Patents
Literature
60 results about "Threshold potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electrophysiology, the threshold potential is the critical level to which a membrane potential must be depolarized to initiate an action potential. In neuroscience, threshold potentials are necessary to regulate and propagate signaling in both the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
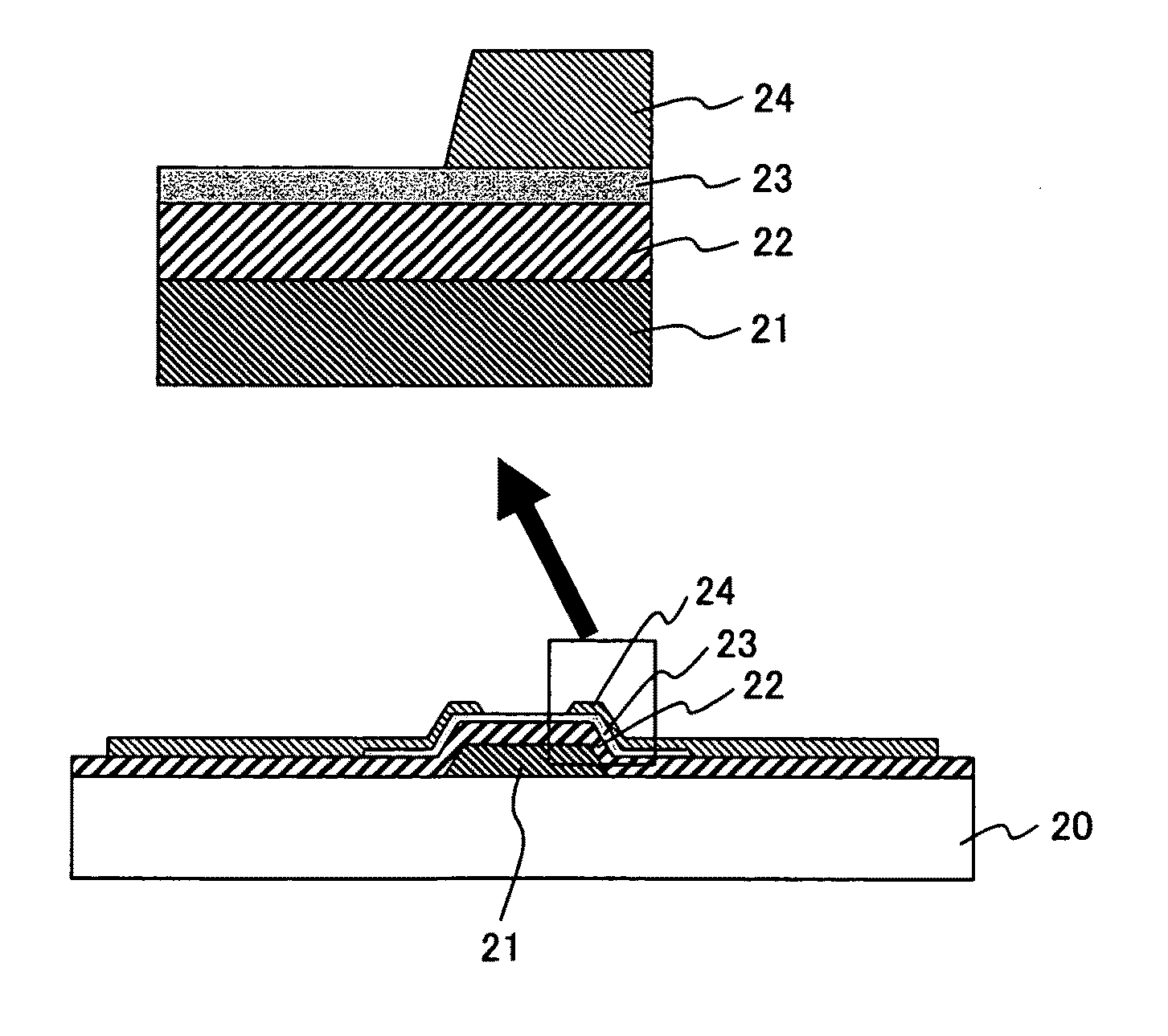
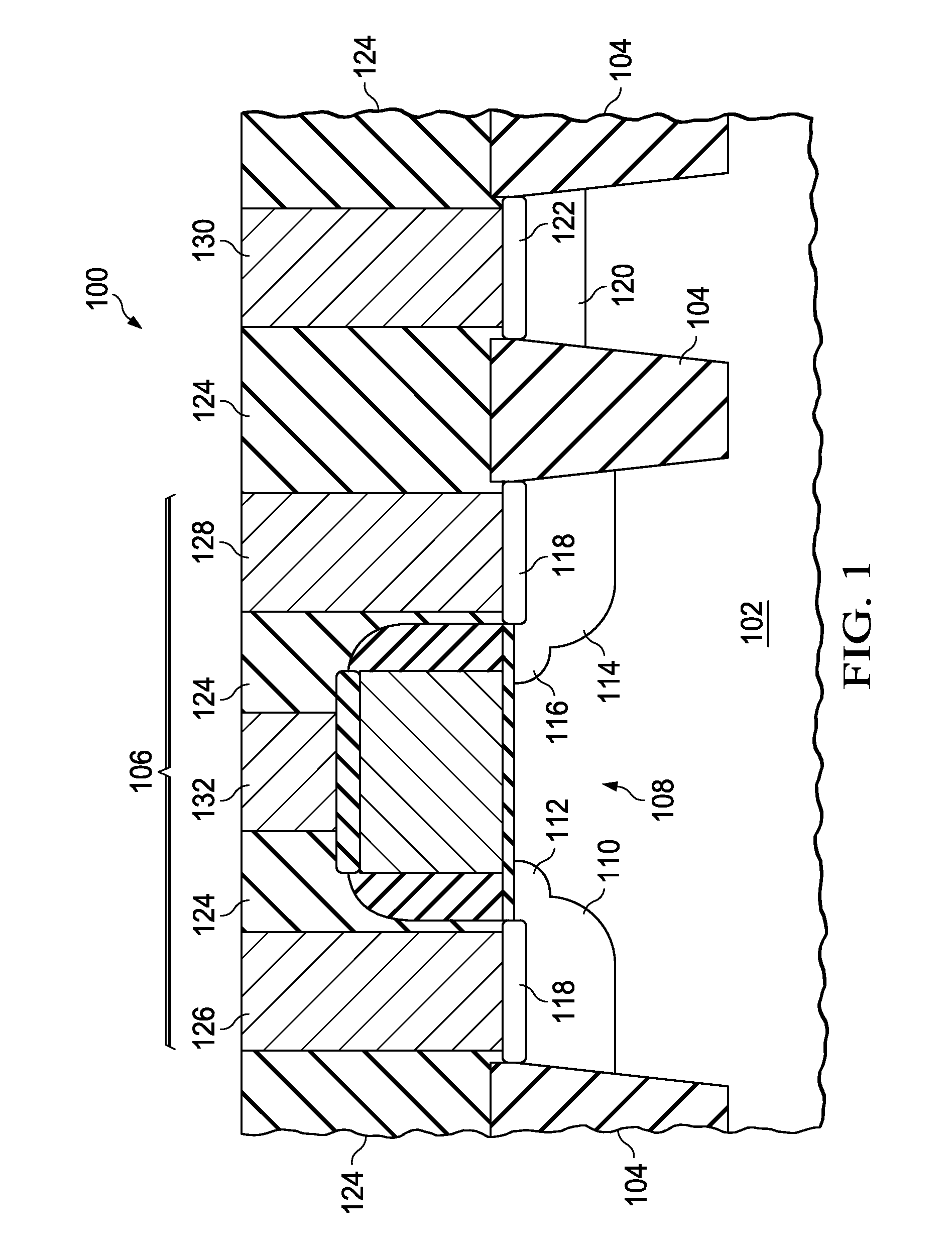
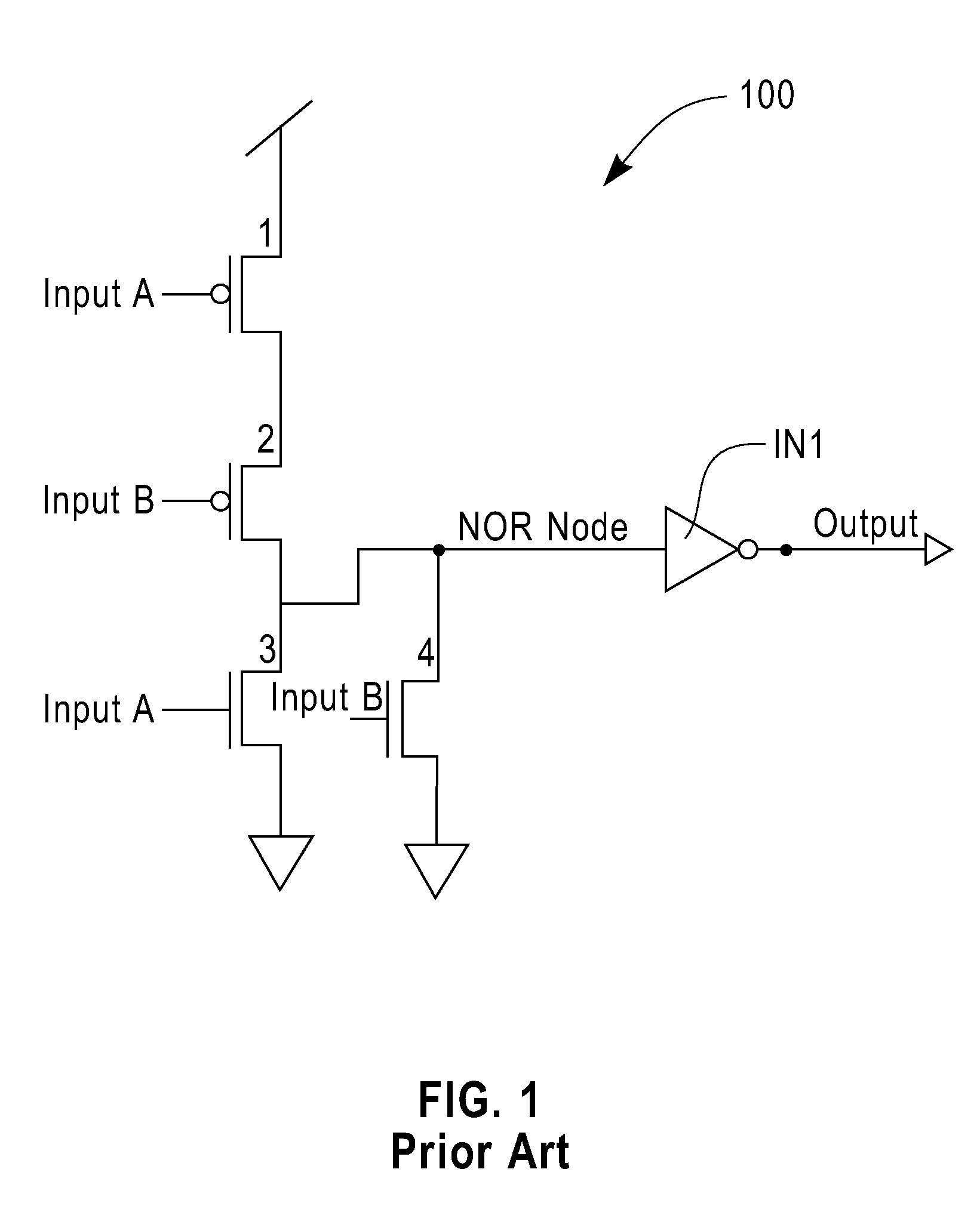
Oxide semiconductor device and surface treatment method of oxide semiconductor
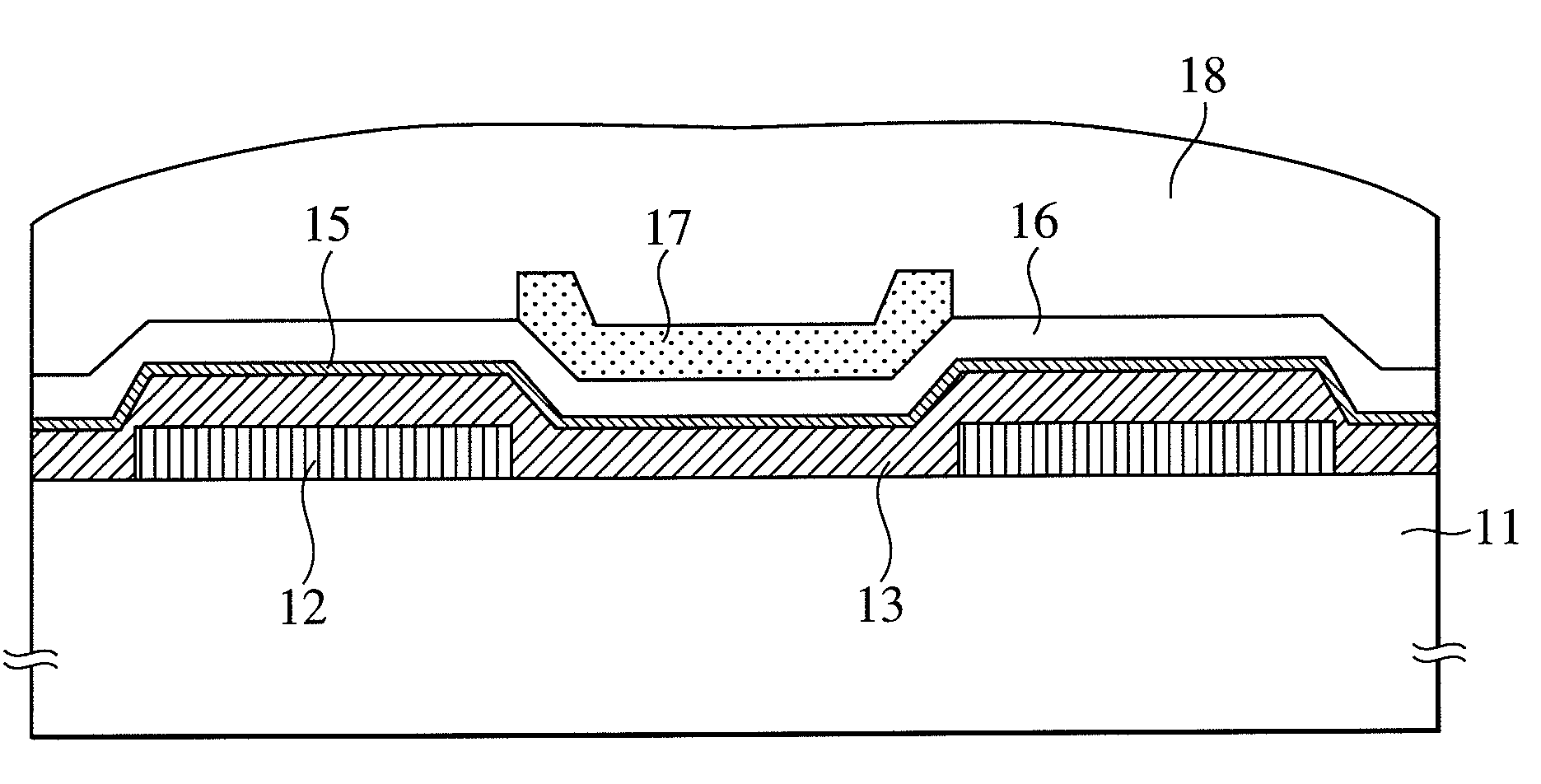
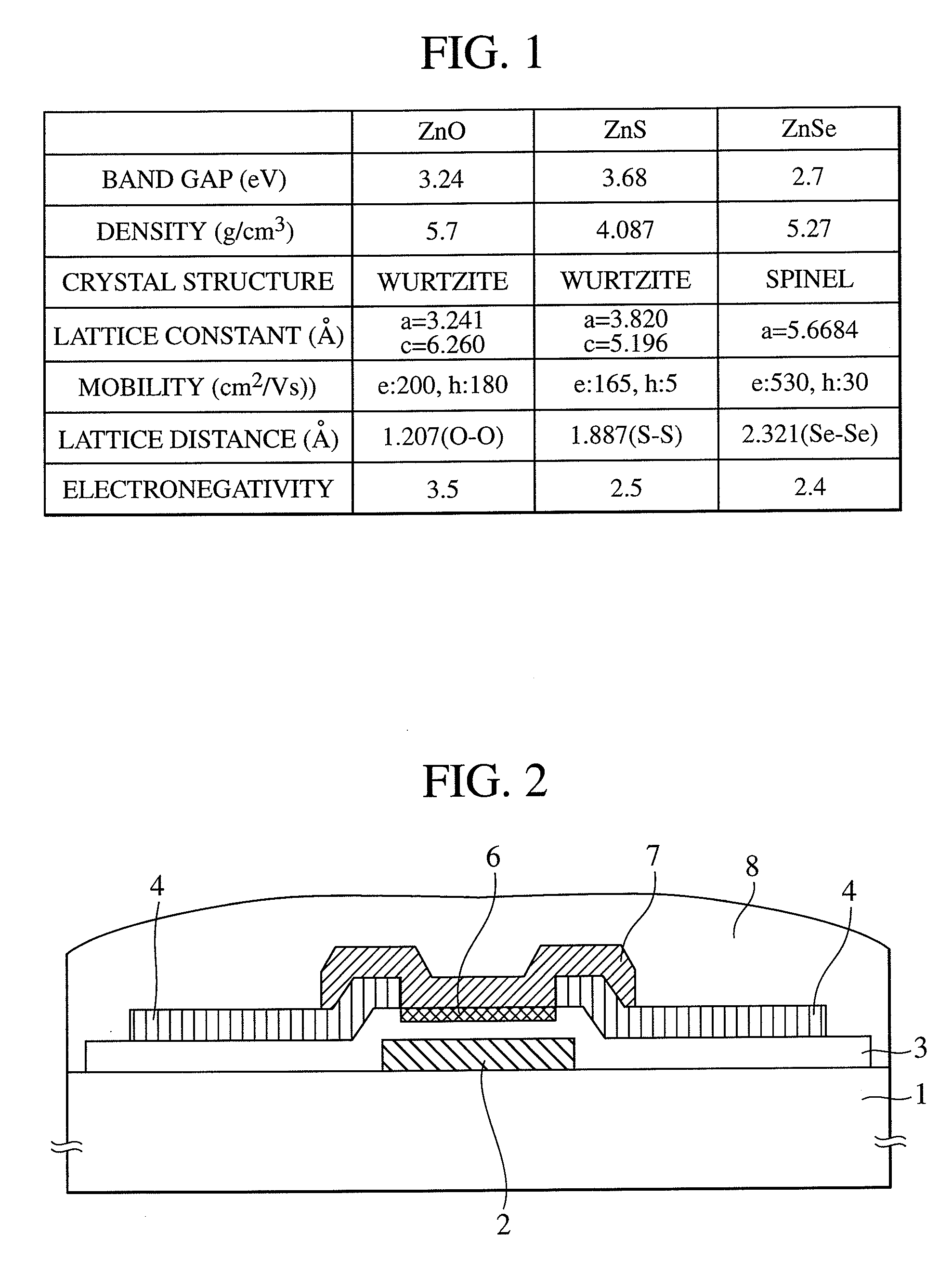
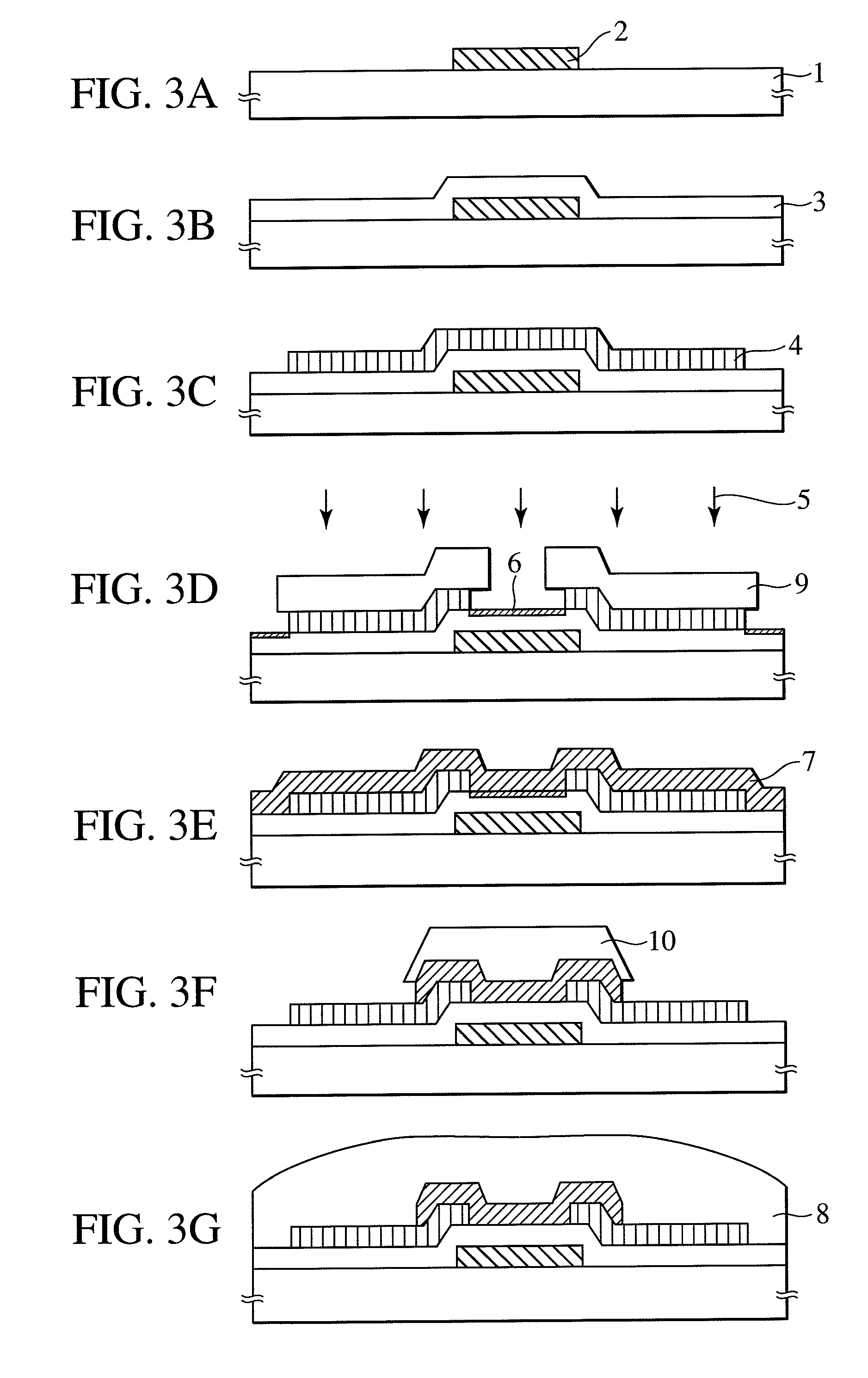
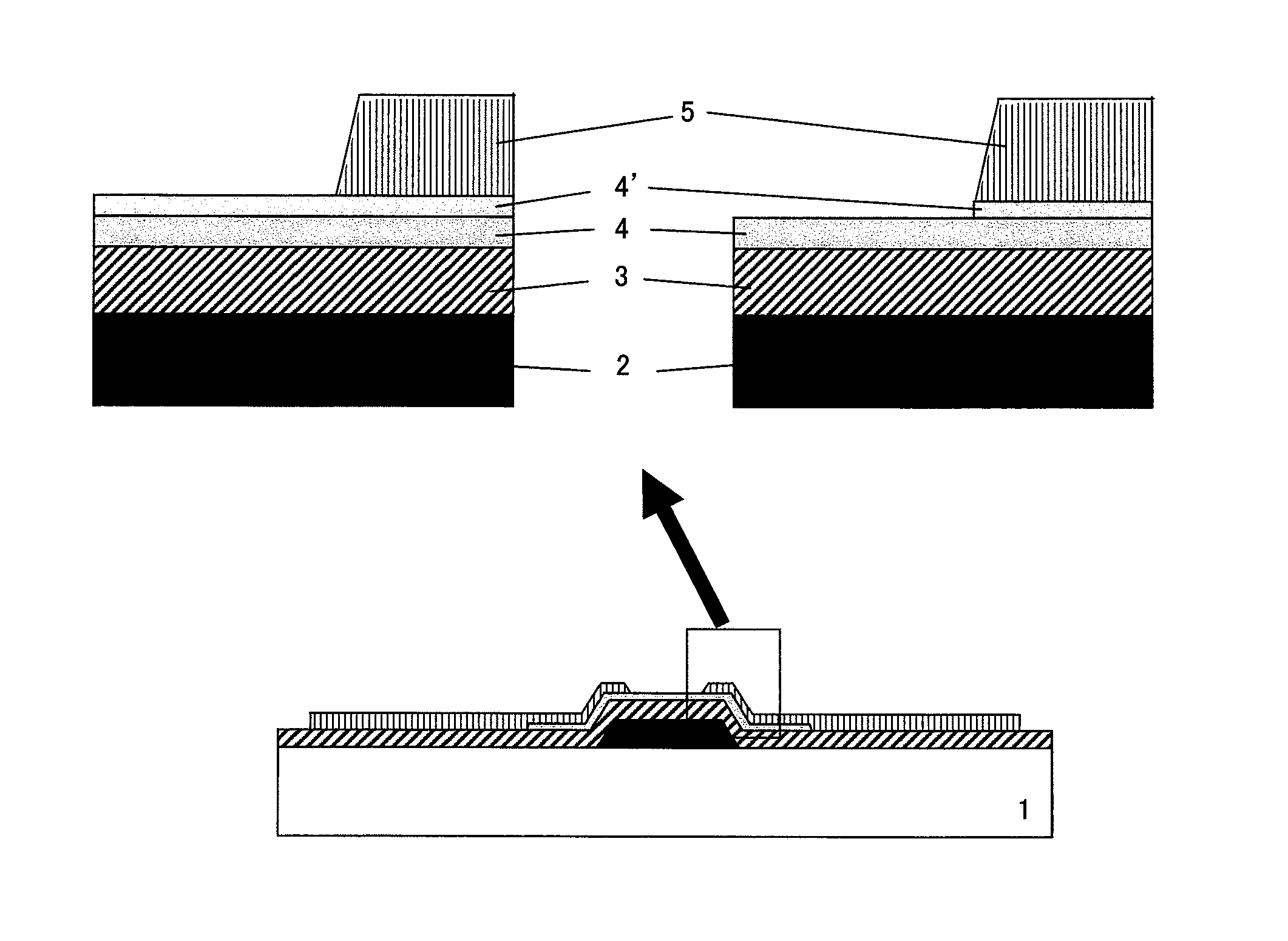
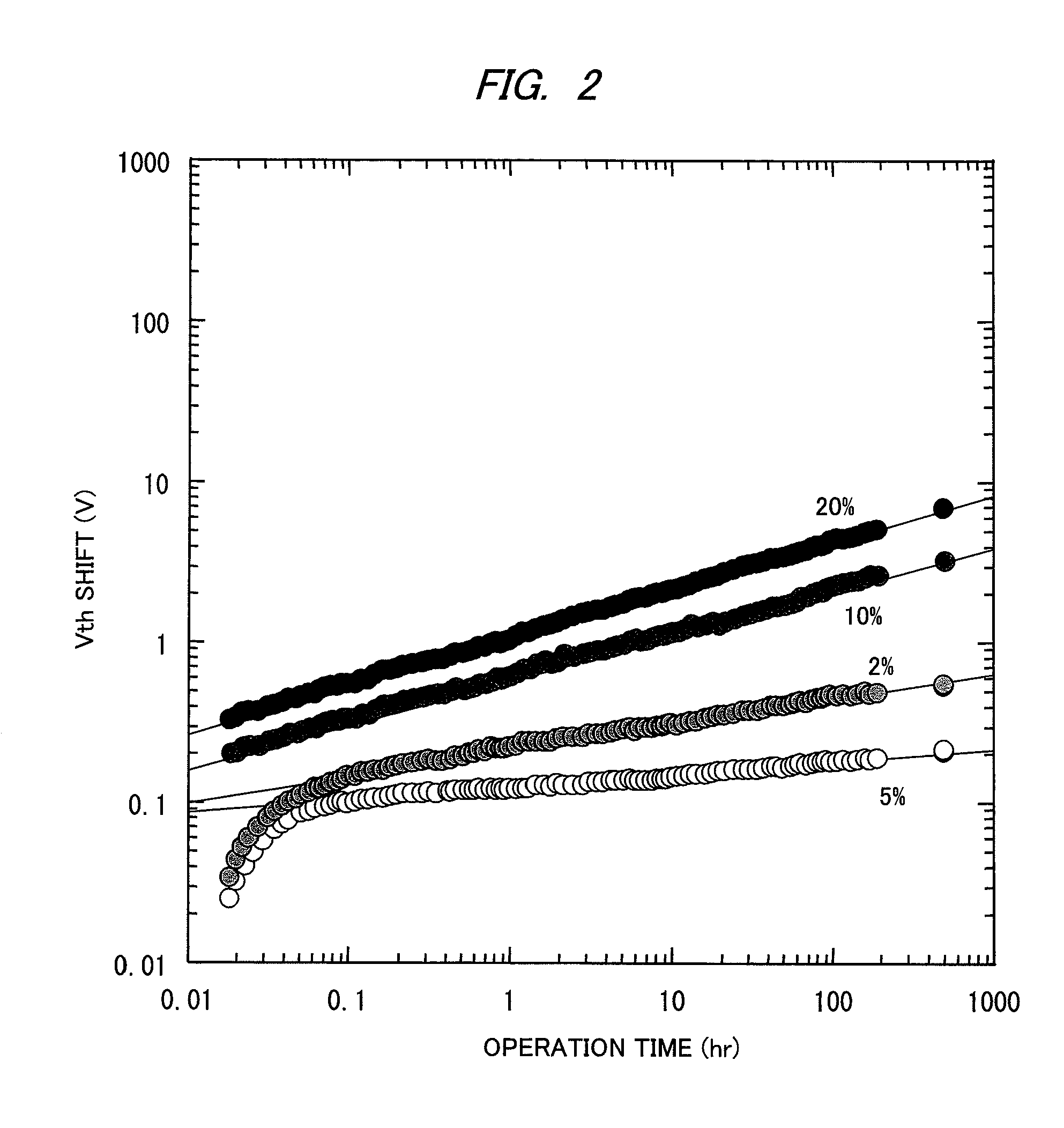
InactiveUS20090166616A1Effectively suppressing the threshold potential shift and occurrence of leak currentPhysical property is lessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseThreshold potential
Oxygen defects formed at the boundary between the zinc oxide type oxide semiconductor and the gate insulator are terminated by a surface treatment using sulfur or selenium as an oxygen group element or a compound thereof, the oxygen group element scarcely occurring physical property value change. Sulfur or selenium atoms effectively substitute oxygen defects to prevent occurrence of electron supplemental sites by merely applying a gas phase or liquid phase treatment to an oxide semiconductor or gate insulator with no remarkable change on the manufacturing process. As a result, this can attain the suppression of the threshold potential shift and the leak current in the characteristics of a thin film transistor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
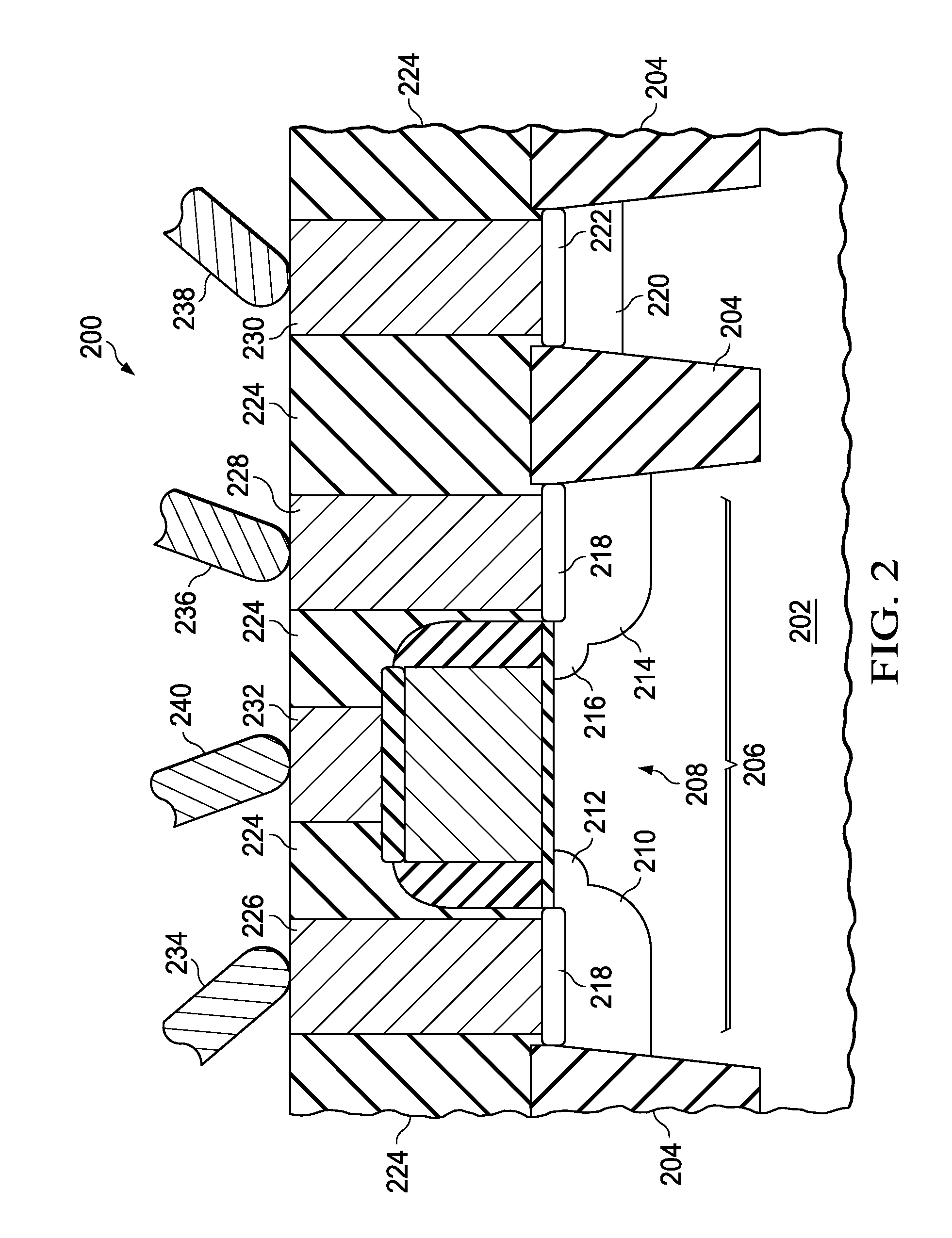
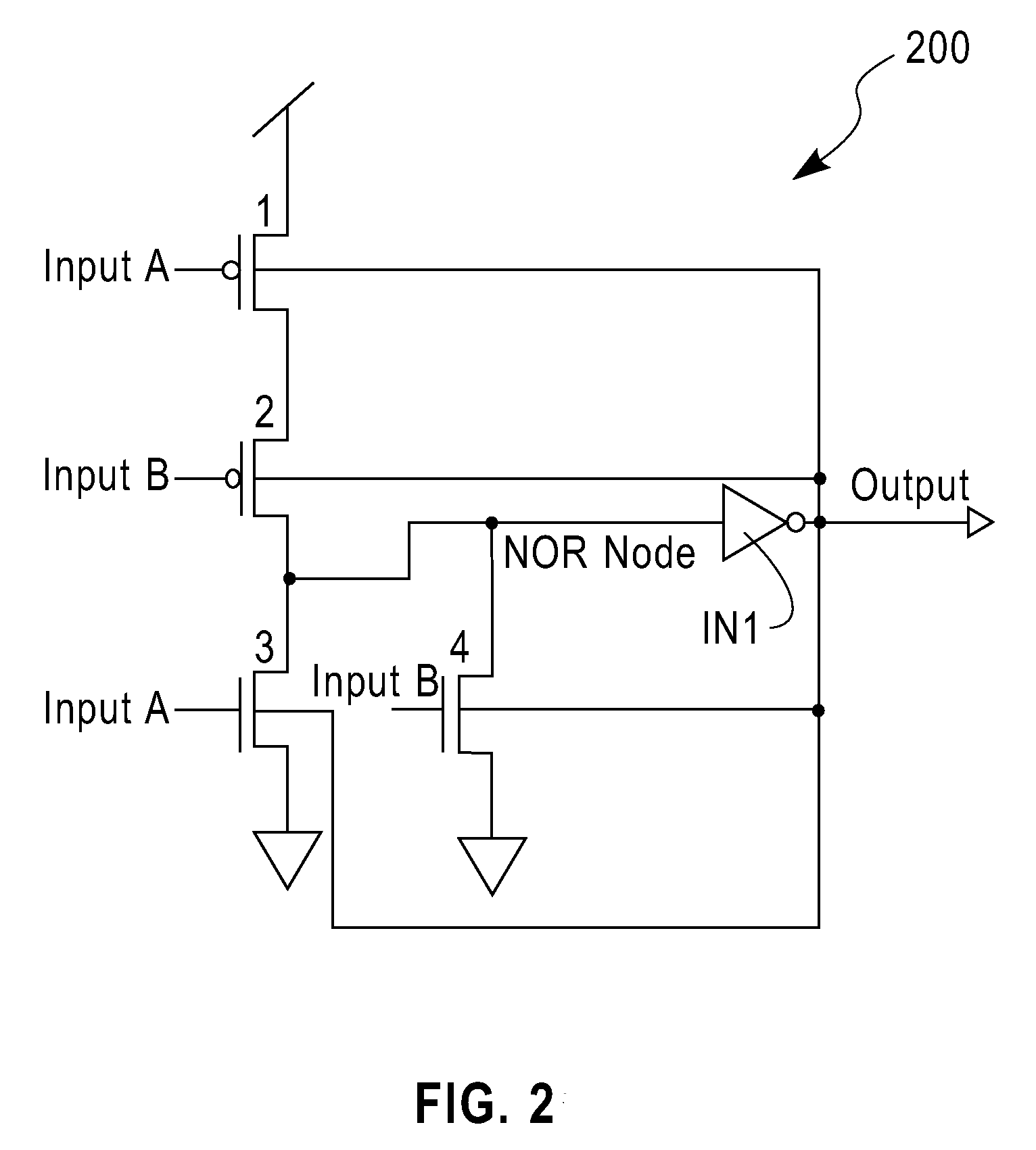
Oxide semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same and active matrix substrate
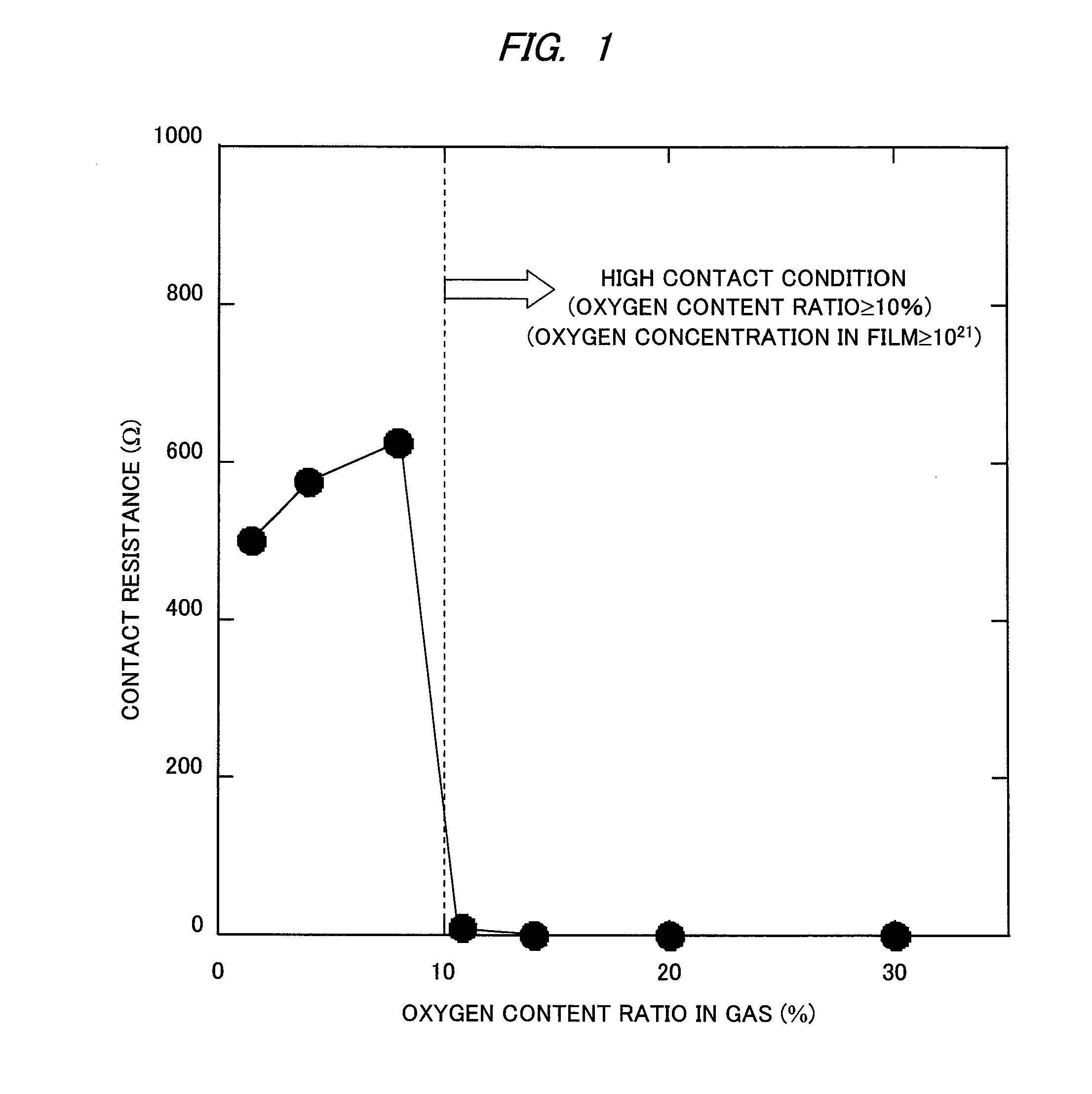
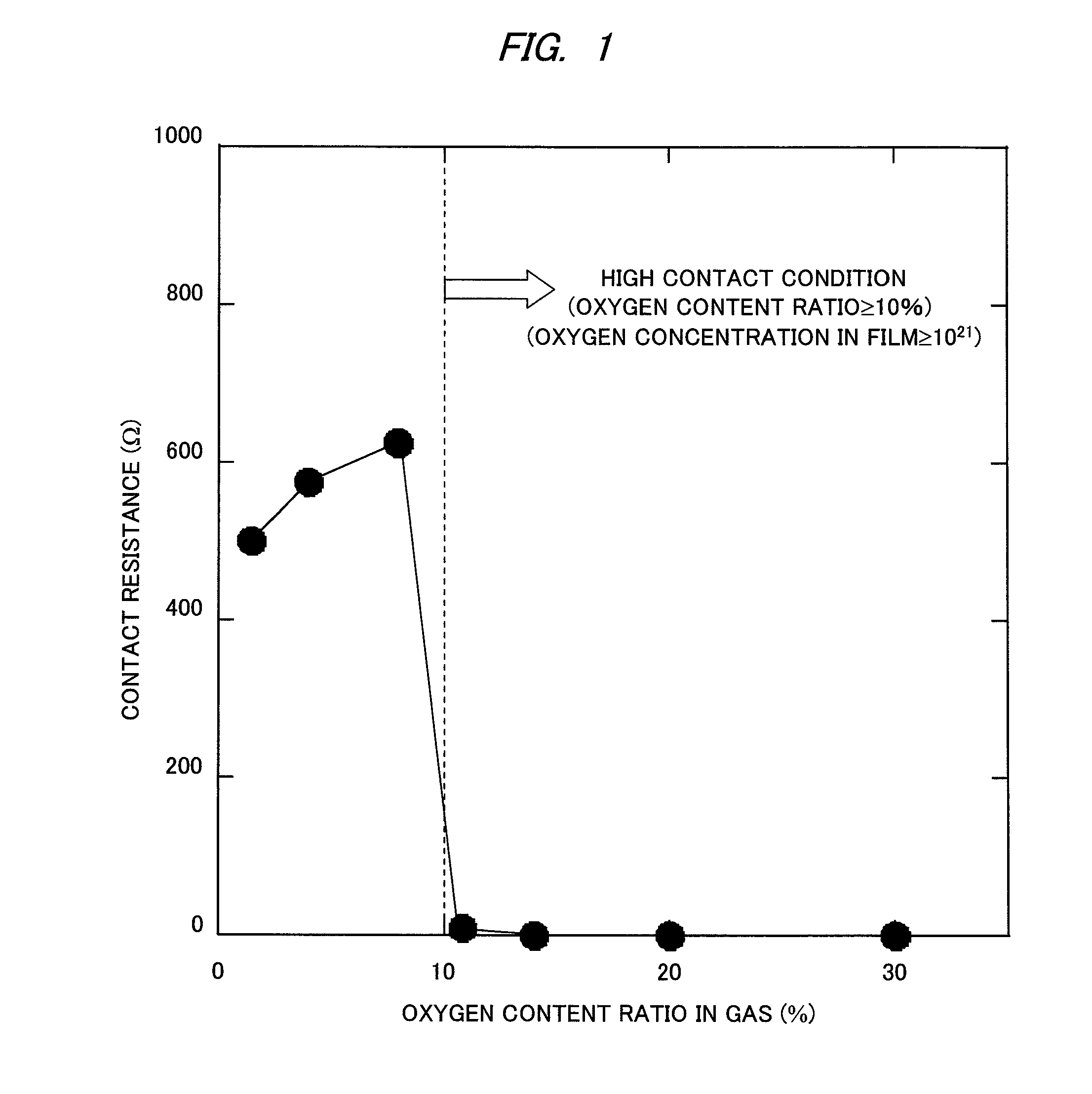
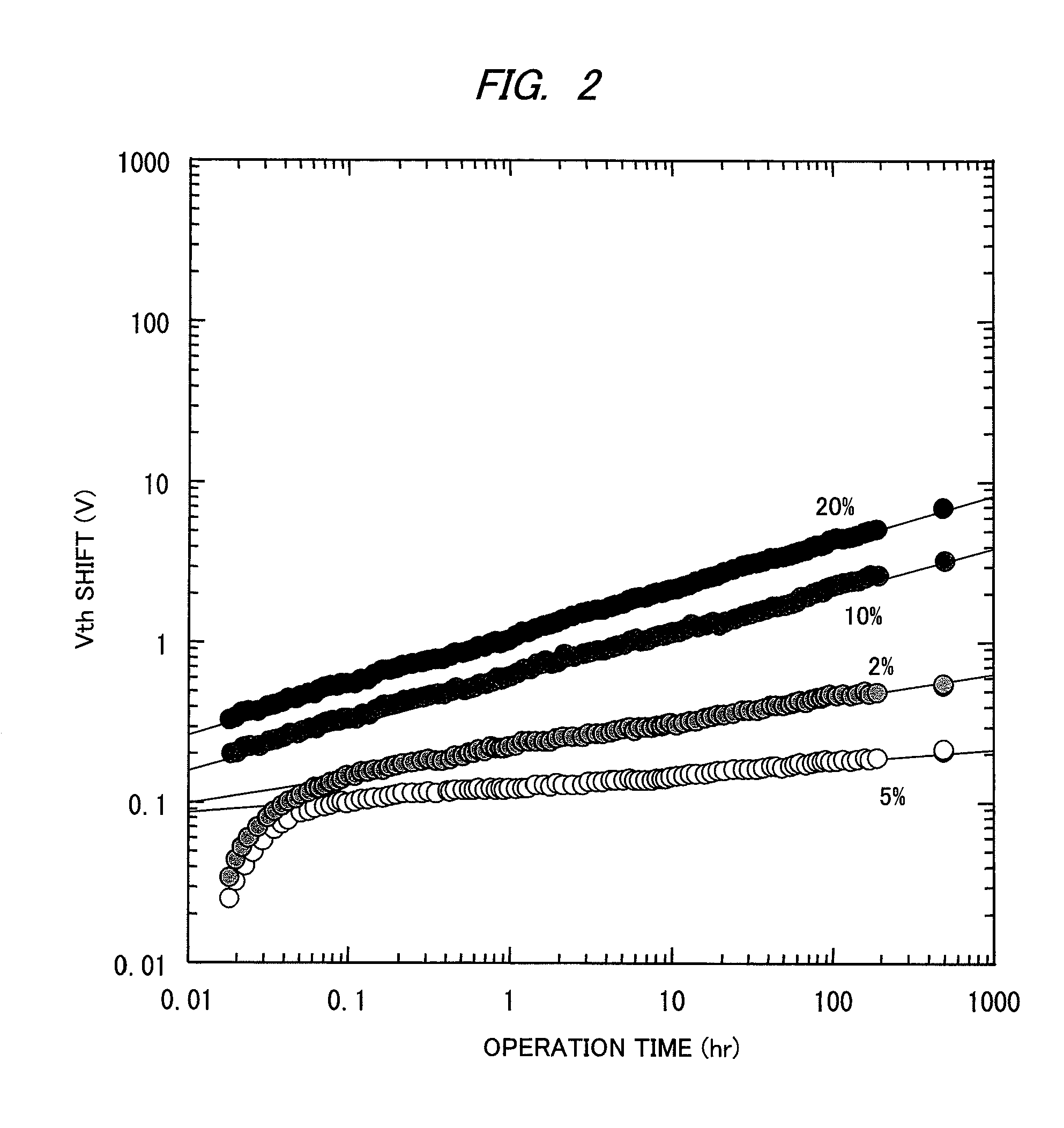
InactiveUS20100140614A1High content ratioImprove contact effectTransistorSolid-state devicesActive matrixThreshold potential
A phenomenon of change of a contact resistance between an oxide semiconductor and a metal depending on an oxygen content ratio in introduced gas upon depositing an oxide semiconductor film made of indium gallium zinc oxide, zinc tin oxide, or others in an oxide semiconductor thin-film transistor. A contact layer is formed with an oxygen content ratio of 10% or higher in a region from a surface, where the metal and the oxide semiconductor are contacted, down to at least 3 nm deep in depth direction, and a region to be a main channel layer is further formed with an oxygen content ratio of 10% or lower, so that a multilayered structure is formed, and both of ohmic characteristics to the electrode metal and reliability such as the suppression of threshold potential shift are achieved.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
