Patents
Literature
161results about "Cold cathodes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
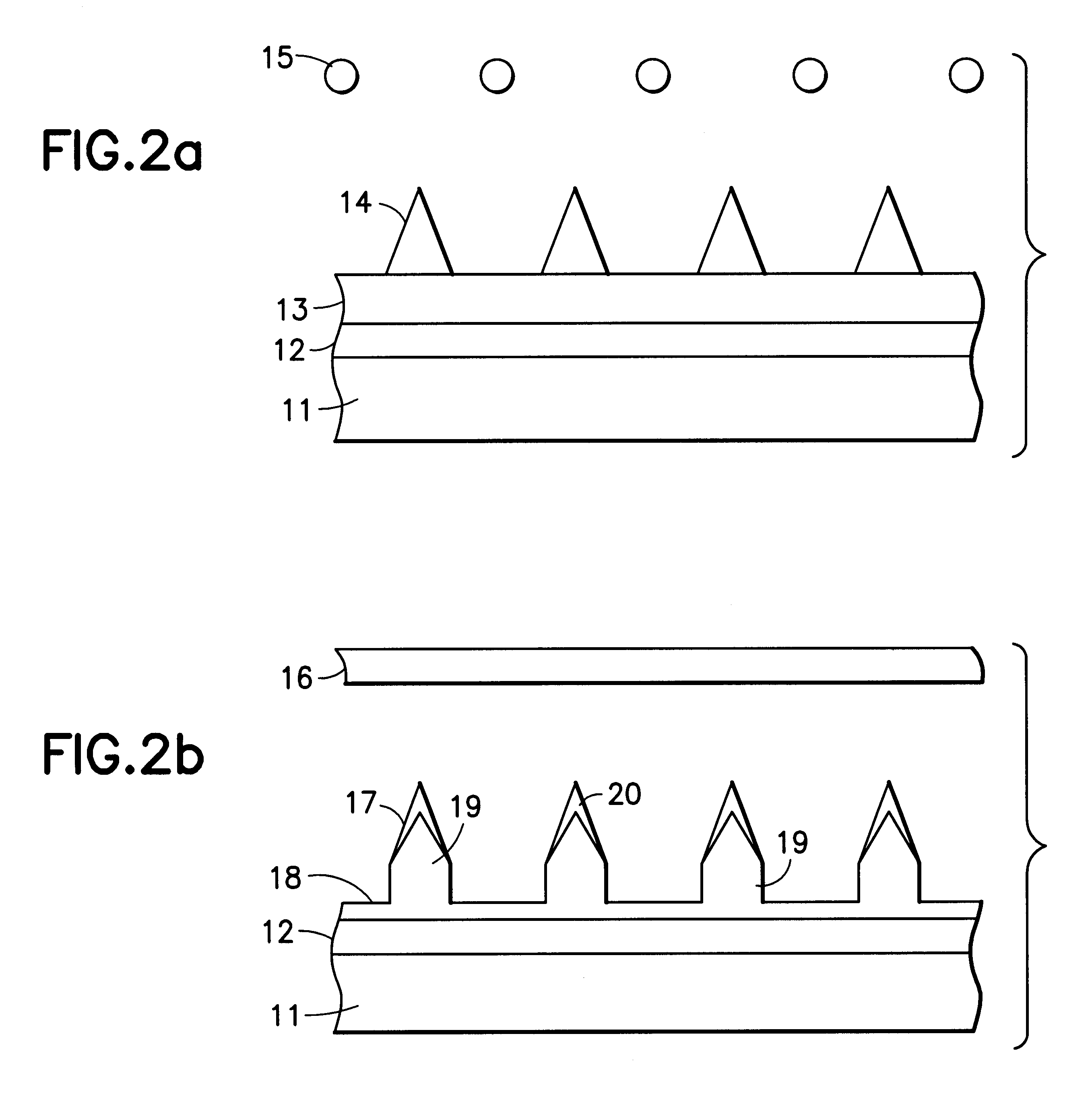
Doped diamond for vacuum diode heat pumps and vacuum diode thermionic generators
InactiveUS6214651B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCold cathodesNitrogen dopedElectron
A novel use of doped carbonaceous material is disclosed, integral to the operation of Vacuum Diode Heat Pumps and Vacuum Diode Thermionic Generators. In the preferred embodiment, the use of nitrogen-doped diamond enhances the operation of Vacuum Diode Heat Pumps and Vacuum Diode Thermionic Generators.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Integrated circuit devices and methods employing amorphous silicon carbide resistor materials
InactiveUS6031250AReduce the temperatureLow implementation costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField emission deviceOxygen
Integrated circuits, including field emission devices, have a resistor element of amorphous SixC1-x wherein 0<x<1, and wherein the SixC1-x incorporates at least one impurity selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogens, nitrogen, oxygen, sulphur, selenium, transition metals, boron, aluminum, phosphorus, gallium, arsenic, lithium, beryllium, sodium and magnesium.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC +1
Peptide nanostructures and methods of generating and using the same
InactiveUS20060079454A1Successfully addressDipeptide ingredientsTripeptide ingredientsNanostructurePeptide
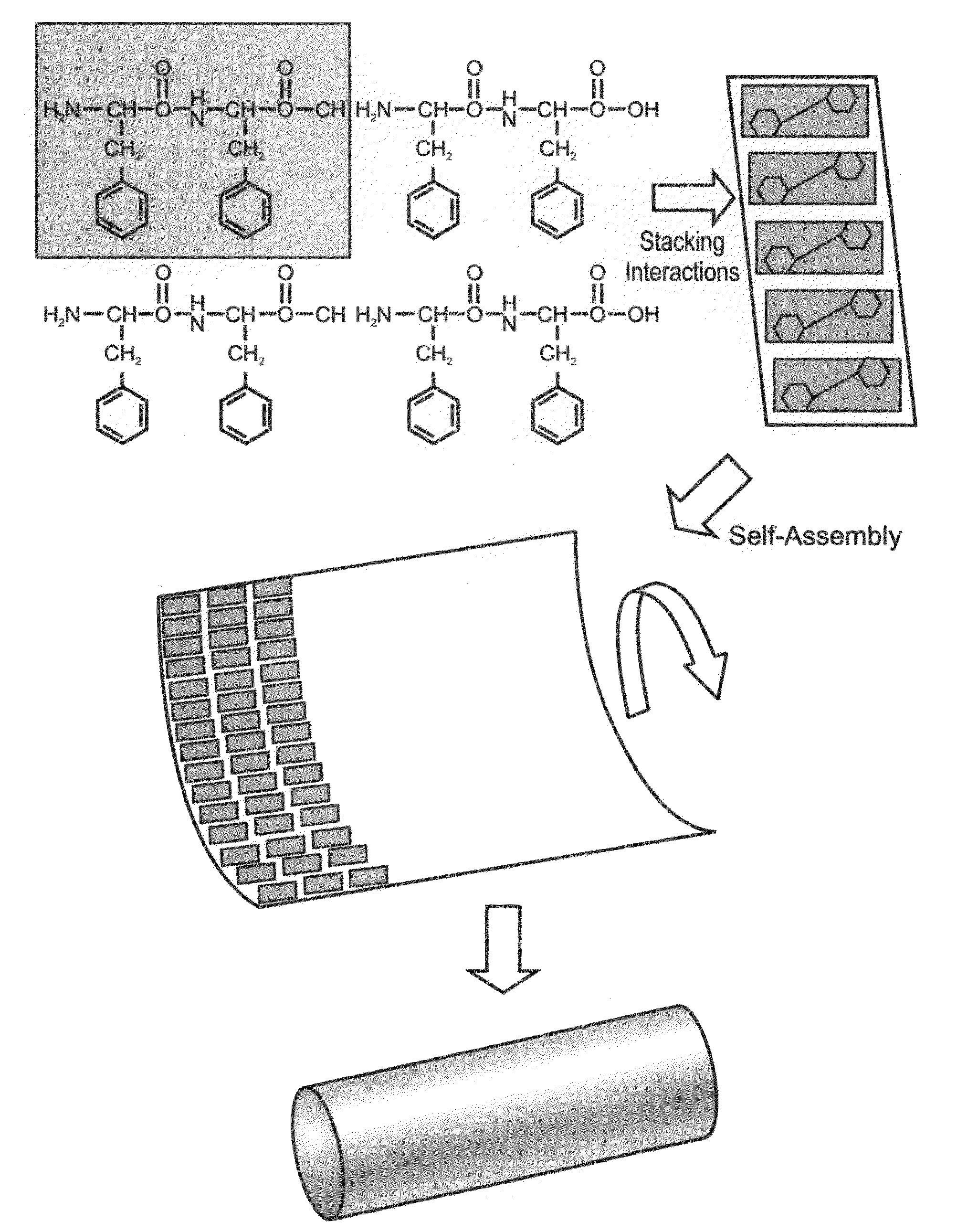
A tubular or spherical nanostructure composed of a plurality of peptides, wherein each of the plurality of peptides includes no more than 4 amino acids and whereas at least one of the 4 amino acids is an aromatic amino acid.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Field emission cathode having an electrically conducting material shaped of a narrow rod or knife edge
InactiveUSRE38223E1Improve emission qualityLong lastingNanoinformaticsThermionic cathodesConfocalConductive materials
A field emission cathode device consisting of an electrically conducting material and with a narrow, rod-shaped geometry or a knife edge, to achieve a high amplification of the electric field strength is characterized in that the electron-emitting part of the field emission cathode at least partly has preferred cylindrical host molecules and / or compounds with host compounds and / or cylindrical atomic networks, possibly with end caps with diameters measuring in the nanometer range.
