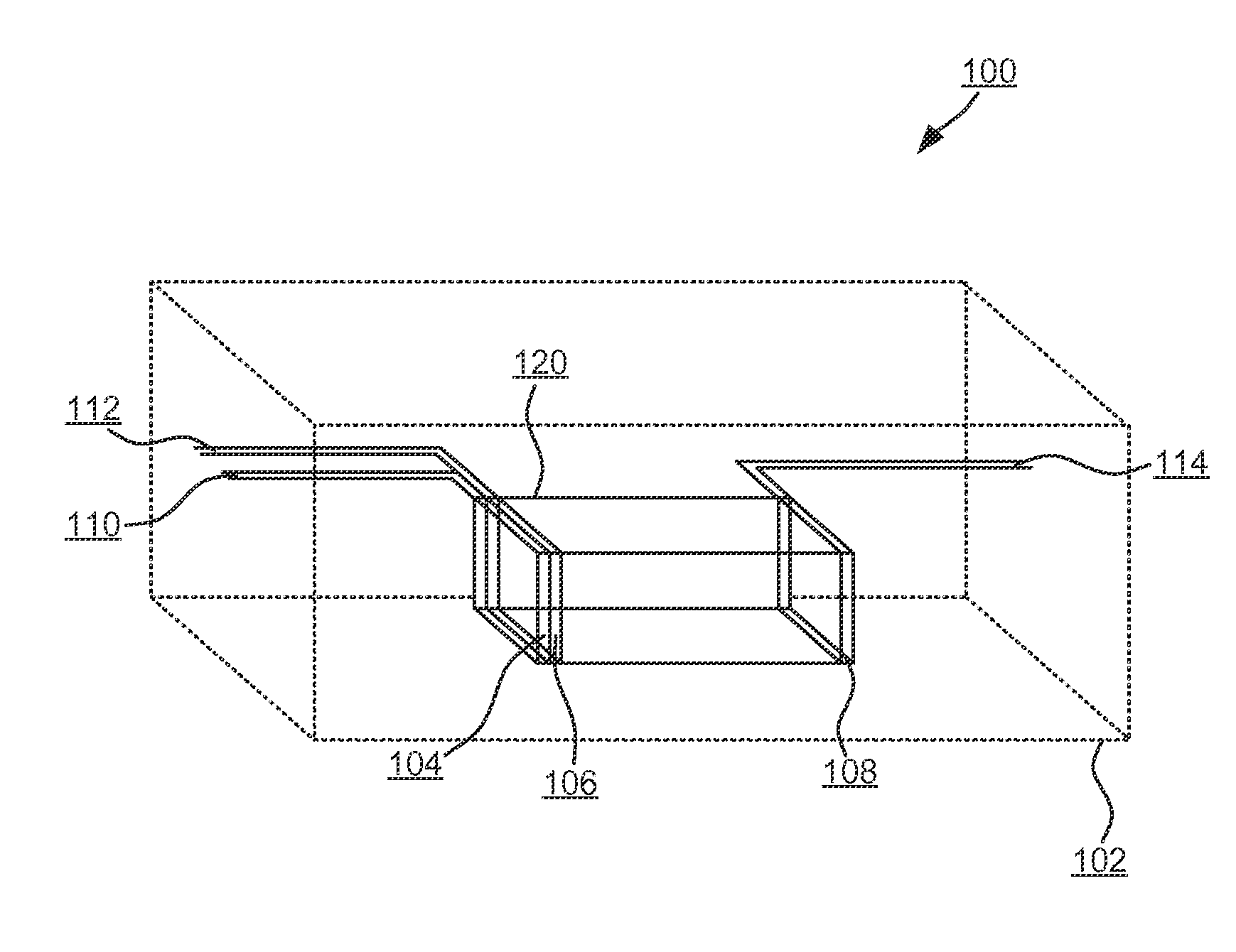
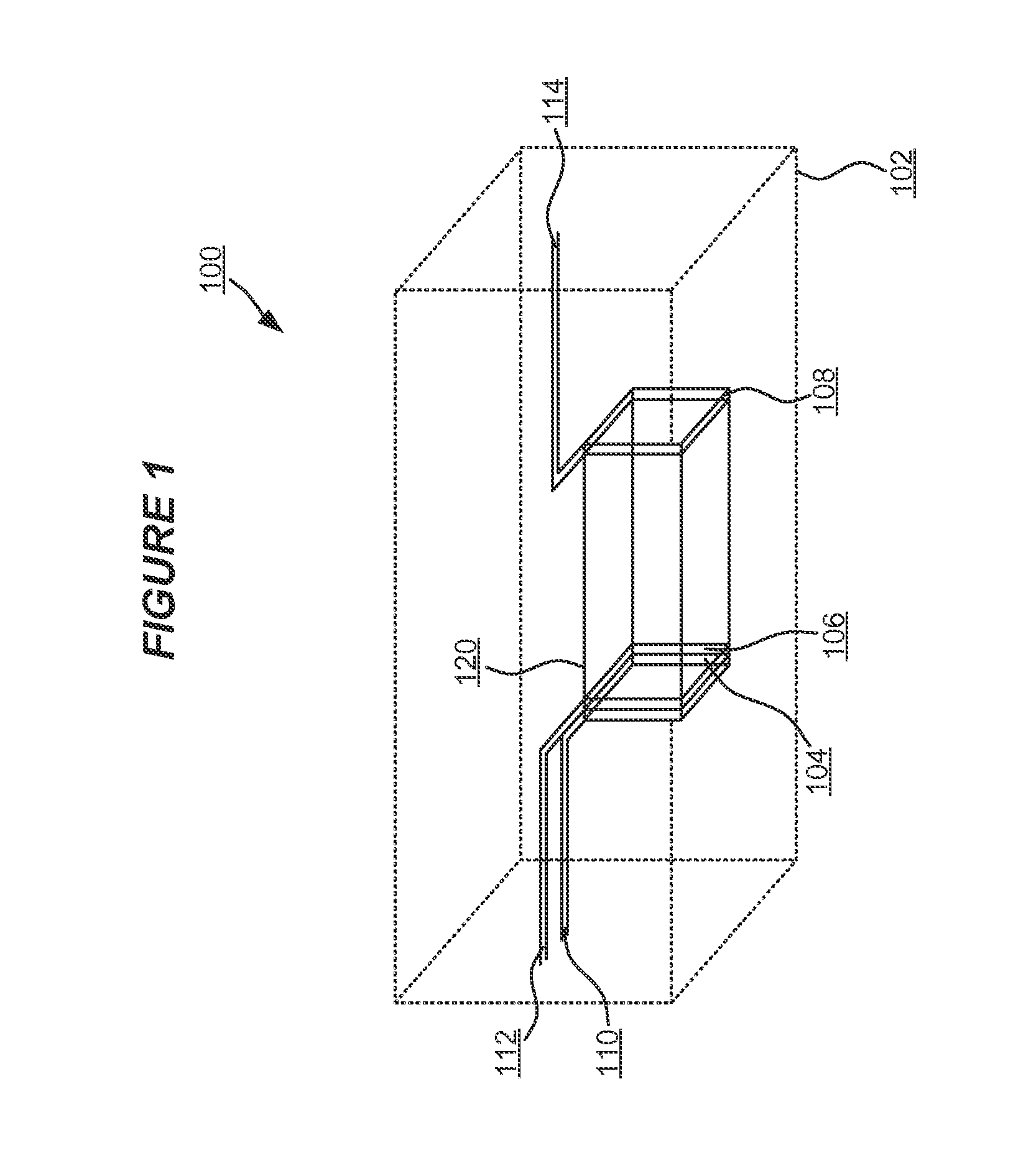
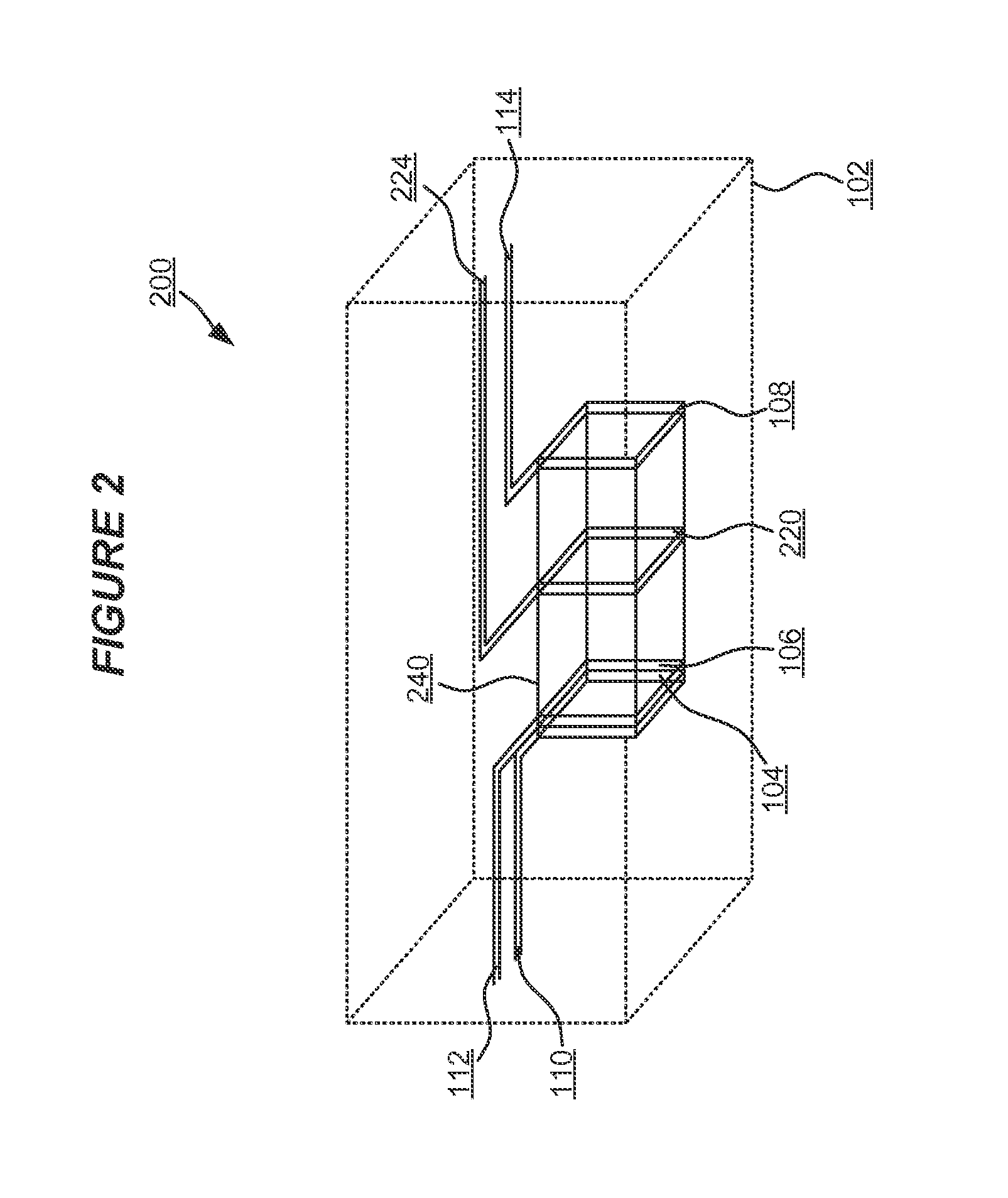
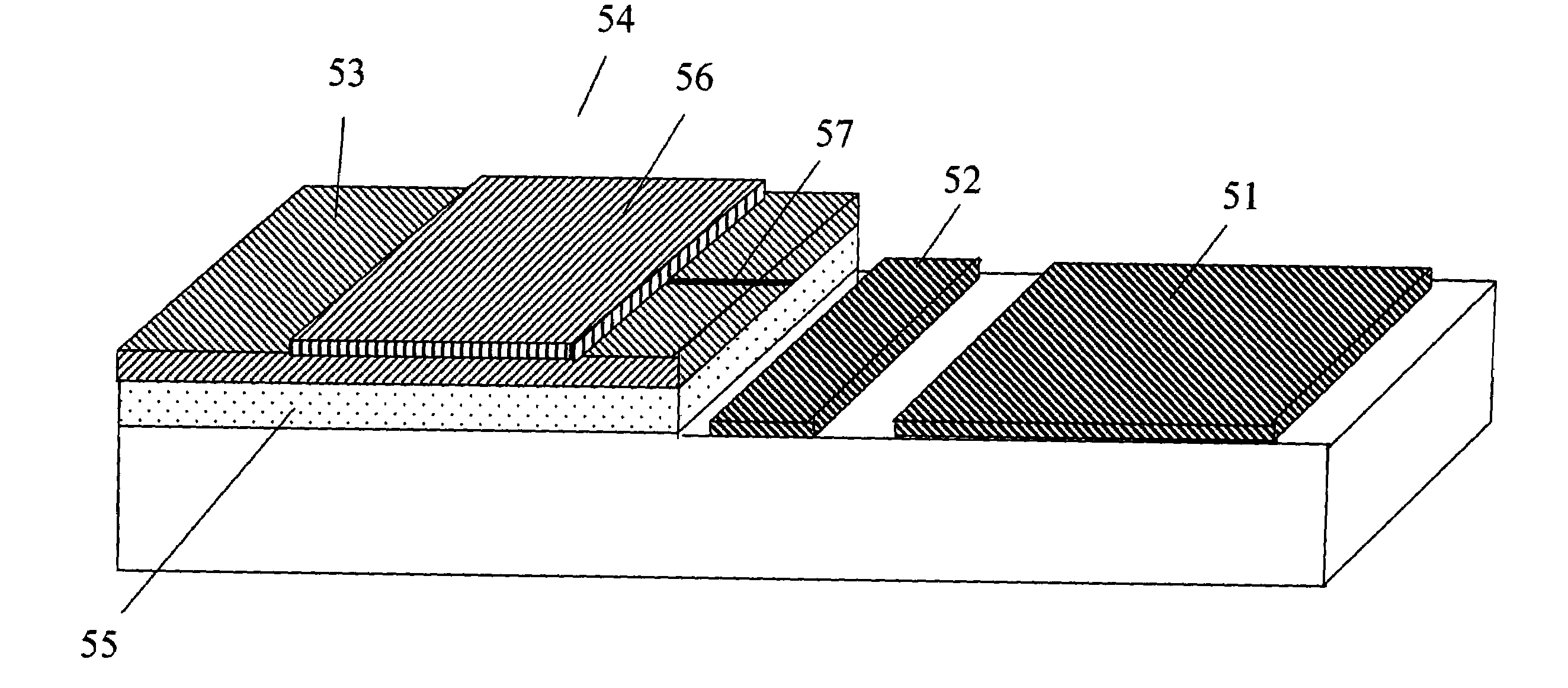
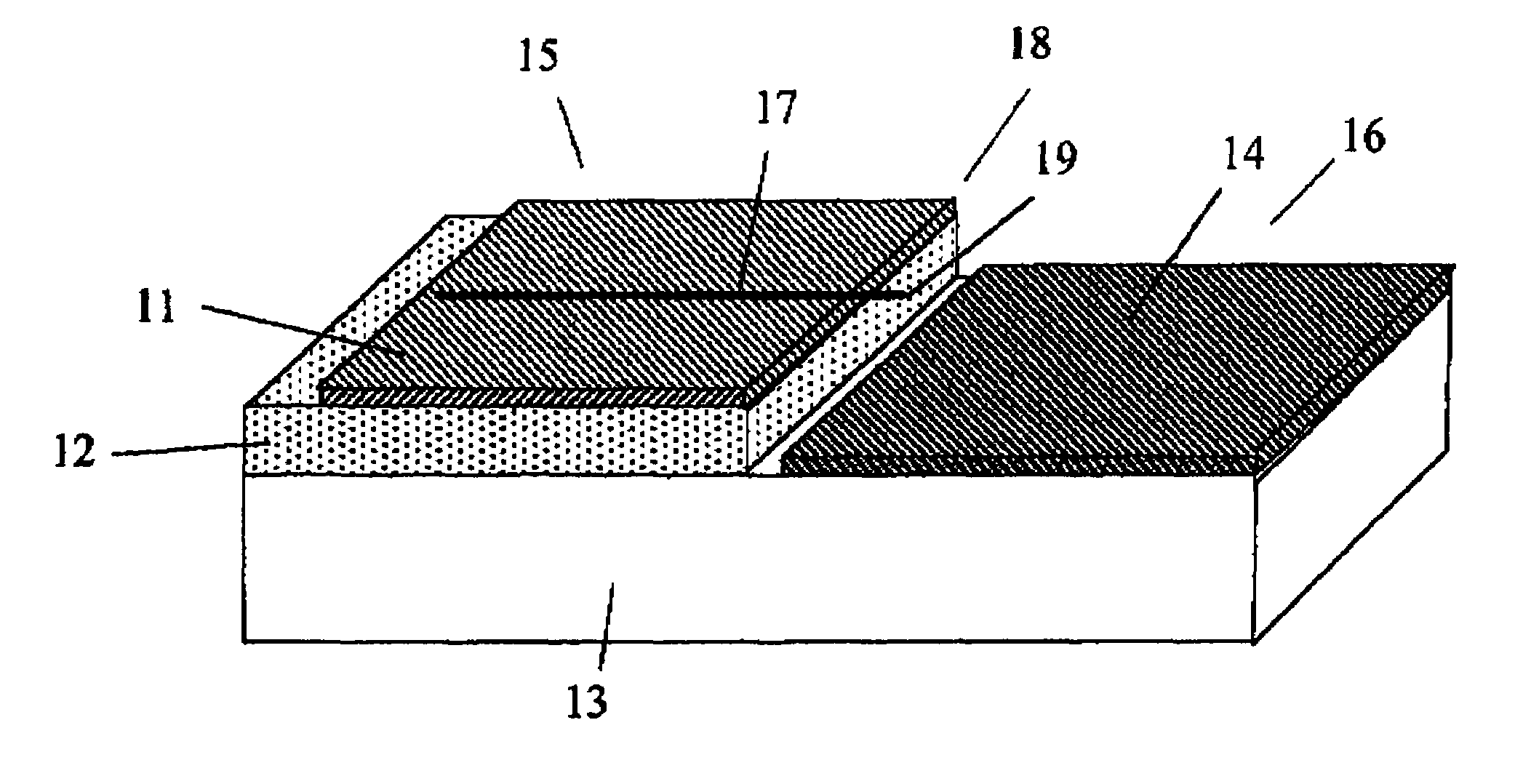
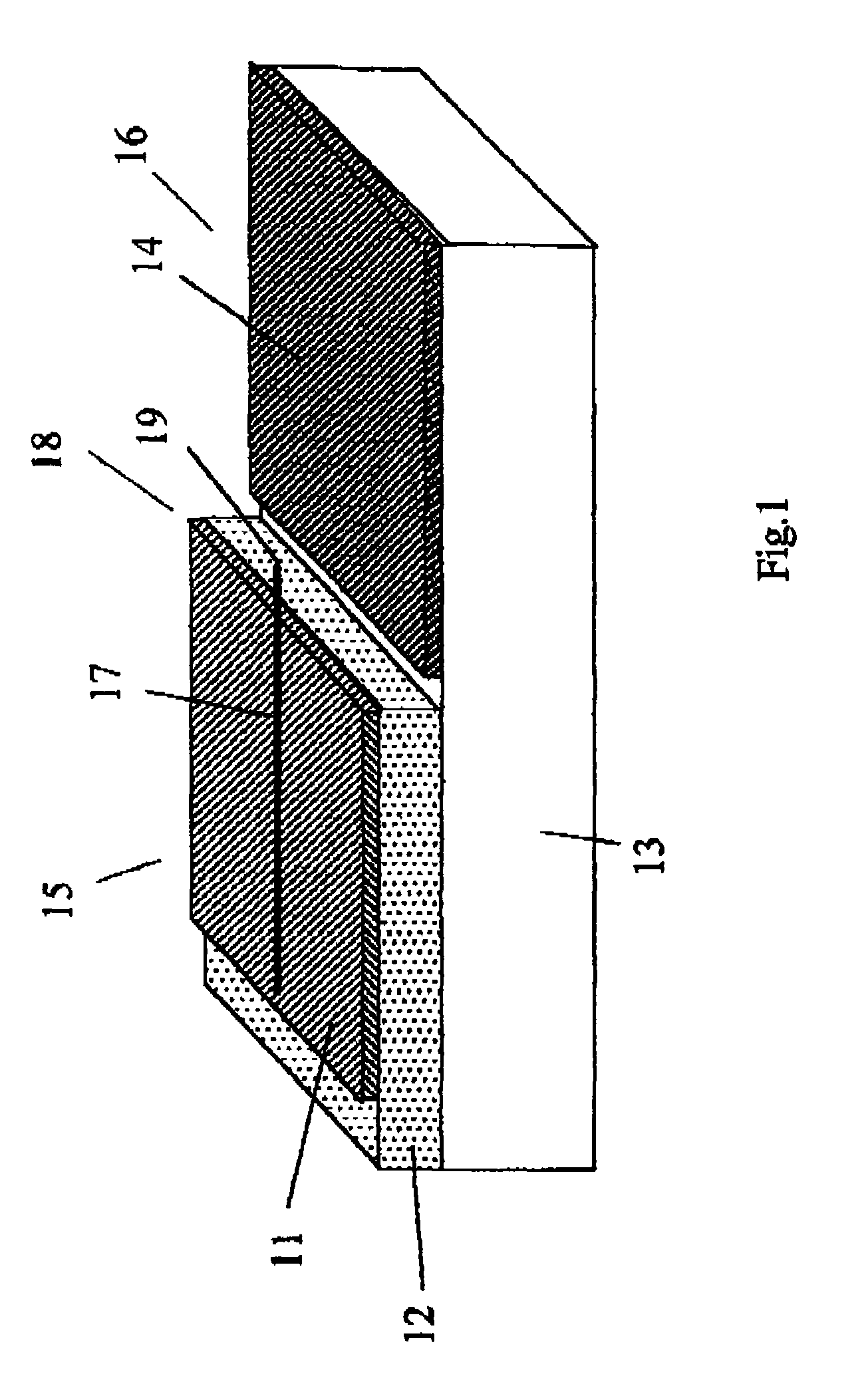
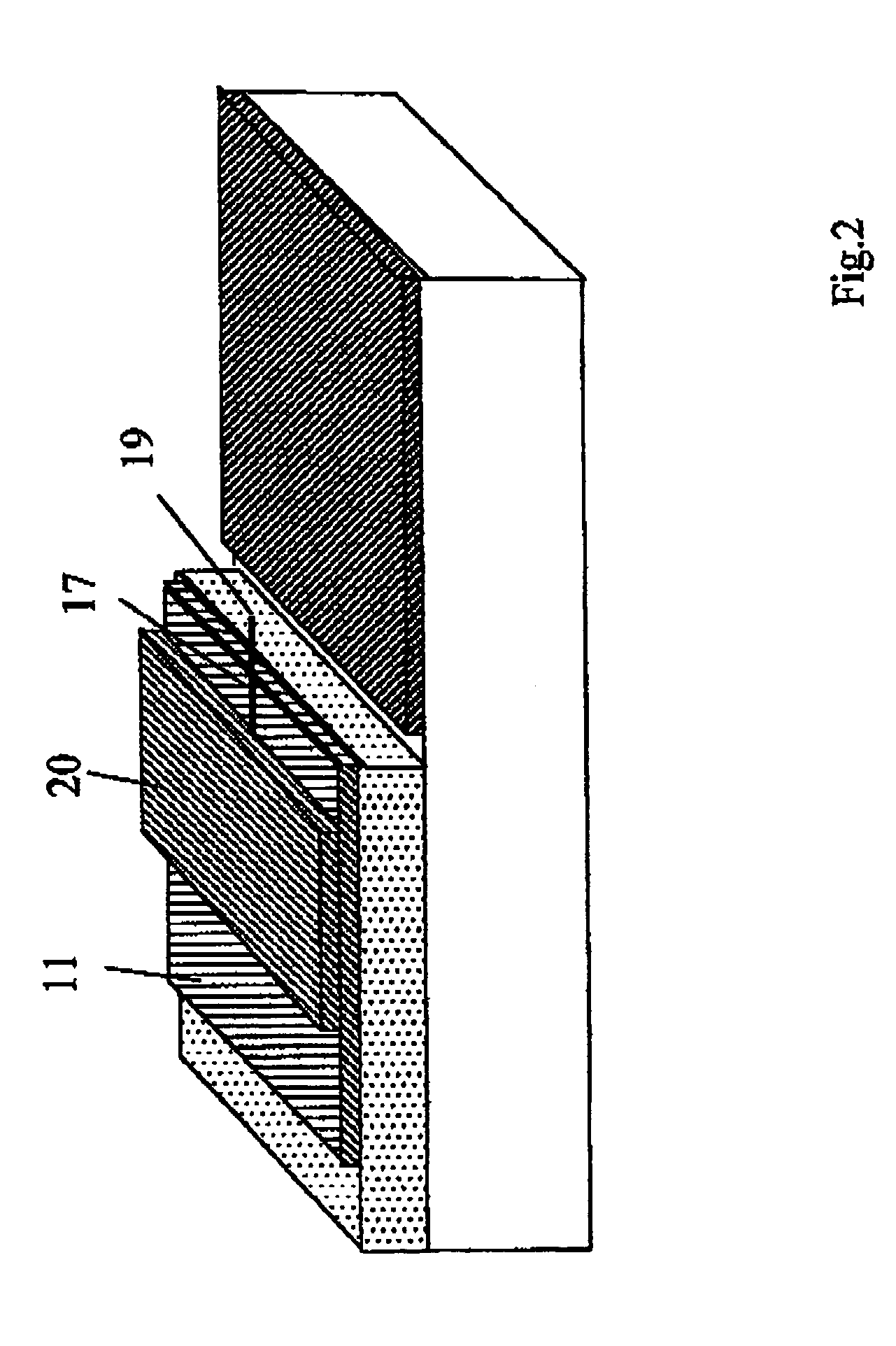
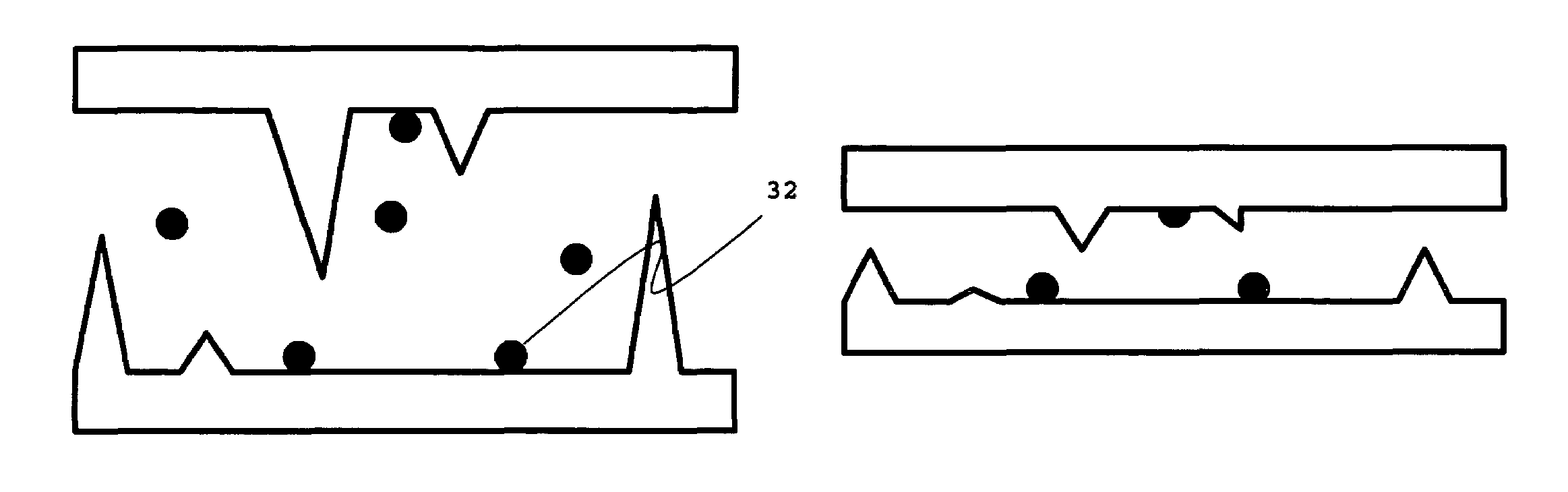
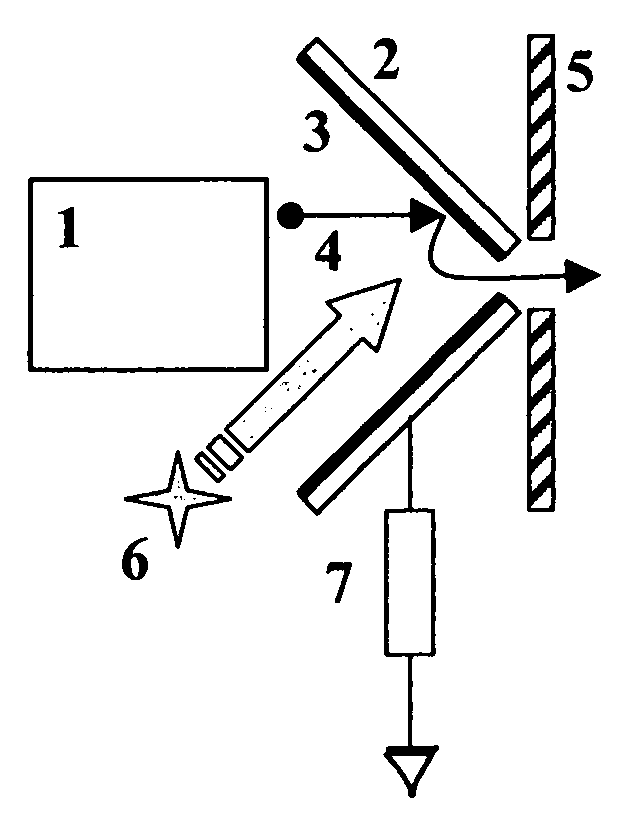
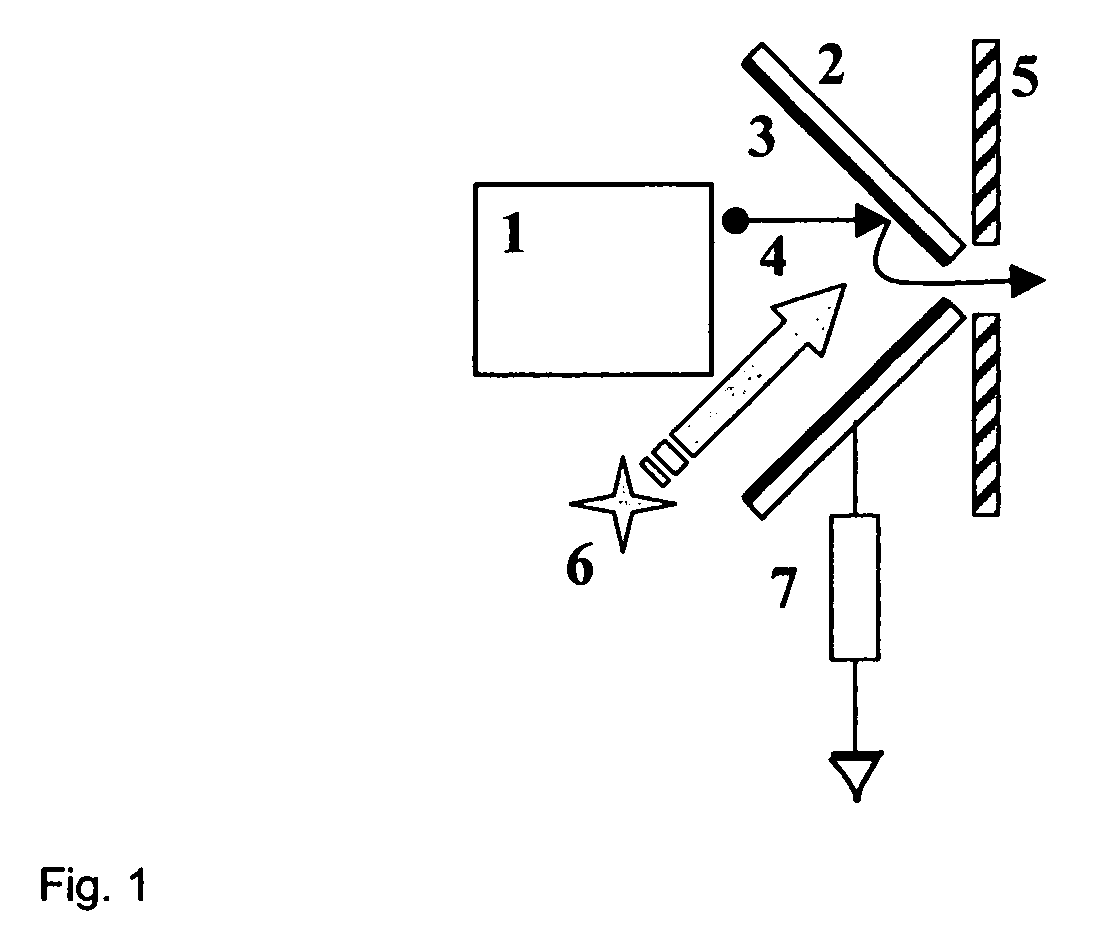
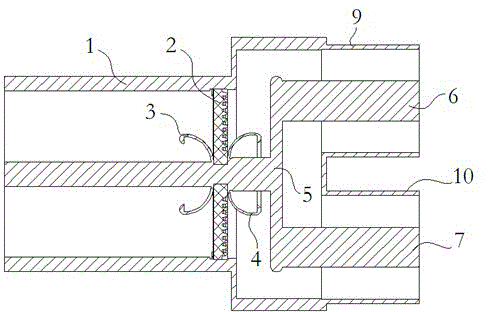
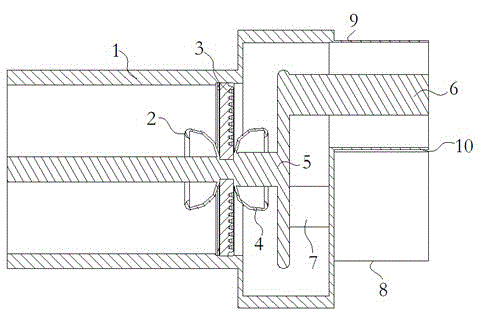
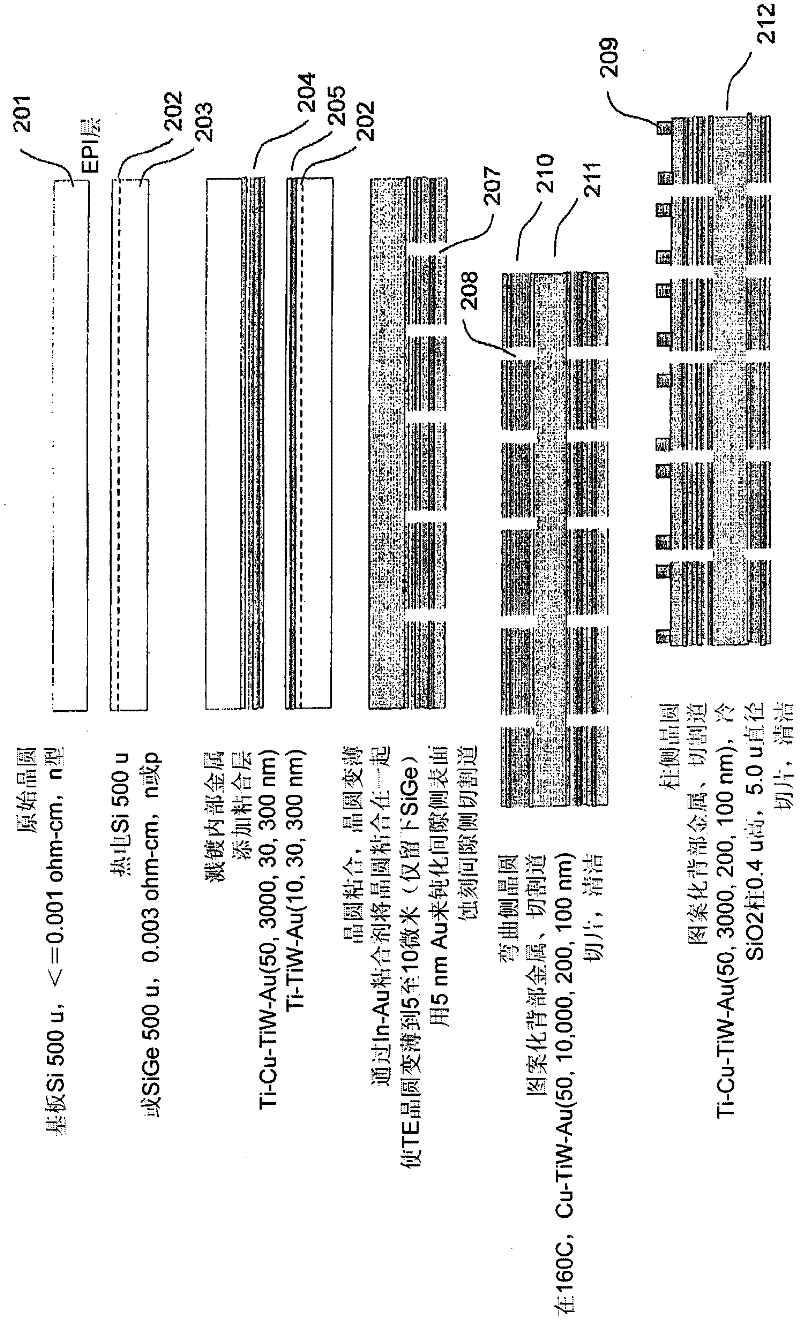
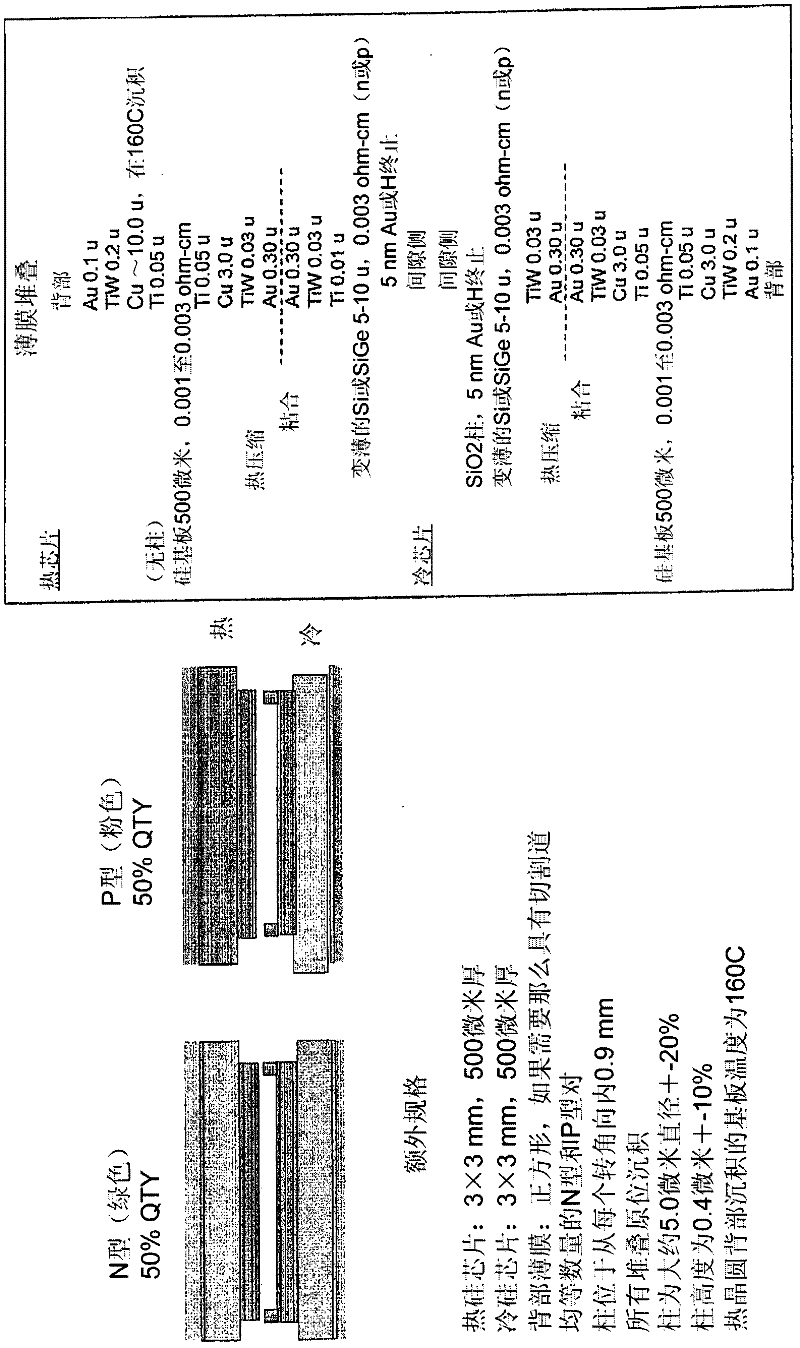
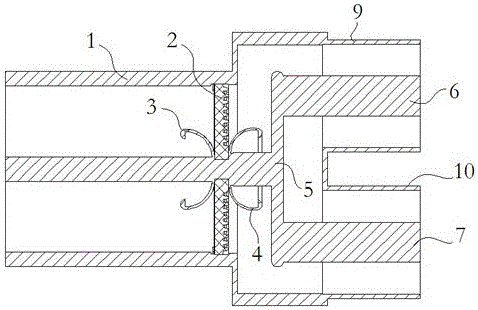
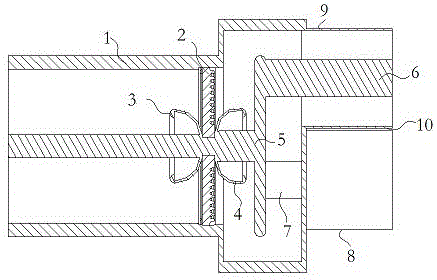
Patents
Literature
38results about "Tubes without control means" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
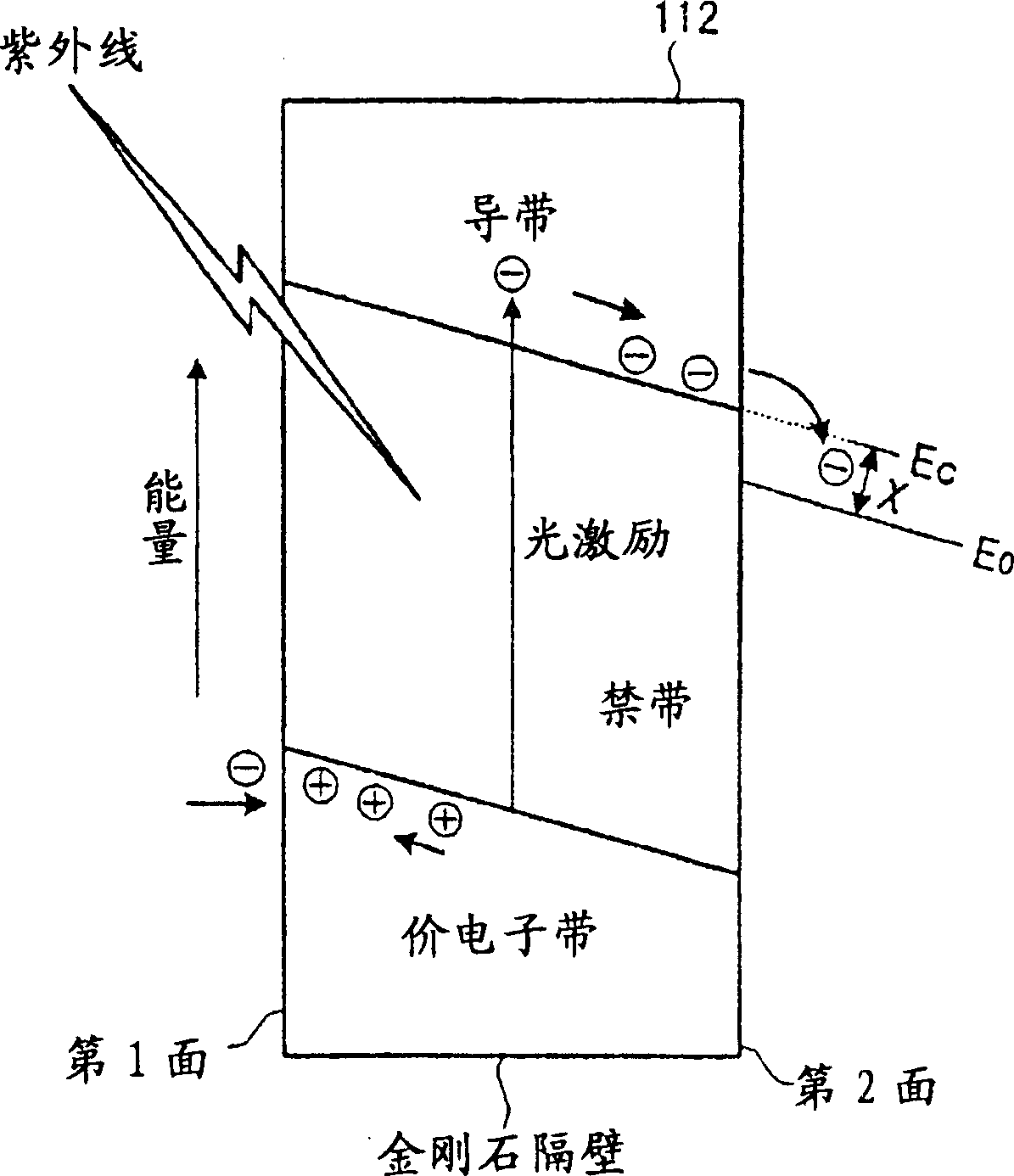
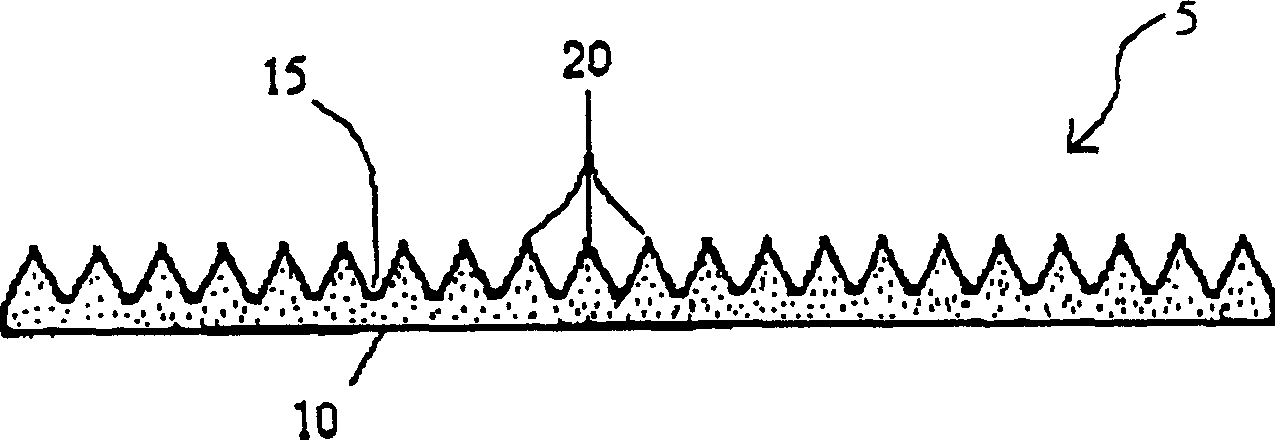
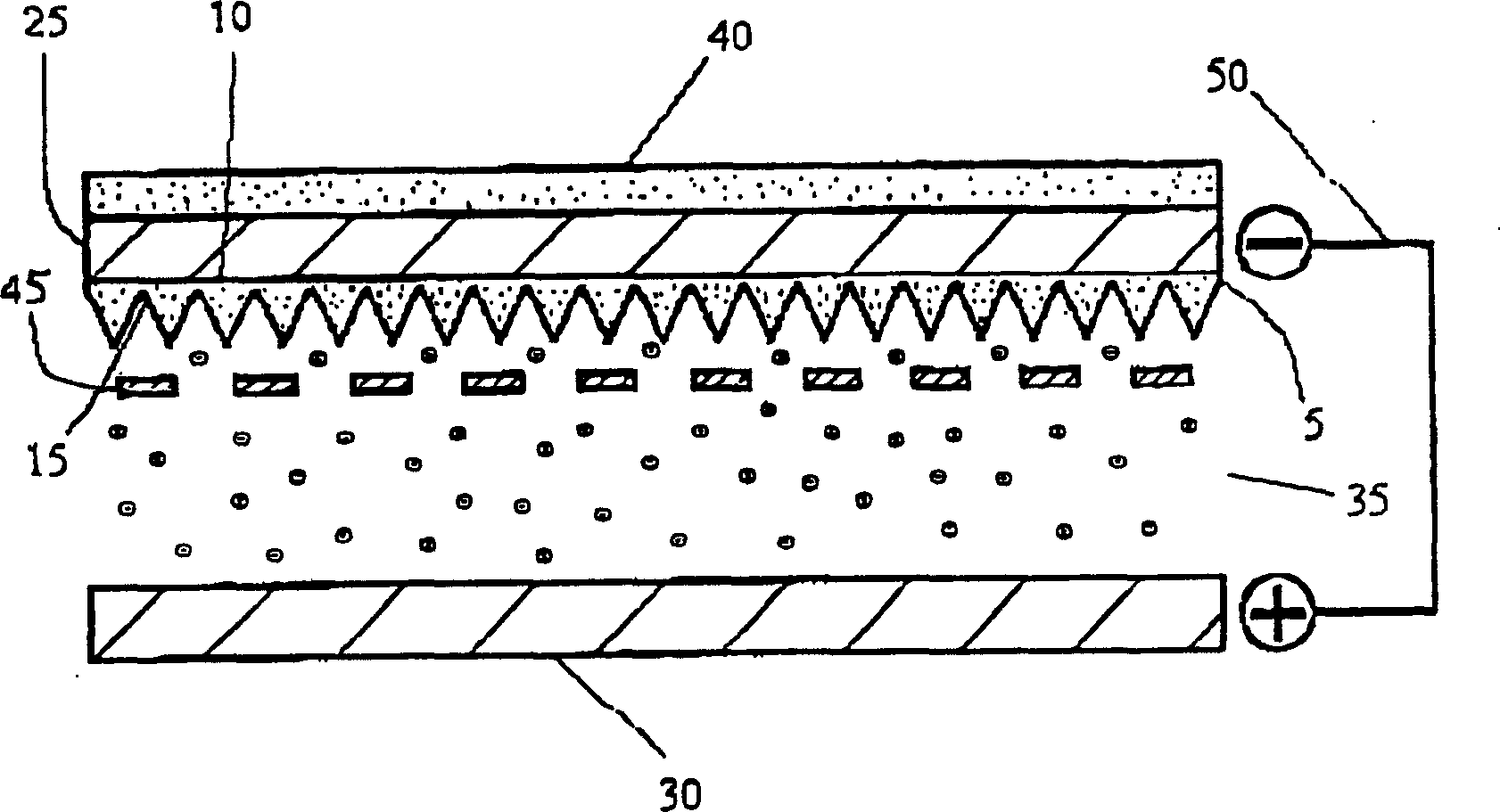
Doped diamond for vacuum diode heat pumps and vacuum diode thermionic generators
InactiveUS6214651B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCold cathodesNitrogen dopedElectron
