Patents
Literature
99results about "Positive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
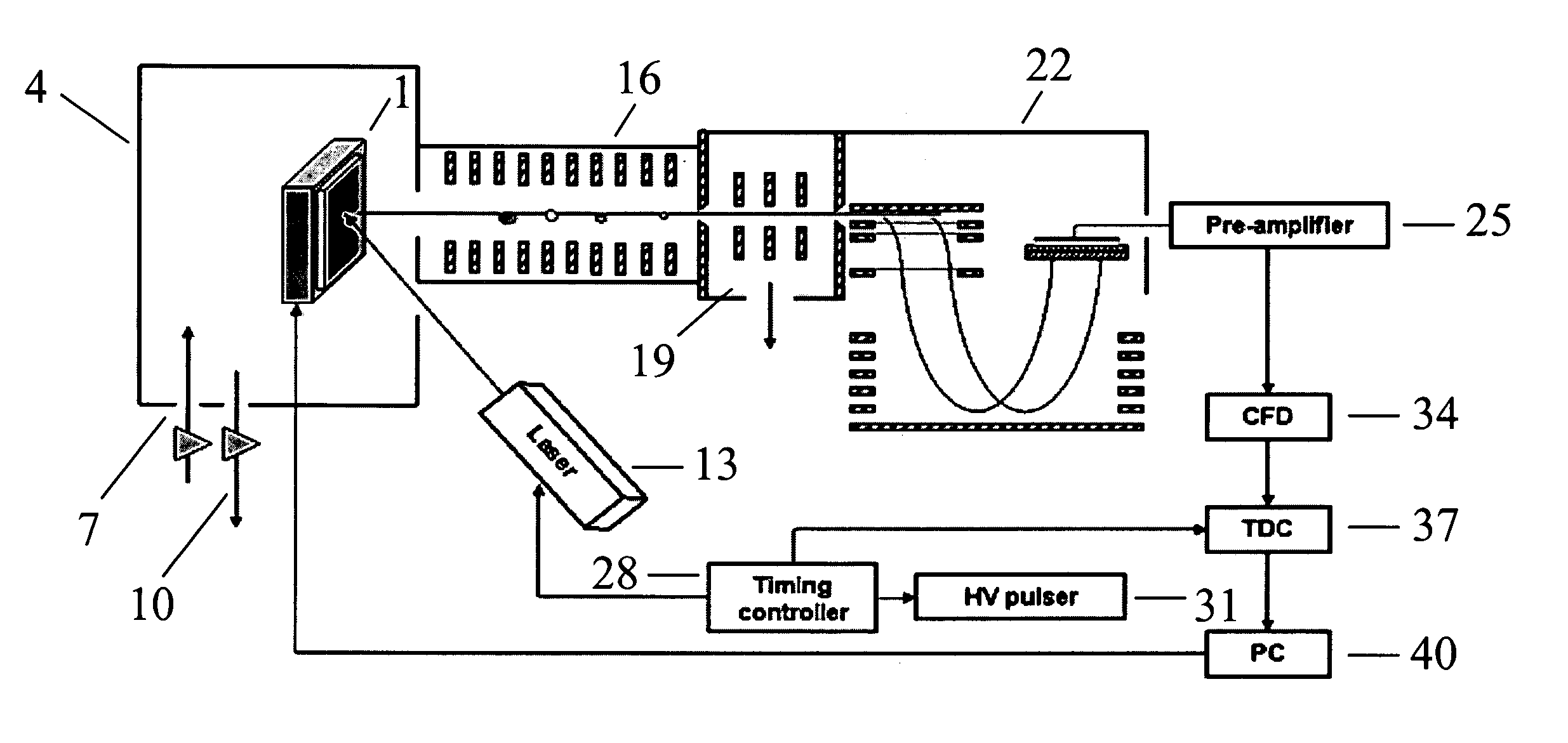
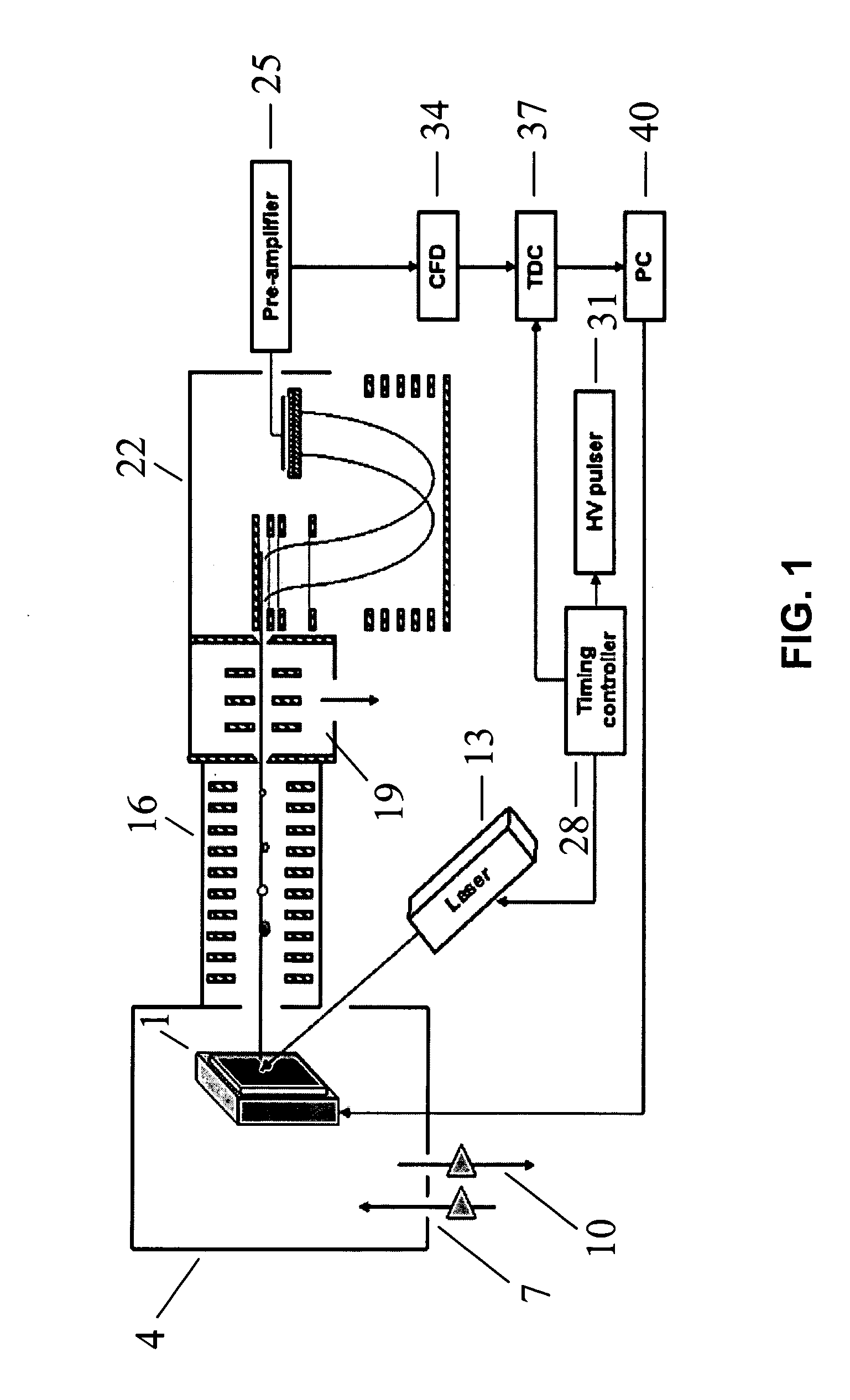
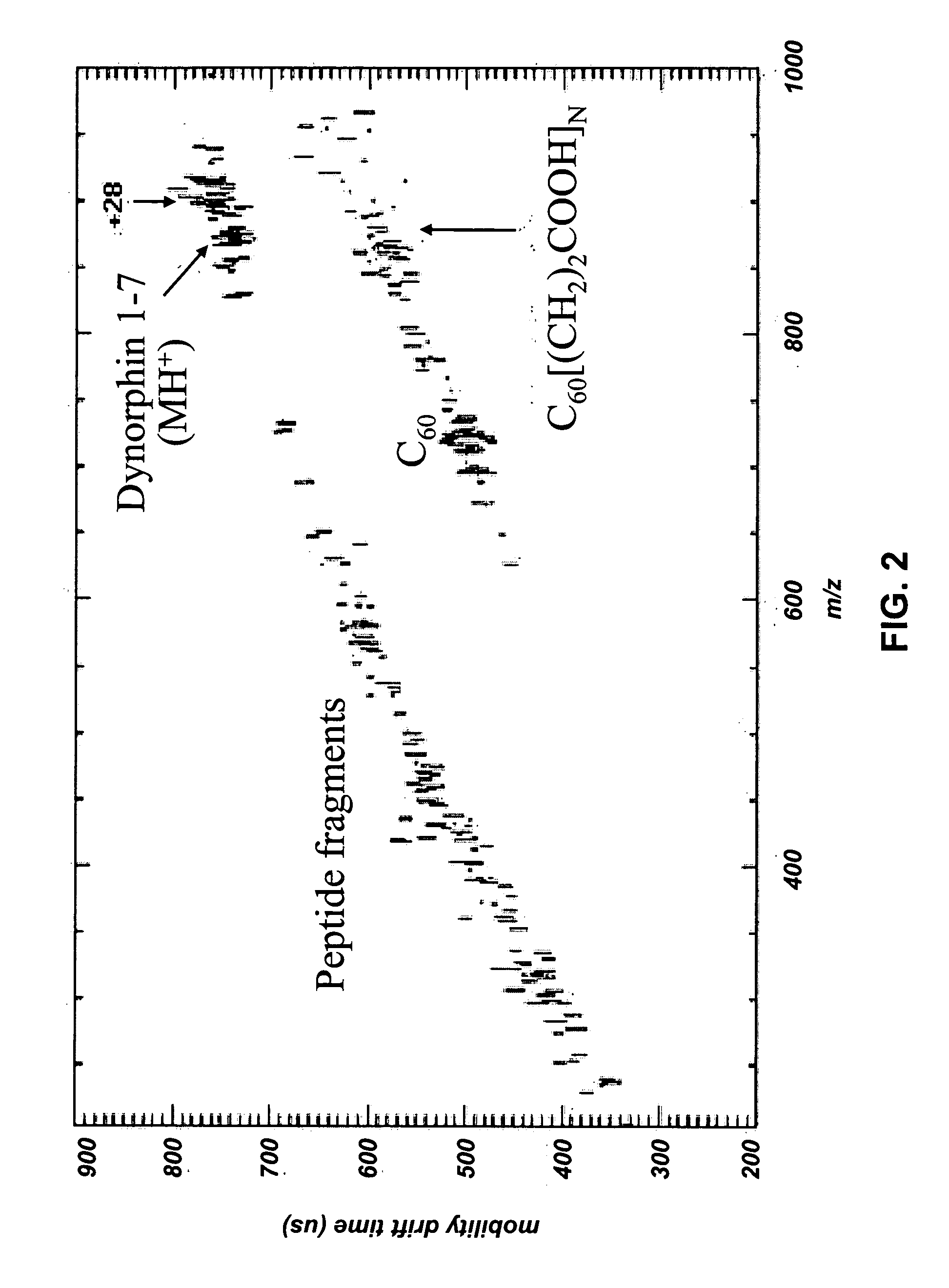
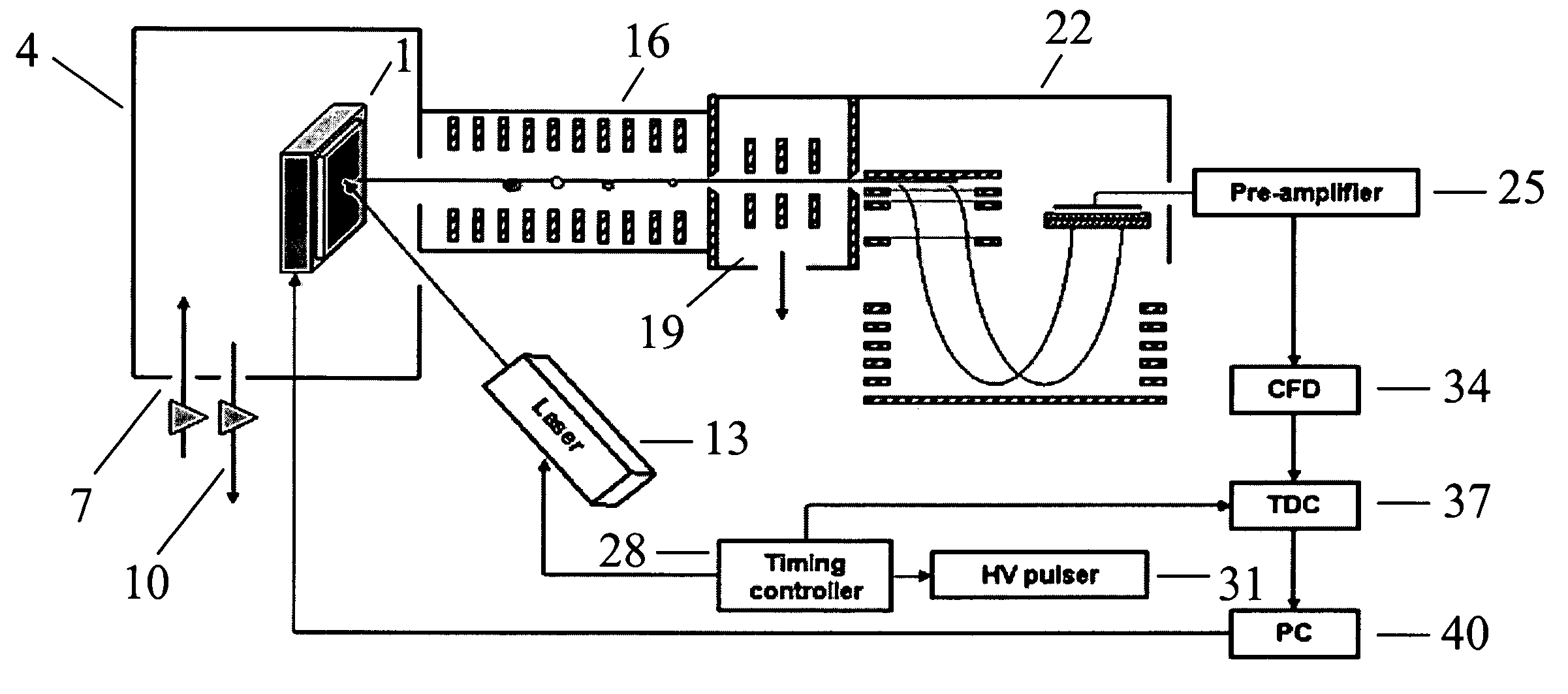
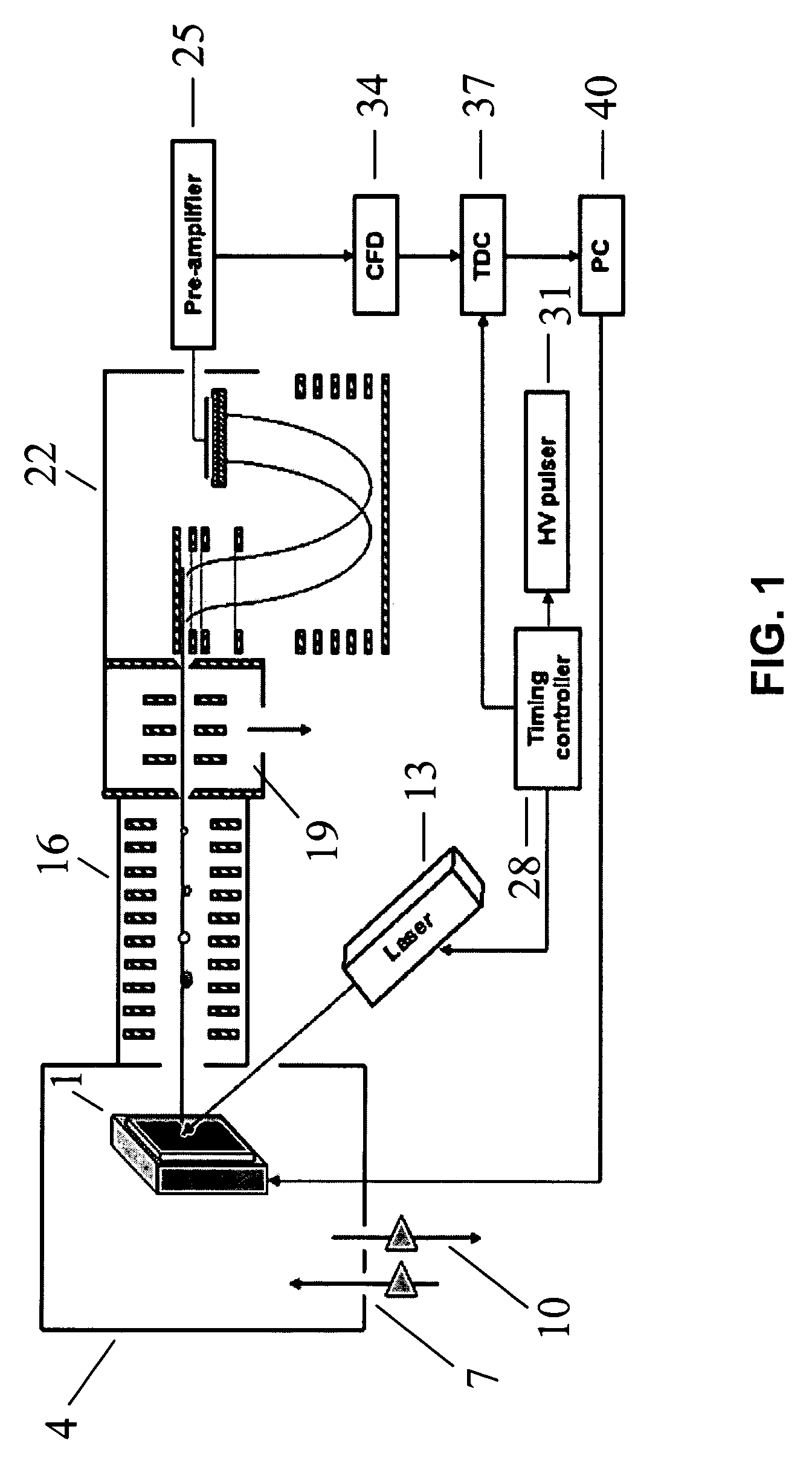
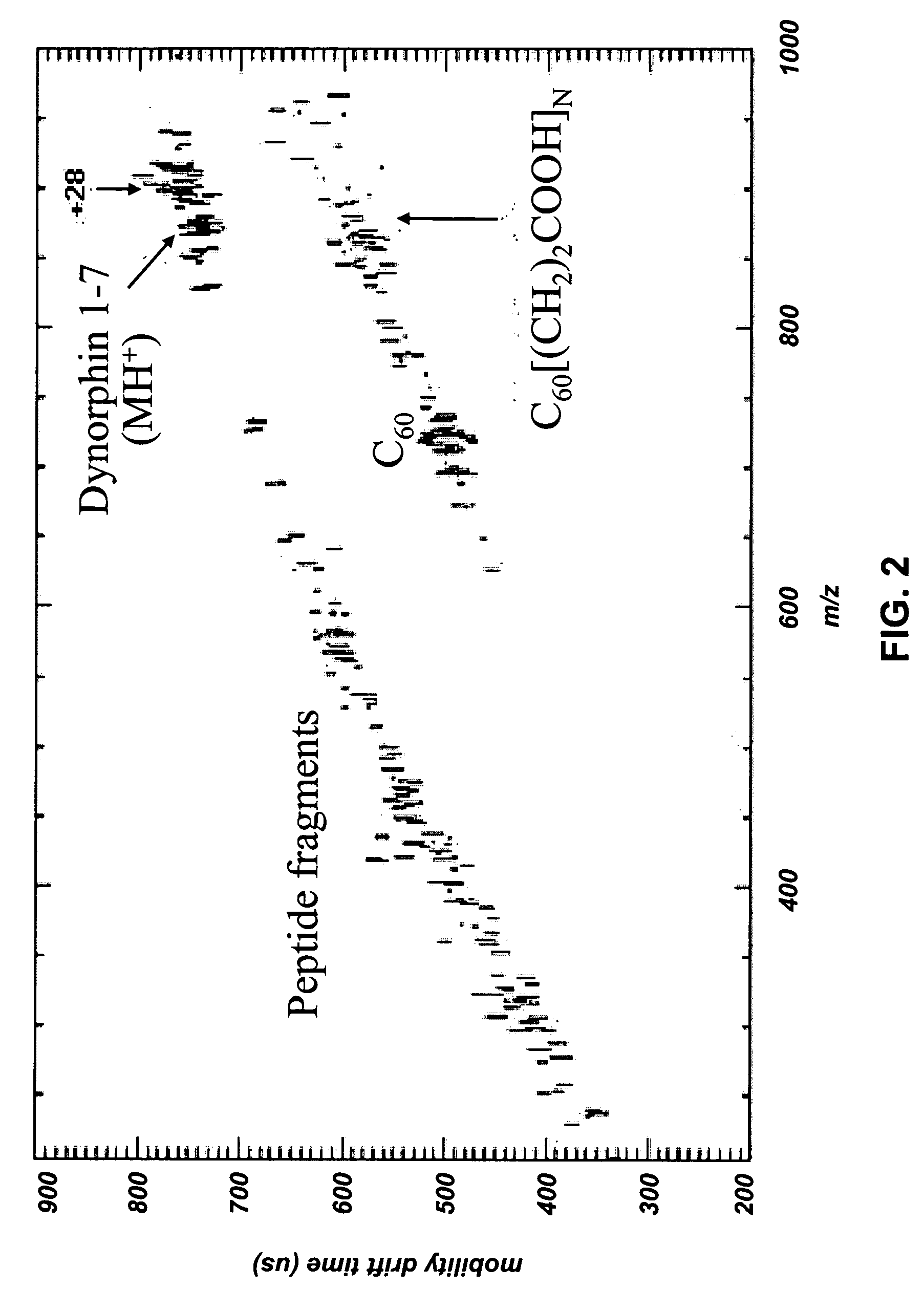
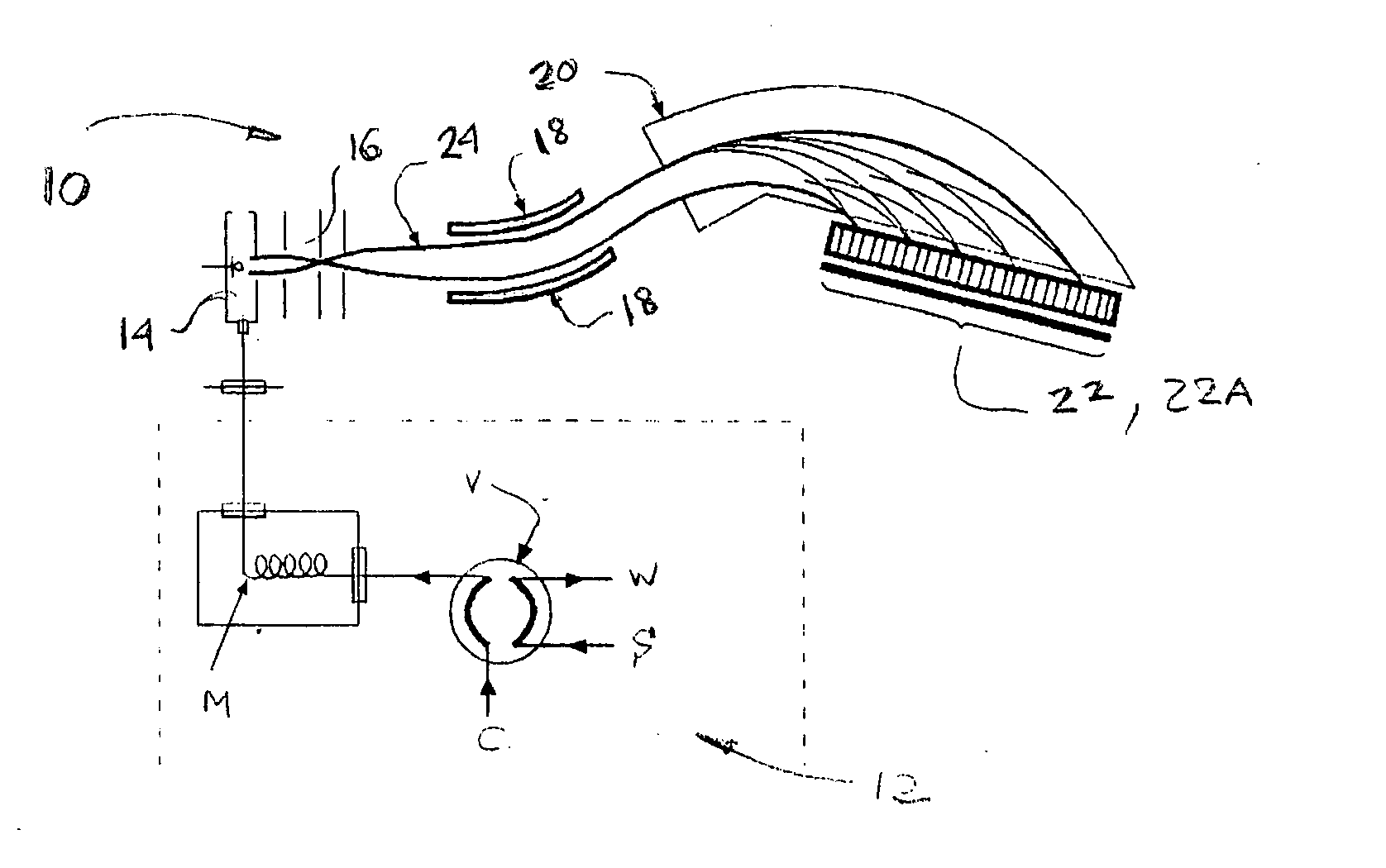
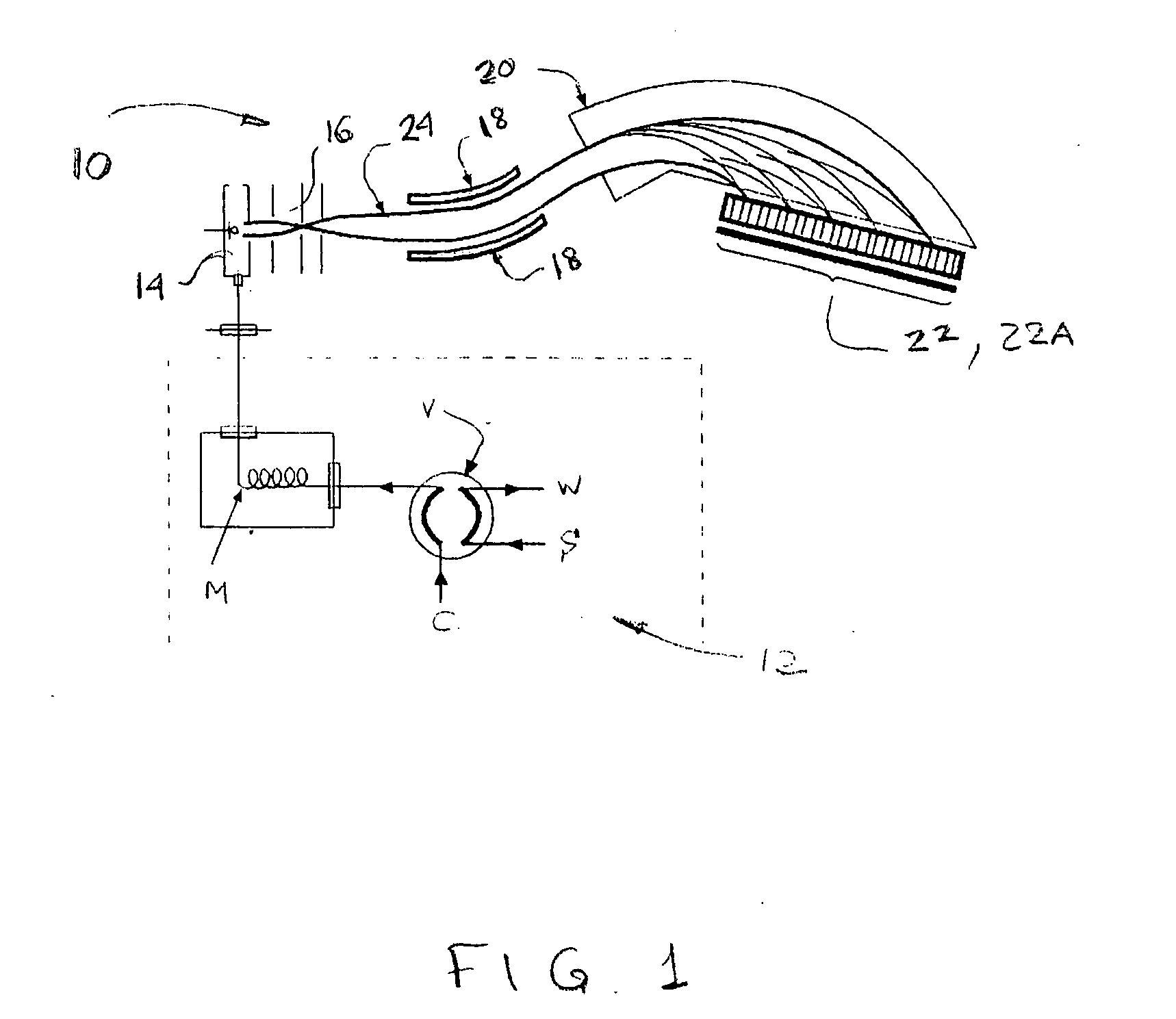
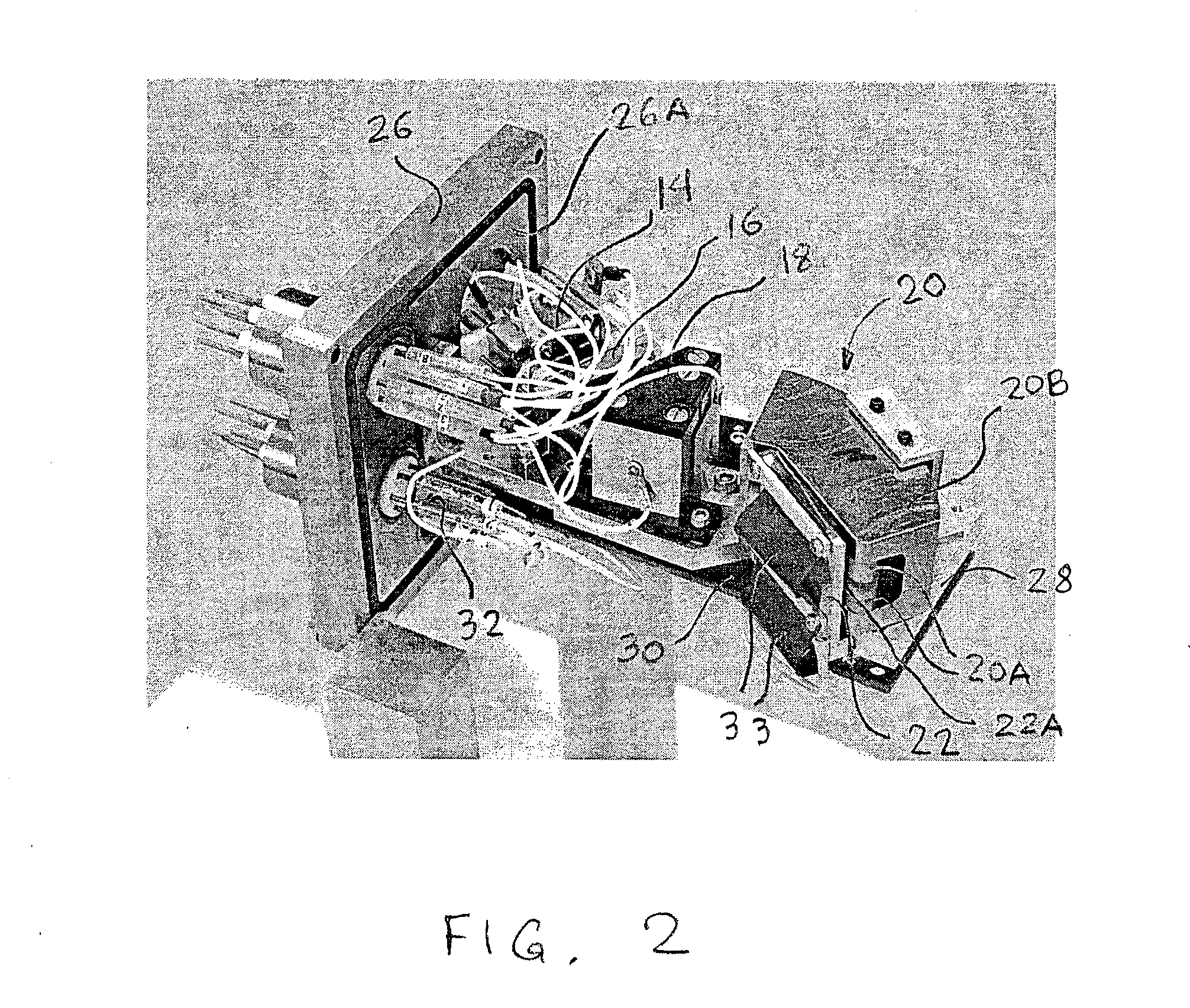
MALDI-IM-ortho-TOF mass spectrometry with simultaneous positive and negative mode detection
InactiveUS20050230615A1Time-of-flight spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryTandem mass spectrometry
An ion mobility / mass spectrometry method and instrument using aerosolized samples and dual positive and negative mode detection is described. Sample preparation methods are also described.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
MALDI-IM-ortho-TOF mass spectrometry with simultaneous positive and negative mode detection
InactiveUS7170052B2Time-of-flight spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationPattern detectionMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
An ion mobility / mass spectrometry method and instrument using aerosolized samples and dual positive and negative mode detection is described. Sample preparation methods are also described.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Mass spectrometer and reaction cell for ion-ion reactions
ActiveUS7196326B2Good effectIncrease probabilityStability-of-path spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationPeptide ionsBiopolymer
The invention relates to a reaction cell for reactions between different types of ion species and a related mass spectrometer to analyze the ion products. The invention consists in an RF-operated straight ion guide with a side inlet, particularly suitable for reactions between positive and negative ion species, one ion species being fed in through the side inlet. Particularly favorable is an ion guide made up of a set of coaxial apertured diaphragms with a slight axial potential gradient. The reactions can be used for a fragmentation of multiply charged protein or peptide ions by electron transfer, or for the removal of excess charges of multiply charged biopolymer ions, for example.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Mass spectrometer and reaction cell for ion-ion reactions
ActiveUS20050279931A1Easy to produceGood effectStability-of-path spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationIonChemistry
The invention relates to a reaction cell for reactions between different types of ion species and a related mass spectrometer to analyze the ion products. The invention consists in an RF-operated straight ion guide with a side inlet, particularly suitable for reactions between positive and negative ion species, one ion species being fed in through the side inlet. Particularly favorable is an ion guide made up of a set of coaxial apertured diaphragms with a slight axial potential gradient. The reactions can be used for a fragmentation of multiply charged protein or peptide ions by electron transfer, or for the removal of excess charges of multiply charged biopolymer ions, for example.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Capacitive discharge plasma ion source
