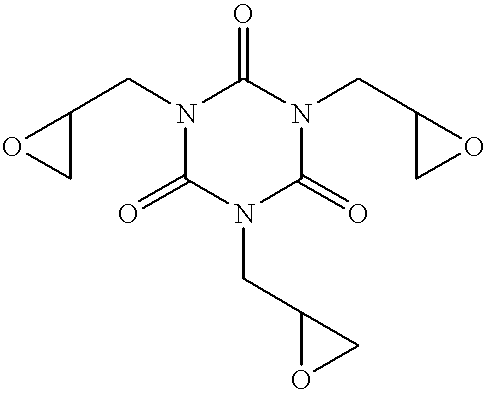
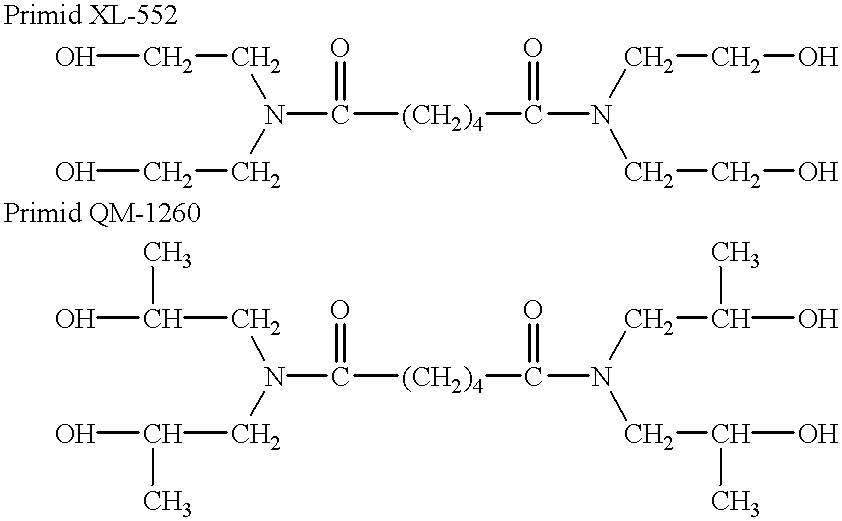
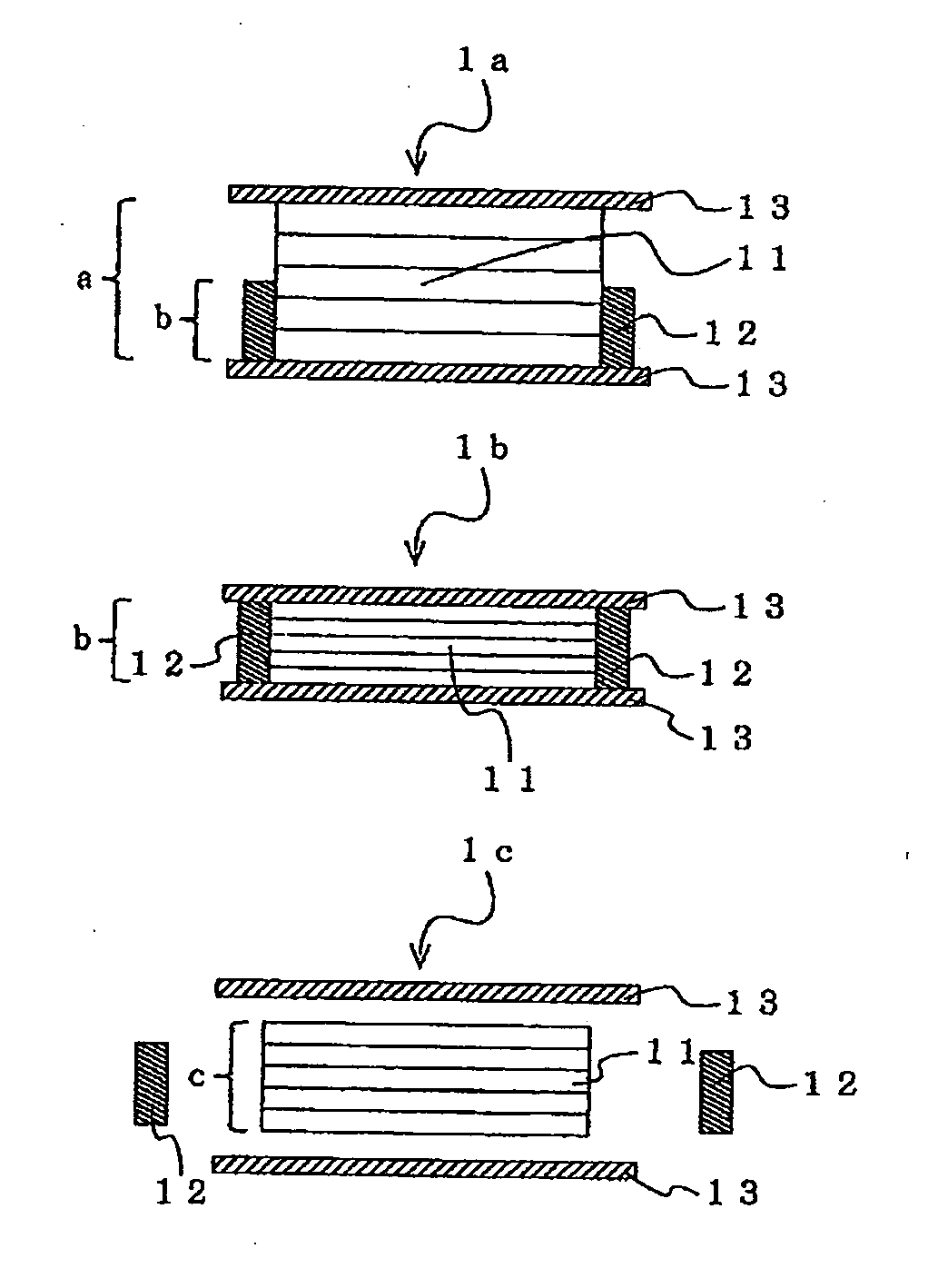
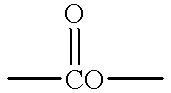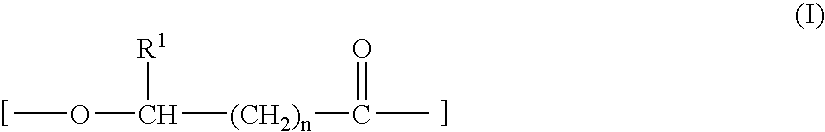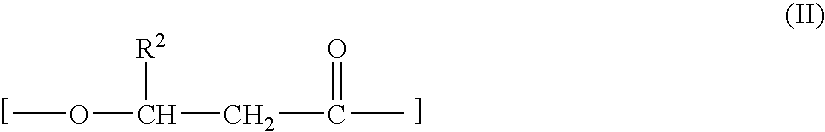Patents
Literature
149results about How to "Outstanding property" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
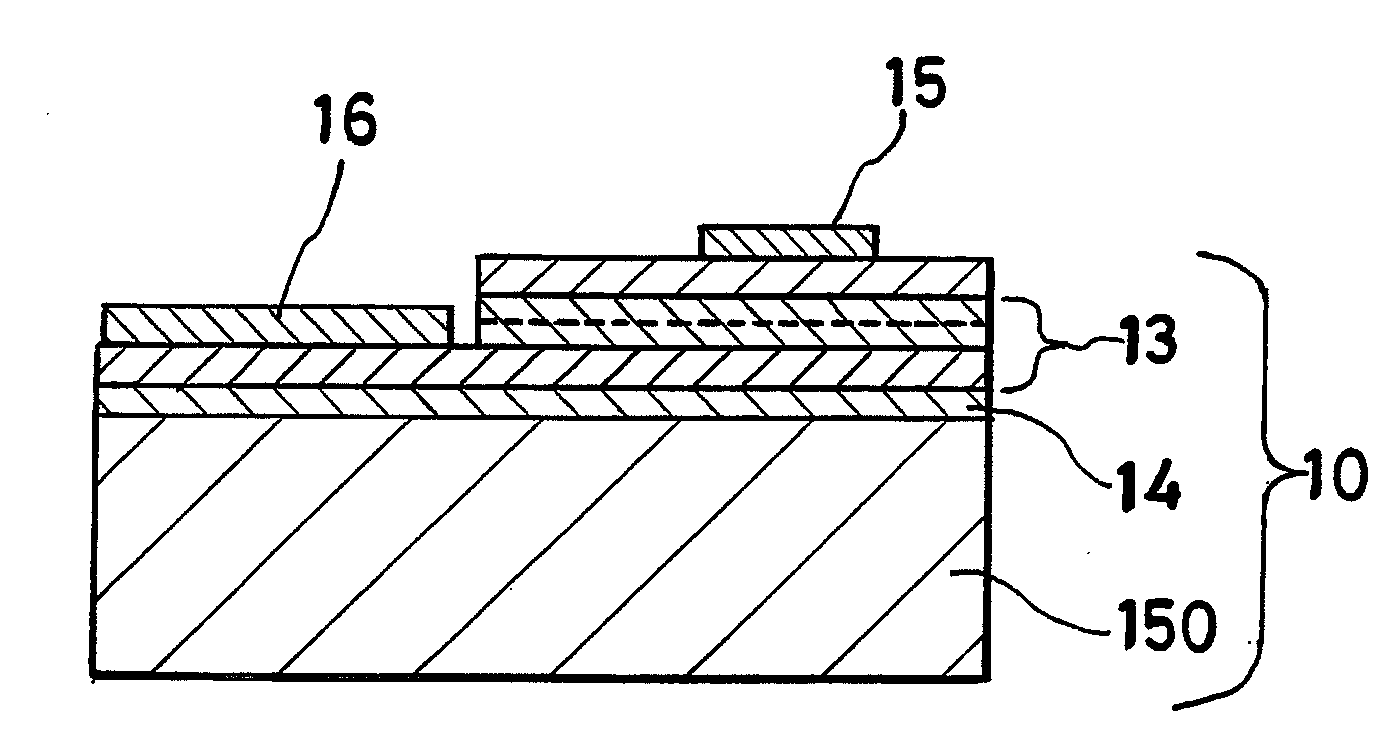
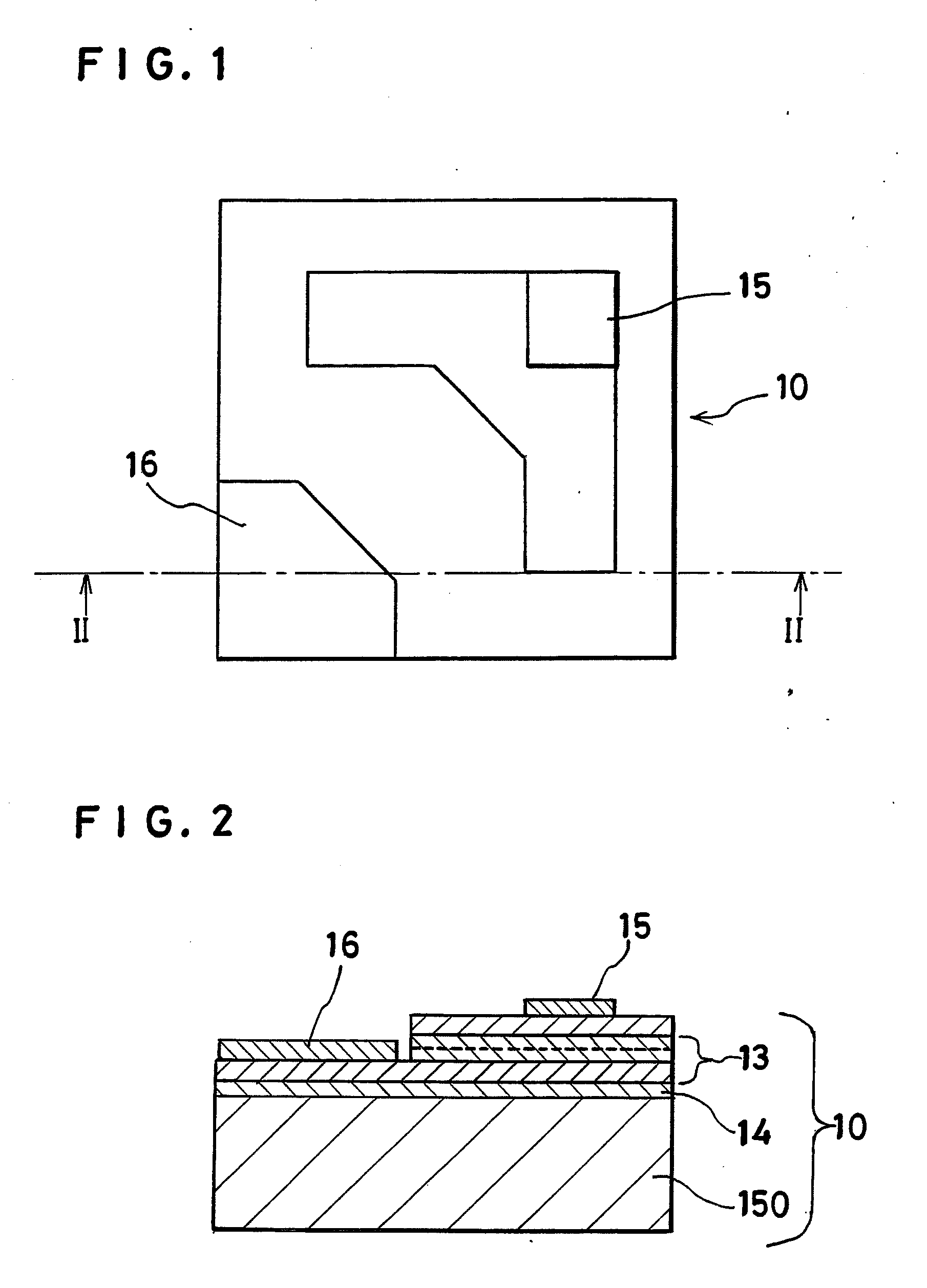
Piezoelectric resonator, piezoelectric filter, duplexer, communication apparatus, and method for manufacturing piezoelectric resonator
InactiveUS6906451B2Improve flatnessOutstanding crystallinityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksOxygenPiezoelectric thin films
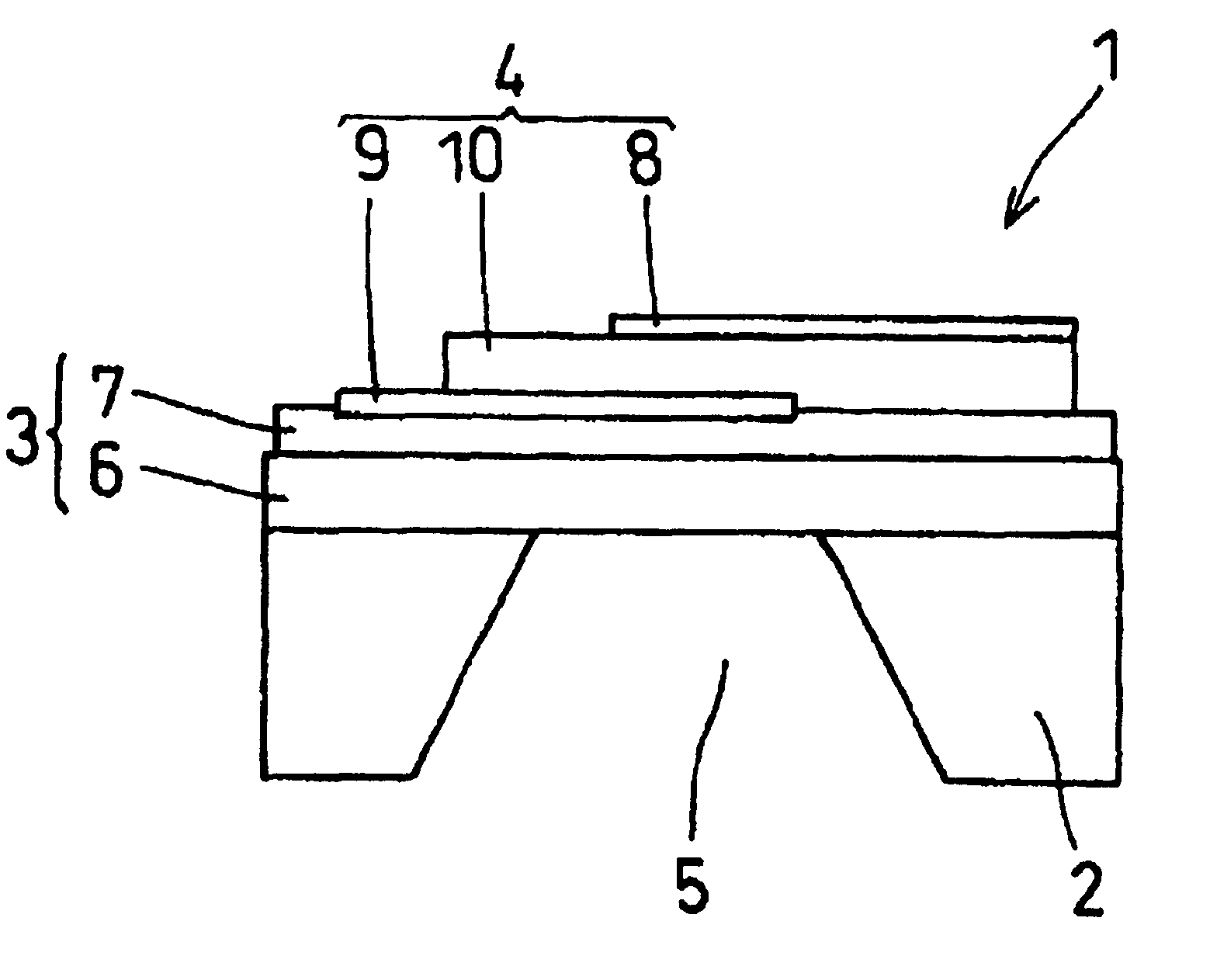
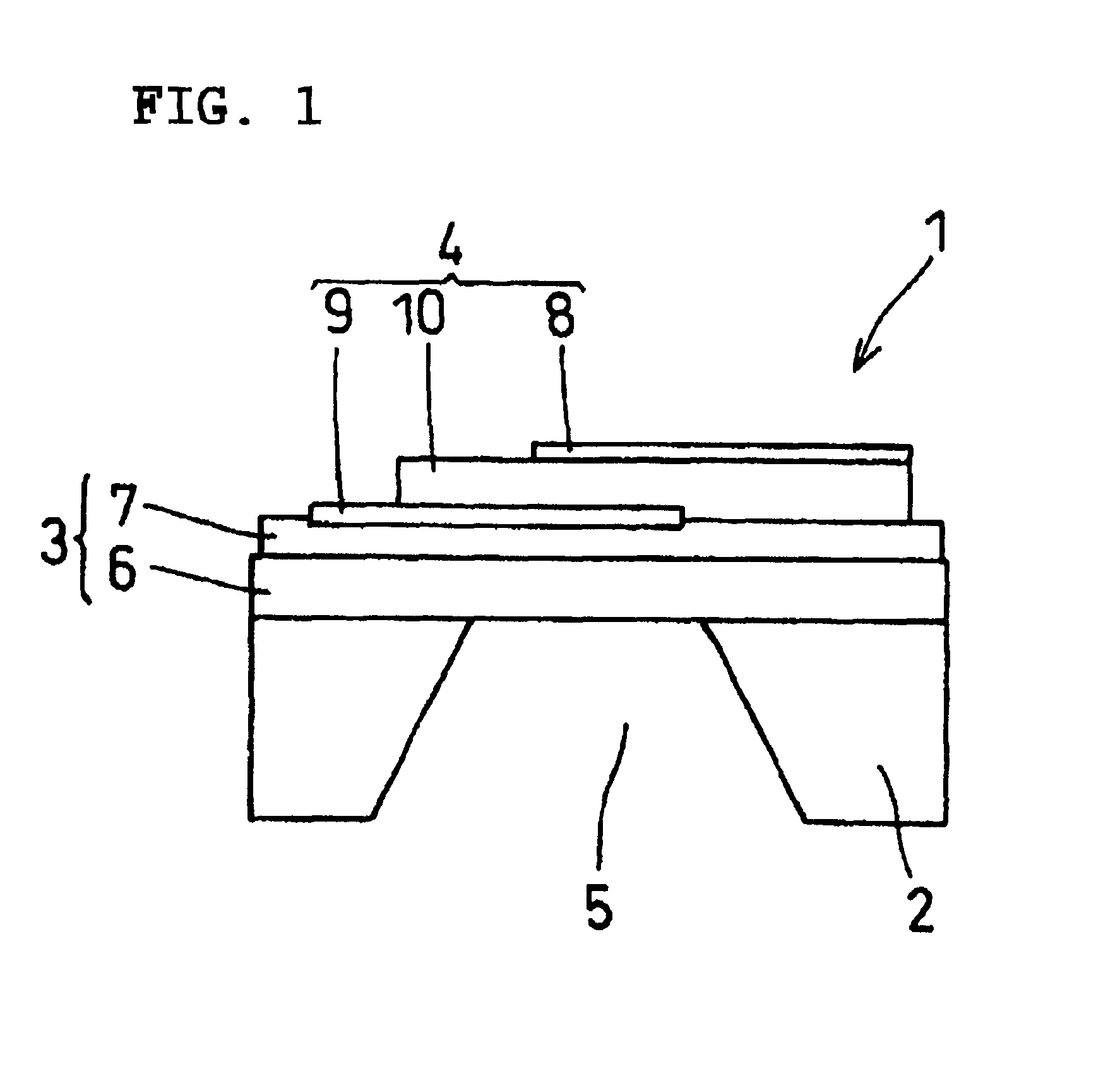
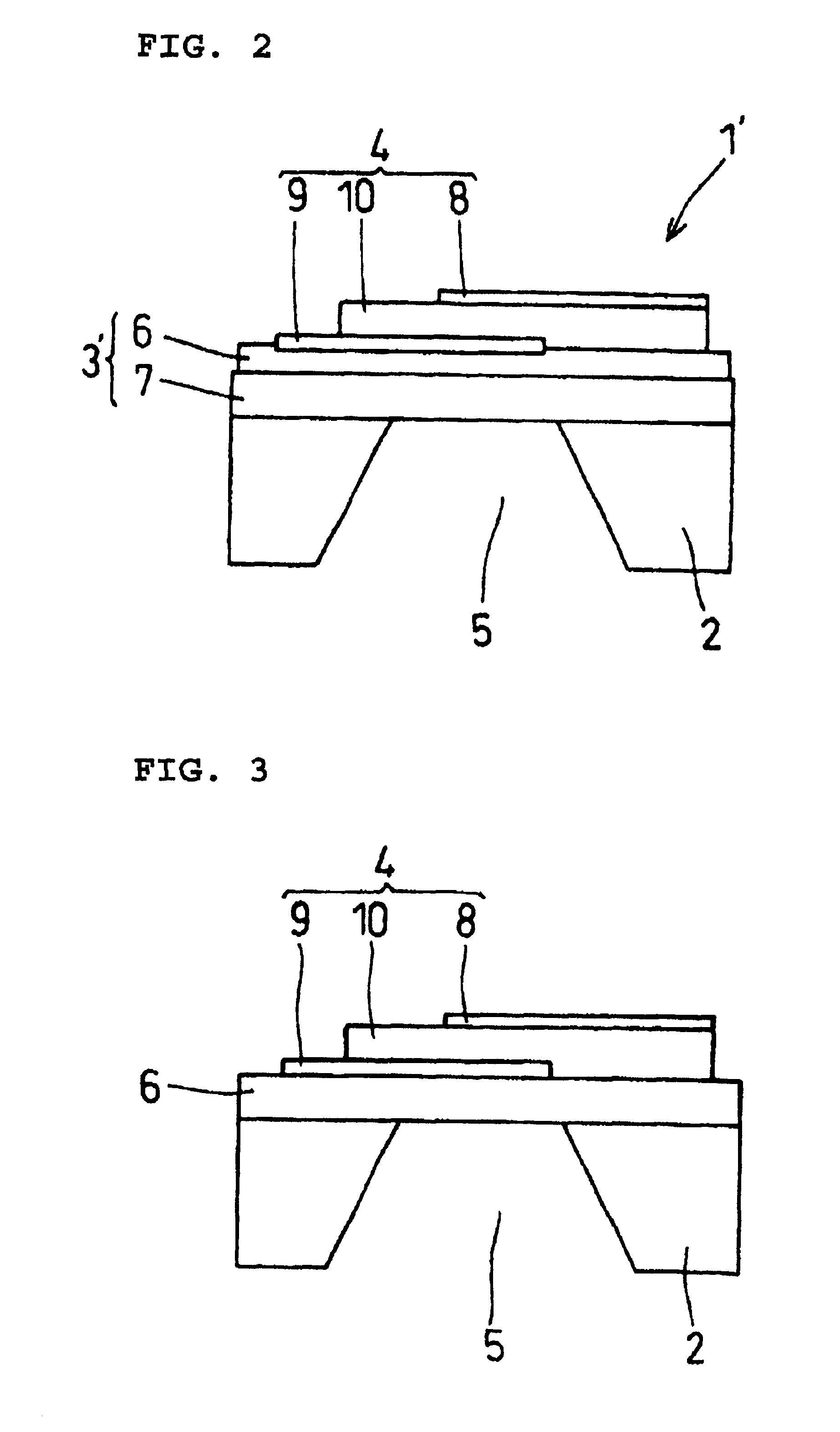
A piezoelectric thin film resonator having a stabilized temperature characteristic of resonant frequency, a method for manufacturing the same, and a communication apparatus using the piezoelectric thin film resonator are provided. The piezoelectric thin film resonator is provided with a substrate having an opening, first and second insulation films which are provided on one surface of the substrate while covering the opening and which primarily include SiO2 and Al2O3, respectively, Al2O3 having oxygen defect and being in an amorphous state, and a piezoelectric thin film which is provided on the second insulation film and is sandwiched between electrodes and which primarily includes ZnO.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Cosmetic composition for care and/or treatment and/or makeup of the emulsion type structured with silicone polymers
InactiveUS20030235548A1Outstanding propertyIncrease flexibilityCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsThiocarbamatePolymer science
Cosmetic emulsion for care and / or makeup, comprising an aqueous phase and a liquid fatty phase dispersed one within the other, said liquid fatty phase comprising at least one silicone oil and being structured with at least one gelling polymer (homopolymer or copolymer) with a weight-average molecular mass ranging from 500 to 500,000, containing at least one moiety comprising: at least one polyorganosiloxane group, composed of 1 to 1000 organosiloxane units in the chain of the moiety or in the form of a graft, and at least two groups capable of establishing hydrogen interactions chosen from among the ester, amide, sulfonamide, carbamate, thiocarbamate, urea, thiourea, oxamido, guanidino, biguanidino groups, and combinations thereof, on condition that at least one of the groups is other than an ester group, the polymer being solid at room temperature and soluble in the liquid fatty phase at a temperature of 25 to 250° C., the aqueous phase, the liquid fatty phase and the gelling polymer forming a physiologically acceptable medium.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Method for production of modified water absorbent resin
InactiveUS20090298963A1Improve production efficiencyOutstanding propertyAbsorbent padsBandagesWater solublePolymer chemistry
