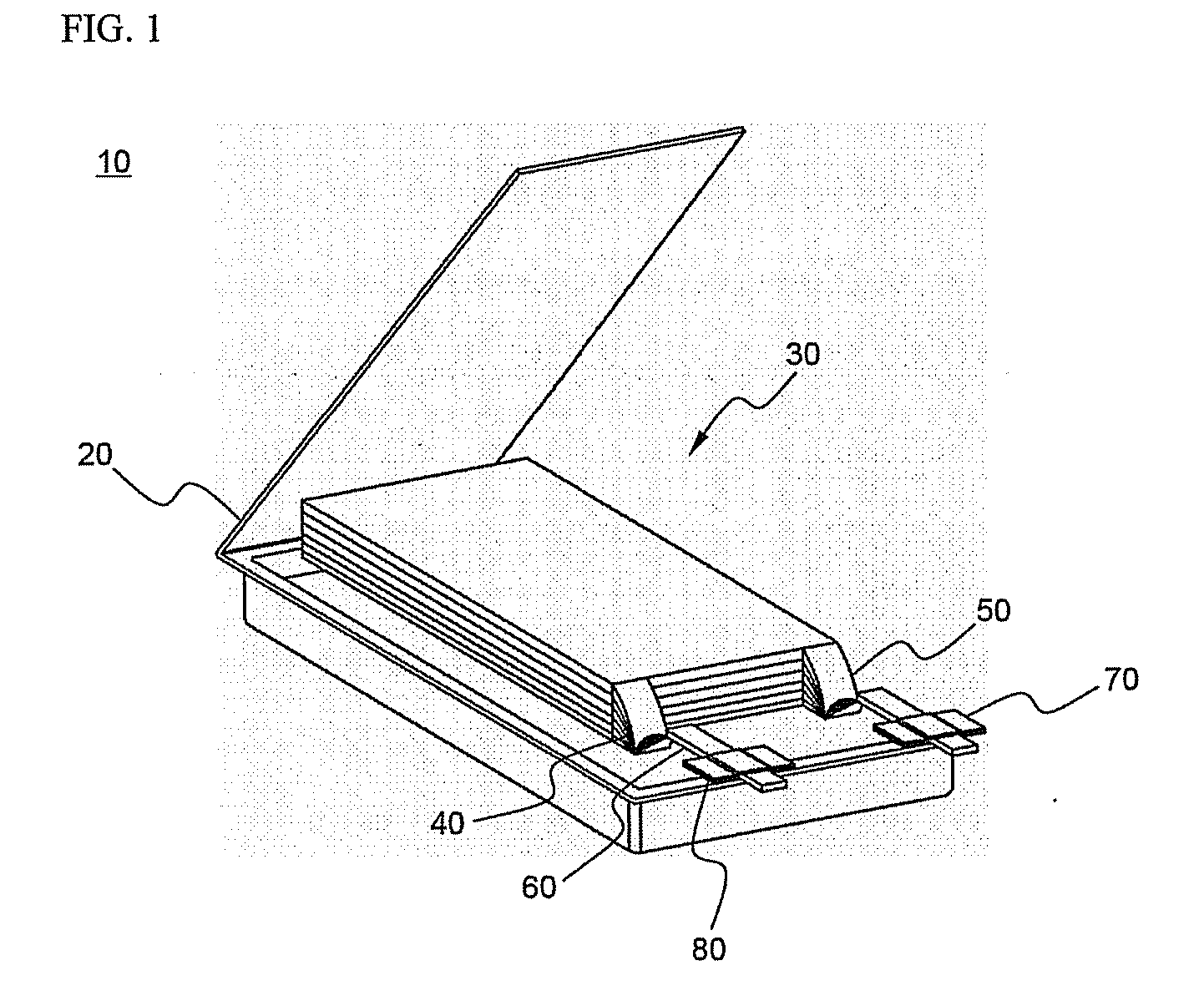
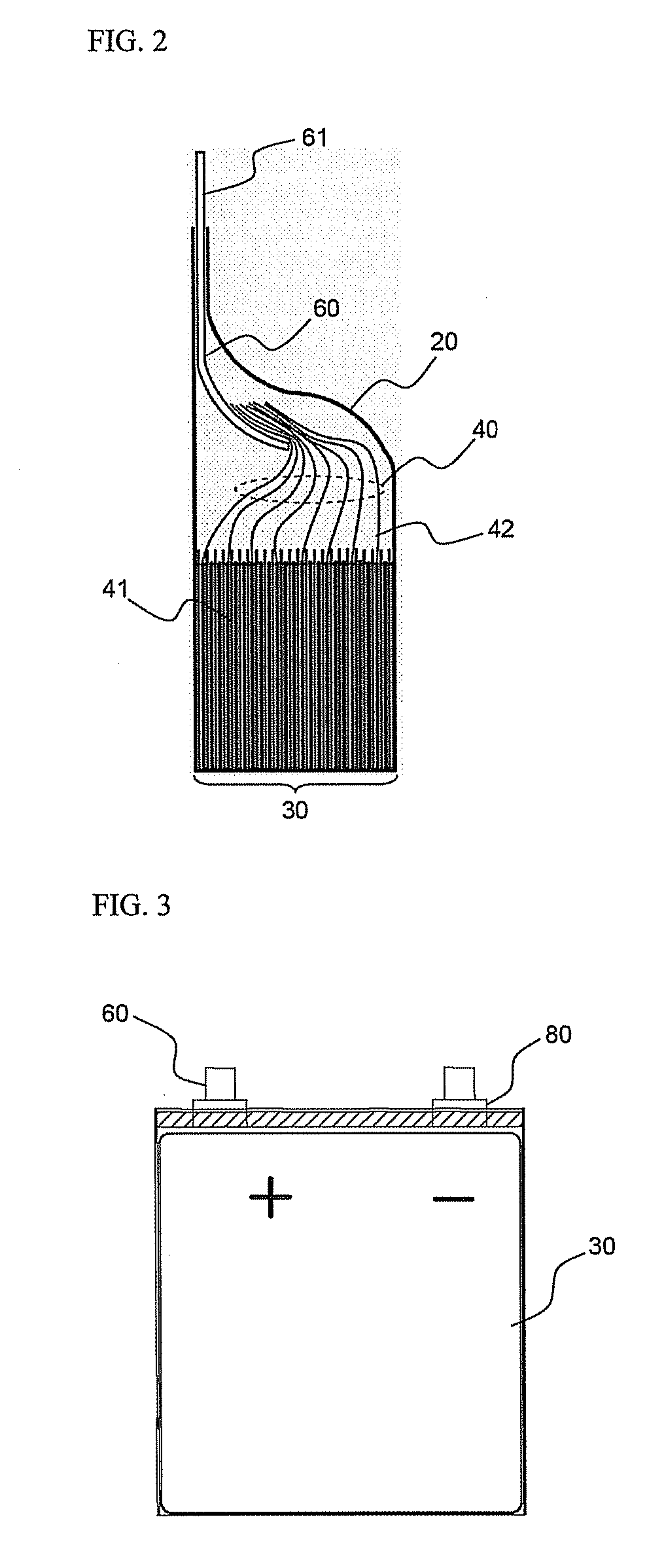
Patents
Literature
251results about How to "Improve battery safety" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
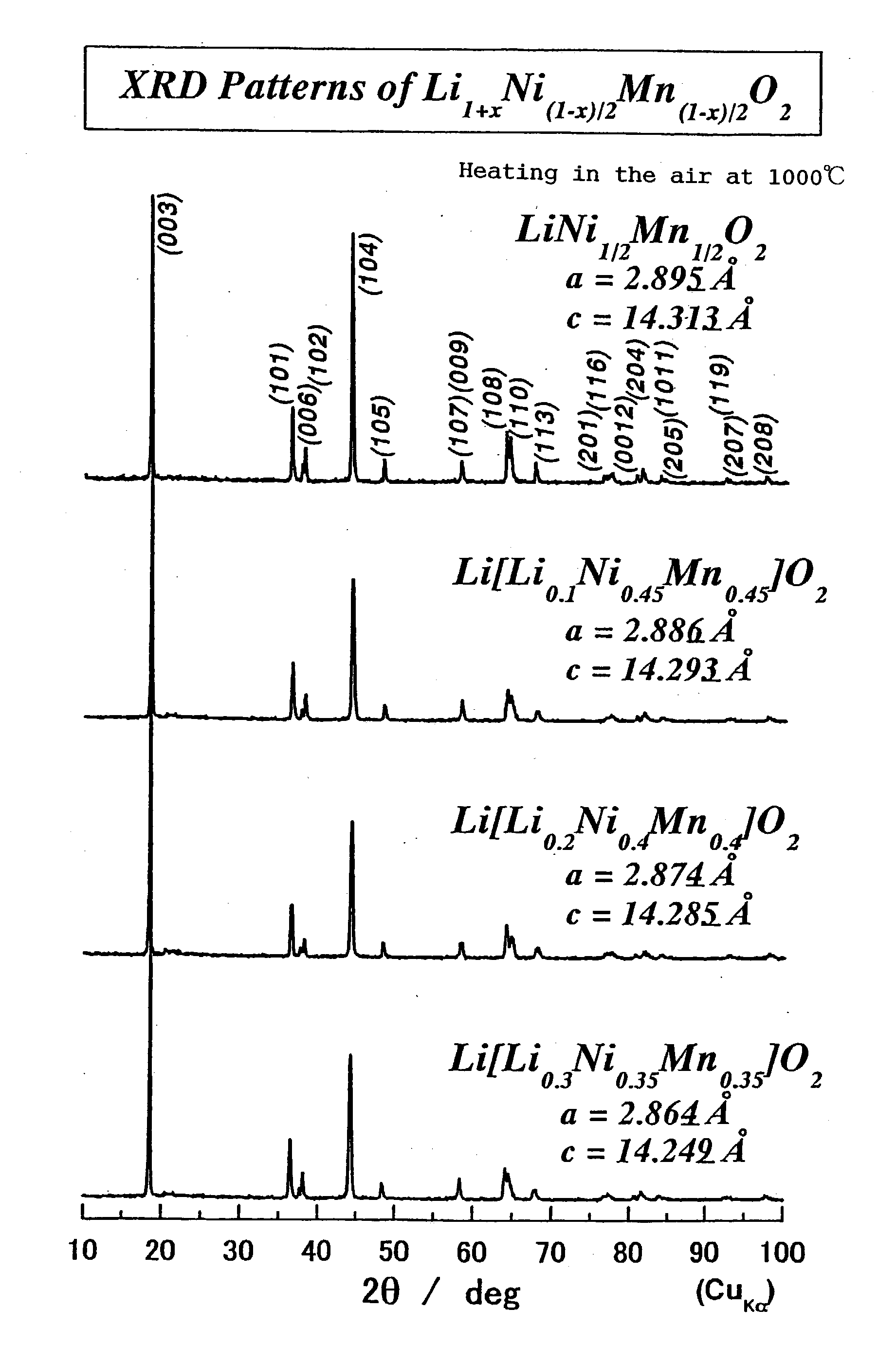
Positive-electrode active material and nonaqueous-electrolyte secondary battery containing the same
InactiveUS20030170540A1Improve the immunityLarge ion permeabilityIron oxides/hydroxidesElectrode thermal treatmentCrystal structureOxygen
The present invention provides a high-capacity and low-cost non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery, comprising: a negative electrode containing, as a negative electrode active material, a ssubstance capable of absorbing / desorbing lithium ions and / or metal lithium; a separator; a positive electrode; and an electrolyte, wherein the positive electrode active material contained in the positive electrode is composed of crystalline particles of an oxide containing two kinds of transition metal elements, the crystalline particles having a layered crystal structure, and oxygen atoms constituting the oxide forming a cubic closest packing structure.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
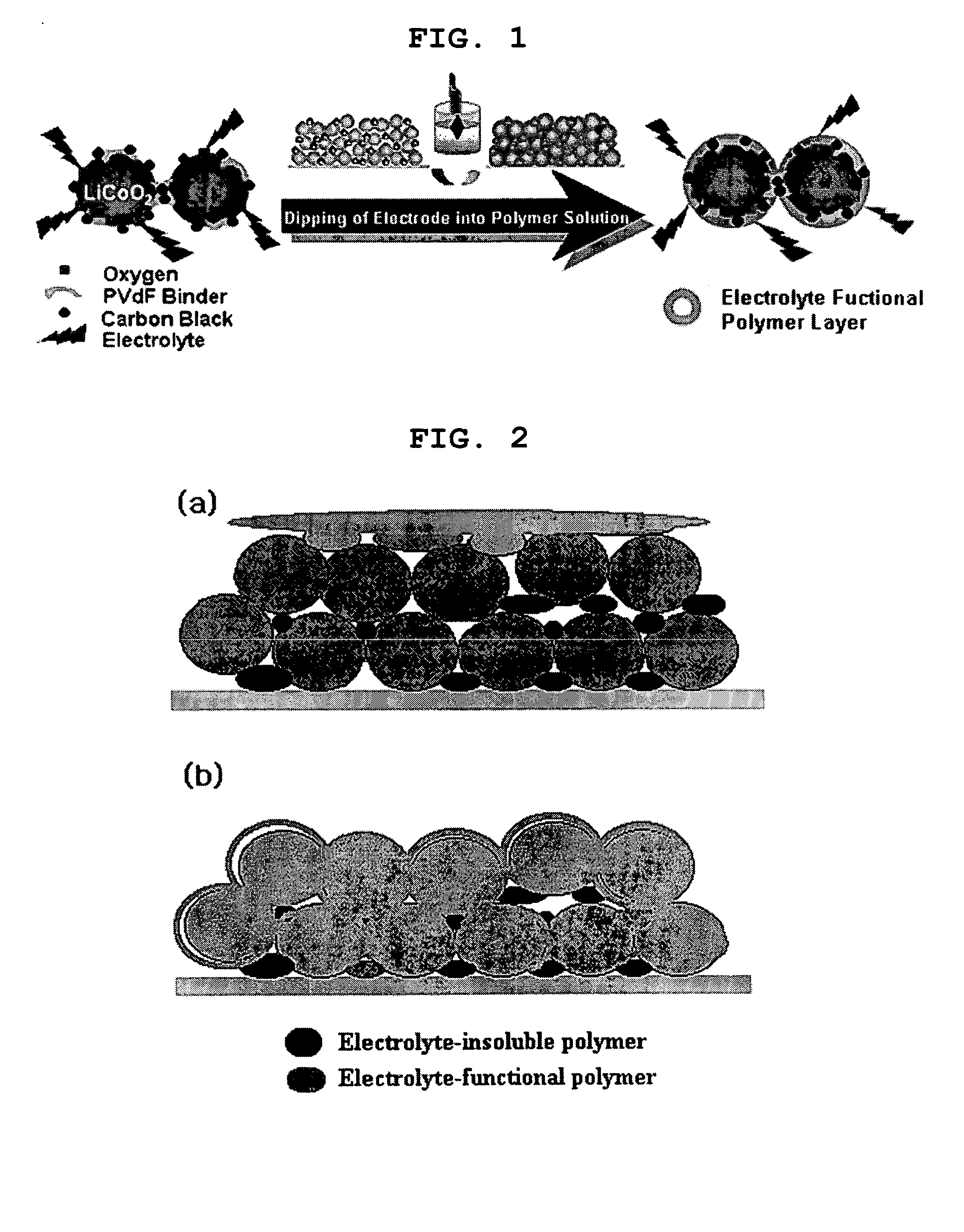
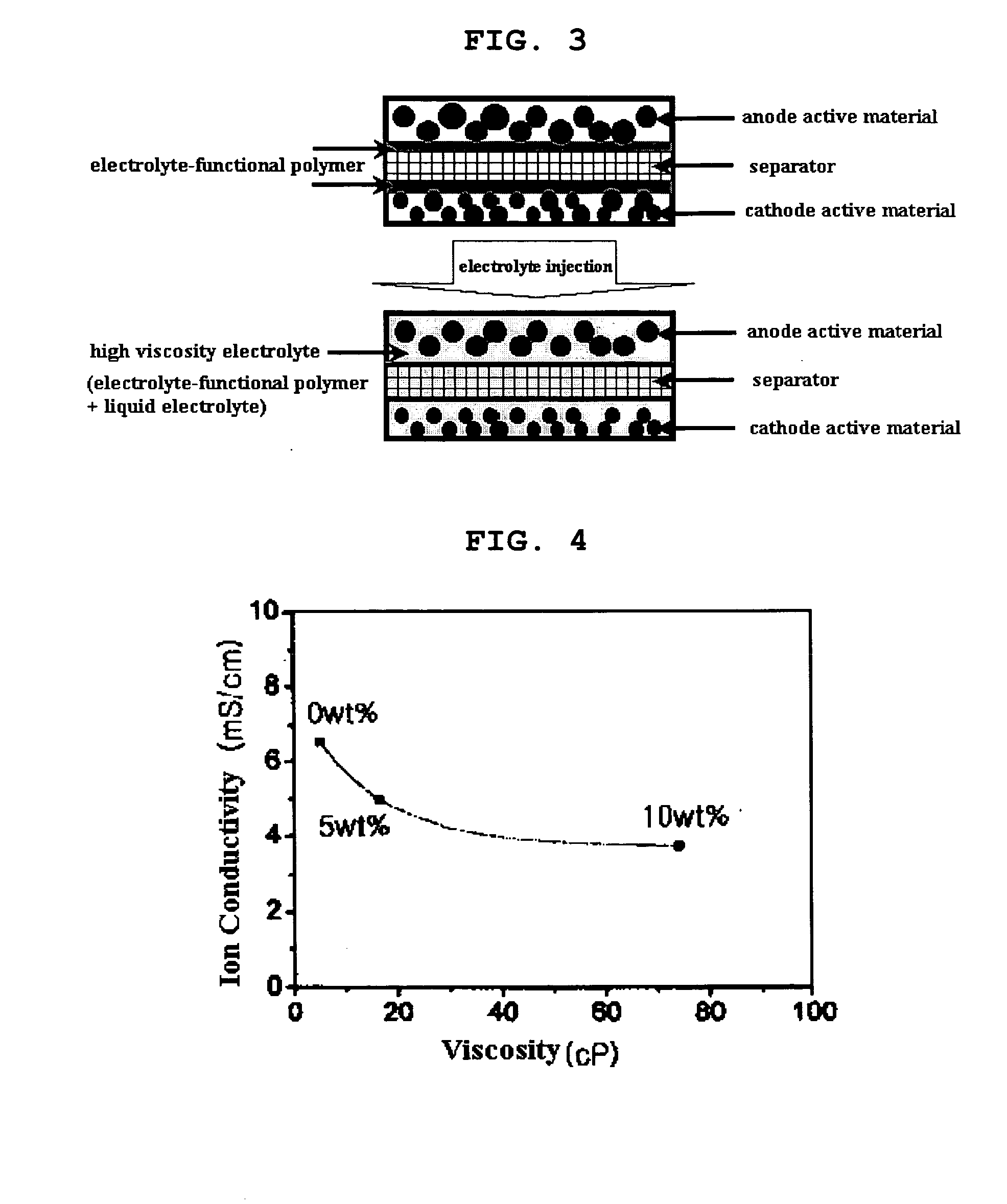
Functional polymer film-coated electrode and electrochemical device using the same
ActiveUS20050118508A1Lower performance requirementsImprove battery safetyGel electrodesElectrode carriers/collectorsSlurryPolymer thin films
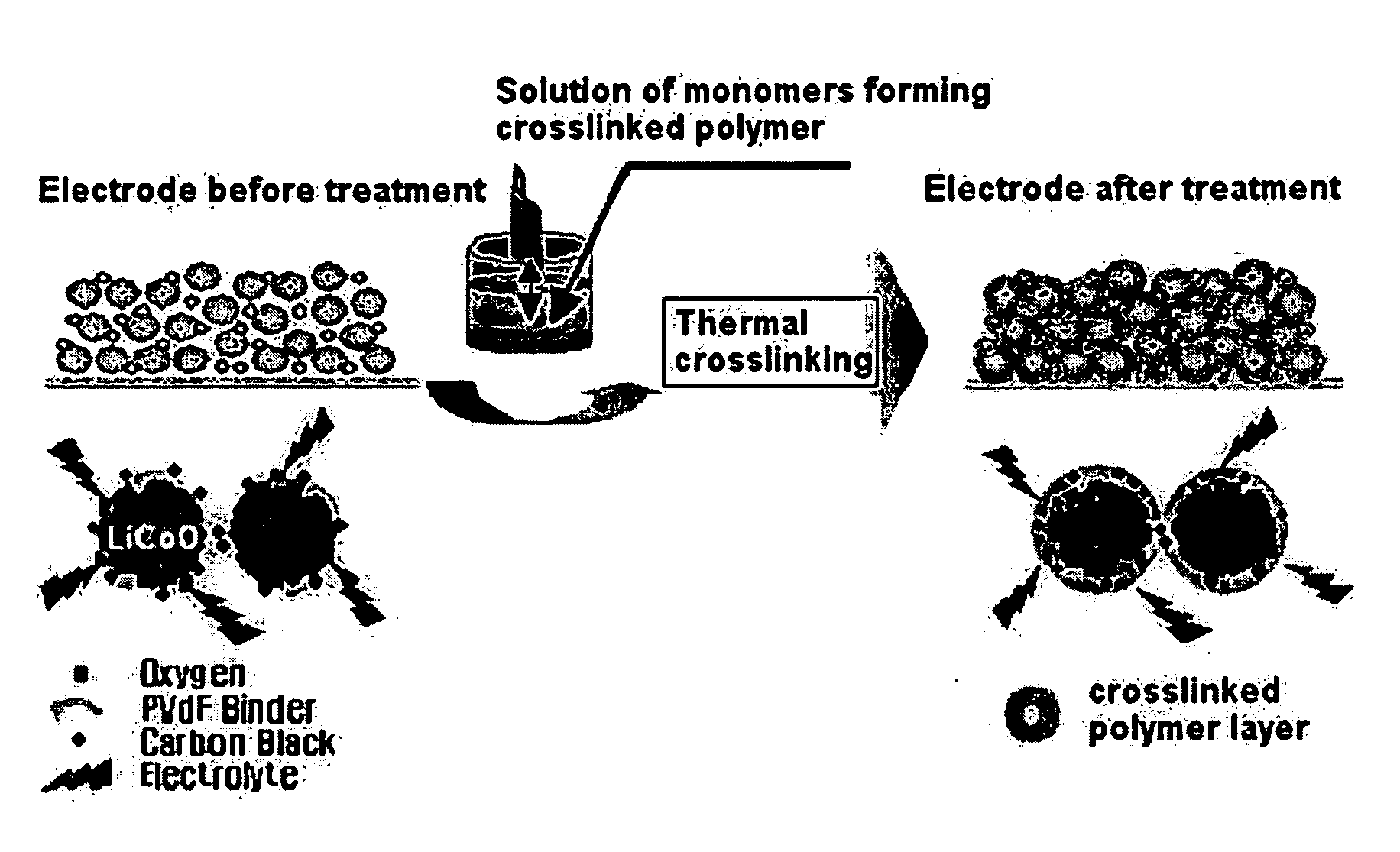
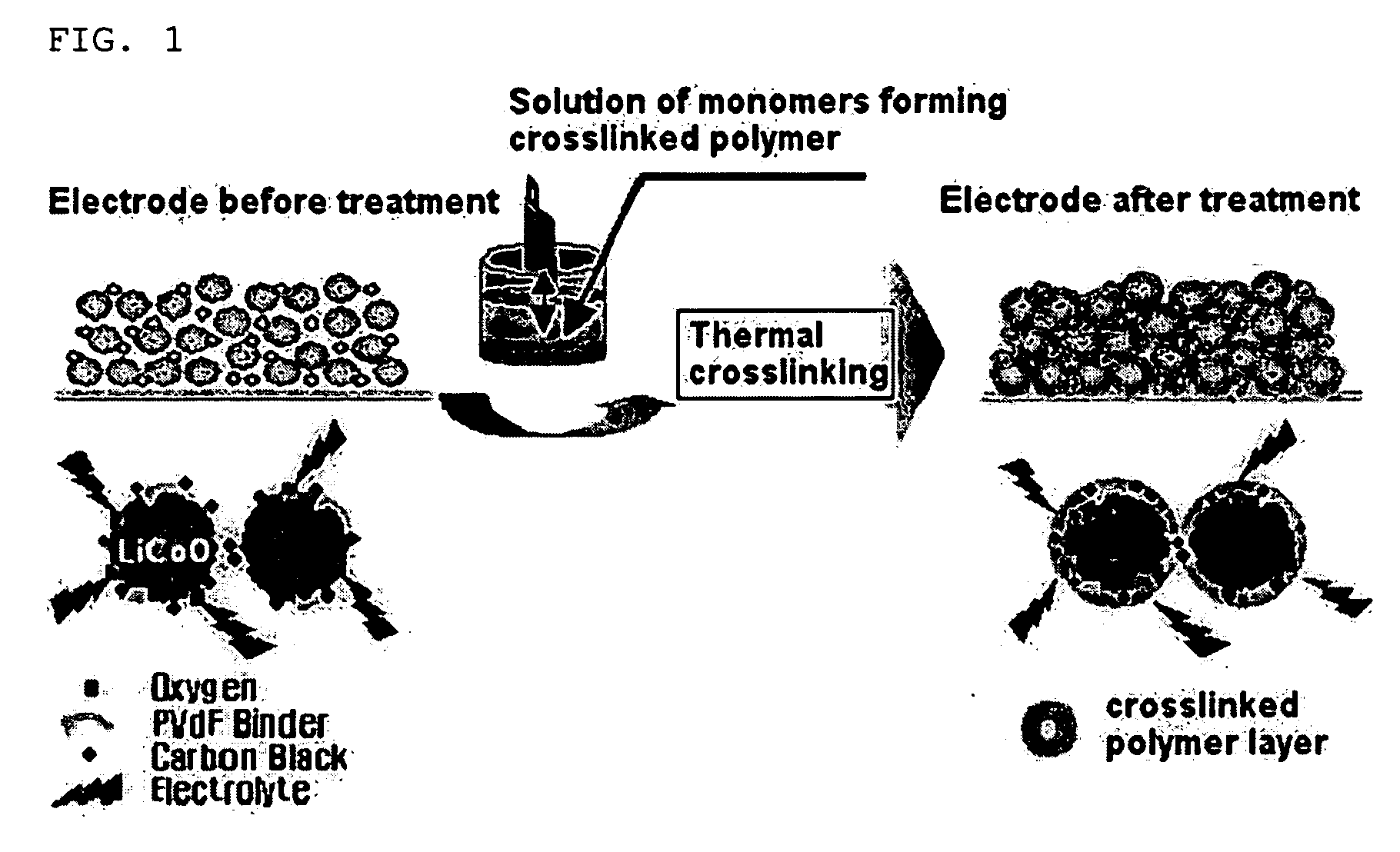
The present invention provides an electrode in which an electrode active material particles as being interconnected are applied on current collector, wherein the interconnected surface of electrode active material particles is coated with a polymer, the polymer being present as an independent phase, while maintaining a pore structure formed among the interconnected electrode active material particles as well as an electrochemical device including the electrode. Also, the present invention provides a method for manufacturing an electrode coated with a polymer present on an interconnected surface of electrode active material as an independent phase, while maintaining a pore structure formed among the electrode active material particles, which comprises the steps of: (a) coating slurry for an electrode including an electrode active material on a current collector and drying it to form an electrode; and (b) dipping the electrode obtained from step (a) into a solution containing the polymer dissolved therein and a method for manufacturing an electrochemical device comprising the electrode obtained by the above method. The electrode coated with a polymer as an independent phase provides an electrochemical device with improved safety and prevents degradation of performance of an electrochemical device.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Nonaqueous secondary battery and method of using the same
ActiveUS20080102369A1Deterioration of characteristicDifficult to formFinal product manufactureActive material electrodesOxideMetal
A nonaqueous secondary battery having a positive electrode having a positive electrode mixture layer, a negative electrode, and a nonaqueous electrolyte, in which the positive electrode contains, as an active material, a lithium-containing transition metal oxide containing a metal element selected from the group consisting of Mg, Ti, Zr, Ge, Nb, Al and Sn, the positive electrode mixture layer has a density of 3.5 g / cm3 or larger, and the nonaqueous electrolyte contains a compound having two or more nitrile groups in the molecule
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
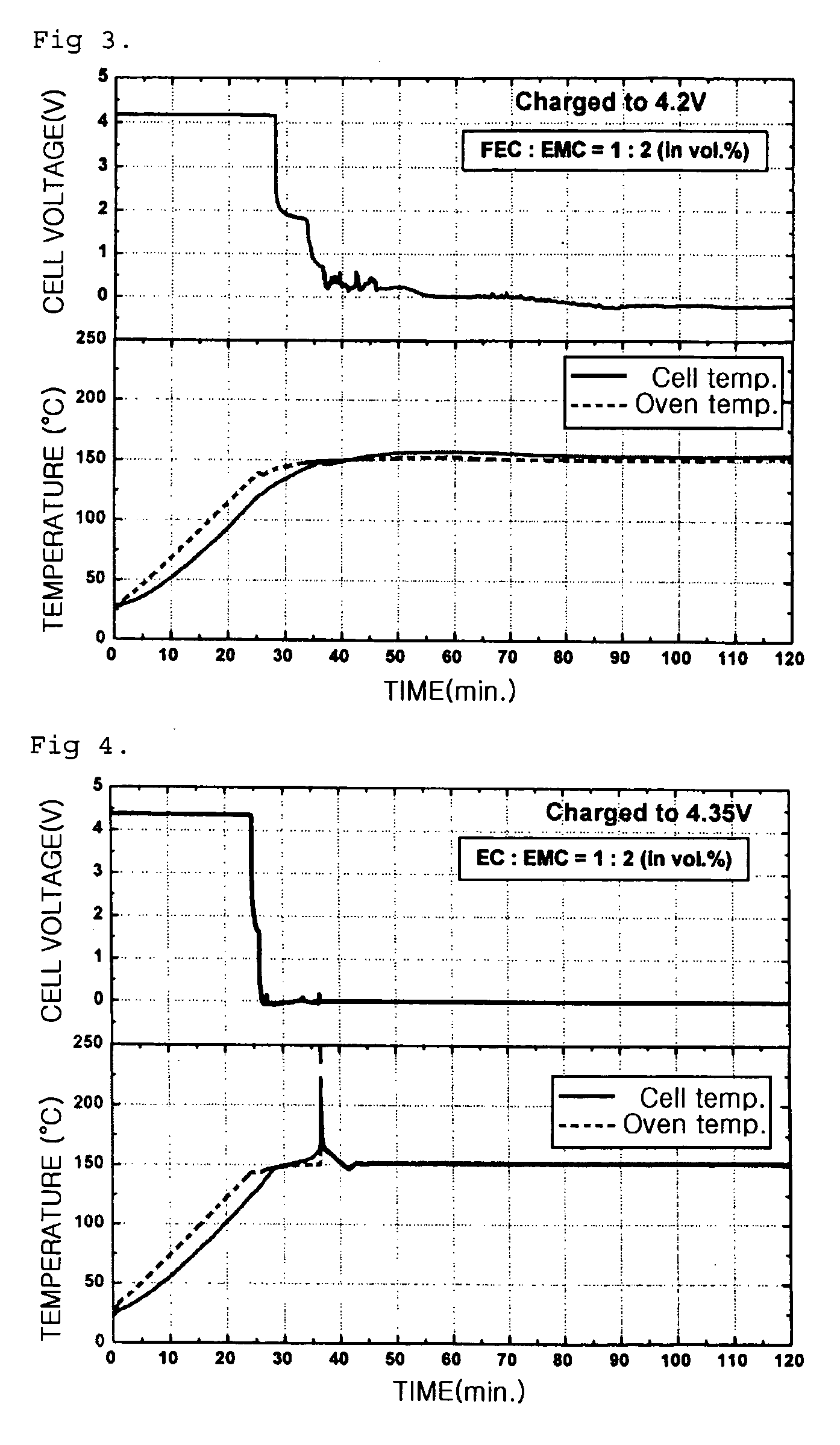
Electrolyte solvent for improving safety of battery and lithium secondary battery comprising the same