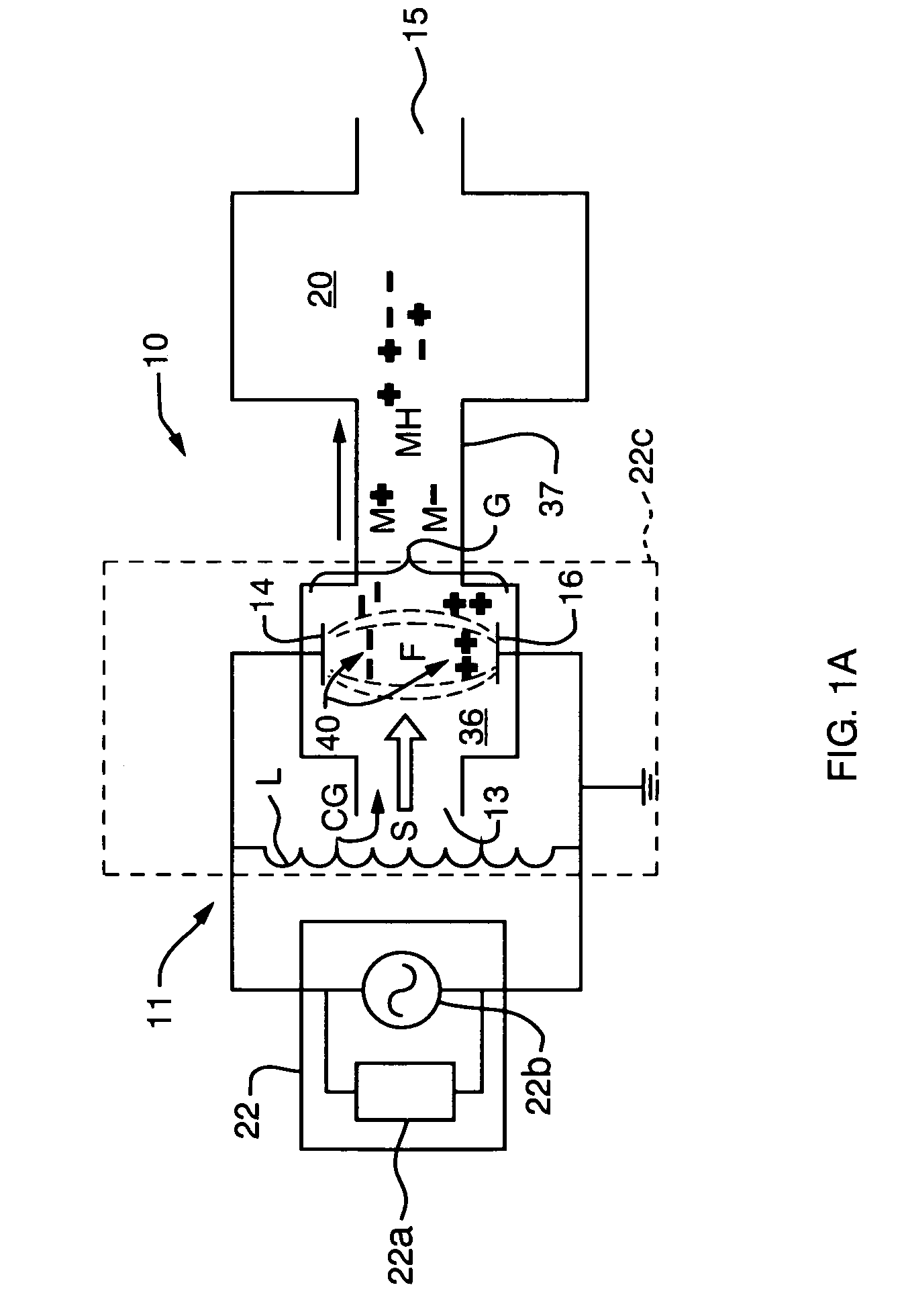
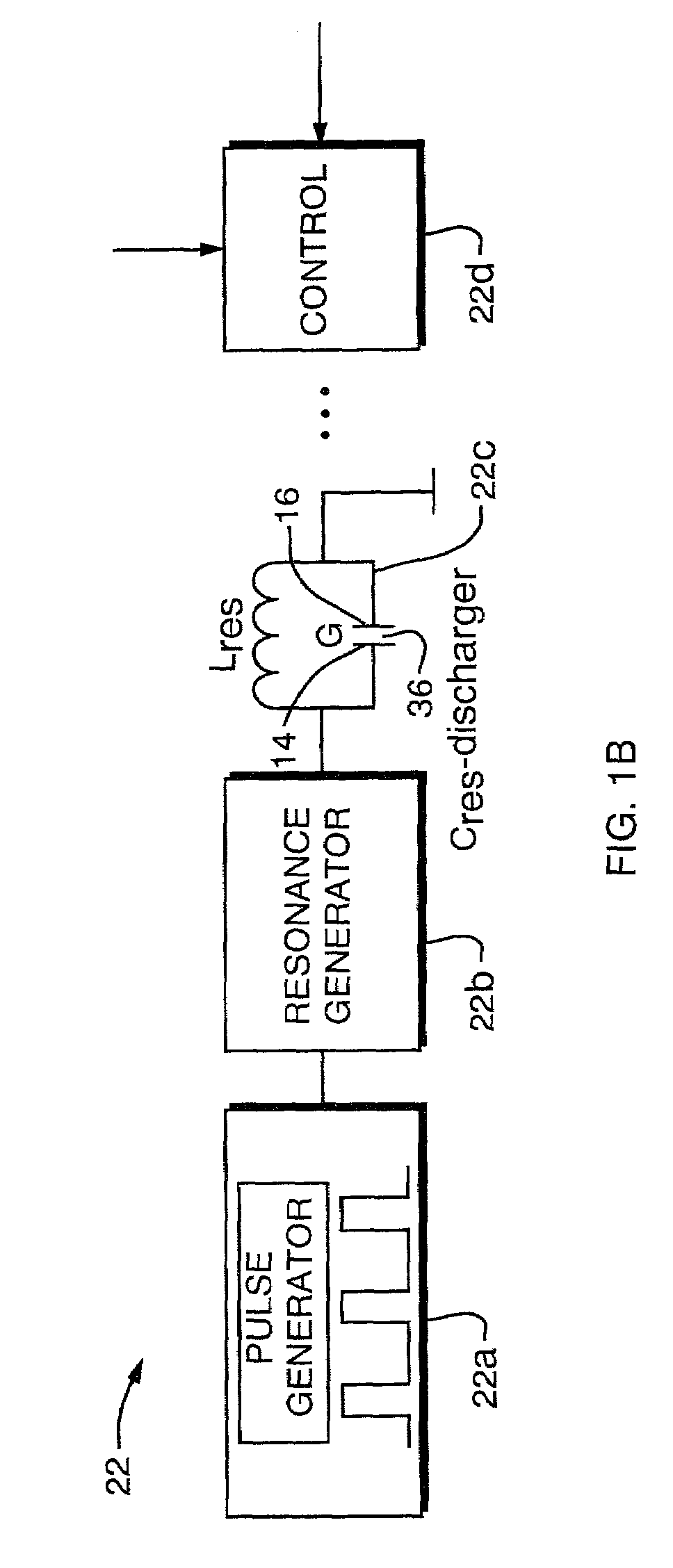
ActiveUS7274015B2Preventing plasma wanderImprove discharge stabilityLaser detailsTime-of-flight spectrometersCapacitanceCapacitive discharge
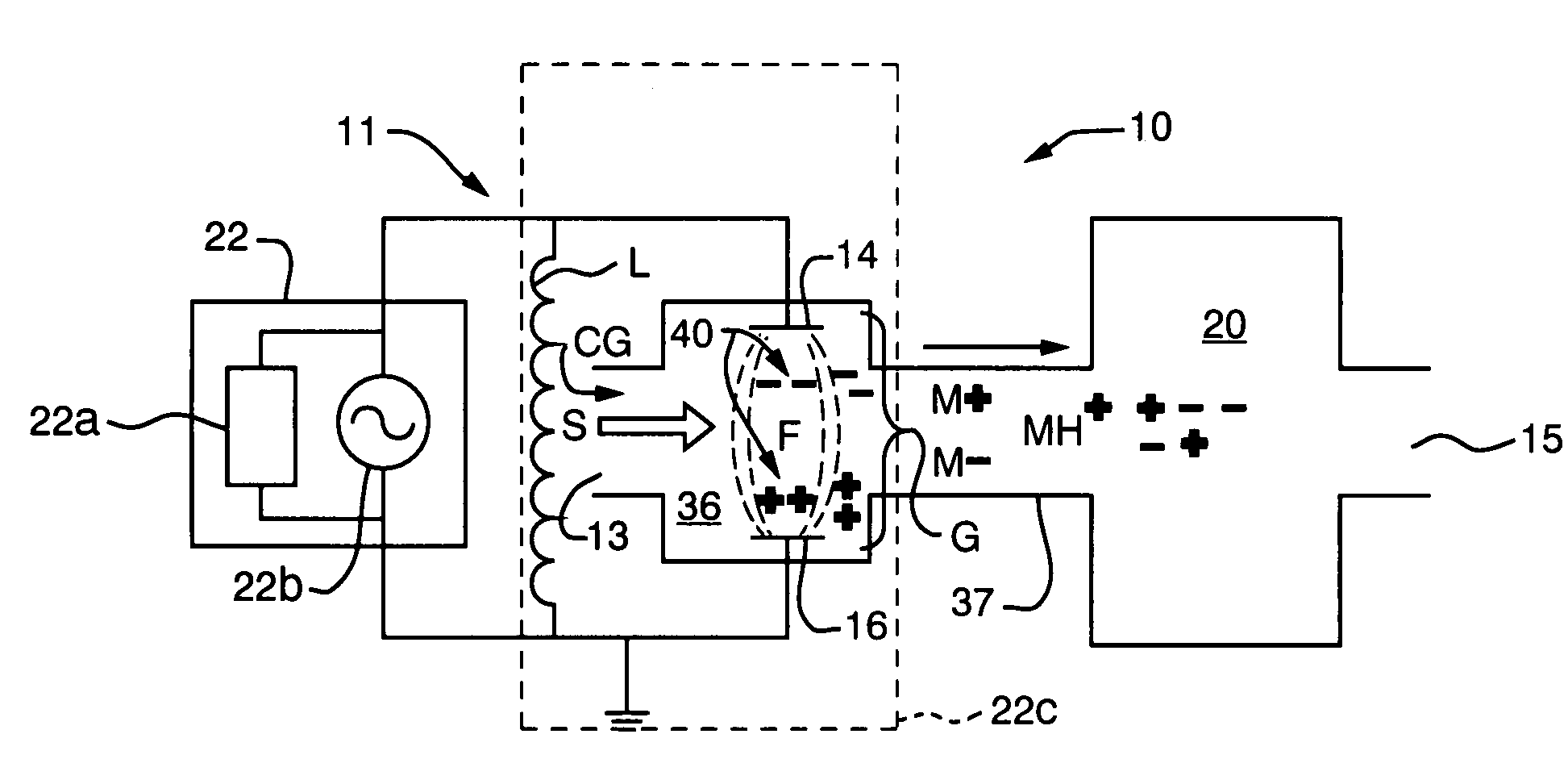
In a system for chemical analysis, an RF-driven plasma ionization device including a pair of spaced-apart and plasma-isolated electrodes, the electrodes are connected to a power source wherein the electrodes act as plates of a capacitor of a resonant circuit, the gas electrically discharges and creates a plasma of both positive and negative ions, and the voltage is applied as a continuous alternating waveform or as a series of pulses, such as a packet waveform.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
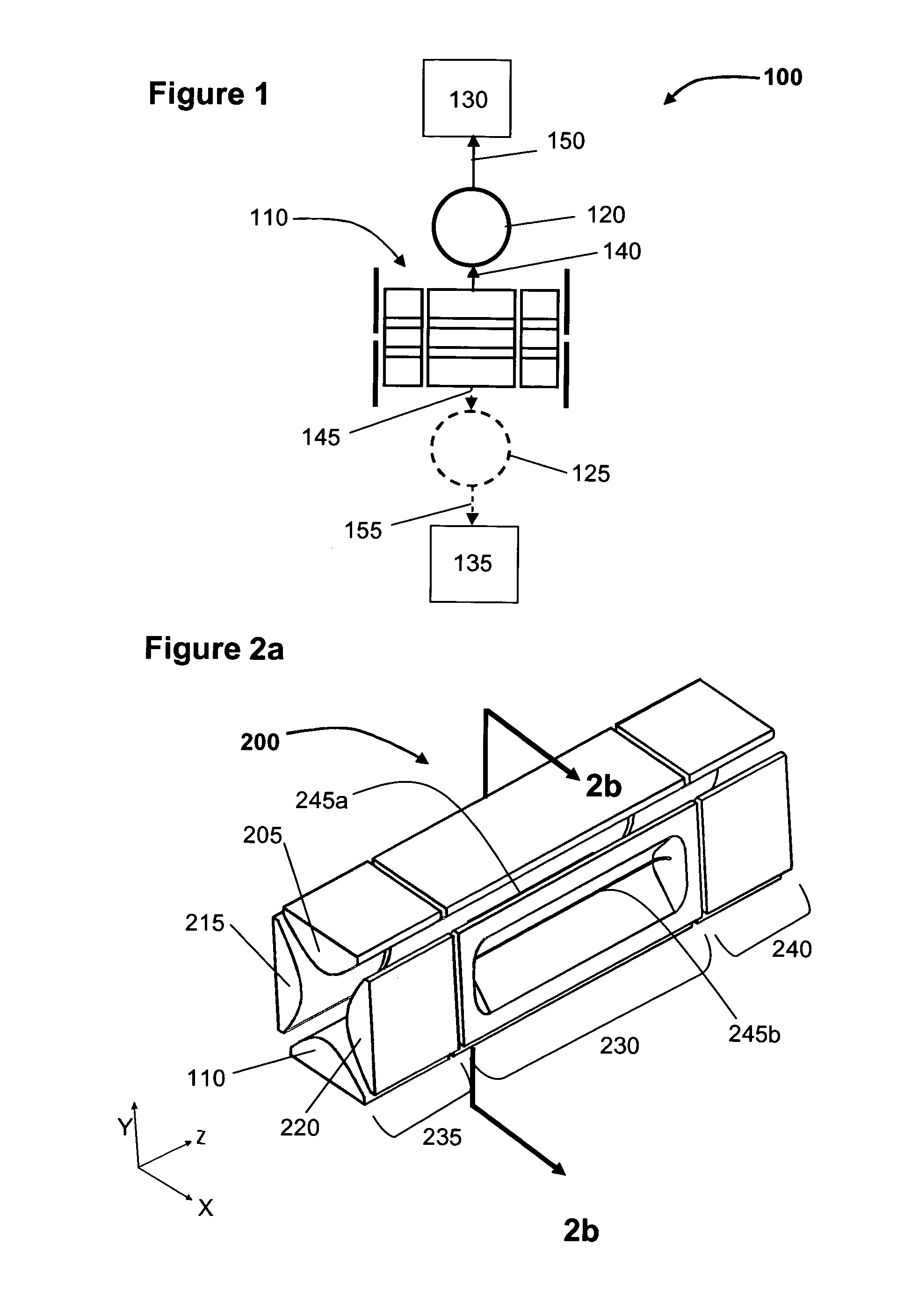
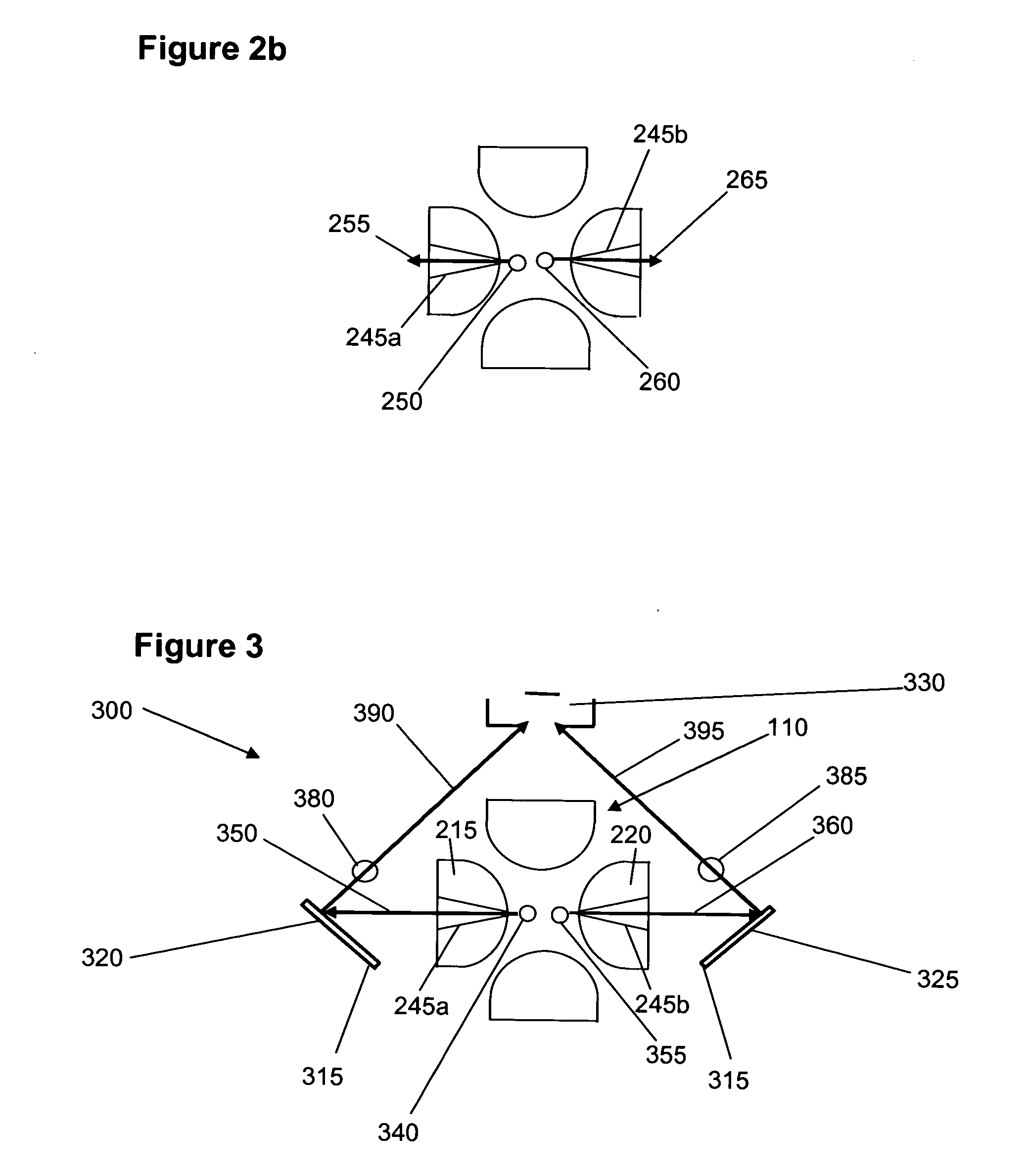
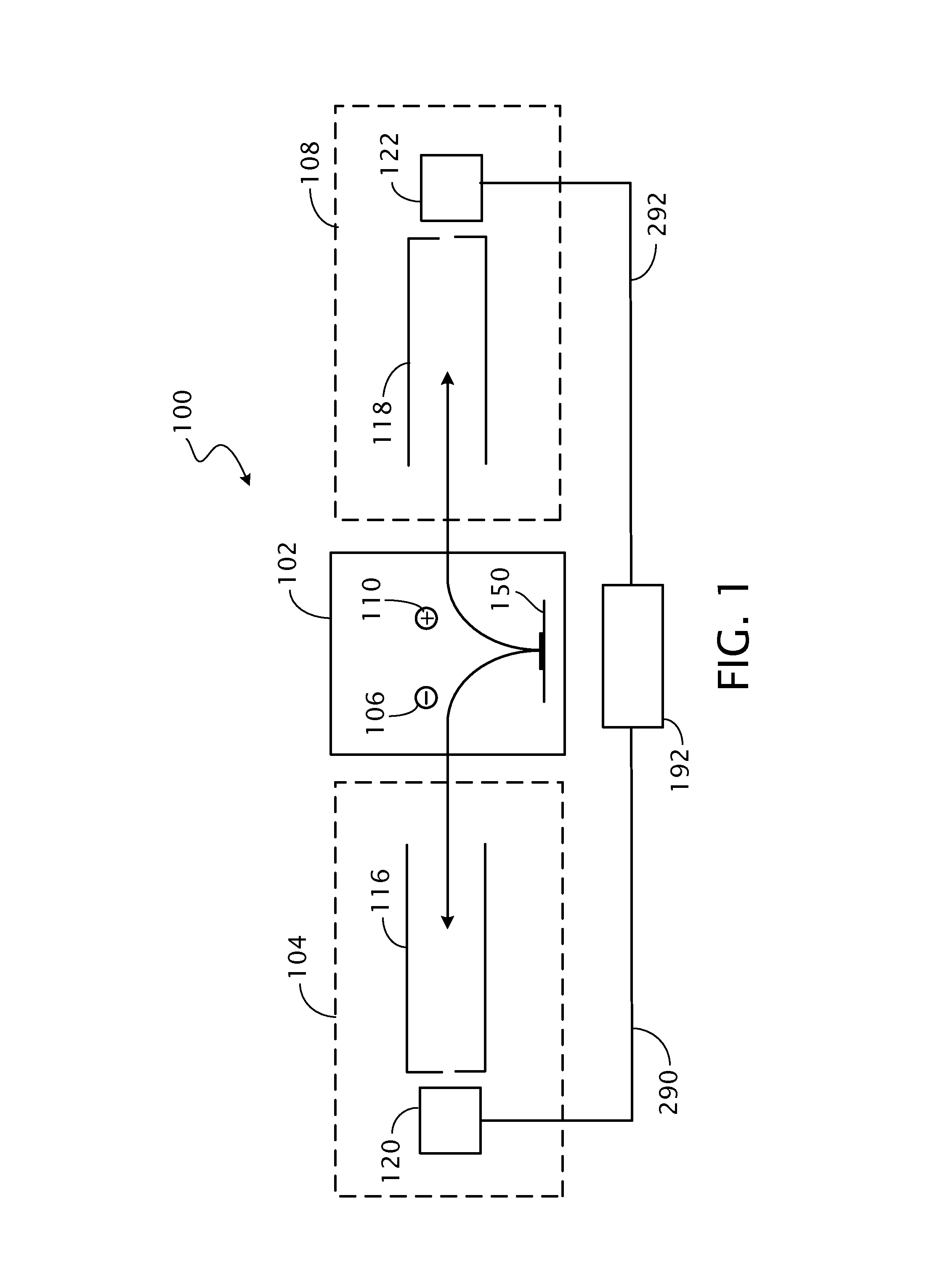
Detection of positive and negative ions
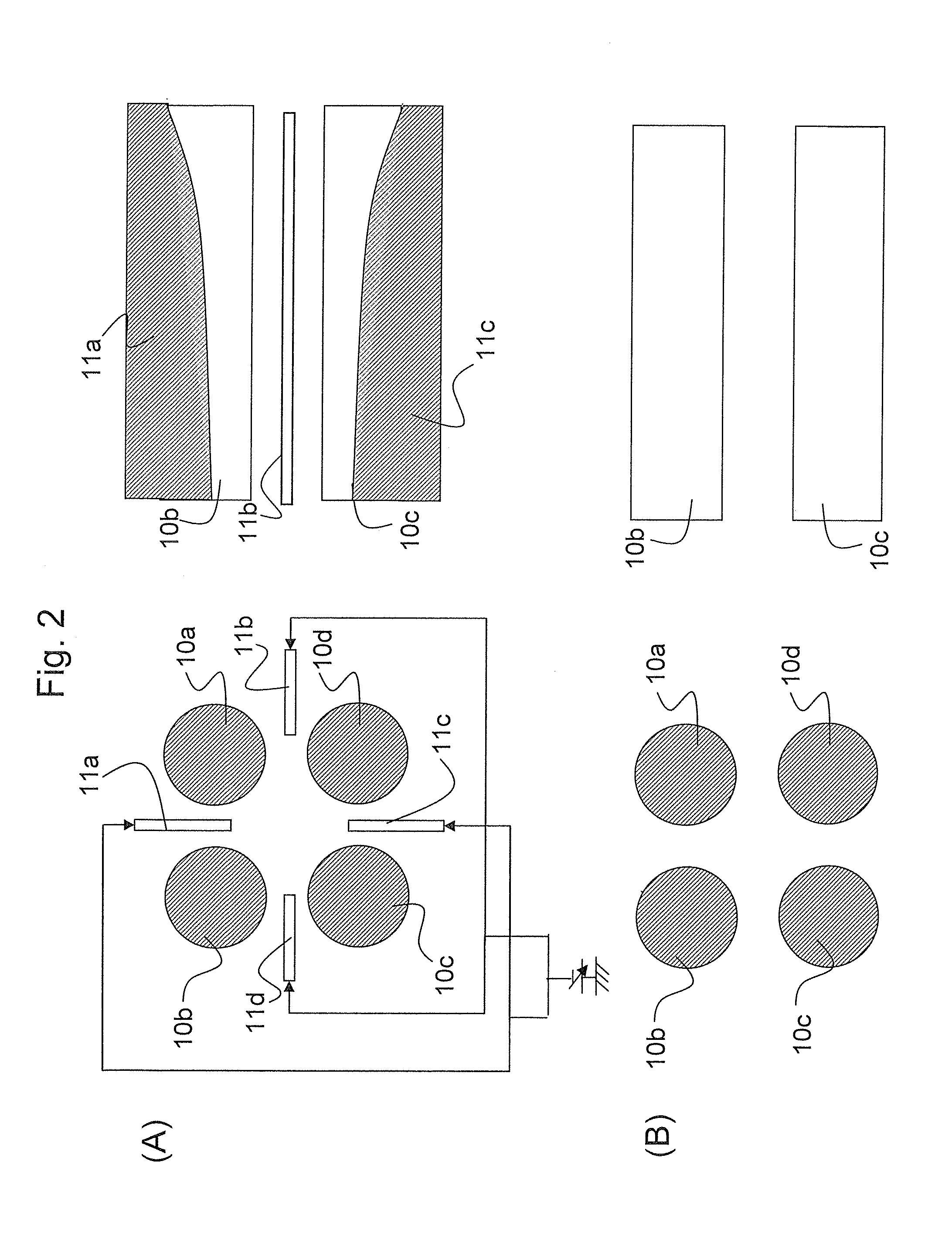
An ion detector comprises an ion guide with electrodes arranged about a first axis; a positive ion detection device with an ion inlet at a first side of the ion output section offset from and at an angle to the first axis; and a negative ion detection device with an ion inlet at a second side opposite the first side, offset from and at an angle to the first axis. A negative voltage bias applied to the positive ion device accelerates positive ions toward the inlet along a path including a component along a second axis orthogonal to the first axis. A positive voltage bias applied to the negative ion detection device accelerates negative ions toward the inlet along a path that includes a component along the second axis orthogonal to the first axis in a direction generally opposite to the path of the positive ions.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Device for manipulating charged particles
ActiveUS20140061457A1Stability-of-path spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationNegatively charged particleChannel use
The present invention is concerned with a device for charged particle transportation and manipulation. Embodiments provide a capability of combining positively and negatively charged particles in a single transported packet. Embodiments contain an aggregate of electrodes arranged to form a channel for transportation of charged particles, as well as a source of power supply that provides supply voltage to be applied to the electrodes, the voltage to ensure creation, inside the said channel, of a non-uniform high-frequency electric field, the pseudopotential of which field has one or more local extrema along the length of the channel used for charged particle transportation, at least, within a certain interval of time, whereas, at least one of the said extrema of the pseudopotential is transposed with time, at least within a certain interval of time, at least within a part of the length of the channel used for charged particle transportation.
