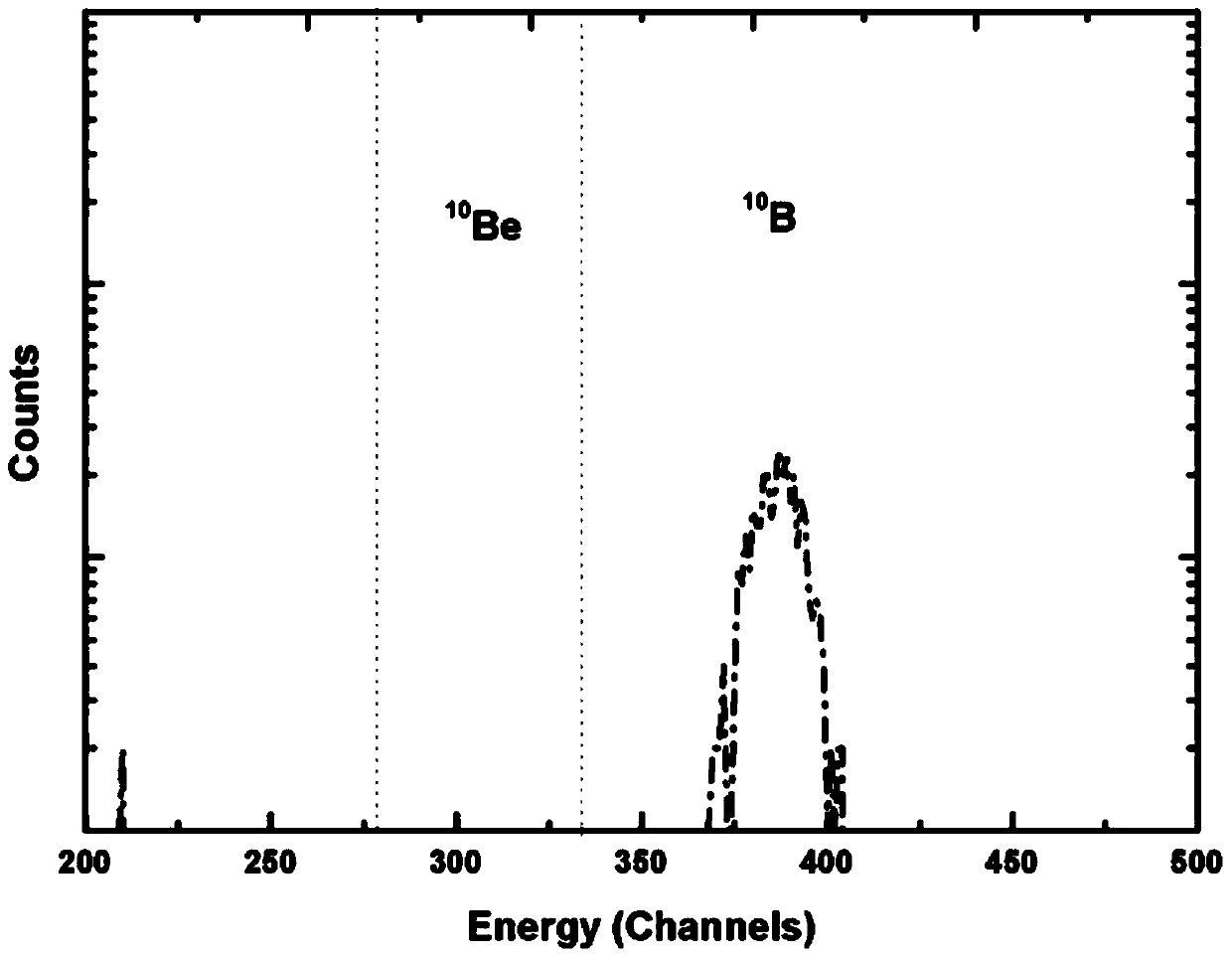
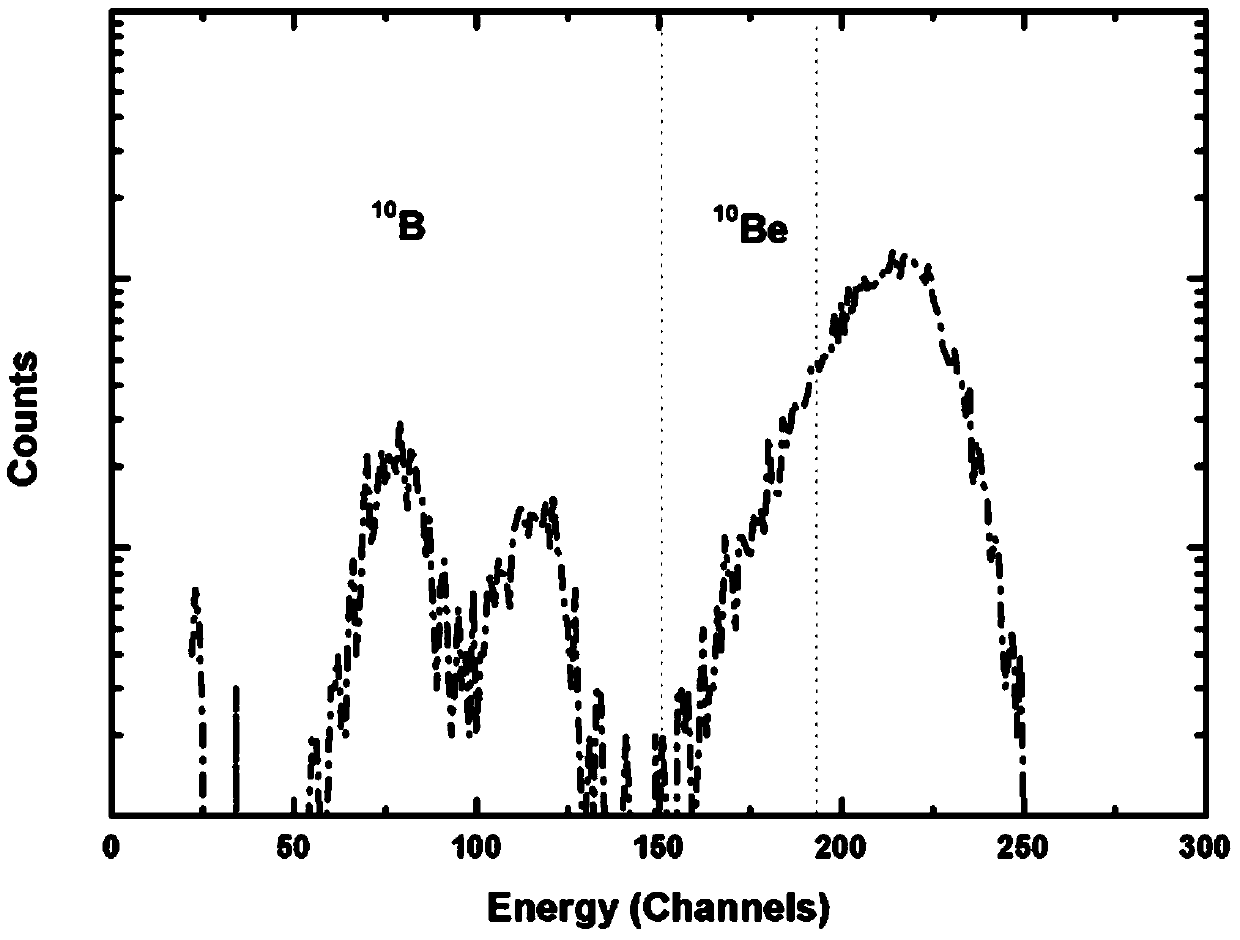
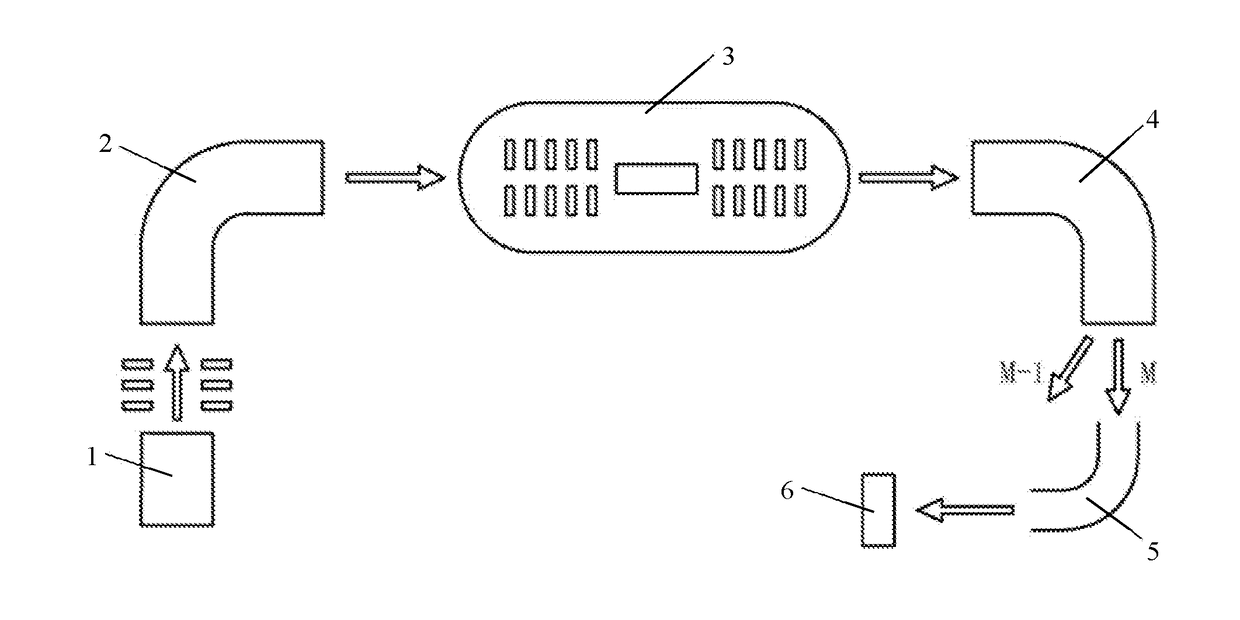
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Accelerator mass spectrometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) is a form of mass spectrometry that accelerates ions to extraordinarily high kinetic energies before mass analysis. The special strength of AMS among the mass spectrometric methods is its power to separate a rare isotope from an abundant neighboring mass ("abundance sensitivity", e.g. C from ¹²C). The method suppresses molecular isobars completely and in many cases can separate atomic isobars (e.g. N from ¹⁴C) also. This makes possible the detection of naturally occurring, long-lived radio-isotopes such as ¹⁰Be, Cl, Al and ¹⁴C. Their typical isotopic abundance ranges from 10⁻¹² to 10⁻¹⁸. AMS can outperform the competing technique of decay counting for all isotopes where the half-life is long enough.
Single-atom detection of isotopes
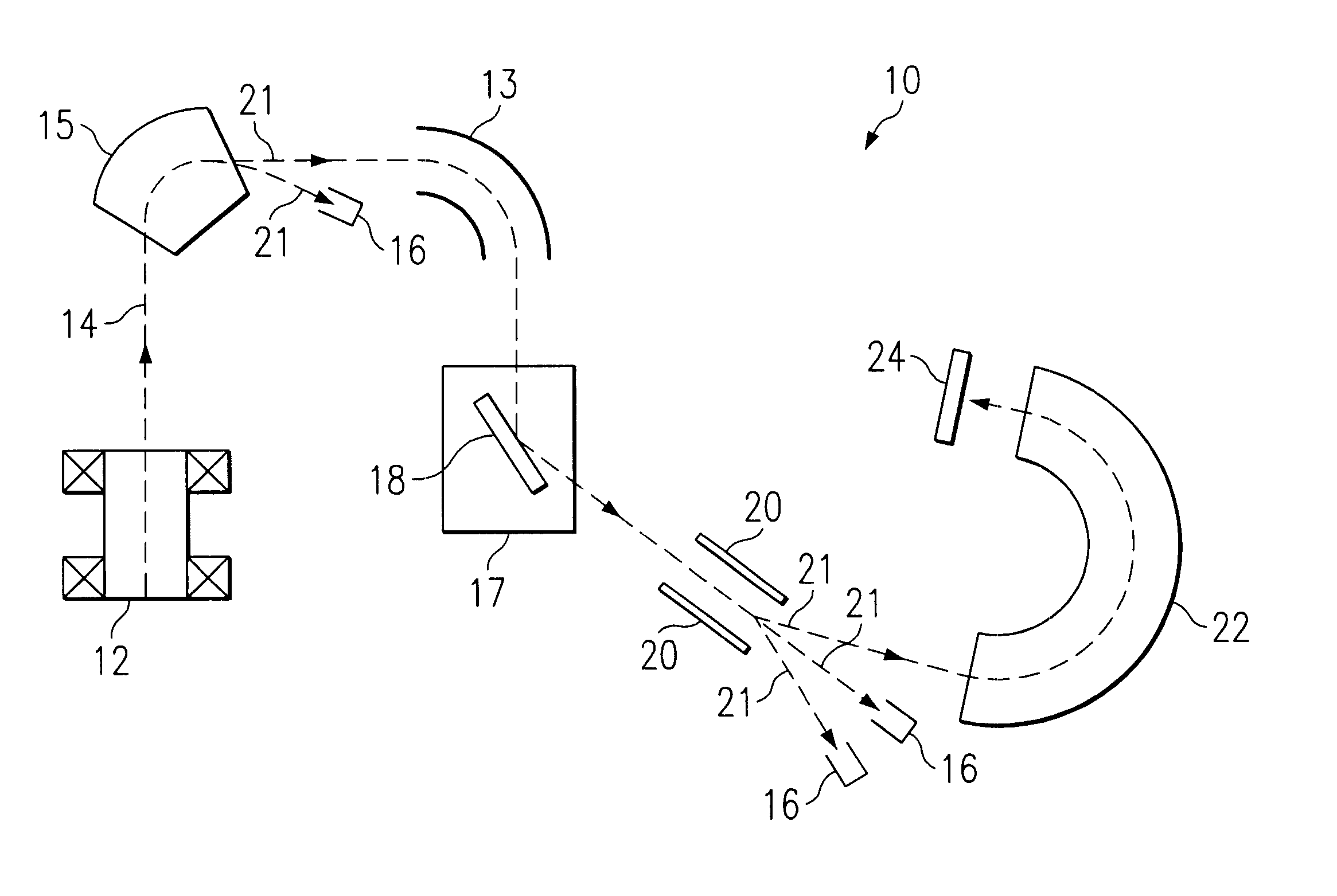
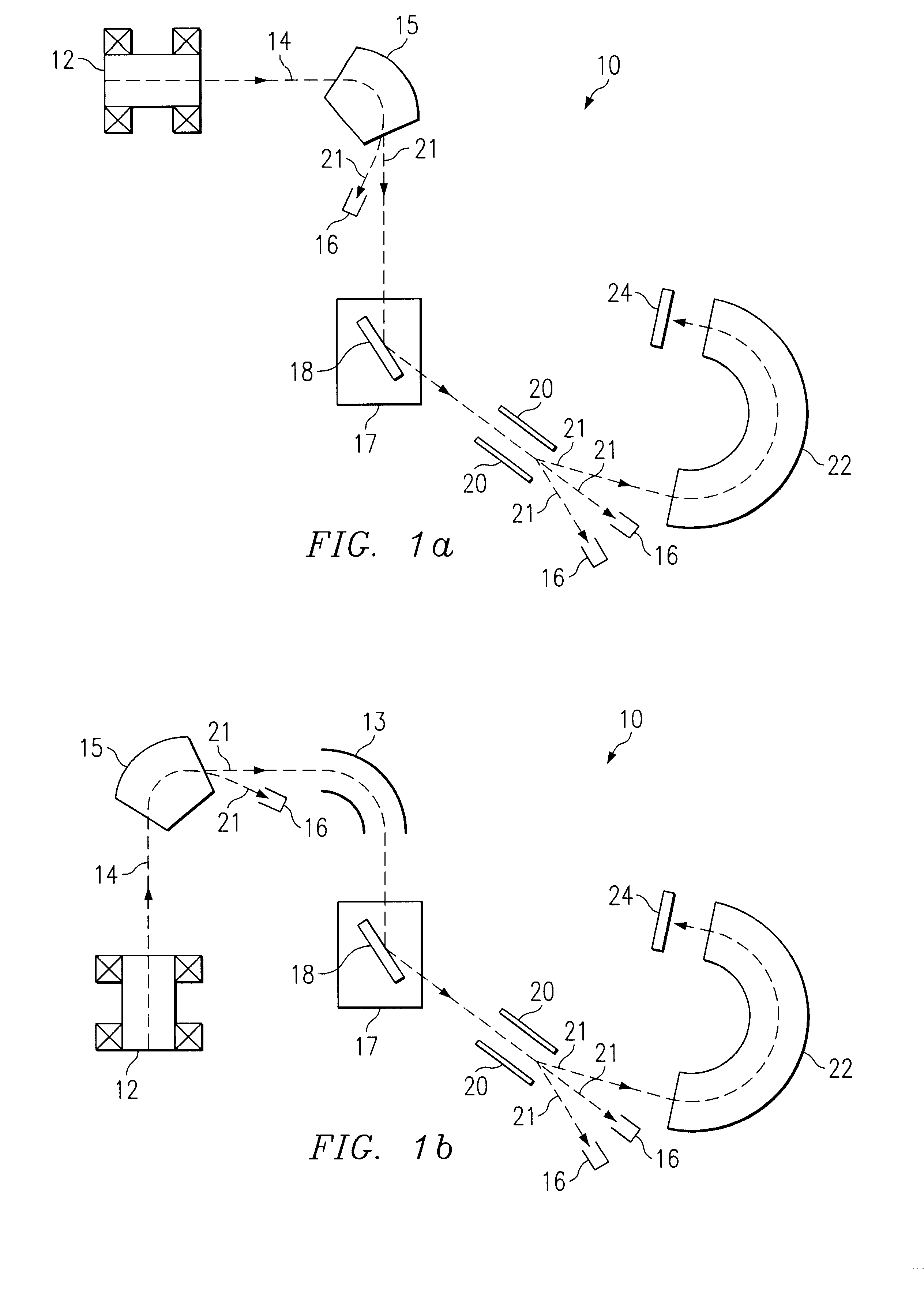
A method for performing accelerator mass spectrometry, includes producing a beam of positive ions having different multiple charges from a multicharged ion source; selecting positive ions having a charge state of from +2 to +4 to define a portion of the beam of positive ions; and scattering at least a portion of the portion of the beam of positive ions off a surface of a target to directly convert a portion of the positive ions in the portion of the beam of positive ions to negative ions.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
Method and apparatus for separation of isobaric interferences
ActiveUS20060113464A1Avoid reactionLow costElectron/ion optical arrangementsIsotope separationTerminal voltageMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
This invention relates to a method and apparatus for separation of rare stable or radioactive isotopes from their atomic or molecular isobars in mass spectrometry (MS). In the present invention, the approach taken to removing atomic isobars utilizes a high transmission device for decelerating ions in combination with low energy reactions, such as ion-molecule reactions or near resonant electron transfer, in RF ion guides. The isobar is selectively depleted by electron transfer or other reactions between negative ions and gaseous targets in pressurized RF ion guides at low energies. The energy is controlled in such a way as to prevent reaction of the ion of interest while inducing reactions with the undesired isobar interference. The technique is of particular relevance to accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) for which it allows substantial reductions in the necessary terminal voltage. The effect is to allow reductions in the size and cost of AMS installations.