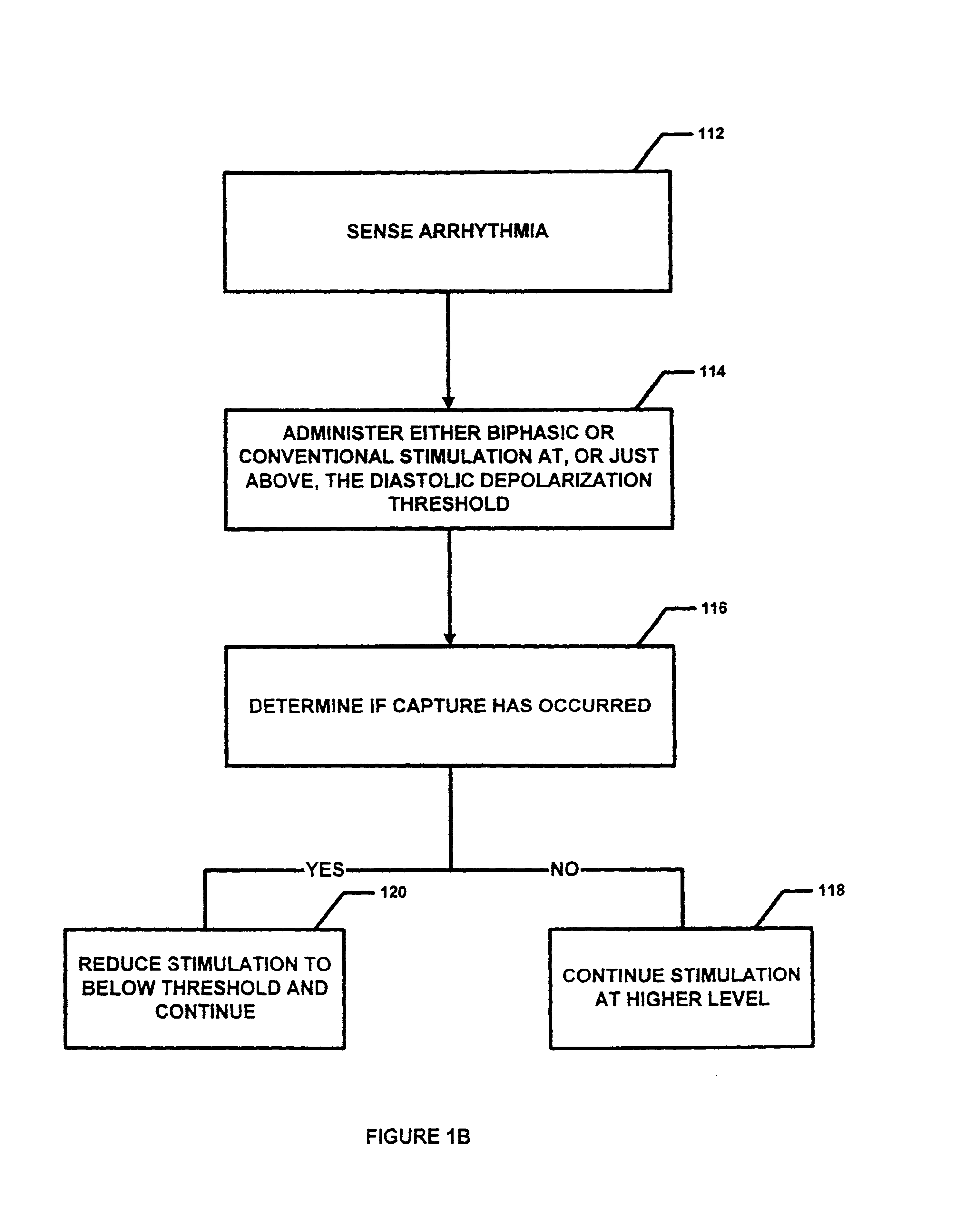
Antitachycardial pacing
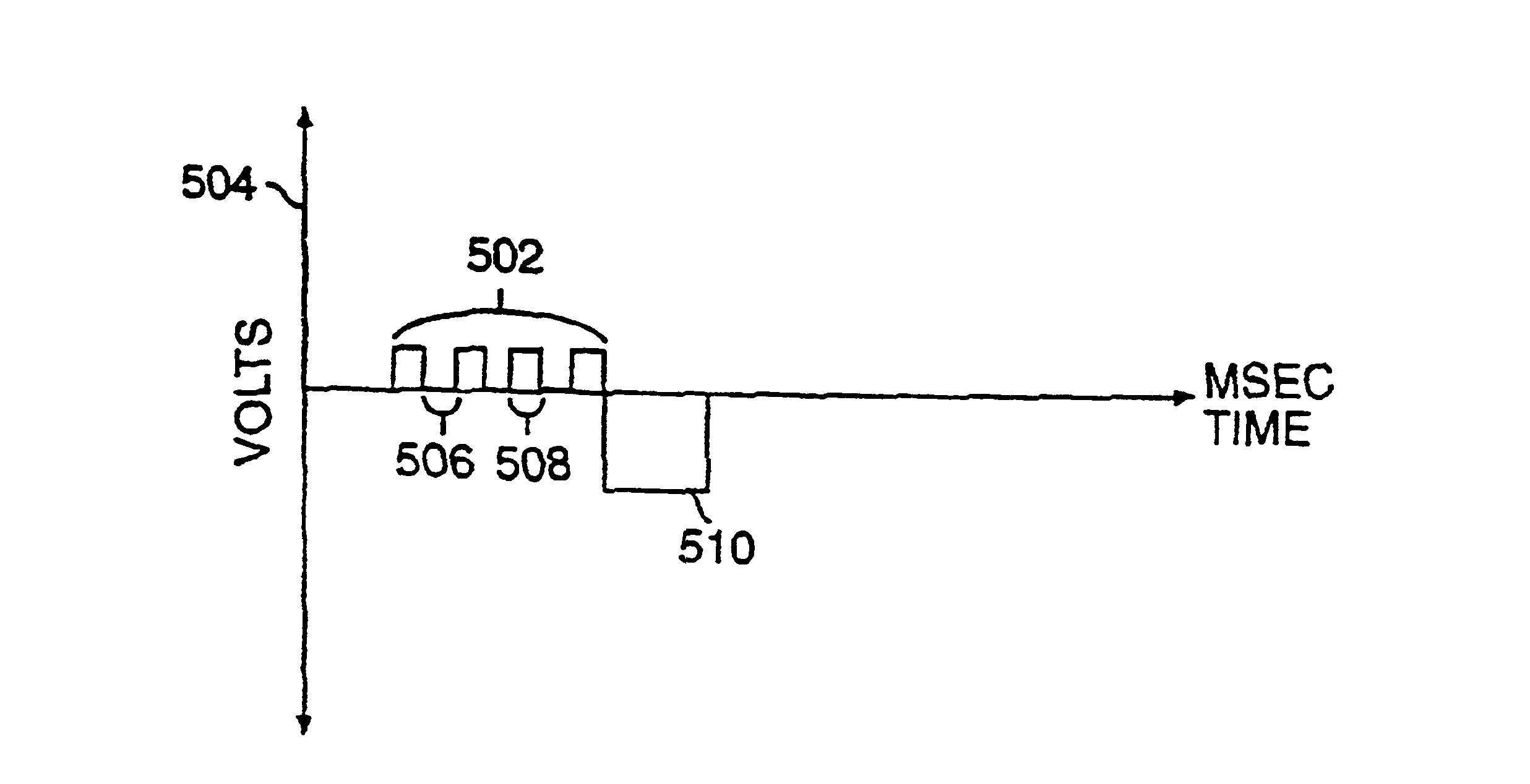
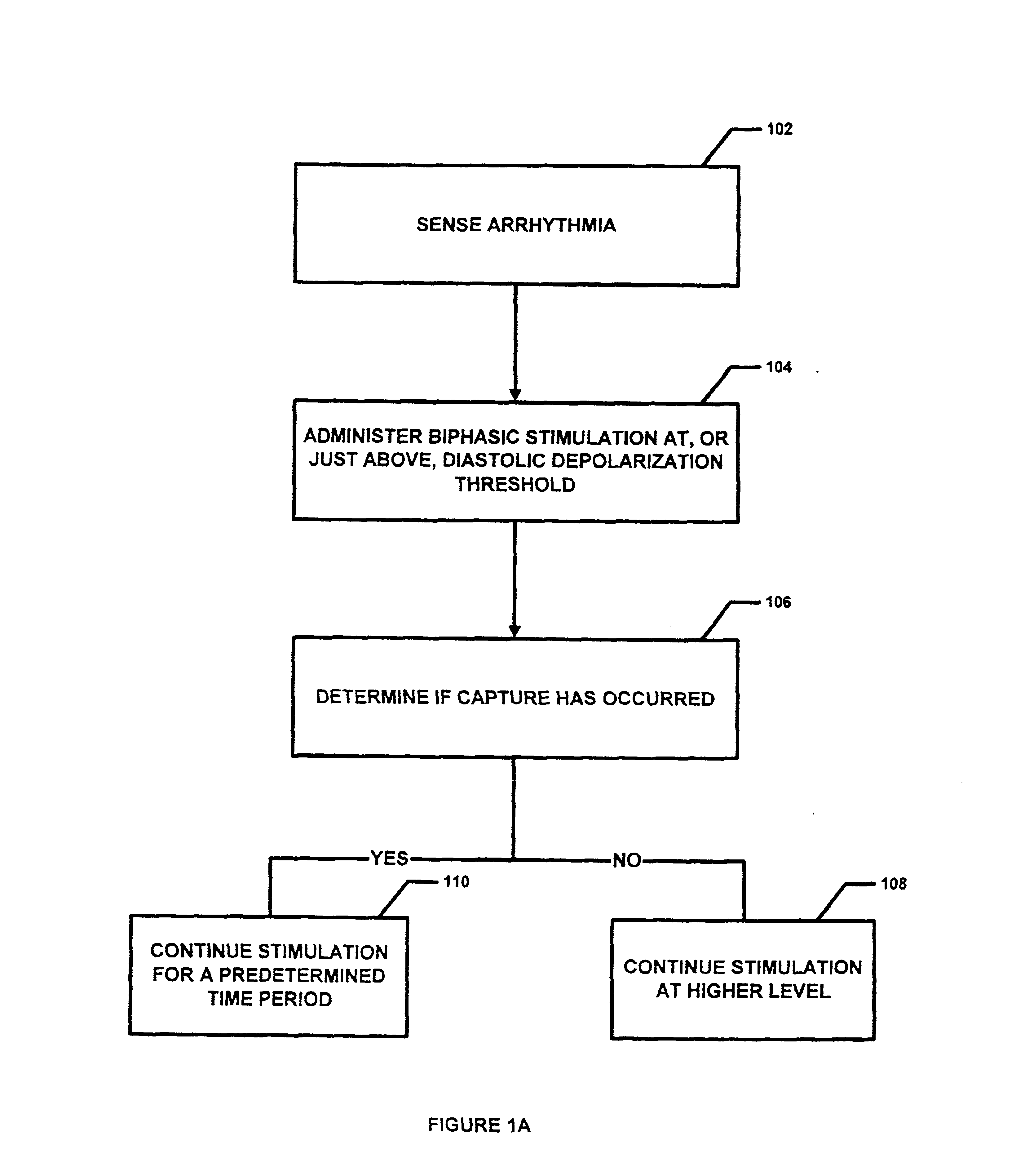
InactiveUS6895274B2Facilitate conductionIncrease contractilityHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsTreatment effectThreshold potential
Protocols for antitachycardial pacing including biphasic stimulation administered at, or just above, the diastolic depolarization threshold potential; biphasic or conventional stimulation initiated at, or just above, the diastolic depolarization threshold potential, reduced, upon capture, to below threshold; and biphasic or conventional stimulation administered at a level set just below the diastolic depolarization threshold potential. These protocols result in reliable cardiac capture with a lower stimulation level, thereby causing less damage to the heart, extending battery life, causing less pain to the patient and having greater therapeutic effectiveness. In those protocols using biphasic cardiac pacing, a first and second stimulation phase is administered. The first stimulation phase has a predefined polarity, amplitude and duration. The second stimulation phase also has a predefined polarity, amplitude and duration. The two phases are applied sequentially. Contrary to current thought, anodal stimulation is first applied and followed by cathodal stimulation. In this fashion, pulse conduction through the cardiac muscle is improved together with the increase in contractility.
Owner:MR3 MEDICAL LLC
Packet energy transfer powered telecommunications system for macro antenna systems and power distribution system therefor
InactiveUS20160294500A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsFibre transmissionEnergy transferThreshold potential
A power-data distribution system including a packet energy transfer (PET) system, a converter, a conductive cable and a fiber optic cable. The PET system transmits discrete packets of digital energy and produces a continuous stream of analog power. The converter reduces the analog power from the first to a second potential, wherein the second potential is lower than a threshold potential. A conductive cable transmits the discrete packets of digital energy from a power source to a load while a fiber optic cable exchanges data between a data source and the target device.
