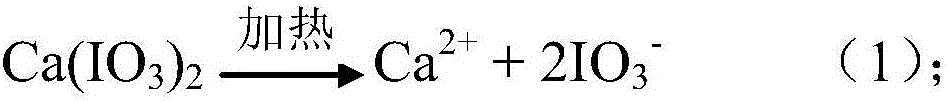Patents
Literature
93 results about "Negatively charged particle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A negatively charged particle within an atom is called an electron. Electrons were discovered in 1897 by a British scientist named J.J. Thomson. All of the electrons found in an atom balance out the protons of the atom.
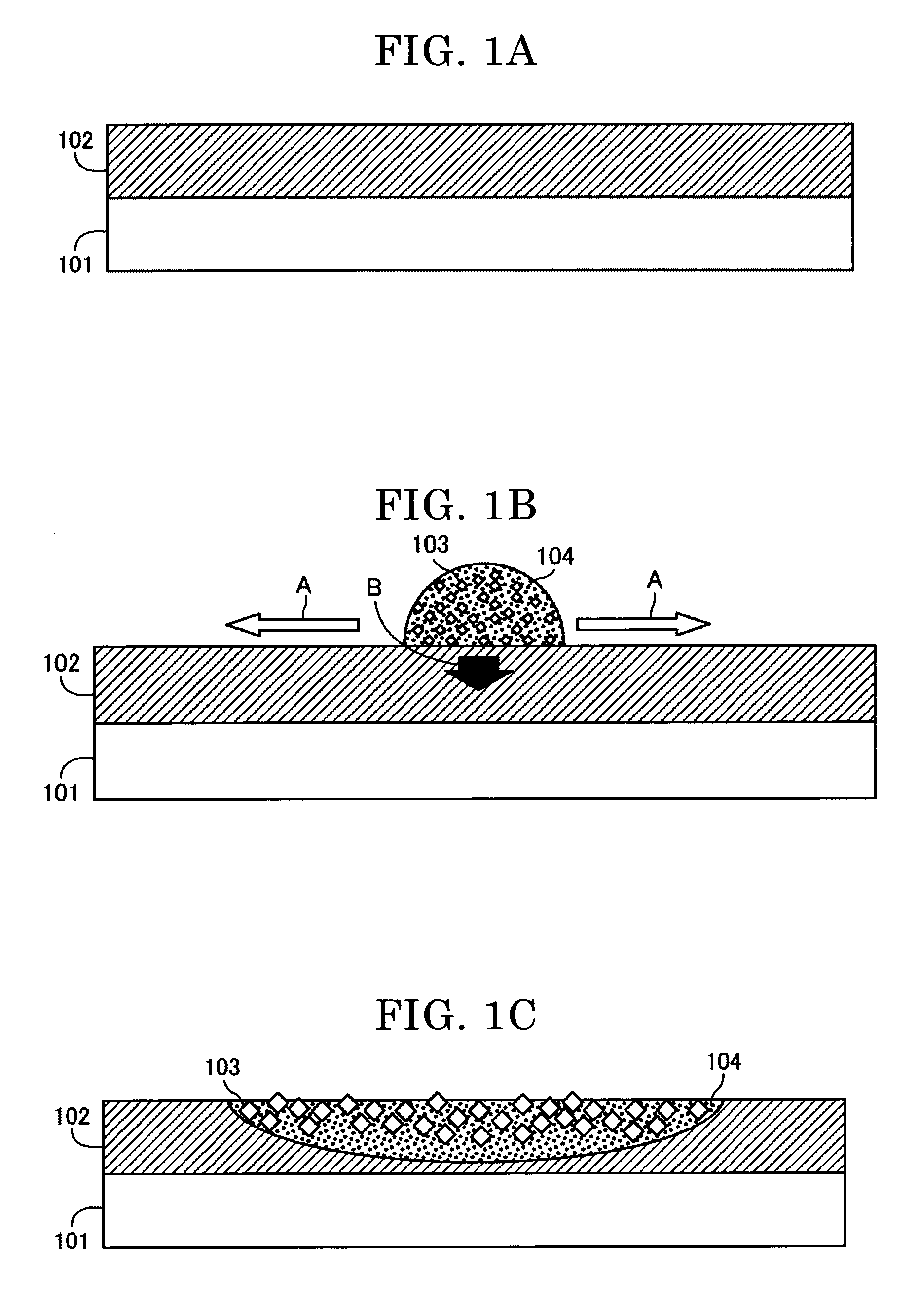
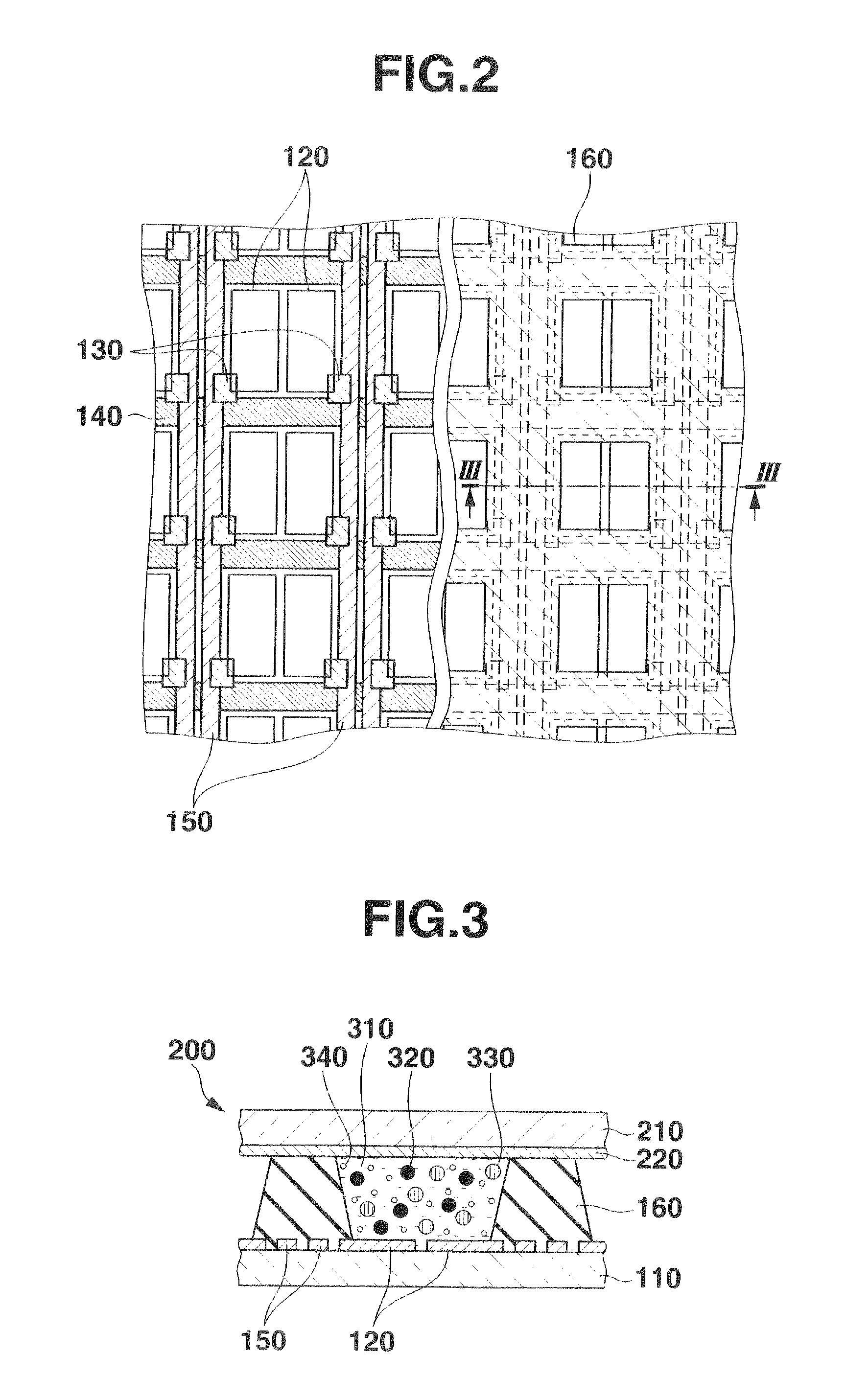
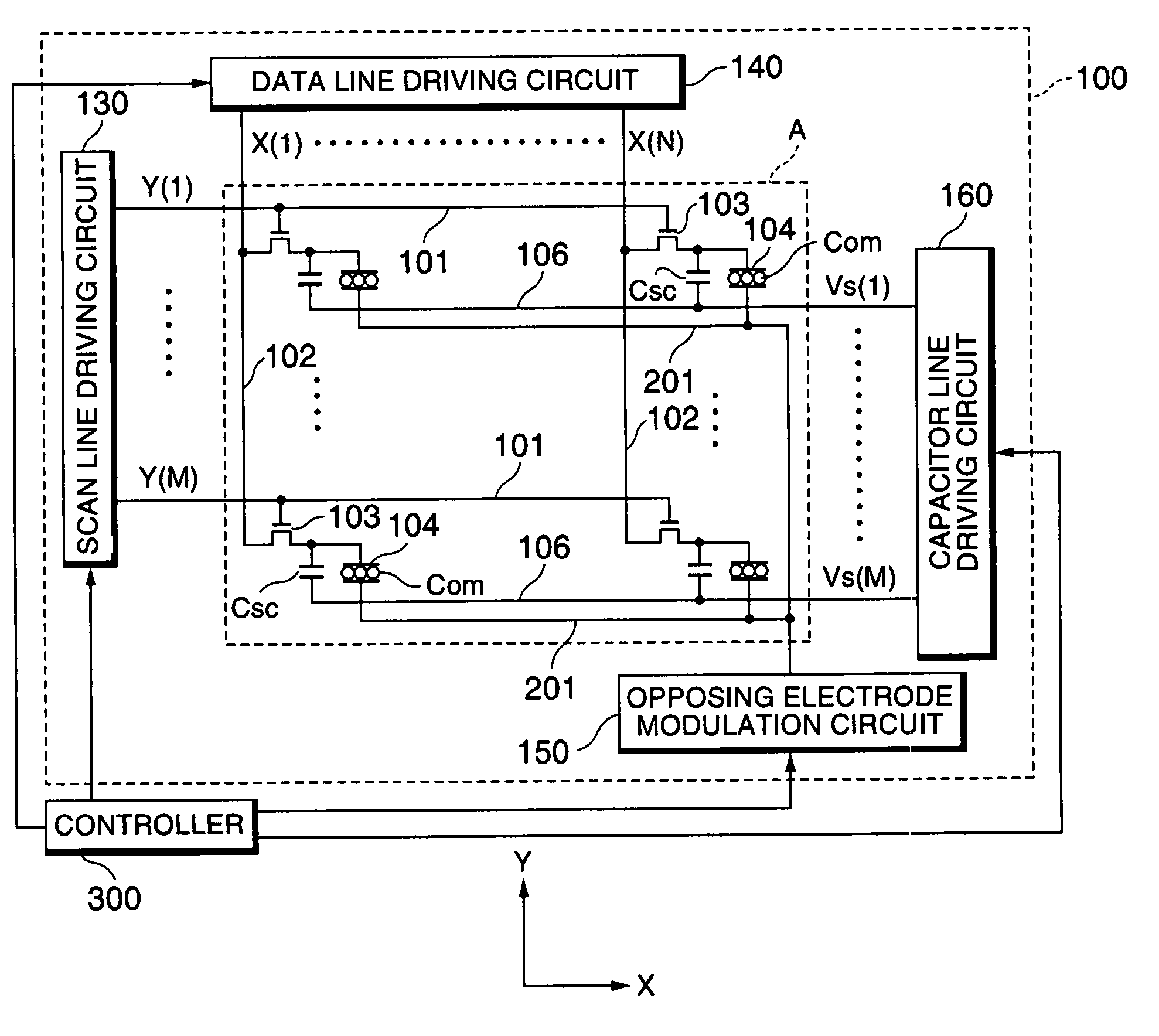
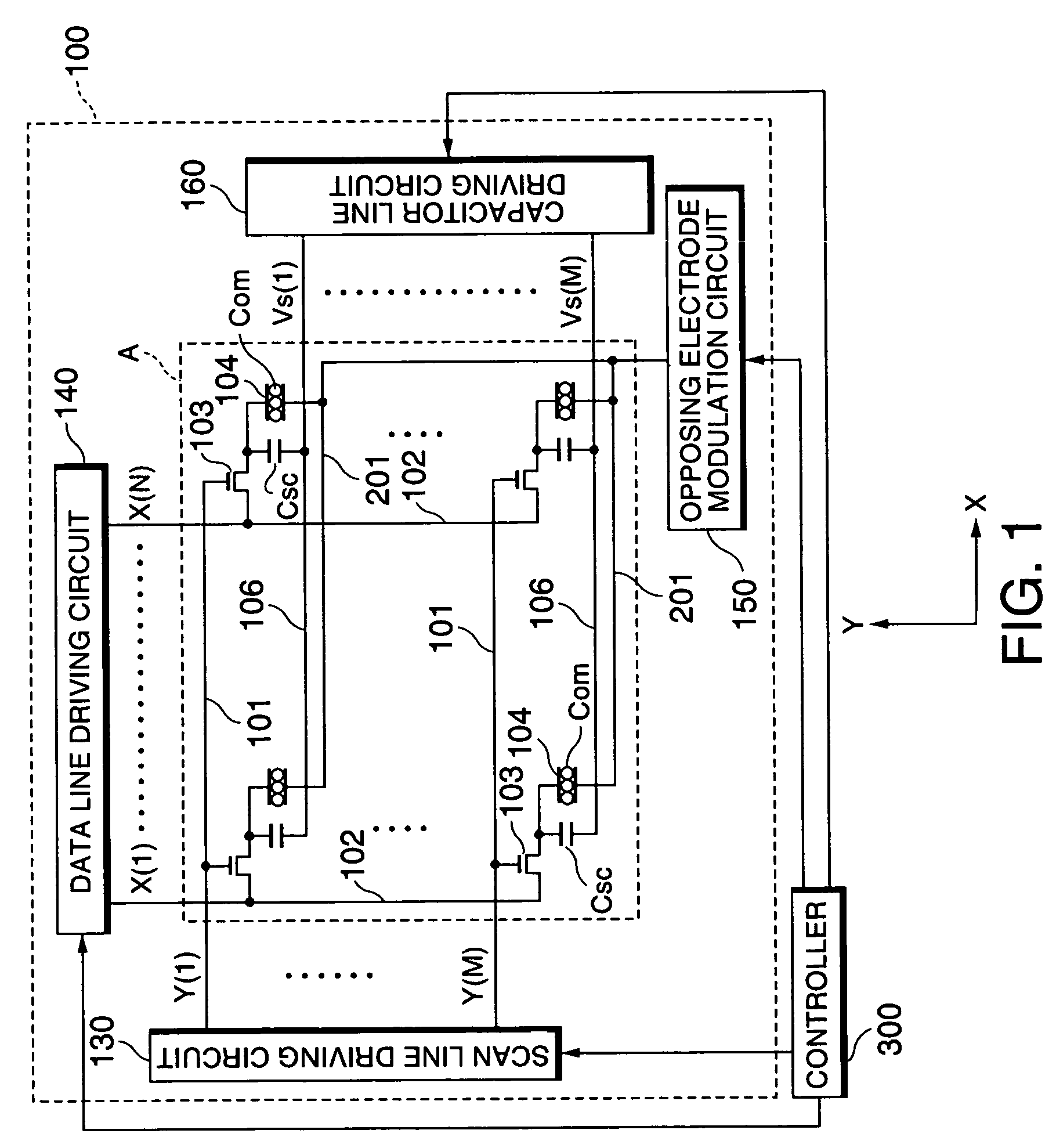
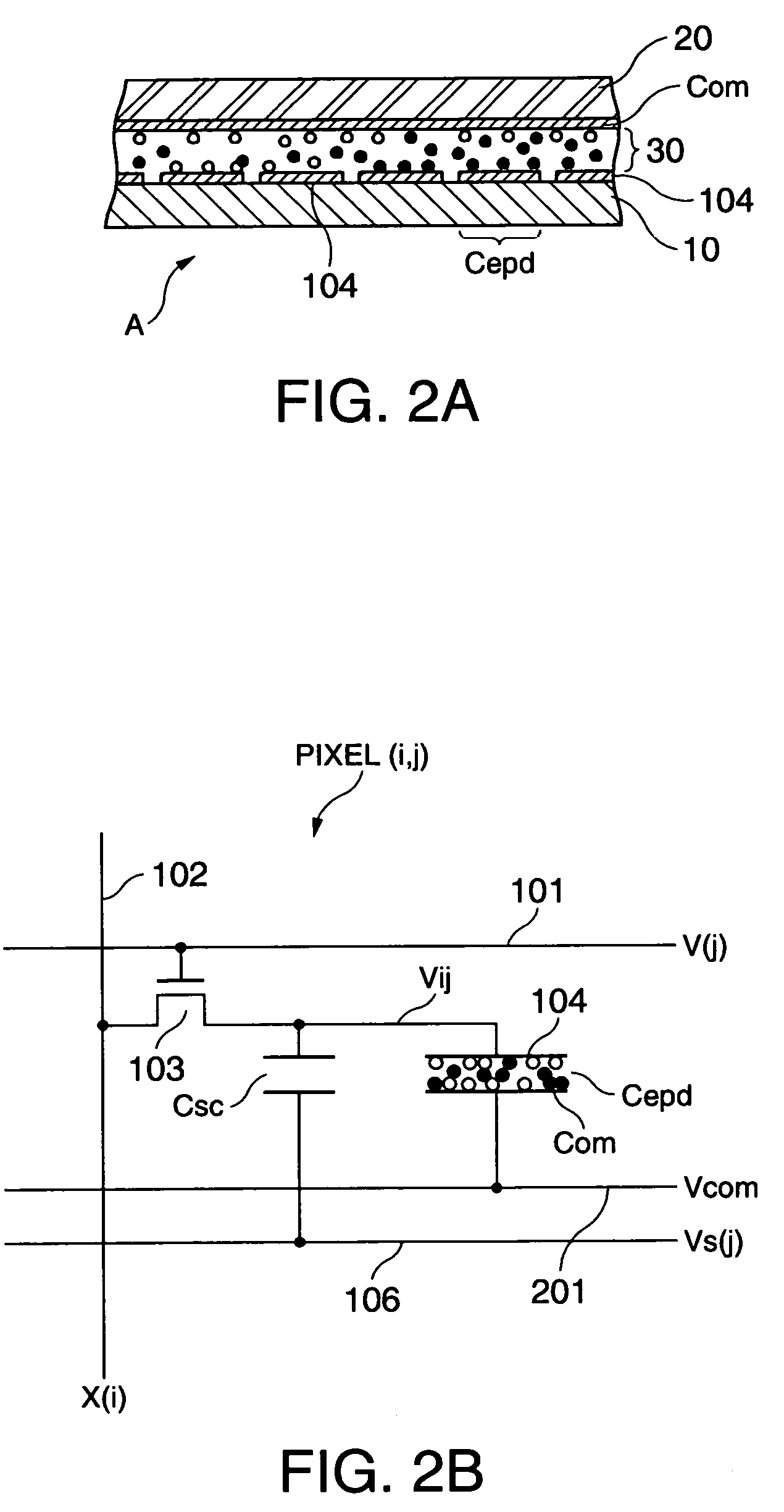
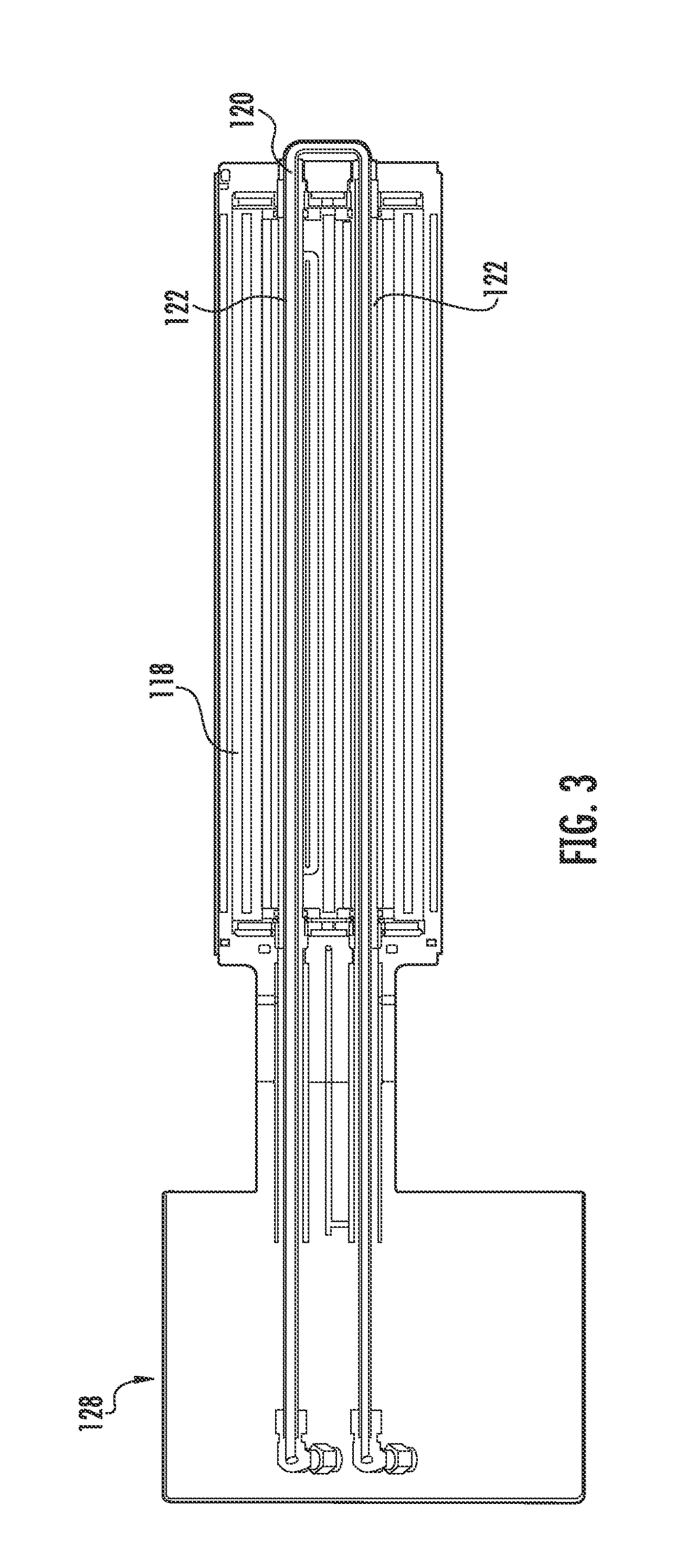
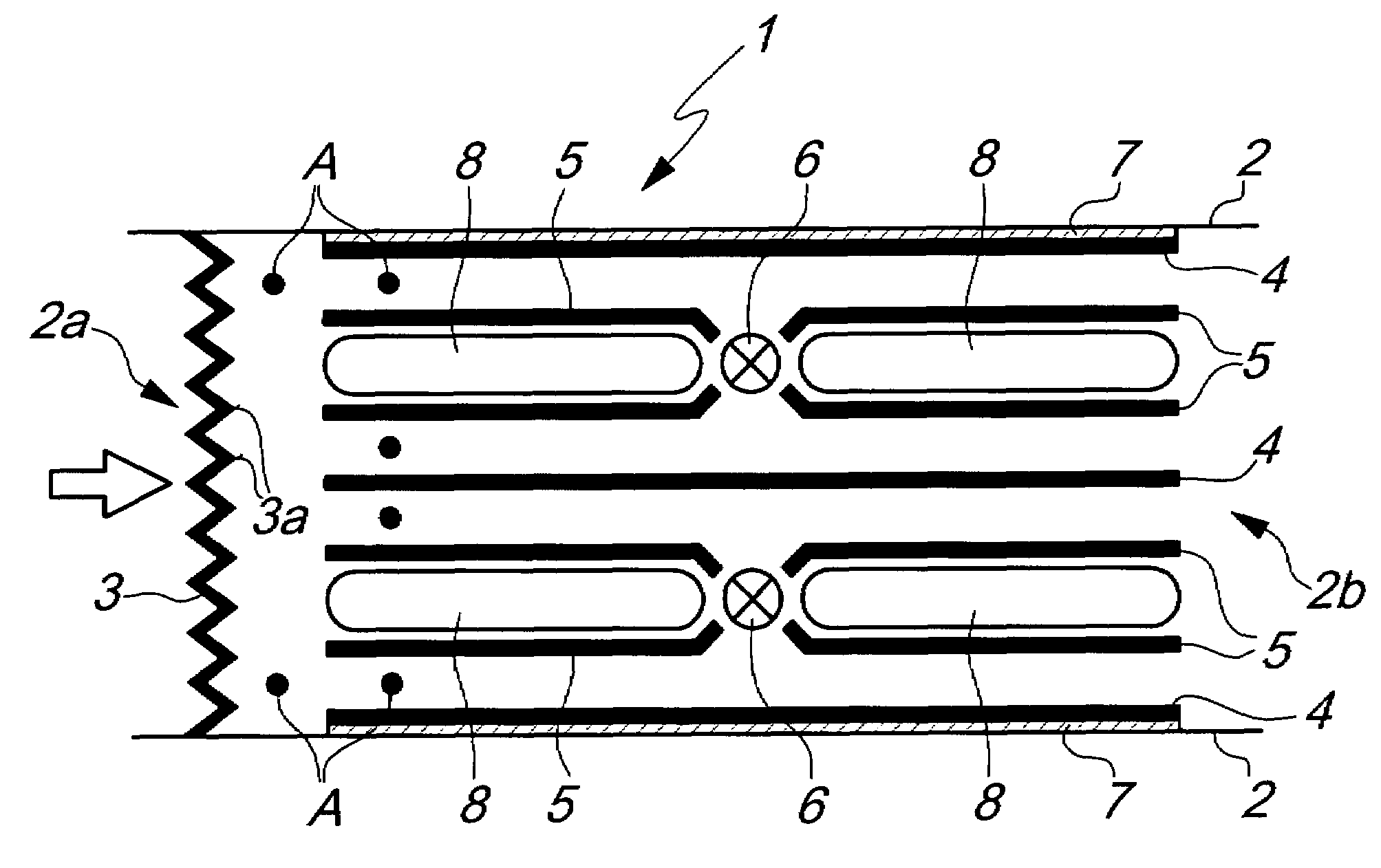
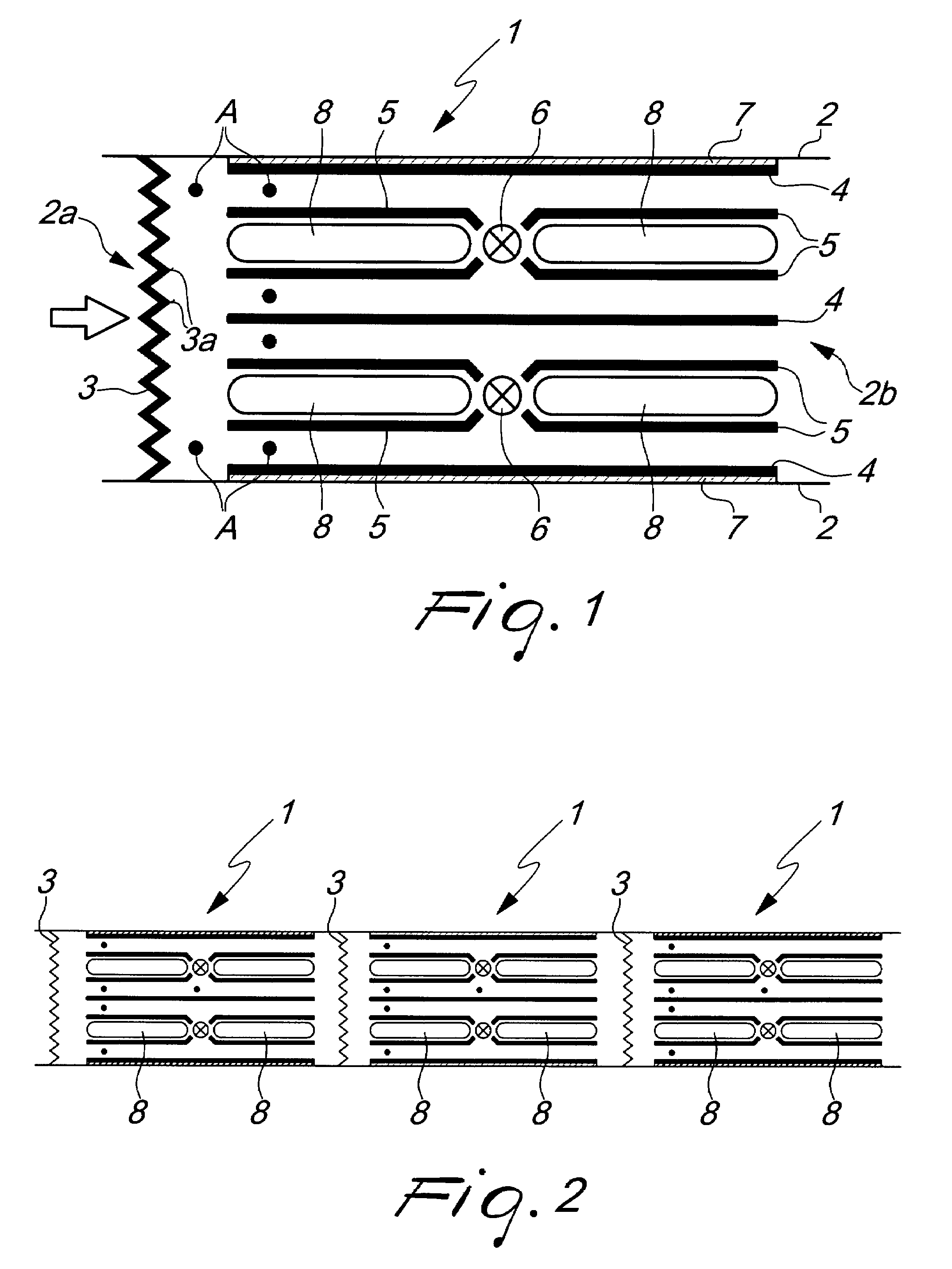
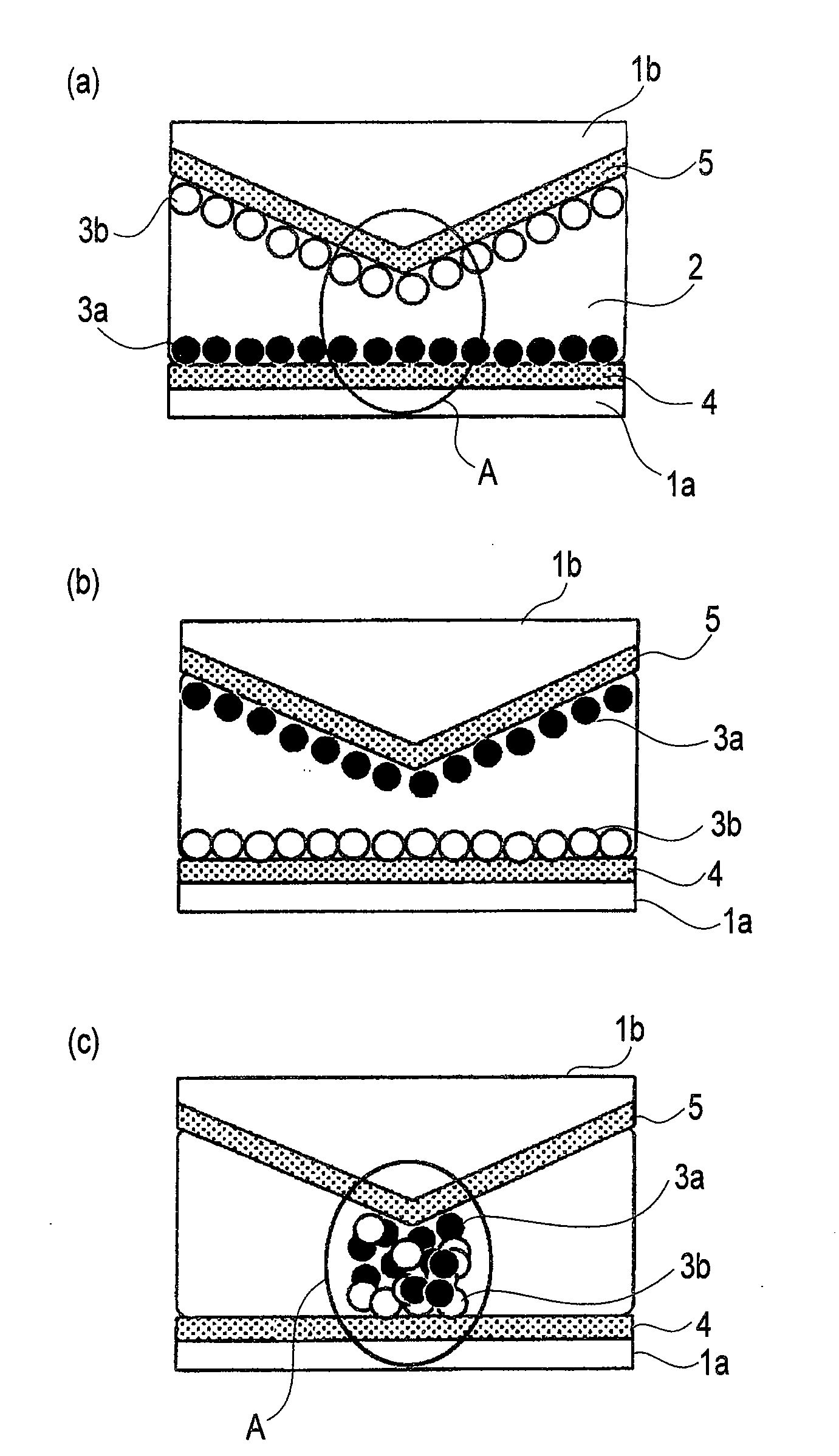
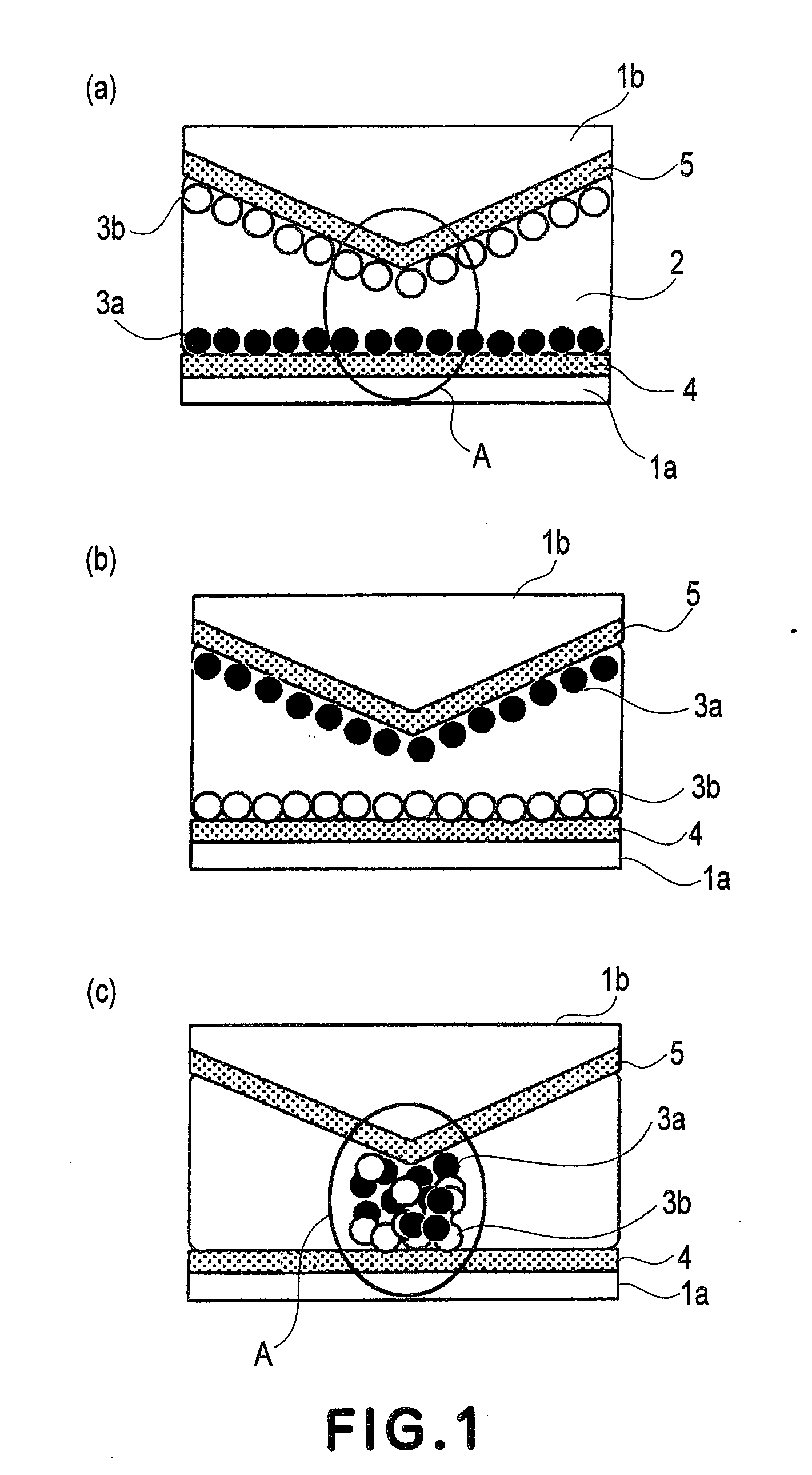
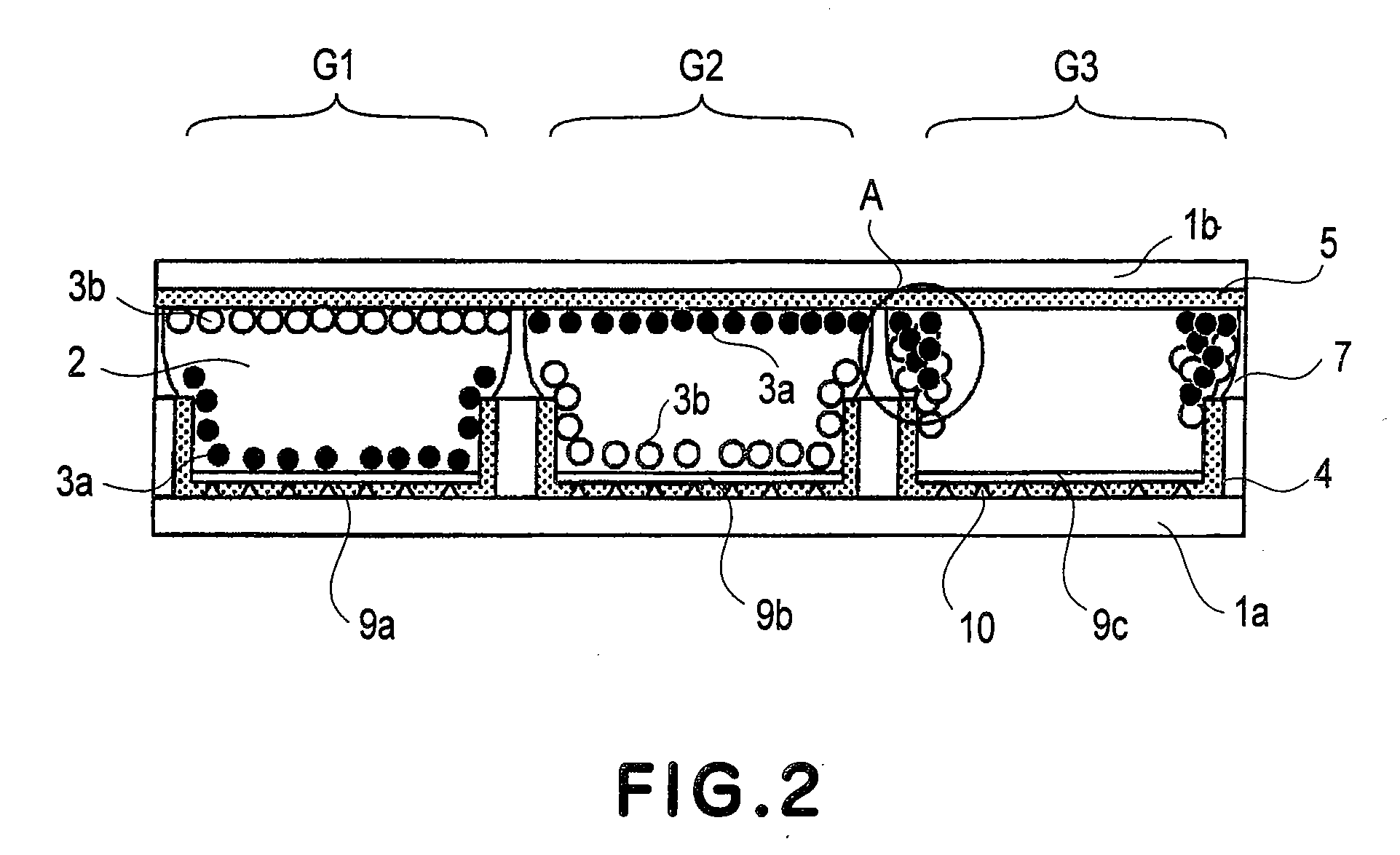
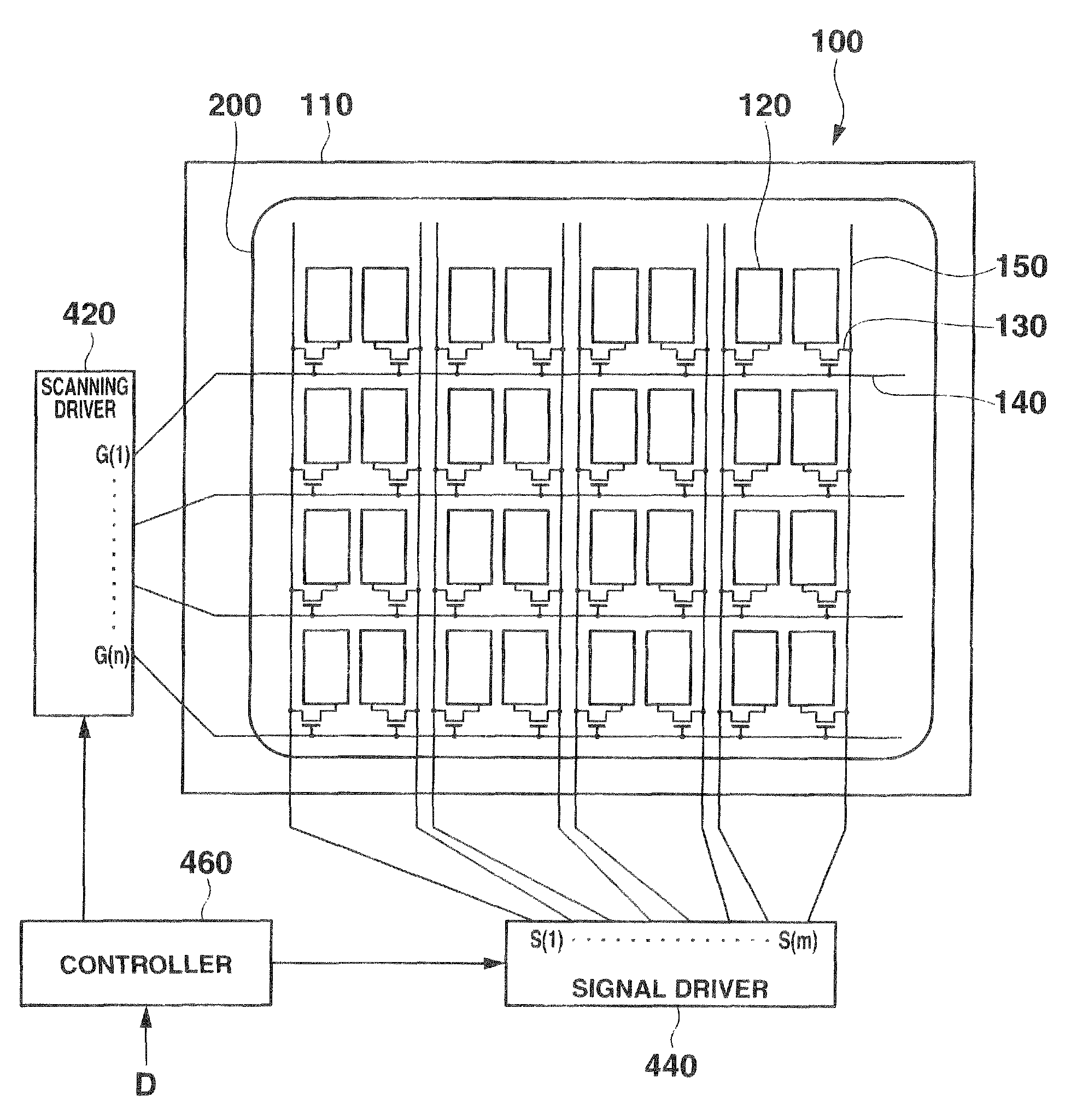
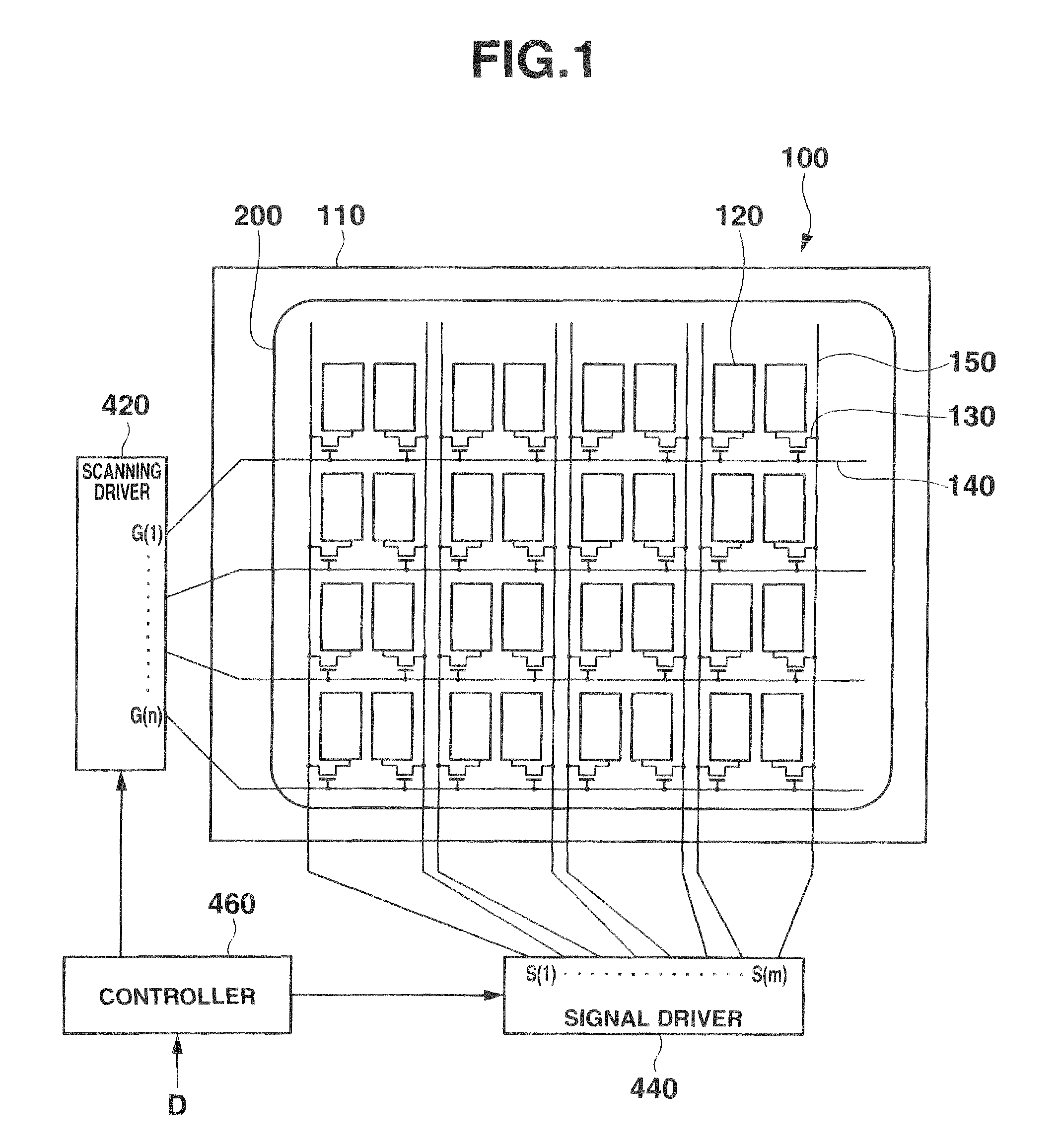
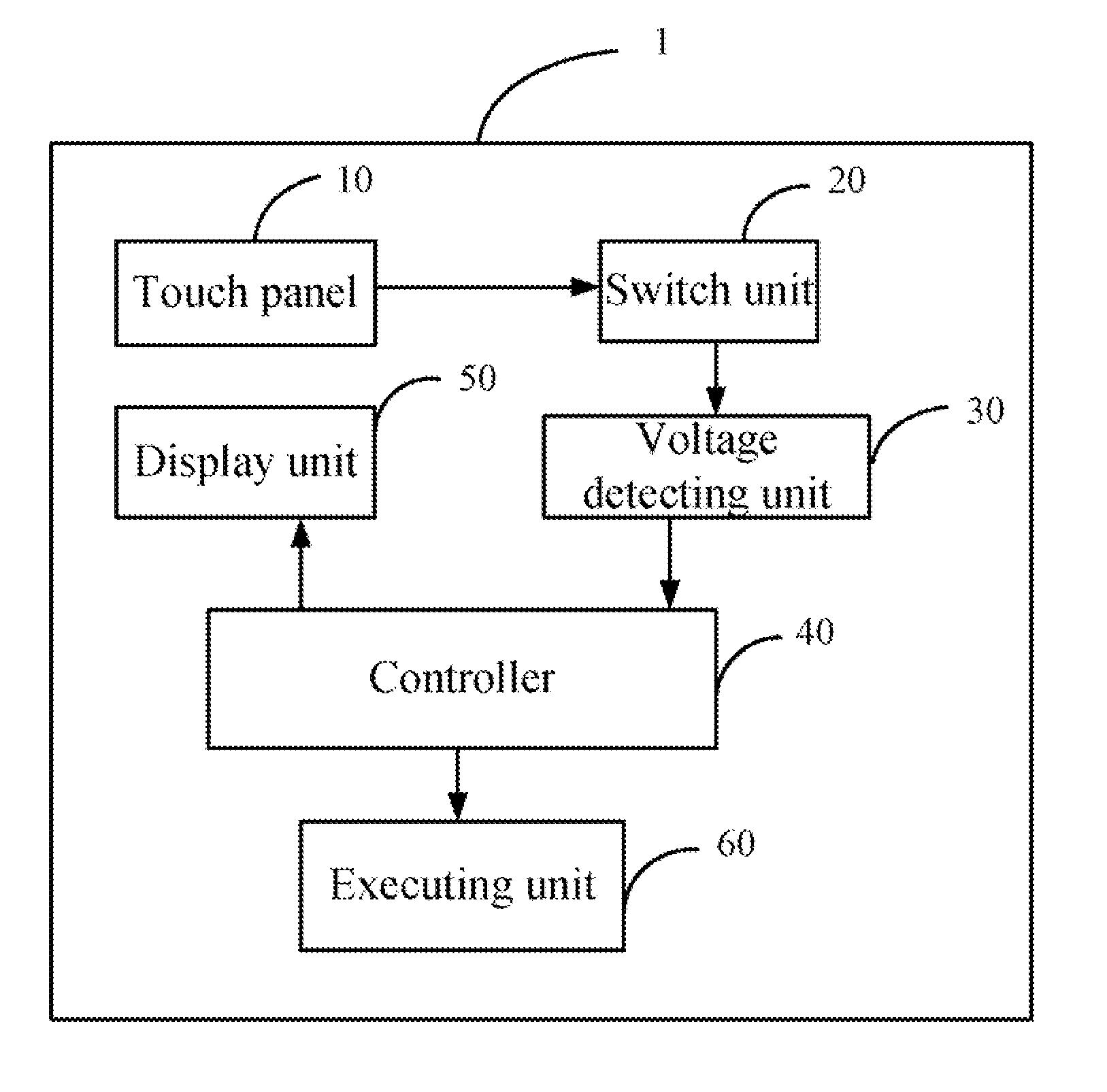
Electrophoretic display device and driving method thereof
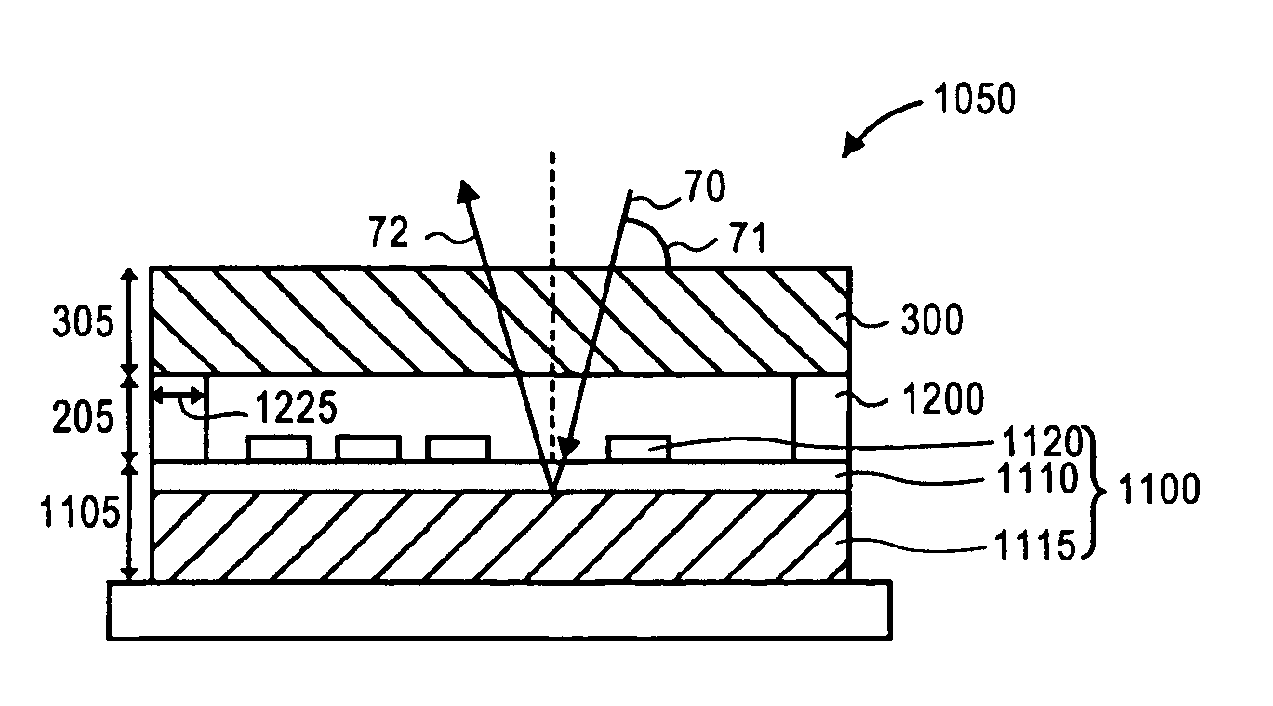
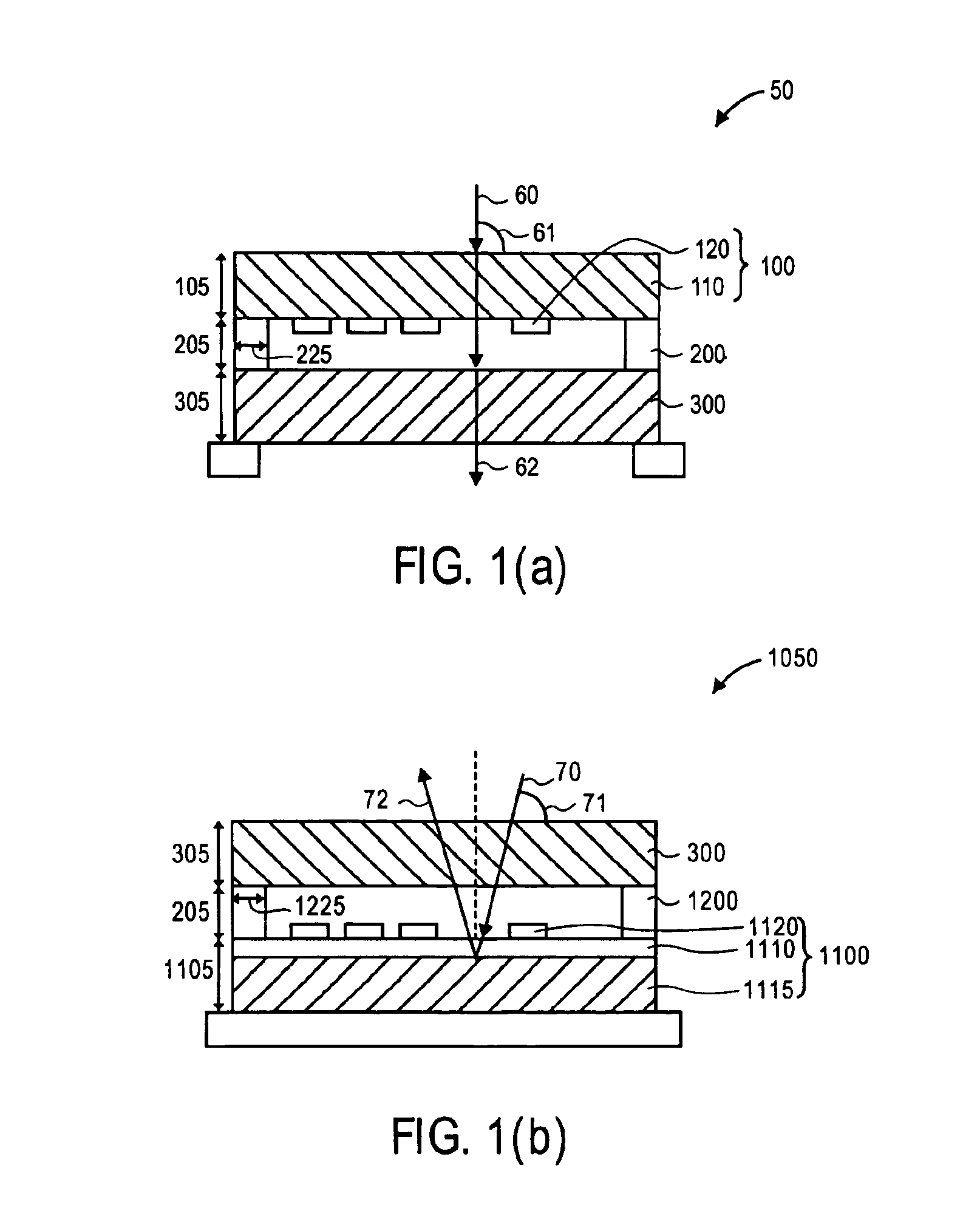
ActiveUS20060209011A1Contrast prevented and improvedPersistence of image and prevented and improvedStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceElectrophoresis
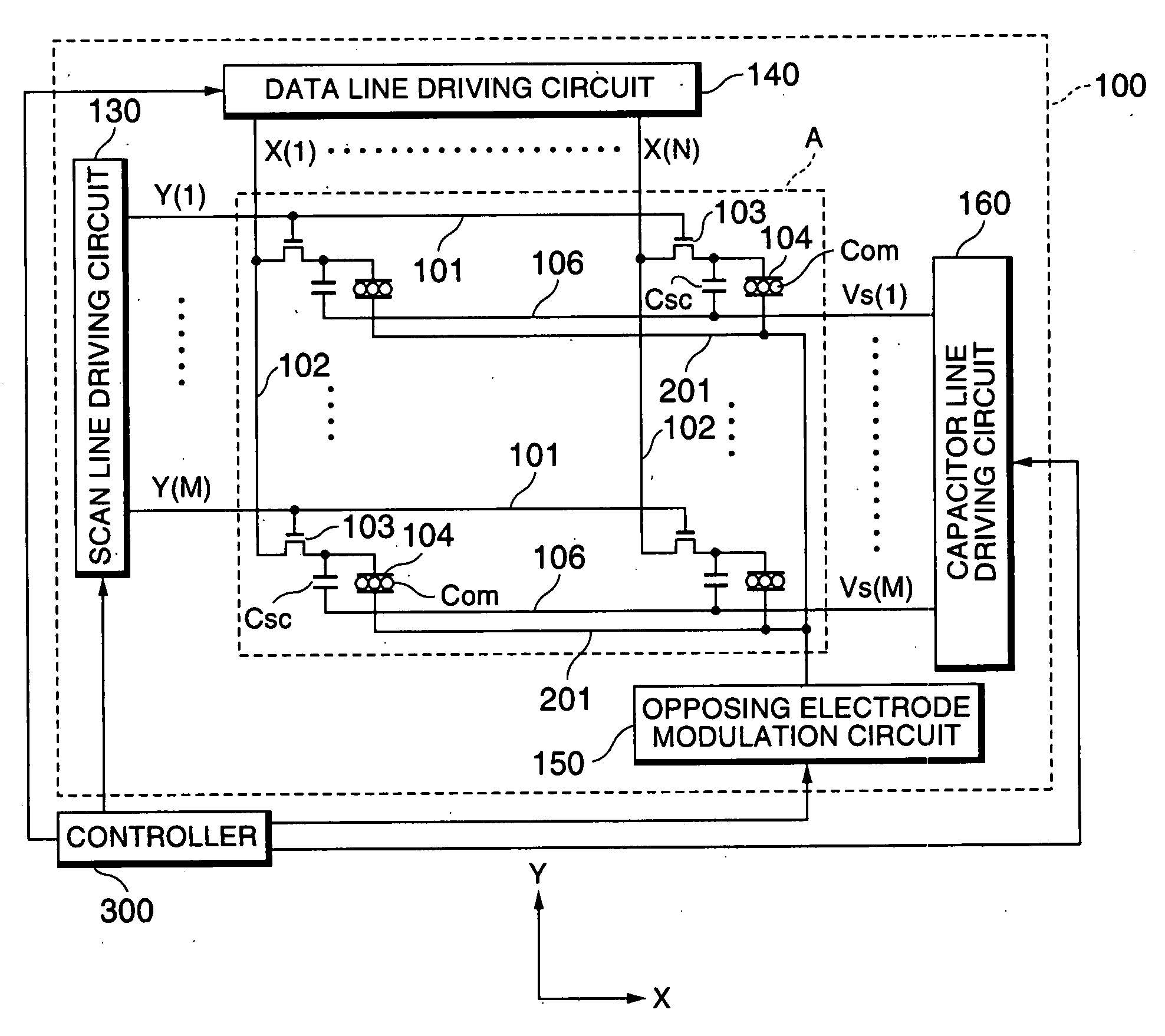
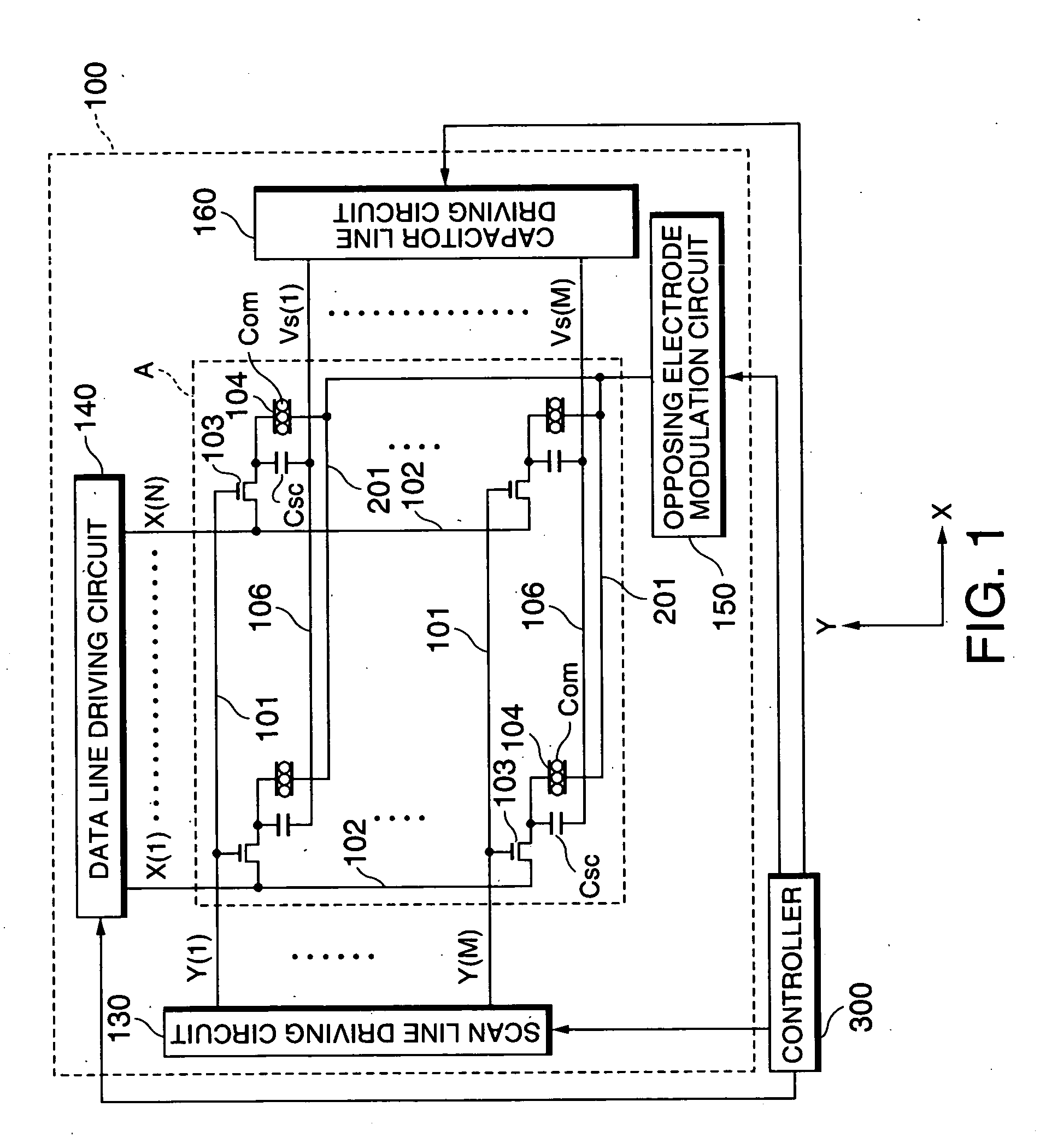
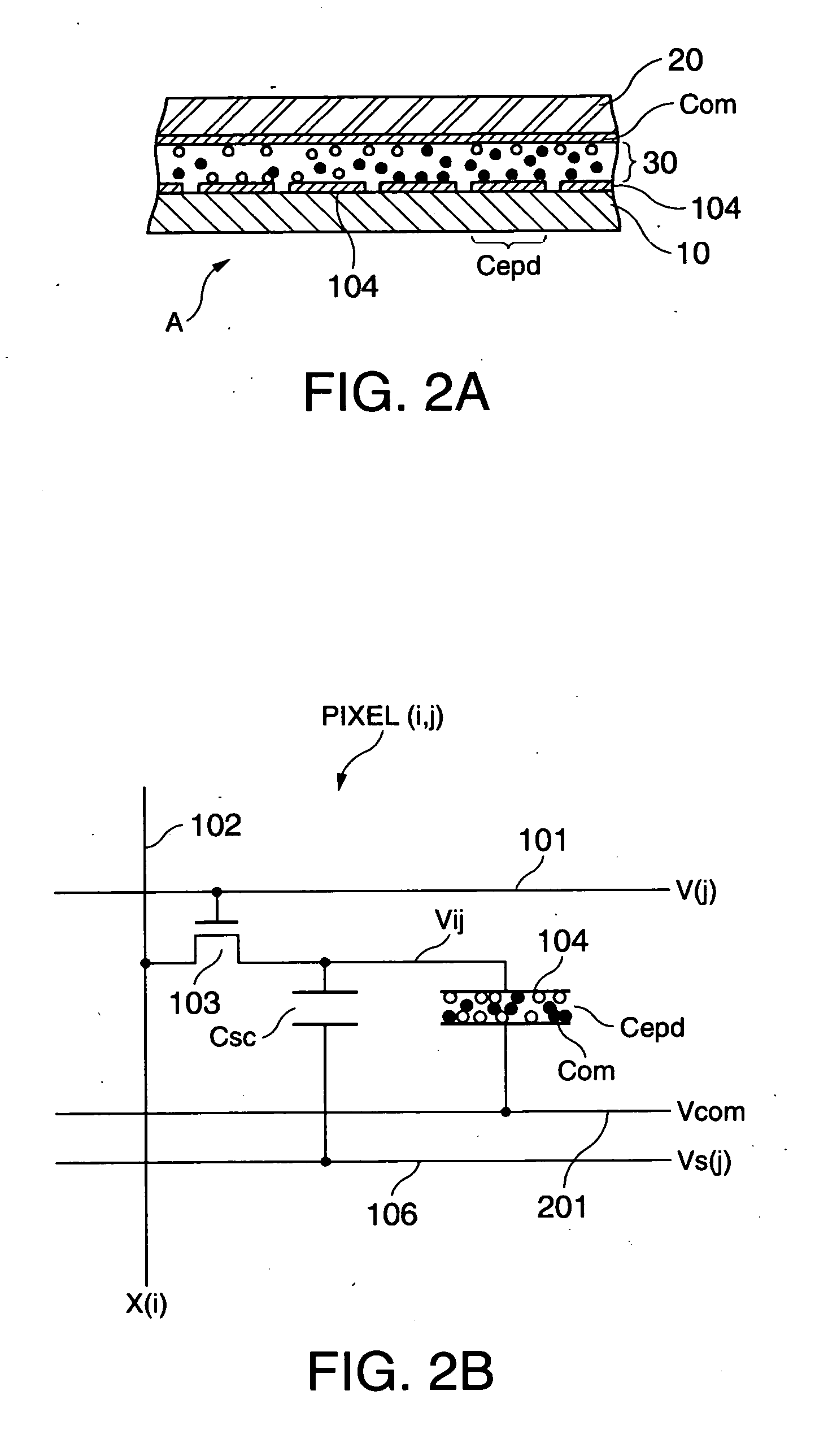
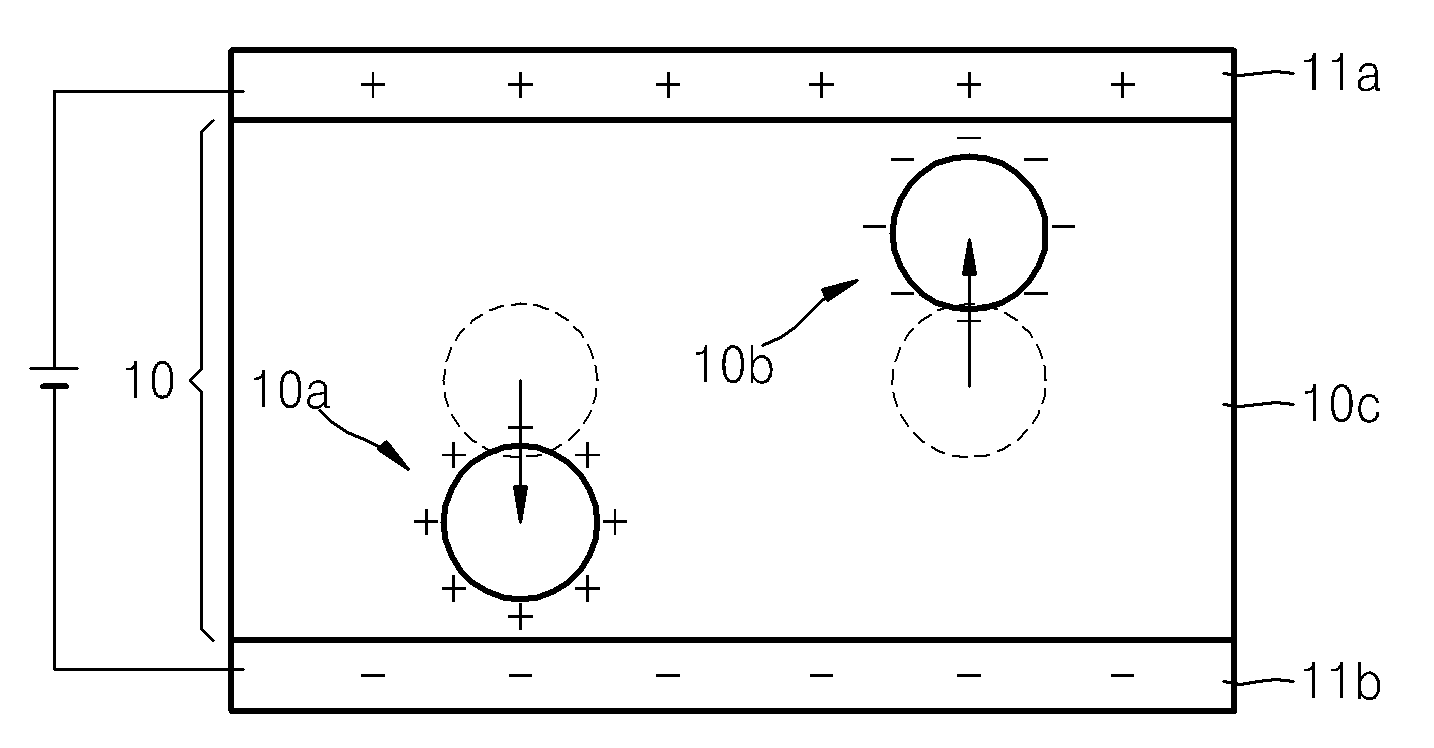
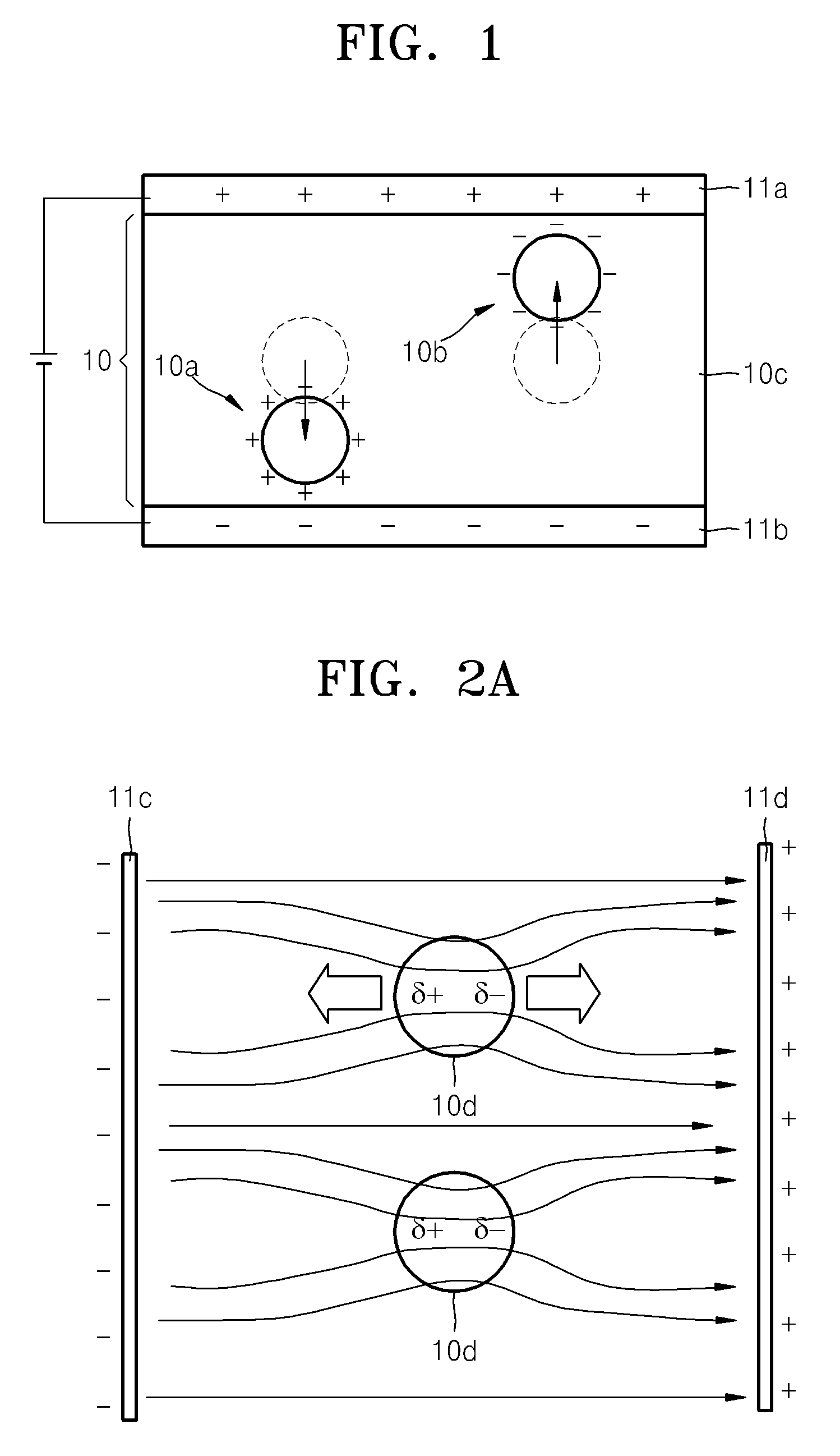
An electrophoretic display device including a first substrate, a second substrate, an electrophoretic material interposed between the first substrate and the second substrate, the electrophoretic material including a positively charged particle and a negatively charged particle, a common electrode provided on the second substrate, a pixel provided at an intersection of a signal line and a scan line, the pixel provided in a plural number and arranged in matrix on the first substrate. The electrophoretic display device further including a pixel electrode provided in the pixel, a capacitor line provided in the pixel, a storage capacitor provided in the pixel, and a second electrode of the storage capacitor being coupled to