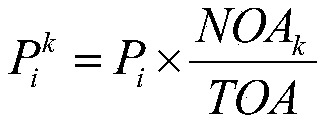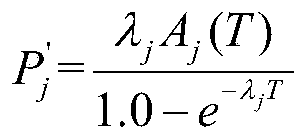Patents
Literature
81 results about "Fission products" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
On this page, a discussion of each of the main elements in the fission product mixture from the nuclear fission of an actinide such as uranium or plutonium is set out by element.
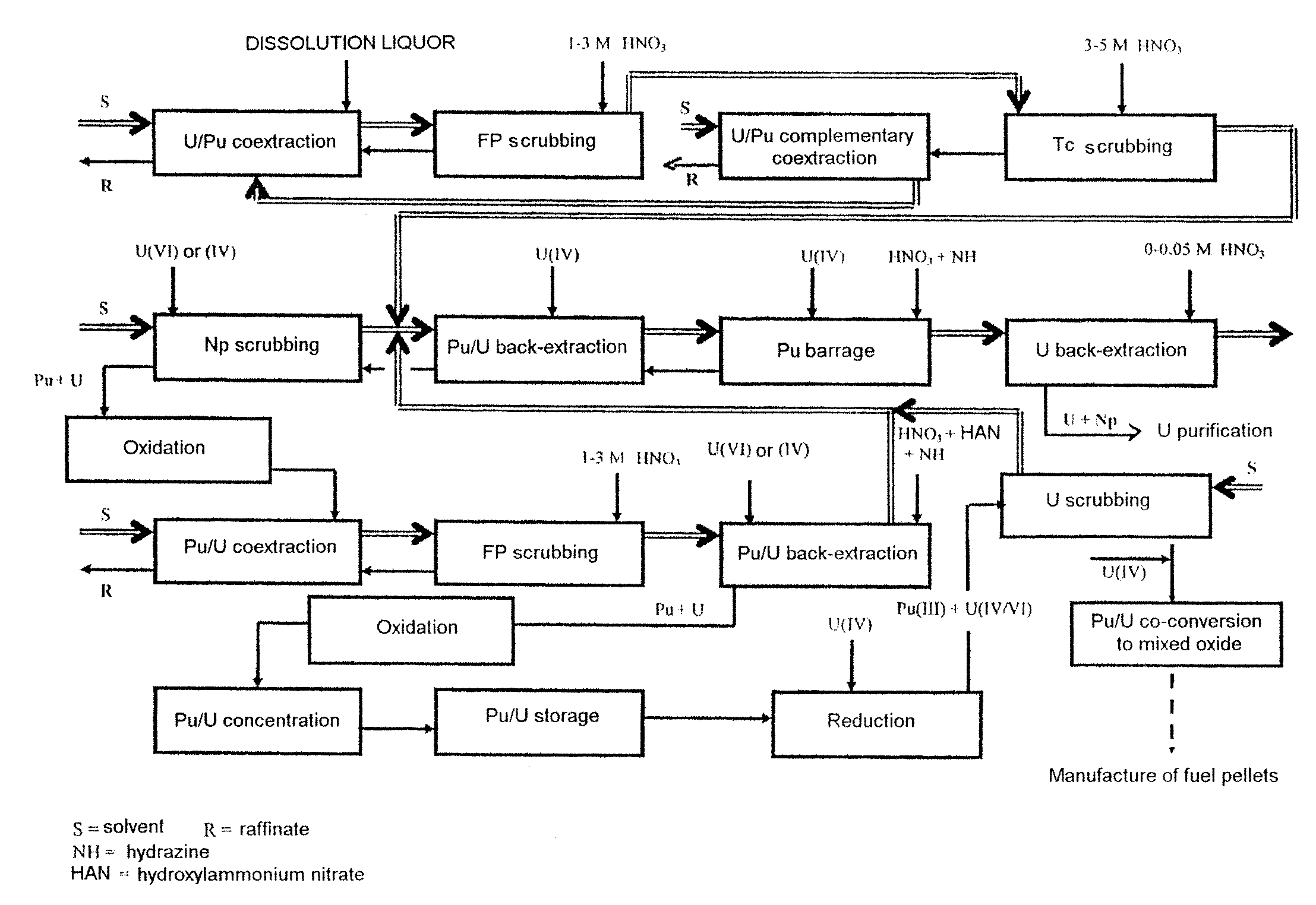
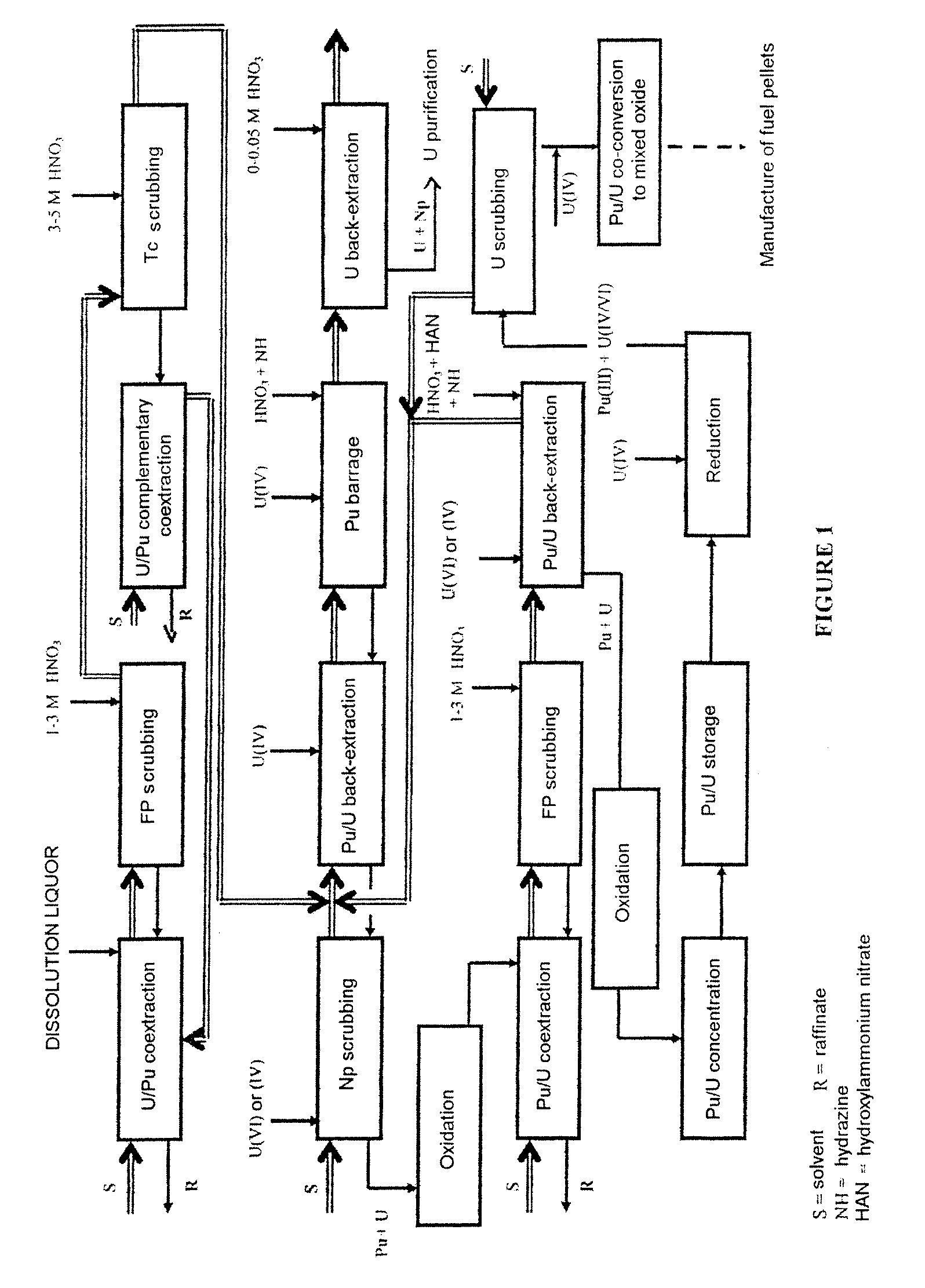
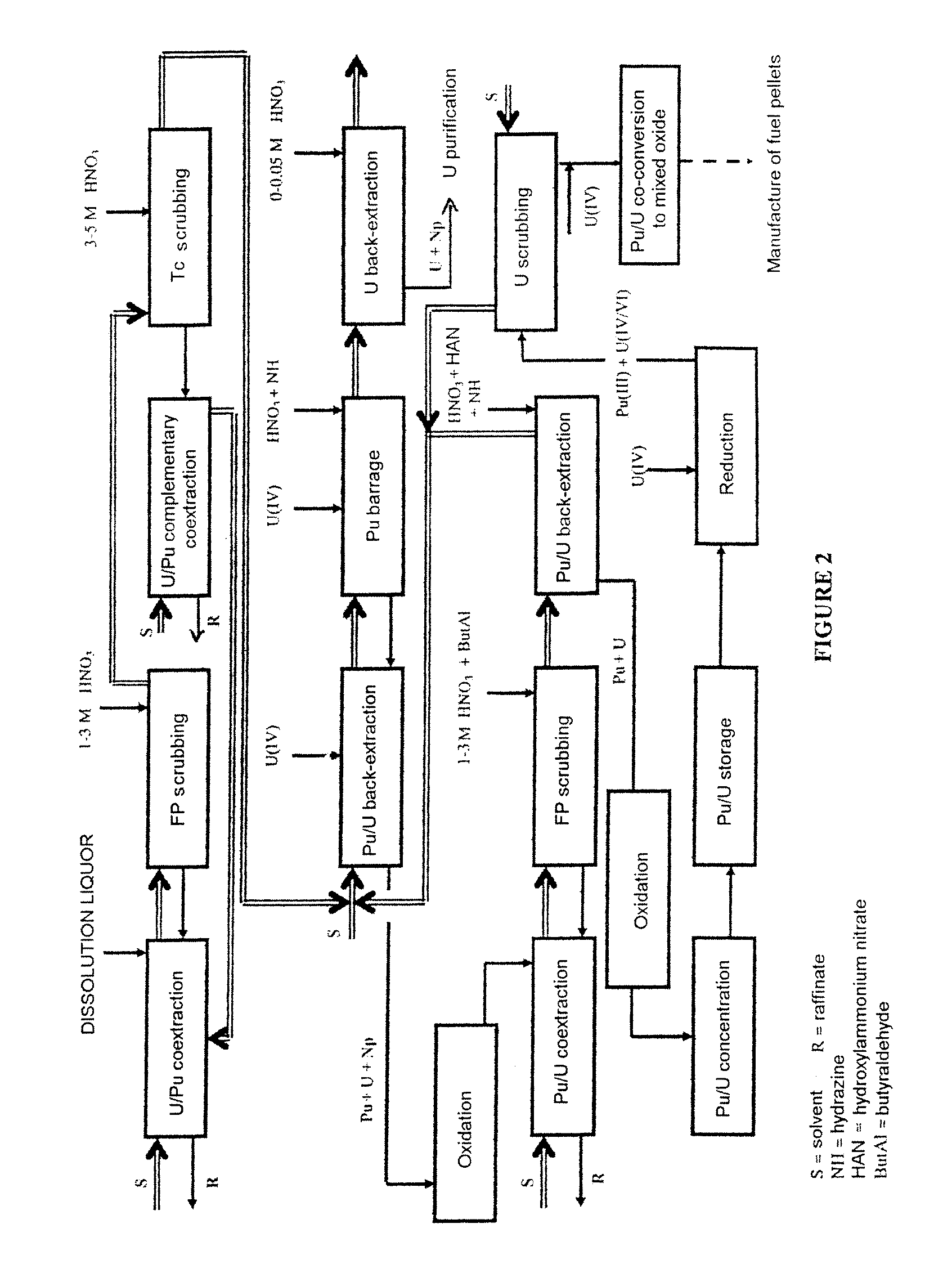
Process for reprocessing a spent nuclear fuel and of preparing a mixed uranium-plutonium oxide
ActiveUS20070290178A1Risk minimizationUranium compounds preparationSolvent extractionUranium oxideDissolution
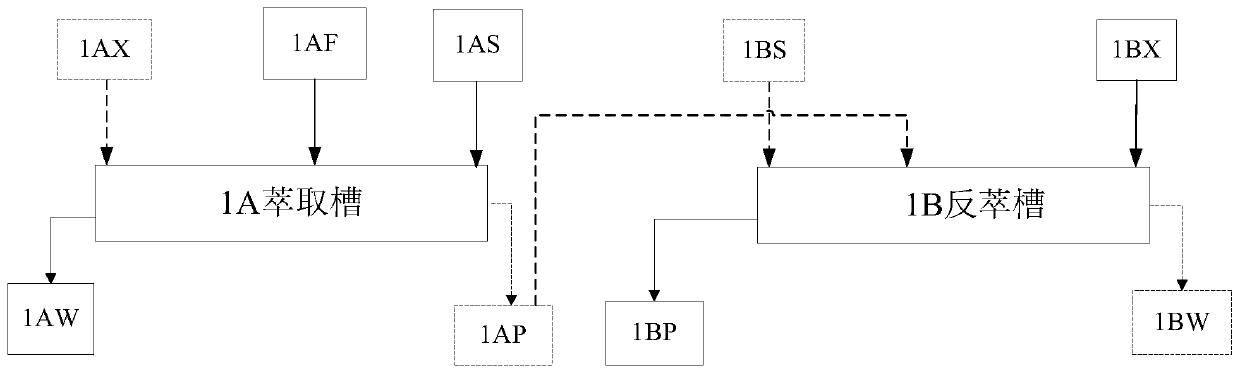
The invention relates to a process for reprocessing a spent nuclear fuel and for preparing a mixed uranium-plutonium oxide, which process comprises: a) the separation of the uranium and plutonium from the fission products, the americium and the curium that are present in an aqueous nitric solution resulting from the dissolution of the fuel in nitric acid, this step including at least one operation of coextracting the uranium and plutonium from said solution by a solvent phase; b) the partition of the coextracted uranium and plutonium to a first aqueous phase containing plutonium and uranium, and a second aqueous phase containing uranium but no plutonium; c) the purification of the plutonium and uranium that are present in the first aqueous phase; and d) a step of coconverting the plutonium and uranium to a mixed uranium / plutonium oxide. Applications: reprocessing of nuclear fuels based on uranium oxide or on mixed uranium-plutonium oxide.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +2
Method and system for subcritical nuclear rubbish treatment and nuclear fuel production based on fissioner neutron breeding
InactiveCN1591700AIncrease productivityImprove processing efficiencyConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsRadioactive decontaminationNatural uraniumBoron carbide
The present invention discloses a method for making subcritical nuclear waste material treatment and nuclear fuel production based on fissionable material neutron proliferation and its system. The exterior of external neutron source generation zone is enclosed successively with actinide elements treating zone, fissionable fuel proliferation zone, fission product treating zone and reflecting and shielding zone, all the zones are separated by means of structure material. The actinide elements treating zone includes actinide elements, fissionable fuel mixture and covering structure material; the fissionable fuel proliferation zone includes natural uranium or thorium or lean uranium and covering structure material; the fission product treating zone includes high radioactive fission product and covering structure material and neutron slowing agent, and the reflecting and shielding zone is formed from graphite, boron carbide, stainless steel and lead, etc.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
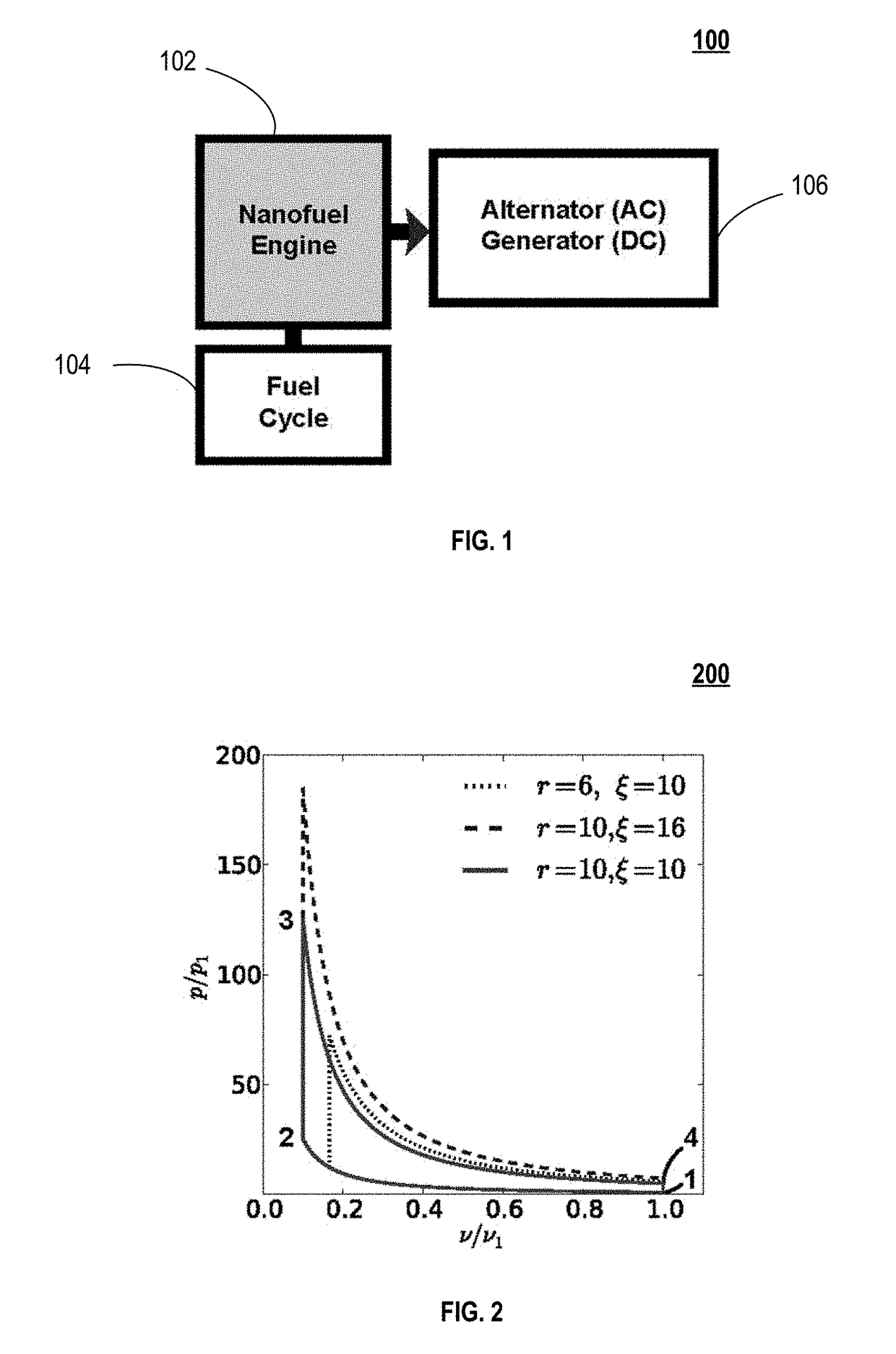
Nanofuel engine apparatus and nanofuel
ActiveUS20150052886A1Improve performanceReduce neutron leakageIntegral reactorsCosmonautic vehiclesMolecular dimensionsWorking fluid
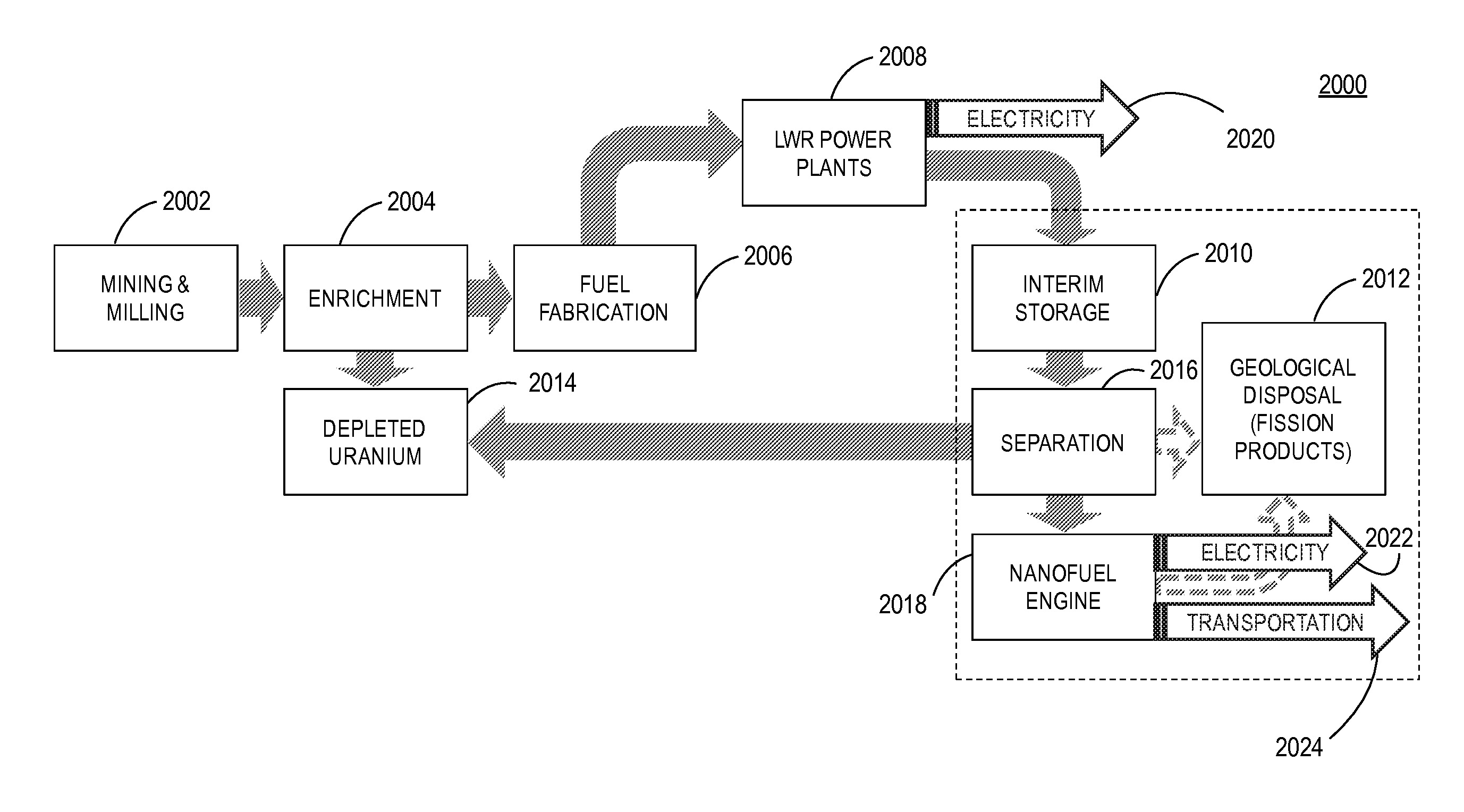
A nanofuel engine including receiving nanofuel (including moderator, nanoscale molecular dimensions & molecular mixture) internally in an internal combustion engine that releases nuclear energy, is set forth. A nanofuel chemical composition of fissile fuel, passive agent, and moderator. A method of obtaining transuranic elements for nanofuel including: receiving spent nuclear fuel (SNF); separating elements from SNF, including a stream of elements with Z>92, fissile fuel, passive agent, fertile fuel, or fission products; and providing elements. A method of using transuranic elements to create nanofuel, including: receiving, converting, and mixing the transuranic elements with a moderator to obtain nanofuel. A method of operating a nanofuel engine loaded with nanofuel in spark or compression ignition mode. A method of cycling a nanofuel engine, including compressing nanofuel; igniting nanofuel; capturing energy released in nanofuel, which is also the working fluid; and using the working fluid to perform mechanical work or generate heat.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY RES ASSOC
System and method for rapidly separating Kr and Xe in complex fission product
ActiveCN109939538ARealize continuous separation and purificationMeet the requirements of rapid separation and purificationConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsWithdrawing sample devicesShort lifeShort lived isotopes
The invention belongs to the technical field of radiochemical separation and purification and discloses a system and method for automatically and quickly separating isotopes of Kr and Xe with short life in a complex gas fission product. The system comprises a quick sampling unit, an iodine removal unit, a xenon purification and collection unit, a krypton purification and collection unit, a controlunit, a vacuum unit, a helium gas storage tank, a xenon gas storage tank, a krypton gas storage tank and a buffer tank, wherein the method comprises the following steps of: (1) setting a vacuum atmosphere; (2) sampling; (3) removing iodine; (4) adsorbing xenon; (5) desorbing impurity gas in a xenon adsorption column; (6) desorbing xenon; (7) adsorbing krypton; and (8) desorbing impurity gas and krypton. According to the system and method, the recovery rate of krypton and xenon is more than 90%, the decontamination factor of iodine is more than 1*104, the decontamination of xenon in krypton ismore than 1*103, the decontamination of krypton in xenon is 3*103, and all process working hours can meet the time requirement of separation and purification of the isotopes of Kr and Xe with short life.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Rapid separation method of activated product gallium in fission product
