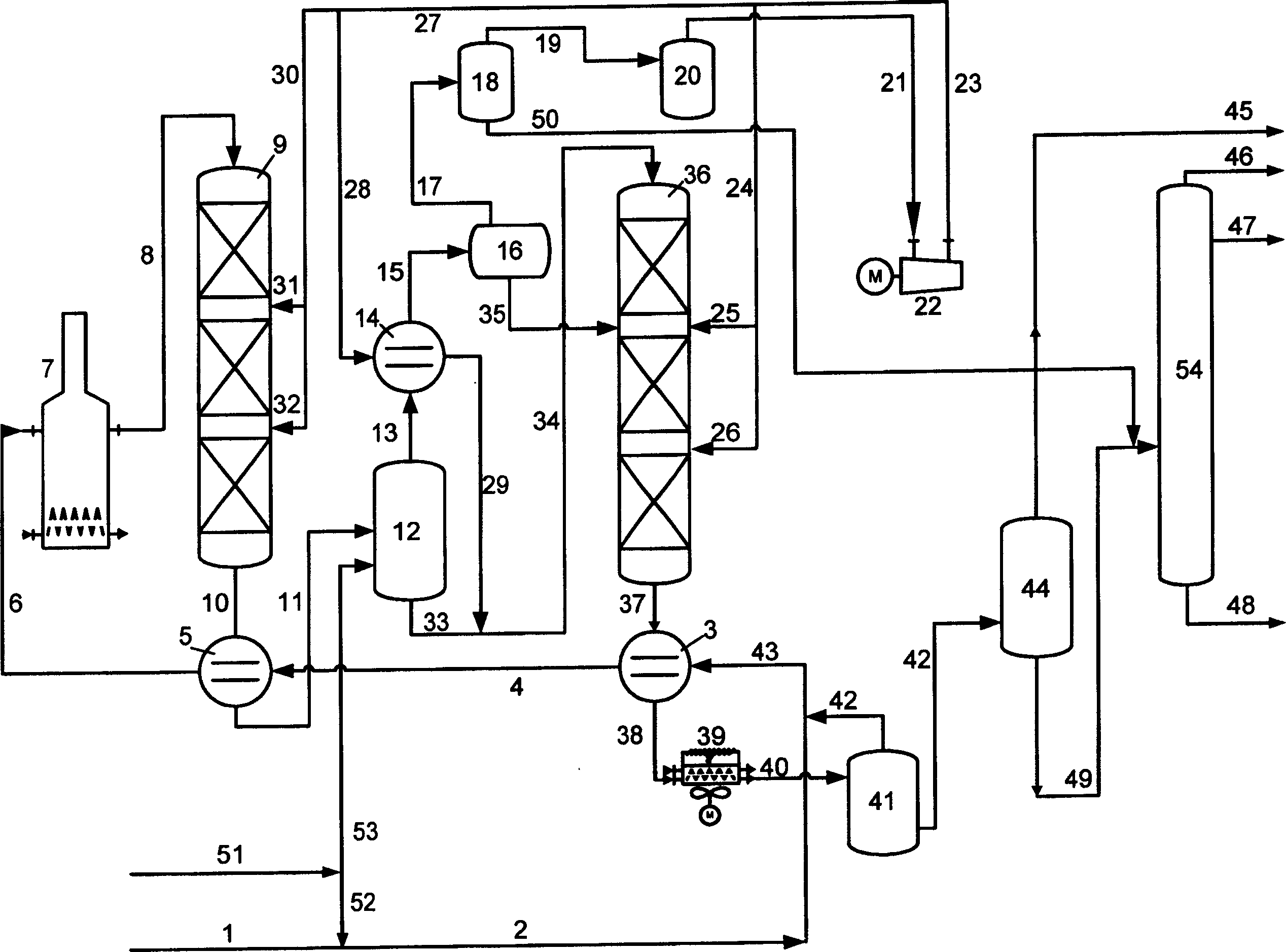
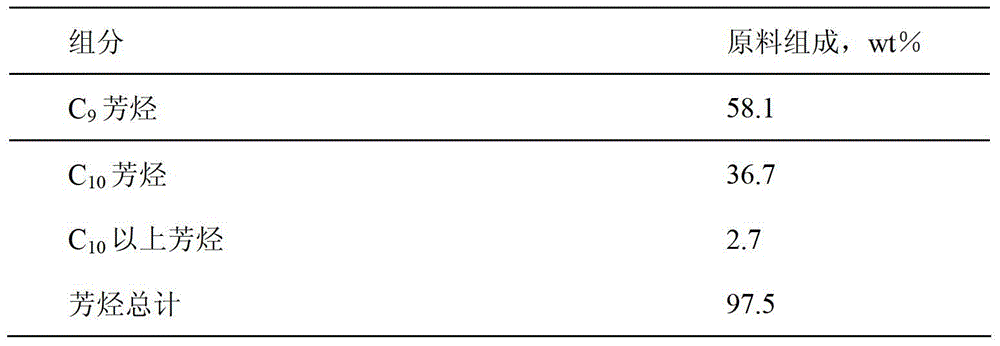
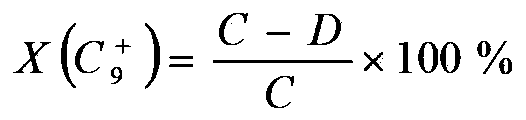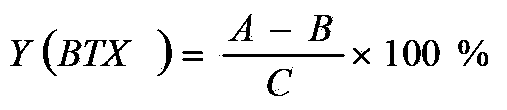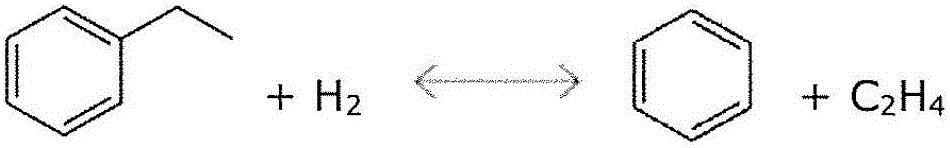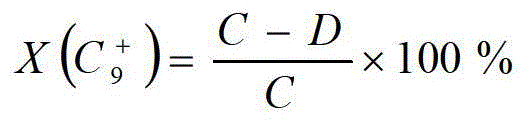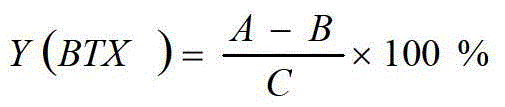Patents
Literature
47 results about "Hydrodealkylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
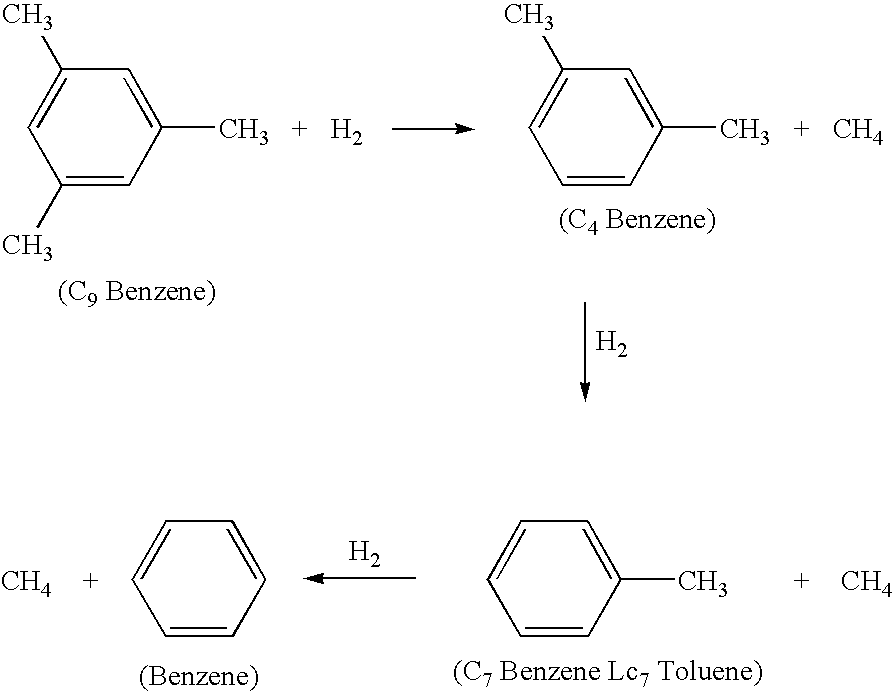
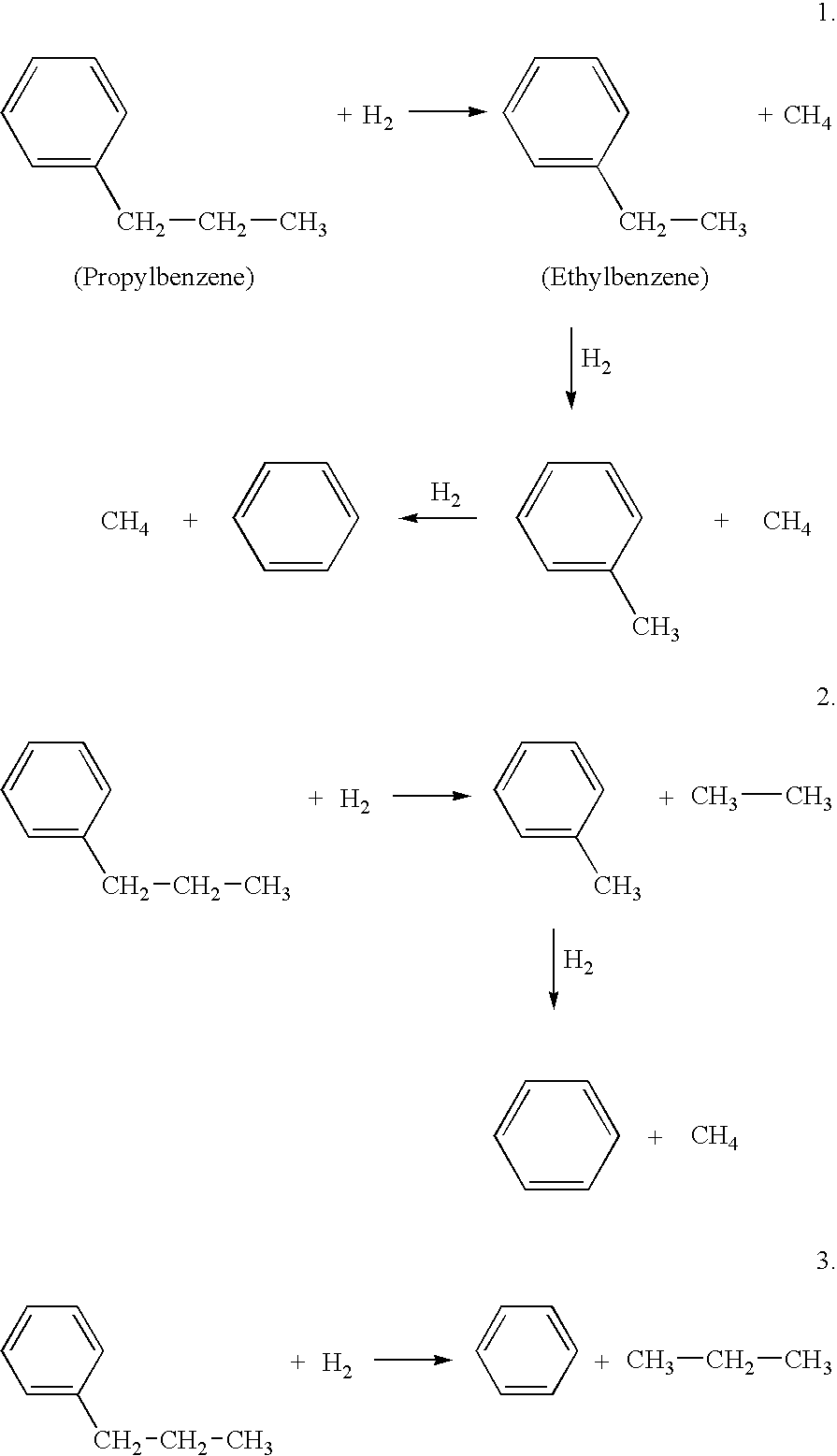
Hydrodealkylation is a chemical reaction that often involves reacting an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as toluene, in the presence of hydrogen gas to form a simpler aromatic hydrocarbon devoid of functional groups. An example is the conversion of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene to xylene. This chemical process usually occurs at high temperature, at high pressure, or in the presence of a catalyst. These are predominantly transition metals, such as chromium or molybdenum.