a storage capacitor line and a thin film transistor (TFT) provided in the pixel, a source electrode of the TFT being coupled to a first electrode of the storage capacitor and the pixel electrode, a drain electrode of the TFT being coupled to the signal line, and a gate electrode of the TFT being coupled to the scan line. A capacitor line low select signal VSL or a capacitor line non-select signal VSC having a higher electric potential than an electric potential of the capacitor line low select signal VSL is supplied to the storage capacitor line.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
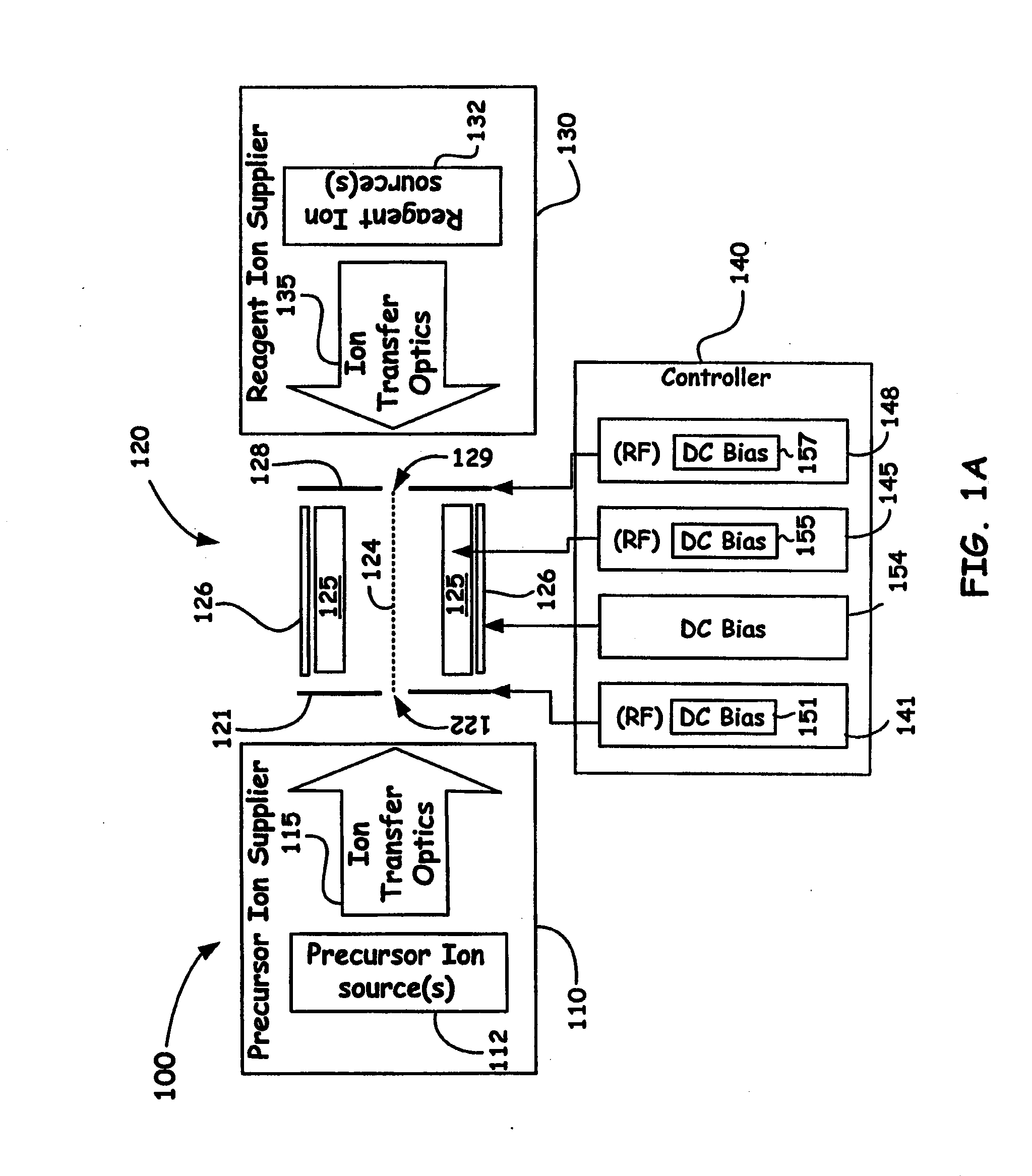
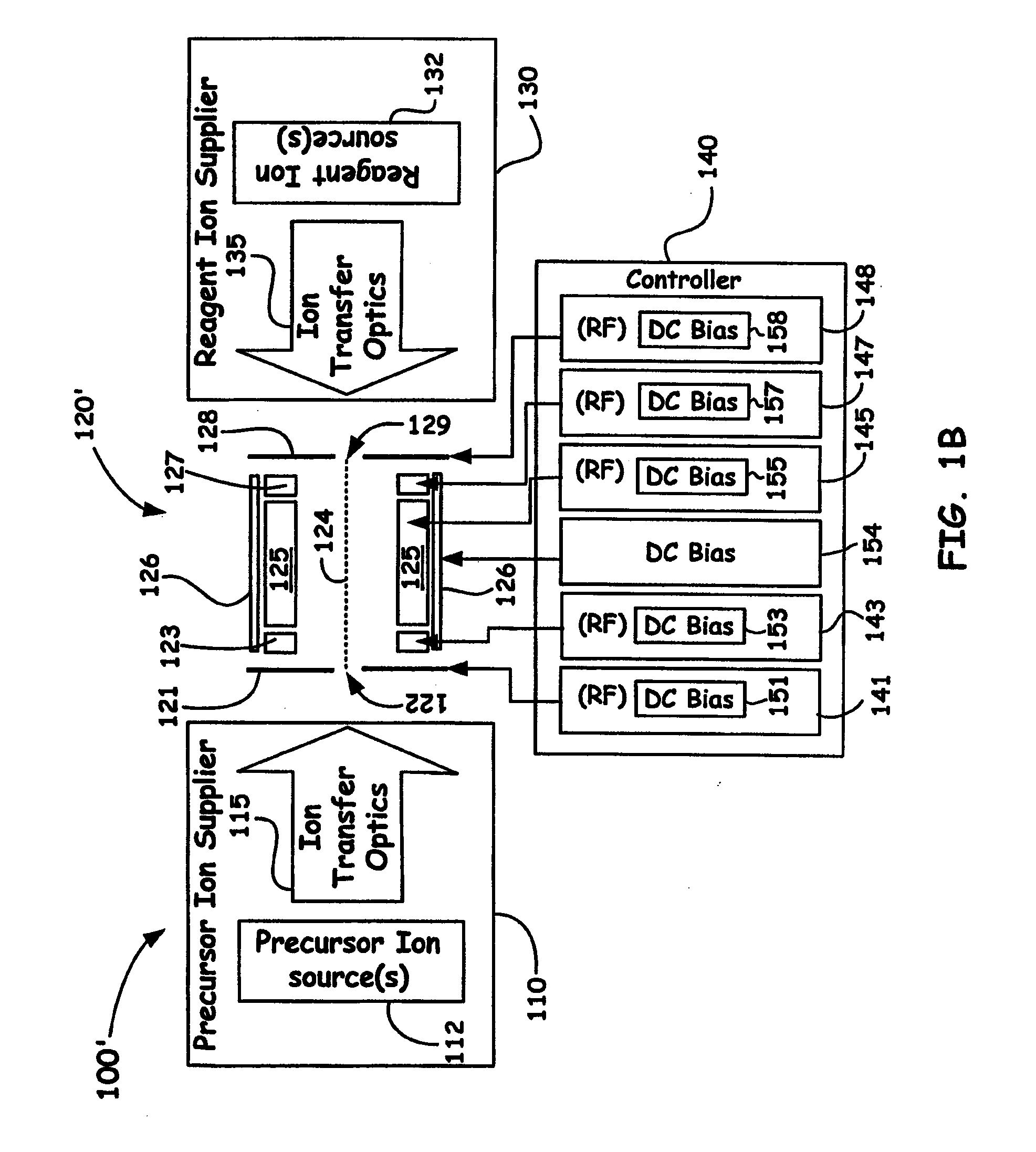
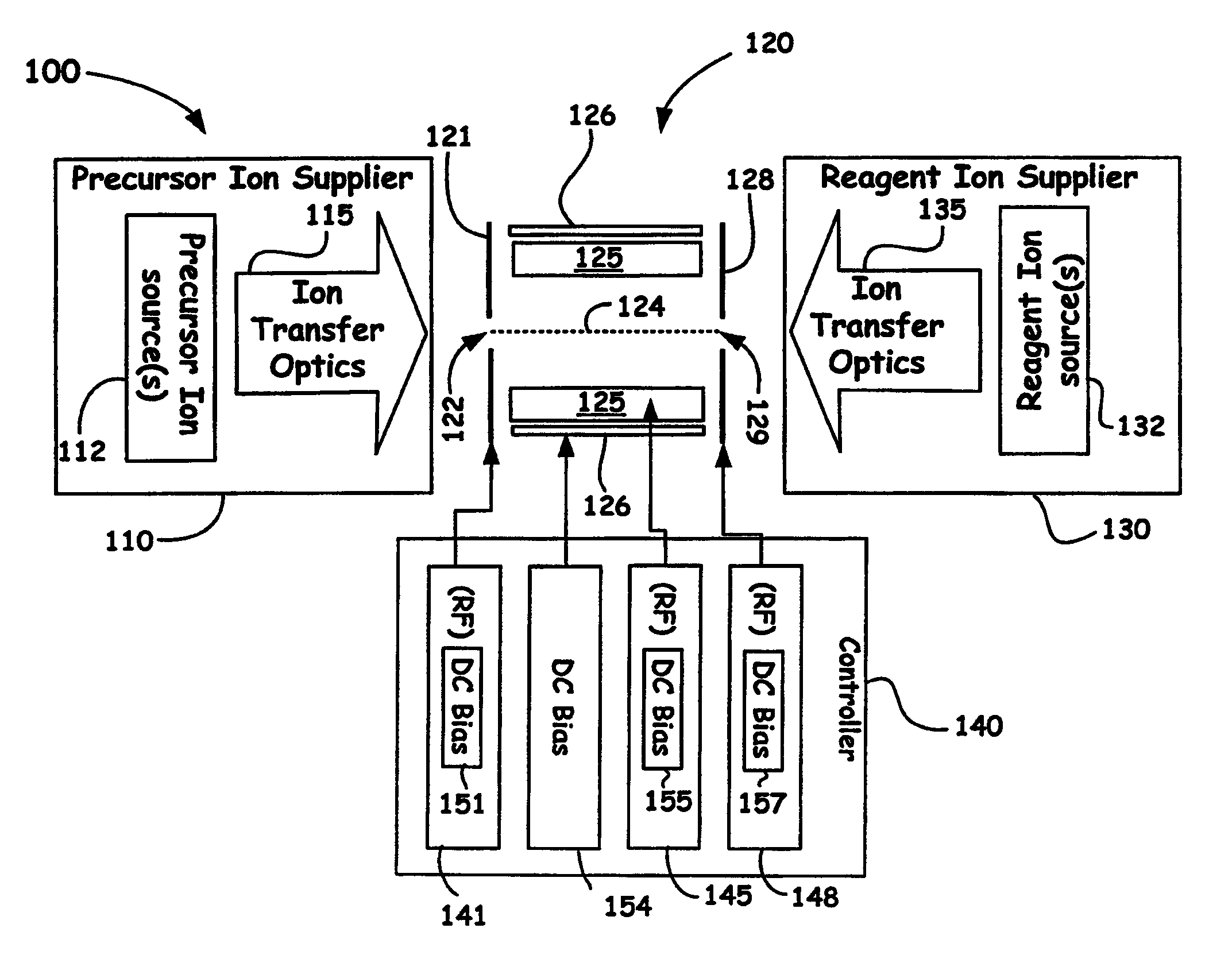
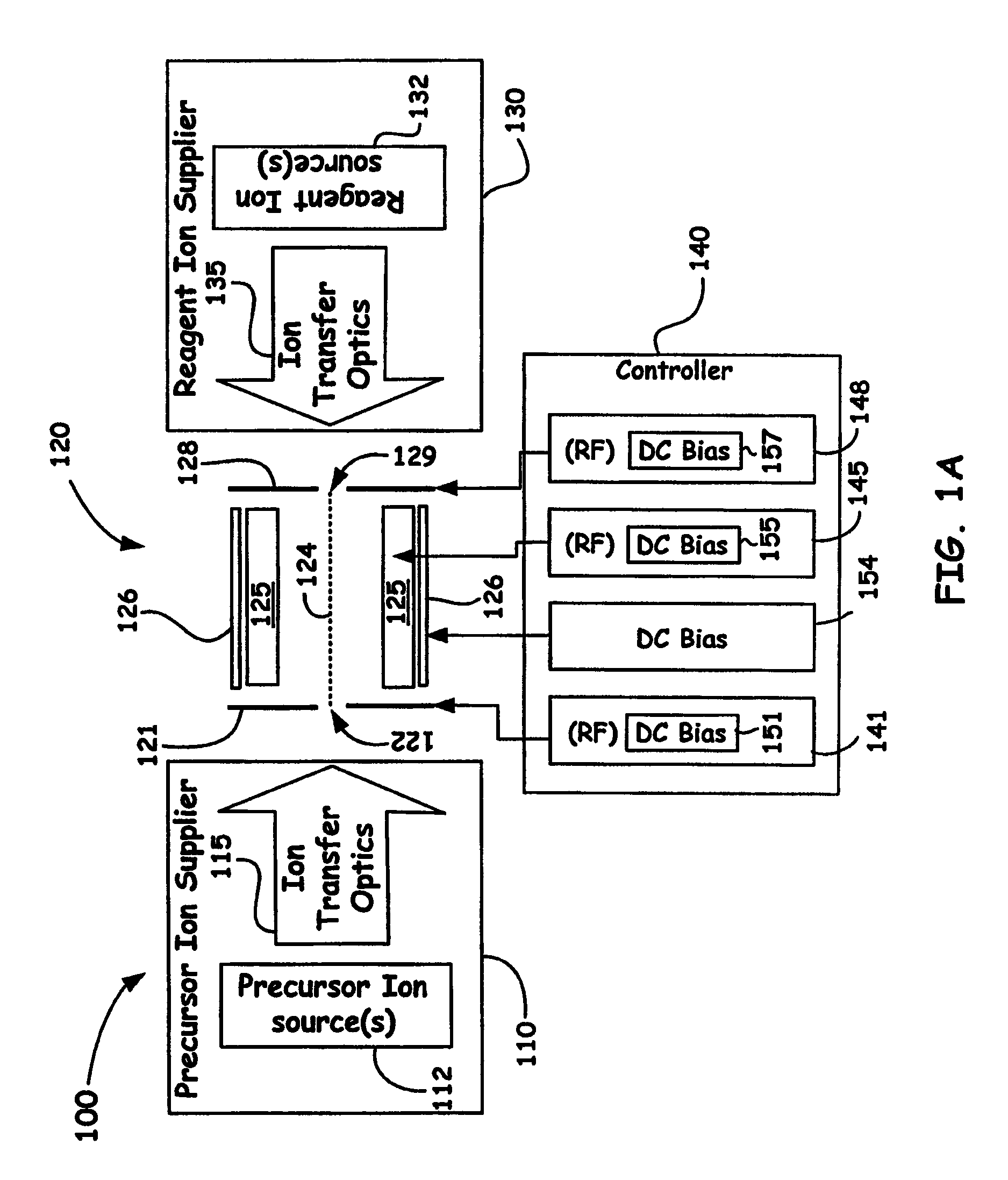
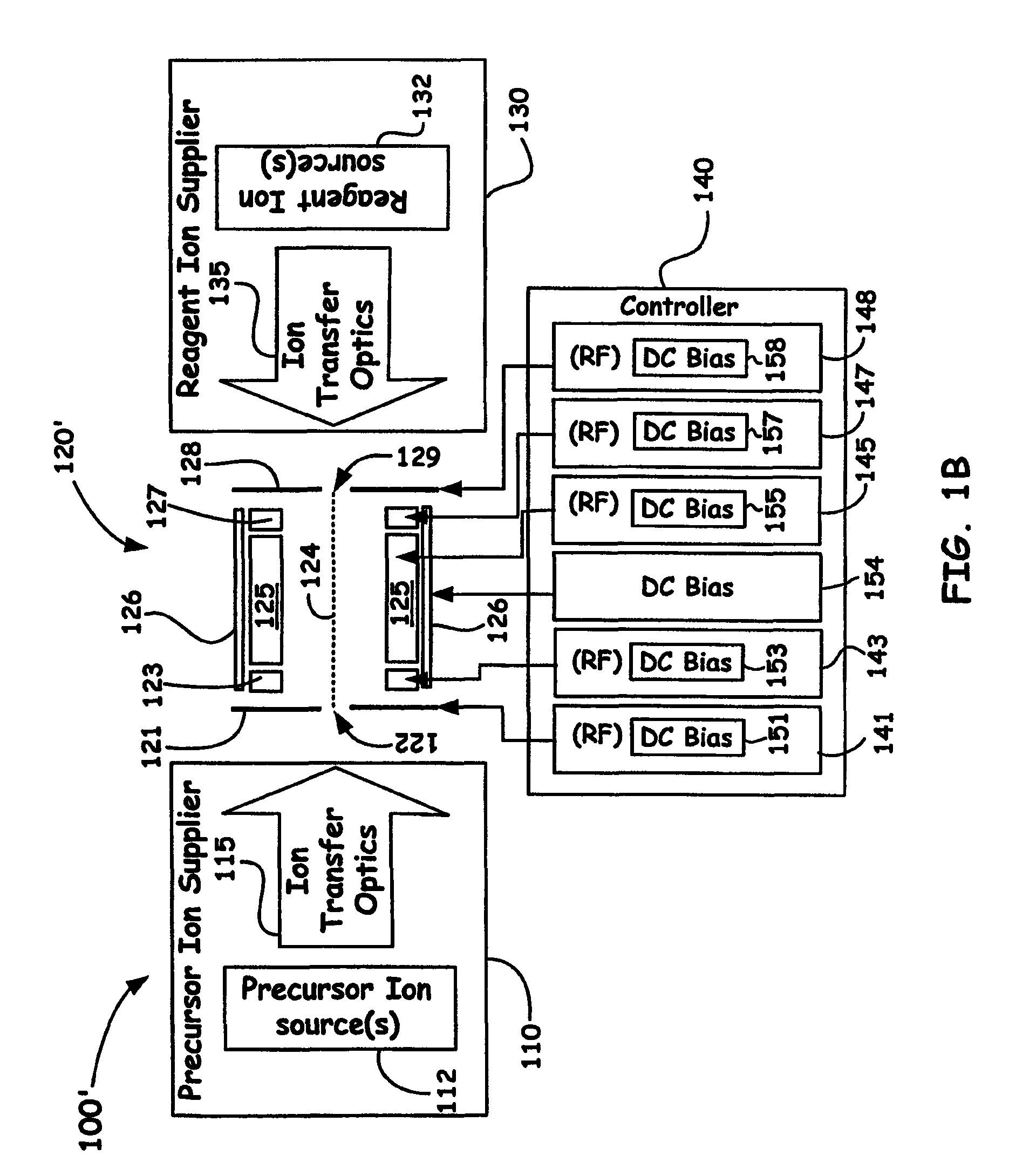
Dual Ion Trapping for Ion/Ion Reactions In A Linear RF Multipole Trap With An Additional DC Gradient
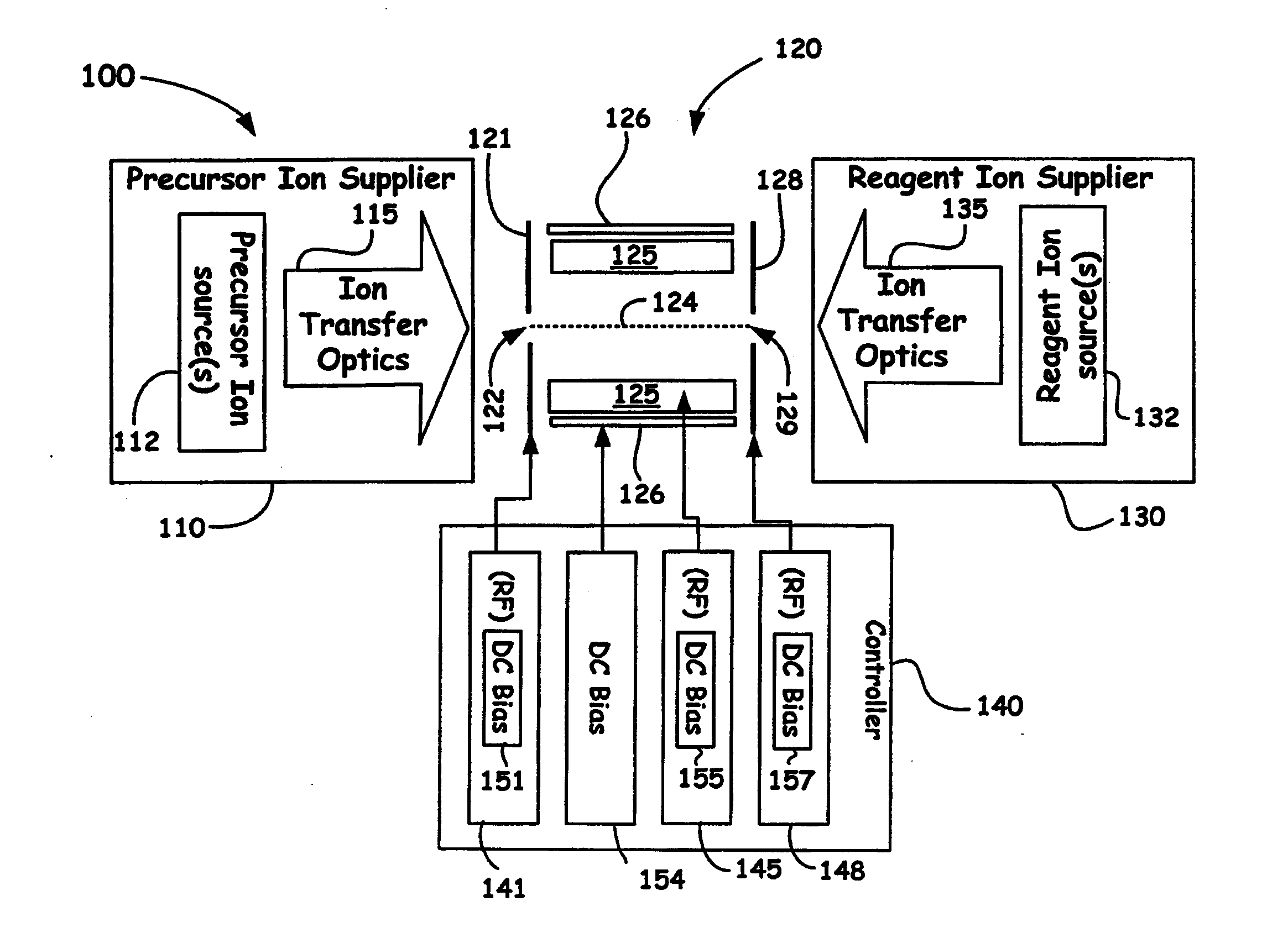
ActiveUS20110186724A1Stability-of-path spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsNegatively charged particleSpectrometer
A novel method and mass spectrometer apparatus is introduced to enable the simultaneous isolation of cations and anions (i.e., precursor and reagent ions) in a linear multipole ion trap via the application of an additional axial DC gradient in combination with coupled RF potential(s). Thus, the combination of the RF and DC voltages in such an arrangement forms a pseudopotential designed to provide for minima for the trapped positively and negatively charged particles that result in the overlap of the ion clouds so as to provide for beneficial ion / ion reactions.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
Device for manipulating charged particles
ActiveUS20140061457A1Stability-of-path spectrometersPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationNegatively charged particleChannel use