The invention discloses a rapid separation method of activated product gallium in a fission product. The rapid separation method comprises the following steps of: preparation of a gallium-containing radioactive solution, preparation of an eluting solution, filling of a chromatographic separation column, control of flow speed, separation of chromatographic, and the like. The rapid separation method comprises the following specific steps of: carrying out adsorption separation by enabling a radioactive solution which is enriched with the fission product and the activated product gallium to pass through a P2O4 chromatographic column, an Al2O3 chromatographic column and a TBP (Tri-Butyl-Phosphate) extracting chromatographic column at a certain flow speed; washing, desorbing the gallium in the TBP extracting chromatographic column by utilizing a low-acid solution; and further purifying an effluent through an Al2O3 and active carbon mixed column and collecting the purified effluent in a sample bottle to obtain a radioactive measuring solution of the activated product gallium. With the adoption of the rapid separation method disclosed by the invention, the radioactive solution enriched with the fission product and the radioactive solution enriched with the activated product gallium are separated; the recycling rate of the gallium is 80-90%; and the decontamination factor of the fission product is superior to 104 and the separation flow can be finished within 2 hours.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
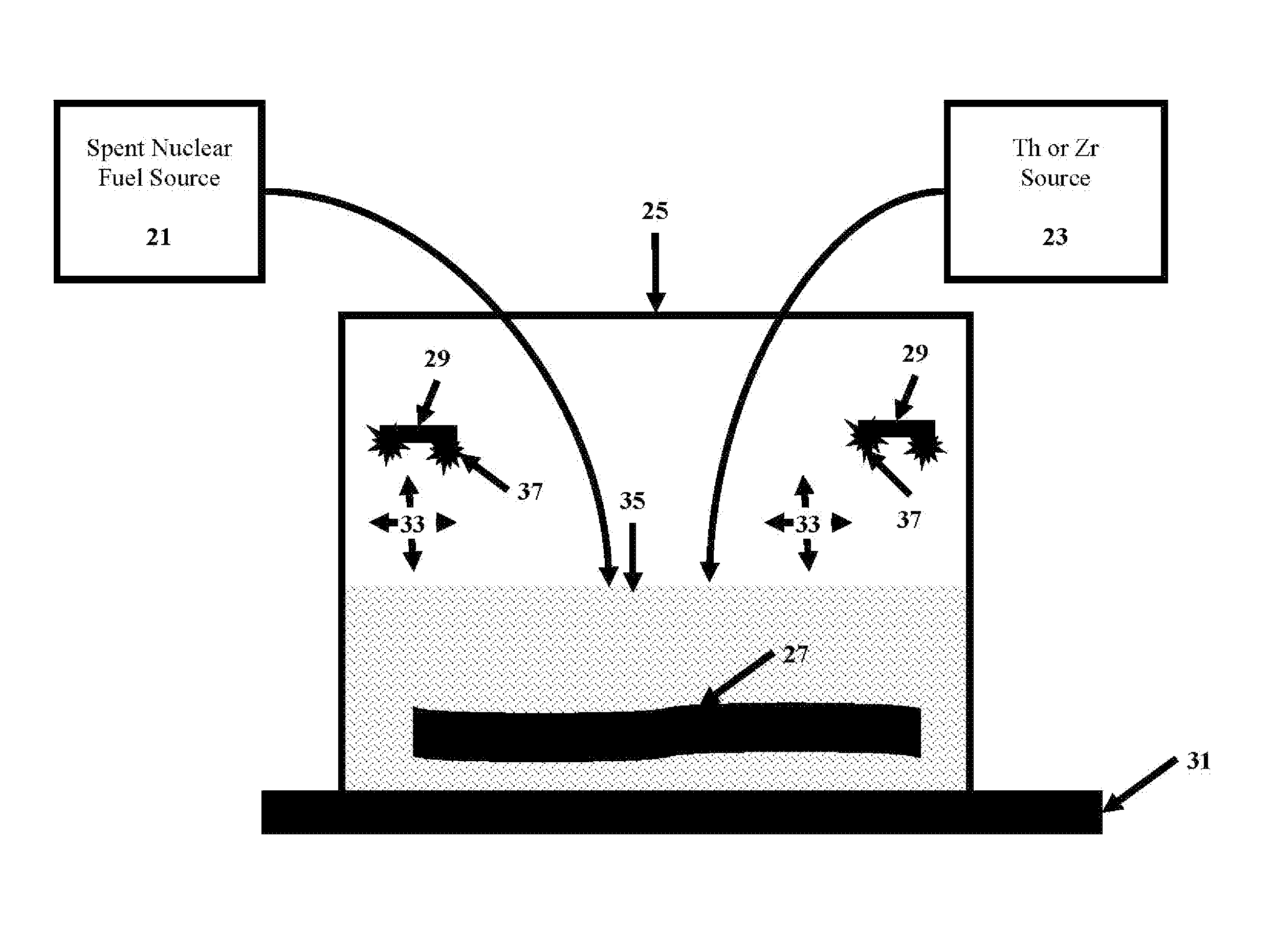
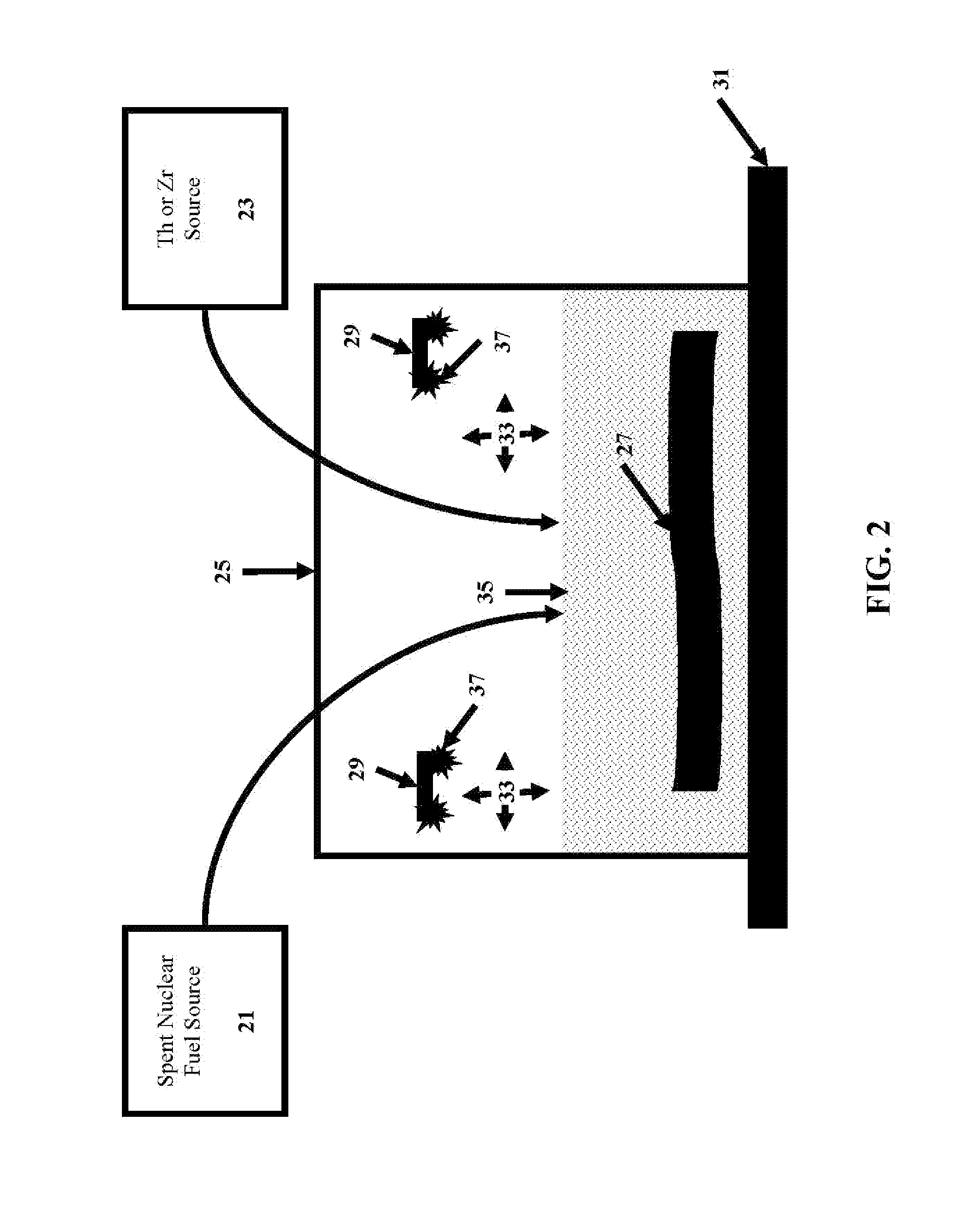
Separation of the rare-earth fission product poisons from spent nuclear fuel
ActiveUS9428401B1Specific isotope recoveryRare earth metal chloridesOxidation reductionRedox cycling
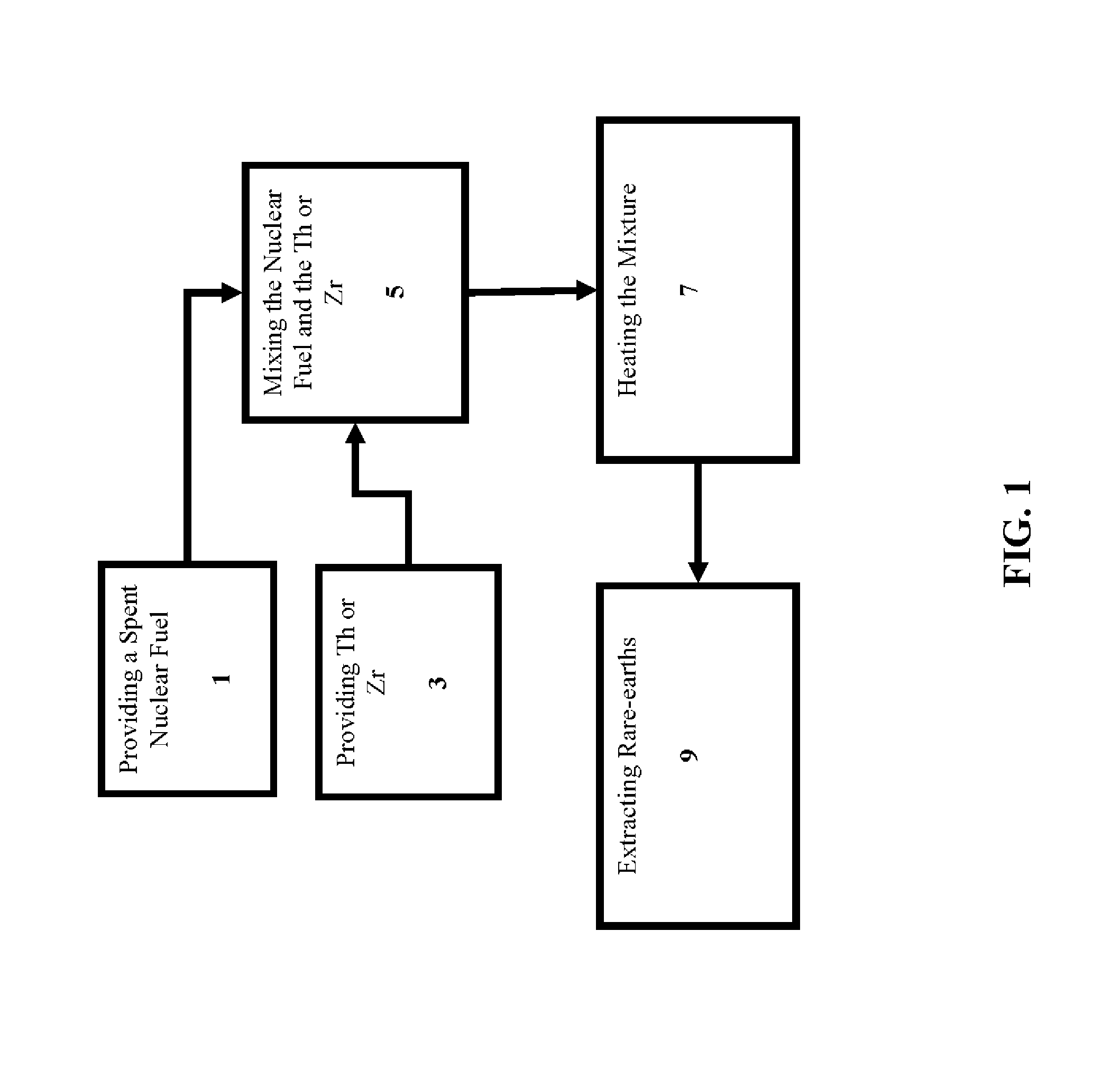
A method for the separation of the rare-earth fission product poisons comprising providing a spent nuclear fuel. The spent nuclear fuel comprises UO2 and rare-earth oxides, preferably Sm, Gd, Nd, Eu oxides, with other elements depending on the fuel composition. Preferably, the provided nuclear fuel is a powder, preferably formed by crushing the nuclear fuel or using one or more oxidation-reduction cycles. A compound comprising Th or Zr, preferably metal, is provided. The provided nuclear fuel is mixed with the Th or Zr, thereby creating a mixture. The mixture is then heated to a temperature sufficient to reduce the UO2 in the nuclear fuel, preferably to at least to 850° C. for Th and up to 600° C. for Zr. Rare-earth metals are then extracted to form the heated mixture thereby producing a treated nuclear fuel. The treated nuclear fuel comprises the provided nuclear fuel having a significant reduction in rare-earths.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
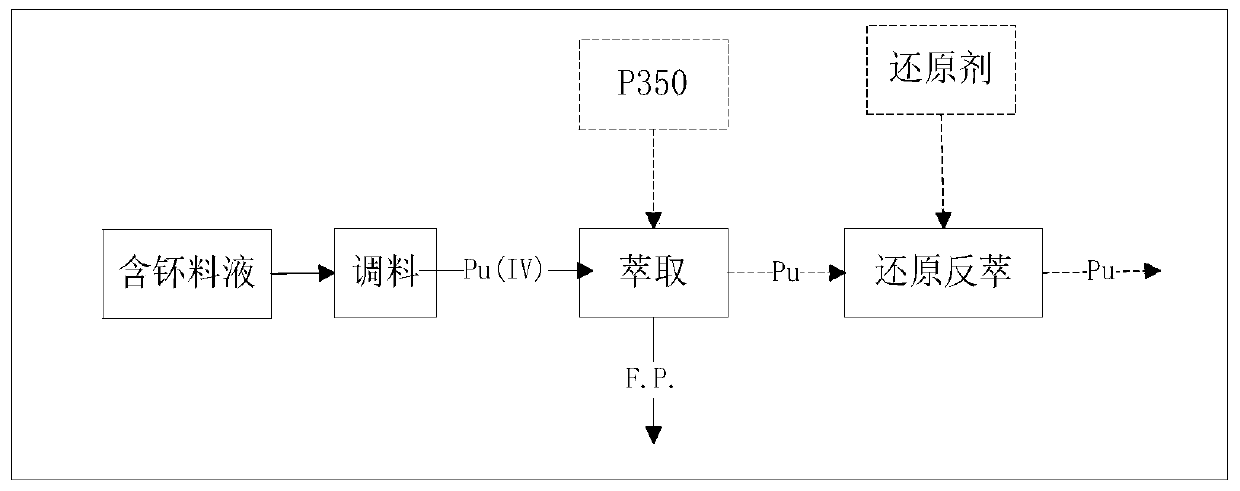
Method for extracting and recovering plutonium from plutonium-containing nitric acid solution
ActiveCN110656247AEfficient separationPurity up to standardProcess efficiency improvementFuel reprocessingPlutonium nitrate
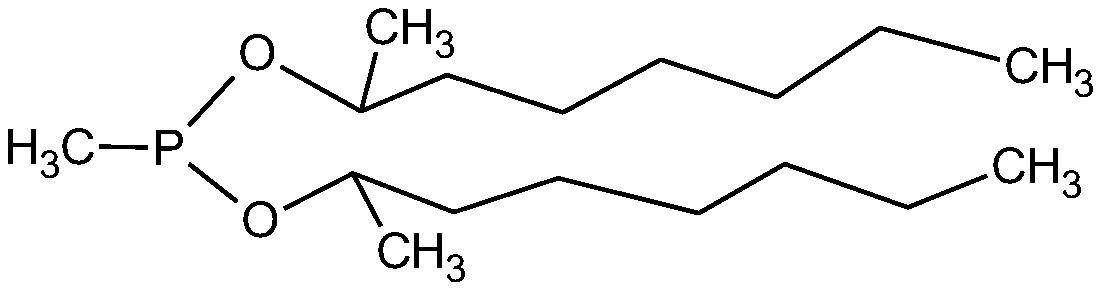
The invention belongs to the technical field of nuclear material extraction and recovery, and relates to a method for extracting and recovering plutonium from a plutonium-containing nitric acid solution. The method comprises the following steps: oxidizing plutonium in the spent fuel reprocessing plutonium-containing nitric acid solution to tetravalent with an oxidant, adding an organic solvent containing DMHMP, Di(1-methyl heptyl)methyl phosphonate for extraction under strong acidic conditions, collecting organic phase, adding a reducing agent, performing back extraction under dilute acidic conditions to selectively reduce the tetravalent plutonium in the organic phase to trivalent, and performing back extraction to form the aqueous phase. The method for extracting and recovering plutoniumfrom the plutonium-containing nitric acid solution can efficiently separate plutonium from other impurities, such as uranium, fission product elements of plutonium, strontium, and cesium, and concentrate plutonium to obtain the plutonium nitrate product solution with standard purity.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Spent nuclear fuel recycling with plasma reduction and etching
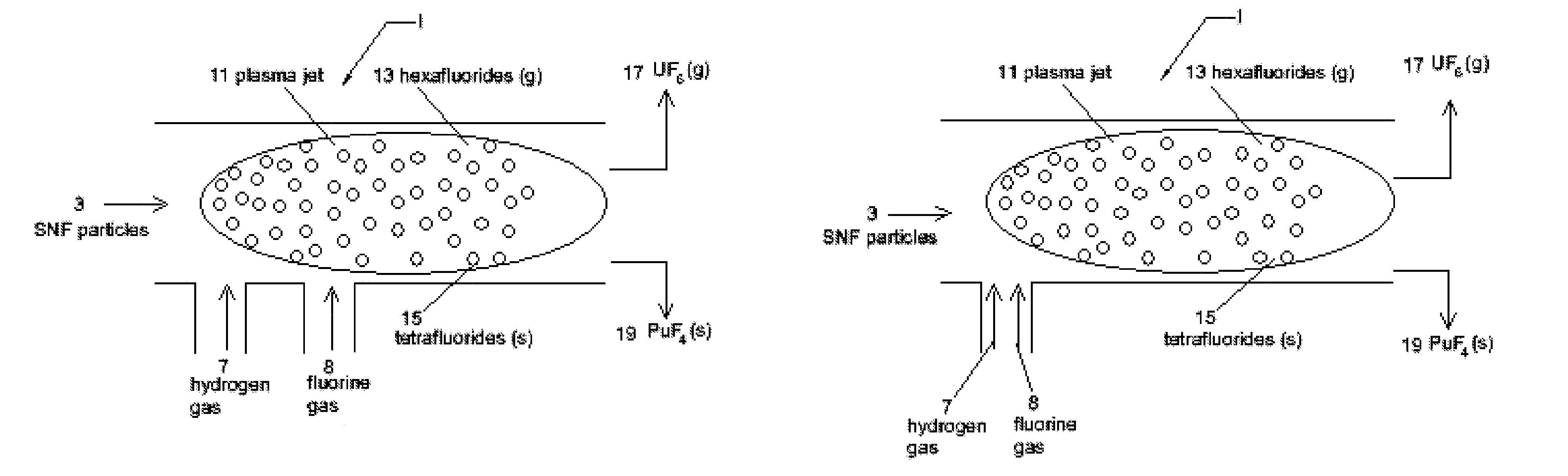
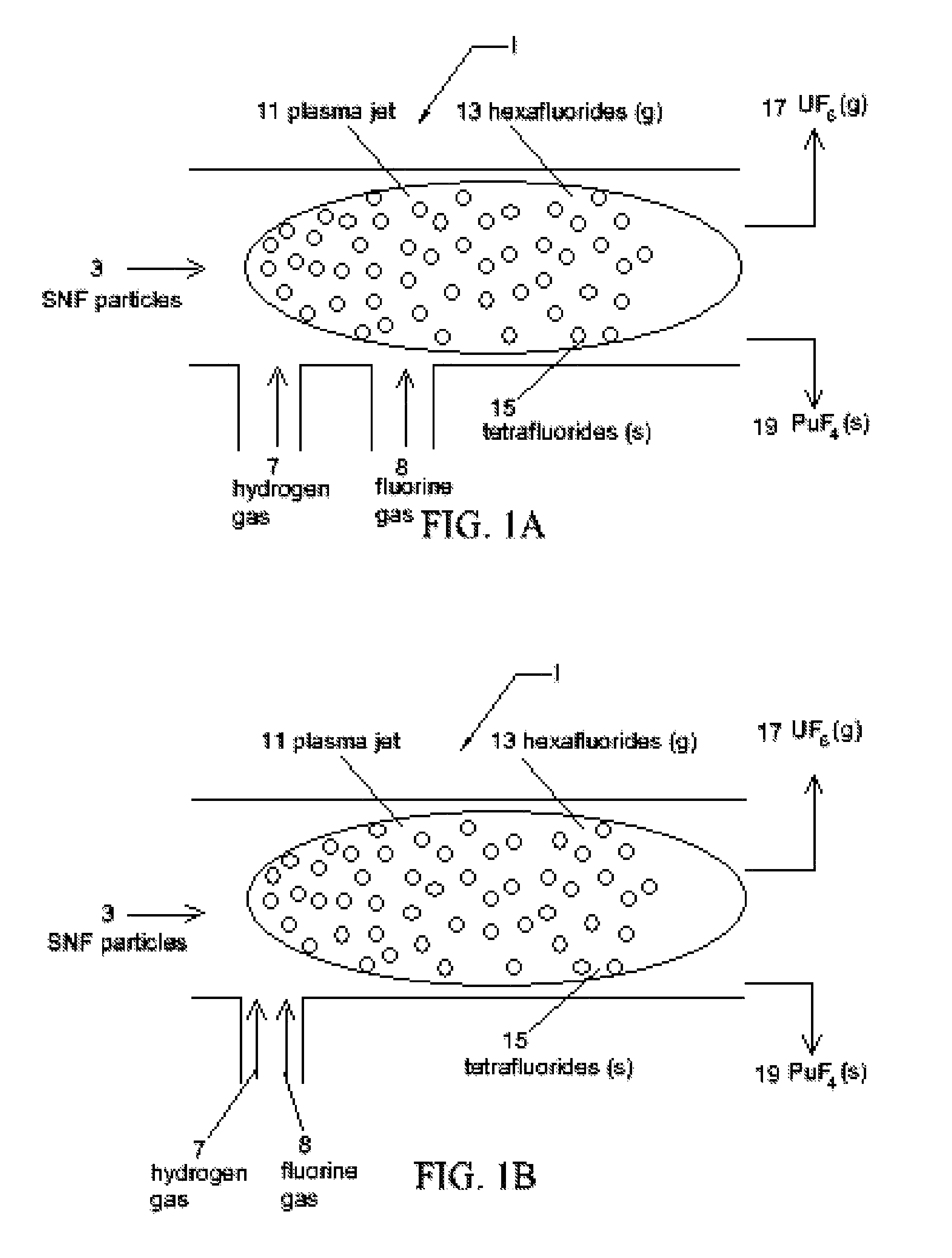
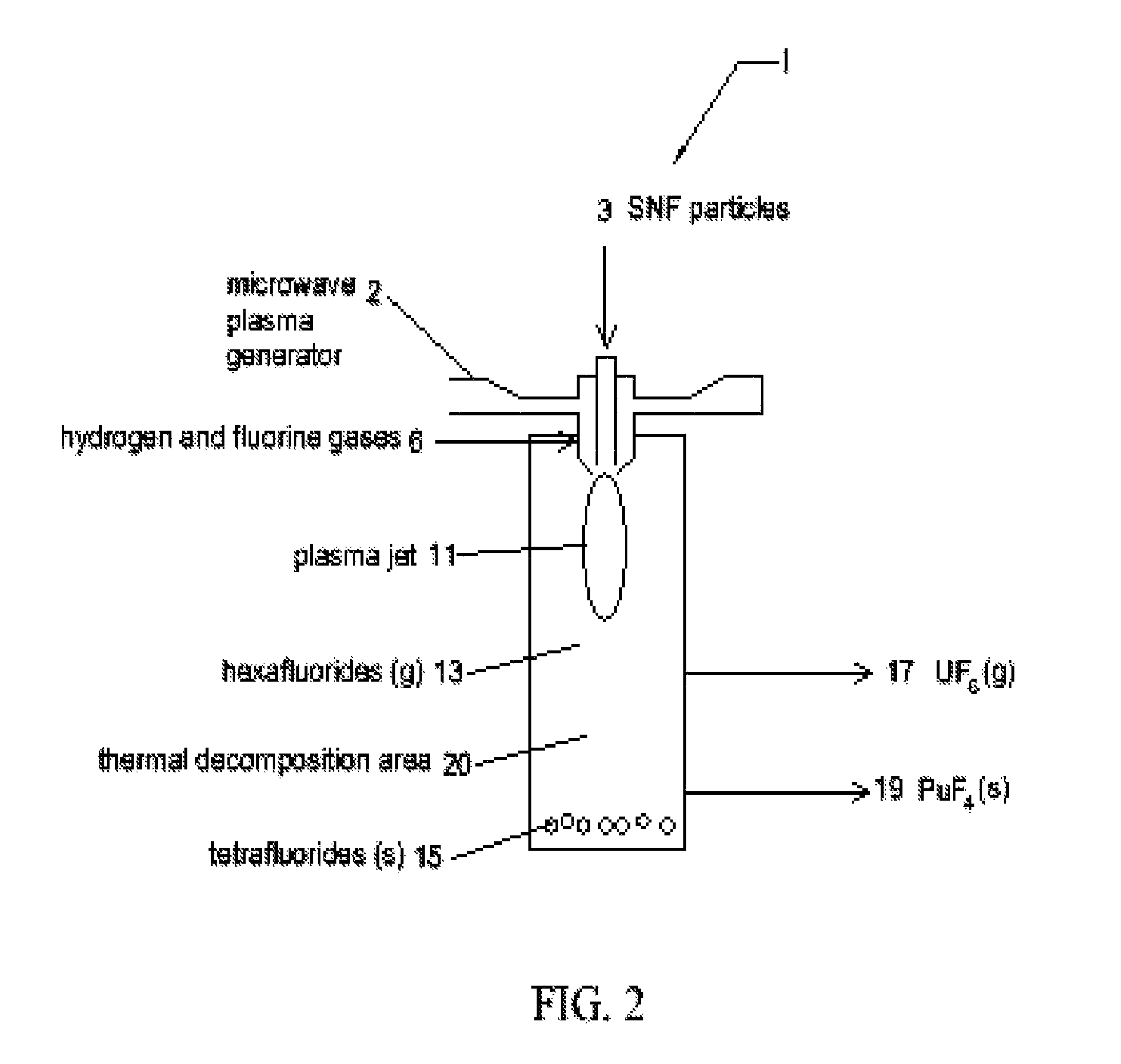
InactiveUS8192704B1Easy extractionEasy to separatePlutonium halidesNuclear energy generationHydrogenHigh-temperature corrosion
A method of extracting uranium from spent nuclear fuel (SNF) particles is disclosed. Spent nuclear fuel (SNF) (containing oxides of uranium, oxides of fission products (FP) and oxides of transuranic (TRU) elements (including plutonium)) are subjected to a hydrogen plasma and a fluorine plasma. The hydrogen plasma reduces the uranium and plutonium oxides from their oxide state. The fluorine plasma etches the SNF metals to form UF6 and PuF4. During subjection of the SNF particles to the fluorine plasma, the temperature is maintained in the range of 1200-2000 deg K to: a) allow any PuF6 (gas) that is formed to decompose back to PuF4 (solid), and b) to maintain stability of the UF6. Uranium (in the form of gaseous UF6) is easily extracted and separated from the plutonium (in the form of solid PuF4). The use of plasmas instead of high temperature reactors or flames mitigates the high temperature corrosive atmosphere and the production of PuF6 (as a final product). Use of plasmas provide faster reaction rates, greater control over the individual electron and ion temperatures, and allow the use of CF4 or NF3 as the fluorine sources instead of F2 or HF.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
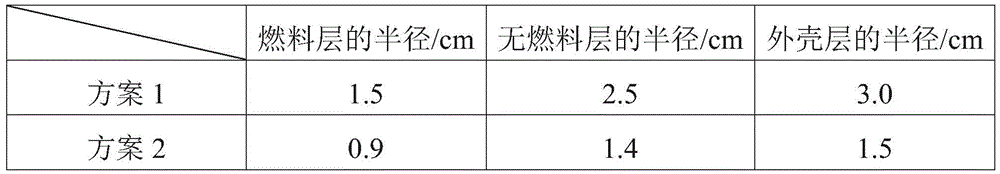
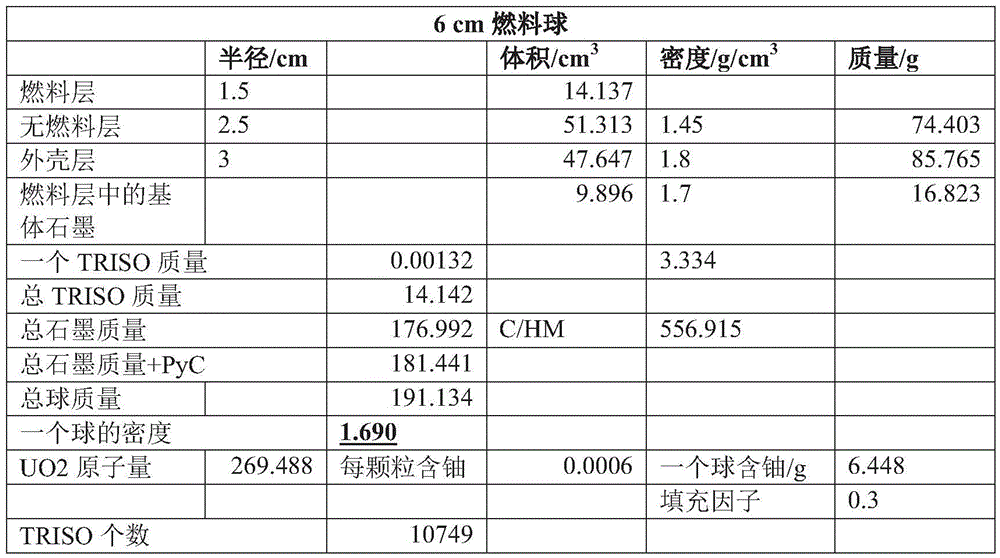
Fuel element as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106128515ALow densityRelieve swellingFuel elementsNuclear energy generationNuclear engineeringMolten salt