ActiveUS20050031963A1Improve safetyImprove battery safetyFinal product manufactureOrganic electrolyte cellsSolventChemistry
The present invention provides an electrolyte solvent for batteries, which comprises fluoroethylene carbonate and linear ester solvent. Also, the present invention provides a lithium secondary battery comprising a positive electrode, a negative electrode and an electrolyte, wherein the electrolyte comprises fluoroethylene carbonate and linear ester solvent. The inventive electrolyte solvent can improve the battery safety without deteriorating the battery performance.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
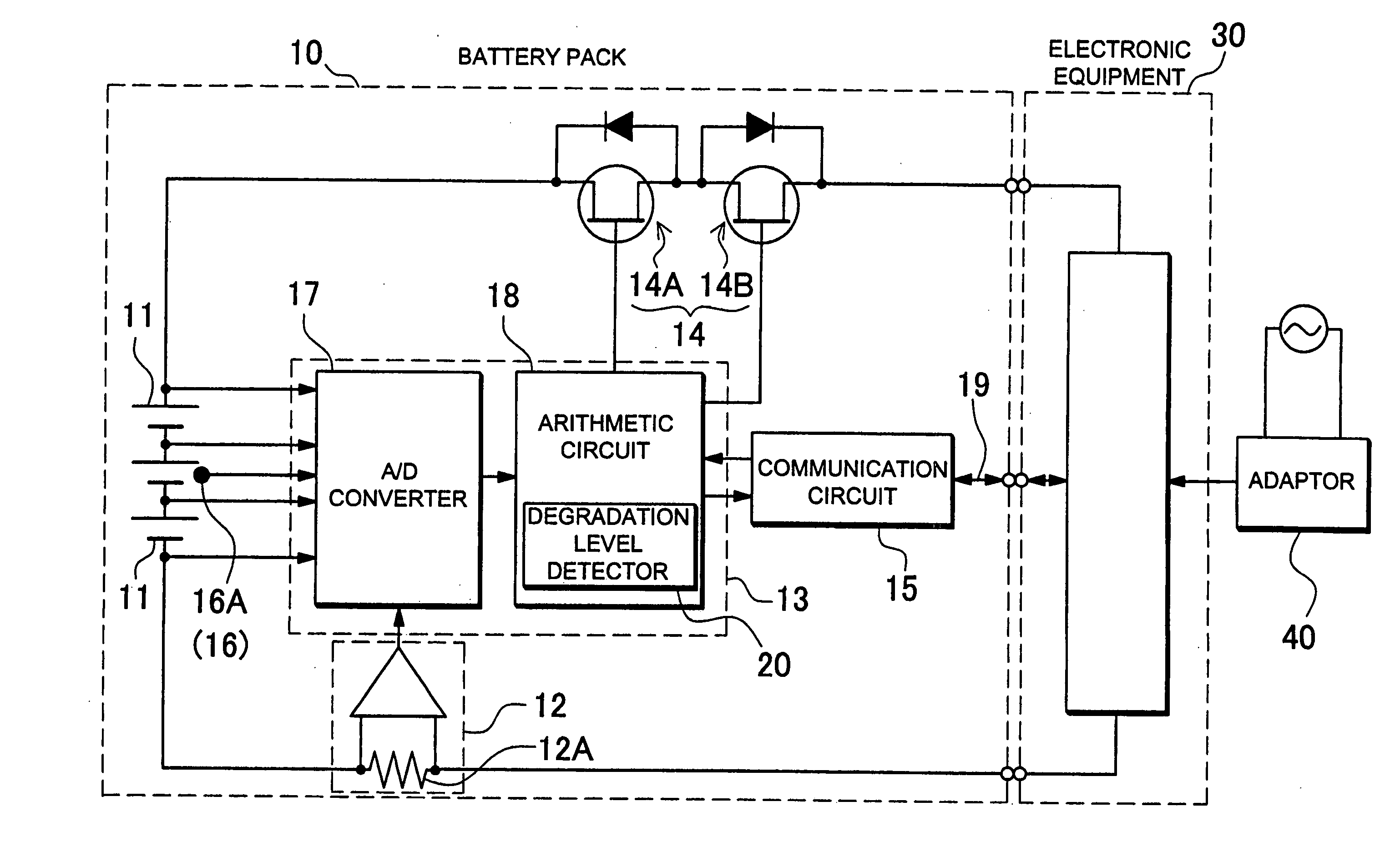
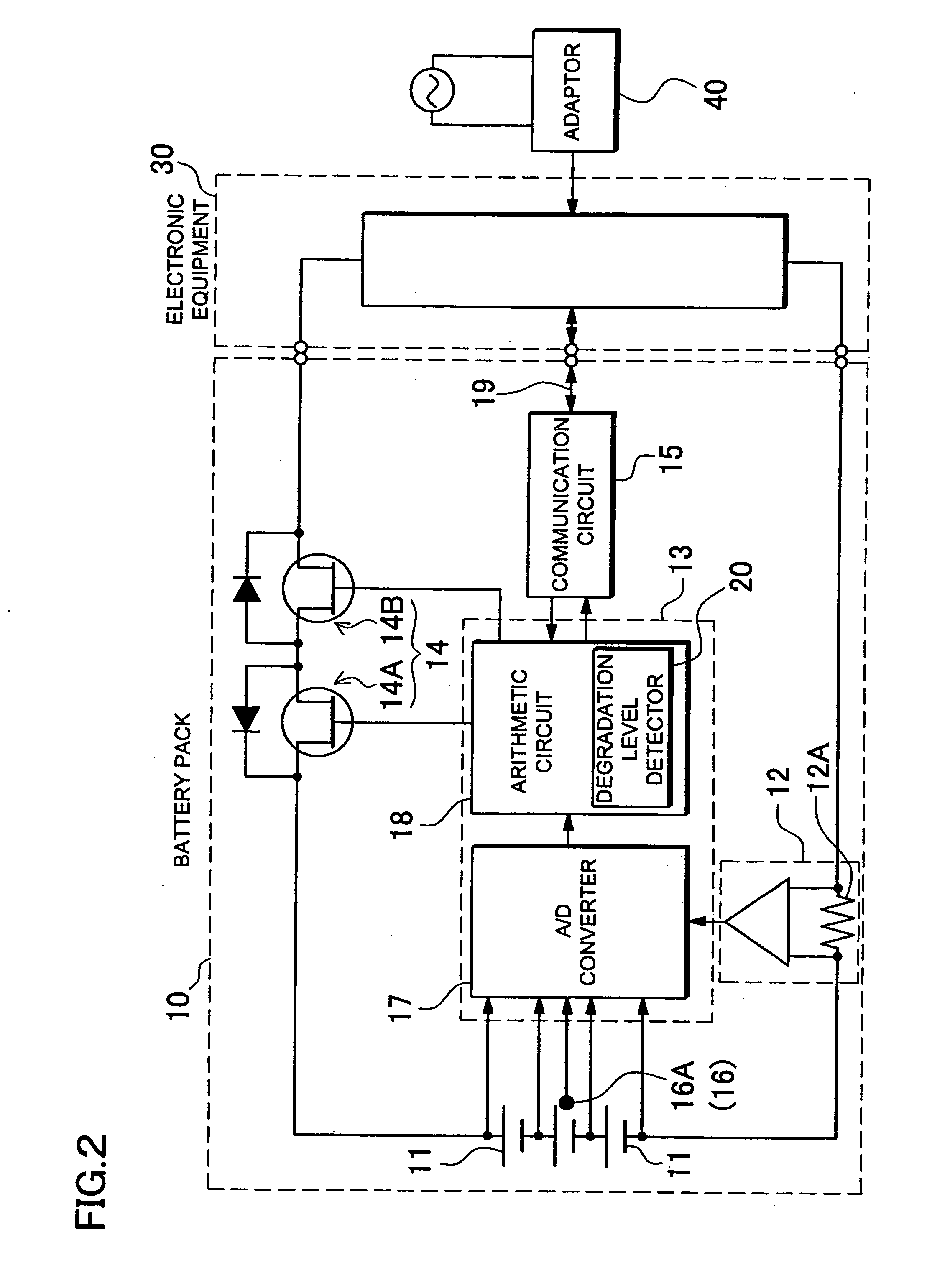
Method for charging battery pack
InactiveUS20080224667A1Improve battery safetyIncrease usable capacityBatteries circuit arrangementsCells structural combinationVoltageLithium
A method for charging a lithium-ion secondary battery is so designed as to fully charge, with a voltage of the lithium-ion secondary battery being limited to a set voltage. Further, the method for charging the lithium-ion secondary battery is so designed that a degradation level of the lithium-ion secondary battery is detected, and when the degradation is advanced, the battery is fully charged with the set voltage being lowered.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Preparation process for preventing deformation of jelly-roll type electrode assembly
ActiveUS20100285341A1Good buffering effectEasy to assembleElectrode manufacturing processesAssembling battery machinesInorganic particleComposite membrane
Provided is a method for fabrication of a jelly-roll type electrode assembly having a cathode / separation membrane / anode laminate structure, including: (a) coating both sides of a porous substrate with organic / inorganic composite layers, each of which includes inorganic particles and an organic polymer as a binder, so as to fabricate a composite membrane; and (b) inserting one end of a sheet laminate comprising a cathode sheet and an anode sheet as well as the composite membrane into a mandrel, winding the sheet laminate around the mandrel, and then, removing the mandrel, wherein the organic / inorganic composite layer includes microfine pores capable of moderating a variation in volume during charge / discharge of a secondary battery and an interfacial friction coefficient between the composite membrane and the mandrel is not more than 0.28.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
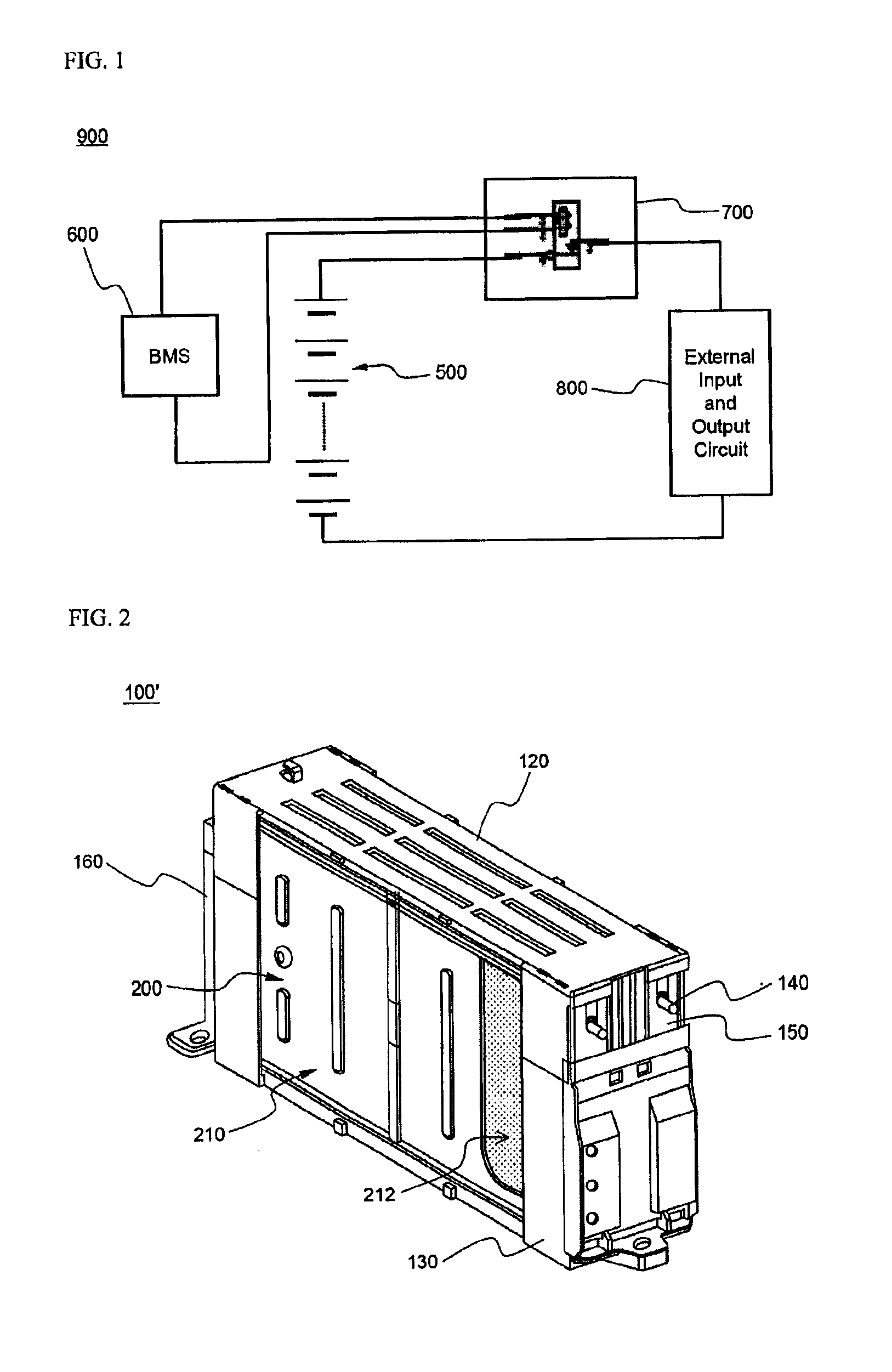
Voltage protection and health monitoring of batteries with reference electrodes
ActiveUS20150147614A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical testingAnode voltageElectrical battery
In some variations, an apparatus provides real-time monitoring of voltage and differential voltage of both anode and cathode in a battery configured with at least one reference electrode. Voltage monitors are connected to a computer programmed for receiving anode voltage signals; receiving cathode voltage signals; calculating the derivative of the anode voltage with respect to time or with respect to capacity; and calculating the derivative of the cathode voltage with respect to time or with respect to capacity. Other variations provide an apparatus for real-time assessment of capacities of both anode and cathode in a battery, comprising a computer programmed for receiving electrode voltage signals; estimating first and second electrode open-circuit voltages at two different times, and correlating the first and second electrode open-circuit voltages to first and second electrode states of charge, respectively, for each of anode and cathode. The anode and cathode capacities may then be estimated independently.
