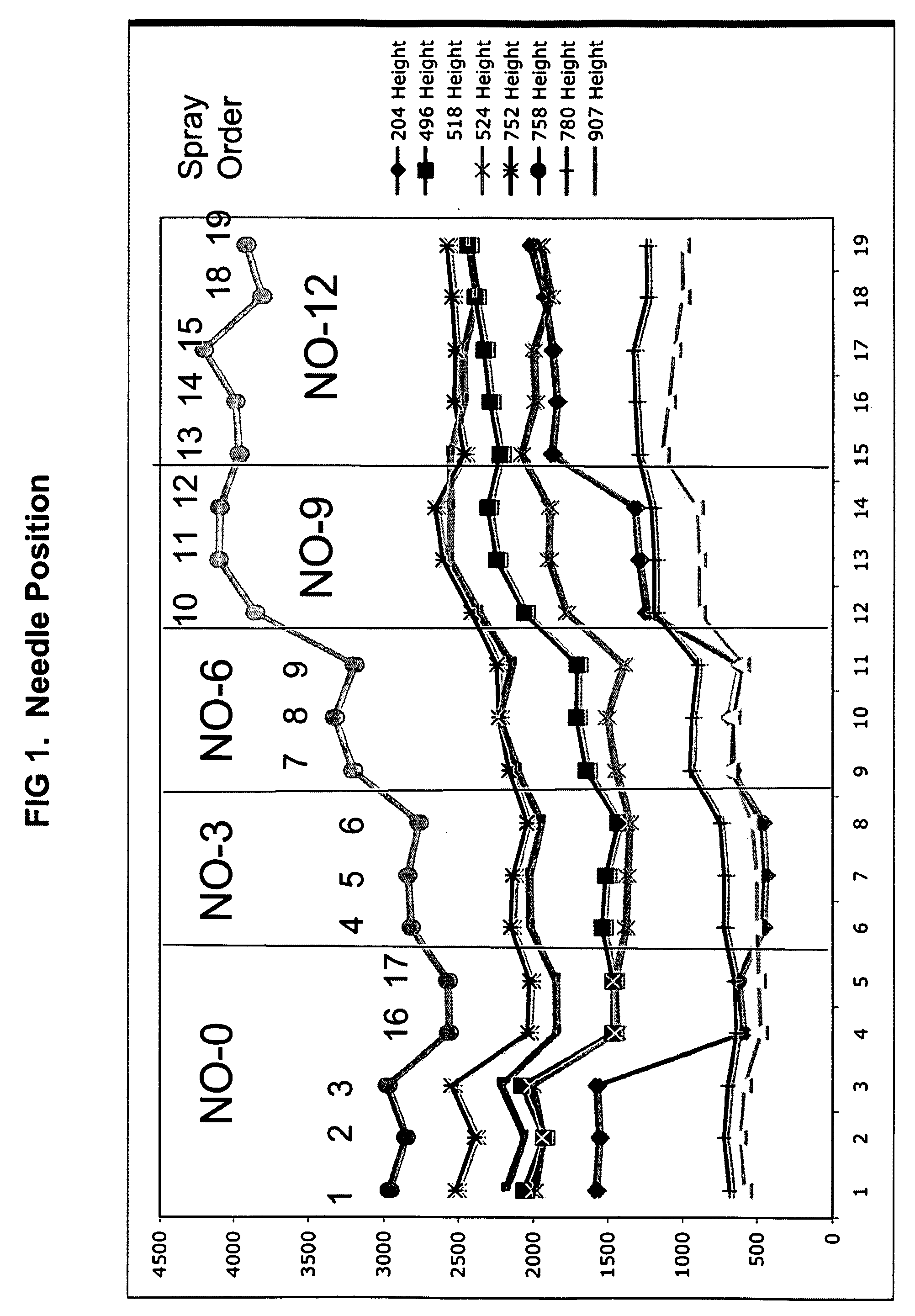
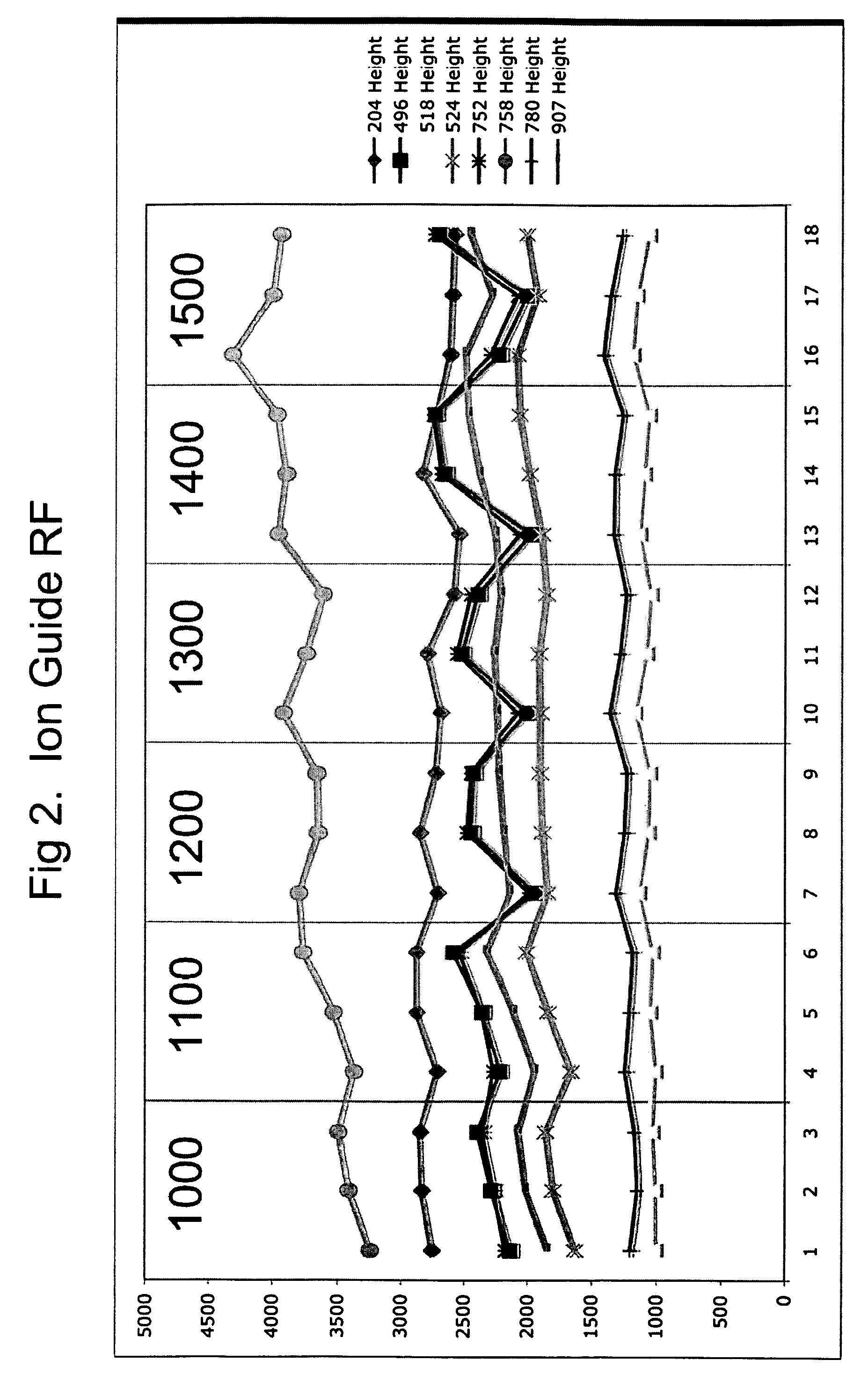
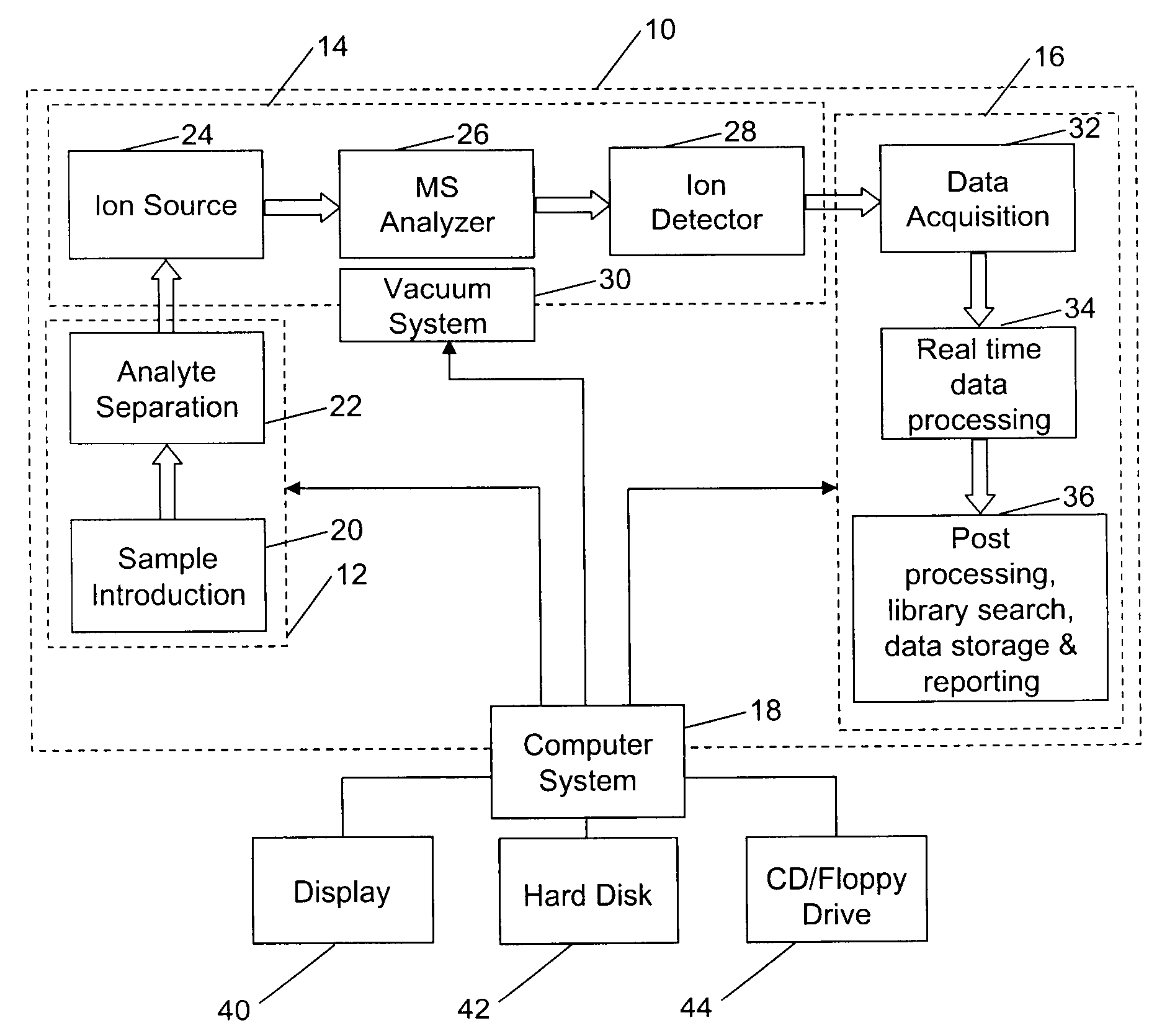
Patents
Literature
424results about "Tube calibration apparatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multi-source ion funnel
InactiveUS6979816B2Enhance ion conductanceMany limitationStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsHigh pressureDc voltage
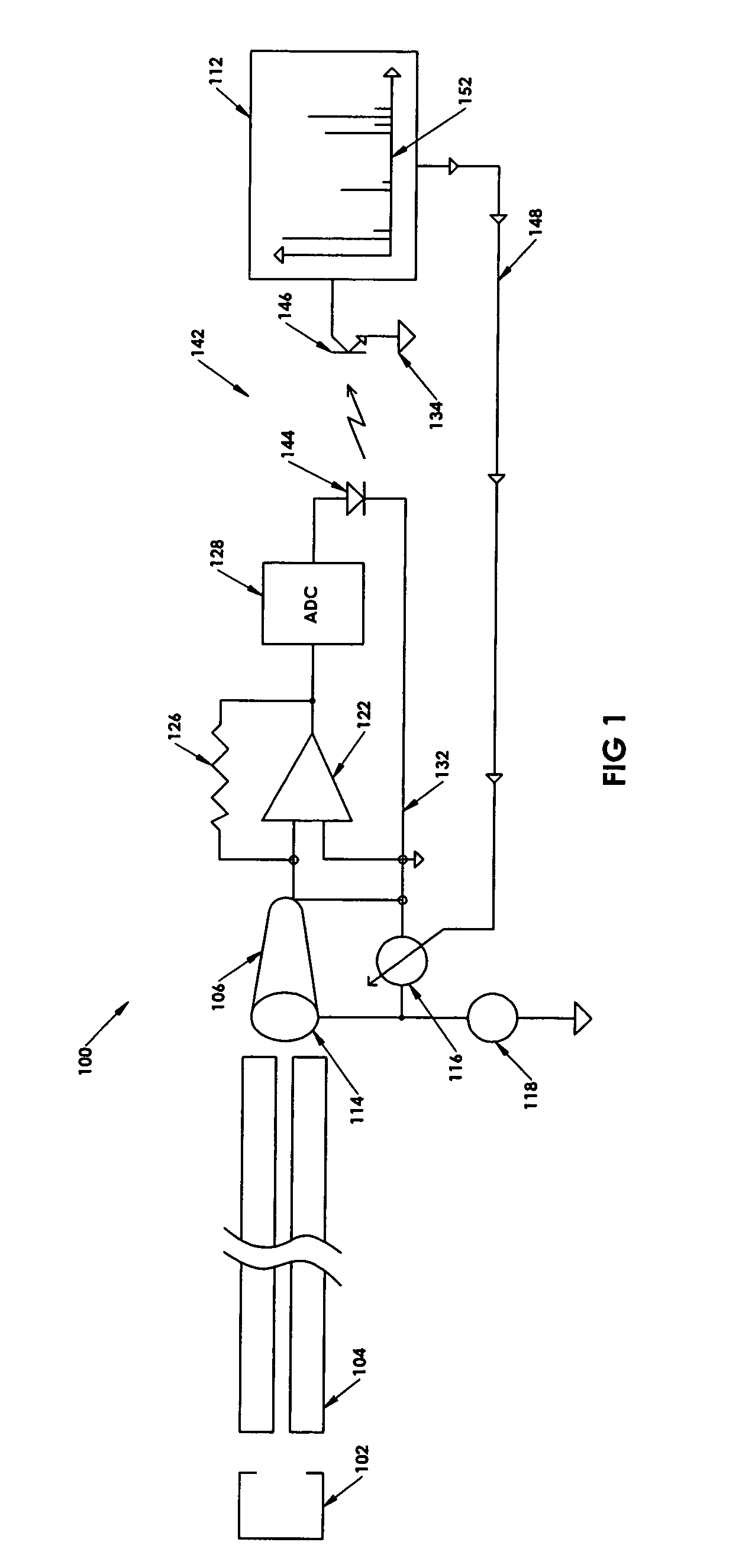
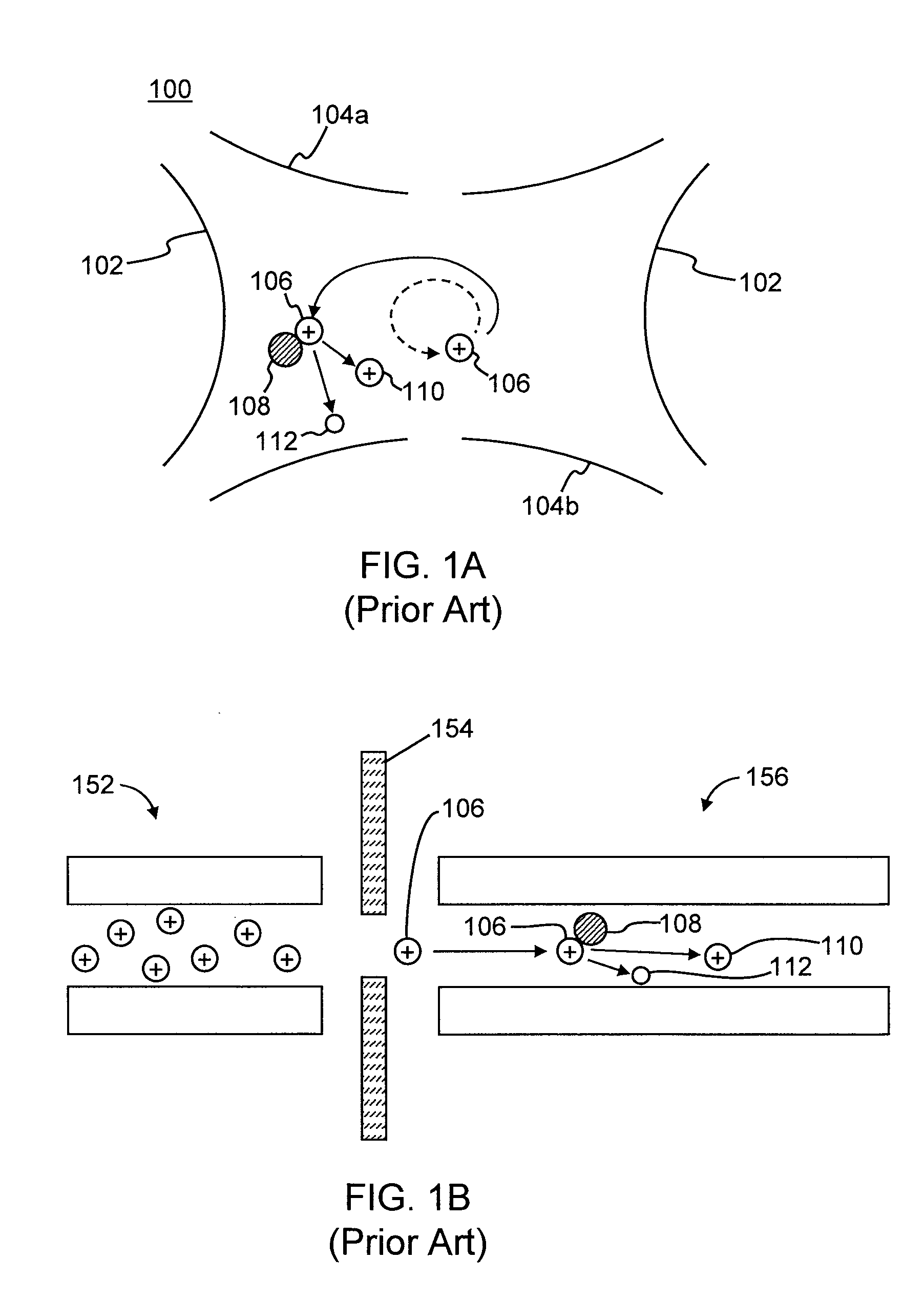
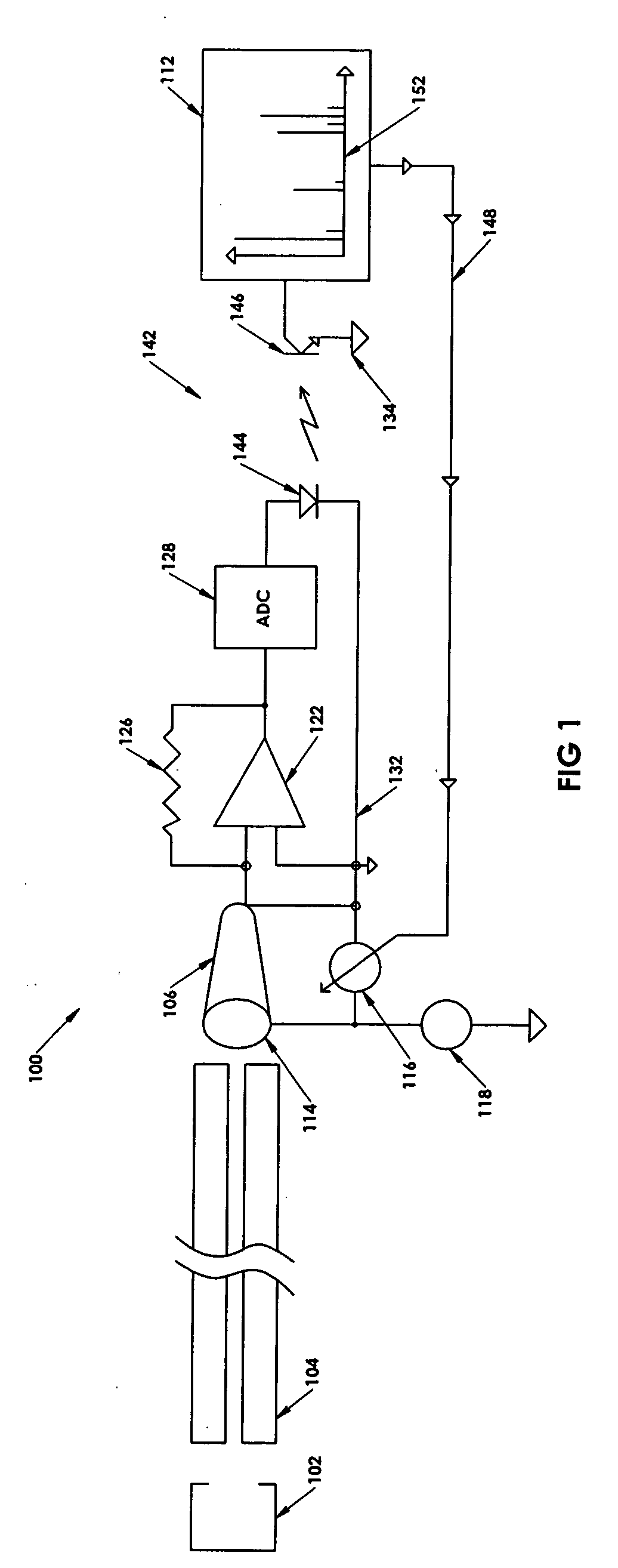
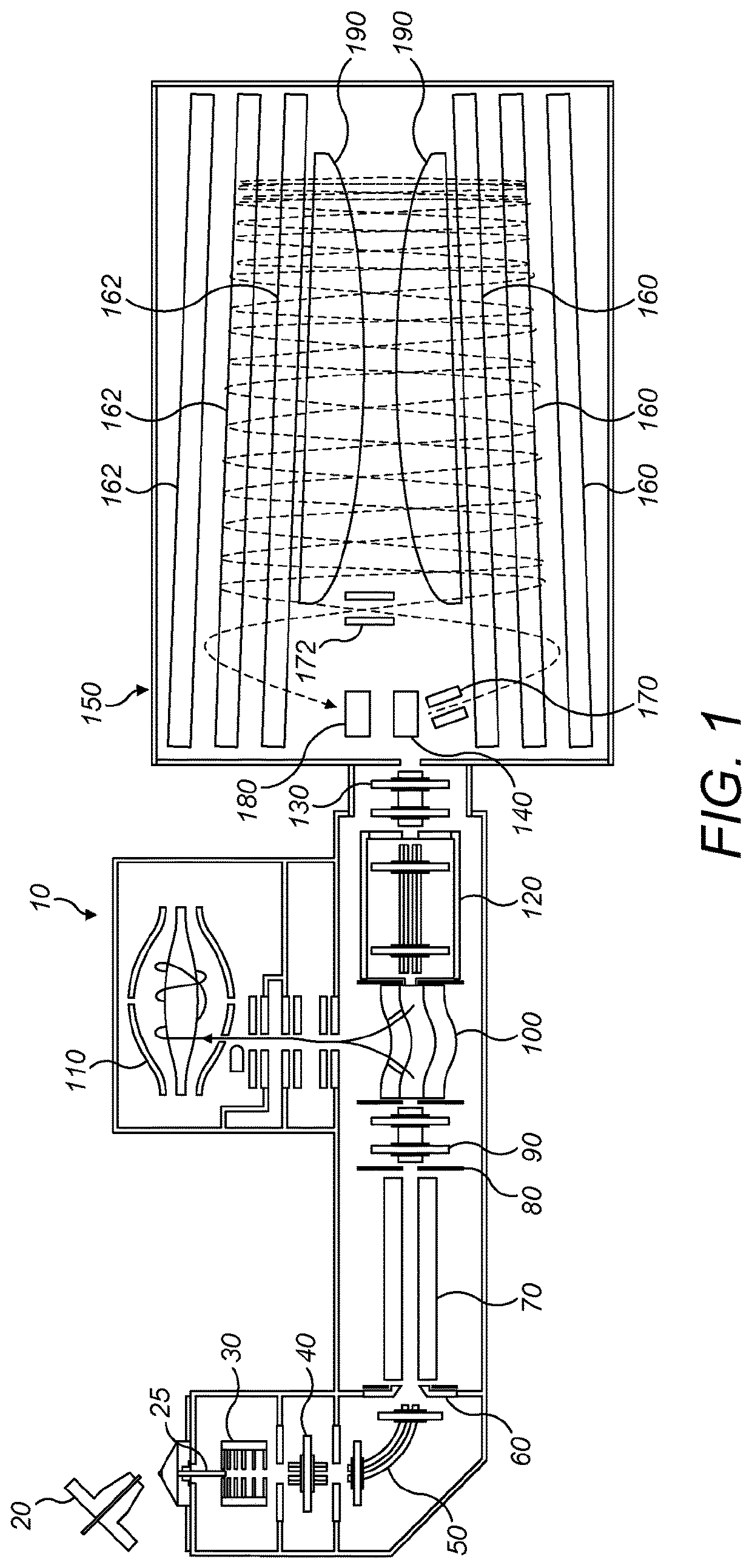
A method for introducing ions generated in a region of relatively high pressure into a region of relatively low pressure by providing at least two electrospray ion sources, providing at least two capillary inlets configured to direct ions generated by the electrospray sources into and through each of the capillary inlets, providing at least two sets of primary elements having apertures, each set of elements having a receiving end and an emitting end, the primary sets of elements configured to receive a ions from the capillary inlets at the receiving ends, and providing a secondary set of elements having apertures having a receiving end and an emitting end, the secondary set of elements configured to receive said ions from the emitting end of the primary sets of elements and emit said ions from said emitting end of the secondary set of elements. The method may further include the step of providing at least one jet disturber positioned within at least one of the sets of primary elements, providing a voltage, such as a dc voltage, in the jet disturber, thereby adjusting the transmission of ions through at least one of the sets of primary elements.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
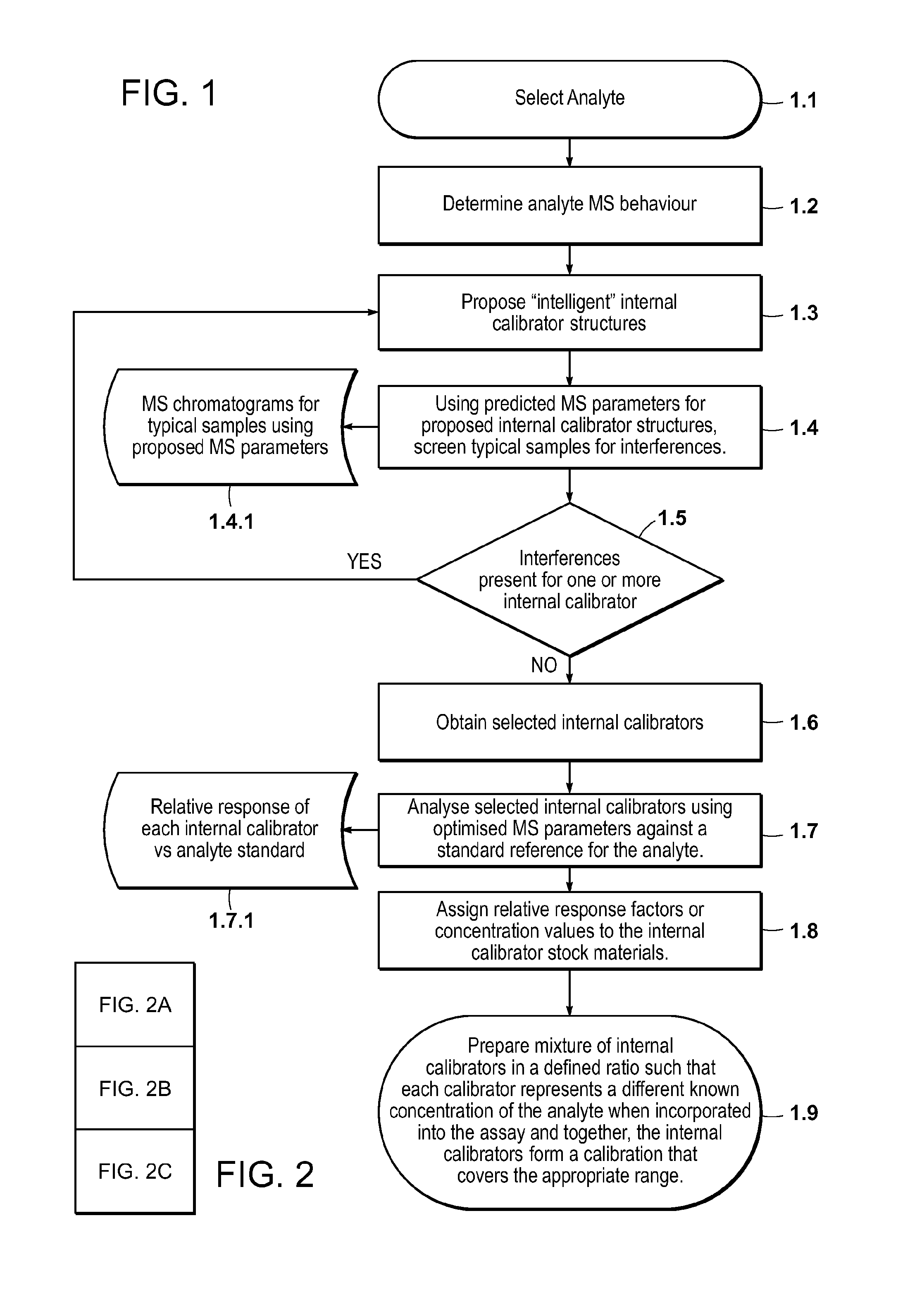
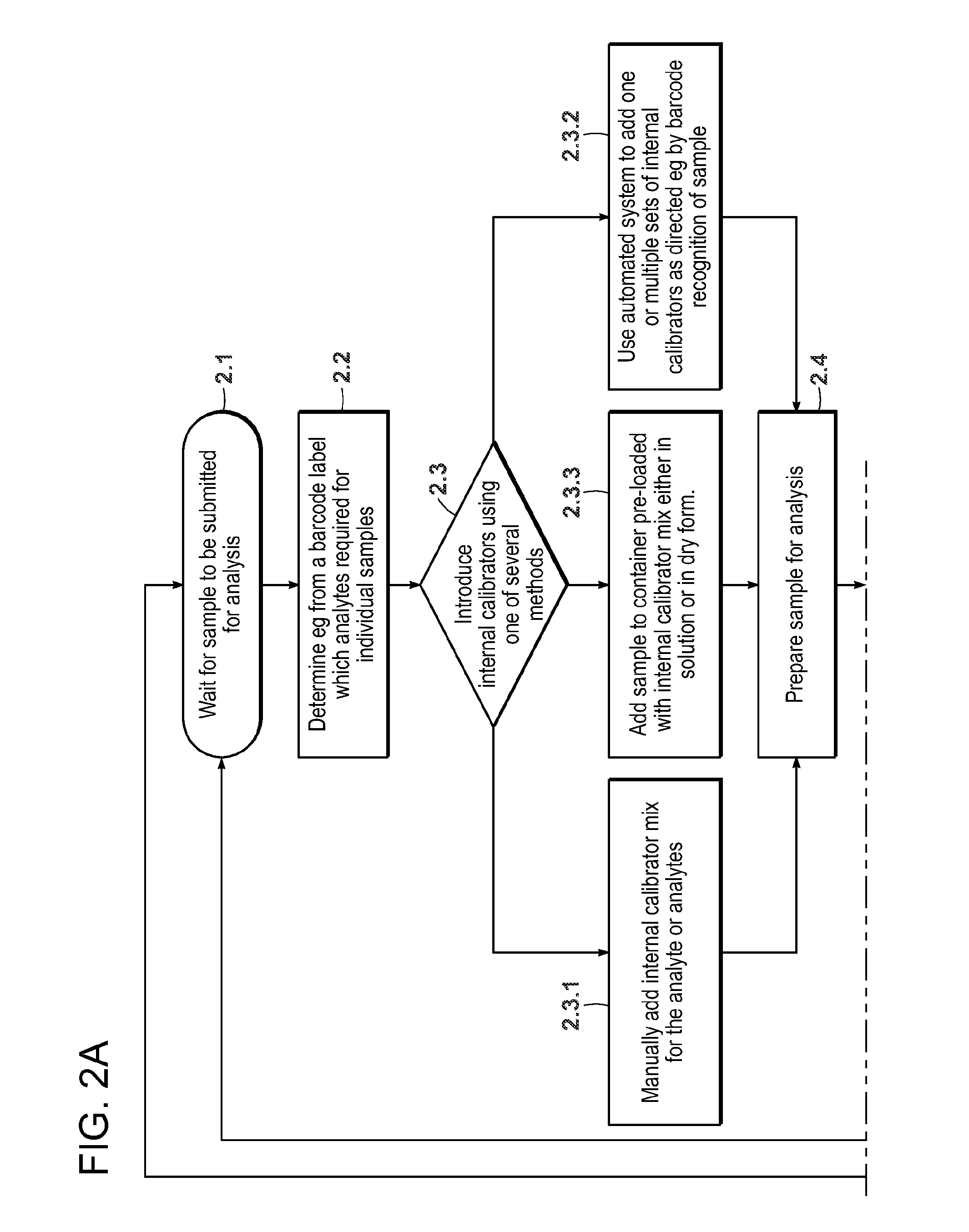
Quantification of analytes using internal standards
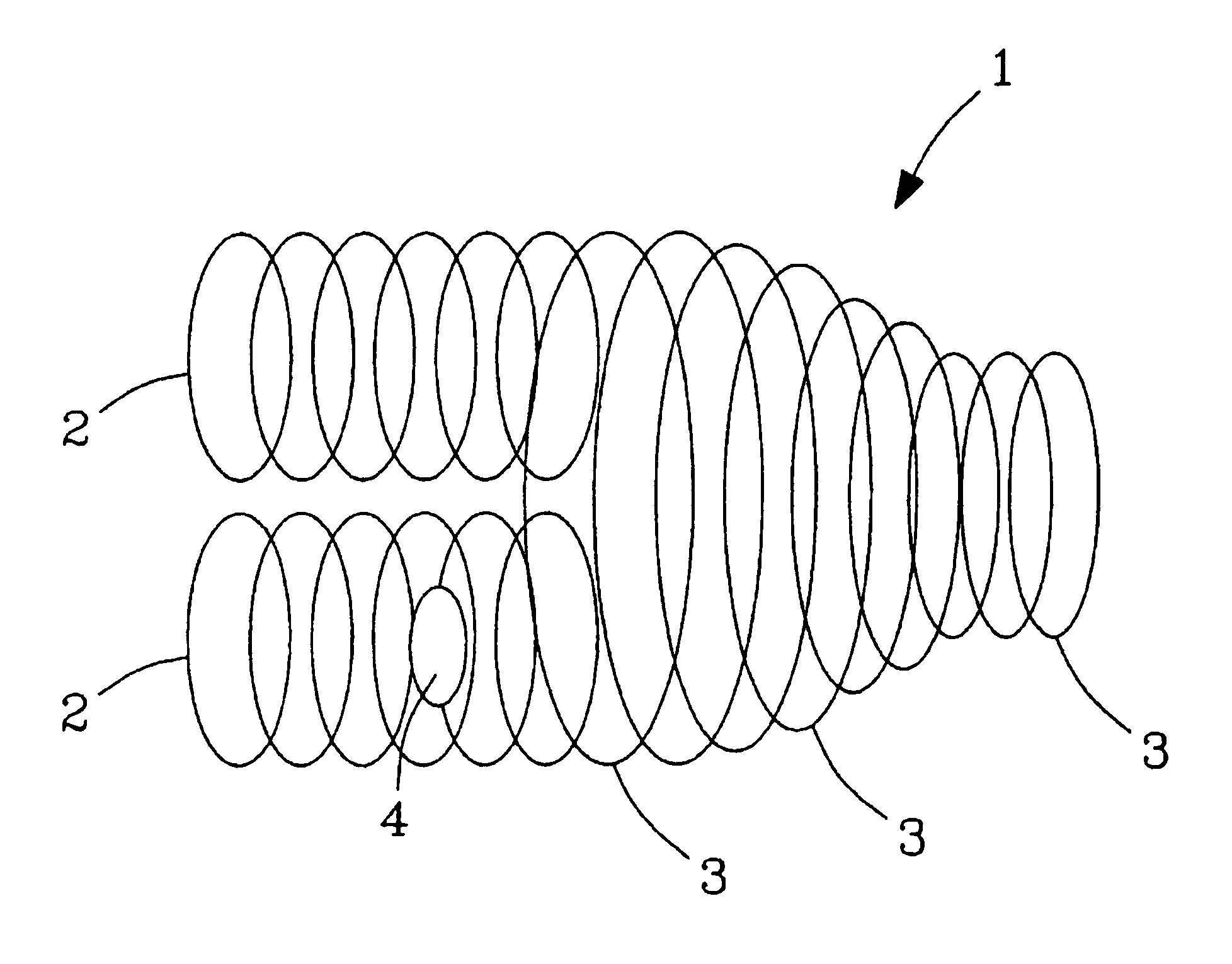
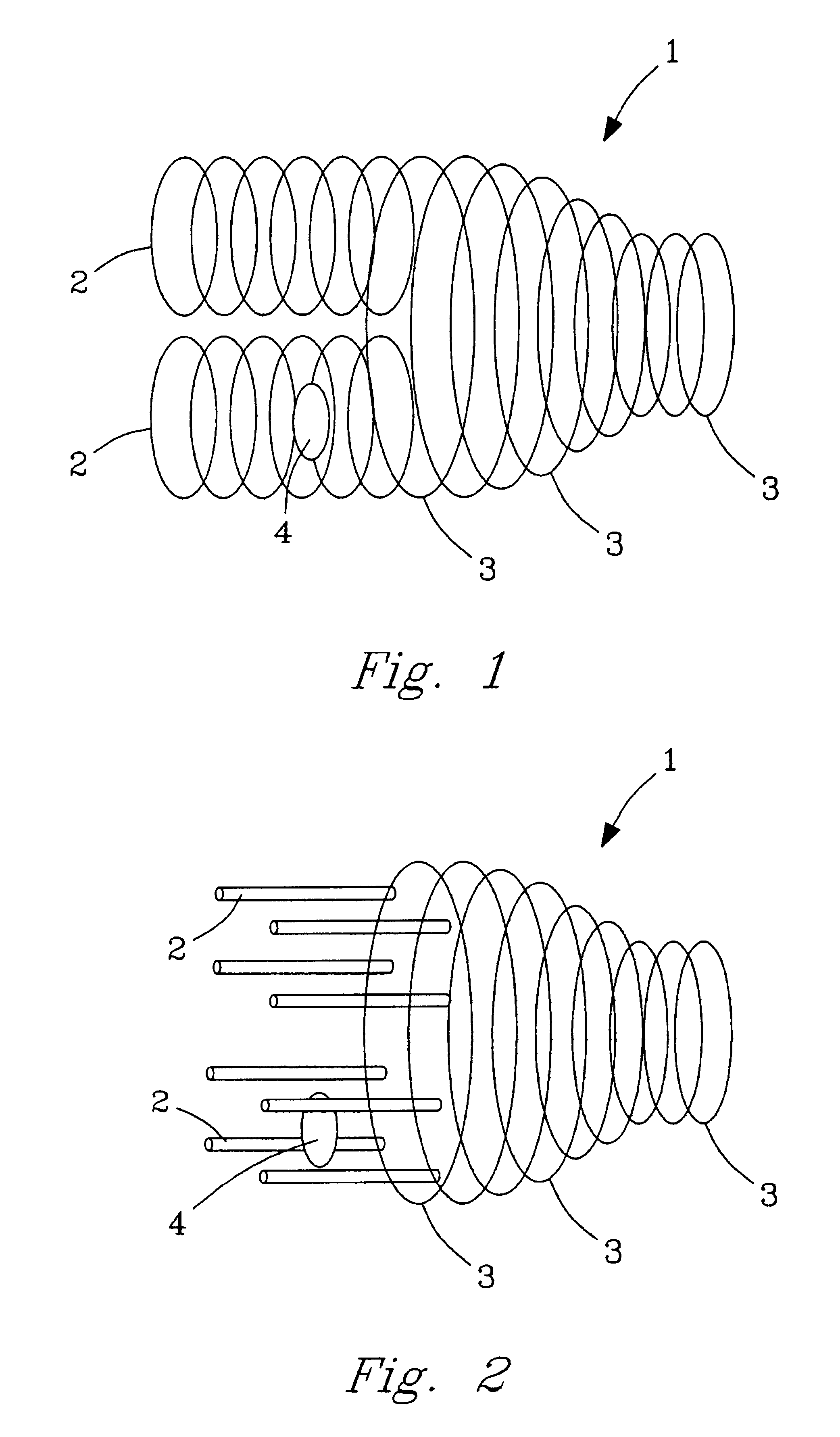
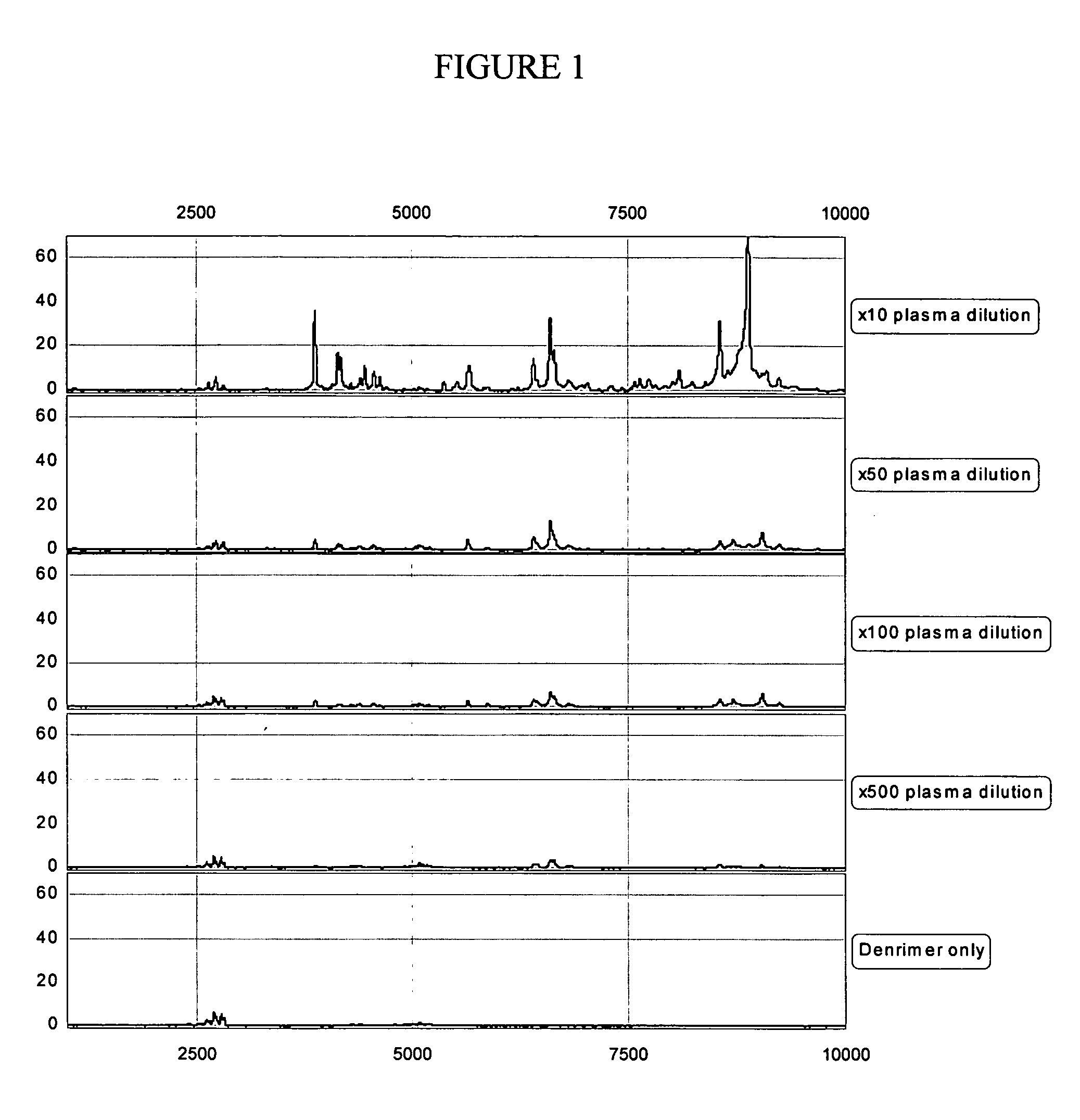
InactiveUS20050112635A1Time-of-flight spectrometersMicrobiological testing/measurementDendrimerAnalyte
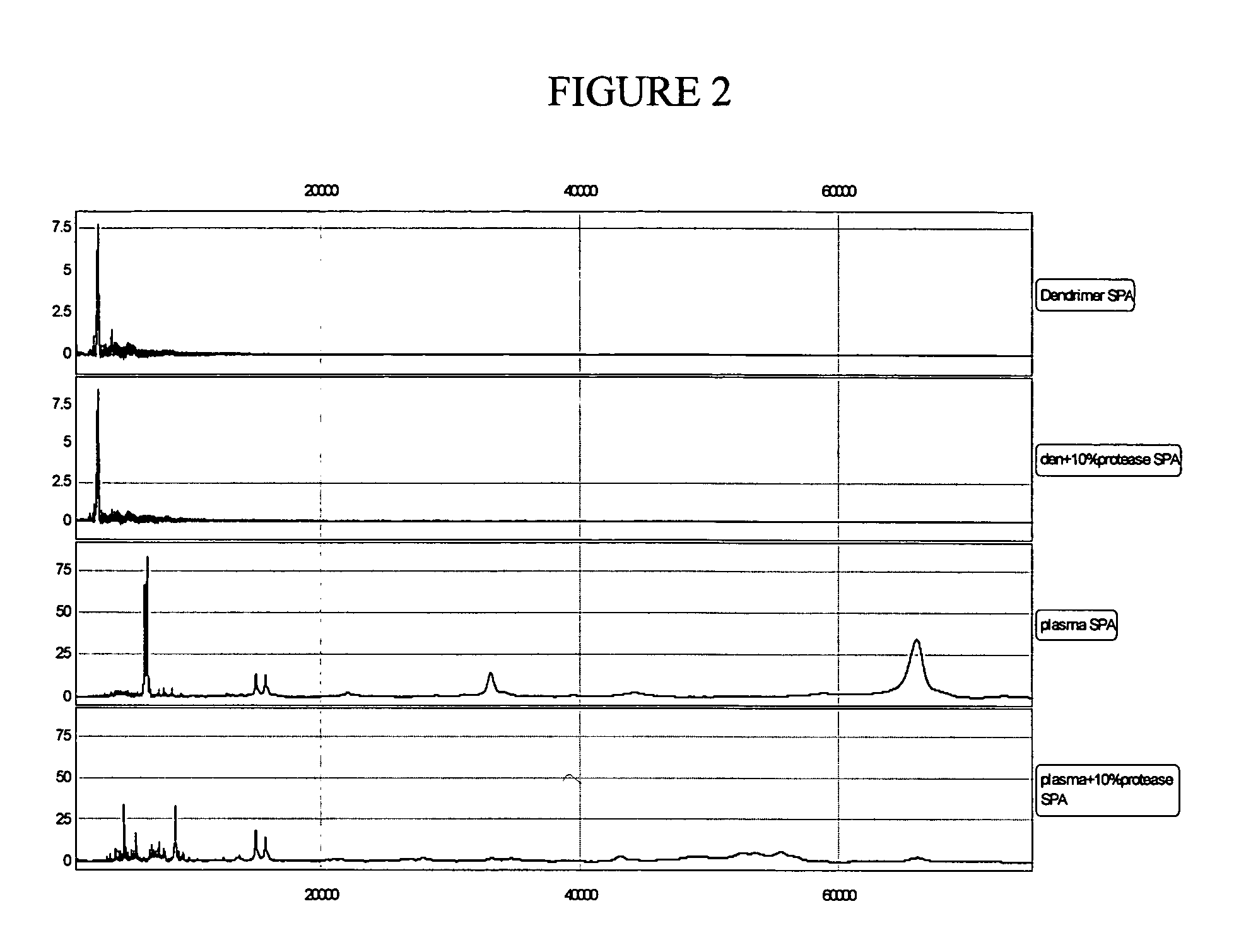
The present invention pertains to methods of quantifying the levels of at least one analyte in a sample or extract comprising adding a known quantity of at least one internal standard to the sample or extract. The present invention also relates to internal standards used in mass spectrometry, as well as compositions thereof. Internal standards for mass spectrometry according to the invention can be used, for example, to assist aligning mass spectra obtained from two different samples, each of which comprises the internal standard. In one aspect of the invention, the internal standard is a dendrimer. A labile internal standard may be used in conjunction with the dendrimer.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Ion detection in mass spectrometry with extended dynamic range
