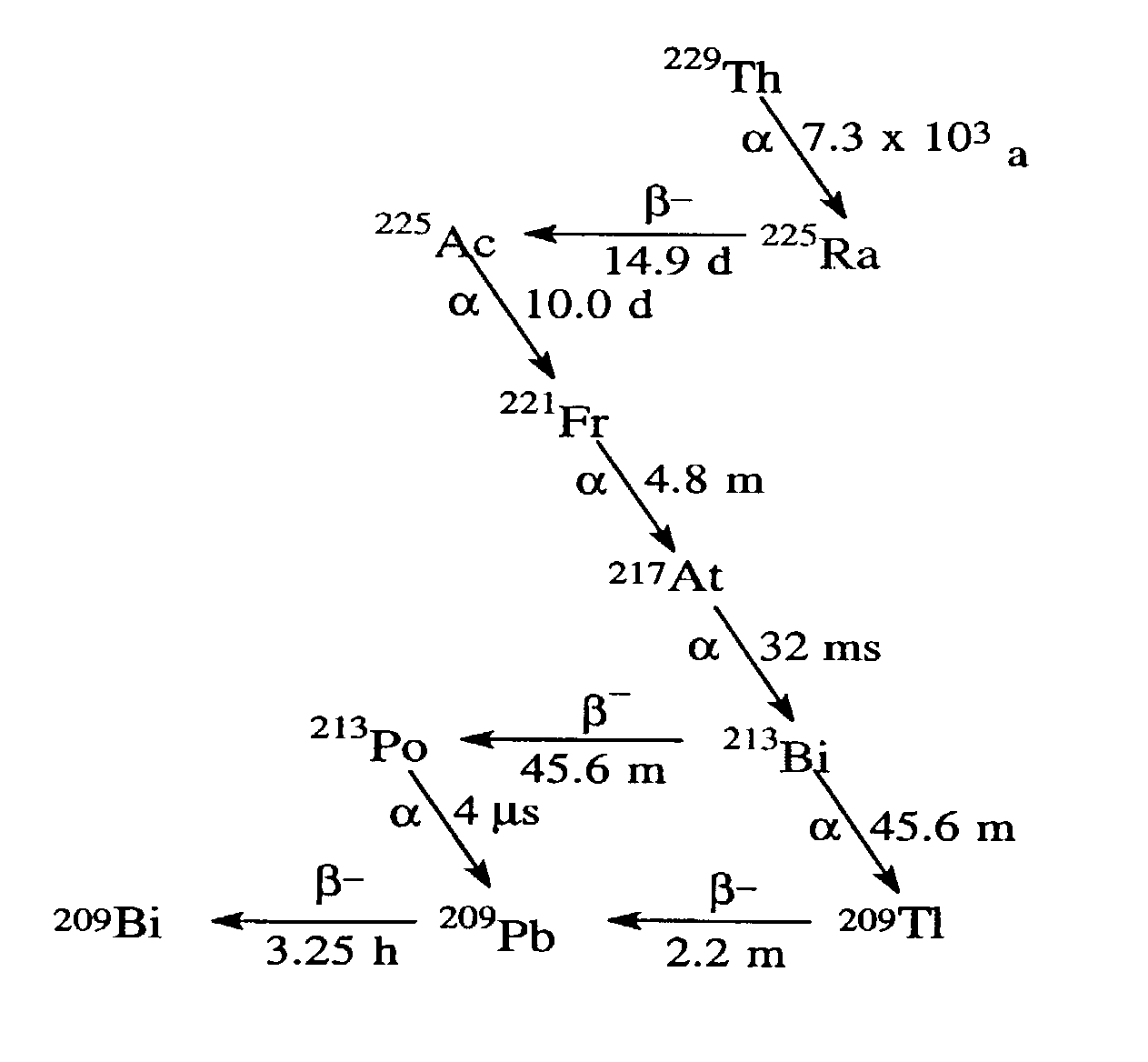Patents
Literature
82 results about "Radiogenic Isotopes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A radiogenic nuclide is a nuclide that is produced by a process of radioactive decay. It may itself be radioactive (a radionuclide) or stable (a stable nuclide). Radiogenic nuclides (more commonly referred to as radiogenic isotopes) form some of the most important tools in geology. They are used in two principal ways:
Magnetic nanoscale particle compositions, and therapeutic methods related thereto
InactiveUS20060142749A1Minimal invasionShort course of treatmentAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryDiseaseMagnetite Nanoparticles
Disclosed are thermotherapeutic compositions for treating disease material, and methods of targeted therapy utilizing such compositions. These compositions comprise a) stable single domain magnetic particles; b) magnetic nanoparticles comprising aggregates of superparamagnetic grains; or c) magnetic nanoparticles comprising aggregates of stable single magnetic domain crystals and superparamagnetic grains. These compositions may also comprise a radio isotope, potential radioactive isotope, chemotherapeutic agent. These methods comprise the administration to a patient's body, body part, body fluid, or tissue of bioprobes (energy susceptive materials attached to a target-specific ligand), and the application of energy to the bioprobes so as to destroy, rupture, or inactivate the target in the patient. Energy forms, such as AMF, are utilized to provide the energy. The disclosed methods may be useful in the treatment of a variety of indications, including cancers, diseases of the immune system, central nervous system and vascular system, and pathogen-borne diseases.
