Process and device in connection with the production of oxygen or oxygen enriched air
a technology of oxygen or oxygen enriched air and process, which is applied in the direction of inorganic chemistry, isotope separation, fuel cells, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the rate of adsorption reaction, affecting the efficiency of zeolite structures used today, and normal nitrogen desorption, etc., to achieve reduced adsorption time, and reduce the time for adsorption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
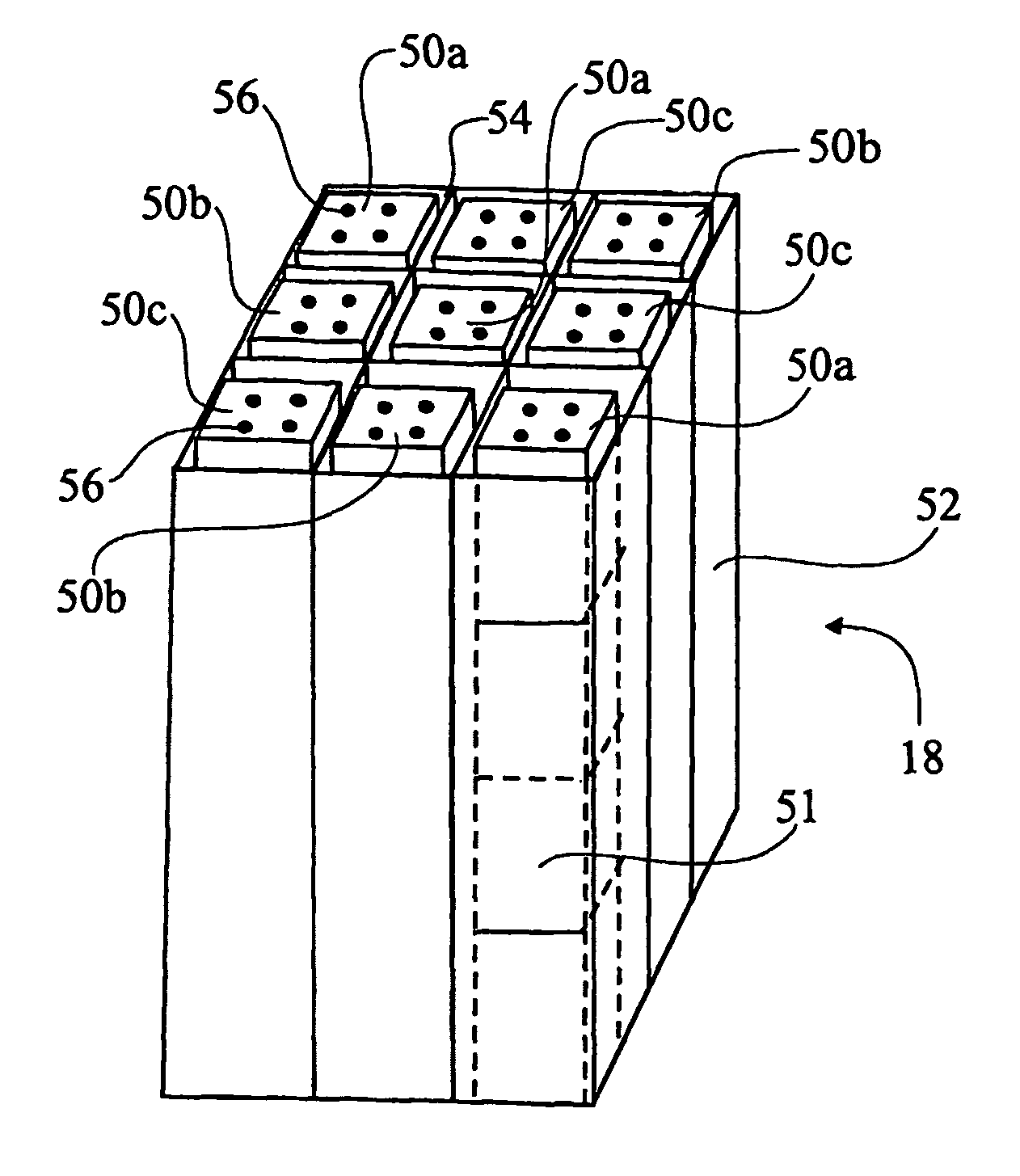