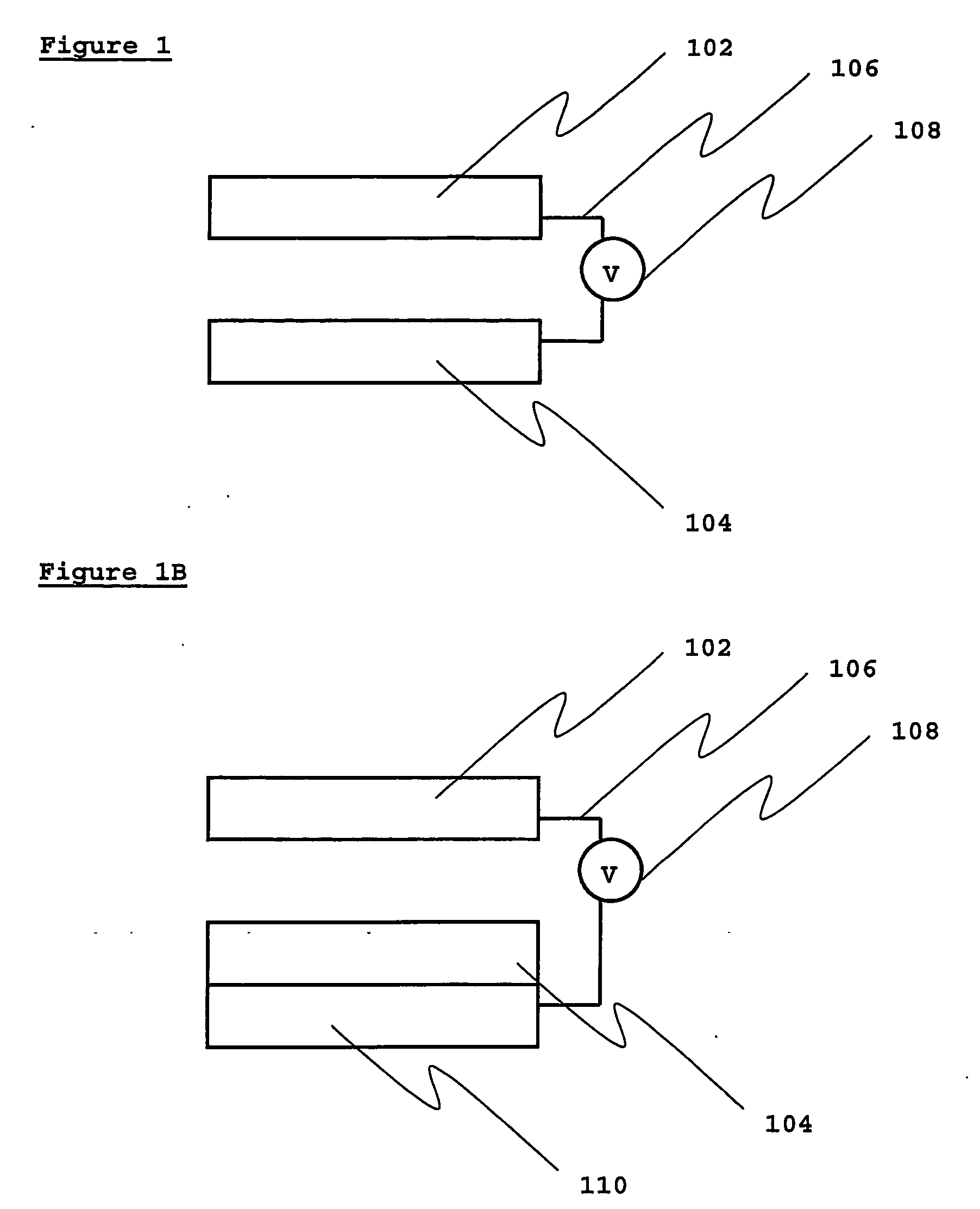
A novel use of doped carbonaceous material is disclosed, integral to the operation of Vacuum Diode Heat Pumps and Vacuum Diode Thermionic Generators. In the preferred embodiment, the use of nitrogen-doped diamond enhances the operation of Vacuum Diode Heat Pumps and Vacuum Diode Thermionic Generators.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Printed active device
ActiveUS20150270089A1Reduce manufacturing costLow costAdditive manufacturing apparatusControl electrodesElement spaceElectrical connection
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Nanotube-based vacuum devices
InactiveUS7102157B2Minimize threshold voltageLow inputNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceTerminal equipment
New, hybrid vacuum electronic devices are proposed, in which the electrons are extracted from the nanotube into vacuum. Each nanotube is either placed on the cathode electrode individually or grown normally to the cathode plane. Arrays of the nanotubes are also considered