The present invention is concerned with a device for charged particle transportation and manipulation. Embodiments provide a capability of combining positively and negatively charged particles in a single transported packet. Embodiments contain an aggregate of electrodes arranged to form a channel for transportation of charged particles, as well as a source of power supply that provides supply voltage to be applied to the electrodes, the voltage to ensure creation, inside the said channel, of a non-uniform high-frequency electric field, the pseudopotential of which field has one or more local extrema along the length of the channel used for charged particle transportation, at least, within a certain interval of time, whereas, at least one of the said extrema of the pseudopotential is transposed with time, at least within a certain interval of time, at least within a part of the length of the channel used for charged particle transportation.
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB EURO
Device for manipulating charged particles via field with pseudopotential having one or more local maxima along length of channel
ActiveUS9536721B2Positive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationElectron/ion optical arrangementsNegatively charged particleChannel use
The present invention is concerned with a device for charged particle transportation and manipulation. Embodiments provide a capability of combining positively and negatively charged particles in a single transported packet. Embodiments contain an aggregate of electrodes arranged to form a channel for transportation of charged particles, as well as a source of power supply that provides supply voltage to be applied to the electrodes, the voltage to ensure creation, inside the said channel, of a non-uniform high-frequency electric field, the pseudopotential of which field has one or more local extrema along the length of the channel used for charged particle transportation, at least, within a certain interval of time, whereas, at least one of the said extrema of the pseudopotential is transposed with time, at least within a certain interval of time, at least within a part of the length of the channel used for charged particle transportation.
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB EURO
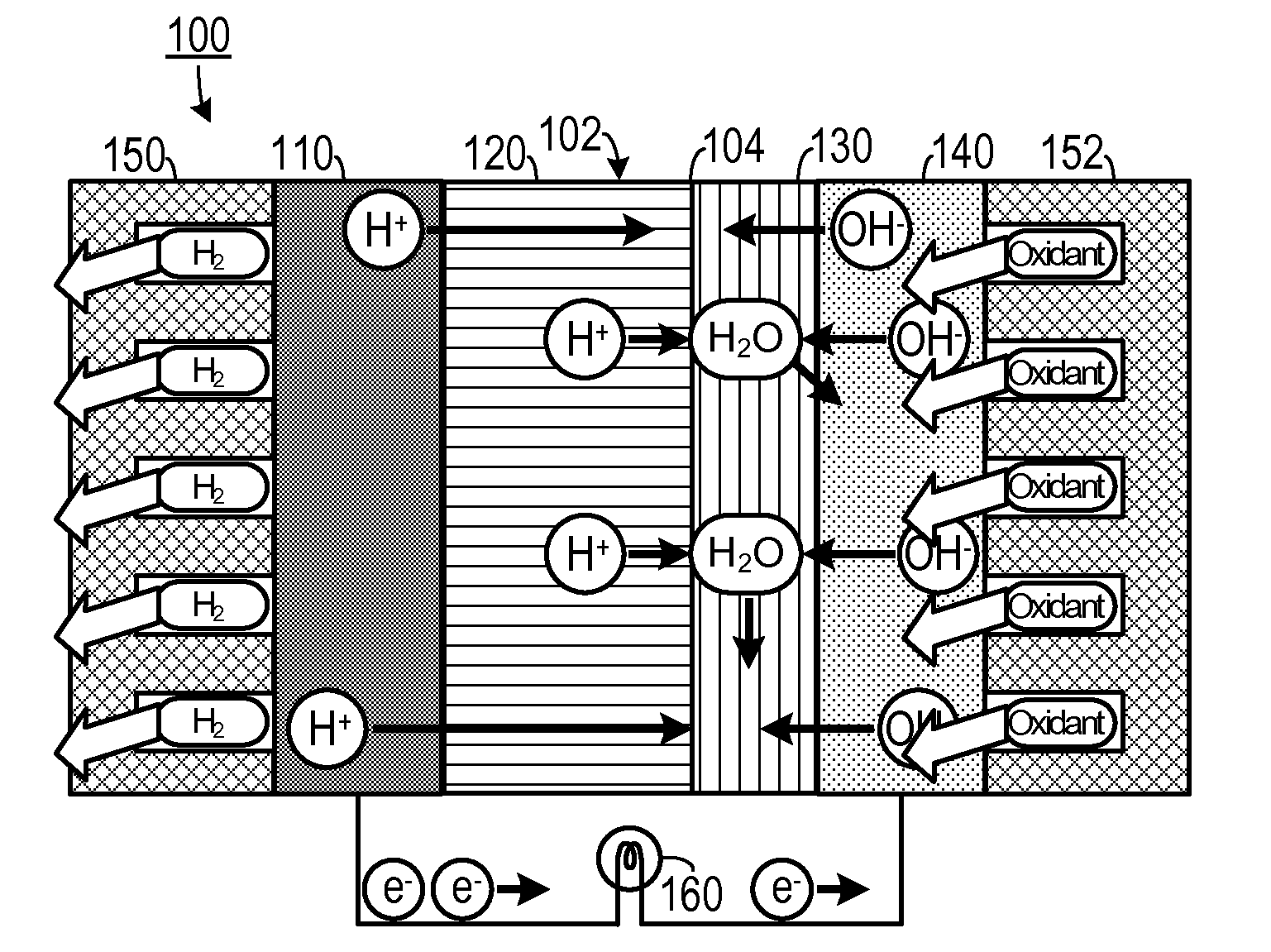
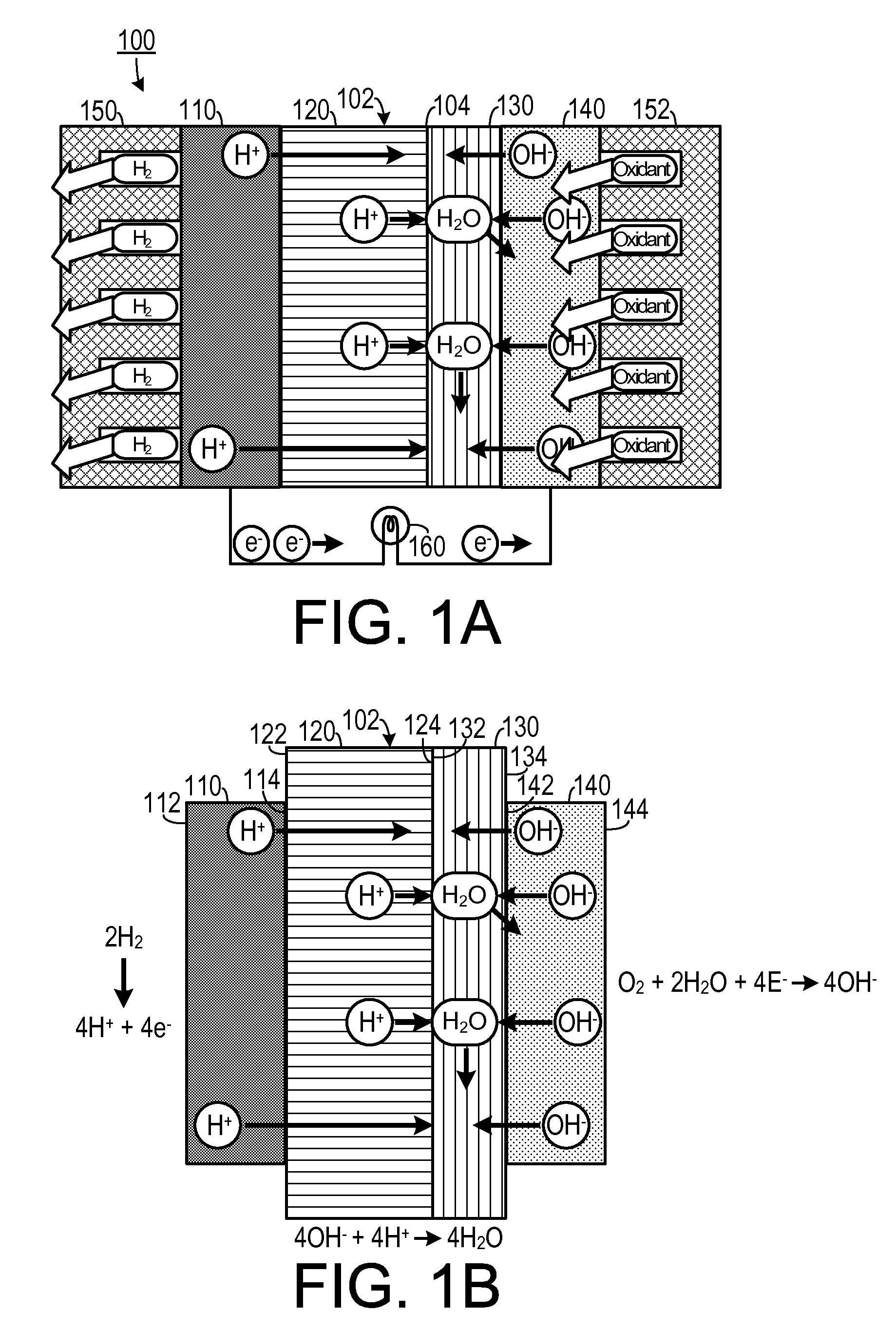
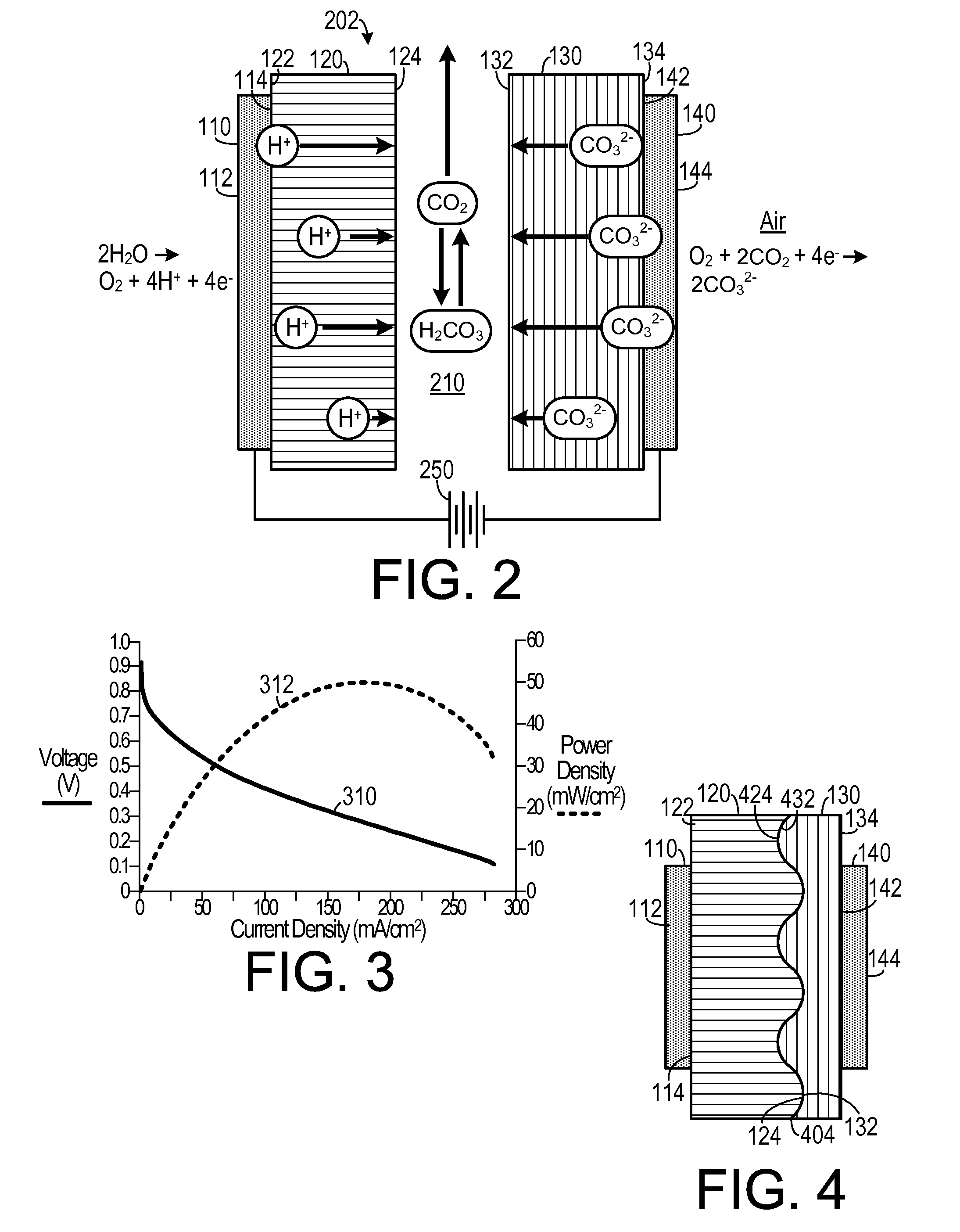
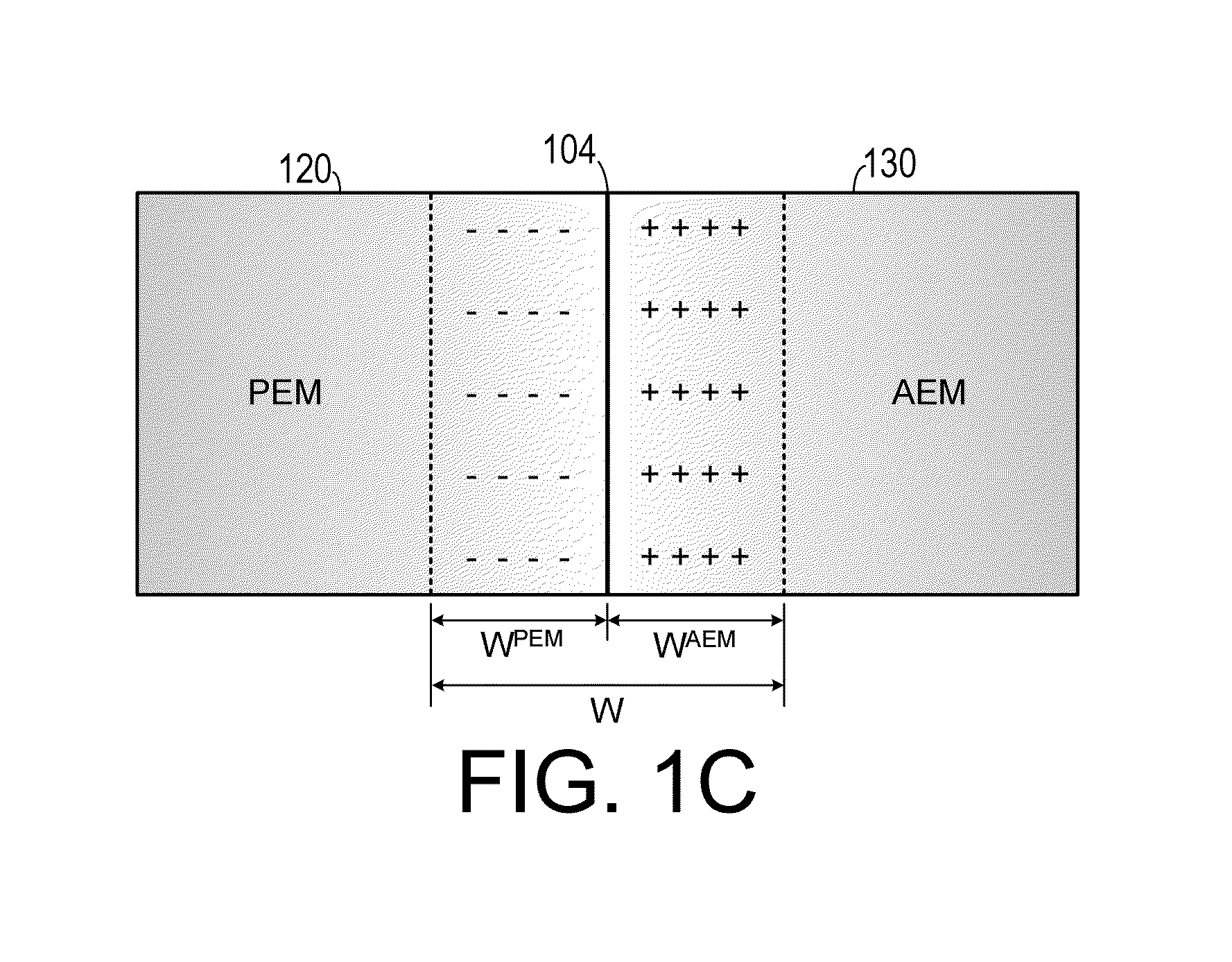
