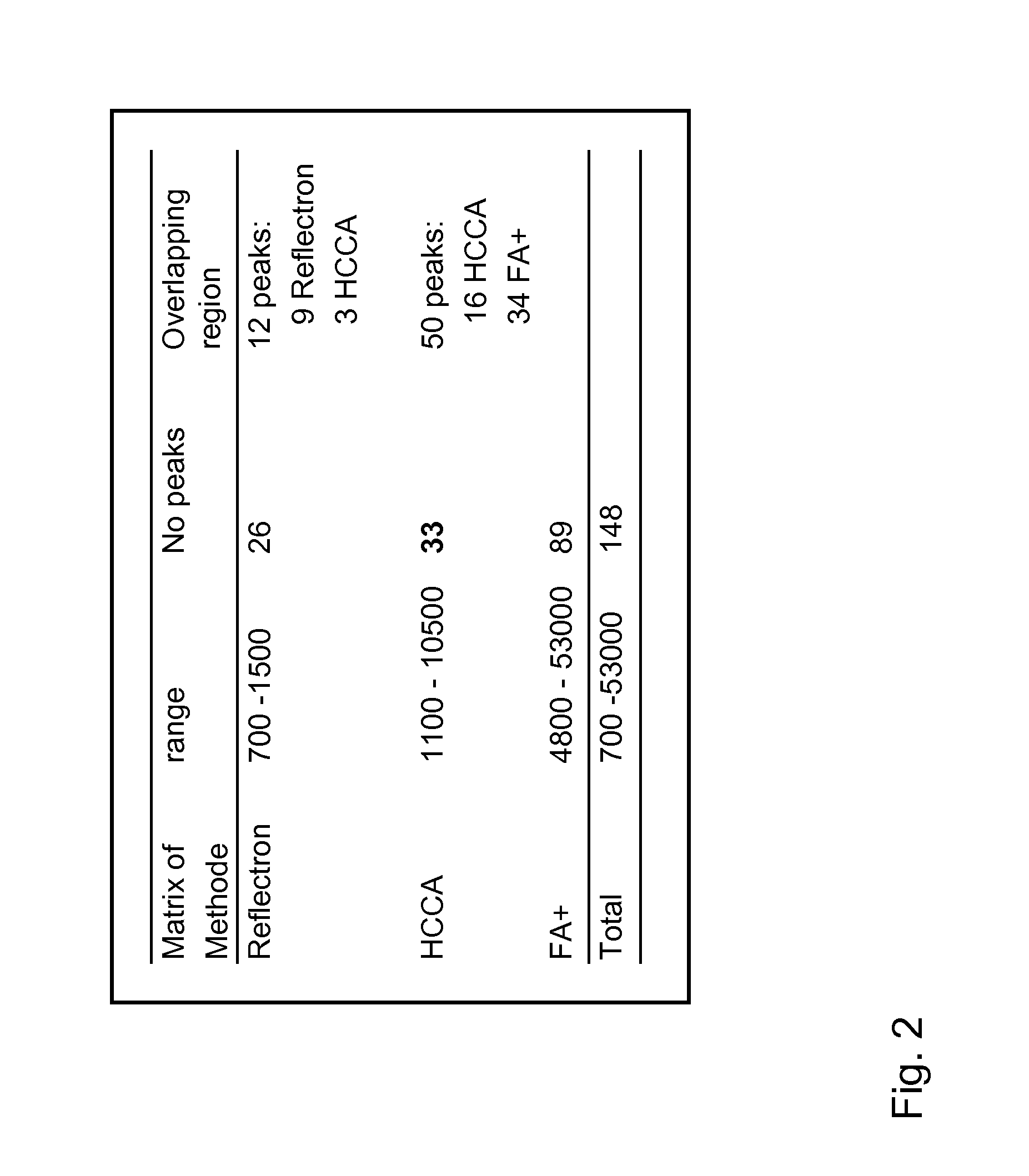
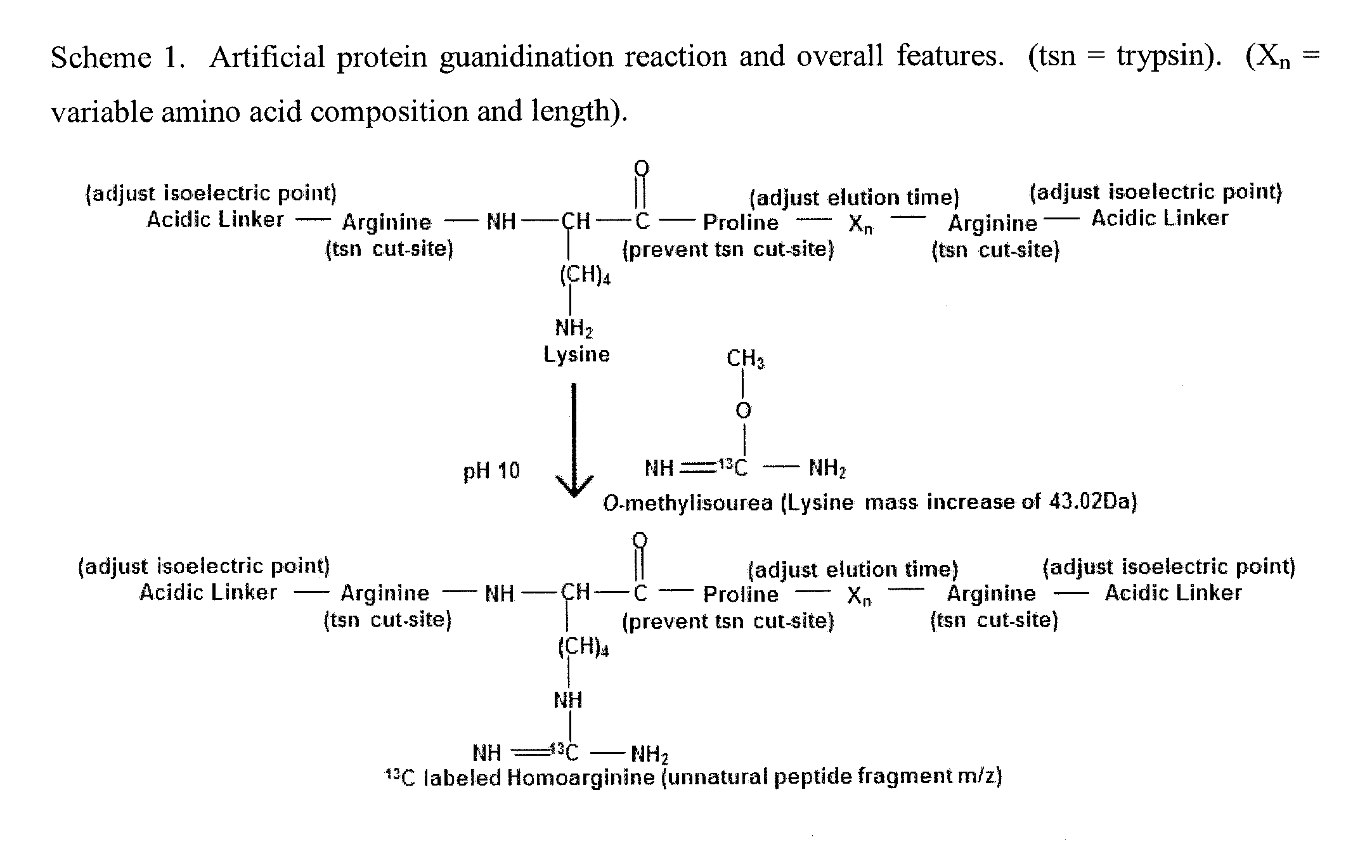
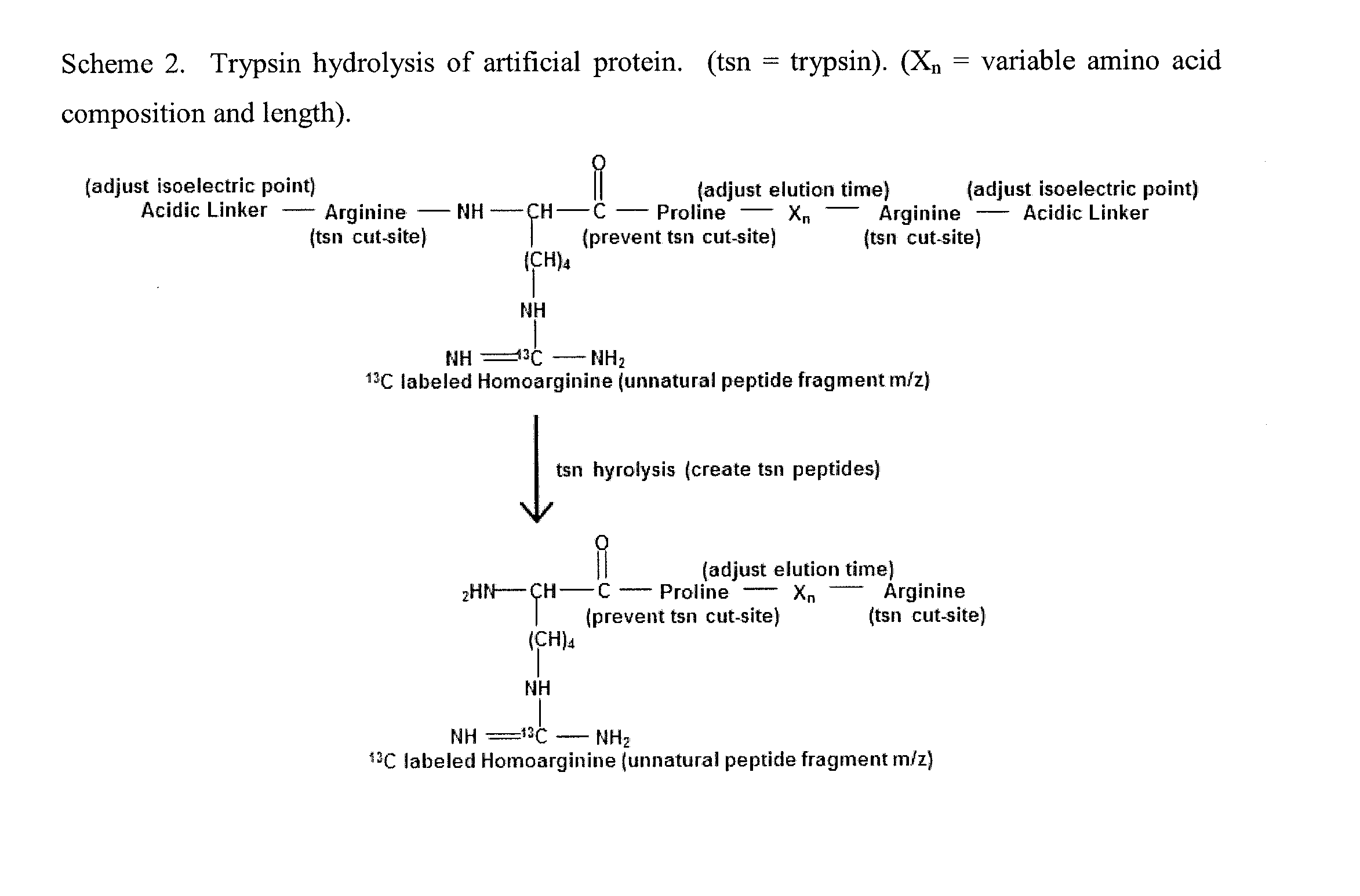
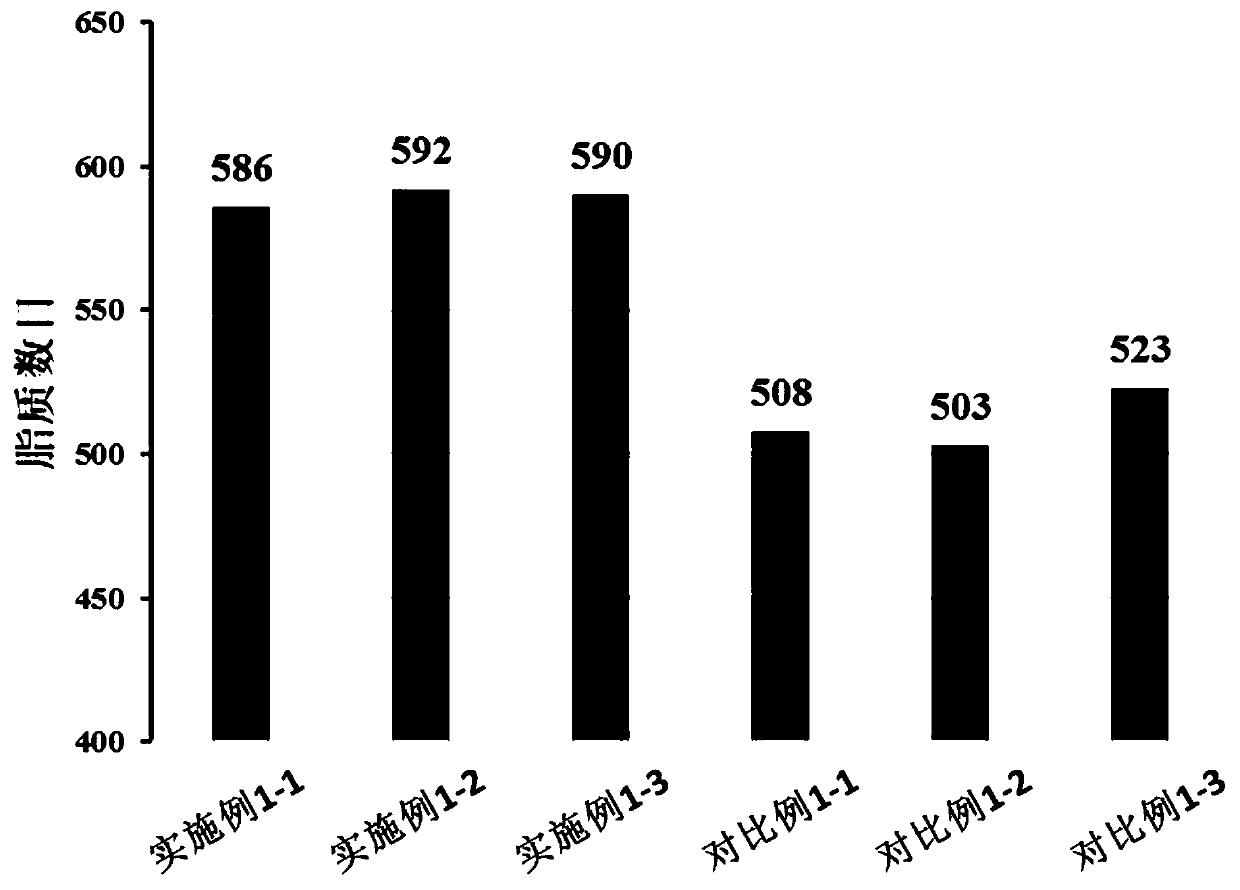
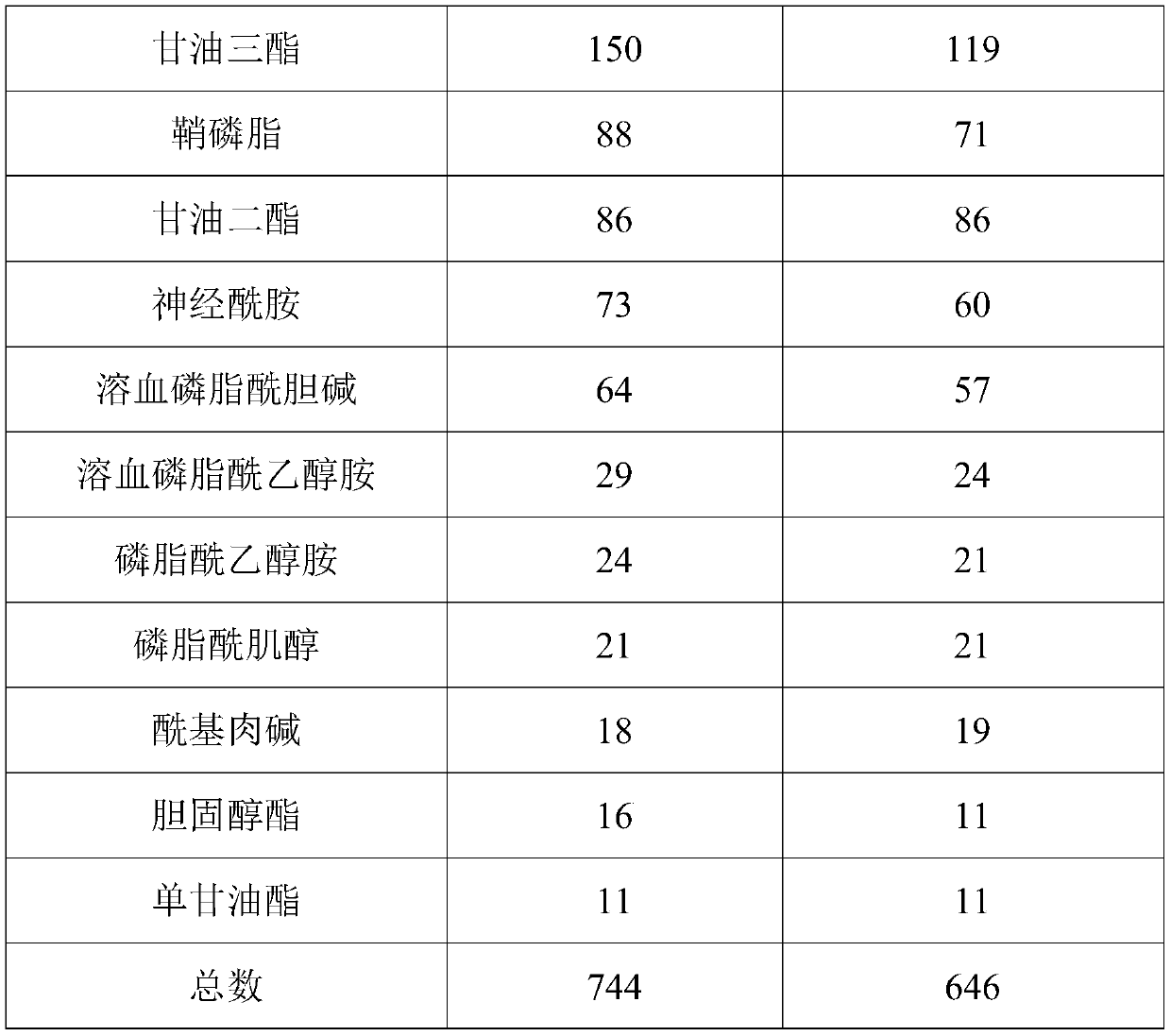
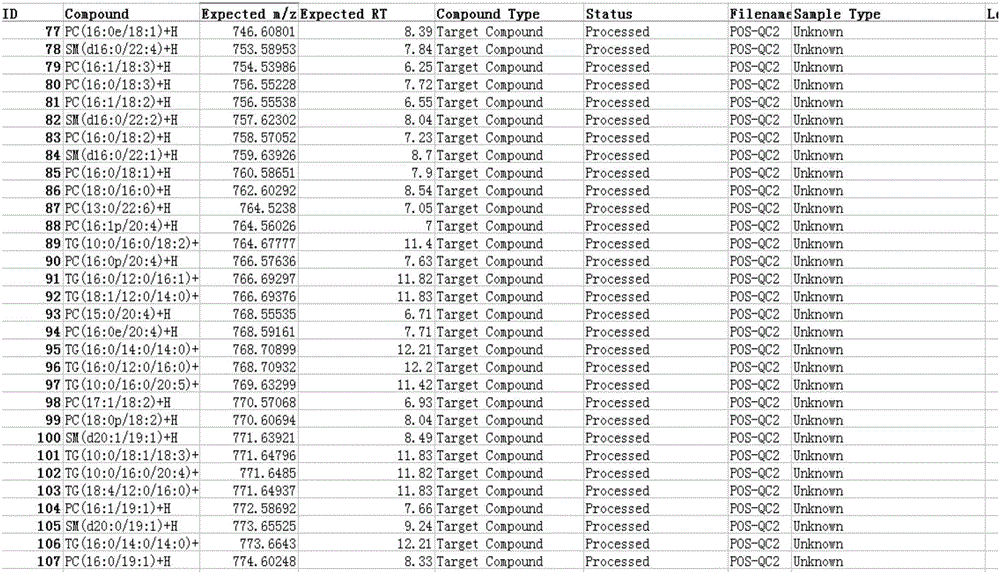
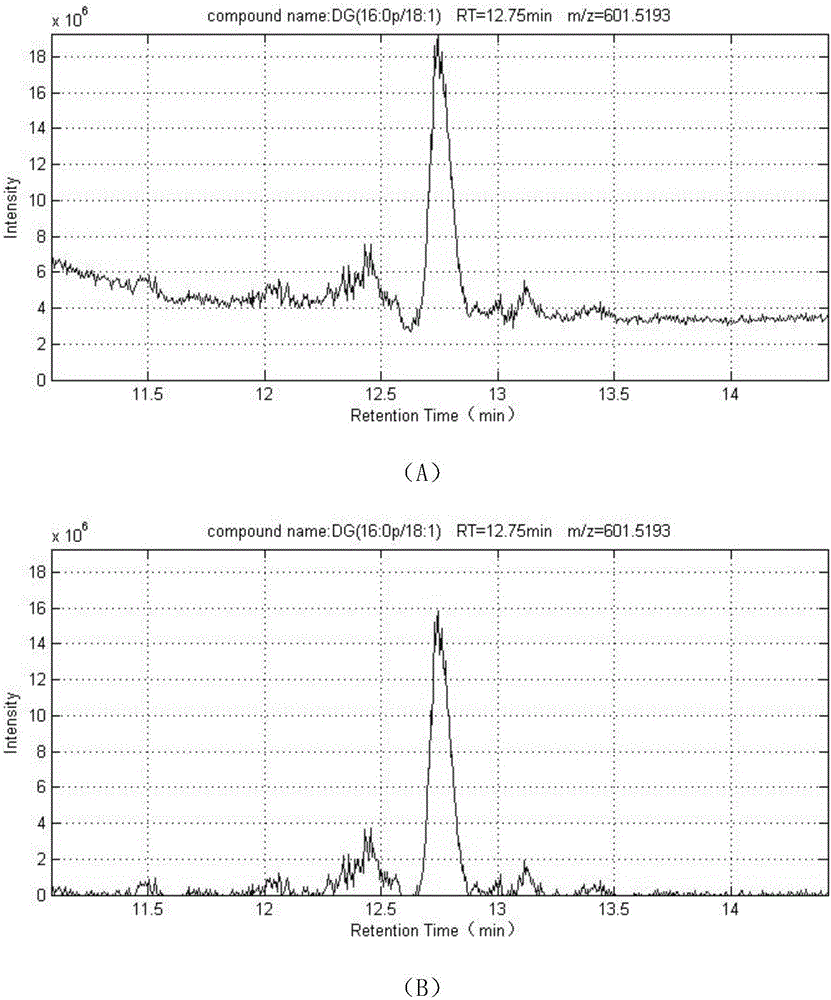
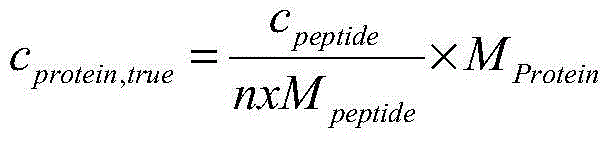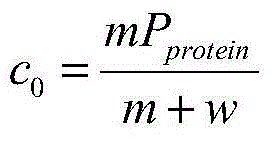Patents
Literature
89 results about "Mass spectrometry measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. It is most generally used to find the composition of a physical sample by generating a mass spectrum representing the masses of sample components. A mass spectrometer is a device that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of ions.