This invention is to provide a method for producing a modified water absorbent resin excelling in water absorbing properties. This invention relates to a method for producing a modified water absorbent resin, which comprises a) mixing a water absorbent resin and a water-soluble radical polymerization initiator or a heat-degradable radical polymerization initiator without addition of an ethylenically unsaturated monomer and b) irradiating the resultant mixture with active energy rays. The method is particularly capable of exalting the absorbency against pressure and the saline flow conductivity.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Process and device for forming ceramic coatings on metals and alloys, and coatings produced by this process
InactiveUS6896785B2Increase usageImprove adhesionAnodisationCellsPlasma electrolytic oxidationCeramic coating
Owner:KERONITE INT LTD
Process for preparing dry extracts
InactiveUS20030104076A1Reduce the amount requiredEasy to handleBiocideGranulation by liquid drop formationFood scienceSpray drying
Owner:J RETTENMAIER & SOEHNE GMBH CO KG ROSENBERG
Thermoplastic resin foam and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20100178488A1Outstanding propertyExcel in flexibilitySynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingElastomerPolymer science
Disclosed is a thermoplastic resin foam which excels typically in strength, flexibility, cushioning properties, and strain recovery and is especially resistant to cell structure shrinkage caused by the restoring force of resin.The thermoplastic resin foam which is obtained by subjecting a thermoplastic resin composition containing a thermoplastic elastomer and an active-energy-ray-curable resin to foam molding to give a foamed structure, and irradiating the foamed structure with an active energy ray to allow the active-energy-ray-curable resin to form a cross-linked structure in the foamed structure. Also, the thermoplastic resin foam which is obtained by subjecting a thermoplastic resin composition containing a thermoplastic elastomer, an active-energy-ray-curable resin, and a thermal cross-linking agent to foam molding to give a foamed structure, irradiating the foamed structure with an active energy ray to allow the active-energy-ray-curable resin to form a cross-linked structure in the foamed structure, and heating the resulting foamed structure bearing the cross-linked structure to thereby allow the thermal cross-linking agent to form another cross-linked structure in the foamed structure.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Fluorescent substance and production method thereof, and light emitting device
ActiveUS20100053932A1Excels substanceImprove efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesFluorescenceUltraviolet lights
Offered is a fluorescent substance consisting of Eu-activated β-sialon and capable of enhancing the brightness of a light emitting device such as a white LED using blue or ultraviolet light as a light source. The fluorescent substance has as its main constituent a β-sialon represented by the general formula Si6-zAlzOzN8-z and containing Eu, wherein the spin density is 2.0×1017 / g or less as measured by electron spin resonance spectroscopy corresponding to an absorption of g=2.00±0.02 at 25° C. In the above fluorescent substance, it is preferable that lattice constant a of the β-sialon be 0.7608-0.7620 nm, the lattice constant c be 0.2908-0.2920 nm, and the Eu content be 0.1-3 mass %.
