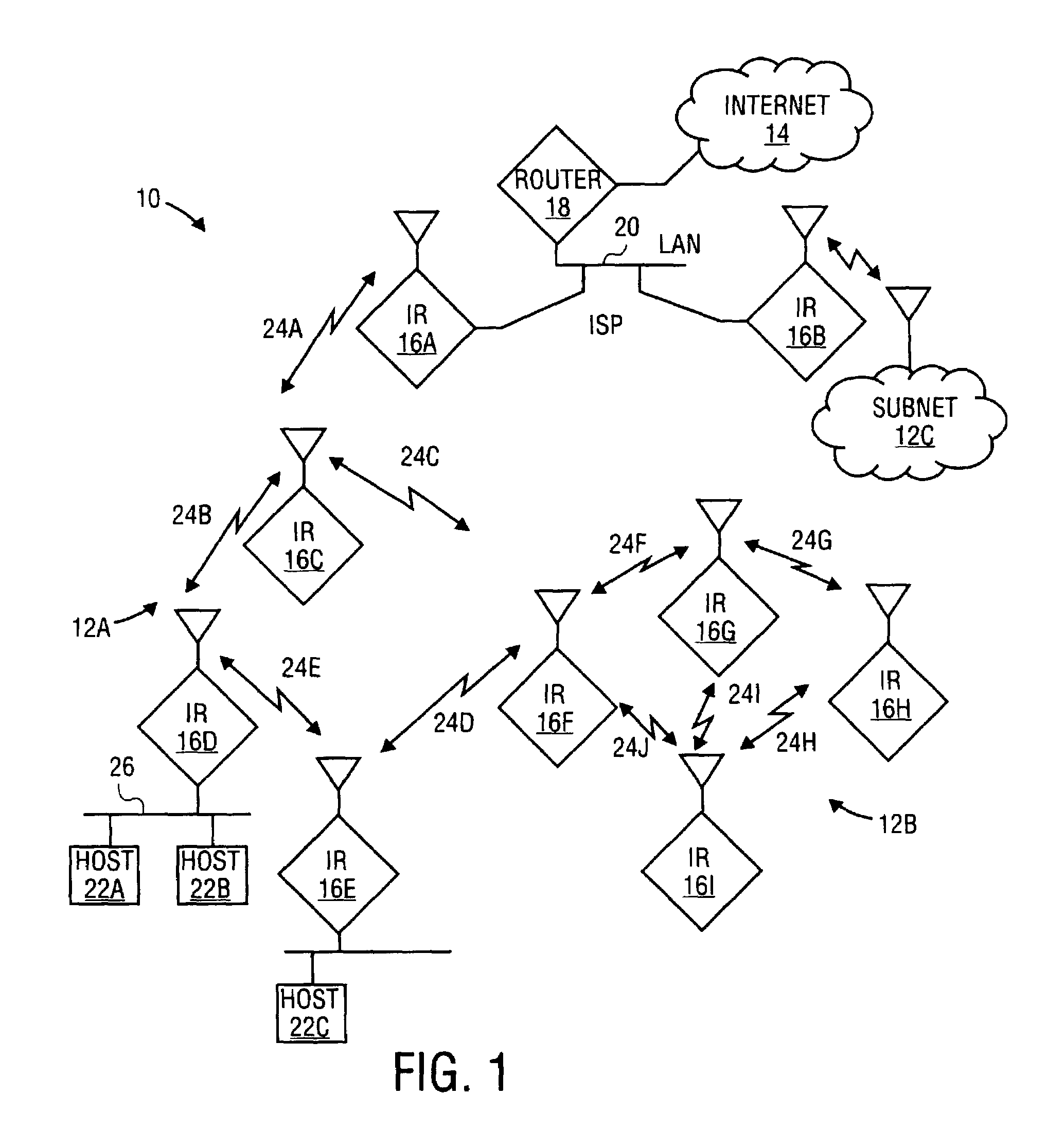
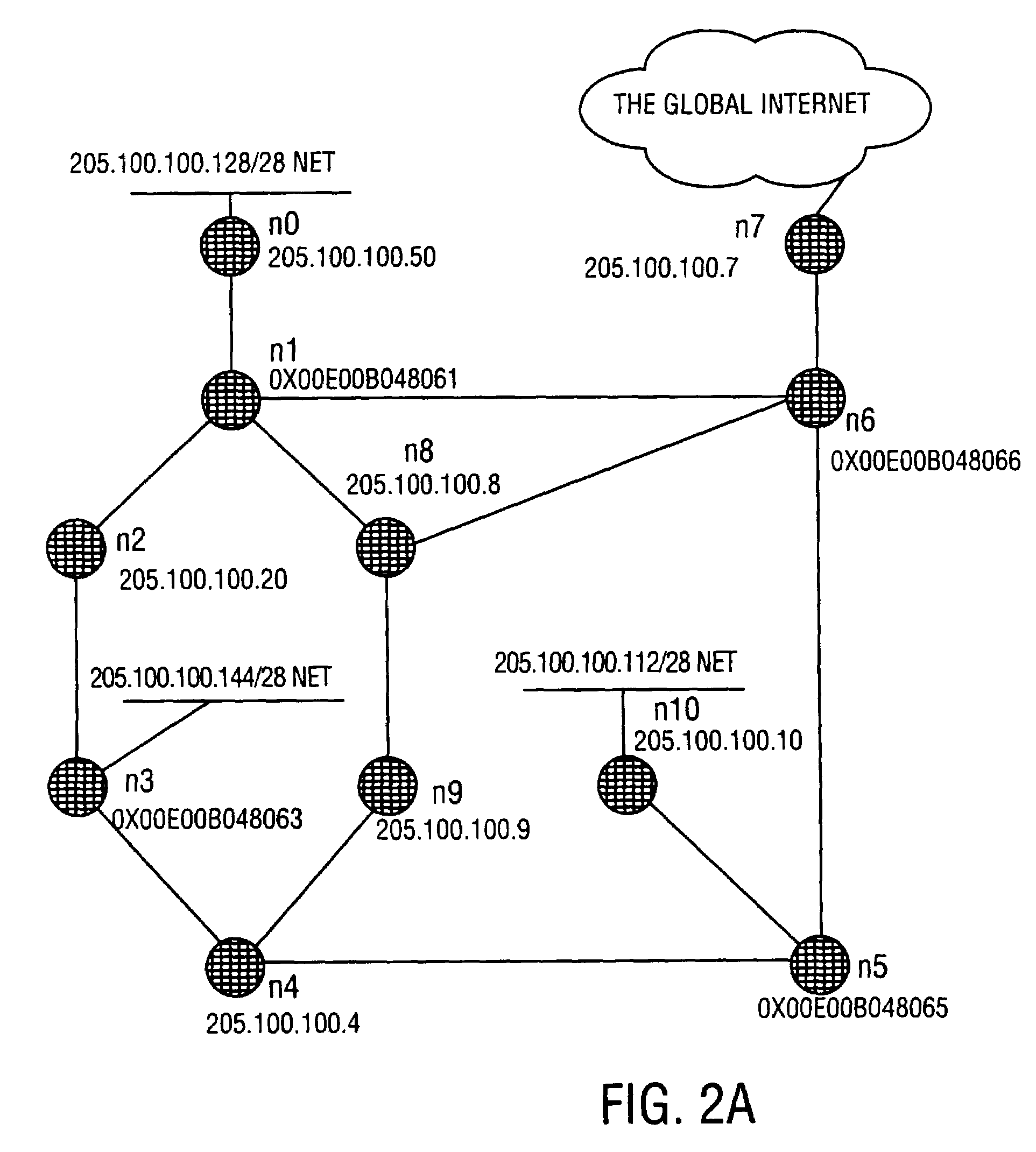
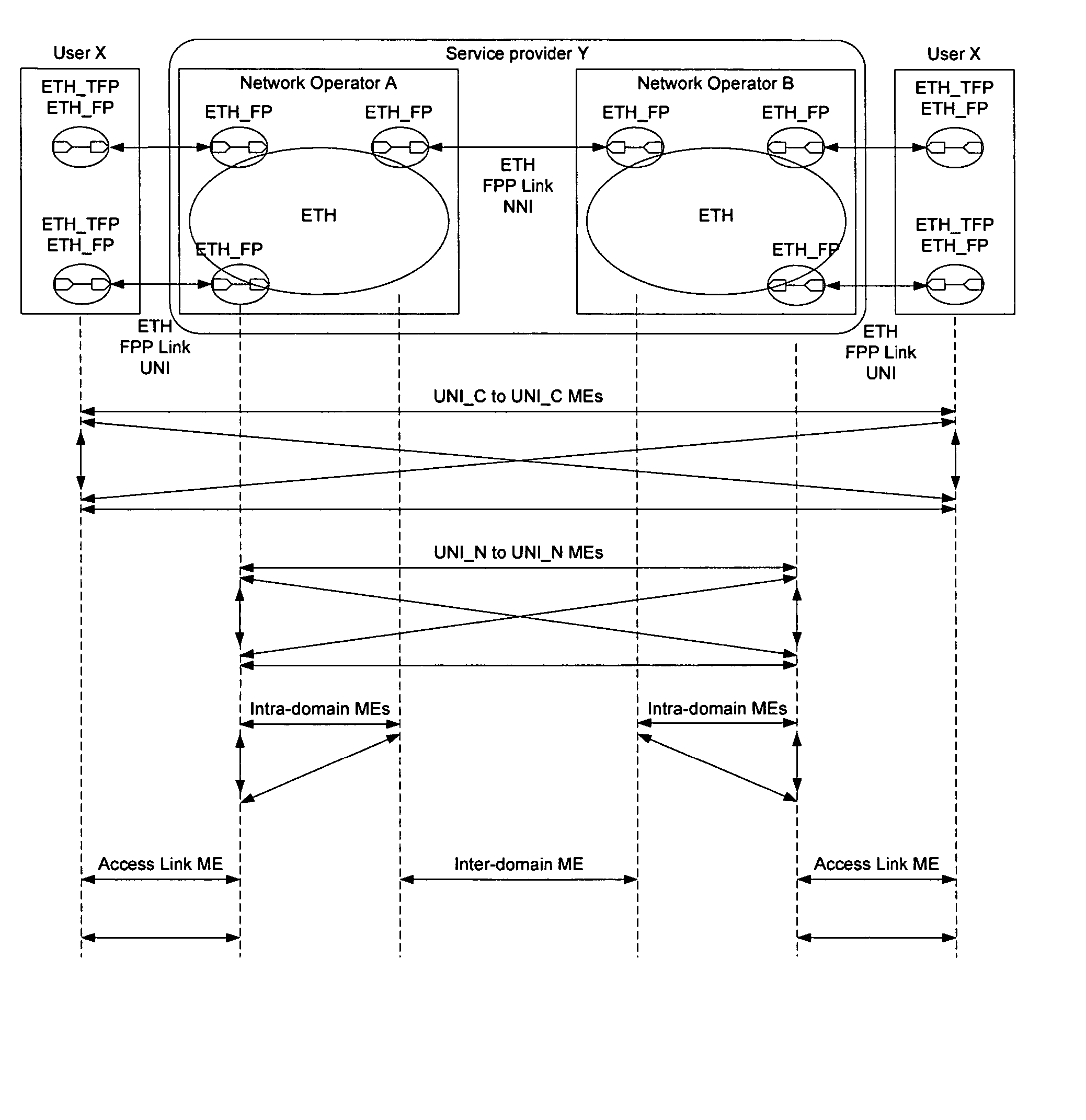
Patents
Literature
144 results about "Link level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
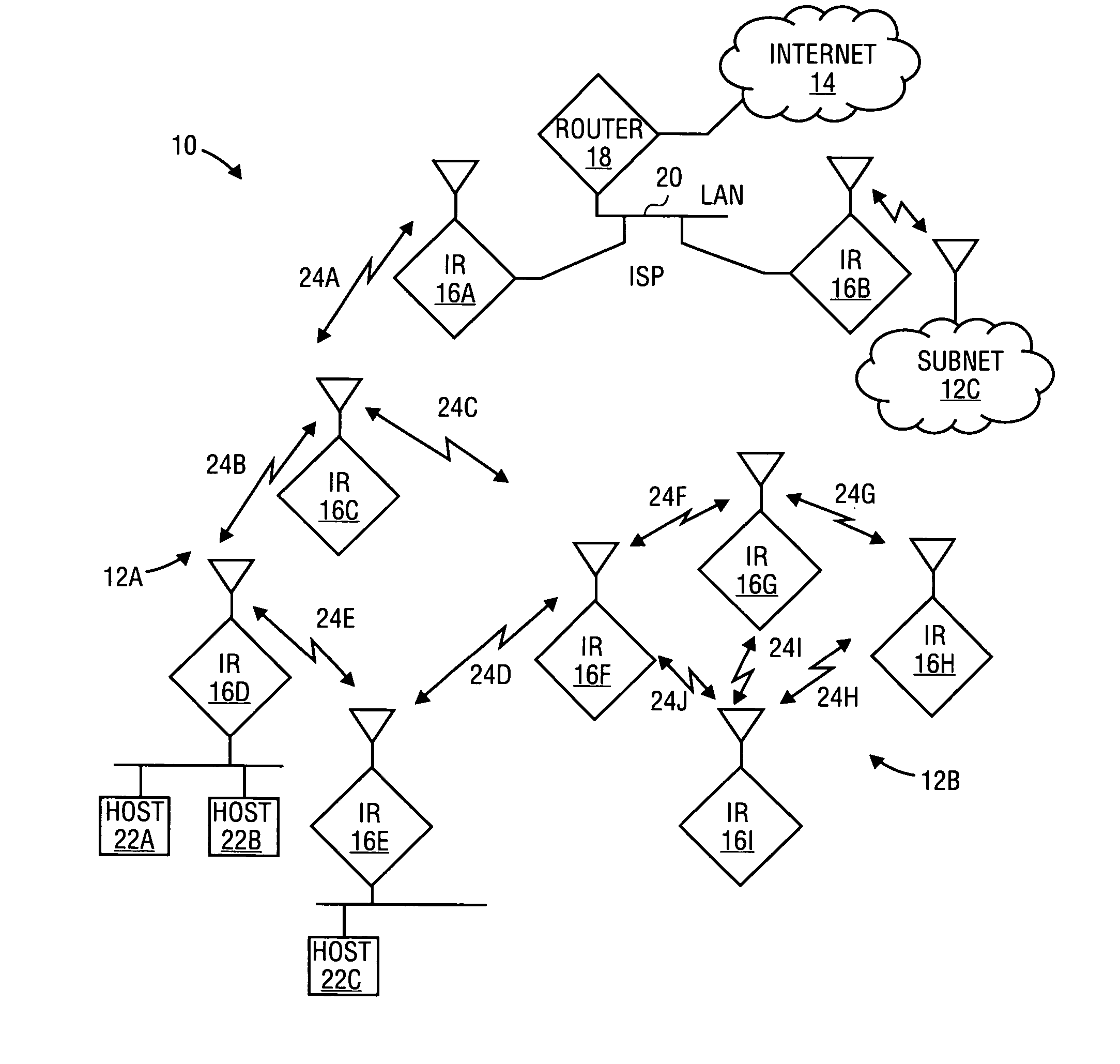
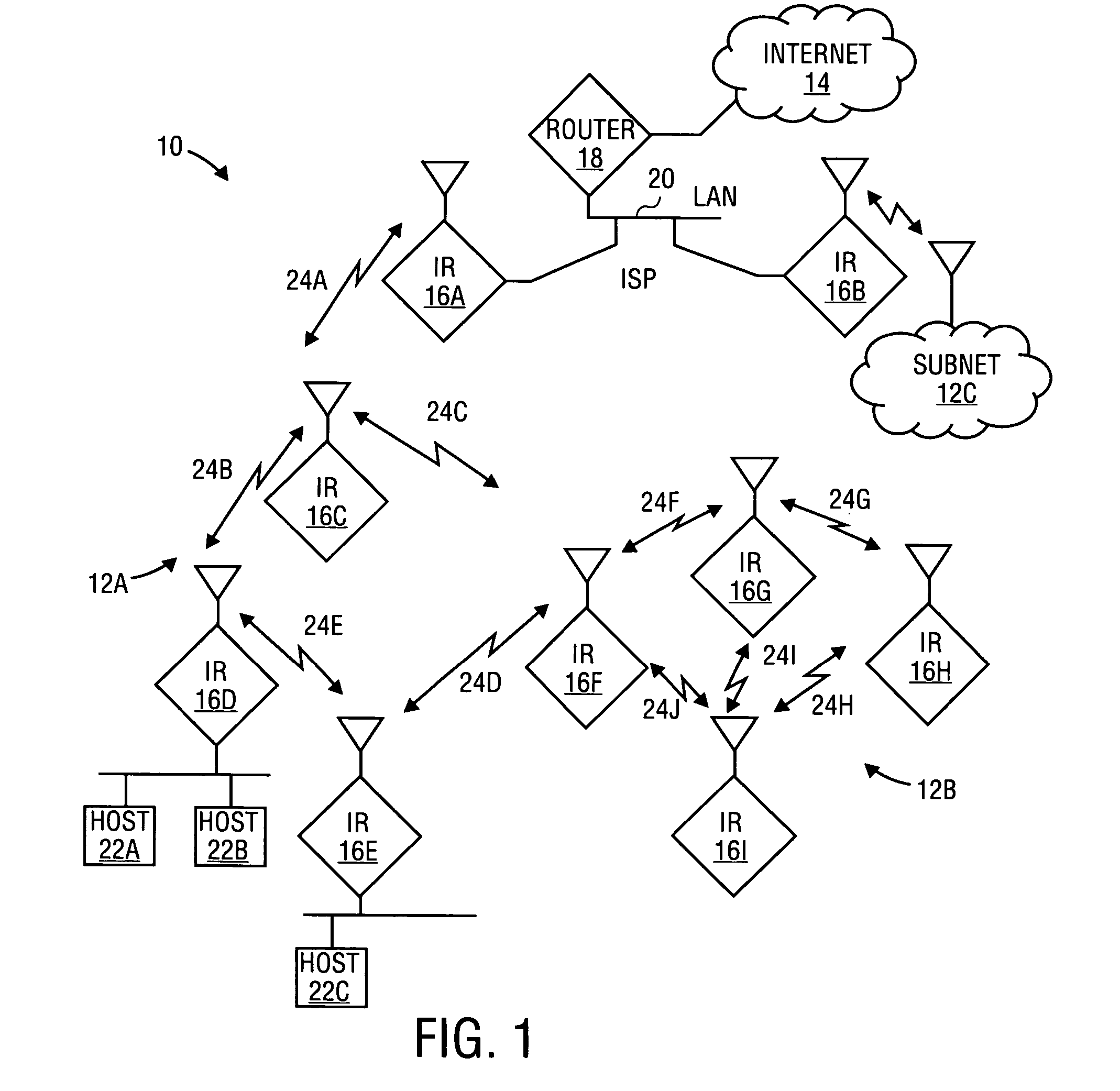
Link level: In the hierarchical structure of a primary or secondary station, the conceptual level of control or data processing logic that controls the data link. Note: Link-level functions provide an interface between the station high-level logic and the data link. Link-level functions include (a) transmit bit injection and receive bit extraction, (b) address and control field interpretation, (c) command response generation, transmission and interpretation, and (d) frame check sequence computation and interpretation.
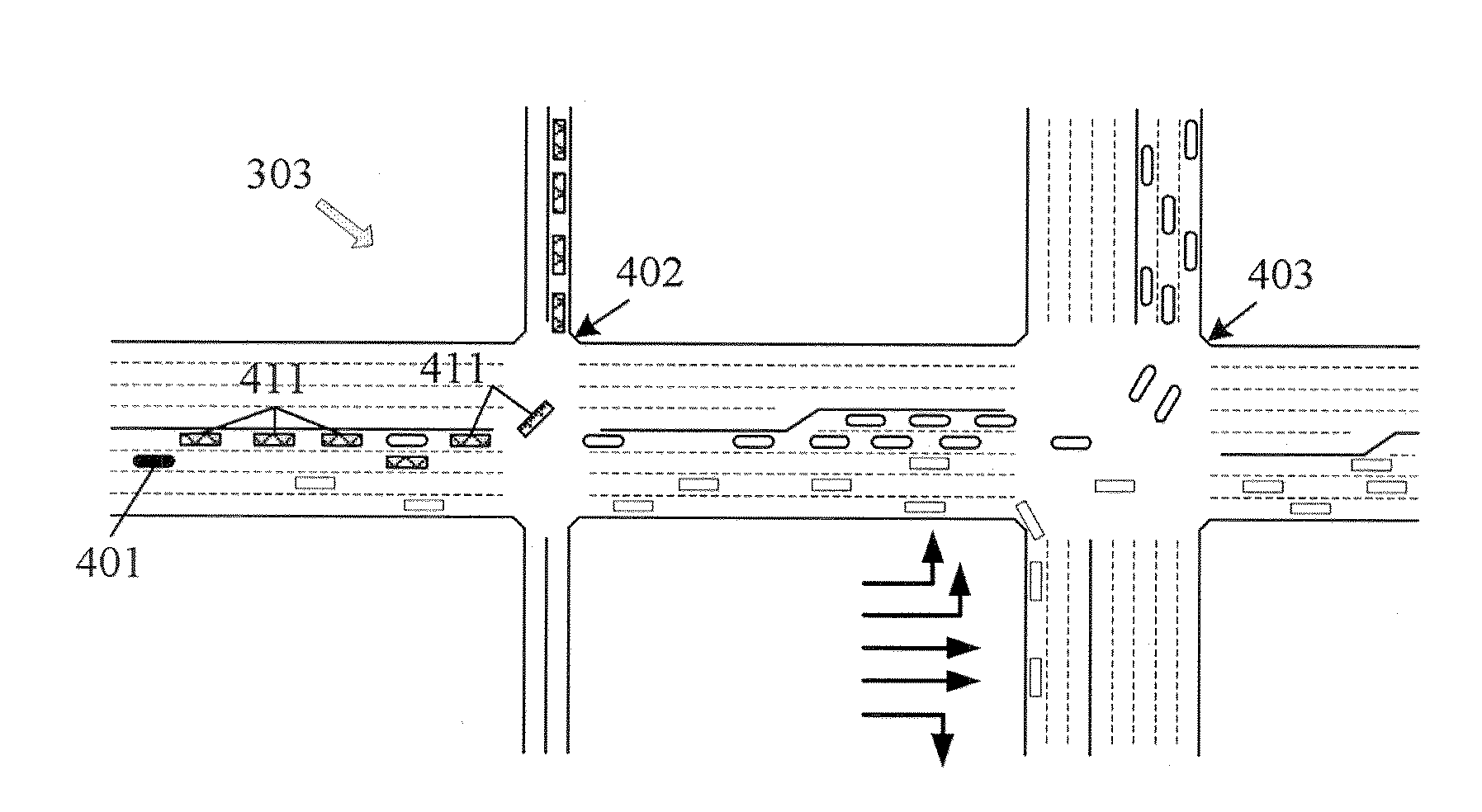
Lane-level vehicle navigation for vehicle routing and traffic management
ActiveUS20140278052A1Improves other aspectSimple methodInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTraffic signalTransportation planning
A lane-level vehicle routing and navigation apparatus includes a simulation module that performs microsimulation of individual vehicles in a traffic stream, and a lane-level optimizer that evaluates conditions along the candidate paths from an origin to a destination as determined by the simulation module, and determines recommended lane-level maneuvers along the candidate paths. A link-level optimizer may determines the candidate paths based on link travel times determined by the simulation module. The simulation may be based on real-time traffic condition data. Recommended candidate paths may be provided to delivery or service or emergency response vehicles, or used for evacuation planning, or to route vehicles such as garbage or postal trucks, or snowplows. Corresponding methods also may be used for traffic planning and management, including determining, based on microsimulation, at least one of (a) altered road geometry, (b) altered traffic signal settings, such as traffic signal timing, or (c) road pricing.
Owner:CALIPER CORPORATION
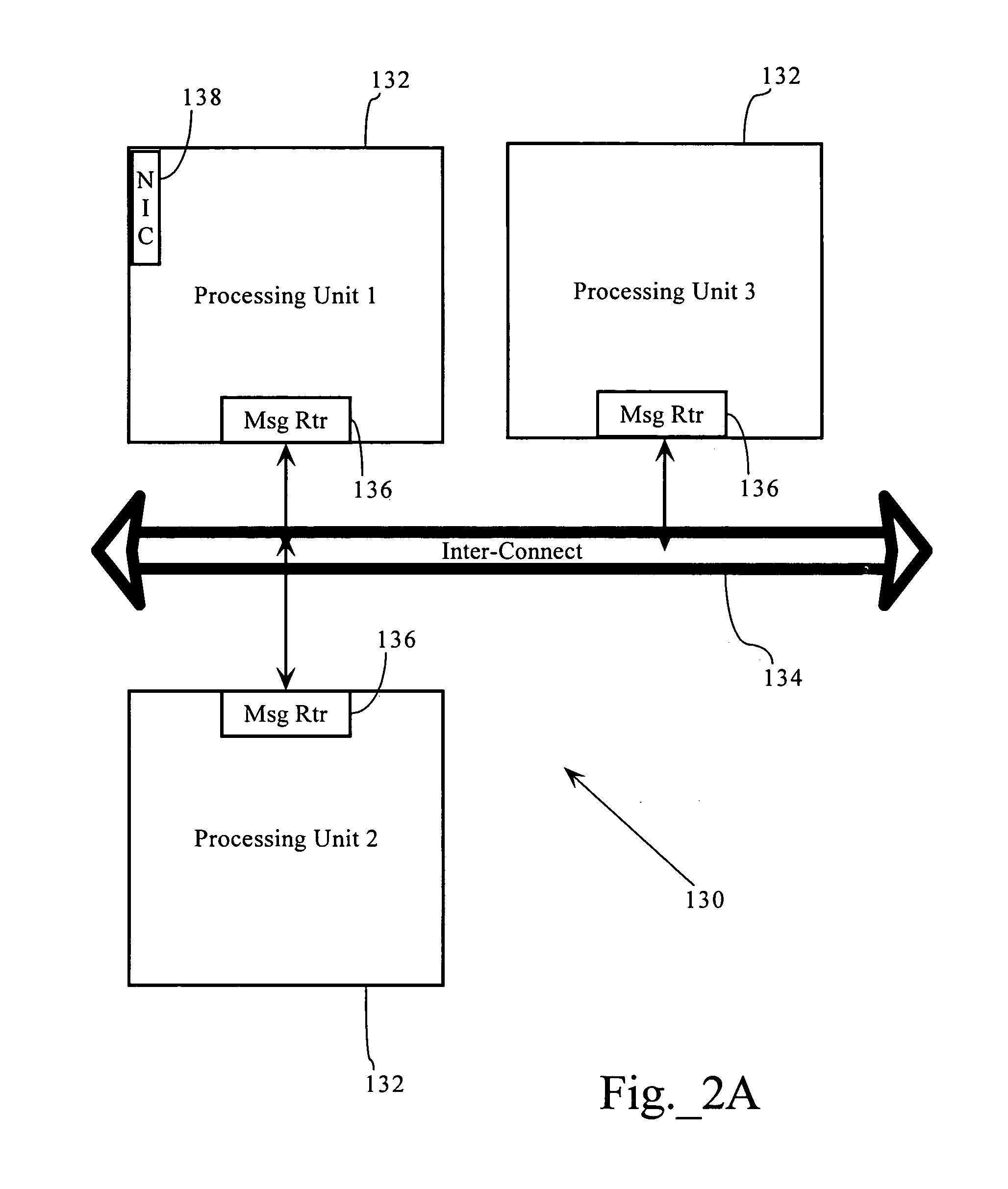
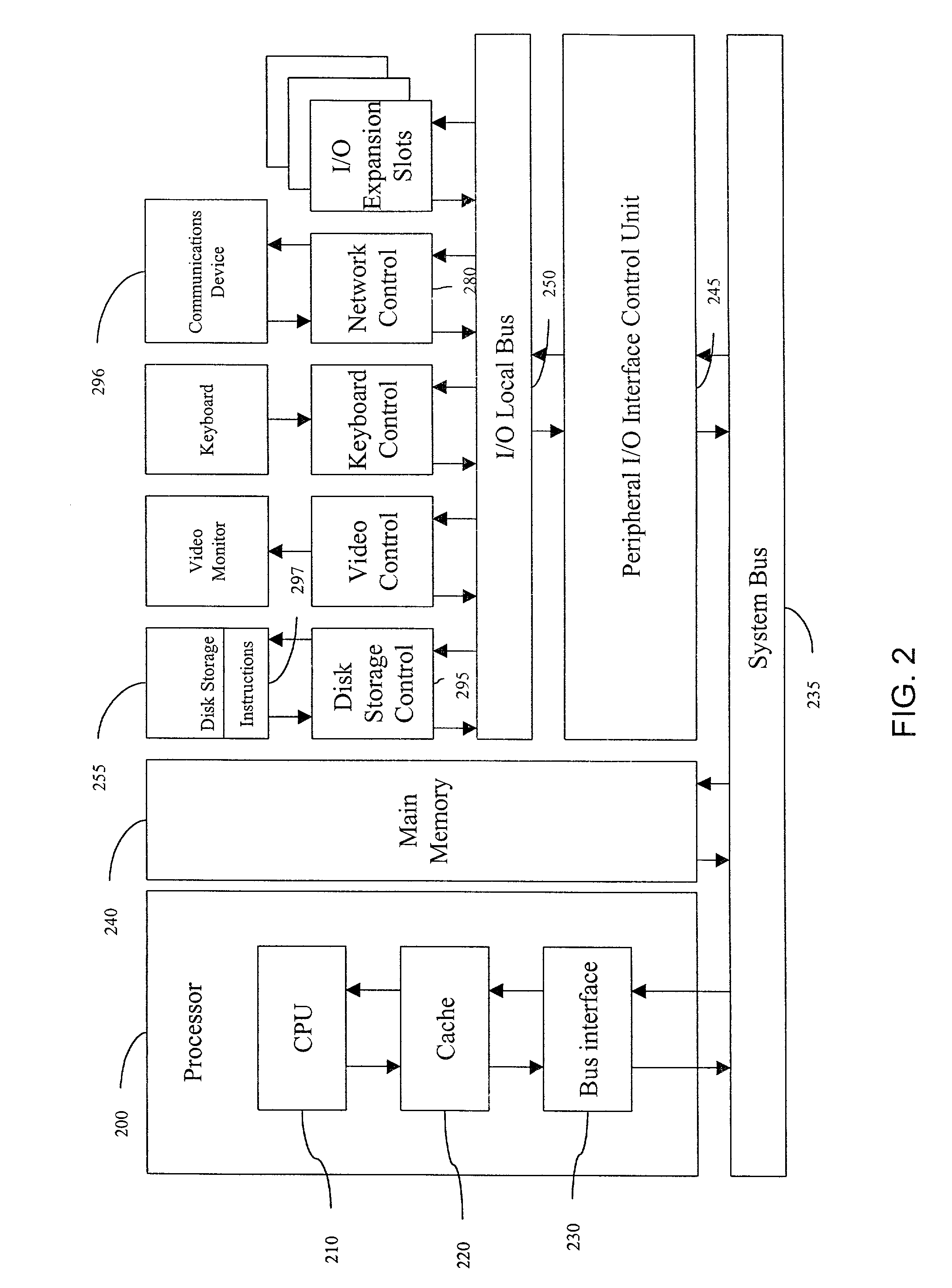
Multi-dimensional computation distribution in a packet processing device having multiple processing architecture
InactiveUS7610330B1High bandwidthHighly-scalableMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionQuality of serviceTraffic capacity
Flow-aware task distribution in network devices having multiple processor architectures. In one embodiment, the present invention can be used for high bandwidth network processing in an application and flow aware Quality of Service (QoS) network device. In some implementations, the present invention provides a task distribution architecture capable of flow state awareness and link level QoS control. In some implementations, the present invention can incorporate one or more processes, such as flow distributors and device distributors, that route packets for processing among different processing units on the basis flow correspondence and / or link or network path attributes. The flow and device distributors, in one implementation, allow for the separation and paralletization of packet processing functionality into flow-specific and link-specific processing units, allowing for a highly-scalable, flow-aware task distribution in a network device that processes network application traffic.