Owner:LITHERLAND ALBERT EDWARD +7
Mass spectrometry system with molecular dissociation and associated method
ActiveUS20130112869A1Effective destructionLess spaceIsotope separationMass spectrometersMass analyzerMass spectrometry imaging
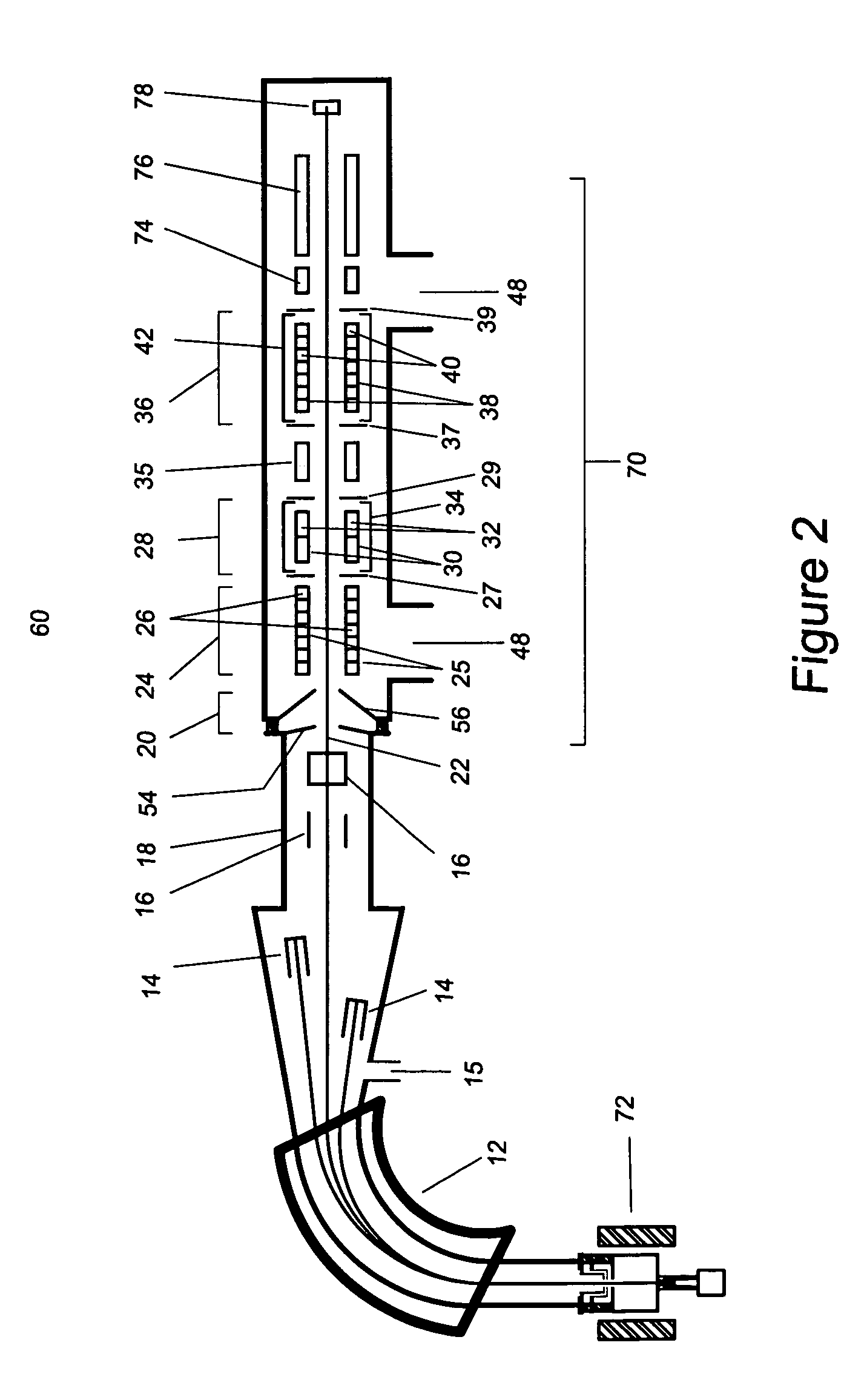
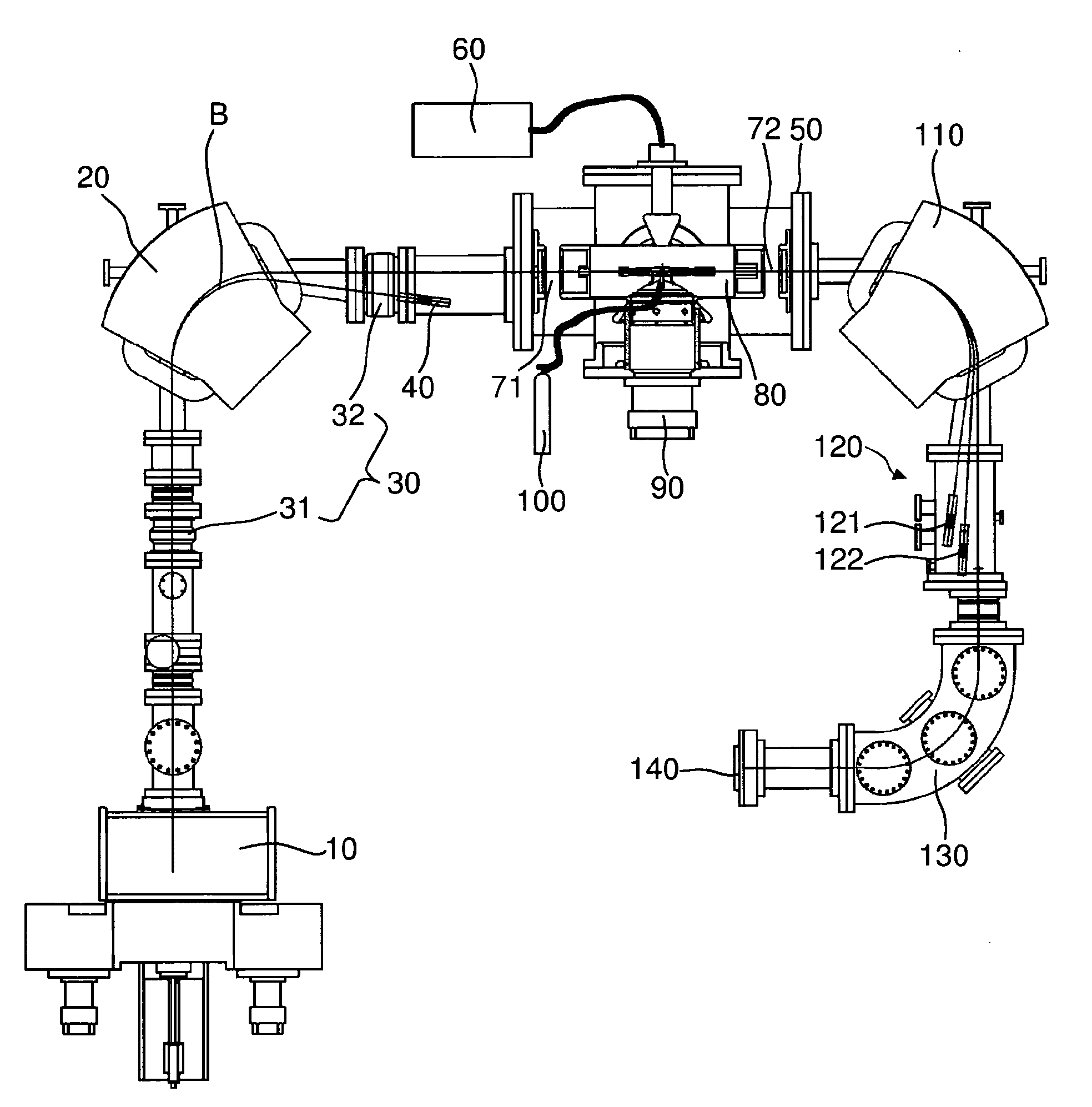
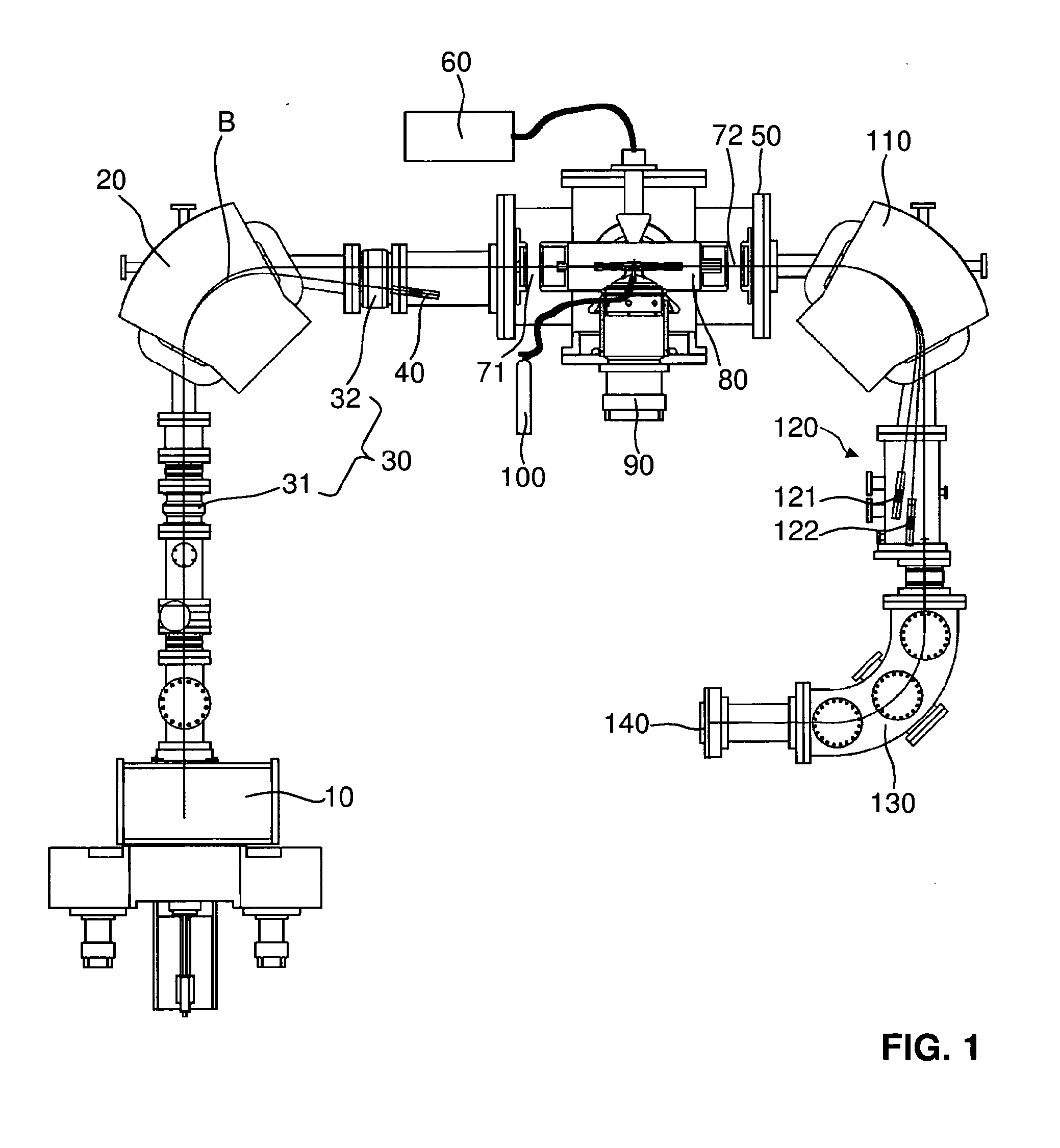
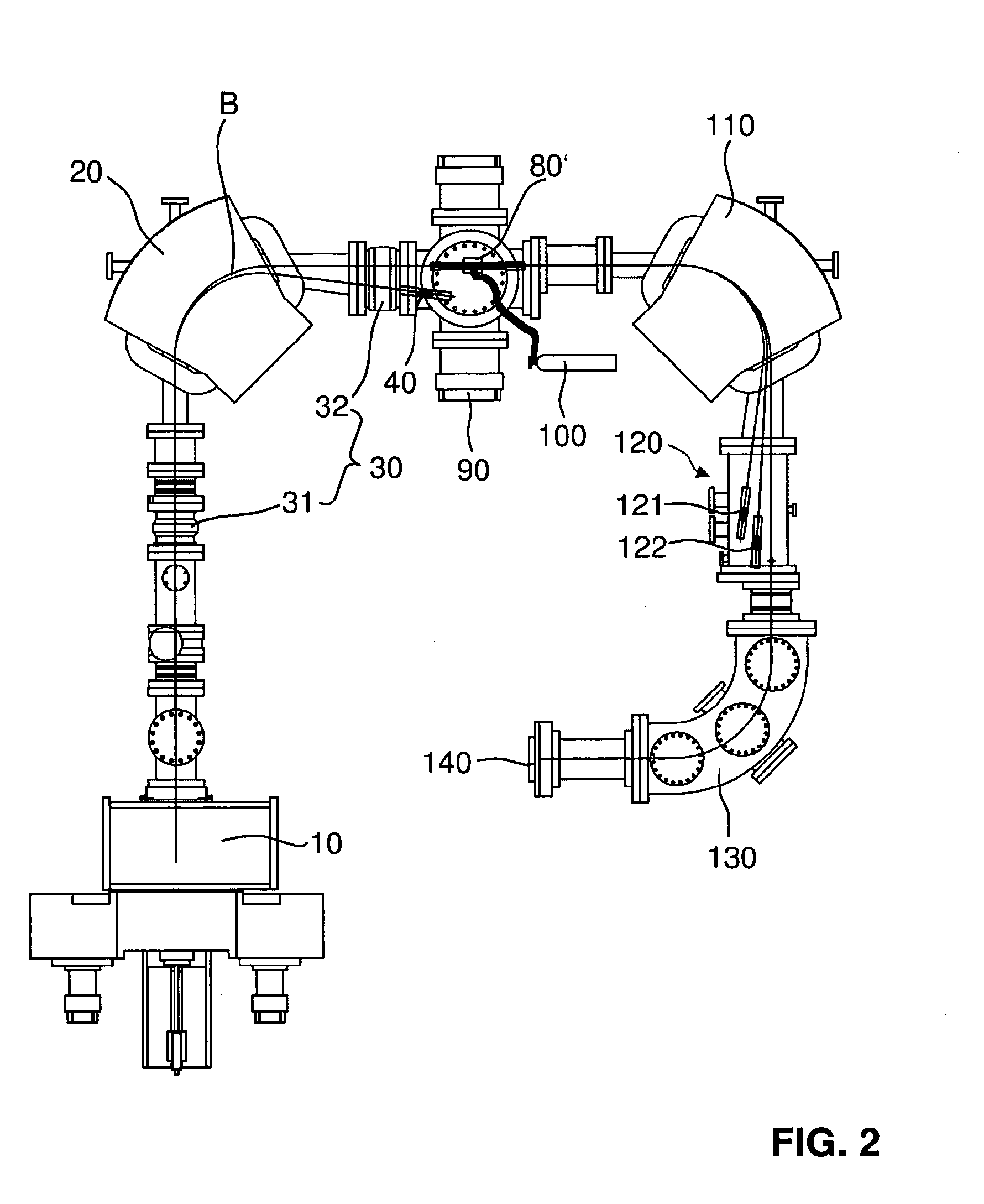
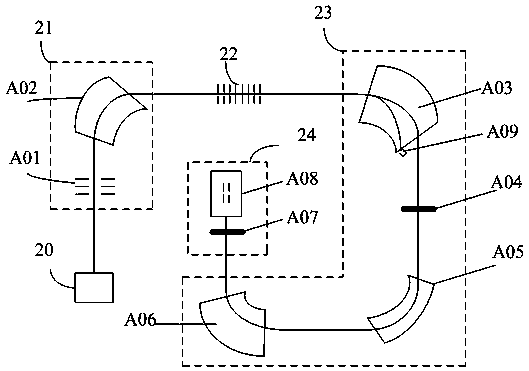
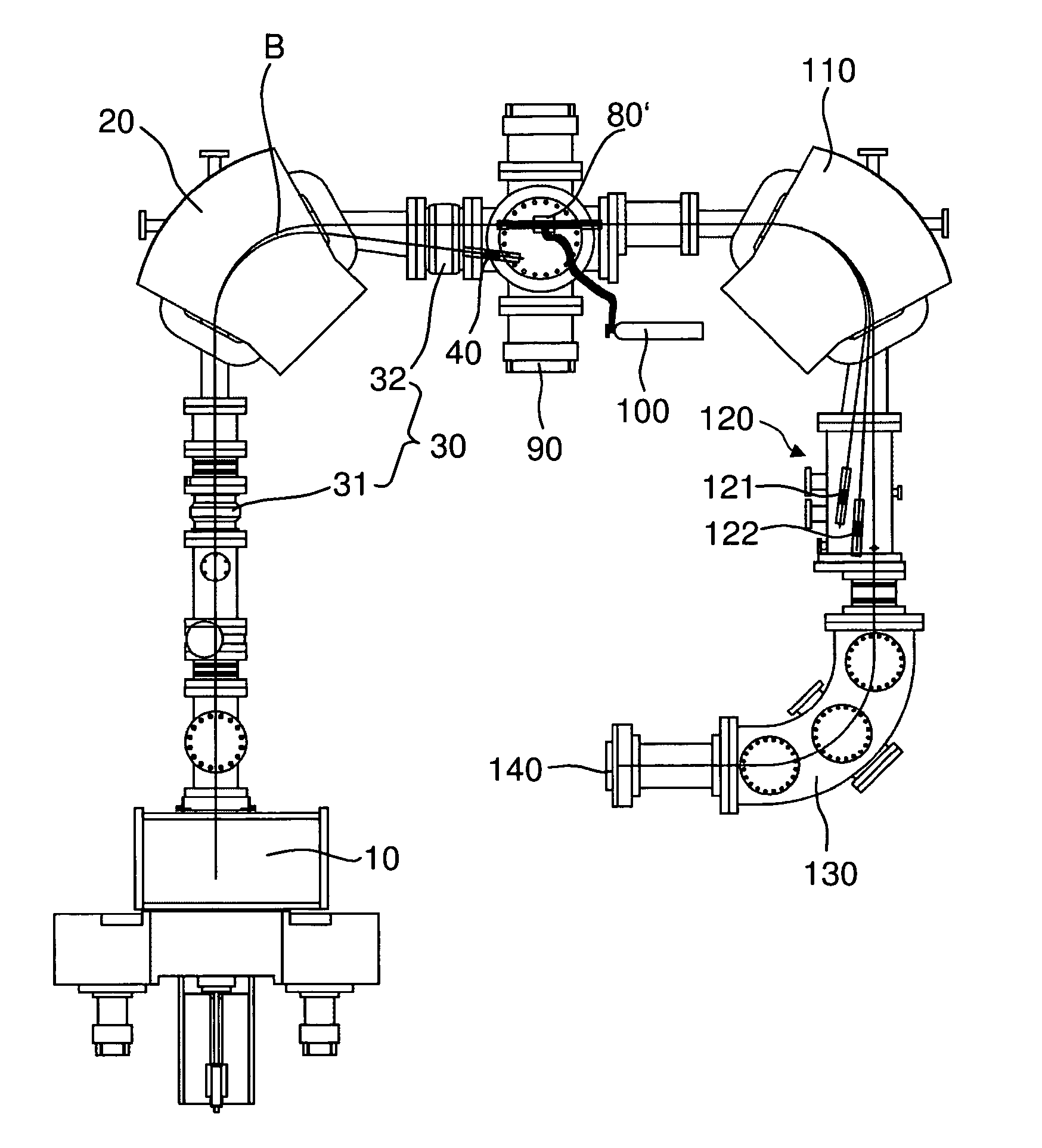
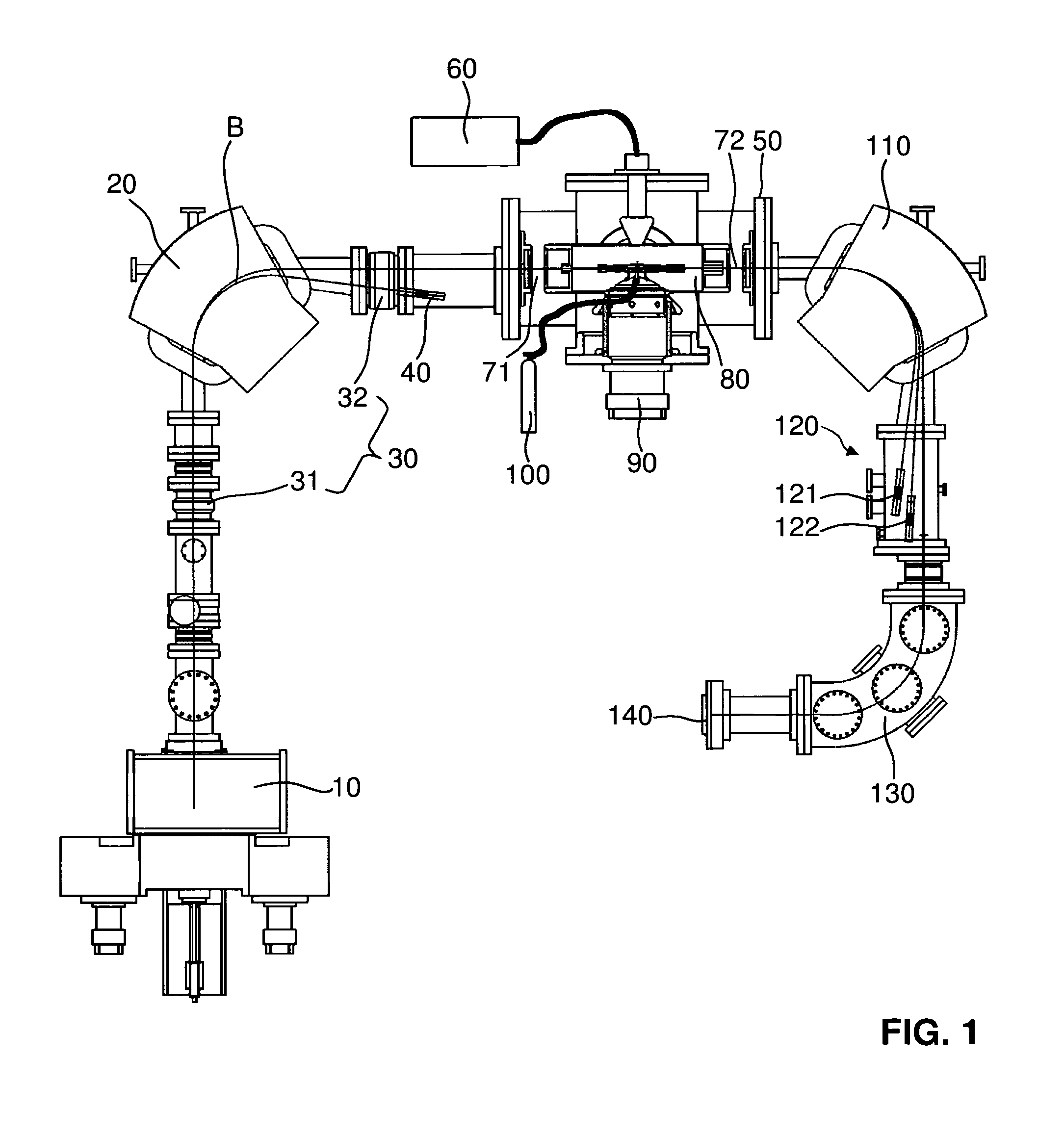
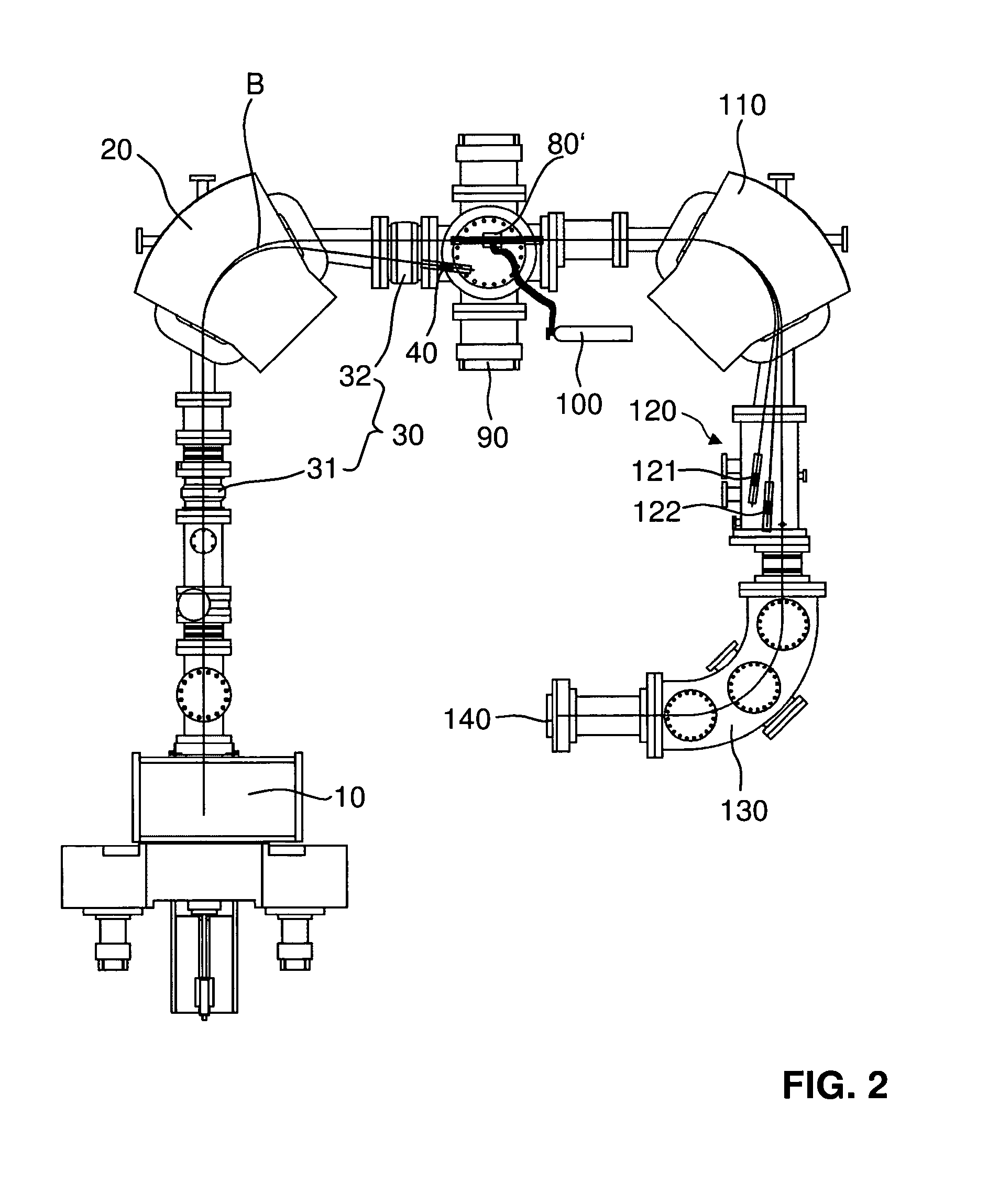
A mass spectrometry system based on the general principle of accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) is disclosed. An ion source (10) generates a beam (B) of ions having a negative charge state. A first mass analyzer (20) transmits only ions having a predetermined mass. The ions are passed through a stripper target (80) comprising helium and / or hydrogen as a stripping gas to change the charge state of said ions from negative to positive charge and to dissociate molecular ions by collisions. A second mass analyzer (110, 130) transmits ions in charge state 1+ having the predetermined mass, which are detected by a detector (140). By using helium and / or hydrogen gas and detecting ions in charge state 1+, it becomes possible to use kinetic energies below 200 keV without excessive transmission losses due to angular straggling. At sufficiently low energies, no additional acceleration is required after ions have been extracted from the ion source. In alternative embodiments, no mass selection is carried out before charge exchange takes place.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Sample preparation method
InactiveUS20070018091A1Reduce bottlenecksCost effectiveTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationCompound (substance)Isotope
The present invention provides a method of sample preparation for use in obtaining elemental isotope ratios of a material by accelerator mass spectrometry. The method comprises forming the material into a sample without any substantial chemical alteration of the material. The invention also provides a sample for use in obtaining elemental isotope ratios of a material.