to multiply the output current. Two- and three-terminal device configurations are discussed. In all the cases considered, the device designs are such that both input and output capacitances are extremely low, while the efficiency of the electron extraction into vacuum is very high, so that the estimated operational frequencies are expected to be in a tera-hertz range. New vacuum triode structure with ballistic electron propagation along the nanotube is also considered.
Owner:ITUS
Field emission microelectronic device
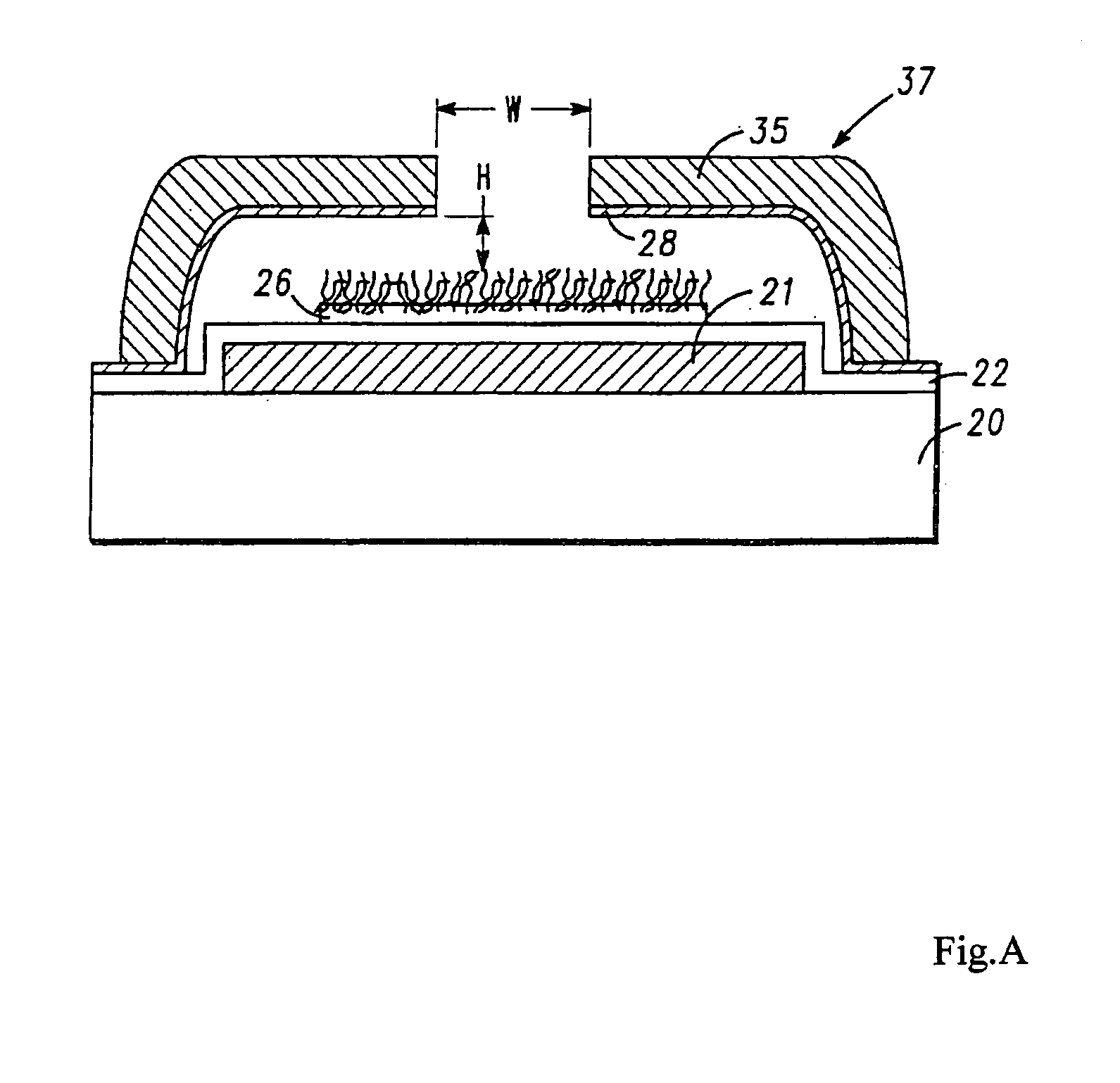
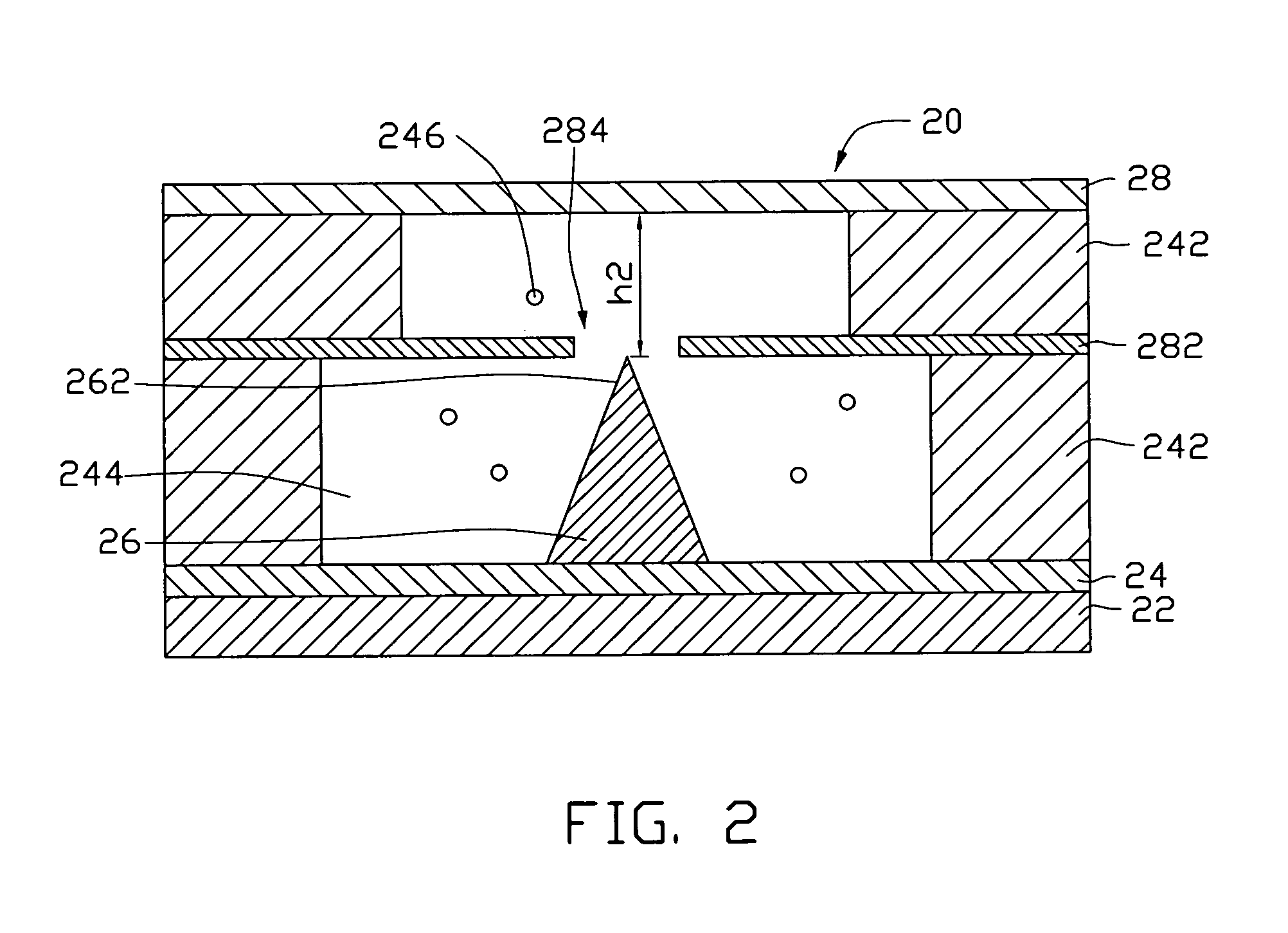
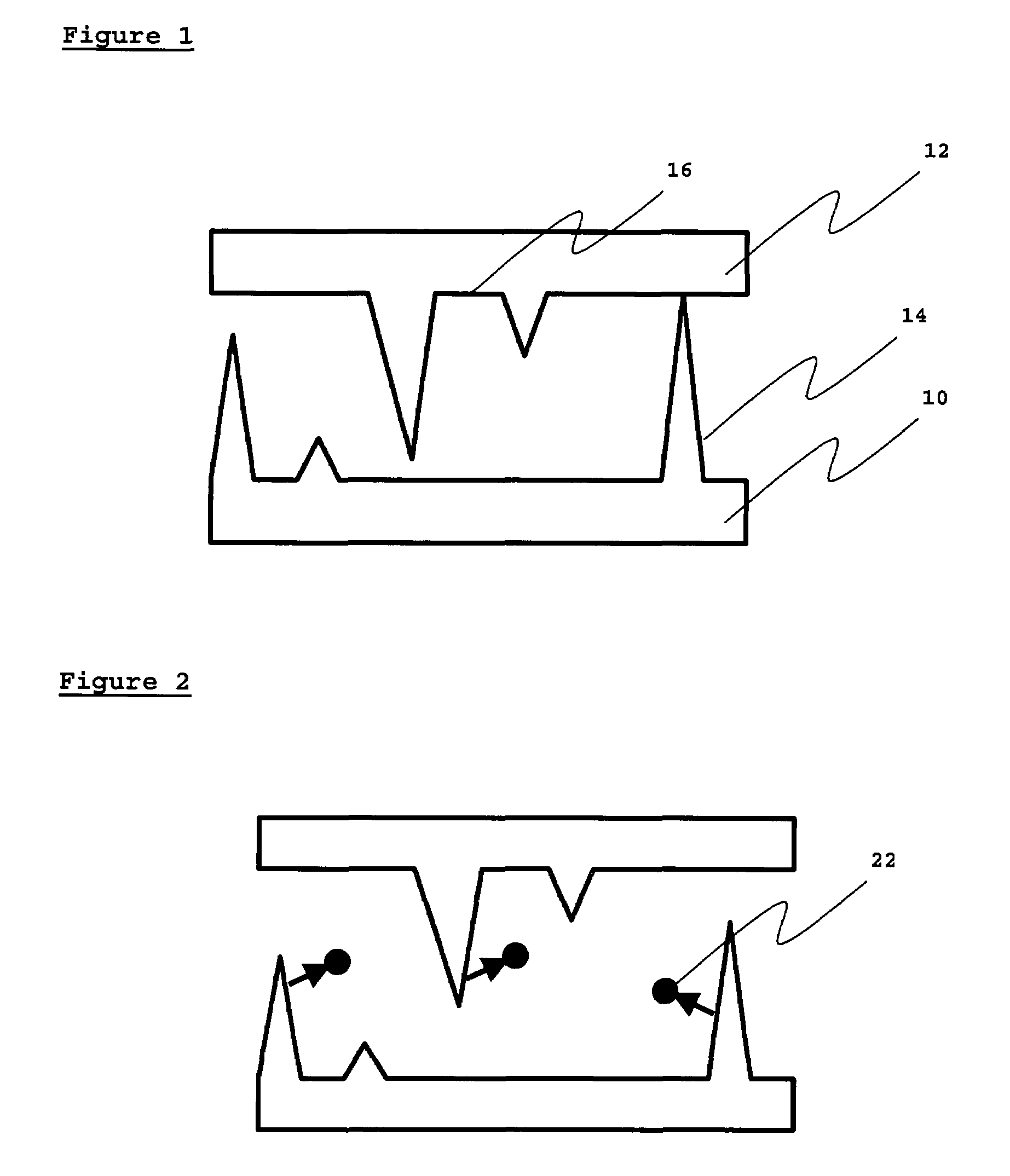
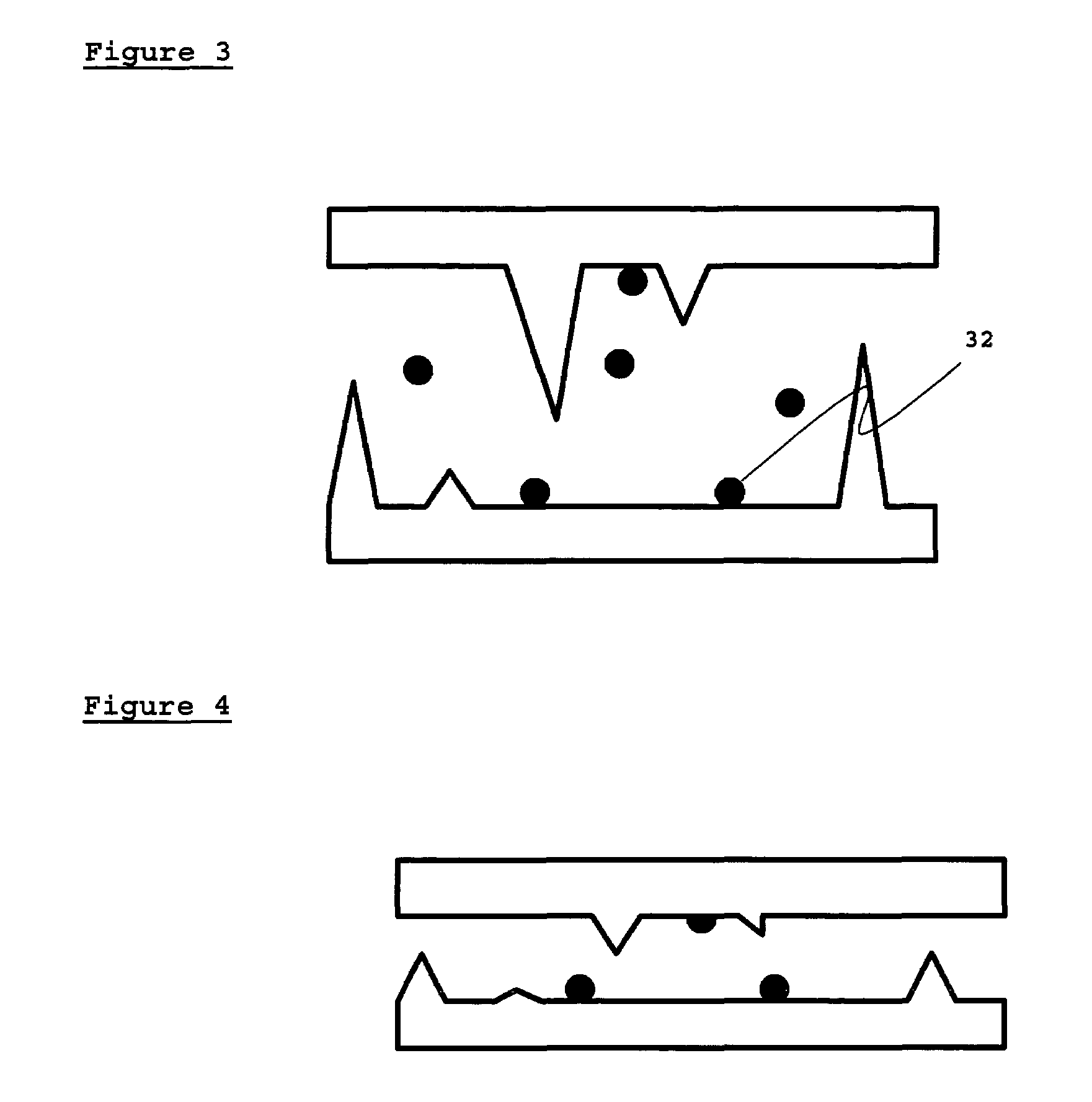
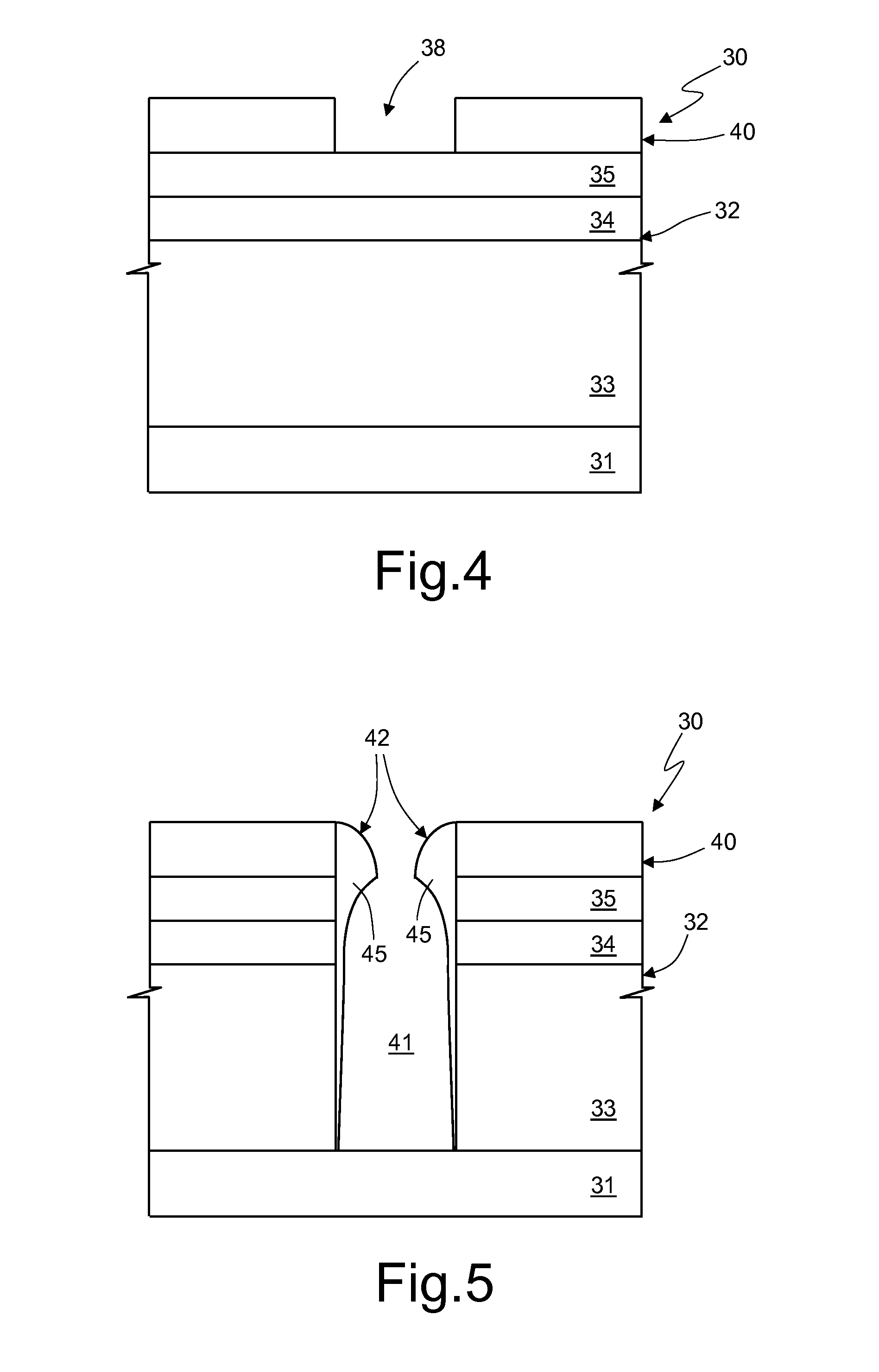
InactiveUS20080001513A1Discharge tube main electrodesTubes without control meansMean free pathField electron emission
A nano-scaled field emission electronic device includes a substrate, a cathode electrode, and an anode electrode. The cathode electrode is placed on the substrate and has an emitter. The anode electrode is positioned