Owner:ASPEN MEDISYS +1
Isotope seeding system that releases radioactive seeds for treatment of cancerous cells
InactiveUS6095967AFacilitate insertionEasy to insertMedical devicesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyAdemetionineBiological body
An isotope seeding system that controls the release of radioactive seeds for treatment of cancerous cells during cancer treatment procedures. The isotope seeding system comprises at least one seed that is chargeable with radioactive isotopes. At least one dissolvable web netting may alternatively be positioned about the at least one seed, and a seed deployment assembly is utilized for delivering the at least one seed, with or without the dissolvable web netting, into an organism's tissue, to surround cancerous cells. The seed deployment assembly includes an elongated cannula, a hub assembly and an obturator. The hub assembly includes an initial inner diameter at its proximal end and an operable length between the proximal end of the hub assembly and the proximal end of the cannula, the ratio of the initial inner diameter relative to the operable length being in the range of 0.075 to 0.175, to preclude against jamming of the at least one seed, with or without the at least one dissolvable web netting wrapped thereabout, within the hub assembly and / or to further preclude against inadvertent migration of such seeds from the web netting when such netting is utilized.
Owner:MANAN MEDICAL PROD
Method and apparatus for separation of isobaric interferences
ActiveUS20060113464A1Avoid reactionLow costElectron/ion optical arrangementsIsotope separationTerminal voltageMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
This invention relates to a method and apparatus for separation of rare stable or radioactive isotopes from their atomic or molecular isobars in mass spectrometry (MS). In the present invention, the approach taken to removing atomic isobars utilizes a high transmission device for decelerating ions in combination with low energy reactions, such as ion-molecule reactions or near resonant electron transfer, in RF ion guides. The isobar is selectively depleted by electron transfer or