Preparation method of rare-earth fluorescent silica nano particle
A technology of silica and nanoparticles, applied in chemical instruments and methods, nanotechnology, nano-optics, etc., can solve the problems of wide application of unfavorable markers, narrow emission spectrum band, time-consuming and labor-intensive, etc., to achieve easy biological functionalization, The preparation process is simple and the controllability is good
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: Preparation of BHHCT-Eu silica nanoparticles
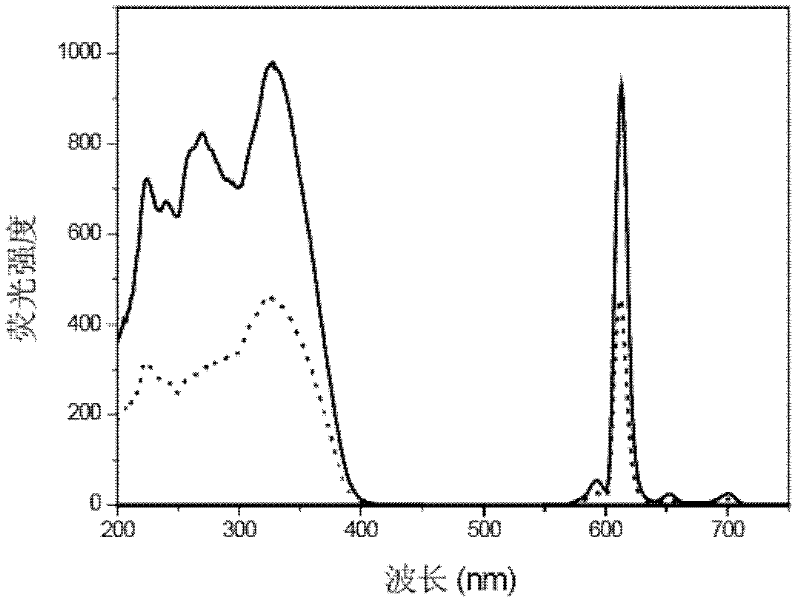
[0031] This example describes the preparation of blank silica nanoparticles in a water-in-oil microemulsion system, and then directly adding the pre-reacted rare earth complex precursor APTMS-BHHCT to the microemulsion system to modify the surface of the particles, and then adding Eu 3+ The process of preparing rare earth fluorescent silica nanoparticles by chelating rare earth ions with rare earth ion complex BHHCT.
[0032] (1) Preparation of blank silica nanoparticles in water-in-oil microemulsion system: Take a conical flask with a magnet, add 6mL cyclohexane, 2mL n-hexanol, 2mL Triton X-100, 0.6 ml ultrapure water to form a water-in-oil microemulsion system. After the solution was uniformly mixed, 60 μL of ammonia water (25%-28%) and 100 μL of TEOS were added in sequence, and reacted at room temperature for 24 hours. Under the catalysis of ammonia water, TEOS polymerized in the water core to form blank ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2: Application of Rare Earth Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles in Rapid Immunochromatographic Detection
[0037] This example describes the implementation process of a rapid immunochromatographic detection system using rare earth fluorescent silica nanoparticles as markers and hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) as a detection model.
[0038] (1) Preparation of rare earth fluorescent silica nanoparticles: same as in Example 1.
[0039] (2) Antibody labeling: Take 0.3mg anti-hepatitis B surface antigen monoclonal antibody and dialyze against 0.05M sodium acetate buffer (pH5.2) for 6h, then add NaIO to the antibody 4 To a final concentration of 0.01M, react at room temperature for 20 minutes to oxidize the hydroxyl groups of antibody sugar chain molecules into aldehyde groups. Then add glycerol to its final concentration of 30mM, mix and shake for 10min to stop the oxidation reaction. The antibody was again dialyzed with 0.05M sodium acetate buffer (pH5.2) ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com