Owner:HRL LAB +1
Battery and process for preparing the same
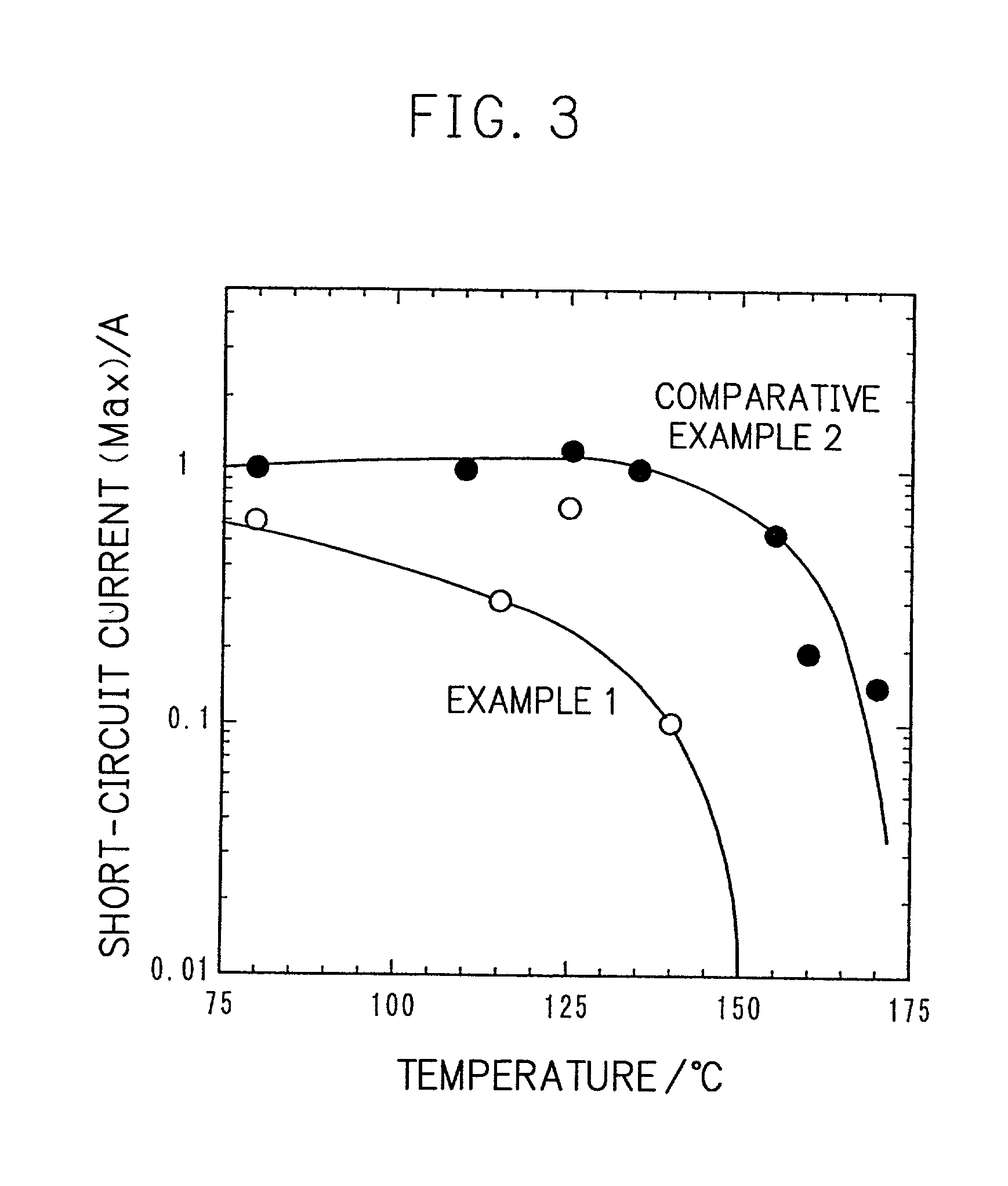
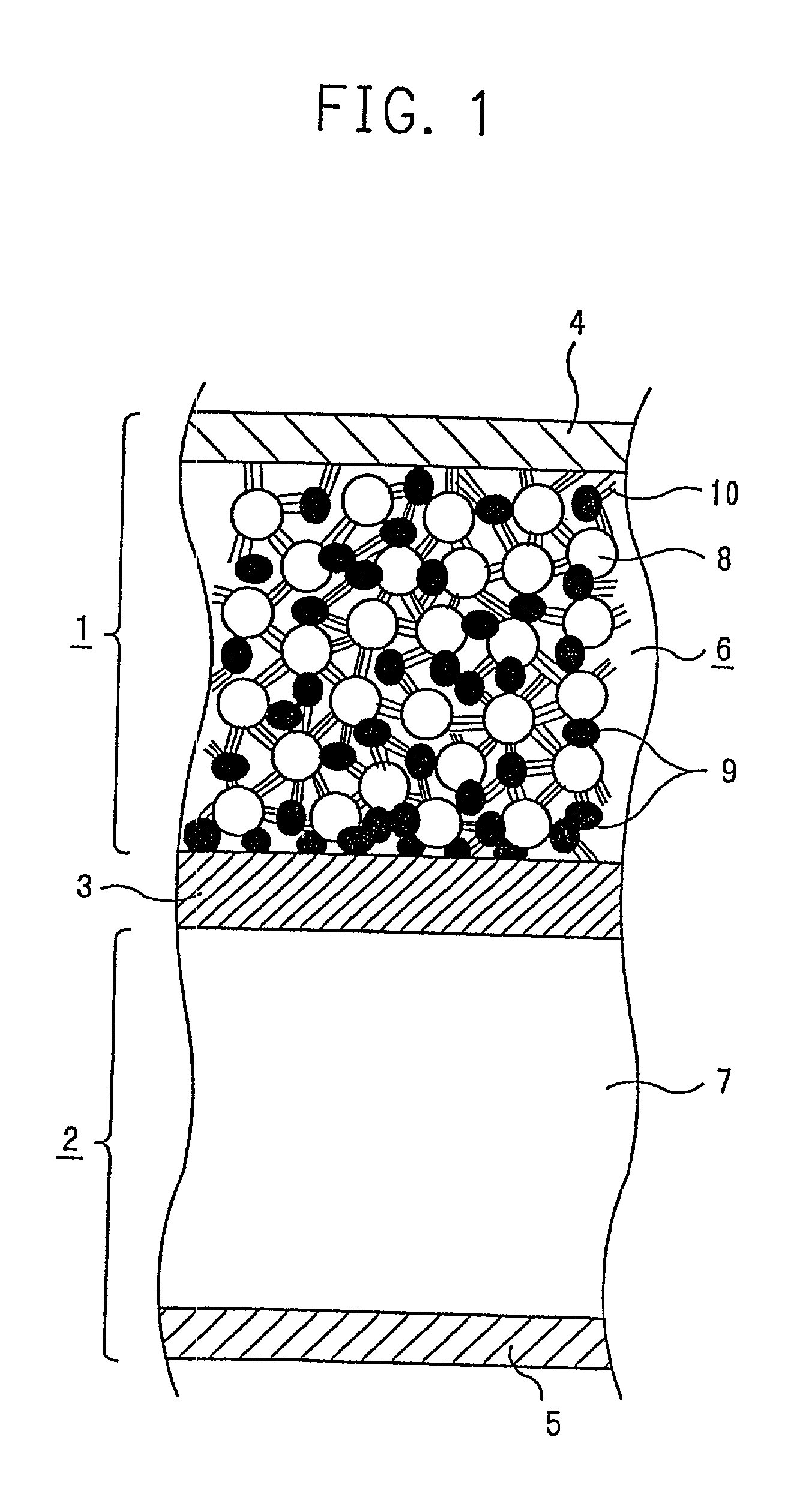
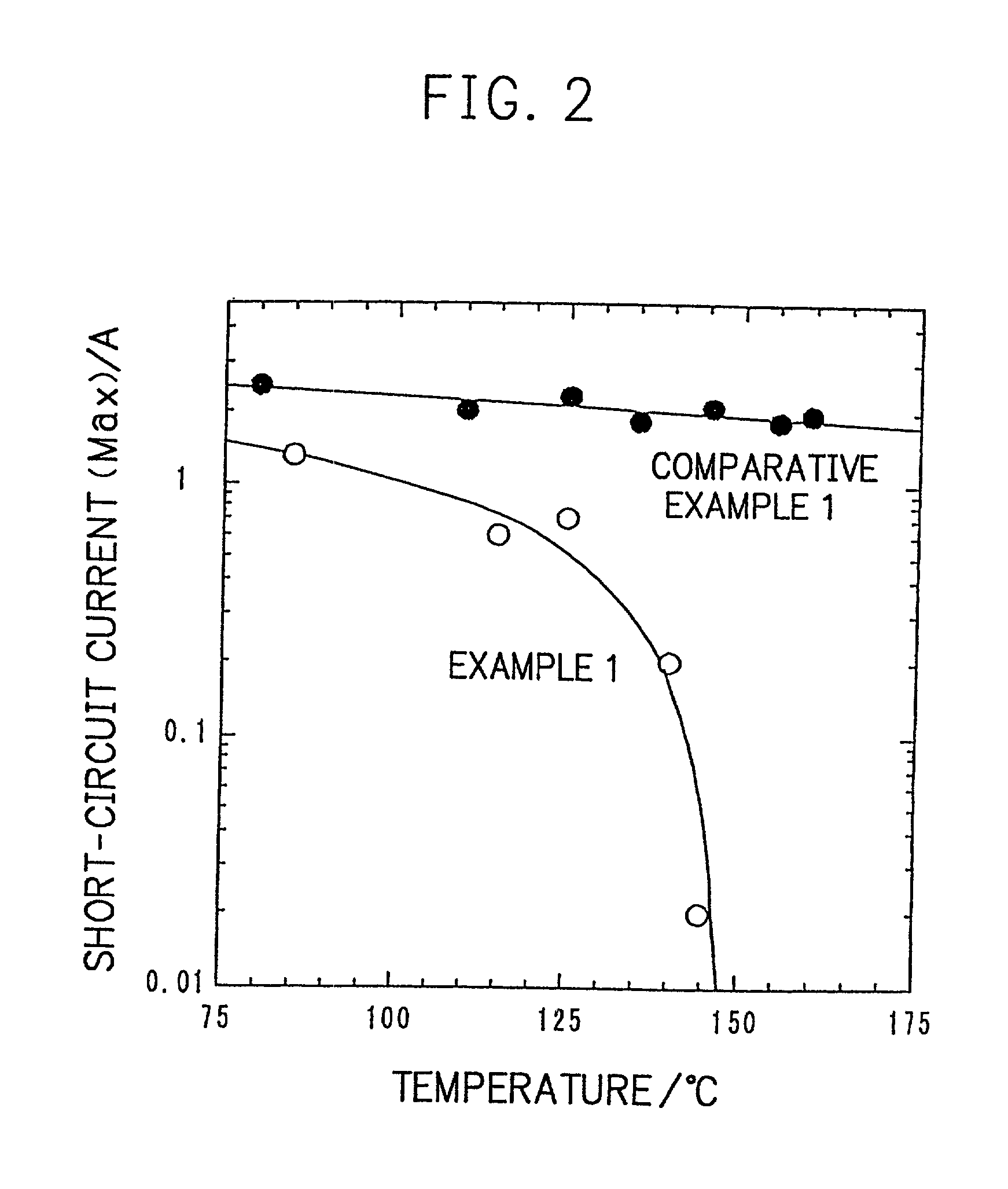
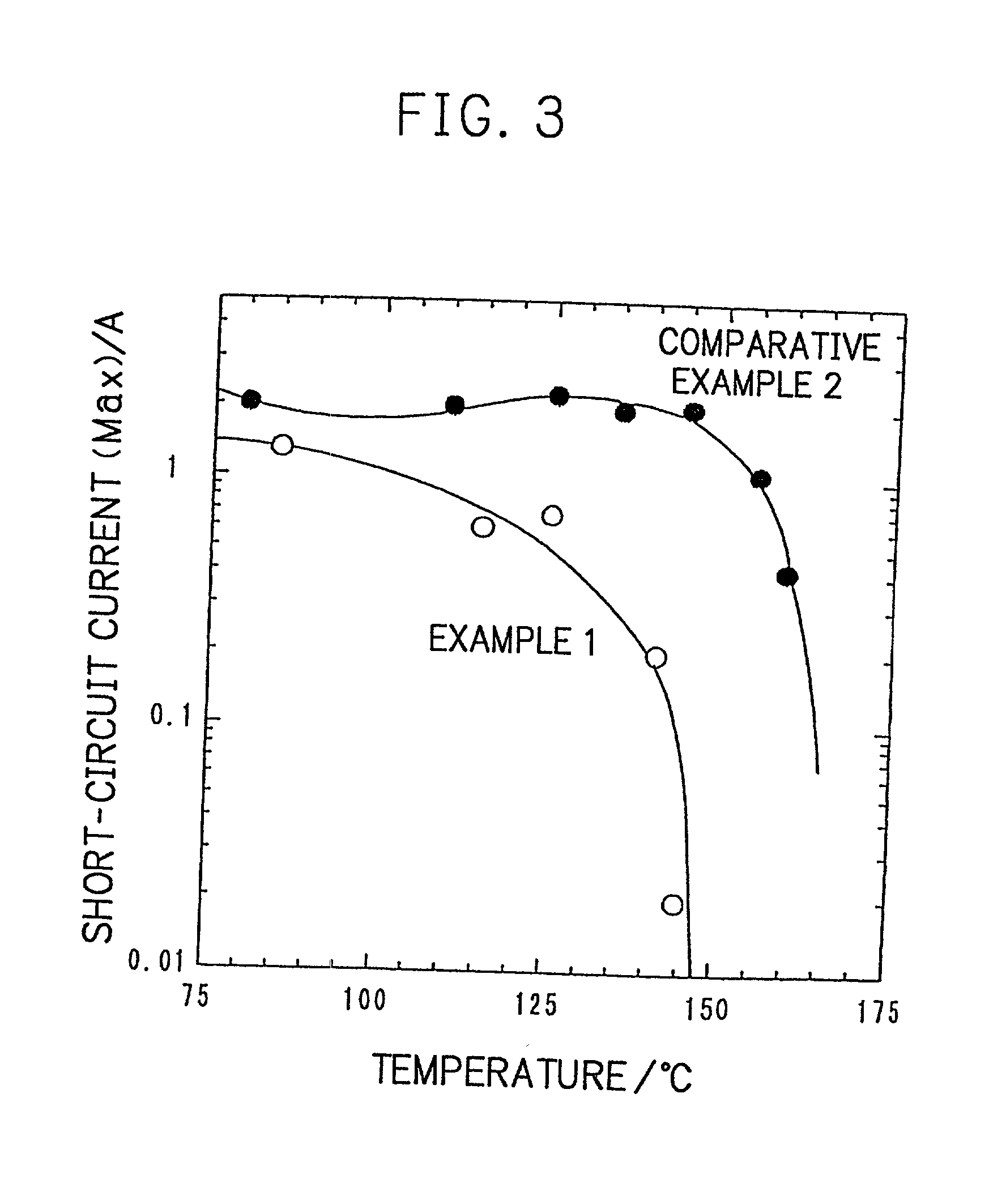
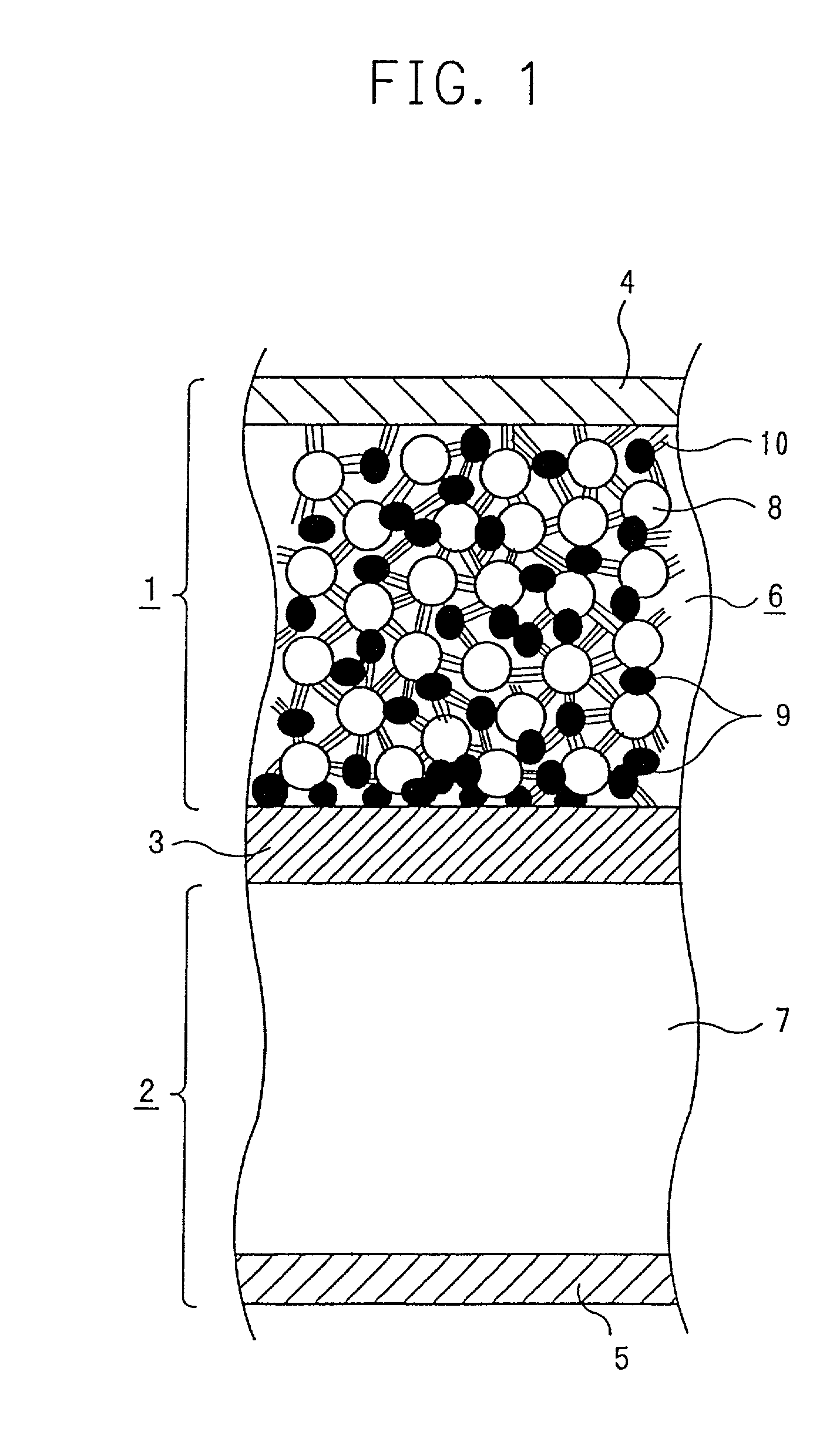
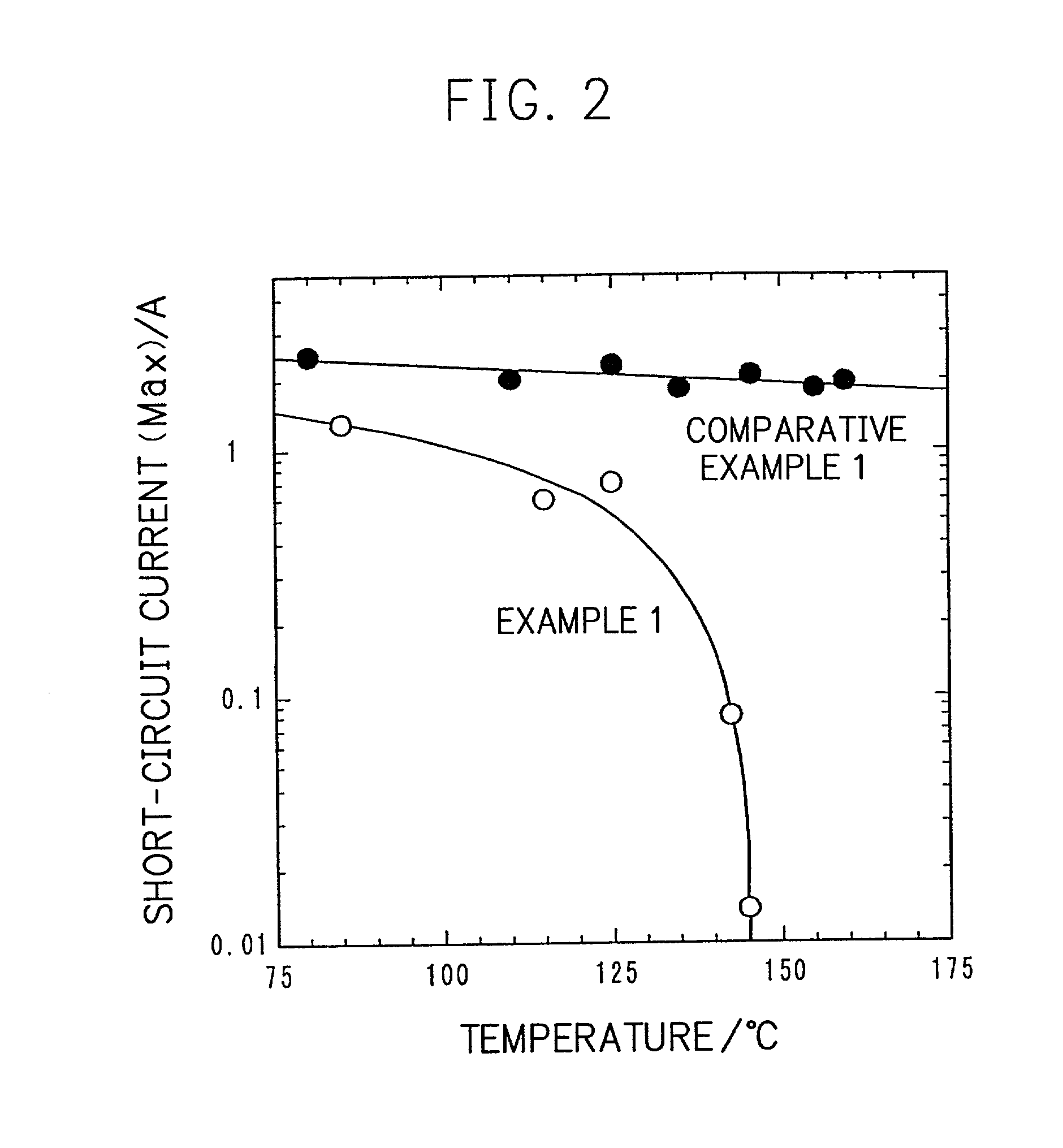
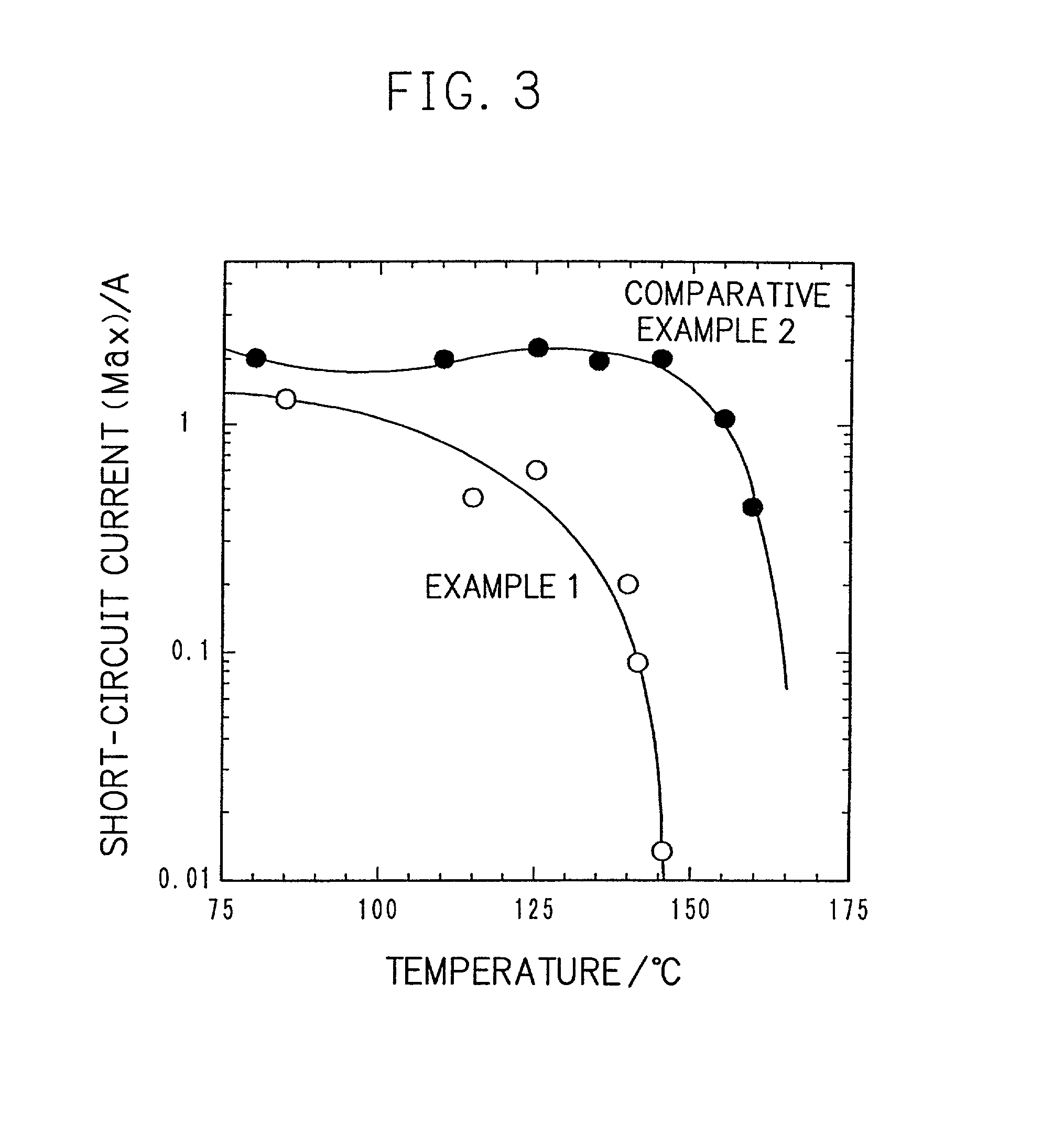
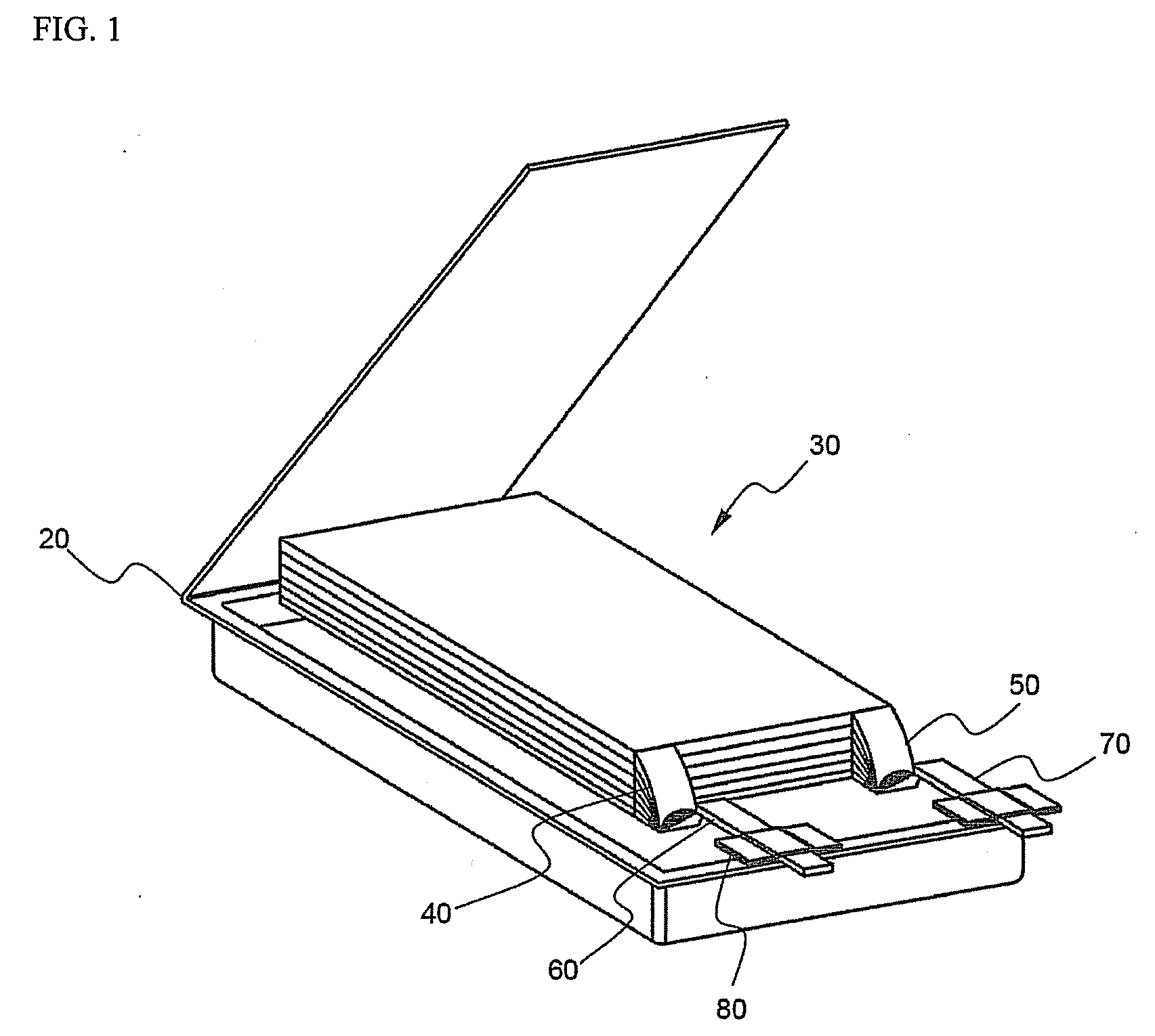
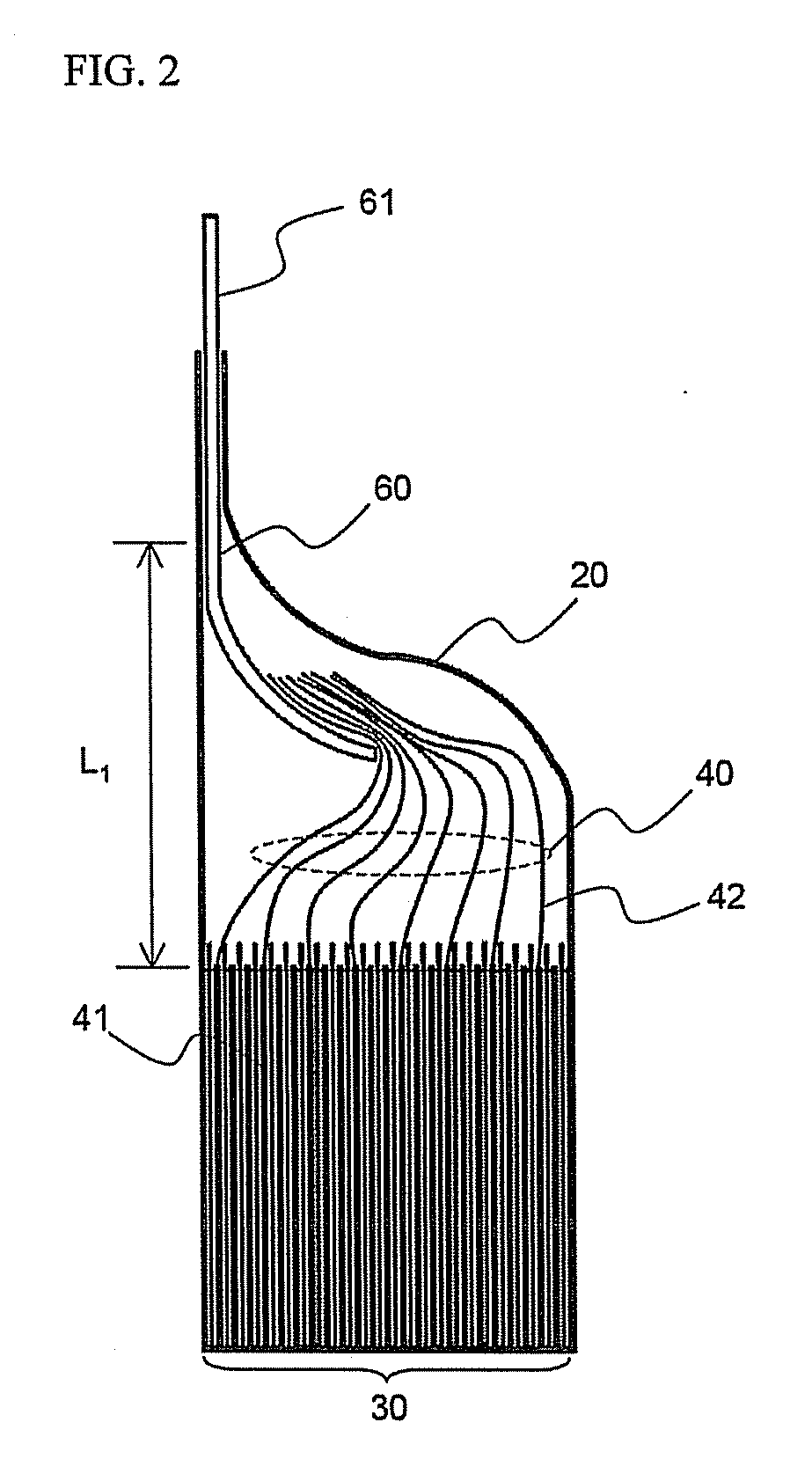
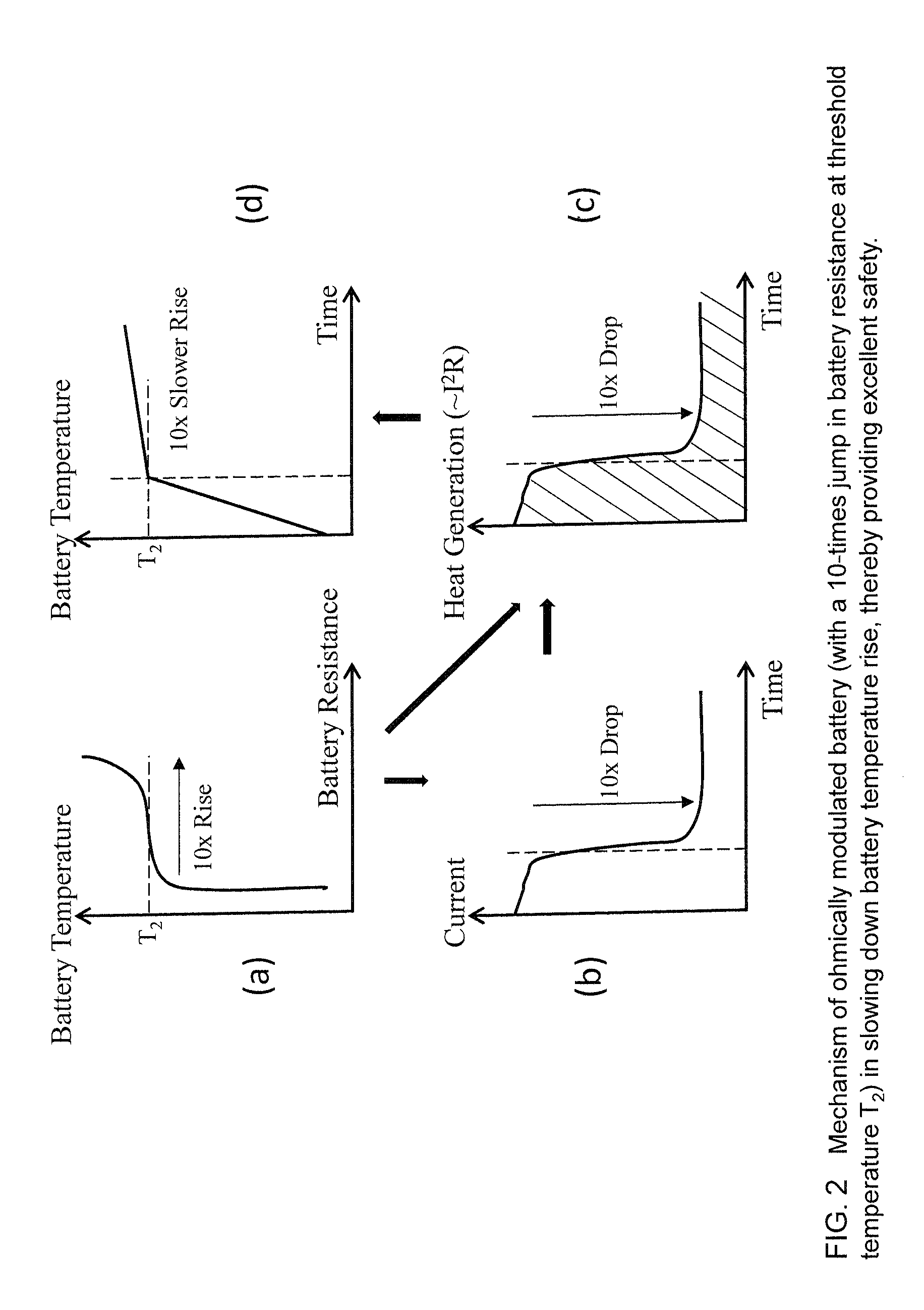
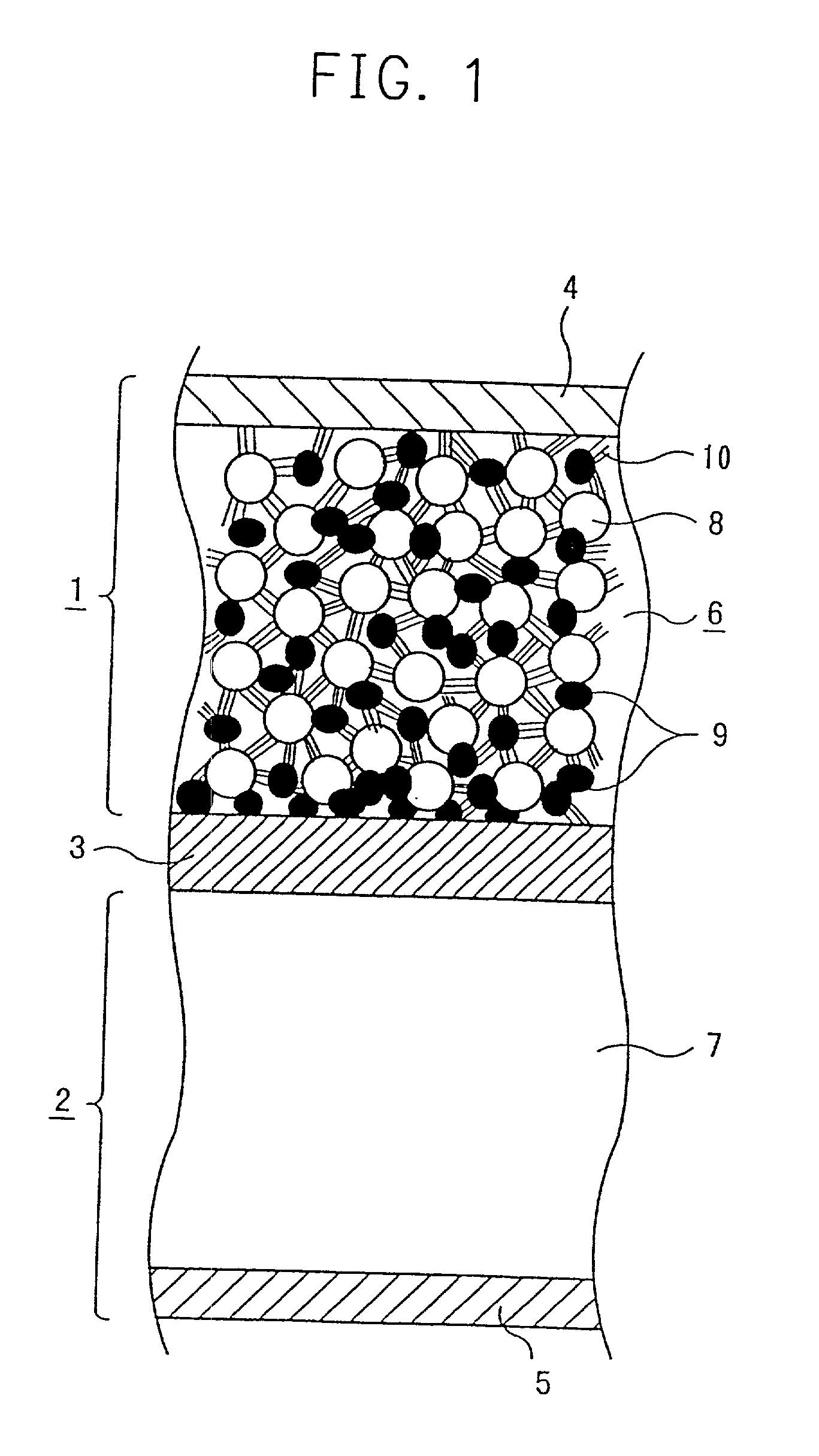
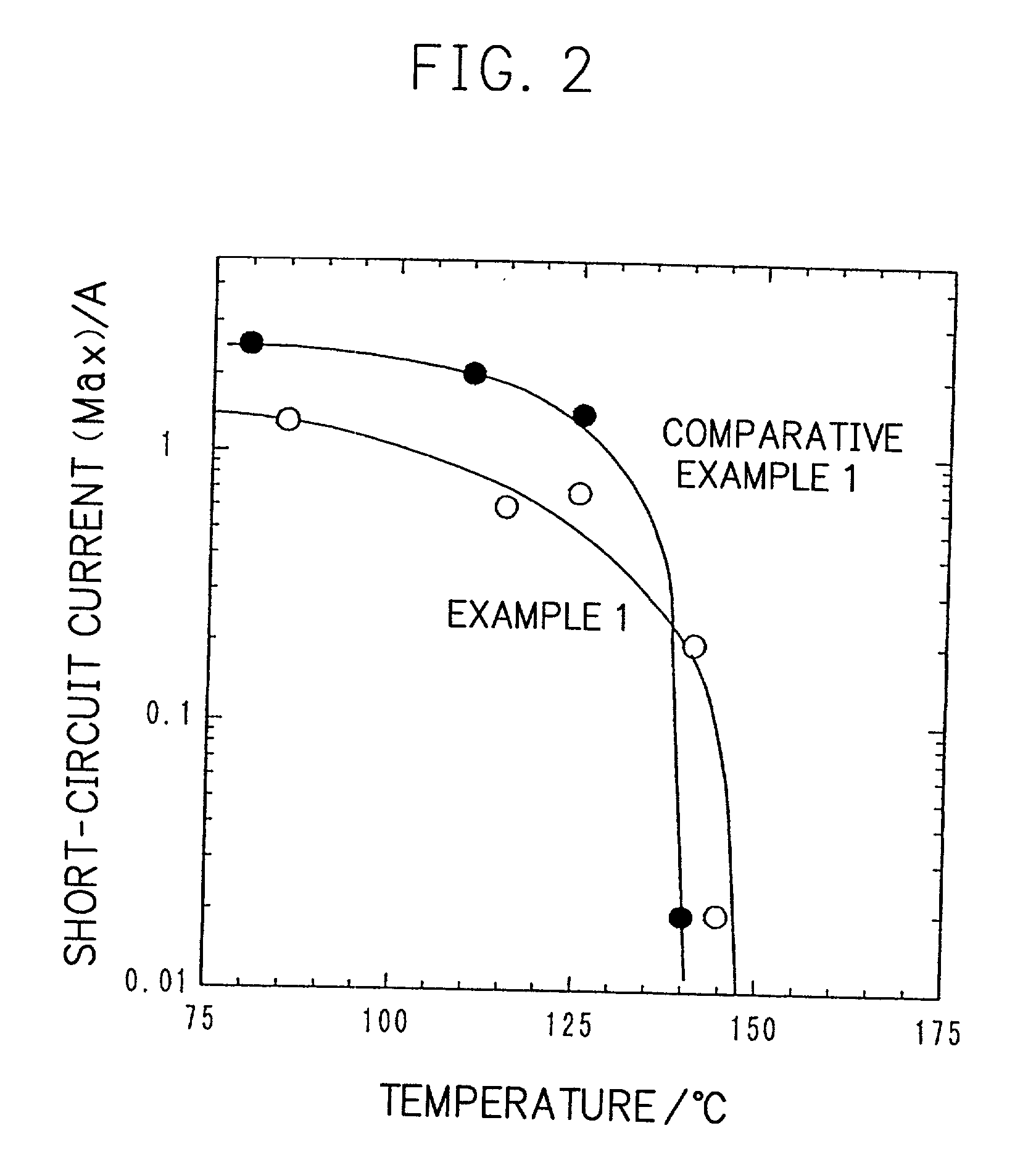
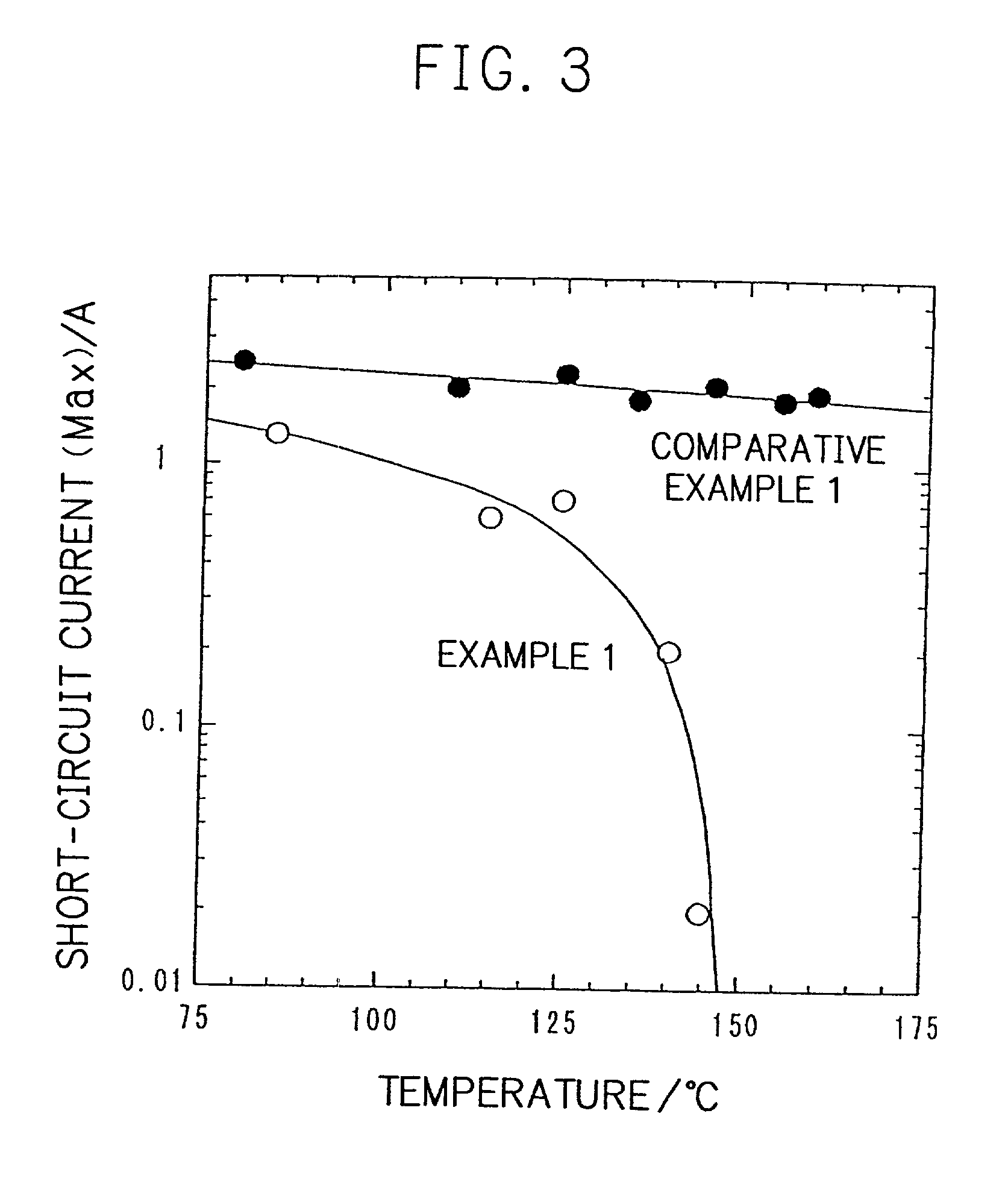
InactiveUS20010005562A1Supplement low electronic conductivityLow electronic conductivityPrimary cell maintainance/servicingElectrode carriers/collectorsElectrical resistance and conductanceConductive materials
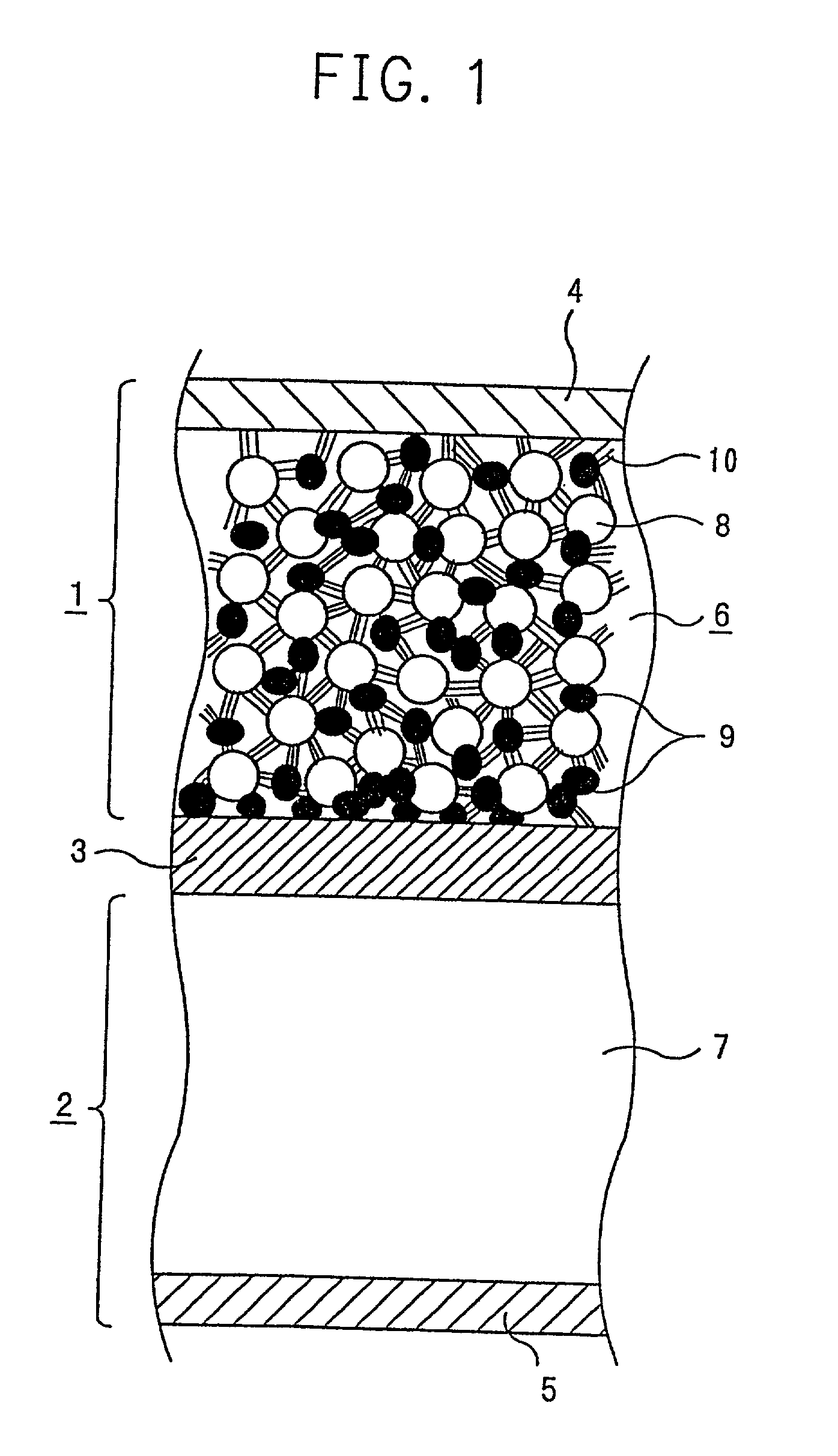
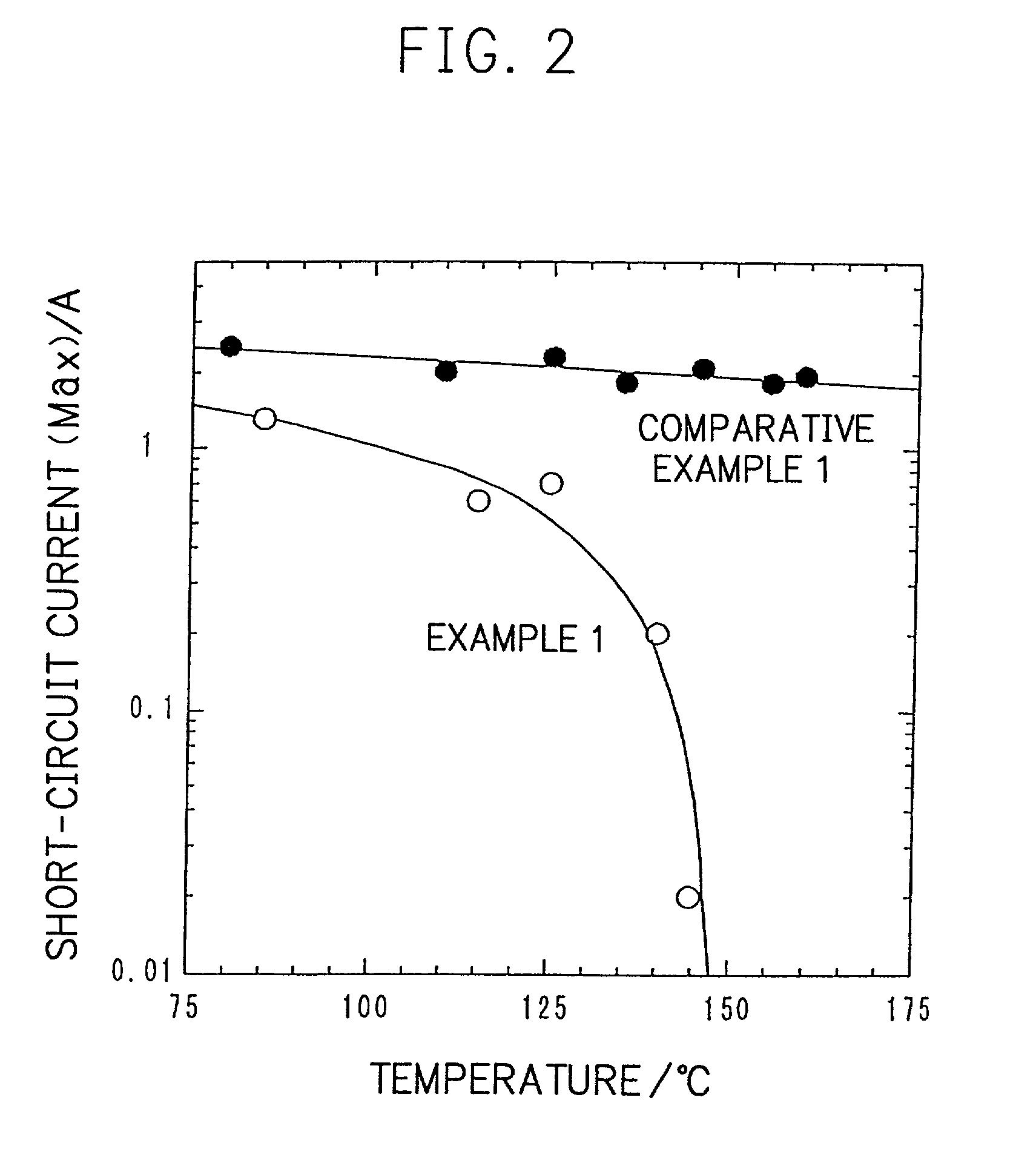
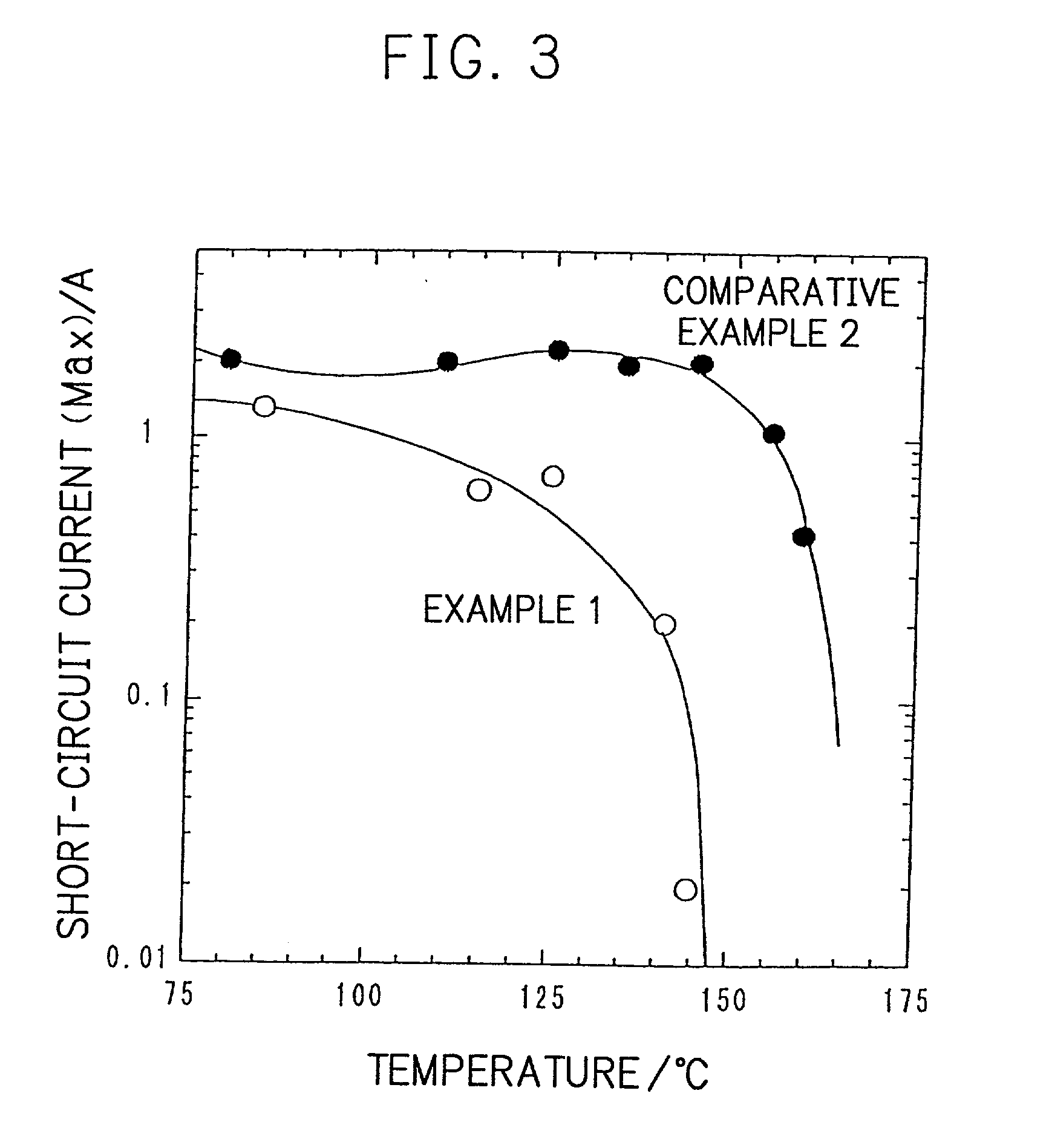
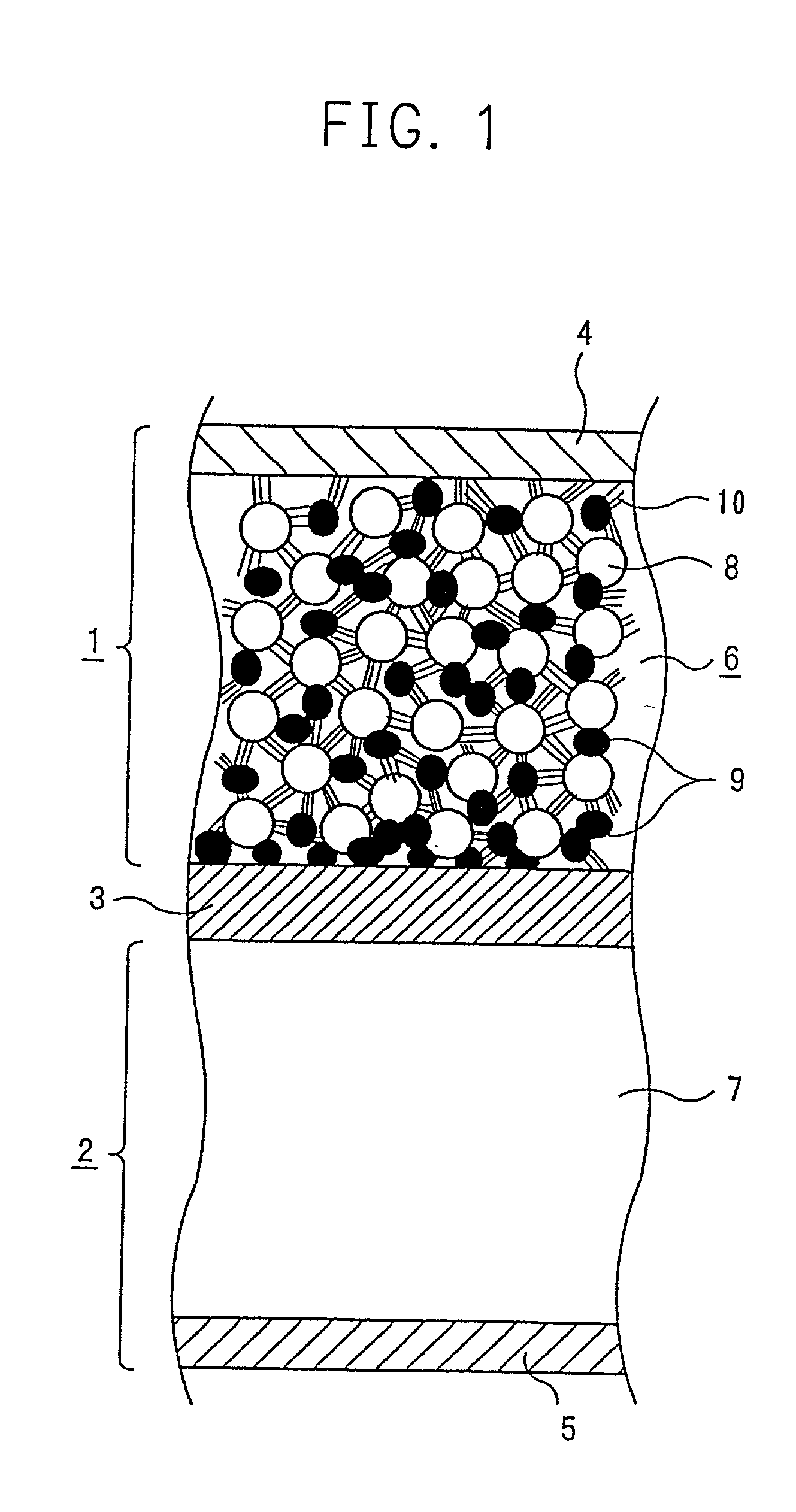
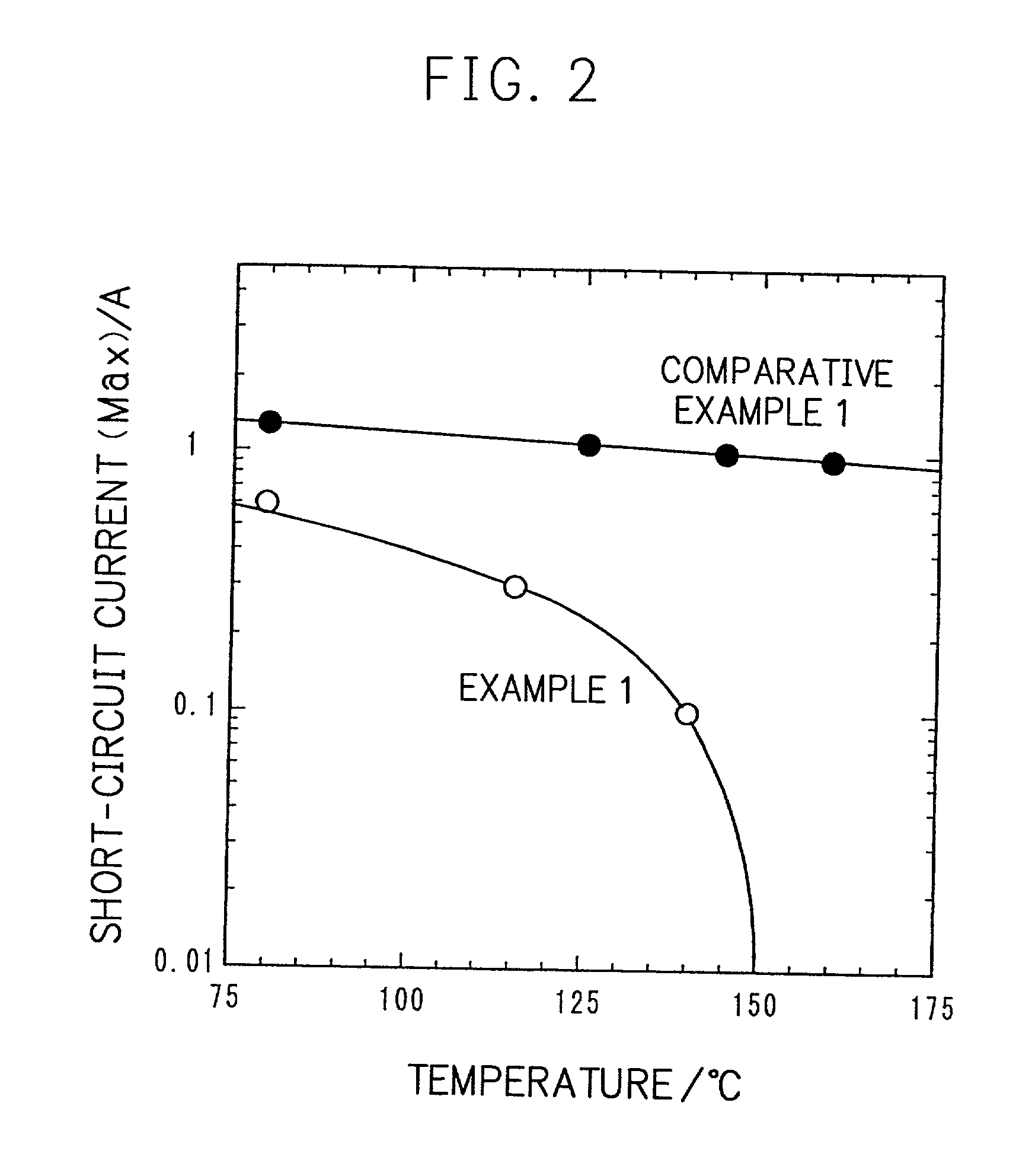
A conventional battery has a problem that a large short-circuit current is generated with temperature rise due to internal short-circuit, and therefore, the temperature of the battery further increases due to heat and the short-circuit current is increased. Also, there is a problem in safety that the sealed part can be easily opened with temperature rise in case of using the aluminum laminated bag as the outer body for sealing the battery body. The present invention has been carried out in order to solve the above problems. The battery of the present invention is a battery wherein at least one of the positive electrode 1 and the negative electrode 2 comprises the active material layer 6 containing the active material 8 and the electronically conductive material 9 contacted to the active material 8; wherein the battery body 11 is constructed by containing the electrolytic layer 3 between the above positive electrode 1 and negative electrode 2, and the above battery body is sealed with the outer body 14 comprising the aluminum 13 and the thermal fusion resin 12; and wherein the electronically conductive material 9 comprises the electrically conductive filler and the resin so that the resistance increases in accordance with temperature rise.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Battery and process for preparing the same