Protein Microscope
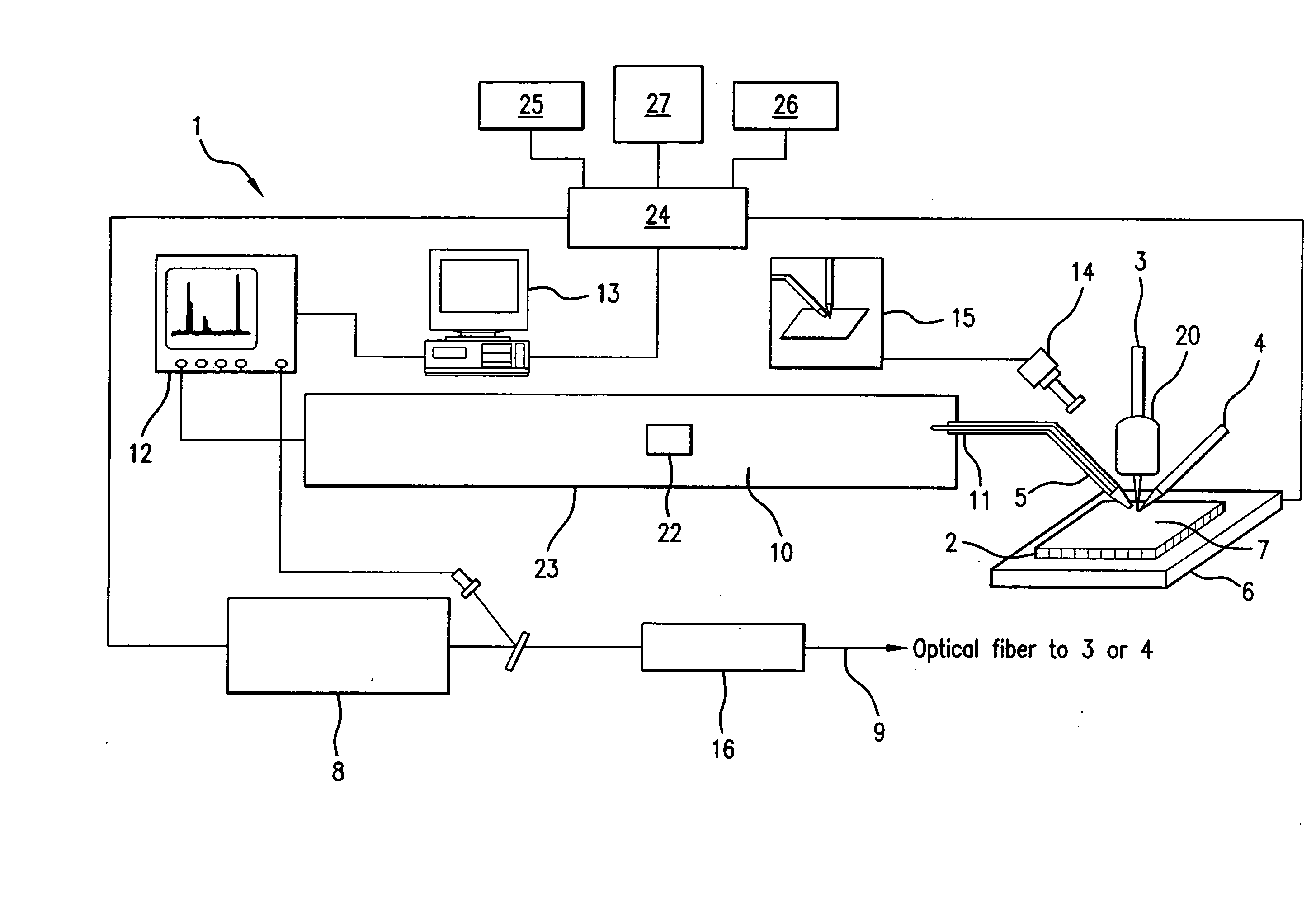
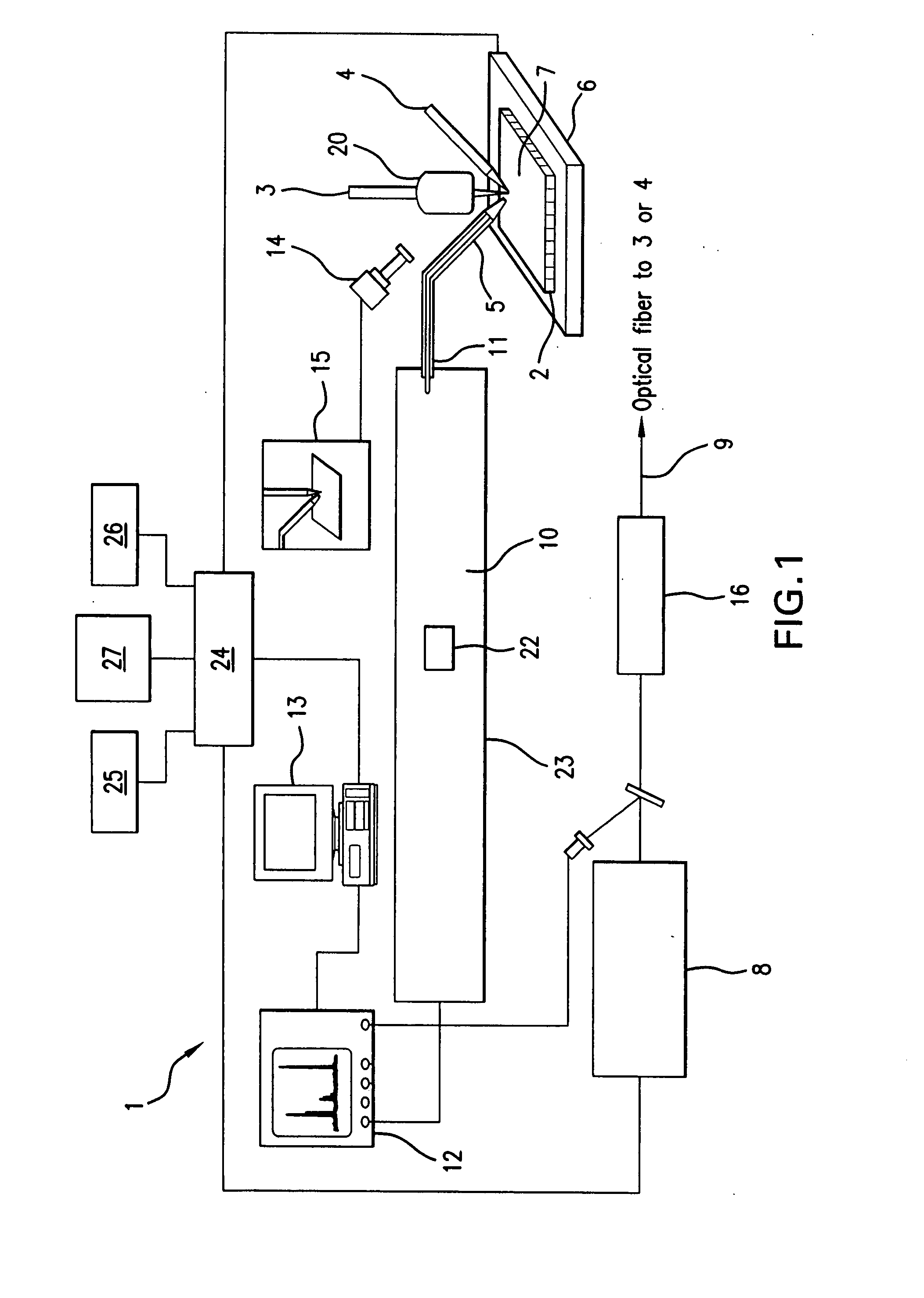
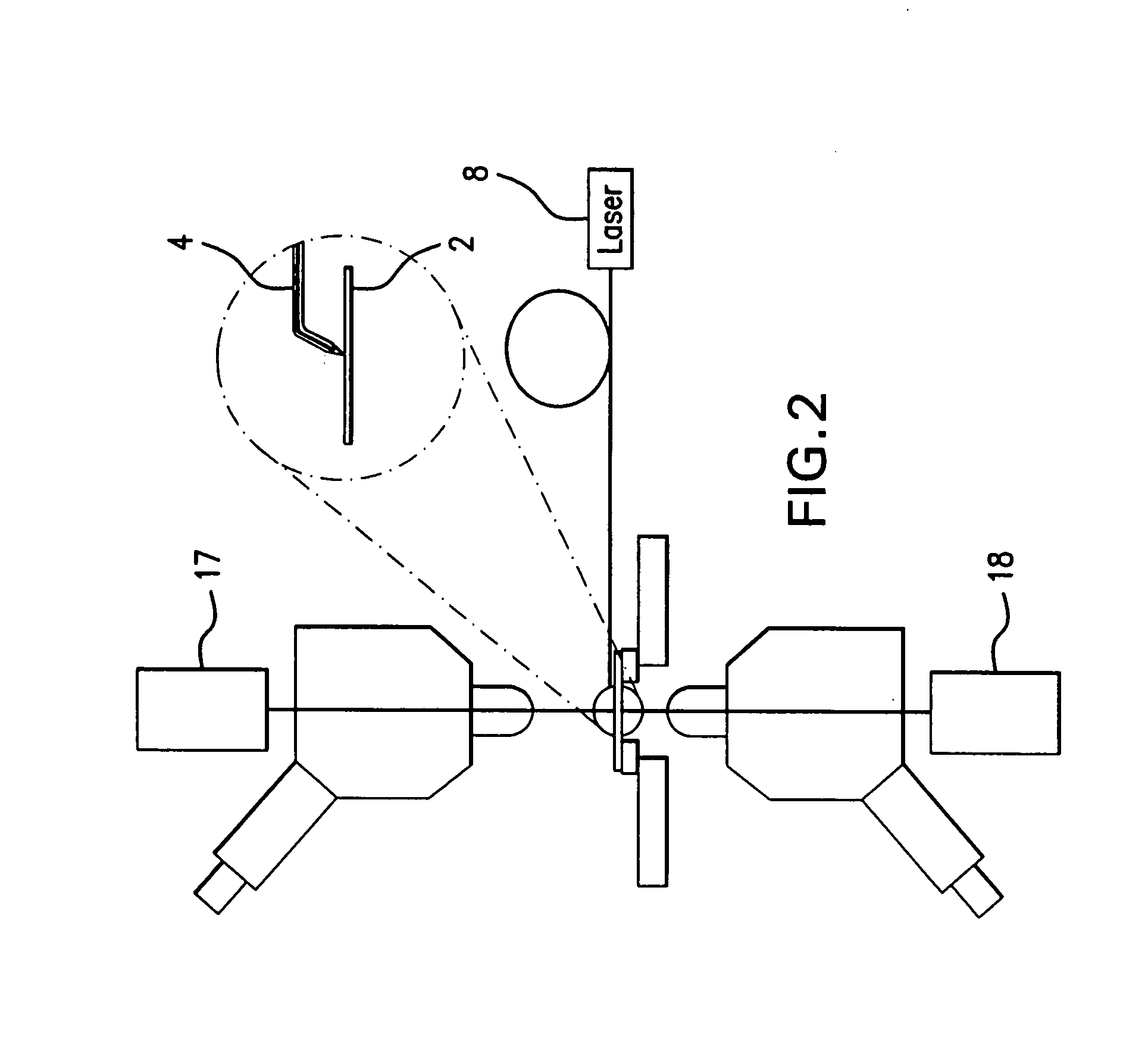
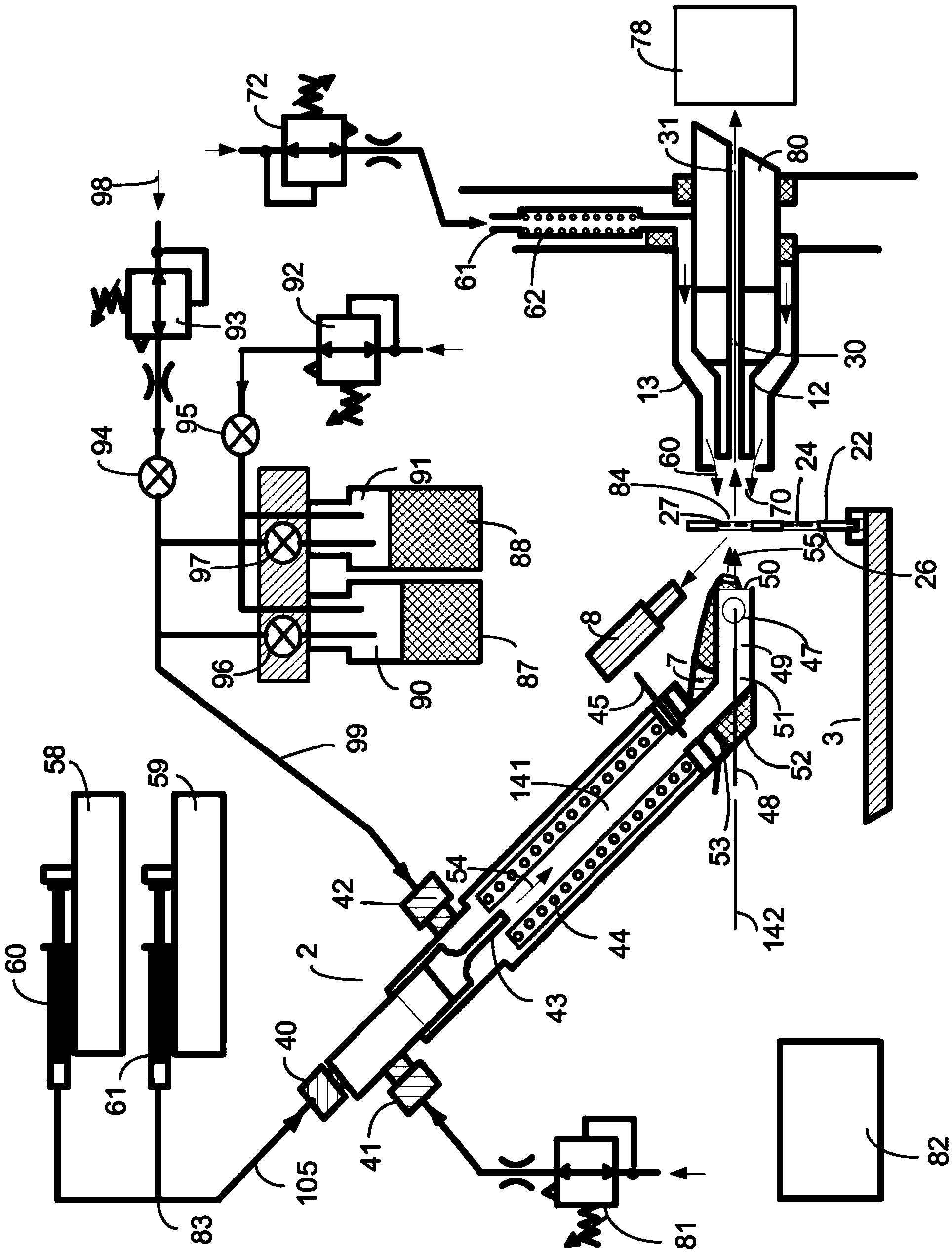
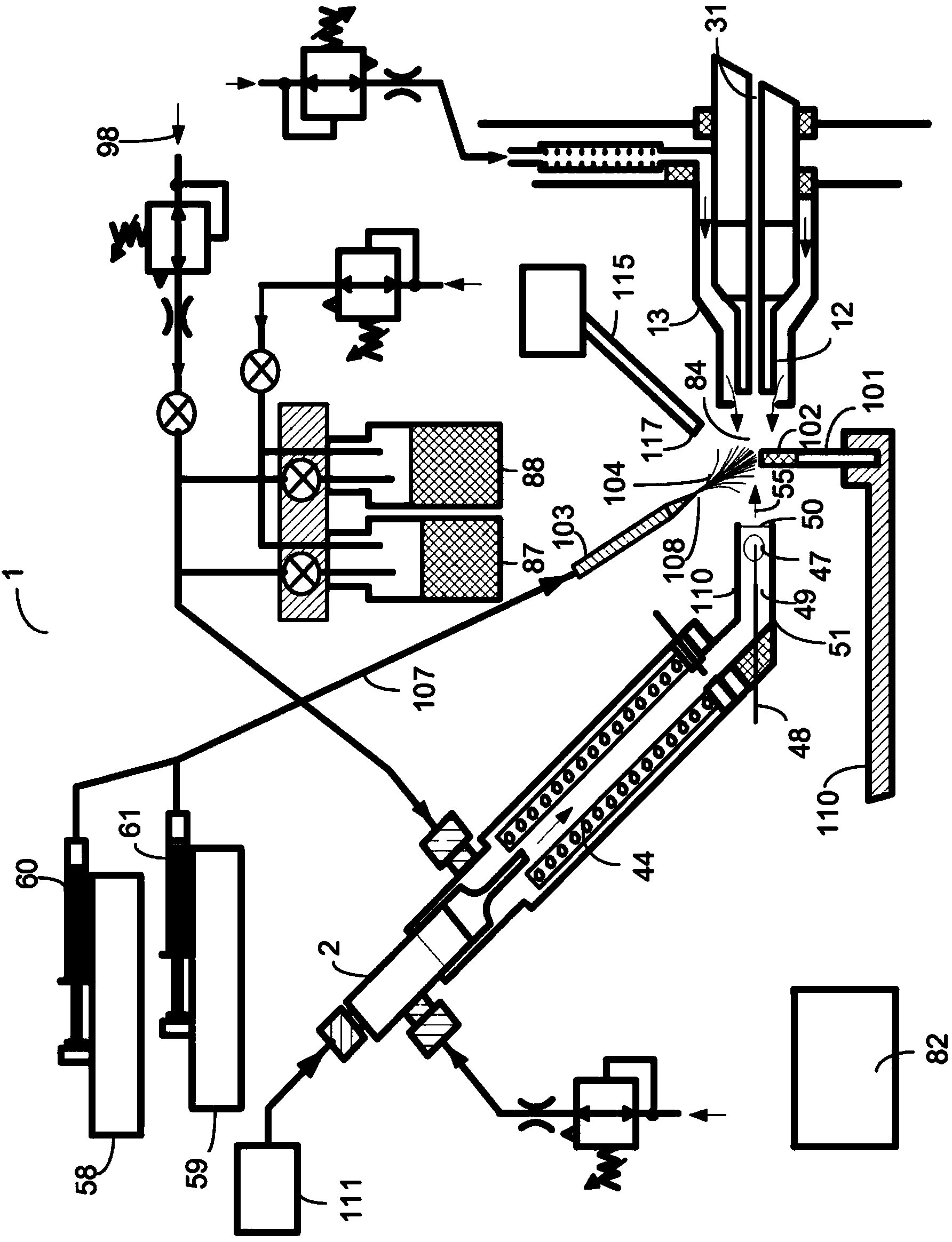
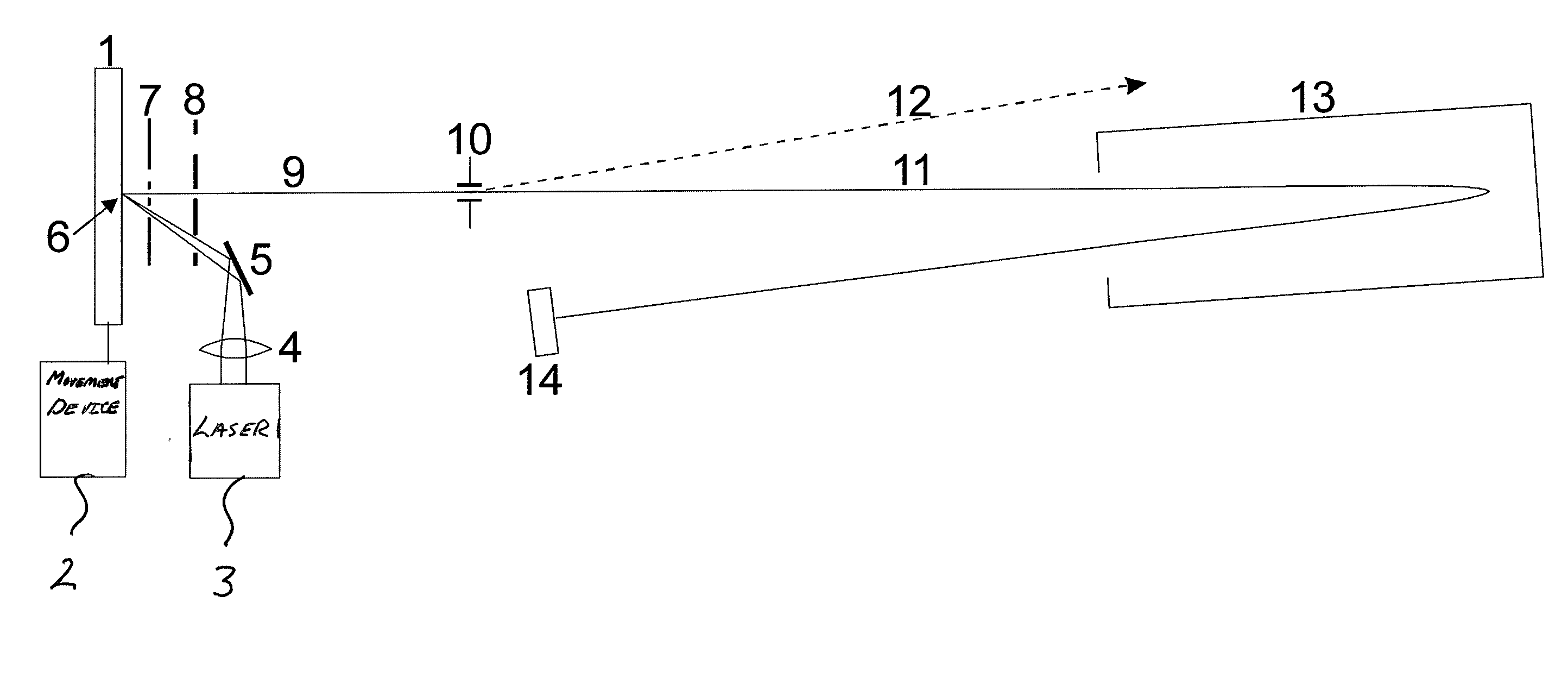
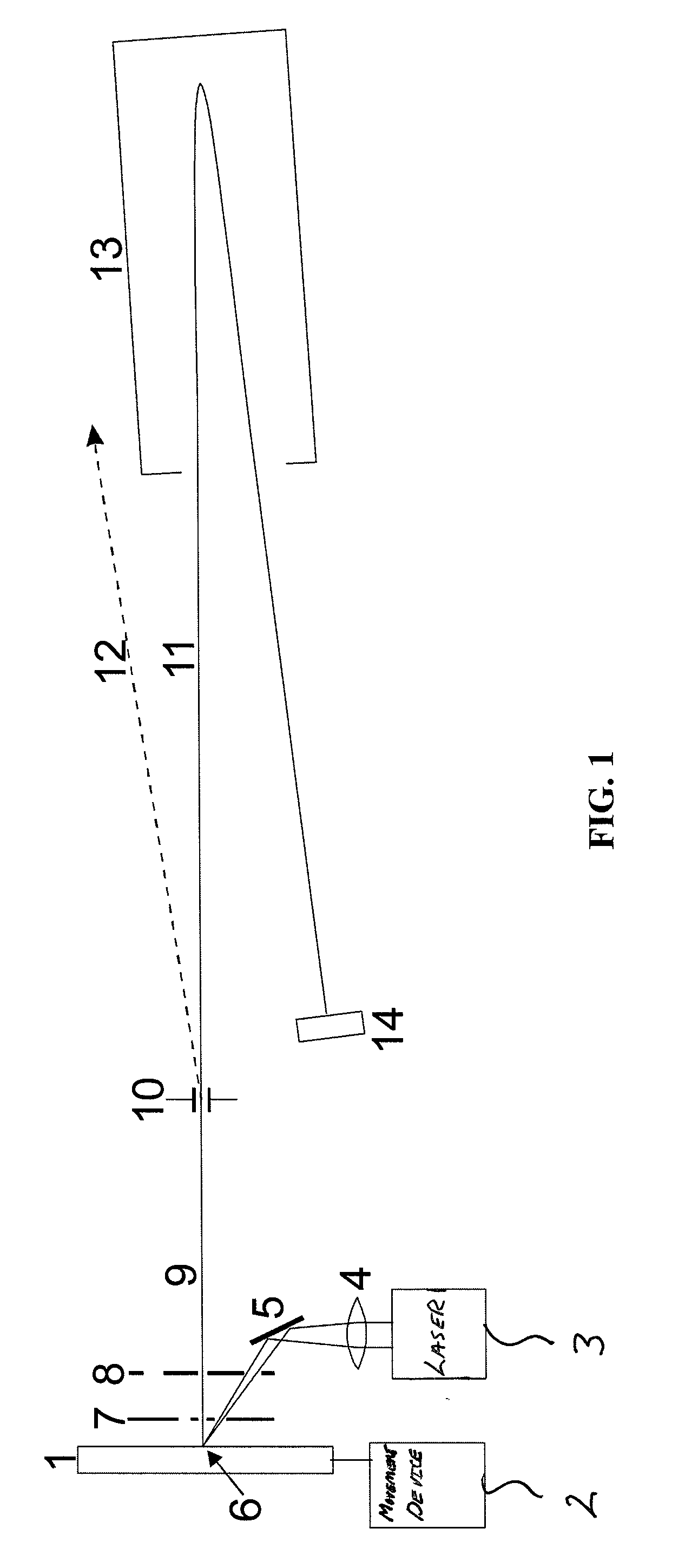
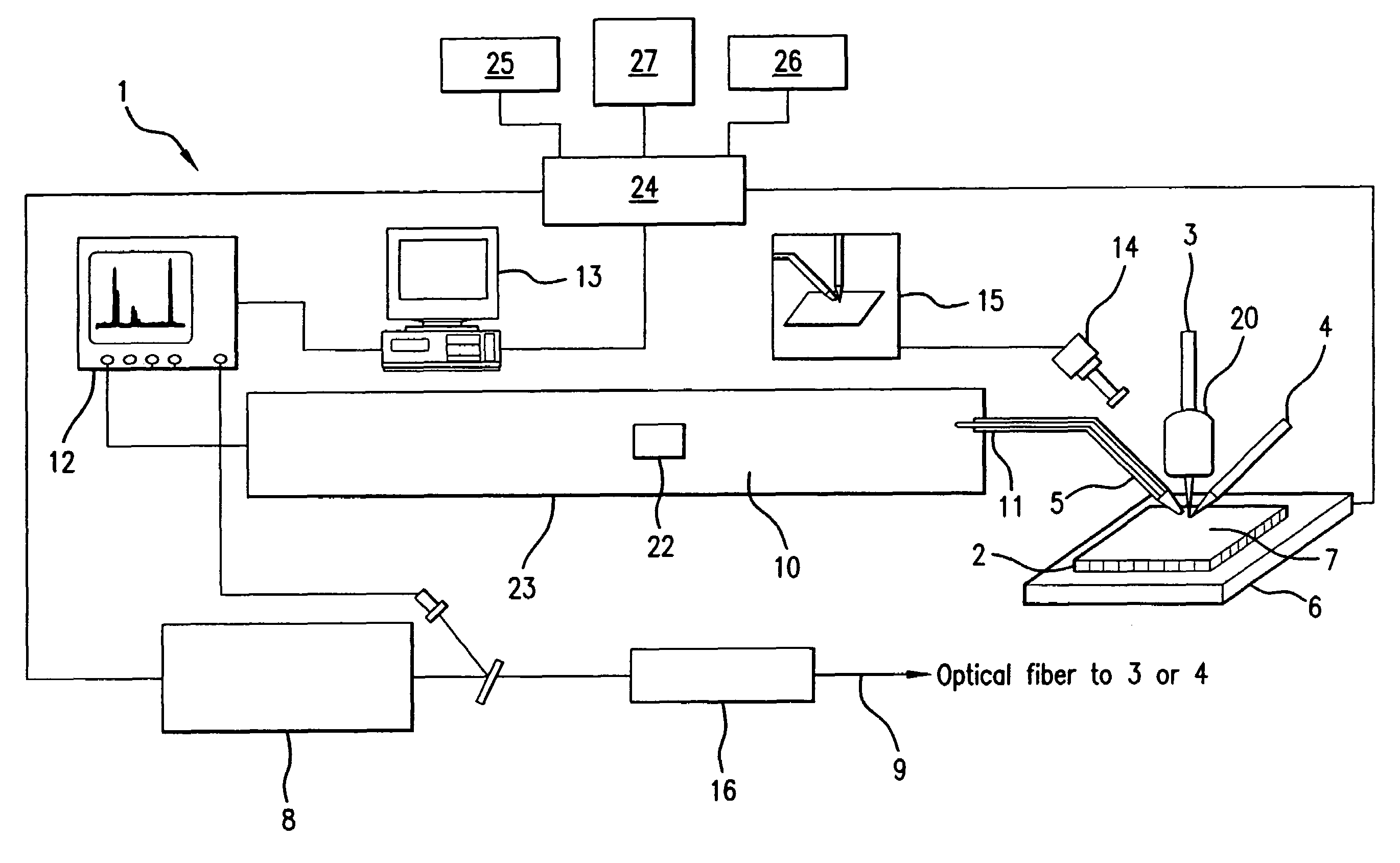
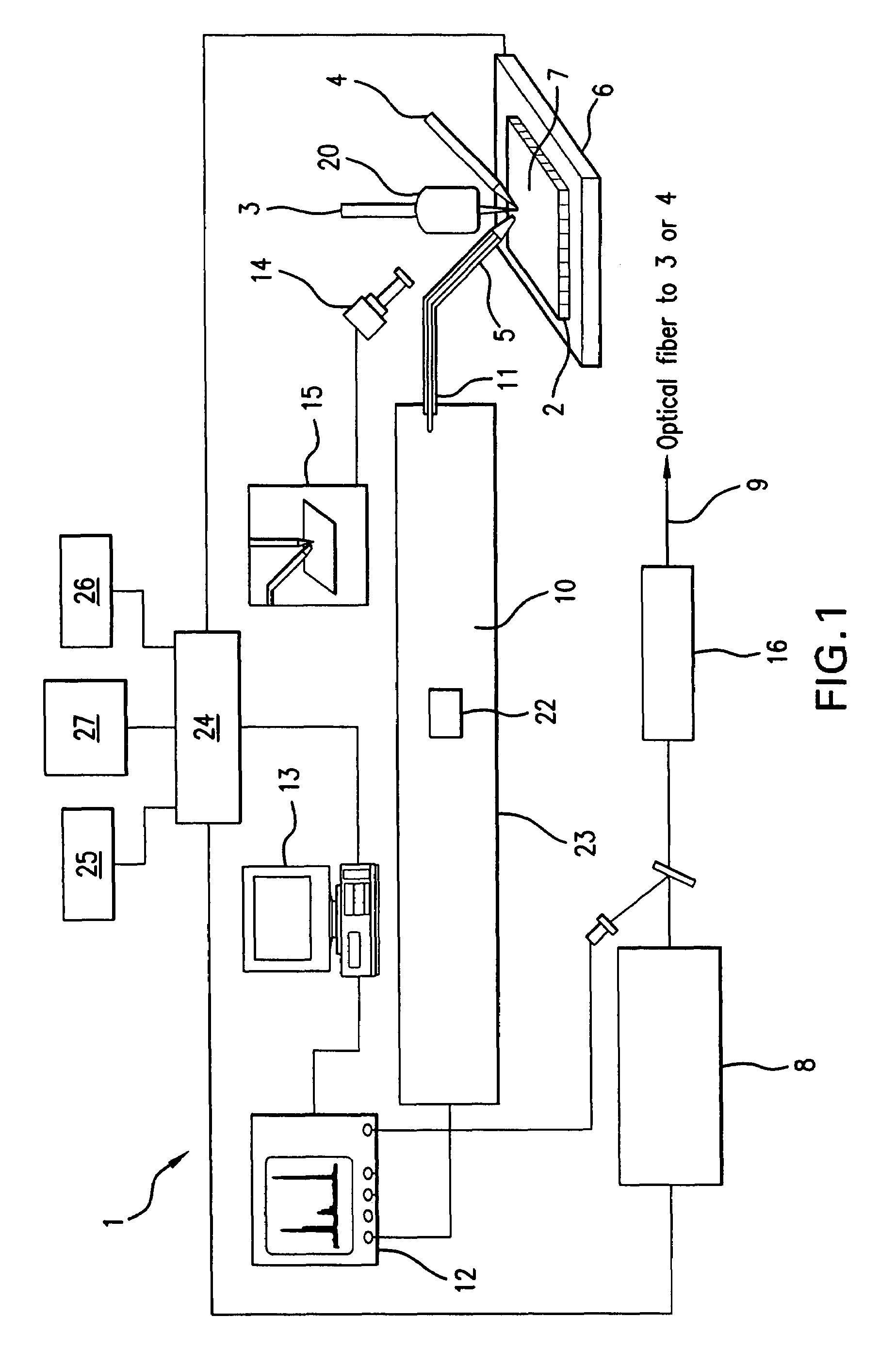
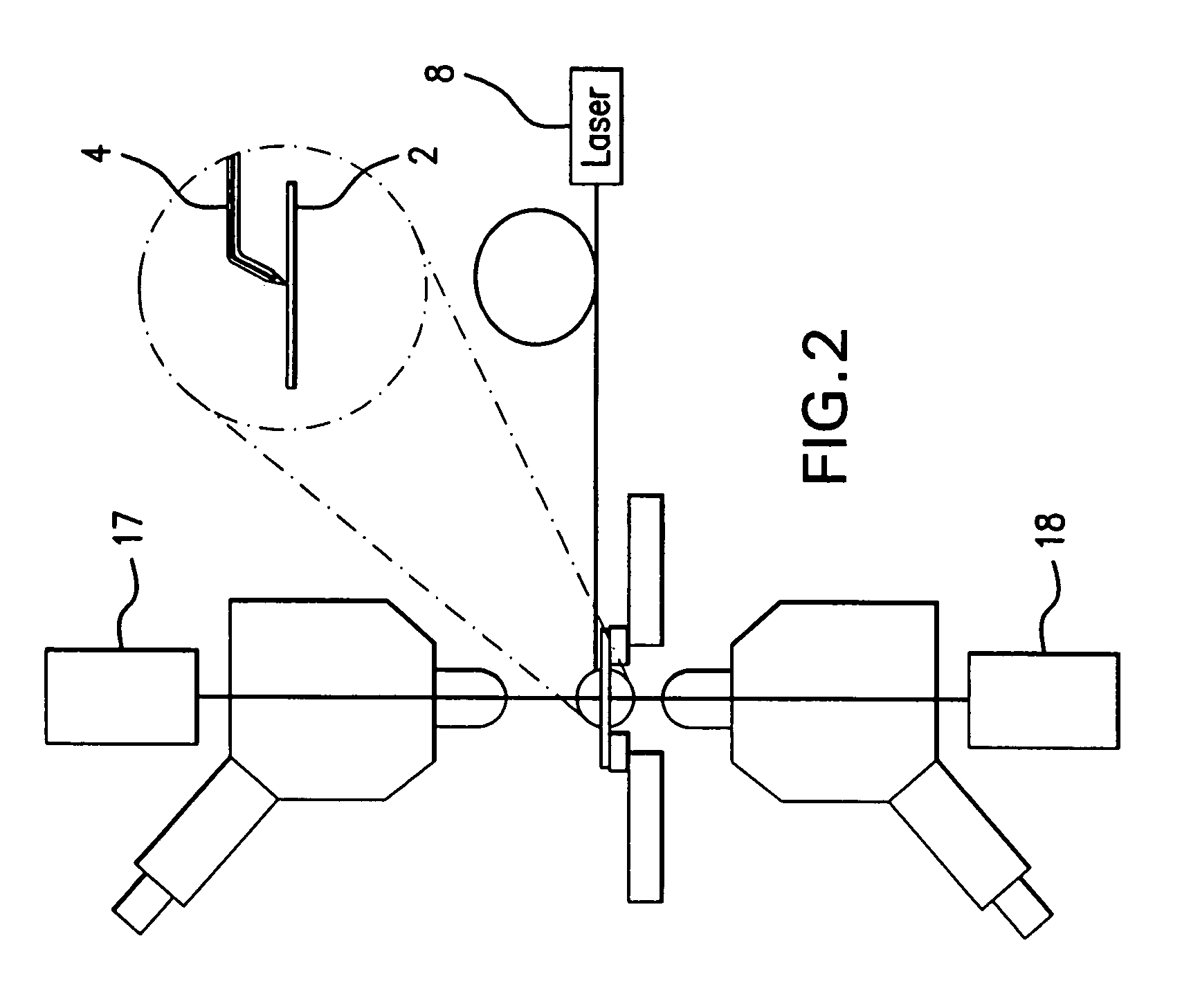
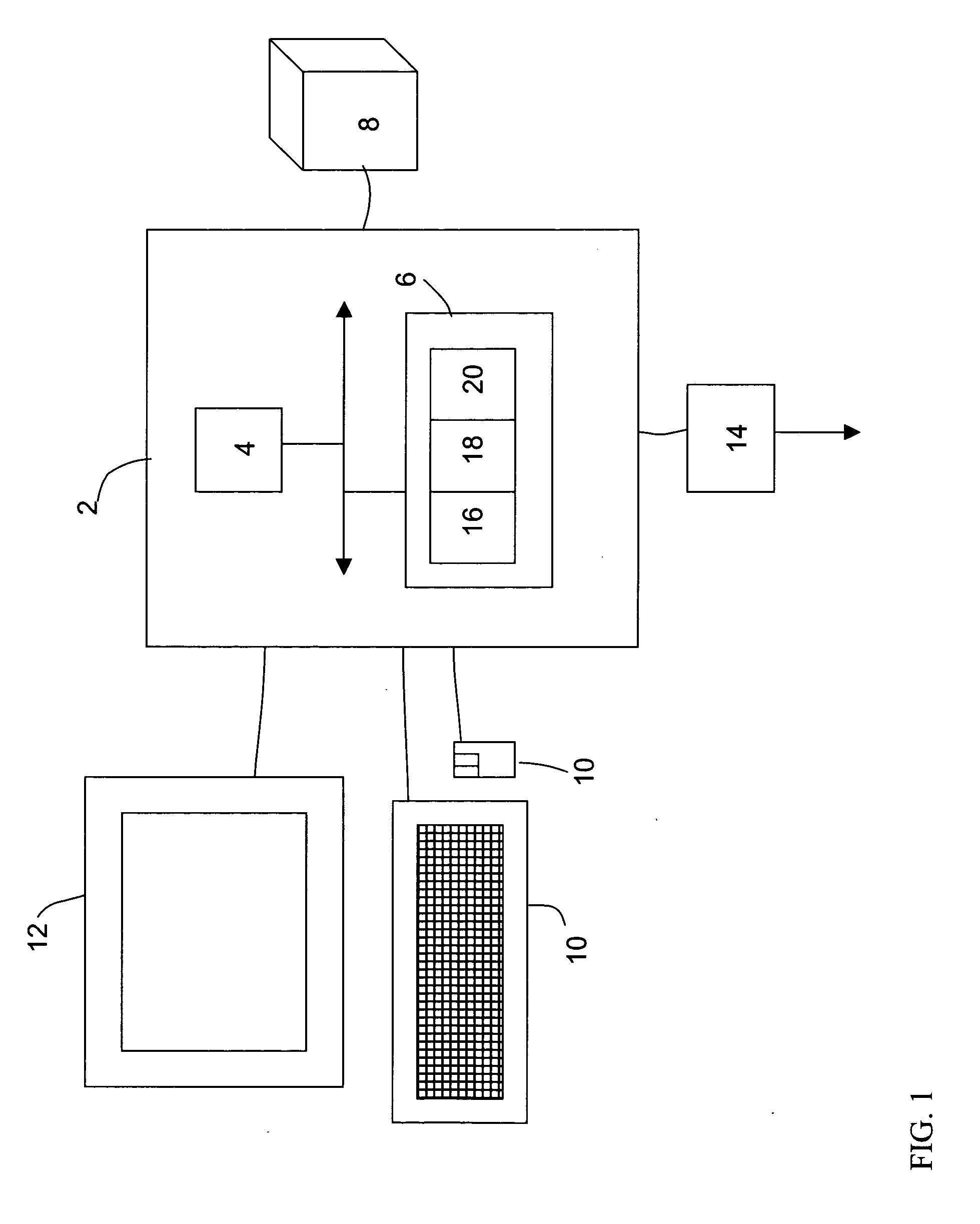
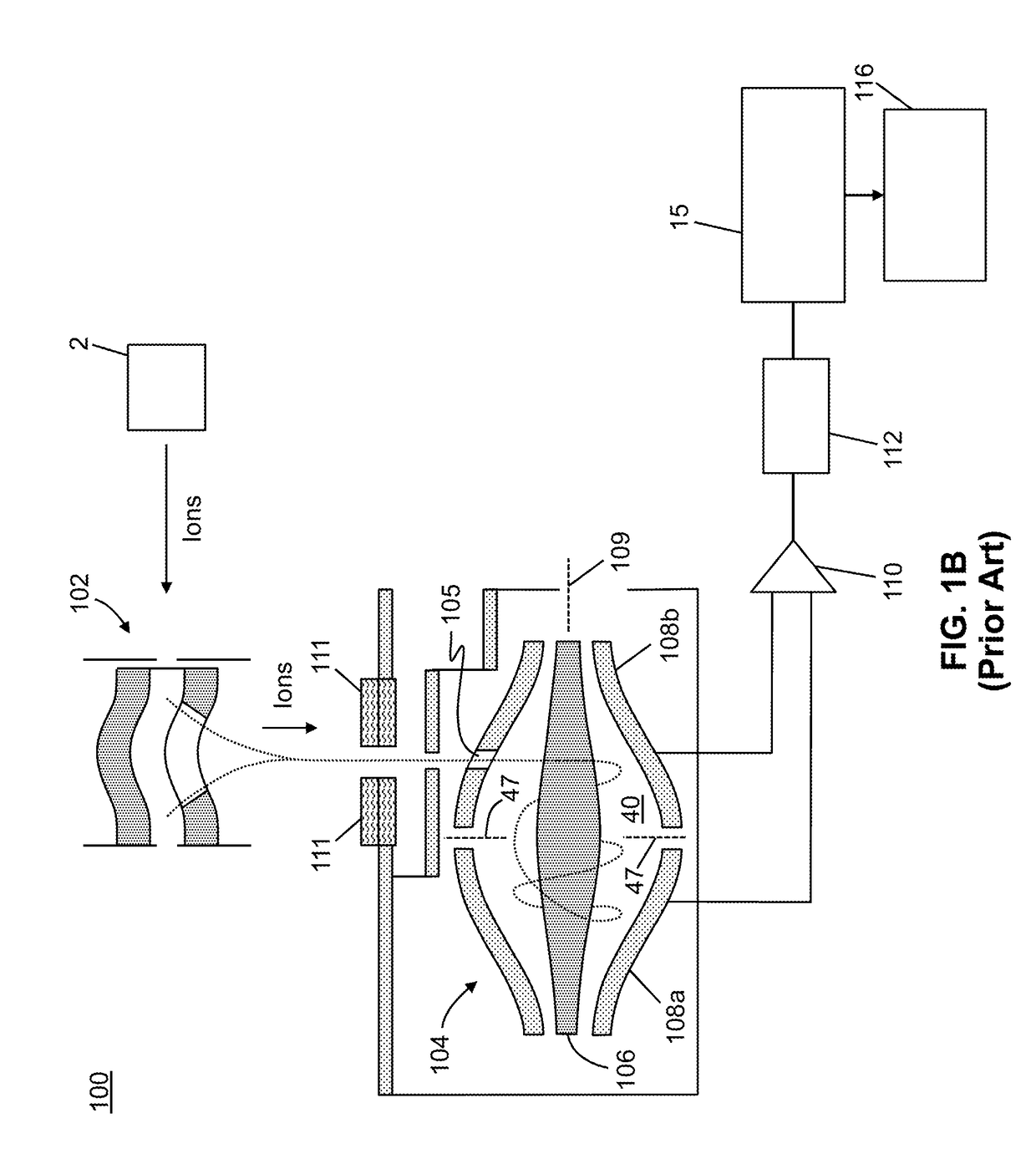
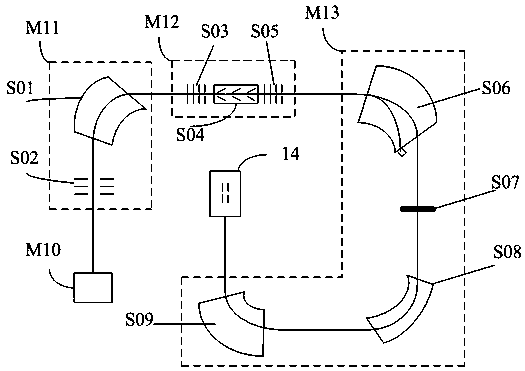
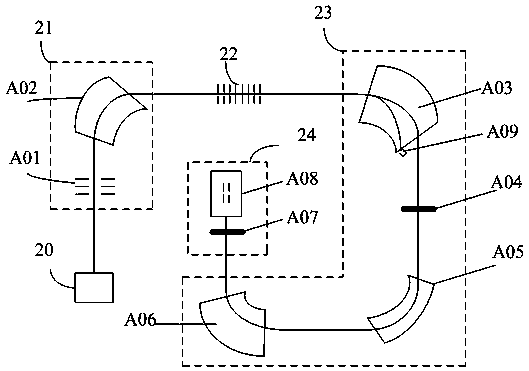
A system and method for analyzing and imaging a sample containing molecules of interest combines modified MALDI mass spectrometer and SNOM devices and techniques, and includes: (A) an atmospheric-pressure or near-atmospheric-pressure ionization region; (B) a sample holder for holding the sample; (C) a laser for illuminating said sample; (D) a mass spectrometer having at least one evacuated vacuum chamber; (E) an atmospheric pressure interface connecting said ionization region and said mass spectrometer; (F) a scanning near-field optical microscopy instrument comprising a near-field probe for scanning the sample; a vacuum capillary nozzle for sucking in particles which are desorbed by said laser, the nozzle being connected to an inlet orifice of said atmospheric pressure interface; a scanner platform connected to the sample holder, the platform being movable to a distance within a near-field distance of the probe; and a controller for maintaining distance information about a current distance between said probe and said sample; (G) a recording device for recording topography and mass spectrum measurements made during scanning of the sample with the near-field probe; (H) a plotting device for plotting said topography and mass spectrum measurements as separate x-y mappings; and (I) an imaging device for providing images of the x-y mappings.
Owner:GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY
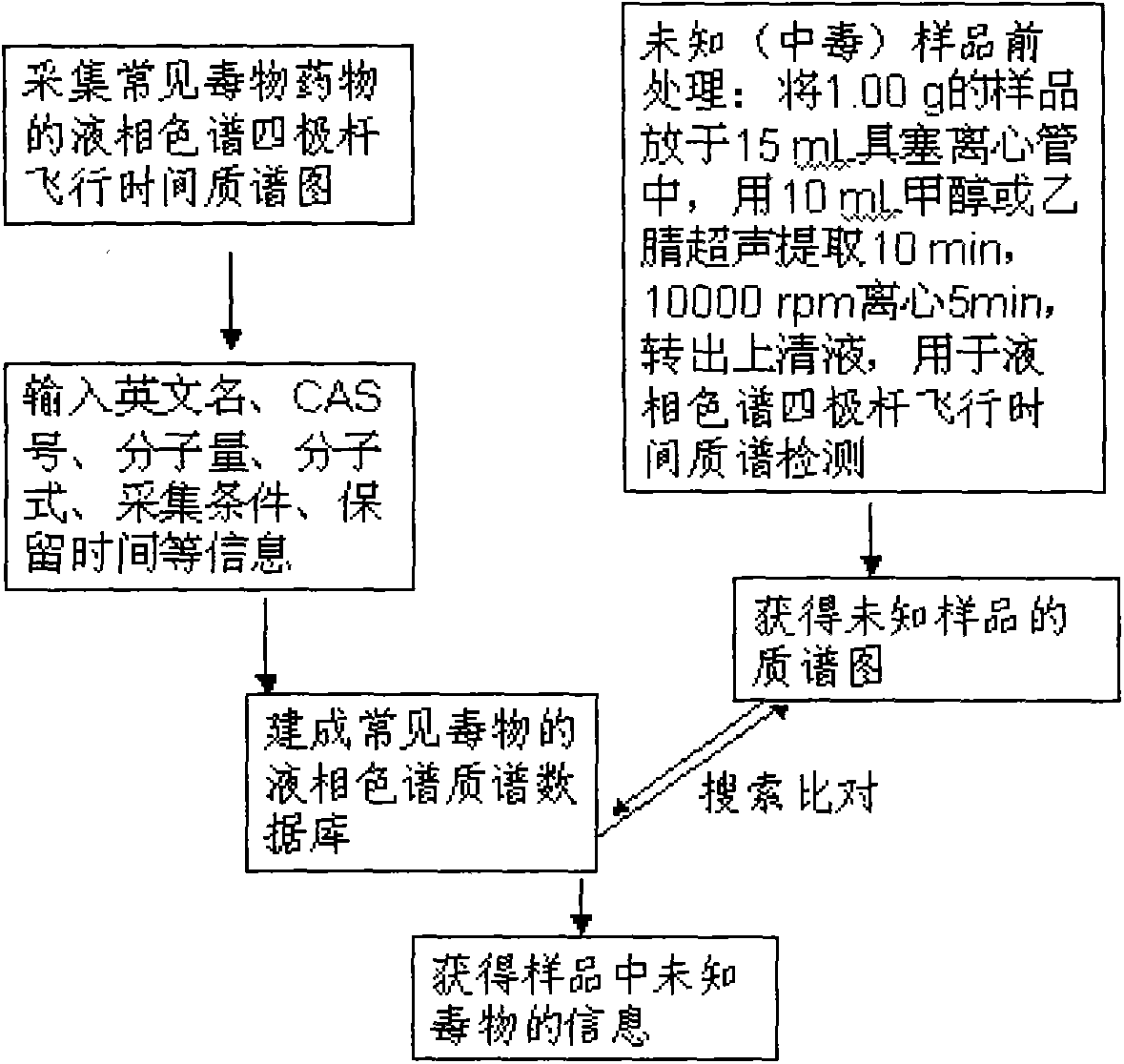
Method for detecting unknown poison by establishing liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry database
ActiveCN103823008AShorten detection timeReduce processing timeComponent separationMass spectrometry measurementToxicant
The invention relates to a method for detecting unknown poison by establishing a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry database, in particular to a method used for detecting unknown poison during food poisoning. According to the method, firstly, an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry method is used for establishing a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry database of common poison; then, a sample is subjected to supersonic extraction with methyl alcohol or acetonitrile, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry data of an extracting solution are measured similarly and searched and compared in the liquid chromatogram-mass spectrometry database of common poison according to the retention time of the sample and mass spectrometry fragments, and the variety of the unknown poison in the sample is judged; and the unknown poisoning sample is simply extracted and directly measured and compared, and a screening result can be acquired in one hour, so that the detecting and treating time of the sample is greatly shortened, the detecting efficiency is improved, and technical support is provided for related events such as food poisoning and the like caused by unknown reasons.
Owner:BEIJING CENT FOR DISEASE PREVENTION & CONTROL
Measuring device and measuring method for measuring gas permeability of material
InactiveCN103115858AHigh measurement sensitivityIncreased permeability measurement sensitivityPermeability/surface area analysisMass spectrometry measurementThermodynamics
The invention discloses a measuring device and a measuring method for measuring gas permeability of a material. The measuring device comprises a gas chamber, a gas accumulation chamber and a high-vacuum chamber, wherein a film of the material to be measured or a thin sheet is installed between the gas chamber and the gas accumulation chamber; the gas chamber is connected with a gas source to be measured and a low-vacuum pump; the accumulation chamber is connected with the high-vacuum chamber through a needle valve; and the high-vacuum chamber is connected with a mass spectra gauge and a super-high-vacuum sucking system. By utilizing the device and the method, after a measured gas which permeates through the measured material is accumulated in the gas accumulation chamber to a relatively large gas quantity, part of the gas is sampled into the high-vacuum chamber to be subjected to mass-spectrometer measurement, so that the sensitivity in permeability measurement is improved; and the longer the accumulation time is, the higher the measurement sensitivity is, for example, the sensitivity in steam permeability measurement can reach the level of 10-7g / m<2>day grade.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