The invention discloses a fuel element as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The fuel element disclosed by the invention is a sphere which sequentially comprises a fuel layer, a non-fuel layer, and a housing layer which are concentric from inside to outside, wherein the non-fuel layer is made from conventional base materials in the field. The fuel element has the advantages of being small in density, having the non-fuel layer which can alleviate swell generated in the service process of the fuel layer, being not liable to rupture, high in power density, fast in heat dissipation and the like; and besides, the housing layer is compact in structure, high in compressive strength, and capable of preventing fused salt from infiltrating and fission products from releasing, and can be used for reactors. The preparation method is simple and low in cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Axial void fraction distribution measurement method and neutron multiplication factor evaluating method
InactiveUS20070076839A1Nuclear energy generationFuel element assembliesNeutron captureCorrelation curve
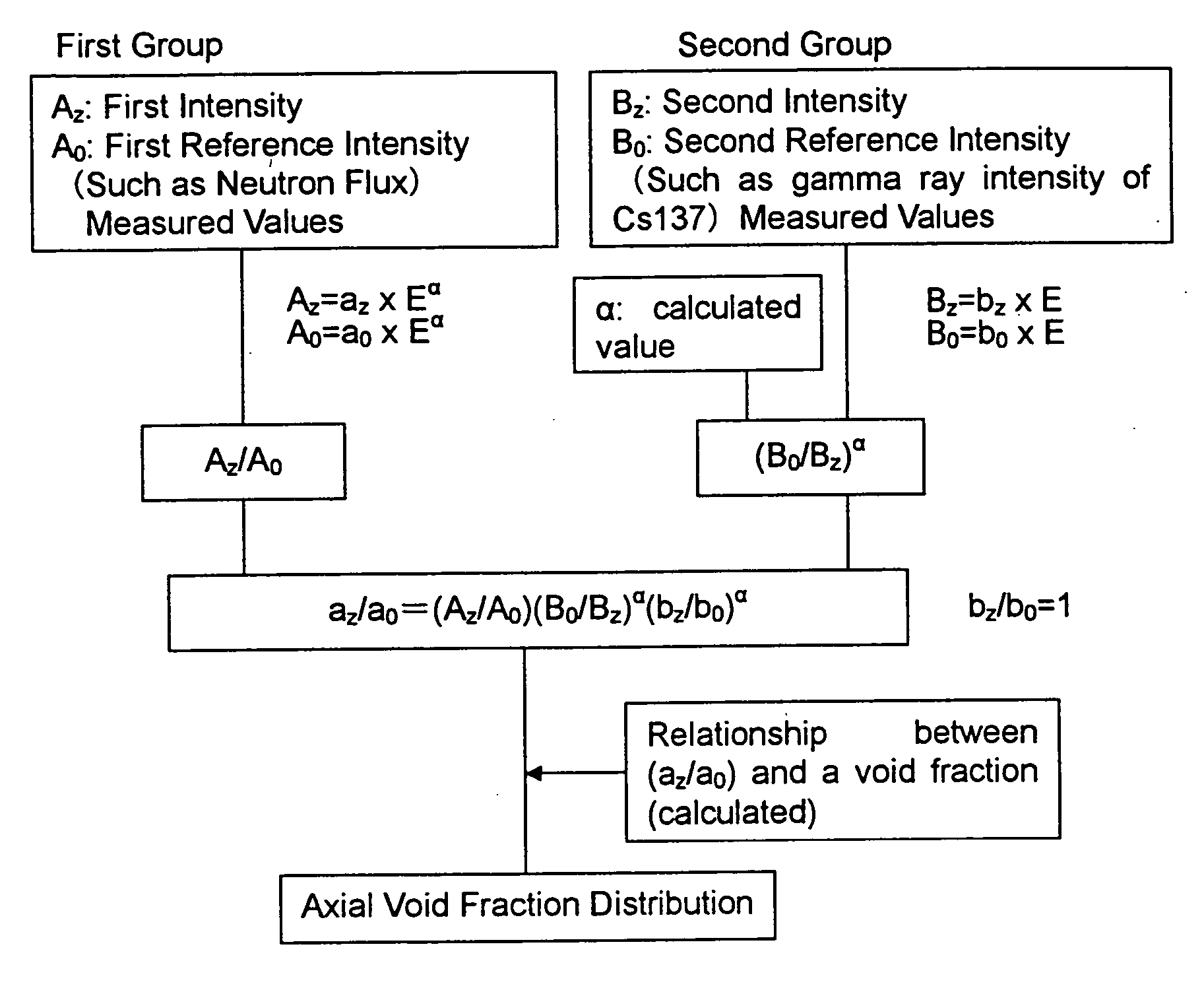
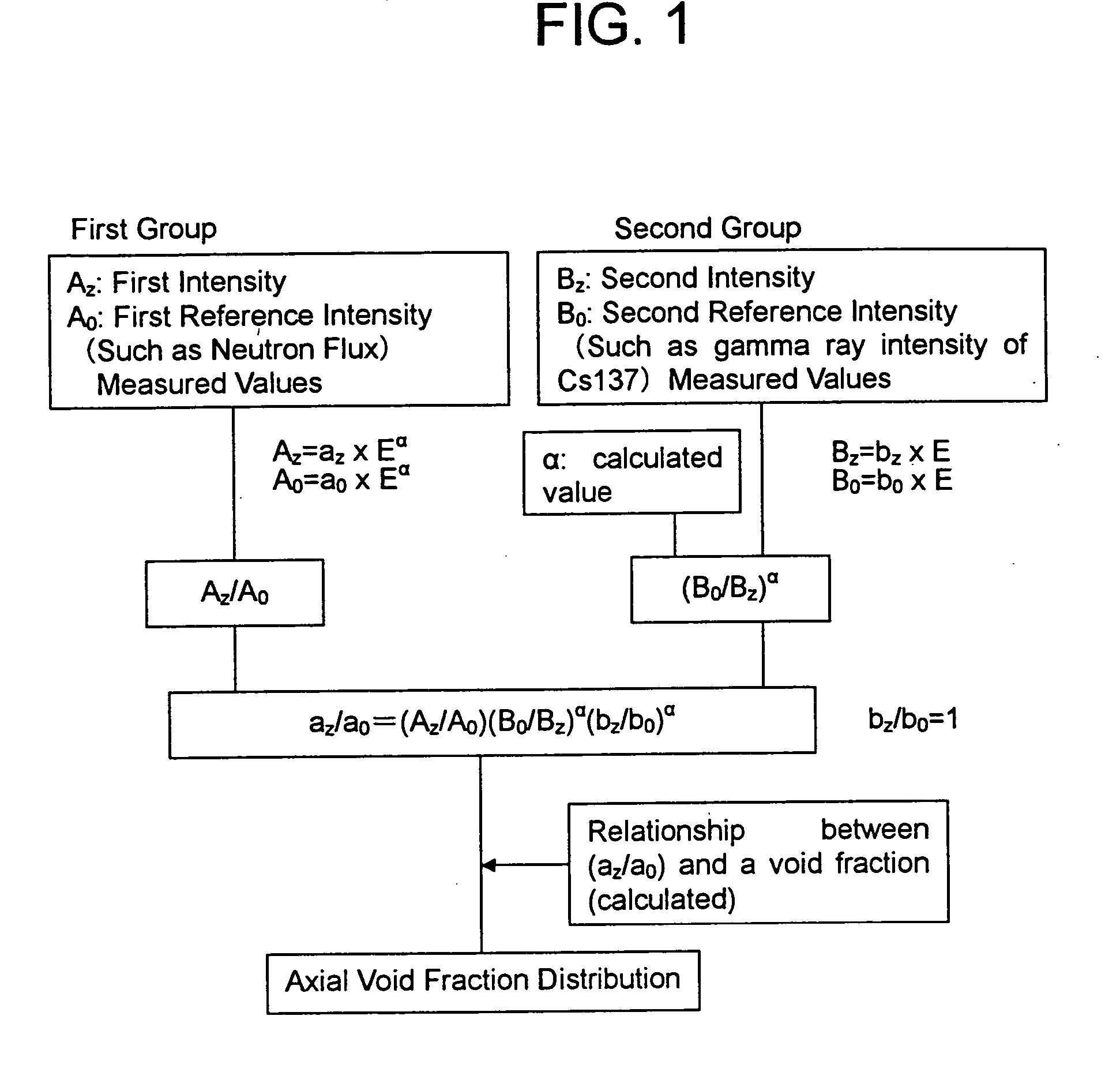
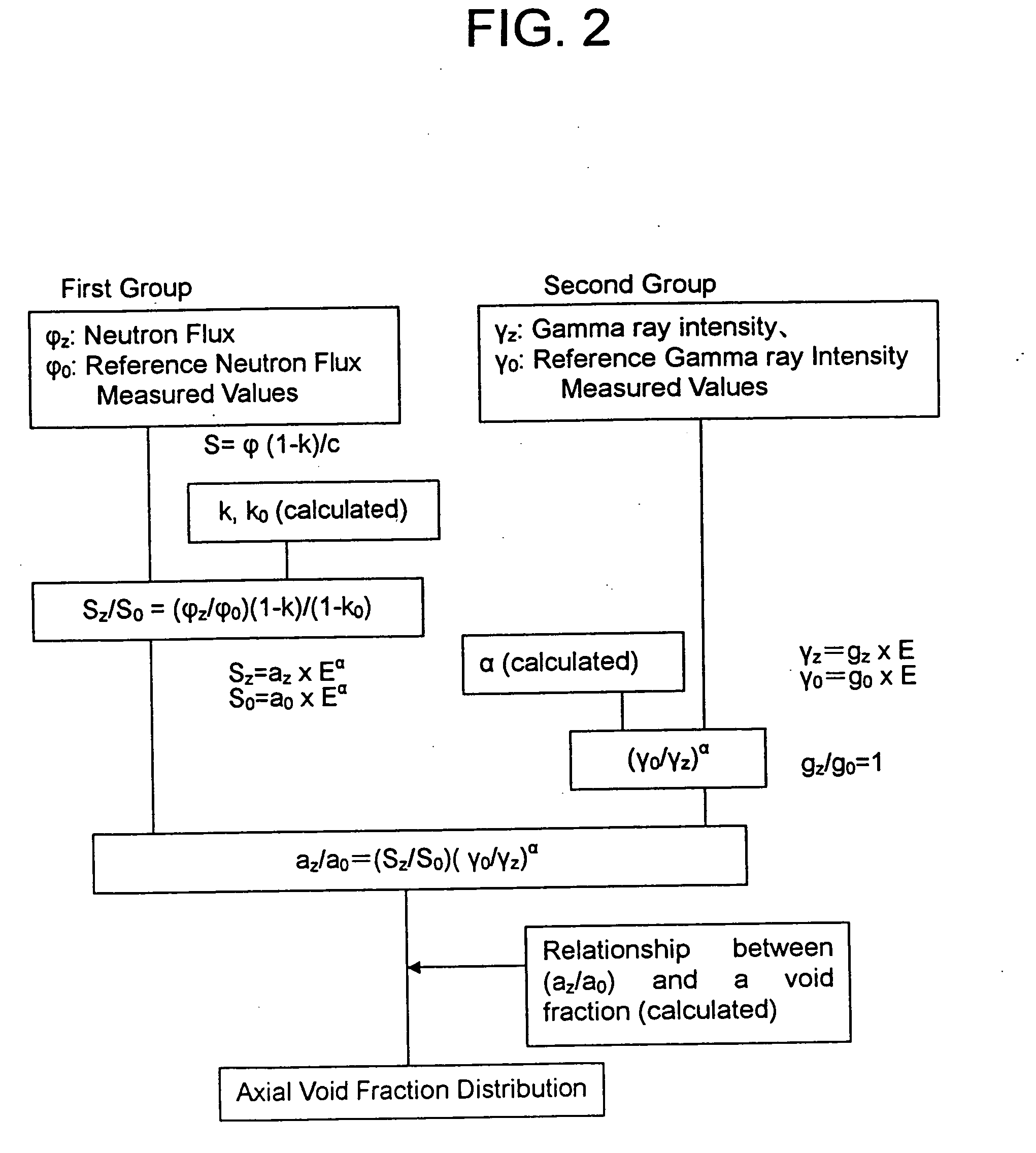
A first intensity Az expressed as Az=az×Eα, a first reference intensity Ao expressed as Ao=ao×Eα, a second intensity Bz expressed as Bz=bz×E, and a second reference intensity Bo=bo×E, are evaluated. The first intensity and the first reference intensity are of radioactive nuclides generated by a neutron capture reaction of a heavy nuclide or a fission product nuclide. The second intensity and the second reference intensity are of radioactive fission product nuclides except nuclides generated by a neutron capture reaction. The reference intensities are measured where the void fraction is known. Also a correlation curve of (az / ao) and a void fraction is evaluated. Finally an axial void fraction distribution is evaluated based on the value of (az / ao) and the correlation curve.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method for specially processing decay heat calculation in compression process of fuel consumption database
ActiveCN112100826AResolved an issue where decay heat calculations could not be performedWill not significantly increase in sizeNuclear energy generationDesign optimisation/simulationFissionBurnup
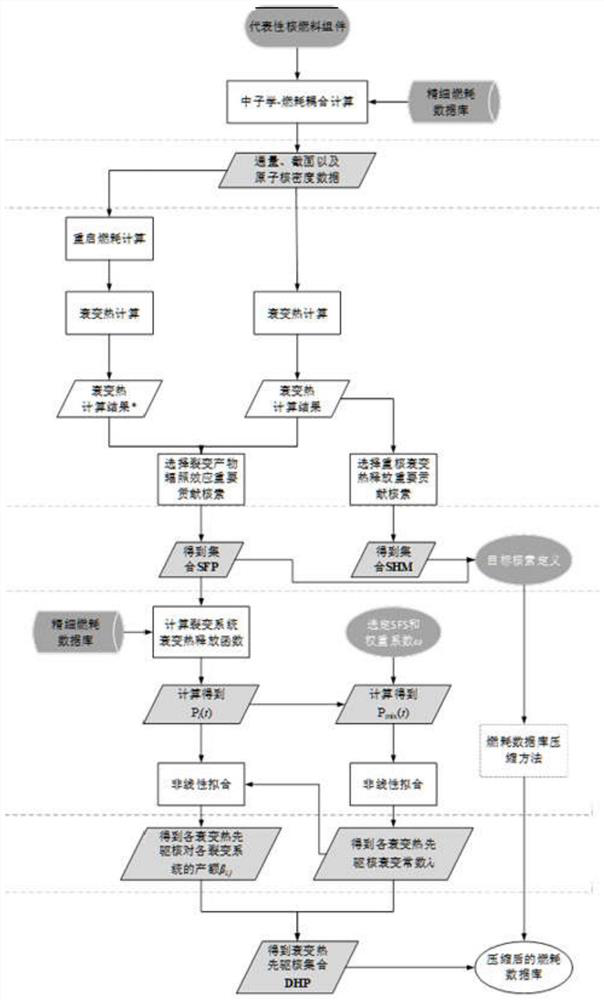
The invention relates to a method for specially processing decay heat calculation in a compression process of a fuel consumption database, which comprises the following steps of: calculating a representative nuclear fuel assembly by using a fine fuel consumption database to obtain a set of related data, and restarting fuel consumption calculation under the condition of assuming that a fission product does not react with neutrons to obtain another set of data; and using two sets of data for carrying out decay heat calculation twice, firstly, selecting a few of heavy nuclides with great contribution of heavy nuclear decay heat, secondly, selecting important contribution nuclides of the fission product irradiation effect, adding a few of heavy nuclides with great contribution and the important contribution nuclides of the fission product irradiation effect into the compressed fuel consumption database, and deducting the fission product irradiation effect from decay heat, so as to obtain afission system decay heat release function, further obtaining a fission sub-system decay heat release function based on the fission product decay hypothesis, finally performing twice nonlinear fitting on the fission sub-system decay heat release function to obtain multiple groups of decay heat precursor kernels, and adding the multiple groups of decay heat precursor kernels into the compressed fuel consumption database. The decay heat result calculated by the method is more accurate.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Concentric spherical surface separation plate type spherical main container
ActiveCN106158052ASolve the purification problemSafe and stable operationNuclear energy generationSubcritical reactorsInter layerNuclear engineering
The invention relates to a concentric spherical surface separation plate type spherical main container, and belongs to the technical field of molten salt reactors. With the molten salt depleted uranium reactor formed from the concentric spherical surface separation plate type spherical main container, the difficult problem of the purification of the fission product inside the spherical main container can be solved, the fission product purification system is not required, the burning mode that the direct input of the depleted uranium and the direct output of the spent fuel are performed on the reactor is achieved, the low-cost long-term safe and stable operating is achieved, and all the excellent performances of the molten salt depleted uranium reactor can be maintained. According to the present invention, the space is divided into the thin sheet by using the multi-layer concentric spherical surface thin separation plate having the material inlet and the material outlet, or the space is divided into the tubular channels by additionally using the radial thin separation plate, valves and the like are arranged on the material inlet, the material outlet and the channel to control the molten salt flowing mode, the internal separation plate uses the modes such as module design, non-welded stacking installation of various modules, and whole replacement of the module, the top portion is provided with the openable cover plate system, and the innermost layer, the outermost layer and the required middle layer are provided with the corresponding channels connected to the corresponding control device and other devices outside the reactor core; and the concentric spherical surface separation plate type spherical main container is mainly used as the neutron source and the small energy source.