opposite to and spaced from the cathode electrode. The nano-scaled field emission electronic device further has at least one kind of inert gas filled therein. The following condition is satisfied: h<λe, wherein h indicates a distance between a tip of the emitter and the anode electrode, and λe indicates an average free path of an electron in the inert gases. More advantageously, the following condition is satisfied:h<λe_10.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Tunneling gap diodes
InactiveUS20060180829A1Good energyImprove power generation efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeTunnel diodeSemiconductor
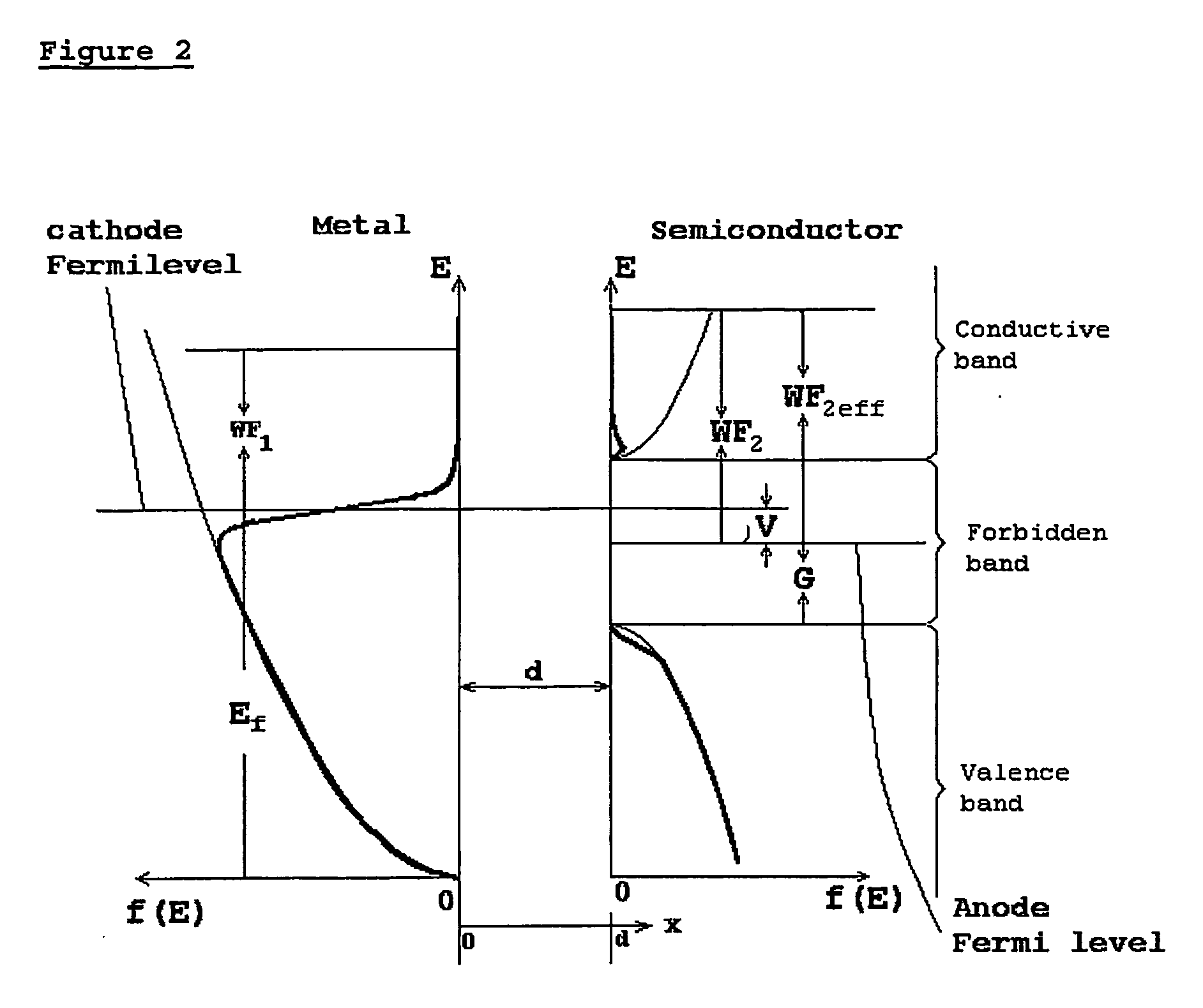
The present invention discloses a tunneling diode having a band gap material as the collector. This increases the tunneling of electrons having greater energy than the Fermi level from emitter to collector, leading to an increase in the efficiency of heat pumping or power generation by the diode. In a further embodiment the collector comprises a semiconductor on which a layer of band gap material is deposited. This approach also reduces back tunneling of electrons from collector to emitter.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Nanotube-based vacuum devices
InactiveUS7176478B2Improve transconductanceRaise the ratioNanoinformaticsCold cathodesCapacitanceTerminal equipment
New, hybrid vacuum electron devices are proposed, in which the electrons are extracted from the nanotube into vacuum. Each nanotube is either placed on the cathode electrode individually or grown normally to the cathode plane. Arrays of the nanotubes are also considered to multiply the output current. Two- and three-terminal device configurations are discussed. In all the cases considered, the device designs are such that both input and output capacitances are extremely low, while the efficiency of the electron extraction into vacuum is very high, so that the estimated operational frequencies are expected to be in a tera-hertz range. New vacuum triode structure with ballistic electron propagation along the nanotube is also considered.
