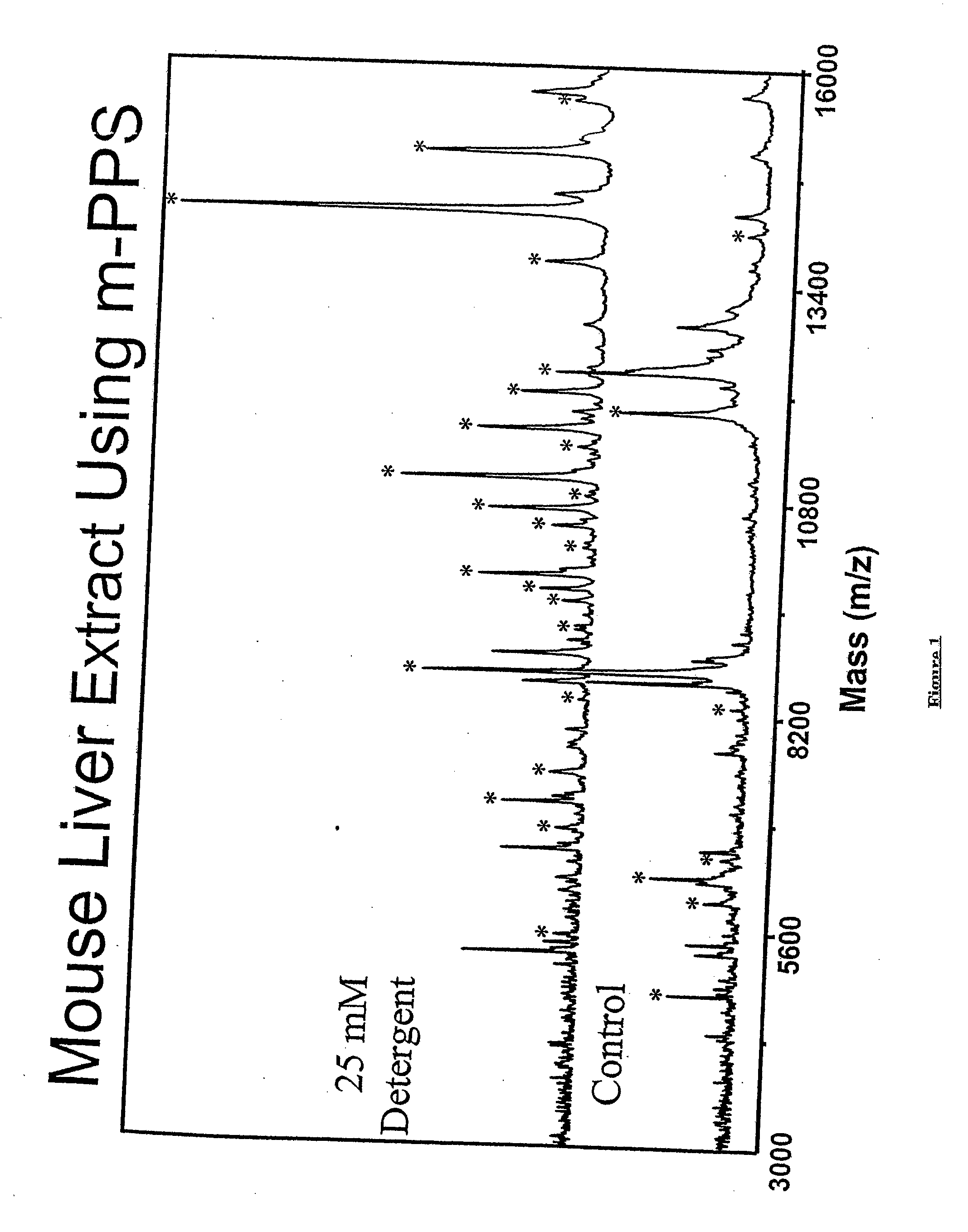
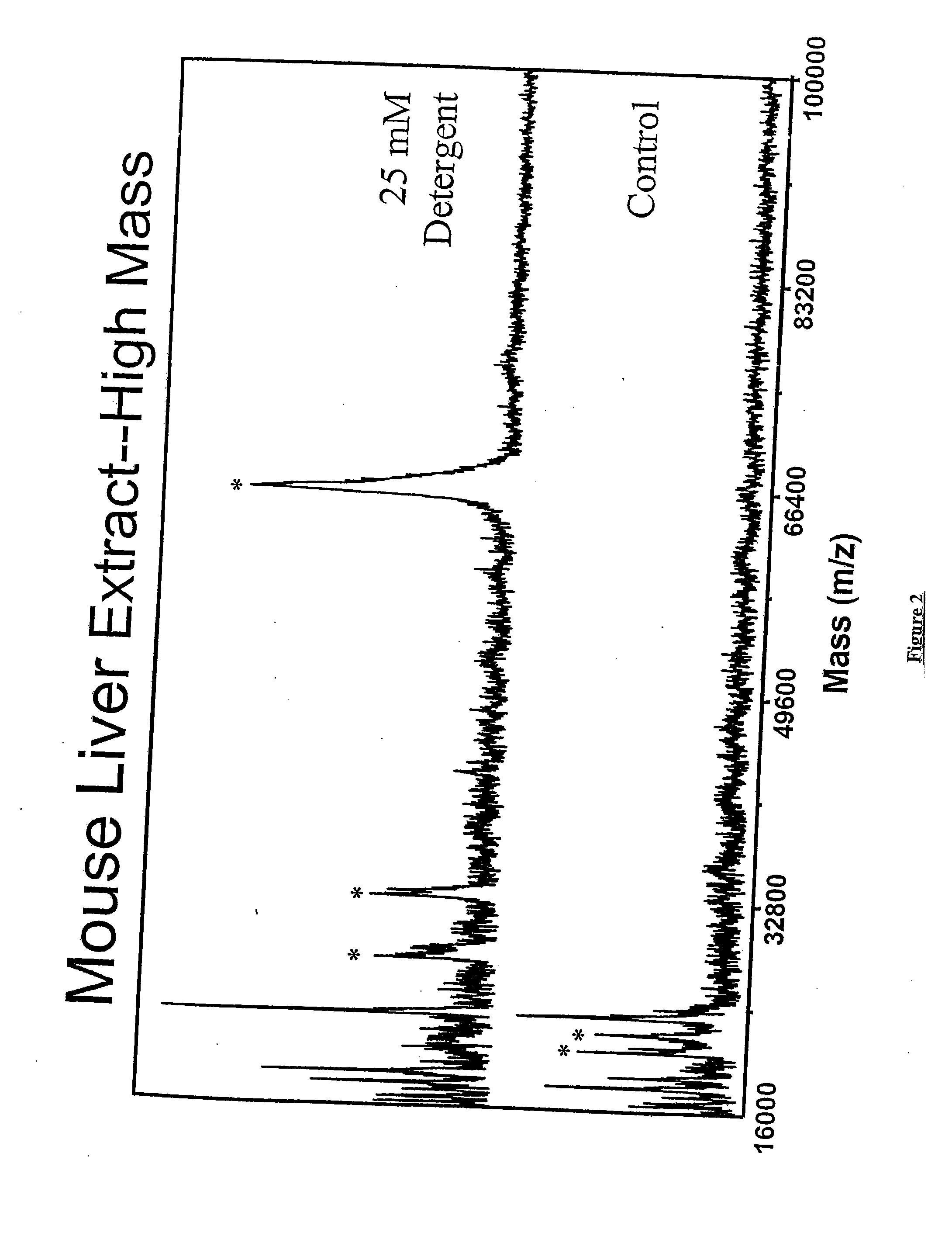
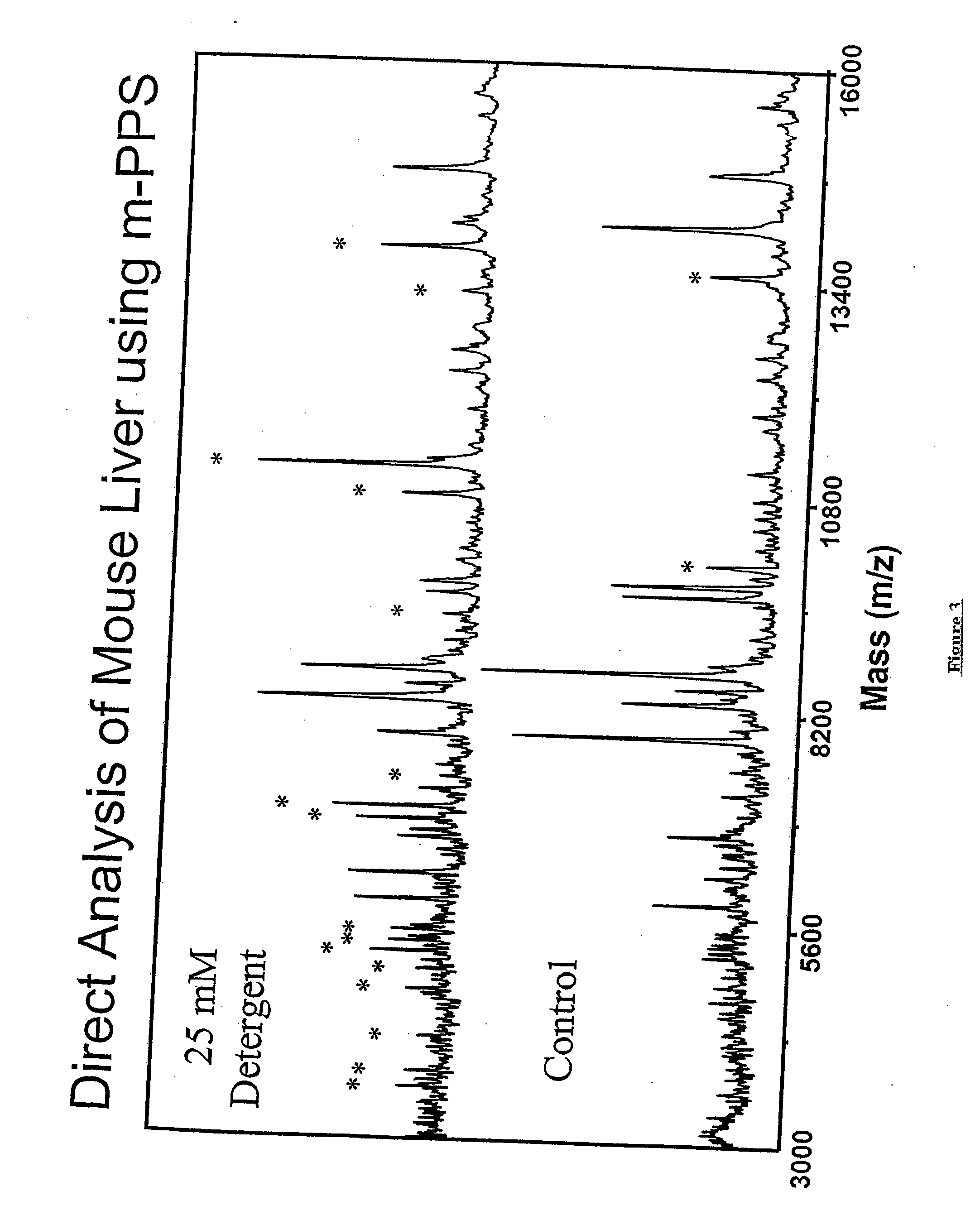
Cleavable surfactants and methods of use thereof
a surfactant and detergent technology, applied in the field of detergents or surfactants, can solve the problems of high analytical system sensitive to the presence high sensitivity of many analytical systems, and high variability in the chemistry of proteins in biological systems and especially in mammals, so as to eliminate the suppressive effect of detergents, increase the signal intensity of high molecular weight proteins, and increase the number of ions detected
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0082] Example 1 is a selection of embodiments of cleavable detergents or surfactants of the present invention, including the hydrophobic tail, cleavable linker, and polar head group.
[0083] X can be SO3−, SO4−, or N+(CH3)3
or a salt thereof, wherein:
[0084] R1 and R2 is each independently —H, -0CH3, —(CH2)1-6CH3, or -0(CH2)1-6CH3;
[0085] R3 and R4 is each independently —H, -0CH3, —OH, —NH2, —(CH2)1-6CH3, or -0(CH2)1-6CH3;
[0086] R5 and R6 are each independently —(CH2)1-19CH3;
[0087] R7 is independently —(CH2)1-19CH3; and
[0088] R8 is independently —(CH2)1-6,