Owner:KEESMANN TILL
Flat panel display with nanotubes
InactiveUS6914381B2Difficult to obtainLarge resistanceDischarge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsFiberPhosphor
A flat panel display includes an electron emitter plate provided with electron emitters, a phosphor plate provided with phosphors and a space defined by the electron emitter plate and the phosphor plate for form a substantial vacuum atmosphere therebetween, wherein a great number of fine recess structures are formed on the surface of a metal film formed on the electron emitter plate, and fine fibered substances or carbon nanotubes or substances containing the fine fibered substances or carbon nanotubes are arranged on the fine recess structures to form electron emitters.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Nanotube-based vacuum devices
InactiveUS7102157B2Minimize threshold voltageLow inputNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceTerminal equipment
New, hybrid vacuum electronic devices are proposed, in which the electrons are extracted from the nanotube into vacuum. Each nanotube is either placed on the cathode electrode individually or grown normally to the cathode plane. Arrays of the nanotubes are also considered to multiply the output current. Two- and three-terminal device configurations are discussed. In all the cases considered, the device designs are such that both input and output capacitances are extremely low, while the efficiency of the electron extraction into vacuum is very high, so that the estimated operational frequencies are expected to be in a tera-hertz range. New vacuum triode structure with ballistic electron propagation along the nanotube is also considered.
Owner:ITUS
Peptide nanostructures and methods of generating and using the same
A tubular or spherical nanostructure composed of a plurality of peptides, wherein each of the plurality of peptides includes no more than 4 amino acids and whereas at least one of the 4 amino acids is an aromatic amino acid.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Double-sided light emitting field emission device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20120248967A1Convenient lightingExtended service lifeDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesField emission devicePhosphor