ActiveUS7047144B2Spectrometer detectorsResistance/reactance/impedenceMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryPeak value
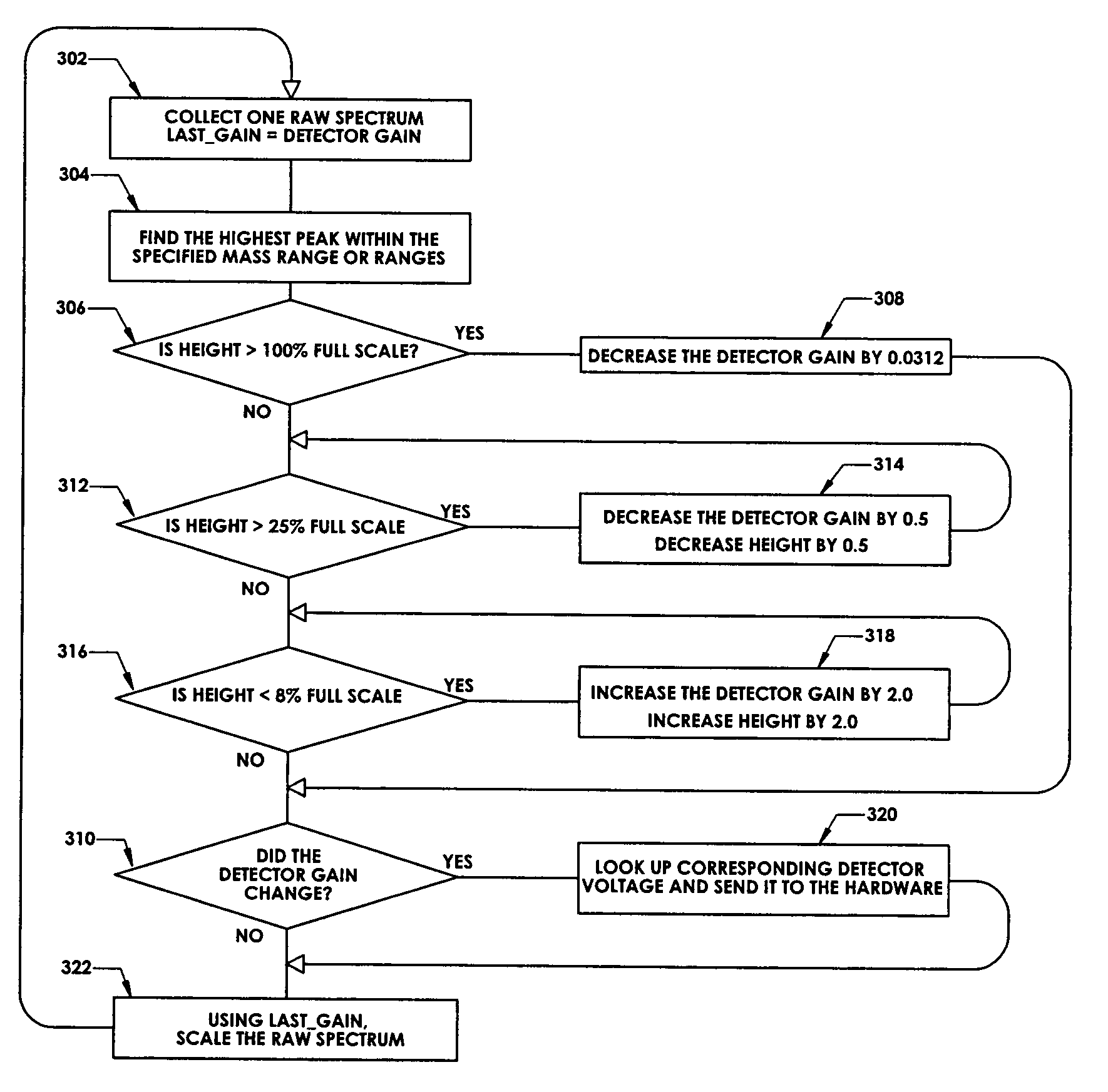
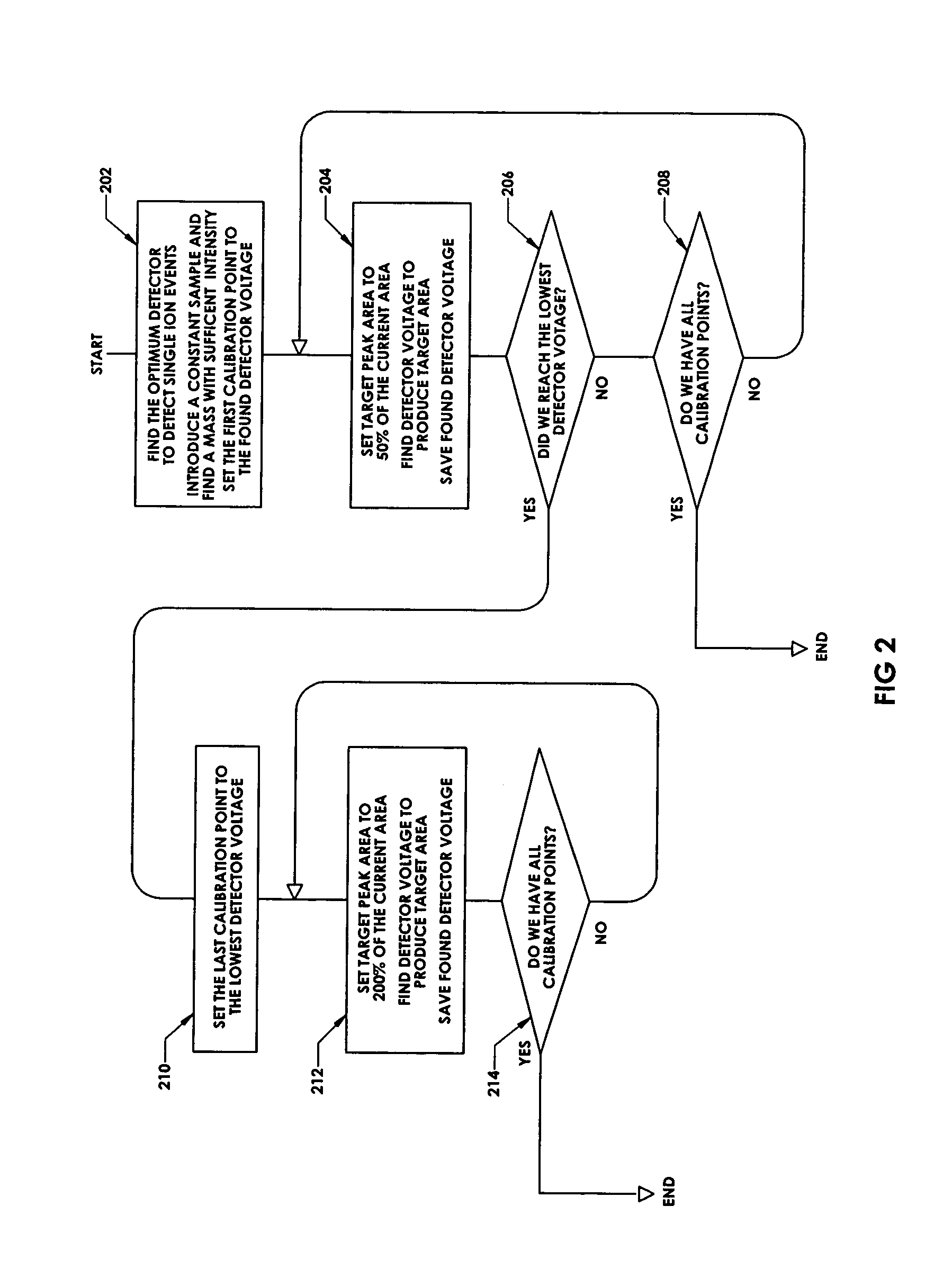
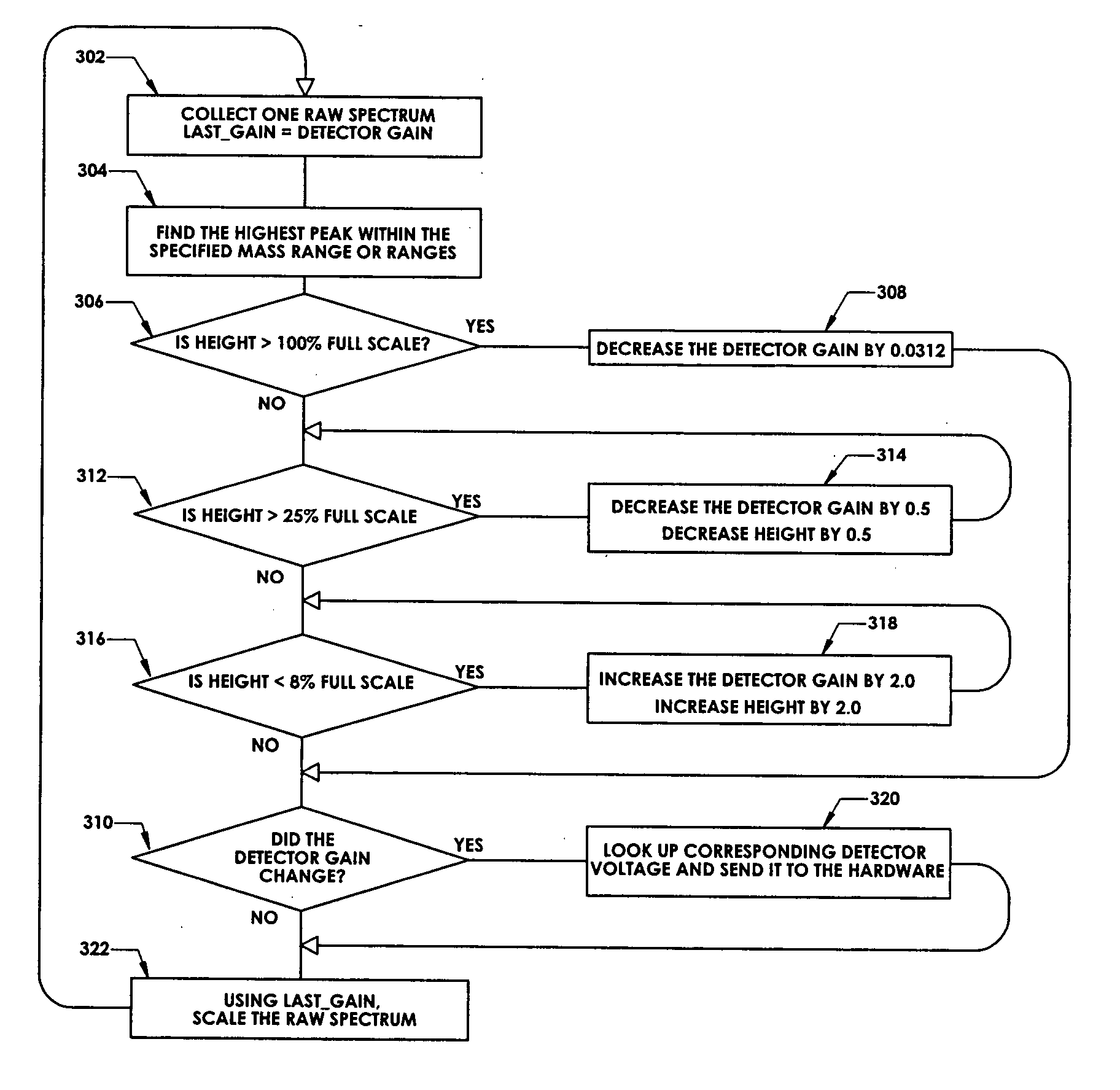
In a method for optimizing an ion detector a control voltage, such as in a mass spectrometry system, an array of mass scan data is acquired. Based on the size of the largest peak in the array or part of the array, a determination is made as to whether the current detector gain should be changed to a new detector gain. If the current detector gain should be changed, the control voltage for the subsequent mass scan is adjusted to a new control voltage corresponding to the new detector gain. The data are scaled based on the current detector gain. In another method, a gain versus control voltage curve is generated for calibration. These methods may be implemented by hardware, software, analog or digital circuitry, and / or computer-readable or signal-bearing media.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Aspects of mass spectral calibration
InactiveUS20060169883A1Improve accuracyHigh resolutionTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by optical meansElemental compositionSpectral response
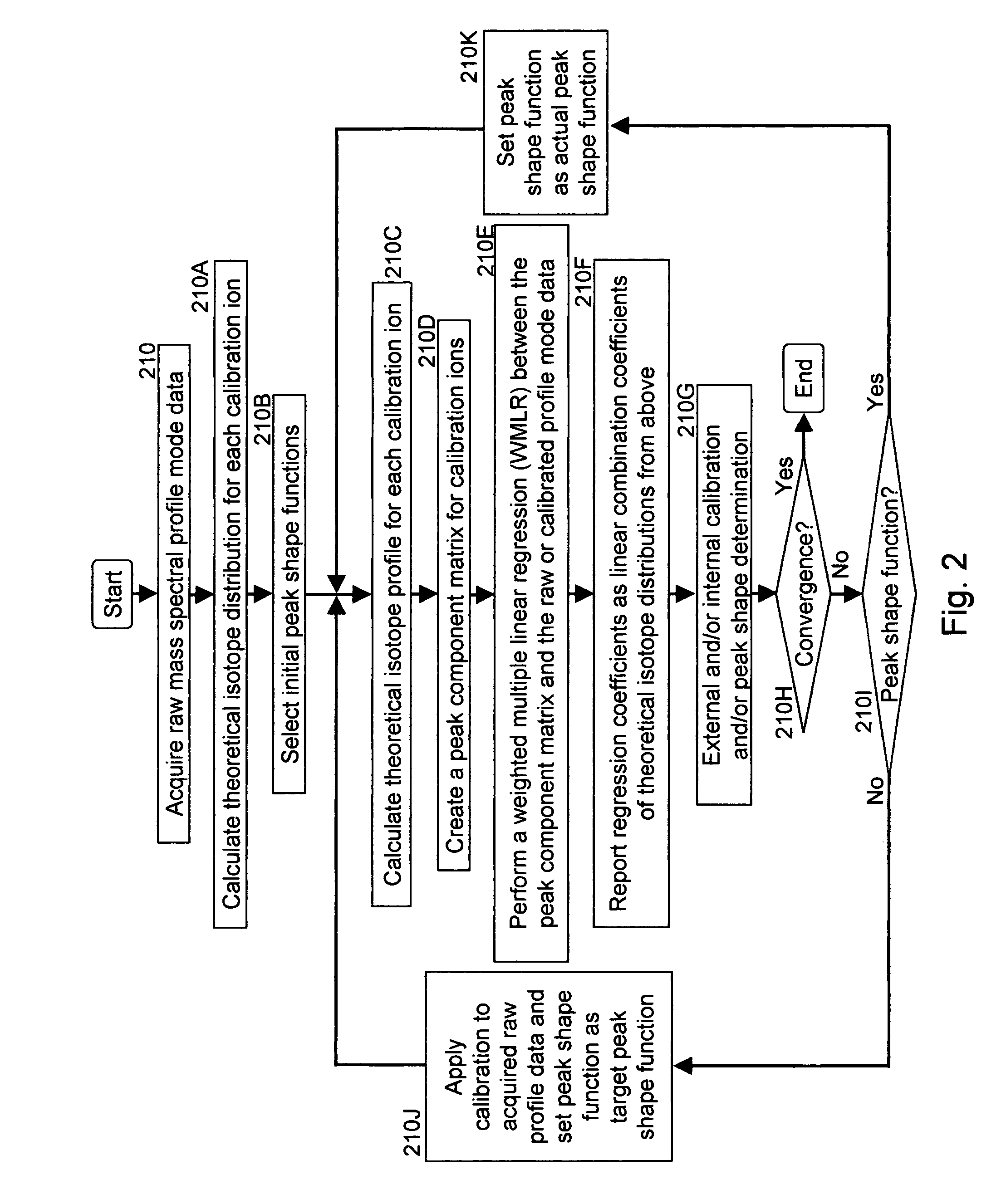
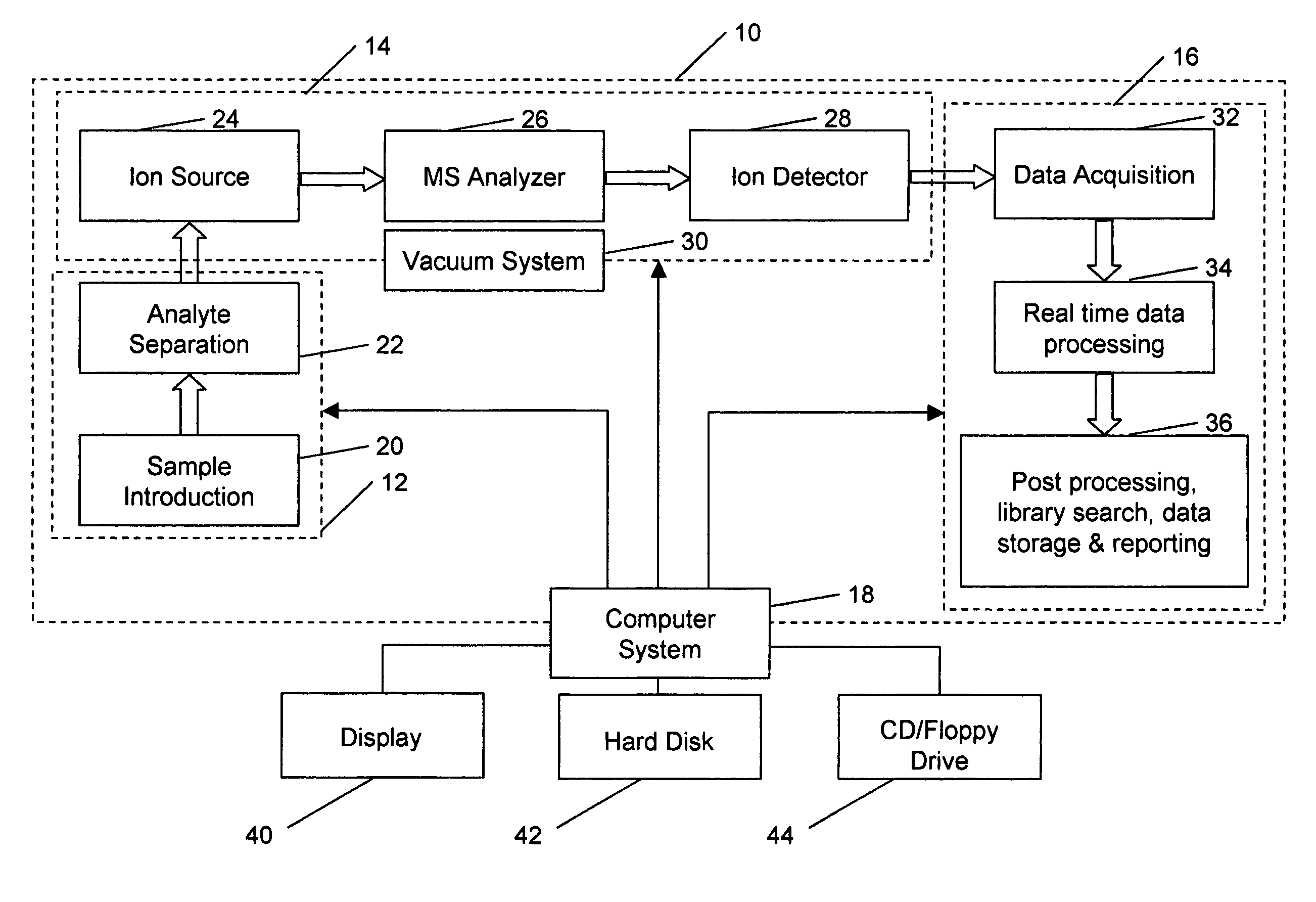
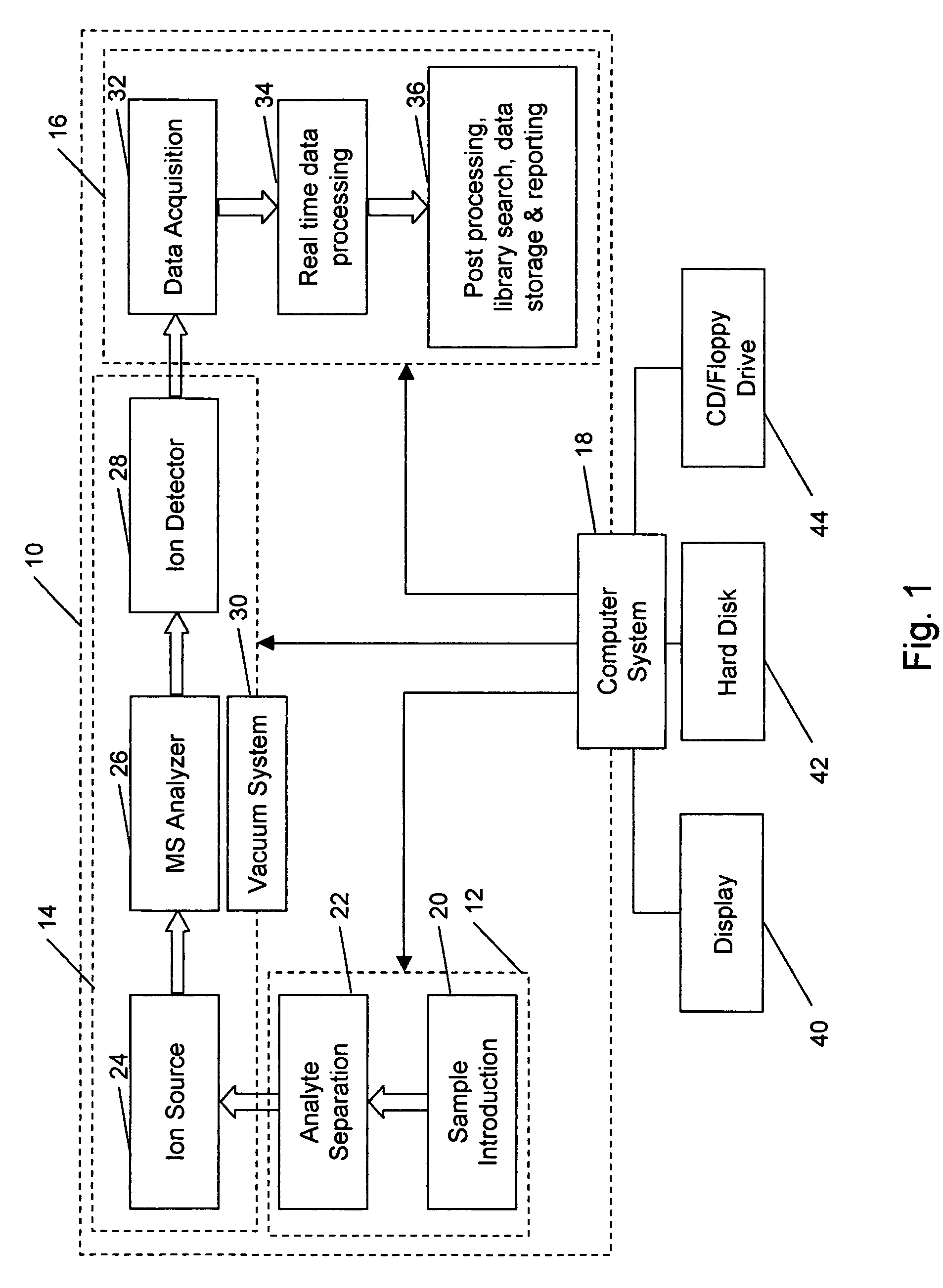
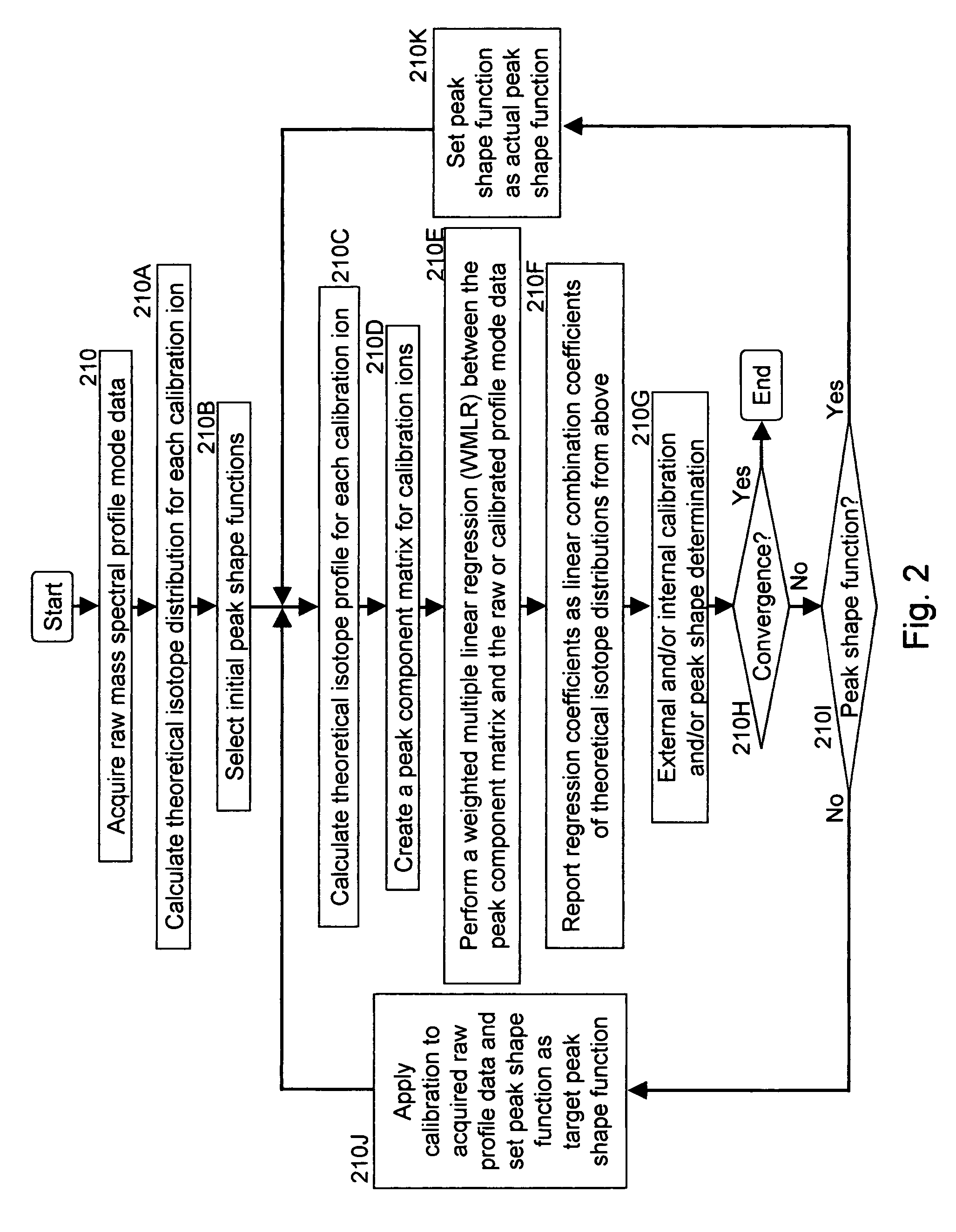
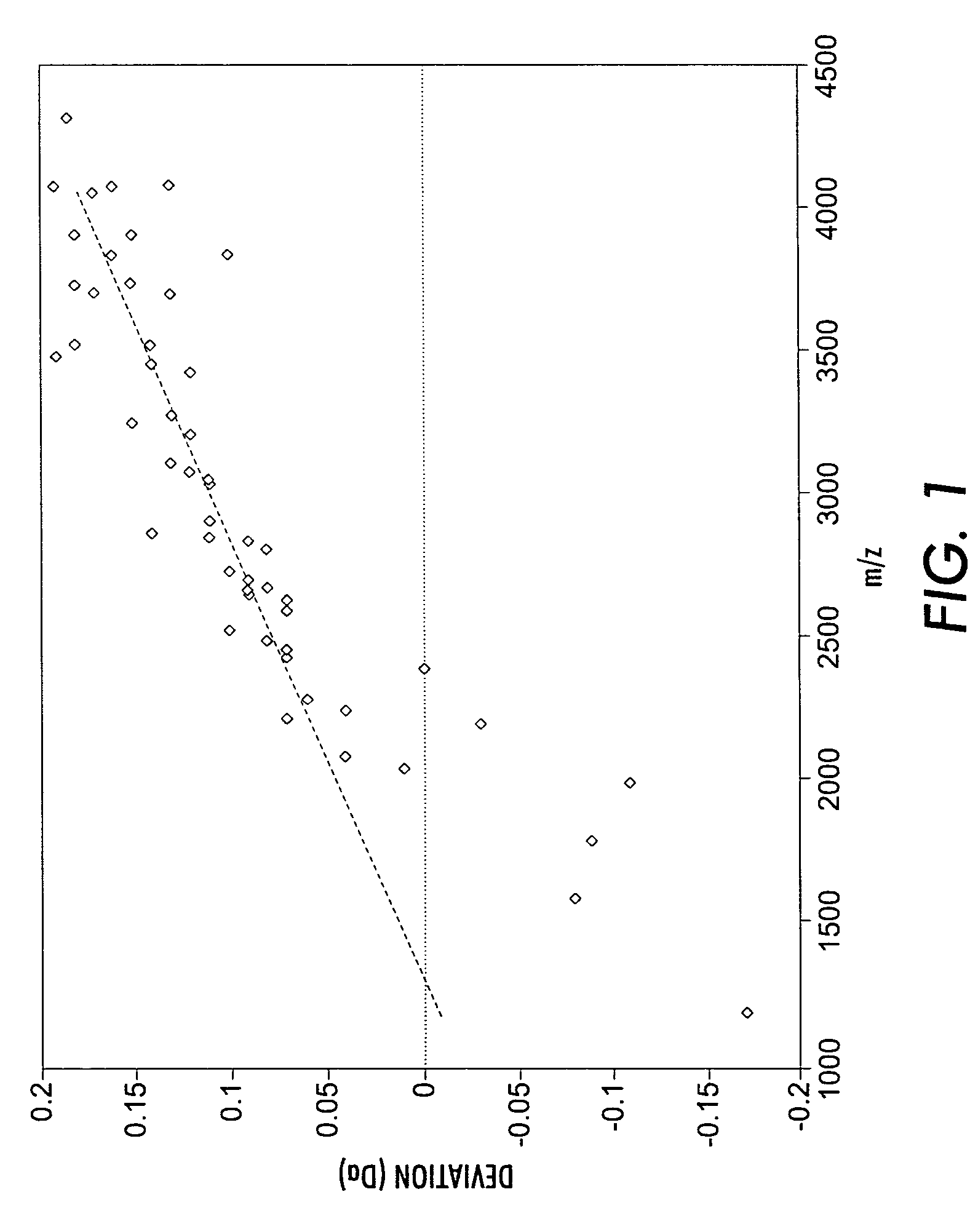
A method for calibrating and analyzing data from a mass spectrometer, comprising the steps of acquiring raw profile mode data containing mass spectral responses of ions with or without isotopes; calculating theoretical isotope distributions for each of at least one calibration ion based on elemental composition; convoluting the theoretical isotope distributions with an initial peak shape function to obtain theoretical isotope profiles for each ion; constructing a peak component matrix including the theoretical isotope profiles for calibration ions as peak components; performing a regression analysis between the raw profile mode mass spectral data and the peak component matrix; and reporting the regression coefficients as the relative concentrations for each of the components. A mass spectrometry system operated in accordance with the method and a computer readable medium having program code thereon for performing the method.