Owner:董沛 +2
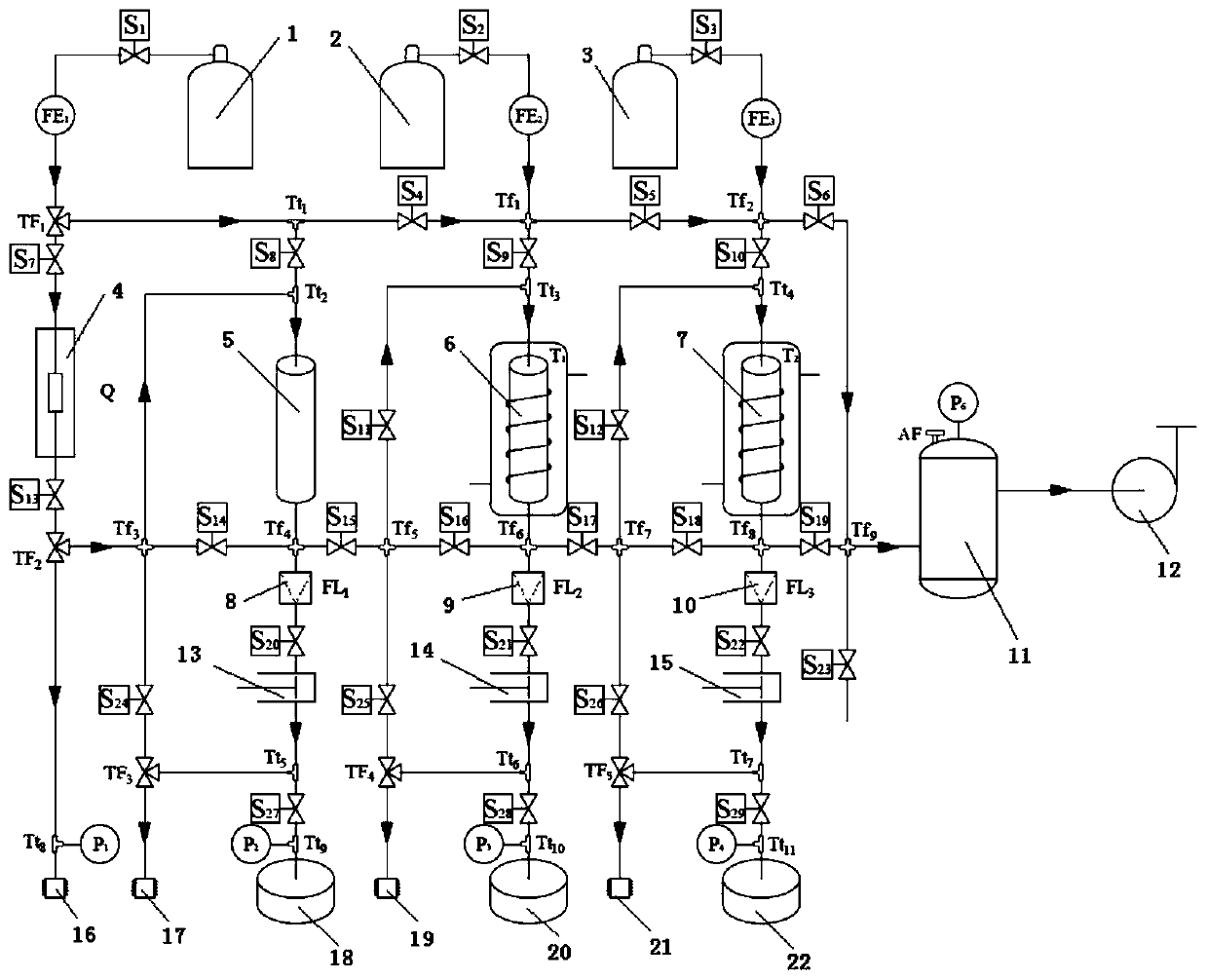
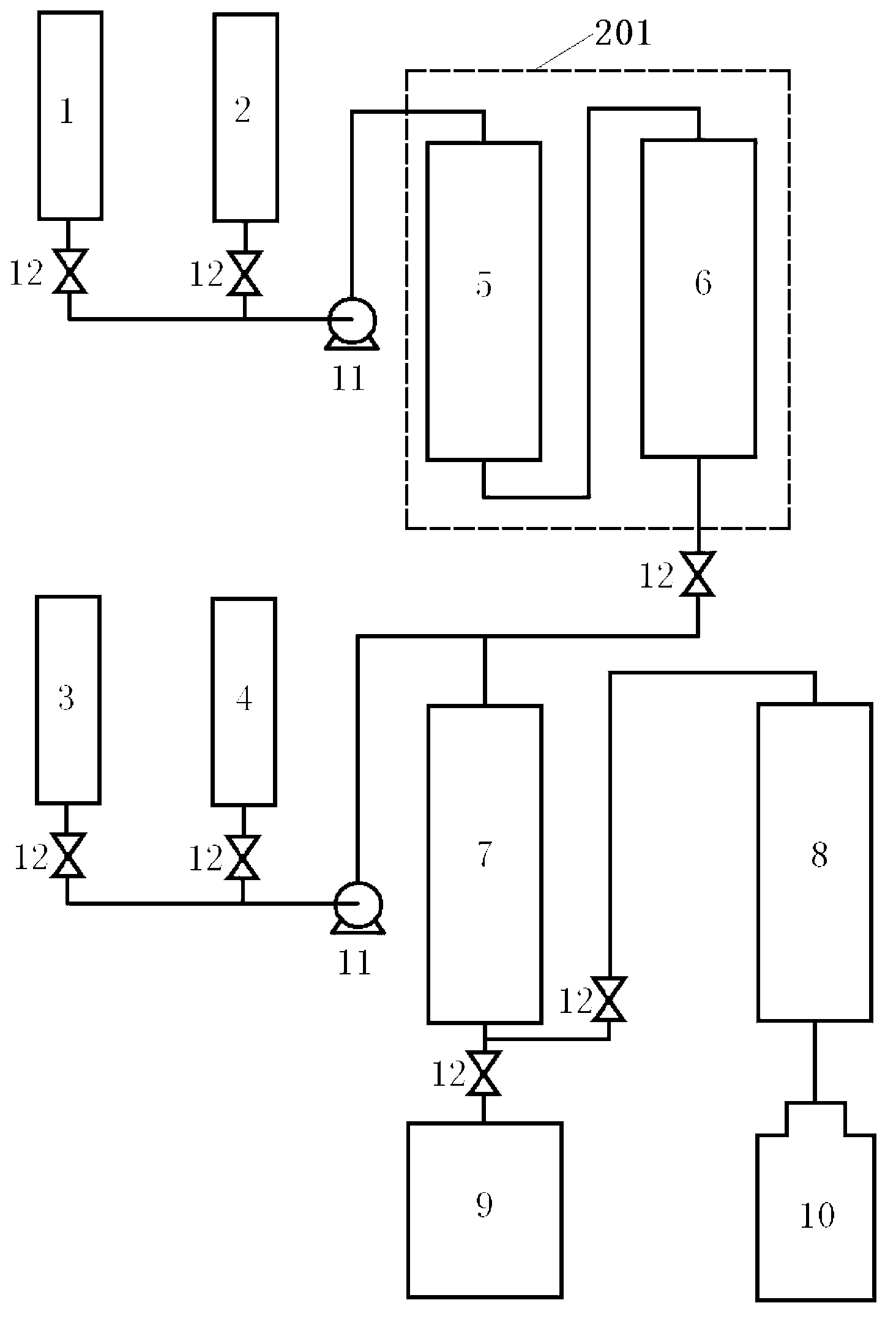
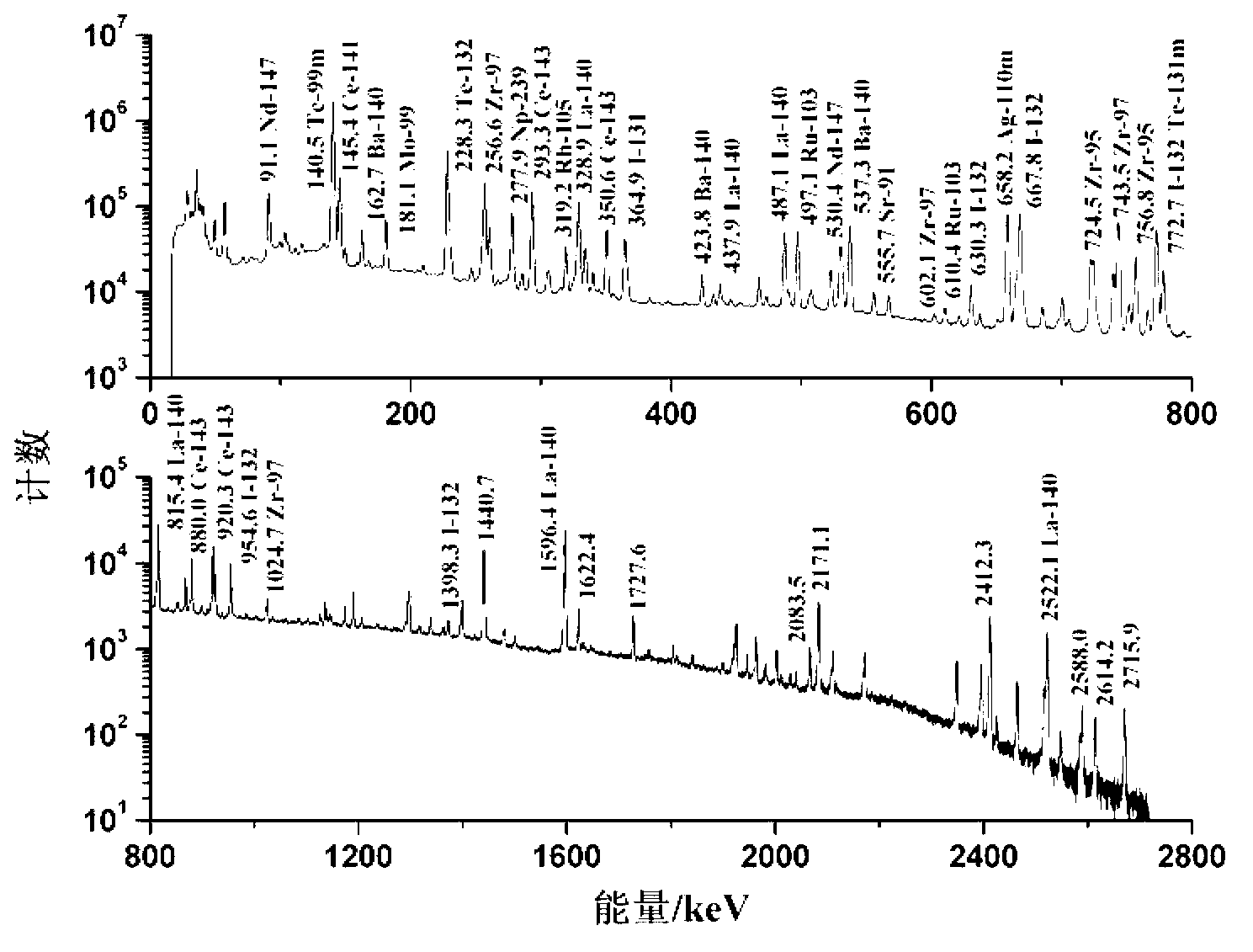
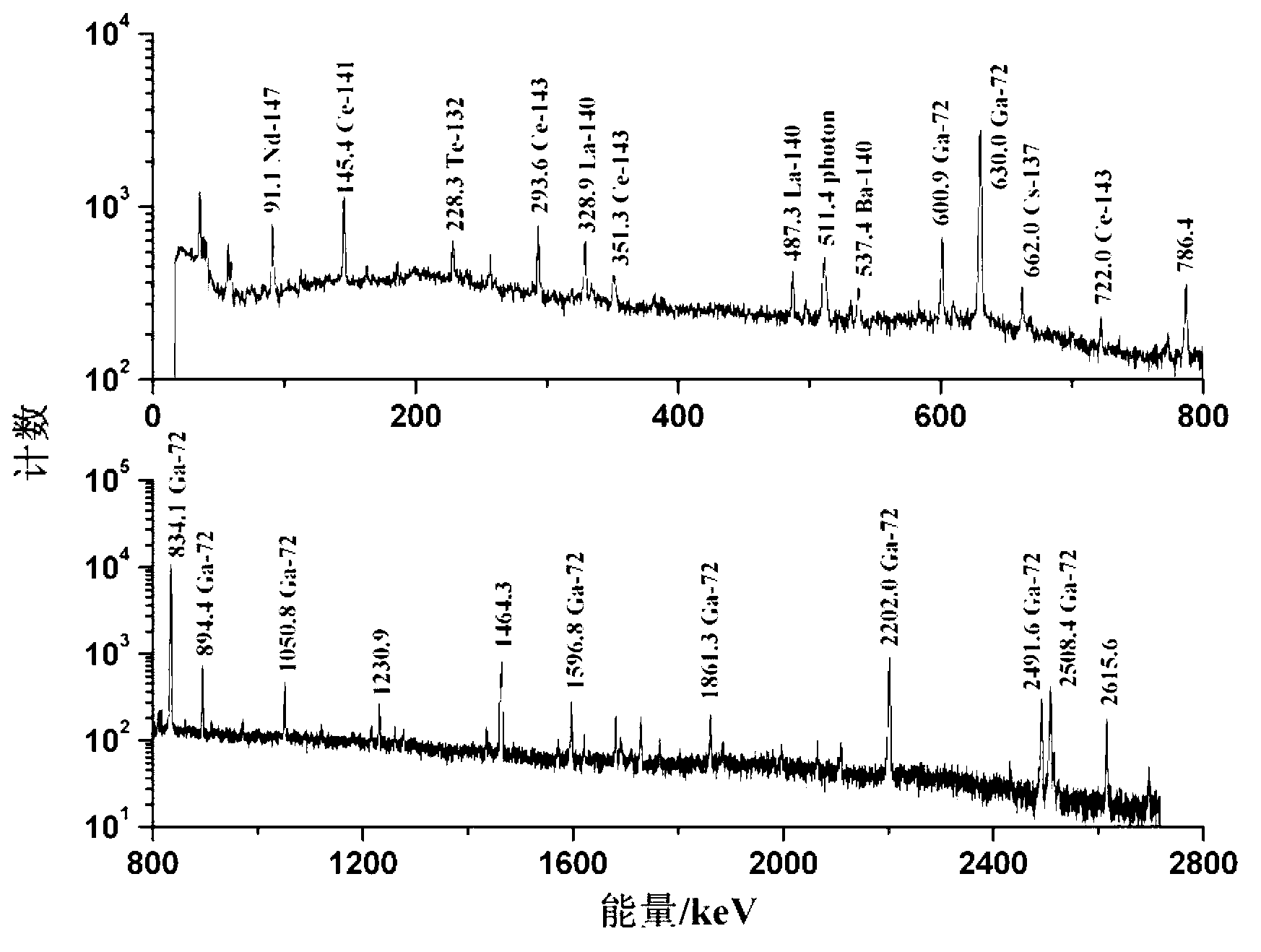
Systems and methods for separating isotopes from a sample of fission products
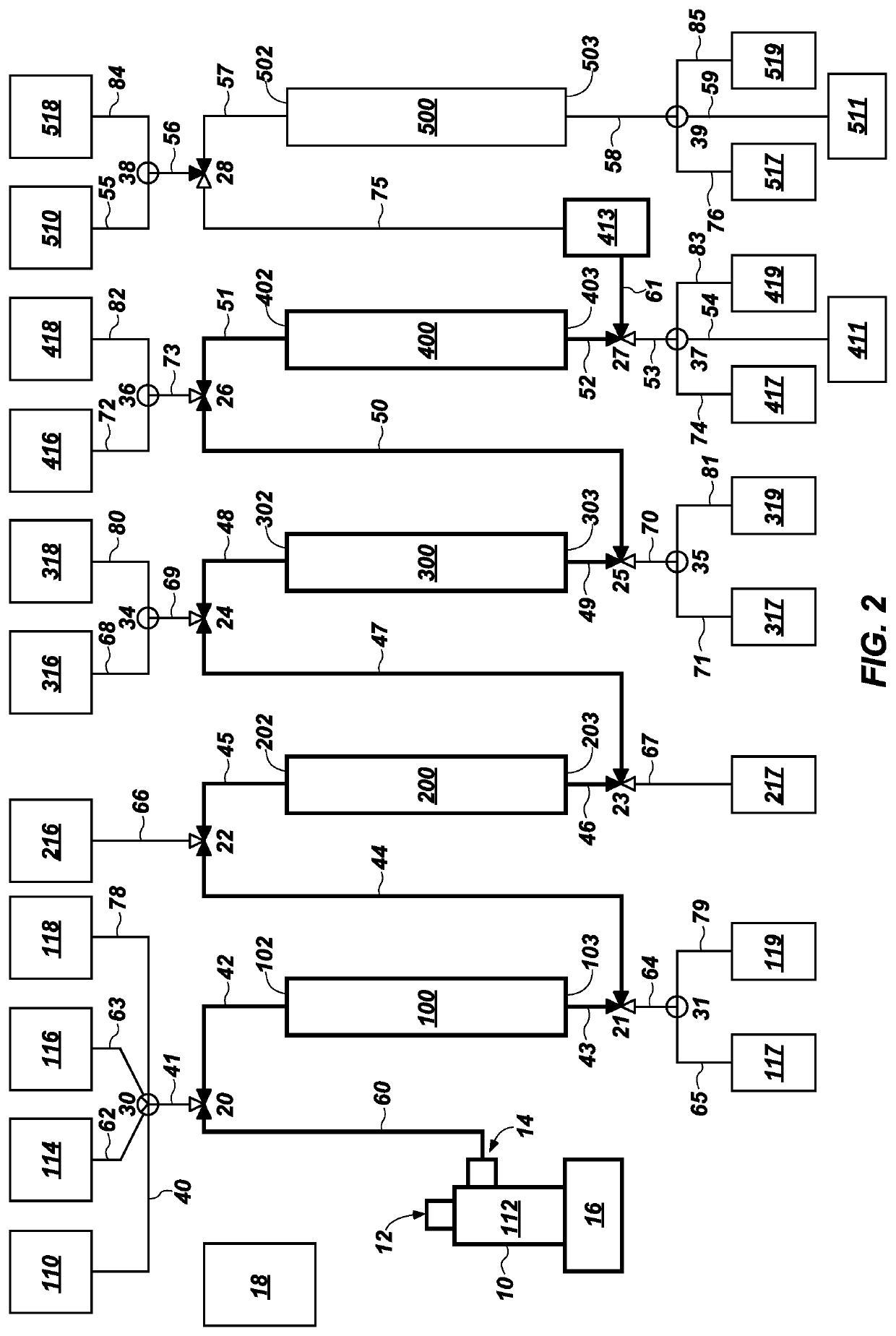
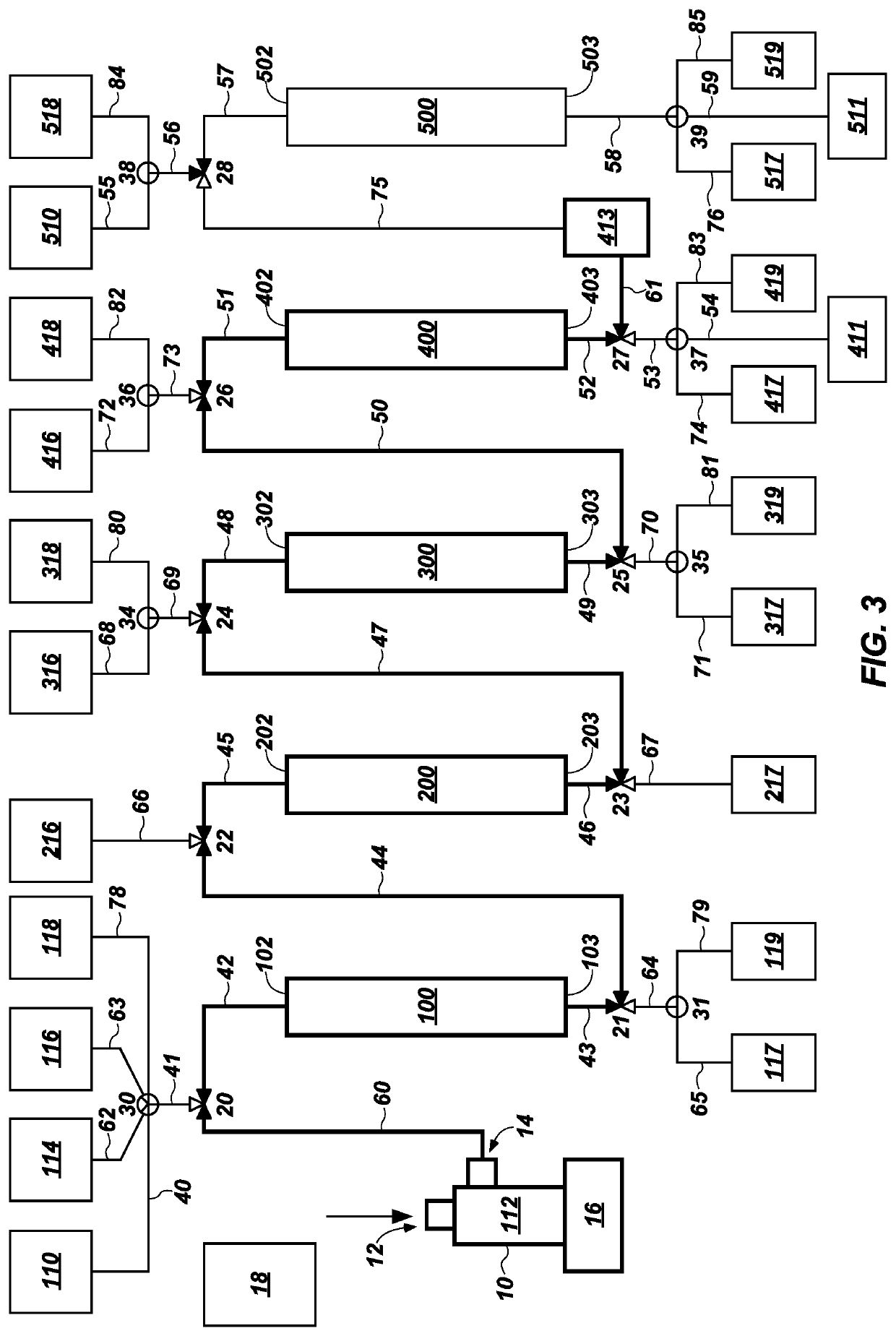
Systems and methods for efficient, effective, and safe separation and isolation of multiple isotopes (e.g., Mo, Zr, Ba, Sr, Te, and lanthanide isotopes) from fission products includes use of a plurality of chromatography columns, each containing a chromatographic resin formulated to target one or more particular isotopes. The system is operable in a “series” configuration to load the multiple columns by a single pass of the sample. Then, the system may be transitioned (e.g., using valves) to a “parallel” configuration in which multiple columns of the system may be operated simultaneously to elute targeted isotopes. Additional parallel operations of the columns, using different eluent compositions, may be used to elute different targeted isotopes. The system may be reconditioned in preparation for a subsequent sample.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Nanofuel Internal Engine
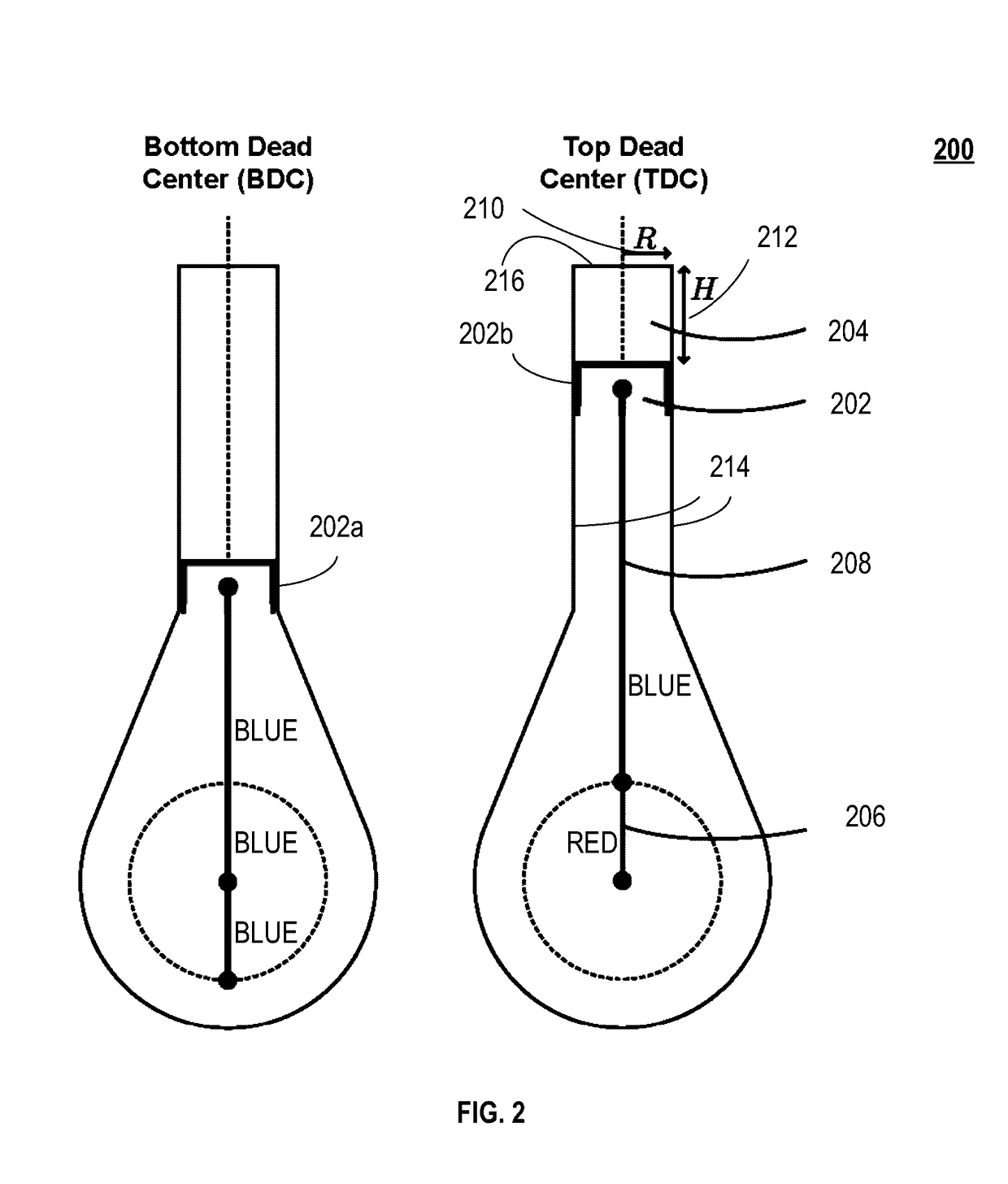
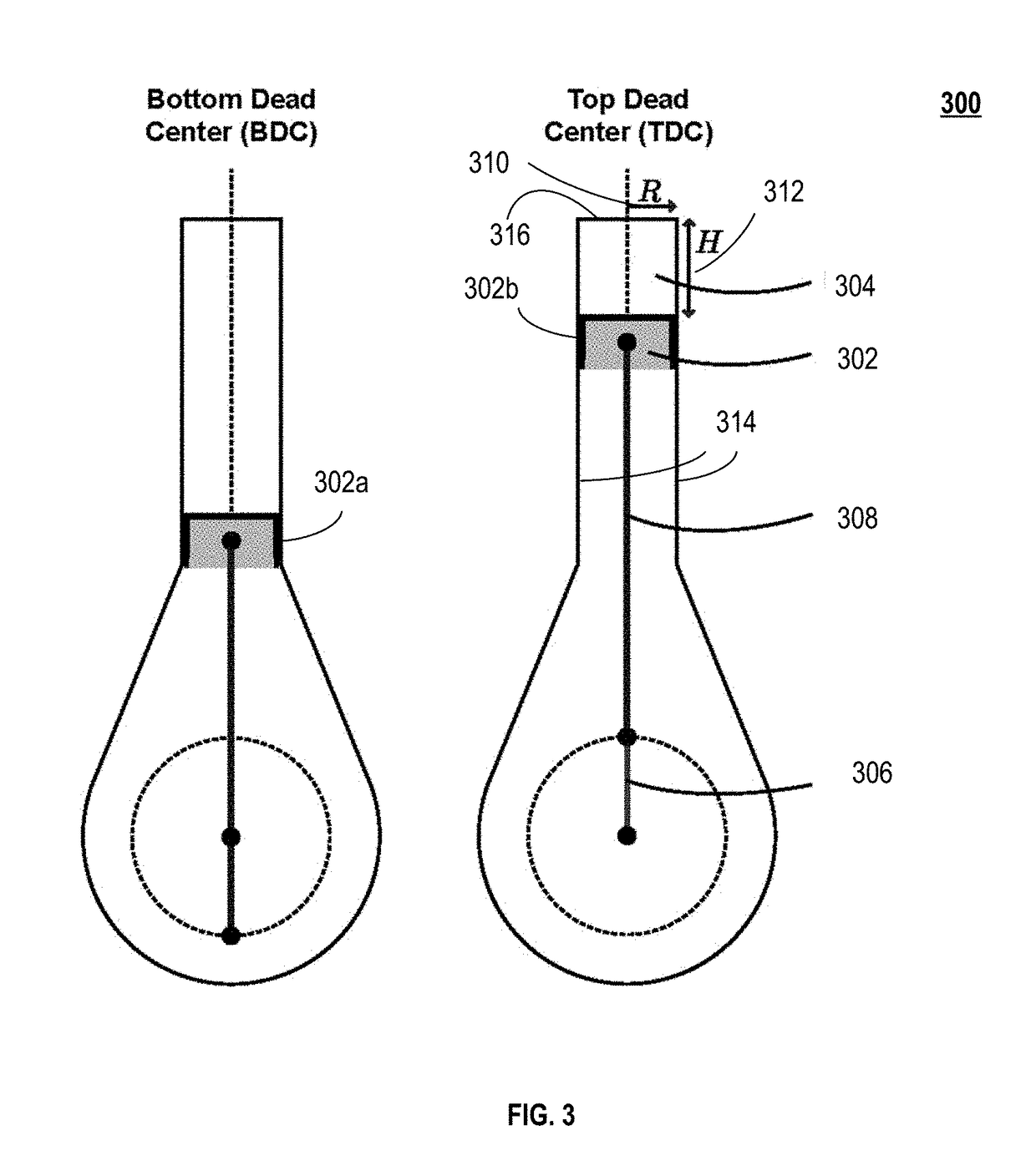
ActiveUS20170069402A1Improve performanceReduce cavitiesIntegral reactorsCosmonautic vehiclesWorking fluidConfiguration design
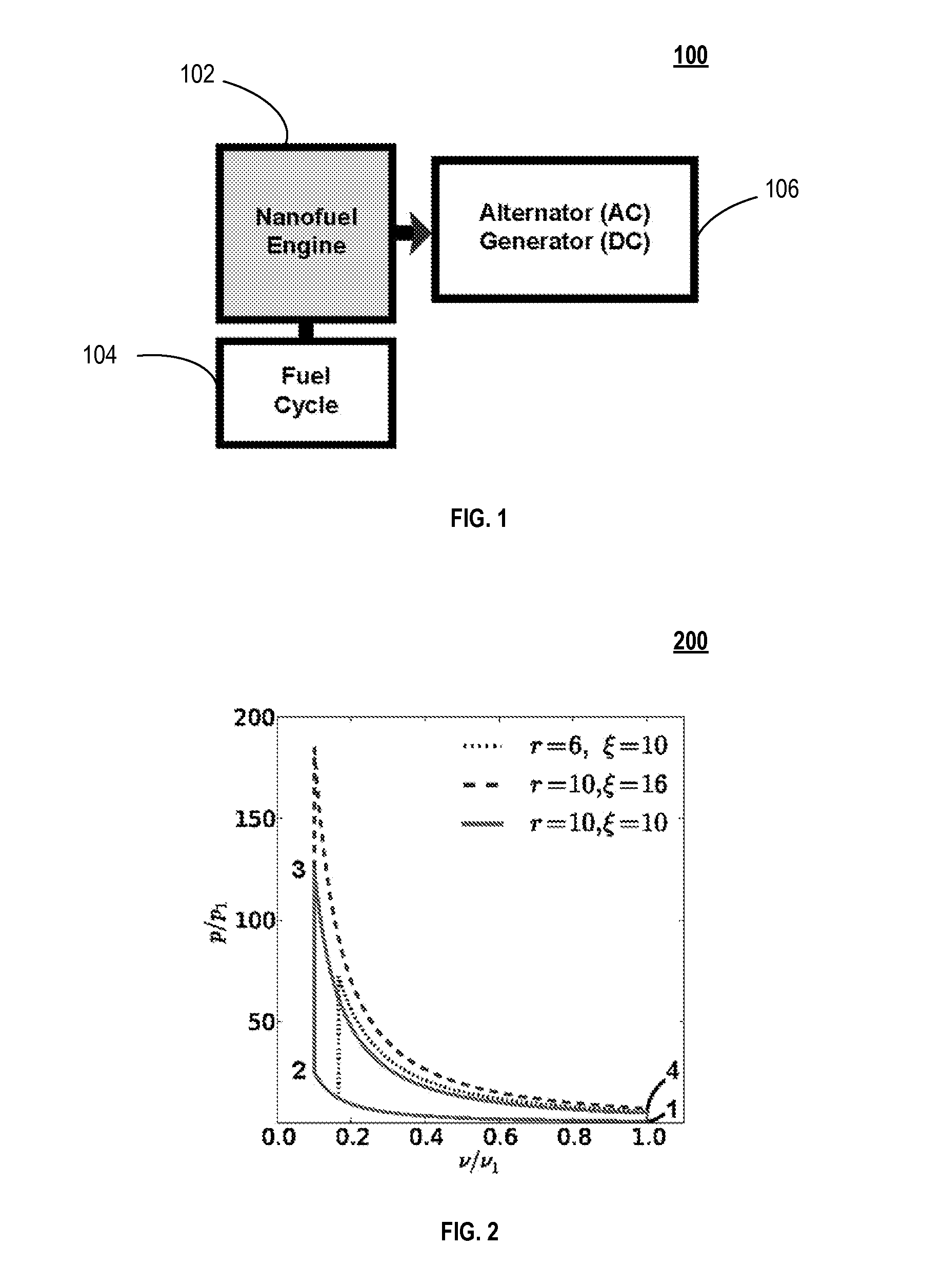
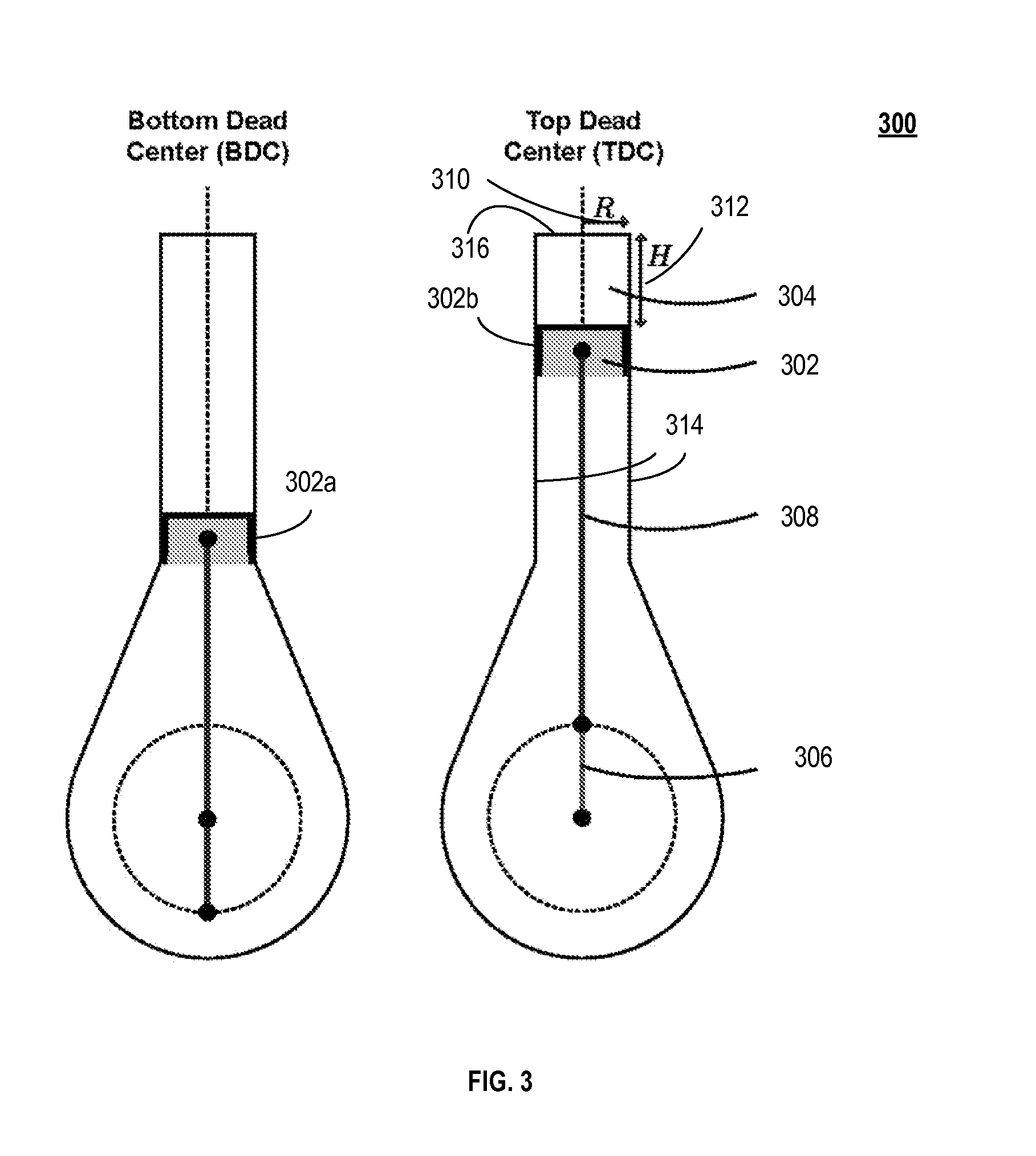
A nanofuel engine including an inventive nanofuel internal engine, whereby nuclear energy is released in the working fluid and directly converted into useful work, with the qualities of an economical advanced small modular gaseous pulsed thermal reactor. Scientific feasibility is established by studying the behavior of nuclear fuels in configurations designed to support a fission chain reaction. Nanofuel is defined as nuclear fuel suitable for use in an internal engine, comprised of six essential ingredients, and can be created from clean fuel or from the transuranic elements found in light-water reactor spent nuclear fuel in a proliferation resistant manner. Three essential ingredients ensure the nanofuel is inherently stable, due to a negative temperature coefficient of reactivity. Reciprocating and Wankel (rotary) internal engine configurations, which operate in an Otto cycle, are adapted to support a fission chain reaction. Dynamic engine cores experience a decrease in criticality as the engine piston or rotor moves away from the top dead center position. In this inherent safety feature, the increase in engine core volume decreases the nanofuel density and increases the neutron leakage. Technological feasibility is demonstrated by examining potential engineering limitations. The nanofuel internal engine can be operated in two modes: spark-ignition with an external neutron source such as a fusion