Owner:CA TECH INC
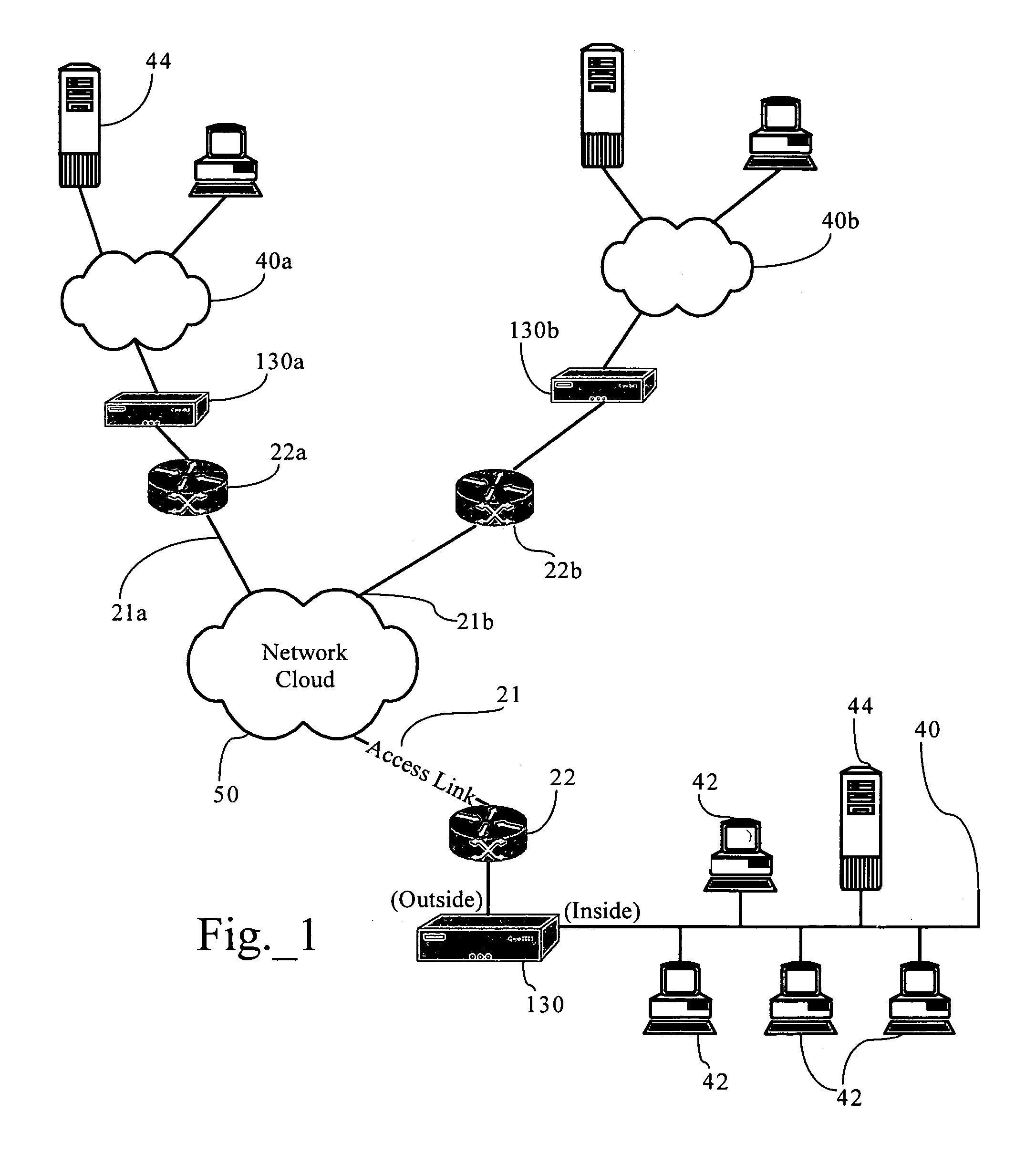
Discovery of unknown MAC addresses using load balancing switch protocols
InactiveUS6456597B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityNetwork switch
A method for discovering addressing information within a network switch for an unknown MAC address received as a destination address of a packet. Where prior techniques flooded the network with the received packet, switch to switch protocols of the present invention reduce the volume of such overhead network traffic required to discover the addressing information. In particular, the present invention propagates query messages through network switches in a load balance domain (a group of switches cooperable in accordance with the protocols described herein). The query messages are propagated using a pruned broadcast tree to reduce the number of transmissions required to reach all switches in the load balance domain. The propagated query message eventual elicits a response from the device which owns the previously unknown destination address. Switches and devices outside the load balance domain are similarly probed for the unknown destination address using link level test messages which elicit a response from the device owning the unknown address without impacting the network higher layer protocols. These techniques reduce the volume of network traffic required to obtain the desired addressing information by forcing the response from the device owning the previously unknown destination address and constructing a unicast path to that device. Creating the unicast path obviates the need to flood the unknown destination address on the network.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
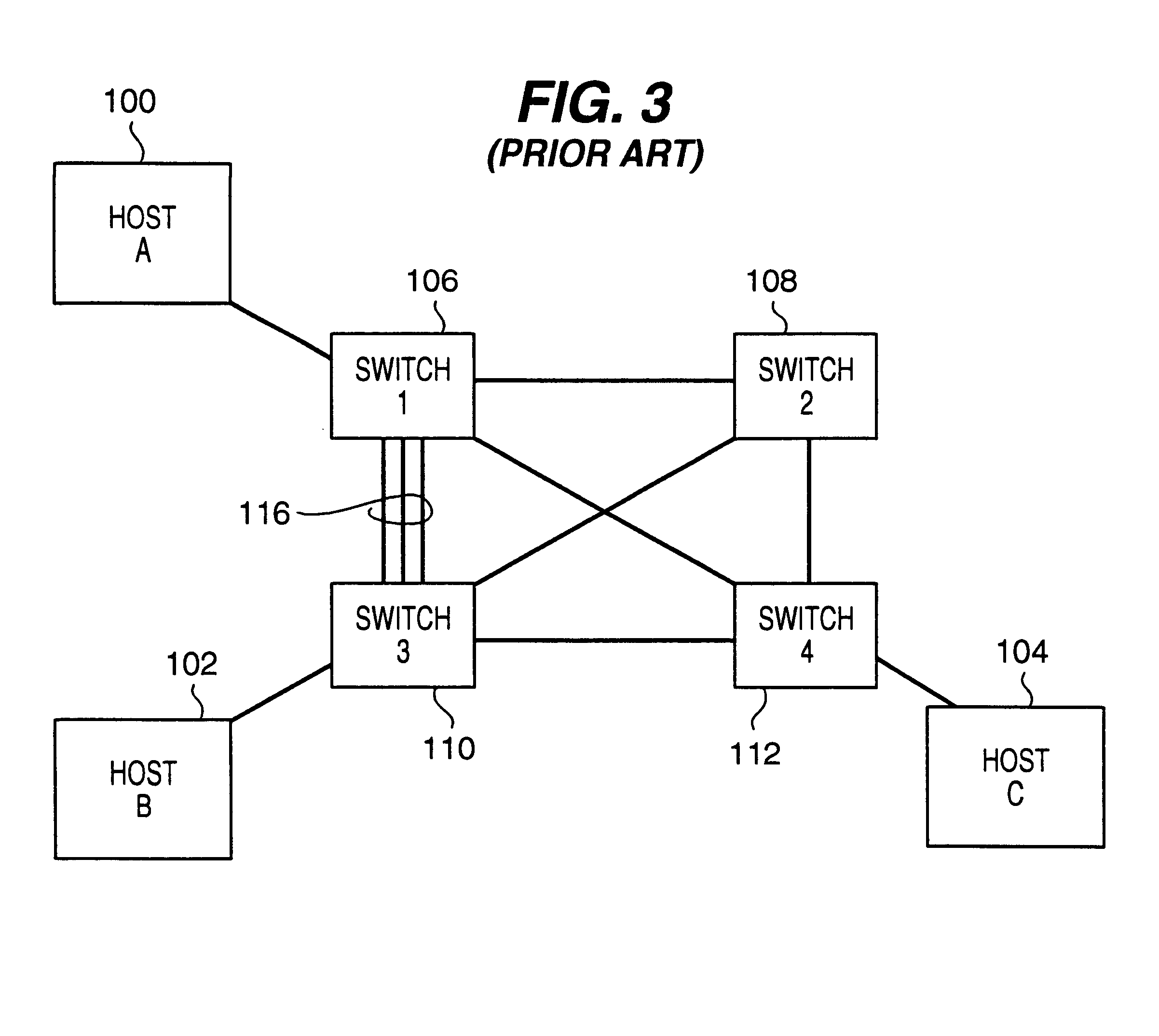
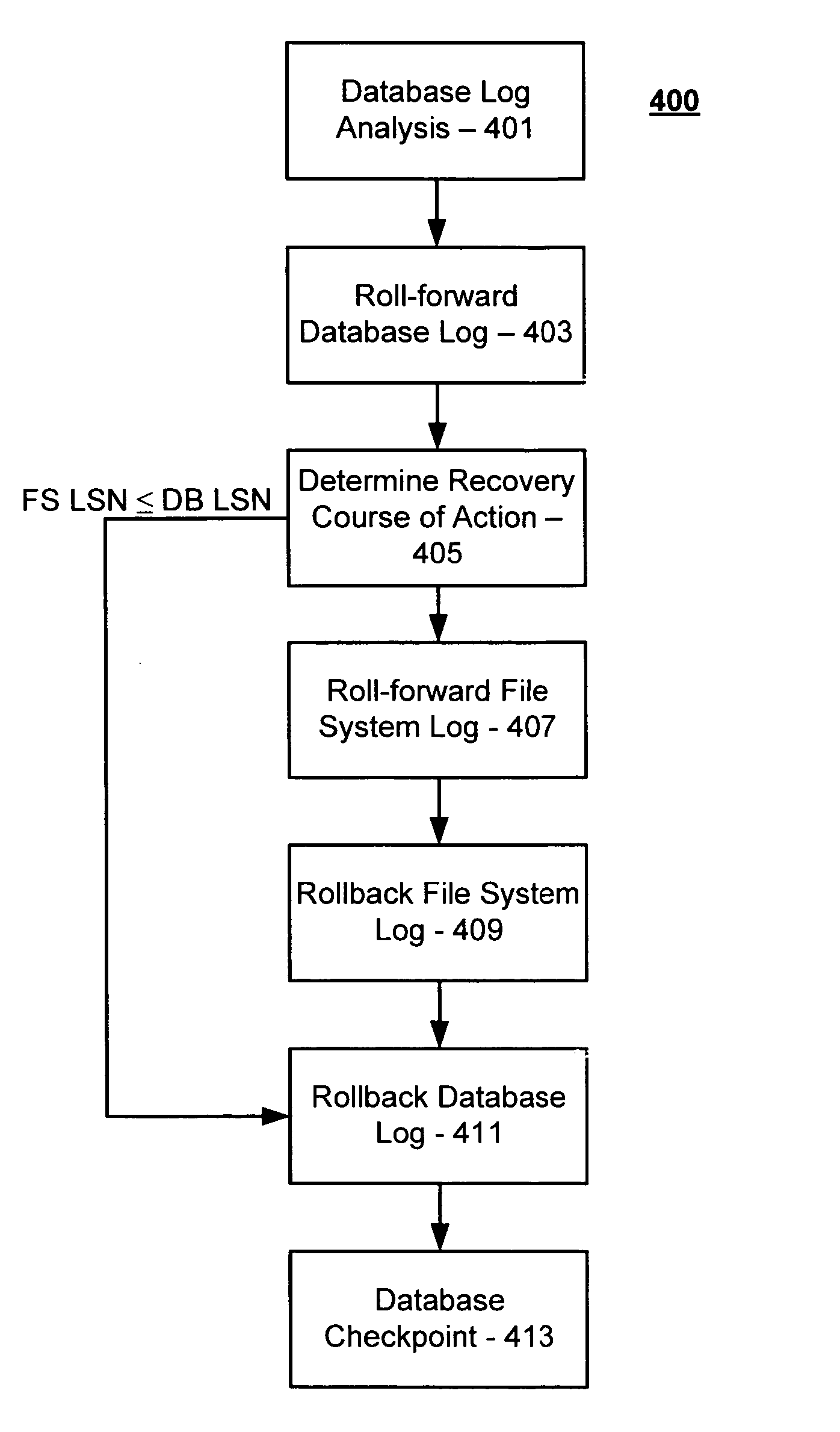
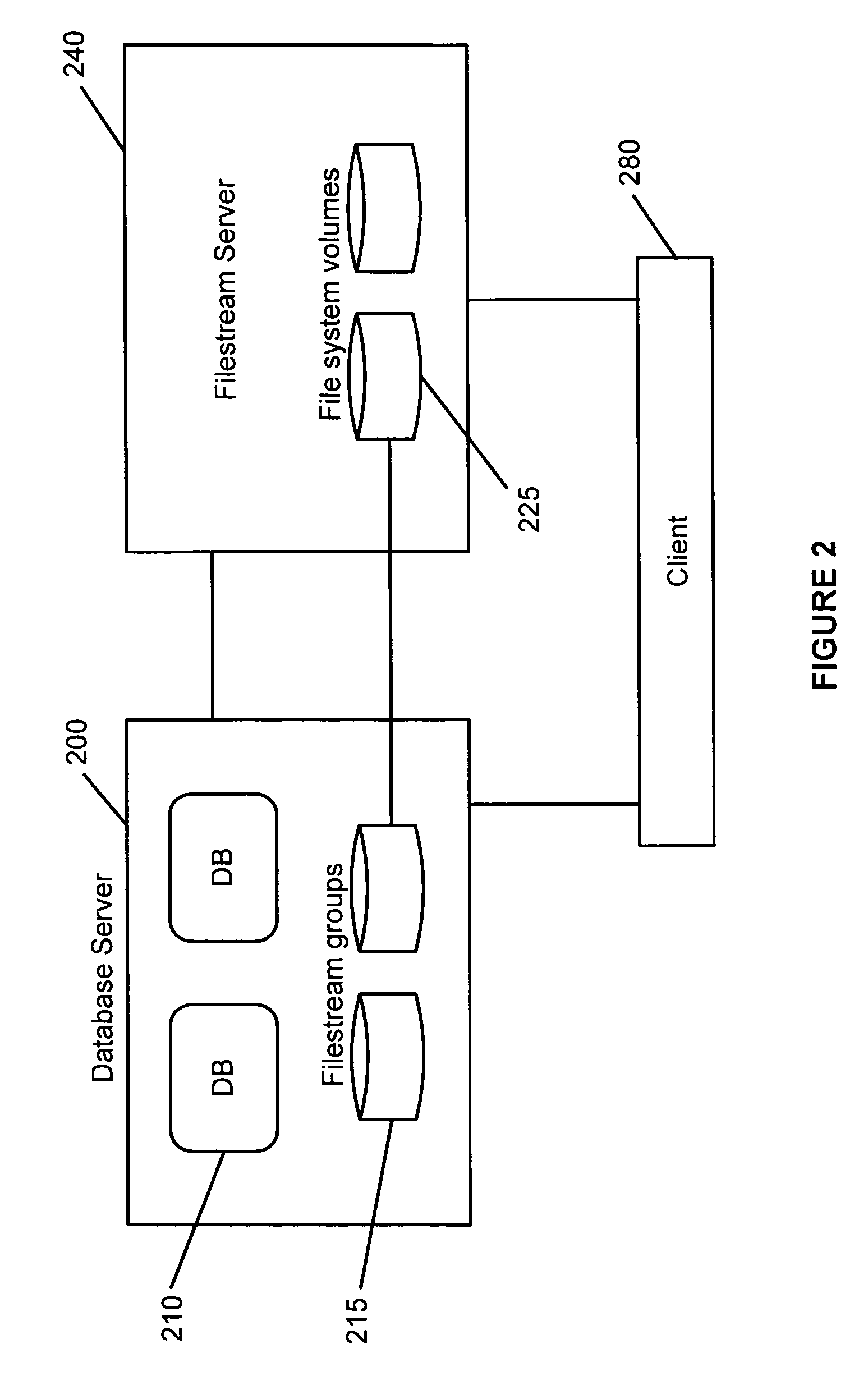
Maintenance of link level consistency between database and file system
Methods and computer-readable media for maintaining transactional link-level consistency between a database and a file system. A file system change is logged in a record of a database log and a file corresponding to the file system change is created in a file system folder. During a restart recovery process, an analysis operation and a conditional redo operation are performed based on the database log, and a conditional redo operation and an undo operation are performed based on the files in the file system folder. An undo operation is then performed based on the database log.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Unified routing scheme for ad-hoc internetworking
InactiveUS7159035B2Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsRouting tableShort path algorithm
Routing table update messages that include both network-level and link-level addresses of nodes of a computer network are exchanged among the nodes of the computer network. Further, a routing table maintained by a first one of the nodes of the computer network may be updated in response to receiving one or more of the update messages. The routing table is preferably updated by selecting a next node to a destination node of the computer network only if every intermediate node in a path from the next node to the destination node satisfies a set of nodal conditions required by the first node for its path to the destination node and the next node offers the shortest distance to the destination node and to every intermediate node along the path from the next node to the destination node. The shortest distance to the destination node may be determined according to one or more link-state and / or node-state metrics regarding communication links and nodes along the path to the destination node. Also, the nodal characteristics of the nodes of the computer system may be exchanged between neighbor nodes, prior to updating the routing table. Preferred paths to one or more destination nodes may be computed according to these nodal characteristics, for example using a Dijkstra shortest-path algorithm.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
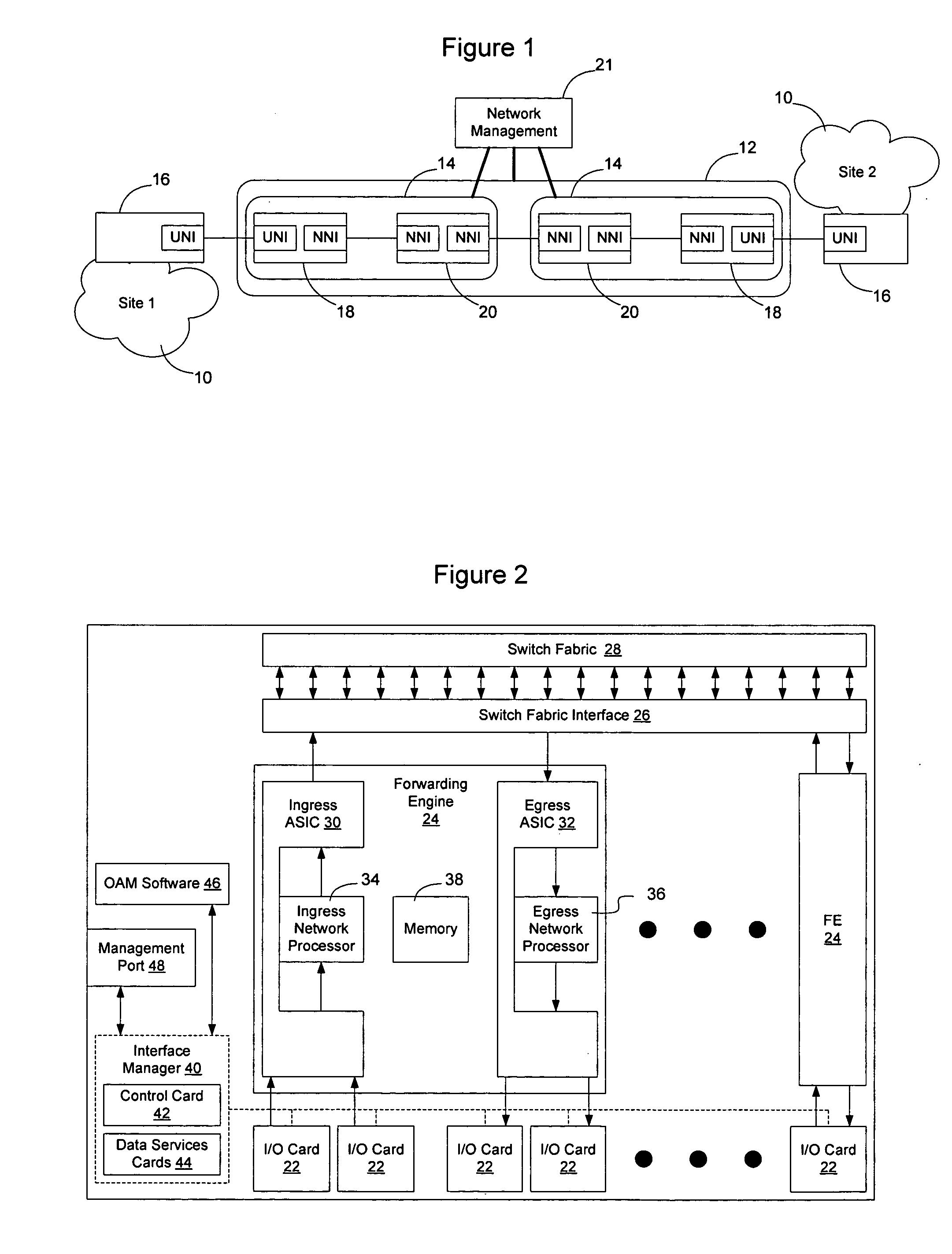
Ethernet OAM network topography discovery
