Method for quickly detecting low-molecular chlorinated organic compounds in papermaking white water, and application
A technology for chlorinated organic matter and white water for papermaking, which is applied in measurement devices, material separation, and analysis of materials, etc., can solve the problems of large interference of white water matrix, cumbersome and time-consuming operation, large solvent consumption, etc., and achieves low detection limit and rapid analysis. , the effect of easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047]A rapid assay method for low-molecular chlorinated organics in papermaking white water, comprising the following steps:
[0048] (1) Pretreatment of samples to be tested
[0049] The paper-making white water to be tested was filtered with medium-speed qualitative filter paper to remove suspended matter, and then 5 grams of paper-making white water and 2.1 g of NaCl were accurately weighed in a 20ml headspace bottle at 40°C for 1 hour.
[0050] (2) Solid phase microextraction (SPME)
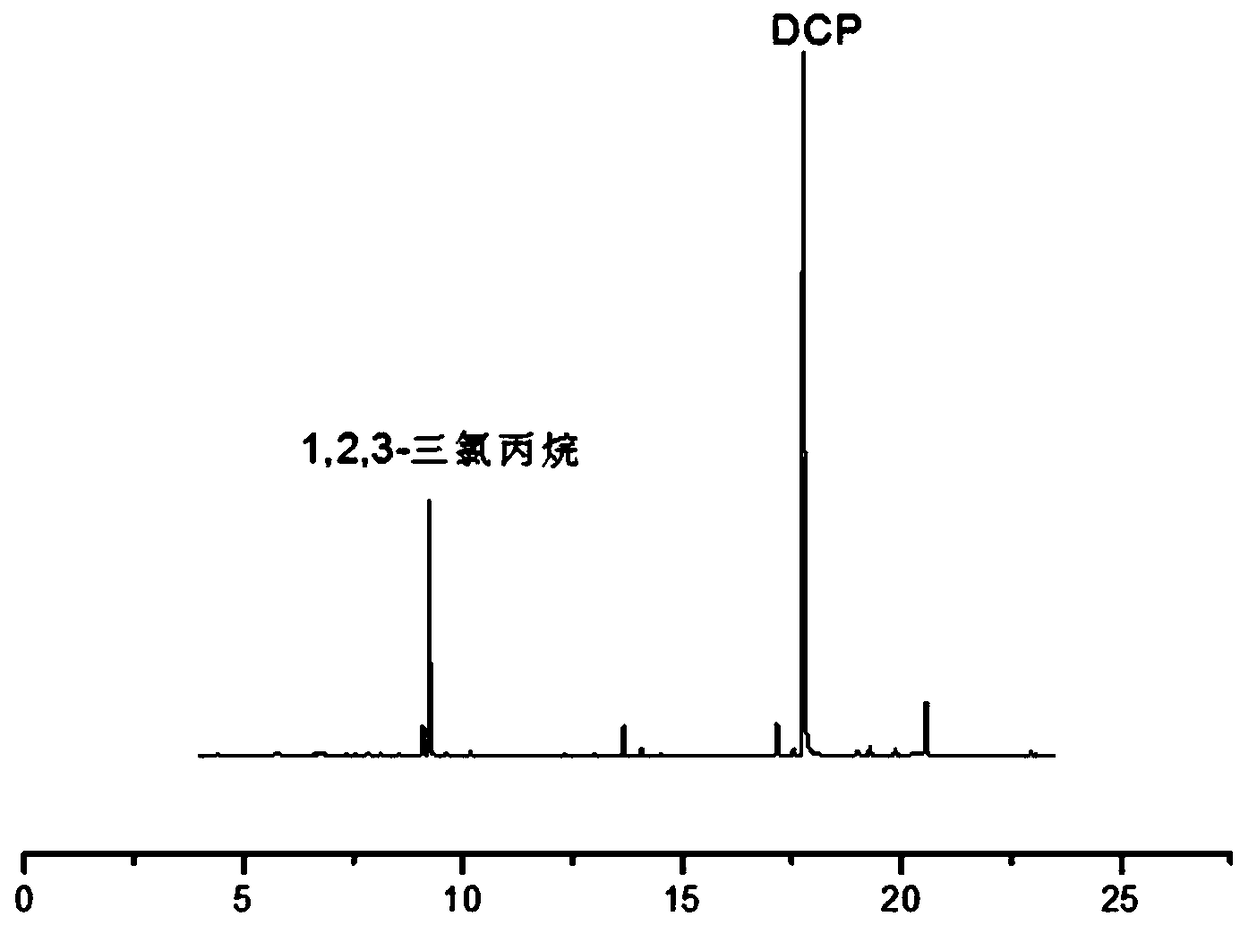
[0051] Perform aging treatment on the solid-phase microextraction fiber head: place the 85 μm polyacrylate (Polyacrylate) extraction head in the GC (gas chromatography) inlet for aging for 15 minutes at a temperature of 250 ° C to remove surface residues; then step (1) Insert the well-balanced sample into the headspace bottle with the aged solid-phase microextraction fiber head (polyacrylate extraction head), and push out the headspace extraction sample of the solid-phase microextraction fi...