Hybrid Ionomer Electrochemical Devices
A membrane electrode assembly for use in a fuel cell includes an anode electrode, a cation exchange membrane, an anion exchange membrane and a cathode electrode. The anode electrode includes a first catalyst. The first catalyst separates a reducing agent into a plurality of positively charged ions and negative charges. The cation exchange membrane is configured to favor transport of positively charged ions therethrough and is also configured to inhibit transport of negatively charged particles therethrough. The anion exchange membrane is configured to favor transport of negatively charged ions therethrough and is also configured to inhibit transport of positively charged ions therethrough. The cathode electrode includes a second catalyst and is disposed adjacent to a second side of the anion exchange membrane. The second catalyst reacts electrons with the at least one oxidizing agent so as to create reduced species.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Air filtration device for closed environments
ActiveUS20070283810A1Preserving healthLess frequent maintenanceCombination devicesMechanical apparatusAir filtrationEngineering
An air filtration device for suppressing biological pollutants for closed environments, comprising at least one enclosure with at least one air inlet, at which at least one perforated conducting grille is located, that has a preset negative electrical potential adapted to emit electrons when air flows, so as to give negative electric charge to particles to which microorganisms adhere, at least one air passage duct being formed between at least one plate having predefined positive potential for collecting negatively charged particles to which microorganisms adhere, at least one deflector plate having a negative potential adapted to divert the particles to which microorganisms adhere, an electrical field being generated between the collector plate and the deflector plate, facing each other, the field to divert and precipitate the particles to which the microorganisms adhere onto the collector plate, and an inactivator for inactivation of the microorganisms provided and at least one filtered air outlet.