Owner:DENKA CO LTD
Process and device in connection with the production of oxygen or oxygen enriched air
Owner:IFO CERAMICS
Copper base alloy, and cast ingot and parts to be contacted with liquid
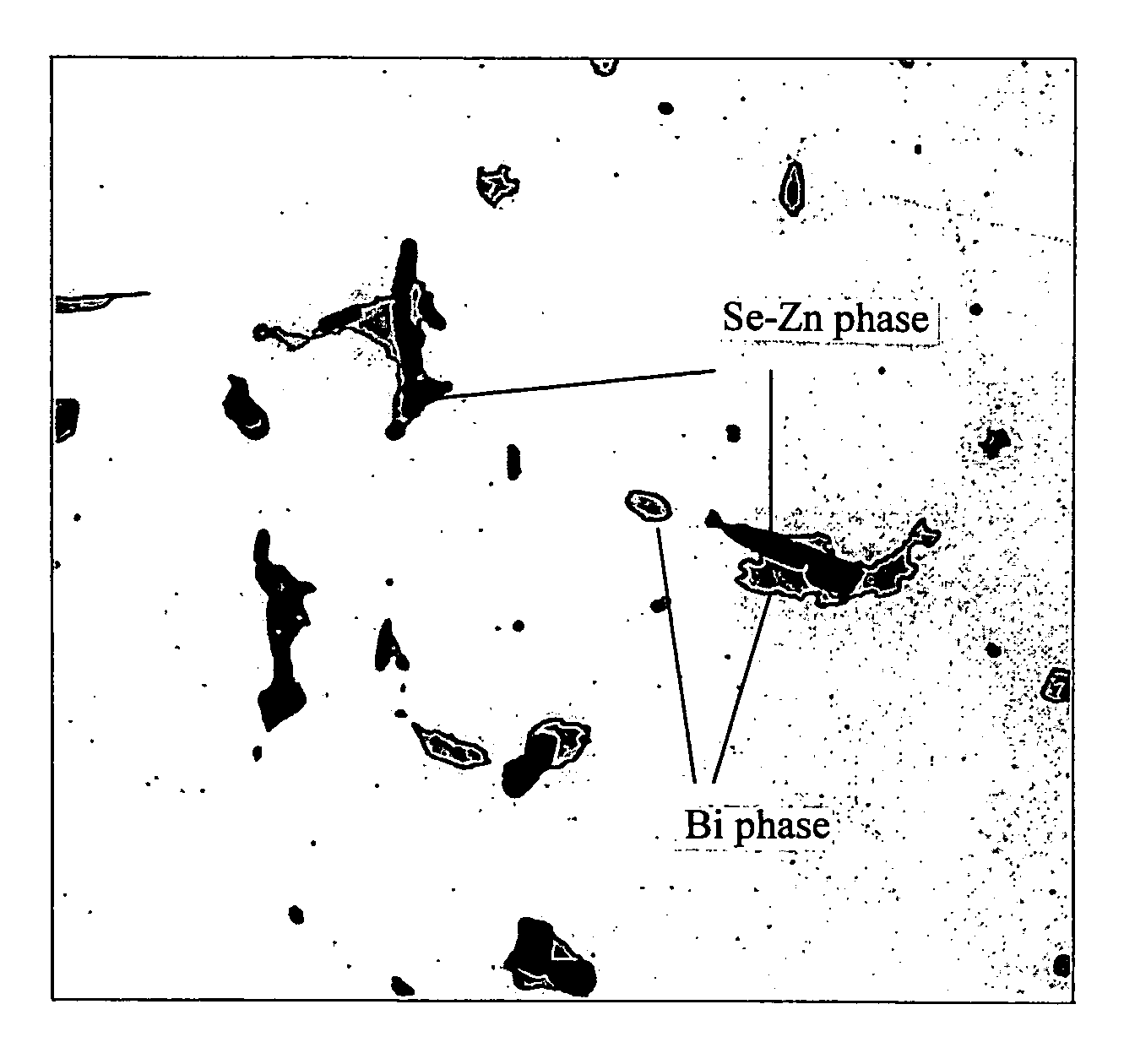
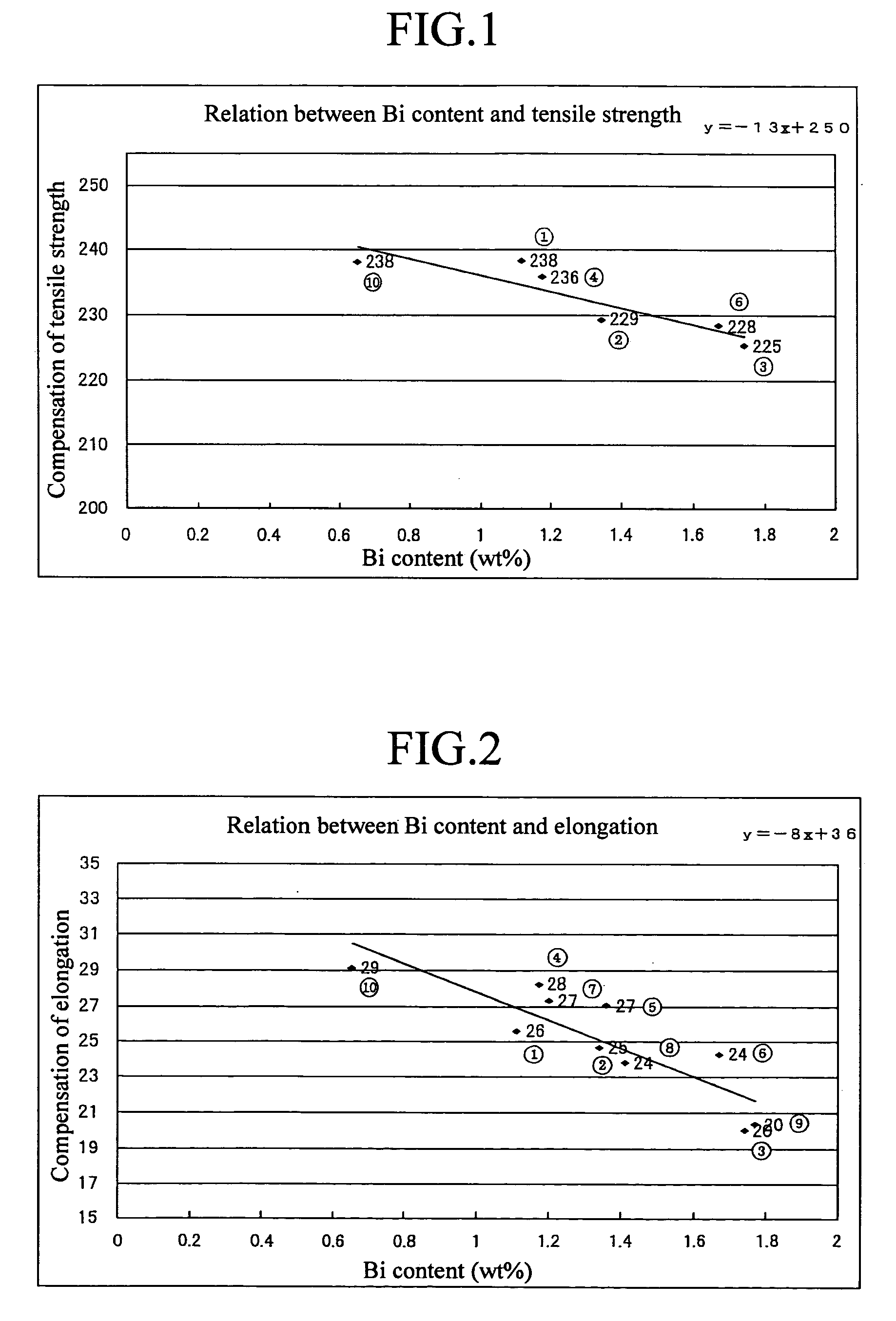
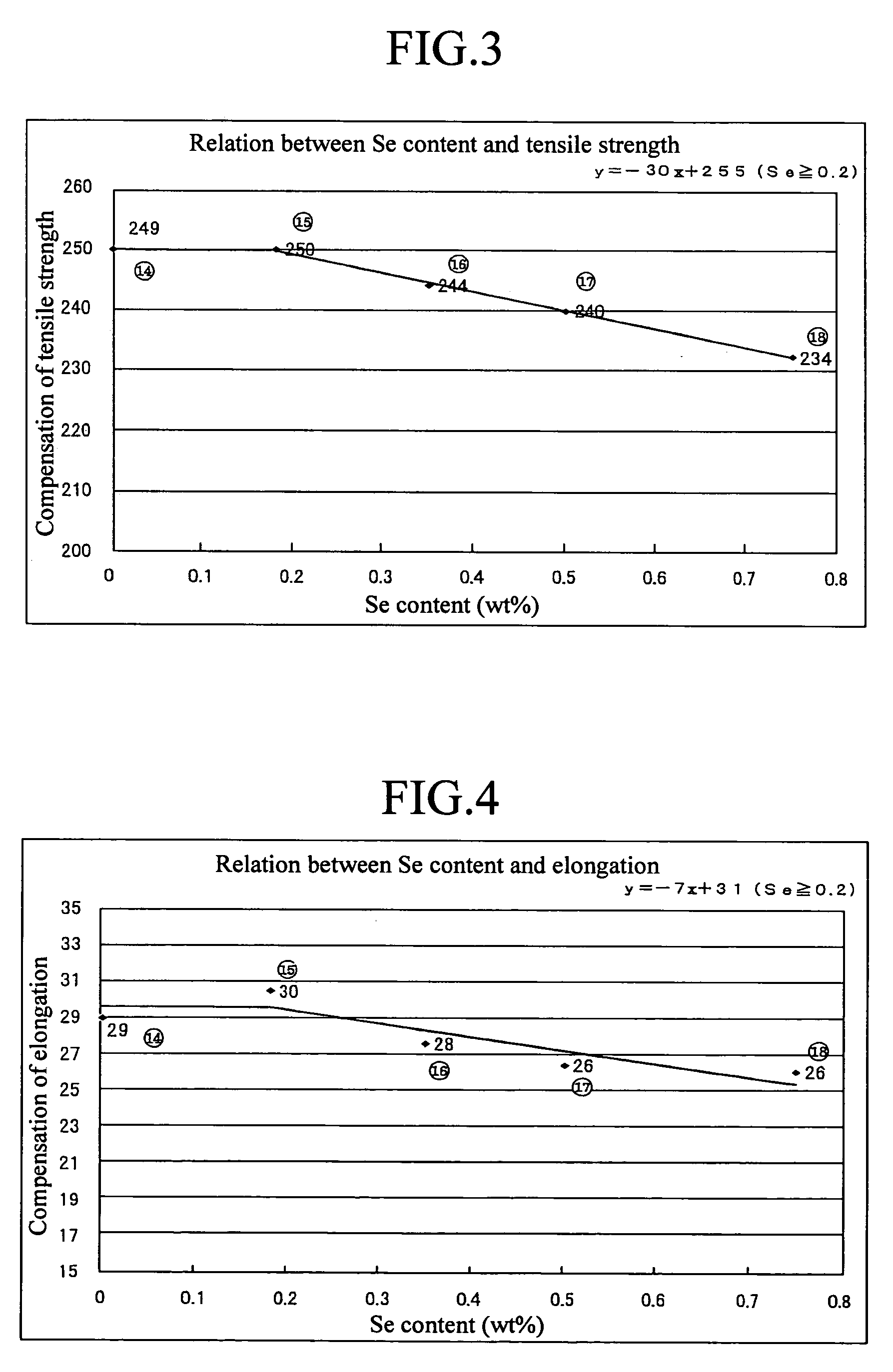
By exactly comprehending the true properties of the rare elements (such as Bi and Se) which are alternative components for Pb, the alloy is enabled to secure machinability equal to the bronze alloy (CAC406) generally used hitherto and acquire mechanical properties at least equal to the CAC406 as well in spite of a decrease in the content of the rare elements (such as Bi and Se) in the alloy. Further, it is possible to suppress the occurrence of casting defects by elucidating the unresolved influence of the decrease of the alternative components (such as Bi and Se) for Pb on the wholesomeness of a casting. Moreover, it is possible, by decreasing the rare elements, to produce a copper-based alloy containing rare elements at a low cost and to provide a cast ingot and a liquid-contacting part each using the alloy. The copper-based alloy, and the cast ingot and liquid-contacting part each using the alloy individually contain at least 2.8 to 5.0 wt % of Sn, 0.4 to 3.0 wt % of Bi and satisfying 0<Se≦0.35 wt % to enable securing prescribed machinability and wholesomeness of a casting and exalt mechanical properties thereof.
Owner:KITZ CORP
Process and device for forming ceramic coatings on metals and alloys, and coatings produced by this process
