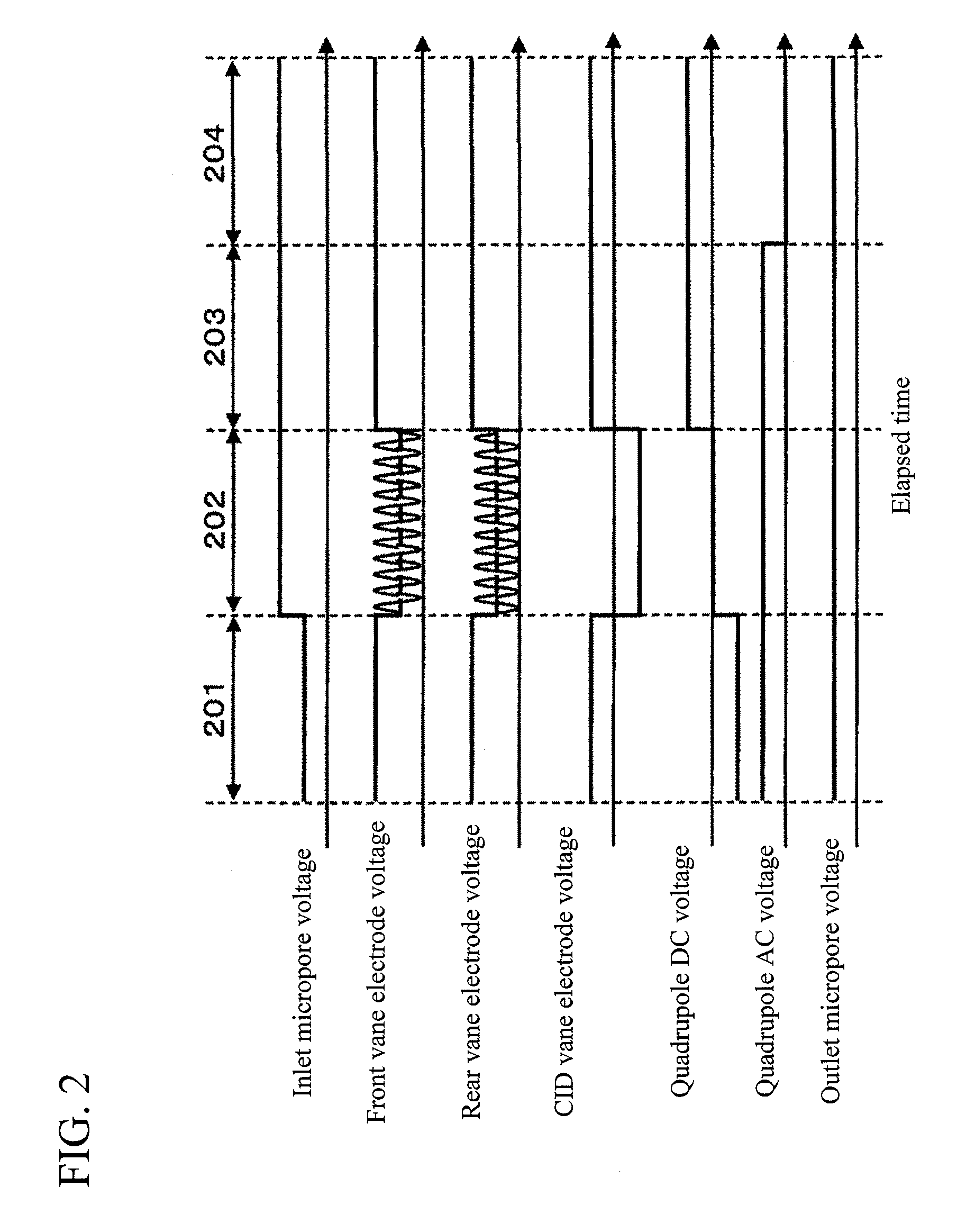
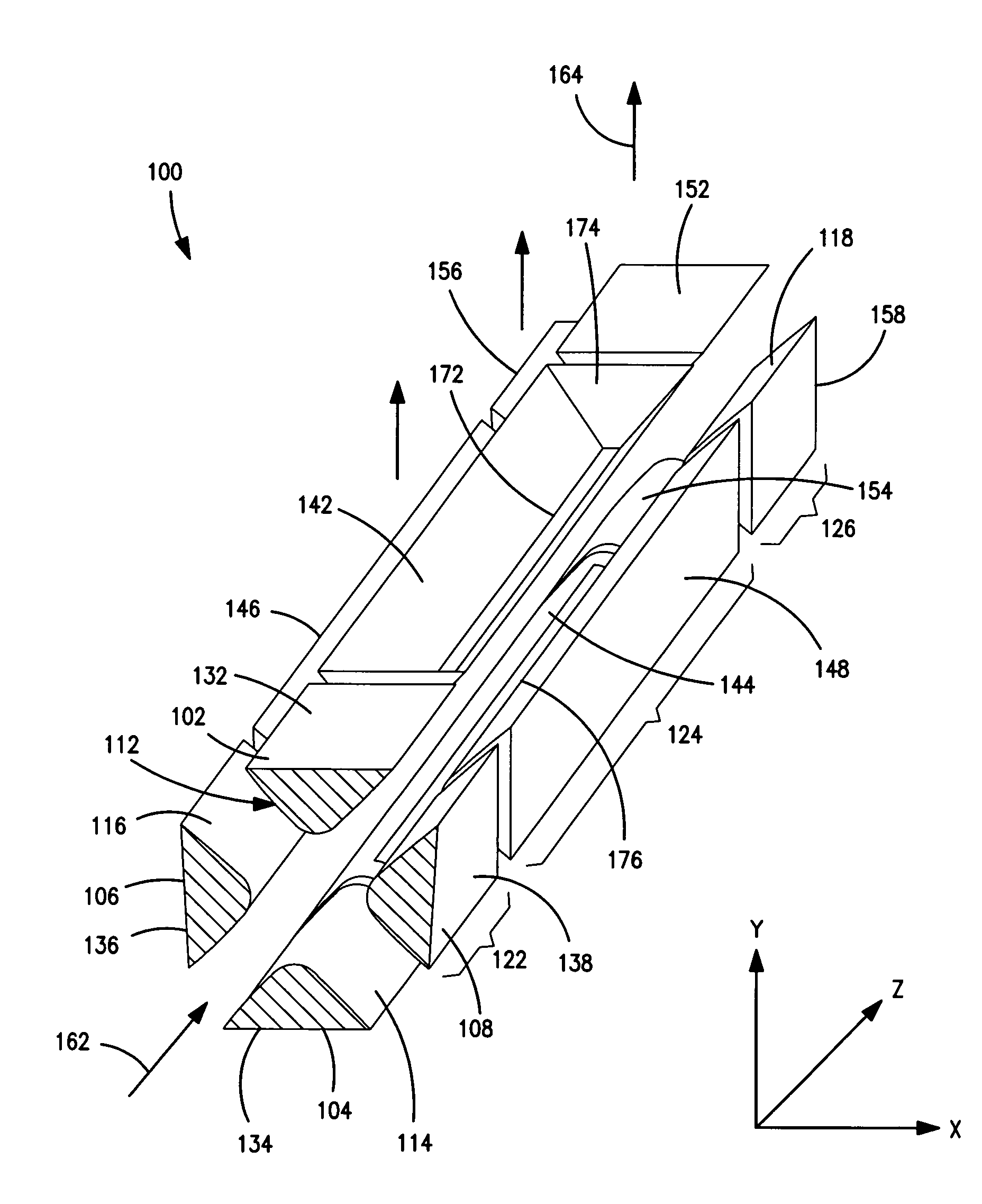
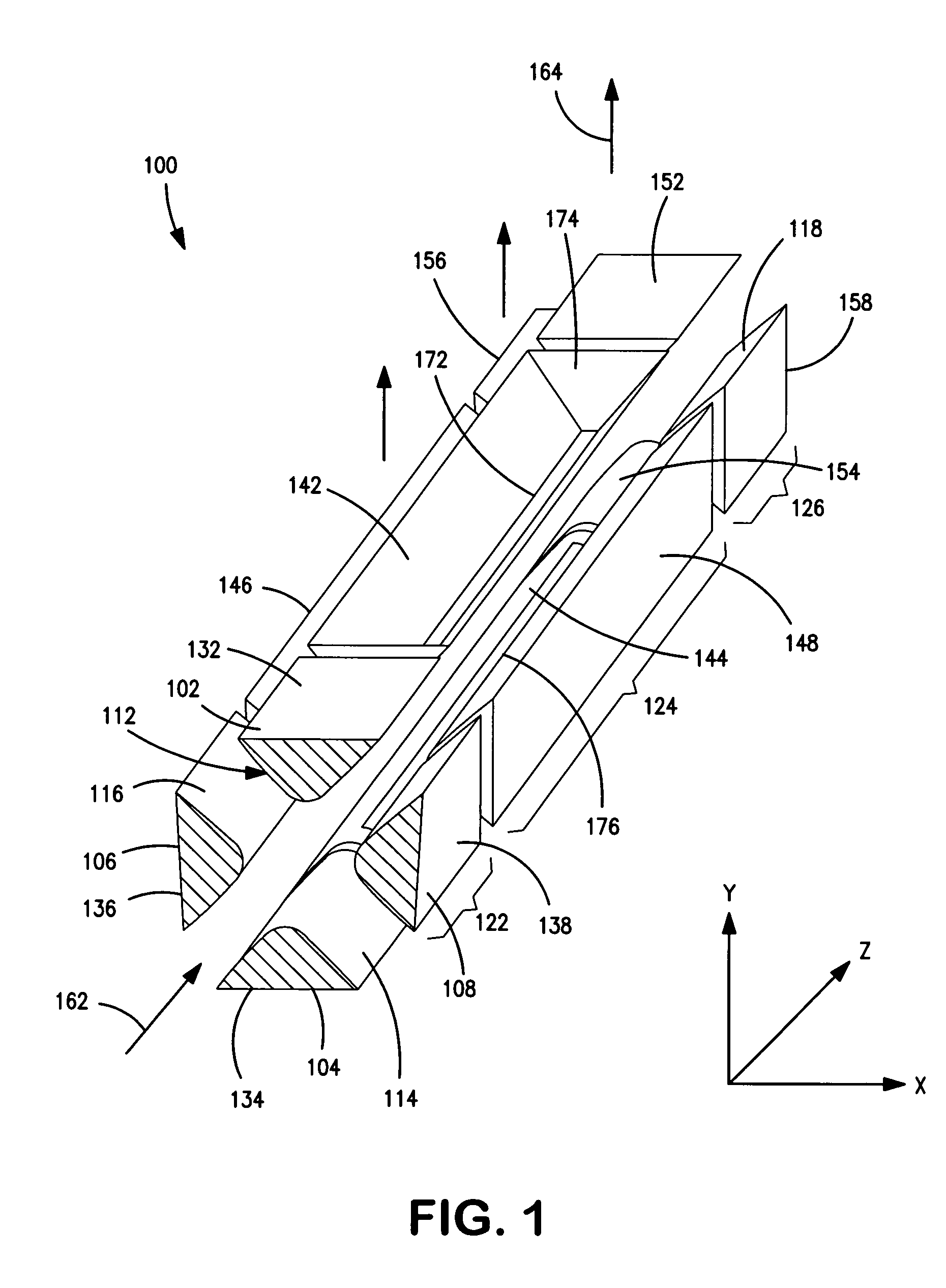
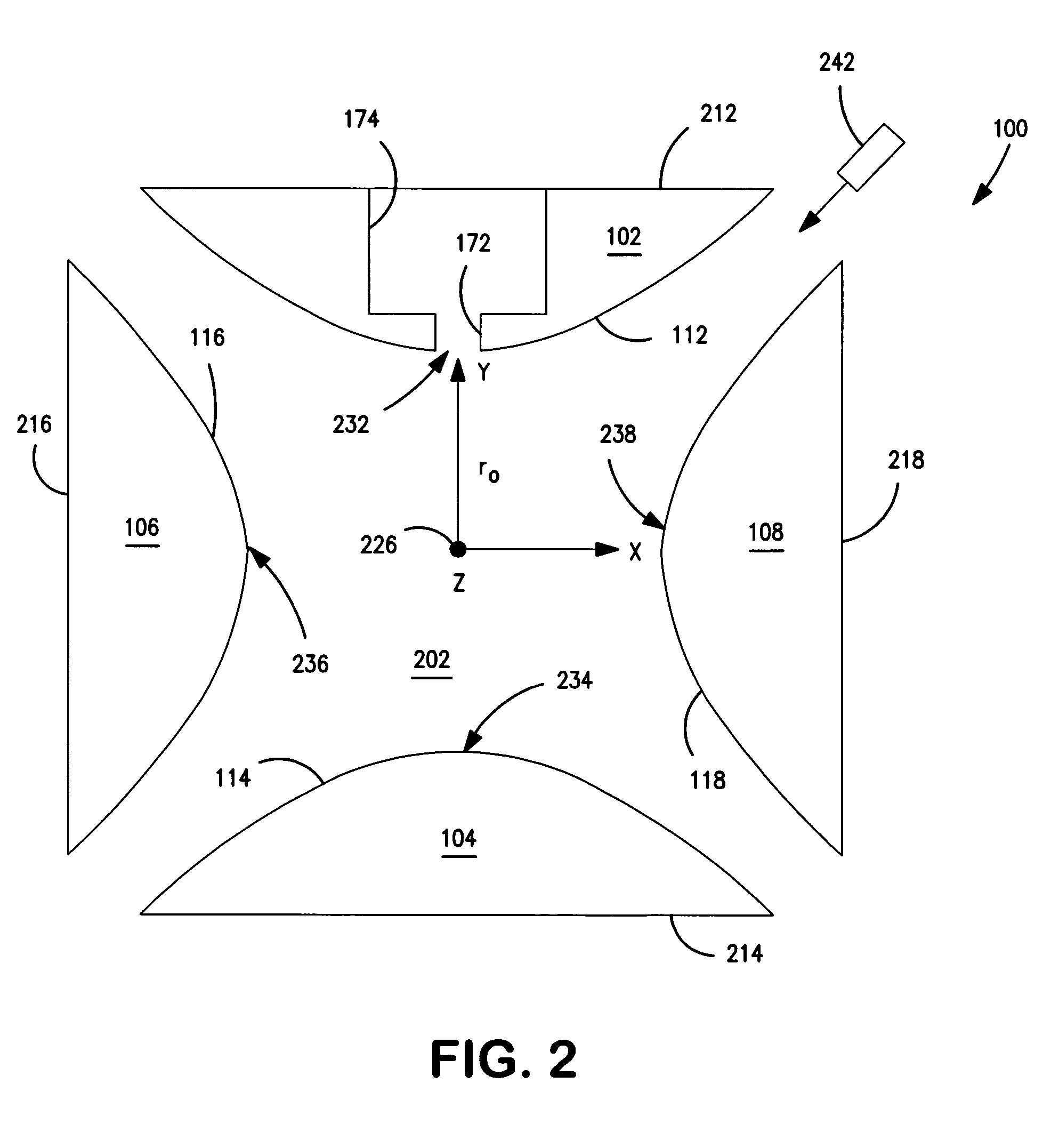
Patents
Literature
107 results about "Collision-induced dissociation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
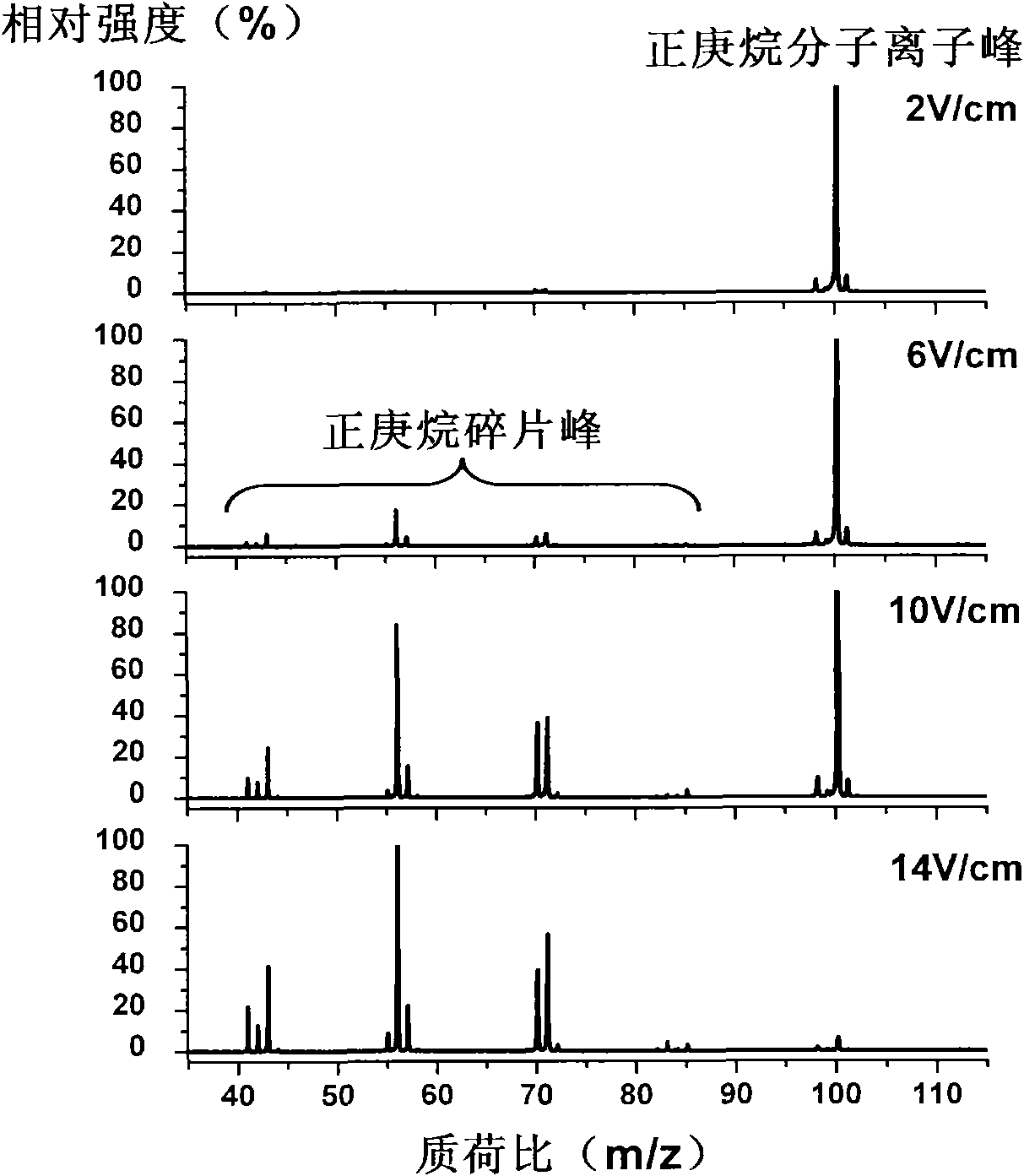
Collision-induced dissociation (CID), also known as collisionally activated dissociation (CAD), is a mass spectrometry technique to induce fragmentation of selected ions in the gas phase. The selected ions (typically molecular ions or protonated molecules) are usually accelerated by applying an electrical potential to increase the ion kinetic energy and then allowed to collide with neutral molecules (often helium, nitrogen or argon). In the collision some of the kinetic energy is converted into internal energy which results in bond breakage and the fragmentation of the molecular ion into smaller fragments. These fragment ions can then be analyzed by tandem mass spectrometry.
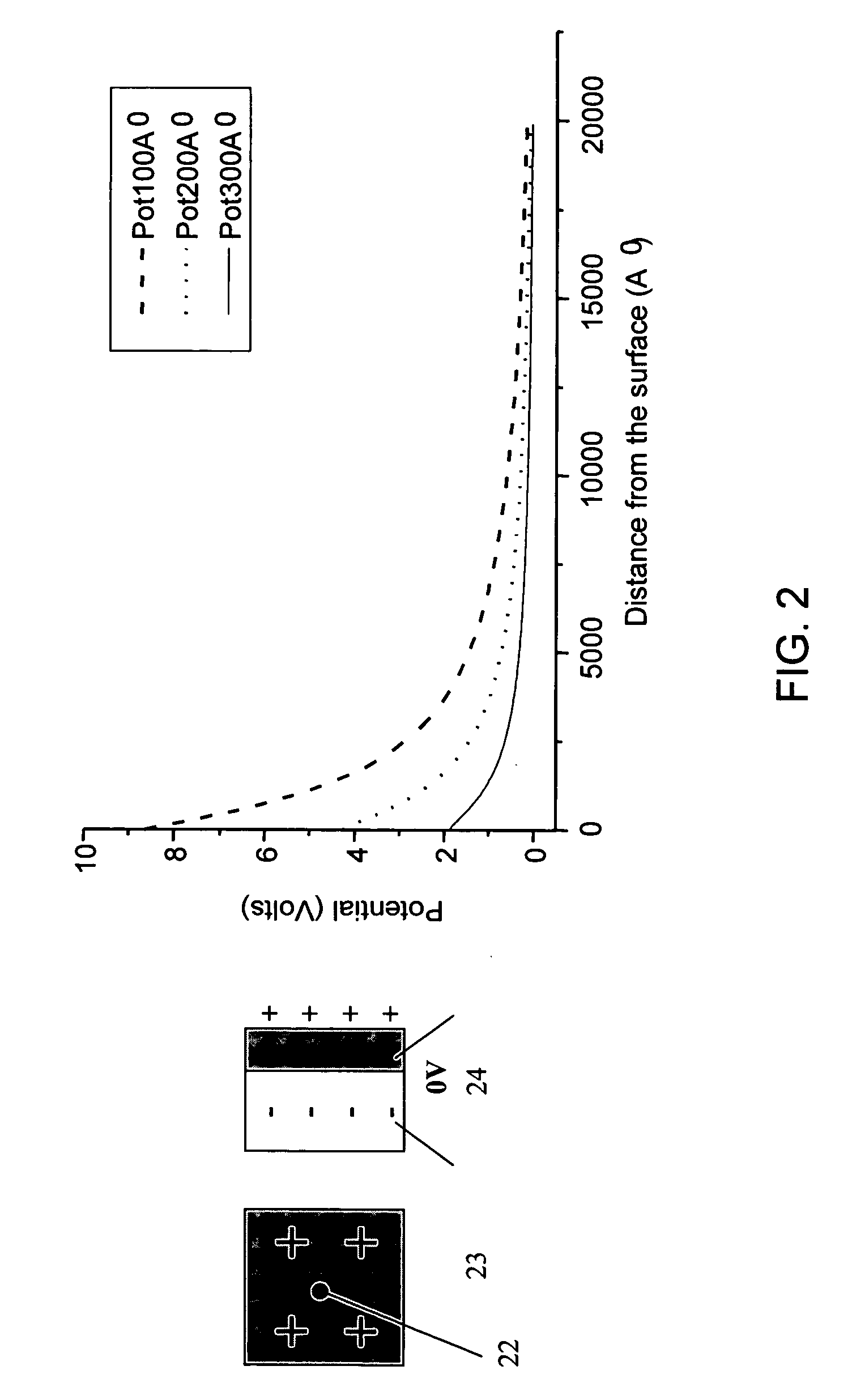
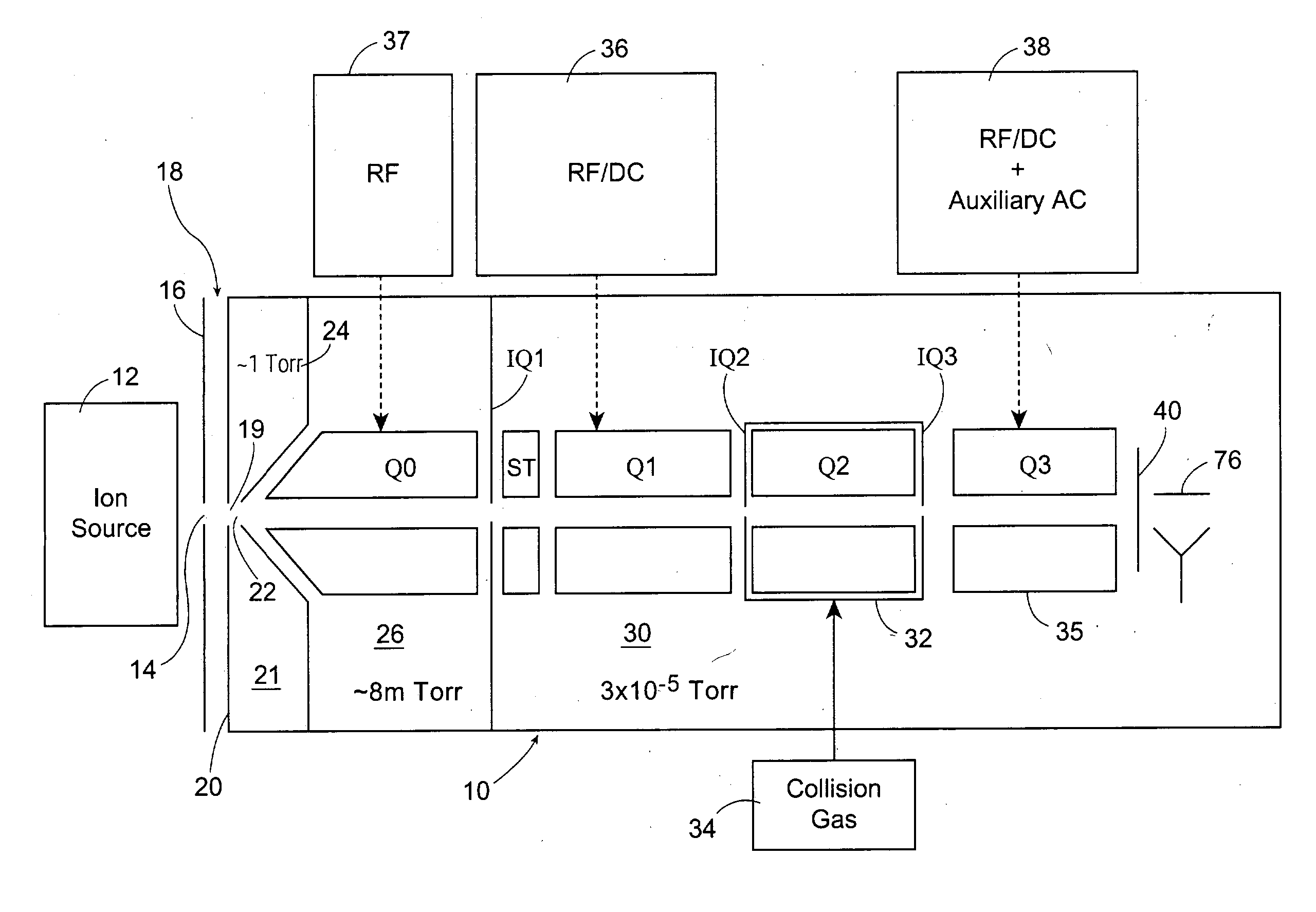
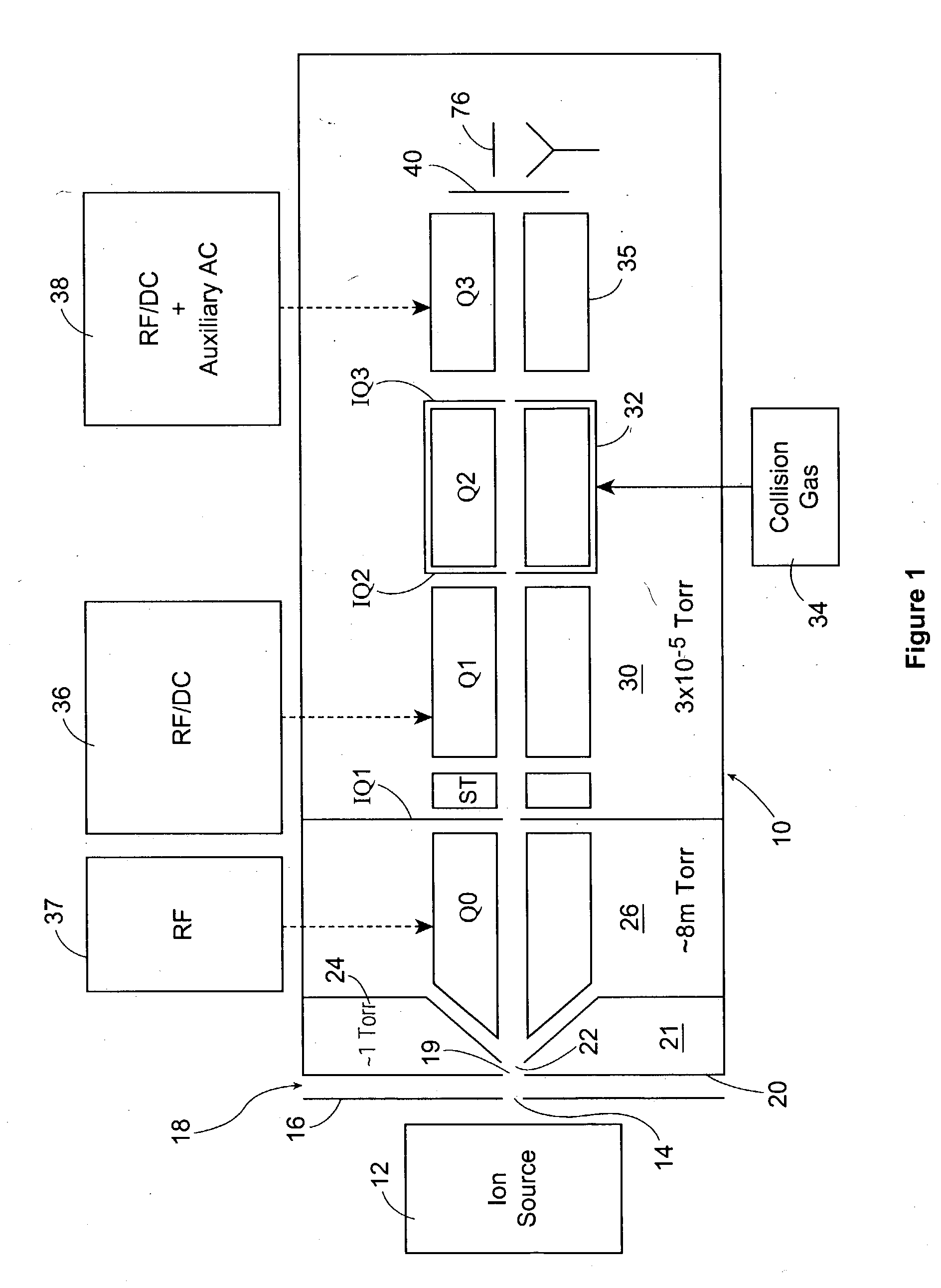
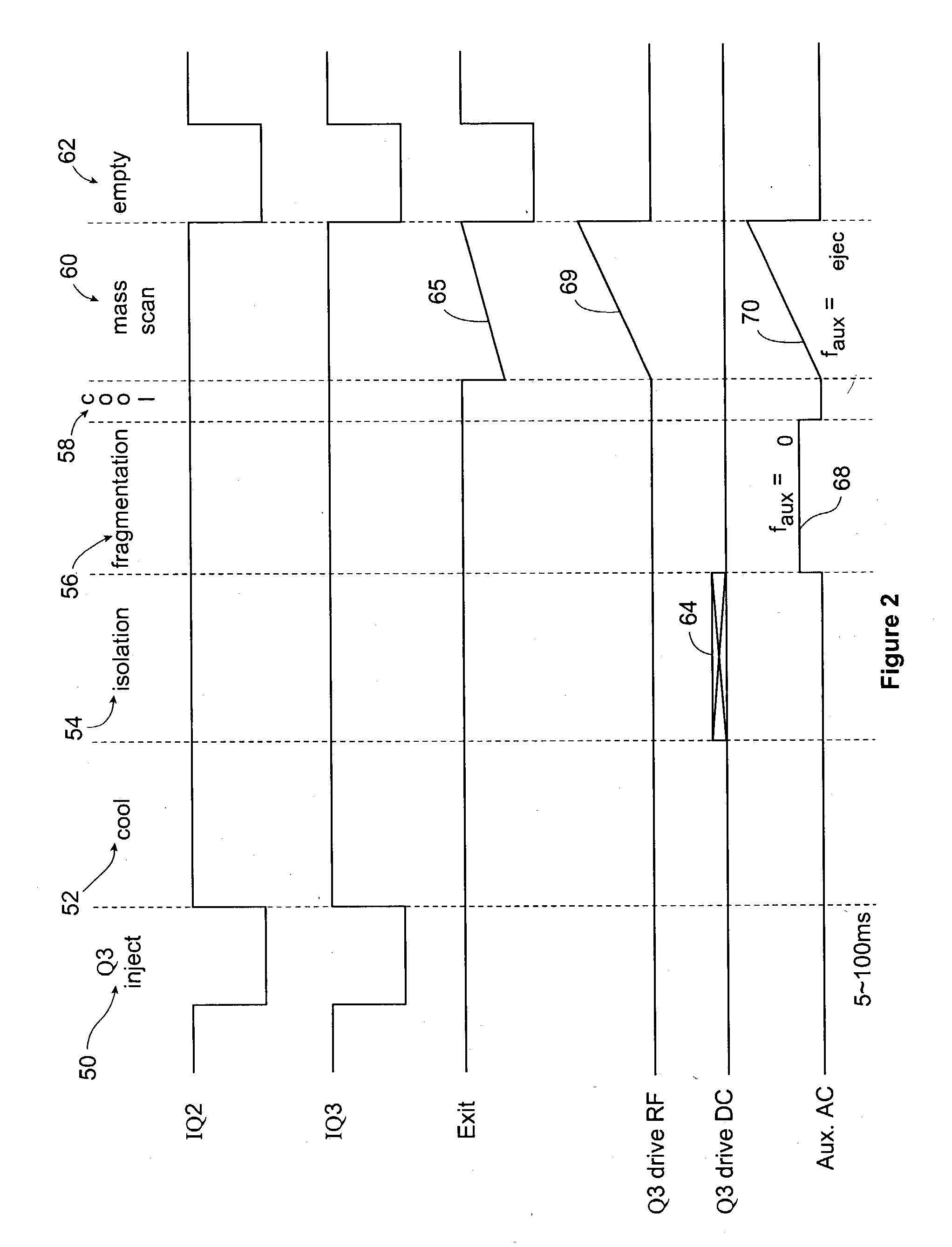
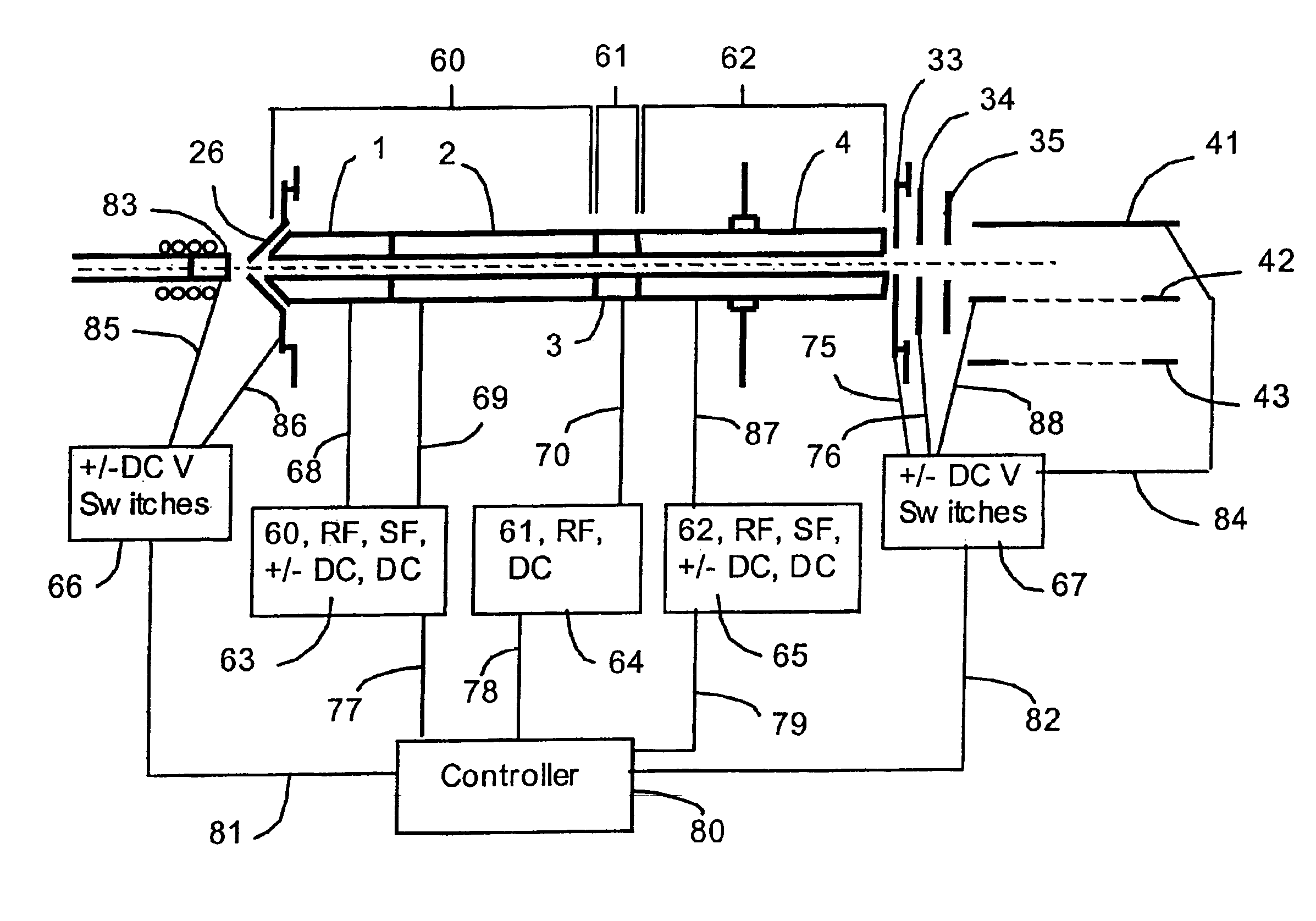
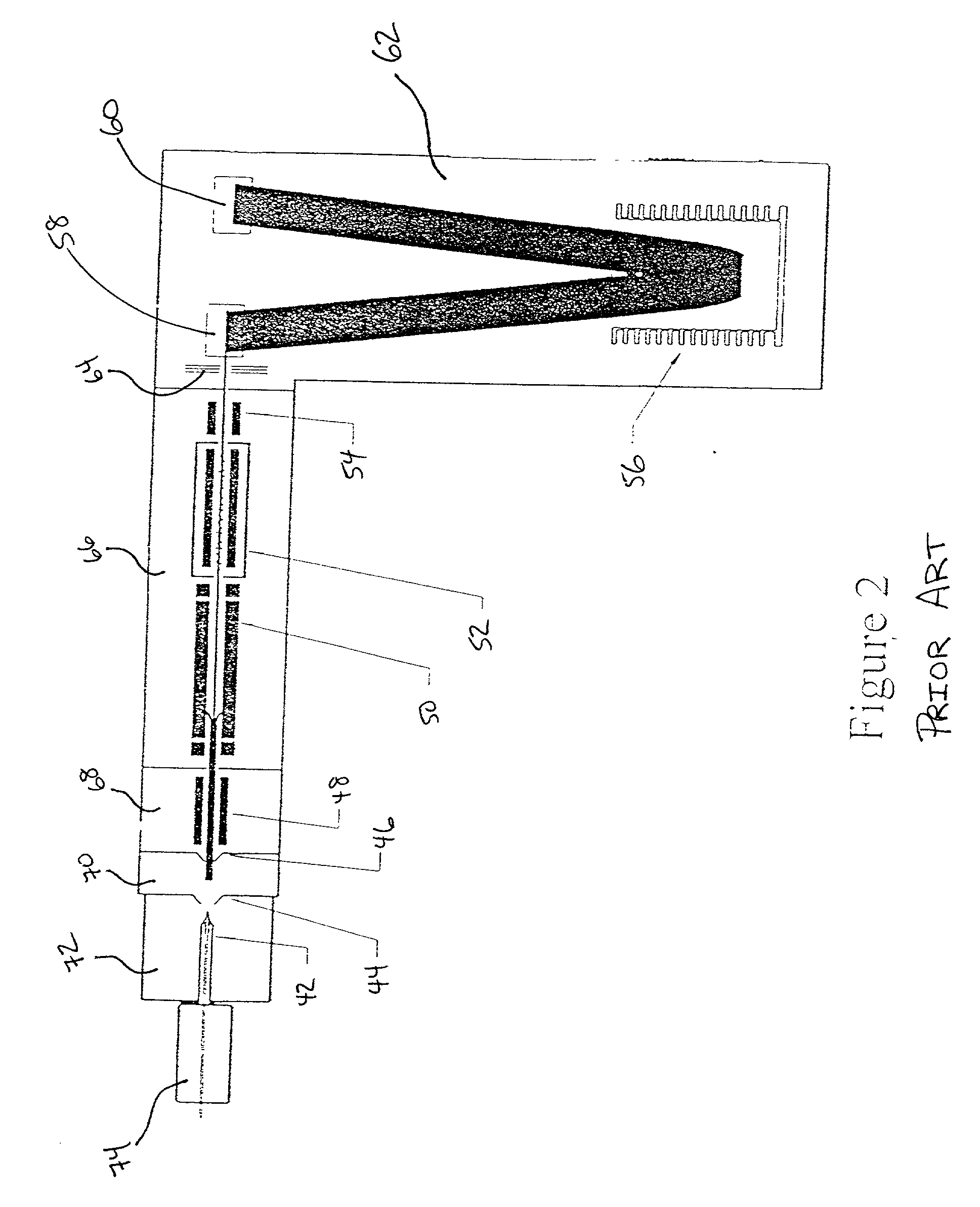
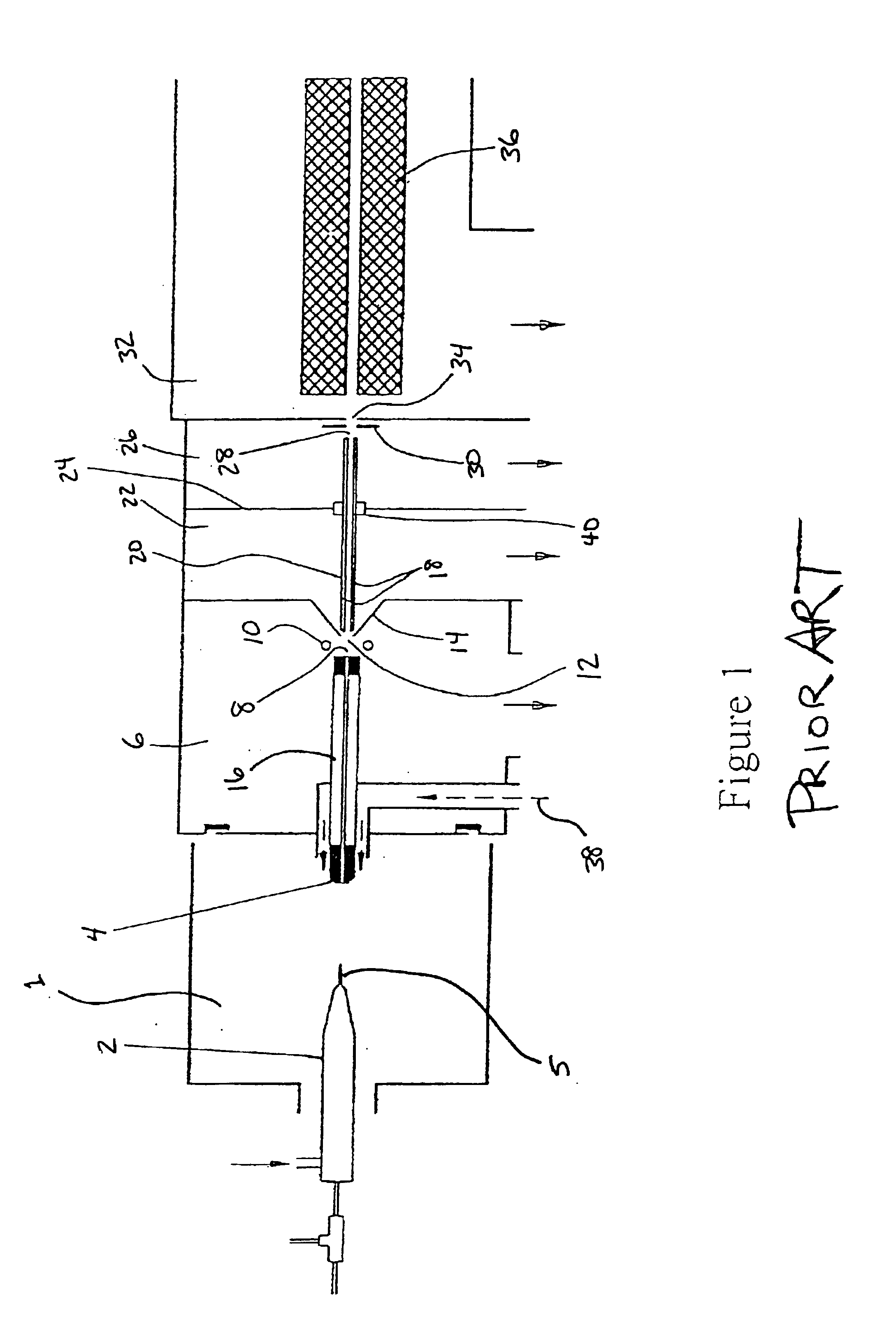
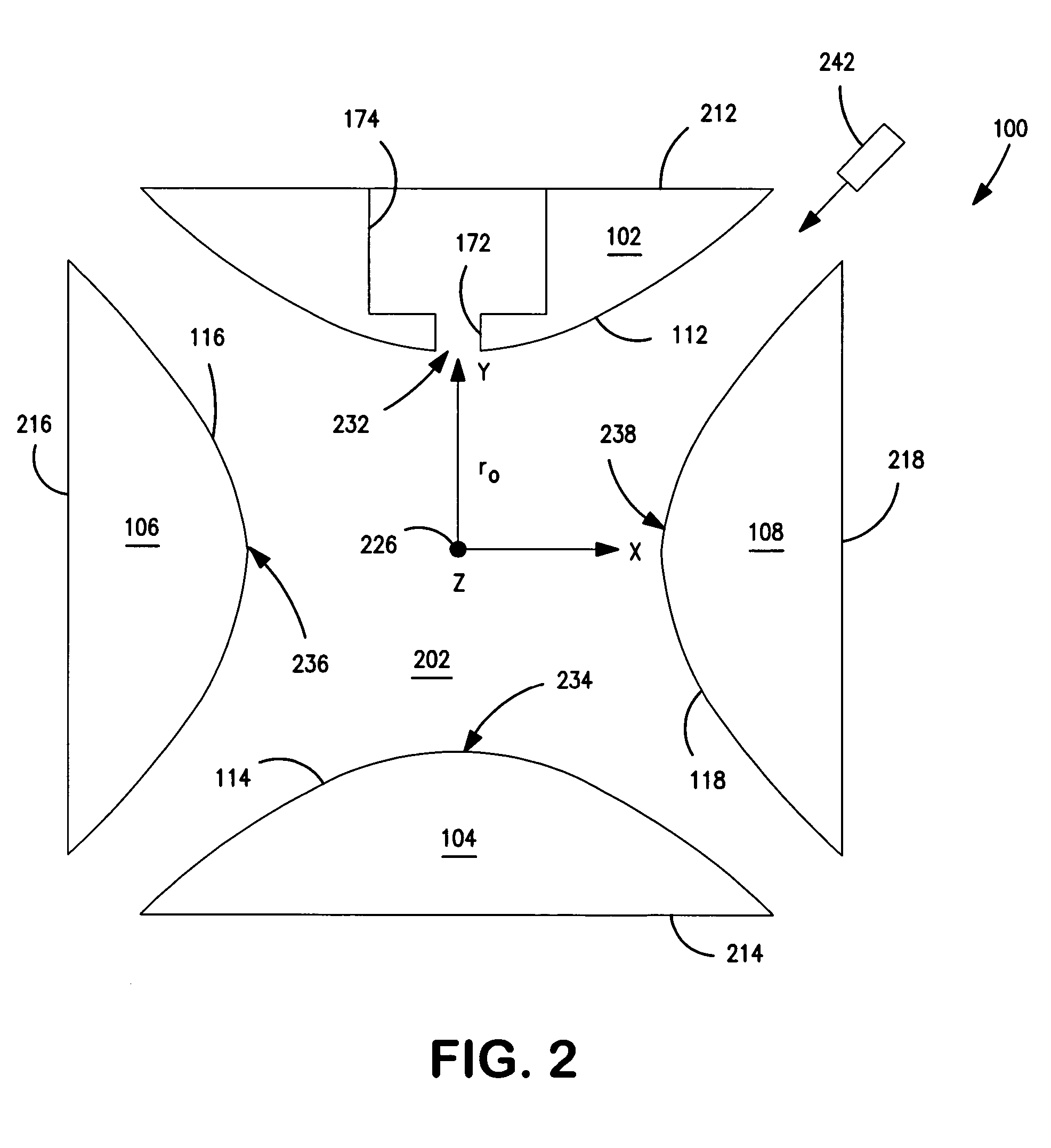
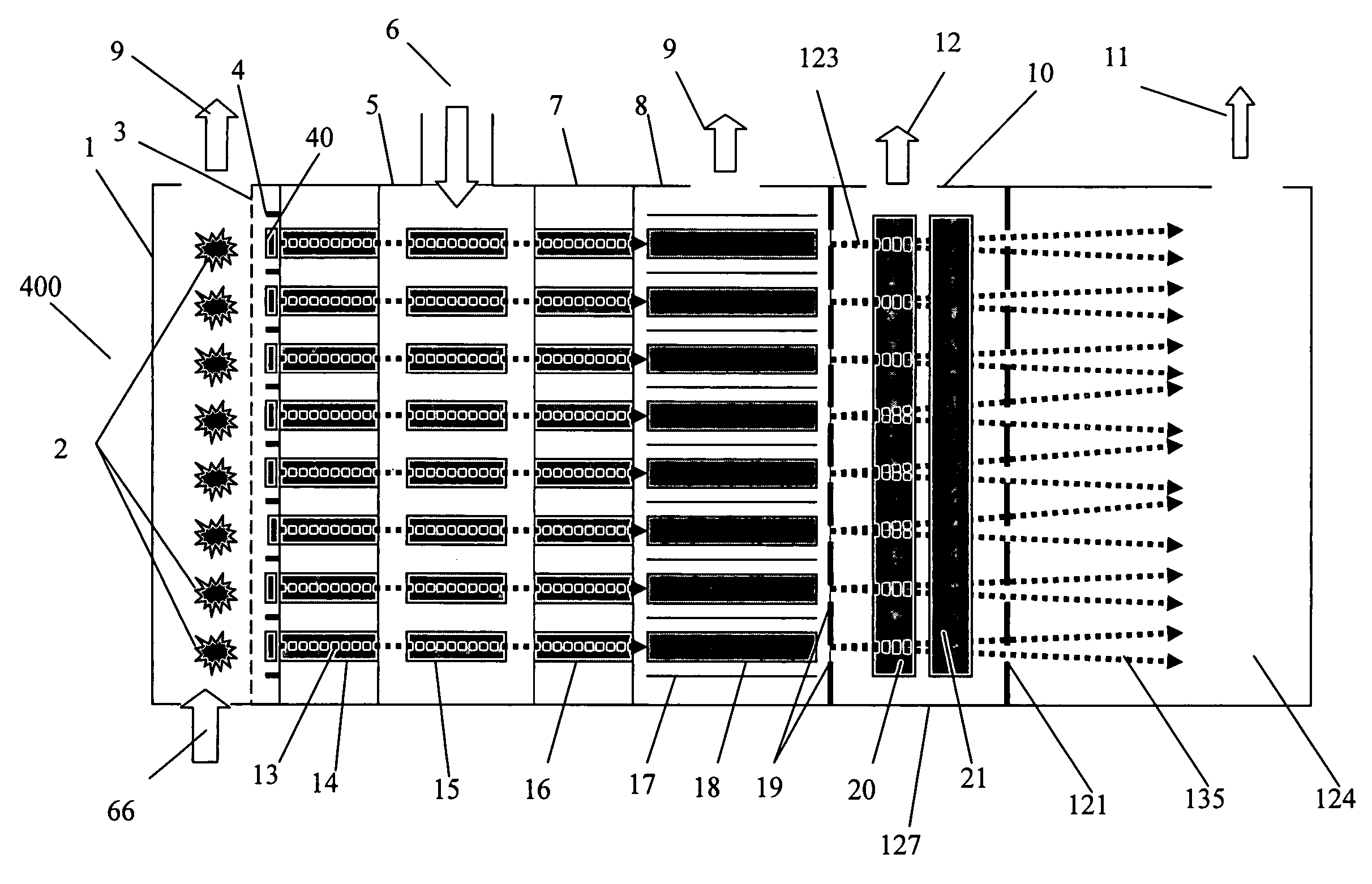
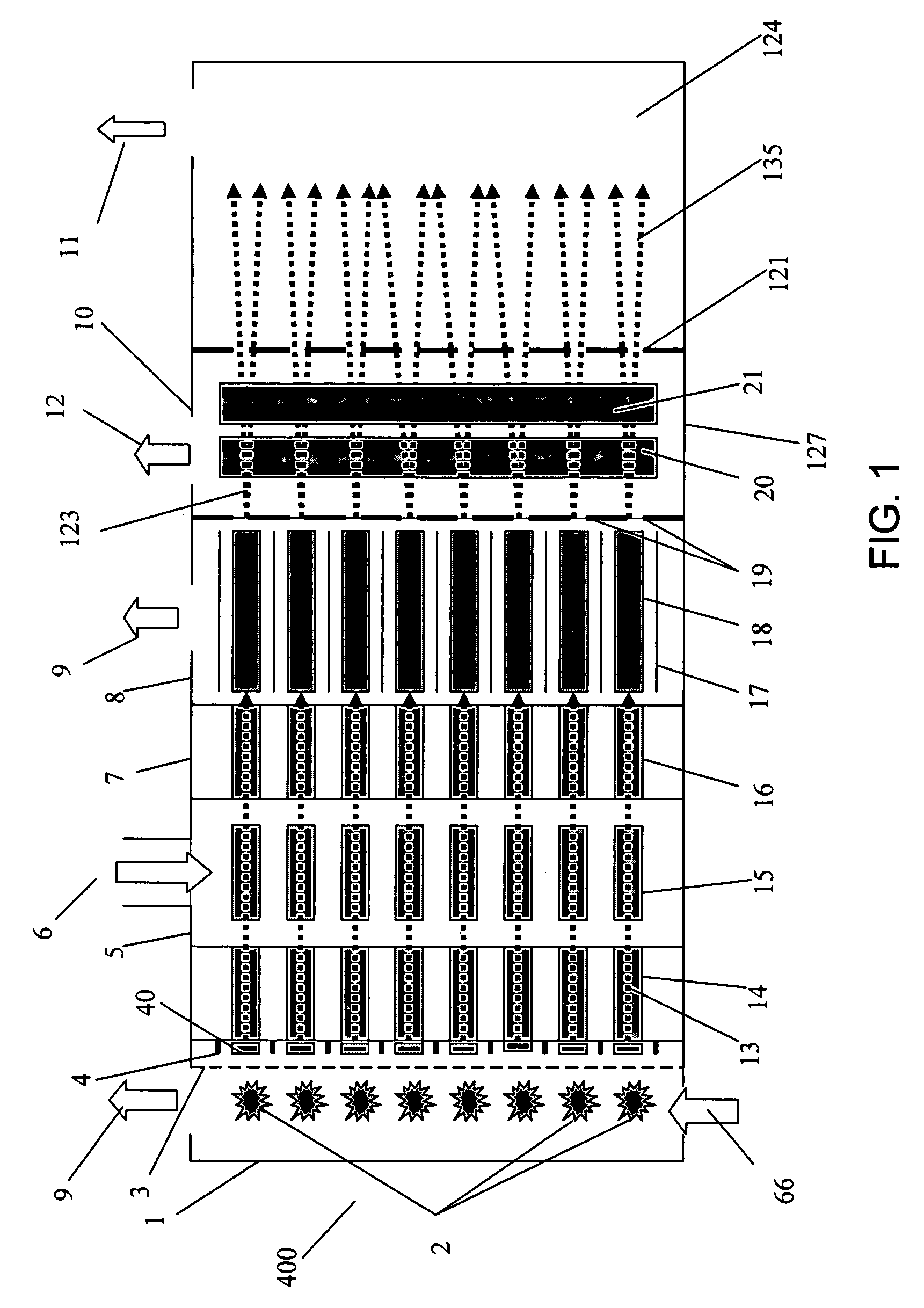
Mass spectrometry with segmented RF multiple ion guides in various pressure regions
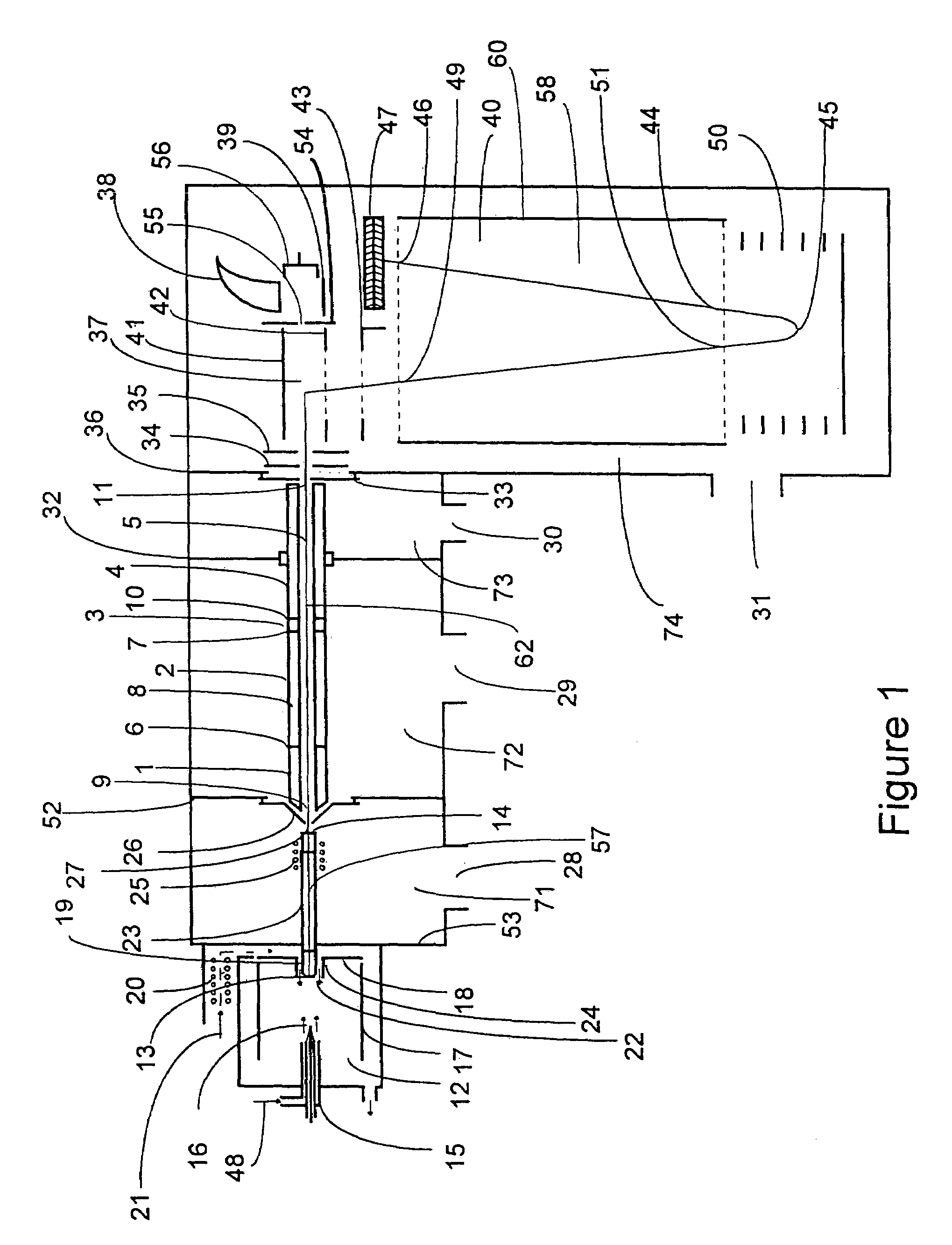
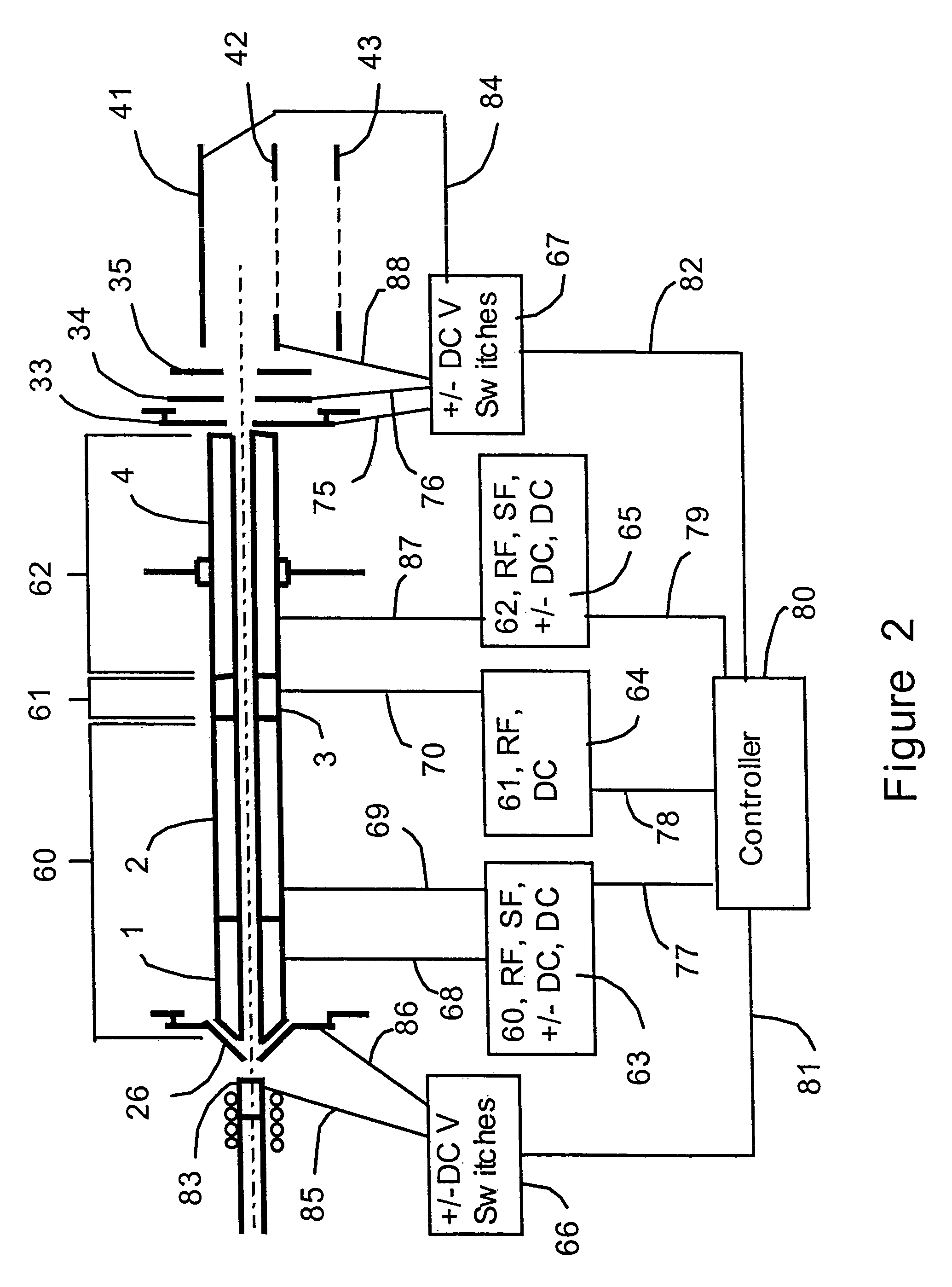
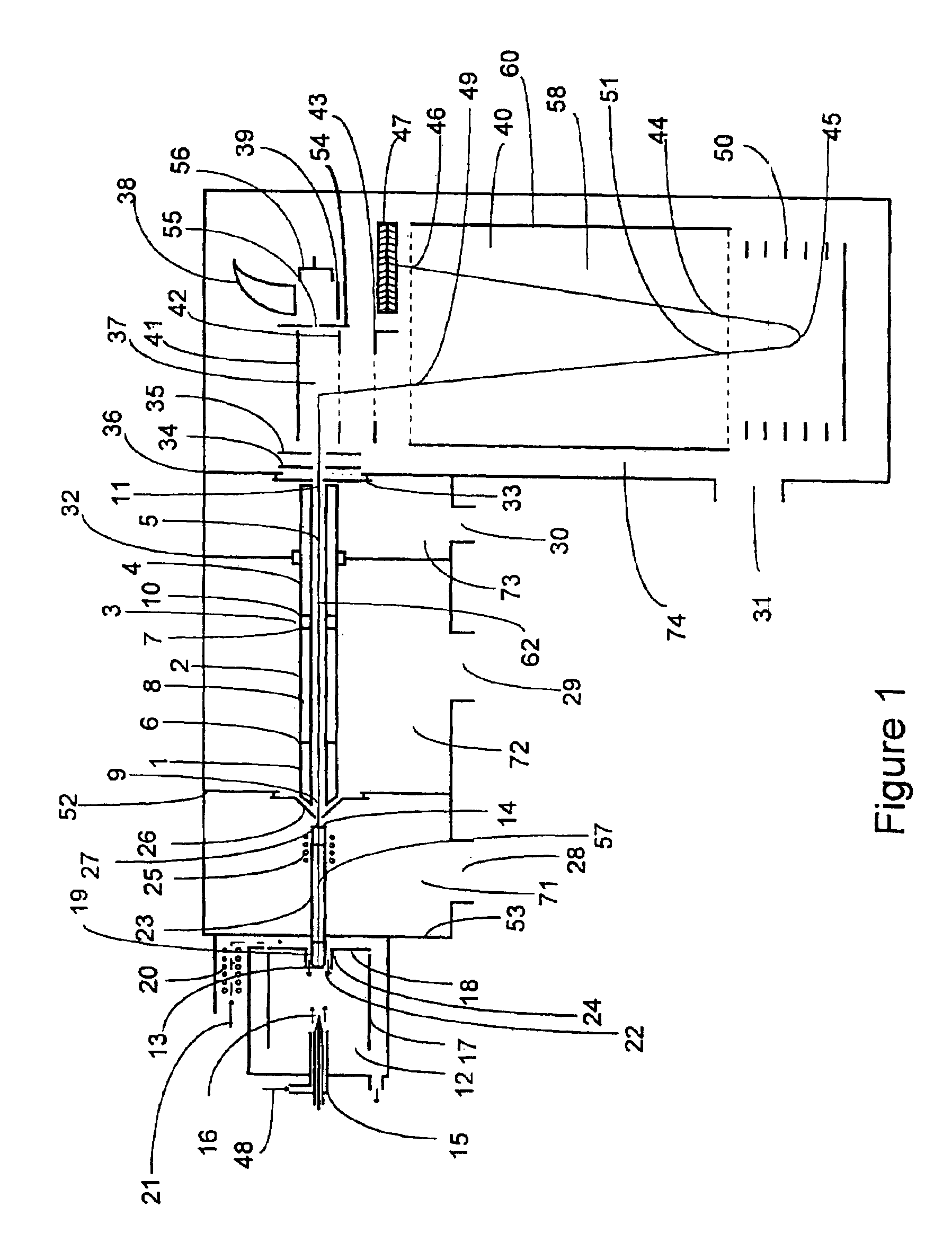
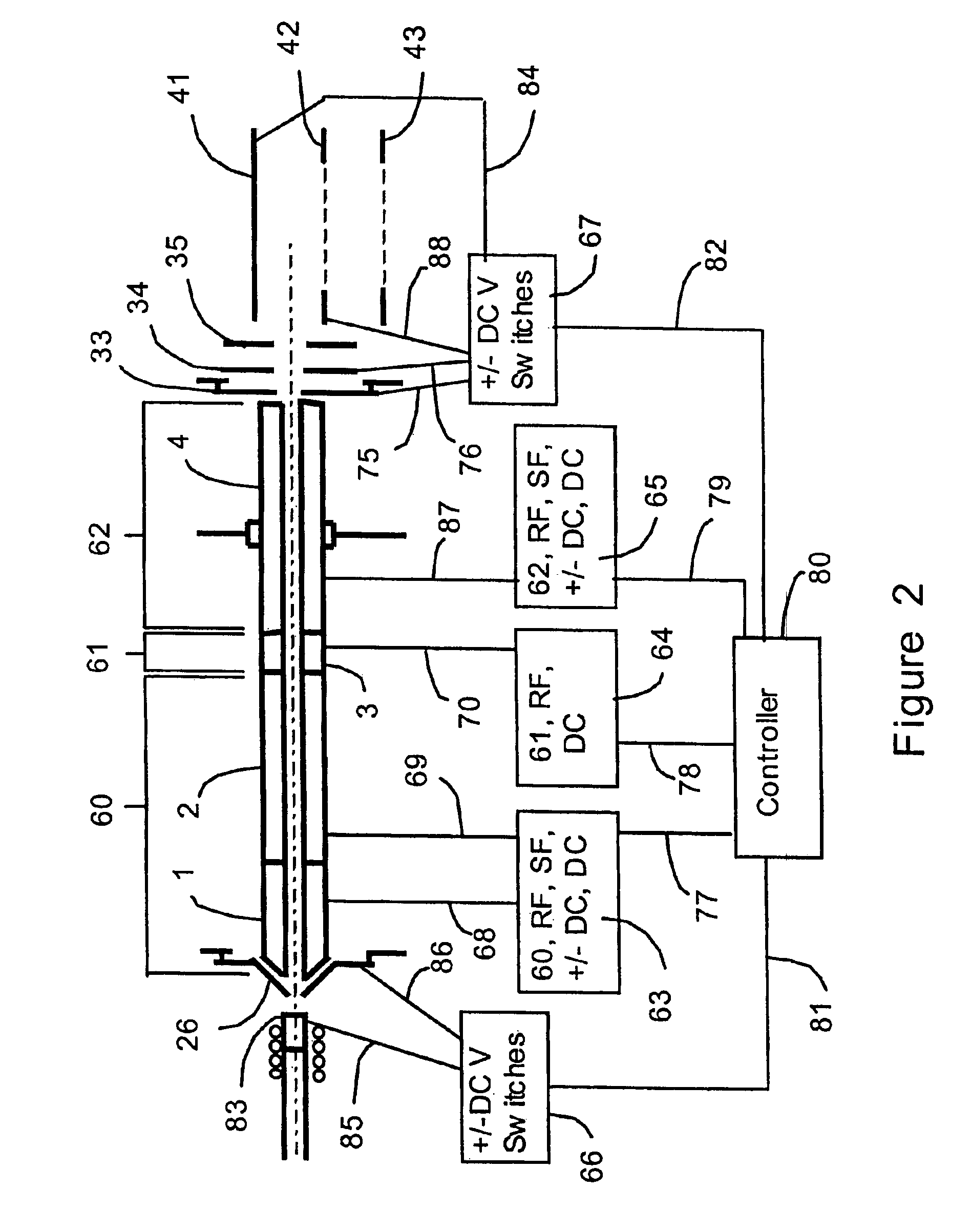
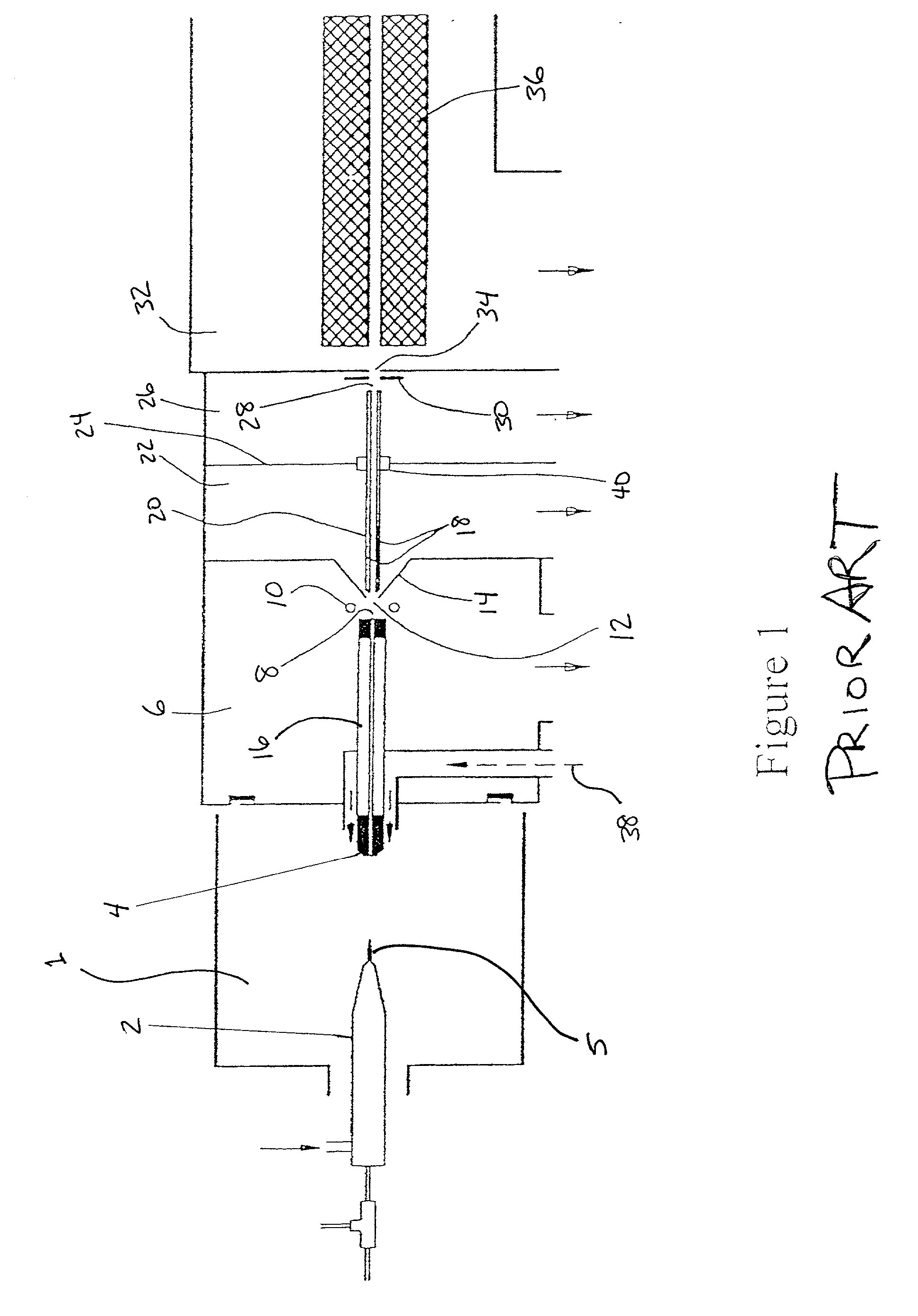
InactiveUS7034292B1Reduce lossesEliminate and reduce numberIsotope separationSpectrometer combinationsFourier transform on finite groupsMass analyzer
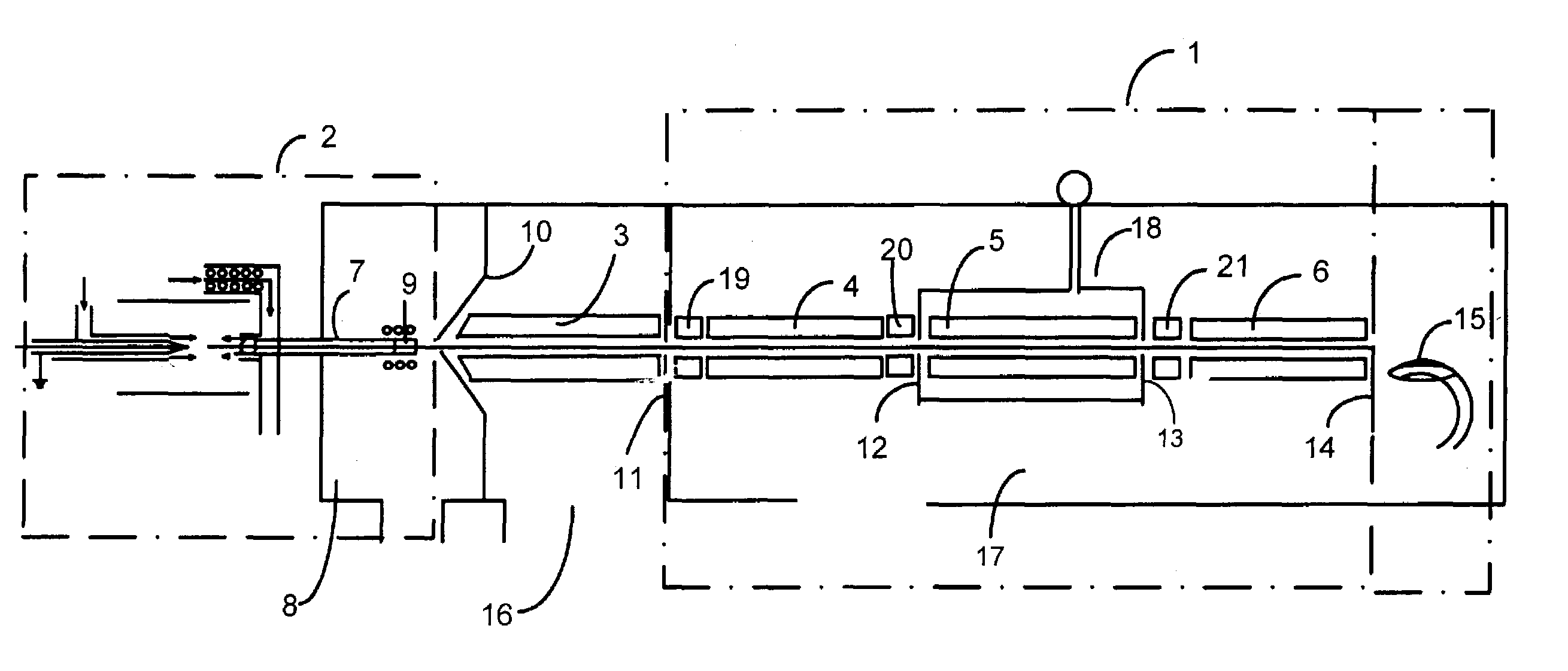
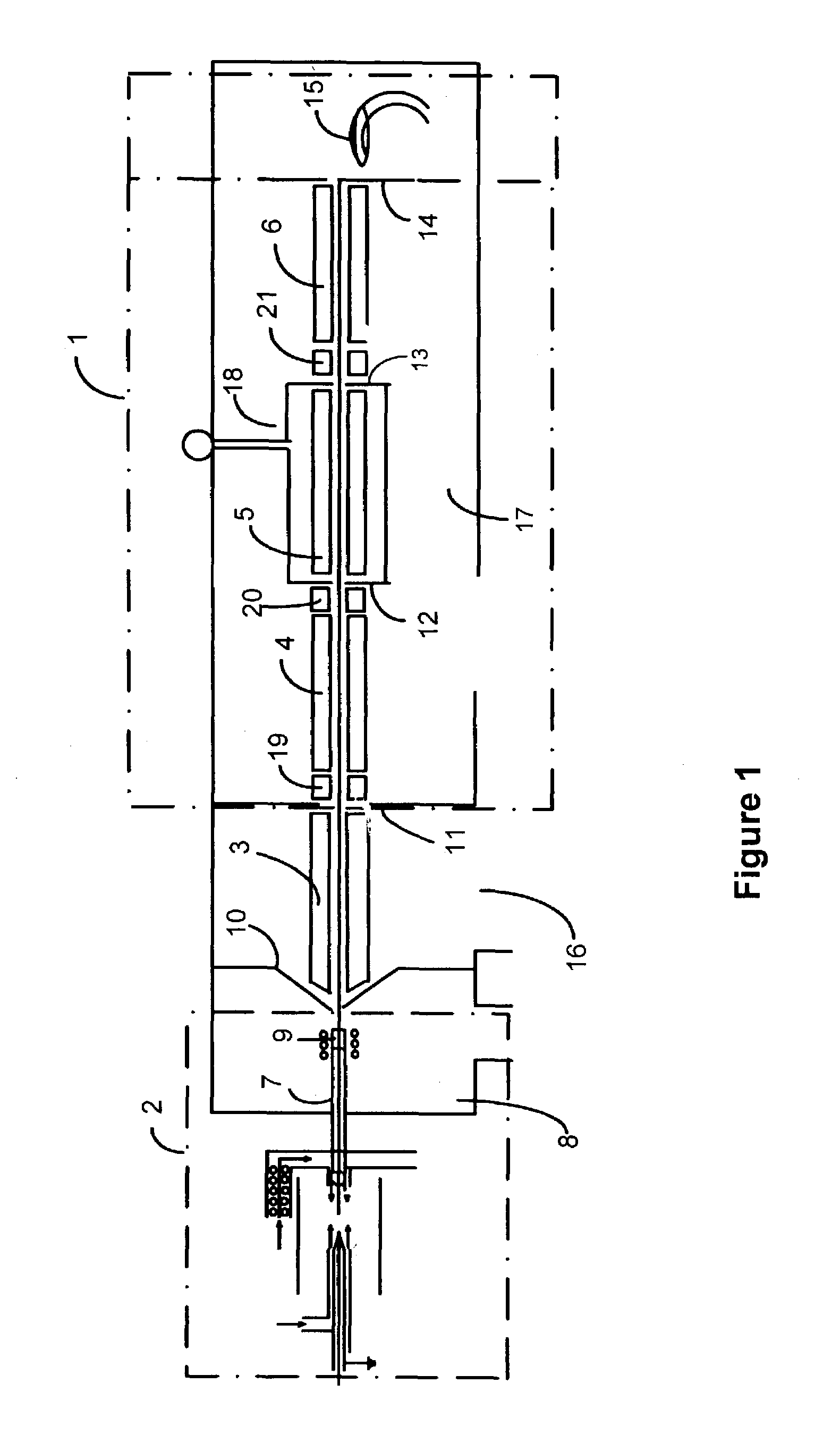
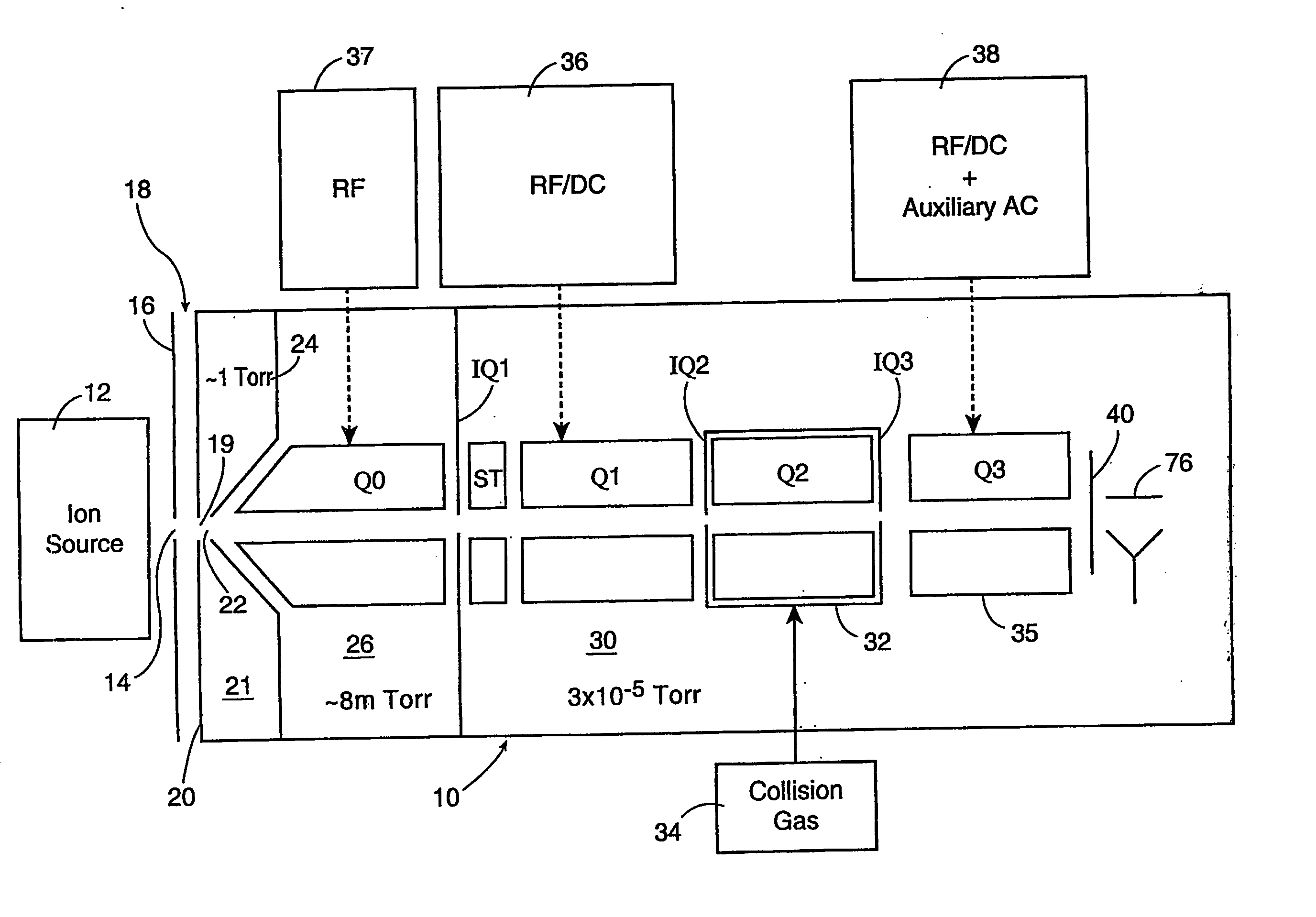
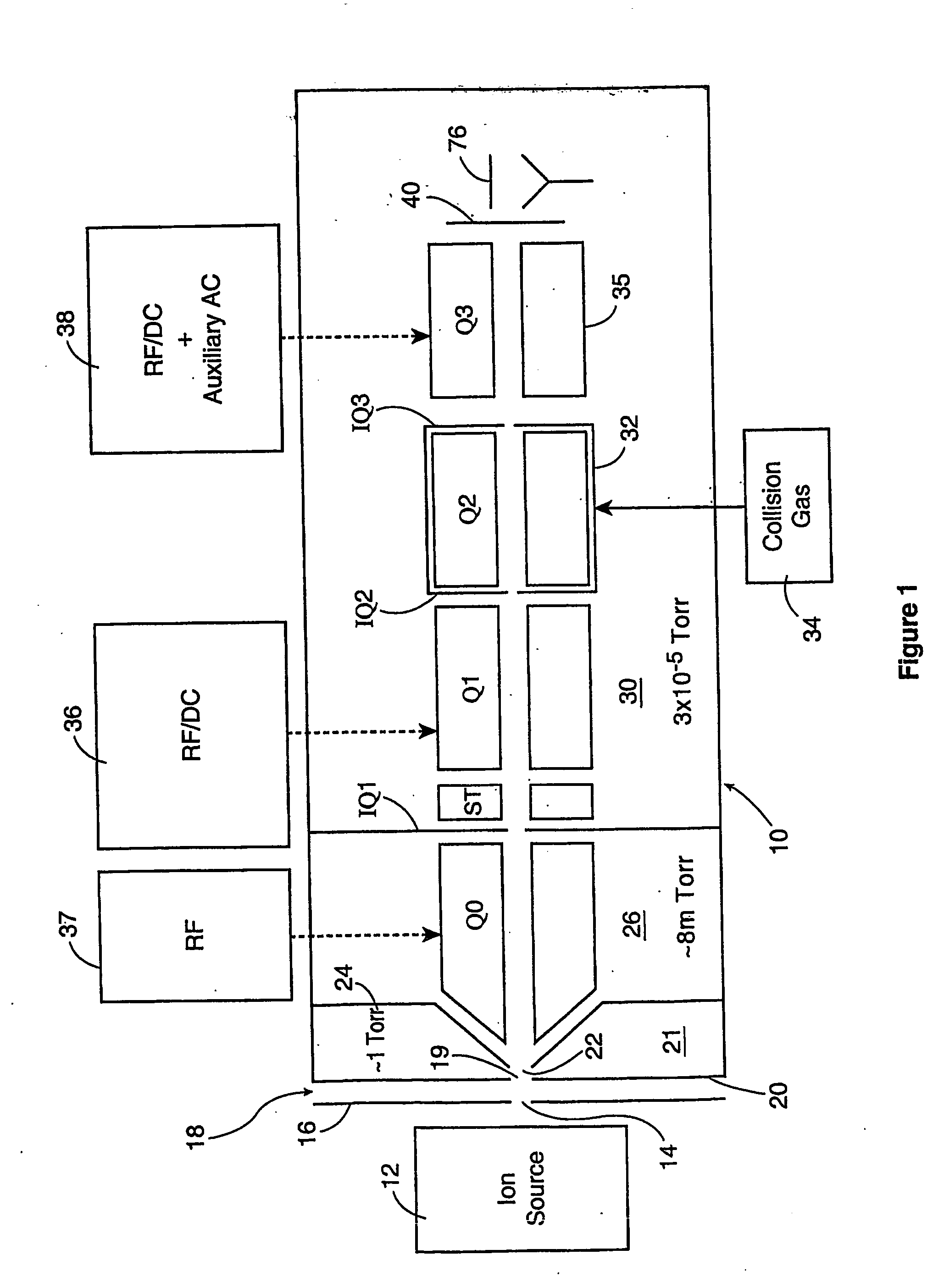