Network topography may be discovered by a network element on an Ethernet network by collecting connectivity check messages periodically issued by other network elements on the network and using the information gleaned from those messages to build a topography database. Since the connectivity check messages may be link level or service instance based, the topography database may include network topography as well as service topography on the Ethernet network. Ethernet OAM loopback frames may also be used to cause network elements on the Ethernet network to issue response frames directed to the initiating network element. By collecting responses from the responding network elements, the initiating network element can build a topography database of network elements on the Ethernet network. This topography database may show the overall network topography or service instances on the network, and may provide visibility within one or more domains.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Broadcast hand-over in a wireless network
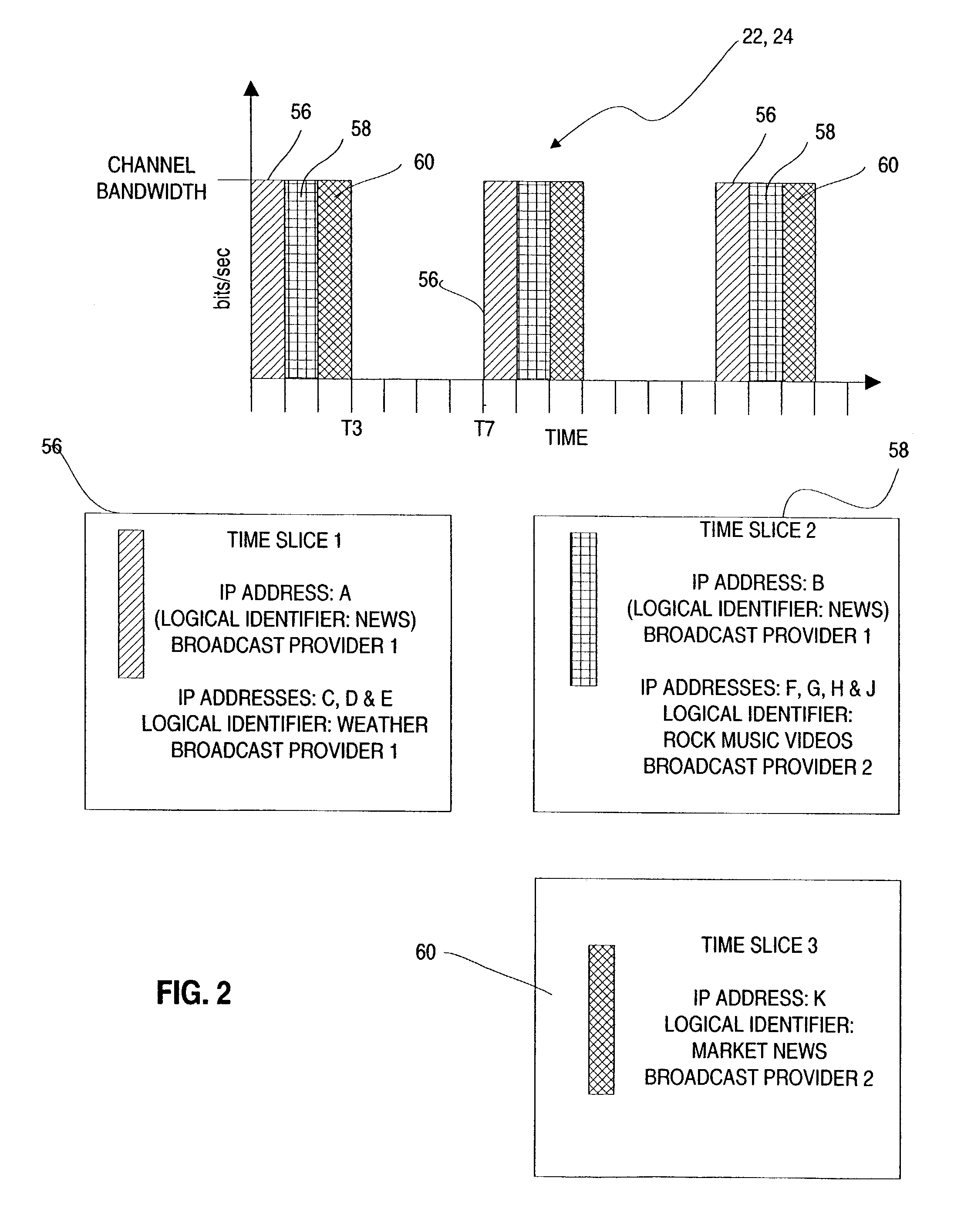
ActiveUS6977914B2Reduce resolutionBroadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexBurst transmissionBroadcasting
A system and method are disclosed for providing multicast channel handover in a mobile device within a mobile network. First and second transmitters within first and second cells broadcast datagrams associated with a logical identifier according to link-level access parameters common to the first and second transmitters. A mobile device receives the broadcast datagrams for the logical identifier from the first transmitter by configuring the common link-level access parameters. As part of handover from the first cell to the second cell, the mobile device continues receiving the broadcast datagrams from the second transmitter by maintaining the common link-level access parameters. In one embodiment, the datagrams are IP datagrams transmitted in an MPEG2 transport stream. The link-level access parameters may include time slice parameters associated with burst transmissions from the first and second transmitters according to an embodiment of the invention.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
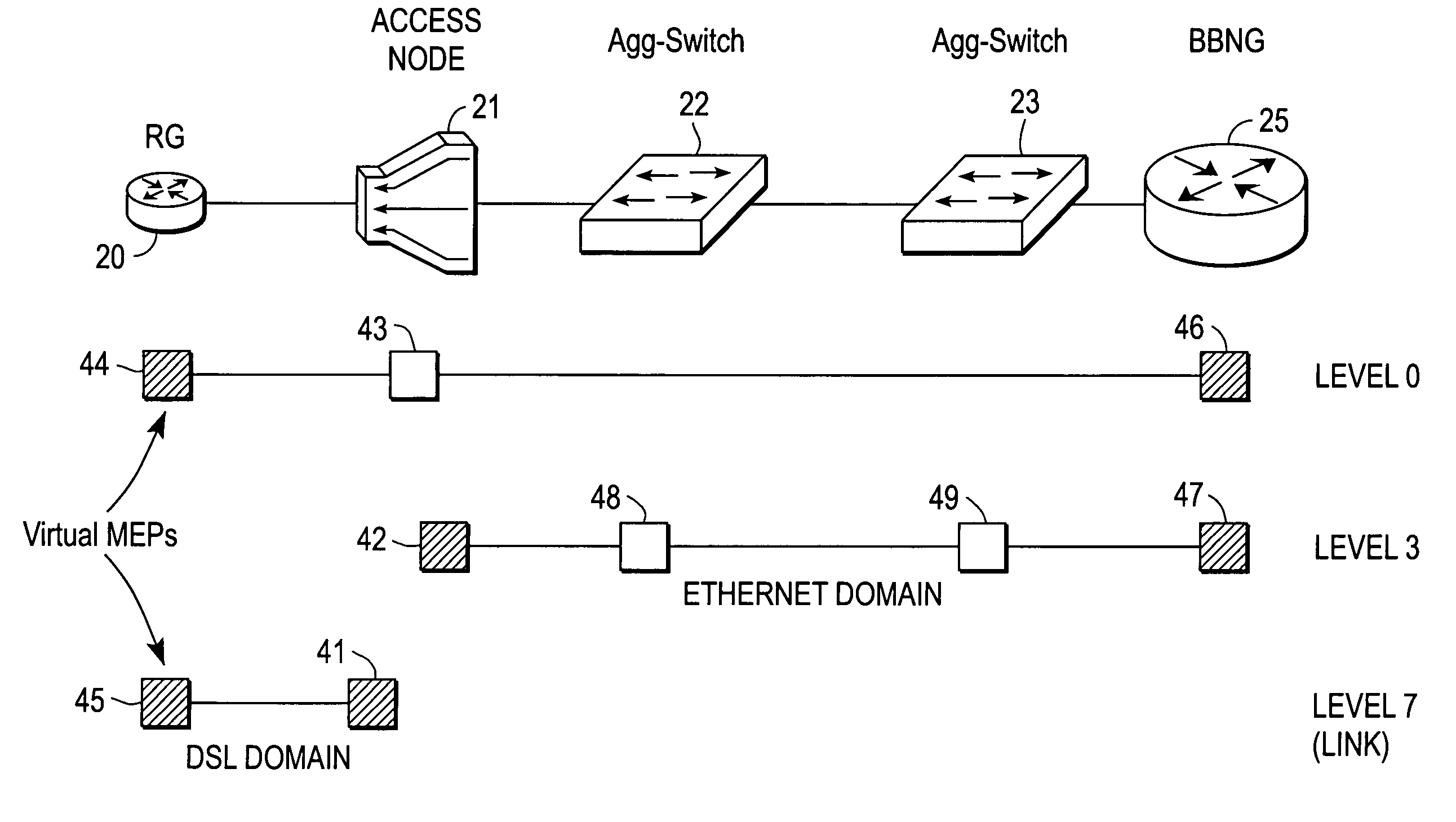
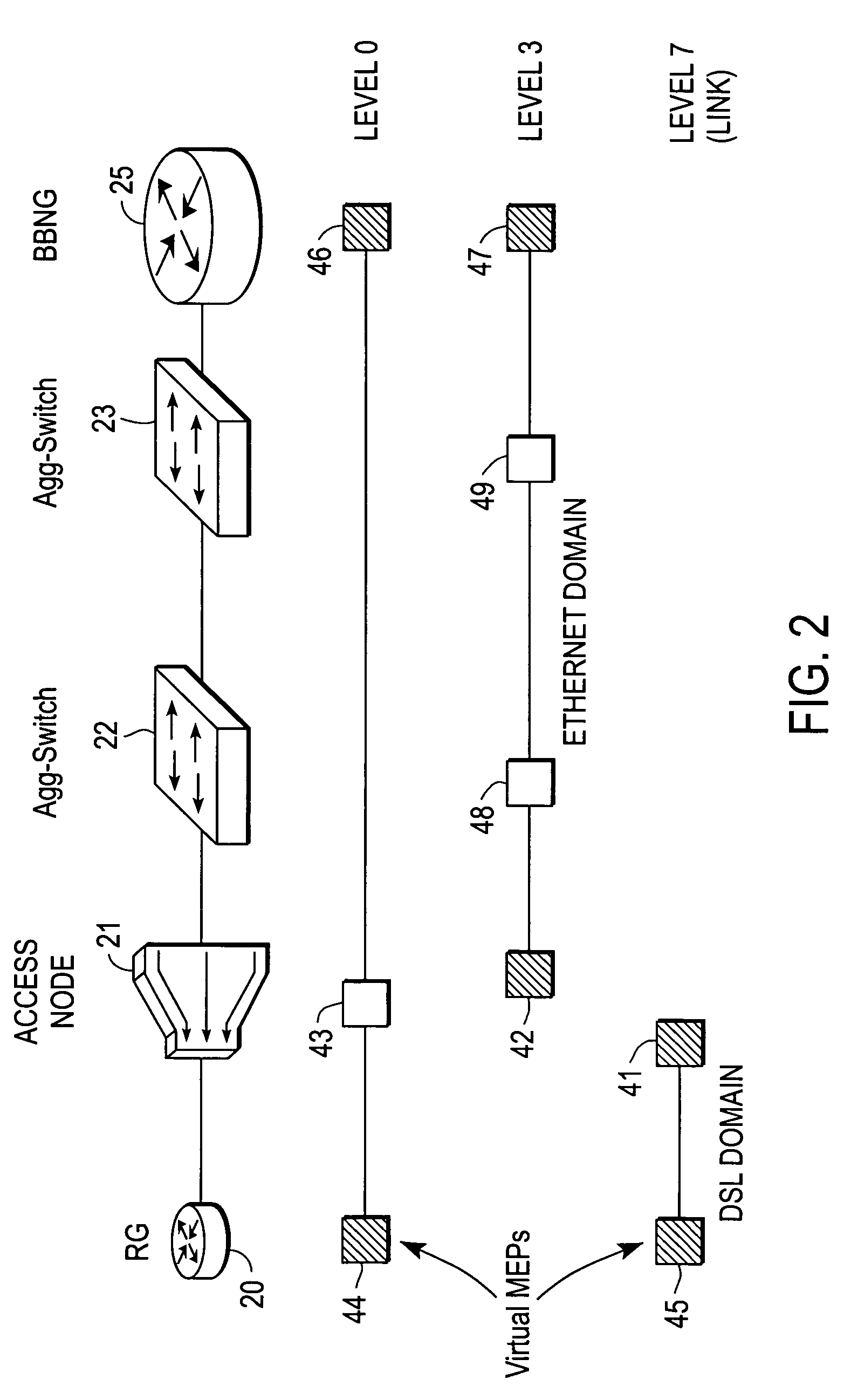
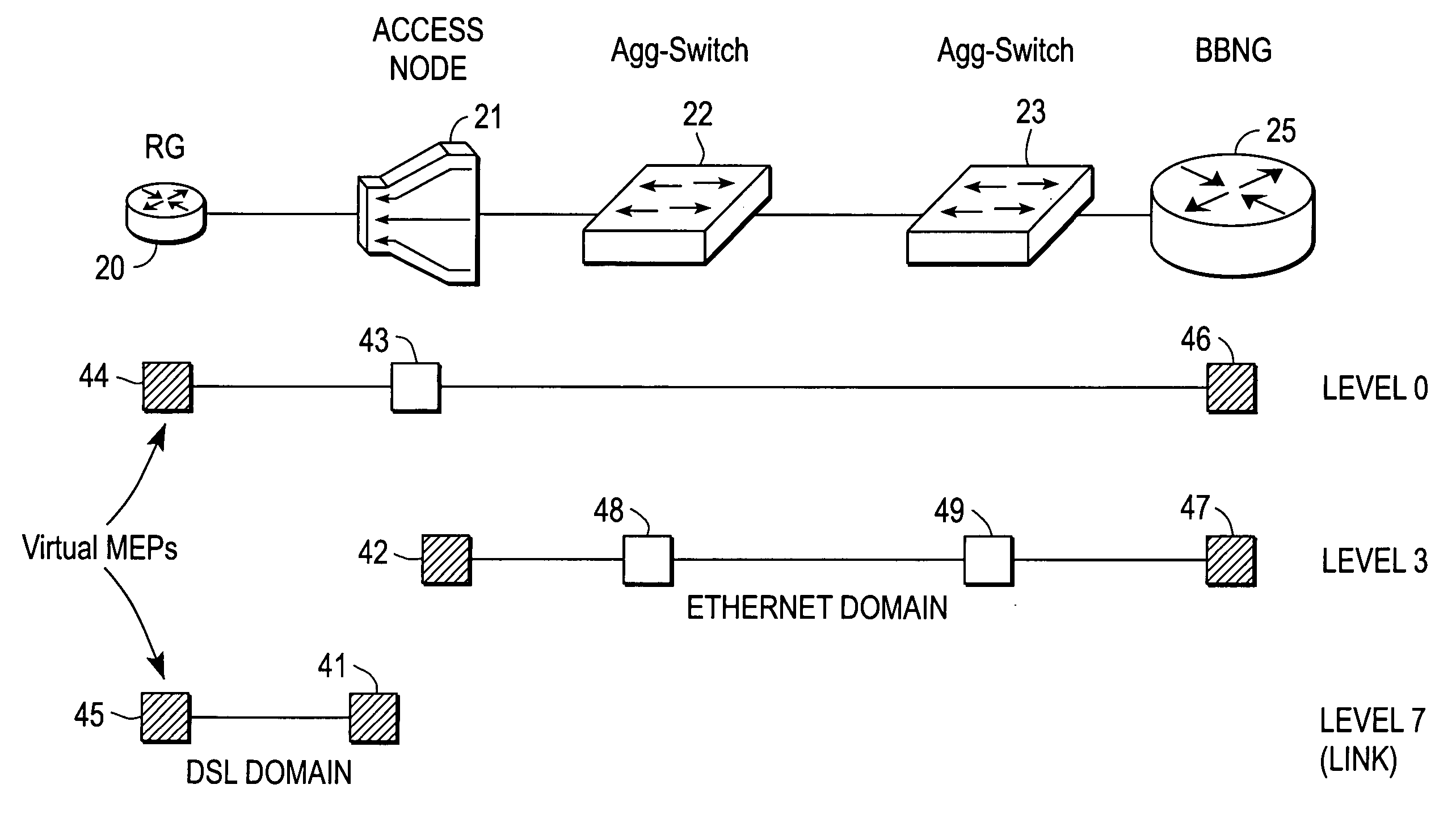
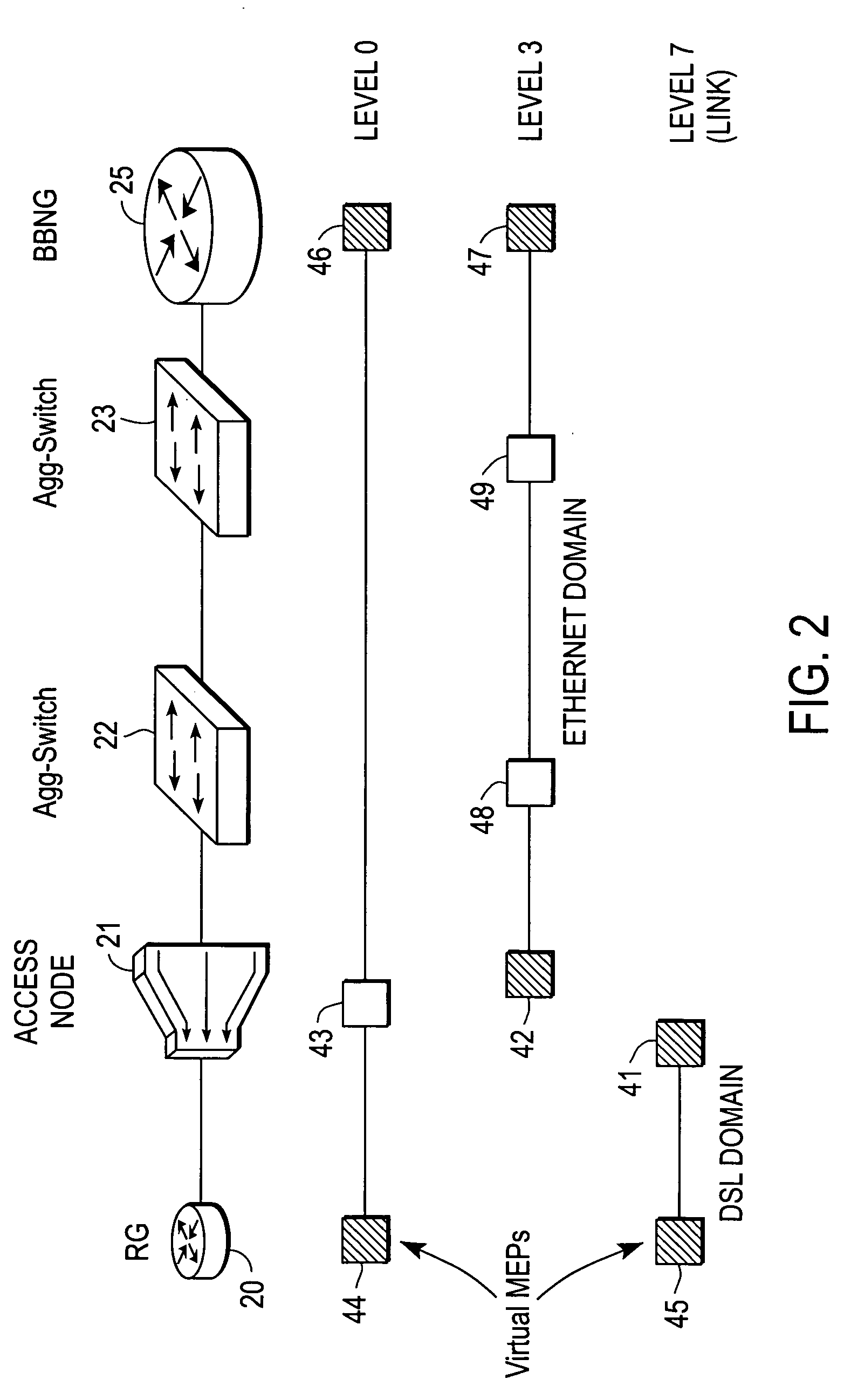
Broadband access note with a virtual maintenance end point
A broadband access node includes a port for connection with a Digital Subscriber Line and a processor to run code that implements a virtual maintenance end point (vMEP). The vMEP translates an IEEE 802.1ag Loopback Message (LBM) received from a device on an Ethernet access network into a legacy operations and maintenance (OAM) message that is transmitted to a residential gateway (RG) device. The legacy OAM message determines a link-level connectivity status between broadband access node and the RG device. The vMEP also transmits a reply message back to the device on an Ethernet access network in compliance with the IEEE 802.1ag specification. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
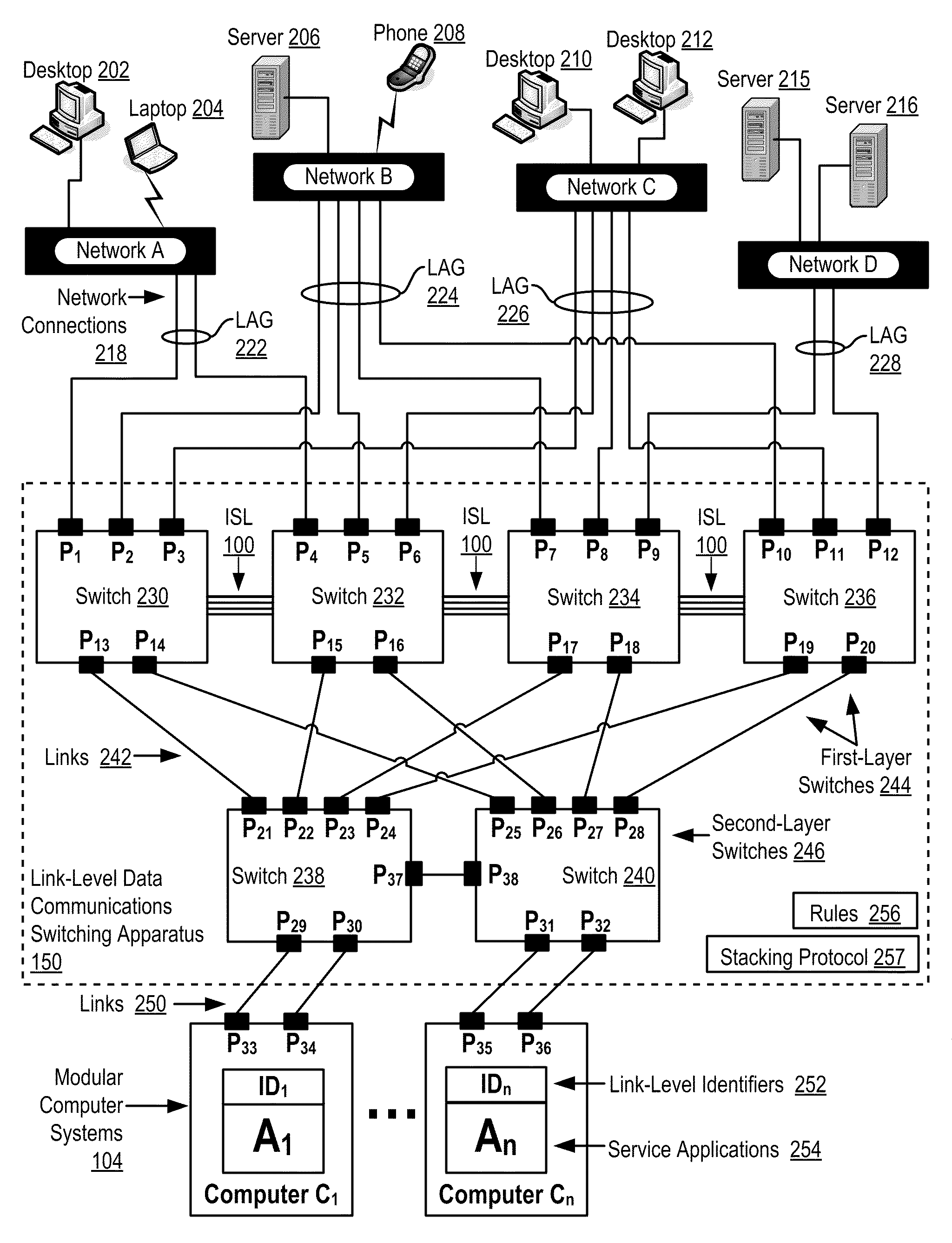
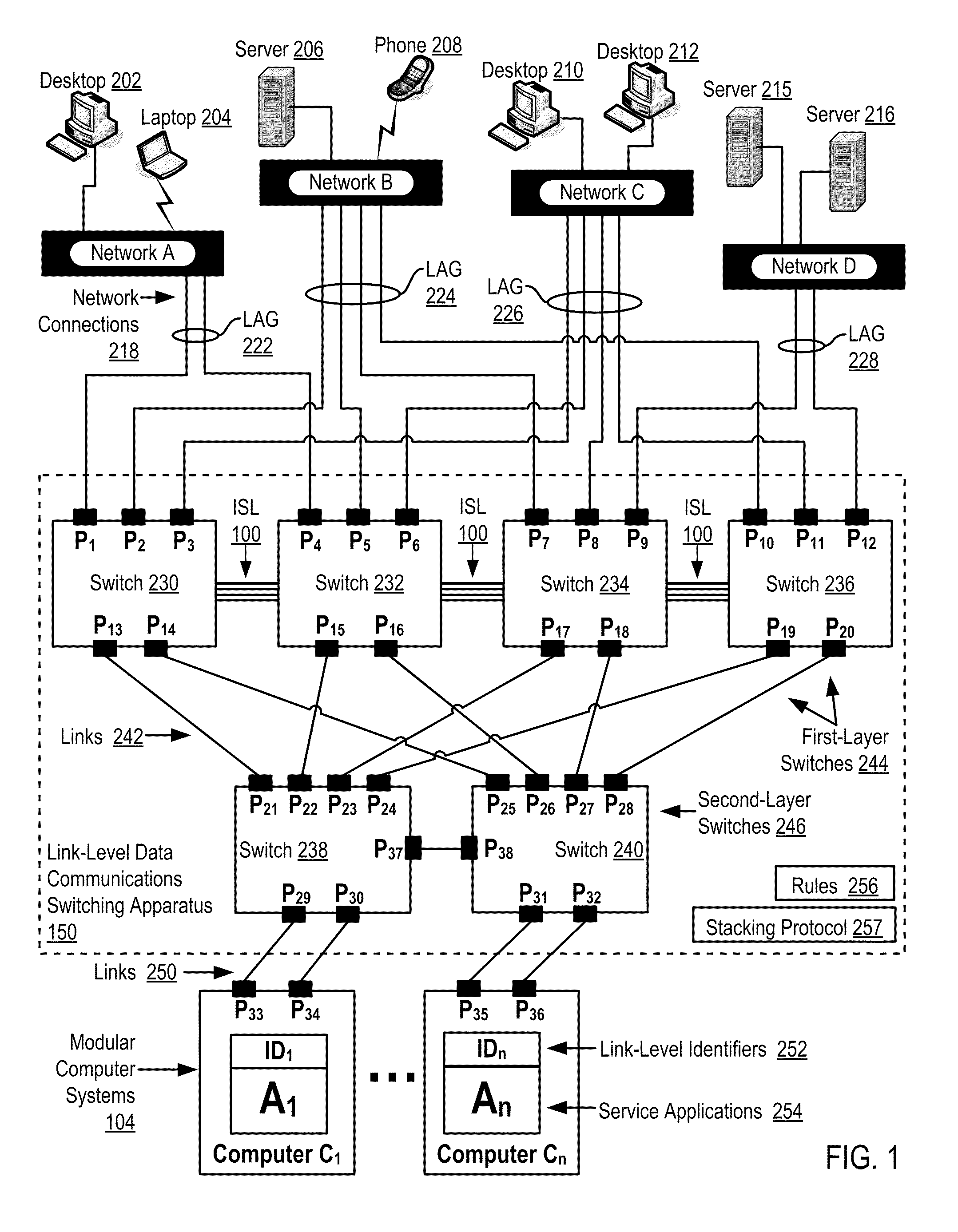
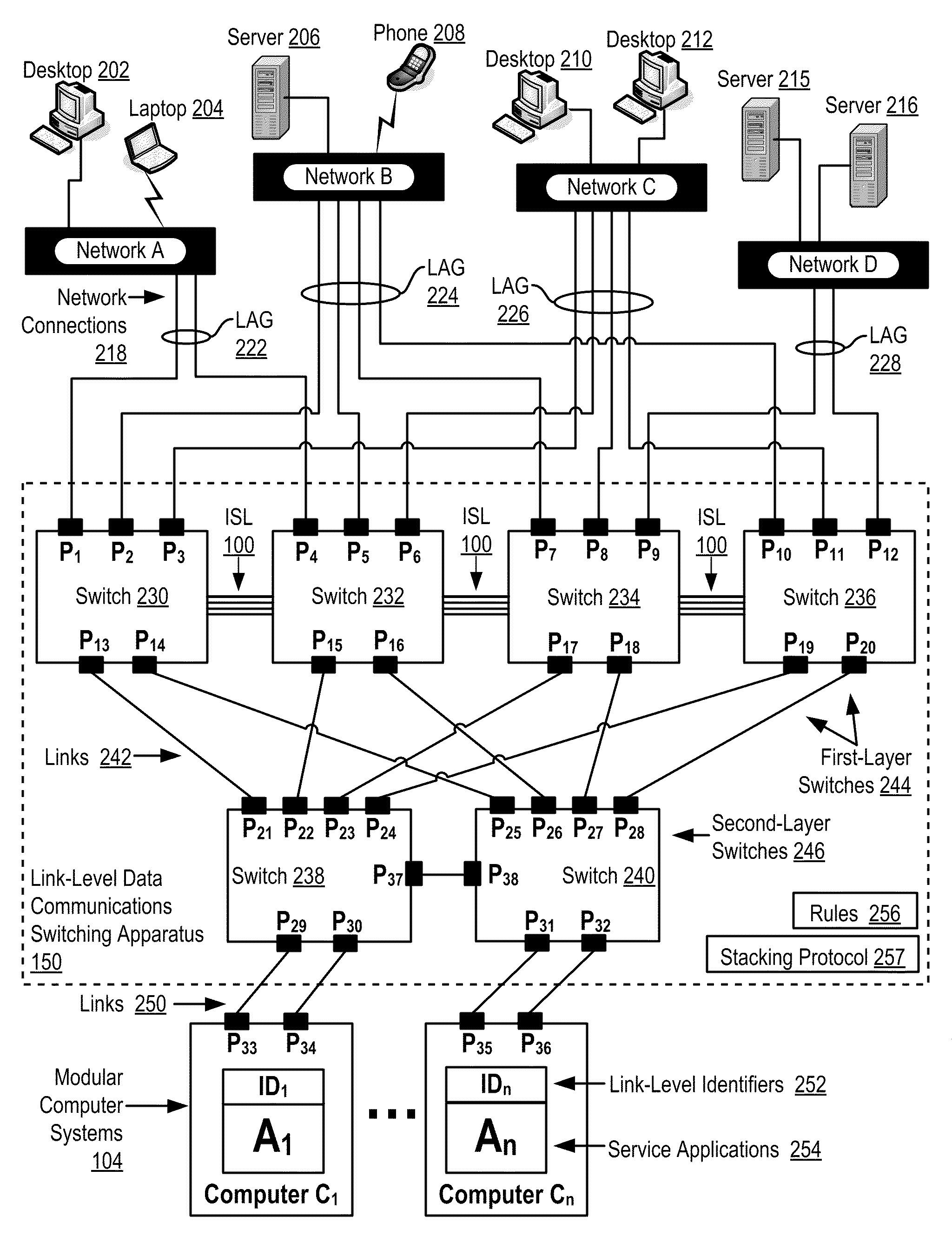
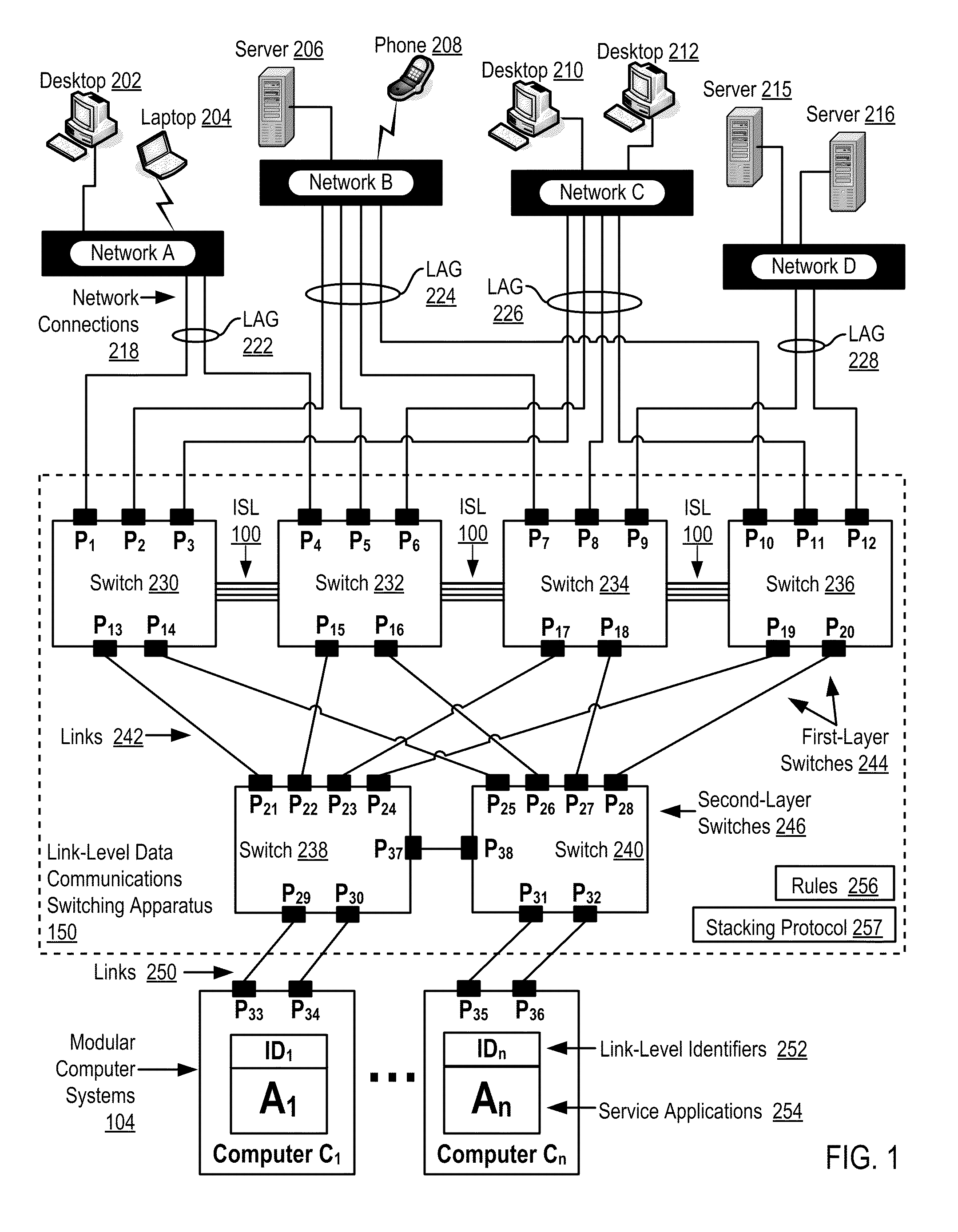
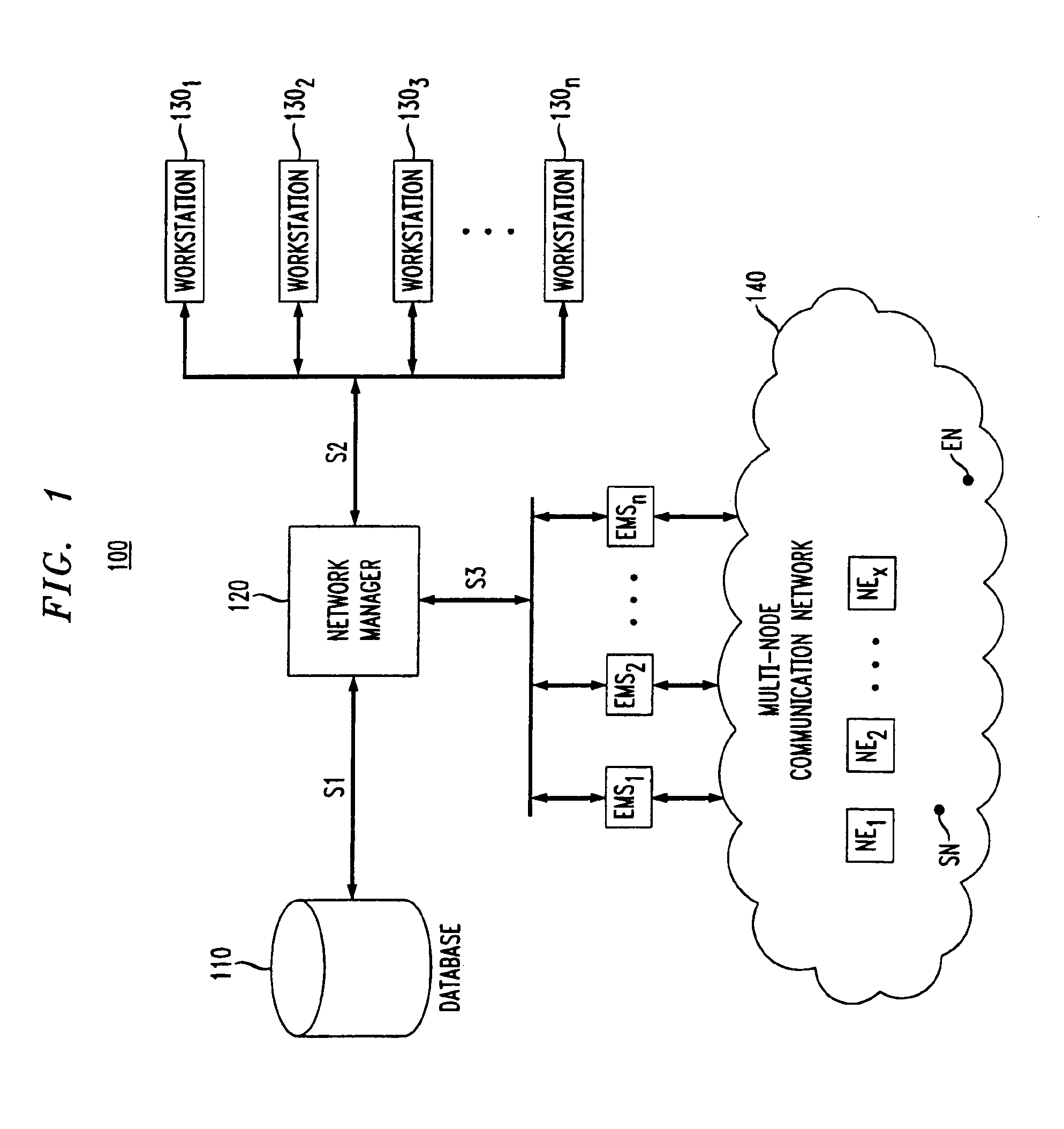
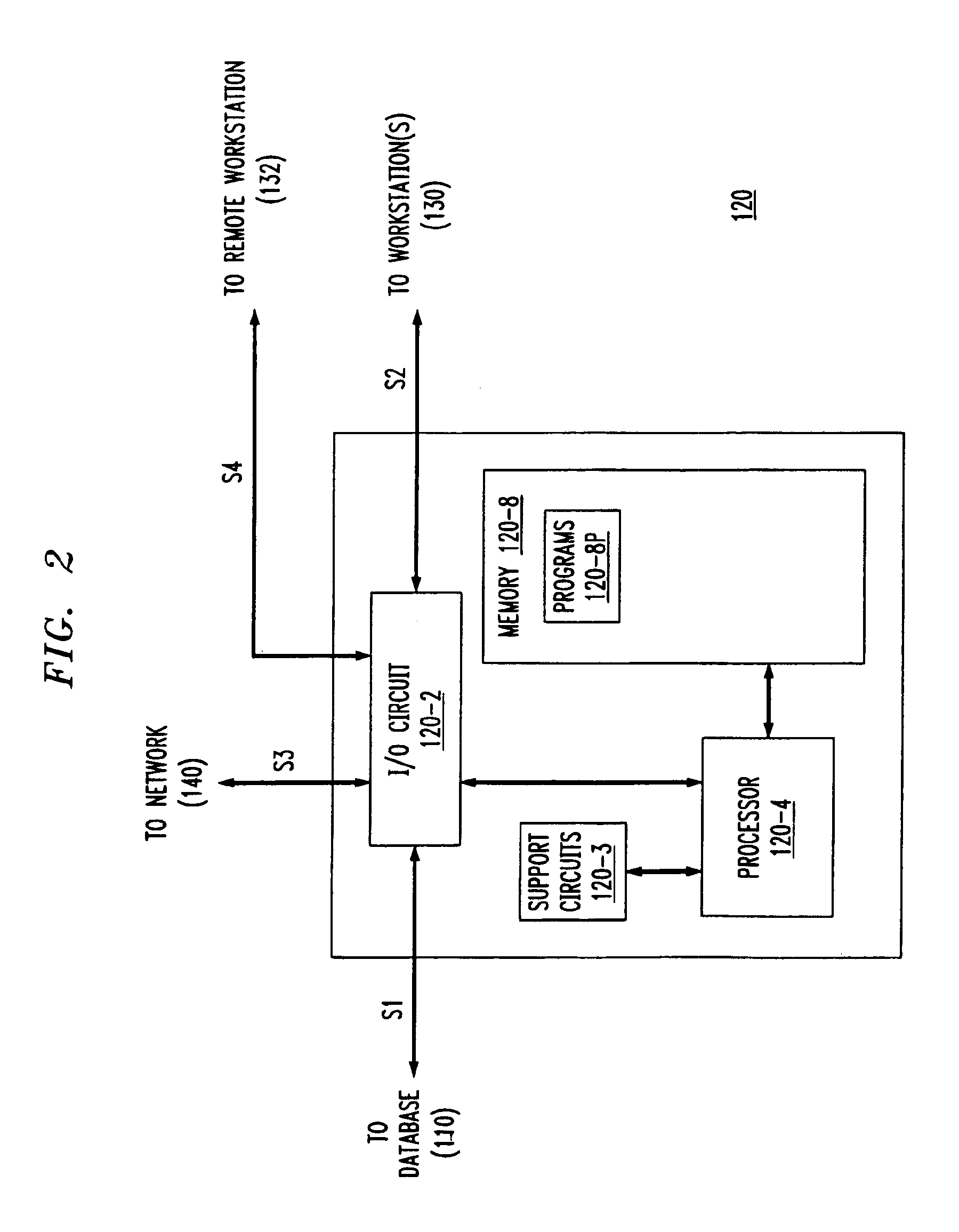
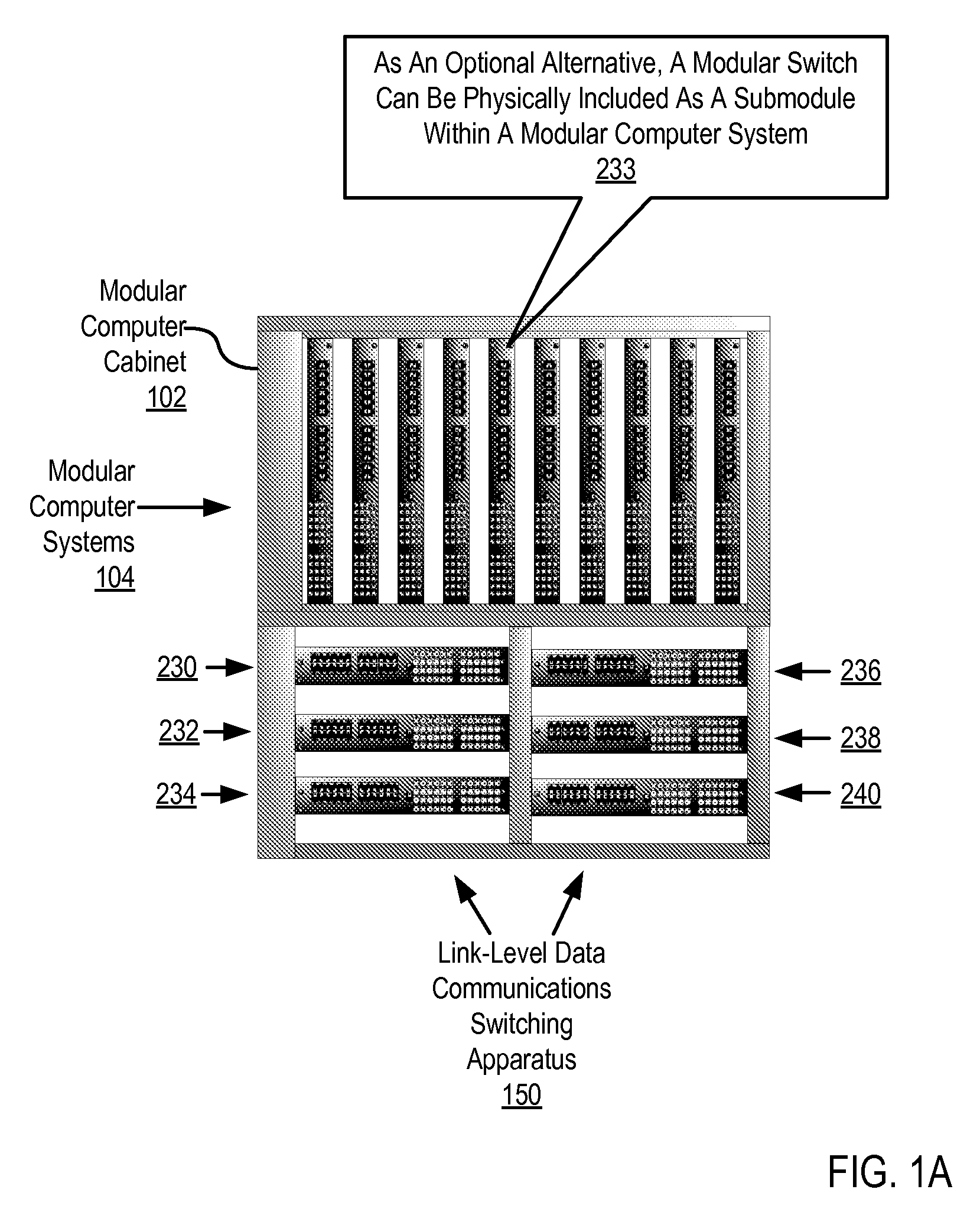
Two-Layer Switch Apparatus To Avoid First Layer Inter-Switch Link Data Traffic In Steering Packets Through Bump-In-The-Wire Service Applications
Link-level data communications carried out in a link-level data communications switching apparatus that includes modular link-level data communications switches; the switching apparatus is configured as two layers of link-level data communications switches; all the switches stacked by a stacking protocol that shares administrative configuration information among the switches and presents the switches as a single logical switch; the switching apparatus includes data communications ports coupling the switching apparatus to data communications networks and to service applications, each service application associated with a unique, link-level identifier; the switching apparatus includes rules governing the steering of packets among service applications and networks; including receiving, in the switching apparatus, packets directed to a destination network; and steering each packet among the service applications to the destination network in accordance with the rules, without using the link-level identifier of any service application.