Owner:JOHN MEZZALINGUA ASSOC LLC
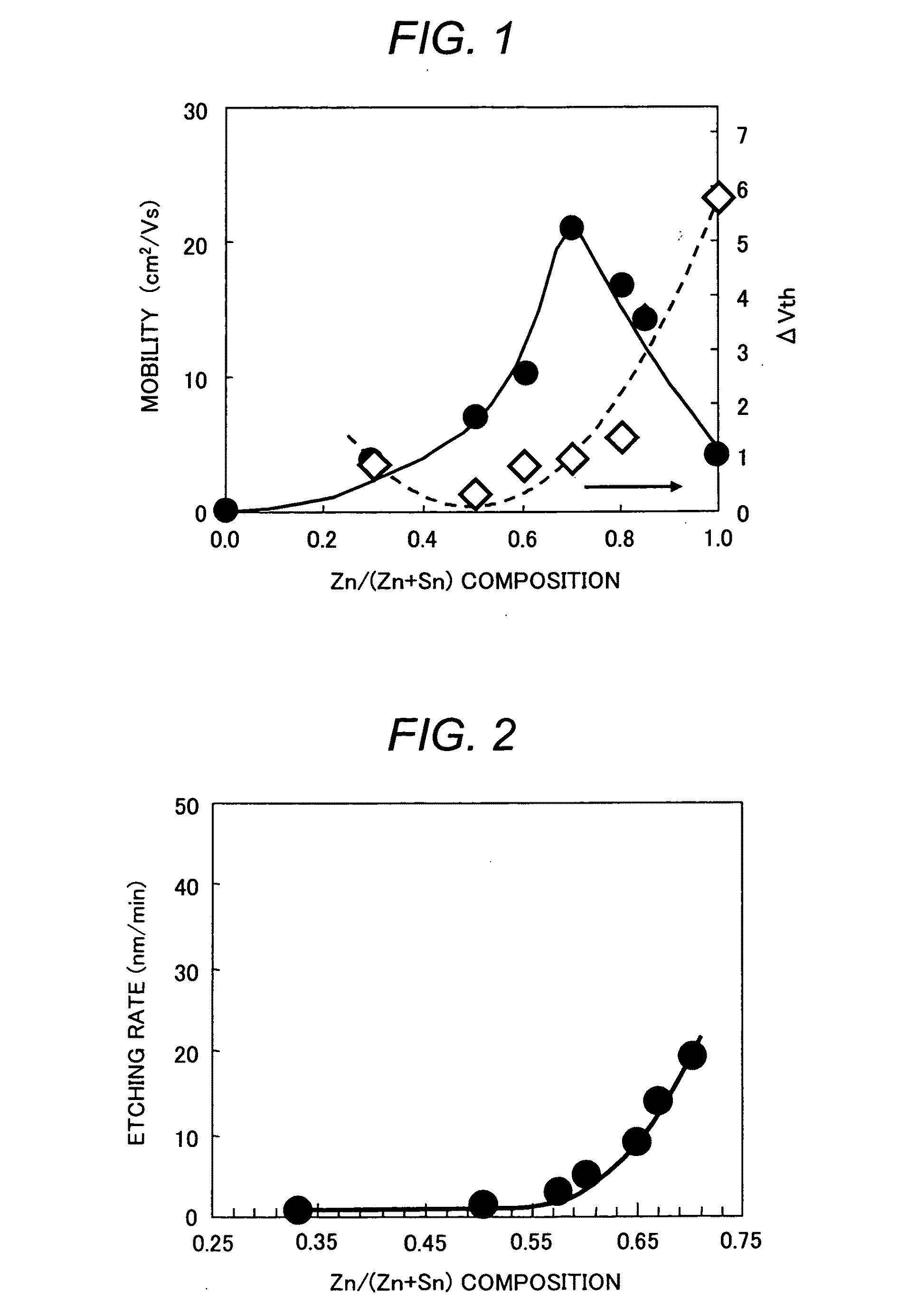
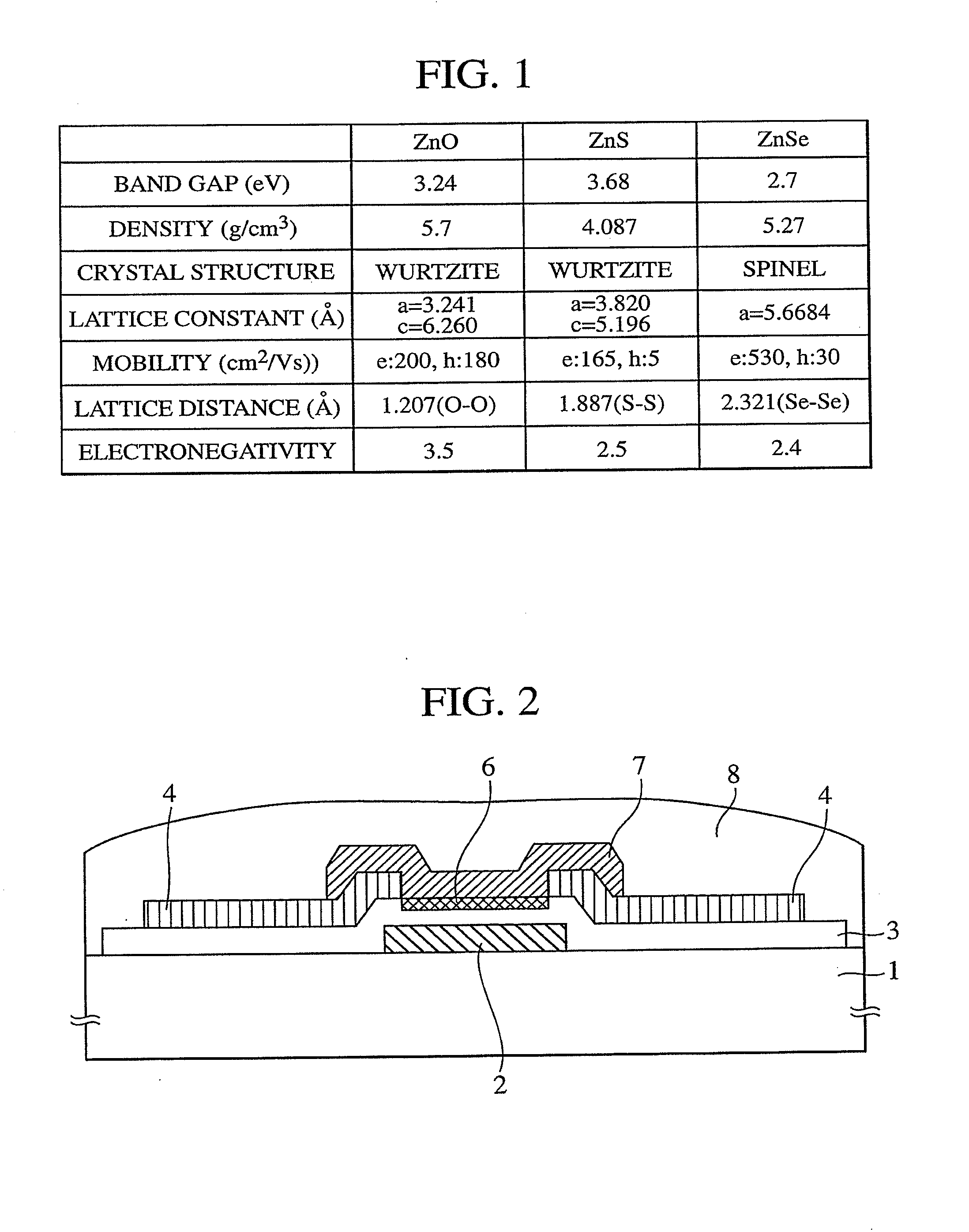
Oxide semiconductor target and manufacturing method of oxide semiconductor device by using the same
InactiveUS20100330738A1Improve mobilityHigh potential stabilityCellsVacuum evaporation coatingHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
An oxide semiconductor target of a ZTO (zinc tin complex oxide) type oxide semiconductor material of an appropriate (Zn / (Zn+Sn)) composition having high mobility and threshold potential stability and with less restriction in view of the cost and the resource and with less restriction in view of the process, and an oxide semiconductor device using the same, in which a sintered Zn tin complex oxide with a (Zn / (Zn+Sn)) composition of 0.6 to 0.8 is used as a target, the resistivity of the target itself is at a high resistance of 1 Ωcm or higher and, further, the total concentration of impurities is controlled to 100 ppm or less.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
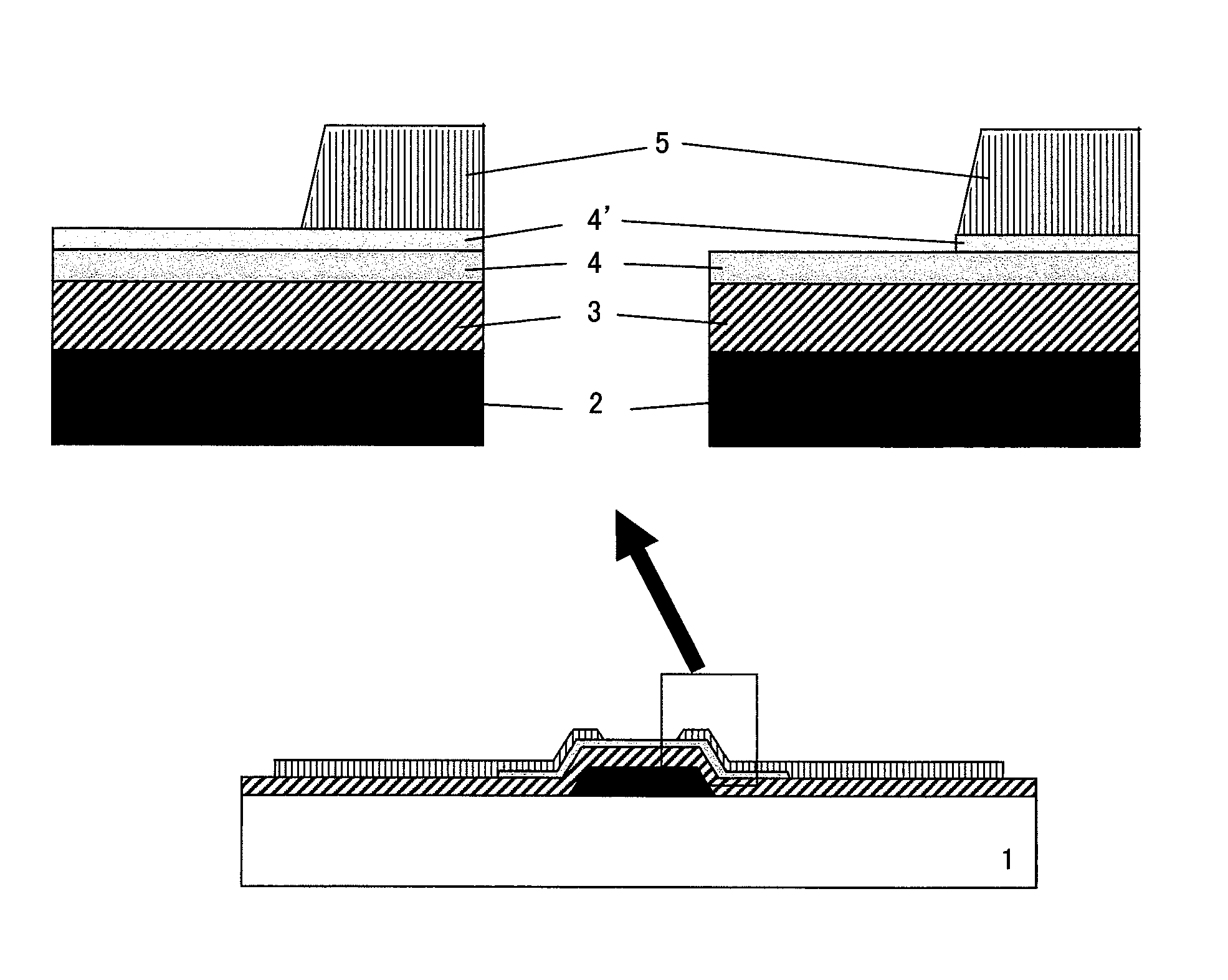
Oxide semiconductor device with oxide semiconductor layers of different oxygen concentrations and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS8368067B2Easiness of flexibilityImprove the level ofTransistorSolid-state devicesThreshold potentialMain channel
A phenomenon of change of a contact resistance between an oxide semiconductor and a metal depending on an oxygen content ratio in introduced gas upon depositing an oxide semiconductor film made of indium gallium zinc oxide, zinc tin oxide, or others in an oxide semiconductor thin-film transistor. A contact layer is formed with an oxygen content ratio of 10% or higher in a region from a surface, where the metal and the oxide semiconductor are contacted, down to at least 3 nm deep in depth direction, and a region to be a main channel layer is further formed with an oxygen content ratio of 10% or lower, so that a multilayered structure is formed, and both of ohmic characteristics to the electrode metal and reliability such as the suppression of threshold potential shift are achieved.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Boosting circuit and RFID tag including boosting circuit
InactiveUS20110215787A1Decrease output potential can be preventedImprove efficiencyTransistorAc-dc conversionThreshold potentialEngineering
One object is to provide a boosting circuit whose boosting efficiency is enhanced. Another object is to provide an RFID tag including a boosting circuit whose boosting efficiency is enhanced. A node corresponding to an output terminal of a unit boosting circuit or a gate electrode of a transistor connected to the node is boosted by bootstrap operation, so that a decrease in potential which corresponds to substantially the same as the threshold potential of the transistor can be prevented and a decrease in output potential of the unit boosting circuit can be prevented.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
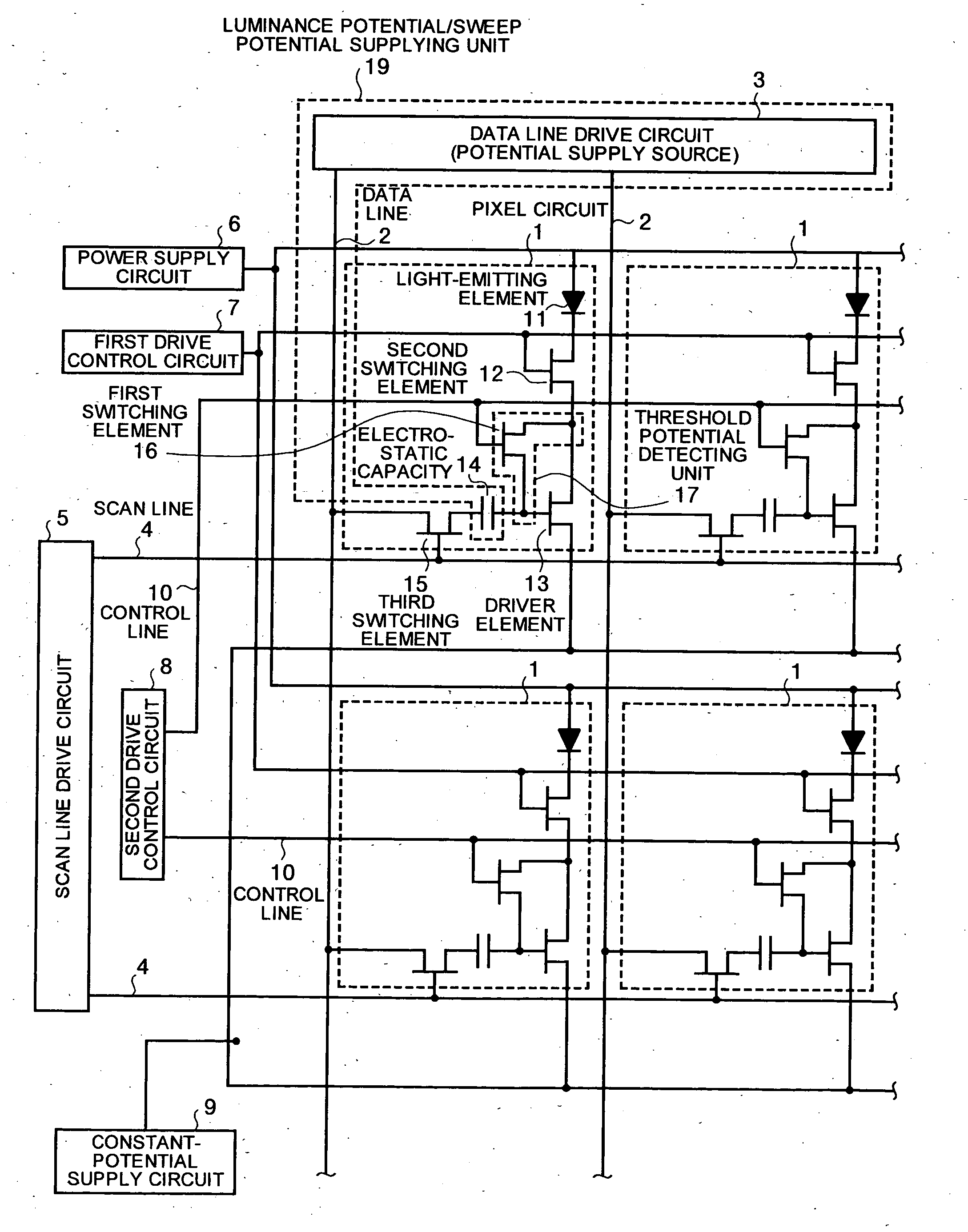
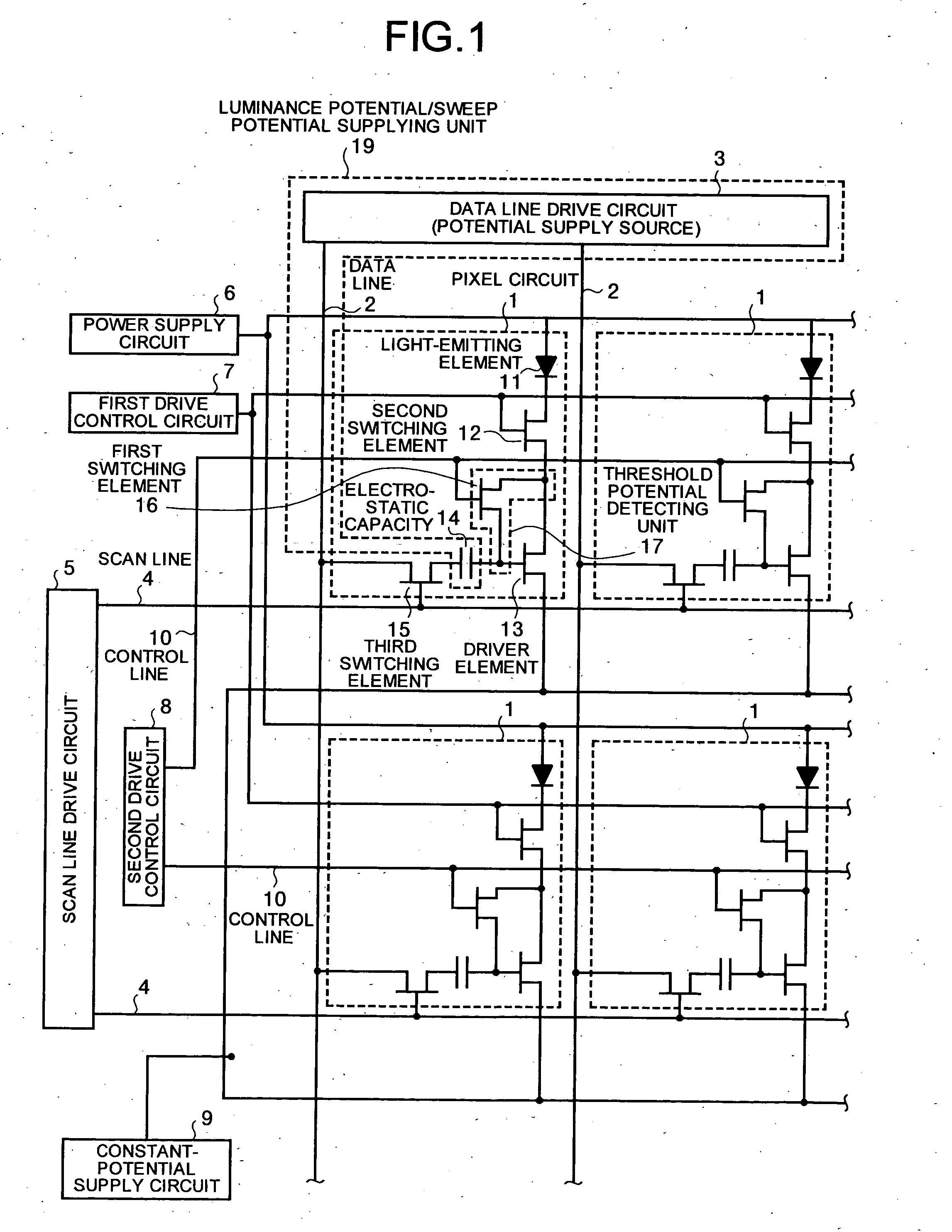
Image display device
ActiveUS20050156832A1Potential differenceStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesPotential differenceThreshold potential
A image display device includes a driving unit that includes a first terminal and a second terminal, and controls current flowing through a light emitting unit based on a potential difference applied between the first terminal and the second terminal. The potential difference is higher than a predetermined drive threshold. The image display device also includes a threshold potential detecting unit that detects the potential difference; a luminance potential supplying unit that changes the potential difference to a value lower than the drive threshold by a luminance potential corresponding to a luminance of the light emitting unit; and a sweep potential supplying unit that controls the driving unit by supplying a sweep potential to the first terminal. The sweep potential is swept in a range between a value lower than the luminance potential and a value higher than the luminance potential.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
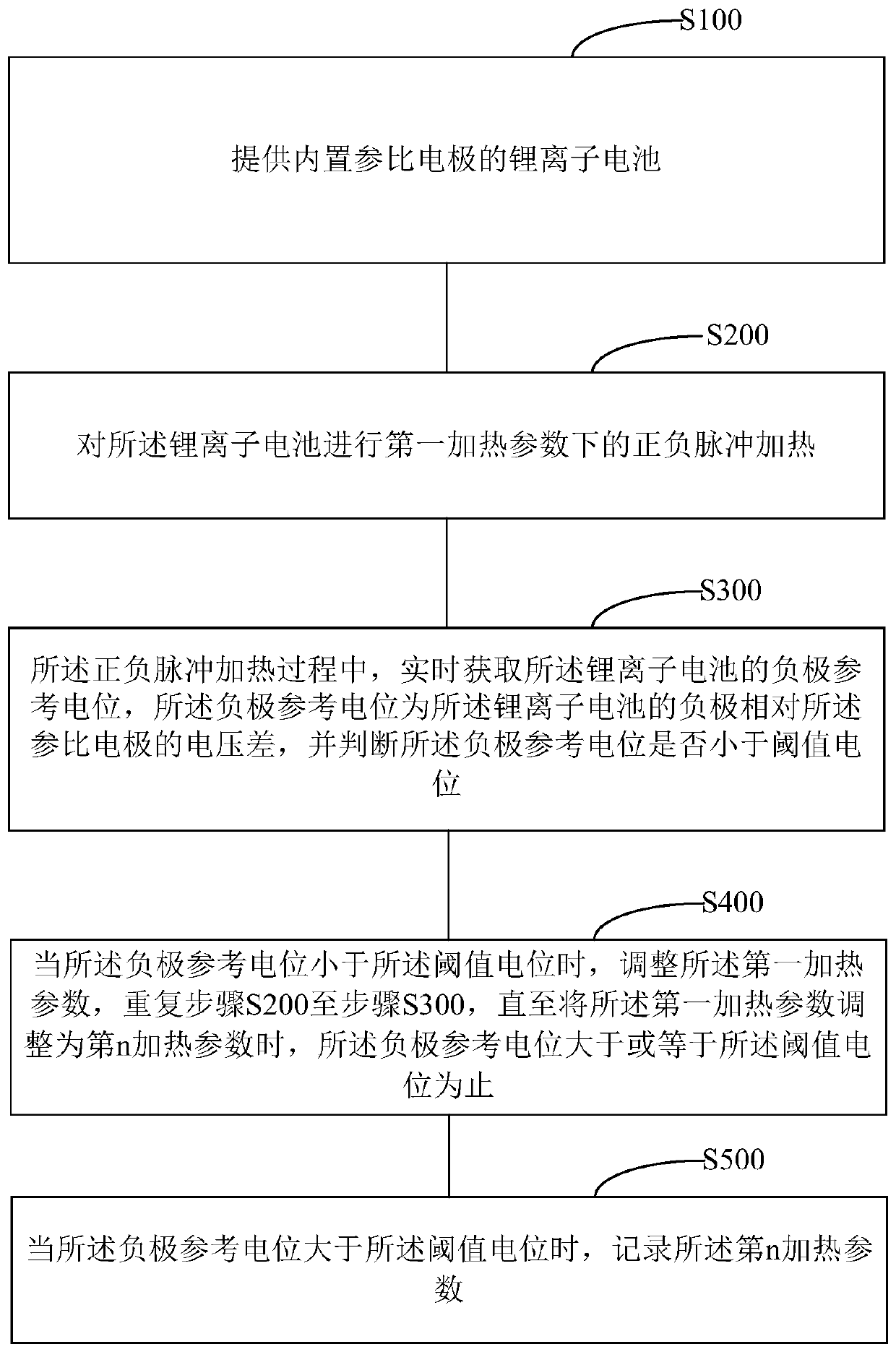
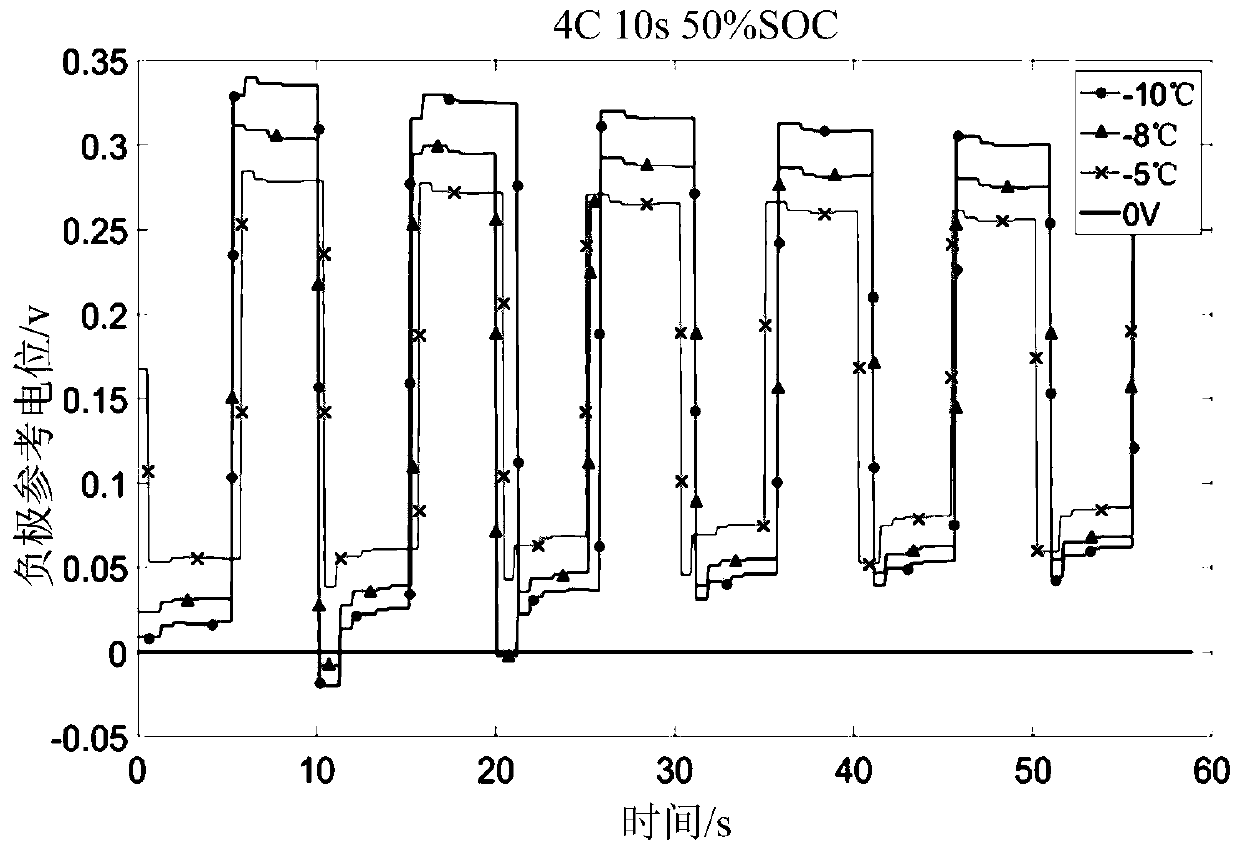
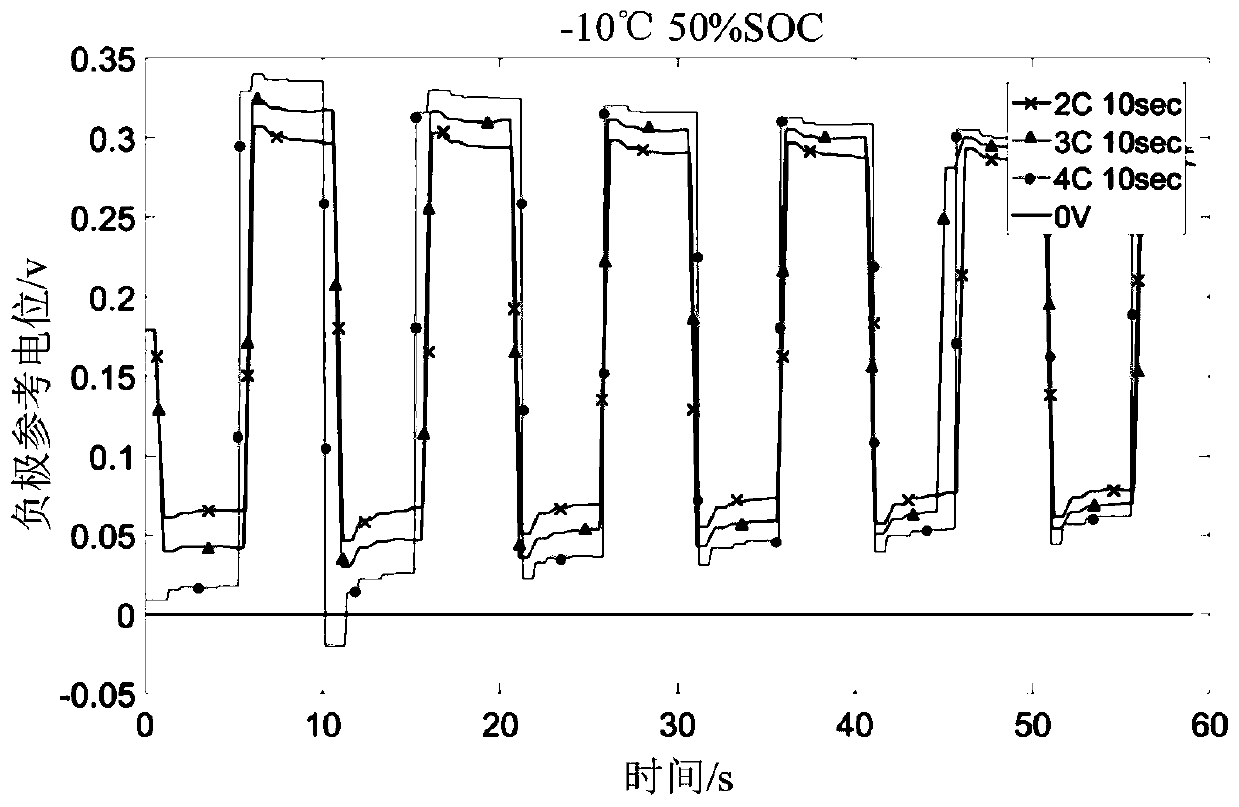
Battery pulse heating parameter determination method and parameter determination system
ActiveCN110556608AExtend your lifeLife expectancyCell electrodesCell temperature controlThreshold potentialElectrical battery
The invention relates to a battery pulse heating parameter determination method and a parameter determination system. The negative reference potential of a lithium ion battery is obtained in real timein the positive and negative pulse heating process under various heating parameters, wherein the negative reference potential is the voltage difference between the negative electrode of the lithium ion battery and a reference electrode. Whether a lithium precipitation phenomenon occurs in the lithium ion battery or not is judged by judging the relationship between the negative reference potentialand a threshold potential. Due to lithium precipitation, the available capacity of the battery may be reduced, dendrites may pierce a diaphragm to cause short circuit in the battery and induce thermal runaway of the battery and the like, and performance reduction, safety risk and other hazards may be caused. Therefore, when the negative reference potential is smaller than the threshold potential,a first heating parameter needs to be adjusted, in order to avoid lithium precipitation and prolong the service life of the battery. By recording the heating parameter when the negative reference potential is greater than the threshold potential, it can be ensured that the pulse heating parameter will not greatly influence the service life of the battery.