Owner:DAITECH SA
Inductively coupled plasma flood gun using an immersed low inductance fr coil and multicusp magnetic arrangement
ActiveUS20120085917A1Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMetallic materialsInductively coupled plasma
A device is disclosed for providing an inductively coupled radio frequency plasma flood gun. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the device is a plasma flood gun in an ion implantation system. The plasma flood gun may comprise a plasma chamber having one or more apertures; a gas source capable of supplying at least one gaseous substance to the plasma chamber; a single-turn coil disposed within the plasma chamber, and a power source coupled to the coil for inductively coupling radio frequency electrical power to excite the at least one gaseous substance in the plasma chamber to generate a plasma. The inner surface of the plasma chamber may be free of metal-containing material and the plasma may not be exposed to any metal-containing component within the plasma chamber. The plasma chamber may include a plurality of magnets for controlling the plasma. An exit aperture may be provided in the plasma chamber to enable negatively charged particles of the resulting plasma to engage an ion beam that is part of the associated ion implantation system. In one embodiment, magnets are disposed on opposite sides of the aperture and are used to manipulate the electrons of the plasma.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
System and method for point-of-use filtration and purification of fluids used in substrate processing
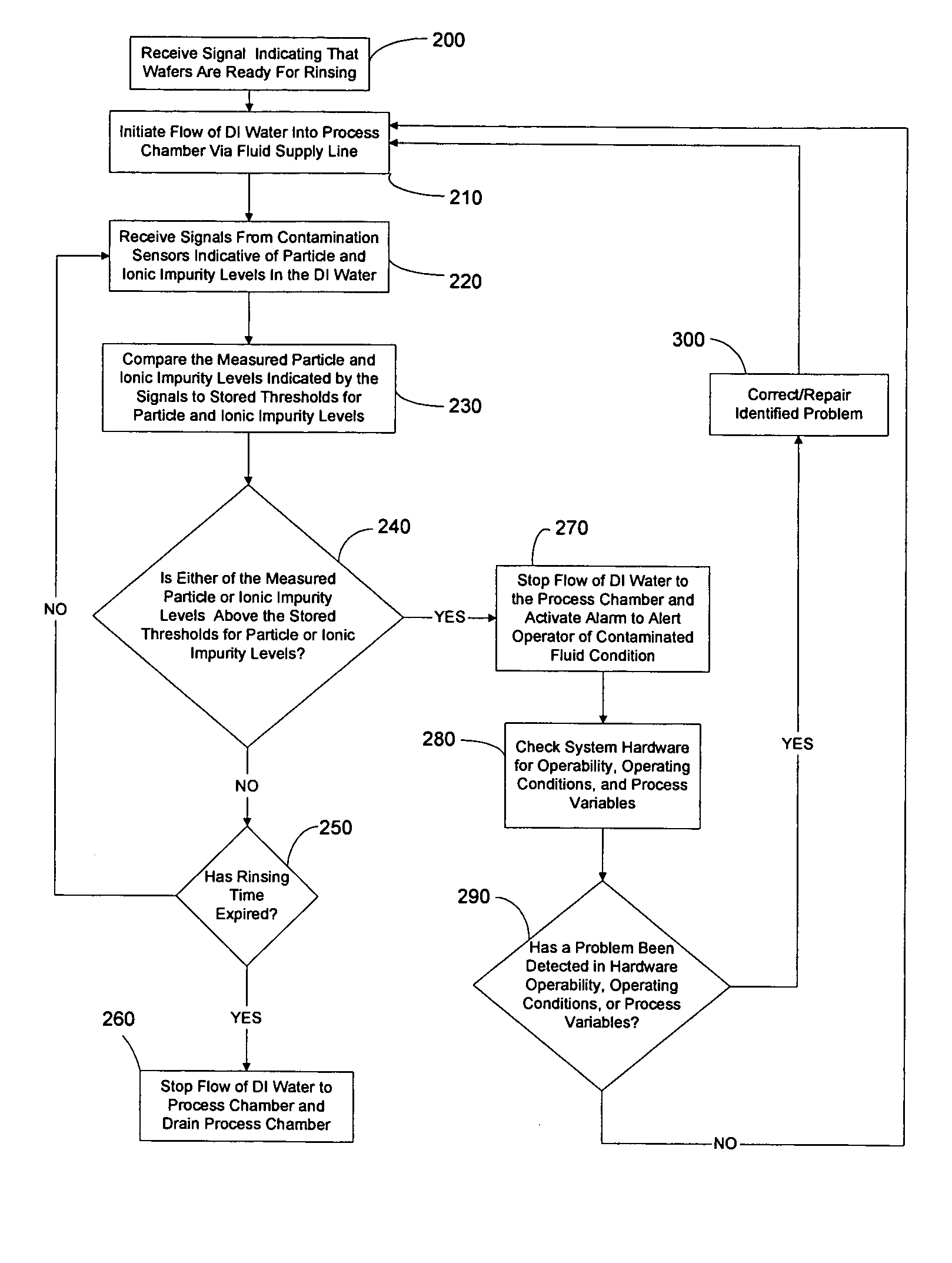
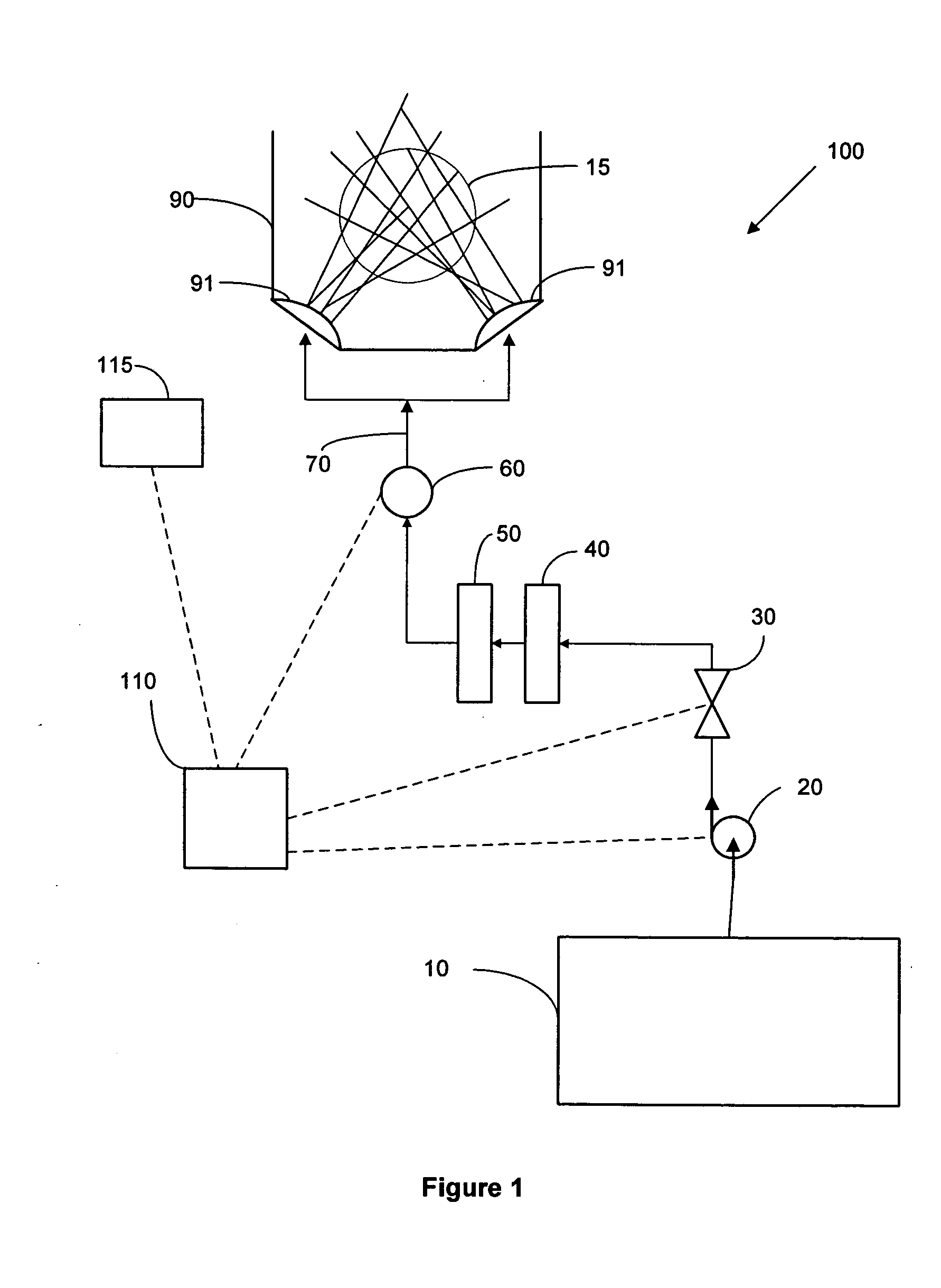
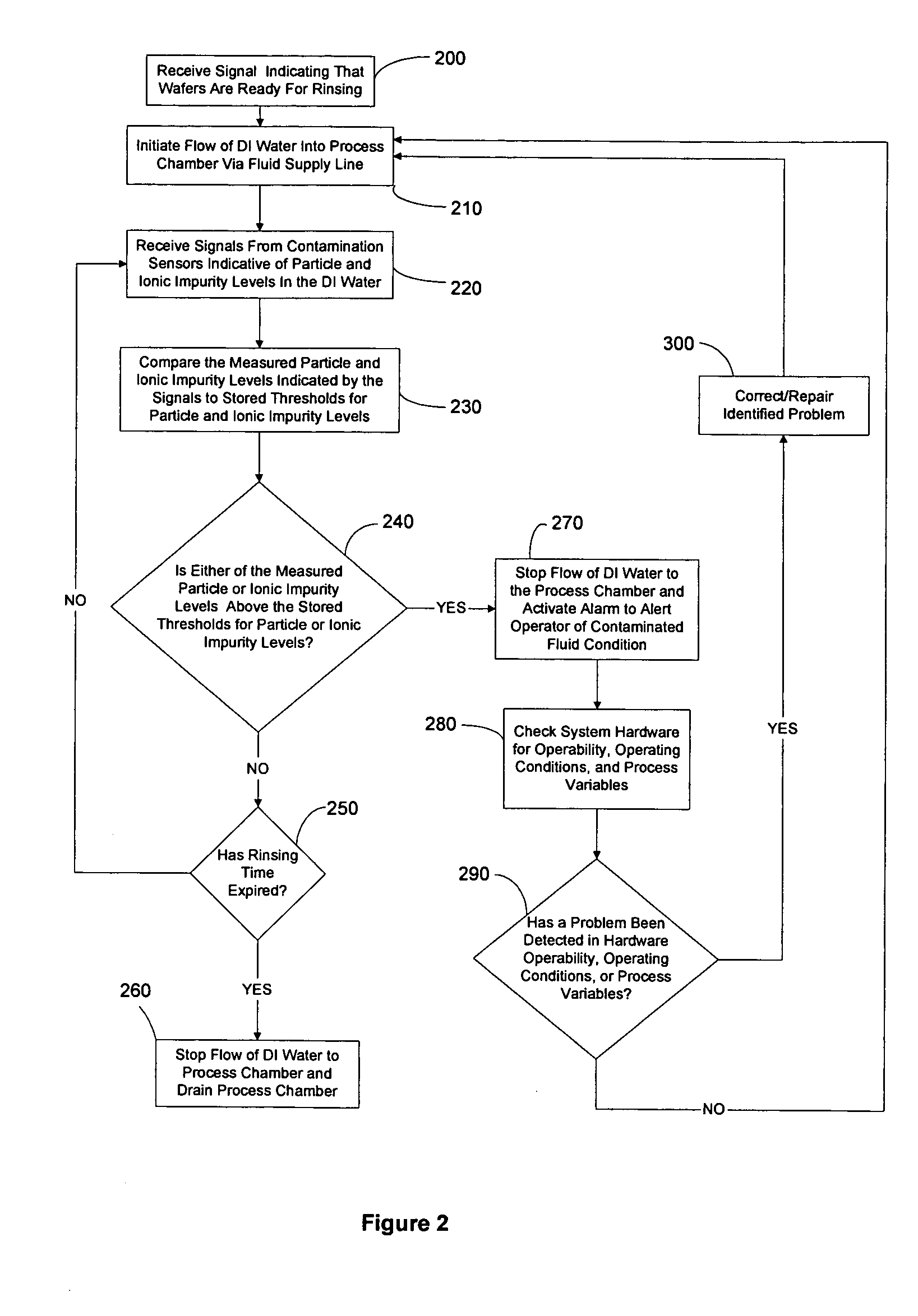
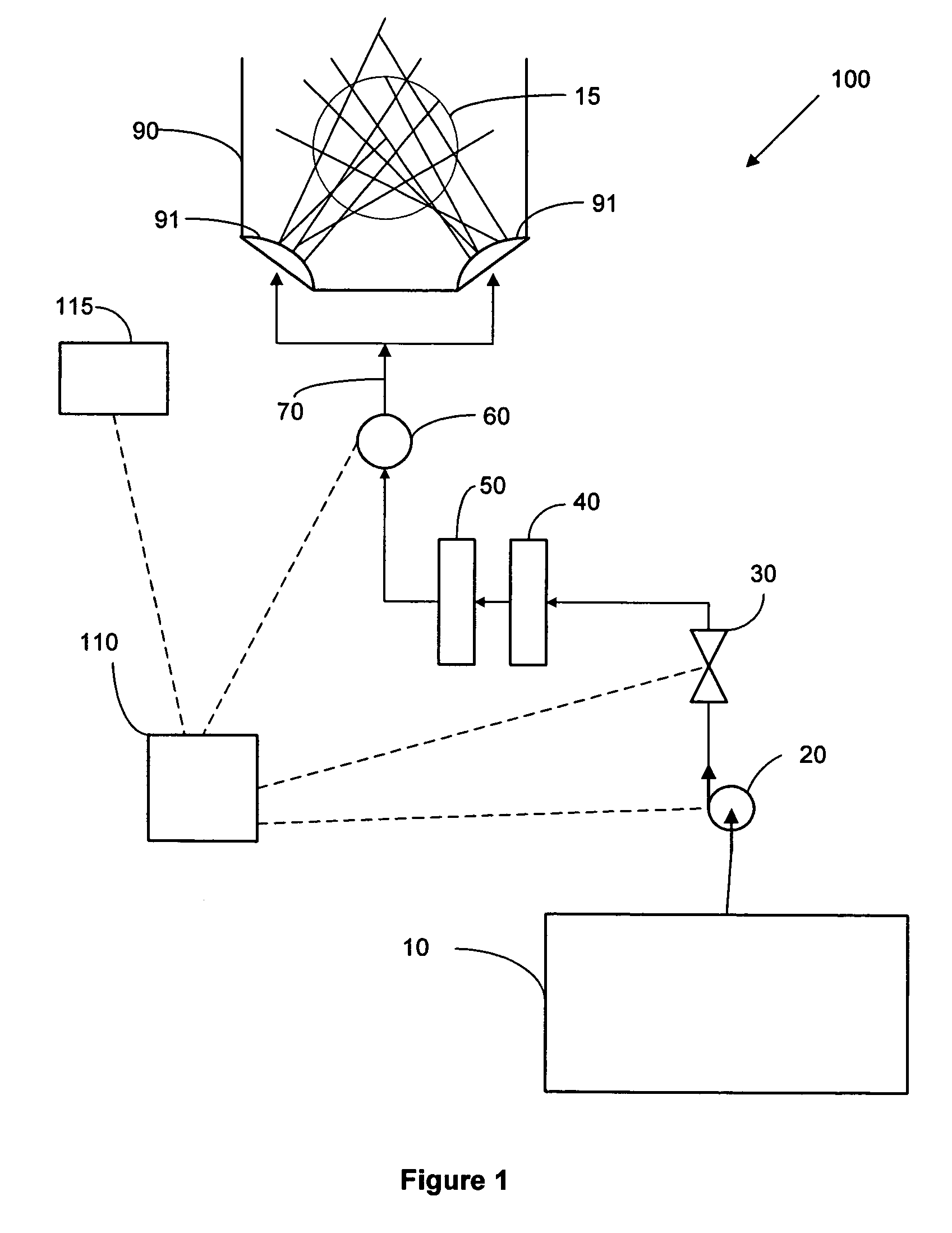
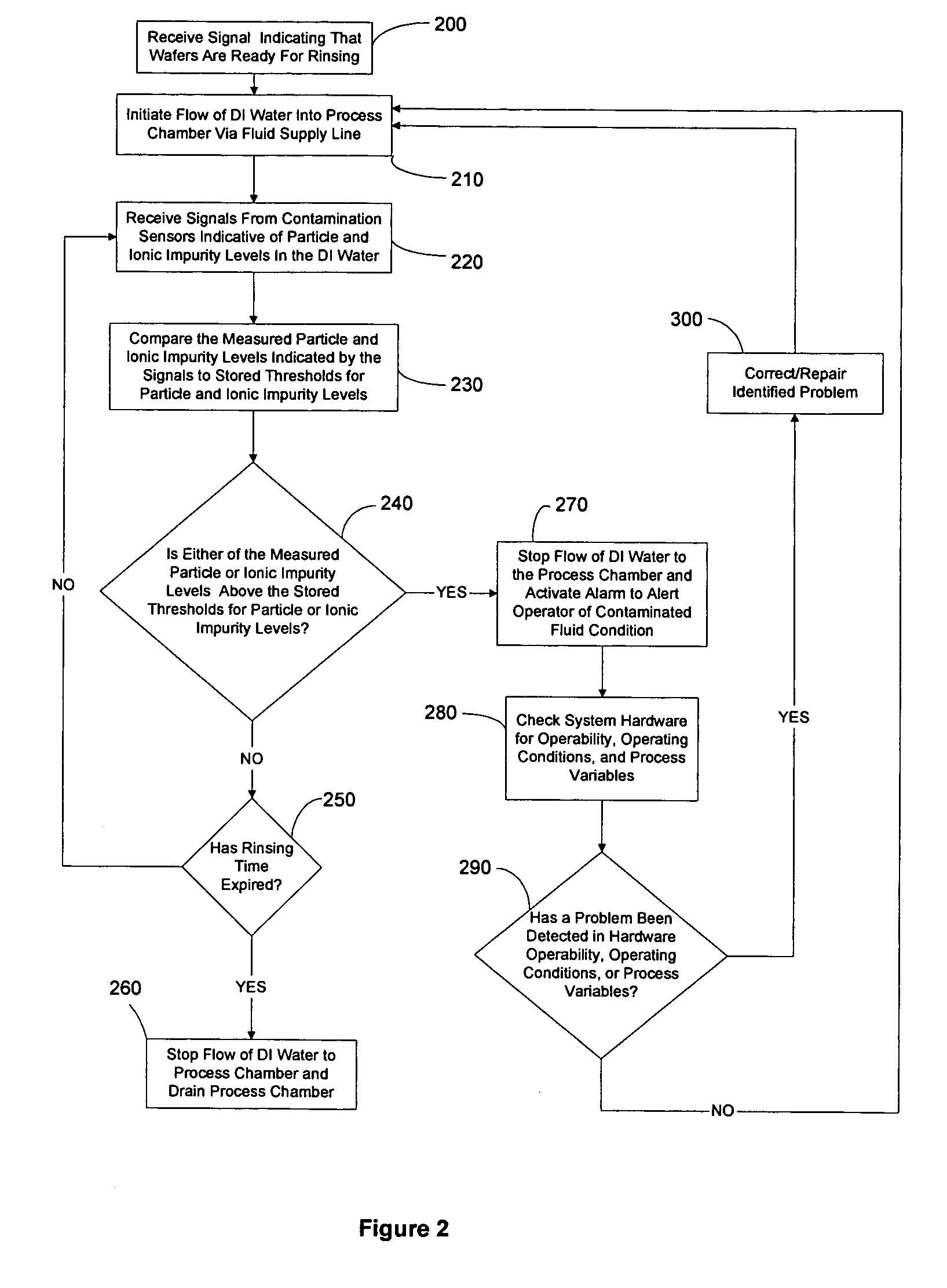
ActiveUS20050016929A1Reduce and eliminate particleReduce and eliminate and ionicIon-exchanger regenerationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityFiltration
A method and system for supplying an ultra-pure fluid to a substrate process chamber using point-of-use filtration and purification. The method and system provide ability to automatically monitor and control contamination levels in fluids in real time and to stop substrate processing when contamination levels exceed predetermined thresholds. In one aspect, the invention is a system comprising: a fluid supply line adapted to supply a fluid to the process chamber; filtration means operably coupled to the fluid supply line for removing positively and negatively charged particles from the fluid prior to the fluid passing into the process chamber; a purifier operably coupled to the fluid supply line in series with the filtration means for removing ionic contaminants from the fluid prior to the fluid passing into the process chamber; sensor means for repetitively measuring particle and ionic impurity levels in the fluid that has passed through the filtration means and the purifier, the sensor means producing signals indicative of the measured particle and ionic impurity levels; a controller electrically coupled to the sensor means for receiving the signals created by the sensor means, the controller adapted to respectively compare the measured particle level and the measured ionic impurity level indicated by the signals to a predetermined particle threshold and a predetermined ionic impurity threshold, wherein upon the controller determining that either the measured particle level is above the predetermined particle threshold and / or that the measured ionic impurity level is above the predetermined ionic impurity threshold, the controller further adapted to (1) activate means to alert a user, (2) cease processing of substrates in the process chamber, and / or (3) prohibit processing of substrates in the process chamber.
Owner:AKRION TECH
Liquid composition, recording method, and recorded matter
ActiveUS20130143008A1Good fixabilityInhibit coloringDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsWater solubleNegatively charged particle
A liquid composition containing: a water-soluble cationic polymer obtained by polymerizing monomers containing epihalohydrin and at least one of amine and amide; and water, wherein the liquid composition is for agglutinating negatively charged particles which are dispersed in a dispersion liquid.