Owner:IBM CORP
Two-layer switch apparatus to avoid first layer inter-switch link data traffic in steering packets through bump-in-the-wire service applications
Link-level data communications carried out in a link-level data communications switching apparatus that includes modular link-level data communications switches; the switching apparatus is configured as two layers of link-level data communications switches; all the switches stacked by a stacking protocol that shares administrative configuration information among the switches and presents the switches as a single logical switch; the switching apparatus includes data communications ports coupling the switching apparatus to data communications networks and to service applications, each service application associated with a unique, link-level identifier; the switching apparatus includes rules governing the steering of packets among service applications and networks; including receiving, in the switching apparatus, packets directed to a destination network; and steering each packet among the service applications to the destination network in accordance with the rules, without using the link-level identifier of any service application.
Owner:IBM CORP
Broadband access node with a virtual maintenance end point
A broadband access node includes a port for connection with a Digital Subscriber Line and a processor to run code that implements a virtual maintenance end point (vMEP). The vMEP translates an IEEE 802.1ag Loopback Message (LBM) received from a device on an Ethernet access network into a legacy operations and maintenance (OAM) message that is transmitted to a residential gateway (RG) device. The legacy OAM message determines a link-level connectivity status between broadband access node and the RG device. The vMEP also transmits a reply message back to the device on an Ethernet access network in compliance with the IEEE 802.1ag specification. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
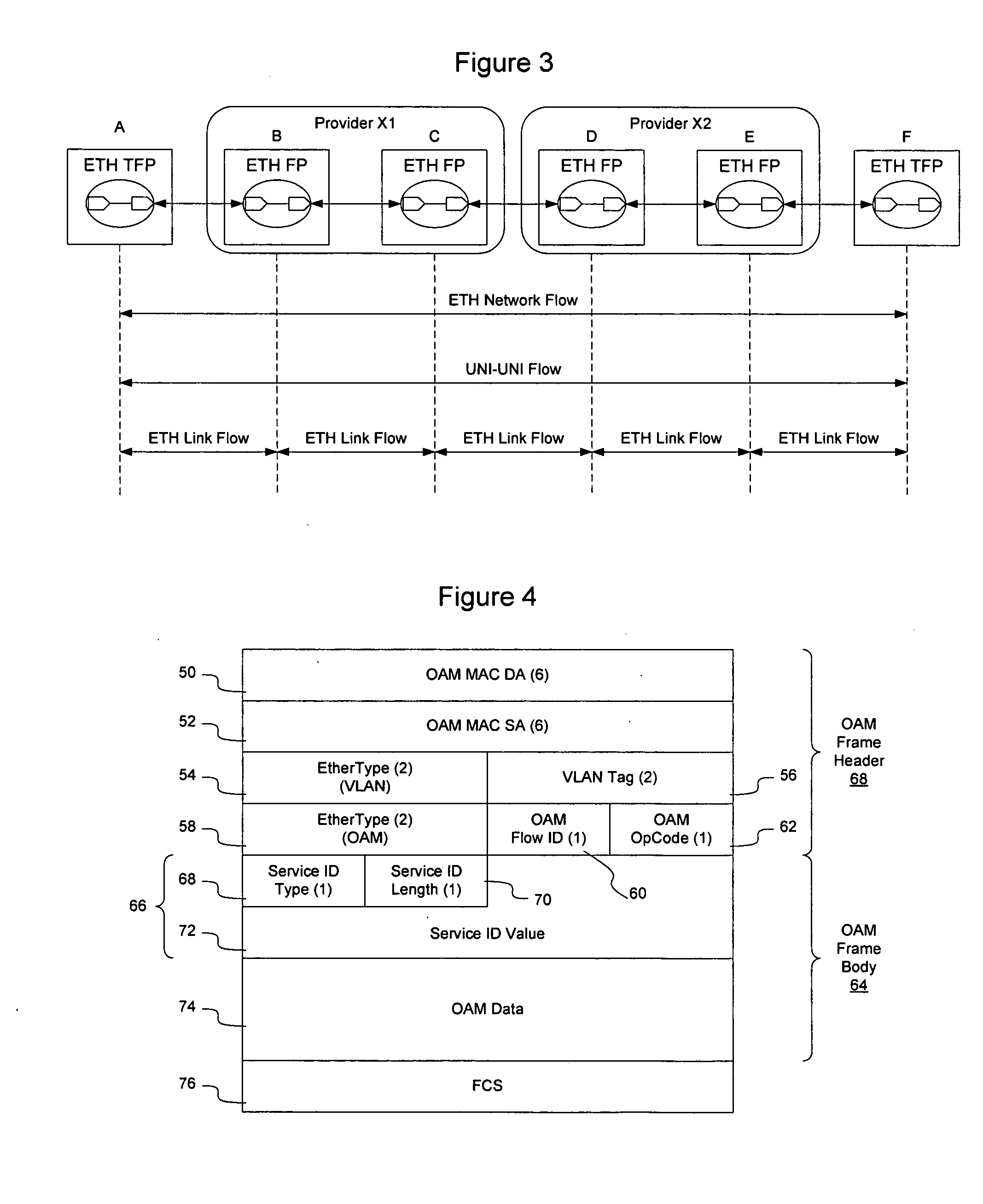
Link-level protection of traffic in a packet-switched network
InactiveUS6901048B1Faster automatic protection switchingLow variabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityAutomatic protection switching
In a packet-switched network having a plurality of nodes interconnected by links, pre-defined protection paths provide protection of a selected plurality of links. Adjacent nodes connected by a protected link are adapted to detect a failure of the protected link, to encapsulate packets within tunnel packets, to differentiate between tunnel packets and non-tunnel packets and to exchange the tunnel packets via a protection path rather than via the failed link. This results in faster automatic protection switching of packet-based traffic. The invention is particularly suited to an Internet Protocol network.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Adaptive communication protocol for wireless networks
InactiveUS7184413B2Network topologiesTime-division multiplexWireless mesh networkNetwork Communication Protocols
A communication protocol that provides link-level and media access control (MAC) level functions for wireless (e.g., ad-hoc) networks and is robust to mobility or other dynamics, and for scaling to dense networks. In a mobile or otherwise dynamic network, any control-packet collisions will be only temporary and fair. In a dense network, the network performance degrades gracefully, ensuring that only a certain percentage of the common channel is consumed with control packets. The integrated protocol allows packets (e.g., data scheduling control packets) to be scheduled in a collision-free and predictable manner (known to all neighbors), multicast packets can be reliably scheduled, as well as streams of delay- or delay-jitter-sensitive traffic. Further, using an optional network code, the scheduling of control packets can appear to observers to be randomized.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
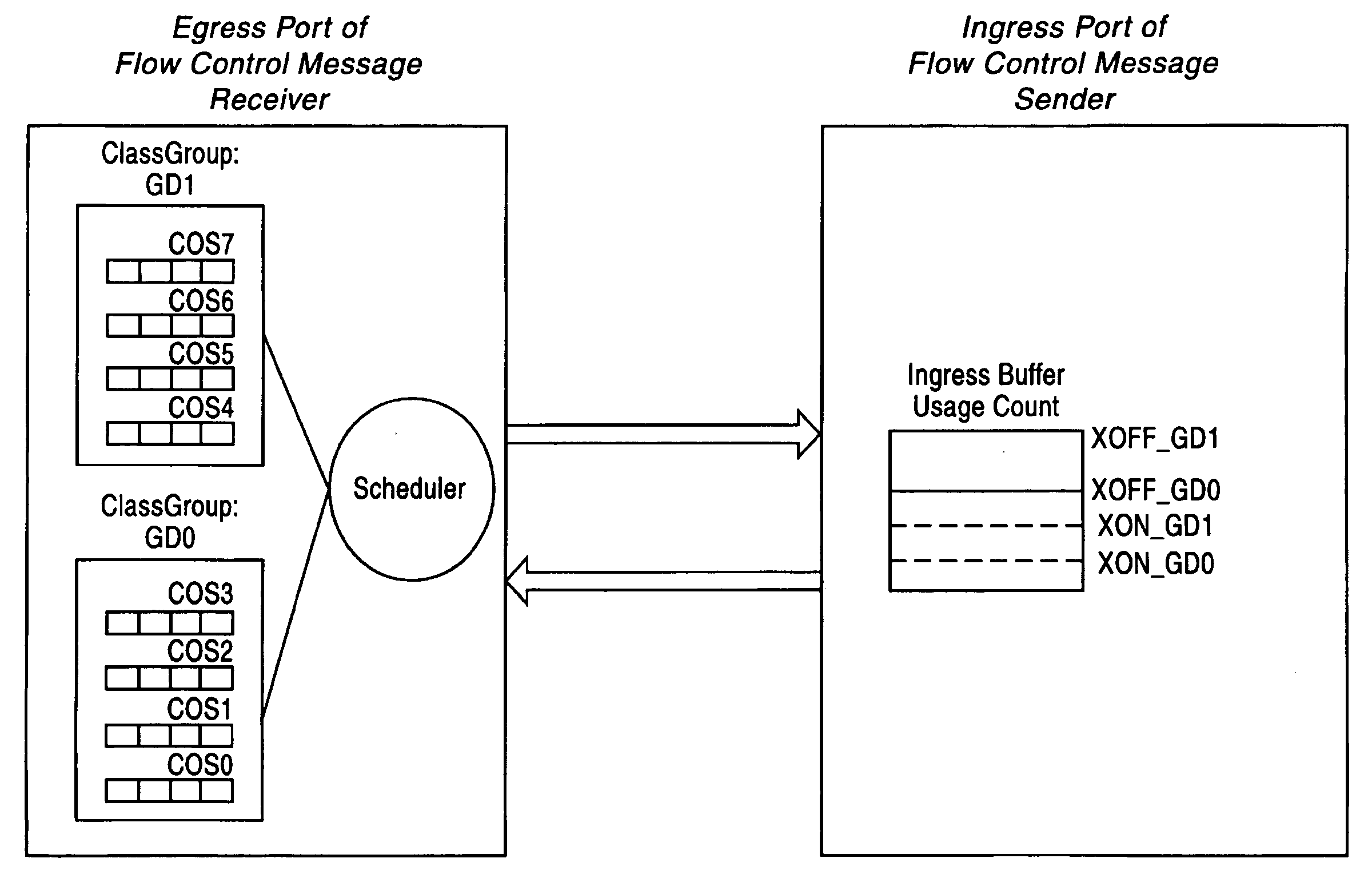
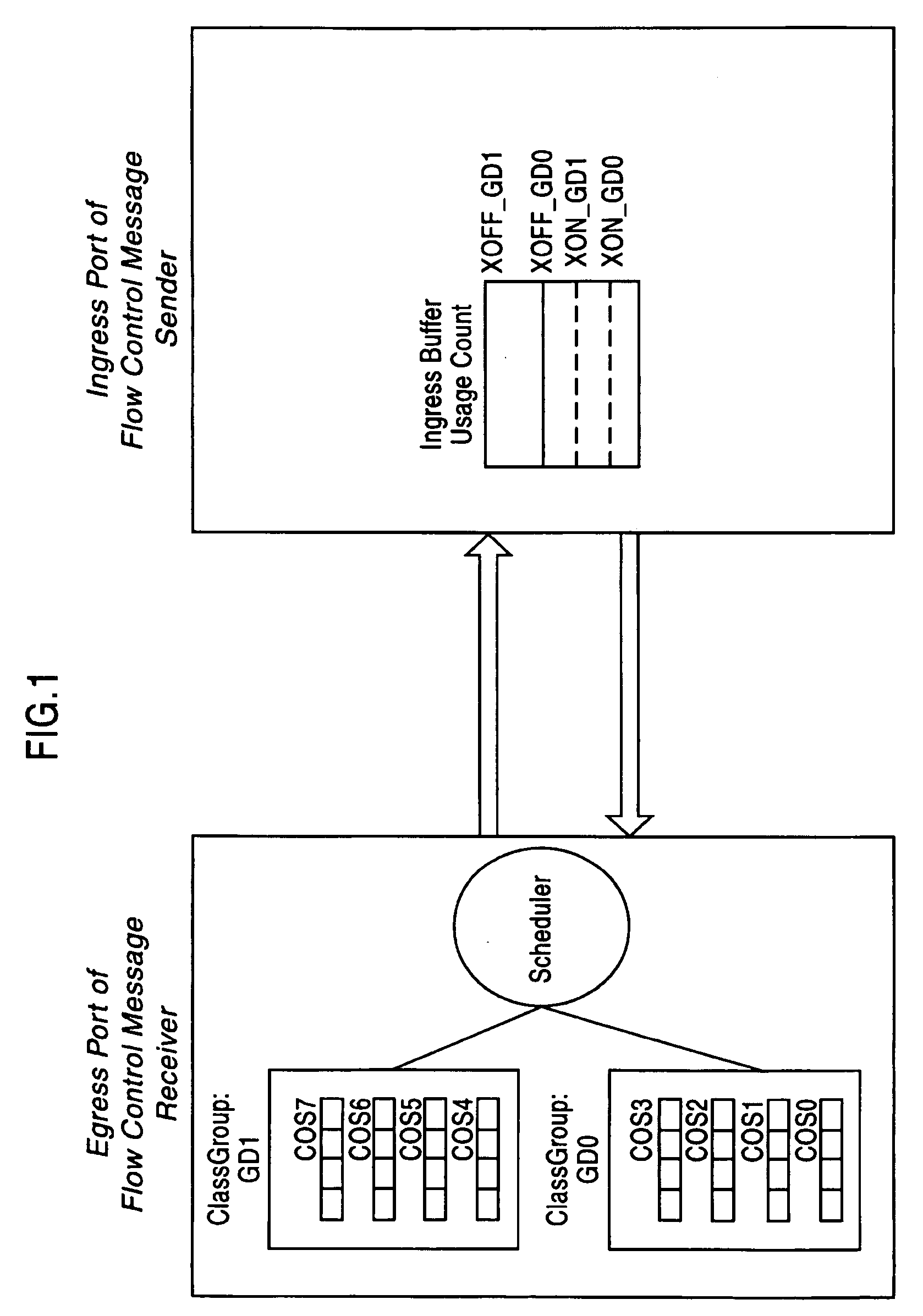
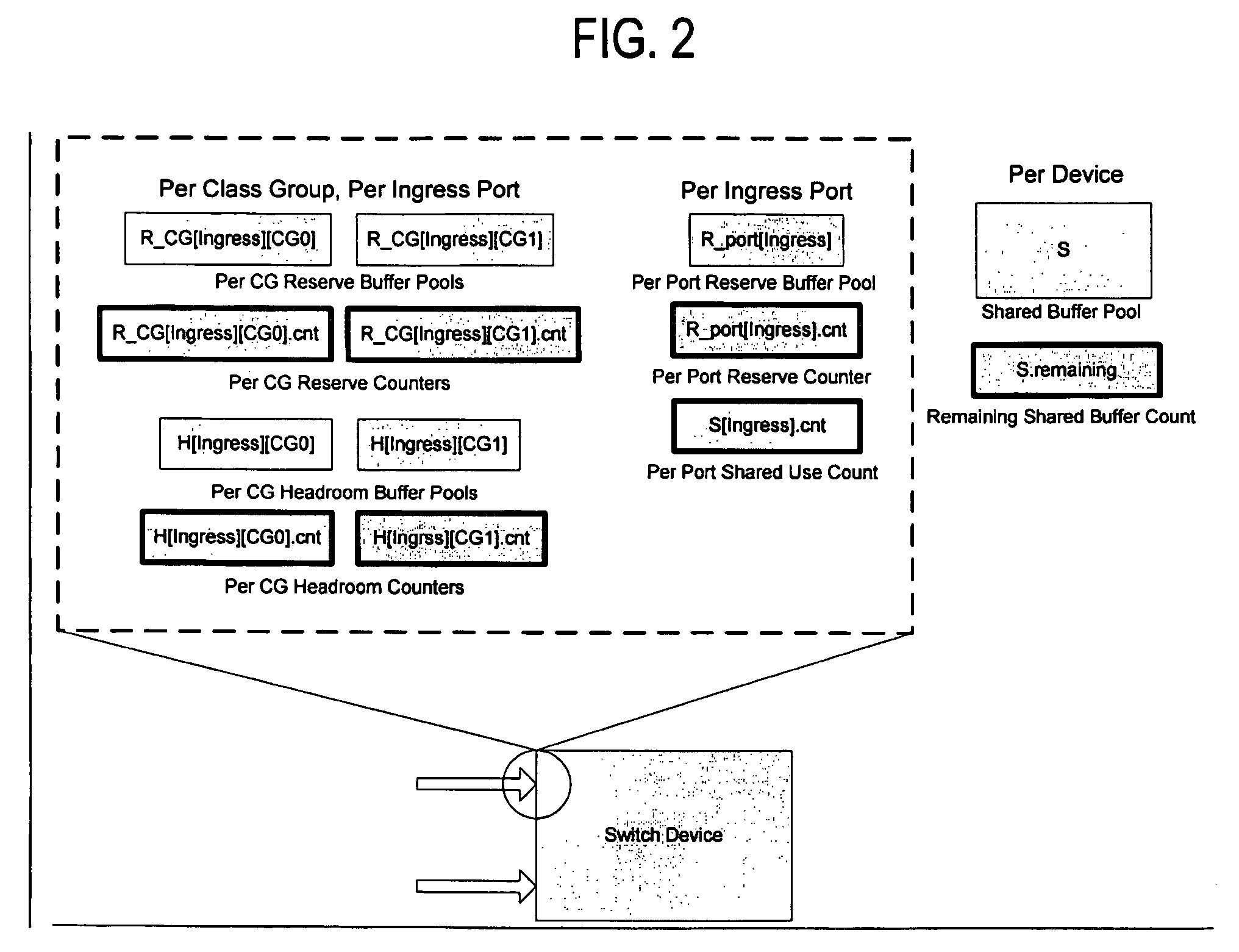
Adaptive dynamic thresholding mechanism for link level flow control scheme