A mass spectrometer is configured with individual multipole ion guides, configured in an assembly in alignment along a common centerline wherein at least a portion of at least one multipole ion guide mounted in the assembly resides in a vacuum region with higher background pressure, and the other portion resides in a vacuum region with lower background pressure. Said multipole ion guides are operated in mass to charge selection and ion fragmentation modes, in either a high or low pressure region, said region being selected according to the optimum pressure or pressure gradient for the function performed. The diameter, lengths and applied frequencies and phases on these contiguous ion guides may be the same or may differ. A variety of MS and MS / MSn analysis functions can be achieved using a series of contiguous multipole ion guides operating in either higher background vacuum pressures, or along pressure gradients in the region where the pressure drops from high to low pressure, or in low pressure regions. Individual sets of RF, + / −DC and resonant frequency waveform voltage supplies provide potentials to the rods of each multipole ion guide allowing the operation of ion transmission, ion trapping, mass to charge selection and ion fragmentation functions independently in each ion guide. The presence of background pressure maintained sufficiently high to cause ion to neutral gas collisions along a portion of each multiple ion guide linear assembly allows the conducting of Collisional Induced Dissociation (CID) fragmentation of ions by axially accelerating ions from one multipole ion guide into an adjacent ion guide. Alternatively ions can be fragmented in one or more multipole ion guides using resonant frequency excitation CID. A multiple multipole ion guide assembly can be configured as the primary mass analyzer in single or triple quadrupole mass analyzers with or without mass selective axial ejection. Alternatively, the multiple multipole ion guide linear assembly can be configured as part of a hybrid Time-Of-Flight, Magnetic Sector, Ion Trap or Fourier Transform mass analyzer.
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
Mass spectrometry with multipole ion guides
InactiveUS6987264B1Efficient transportImprove duty cycleStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass analyzer