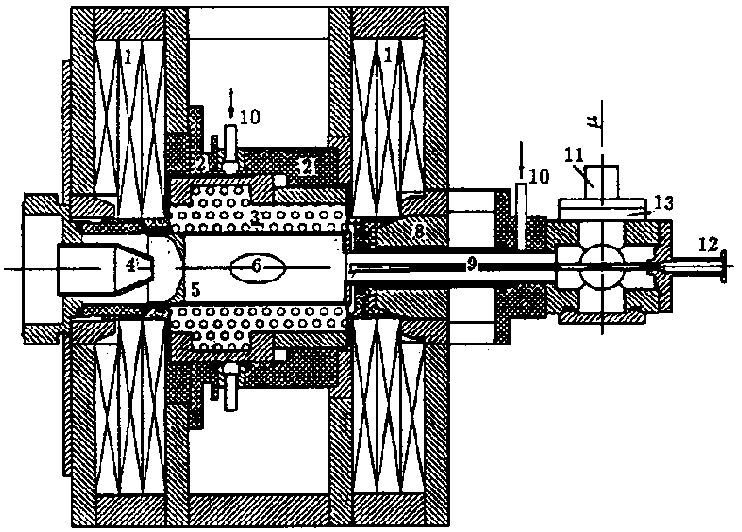
Direct sample analysis ion source
ActiveCN103797559ASamples introduction/extractionTube vacuum systemsMass spectrometry measurementGas phase
A Direct Sample Analysis (DSA) ion source system operating at essentially atmospheric pressure is configured to facilitate the ionization, or desorption and ionization, of sample species from a wide variety of gaseous, liquid, and / or solid samples, for chemical analysis by mass spectrometry or other gas phase ion detectors. The DSA system includes one or more means of ionizing samples and includes a sealed enclosure which provides protection from high voltages and hazardous vapors, and in which the local background gas environment may be monitored and well-controlled. The DSA system is configured to accommodate single or multiple samples at any one time, and provide external control of individual sample positioning, sample conditioning, sample heating, positional sensing, and temperature measurement.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Imaging mass spectrometry for small molecules in two-dimensional samples
ActiveUS20080296488A1Improve quality resolutionIncrease choiceTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationMass spectrometry measurementMetabolite
The invention relates to spatially resolved mass spectrometric measurement and visualization of the distribution of small molecules in a mass range from approximately 150 to 500 Daltons, for example drugs and their metabolites, in thin sections or other two-dimensional samples, preferably with ionization of the molecules by matrix-assisted laser desorption. The invention includes the steps measuring a daughter ion produced by forced decomposition of the molecular ion instead of the ionized analyte molecule itself, the daughter ion having a much better signal-to-noise ratio. The daughter ions are detected in a relatively simple reflector time-of-flight mass spectrometer instead of using an expensive time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometers for the measurement of the daughter ions. Advantageously, substantially faster and less expensive scanning of the thousands of mass spectra which serve as the basis for visualizing the spatial distribution of the analyte molecule is achieved, while the mass resolution and sensitivity are at least equally good.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Protein microscope
InactiveUS7735146B2Time-of-flight spectrometersNanoopticsMass spectrometry measurementNear field optical microscope
A system and method for analyzing and imaging a sample containing molecules of interest combines modified MALDI mass spectrometer and SNOM devices and techniques, and includes: (A) an atmospheric-pressure or near-atmospheric-pressure ionization region; (B) a sample holder for holding the sample; (C) a laser for illuminating said sample; (D) a mass spectrometer having at least one evacuated vacuum chamber; (E) an atmospheric pressure interface connecting said ionization region and said mass spectrometer; (F) a scanning near-field optical microscopy instrument comprising a near-field probe for scanning the sample; a vacuum capillary nozzle for sucking in particles which are desorbed by said laser, the nozzle being connected to an inlet orifice of said atmospheric pressure interface; a scanner platform connected to the sample holder, the platform being movable to a distance within a near-field distance of the probe; and a controller for maintaining distance information about a current distance between said probe and said sample; (G) a recording device for recording topography and mass spectrum measurements made during scanning of the sample with the near-field probe; (H) a plotting device for plotting said topography and mass spectrum measurements as separate x-y mappings; and (I) an imaging device for providing images of the x-y mappings.
Owner:GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY
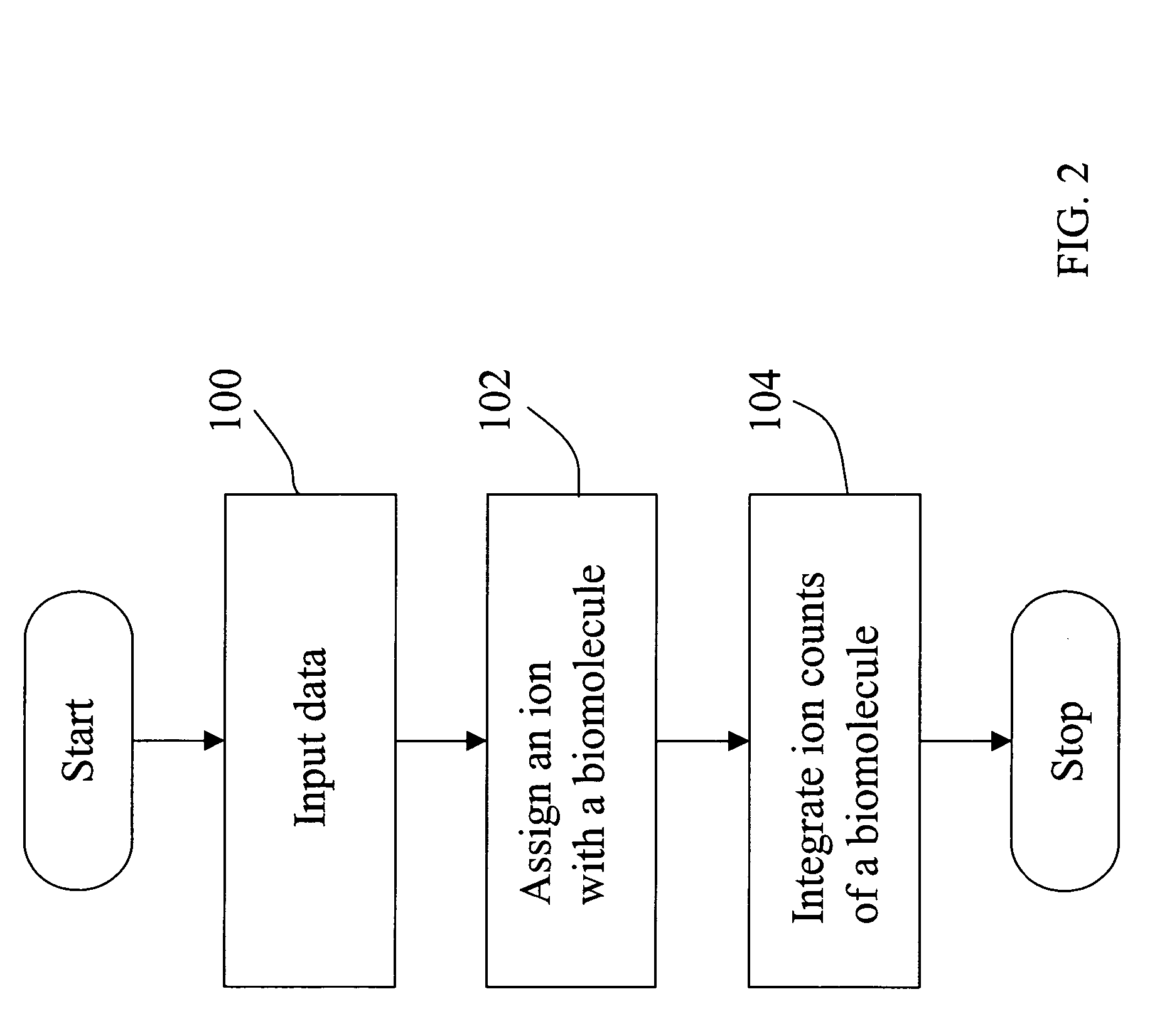
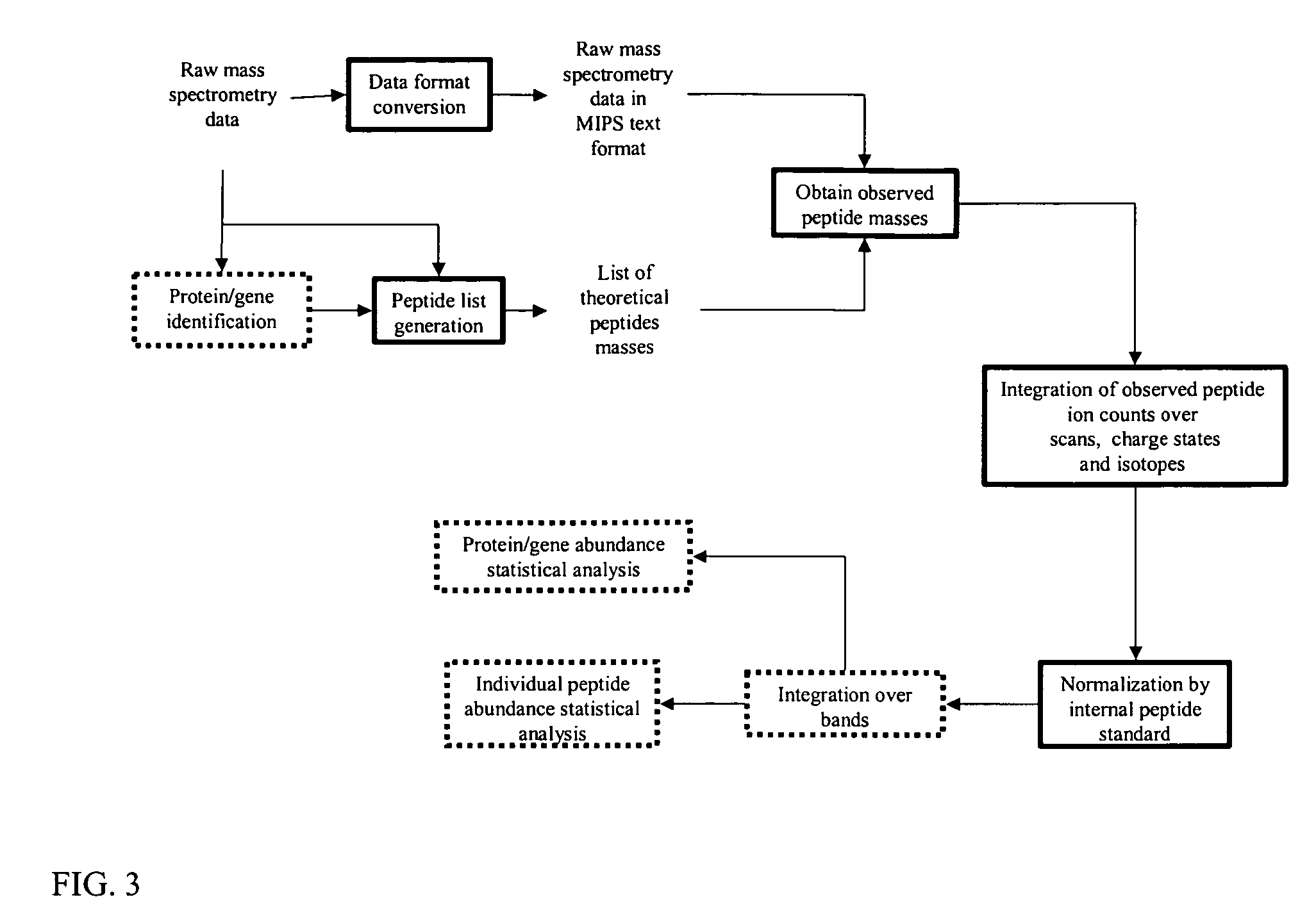
Mass intensity profiling system and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060003385A1Rapid and efficient identificationQuick SetupComponent separationOther chemical processesMass spectrometry measurementMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention is directed to computer automated methods and systems for identifying and characterizing biomolecules in a biological sample. Mass spectrometry measurements are obtained on biomolecules in a sample. These measurements are analyzed to determine the abundance of the biomolecules in the sample, and the abundance measurements are coupled with one or more distinguishing characteristics of biomolecules they are associated with, thereby permitting computer-mediated comparison of abundances of biomolecules from multiple biological samples.