A dynamic threshold apparatus and method are provided including a flow control sender and a flow control receiver. The flow control sender includes an ingress port with one or more Class Groups (CG) defined including a shared buffer pool, a shared counter per ingress port per CG tracking an amount of the shared buffer pool utilized by each CG, an ingress port utilization counter per ingress port tracking an amount of the shared buffer pool utilized by the ingress port, and a controller computing a dynamic threshold for each CG, comparing the dynamic threshold of each CG with the ingress port utilization counter, and determining a particular CG experiencing congestion when the ingress port utilization counter is greater than the dynamic threshold for the particular CG. The flow control receiver ceases transmission of data packets to the particular CG experiencing congestion and allows transmission of the data packets corresponding to other CGs.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
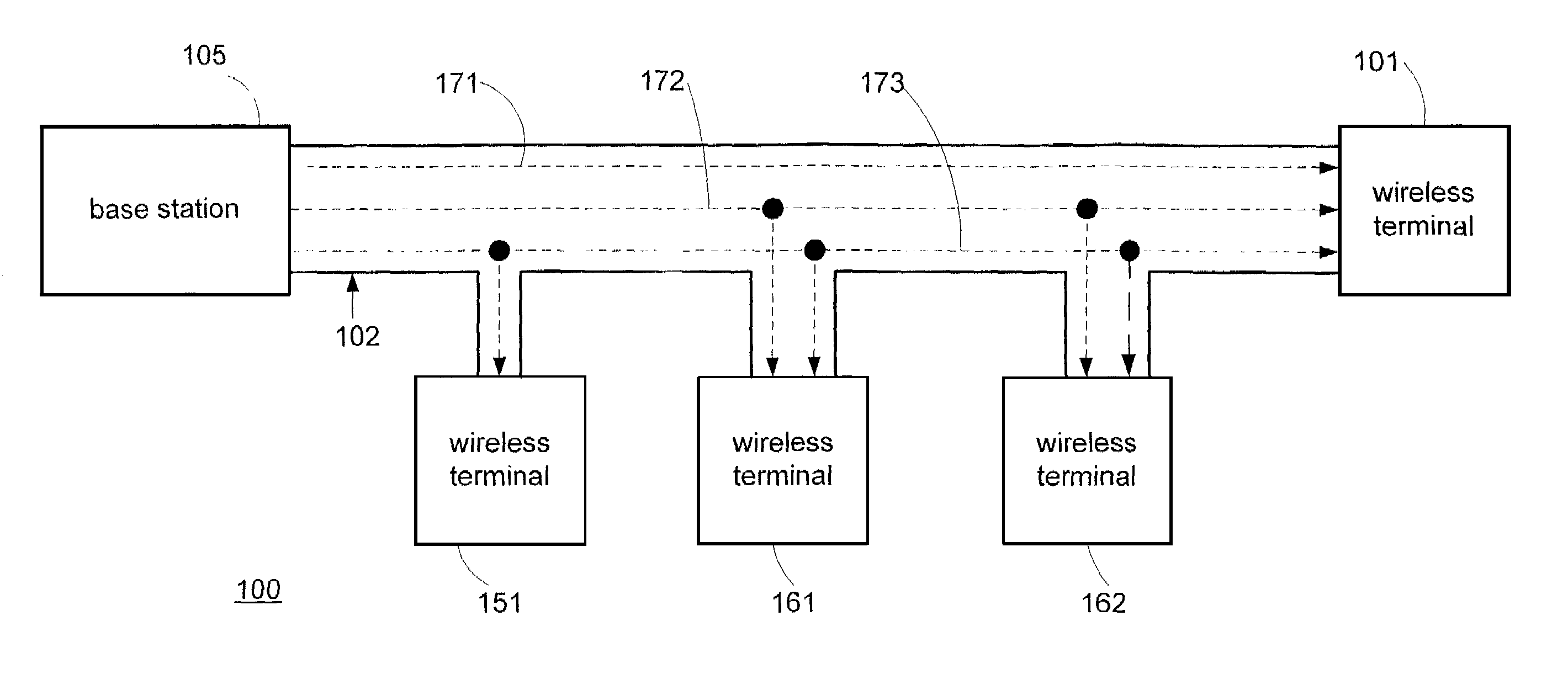
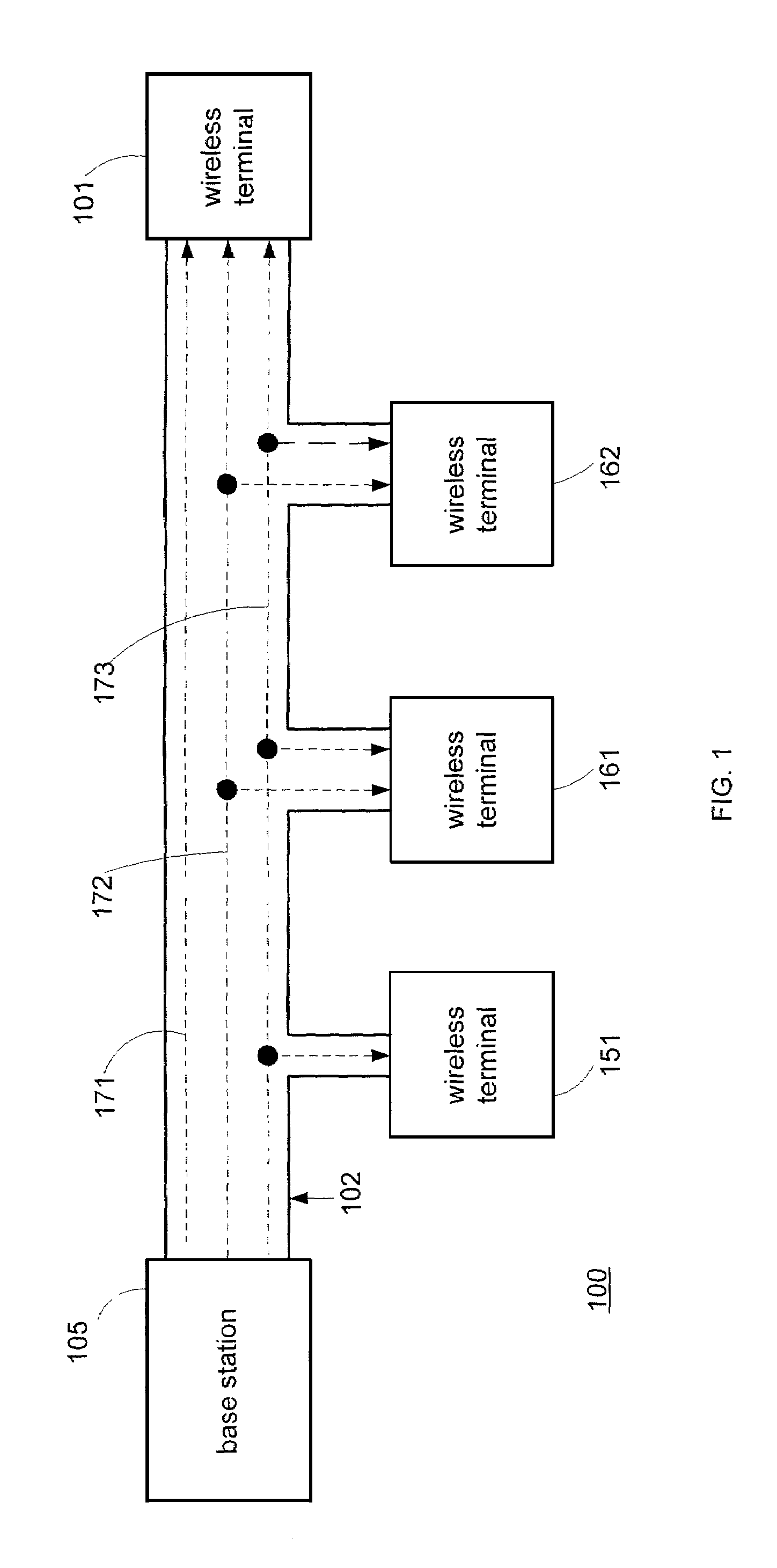
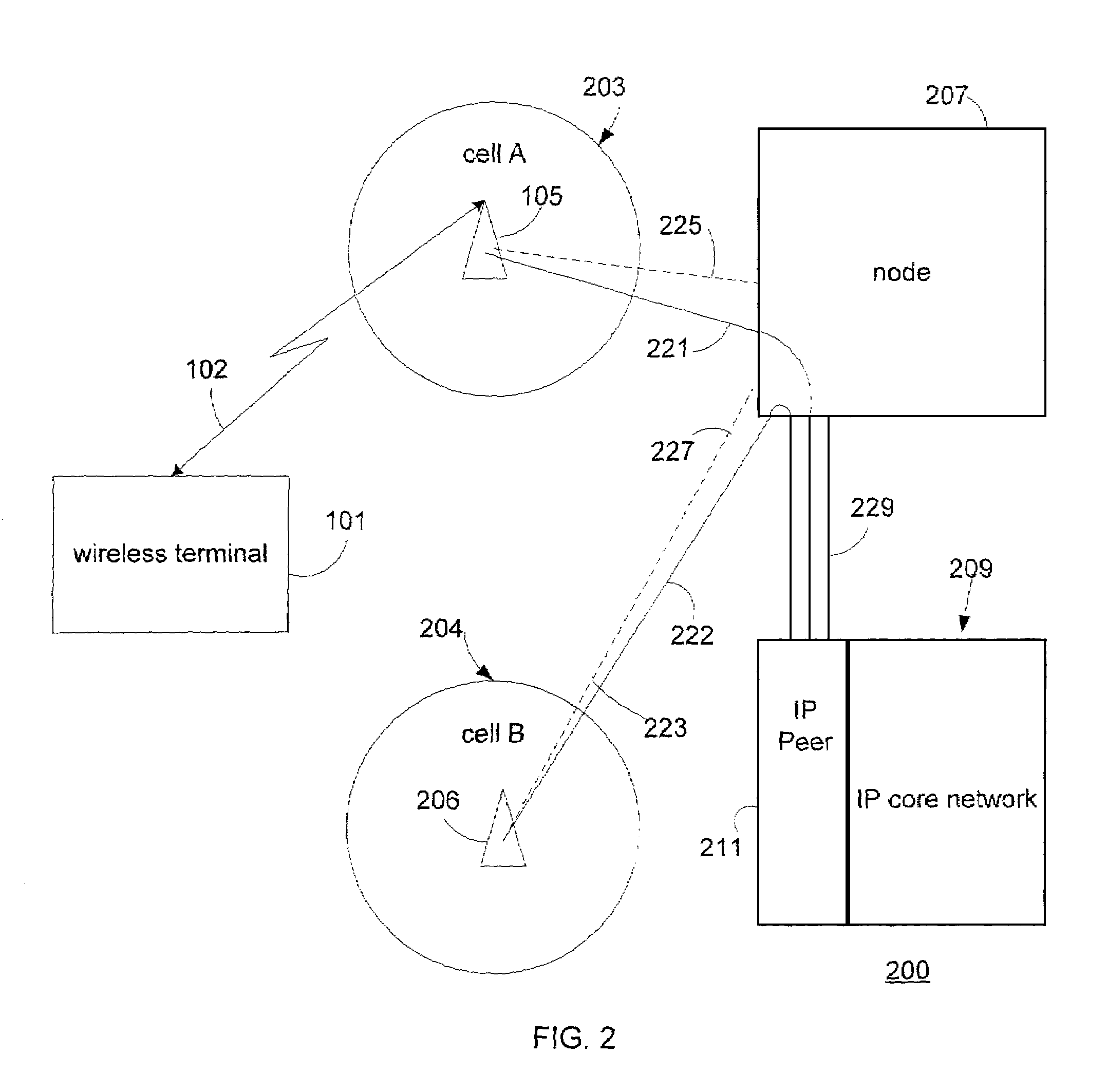
System for rate control of multicast data delivery in a wireless network
ActiveUS7054643B2Optimize networkSpecial service provision for substationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorMulticast addressData rate
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for transmitting multicast data over a wireless channel. At least one wireless terminal requests a multicast service corresponding to at least one requested layer. A wireless infrastructure comprising a base station and a node determines a data rate that the at least one wireless terminal can receive reliably and correspondingly configures a multicast session for at least one layer. The node utilizes measurements provided by the wireless terminal. The node through the base station signals the wireless terminal about a link-level multicast address corresponding to a time slot for which the wireless terminal shall process packets. An associated point of attachment with a core data network controls a data flow from a multicast content source through the core data network in order to match the data rate over the wireless channel.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
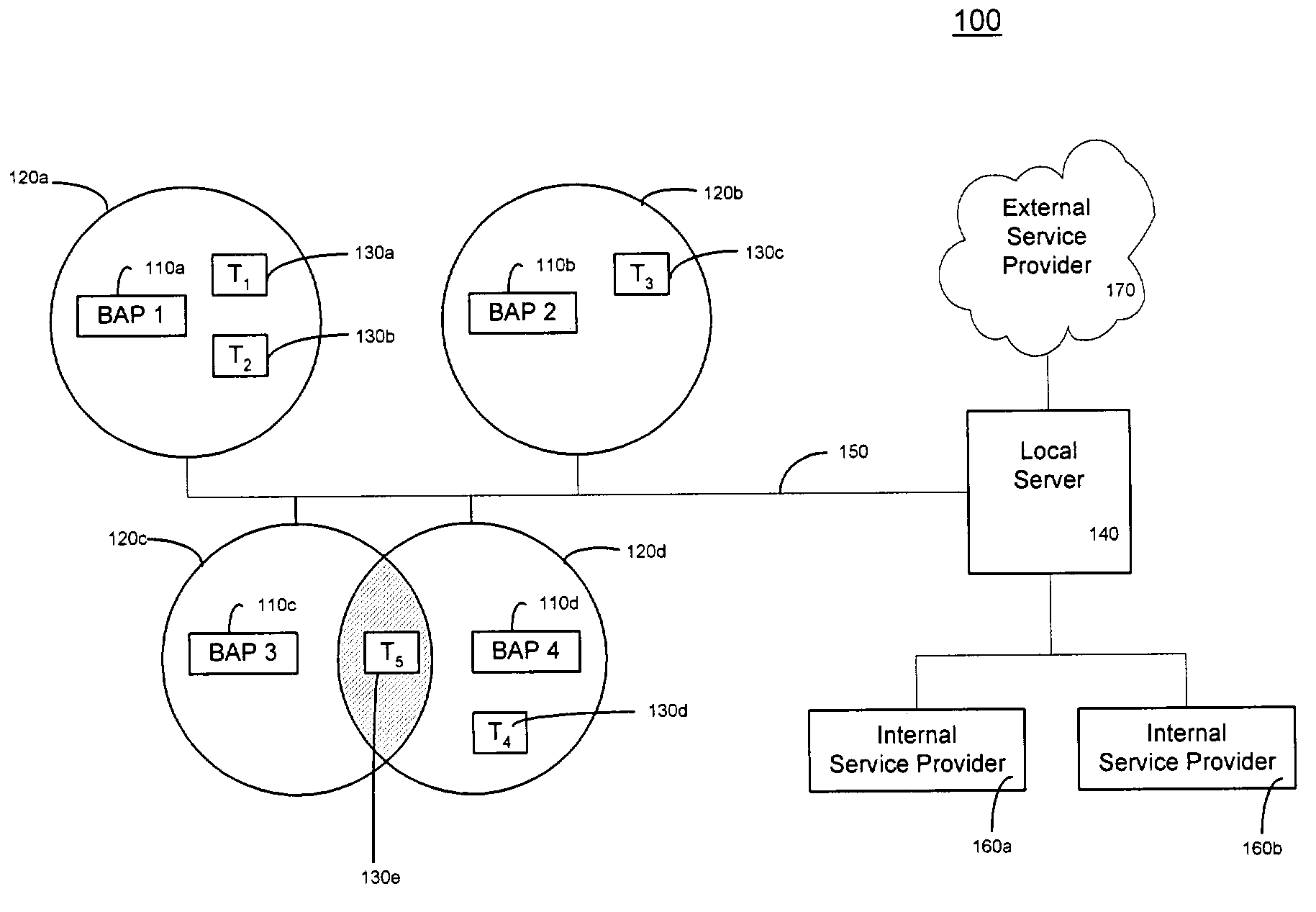
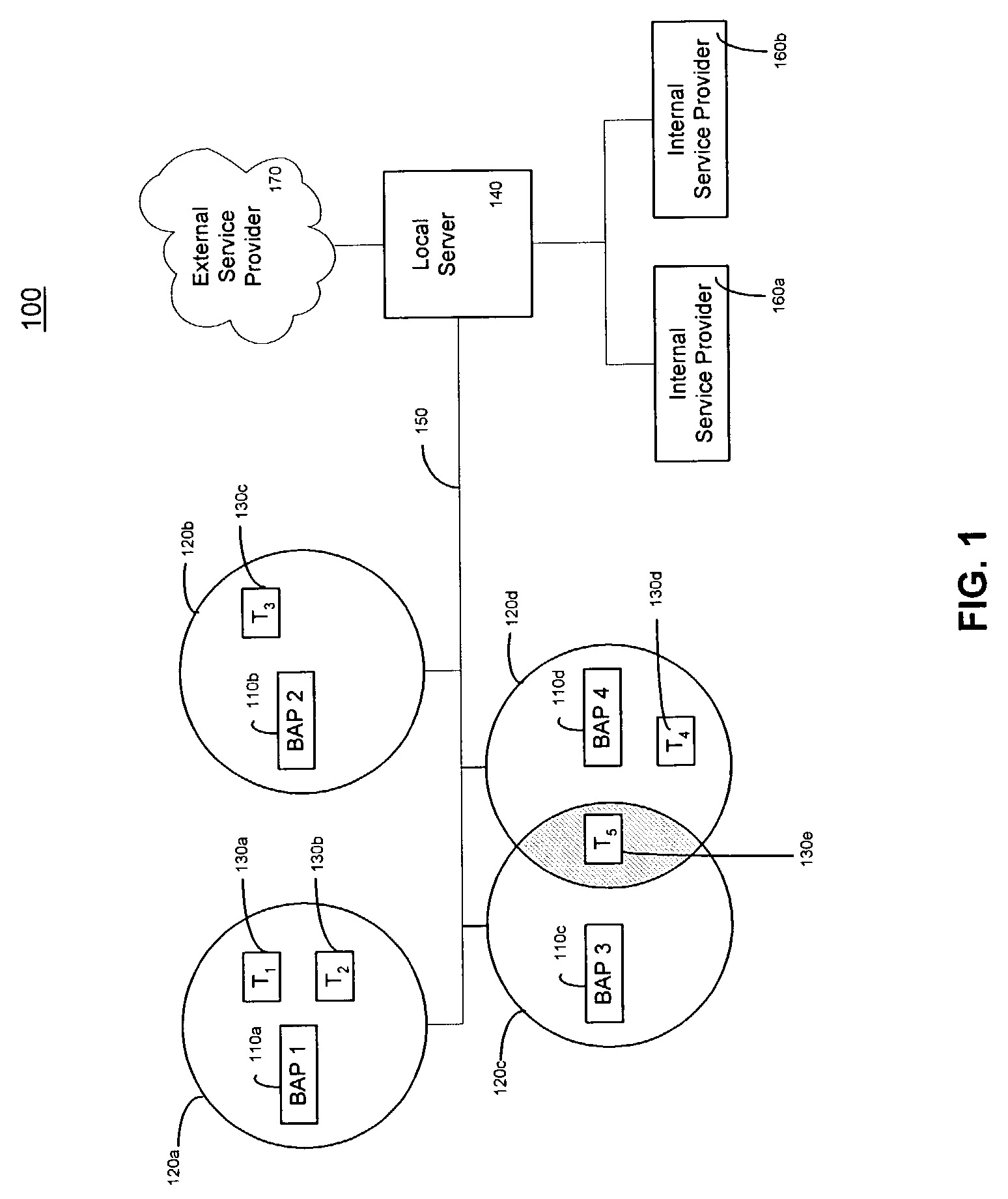
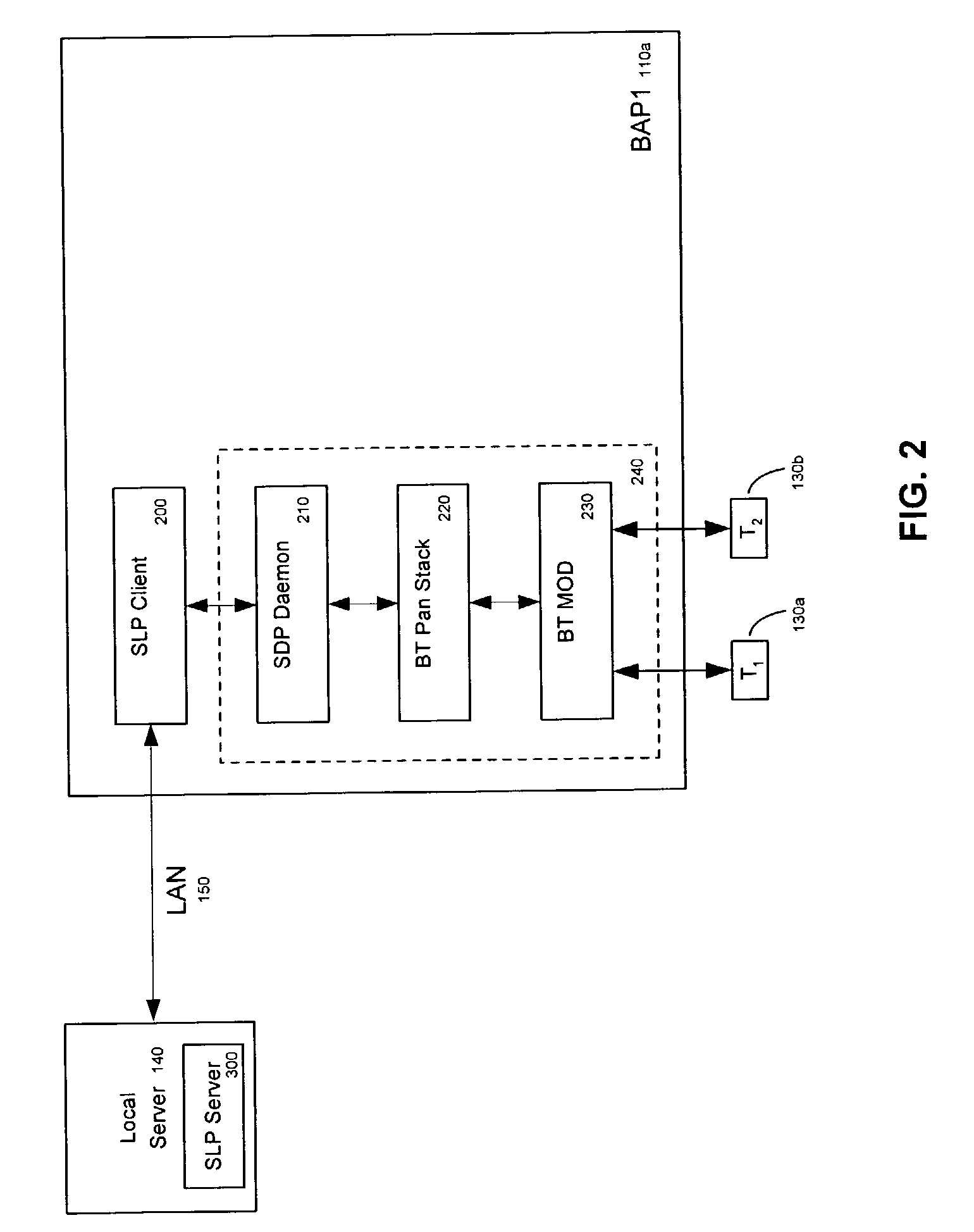
Automatic and dynamic service information delivery from service providers to data terminals in an access point network
InactiveUS7379958B2Reduce needMultiple digital computer combinationsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsData terminalAccess network
A system and method for dynamically updating service information from a service provider to a data terminal in an access point network wherein an access point requests service information from a local server; in response, the access point receives service information from the local server. Subsequently, the access point maps the service information to a link-level communication Service Discovery Protocol (SDP). The access point then sends the mapped service information to a data terminal.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Peer-to-peer communication method for near field communication
ActiveUS20080065877A1Stricter securityNear-field transmissionRadio transmissionPeer-to-peerPeer communication
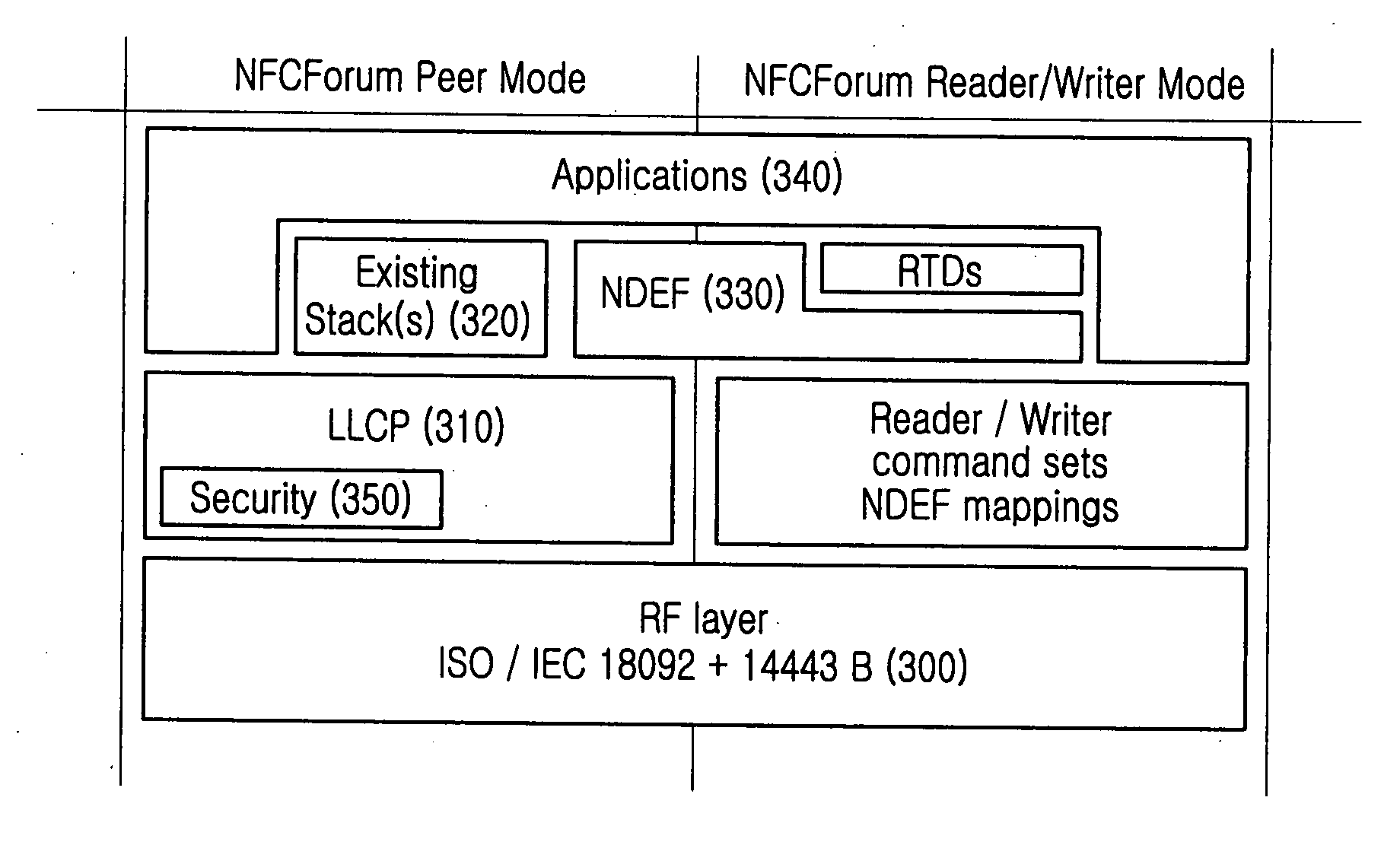
A peer-to-peer communication method for NFC is provided. A link-level security is started by exchanging a link-level security request and a link-level security response between an initiator terminal and a target terminal, then transmission data are encrypted at link-level security layers of the initiator terminal and the target terminal, and the encrypted data are exchanged between the initiator terminal and the target terminal. The link-level security is released by exchanging a link-level security release request and a link-level security release response between the initiator terminal and the target terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
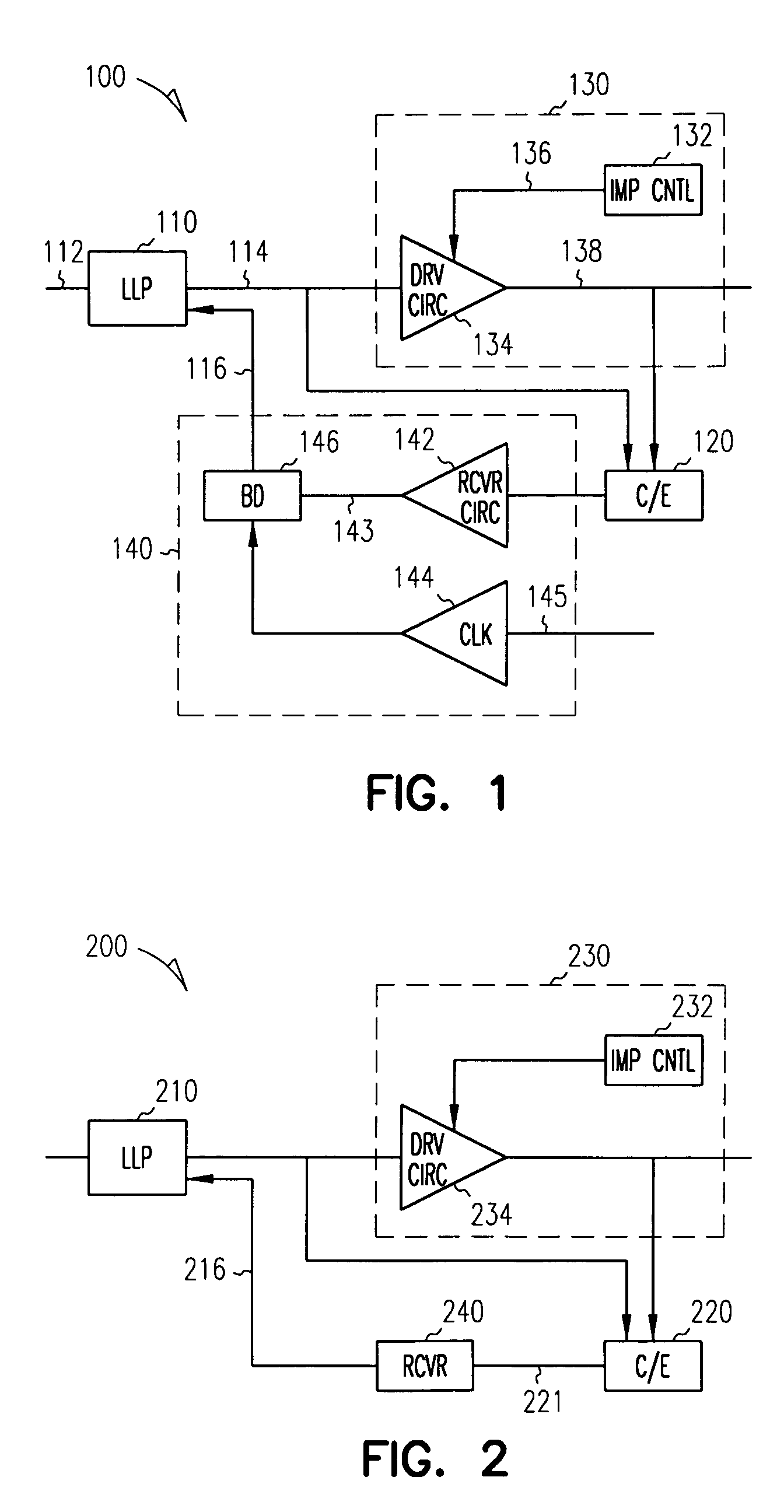
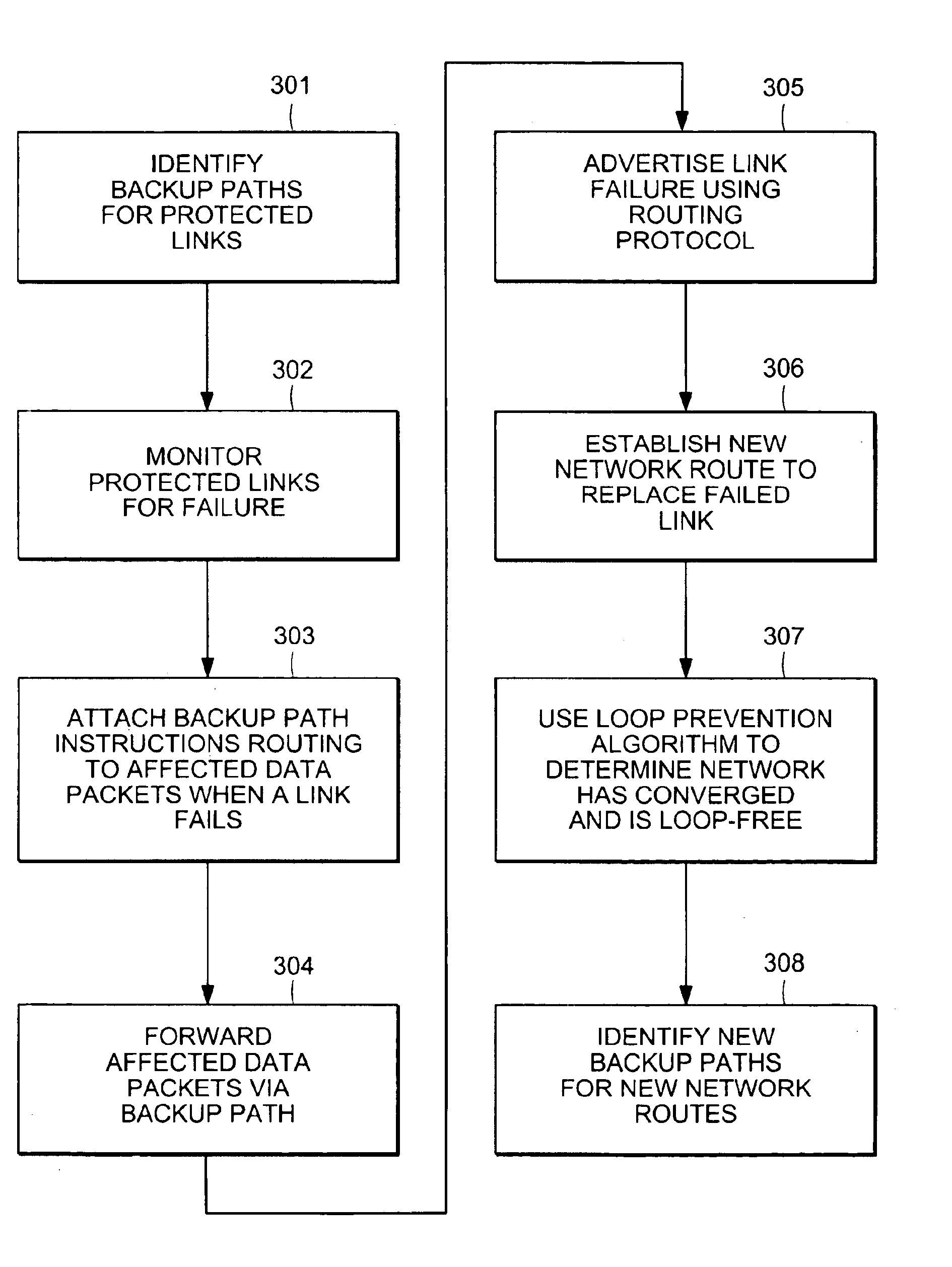
Automatic protection switching using link-level redundancy supporting multi-protocol label switching
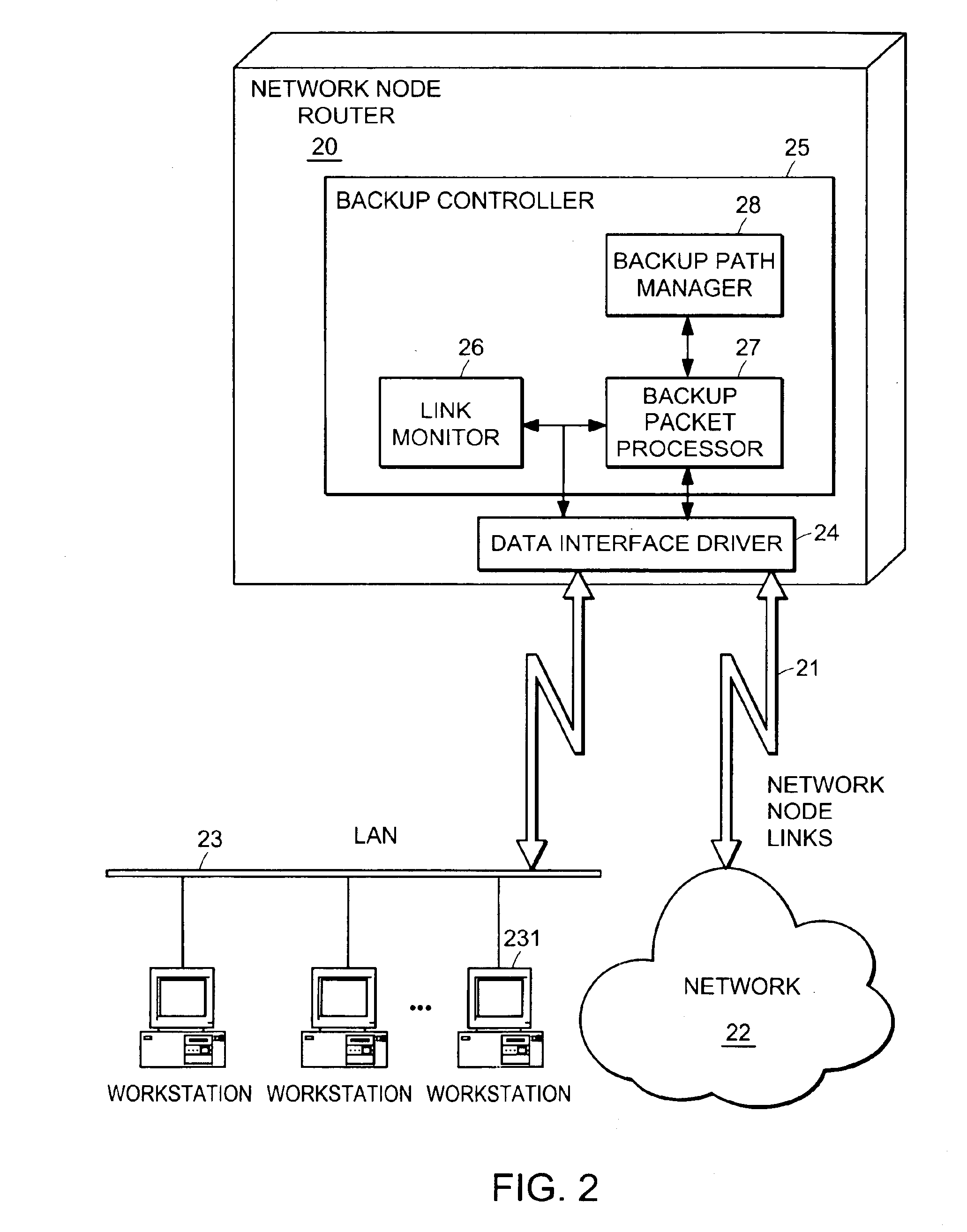
InactiveUS20050265228A1Error preventionTransmission systemsAutomatic protection switchingNetwork packet
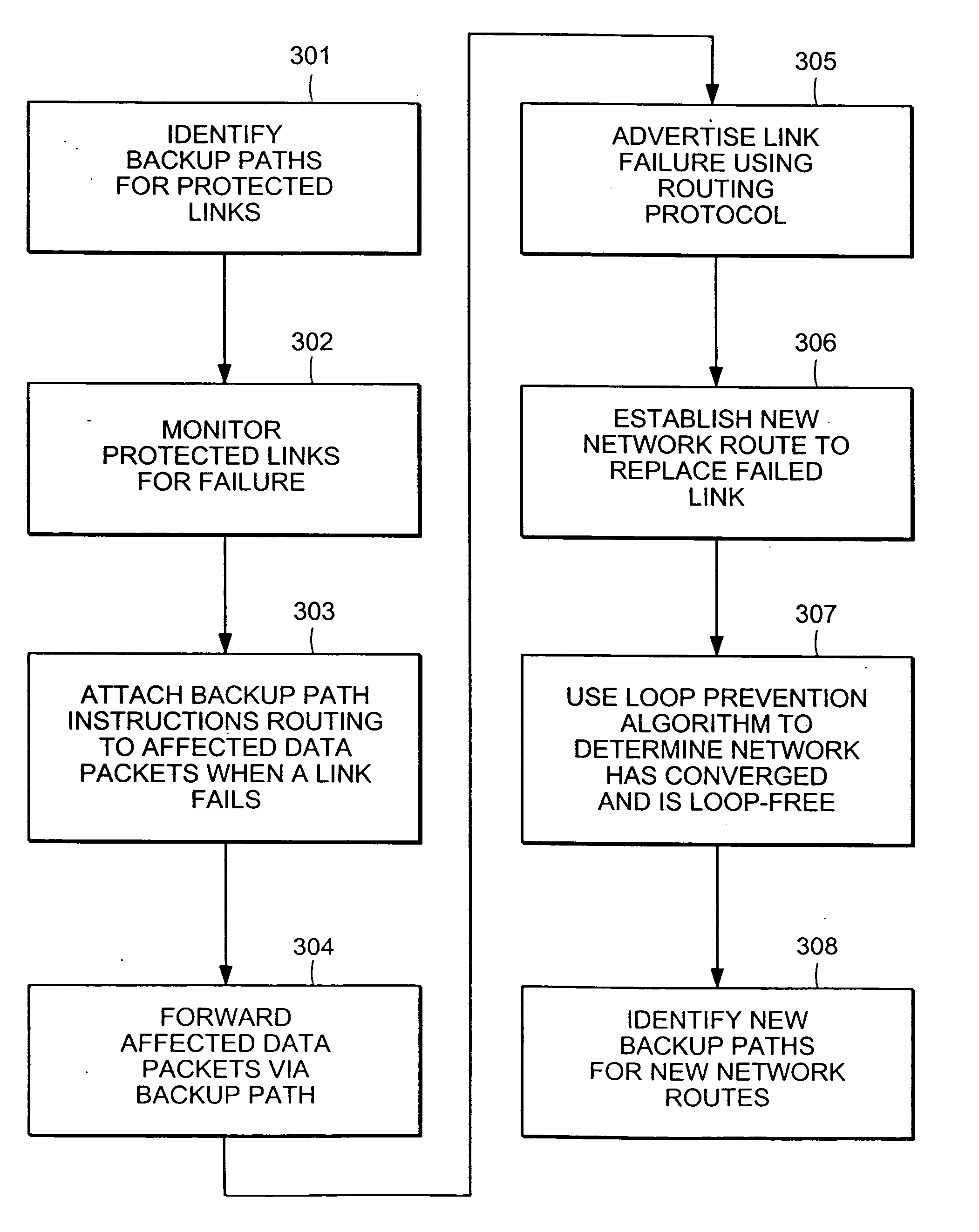
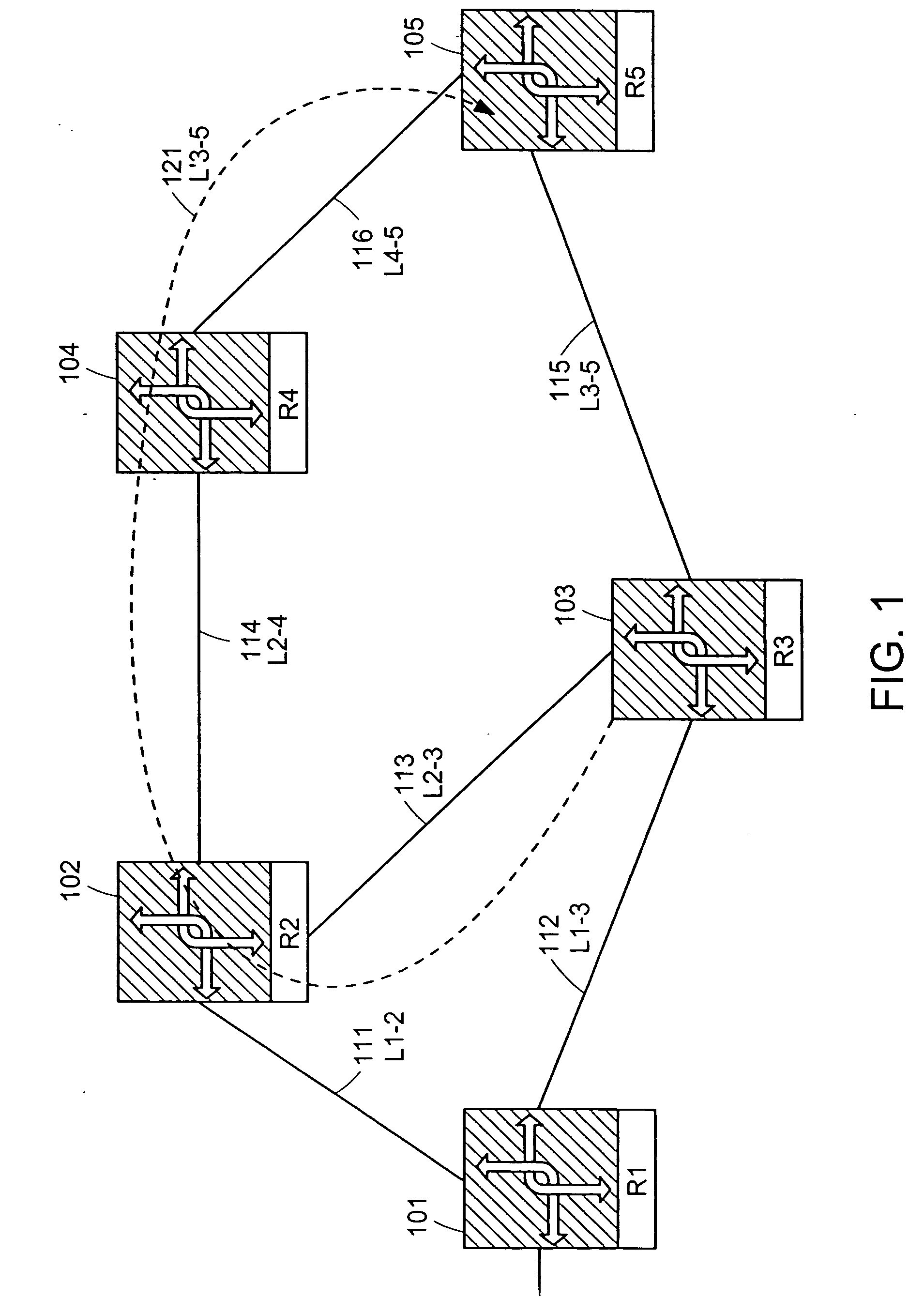
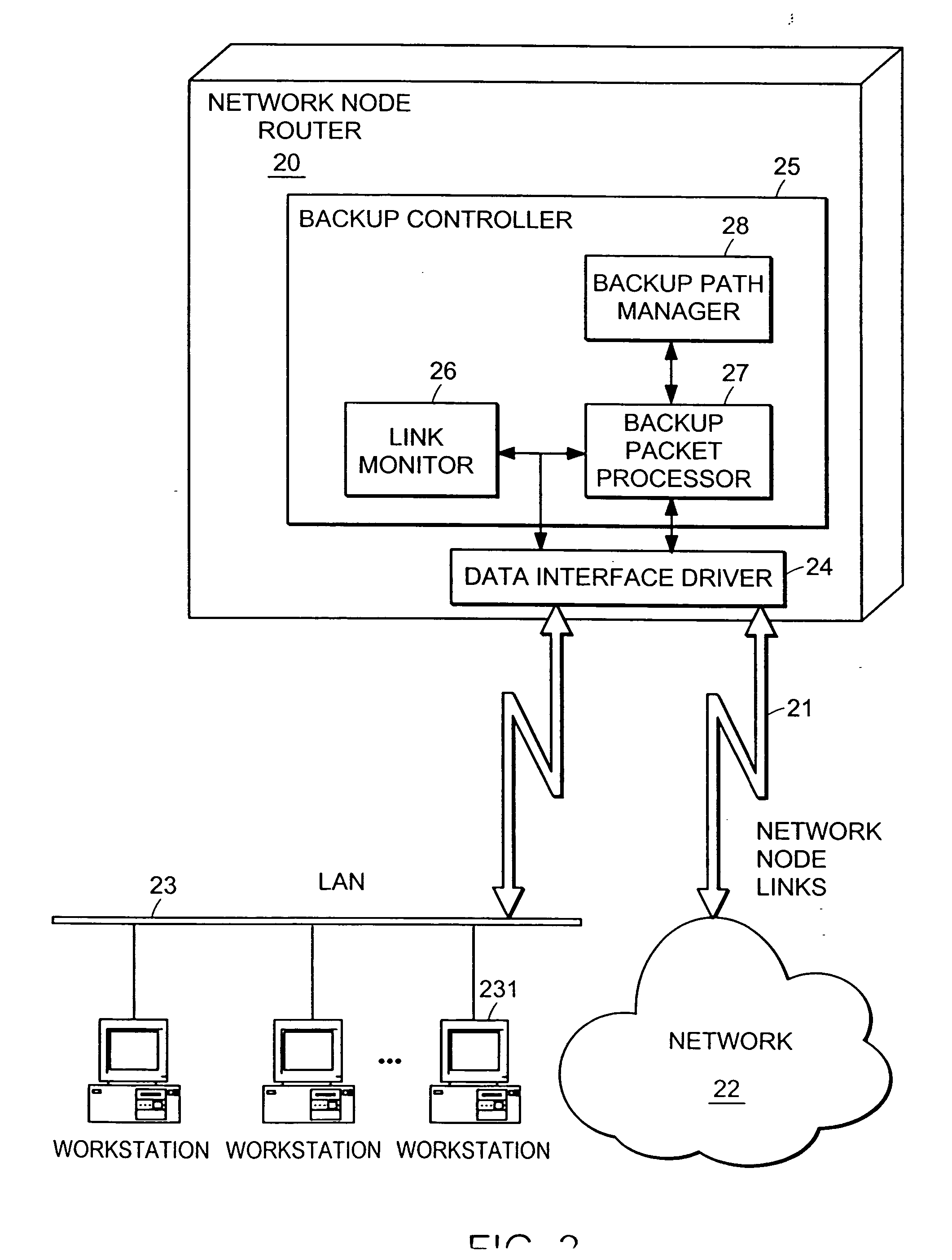
