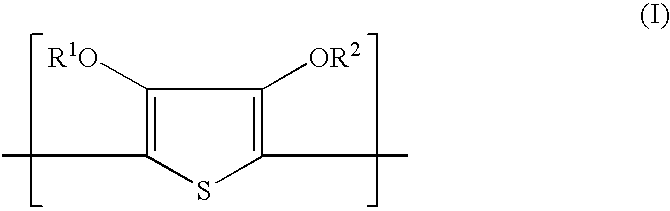
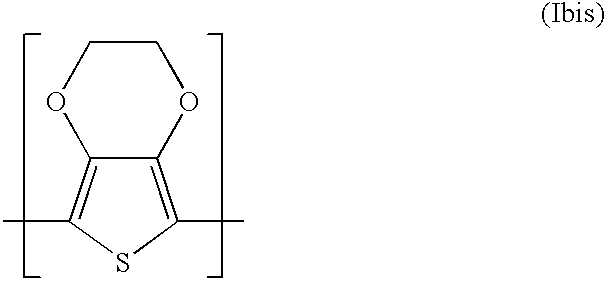
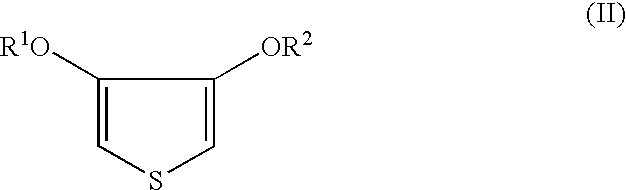
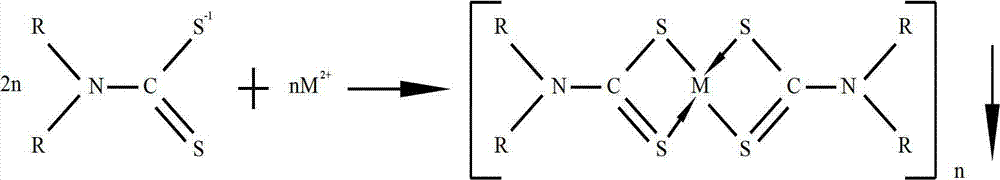
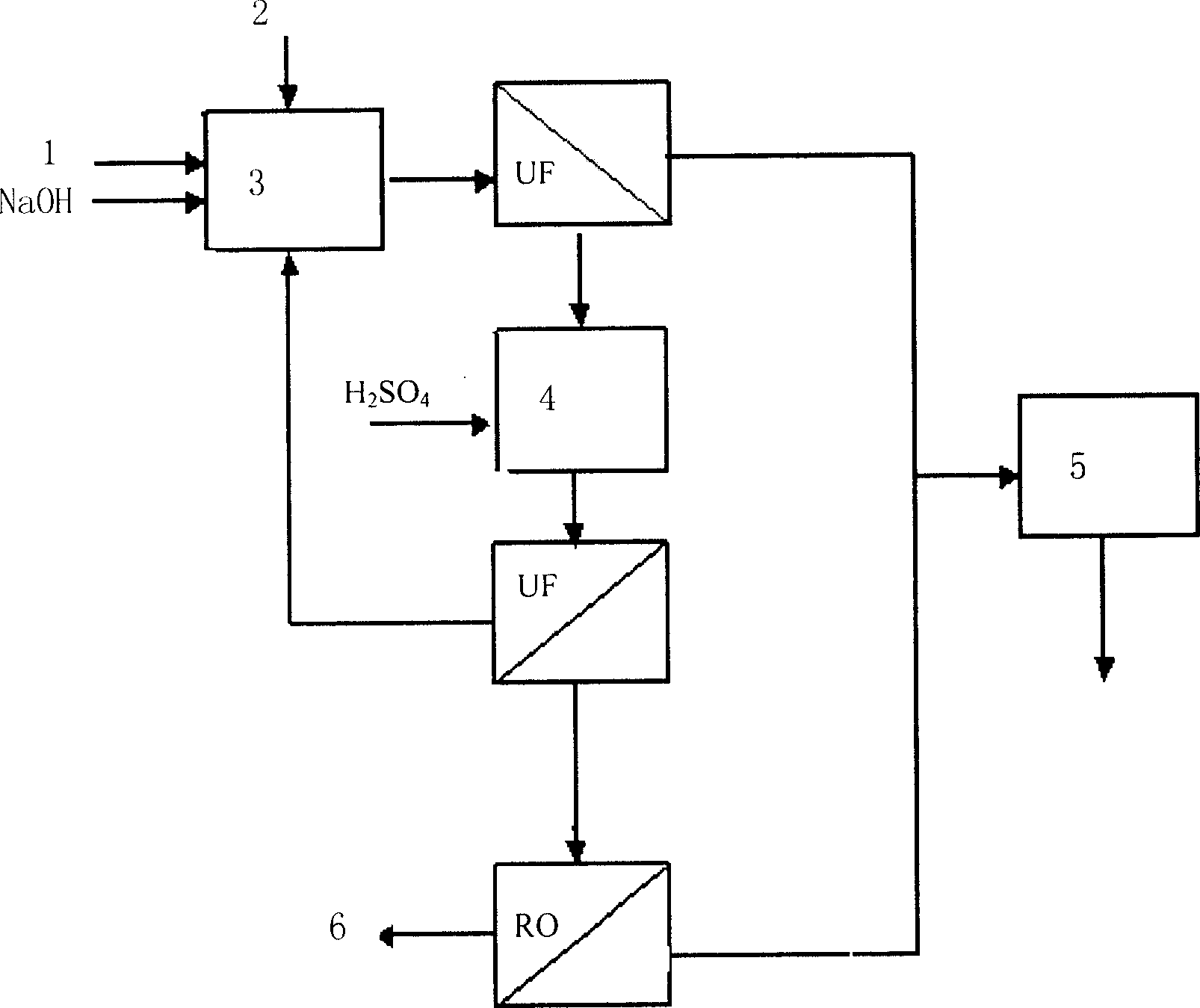
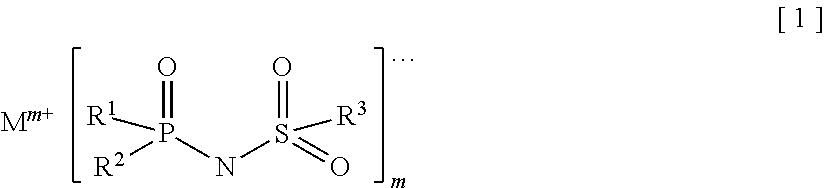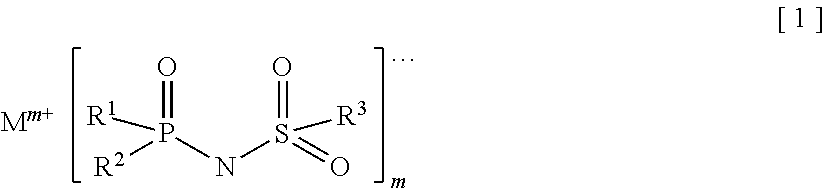Patents
Literature
250 results about "Ionic complex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Complex Ion Definition: Complex ions are ions with a central metal ion bonded to one or more molecules or ions. They are a type of coordination complex. The central ion is the coordination center, while the molecules or ions bound to it are termed complexing agents or ligands. Examples: The copper ammine ion, Cu(NH 3) 6 2+ is a complex ion.
Metal-air cell with performance enhancing additive
ActiveUS20110281184A1Improves oxygen reduction thermodynamicsImproved kineticsFuel and primary cellsFuel and secondary cellsOxygenElectrochemical cell
Systems and methods drawn to an electrochemical cell comprising a low temperature ionic liquid comprising positive ions and negative ions and a performance enhancing additive added to the low temperature ionic liquid. The additive dissolves in the ionic liquid to form cations, which are coordinated with one or more negative ions forming ion complexes. The electrochemical cell also includes an air electrode configured to absorb and reduce oxygen. The ion complexes improve oxygen reduction thermodynamics and / or kinetics relative to the ionic liquid without the additive.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Polymerization process for olefin copolymers using bridged hafnocene compounds
InactiveUS6218488B1High Mooney viscosityIncrease pointsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationElastomerSide chain
The invention is a polymerization process for ethylene copolymers having a density less than 0.915 comprising contacting ethylene, one or more alpha-olefin monomer, and optionally one or more diene monomer, with a catalyst composition comprising the reaction product of at least one organometallic Group 4 metallocene compound derived from a bridged, fused-ring ligand containing biscyclopentadienyl hafnocene, said bridge being a substituted or unsubstituted carbon or silicon atom connecting the biscyclopentadienyl ligands, and a salt of a Group 13 element anionic complex having halogenated aromatic ligands in an essentially tetrahedral structure wherein the aromatic groups are polycyclic fused or pendant aromatic rings. The process is particularly suitable for the preparation of high comonomer content and high molecular weight ethylene-alpha-olefin plastomers and ethylene-propylene or ethylene-propylene-diene monomer elastomers.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Polymerized cycloolefins using transition metal catalyst and end products thereof
InactiveUS6903171B2Low level of residual GroupPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical apparatusElectron donorCoordination complex
Methods for the addition polymerization of cycloolefins using a cationic Group 10 metal complex and a weakly coordinating anion of the formula:[(R′)zM(L′)x(L″)y]b[WCA]dwherein [(R′)zM(L′)x(L″)y] is a cation complex where M represents a Group 10 transition metal; R′ represents an anionic hydrocarbyl containing ligand; L′ represents a Group 15 neutral electron donor ligand; L″ represents a labile neutral electron donor ligand; x is 1 or 2; and y is 0, 1, 2, or 3; and z is 0 or 1, wherein the sum of x, y, and z is 4; and [WCA] represents a weakly coordinating counteranion complex; and b and d are numbers representing the number of times the cation complex and weakly coordinating counteranion complex are taken to balance the electronic charge on the overall catalyst complex.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
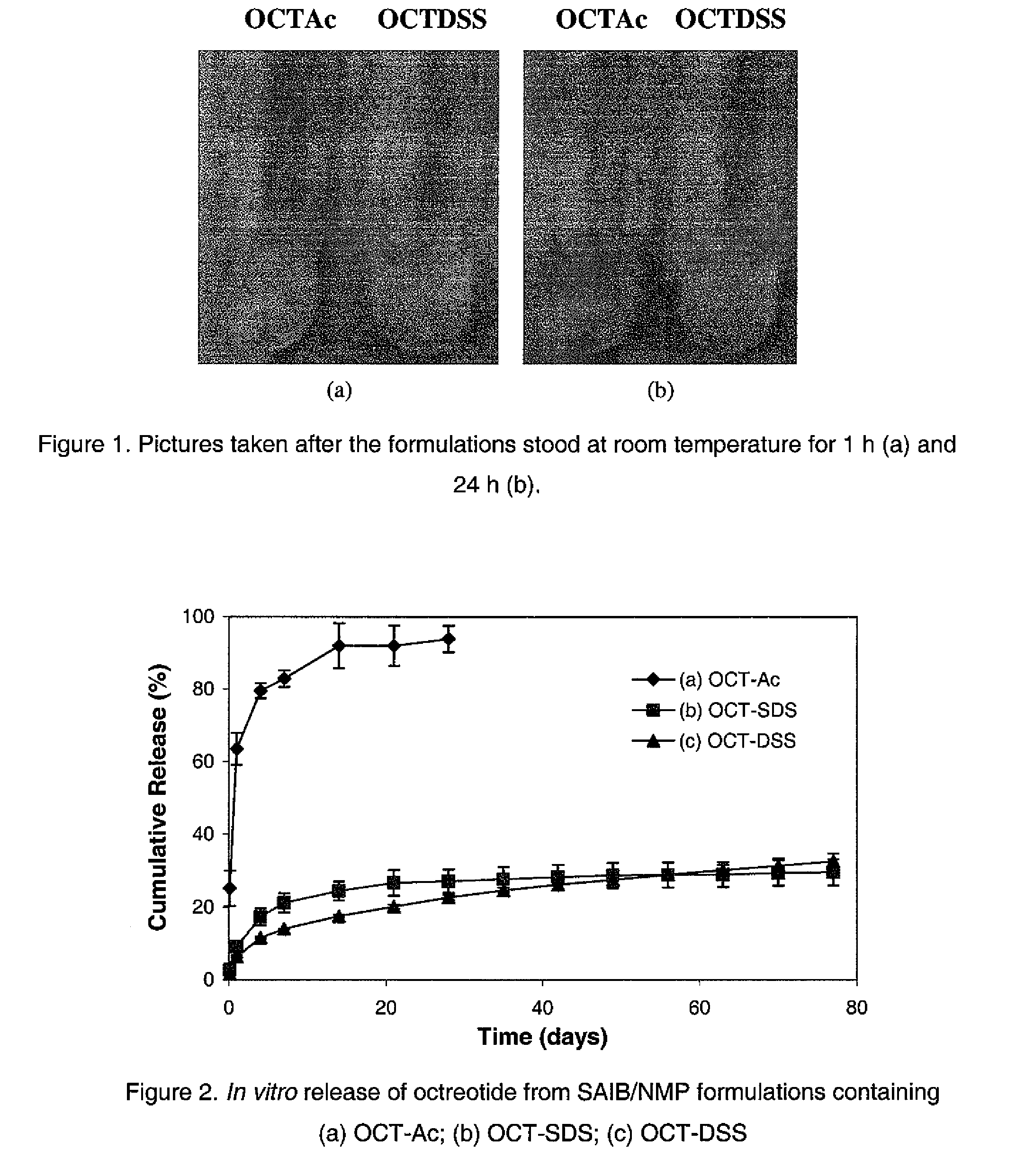
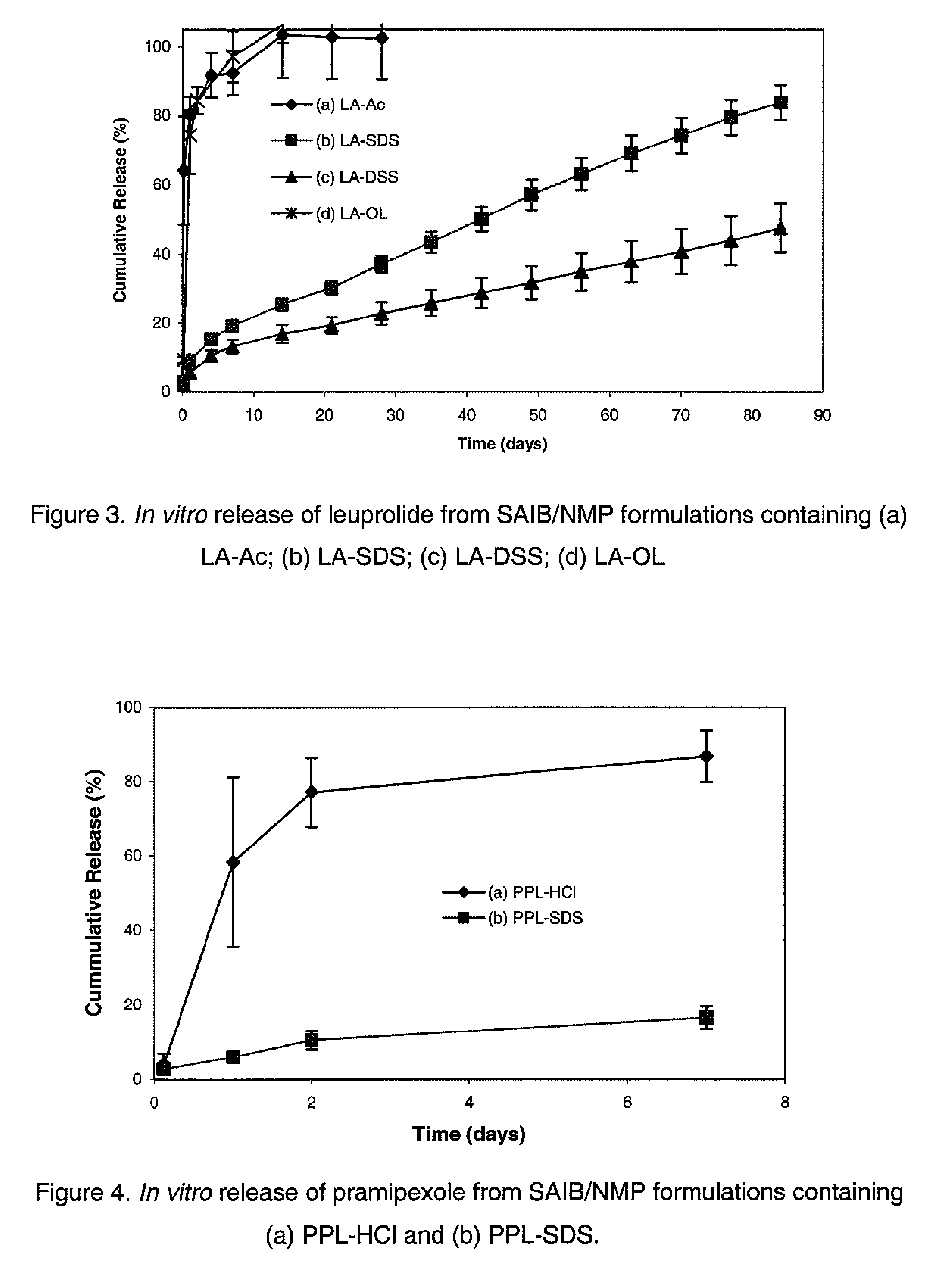
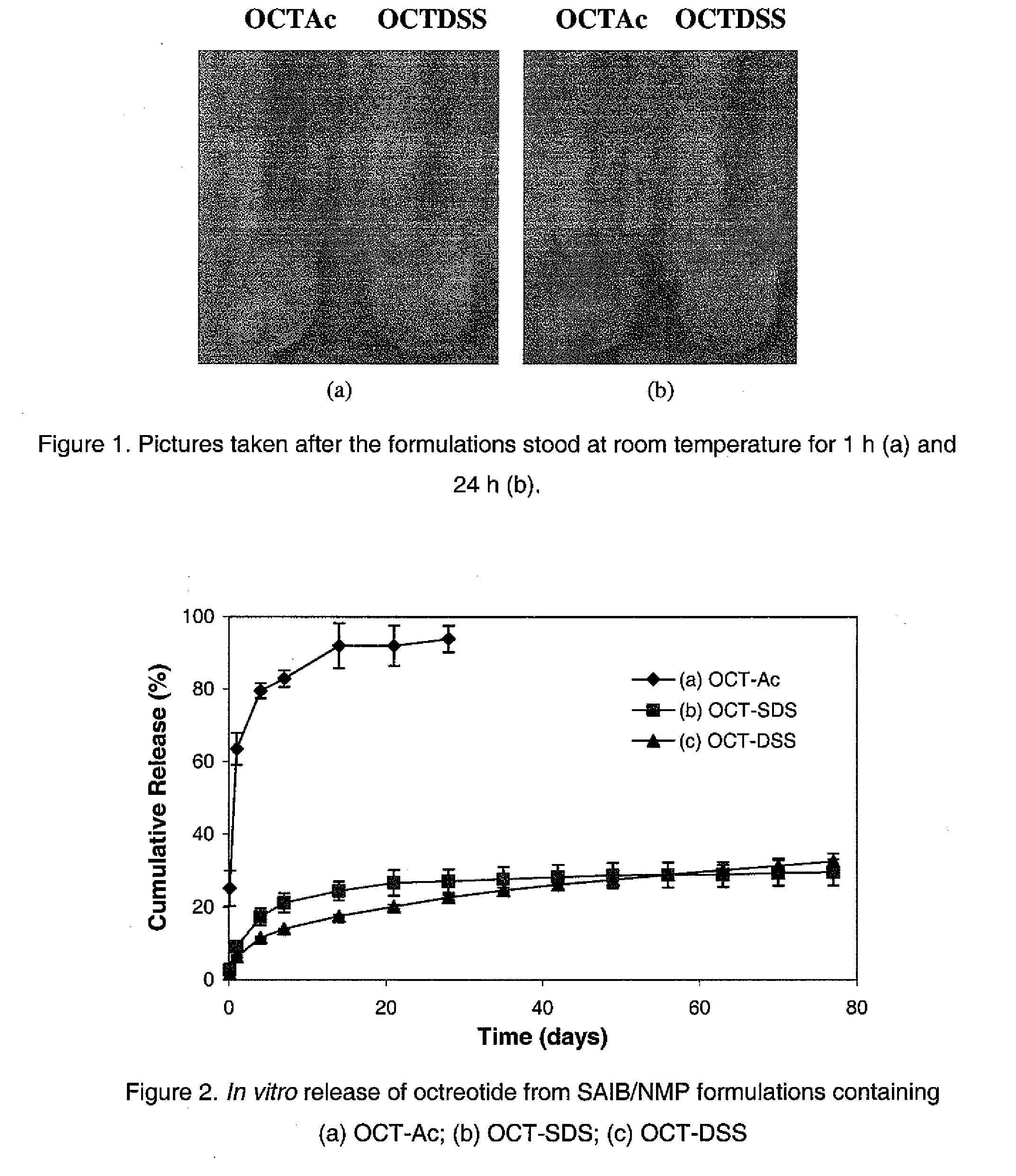
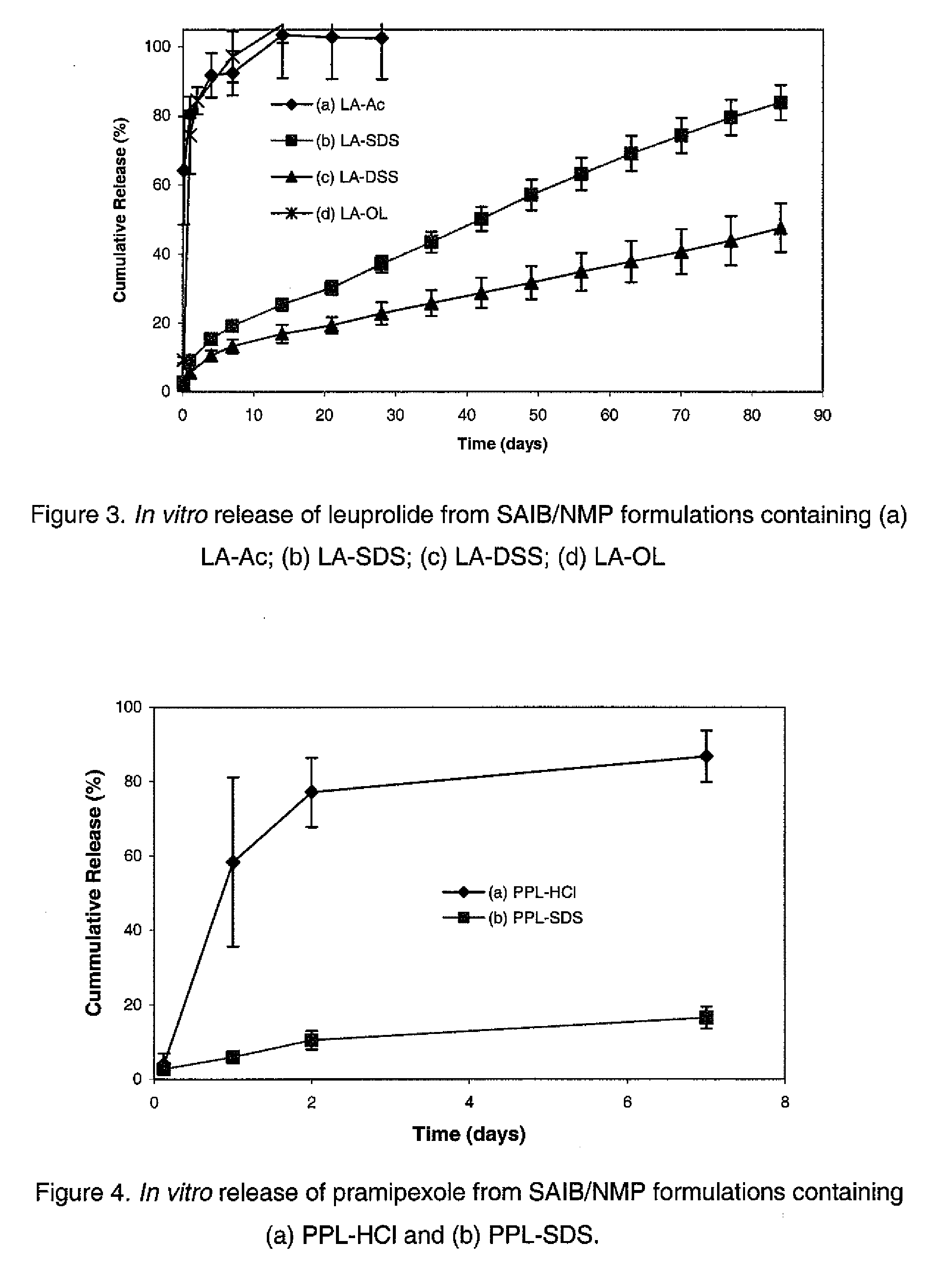
Pharmaceutical formulations for sustained release
InactiveUS20060293217A1Sustained deliveryOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHigh concentrationActive component
