Mass spectrometry assay method for detection and quantitation of organic acid metabolites
A mass spectrometry, caproic acid technology, applied in the field of mass spectrometry for detecting and quantifying organic acid metabolites, can solve the problems of reduced sensitivity, difficult to detect SCFA, difficult to retain, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0115] Example 1: Measuring SCFA and energy metabolites
[0116] Chromatographic method
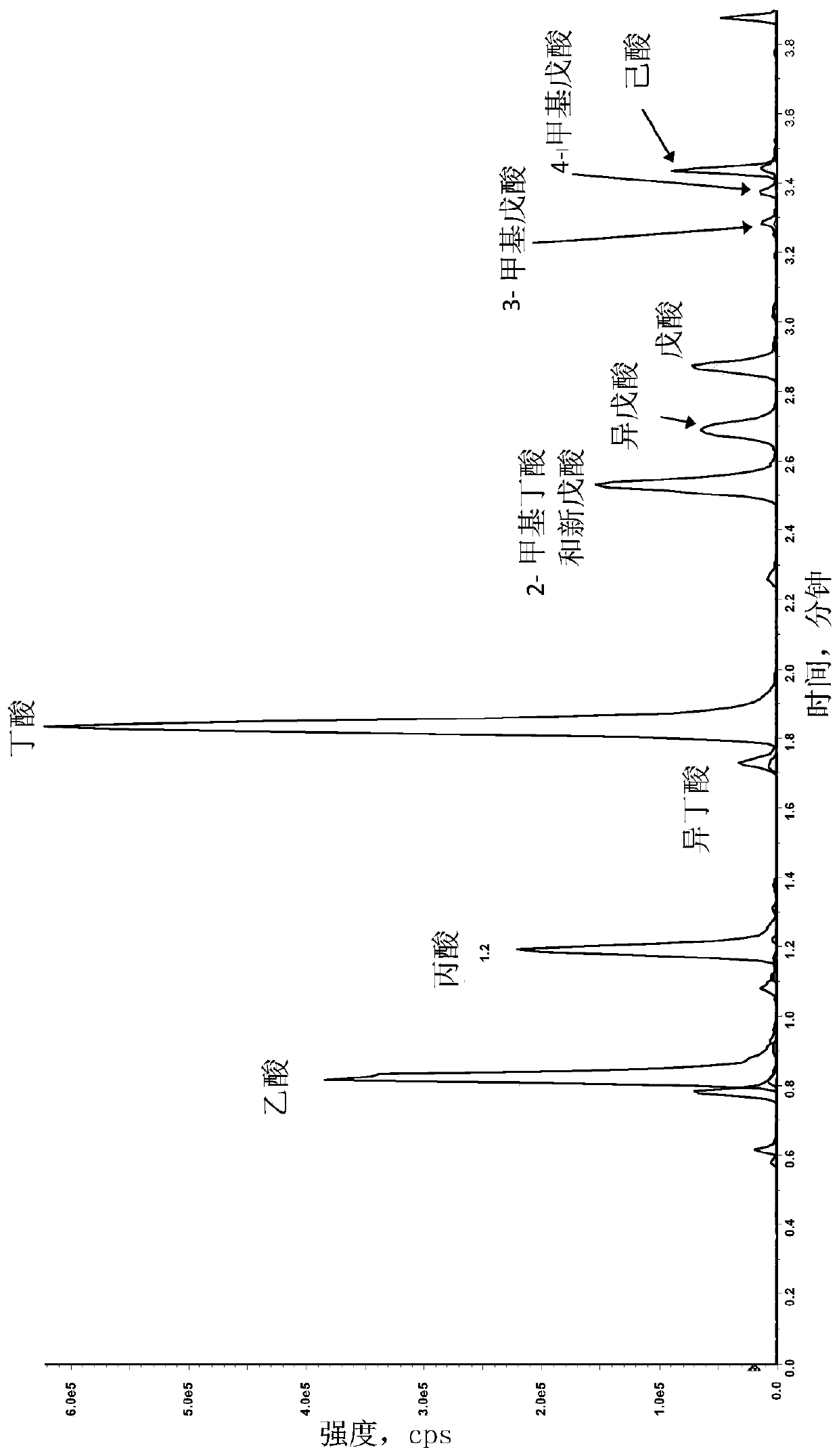
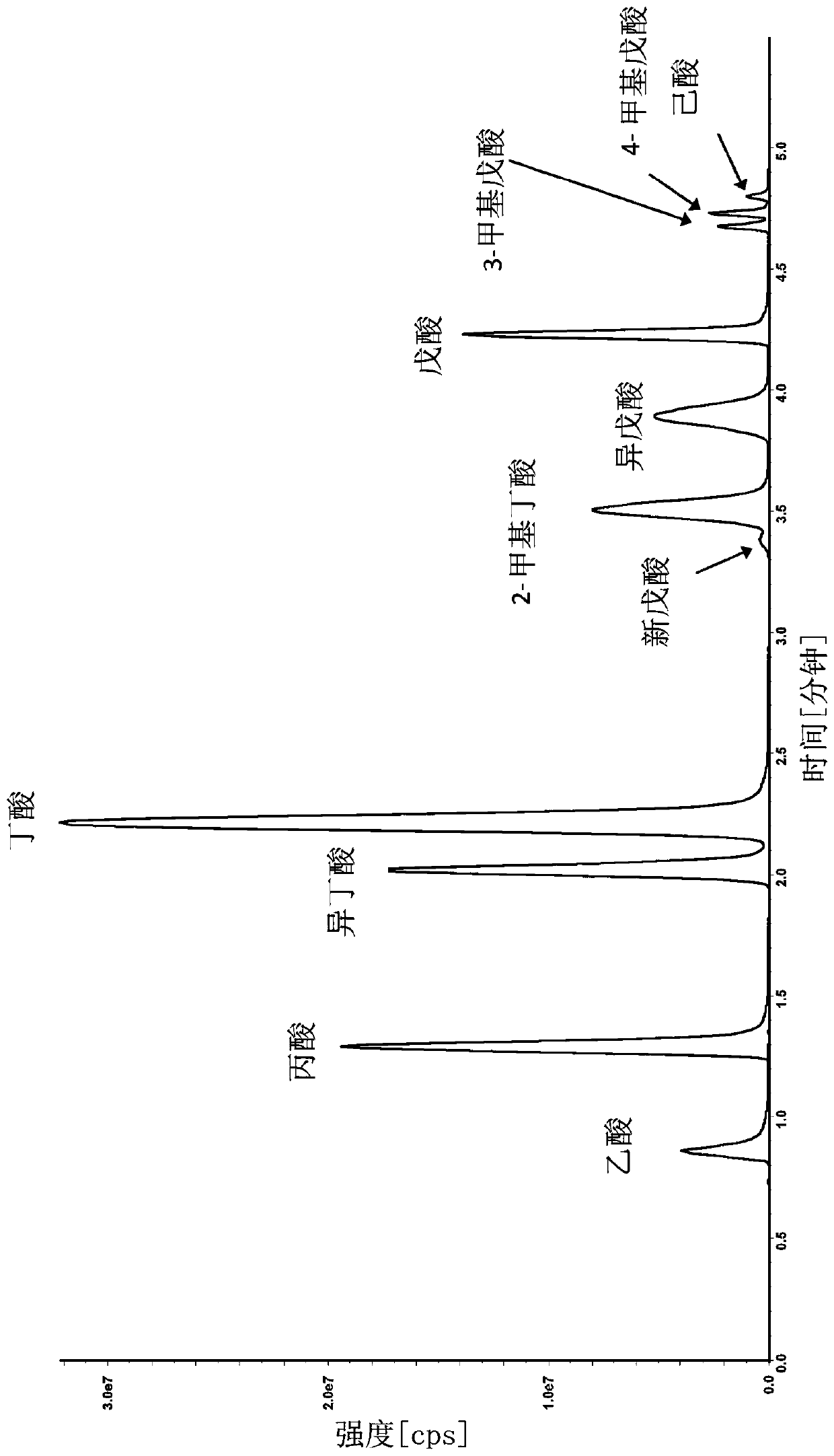
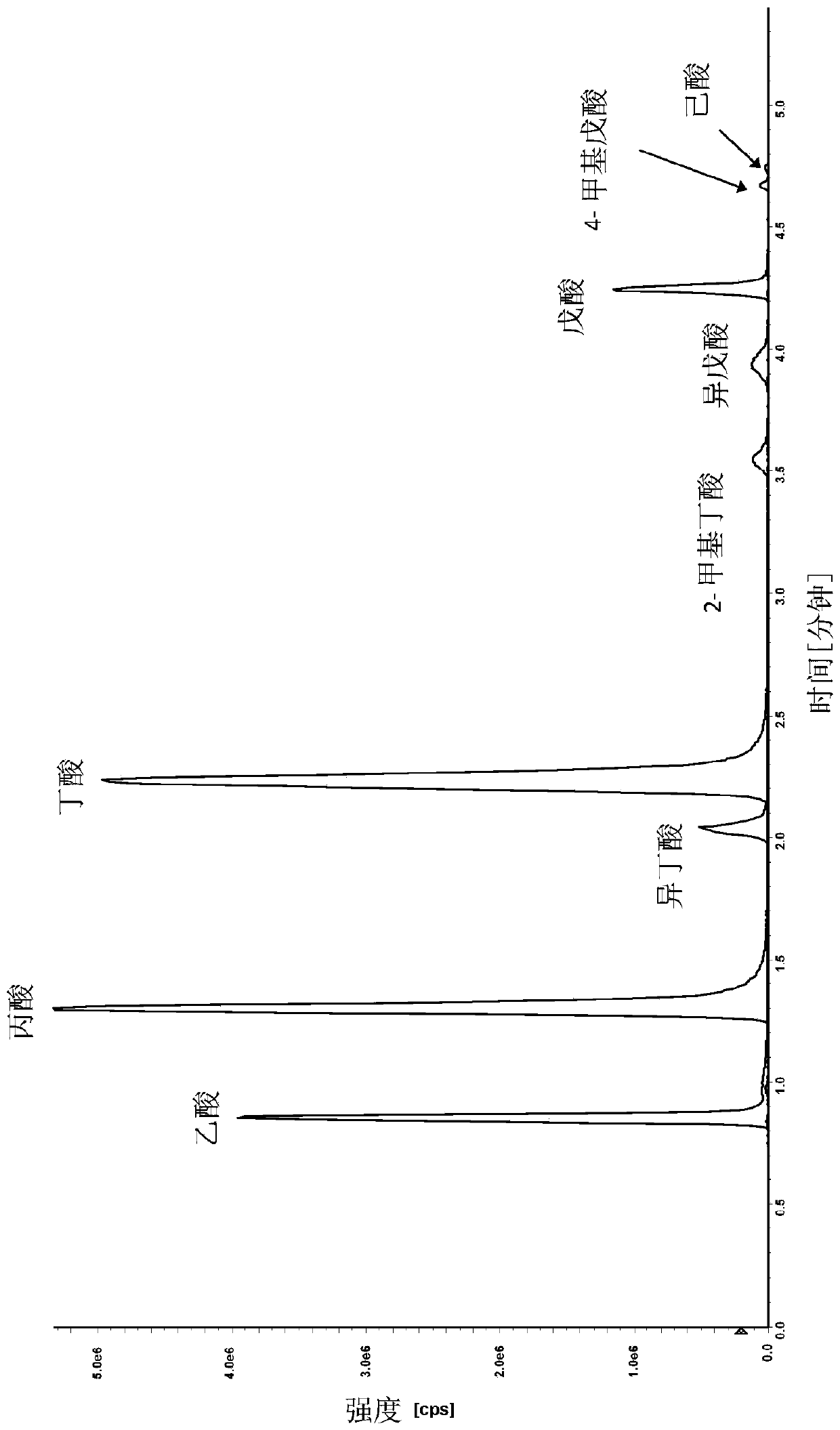
[0117] A liquid chromatography method was developed for the purification and separation of one or more, two or more and up to a total of twelve analytes selected from the group consisting of acetic acid (C2) , propionic acid (C3), isobutyric acid (C4), butyric acid (C4), 