Owner:RICOH KK
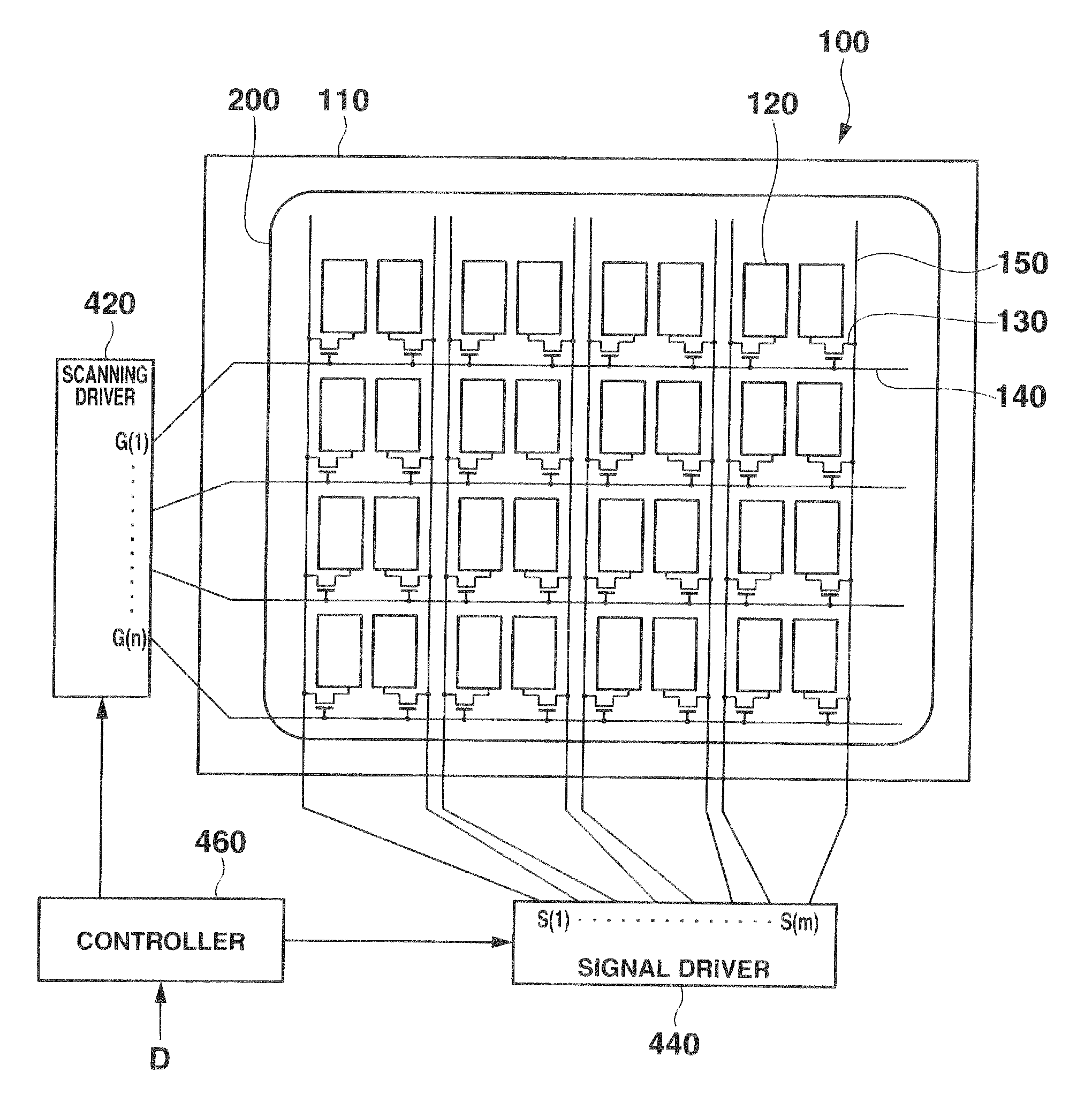
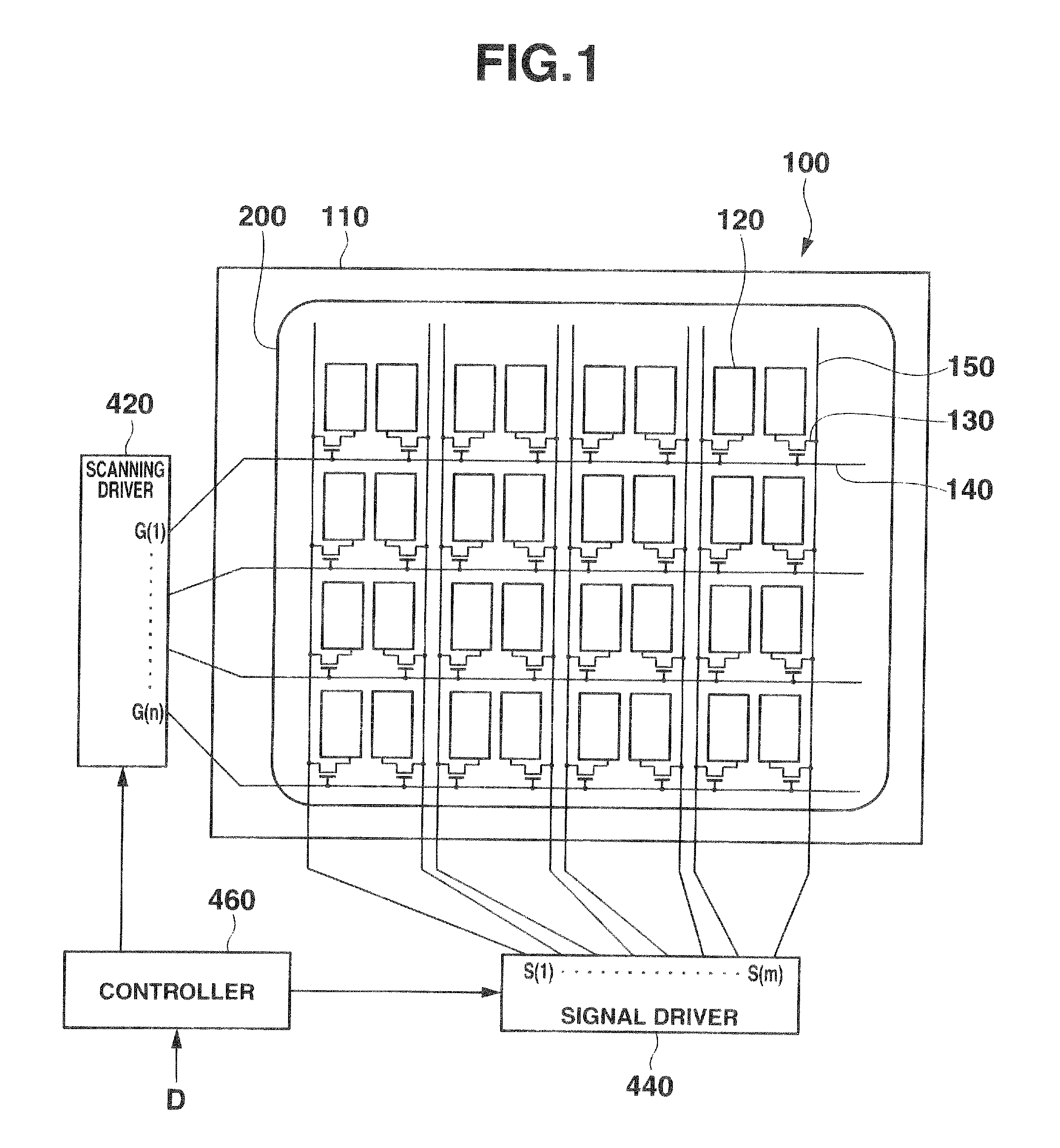
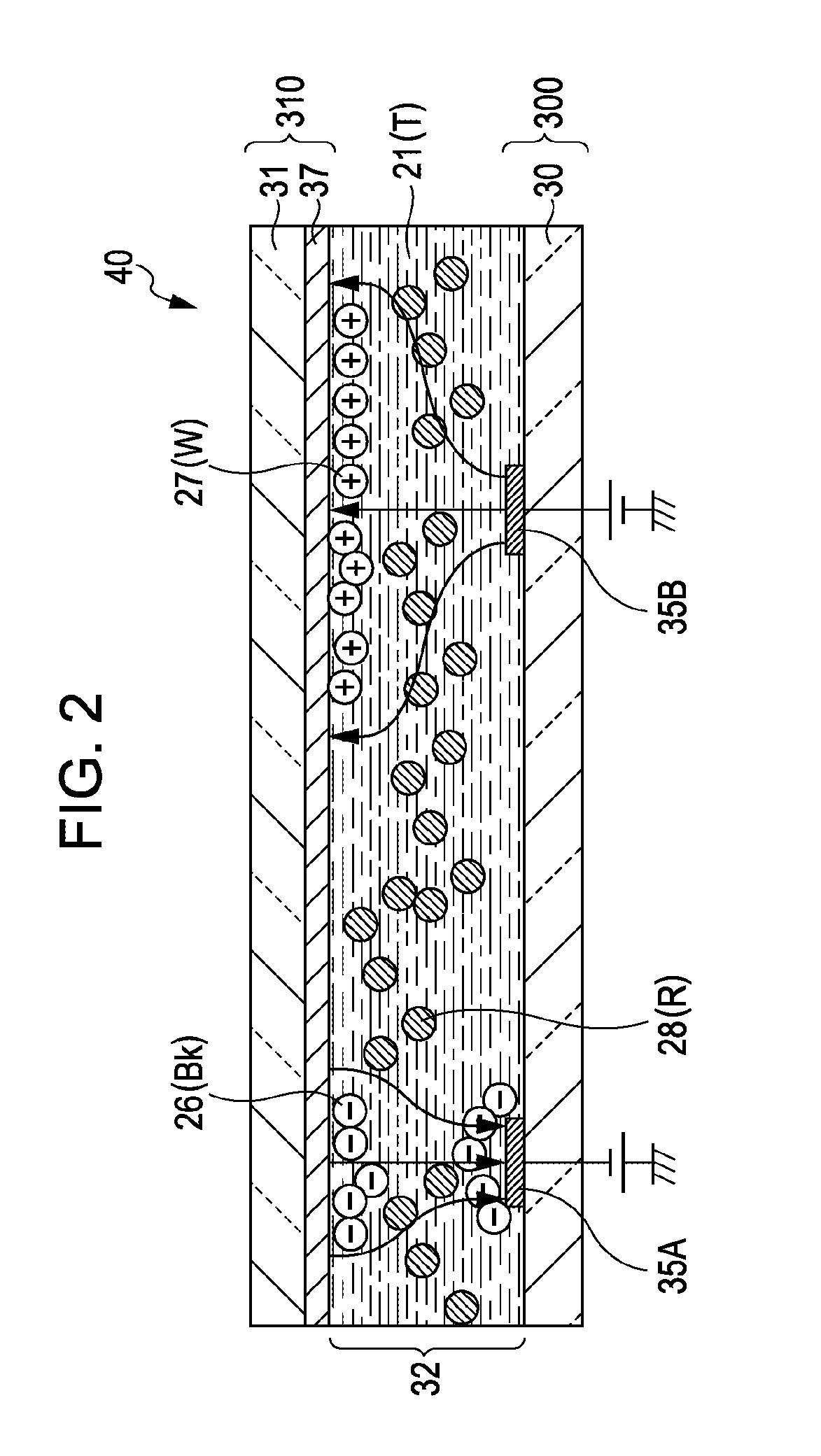
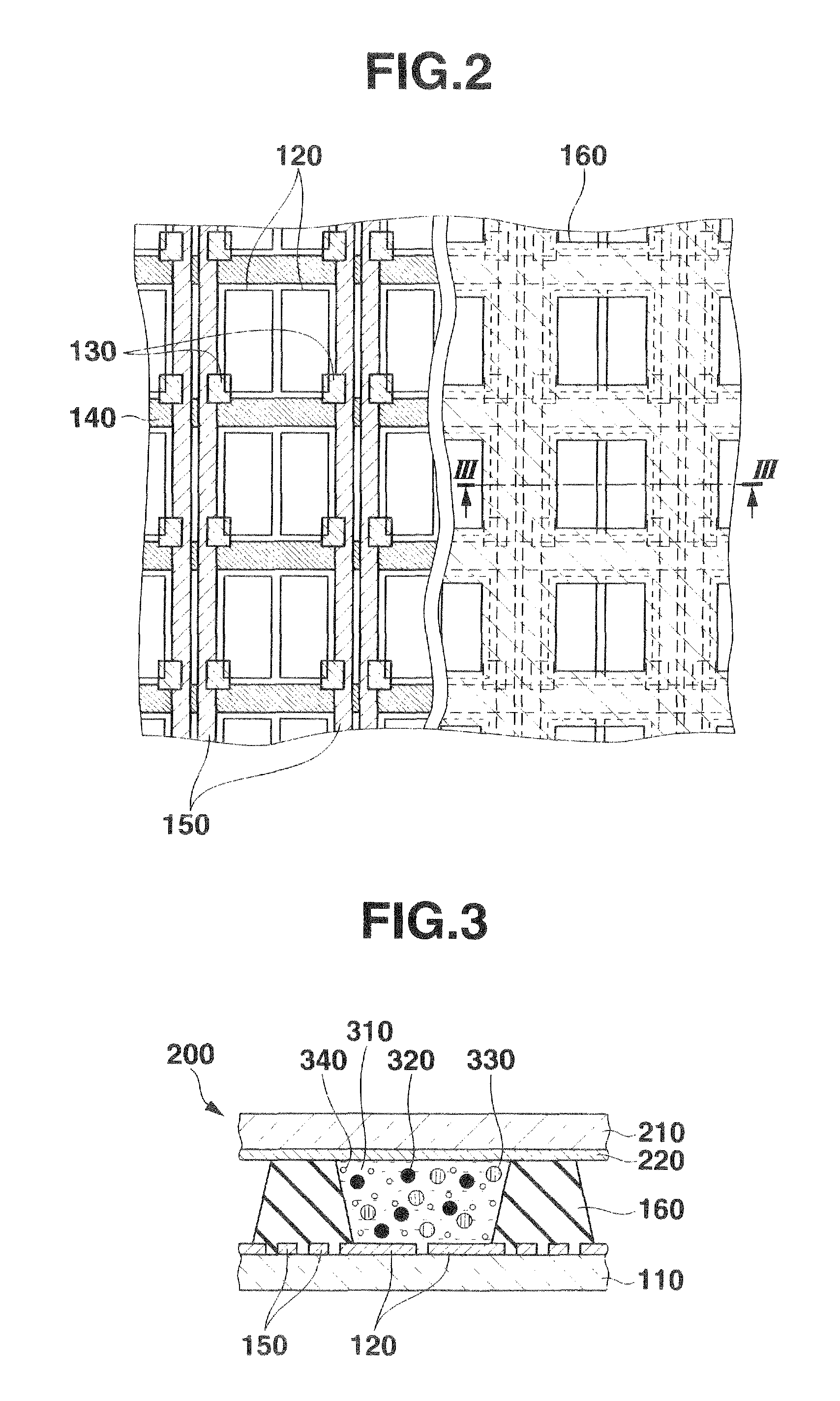
Electrophoretic display panel
An electrophoretic display panel includes a first substrate, a second substrate, a partition wall, first electrodes, a second electrode, a dispersant, positively-charged particles, negatively-charged particles, weakly-charged particles, switching thin film transistors, scanning lines, and signal lines. Pixel spaces are surrounded by the partition wall, the first substrate and the second substrate. Two of the first electrodes are formed on the first substrate in each pixel. The second electrode facing the first electrodes is formed on the second substrate. The dispersant with the positively-charged particles, the negatively-charged particles, and weakly-charged particles is contained in the pixel spaces. The switching thin film transistors are connected to the first electrode, and the signal line. The scanning lines supply scanning signals to gate electrodes of the switching thin film transistors. The signal lines input a data signal to the switching thin film transistors.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Dual ion trapping for ion/ion reactions in a linear RF multipole trap with an additional DC gradient
ActiveUS8604419B2Stability-of-path spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsMass analyzerNegatively charged particle
A novel method and mass spectrometer apparatus is introduced to enable the simultaneous isolation of cations and anions (i.e., precursor and reagent ions) in a linear multipole ion trap via the application of an additional axial DC gradient in combination with coupled RF potential(s). Thus, the combination of the RF and DC voltages in such an arrangement forms a pseudopotential designed to provide for minima for the trapped positively and negatively charged particles that result in the overlap of the ion clouds so as to provide for beneficial ion / ion reactions.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
Electrophoretic display device and driving method thereof
ActiveUS7755599B2Contrast prevented and improvedPersistence of and prevented and improvedStatic indicating devicesElectrophoresisScan line
An electrophoretic display device including a first substrate, a second substrate, an electrophoretic material interposed between the first substrate and the second substrate, the electrophoretic material including a positively charged particle and a negatively charged particle, a common electrode provided on the second substrate, a pixel provided at an intersection of a signal line and a scan line, the pixel provided in a plural number and arranged in matrix on the first substrate. The electrophoretic display device further including a pixel electrode provided in the pixel, a capacitor line provided in the pixel, a storage capacitor provided in the pixel, and a second electrode of the storage capacitor being coupled to a storage capacitor line and a thin film transistor (TFT) provided in the pixel, a source electrode of the TFT being coupled to a first electrode of the storage capacitor and the pixel electrode, a drain electrode of the TFT being coupled to the signal line, and a gate electrode of the TFT being coupled to the scan line. A capacitor line low select signal VSL or a capacitor line non-select signal VSC having a higher electric potential than an electric potential of the capacitor line low select signal VSL is supplied to the storage capacitor line.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
System and method for point-of-use filtration and purification of fluids used in substrate processing
ActiveUS7311847B2Reduce and eliminate particleReduce and eliminate and ionicIon-exchanger regenerationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityFiltration
Owner:AKRION TECH
Inductively coupled plasma flood gun using an immersed low inductance FR coil and multicusp magnetic arrangement
A device is disclosed for providing an inductively coupled radio frequency plasma flood gun. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the device is a plasma flood gun in an ion implantation system. The plasma flood gun may comprise a plasma chamber having one or more apertures; a gas source capable of supplying at least one gaseous substance to the plasma chamber; a single-turn coil disposed within the plasma chamber, and a power source coupled to the coil for inductively coupling radio frequency electrical power to excite the at least one gaseous substance in the plasma chamber to generate a plasma. The inner surface of the plasma chamber may be free of metal-containing material and the plasma may not be exposed to any metal-containing component within the plasma chamber. The plasma chamber may include a plurality of magnets for controlling the plasma. An exit aperture may be provided in the plasma chamber to enable negatively charged particles of the resulting plasma to engage an ion beam that is part of the associated ion implantation system. In one embodiment, magnets are disposed on opposite sides of the aperture and are used to manipulate the electrons of the plasma.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
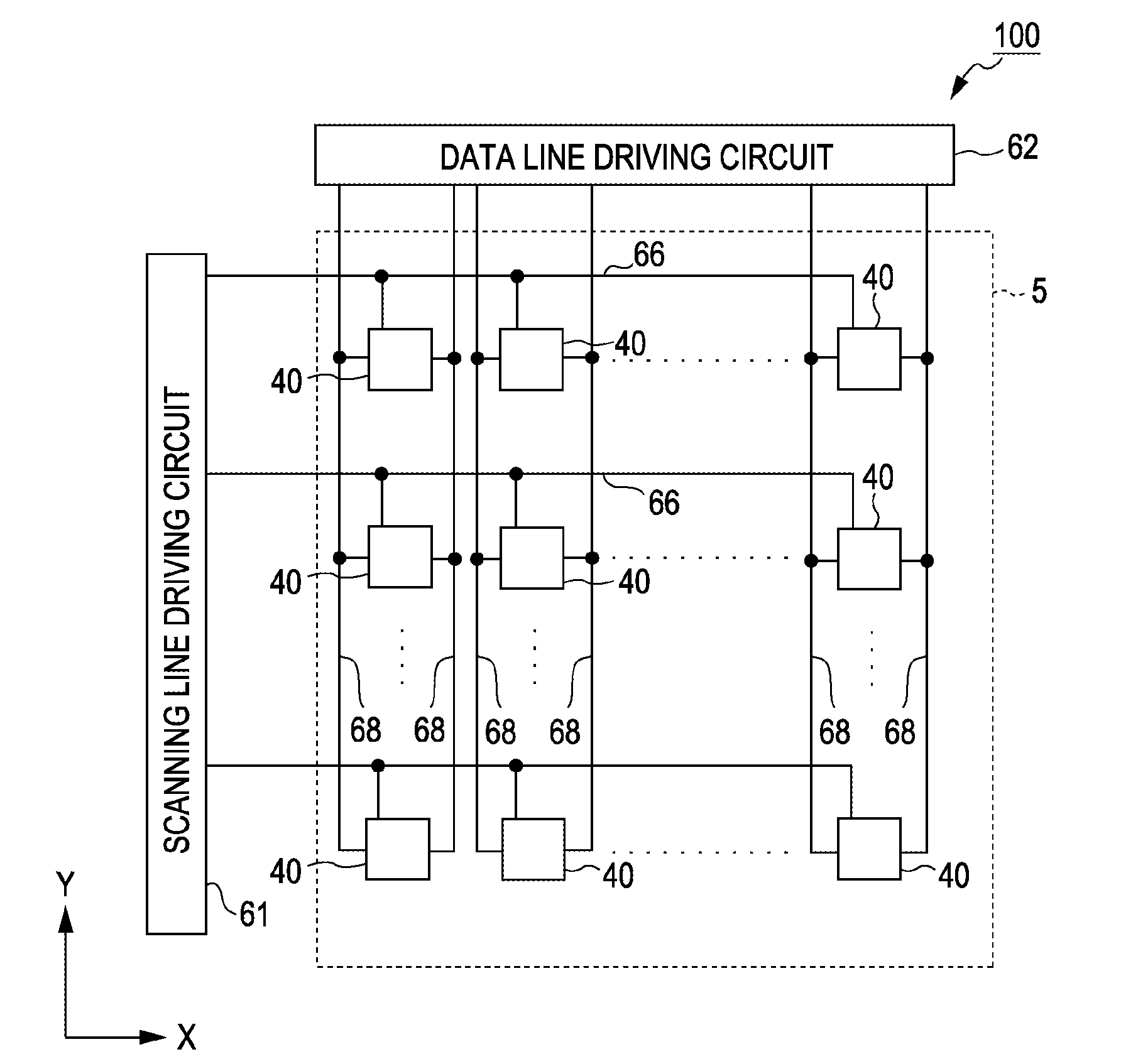
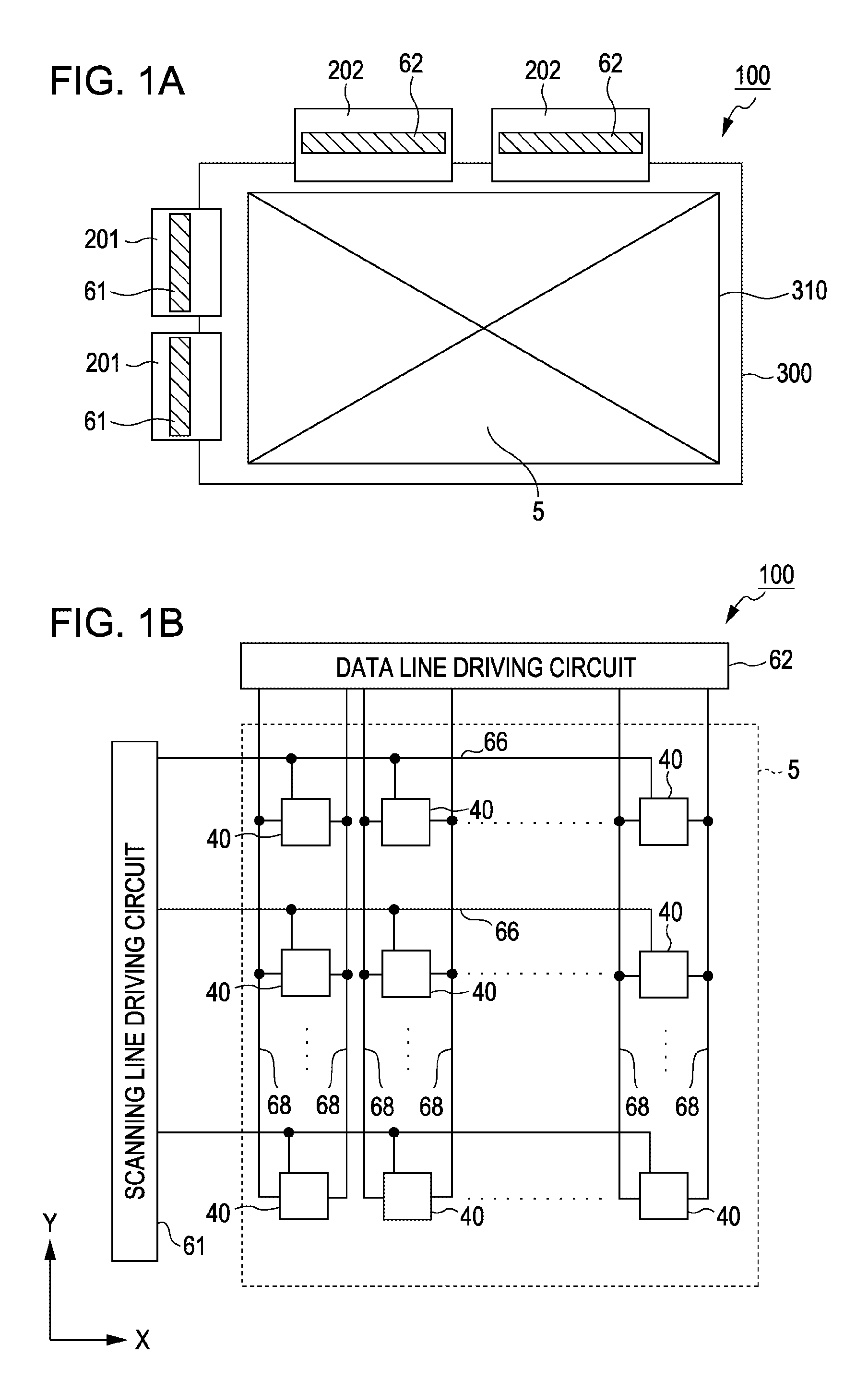
Electrophoretic display device, driving method therefor, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20110285756A1Smooth movementImprove color displayCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsElectrophoresisDisplay device
An electrophoretic display device includes a first substrate and a second substrate, an electrophoretic layer disposed between the first substrate and the second substrate and containing at least a dispersion medium and positively or negatively charged particles mixed in the dispersion medium, first electrodes formed in island shapes and driven independently in respective pixels on a side of the electrophoretic layer of the first substrate, a second electrode formed on a side of the electrophoretic layer of the second substrate and having a larger area than the first electrodes, transistors connected to the first electrodes, and a first control electrode disposed in at least part of an area where the first electrodes are absent above a drain electrode of a first transistor of the transistors. A potential for repelling the particles is applied to the first control electrode.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Electrostatic pellicle system for a mask
InactiveUS6921613B2Picture framesNanoinformaticsNegatively charged particlePositively charged particle
The present invention describes an apparatus comprising a mask; a pellicle spacer, the pellicle spacer attached to the mask; and an electrostatic pellicle system, the electrostatic pellicle system attached to the pellicle spacer.The present invention further describes a method of keeping contaminants away from a vicinity of a mask during exposure, the contaminants including an uncharged or neutral particle, a positively-charged particle, or a negatively-charged particle, comprising: inducing a positive or negative charge on the uncharged or neutral particle; attracting the positively-charged particle with a negatively-charged electric field; and attracting the negatively-charged particle with a positively-charged electric field.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Stripping member, a stripping assembly and a method for extracting a particle beam from a cyclotron