Owner:北京昇科能源科技有限责任公司
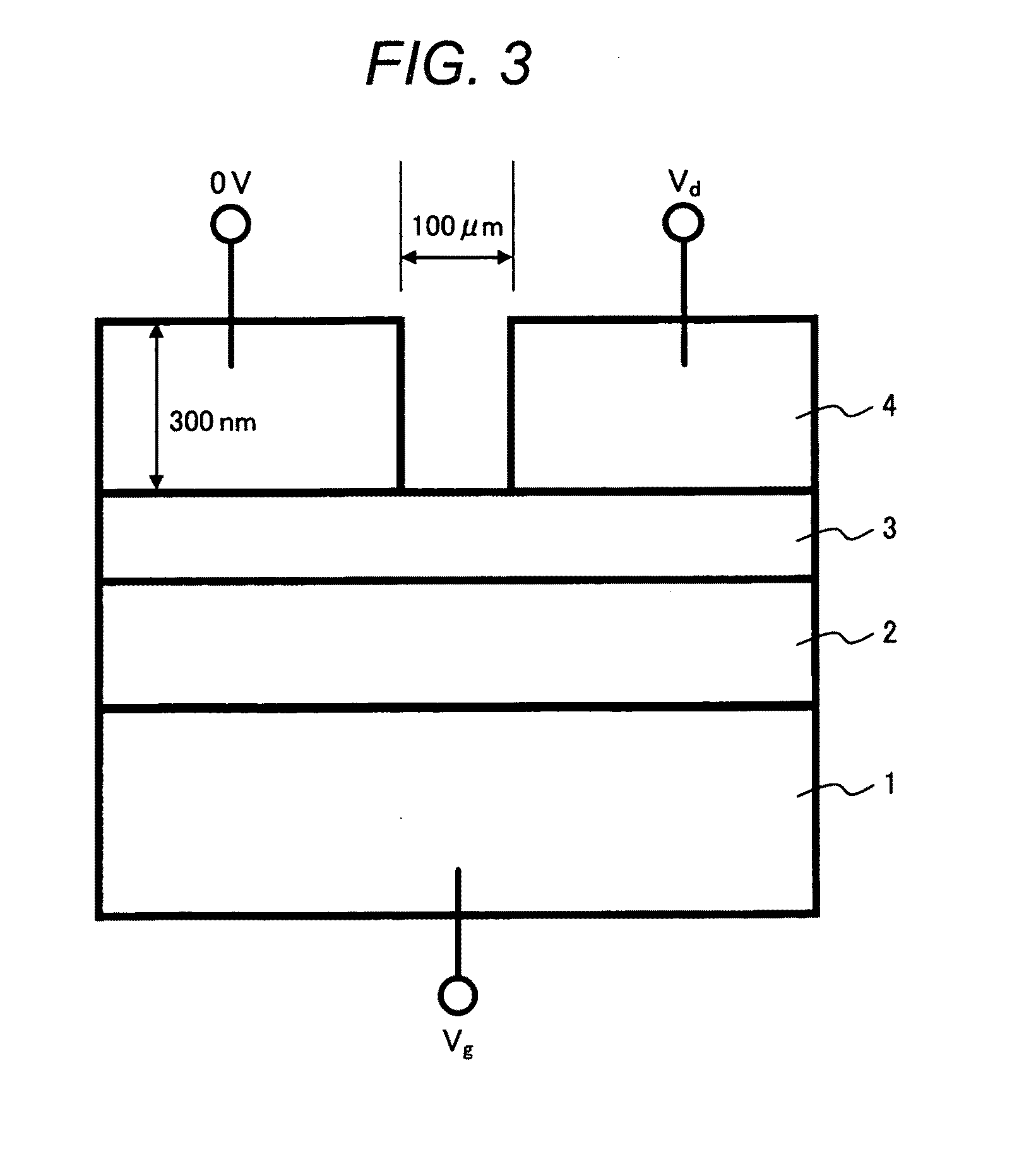
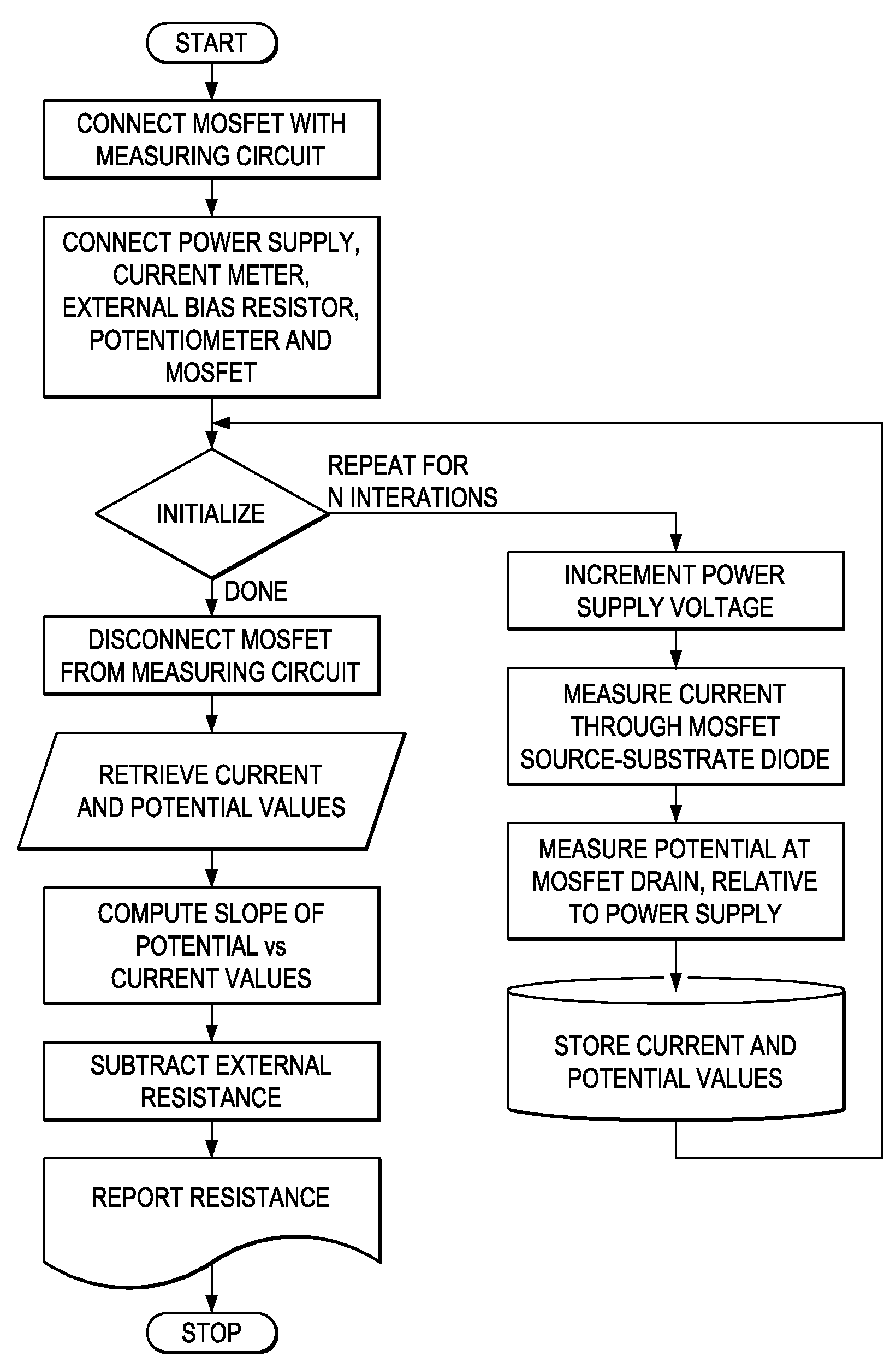
Method to Accurately Estimate the Source and Drain Resistance of a MOSFET
ActiveUS20090079446A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceThreshold potential
Measurements of parameters of MOS transistors, also known as MOSFETs, such as threshold potentials, require accurate estimates of source and drain series resistance. In cases where connections to the MOSFET include significant external series resistance, as occurs in probing transistors that are partially fabricated or deprocessed, accurate estimates of external resistances are also required. This invention comprises a method for estimating series resistances of MOSFETs, including resistances associated with connections to the MOSFET, such as probe contacts. This method is applicable to any MOSFET which can be accessed on source, drain, gate and substrate terminals, and does not require other test structures or special connections, such as Kelvin connections.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
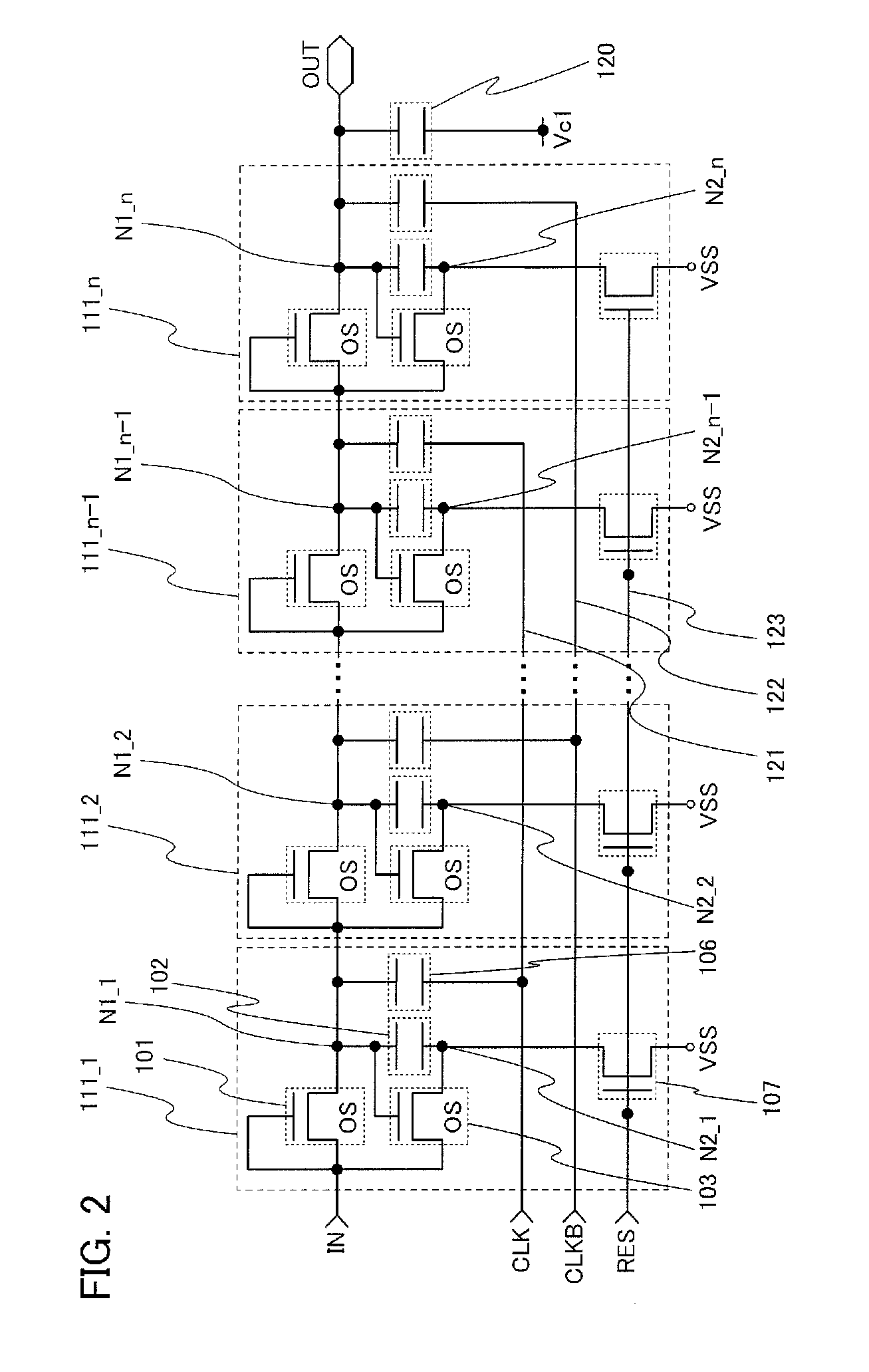
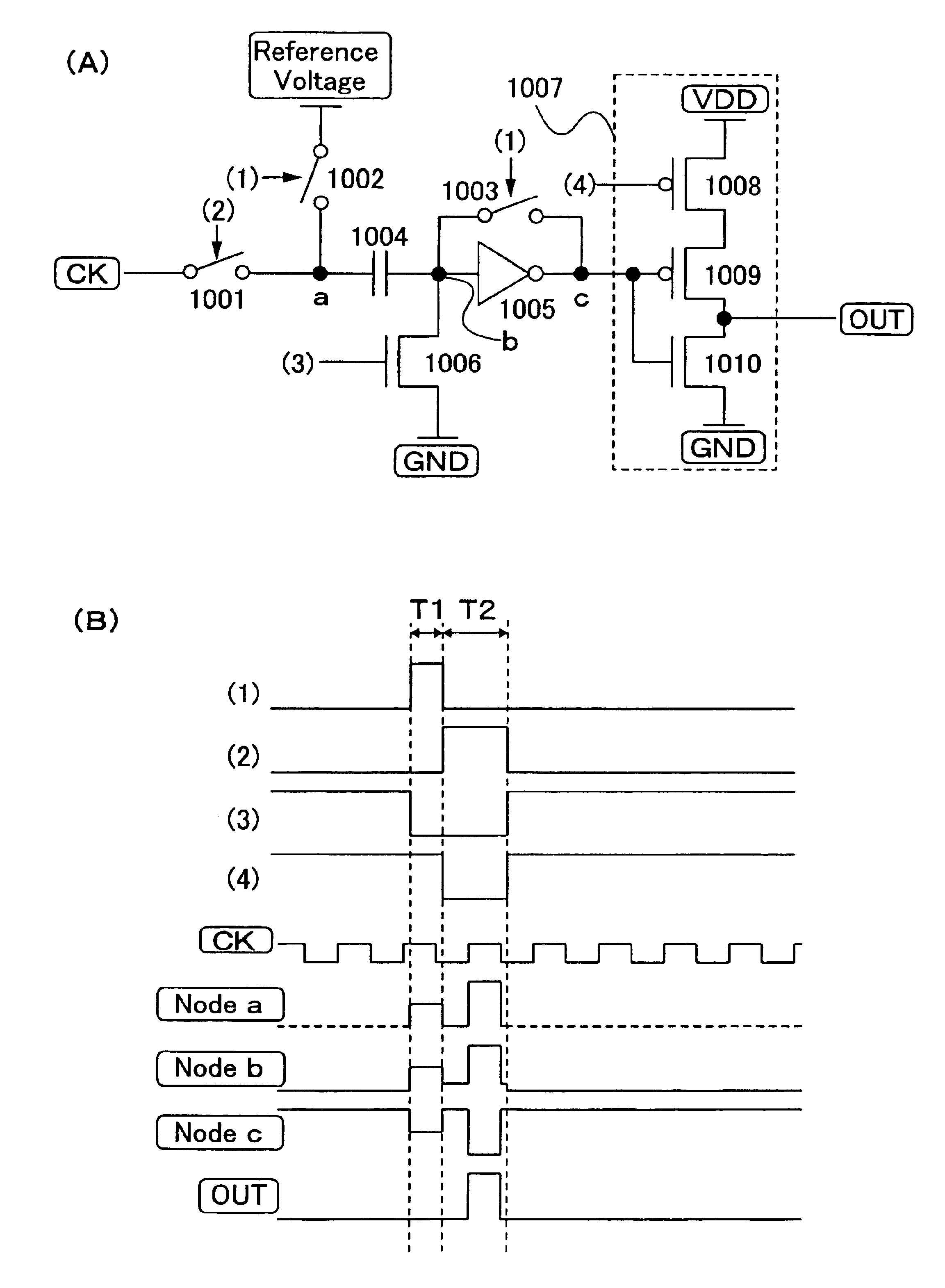
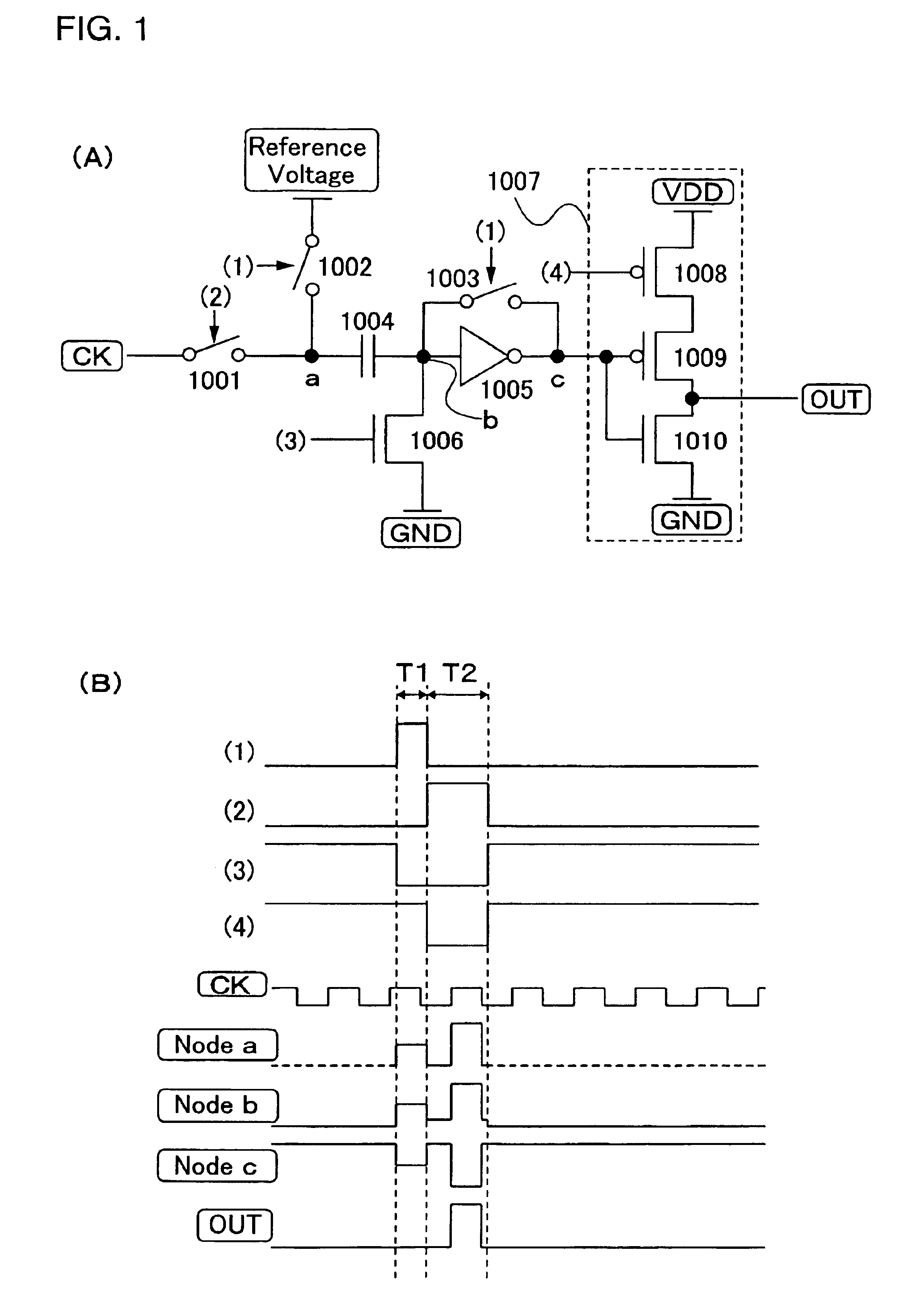
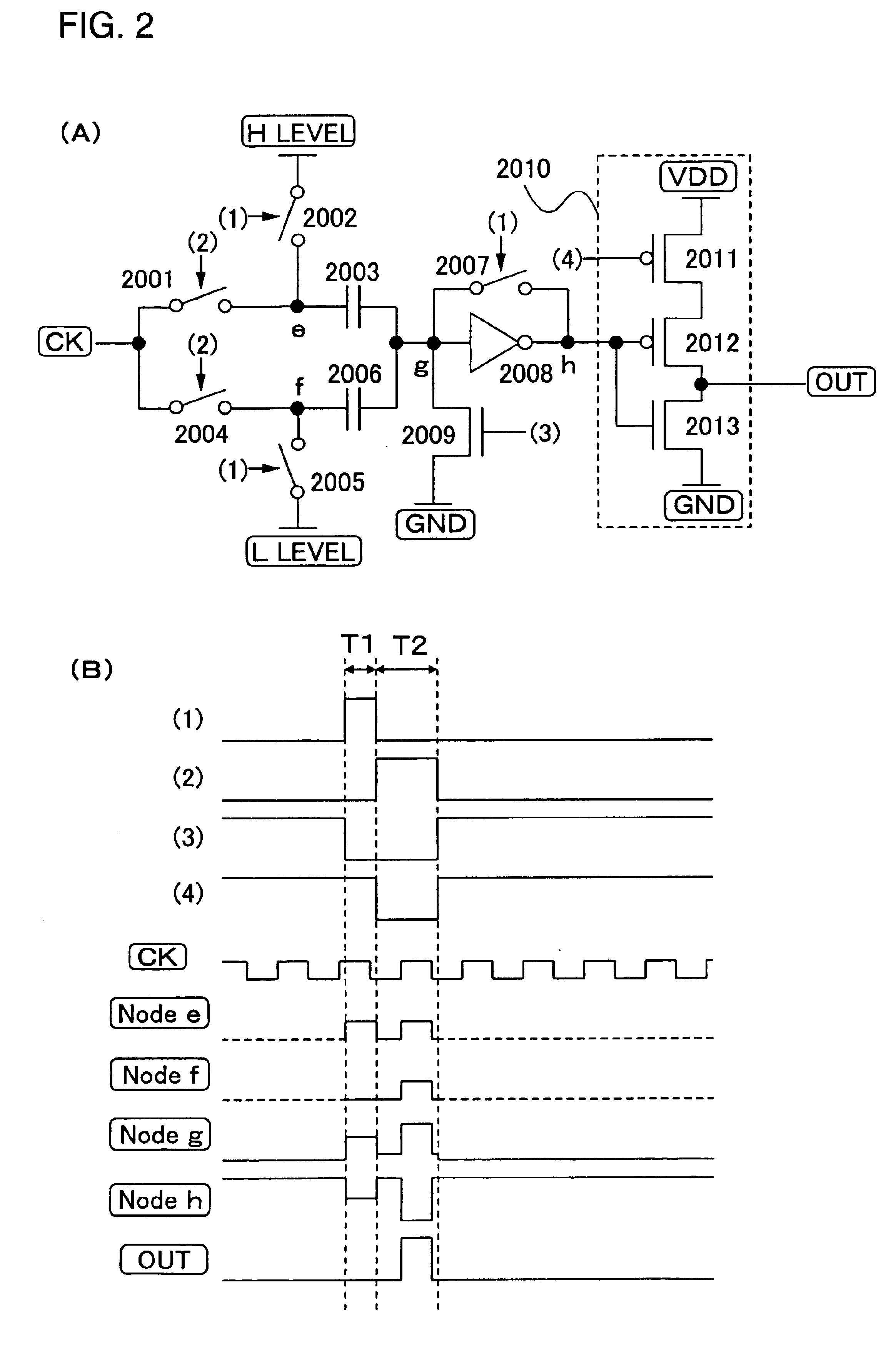
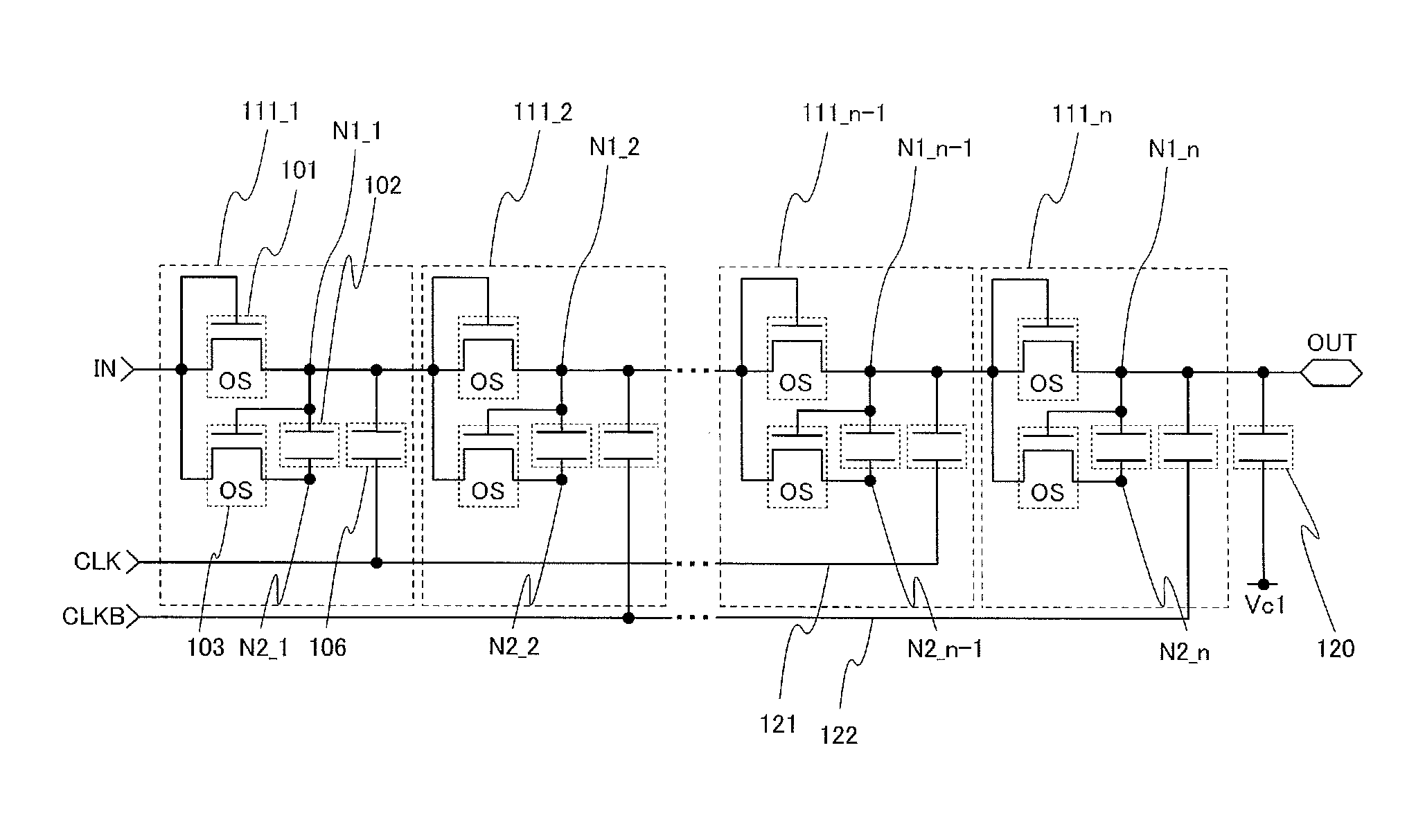
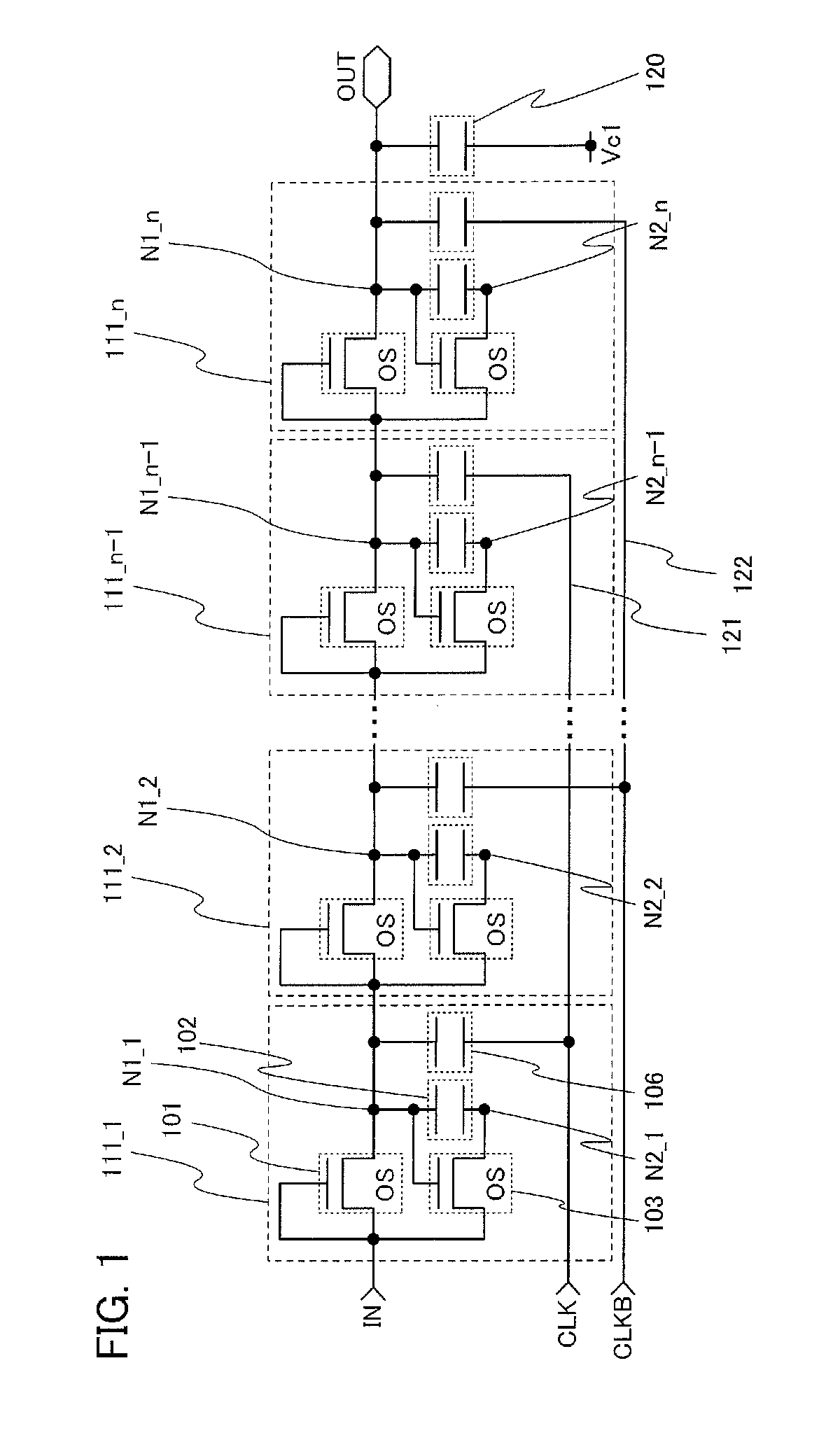
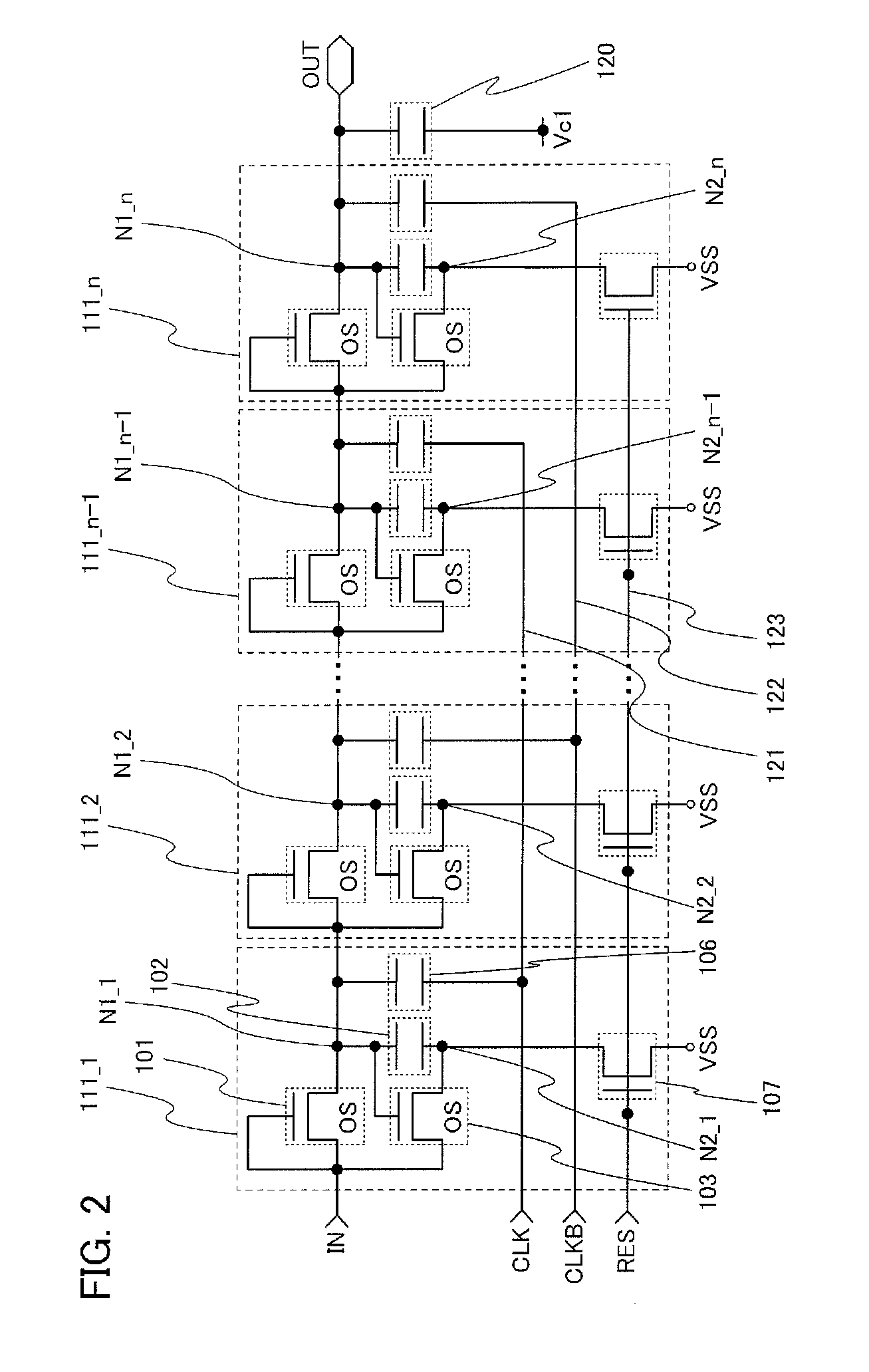
Shift register and driving method thereof
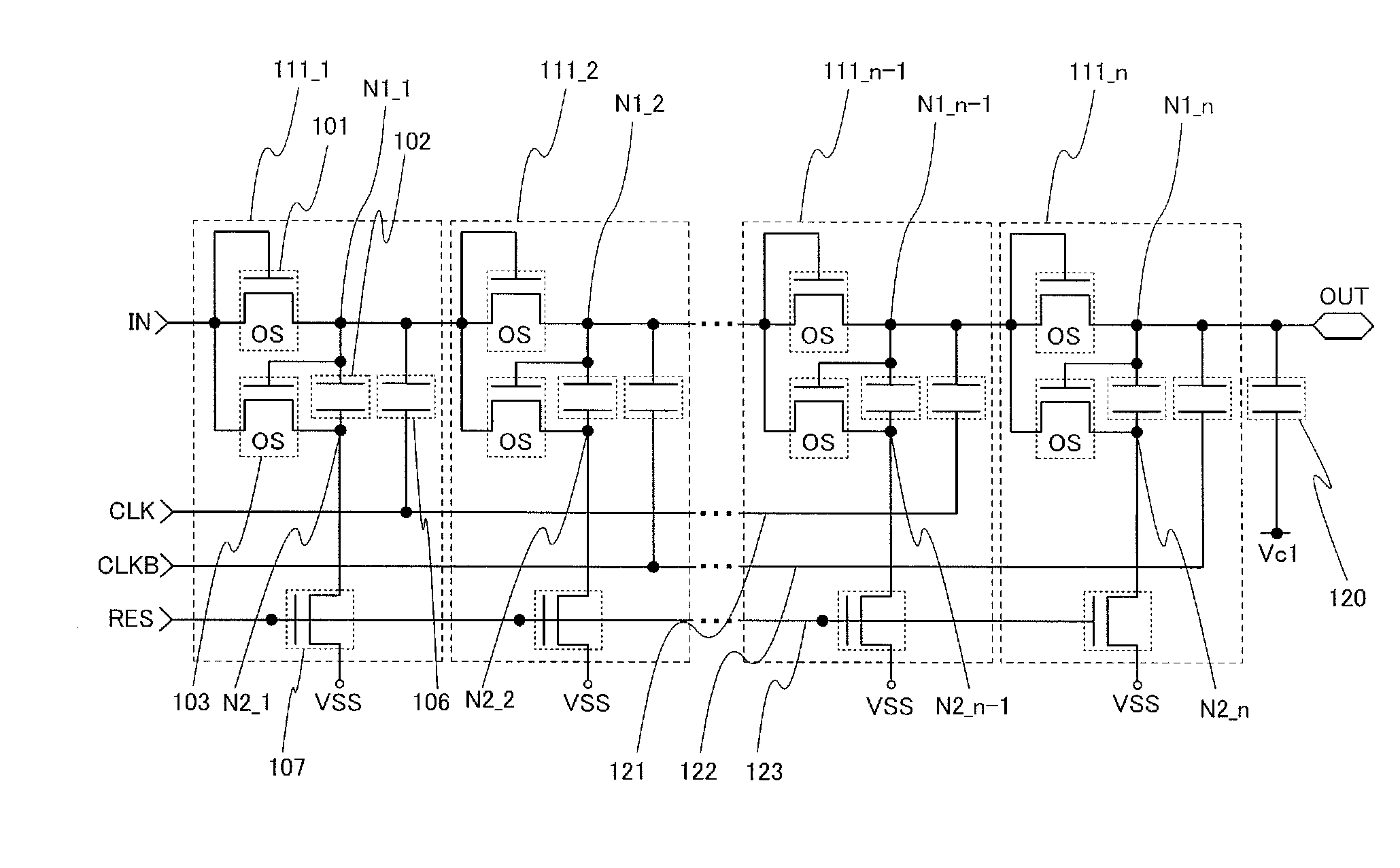
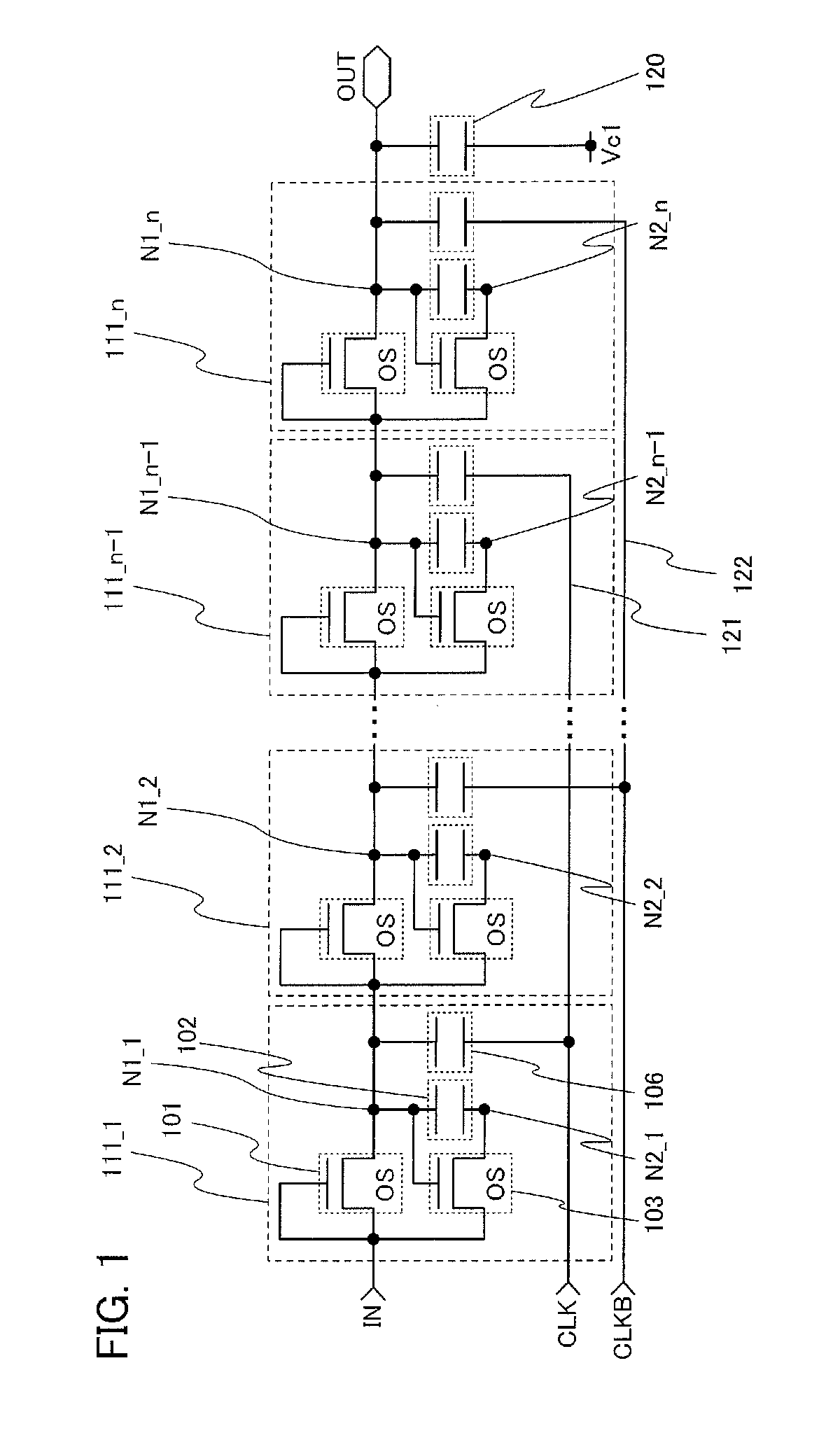
ActiveUS6870895B2Reduce power consumptionMultiple input and output pulse circuitsStatic indicating devicesPower inverterShift register
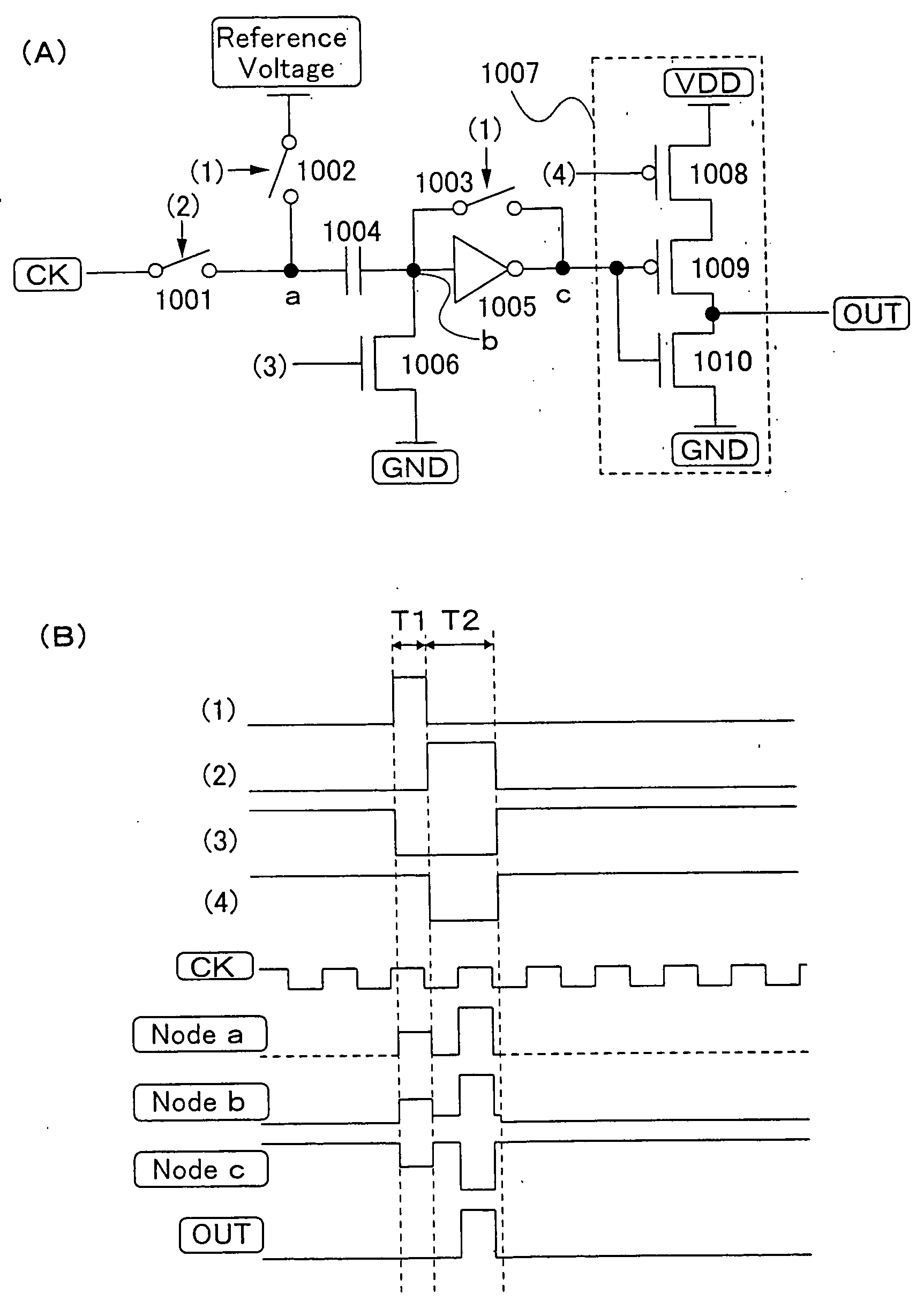
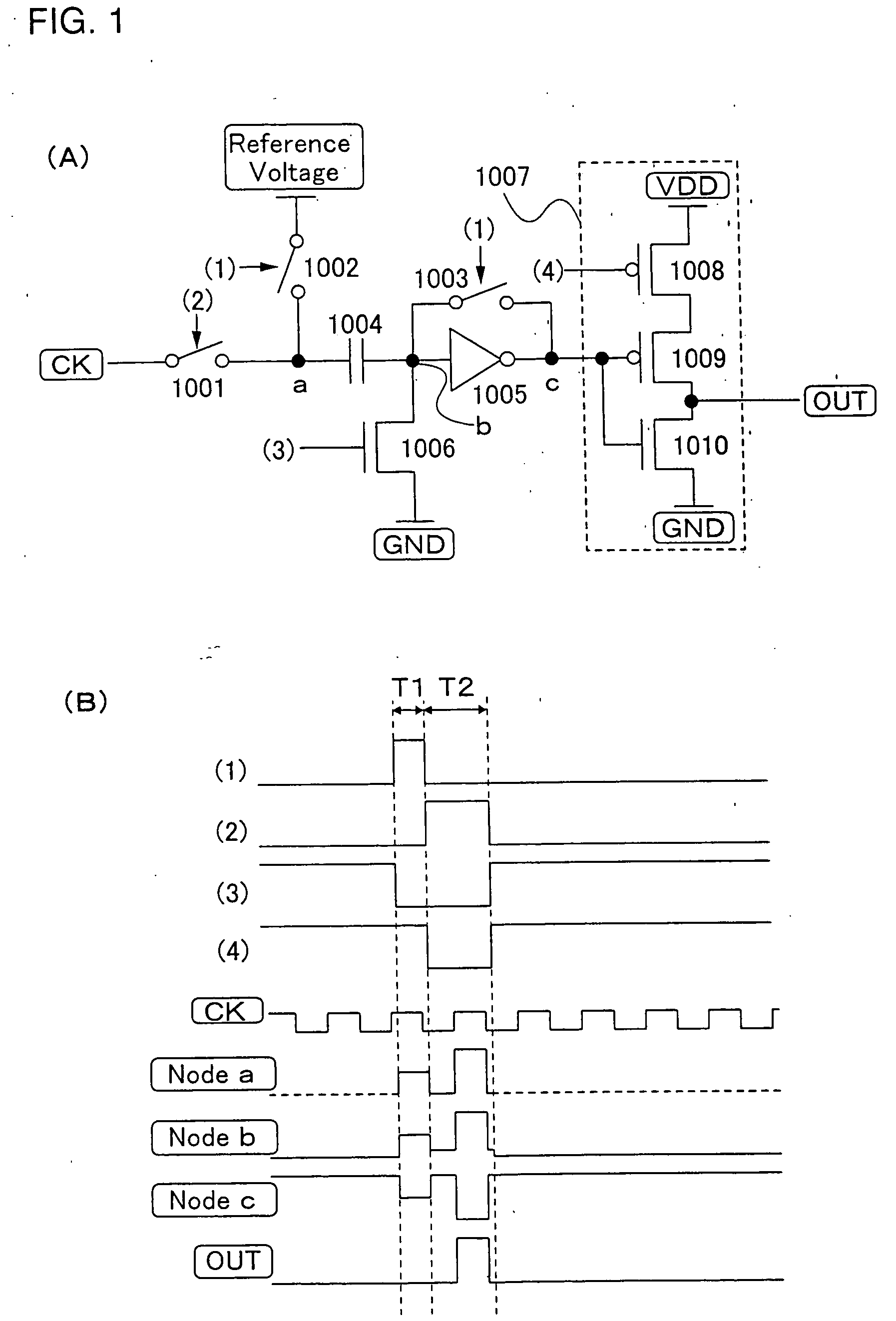
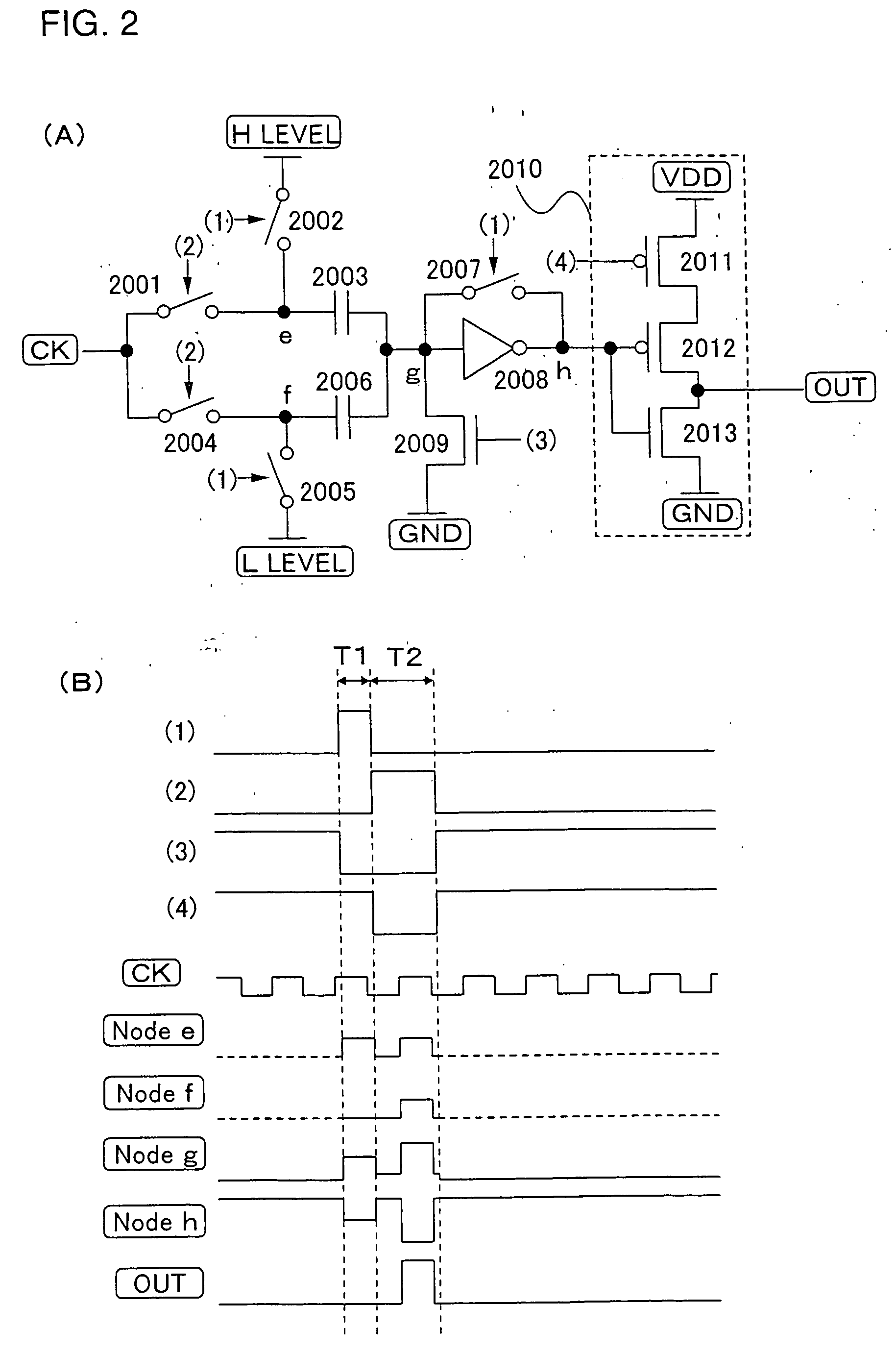