Sustained delivery pharmaceutical compositions comprising a solid ionic complex of a pharmaceutically active compound and an ionic macromolecule are provided by the present invention. The pharmaceutical compositions of the invention allow for loading of high concentrations of pharmaceutically active compounds and for delivery of a pharmaceutically active compound for prolonged periods of time, e.g., one month, after administration. Methods for preparing these pharmaceutical compositions, as well as methods of using them to treat a subject are also provided.
Owner:PRAECIS PHARM INC
Thin film inorganic light emitting diode
InactiveUS6706551B2Economical and simpleEasy and economical to manufactureMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentZinc sulfideLight-emitting diode
A method for the manufacturing of a Thin Film Inorganic Light Emitting Diode is disclosed. The device contains in one single layer or in a double layer a dispersion of zinc sulfide doped with a luminescent centre, and a water-compatible p-type semiconductive polymer, preferably a polythiophene / polymeric polyanion complex.
Owner:AGFA GEVAERT AG
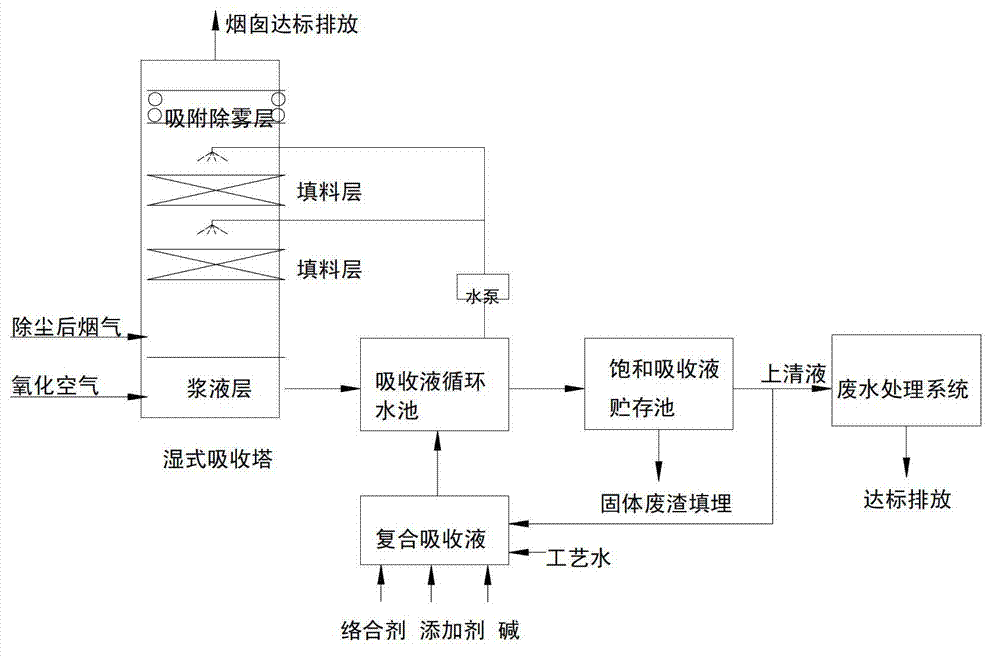
Method for collaboratively controlling multi-pollutants produced from waste incineration smokes
ActiveCN102921278AEfficient removalConvenient sourceDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementMulti pollutantLitter
The invention discloses a method for collaboratively controlling multi-pollutants produced from waste incineration smokes. By developing a novel compound absorption liquid and improving the structure of the conventional absorption tower, multiple pollutants in waste incineration smokes are simultaneously and efficiently removed in a same device with the adoption of a two-stage serial processing mode of oxidation absorption / complexation and adsorption. The method concretely comprises the following steps of: cleaning and removing SO2, HCl, HF, NOX, heavy metal and part of dioxin in waste incineration smokes by using a mixed absorption liquid of alkali, an oxide addition and a heavy metal ionic complex agent, and stabilizing the heavy metal so as to avoid secondary volatilization of the heavy metal; and further absorbing the dioxin and the heavy metal in the smokes via a demister which is made of an adsorption material and serially connected at the top of the absorption tower so that the discharge of the smokes is finally up to the standard. The invention has the advantages of simple method and device, easiness in operation, running and management, small occupied area, low overall operating cost, high pollutant removing efficiency and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MEP
Treating, recovering and reutilizing method for electroplating waste liquid containing heavy metals
ActiveCN1899985AReduce concentrationAvoid harmWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisMultistage water/sewage treatmentLiquid wasteReverse osmosis
The present invention relates to treatment of waste electroplating solution, and is especially method of treating waste electroplating solution containing Cu, Cr, Cd, Ni and other heavy metals and recovering heavy metals. The method includes the following steps: adding water soluble great molecular weight polymer into the waste electroplating solution to form complex of heavy metal ions, ultrafiltering to obtain concentrated liquid with enriched heavy metal ions, adding sulfuric acid to the ultrafiltrate to acidify and decomplex the heavy metal ions, ulterfiltering the decomplexed solution, returning the concentrated liquid with enriched complex agent to the complexing step, treating the ultrafiltered dialysate through reverse osmosis to obtain concentrated heavy ion solution, and returning the concentrated heavy ion solution to the electroplating step.
Owner:SANDA FILM SCI & TECH XIAMEN
Ion complex, coated product and coating method
InactiveUS6555225B1Inhibition of dissolutionMaintain stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsPharmaceutical containersOrganic solventWater insoluble
An ion complex which comprises a water-insoluble polyion (P) and a water-soluble polyion (A); and is insoluble in water and soluble in an aqueous organic solvent. Such an ion complex becomes a coating material which can preferably be used for coating of various ionic substances (e.g., substance having biological activity such as an anticoagulant property or an antibacterial property).