Owner:CERNO BIOSCI
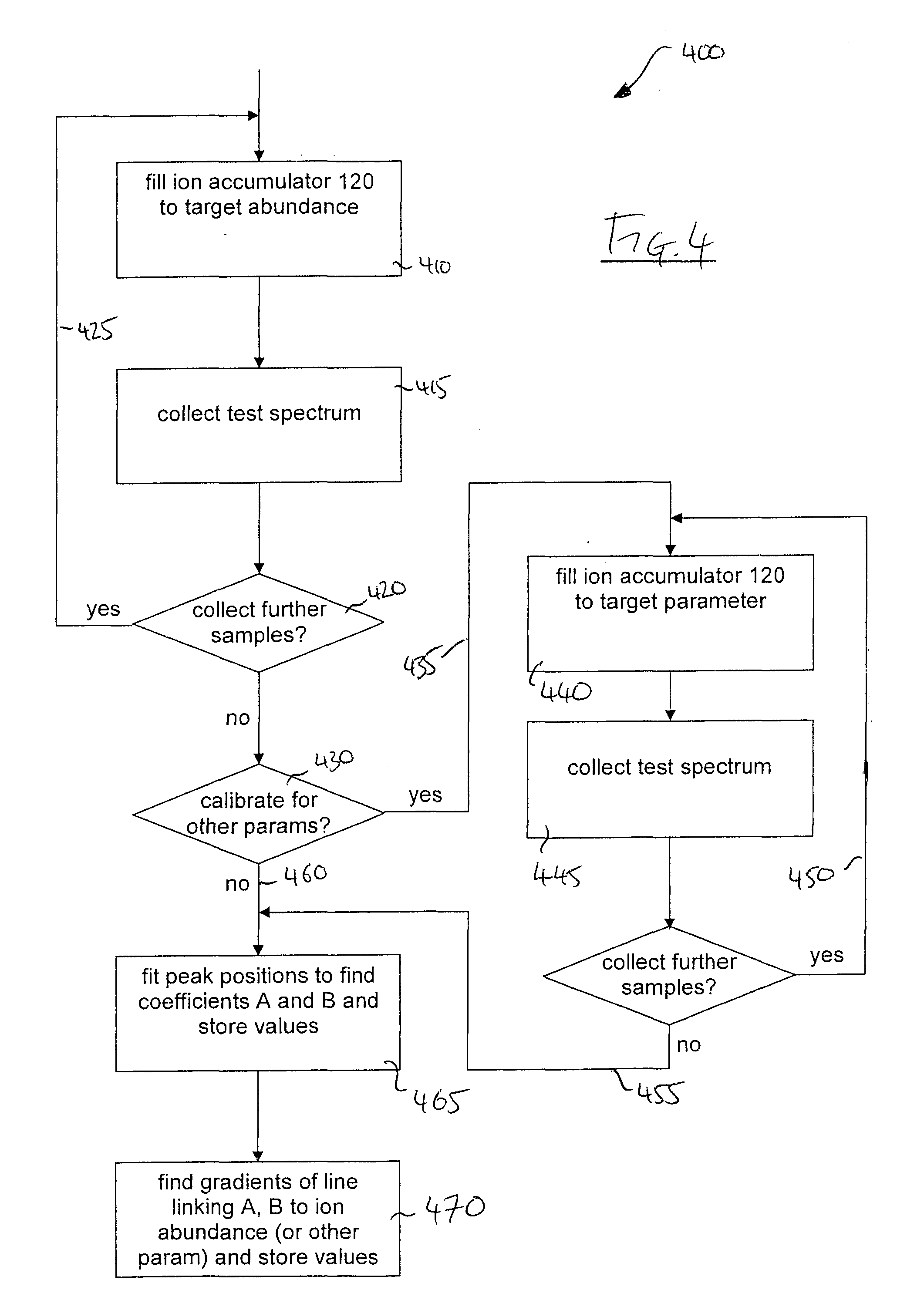
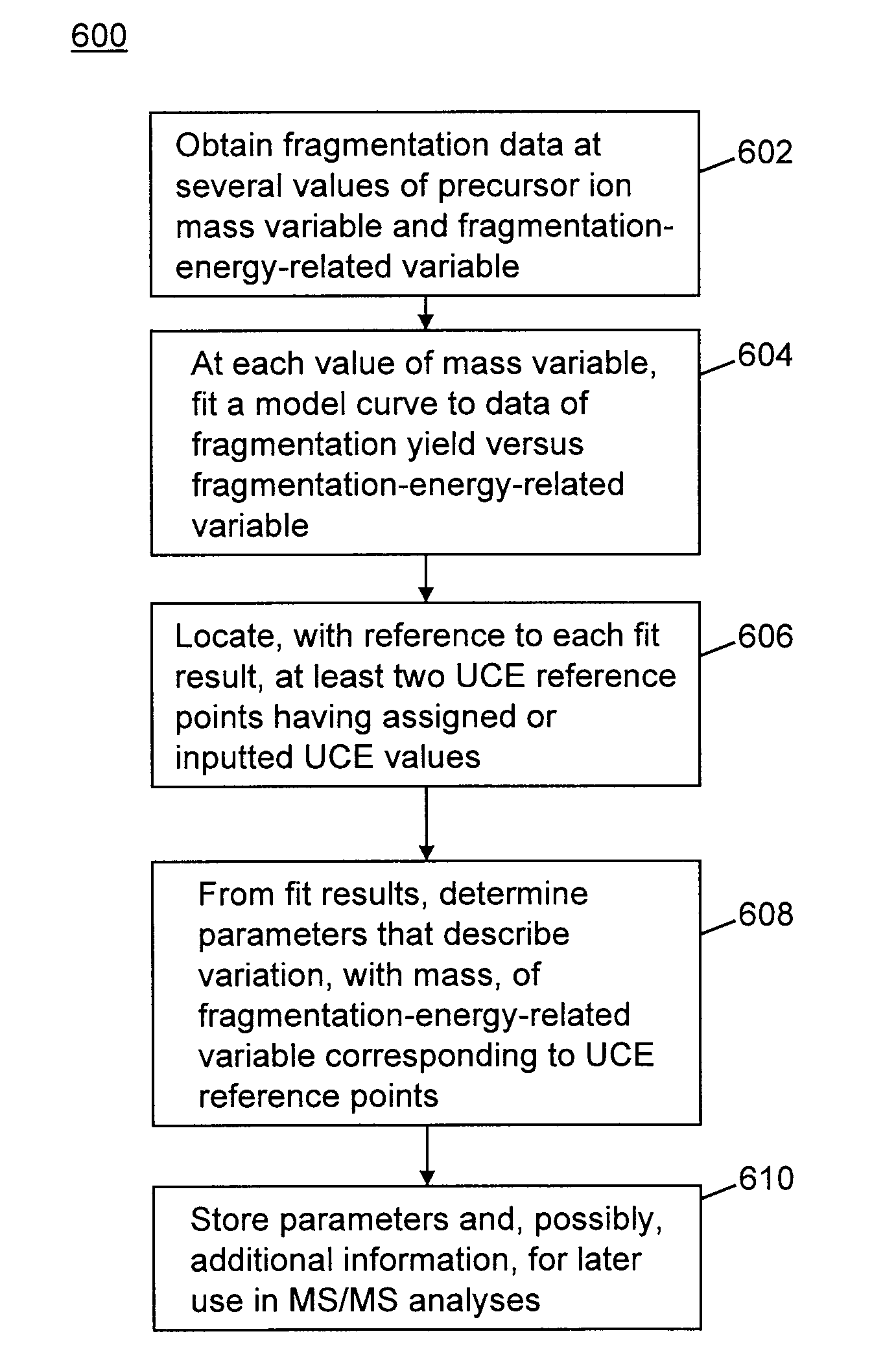
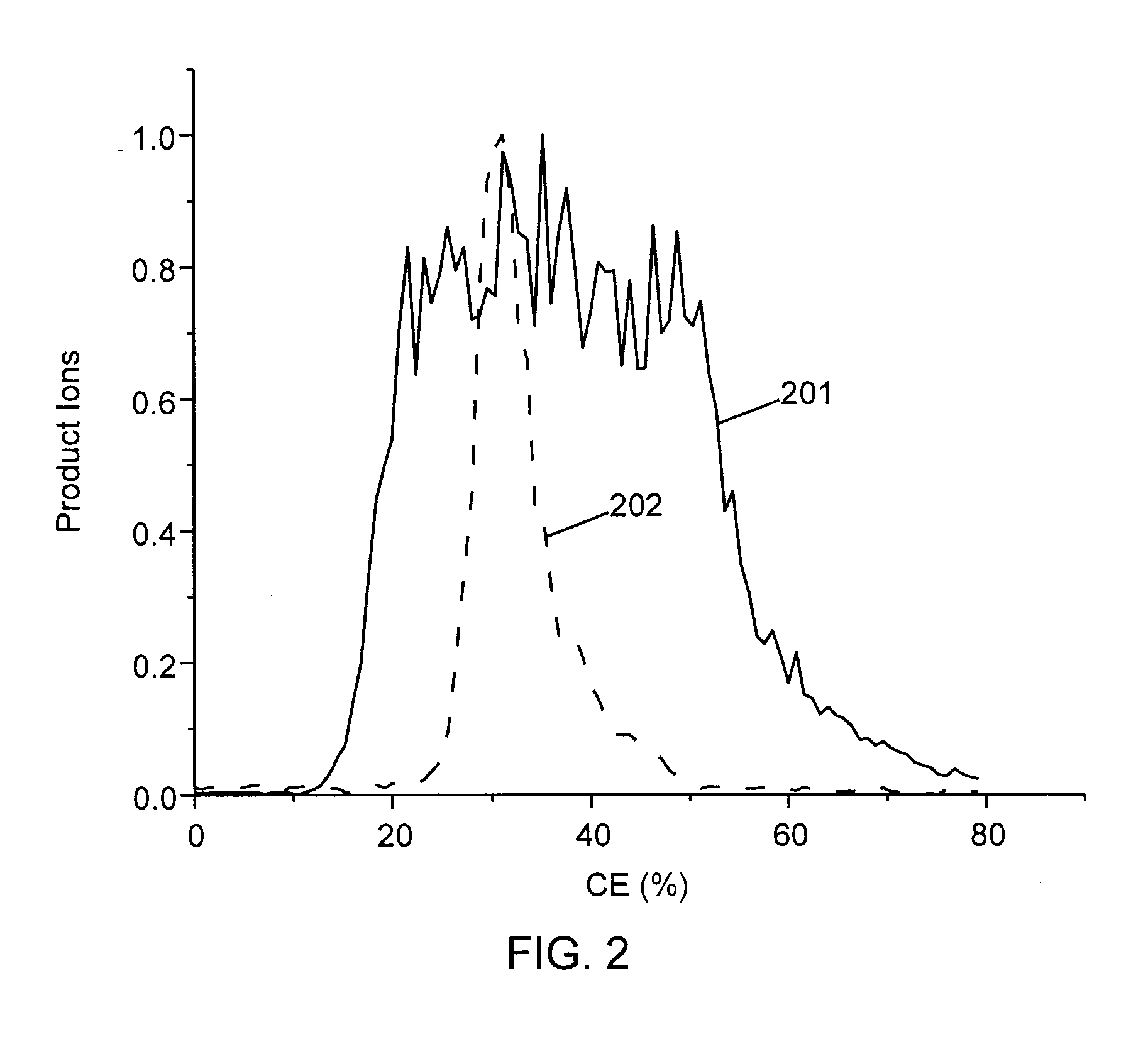
Methods for calibration of usable fragmentation energy in mass spectrometry
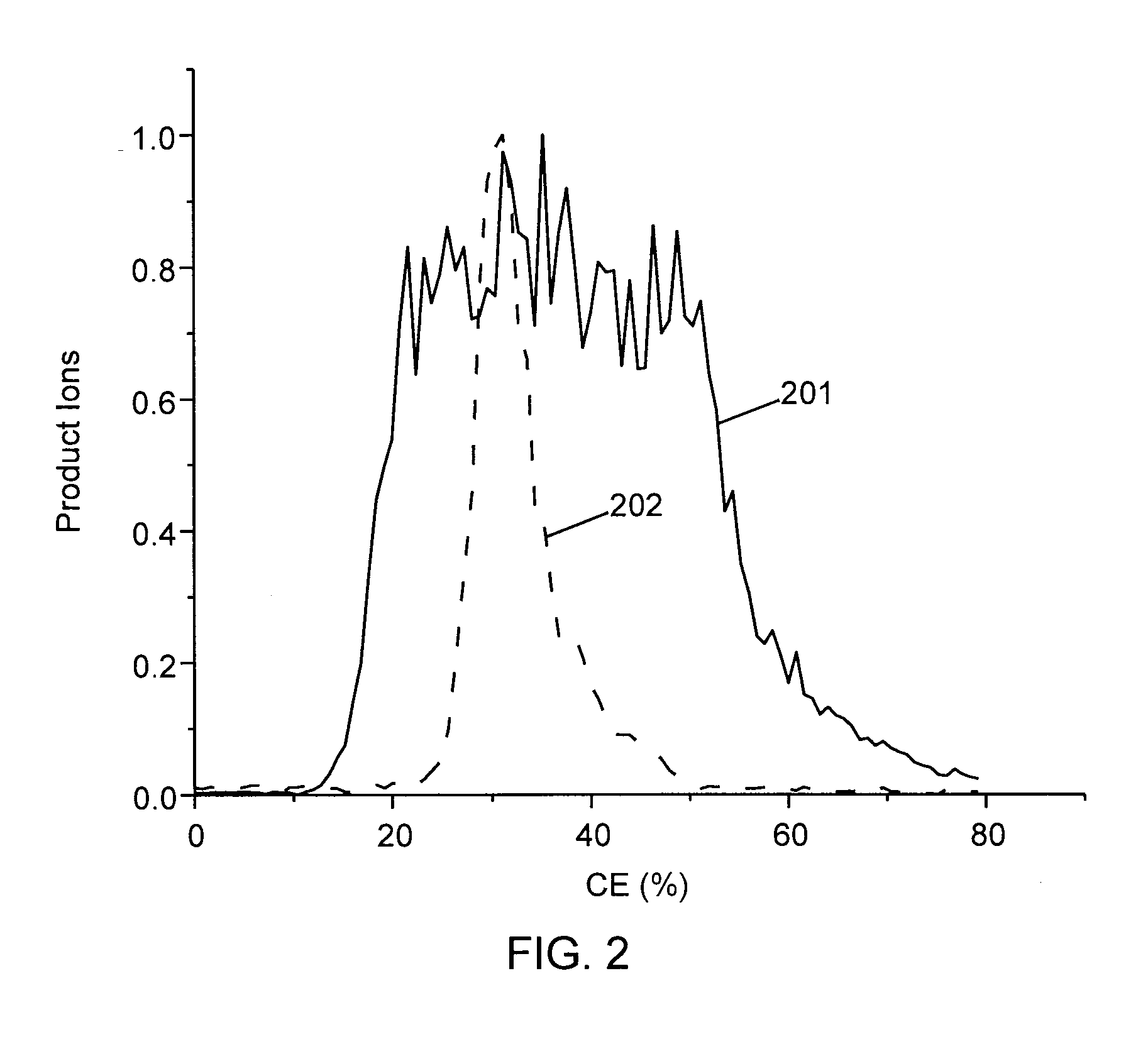
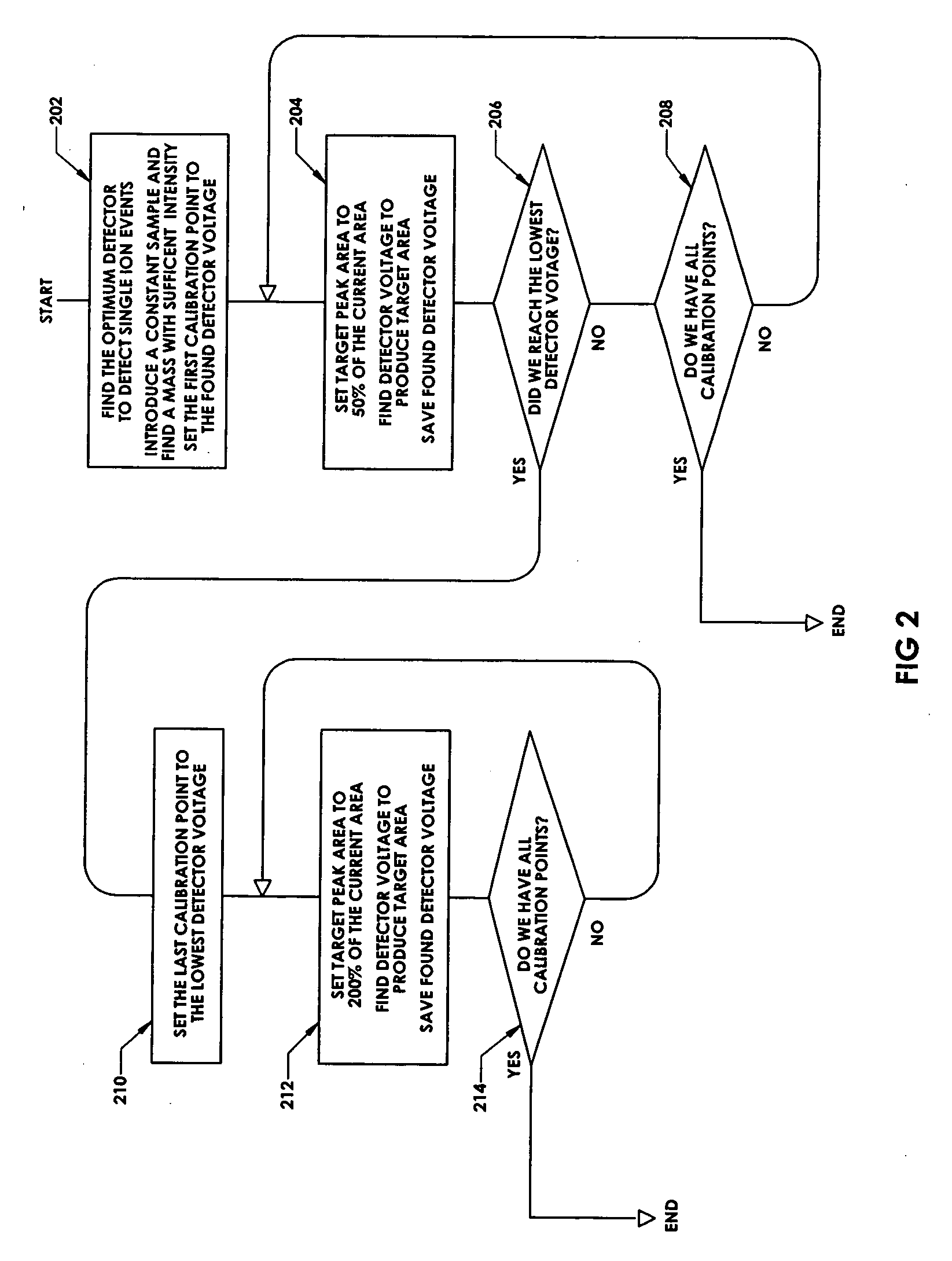
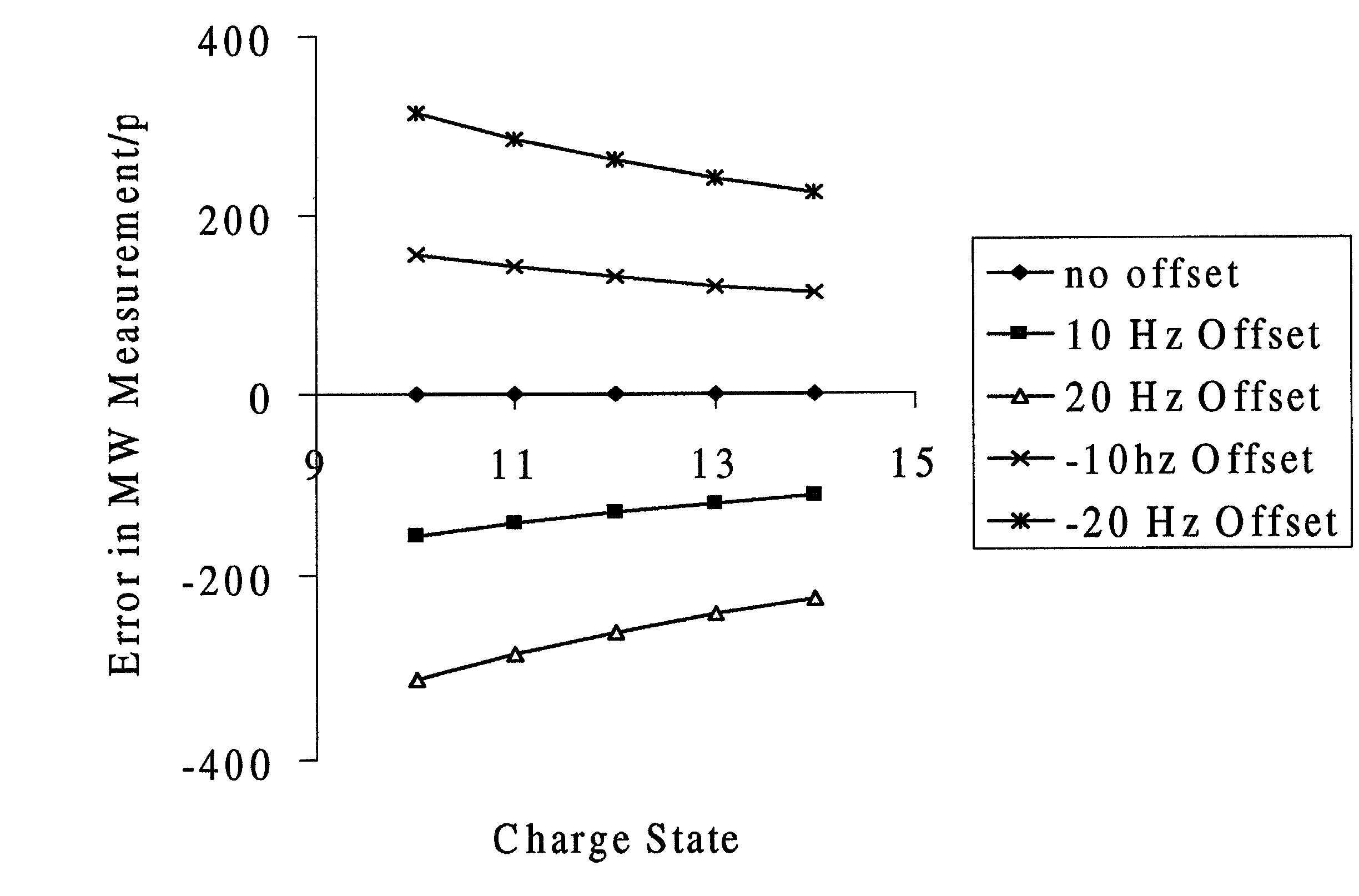
ActiveUS8278620B2Isotope separationCalibration apparatusMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass analyzer
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Ion detection in mass spectrometry with extended dynamic range
ActiveUS20060080045A1Small sizeIncrease in sizeSpectrometer detectorsResistance/reactance/impedenceMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryPeak value
In a method for optimizing an ion detector a control voltage, such as in a mass spectrometry system, an array of mass scan data is acquired. Based on the size of the largest peak in the array or part of the array, a determination is made as to whether the current detector gain should be changed to a new detector gain. If the current detector gain should be changed, the control voltage for the subsequent mass scan is adjusted to a new control voltage corresponding to the new detector gain. The data are scaled based on the current detector gain. In another method, a gain versus control voltage curve is generated for calibration. These methods may be implemented by hardware, software, analog or digital circuitry, and / or computer-readable or signal-bearing media.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Method for accurate mass determination with ion trap/time-of-flight mass spectrometer
ActiveUS20050151073A1Accurate mass determinationImprove accuracyStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryAnalyte
Accurate mass measurement is carried out for product ions of a sample. A method for accurate mass determination of ions with Trap-TOF / μs includes steps of generating ions of an analyte sample and a standard material; introducing the ions of the analyte sample and the standard material together into an ion trap to trap them; selecting a precursor ion from the ions of the analyte sample to leave the precursor ion and a standard material ion in the ion trap and eliminate other ions; exciting and dissociating the precursor ion to generate product ions; ejecting the precursor ion, its product ions, and the standard material ion trapped in the ion trap to introduce these ions into the TOF mass spectrometer; and measuring a mass spectrum with the TOF mass spectrometer, where correction for accurate masses of the product ions is carried out based on the standard material ion measured.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Particles containing detectable elemental code
InactiveUS20100144056A1Direct contact guaranteeBiological testingTube calibration apparatusAnalysis methodSpectrometer
The invention relates to a new type of element encoded particles suitable for the attachment of bio molecules to enable massively multiplex bio-analytical methods, and to calibrate and tune the elemental flow cytometer mass spectrometer (FC-MS).
Owner:FLUIDIGM CANADA INC
Method for Calibrating an Analytical Instrument
InactiveUS20080201095A1Minimize the differenceOptimize locationMaterial analysis by optical meansElectrical measurementsComputer scienceSpectrometer
Methods are provided for calibrating analytical instruments that comprise a quantitative device, such as spectrometers, particularly where a complex mixture is analyzed over a broad spectral range. Associated computer and analytical systems as well as software are also provided.