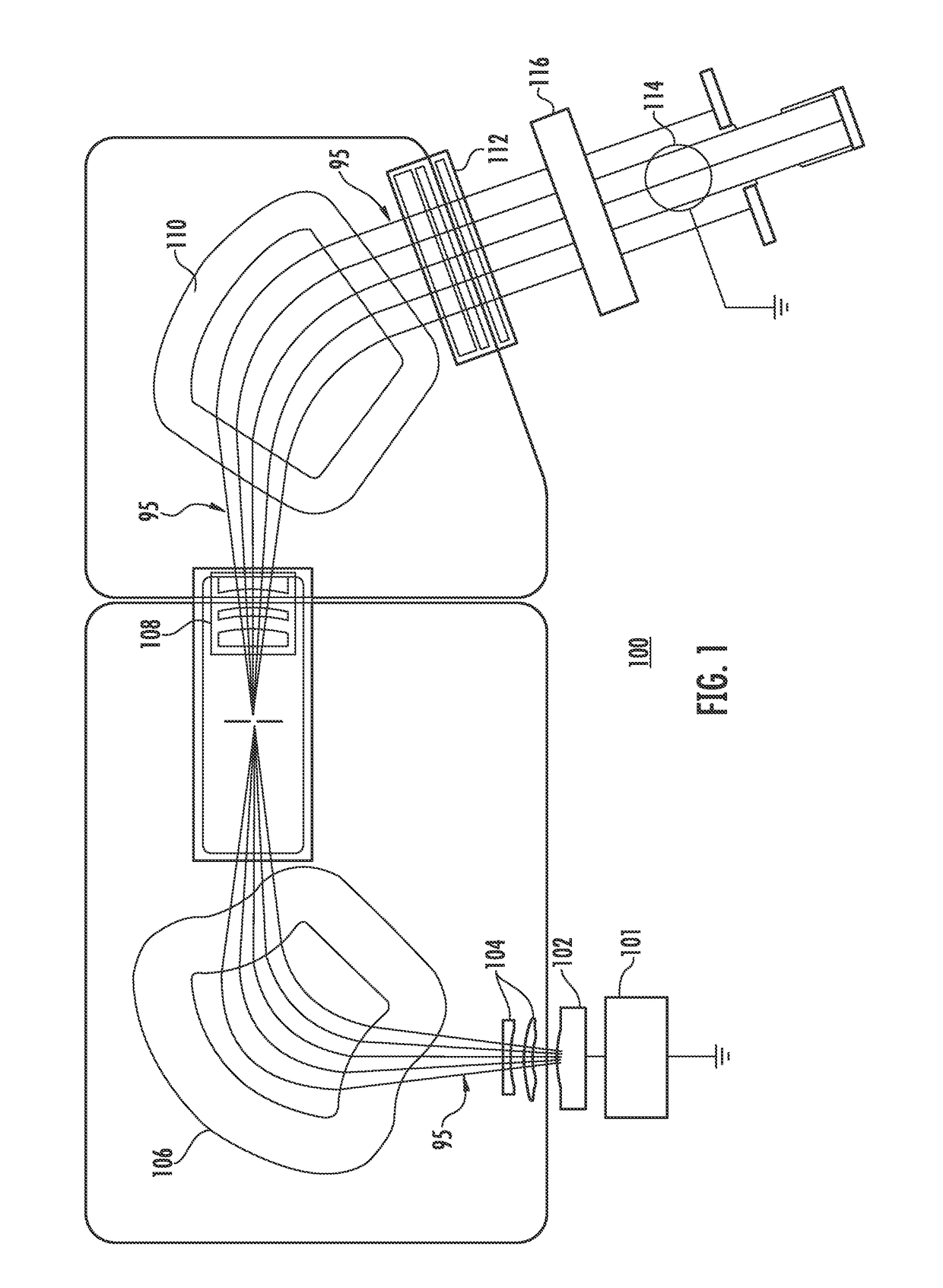
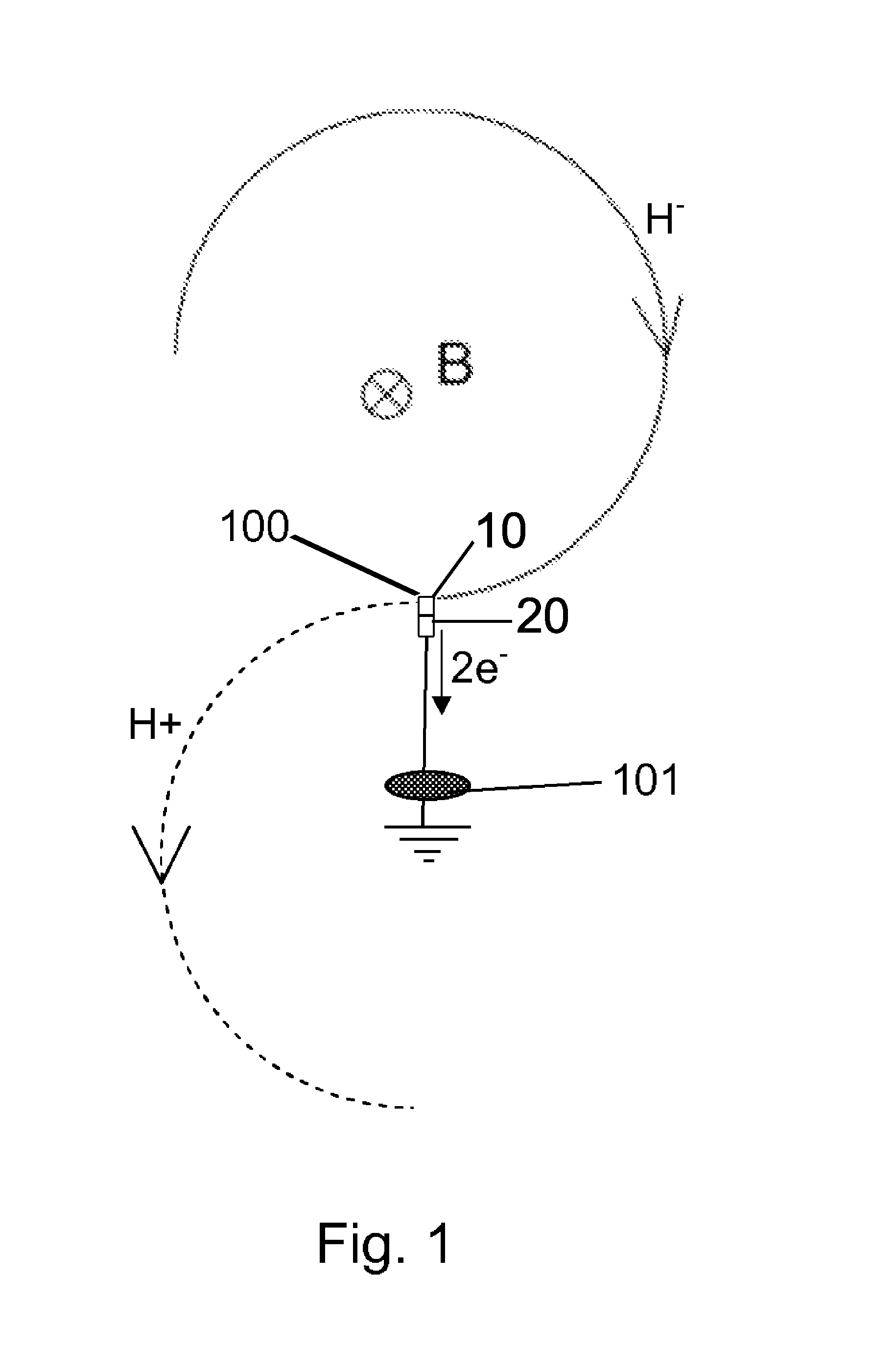
ActiveUS8432090B2Improve extraction efficiencyMagnetic resonance acceleratorsHandling using charge exchange devicesParticle beamNegatively charged particle
The present invention relates to a stripping member for stripping electrons off a negatively charged particle beam at the periphery of a cyclotron for extracting a particle beam out of said cyclotron, said stripping member comprising a first stripper foil adapted for being located at the periphery of said cyclotron so that said particle beam passes through said first stripper foil, characterized in that it comprises a second stripper foil adapted for being located side-by-side with the first foil at the periphery of said cyclotron at a more peripheral radius than said first stripper foil so that said negatively charged particle beam passes through said second stripper foil when said first stripper foil is damaged.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Electro-dielectro-phoretic display device and method thereof
ActiveUS20090046051A1Difficult to displayStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsElectrophoresisDisplay device
Electrophoretic particles and dielectrophoretic particles are included together in a unit pixel. Each of the electrophoretic particles and the dielectrophoretic particles includes two kinds of particles having different electric properties. The electrophoretic particles include positively charged particles and negatively charged particles. The dielectrophoretic particles include particles having low dielectric constant and particles having high dielectric constant. A first electric field for moving the electrophoretic particles and a second electric field for moving the dielectrophoretic particles are applied to the unit pixel. The second electric field has an asymmetric gradient in the direction where the dielectrophoretic particles move to determine movement directions of the dielectrophoretic particles having different dielectric constants.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
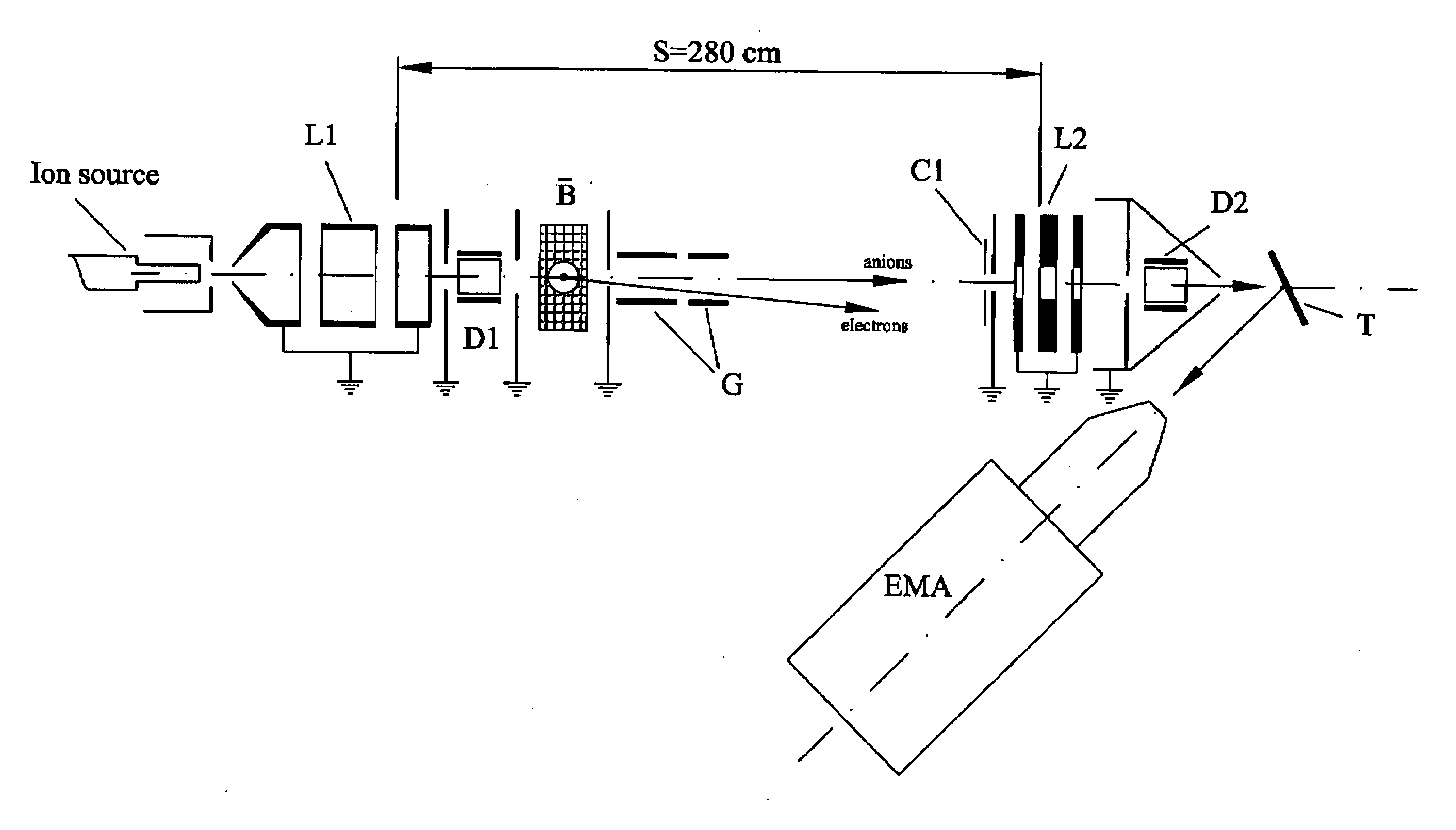
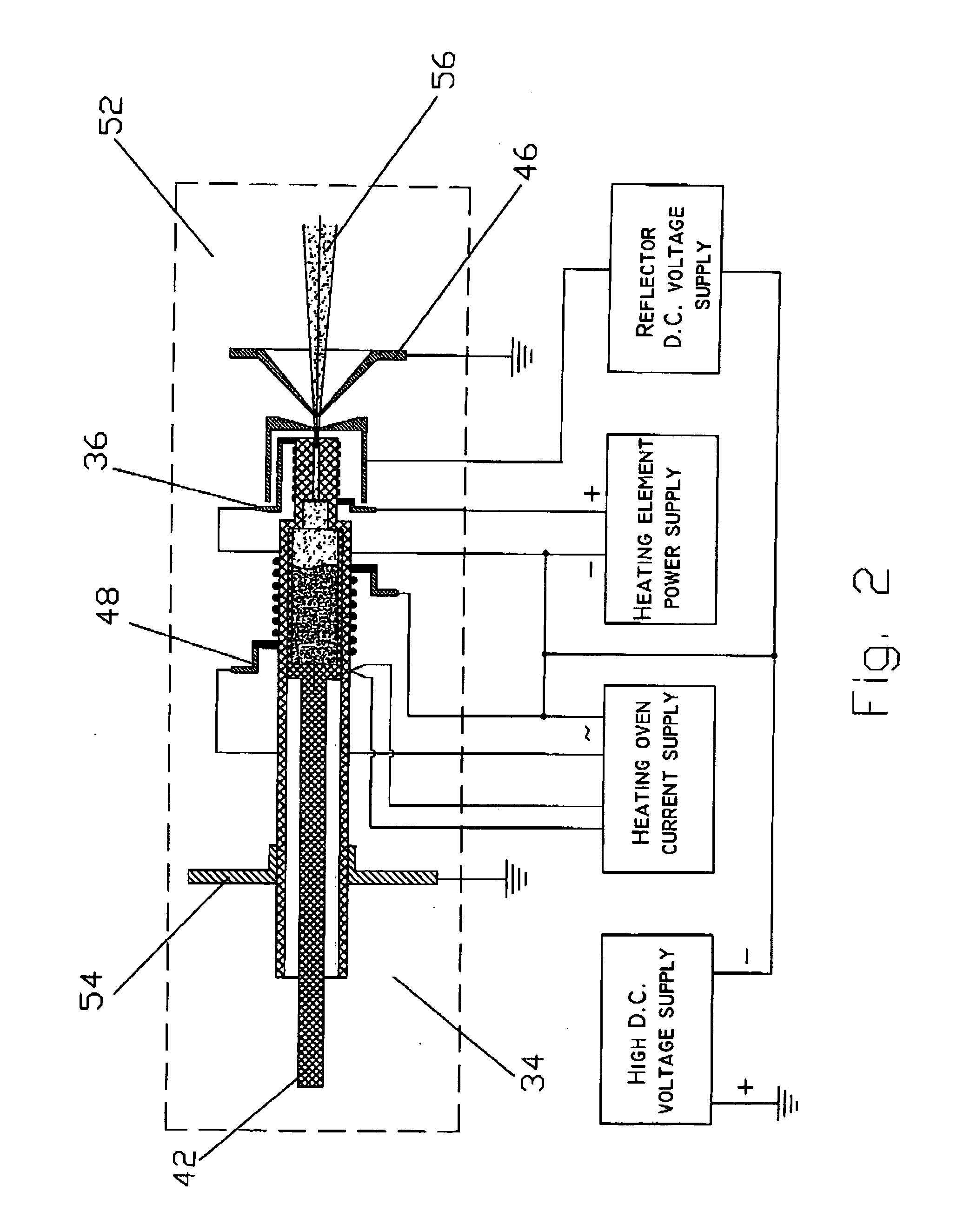
Method and apparatus for the generation of anionic and neutral particulate beams and a system using same
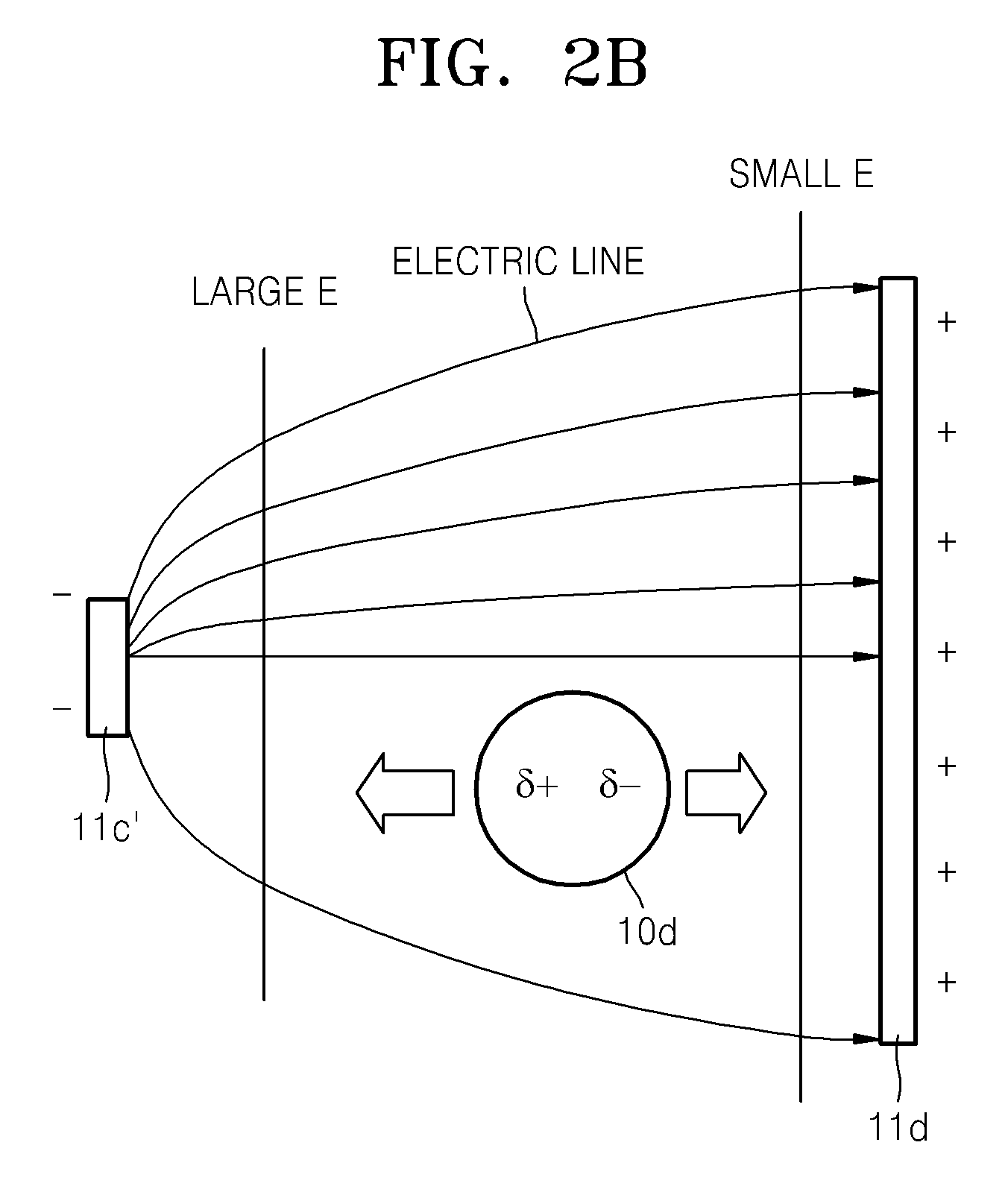
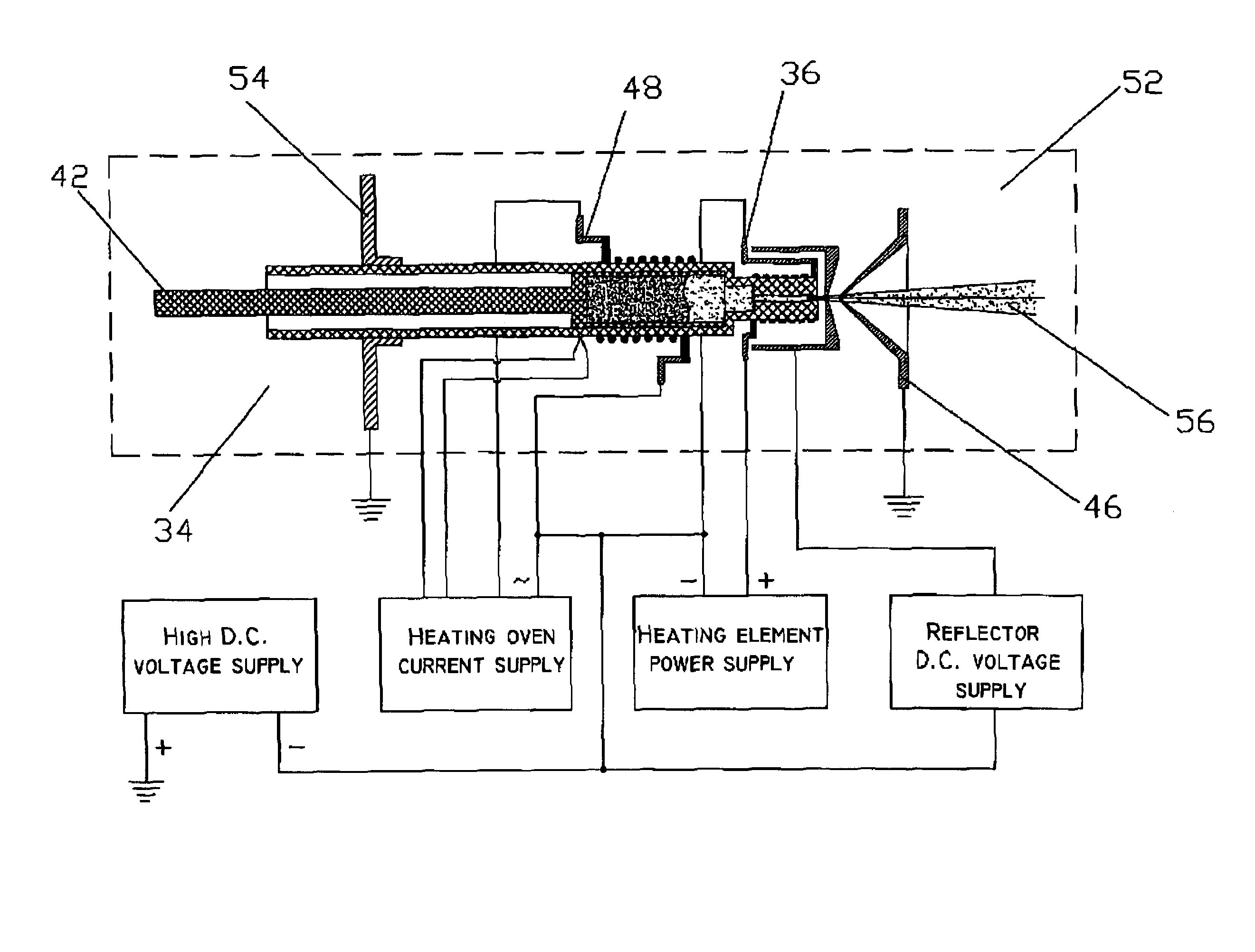
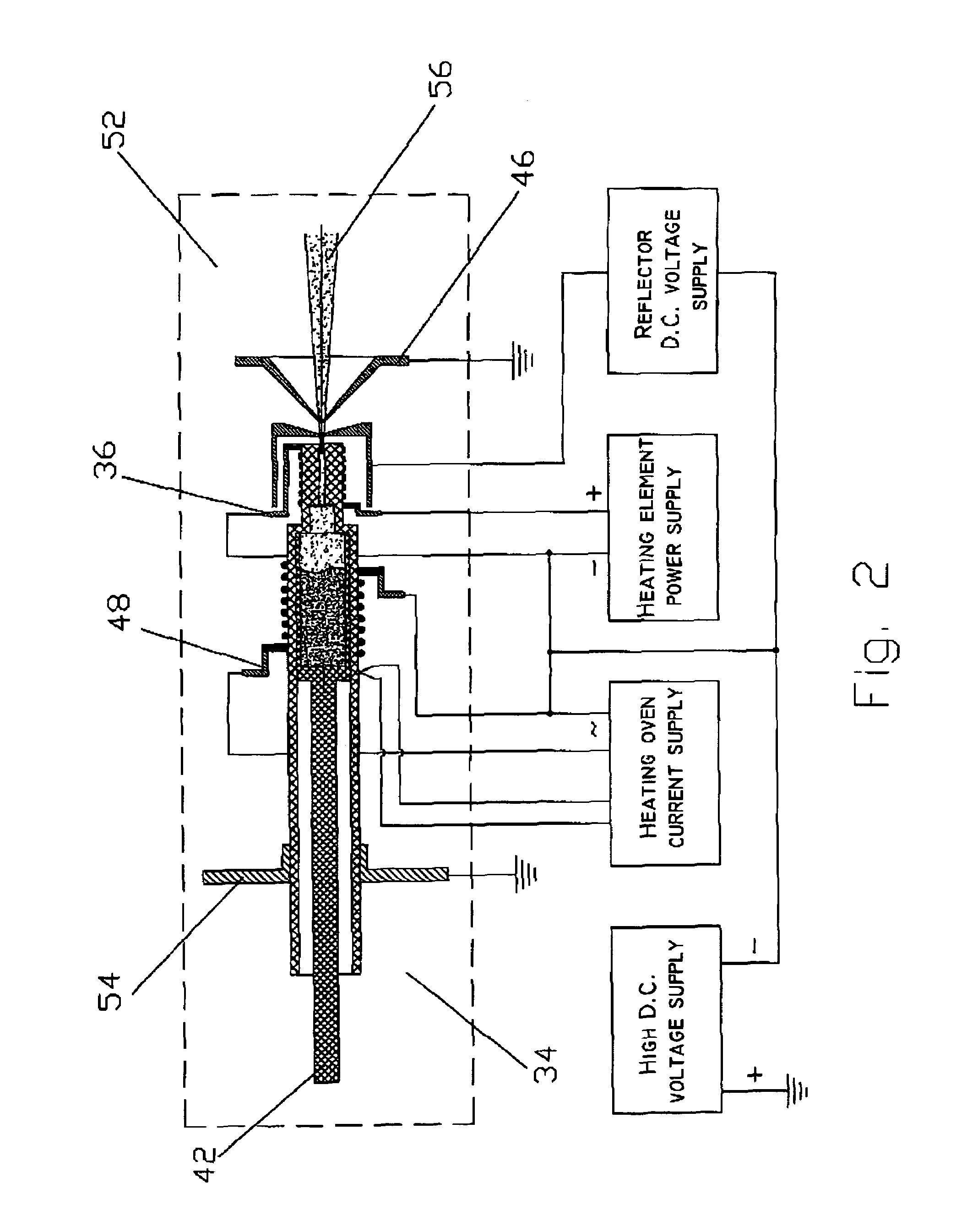
InactiveUS7235796B2Increase productionImprove efficiencyThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersParticulatesNegatively charged particle
An apparatus for the generation of anionic and neutral particulate beams is described. The apparatus comprises a duct defined by walls having an inner surface capable of sustaining a temperature above an electron emission temperature of the surface, so as to negatively charge electrically neutral particles being passed through the duct when the surface is heated to the temperature; a heating element for heating the inner surface to the temperature; and an acceleration electrode for ion-optically controlling and manipulating the negatively charged particles into the anion beam. The apparatus may further comprise a protection electrode defining a protected region, which substantially prevent emitted electrons from escaping the protected region. Moreover, a system for analyzing substances ejected from a surface of a sample bombarded with an anion beam generated by the apparatus is described. The system further comprises a detector for detecting the substances once ejected of the surface. Further, a method of generating an anion beam is described.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Air filtration device for closed environments
ActiveUS7473304B2Preserving healthLess frequent maintenanceCombination devicesMechanical apparatusAir filtrationEngineering
An air filtration device for suppressing biological pollutants for closed environments, including at least one enclosure with at least one air inlet, at which at least one perforated conducting grille is located, that has a present negative electrical potential adapted to emit electrons when air flows, so as to give negative electric charge to particles to which microorganisms adhere, at least one air passage duct being formed between at least one plate having predefined positive potential for collecting negatively charged particles to which microorganisms adhere, at least one deflector plate having a negative potential adapted to divert the particles to which microorganisms adhere, an electrical field being generated between the collector plate and the deflector plate, facing each other, the field to divert and precipitate the particles to which the microorganism adhere onto the collector plate, and an inactivator for inactivation of the microorganisms provided and at least one filtered air outlet.
Owner:DAITECH SA
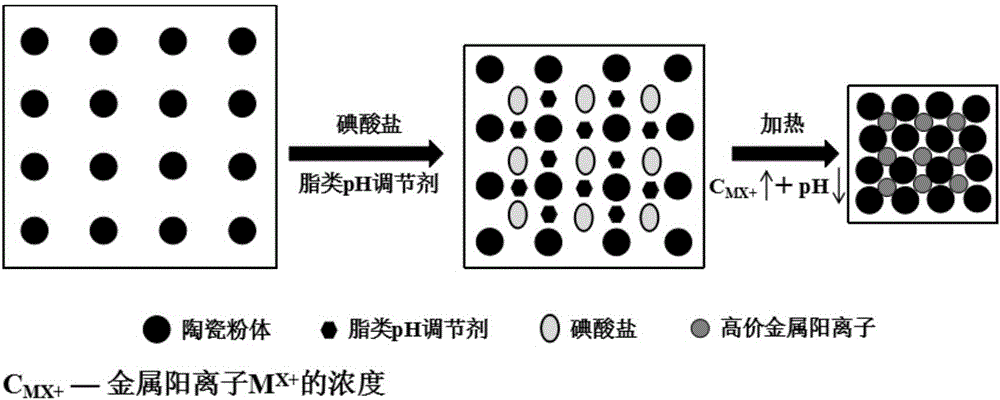
Method for rapidly curing ceramic slurry
InactiveCN106348736AIncrease ionic strengthAchieve direct curing moldingCeramic sinteringTemperature control
The invention discloses a method for rapidly curing ceramic slurry. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, mixing ceramic powder, a dispersant and water and sufficiently carrying out ball milling to prepare the ceramic slurry with a negatively-charged particle surface; then, adding iodate of high-valence metal cations and carrying out the ball milling; stirring the obtained slurry under a vacuum condition and degassing; then adding an esters pH (Potential of Hydrogen) regulator; after uniformly stirring, injecting the slurry into a pore-free mold; storing the pore-free mold at 45 DEG C to 70 DEG C for 15 minutes to 45 minutes; de-molding to obtain a ceramic wet blank; drying the ceramic wet blank to obtain a dry blank; then putting the dry blank into a sintering furnace and sintering to obtain a sintered ceramic body. According to the method provided by the invention, the common effect of decomposing the iodate through temperature control to release the high-valence metal cations and decomposing and regulating the pH value to an isoelectric point through the esters pH regulator realizes rapid curing and molding of the ceramic slurry; the method has the advantages that the method is suitable for any ceramic slurry with negative charges, is rapid in curing speed, high in slurry molding efficiency, environment-friendly, excellent in performance and simple to operate, is convenient for large-scale production and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Display apparatus and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20080316168A1Reduce contrastInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsNegatively charged particlePositively charged particle
A display apparatus includes a first substrate provided with a plurality of closed containers, a fluid filled in the closed containers, a plurality of positively charged particles which have a relative dielectric constant different from the fluid and are dispersed and held in the fluid, a plurality of negatively charged particles which have a same color as the positively charged particles and a relative dielectric constant different from the fluid and are dispersed and held in the fluid, and a pair of electrodes for generating an electric field in the closed containers. The display apparatus displays an image formed by a positional distribution of positively and negatively charged particles in each of the closed containers.