Owner:MEBIOL +1
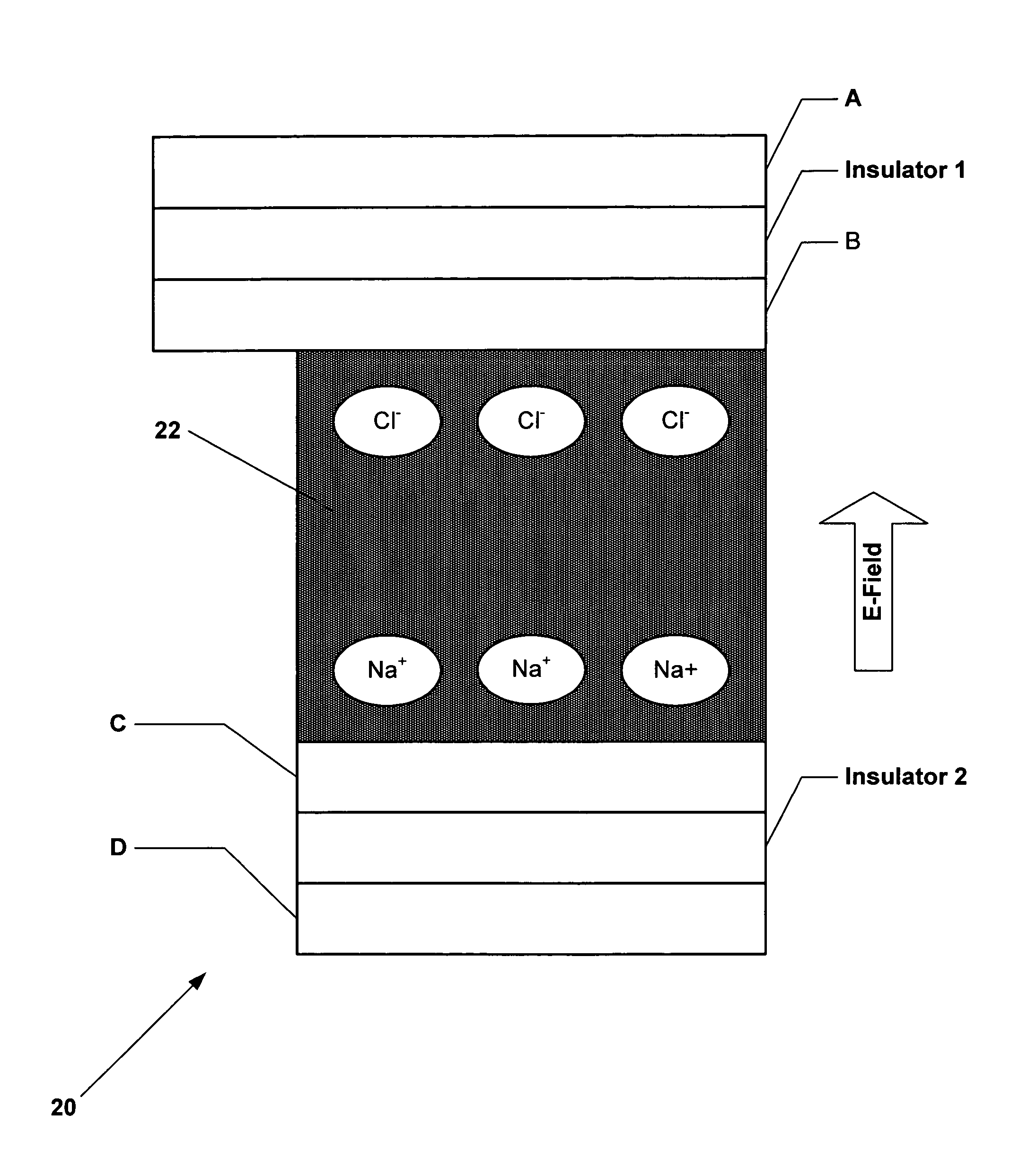
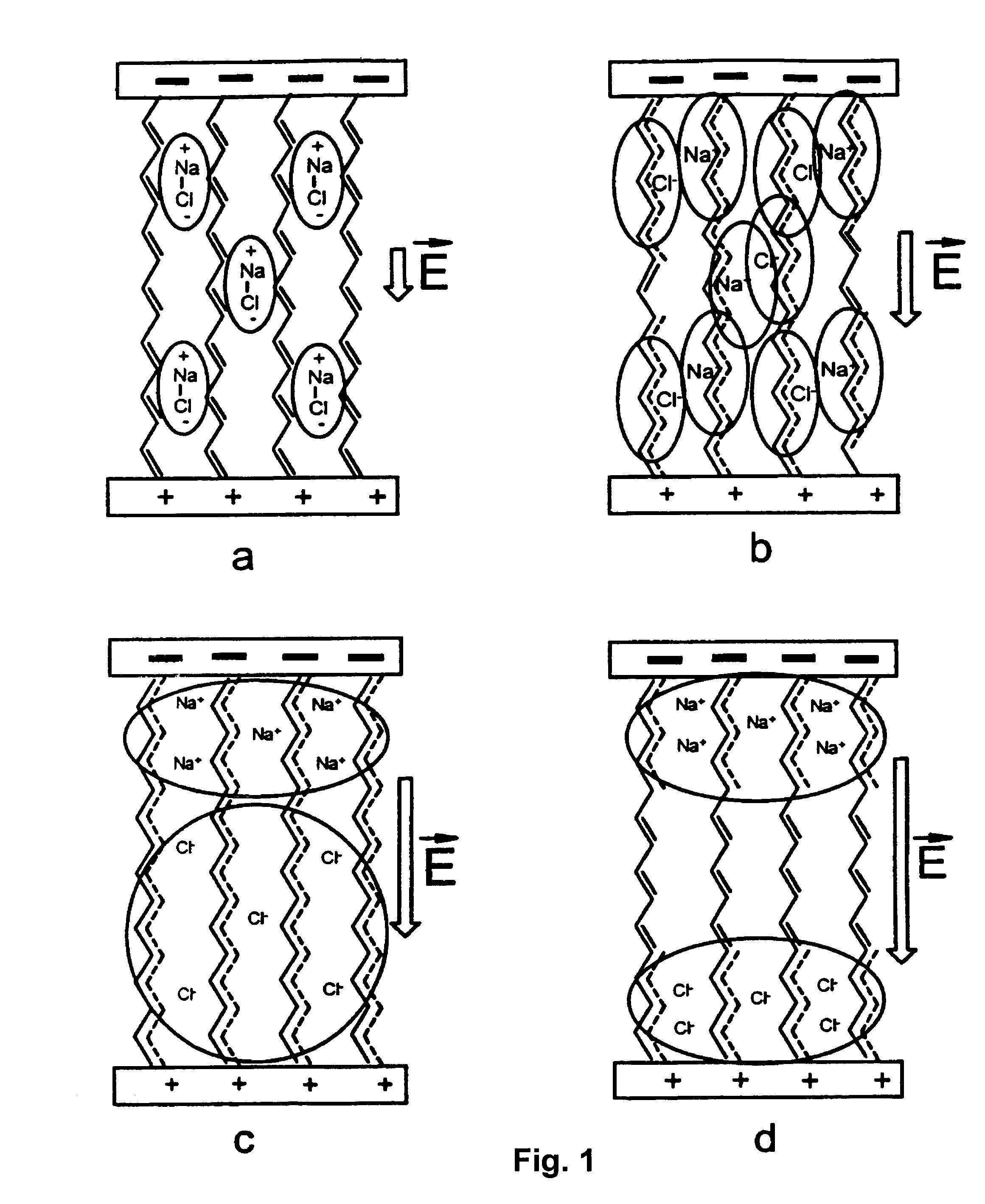
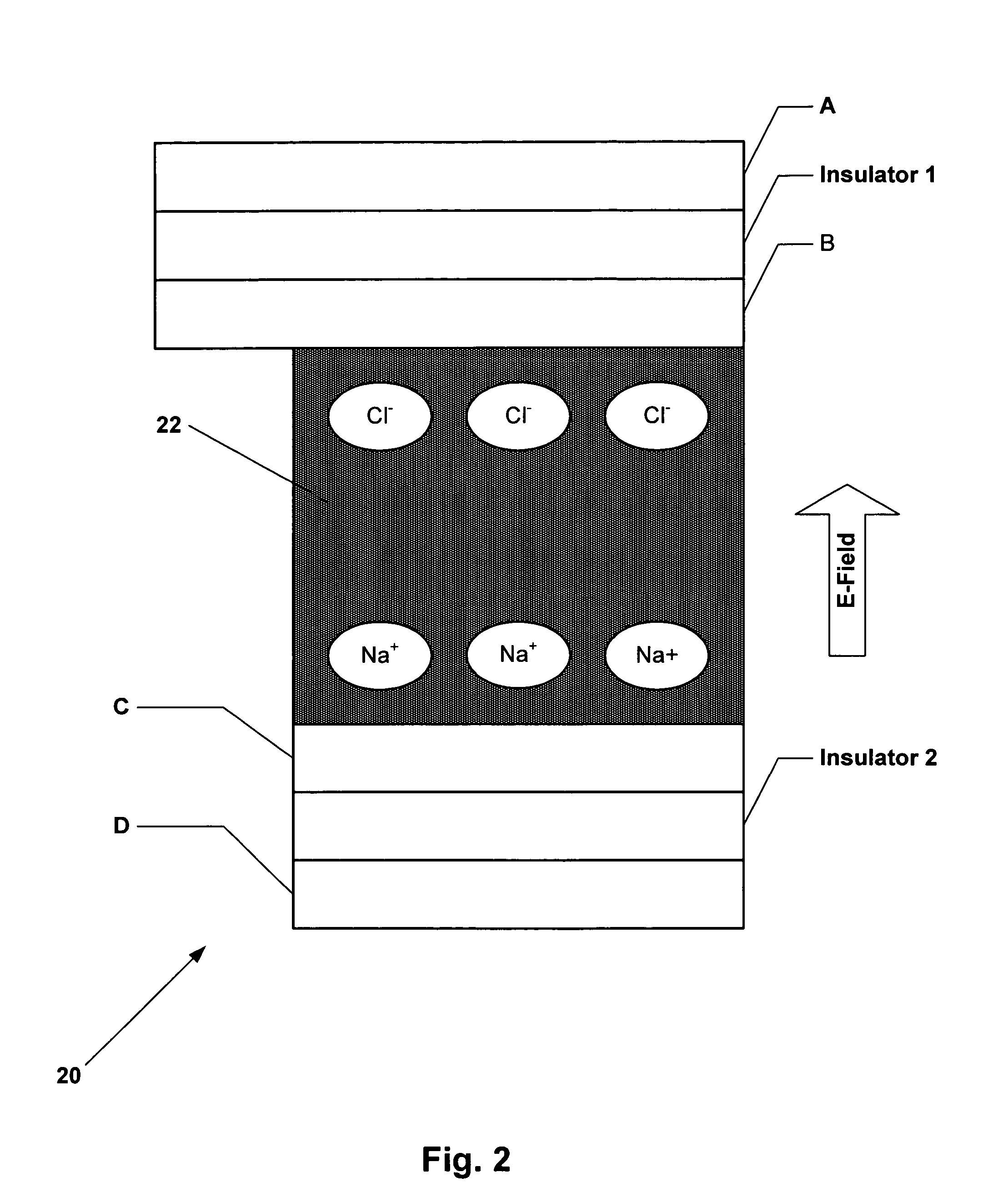
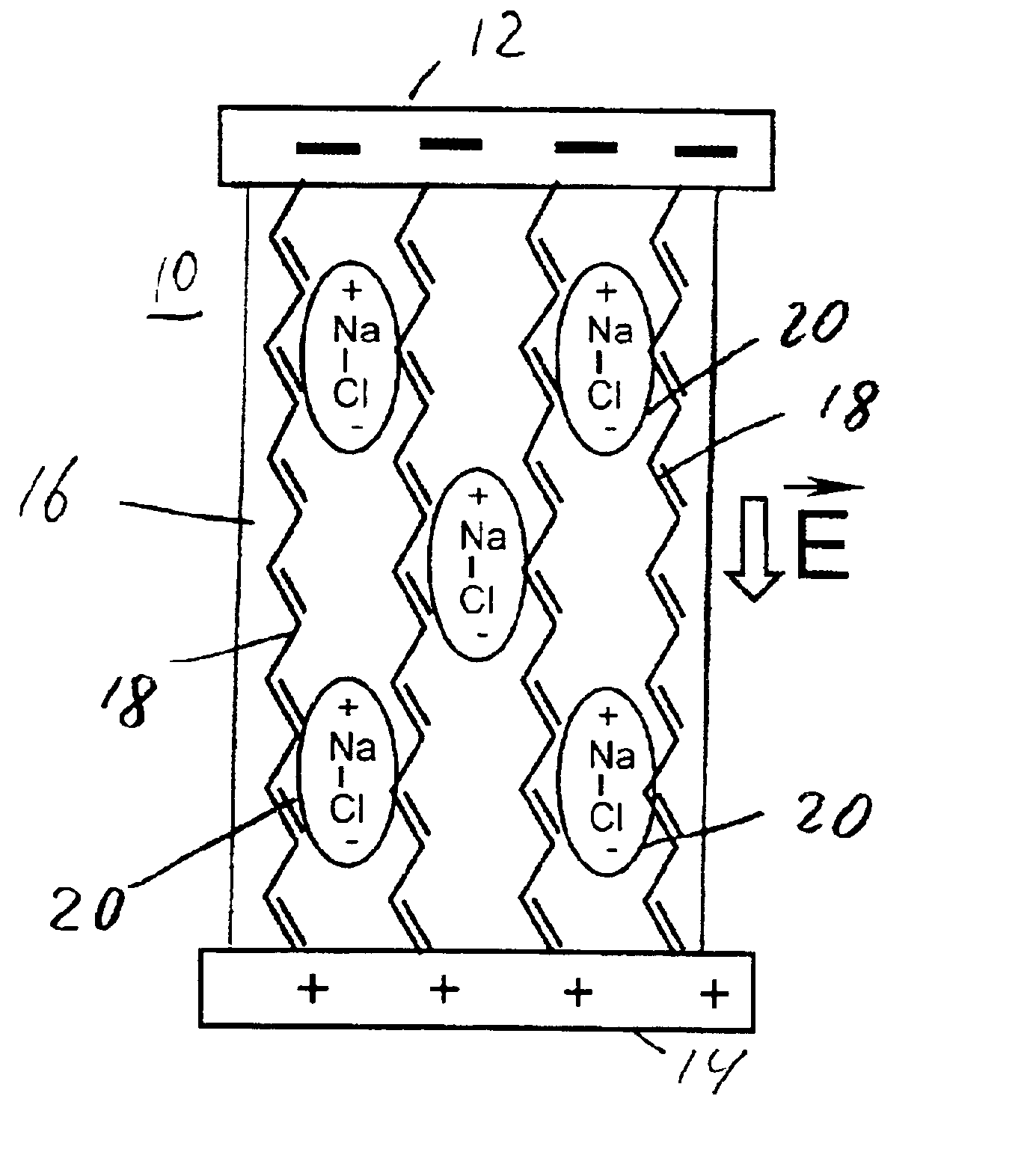
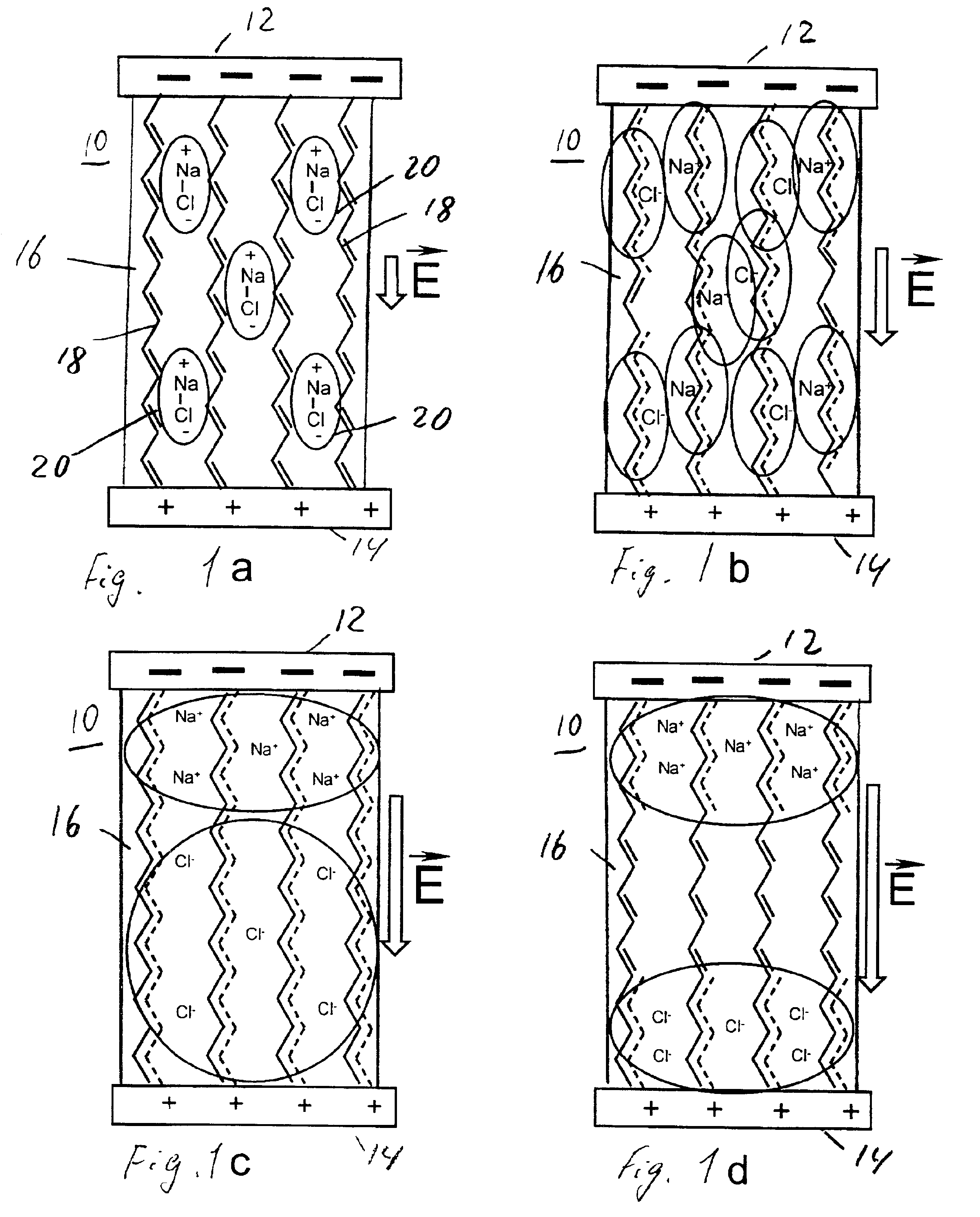
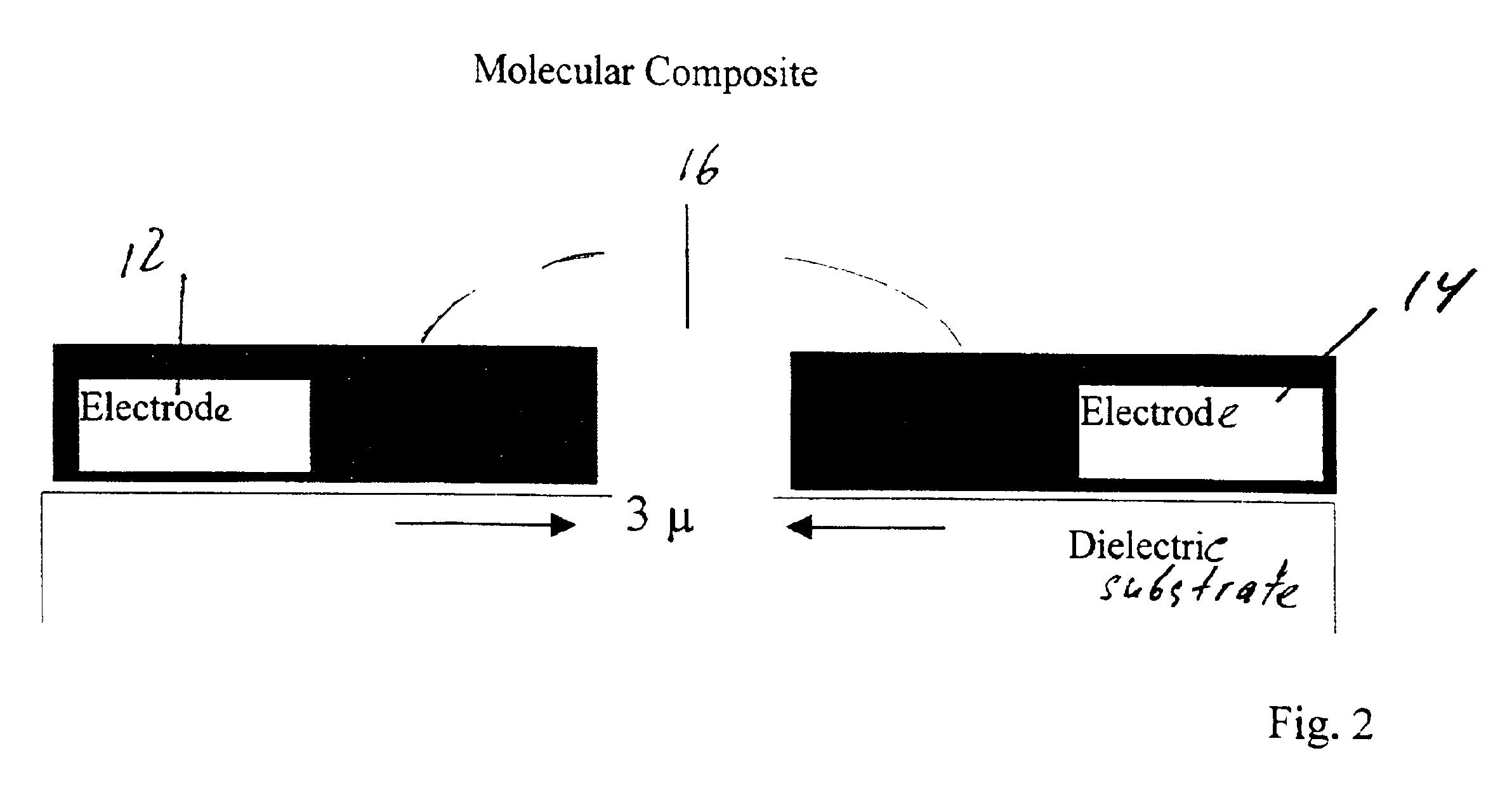
Molecular memory device
InactiveUS20050116256A1Reduce leakage currentNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesWork functionElectric field
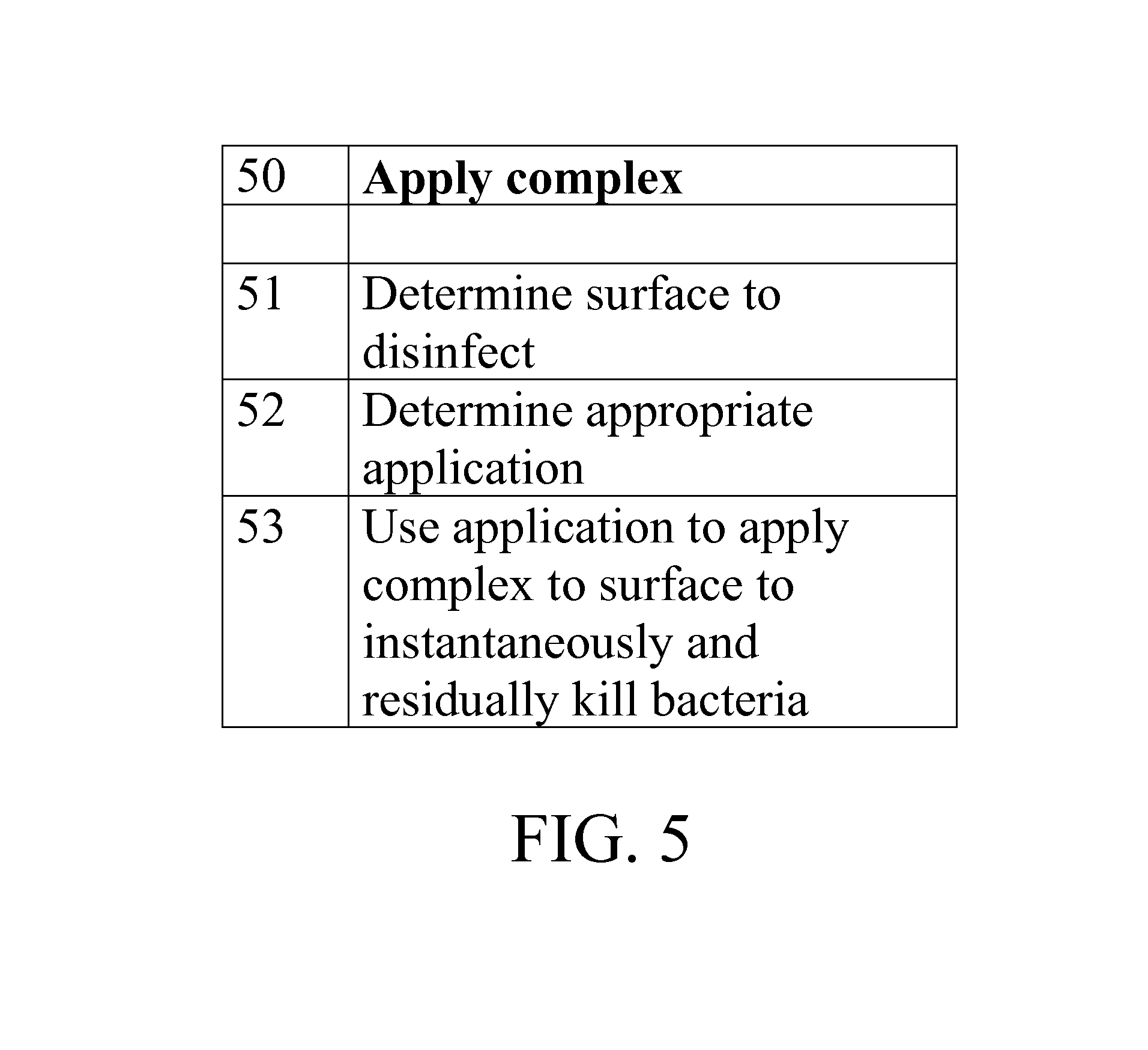
A novel memory cell is provided with an active region including a molecular system and ionic complexes distributed in the molecular system. A pair of write electrodes are arranged for writing information to the memory cell. The active region is responsive to an electric field applied between the pair of write electrodes for switching between an on state and an off state. The active region has a high impedance in the off state and a low impedance in the on state. A pair of read electrodes is used to detect whether the active region is in the on state or in the off state to read the information from the memory cell. Read electrodes may be made of different materials having different work functions to reduce leakage current.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
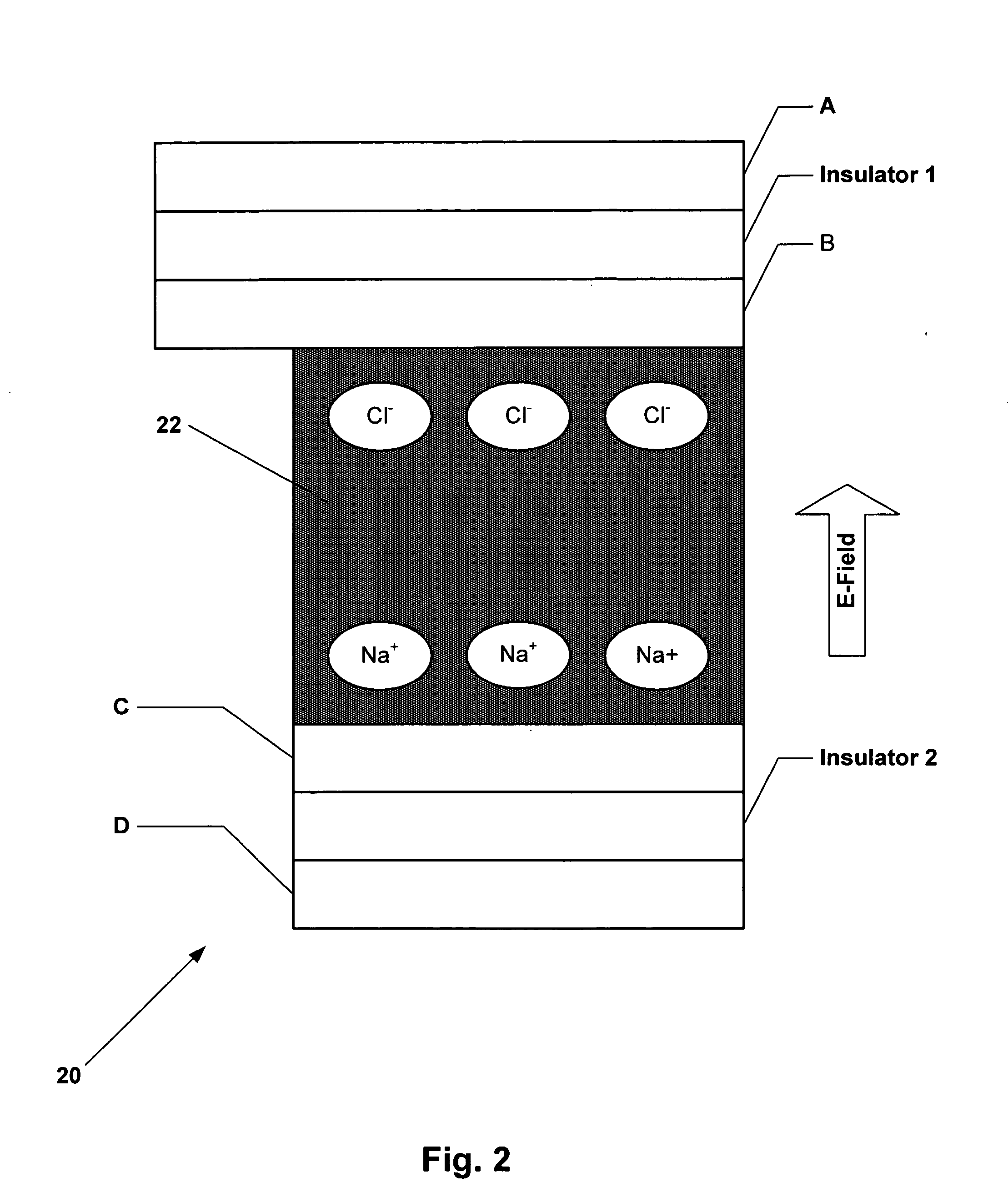
Method of Screening Crude Oil for Low Molecular Weight Naphthenic Acids
InactiveUS20070298505A1Simple to learnSimple to runComponent separationSolid sorbent liquid separationPhysical chemistryIon exchange
A method for the quantitation of the naphthenic acid content of molecular weight less than 600 Daltons in a hydrocarbon composition, in which naphthenic acids are separated from the hydrocarbon composition and applied to a macroreticular ion-exchange resin. The resin is washed and the naphthenic acid-metal ion complexes are eluted from the resin. The number of naphthenic acid-metal ion complexes present in the eluate from the resin are then quantitated.
Owner:OIL PLUS
Low dosage naphthenate inhibitors
InactiveUS20050282711A1Avoid interactionInhibition formationDewatering/demulsification with chemical meansTransportation and packagingOrganic acidHydrotrope