InactiveUS20030188972A1Reduce roughnessImprove thickness uniformityAnodisationCellsElectrolytic agentPlasma electrolytic oxidation
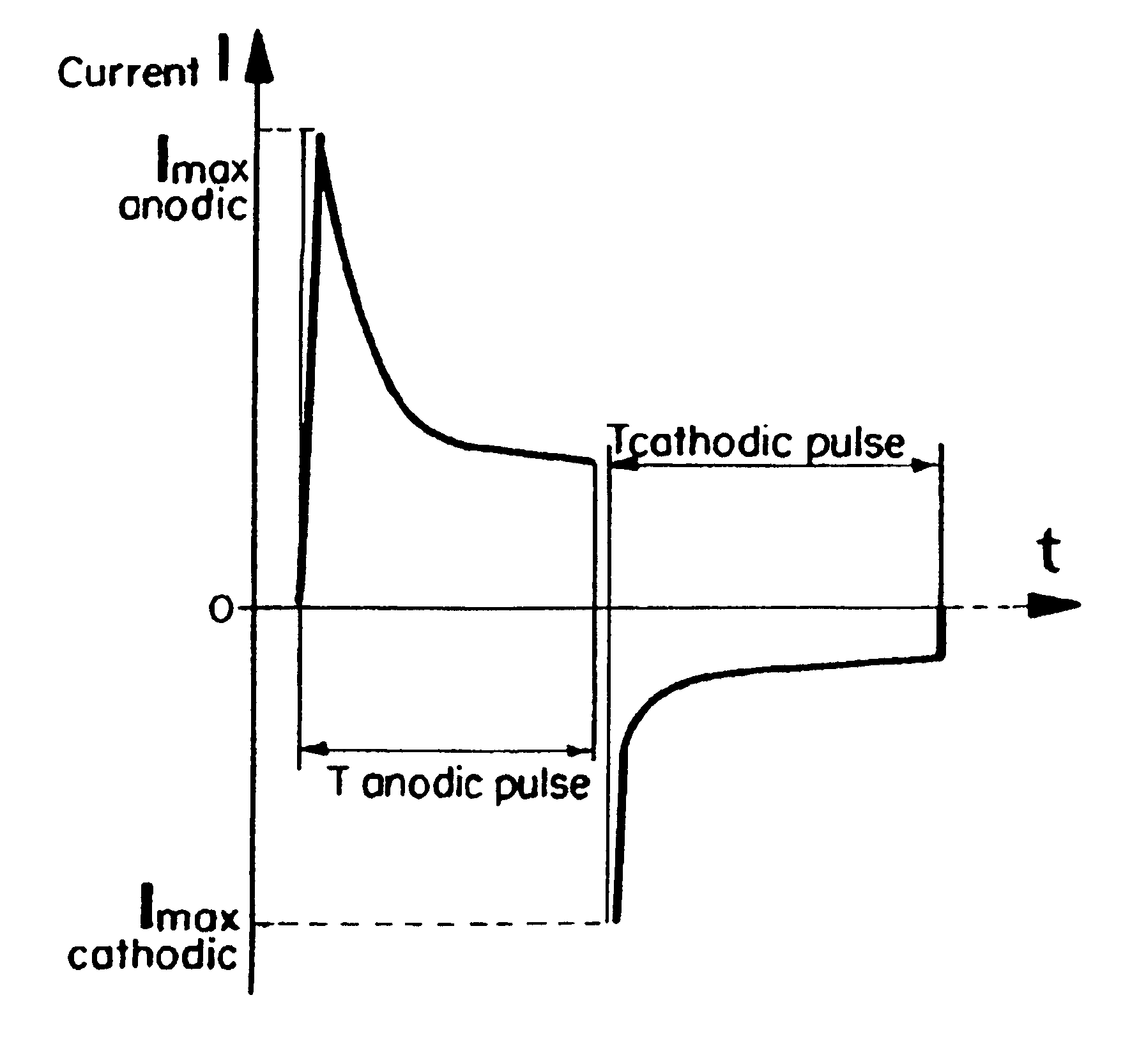
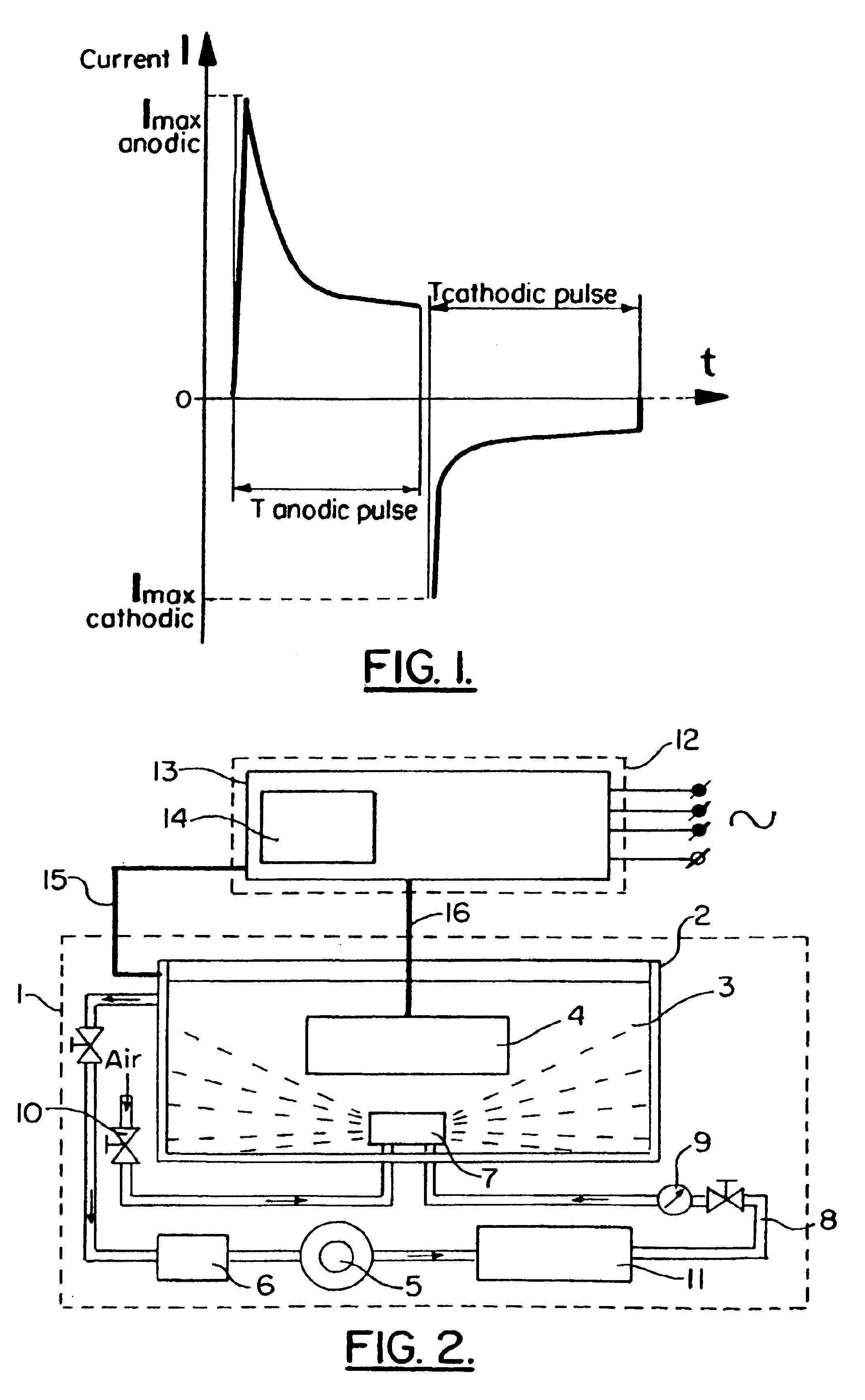
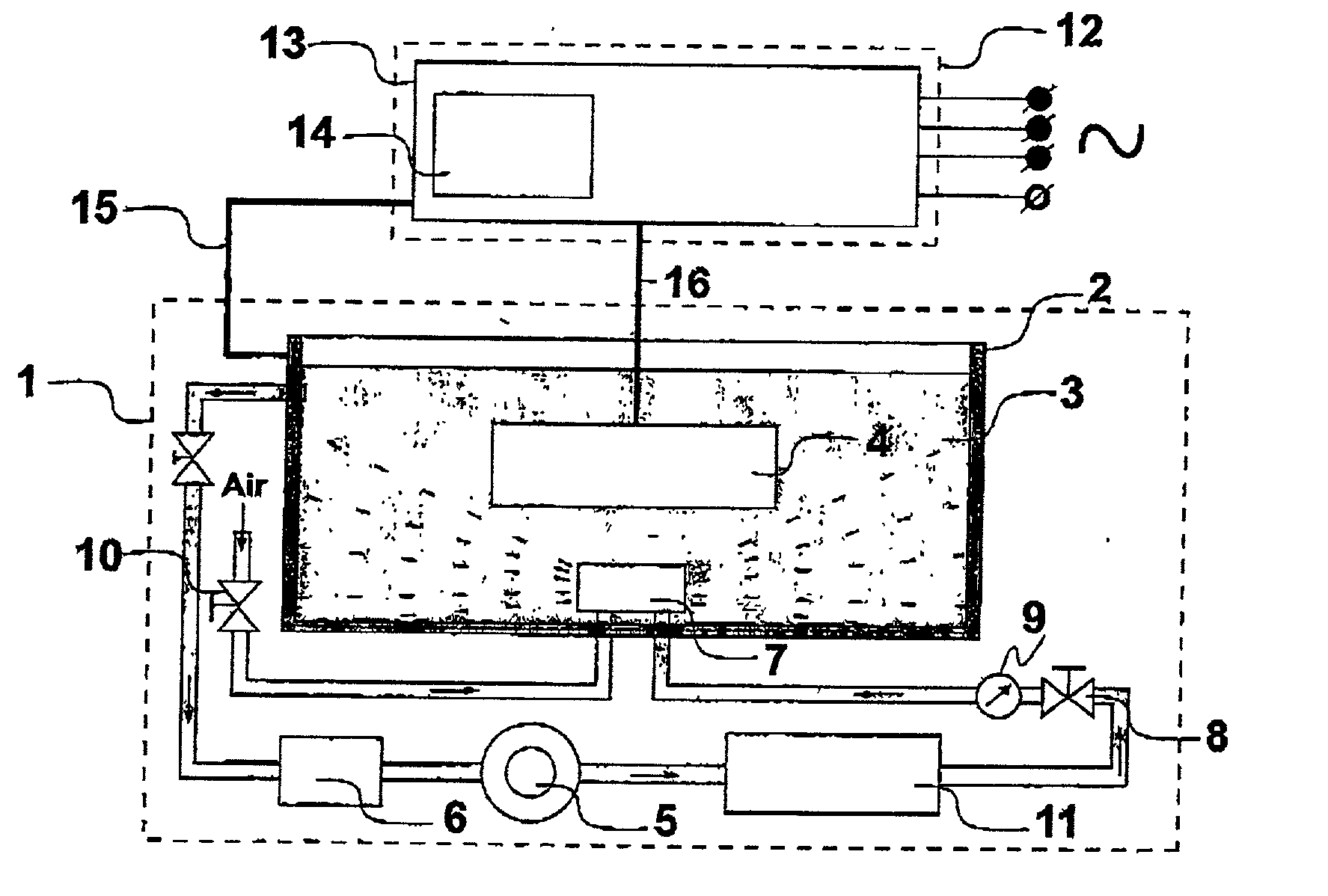
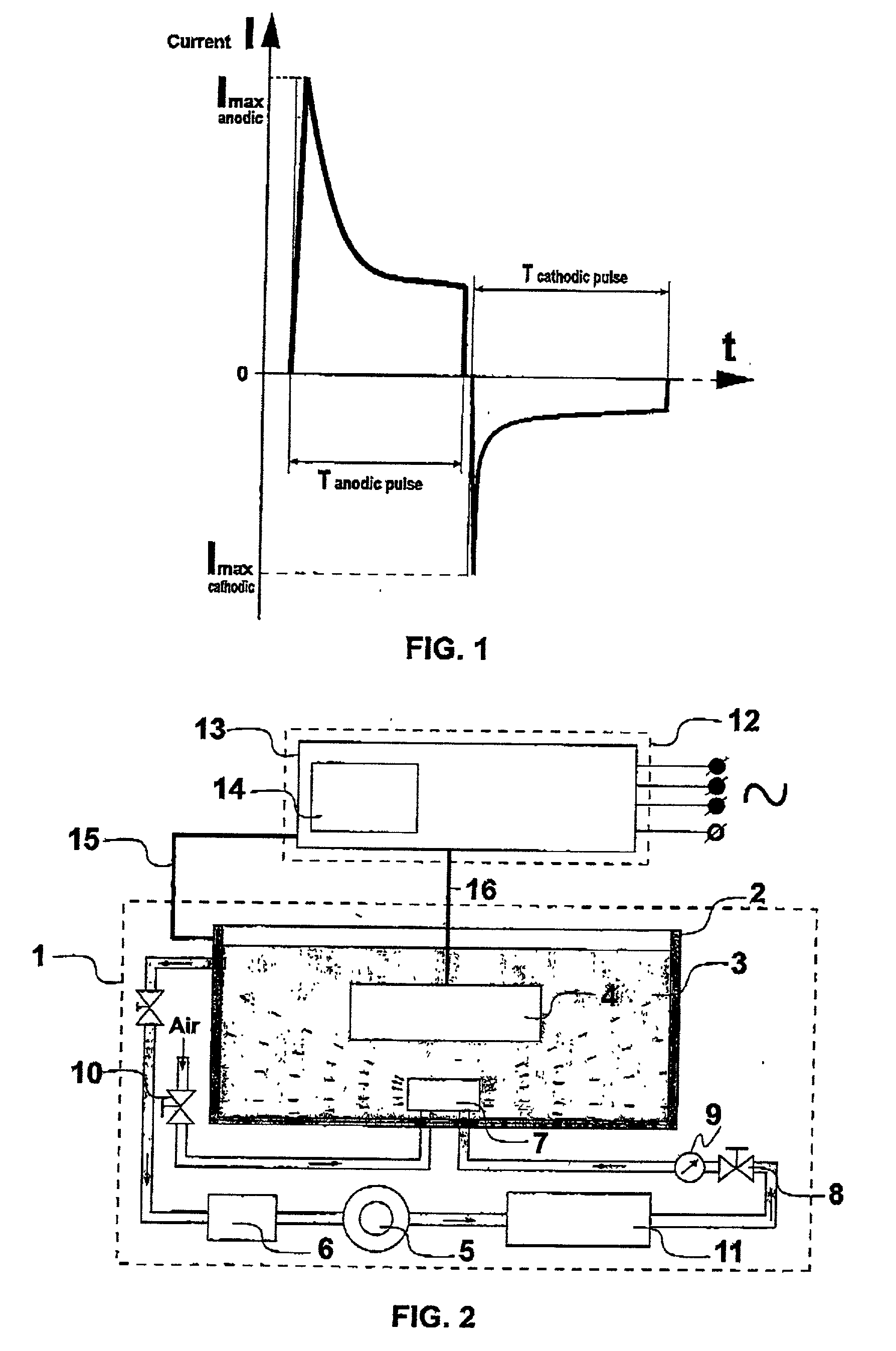
There is disclosed a process and apparatus for carrying out plasma electrolytic oxidation of metals and alloys, forming ceramic coatings on surfaces thereof at a rate of 2-10 microns per minute. The process comprises the use of high-frequency current pulses of a certain form and having a given frequency range, combined with the generation of acoustic vibrations in a sonic frequency range in the electrolyte, the frequency ranges of the current pulses and the acoustic vibrations being overlapping. The process makes it possible to introduce ultra-disperse powders into the electrolyte, with the acoustic vibrations helping to form a stable hydrosol, and to create coatings with set properties. The process makes it possible to produce dense hard microcrystalline ceramic coatings of thickness up to 150 microns. The coatings are characterised by reduced specific thickness of an external porous layer (less than 14% of the total coating thickness) and low roughness of the oxidised surface, Ra 0.6-2.1 microns.
Owner:KERONITE INT LTD
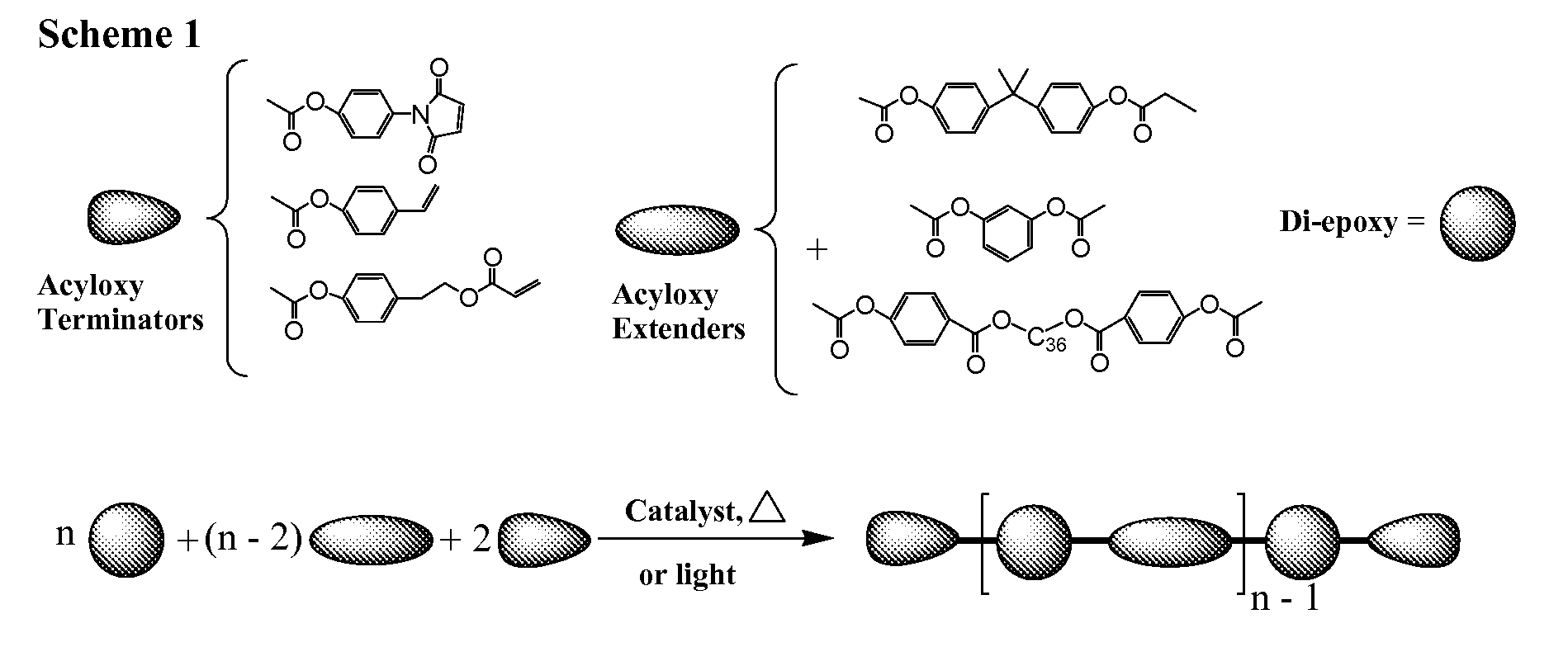
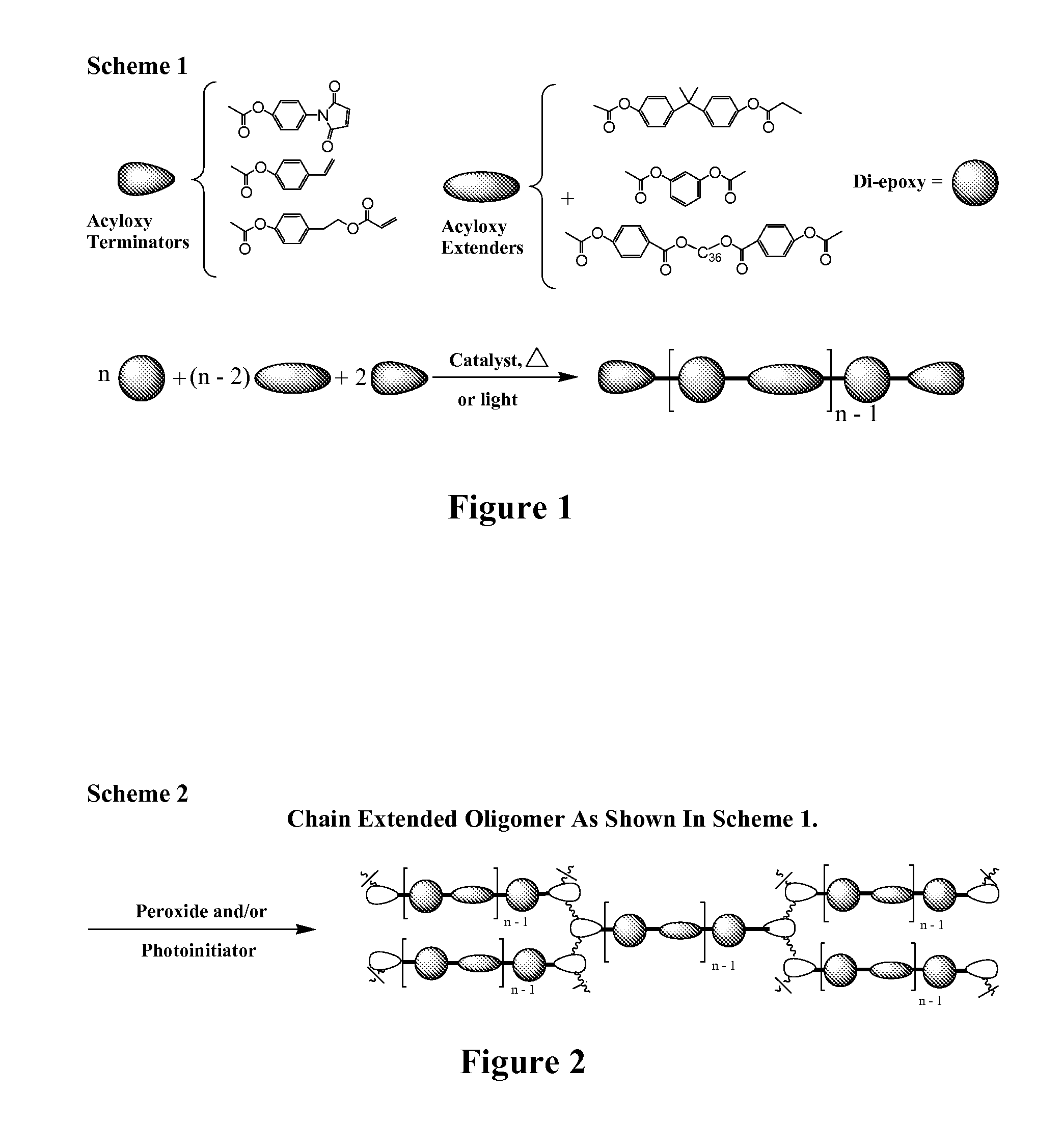
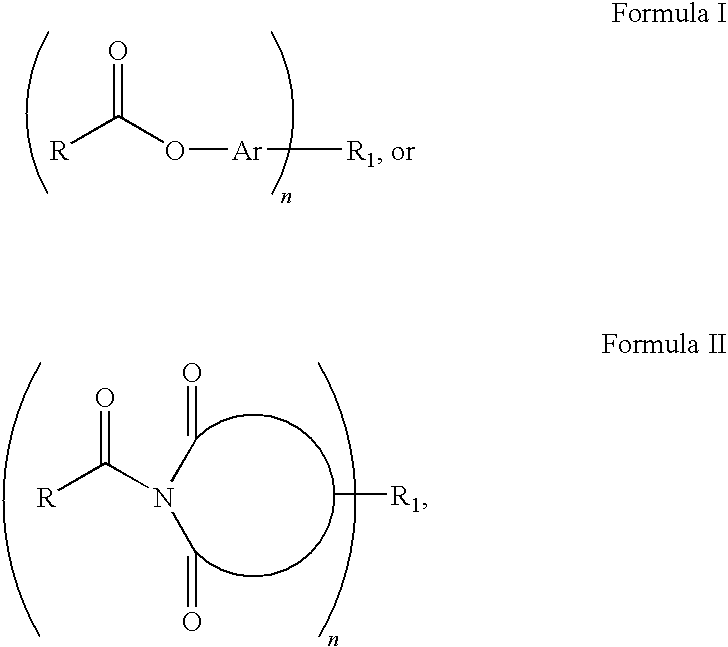
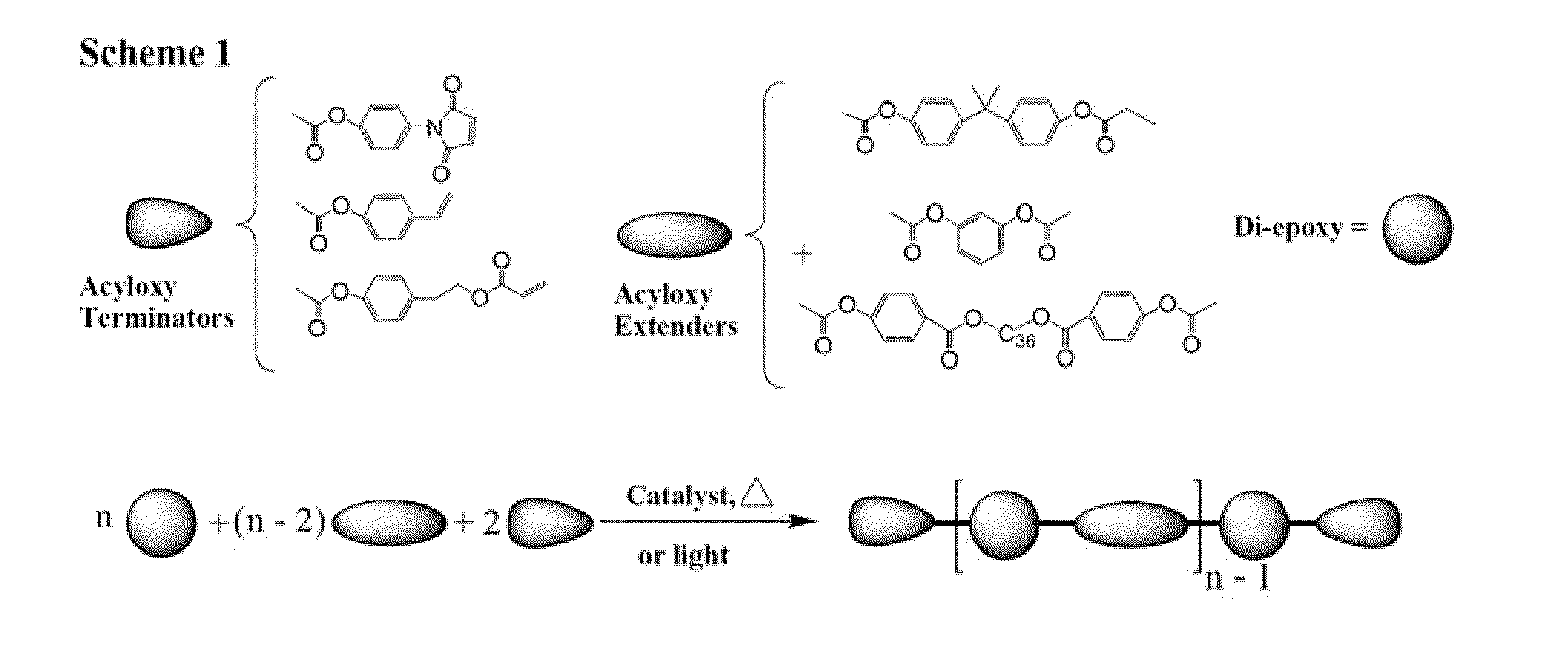