Owner:ITUS
Method for flat electrodes
InactiveUS7005381B1Reduce roughnessPromotes preferential evaporationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTubes without control meansEvaporationSurface roughness
The present invention is a method for reducing nanoscale surface roughness. The method involves exposing the surface to an environment that preferentially promotes evaporation of material from the region of nanoscale roughness. The methods involve either heating the surface, or flushing an inert gas across the surface, or a combination of both.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Nanotube-based vacuum devices
InactiveUS20050161668A1Improve transconductanceRaise the ratioNanoinformaticsCold cathodesCapacitanceTerminal equipment
New, hybrid vacuum electron devices are proposed, in which the electrons are extracted from the nanotube into vacuum. Each nanotube is either placed on the cathode electrode individually or grown normally to the cathode plane. Arrays of the nanotubes are also considered to multiply the output current. Two- and three-terminal device configurations are discussed. In all the cases considered, the device designs are such that both input and output capacitances are extremely low, while the efficiency of the electron extraction into vacuum is very high, so that the estimated operational frequencies are expected to be in a tera-hertz range. New vacuum triode structure with ballistic electron propagation along the nanotube is also considered.
Owner:ITUS
Conical housing
InactiveUS20060006515A1Wide temperature rangeWide rangeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEnergy efficient heating/coolingHermetic sealEngineering
A conical diode device is disclosed, comprising a pair of electrodes and a conical housing. The conical housing ensures that the hermetic seal between the electrodes and the housing remains strong despite thermal imbalances between the two electrodes when the device is in operation. In one embodiment, the conical housing additionally serves as a means for controlling the separation between the electrode pair. In a preferred embodiment, the conical actuating element is a quartz piezo-electric cone. In another embodiment, a modified electrode for use in a diode device of the present invention is disclosed, in which indents are made on the surface of the electrode.
Owner:COX ISAIAH WATAS
Optical modulator of electron beam
InactiveUS7728520B2Electrode and associated part arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansElectron currentElectromagnetic radiation
An optoelectronic modulator is based on the concentration of an electron beam from an electron gun by a tapered cavity, which sides are photosensitive and change the electrical conductivity under the illumination of light (electromagnetic radiation). The light modulation causes the corresponding changes in the current transported across the walls of the cavity. The remaining part of the electron current exits the cavity aperture and forms an amplitude-modulated divergent electron beam.
Owner:APPLIED NANOTECH HLDG
Combined-type vacuum diode
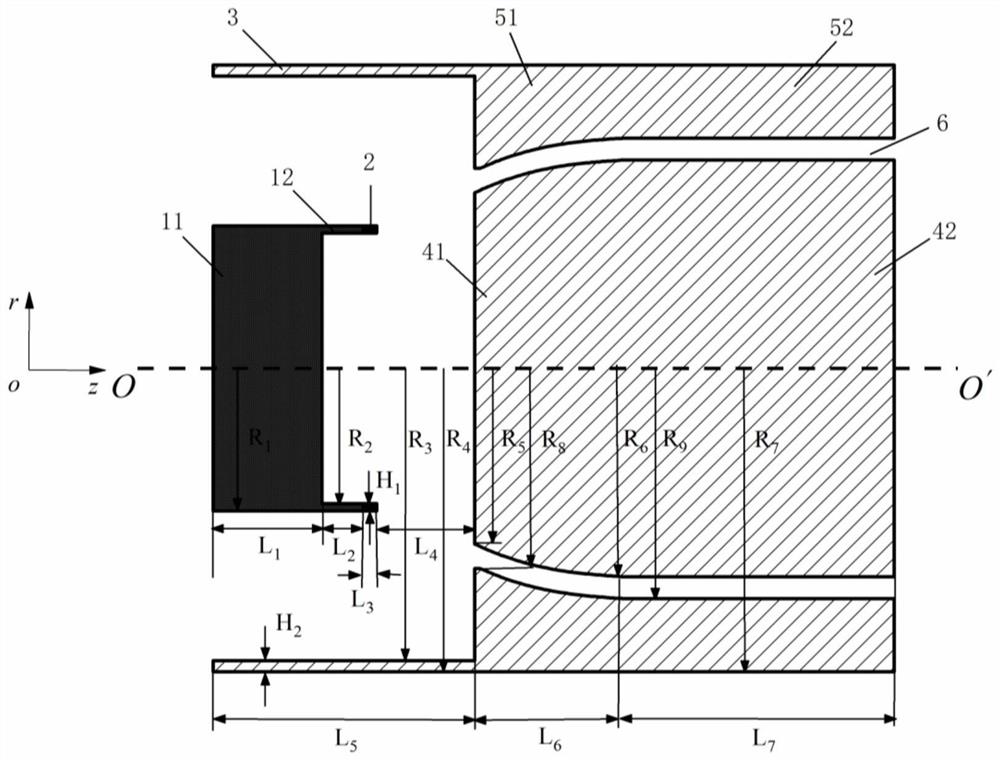
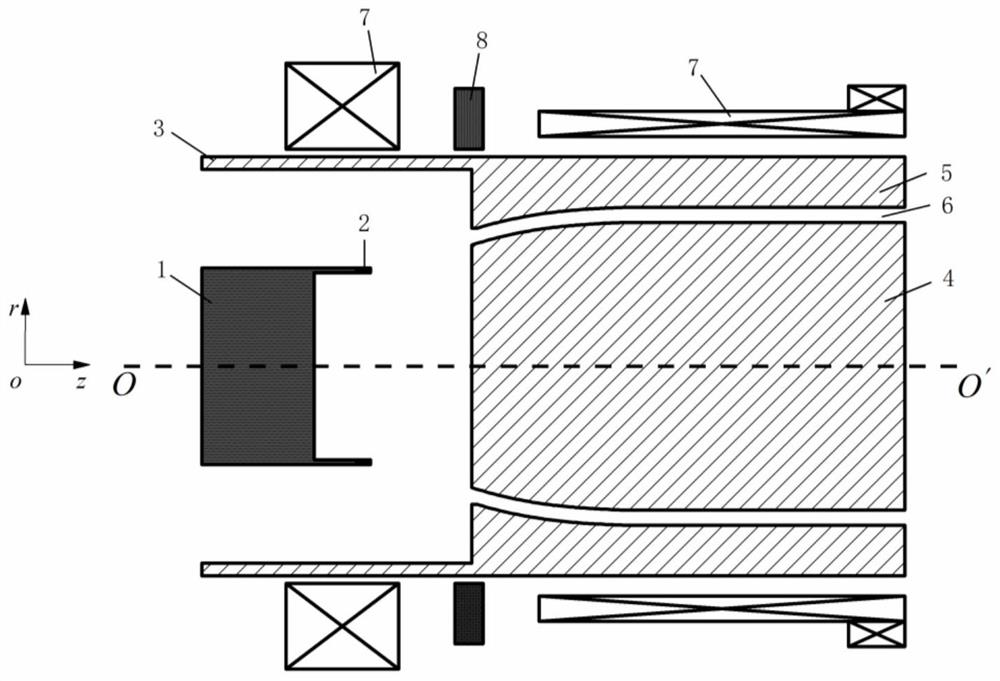
ActiveCN104900464AIncrease powerReduce volumeElectrode assembly mountingTubes without control meansElectricityMicrowave
The present invention discloses a combined-type vacuum diode used for a high-power microwave source. The combined-type vacuum diode comprises a large outer cylinder which may be connected with the high-power microwave source, a microwave source shielding ring, an insulator, a vacuum side shielding ring, a cathode pedestal, cathodes, a small outer cylinder and anodes. According to the combined-type vacuum diode, a plurality of cathode and anode structures share one insulator, and thus the cathode and anode structures or high-power microwave devices are combined for parallel drive to generate high-power electron beams.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Nanotube-based vacuum devices
InactiveUS20050247929A1Minimize threshold voltageLow inputNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceTerminal equipment
New, hybrid vacuum electronic devices are proposed, in which the electrons are extracted from the nanotube into vacuum. Each nanotube is either placed on the cathode electrode individually or grown normally to the cathode plane. Arrays of the nanotubes are also considered to multiply the output current. Two- and three-terminal device configurations are discussed. In all the cases considered, the device designs are such that both input and output capacitances are extremely low, while the efficiency of the electron extraction into vacuum is very high, so that the estimated operational frequencies are expected to be in a tera-hertz range. New vacuum triode structure with ballistic electron propagation along the nanotube is also considered.
Owner:ITUS
Tunneling gap diodes
InactiveUS20070057277A1Good energyImprove efficiencyDiodeTubes without control meansTunnel diodeFermi level
The present invention discloses a tunneling diode having a band gap material as the collector. This increases the tunneling of electrons having greater energy than the Fermi level from emitter to collector, leading to an increase in the efficiency of heat pumping or power generation by the diode. This approach also reduces back tunneling of electrons from collector to emitter.
Owner:MARTSINOVSKY ARTEMI +1
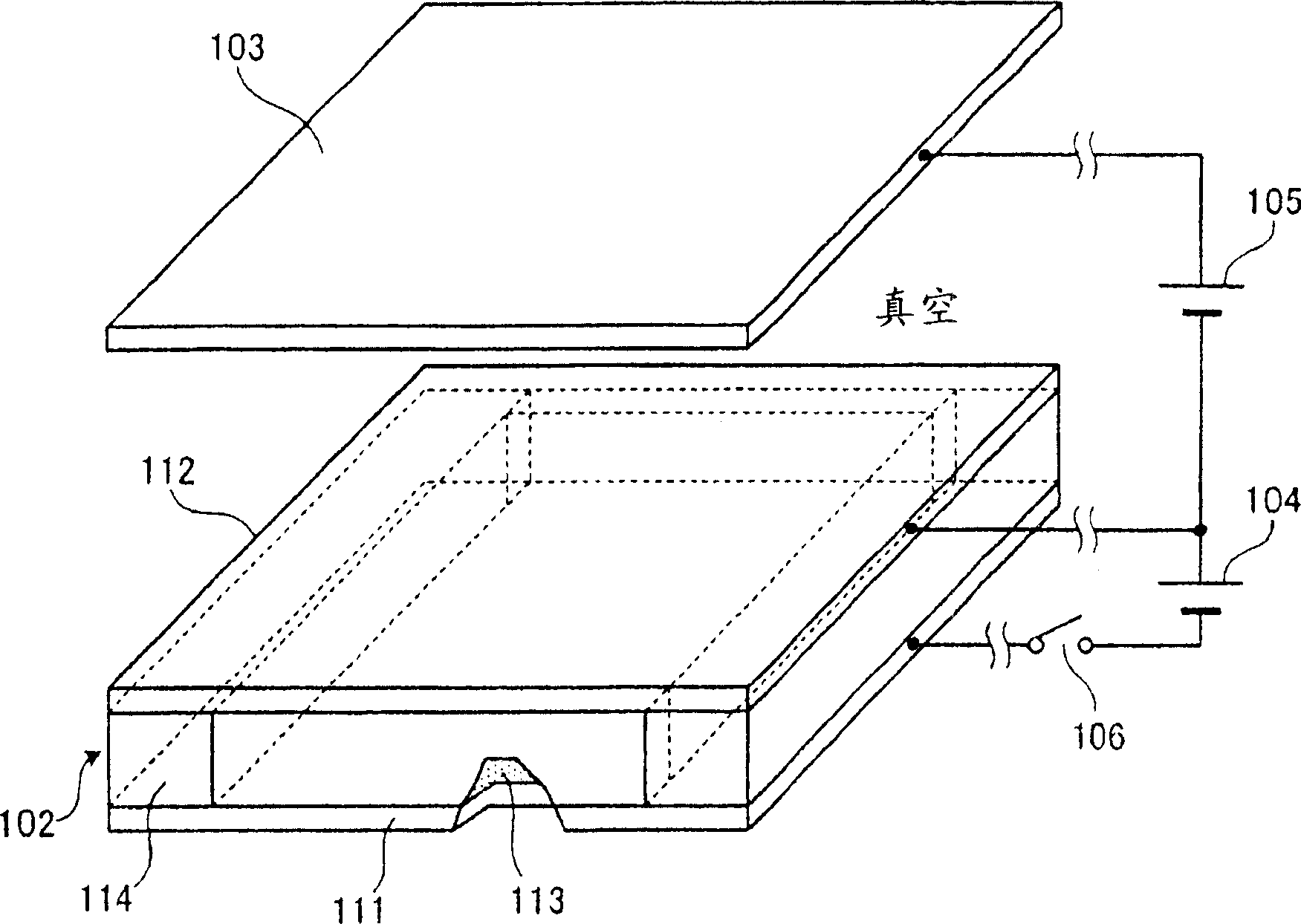
Electronic heat pump device, electronic equipment using electronic heat pump device and method of manufacturing electronic heat pump device
InactiveCN1661757AHeat pumpsThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermodynamicsEngineering
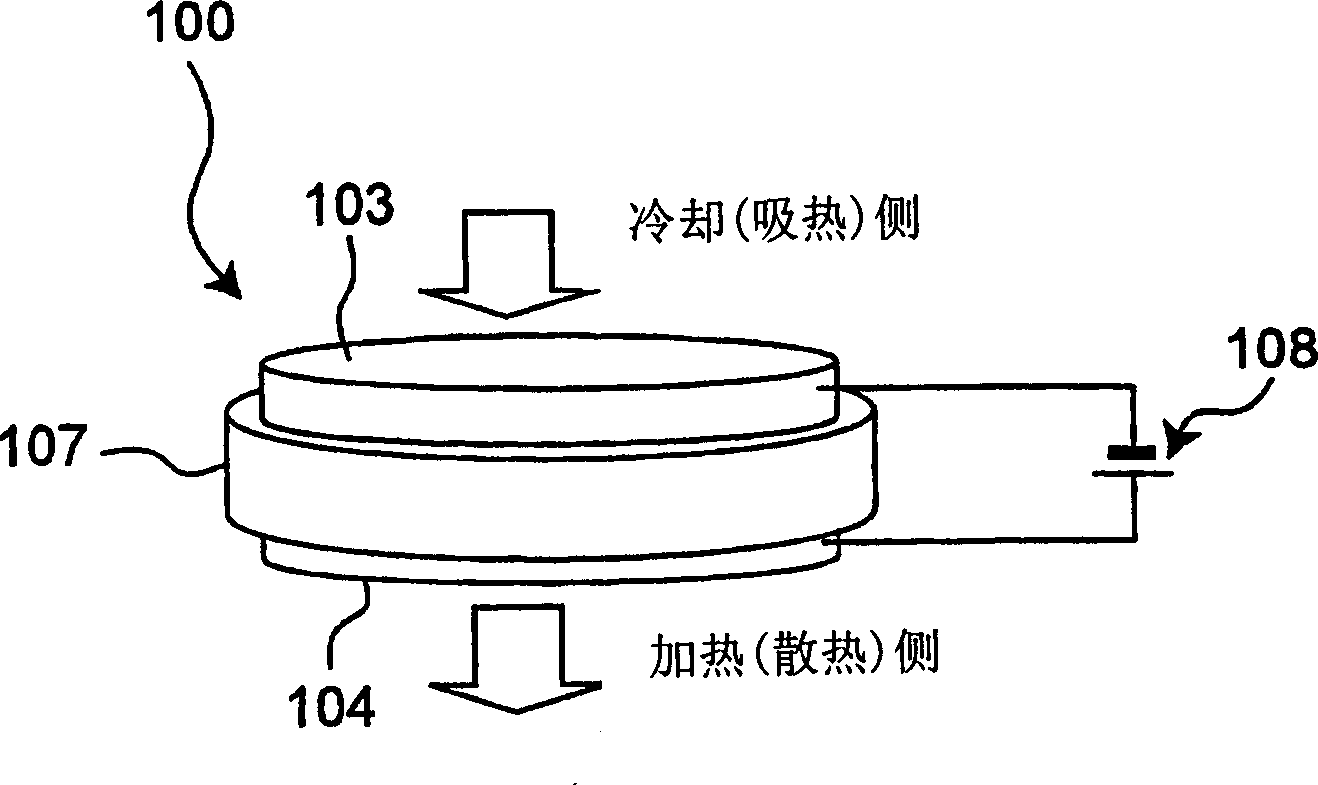
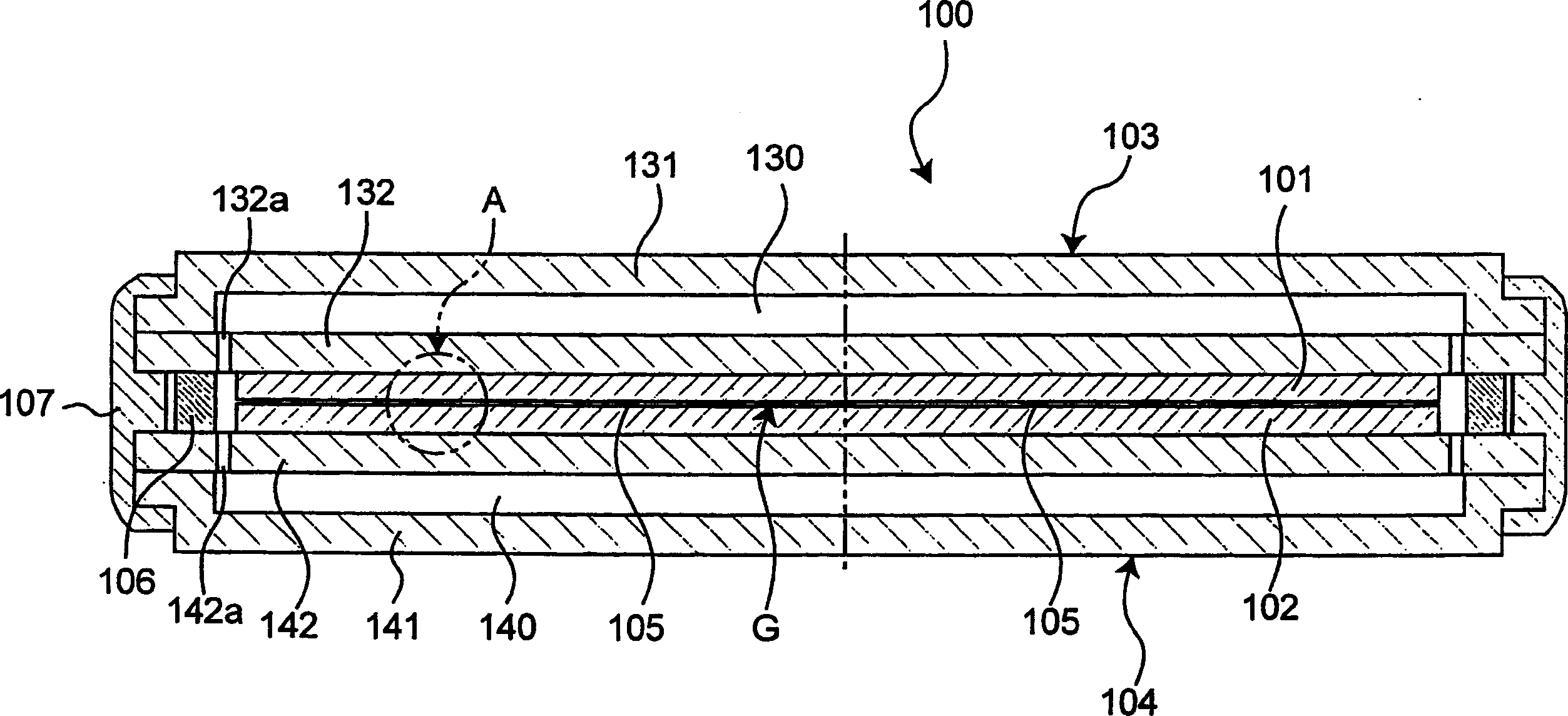
An electronic heat pump device has an emitter and a collector, stems supporting these components, a spacing retention member for keeping a spacing between the stems constant, and a sealing member for maintaining a vacuum between the stems. The emitter has a first semiconductor substrate and an emitter electrode, while the collector has a second semiconductor substrate and a collector electrode. The emitter electrode and the collector electrode are disposed so as to be opposed to each other with a space interposed therebetween. At least one of the first and second semiconductor substrates is integrally formed with electrically and thermally insulative spacers that keep the space between the emitter electrode and the collector electrode constant.