Multipole ion guides configured with one or mote segments and positioned in a higher pressure vacuum region, are operated in mass to charge selection and ion fragmentation modes. Individual multipole ion guides are mounted in a linear assembly with no electrodes configured in between each multipole ion guide. At least a portion of each multipole ion guide mounted in a linear assembly resides in a vacuum region with higher background pressure. At least one ion guide can be configured to extend continuously from one vacuum stage into another. Individual sets of RF, + / − DC and secular frequency voltage supplies provide potentials to the rods of each multipole ion guide allowing the operation of ion transmission, ion trapping, mass to charge selection and ion fragmentation functions independently in each ion guide. The presence of higher background pressure along a portion of the multiple ion guide linear assembly allows the Collisional Induced Dissociation (CID) fragmentation of ions by axially accelerating ions from one multipole ion guide to an adjacent ion guide, analogous to a triple quadrupole function. A variety of MS and MS / MSn analysis functions can be achieved with a mass analyzer configured with multiple ion guide linear assembly operated in a higher background pressure.
Owner:ANALYTICA OF BRANFORD
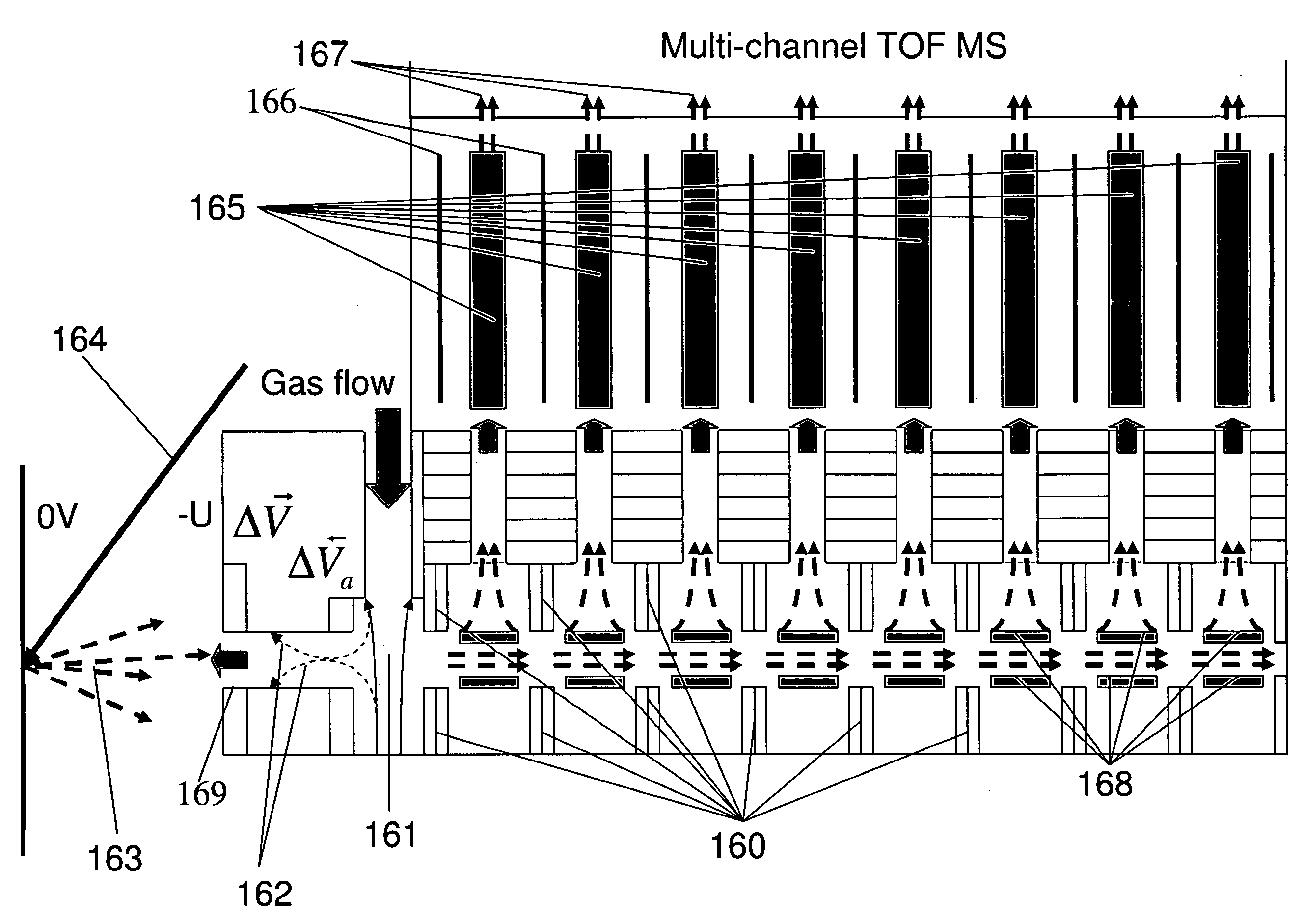
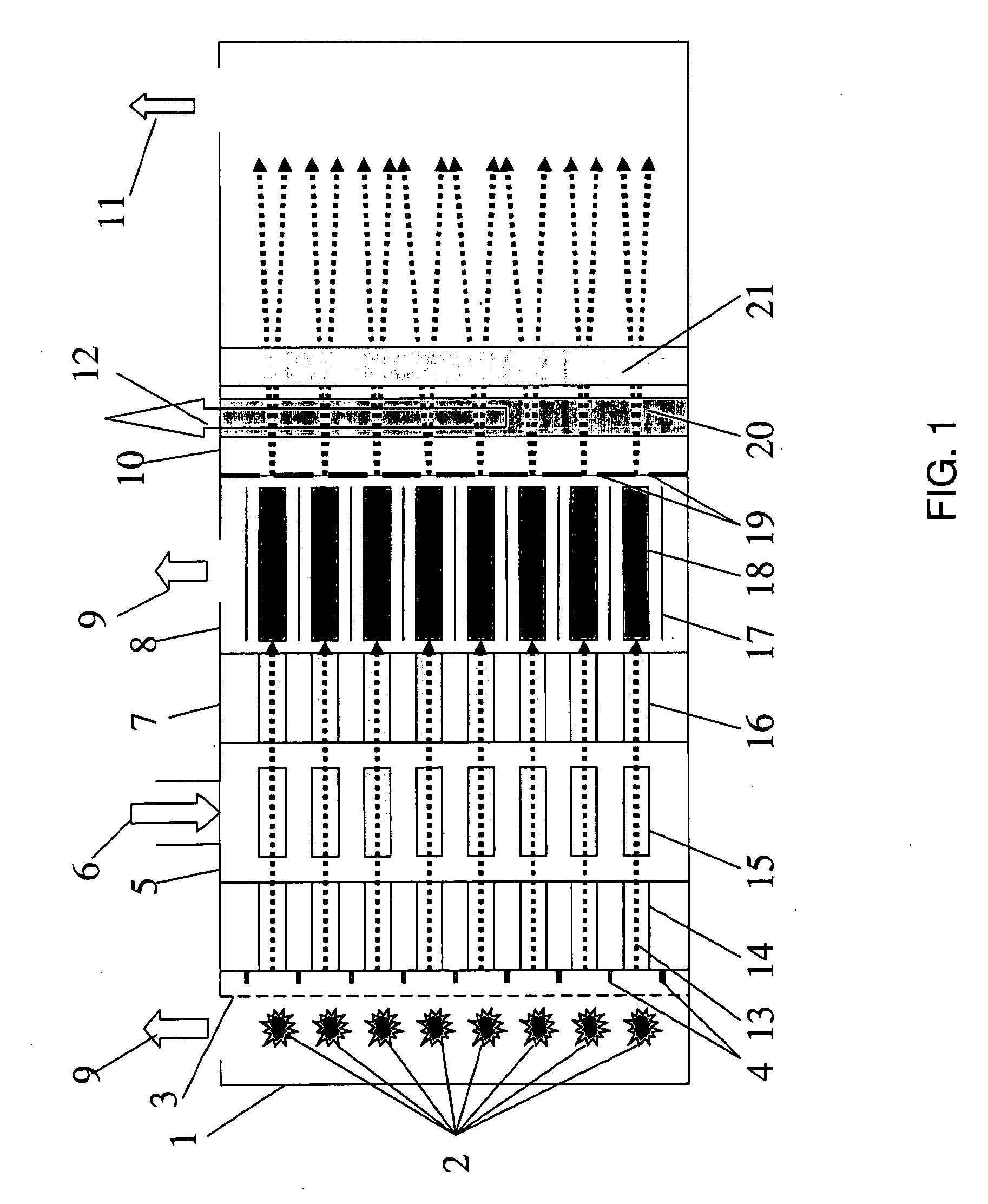
Multi-beam ion mobility time-of-flight mass spectrometry with multi-channel data recording
InactiveUS20060289746A1Improve efficiencyFacilitates ion transportTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansData recordingLinearity
The content of the invention comprises a concept of multi-beam ion pre-selection from a single sample, coordinated mobility (against the gas flow) separation, cooling ions in supersonic gas flow and mass separation of thus low divergent ions by single or plural compact high-resolution orthogonal time-of-flight mass spectrometers both linear or reflectron type with controlled collision-induced dissociation (CID) and multi-channel data recording for the optimization of sample use in the analysis, and obtaining as much useful information about the sample as possible in a reasonably short time.