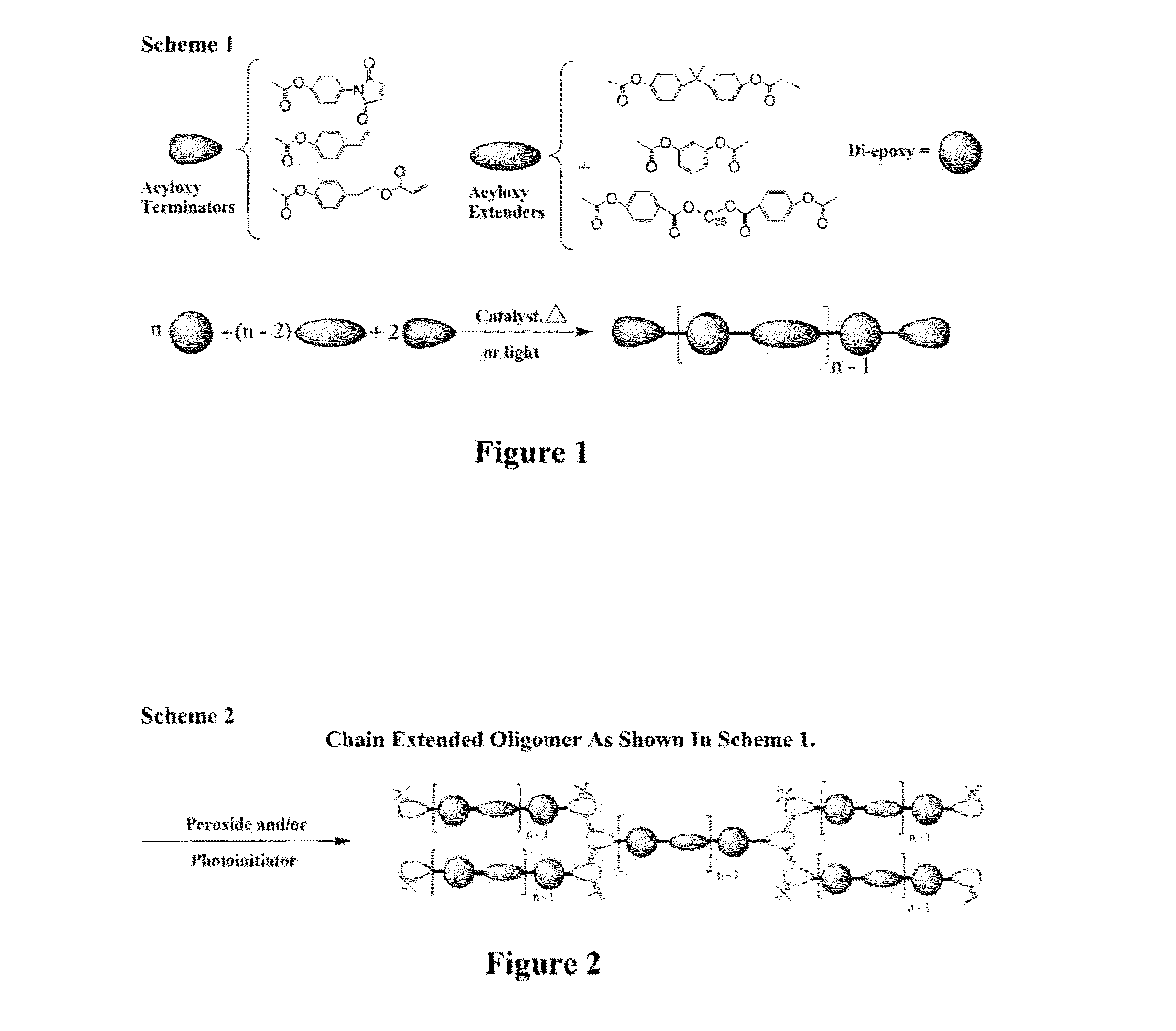
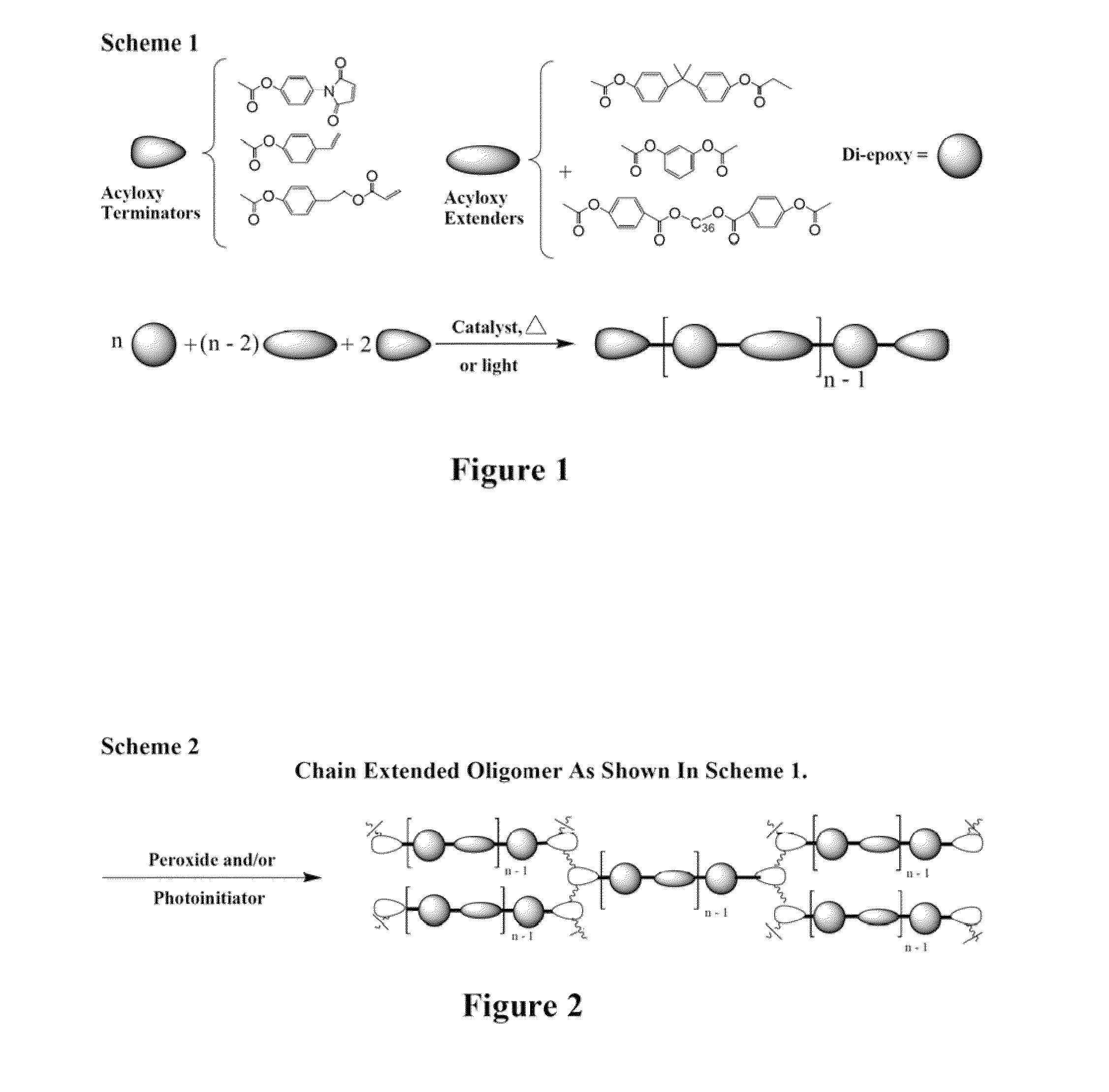
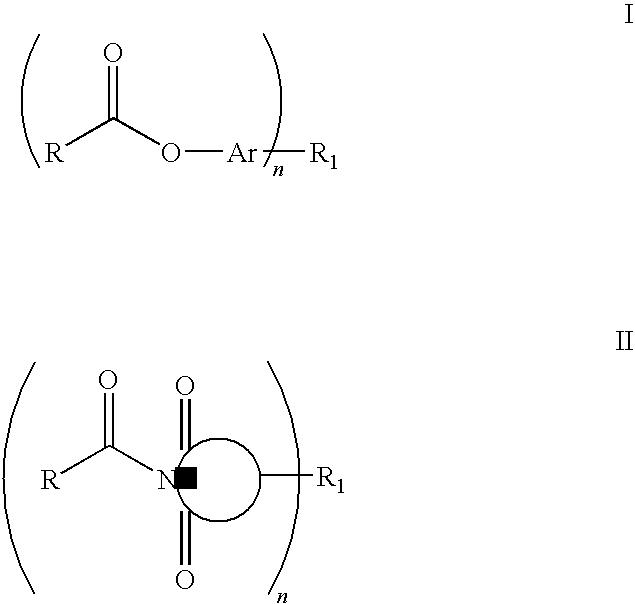
Curatives for epoxy adhesive compositions
InactiveUS20100113643A1Increase opportunitiesReduce hydrophilicitySilicon organic compoundsCosmetic preparationsFirming agentEpoxy adhesive
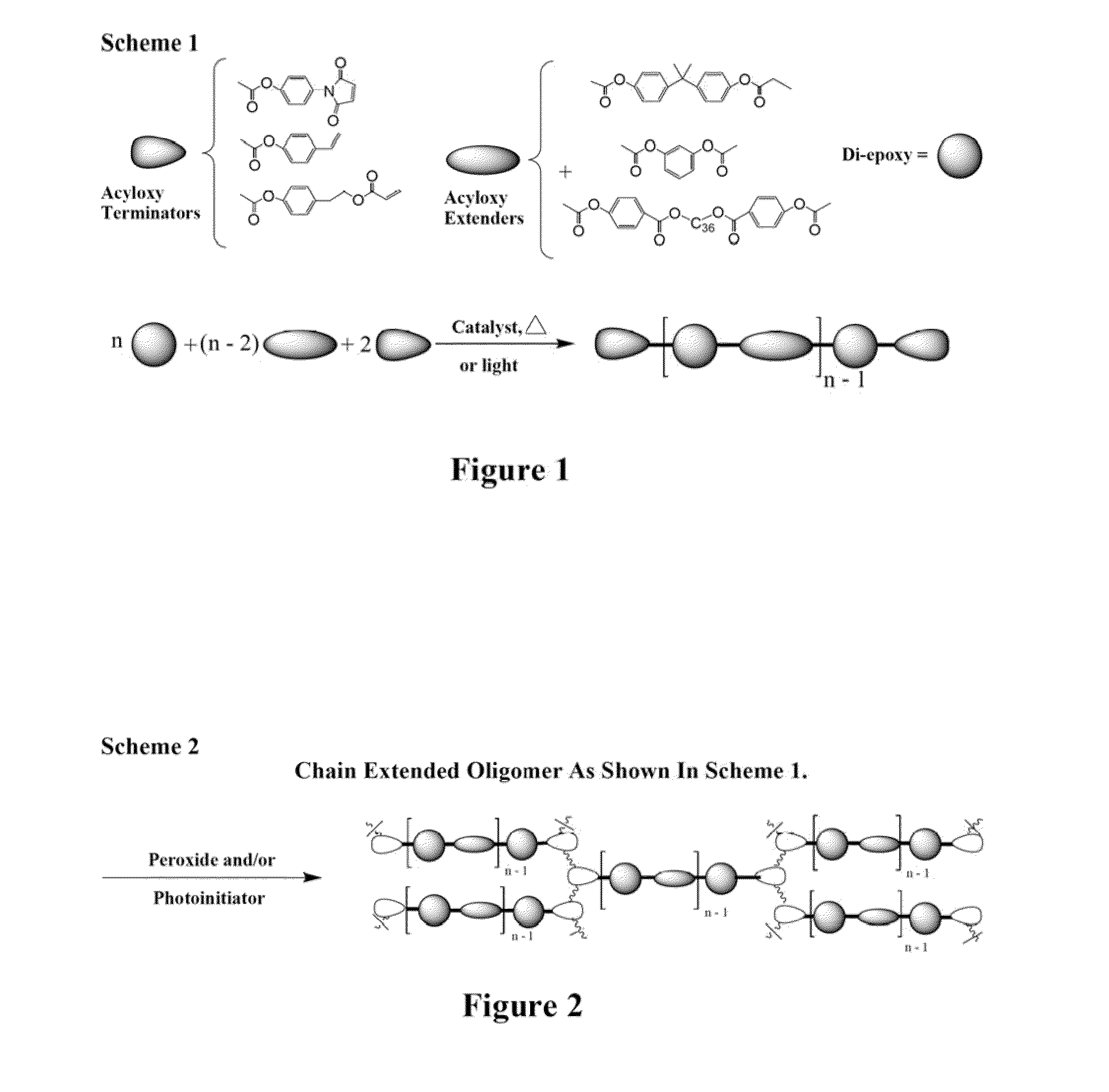
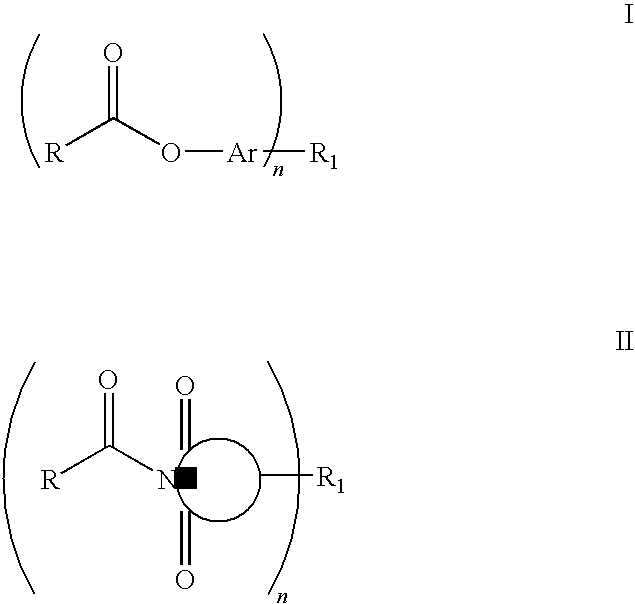
The invention provides epoxy and oxetane compositions including the novel acyloxy and N-acyl curing agents described herein. Use of invention curing agents result in cured adhesive compositions with remarkably increased adhesion and reduced hydrophilicity when compared to resins cured with other types of curing agents. Furthermore, the curatives of this invention do not interfere with free-radical cure and are thus suited for use in hybrid cure thermoset compositions.
Owner:DESIGNER MOLECULES
Curatives for epoxy compositions
ActiveUS20100249276A1Improve adhesionLow viscositySilicon organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationEpoxyChemistry
The invention provides epoxy and oxetane compositions including the novel acyloxy and N-acyl curing agents described herein. Use of invention curing agents result in cured adhesive compositions with remarkably increased adhesion and reduced hydrophilicity when compared to resins cured with other types of curing agents. Furthermore, the curatives of this invention do not interfere with free-radical cure and are thus suited for use in hybrid cure thermoset compositions.