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB EURO
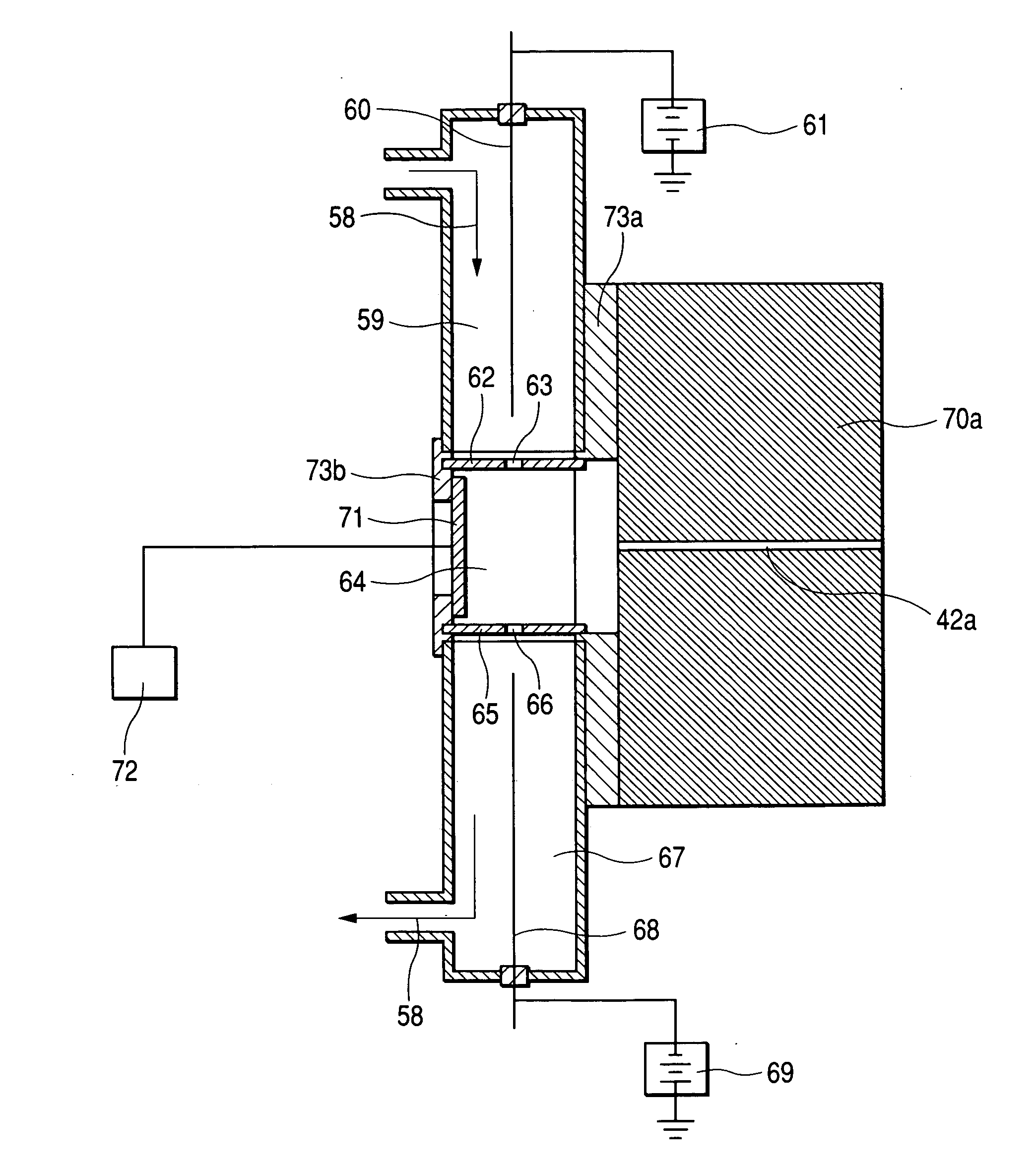
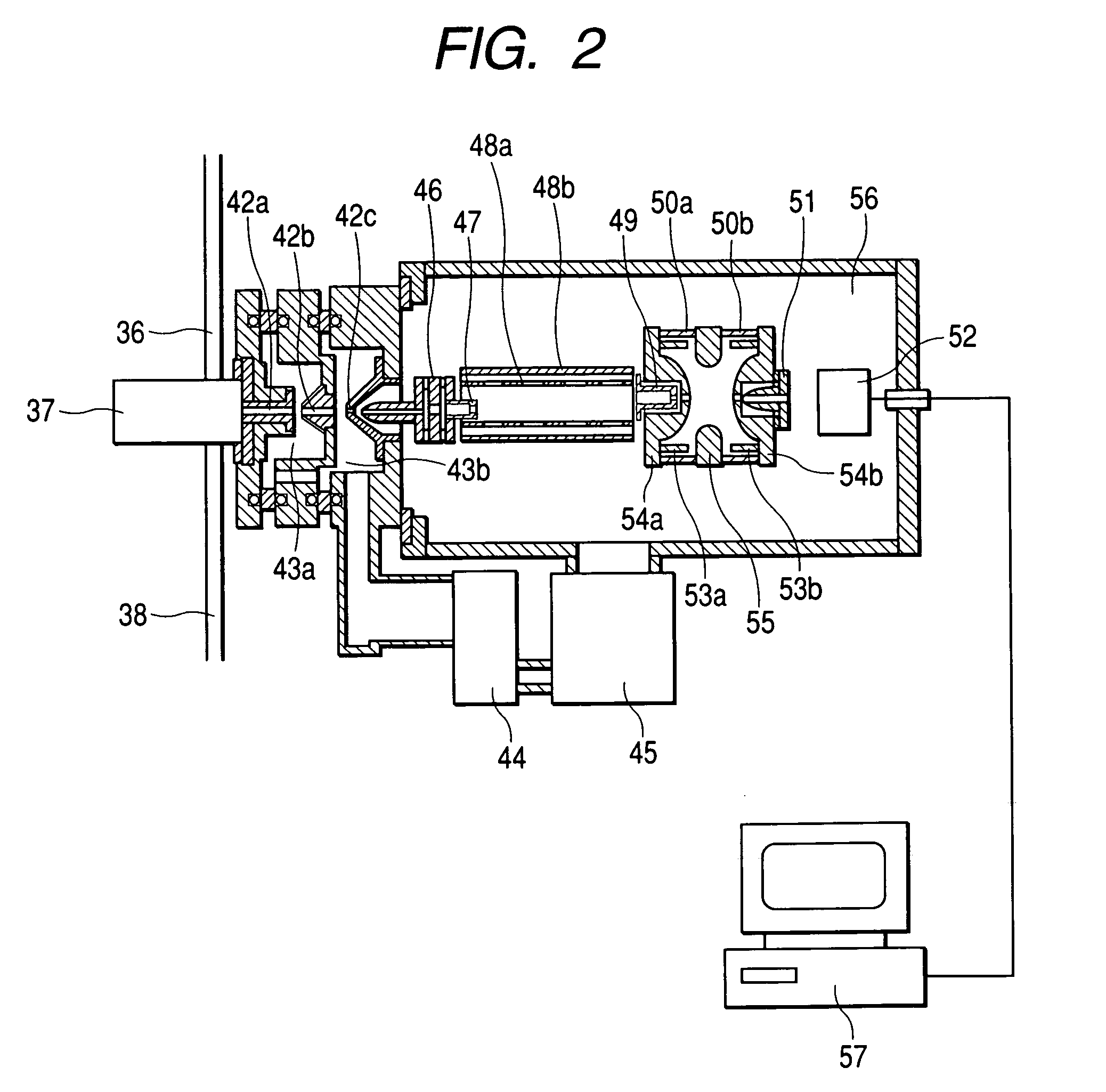
Mass spectrometric apparatus and ion source
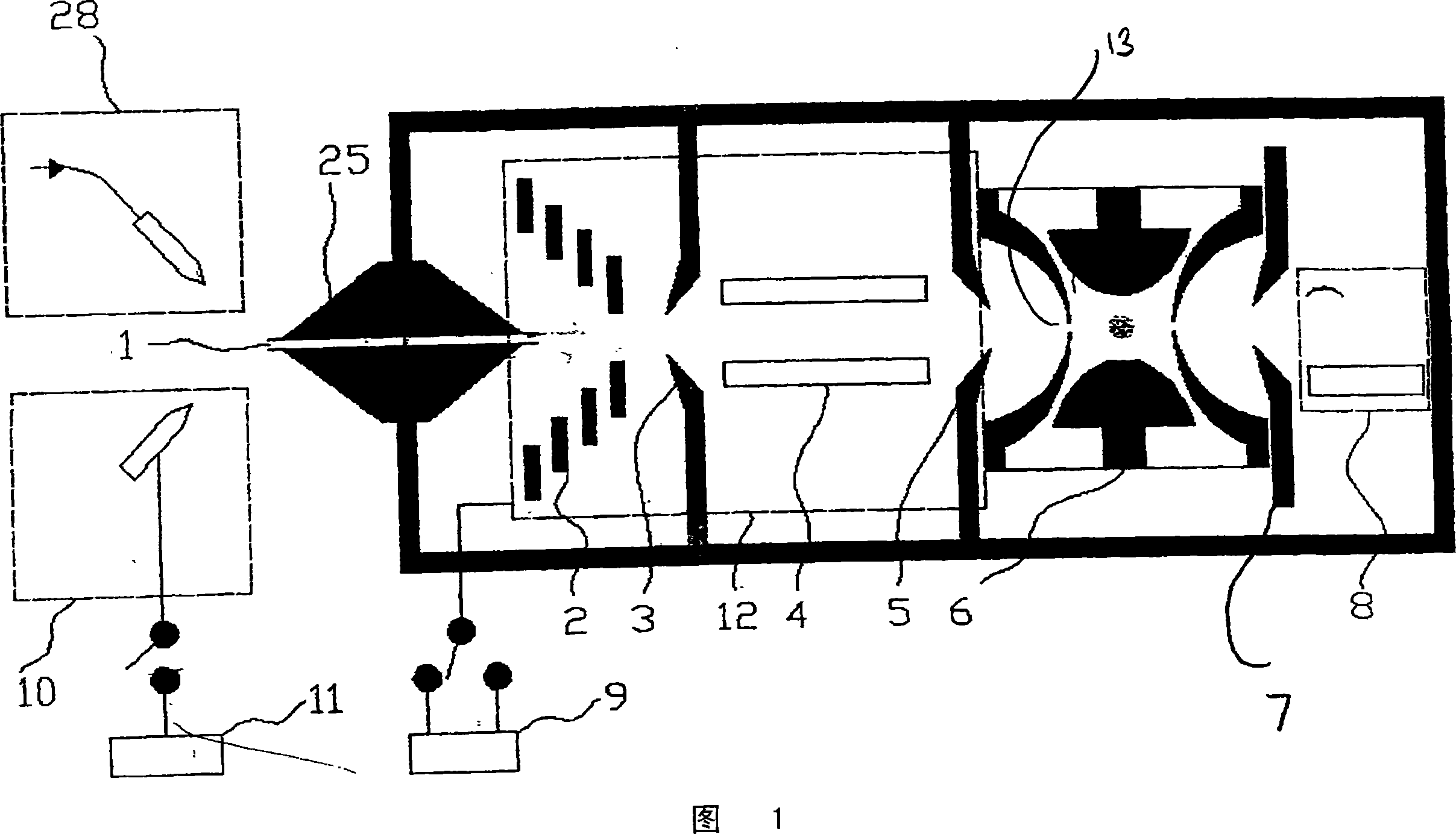
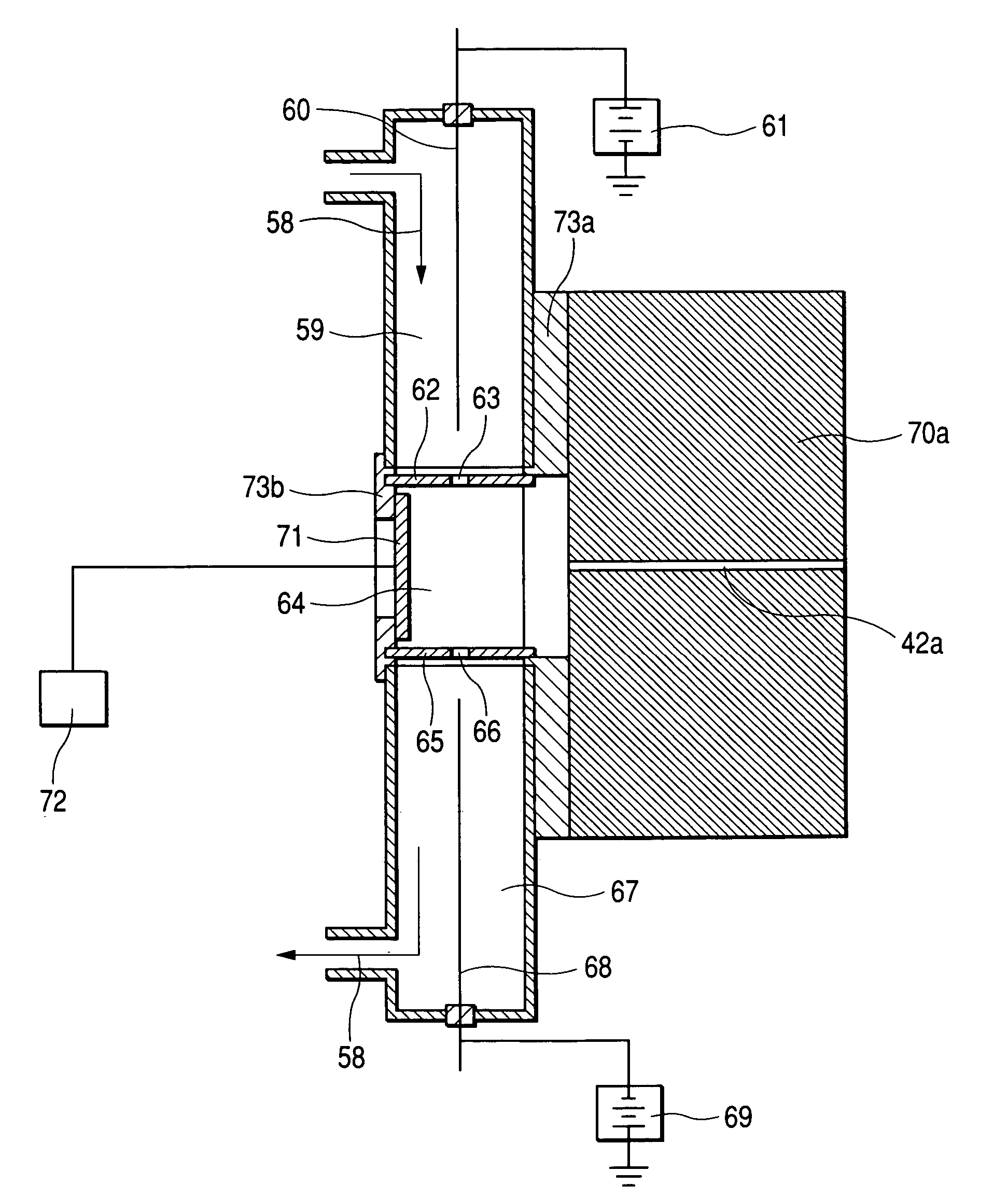
InactiveUS20050199799A1Easier/reduced maintenanceExtended service lifePositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass spectrometricSpectrometer
A mass spectrometric apparatus capable of generating and detecting positive and negative ions stably at the same time. The apparatus preferably comprises: an opening through which a sample gas is introduced; an ion source to generate ions of the sample gas; and a mass spectrometer to analyze the mass of the generated ions. The ion source utilized with the mass spectrometric device comprises: a first needle electrode on which a voltage is applied in order to generate positive ions of the sample gas introduced through the opening; a first counter electrode having a first opening through which the sample gas and the positive ions pass; a second counter electrode disposed opposite the first counter electrode having a second opening through which the sample gas and the positive ions pass; a second needle electrode on which voltage is applied in order to generate negative ions of the sample gas; and a vent through which the sample gas is ejected. Generated ions are then introduced into a vacuum region via an aperture and subjected to mass analysis.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Device for manipulating charged particles via field with pseudopotential having one or more local maxima along length of channel
ActiveUS9536721B2Positive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationElectron/ion optical arrangementsNegatively charged particleChannel use
The present invention is concerned with a device for charged particle transportation and manipulation. Embodiments provide a capability of combining positively and negatively charged particles in a single transported packet. Embodiments contain an aggregate of electrodes arranged to form a channel for transportation of charged particles, as well as a source of power supply that provides supply voltage to be applied to the electrodes, the voltage to ensure creation, inside the said channel, of a non-uniform high-frequency electric field, the pseudopotential of which field has one or more local extrema along the length of the channel used for charged particle transportation, at least, within a certain interval of time, whereas, at least one of the said extrema of the pseudopotential is transposed with time, at least within a certain interval of time, at least within a part of the length of the channel used for charged particle transportation.
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB EURO
Method for introducing ions into an ion trap and an ion storage apparatus
InactiveUS20090127453A1Reduce the impactSmall sizeStability-of-path spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationIon trap mass spectrometryPhysical chemistry