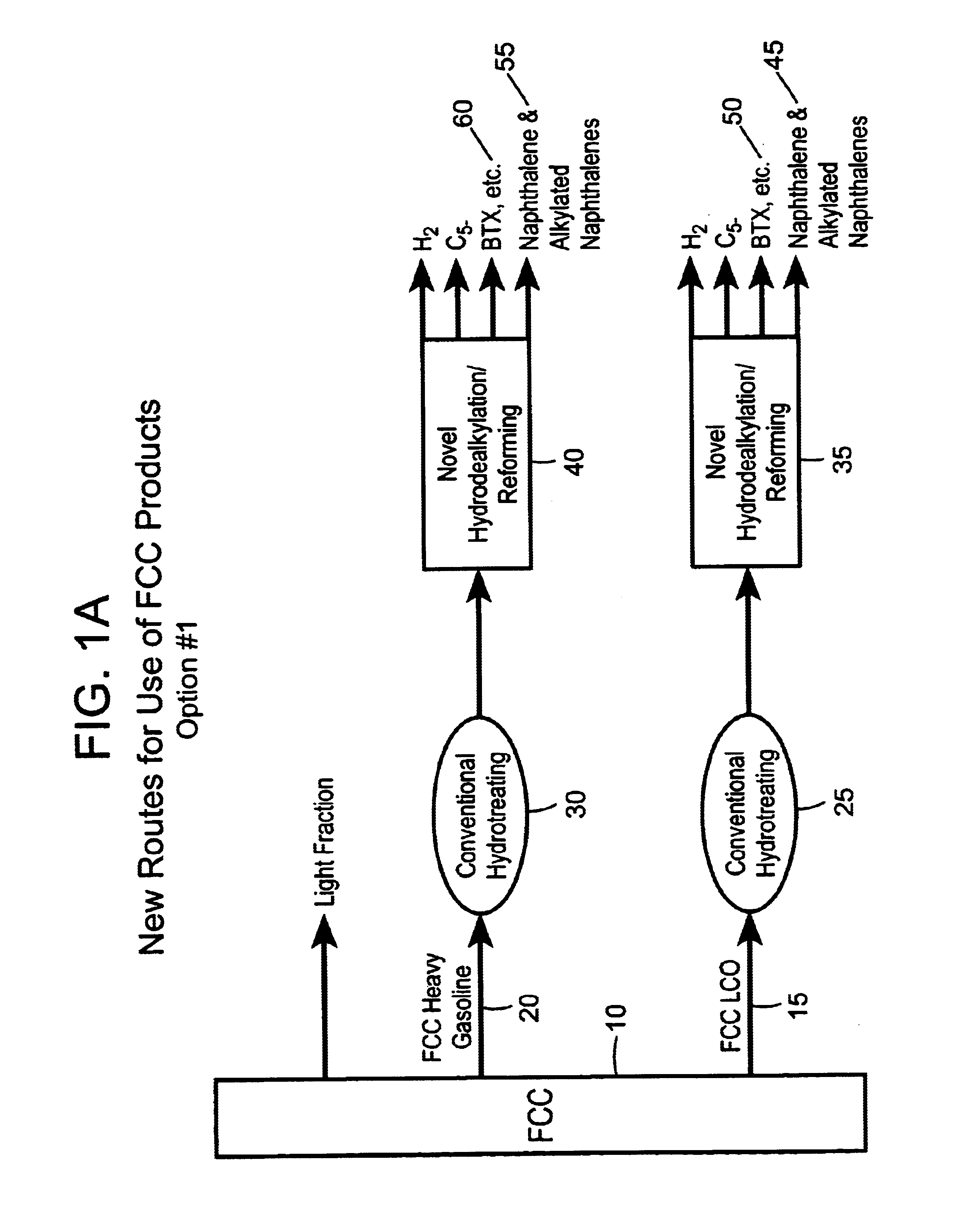
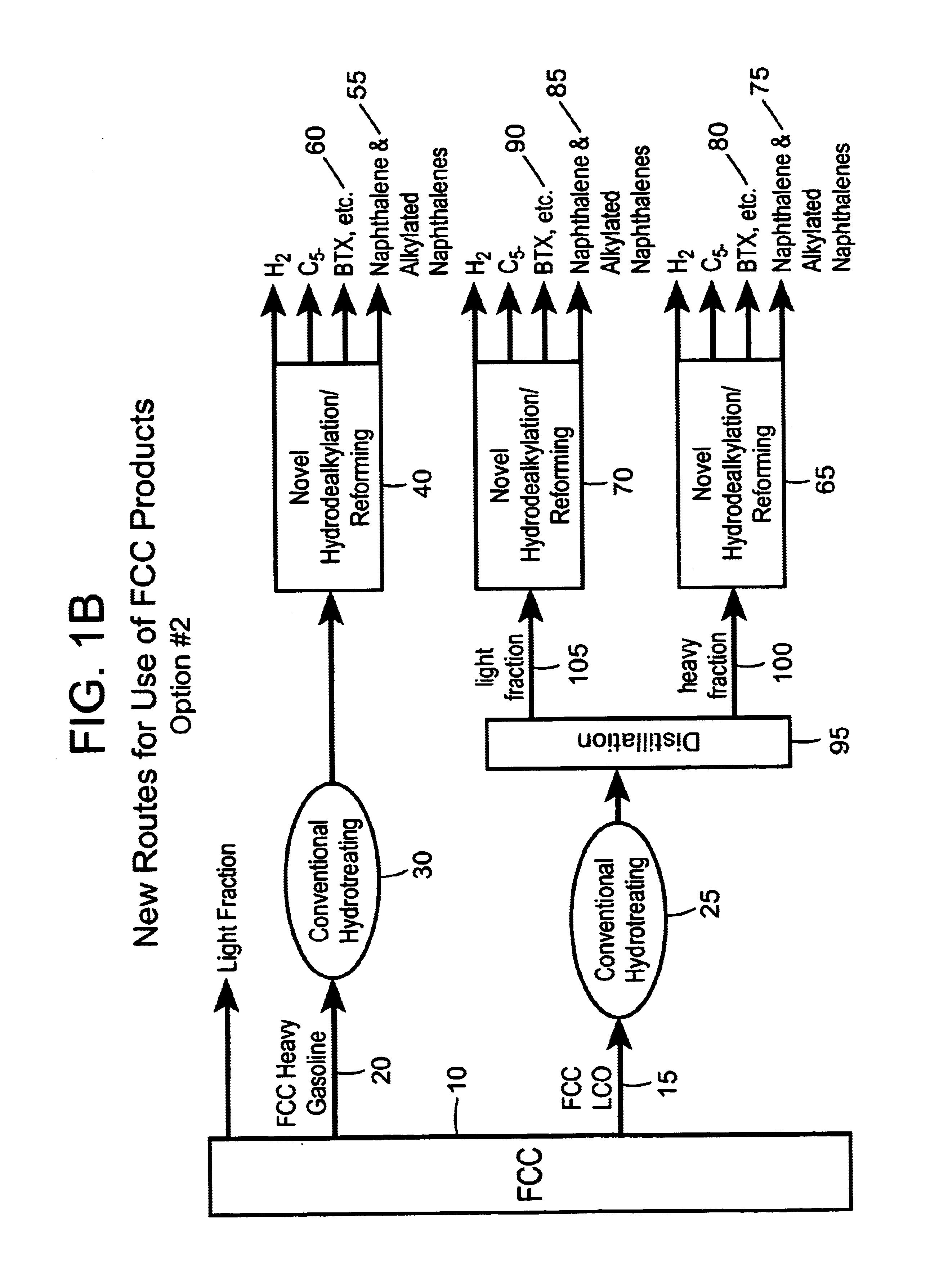
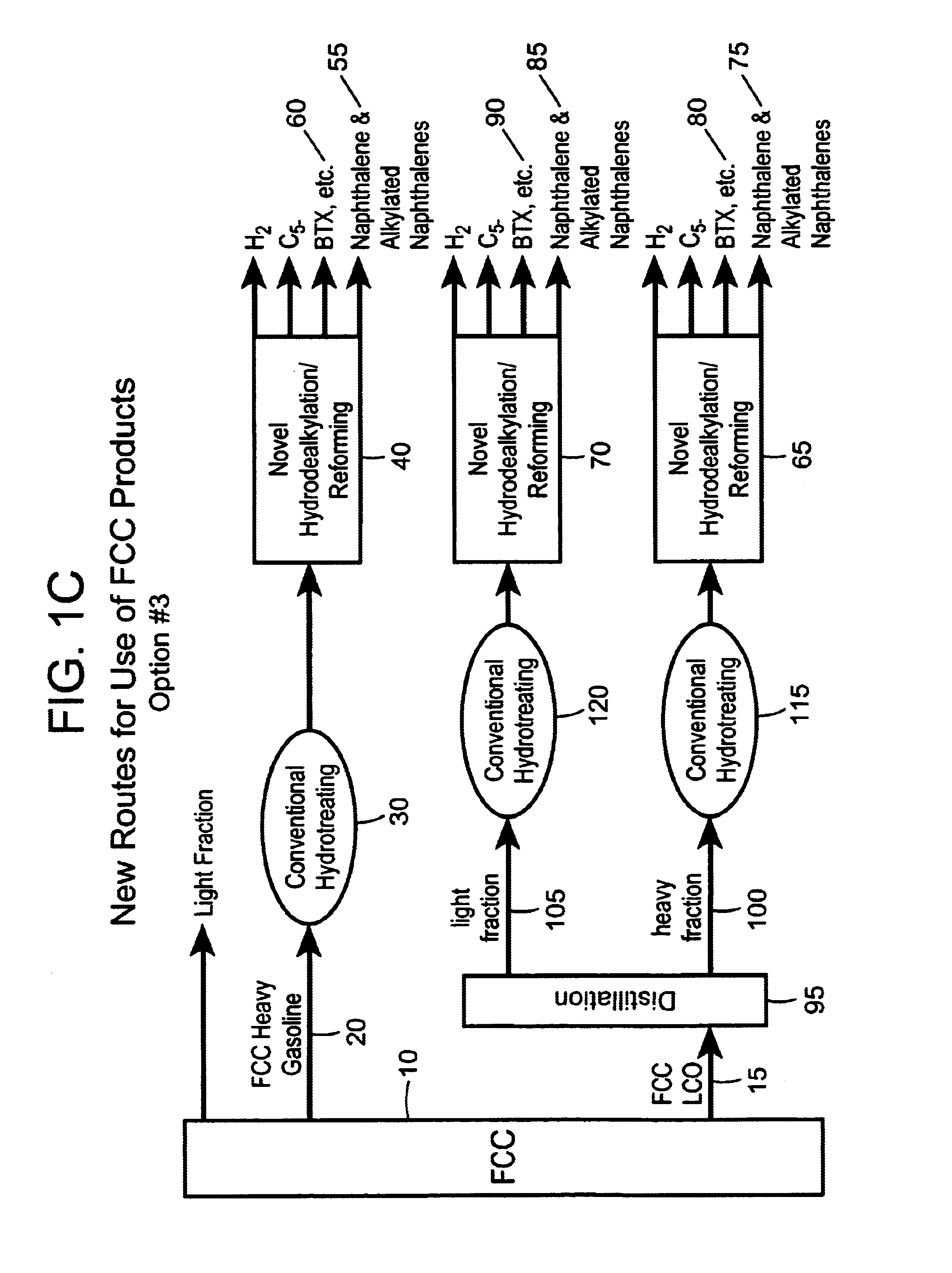
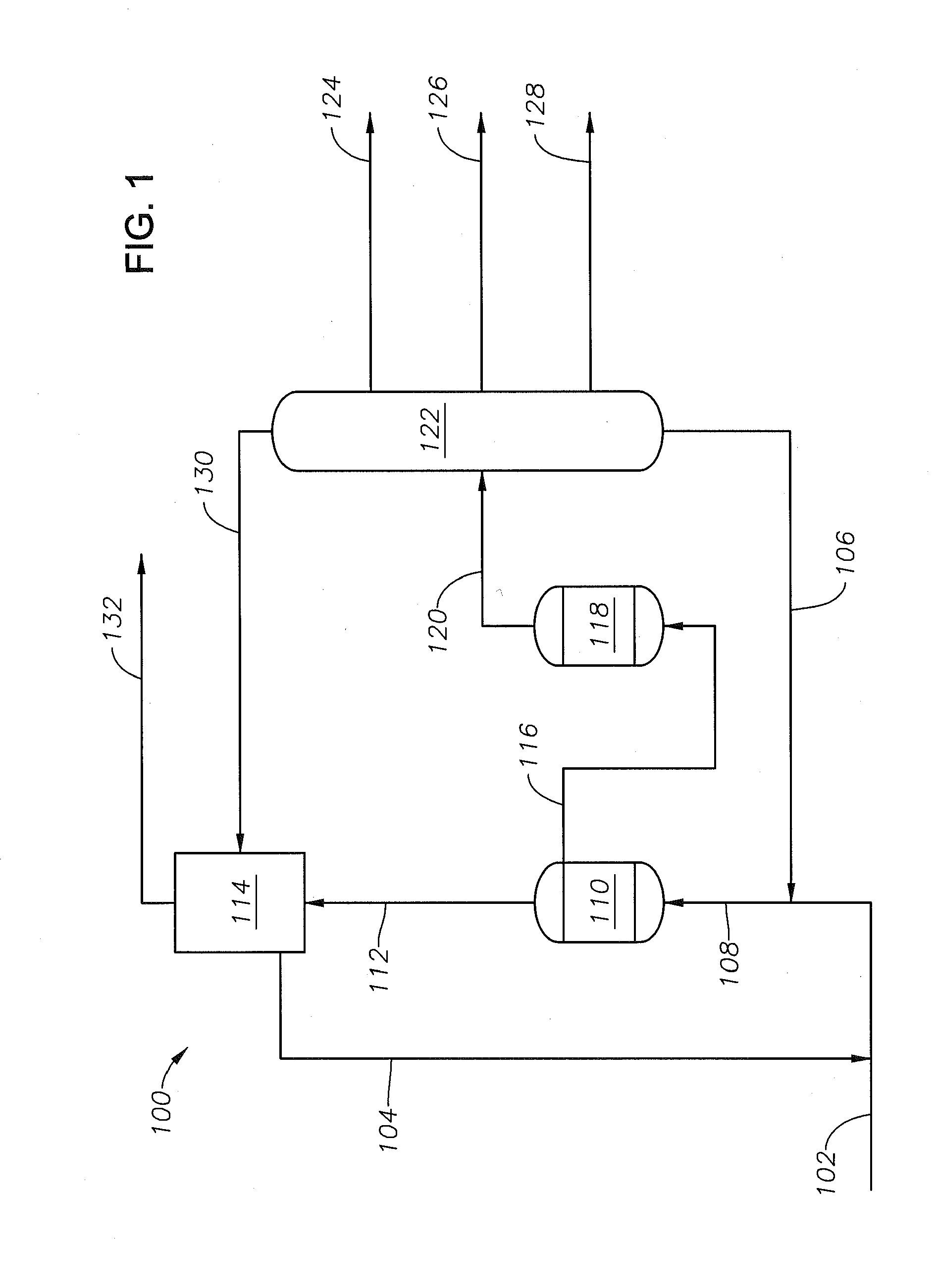
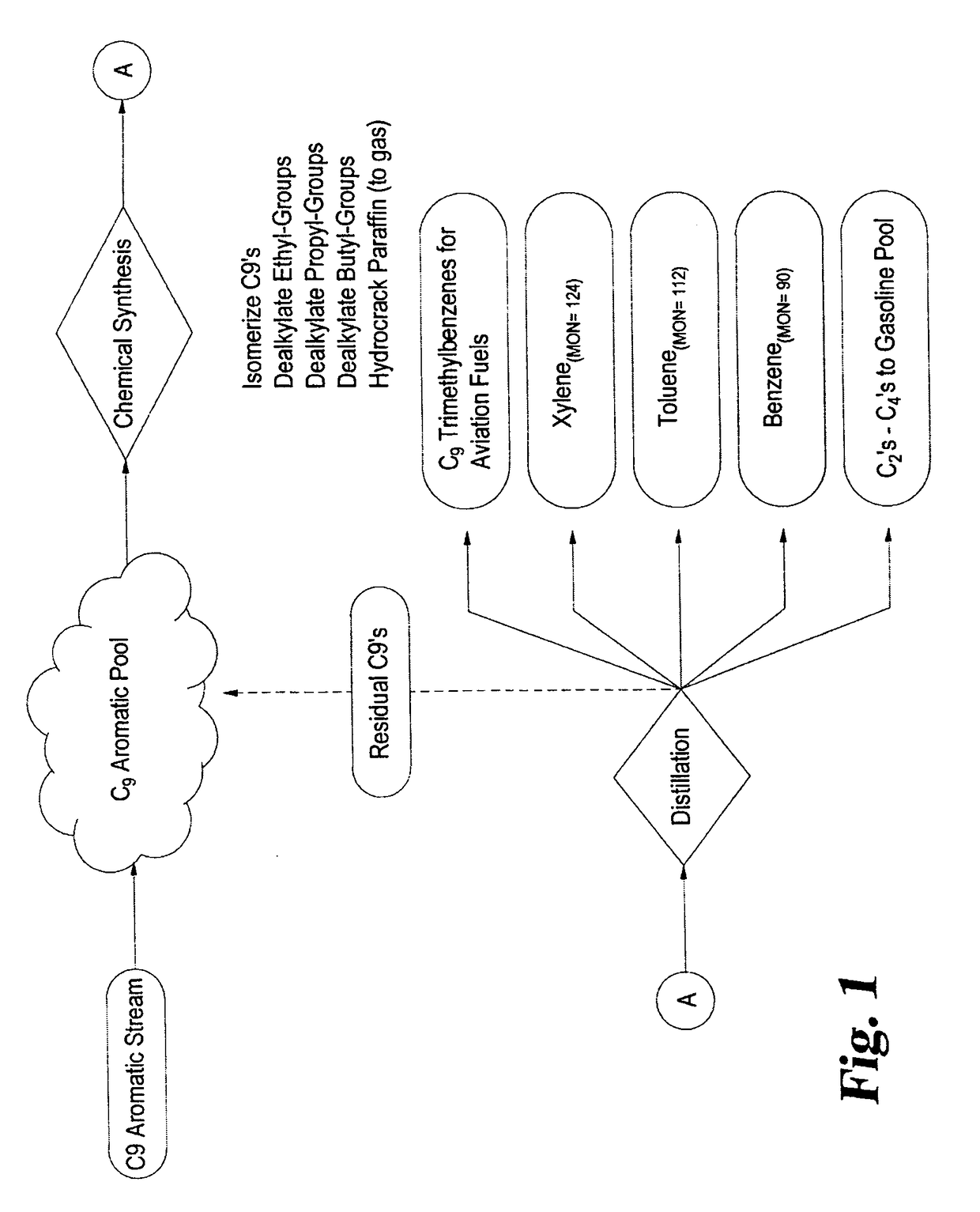
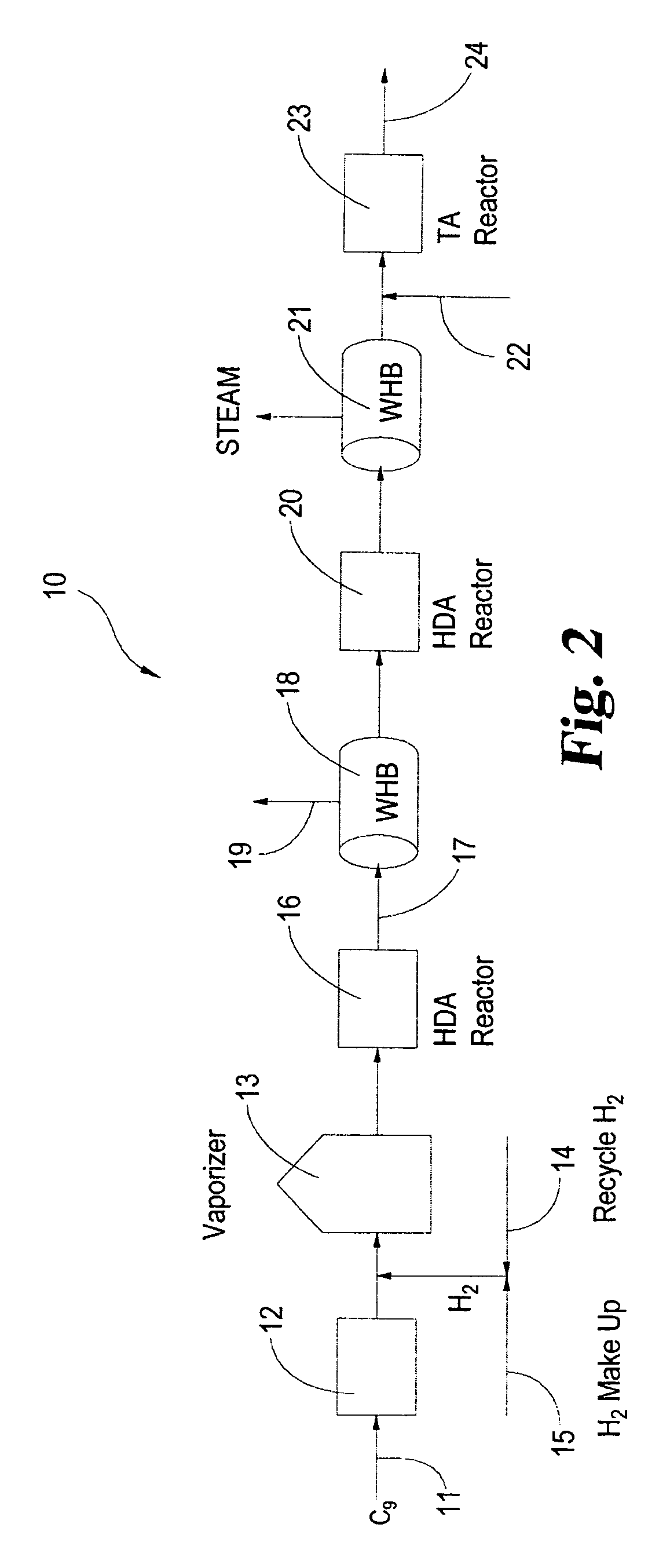
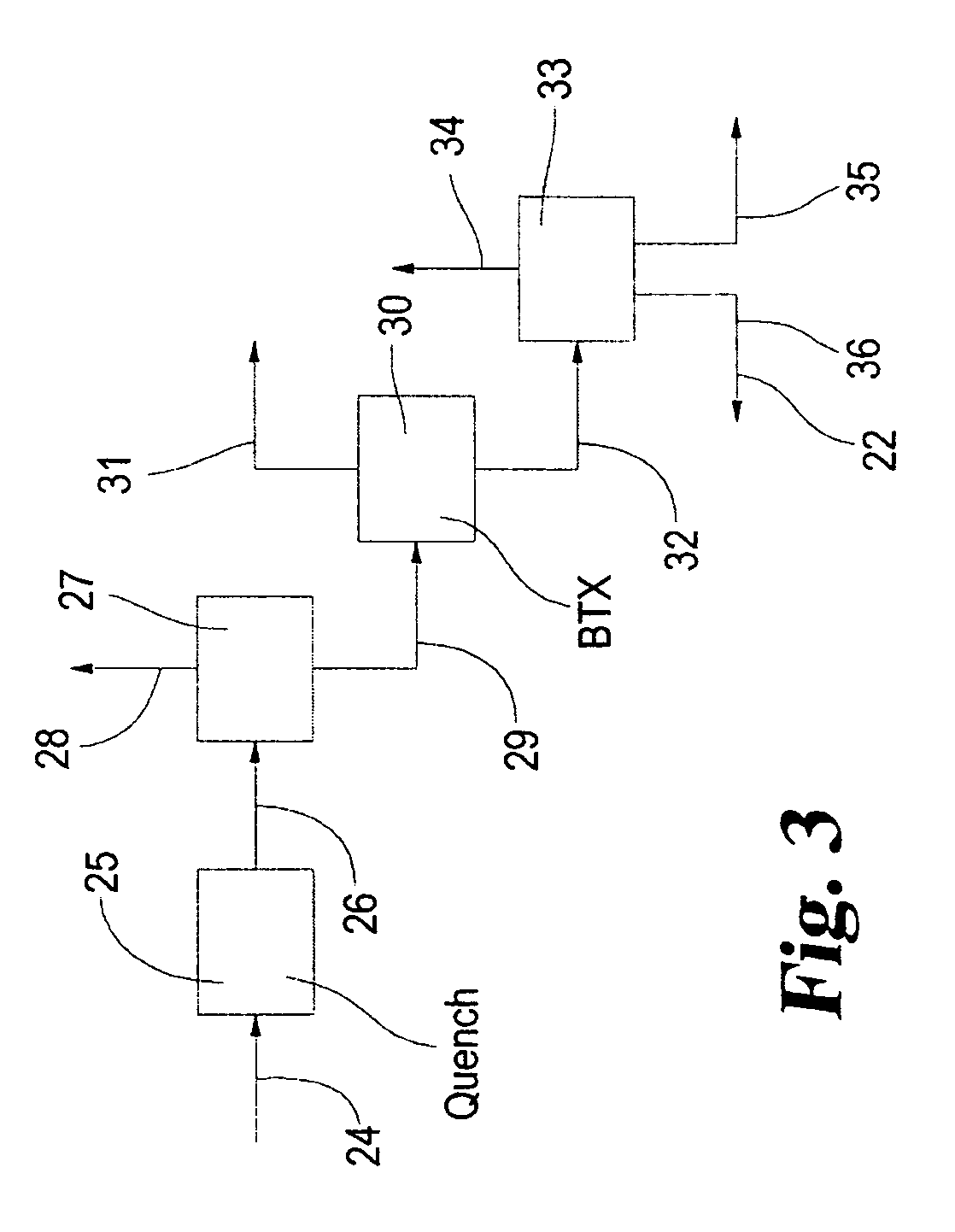
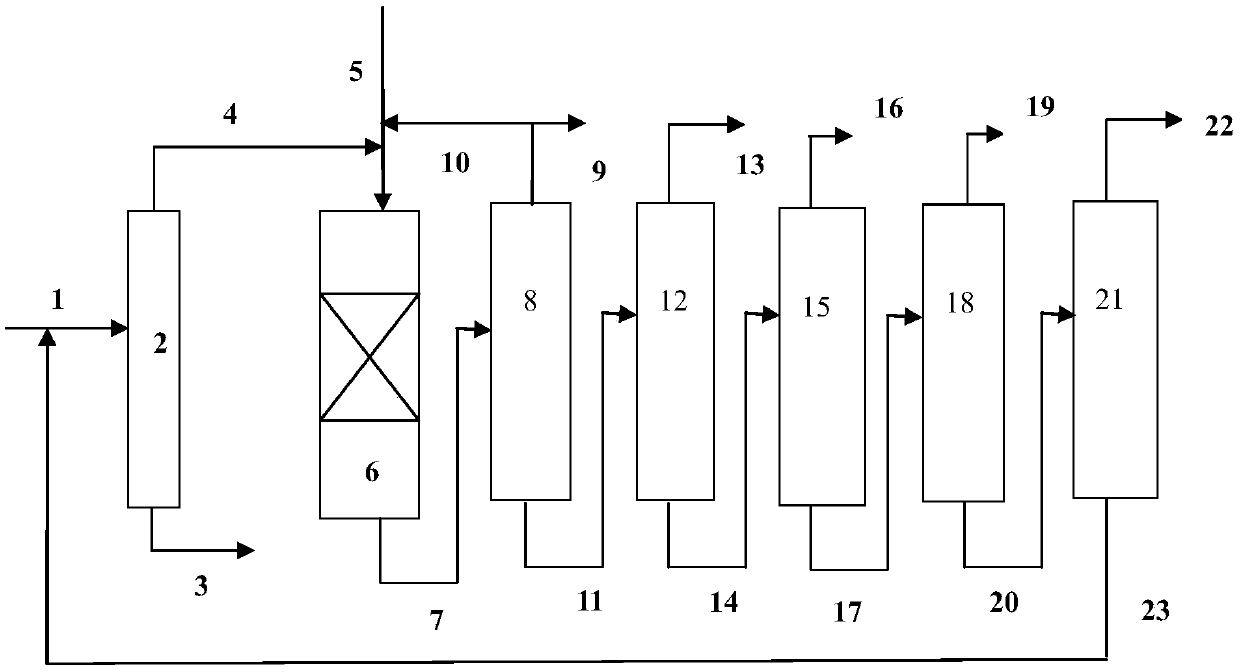
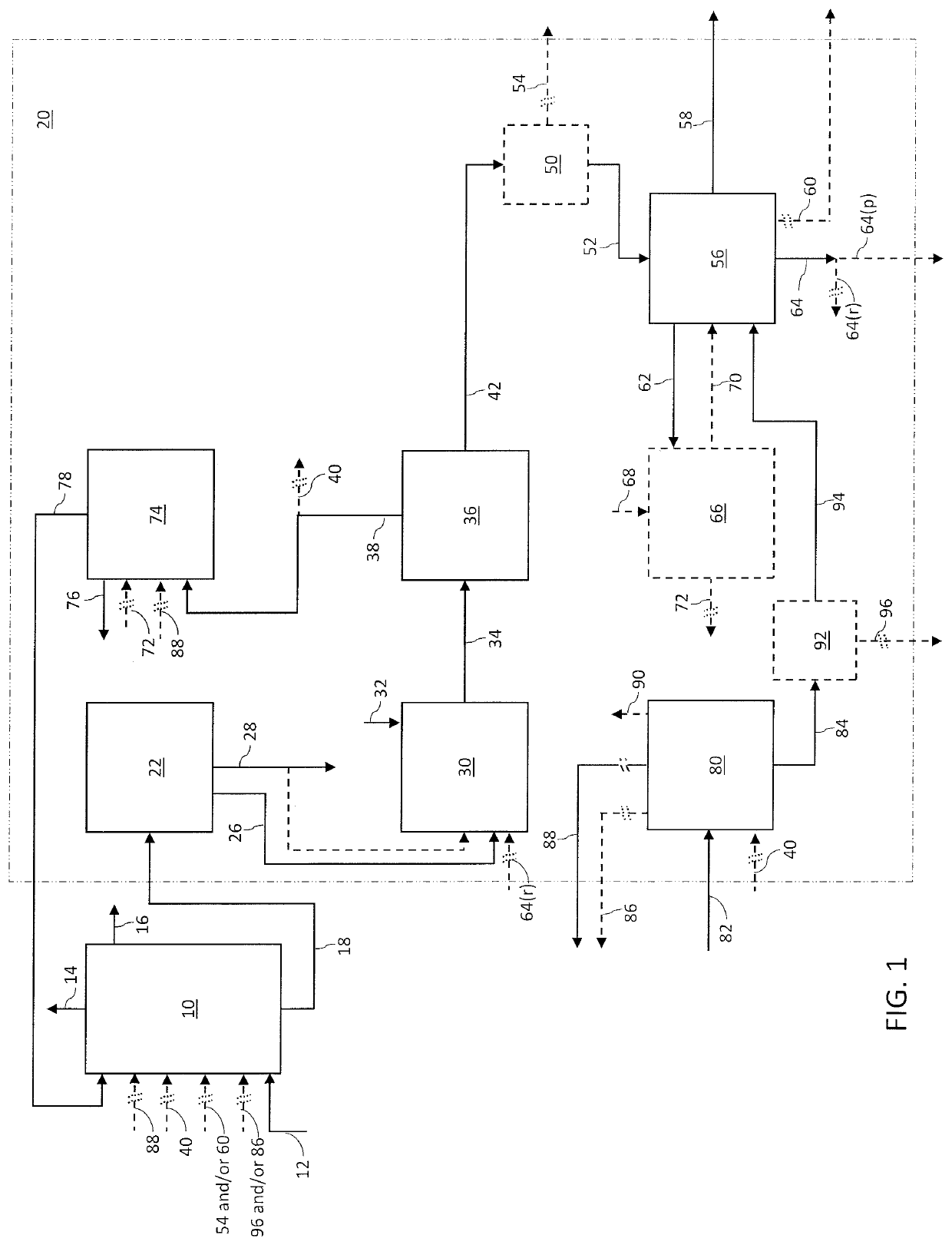
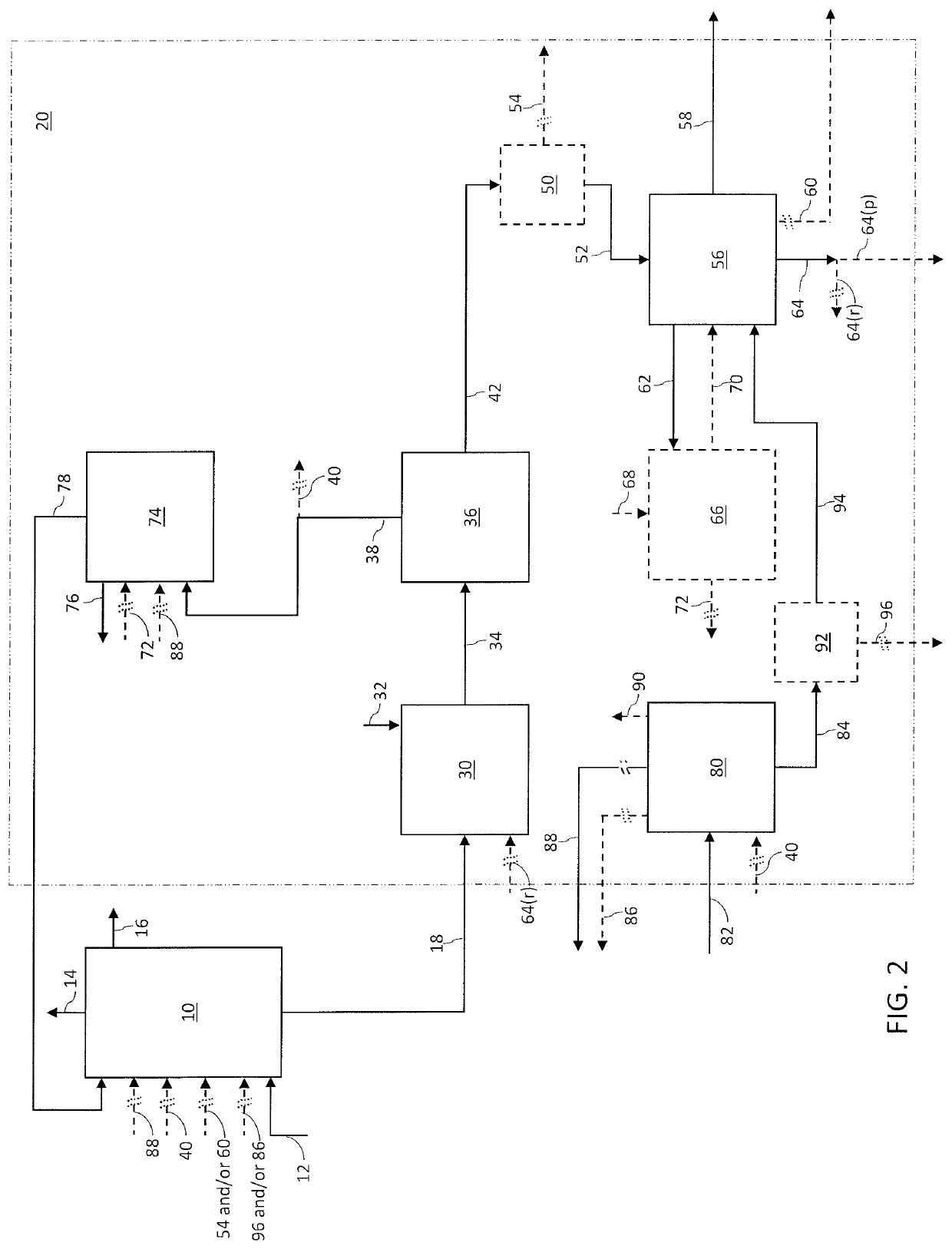
Process for converting heavy hydrocarbon feeds to high octane gasoline, BTX and other valuable aromatics
InactiveUS6900365B2High yieldOutstanding propertyCatalytic naphtha reformingHydrocarbonsMolecular sieveDehydrogenation
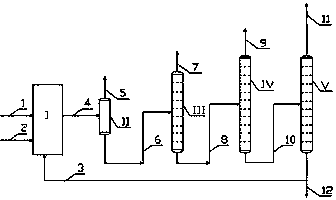
A catalytic hydrodealkylation / reforming process which comprises contacting a heavy hydrocarbon feedstream under catalytic hydrodealkylation / reforming conditions with a composition comprising borosilicate molecular sieves having a pore size greater than about 5.0 Angstroms and a Constraint Index smaller than about 1.0; further containing a hydrogenation / dehydrogenation component; wherein at least a portion of the heavy hydrocarbon feedstream is converted to a product comprising benzene, toluene, xylenes and ethylbenzene.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Heavy aromatic hydrocarbon light catalyst, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101607207AHigh aromatics conversion activityHigh yieldMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oils refiningRheniumCatalytic effect