Owner:CAPRION PHARMA
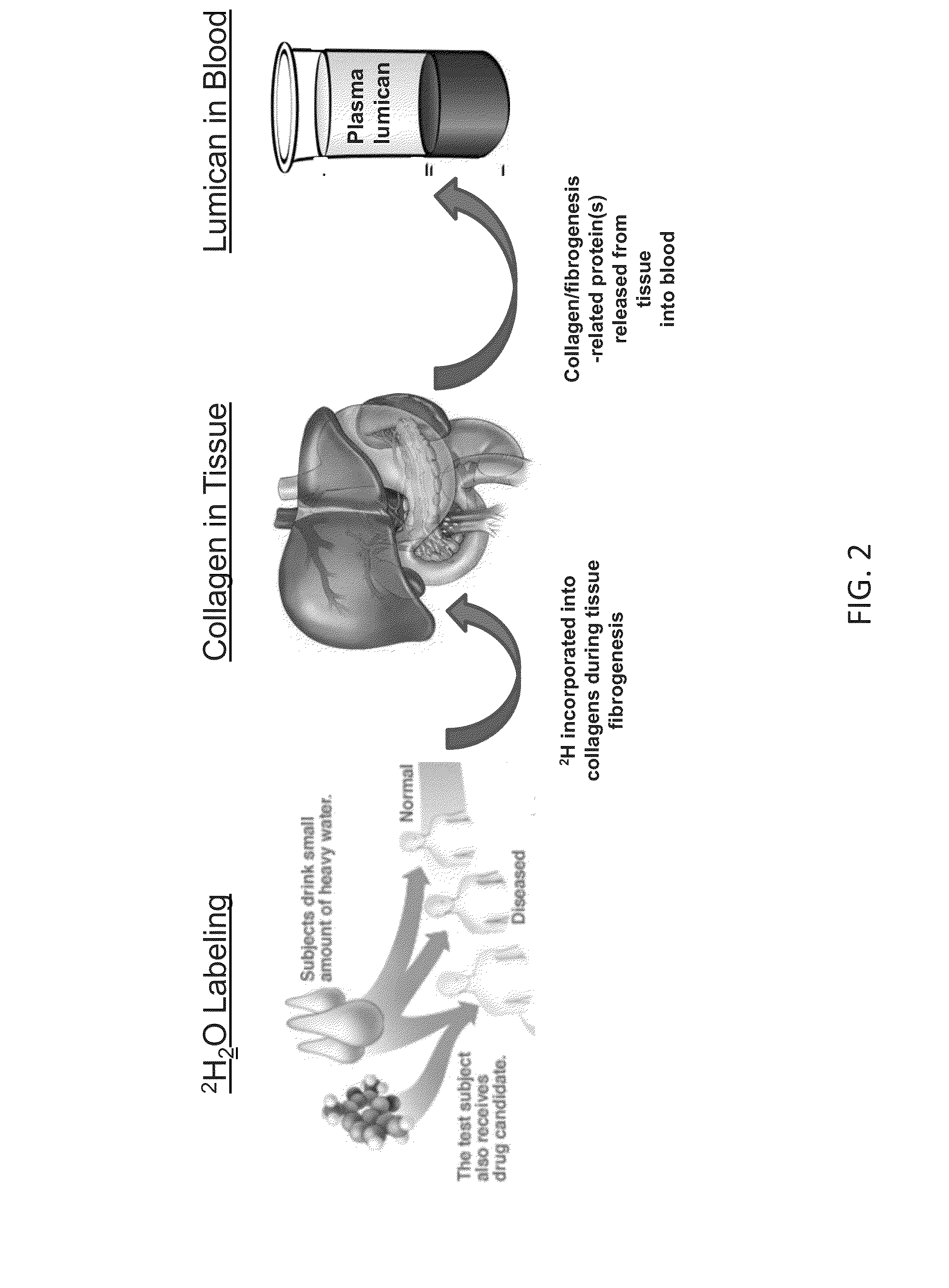
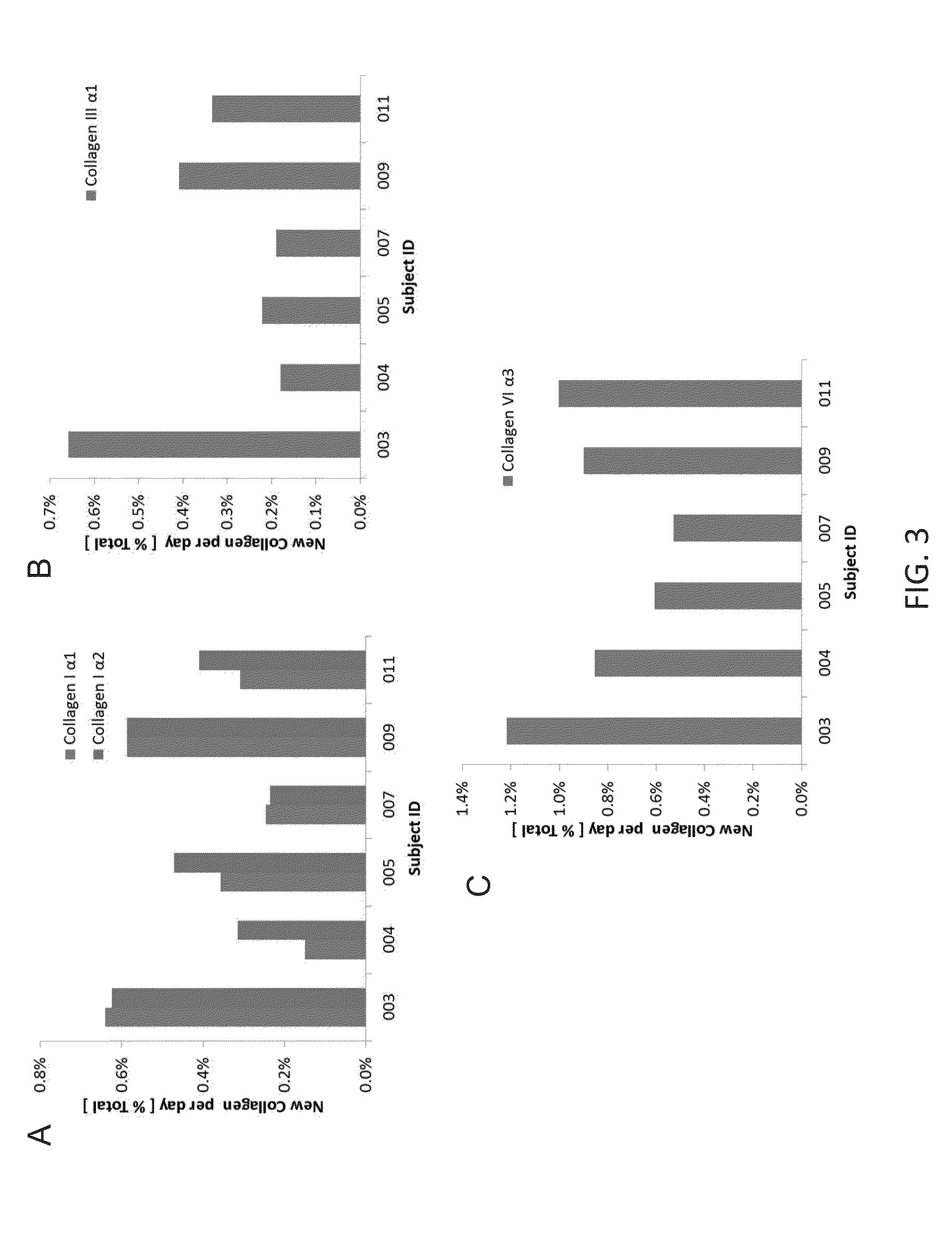
Method for replacing biomarkers of protein kinetics from tissue samples by biomarkers of protein kinetics from body fluids after isotopic labeling in vivo
ActiveUS20140273044A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisProtein targetIsotopic labeling
Provided herein are method for measuring the rate of synthesis, breakdown, transport, or other kinetic parameters of a protein in a tissue of medical interest, without requiring physical sampling of the tissue, by a measurement of the protein in a body fluid. Methods may include selecting one or more target proteins in a tissue; administering an isotope-labeled molecule to a subject for a period of time sufficient for said isotope-labeled molecule to enter into and label the one or more target proteins to produce one or more isotope-labeled target proteins; collecting a volume of a body fluid, wherein the volume comprises one or more isotope-labeled target proteins that escaped or were released from the tissue; enriching or isolating the one or more isotope-labeled target proteins from the volume; performing a mass spectrometric measurement of the isotopic content, rate of incorporation, and / or pattern or rate of change in isotopic content and / or pattern of isotope labeling of the one or more enriched or isolated isotope-labeled target proteins; and calculating at least one kinetic parameter of the one or more enriched or isolated isotope-labeled target proteins, where the kinetic parameter of the one or more isotope-labeled target proteins from the volume of a body fluid reflects the corresponding kinetic parameter of the one or more target proteins in the tissue; and inferring the at least one kinetic parameter of the one or more target proteins in the tissue based on the corresponding at least one kinetic parameter of the one or more target proteins in the body fluid.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
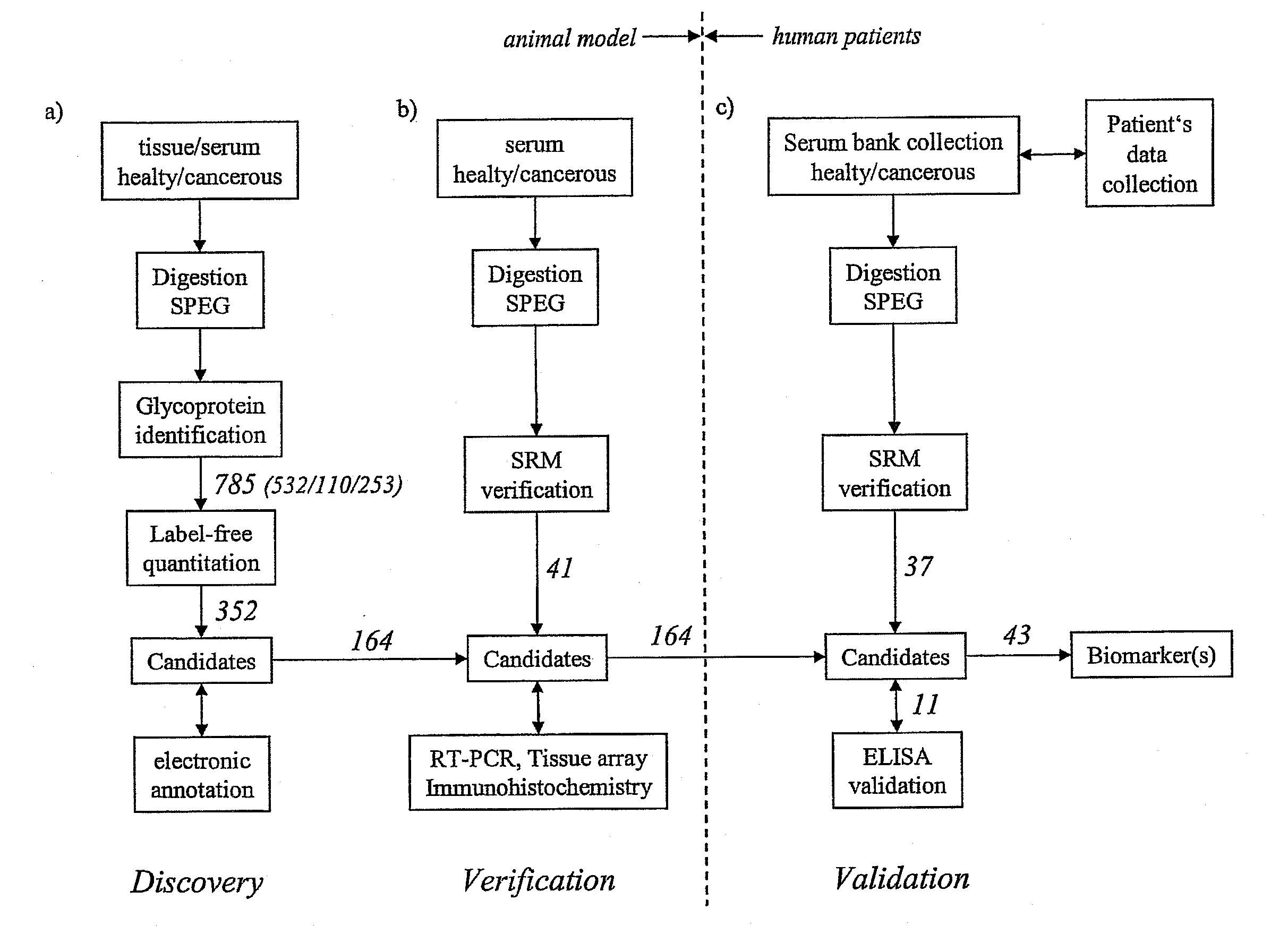
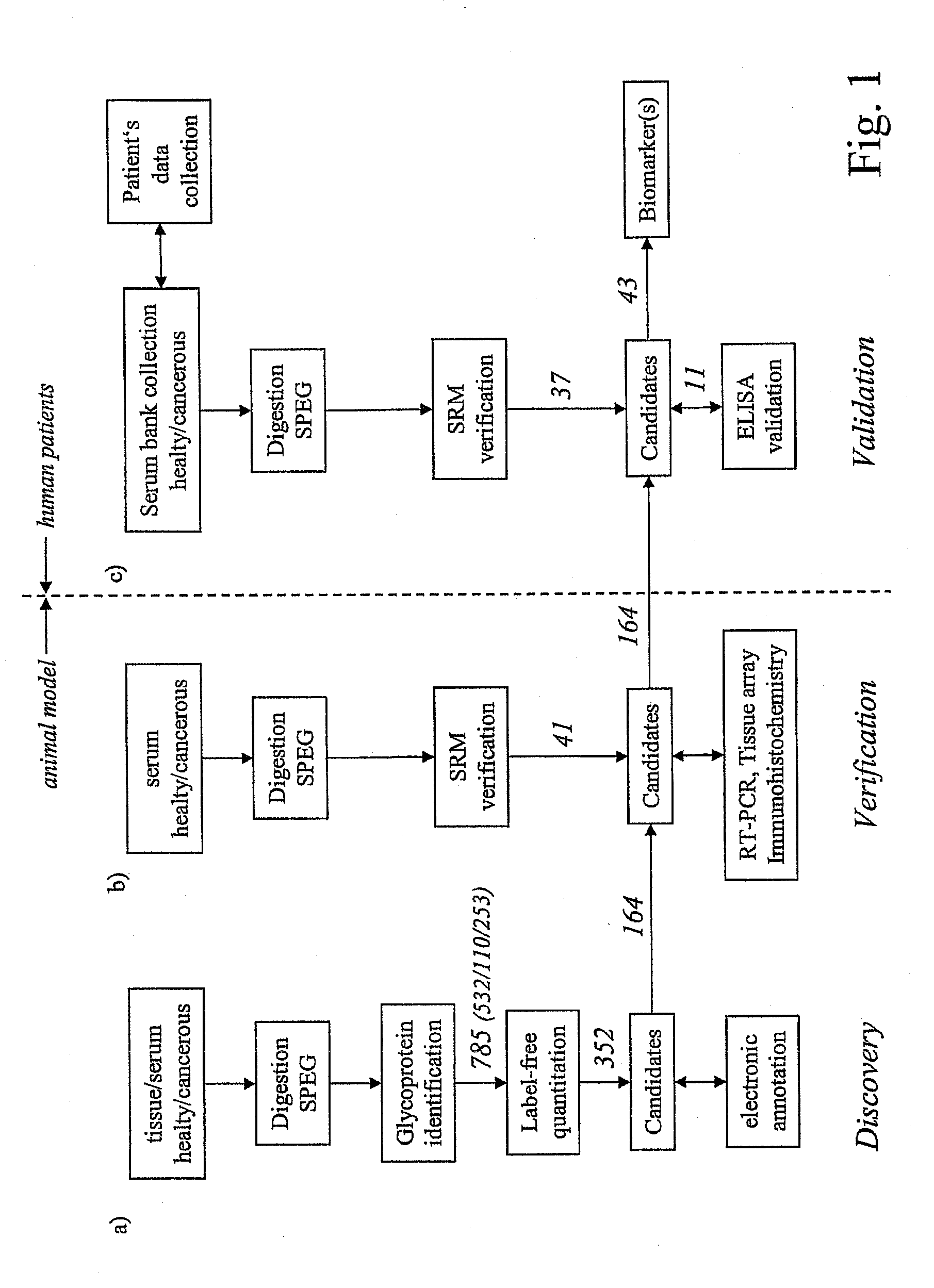
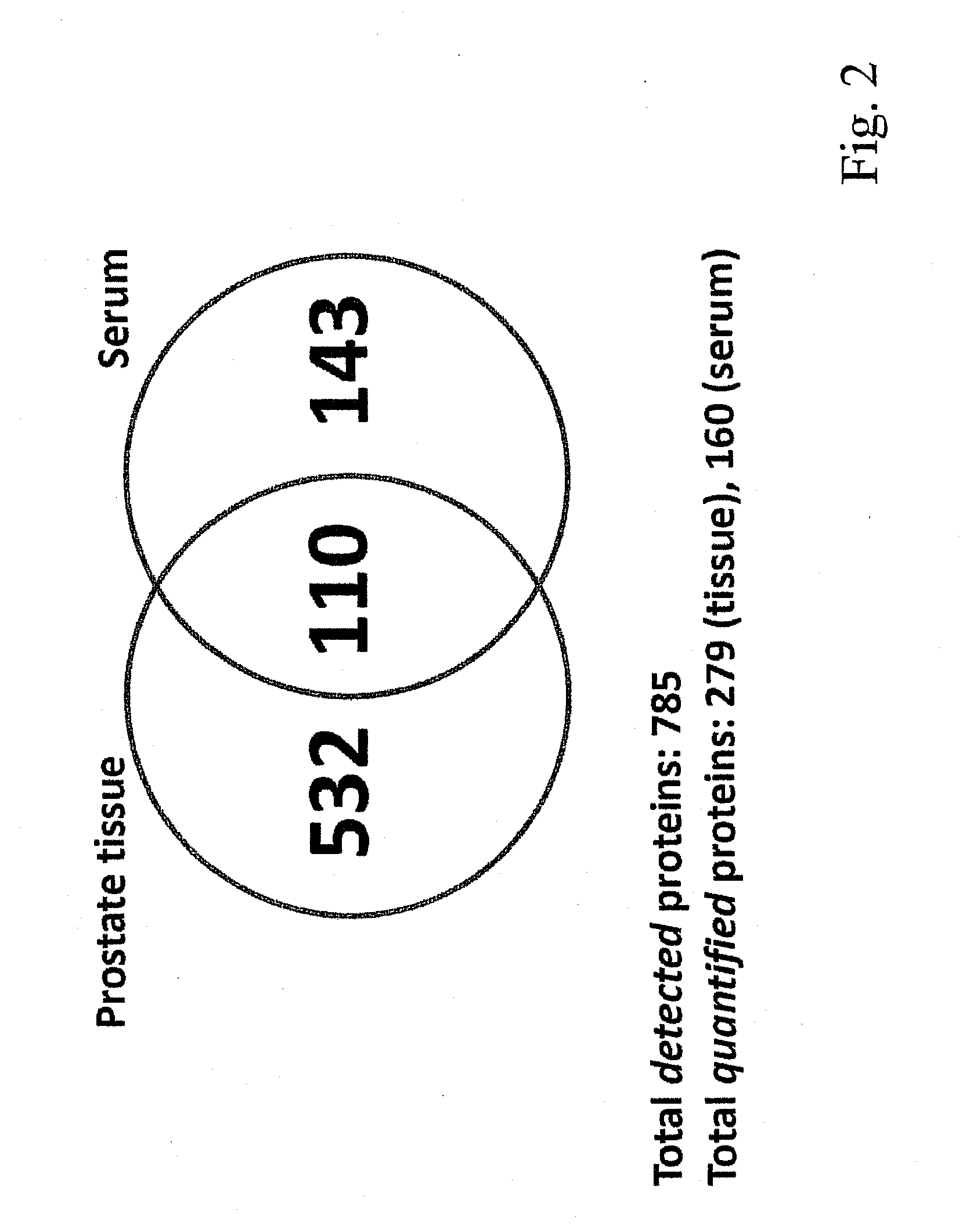
Method for biomarker and drug-target discovery for prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment as well as biomarker assays determined therewith
InactiveUS20110065605A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProtein proteinAntibody
The invention relates to a method for the determination of a cancer diagnostic / therapeutic biomarker assay and drug-targets including the following steps: (a) identification of potential candidate protein / peptide biomarkers and drug-targets based on the measurement of protein / peptide constituent concentrations in tissue sample proteomes as well as serum, plasma or any other derivatives of blood, or blood itself sample proteomes derived from healthy non-human mammalian individuals as well as from cancerous non-human mammalian individuals and qualitatively selecting as potential candidate protein / peptide biomarkers those which show a pronounced differential behaviour between healthy and cancerous sample proteomes; (b) optional verification of the potential candidate protein / peptide biomarkers as identified in step (a) by quantitative mass spectrometric measurement of the potential candidate protein biomarkers in serum, plasma or any other derivatives of blood, or blood itself sample proteomes derived from healthy non-human mammalian individuals as well as from cancerous non-human mammalian individuals and selecting as candidate protein / peptide biomarkers those which show a mass-spectrometrically measurable quantitative differential behaviour between healthy and cancerous sample proteomes; (c) validation of the candidate protein / peptide biomarkers as identified in step (a), or as optionally verified in step (b), by mass spectrometric measurement and / or antibody-based assays such as an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) determination of the candidate protein biomarkers in serum, plasma or any other derivatives of blood, or blood itself sample proteomes derived from healthy human individuals as well as from cancerous human individuals and selecting as protein / peptide biomarkers those which show a mass-spectrometrically measurable and / or antibody-based assay detectable differential behaviour between healthy and cancerous sample proteomes; (d) application of statistical methods to uncover single or groups of protein / peptide biomarkers as validated in step (c) as signatures for the detection of patients with cancer. The invention furthermore relates to specific biomarker assays for the highly reliable diagnosis of cancer, specifically of localized or non-localized prostate cancer, using human serum, plasma or any other derivatives of blood, or blood itself.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH +1
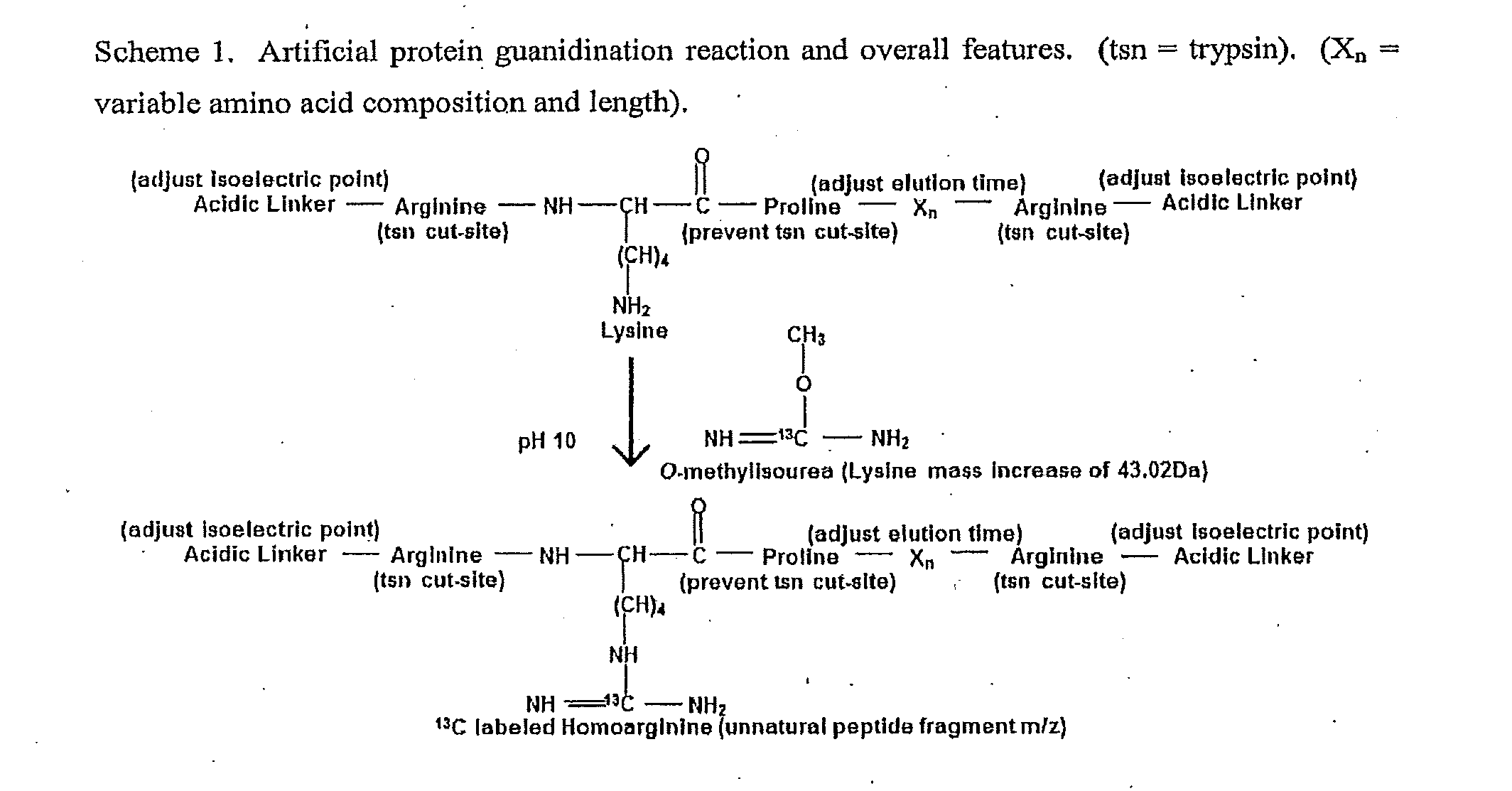
General Mass Spectrometry Assay Using Continuously Eluting Co-Fractionating Reporters of Mass Spectrometry Detection Efficiency
InactiveUS20140252221A1Component separationParticle spectrometer methodsMass spectrometry measurementFractionation
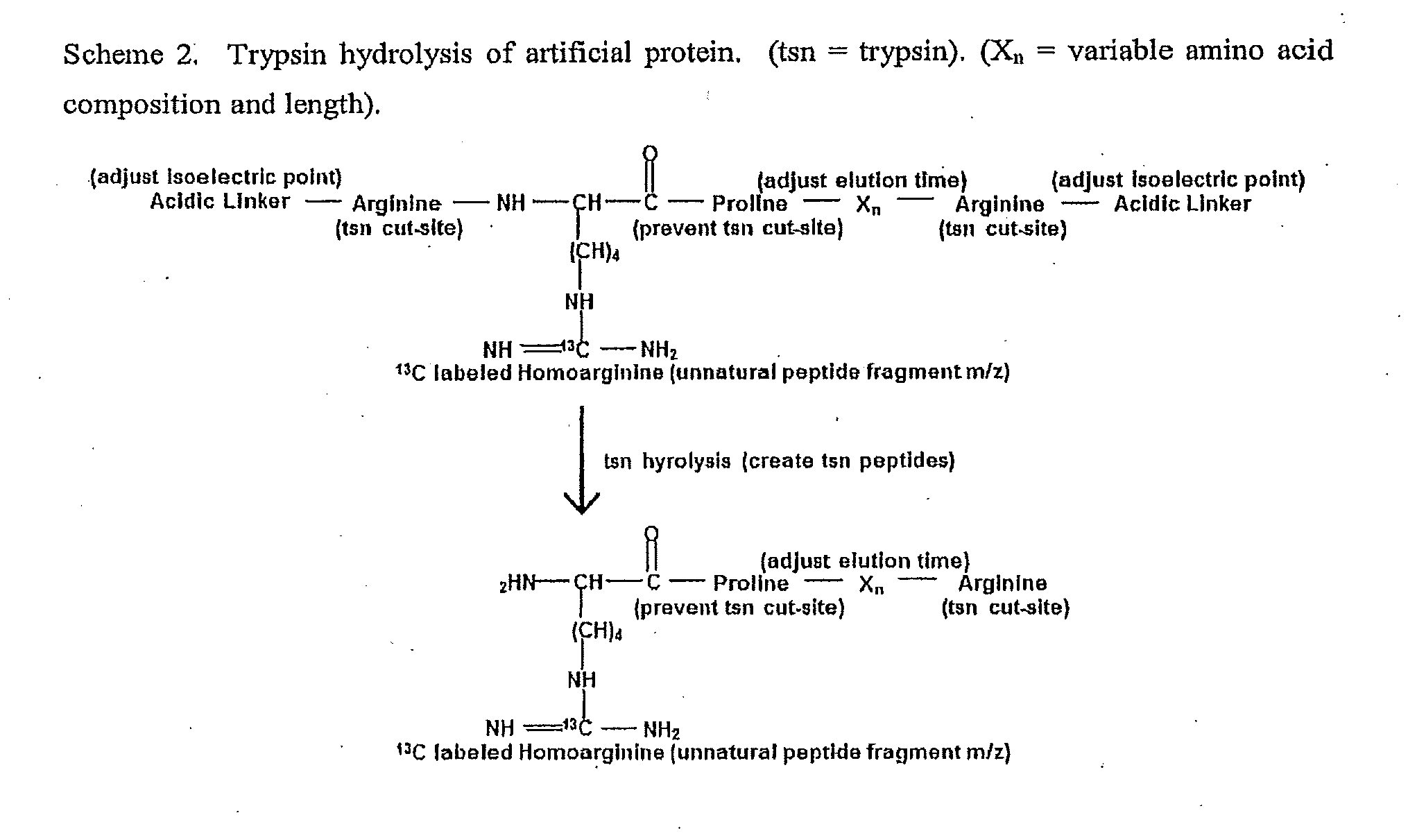
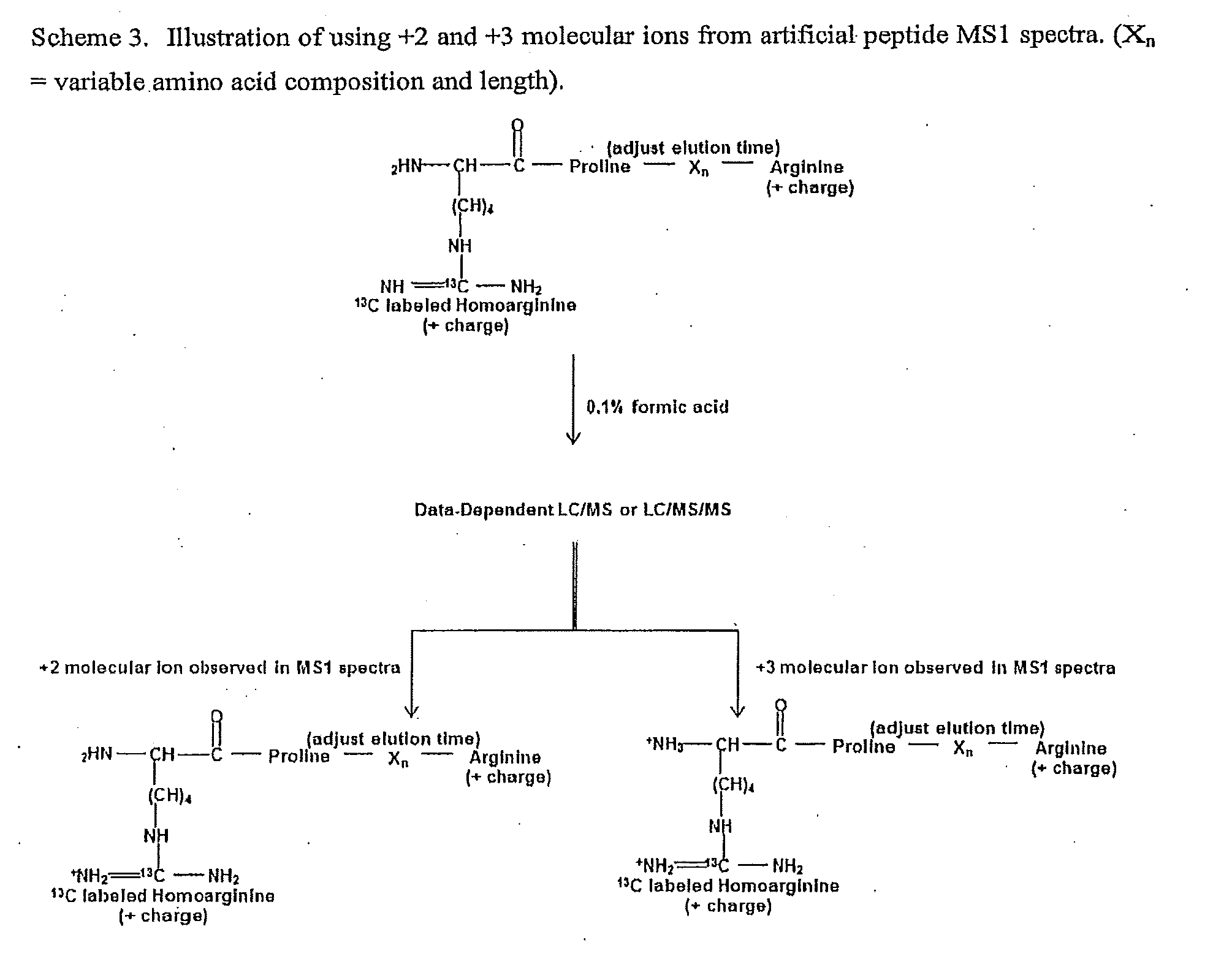
The invention provides general methods for quantifying any conceivable compound including small organic molecules and biological molecules in mass spectrometric measurements. The methods include the use of chemical or biological reporters such as artificial polypeptides containing proteolytic cleavage sites, which provide proteolytic reporter peptides for standardization of mass spectrometric detection efficiency. In addition to mass spectrometry standardization between different samples, the artificial polypeptides also standardize sample preparation amongst different samples undergoing mass spectrometric analysis when using electrophoresis separation prior to mass spectrometric analysis. Methods of the present invention also include methods for designing artificial polypeptides with peak to peak continuous liquid chromatography elution profiles spanning the complete or partial analyte elution profile for organic and biological molecules. Also included are the artificial polypeptides predigested with protease, which is compatible for use in experiments with native PAGE, in-solution proteolytic digestion of polypeptides, and small organic molecules undergoing fractionation separation followed by mass spectrometric evaluation.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Methods for Optimizing Mass Spectrometer Parameters