other reactions between negative ions and gaseous targets in pressurized RF ion guides at low energies. The energy is controlled in such a way as to prevent reaction of the ion of interest while inducing reactions with the undesired isobar interference. The technique is of particular relevance to accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) for which it allows substantial reductions in the necessary terminal voltage. The effect is to allow reductions in the size and cost of AMS installations.
Owner:LITHERLAND ALBERT EDWARD +7
Prompt gamma-ray detection apparatus for analyzing chemical materials using femtosecond pulse laser-induced neutrons
ActiveUS20120183111A1Easy to moveSystem mobilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsFemtosecond pulsed laserIsotope
Disclosed herein is a prompt gamma-ray detection apparatus for analyzing chemical materials using femtosecond pulse laser-induced neutrons, which can be effectively used in the nondestructive inspection of various materials, such as metals, coal, cement, radioactive materials and the like as well as explosives and chemical materials, and which can provide better measurement results for the analysis of basic materials, and a method of measuring prompt gamma-rays using the apparatus. The prompt gamma-ray detection apparatus is advantageous because it can non-destructively analyze the elements in a chemical sample using a femtosecond pulse laser-induced neutron generator that solves the problems of an atomic reactor for research or a radioactive isotope as a neutron radiation source.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Real-time list mode reconstruction
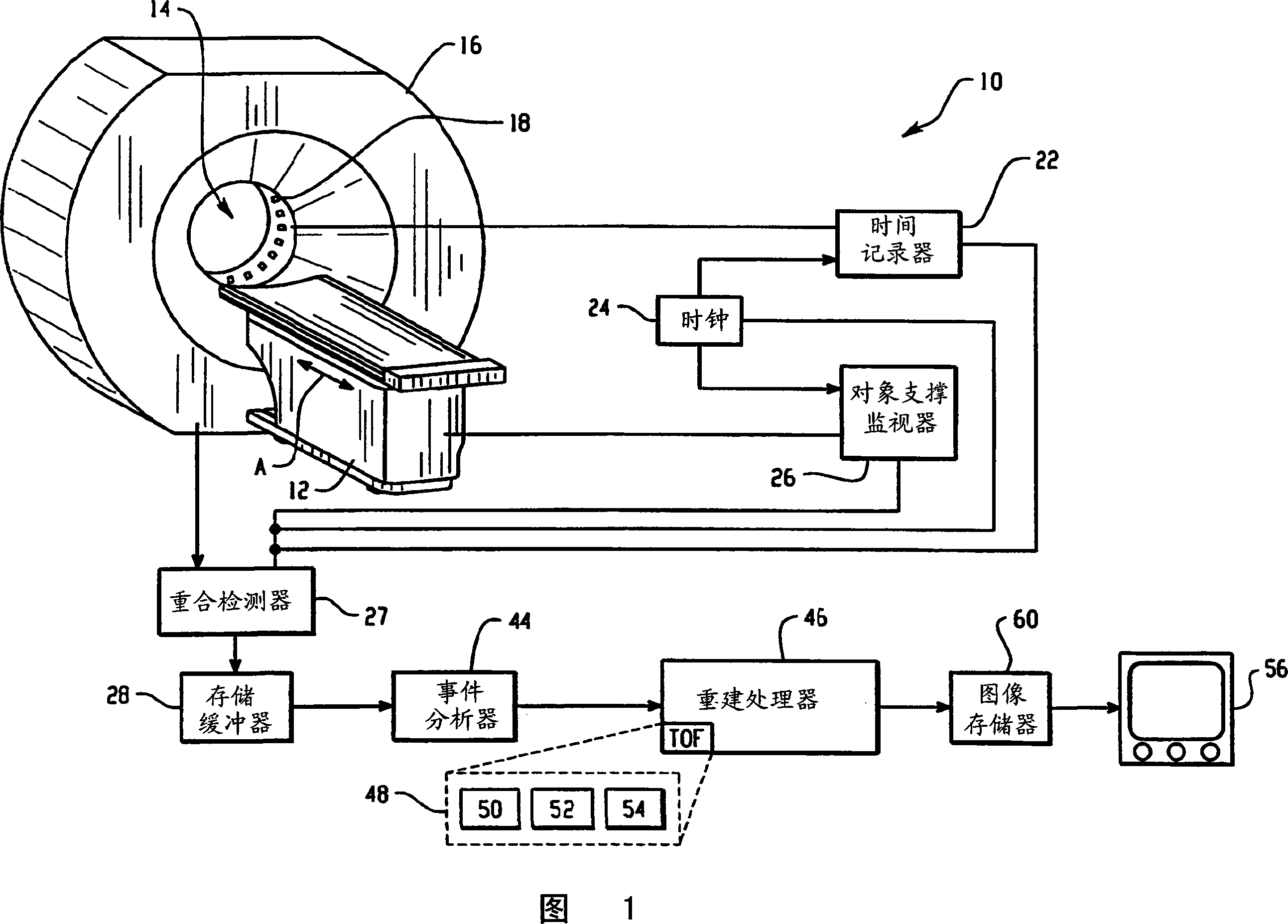
ActiveCN101088028AIncrease throughputTomographyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentData reconstructionMechanical engineering