Low dosage naphthenate inhibitors, such as a surfactant or hydrotrope, delivered into production fluids for contact with mixtures of oil and water, such as in a hydrocarbon producing formation, production equipment, or processing systems. Inhibitor compounds such as monophosphate esters and diphosphate esters exhibit surface-active properties that cause the inhibitors to self-associate at oil-water interfaces and inhibit interactions between organic acids in the oil with cations or cation complexes in the water. These compounds also inhibit aggregation of organic acid carboxylate salts that form when pH and pressure conditions are amenable to organic acid ionization. Preferred inhibitors do not form emulsions due to the formation of unstable mixed interface structures that result in coalescence of dispersed droplets. Naphthenate inhibitor compound dosages of less than 100 ppm can effectively inhibit naphthenate salts or other organic acid salts that can form precipitates or emulsions during crude oil production or processing.
Owner:CHAMPIONX USA INC
Polymer micelle complex including nucleic acid
ActiveUS20090258416A1Efficient expressionMicroencapsulation basedGenetic material ingredientsViral GenesPolyethylene glycol
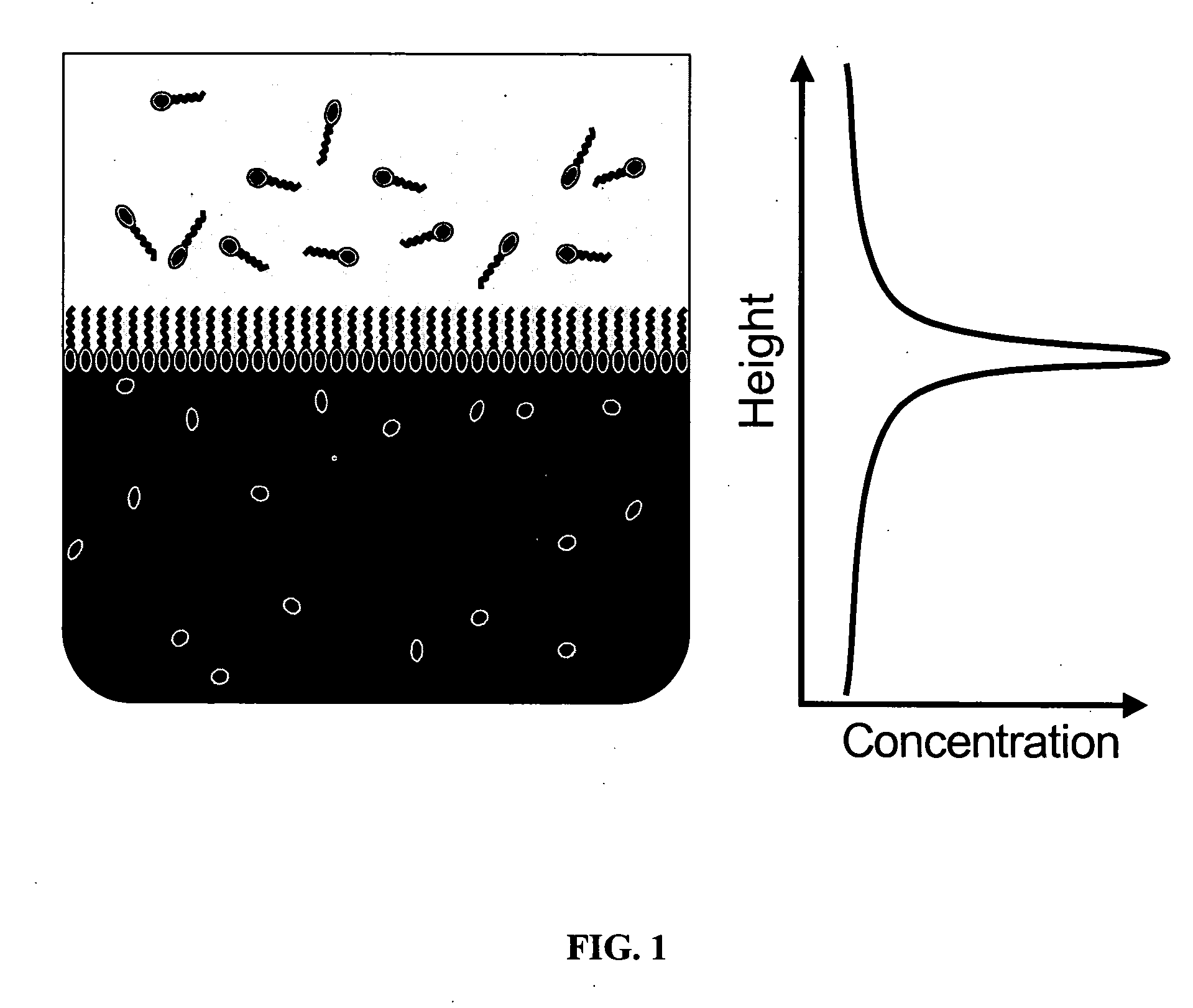
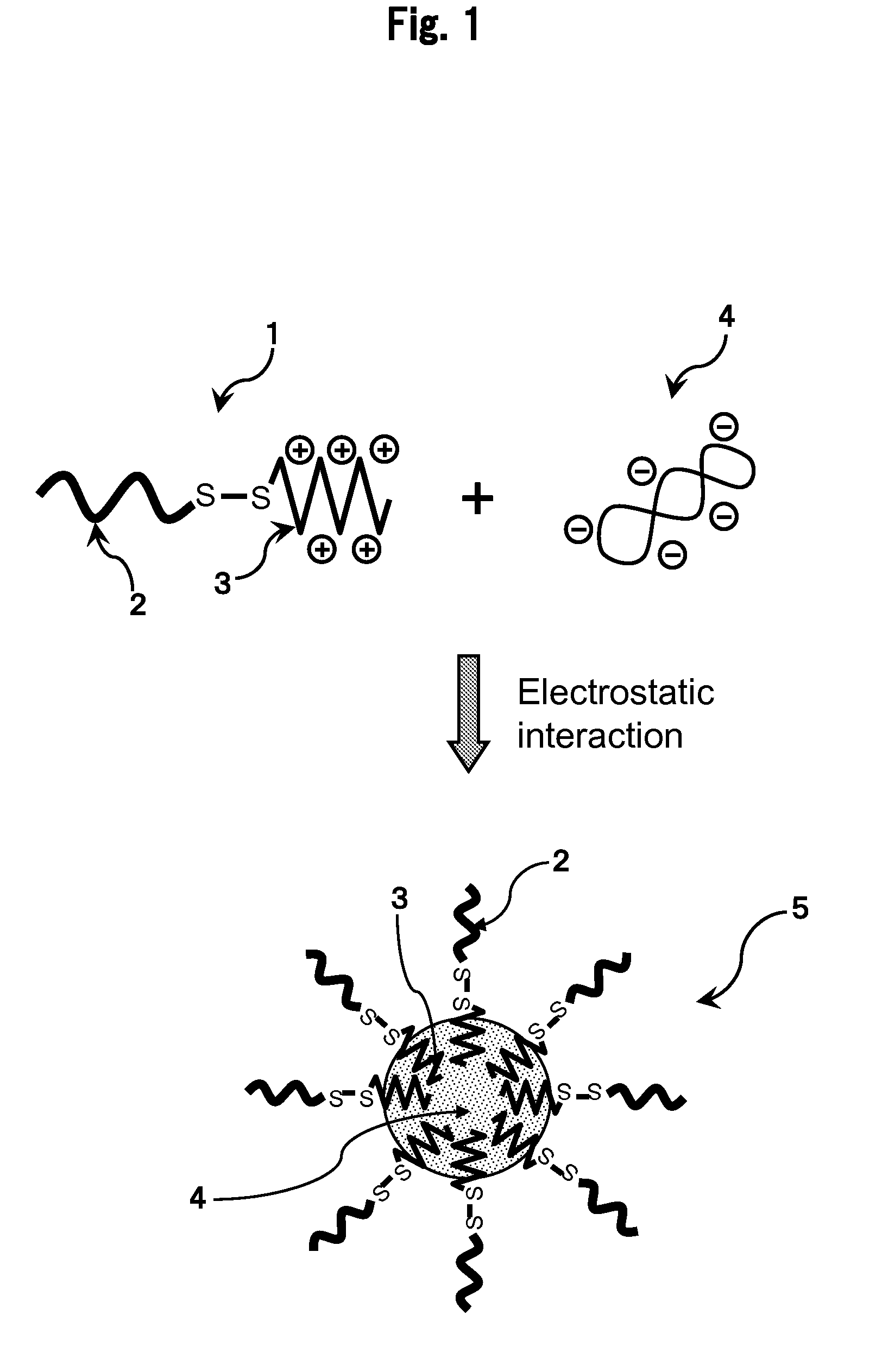
It is an object of the present invention to provide a polyion complex used as a non-viral gene vector, which achieves sufficiently high gene expression efficiency to a target cell. The polyion complex of the present invention comprises a block copolymer formed by binding polyethylene glycol to polycation via a disulfide group and a nucleic acid.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Antiseptics for improving hydrogen peroxide sterilizing activity and preparing process thereof
InactiveCN1552211AHigh bactericidal activityIncrease free radical concentrationBiocideAnimal repellantsGlutaric anhydrideButanedioic acid
A disinfectant able to increase the bactericiding activity of hydrogen peroxide is prepared from the aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide, the activating agent chosen from the complex of metallic ion (Fe, Cu, Ag or Mg), the anhydride of acetic acid, propionic acid, butanedioic acid, etc and the stabilizer chosen from organic acid and inorganic acid through proportional mixing, and controlling pH=0.5-4 and temp to be lower than 100 deg.C. Its advantages are high bactericiding power, broad spectrum and high stability.