InactiveUS20010005558A1Supplement low electronic conductivityLow electronic conductivityPrimary cell maintainance/servicingFinal product manufactureElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrolysis
A conventional battery has a problem that a large short-circuit current was generated with temperature rise due to internal short-circuit or the like, and therefore, the temperature of the battery further increases due to exothermic reaction to increase the short-circuit current. The present invention has been carried out in order to solve the above problems. The battery of the present invention is a battery wherein at least one of a positive electrode 1 and a negative electrode 2 comprises an active material layer 6 containing an active material 8 and an electronically conductive material 9 contacted to the active material 8, wherein a solid electrolytic layer 3 is interposed between the above positive electrode 1 and the negative electrode 2, and wherein the above electronically conductive material 9 comprises an electrically conductive filler and a resin so that resistance increases with temperature rise.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Battery and process for preparing the same
InactiveUS20010007726A1Low electronic conductivityHigh volume specific resistanceNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsPrimary cellsElectrical resistance and conductanceLithium metal
In a conventional battery containing metal lithium in the negative electrode, there is a problem that large short-circuit current was generated with temperature rise due to internal short-circuit or the like, and therefore, the temperature of the battery further increases due to exothermic reaction to increase the short-circuit current. The present invention has been carried out in order to solve the above problems. The battery of the present invention comprises a negative electrode 2 containing lithium metal, a positive electrode 1 containing a positive electrode active material 8 and an electronically conductive material 9 contacted to the positive electrode active material 8, and an electrolytic layer 3 between the positive electrode 1 and the negative electrode 2, wherein the electronically conductive material 9 comprises an electrically conductive filler and a resin and resistance thereof is increased with temperature rise.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