A method of introducing ions into an ion trap and an ion storage apparatus are described. Introduction means are used to introduce first ions into an ion trap through an entrance aperture to the ion trap. An operating condition of the introduction means is adjusted to cause second ions, of different polarity to the first ions to be introduced into the ion trap through the same entrance aperture.
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB EURO
Detection of positive and negative ions
An ion detector comprises an ion guide with electrodes arranged about a first axis; a positive ion detection device with an ion inlet at a first side of the ion output section offset from and at an angle to the first axis; and a negative ion detection device with an ion inlet at a second side opposite the first side, offset from and at an angle to the first axis. A negative voltage bias applied to the positive ion device accelerates positive ions toward the inlet along a path including a component along a second axis orthogonal to the first axis. A positive voltage bias applied to the negative ion detection device accelerates negative ions toward the inlet along a path that includes a component along the second axis orthogonal to the first axis in a direction generally opposite to the path of the positive ions.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
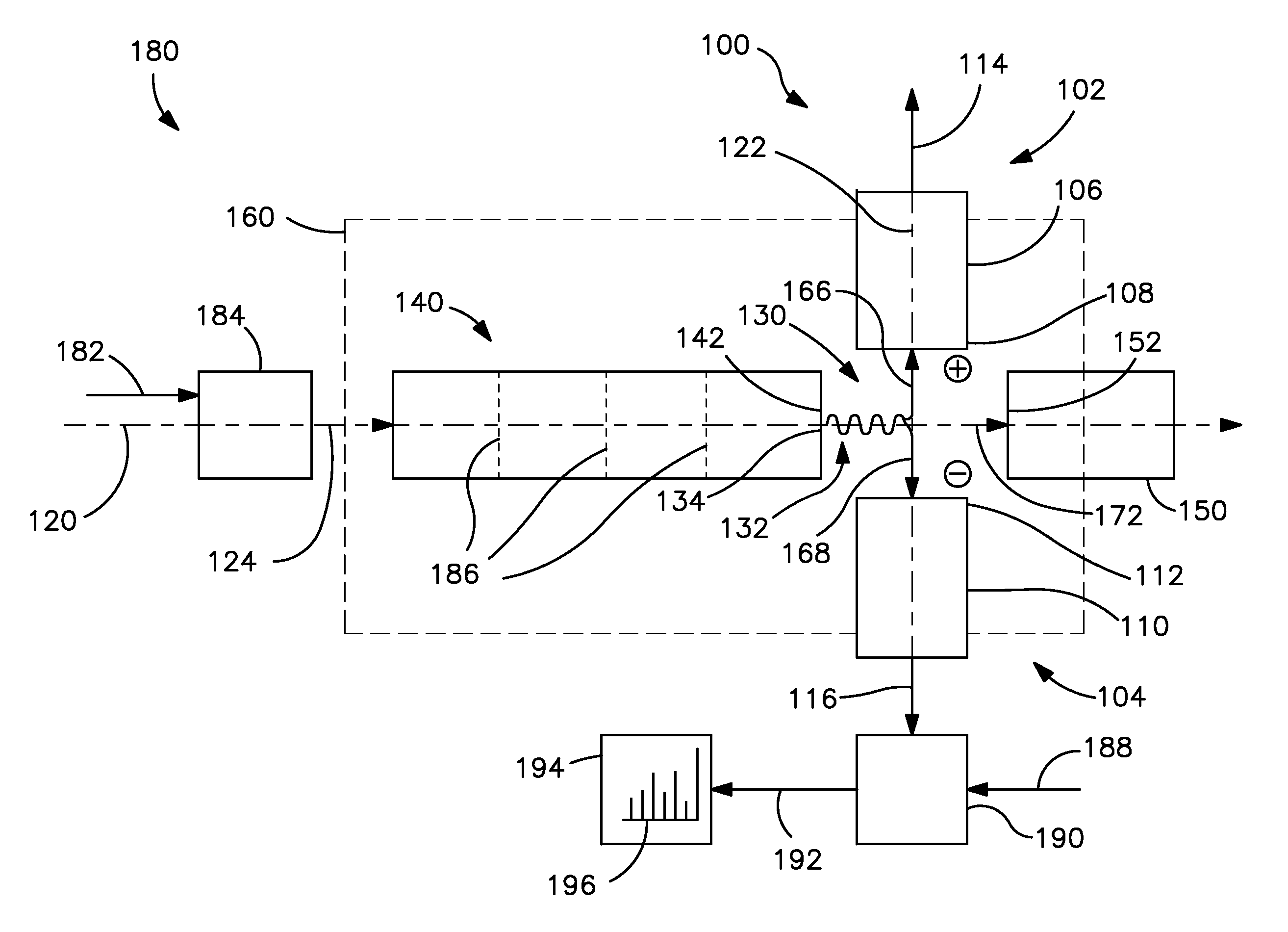
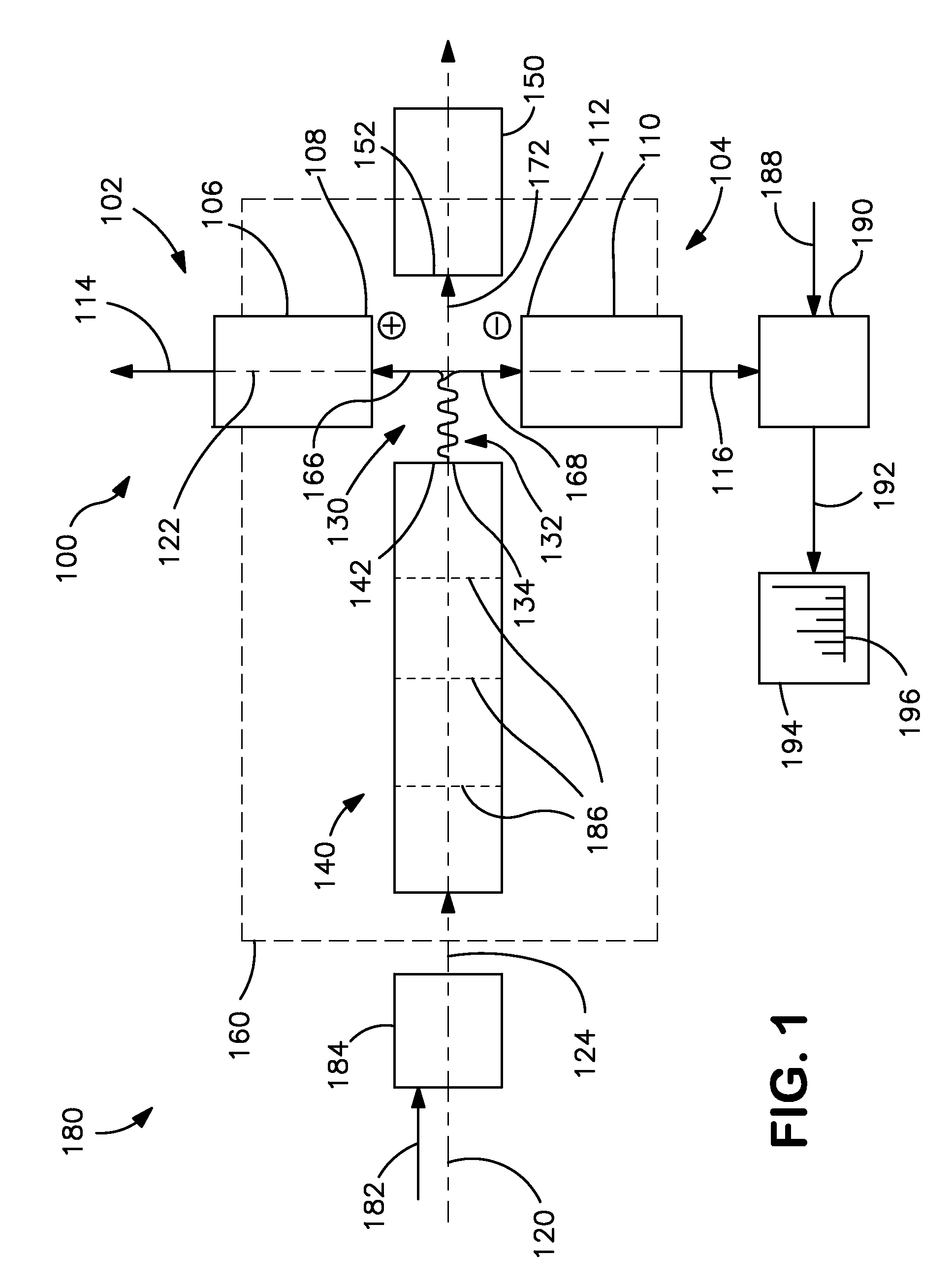
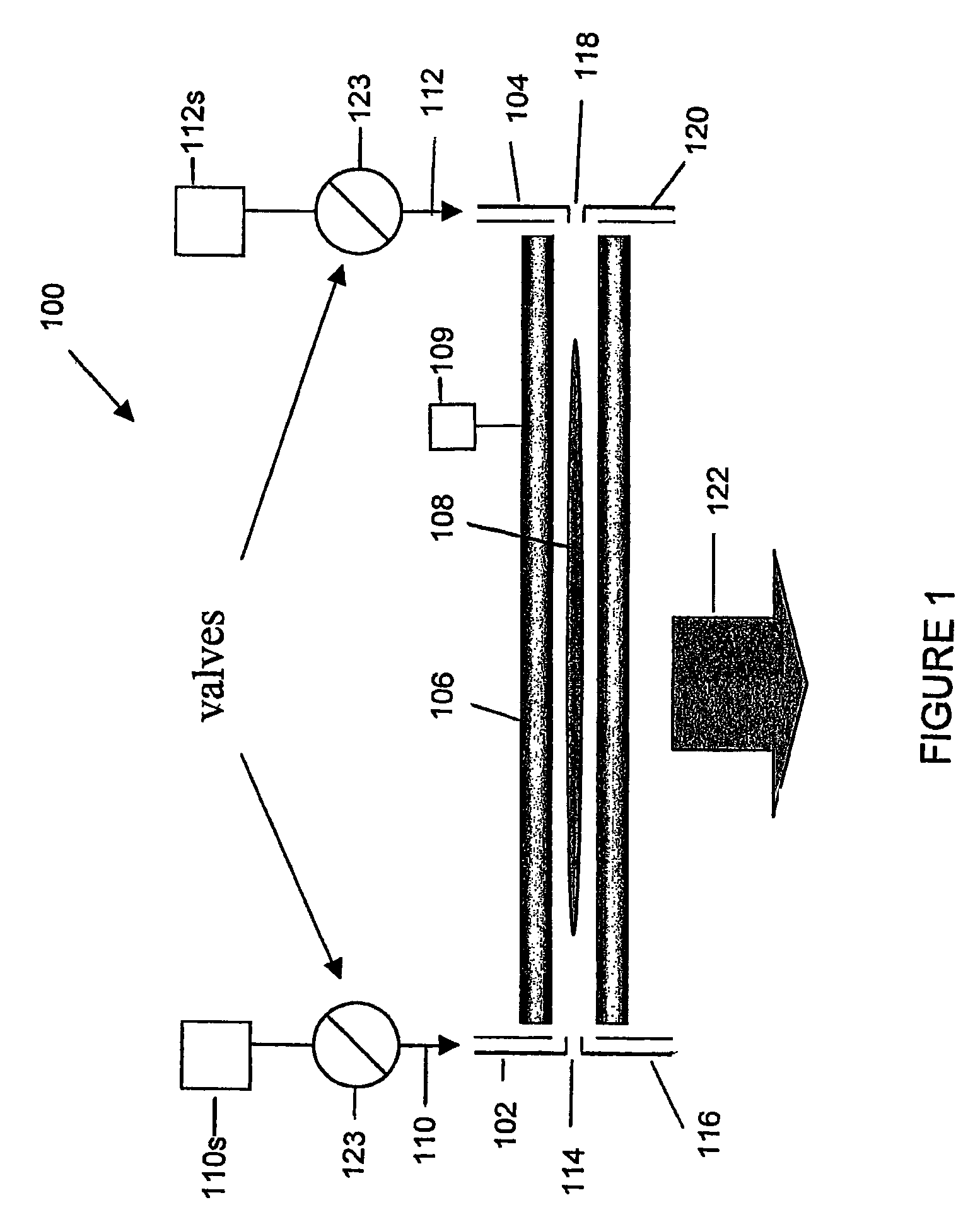
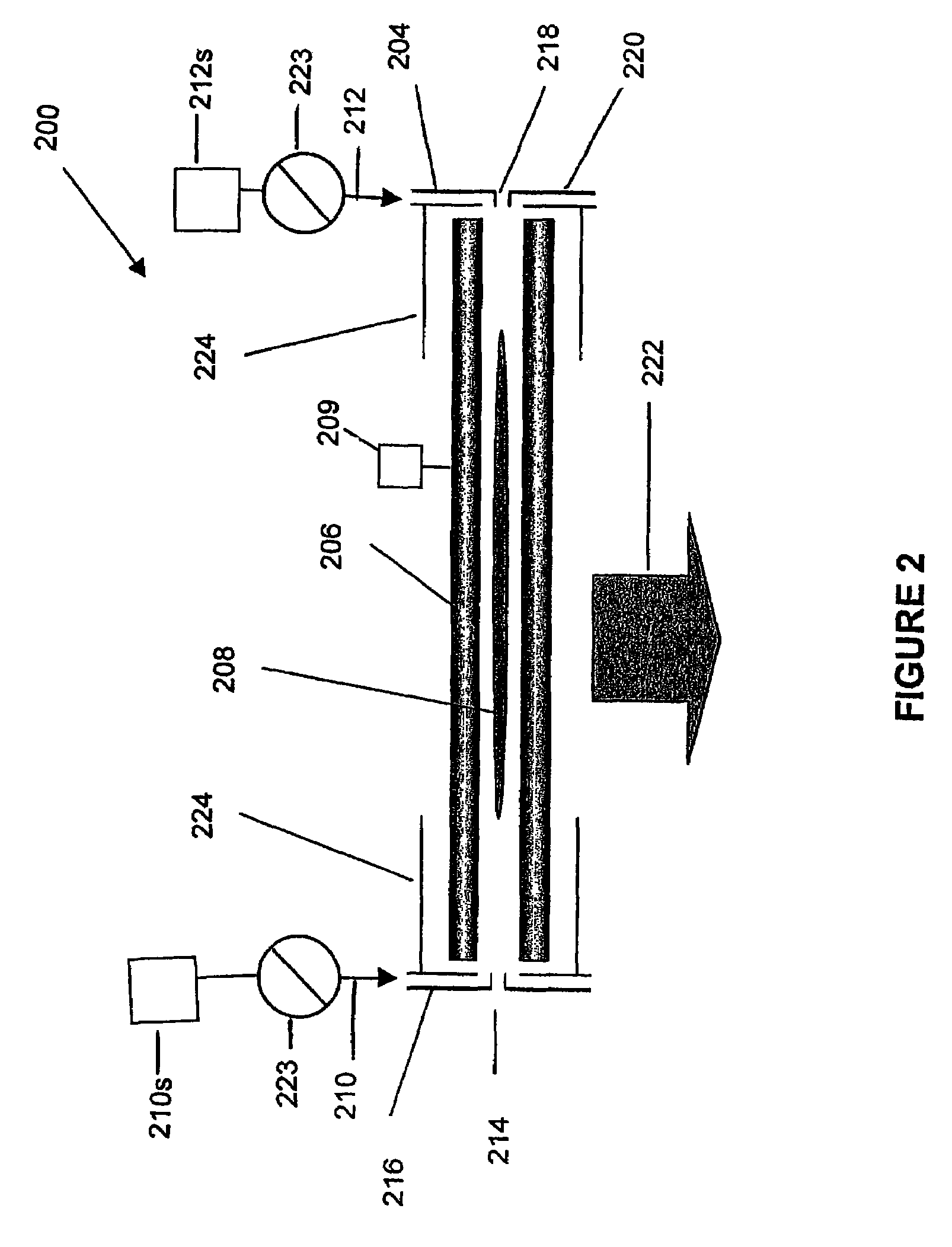
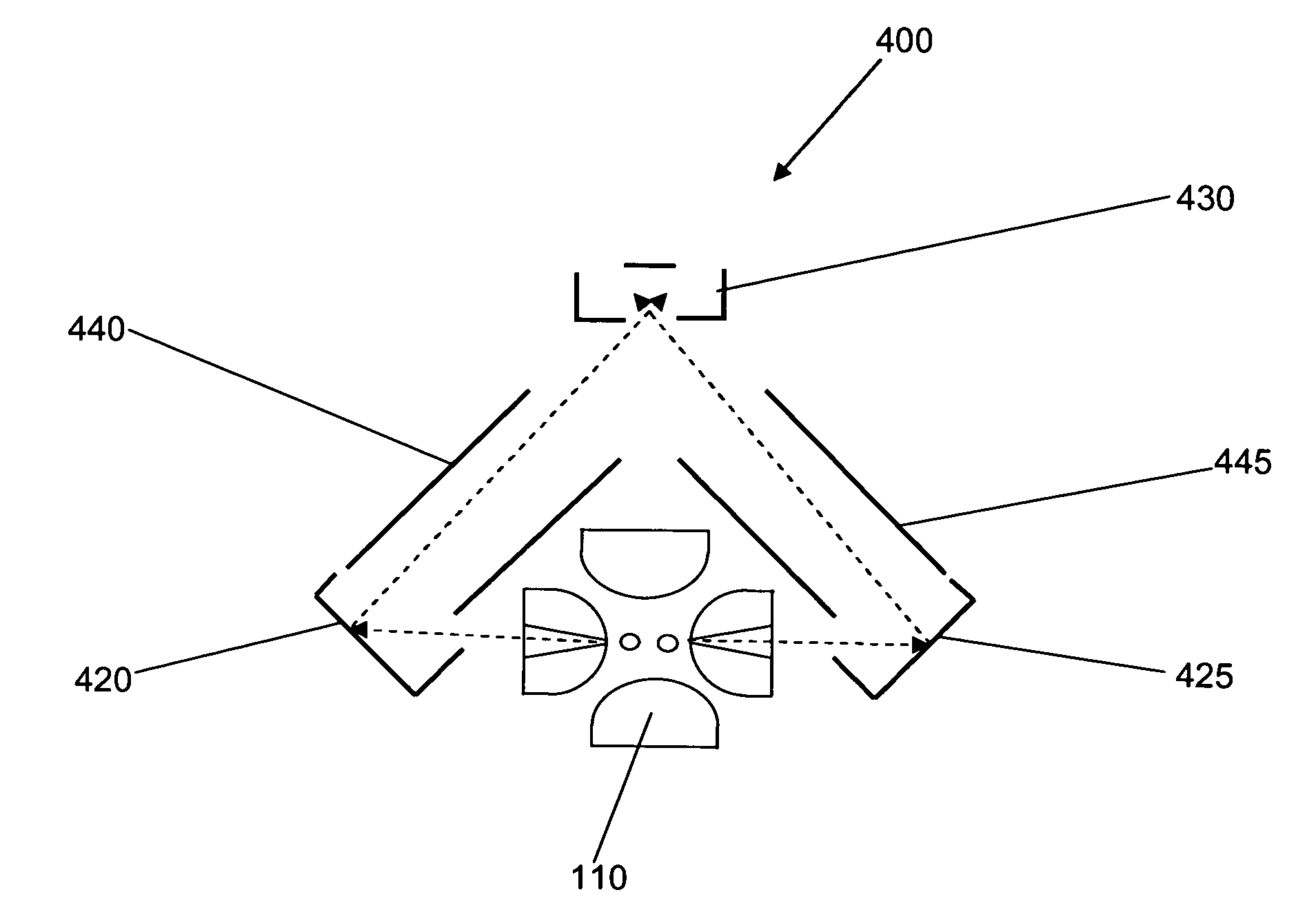
Mass spectrometer for both positive and negative particle detection
A mass spectrometer suitable to measure both positive and negative particles, such as ions for example in a vacuum chamber. This spectrometer is provided with a turnable permanent magnet segment, which provides the gap of a yoke with adequate magnetic flux having the appropriate direction to separate the positive or the negative particles. Changing the polarity adjusts the flight path of the ions. Thus, negatively charged ions and positively charged ions will follow similar flight paths under opposite polarities, permitting the use of a single array of detectors. One or more coils may be used in place of or in addition to the turnable permanent magnet segment in order to provide the appropriate magnetic flux to the gap, and / or facilitate the turning process of the turnable magnet segment. The turnable magnet and / or the coils may be inside or outside the vacuum chamber. The detector may comprise at least one detector area, two charge mode amplifiers coupled to the detector area, a first CCD shift register coupled to a first one of the charge mode amplifiers and a second CCD shift register coupled to a second one of the charge mode amplifiers.
Owner:O I CORP
Mass Spectrometer With Beam Expander