A double-sided light-emitting field emission device and method of manufacturing same, said device comprising at least two transparent conductive layers, mixed field emission layers, and transparent package device. Wherein, the mixed field emission layer of field emission source and phosphor are utilized directly to serve as anode and cathode alternatively, such that on applying an AC power supply, roles of anode and cathode are changed alternatively along with frequency, hereby forming double-sided light-emitting structure. Therefore, the applications of said double-sided light-emitting field emission device are pretty wide, and having advantages of protecting field emission source, activating field emission source, reducing field emission arcing effect, having conductive phosphor, and raising illumination.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG CHENG UNIV
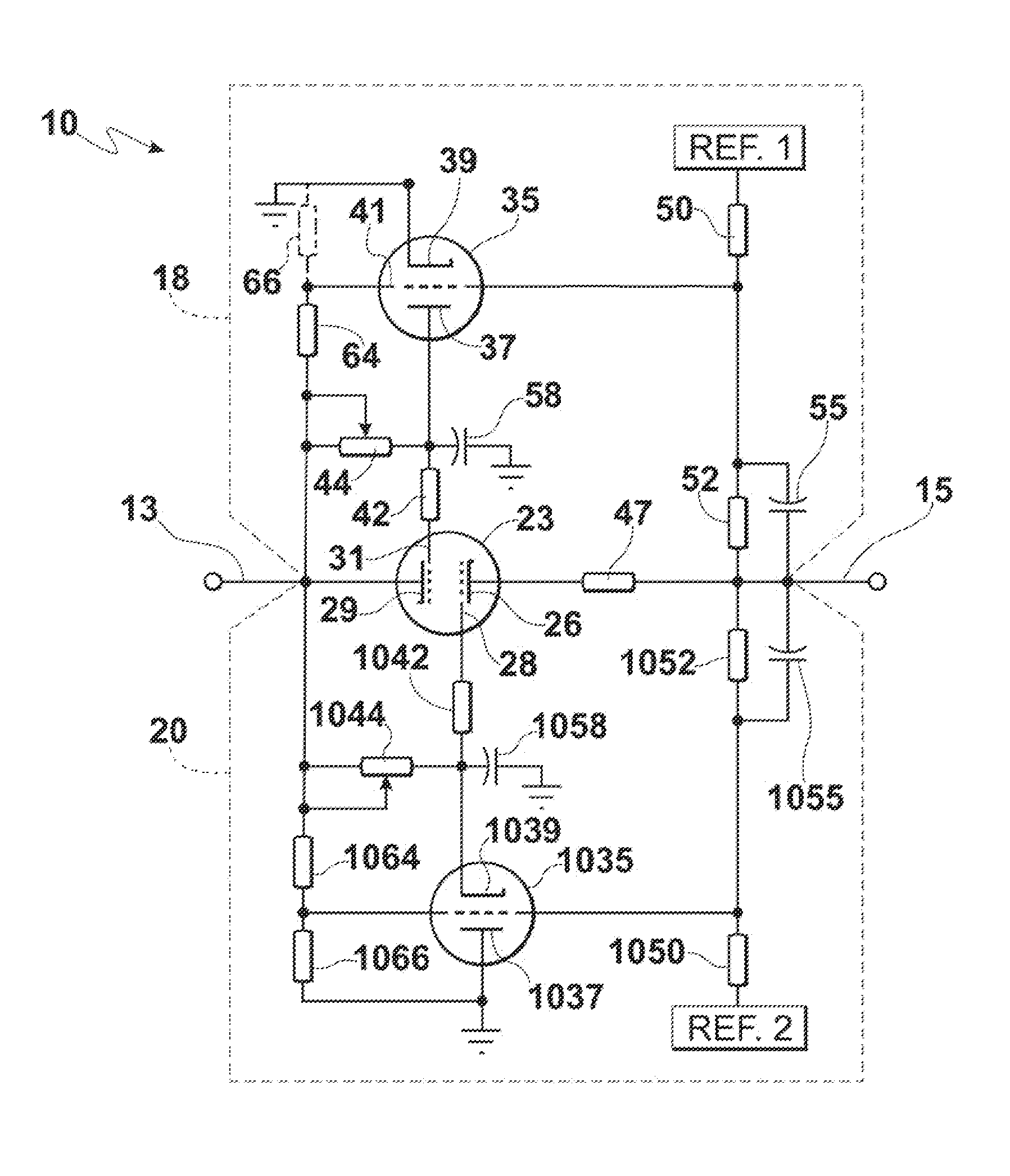
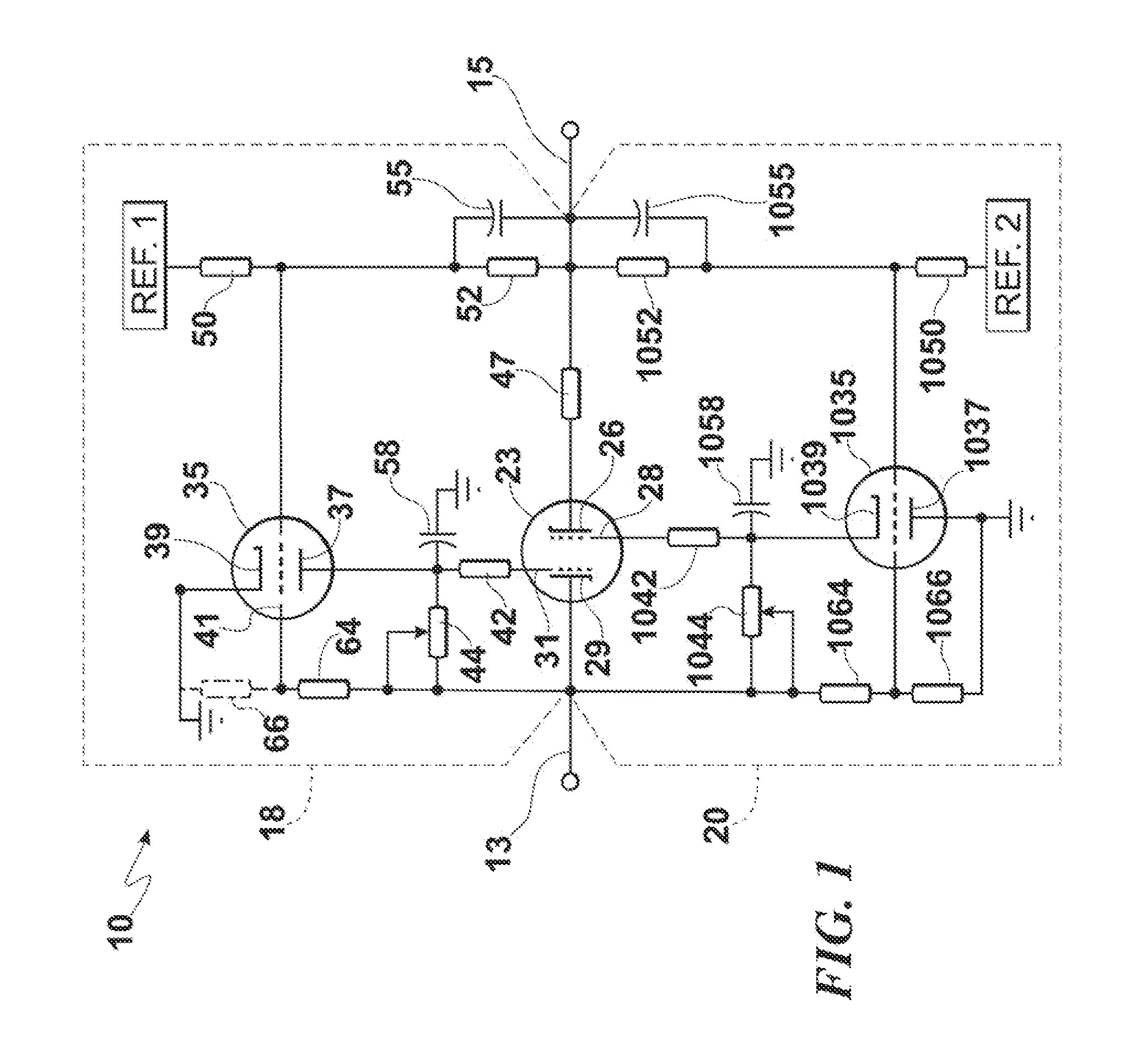
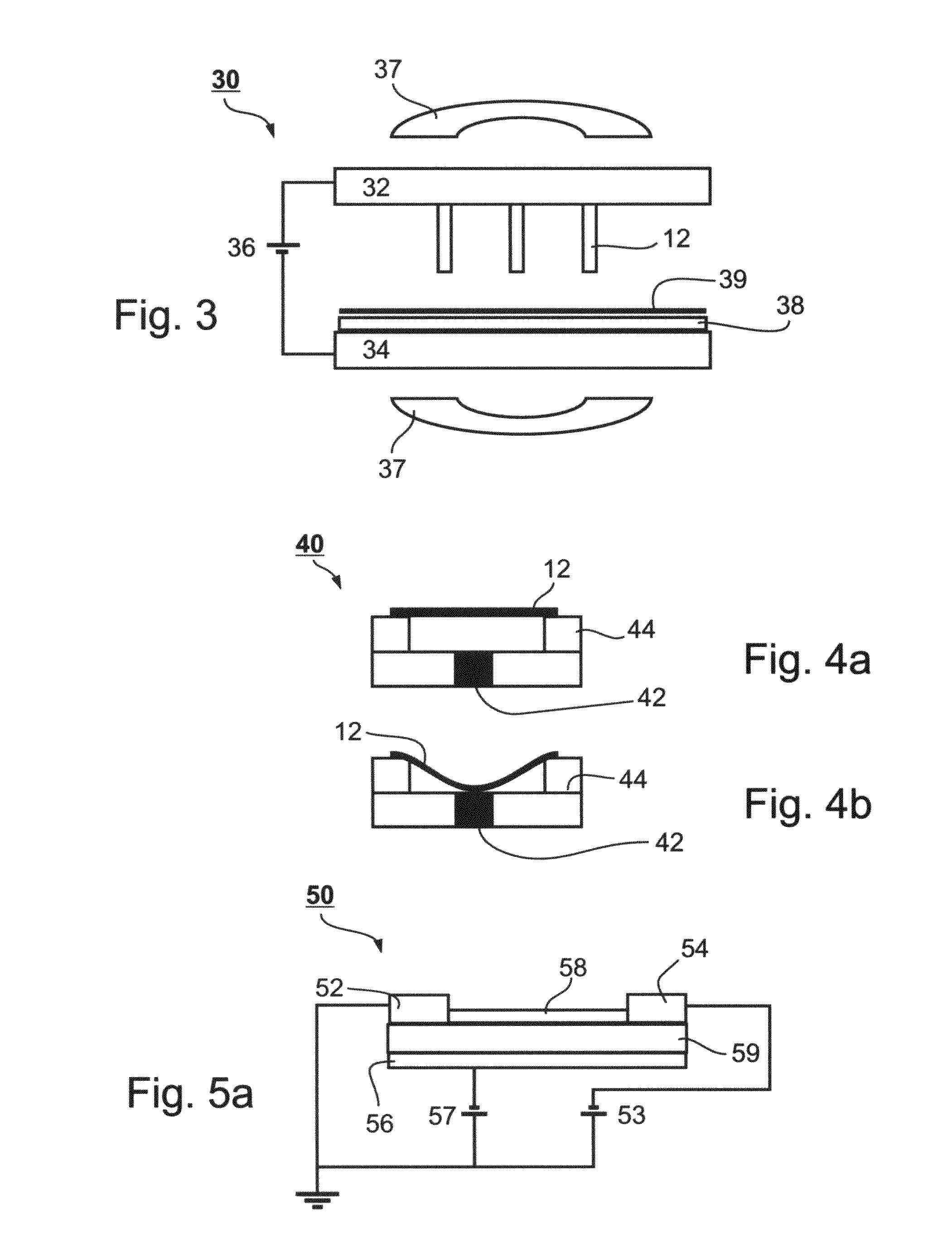
High Voltage High Current Regulator
ActiveUS20120081097A1Minimized size requirementPreventing internal electrical short circuitAnti-noise capacitorsElectrode assembly support/mounting/spacing/insulationHigh voltage igbtControl signal
High voltage high current regulator circuit for regulating current is interposed between first and second terminals connected to an external circuit and comprises at least one main-current carrying cold-cathode field emission electron tube conducting current between the first and second terminals. First and second grid-control cold-cathode field emission electron tubes provide control signals for first and second grids of the at least one main-current carrying cold-cathode field emission electron tube for positive and negative excursions of voltage on the first and second terminals, respectively. The current regulator circuit may be accompanied by a voltage-clamping circuit that includes at least one cold-cathode field emission electron tube. At least two cold-cathode field emission electron tubes, configured to operate at high voltage and high current, are preferably contained within a single vacuum enclosure and are interconnected to provide a circuit function, so as to form a high voltage high current vacuum integrated circuit.
Owner:ADVANCED FUSION SYST LLC
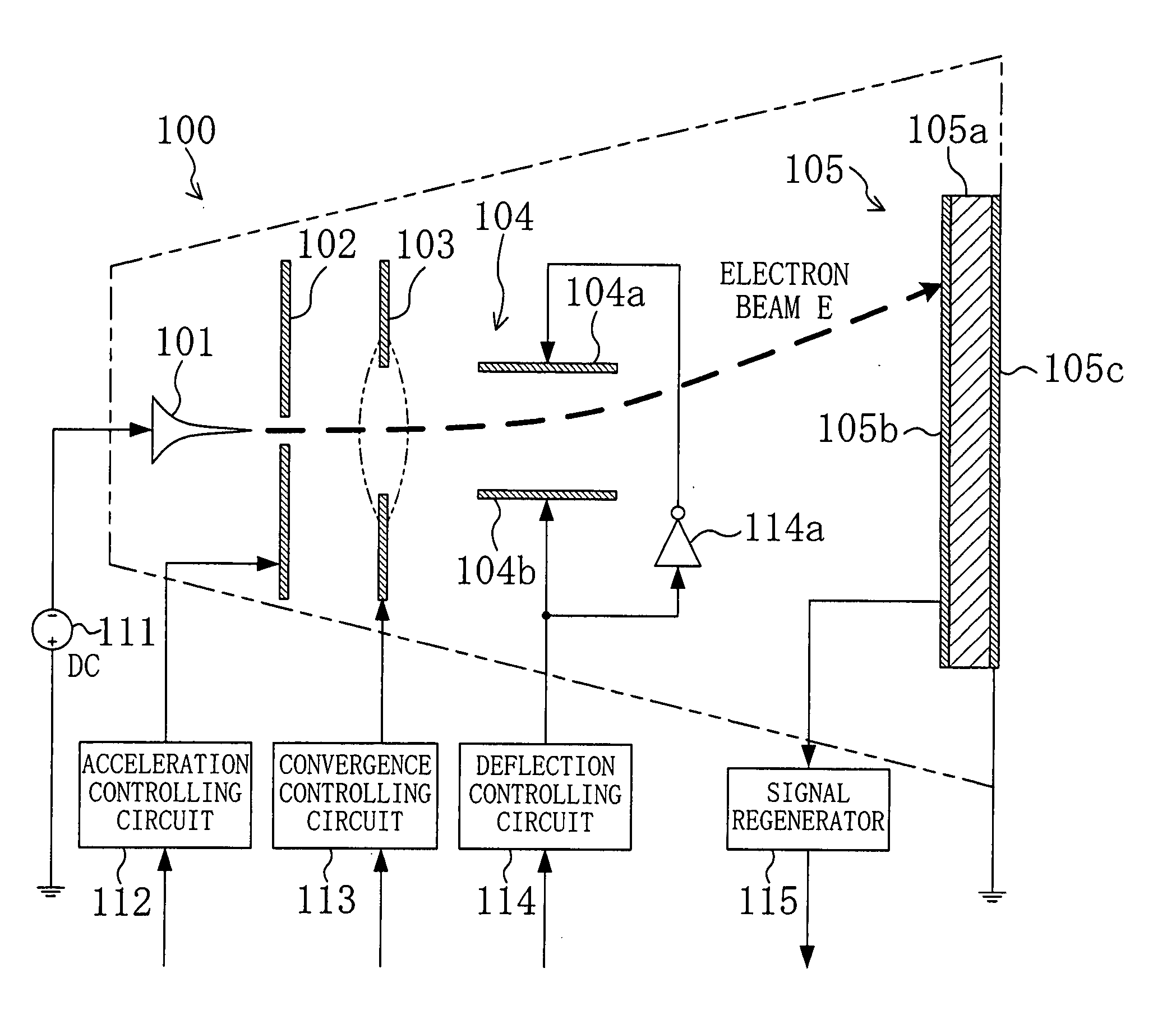
Information storage
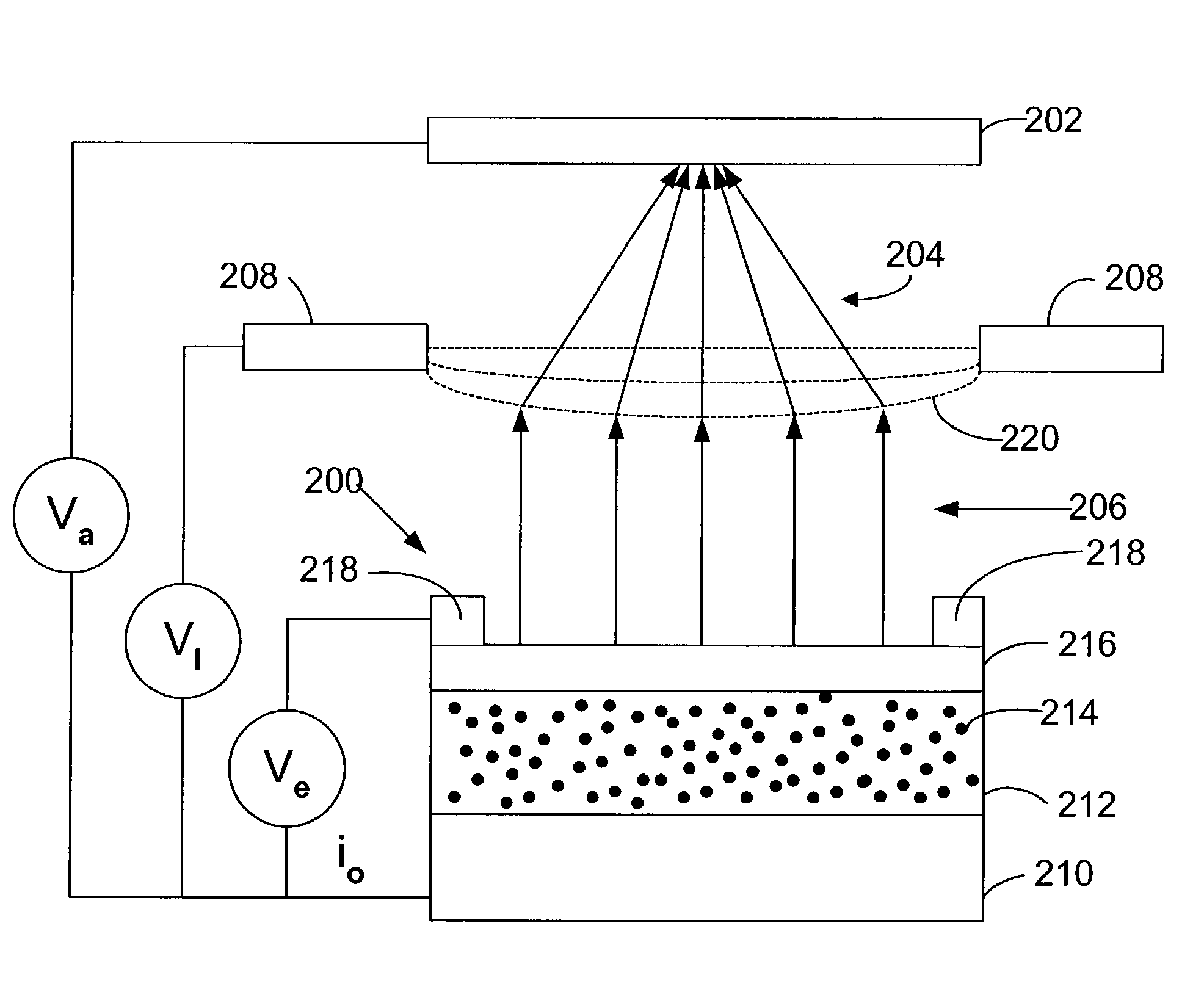
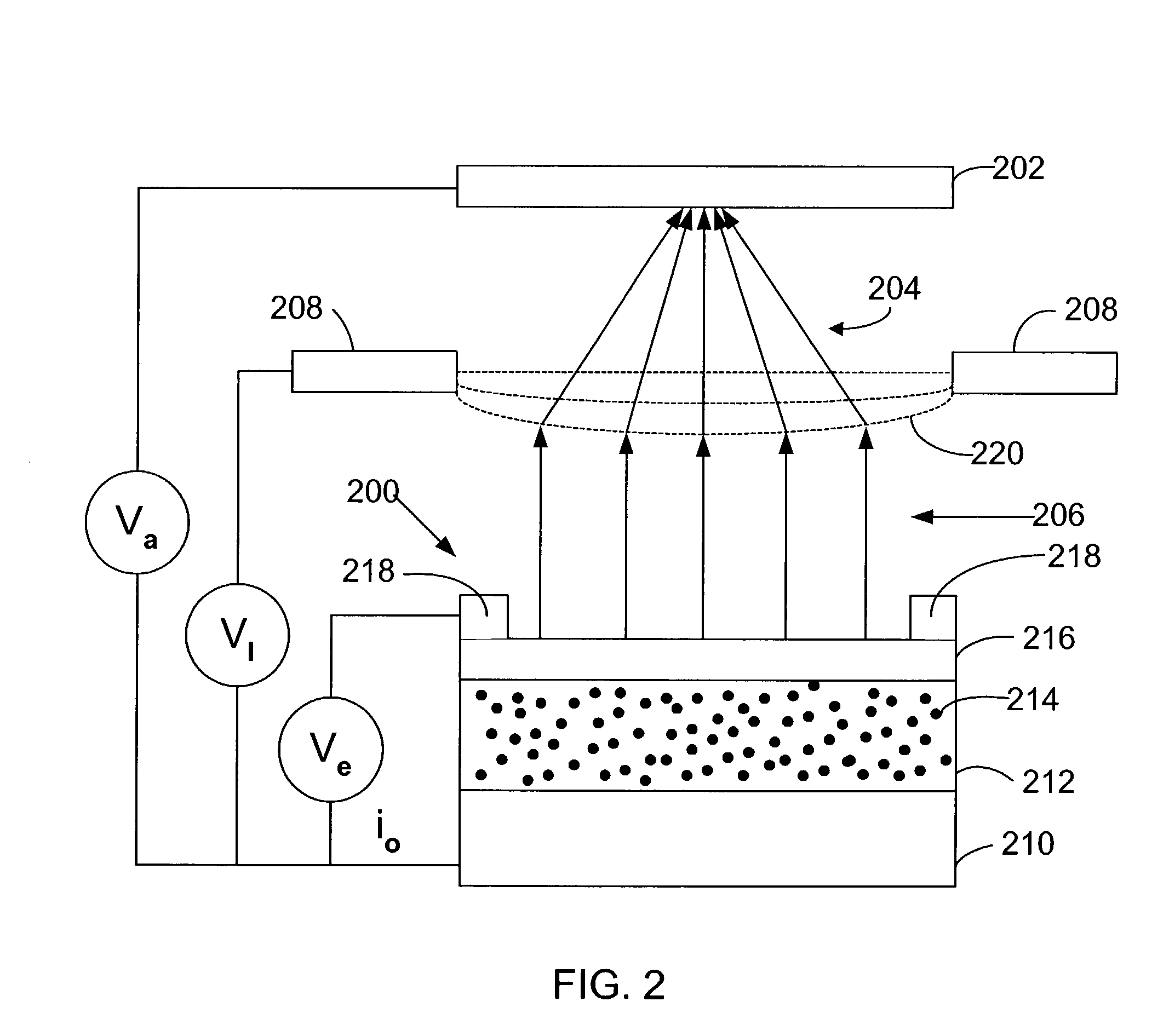
InactiveUS20060072427A1Increase speedImprove accuracyRead-only memoriesRecord information storageHigh energyPotential difference
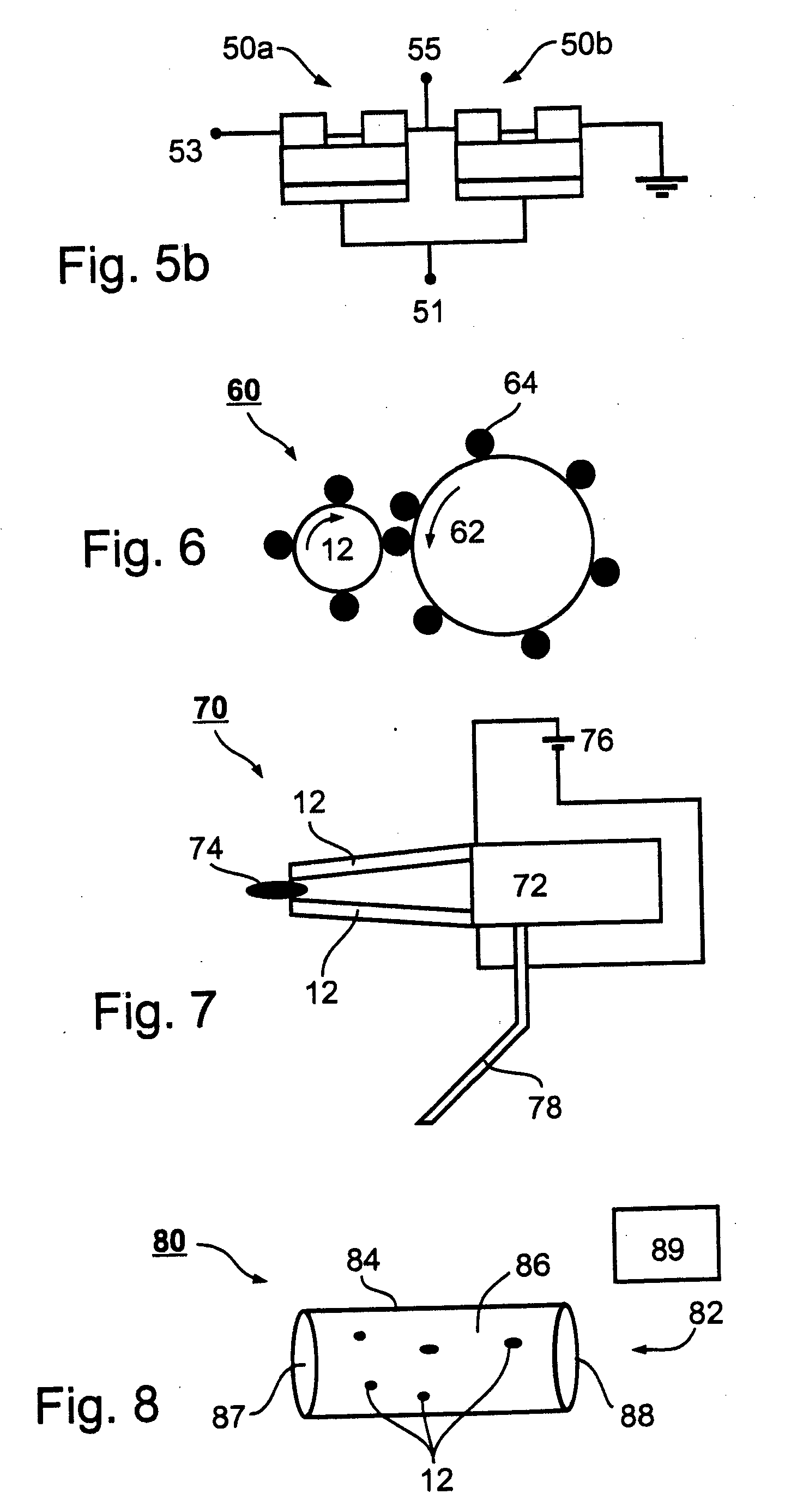
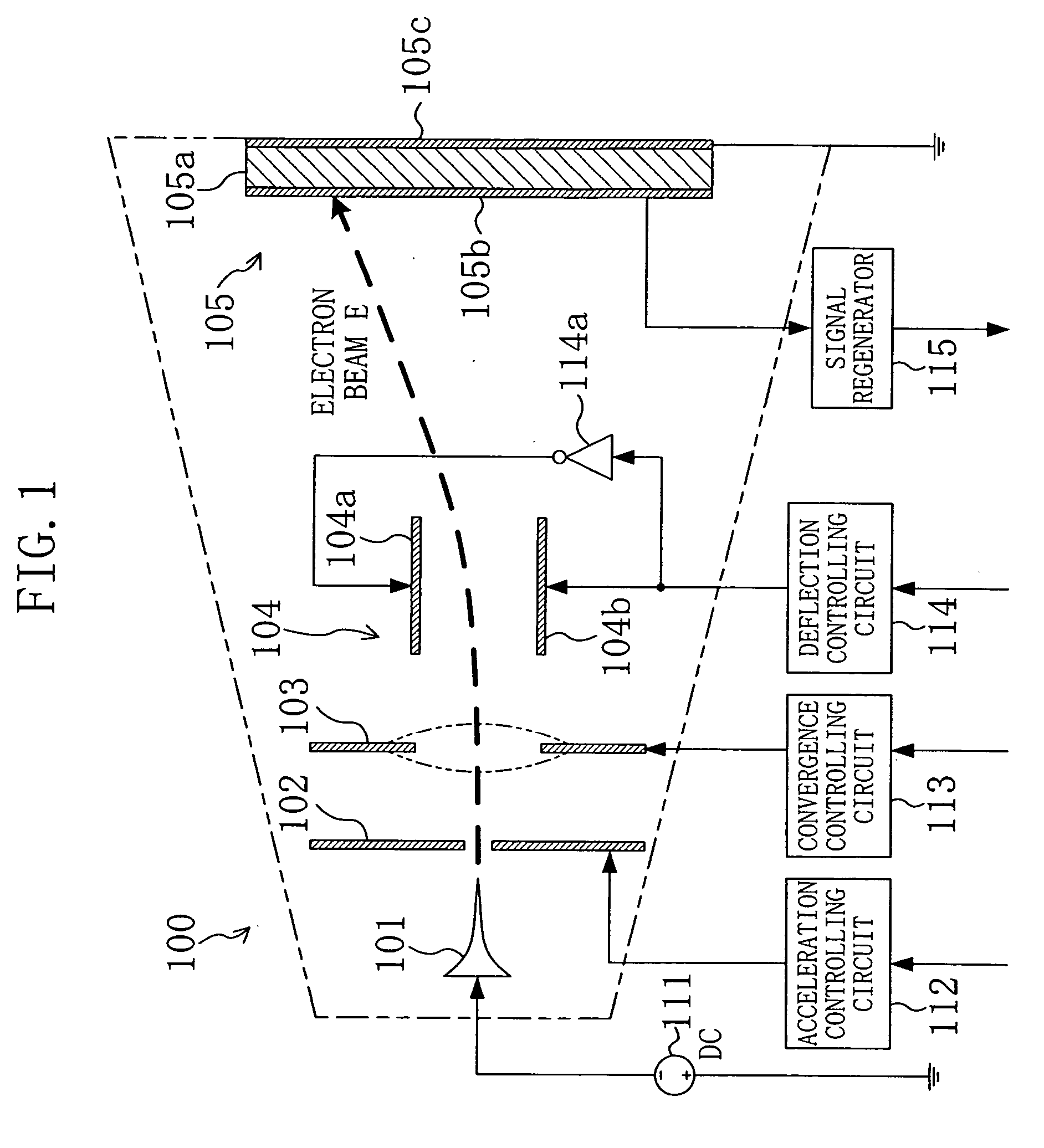
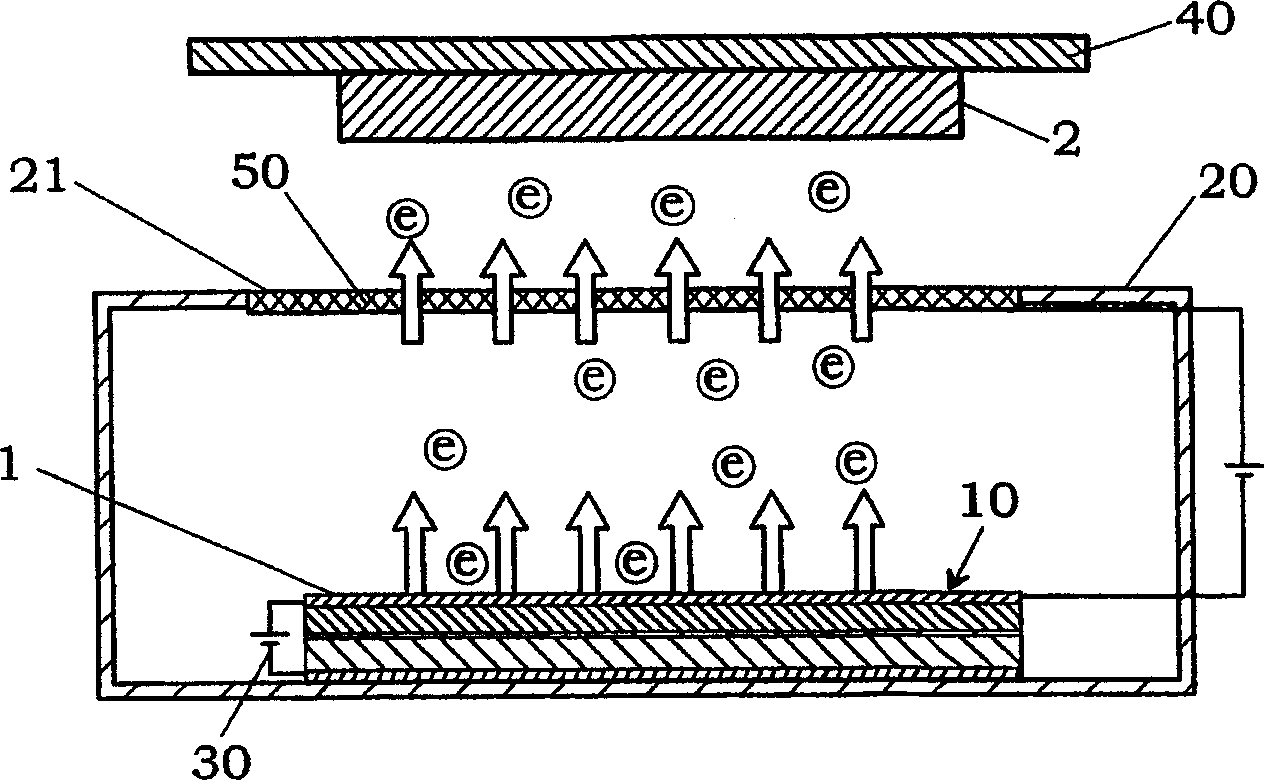