The invention relates to a heavy aromatic hydrocarbon light catalyst, a preparation method and application thereof. In a composite carrier, H type MCM-56 zeolite is between 50 and 80 wt percent, Al2O3 is between 20 and 50 wt percent, metals or oxides thereof of tin, bismuth, lanthanum, molybdenum, nickel, chrome and cobalt are 3 to 20 wt percent, or platinum, palladium, rhenium or oxide thereof are 0.1 to 2wt percent. The catalyst is applicable to the light preparation of benzene, methylbenzene and dimethylbenzene by heavy aromatic hydrocarbon; and the catalyst has good catalytic effect on a hydrodealkylation light reaction of C9 heavy aromatic hydrocarbon, the transformation ratio of C9 aromatic hydrocarbon is 76.89 wt percent, the yield of BTX is 48.37 wt percent, the selectivity of the BTX is 80.50 mol percent, no phenylethane is generated in a product, and the dimethylbenzene has high content.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
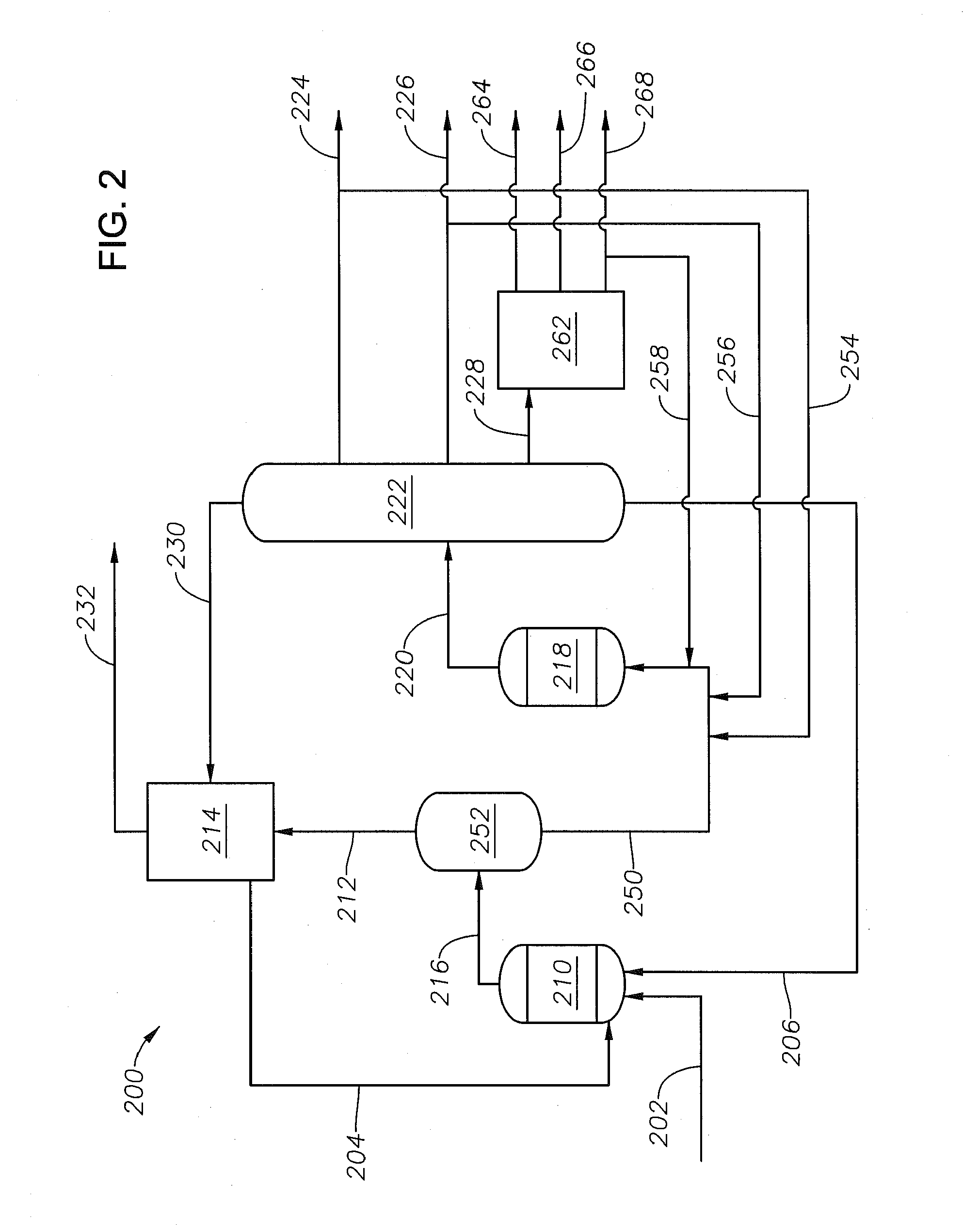
Combined heavy reformate dealkylation-transalkylation process for maximizing xylenes production
ActiveUS20130281750A1Easy to understandDescribed being slowOrganic compound preparationMolecular sieve catalystMethyl benzeneHydrodealkylation
A method of forming mixed xylenes from a heavy reformate using a dealkylation-transalkylation system includes the step of introducing both a heavy reformate containing methyl ethyl benzenes and tri-methyl benzenes and that is sufficiently free of toluene and a hydrogen-containing material into the dealkylation stage such that the heavy reformate and the hydrogen-containing material intermingle and contact the hydrodealkylation catalyst. The dealkylation-transalkylation system includes dealkylation, non-aromatic product gas separations and transalkylation stages. Toluene forms from the reaction of methyl ethyl benzenes and hydrogen in the presence of the hydrodealkylation catalyst. The method also includes the step of introducing a dealkylated heavy reformate into the transalkylation stage such that the dealkylated heavy reformate contacts a transalkylation catalyst, forming a transalkylation stage product mixture includes mixed xylenes.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Process for producing aromatic hydrocarbon compounds and liquefied petroleum gas from hydrocarbon feedstock
InactiveCN1478139AHigh purityHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsGas phaseDistillation
Fisclosed are a process for producing aromatic hydrocarbon compounds and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) from a hydrocarbon feedstock having boiling points of 30-250 DEG C and a catalyst useful therefor. In the presence of said catalyst, aromatic components in the hydrocarbon feedstock are converted to BTX-enriched components of liquid phase through hydrodealkylation and / or transalkylation, and non-aromatic components are converted to LPG-enriched gaseous materials through hydrocracking. The products of liquid phase may be separated as benzene, toluene, xylene, and C9 or higher aromatic compounds, respectively according to their different boiling points, while LPG is separated from the gaseous products, in a distillation tower.