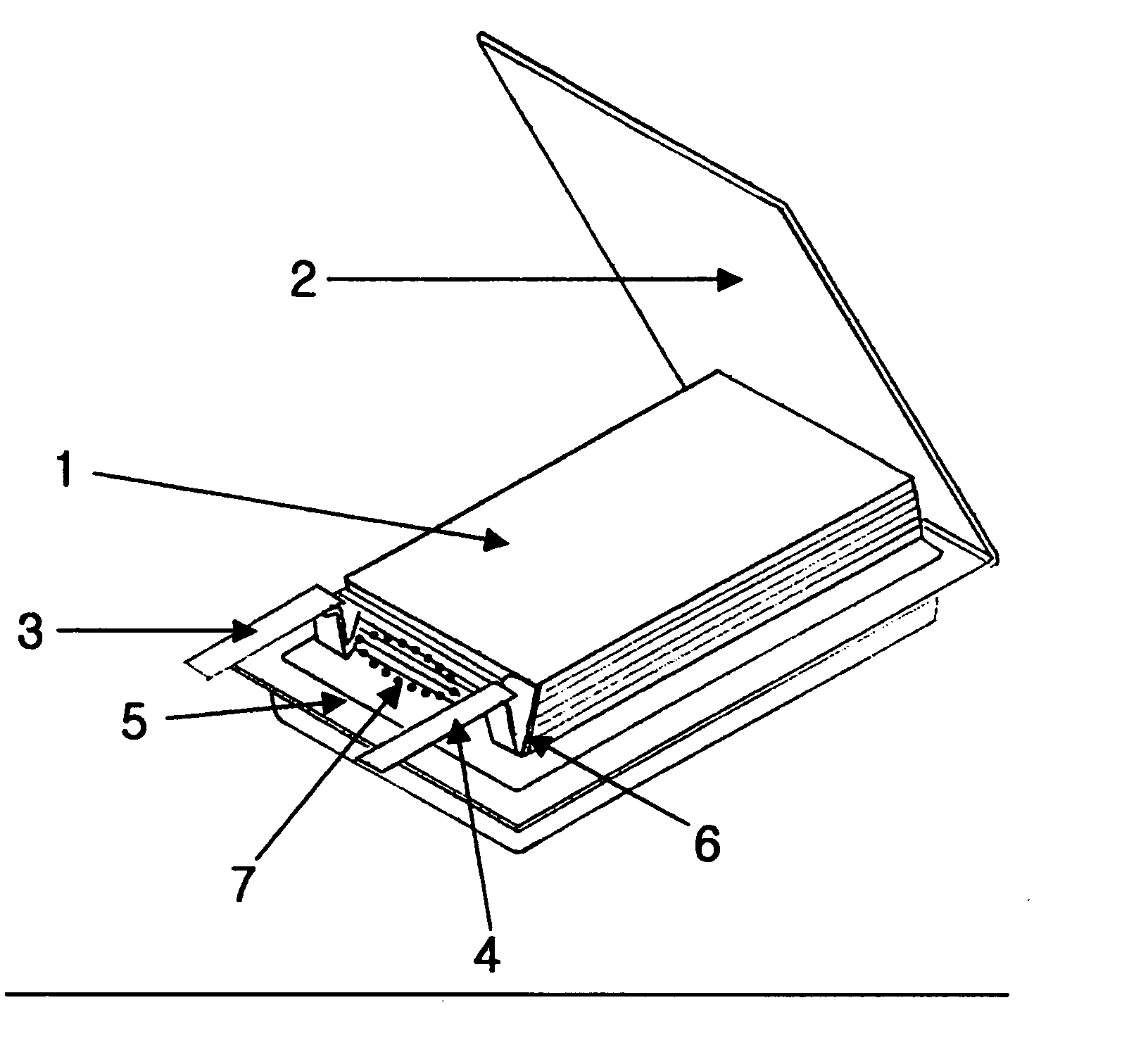
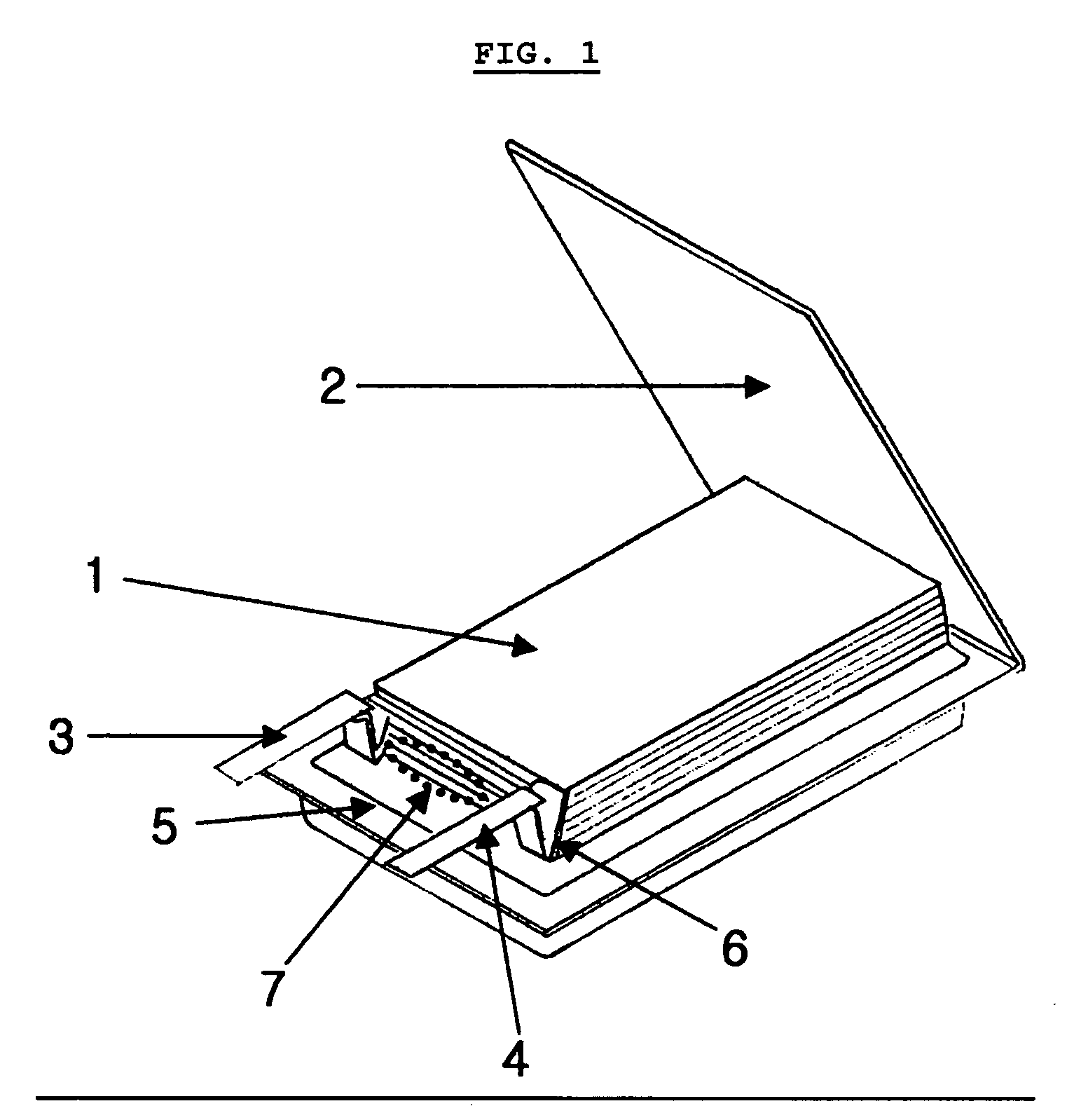
Electrochemical device comprising electrode lead having protection device
ActiveUS20060008698A1Minimized dropImprove the immunityPrimary cell maintainance/servicingNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsEngineeringElectrochemistry
Disclosed is an electrochemical device including an electrode assembly having a cathode, anode and an electrolyte, and a casing surrounding the electrode assembly. The device further includes a protection device to which either or both of a cathode lead for connecting a cathode with an outer terminal and an anode lead for connecting an anode with an outer terminal are connected electrically, wherein the protection device is disposed in the inner space of the casing and the electrode lead equipped with the protection device is folded at both sides of the protection device so that the largest surface of the protection device is layered on a lateral surface of the casing where the electrode lead is present.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
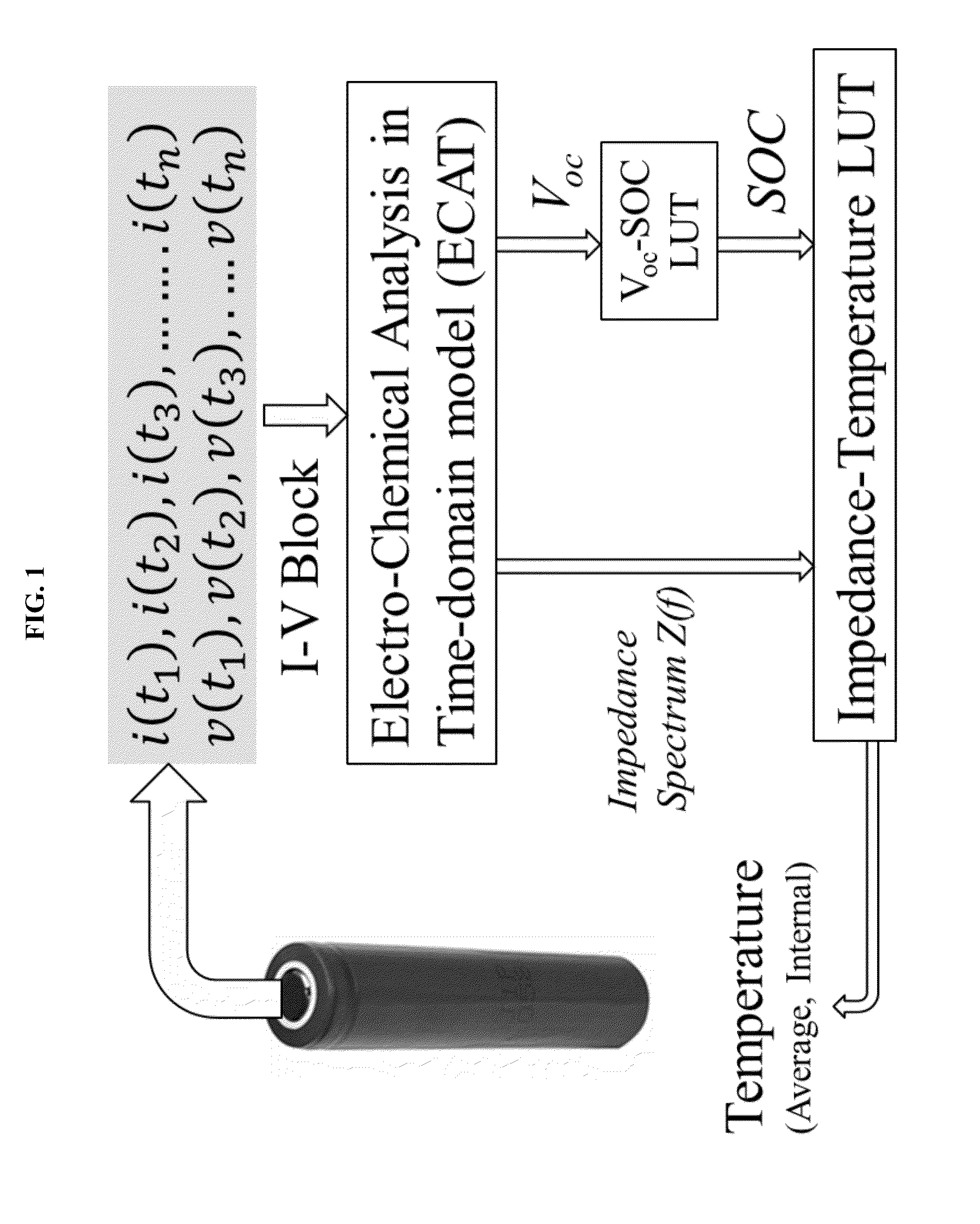
Methods and apparatus for sensing the internal temperature of an electrochemical device
ActiveUS20140372055A1Improve accuracy and reliabilityImprove battery safetyElectric devicesThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectrical batteryEngineering
The internal temperature of an electrochemical device may be probed without a thermocouple, infrared detector, or other auxiliary device to measure temperature. Some methods include exciting an electrochemical device with a driving profile; acquiring voltage and current data from the electrochemical device, in response to the driving profile; calculating an impulse response from the current and voltage data; calculating an impedance spectrum of the electrochemical device from the impulse response; calculating a state-of-charge of the electrochemical device; and then estimating internal temperature of the electrochemical device based on a temperature-impedance-state-of-charge relationship. The electrochemical device may be a battery, fuel cell, electrolytic cell, or capacitor, for example. The procedure is useful for on-line applications which benefit from real-time temperature sensing capabilities during operations. These methods may be readily implemented as part of a device management and safety system.