To greatly increase the storage density of a storage apparatus, an electron beam E emitted from a cold cathode 101 is accelerated by an accelerating electrode 102, caused to converge by a convergence electrode 103, deflected by a deflection electrode 104 and applied to a minute region of a storage film 105. The storage film 105 includes, for example, a phase change film 105a. The film is rapidly heated and cooled to change into an amorphous state upon irradiation with an electron beam E with high energy, while being gradually cooled to change into a crystallized state upon irradiation with an electron beam E with approximately intermediate energy, thereby storing data. Upon irradiation with an electron beam E with low energy, the potential difference between a detection electrode 105b and an anode 105c is detected depending on the state, i.e., the amorphous or crystallized state, thereby reading stored data.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Peptide nanostructures and methods of generating and using the same
A tubular or spherical nanostructure composed of a plurality of peptides, wherein each of the plurality of peptides includes no more than 4 amino acids and whereas at least one of the 4 amino acids is an aromatic amino acid.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Electron emitting devices having metal-based film formed over an electro-conductive film element
InactiveUS7271529B2Keep the homogeneity of brightness over a long period of timeDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPhosphorEngineering
An image display apparatus including a rear plate and a face plate disposed opposite to each other, the rear plate being equipped with a plurality of electron-emitting devices, each provided with a pair of electrodes and an electroconductive film including an electron-emitting region disposed between the electrodes, the face plate being equipped with a phosphor for displaying an image and a film exposed on a surface of the phosphor, the film comprising a metal or a metal compound material. A film comprising the same metal or the same metal compound material as the metal or the metal compound material constituting the film exposed on the surface of the phosphor is formed on each of the electroconductive films of the plurality of electron-emitting devices to have a thickness in a range from 0.2 nm to 4.5 nm.
Owner:CANON KK
Process for improving the emission of electron field emitters
InactiveUS20060049741A1Improve launch performanceImprove adhesionNanoinformaticsThermionic cathodesField electron emissionSemiconductor