Owner:XCELERON LTD
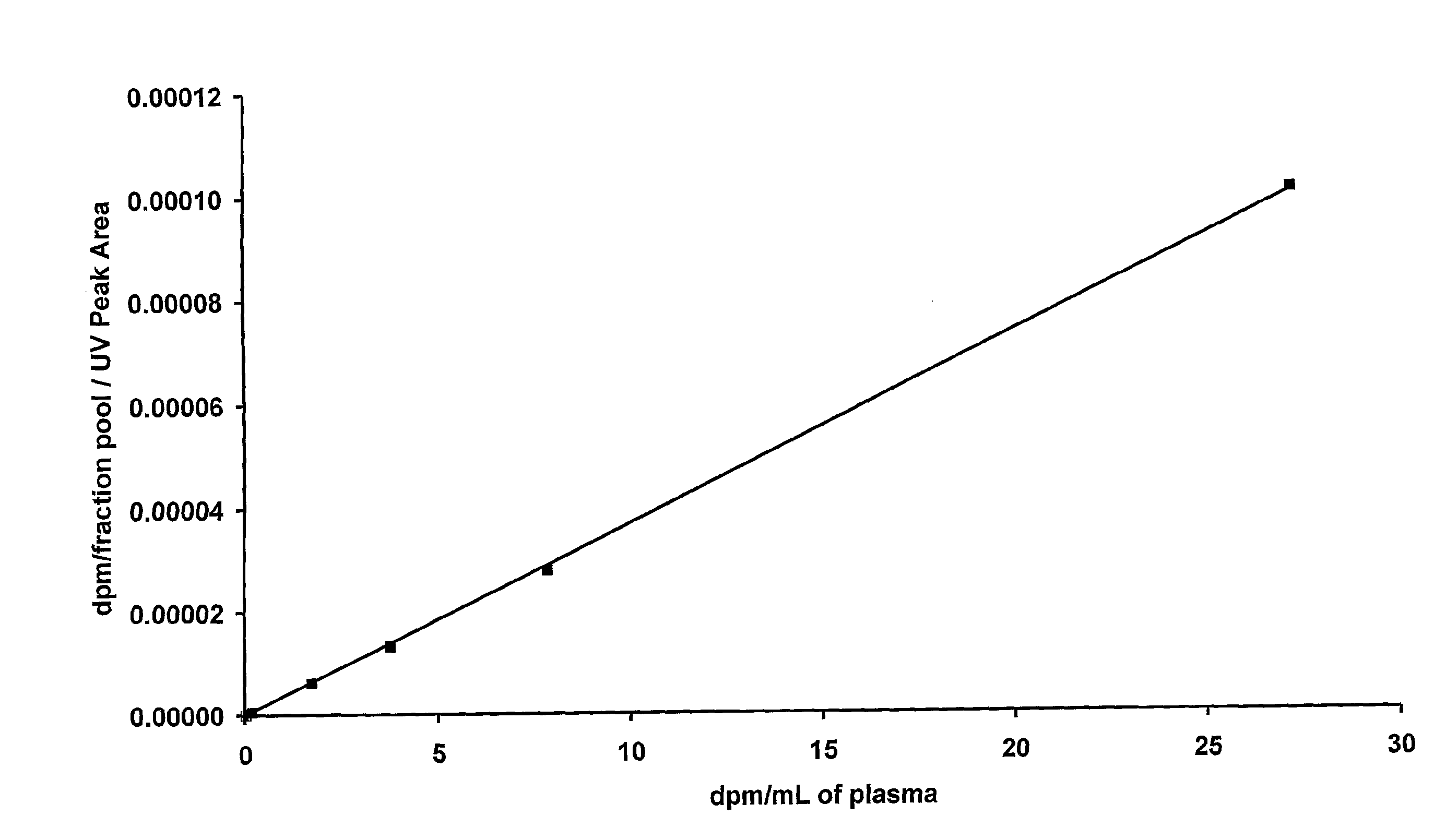
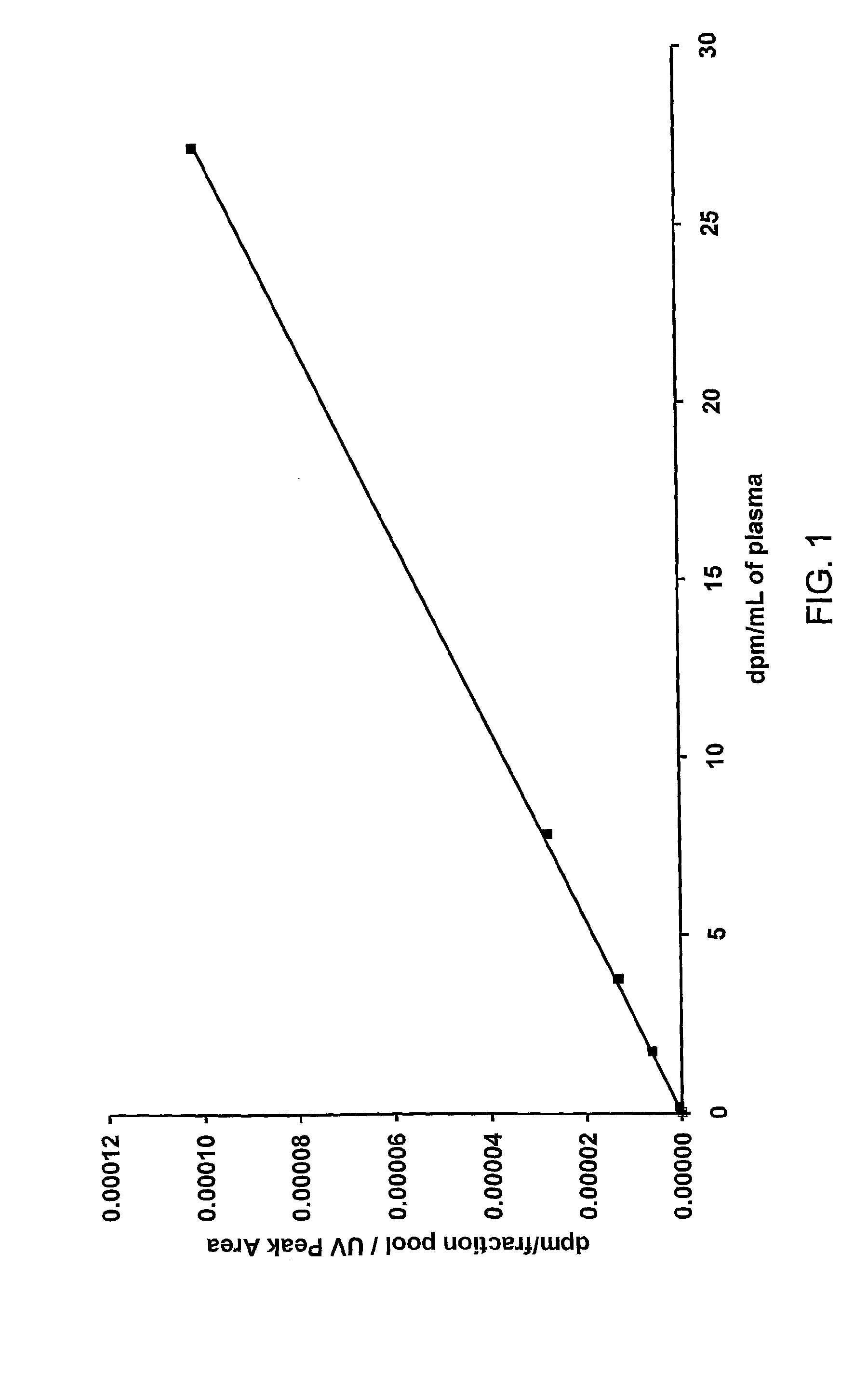
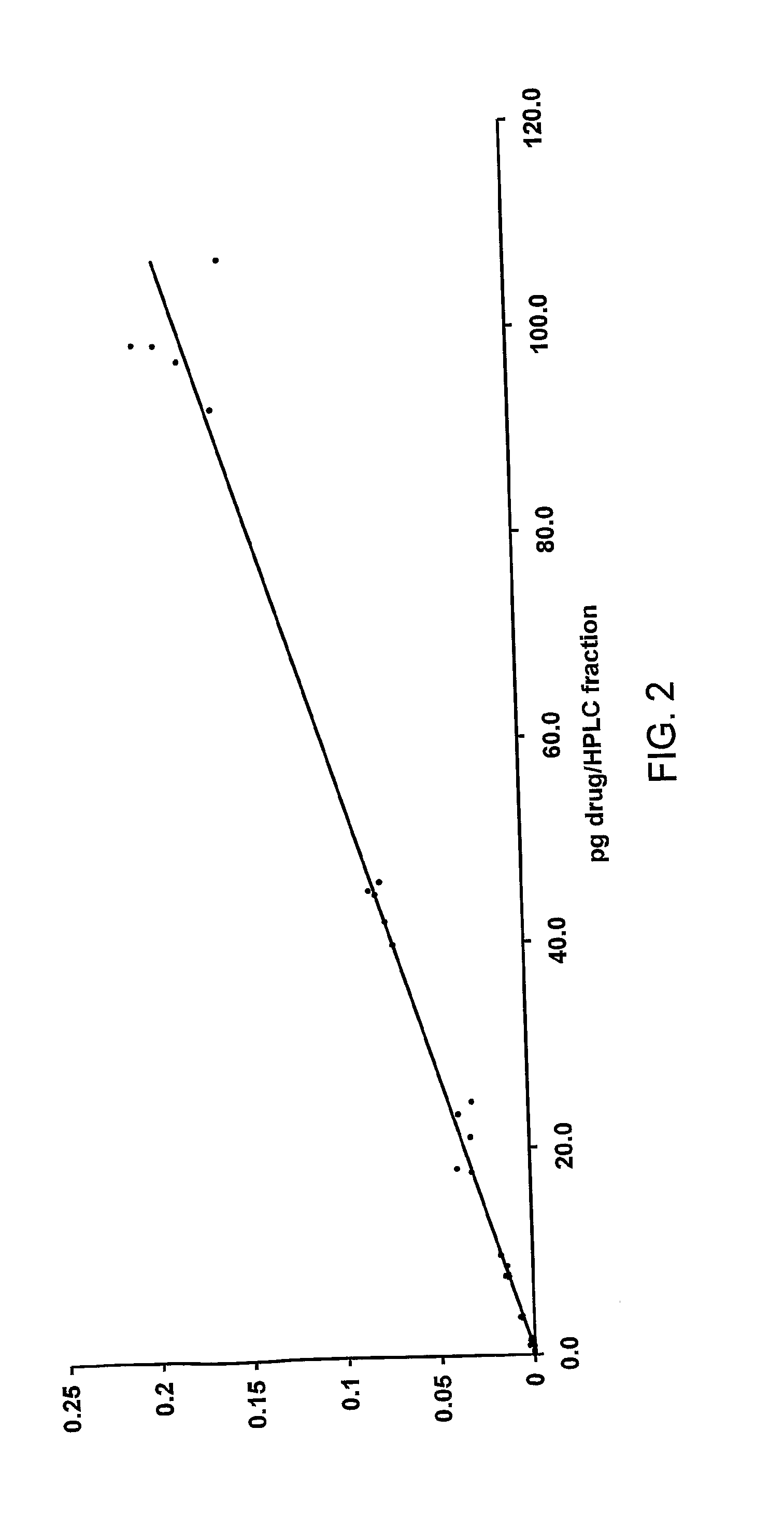
Quantification of analytes using accelerator mass spectrometry
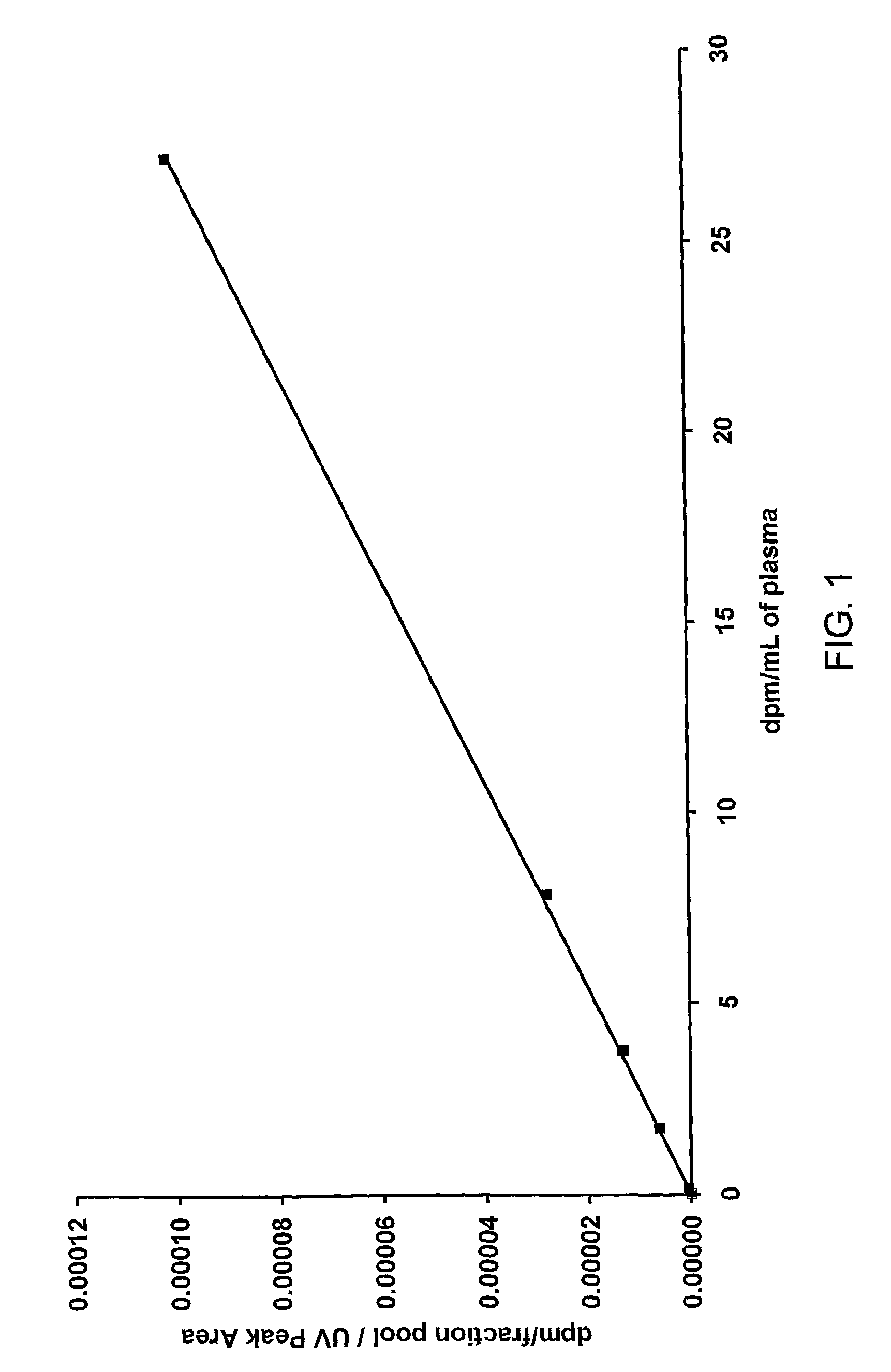
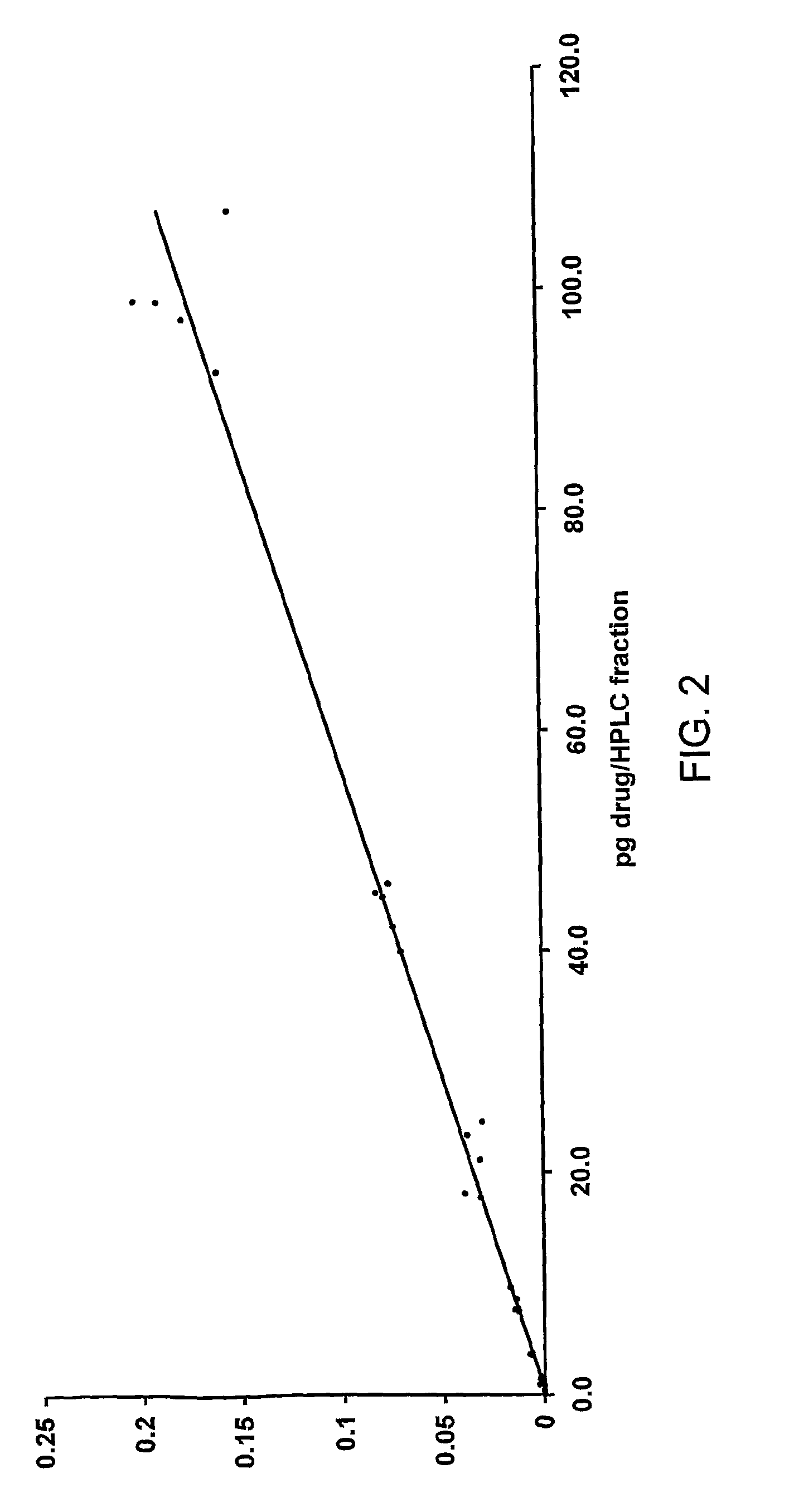
The invention provides a calibrating method for use in a method of determining the quantity of an analyte labelled with an AMS isotope in a test sample, said calibrating method comprising: (i) contacting a plurality of samples contaminated with neither said analyte nor a non-labelled counterpart analyte with a known quantity of said counterpart analyte and a quantity C of analyte to afford a plurality of calibrating samples, wherein each of said calibrating samples contains a known quantity of counterpart analyte but a different quantity of C; (ii) measuring by AMS the quantity C of analyte added to each of the plurality of samples; (iii) separating the analyte and counterpart analyte from other species in the plurality of samples to afford a plurality of purified samples; (iv) measuring a quantity A of analyte in said purified samples by AMS; and (v) measuring a quantity B of counterpart analyte in said purified samples.