Owner:HRL LAB
Electrolyte for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery comprising same
ActiveUS20060003232A1Improve battery safetyGood electrochemical propertiesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsOrganic electrolyte cellsHigh temperature storageLithium
An electrolyte for a lithium secondary battery is provided. The electrolyte improves battery safety, high temperature storage characteristics, and electrochemical properties of lithium batteries. The electrolyte comprises at least one lithium salt and a non-aqueous organic solvent comprising a cyclic carbonate and a lactone-based compound. The lactone based compound comprises substituents selected from the group consisting of alkyl groups, alkenyl groups, alkynyl groups, aryl groups, and combinations thereof. A lithium battery is also provided, which comprises a negative electrode capable of intercalating / deintercalating lithium, a positive electrode capable of intercalating / deintercalating lithium, and an inventive electrolyte.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
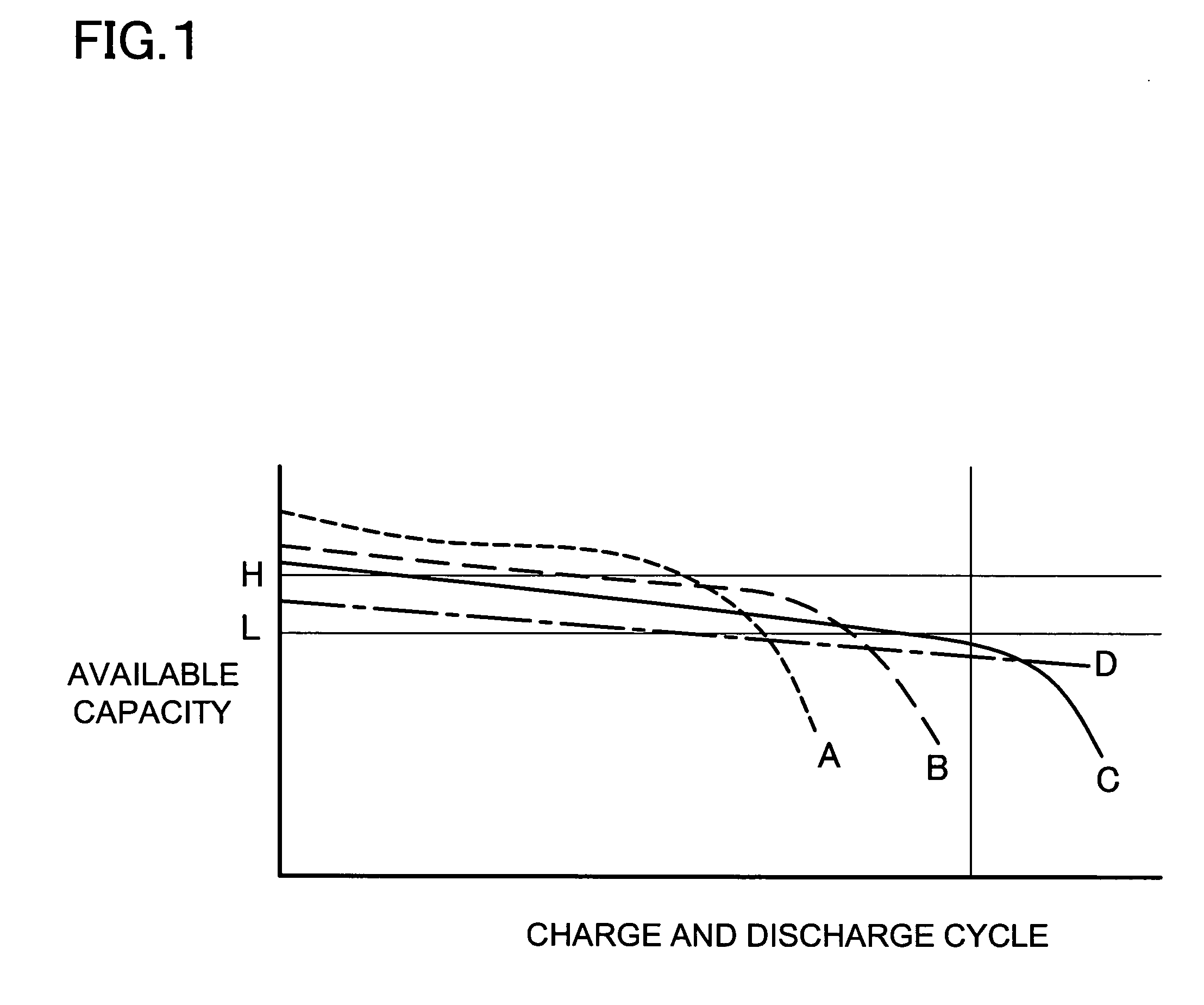
Apparatus and method for estimating state of health of battery
ActiveUS20140009123A1Over-charging or over-discharging may be preventedImprove battery safetyBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical testingState of healthVoltage range
The present disclosure describes an apparatus and method for estimating state of health (SOH) of a battery. The apparatus for estimating state of health of a battery includes a sensing unit for measuring a battery voltage and current within a predetermined charging voltage range; a memory unit storing the battery voltage and current values measured by the sensing unit and SOH-based ampere counting values, obtained by an ampere counting experiment of a battery whose actual degradation degree is known; and a control unit for calculating an ampere counting value by counting the measured current values stored in the memory unit within the charging voltage range, and estimating a SOH value by mapping the SOH value corresponding to the calculated ampere counting value from the SOH-based ampere counting values stored in the memory unit.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
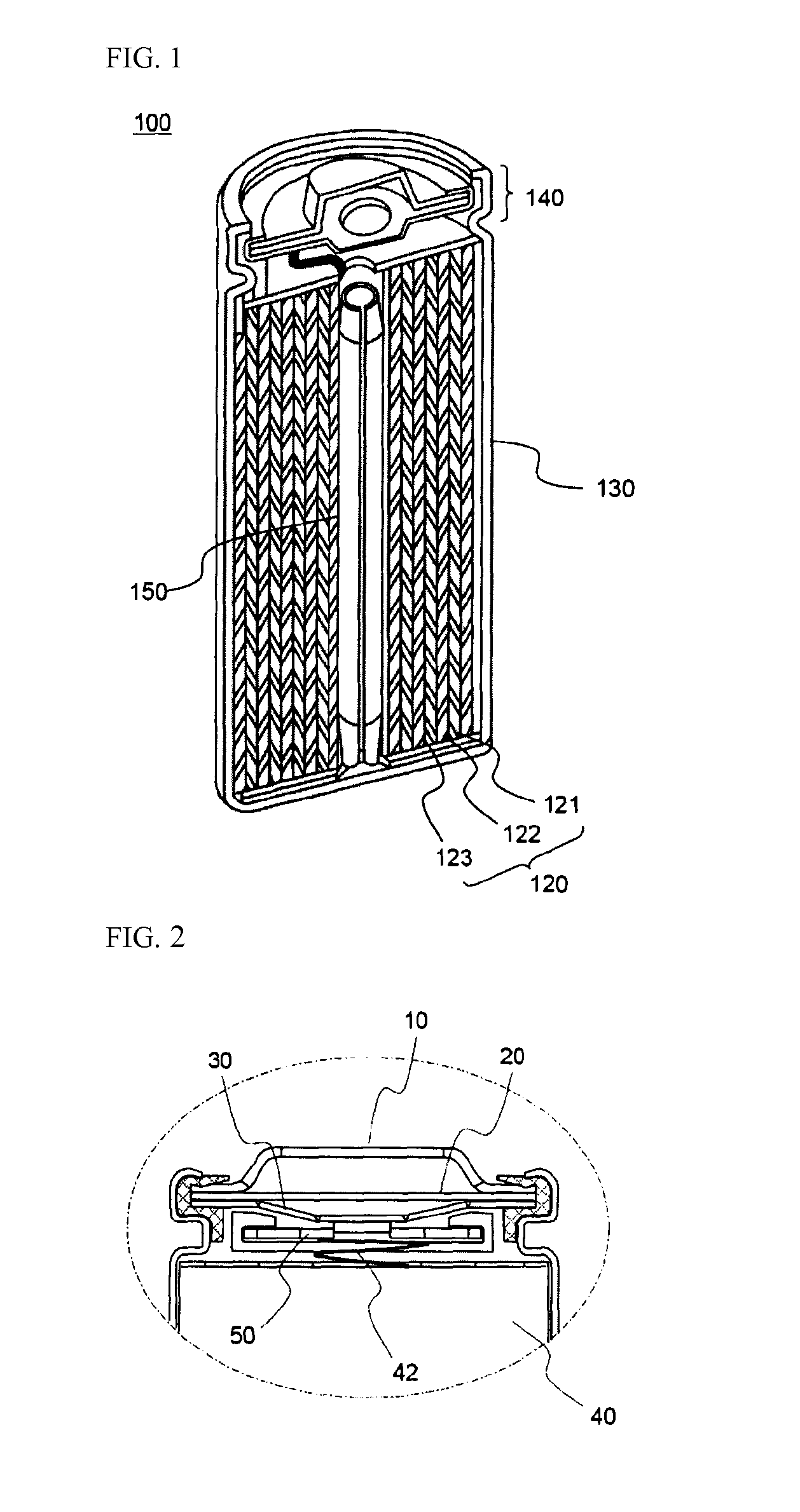
Cylindrical secondary battery of improved safety
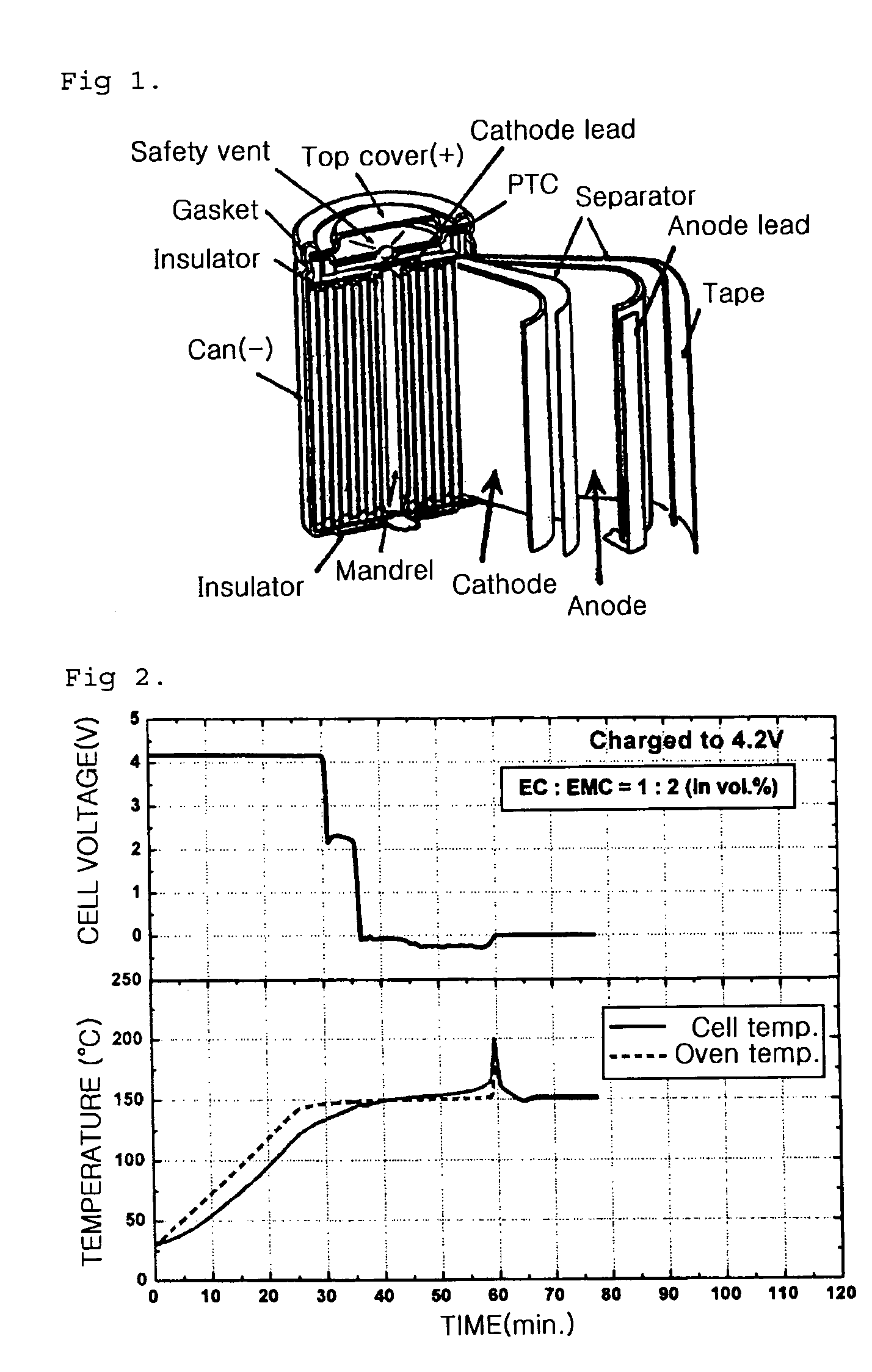
ActiveUS20120114979A1Efficient dischargeIncrease the areaFinal product manufactureWound/folded electrode electrodesEngineeringHigh pressure
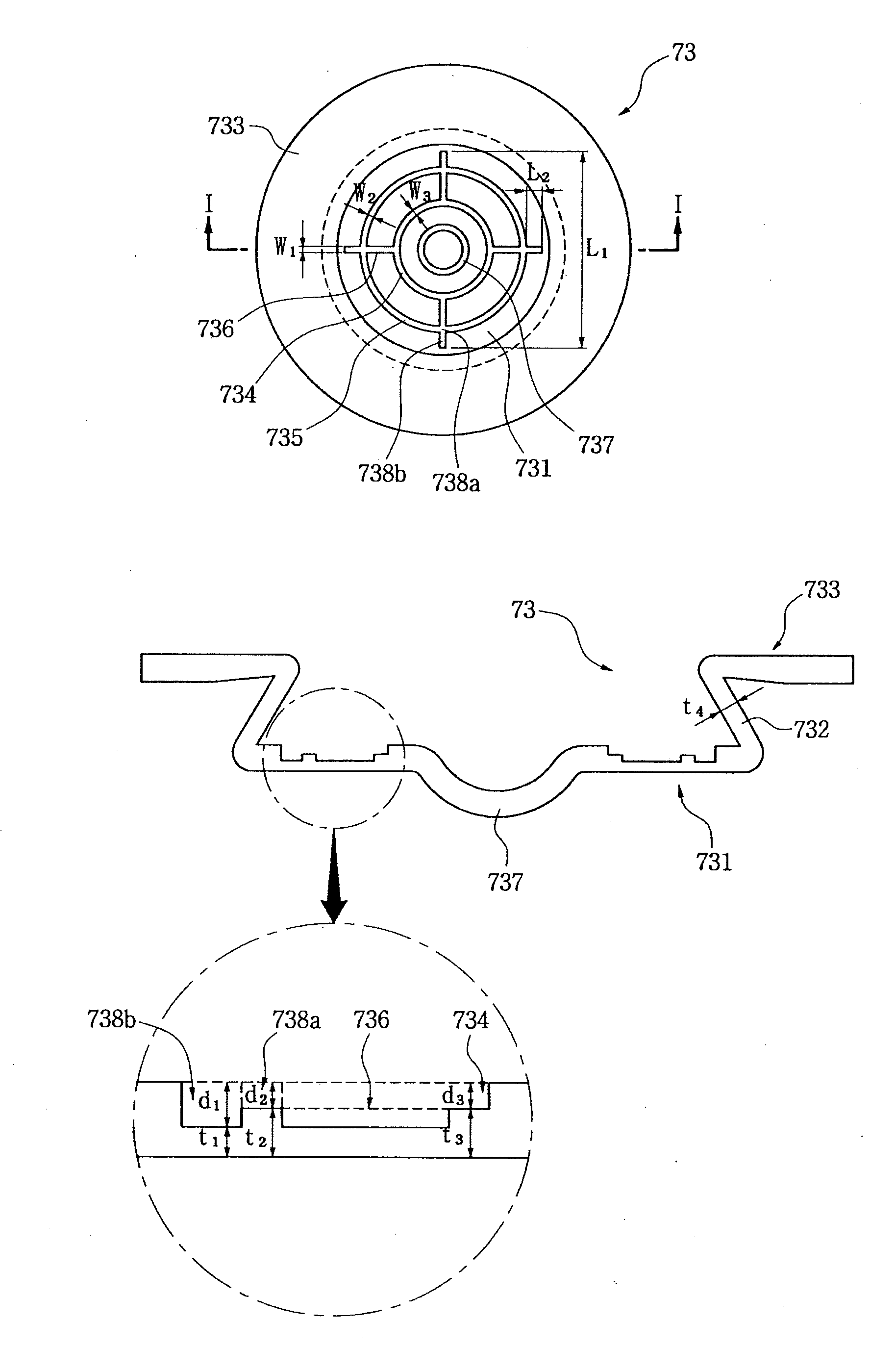
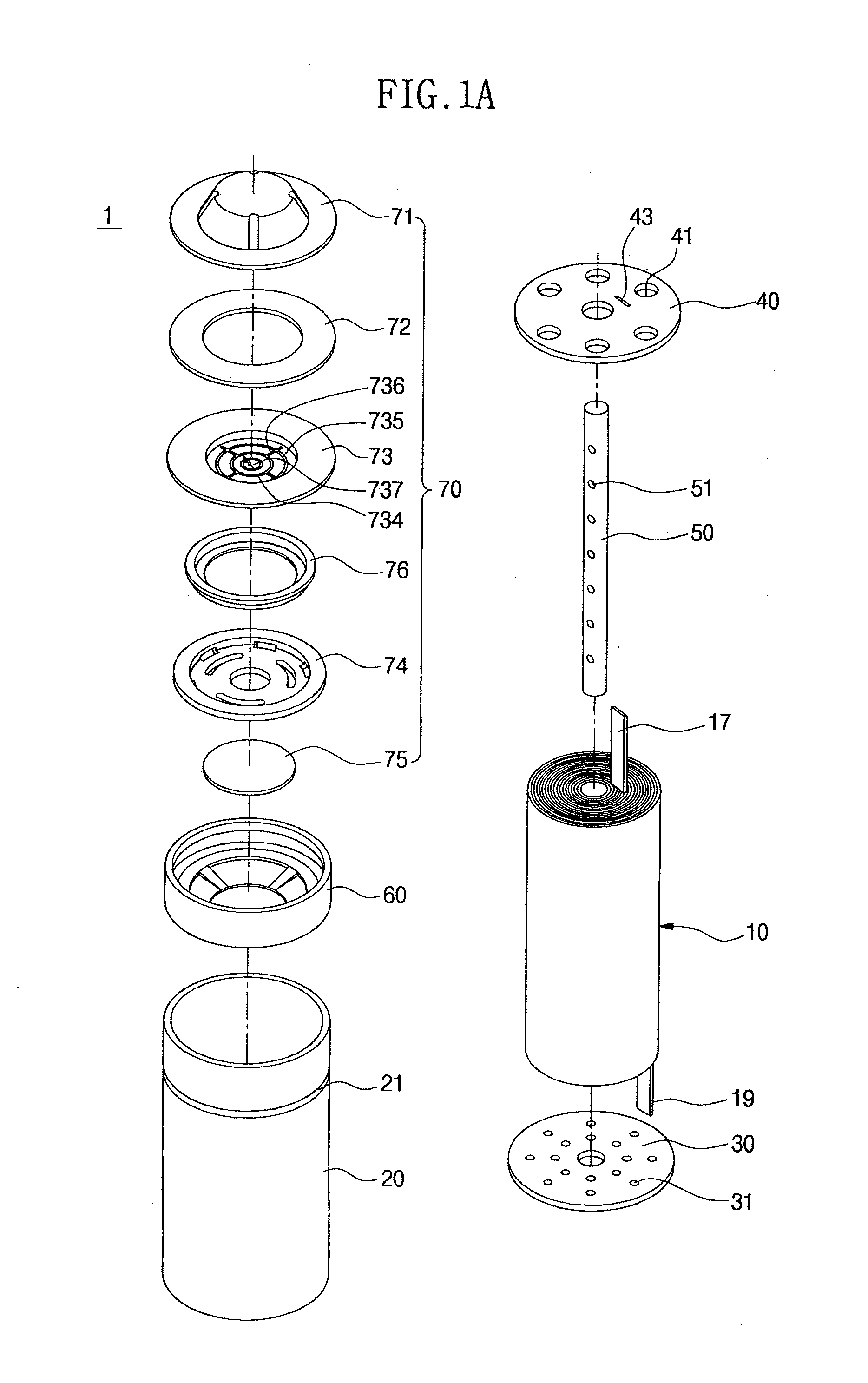
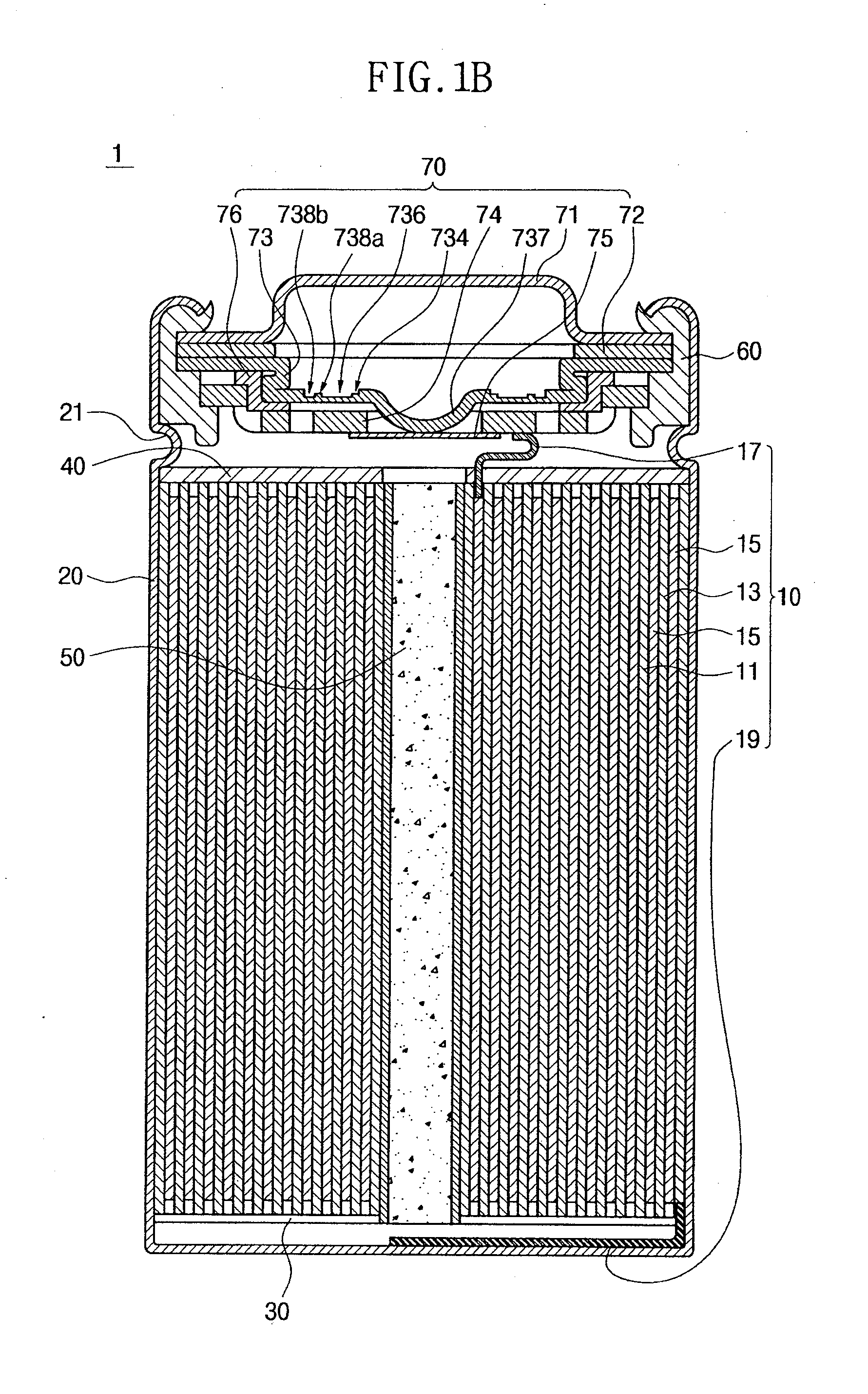
Provided is a cylindrical battery in which an electrode assembly fabricated by rolling a cathode / separator / anode and an electrolyte are provided in a cylindrical can, wherein a cap assembly mounted on the opening top of the cylindrical can comprises: a safety vent provided with a predetermined notch, to allow breakage due to high-pressure gas of the battery, a current interruptive device to interrupt current, welded to the bottom of the safety vent, and a gasket for the current interruptive device to surround the periphery of the current interruptive device, wherein the current interruptive device comprises two or more through holes to allow exhaustion of gas, wherein the through holes have a size of 20 to 50% with respect to the total area of the current interruptive device.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
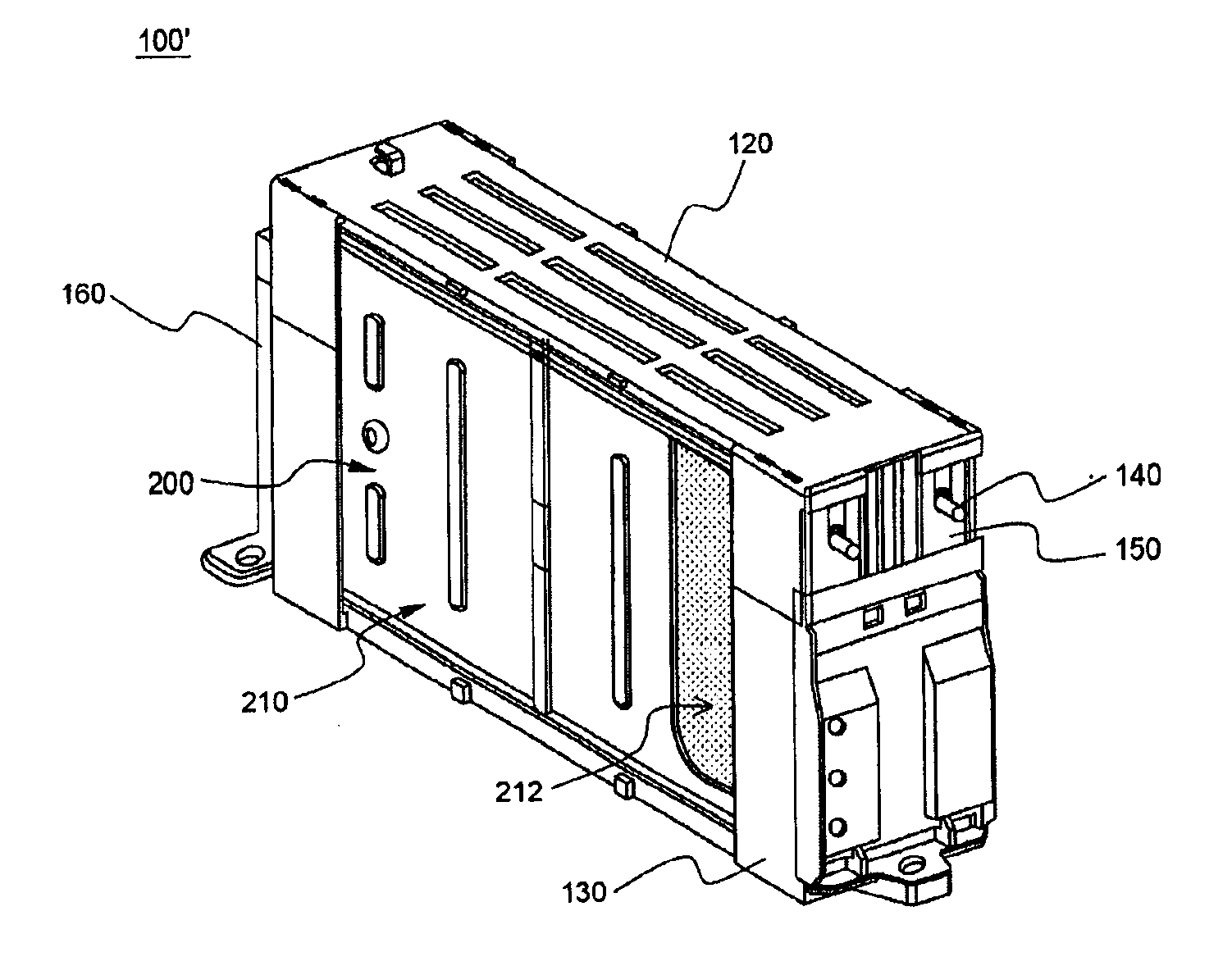
Battery module of improved safety and middle or large-sized battery pack containing the same
ActiveUS20100297482A1Improve battery safetyImprove securityLarge-sized flat cells/batteriesFinal product manufactureBattery cellBattery pack
Disclosed herein is a high-power, large-capacity battery module including a plurality of battery cells or unit modules connected in series to each other such that the battery cells or the unit modules are stacked while being in tight contact with each other or being adjacent to each other, wherein the battery module is fixed such that the stacked state of the battery cells or the unit modules is maintained even when the volume of the battery cells or the unit modules changes at the time of charging and discharging the battery cells or the unit modules, and a portion of an electrode terminal connection region between the battery cells or between the unit modules is weak with respect to the volume expansion of the battery cells or the unit modules such that an expansion stress caused by the swelling of the battery cells is concentrated on the electrode terminal connection region, whereby the electrode terminal connection region is broken, and therefore, an electrical cut-off occurs at the electrode terminal connection region, when the swelling exceeds a predetermined value.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
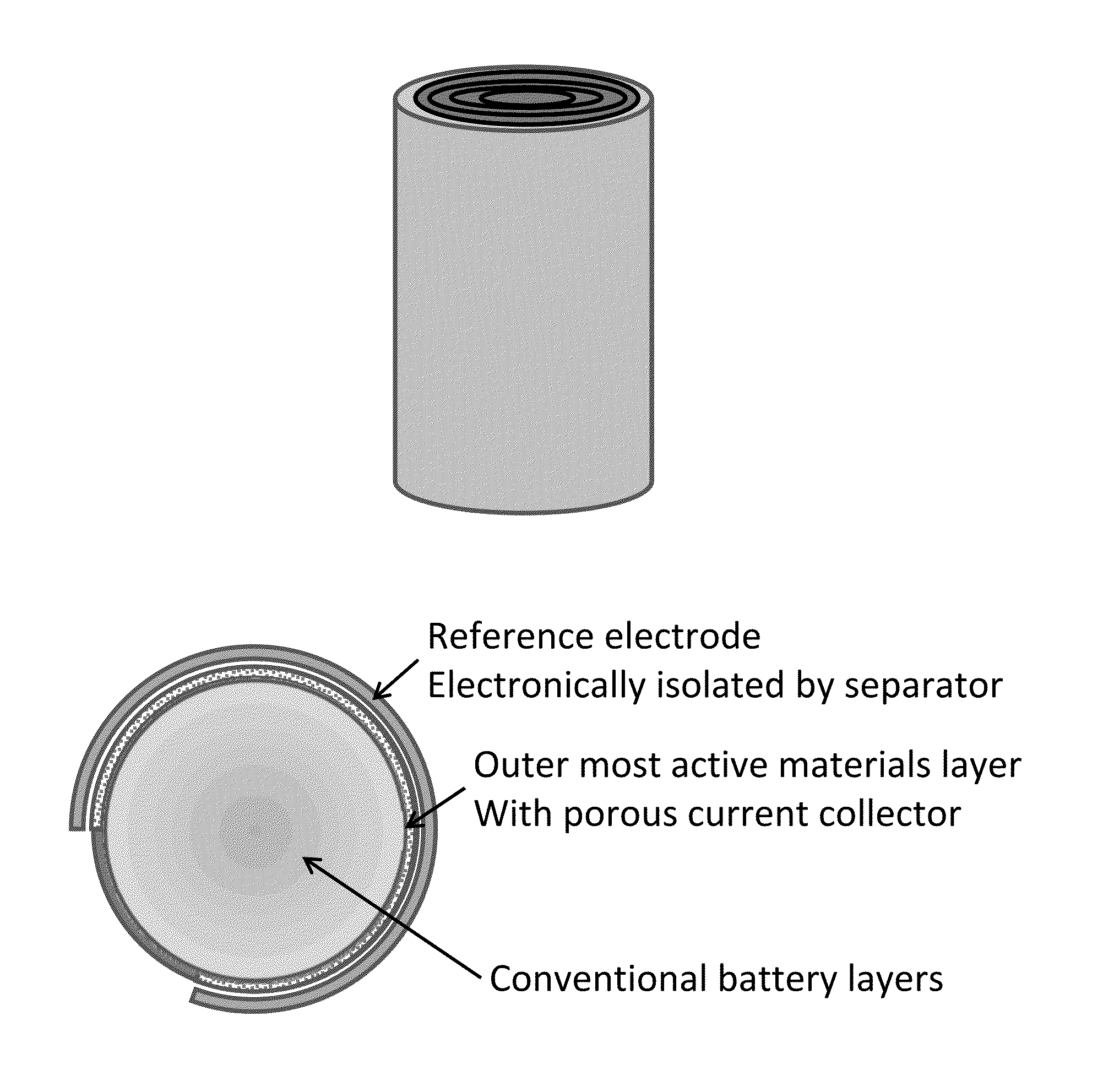
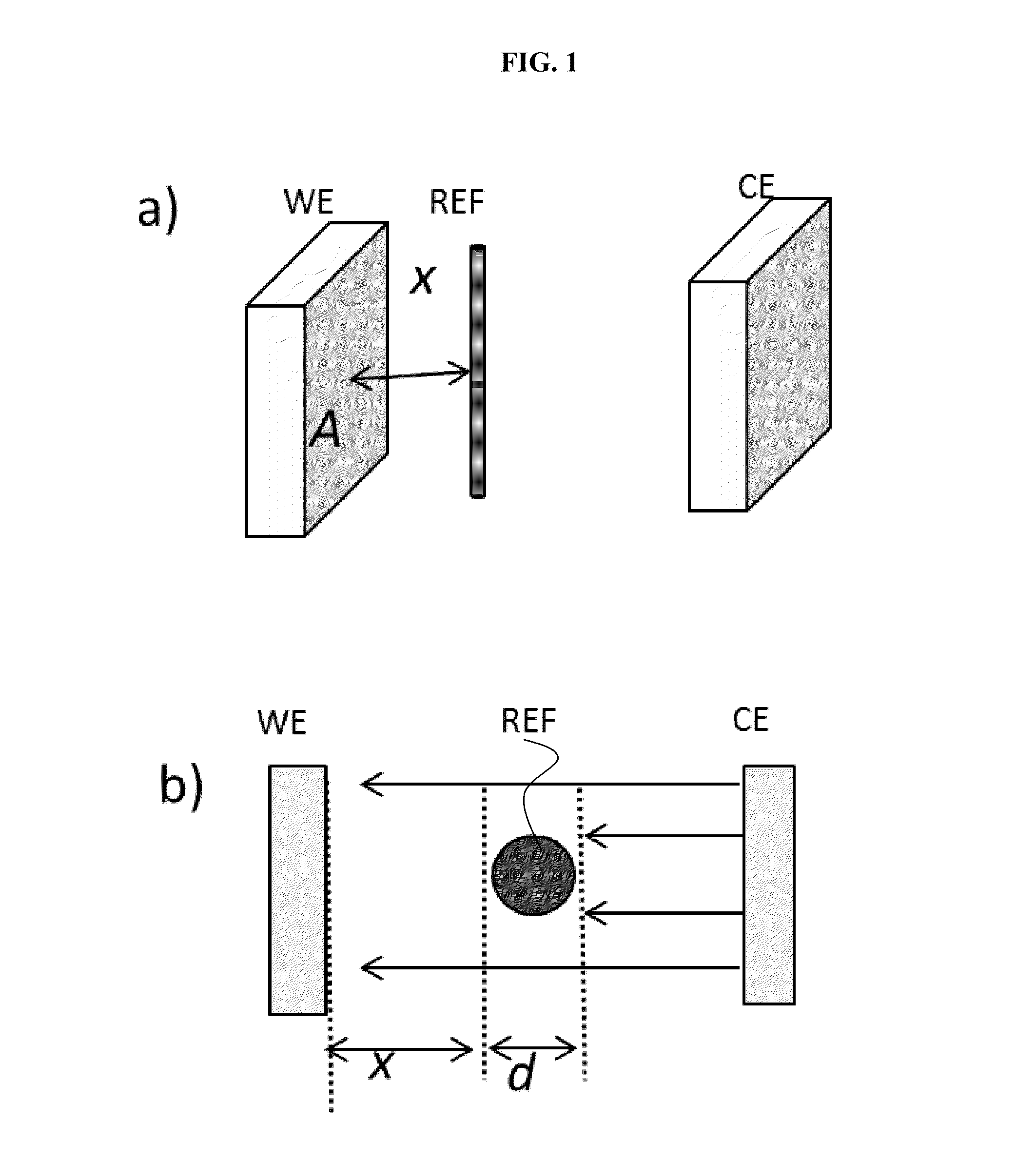