In positron emission tomography, a nuclear medicine scanner (10) is used to detect gamma-ray events generated by positron annihilation events. Molecules of known behavior are labeled with radioactive isotopes that decay into pairs of gamma rays that are detected coincidentally, ie in a nearly simultaneous manner, by radiation detectors (18). A time recorder (22) and subject support monitor (26) indicate the time when the coincident gamma rays were detected and the position of the subject. The storage buffer (28) collects gamma ray detection time and position and support position. A batch of data acquired in the buffer (28) is reconstructed (48) into an overlapping portion of the image memory every 1 / 100 to 1 / 10 of a second while the support surface (12) is continuously moved across the scanner.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS NV
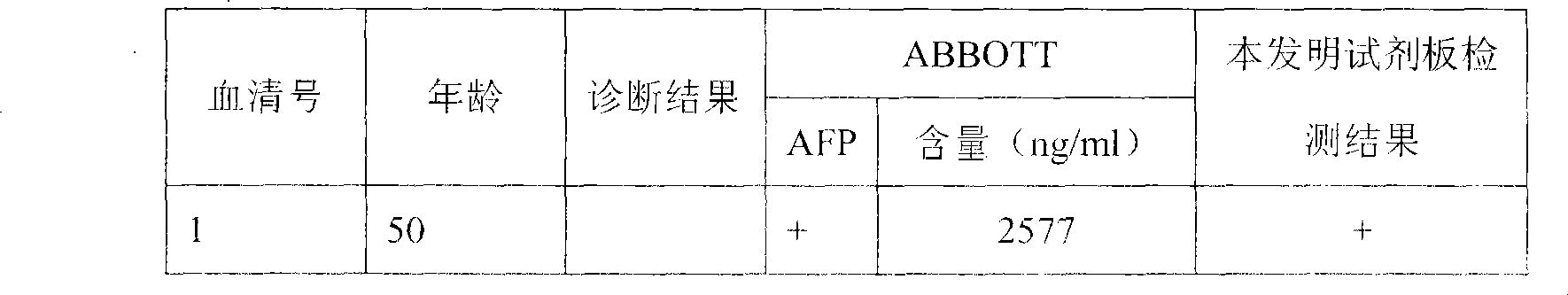
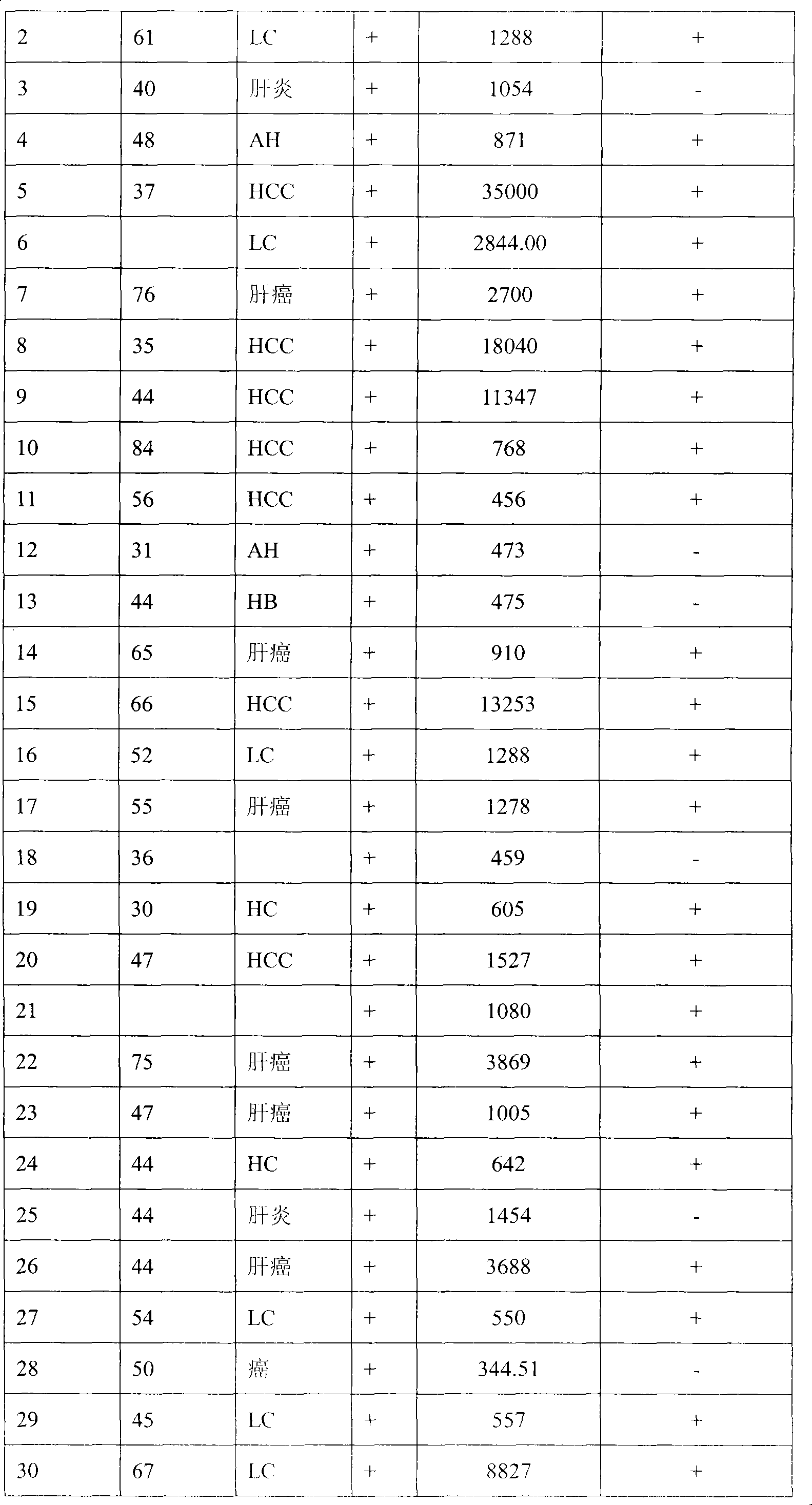
Reagent plate for rapidly detecting hepatocarcinoma, making method thereof and applications
InactiveCN101424690AFor long-term storageApplicable to on-site inspectionMaterial analysisReagent stripAgglutinin-B
The invention discloses an agent plate for testing hepatocarcinoma and a preparation method and the application thereof. The agent plate is composed of a rigid plate and an agent strip attached to the rigid plate, and the agent strip is formed by sequentially and closely splicing absorbent filter paper, a pyroxylin membrane, a glass fibre membrane and a sample adsorption glass fibre membrane from top to bottom, wherein a gold-labeled anti-mouse AFP monoclonal antibody is absorbed by the glass fibre membrane; an agglutinin coated detection line is arranged at one end of the pyroxylin membrane, which is adjacent to the glass fibre membrane, and a goat anti mouse IgG coated contrast line is arranged at the other end which is adjacent to the absorbent filter paper; and the lower end of the sample adsorption glass fibre membrane is provided with a row of loading holes. The agent plate for testing hepatocarcinoma has the advantages that a fluorescence microscope, an Elisa tester and other expensive instruments are not needed, and the agent plate is much more suitable for field test; the agent plate is safer since radioactive isotopes, TMB and other harmful substances or chemical substances are not needed in testing processes; test results can be preserved for a long time; and the operation of the agent plate is easy and fast, and the agent plate can be operated by a single person.