Owner:SHARP KK
Electromagnetic wave generation apparatus and manufacturing method of electromagnetic wave generation apparatus
InactiveUS20060028110A1Increase powerFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLength waveWavelength modulation
The present invention provides an electromagnetic wave generation apparatus that is compact and generates a high power terahertz wave. An electromagnetic wave generation apparatus includes: a substrate; a first electrode, having a photoelectron emitting part, formed on one of the surfaces of the substrate; a second electrode formed on the surface of the substrate; a power supply source that applies voltage to between the first electrode and the second electrode so that the potential of the second electrode becomes higher than the potential of the first electrode; and a light source that radiates one of time modulated light and wavelength modulated light, and in the apparatus, the photoelectron emitting part (a) emits electrons when light is irradiated and (b) is placed at a position which an incident light from the light source enters and from which the emitted electrons run to the electron incidence plane of the second electrode.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Electron emission device
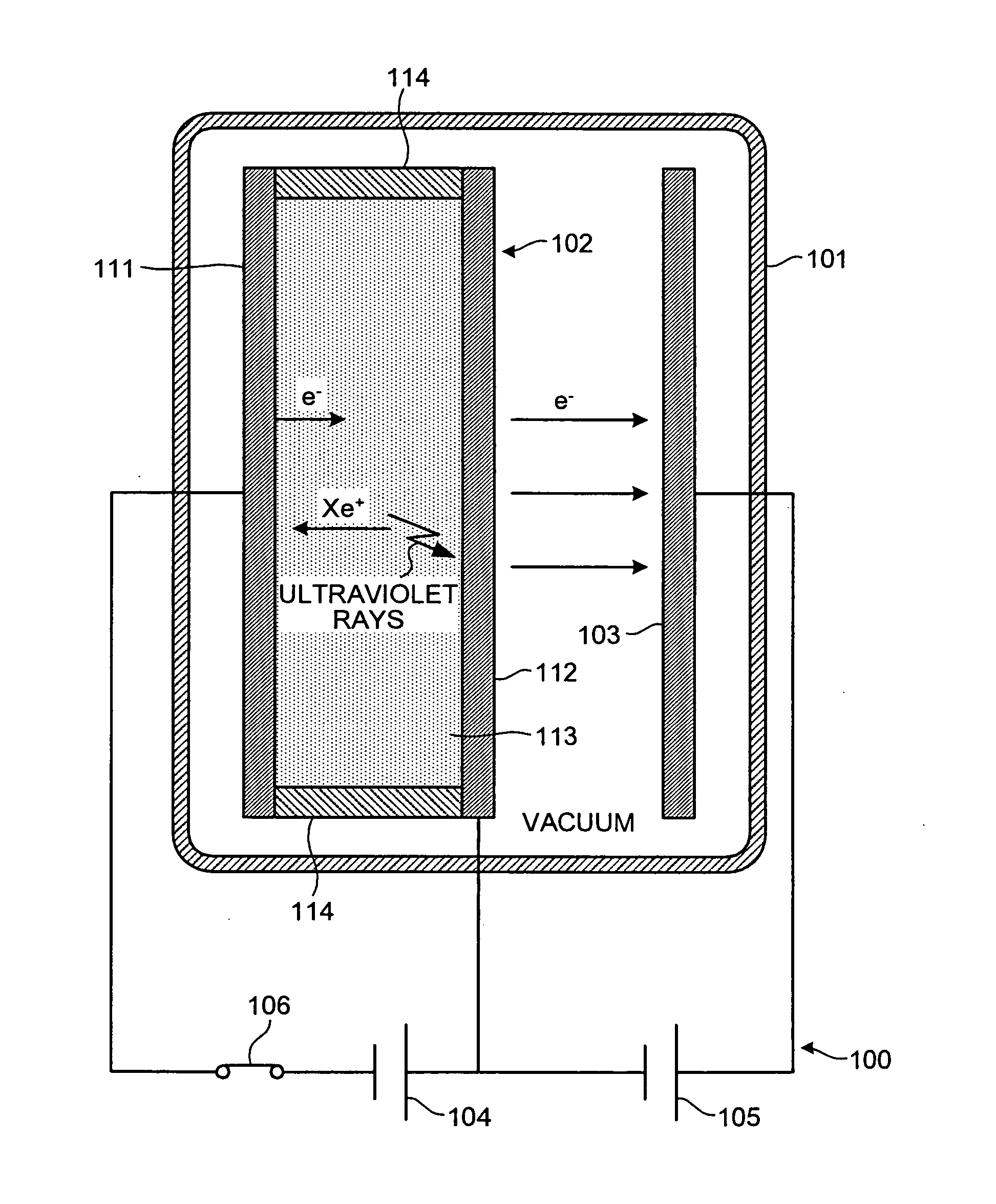
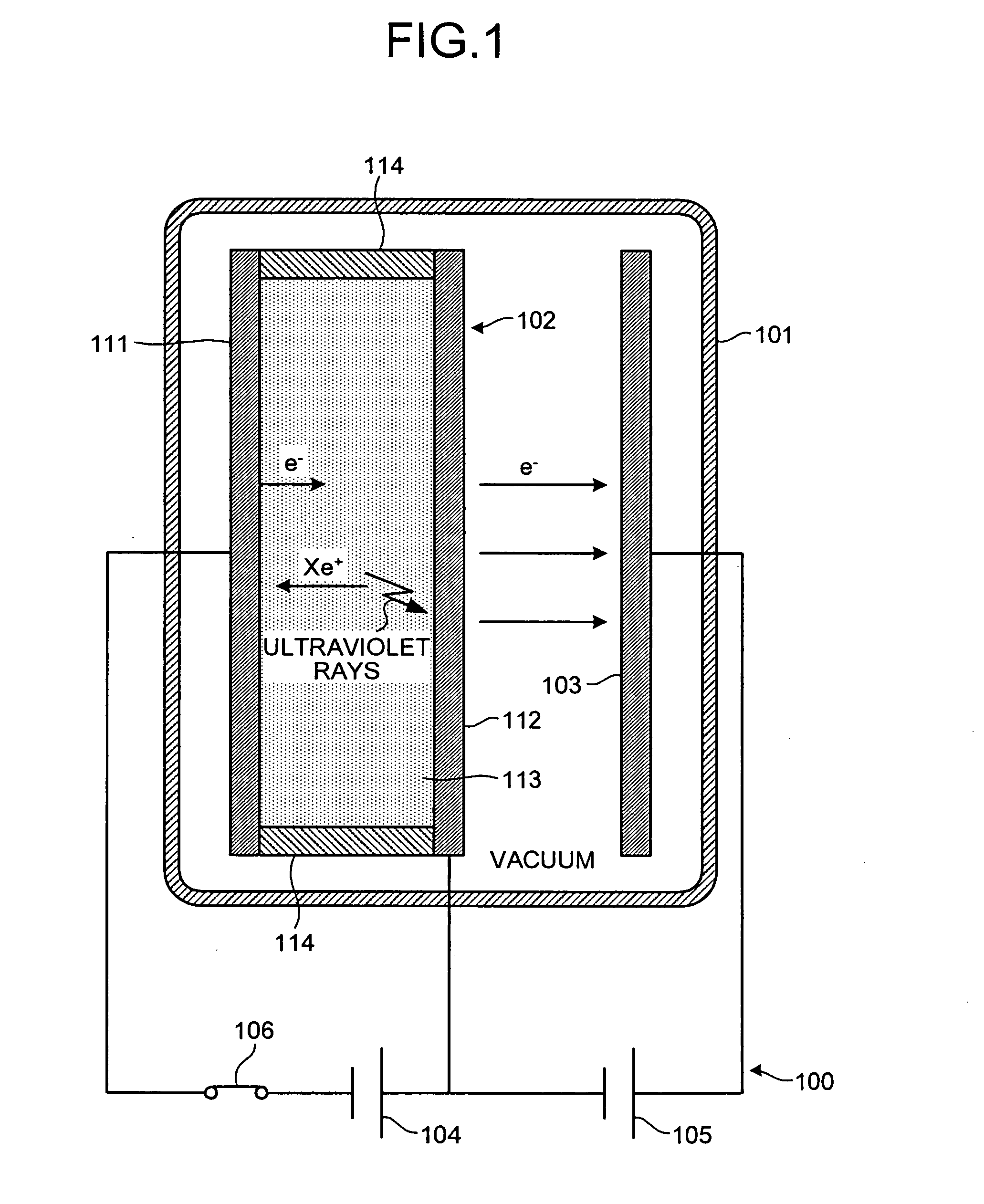
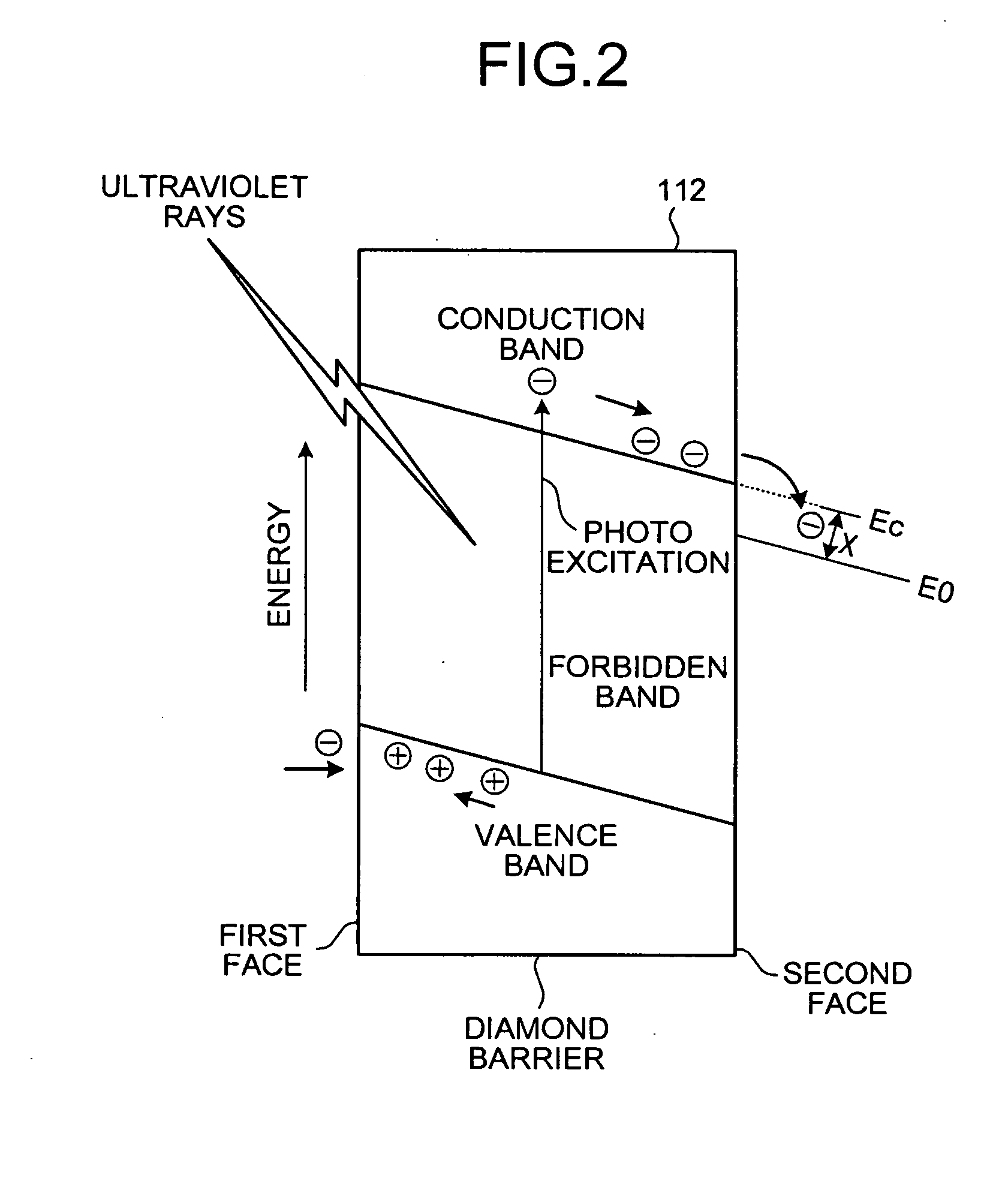
InactiveUS20070029935A1Instantly switchedDischarge tube/lamp detailsSolid cathode detailsElectronWide-bandgap semiconductor
The electron emission device includes a first electrode; a semiconductor barrier that has a first face disposed to face the first electrode and a second face which is opposite face of the first face, and is formed with a wide bandgap semiconductor; an insulating material that forms a space sealed between the first electrode and the semiconductor barrier; an inert gas that is encapsulated in the space; a second electrode that is disposed to face a second face of the semiconductor barrier interposing vacuum therebetween; a first voltage applying unit that applies a voltage between the first electrode and the semiconductor barrier; and a second voltage applying unit that applies a voltage between the semiconductor barrier and the second electrode.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Printed active device
ActiveUS20170345610A1Reduce manufacturing costLow costLiquid surface applicatorsAdditive manufacturing apparatusElement spaceElectrical connection
A method of manufacturing an article with integral active electronic component comprising: using an additive manufacturing process to: a) form a non-electrically conductive substrate; b) form a non-electrically conductive perforated layer having an aperture; c) form electrically conductive anode and cathode elements spaced in the aperture; d) deposit a conductive electrical connection to each of the elements suitable for imparting an electrical potential difference between the elements; e) form a non-electrically conductive sealing layer atop the perforated layer so as to retain and seal the aperture in the perforated layer.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Optical modulator of electron beam
InactiveUS20050156521A1Electrode and associated part arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansElectron currentElectromagnetic radiation
An optoelectronic modulator is based on the concentration of an electron beam from an electron gun by a tapered cavity, which sides are photosensitive and change the electrical conductivity under the illumination of light (electromagnetic radiation). The light modulation causes the corresponding changes in the current transported across the walls of the cavity. The remaining part of the electron current exits the cavity aperture and forms an amplitude-modulated divergent electron beam.