neutron generator; and compression-ignition with an internal neutron source. The structural integrity can be maintained using standard internal combustion engine design and operation practices. The fuel system can be operated in a closed thermodynamic cycle, which allows for complete fuel utilization, continuous refueling, and easy fission product extraction. Nanofuel engine power plant configurations offer favorable economic, safety, and waste management attributes when compared to existing power generation technology. The initial (first-of-a-kind) overnight capital cost is approximately $400 per kilowatt-electric. Obvious safety features include an underground installation, autonomous operation, and an ultra-low nuclear material inventory.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY RES ASSOC
Process for Converting Alkaline-Earth Metal Chlorides to Tungstates and Molybdates and Applications Thereof
The invention relates to a process for converting an alkaline-earth metal chloride to at least one salt chosen from the tungstates and molybdates of this metal, which comprises the reaction of the alkaline-earth metal chloride with at least one precursor of tungsten or of molybdenum chosen from tungsten oxides, molybdenum oxides, tungstates and molybdates, this reaction being carried out in a solvent constituted by KCl or by an LiCl / KCl mixture and at a temperature at least equal to the melting point of this solvent.Applications: synthesis of alkaline-earth metal tungstates and molybdates, extraction of alkaline-earth metals from media in which they are found in the form of chlorides, recovery of alkaline-earth fission products from a salt flux in the context of the reprocessing of a spent nuclear fuel in molten chloride media, etc.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Emergency Cooling System for Improved Reliability for Light Water Reactors
InactiveUS20160042817A1Sufficient powerReduce pressureNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear powerCapital cost
A passive cooling system using only reactive processes without moving parts to power its startup and operation is designed to maximize the reliability of decay heat removal for the current generation of nuclear power plants and for advanced passive reactors. In order to reduce the number of failure modes processes independent from any external power source—such as the electrical power grid or Diesel generators—are used exclusively for all safety functions.The system uses the very energy that could cause an accident to circulate cooling water through the steam generator to remove the decay heat, simplifying the design and reducing capital costs significantly. Decay heat generated by the nuclear fuel after reactor shutdown induces coolant circulation from the steam generator to the ultimate heat sink keeping the nuclear fuel at safe temperatures and preventing any release of radioactive fission products to the environment.