Owner:DESIGNER MOLECULES
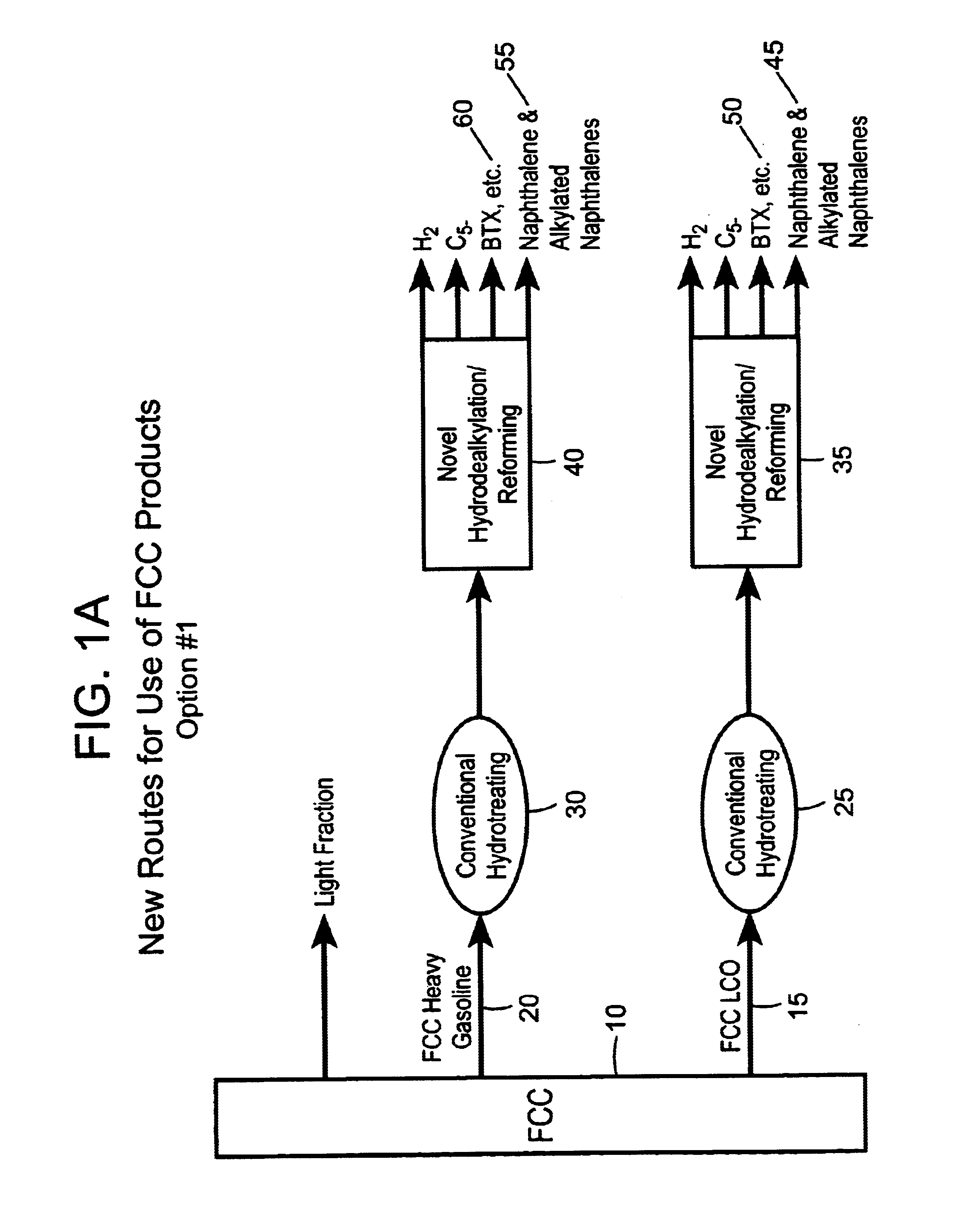
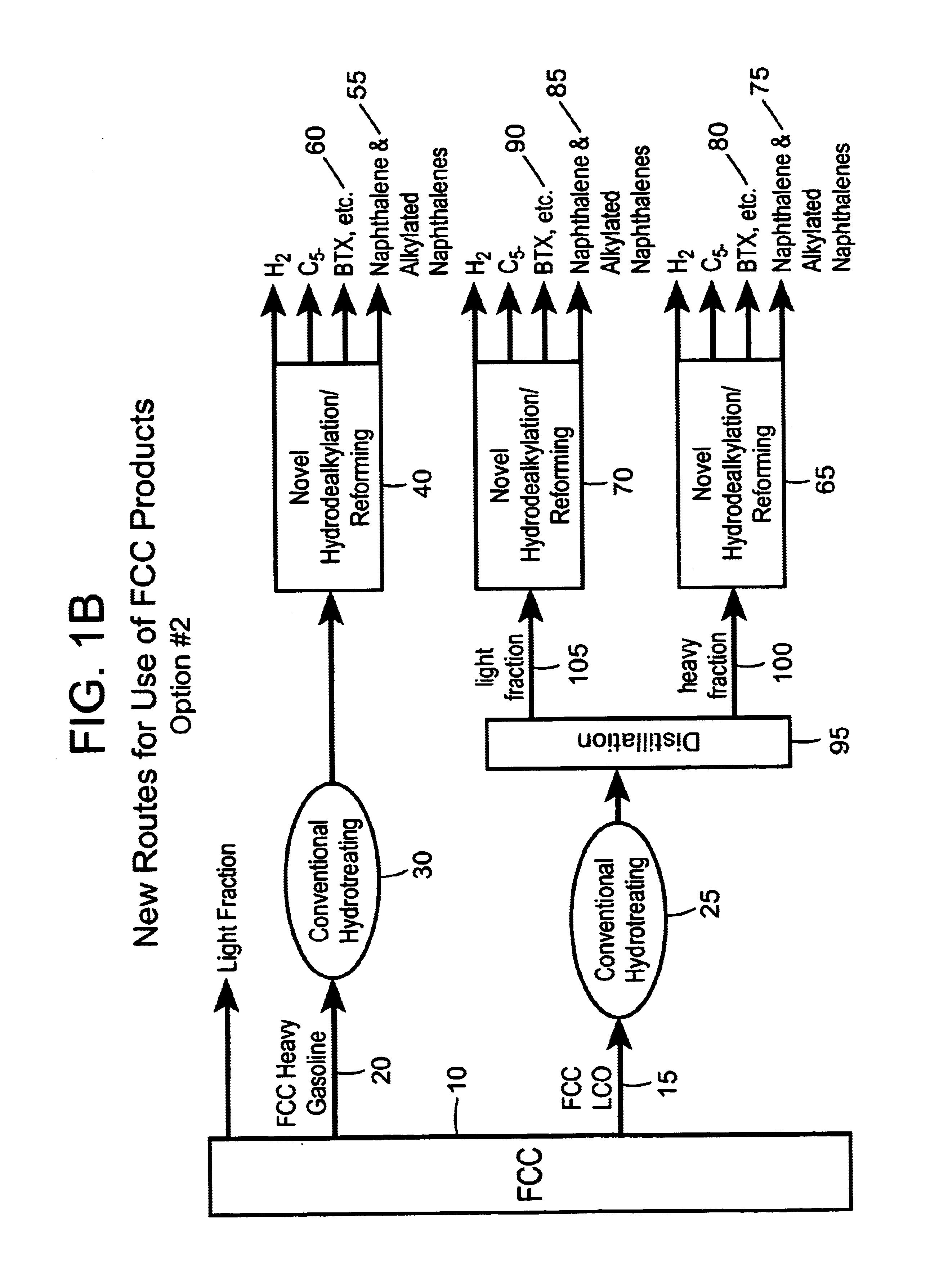
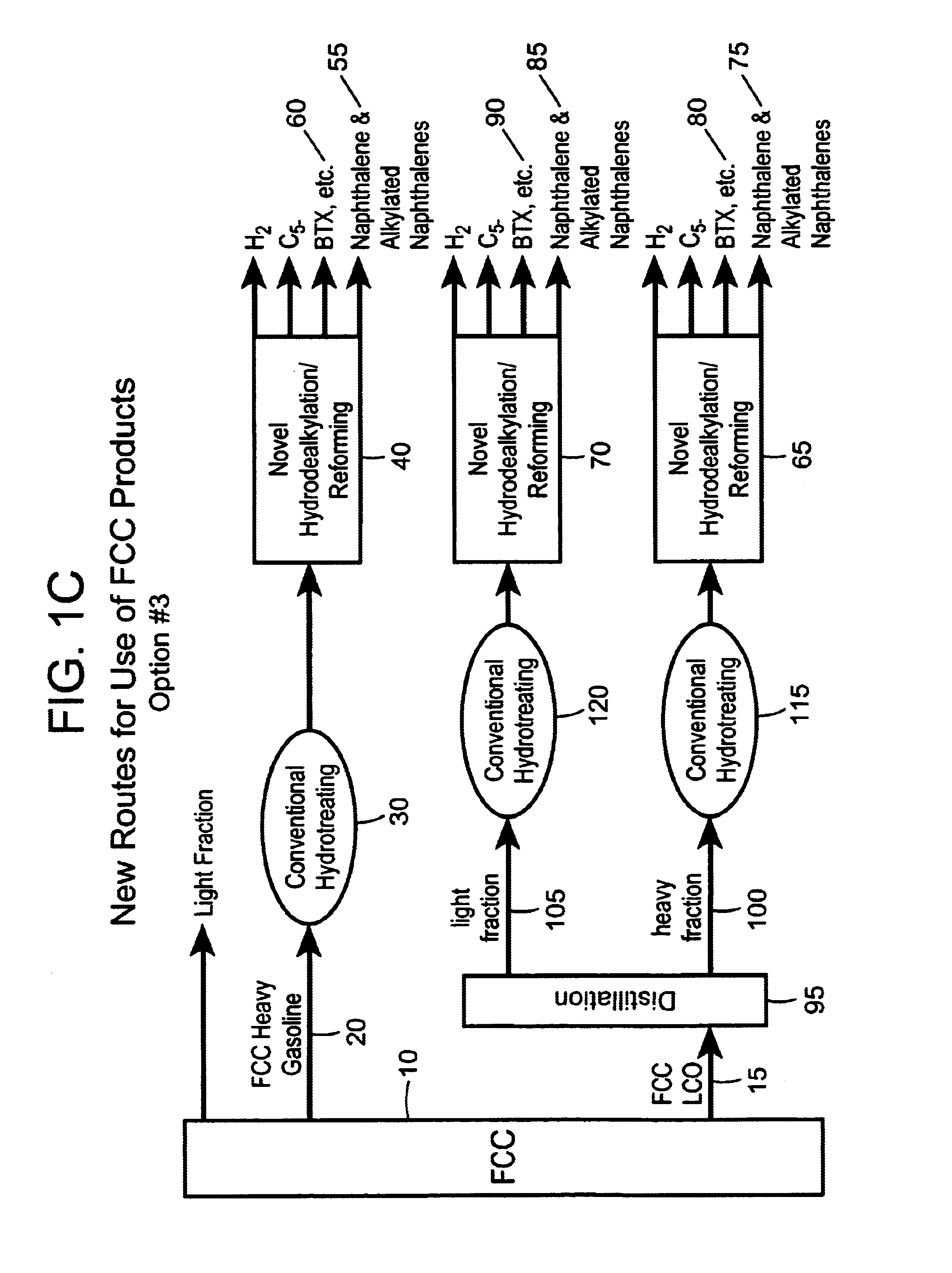
Process for converting heavy hydrocarbon feeds to high octane gasoline, BTX and other valuable aromatics
InactiveUS6900365B2High yieldOutstanding propertyCatalytic naphtha reformingHydrocarbonsMolecular sieveDehydrogenation
A catalytic hydrodealkylation / reforming process which comprises contacting a heavy hydrocarbon feedstream under catalytic hydrodealkylation / reforming conditions with a composition comprising borosilicate molecular sieves having a pore size greater than about 5.0 Angstroms and a Constraint Index smaller than about 1.0; further containing a hydrogenation / dehydrogenation component; wherein at least a portion of the heavy hydrocarbon feedstream is converted to a product comprising benzene, toluene, xylenes and ethylbenzene.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
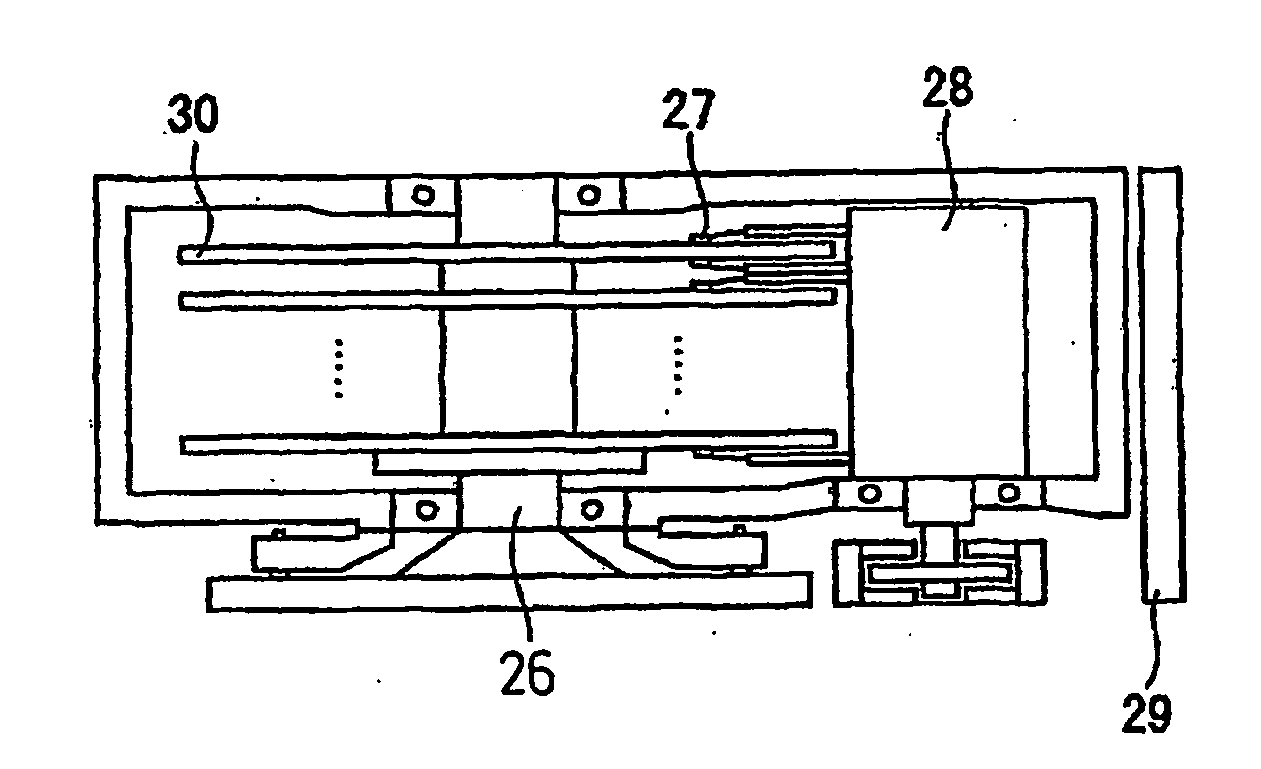
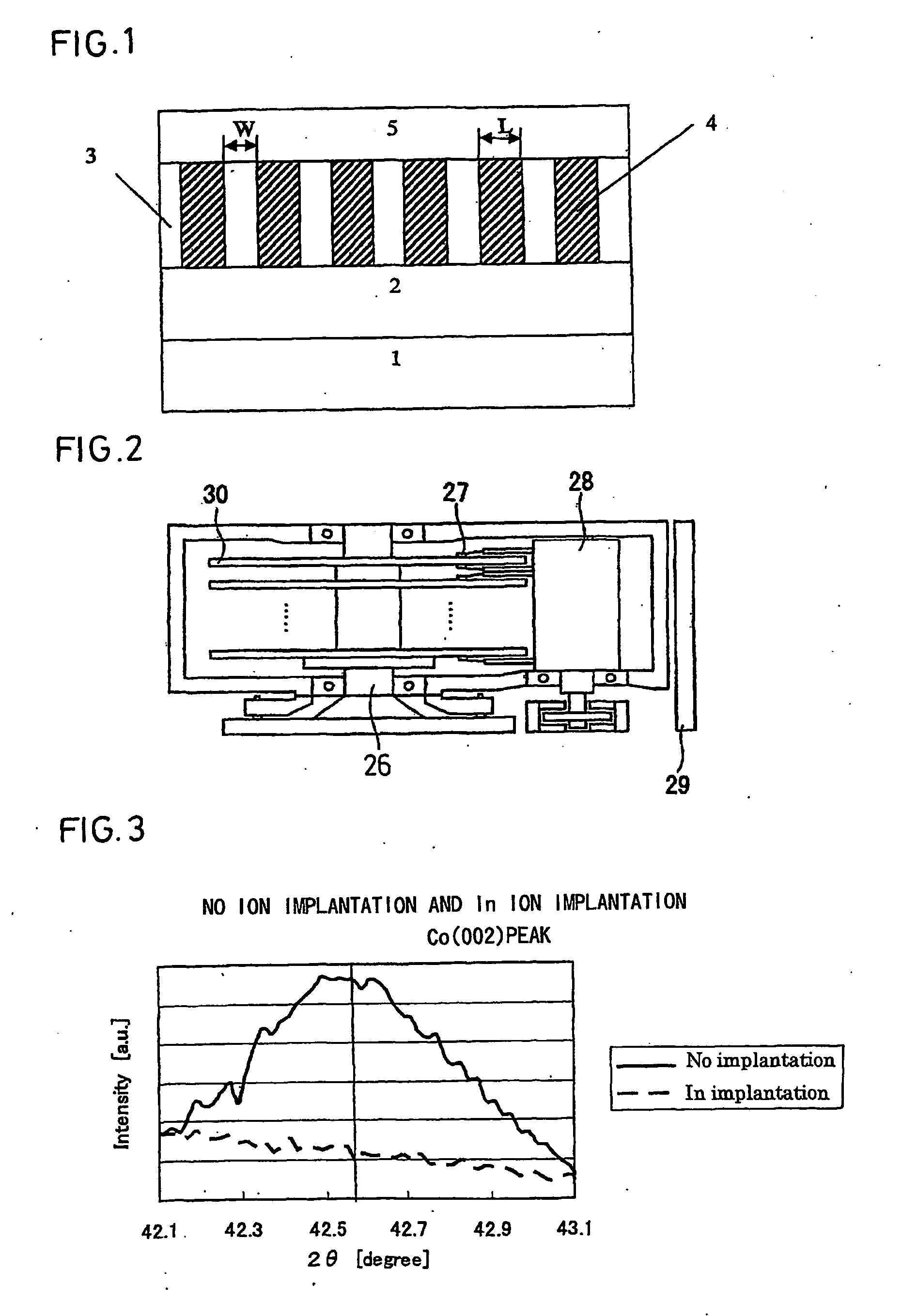
Magnetic recording medium, method for production thereof and magnetic recording and reproducing device
ActiveUS20090323219A1Guaranteed smooth progressExcellent ability to separate magnetic recording patternManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageX-rayNon magnetic
A method for the production of a magnetic recording medium (30) includes the steps of depositing a magnetic layer or Co-containing magnetic layer (3) on at least one side of a nonmagnetic substrate (1) and partially implanting atoms into the magnetic layer or Co-containing magnetic layer to partially unmagnetize the magnetic layer or Co-containing magnetic layer, thereby forming nonmagnetic parts (4) and a magnetic recording pattern magnetically separated by the nonmagnetic parts and, in the case of the Co-containing magnetic layer, lowering Co (002) or Co (110) peak strength of a relevant part of the Co-containing magnetic layer as determined by the X-ray diffraction to ½ or less. A magnetic recording and reproducing device includes the magnetic recording medium (30), a driving part (26) for driving the magnetic recording medium in a direction of recording, a magnetic head (27) consisting of a recording part and a regenerating part, means (28) for moving the magnetic head relative to the magnetic recording medium, and recording and reproducing signal processing means (29) adapted to enter a signal into the magnetic head and regenerate an output signal from the magnetic head.