Owner:西藏大昭圣泉实业有限公司
High stable water chain alkyl silane emulsion and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a highly stable aqueous chain alkyl silane emulsion and a preparation method. The emulsion includes continuous aqueous phase, dispersed hydrolyzable alkoxy silane oil phase and emulsifier; the weight ratio of hydrolyzable alkoxy silane, emulsifier and water is 10 to 65:2 to 15:20 to 88. The hydrolyzable alkoxy silane oil phase is composed of chain alkyl trialkoxysilane R1Si (OR2) 3, trialkoxysilane R3Si (OR2) 3 or dialkoxysilane R4R5Si (OR2) 2 and the corresponding hydrolysis polycondensation oligomer, wherein, substituents R1 and R4 are C1 to 18 chain alkyls, R2 is methyl, ethyl, propyl, etc., and R3 and R5 are acryloyl oxy propyl, ethenyl, amino propyl, Gamma-glycidyl ether oxyl, etc. The emulsifier is nonionic and ionic complex, including OP series, Span series, Tween series and a composite system composed of sodium dodecyl sulfonate, sodium dodecyl sulfate and dodecyl benzene sulfonate.
Owner:湖北德邦化工新材料有限公司 +1
Pharmaceutical formulations for sustained release
InactiveUS20060198815A1Sustained deliveryBiocideNervous disorderHigh concentrationPharmaceutical formulation
Sustained delivery pharmaceutical compositions comprising a solid ionic complex of a pharmaceutically active compound and an ionic macromolecule are provided by the present invention. The pharmaceutical compositions of the invention allow for loading of high concentrations of pharmaceutically active compounds and for delivery of a pharmaceutically active compound for prolonged periods of time, e.g., one month, after administration. Methods for preparing these pharmaceutical compositions, as well as methods of using them to treat a subject are also provided.
Owner:GLAXO SMITHKLINE LLC
Non-polymeric compositions for controlled drug delivery
InactiveUS8586103B2Maintain physical stabilityEnhanced chemical and physical stabilityAntibacterial agentsBiocidePharmaceutical SubstancesCompatibilization
The present invention provides a novel liquid composition suitable for in-situ formation of a depot system to deliver a bioactive substance in a controlled manner. The composition of the present invention comprises: (a) a hydrophobic non-polymeric carrier material; (b) a water miscible biocompatible organic solvent that dissolves the hydrophobic non-polymeric material; (c) an ionic complex that is formed between an amphiphilic molecule and a bioactive substance having a net charge at neutral pH in water. The present invention also provides a method of manufacturing and use of the composition thereof.
Owner:FORESEE PHARMA CO LTD
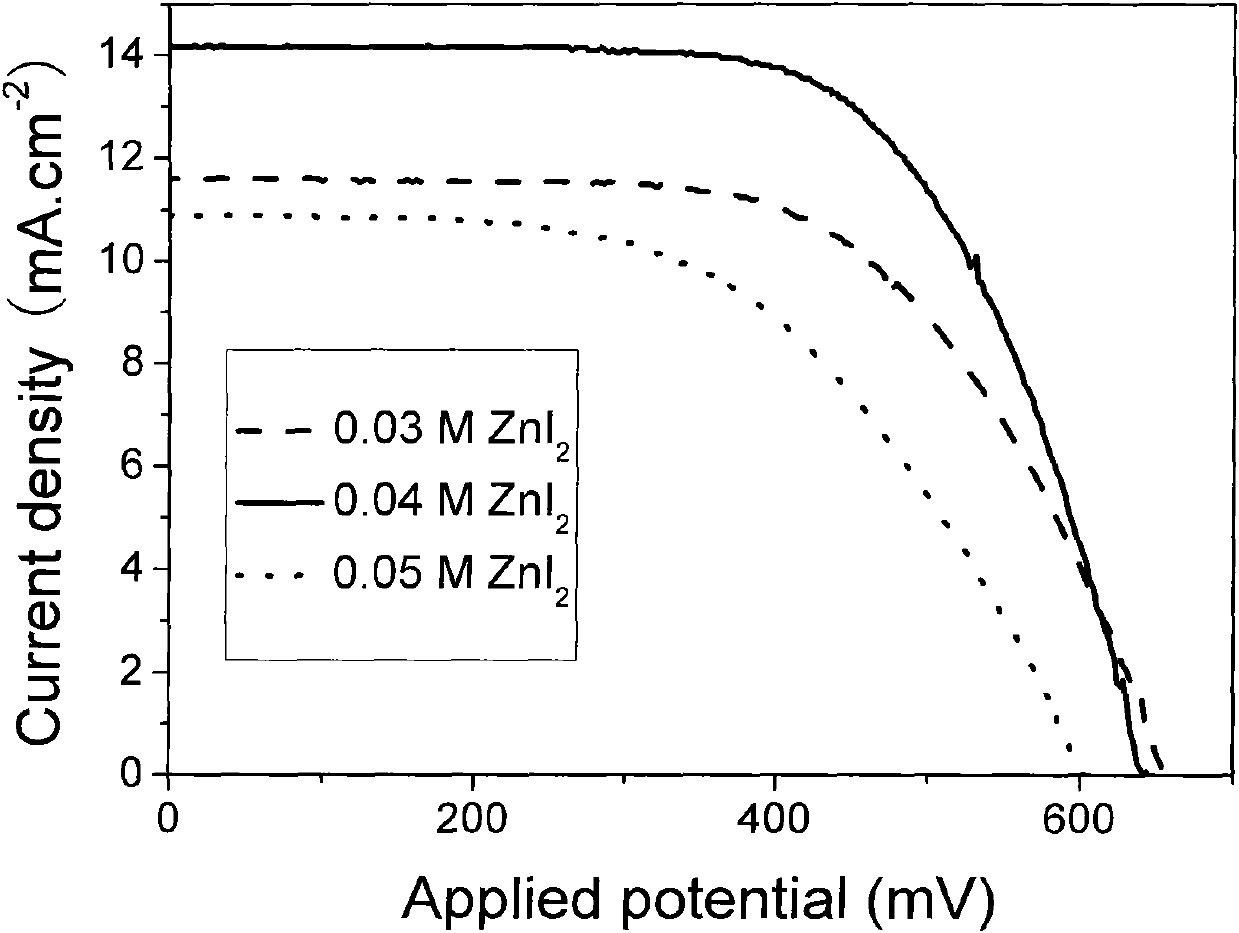
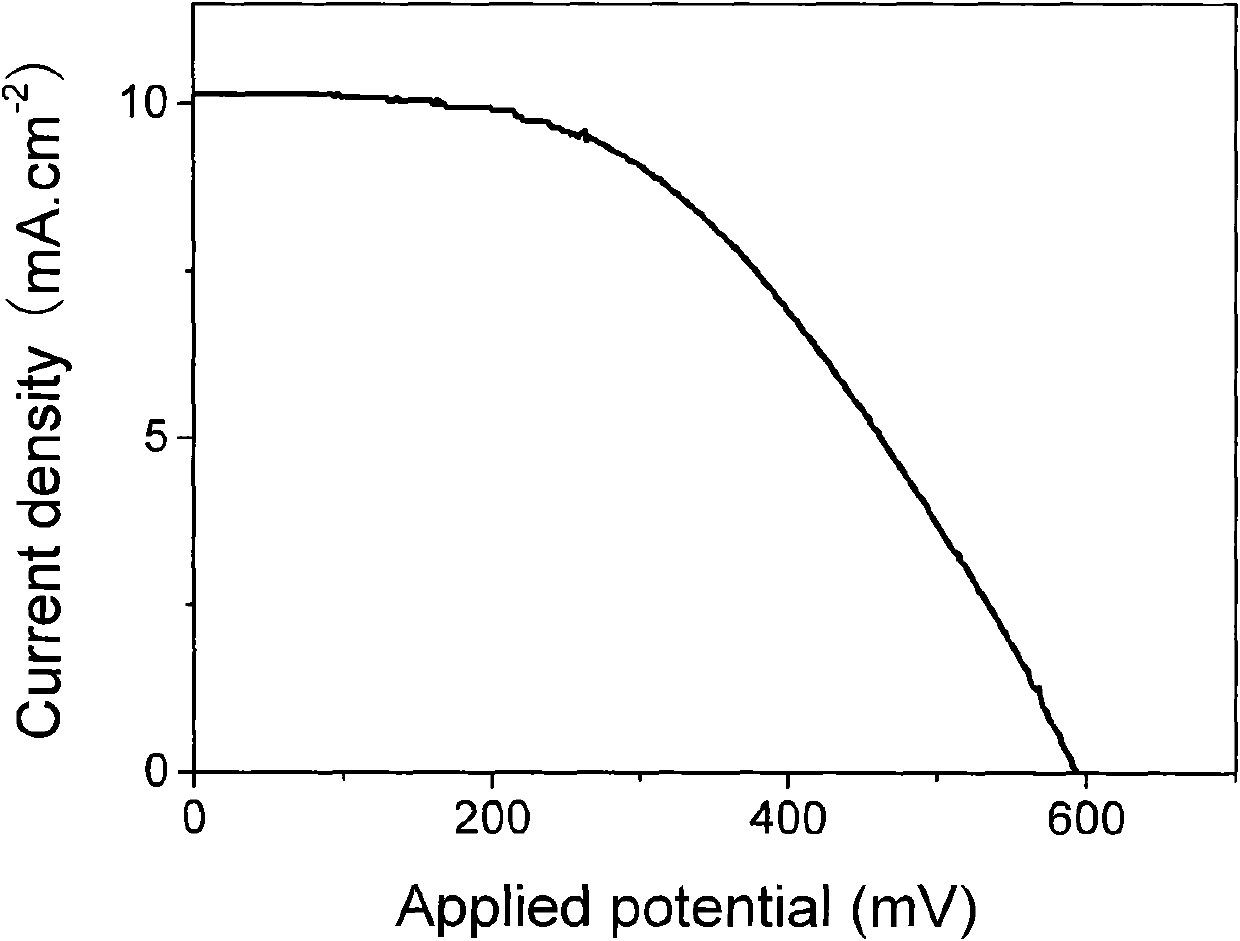
Polymer-metal ion complex gel electrolyte and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102020748AImprove machinabilityOvercome the defects of poor preparation operability and poor interface contactLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesPolymer metalPlasticizer