ActiveUS20170370889A1Reduce effortShorten the timeMolecular entity identificationParticle separator tubesMass spectrometry measurementMass analyzer
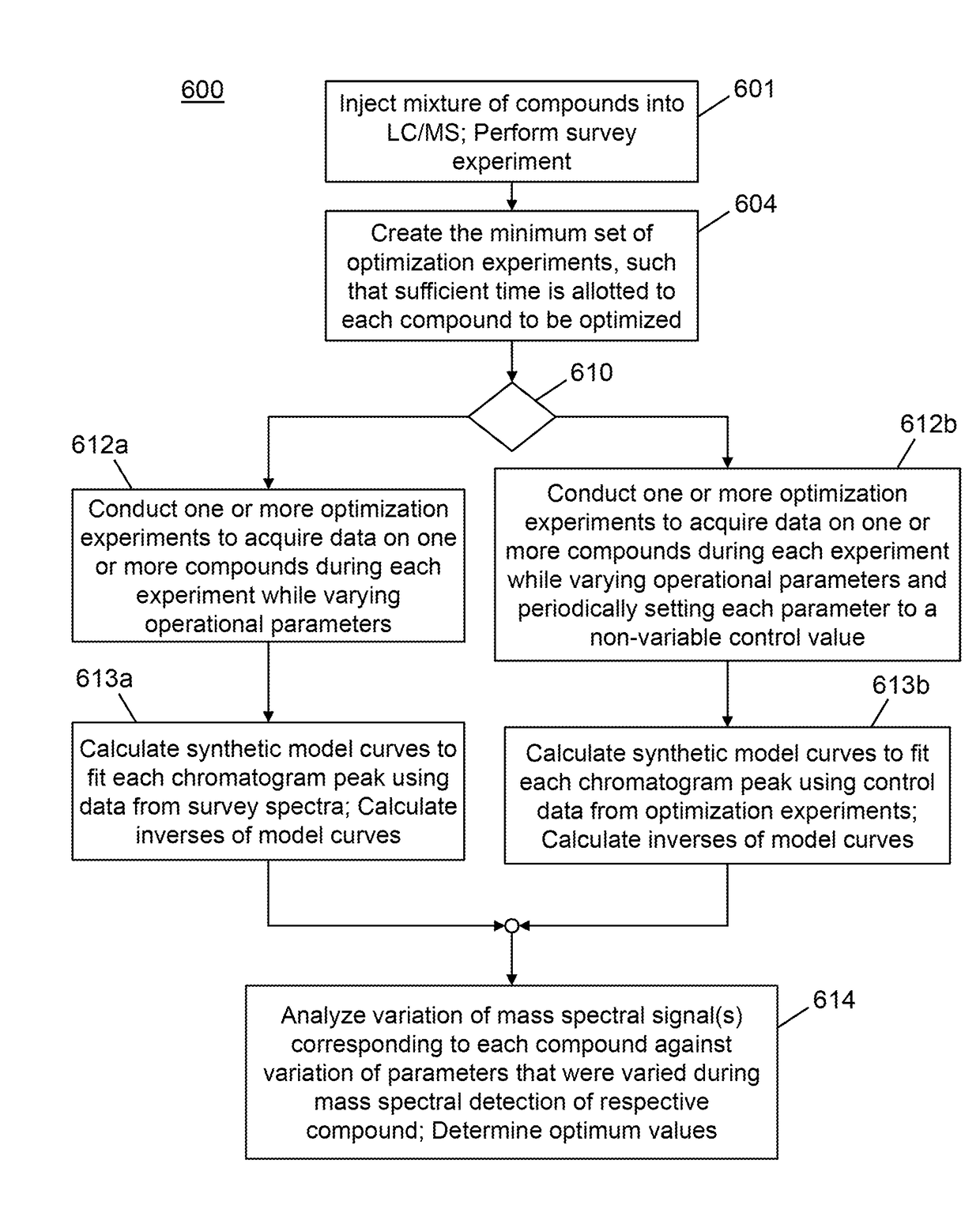
A method for determining optimal values of a mass spectral operating parameter for mass spectral analysis of each of a plurality of compounds comprises: acquiring a plurality of mass spectral measurements of each of at least one characteristic ion species of each respective compound during its introduction into a mass spectrometer while a quantity of each introduced compound varies with time wherein, for each characteristic ion species, the operational parameter is caused to vary between successive mass spectral measurements of the said species; calculating, for each characteristic ion species, a corrected intensity of at least a portion of the plurality of mass spectral measurements of said each species, based on a best-fit synthetic model curve that relates to the time variation of the respective corresponding compound; and determining the optimal values of the operating parameter from analyses of variation of the corrected intensities with respect to the operational parameter variation.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
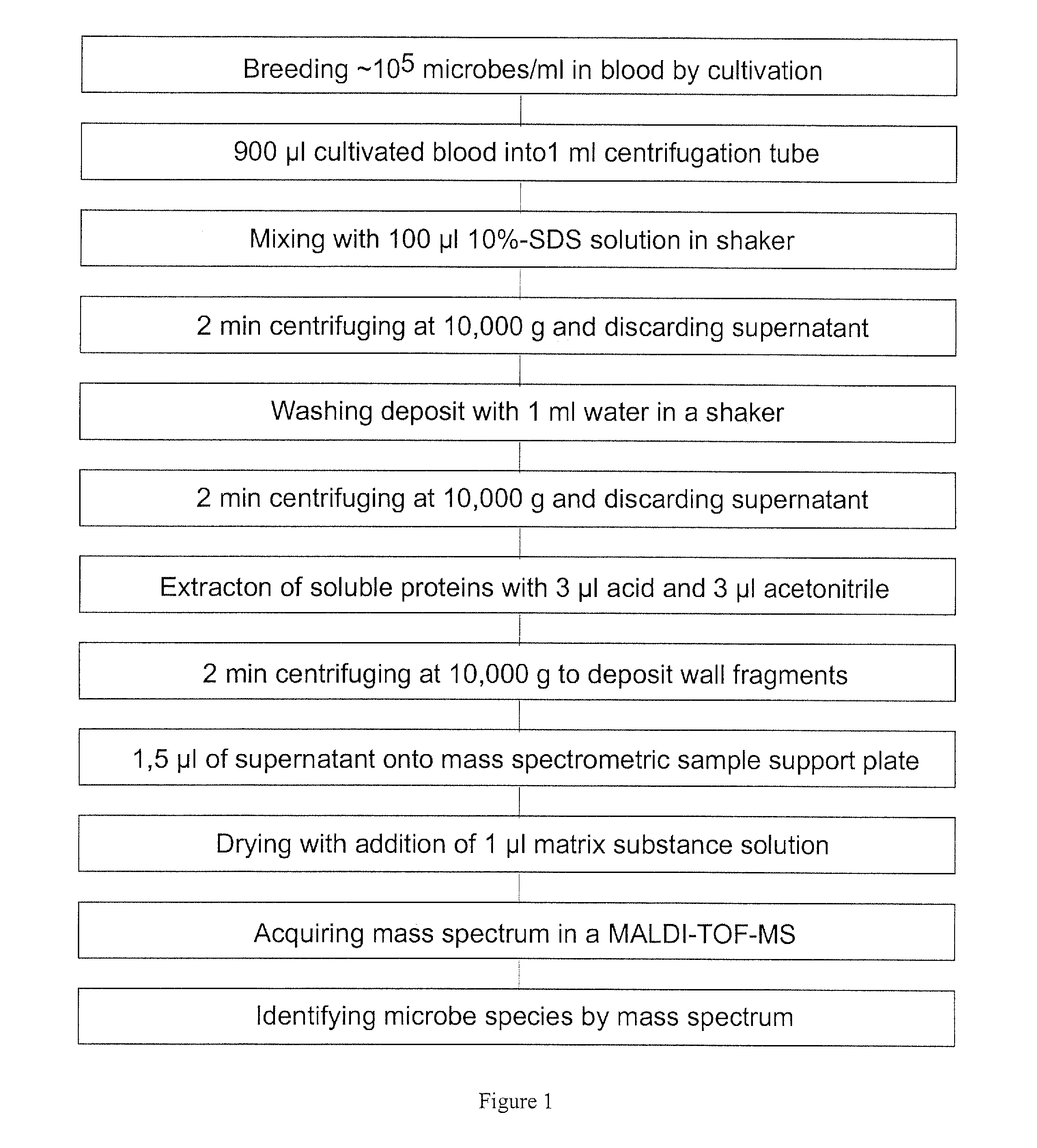
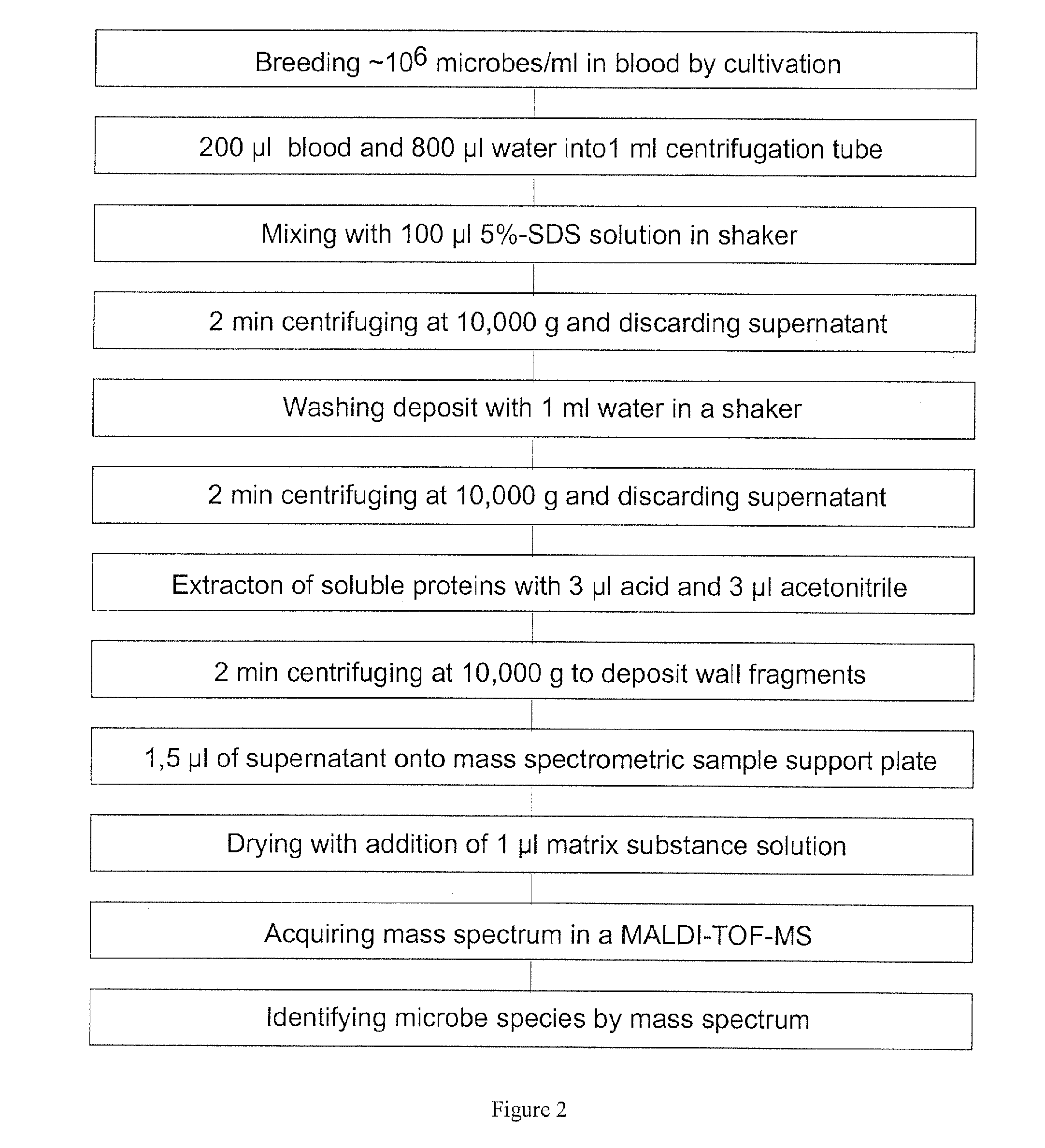
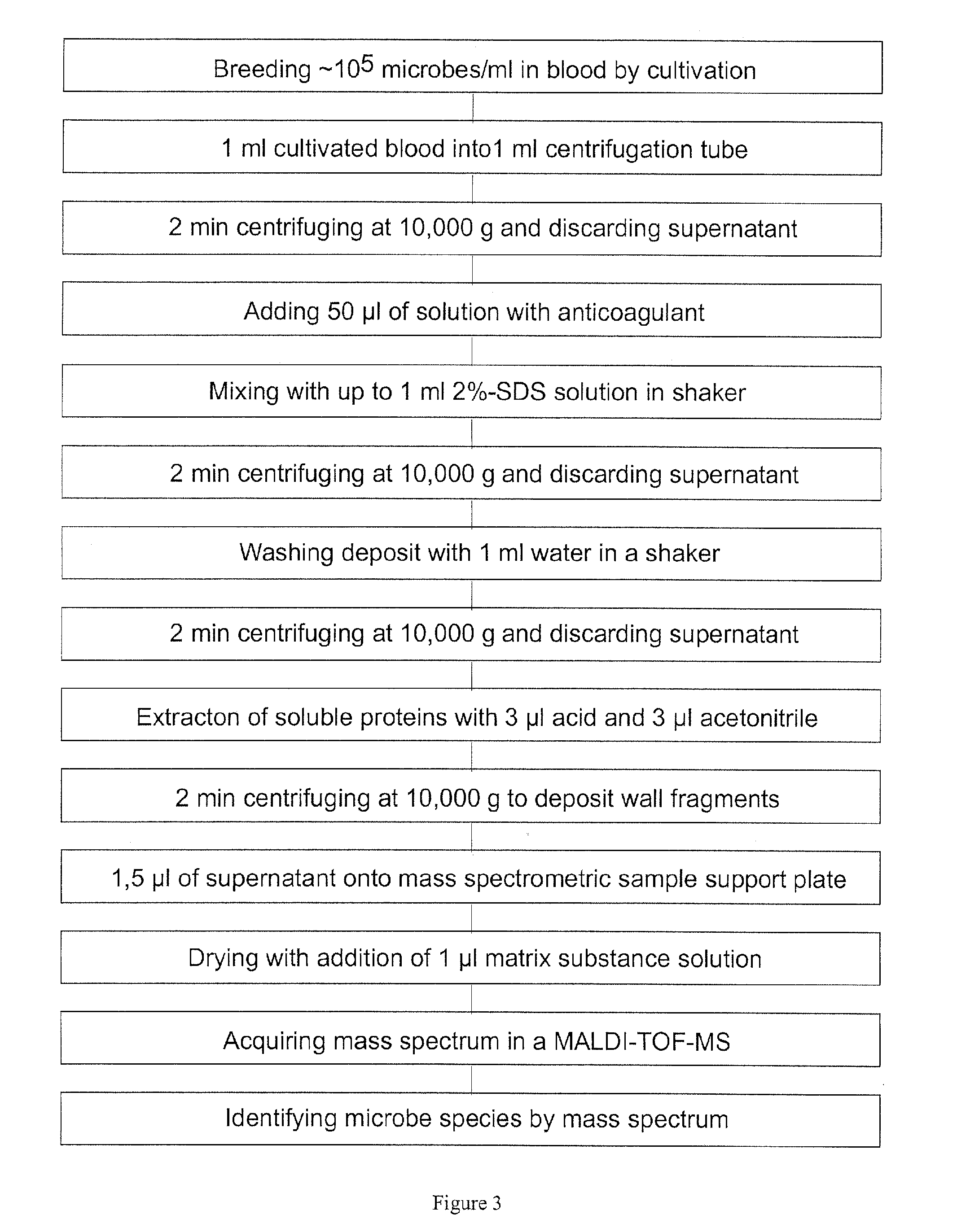
Mass spectrometric diagnosis of septicemia
ActiveUS8569010B2Microbiological testing/measurementMass spectrometric analysisProtein profilingMass spectrometry measurement
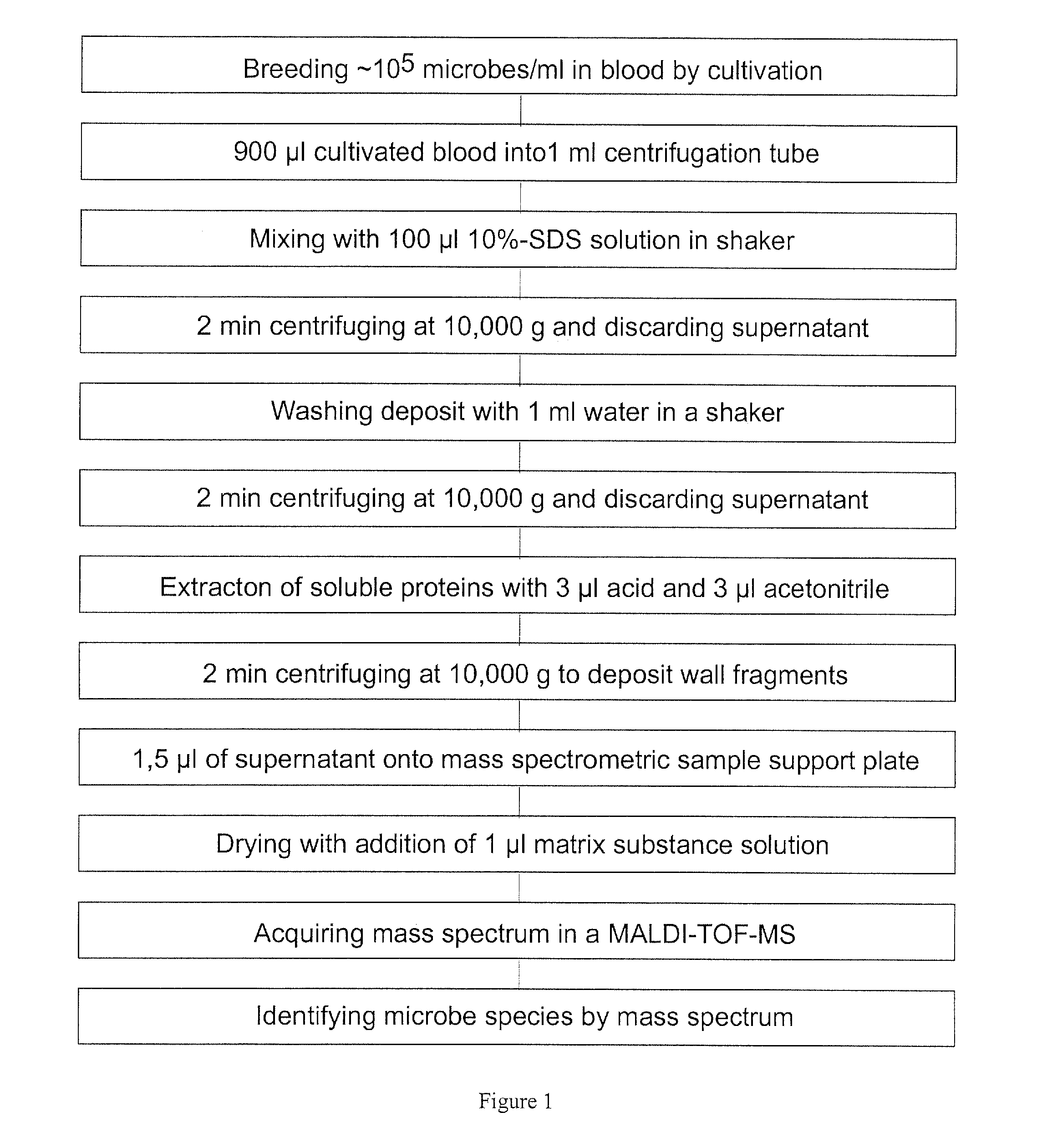
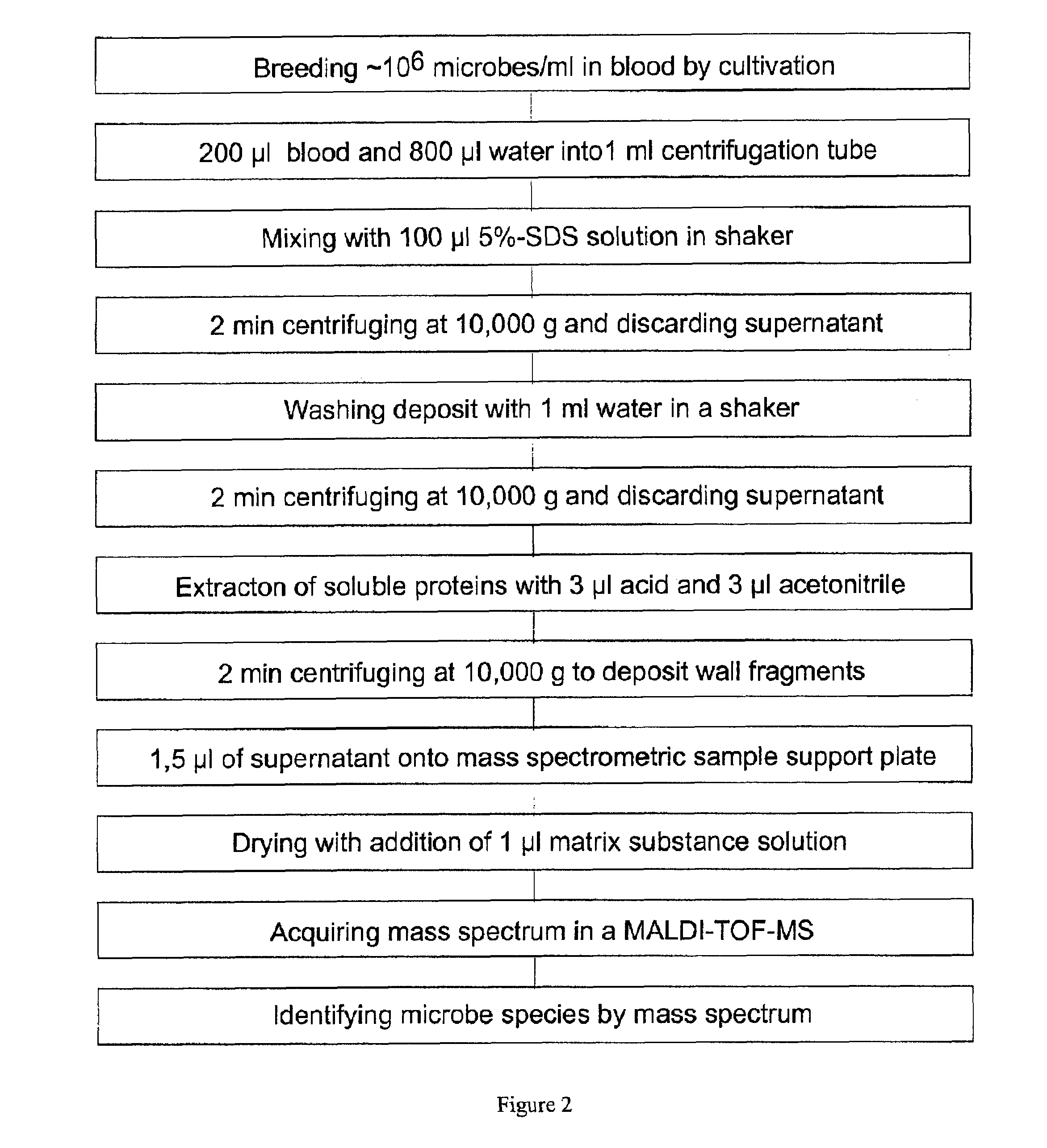
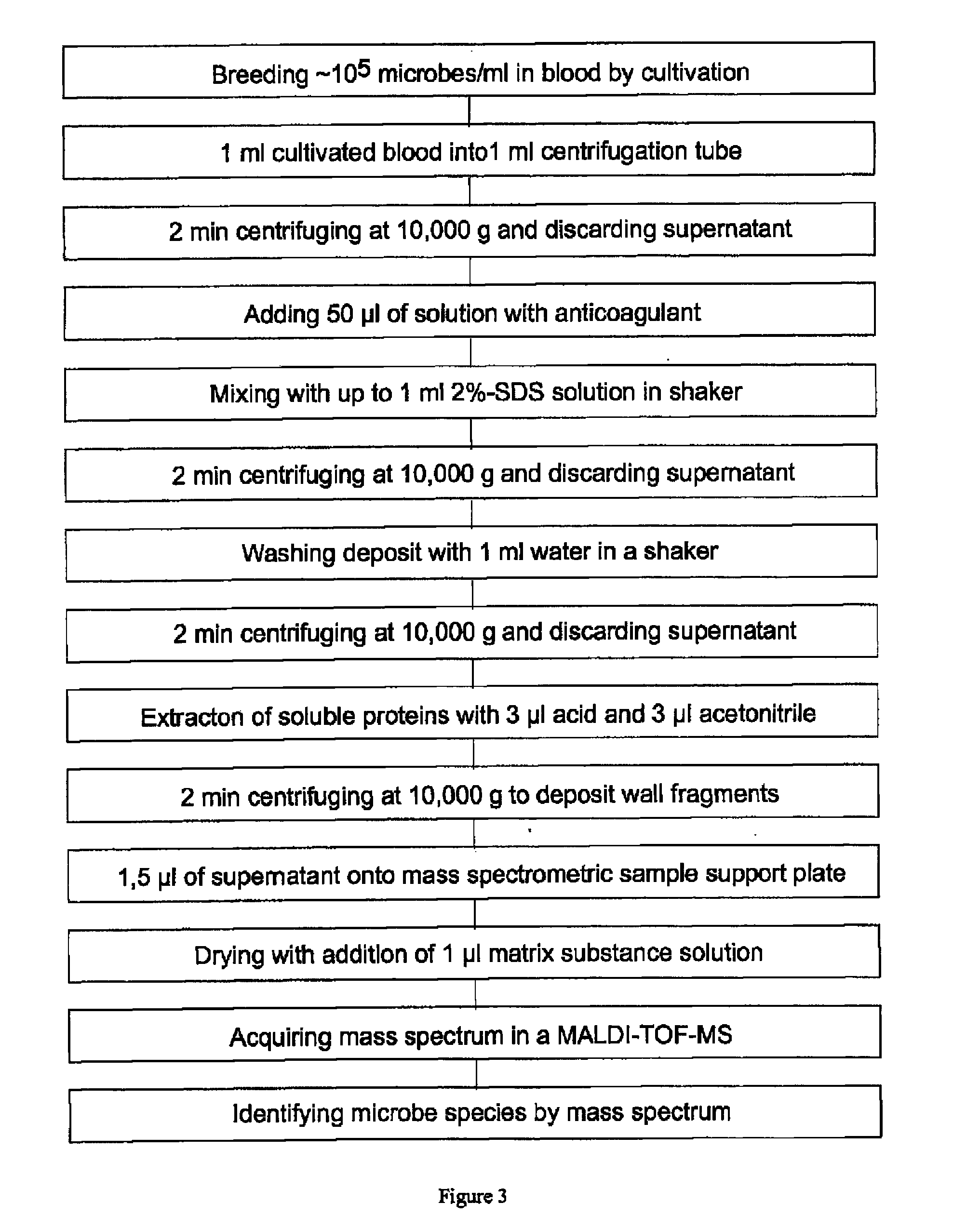
The invention mainly relates to the mass spectrometric identification of pathogens in blood cultures from blood-stream infections (septicemia). The invention provides a method with which microbial pathogens can be separated in purified form from blood after a relatively brief cultivation in a blood culture flask, without any interfering human proteins or any residual fractions of blood particles such as erythrocytes and leukocytes, and can be directly identified by mass spectrometric measurement of their protein profiles. The method is based on the use of relatively strong tensides to destroy the blood particles by dissolving the weak cell membranes and most of the internal structures of the blood particles; in spite of the fact that tensides are regarded as strong ionization inhibitors in MALDI and other ionization processes required for mass spectrometric measurements. This method allows unknown pathogens to be obtained in their pure form by centrifuging or filtration and to be identified on the taxonomic level of species or subspecies. Problems with DNA from high levels of leukocytes can be resolved by special measures. After sufficient cultivation, the identification in a mass spectrometric laboratory takes only half an hour.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Assessing the contamination in a mass-spectrometric maldi ion source
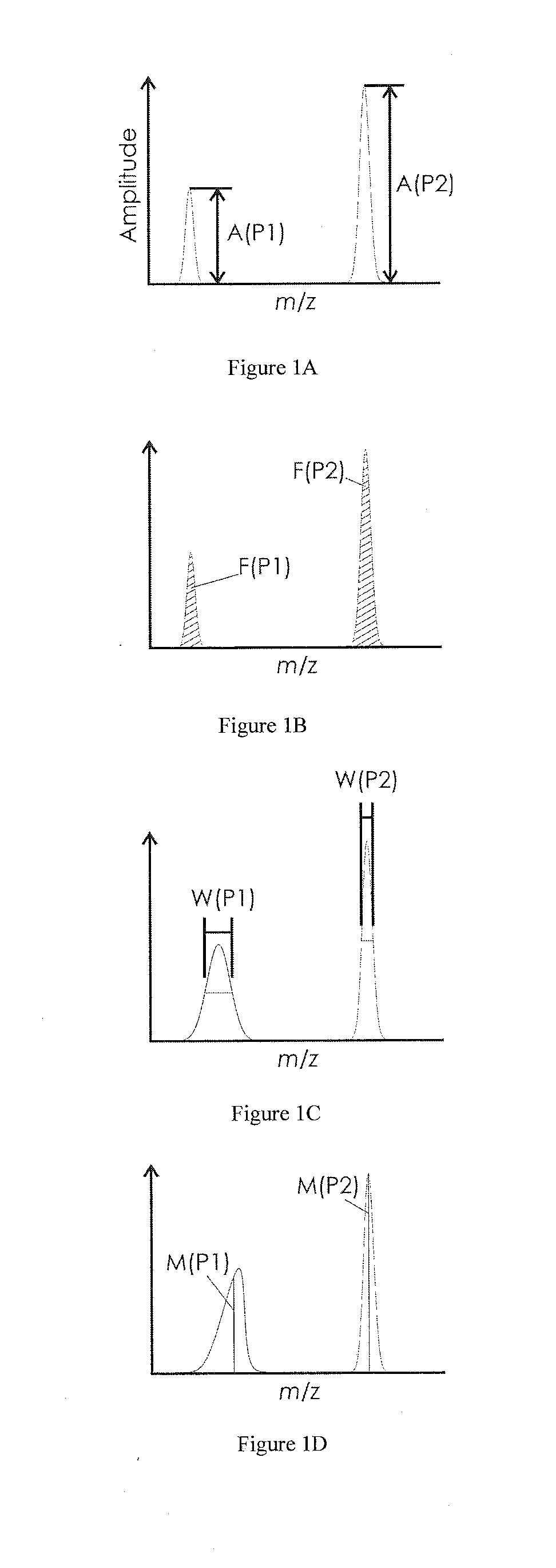
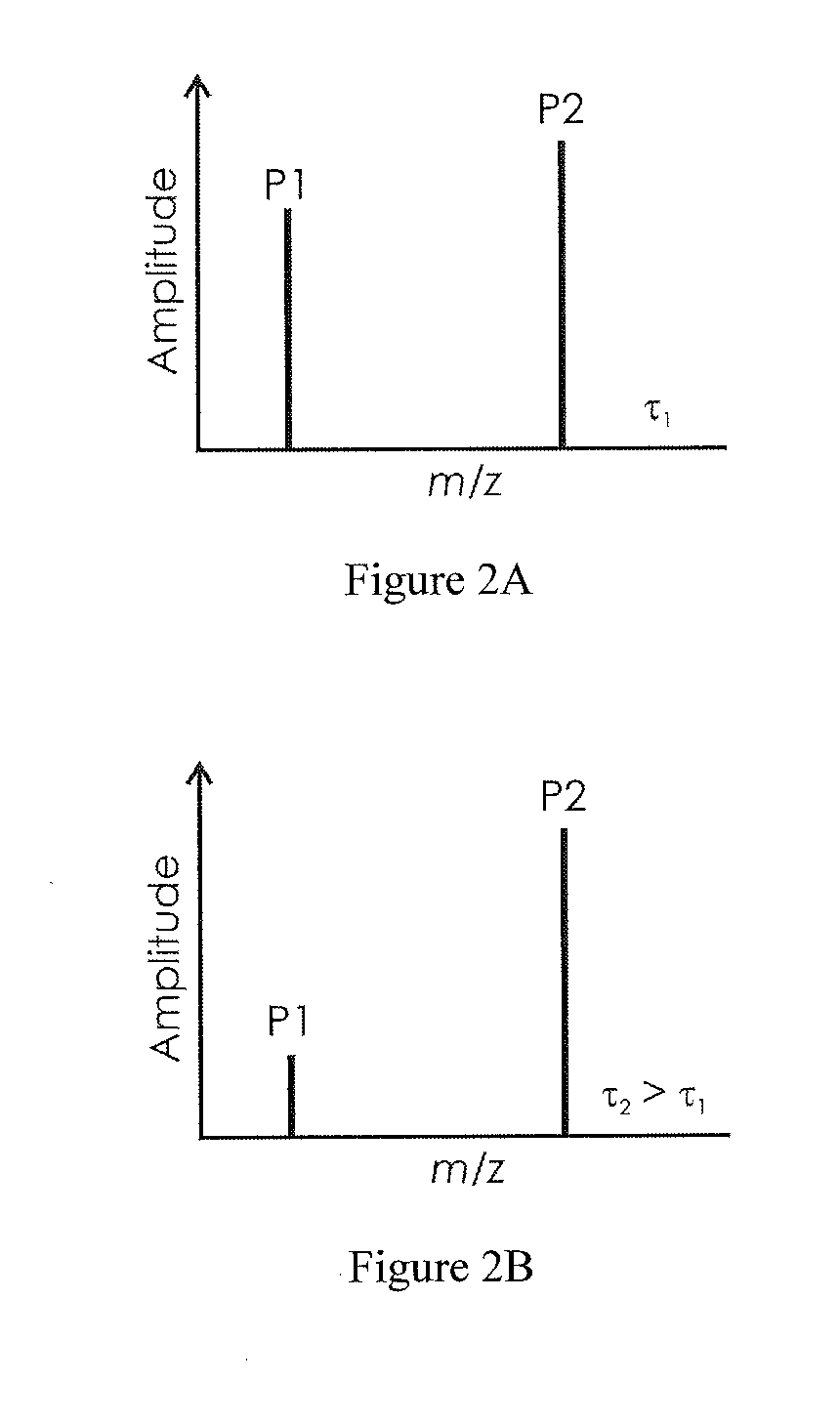
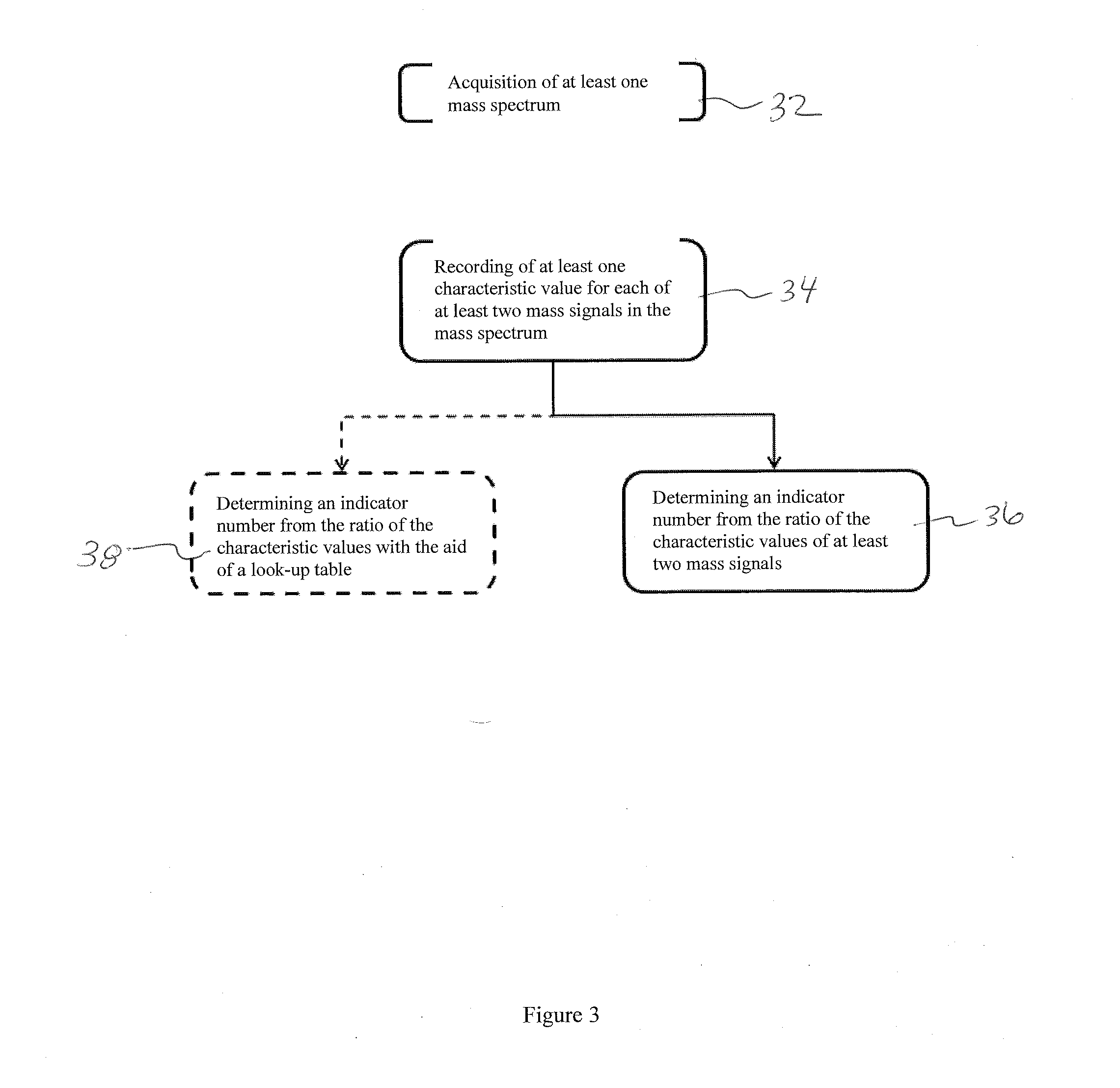
ActiveUS20120228489A1High resolutionReduce the average velocityIsotope separationMass spectrometersMass spectrometry measurementMass analyzer
The invention relates to a method by which the operator of a mass spectrometer with a MALDI ion source, particularly one which operates with delayed extraction of the ions, is provided with a technique for determining the degree of contamination, in particular to determine when the ion source must be cleaned. The method comprises the acquisition of at least one mass spectrum of ions which are generated in the ion source, the recording of at least one characteristic value for each of at least two mass signals in the mass spectrum, and the determination of an indicator number, derived from the characteristic values of at least two mass signals, which shows how urgently the ion source must be cleaned. The invention also relates to a mass spectrometer with a MALDI ion source which can be characterized accordingly.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Method for accurately testing digestion efficiency of proteins in matrix
ActiveCN104569134AAccurate measurementImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProtein targetMass spectrometry measurement
The invention discloses a method for accurately testing the digestion efficiency of proteins in a matrix. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing specific peptide fragment screening and digestion on target proteins for determining specific digestion peptide fragments; (2) synthesizing the specific peptide fragments; (3) preparing a standard protein mother liquor; (4) performing preliminary measurement on the concentration of the target proteins; (5) performing the digestion and measuring the concentration; (6) adding a diluent, performing the digestion and performing isotopic dilution mass spectrometry measurement on the concentration of the specific peptide fragments; (7) calculating the concentration of the proteins according to the concentration of the specific peptide fragments; (8) calculating the digestion efficiency when the concentration of added target proteins is used in the step (6); (9) repeating the steps (6)-(8), and adding different protein amounts every time to obtain a series of digestion efficiency values; and (10) plotting according to the protein addition amount and the digestion efficiency and extrapolating the digestion efficiency when the added protein amount is zero so as to obtain the accurate digestion efficiency of the proteins. The method has the advantages of high accuracy and good traceability.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