Owner:BEIJING WANTAI BIOLOGICAL PHARMACY ENTERPRISE
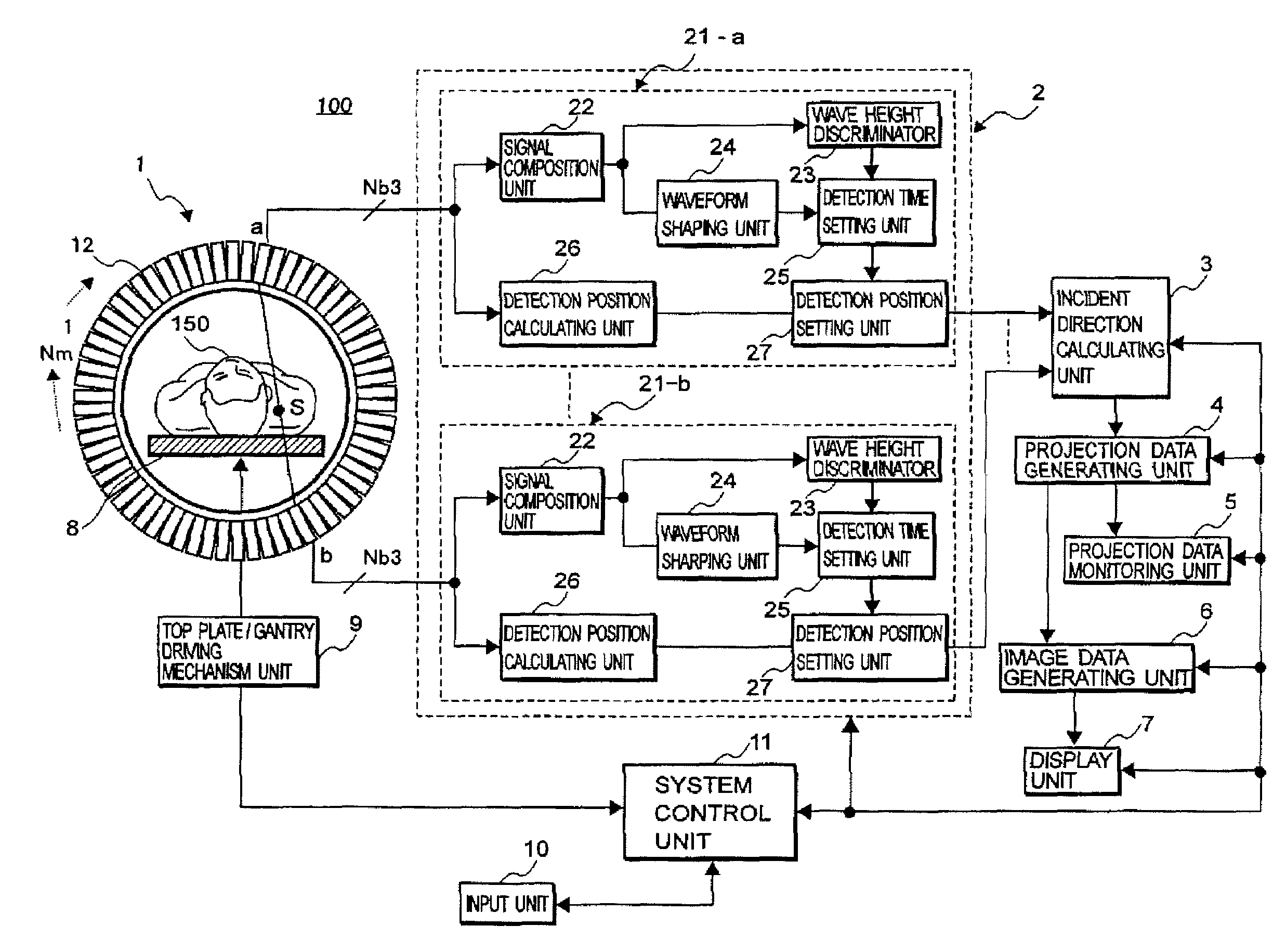
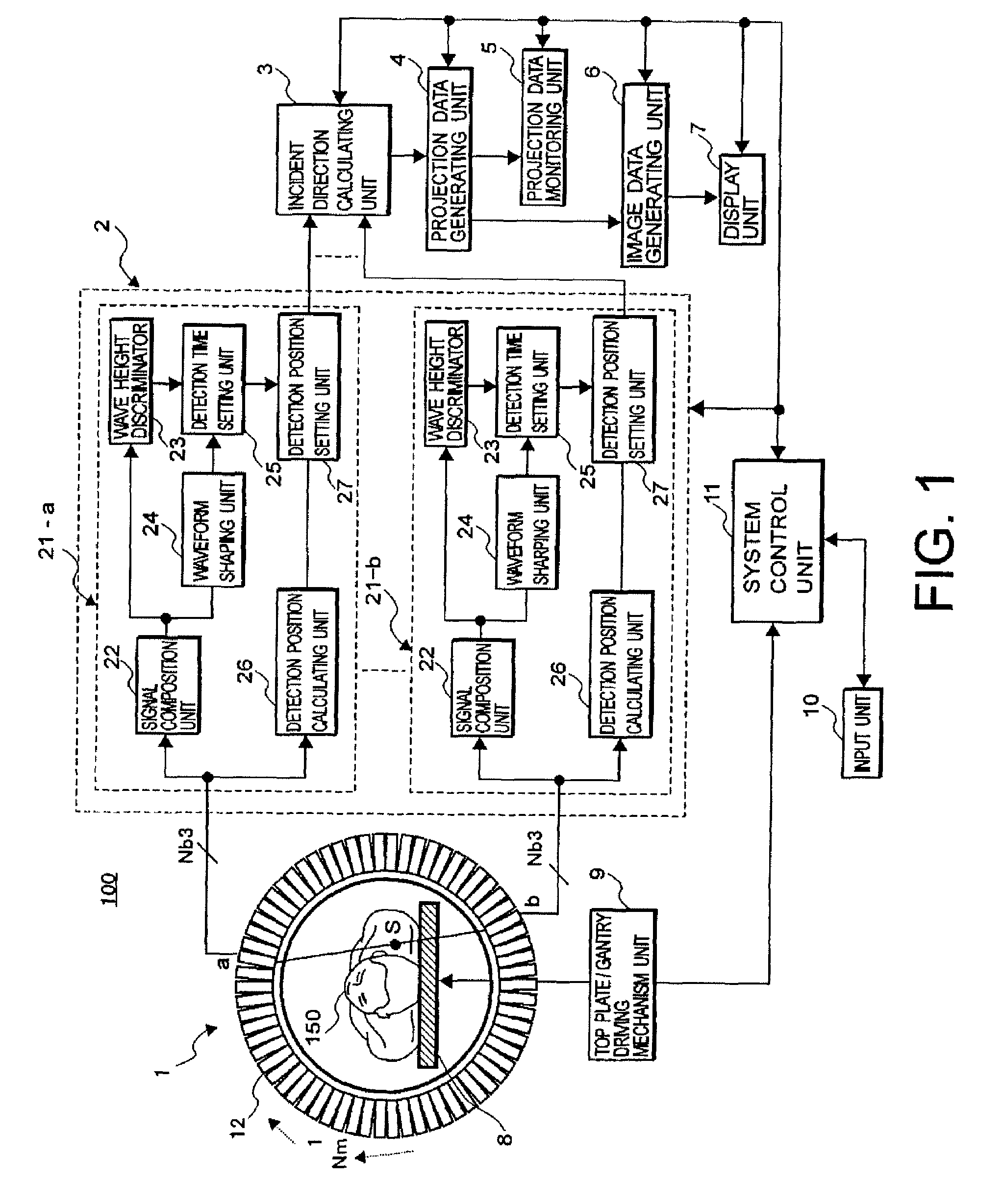
Nuclear medicine imaging apparatus and a method for generating image data
ActiveUS7718971B2Reduce the burden onImprove examinationMaterial analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentImaging processingBody movement
The present invention provides a nuclear medicine imaging apparatus and image data generation method that achieves restarting of the generation of projection data and at an early stage while monitoring a variation of count values for detecting an occurrence of non-permissible body movement of a patient. The image processing apparatus consistent with the present invention detects a pair of gamma-rays successively emitted from an object with a radioactive isotope through a pair of detector modules in a data detecting unit. A data processing unit and an incident direction calculating unit in the image processing apparatus respectively calculate a gamma-ray detection position and a gamma-ray incident direction based on the acquired detection signals. A projection data generating unit in the apparatus generates monitoring projection data based on each count value of the detection signals in correspondence to the gamma-ray detection position and the gamma-ray incident direction. A projection data monitoring unit calculates a body movement index of the object by comparing count values of the monitoring projection data that are generated in each of two preferably adjoining monitoring periods. A system control unit generates an alarm signal for performing repetition of the monitoring projection data when the body movement index exceeds a threshold value and displays the alarm signal on a display unit.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
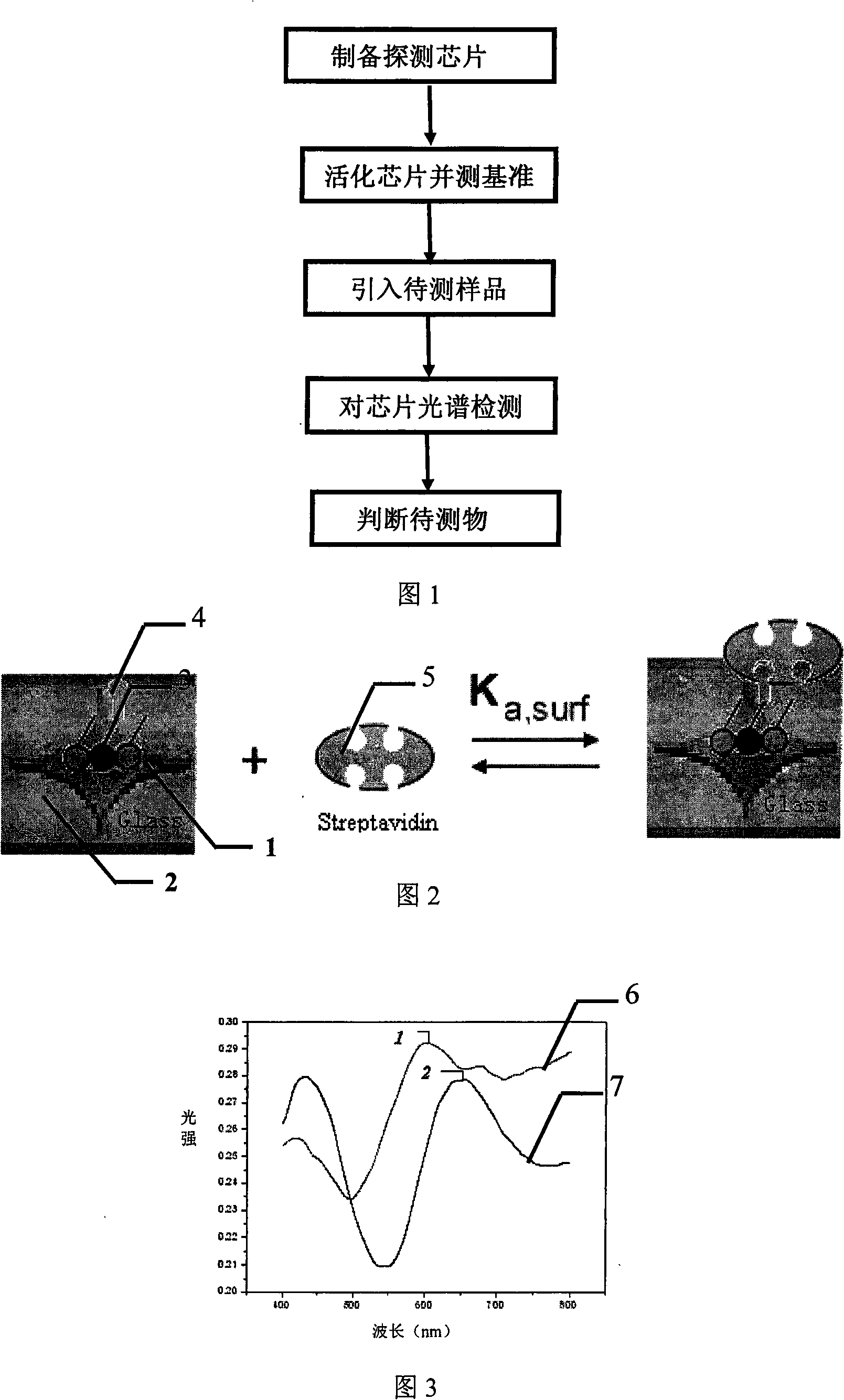
Label-free biochemical detection method reinforced by utilizing local surface plasma
InactiveCN101514986ALow costHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological testingSystem testingFluorescence