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD
Combined heavy reformate dealkylation-transalkylation process for maximizing xylenes production
A method of forming mixed xylenes from a heavy reformate using a dealkylation-transalkylation system includes the step of introducing both a heavy reformate containing methyl ethyl benzenes and tri-methyl benzenes and that is sufficiently free of toluene and a hydrogen-containing material into the dealkylation stage such that the heavy reformate and the hydrogen-containing material intermingle and contact the hydrodealkylation catalyst. The dealkylation-transalkylation system includes dealkylation, non-aromatic product gas separations and transalkylation stages. Toluene forms from the reaction of methyl ethyl benzenes and hydrogen in the presence of the hydrodealkylation catalyst. The method also includes the step of introducing a dealkylated heavy reformate into the transalkylation stage such that the dealkylated heavy reformate contacts a transalkylation catalyst, forming a transalkylation stage product mixture includes mixed xylenes.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Process for improving cetane number of diesel oil and reducing aromatic hydrocarbon of diesel oil simultaneously
InactiveCN1566284AHigh quality low sulfurIncrease cetane numberTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHydrodealkylationAromatic hydrocarbon
The invention provides a process for improving cetane number of diesel oil and reducing aromatic hydrocarbon of diesel oil simultaneously which comprises, charging the diesel raw material and hydrogen gas into a first reactor, contacting non-noble metal hydrogenation catalyst, charging the reaction effluent from the first reactor into a second reactor, contacting noble metal hydrodealkylation catalyst, isolating the reaction effluent from the second reactor to obtain the diesel product.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Hydrocatalyst for preparing fuel by hydrodealkylation of coal-tar pitch and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101302439AImprove qualityVersatilityRefining to eliminate hetero atomsHydrodealkylationBiological activation
The invention relates to hydrosenation catalyst for producing oil by converting heavy coal tar pitch into light coal tar pitch, which is characterized in that: 100 portions of macroporous alumina is immersed into 100 portions of solution which consists of 3.5 to 20.5 weight percent of nickel nitrate and 3.0 to 25.0 weight percent of molybdenum nitrate for 2 hours at a temperature of between 50 and 60 DEG C; the mixture stands and supernatant is poured out, and then the mixture is dried for 4 hours at a temperature of 120 DEG C, activated for 5 hours at a temperature of 480 DEG C, and then immersed into cupric nitrate solution, cobalt nitrate solution, silver nitrate solution, ferric nitrate solution or bismuth nitrate solution with a concentration between 1.1 and 12.0 weight percent; and the catalyst is prepared through immersion, drying and activation which are the same as the above. The content of the nickel oxide and the molybdenum oxide in the catalyst is respectively 1.2 to 11.2 weight percent and 1.1 to 15.4 weight percent of the weight of carrier, and the content of cupric oxide, cobalt oxide, silver oxide, ferric oxide or bismuth oxide is 1.1 to 7.8 weight percent of the weight of the carrier. The hydrogenation catalyst has good adaptability to various coal tar pitch raw materials, high hydrogenation degree, strong controllability, low operating cost, and high yield of the oil produced by converting the heavy coal tar pitch into the light coal tar pitch; and the overall oil yield of fuel can reach over 75 percent.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Process for the preparation of hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20120088944A1Attractive for productionRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocotyle bowlesioidesHydrodealkylation
The invention provides a process for the preparation of hydrocarbons comprising the steps of:(a) contacting a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at an elevated temperature and pressure with a mixture of a methanol synthesis catalyst and a methanol conversion catalyst thereby forming C5+ hydrocarbons;(b) separating at least part of the C5+ hydrocarbons as obtained in step (a) into a light stream and a heavy durene-rich stream;(c) subjecting at least part of the heavy durene-rich stream to a hydrodealkylation treatment in the presence of hydrogen to obtain a stream of hydrocarbons having a reduced durene content; and(d) mixing at least part of the light stream as obtained in step (b) with at least part of the stream of hydrocarbons having a reduced durene content as obtained in step (c).
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
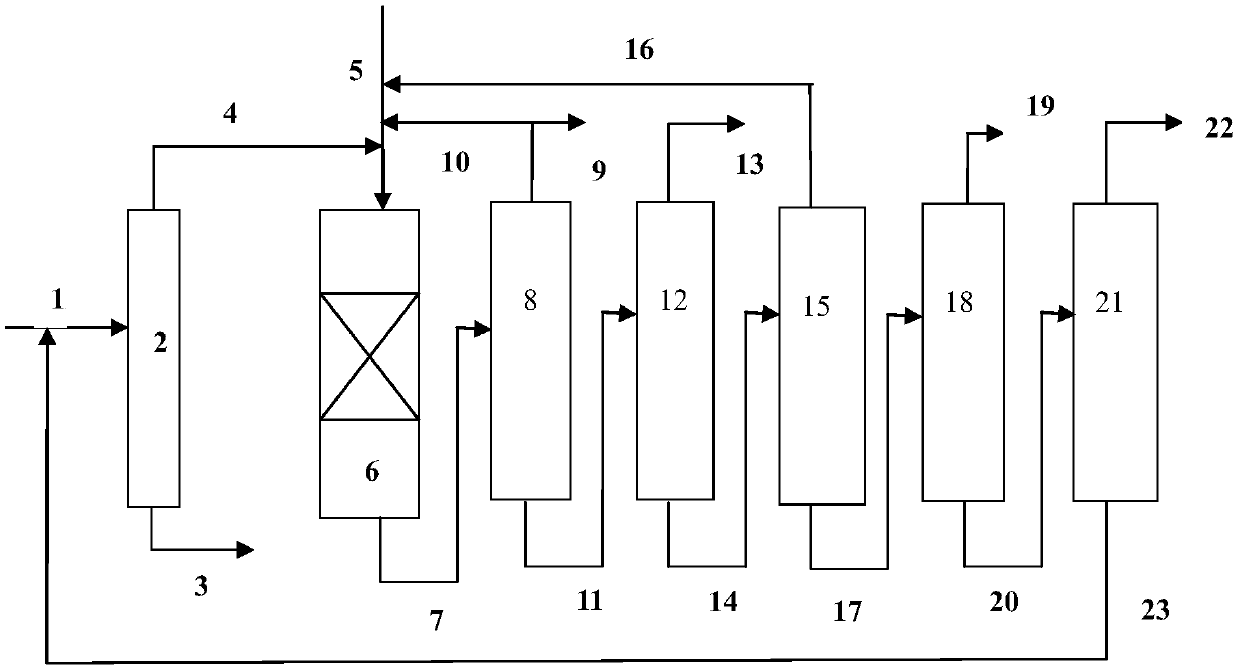
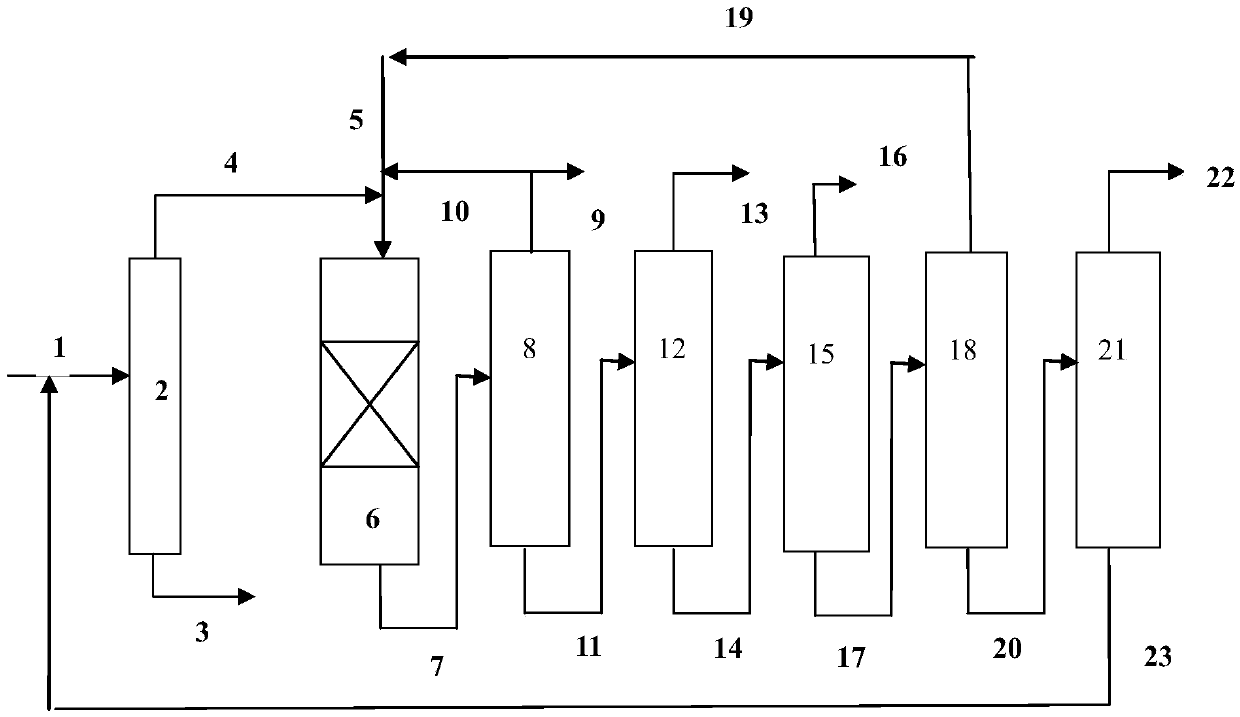
Catalyst for C10+ heavy arene hydrodealkylation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110075911ARegulate acidityImprove pore structureMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsMolecular sieveActive component
The invention provides a catalyst for C10+ heavy arene hydrodealkylation and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst adopts a modified beta molecular sieve with a micropore-mesoporous composite structure as a carrier, and transition metal oxide and rare earth oxides as active components, wherein the transition metal oxide is a mixture of one or more of MoO3, Bi2O3, Co3O4 or CuO and NiO; the rare earth oxide is one or two of La2O3 or CeO2; the content of NiO is 2-16% of the mass of the carrier; the content of one or more of MoO3, Bi2O3, Co3O4 or CuO is 1-5% of the mass of the carrier; the content of the rare earth oxide is 0.4-2% of the mass of the carrier. The catalyst provided by the invention adopts the micropore-mesoporous composite structure, has stronger processing capacity to C10+heavy arene (equal to or greater than 40wt%), and can improve the C10+ heavy arene conversion rate and the mixed xylene selectivity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Enhanced aromatics production by low pressure end point reduction and selective hydrogenation and hydrodealkylation
A reforming process includes an endpoint reduction zone for converting C11+ components via selective hydrogenation and hydrodealkylation to lower boiling point aromatics, such as benzene, toluene, and xylene, or their single ring aromatic C9-C10 precursors.