Owner:RESONAC CORP
Protection of fragrance in a wax candle using an antioxidant
InactiveUS7220288B2Outstanding propertyProtects the candle from fragrance discolorationSolid fuelsCandle ingredientsParaffin waxPolymer science
Disclosed is a fragranced wax candle and fragranced wax composition comprising paraffin wax, a fragrance containing an antioxidant, with or without vegetable wax and / or beeswax, saturated fatty acid, hindered amine, and an additive. Also disclosed is a method for incorporating an antioxidant into the fragranced candle wax composition.
Owner:SCENT2MARKET
Production of starch-gel-based shaped bodies
InactiveUS20050163833A1Simple methodOutstanding propertyPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCoatingsGel basedActive ingredient
Starch gels and a method for the production of shaped bodies therefrom containing active ingredients, especially gelatin-free soft capsules. Significant improvements, especially with regard to brittleness, storage stability in changing conditions and sorption behaviour, are provided in comparison with existing approaches to solving the gelatin problem in soft capsules. Gelatin-free soft capsules have resistant properties and reduced glyceamic index in comparison with starch or thermoplastic starch.
Owner:INNOGEL AG
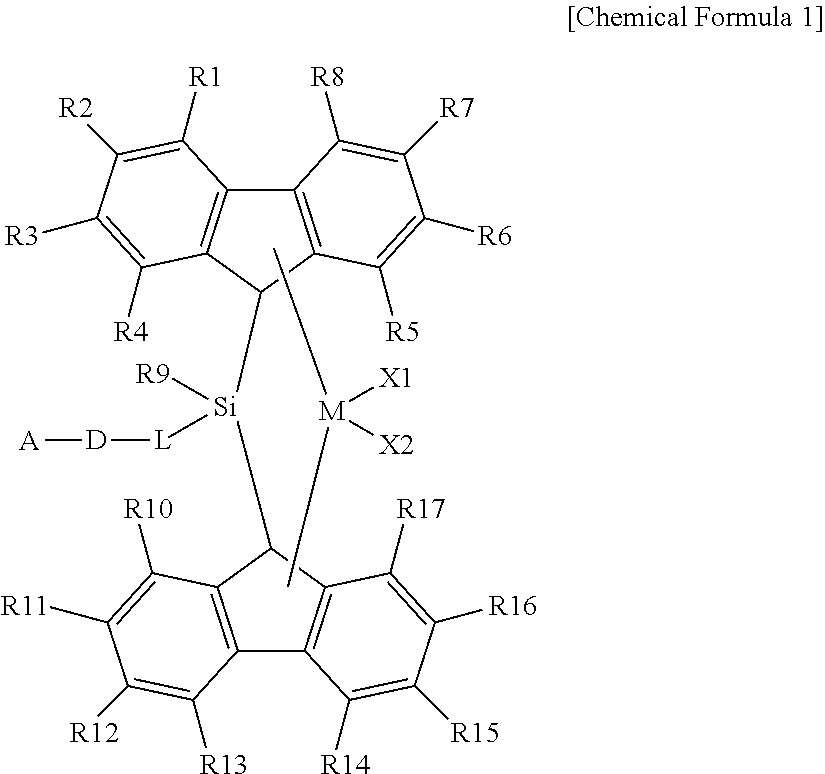
Metallocene compound, catalyst composition comprising the same, and an olefinic polymer produced using the same
ActiveUS20120123078A1Improve copolymerization performanceHigh molecular weightOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationHeat resistanceOlefin polymerization
The present invention relates to a novel metallocene compound, a catalyst composition comprising the same, and to olefinic polymers produced using the same. The metallocene compound according to the present invention and the catalyst composition comprising the same can be used when producing olefinic polymers, have outstanding copolymerisation properties, and can produce olefinic polymers of high molecular weight. In particular, when the metallocene compound according to the present invention is employed, highly heat resistant block copolymers can be produced, and olefinic polymers can be produced which have a high melting point (Tm) even if the comonomer content is increased when producing the olefinic polymer.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Protection of fragrance in a wax candle using an antioxidant
InactiveUS20040031191A1Outstanding propertyProtects the candle from fragrance discolorationSolid fuelsCandle ingredientsParaffin waxFlavor
Disclosed is a fragranced wax candle and fragranced wax composition comprising paraffin wax, a fragrance containing an antioxidant, with or without vegetable wax and / or beeswax, saturated fatty acid, hindered amine, and an additive. Also disclosed is a method for incorporating an antioxidant into the fragranced candle wax composition.
Owner:SCENT2MARKET
Light-Emitting Diode and Method For Fabrication Thereof
InactiveUS20080315176A1Improve pressure resistanceOutstanding resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh resistanceP–n junction
A light-emitting diode includes a substrate, a compound semiconductor layer including a p-n junction-type light-emitting part formed on the substrate, an electric conductor disposed on the compound semiconductor layer and formed of an electrically conductive material optically transparent to the light emitted from the light-emitting part and a high resistance layer possessing higher resistance than the electric conductor and provided in the middle between the compound semiconductor layer and the electric conductor. In the configuration of a light-emitting diode lamp, the electric conductor and the electrode disposed on the semiconductor layer on the side opposite to the electric conductor across the light-emitting layer are made to assume an equal electric potential by means of wire bonding. The light-emitting diode abounds in luminance and excels in electrostatic breakdown voltage.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Oil-based ink composition for inkjet recording
ActiveUS20070167538A1Outstanding propertyNot easy to dissolveFilm/foil adhesivesDuplicating/marking methodsSolubilityAcrylic resin
An oil-based ink composition for inkjet recording capable of exhibiting desired properties of drying after print, rubfastness and re-solubility is achieved by performing solubilization on an acrylic resin which is not easily dissolved conventionally. The oil-based ink composition for inkjet printing comprises glycol ether dialkyl ethers as a prime solvent; and an acrylic resin that results from solution polymerization in a solvent of the glycol ether dialkyl ethers by use of a radical polymerization initiator.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP +1
Curatives for epoxy compositions
InactiveUS20130199724A1Improve adhesionLow viscositySilicon organic compoundsEpoxy resin adhesivesEpoxyChemistry
The invention provides epoxy and oxetane compositions including the novel acyloxy and N-acyl curing agents described herein. Use of invention curing agents result in cured adhesive compositions with remarkably increased adhesion and reduced hydrophilicity when compared to resins cured with other types of curing agents. Furthermore, the curatives of this invention do not interfere with free-radical cure and are thus suited for use in hybrid cure thermoset compositions.
Owner:DESIGNER MOLECULES
Superalloy for single crystal turbine vanes
InactiveUS7011721B2Improve toleranceImprove casting yieldBlade accessoriesGas turbine plantsRheniumSingle crystal
A nickel-base superalloy that is useful for making single crystal castings exhibiting outstanding stress-rupture properties, creep-rupture properties, and an increased tolerance for grain defects contains, in percentages by weight, from about 4.7% to about 4.9% chromium, (Cr), from about 9% to about 10% cobalt (Co), from about 0.6% to about 0.8% molybdenum (Mo), from about 8.4% to about 8.8% tungsten (W), from about 4.3% to about 4.8% tantalum (Ta), from about 0.6% to about 0.8% titanium (Ti), from about 5.6% to about 5.8% aluminum (Al), from about 2.8% to about 3.1% rhenium (Re), from about 1.1% to about 1.5% hafnium (Hf), from about 0.06% to about 0.08% carbon (C), from about 0.012% to about 0.020% boron (B), from about 0.004% to about 0.010% zirconium (Zr), the balance being nickel and incidental impurities. The nickel-base superalloy provides improved casting yield and reduce component cost due to a reduction in rejectable grain defects as compared with conventional directionally solidified casting alloys and conventional single crystal alloys.