Owner:DYNAC SYST LLC
Silicon carbide reinforced zirconium based cladding
ActiveUS20200020455A1Gap minimizationEliminate gapsMolten spray coatingOptical rangefindersCarbide siliconThermal deposition
A method for making an improved nuclear fuel cladding tube includes reinforcing a Zr alloy tube by first winding or braiding ceramic yarn directly around the tube to form a ceramic covering, then physically bonding the ceramic covering to the tube by applying a first coating selected from the group consisting of Nb, Nb alloy, Nb oxide, Cr, Cr oxide, Cr alloy, or combinations thereof, by one of a thermal deposition process or a physical deposition process to provide structural support member for the Zr tube, and optionally applying a second coating and optionally applying a third coating by one of a thermal deposition process or a physical deposition process. If the tube softens at 800° C.-1000° C., the structural support tube will reinforce the Zr alloy tube against ballooning and bursting, thereby preventing the release of fission products to the reactor coolant.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Nuclear powered internal engine nuclear fuel cycle and housing design improvement
ActiveUS20180170496A1Stable internal performanceImprove performanceCosmonautic vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesWorking fluidChemical composition
A nanofuel engine including receiving nanofuel (including moderator, nanoscale molecular dimensions & molecular mixture) internally in an internal combustion engine that releases nuclear energy, is set forth. A nanofuel chemical composition of fissile fuel, passive agent, and moderator. A method of obtaining transuranic elements for nanofuel including: receiving spent nuclear fuel (SNF); separating elements from SNF, including a stream of elements with Z>92, fissile fuel, passive agent, fertile fuel, or fission products; and providing elements. A method of using transuranic elements to create nanofuel, including: receiving, converting, and mixing the transuranic elements with a moderator to obtain nanofuel. A method of operating a nanofuel engine loaded with nanofuel in spark or compression ignition mode. A method of cycling a nanofuel engine, including compressing nanofuel; igniting nanofuel; capturing energy released in nanofuel, which is also the working fluid; and using the working fluid to perform mechanical work or generate heat.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY RES ASSOC
Method and system to detect and locate the in-core position of fuel bundles with cladding perforations in candu-style nuclear reactors
A method for detecting a leak in a cladding tube in a nuclear reactor is described. The method is well-suited for use in a reactor having a plurality of cladding tubes housed in a plurality of linearly arranged channels for flowing coolant past the cladding tubes. The method includes monitoring the channels for the occurrence of an increase in radiation above a selected base line indicative of the presence of at least one fission product in the coolant in at least one of the plurality of channels, and monitoring the channels for the occurrence of time dependent changes in the strength of radiation in the coolant above the base line along the length of the at least one of the plurality of channels. The leak location is calculated by triangulating the radiation readings from a fixed linear array of detectors positioned adjacent to the channels to determine the location of the strongest radiation reading and the location along the length of the channel where the increase in radiation occurred.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Detecting special nuclear materials in suspect containers using high-energy gamma rays emitted by fission products
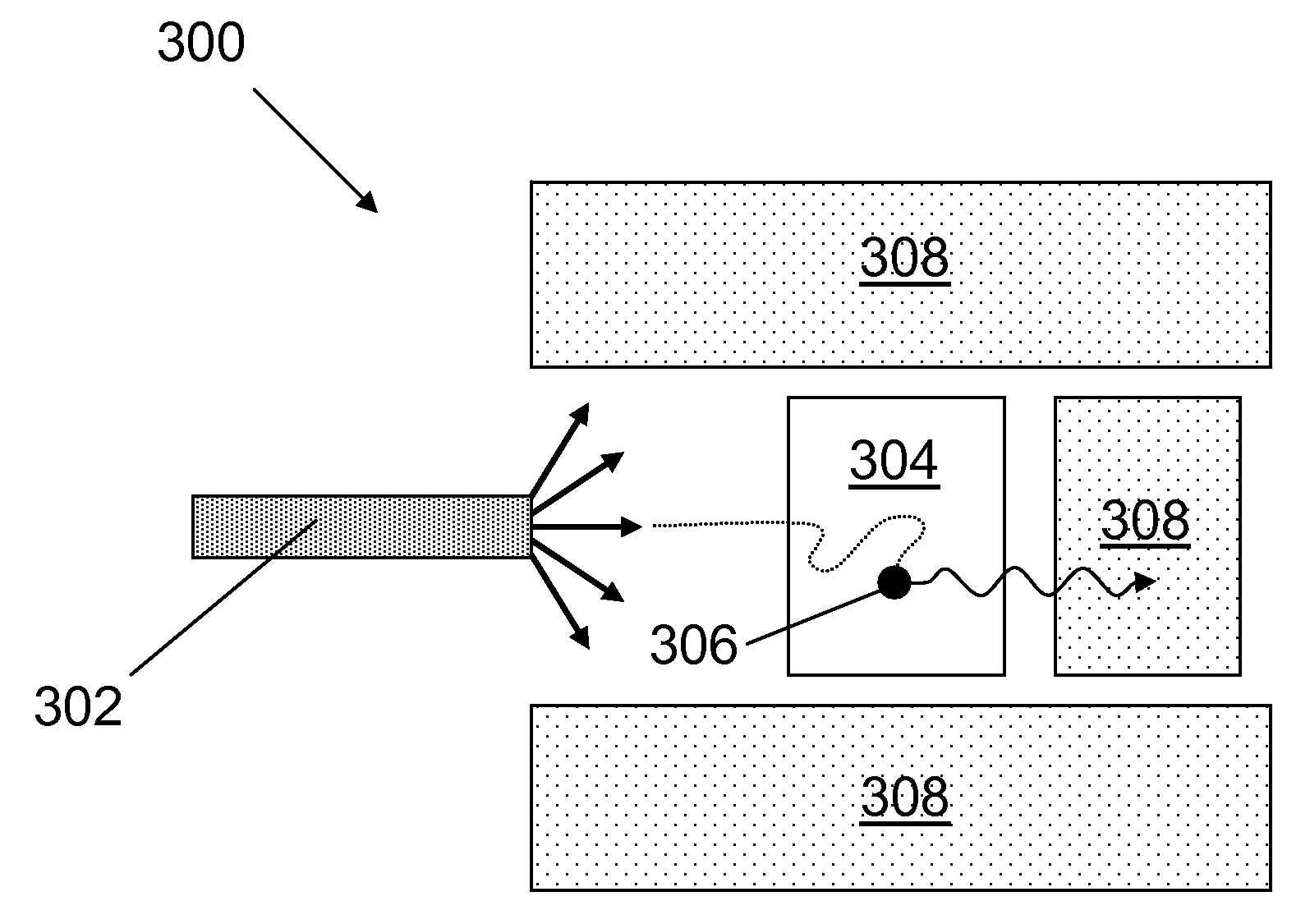
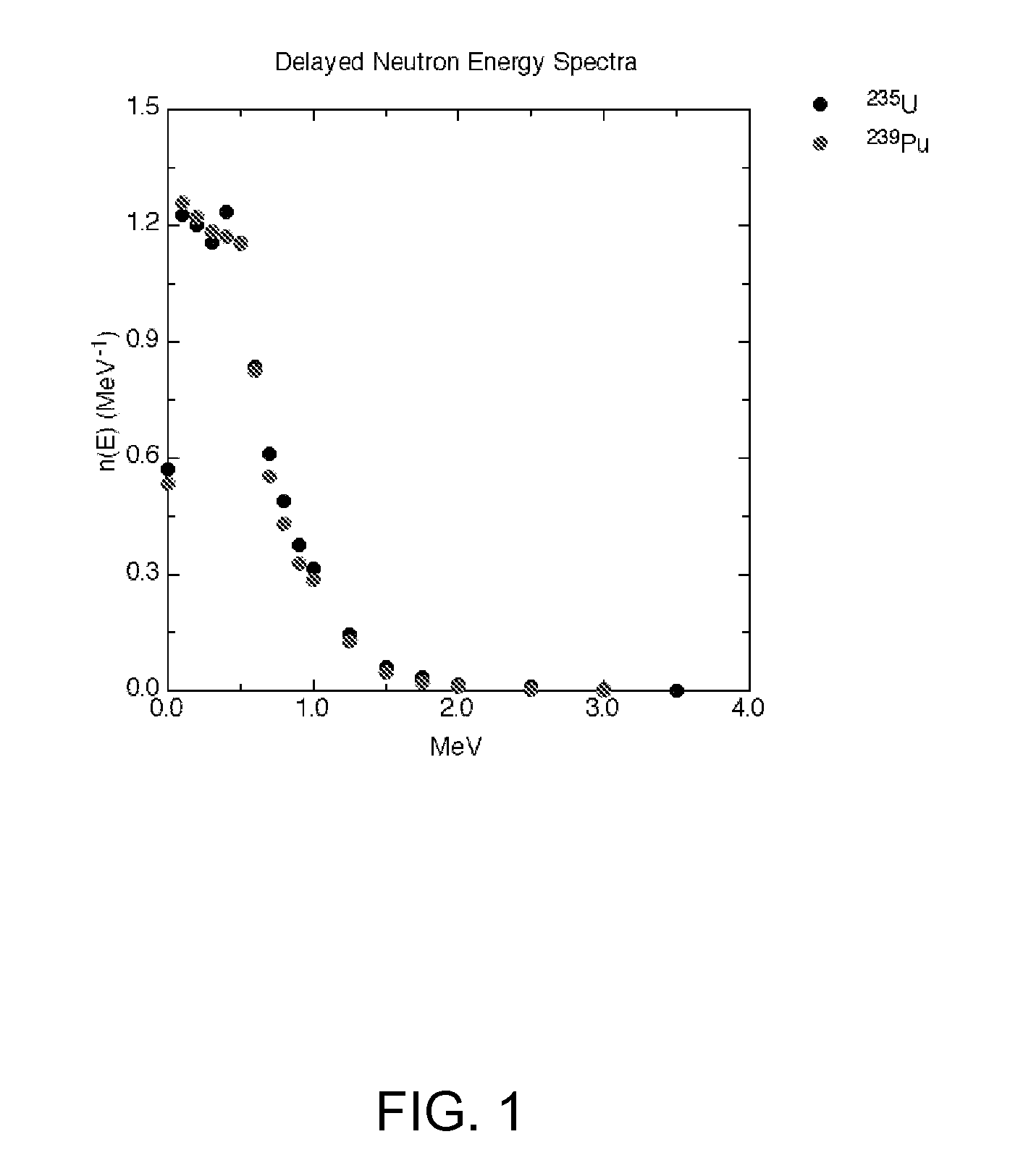
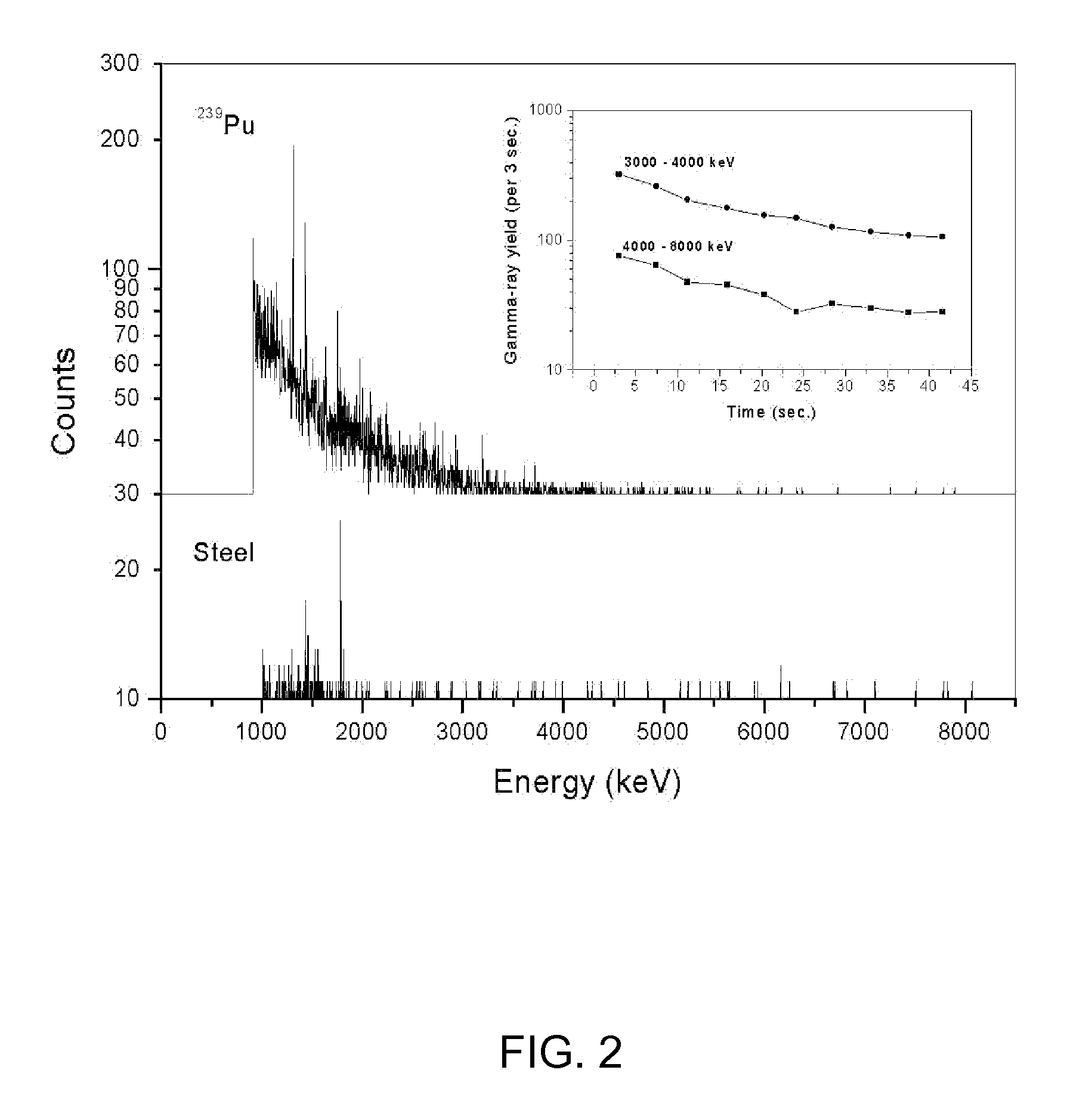
InactiveUS20080192878A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsGamma rayFission
A method and a system for detecting the presence of special nuclear materials in a suspect container. The system and its method include irradiating the suspect container with a beam of neutrons, so as to induce a thermal fission in a portion of the special nuclear materials, detecting the gamma rays that are emitted from the fission products formed by the thermal fission, to produce a detector signal, comparing the detector signal with a threshold value to form a comparison, and detecting the presence of the special nuclear materials using the comparison.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
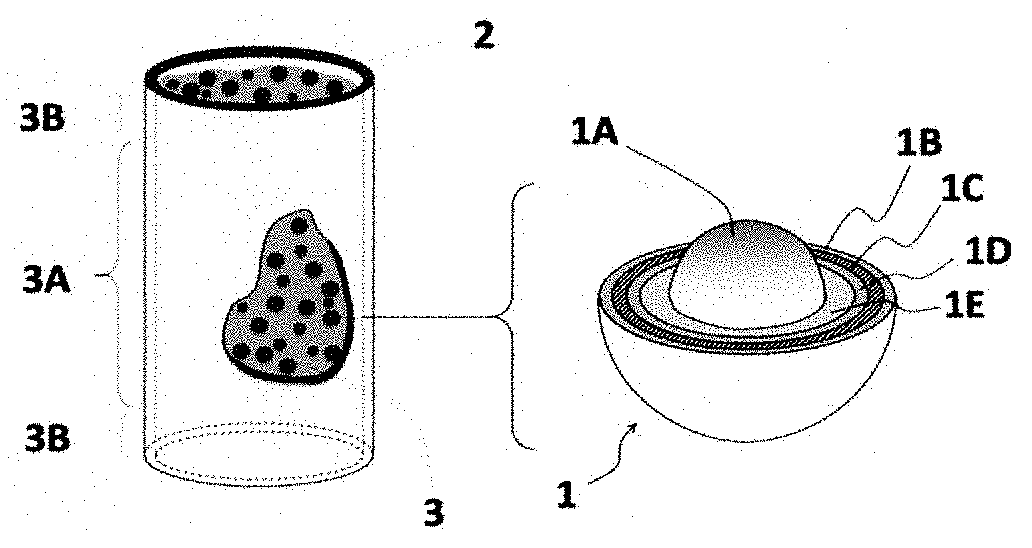
Processing ultra high temperature zirconium carbide microencapsulated nuclear fuel
The known fully ceramic microencapsulated fuel (FCM) entrains fission products within a primary encapsulation that is the consolidated within a secondary ultra-high-temperature-ceramic of Silicon Carbide (SiC). In this way the potential for fission product release to the environment is significantly limited. In order to extend the performance of this fuel to higher temperature and more aggressive coolant environments, such as the hot-hydrogen of proposed nuclear rockets, a zirconium carbide matrix version of the FCM fuel has been invented. In addition to the novel nature to this very high temperature fuel, the ability to form these fragile TRISO microencapsulations within fully dense ZrC represent a significant achievement.
Owner:ULTRA SAFE NUCLEAR CORP
Method for rapidly calculating stock of short-life inert gas fission product reactor core disk
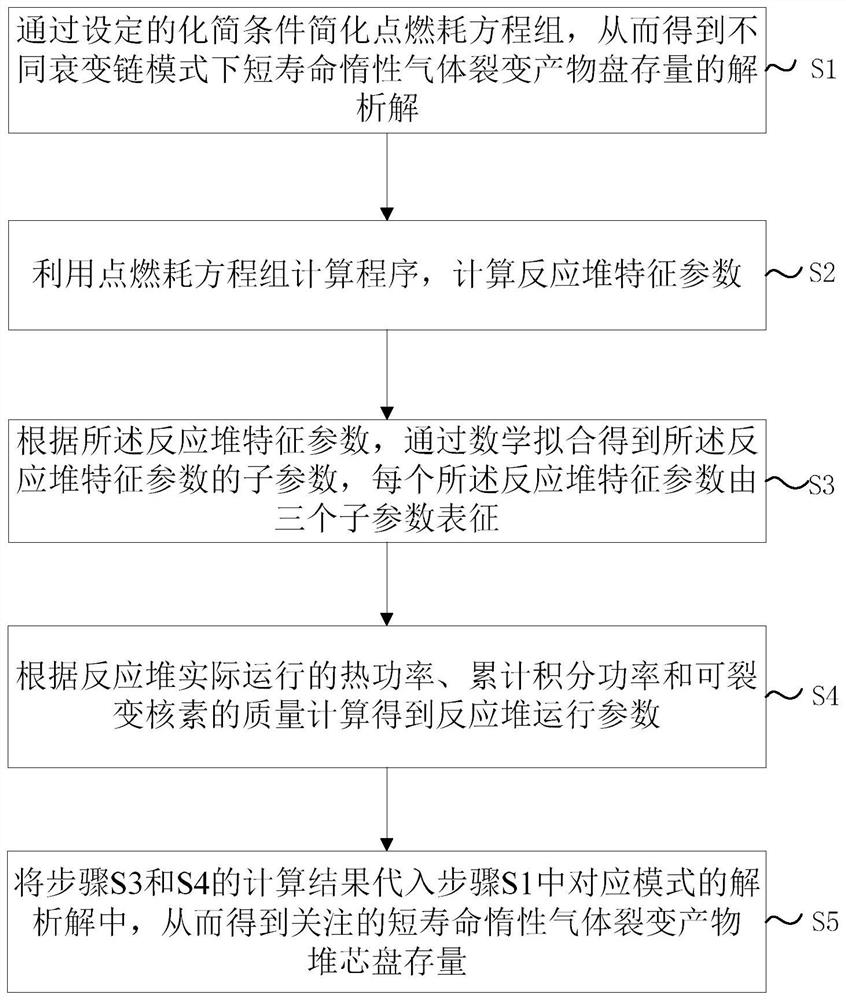
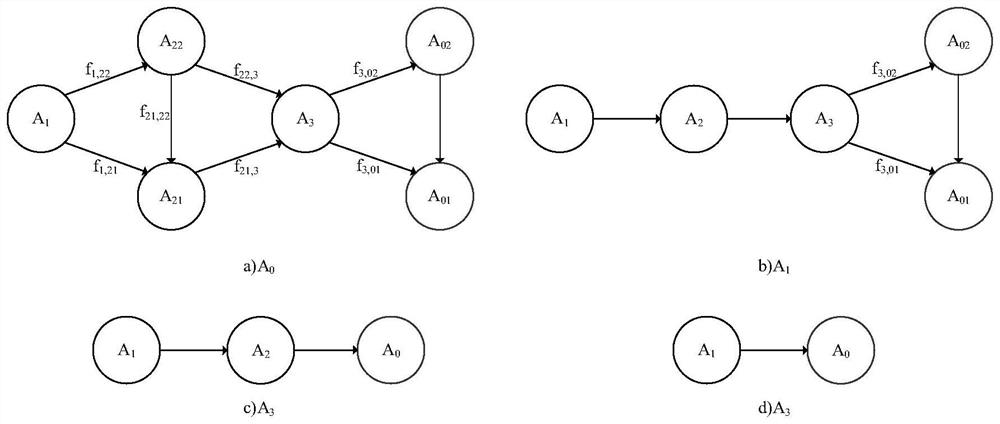
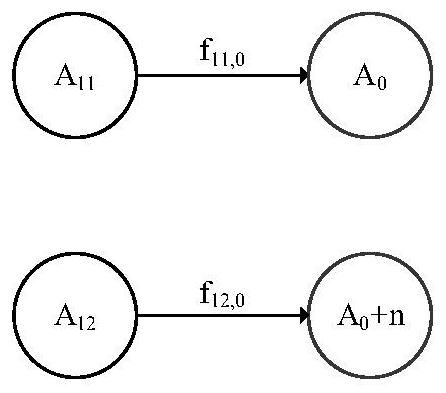
The invention relates to a method for rapidly calculating the stock of a short-life inert gas fission product reactor core disk, and belongs to the technical field of reactor engineering.The method comprises the following steps that S1, an ignition consumption equation set is simplified by setting a simplification condition, and an analytical solution of the stock of the short-life inert gas fission product disk in different decay chain modes is obtained; s2, calculating reactor characteristic parameters by using an ignition consumption calculation program; s3, obtaining sub-parameters of the reactor through mathematical fitting according to the reactor characteristic parameters; s4, calculating reactor operation parameters according to the actual operation thermal power, the accumulated integral power and the fissible nuclide mass of the reactor; and S5, substituting the calculation results of the step S3 and the step S4 into the corresponding analytical solution in the step S1 to obtain the stock of the short-life inert gas fission product reactor core disk. The method provided by the invention can be used for rapidly calculating the short-life inert gas fission product disk stock of balanced cores or non-balanced cores of various types of nuclear fission reactors, and is accurate enough in engineering application.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method of positioning damaged fuel assembly
InactiveCN111799003AImprove screening efficiencyReduce difficultyNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringPressurized water reactorNuclear power
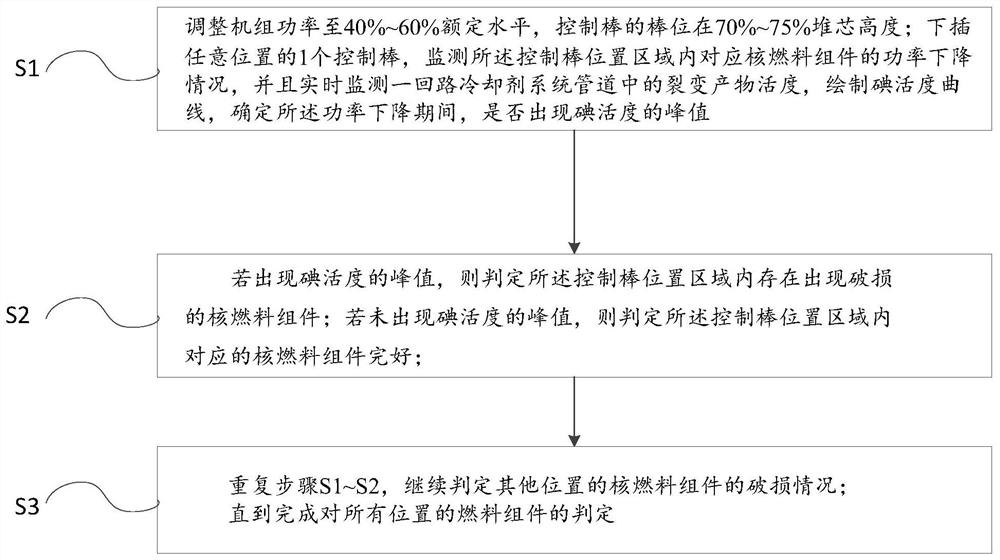
The invention relates to the field of nuclear power, in particular to a method for positioning a damaged fuel assembly. The method for positioning a damaged fuel assembly comprises the following steps: adjusting the unit power to 40%-60% of a rated level, controlling the rod position of a control rod to be 70%-75% of the height of a reactor core; inserting one control rod downwards, monitoring thepower reduction condition of the corresponding fuel assembly in the control rod position area, monitoring the fission product activity in a primary loop coolant system pipeline in real time, drawingan iodine activity curve, and determining whether a peak value of iodine activity occurs or not during the power reduction period; if the peak value of the iodine activity appears, judging that a damaged fuel assembly exists in the control rod position area; if the peak value of the iodine activity does not appear, judging that the fuel assembly in the control rod position area is intact; repeating the steps, and continuously judging the damage conditions of the fuel assemblies at other positions. According to the method, the pressurized water reactor nuclear power unit can locate the positionof the damaged fuel assembly during power operation, and the discrimination efficiency is high.