A label-free biochemical detection method reinforced by utilizing local surface plasma is characterized in that the label-free biochemical detection method comprises the steps as follows: (1) preparing an LSPR detection chip according to a detected object; (2) selecting a specific biological molecule to activate the chip according to the detected object, and testing the spectrum reference value of the chip by a spectrum test system; (3) leading in a to-be-detected sample for detection, and obtaining a spectrum curve by test; and (4) judging whether the to-be-detected sample contains the detected object by analysing the spectral peak movement state of the spectrum, so as to quickly detect the detected object with high sensitivity and without a label, meanwhile, the array chip is used for realising high-efficiency and multi-channel detection. The method of the invention does not need complex equipment and does not use radioactive isotope, enzyme or fluorescence as a label, has the remarkable characteristics of low cost and high sensitivity, and can realise array chip. The method provides a simple and practical new method for fast detection of biochemical molecule.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
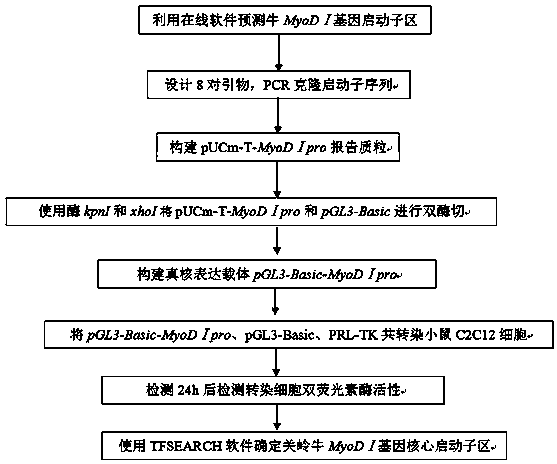
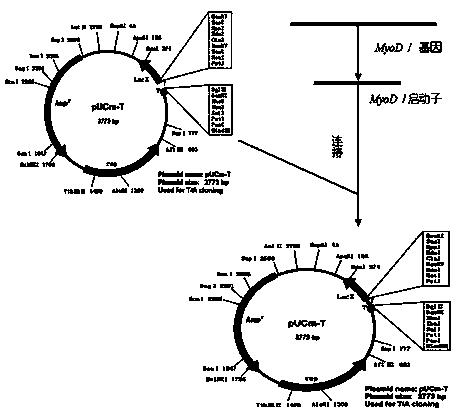
Method for determining Guanling cattle MyoDI gene core promoter by using dual-luciferase report gene
InactiveCN103571941AHigh sensitivityThe detection process is fastMicrobiological testing/measurementLipofectamineSubcloning
The invention discloses a method for determining a Guanling cattle MyoDI gene core promoter by using a dual-luciferase report gene. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a recombinant vector containing a Guanling cattle MyoDI gene promoter full-length fragment and a subcloning fragment; culturing skeletal muscle growth-related cells and planking; preparing a promoter recon / liposome mixture, and carrying out transfection on the cells obtained in the step (2); carrying out dual-luciferase activity detection on the transfection cells obtained in the step (3) by using the dual-luciferase report gene. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, fastness in detection speed and low cost and does not need radioactive isotopes and the like; as a used pGL3-Basic report gene does not comprise the promoter and an enhancer, the expression of the luciferase report gene can be used for detecting the starting activity of inserted promoters and comparing the intensity of the promoters, and further a core promoter region is preliminarily determined.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Wide-energy-spectrum BF3 long neutron counter measurement system
ActiveCN111257922ASuppression of the sharp decline in relative detection efficiencyNuclear energy generationNeutron radiation measurementNuclear technologyNuclear engineering
The invention belongs to the field of nuclear technology application and particularly relates to a wide-energy-spectrum BF3 long neutron counter, the average energy response of the long neutron counter is 3.01 cm<2>, and the average relative deviation is 6.87%. An MCNP5 program is used for controlling a simulation calculation result to be within a statistical error range of 0.78 percent; the relative detection efficiency of the long neutron counter at the position 150 cm away from a point source is simulated, the relative detection efficiency is 2.05*10<-3> to 2.62*10<-3> within the energy range of 1 KeV to 15.2 MeV, the average relative detection efficiency epsilon is 2.31*10<-3>, and the average deviation is 6.84%. The long neutron counter overcomes the problems that in the prior art, the energy lower limit of a neutron counter is high, the energy response is sharply reduced in a range of above 5 MeV, the energy response flat range is not long enough and the like, and the requirements of high-flux-rate monitoring of most accelerator neutron sources or neutron fluence rate calibration of radioactive isotope neutron sources can be met.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of adsorbent containing SnO2/Sb2O5, product and application of adsorbent
ActiveCN103861550AImprove adsorption capacityEnhanced interactionOther chemical processesRadioactive decontaminationSorbentUltraviolet