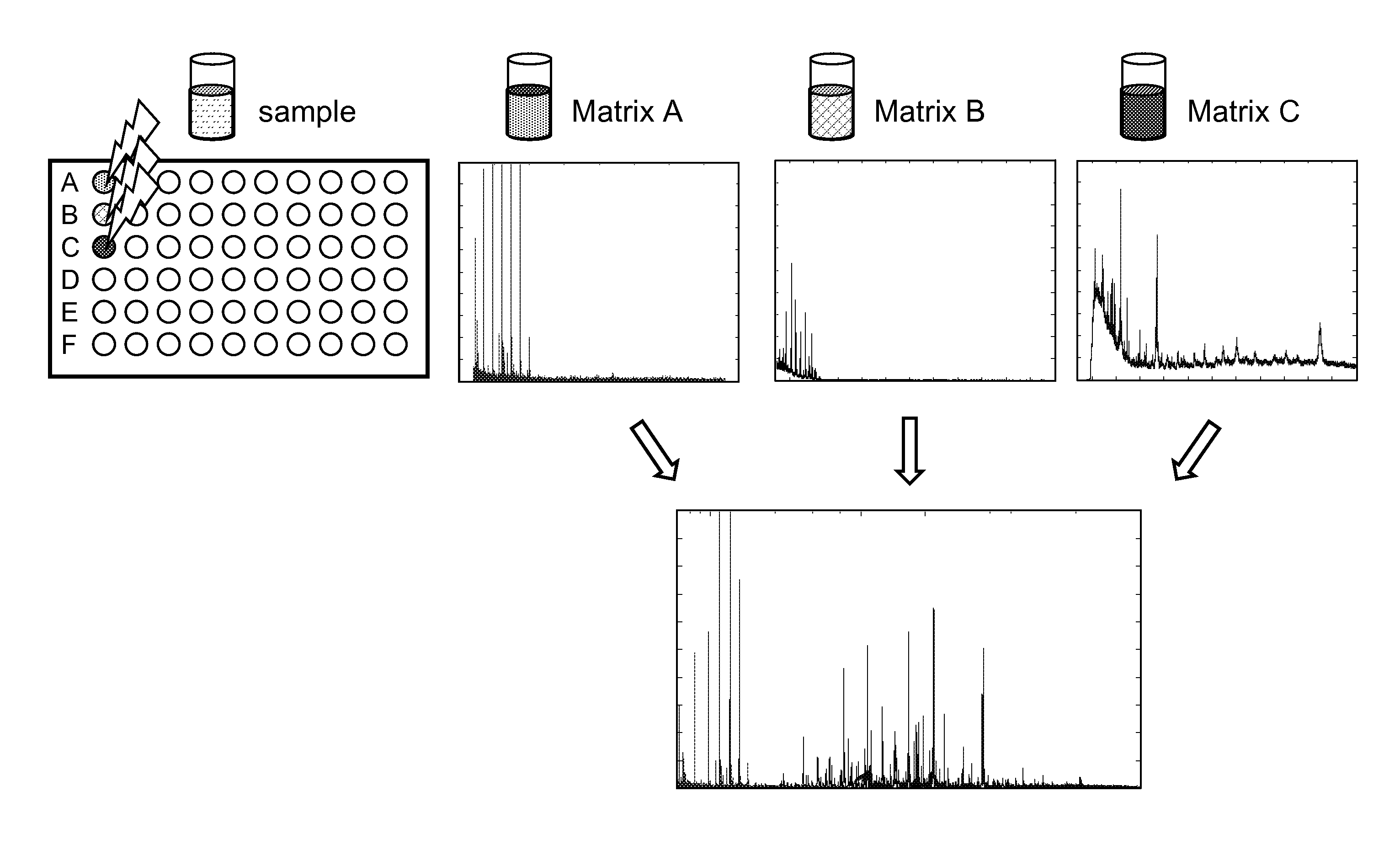
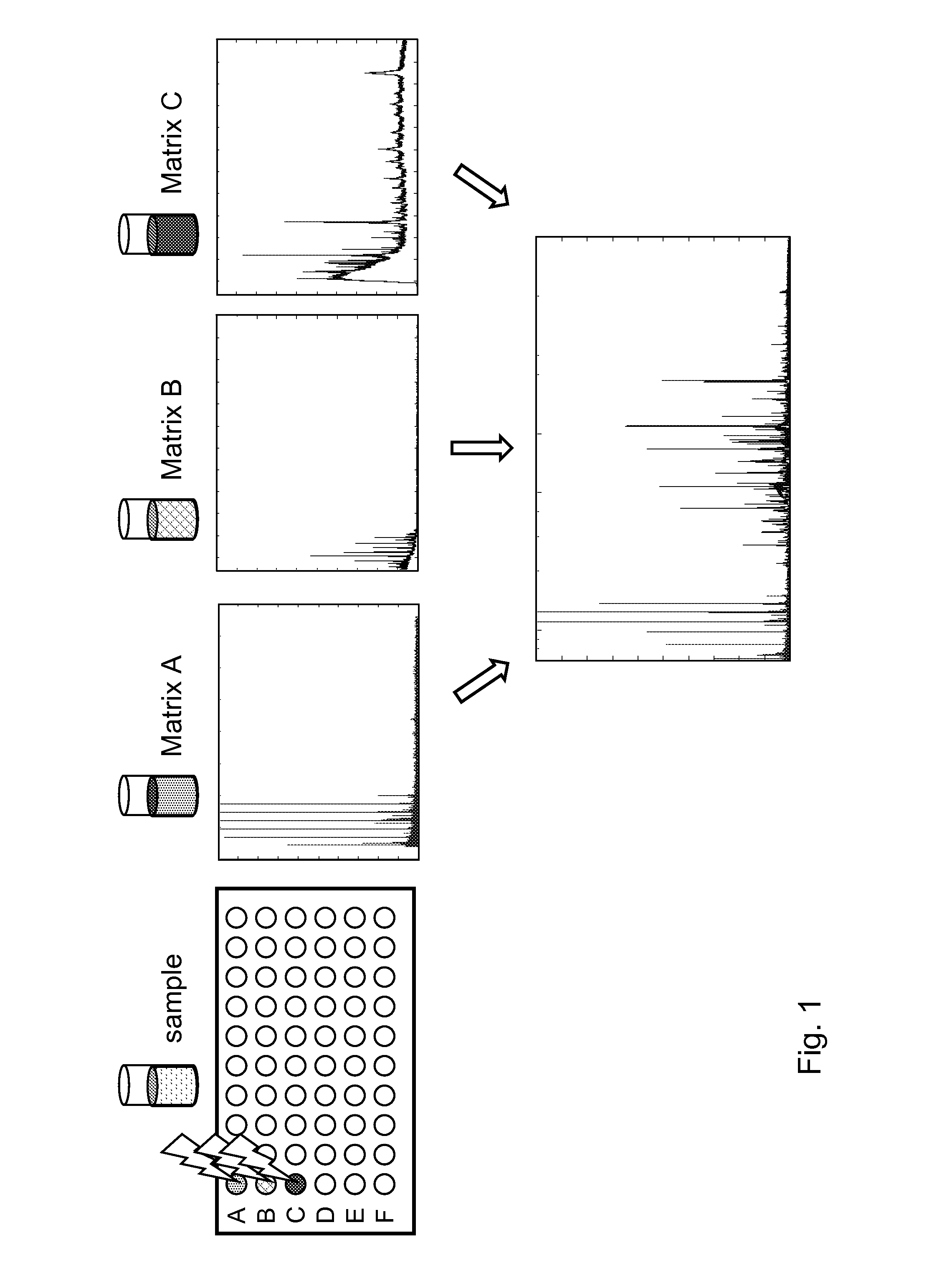
Classification method for spectral data
InactiveUS20150186754A1Particle separator tubesMicrobiological testing/measurementFrequency spectrumMass spectrometry measurement
The present invention relates to a new method for classification of spectral data comprising:a. obtaining at least two spectrograms of different mass range of a sample by performing at least two different mass spectrography measurements, each with a different matrix;b. adding the at least two spectrograms;c. comparing the sample spectrogram resulting from step b) with one or more spectrograms of known samples;d. if there is no difference between the sample spectrogram and a spectrogram of a known sample, declaring the sample identical to the known sample.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
General Mass Spectrometry Assay Using Continuously Eluting Co-Fractionating Reporters of Mass Spectrometry Detection Efficiency
InactiveUS20130068943A1Easy to understandComponent separationParticle spectrometer methodsMass spectrometry measurementFractionation
The invention provides general methods for quantifying any conceivable compound including small organic molecules and biological molecules in mass spectrometric measurements. The methods include the use of chemical or biological reporters such as artificial polypeptides containing proteolytic cleavage sites, which provide proteolytic reporter peptides for standardization of mass spectrometric detection efficiency. In addition to mass spectrometry standardization between different samples, the artificial polypeptides also standardize sample preparation amongst different samples undergoing mass spectrometric analysis when using electrophoresis separation prior to mass spectrometric analysis. Methods of the present invention also include methods for designing artificial polypeptides with peak to peak continuous liquid chromatography elution profiles spanning the complete or partial analyte elution profile for organic and biological molecules. Also included are the artificial polypeptides predigested with protease, which is compatible for use in experiments with native PAGE, in-solution proteolytic digestion of polypeptides, and small organic molecules undergoing fractionation separation followed by mass spectrometric evaluation.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
System and method for analyzing oxygen isotope composition in water of oxygen-free mineral inclusion
PendingCN107422024AIncrease vacuumGuaranteed vacuumPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCooking & bakingMass spectrometry measurement
The invention belongs to the field of measurement of isotope composition in water of mineral inclusions and particularly discloses a system and a method for analyzing oxygen isotope composition in water of an oxygen-free mineral inclusion. One end of an inclusion burst extraction / purification separation / extract conversion system of the system is connected with a product collection and measurement system, and the other end of the inclusion burst extraction / purification separation / extract conversion system is connected with a waste treatment system. The method comprises steps as follows: sampling of a mineral sample; baking and vacuum degassing; bursting, extraction and purification of the mineral inclusion; conversion of the water in the mineral inclusion; collection and mass spectrometric measurement of a converted product; waste treatment of a reaction product. The problems that water extraction of the mineral inclusion is not thorough, impurity ingredient separation is not complete, oxygen isotope fractionation is easily caused in the conversion process and the like are solved, and the analysis and test accuracy and the analysis and test efficiency are improved.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
Mass spectrometric measurement of b-lactamase resistances
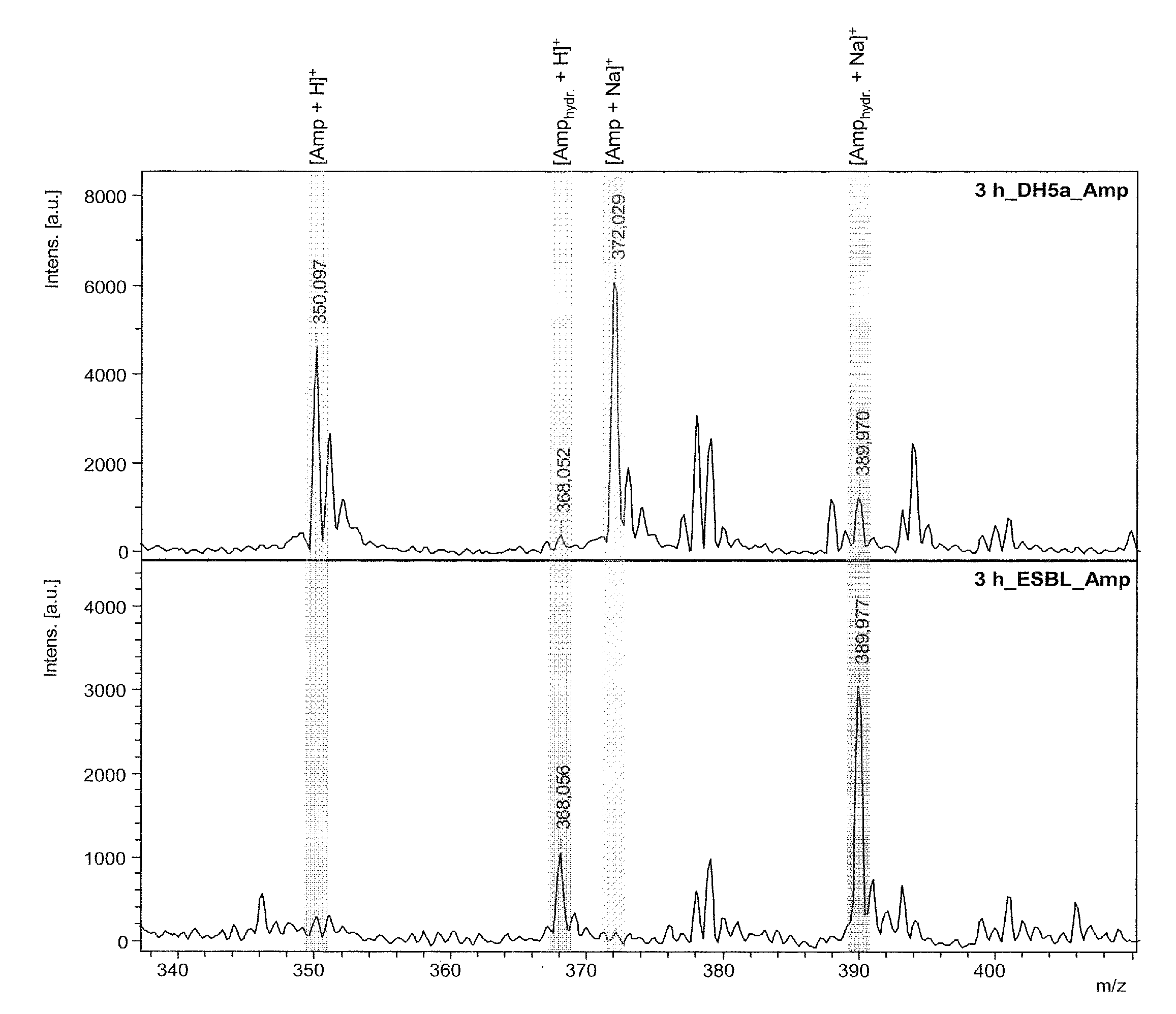
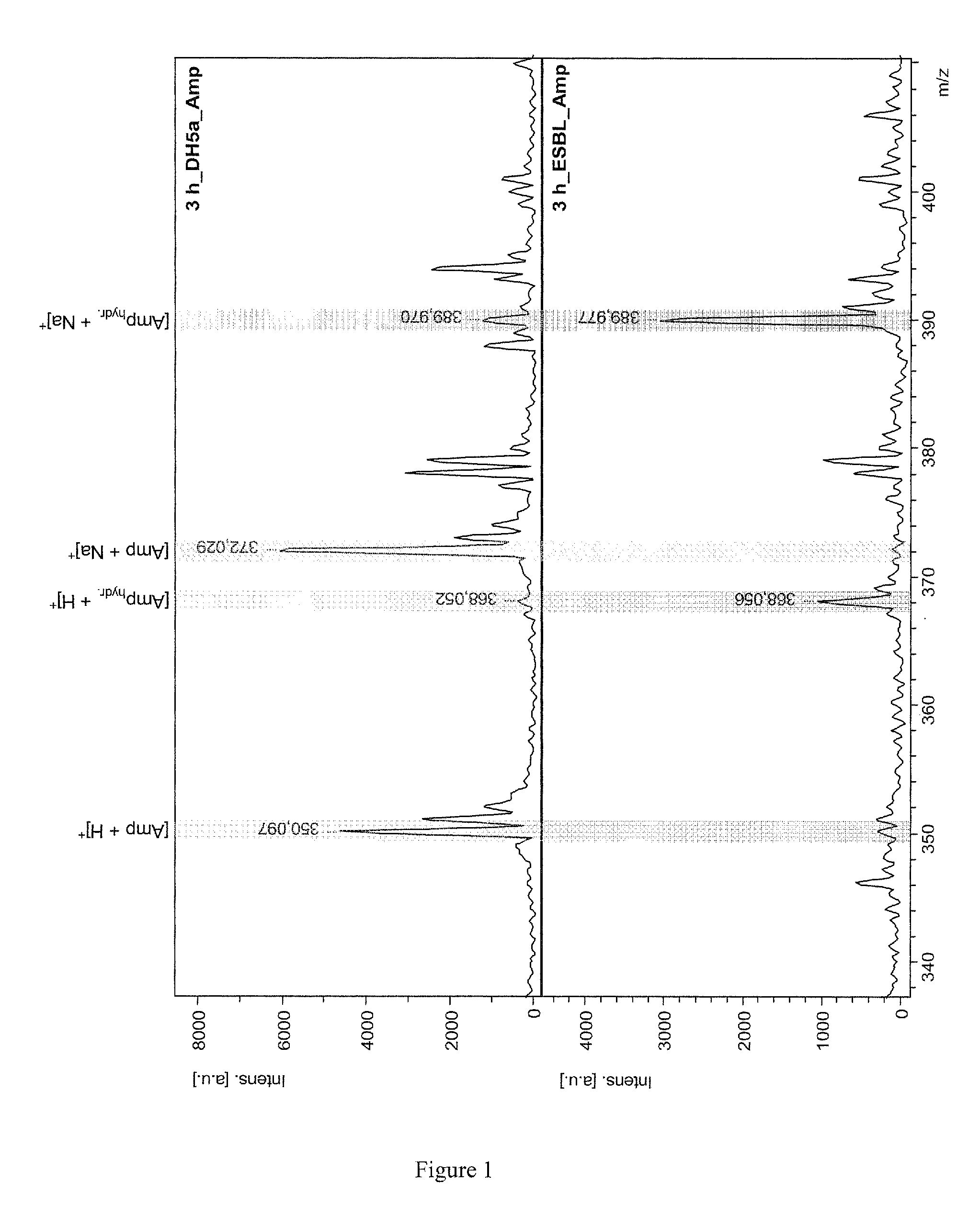
PendingUS20130095511A1Quickly and easily measureDecrease in amountMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisChemistryMass spectrometry
The invention relates to the determination of resistances of microorganisms which produce β-lactamases, in particular “extended spectrum β-lactamases” (ESBL). The invention provides a method whereby the microbial resistance can be measured very simply and quickly by means of the catalytic effect of the microbially produced β-lactamases on β-lactam antibiotics, which consists in a hydrolytic cleavage of the β-lactam ring. The method determines the resistance of the bacteria a few hours after a suitable substrate, either a β-lactam antibiotic or a customized β-lactam derivative, has been added to a suspension of the microbes, by direct mass spectrometric measurement of the substrate breakdown caused by the β-lactamases.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
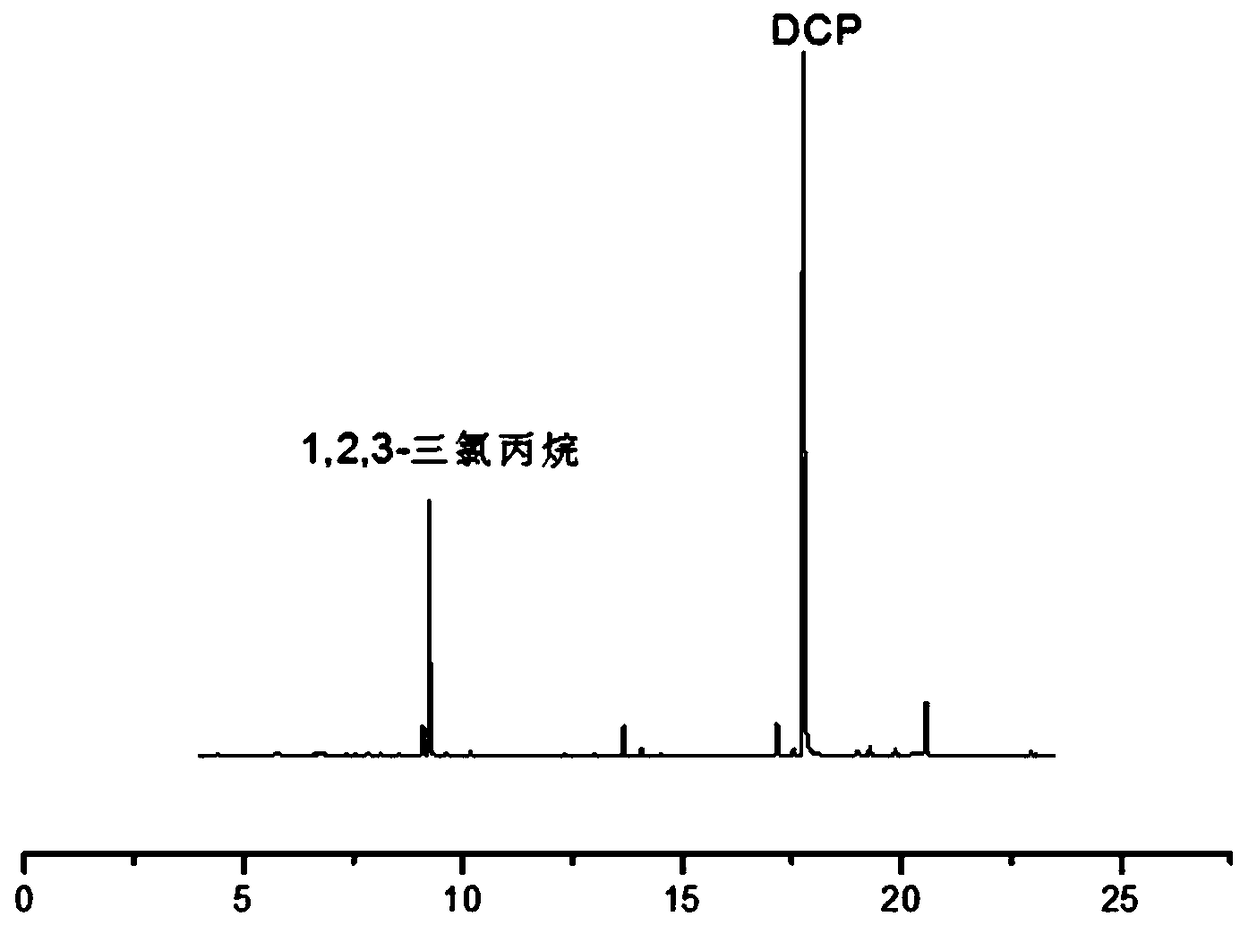
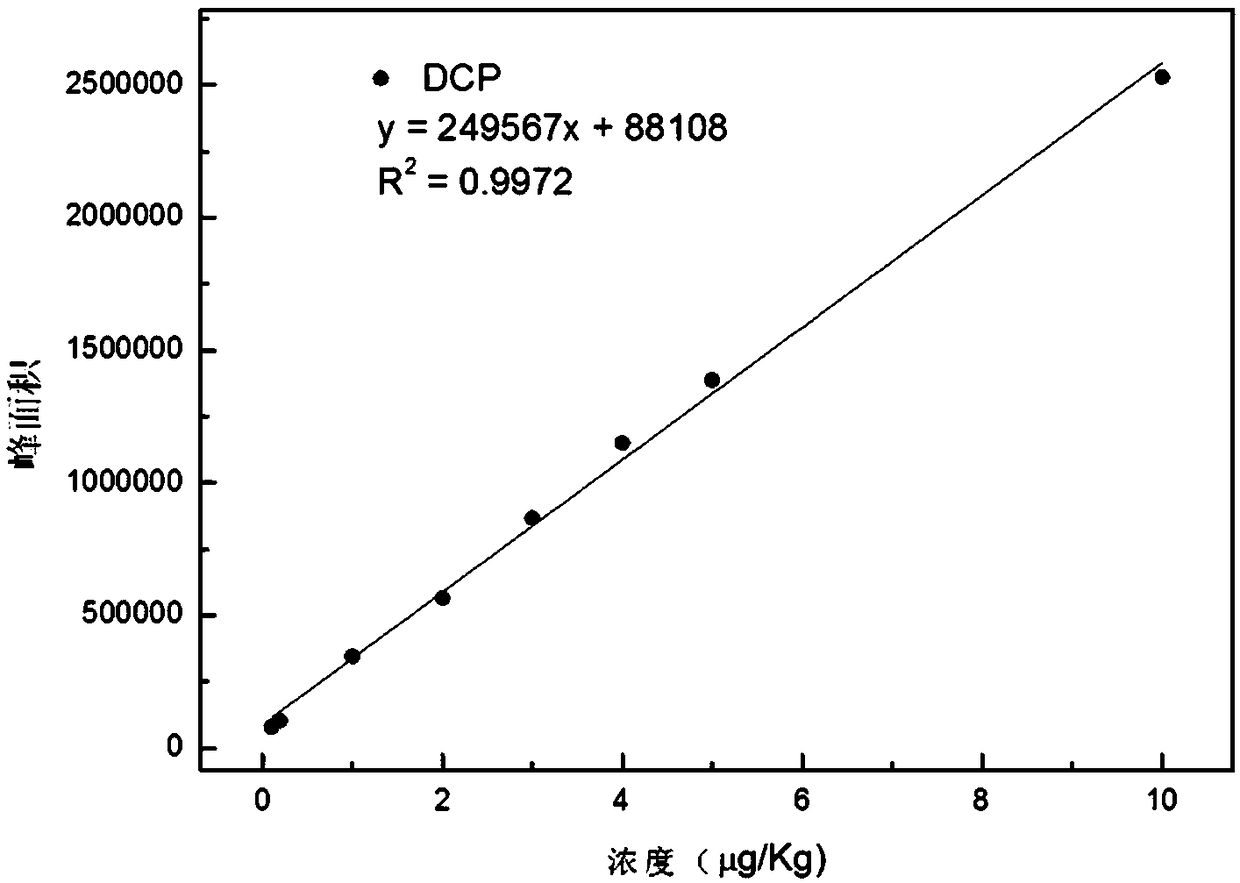
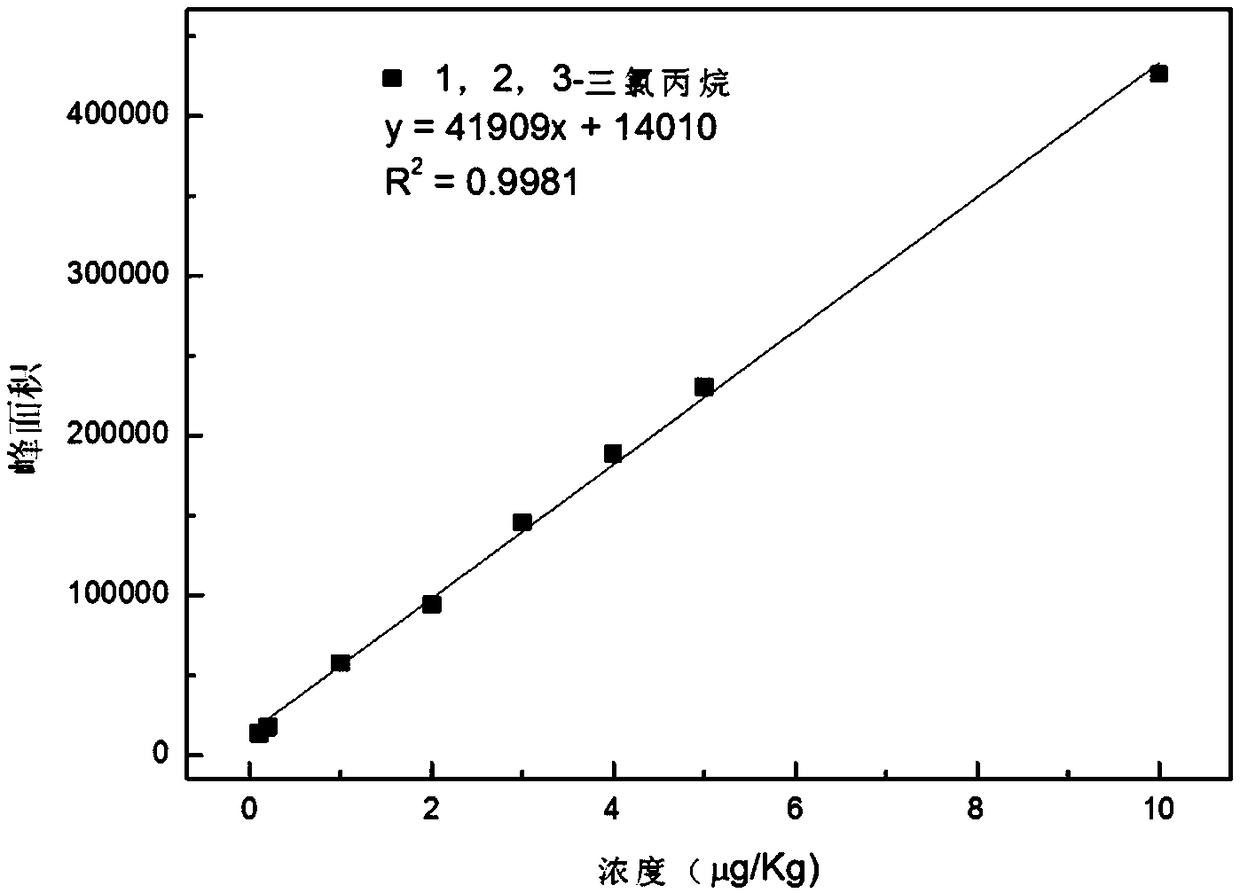
Method for quickly detecting low-molecular chlorinated organic compounds in papermaking white water, and application