Owner:IONWERKS
Fragmentation of ions by resonant excitation in a high order multipole field, low pressure ion trap
InactiveUS20030189171A1Promote collision-induced dissociationIncrease probabilityStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRf fieldIon trap mass spectrometry
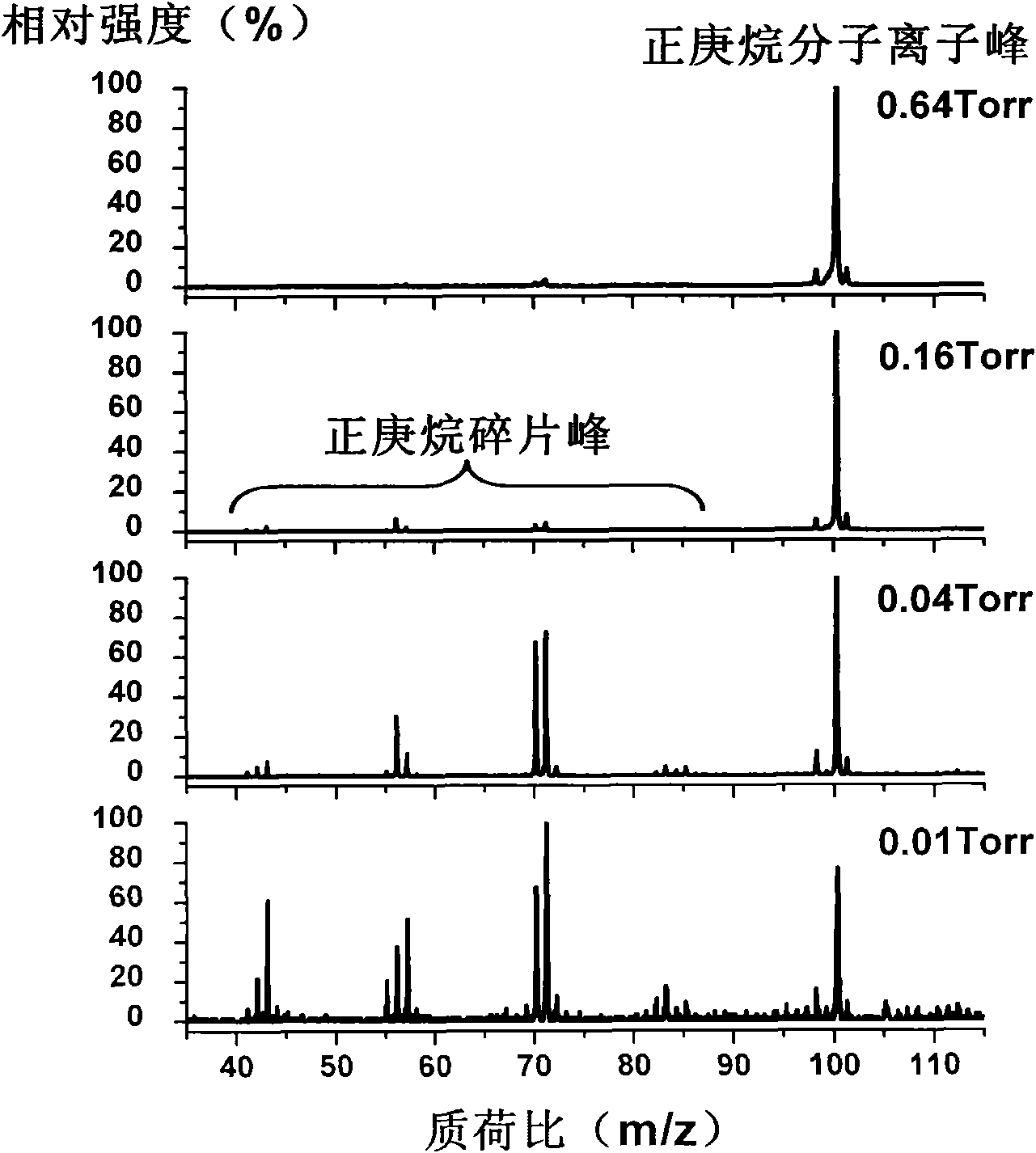
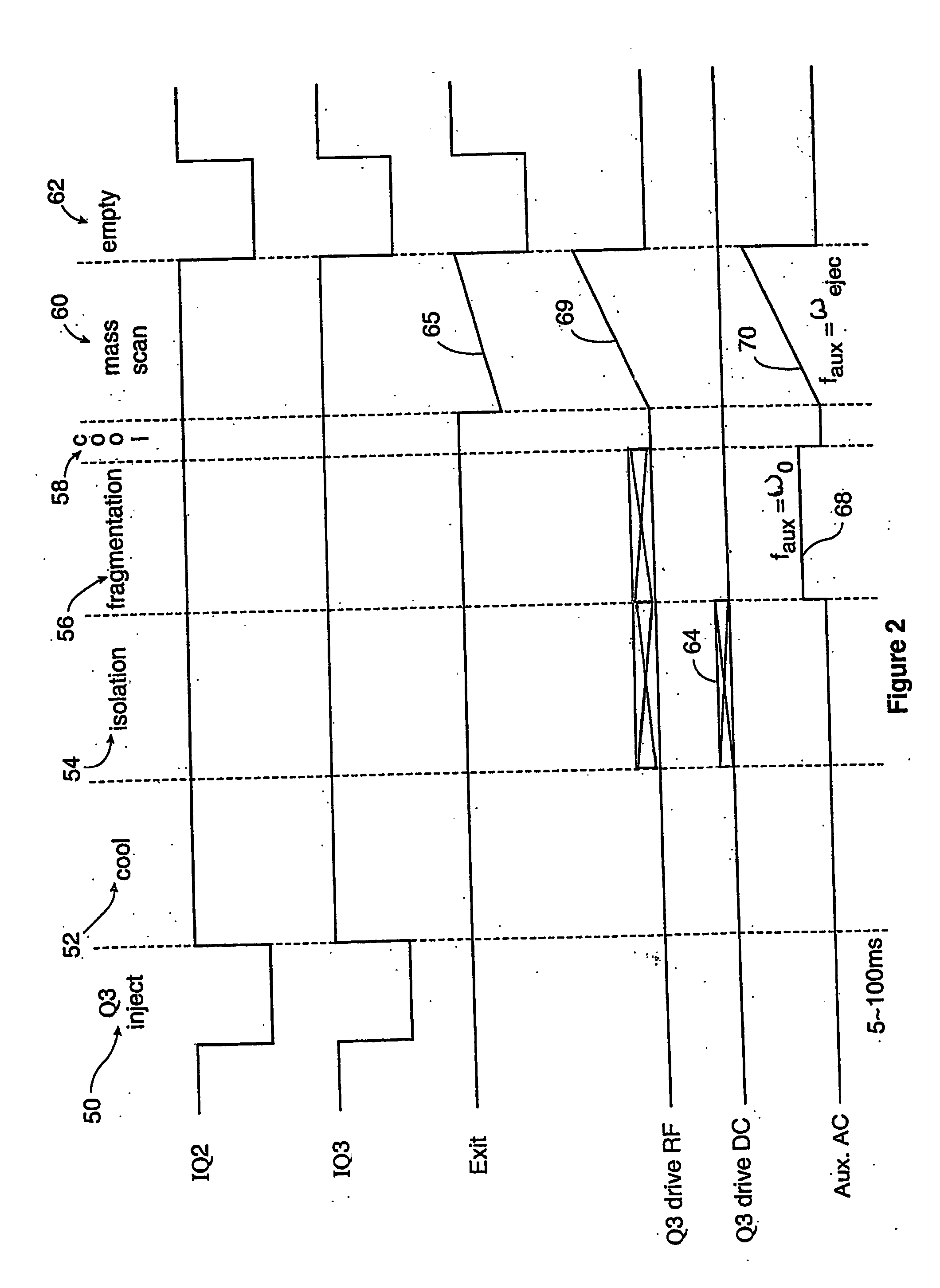
In the field of mass spectrometry, a method and apparatus for fragmenting ions with a relatively high degree of resolution and efficiency. The technique includes trapping the ions in a linear ion trap, in which the background or neutral gas pressure is preferably on the order of 10<-5 >Torr. The trapped ions are resonantly excited for a relatively extended period of time, e.g., exceeding 50 ms, at relatively low excitation levels, e.g., less than 1 Volt(0-pk). The technique allows selective dissociation of ions with a high discrimination. High fragmentation efficiency may be achieved by superimposing a higher order multipole field onto the quadrupolar RF field used to trap the ions. The multipole field, preferably an octopole field, dampens the radial oscillatory motion of resonantly excited ions at the periphery of the trap. This reduces the probability that ions will eject radially from the trap thus increasing the probability of collision induced dissociation.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
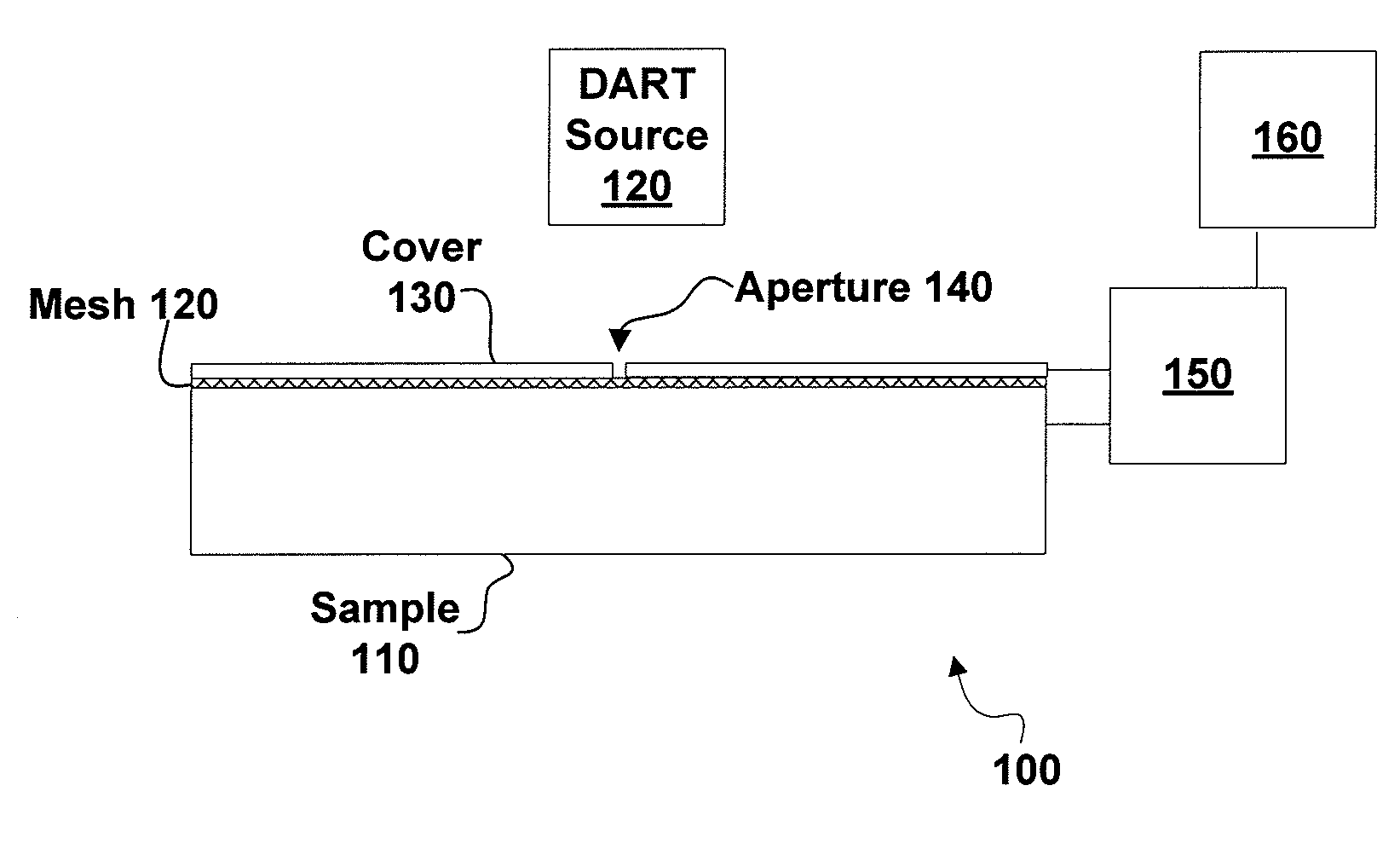
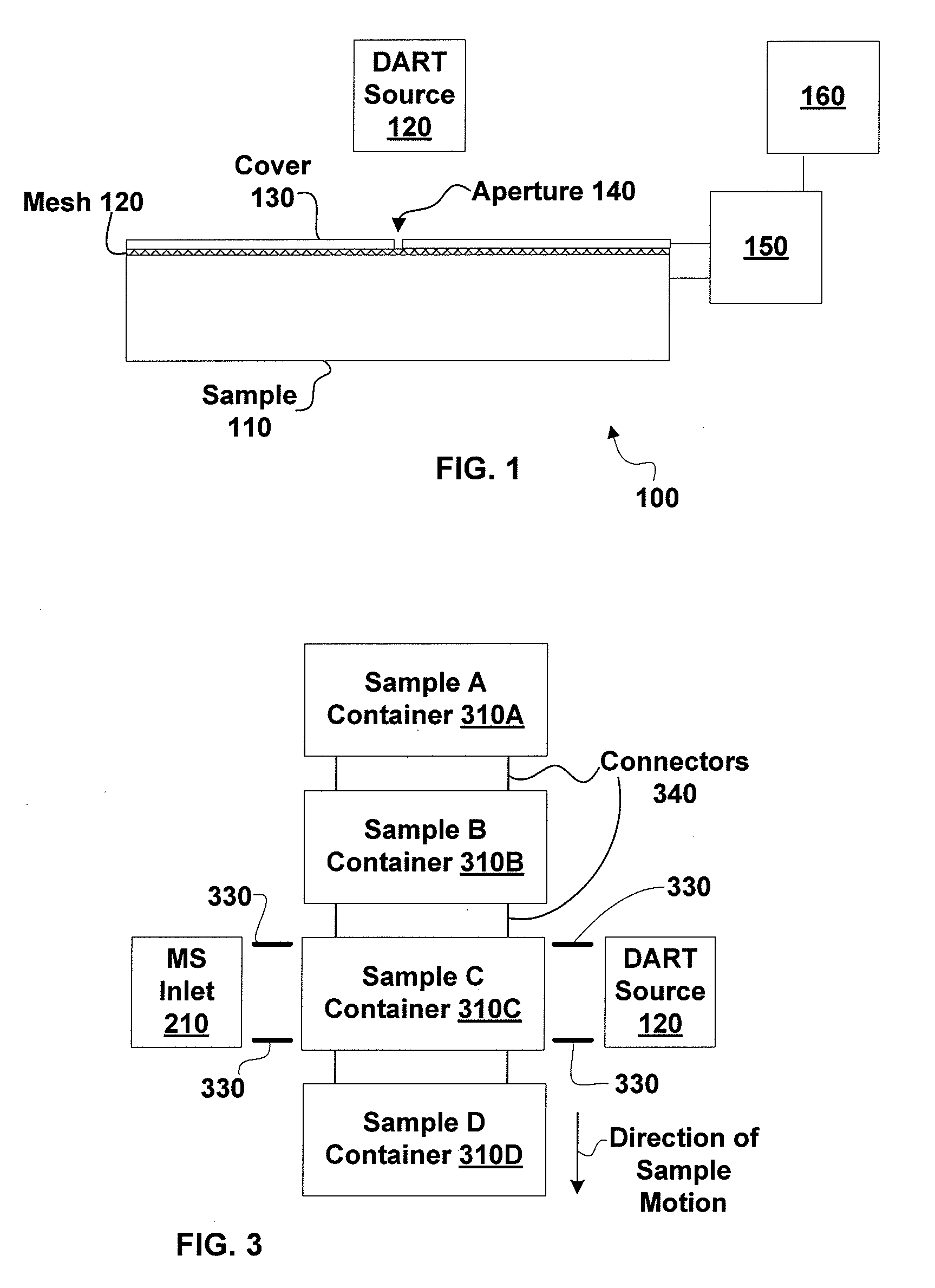
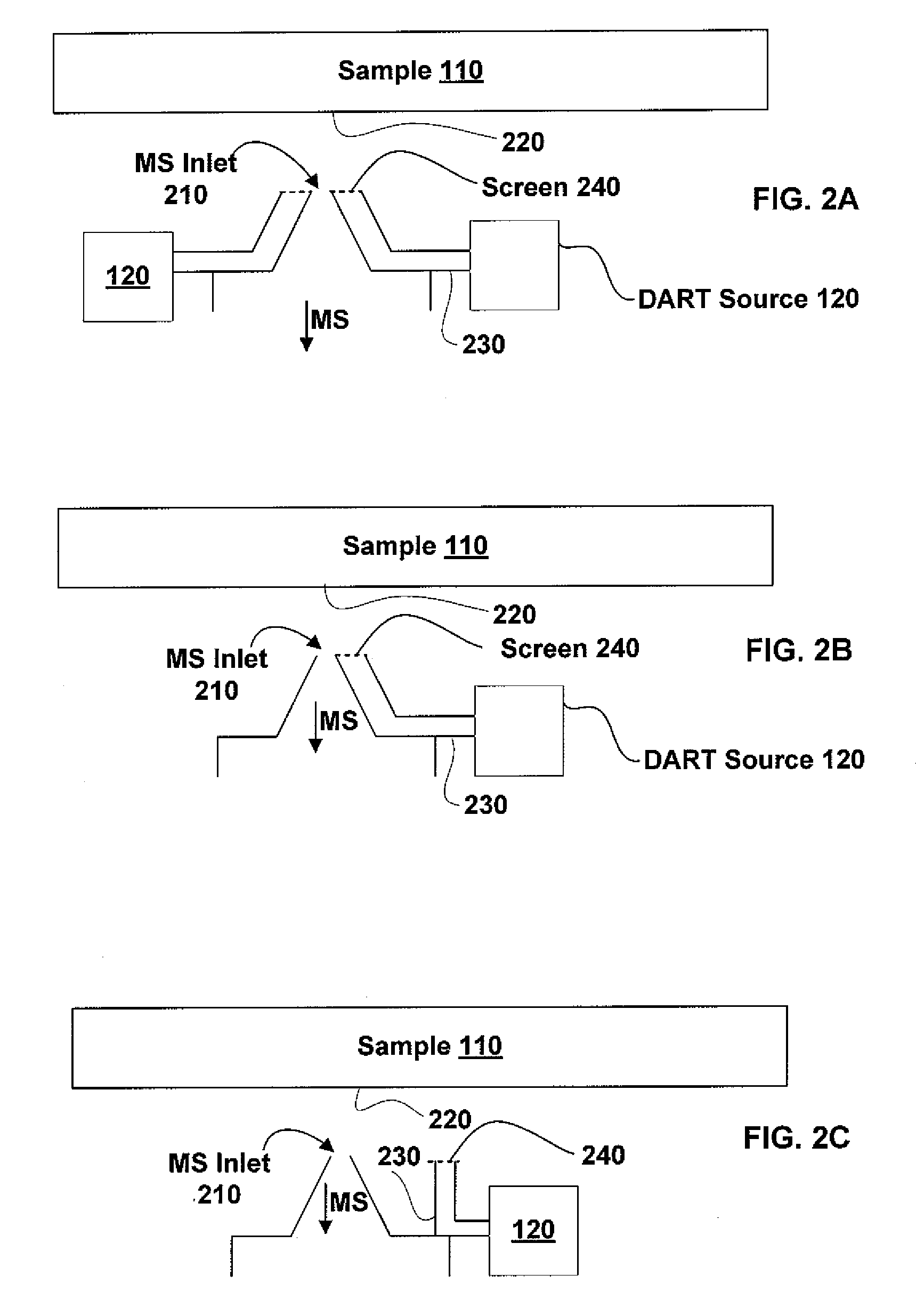
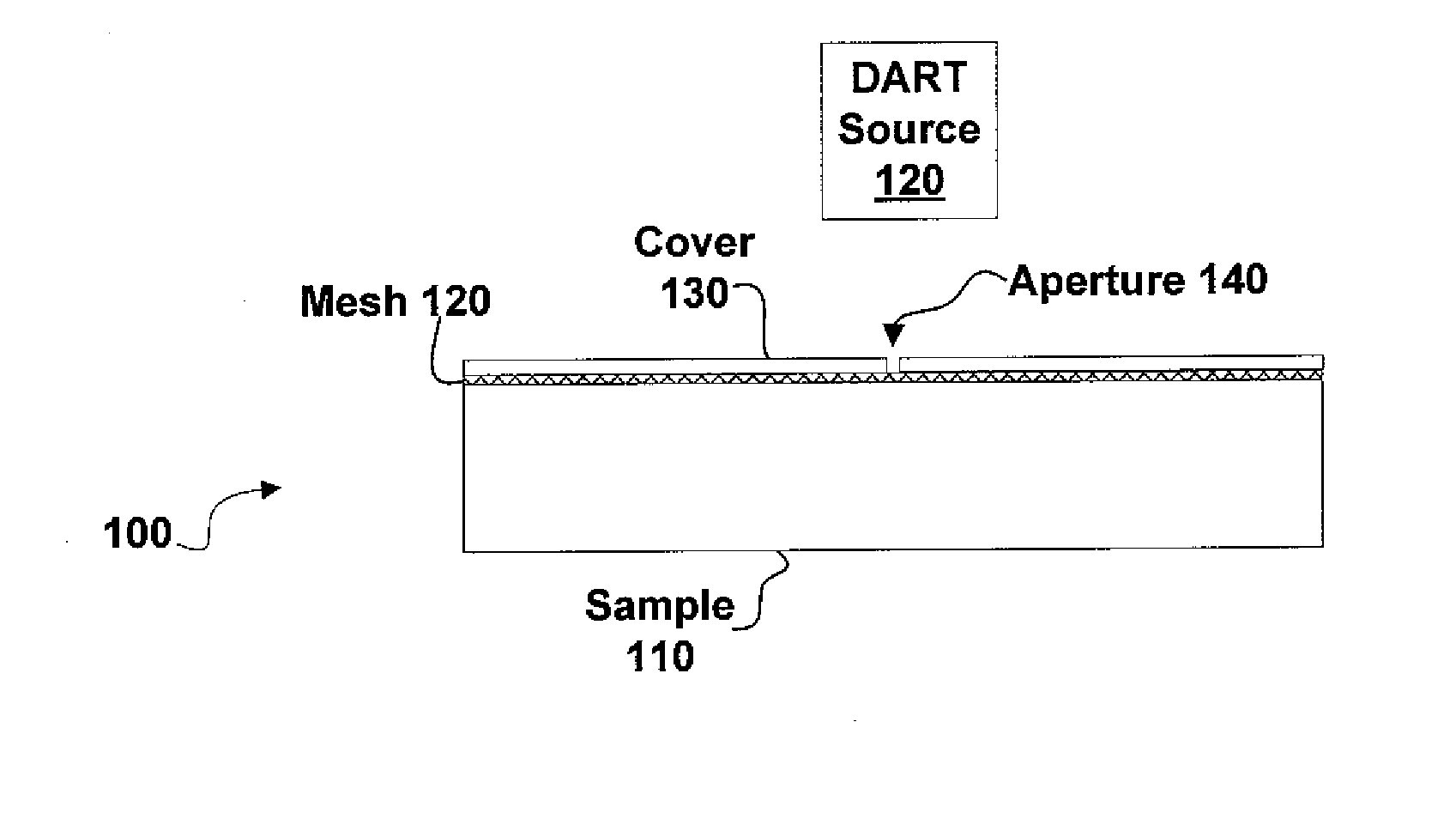
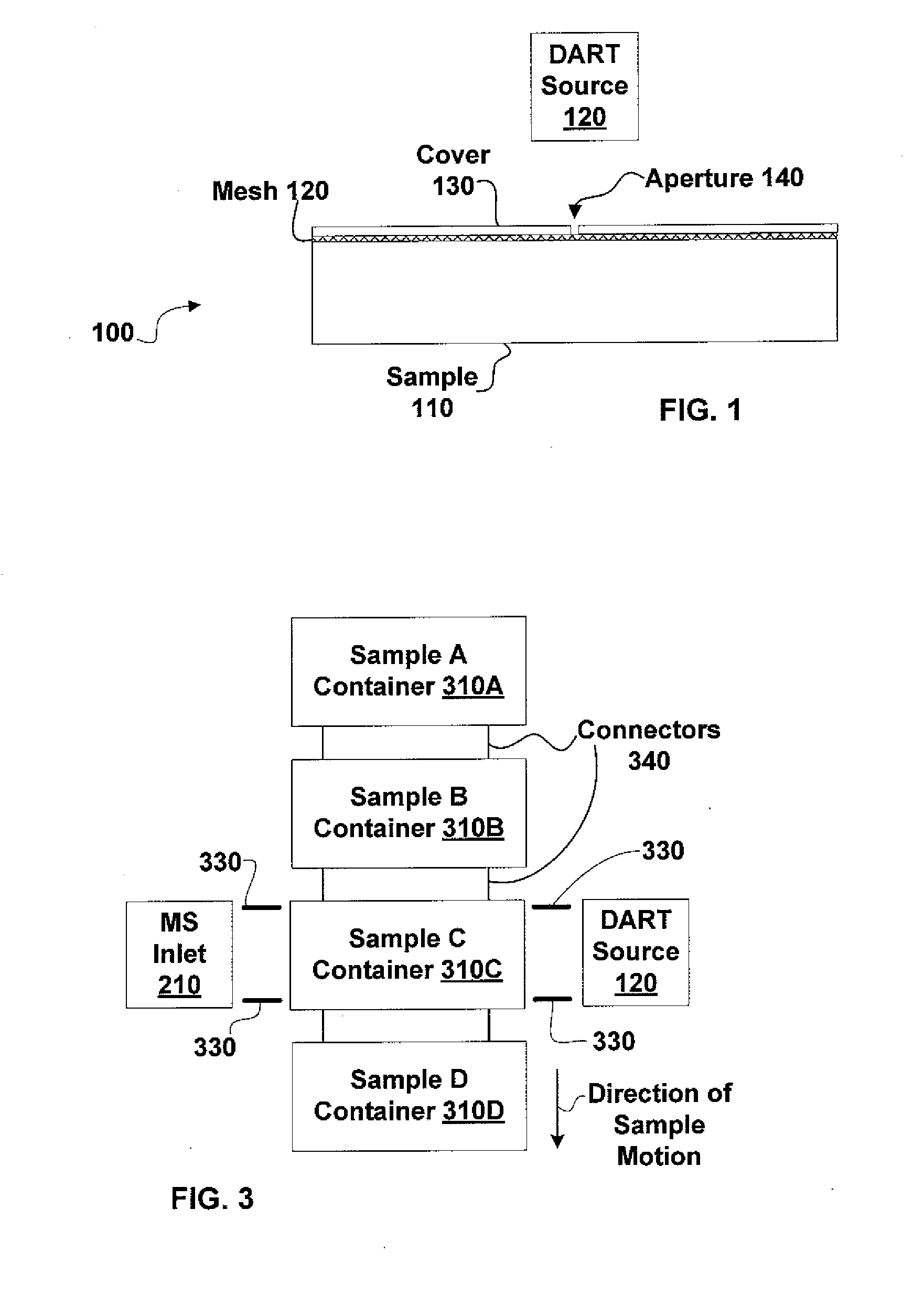
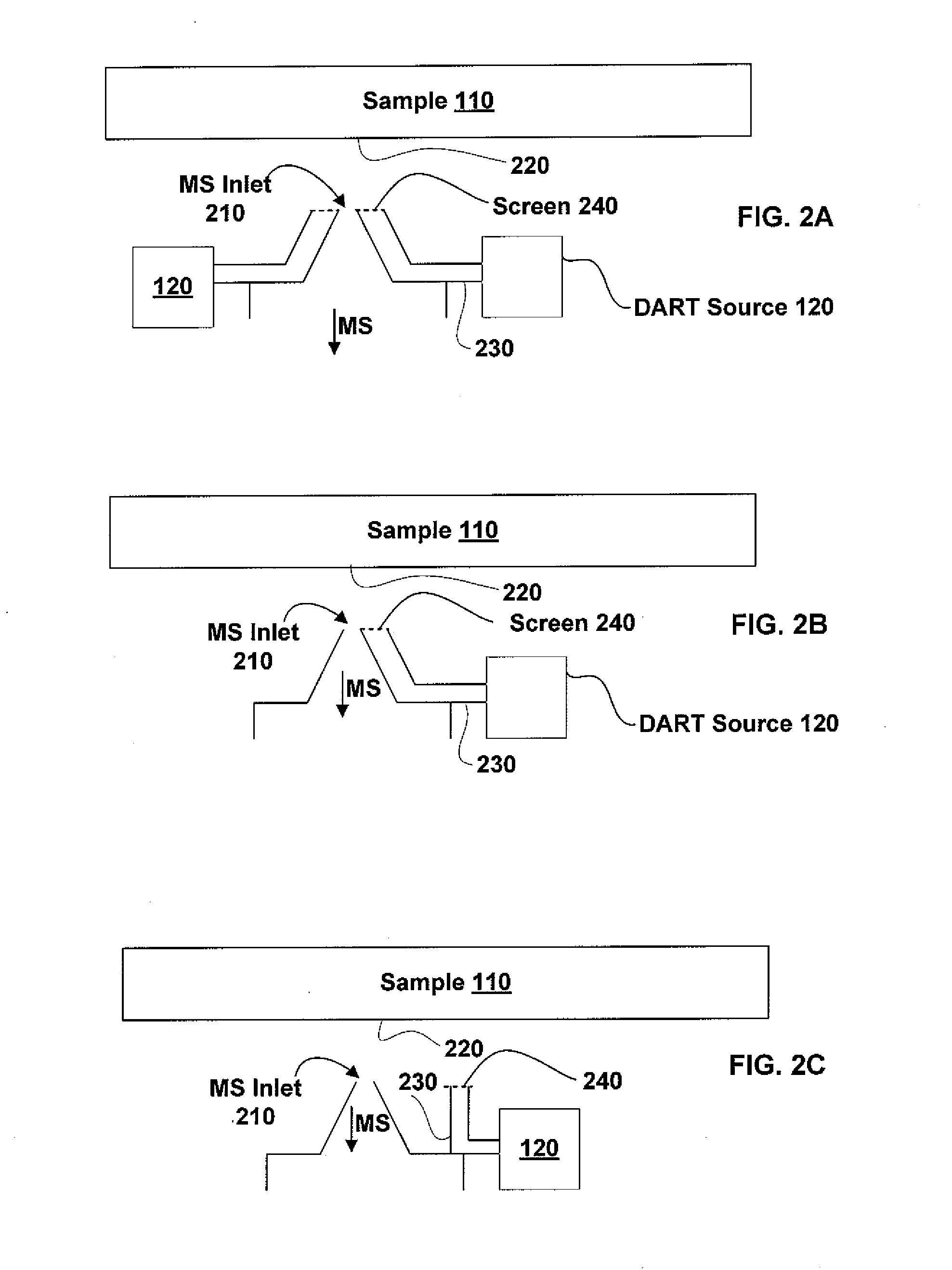
Sample imaging
InactiveUS7196525B2Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansImaging particle spectrometryAtmospheric pressureIonization
Systems and methods of generating ions at atmospheric pressure are presented. These systems and methods include spatially dependent analysis of a sample using an effusive ionization source. Systems and methods of isolating samples at atmospheric pressure are presented. These systems and methods include using a barrier to prevent metastables or electrons from an effusive ion source from reaching a sample unless the sample is in an analysis position. Systems and methods of using metastables in collisionally induced dissociation are presented.
Owner:SPARKMAN O DAVID +1
Mass spectrometry with multipole ion guides
ActiveUS7189967B1Efficient transportImprove duty cycleStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass analyzer
Multipole ion guides configured with one or more segments and positioned in a higher pressure vacuum region, are operated in mass to charge selection and ion fragmentation modes. Individual multipole ion guides are mounted in a linear assembly with no electrodes configured in between each multipole ion guide. At least a portion of each multipole ion guide mounted in a linear assembly resides in a vacuum region with higher background pressure. At least one ion guide can be configured to extend continuously from one vacuum stage into another. Individual sets of RF, + / −DC and secular frequency voltage supplies provide potentials to the rods of each multipole ion guide allowing the operation of ion transmission, ion trapping, mass to charge selection and ion fragmentation functions independently in each ion guide. The presence of higher background pressure along a portion of the multiple ion guide linear assembly allows the Collisional Induced Dissociation (CID) fragmentation of ions by axially accelerating ions from one multipole ion guide to an adjacent ion guide, analogous to a triple quadrupole function. A variety of MS and MS / MSn analysis functions can be achieved with a mass analyzer configured with multiple ion guide linear assembly operated in a higher background pressure.