Owner:VERMILLION INC
Automated mass spectral identification
InactiveUS20080237458A1Identification results are reliableConfidenceIsotope separationTube calibration apparatusIonPhysics
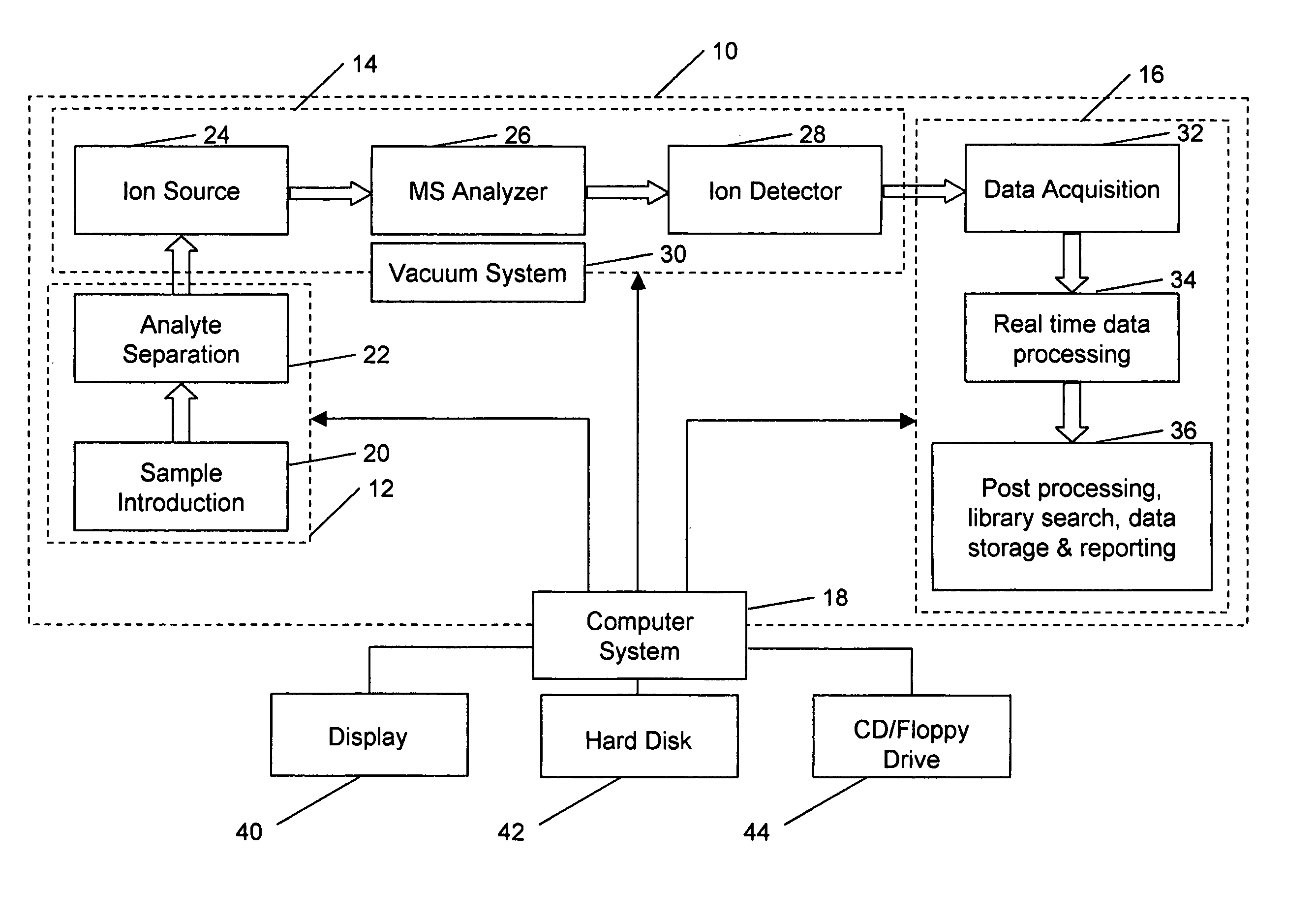
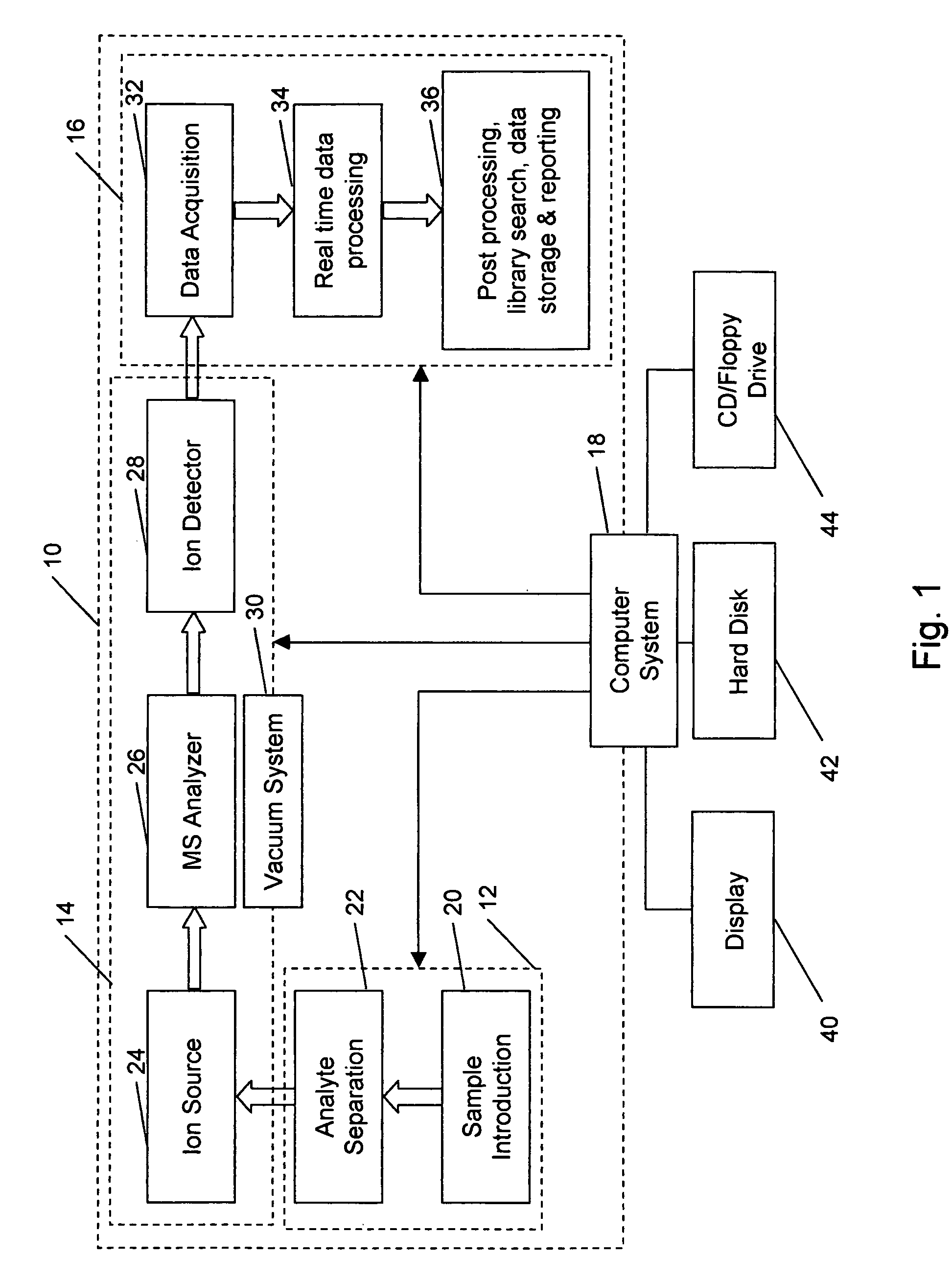
An automated or fully automated mass spectral system and a method of operating the system to identify a sample ion or compound. The system includes at least one computer addressable holder for at least one of standard and sample; at least one mass spectrometer configured to acquire one of continuum, profile, and raw mode mass spectral data; a computer system including a first software component to control introduction of at least one of the sample and the standard, data acquisition, and data analysis; a second software component for performing a mass spectral calibration involving at least m / z value, to report at least one of accurate mass, a list of possible elemental compositions, and a measurement statistic; and a third software component capable of acting on reported result or measurement statistic to change at least one of the introduction of at least one of the sample and the standard, data acquisition, data analysis, reported result, and measurement statistic. A computer readable medium having computer readable program code therein for use in the method or system.
Owner:CERNO BIOSCI
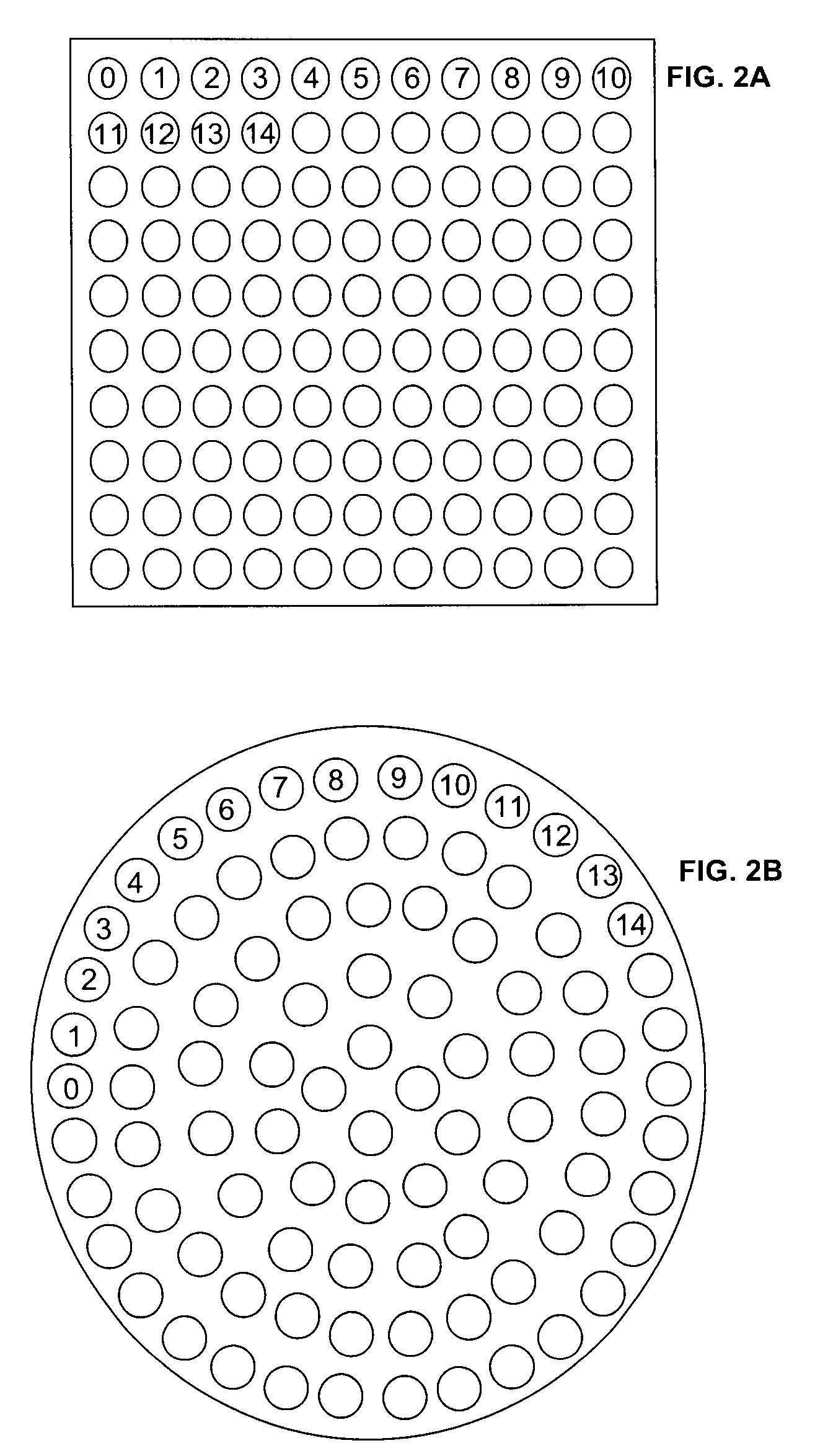
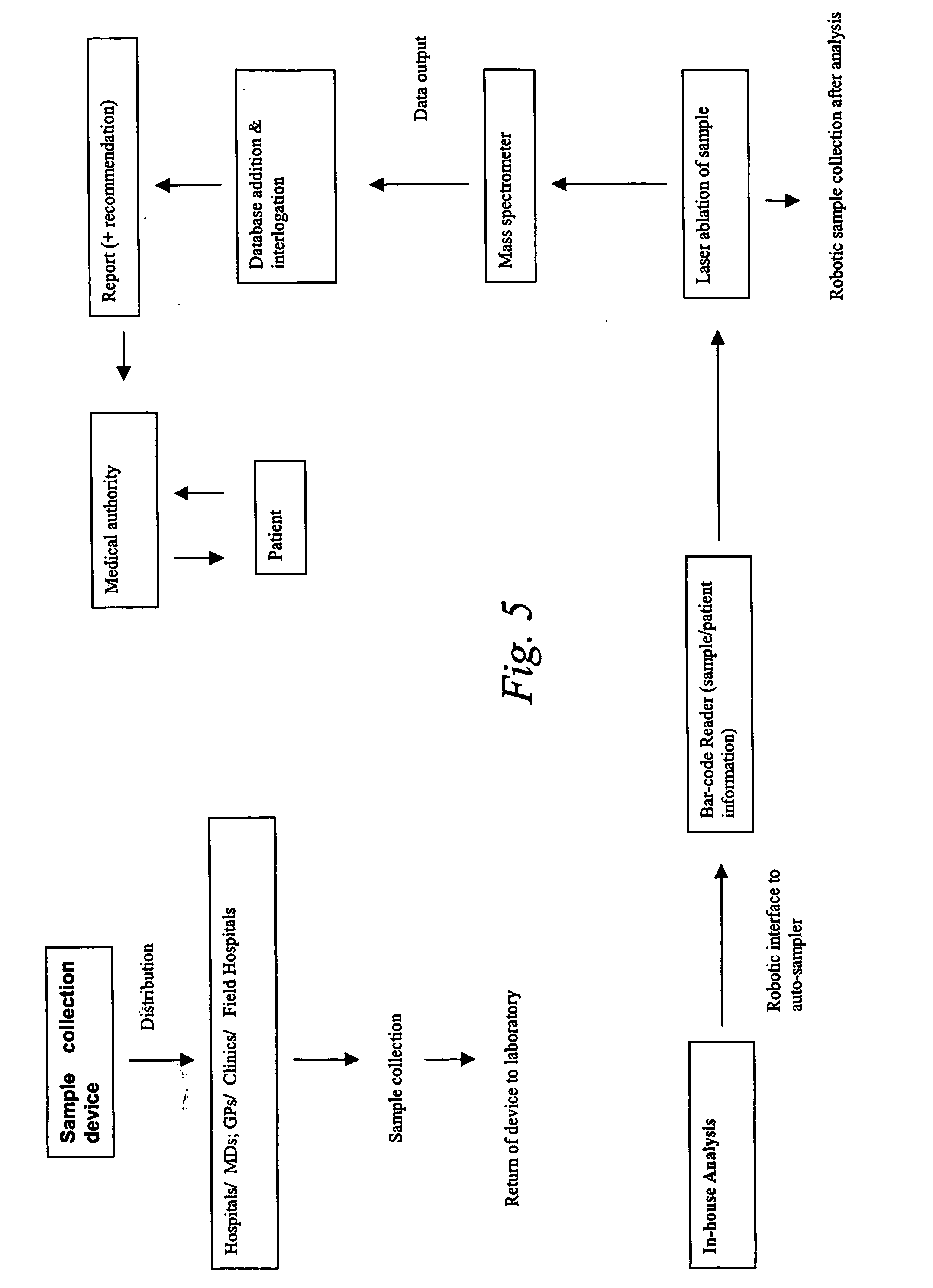
Sample collecting device and mass spectrometry of device
InactiveUS20060057554A1Facilitate matrix matchingImprove propertiesTesting starch susbtancesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReference sampleMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A sample collection device comprising a support bearing an inert absorbing matrix for a fluid sample is described. The device may or may not have a lancet. Also described for a sample device is a method of using a mass spectrometer in a laboratory where the sample in its matrix is ionised and the plurality of elements is detected. The results may or may not be quantised in relation to the original sample and an internal ionised reference sample may also be used.
Owner:DIAKYNE PTY LTD
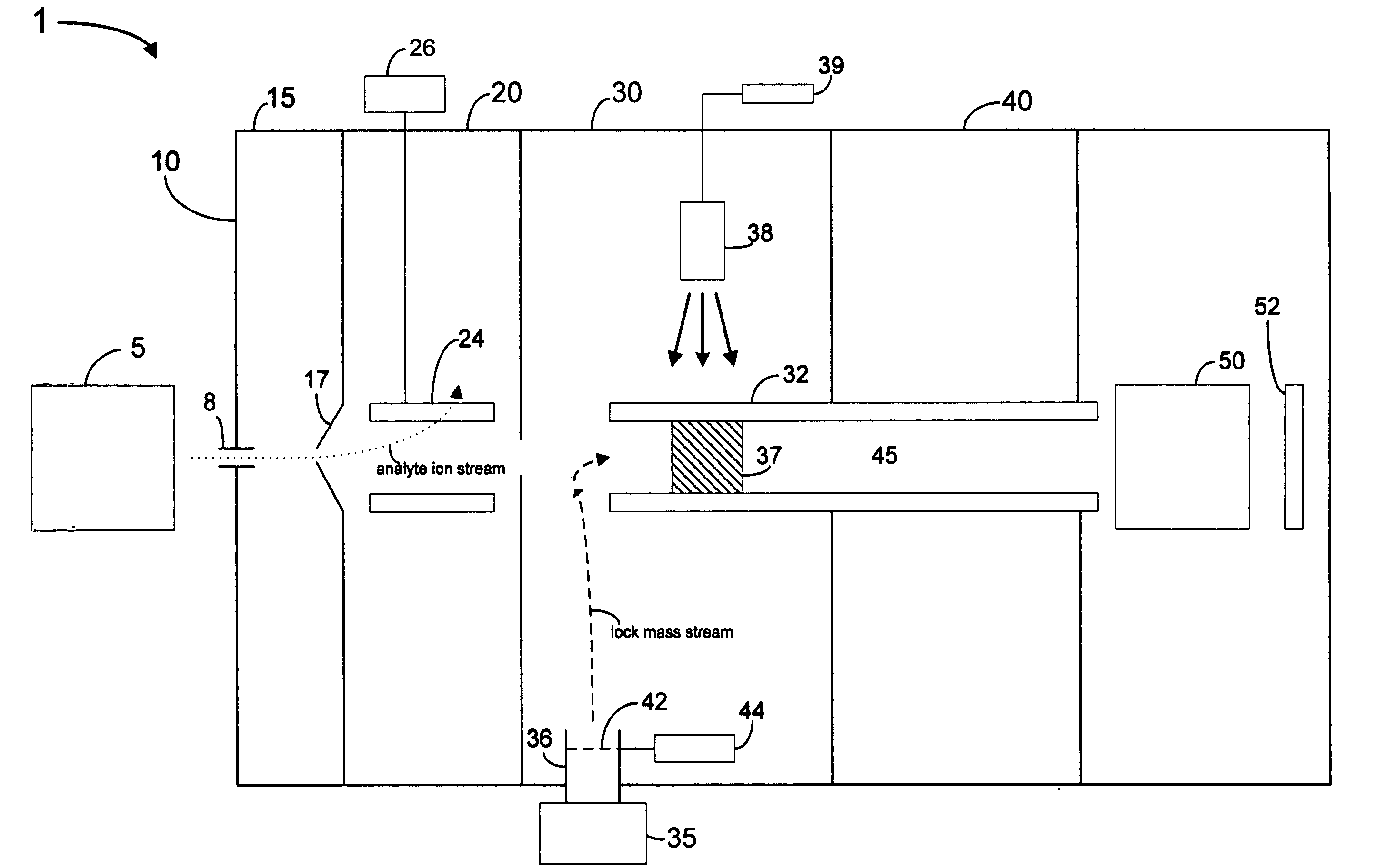
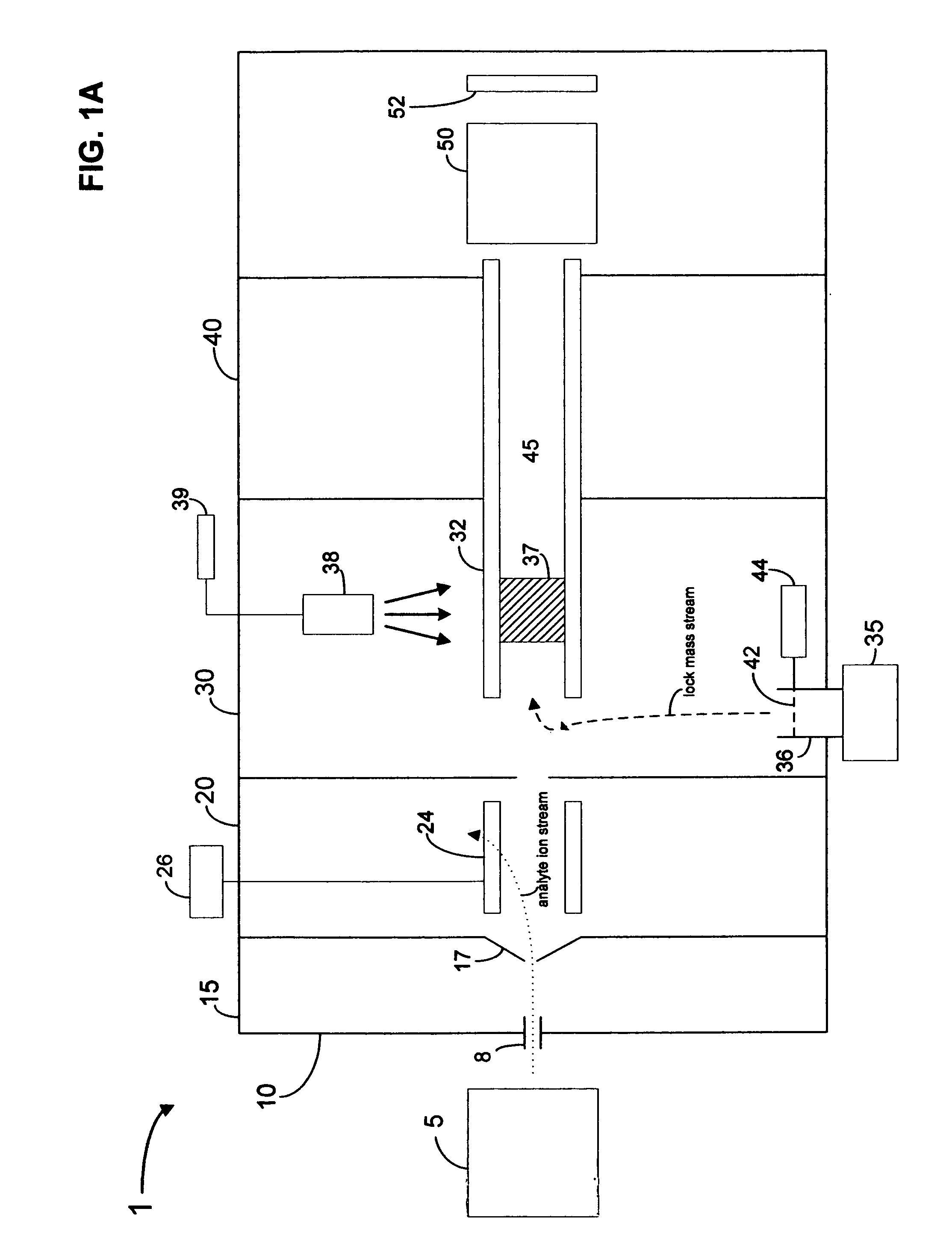
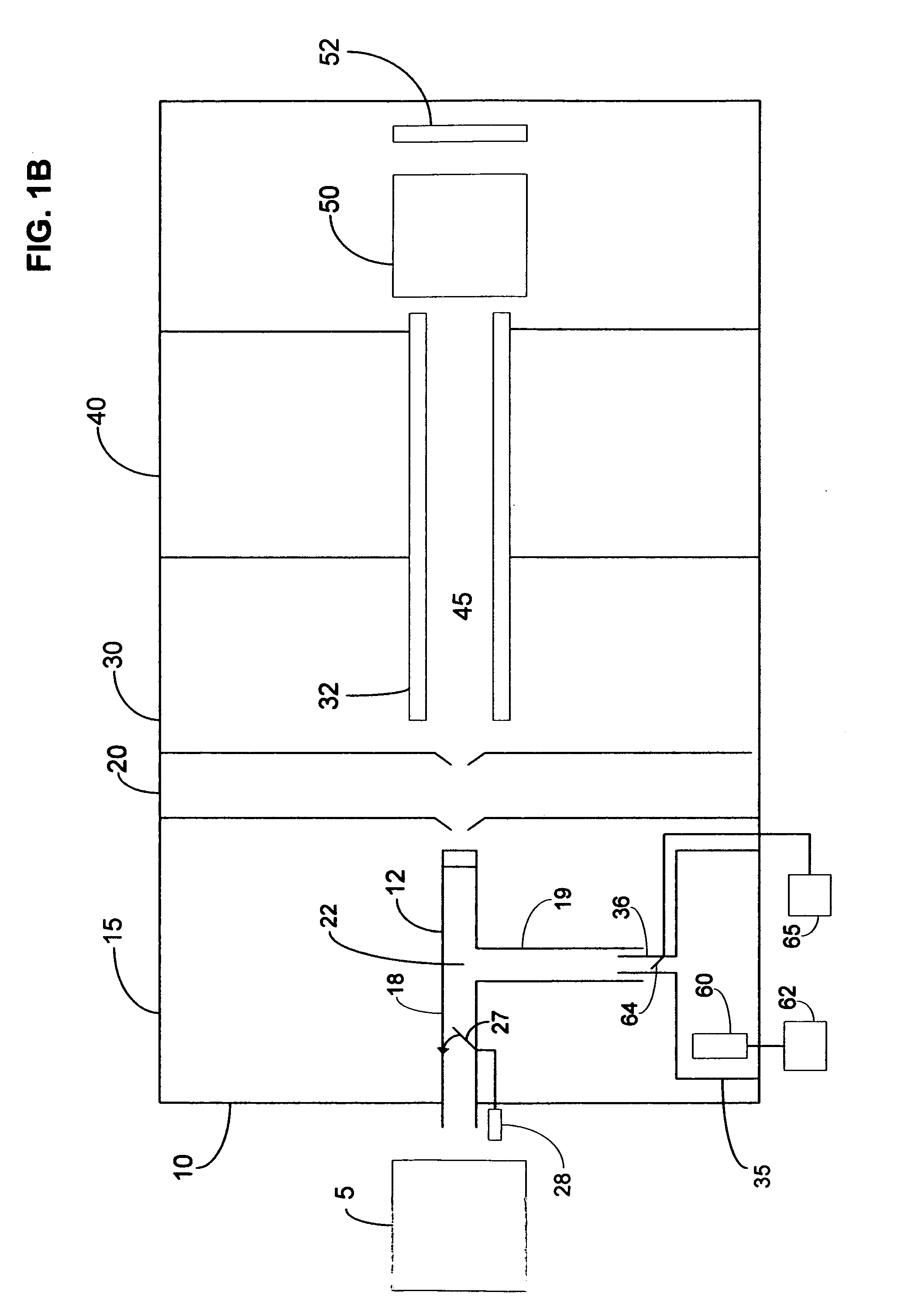
Pulsed internal lock mass for axis calibration
InactiveUS20070200060A1Samples introduction/extractionIsotope separationAnalyteMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A method and apparatus for calibrating a mass spectrometry system in which lock mass ions are introduced into the transport region of a mass spectrometer intermittently in a pulsed manner and analyte ions and / or lock mass ions are then detected at the mass analyzer. In one embodiment, analyte ions are also introduced into the transport region of the mass spectrometer from the analyte ion source intermittently in a pulsed manner.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
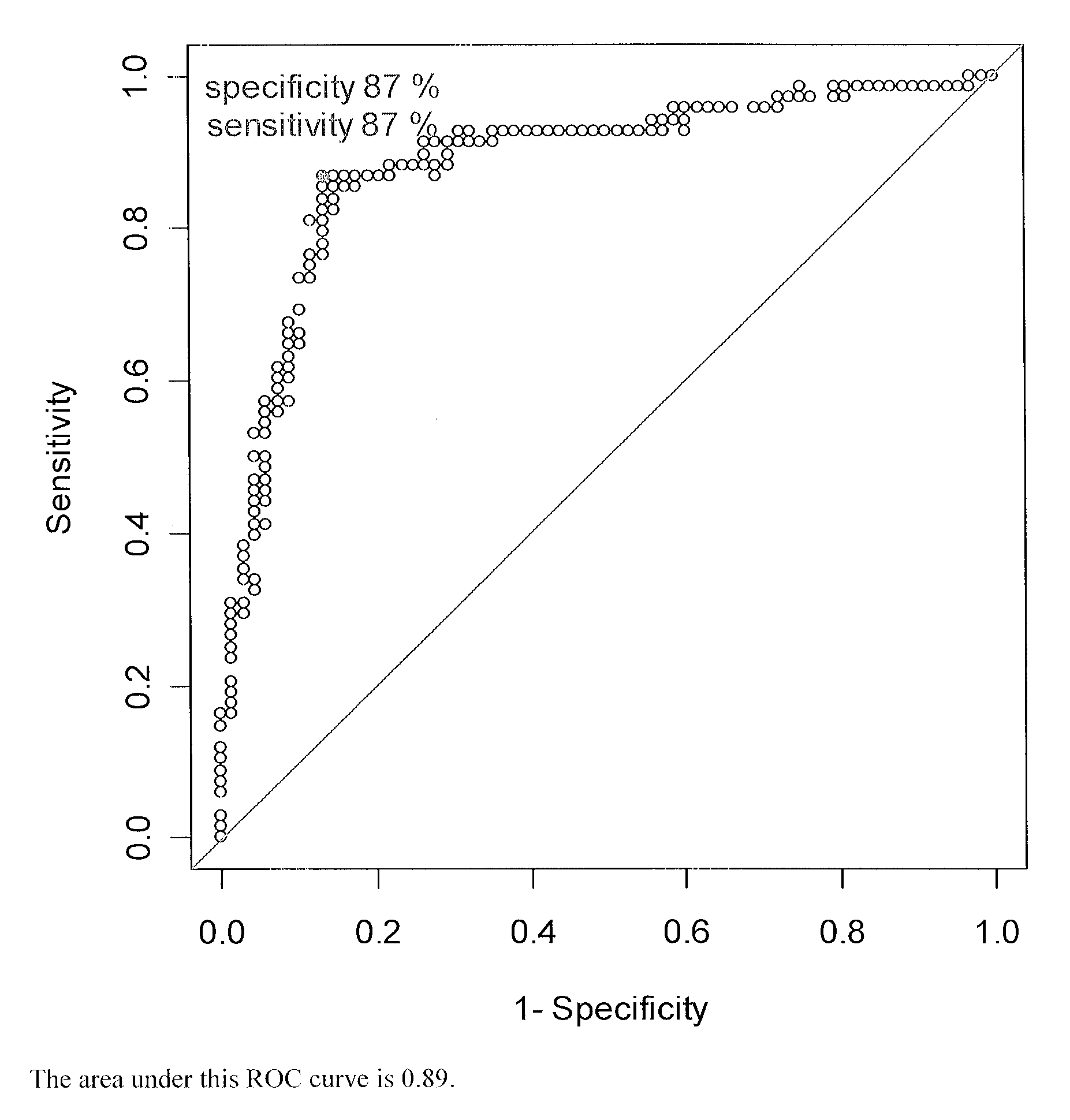
Methods for detecting major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events
InactiveUS20110045514A1Raise the possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisTissue factorAnalyte
The present teachings relate to a method of assessing the probability of a major adverse cardiovascular or cerebrovascular event in a human. The method can include measuring a concentration, in a blood-based sample of a human, of a set of analytes, for example, alpha-fetoprotein, cancer antigen 125, glutathione S-transferase, and tissue factor. The method also can include determining a MACCE index for the set of analytes and identifying the human as having an increased likelihood of a major adverse cardiovascular or cerebrovascular event if the MACCE index is greater than zero, or a decreased likelihood of a major adverse cardiovascular or cerebrovascular event if the MACCE index is less than or equal to zero.