The invention discloses a method for quickly detecting low-molecular chlorinated organic compounds in papermaking white water, and application. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) the preprocessing of a sample to be detected: filtering papermaking white water of a water sample to be detected, and adding chloride salt to obtain a sample to be tested; (2) standard solution preparation: adding 1,3-dichloro-2-propyl alcohol and 1,2,3-trichloropropane into the papermaking white water to prepare standard solutions of at least five concentrations; and (3) solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry detection: independently adopting a headspace solid-phase microextraction way to extract the sample to be detected and the standard solutions in the (2), inserting an extraction head into the sample introduction hole of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to carry out desorption, and carrying out gas chromatography-mass spectrometry measurement to calculate thecontents of 1,3-dichloro-2-propyl alcohol and 1,2,3-trichloropropane in the sample. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being simple, efficient and sensitive in operation, highin recovery rate and low in cost and is suitable for analyzing volatile chlorinated organic compounds in the papermaking white water.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Mass spectrometric diagnosis of septicemia
ActiveUS20120115182A1Microbiological testing/measurementMass spectrometric analysisProtein profilingMass spectrometry measurement
The invention mainly relates to the mass spectrometric identification of pathogens in blood cultures from blood-stream infections (septicemia). The invention provides a method with which microbial pathogens can be separated in purified form from blood after a relatively brief cultivation in a blood culture flask, without any interfering human proteins or any residual fractions of blood particles such as erythrocytes and leukocytes, and can be directly identified by mass spectrometric measurement of their protein profiles. The method is based on the use of relatively strong tensides to destroy the blood particles by dissolving the weak cell membranes and most of the internal structures of the blood particles; in spite of the fact that tensides are regarded as strong ionization inhibitors in MALDI and other ionization processes required for mass spectrometric measurements. This method allows unknown pathogens to be obtained in their pure form by centrifuging or filtration and to be identified on the taxonomic level of species or subspecies. Problems with DNA from high levels of leukocytes can be resolved by special measures. After sufficient cultivation, the identification in a mass spectrometric laboratory takes only half an hour.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Method for measuring isotopic abundance ratio of uranium in particles through accelerator mass spectrometry
InactiveCN104535598AImprove accuracyEliminate distractionsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionMass spectrometry measurementMicroparticle
The invention relates to a control device for the irradiation dose of an irradiation device, and provides a method for measuring the isotopic abundance ratio of uranium in particles through accelerator mass spectrometry. The method aims to solve the problems that an analysis method for the isotopic abundance ratio of uranium in existing environment sample particles is not high in analysis result accuracy, and interference is serious in the analysis process. The method comprises the following steps that 1, the sample particles are separated from a carrier and transferred to a graphite flake through ultrasonic oscillation; 2, the sample particles are transferred into a scanning electron microscope; 3, the uranium-bearing particles are found; 4, the uranium-bearing particles are dissolved; 5, a target is manufactured; 6, ruling is carried out; 7, accelerator parameters needed by each uranium isotope are determined; 8, the counting rate of each uranium isotope is measured; 9, the isotopic abundance ratio of the uranium is calculated. The problem that isotopic abundance ratio analysis of the uranium in the particles has polyatomic ion interference is solved, abundance sensitivity is obviously improved, the obtained analysis result is accurate, and the defect in an existing analysis method is overcome.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
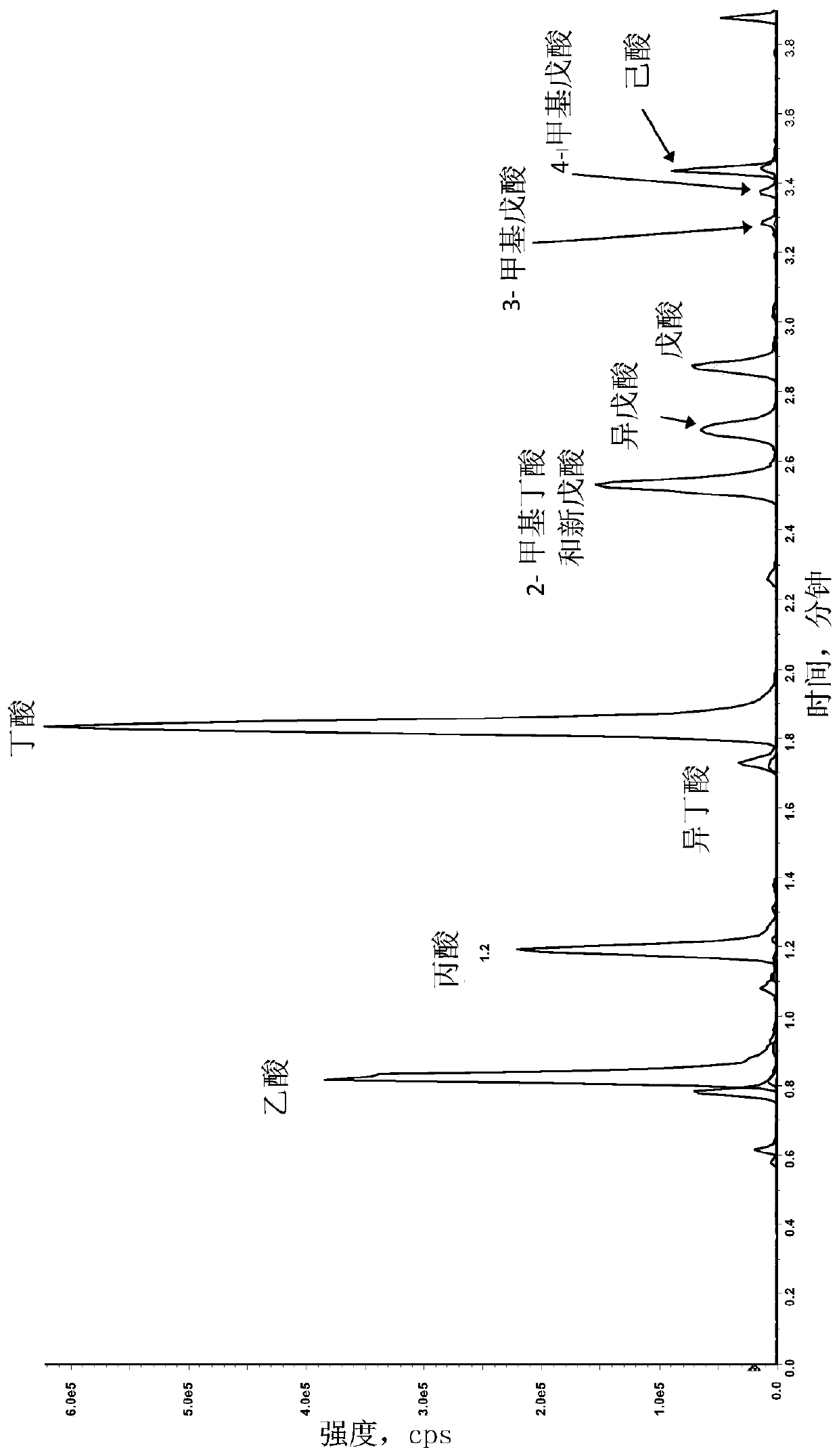
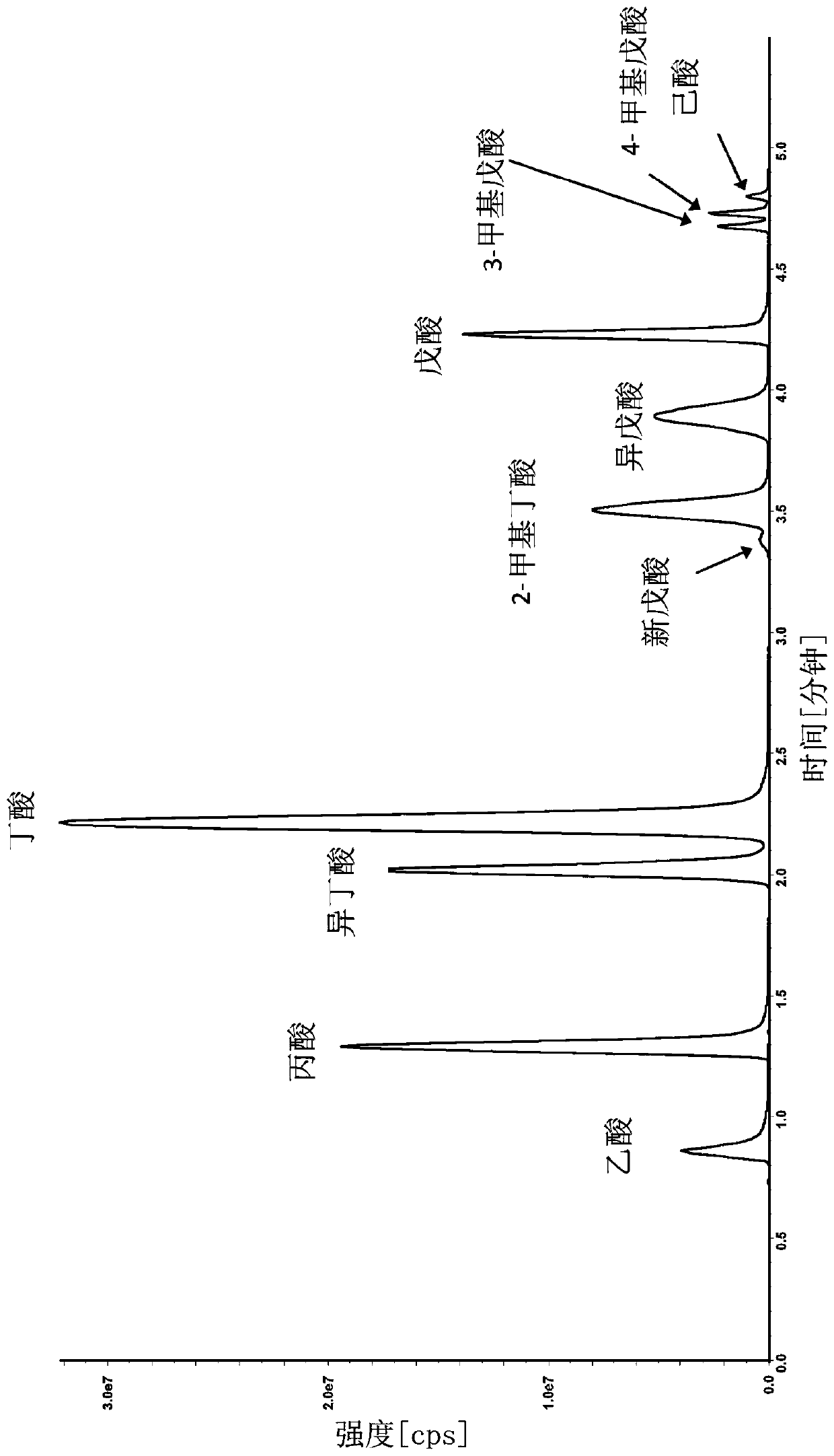
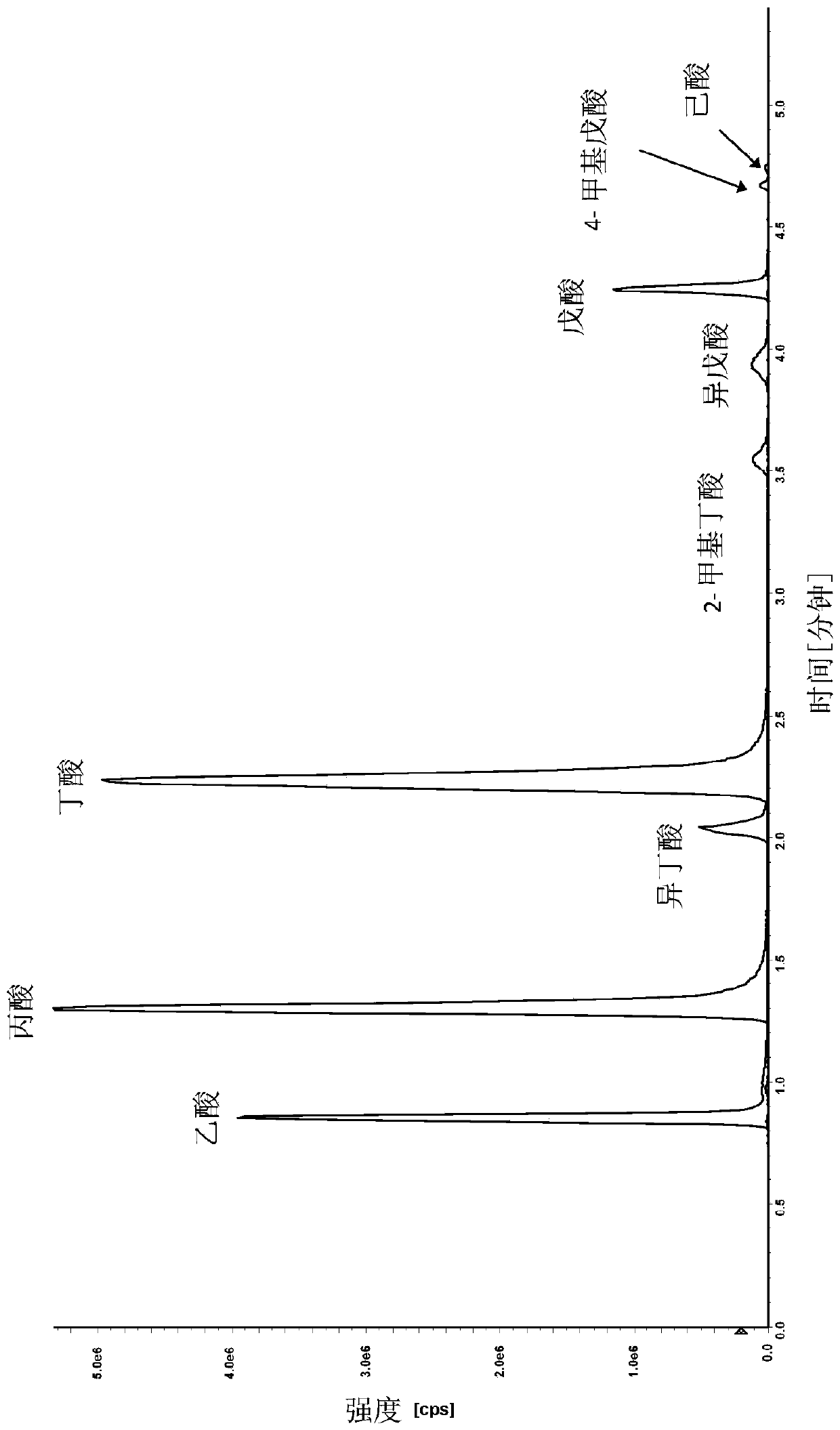
Mass spectrometry assay method for detection and quantitation of organic acid metabolites
A method for determining in a sample, by mass spectrometry, the presence, absence, or amount of one or more analytes is described herein. The run time is less than six minutes. The method includes subjecting the sample to an ionization source under conditions suitable to produce one or more ions detectable by mass spectrometry from each of the one or more analytes, wherein the one or more analytesare derivatized prior to ionization; measuring, in a single injection, by mass spectrometry, the amount of the one or more ions from each of the one or more analytes; and using the measured amount ofthe one or more ions to determine the amount of each of the one or more analytes in the sample.
Owner:METABOLON
Accelerator mass spectrometry method and system
ActiveCN109830423ABeam highIncrease beam intensityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIon sources/gunsMass spectrometry measurementResolution (mass spectrometry)
The embodiment of the application provides an accelerator mass spectrometry system and relates to the technical field of AMS. The accelerator mass spectrometry system comprises an ECR strong current positive ion source subsystem, an injector subsystem, a strong current accelerator subsystem, a high-energy analysis subsystem and a high-resolution detector subsystem which are successively connected.The ECR strong current positive ion source subsystem is configured to generate strong current positive ions in multiple charge states. The strong current accelerator subsystem is configured to directly accelerate the strong current positive ions. The accelerator mass spectrometry system has the advantages of strong beam current, high total efficiency, and good background lowering capability, andcan greatly improve the abundance sensitivity of the spectrometry.