Owner:XCELERON INC
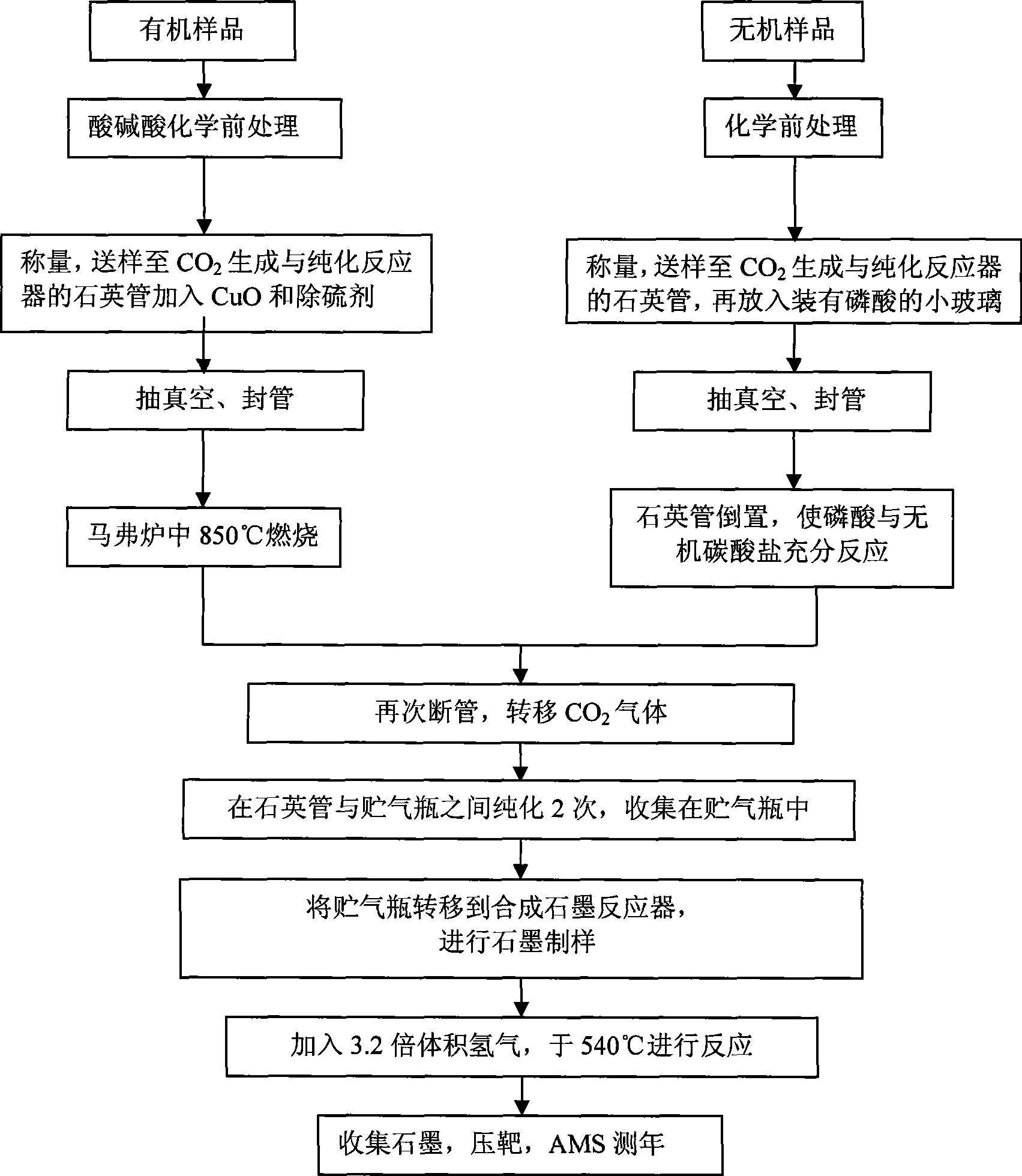
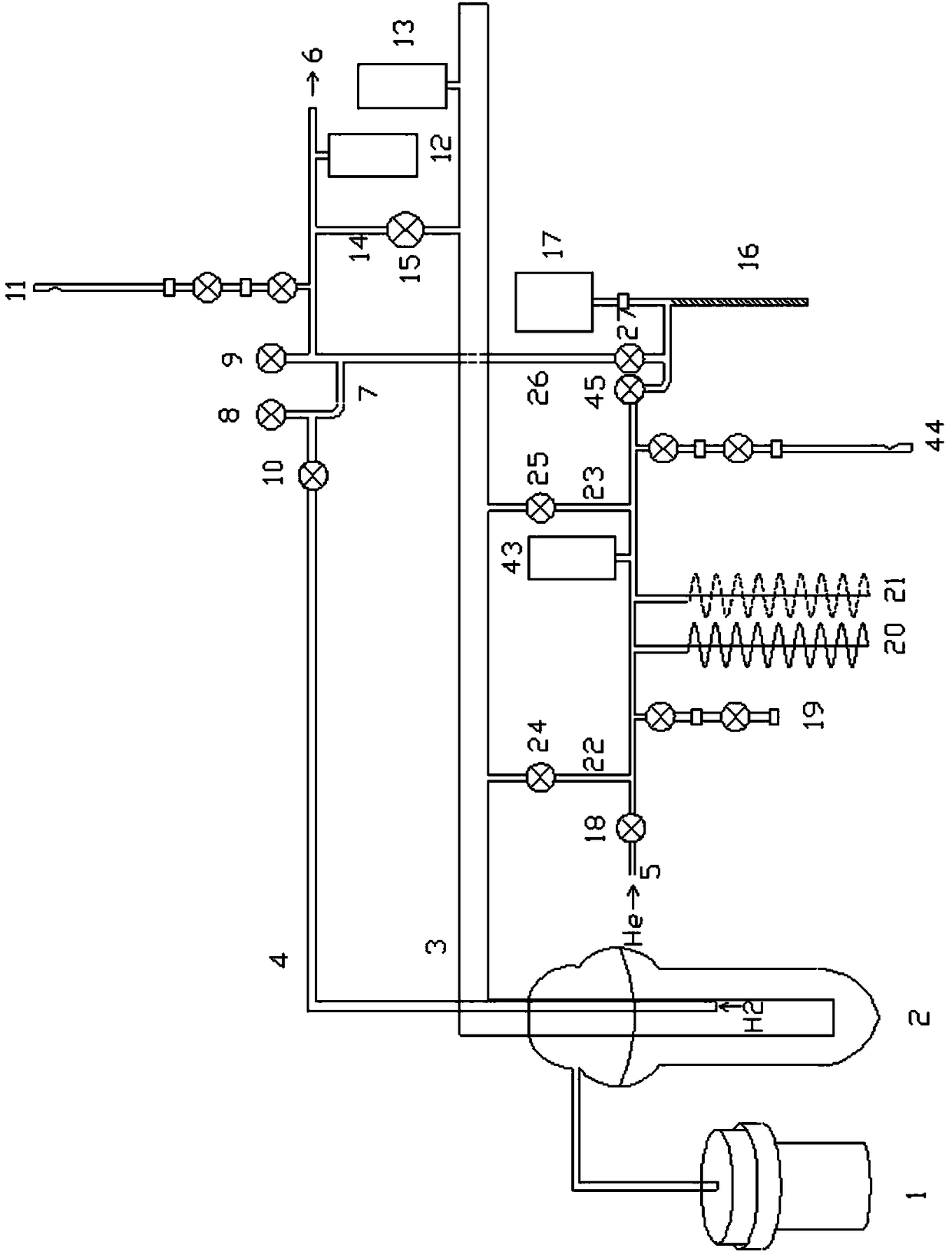
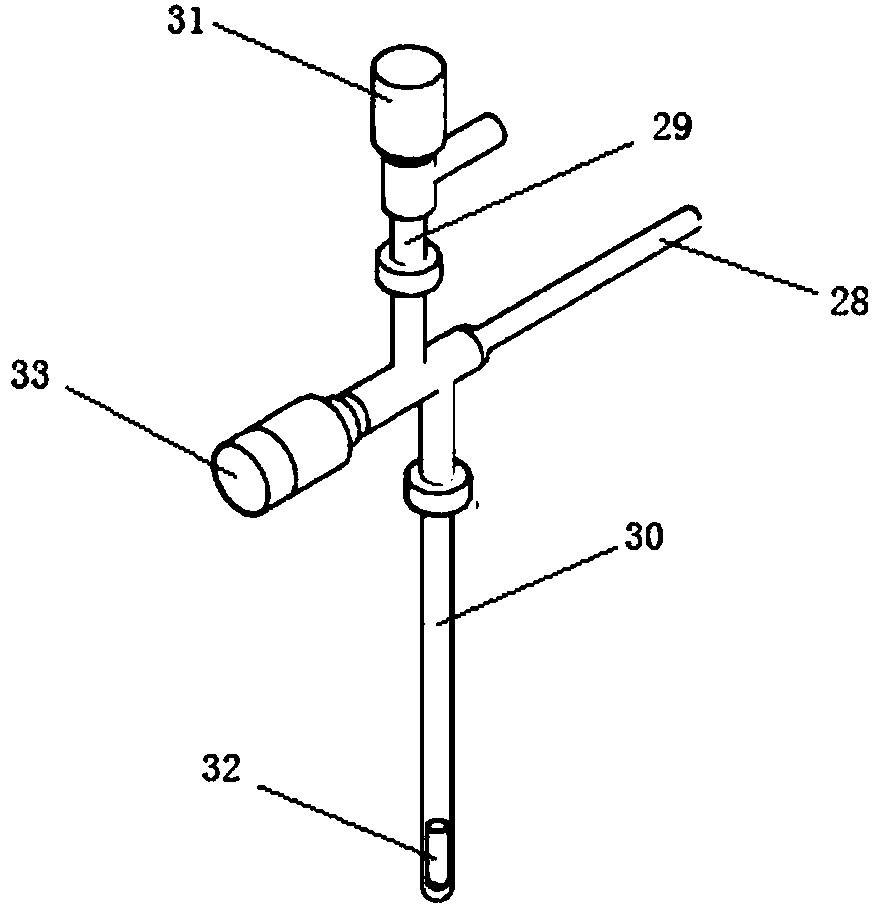
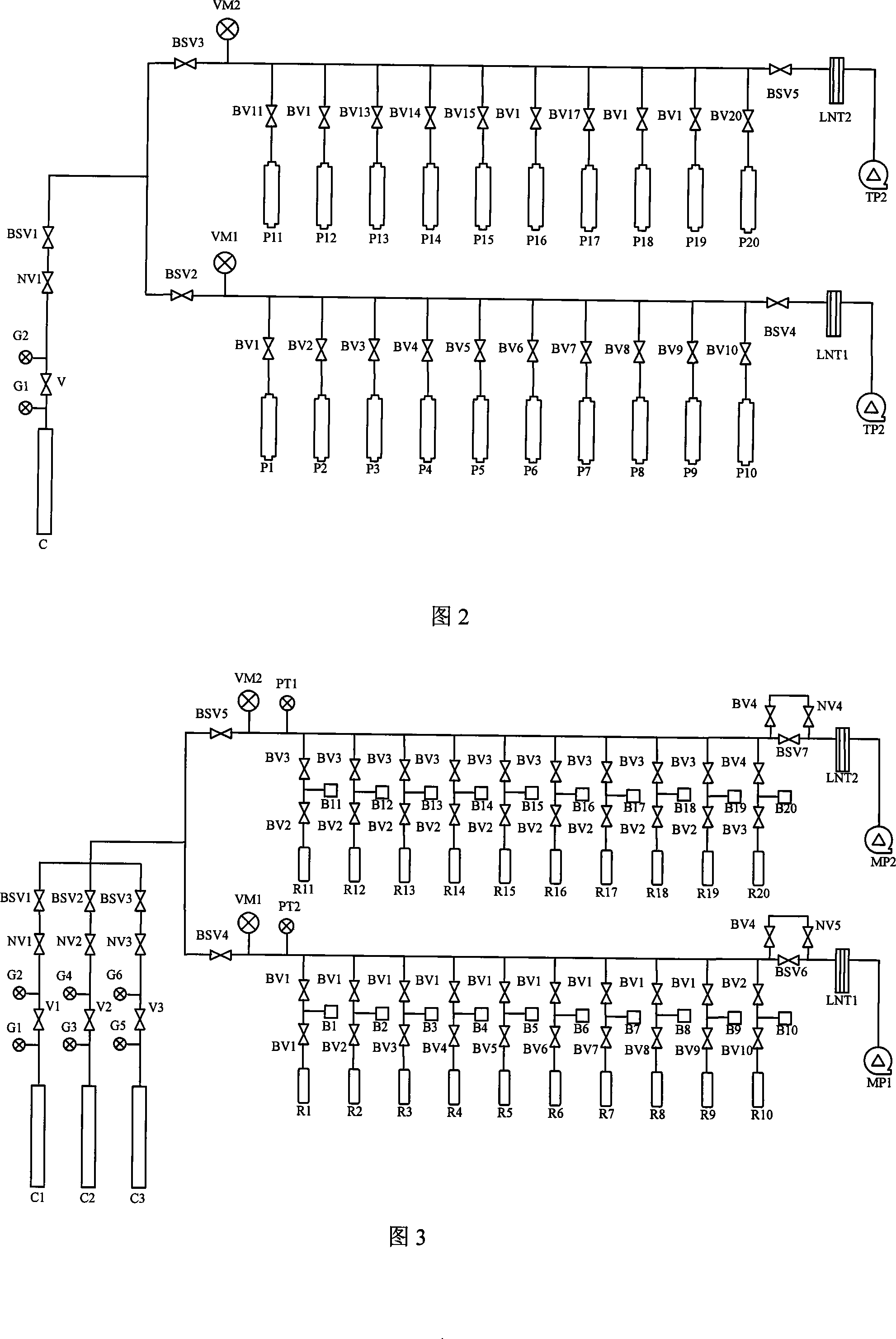
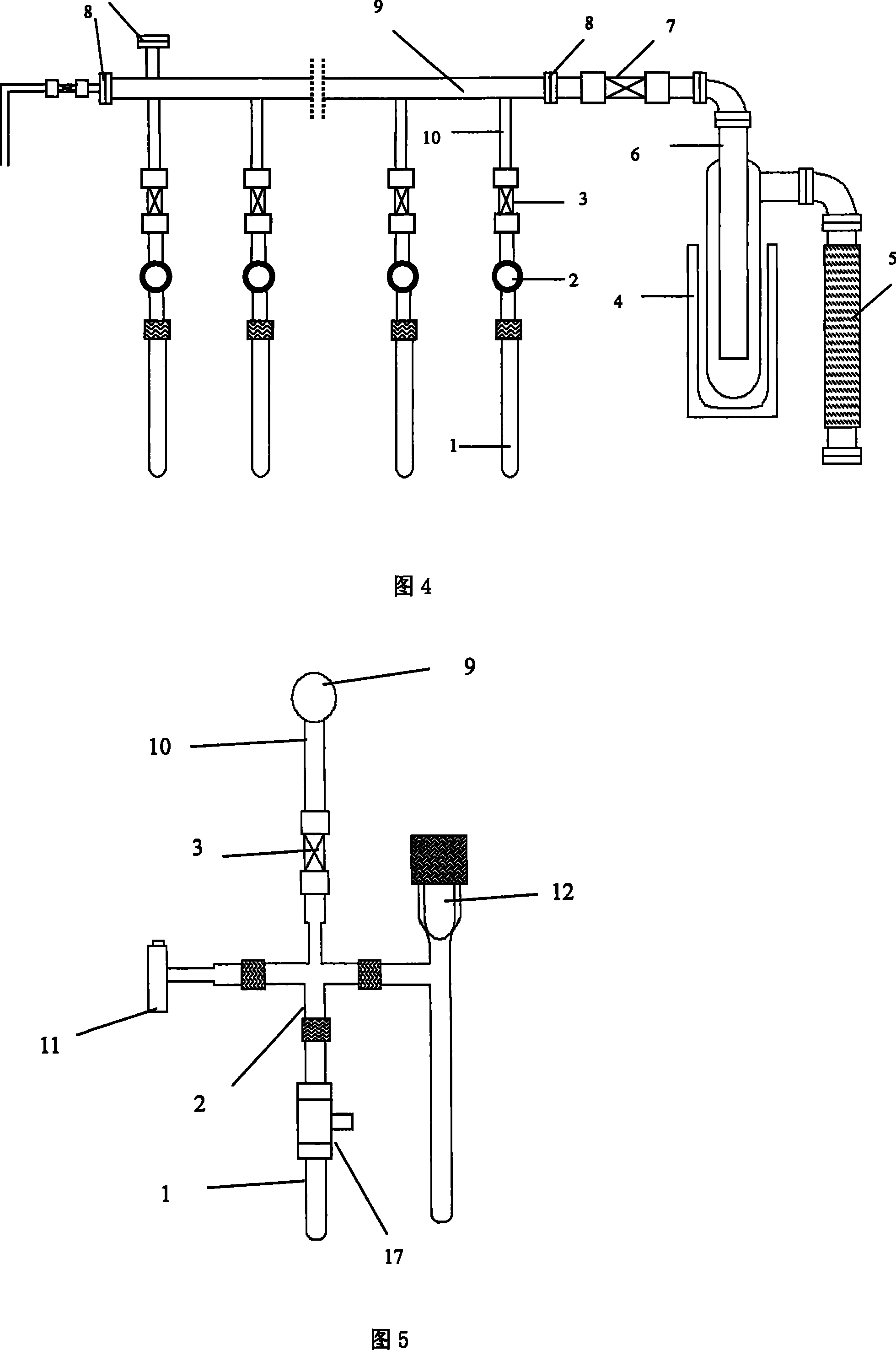
Accelerator mass spectrometry carbon-14 dating and sampling device
ActiveCN101446527AAccurate temperature controlAccurately monitor the progress of the reactionPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGas cylinderEngineering
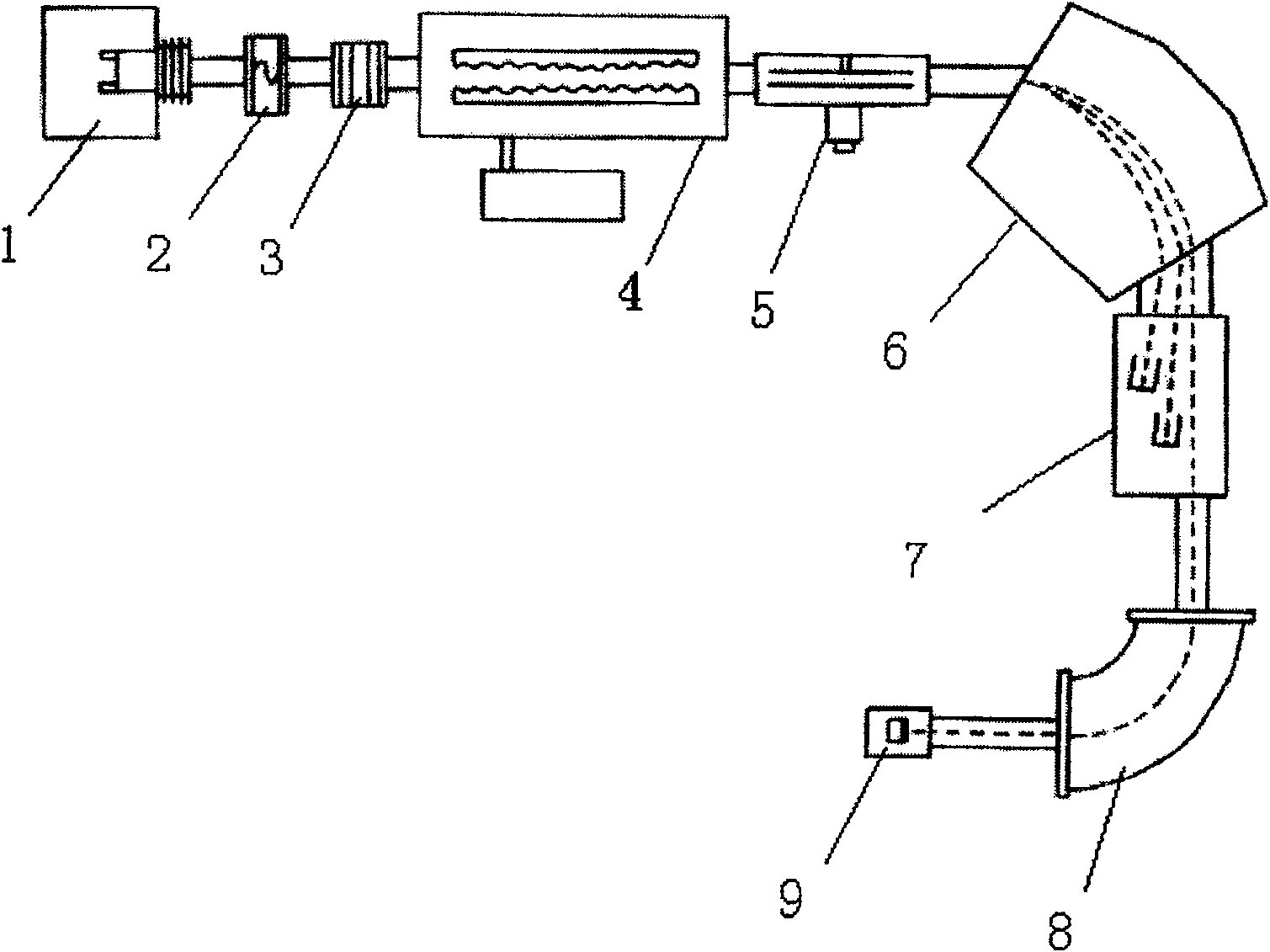
The invention discloses an accelerator mass spectrometry carbon-14 dating and sampling device, and belongs to the technical field of radiocarbon (<14>C) dating. The device comprises a CO2 generation and purification apparatus and a graphite synthesis apparatus, wherein, a reactor of the CO2 generation and purification apparatus comprises a vacuum joint, a quartz tube, a quartz tube cutter, an air bottle and a ball valve; the vacuum joint is provided with four interfaces, the upper interface is connected with the ball valve, the rear interface is connected with a pressure sensor, the front interface is movably connected with the air bottle, the lower interface is connected with the quartz tube or the quartz tube cutter; and the reactor of the graphite synthesis apparatus comprises the two quartz tubes, a vacuum joint and a ball valve, the vacuum joint is also provided with four interfaces, wherein, the upper interface is connected with the ball valve, the rear interface is connected with a pressure sensor, and the lower interface and the front interface are respectively connected with two quartz tubes. The device is applicable to preparing a small graphite target sample, and the obtained target material has excellent performance.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Polyacrylic acid (SALT), polyacrylic acid (SALT)-based water-absorbing resin, and process for producing same
A polyacrylic acid (salt), or a polyacrylic acid (salt)-based water-absorbing resin, contains a tracer for detecting various troubles in the water-absorbing resin during the period from the production of the water-absorbing resin to the use and discard thereof by a consumer. The polyacrylic acid (salt)-based water-absorbing resin has a stable carbon isotope ratio, as determined by accelerator mass spectrometry, of less than −20% and a radioactive carbon content of 1.0×10−14 or mole. The polyacrylic acid (salt)-based water-absorbing resin has: a CRC of 10 [g / g] or mole; an AAP of 20 [g / g] or mole; an Ext of 35 wt. % or less; a content of residual monomers of 1,000 ppm or less; a PSD in which the proportion of particles having a particle diameter of 150 μm or larger but less than 850 μm is 90 wt. % or more; and an FSR of 0.15 [g / g / s] or more.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Quantification of analytes using accelerator mass spectrometry
The invention provides a calibrating method for use in a method of determining the quantity of an analyte labeled with an accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) isotope in a test sample. The samples can include, for example, urine, faeces, plasma or blood. The analyte can be, for example, a drug or metabolite of a drug.