Owner:BG MEDICINE
MS/MS mass spectrometer
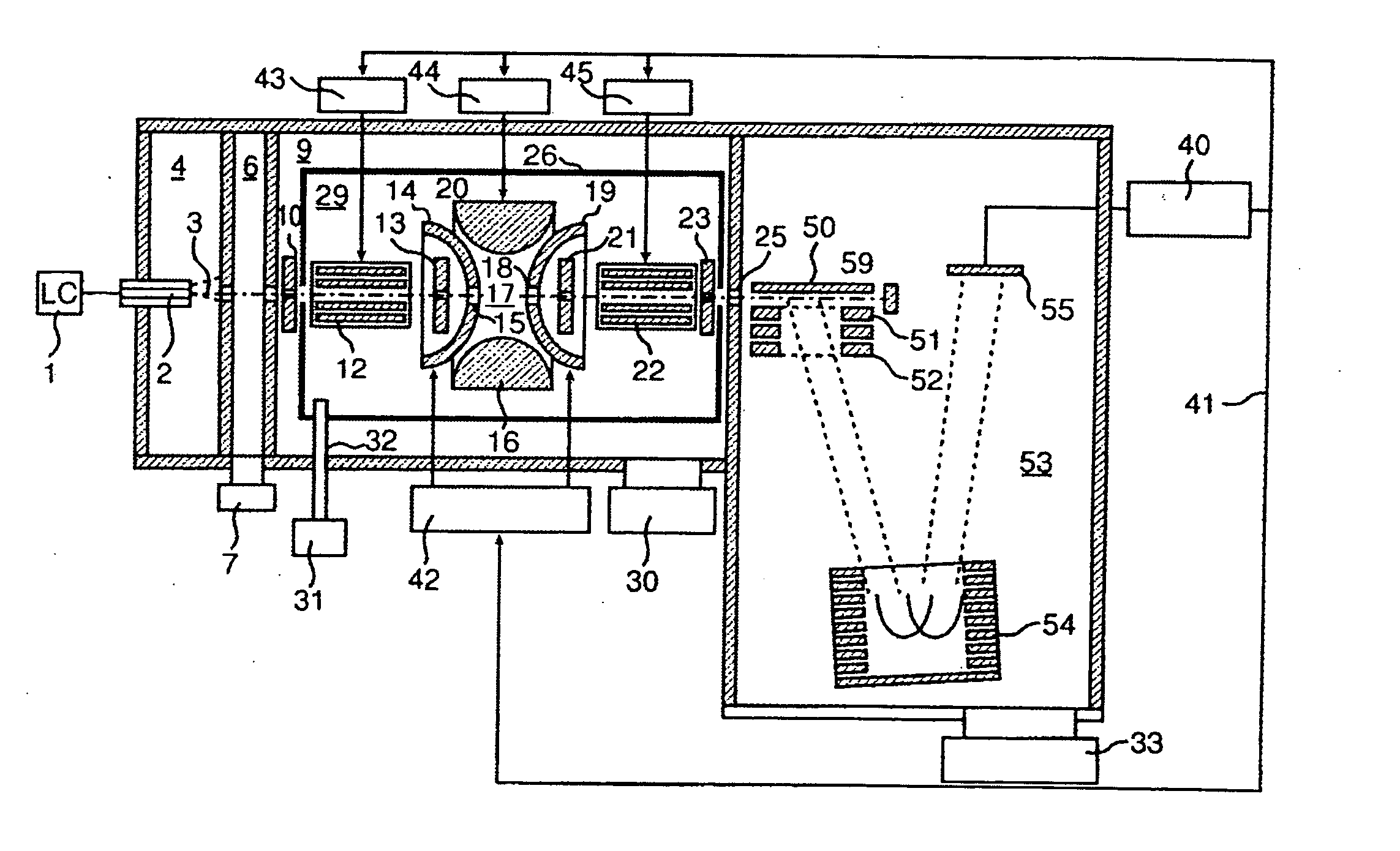
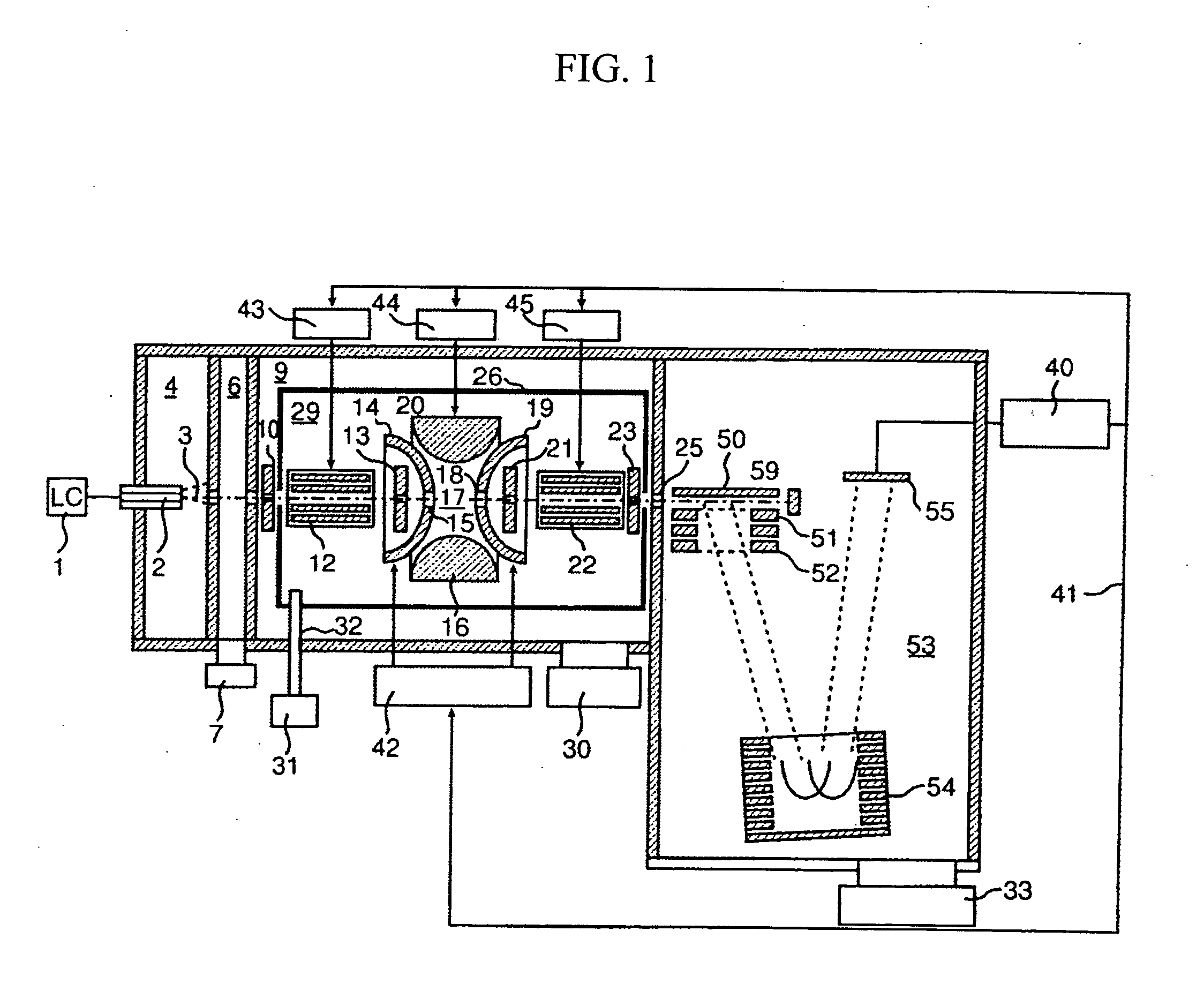
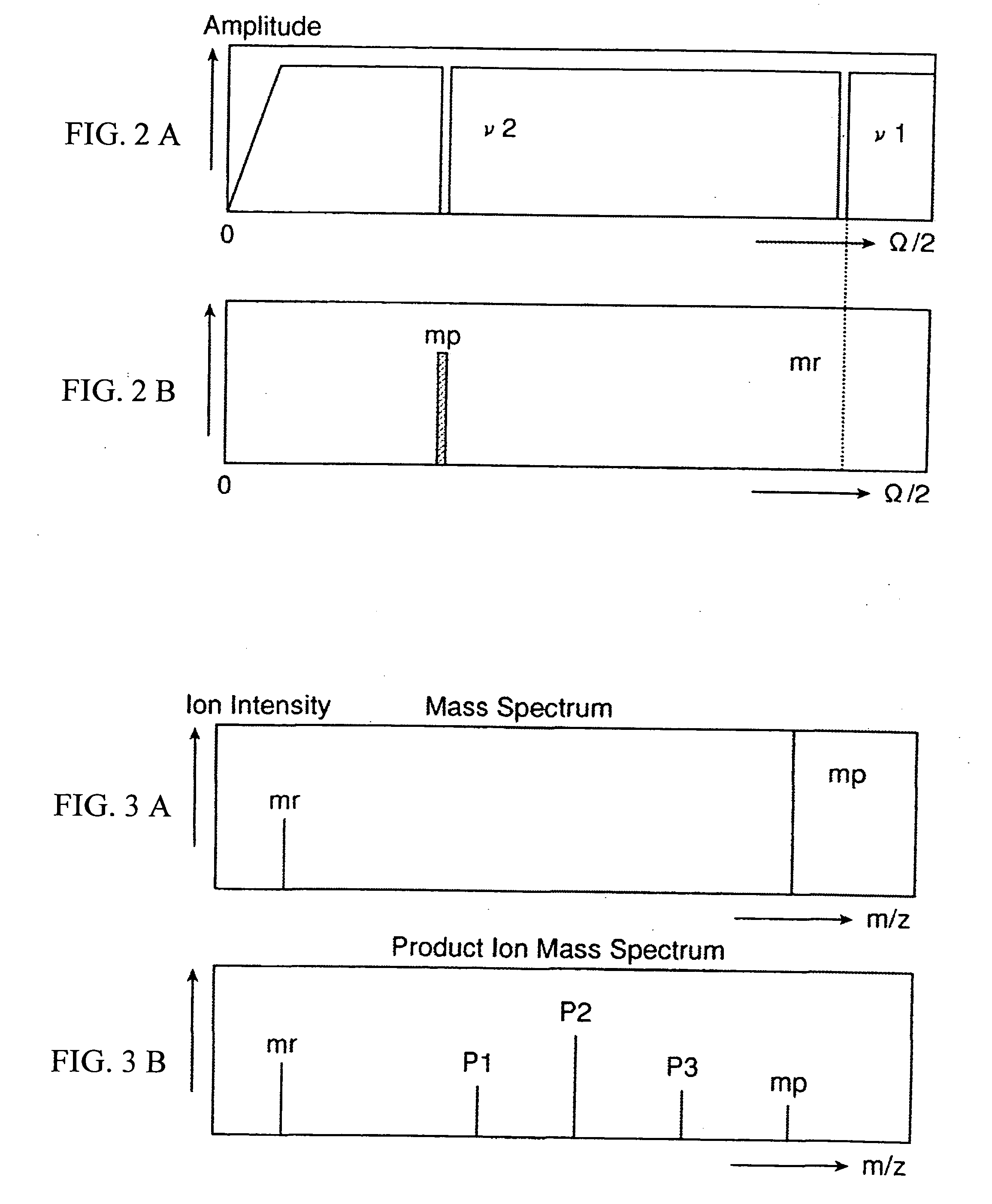
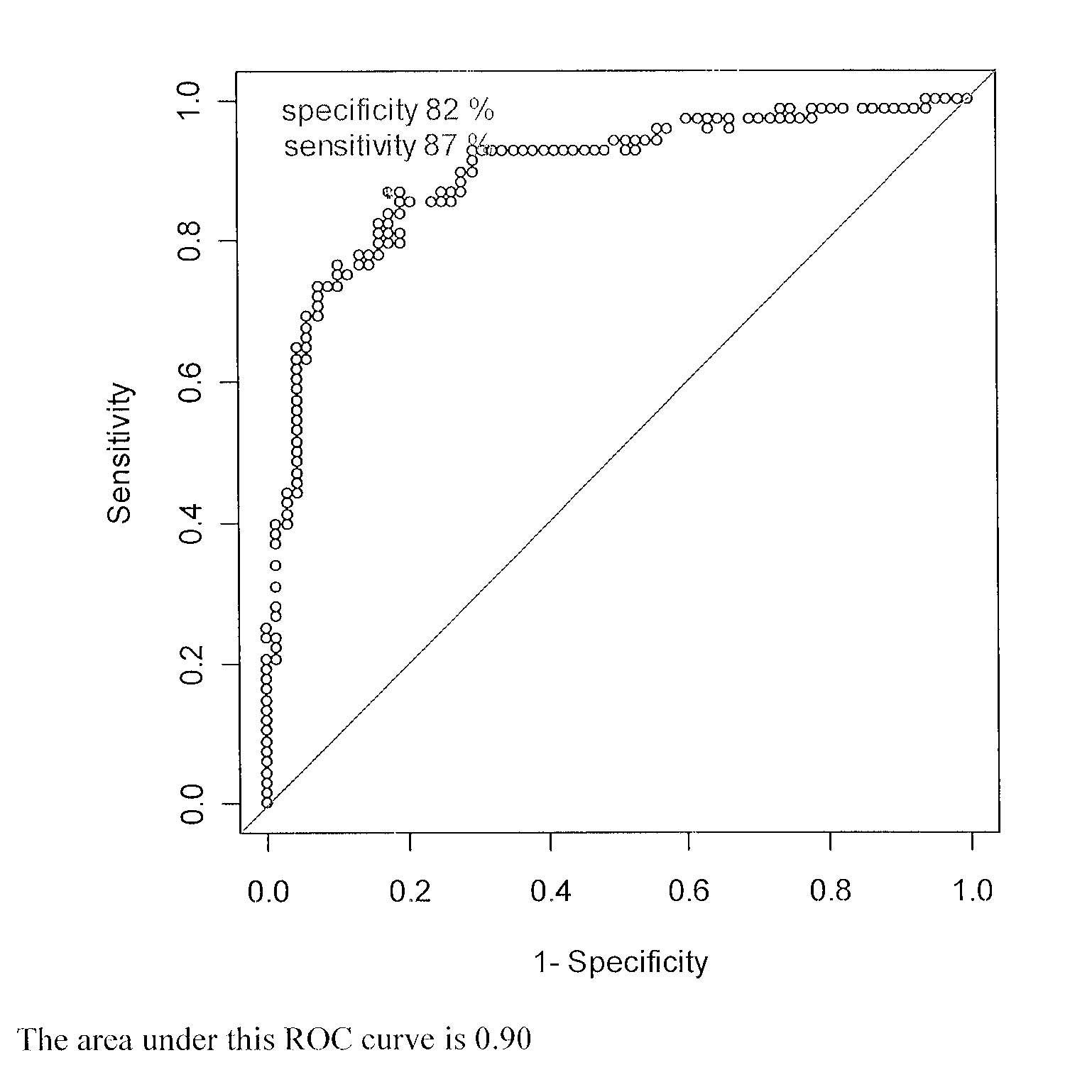
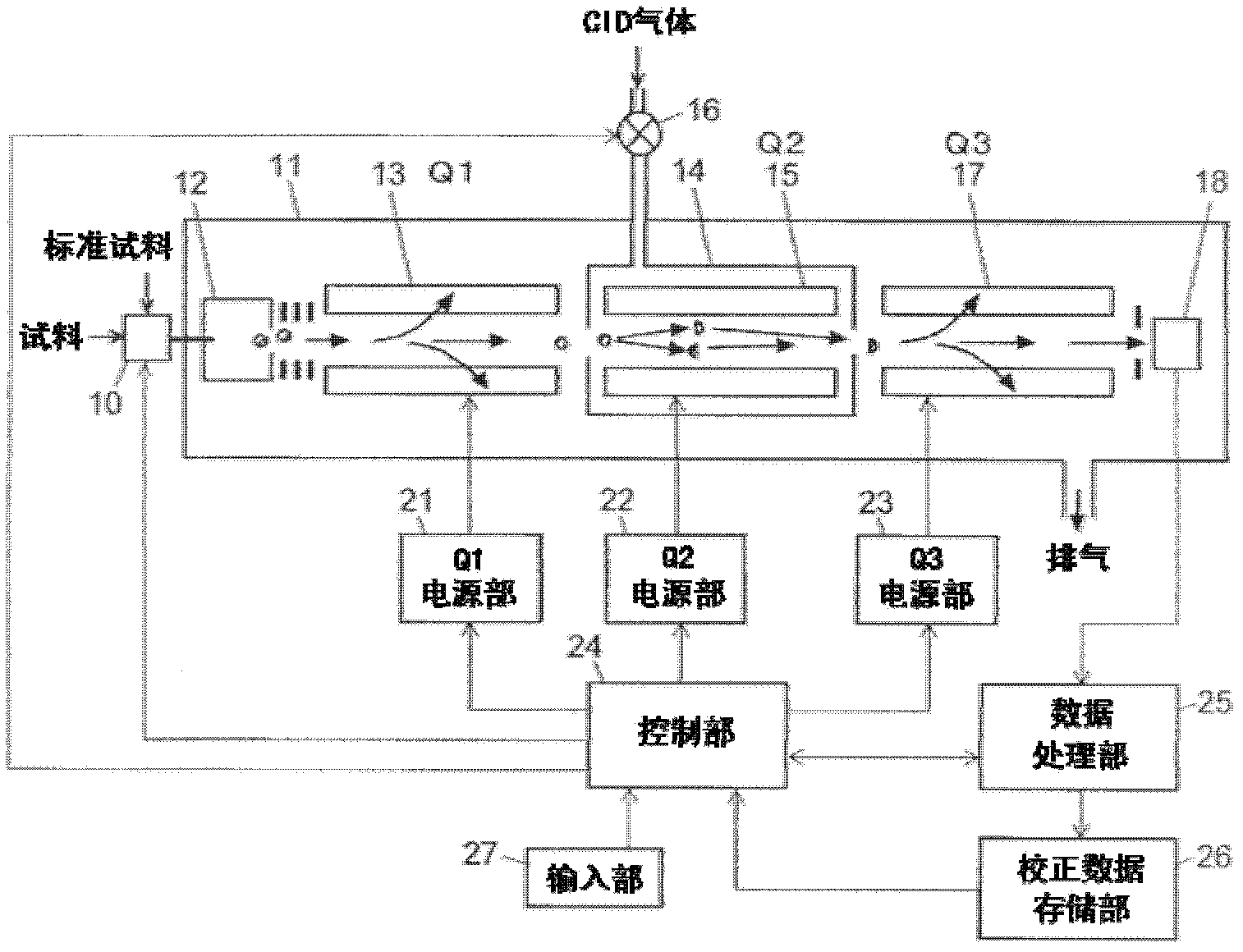
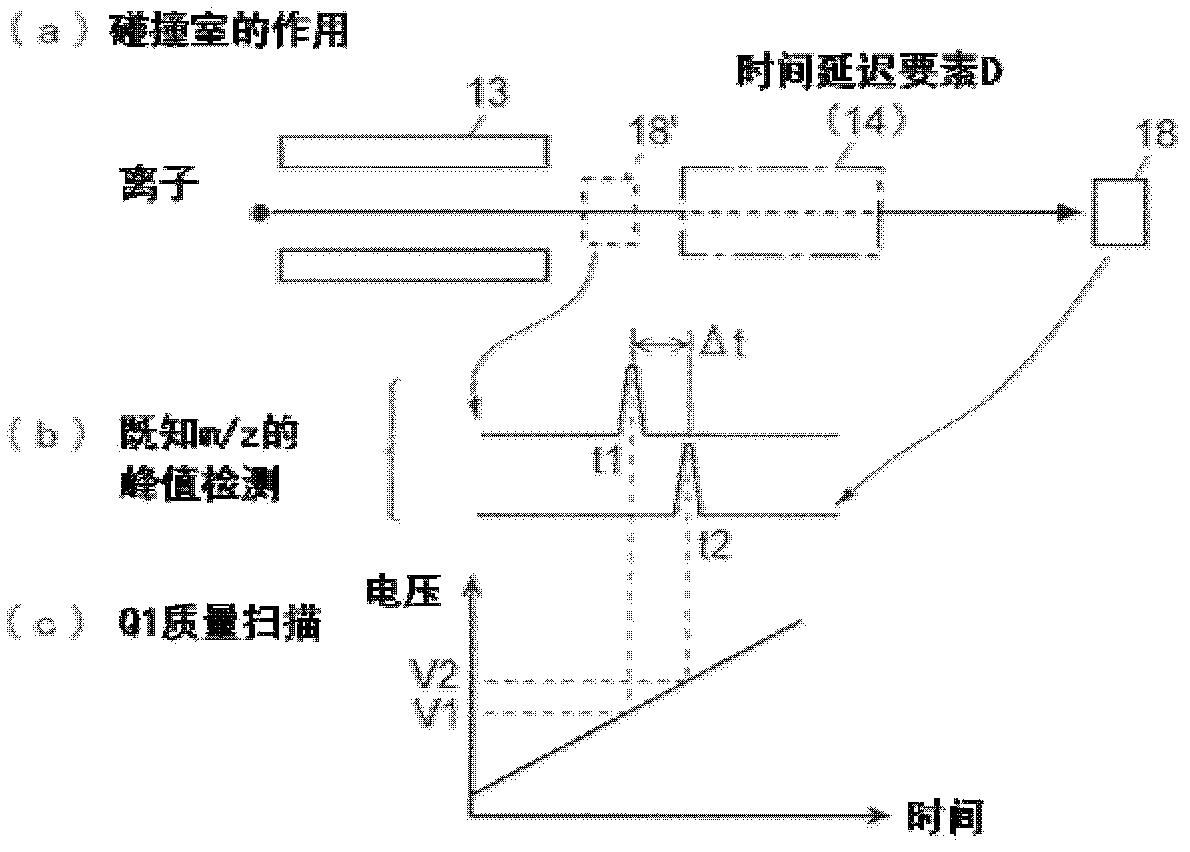
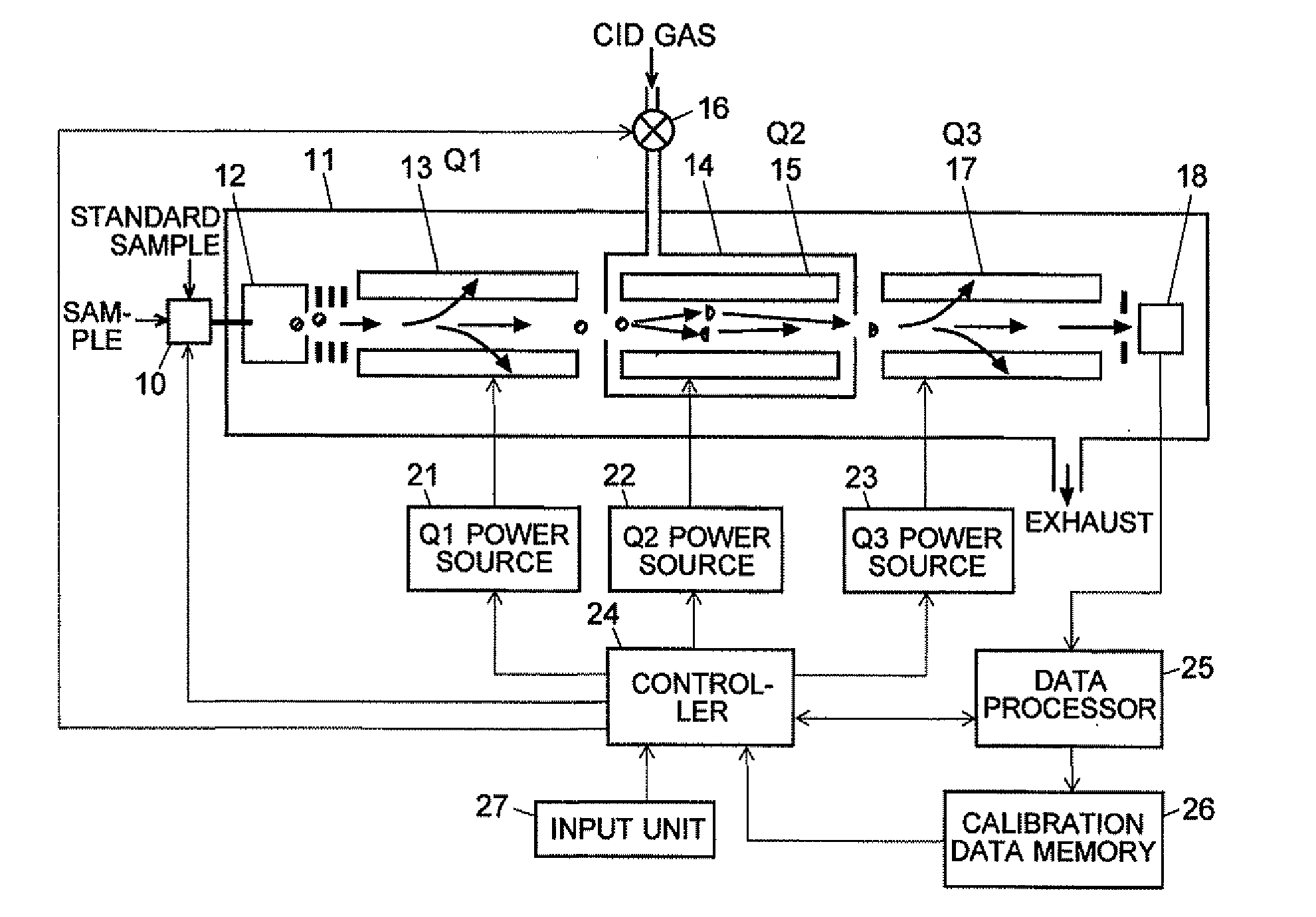
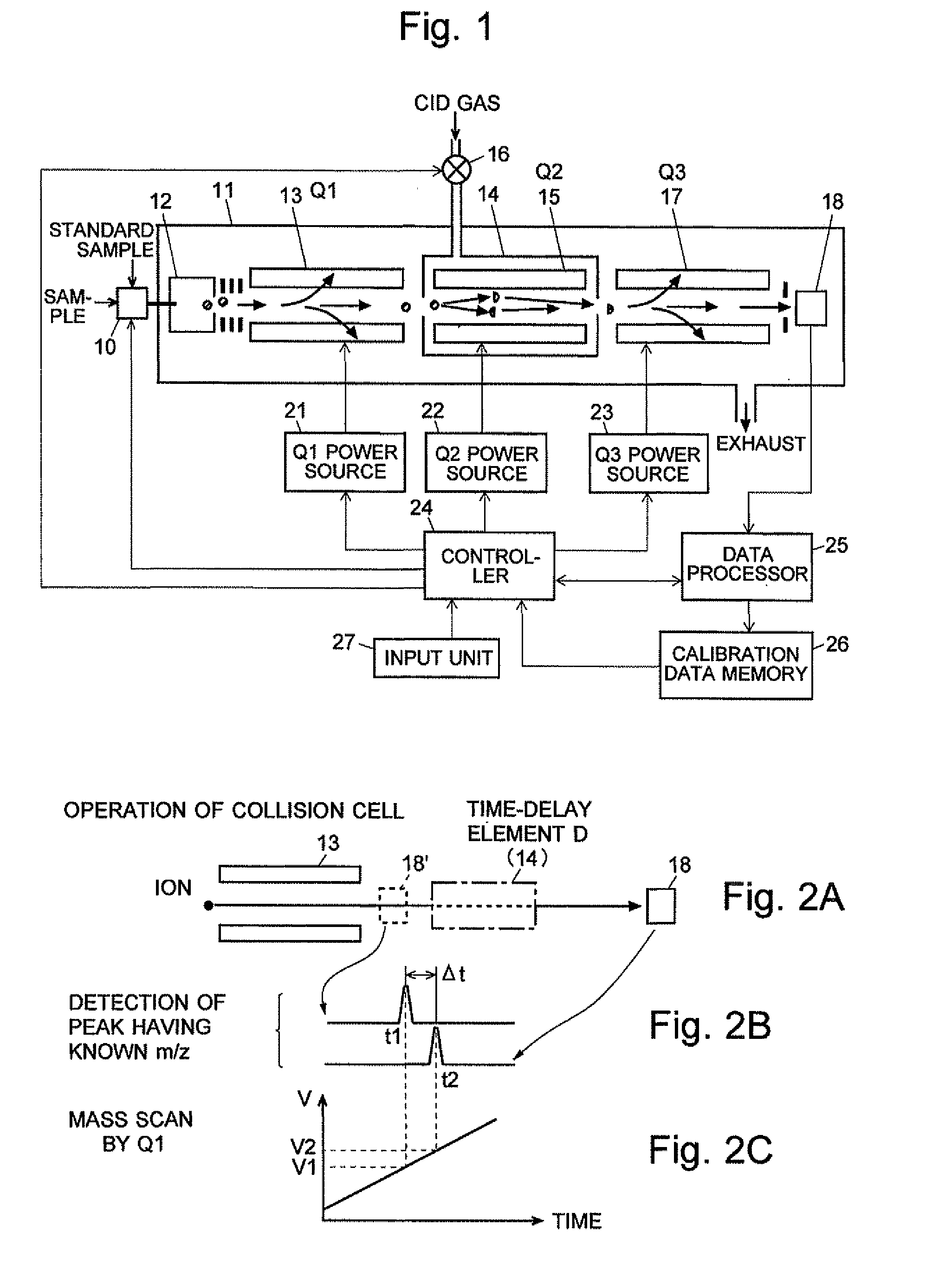
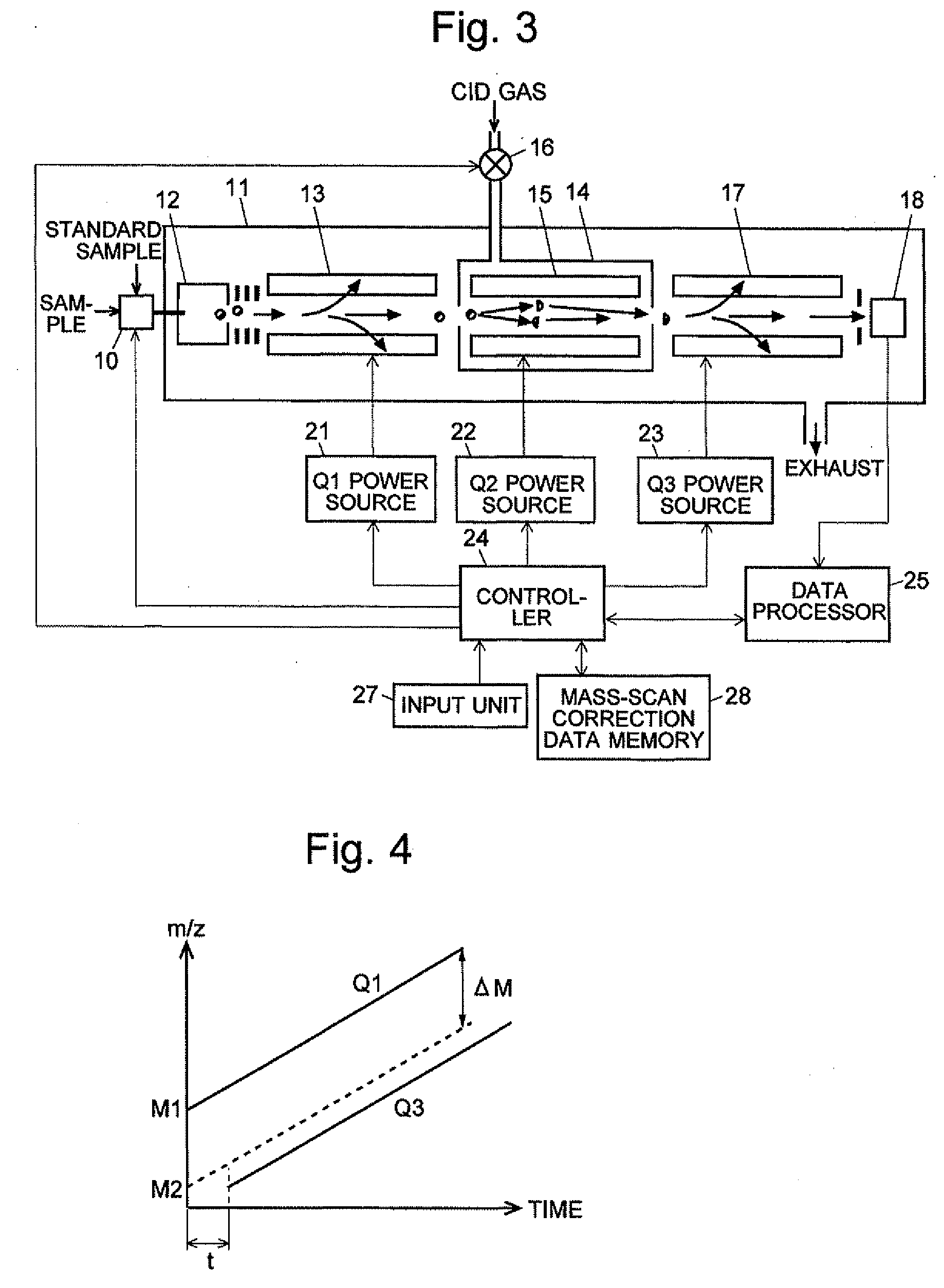
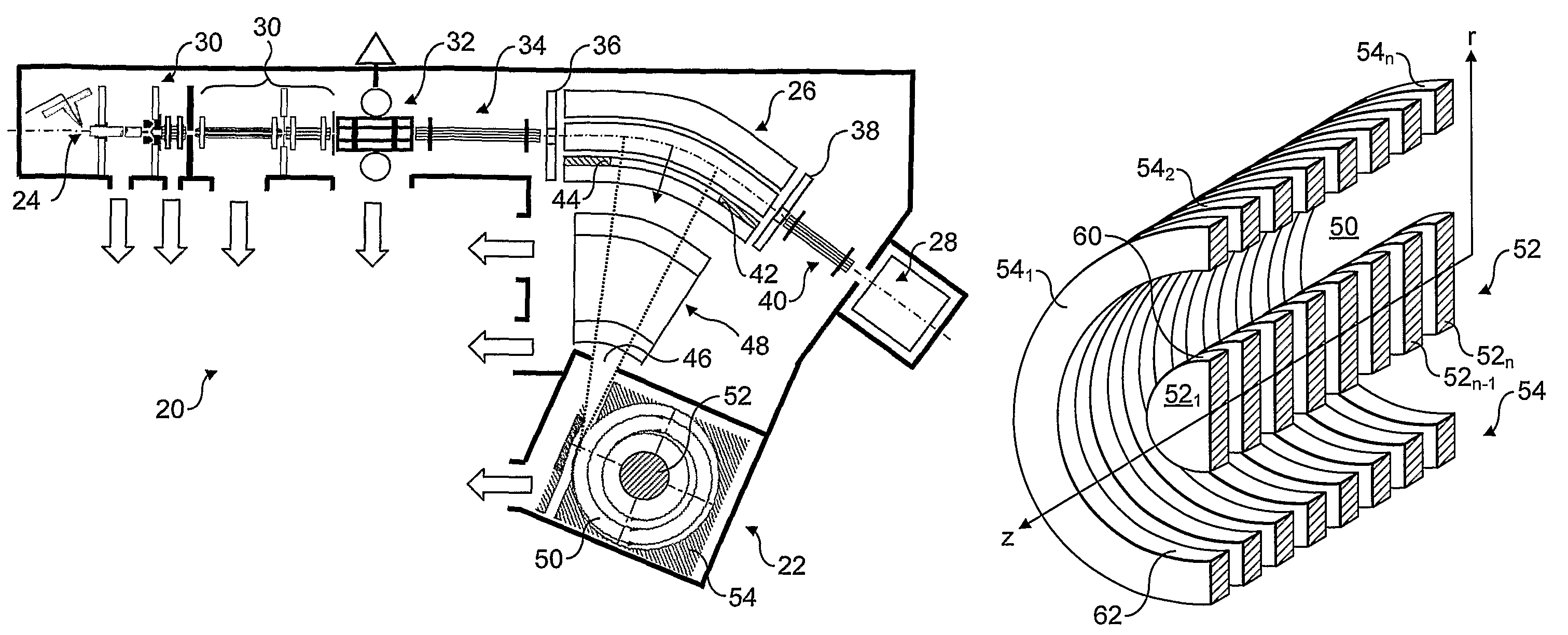
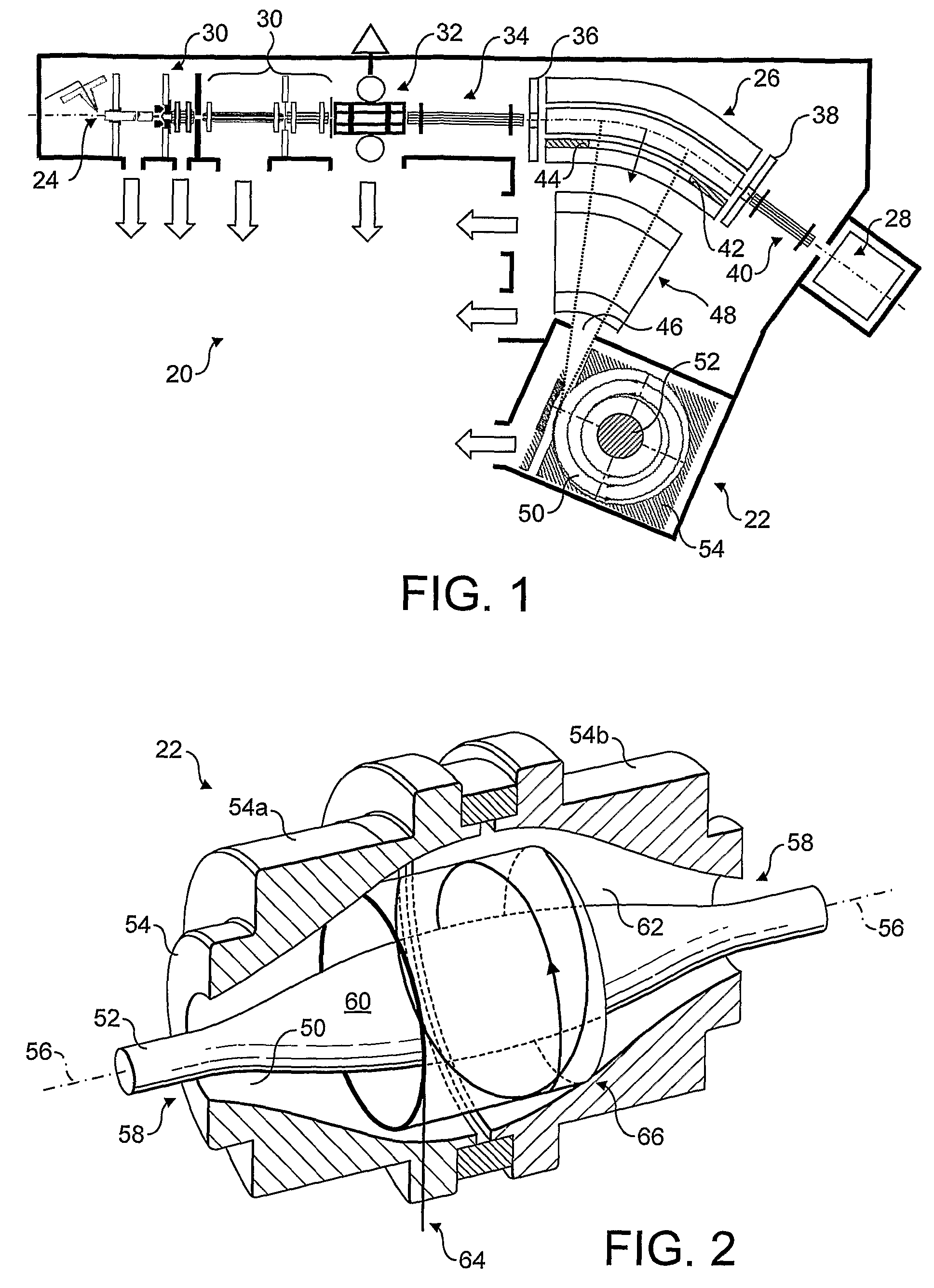
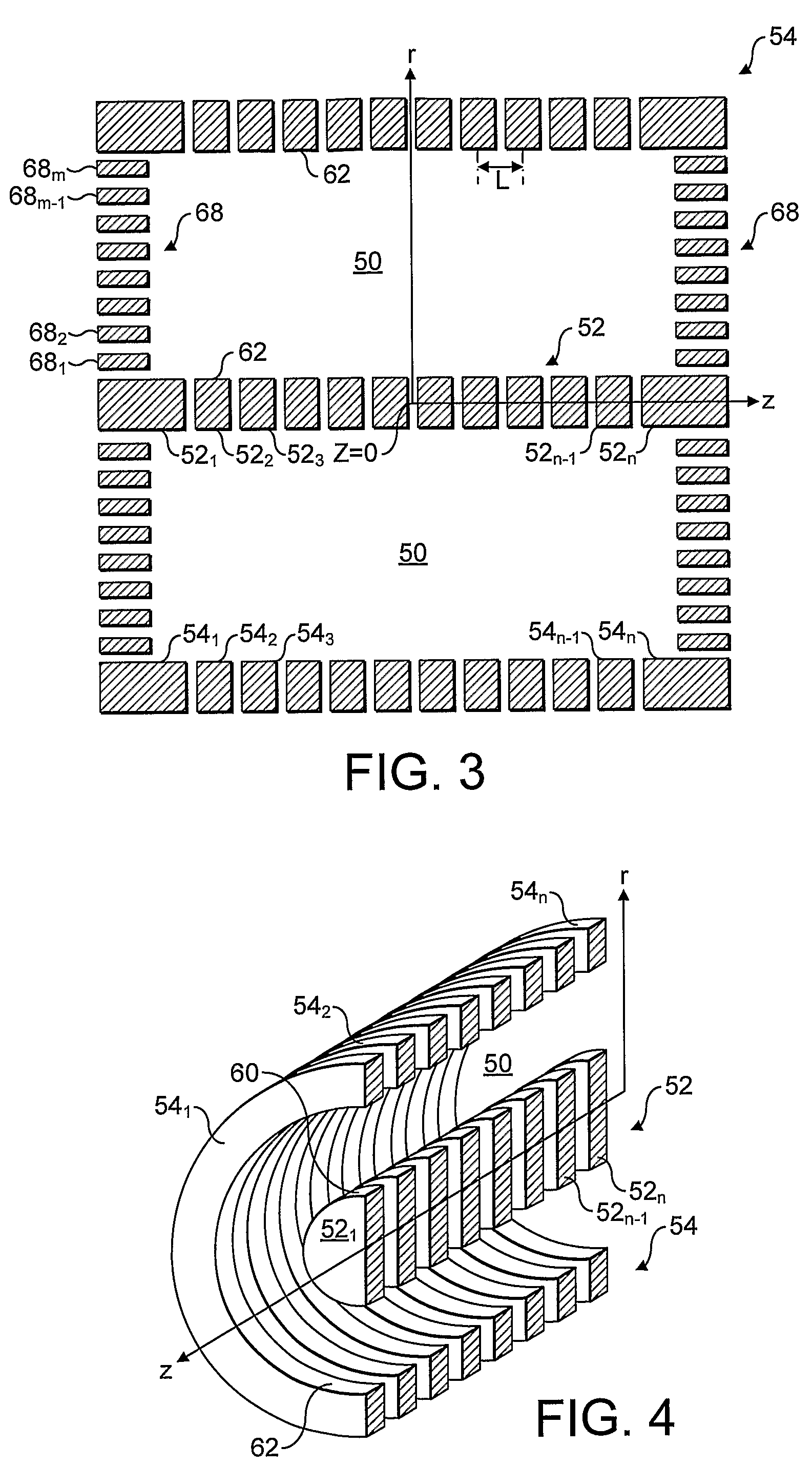
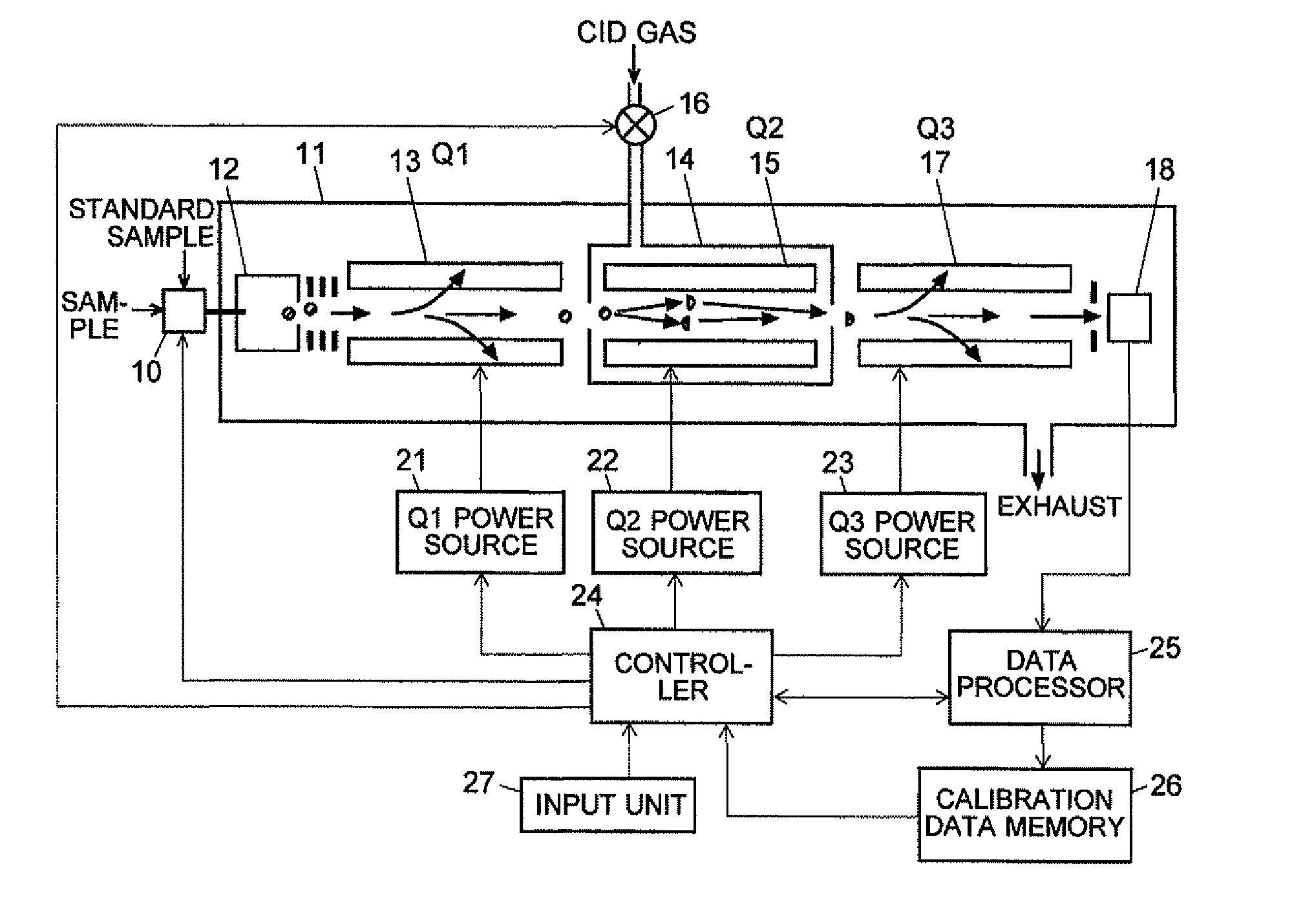
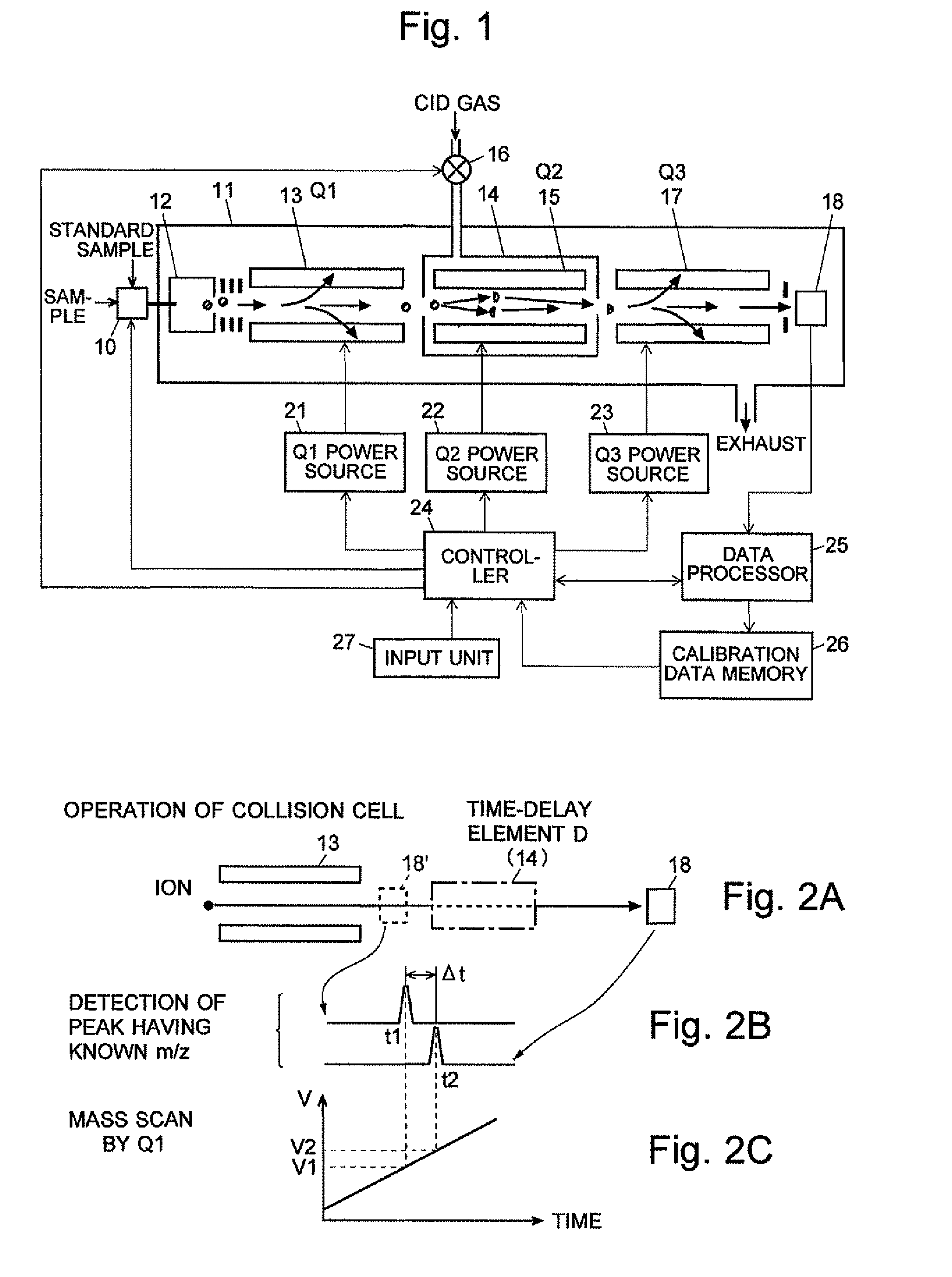
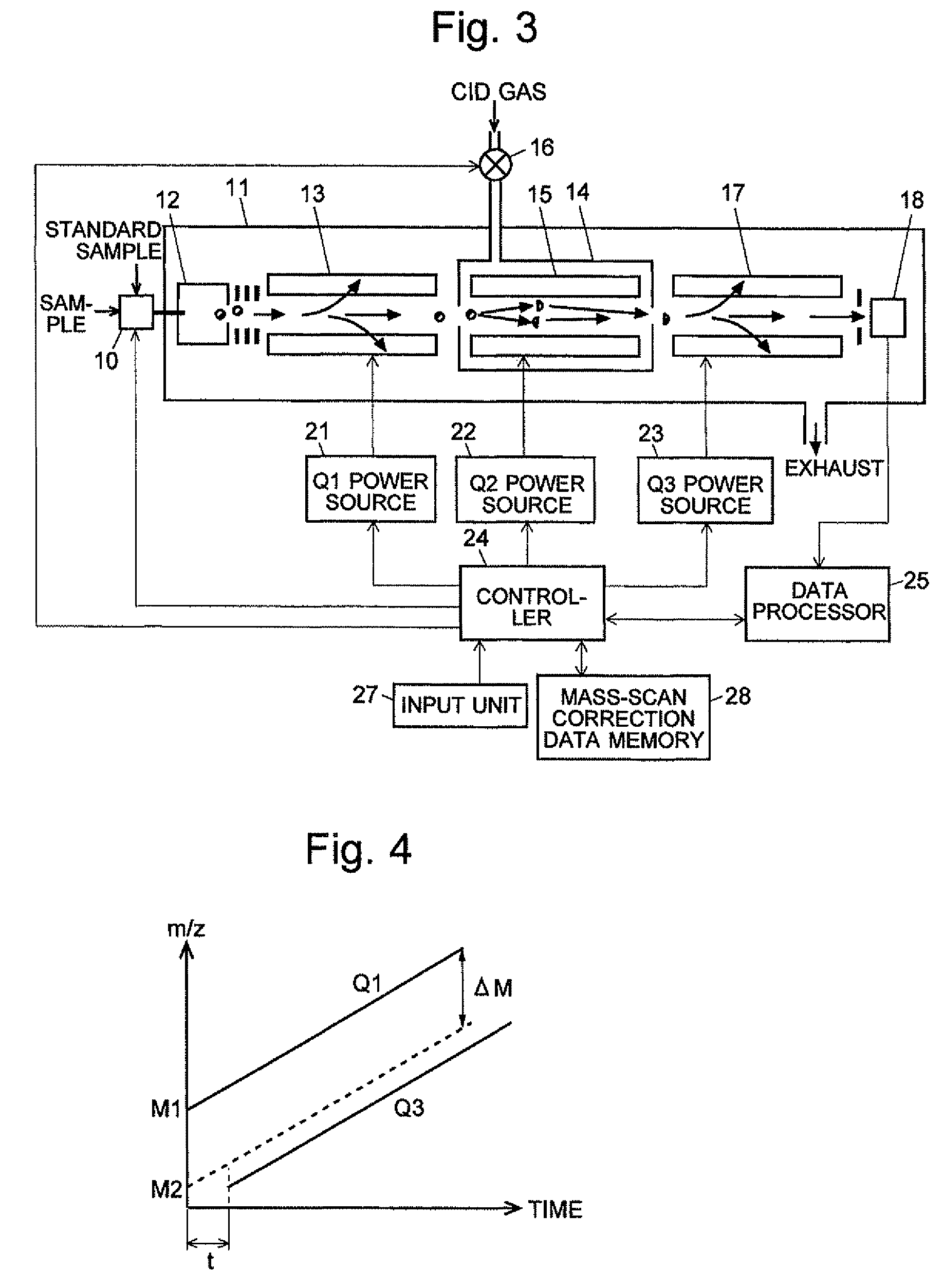
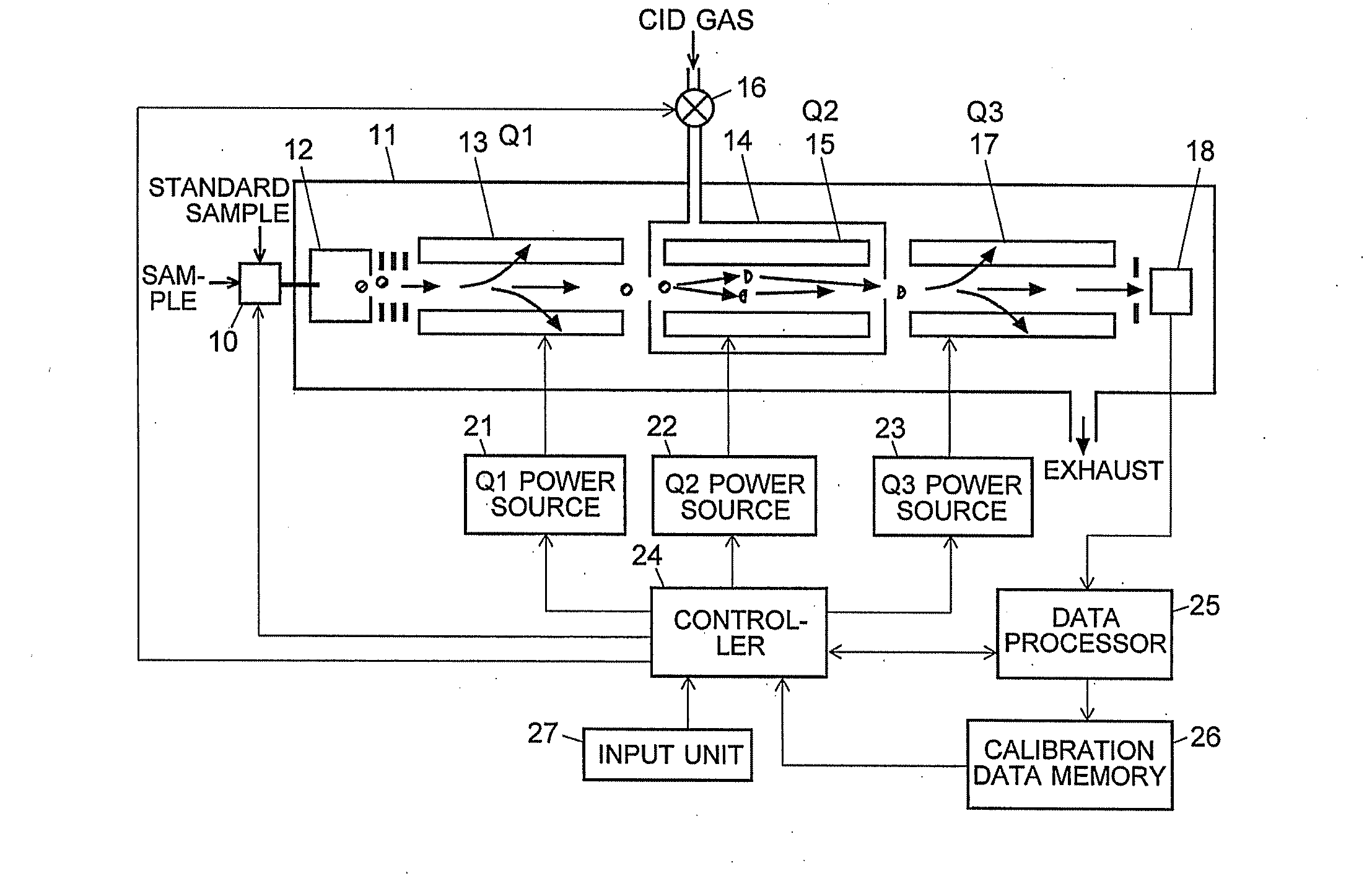
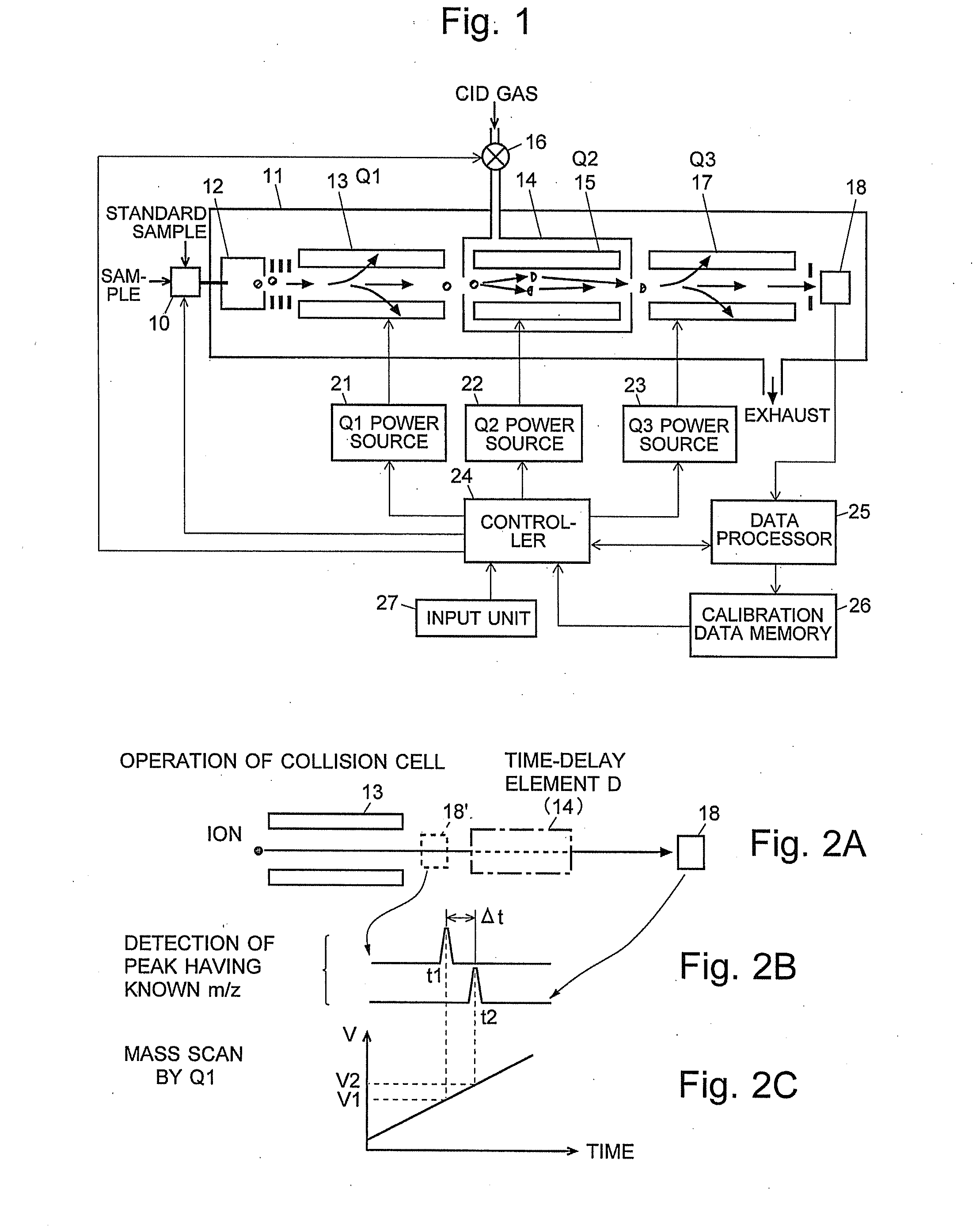
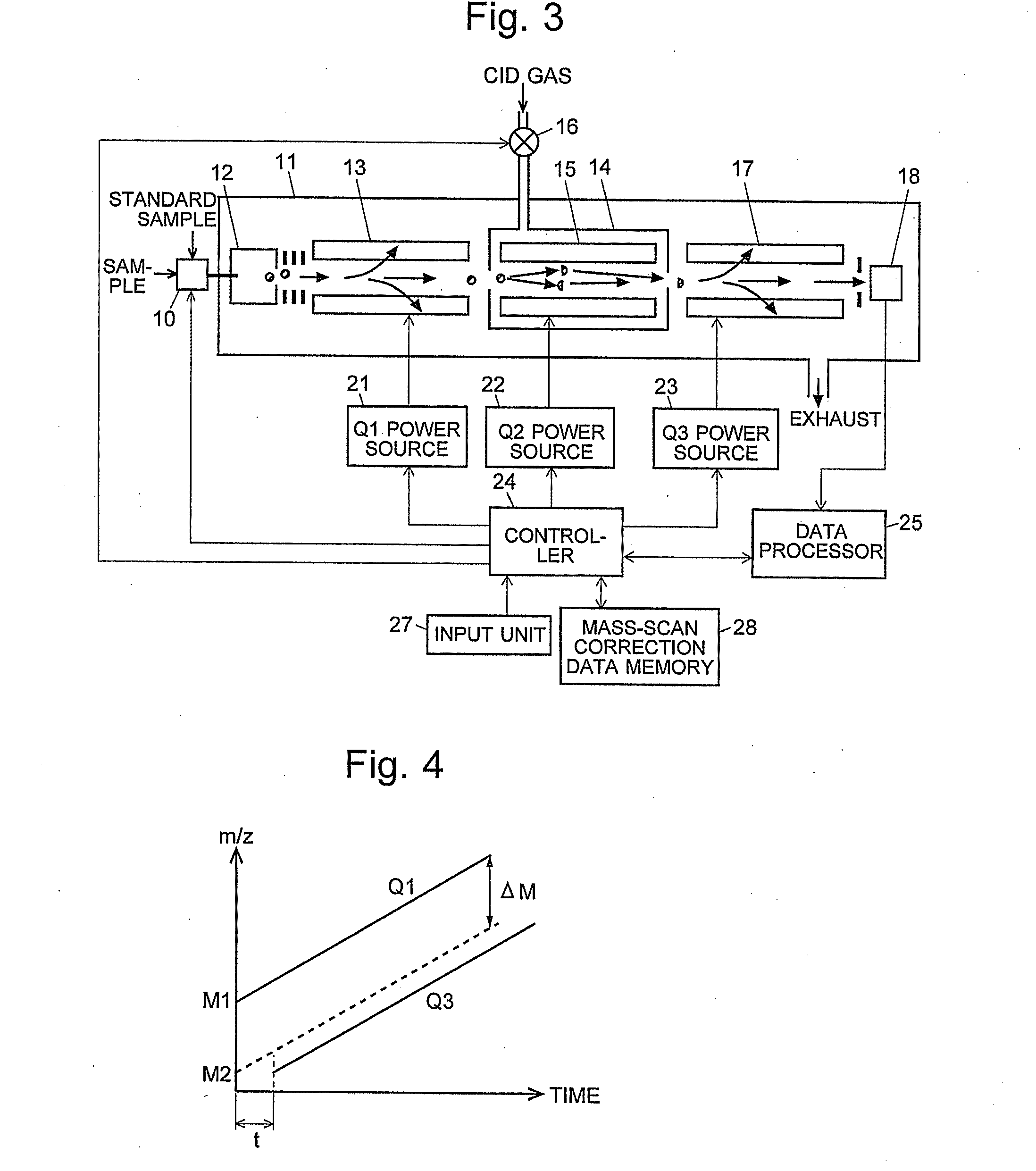
ActiveCN102308361AReduce the effect of time delayHigh detection sensitivityStability-of-path spectrometersParticle spectrometer methodsReference sampleTime delays
A CID gas is introduced into a collision cell (14). An application voltage is set so that mass separation is not substantially effected by a third-stage quadrupole (17). While mass scanning in a predetermined range is effected by a first-stage quadrupole (13), mass spectrometry of a reference sample whose mass / charge ratio is known is effected. Various species of product ions originated from precursor ions selected by the first-stage quadrupole (13) are not separated, reach a detector (18), and are detected. Therefore, a data processing unit (25) acquires the relation between the voltage applied to the first-stage quadrupole (13) and the determined mass / charge ratio of the ions on the basis of the detected data. The relation reflects the time delay at the collision cell and is stored in a calibration data storage unit (26). By using the relation for neutral loss scanning measurement, the mass variation due to the time delay at the collision cell (14) is solved, and product ions over the whole mass range can be detected with high sensitivity. A mass spectrum having a high-accuracy mass axis can be created.
Owner:SHIMADZU SEISAKUSHO LTD
Aspects of mass spectral calibration
InactiveUS7348553B2Improve accuracyHigh resolutionIon-exchange process apparatusTime-of-flight spectrometersElemental compositionSpectral response
A method for calibrating and analyzing data from a mass spectrometer, comprising the steps of acquiring raw profile mode data containing mass spectral responses of ions with or without isotopes; calculating theoretical isotope distributions for each of at least one calibration ion based on elemental composition; convoluting the theoretical isotope distributions with an initial peak shape function to obtain theoretical isotope profiles for each ion; constructing a peak component matrix including the theoretical isotope profiles for calibration ions as peak components; performing a regression analysis between the raw profile mode mass spectral data and the peak component matrix; and reporting the regression coefficients as the relative concentrations for each of the components. A mass spectrometry system operated in accordance with the method and a computer readable medium having program code thereon for performing the method.