Embodiment 2
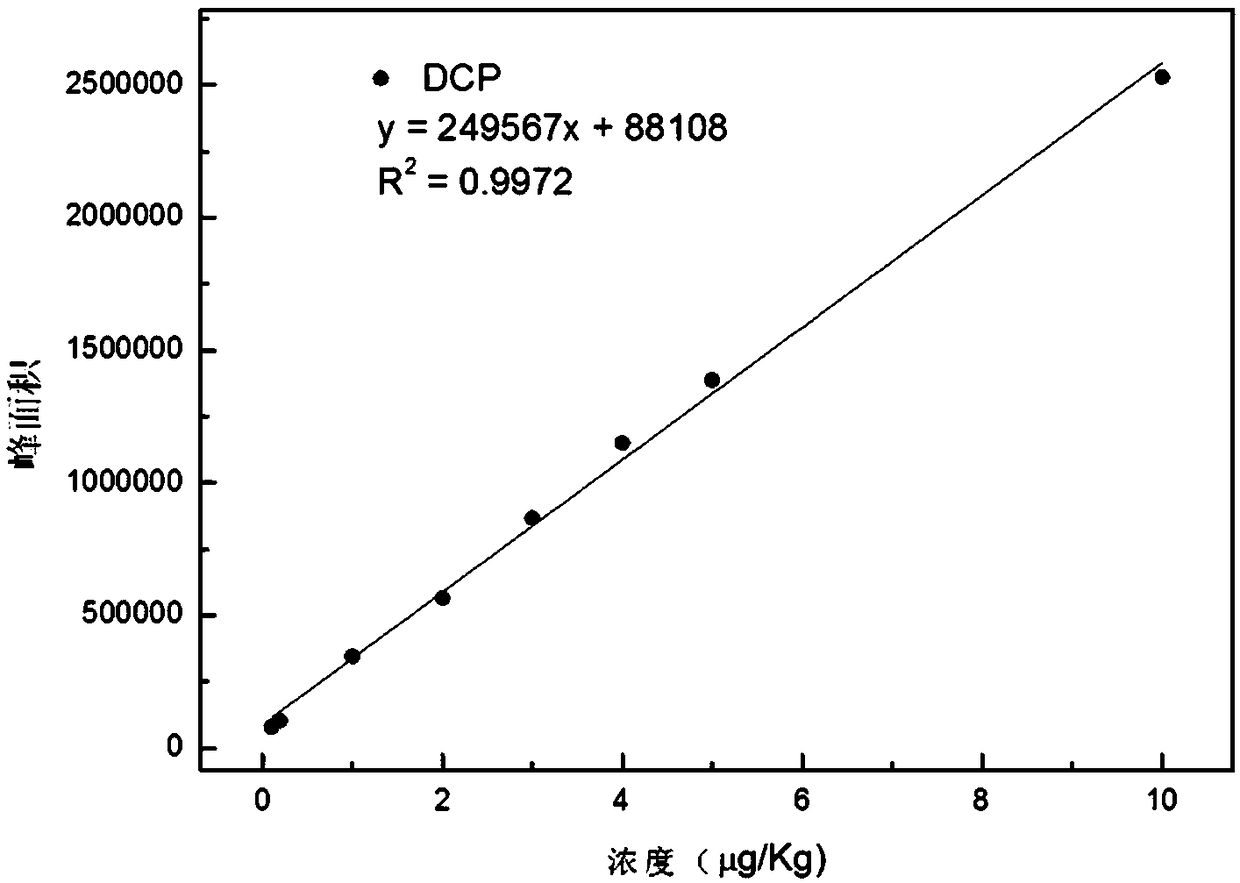
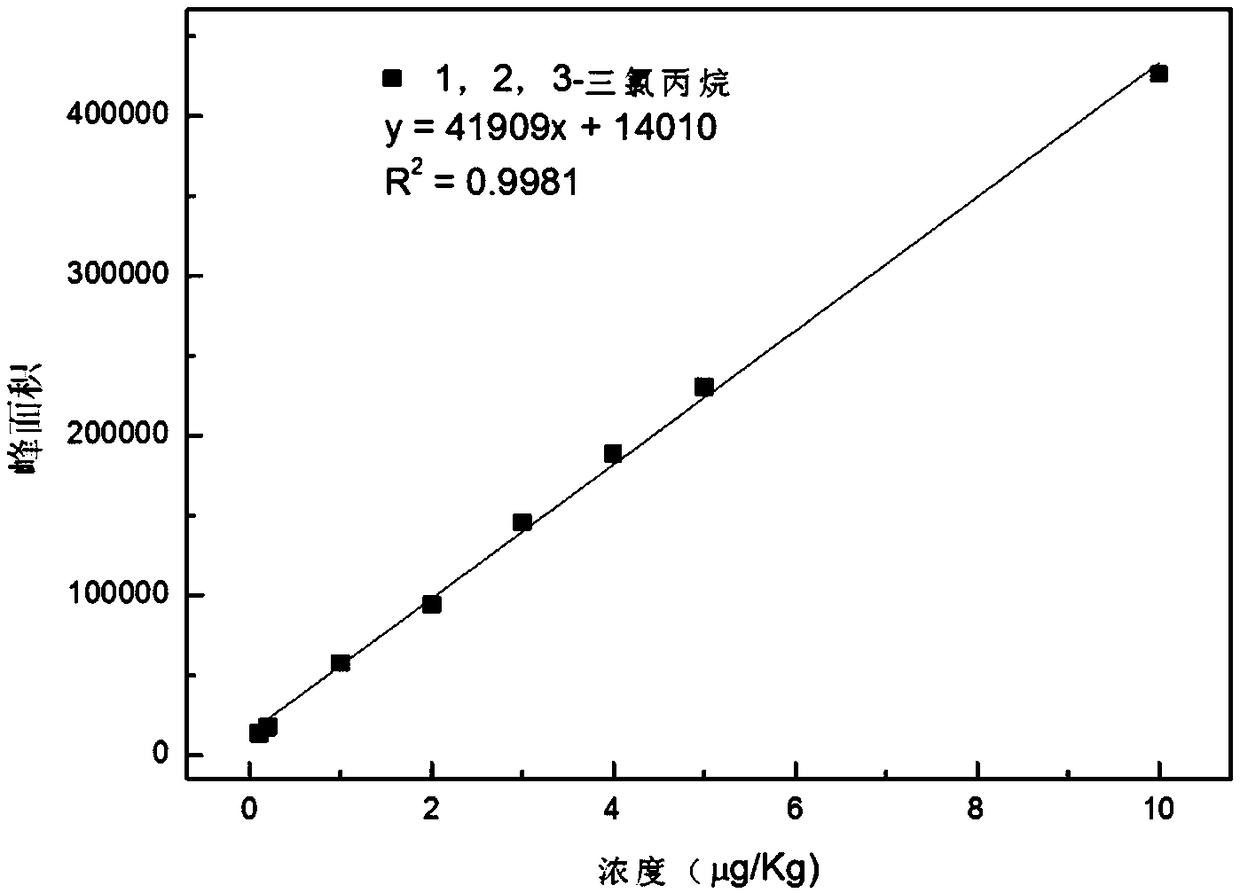
[0067] Detect according to the method of Example 1, the difference is: the time of solid phase microextraction (SPME) in step (2) is 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60min. Its detection signal is as Figure 4 shown. In the SPME process, the extraction time is generally increased to ensure the maximum volatilization of volatile substances into the headspace to improve the detection sensitivity, but by Figure 4 It can be seen that after 40 minutes, the sensitivity of 1,2,3-trichloropropane decreased significantly, while DCP gradually increased, which is the performance of adsorption competition. In order to ensure the accurate detection of the two substances, the optimal extraction time was 40 minutes.
Embodiment 3
[0069] Detect according to the method of Example 1, the difference is: the quality of NaCl added during the pretreatment of the sample to be tested in step (1) is 0.3, 0.6, 0.9, 1.2, 1.5, 1.8, 2.1 grams. Its detection signal is as Figure 5 shown. The ionic effect will reduce the solubility of substances in water, and the addition of salts containing chlorine will increase the volatility of chlorinated organic compounds. Depend on Figure 5 It can be seen that the addition of NaCl significantly increases the sensitivity of the two substances to be detected, therefore, the detection sensitivity of low-molecular chlorinated organic compounds in white water can be improved by adding NaCl.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com