Owner:APPLIED NANOTECH HLDG
Electromagnetic wave generation apparatus and manufacturing method of electromagnetic wave generation apparatus
InactiveUS7595498B2Increase powerFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron flowWavelength modulation
The present invention provides an electromagnetic wave generation apparatus that is compact and generates a high power terahertz wave. An electromagnetic wave generation apparatus includes: a substrate; a first electrode, having a photoelectron emitting part, formed on one of the surfaces of the substrate; a second electrode formed on the surface of the substrate; a power supply source that applies voltage to between the first electrode and the second electrode so that the potential of the second electrode becomes higher than the potential of the first electrode; and a light source that radiates one of time modulated light and wavelength modulated light, and in the apparatus, the photoelectron emitting part (a) emits electrons when light is irradiated and (b) is placed at a position which an incident light from the light source enters and from which the emitted electrons run to the electron incidence plane of the second electrode.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Electron emission device
InactiveCN1909142ALaunch stableHigh outputPhoto-emissive cathodesDischarge tube cold cathodesLow voltageElectron
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Process for manufacturing a semiconductor device comprising an empty trench structure and semiconductor device manufactured thereby
ActiveUS9553209B2Improve performancePrevent penetrationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCold cathodesPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor
The process is based upon the steps of: forming a trench in a body including a substrate and at least one insulating layer; and depositing a metal layer above the body for closing the open end or mouth of the trench. The trench is formed by selectively etching the body, wherein the reaction by-products deposit on the walls of the trench and form a passivation layer along the walls of the trench and a restriction element in proximity of the mouth of the trench.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Array type terahertz vacuum diode device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN109801822AReduce contact areaVacuum tube vessels/containers/shieldsPhoto-emissive cathodes manufacturePhotocathodeEngineering
The embodiments of the present invention disclose an array type terahertz vacuum diode device and a manufacturing method thereof. The array type terahertz vacuum diode device comprises a substrate anda plurality of terahertz vacuum diodes; the plurality of terahertz vacuum diodes are arranged in an array on the substrate; each of the terahertz vacuum diodes comprises a photocathode, a vacuum channel layer and an anode; the vacuum channel layer is provided with a vacuum channel; the vacuum channel extends through the vacuum channel layer; the photocathode and the anode are disposed at two endsof the vacuum channel respectively; a sealed cavity is formed among the photocathode, the vacuum channel layer and the anode; the vacuum channel is in the shape of a circular truncated cone; and thecontact area of the photocathode and the vacuum channel is smaller than the contact area of the anode and the vacuum channel. The array type terahertz vacuum diode device provided by the embodiments of the present invention is a novel terahertz vacuum electronic device.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Process for manufacturing a semiconductor device comprising an empty trench structure and semiconductor device manufactured thereby
ActiveUS20160141428A1Not always easyImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCold cathodesSemiconductorMetal
The process is based upon the steps of: forming a trench in a body including a substrate and at least one insulating layer; and depositing a metal layer above the body for closing the open end or mouth of the trench. The trench is formed by selectively etching the body, wherein the reaction by-products deposit on the walls of the trench and form a passivation layer along the walls of the trench and a restriction element in proximity of the mouth of the trench.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Devices for energy conversion, electrical switching and thermal switching
InactiveCN102272957AThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device detailsEngineeringElectron
The present invention discloses an improvement for maintaining nanometer separation between electrodes in tunneling, thermal tunneling, diode, thermionic, thermoelectric, thermophotovoltaic, current limiting, resettable fusing, relays, circuit breakers and other devices the design of. At least one electrode has a curved shape, the curvature of which is changed by temperature. Some embodiments use nanoseparation to limit or stop the electrical current. Other embodiments reduce heat conduction between the two electrodes when compared to the prior art. The result is an electronic device that maintains two close parallel electrodes in a stable equilibrium with a nanogap between the two electrodes over a large area in a simple configuration for ease of manufacturability, and the resulting The devices described above are used to convert heat into electricity for cooling, or to limit or interrupt current flow.
Owner:TEMPRONICS INC
A Combined Vacuum Diode
ActiveCN104900464BIncrease powerReduce volumeElectrode assembly mountingTubes without control meansMicrowaveEngineering
The present invention discloses a combined-type vacuum diode used for a high-power microwave source. The combined-type vacuum diode comprises a large outer cylinder which may be connected with the high-power microwave source, a microwave source shielding ring, an insulator, a vacuum side shielding ring, a cathode pedestal, cathodes, a small outer cylinder and anodes. According to the combined-type vacuum diode, a plurality of cathode and anode structures share one insulator, and thus the cathode and anode structures or high-power microwave devices are combined for parallel drive to generate high-power electron beams.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Use of non-crystal diamond material
InactiveCN1779880ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectronMaterials science
An application of non-crystal diamond is disclosed. It can emit the greatest deal of electrons in vacuum by supplying the lowest energy to it. It contains the carbon atoms (at least 90%) and has a emitting surface with the roughness of 10-10000nm. It can be used for various vacuum devices such as switch, laser diode, etc.
Owner:宋健民
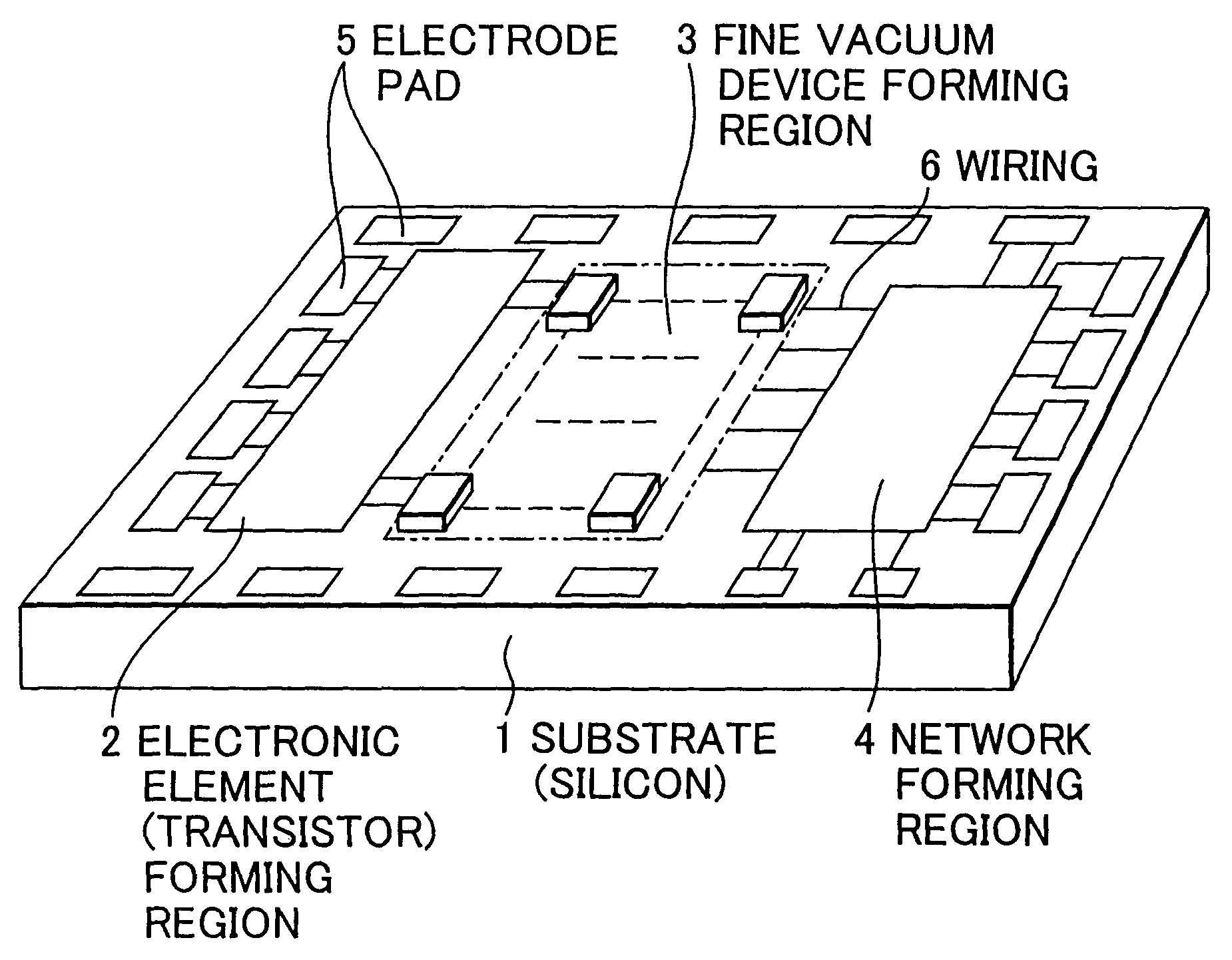
Integrated circuit
InactiveUS7732807B2Increase speedAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsElectric field sensorField electron emission
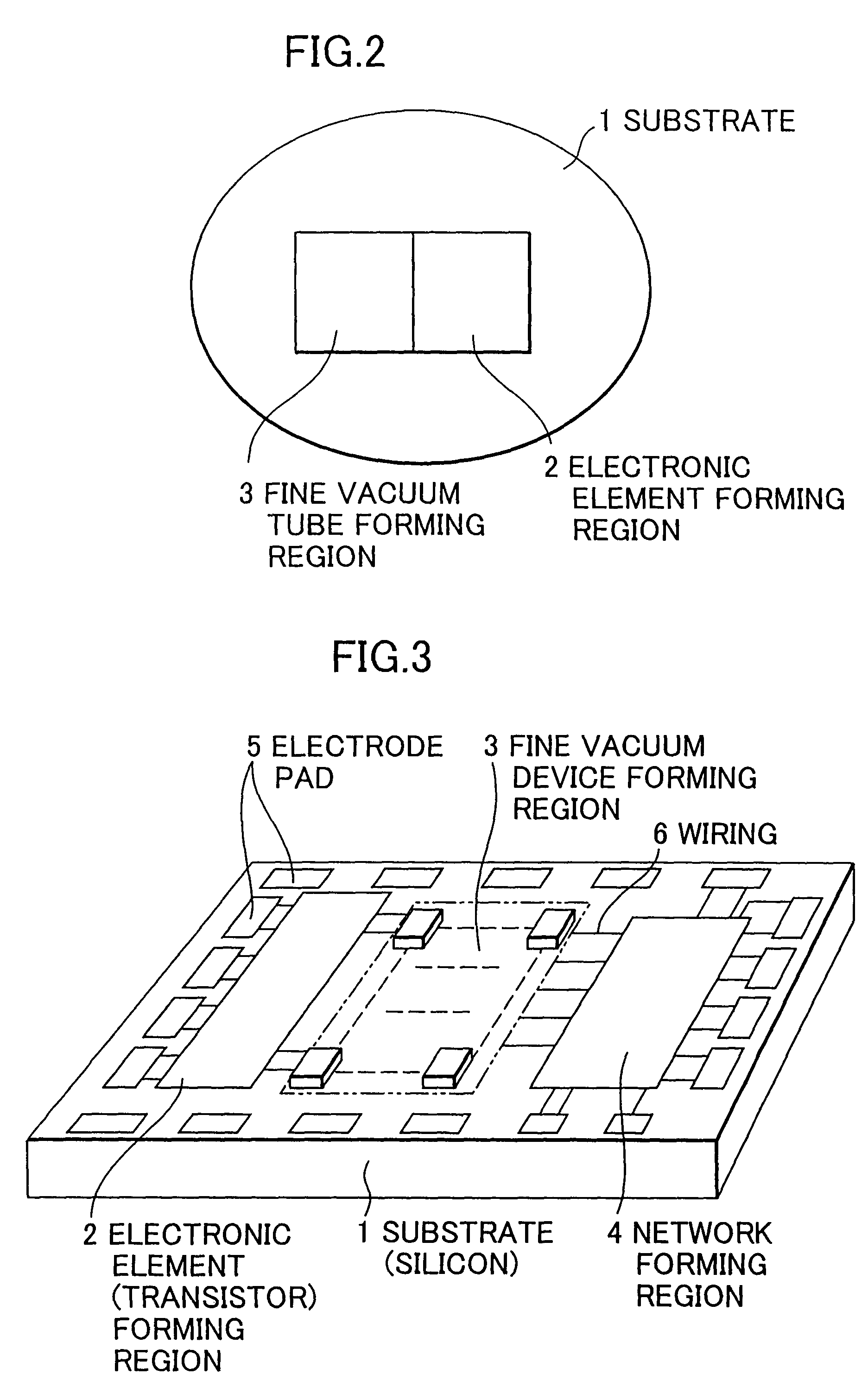
A fine vacuum tube element and other electronic elements are integrated and formed on a semiconductor substrate, and the fine vacuum tube element and the other electronic elements transmit signals to and from each other. When integrating the vacuum tube element with the other electronic elements, a quantum effect is realized in a room temperature environment by utilizing ballistic electrons (non-scattering electrons) traveling through the vacuum, and in the integrated circuit, an A / D converter is constructed by an interference system such as a Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Also an integrated circuit of an advanced function-integrated type is provided, comprising an interference system such as a Mach-Zehnder interferometer wherein weighting of the Mach-Zehnder interferometer is constituted for image processing and signal code conversion. A very high-speed light-receiving integrated circuit for optical communication is constructed by utilizing a very high-speed optical response characteristic of electron emission of the vacuum element, and a sensor such as a magnetic / electric field sensor is constructed by utilizing a quantum effect of ballistically traveling electrons.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Electrode coating for electron emission devices within cavities
ActiveCN105006413AVacuum tube vessels/containers/shieldsSolid-state devicesField electron emissionElectrostatic discharge
Embodiments of a method for forming a field emission diode for an electrostatic discharge device include forming a first electrode, a sacrificial layer, and a second electrode. The sacrificial layer separates the first and second electrodes. The method further includes forming a cavity between the first and second electrode by removing the sacrificial layer. The cavity separates the first and second electrodes. The method further includes depositing an electron emission material on at least one of the first and second electrodes through at least one access hole after formation of the first and second electrodes. The access hole is located remotely from a location of electron emission on the first and second electrode.
Owner:NEXPERIA BV
Use of non-crystal diamond material
InactiveCN100356495CSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectronMaterials science
Owner:宋健民
High-current diode based on gradient magnetic field and gradient magnetic field device
PendingCN113921357ASmall sizeSufficient magnetic field strengthTubes with magnetic controlTubes with electrostatic and magnetic controlElectrical conductorEngineering
The invention discloses a gradient magnetic field device which comprises a guiding magnetic field for guiding transmission of a high-current relativistic electron beam; the guide magnetic field comprises a solenoid coil; the solenoid coil is wound around the high-current diode so as to form a gradient magnetic field enabling the high-current relativistic electron beam to generate radial deflection, and the solenoid coil comprises a first sub-coil, a second sub-coil and a third sub-coil; the first sub-coil is wound on the outer side of an anode of the high-current diode, the second sub-coil is wound on the outer side of an outer conductor of the high-current diode, and the third sub-coil is wound on the outer side of the second sub-coil; the guide magnetic field further comprises an adjusting magnetic field; and the adjusting magnetic field is fixedly arranged between the first sub-coil and the second sub-coil, is wound around the high-current diode and is used for adjusting the radius change speed of the high-current relativistic electron beam. The invention further discloses a high-current diode based on the gradient magnetic field. The high-current diode comprises the gradient magnetic field device. The problem that the size of a high-impedance diode is difficult to reduce can be solved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com