This invention provides a process for improving the field emission of an electron field emitter comprised of an acicular emitting substance such as acicular carbon, an acicular semiconductor, an acicular metal or a mixture thereof, comprising applying a force to the surface of the electron field emitter wherein the force results in the removal of a portion of the electron field emitter thereby forming a new surface of the electron field emitter.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Process for improving the emissions of electron field emitters
InactiveUS20070160758A1Improve launch performanceImprove adhesionNanoinformaticsCold cathodesField electron emissionSemiconductor
This invention provides a process for improving the field emission of an electron field emitter comprised of an acicular emitting substance such as acicular carbon, an acicular semiconductor, an acicular metal or a mixture thereof, comprising applying a force to the surface of the electron field emitter wherein the force results in the removal of a portion of the electron field emitter thereby forming a new surface of the electron field emitter.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Planar electron emitter (PEE)
Owner:VISCOR PETR +3
Low voltage nanoscale vacuum electronic devices
ActiveUS9331189B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow voltageOptoelectronics
An electronic device including a first conducting layer, a second conducting layer, and an insulating layer provided between the conducting layers. At least one side wall extends from the first conducting layer to the second conducting layer and includes at least a portion of the first conducting layer, the second conducting layer and the insulating layer. A bias voltage is applied between the first and second conducting layers, wherein responsive to the bias voltage, a two dimensional electron system is induced at least in one of the first conducting layer and the second conducting layer, and wherein electrons from the two dimensional electron system are emitted from the side wall side wall as a result of Coulombic repulsion and travel in air from the one of the first conducting layer and the second conducting layer to the other of the first conducting layer and the second conducting layer.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
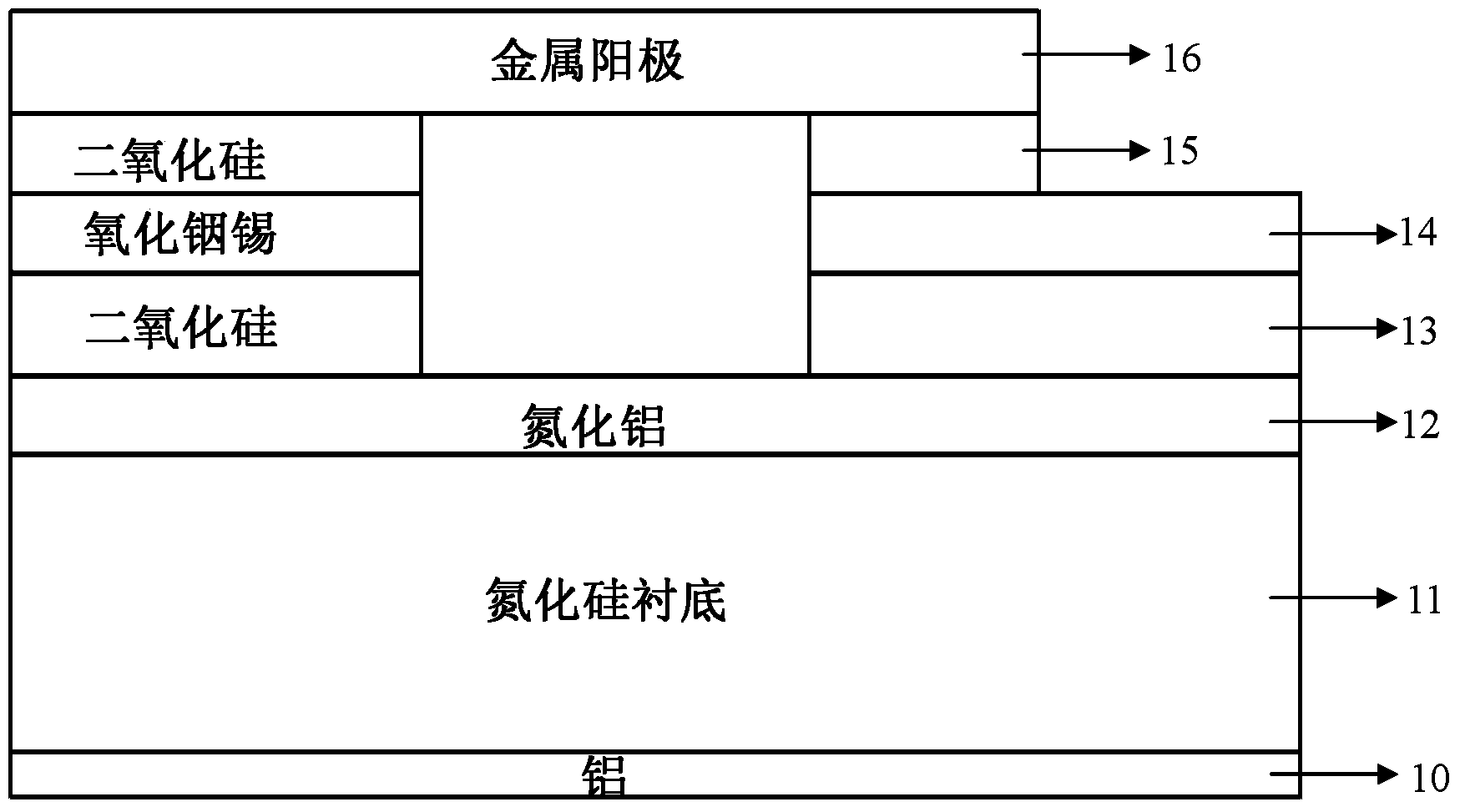
Nano vacuum triode with planar emitting cathode and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104299988AReduced vacuum requirementsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerIndium tin oxide