The present invention discloses a polymer-metal ion complex gel electrolyte and preparation method and application thereof. The polymer-metal ion complex provided by the present invention is prepared by the complexation of polymers and polyvalent metal salts. The polymer gel electrolyte prepared by the polymer-metal ion complex comprises polymers, polar small molecular plasticizers, polyvalent metal salts, monovalent metal salts, and iodine. The present invention also discloses a preparation method of the metal ion complex gel electrolyte. The polymer-metal ion complex gel electrolyte provided by the present invention overcomes the defects of poor maneuverability of electrolyte preparations and poor contact between interfaces in the prior art. The gel electrolyte is especially applicable to prepare dye-sensitized solar cells, which allows the photoelectric conversion efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells to be above 5%.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Supported catalysts with controlled metal cluster size
ActiveUS7582586B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationDendrimerSolvent
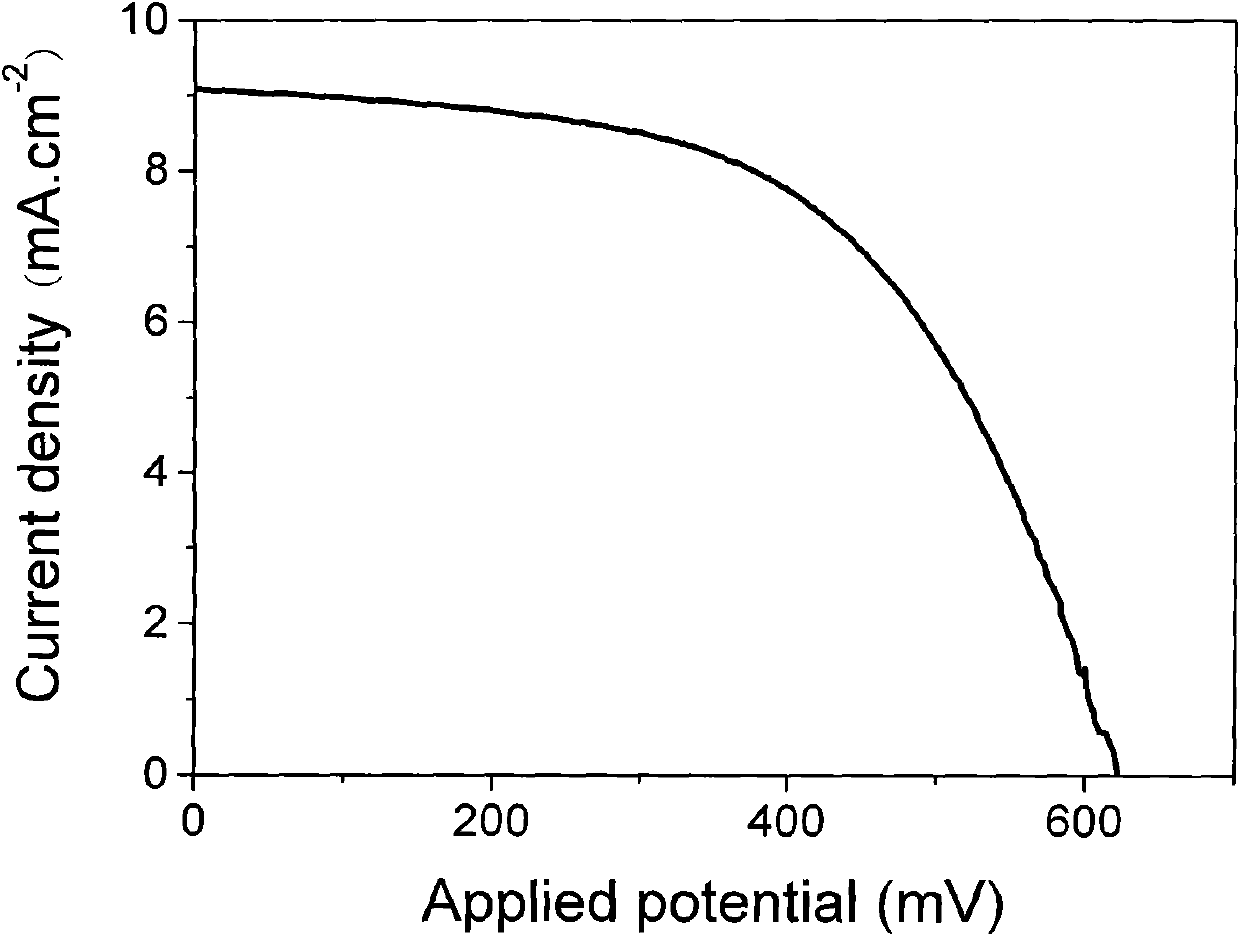
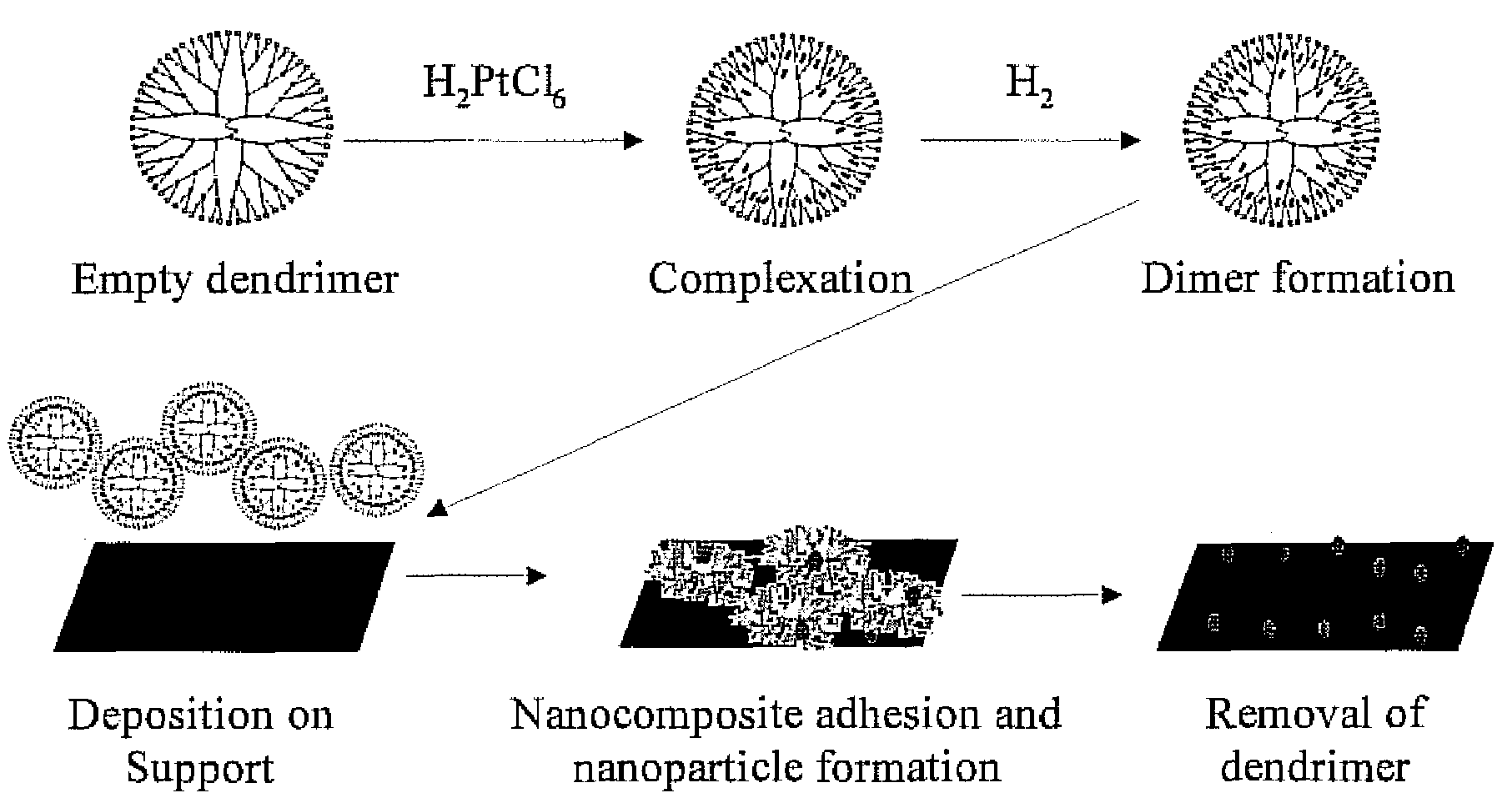
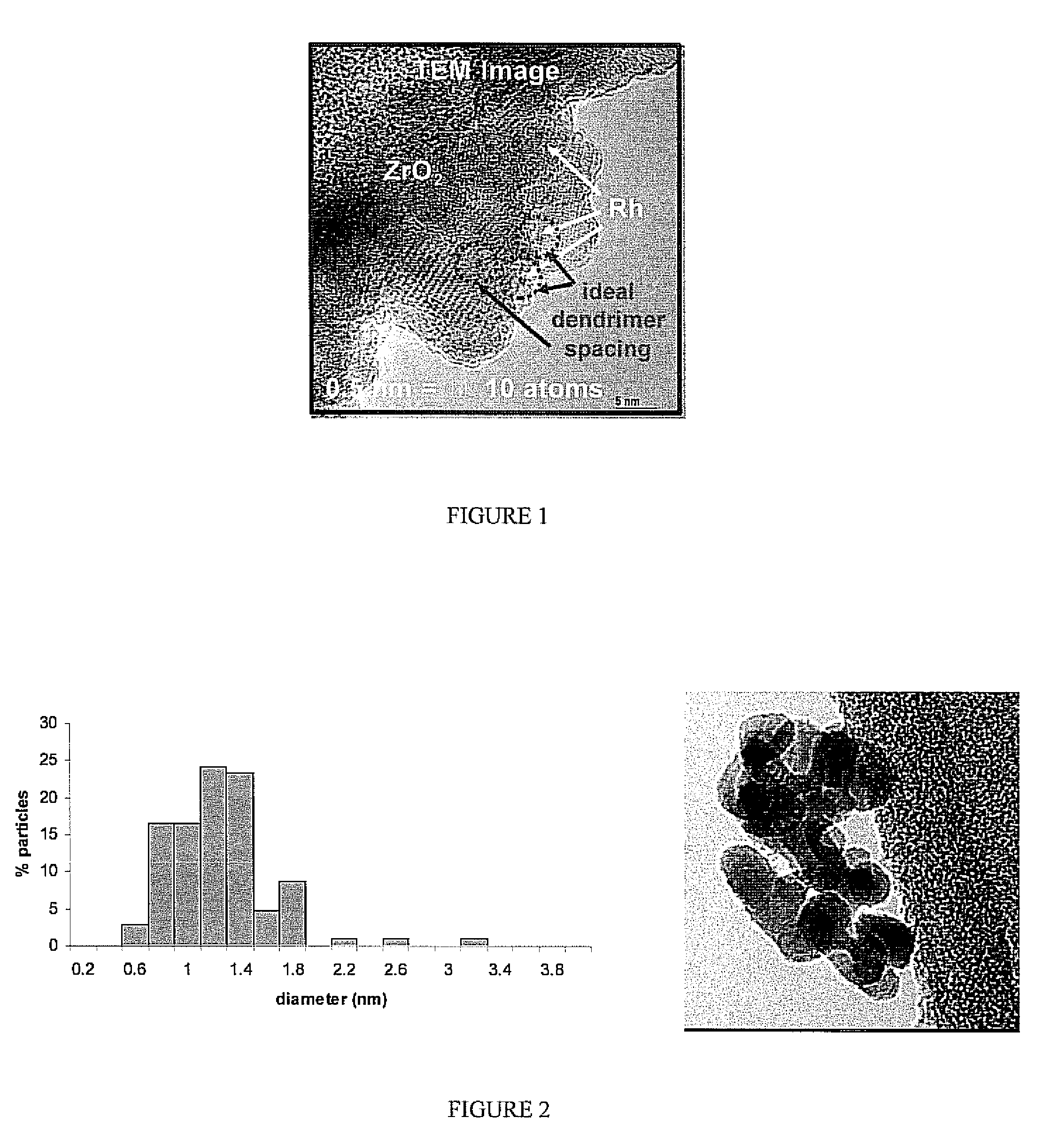
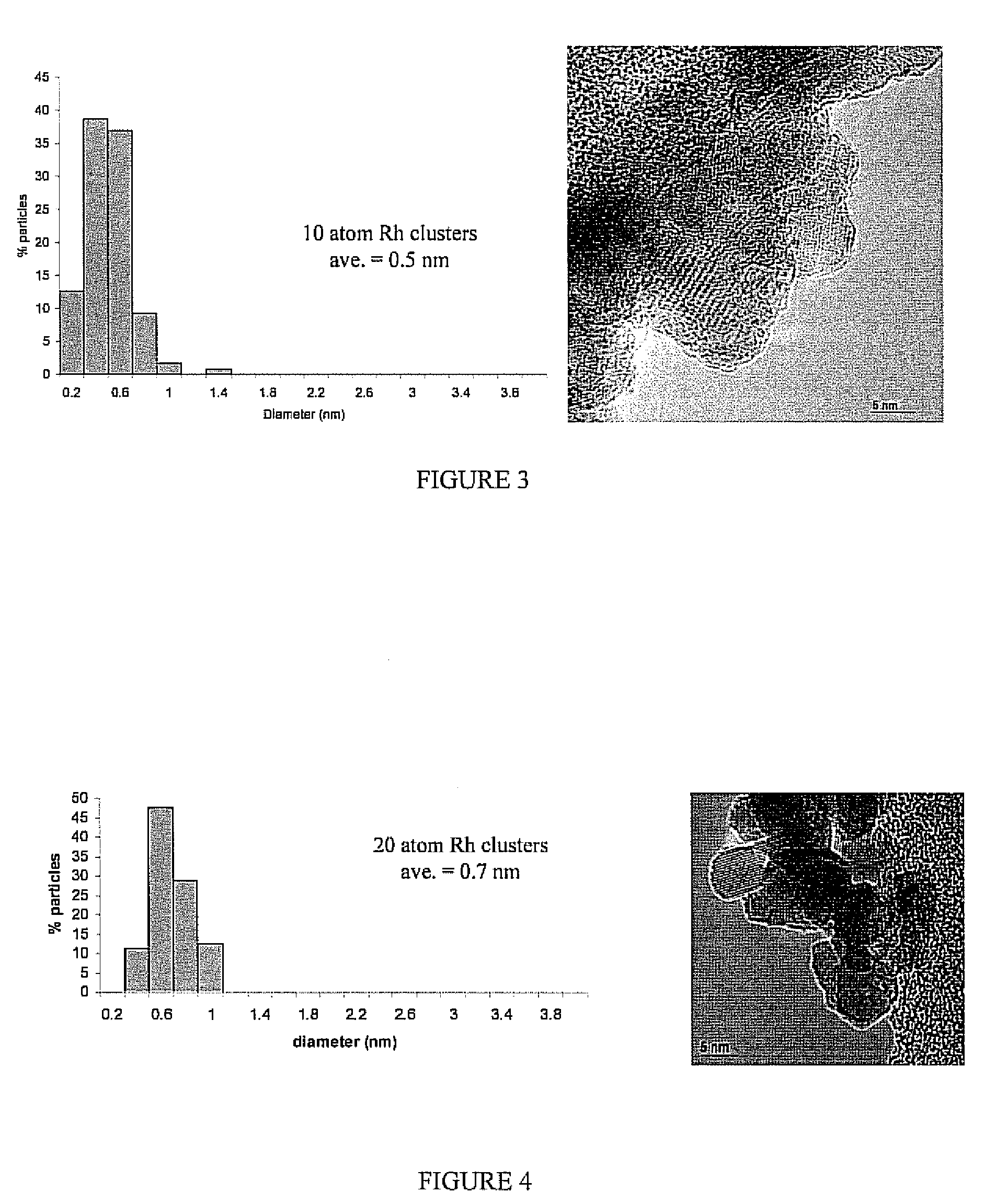
There is disclosed a process for producing a catalyst. The process includes the steps of: a) combining a dendrimer polymer and metal salt in solution forming a metal ion complex; b) exposing the metal ion complex to a reducing environment forming a dendrimer metal nanocomposite; c) depositing the dendrimer metal nanocomposite onto a catalyst support material; d) removing a solvent from the dendrimer metal nanocomposite forming metal clusters; and e) removing the dendrimer polymer forming a catalyst. Additionally, there is disclosed a catalyst having a catalytic metal deposited on a substrate. The catalytic metal is formed in clusters having a size of from 2 to 150 atoms. In another aspect, the clusters may have a spacing of from 2 to 100 nanometers between adjacent metal clusters. Further, in another aspect, the metal clusters which comprise the catalyst have a size distribution in which 70% of the clusters are within 0.6 nm of the average diameter and 99% of the particles are within 1.5 nm of the average diameter.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA +1
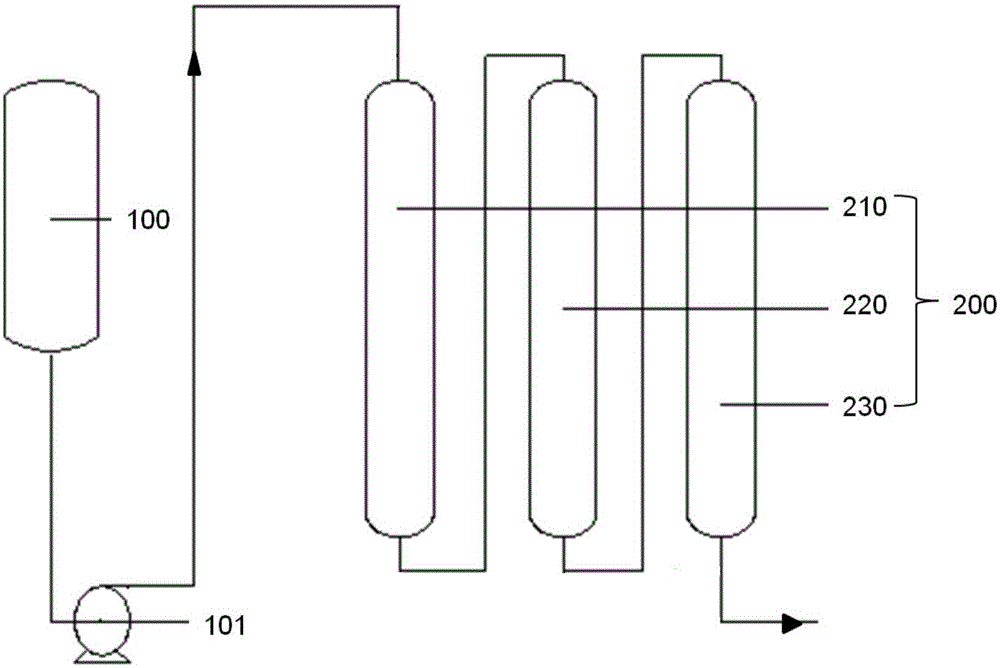
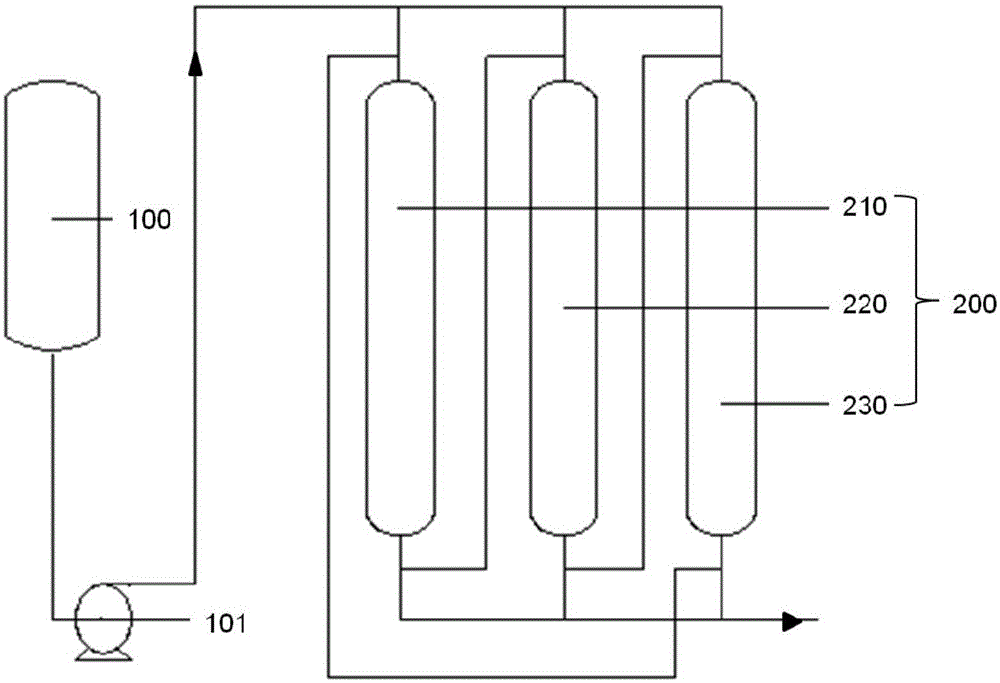
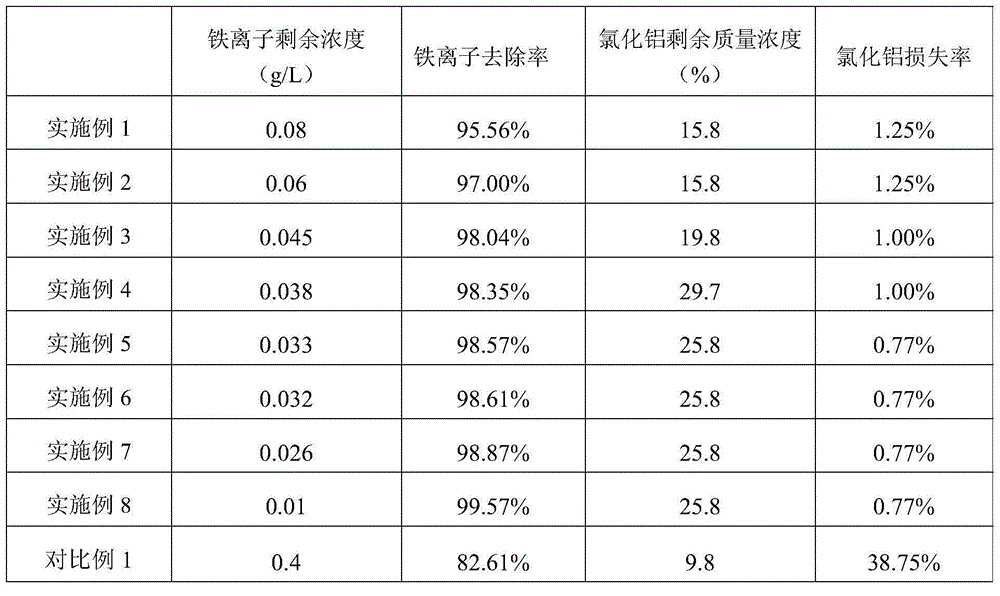
Iron-containing aluminum chloride solution iron removal method
InactiveCN105016368AHighly selective adsorptionHigh iron removal rateAluminium chloridesAluminum IonAluminium chloride
The invention discloses an iron-containing aluminum chloride solution iron removal method. The method comprises treating an iron-containing aluminum chloride solution by an anion exchange resin column so that iron ions are adsorbed by the resin column and the ion adsorption resin column and the aluminum chloride solution without iron are obtained. The iron-containing aluminum chloride solution iron removal method has anion exchange resin-based iron ion selective adsorptivity better than aluminum ion selective adsorptivity because of easy iron ion complexation effects. When the iron-containing aluminum chloride solution goes through the anion exchange resin column, iron ions in the aluminum chloride solution and anions in the resin are compounded and form a negative ion complex so that iron ions can be adsorbed by the resin column and iron removal is realized. The anion exchange resin-based iron selective adsorption removal method has a high iron removal rate and a low cost and does not produce additional pollution.