InactiveUS20130256524A1Reduce turnaround timeExtended flight timeTime-of-flight spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationBeam expanderLight beam
A mass spectrometer is disclosed comprising a RF confinement device, a beam expander and a Time of Flight mass analyser. The beam expander is arranged to expand an ion beam emerging from the RF confinement device so that the ion beam is expanded to a diameter of at least 3 mm in the orthogonal acceleration extraction region of the Time of Flight mass analyser.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
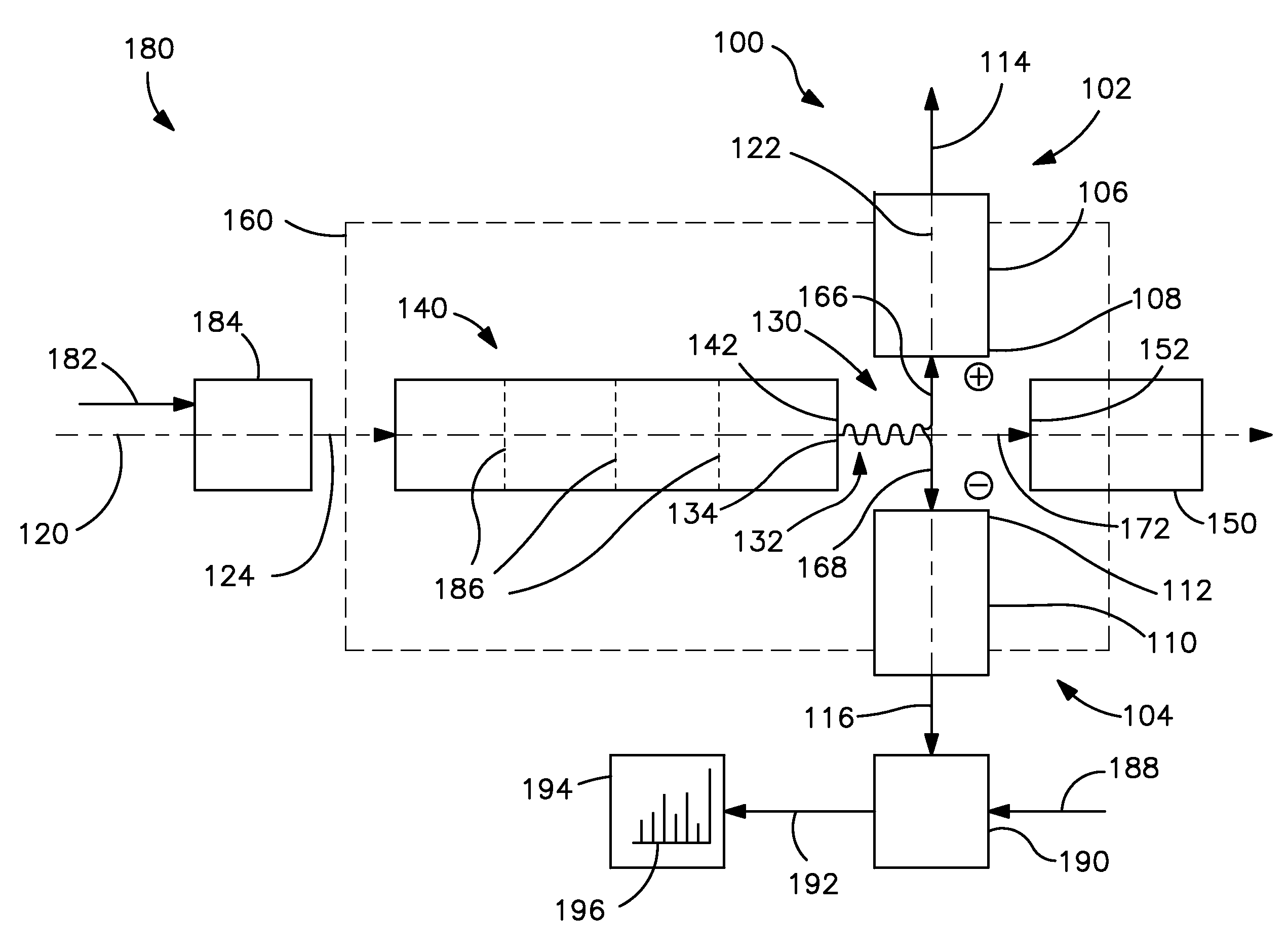
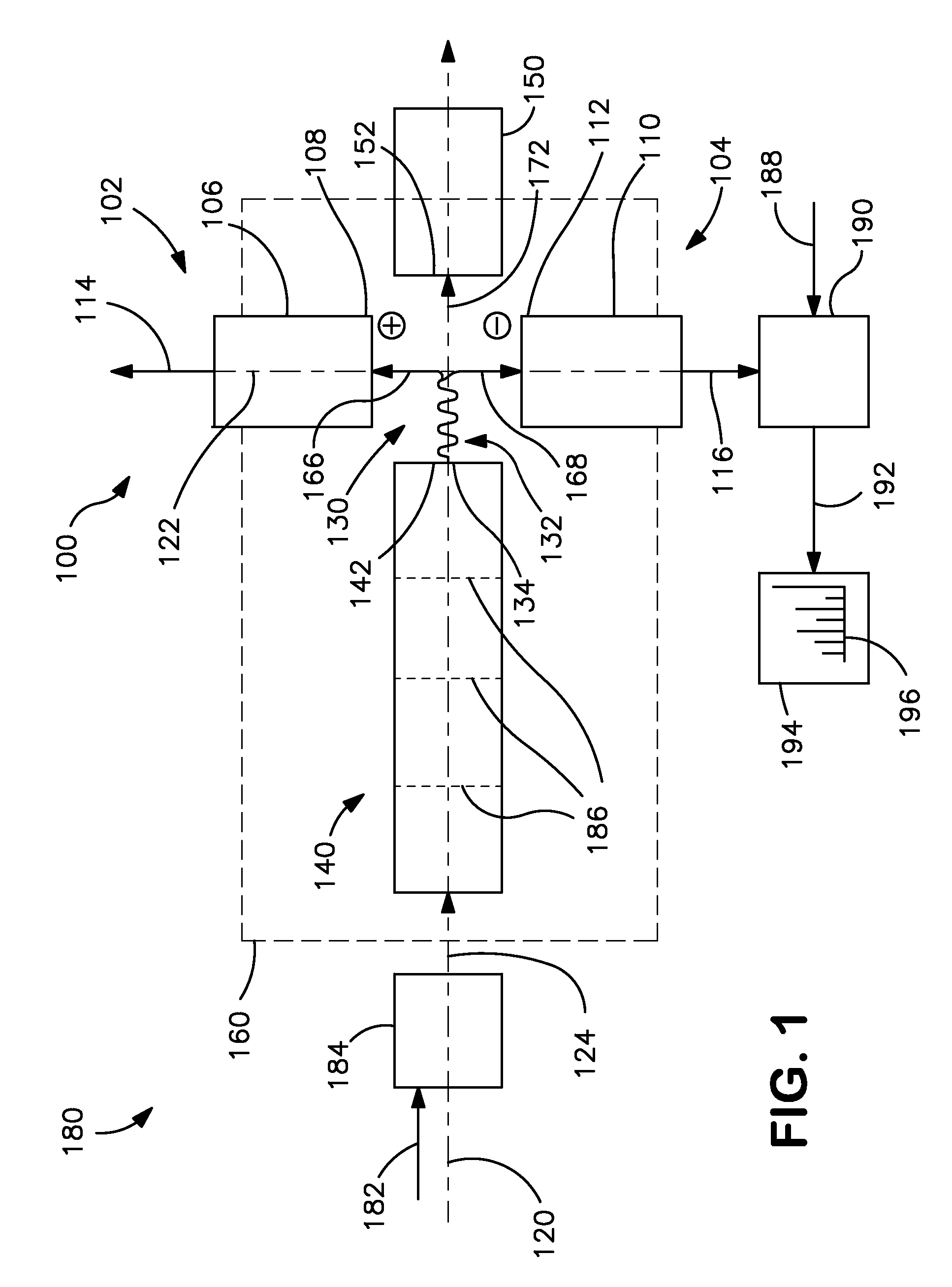
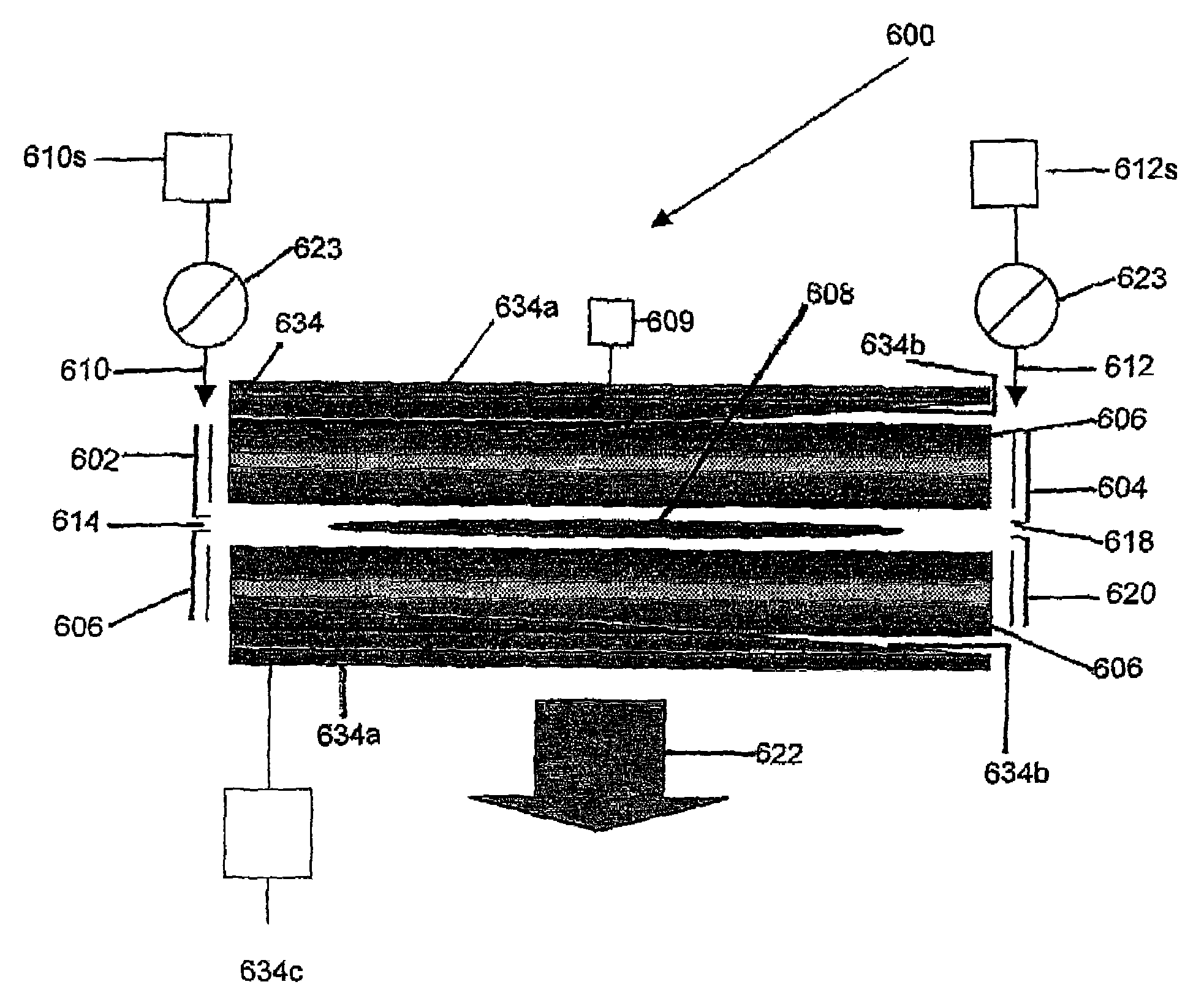
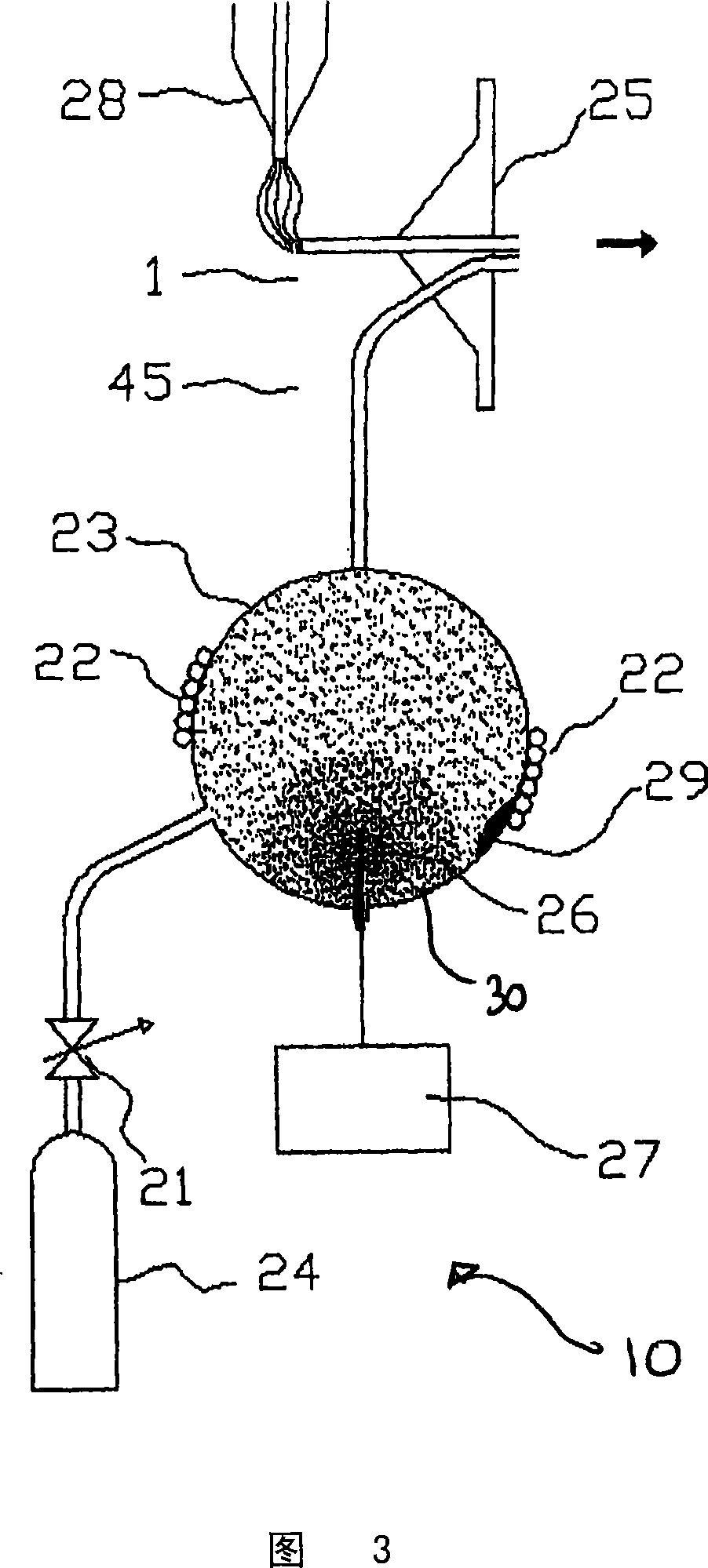
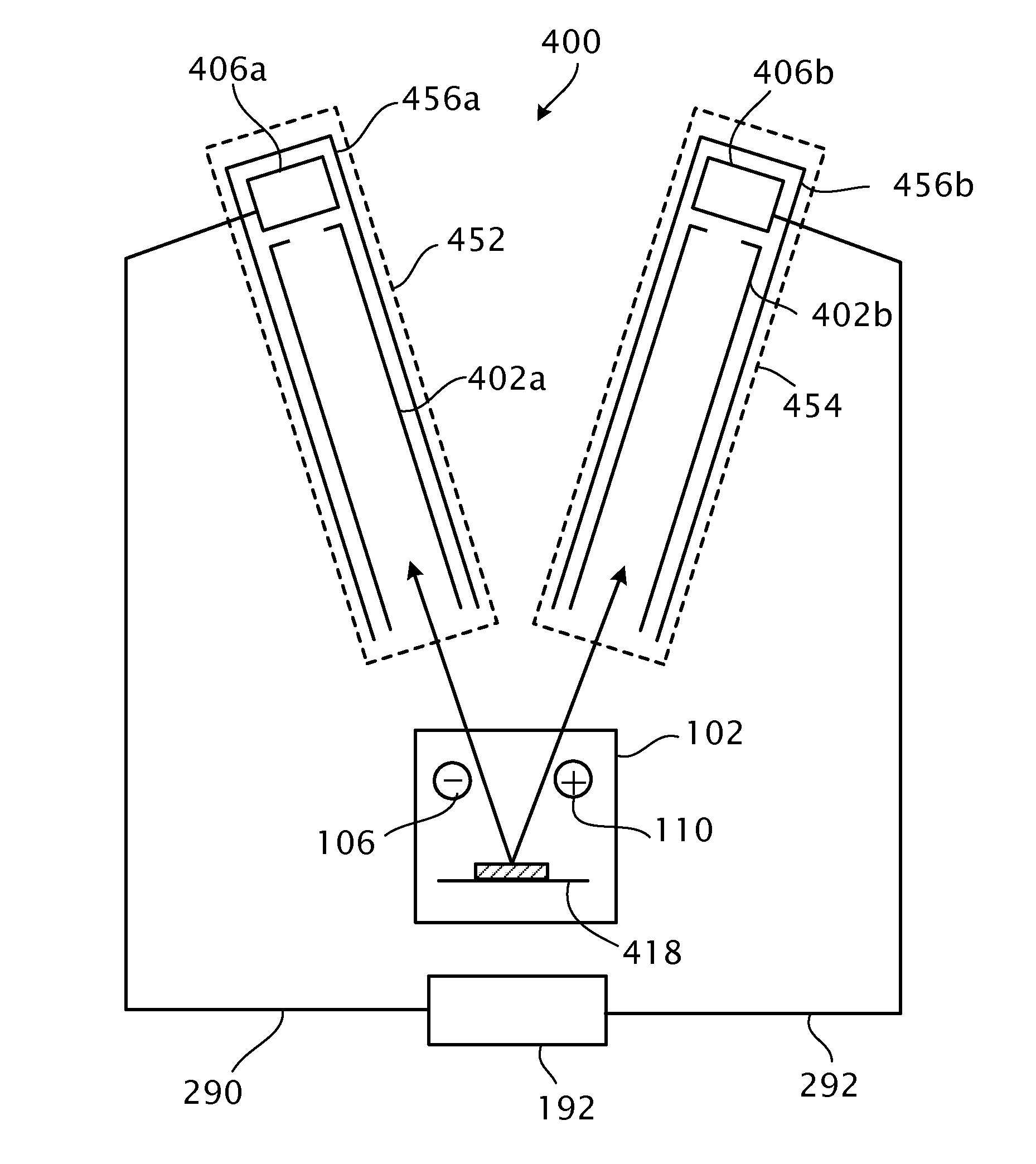
Dual-polarity mass spectrometer
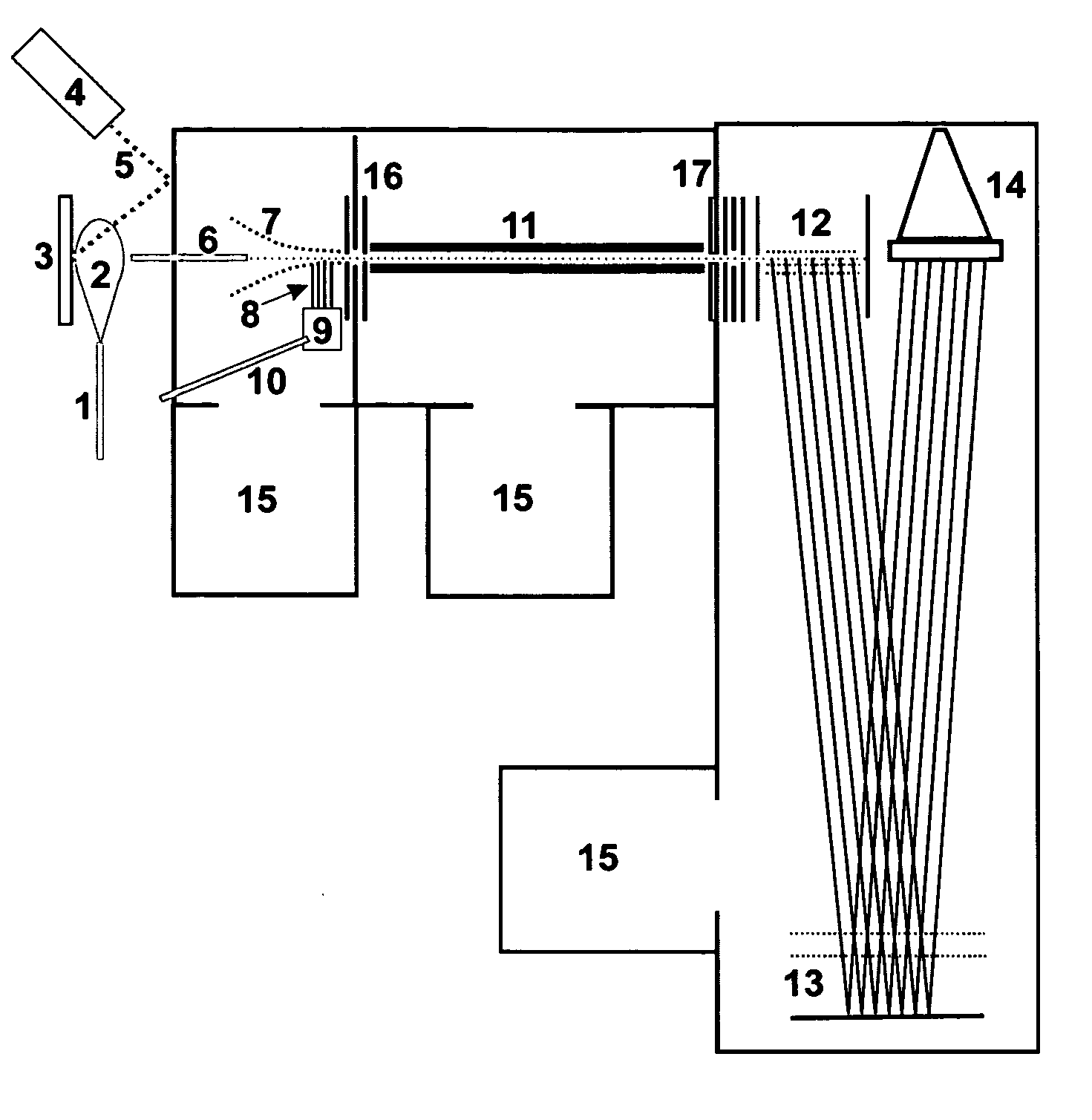
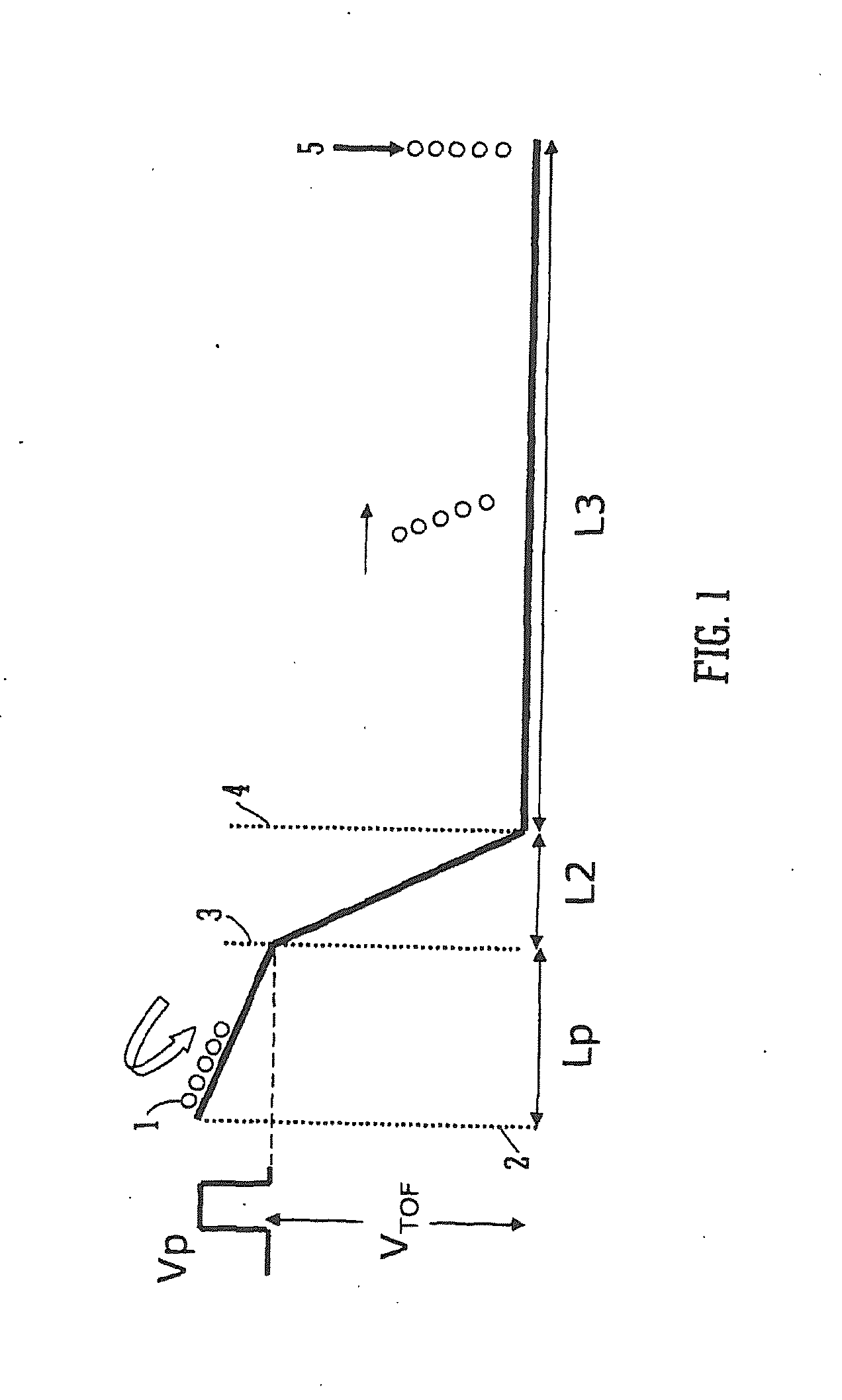
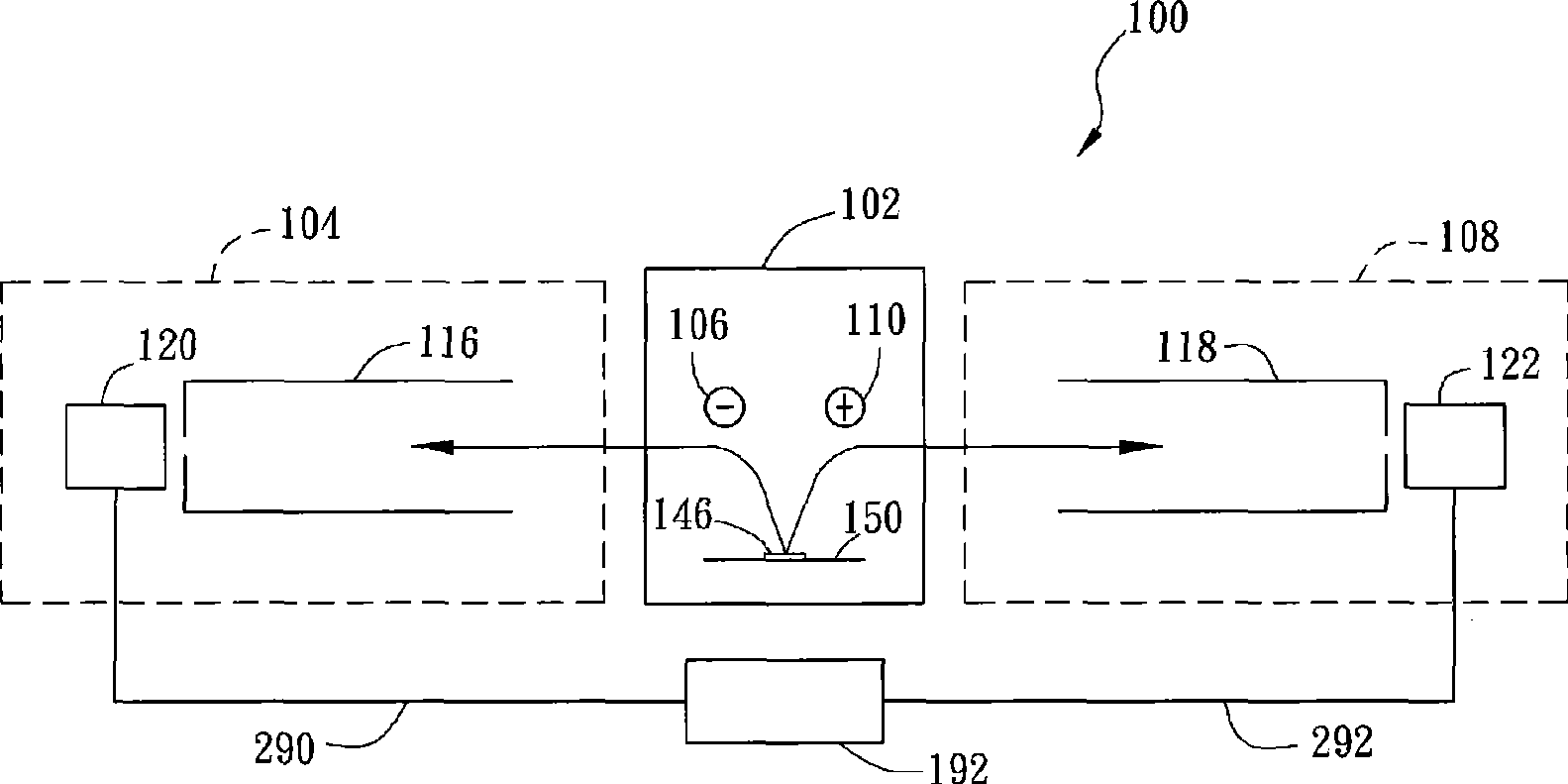
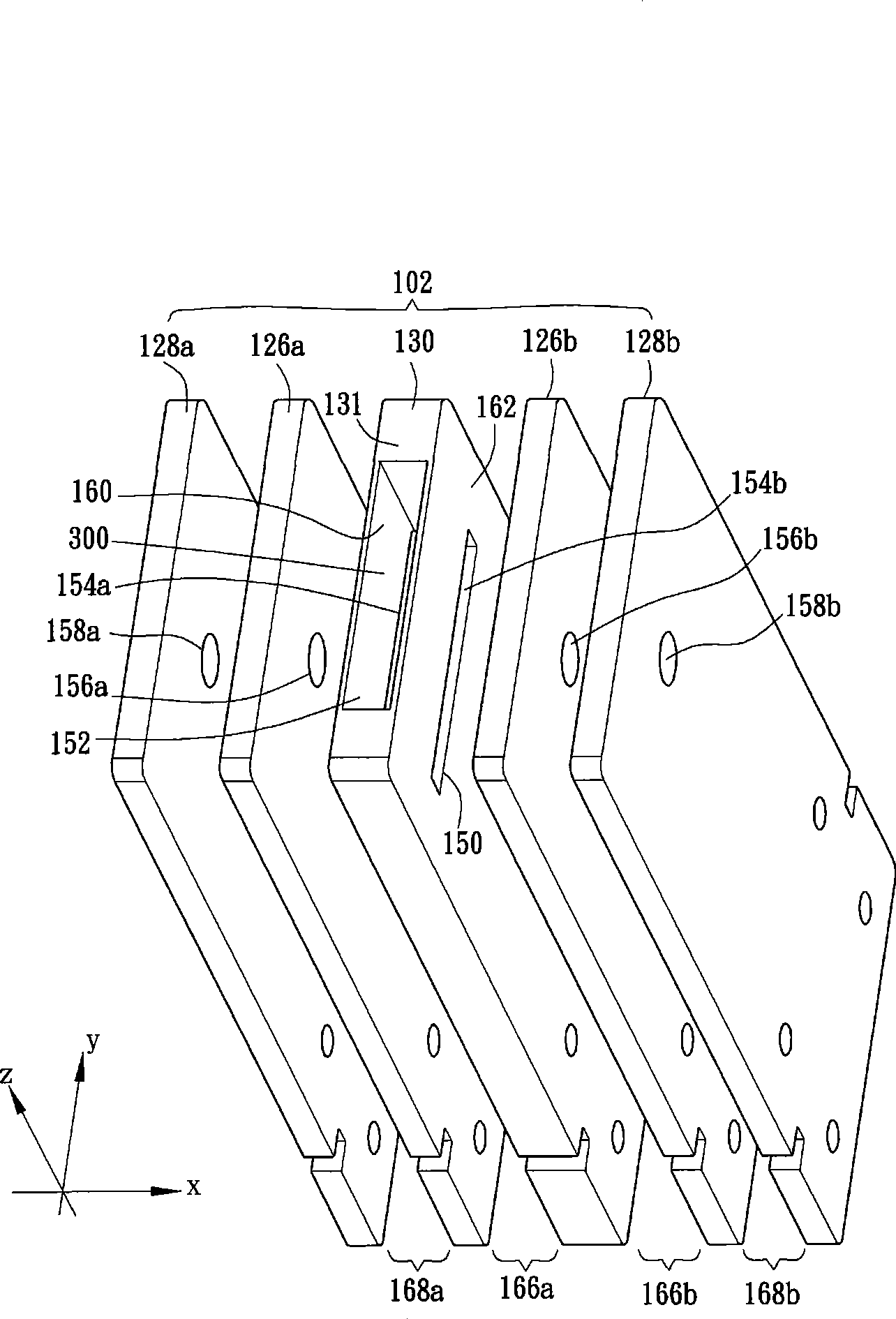
InactiveCN101523547AAccurate and real-time detectionTime-of-flight spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationMass analyzerLaser beams
A dual-polarity mass spectrometer includes an ion source, a negative ion mass analyzer, and a positive ion mass analyzer to measure both the negative and positive ion spectra of a sample material simultaneously. The ion source includes a sample surface on which the sample material is positioned, the sample material providing positive ions and negative ions when excited by a laser beam or an energetic particle stream. A first extraction electrode is connected to a voltage higher than the sample surface to attract the negative ions from the sample electrode. A second extraction electrode is connected to a voltage lower than the sample surface to attract the positive ions from the sample electrode. The negative and positive ions are analyzed simultaneously by the negative ion mass analyzer and the positive ion mass analyzer, respectively.
Owner:ACAD SINICA
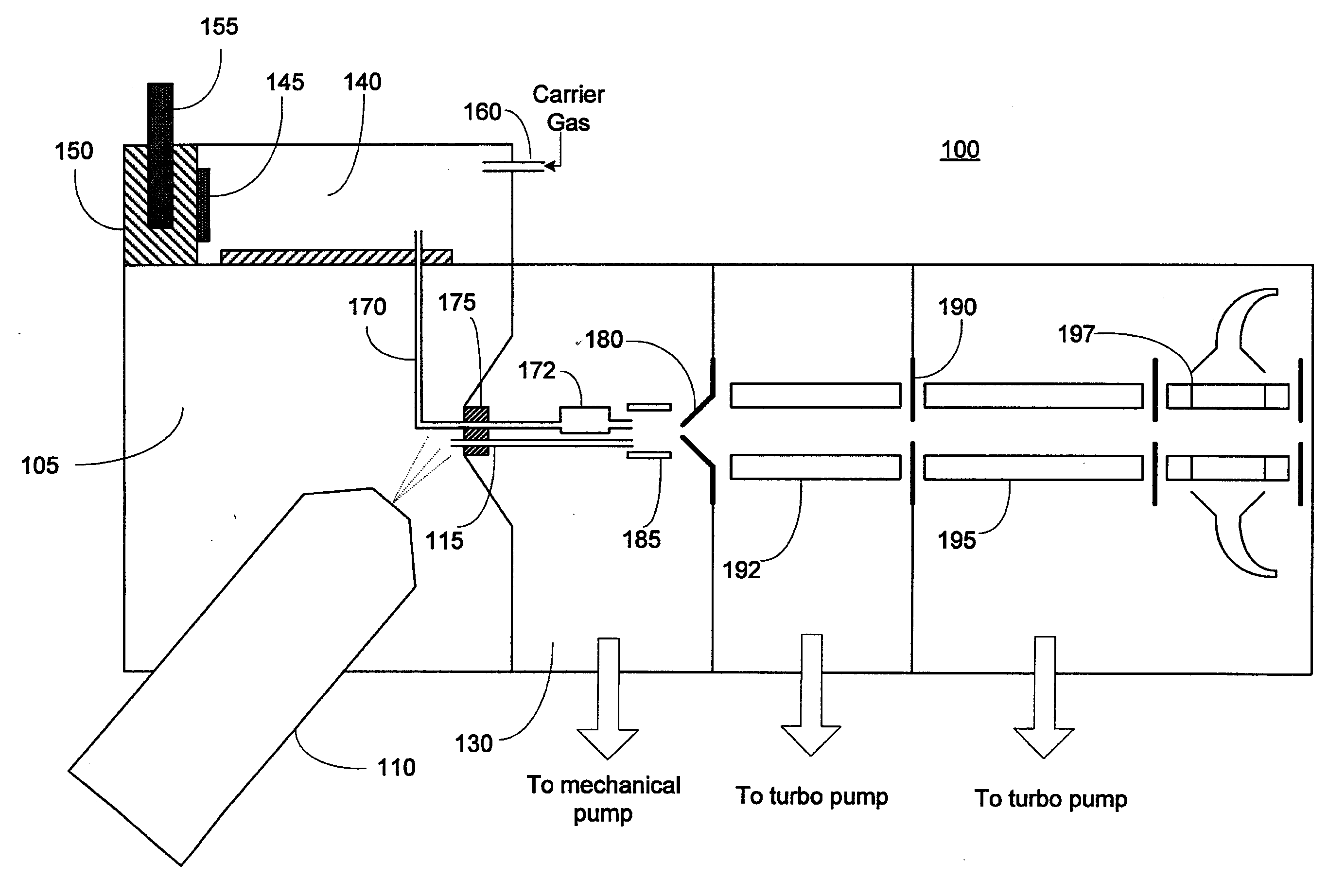
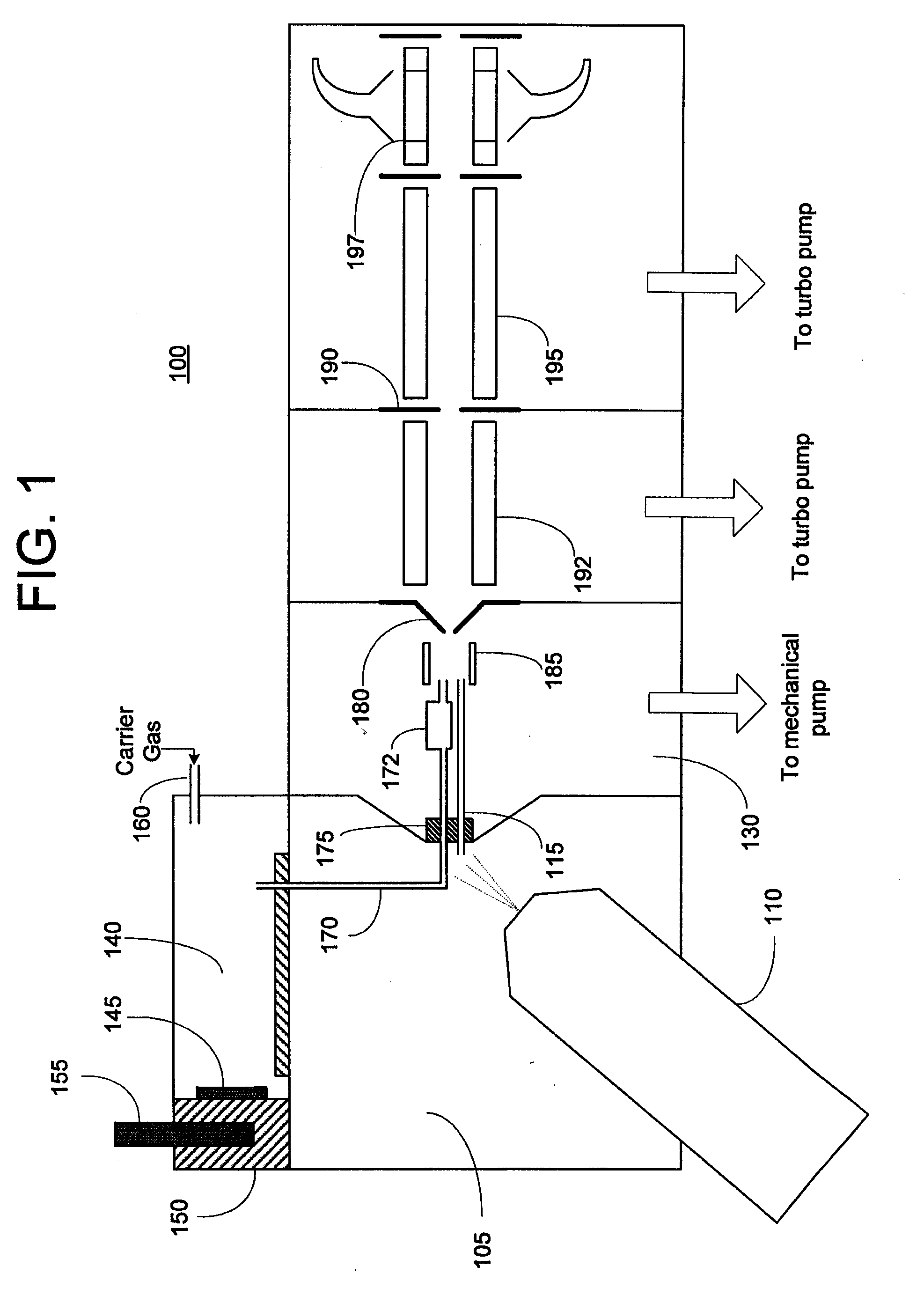
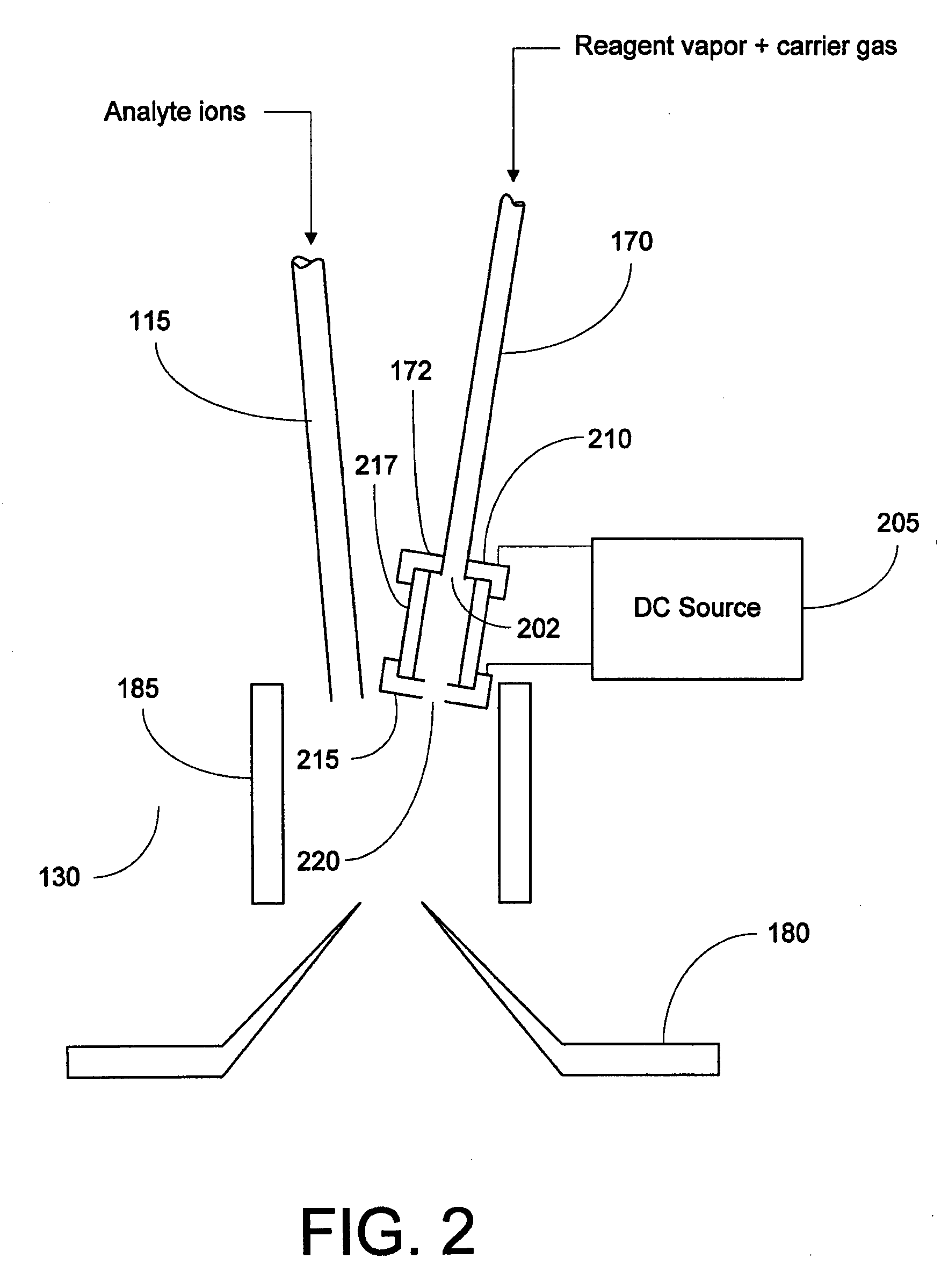
Method and Apparatus for Generation of Reagent Ions in a Mass Spectrometer
ActiveUS20090294649A1Production controlPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationMaterial analysis by optical meansAnalyteMass analyzer
A front-end reagent ion source for a mass spectrometer is disclosed. Reagent vapor is supplied to a reagent ionization volume located within a chamber of the mass spectrometer and maintained at a low vacuum pressure. Reagent ions are formed by interaction of the reagent vapor molecules with an electrical discharge (e.g., a glow discharge) within the ionization volume, and pass into the chamber of the mass spectrometer. At least one ion optical element located along the analyte ion path transports the reagent ions to successive chambers of the mass spectrometer. The reagent ions may be combined with the analyte ions to perform ion-ion studies such as electron transfer dissociation (ETD).