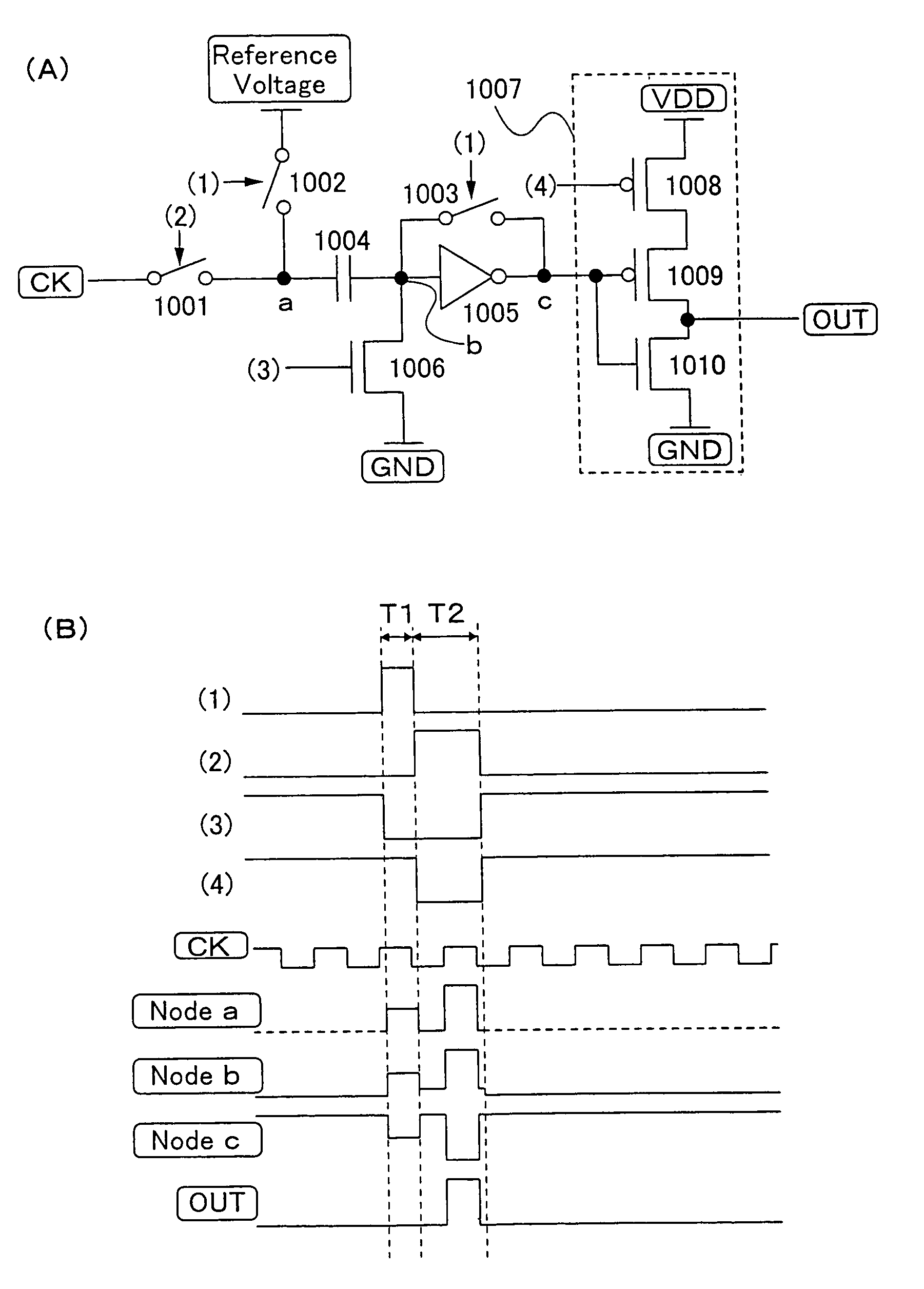
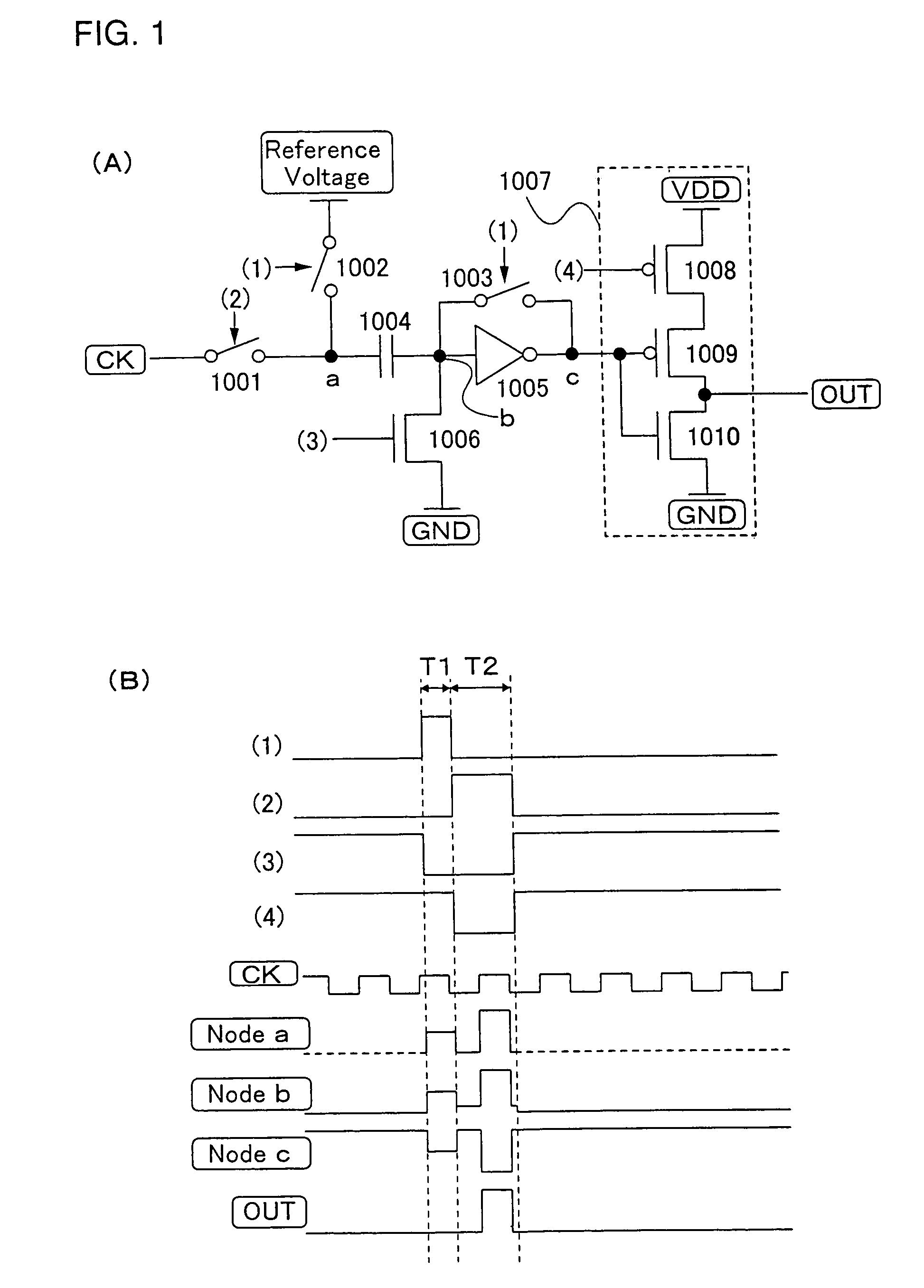
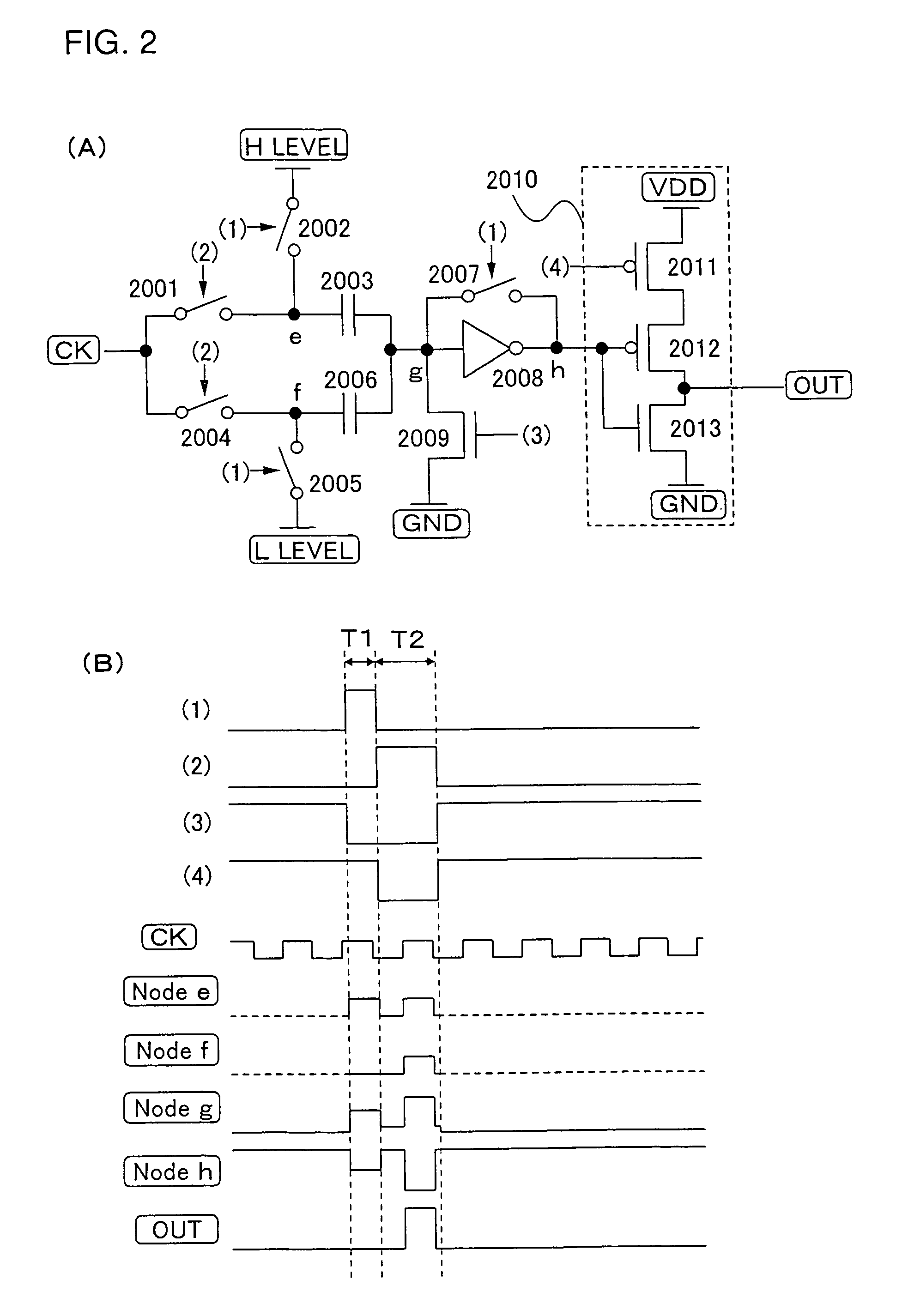
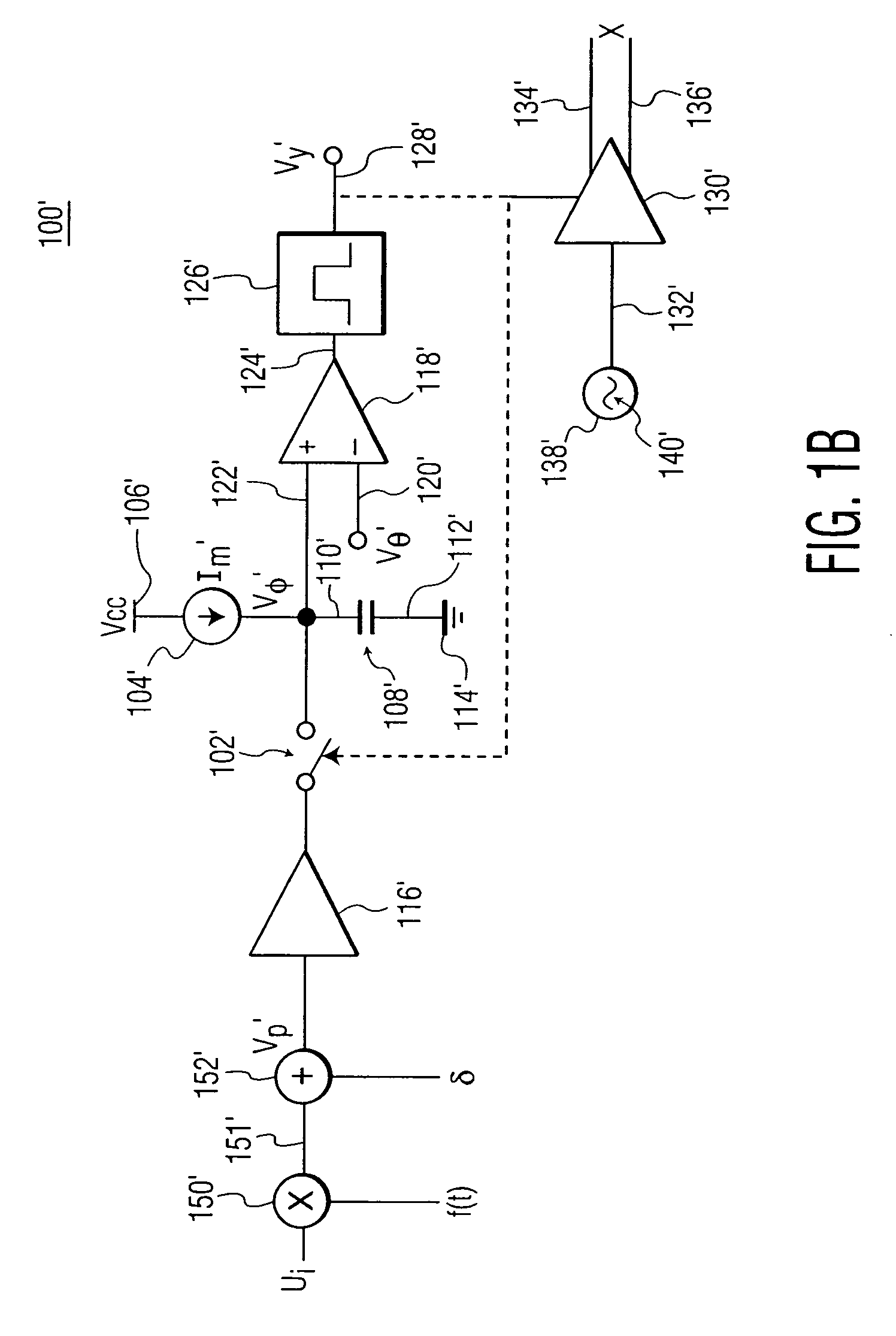
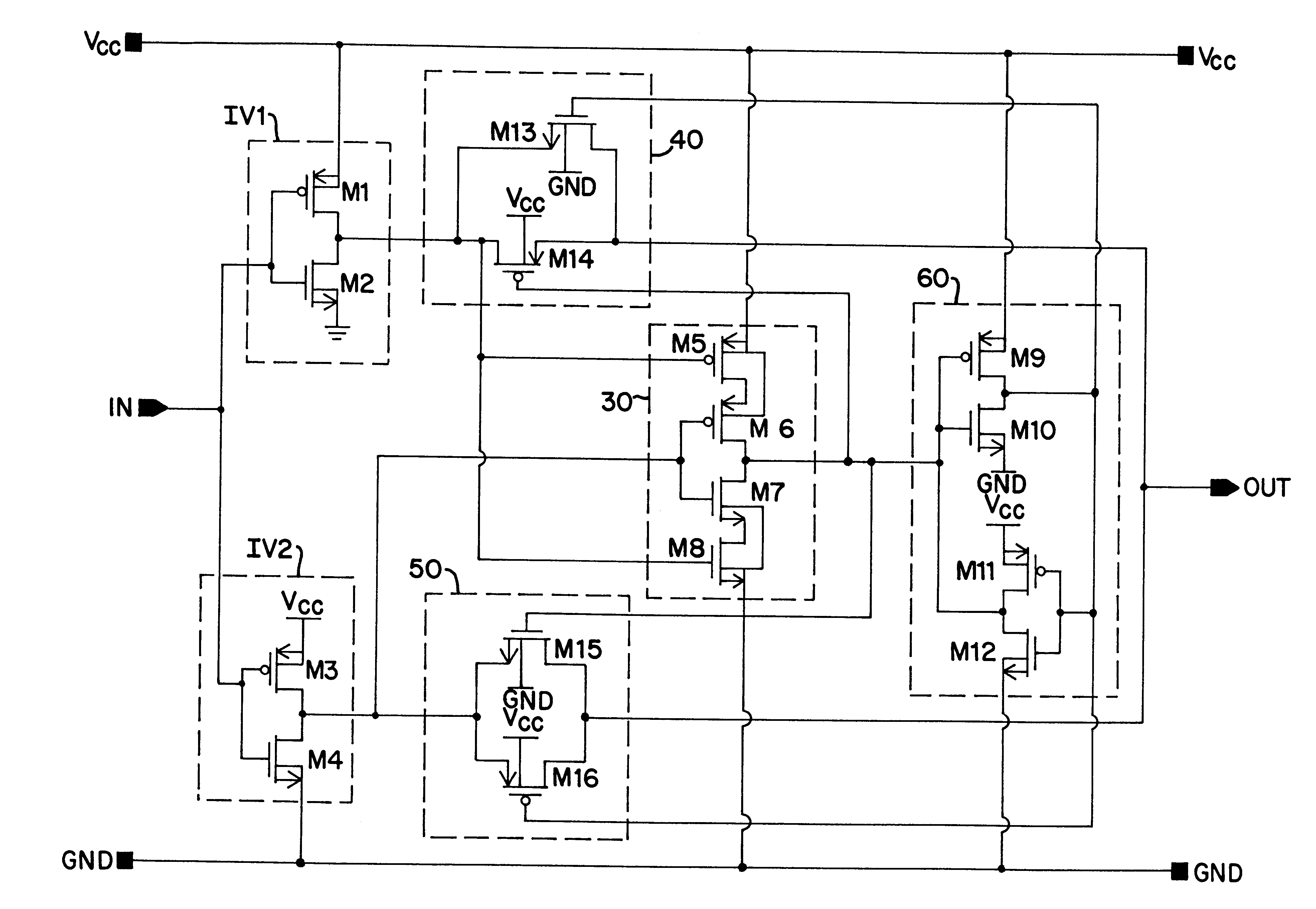
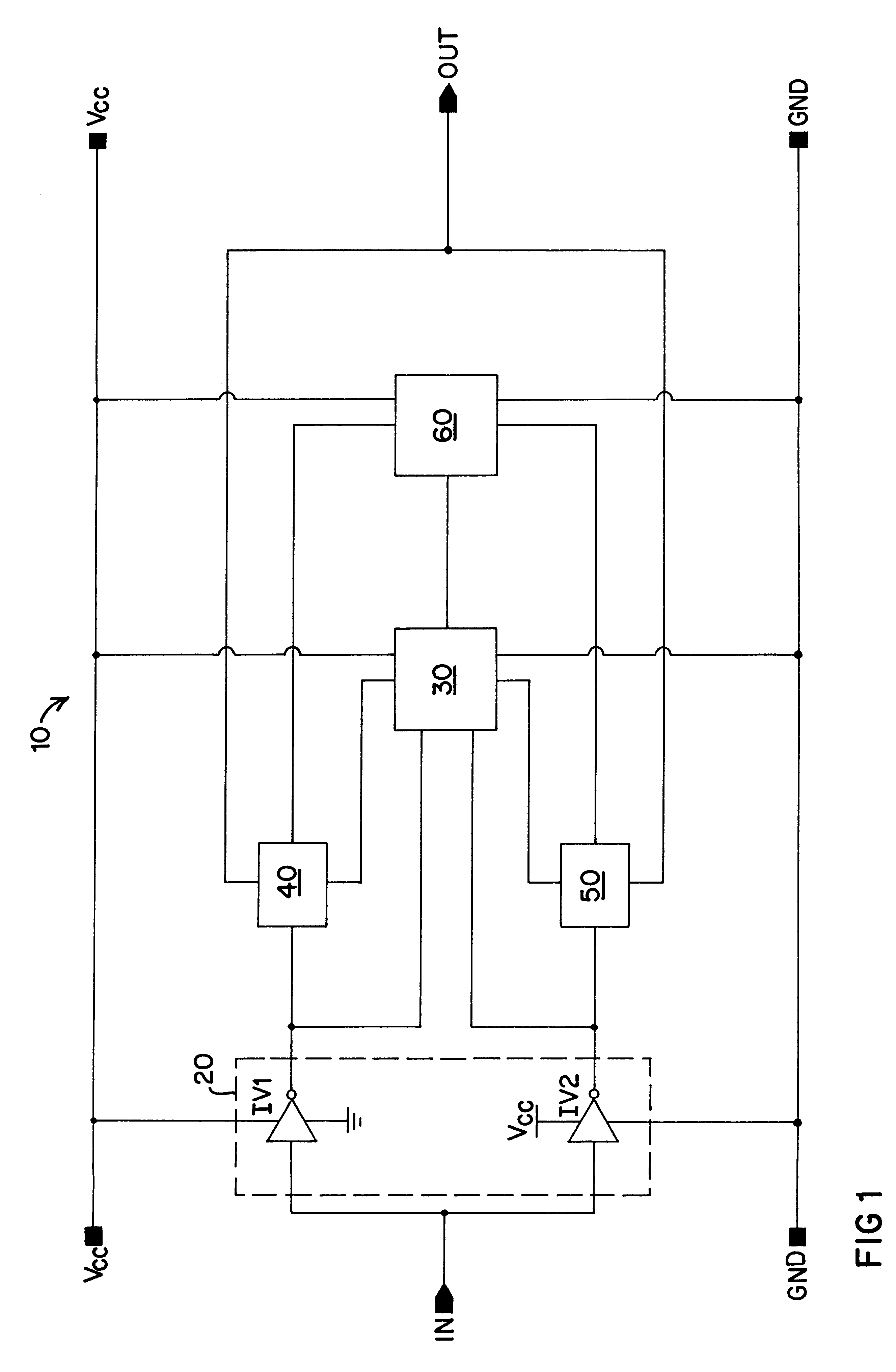
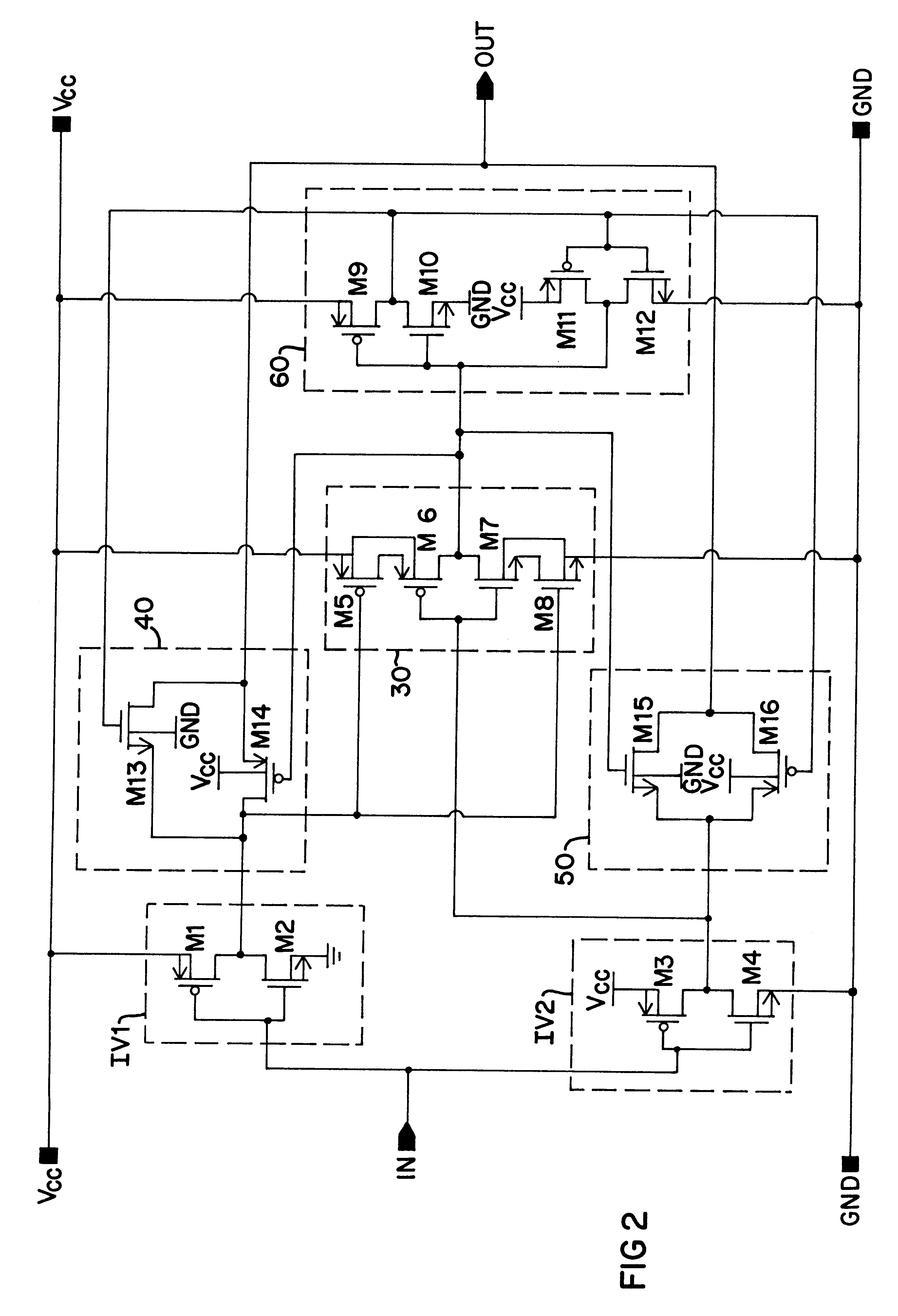
A low power consumption shift register which inputs a CK signal with a low voltage with almost no effect of variation in characteristics of transistors. In the invention, an input portion of an inverter is set at a threshold voltage thereof and a CK signal is inputted to the input portion of the inverter through a capacitor means. In this manner, the CK signal is amplified, which is sent to the shift register. That is, by obtaining the threshold potential of the inverter, the shift register which operates with almost no effect of variation in characteristics of transistors can be provided. A level shifter of the CK signal is generated from an output pulse of the shift register, therefore, the low power consumption shift register having the level shifter which flows a shoot-through current for a short period can be provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Information processing method and device for simulating biological neuron information processing mechanism
InactiveCN101770560AComputing operations for integration/differentiationAnalogue processes for specific applicationsInformation processingProcess mechanism
The invention discloses an information processing method and device simulating a biological neuron information processing mechanism, which comprises a signal input circuit, an integrating circuit, a pulse generating circuit and a decoding circuit. The signal input circuit simulates and generates the nerve impulse of neuron. The integrating circuit analogous to