A computer network has a plurality of routers that deliver data packets to the network via a plurality of links. At least one router provides automatic protection switching in the event of a link failure. The at least one router includes a plurality of data interfaces for streams of data packets to enter and exit the at least one router; and a backup controller. The backup controller includes a backup path manager, a link monitor, and a backup packet processor. For at least one link of the routing node, the backup path manager identifies a backup routing path for forwarding affected data packets in the event of a failure of the at least one link. The link monitor monitors the plurality of links to determine when a link fails. When a link which has a backup routing path fails, the backup packet processor attaches backup routing path instructions to affected data packets routed over the failed link, and forwards the affected data packets via the backup routing path.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method and apparatus for a bandwidth broker in a packet network
InactiveUS7257632B2Digital computer detailsData switching networksBandwidth BrokerDistributed computing
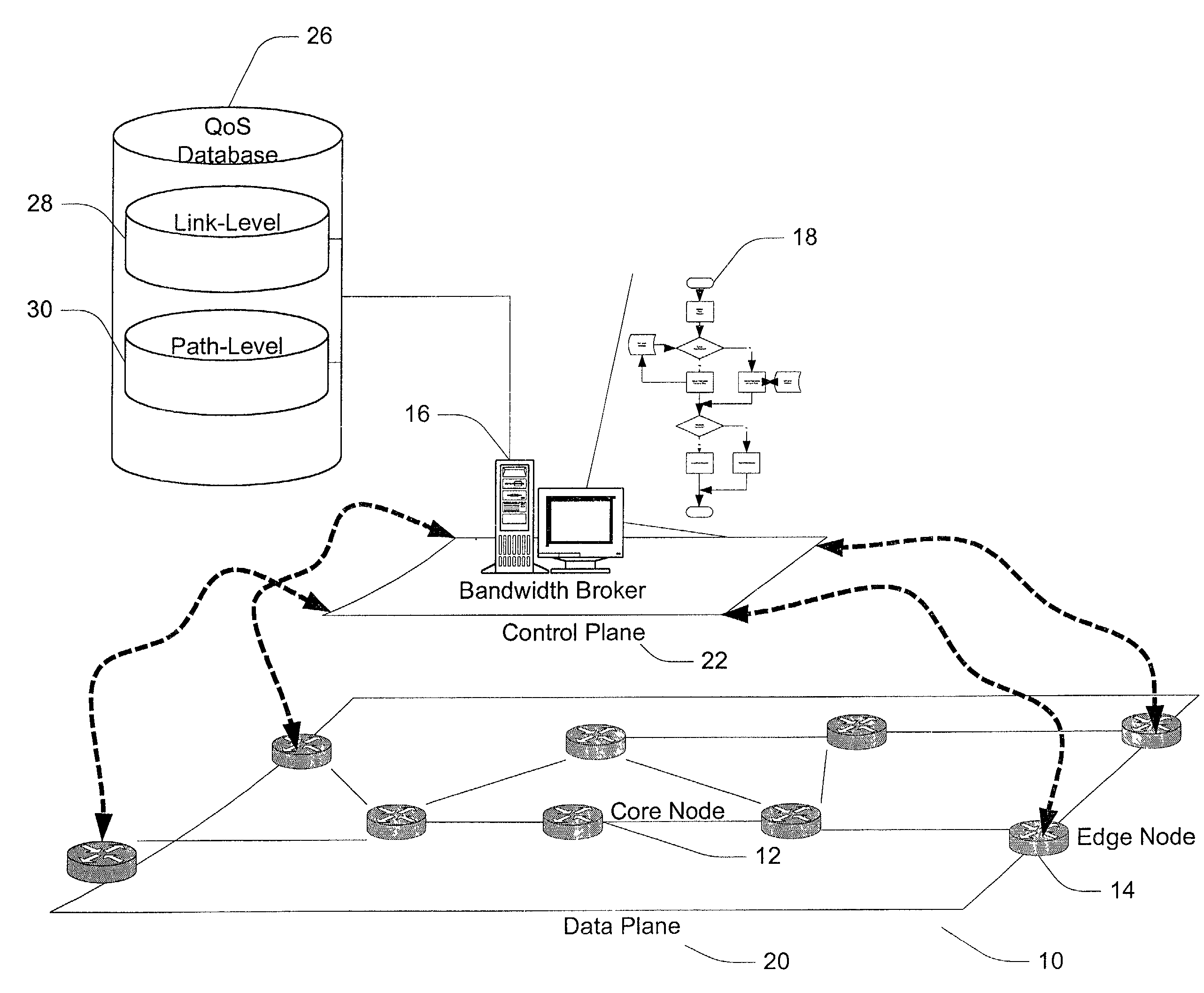
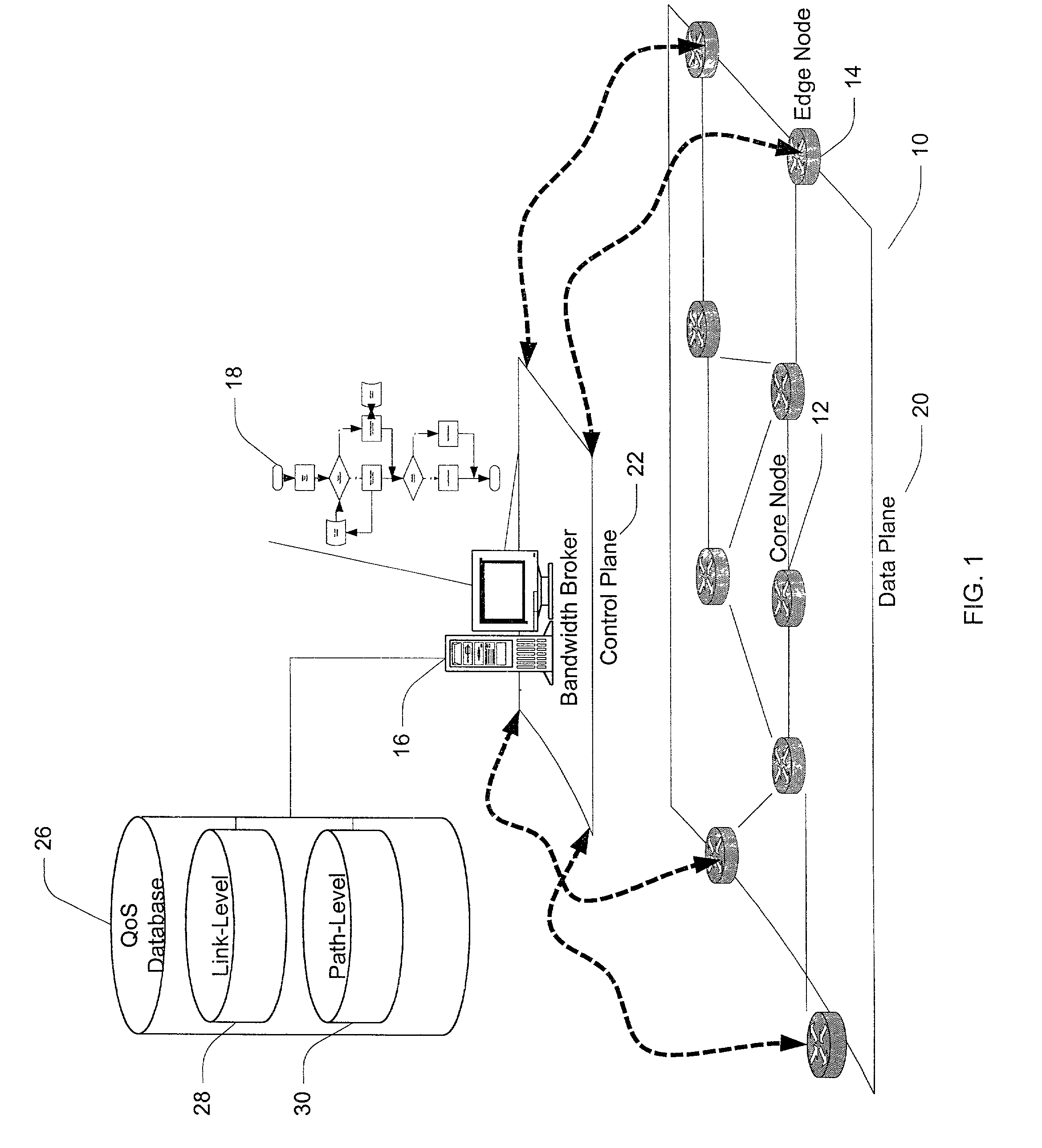
A method and apparatus for allocating bandwidth within a network domain. A centralized bandwidth broker maintains a link-level database including detailed flow data for individual links in a network domain and a path-level database including summarized flow data for individual paths in the network domain. The bandwidth broker determines bandwidth allocations at a path-level by allocating discrete amounts of bandwidth, termed quotas, based on flow requests. If a flow request cannot be satisfied by allocating quotas, then the bandwidth broker uses the link-level database to recover bandwidth from unused bandwidth by other paths on the same link in order to satisfy the flow request. In another embodiment of a bandwidth broker, the centralized bandwidth broker is replaced by a distributed bandwidth broker including a central bandwidth broker and one or more edge bandwidth brokers. An edge bandwidth broker conducts path-level allocations and requests or releases quotas from and to the central bandwidth broker. The central bandwidth broker conducts link-level allocations and allocates or de-allocates quotas to and from the path maintained by the edge bandwidth broker.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
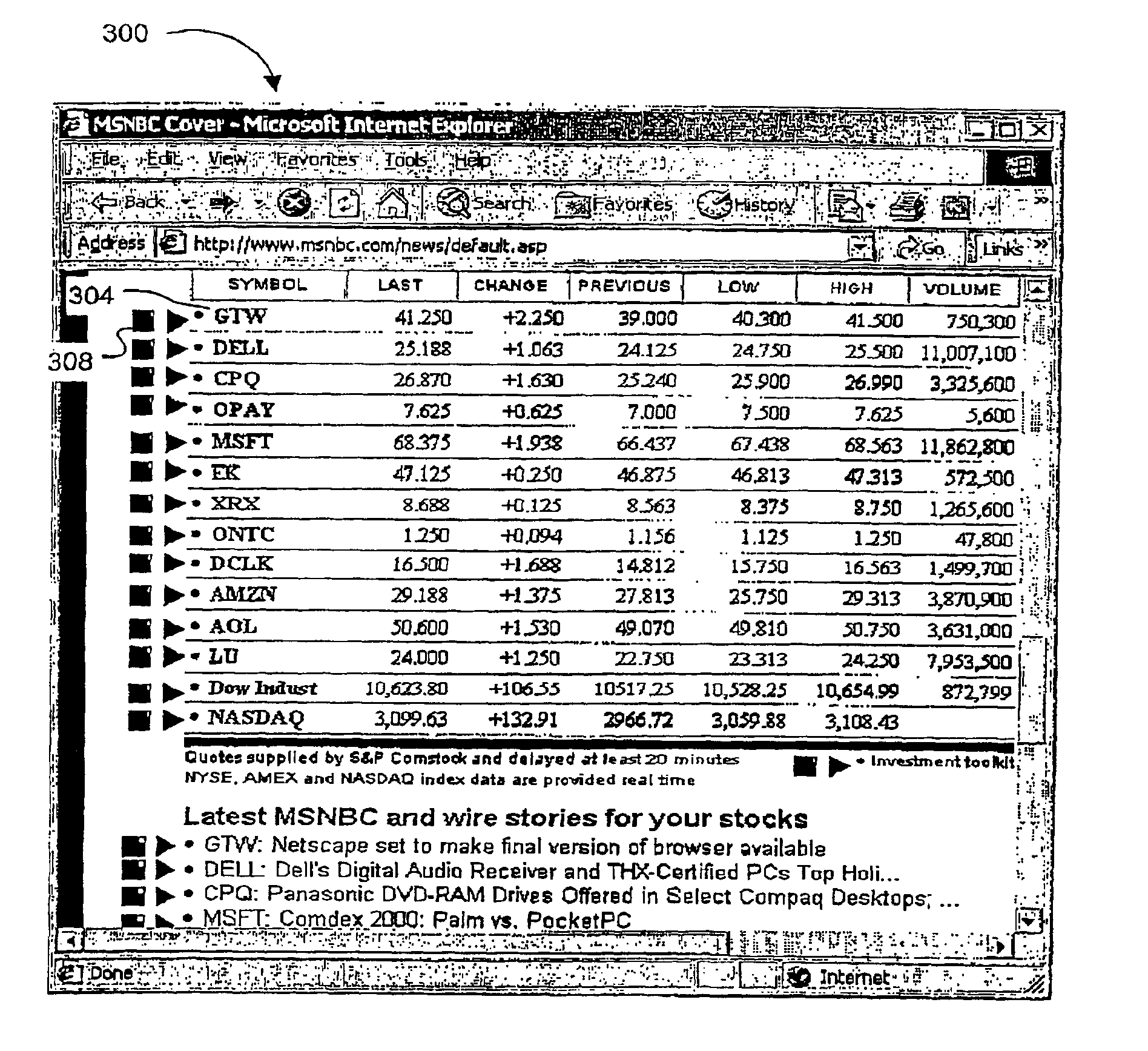
Link-level browser instance control
InactiveUS6904569B1Digital data information retrievalCathode-ray tube indicatorsBiological activationWorld Wide Web
A method for processing data contains links to information in a data browsing system, thereby providing user control over link activation behavior. As data is received, it is parsed to identify a link. Link-option data is then generated and inserted into the received data, such that a user may retrieve the information identified by the link in response to selection of the link-option data independent of retrieving the information in response to selection of the link. For example, the link-option data may be capable of retrieving the information for display in a current presentation instance, in a separate presentation instance overlaid upon the current presentation instance, in a separate presentation instance side-by-side with the current presentation instance, or in a separate presentation instance with minimization of the current presentation instance.
Owner:GATEWAY
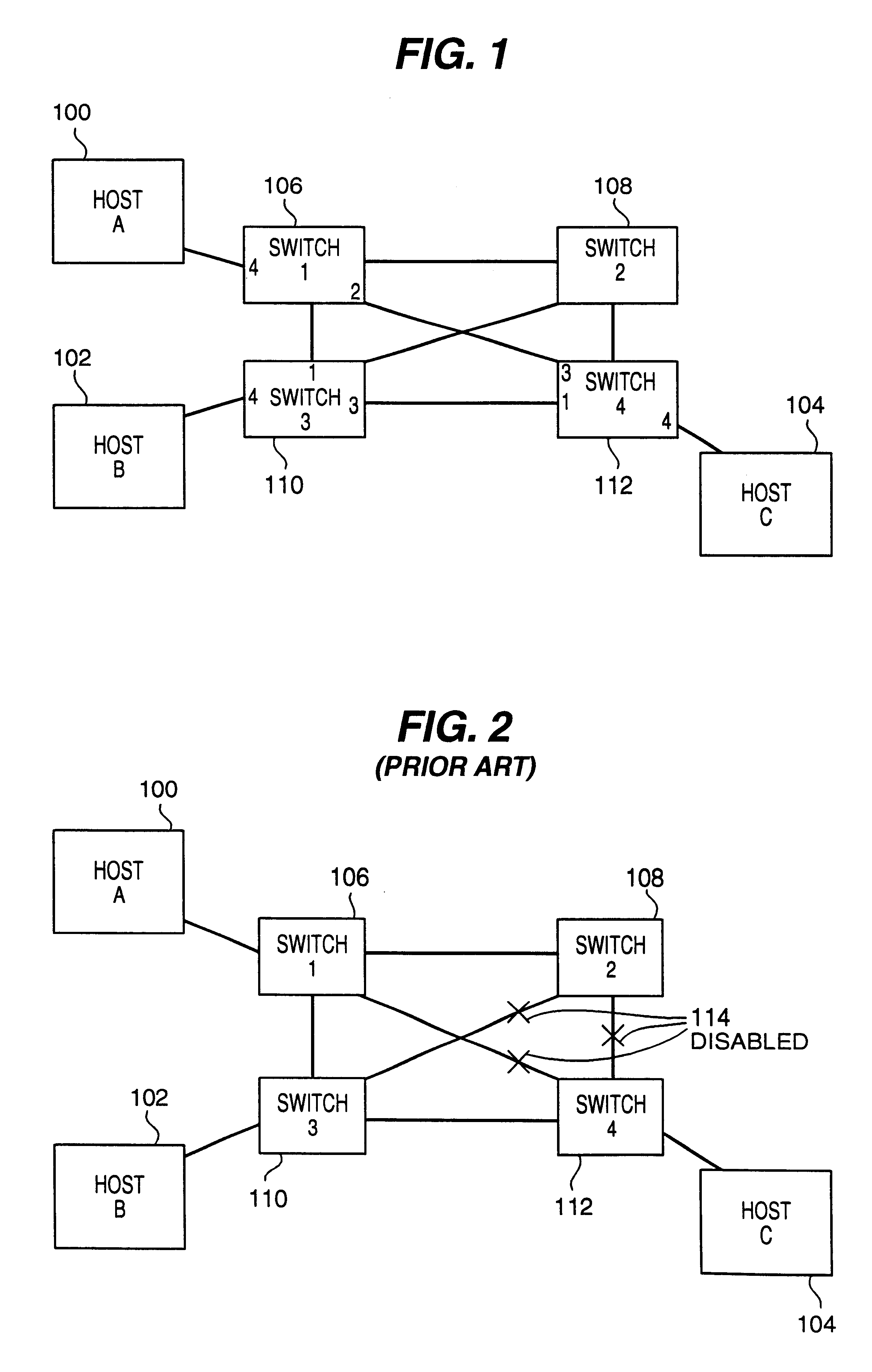
Techniques for link redundancy in layer 2 networks
ActiveUS20110228669A1Facilitating link redundancyProvides redundancyError preventionTransmission systemsTier 2 networkVirtual switch
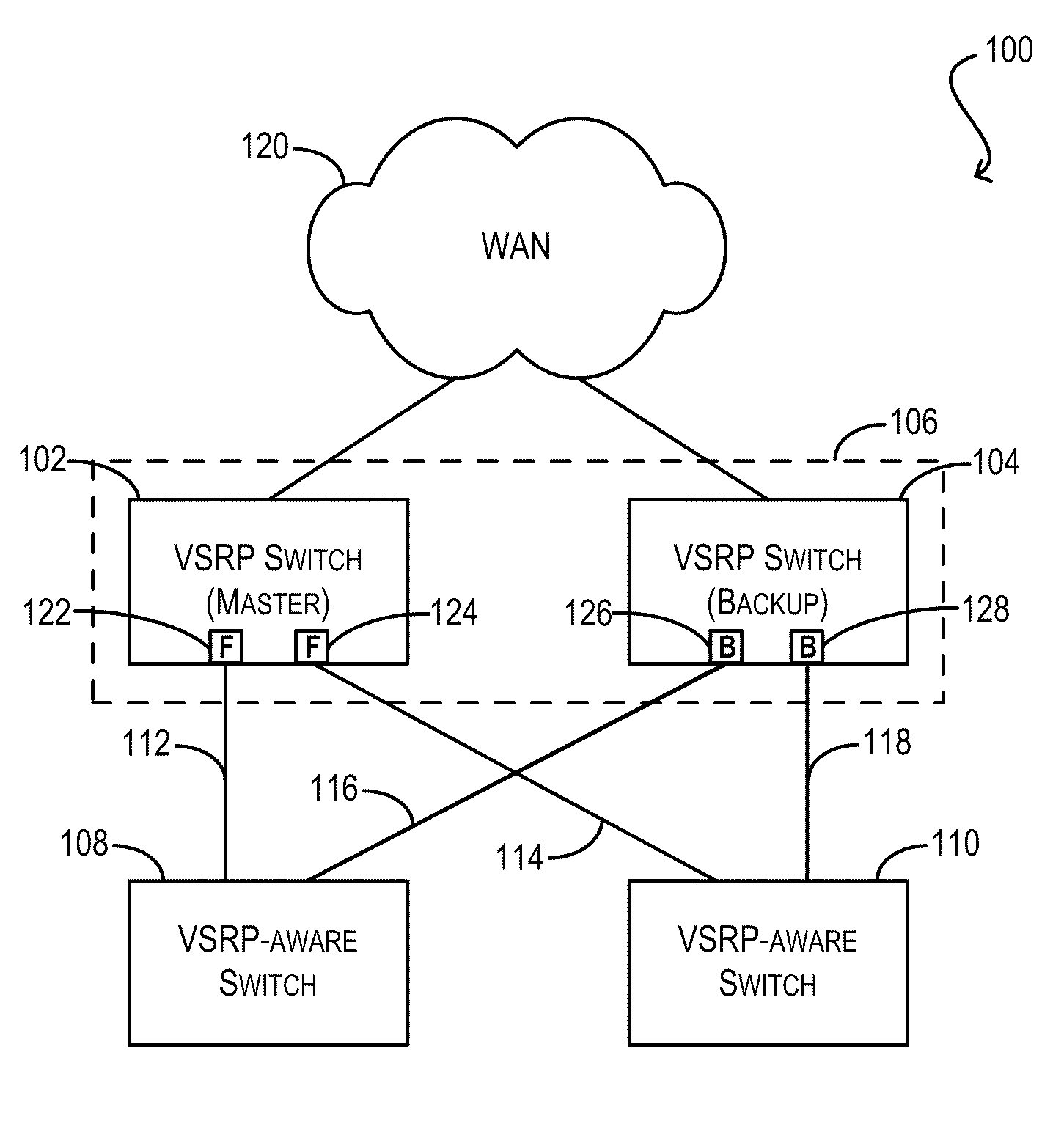
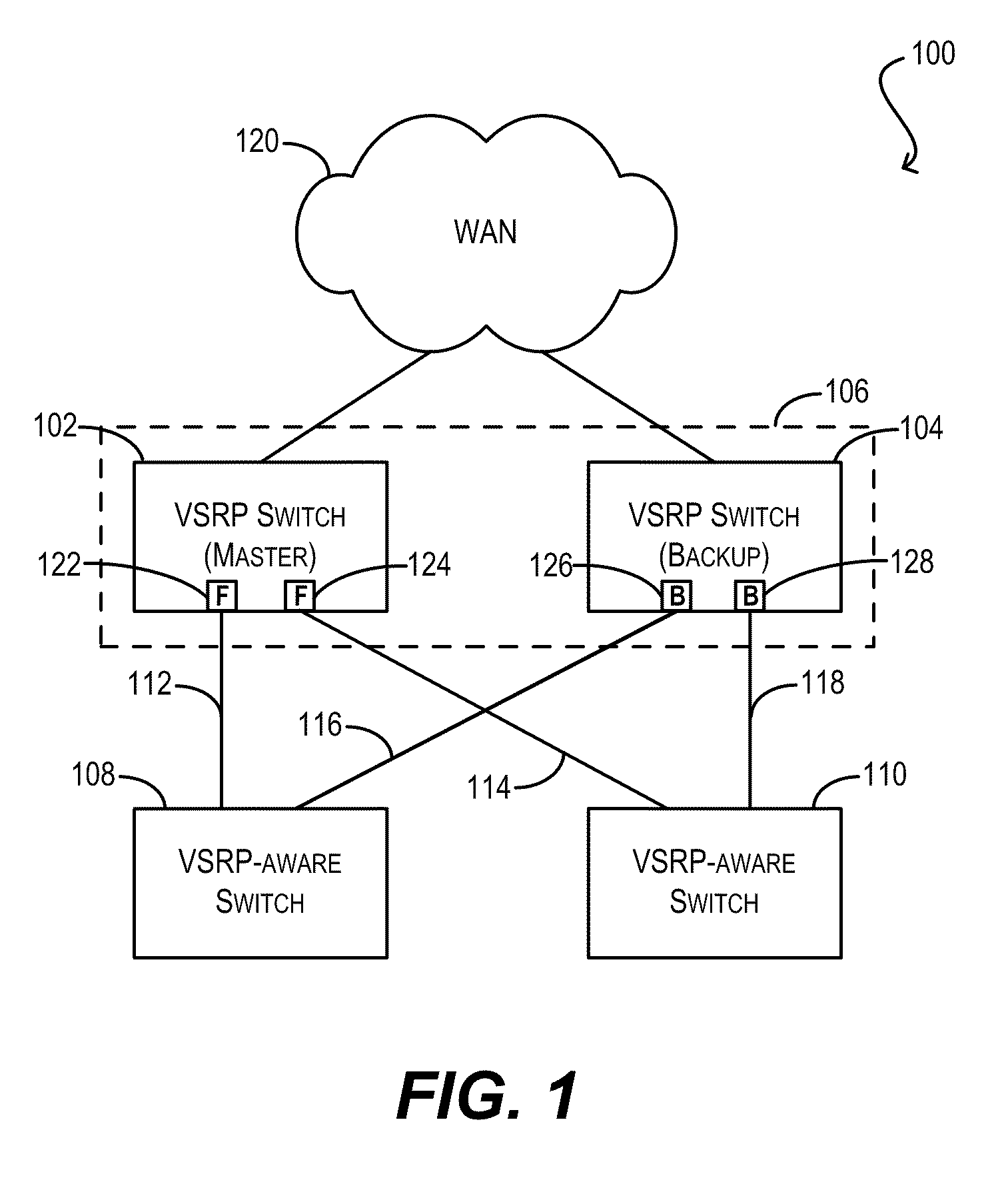
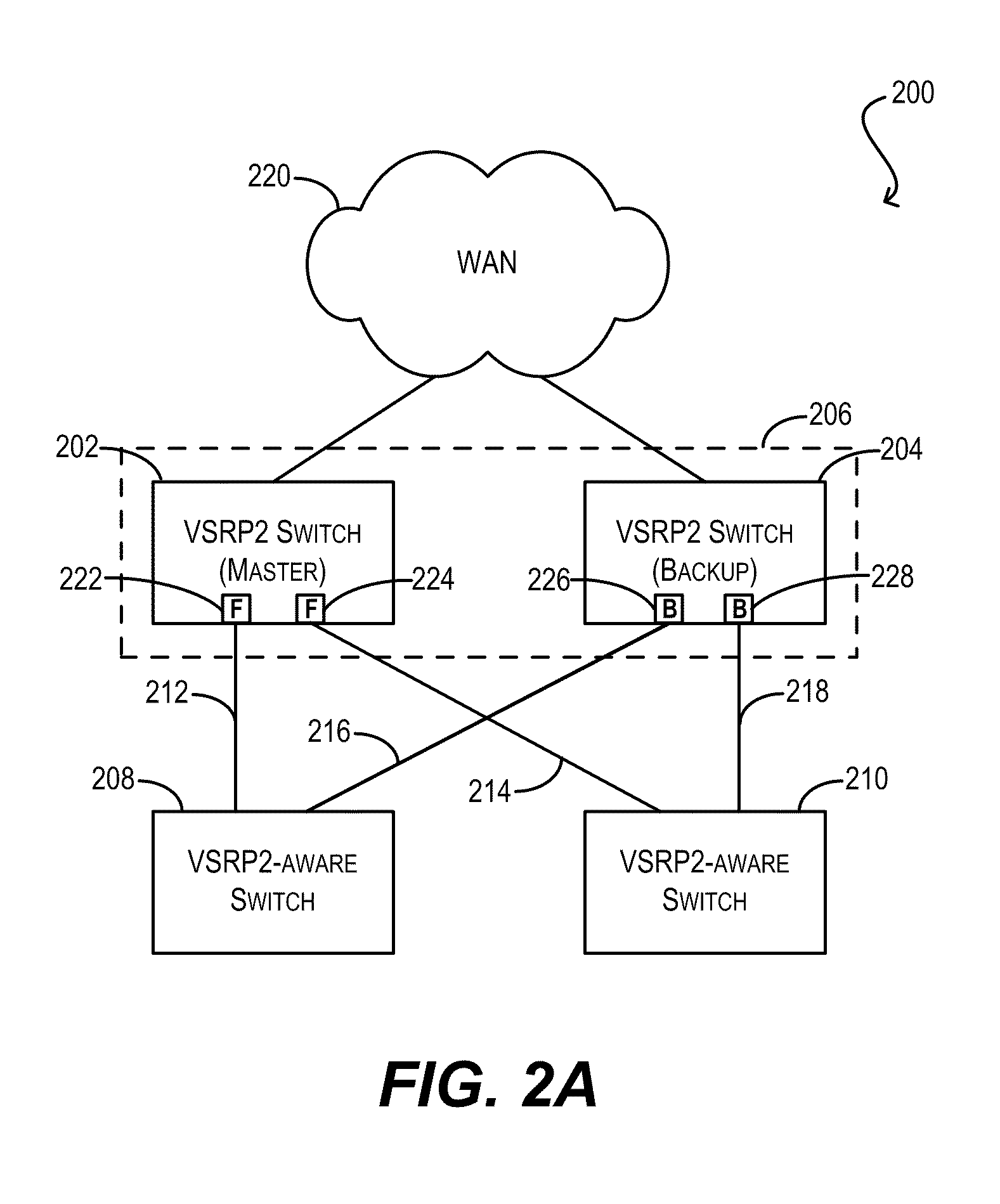
Techniques for facilitating link redundancy using an enhanced version of Virtual Switch Redundancy Protocol (VSRP), referred to herein as VSRP2. In one set of embodiments, a group of Layer 2 and / or Layer 2 / 3 devices (switches) can act in concert as a VSRP2 virtual switch. A first switch in the group (a VSRP2 master switch) can forward, via a first link, data traffic to / from a network device in a connected Layer 2 network. A second switch in the group (a VSRP2 backup switch) can block, at a second link, data traffic to / from the same network device. If the first link fails or otherwise becomes unavailable, the VSRP2 backup switch can detect the link failure and begin forwarding, via the second link, data traffic to / from the network device. In this manner, redundancy can be provided at the link level between the VSRP2 virtual switch and the Layer 2 network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