Owner:JIANGSU NUCLEAR POWER CORP
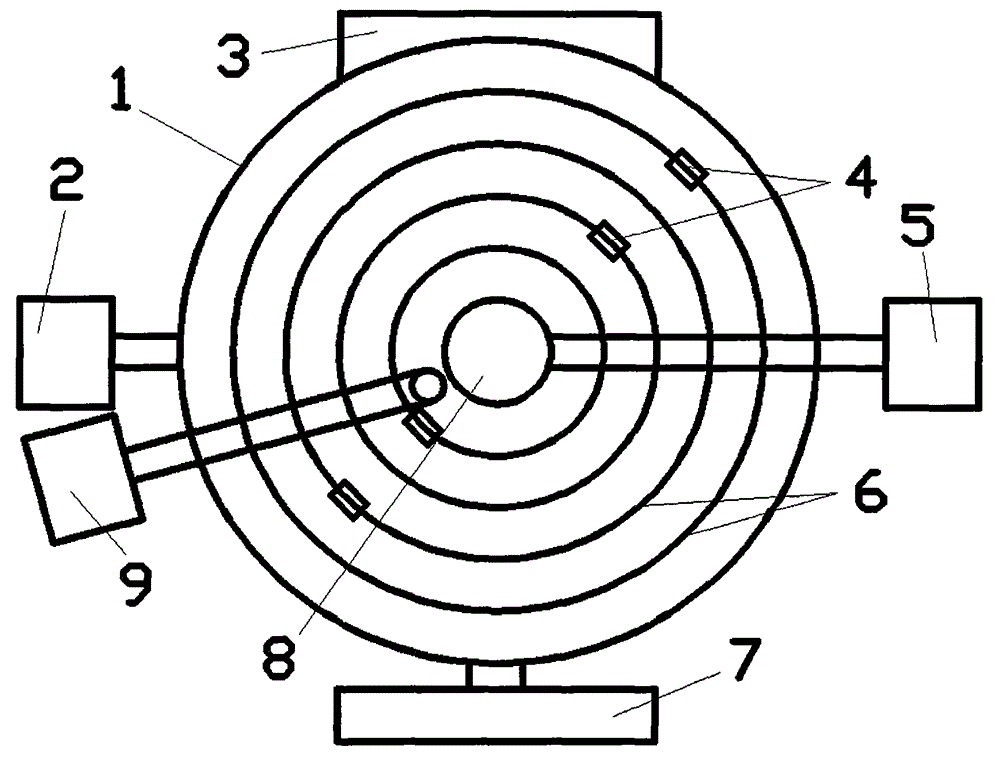
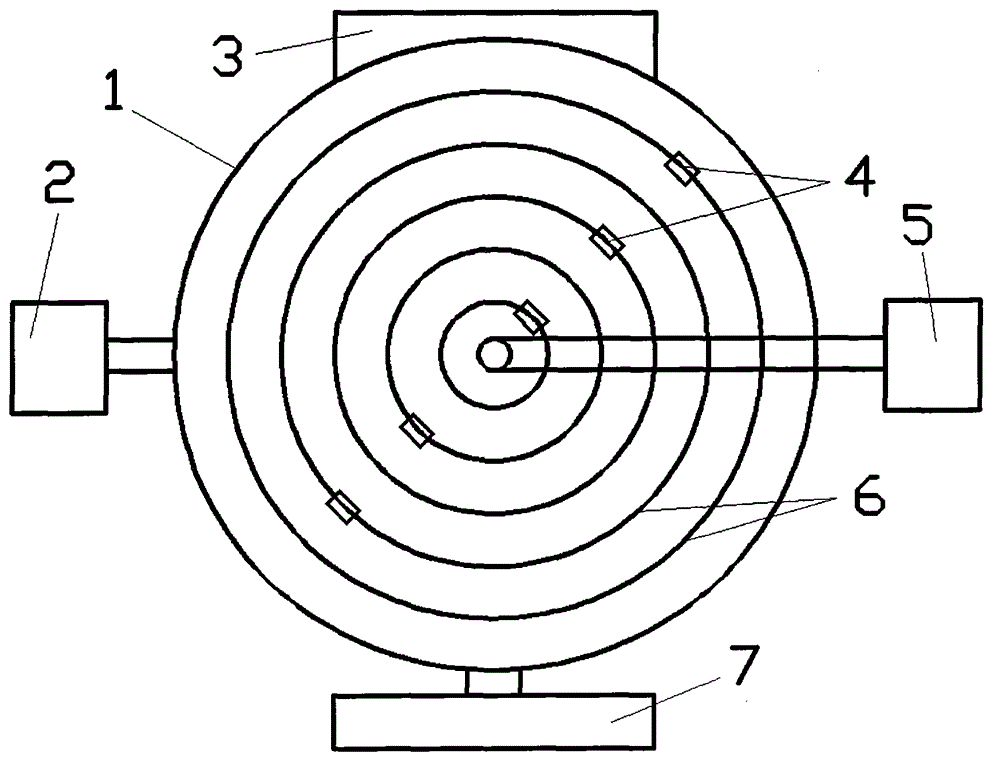
Sampling type fission ionization chamber and fission total number measuring method based on same
PendingCN111370290AAvoid inconsistenciesRealize simultaneous measurementIon sources/gunsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNeutron energy spectrumIonization chamber
The invention relates to a fission ionization chamber, in particular to a sampling fission ionization chamber and a fission total number measuring method based on the same. The problems that when an existing ionization chamber is used for measuring the fission yield, due to the fact that the ionization chamber has self-shielding and is poor in neutron energy spectrum consistency, large measurementuncertainty is introduced, gas fission products and short-life fission products cannot be measured, and the influence on the health of measuring personnel is large are solved. The ionization chamberis characterized by comprising a cathode support, a cathode and an anode support, wherein the cathode support and the cathode are coaxially arranged in sequence from bottom to top, and the anode support is arranged in an inner cavity of the cathode and is coaxial with the cathode. An annular sealing boss and an isolation boss are arranged on the lower bottom surface of the anode support. The sealing boss is positioned on the outer side of the isolation boss. The lower end surface of the sealing boss is hermetically and fixedly connected with the bottom inner surface of the cathode. A gap is formed between the lowermost end of the isolation boss and the inner surface of the cathode bottom. The sampling anode and the annular anode are attached to the lower bottom surface of the anode support, and the sampling anode is located in the isolation boss. The annular anode is located between the isolation boss and the sealing boss.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Mobile integrated two-flow gas cooled reactor system and working method thereof
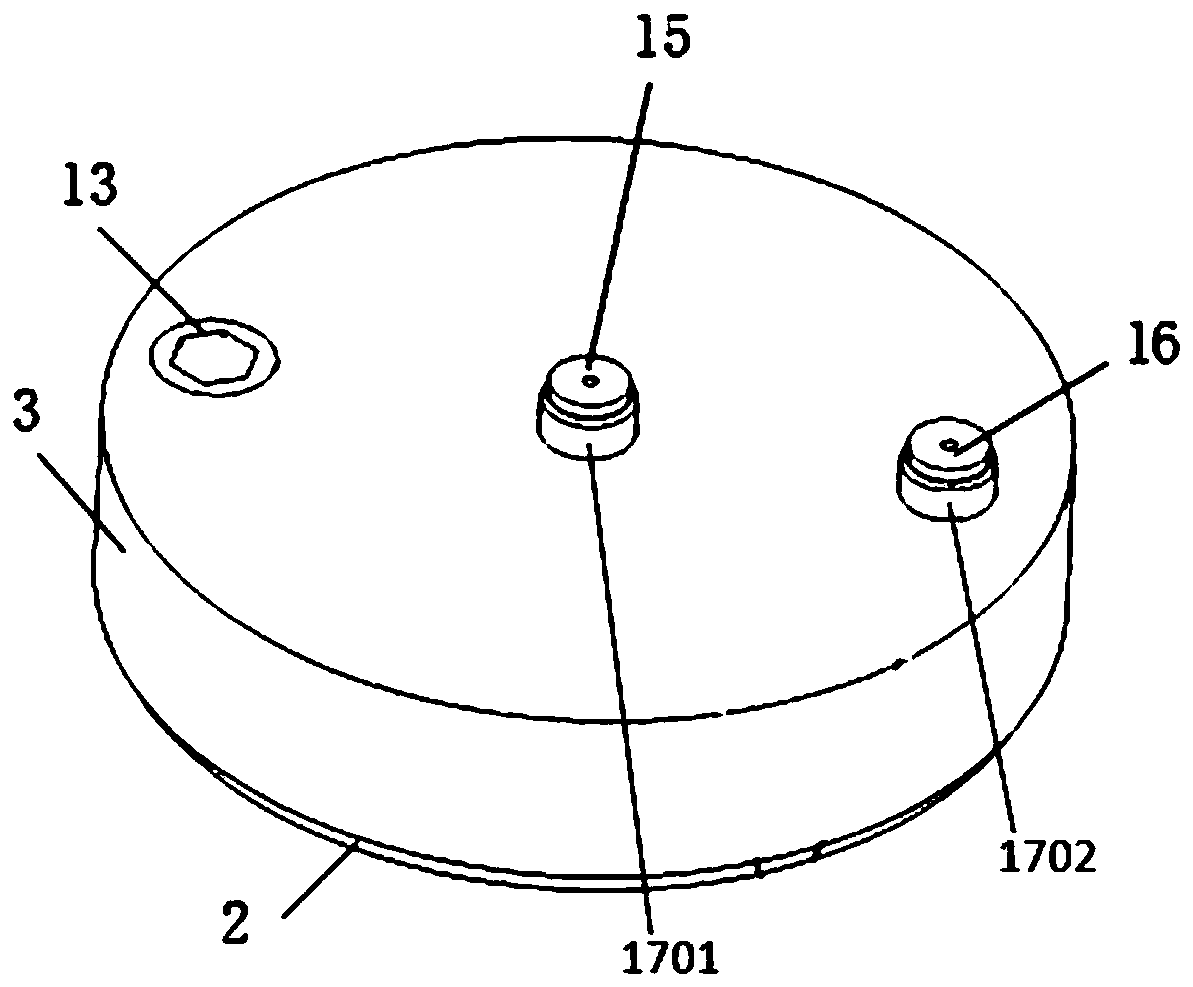
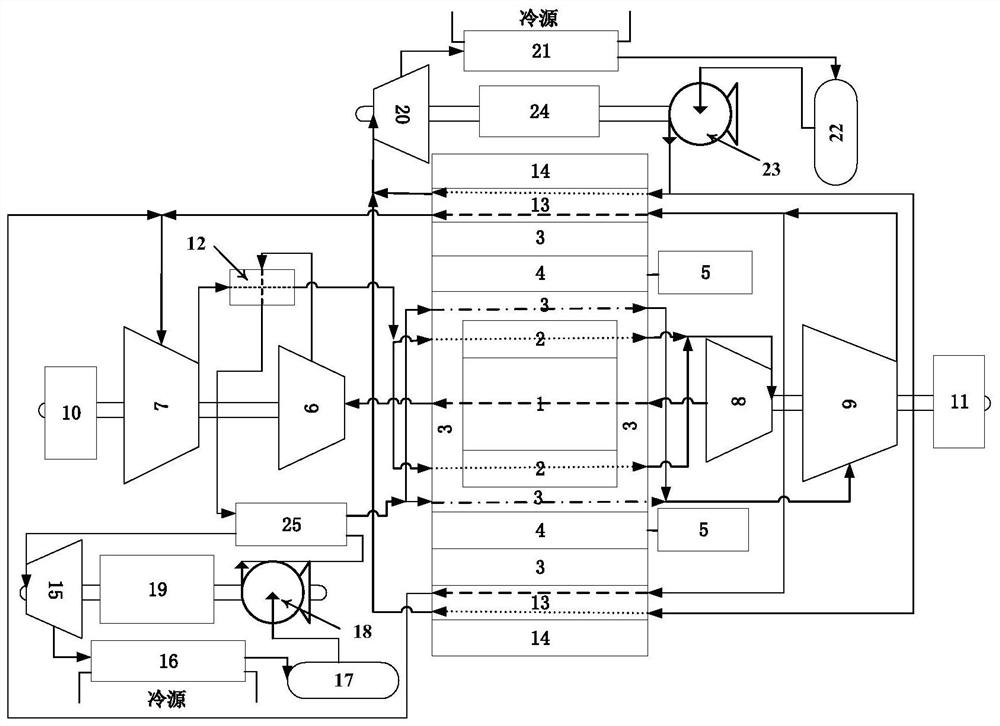
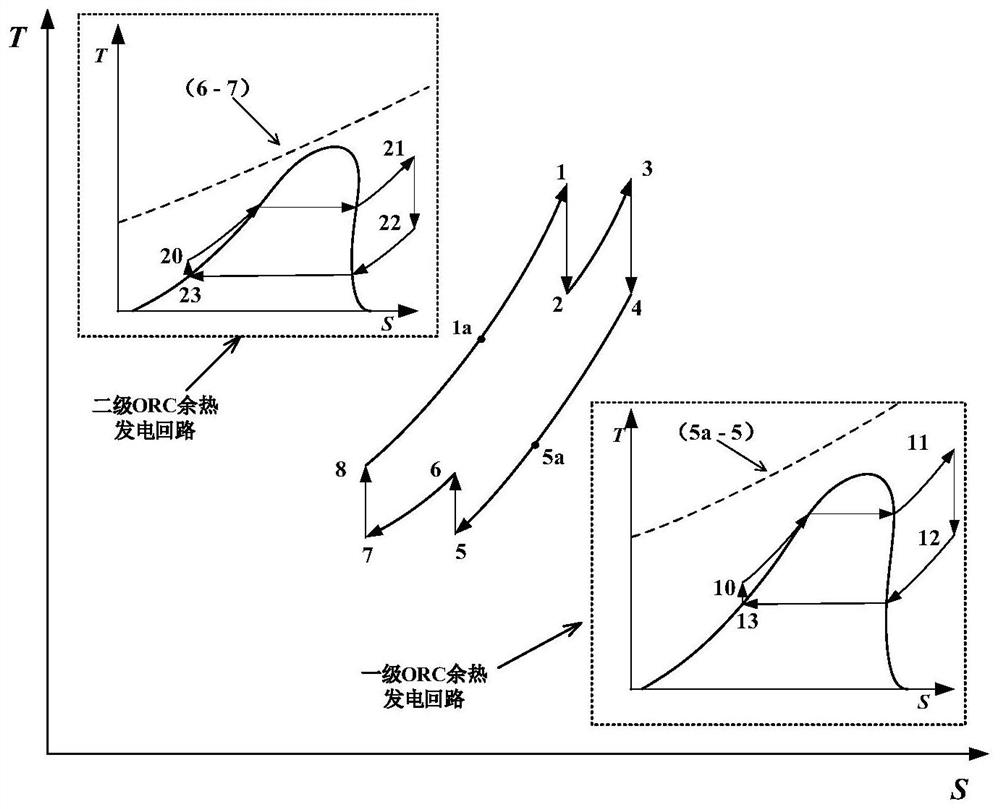
The invention discloses a mobile integrated two-process gas cooled reactor system and a working method thereof. The system adopts a Brayton-organic Rankine combined cycle, and the whole system comprises a gas cooled reactor part, a main power generation part and an ORC waste heat power generation part; a core part of the gas cooled reactor part is composed of an inner fuel tank and an outer fuel tank which are different in internal coolant working medium pressure and opposite in flowing direction; the inner fuel tank and the outer fuel tank are arranged in a reflecting layer with coolant working medium flowing pore passages; the two axial ends of the reflecting layer are tightly connected with a gas turbine, a gas compressor and a power generation unit which are coaxially designed respectively, and the main power generation part is formed together with a heat regenerator; and the ORC waste heat power generation part consists of two stages of ORC waste heat power generation loops and is coupled with the main power generation part for discharging and recycling waste heat of the reactor core. According to the system, multiple sets of energy utilization equipment, an integrated double-process and fuel tank design are adopted, fission products can be contained, the equipment safety redundancy requirement is met, energy gradient utilization is achieved, and the system has the advantages of being compact, small in size, high in safety and high in energy utilization rate.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for calculating yield of multi-group slow luminophores by using fission yield and decay data
ActiveCN114694863AImprove calculation accuracyImprove computing efficiencyNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringLuminophoreDecay chain
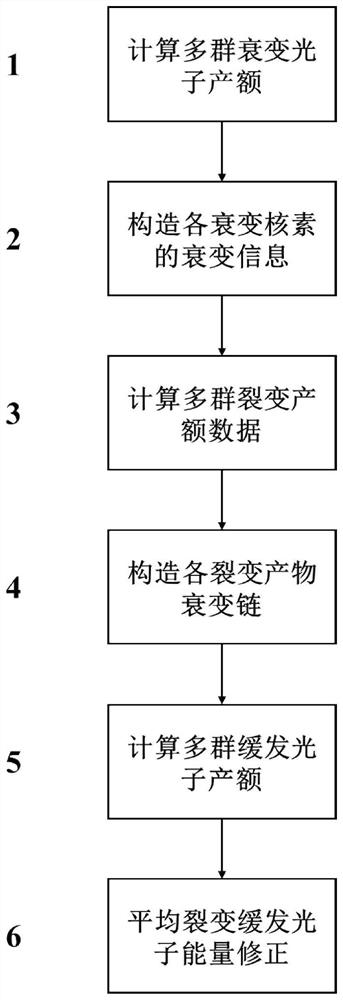
The invention discloses a method for calculating a multi-group slow luminescence photon yield by using a fission yield and decay data. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, calculating a multi-group decay photon yield of each nuclide based on a decay photon energy spectrum given in a decay sub-library of an evaluation nuclear database; constructing decay information of each nuclide according to the decay mode and the branching ratio data; secondly, fission yield data under different neutron incident energies are selected according to different requirements; then constructing decay chain information of all fission products until each fission product decays to a stable nuclide; according to fission yield data, adding decay photons generated in the process of decaying fission products to stable nuclides in different energy ranges, so as to obtain the multi-group slow luminescence photon yield of the fission nuclides; and finally, in order to ensure the accuracy of heat release calculation of the slow luminophores, correcting the yield of the multi-group slow luminophores obtained by calculation by using the average fission slow luminophore energy given in the evaluation kernel database. The method is high in calculation precision and calculation efficiency.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Laser welding pipe plugging device and method for water supply end of high-temperature gas cooled reactor steam generator
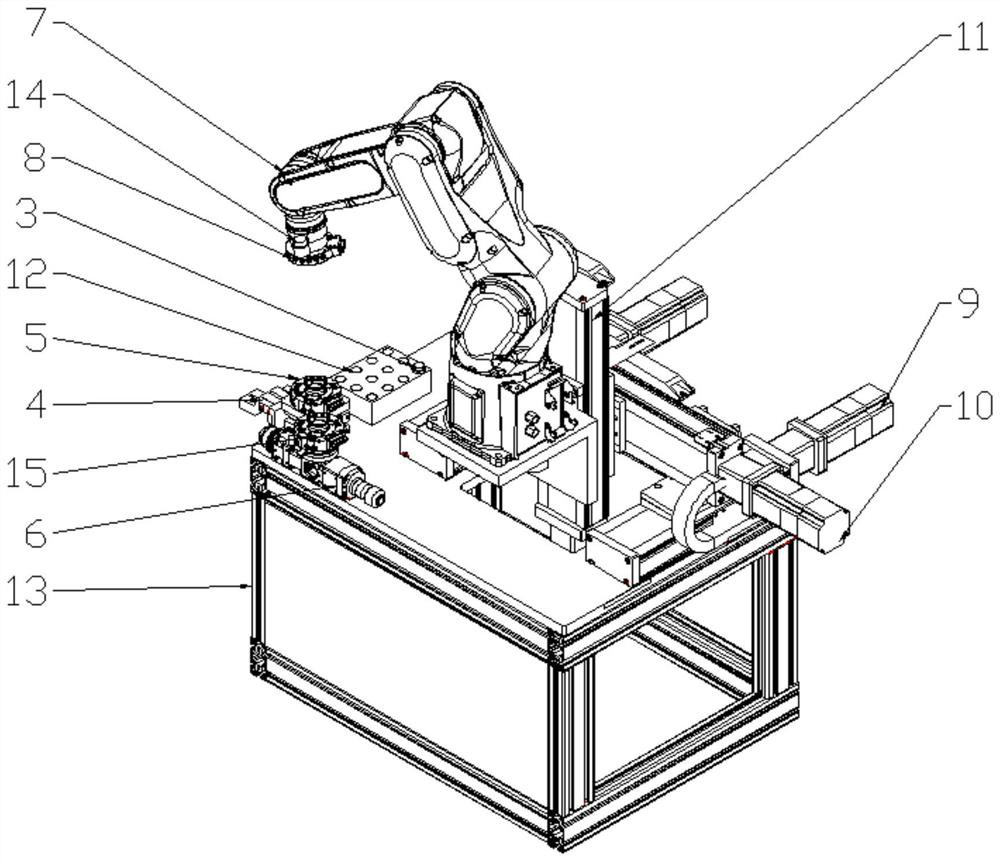
InactiveCN114260568AHigh positioning accuracyHigh degree of automationLaser beam welding apparatusHigh radiationLaser soldering
The steam generator is one of key equipment in a high-temperature gas cooled reactor nuclear power system. A steam generator heat transfer pipe is an important component of a loop pressure boundary and is an important barrier for preventing radioactive fission products from leaking. A heat transfer pipe is prone to causing serious damage accidents under the action of high temperature, high pressure and high radiation for a long time, and therefore blocking operation on the heat transfer pipe in the early stage of a fault is crucial. The invention provides a high-temperature gas cooled reactor steam generator water supply end laser welding pipe plugging device and method based on a multi-axis robot and a laser welding process aiming at a special structure of a high-temperature gas cooled reactor steam generator water supply end. By means of the device, the water supply end pipe plugging operation precision and the automation degree can be improved, and the manual operation time is shortened. The invention provides an innovative solution for laser welding pipe plugging at the water supply end of the steam generator of the high-temperature gas cooled reactor nuclear power station.