membrane potential integrates the input signals of the signal input circuit. The pulse generating circuit compares the integrating result of the analogous membrane potential integrating circuit with a predetermined threshold potential in order to generate analogous motion potential pulse. The decoding circuit ingrates the analogous motion potential impulse in order to obtain the analogous motion potential pulse coding signals of output signals consistent with the input signals. The invention simulates the information processing mechanism of the biological neuron and realizes the biological neuron manner with a circuit method.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
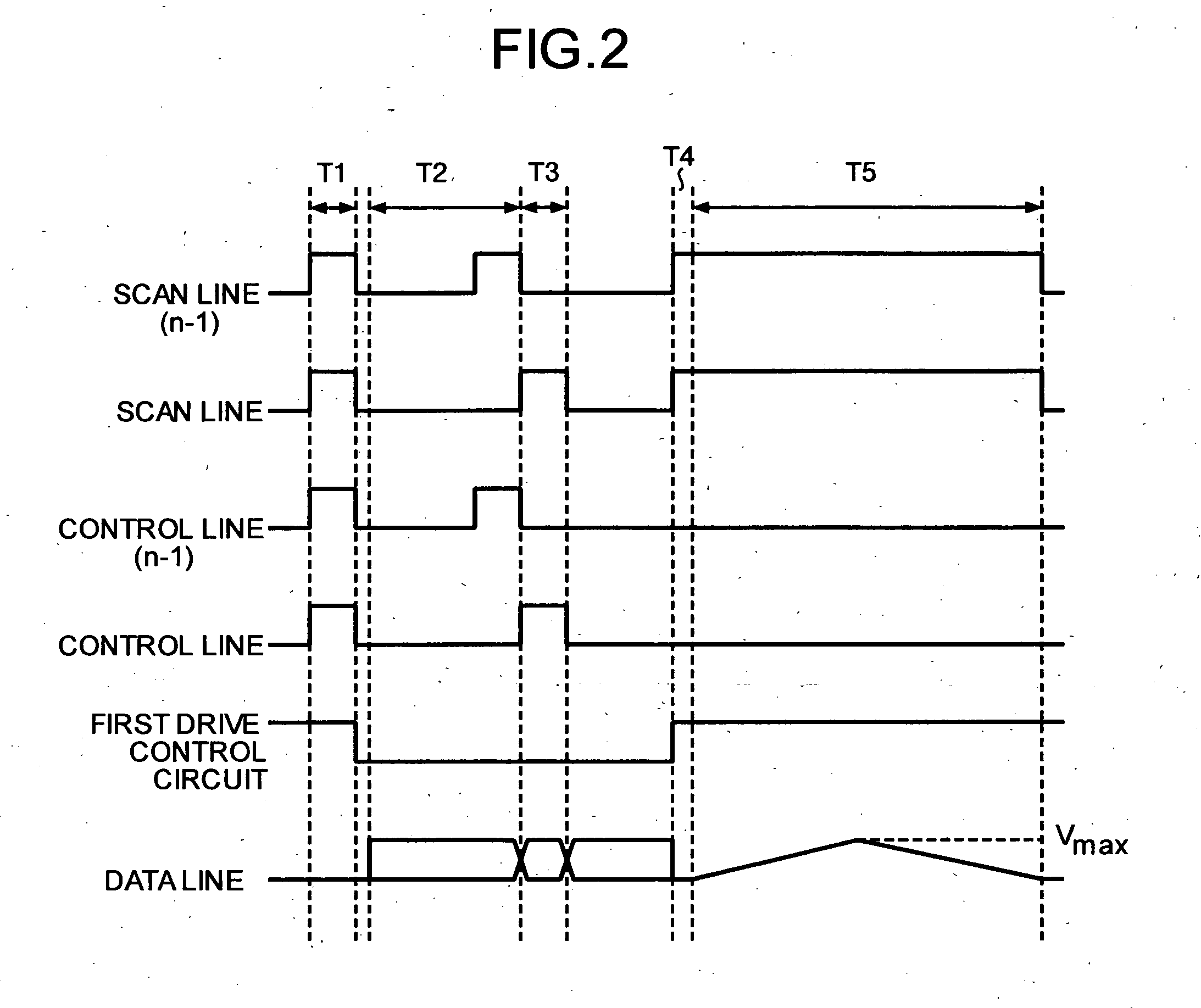
Display apparatus
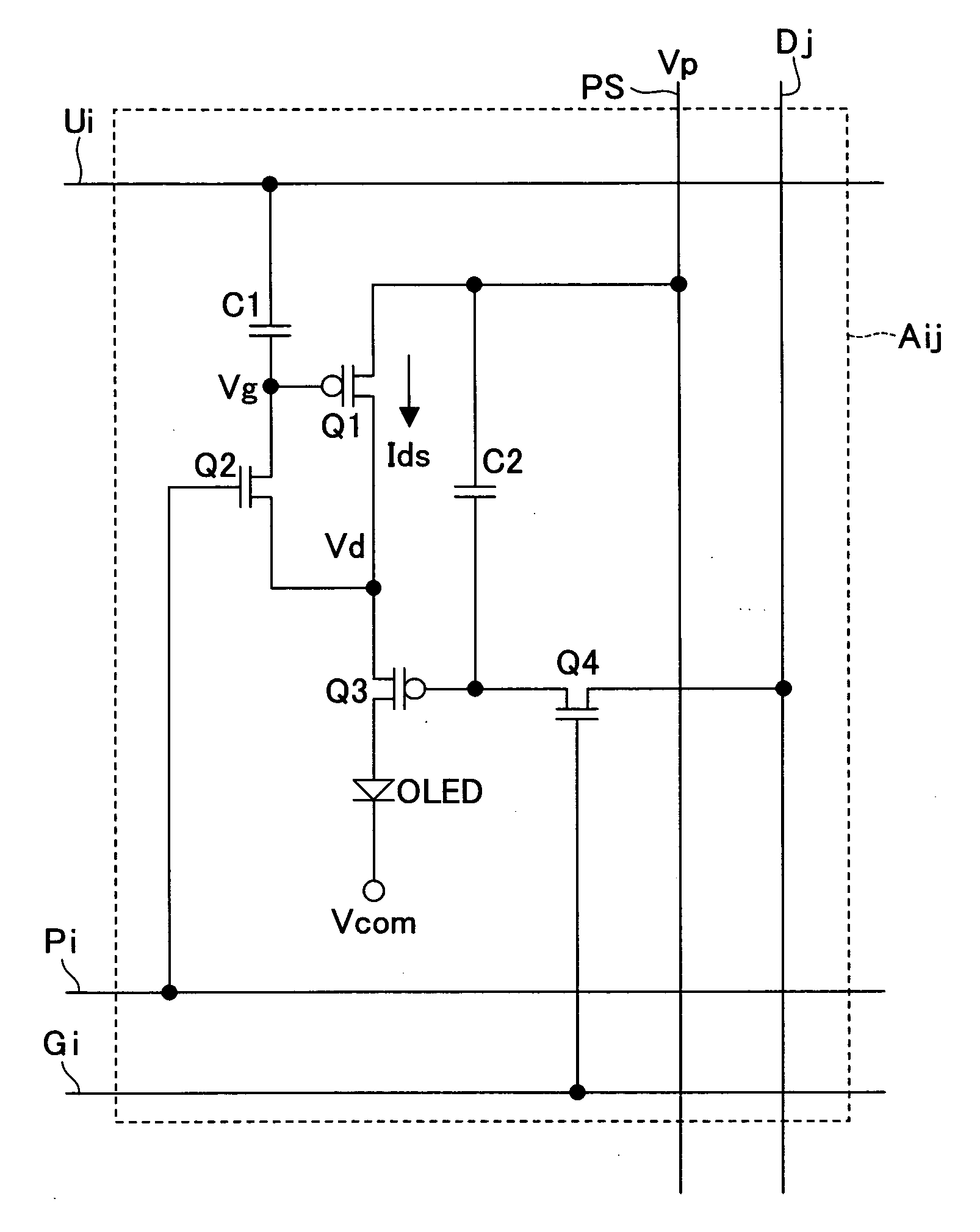
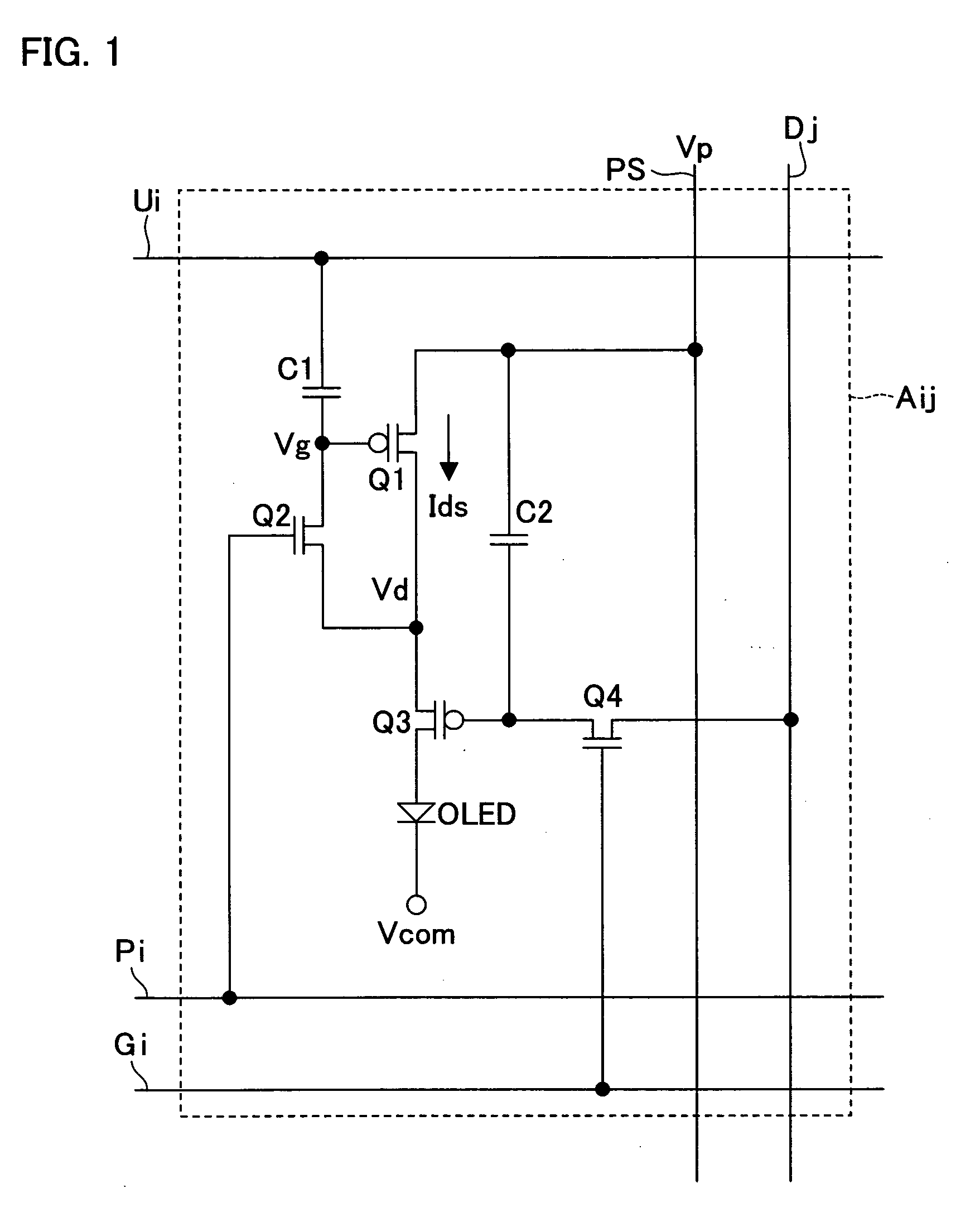
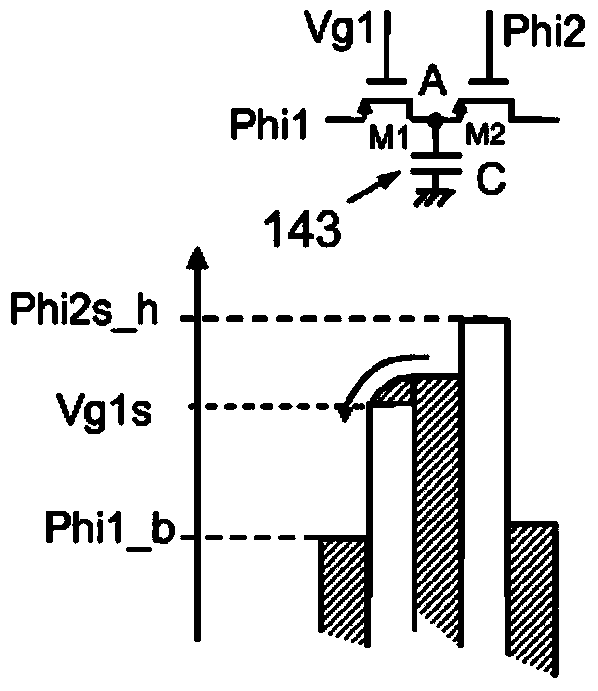
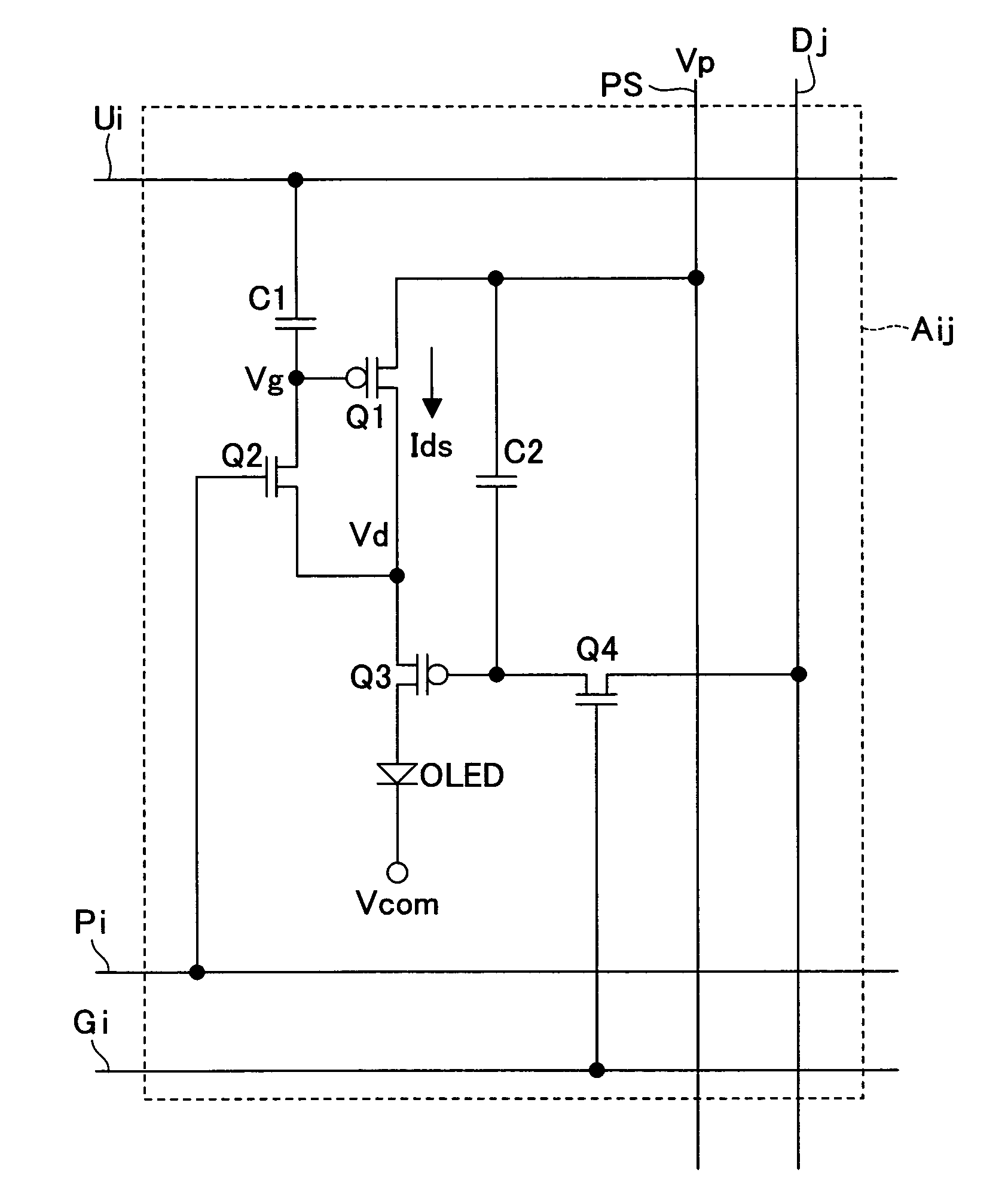
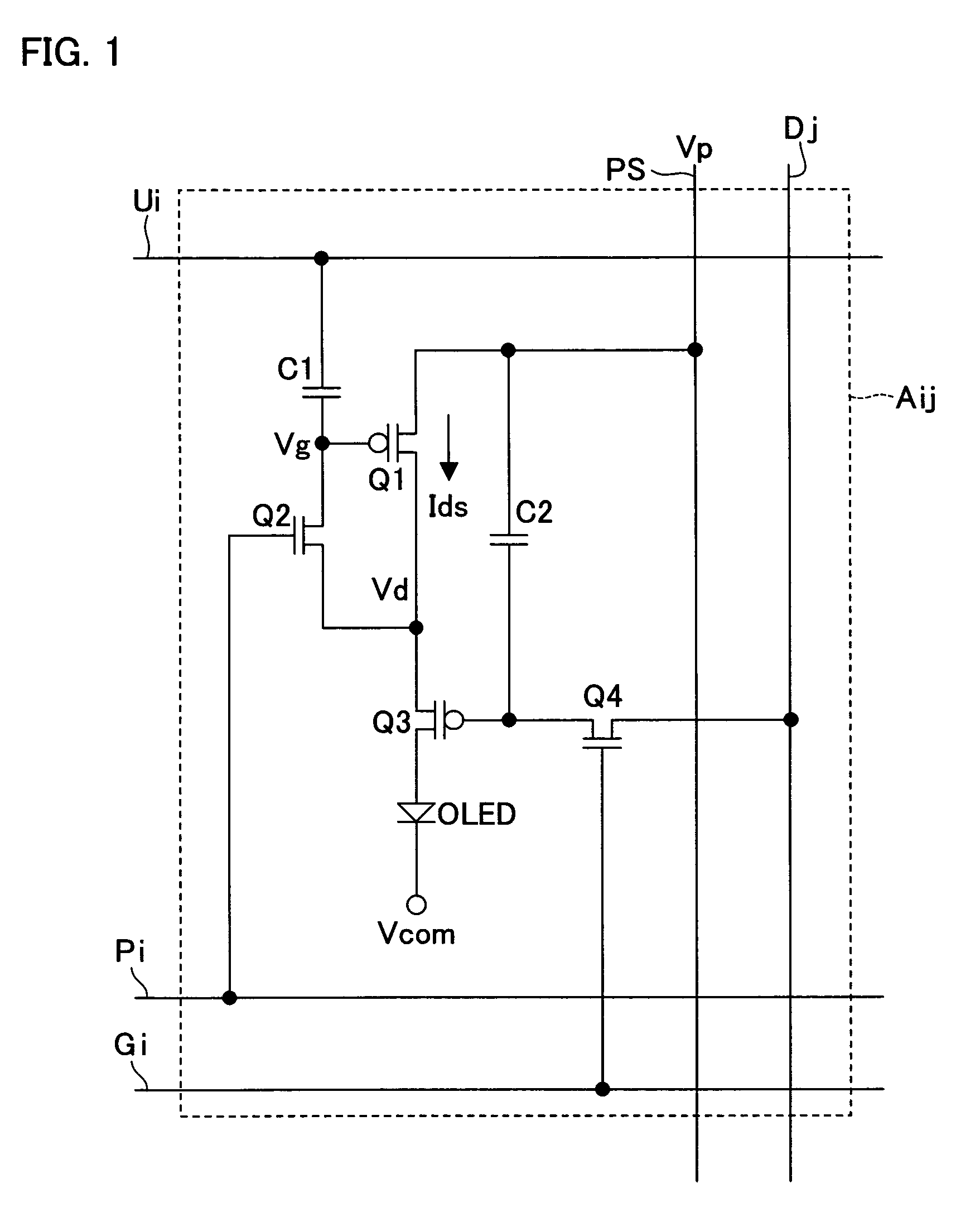
ActiveUS20050275647A1Shorten the timeSuitable for useCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingThreshold potentialEngineering
When the transistor Q3 is OFF, a predetermined potential is supplied to a potential wire Ui such that a switching transistor Q2 becomes ON. This changes a gate potential of a driving transistor Q1 from an ON potential to a threshold potential. Thereafter, the transistor Q2 is turned OFF, with the result that the potential of the potential wire Ui is changed (in cases where the transistor Q1 is a p-type transistor, the potential is decreased). With this, the transistor Q1 allows a current to constantly flows therethrough, irrespective of the threshold potential. This shortens time for setting an output current of the driving TFT for driving a current driving type display element.