Owner:QIXIANHE (BEIJING) TECH CO LTD
High-throughput mass-spectrometric characterization of samples
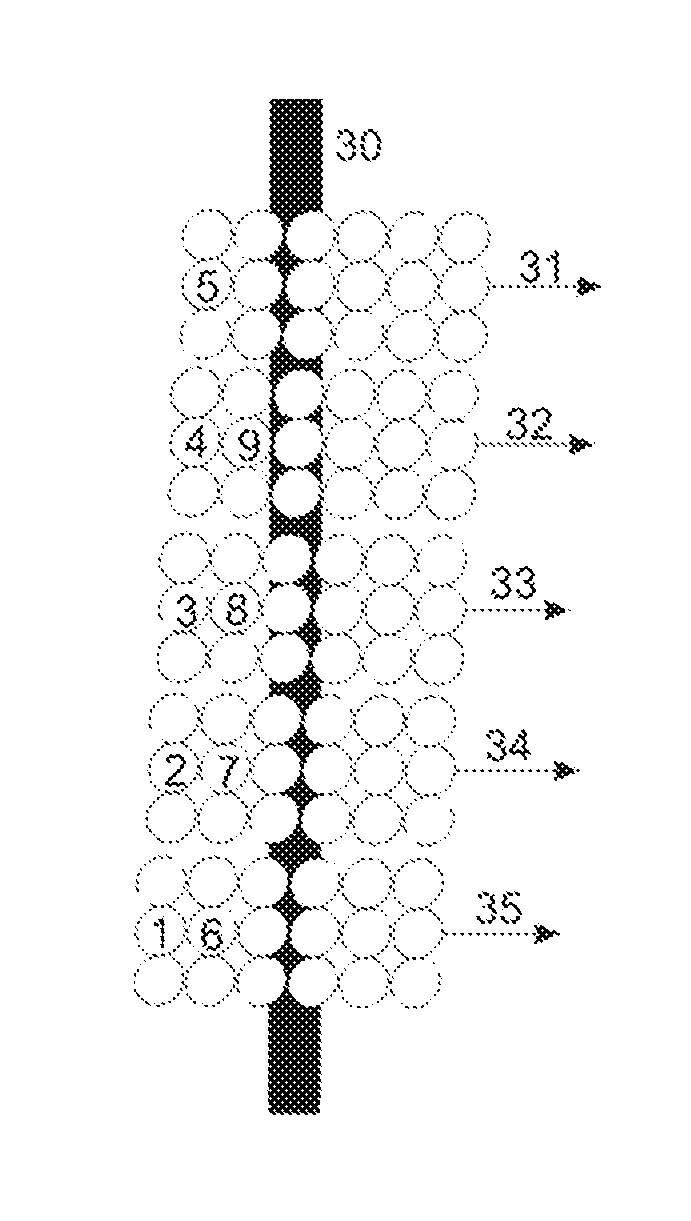
ActiveUS20140306104A1High sensitivityEasy to findChemical library matterPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationMass spectrometry measurementRegular pattern
The invention relates to the characterization of samples which are located in their many hundreds up to tens or hundreds of thousands on a sample support plate in a regular pattern, a so-called array, by ionization with matrix-assisted laser desorption and mass spectrometric measurement, for example. The invention proposes that the position of the sample pattern, and thus the position of each sample in the measuring instrument, for example a mass spectrometer, should be determined by measuring at least two finely structured internal position recognition patterns, such as fine crosses. The position recognition patterns are preferably applied as the samples are generated, with the same apparatus which also generates the sample pattern. A mass spectrometer in which laser spots with diameters of only four to five micrometers can be generated, which can preferably be positioned with an accuracy of one micrometer or better, is particularly suitable for the characterization.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
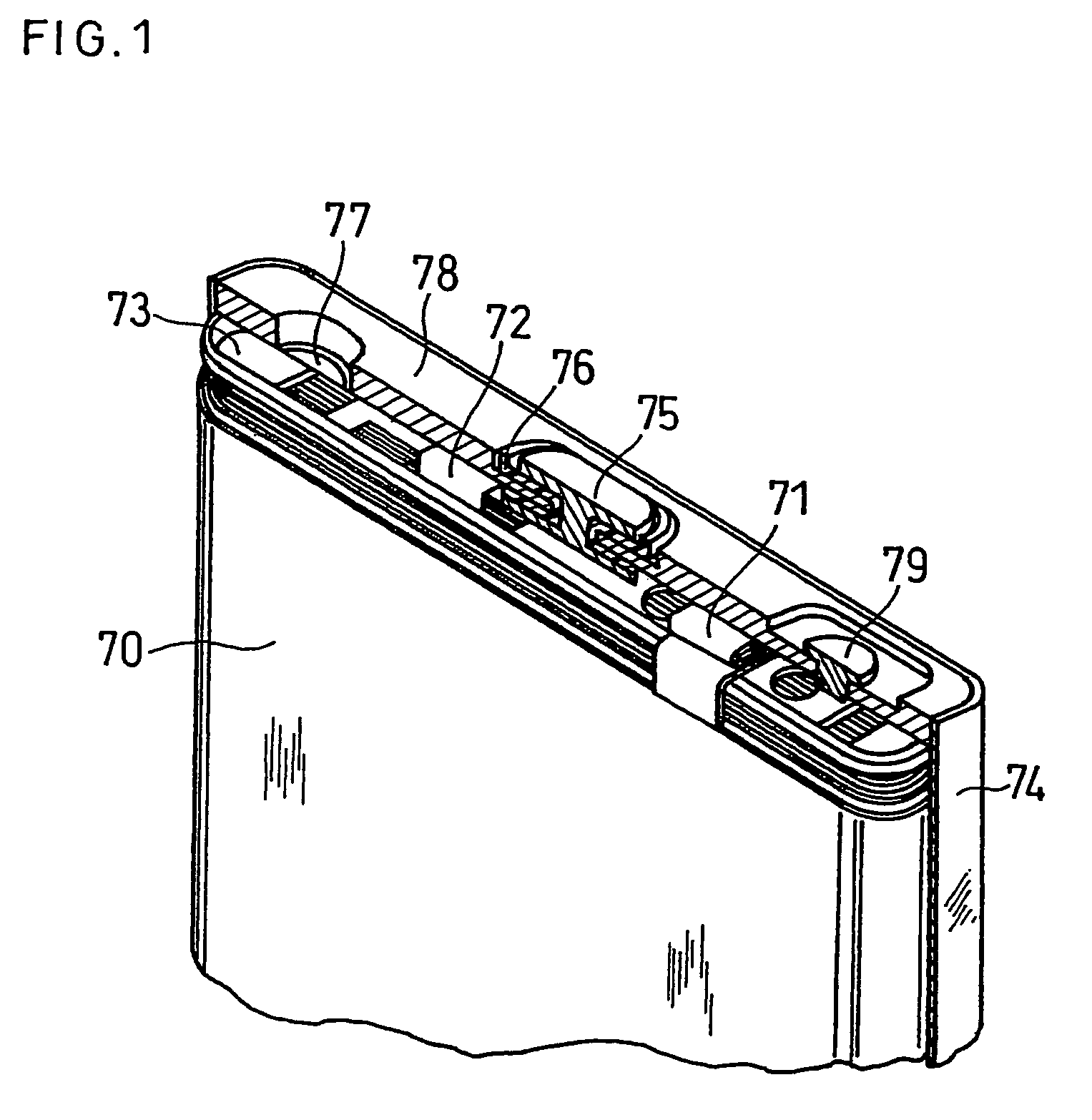
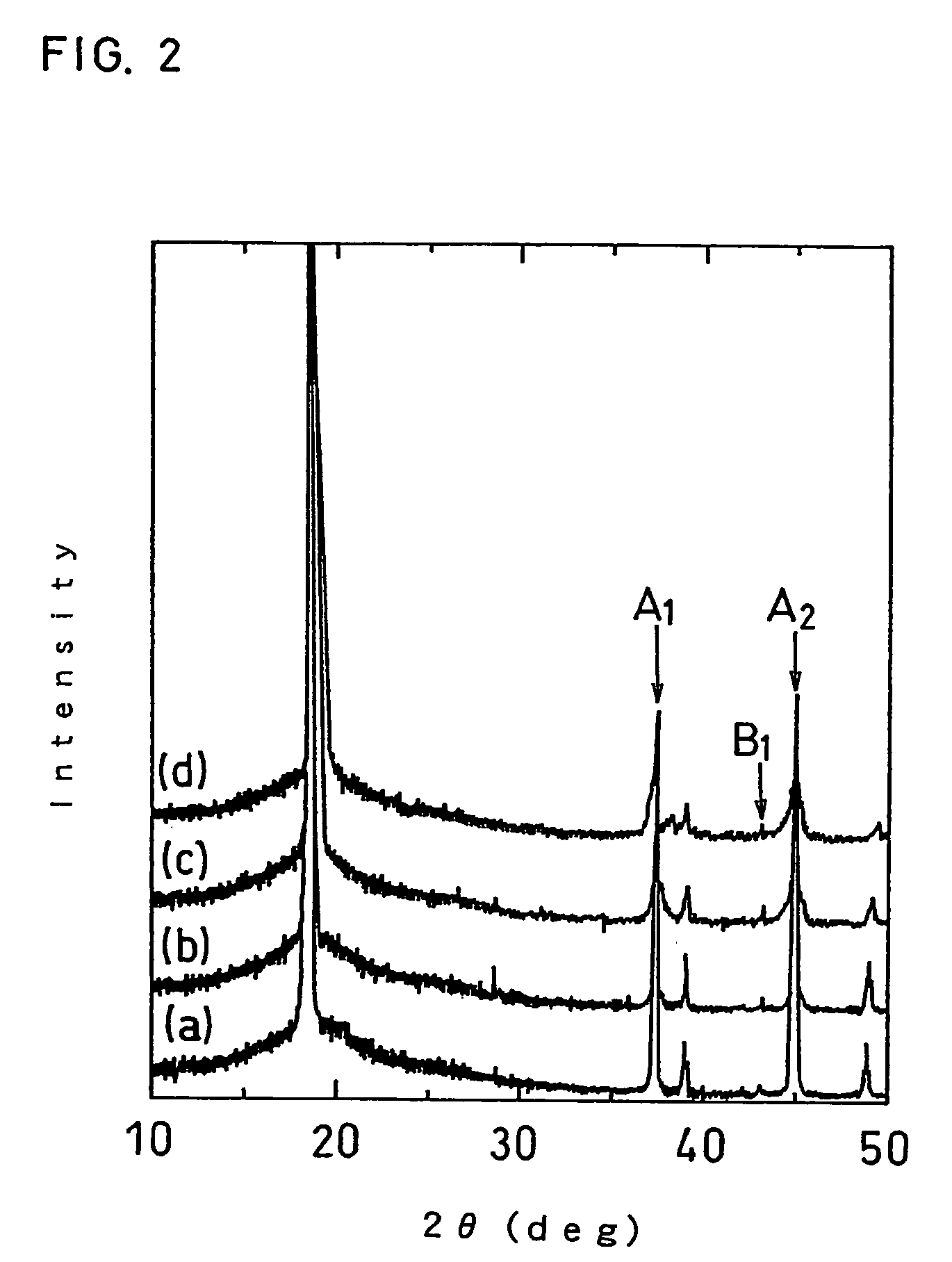
Positive electrode active material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
ActiveUS7381497B2Improve stabilityImprove battery safetyElectrode rolling/calenderingElectrode carriers/collectorsMass spectrometry measurementCrystal structure
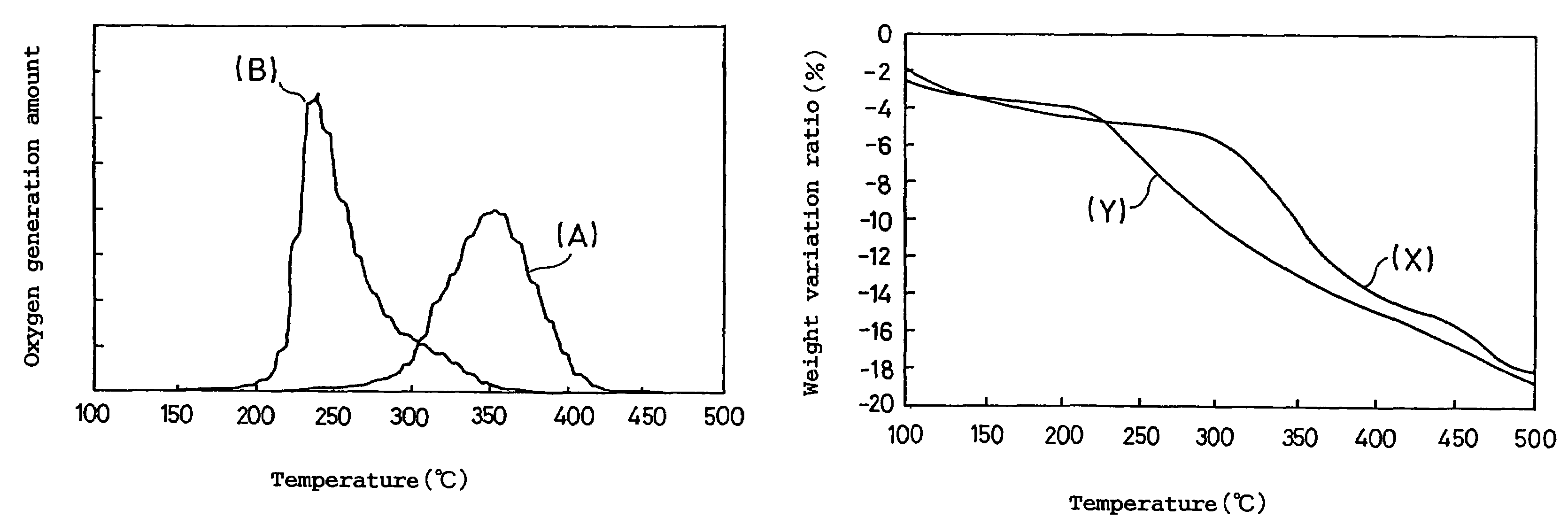
A positive electrode active material for a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery, comprising a lithium-containing composite oxide, wherein the composite oxide is represented by the general formula: LizCo1-x-yMgxMyO2, the element M included in the general formula is at least one selected from the group consisting of Al, Ti, Sr, Mn, Ni and Ca, the values x, y and z included in the general formula satisfy: (i) 0≦z≦1.03; (ii) 0.005≦x≦0.1; and (iii) 0.001≦y≦0.03, the composite oxide has a crystal structure attributed to a hexagonal system in an overcharged state having a potential over 4.25 V relative to metallic Li, and a maximum value of an oxygen generation peak in a gas chromatograph mass spectrometry measurement of the composite oxide in the overcharged state is in the range of 330 to 370° C.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for preparing isotope-labeled recombinant C reactive protein
ActiveCN101974556AImprove comparabilityOffset UncertaintyPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesMass spectrometry measurementIsotopic labeling
The invention relates to a method for preparing an isotope-labeled recombinant C reactive protein, which comprises the following steps of: constructing a C reactive protein gene-containing recombinant vector; transferring the recombinant vector into a host cell for recombinant expression, wherein a stable isotope is added into a culture medium for recombinant expression; and purifying the expressed recombinant vector and measuring the purity thereof. The method has the advantages that: the isotope 15N-labeled recombinant C reactive protein is designed, an N source in the culture medium is replaced, the expressed and purified product is taken as an interior label and subjected to enzyme cutting with a target C reactive protein, and mass-spectrometer measurement is preformed, so the uncertainty of incomplete enzyme cutting on the measured result can be eliminated, more accurate quantification on the protein is achieved, the measurement error caused by incomplete enzymolysis and hydrolysis of the protein in the prior art is avoided, the uncertainty in the measurement process is greatly reduced and the measurement accuracy is improved.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
Gas concentration quasi-static regulation device based on mass spectrum feedback and regulation method
ActiveCN105181860AHigh sensitivityImprove stabilityComponent separationMass spectrometry measurementEngineering
The present invention discloses a gas concentration quasi-static regulation device based on mass spectrum feedback and a regulation method. The device comprises a gas distribution apparatus, a mass spectrometer in communication with the gas distribution apparatus, and an embedded control system. The mass spectrometer uses the embedded control system to conduct mass spectrometry measurements on the gas within the gas distribution apparatus. The gas distribution apparatus includes a cylinder, a piston fitted in the cylinder, and a motor for driving displacement of the piston; and the piston and the bottom of the cylinder form a main cavity communicating with the mass spectrometer; the main cavity inputs test gas through a valve 1, and inputs a test gas through a valve 2. The embedded control system and electrical mechanical are in electrical connection; and according to the measurement results of the mass spectrometer, the motor adjusts the shift amount of the piston. The present invention also discloses a regulation method of the gas concentration quasi-static regulation device based on mass spectrum feedback.
Owner:KUSN HEXIN MASS PECTRUM TECH +2
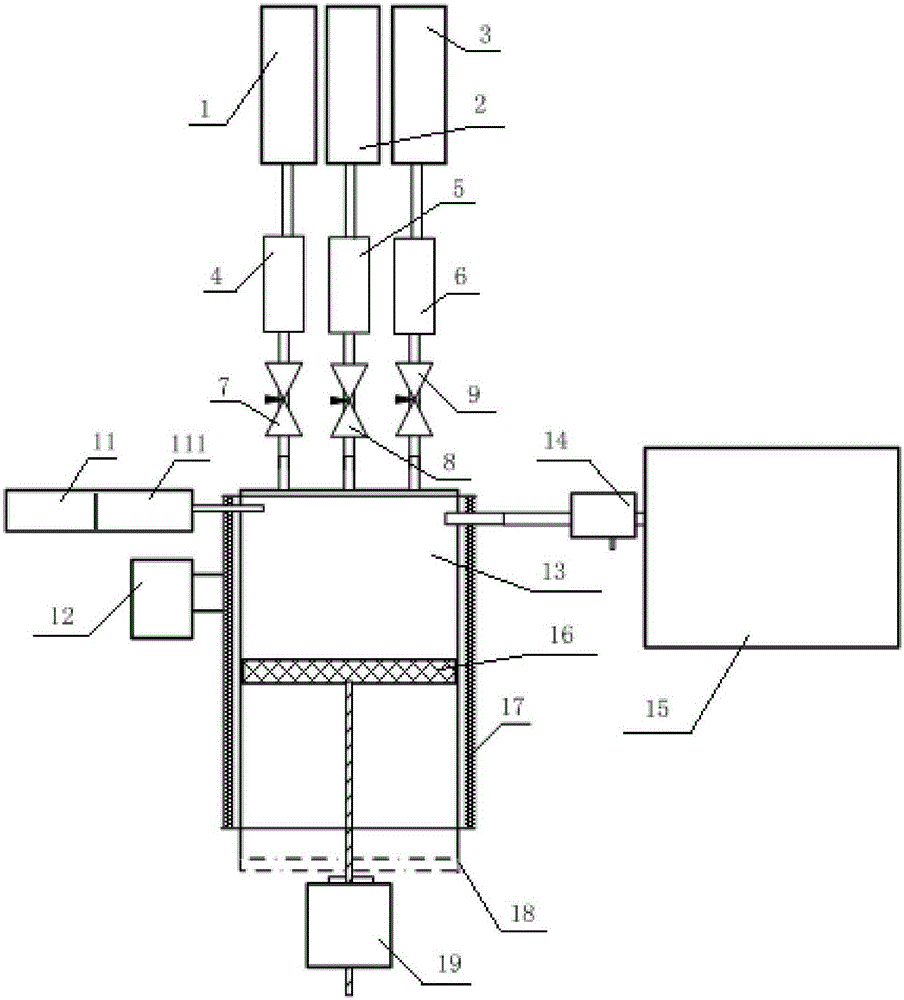
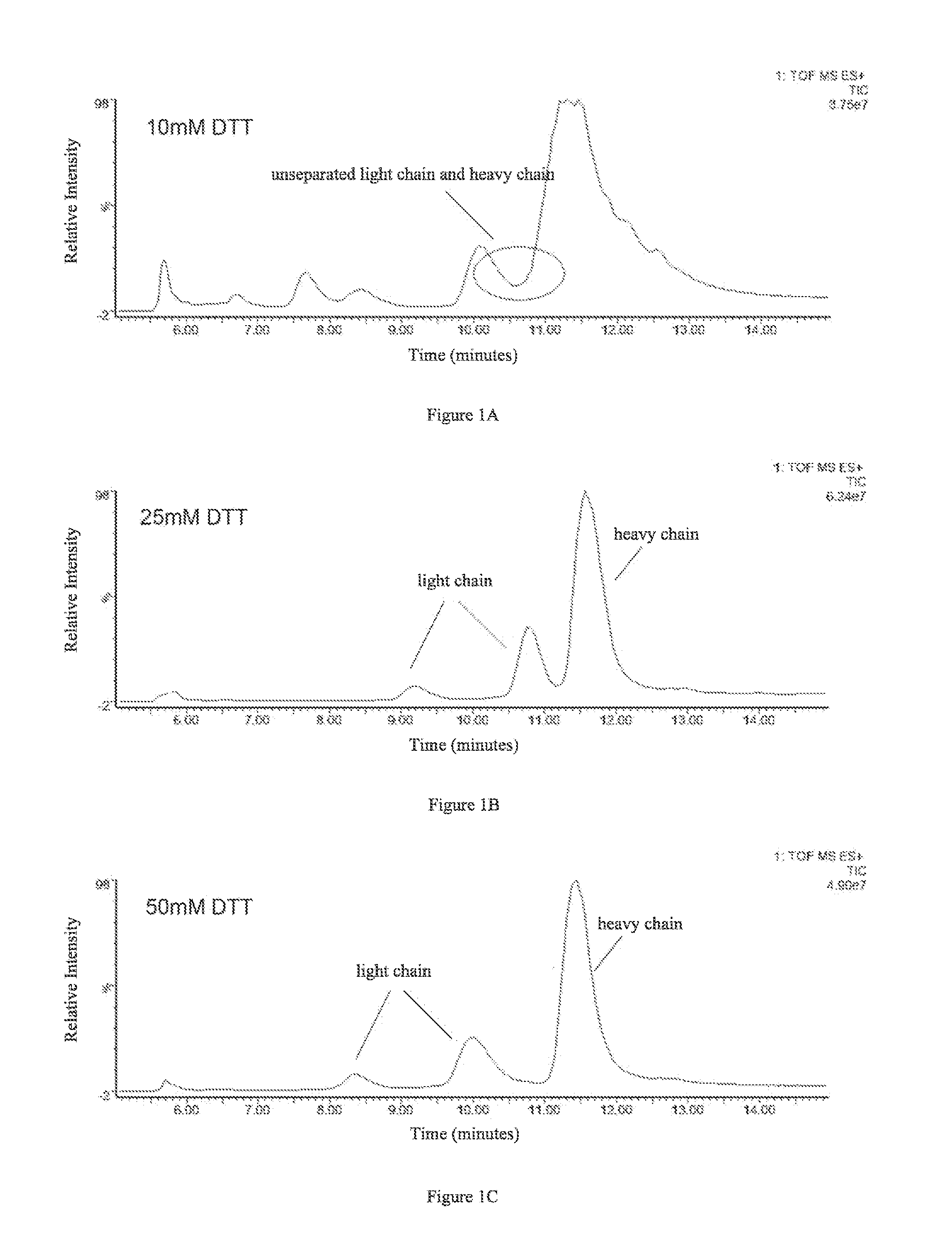
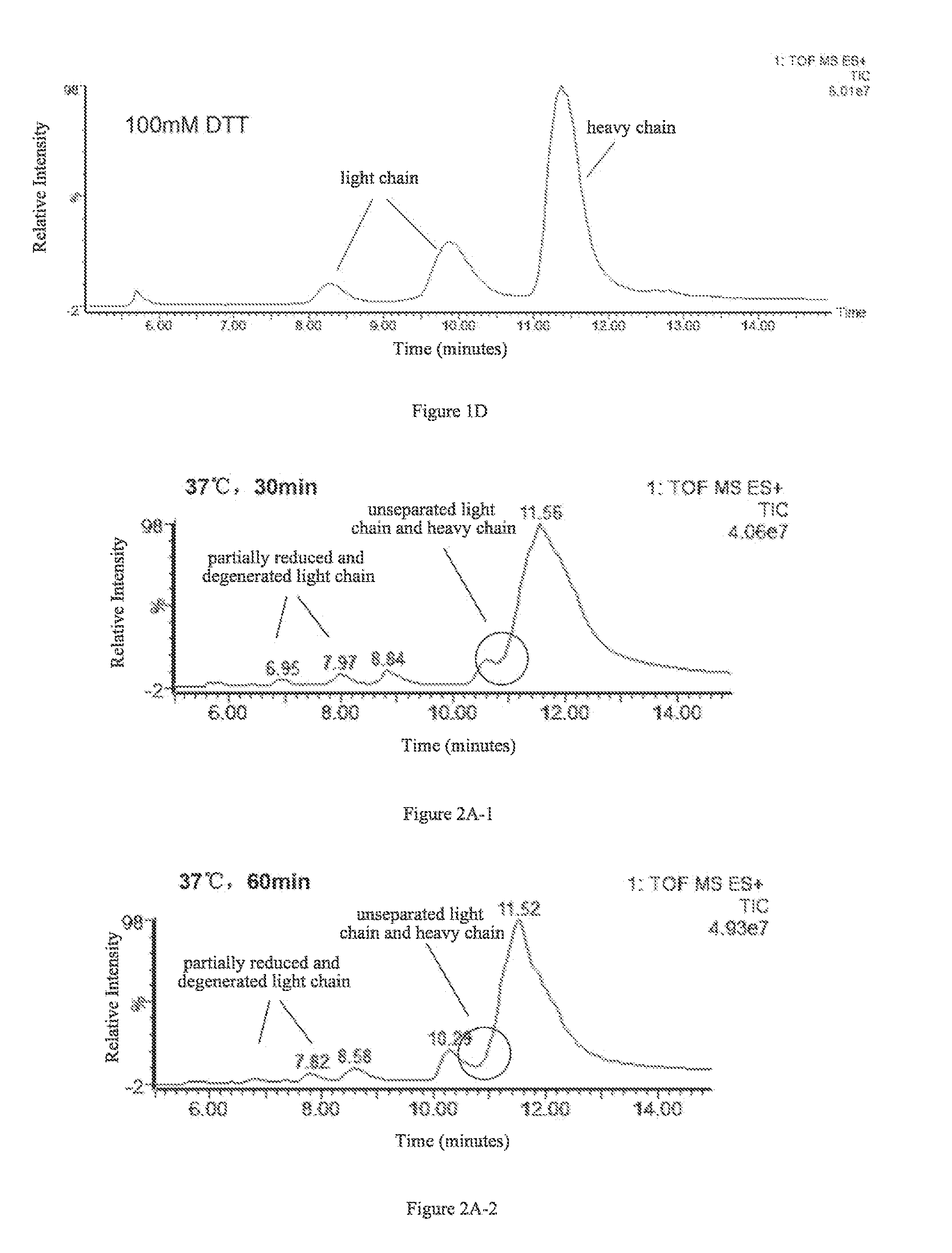
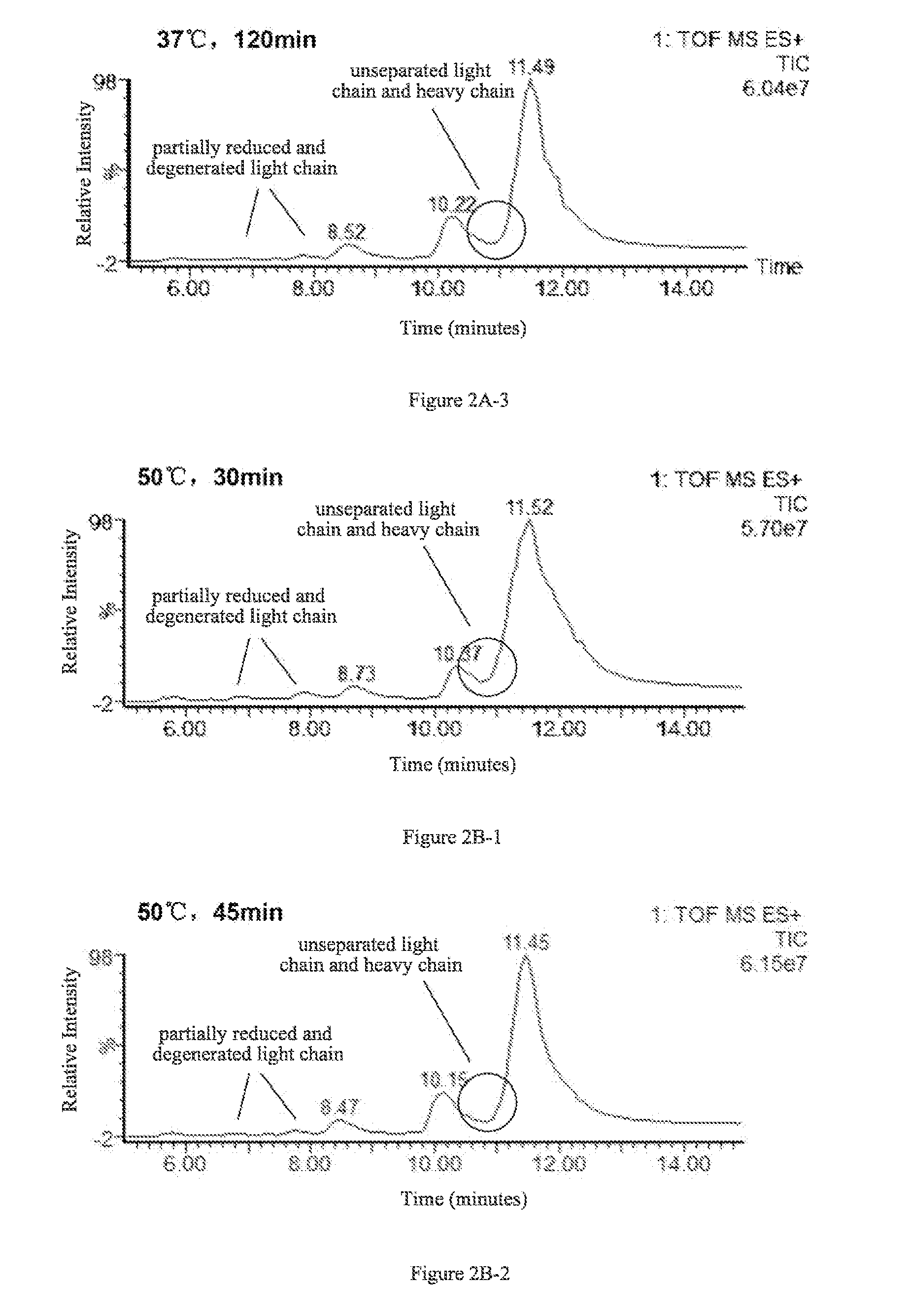
A method for determining glycosylation and terminal modification of samples during protein purification process
ActiveUS20150362506A1Improve accuracyImprove resolutionComponent separationMass spectrometric analysisS glutathiolationMass spectrometry measurement
The present invention provides a method for determining glycosylation and terminal modifications of immunoglobulin during immunoglobulin purification process, which can simultaneously and rapidly determine glycosylation, N-terminal pyroglutamination and C-terminal de-lysination of immunoglobulin. The method comprises: 1) separating immunoglobulin by using cation-exchange resin, and collecting different components in according to retention time; 2) denaturing the components of immunoglobulin obtained in step 1) with a denaturant, followed by reducing them with a reducing agent, to separate the light chain and heavy chain; 3) separating the light chain and heavy chain of immunoglobulin of step 2) by using reverse phase ultrahigh pressure liquid chromatography; 4) measuring the molecular weights of the light chain and heavy chain obtained in step 3) with mass spectrum; 5) analyzing the chromatographic data obtained in step 3) and the mass spectrometric data obtained in step 4) to determine glycosylation and terminal modifications of said immunoglobulin.
Owner:LIVZON MABPHARM
Biomolecules mass spectrometry detection method
ActiveCN110243985AHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyComponent separationMolecular identificationMass spectrometry measurement
The present invention provides a biomolecules mass spectrometry detection method. The mass spectrometry detection method comprises following steps: firstly performing data-independent mass spectrometry acquisition on a sample to be tested, to obtain mass spectrometry data; and then processing the mass spectrometry data, to obtain a detection result; wherein a cyclic scan mode of the data-independent mass spectrometry acquisition includes a first-level full scan and a data-independent secondary scan, and a fragmentation mode of the data-independent secondary scan is mixed fragmentation of intra-source collision-induced dissociation and high-energy collision dissociation. The mixed fragmentation mode in the mass spectrometric detection method significantly improves secondary fragmentation efficiency of parent ions, and obtains more abundant fragmentation information and a more complete secondary spectrum. When used for biomolecule detection, especially for lipidomics analysis, the method can significantly improve molecular identification quantity, and has high sensitivity, high accuracy and high throughput.
Owner:JIANGSU QLIFE MEDICAL TECH GRP CO LTD
New method for quantitative analysis on chromatographic peak under complex environment in liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry data
ActiveCN106596814AReduce the impactObvious superiorityComponent separationMass spectrometry measurementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a new method for quantitative analysis on chromatographic peaks under a complex environment in liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry data and belongs to the field of analyticchemistry. The method includes the steps of: a) quickly reading an XML file of original mass spectrometry data to obtain extract ion chromatogram map of each to-be-quantified substance, and finding potential chromatographic peaks in the extract ion chromatogram map by means of chromatographic peak span value, which is an index having definite physical meaning; b) on the basis of a result in the step a), comparing adjacent potential chromatographic peaks according to chromatographic attribute features such as peak height, peak distance, peak area and the like, and further performing effectivefusion; and c) according to the characters of the chromatography-mass spectrometry data, comprehensively analyzing possible chromatographic peak shapes and noise influence in the liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis process to dynamically regulate the chromatographic peaks. By means of the new method for accurate quantification on the basis of complex liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry data, number, position, height and area of the chromatographic peaks within the same retention time range can be obtained. The method is suitable for quick, accurate, batched and quantitative analysis for high-resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry data under low signal to noise ratio and under a complex background.
Owner:DALIAN CHEM DATA SOLUTION TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com