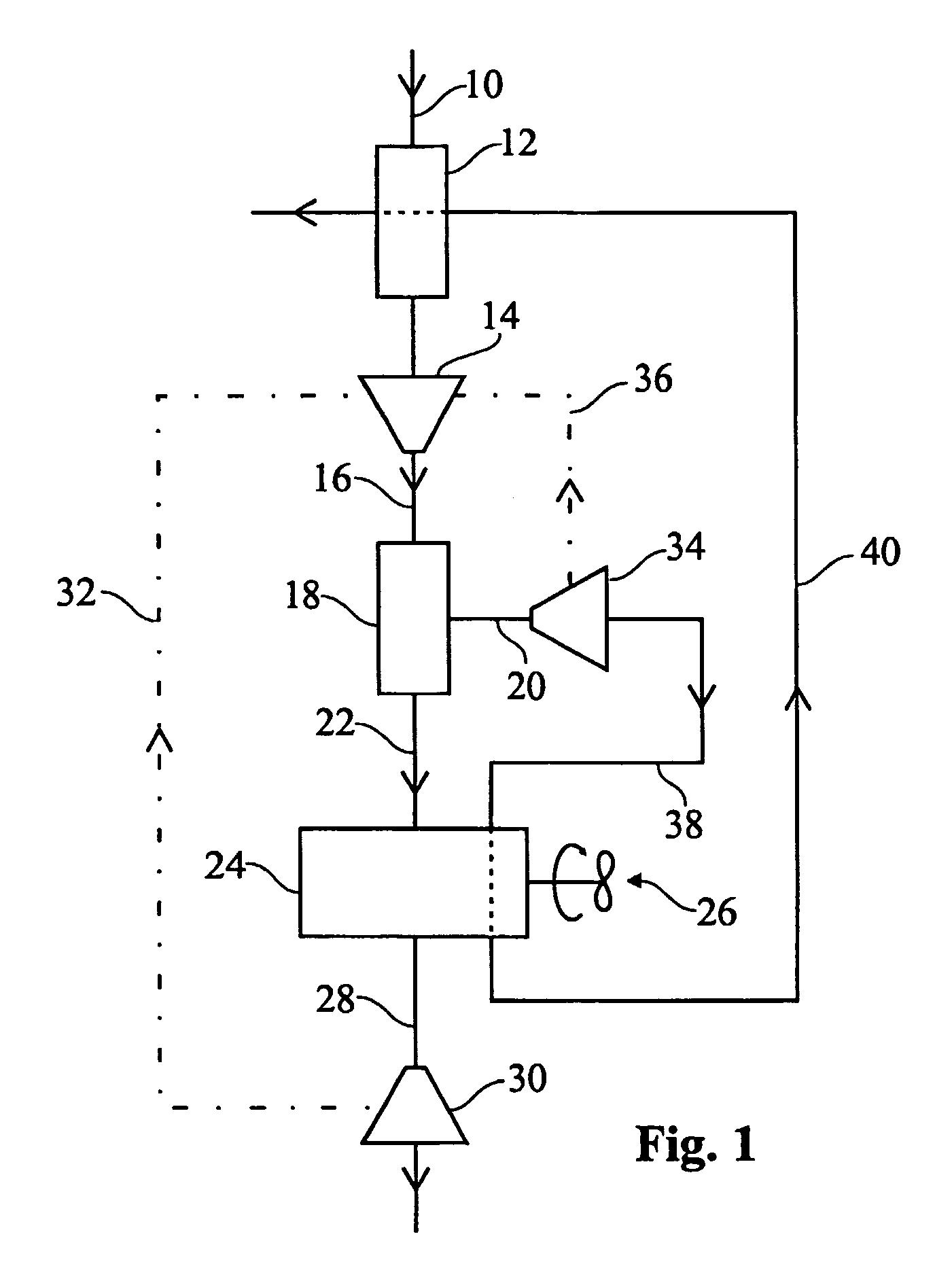
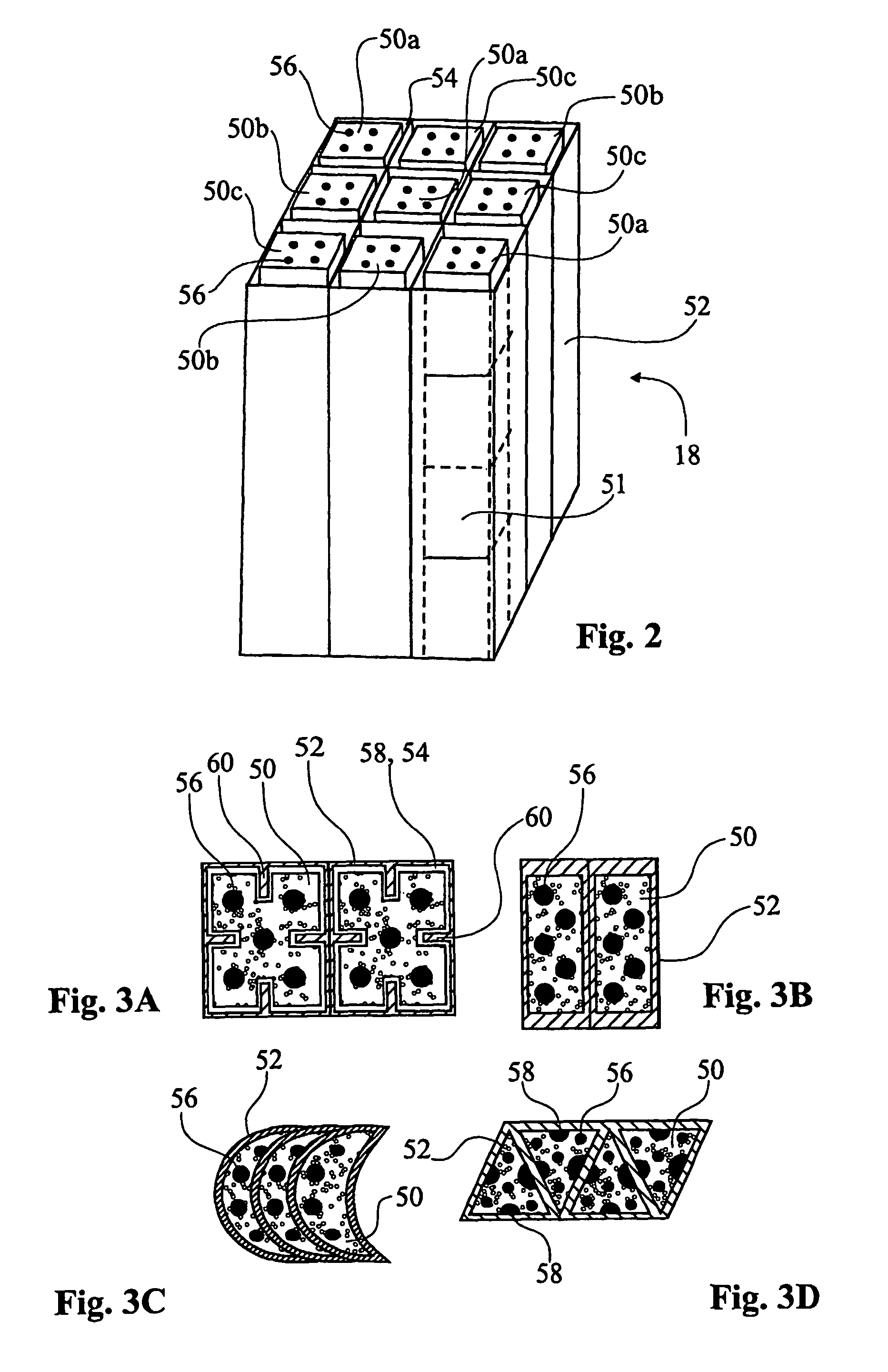
[0006]The present invention aims at addressing the above problems and thus to offer new design and technique for nitrogen adsorbing zeolites or other materials (sorbent materials) with similar nitrogen and oxygen adsorbing properties as the zeolites used today for production of oxygen or oxygen enriched air. In the following text this group of materials will only be referred to as “zeolite” or “zeolites”. Thus, by introduction of serially (consecutively) interlinked zeolite units operating in a certain sequence, the present invention aims at offering a new and highly efficient process and device in connection with the production of oxygen or oxygen enriched air by aid of nitrogen adsorbing zeolites. Moreover, the present invention aims at offering a device which is at least as efficient as known devices but which is smaller in size. By new design and technique the problems related to diminished reaction rates due to excessive production or consumption of heat are solved too. Moreove...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com