Owner:XIAN THERMAL POWER RES INST CO LTD +1
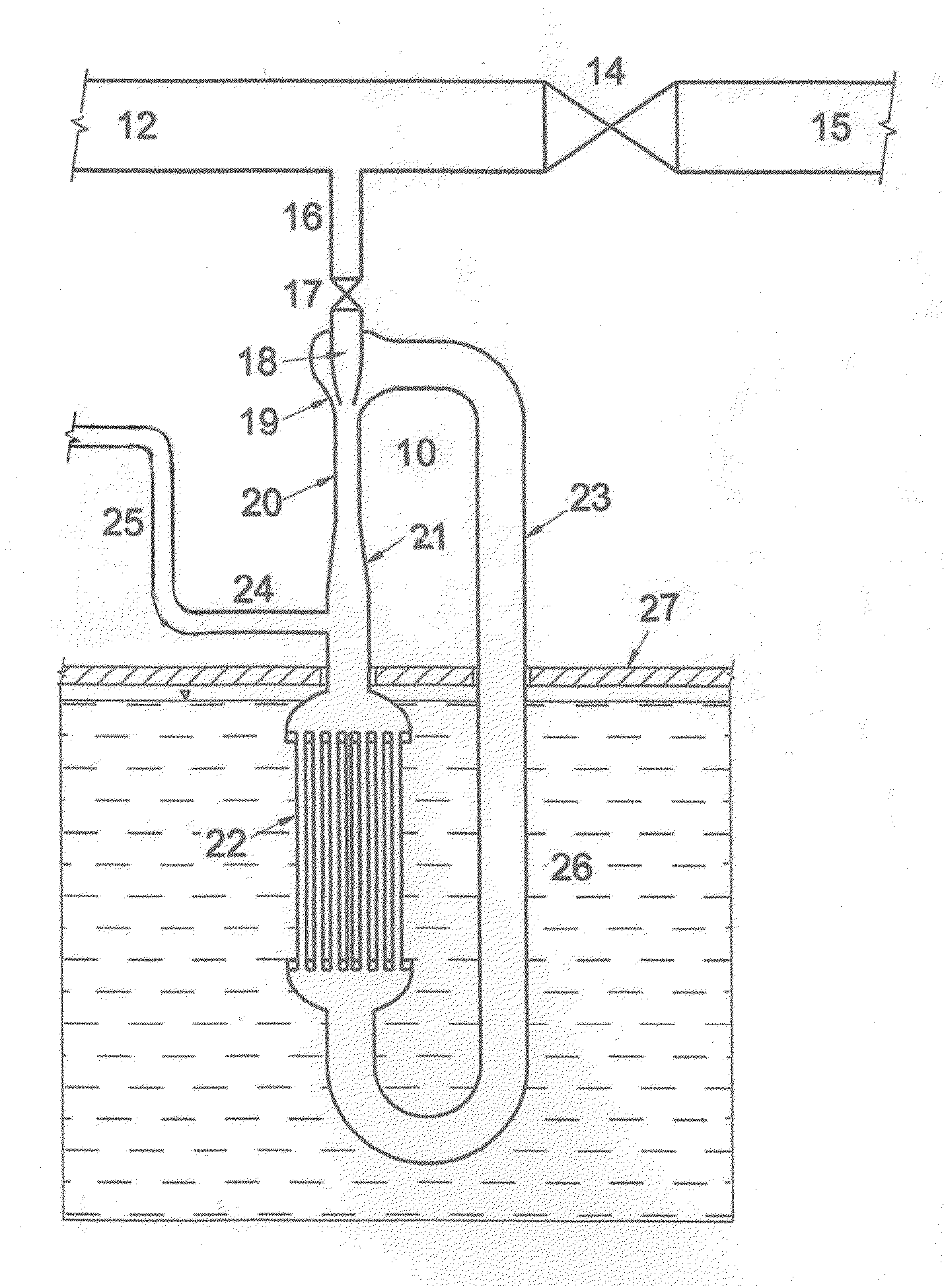
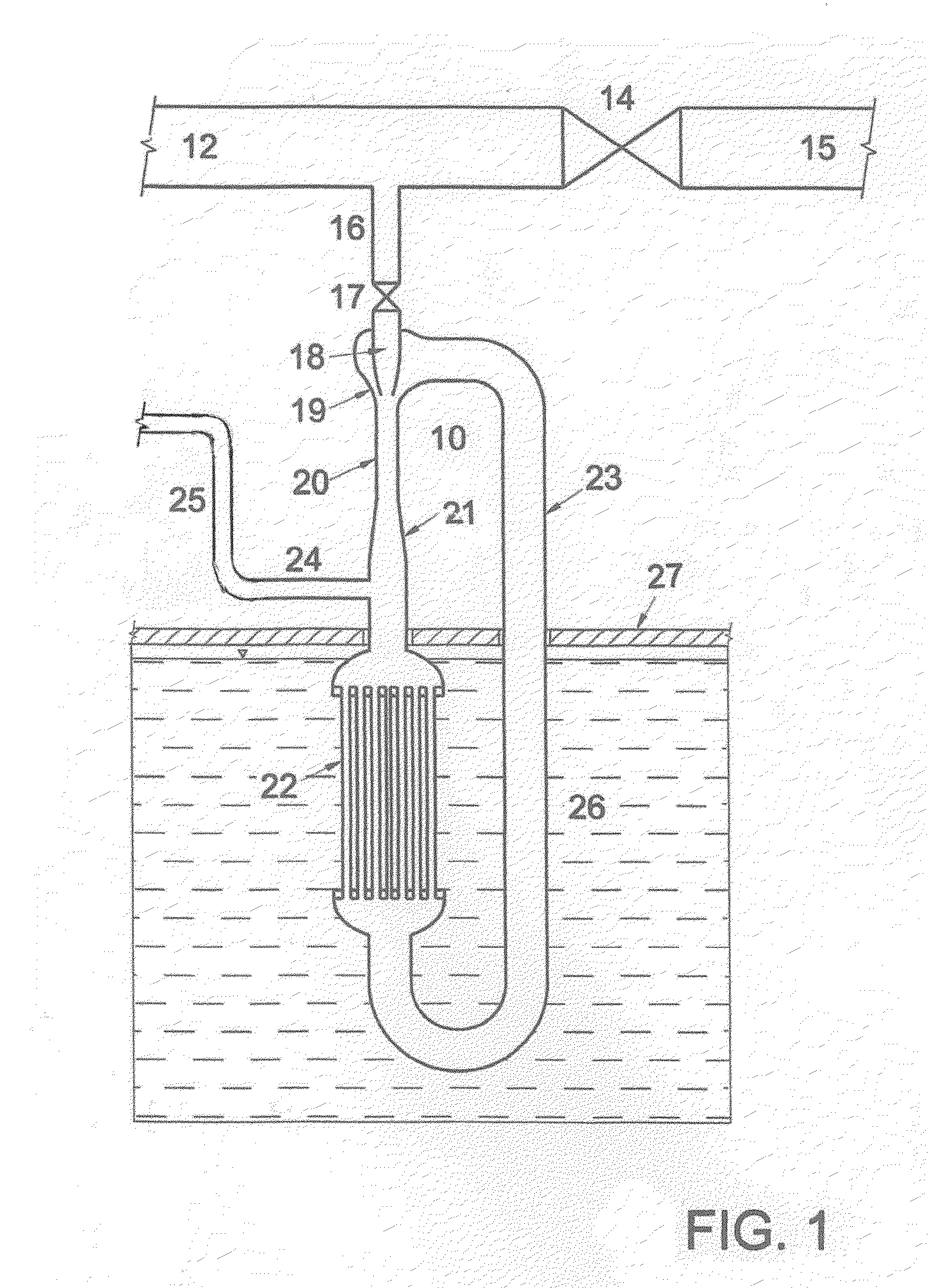
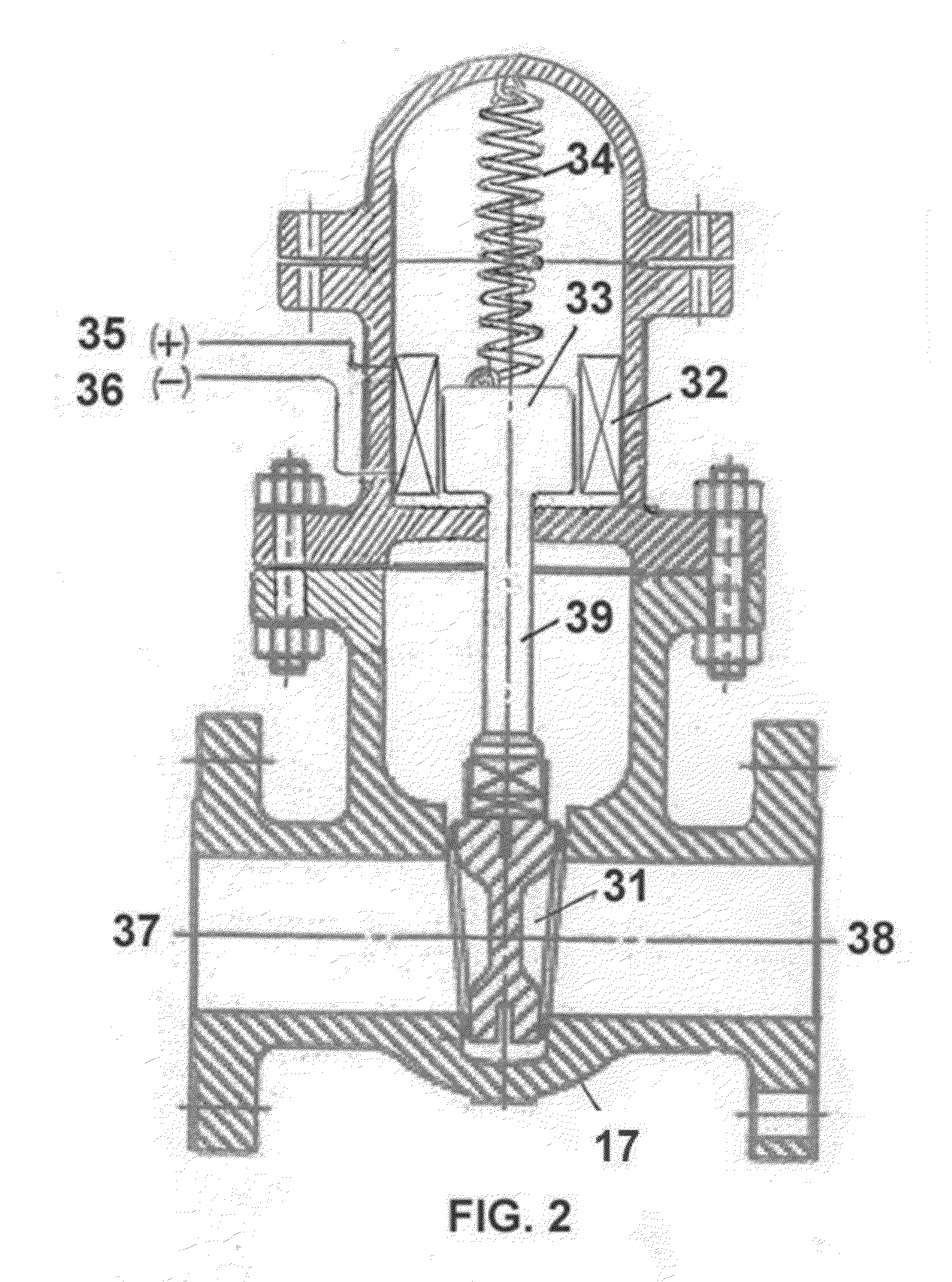
Secondary startup neutron source
ActiveUS10636537B2Improve reliabilityImprovement of fail-free operationNuclear energy generationNeutron sourcesNiobiumAlloy
The invention relates to nuclear engineering and more particularly to controlled reactor start-up. The invention addresses a secondary startup neutron source by creating additional safety barriers between the coolant and the source active part materials. The secondary startup neutron source is designed as a steel enclosure housing an ampule containing antimony in the central enclosure made of a niobium-based alloy unreactive with antimony, with a beryllium powder bed located between the antimony enclosure and the ampule enclosure. An upper gas collector, located above the ampule serves as a compensation volume collecting gaseous fission products. The ampule is supported by a reflector and a bottom gas collector. The gas collectors, reflector, ampule enclosure and washers are made of martensite-ferrite grade steel.
Owner:JOINT CO AKME ENG
Real-time estimation method for reactor core accumulation amount based on Hualong-1
The invention provides a Hualong-1-based reactor core accumulation amount real-time estimation method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) determining the total batch number NOB of fuel loaded by a Hualong-1 reactor core and the number NOA of fuel components of each batch in emergency of an accident; 2) determining the fuel power history of each batch of the reactor core; 3) estimating the reactor core accumulation amount of each batch of fuel accidents, 3.1) determining the nuclide generation rate, 3.2) estimating the train change product accumulation amount in the first irradiationperiod, 3.3) estimating the fission product accumulation amount in the subsequent irradiation or refueling period, and 4) estimating the reactor core accumulation amount, namely summing the fuel accumulation amounts of each batch.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
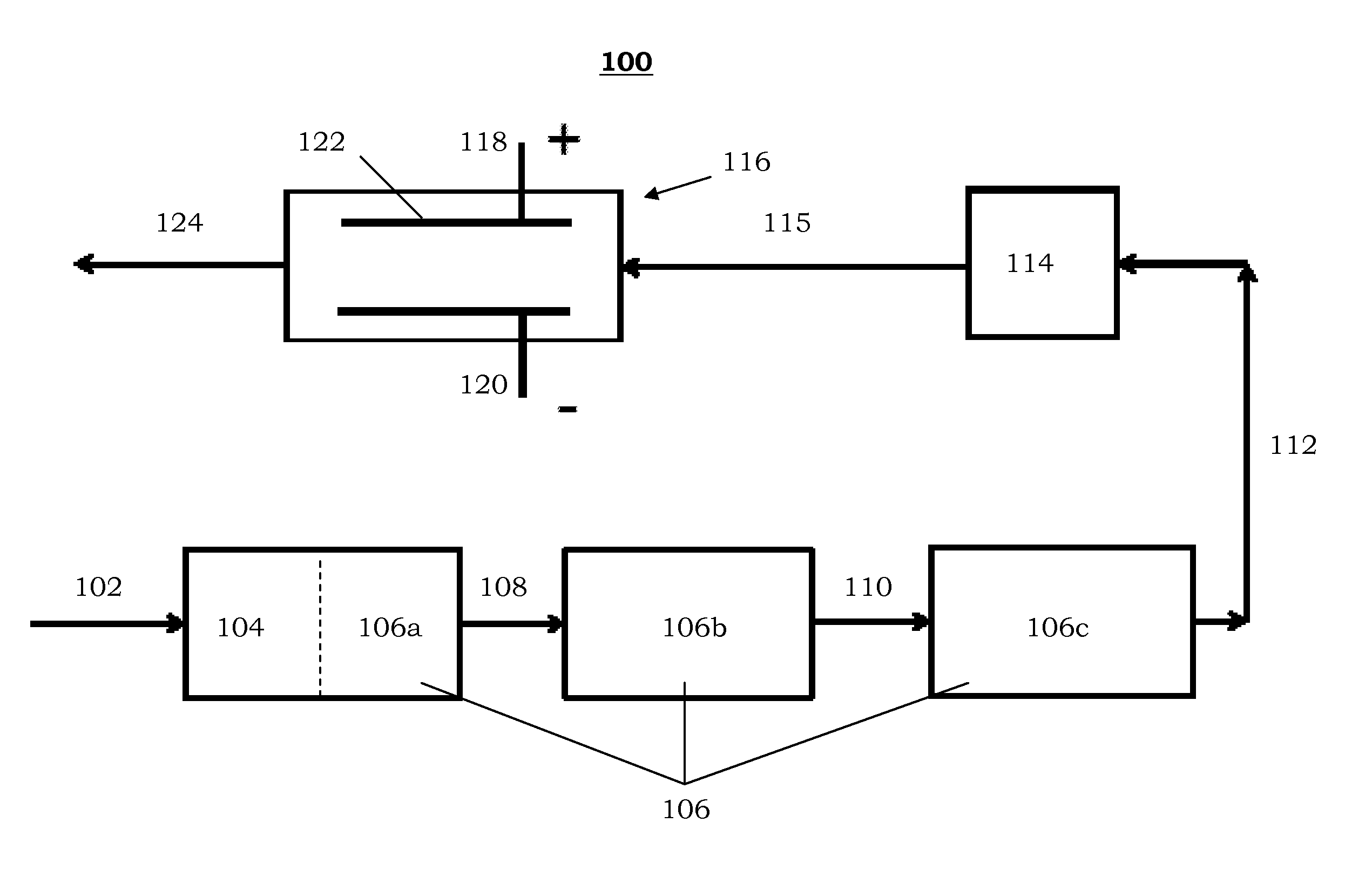
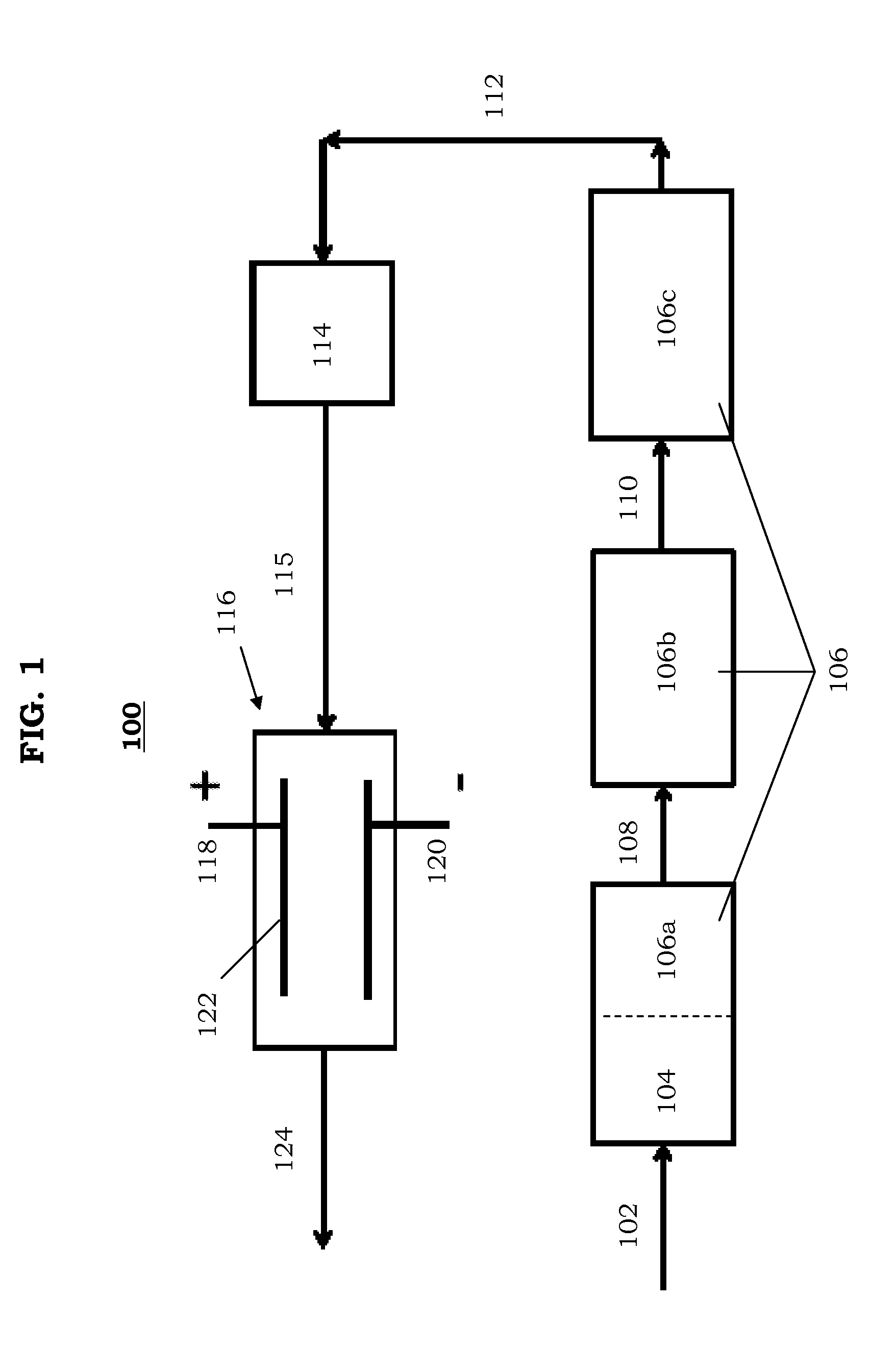
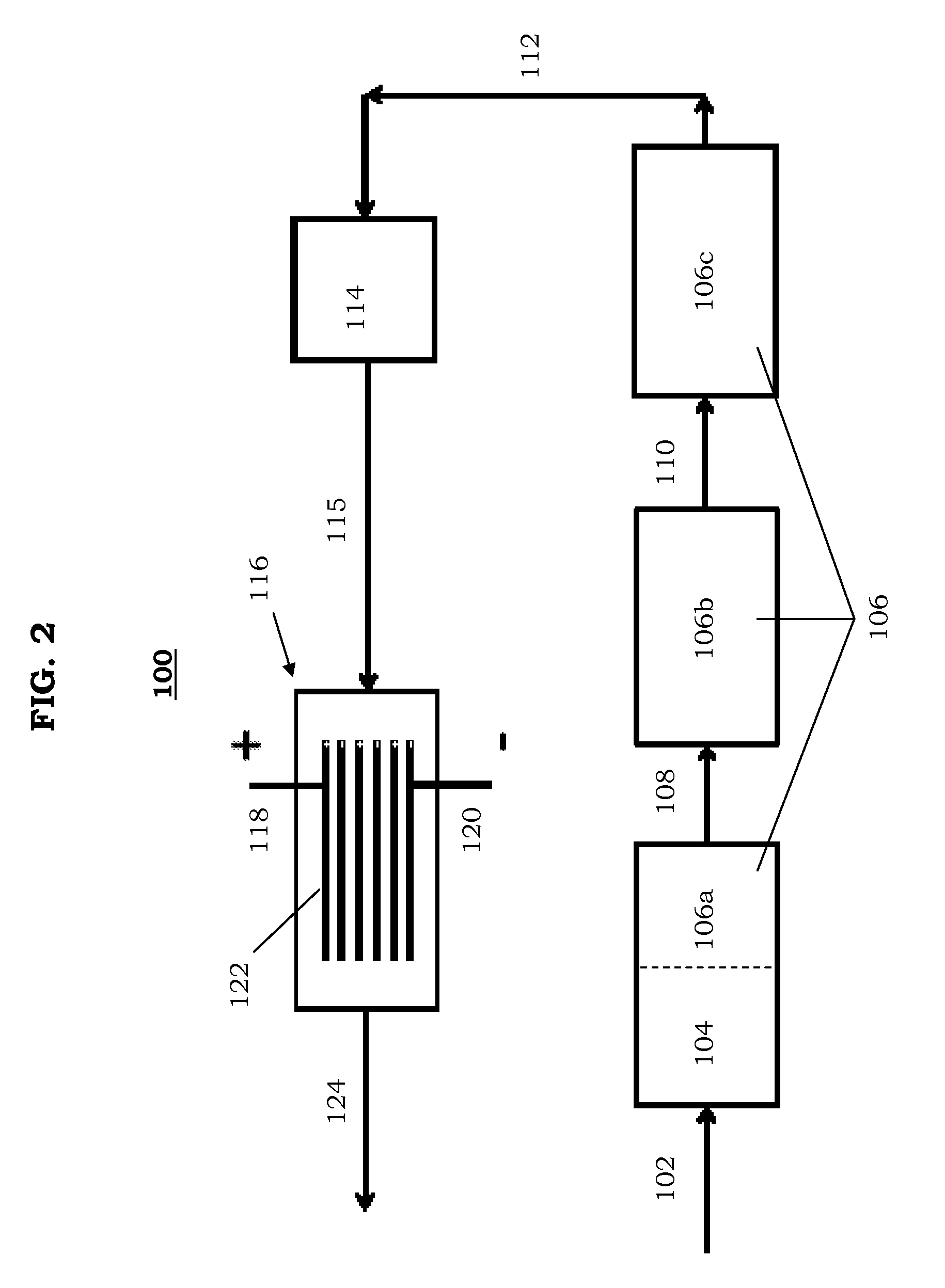
Post-accident fission product removal system and method of removing post-accident fission product
ActiveUS20130170600A1Facilitate electrostatic captureProduce cleanReactor fuel elementsRadioactive decontaminationIonization chamberEngineering
A post-accident fission product removal system may include an air mover, a filter assembly, and / or an ionization chamber. The air mover may be configured to move contaminated air through the filter assembly to produce filtered air. The ionization chamber may be connected to the filter assembly. The ionization chamber may include an anode and a cathode. The ionization chamber may be configured to receive the filtered air from the filter assembly and to ionize and capture radioisotopes from the filtered air to produce clean air.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com