Owner:XCELERON INC
Method and apparatus for separation of isobaric interferences
ActiveUS7439498B2Reduction size and costAvoid reactionTime-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsTerminal voltageMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
This invention relates to a method and apparatus for separation of rare stable or radioactive isotopes from their atomic or molecular isobars in mass spectrometry (MS). In the present invention, the approach taken to removing atomic isobars utilizes a high transmission device for decelerating ions in combination with low energy reactions, such as ion-molecule reactions or near resonant electron transfer, in RF ion guides. The isobar is selectively depleted by electron transfer or other reactions between negative ions and gaseous targets in pressurized RF ion guides at low energies. The energy is controlled in such a way as to prevent reaction of the ion of interest while inducing reactions with the undesired isobar interference. The technique is of particular relevance to accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) for which it allows substantial reductions in the necessary terminal voltage. The effect is to allow reductions in the size and cost of AMS installations.
Owner:LITHERLAND ALBERT EDWARD +7
Method for measuring isotopic abundance ratio of uranium in particles through accelerator mass spectrometry
InactiveCN104535598AImprove accuracyEliminate distractionsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionMass spectrometry measurementMicroparticle
The invention relates to a control device for the irradiation dose of an irradiation device, and provides a method for measuring the isotopic abundance ratio of uranium in particles through accelerator mass spectrometry. The method aims to solve the problems that an analysis method for the isotopic abundance ratio of uranium in existing environment sample particles is not high in analysis result accuracy, and interference is serious in the analysis process. The method comprises the following steps that 1, the sample particles are separated from a carrier and transferred to a graphite flake through ultrasonic oscillation; 2, the sample particles are transferred into a scanning electron microscope; 3, the uranium-bearing particles are found; 4, the uranium-bearing particles are dissolved; 5, a target is manufactured; 6, ruling is carried out; 7, accelerator parameters needed by each uranium isotope are determined; 8, the counting rate of each uranium isotope is measured; 9, the isotopic abundance ratio of the uranium is calculated. The problem that isotopic abundance ratio analysis of the uranium in the particles has polyatomic ion interference is solved, abundance sensitivity is obviously improved, the obtained analysis result is accurate, and the defect in an existing analysis method is overcome.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Isotopic tracing method for monitoring cancer cell osseous metastasis
ActiveCN104698063ABest Separation SchemeExtended marking timeIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSocial benefitsCancer cell
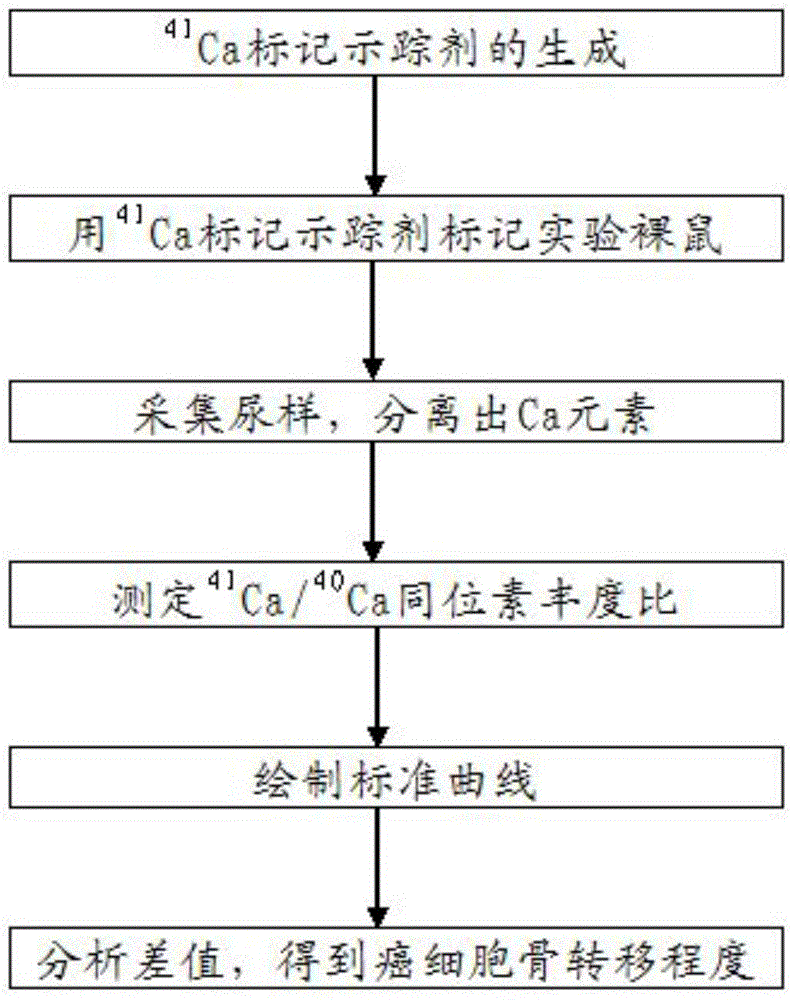
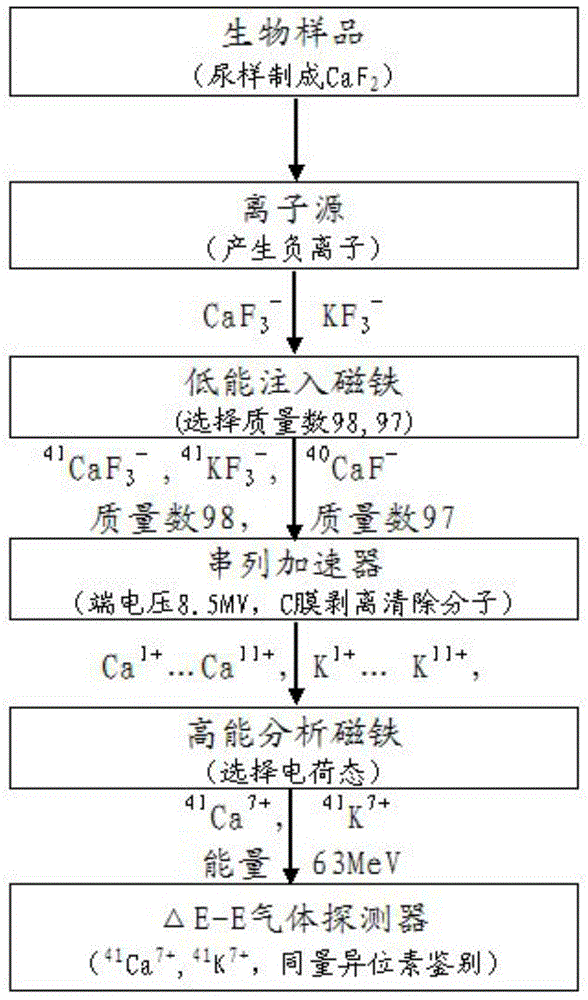
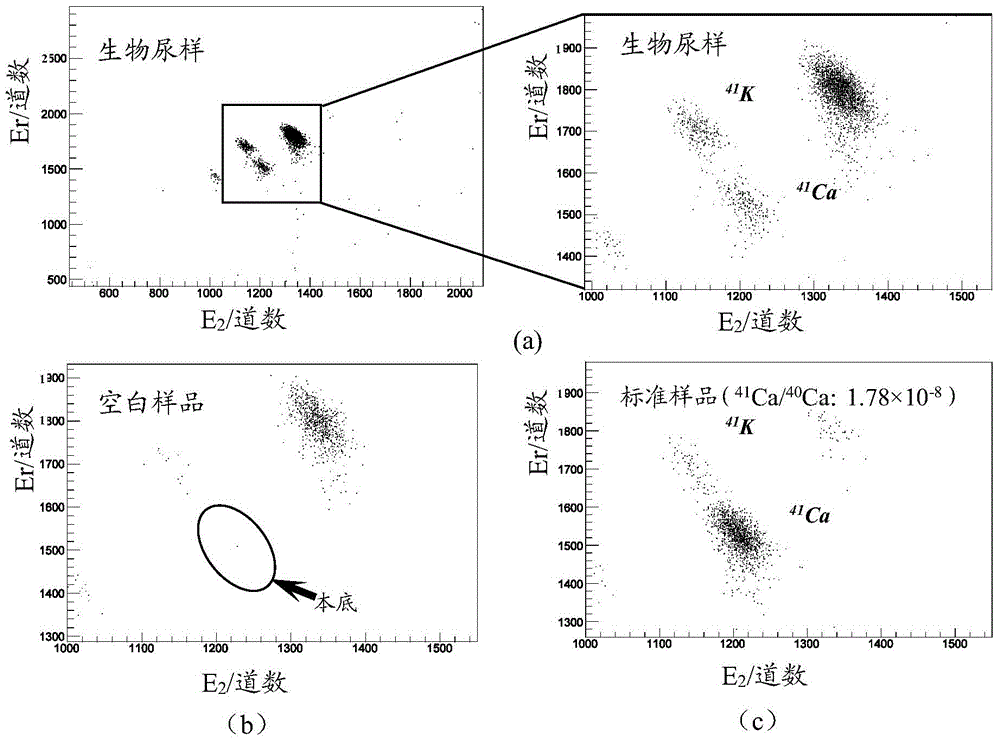
The invention discloses an isotopic tracing method for monitoring cancer cell osseous metastasis. The method refers to a measurement method by taking 41Ca as a tracer agent and taking accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) as a tracer agent and is used for monitoring the occurrence, development and resolution processes of the cancer cell osseous metastasis, and belongs to the technical field of nuclear technologies. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) generating a 41Ca marked tracer agent; (2) marking an experimental nude mouse by using the 41Ca marked tracer agent; (3) collecting a urine sample of the nude mouse in the step (2), and separating the element Ca; (4) measuring the 41Ca / 40Ca isotope abundance ratio in the calcium fluoride powder obtained in the step (3); and (5) drawing a standard curve; and (6) analyzing the difference, so as to obtain the cancer cell osseous metastasis degree. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the problems that the sensitivity of a conventional monitoring means is relatively low and the early monitoring of the cancer cell osseous metastasis is difficultly realized are solved, and the method has high clinical application values and social benefits.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
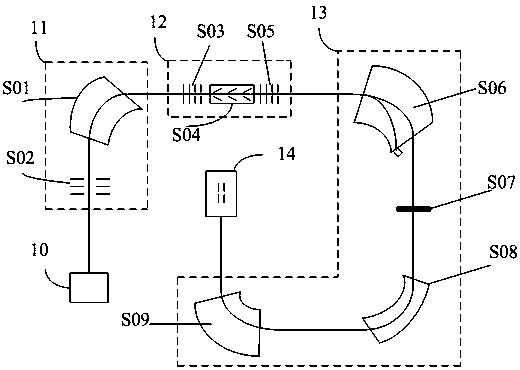
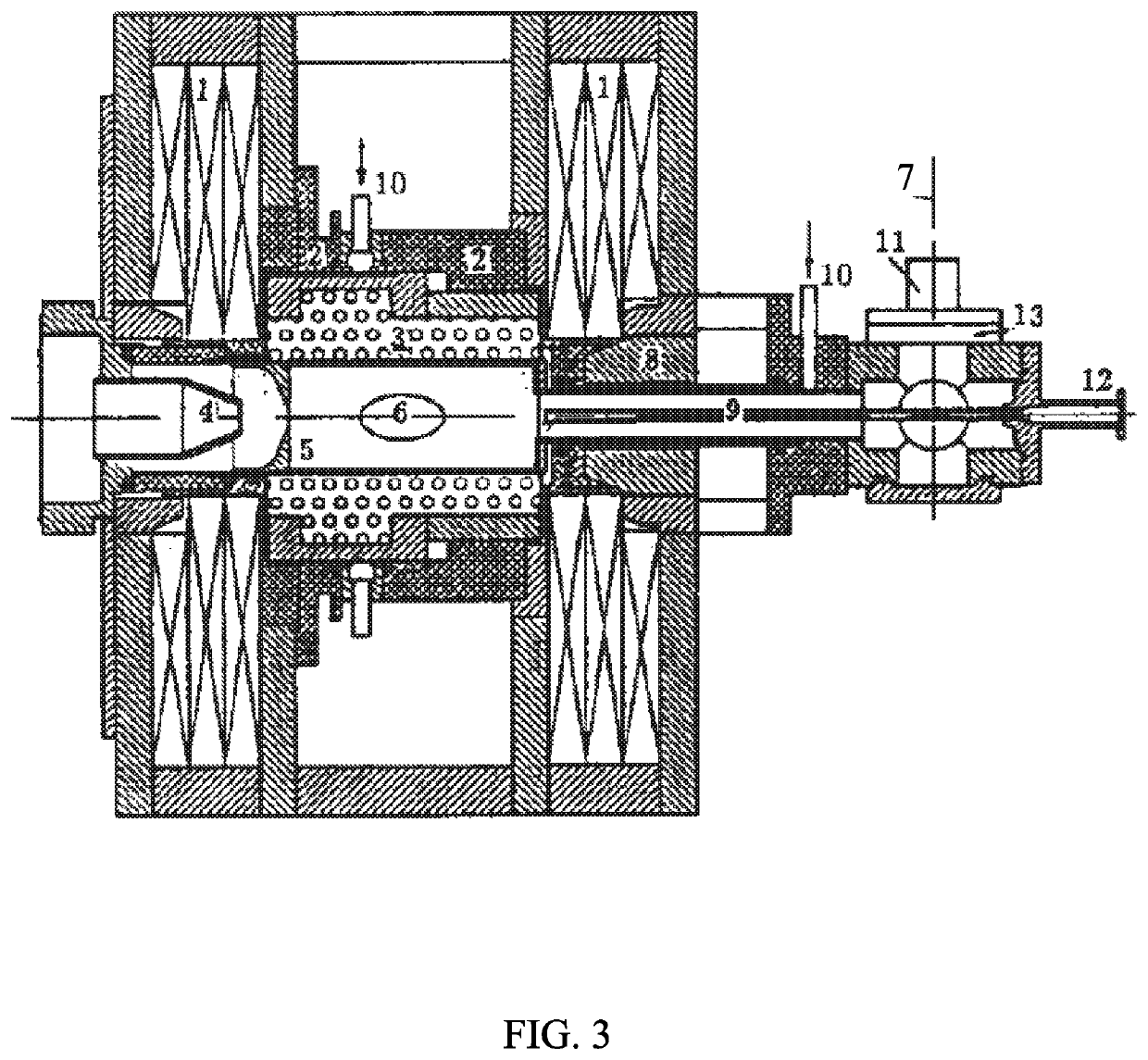
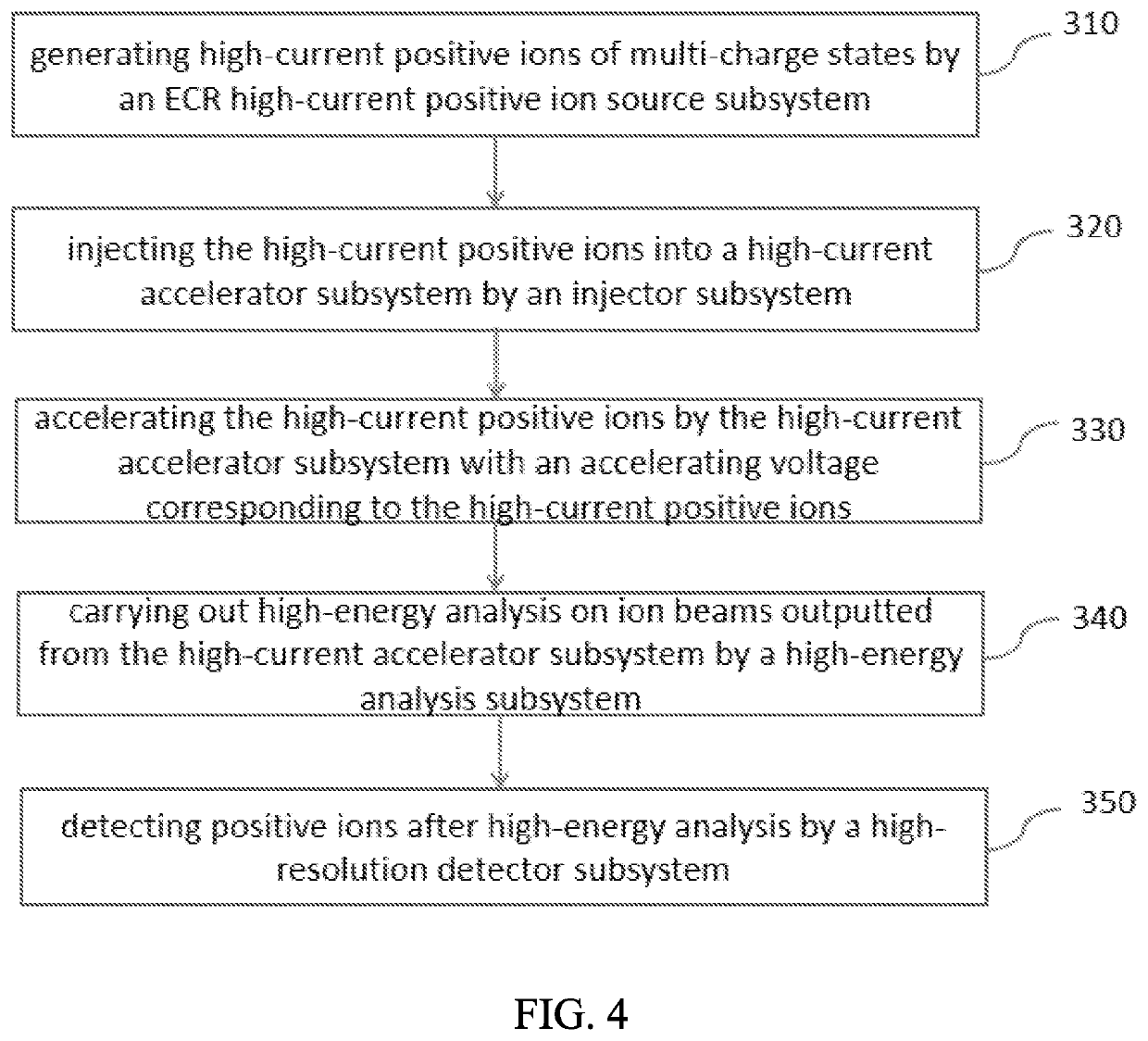
Accelerator mass spectrometry method and system
ActiveCN109830423ABeam highIncrease beam intensityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIon sources/gunsMass spectrometry measurementResolution (mass spectrometry)
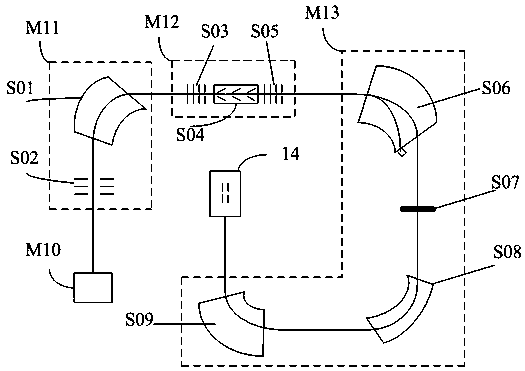
The embodiment of the application provides an accelerator mass spectrometry system and relates to the technical field of AMS. The accelerator mass spectrometry system comprises an ECR strong current positive ion source subsystem, an injector subsystem, a strong current accelerator subsystem, a high-energy analysis subsystem and a high-resolution detector subsystem which are successively connected.The ECR strong current positive ion source subsystem is configured to generate strong current positive ions in multiple charge states. The strong current accelerator subsystem is configured to directly accelerate the strong current positive ions. The accelerator mass spectrometry system has the advantages of strong beam current, high total efficiency, and good background lowering capability, andcan greatly improve the abundance sensitivity of the spectrometry.