Owner:ANALYTICA OF BRANFORD
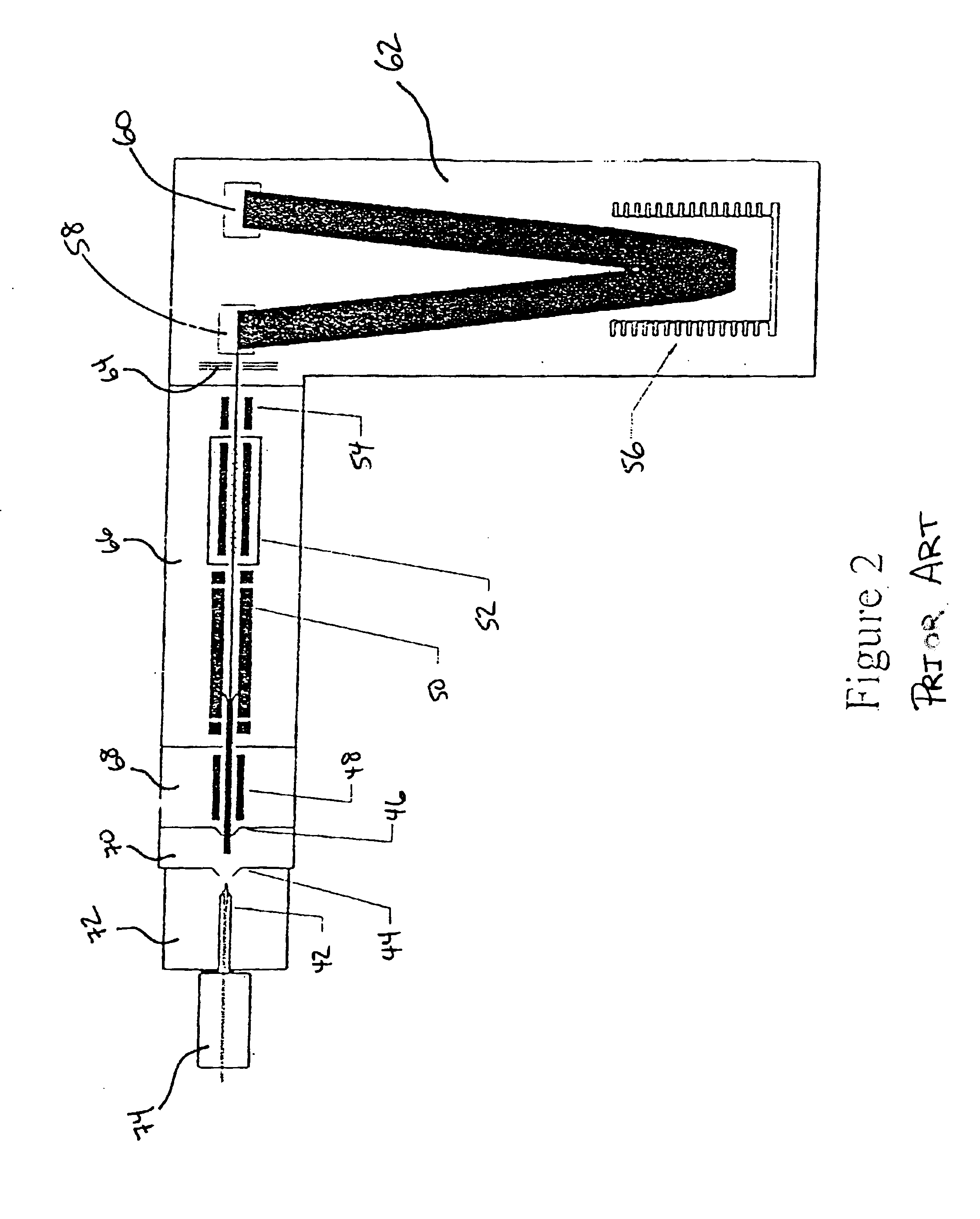
Means and method for a quadrupole surface induced dissociation quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer
InactiveUS20030042412A1Time-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationTime-of-flight mass spectrometryMass analyzer
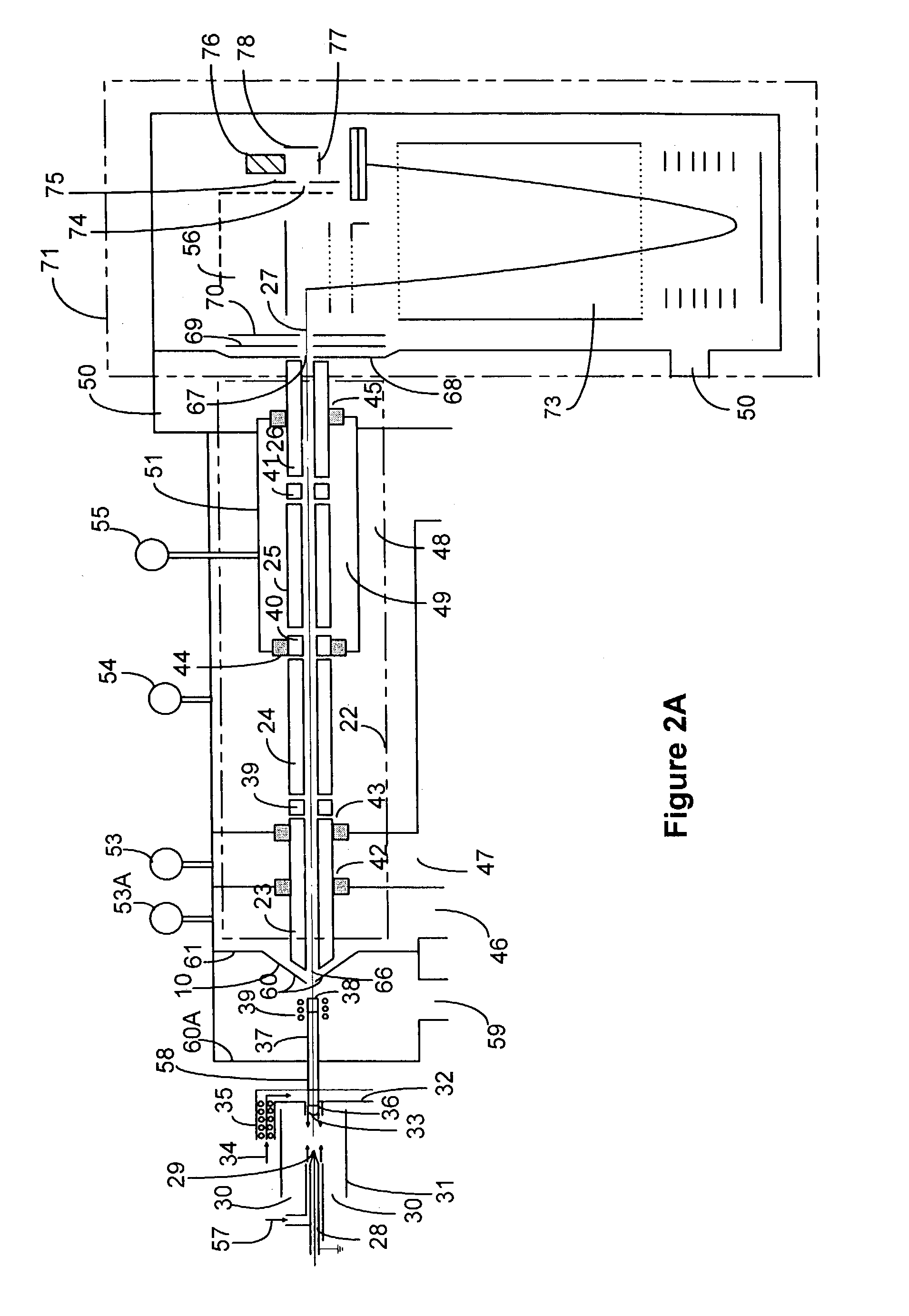
A means and method are disclosed whereby ions from an ion source can be selected and transferred to a time-of-flight mass analyzer via an arrangement of multipoles in such a way that fragmented ions may be generated by collision-induced dissociation or surface-induced dissociation. First, ions from the source are collisionally cooled by a first multipole. Second, the m / z range of the ions is then selected by a second multipole (preferably a quadrupole). Third, the selected ions are allowed to collide with a "collision surface" capable of producing fragment ions. Fourth, these fragment ions are collisionally cooled in a third multipole and delivered into a TOF mass analyzer for subsequent analysis of the fragmented ions.
Owner:BRUKER SCI LLC
Multi-beam ion mobility time-of-flight mass spectrometry with multi-channel data recording
InactiveUS20090140140A1Improve efficiencyReduce divergenceTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDense bodyData recording
The content of the invention comprises a concept of multi-beam ion pre-selection from a single sample, coordinated mobility (against the gas flow) separation, cooling ions in supersonic gas flow and mass separation of thus low divergent ions by single or plural compact high-resolution orthogonal time-of-flight mass spectrometers both linear or reflectron type with controlled collision-induced dissociation (CID) and multi-channel data recording for the optimization of sample use in the analysis, and obtaining as much useful information about the sample as possible in a reasonably short time.
Owner:IONWERKS
Metastable CID
InactiveUS20060250138A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansImaging particle spectrometryAtmospheric pressureIonization
Systems and methods of generating ions at atmospheric pressure are presented. These systems and methods include spatially dependent analysis of a sample using an effusive ionization source. Systems and methods of isolating samples at atmospheric pressure are presented. These systems and methods include using a barrier to prevent metastables or electrons from an effusive ion source from reaching a sample unless the sample is in an analysis position. Systems and methods of using metastables in collisionally induced dissociation are presented.
Owner:SPARKMAN O DAVID +1
Means and method for a quadrupole surface induced dissociation quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer
InactiveUS6744040B2Time-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsTime-of-flight mass spectrometryMass analyzer
A means and method are disclosed whereby ions from an ion source can be selected and transferred to a time-of-flight mass analyzer via an arrangement of multipoles in such a way that fragmented ions may be generated by collision-induced dissociation or surface-induced dissociation. First, ions from the source are collisionally cooled by a first multipole. Second, the m / z range of the ions is then selected by a second multipole (preferably a quadrupole). Third, the selected ions are allowed to collide with a "collision surface" capable of producing fragment ions. Fourth, these fragment ions are collisionally cooled in a third multipole and delivered into a TOF mass analyzer for subsequent analysis of the fragmented ions.
Owner:BRUKER SCI LLC
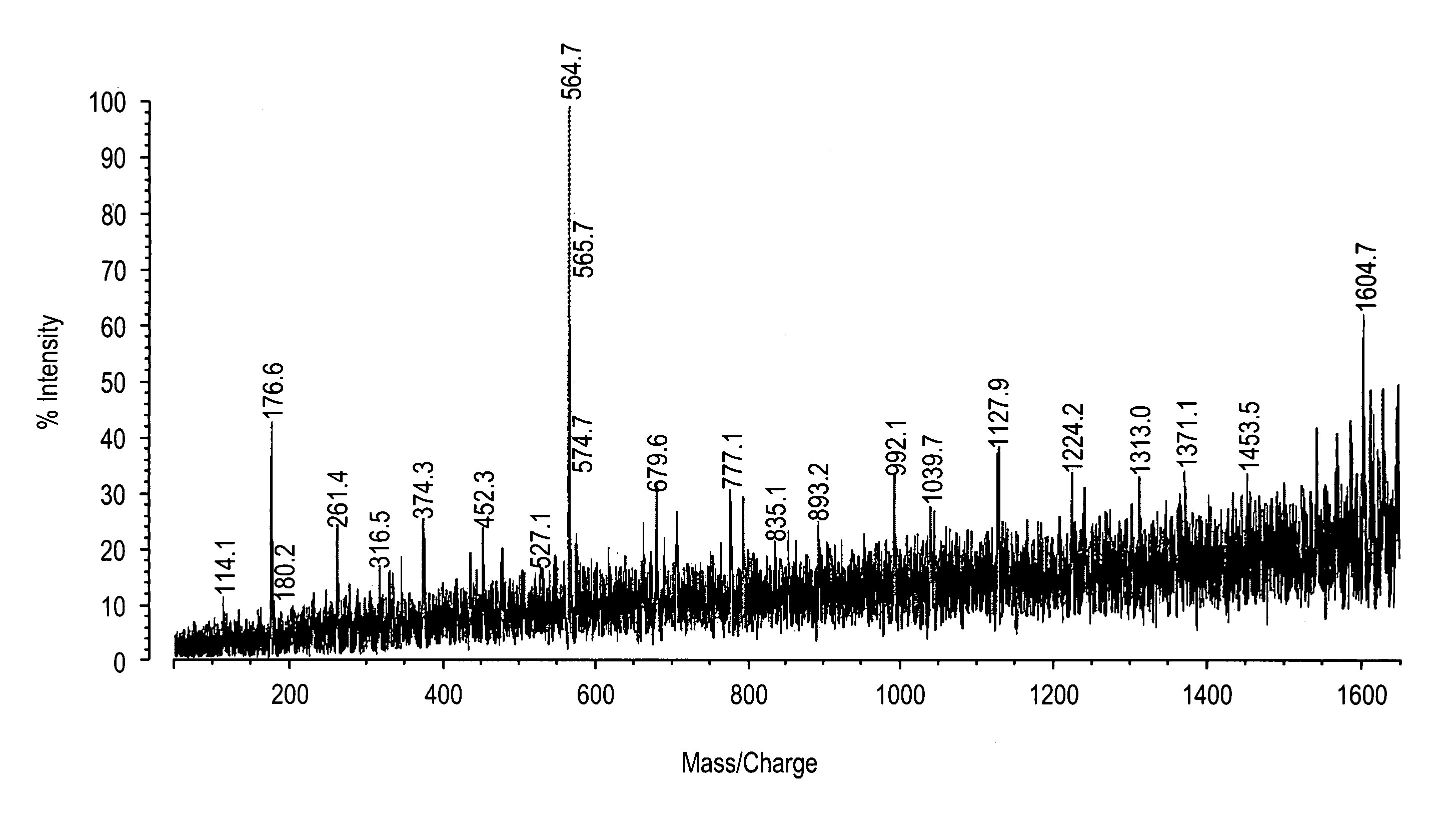
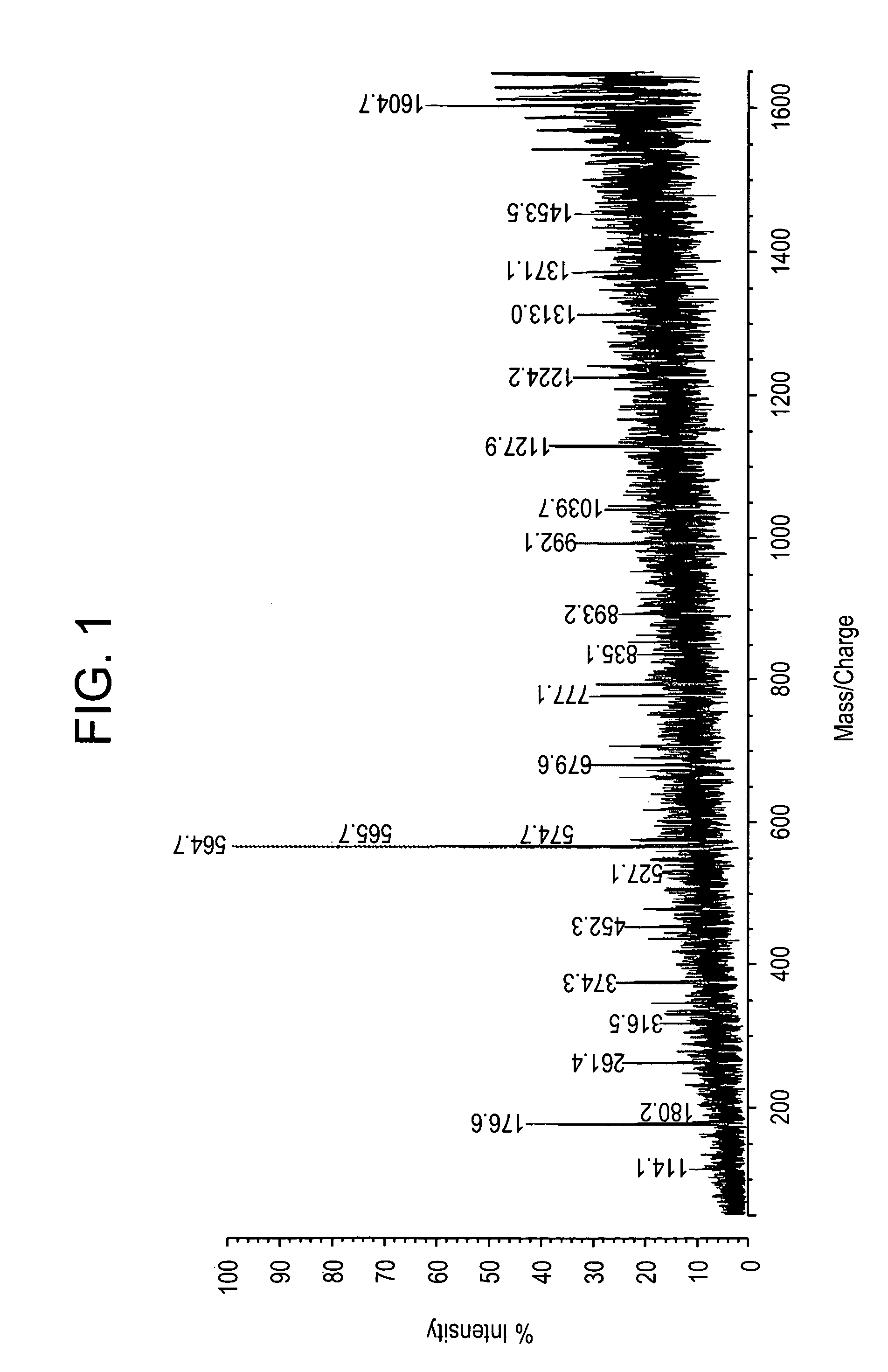
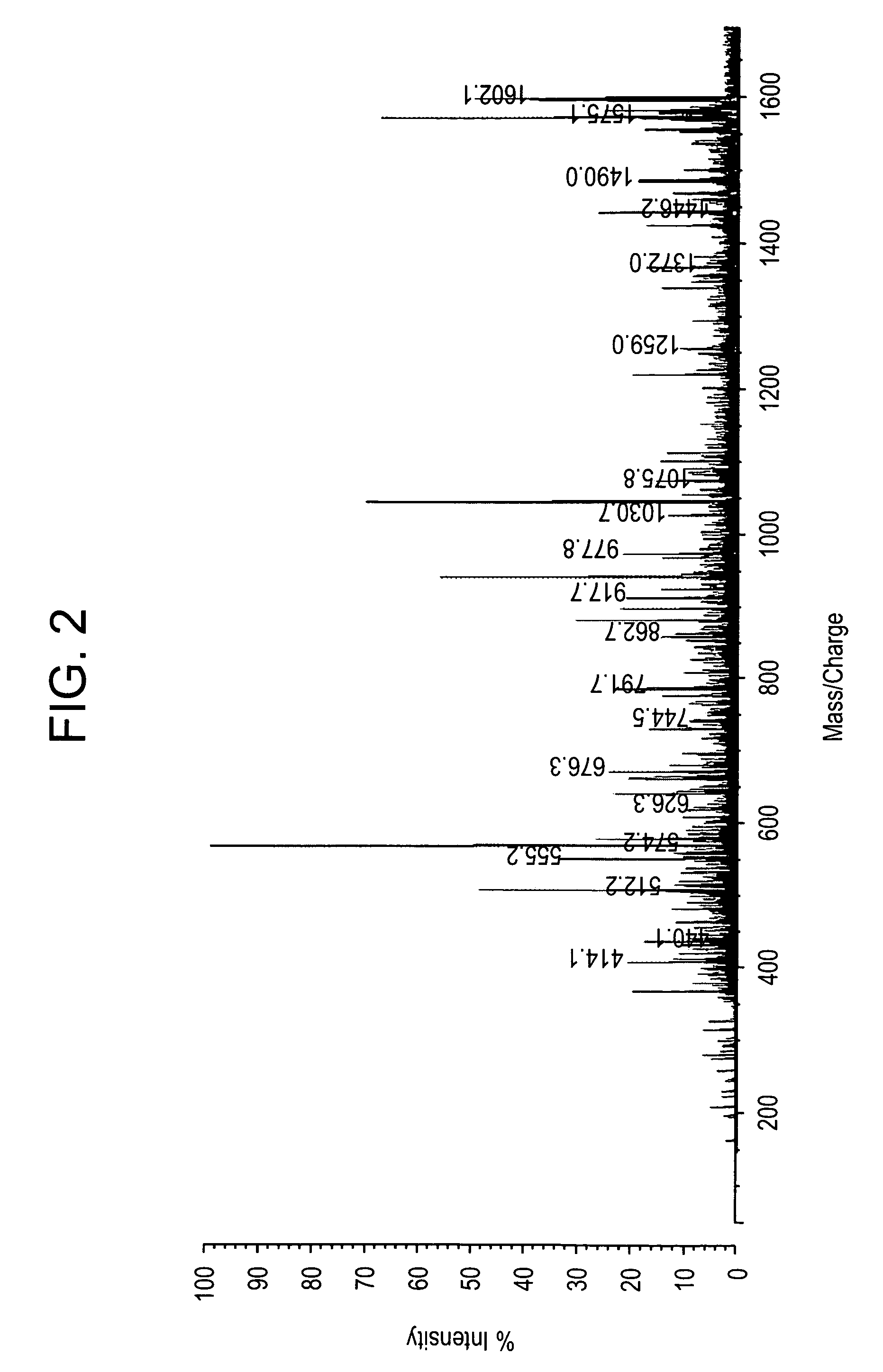
Methods for direct biomolecule identification by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20070114375A1Particle separator tubesIsotope separationLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometryMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
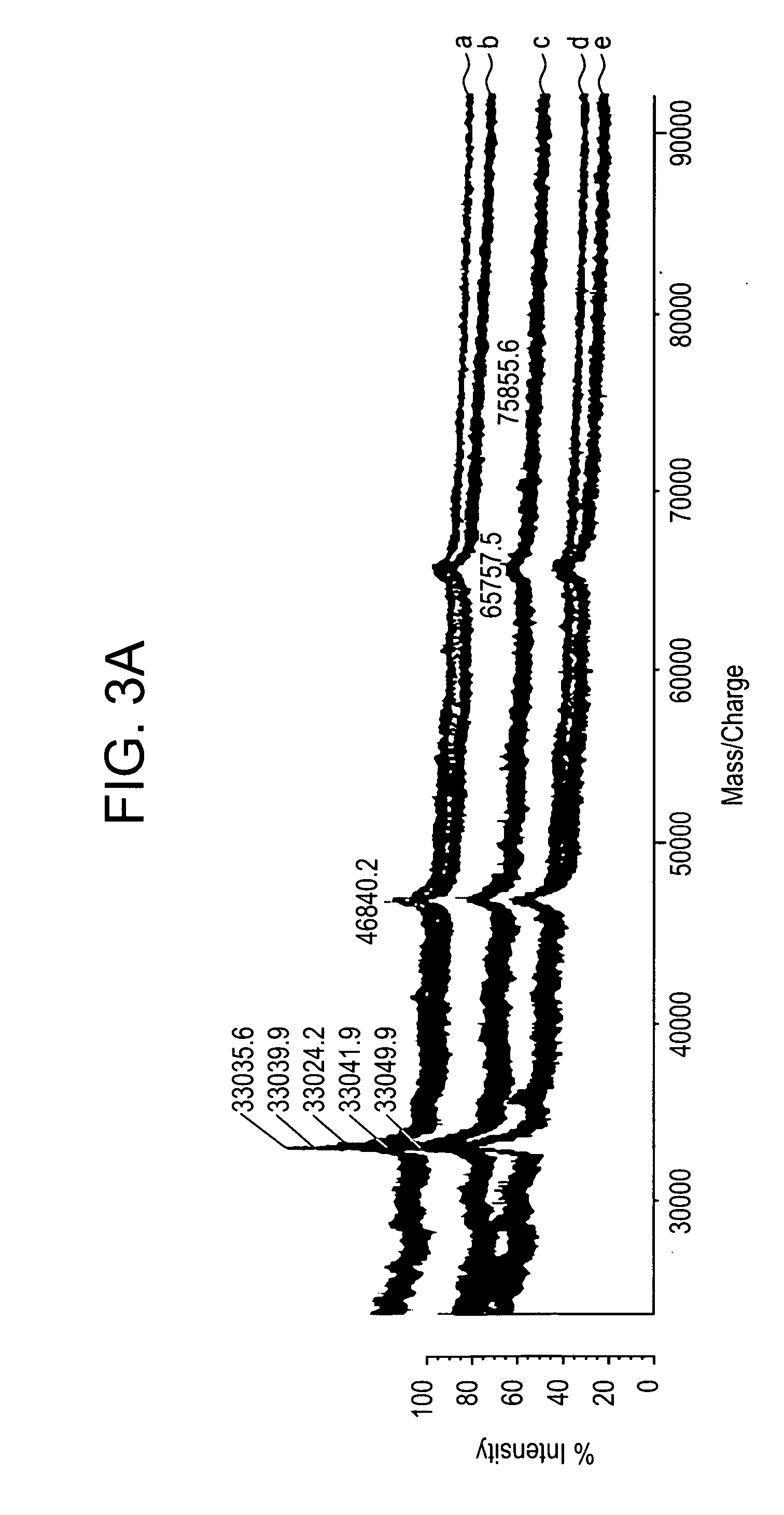
The present invention relates to the use of post source decay (PSD) or collision induced dissociation (CID) direct tissue (DT) MALDI-TOF or DT-MALDI-TOF-TOF mass spectrographic identification of biological molecules in a tissue or cellular sample without the need for further protein extraction. This method provides for studying cells or tissues by direct tissue MALDI (DT-MALDI), thereby substituting in situ protein release for further protein extraction. Mass / intensity data was processed with Mascot© software interrogation of the NCBI database. These results are proof of principle that DT-MALDI, combined with bioinformatics, can directly identify proteins in cells and tissues from their mass spectra.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Photoactivated collision induced dissociation (PACID) (apparatus and method)
ActiveUS20080042056A1Ion sources/gunsIsotope separationMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryElectronic component
The invention provides a system apparatus and methods for fragmenting various molecules. In particular, the invention may be employed for fragmenting biomolecules like peptides to determine sequence information. The invention provides a mass spectrometry system for photo-activated collision induced dissociation. The mass spectrometry system or device includes an ion source for producing ions, a photon source adjacent to the ion source for photo-activating ions produced by the ion source, an electrical element adjacent to the photon source for creating an electric field for accelerating ions produced by the ion source and photo-activated by the photon source; wherein ions are produced by the ion source, photo-activated by the photon source and accelerated into a surface to cause dissociation of the activated ions; and a detector downstream from the ion source for detecting the collision induced and dissociated ions.Methods for molecule and / or peptide fragmentation are also disclosed.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
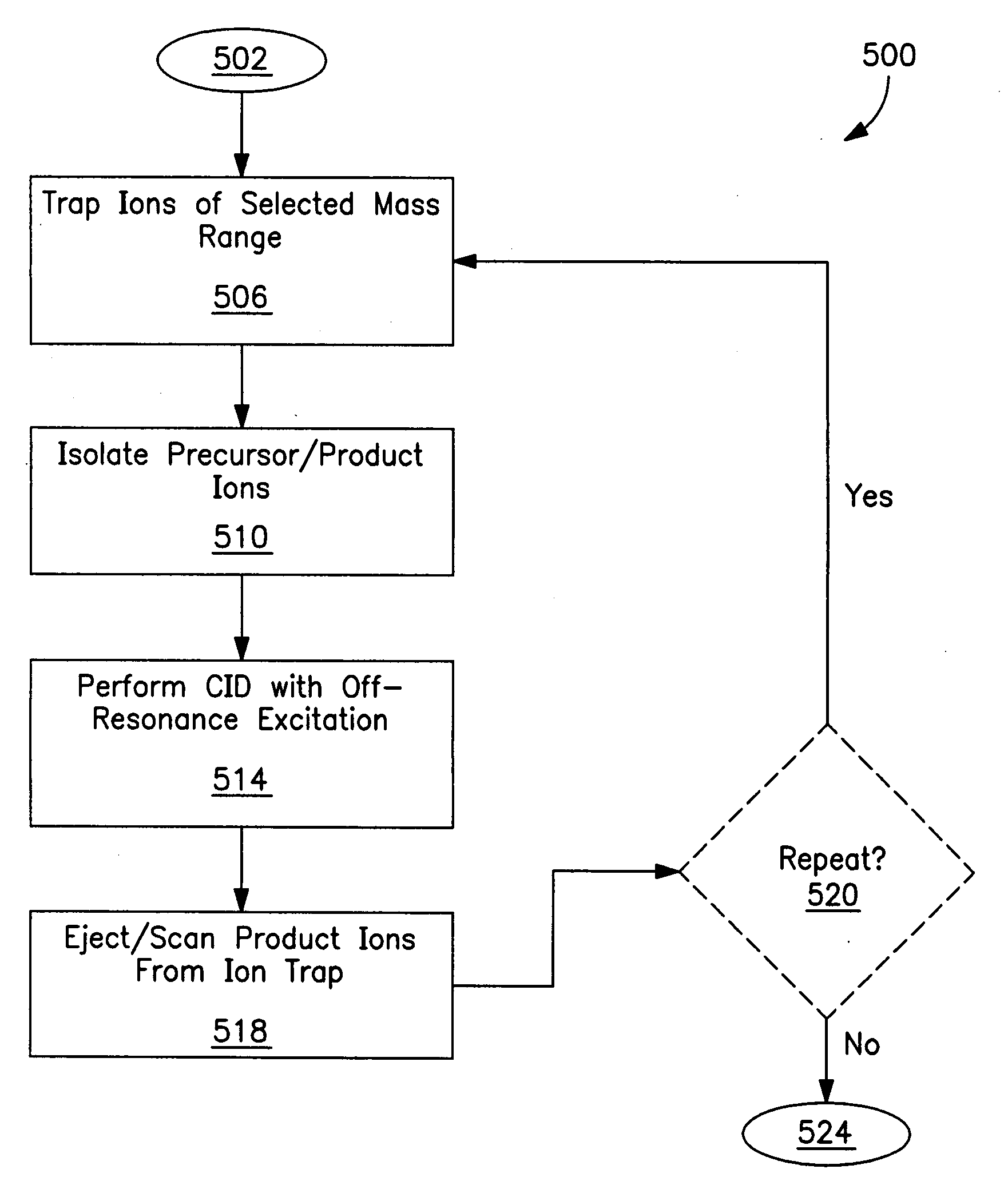
Cascade mass spectrometry method performed in ion trap mass analyzer
ActiveCN103413751AAchieve dissociationSimplify the experimental processStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansHigh energyMass analyzer