Owner:SHARP KK
CMOS back-gated keeper technique
InactiveUS20090224803A1Reduce leakage currentImprove noise immunityPower consumption reductionLogic circuits characterised by logic functionMOSFETCMOS
A novel methodology for the construction and operation of logical circuits and gates that make use of and contact to a fourth terminal (substrates / bodies) of MOSFET devices is described in detail. The novel construction and operation provides for maintaining such body-contacted MOSFET devices at a lower threshold voltage (VTh) when actively on (to increase overdrive and performance), and at a higher relative threshold voltage when off (to reduce leakage power). Because the threshold potential of a gate moves inversely to its body potential, it follows then that in general, the body of a given device must be tied to the inverse of the device's drain voltage to achieve such a desirable threshold potential modulation effect for improved device, circuit, gate and logical family operation.
Owner:IBM CORP
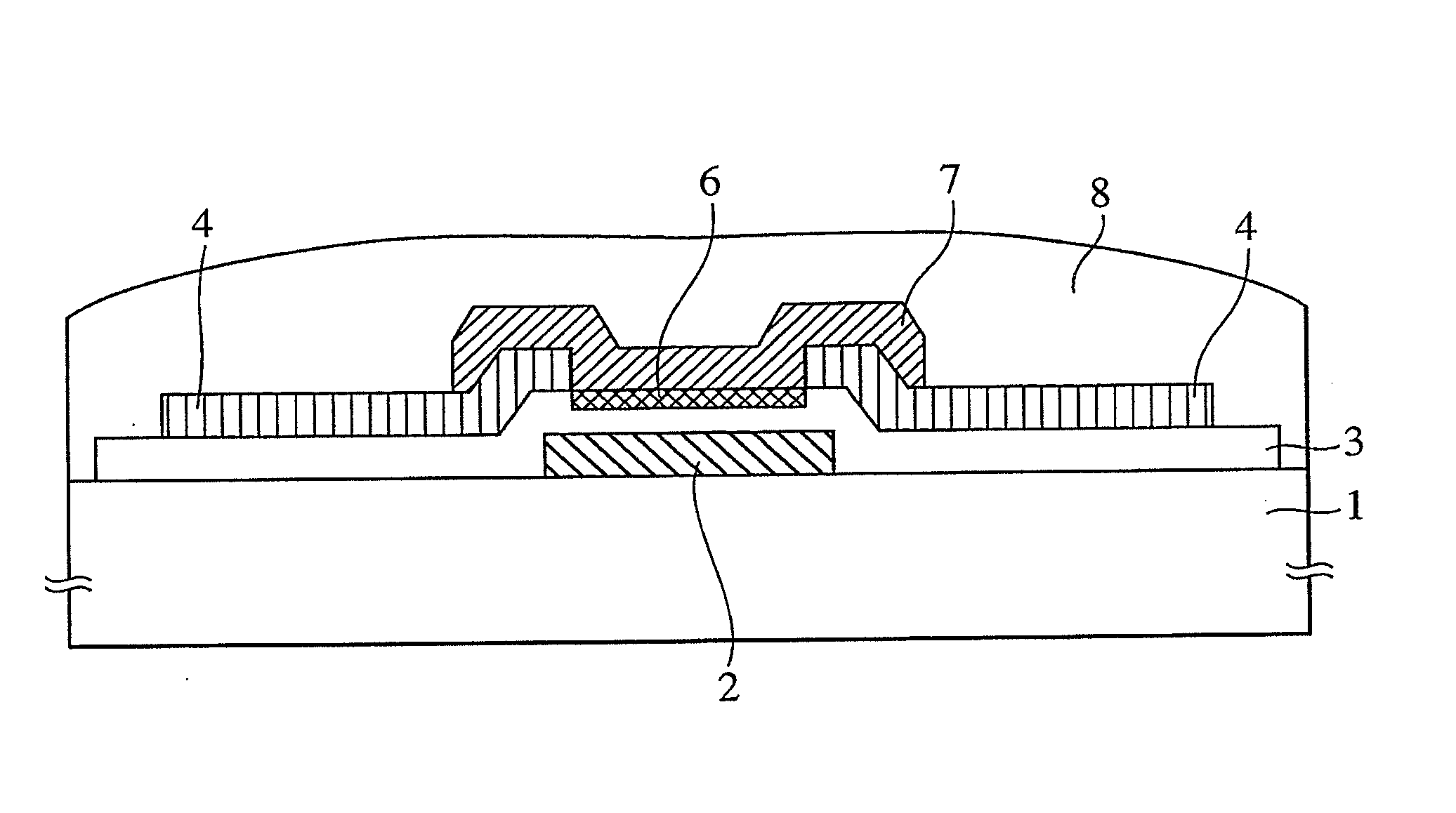
Oxide Semiconductor Device and Surface Treatment Method of Oxide Semiconductor
InactiveUS20140175437A1Effectively suppressing the threshold potential shift and occurrence of leak currentPhysical property is lessTransistorSolid-state devicesThreshold potentialGas phase
Oxygen defects formed at the boundary between the zinc oxide type oxide semiconductor and the gate insulator are terminated by a surface treatment using sulfur or selenium as an oxygen group element or a compound thereof, the oxygen group element scarcely occurring physical property value change. Sulfur or selenium atoms effectively substitute oxygen defects to prevent occurrence of electron supplemental sites by merely applying a gas phase or liquid phase treatment to an oxide semiconductor or gate insulator with no remarkable change on the manufacturing process. As a result, this can attain the suppression of the threshold potential shift and the leak current in the characteristics of a thin film transistor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Shift register and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20050134325A1Reduce power consumptionMultiple input and output pulse circuitsStatic indicating devicesShift registerLow voltage
A low power consumption shift register which inputs a CK signal with a low voltage with almost no effect of variation in characteristics of transistors. In the invention, an input portion of an inverter is set at a threshold voltage thereof and a CK signal is inputted to the input portion of the inverter through a capacitor means. In this manner, the CK signal is amplified, which is sent to the shift register. That is, by obtaining the threshold potential of the inverter, the shift register which operates with almost no effect of variation in characteristics of transistors can be provided. A level shifter of the CK signal is generated from an output pulse of the shift register, therefore, the low power consumption shift register having the level shifter which flows a shoot-through current for a short period can be provided
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Shift register and driving method thereof
InactiveUS7079617B2Reduce power consumptionMultiple input and output pulse circuitsStatic indicating devicesPower inverterShift register
A low power consumption shift register which inputs a CK signal with a low voltage with almost no effect of variation in characteristics of transistors. In the invention, an input portion of an inverter is set at a threshold voltage thereof and a CK signal is inputted to the input portion of the inverter through a capacitor means. In this manner, the CK signal is amplified, which is sent to the shift register. That is, by obtaining the threshold potential of the inverter, the shift register which operates with almost no effect of variation in characteristics of transistors can be provided. A level shifter of the CK signal is generated from an output pulse of the shift register, therefore, the low power consumption shift register having the level shifter which flows a shoot-through current for a short period can be provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Capacitive touch panel
InactiveUS20120019265A1Small gradientLittle changeResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic switchingElectrical resistance and conductanceResting time
Changes of the stray capacitances of a large number of sensing electrodes can be detected simultaneously. Further, even if a stray capacitance changes slightly, an input operation to a sensing electrode can be detected based on elapsed time until the electric potential of the sensing electrode becomes the same as a threshold potential. The stray capacitance of a sensing electrode and a resistor of the sensing electrode form a CR time constant circuit. Charge or discharge of the stray capacitance of the sensing electrode is controlled while a rest time in a predetermined time ratio is set. A stray capacitance that slightly increases in response to an input operation made near a sensing electrode can be detected by detecting the stray capacitance in extended elapsed time until the electric potential of the sensing electrode becomes the same as the threshold potential.
Owner:SMK CORP
Cort_x: a dynamic brain model
InactiveUS20060271342A1Digital computer detailsComputation using non-denominational number representationCapacitanceCapacitor voltage
A cortical column emulation circuit includes a capacitor which is coupled at a first end to a source of reference potential by a switch, a current source coupled to the first end of the capacitor for charging the capacitor when the switch is open to develop a capacitor voltage between the first end and the second end of the capacitor; and a comparator which compares the voltage across the capacitor to a threshold potential and generates a pulse signal when the capacitor voltage is greater than the threshold voltage. The pulse signal closes the switch to connect the first end of the capacitor to the source of reference potential. A set of cortical column emulation circuits may be coupled together by an adaptive coupling to form a cortical region emulation circuit. The adaptive coupling circuit weights an input stimulus and a plurality of state vector elements by variable coupling coefficients.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Circuit for dynamic switching of a buffer threshold
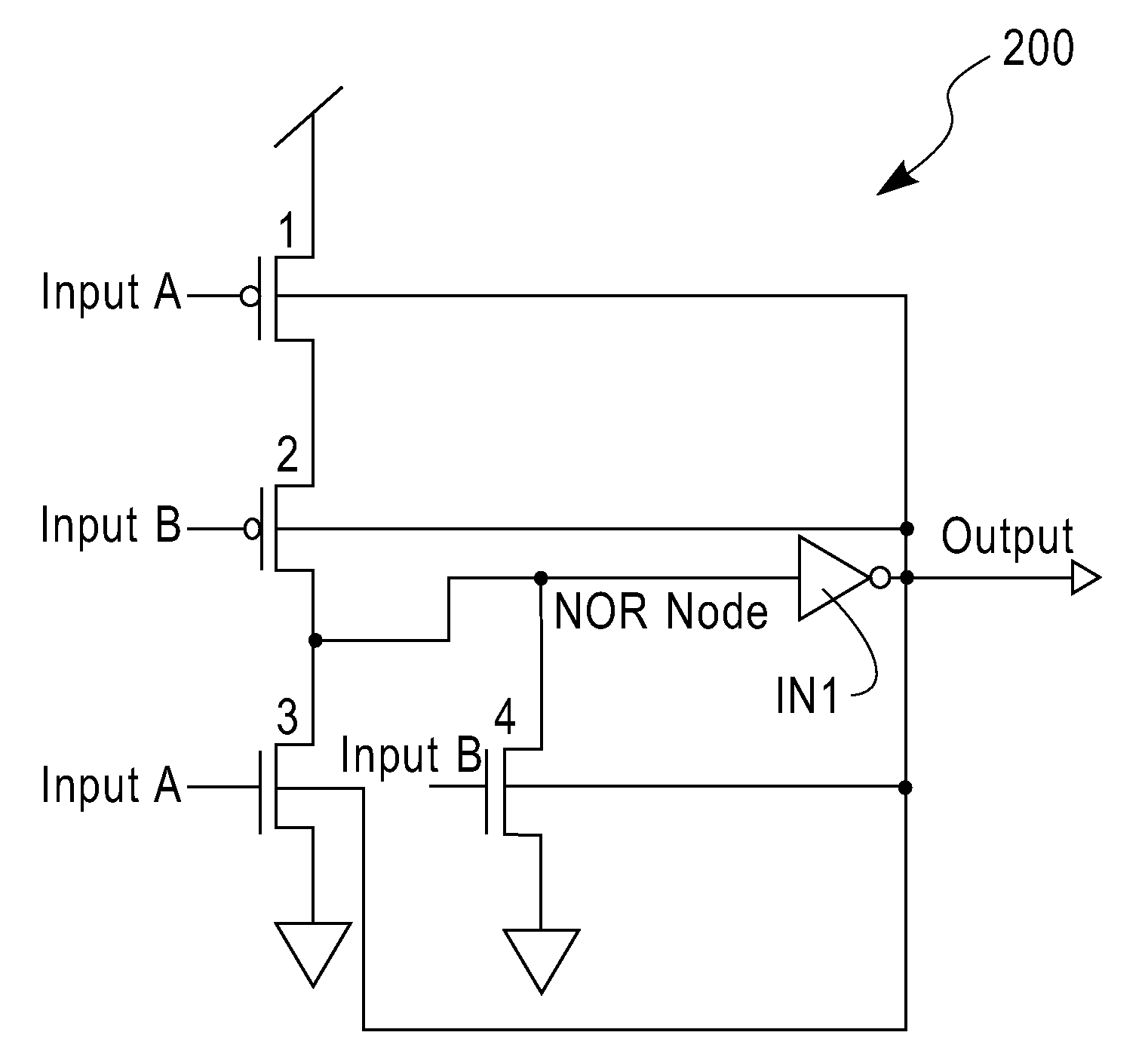
InactiveUS6198308B1Reduce degradationReduce sensitivitySwitching accelaration modificationsThreshold modification in field effect transistorsPropagation delayThreshold potential
A buffer circuit for providing dynamic threshold control. The buffer circuit includes a pair of input inverters designed with different skewed threshold potential characteristics. The outputs of the skewed inverters are directed to a logic circuit designed to select either the faster or the slower signal received from the two inverters for transmission to passgate devices coupled to the respective inverters. Only one of the passgate devices is enabled to ensure that only one of the output signals from the two inverters is propagated through the buffer. A latch is preferably connected between the logic circuit and the two passgate devices to maintain the states of the inverters and the logic circuit. The circuit can be designed to define the threshold potential at which switching will occur so as to reduce propagation delay or increase it as desired. It is therefore possible using the circuit to increase transmission rates with minimal affect on signal noise.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Semiconductor device having standby mode and active mode
InactiveUS7023754B2Stably raisingSuppressing a standby current to be lowTransistorSolid-state devicesThreshold potentialDevice material
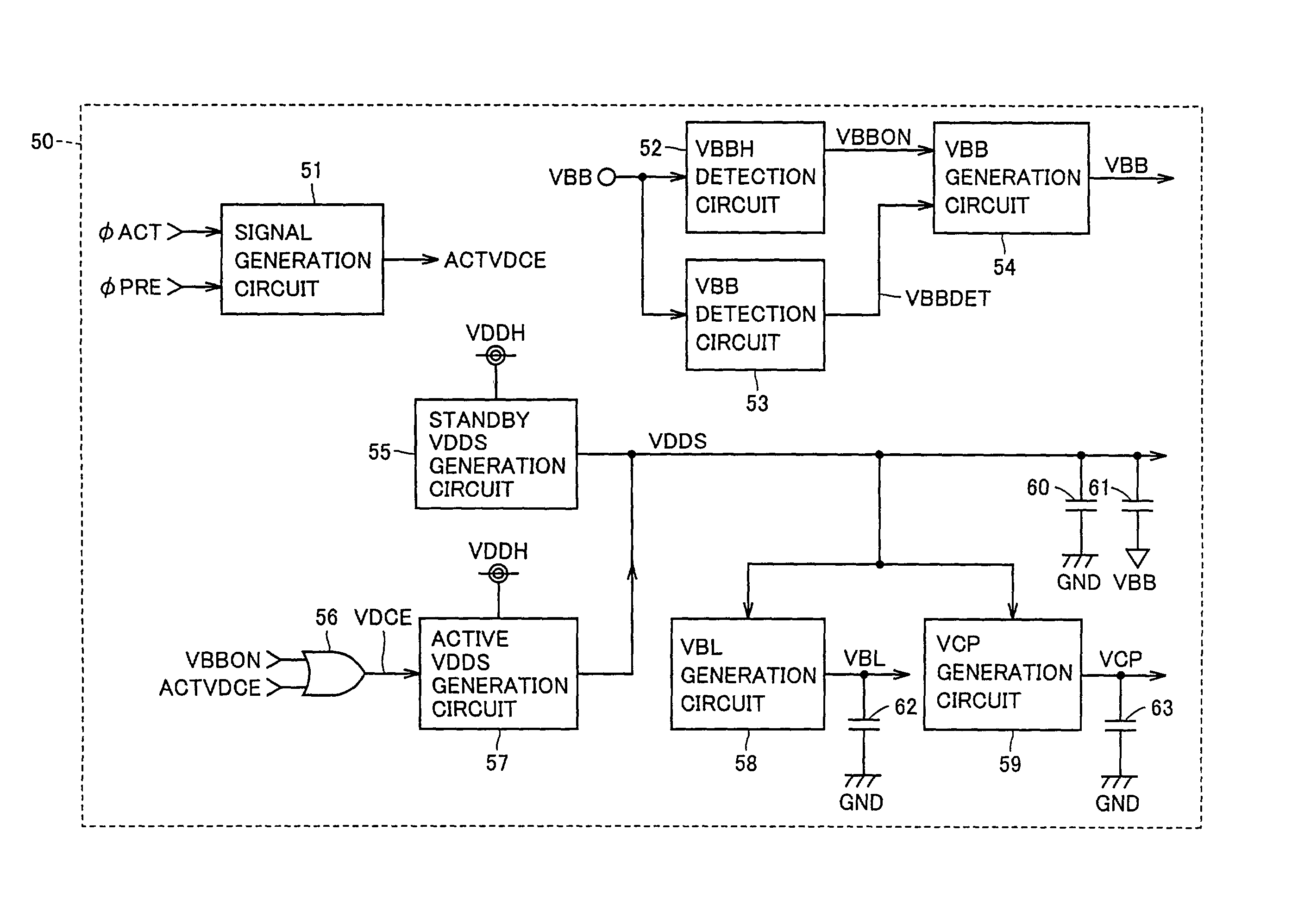
An internal potential generation circuit of an SDRAM includes a standby VDDS generation circuit which has a relatively low current driving force and which generates an internal power supply potential, and an active VDDS generation circuit which has a relatively high current driving force, which is activated during a period after an external power supply potential is applied until a negative potential reaches a threshold potential, and in an activation period, and which generates the internal power supply potential. Therefore, it is possible to raise the internal power supply potential stably without increasing standby current when the power supply is turned on.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
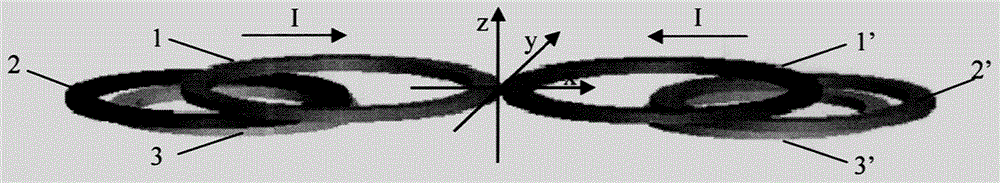
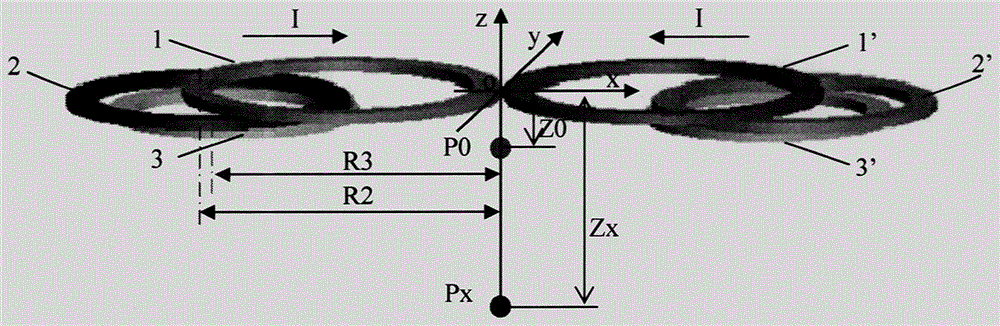
Multilayer eccentric 8-shaped coil for deep site transcranial magnetic stimulation
The invention discloses a multilayer eccentric 8-shaped coil for deep site transcranial magnetic stimulation. Multiple layers of coils are arranged; the first layer forms a basic 8-shaped coil, the below coils are symmetrically distributed along the central line of the 8-shaped coil, and thus the magnetic field and a sensing electric field are adjusted. The distance between the central line of each coil layer and the symmetrical axis is determined through an optimization method, and the optimization target is to enable the ratio of the sensing electric field E (z0) generated on the surface of the coil to the deep site sensing electric field E (z) to be the minimal. Each coil layer can be arranged on the same plane or can be crossed for a certain angle. When the deep site achieves a threshold potential, the sensing electric field on the surface of the coil can be in a safe range, and good focusing can be achieved in the deep site. The attenuation index of the sensing electric field along the depth direction of the multilayer eccentric 8-shaped coil is close to or even better than that of an H coil.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
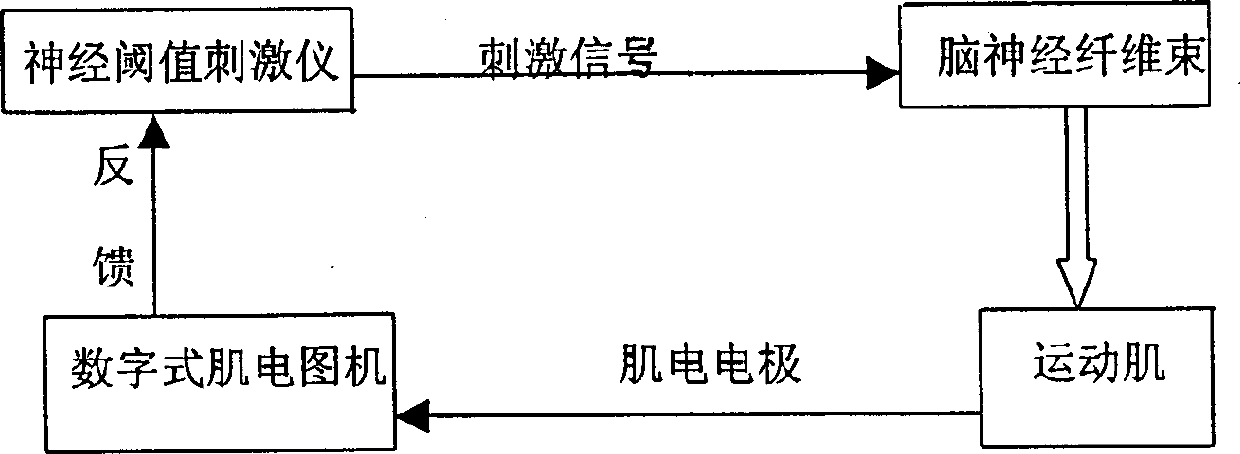
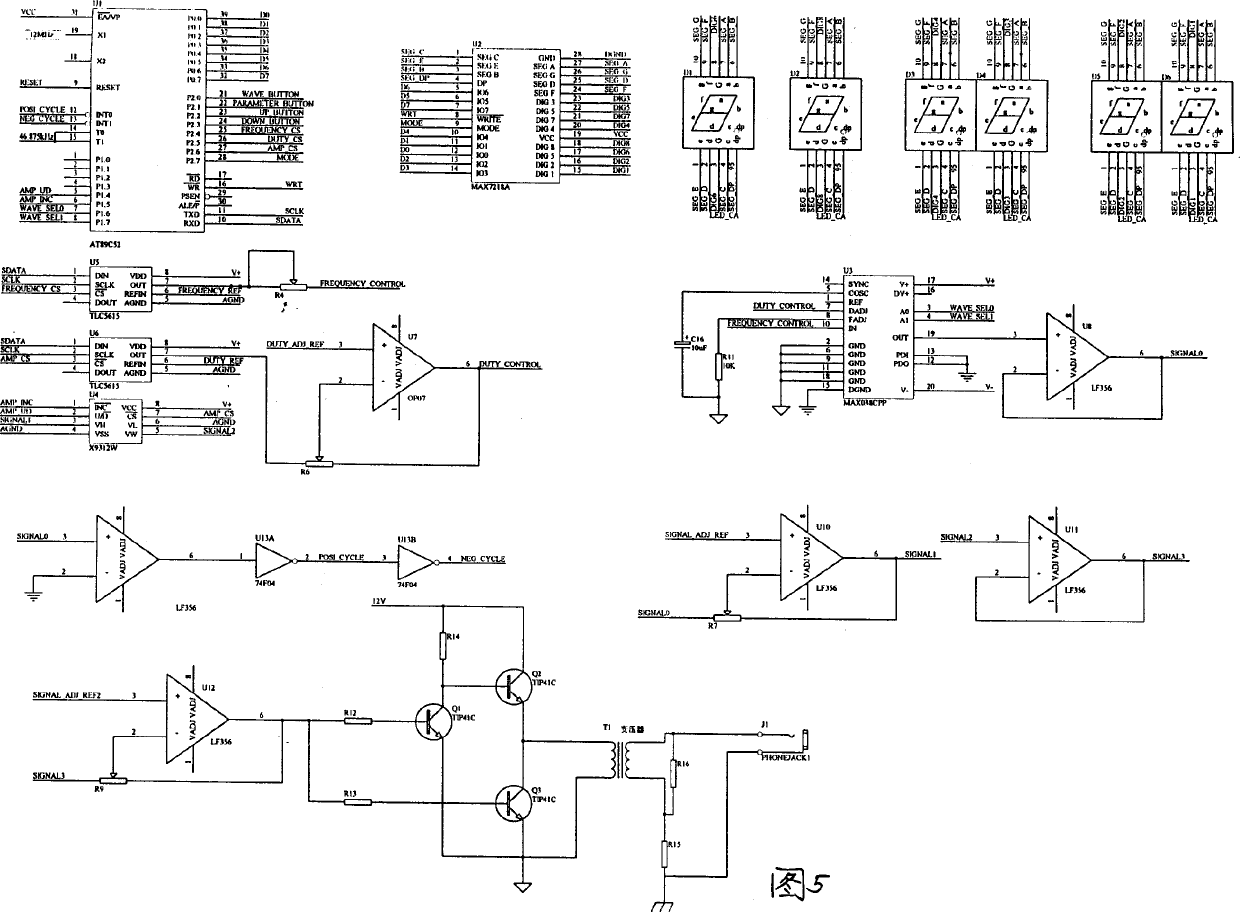
Method and system for testing human nerve threshold value
InactiveCN1401294APrecise digital adjustmentAccurate amplitudeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNerve thresholdThreshold potential
A method for measuring the threshold value of human nerve includes opening human skull, applying electric stimualting signal to the nerve to be measured, measuring the electromyographic signal of the muscle controlled by said nerve, and finding out the threshold value and relative parameters. Its system is composed of a nerve threshold stimulator, a digital electromyograph and a computer.