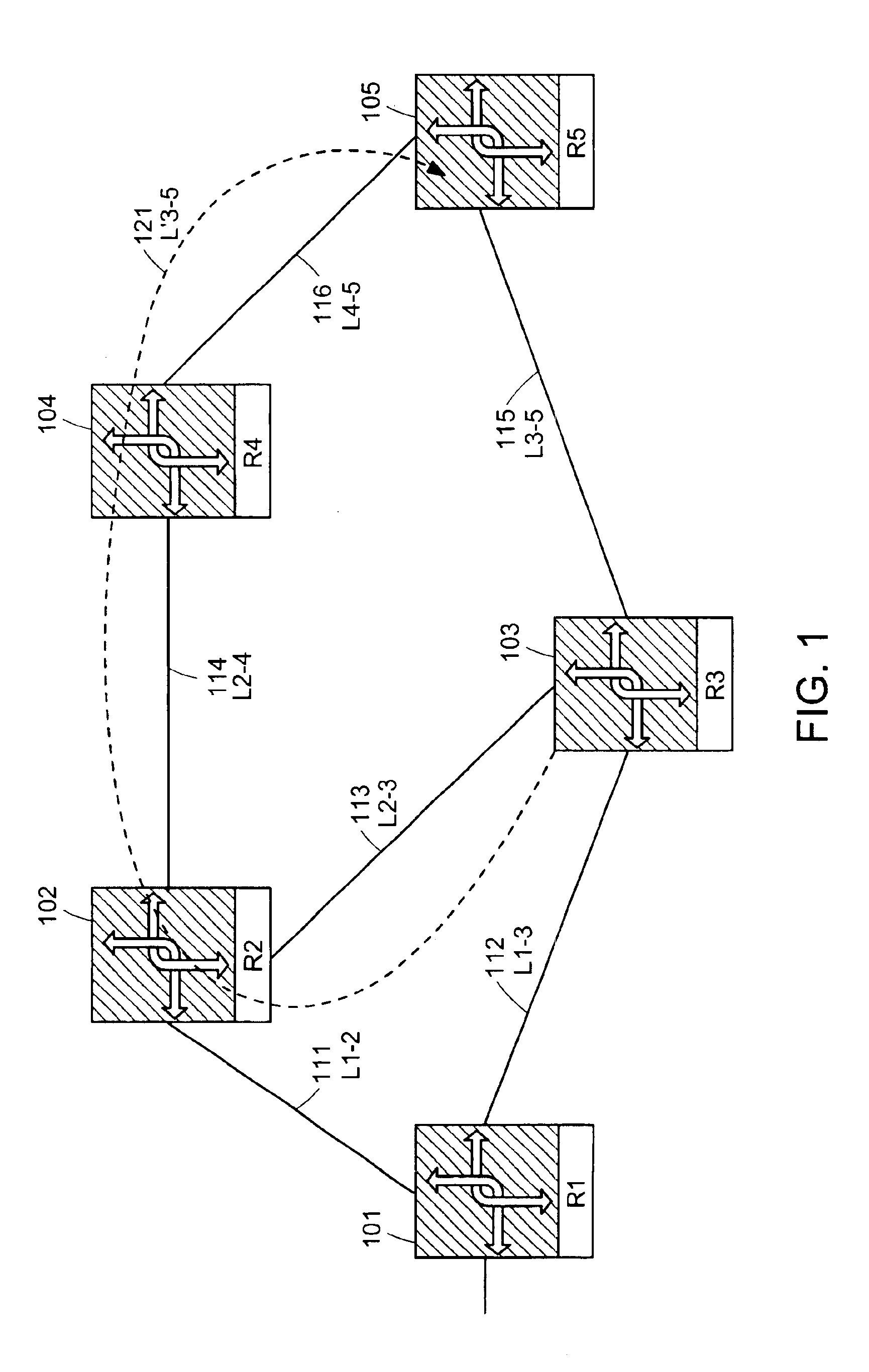
Method and apparatus for computing the shortest path between nodes based on the bandwidth utilization link level
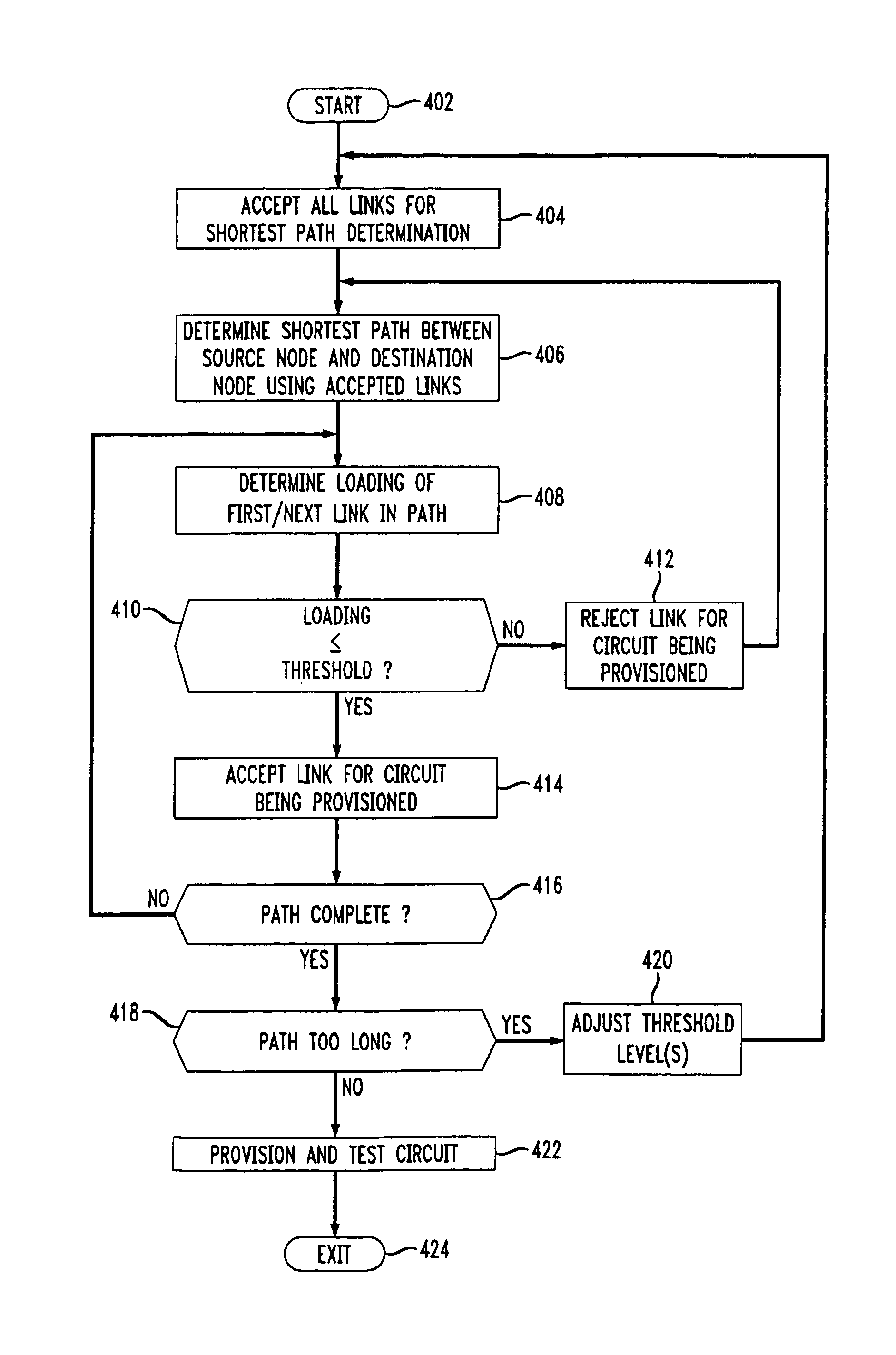
InactiveUS6963927B1Avoids over utilizing and overloadingError preventionTransmission systemsTelecommunications linkShort path algorithm
A method and apparatus for determining a circuit path between a source node and a destination node within a network comprising a plurality of nodes by iteratively selecting appropriate next nodes using a shortest path algorithm and accepting or rejecting the selected next node based upon the bandwidth utilization level of the communications link to the next node. In the case of a lack of acceptable communication links or a determined circuit path exceeding an ideal circuit path by a predetermined amount, the threshold levels defining acceptable links are adjusted.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
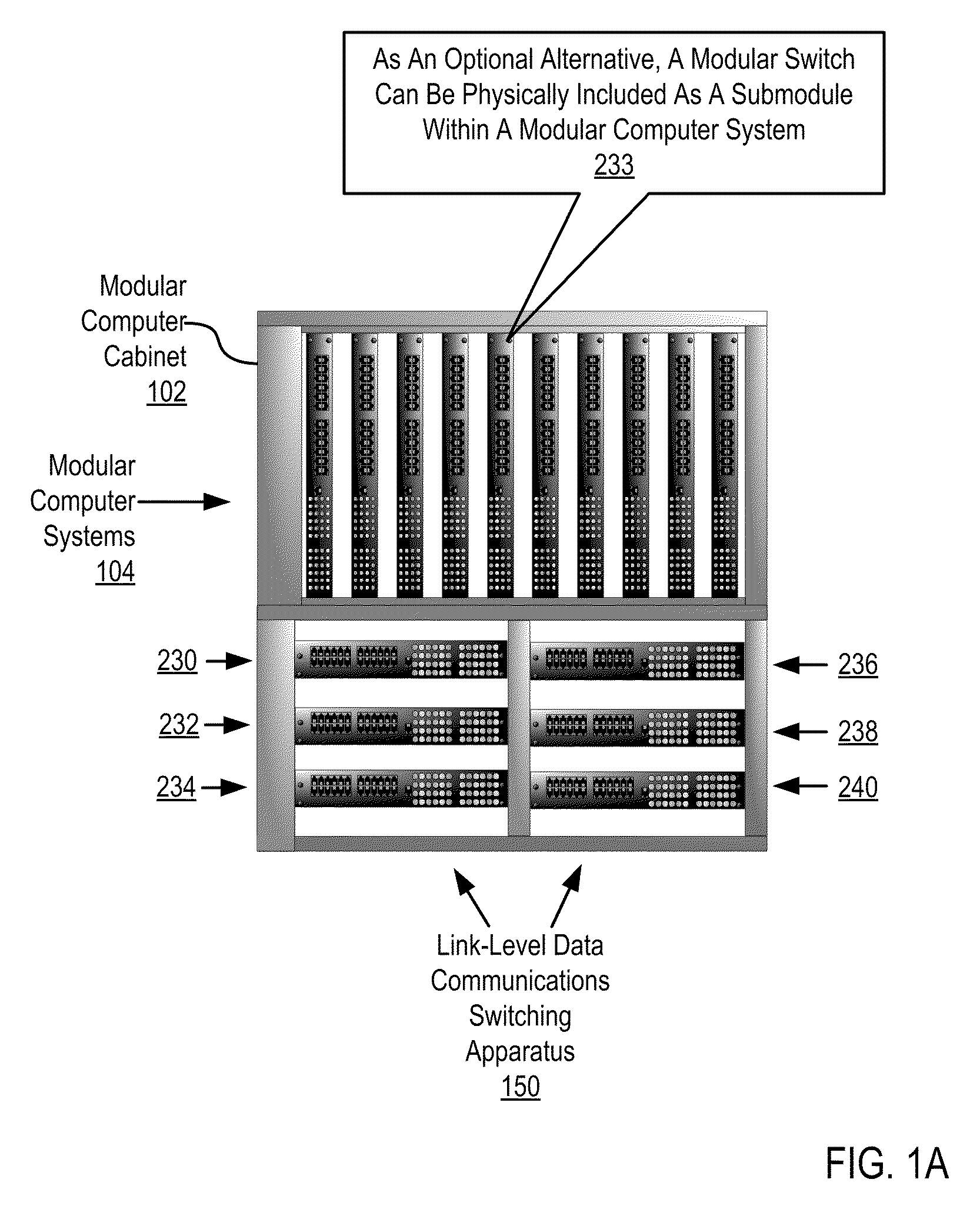
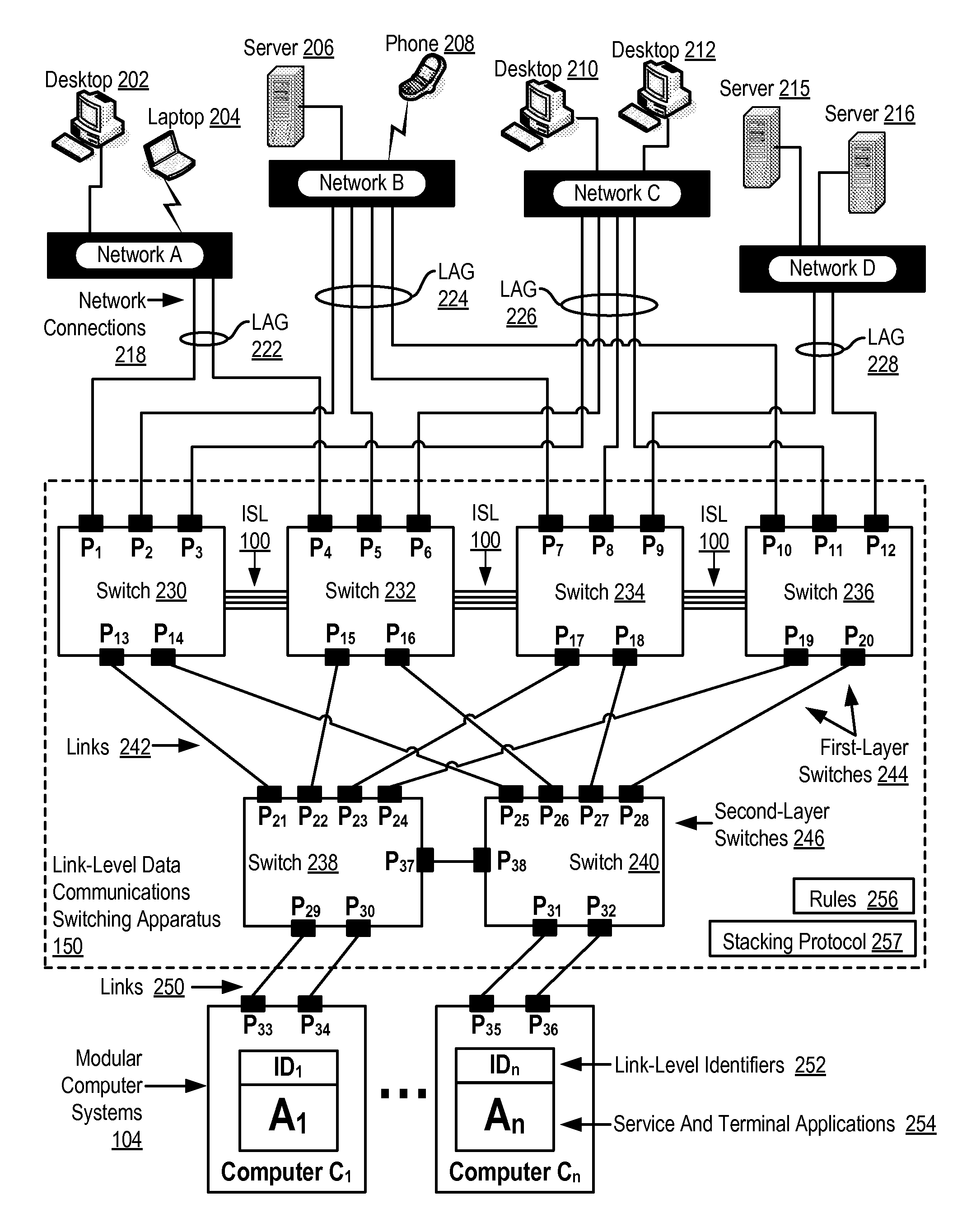
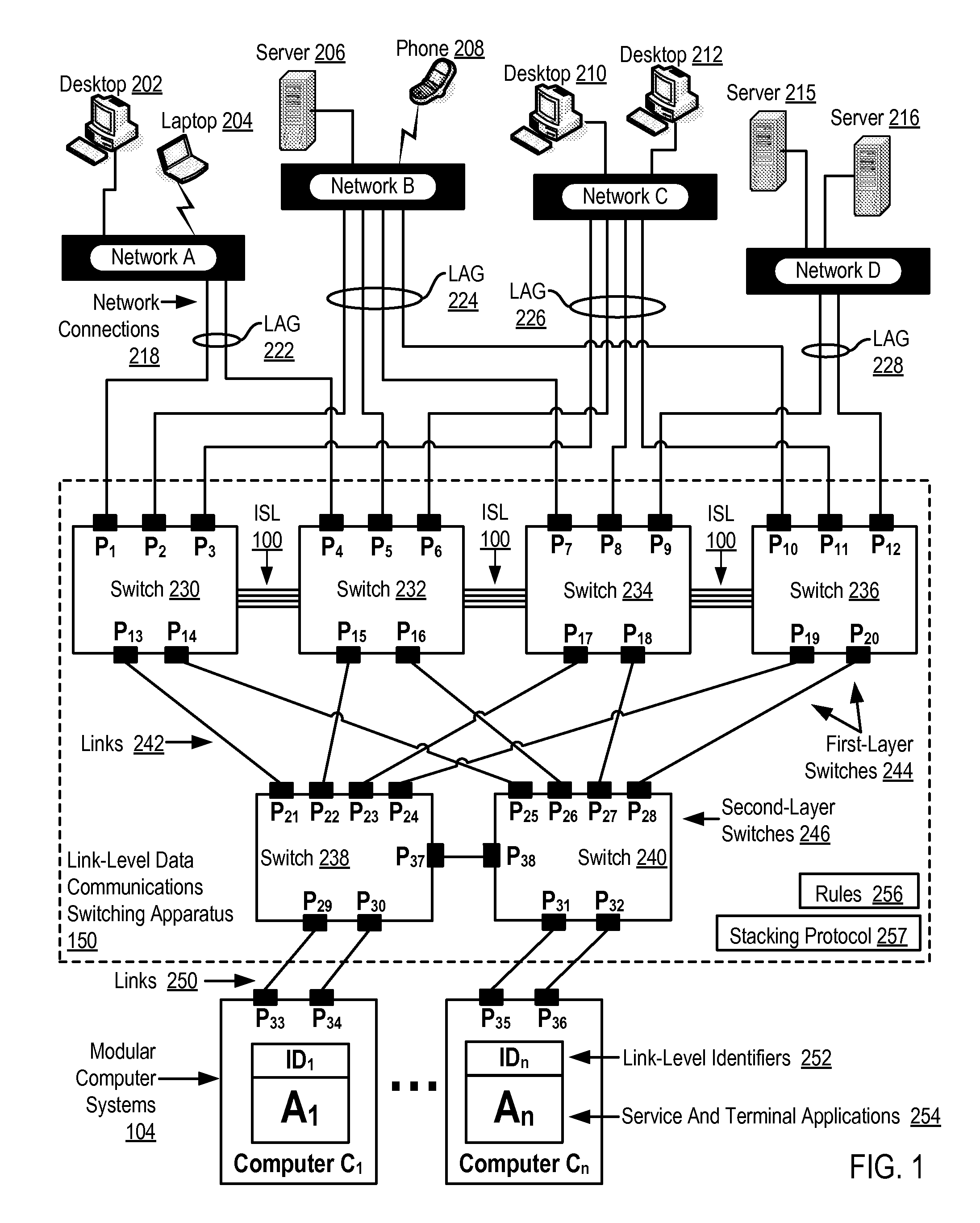
Two-Layer Switch Apparatus Avoiding First Layer Inter-Switch Traffic In Steering Packets Through The Apparatus
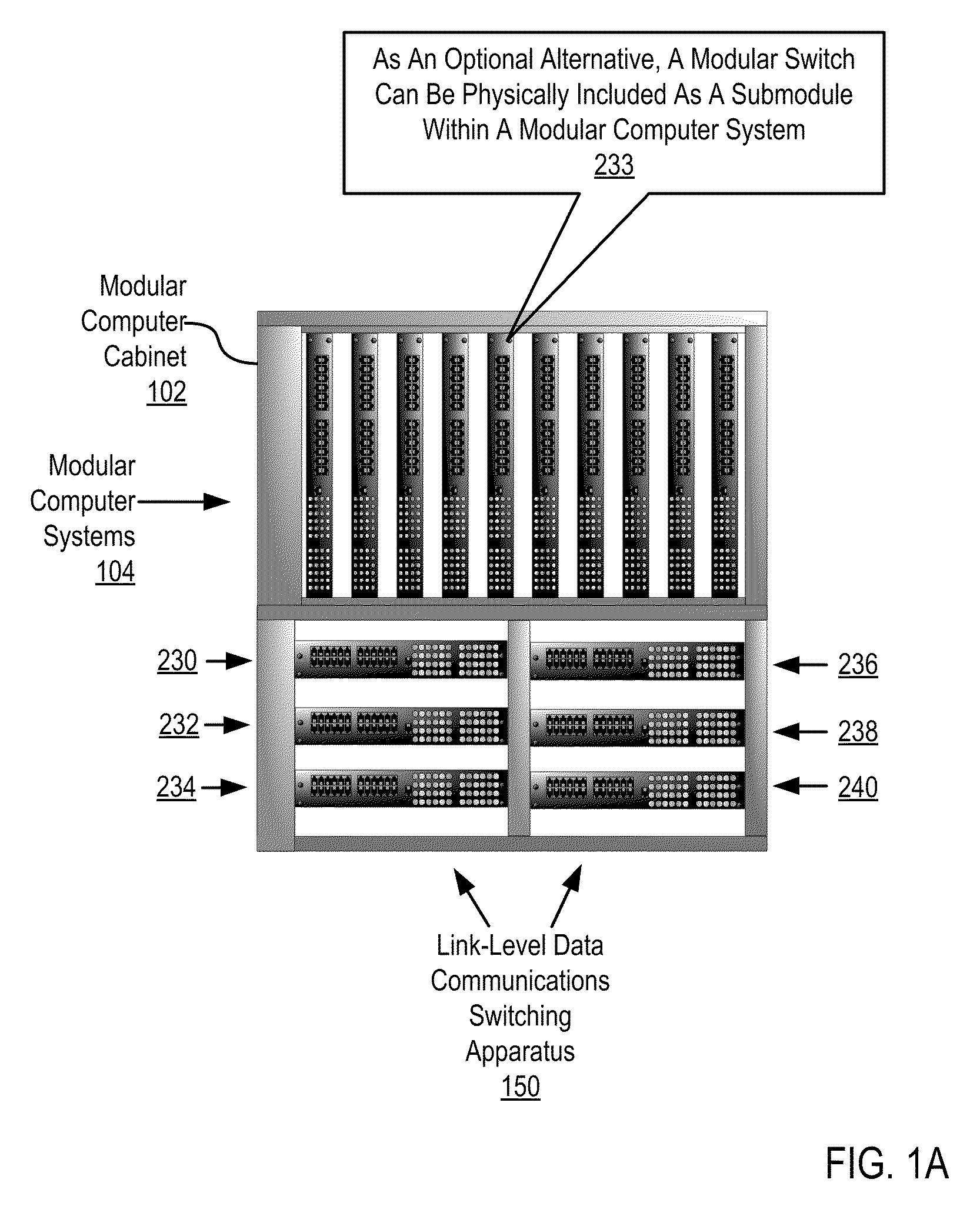
InactiveUS20100316055A1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityEngineering
Link-level data communications implemented in switching apparatus comprising modular switches disposed within a modular computer cabinet that includes modular computer systems; the switching apparatus configured as two layers of switches, the first layer switches coupled to one another for communications by inter-switch links, each second layer switch coupled for communications to the modular computer systems; all the switches stacked by a stacking protocol that shares administrative configuration information among the switches through the inter-switch links and presents all the switches as a single logical switch; the switching apparatus including ports coupling the apparatus to networks and to service applications and terminating applications on the modular computer systems; and sending the packet from network to modular computer system to which the packet is directed, or from modular computer system to network to which the packet is directed, the packet traversing none of the inter-switch links among the first layer switches.
Owner:IBM CORP
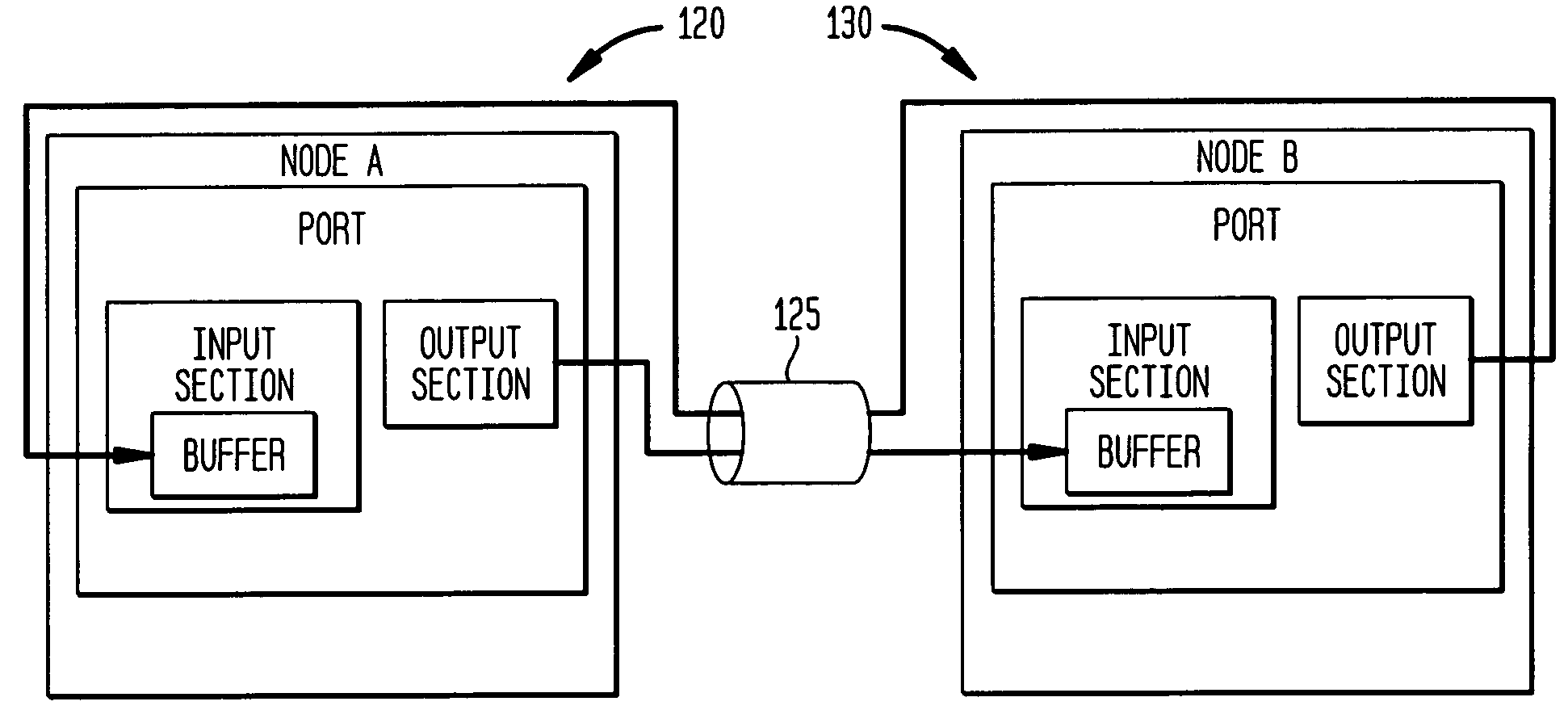
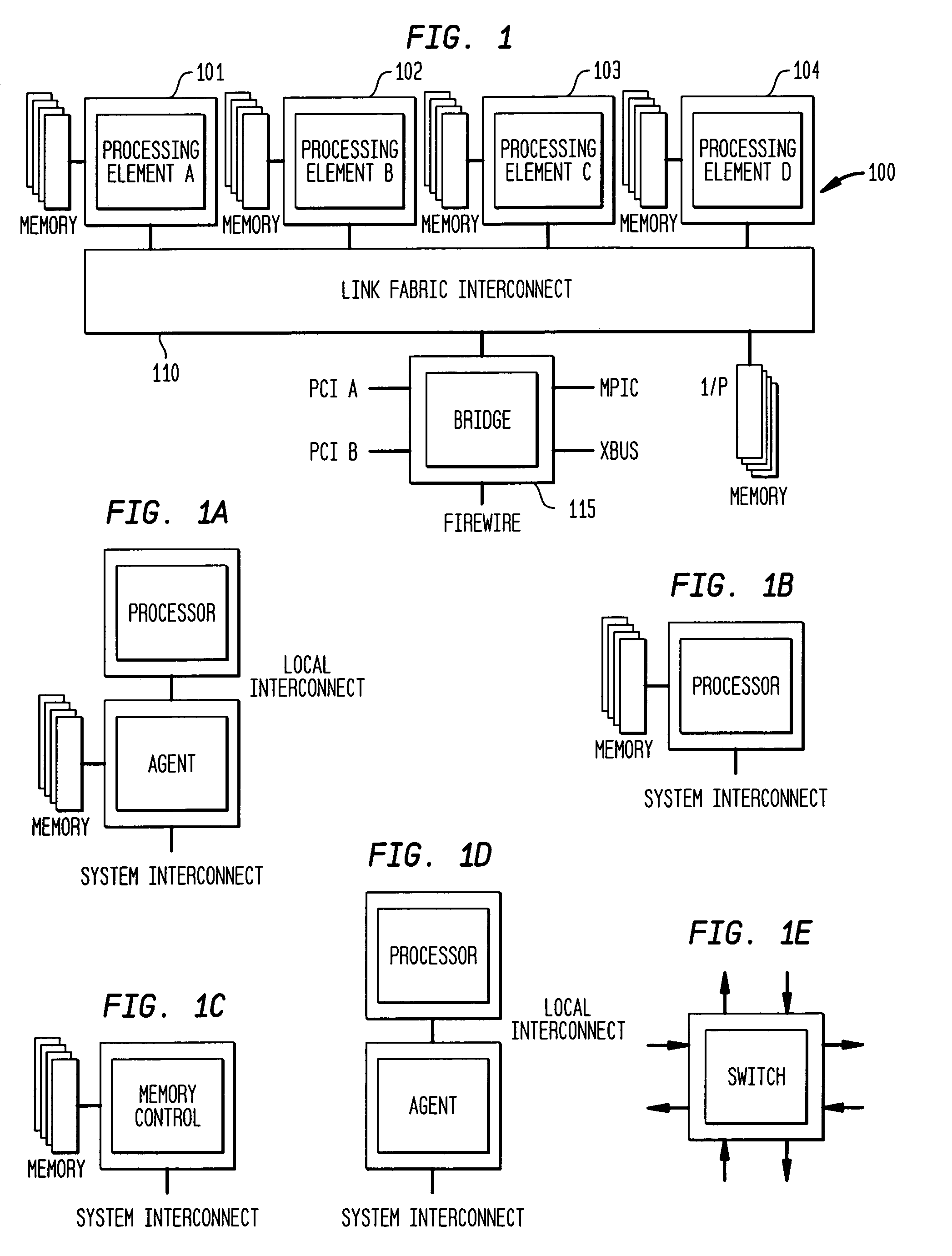
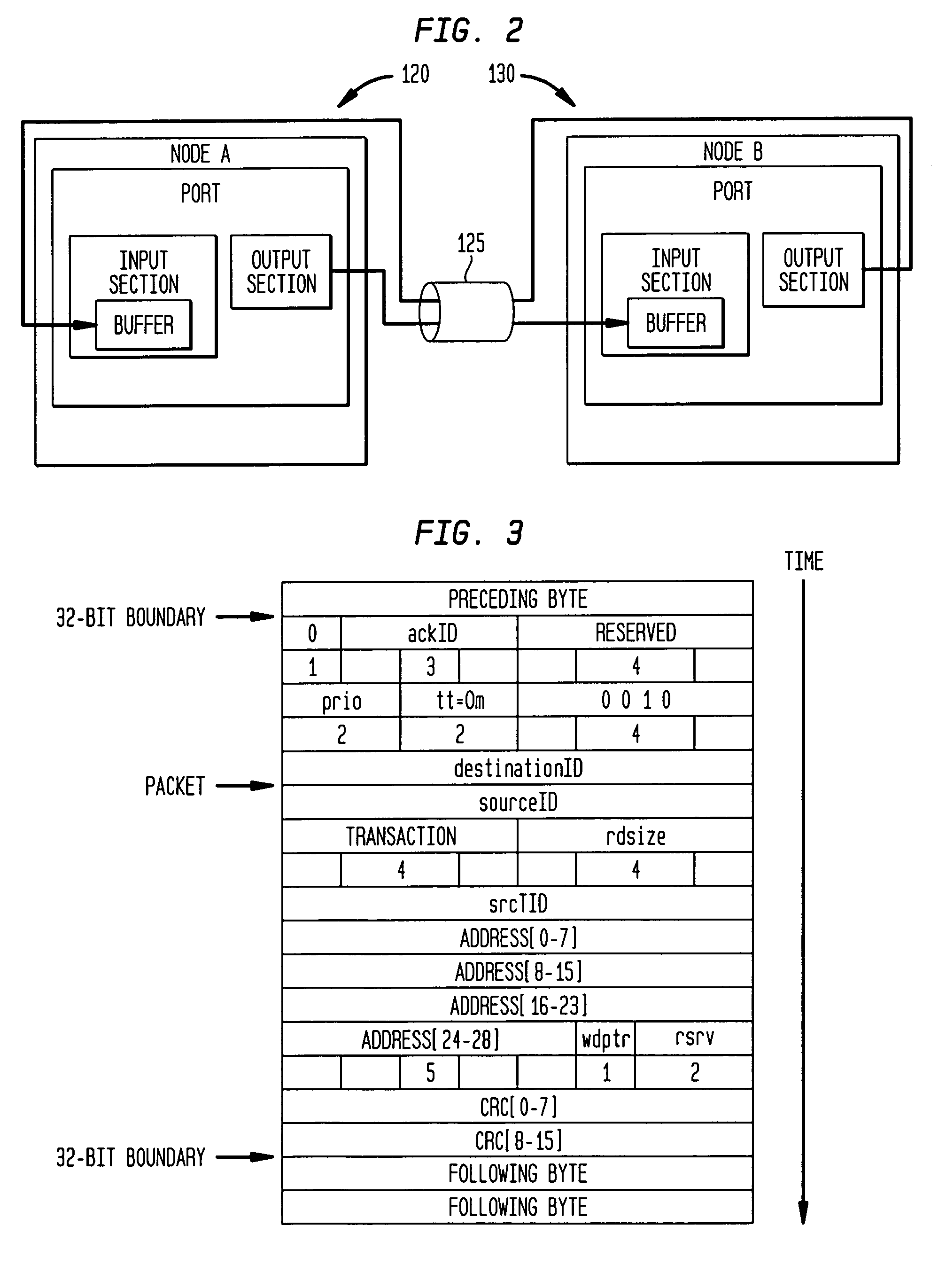
Digital data system with link level message flow control
InactiveUS7031258B1Keep openEnhance speed and accuracy and efficiencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDigital dataError checking
A digital data system comprises a plurality of links for passing messages between nodes, which may be end points such as memory or processing units, or intermediate or branch points such as routers or other devices in the system. A link level flow control is implemented by control symbols passed between adjacent nodes on a link to efficiently regulate message burden on the link. The control symbols may be embedded within in a message packet to quickly effect control on a link—such as reducing data flow, requesting retransmission of corrupted data, or other intervention—without disruption of the ongoing packet reception. A control symbol may be recognized within the packet by a flag bit, a marker such as a transition in a signal, or a combination of characteristics. The control symbol may be a short word, having a control action identifier code at defined bit positions to indicate the desired link-level control function. A node receiving the control symbol implements the designated control action while maintaining packet order data (such a bit positions and byte counts), and applying message housekeeping processing (such as error checking) as though the control symbol were absent. The control symbol is thus embedded in a manner such that a receiving node need not receive a complete message, or even a complete packet, before acting on the control symbol. The beginning and end of the interrupted packet, meanwhile, are handled as a single message packet, and are processed by the receiving node in properly-aligned bit positions, allowing message flow to continue along the link without interruption. Thus, retransmission of the affected packet or message is not required. The result is that control operations dictated by the embedded control symbol are effected immediately and without slowing down communications.