Owner:UOP LLC
Treating c8-c10 aromatic feed streams to prepare and recover trimethylated benzenes
ActiveUS20140316174A1Boost octaneIncrease severityHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystHydrodealkylationMethyl group
Methods are provided for the treatment of a feed stream containing C9 aromatic components to produce mesitylene-containing products. The methods include hydrodealkylating the feed stream to remove C2 and higher alkyl groups from the aromatic components and transalkylating the feed stream to rearrange the distribution of methyl groups among the aromatic components. Disclosed methods also include the treatment of a hydrocarbon feedstock by hydrodealkylation and / or transalkylation in order to produce a hydrocarbon product having an increased mass percentage of mesitylene.
Owner:SWIFT FUELS
System and process for steam cracking and pfo treatment integrating hydrodealkylation and naphtha reforming
ActiveUS20210130712A1Refining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonCatalytic naphtha reformingThermodynamicsNaphtha
A process for treatment of PFO from a steam cracking zone includes hydrodealkylating PFO or a portion thereof for conversion of polyaromatics compounds contained in the PFO into hydrodealkylated aromatic compounds with one benzene ring, a hydrodealkylated BTX+ stream. In addition, a naphtha reformer is integrated, so that the hydrodealkylated BTX+ stream and a reformate stream are separated into BTX compounds.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Method for preparation of benzene, toluene and xylene from ethene cracking C9
ActiveCN104211557AAvoid Hydrogenation LossImprove stabilityTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon crackingTetraglycolDistillation
The invention relates to a method for preparation of benzene, toluene and xylene from ethene cracking C9; an ethene cracking C9 raw material is extracted for separation of aromatic fractions and other non aromatic components, separation of aromatics can be performed in an extraction column, the separation temperature is 50 to 70 DEG C, the feeding weight ratio of an extracting agent to the ethene cracking C9 raw material is 4-10:1, the extracting agent is tetraglycol; the distillation range of aromatics extraction is controlled in the range of 135 to 220 DEG C; unsaturated aromatics are pre hydrogenated for hydrogenation saturation, pre hydrogenated C9 + aromatics is processed for lightening of heavyweight aromatics by catalytic hydrodealkylation method for preparation of the benzene, the toluene and the xylene; according to the method, the conversion rate of X (C9+) aromatics is 61.6 to 62.2; Y (BTX) (benzene, toluene and xylene) yield is 40.8-42.8; and S (BTX) selectivity is 67.96-8.8.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Hydrodealkylation processes
InactiveUSRE38532E1Reduce sulfide corrosionImprove product valueHydrogenOrganic compound preparationMetal dustingEngineering
Carburization and metal-dusting while hydrodealkylating a hydrodealkylatable hydrocarbon are reduced even in the substantial absence of added sulfur.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Method of cracking multi-production of trimethylbenzene with C9 and above heavyweight aromatic hydrocarbon ingredients
ActiveCN103772121AAchieve self-sufficiencyHigh-quality production increaseHydrocarbon by isomerisationDistillation purification/separationHemimelliteneBoiling point
The invention relates to a method of catalytic cracking multi-production of trimethylbenzene with C9 and above heavyweight aromatic hydrocarbon ingredients. The method mainly solves the problems that a lightweight aromatic hydrocarbon product contains much toluene, and separated heavyweight aromatic hydrocarbon and non-aromatic hydrocarbon are lower in use value since BTX (B: Benzene, T: Toluene, and X: Xylol) aromatic hydrocarbon is just simply separated in a traditional gasoline cracking and C9 reforming process. With the adoption of the technical scheme that a C9<+> heavyweight aromatic hydrocarbon raw material is subjected to hydrodealkylation and performs transalkylation reaction with lightweight aromatic hydrocarbon in the presence of a catalyst, trimethylbenzene in C9 aromatic hydrocarbon is gathered, light hydrocarbon, BTX, mesitylene and pseudocumene, C9 and hemimellitene fractions are separated from a liquid phase product respectively according to different boiling points, and C9 and hemimellitene can return to be processed continuously as a feed material, the method better solves the technical problems, and can be used for industrial production of heavyweight aromatic hydrocarbon.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process for producing aromatic hydrocarbon compounds and liquefied petroleum gas from hydrocarbon feedstock
InactiveCN1217892CHigh purityHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsGas phaseDistillation
Fisclosed are a process for producing aromatic hydrocarbon compounds and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) from a hydrocarbon feedstock having boiling points of 30-250 DEG C and a catalyst useful therefor. In the presence of said catalyst, aromatic components in the hydrocarbon feedstock are converted to BTX-enriched components of liquid phase through hydrodealkylation and / or transalkylation, and non-aromatic components are converted to LPG-enriched gaseous materials through hydrocracking. The products of liquid phase may be separated as benzene, toluene, xylene, and C9 or higher aromatic compounds, respectively according to their different boiling points, while LPG is separated from the gaseous products, in a distillation tower.
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD
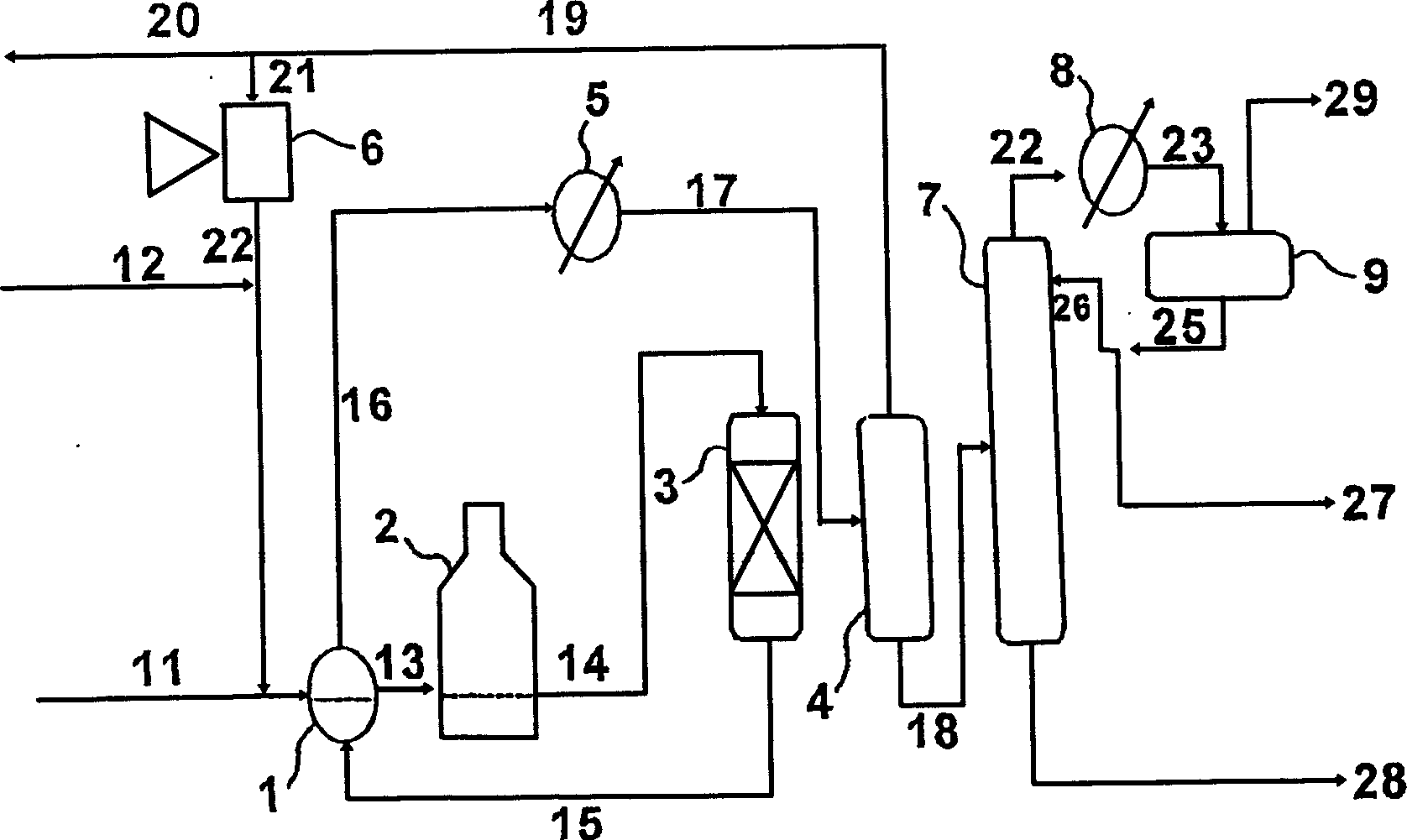
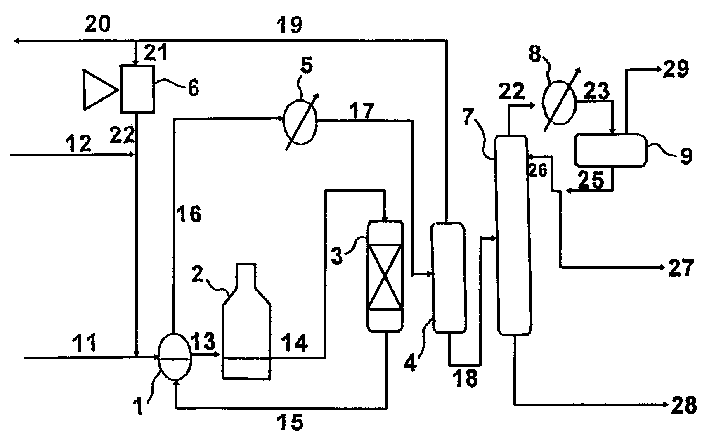
Process for deep dearylation of hydrocarbon oil
The invention discloses a process for deep dearylation of hydrocarbon oil which comprises, charging raw oil and hydrogen gas into hydrogenation reactor, contacting hydrodealkylation catalyst, isolating the reacted articles to obtain gaseous phase and liquid phase product, wherein the gaseous phase product is compressed for cycling use, the liquid phase product is isolated to obtain destination product of low aromatic hydrocarbons.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Transalkylation / disproportionation or thermal hydrodealkylation hydrocarbon processing methods and systems employing an increased ethylbenzene feed content
InactiveUS20160060189A1Reduce contentReduced ethylbenzene contentHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon by metathesis reactionHydrodealkylationAromatic hydrocarbon
Methods and apparatus for processing hydrocarbons are provided. In one example, a method for processing hydrocarbons includes the step of providing feed stream including toluene, ethylbenzene, mixed xylenes, and C9 hydrocarbons. Ethylbenzene is present in the feed stream in an amount of at least about 20% by weight of total C8 aromatic hydrocarbons present in the feed stream. The method further includes the step of subjecting the feed stream to ethylbenzene conversion to form a benzene-containing product stream that includes benzene.