Owner:CHINA SHENHUA ENERGY CO LTD +1
Non-Polymeric Compositions for Controlled Drug Delivery
InactiveUS20100034801A1Prevent and minimize phase separationMaintain physical stabilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideControl mannerPolymer
The present invention provides a novel liquid composition suitable for in-situ formation of a depot system to deliver a bioactive substance in a controlled manner. The composition of the present invention comprises: (a) a hydrophobic non-polymeric carrier material; (b) a water miscible biocompatible organic solvent that dissolves the hydrophobic non-polymeric material; (c) an ionic complex that is formed between an amphiphilic molecule and a bioactive substance having a net charge at neutral pH in water. The present invention also provides a method of manufacturing and use of the composition thereof.
Owner:FORESEE PHARMA CO LTD
Molecular memory device
InactiveUS7157750B2Reduce leakage currentNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesWork functionLeakage current reduction
A novel memory cell is provided with an active region including a molecular system and ionic complexes distributed in the molecular system. A pair of write electrodes are arranged for writing information to the memory cell. The active region is responsive to an electric field applied between the pair of write electrodes for switching between an on state and an off state. The active region has a high impedance in the off state and a low impedance in the on state. A pair of read electrodes is used to detect whether the active region is in the on state or in the off state to read the information from the memory cell. Read electrodes may be made of different materials having different work functions to reduce leakage current.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Molecular memory cell
A memory cell is provided with a pair of electrodes, and an active layer sandwiched between the electrodes and including a molecular system and ionic complexes distributed in the molecular system. The active layer having a high-impedance state and a low-impedance state switches from the high-impedance state to the low-impedance state when an amplitude of a writing signal exceeds a writing threshold level, to enable writing information into the memory cell. The active layer switches from the low-impedance state to the high-impedance state when an amplitude of an erasing signal having opposite polarity with respect to the writing signal exceeds an erasing threshold level, to enable erasing information from the memory cell.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Electrolyte for non-aqueous electrolyte cell, and non-aqueous electrolyte cell wherein same is used
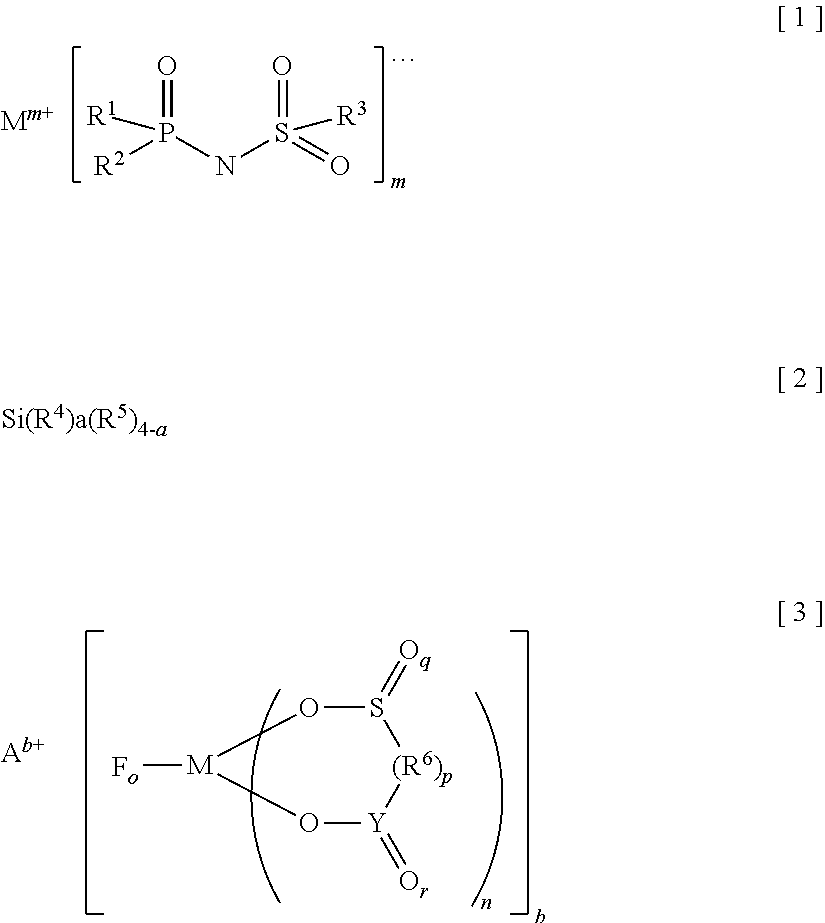
ActiveUS20180375158A1Lower internal resistanceSuppress amount of gasHybrid capacitor electrolytesHybrid capacitor electrodesImideSilane compounds
Provided is an electrolyte for a non-aqueous electrolyte battery, which can provide, when used in a non-aqueous electrolyte battery, in a good balance, an effect to suppress an increase in an internal resistance at a low temperature and an effect to suppress an increase in an amount of gas generated at a high temperature, as well as a non-aqueous electrolyte battery containing such an electrolyte. The non-aqueous electrolyte comprises a non-aqueous solvent and at least a hexafluorophosphate and / or tetrafluoroborate as a solute, and further comprises at least one imide anion-containing salt represented by the following general formula [1] but does not contain a silane compound represented by the following general formula [2] or an ionic complex represented by, for example, the following general formula [3].
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Polymer mixtures of anionic and cationic polysaccharides anduse thereof
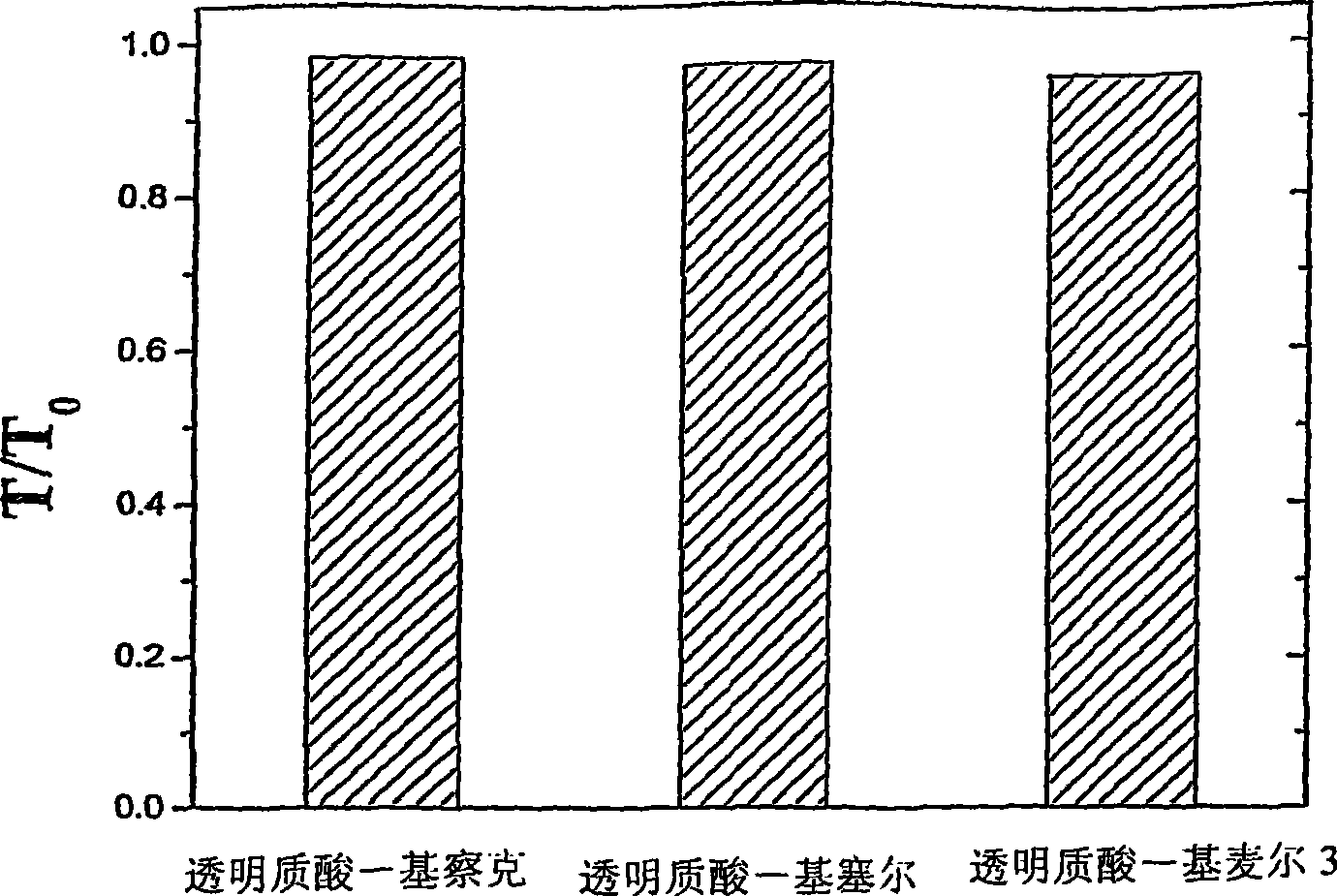
Described in the present application are compositions comprising mixtures of polyanionic polysaccharides and polycationic polysaccharides consisting of oligosaccharide derivatives of chitosan. In the compositions of the invention said mixtures have proven to be soluble in aqueous environments, despite ionic complexes forming between the acid polysaccharides and chitosan derivatives. Said compositions have also demonstrated significant rheological behaviour with an unexpected increase in viscosity and viscoelasticity, although the polysaccharides used have relatively low average molecular weights. The said solubility and rheological behaviour renders the compositions of the invention particularly advantageous from the biomedical application viewpoint, in particular for viscosupplementation and particularly in the field of articular pathologies and of ophthalmic surgery.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI TRIESTE
Method for fabricating hafnia films
InactiveUS20060030135A1Quality improvementMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsCross-linkSelf-assembled monolayer
The present invention comprises a method for fabricating hafnia film comprising the steps of providing a substrate having a surface that allows formation of a self-assembled monolayer thereon via covalent bonding; providing an aqueous solution that provides homogeneous hafnium ionic complexes and hafnium nanoclusters wherein the aqueous solution is capable of undergoing homogeneous precipitation under controlled conditions for a desired period of time at a controlled temperature and controlled solution acidity for desired nanocluster nucleation and growth kinetics, desired nanocluster size, desired growth rate of film thickness and desired film surface characteristics. The method further comprising forming the self-assembled monolayer on the surface of the substrate wherein the self-assembled monolayer comprises a plurality of hydrocarbon chains cross-linked together along the surface of the substrate, the hydrocarbon chains being uniformly spaced from one another and wherein each of the hydrocarbon chains having a functional anchoring group at a first end of the chain covalently bonded with the surface of the substrate and each of the hydrocarbon chains having a functional terminating group projected away from the surface wherein the functional terminating group provides a bonding site for the hafnium film to grow; and exposing the substrate to the aqueous solution for a desired period of time at a controlled temperature wherein the hafnium ionic complexes and the hafnium nanoclusters are deposited on the bonding site of the functional terminating group thereby forming the hafnia film wherein the hafnium bonded to the hydrocarbons and to one another provide a uniform ordered arrangement defined by the uniform arrangement of the hydrocarbons.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Antimicrobial solution and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS9132296B2Promote absorptionHigh immediate and short-term effectivenessBiocideCosmetic preparationsCarboxylic acidEthylene Homopolymers
A chitosan solution is formed from chitin, which is a homopolymer of beta (1-4)-linked N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. Rinsed, dried and ground chitin undergoes a process of deacetylation to convert some N-acetyl glucosamine to glucosamine, a primary component of chitosan. The chitosan solution is prepared by mixing 5chitosan with an alpha-hydroxy acid such as glycolic acid. An aqueous chelated silver solution is prepared by mixing silver oxide with a carboxylic acid such as citric acid. The chitosan solution can then be mixed with the silver solution resulting in a cationic complex. The cationic complex of the present invention may then be electrostatically bonded with generally negatively charged surfaces. In use, citrate promotes uptake of the silver by microbes. The antimicrobial complex can be applied via several methods of application, including an impregnated wipe, a foam, a gel, a spray, a lotion and an ointment.