Owner:MERCURY SISTEMS INC +1
Maintenance of link level consistency between database and file system
Methods and computer-readable media for maintaining transactional link-level consistency between a database and a file system. A file system change is logged in a record of a database log and a file corresponding to the file system change is created in a file system folder. During a restart recovery process, an analysis operation and a conditional redo operation are performed based on the database log, and a conditional redo operation and an undo operation are performed based on the files in the file system folder. An undo operation is then performed based on the database log.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
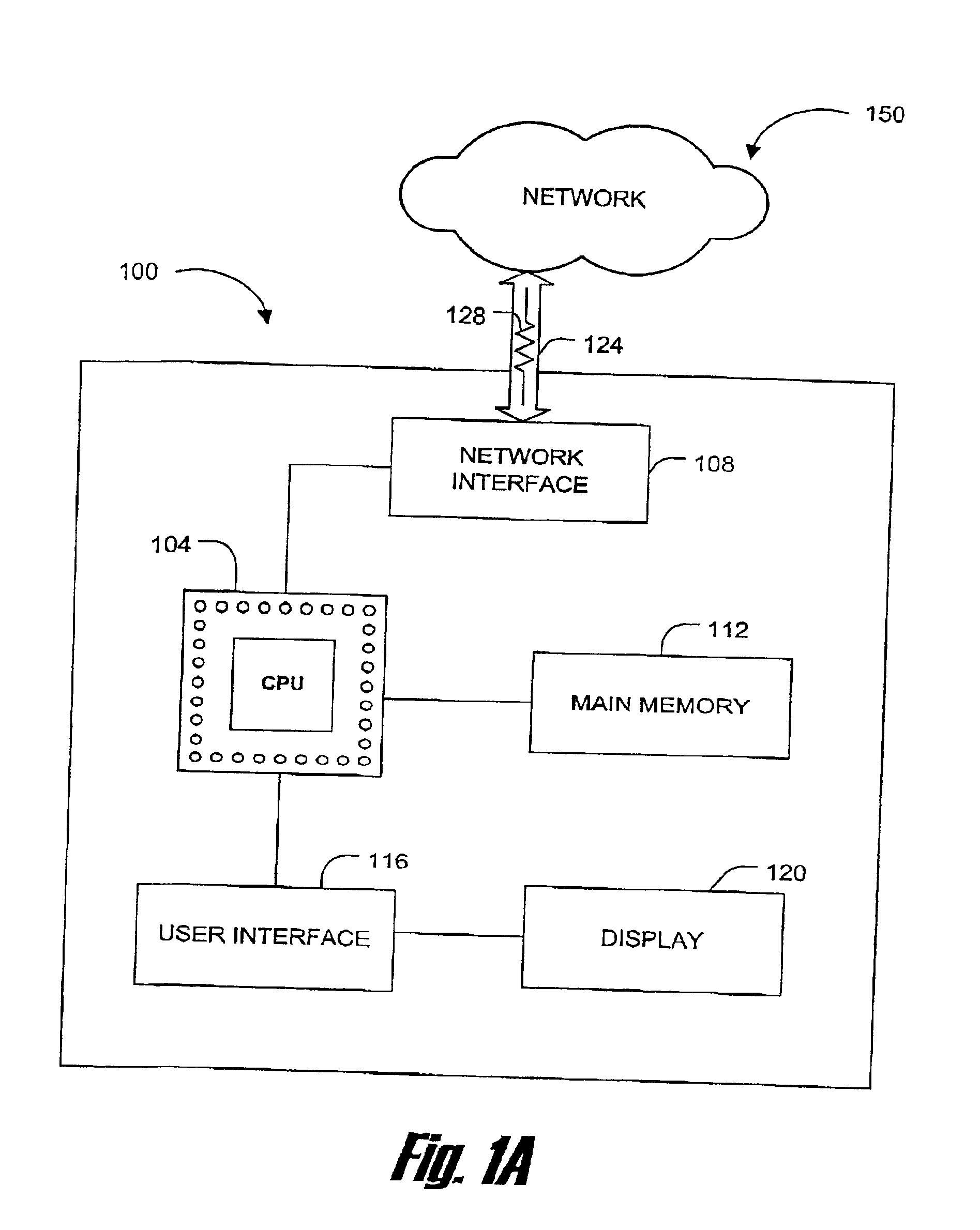
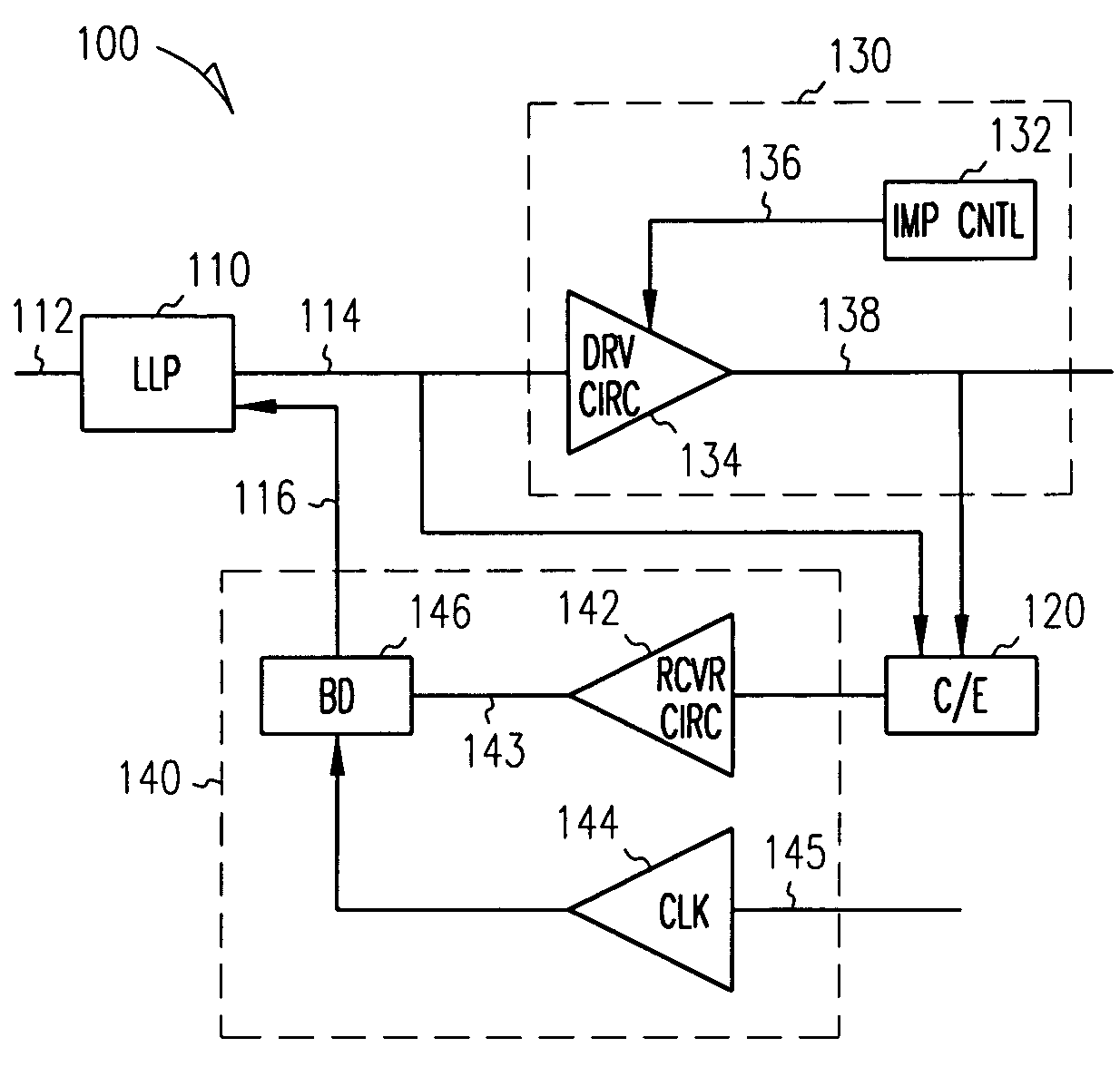
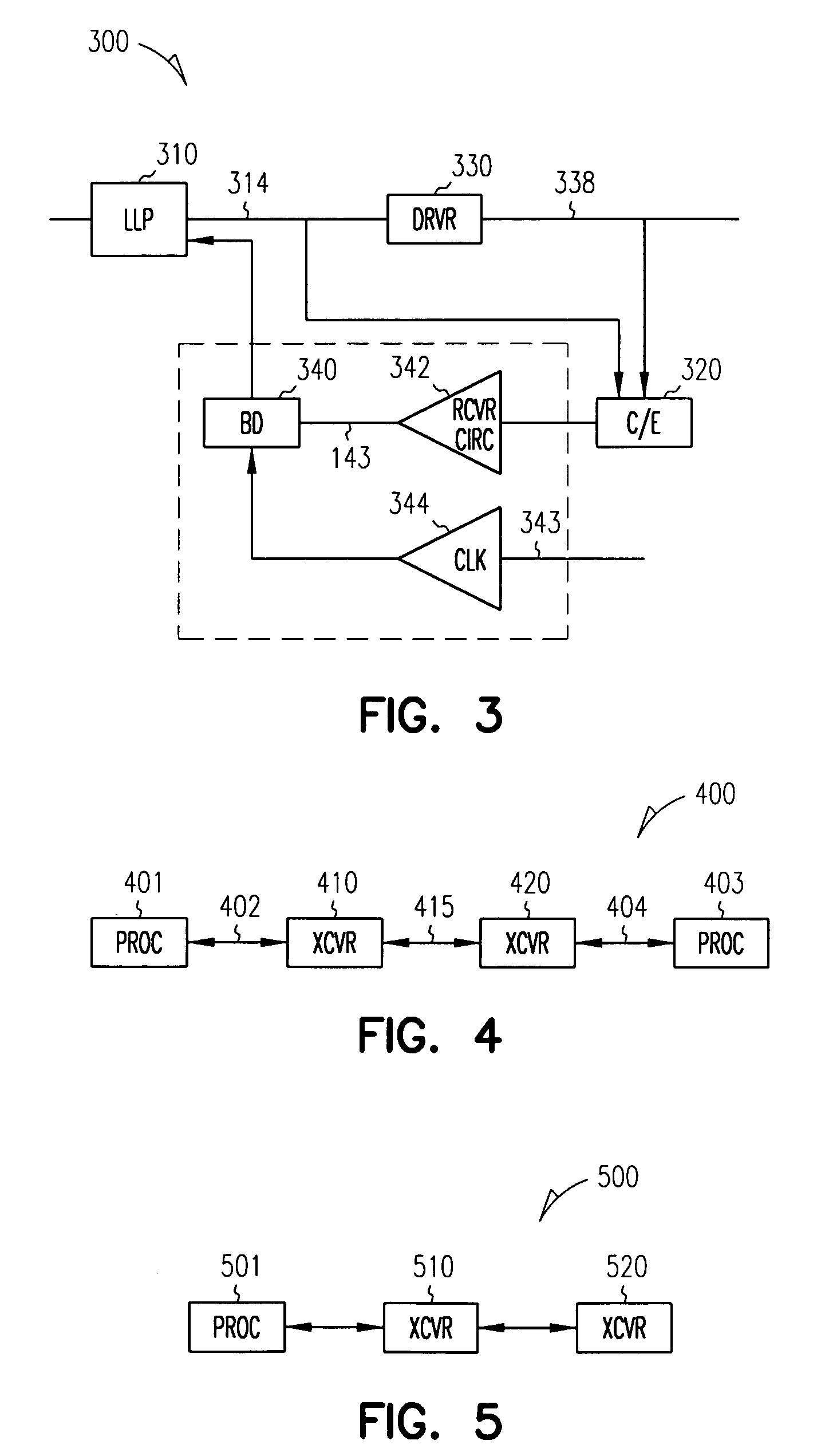
Method and apparatus for communicating computer data from one point to another over a communications medium
InactiveUS7248635B1Clearer and fast data transferIncrease the number ofMultiple-port networksSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionData signalEqualization
The present invention is directed toward a communications channel comprising a link level protocol, a driver, a receiver, and a canceller / equalizer. The link level protocol provides logic for DC-free signal encoding and recovery as well as supporting many features including CRC error detection and message resend to accommodate infrequent bit errors across the medium. The canceller / equalizer provides equalization for destabilized data signals and also provides simultaneous bi-directional data transfer. The receiver provides bit deskewing by removing synchronization error, or skewing, between data signals. The driver provides impedance controlling by monitoring the characteristics of the communications medium, like voltage or temperature, and providing a matching output impedance in the signal driver so that fewer distortions occur while the data travels across the communications medium.
Owner:MORGAN STANLEY
Automatic protection switching using link-level redundancy supporting multi-protocol label switching
A computer network has a plurality of routers that deliver data packets to the network via a plurality of links. At least one router provides automatic protection switching in the event of a link failure. The at least one router includes a plurality of data interfaces for streams of data packets to enter and exit the at least one router; and a backup controller. The backup controller includes a backup path manager, a link monitor, and a backup packet processor. For at least one link of the routing node, the backup path manager identifies a backup routing path for forwarding affected data packets in the event of a failure of the at least one link. The link monitor monitors the plurality of links to determine when a link fails. When a link which has a backup routing path fails, the backup packet processor attaches backup routing path instructions to affected data packets routed over the failed link, and forwards the affected data packets via the backup routing path.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Lane-level vehicle navigation for vehicle routing and traffic management
ActiveUS20180299290A1Improves other aspectInstruments for road network navigationDetection of traffic movementTraffic signalTransportation planning
A lane-level vehicle routing and navigation apparatus includes a simulation module that performs microsimulation of individual vehicles in a traffic stream, and a lane-level optimizer that evaluates conditions along the candidate paths from an origin to a destination as determined by the simulation module, and determines recommended lane-level maneuvers along the candidate paths. A link-level optimizer may determines the candidate paths based on link travel times determined by the simulation module. The simulation may be based on real-time traffic condition data. Recommended candidate paths may be provided to delivery or service or emergency response vehicles, or used for evacuation planning, or to route vehicles such as garbage or postal trucks, or snowplows. Corresponding methods also may be used for traffic planning and management, including determining, based on microsimulation, at least one of (a) altered road geometry, (b) altered traffic signal settings, such as traffic signal timing, or (c) road pricing.
Owner:CALIPER CORPORATION
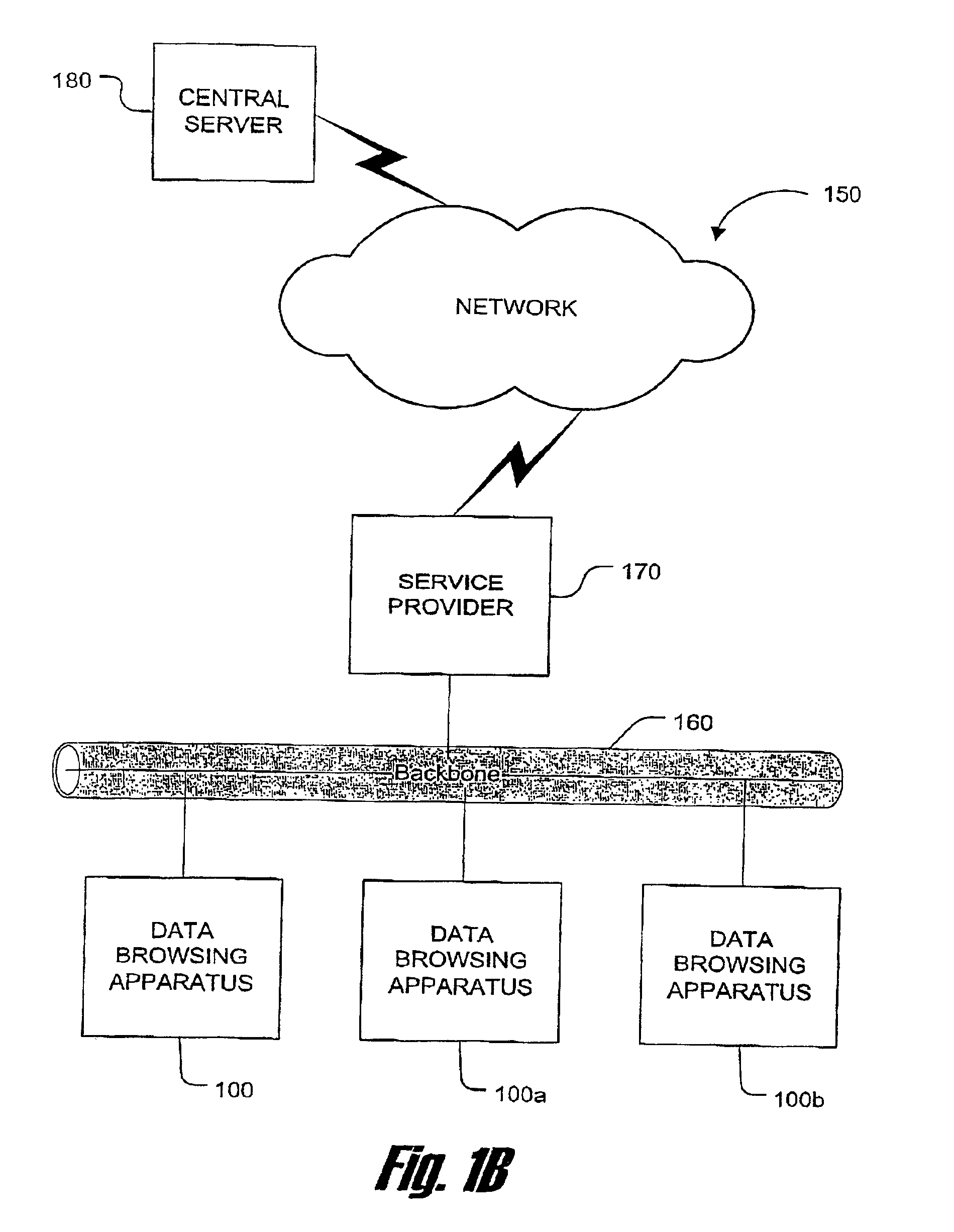
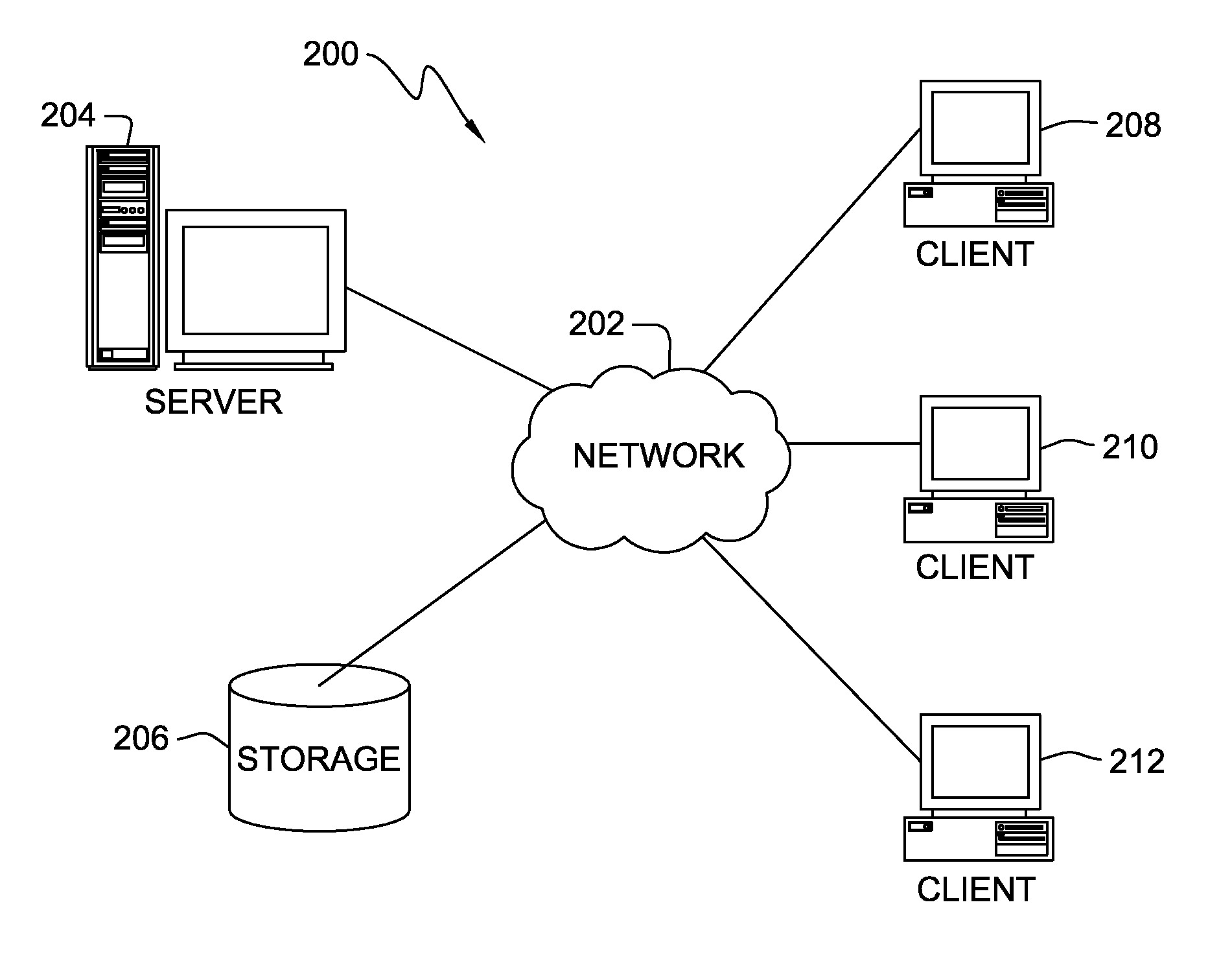
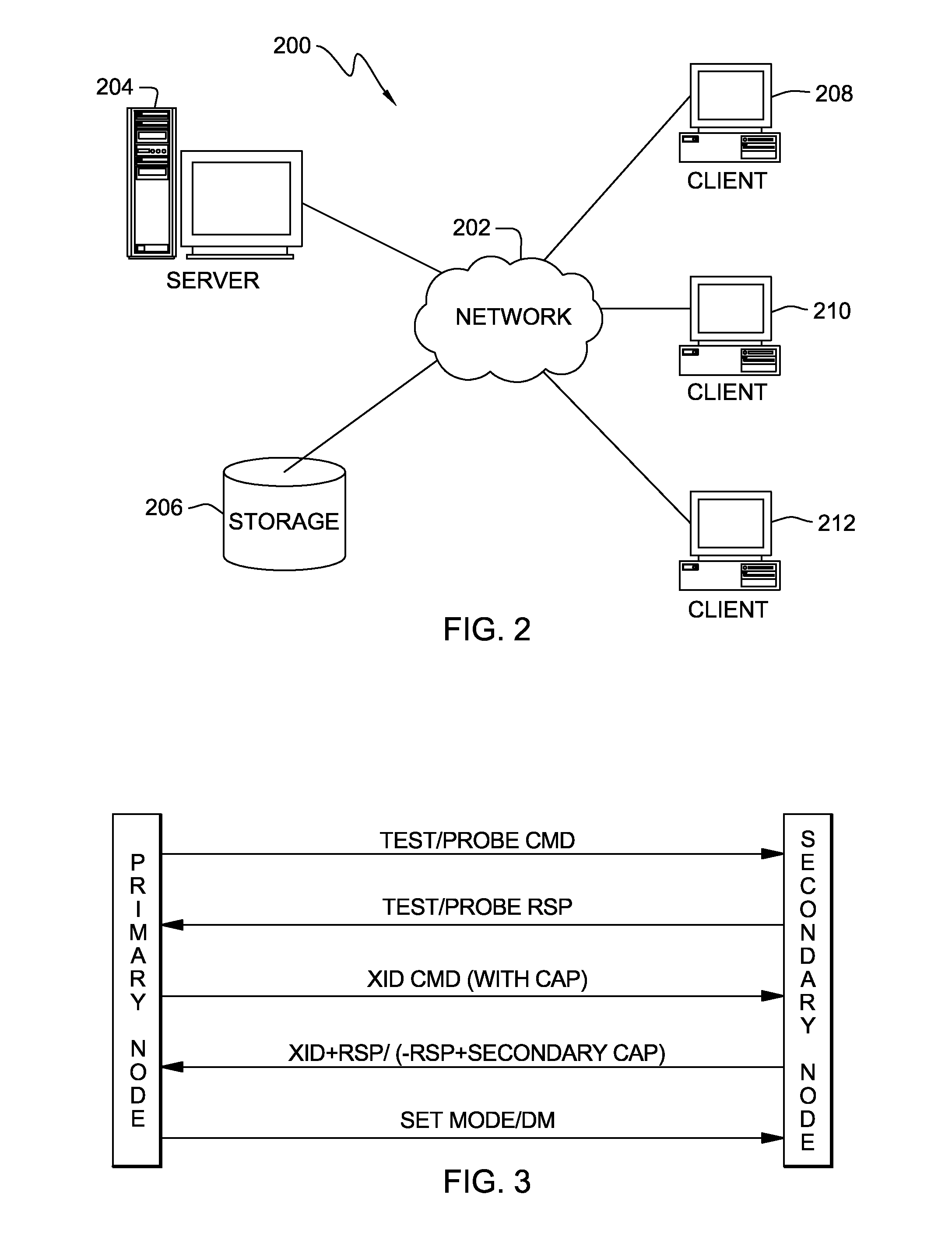
Method and system for establishing connections between nodes in a communication network
InactiveUS20110066736A1Simple procedureReduce in quantityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionComputer networkLink level
A method, system and article of manufacture are disclosed for establishing a connection between a plurality of nodes in a communication network, the plurality of nodes including at least first and second nodes. The method comprises the steps of verifying availability of the second node by the first node; and sending an exchange identification request by the first node to the second node, this request including information related to protocols supported by the first node. An exchange identification response is received by the first node from the second node, this response including information related to protocols supported by the second node. Also, the verifying step includes the steps of sending a request to the second node to initiate a link level connection between the first node and the second node, and confirming this connection upon receiving a response from the second node.
Owner:IBM CORP
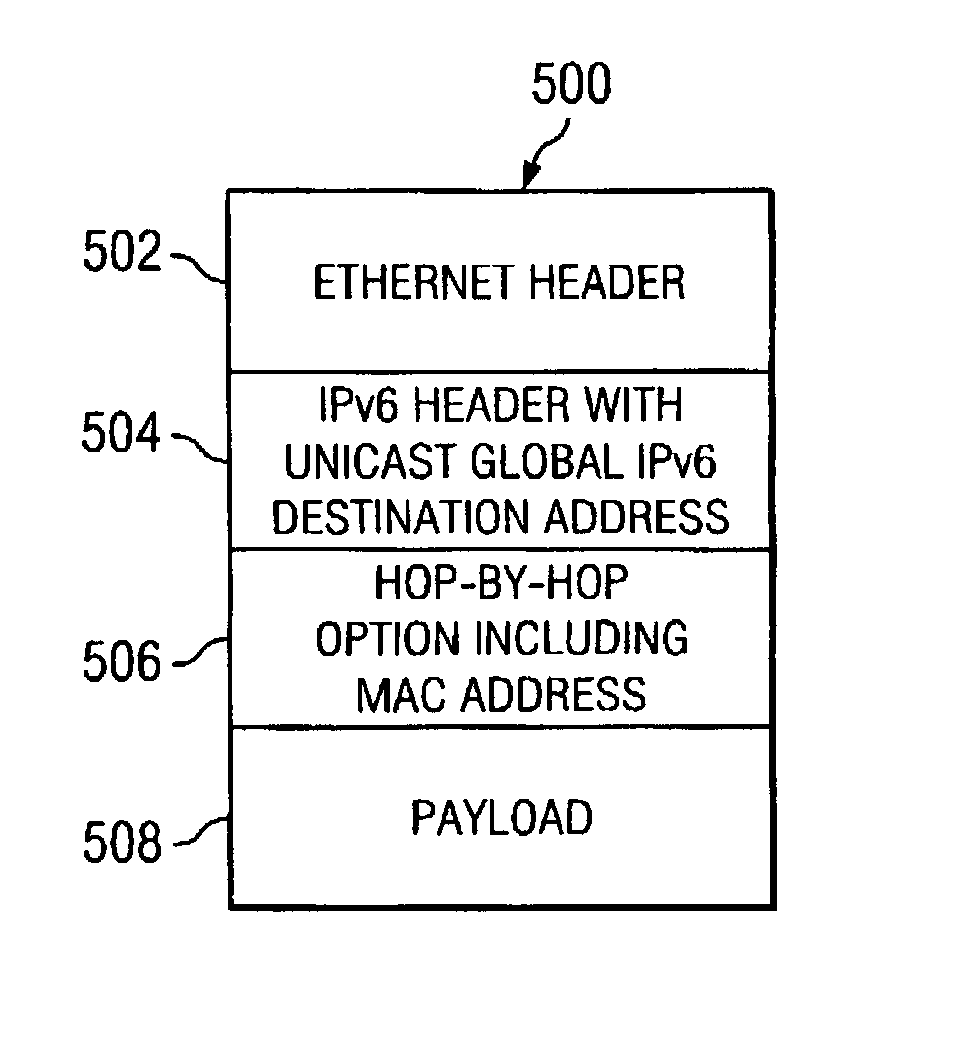
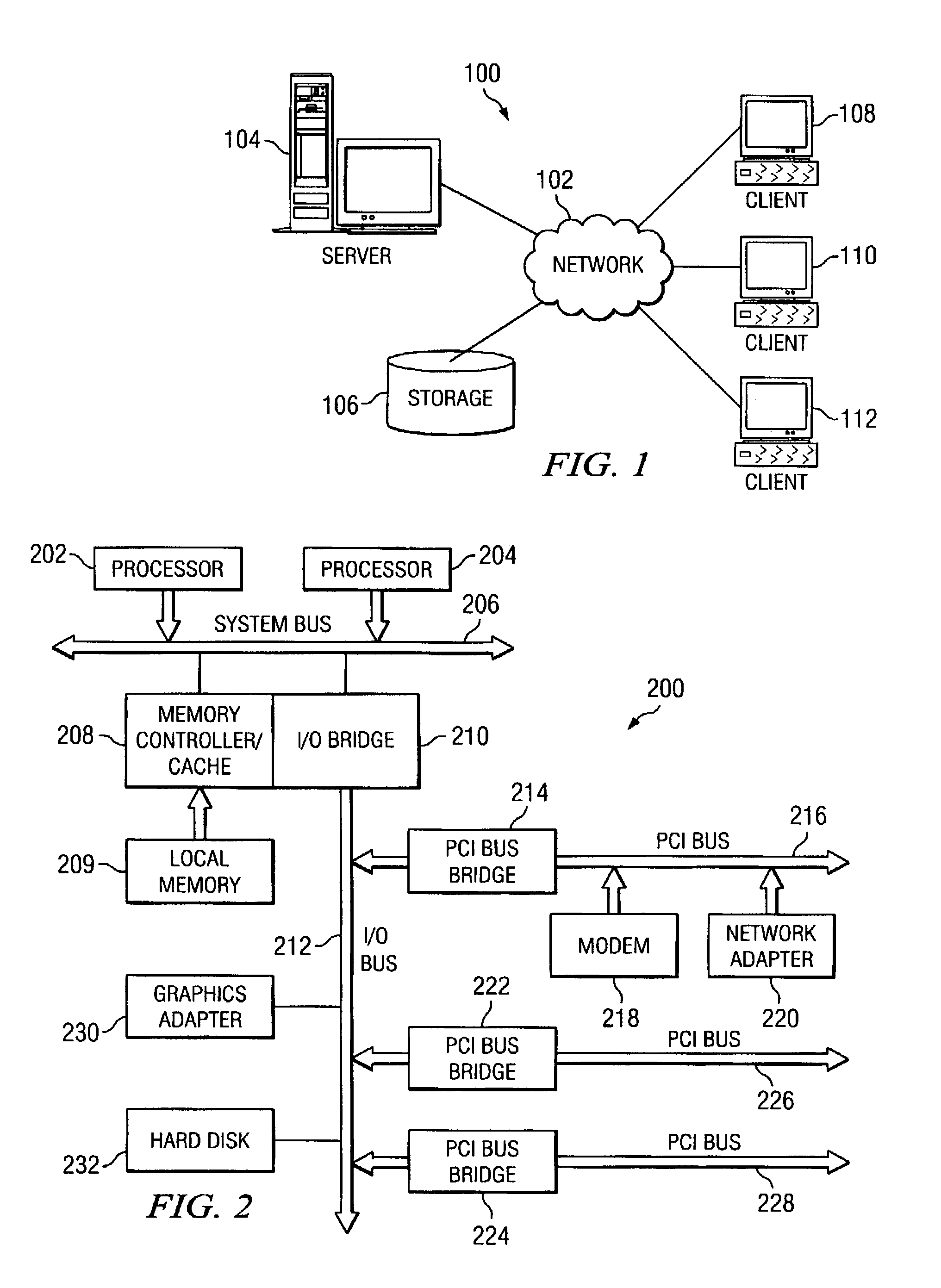
Method and apparatus for transmitting wake-up packets over a network data processing system
InactiveUS7324518B2Energy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsData processing systemNetwork data
A method in a data processing system for routing a packet to a target data processing system. With the method and apparatus, a global address for the target data processing system is placed in the packet. A hop-by-hop option may then be set in the packet, which contains a media access control address for the final destination. This option causes a router for a subnet on which the target data processing system is located to send the packet to the target data processing system using the media access control address without performing a link level address discovery operation.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com