Owner:UOP LLC
Catalyst for preparing low carbon aromatic hydrocarbon by hydrodealkylation of C10+ heavyweight aromatic hydrocarbon and preparation method of catalyst
InactiveCN110075912AGood dispersionRich acid center typeMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oil crackingMolecular sieveActive component
The invention provides a catalyst for preparing low carbon aromatic hydrocarbon by hydrodealkylation of C10+ heavyweight aromatic hydrocarbon. The catalyst is characterized in that the catalyst takesa composite molecular sieve as a carrier and a transition metal oxide and a rare earth oxide as active components, wherein the transition metal oxide is MoO3, and one or more of NiO, Bi2O3, Co3O4 or CuO; the rare earth oxide is one or two of La2O3 and CeO2; a content of MoO3 is 3-12% of the mass of the carrier; a content of NiO, Bi2O3 or Co3O4 is 0.5-2% of the mass of the carrier; and a content ofthe rare earth oxide is 0.2-1% of the mass of the carrier. A method of preparing low carbon aromatic hydrocarbon by the hydrodealkylation of C10+ heavyweight aromatic hydrocarbon has stronger processing capacity of C10+ heavyweight aromatic hydrocarbon (greater than or equal to 40wt%); a conversion rate of C10+ heavyweight aromatic hydrocarbon can be increased; and selectivity of low carbon aromatic hydrocarbon can be improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Treating C8-C10 aromatic feed streams to prepare and recover trimethylated benzenes
ActiveUS9890095B2Boost octaneIncrease severityMolecular sieve catalystCatalystsHydrodealkylationMethyl group
Owner:SWIFT FUELS
Process method for producing xylene from C<9><+> heavy aromatic hydrocarbons
ActiveCN110642665AHydrocarbonsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystHydrocotyle bowlesioides
The invention discloses a process method for producing xylene from C<9><+> heavy aromatic hydrocarbons. The process method comprises the following steps: low-boiling-point heavy aromatic hydrocarbonsand high-boiling-point heavy aromatic hydrocarbons are separated from the C<9><+> heavy aromatic hydrocarbons in a heavy aromatic hydrocarbon separation tower; in the presence of hydrogen, the low-boiling-point heavy aromatic hydrocarbons is allowed to be in contact with a hydrodealkylation and transalkylation catalyst to be subjected to a reaction in a hydrodealkylation and transalkylation reaction unit to obtain a material stream containing benzene, toluene and xylene aromatic hydrocarbons, non-aromatic hydrocarbons, unreacted heavy aromatic hydrocarbons and hydrogen; and the material streamcontaining benzene, toluene and xylene aromatic hydrocarbons, non-aromatic hydrocarbons, unreacted heavy aromatic hydrocarbons and hydrogen sequentially passes through a gas-liquid separator, a stripping tower, a benzene separation tower, a toluene separation tower, and a xylene separation tower to sequentially separate hydrogen, the non-aromatic hydrocarbons, benzene, toluene and xylene aromatichydrocarbon products, and the unreacted heavy aromatic hydrocarbons.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
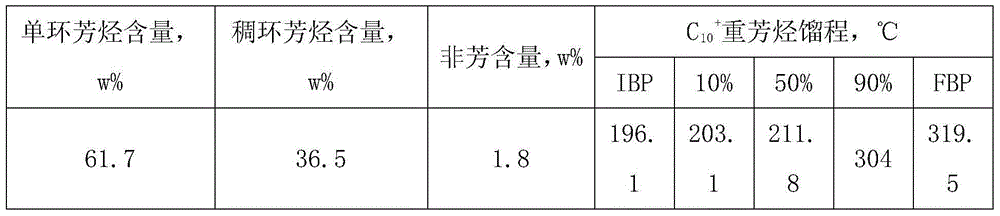
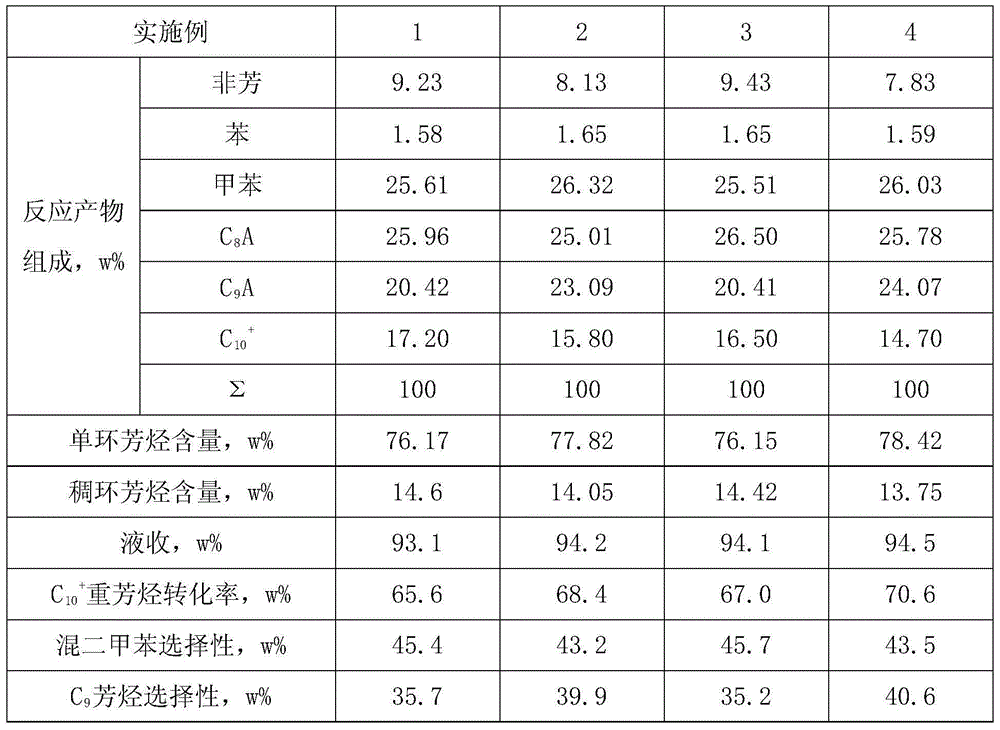
C10+ heavy aromatic hydrocarbon hydrodealkylation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104353486ADiffusion is fastSlow down carbon deposition and deactivationMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsCarbon numberPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
The invention relates to a C10+ heavy aromatic hydrocarbon hydrodealkylation catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The C10+ heavy aromatic hydrocarbon indicates monocyclic / polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with a carbon number more than or equal to 10 and a final boiling point not more than 300 DEG C. The C10+ heavy aromatic hydrocarbon hydrodealkylation catalyst provided by the invention is capable of treating the C10+ heavy aromatic hydrocarbon under the condition of hydrogenation and has the advantages of high C10+ heavy aromatic hydrocarbon transformation rate and high mixed xylene selectivity and C9 aromatic hydrocarbon selectivity and can be used for realizing the conversion to light fraction of the C10+ heavy aromatic hydrocarbon. The preparation method disclosed by the invention can be used for increasing the yield of BTX aromatic hydrocarbon and high-quality disproportionate raw materials by carrying out hydrodealkylation reaction by adopting a rare earth metal and transition metal modified mixed molecular sieve catalyst and taking the C10+ heavy aromatic hydrocarbon and light aromatic hydrocarbon which includes benzene and / or methylbenzene as raw materials.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +3
System and process for steam cracking and PFO treatment integrating hydrodealkylation and naphtha reforming
ActiveUS11377609B2Refining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonCatalytic naphtha reformingThermodynamicsNaphtha
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
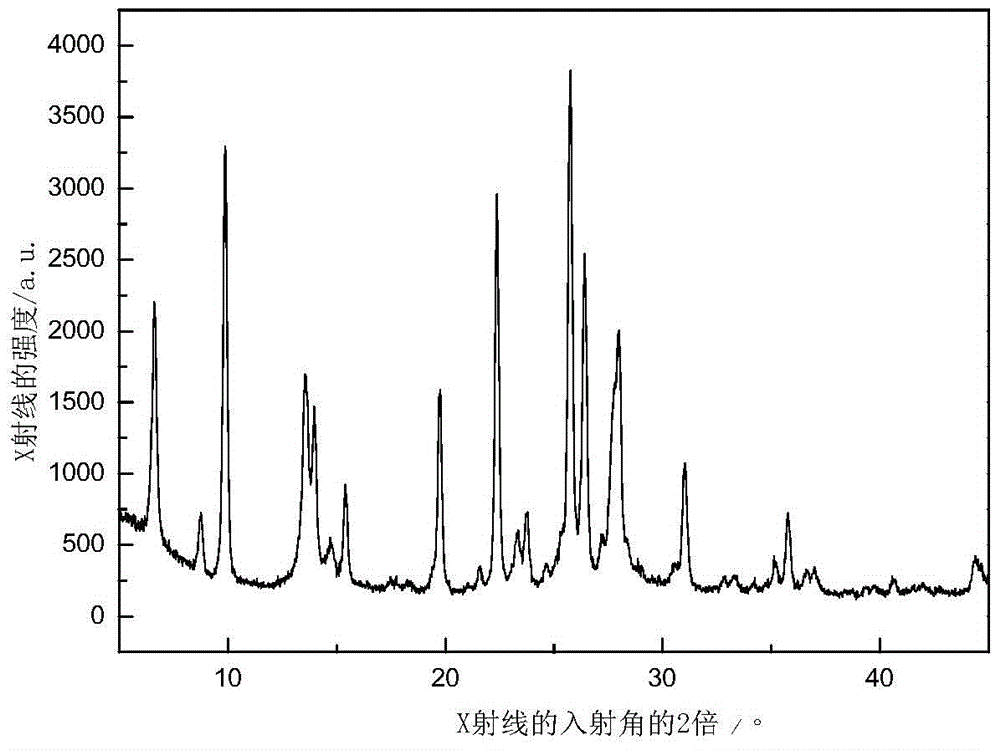
A kind of preparation method of nanometer step hole mordenite molecular sieve
InactiveCN104843731BReduce the degree of polymerizationSmall grain sizeCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesMolecular sieveFiltration
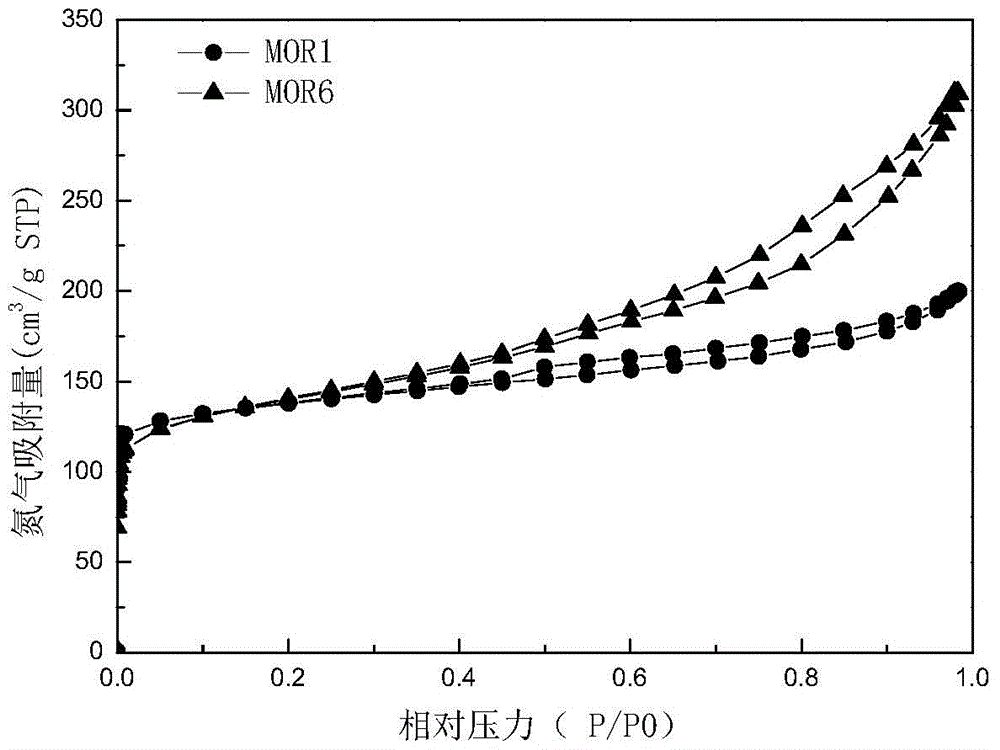
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nanometer stepped hole mordenite molecular sieve. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving sodium hydroxide in water and then adding a silicon source at room temperature to stir for 0.5-1.5 h to obtain alkaline silicon source solution; adding an aluminum source dissolved by using the water into the alkaline silicon source solution, stirring for 1 h at the room temperature to form uniform silicon and aluminum mixed solution, adding a mesoporous soft template (R) for 1 h, then adding a seed crystal (M) and stirring for 1 h to form a gel mixture, and then dynamically crystallizing at 100-180 DEG C for 12-96 h; cooling, performing extraction filtration and washing the product after crystallization until pH is about 7, drying at 100 DEG C for 12 h, roasting at the constant temperature of 110 DEG C for 3 h and then rising temperature to 500 DEG C to roast for 3 h to obtain a nanometer stepped hole mordenite product. The mordenite molecular sieve prepared by the invention has the typical nanometer stepped hole characteristic, and the hydrodealkylation performance of the Pt / MOR catalyst loaded with the sieve as a carrier is obviously improved.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
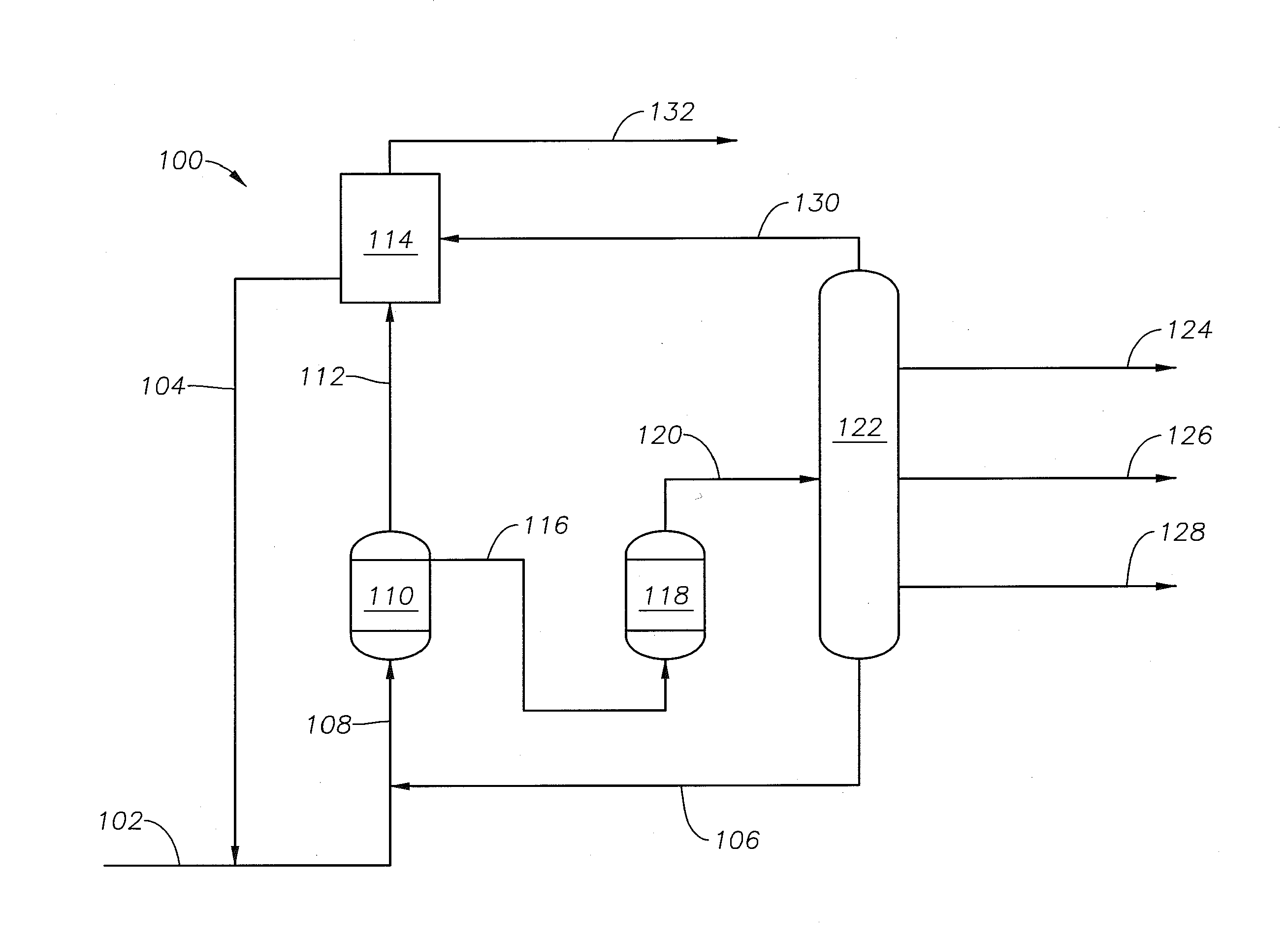
Process for producing benzene from a c5-c12 hydrocarbon mixture