Battery with reference electrode for voltage monitoring
ActiveUS20140375325A1Improve accuracy and reliabilitySimple designFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsLithium metalElectrical battery
A lithium-ion battery structure with a third electrode as reference electrode is disclosed. The reference electrode may be fabricated from lithium metal, lithiated carbon, or a variety of other lithium-containing electrode materials. A porous current collector allows permeation of reference lithium ions from the reference electrode to the cathode or anode, enabling voltage monitoring under actual operation of a lithium-ion battery. The reference electrode therefore does not need to be spatially between the battery anode and cathode, thus avoiding a shielding effect. The battery structure includes an external reference circuit to dynamically display the anode and cathode voltage. The battery structure can result in improved battery monitoring, enhanced battery safety, and extended battery life.
Owner:HRL LAB +1
Microporous polymer membrane modified by aqueous polymer, manufacturing method and use thereof
ActiveUS20110229768A1Low costImprove performanceRadiation applicationsDouble layer capacitorsHydrophilic monomerPolyolefin
Microporous polyolefin membrane modified by aqueous polymer of the invention is obtained by the following steps: copolymerizing 100 parts of a water-soluble polymer, 30-500 parts of a hydrophobic monomer, 0-200 parts of a hydrophilic monomer and 1-5 parts of an initiator into polymeric colloid emulsion; adding 0-100% of an inorganic filler and 20-100% of a plasticizer based on 100% solid content of the polymeric colloid emulsion to obtain slurry; and coating the slurry on one or two surfaces of the surface modified microporous polyolefin membrane and then drying. The microporous polyolefin membrane modified by aqueous polymer has thermal shutdown effect and little thermal shrinkage, and improves the main problem of shrinkage of the microporous polyolefin membrane at high temperature.
Owner:SICHUAN INDIGO TECH CO LTD
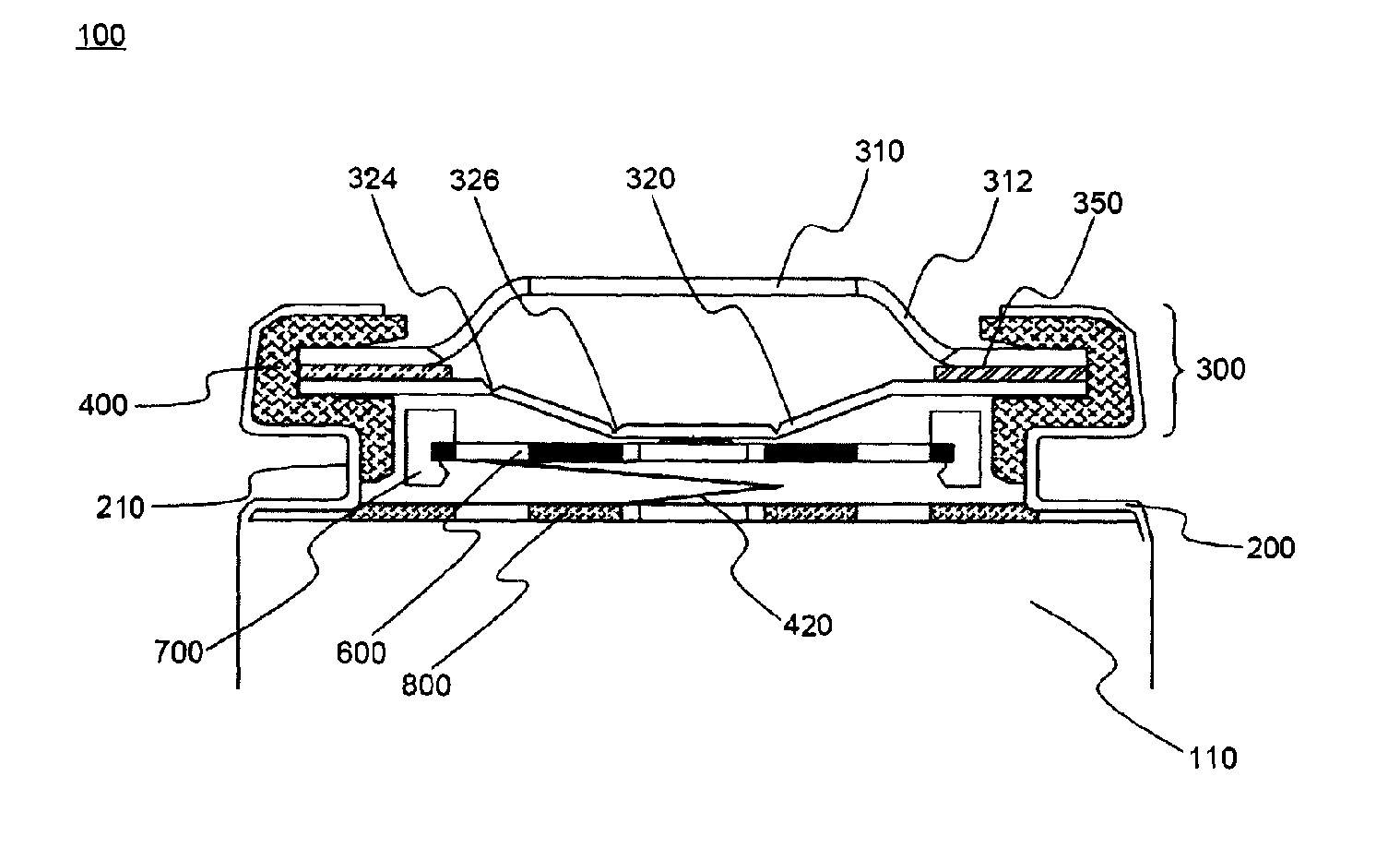
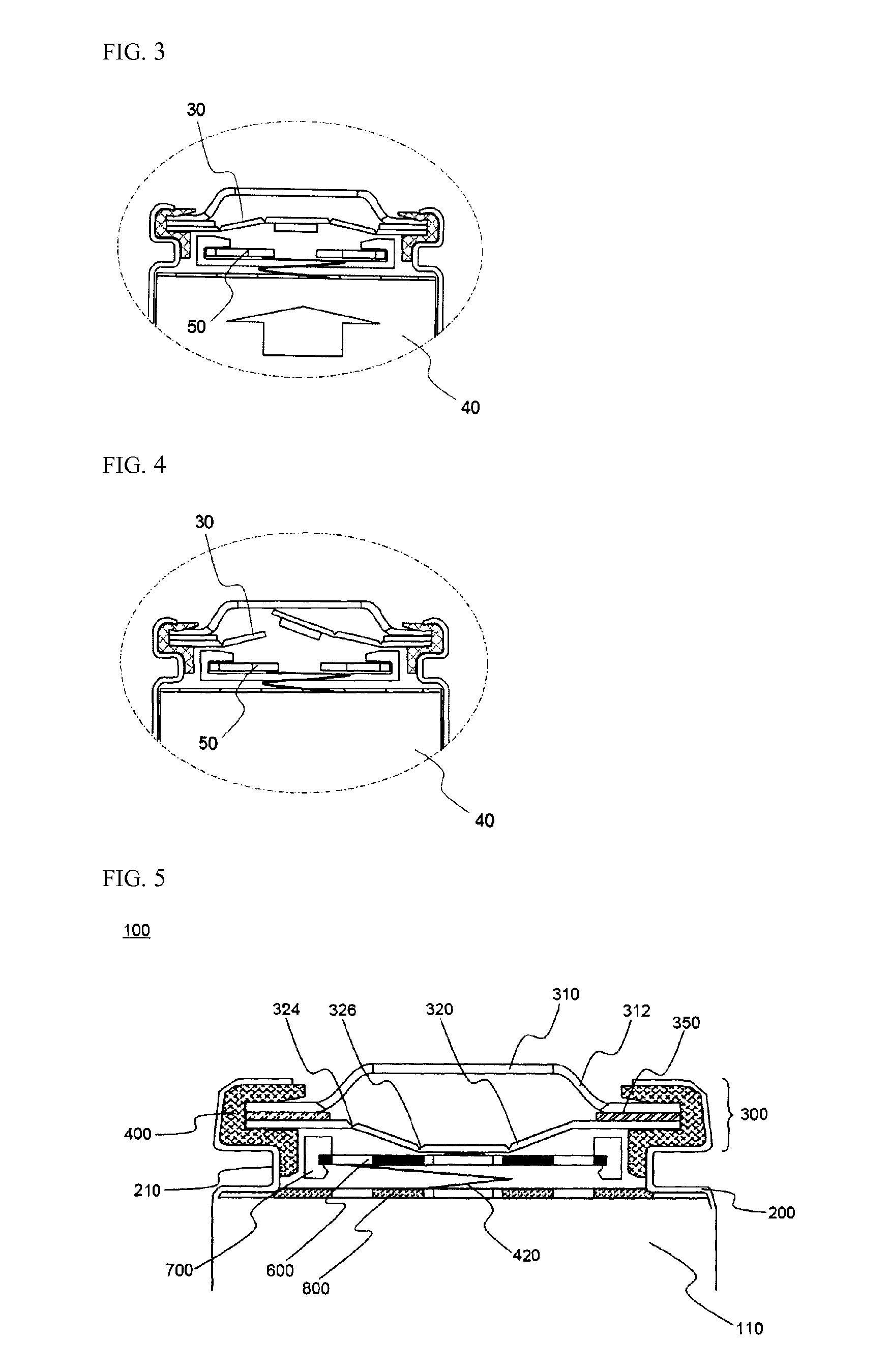
Cap assembly and secondary battery using the same
ActiveUS20100136388A1Improve battery safetyCurrent conducting connectionsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A cap assembly for a battery and a battery incorporating the cap assembly. The cap assembly includes a plate that connects the electrodes of the bare cell of the battery. The cap assembly includes a vent member that includes a protrusion that is physically connected to the plate. Excess pressure within the bare cell results in the protrusion disconnecting from the plate thereby interrupting current. The vent further includes two circular notches, an inner notch and an outer notch. The vent further includes a cross notch that extends radially outward so as to intersect and extend beyond both the first and second notches. The notches are configured to release when the pressure within the bare cell exceeds a burst pressure.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Secondary battery having electrode terminal whose position is adjustable and improved safety
ActiveUS20080070067A1Increase productionLarge capacityFinal product manufactureSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsEngineeringHigh heat
Disclosed herein is a secondary battery including a safety connection member constructed in a structure in which a horizontal connection terminal (a), which is connected to an electrode lead of a battery, is connected to one end of a safety element, and a vertical connection terminal (b) is connected to the other end of the safety element. The position of the electrode lead of the battery is easily adjusted due to the safety connection member. Also, the high-temperature safety of the battery is improved due to the safety element.
Owner:LG TWIN TOWERS 20 +1
Lithium secondary battery and electrode for lithium secondary battery
InactiveUS20080268348A1Improve reliabilityImprove featuresSolid electrolyte cellsLi-accumulatorsMolten saltLithium-ion battery
An object of the invention is to provide a lithium secondary battery using a fused salt at ambient temperature where a high capacity is able to be maintained even when it is stored at a high temperature environment or even when it is subjected to charge and discharge repeatedly and also to provide an electrode for a nonaqueous electrolytic lithium secondary battery. There is disclosed a lithium secondary battery using at least a fused salt at ambient temperature having ionic conductivity in which at least one of the positive and negative electrode contains a powder which solely comprises an inorganic solid electrolyte having lithium ionic conductivity. There is also disclosed an electrode for a lithium secondary battery using, at least, a ionic liquid having ionic conductivity which contains a powder solely comprising inorganic solid electrolyte having lithium ionic conductivity.