The invention belongs to the technical field of mass spectrometry and particularly relates to a cascade mass spectrometry method performed in an ion trap mass analyzer. The cascade mass spectrometry method performed in the ion trap mass analyzer specifically comprises three stages of ion selective segregation, collision induction dissociation and mass scanning and analyzing. According to the cascade mass spectrometry method performed in the ion trap mass analyzer, in the stage of collision induction dissociation, by changing the period of a radio frequency signal, namely changing the frequency of radio-frequency voltage loaded on an ion trap, parent ions with a certain mass-to-charge ratio undergo resonance excitation so as to obtain energy. The high-energy ions which undergo resonance excitation collide with neutral molecules in the ion trap and are dissociated, outcome ions are generated, and the cascade mass spectrometry is achieved. The cascade mass spectrometry method performed in the ion trap mass analyzer has the advantages that only arrangement of software can be used for changing the scanning period of the stage of collision induction dissociation in order to achieve collision induction dissociation, and thus, an experiment device and a method of cascade mass spectrometry can be obviously simplified.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
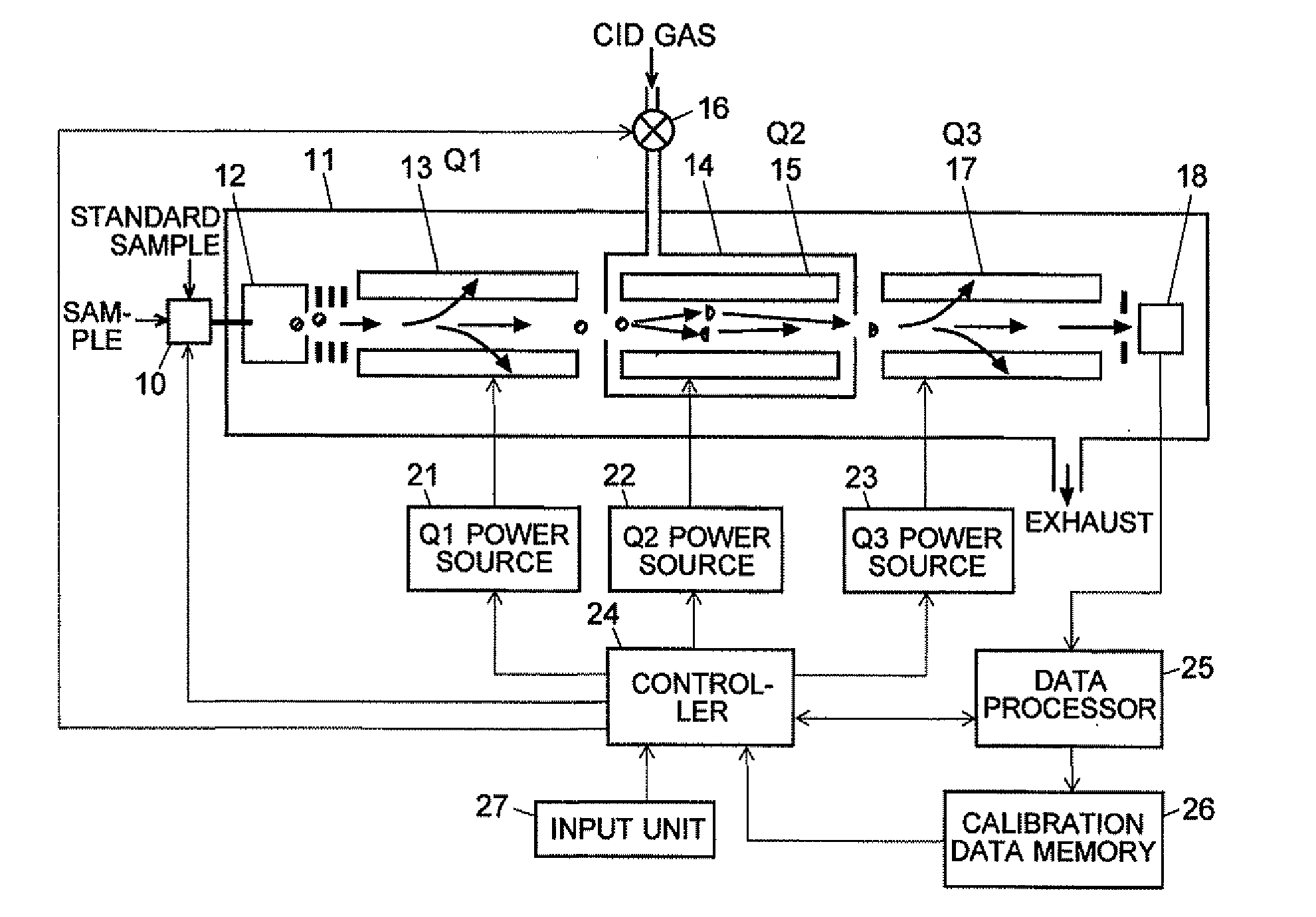
MS/MS Mass Spectrometer
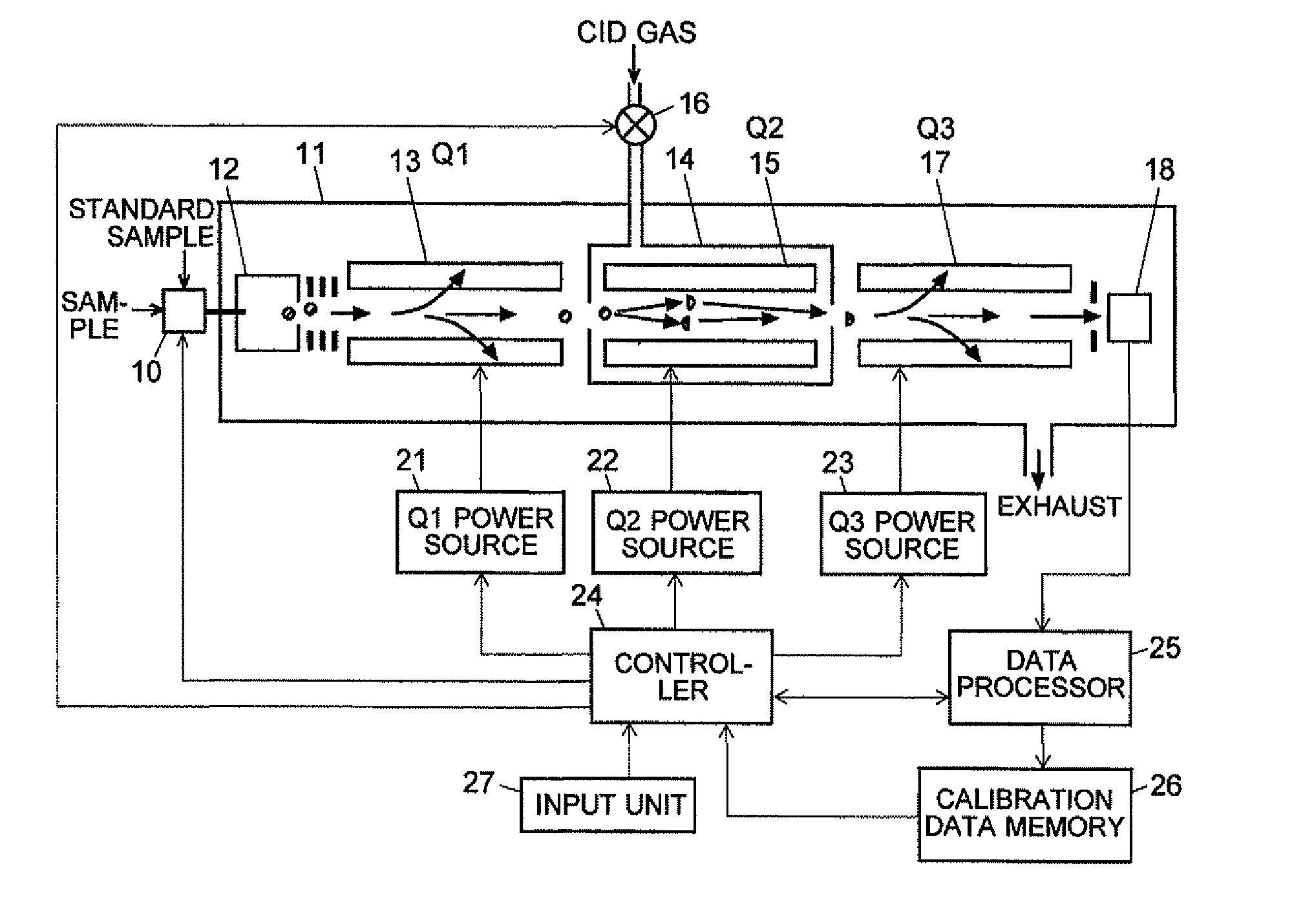
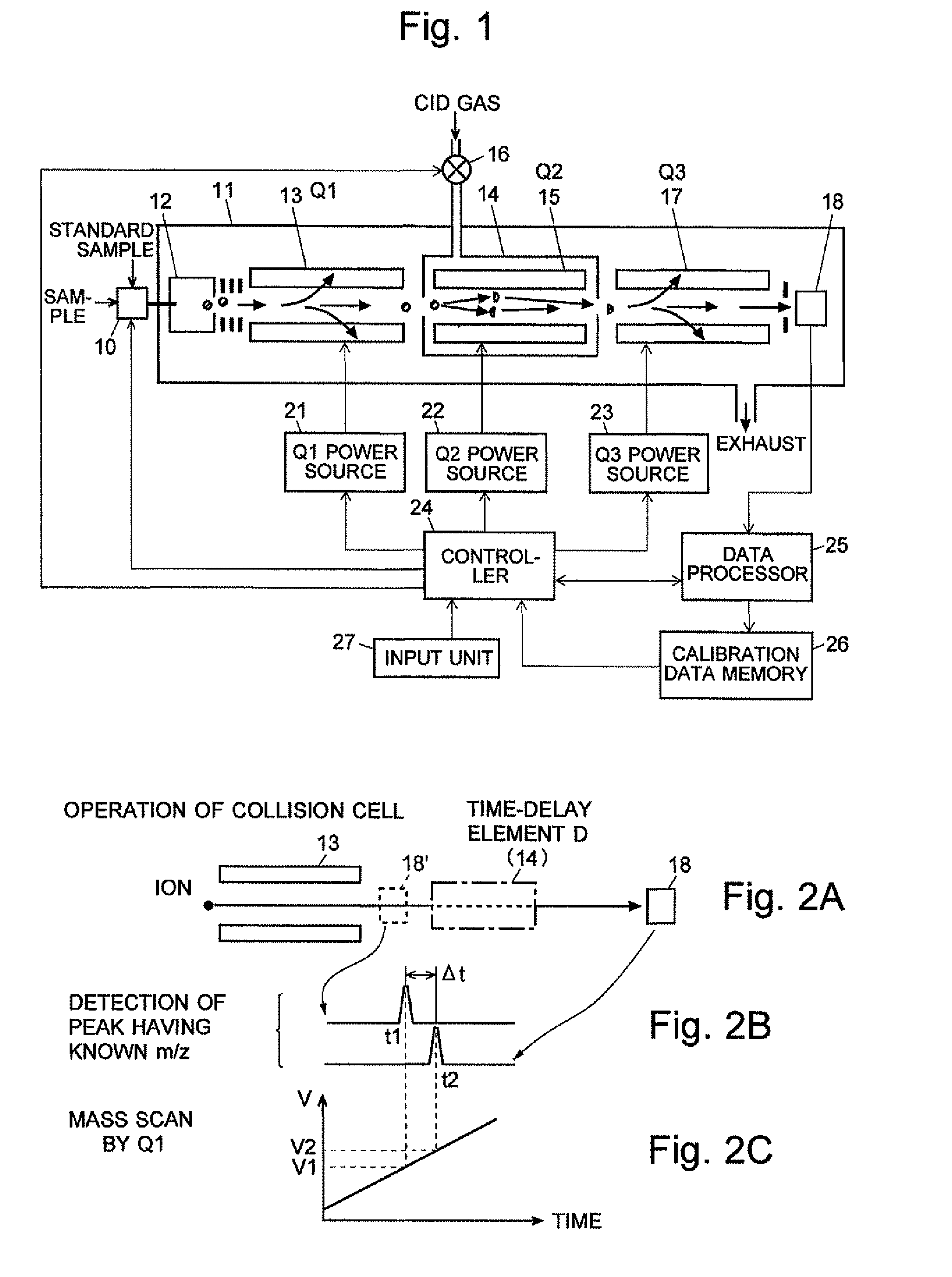
ActiveUS20110284740A1High detection sensitivityIncrease in mass accuracySamples introduction/extractionParticle spectrometer methodsData memoryQuadrupole
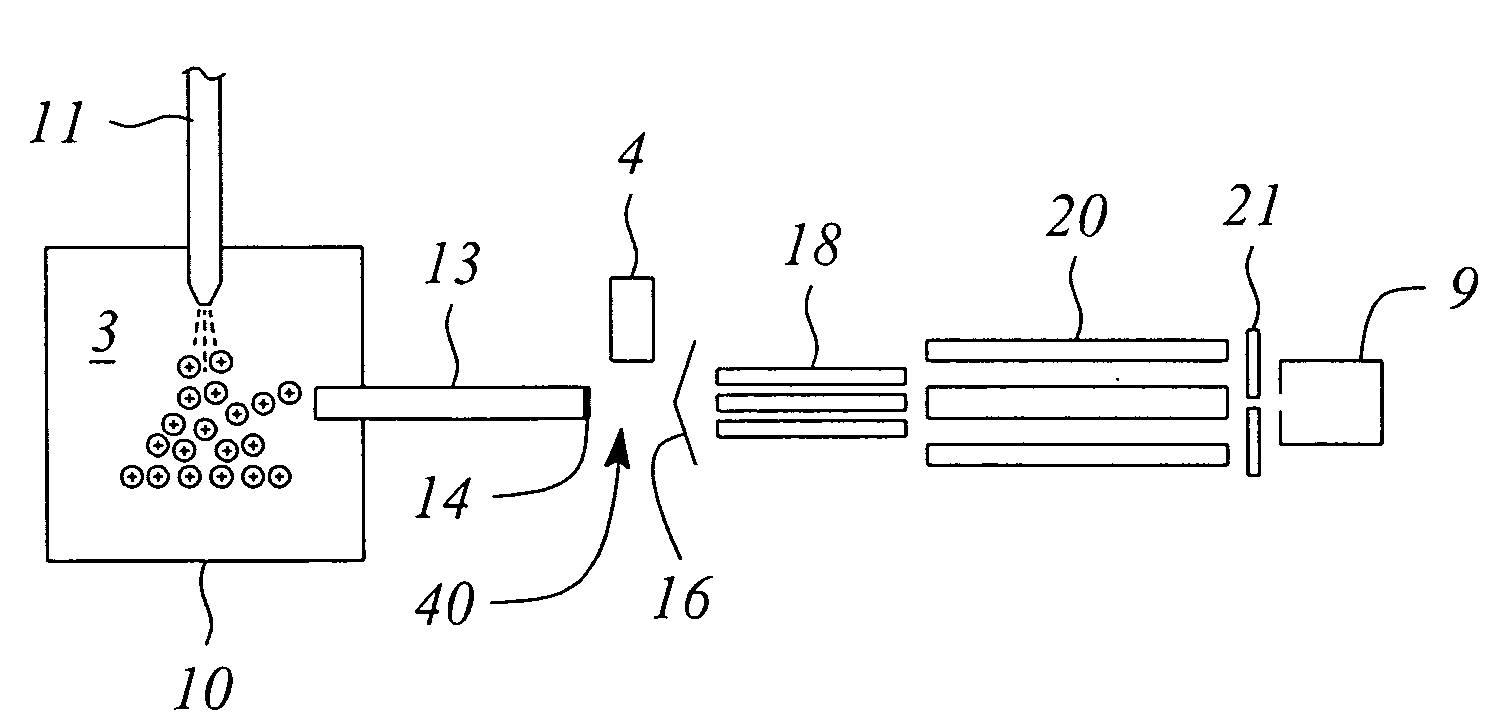
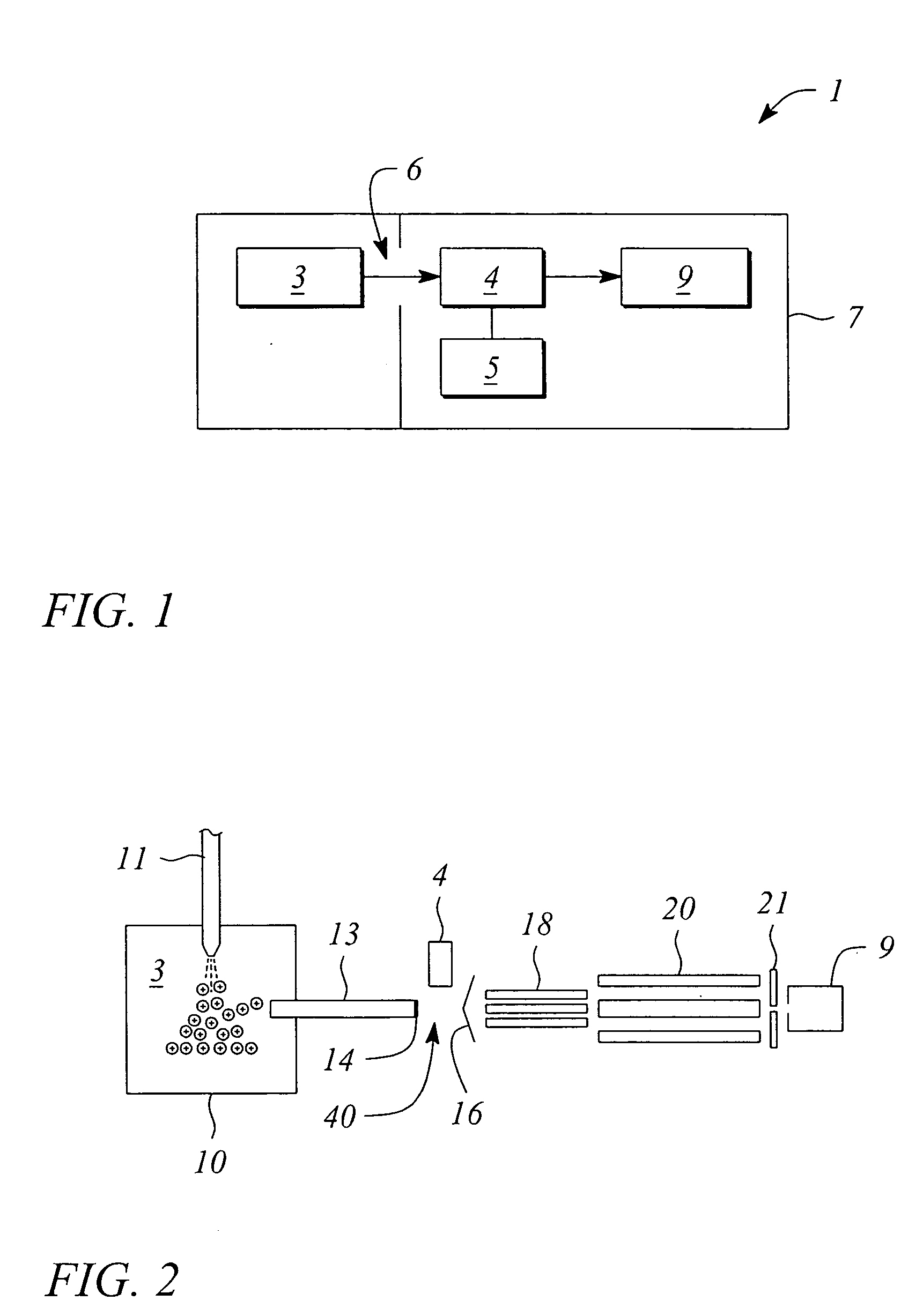
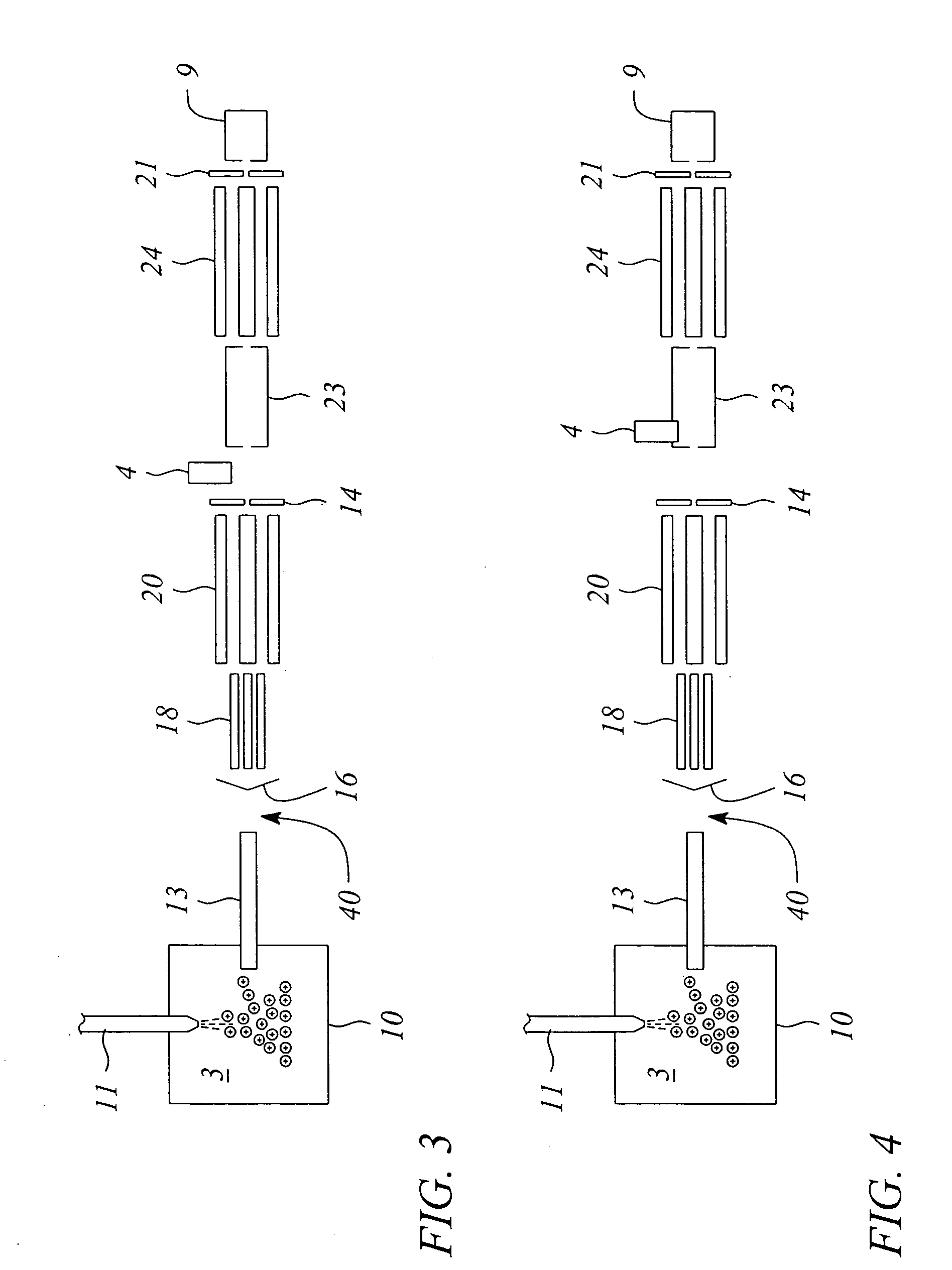
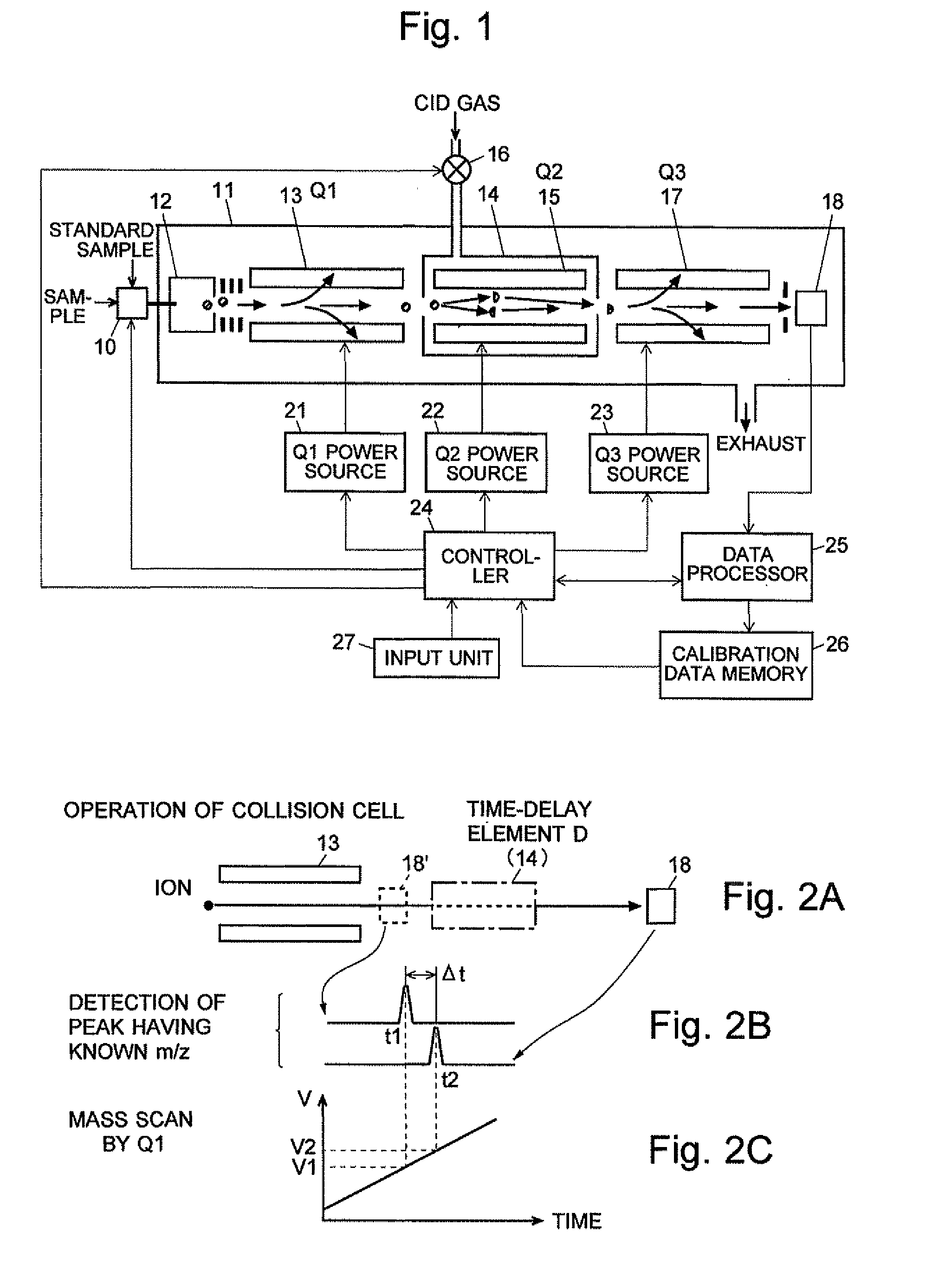
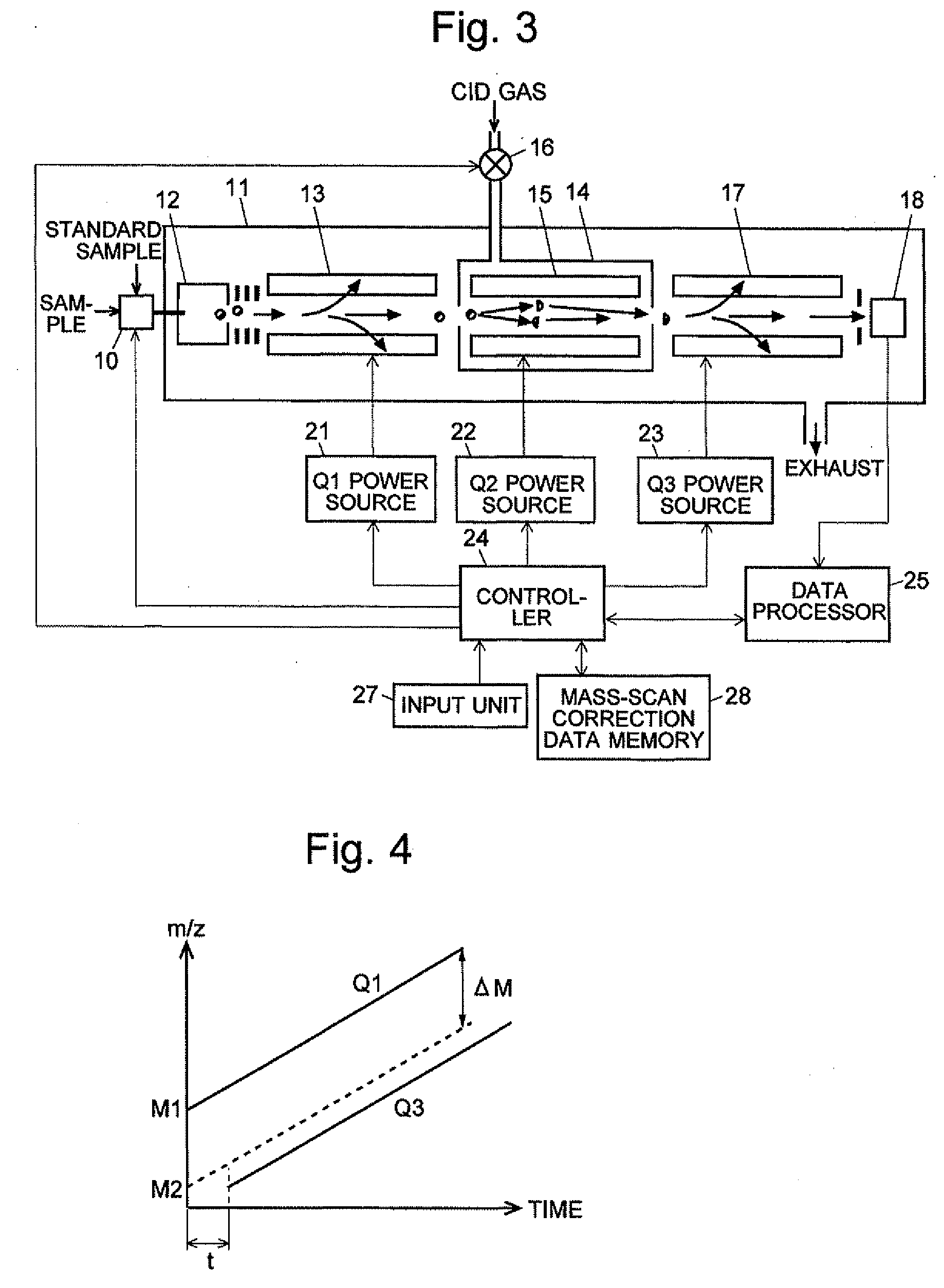
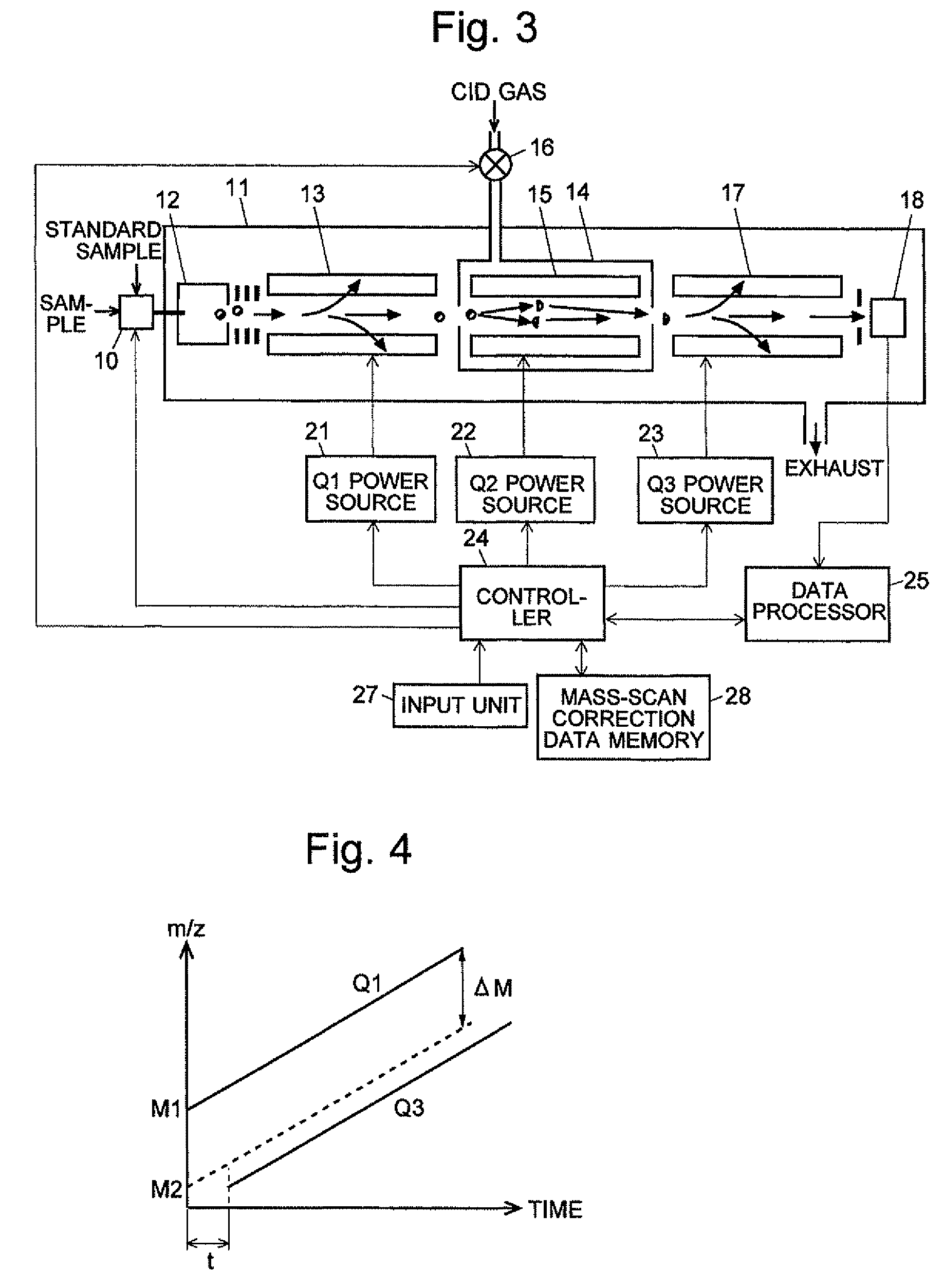
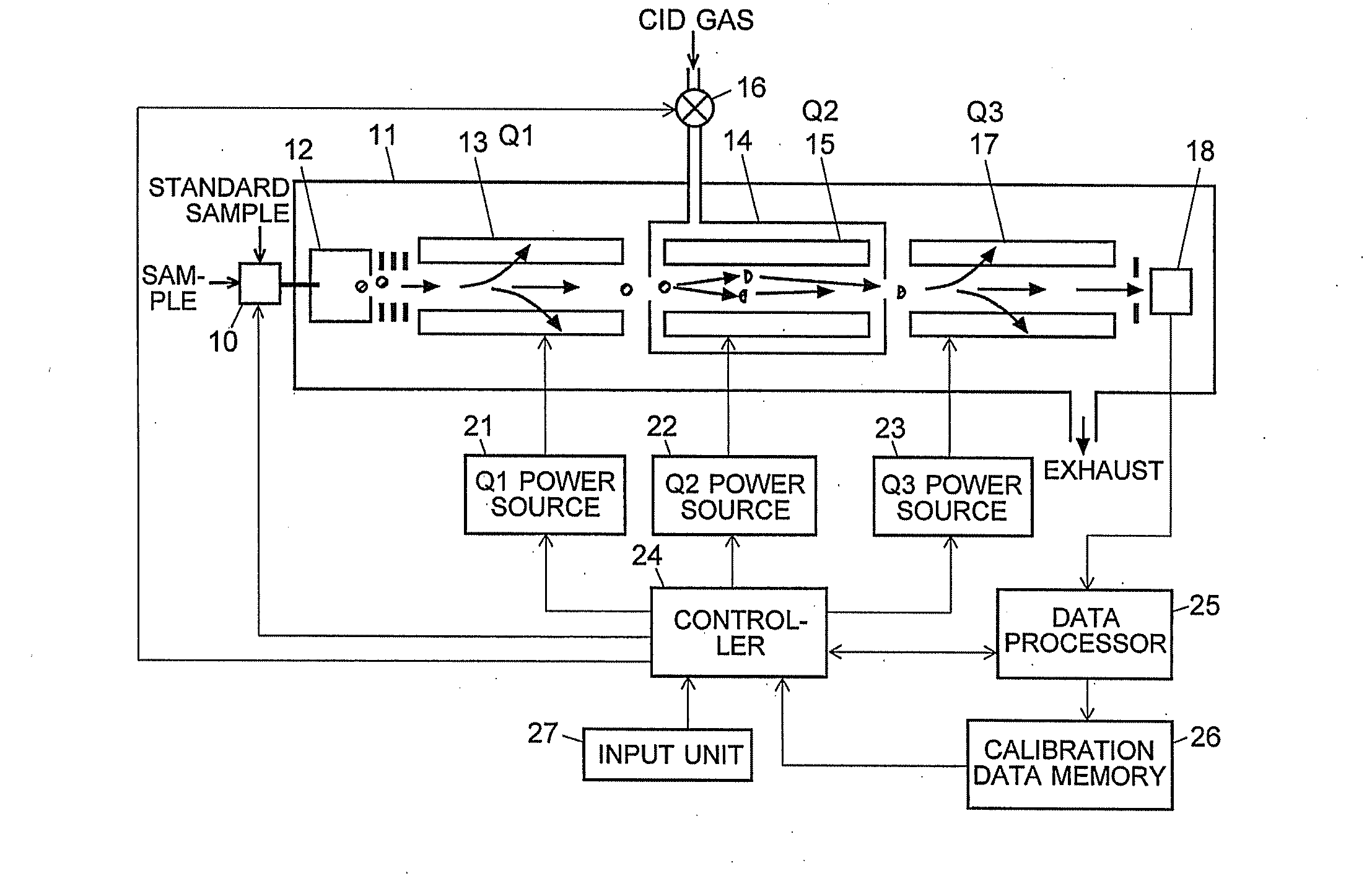
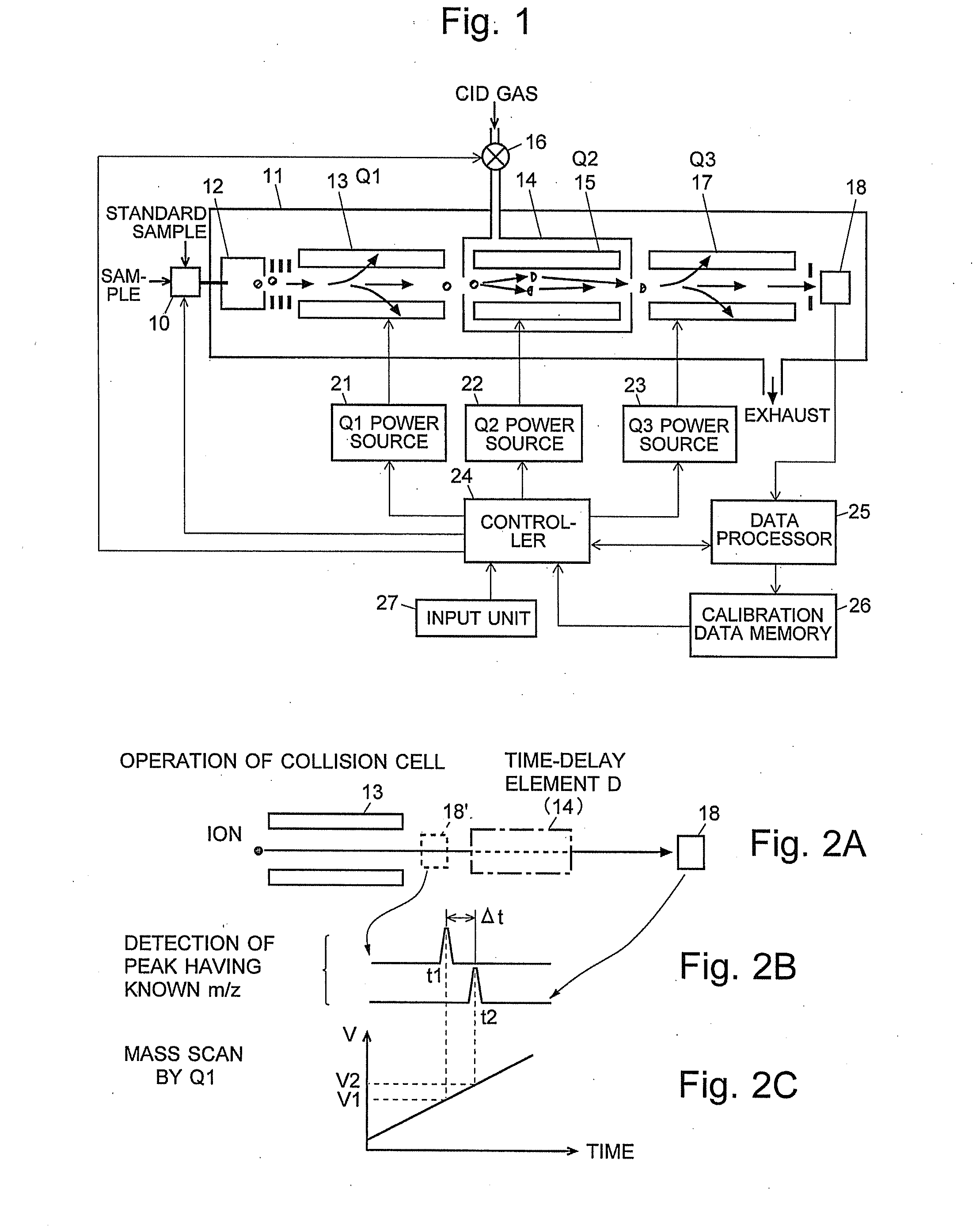
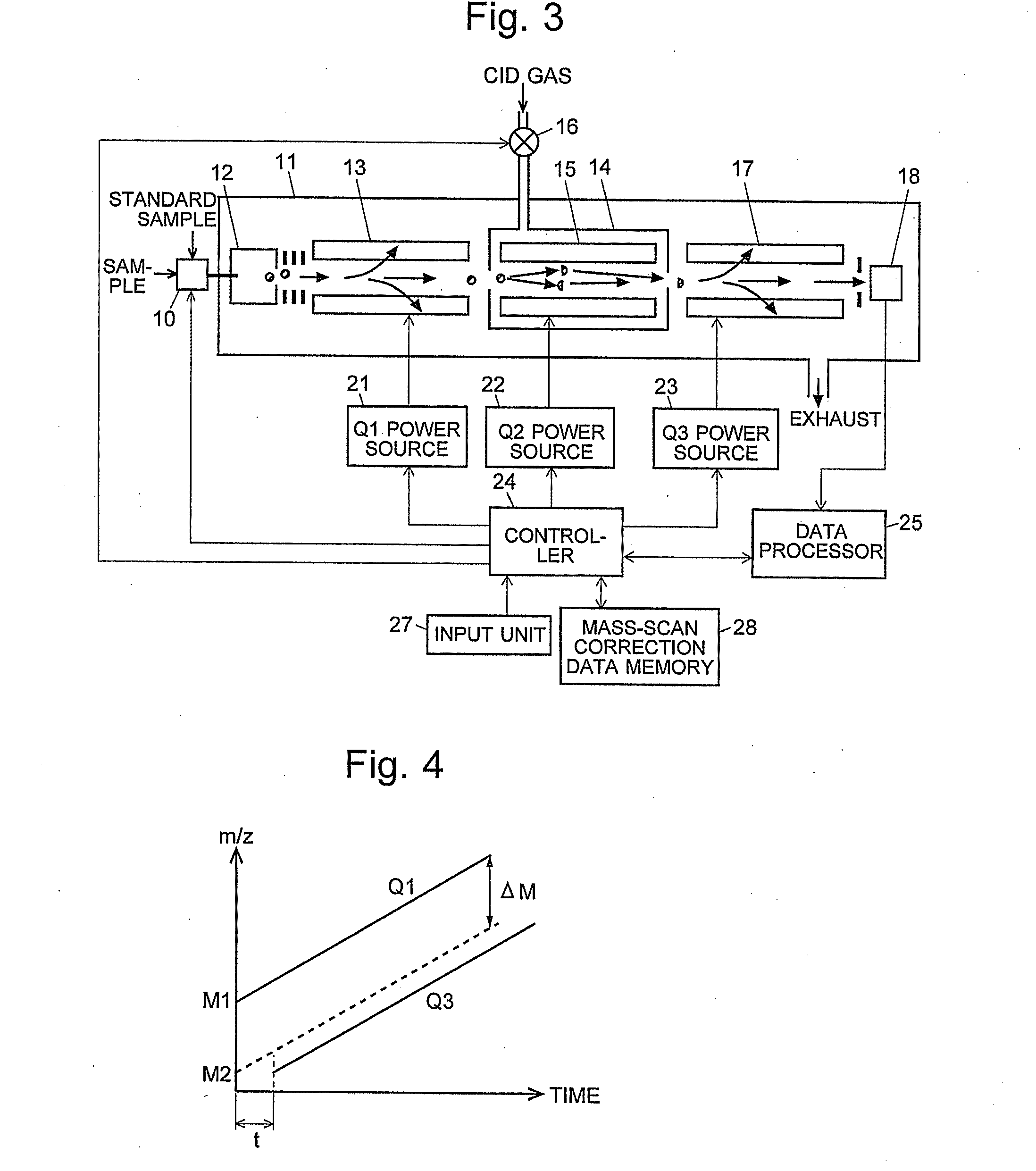
A mass analysis of a standard sample having a known mass-to-charge ratio is carried out by performing a mass scan at a first-stage quadrupole (13) over a predetermined mass range, under the condition that a collision induced dissociation (CID) gas is introduced into a collision cell (14) and a voltage applied to a third-stage quadrupole (17) is set so that no substantial mass separation occurs in this quadrupole. Various kinds of product ions originating from a precursor ion selected by the first-stage quadrupole (13) arrive at and are detected by a detector (18) without being mass separated. Accordingly, based on the detection data, a data processor (25) can obtain a relationship between the voltage applied to the first-stage quadrupole (13) and the mass-to-charge ratio of the selected ions, with a time delay in the collision cell (14) reflected in that relationship. This relationship is stored in a calibration data memory (26), to be utilized in a neutral loss scan measurement or the like. By using this relationship, a mass shift due to the time delay in the collision cell (14) can be cancelled, so that the product ions can be detected with high sensitivity over the entire mass range. Furthermore, a mass spectrum having an accurate mass axis can be created.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Mass spectrum VUV (Vacuum Ultraviolet) photoionization source device for in-source collision induced dissociation
ActiveCN102117728AQuick analysisQuick Qualitative AnalysisDynamic spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIon accelerationCollision-induced dissociation
The invention relates to a mass spectrum analyzer, in particular to a mass spectrum VUV (Vacuum Ultraviolet) photoionization source device for in-source collision induced dissociation, which comprises a sample injecting capillary tube, an ion repelling electrode, an ion accelerating electrode, a vacuum ultraviolet lamp, a side pumping valve and an ionization source cavity, wherein the ion repelling electrode and the ion accelerating electrode are placed in the ionization source cavity at interval in parallel, the sample injecting capillary tube passes through the outer wall of the ionization source cavity, and one end of the sample injecting capillary tube is arranged in a central small hole of the ion repelling electrodes; a light emitting window of the vacuum ultraviolet lamp is placed opposite to a gap between the ion repelling electrode and the ion accelerating electrode; and an air outlet is arranged on the side wall of the ionization source cavity, and the side pumping valve is connected with the air outlet through a pipeline. The mass spectrum VUV photoionization source device can be used together with any types of quality analyzers, can simultaneously obtain the molecular weight and the structural information of a matter to be analyzed and also be used for rapidly distinguishing isomerides by utilizing in-source collision induced dissociation.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chemical structure-insensitive method and apparatus for dissociating ions
ActiveUS20080217527A1Isotope separationSpecific reaction combinationsChemical structureIon trap mass spectrometry
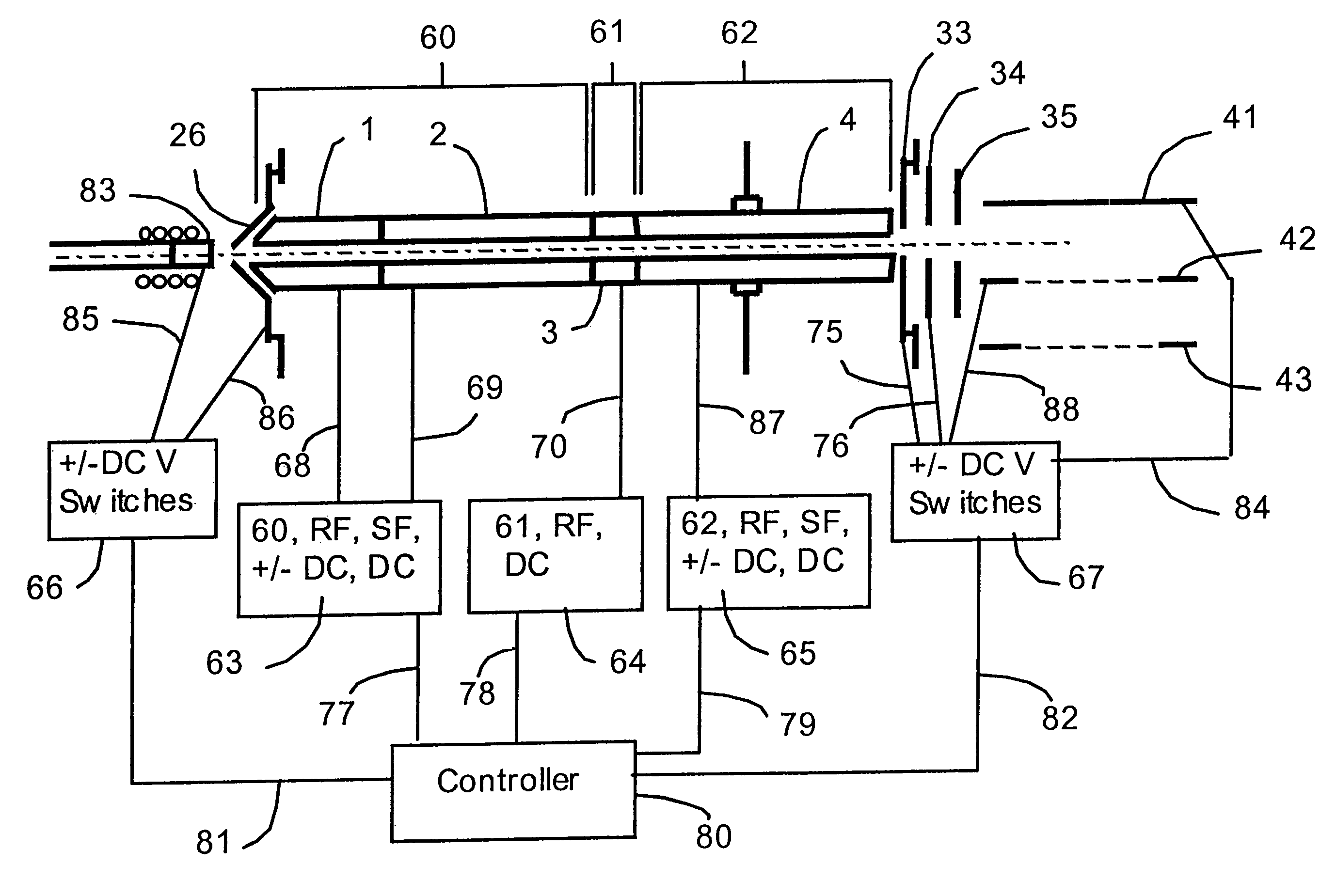
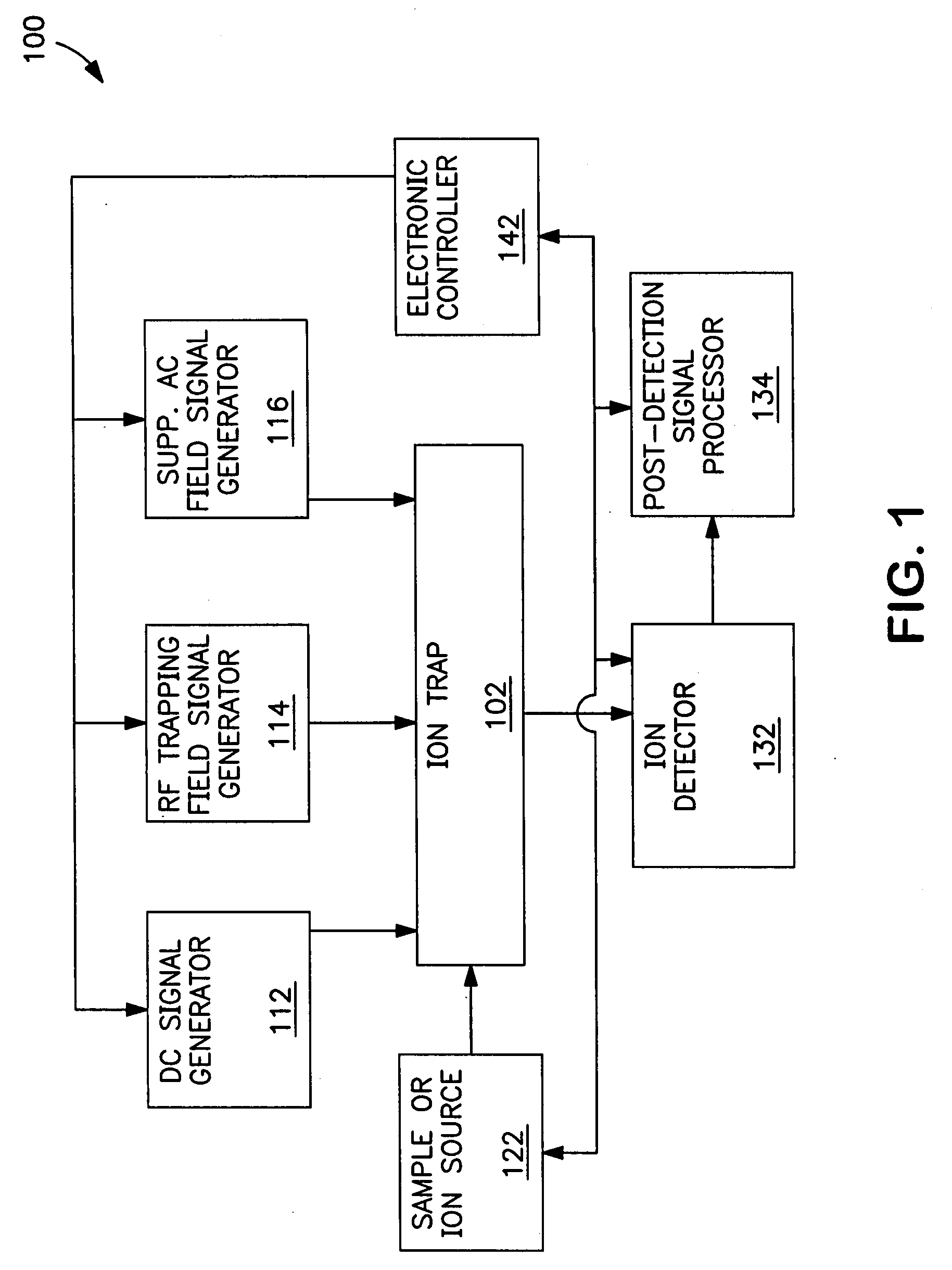
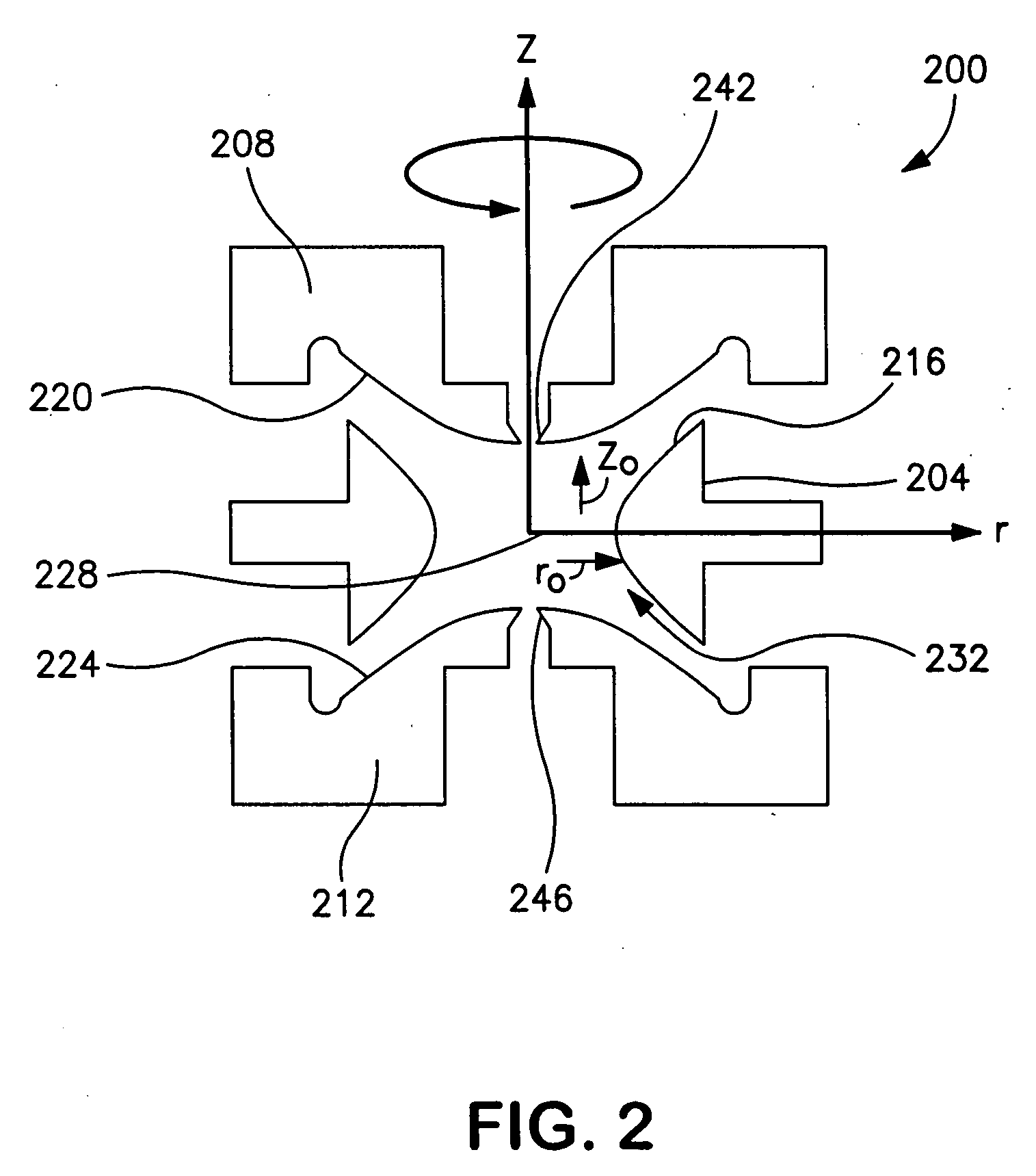
In a method for exciting a precursor ion in an ion trap, the ion is trapped in a nonlinear trapping field that includes a quadrupolar field and a multipole field. The quadrupolar field is generated by applying a radio-frequency (RF) trapping voltage to the ion trap at a trapping amplitude and trapping frequency. A supplemental alternating-current (AC) voltage is applied to the ion trap at a supplemental amplitude and supplemental frequency. The supplemental amplitude is low enough to prevent ejection of the ion from the ion trap, and the supplemental frequency differs from the secular frequency of the ion by an offset amount. One or more operating parameters of the ion trap are adjusted, such that the ion absorbs energy from the supplemental field sufficient to undergo collision-induced dissociation (CID) without being in resonance with the supplemental field.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Fragmentation of ions by resonant excitation in a high order multipole field, low pressure ion trap
InactiveUS20050178963A1Promote collision-induced dissociationIncrease probabilityStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIon trap mass spectrometryRf field