Owner:QIXIANHE (BEIJING) TECH CO LTD
Mass spectrometry system with molecular dissociation and associated method
ActiveUS8791410B2Effective destructionLess spaceMaterial analysis by optical meansIon sources/gunsMass analyzerMass spectrometry imaging
A mass spectrometry system based on the general principle of accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) is disclosed. An ion source (10) generates a beam (B) of ions having a negative charge state. A first mass analyzer (20) transmits only ions having a predetermined mass. The ions are passed through a stripper target (80) comprising helium and / or hydrogen as a stripping gas to change the charge state of said ions from negative to positive charge and to dissociate molecular ions by collisions. A second mass analyzer (110, 130) transmits ions in charge state 1+ having the predetermined mass, which are detected by a detector (140). By using helium and / or hydrogen gas and detecting ions in charge state 1+, it becomes possible to use kinetic energies below 200 keV without excessive transmission losses due to angular straggling. At sufficiently low energies, no additional acceleration is required after ions have been extracted from the ion source. In alternative embodiments, no mass selection is carried out before charge exchange takes place.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Accelerator mass spectrometry device for simultaneously measuring isotopes
ActiveUS10395910B2Promote popularizationSimple structureIon sources/gunsStatic spectrometersMass analyzerAccelerator mass spectrometry
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
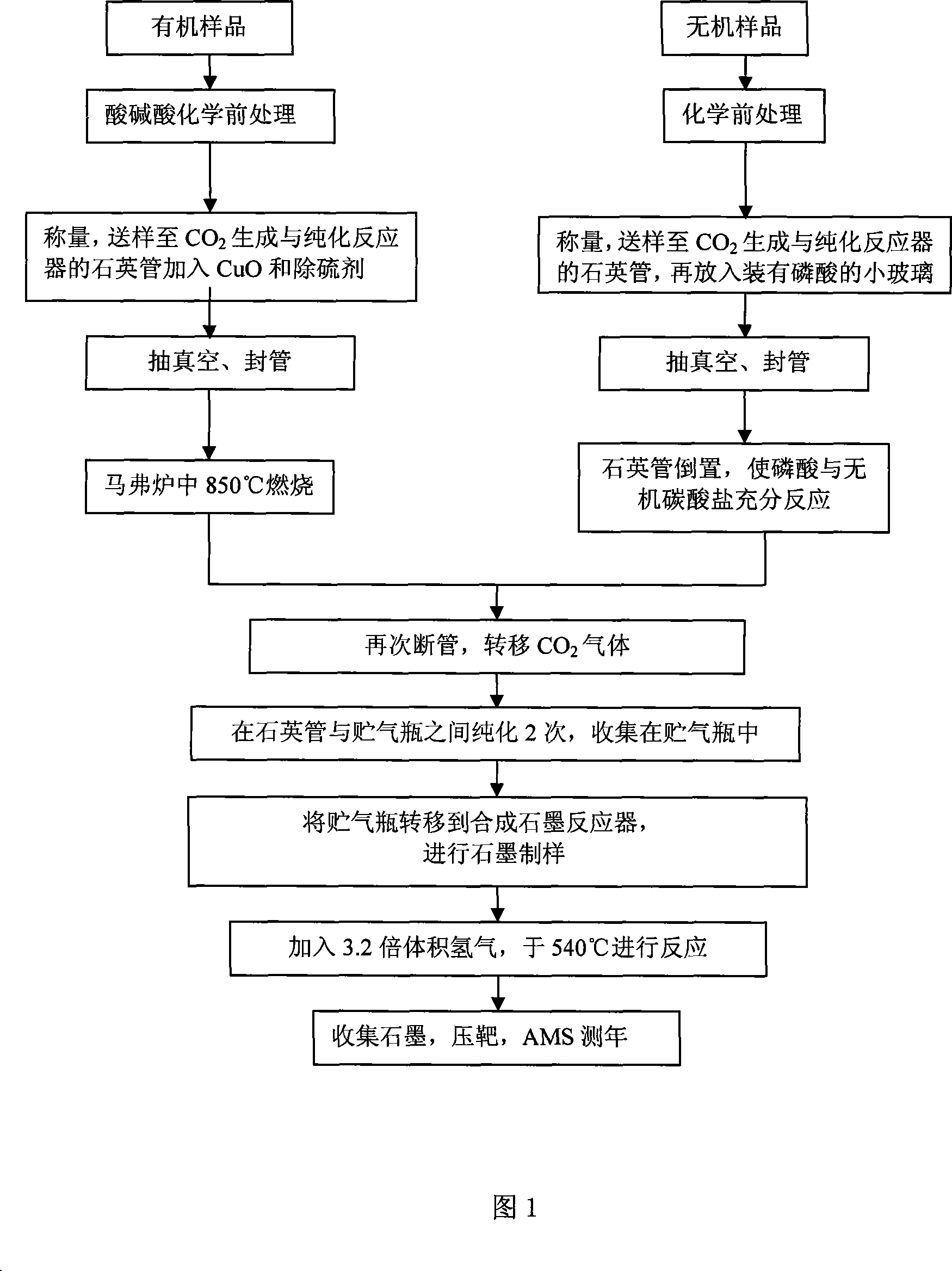
<14>C sample preparation system for both hydrogen method and zinc method
PendingCN108303297AImprove the level ofEasy to usePreparing sample for investigationHydrogenVacuum pressure
The invention relates to a <14>C sample preparation system for both hydrogen method and zinc method. The main application of the <14>C sample preparation system is to prepare a <14>C sample and supplyraw materials to an AMS (accelerator mass spectrometry) accelerator. After a primary sample is taken, the <14>C sample can be prepared by the system with the hydrogen method and the zinc method. Thesystem adopts glass as a main structural material, and mainly comprises four parts: a vacuum power treatment part, a sample vacuumization part, a CO2 purification part and a CO2 reduction part. The system comprises main components as follows: reaction devices, valves, cold traps, resistance wires, pressure vacuum gauges, a muffle furnace, a reaction furnace and the like. The preparation system hasthe characteristics as follows: the sample can be prepared with the hydrogen method and the zinc method simultaneously, a high-vacuum system is utilized efficiently, the system is high in safety coefficient, relatively low in manufacturing cost, compact in structure and convenient to operate, mutual pollution is avoided, and working level of an assembly line is improved.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Rapid online analyzer for <14>C-AMS
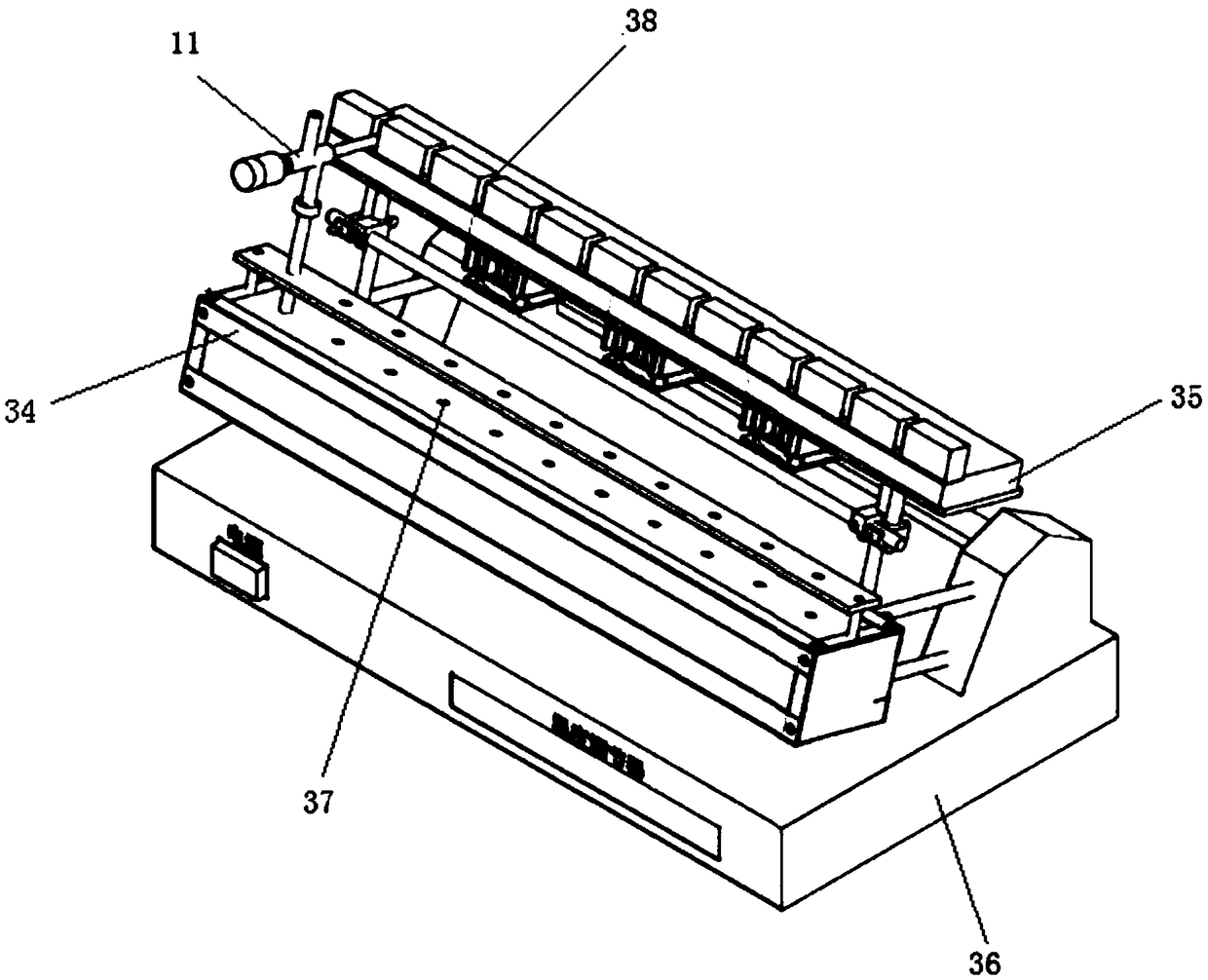
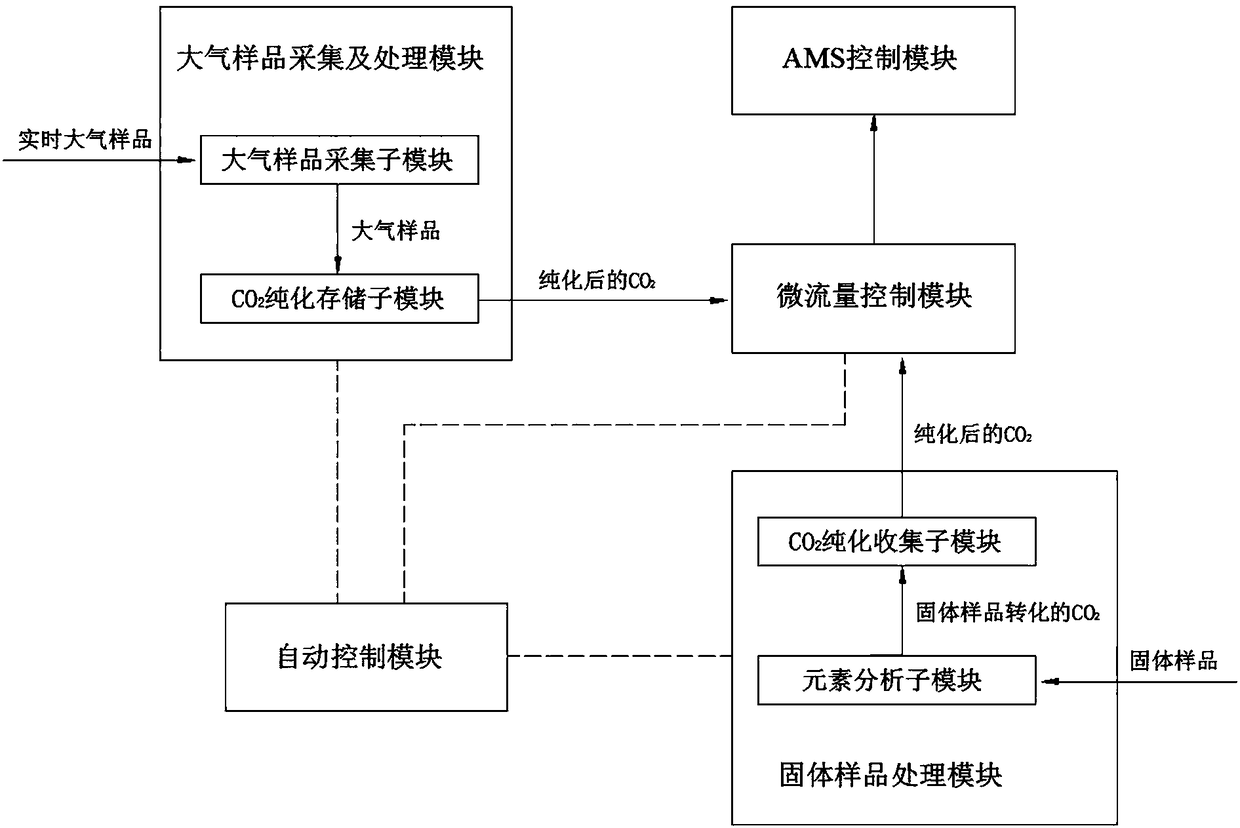
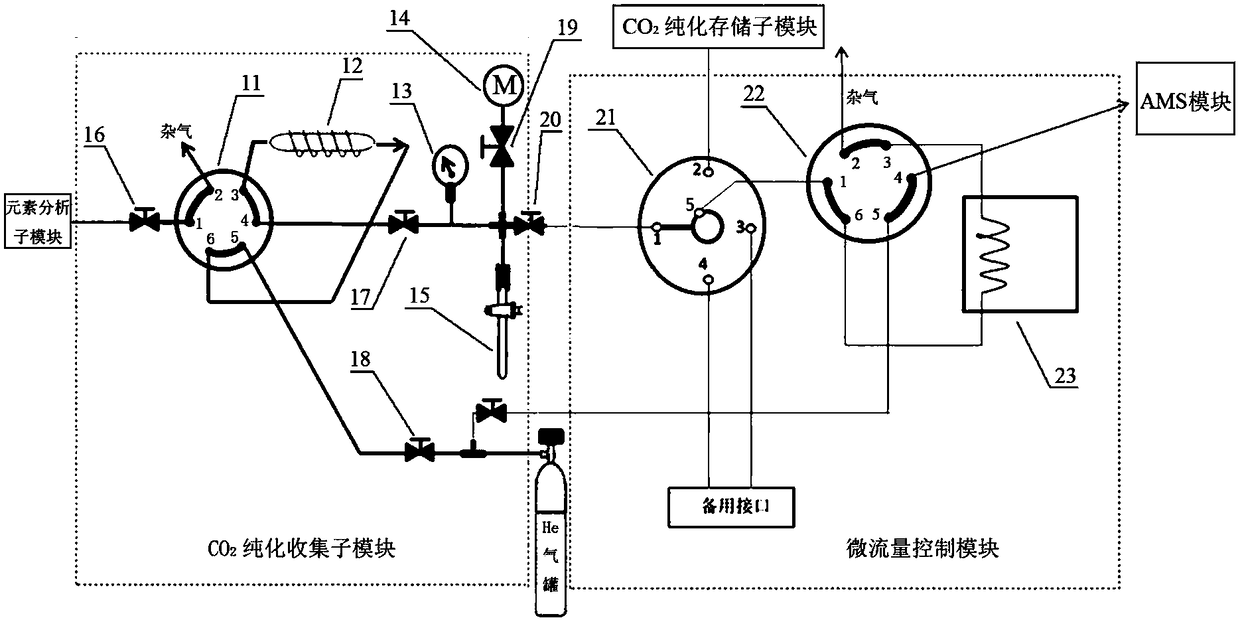
InactiveCN108226274AEfficient analysisReduced Possibility of ContaminationChemical analysis using combustionDynamic spectrometersAutomatic controlAccelerator mass spectrometry
The invention discloses a rapid online analyzer for <14>C-AMS (Accelerator Mass Spectrometry). The rapid online analyzer comprises a solid-sample treating module, an atmosphere-sample collecting and treating module, a micro-flow control module, an AMS module and an automatic control module. The rapid online analyzer disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that sample preparation andAMS measurement are fused, not only can <14>C samples (including solid samples and atmosphere samples) be analyzed in a rapid and high-efficiency manner and can the possibility that the samples are polluted be reduced, but also the capabilities of analyzing and testing the <14>C samples can be greatly improved for an AMS laboratory in a limited machine hour, and meanwhile another scheme with faster speed and stronger anti-pollution capability also can be provided for measuring extremely-trace samples (the content is a few of micrograms); the solid original samples are directly transformed intoCO2 gas to be subjected to AMS measurement without being specially treated by a chemical laboratory, the atmosphere samples can be collected in real time for AMS analysis, so that the process of firstly preparing the samples and then carrying out <14>C-AMS measurement in the original special chemical laboratory is completely changed.
Owner:INST OF EARTH ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Sample preparation method
InactiveUS7368710B2Cost effectiveMinimal amountTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationCompound (substance)Isotope
Owner:XCELERON LTD
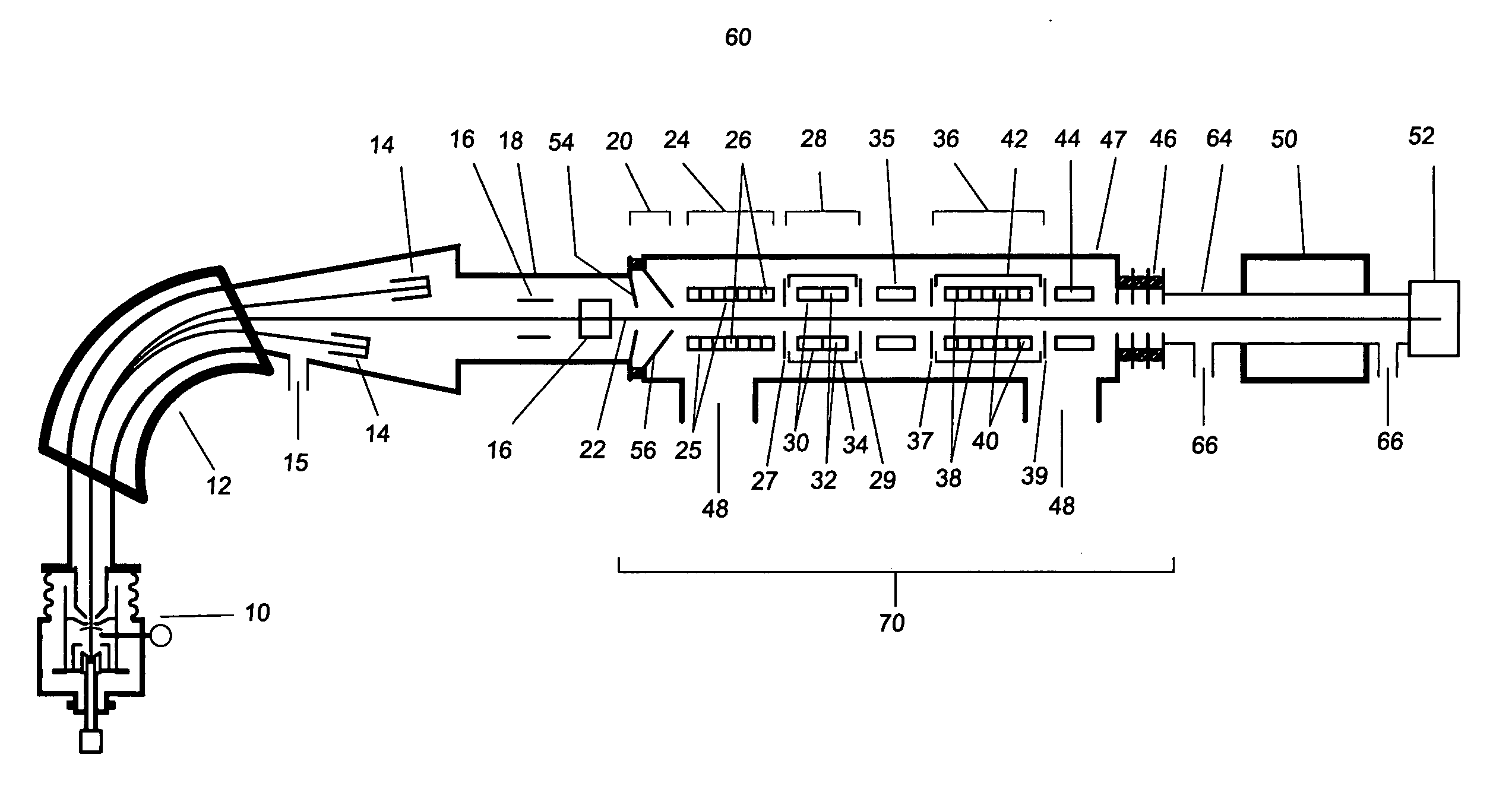
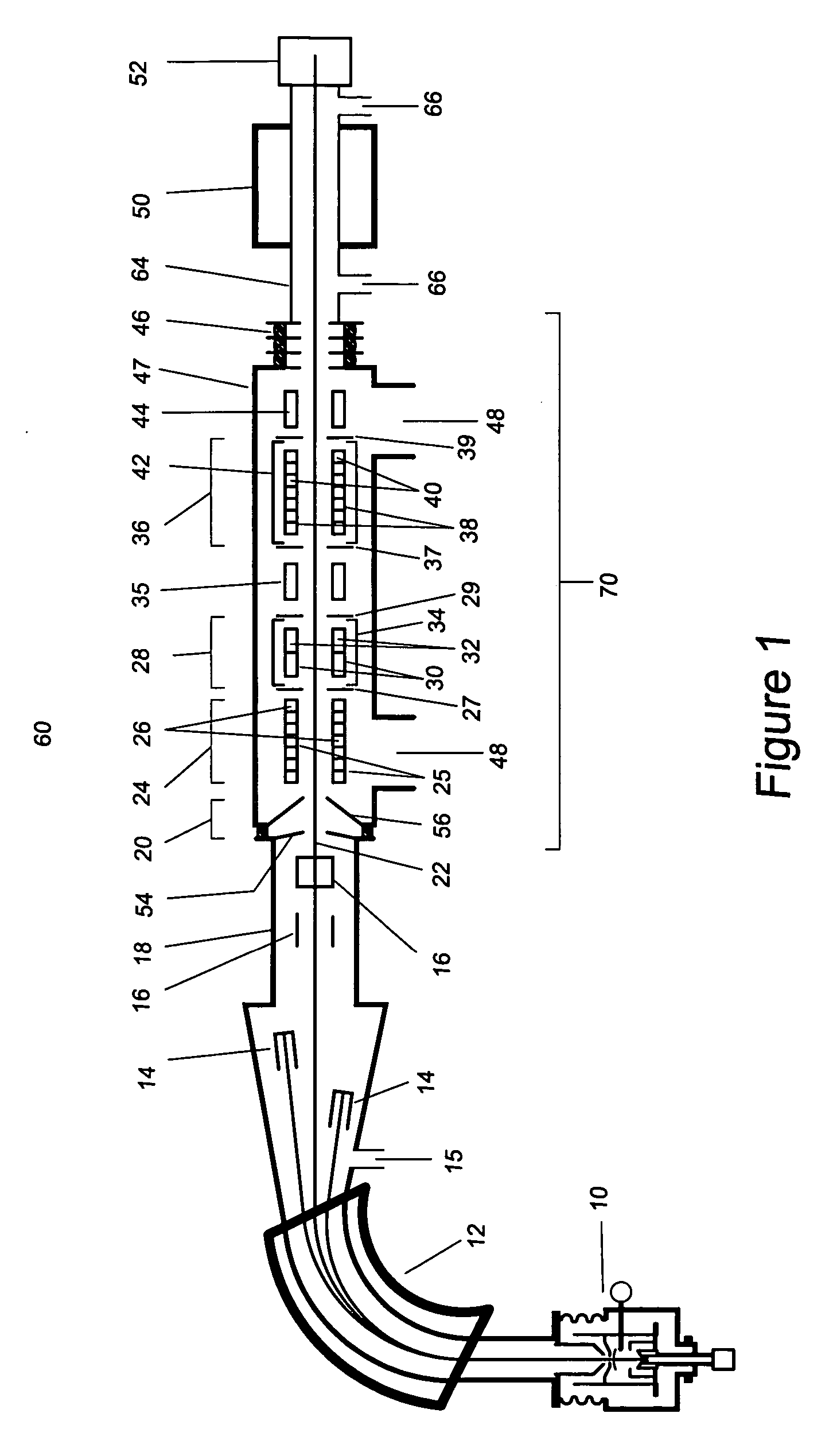
Accelerator mass spectrometry system and associated method
ActiveUS20190385830A1Lower Level RequirementsEfficient and cost-effectiveStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTandem acceleratorMass analyzer
An accelerator mass spectrometry system for measuring an isotopic ratio of a chemical element in a sample. The system includes an ion source generating a beam of negative ions of the chemical element containing ions of first and second isotopes of the chemical element, a first analyzer section, comprising a first mass analyzer; a tandem accelerator comprising a first accelerating section, a charge stripping section for converting the negative ions into positive ions, and a second accelerating section behind the charge stripping section. A second analyzer section includes a second mass analyzer and an electrostatic analyzer; a particle detector; and a controller system configured to control the first mass analyzer section and the second analyzer section such that the ions of the first and second isotopes traverse the tandem accelerator and ions of only one of the first and second isotopes enter the particle detector. An additional analyzer is located in between the charge stripping section and the second accelerating section and is configured to receive positive ions that have exited the charge stripping section and to separate positive ions having a charge state corresponding to a predetermined charge-state value from positive ions having a charge state not corresponding to the predetermined charge-state value, so as to transmit ions with different charge states in mutually different directions such that only ions having a charge state corresponding to the predetermined charge-state value are transmitted towards the particle detector.