2-methylbutyric acid (C5), isovaleric acid (C5), valeric acid (C5), 3-methylvaleric acid, 4-Methylpentanoic acid (isocaproic acid), caproic acid (caproic acid, C6), pivalic acid, lactic acid, pyruvic acid, fumaric acid, succinic acid, malic acid, alpha-ketoglutaric acid, aconitic acid , citric acid, isocitric acid and combinations thereof. An Agilent 1290 Infinity UHPLC system equipped with a binary solvent pump unit, a refrigerated autosampler (set at 18°C) and a column heater (set at 60°C) was used with a reversed-phase column (Waters ACQUIT Y C18 BEH Shield, 1.7 μm, 2.1x100 mm) liquid chromatography. Mobile phase A...
Embodiment 2
[0131] Example 2: Measurement of SCFA Analytes in Experimental Samples
[0132] SCFAs in the samples were measured using derivatization method 2 using the method described in Example 1. The method was developed for the determination of the SCFA analytes acetate (C2), propionate (C3), isobutyrate (C4), Absolute amounts of butyric acid (C4), 2-methylbutyric acid (C5), isovaleric acid (C5), valeric acid (C5), caproic acid (caproic acid, C6).
[0133] In another example, 8 SCFA analytes were measured in 59 plasma samples. Results for representative samples are presented in Table 6.
[0134] In another example, 8 SCFA analytes were measured in 120 serum samples. Results for representative samples are presented in Table 6.
[0135] In another example, 8 SCFA analytes were measured in 50 urine samples. Results for representative samples are presented in Table 6.
[0136] In another example, 8 SCFA analytes were measured in 197 stool samples. Results for representative samples ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| collision energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com