In the field of mass spectrometry, a method and apparatus for fragmenting ions with a relatively high degree of resolution and efficiency. The technique includes trapping the ions in a linear ion trap, in which the background or neutral gas pressure is preferably on the order of 10-5 Torr. The trapped ions are resonantly excited for a relatively extended period of time, e.g., exceeding 50 ms, at relatively low excitation levels, e.g., less than 1 Volt (0-pk). The technique allows selective dissociation of ions with a high discrimination. High fragmentation efficiency may be achieved by superimposing a higher order multipole field onto the quadrupolar RF field used to trap the ions. The multipole field, preferably an octopole field, dampens the radial oscillatory motion of resonantly excited ions at the periphery of the trap. This reduces the probability that ions will eject radially from the trap thus increasing the probability of collision induced dissociation.
Owner:MDS CO LTD +2
Tandem mass spectrometry analysis method performed in ion traps
InactiveCN102937622AEnrich ion fragment informationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDipole excitationParticle physics
The invention belongs to the technical field of mass analysis, in particular to a tandem mass spectrometry analysis method performed in ion traps. The method comprises ion selective isolation, collision induced dissociation and quality scanning analysis. Dipole excitation voltages with asymmetric wave shapes are imposed on a pair of electrodes to generate dipole direct voltages, so that isolated parent ions obtain energy to be excited, collided with neutral molecules in the ion traps and dissociated, and tandem mass spectrometry analysis is achieved. The tandem mass spectrometry analysis method performed in ion traps has the advantages that additional direct current power supplies are not needed, and the dipole direct voltages can be obtained only through the control of software, and experiment devices and methods can be simplified apparently. Simultaneously, the parent ions are subjected to a non-resonance excited dissociation mode under the action of the dipole direct voltages, and abundant ion fragment information can be given through the non-resonance excitation of collision and dissociation.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
MS/MS mass spectrometer
ActiveUS8269166B2Reduce impactHigh detection sensitivityStability-of-path spectrometersParticle spectrometer methodsTime delaysData memory
A mass analysis of a standard sample having a known mass-to-charge ratio is carried out by performing a mass scan at a first-stage quadrupole (13) over a predetermined mass range, under the condition that a collision induced dissociation (CID) gas is introduced into a collision cell (14) and a voltage applied to a third-stage quadrupole (17) is set so that no substantial mass separation occurs in this quadrupole. Various kinds of product ions originating from a precursor ion selected by the first-stage quadrupole (13) arrive at and are detected by a detector (18) without being mass separated. Accordingly, based on the detection data, a data processor (25) can obtain a relationship between the voltage applied to the first-stage quadrupole (13) and the mass-to-charge ratio of the selected ions, with a time delay in the collision cell (14) reflected in that relationship. This relationship is stored in a calibration data memory (26), to be utilized in a neutral loss scan measurement or the like. By using this relationship, a mass shift due to the time delay in the collision cell (14) can be cancelled, so that the product ions can be detected with high sensitivity over the entire mass range. Furthermore, a mass spectrum having an accurate mass axis can be created.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Quantification of vitellogenin
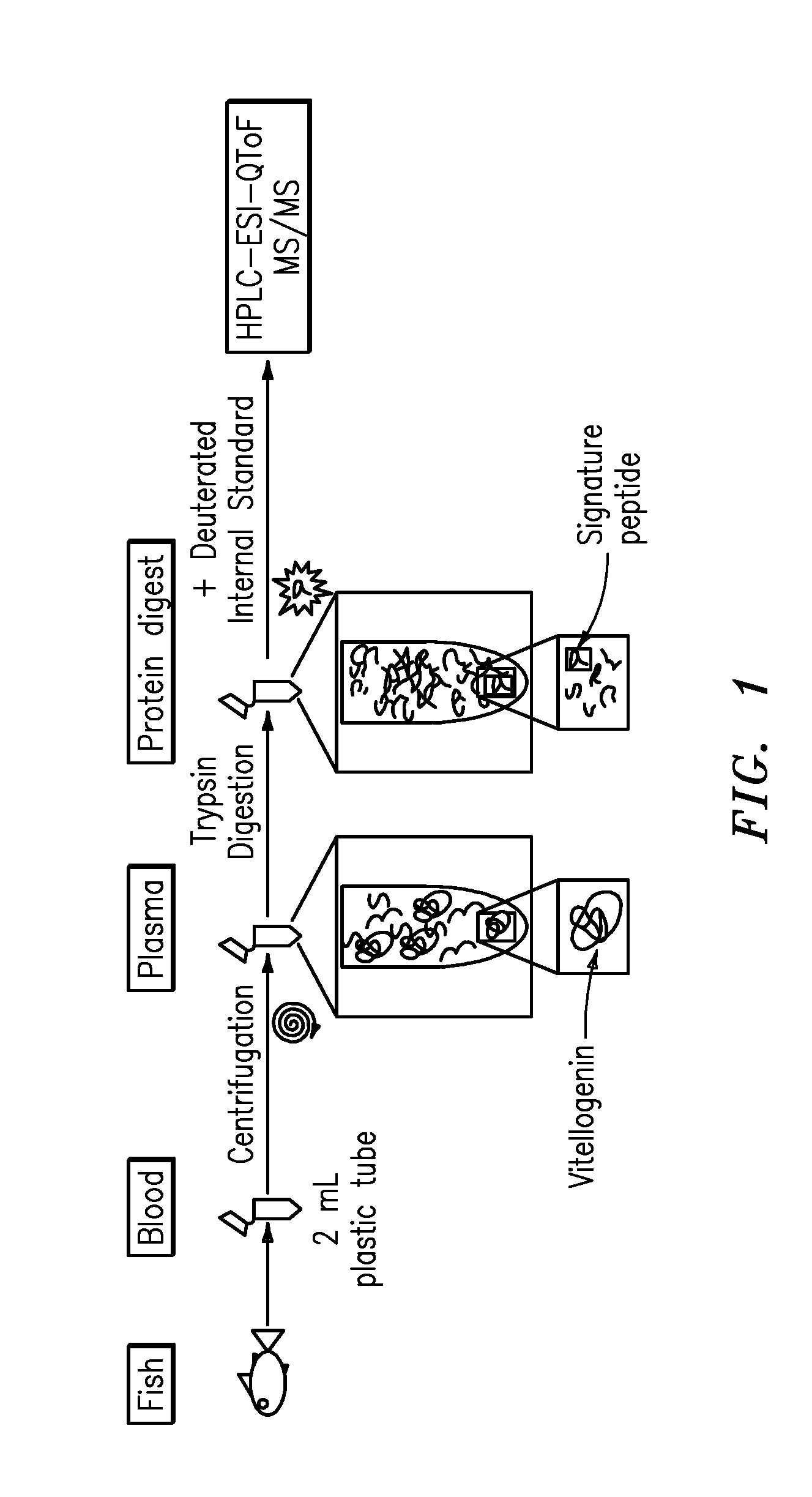
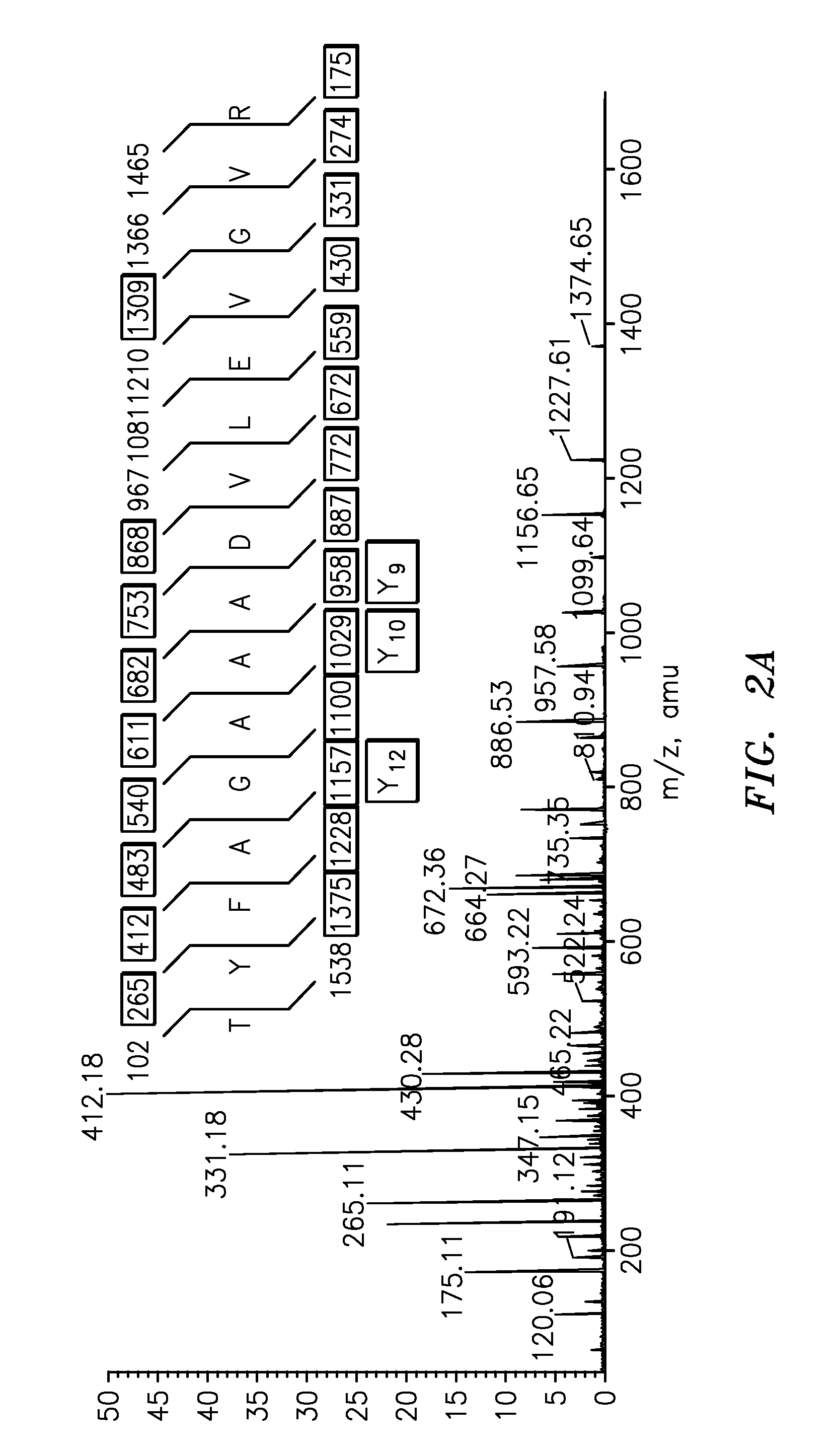
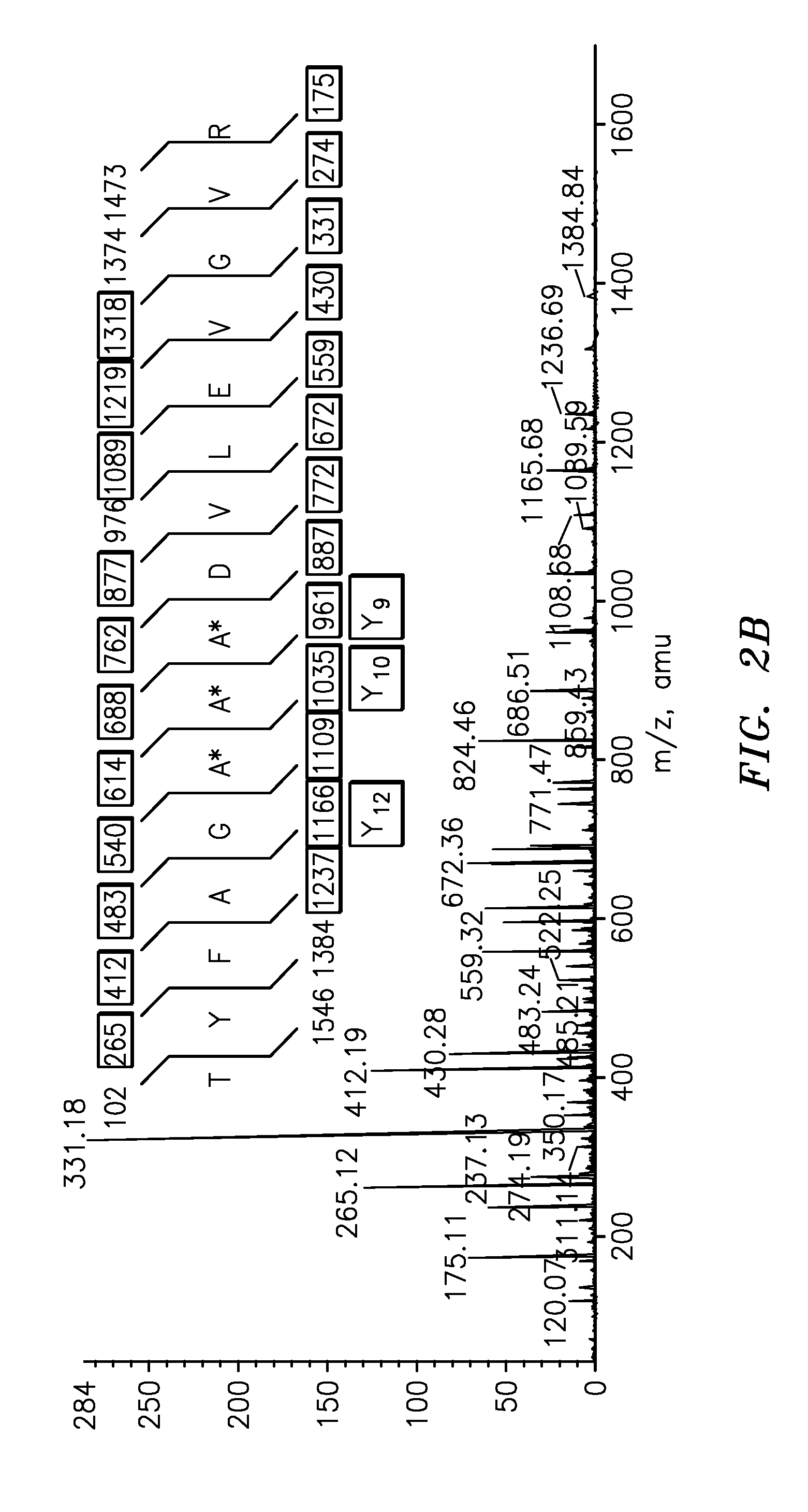
InactiveUS20090011447A1Simple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesVitellogeninsGlu-Val-Gly
The present invention is directed to a simple method for absolute quantification of plasma vitellogenin from two or more different fish species such as Rainbow trout and Atlantic salmon, or Atlantic cod and haddock. In the case of Rainbow trout and Atlantic salmon, plasma samples obtained from control and β-estradiol induced fish were digested with trypsin. A characteristic ‘signature peptide’ was selected and analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography coupled to an electrospray quadrupole-time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometer, using a deuterated homologue peptide as an internal standard. The hybrid tandem mass spectrometer was operated in a ‘pseudo’ selected reaction monitoring mode by which three diagnostic product ions were monitored for identification and quantification purposes. The reproducibility (coefficient of variation ˜5%) and sensitivity (limit of quantification of 0.009 mg / mL) achieved by this simple assay allow it to be considered as an alternative to immunological assays. In the case of Atlantic cod and haddock, the amino acid sequence of the vitellogenin protein has not yet been determined, but, the Atlantic cod vitellogenin has been characterized using a ‘bottom-up’ mass spectrometric approach. Vitellogenin synthesis was induced ‘in vivo’ with β-Estradiol, and subjected to trypsin digestion for characterization by matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization-Quadrupole-Time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. A peptide mass fingerprint was obtained and ‘de novo’ sequencing of the most abundant tryptic peptides was performed by low energy collision induced dissociation-tandem mass spectrometry. Thus, the sequences of various tryptic peptides have been elucidated. It has also been determined that Atlantic cod vitellogenin shares a series of common peptides with the two different known vitellogenin sequences of Haddock, a closely related species. There are also disclosed novel isolated signature peptides, namely Thr-Tyr-Phe-Ala-Gly-Ala-Ala-Ala-Asp-Val-Leu-Glu-Val-Gly-Val-Arg, Asp Leu Gly Leu Ala Tyr Thr Glu Lys, Phe Phe Gly Gln Glu Ile Ala Asn Ile Asp Lys, Glu Ile Val Leu Leu Gly Tyr Gly Thr Met Ile Ser Lys and Tyr Glu Ser Phe Ala Val Ala Arg.