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +1
Ion sampling apparatuses in fast polarity-switching ion sources
ActiveUS20080197275A1Time-of-flight spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationPhysical chemistryElectric field
The present invention provides ion sampling apparatuses that can be used in a fast polarity-switching electric field. In some embodiments, the ion sampling apparatus comprises a capillary made with an insulator, with a resistive inner or outer surface. Devices and systems comprising the ion sampling apparatuses, as well as methods of use thereof, are also provided.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
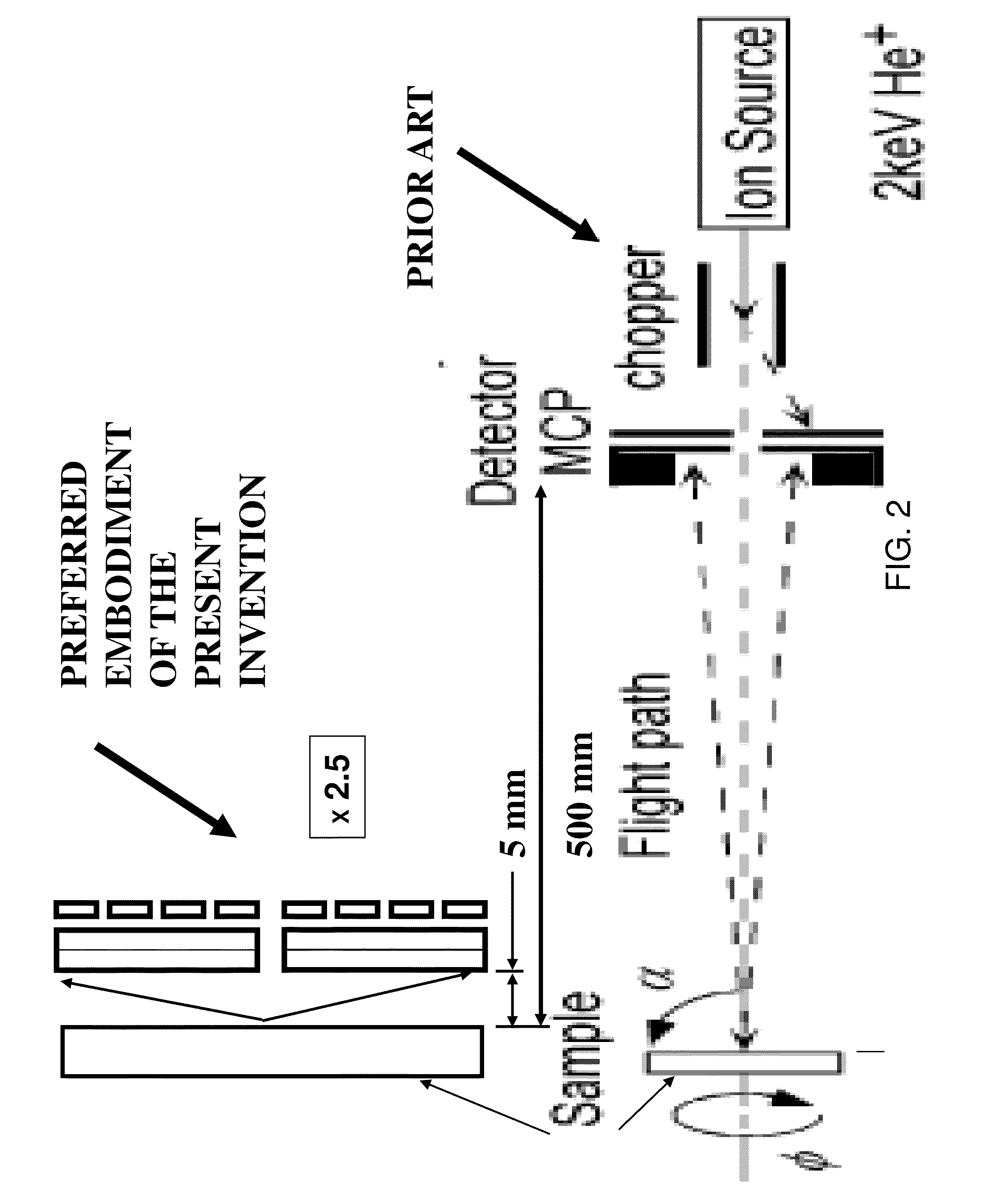
Time-of-flight spectrometry and spectroscopy of surfaces
ActiveUS20110147578A1FocusTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationParticle beamSpectroscopy
Described is an analytical method and apparatus for counting and measuring the flight time of secondary electrons, secondary ions and neutrals, scattered ions and / or neutrals and for correlating coincidences between these while maintaining a continuous un-pulsed, micro-focused, primary particle beam for impinging a surface for purposes of microprobe imaging and microanalysis.
Owner:IONWERKS
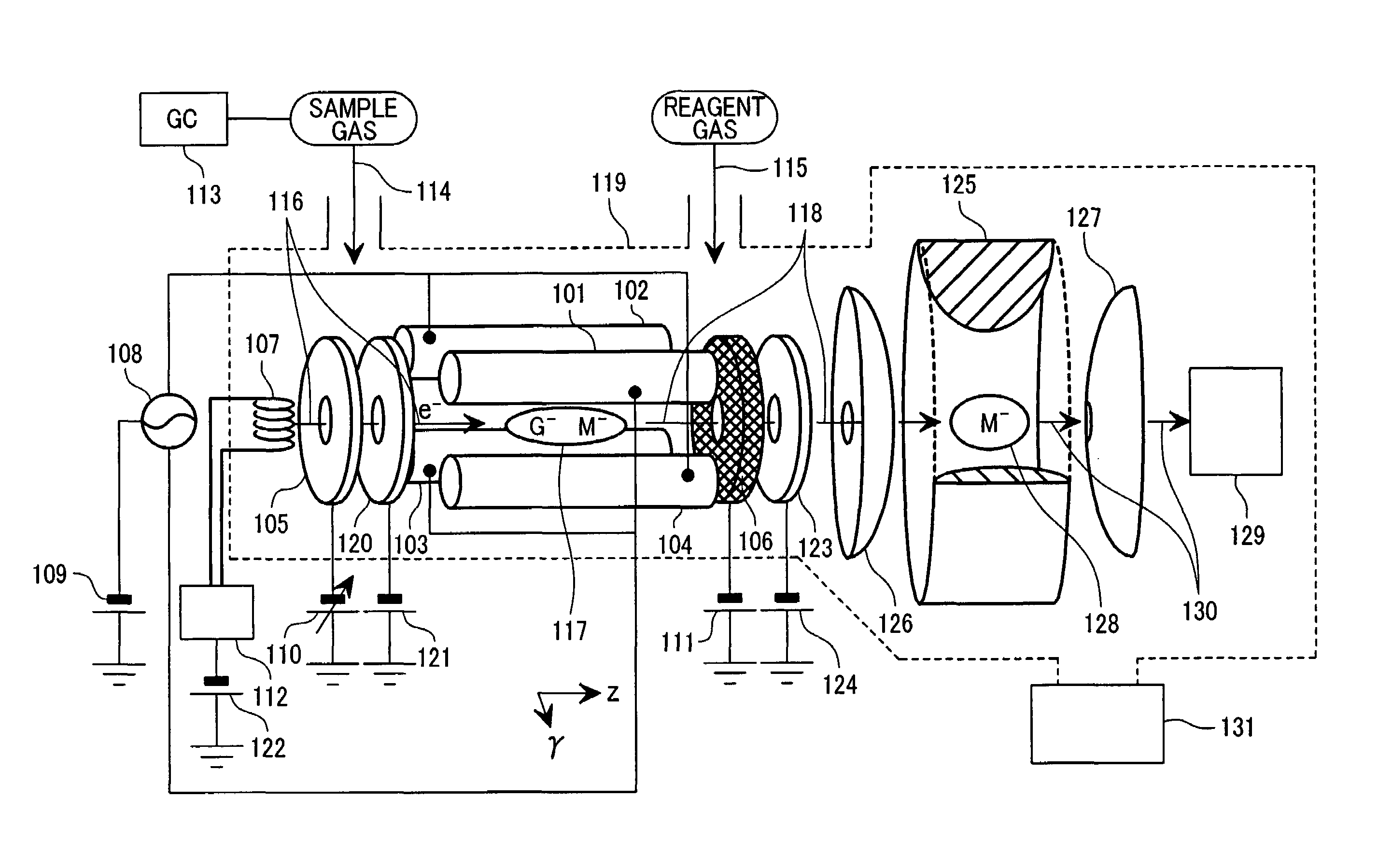
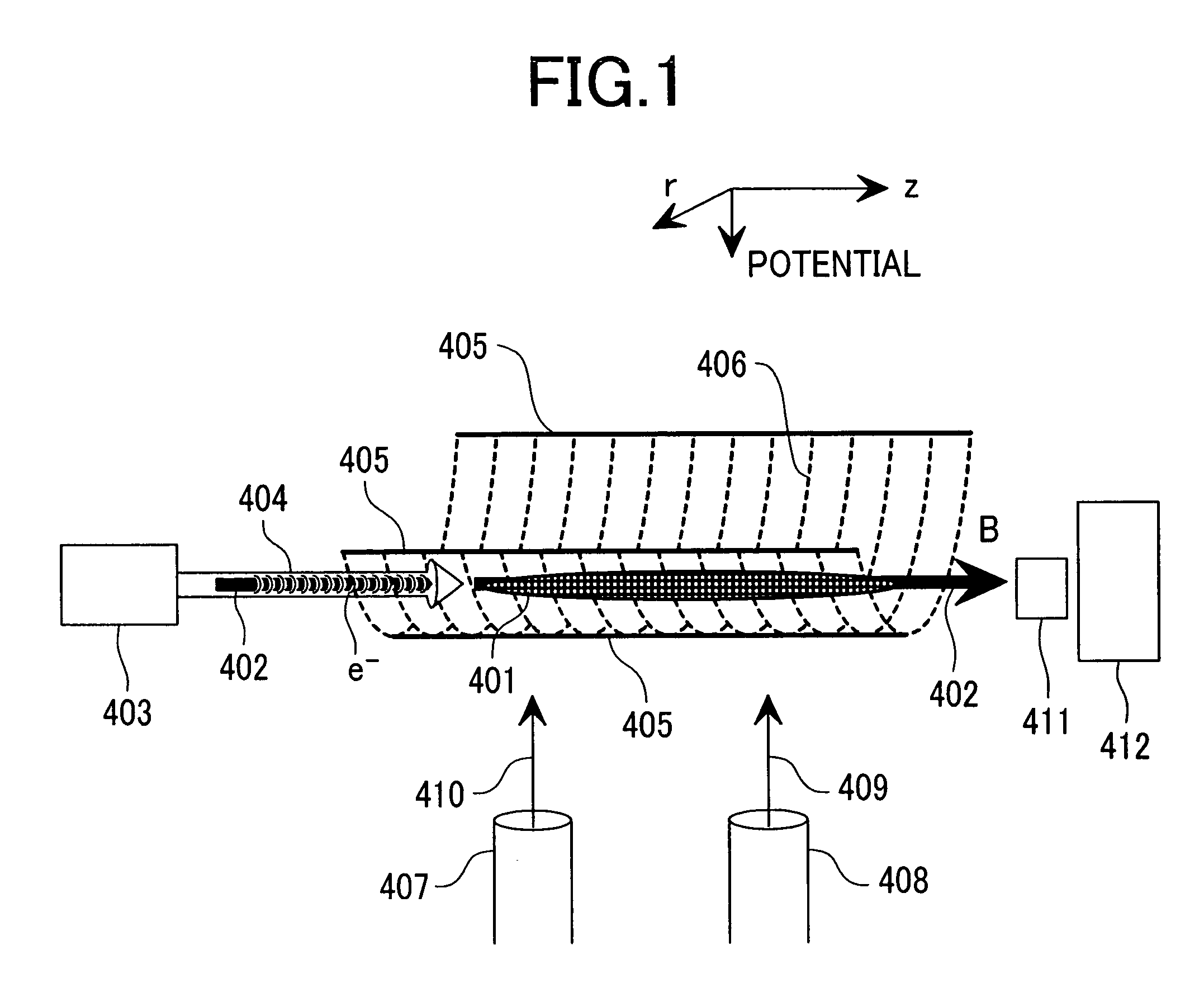
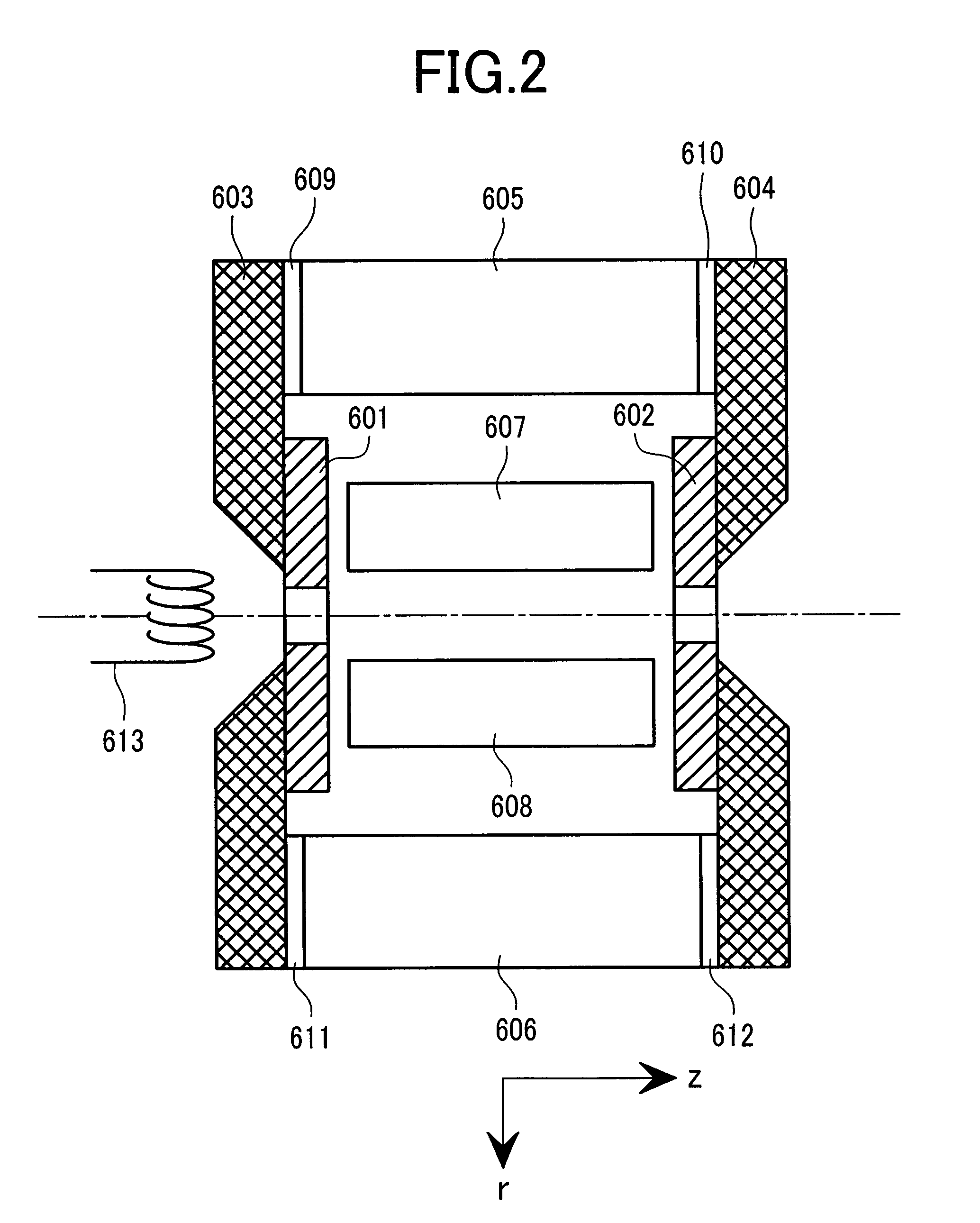
Mass spectrometer
ActiveUS7129478B2Improve detection efficiencyEffective massStability-of-path spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationElectron sourceMass analyzer
A mass spectrometer having an ion source section capable of creating positive ions and negative ions at high efficiency. The ion source is comprised of an ion source section for creating ions of a sample gas, a mass spectrometric section for conducting mass separation of created ions, linear RF generating multipole electrodes, magnetic fields generation means, a sample gas introduction system, a reaction gas introduction system and an electron source in which the linear RF generating multipole electrodes generate linear RF multipole electric fields. A static magnetic fields is applied in parallel on the center axis where the linear RF multipole electric fields are zero. A sample gas and a reagent gas are introduced into the ion source section. Electrons are injected for creating reaction of the positive ions or negative ions.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Mass spectrometer for both positive and negative particle detection
A mass spectrometer suitable to measure both positive and negative particles, such as ions for example in a vacuum chamber. This spectrometer is provided with a turnable permanent magnet segment, which provides the gap of a yoke with adequate magnetic flux having the appropriate direction to separate the positive or the negative particles. Changing the polarity adjusts the flight path of the ions. Thus, negatively charged ions and positively charged ions will follow similar flight paths under opposite polarities, permitting the use of a single array of detectors. One or more coils may be used in place of or in addition to the turnable permanent magnet segment in order to provide the appropriate magnetic flux to the gap, and / or facilitate the turning process of the turnable magnet segment. The turnable magnet and / or the coils may be inside or outside the vacuum chamber. The detector may comprise at least one detector area, two charge mode amplifiers coupled to the detector area, a first CCD shift register coupled to a first one of the charge mode amplifiers and a second CCD shift register coupled to a second one of the charge mode amplifiers.
Owner:O I CORP
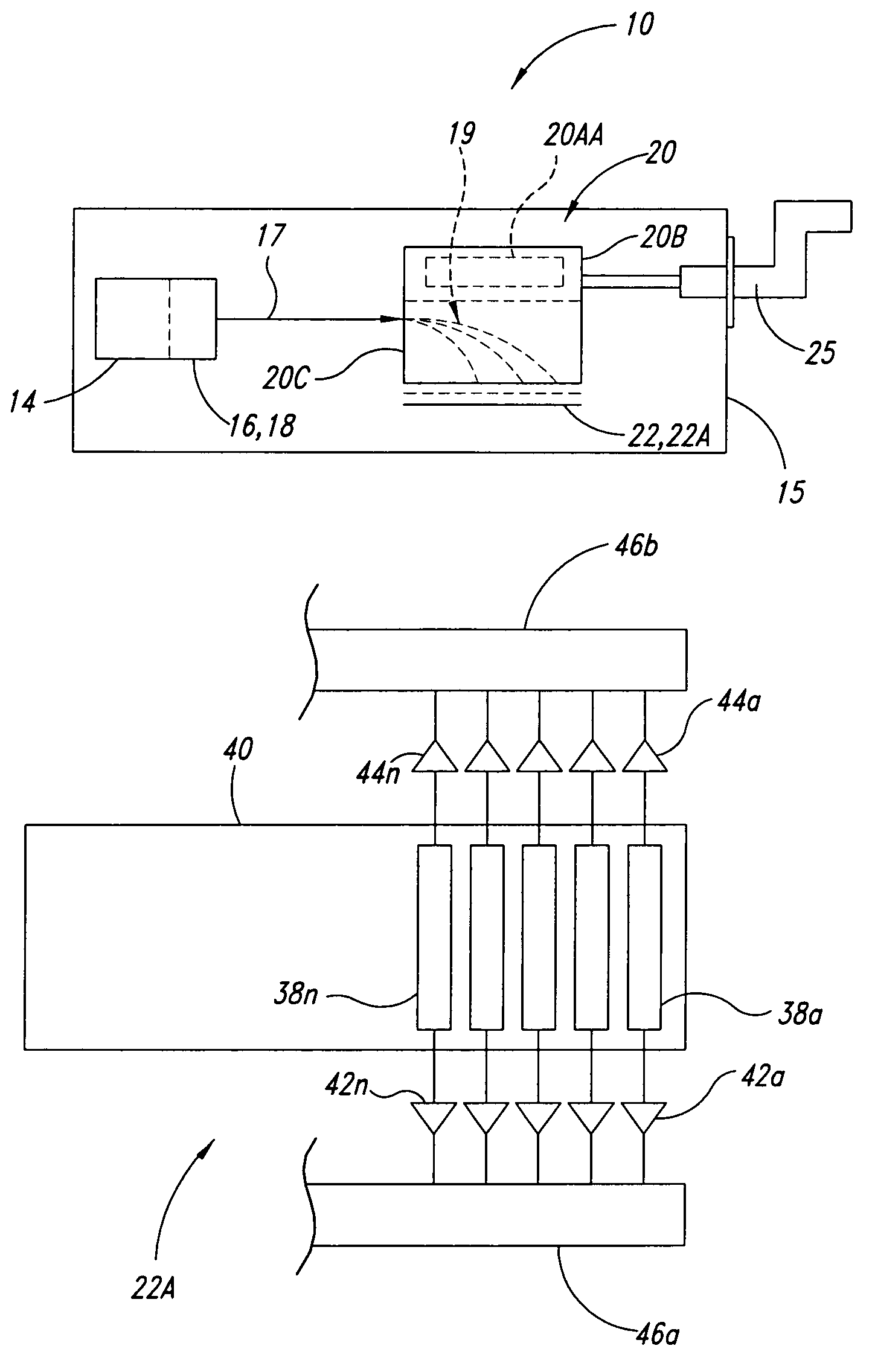
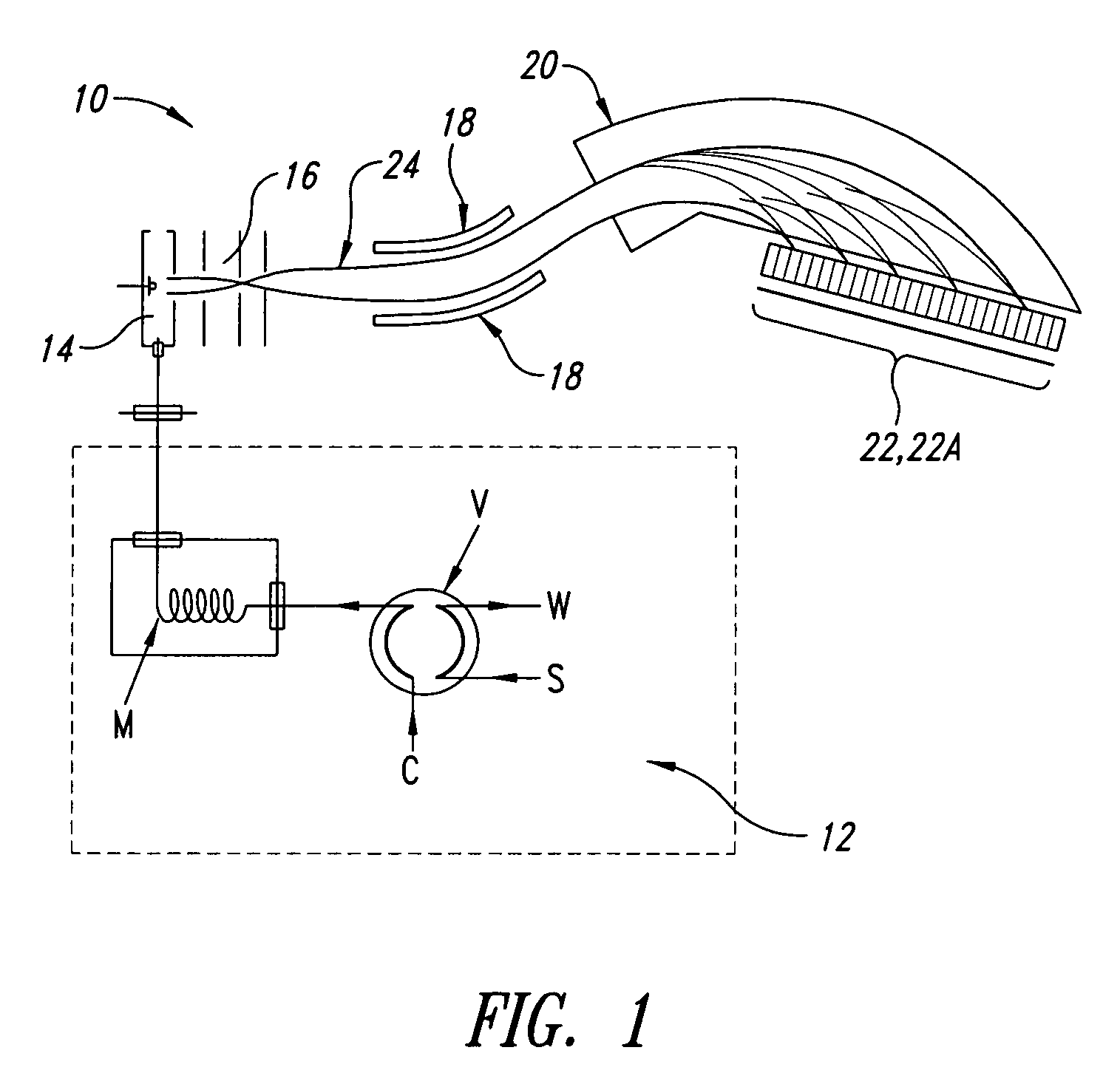
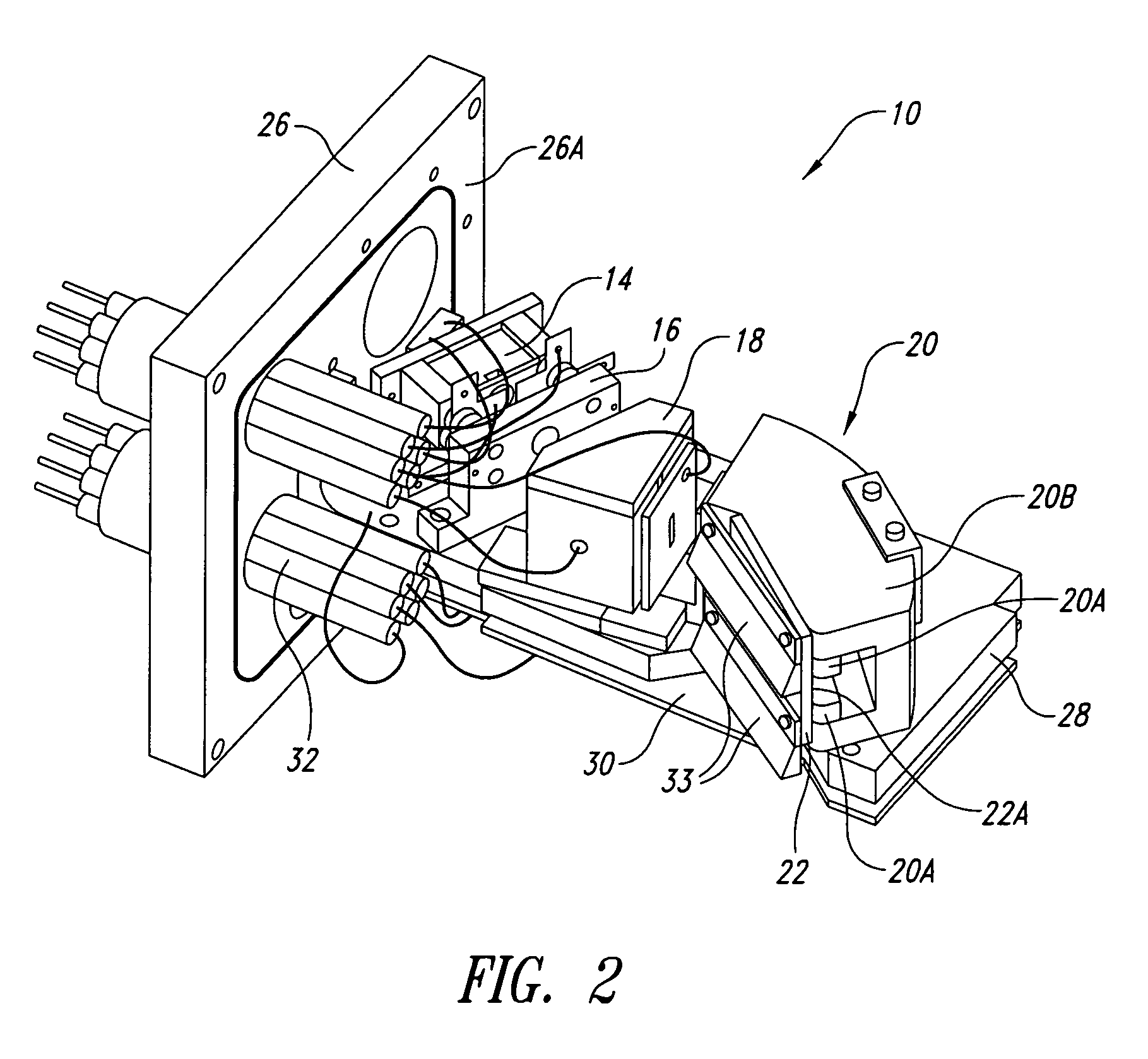
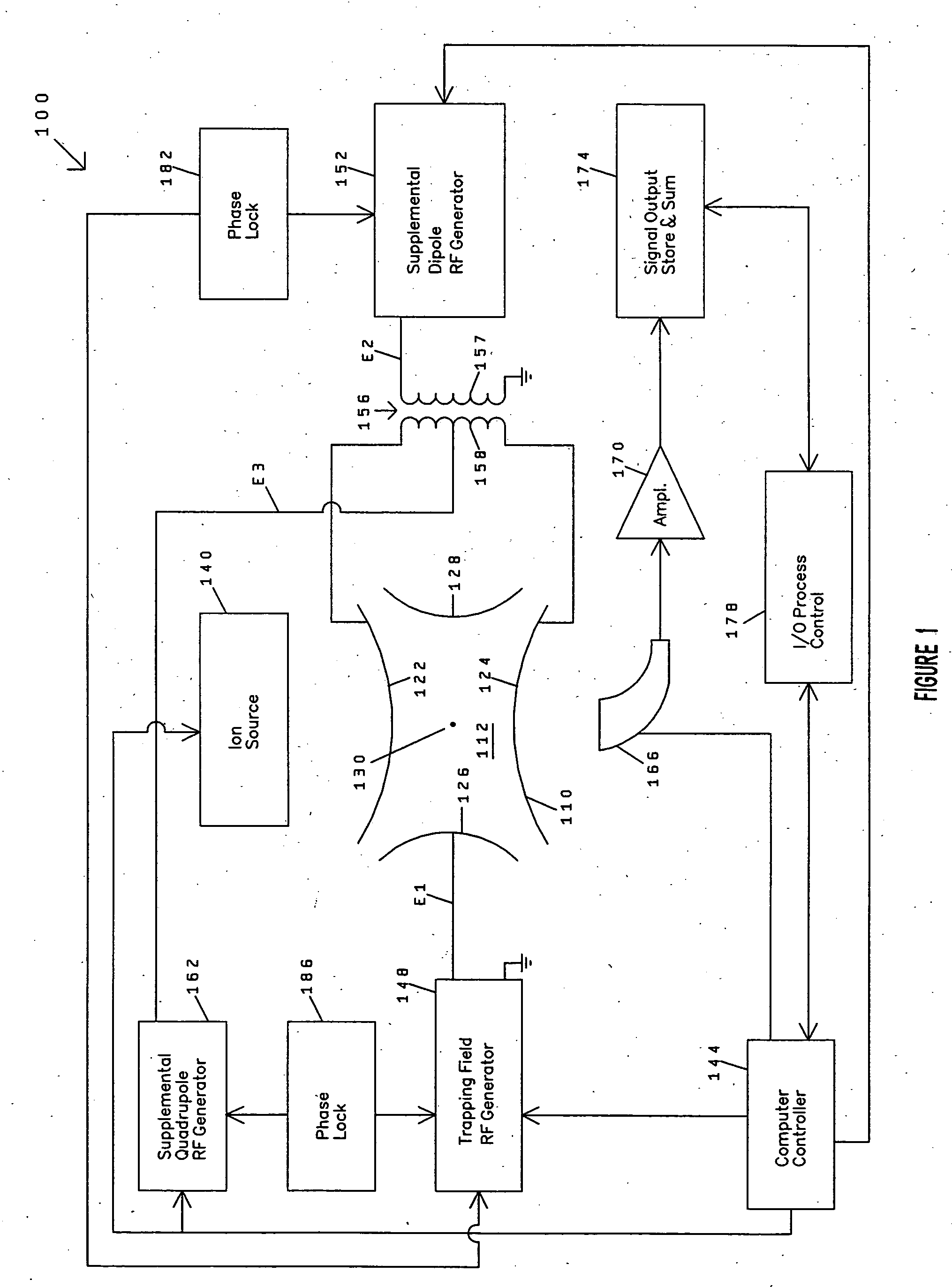
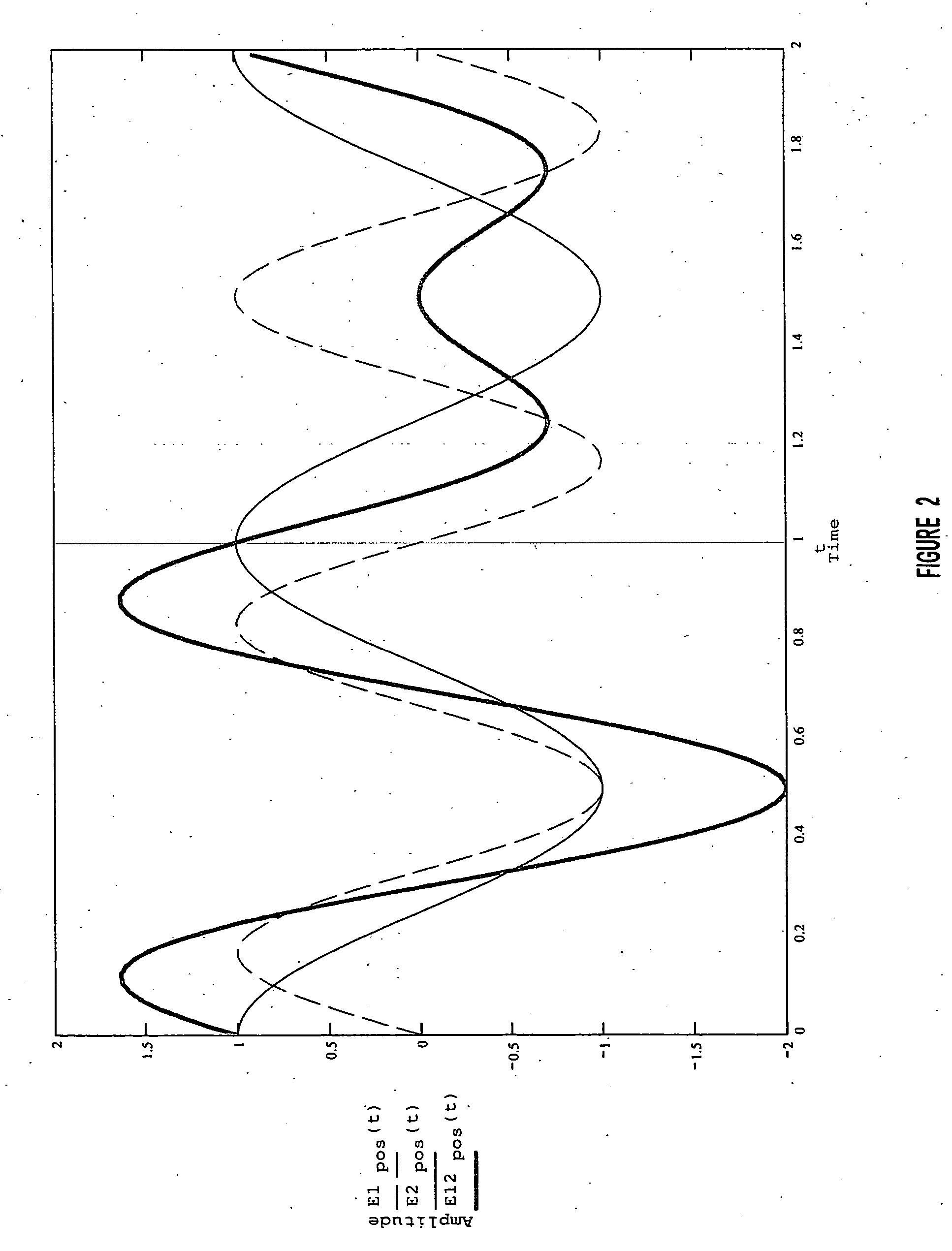
Correcting phases for ion polarity in ion trap mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20060163472A1Increase typePositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryComposite field
In a method and apparatus for adjusting a composite electric field to be applied to an ion trap to accommodate switching the operation of the ion trap between a positive ion mode and a negative ion mode, the composite electric field includes a plurality of component fields including at least one AC trapping field and one or more supplemental AC fields. A phase of one or more of the component fields is adjusted such that a force imparted by the composite field to a negative ion in the ion trap will be substantially the same as the force imparted by the composite field to a positive ion in the ion trap.