The invention provides a nano vacuum triode with a planar emitting cathode and a manufacturing method of the nano vacuum triode with the planar emitting cathode. The method comprises the steps that a substrate, a back electrode, the planar cold cathode, a first insulation layer, a grid layer, a second insulation layer, a small cylindrical hole, a grid layer step and an anode layer are included; the back electrode is manufactured on the back face of the substrate; the planar cold cathode is manufactured on the front face of the substrate; the first insulation layer is manufactured on the planer cold cathode; the grid layer is manufactured on the first insulation layer; the second insulation layer is manufactured on the indium tin oxide thin film grid layer; the small cylindrical hole penetrates through the first insulation layer, the grid layer and the second insulation layer; the grid layer step is formed by etching the second insulation layer to the grid layer; the anode layer is manufactured on the second insulation layer; the total thickness of the first insulation layer, the indium tin oxide thin film grid layer and the second insulation layer ranges from 10 nanometers to 100 manometers. The defect that the electron emitting density of a tip structure is uneven, and a tip is prone to being damaged is overcome, and meanwhile the defect that the planar cathode needs higher threshold electric field intensity is overcome through the negative electron affinity characteristic of aluminum nitride materials.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Field emission display devices
InactiveUS6087766AImprove efficiencyExcellent optical propertiesDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectrode and associated part arrangementsSecondary emissionDisplay device
Cathodoluminescent field emission display devices feature phosphor biasing, amplification material layers for secondary electron emissions, oxide secondary emission enhancement layers, and ion barrier layers of silicon nitride, to provide high-efficiency, high-brightness field emission displays with improved operating characteristics and durability. The amplification materials include copper-barium, copper-beryllium, gold-barium, gold-calcium, silver-magnesium and tungsten-barium-gold, and other high amplification factor materials fashioned to produce high-level secondary electron emissions within a field emission display device. For enhanced secondary electron emissions, an amplification material layer can be coated with a near mono-molecular film consisting essentially of an oxide of barium, beryllium, calcium, magnesium or strontium. Use of a high amplification factor film as a phosphor biasing electrode, and variability of the phosphor biasing potential to achieve brightness or gray scale control are further described in the disclosure.