Owner:BANOUB JOSEPH H +2
MS/MS Mass Spectrometer
ActiveUS20130214146A1Reduce impactHigh detection sensitivityIsotope separationTube calibration apparatusTime delaysData memory
A mass analysis of a sample having a known mass-to-charge ratio is carried out by performing a scan at a first-stage quadrupole over a predetermined mass range, under the condition that a collision induced dissociation gas is introduced into a collision cell and a voltage applied to a third-stage quadrupole is set so that no substantial mass separation occurs in this quadrupole. Various product ions originating from a precursor ion selected by the first-stage quadrupole arrive at and are detected by a detector without being mass separated. Accordingly, based on the detection data, a data processor can obtain a relationship between the voltage applied to the first-stage quadrupole and the mass-to-charge ratio of the selected ions, with a time delay in the collision cell reflected in that relationship. This relationship is stored in a calibration data memory, to be utilized in a neutral loss scan measurement or the like.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
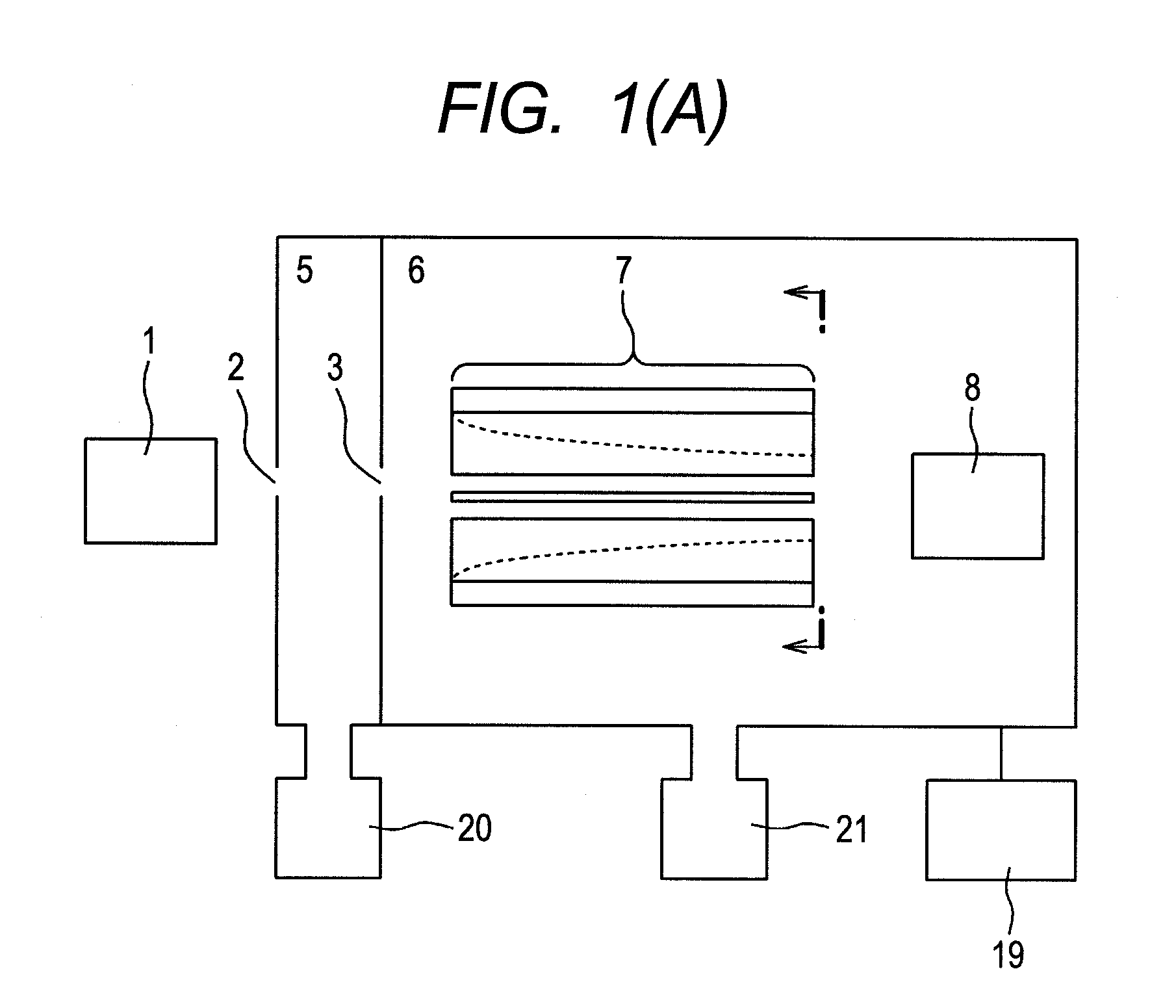
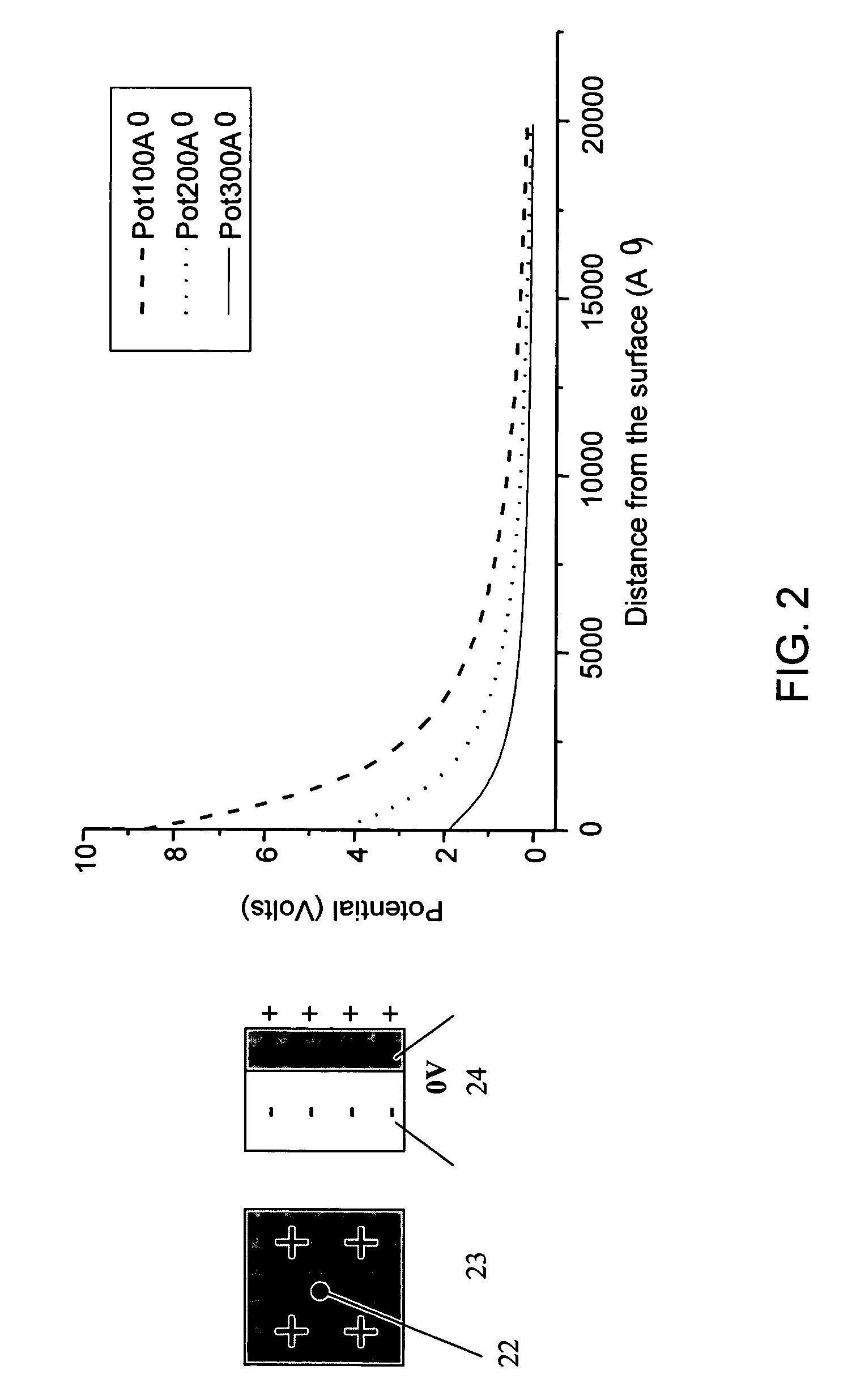
Mass spectrometer and mass spectrometry method
InactiveUS20110248157A1Improve ion transmission efficiencyLow costStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationMass analyzerHigh pressure
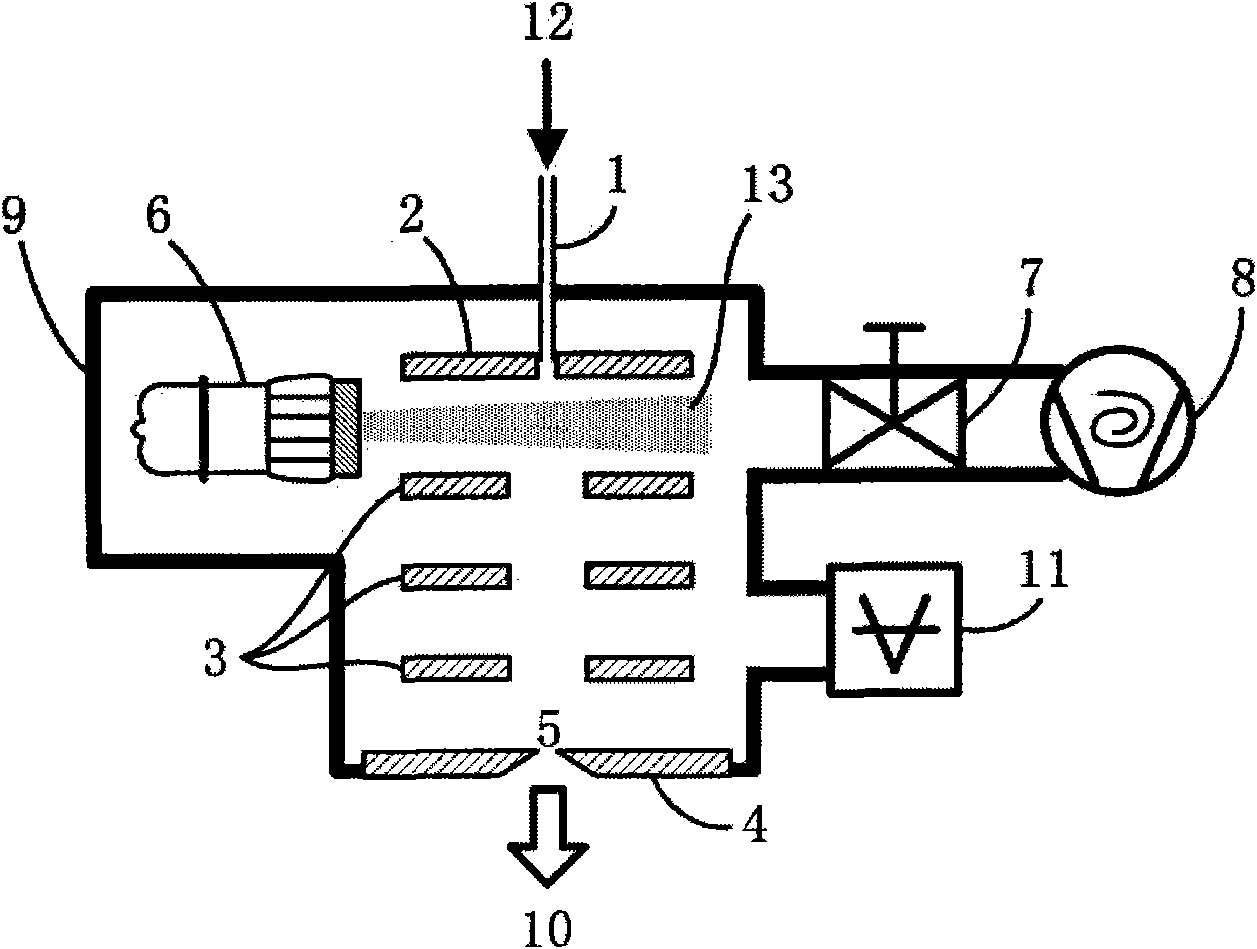
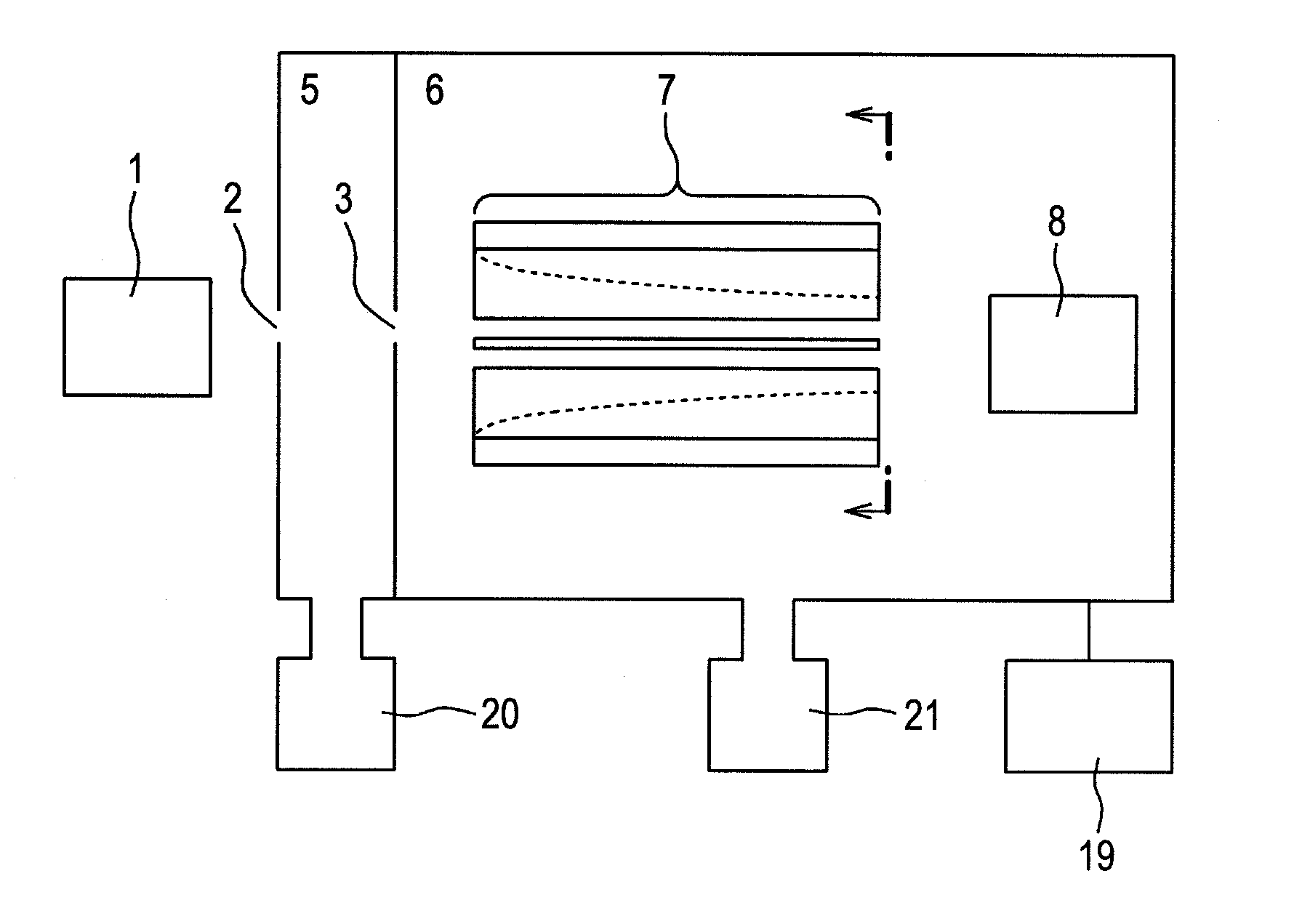
Objects of the present invention is to provide a quadrupole mass filter that can be fabricated at low cost and has a high transmission efficiency even under a high pressure (0.5 mTorr or more), and to provide a mass spectrometer or mass spectrometry method that reduces crosstalk in a wide mass range. Now, in a mass spectrometer, an ion separating unit is configured to include quadrupole rod electrodes that form a quadrupole radio-frequency electric field, electrodes that form a quadrupole electrostatic field, and a power supply that allows the voltage of the electrodes to form a quadrupole electrostatic field to change. In a collision cell configured to perform collision induced dissociation, harmonic potentials in a plurality of stages are produced to resonance excite ions in the axial direction, so that the ions obtain kinetic energy to move in the direction of the detector. This energy allows a time period to shorten for which ions stay in the collision cell.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
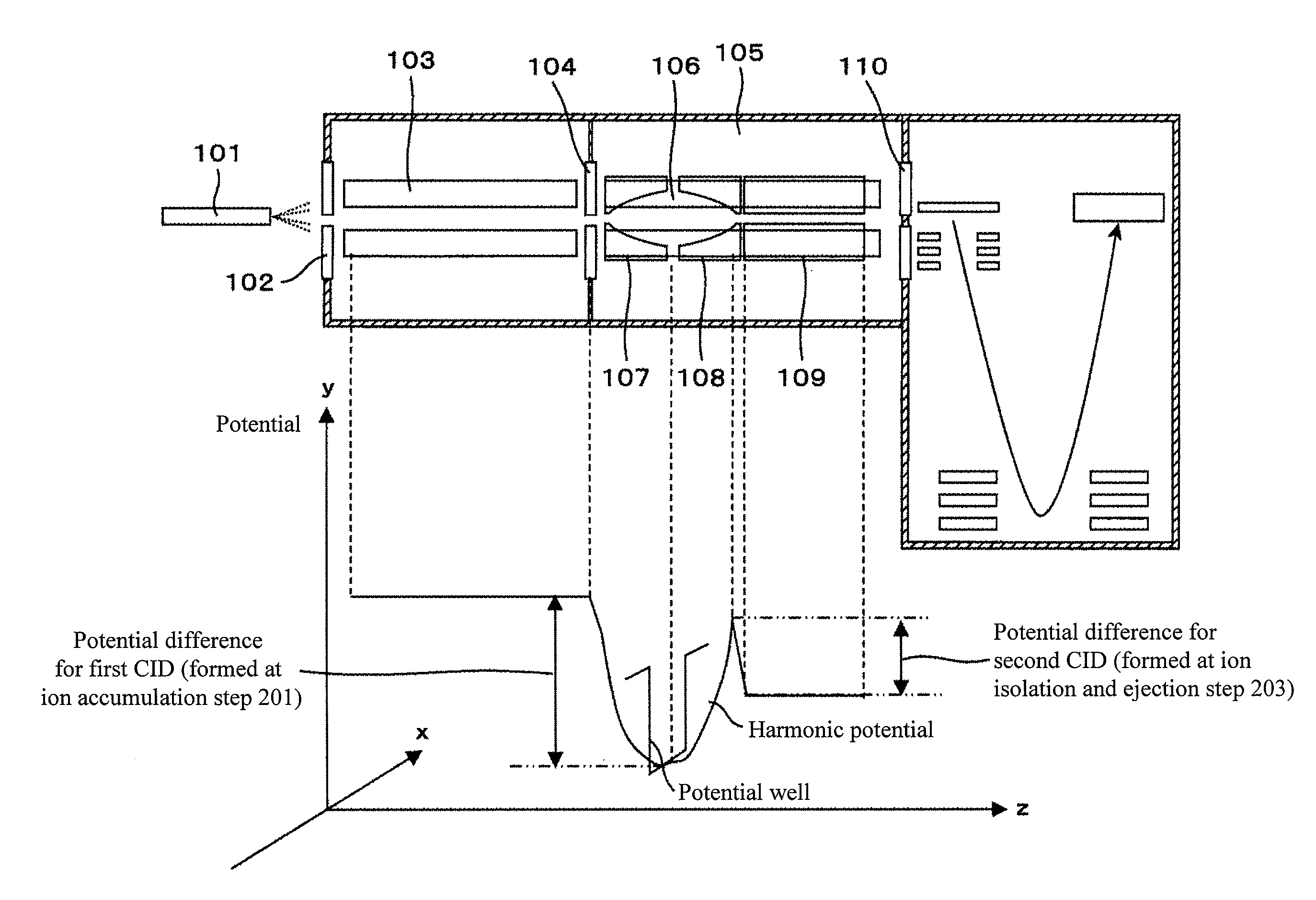
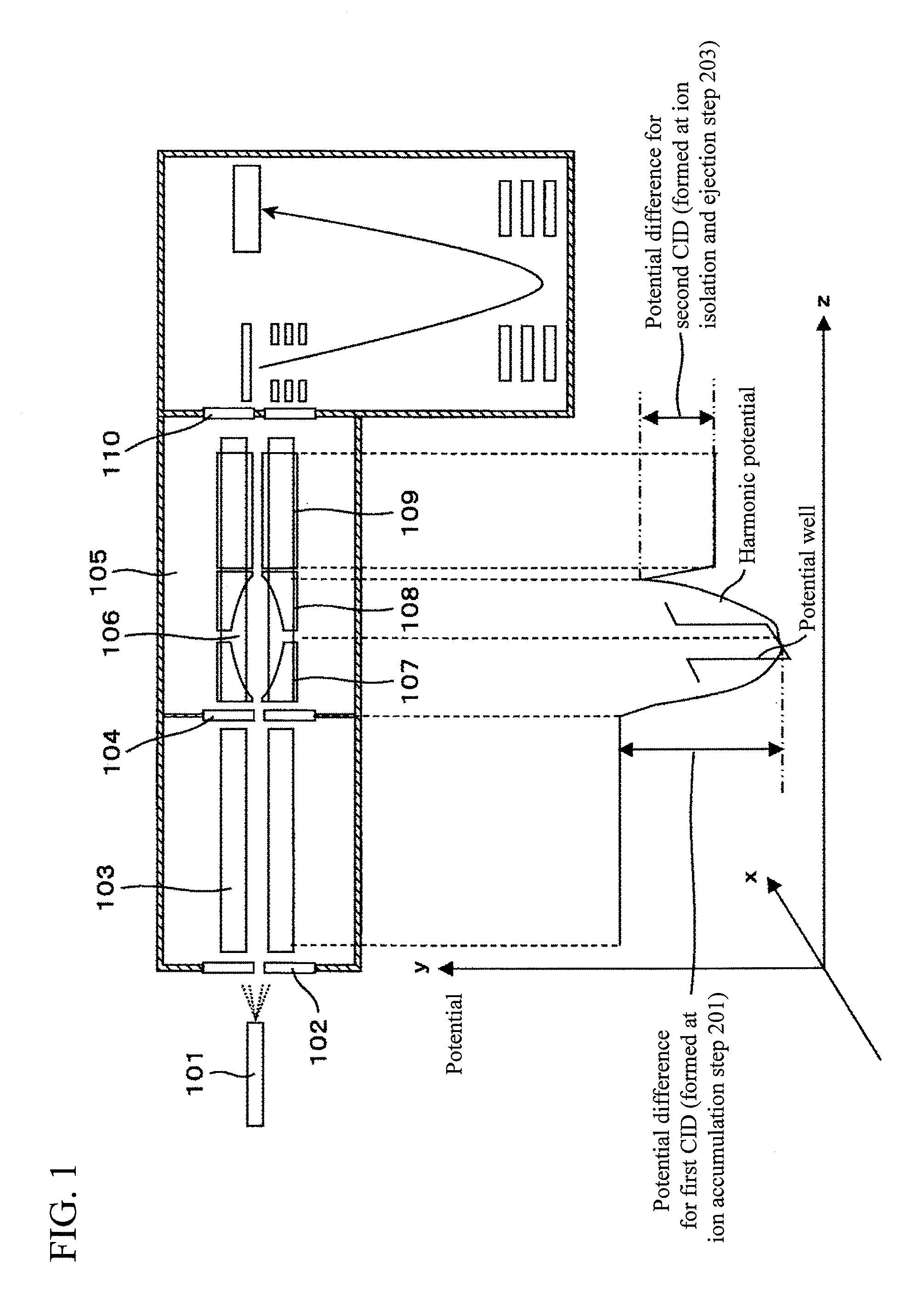
Mass spectrometer and mass spectrometry method
InactiveUS20090179148A1Avoid sizeLower ratioIsotope separationSpectrometer combinationsHarmonic potentialPotential difference
Performing an MS3 with a tandem mass spectrometer causes problems of increase in size of the device and of increase in cost. Likewise, a plural number of times MS / MS analyses are even more difficult. An electrode to create a harmonic potential is disposed in a collision cell, and fragment ions produced by the first-time collision induced dissociation are accumulated in the harmonic potential. Target ions of the subsequent stage are let out, by means of an axial resonance excitation, selectively from the accumulated ions. The ions are excited in the axial direction to have a potential exceeding the harmonic potential. Thereby, the second-time collision induced dissociation is performed by means of a potential difference provided at the subsequent stage. In addition, an operation to return the ions back to the harmonic potential enables a plural number of times MS / MS analyses to be performed.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Increasing ion kinetic energy along axis of linear ion processing devices
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Field conditions for ion excitation in linear ion processing apparatus
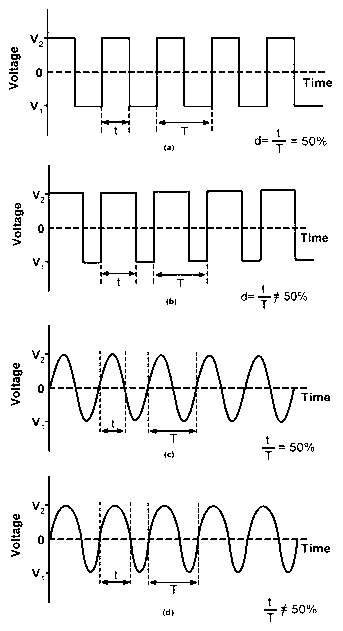
Methods for applying an RF field in a two-dimensional electrode structure include applying RF voltages to main electrodes and to compensation electrodes. The voltages on the compensation electrodes may be proportional to the voltages on the main electrodes so as to optimize the RF field for processes involving ion excitation, including collision-induced dissociation. Electrode structures may include main trapping electrodes, one or more compensation electrodes, one or more ion exit apertures, and a device or circuitry for applying the various desired voltages.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Increasing ion kinetic energy along axis of linear ion processing devices
ActiveUS20070158550A1High ion energyStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationPotential wellEngineering
In a method for increasing the kinetic energy of an ion in a linear electrode structure, axial motion of the ion is constrained substantially to a selected axial end the electrode structure. The ion is driven to move axially from the selected end toward the other end and to reflect back toward the selected end. Constraining may be effected by adjusting one or more DC voltages applied to the ends and a central region of the electrode structure to create an axial potential well in the selected end. Driving may be affected by adjusting the DC voltage applied to the selected end to a magnitude greater than the value applied during the constraining step. The constraining and driving steps may be repeated a number of times. The method may be performed in connection with collision-induced dissociation.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Methods for direct biomolecule identification by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7714276B2Particle separator tubesIsotope separationMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass spectrometry imaging
The present invention relates to the use of post source decay (PSD) or collision induced dissociation (CID) direct tissue (DT) MALDI-TOF or DT-MALDI-TOF-TOF mass spectrographic identification of biological molecules in a tissue or cellular sample without the need for further protein extraction. This method provides for studying cells or tissues by direct tissue MALDI (DT-MALDI), thereby substituting in situ protein release for further protein extraction. Mass / intensity data was processed with Mascot© software interrogation of the NCBI database. These results are proof of principle that DT-MALDI, combined with bioinformatics, can directly identify proteins in cells and tissues from their mass spectra.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Multi-beam ion mobility time-of-flight mass spectrometry with multi-channel data recording
InactiveUS7482582B2Improve efficiencyReduce divergenceTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansData recordingTime of flight
The content of the invention comprises a concept of multi-beam ion pre-selection from a single sample, coordinated mobility (against the gas flow) separation, cooling ions in supersonic gas flow and mass separation of thus low divergent ions by single or plural compact high-resolution orthogonal time-of-flight mass spectrometers both linear or reflectron type with controlled collision-induced dissociation (CID) and multi-channel data recording for the optimization of sample use in the analysis, and obtaining as much useful information about the sample as possible in a reasonably short time.
Owner:IONWERKS
Detection method for dammarane type four-ring triterpenoid saponin
The invention relates to a method for detecting dammarane tetracyclic triterpenoid saponin and secondary aglycone. The inventive method uses high-efficiency liquid color spectrum-mass spectrum coupled device, wherein the conditions of high-efficiency liquid color spectrum comprises: color spectrum column is ODSC18 column; the column temperature is 20-38Deg. C; the conditions of mass spectrum comprise: the ion source is Turbo Ionspray source; the ejecting voltage is 3000-5000V; the Tem is 250-300Deg. C; the detector uses triplicate four-electrode serial mass spectrum detection and positive ion detection; the scanning method uses multi-reaction detection (MRM); CE is 17-36V; DP is 8-110V; the ion detection comprises: processing impact induce dissociation on the quasi-molecule ion peak of said saponin of first-stage scanning mass spectrum, to obtain the second-stage fragment ion; and uses multi-reaction detection (MRM) scanning method to analyze the ion reaction quantitatively, to represent the blood drug density of monomer saponin and secondary aglycone.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
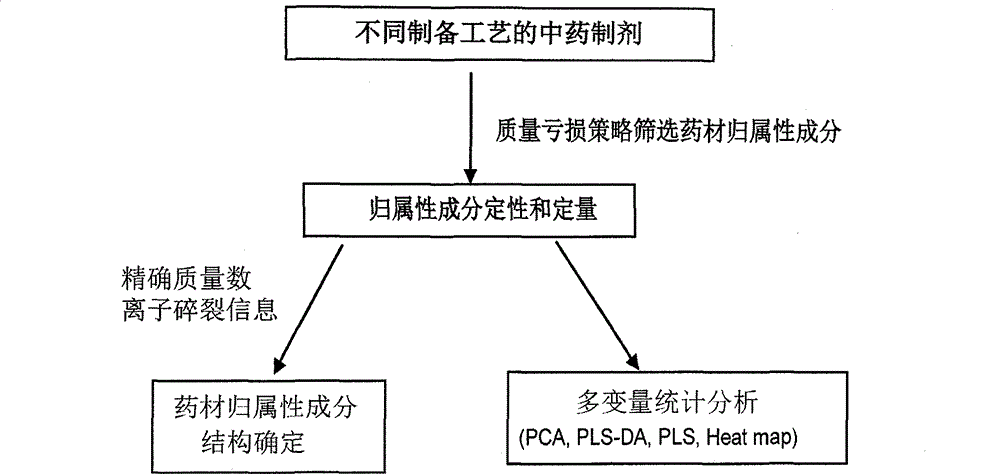
Method for evaluating traditional Chinese medicine preparation making technology based on metabonomics technology
InactiveCN102749409AAvoid processing powerAvoid generalizationComponent separationMass numberMedicine
The invention discloses a method for evaluating a traditional Chinese medicine preparation making technology based on a metabonomics technology, which comprises the following steps: 1, an orthogonal experiment design or a parallel contrast experiment design are used for acquiring traditional Chinese medicine preparation products with different preparation technologies; 2, the prepared products are subjected to sample pre-treatment; 3, a liquid phase series high resolution mass spectrometer is used for acquiring a chromatogram of the traditional Chinese medicine preparation product; 4, the belongingness components of the traditional Chinese medicine are found in the chromatogram according to mass loss strategy; 5, each component structure can be deducted according to fragment information obtained by determined accurate mass number and collision induced dissociation; 6, all belongingness components content in each product are subjected to quantitative analysis; and 7) the influence of the preparation technology on the preparation can be evaluated through multivariable data statistics analysis method. The method of the invention has the advantages of accuracy and sensitivity, and is not depend on standard compounds, and the change of belongingness components of the traditional Chinese medicine in the preparation product can be integrally traced.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com