Owner:VARIAN INC
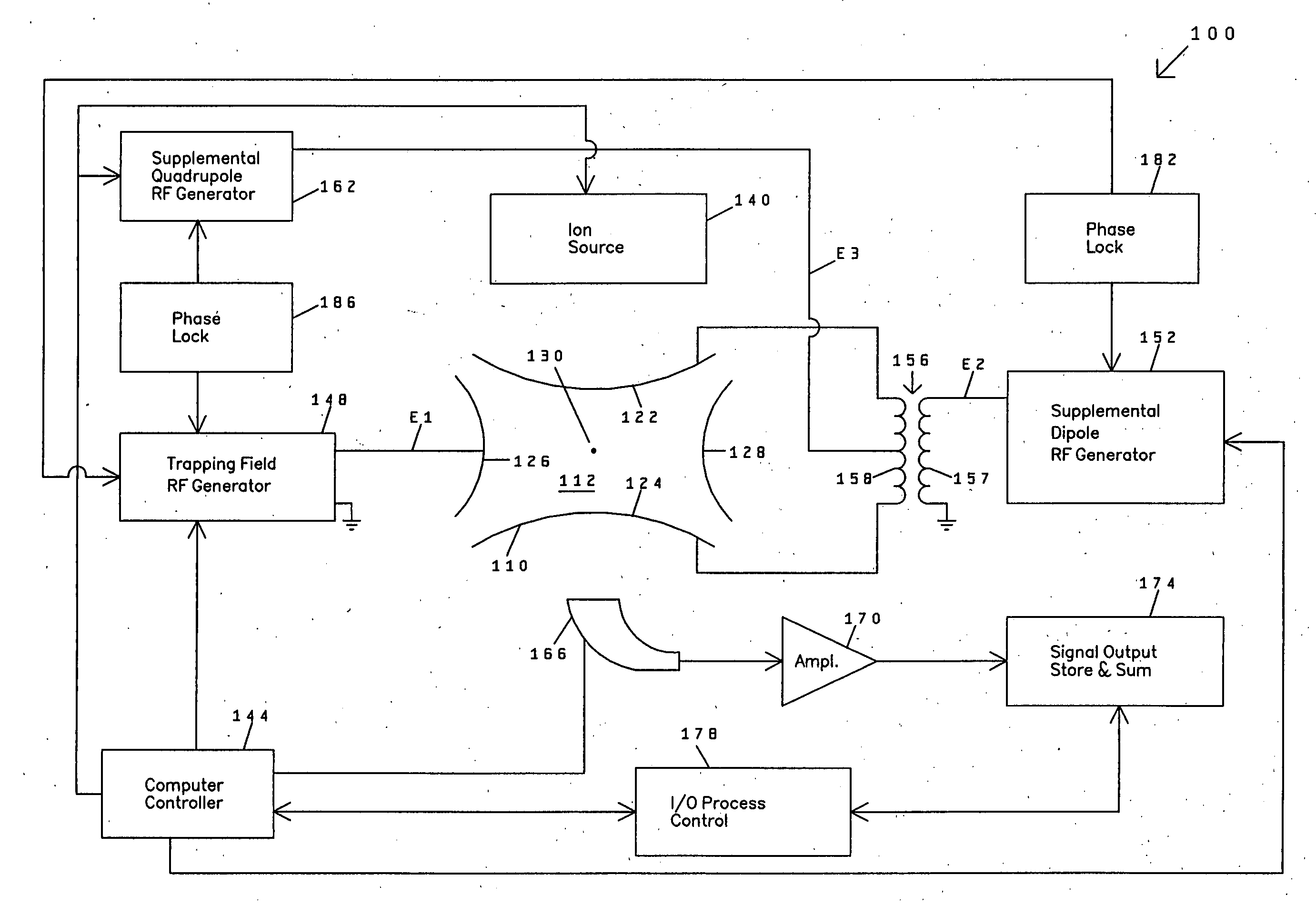
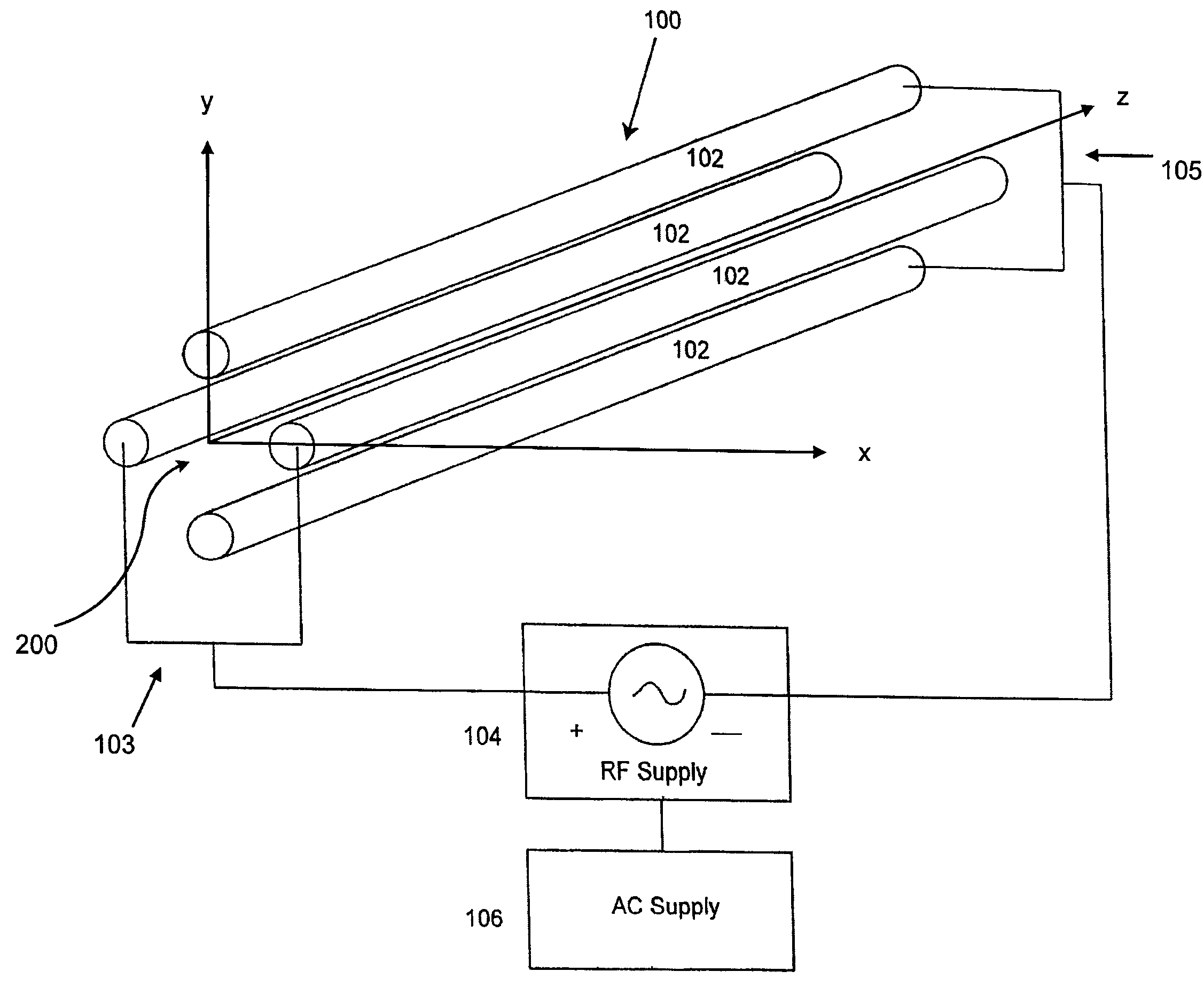
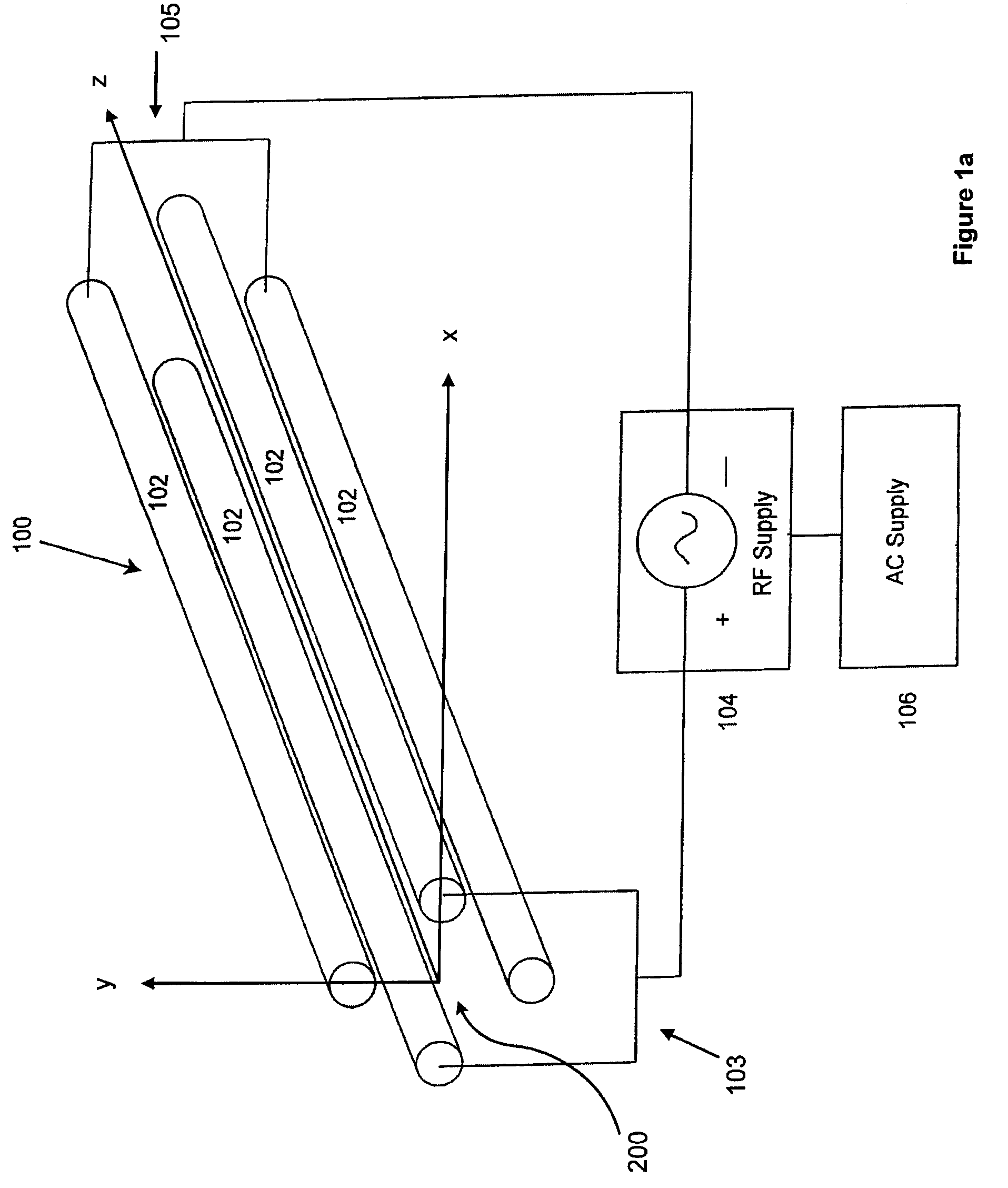
Confining ions with fast-oscillating electric fields
ActiveUS7557344B2Raise the possibilityStability-of-path spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationRadio frequencySpectrometer
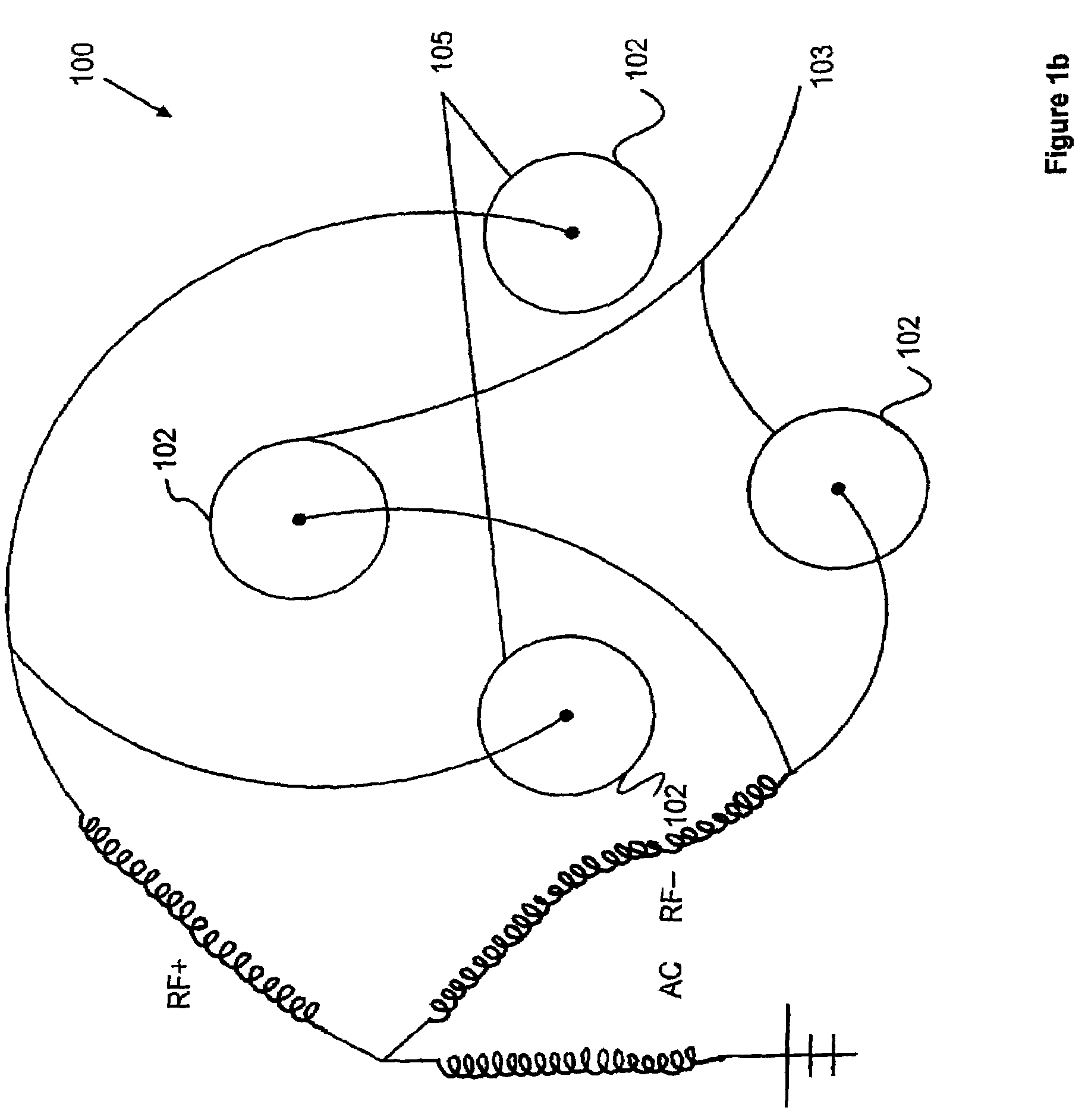
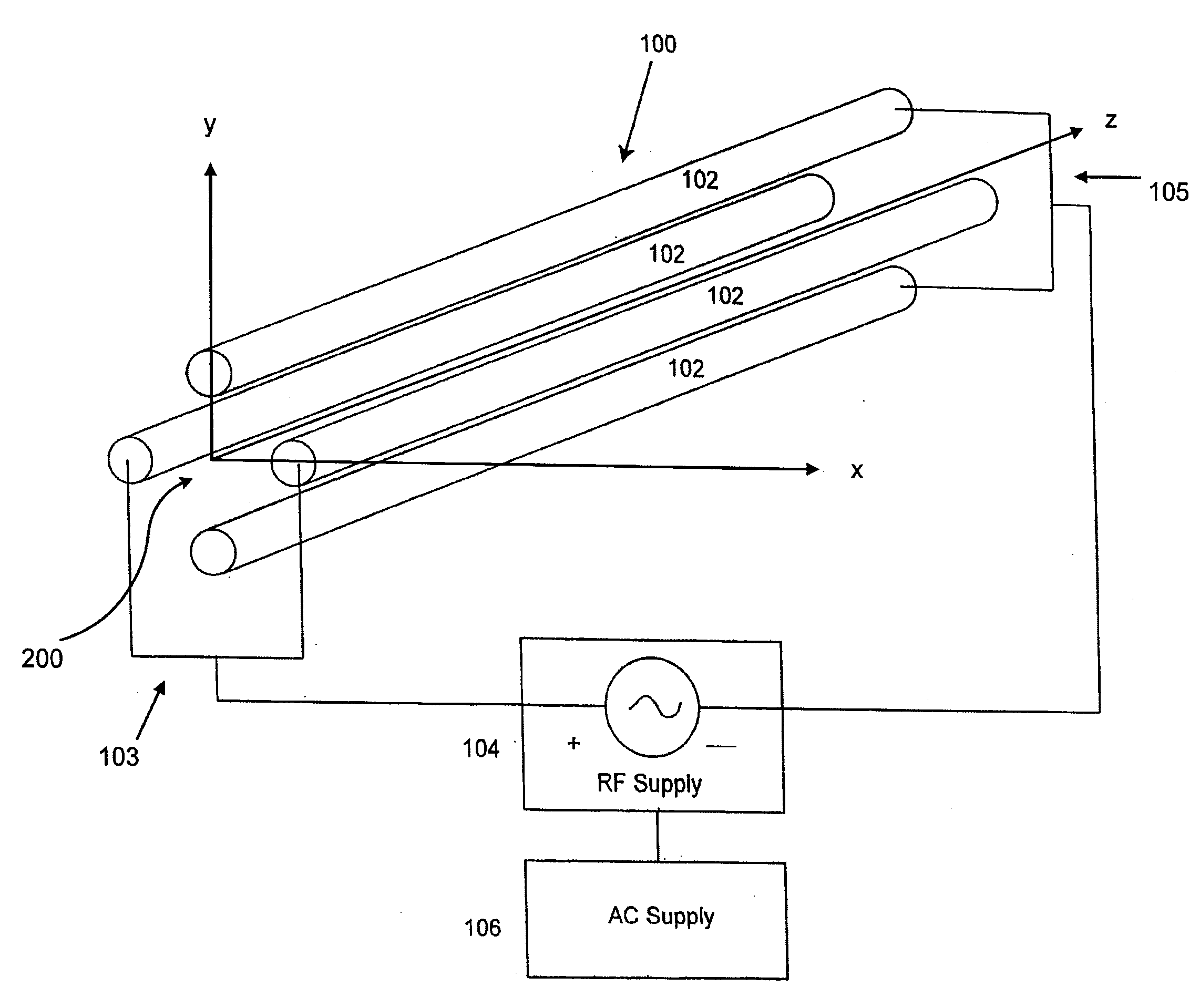
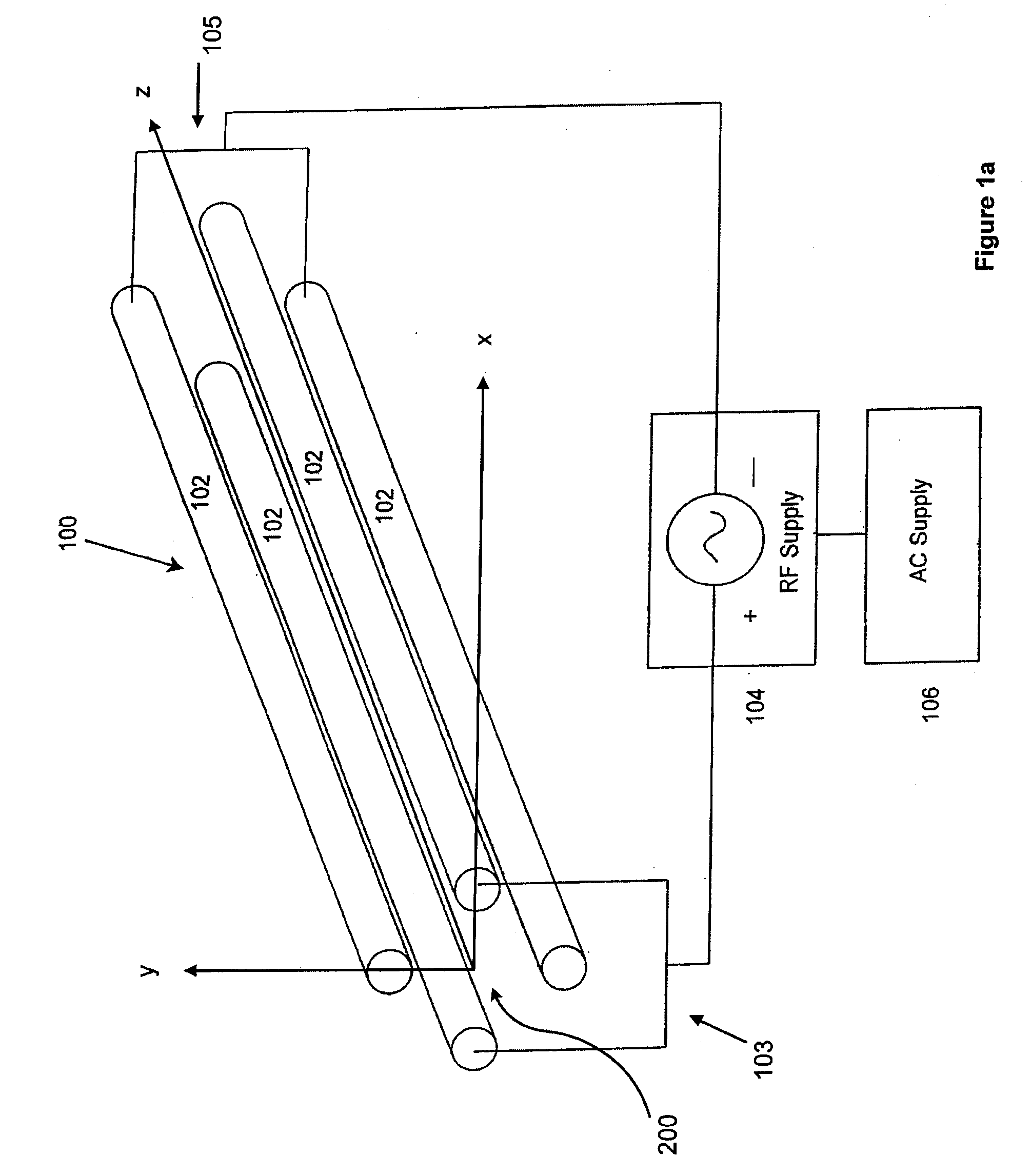
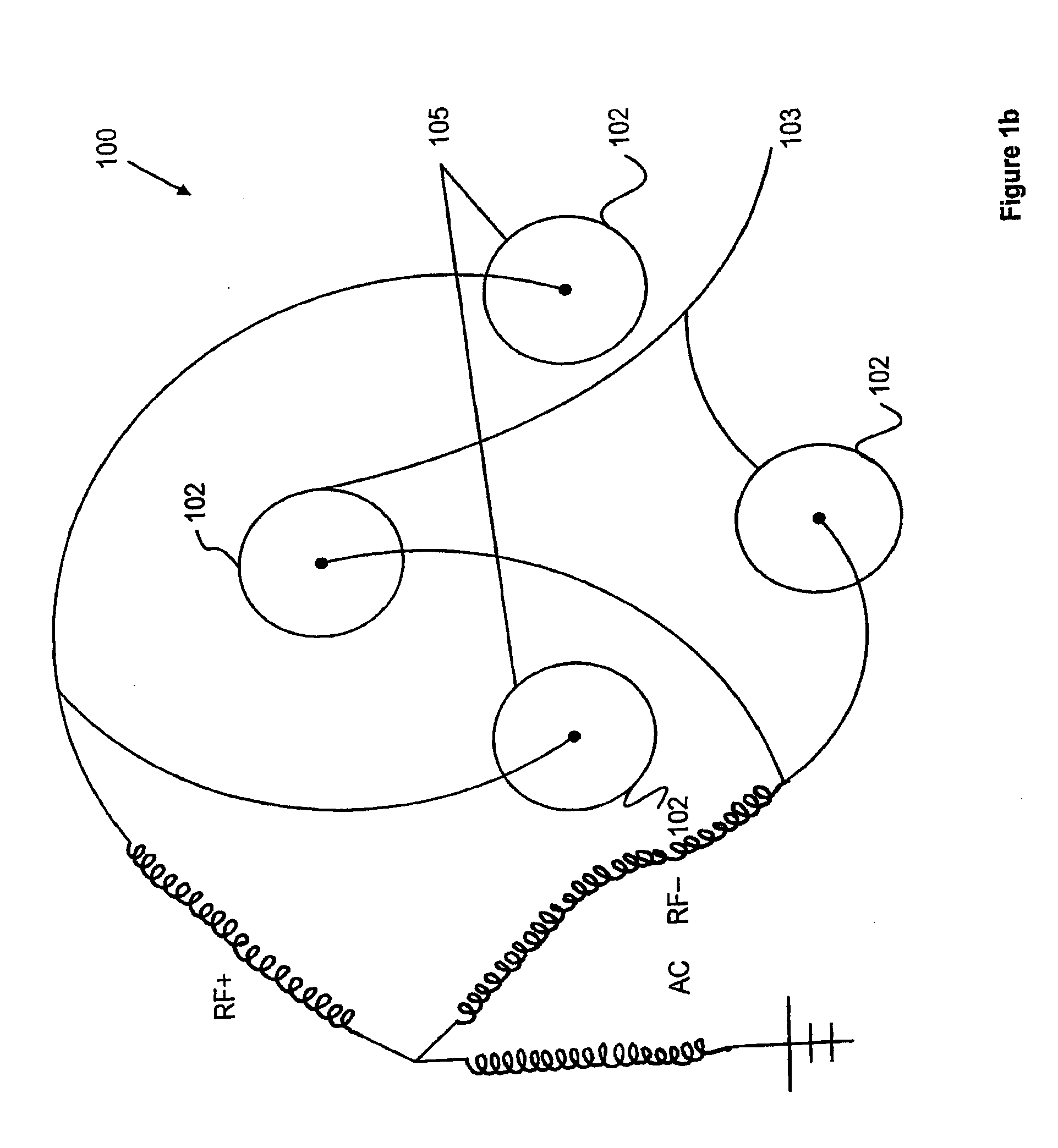
The applicants' teachings provide methods, systems, and apparatus useful in operating mass spectrometers and other devices incorporating multipole rod sets or other multi-electrode devices to simultaneously contain ions of both positive and negative charges through the simultaneous application to the rods or other electrodes of both radio-frequency (RF) and alternating (AC) currents.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
Confining ions with fast-oscillating electric fields
ActiveUS20090014645A1Increase analytic possibilityRaise the possibilityStability-of-path spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationRadio frequencySpectrometer
The applicants' teachings provide methods, systems, and apparatus useful in operating mass spectrometers and other devices incorporating multipole rod sets or other multi-electrode devices to simultaneously contain ions of both positive and negative charges through the simultaneous application to the rods or other electrodes of both radio-frequency (RF) and alternating (AC) currents.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
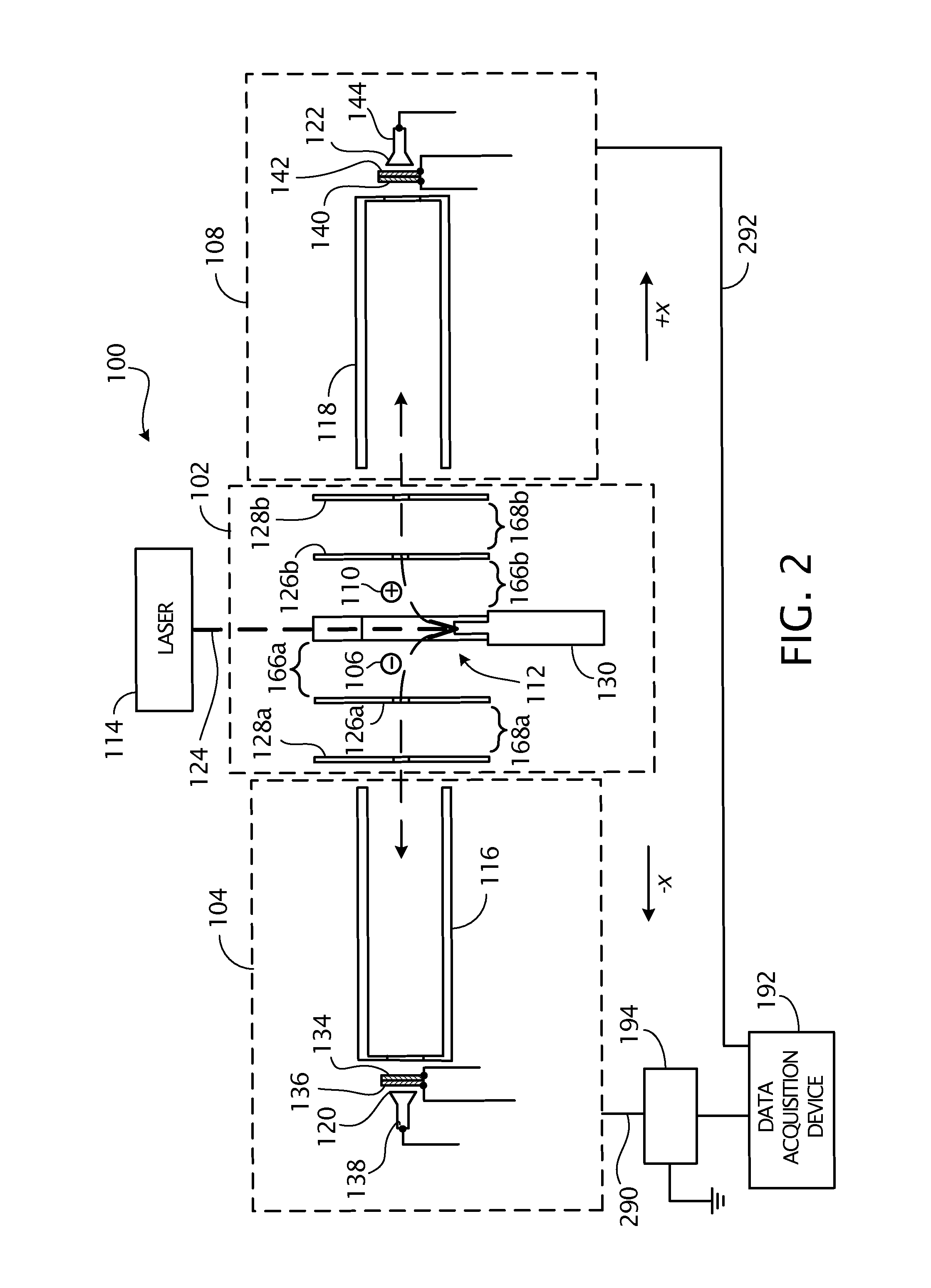
Method and apparatus for providing ion barriers at the entrance and exit ends of a mass spectrometer
InactiveUS7495213B2Time-of-flight spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationIon trap mass spectrometryPhysical chemistry
There is provided a linear ion trap having an ion guide and a method of operating same. The ion guide has a first end and a second end. The method involves a) providing a first group of ions within the ion guide; b) providing a second group of ions within the ion guide, the second group of ions being opposite in polarity to the first group of ions; c) providing an RF drive voltage to the ion guide to radially confine the first group of ions and the second group of ions in the ion guide; d) providing a gas flow of an inert gas in a first axial direction away from the first end of the ion guide and toward a middle of the ion guide to repel both the first group of ions and the second group of ions from the first end of the ion guide; and, e) providing a trapping region barrier for repelling both the first group of ions and the second group of ions away from the second end of the ion guide. The gas flow in the first axial direction and the trapping region barrier together define a main trapping region for trapping both the first group of ions and the second group of ions.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
Mass spectrometer
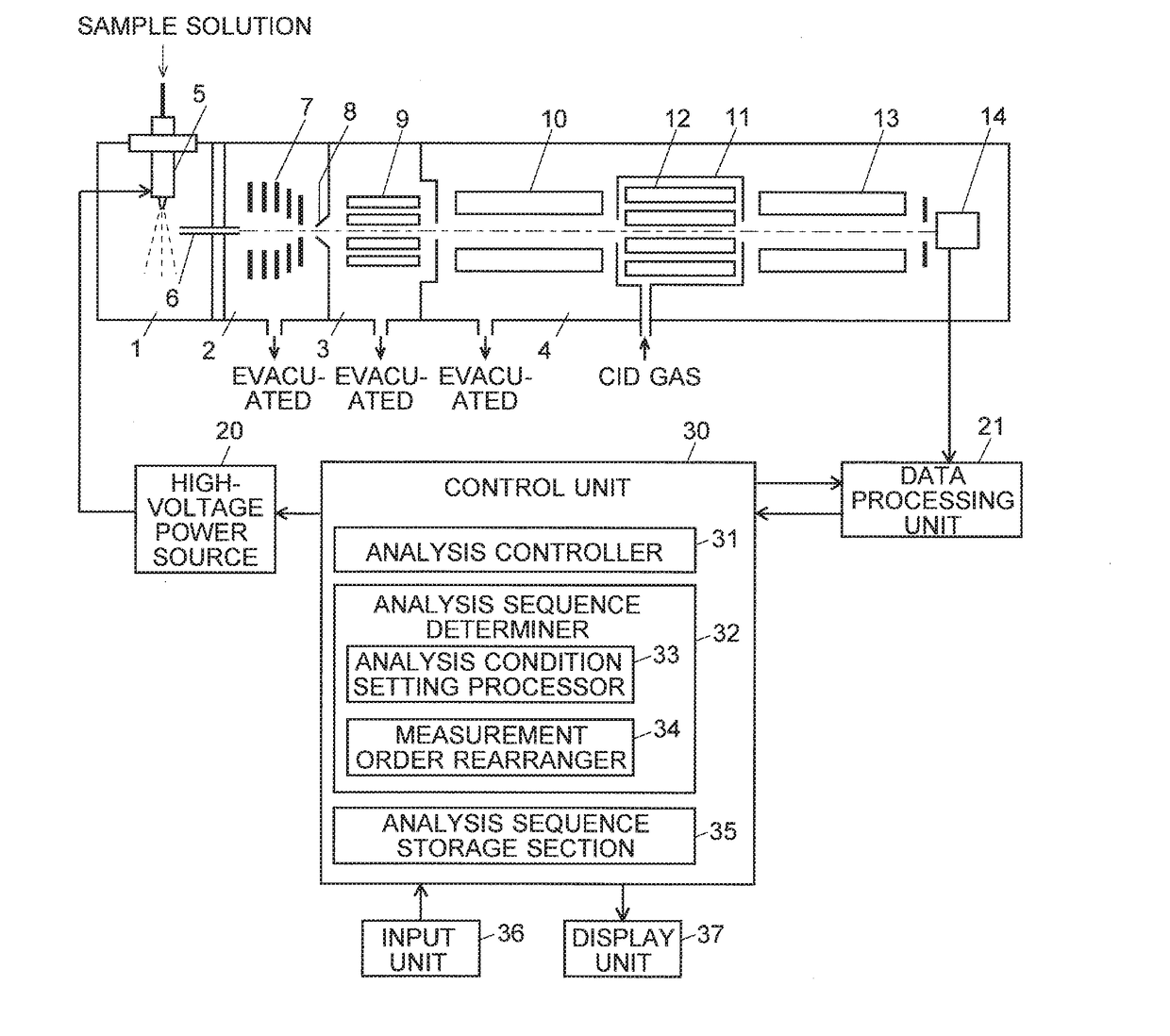
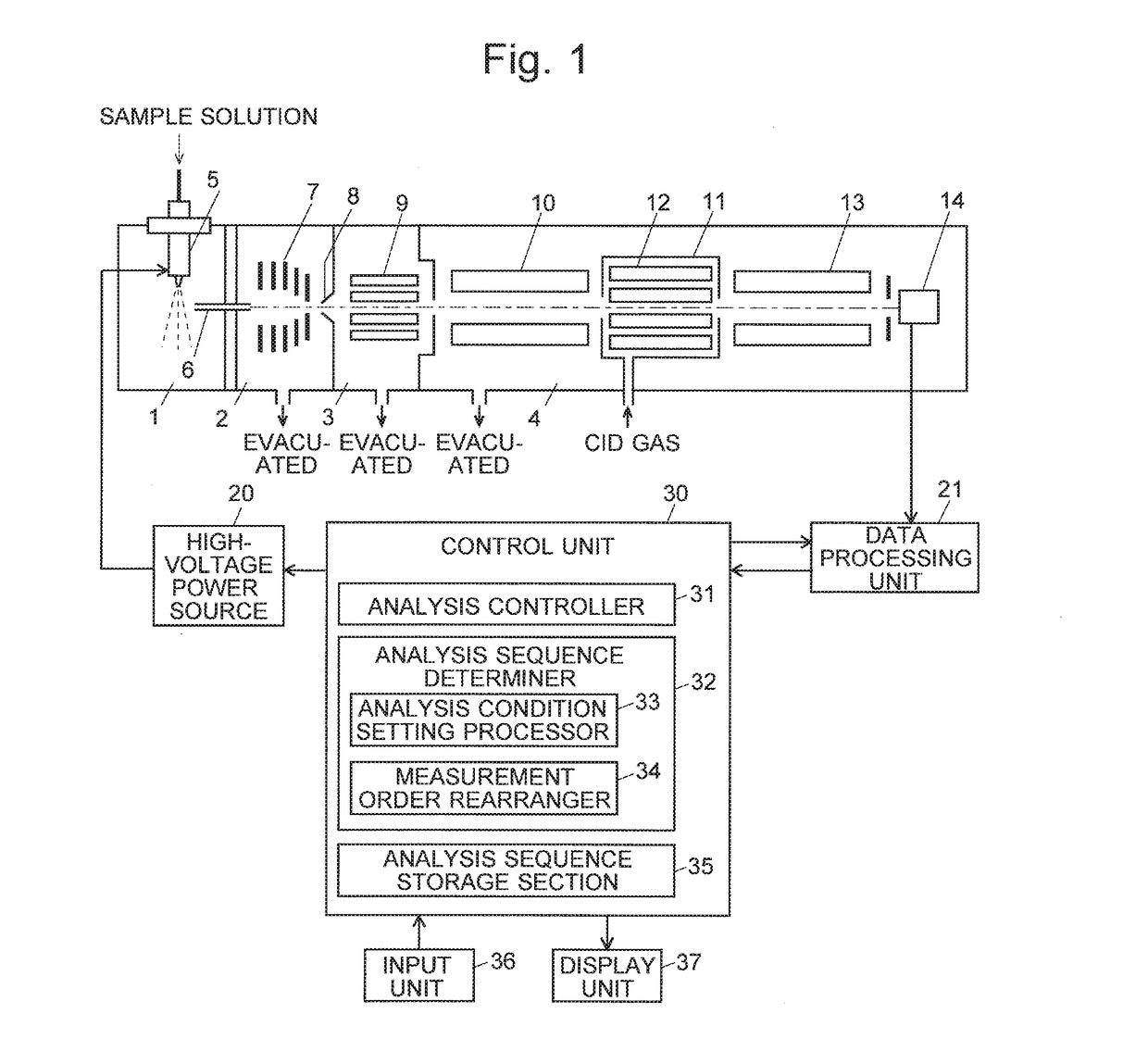
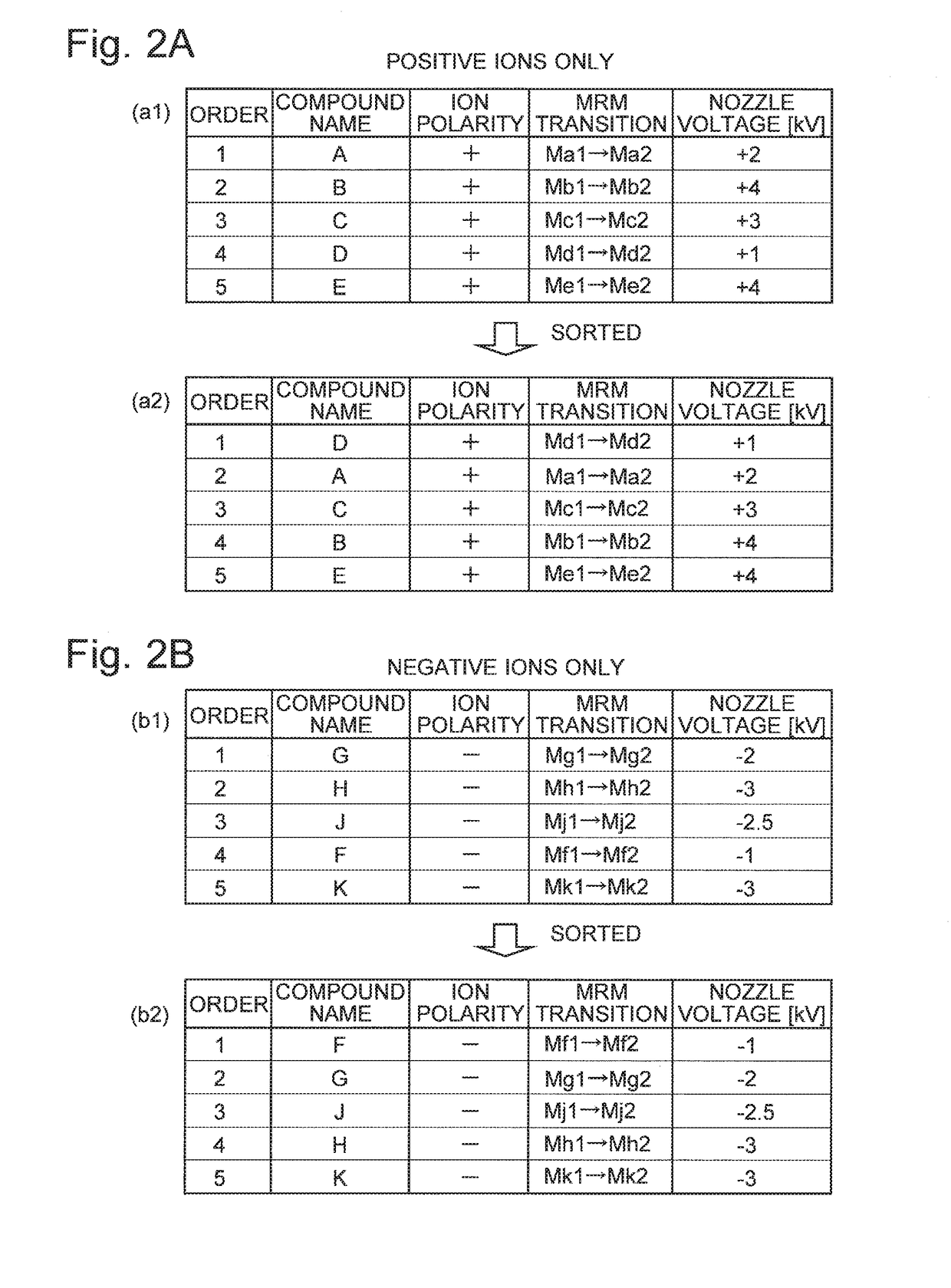
ActiveUS20170287691A1High detection sensitivityHigh quantitative accuracyStability-of-path spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationIonizationAnalytical control
In a mass spectrometer according to the present invention, when MRM measurements for a plurality of MRM transitions need to be performed within one cycle, a measurement order rearranger determines an analysis sequence by sorting the measurement in ascending order of the absolute value of an optimum application voltage (an application voltage which gives the highest ionization efficiency) to the nozzle of the ESI probe. An analysis controller performs the analysis by controlling the high-voltage power source and other relevant units according to the determined analysis sequence. Since the voltage applied to the nozzle within one cycle has no period in which the voltage is changed in the decreasing direction with the same polarity, the cycle time becomes shorter than in a conventional device.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Method for introducing ions into an ion trap and an ion storage apparatus
InactiveCN101238544AStability-of-path spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationIon trap mass spectrometryPhysical chemistry
The present invention describes a method of introducing ions into an ion trap and an ion storage device. The first ions are introduced into the ion trap through an entrance aperture to the ion trap by means of introducing means. Operating conditions of said introduction means are adjusted to introduce a second ion having a different polarity than the first ion into the ion trap through said same entrance aperture.