[0089] X is independently SO3−, SO4−, or NH3+.
[0090] A preferred embodiment of formula 14 is where that R1 and R4 are H, and R7 is methyl. The basic structure defined by R5-O—C—O—R6 is that of a ketal linkage. The present set of structures is especially useful for the ability to degrade the surfactant by cleavage at the ketal yielding molecules with reduced MALDI signal suppression.
[0091] or a salt thereof, wherein:
[0092]...
example 2
[0135] This Example describes the synthesis and cleavage of alpha-cyano-4-hydroxy-cinnamic acid detergent, a preferred embodiment of the present invention.
[0136] Synthesis of Chloromethyl ether: A volume of 5 mL (39.4 mmol) of chlorotrimethylsilane (TMS-Cl) and 0.3 g of paraformaldehyde were placed in a flame dried 25 mL round bottom flask. The reagents are allowed to stir under inert atmosphere until homogeneous. A volume of 2.27 mL (10 mmol) of n-dodecanol were added drop wise to the reaction vessel. The reagents react at room temperature for a period of two hours. The TMS-Cl is removed under vacuum followed by a vacuum distillation of the product, chloromethyl ether. A total of 0.973 g (41% yield) of product were collected at 106°-109° C. at 0.4 torr.
[0137] Synthesis of the methoxyalkyl ether of α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid: Powdered NaOH (107 mg, 2.68 mmol) was dissolved in 2 mL of dimethylsulfoxide in a flame dried 25 mL round bottom flask. To this mixture, 0.302 g (1.35 m...
example 3
[0139] This Example describes the synthesis and cleavage of sinapinic acid detergent, a preferred embodiment of the present invention.
[0140] Synthesis of Chloromethyl ether: A volume of 5 mL (39.4 mmol) of chiorotrimethylsilane (TMS-Cl) and 0.3 g of paraformaldehyde were placed in a flame dried 25 mL round bottom flask. The reagents are allowed to stir under inert atmosphere until homogeneous. A volume of 2.27 mL (10 mmol) of n-dodecanol were added drop wise to the reaction vessel. The reagents react at room temperature for a period of two hours. The TMS-Cl is removed under vacuum followed by a vacuum distillation of the product, chloromethyl ether. A total of 0.973 g (41% yield) of product were collected at 106°-109° C. at 0.4 torr.
[0141] Synthesis of protected sinapinic acid (5): [0142] Synthesis of trimethylsilylethyl bromoacetate (3): In a dry 50 mL round bottom flask, 1.65 mL (11.54 mmol) of trimethylsilyl ethanol (1), 0.88 mL (11 mmol) of pyridine, 0.124 g (1 mmol) of N,N-d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com