InactiveCN106660900ARefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbon mixturesHydrodealkylation
The present invention relates to a process for producing benzene comprising the steps of: a) separating a source feedstream comprising C5-C12 hydrocarbons including benzene and alkylbenzenes into a first feedstream comprising a higher proportion of benzene than the source feedstream and a second feedstream comprising a lower proportion of benzene than the source feedstream and subsequently, b) contacting the first feedstream in the presence of hydrogen with a first hydrocracking catalyst comprising 0.01-1 wt-% hydrogenation metal in relation to the total catalyst weight and a zeolite having a pore size (as shown in the description) and a silica (SiO2) to alumina (Al2O3) molar ratio of 5-200 under first process conditions to produce a first product stream comprising benzene, wherein the first process conditions include a temperature of 425-580 DEG C, a pressure of 300-5000 kPa gauge and a Weight Hourly Space Velocity of 0.1-15 h-1, and c) contacting the second feedstream with hydrogen under second process conditions to produce a second product stream comprising benzene, wherein i) the second process conditions are suitable for hydrocracking and step (c) involves contacting the second feedstream in the presence of hydrogen with a second hydrocracking catalyst comprising 0.01-1 wt-% hydrogenation metal in relation to the total catalyst weight and a zeolite having a pore size of 5-8 and a silica (SiO2) to alumina (Al2O3) molar ratio of 5-200 under the second process conditions which include a temperature of 300-600 DEG C, a pressure of 300-5000 kPa gauge and a Weight Hourly Space Velocity of 0.1-15 h-1, ii) the second process conditions are suitable for toluene disproportionation and involve contacting the second feedstream with a toluene disproportionation catalyst, or iii) the second process conditions are suitable for hydrodealkylation.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
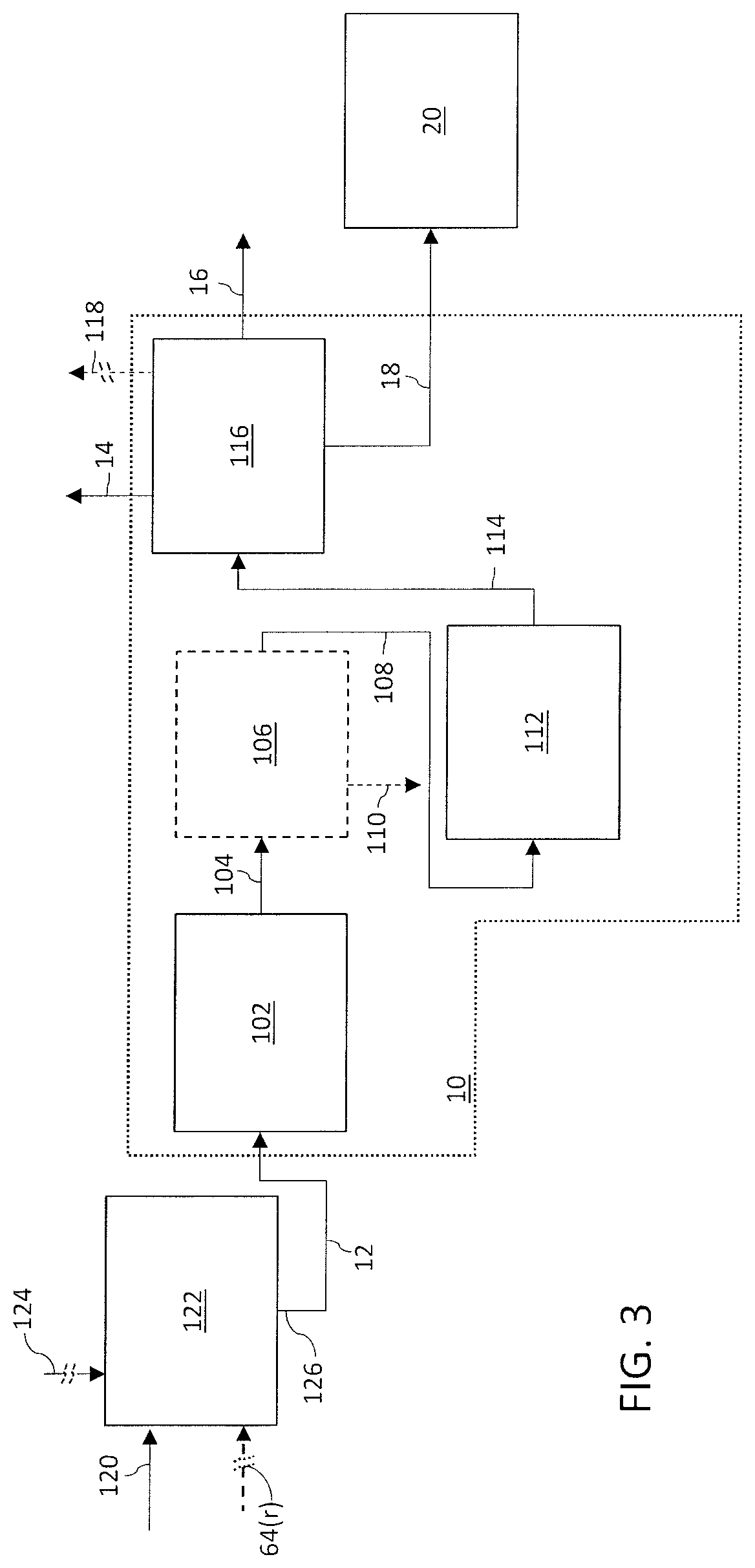
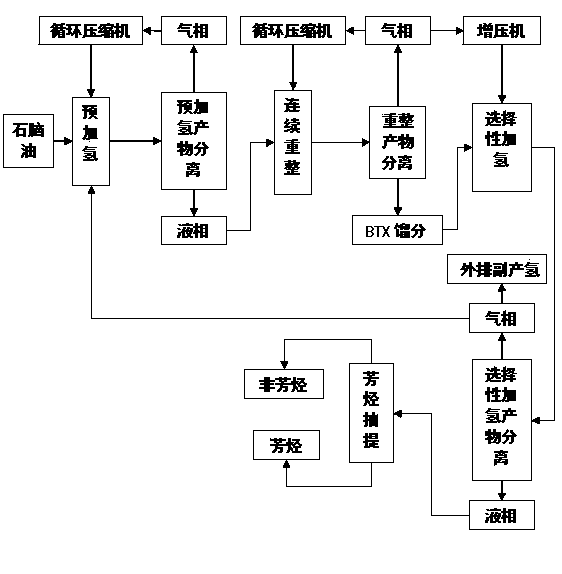
Process for producing arene through continuous reforming
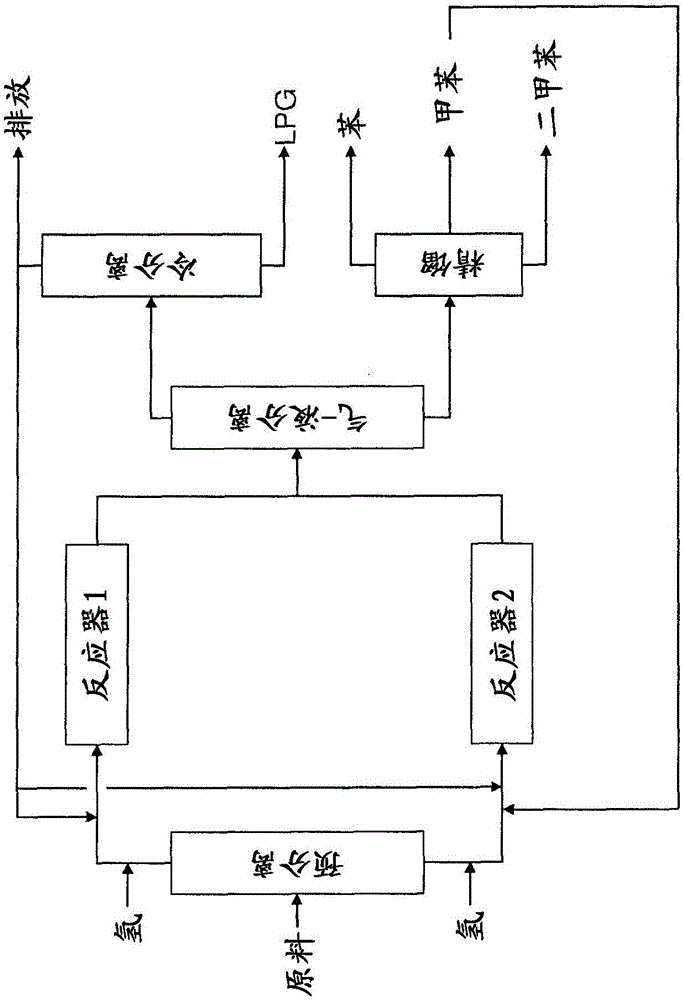
InactiveCN102051231BExtensive sources of raw materialsWide variety of sourcesTreatment with hydrotreatment processesCatalytic reformingHydrogen purity
The invention discloses a process for producing arene through continuous reforming. The process comprises the following steps: pre-hydrogenation treatment is performed on a naphtha raw material, catalytic reforming is performed on the oil generated through pre-hydrogenation treatment so that at least a part of paraffin and a part of cycloparaffin are converted to arene, selective hydrodealkylation is performed on the oil generated through catalytic reforming, the oil generated through selective hydrogenation is separated to obtain arene; a part of the gas with rich hydrogen, generated by catalytic reforming device is circulated to the catalytic reforming device and the residual gas is pressurized to perform selective hydrogenation reaction with the oil generated through catalytic reforming to remove the olefin in the oil, wherein the selective hydrogenation of the oil generated through catalytic reforming adopts hydrogen single-pass flow, the effluent of the selective hydrogenation reaction is separated to gaseous phase and liquid phase; a part of gaseous phase is used as the hydrogen make-up of the naphtha raw material pre-hydrogenation device, the rest part is discharged out of the device; and the liquid phase is used for the separation of the arene product. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the raw material adaptability is high, the byproduct discharged to the outside has high hydrogen content and the economy of the catalytic reforming device is high and the like.
Owner:赵丽
System and process for steam cracking and pfo treatment integrating hydrodealkylation
ActiveUS20210130714A1Refining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonGaseous fuelsProcess engineeringHydrodealkylation
A process for treatment of PFO from a steam cracking zone includes hydrodealkylating PFO or a portion thereof for conversion of polyaromatics compounds contained in the PFO into hydrodealkylated aromatic compounds with one benzene ring, a hydrodealkylated BTX+ stream. The hydrodealkylated BTX+ stream is separated into BTX compounds.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Process for improving cetane number of diesel oil and reducing aromatic hydrocarbon of diesel oil simultaneously
InactiveCN1261543CHigh quality low sulfurIncrease cetane numberTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHydrodealkylationAromatic hydrocarbon
The invention provides a process for improving cetane number of diesel oil and reducing aromatic hydrocarbon of diesel oil simultaneously which comprises, charging the diesel raw material and hydrogen gas into a first reactor, contacting non-noble metal hydrogenation catalyst, charging the reaction effluent from the first reactor into a second reactor, contacting noble metal hydrodealkylation catalyst, isolating the reaction effluent from the second reactor to obtain the diesel product.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
an ethylene cracker c 9 Process for preparing benzene, toluene, xylene
ActiveCN104211557BTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon crackingTetraglycolDistillation
The invention relates to a method for preparation of benzene, toluene and xylene from ethene cracking C9; an ethene cracking C9 raw material is extracted for separation of aromatic fractions and other non aromatic components, separation of aromatics can be performed in an extraction column, the separation temperature is 50 to 70 DEG C, the feeding weight ratio of an extracting agent to the ethene cracking C9 raw material is 4-10:1, the extracting agent is tetraglycol; the distillation range of aromatics extraction is controlled in the range of 135 to 220 DEG C; unsaturated aromatics are pre hydrogenated for hydrogenation saturation, pre hydrogenated C9 + aromatics is processed for lightening of heavyweight aromatics by catalytic hydrodealkylation method for preparation of the benzene, the toluene and the xylene; according to the method, the conversion rate of X (C9+) aromatics is 61.6 to 62.2; Y (BTX) (benzene, toluene and xylene) yield is 40.8-42.8; and S (BTX) selectivity is 67.96-8.8.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Modified ultra-stable Y (USY) zeolite catalyst for dealkylation of aromatics
ActiveUS11484869B2Reduce formationRaise the ratioMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
Owner:JGC CATALYSTS & CHEM LTD +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com