Owner:CERNO BIOSCI
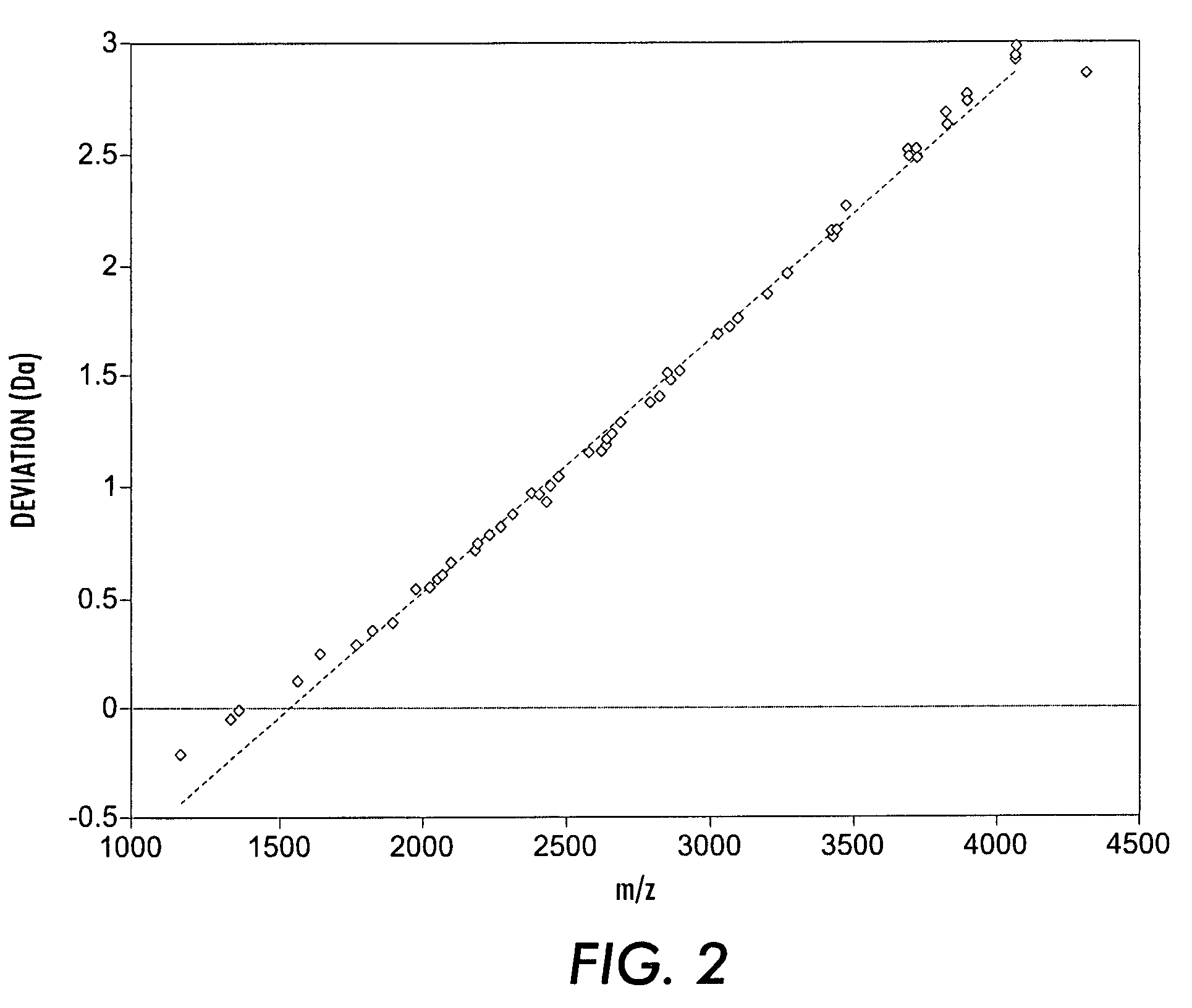
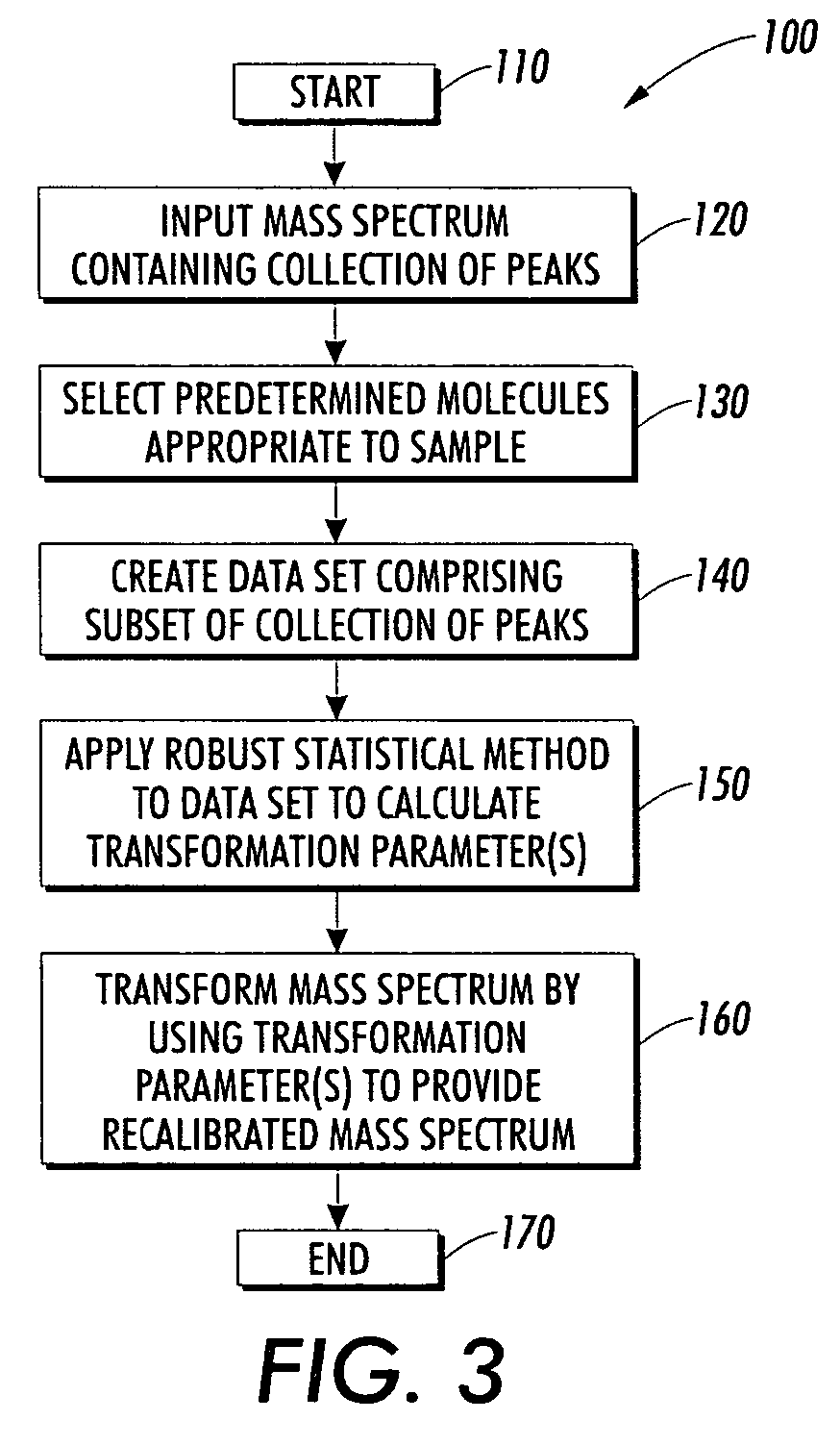
Self-calibration of mass spectra using robust statistical methods
ActiveUS7979258B2High precisionEasy to identifySpectral/fourier analysisSamplingMeasuring instrumentComputational physics
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method Of Improving A Mass Spectrum
InactiveUS20070203652A1Increase valueImprove positionStability-of-path spectrometersOmegatronsMass spectrometricSpectrometer
The present invention provides a method of improving a mass spectrum collected from a mass spectrometer comprising a detector for collecting a mass spectrum from ions stored in or released from an ion trapping volume, wherein assignment of masses to peaks appearing in the mass spectrum is sensitive to an experimental parameter related to the mass spectrometer or the operation thereof, such as ion abundance, the method comprising: determining a positional value of a peak; determining the experimental parameter associated with the mass spectrum; comparing the determined positional value with positional values of peaks contained in a calibration dataset; and improving the determined positional value of the peak from adjacent peak positional values by interpolation thereby to provide a corrected mass assignment for the peak. The present invention also provides a method of calibrating such a mass spectrometer.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Methods for Calibration of Usable Fragmentation Energy in Mass Spectrometry
ActiveUS20110266426A1Isotope separationCalibration apparatusMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass analyzer
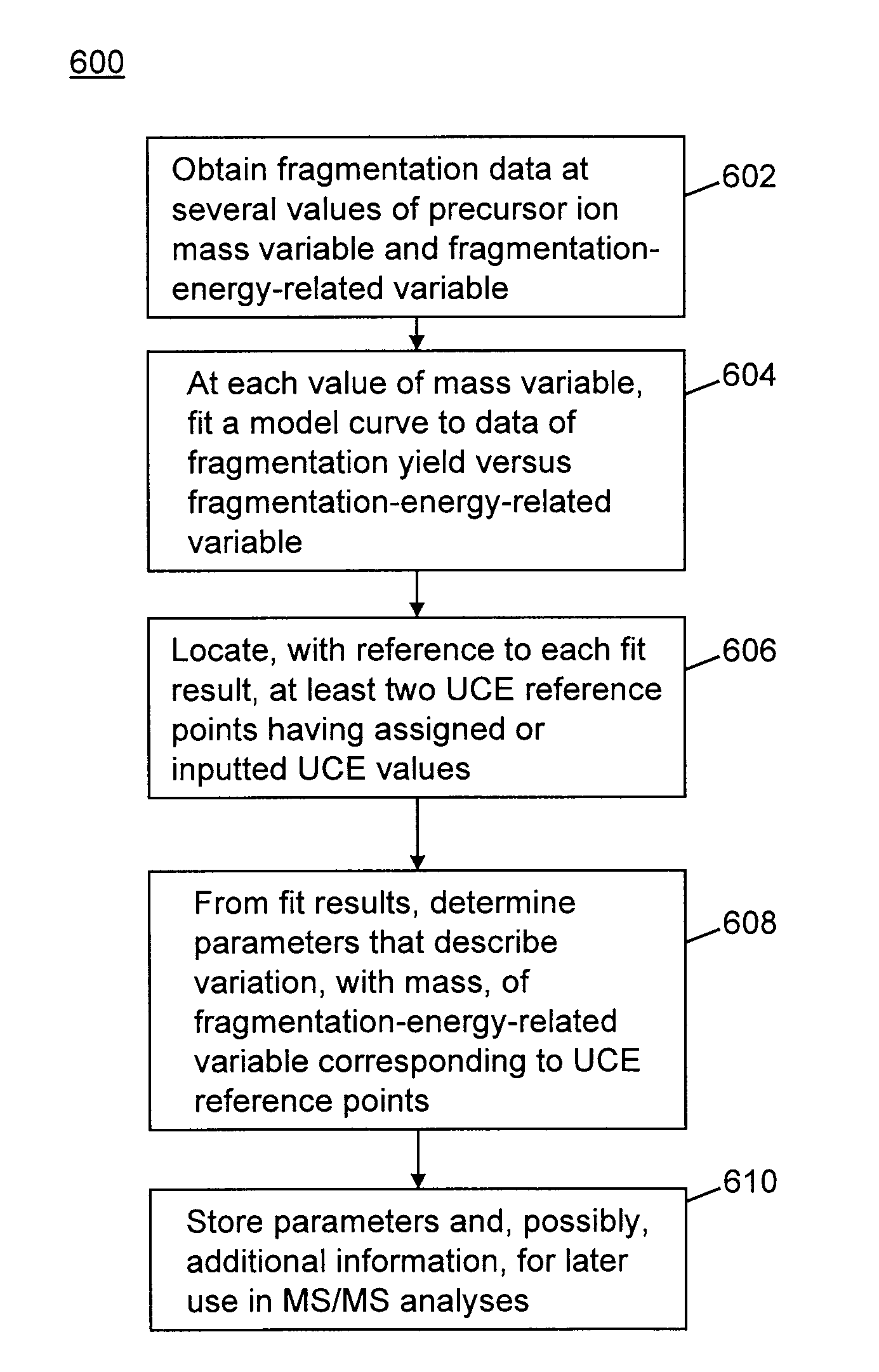
A method of calibrating ion collision energy used in a mass spectrometer, comprises: (a) obtaining fragment ion yield data for each of a plurality of precursor ion populations having respective mass-to-charge ratios at each of a plurality of settings of a fragmentation-energy-related variable; (b) locating, for each mass-to-charge ratio, reference values of the fragmentation-energy-related variable, each reference value corresponding to a respective reference feature of the ion yield data at the mass-to-charge ratio; (c) determining, from the plurality of locating steps, the variation, with mass-to-charge-ratio, of each of the reference values of the fragmentation-energy-related variable; (d) associating each of the reference values of the fragmentation-energy related variable with respective reference values of a dimensionless useable-fragmentation-energy variable; and (e) storing parameters describing the variation of each of the reference values of the fragmentation-energy-related variable with mass-to-charge ratio, wherein the parameters comprise coefficients of at least one non-linear equation.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
MS/MS Mass Spectrometer
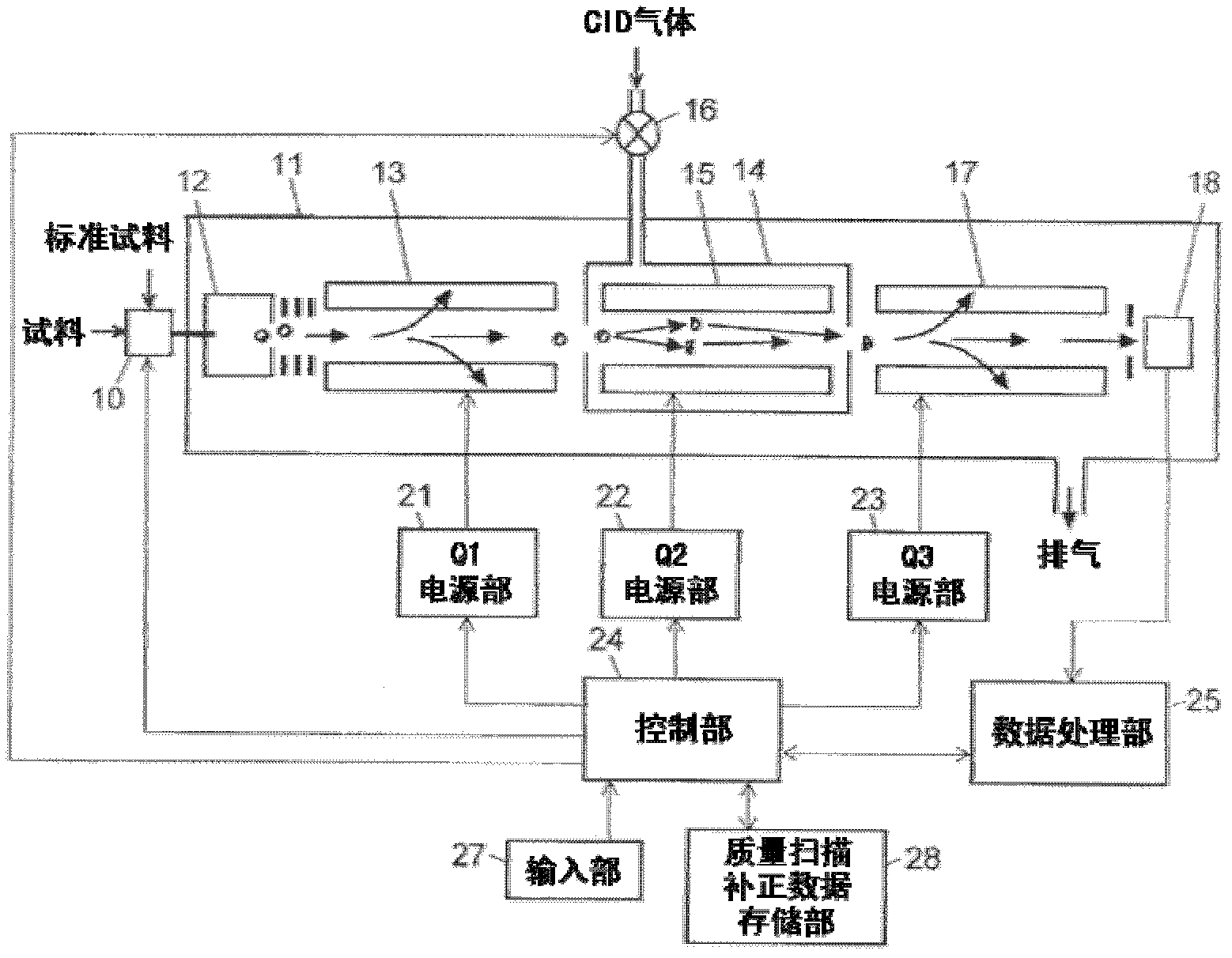
ActiveUS20110284740A1High detection sensitivityIncrease in mass accuracySamples introduction/extractionParticle spectrometer methodsData memoryQuadrupole
A mass analysis of a standard sample having a known mass-to-charge ratio is carried out by performing a mass scan at a first-stage quadrupole (13) over a predetermined mass range, under the condition that a collision induced dissociation (CID) gas is introduced into a collision cell (14) and a voltage applied to a third-stage quadrupole (17) is set so that no substantial mass separation occurs in this quadrupole. Various kinds of product ions originating from a precursor ion selected by the first-stage quadrupole (13) arrive at and are detected by a detector (18) without being mass separated. Accordingly, based on the detection data, a data processor (25) can obtain a relationship between the voltage applied to the first-stage quadrupole (13) and the mass-to-charge ratio of the selected ions, with a time delay in the collision cell (14) reflected in that relationship. This relationship is stored in a calibration data memory (26), to be utilized in a neutral loss scan measurement or the like. By using this relationship, a mass shift due to the time delay in the collision cell (14) can be cancelled, so that the product ions can be detected with high sensitivity over the entire mass range. Furthermore, a mass spectrum having an accurate mass axis can be created.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Method for calibrating mass spectrometers
InactiveUS20020130259A1Improved mass measurement accuracyHigh measurement accuracyCalibration apparatusIsotope separationMass analyzerQuantum electrodynamics
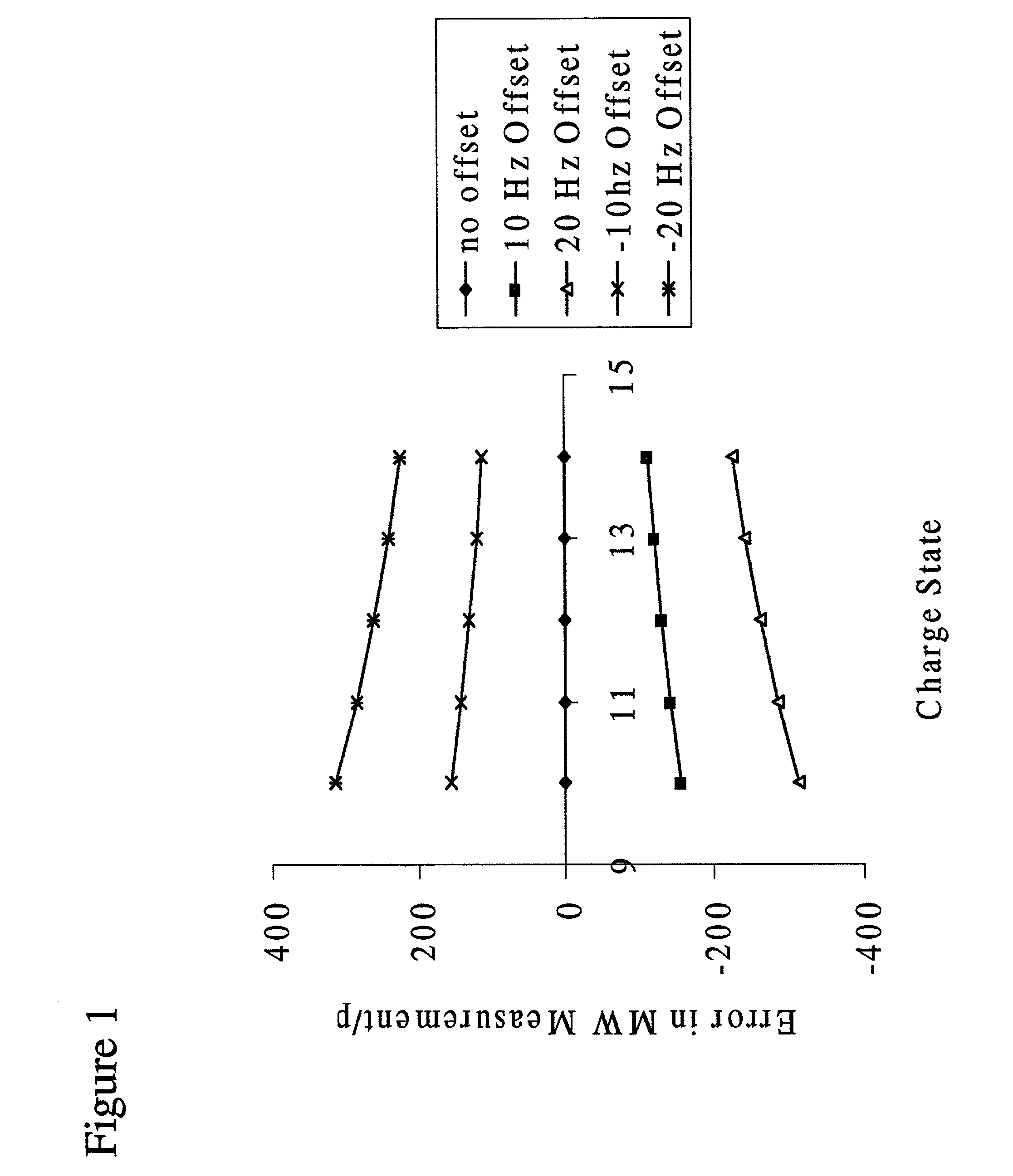
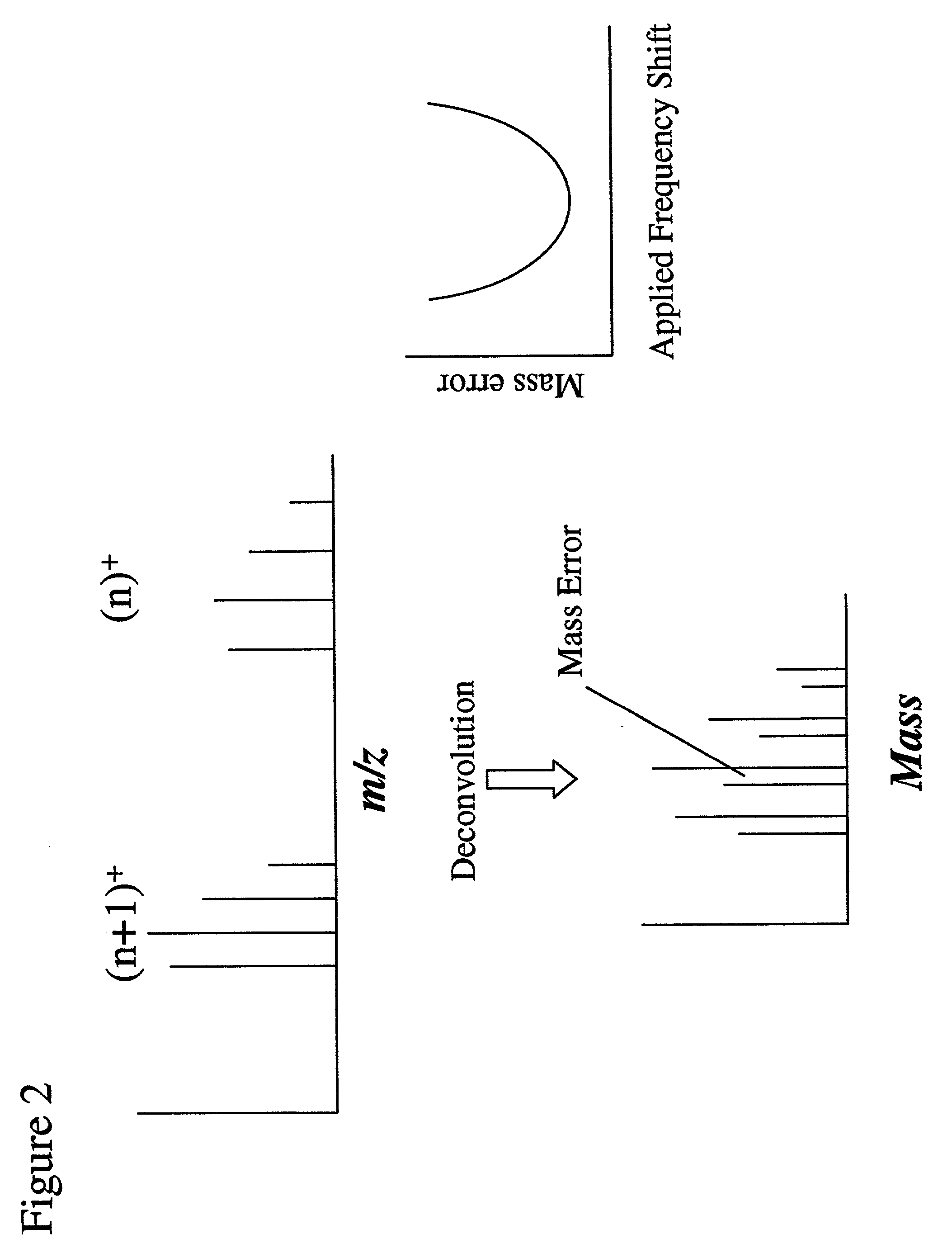
A method whereby a mass spectra generated by a mass spectrometer is calibrated by shifting the parameters used by the spectrometer to assign masses to the spectra in a manner which reconciles the signal of ions within the spectra having equal mass but differing charge states, or by reconciling ions having known differences in mass to relative values consistent with those known differences. In this manner, the mass spectrometer is calibrated without the need for standards while allowing the generation of a highly accurate mass spectra by the instrument.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
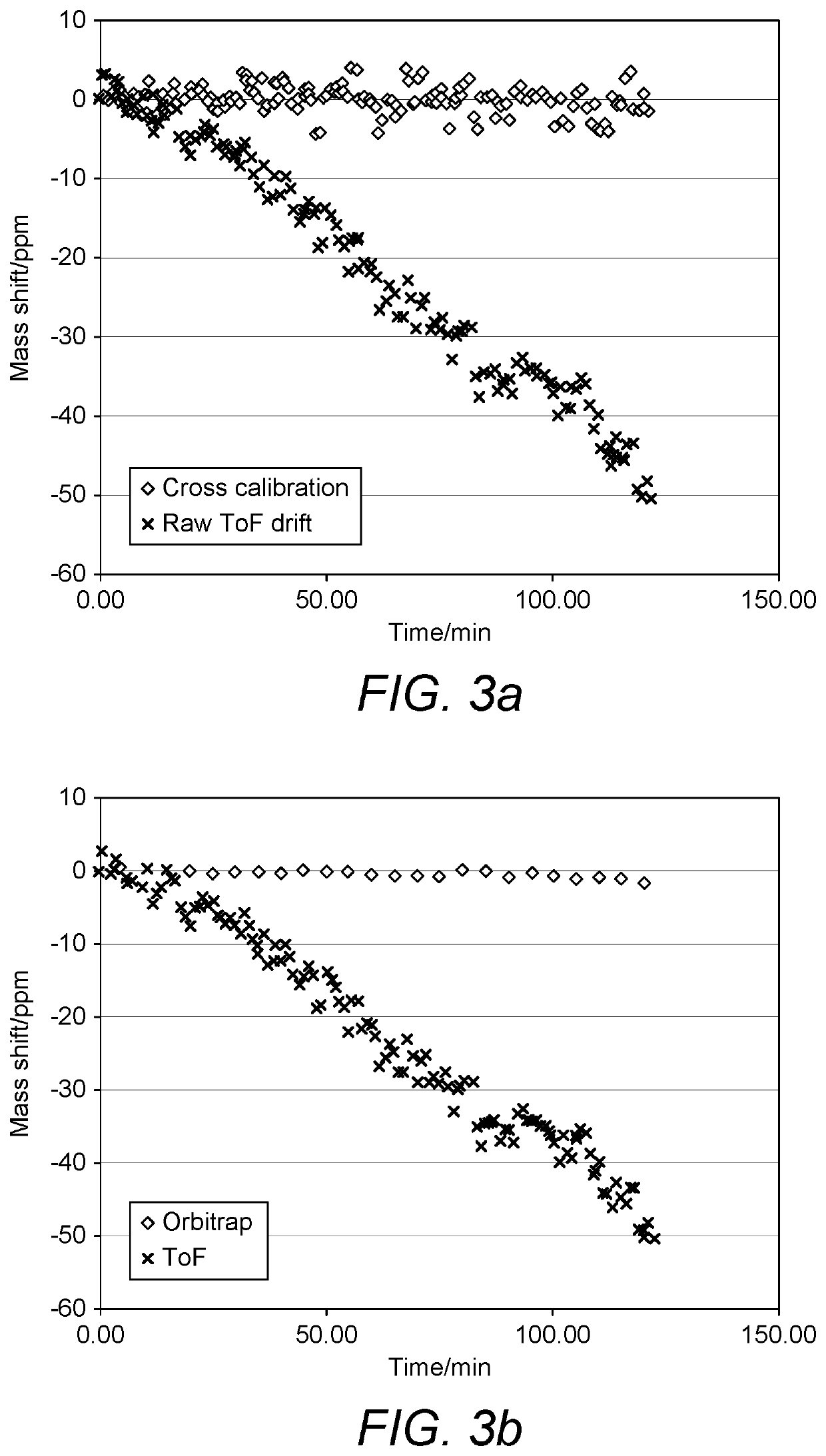
Mass error correction due to thermal drift in a time of flight mass spectrometer
ActiveUS10593525B2Easy CalibrationStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersMass analyzerMass
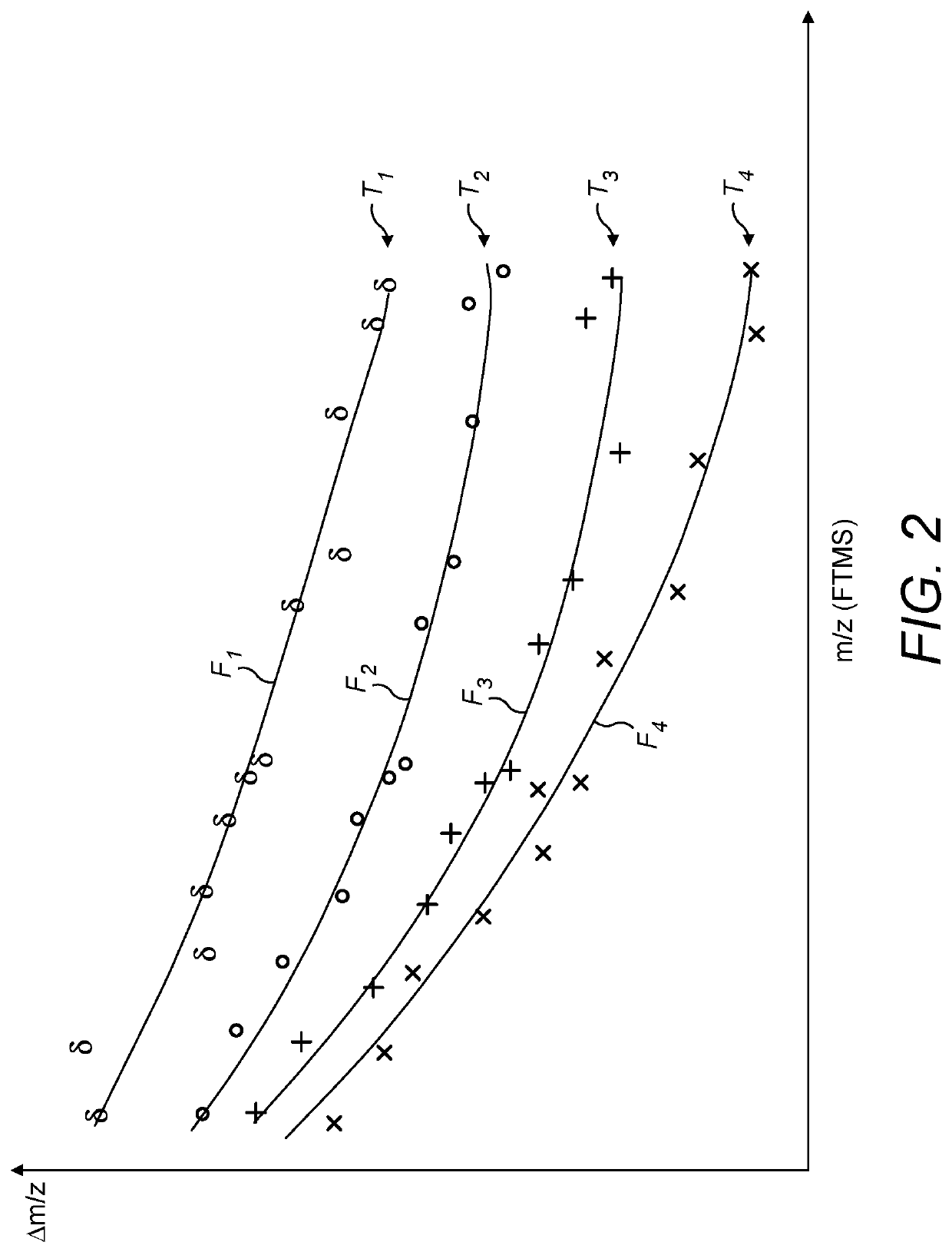
A method of calibrating a TOF-MS mass spectrum, to account for temperature changes, is disclosed. Ions are introduced into a Fourier Transform Mass Spectrometer and their mass to charge ratios are determined. Ions, including calibrant ions, are also introduced into a time of flight mass spectrometer and the mass to charge ratios of the calibrant ions at least are also determined. Specific peaks representative of calibrant ions are selected and matched between the TOF MS and FTMS spectra. The relative position of matched peaks in each spectrum is then used to determine a temperature correction factor for the TOF MS data, based upon the relative independence of the FTMS spectrum with respect to temperature.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
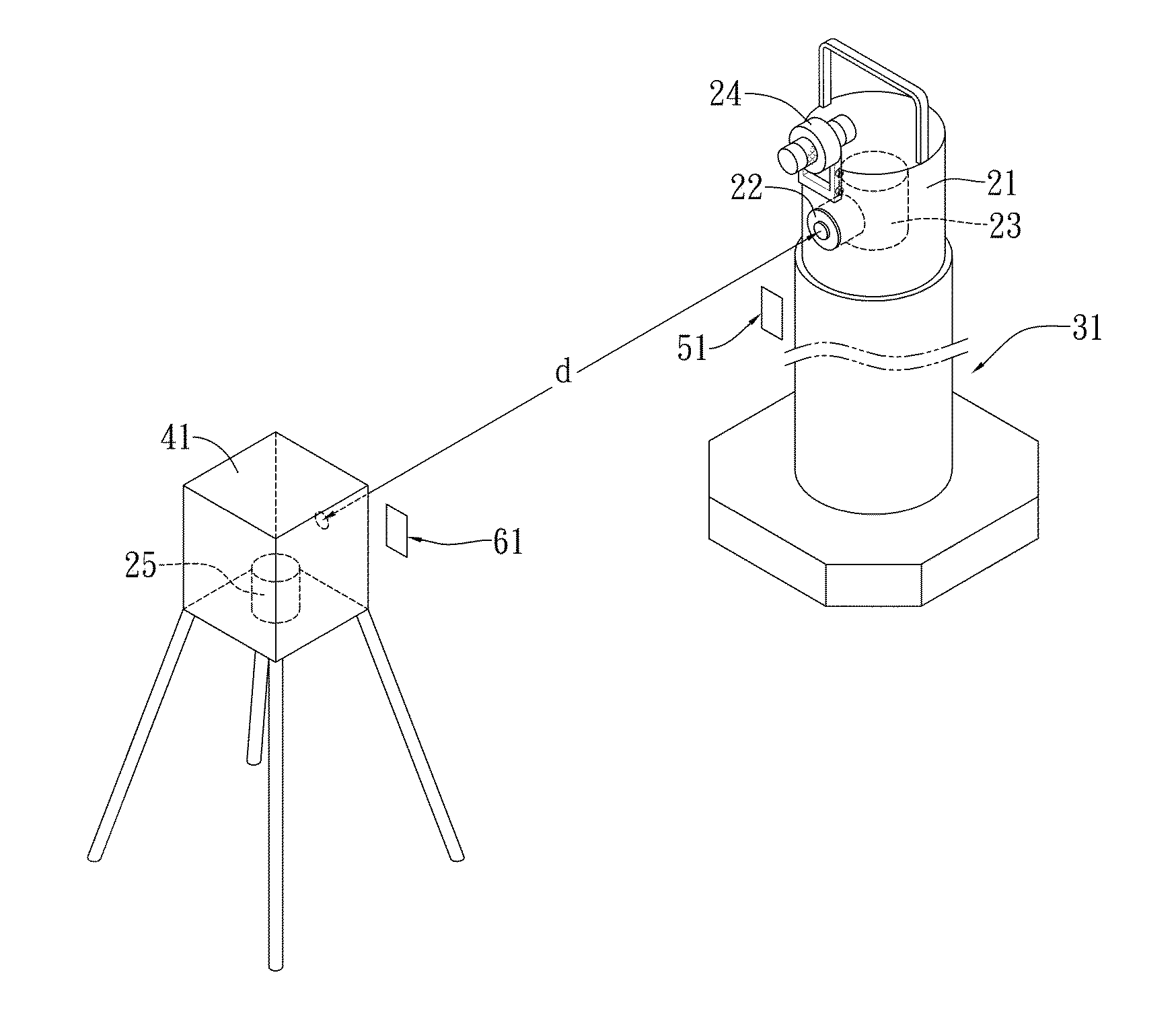
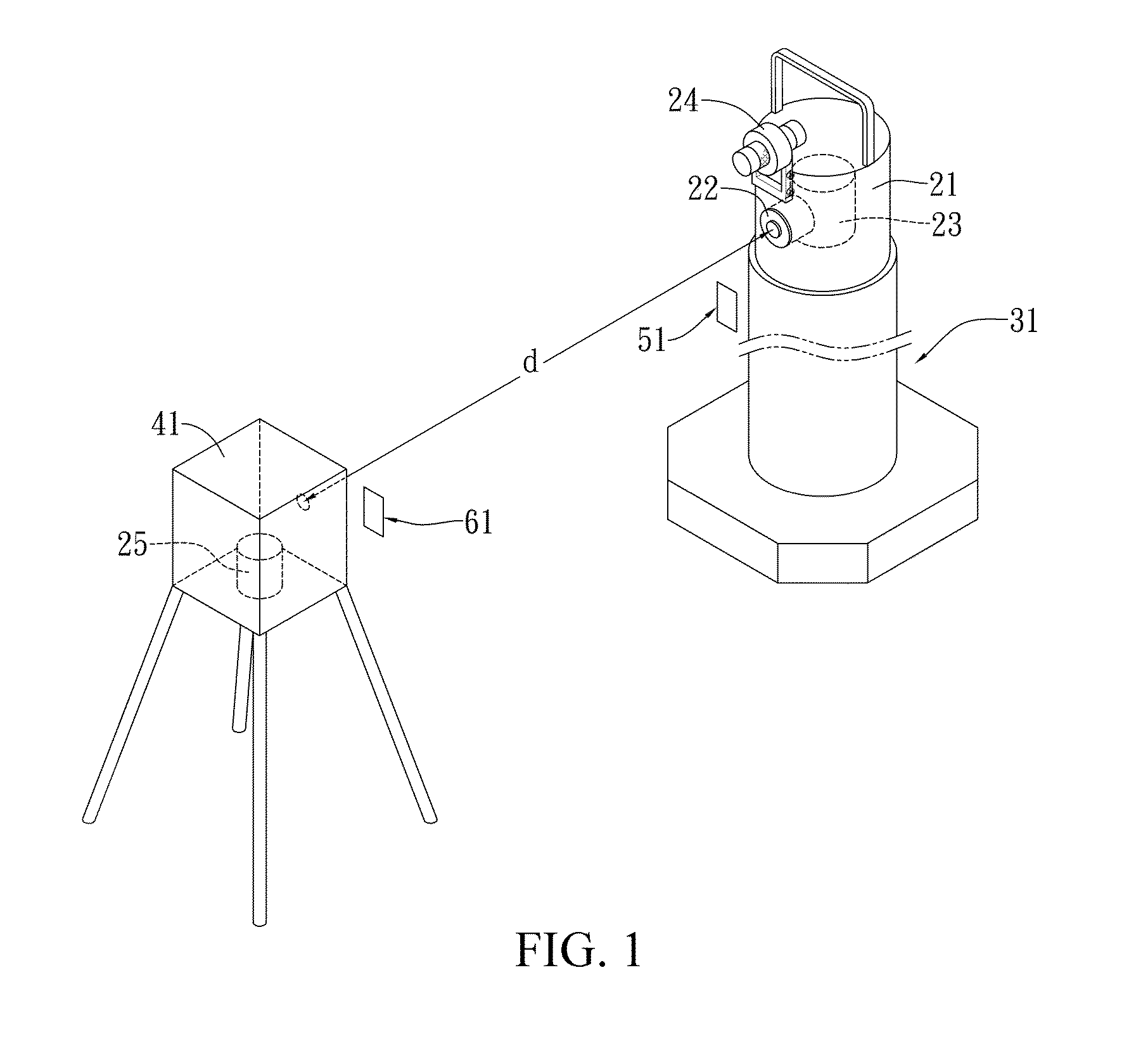
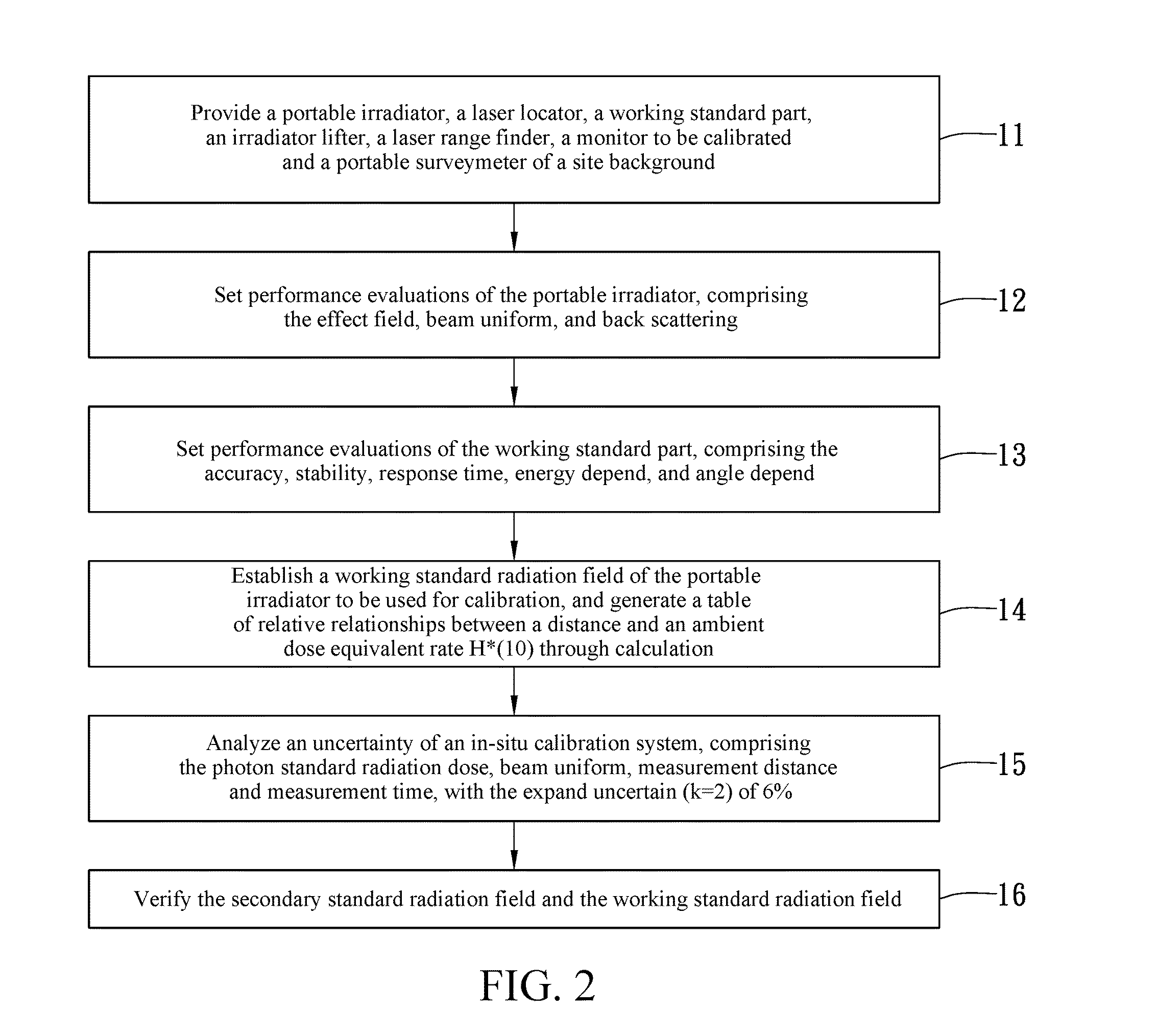
In-situ calibration system and method for radiation monitors
InactiveUS20140042309A1High measurement accuracyMaintain accuracy and reliabilityDosimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansNuclear powerIn situ calibration
By using a scintillation surveymeter with good calibration performance evaluation for a secondary standard radiation field, and a working standard part obtaining an ambient dose equivalent rate, in cooperation with a portable irradiator, and an irradiator lifter, a laser range finder and a laser locator of a relevant radiation source, in-situ calibration is capable of being performed on fixed, or large-scale, or continuous monitoring type radiation monitors to be calibrated stationed in nuclear power plants, nuclear medical departments, and other nuclear facility operating institutions. Moreover, a time-efficient and effective in-situ calibration method is further provided, which can be performed based upon a standard calibration field that is achieved using a portable 137Cs radiation source. The in-situ calibration method is capable of saving the trouble of delivering large-scale monitors, or monitors difficult to move, or monitors requiring continuous monitoring to calibration laboratories for scheduled calibration.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Multi-electrode ion trap
ActiveUS7767960B2Better trapping fieldSpreadStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryTrapping
This invention relates generally to multi-reflection electrostatic systems, and more particularly to improvements in and relating to the Orbitrap electrostatic ion trap. A method of operating an electrostatic ion trapping device having an array of electrodes operable to mimic a single electrode is proposed, the method comprising determining three or more different voltages that, when applied to respective electrodes of the plurality of electrodes, generate an electrostatic trapping field that approximates the field that would be generated by applying a voltage to the single electrode, and applying the three or more so determined voltages to the respective electrodes. Further improvements lie in measuring a plurality of features from peaks with different intensities from one or more collected mass spectra to derive characteristics, and using the measured characteristics to improve the voltages to be applied to the plurality of electrodes.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
MS/MS mass spectrometer
ActiveUS8269166B2Reduce impactHigh detection sensitivityStability-of-path spectrometersParticle spectrometer methodsTime delaysData memory
A mass analysis of a standard sample having a known mass-to-charge ratio is carried out by performing a mass scan at a first-stage quadrupole (13) over a predetermined mass range, under the condition that a collision induced dissociation (CID) gas is introduced into a collision cell (14) and a voltage applied to a third-stage quadrupole (17) is set so that no substantial mass separation occurs in this quadrupole. Various kinds of product ions originating from a precursor ion selected by the first-stage quadrupole (13) arrive at and are detected by a detector (18) without being mass separated. Accordingly, based on the detection data, a data processor (25) can obtain a relationship between the voltage applied to the first-stage quadrupole (13) and the mass-to-charge ratio of the selected ions, with a time delay in the collision cell (14) reflected in that relationship. This relationship is stored in a calibration data memory (26), to be utilized in a neutral loss scan measurement or the like. By using this relationship, a mass shift due to the time delay in the collision cell (14) can be cancelled, so that the product ions can be detected with high sensitivity over the entire mass range. Furthermore, a mass spectrum having an accurate mass axis can be created.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
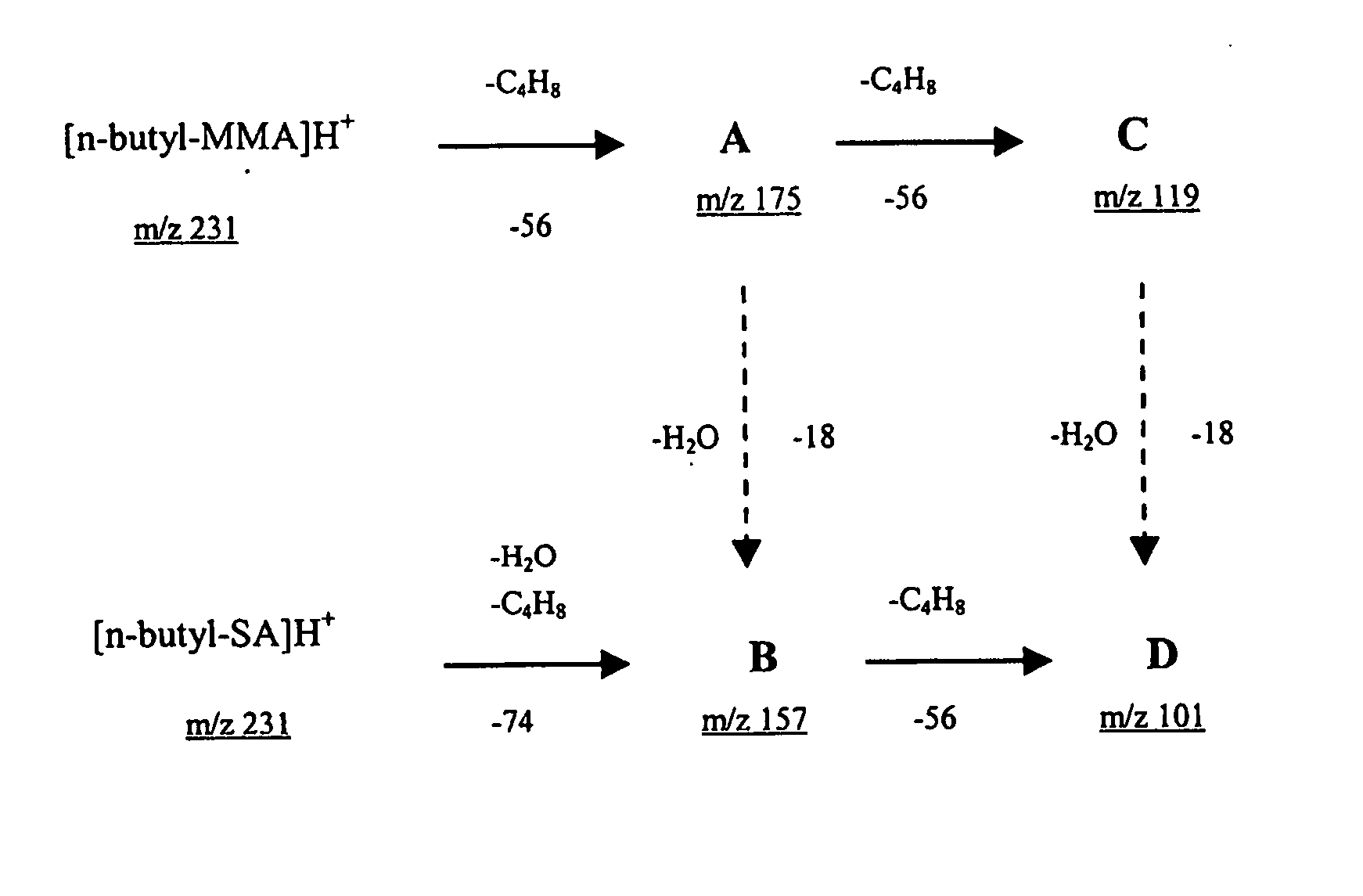
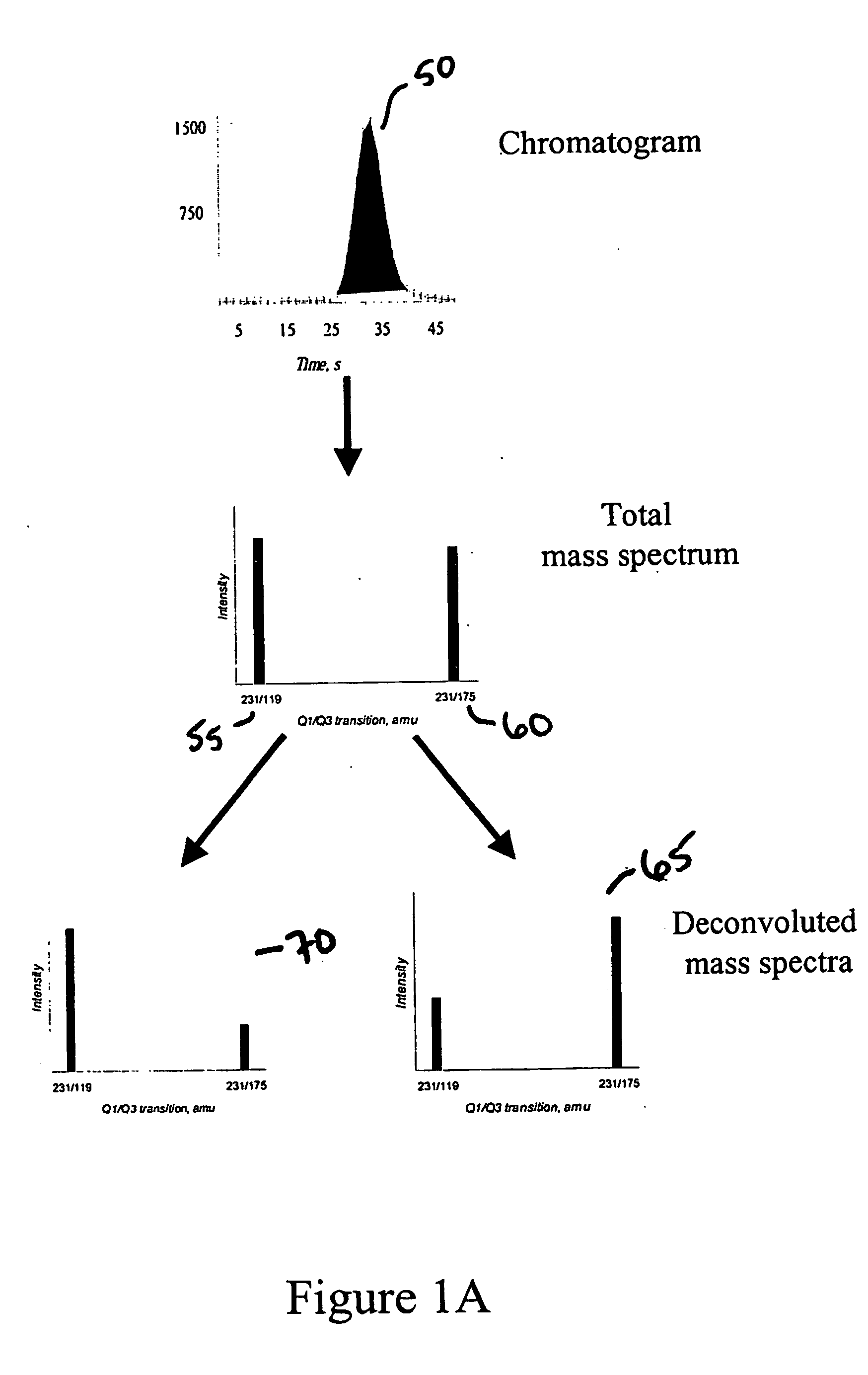
Methods for quantitative analysis by tandem mass spectrometry
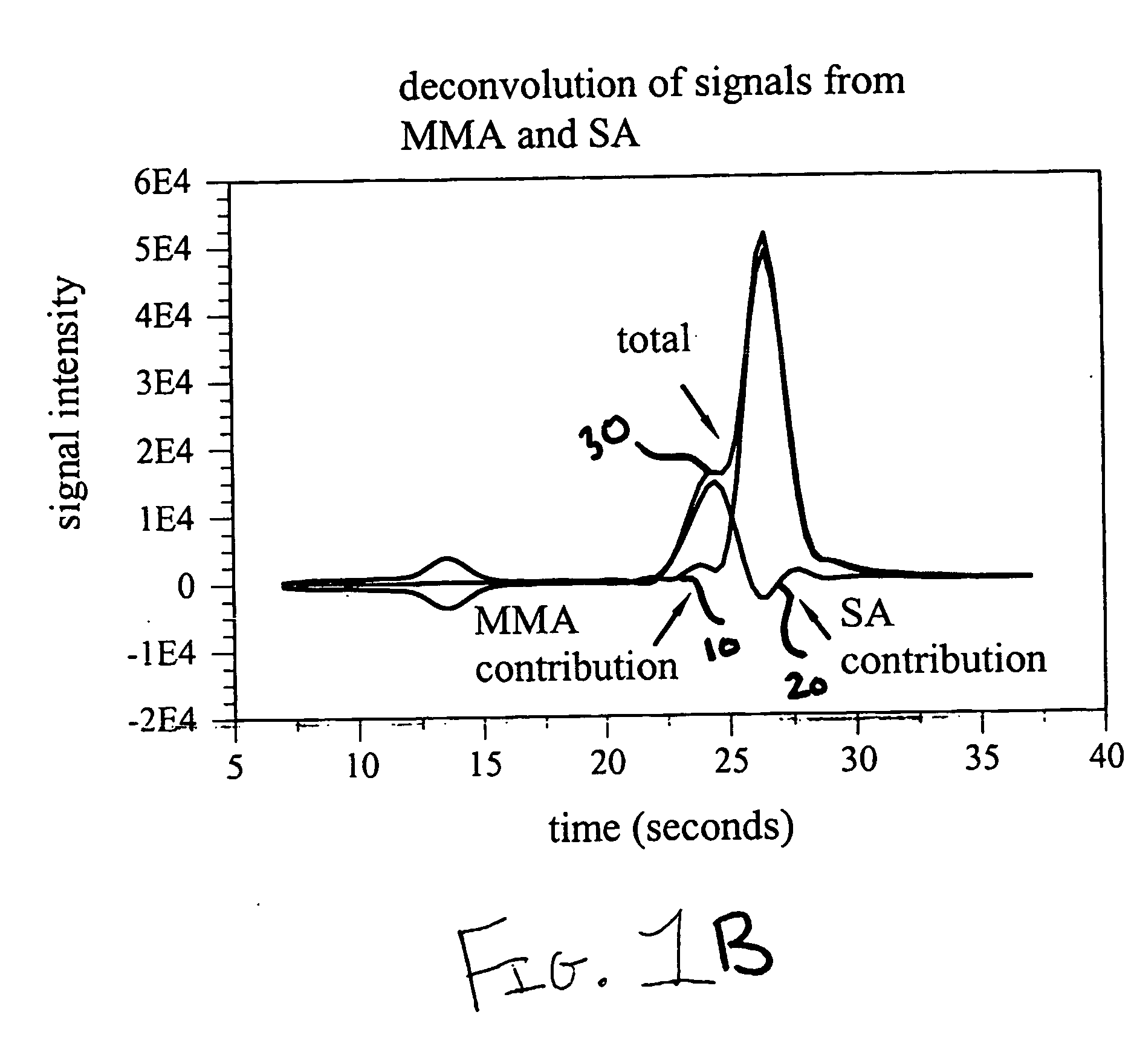
The present invention provides methods for high throughput analysis of analytes in complex mixtures for unresolved chromatographic peaks including specific embodiment for summing intensities for each mass transition of interest over a selected chromatographic peak (50) to generate a signal corresponding to total intensity for each transition (55, 60). The intensities are deconvoluted into intensities of individual analytes (65, 70), based on branching ratios acquired from authentic standards, and a comparison to calibration curve is performed to obtain a quantitative concentration measurement of a particular analyte in a sample.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Saturation correction for ion signals in time-of-flight mass spectrometers
InactiveUS20110226943A1Increased dynamic measurement rangeTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationTime-of-flight mass spectrometryFrequency spectrum
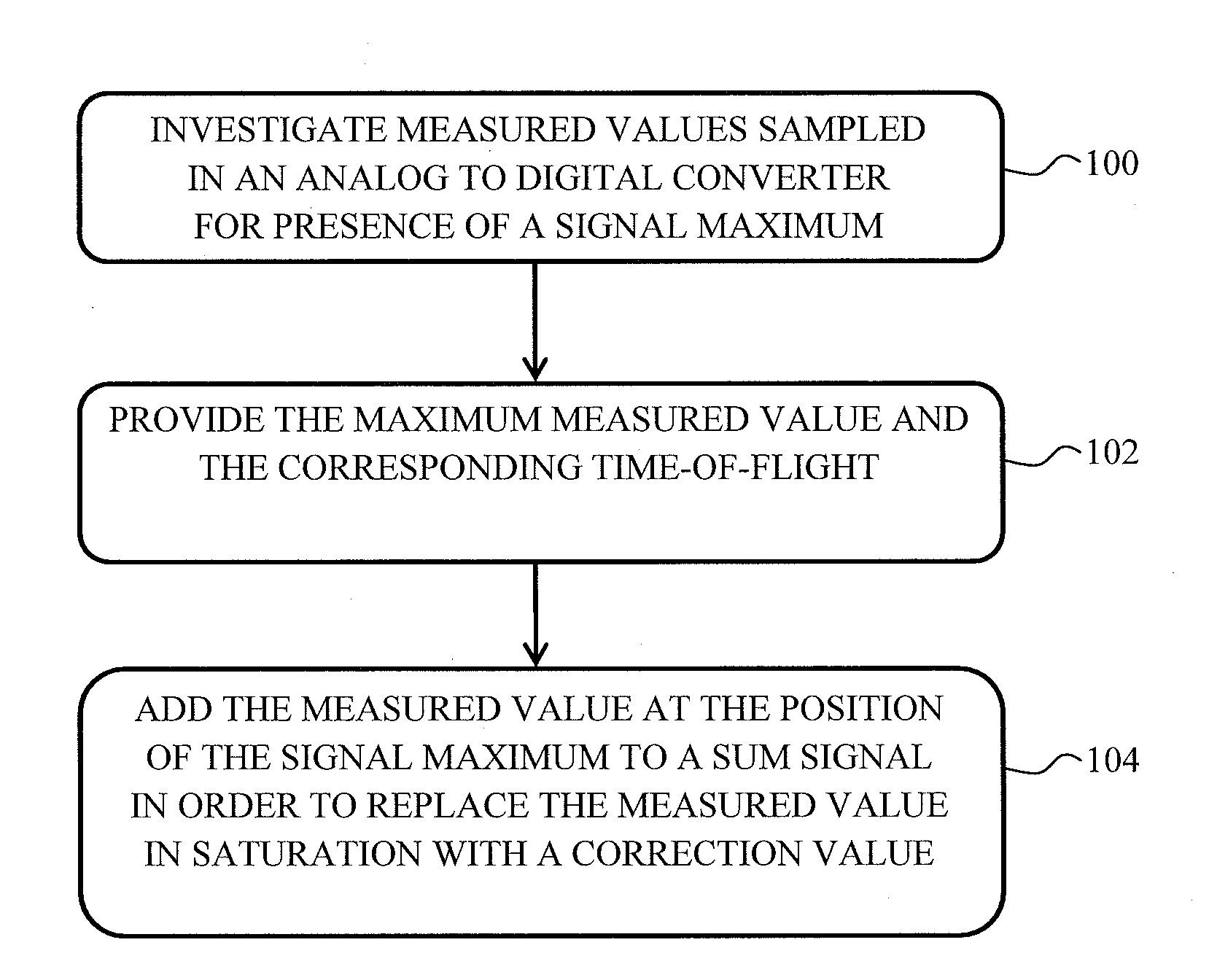
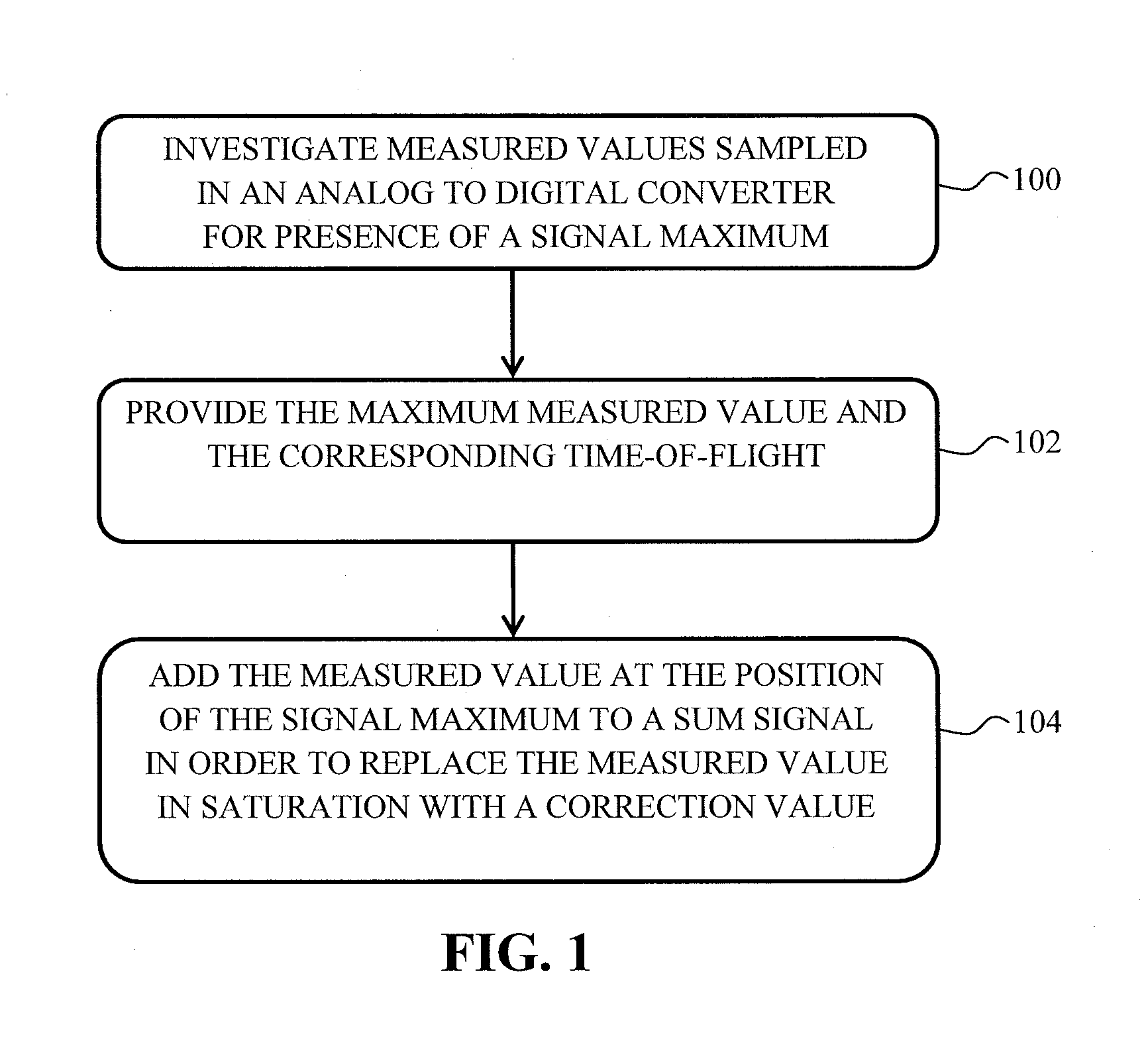
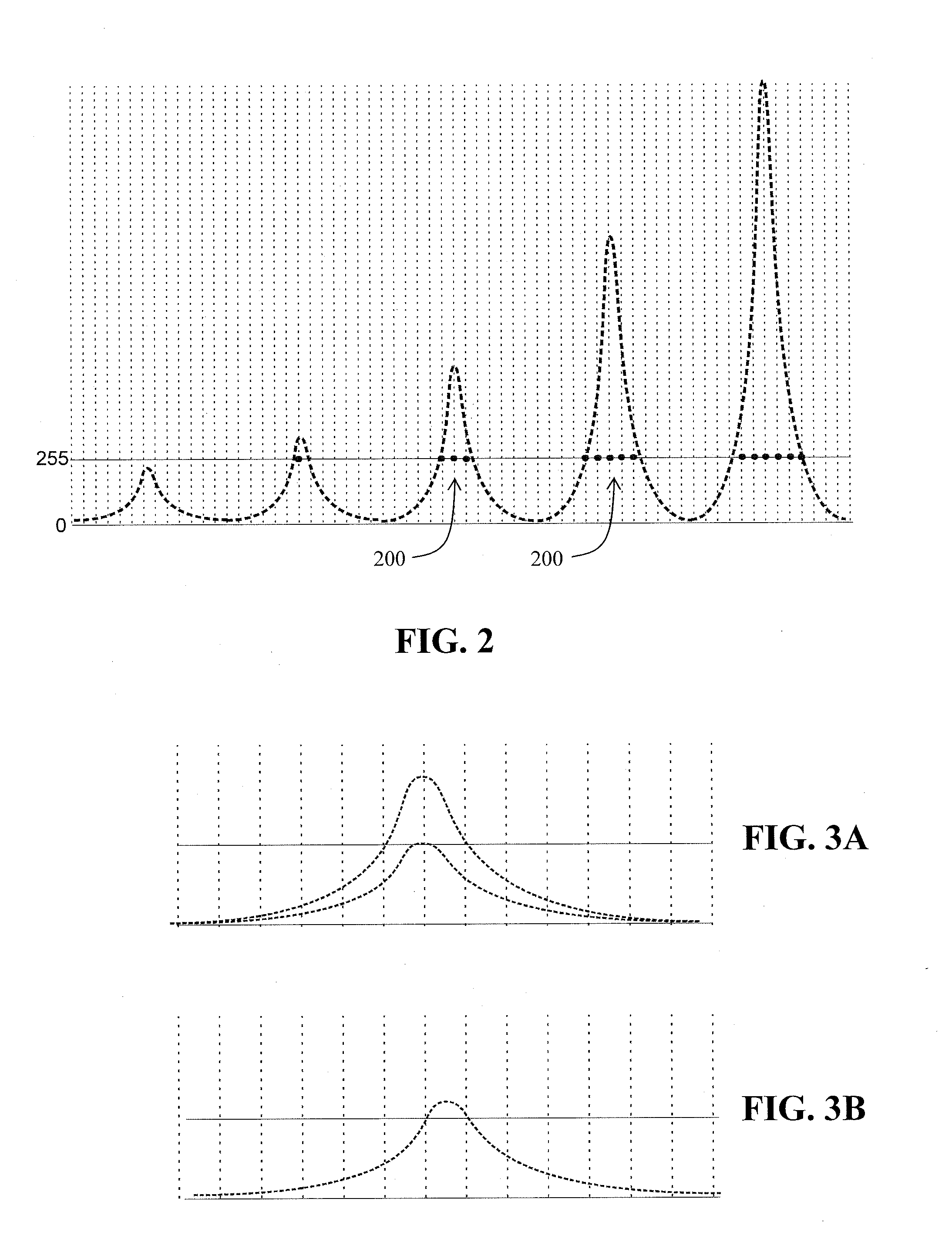
A method for increasing a dynamic measurement range of a mass spectrometer, includes replacing measured values in saturation with correction values, and summing the correction values to provide a sum spectrum.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH
MS/MS Mass Spectrometer
ActiveUS20130214146A1Reduce impactHigh detection sensitivityIsotope separationTube calibration apparatusTime delaysData memory
A mass analysis of a sample having a known mass-to-charge ratio is carried out by performing a scan at a first-stage quadrupole over a predetermined mass range, under the condition that a collision induced dissociation gas is introduced into a collision cell and a voltage applied to a third-stage quadrupole is set so that no substantial mass separation occurs in this quadrupole. Various product ions originating from a precursor ion selected by the first-stage quadrupole arrive at and are detected by a detector without being mass separated. Accordingly, based on the detection data, a data processor can obtain a relationship between the voltage applied to the first-stage quadrupole and the mass-to-charge ratio of the selected ions, with a time delay in the collision cell reflected in that relationship. This relationship is stored in a calibration data memory, to be utilized in a neutral loss scan measurement or the like.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Compositions, methods, and kits for quantifying target analytes in a sample
ActiveUS20140158881A1Effectively indistinguishableImprove productivityComponent separationIsotope separationSingle sampleAnalyte
A method of quantifying a target analyte by mass spectrometry includes obtaining a mass spectrometer signal comprising a first calibrator signal, comprising a second calibrator signal, and potentially comprising a target analyte signal from a single sample comprising a first known quantity of a first calibrator, comprising a second known quantity of a second calibrator, and potentially comprising a target analyte. The first known quantity and the second known quantity are different, and wherein the first calibrator, the second calibrator, and the target analyte are each distinguishable in the single sample by mass spectrometry. The method also includes quantifying the target analyte in the single sample using the first calibrator signal, the second calibrator signal, and the target analyte signal.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
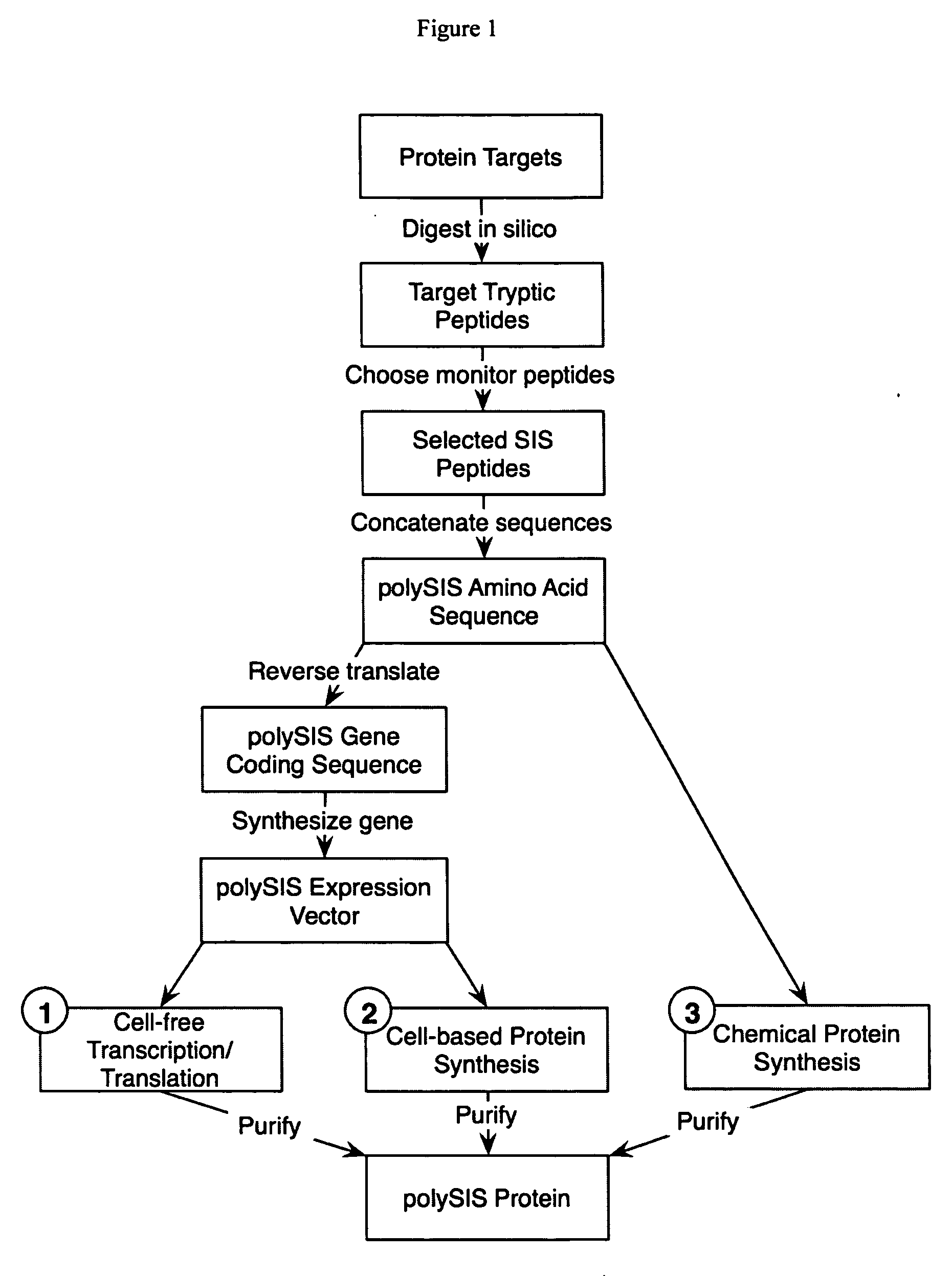
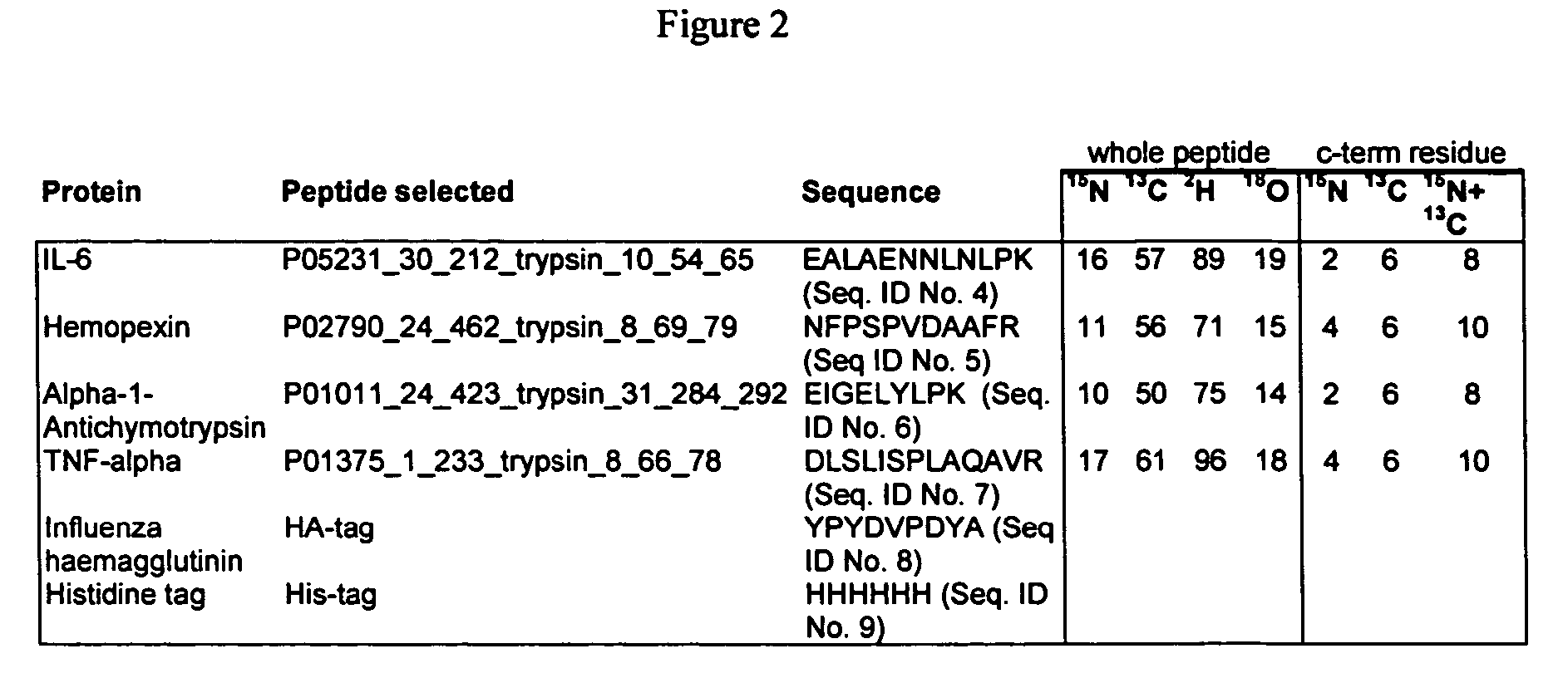
Stable isotope labeled polypeptide standards for protein quantitation
InactiveUS20060154318A1Increase heightDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsStable Isotope LabelingProtein target
This invention relates to proteins having an amino acid sequence containing several amino acid subsequences found in nature and wherein at least two different subsequences act as monitor sequences, said subsequences being part of at least one natural protein which is a target protein, wherein the end of each of said two different subsequences have a cleavage site that will be cleaved by the same site-specific proteolytic treatment to release said subsequences.
Owner:ANDERSON FORSCHUNG GROUP
Calibration method
InactiveUS7071463B2Compensation effectAvoid offsetTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass analyzerPeak value
In its most general terms the invention compensates for the effect of the mass offset in the prior art calibration method. This can be achieved either by correcting for the offset or assigning mass to the peaks in such a way that the offset is avoided. Accordingly in a first aspect there is provided a method of calibrating a reflectron time-of-flight mass spectrometer using a spectrum generated by fragment ions wherein a measured mass value is modified to take account of the effect of post source decay and that modified value is used for calibration. A modified calibration function can then be defined and used to determine actual fragment ion masses of an unknown compound.
Owner:KRATOS ANALYTICAL
Popular searches
Beam/ray deflecting arrangements Electron/ion optical arrangements Beam deviation/focusing by electric/magnetic means Material analysis by using resonance Immunoassays Current/voltage measurement Voltage-current phase angle Special data processing applications Chemical methods analysis Testing/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devices
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com