Owner:ST CLAIR INTPROP CONSULTANTS
Electric field emitting source, element using same, and production method therefor
An electric field emitting source is equipped with an electron emitting film which comprises a nano-sized electron emitting substance and has a first surface and a second surface constituting the surface opposite thereto, and a cathode which secures one end of the electron emitting film and comprises a first block and a second block respectively corresponding to the first surface and the second surface of the electron emitting film.
Owner:LUMINAX CO LTD
Nanotube-based vacuum devices
InactiveUS7176478B2Improve transconductanceRaise the ratioNanoinformaticsCold cathodesCapacitanceTerminal equipment
New, hybrid vacuum electron devices are proposed, in which the electrons are extracted from the nanotube into vacuum. Each nanotube is either placed on the cathode electrode individually or grown normally to the cathode plane. Arrays of the nanotubes are also considered to multiply the output current. Two- and three-terminal device configurations are discussed. In all the cases considered, the device designs are such that both input and output capacitances are extremely low, while the efficiency of the electron extraction into vacuum is very high, so that the estimated operational frequencies are expected to be in a tera-hertz range. New vacuum triode structure with ballistic electron propagation along the nanotube is also considered.
Owner:ITUS
Nanotube-based vacuum devices
InactiveUS20050161668A1Improve transconductanceRaise the ratioNanoinformaticsCold cathodesCapacitanceTerminal equipment
New, hybrid vacuum electron devices are proposed, in which the electrons are extracted from the nanotube into vacuum. Each nanotube is either placed on the cathode electrode individually or grown normally to the cathode plane. Arrays of the nanotubes are also considered to multiply the output current. Two- and three-terminal device configurations are discussed. In all the cases considered, the device designs are such that both input and output capacitances are extremely low, while the efficiency of the electron extraction into vacuum is very high, so that the estimated operational frequencies are expected to be in a tera-hertz range. New vacuum triode structure with ballistic electron propagation along the nanotube is also considered.
Owner:ITUS
Field emission display devices
InactiveUS6084345ALow costImprove efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectrode and associated part arrangementsSecondary emissionDisplay device
Cathodoluminescent field emission display devices feature phosphor biasing, amplification material layers for secondary electron emissions, oxide secondary emission enhancement layers, and ion barrier layers of silicon nitride, to provide high-efficiency, high-brightness field emission displays with improved operating characteristics and durability. The amplification materials include copper-barium, copper-beryllium, gold-barium, gold-calcium, silver-magnesium and tungsten-barium-gold, and other high amplification factor materials fashioned to produce high-level secondary electron emissions within a field emission display device. For enhanced secondary electron emissions, an amplification material layer can be coated with a near mono-molecular film consisting essentially of an oxide of barium, beryllium, calcium, magnesium or strontium. Use of a high amplification factor film as a phosphor biasing electrode, and variability of the phosphor biasing potential to achieve brightness or gray scale control are further described in the disclosure.
Owner:ST CLAIR INTPROP CONSULTANTS
Arrangement and a method for emitting light
InactiveUS20050062413A1Easily be dimmedBright lightElectric circuit arrangementsCathode ray/electron stream lampsSpelunkingFluorescence
The present invention relates to an arrangement for emitting light comprising: a hermetically sealed caving (4) including a transparent or translucent window (10); a layer (3) of a fluorescent substance arranged within said casing covering at least a major part of said window; an electron emitting cathode (1) arranged within said casing for emission of electrons; and an anode (2). Said caving is filled with a has suitable for electron avalanche amplification. Said cathode and anode are, during use, held at electric potentials such that said emitted electrons are accelerated and avalanche amplified in said gas: and said layer is arranged to emit light through raid window in response to being bombarded by avalanche amplified electrons and / or in response to being exposed to ultraviolet light as being emitted in the gas due w interactions between the avalanche amplified electrons and the gas.
Owner:LIGHTLAB
Pulse mode electron generator
InactiveUS6388384B1Reduce power consumptionEasy to controlStatic indicating devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansVoltage generatorPulse mode
The pulse mode electron generator of the invention includes a field emission cathode with electron-emitting micropoints associated with a grid biased by means for positively biasing the grid and an anode attracting electrons emitted by the cathode. The grid is biased by a permanent positive pre-bias voltage generator delivering a rest voltage which is slightly lower than the emission threshold voltage of the cathode and in series with a positive pulse voltage generator delivering a pulse component of sufficient value to exceed the emission threshold voltage of the cathode. This facilitates the pulse mode production of electrons and reduces the power consumption needed to produce the electrons.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method and apparatus for modifying object with electrons generated from cold cathode electron emitter