Owner:HIGH VOLTAGE ENG EUROPA
Method for inversion of earthquake generation time by using stalagmite
InactiveCN106093175AHard natureEasy to storeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAccelerator mass spectrometryGeneration time
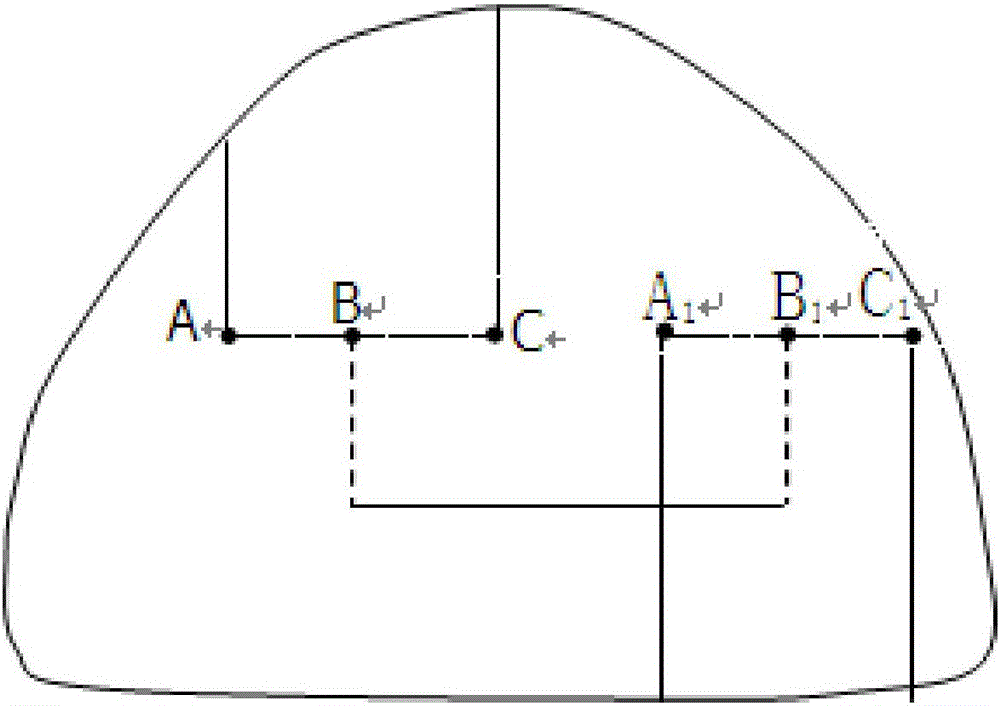
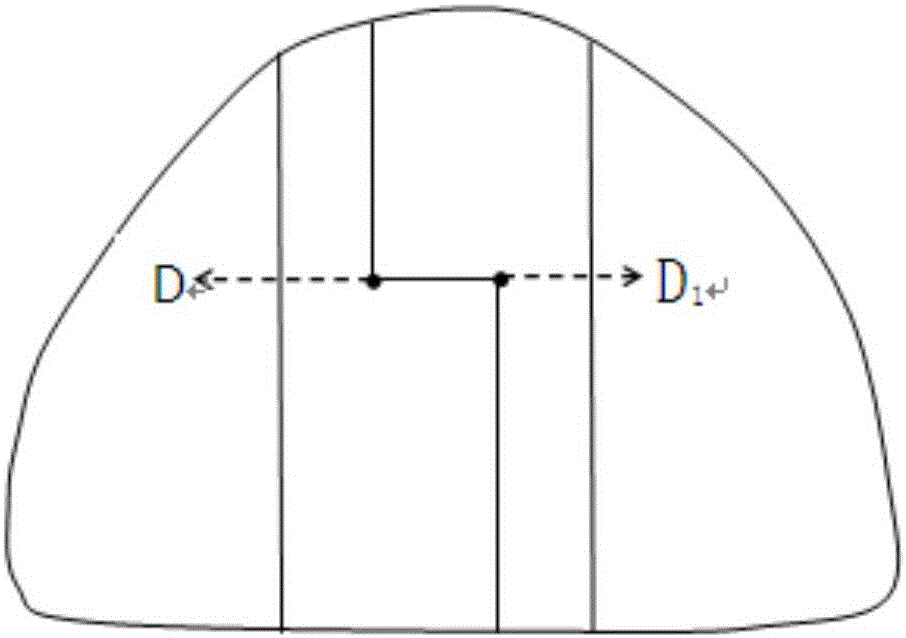
The invention discloses a method for inversion of earthquake generation time by using a stalagmite. The method comprises the following steps: a step 1, a stalagmite which has fractures and displacement or a stalagmite whose core is dislocated is used as a measurement object; a step 2, three sampling sites A, B and C which are equidistant are selected on a first ruptured surface of the stalagmite with fractures and displacement, and three sampling sites A1, B1 and C1 which are equidistant are selected on a second ruptured surface; a step 3, samples are acquired on each sampling site and preserved with packaging; a step 4, an accelerator mass spectrometry AMS is used for determining 14C deposition time of the acquired samples; a step 5, earthquake generation time is calculated. The method solves the technical problems of high cost and low measuring precision and the like existed in determination of earthquake generation time in the prior art.
Owner:INST OF GEOCHEM CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Online accelerator mass spectrometry measurement method and system
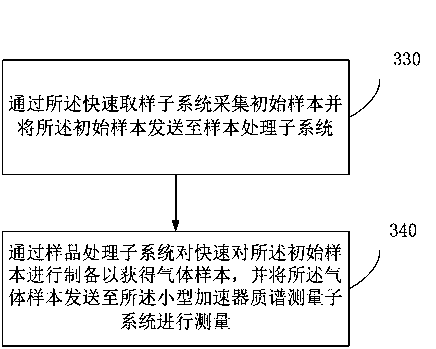
ActiveCN109841487AAchieve installationEasy to installSamples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass spectrometry measurementAccelerator mass spectrometry
An online accelerator mass spectrometry measurement system includes a fast sampling subsystem, a sample processing subsystem and a small accelerator mass spectrometry measurement subsystem. The fast sampling subsystem, the sample processing subsystem and the small accelerator mass spectrometry measurement subsystem are sequentially connected. The fast sampling subsystem is used for collecting an initial sample and sending the initial sample to the sample processing subsystem. The sample processing subsystem is used for preparing the initial sample quickly to obtain a gas sample and sending thegas sample to the small accelerator mass spectrometry measurement subsystem for measurement. The system of the invention has the following advantages: firstly, installation on a measurement site canbe realized; secondly, on-line or quasi-on-line measurement can be realized; and thirdly, the application scope of AMS (Accelerator Mass Spectrometry) can be expanded.
Owner:启先核(北京)科技有限公司
Quick measurement method of 14C based on accelerator mass spectrometry
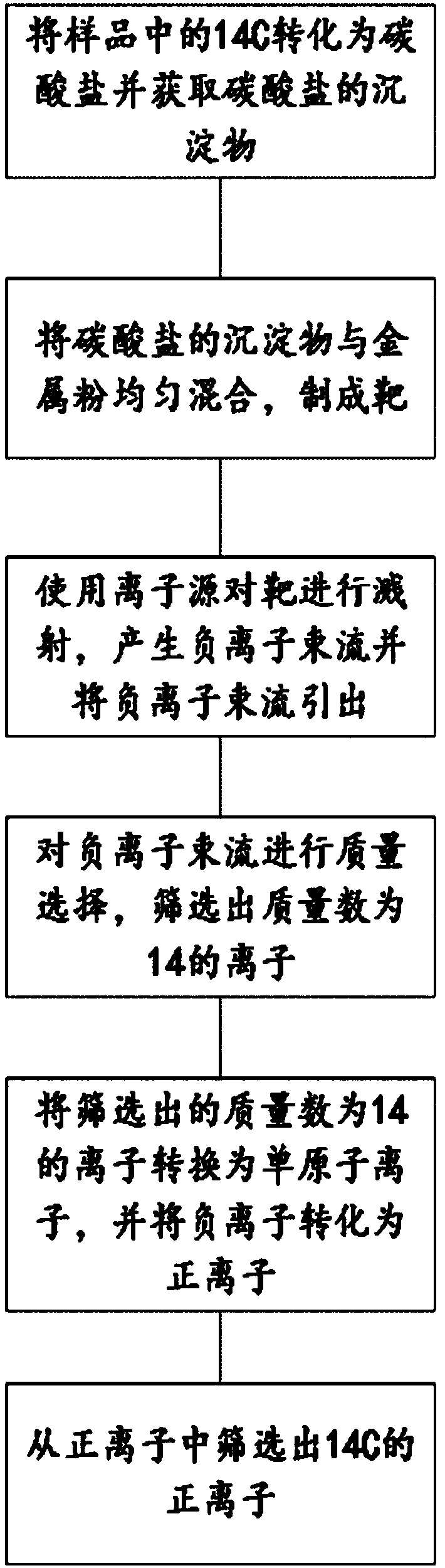
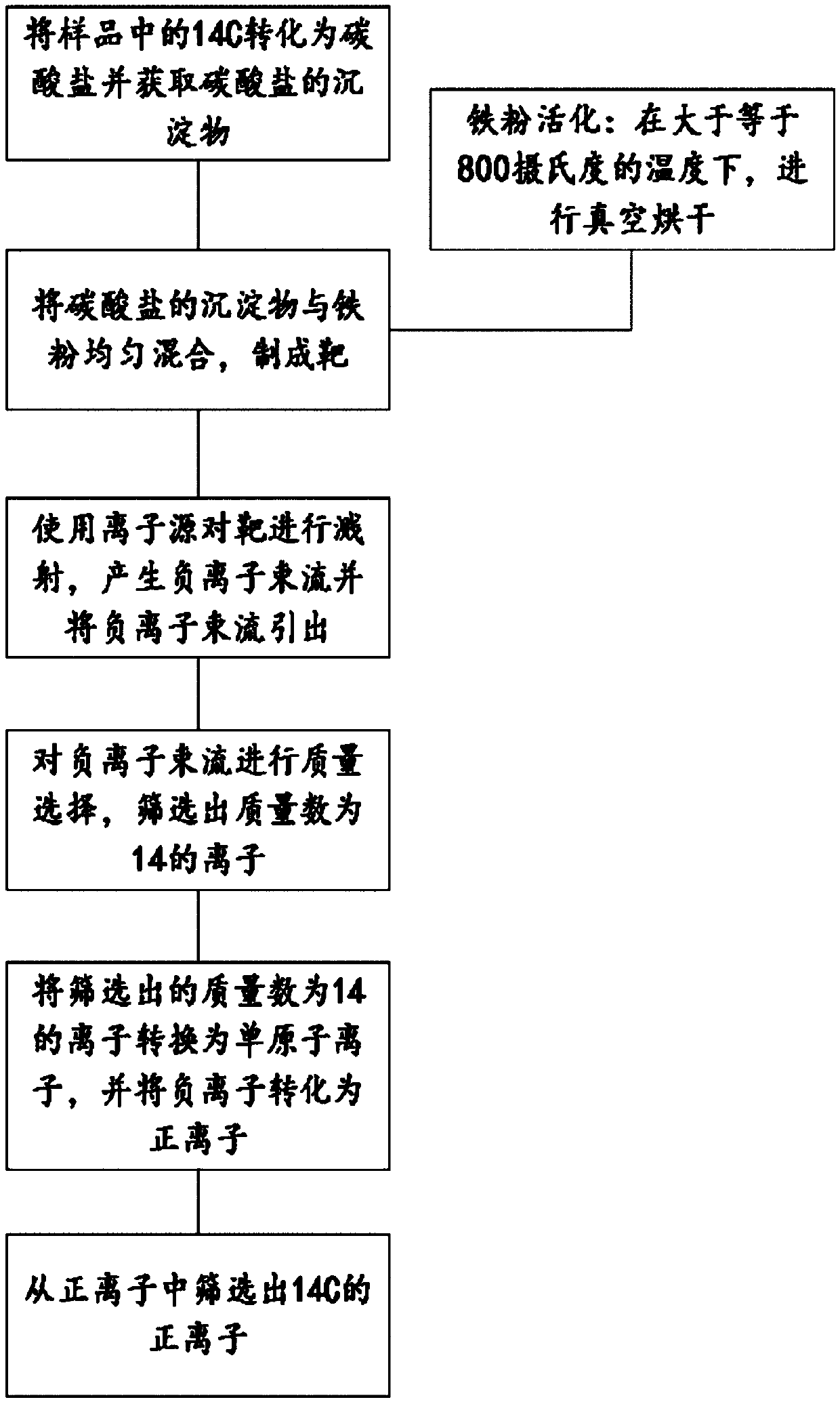
The invention provides a measurement method of 14C, comprising: converting 14C in a 14C-containing sample into a carbonate; acquiring carbonate deposit; mixing well the carbonate deposit with metal powder to obtain a target; using an ion source to sputter the target and generate an anion beam, and guiding out the anion beam; subjecting the anion beam to mass selection to screen out ions having themass number of 14; converting the screened ions having the mass number of 14 into monatomic ions, and converting the anions into cations; screening 14C cations from the cations; detecting the 14C cations.
Owner:INST OF HYDROGEOLOGY & ENVIRONMENTAL GEOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
Method for carrying out accelerator mass spectrometry measurement by using super halogen anions of beryllium
InactiveCN104181223ASuppress interferenceGuaranteed transmission efficiencyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass spectrometry measurementGas detector
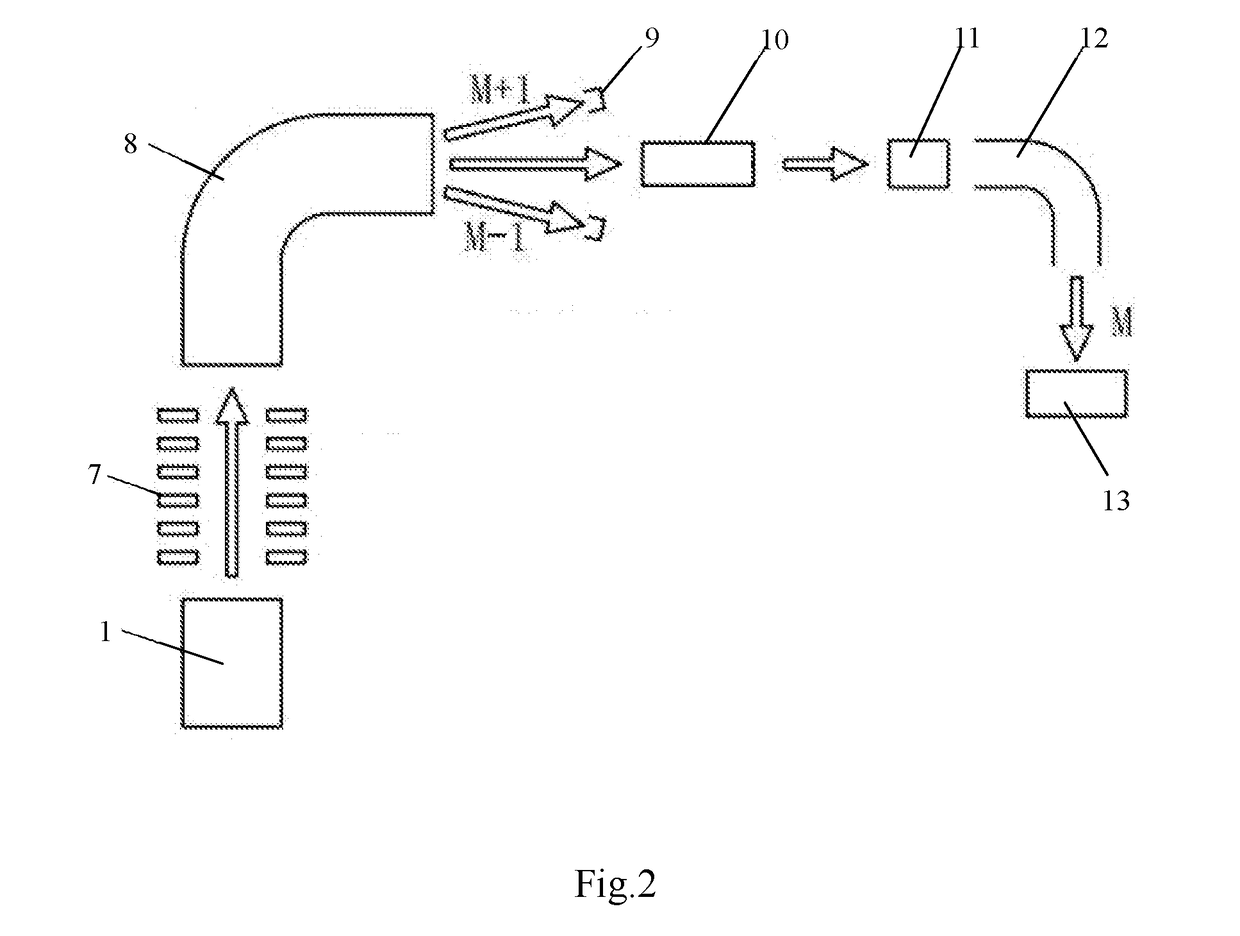
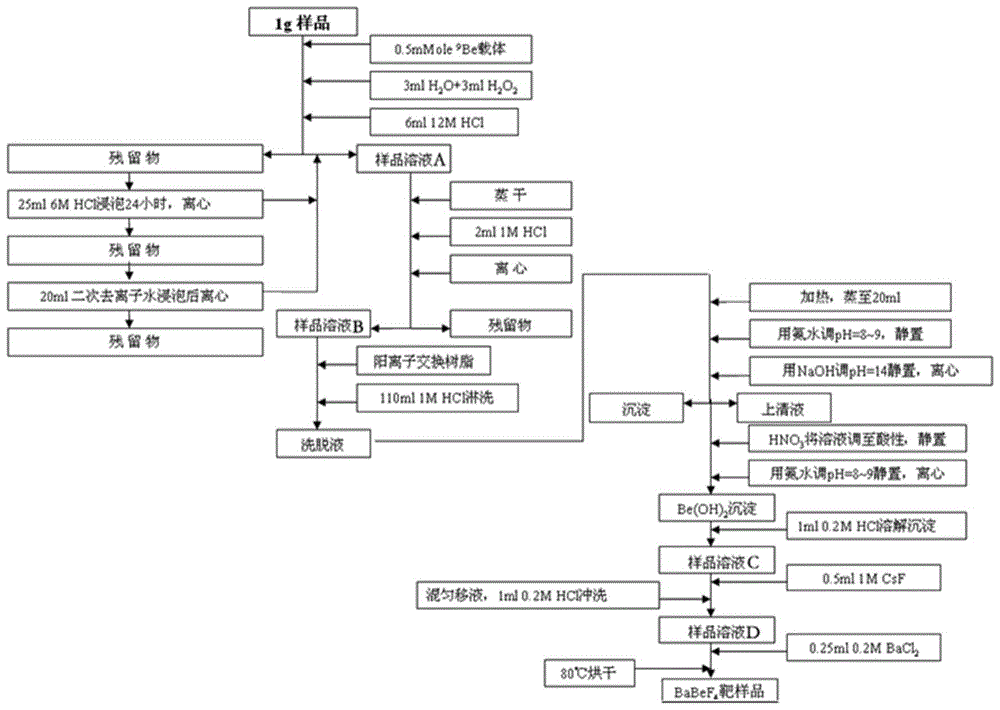
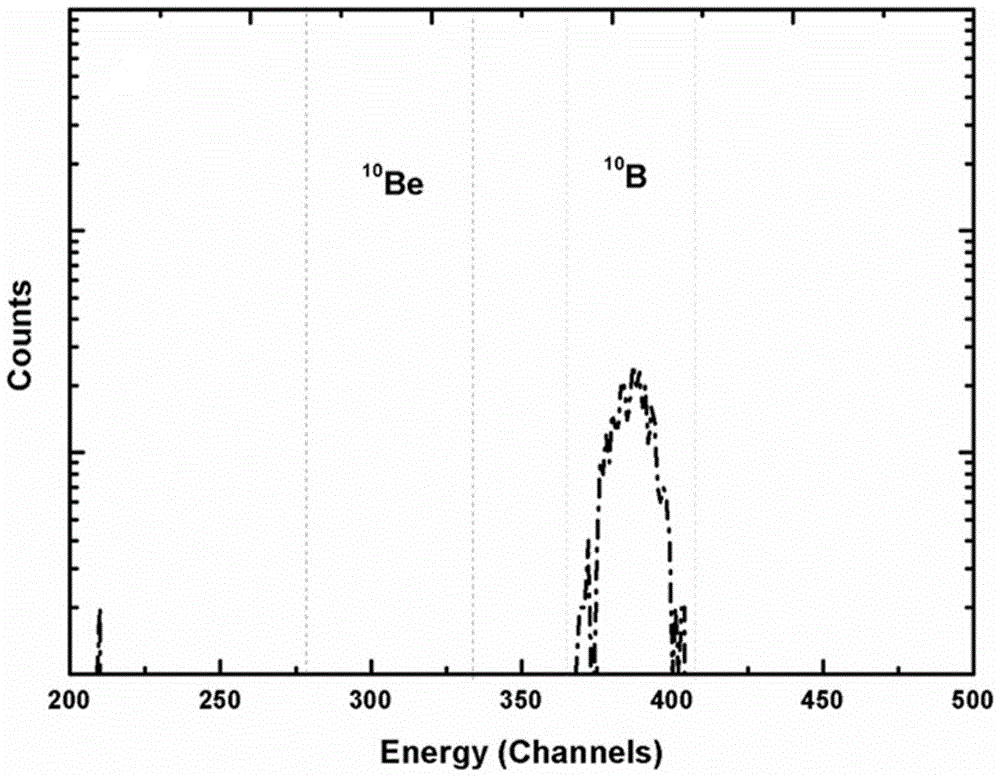
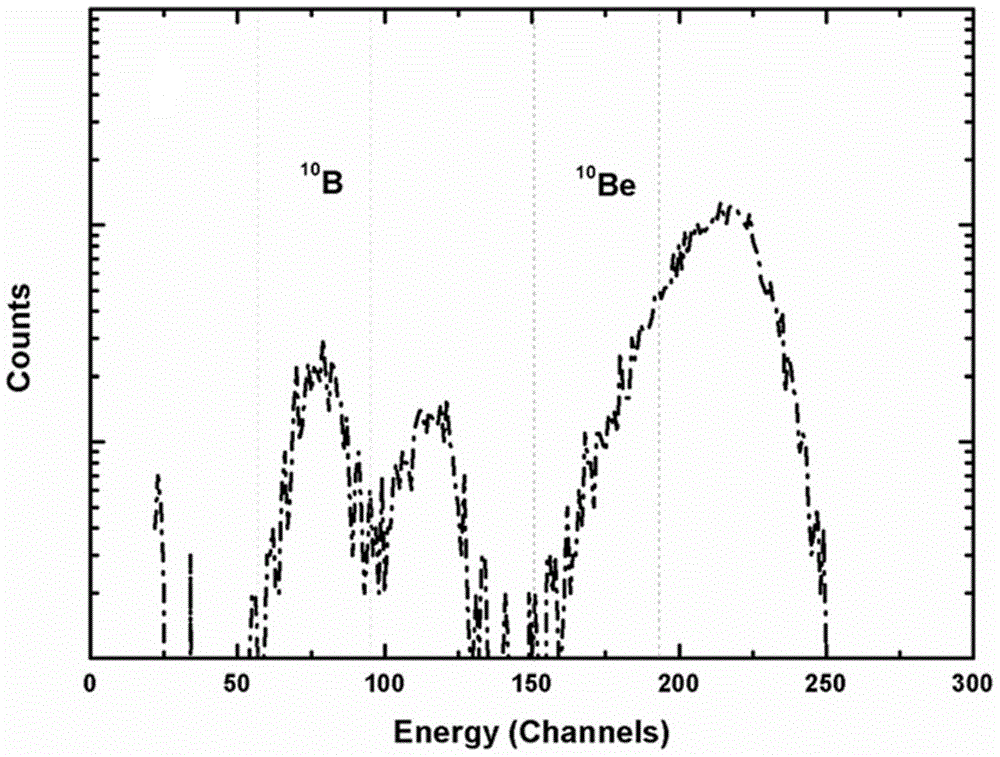
The invention discloses a method for carrying out accelerator mass spectrometry measurement by using super halogen anions of beryllium. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: preparing a target sample capable of producing super halogen anions BeF3<->; bombarding the target sample and a PbF2 powder mixing target cone to generate a BeF3<-> beam; crushing the BeF3<-> beam in a tandem accelerator; enabling <9>Be<2+> to enter a mobile Faraday cup for measurement after passing through a main analysis magnet; enabling <10>Be<2+> to pass through along a main beam line and to directly pass through a main electrostatic analyzer and a second magnet at the high-energy end; and finally entering a gas detector for analysis. The method has the beneficial effects that interference of <10>B is effectively inhibited at the extraction stage by the extracted beam which is measured by taking BeF3<-> as <10>Be-AMS, so that the high-energy end of a miniature AMS does not need to be peeled off twice by using an energy-reducing film, and the transmission efficiency of the <10>Be beam is ensured (the high-energy end achieves 100% transmission), the original good beam quality is maintained in the absence of the film, and the risks to experimenters due to the fact that BeO as airborne dust has high toxicity are effectively avoided.