Owner:CANNON MUSKEGON CORP
TiAlCN Layers With Lamellar Structure
ActiveUS20160333473A1Outstanding propertyImprove wear resistanceWorkpiecesTurning toolsPeriodic alternatingHard metal
A tool has a main part of hard metal, cermet, ceramic, steel, high-speed steel, and a single or multilayer wear protection coating applied onto the main part by CVD and which has a thickness from 3 μm to 25 μm. The wear protection coating has at least one Ti1-xAlxCyNz layer with stoichiometric coefficients 0.70≦x<1.0≦y<0.25 and 0.75≦z<1.15 and a thickness from 1.5 μm to 17 μm. The T1-xAlxCyNz layer has a lamellar structure with lamellae with thickness of no more than 150 nm, preferably no more than 100 nm, particularly preferably no more than 50 nm. Lamellae are made of periodically alternating regions of the Ti1-xAlxCyNz layer with alternatingly different stoichiometric proportions of Ti and Al, having the same crystal structure (crystallographic phase), and the Ti1-xAlxCyNz layer has at least 90% vol. % of face centered cubic (fcc) crystal structure.
Owner:WALTER AG
Biodegradable polyester blend compositions and methods of making the same
The present invention relates to tough and ductile biodegradable, aliphatic polyester blend compositions and methods for preparing such compositions. It relates to products made out of such blend compositions, including, but not limited to, films, fibers, nonwovens, sheets, coatings, binders, foams and molded products for packaging. The products exhibit a desirable combination of high strength, ductility and toughness, while maintaining flexibility, biodegradability and compostability. The products are useful for a variety of biodegradable articles, such as diaper topsheets, diaper backsheets, disposable wipes, shopping and lawn / leaf bags, agricultural films, disposable garments, medical disposables, paper coatings, biodegradable packaging, binders for cellulose fibers or synthetics, and the like.
Owner:DANIMER IPCO LLC +1
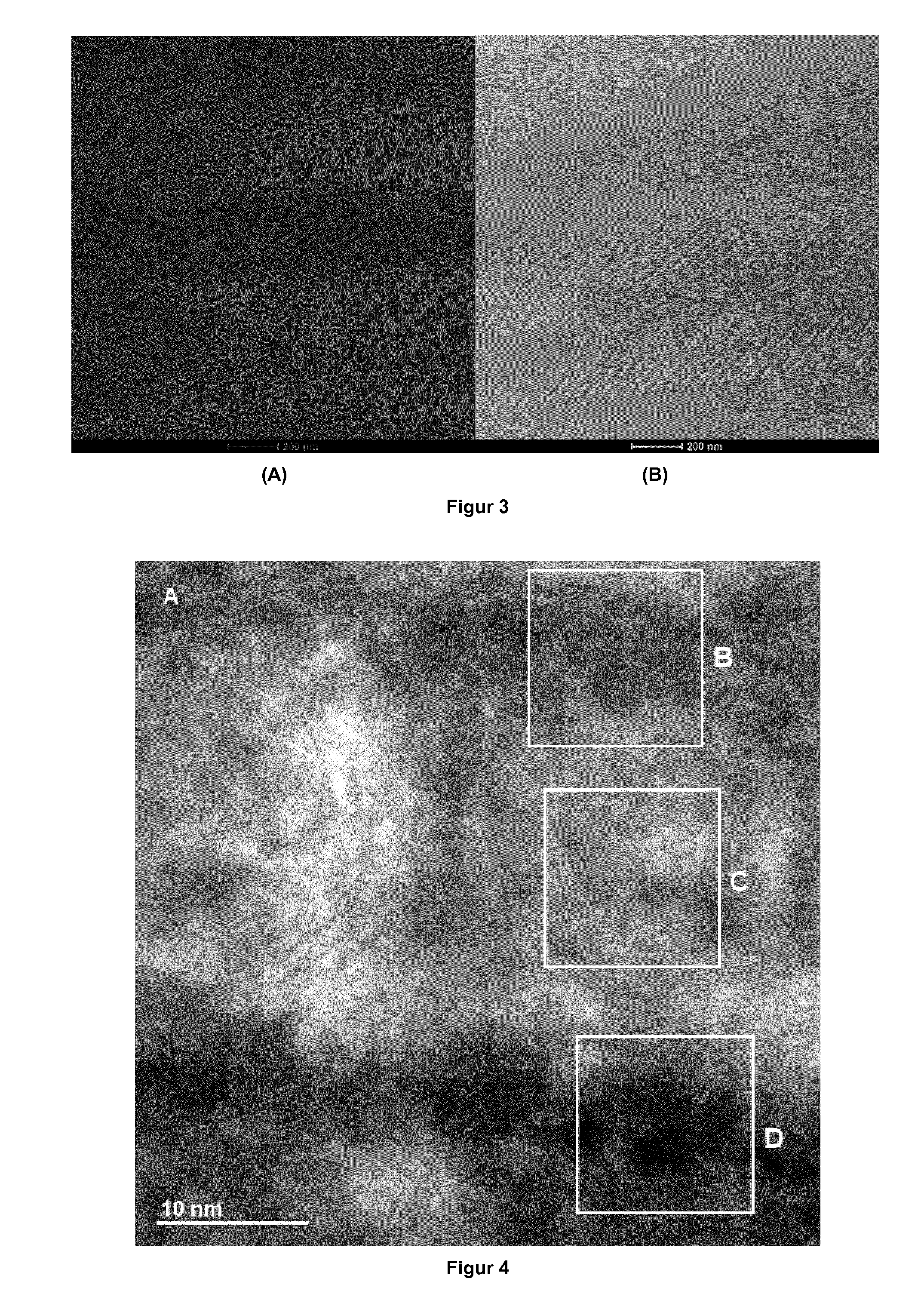
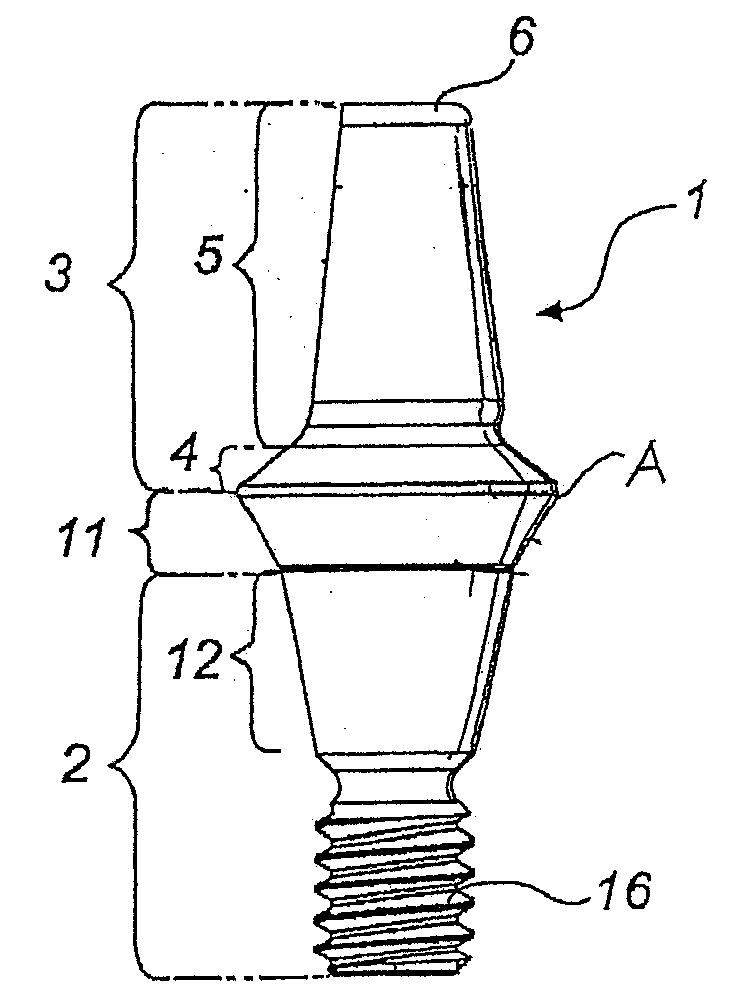
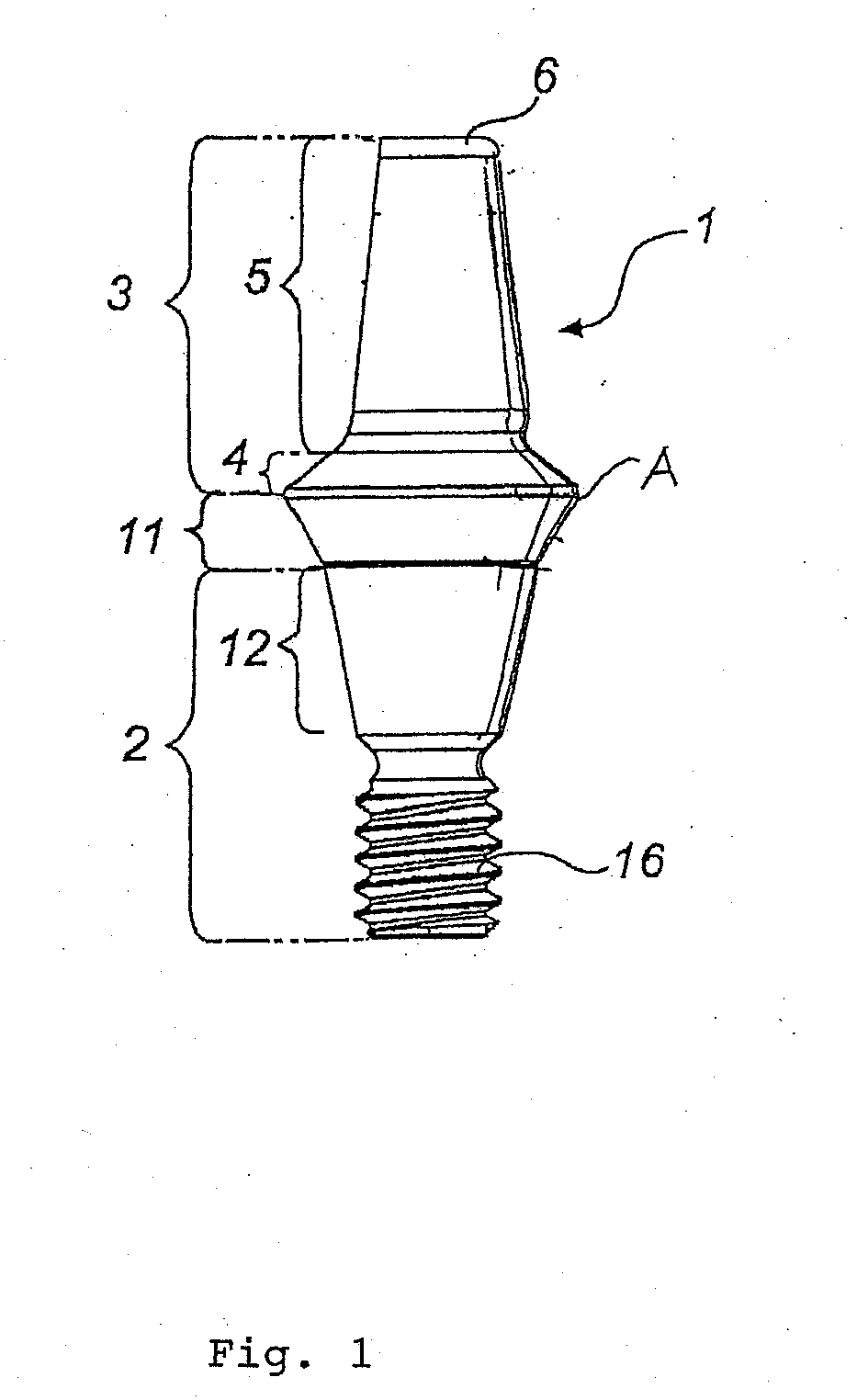
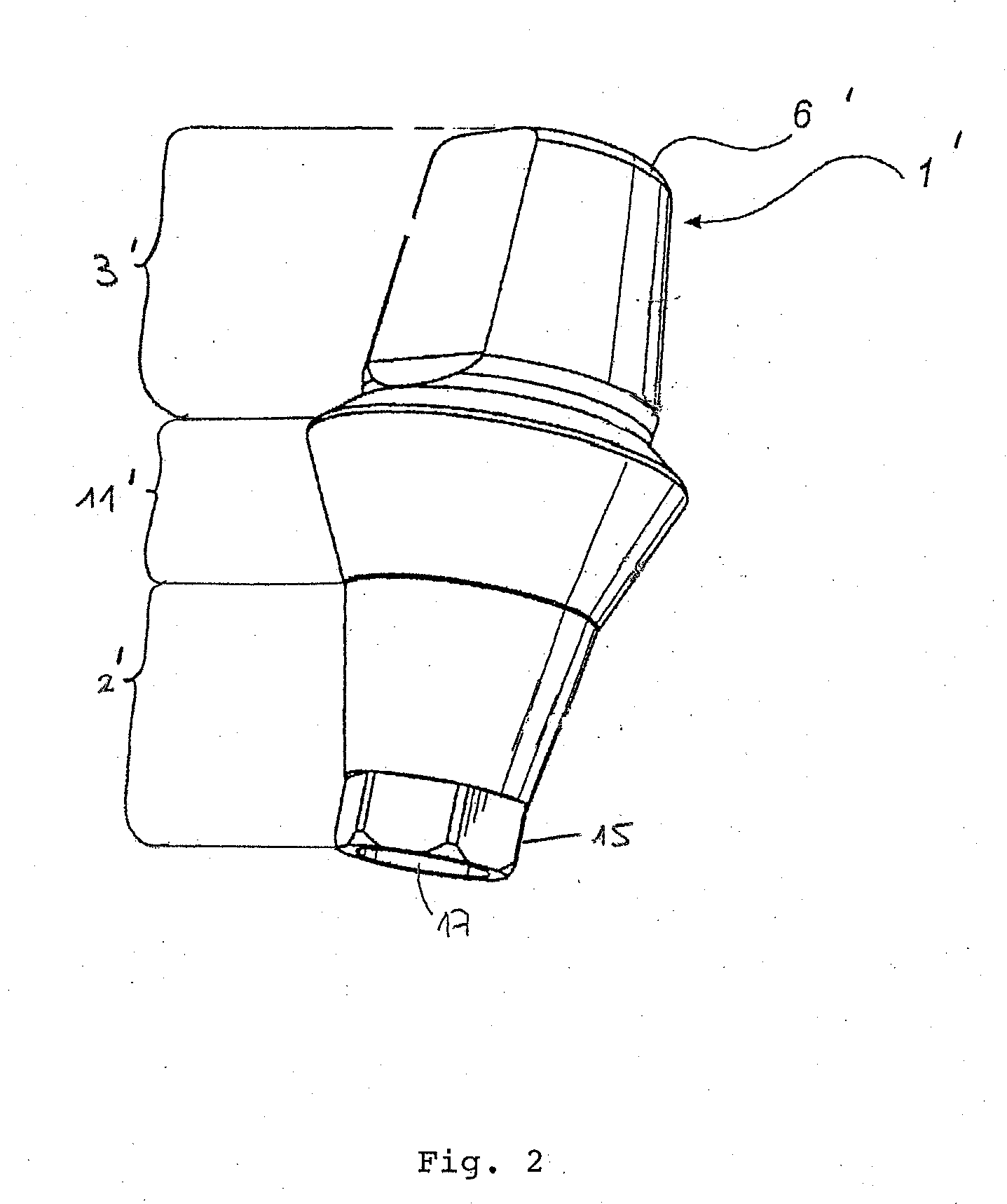
Abutment with a Hydroxylated Surface
ActiveUS20070202462A1Improve wettabilityAvoid accumulationDental implantsFastening prosthesisProsthesisBiomedical engineering
Abutment of a dental implant system, having at the top a support region intended for receiving a prosthetic build-up construction and at the bottom an implant contact region intended for insertion into a receiving hole of an implant, and wherein the abutment has between the support region and the implant contact region a soft tissue contact surface. Said soft tissue contact surface is at least partially hydroxylated or silanated.
Owner:STRAUMANN HLDG AG
Curatives for epoxy compositions
ActiveUS8431655B2Reduce hydrophilicityLow viscosityGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsPolyether coatingsEpoxyChemistry
The invention provides epoxy and oxetane compositions including the novel acyloxy and N-acyl curing agents described herein. Use of invention curing agents result in cured adhesive compositions with remarkably increased adhesion and reduced hydrophilicity when compared to resins cured with other types of curing agents. Furthermore, the curatives of this invention do not interfere with free-radical cure and are thus suited for use in hybrid cure thermoset compositions.
Owner:DESIGNER MOLECULES
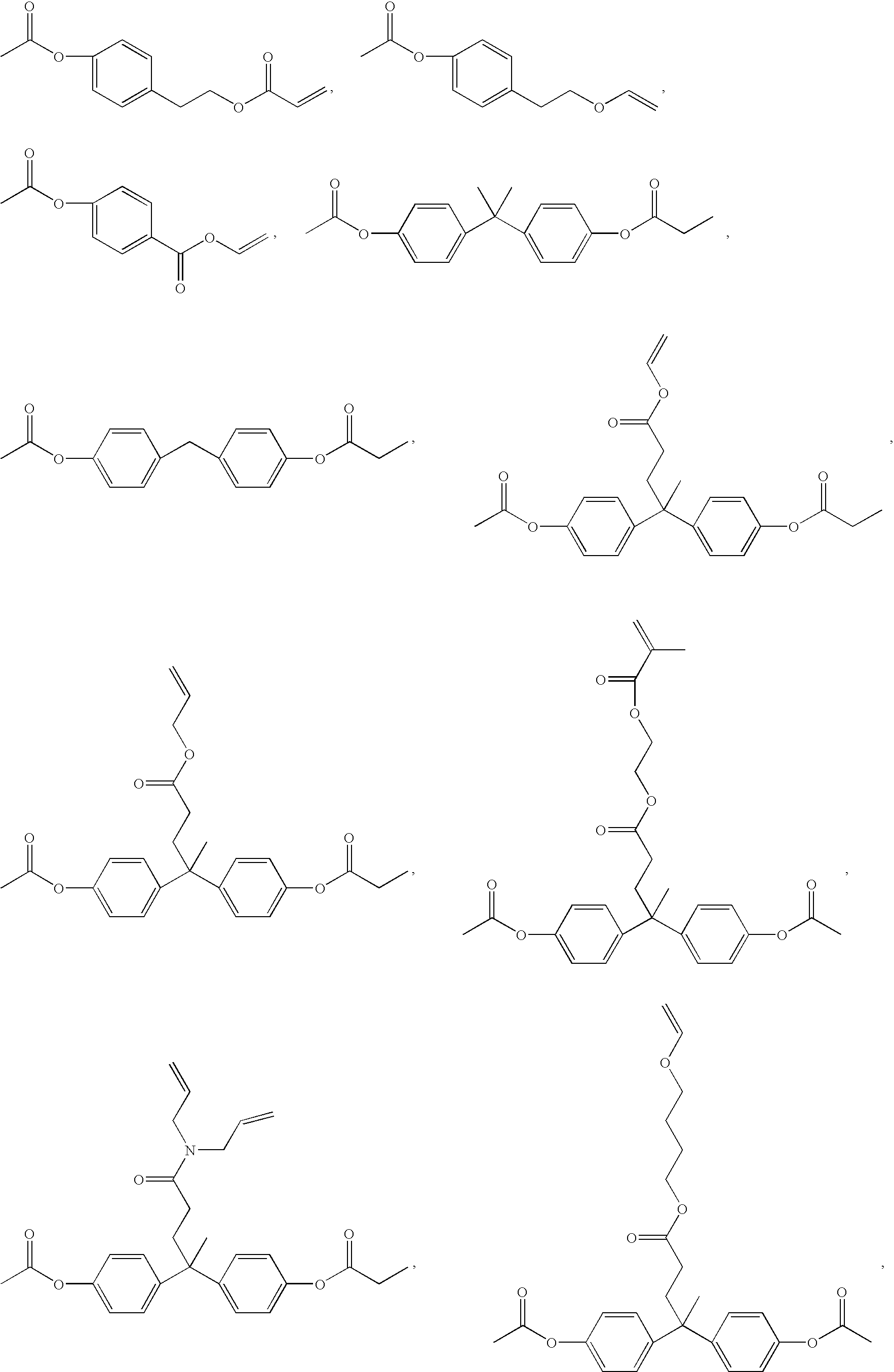
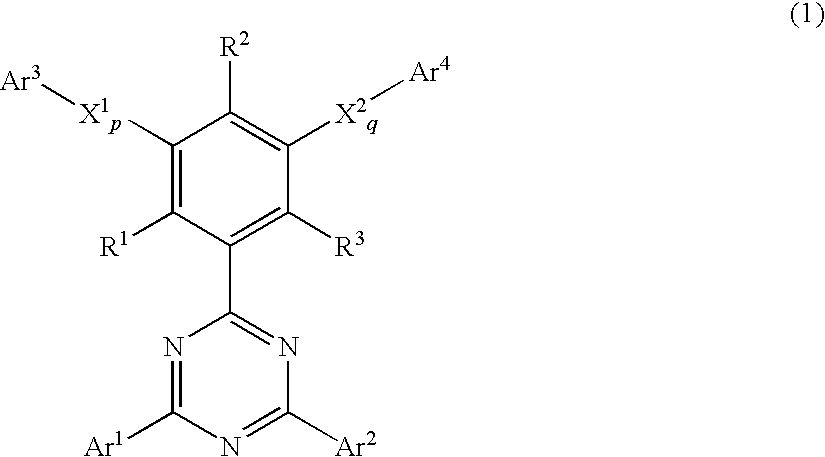
Phenyl-substituted 1,3.5-triazine compound, process for producing the same, and organic electroluminescent device containing the same as component
ActiveUS20100249406A1Outstanding propertyOrganic chemistryElectroluminescent light sources1,3,5-TriazineHydrogen atom
A phenyl-substituted 1,3,5-triazine compound represented by the general formula (1);wherein Ar1 and Ar2 independently represent substituted or unsubstituted phenyl, naphthyl or biphenylyl group; R1, R2 and R3 independently represent hydrogen atom or methyl group; X1 and X2 independently represent substituted or unsubstituted phenylene, naphthylene or pyridylene group; p and q independently represent an integer of 0 to 2; and Ar3 and Ar4 independently represent substituted or unsubstituted pyridyl or phenyl group. This compound is suitable for an organic electroluminescent device.
Owner:SAGAMI CHEM RES CENT +1
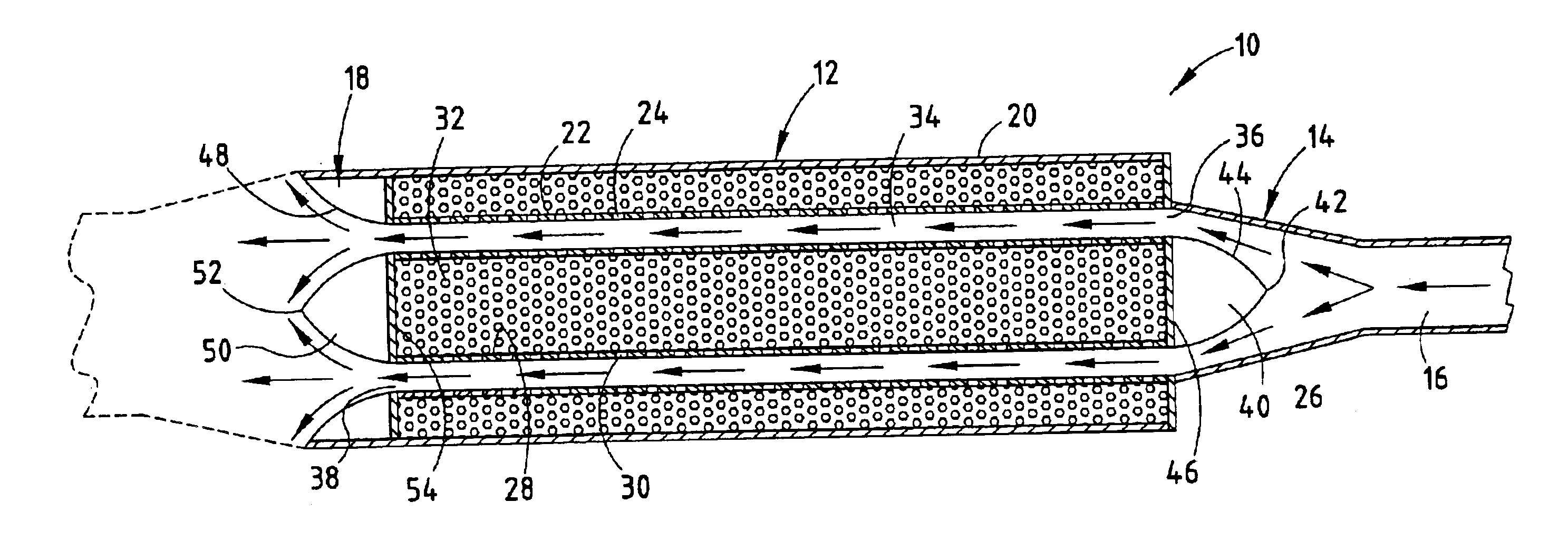
Exhaust silencer system
InactiveUS6868939B2Outstanding sound muffling/silencing propertyHigh performance outputExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusNegative pressure waveDual core
An improved exhaust system for an internal combustion engine generally comprises two expanding megaphones, separated by a dual core annular flow silencing section. The two or split megaphone design facilitates broadening of the time of the negative pressure wave to provide a desirable broad range power output while substantially reducing obnoxious sound output.
Owner:VICIOUS CYCLE PERFORMANCE
Cross-linked resin foam and process for producing the same
Disclosed is a resin foam which excels in properties such as strength, flexibility, cushioning properties, and strain recovery, particularly has a cell structure resistant to shrinkage caused by the restoring force of the resin, and has a high expansion ratio.The cross-linked resin foam is obtained by heating a resin composition containing an elastomer, an active-energy-ray-curable compound, and a thermal crosslinking agent to form a cross-linked structure derived from the thermal crosslinking agent in the resin composition; subjecting the cross-linked-structure-containing resin composition to foam molding to give a foamed structure; and irradiating the foamed structure with an active energy ray to form another cross-linked structure derived from the active-energy-ray-curable compound to give the cross-linked resin foam.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com