Owner:CANON KK
Electrophoretic display panel
An electrophoretic display panel includes a first substrate, a second substrate, a partition wall, first electrodes, a second electrode, a dispersant, positively-charged particles, negatively-charged particles, weakly-charged particles, switching thin film transistors, scanning lines, and signal lines. Pixel spaces are surrounded by the partition wall, the first substrate and the second substrate. Two of the first electrodes are formed on the first substrate in each pixel. The second electrode facing the first electrodes is formed on the second substrate. The dispersant with the positively-charged particles, the negatively-charged particles, and weakly-charged particles is contained in the pixel spaces. The switching thin film transistors are connected to the first electrode, and the signal line. The scanning lines supply scanning signals to gate electrodes of the switching thin film transistors. The signal lines input a data signal to the switching thin film transistors.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
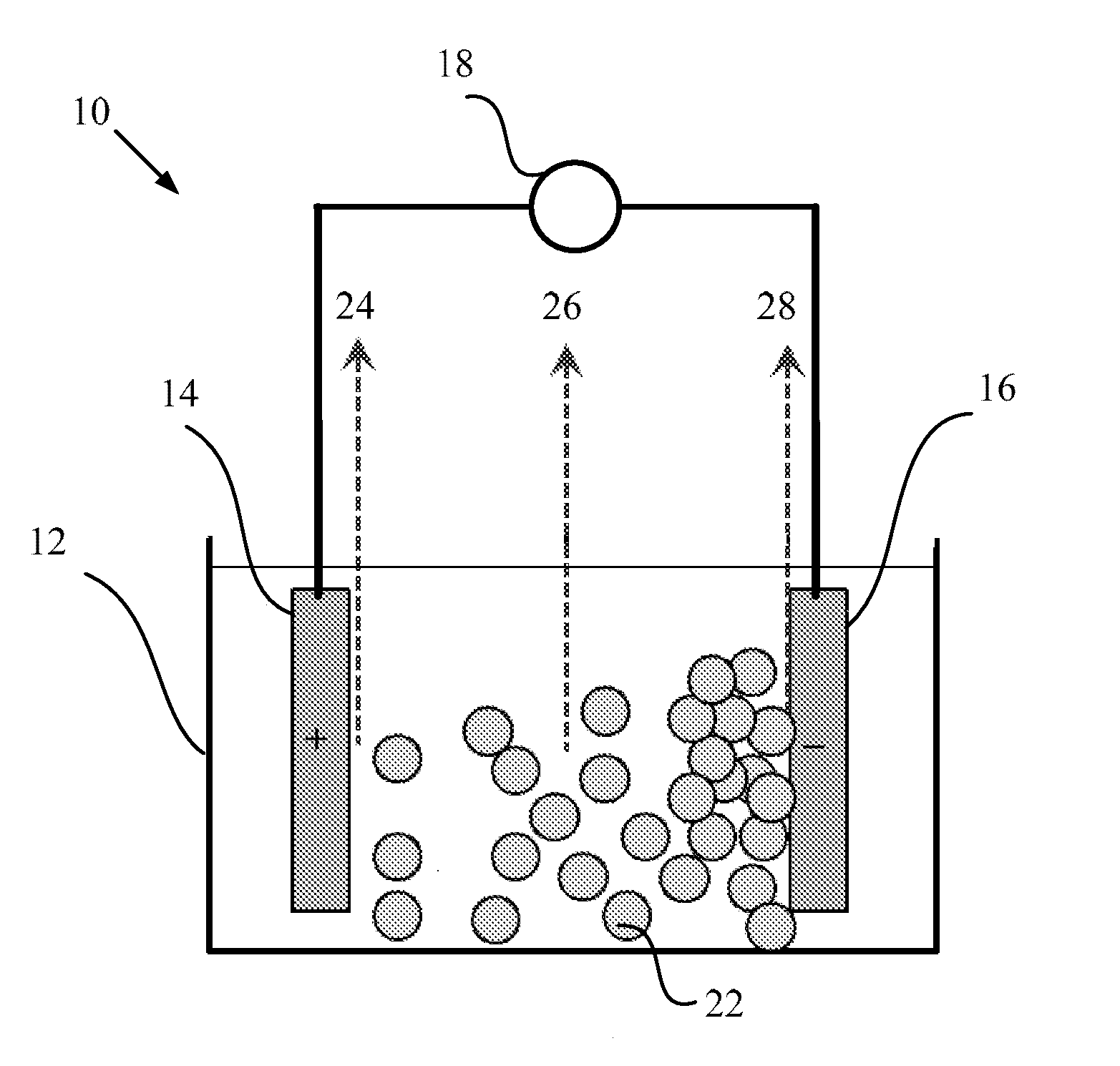
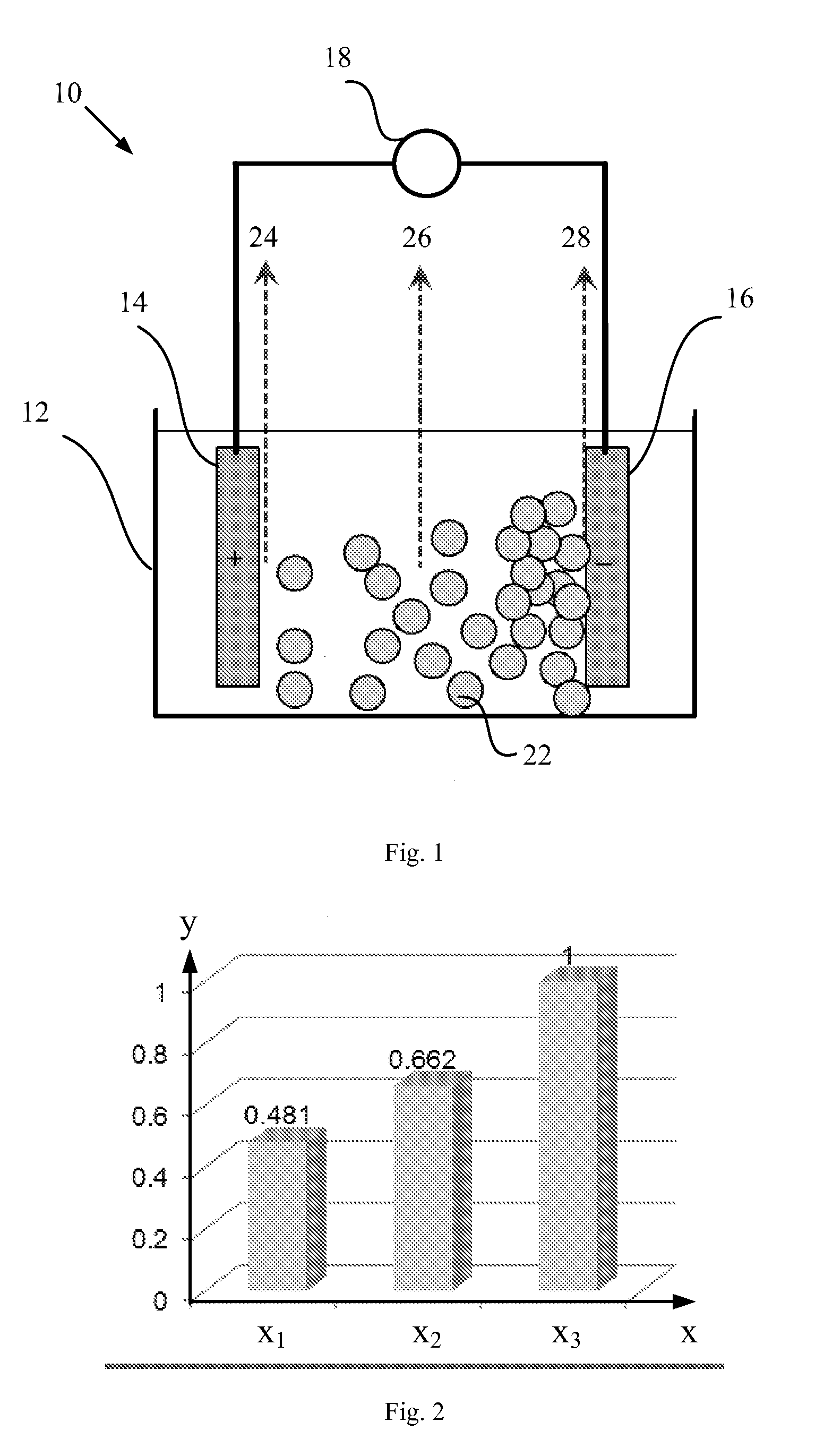
Method and device for sensing a liquid
InactiveUS20150293056A1High sensitivitySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementNegatively charged particlePositively charged particle
The invention proposes a method and device for sensing a liquid that contains positively charged particles and / or negatively charged particles. An electrical field is imposed to the liquid by applying a voltage to a positive electrode and a negative electrode disposed in the liquid, for attracting the negatively charged particles toward the positive electrode to concentrate the negatively charged particles in a first part of the liquid and attracting the positively charged particles toward the negative electrode to concentrate the positively charged particles in a second part of the liquid. A first sensing result is obtained by sensing at least one part of liquid of the first part of the liquid, the second part of the liquid, and a third part of the liquid in which the negatively charged particles and the positively charged particles are deconcentrated. Accordingly, the sensing is conducted in at least one part of liquid in which the concentration of the charged particles is changed. Since the concentration of the particles in the liquid impacts the sensitivity of the sensing of the liquid, it is possible to improve the sensitivity.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method for solidifying ceramic slurry by employing metal ions in temperature-controlled slow-release sintering aid
ActiveCN106747480ARealize direct solidification moldingImprove uniformityCeramic materials productionCeramic sinteringTemperature control
The invention discloses a method for solidifying ceramic slurry by employing metal ions in a temperature-controlled slow-release sintering aid. The method comprises the following steps of firstly mixing ceramic powder, a dispersing agent, a metallic oxide sintering aid and water, carrying out full ball-milling to obtain the ceramic slurry with negatively charged particle surfaces; carrying out vacuum mixing on the slurry to degas and then adding an ester pH modifier, stirring evenly and then injecting a mixture into a mold, standing at 35-70 DEG C for 1-5 hours, demolding to obtain a wet ceramic body and drying to obtain a dry body; and then sintering to obtain a ceramic sintering body. An acid is decomposed from the ester pH modifier through temperature control to react with the sintering aid in the slurry to release highly-valence counter ions, so that direct coagulation casting of the ceramic slurry is achieved. A biscuit prepared by the method is good in uniformity; the sintering temperature can be effectively reduced and the consistency and the overall mechanical property of a sintered part can be effectively improved through adding the sintering aid; the method has the advantages of being suitable for any negatively charged ceramic slurry, friendly to environment and simple in operation; and massive production is easy to implement.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Hybrid Ionomer Electrochemical Devices
InactiveUS20150064581A1Reduced specieOvercome disadvantagesSolid electrolytesCell electrodesIonomerProton
A membrane electrode assembly for use in a fuel cell includes an anode electrode, a proton exchange membrane, an anion exchange membrane and a cathode electrode. The anode electrode includes a first catalyst. The first catalyst separates a reducing agent into a plurality of positively charged ions and negative charges. The proton exchange membrane is configured to favor transport of positively charged ions therethrough and is also configured to inhibit transport of negatively charged particles therethrough. The anion exchange membrane is configured to favor transport of negatively charged ions therethrough and is also configured to inhibit transport of positively charged ions therethrough. The cathode electrode includes a second catalyst and is disposed adjacent to a second side of the anion exchange membrane. The second catalyst reacts electrons with the at least one oxidizing agent so as to generate+reduced species.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Method and apparatus for the generation of anionic and neutral particulate beams and a system using same
InactiveUS20060118405A1Increase productionImprove efficiencyThermometer detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansParticulatesNegatively charged particle
An apparatus for the generation of anionic and neutral particulate beams is described. The apparatus comprises a duct defined by walls having an inner surface capable of sustaining a temperature above an electron emission temperature of the surface, so as to negatively charge electrically neutral particles being passed through the duct when the surface is heated to the temperature; a heating element for heating the inner surface to the temperature; and an acceleration electrode for ion-optically controlling and manipulating the negatively charged particles into the anion beam. The apparatus may further comprise a protection electrode defining a protected region, which substantially prevent emitted electrons from escaping the protected region. Moreover, a system for analyzing substances ejected from a surface of a sample bombarded with an anion beam generated by the apparatus is described. The system further comprises a detector for detecting the substances once ejected of the surface. Further, a method of generating an anion beam is described.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
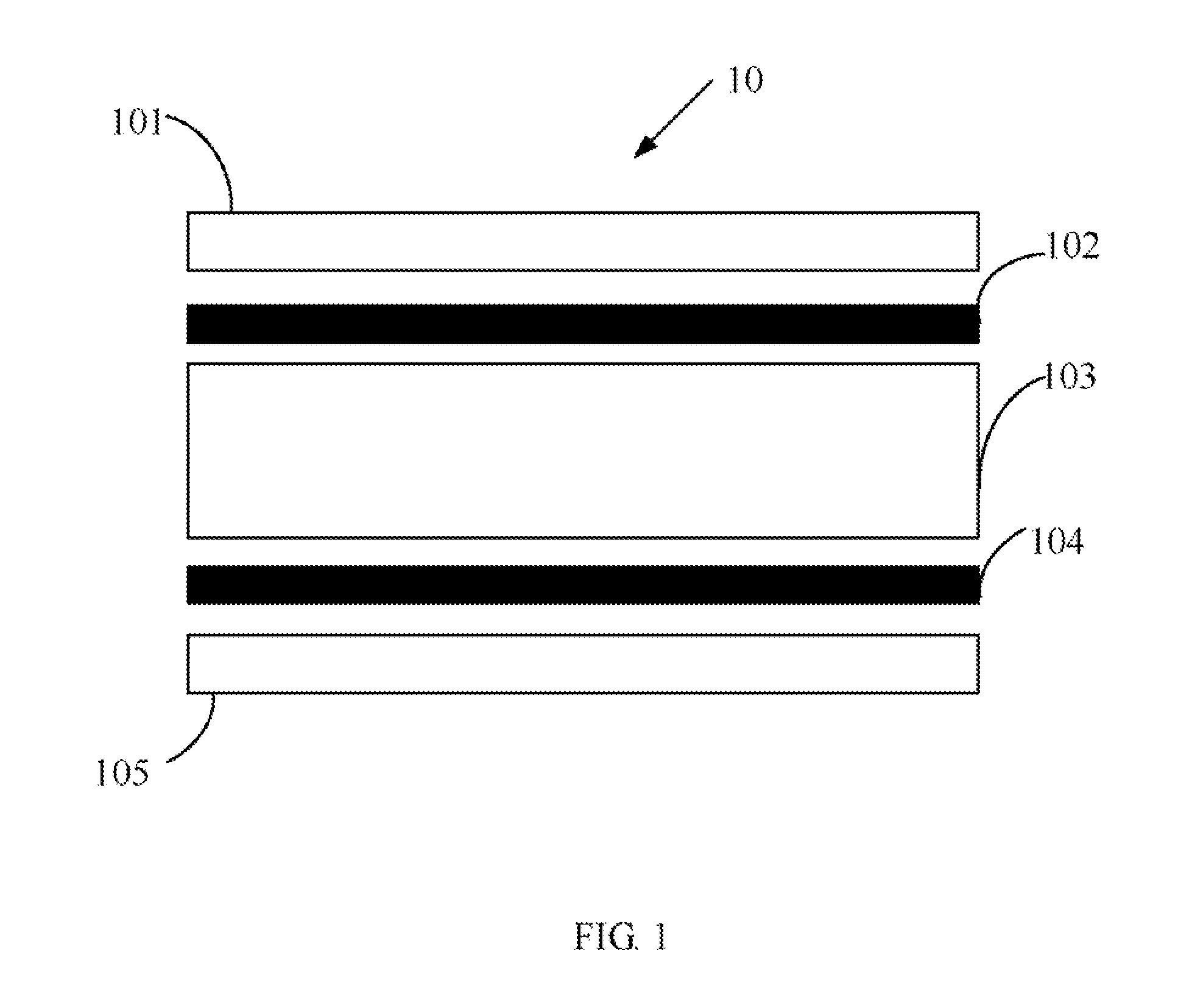
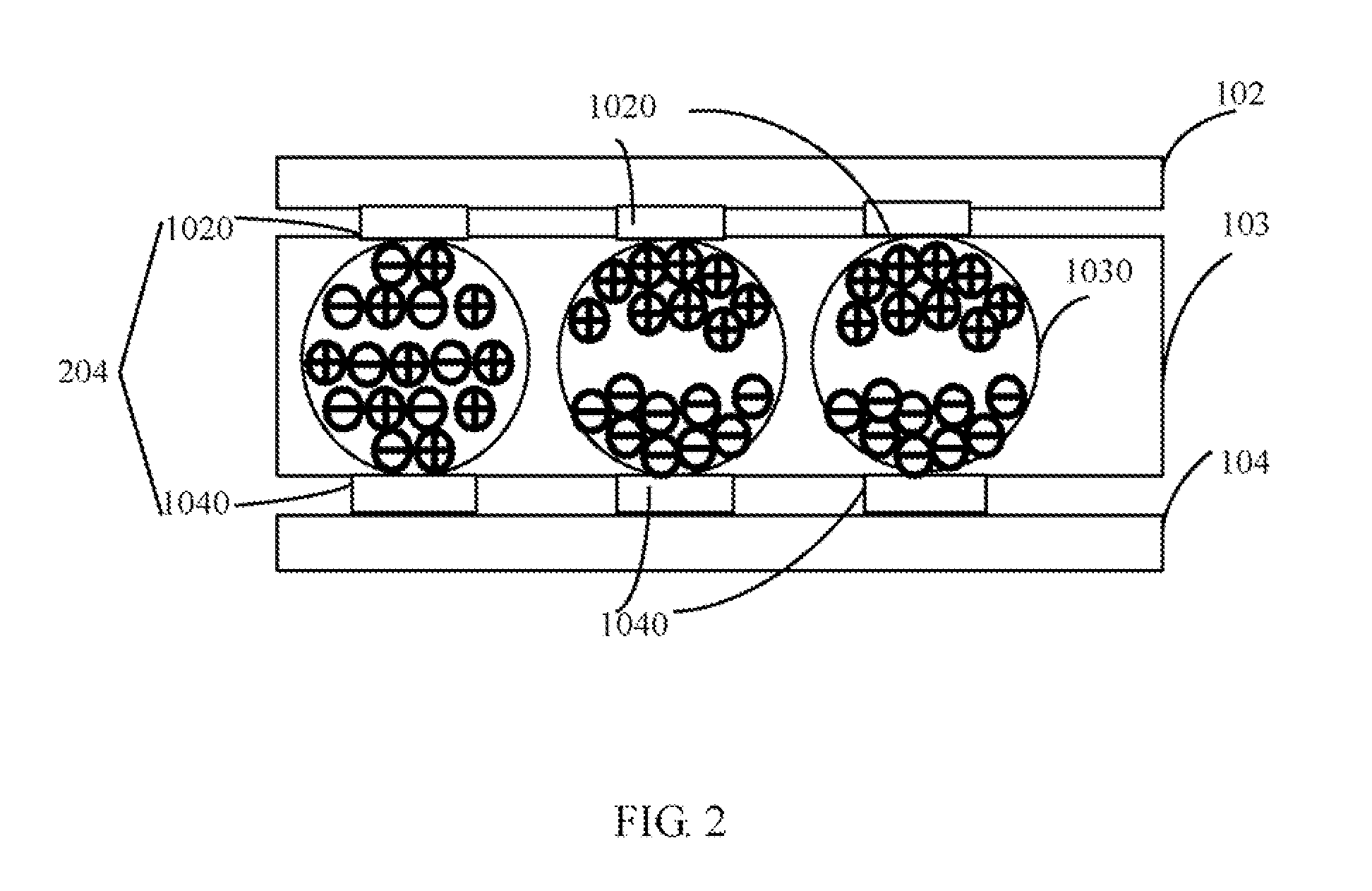
Touch panel and electronic device using the same
InactiveUS20110032195A1Static indicating devicesInput/output processes for data processingIndium tin oxideEngineering
A touch panel includes a touch layer, a first Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) electrode layer, a second ITO layer, and a microcapsule layer. The first ITO electrode layer includes a plurality of first ITO electrode. The second ITO electrode layer includes a plurality of second ITO electrodes. Each of the first ITO electrodes and one corresponding second ITO electrode forms an electrode unit. The microcapsule layer includes a plurality of microcapsules. Each microcapsule is connected to the first ITO electrode and the corresponding second ITO electrode. Each microcapsule comprises a plurality of positively charged particles and negatively charged particles. When the touch panel is touched, the distribution of the positively and negatively charged particles in the microcapsule corresponding to the touch portion of the touch layer is placed in a polarization state. An electronic device using the touch panel is also provided.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Negative static electrically charged coating method and composition for repelling dust from glass
A liquid which has a negative static electrical charge is coated onto positive static electrically charged glass windows, automobile and truck windshields and glass mirrors, causing the surfaces to become negatively charged. Since like static electrical charges will repel each other, the negative static electrically charged liquid coating will repel negative static electrically charged human fibers, dust and other negatively charged particles. The liquid can be coated onto the surface and then rubbed to a thin film by using a paper or fabric sheet or a circular rotating polisher. The liquid can also be pre-coated onto a paper or fabric sheet or a circular rotating polisher and then rubbed onto the surface to produce a thin film. If the film is not thin, the coating will be streaked. The coating is water insoluble and preferably is a water insoluble silicone, preferably in an amount of at least 70% silicone and most preferably comprises dimethylsiloxane or polydimethylsiloxane. The coating can be mixed with a water insoluble organic solvent and should have a viscosity in the range of 5-50 centistokes.
Owner:ROOD LEONARD D
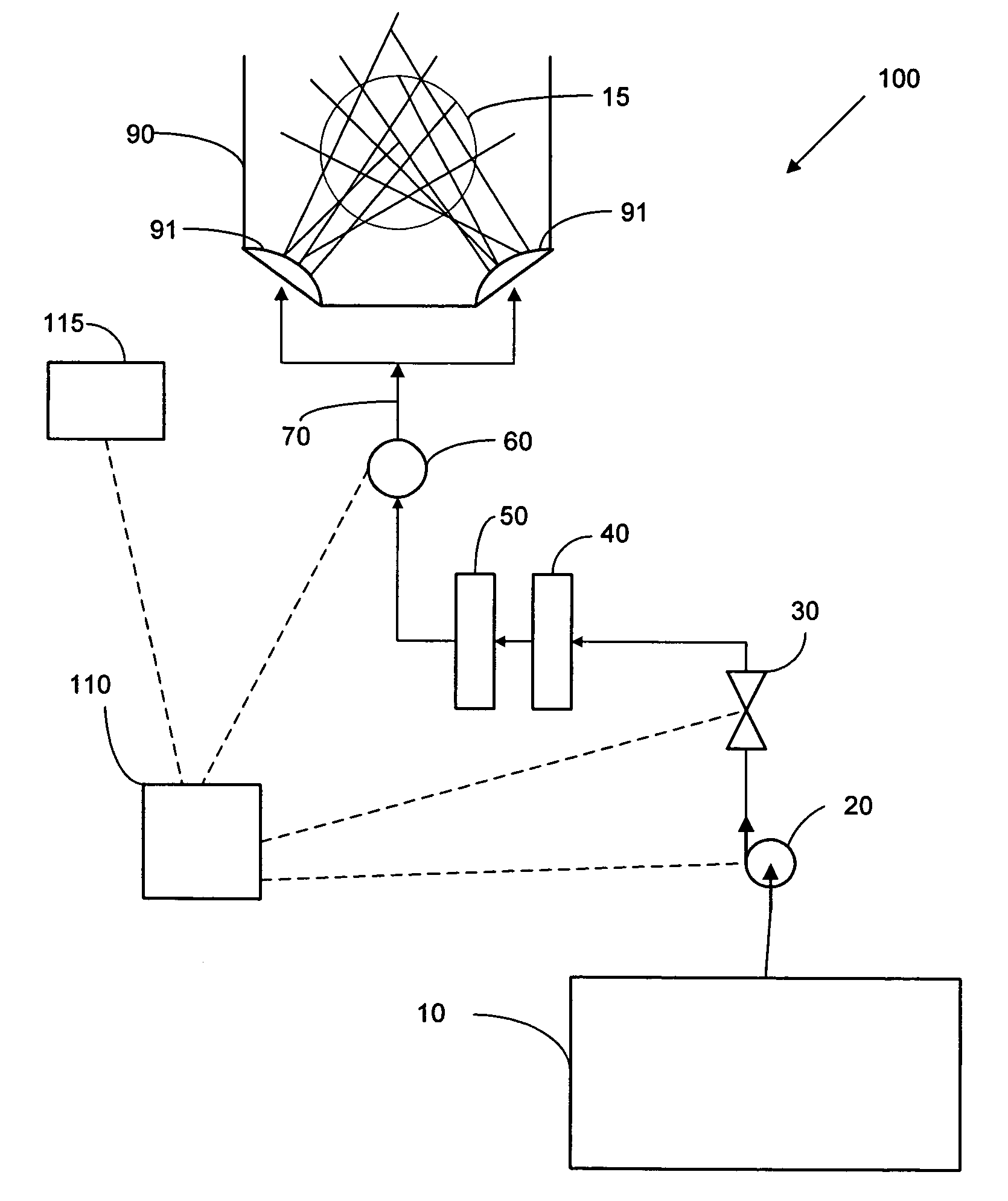
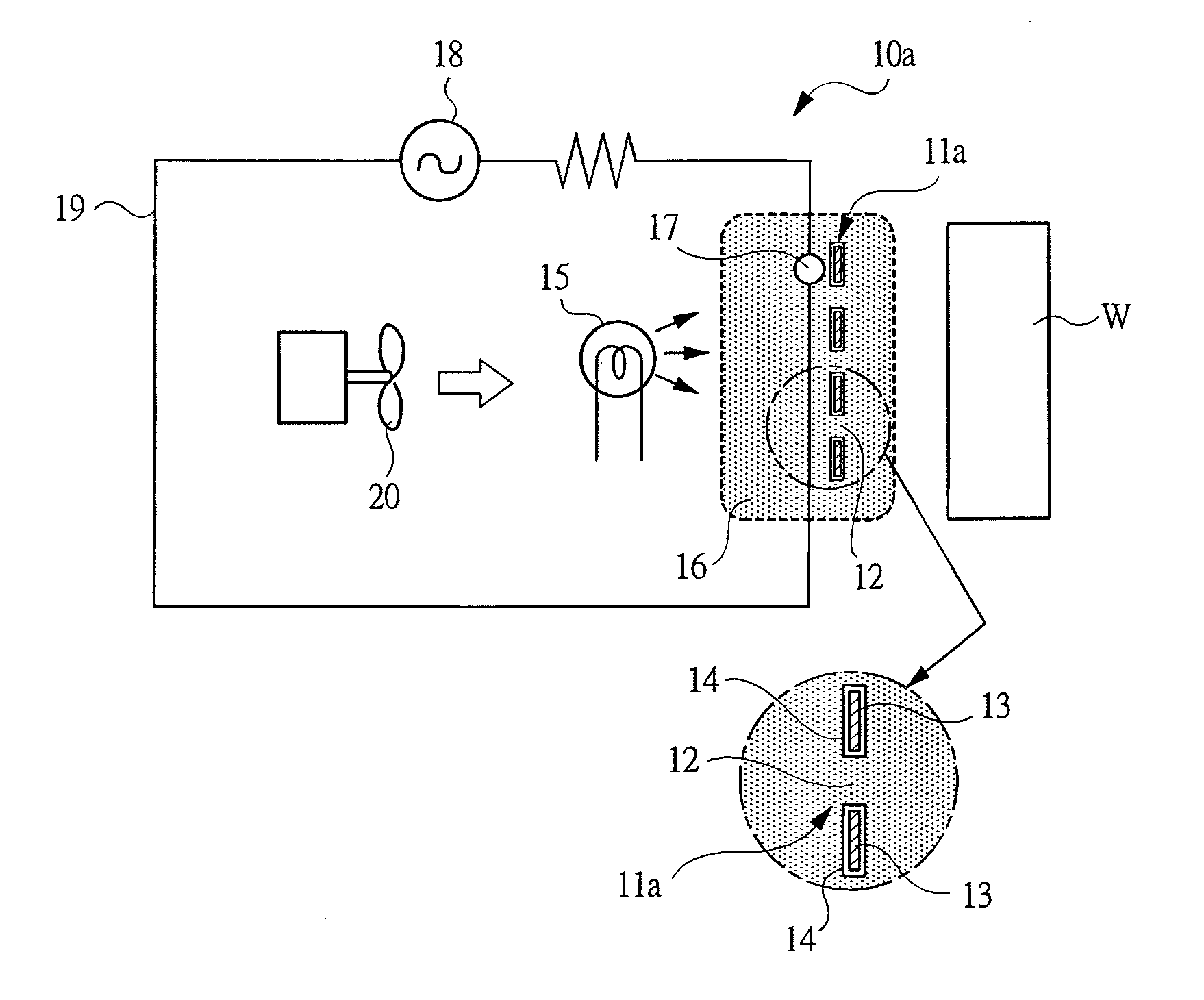
Ion generator
InactiveUS20100172808A1A large amountEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesElectrostatic chargesForeign matterElectricity
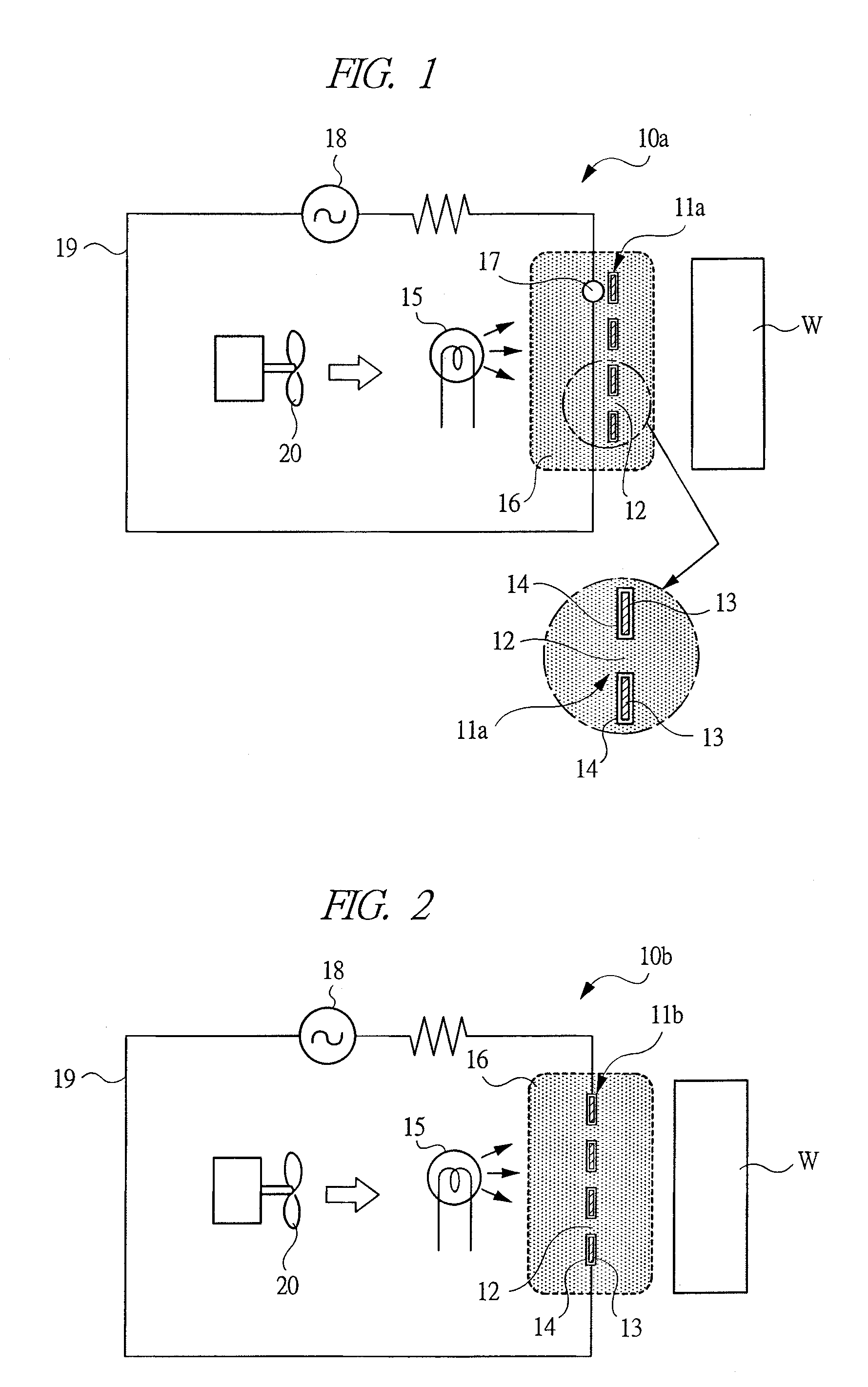
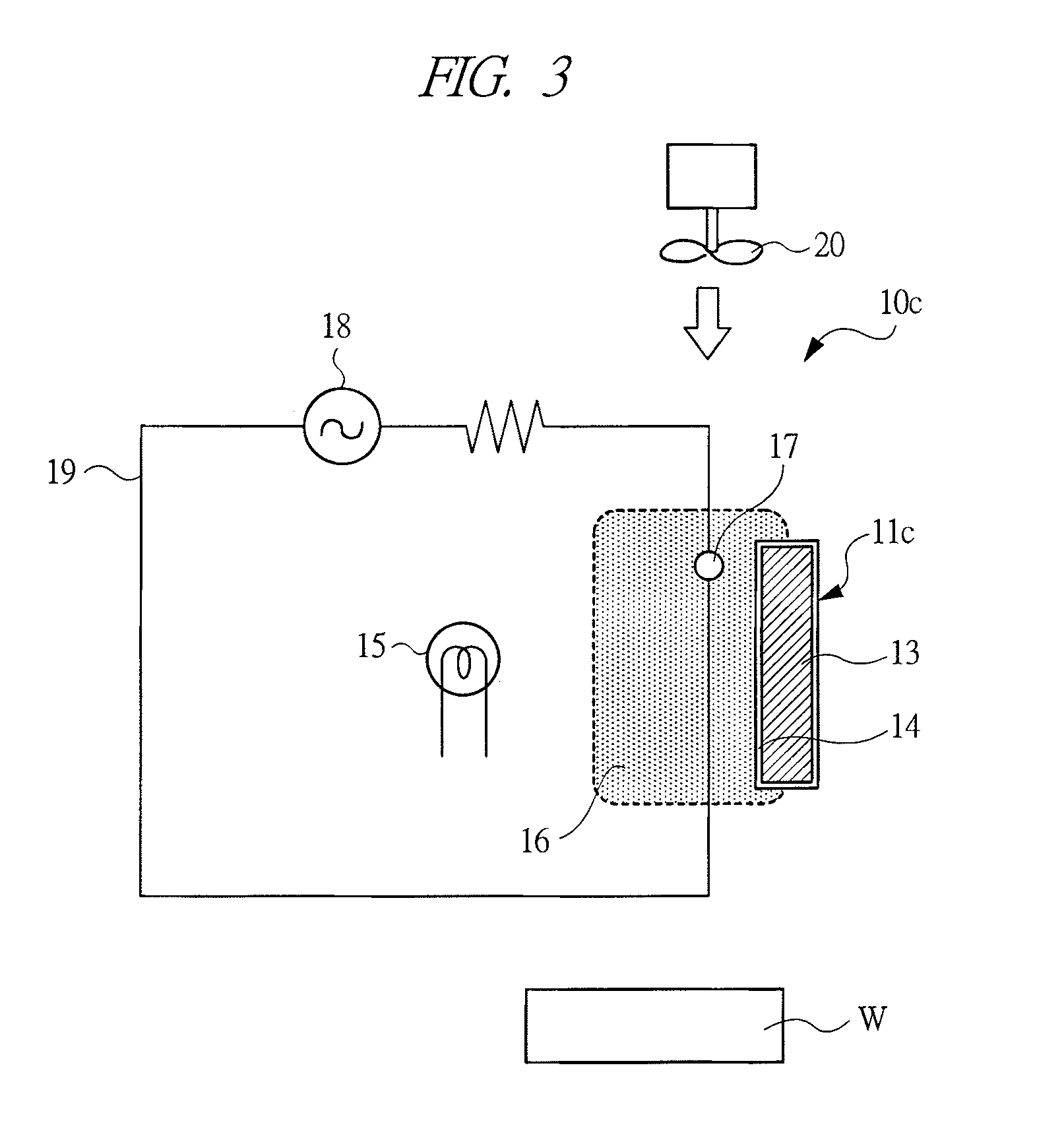
An ion generator can generate clean ionized gas, in which no foreign matters are mixed, and apply the same to a treated object.Ultraviolet rays from an ultraviolet generating source 15 are irradiated to a photo receiver 11a provided with a coating layer 14 made of titanium oxide, and air surrounding the photo receiver is electrically separated to generate positively charged particles and negatively charged particles. An electric field is created by the electrode 17 in a space containing the electrically separated air to ionize the charged particles. The ionized charged particles are blown toward the treated object W by a blower 20.
Owner:KOGANEI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com