Owner:OHARA
Battery and process for preparing the same
InactiveUS20010049050A1Low electronic conductivityHigh volume specific resistancePrimary cell maintainance/servicingCell temperature controlElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A conventional battery has a problem that when a temperature of the battery reaches at least 100° C. due to internal short-circuit or the like, large short-circuit current is generated, and therefore, a temperature of the battery further increases due to exothermic reaction to increase the short-circuit current. Also, if an aluminum laminated pack and the like are used as a casing material for the purpose of lightweight and improved energy density of the battery, and if an adhesive agent is used to joint an electrode with a separator to maintain the contact thereof, there is a problem that the adhesive agent intrudes into the opening part of the separator and the opening part area and the hole diameter decrease to bring about unfavorable results for discharge load characteristics of the battery. The present invention has been carried out in order to solve the above problems. The battery of the present invention comprises the active material layer 6 having the active material 8 and the electronically conductive material 9 contacted to the active material 8 and the electrolytic layer 3 jointed with the active material layer 6, wherein the electronically conductive material 9 contains an electrically conductive filler and a resin so that resistance can be increased with temperature rise, and wherein the active material layer 6 and the electrolytic layer 3 are laminated and jointed by thermal treatment.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Secondary battery of improved safety
ActiveUS20070231683A1Low mechanical strengthEasy to transformFinal product manufactureSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsAnodeCathode
Disclosed herein is a secondary battery having an electrode assembly received in a receiving part of a battery case, the electrode assembly being constructed in a structure in which pluralities of cathodes and anodes are stacked one on another while separators are disposed between the respective cathodes and anodes, and electrode taps extending from the stacked cathodes and anodes are coupled to electrode leads, wherein the receiving part of the battery case is provided at the outer upper end thereof with a depressed step such that at least a portion of the inner upper end of the receiving part of the battery case excluding the electrode taps-electrode lead coupling parts of the electrode assembly is in tight contact with the upper end of the electrode assembly.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Polyolefin microporous membrane
ActiveCN101331178AExcellent battery characteristicsImprove battery safetyMembranesSemi-permeable membranesPorosityPolyolefin
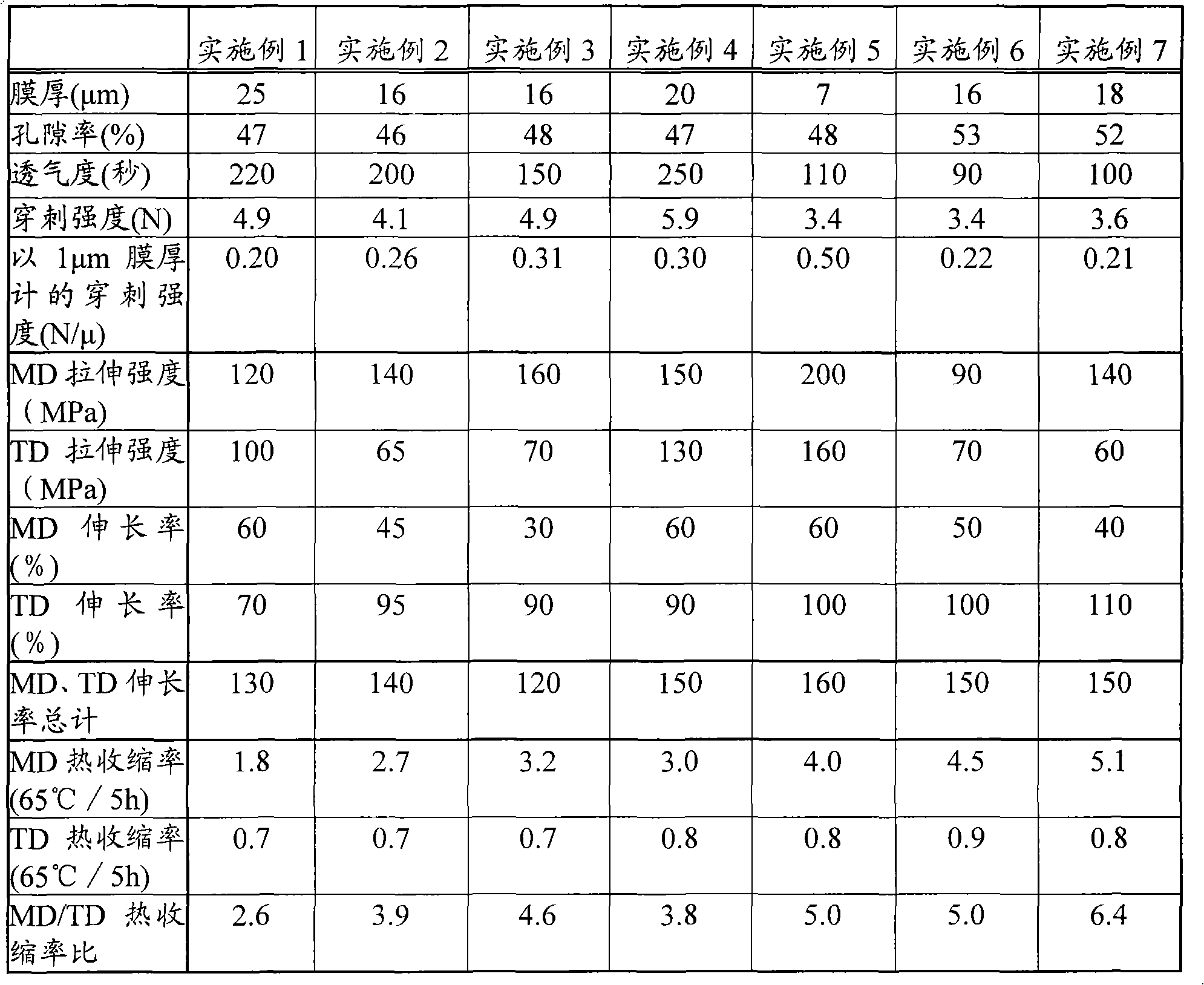
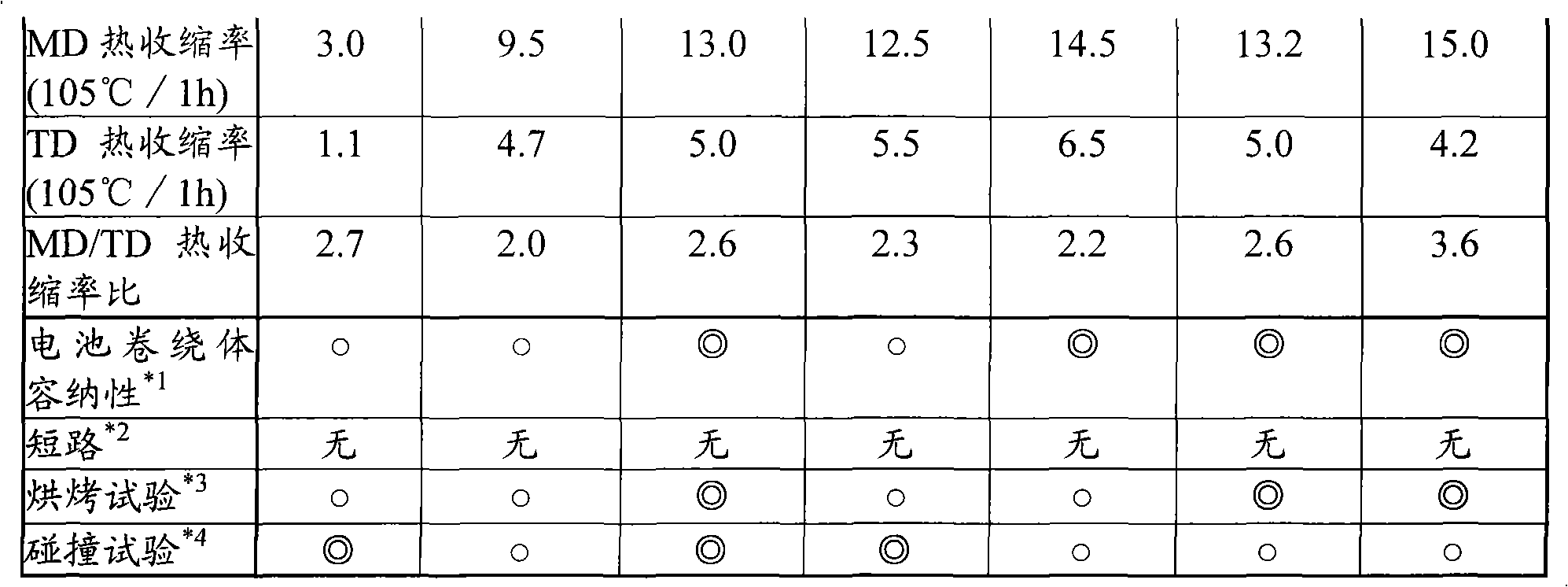
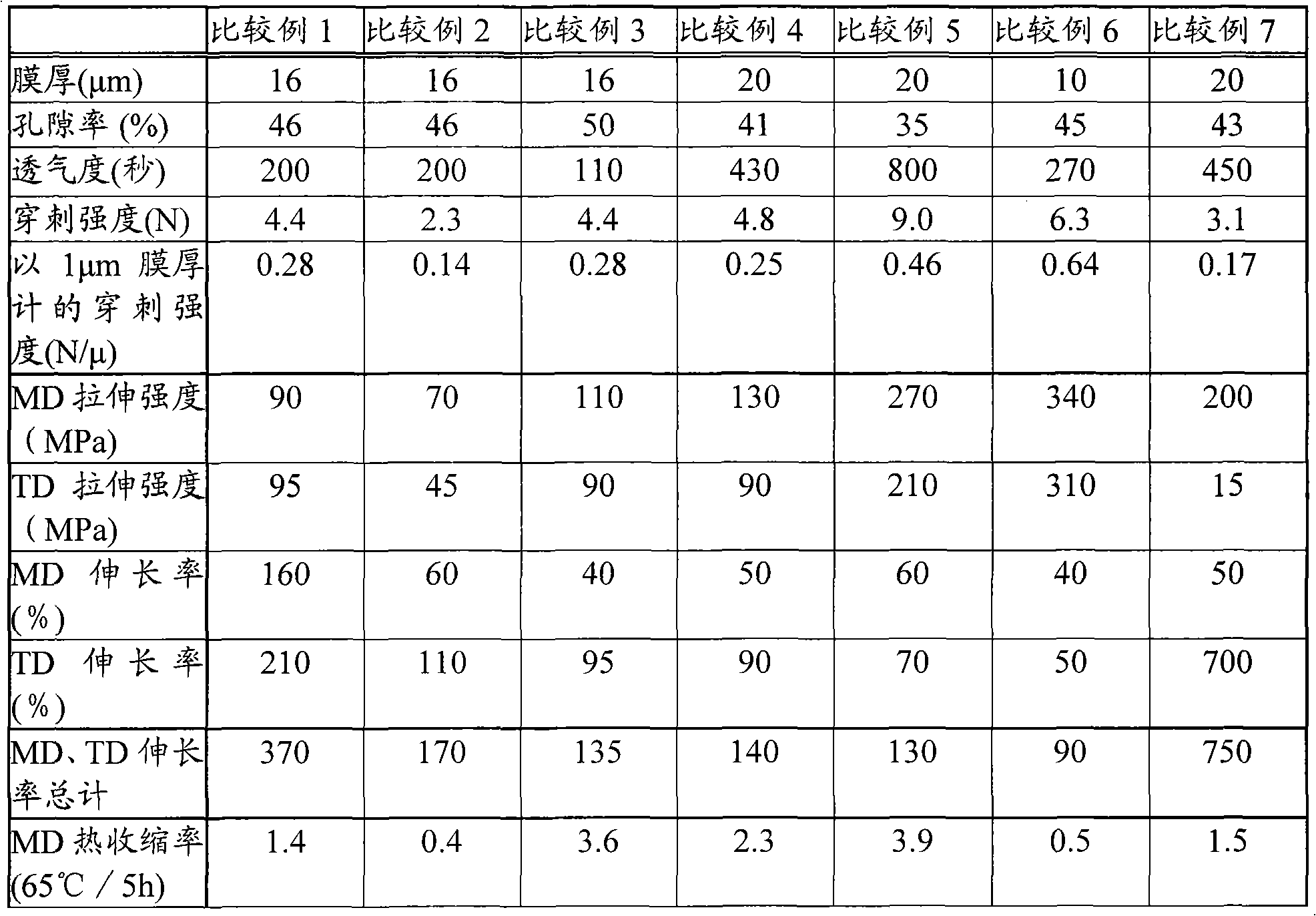
Disclosed is a polyolefin microporous membrane having a thickness of not less than 1[mu]m and not more than 50 [mu]m, a porosity of not less than 30 percent and not more than 70 percent, a puncture strength in terms of a 1[mu]m thick film of not less than 0.15 N / [mu]m, a tensile strength in the machine direction (MD tensile strength) of not less than 30 MPa, a tensile strength in the transverse direction (TD tensile strength) of not less than 30MPa, a thermal shrinkage at 65 DEG C in the transverse direction (TD thermal shrinkage) of not more than 1 percent, and a ratio between the thermal shrinkage at 65 DEG C in the machine direction and the thermal shrinkage at 65 DEG C in the transverse direction (MD thermal shrinkage / TD thermal shrinkage) of more than 2. Also disclosed are a method for producing such a polyolefin microporous membrane and a nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery using such a polyolefin microporous membrane.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Electrochemical device comprising aliphatic mono-nitrile compound
ActiveUS20060204834A1Low viscosityImprove ionic conductivitySolid electrolytesFinal product manufactureSolventElectrochemical cell
Disclosed is a cathode comprising a complex formed between the surface of a cathode active material and an aliphatic mono-nitrile compound, and an electrochemical device comprising the cathode. A non-aqueous electrolyte containing a lithium salt, a solvent and an aliphatic mono-nitrile compound, and an electrochemical device comprising the electrolyte are also disclosed. The electrochemical device shows excellent low-temperature characteristics, high-temperature life characteristics and safety.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Secondary battery and method for producing the same
ActiveUS7402184B2Improve discharge characteristicsImprove battery safetyAlkaline accumulatorsElectrode manufacturing processesSlurryBattery cell
In a secondary battery including a positive electrode, a negative electrode and a porous film bonded to the surface of at least one of the positive electrode and the negative electrode, the porous film includes ceramic particles and a binder, and the ceramic particles include polycrystalline particles obtained by mechanically crushing a fired material comprising a ceramic that is directly synthesized from a ceramic precursor. The porous film has a porosity of 40 to 80%, for example. The porous film can be formed by a method including the steps of: obtaining a fired material comprising a ceramic from a ceramic precursor; obtaining ceramic particles by mechanically crushing the fired material of the ceramic; obtaining a slurry including the ceramic particles and a binder; and applying the slurry onto the surface of an electrode, followed by drying.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Safety-improved electrode by introducing crosslinkable polymer and electrochemical device comprising the same
ActiveUS20060246354A1Improve battery safetyMinimize degradationElectrode thermal treatmentPrimary cellsCrosslinked polymersElectrochemistry
Disclosed is an electrode, comprising a coating layer of crosslinked polymer, formed on a surface of electrode active material particles, while maintaining a pore structure formed among the electrode active material particles interconnected to each other in the electrode. A method for manufacturing the electrode and an electrochemical device comprising the electrode are also disclosed. The electrode, which comprises a coating layer of crosslinked polymer formed on the surface of the electrode active material particles, can improve the safety of a battery, while minimizing degradation in the quality of a battery.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD +1
Method and apparatus of battery charging
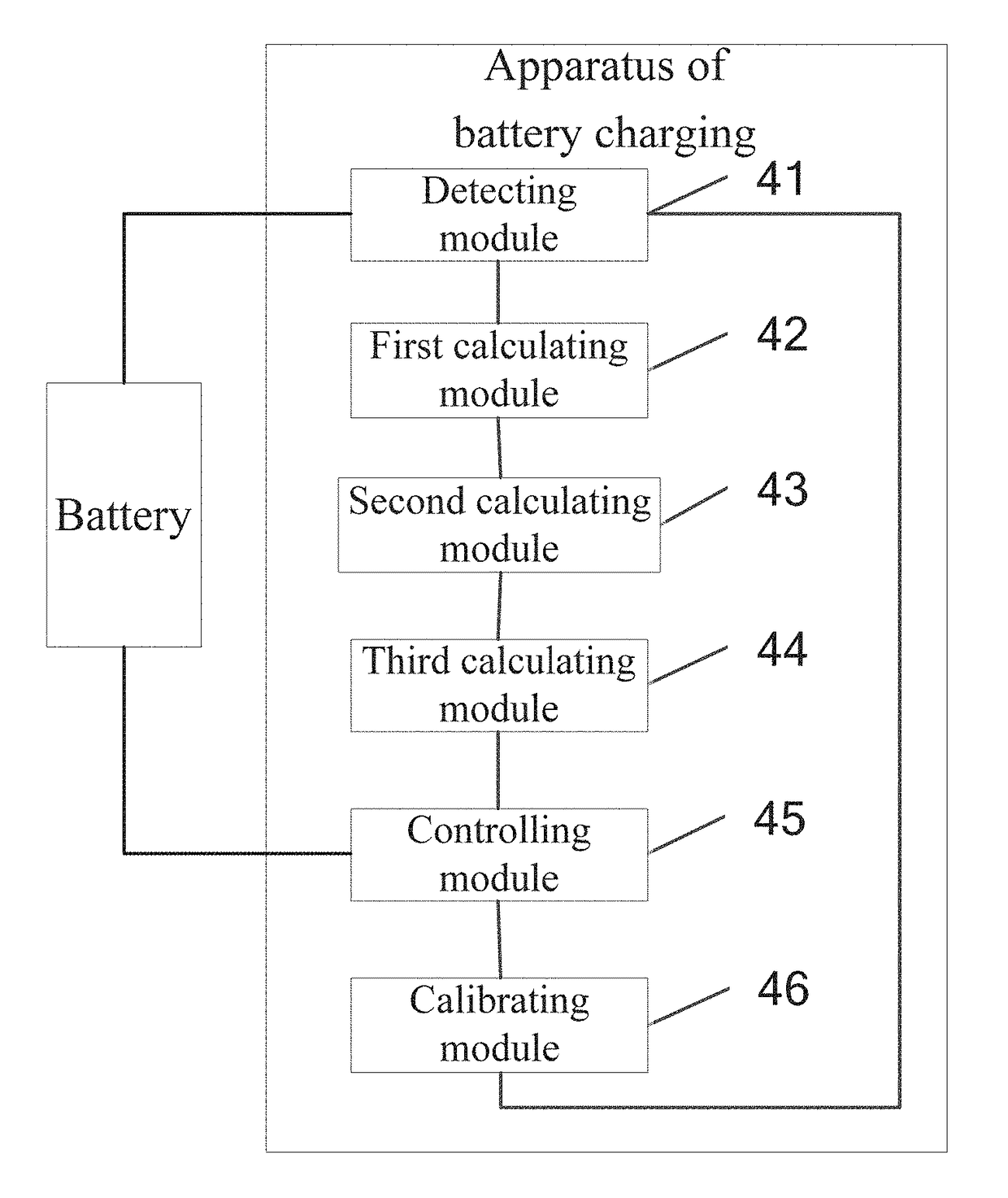
ActiveUS20170366015A1Improve safety of batteryImprove speedSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectric powerState of chargeElectrical battery
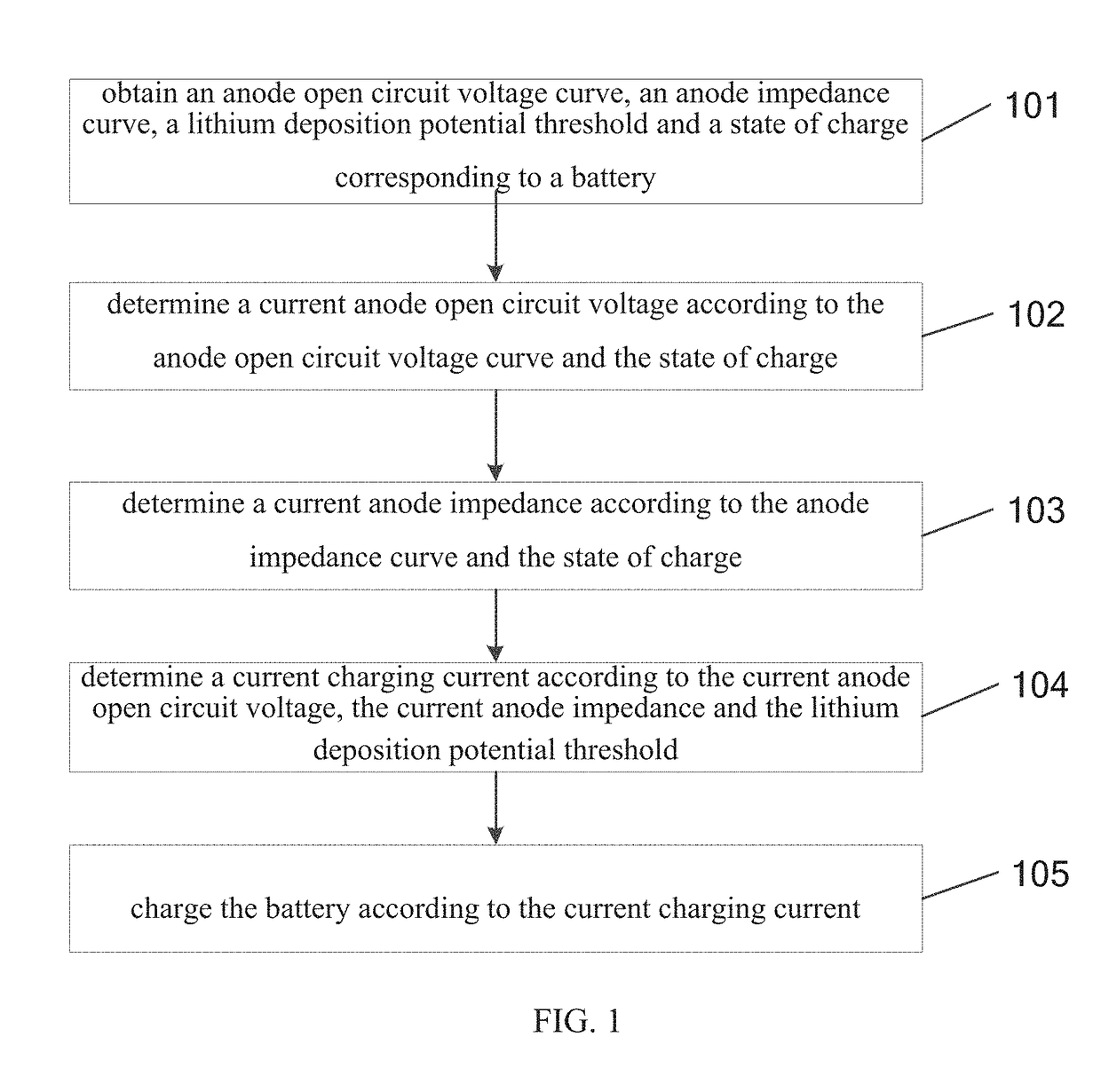
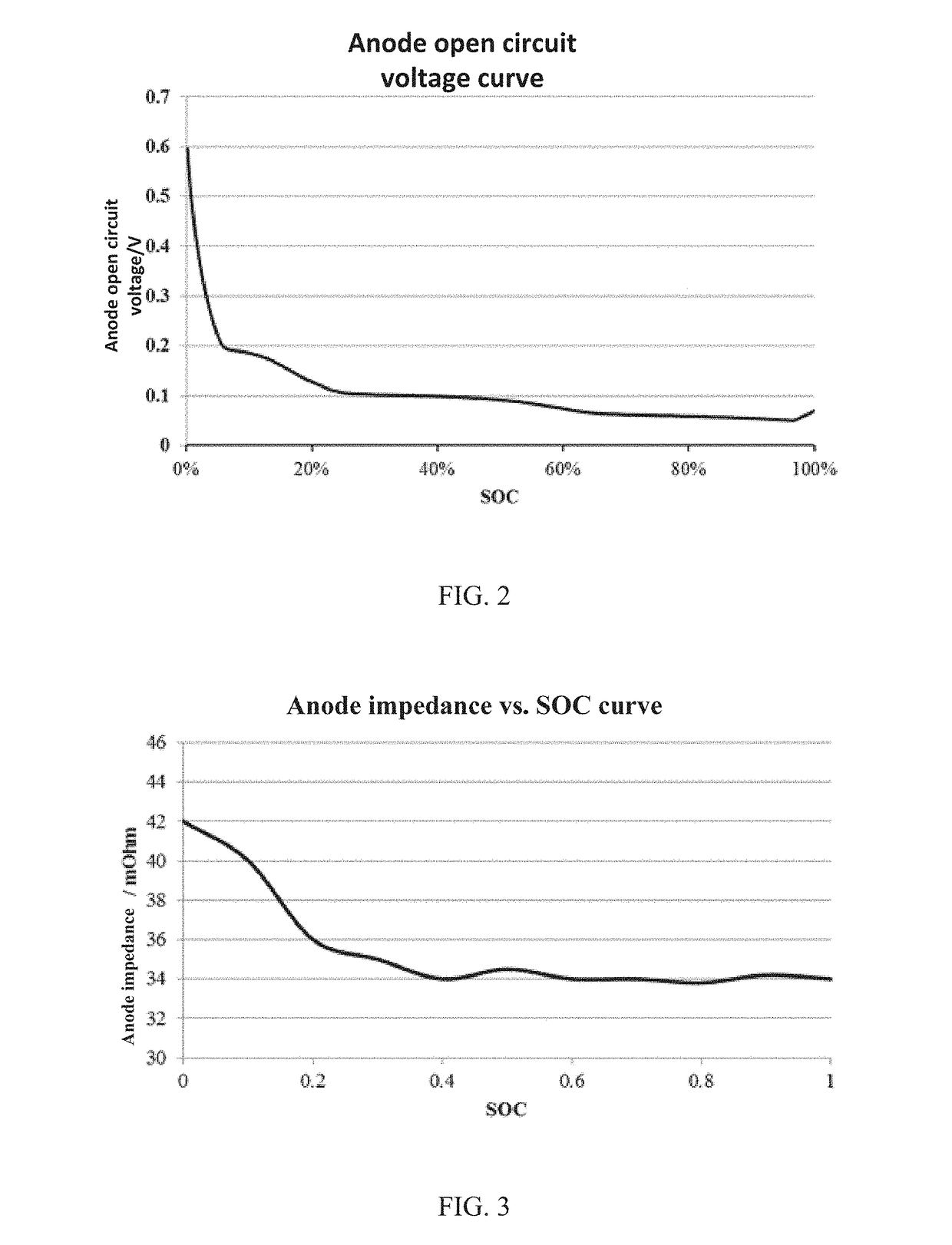
Embodiments of the present application provide a method of battery charging, which relates to the field of battery charging and is capable of effectively improving safety performance of the battery. The method includes: obtaining an anode open circuit voltage curve, an anode impedance curve, a lithium deposition potential threshold and a state of charge, corresponding to a battery; determining a current anode open circuit voltage according to the anode open circuit voltage curve and the state of charge; determining a current anode impedance according to the anode impedance curve and the state of charge; determining a current charging current according to the current anode open circuit voltage, the current anode impedance and the lithium deposition potential threshold; and charging the battery according to the current charging current. Embodiments of the present application are applicable to a rapid battery charging process.
Owner:NINGDE AMPEREX TECH
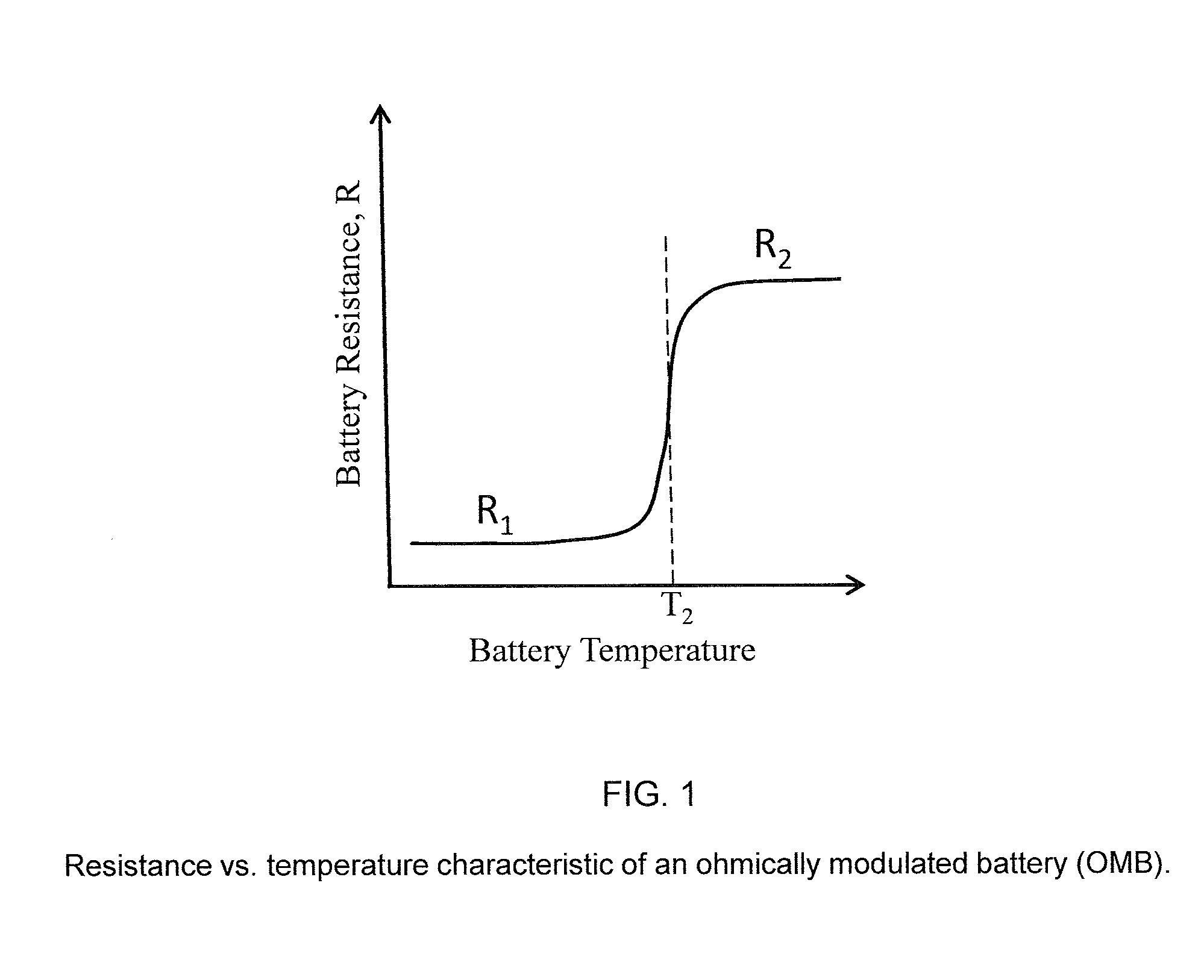
Ohmically modulated battery
ActiveUS20150104681A1Improve performance and securityHigh currentNuclear energy generationFinal product manufactureEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:EC POWER LLC
Battery and process for preparing the same
InactiveUS20010005559A1Improve battery safetyImprove securityPrimary cell maintainance/servicingCell temperature controlElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrolysis
A conventional battery has a problem that since a device having PTC function was placed outside the battery or outside the electrode of the battery as a safety device in case of temperature rise due to short-circuit current generated by external short-circuit or the like, a large short-circuit current was generated with temperature rise due to internal short-circuit. And therefore, a temperature of the battery further increases due to exothermic reaction to increase the short-circuit current. Also, there is a problem that structure of the battery become complicated and volume energy density is lowered. The present invention has been carried out in order to solve the above problems. The battery of the present invention is a battery wherein at least one of a positive electrode (1) and a negative electrode (2) comprises an active material layer (6) containing an active material (8) and an electronically conductive material (9) contacted to the active material (8), and the battery body has an electrolytic layer (3) between the above positive electrode (1) and the negative electrode (2), wherein the electronically conductive material (9) comprises an electrically conductive filler and a resin and resistance thereof can be increased with temperature rise, and wherein the battery body is sealed with the outer can (20) without forming extra space.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com