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB EURO
Efficient detection for ion traps
InactiveUS7456398B2Efficient detectionLow costSpectrometer detectorsPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationIon trap mass spectrometryDynode
An apparatus and method are disclosed for efficient detection of ions ejected from a quadrupolar ion trap, in which the ions are ejected as first and second groups of ions having different directions. The first and second groups of ions are received by a conversion dynode structure, which responsively emits secondary particles that are directed to a shared detector, such as an electron multiplier. The conversion dynode structure may be implemented as a common dynode or as two dynodes (or sets of dynodes), with each dynode positioned to receive one of the groups of ions.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Mass spectrometer and mass spectrometry method
InactiveUS20120112059A1High duty cyclePositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
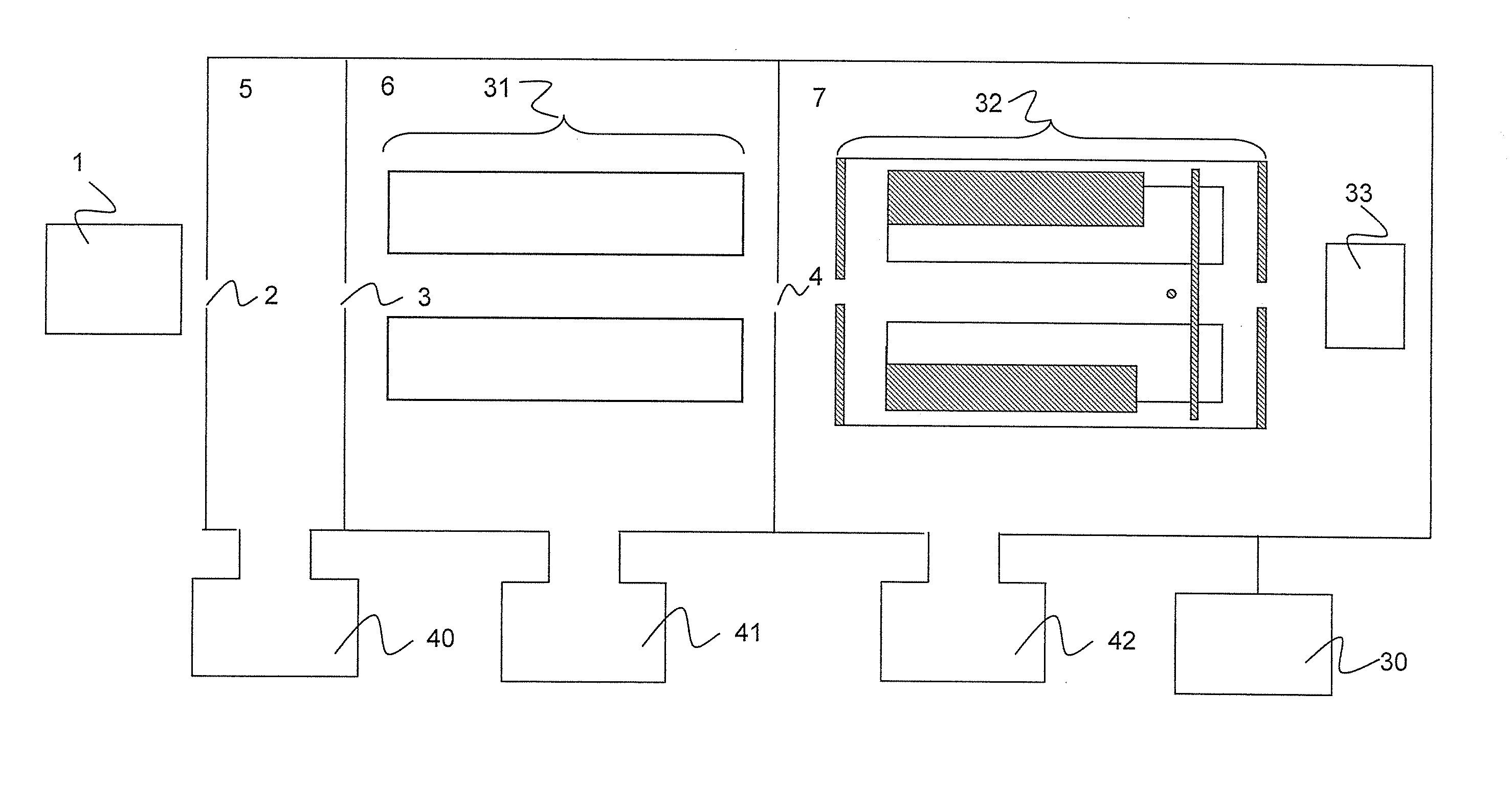
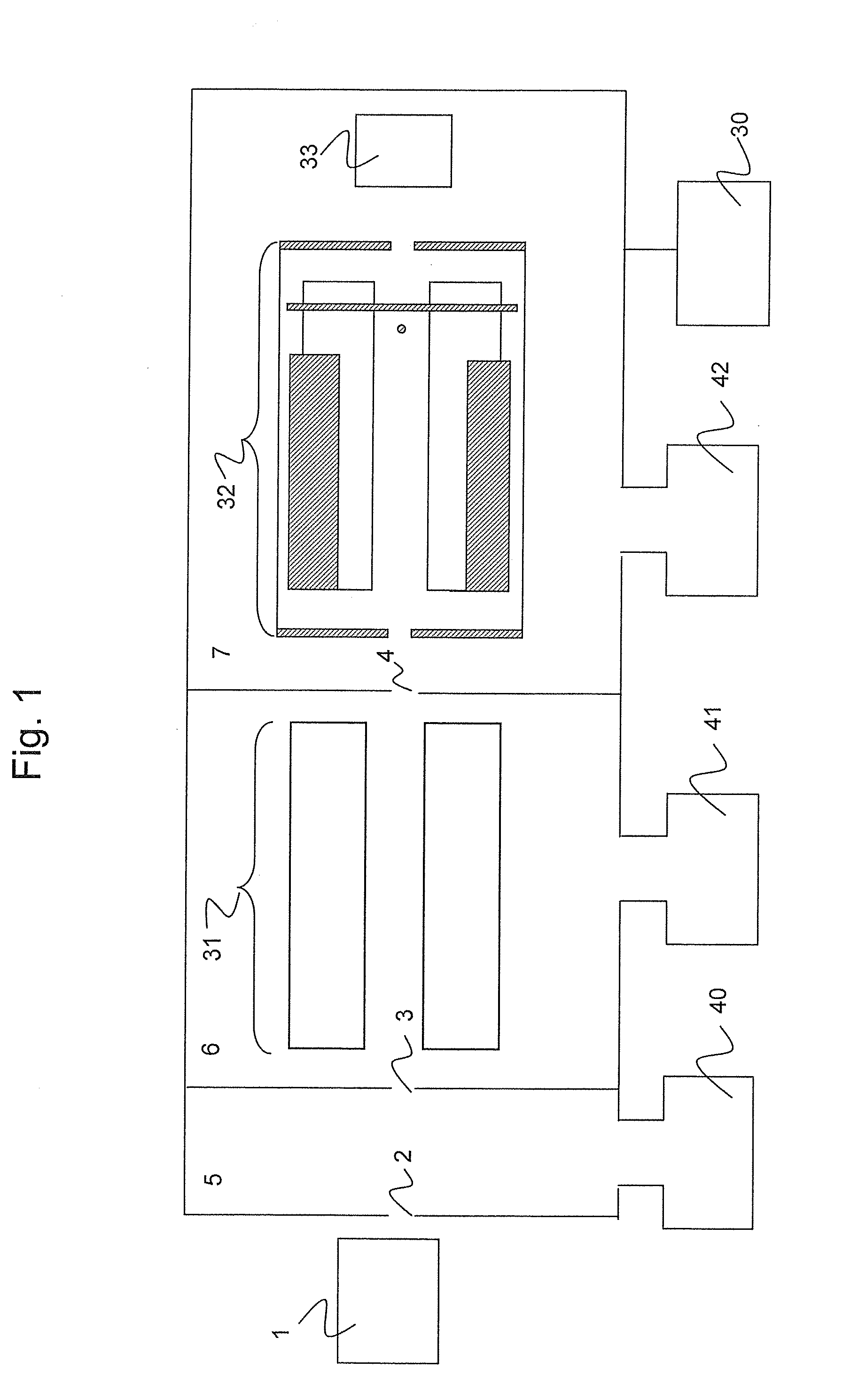
An object is to measure both cations and anions with high duty cycle. In a mass spectrometer comprising an ion source (1), an ion guide part (31), and an ion trap (32), while ions are being mass-selectively ejected from the ion trap, ions having a polarity reverse to that of the ions trapped in the ion trap are introduced into the ion guide part.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Efficient detection for ion traps
InactiveUS20080067361A1Efficient detectionLow costStability-of-path spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsIon trap mass spectrometryElectron multiplier
An apparatus and method are disclosed for efficient detection of ions ejected from a quadrupolar ion trap, in which the ions are ejected as first and second groups of ions having different directions. The first and second groups of ions are received by a conversion dynode structure, which responsively emits secondary particles that are directed to a shared detector, such as an electron multiplier. The conversion dynode structure may be implemented as a common dynode or as two dynodes (or sets of dynodes), with each dynode positioned to receive one of the groups of ions.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Mass spectrometric apparatus and ion source
InactiveUS7164124B2Easier/reduced maintenanceGenerate positive ions and negative ions substantially simultaneously and stablyPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass analyzerSpectrometer
A mass spectrometric apparatus capable of generating and detecting positive and negative ions stably at the same time. The apparatus preferably comprises: an opening through which a sample gas is introduced; an ion source to generate ions of the sample gas; and a mass spectrometer to analyze the mass of the generated ions. The ion source utilized with the mass spectrometric device comprises: a first needle electrode on which a voltage is applied in order to generate positive ions of the sample gas introduced through the opening; a first counter electrode having a first opening through which the sample gas and the positive ions pass; a second counter electrode disposed opposite the first counter electrode having a second opening through which the sample gas and the positive ions pass; a second needle electrode on which voltage is applied in order to generate negative ions of the sample gas; and a vent through which the sample gas is ejected. Generated ions are then introduced into a vacuum region via an aperture and subjected to mass analysis.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Angled dual-polarity mass spectrometer
ActiveUS8309913B2Accurate measurementTime-of-flight spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationMass analyzerSpectrometer
An angled dual-polarity mass spectrometer includes a dual-polarity ion generator, a first mass analyzer, and a second mass analyzer. The dual-polarity ion generator includes an ion source to generate positive ions and negative ions from a sample, and electrodes to generate electric fields for guiding the negative ions into a beam of negative ions and guiding the positive ions into a beam of positive ions. The first mass analyzer can analyze the negative ions, and the second mass analyzer can analyze the positive ions. The central axes of the first and the second mass analyzers are at an angle between 0 to 179 degrees.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com