Owner:AG TECH LLC
Phytic acid-metal ion complex composite nano-filtration membrane and preparation method thereof
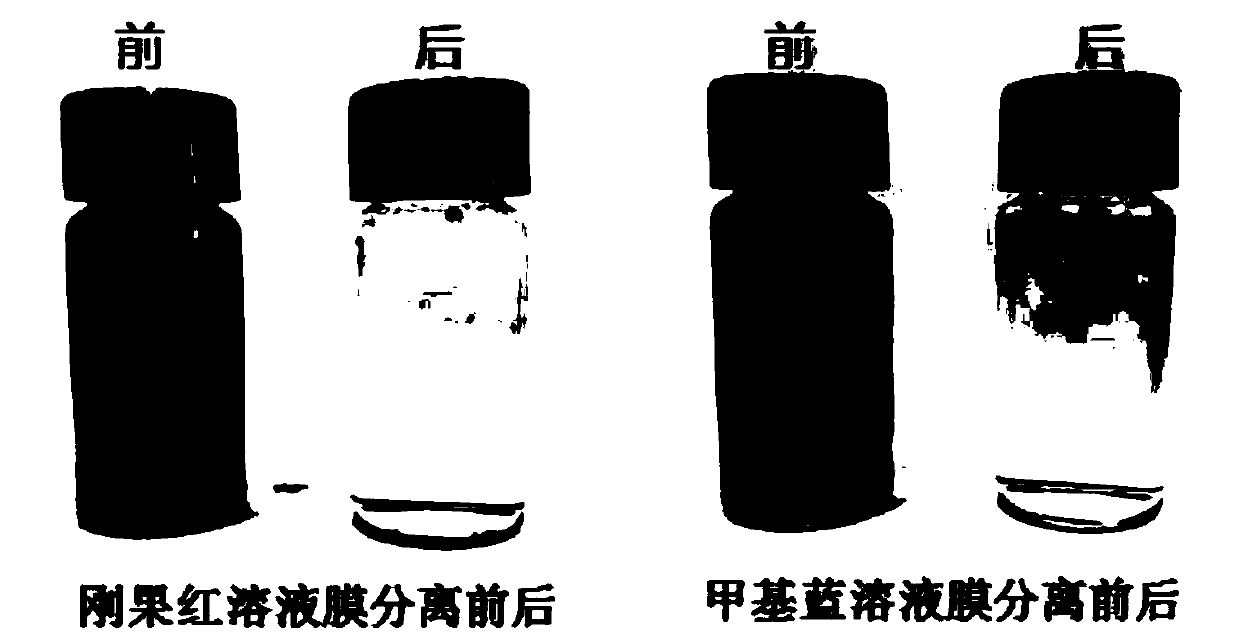
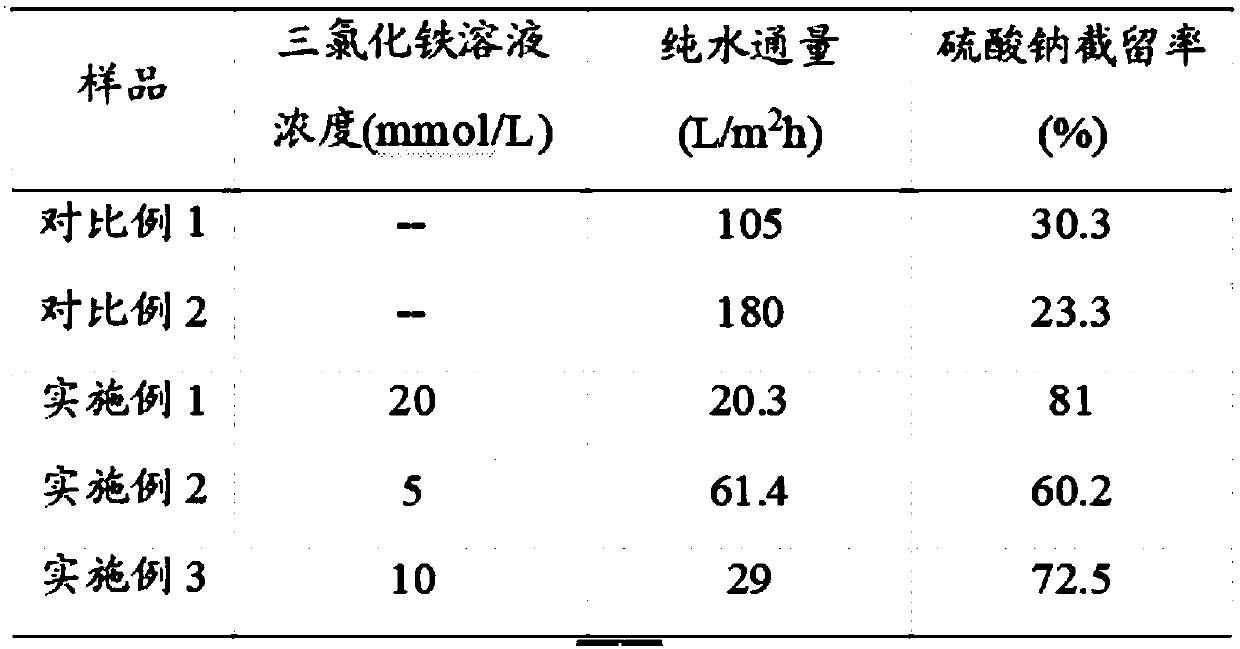
ActiveCN108671772AImprove permeabilityImprove anti-pollution performanceWater contaminantsReverse osmosisFiltration membraneMembrane technology
The invention provides a composite nano-filtration membrane using a phytic acid-metal ion complex as a separation layer, and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the field of membrane technologies. First, the surface of a polymer porous support membrane is pretreated, and then a phytic acid-metal ion complex functional surface layer is deposited on the modified porous support membrane by one step. The surface layer has a strong chemical force with the porous support membrane, is uniform and stable in structure, and has very high hydrophilicity. The prepared composite nano-filtration membrane has excellent separation function, anti-pollution performance and long-term use stability. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple and convenient to operate, mild in condition, low in cost and environmentally friendly, and has prospects in industrial production and commercial application.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV OF TECH
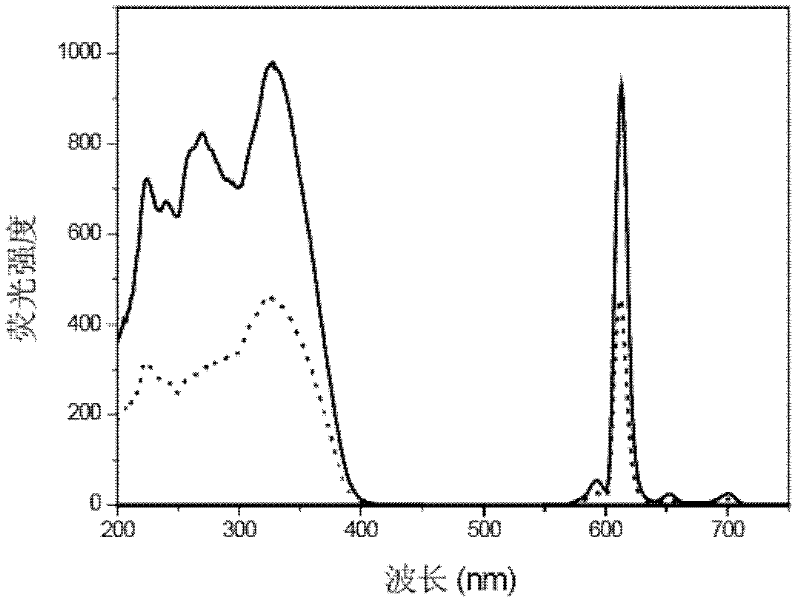
Preparation method of rare-earth fluorescent silica nano particle
ActiveCN102504808AEasy to makeEasy to operateNanoopticsLuminescent compositionsSilanesSilicon dioxide
Provided is a preparation method of rare-earth fluorescent silica nano particle, relating to nano material particles. The preparation method comprises the following steps:: mixing water, oil, surfactant and co-surfactant to spontaneously form anisotropic transparent disperse system with stable thermodynamics, so as to obtain silica nano particle with hydroxyl at the surface thereof; reacting silane reagent with functional group with rare earth ionic complex to obtain rare earth ionic complex precursor; mixing the prepared rare earth ionic complex precursor with tetraethoxy silane, and then adding the mixture into the obtained silica nano particle with hydroxyl at the surface thereof, wherein the rare earth ionic complex is bonded on the surface of the silica nano particle; and adding rare earth ions into a water-in-oil micro-emulsion system to form fluorescent rare earth complex by chelating with the earth ionic complex fixed on the surface of the silica nano particle, sealing the reaction system by acetone, and rinsing to obtain the product rare-earth fluorescent silica nano particles. The operation is simple, the implementation is easy and the fluorescent intensity is higher.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Functional molybdate film and its prepn
InactiveCN1888134APromote crystallizationFlawlessMolybdeum compoundsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingAlkaline earth metalSolvent
The functional molybdate film on substrate of conductive or non-conductive and crystalline or amorphous material has crystal grain size of 10-500 nm and thickness of 100-3000 nm. Its preparation process includes the following steps: 1. compounding Mo ion complex solution with ammonium molybdate and / or molybdic acid as solute, and propylene glycol, glycerine or the mixture of propylene glycol or glycerine, propylene glycol methyl ether and glacial acetic acid as solvent; 2. compound metal ion complex solution with carbonate of alkali metal or alkali earth metal and / or nitrate of transition metal or rare metal as solute, and propylene glycol, glycerine or the mixture of propylene glycol or glycerine, propylene glycol methyl ether and glacial acetic acid as solvent; 3. preparing molybdate precursor solution through mixing the solutions prepared in the forgoing steps and standing for at least 40 min; and 4. spin coating to form film and drying.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
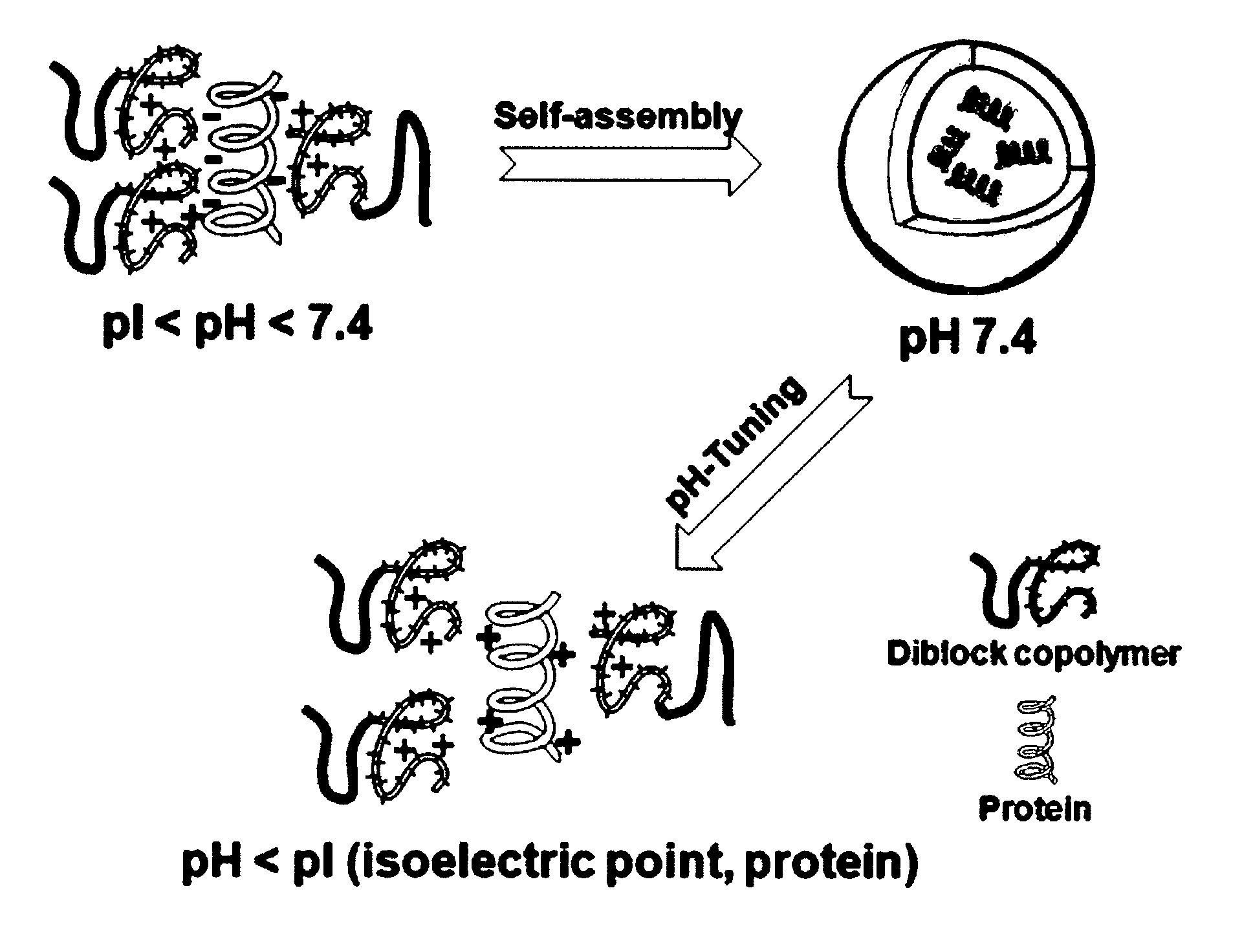
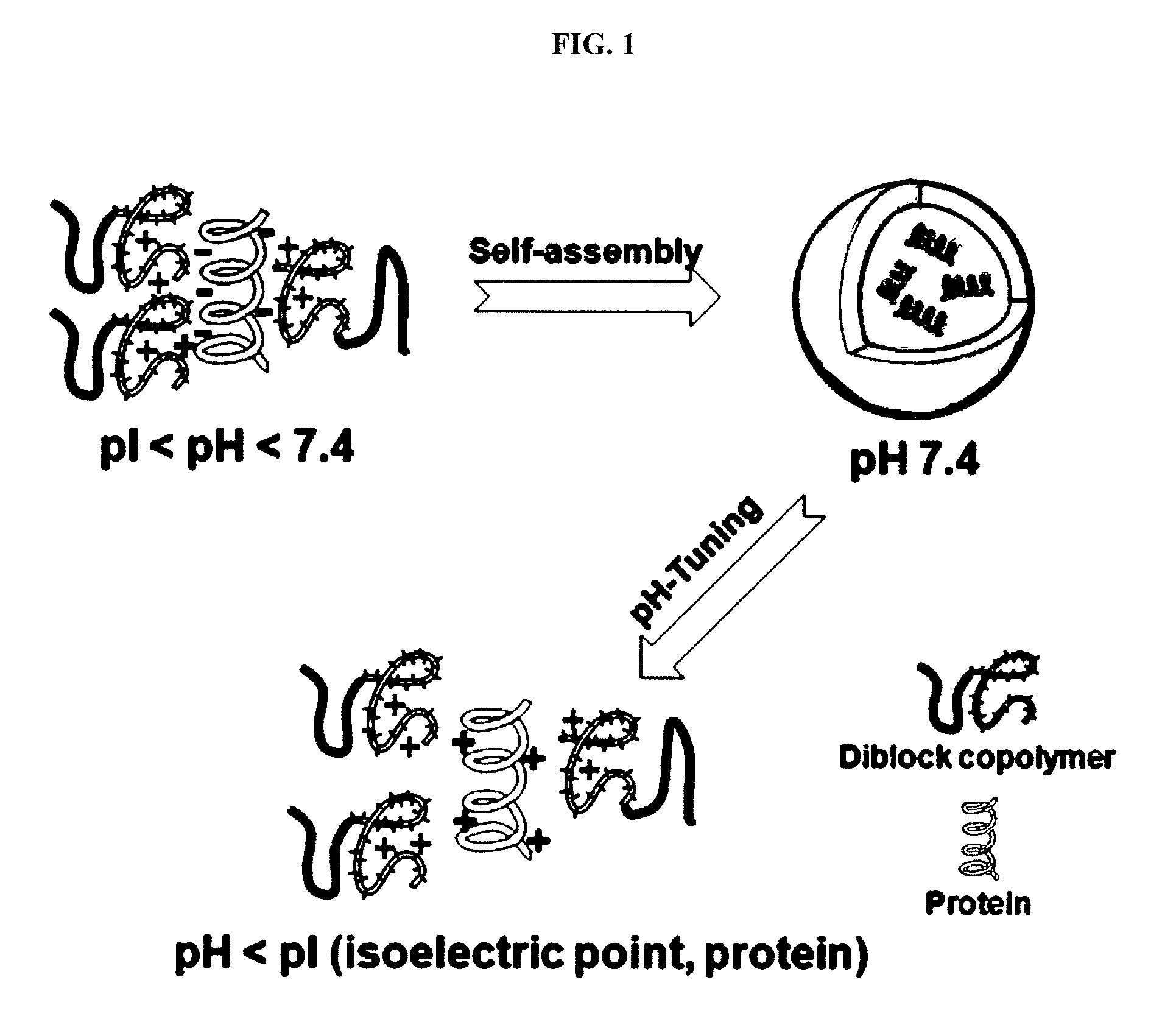
Ph-sensitive block copolymer forming polyionic complex micelles and drug or protein carrier using the same
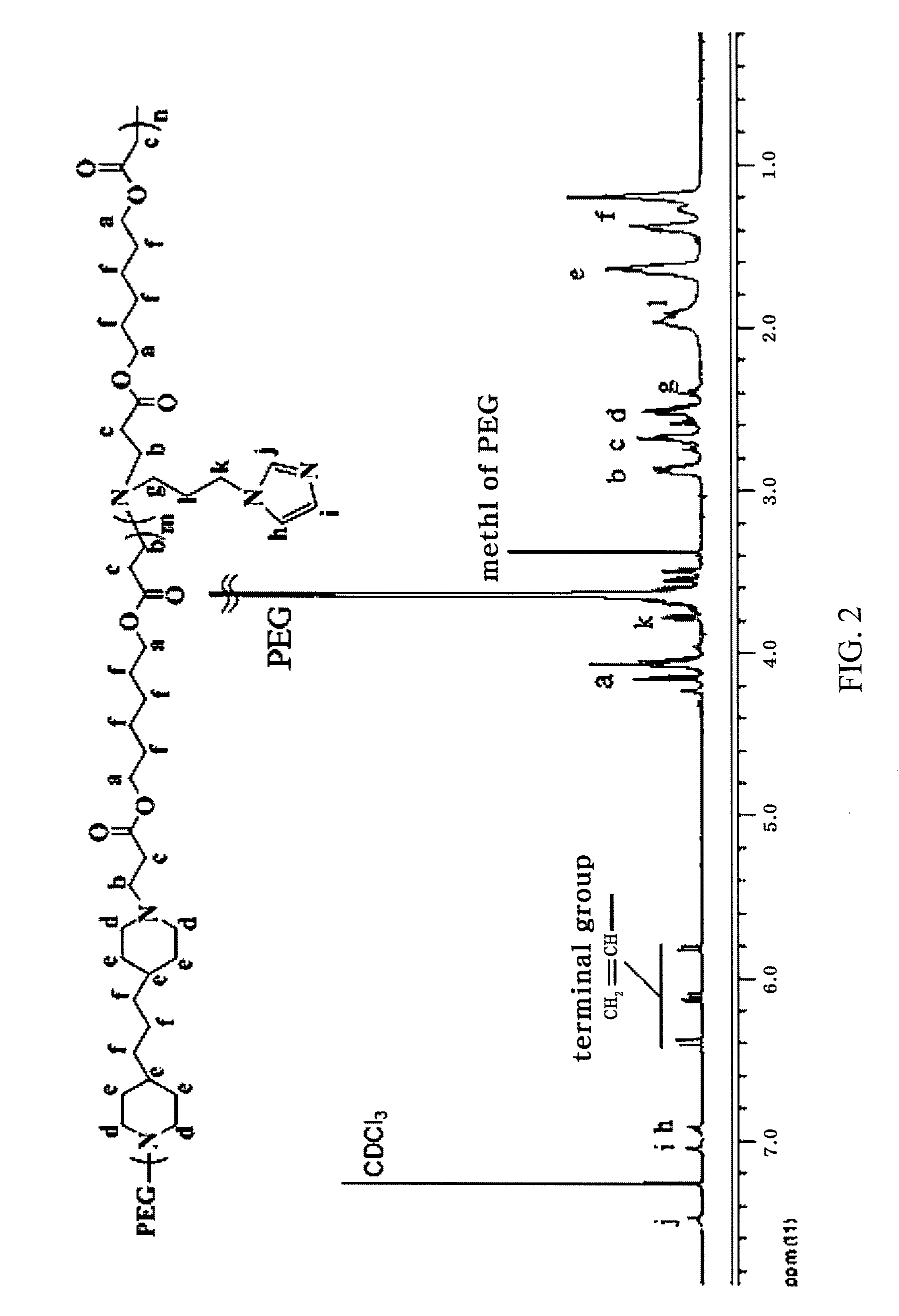
ActiveUS20110150978A1Efficient deliveryStably containPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticAlkyl amineCopolymer
Disclosed is a pH-sensitive block copolymer that forms polyionic complex micelles. The block copolymer is prepared by copolymerization of (a) a polyethylene glycol compound, (b) a poly(amino acid) compound, and (c) a heterocyclic alkyl amine compound having the ability to induce the formation of ionic complexes. Further disclosed is a drug or protein carrier using the block copolymer.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com