InactiveCN1849673AImprove processing efficiencyImprove uniformityRadiation/particle handlingCold cathodesCold cathodeNanocrystalline silicon
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for treating and improving a target object using electrons, by which it is possible to use electrons to uniformly And effectively deal with and improve the target audience. The method uses a cold-cathode electron emitter having the ability to emit electrons from a planar electron-emitting portion according to the tunneling effect, and preferably includes a pair of electrodes and a strong field drift layer comprising nanocrystalline silicon disposed between the electrodes . A target object is exposed to electrons emitted from the planar electron emitting portion by applying a voltage between the electrodes. Preferably, the energy of the emitted electrons is selected from the range of 1 eV to 50 keV, preferably 1 eV to 100 eV.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Diamond triode devices with a diamond microtip emitter
InactiveUS20050062389A1Improve performanceImprove emission effectAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNanoinformaticsDisplay deviceCarbon graphite
Diamond microtip field emitters are used in triode vacuum microelectronic devices, sensors and displays. Diamond triode devices having integral anode and grid structures can be fabricated. Ultra-sharp tips are formed on the emitters in a fabrication process in which diamond is deposited into mold cavities in a two-step deposition sequence. During deposition of the diamond, the carbon graphite content is carefully controlled to enhance emission performance. The tips or the emitters are treated by post-fabrication processes to further enhance performance.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Integrated circuit devices and methods employing amorphous silicon carbide resistor materials
InactiveUS6268229B1Low implementation costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField emission deviceOxygen
Integrated circuits, including field emission devices, have a resistor element of amorphous SixC1-x wherein 0<x<1, and wherein the SixC1-x incorporates at least one impurity selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogens, nitrogen, oxygen, sulphur, selenium, transition metals, boron, aluminum, phosphorus, gallium, arsenic, lithium, beryllium, sodium and magnesium.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC +1
Low voltage nanoscale vacuum electronic devices
ActiveUS20130299773A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow voltageOptoelectronics
An electronic device including a first conducting layer, a second conducting layer, and an insulating layer provided between the conducting layers. At least one side wall extends from the first conducting layer to the second conducting layer and includes at least a portion of the first conducting layer, the second conducting layer and the insulating layer. A bias voltage is applied between the first and second conducting layers, wherein responsive to the bias voltage, a two dimensional electron system is induced at least in one of the first conducting layer and the second conducting layer, and wherein electrons from the two dimensional electron system are emitted from the side wall side wall as a result of Coulombic repulsion and travel in air from the one of the first conducting layer and the second conducting layer to the other of the first conducting layer and the second conducting layer.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Emitter with dielectric layer having implanted conducting centers
ActiveUS7170223B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesThin metalElectrical conductor
An emitter has a dielectric layer formed on a conductor, with a thin metal layer over the dielectric. A plurality of conducting centers is in the dielectric layer to allow electrons to pass through the dielectric from the conductor to the thin metal layer via quantum tunneling.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Field emission display device
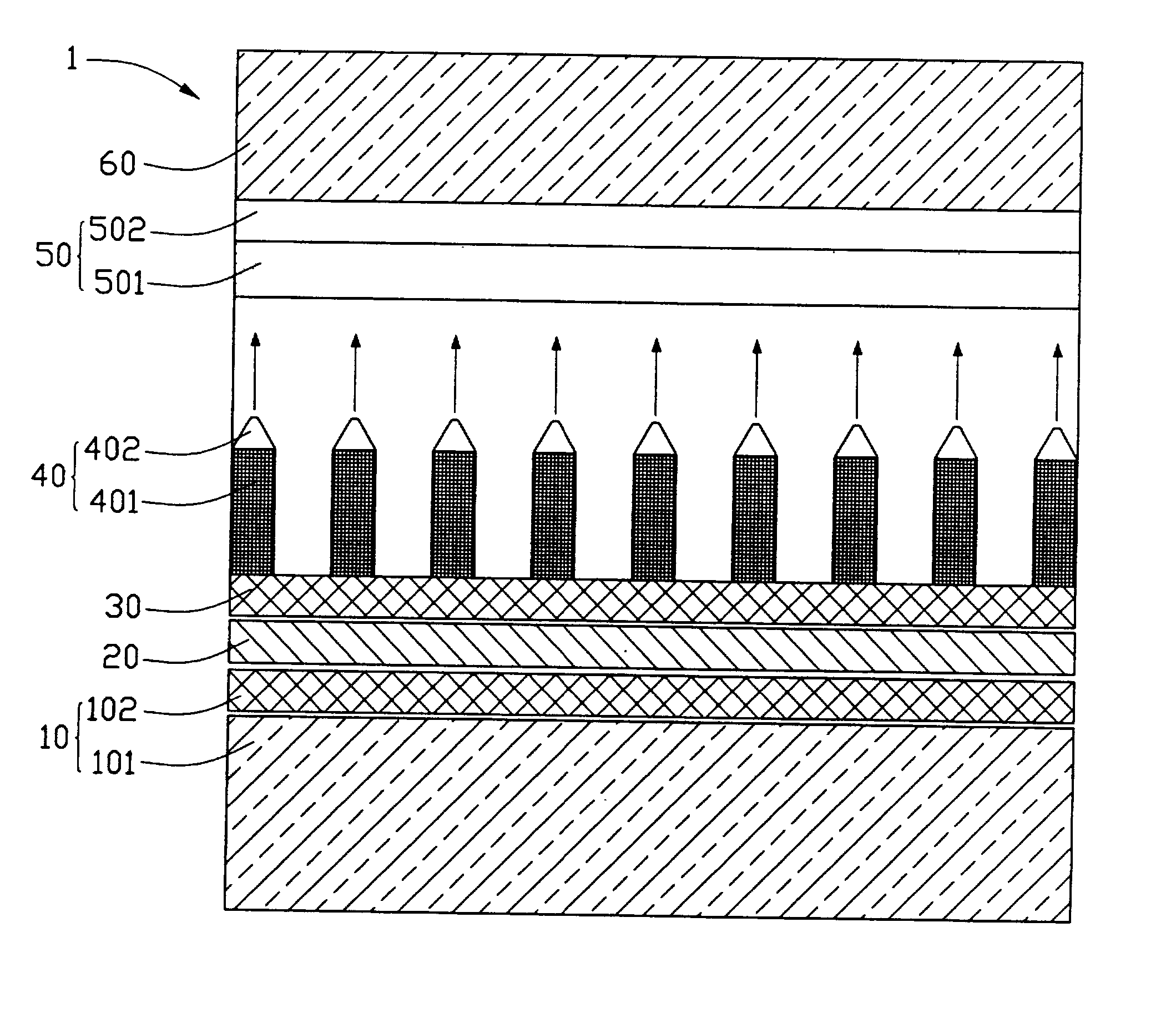
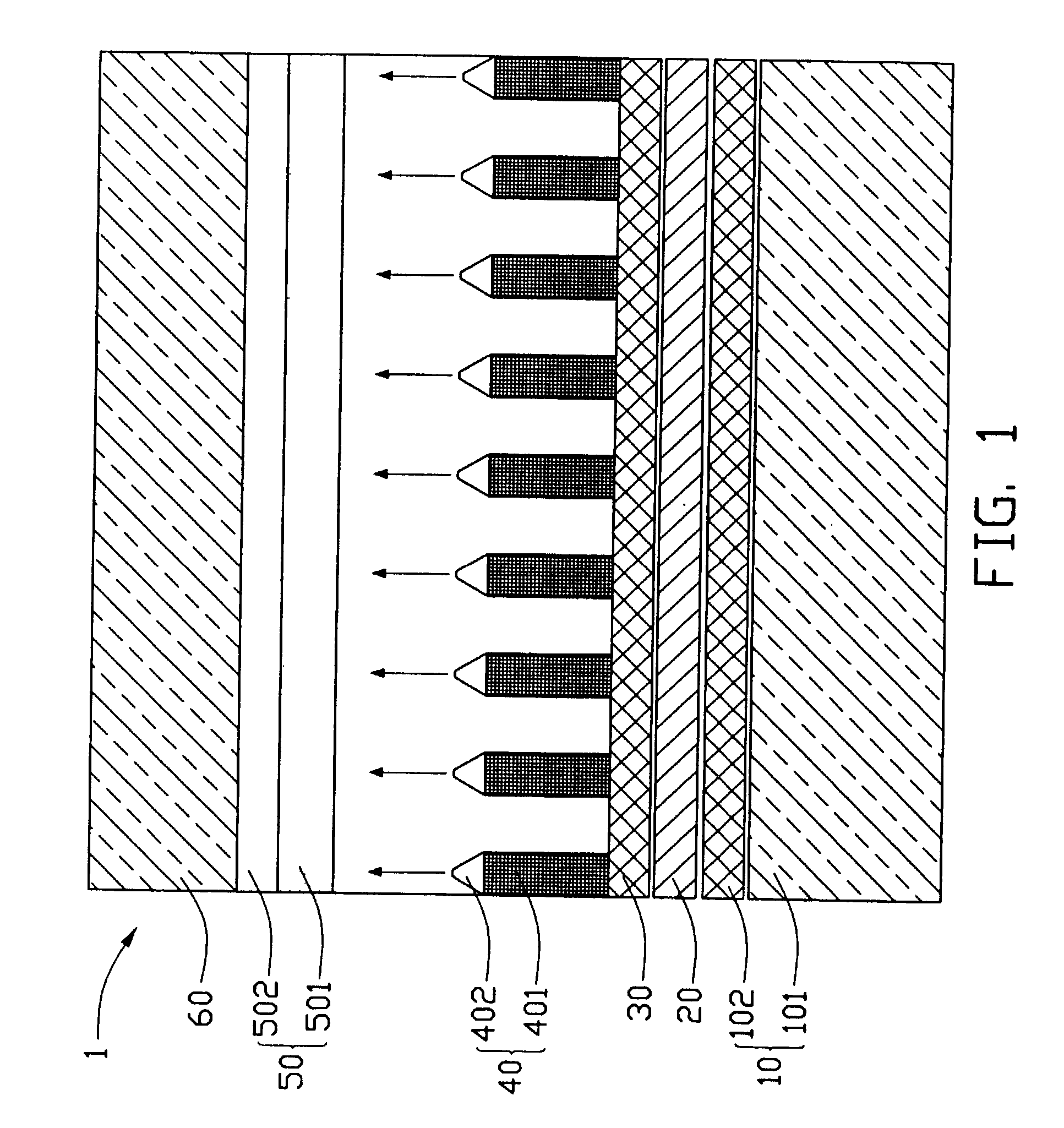
InactiveUS20040007964A1Reduce emission voltageImprove mechanical propertiesNanotechDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectrical resistance and conductanceField emission display
A field emission display device (1) includes a cathode plate (20), a resistive buffer (30) in contact with the cathode plate, a plurality of electron emitters (40) formed on the buffer, and an anode plate (50) spaced from the electron emitters. Each electron emitter includes a nano-rod first part (401) and a conical second part (402). The buffer and the nano-rods are made from silicon carbide (SiCX). The combined buffer and nano-rods has a gradient distribution of electrical resistivity such that highest electrical resistivity is nearest the cathode plate and lowest electrical resistivity is nearest-the anode plate. The conical parts are made from molybdenum. When emitting voltage is applied between the cathode and anode plates, electrons emitted from the electron emitters traverse the interspace region and are received by the anode plate. Because of the gradient distribution of electrical resistivity, only a very low emitting voltage is needed.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com