Owner:INST OF EARTH ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Accelerator mass spectrometry device for simultaneously measuring isotopes
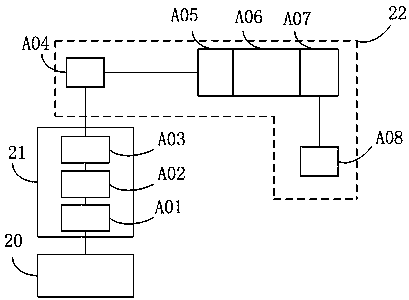
ActiveUS20180082828A1Simple structureGuaranteed uptimeIon sources/gunsStatic spectrometersAccelerator mass spectrometryIon source
The present invention provides an accelerator mass spectrometry device for simultaneously measuring isotopes. In one embodiment, the device comprises a sputtering negative ion source for generating negative ions; the sputtering negative ion source being connected to an accelerating tube for simultaneously accelerating a plurality of isotopic ions; an output end of the accelerating tube being connected to an isotope mass resolution system; the isotope mass resolution system being connected to a charge conversion analysis and multi-receiving measurement system; the charge conversion analysis and multi-receiving measurement system being connected to an ion detection system. The present invention is capable of accelerating a plurality of isotopic negative ions simultaneously. The accelerated isotopic negative ions are separated. Stable isotopic negative ions are measured by a stable isotope receiver. Unstable isotope negative ions are converted to positive ions and then measured by a detector.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Polyacrylic acid (SALT), polyacrylic acid (SALT)-based water-absorbing resin, and process for producing same
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
A method for accelerator mass spectrometry using beryllium superhalogen anions
InactiveCN104181223BSuppress interferenceGuaranteed transmission efficiencyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass spectrometry measurementGas detector
Owner:INST OF EARTH ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mass spectrum equipment of accelerator, and method for measuring mass spectrum 14C of accelerator
InactiveCN100561221CEliminates cycle dryingImprove protectionStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansHigh energyEnergy dispersion
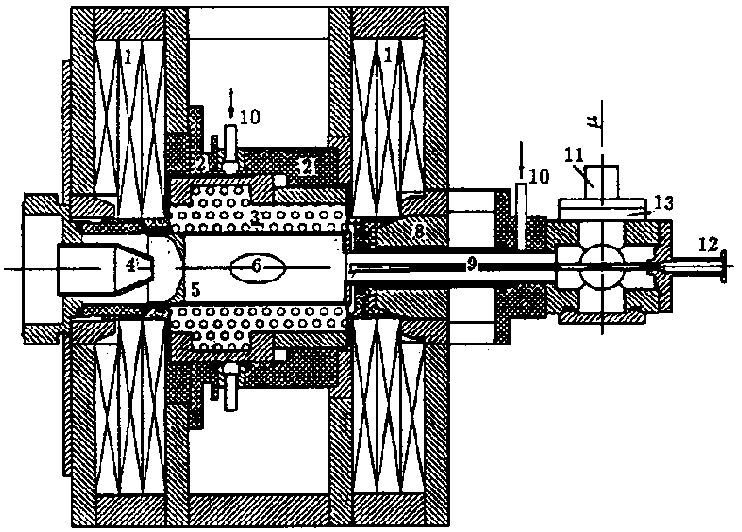
The invention provides an accelerator mass spectrometry device based on a low energy dispersion RFQ accelerator and a corresponding accelerator mass spectrometry 14C measurement method, belonging to the technical field of accelerator mass spectrometry. The accelerator mass spectrometry device includes: an ion source, a buncher, an RFQ accelerator, an electron stripper, a high-energy analysis system, and a detector, the above components are connected in sequence, and the RFQ accelerator accelerates 14C, 12C, and 13C ions to a certain energy to carry out electron analysis. Stripping to remove molecular ion interference. The invention uses a low-energy-dispersion RFQ acceleration structure as the ion acceleration device in the 14C measurement accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) system, and realizes the alternate acceleration of 14C, 12C, and 13C ions by alternately changing the RF power fed into the RFQ accelerator. There is no need for steel cylinders, insulating gas, alternate injection systems, etc. in traditional AMS, and the overall structure is simplified.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Accelerator mass spectrometry carbon-14 dating and sampling device
ActiveCN101446527BImprove efficiencyStable structurePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGas cylinderGraphite
The invention discloses an accelerator mass spectrometry carbon-14 dating and sampling device, and belongs to the technical field of radiocarbon (<14>C) dating. The device comprises a CO2 generation and purification apparatus and a graphite synthesis apparatus, wherein, a reactor of the CO2 generation and purification apparatus comprises a vacuum joint, a quartz tube, a quartz tube cutter, an airbottle and a ball valve; the vacuum joint is provided with four interfaces, the upper interface is connected with the ball valve, the rear interface is connected with a pressure sensor, the front interface is movably connected with the air bottle, the lower interface is connected with the quartz tube or the quartz tube cutter; and the reactor of the graphite synthesis apparatus comprises the two quartz tubes, a vacuum joint and a ball valve, the vacuum joint is also provided with four interfaces, wherein, the upper interface is connected with the ball valve, the rear interface is connected with a pressure sensor, and the lower interface and the front interface are respectively connected with two quartz tubes. The device is applicable to preparing a small graphite target sample, and the obtained target material has excellent performance.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
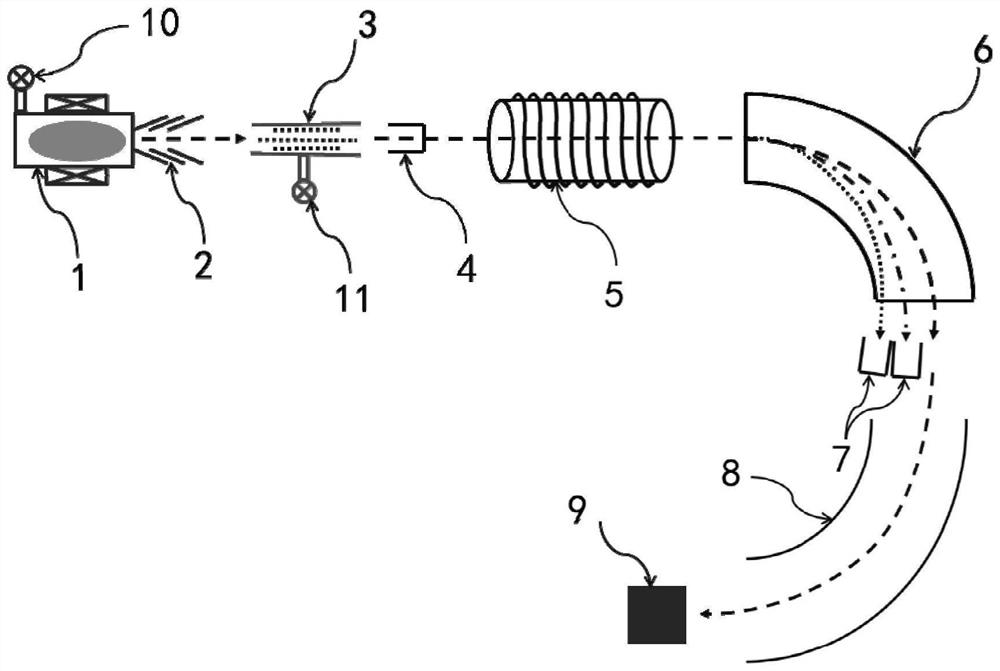
Positive ion mass spectrometry 14C measuring method and positive ion mass spectrometry device
InactiveCN113866258AAvoid operabilityAvoid maintenanceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAccelerator mass spectrometryAllene
The invention provides a positive ion mass spectrometry 14C measuring method and a positive ion mass spectrometry device, and belongs to the technical field of accelerator mass spectrometry. The device comprises a 2.45 GHz ECR ion source, a non-metal gas charge exchanger, a solenoid, an analysis system and a particle detector which are connected in sequence, the 2.45 GHz ECR ion source generates C2 + ions, and the non-metal gas charge exchanger selects one or a mixture gas of isobutane, isobutene, ethylene, propylene, propyne, allene, butylene and 1, 3-propylene as a charge exchange target, C2 + ions generated by an ion source are converted into C-ions, focusing is performed on a C-ion beam formed after charge exchange by a solenoid, and the C-ion beam is sent the focused C-ion beam into an analysis magnet; the analysis magnet is used for separating 12C-, 13C- and 14C- ions; 12C- and 13C- are measured through a bias Faraday cup behind an analysis magnet; 14C- ions enter the particle detector through the electrostatic analyzer to be measured, and finally the ratio of 14C to 12C or 13 C is obtained. According to the invention, high-precision measurement of 14C can be realized.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Accelerator mass spectrometry measuring method and system
ActiveUS20200411300A1Simple structureMiniaturizationIon sources/gunsIsotope separationMass spectrometry measurementResolution (mass spectrometry)
An accelerator mass spectrometry measuring system is disclosed, including: an ECR high-current positive ion source subsystem; an injector subsystem; a high-current accelerator subsystem; a high-energy analysis subsystem; and a high-resolution detector subsystem; of which, the ECR high-current positive ion source subsystem, the injector subsystem, the high-current accelerator subsystem, high-energy analysis subsystem and a high-resolution detector subsystem are connected sequentially; the ECR high-current positive ion source subsystem is configured for generating high-current positive ions of multi-charge states; the high-current accelerator subsystem is configured for accelerating the high-current positive ions. The AMS system is high in beam, high in overall efficiency, and strong in how-down capability, and can greatly improve the abundance sensitivity of measurement.
Owner:QIXIANHE (BEIJING) TECH CO LTD
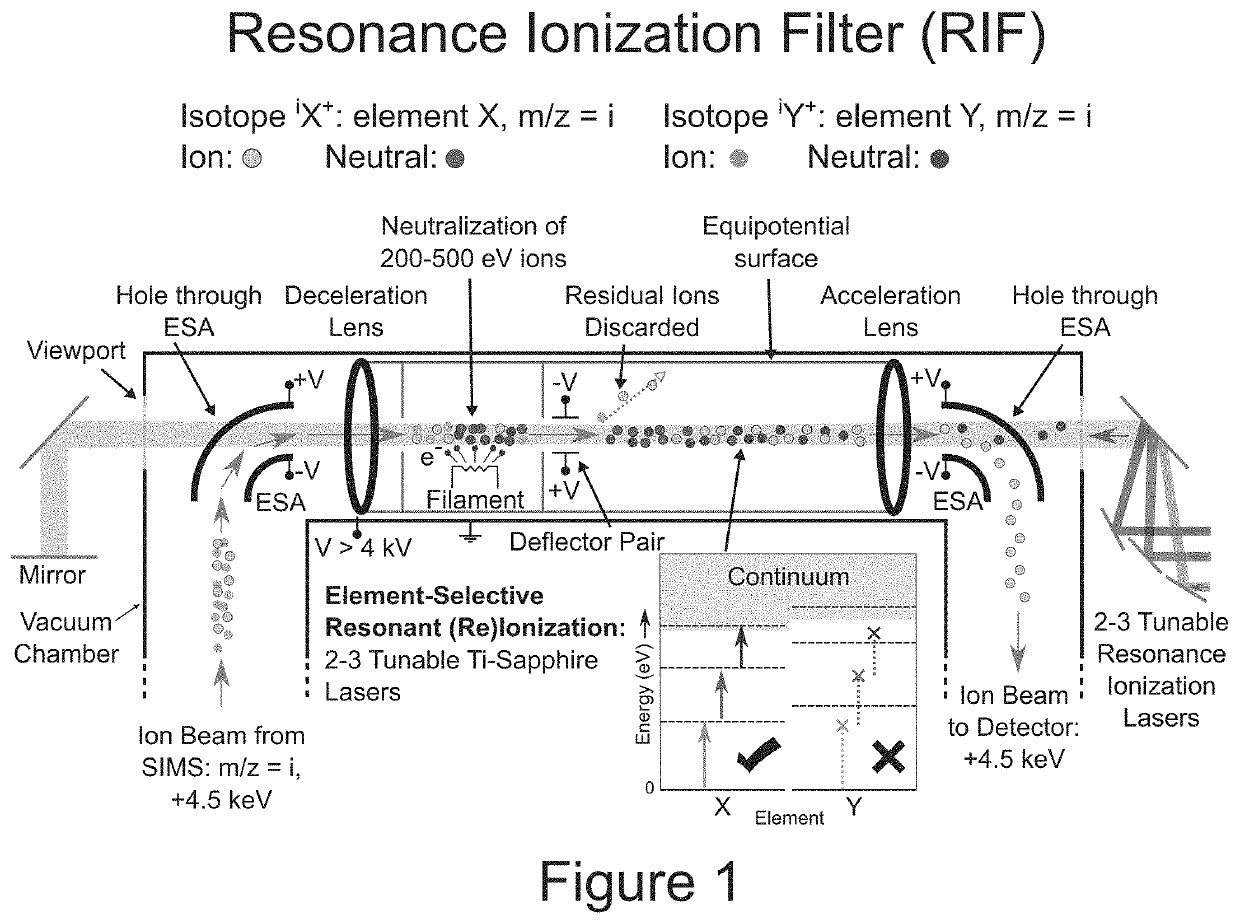
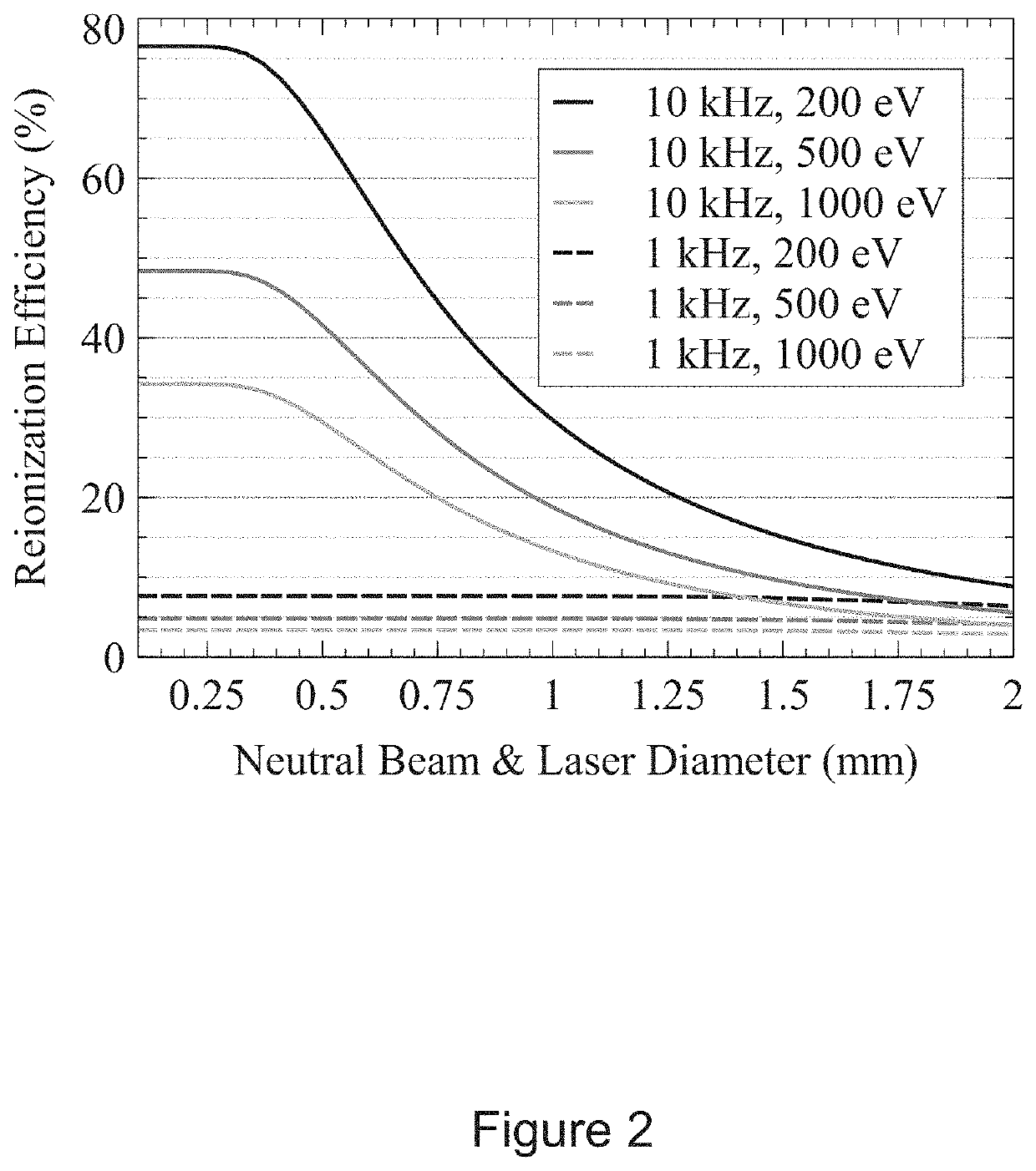
Resonance ionization filter for secondary ion and accelerator mass spectrometry
ActiveUS11501960B2Mitigate such drawbackTime-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsElectron sourceIon beam
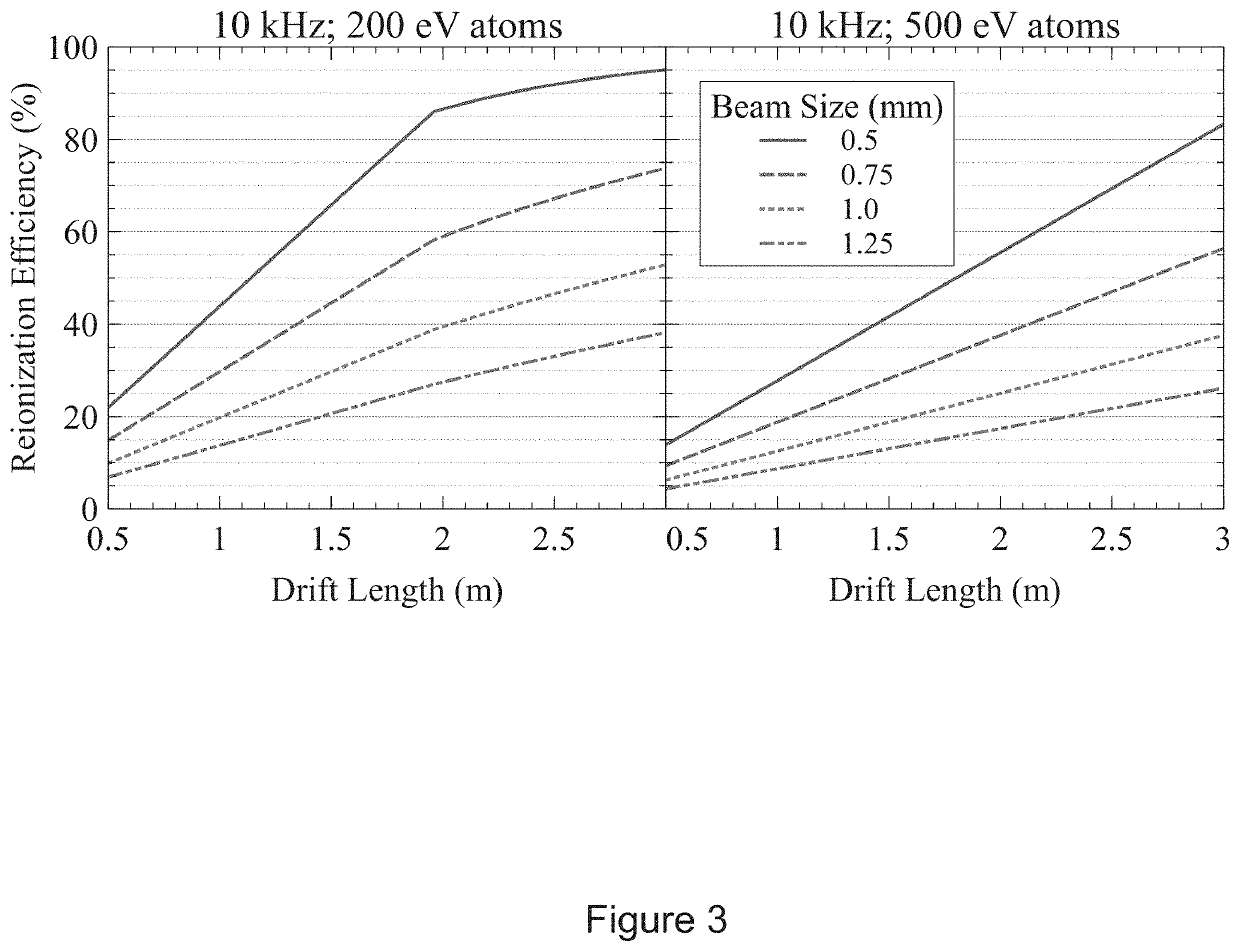
A method of removing nuclear isobars from a mass spectrometric technique comprising directing ions, decelerating the ions, neutralizing a first portion of the ions, creating residual ions and a second portion of the ions, reionizing a selective portion of the ions, re-accelerating the selective reionized portion of ions, and directing the reionized portion of ions to a detector. An apparatus to remove nuclear isobars comprising a deceleration lens, an equipotential surface, an electron source to neutralize a portion of the ion beam, a deflector pair, a tunable resonance ionization laser for selective resonant reionization, and an acceleration lens.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com