Owner:NANJING GENERAL HOSPITAL NANJING MILLITARY COMMAND P L A +1
Boosting circuit and RFID tag including boosting circuit
InactiveUS8593840B2Potential boosted in each unit boosting circuit is reducedImprove efficiencyTransistorAc-dc conversionThreshold potentialTransistor
One object is to provide a boosting circuit whose boosting efficiency is enhanced. Another object is to provide an RFID tag including a boosting circuit whose boosting efficiency is enhanced. A node corresponding to an output terminal of a unit boosting circuit or a gate electrode of a transistor connected to the node is boosted by bootstrap operation, so that a decrease in potential which corresponds to substantially the same as the threshold potential of the transistor can be prevented and a decrease in output potential of the unit boosting circuit can be prevented.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
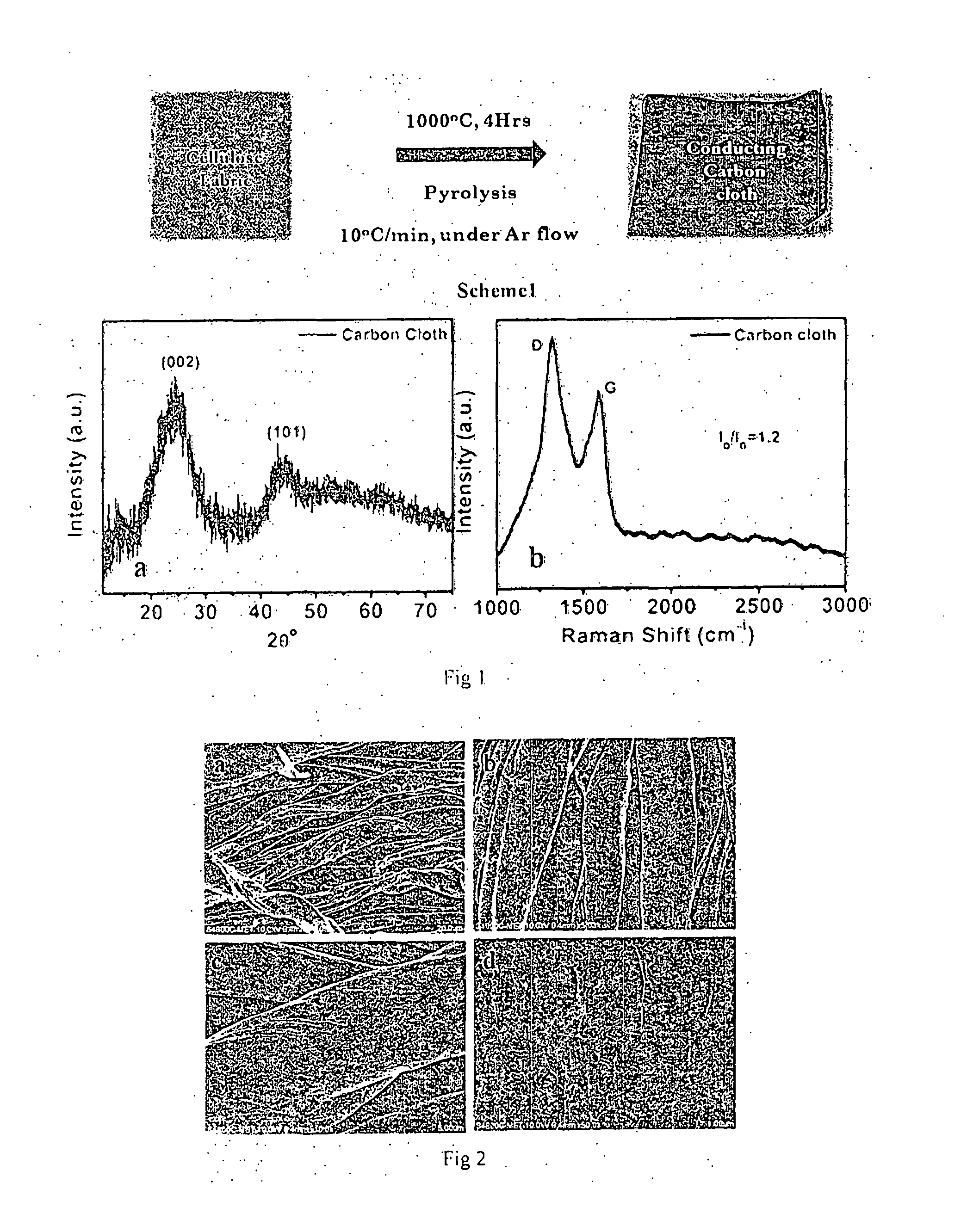
Conducting Carbon Cloth Electrode for Hydrogen Generation and Dye Sensitized Solar Cells
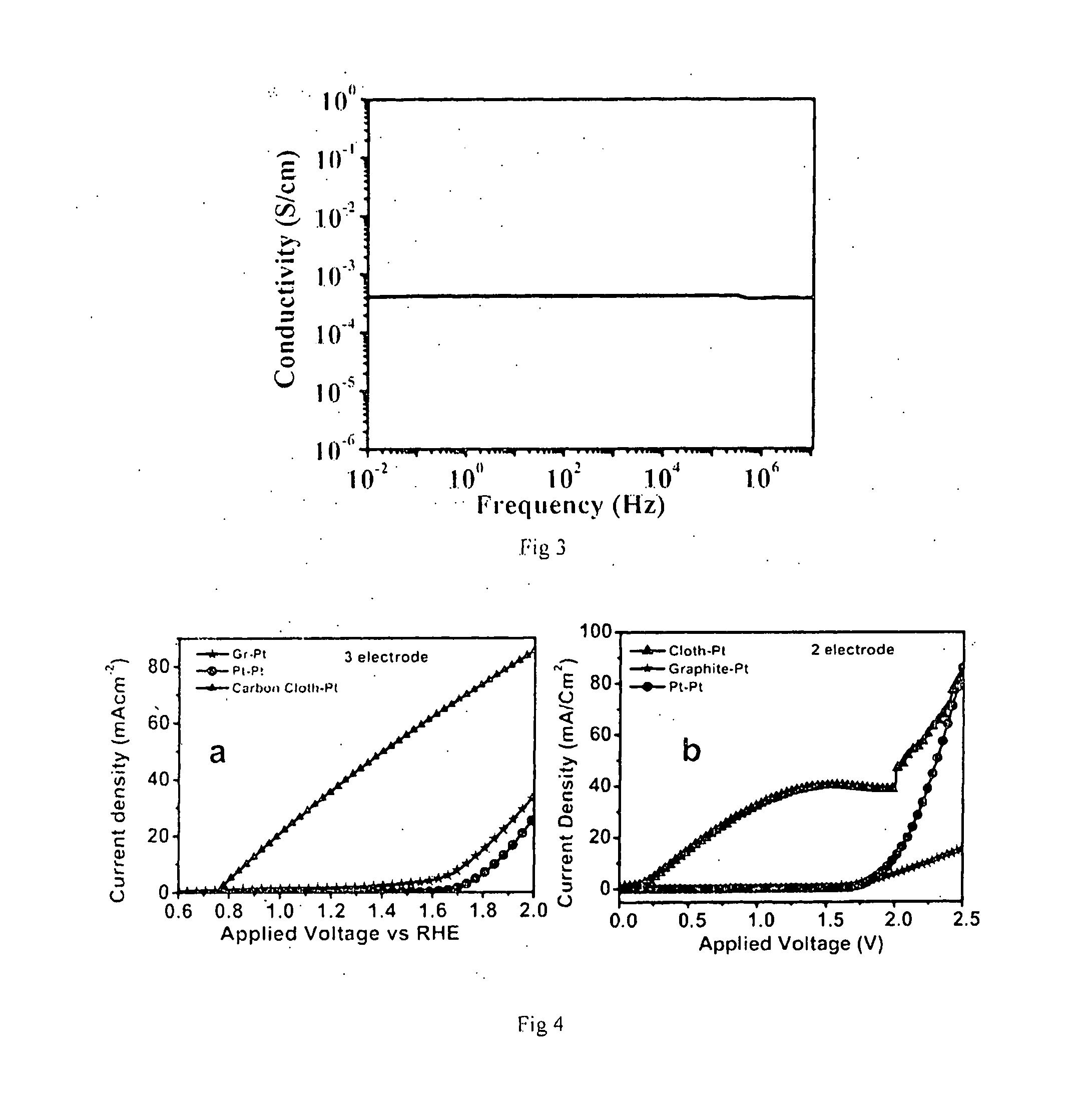
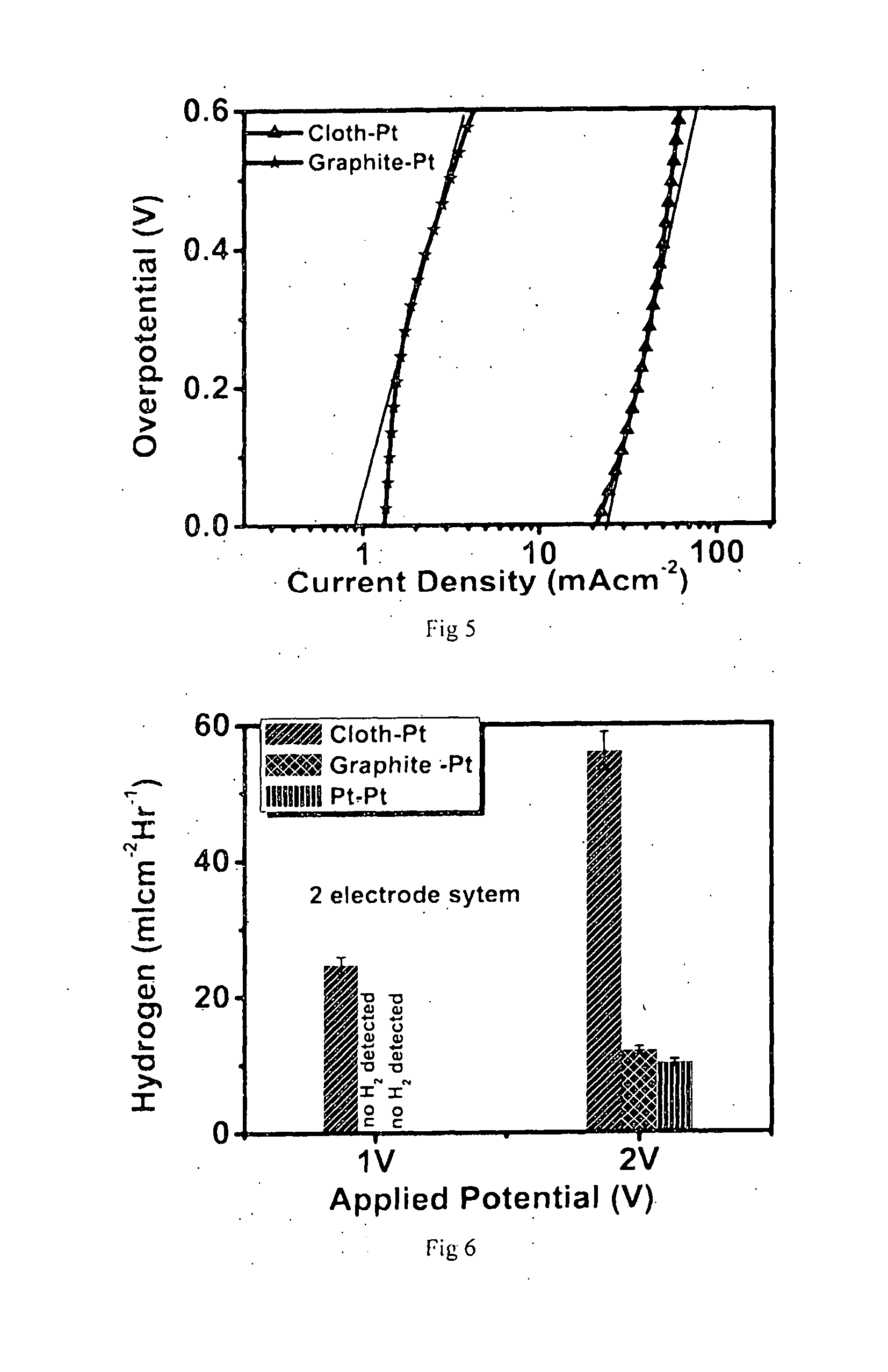
InactiveUS20160201206A1Simple and convenient and cost-effective fabricationLow costLight-sensitive devicesElectrolytic organic productionSub thresholdHydrogen
Disclosed herein is functional conducting carbon cloth with permeability and turbostratic disorder, and process for preparation of the same. Further it describes use of said carbon cloth as anode in alkaline water electrolysis for generation of hydrogen at sub-threshold potential (<1.23V) and generation of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) at super-threshold potential (>1.23V). The invention also relates to the efficient use of the said carbon cloth as counter electrode in Dye Sensitized Solar Cells (DSSCs).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Radiation detector comprising a circuit for injecting a calibrated quantity of counter-charges
InactiveCN103874933ASmall amount-Q0Improve accuracyTransistorRadiation controlled devicesThreshold potentialEngineering
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Display apparatus
ActiveUS7786959B2Requirement for numberSuitable for useCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingThreshold potentialElectrical current
When the transistor Q3 is OFF, a predetermined potential is supplied to a potential wire Ui such that a switching transistor Q2 becomes ON. This changes a gate potential of a driving transistor Q1 from an ON potential to a threshold potential. Thereafter, the transistor Q2 is turned OFF, with the result that the potential of the potential wire Ui is changed (in cases where the transistor Q1 is a p-type transistor, the potential is decreased). With this, the transistor Q1 allows a current to constantly flows therethrough, irrespective of the threshold potential. This shortens time for setting an output current of the driving TFT for driving a current driving type display element.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method to accurately estimate the source and drain resistance of a MOSFET
ActiveUS7595649B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceThreshold potential
Measurements of parameters of MOS transistors, also known as MOSFETs, such as threshold potentials, require accurate estimates of source and drain series resistance. In cases where connections to the MOSFET include significant external series resistance, as occurs in probing transistors that are partially fabricated or deprocessed, accurate estimates of external resistances are also required. This invention comprises a method for estimating series resistances of MOSFETs, including resistances associated with connections to the MOSFET, such as probe contacts. This method is applicable to any MOSFET which can be accessed on source, drain, gate and substrate terminals, and does not require other test structures or special connections, such as Kelvin connections.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Multi-stage input logic judging circuit
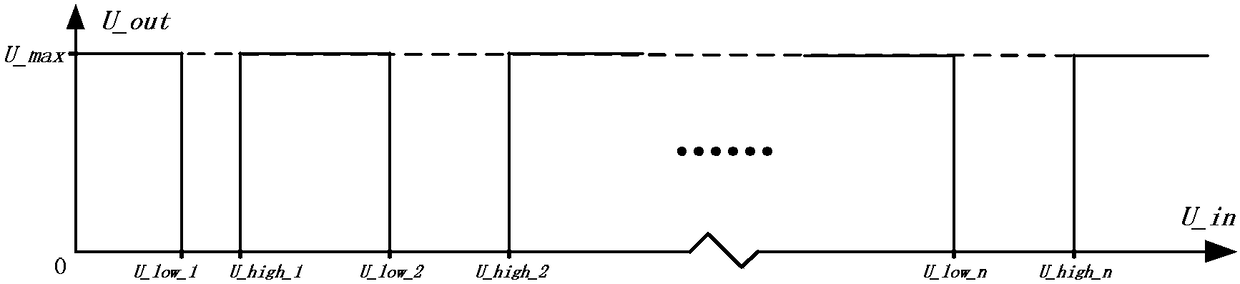
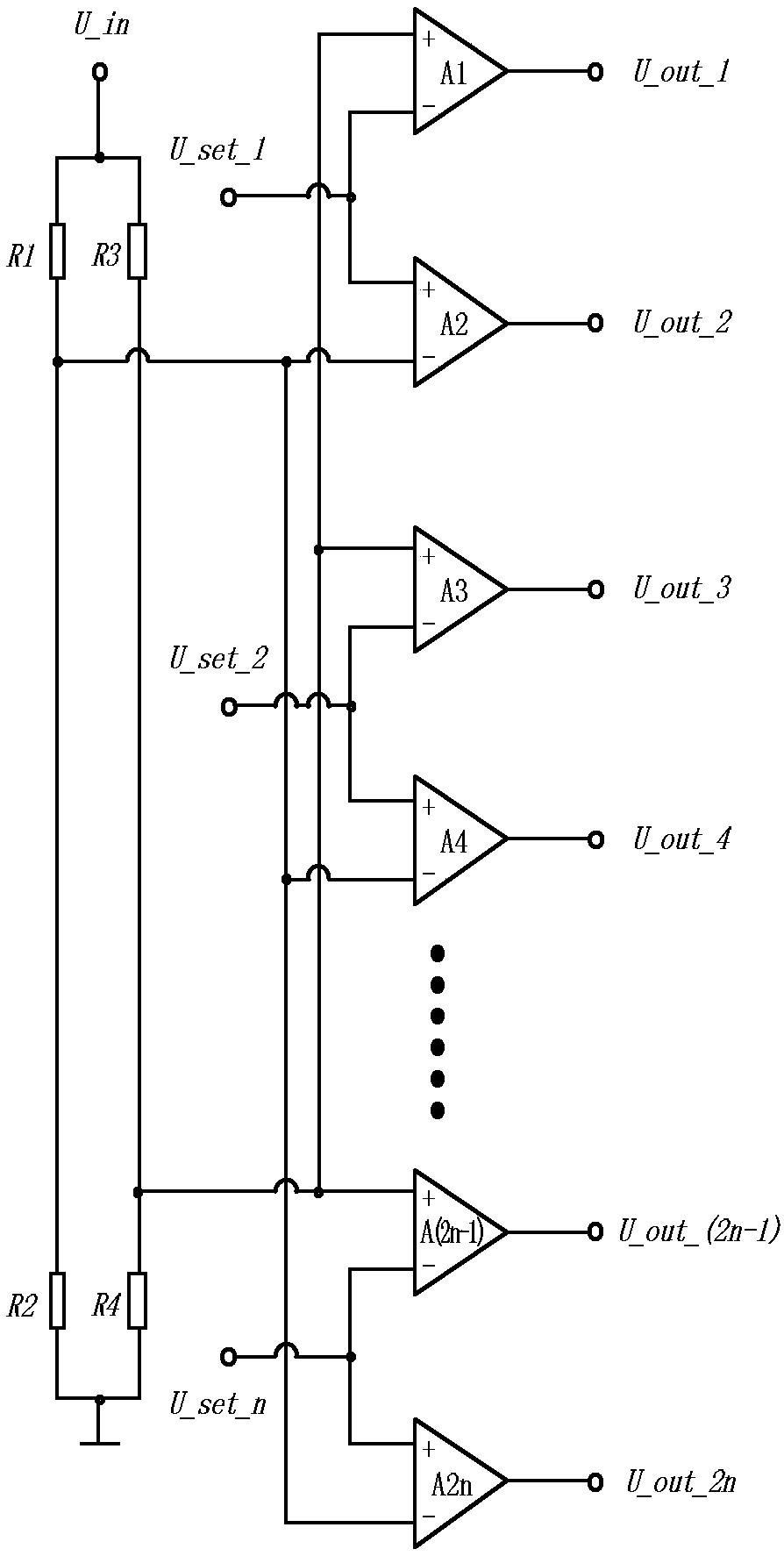
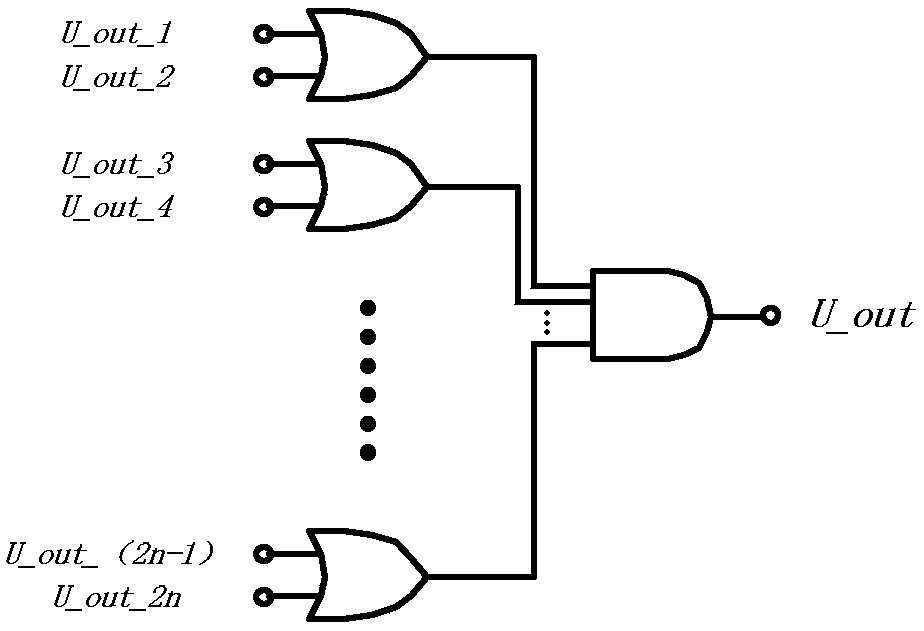
PendingCN108347233ANo "crash" problemQuick responseMultiple input and output pulse circuitsMulti inputOvervoltage
The invention discloses a multi-stage input logic judging circuit. The comparator circuit has n groups of comparators and n threshold point potentials, each group of comparators has two comparators toobtain 2n comparison output voltages, undervoltage and overvoltage sampling of a compared voltage are input to divide the voltage into two independent voltage-dividing branches, voltages obtained bydividing the voltages of R1 and R2 are respectively sent to inverting ends of even-numbered comparators and are compared with the threshold potentials of the non-inverting ends, the voltages obtainedby dividing the voltages of R3 and R4 are respectively sent to the non-inverting ends of odd-numbered comparators and are compared with the threshold potentials of the inverting ends, at this time, the odd-numbered comparators obtain the overvoltage state of each of the n path (when the output level is high, it is in an overvoltage state, and when the output level is low, it is in a non-overvoltage state). According to the multi-stage input logic judging circuit, the function of multi-input potential logic judgment is achieved by designing the hardware circuit of the improved window comparator.
Owner:SHUNDE POLYTECHNIC
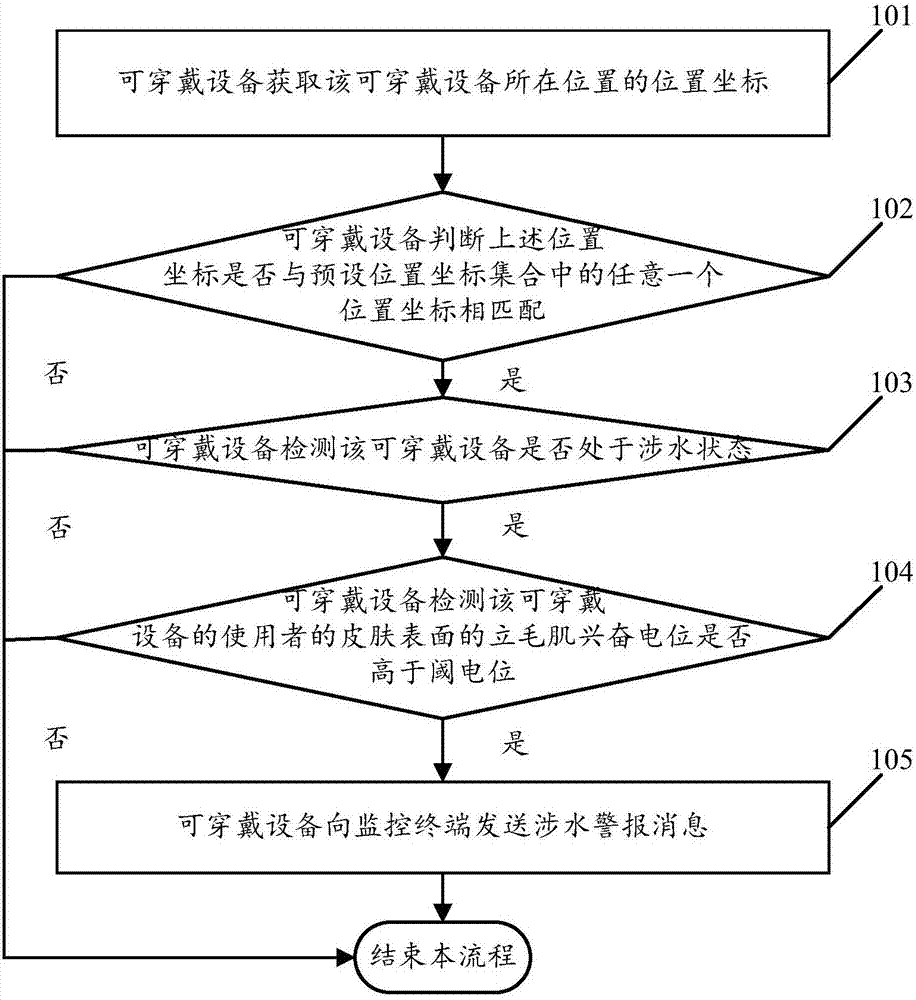
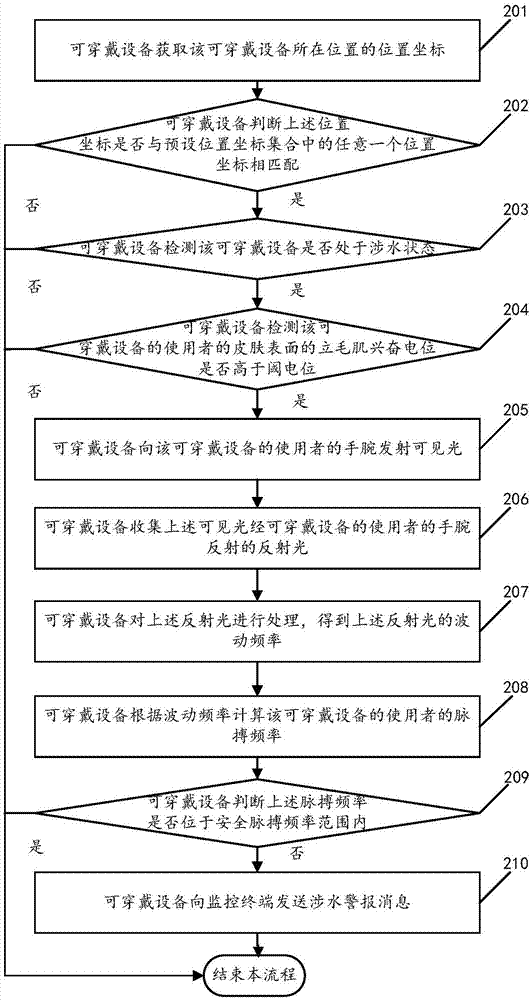
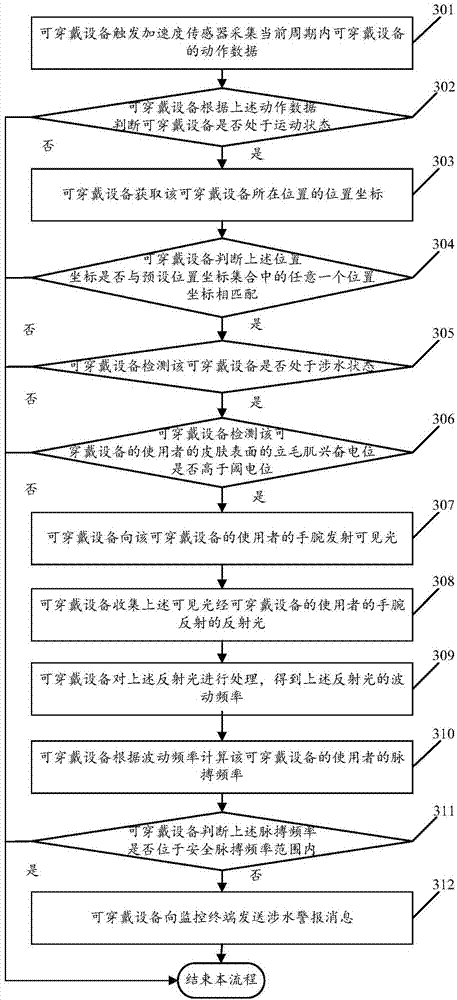
Positioning based fording alarm method and wearable equipment
The invention relates to a positioning based fording alarm method and wearable equipment, and relates to the technical field of electronic equipment. The method comprises that the wearable equipment obtains a positional coordinate of itself and determines whether the positional coordinate matches any positional coordinate in a preset positional coordinate set, if YES, whether the wearable equipment is in a fording state is detected, if the wearable equipment is in the fording state, whether an arrector excitement potential in the skin surface of a user of the wearable equipment is higher thana threshold potential is detected, and if the arrector excitement potential is higher than the threshold potential, a fording alarm message is sent to a monitoring terminal. Thus, fording situation ofkids can be mastered timely.
Owner:GUANGDONG XIAOTIANCAI TECH CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com