The invention relates to a preparation method of an adsorbent containing SnO2 / Sb2O5. According to the method, SbCl3 with a stable chemical property and low toxicity is taken as a Sb source, sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate, namely SnCl4, is utilized as a Sn source, and a SnO2 / Sb2O5 binary composite oxide is prepared. The preparation method comprises the following steps of oxidizing Sb<3+> as Sb(V) in a non-water system taking alcohol as a solvent by adopting the combination of H2O2 oxidation and ultraviolet irradiation, further carrying out hydrolytic precipitation on Sb(V) and Sb<4+> by utilizing a small amount of water introduced by utilizing H2O2 solution as a reactant, and forming a binary SnO2 / Sb2O5 composite oxide. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the hydrolyzing speed of Sb<3+> is slow, the generation of the Sb2O3 is effectively controlled, the Sn / Sb2O5 binary composite oxide with the Sb<3+> oxygenation efficiency being 100% is obtained, the adsorbent can remove the radioactive isotope Co ions and a complex thereof and stable isotope Co ions and a complex thereof, and the adsorptive property of the SnO2 / Sb2O5 binary composite oxide and pure Sb2O5 obtained by the introduction of Sb is improved by 200 times.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
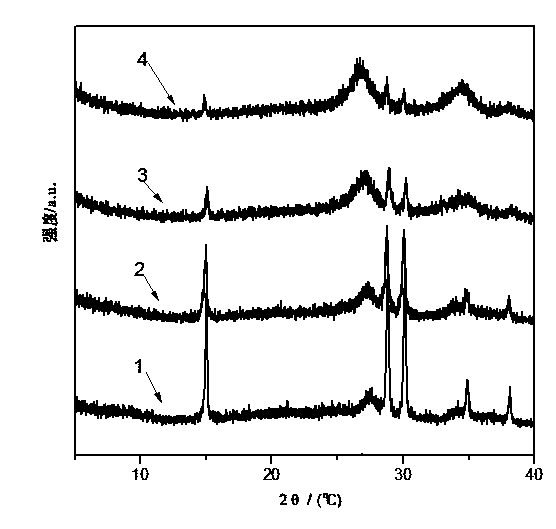
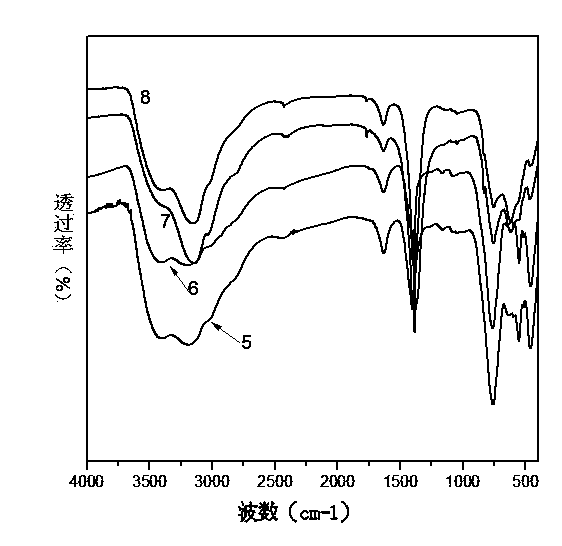
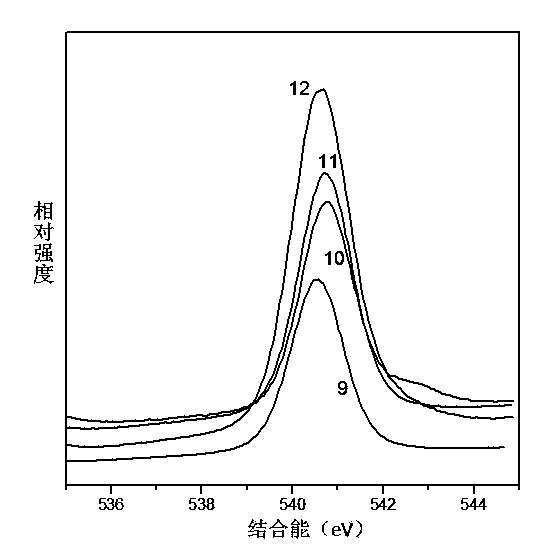
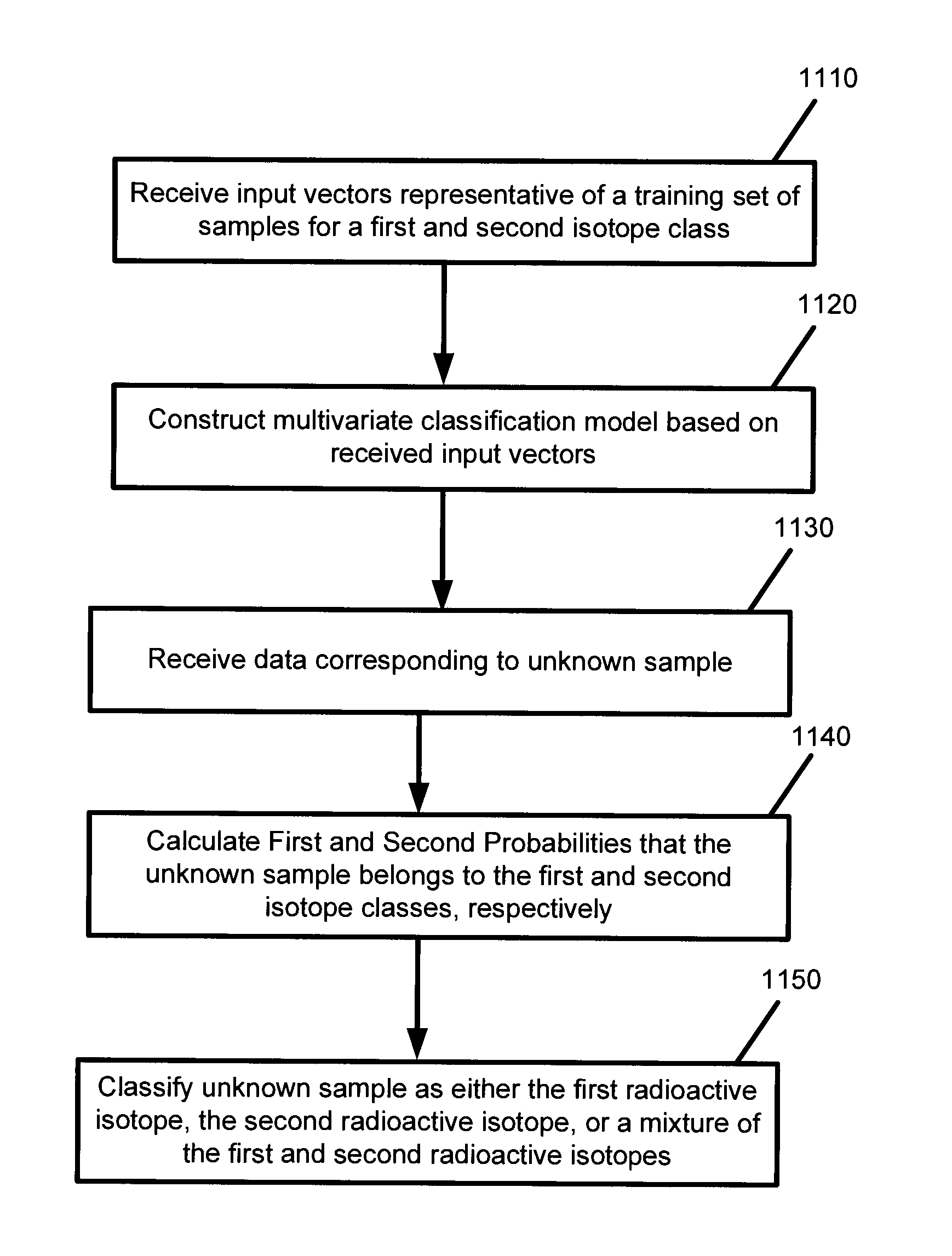
Multi-dimensional spectral analysis for improved identification and confirmation of radioactive isotopes
InactiveUS20110113003A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationFuzzy logic based systemsMultivariate classificationIsotope
A method and system for classifies an unknown sample that contains either a first radioactive isotope, a second radioactive isotope, or a mixture of the first and second radioactive isotopes. Input vectors representative of a training set of samples for a first isotope class and a second isotope class are received. A multivariate classification model is constructed based on the received input vectors. Data is received corresponding to the unknown sample. First and second probabilities that the unknown sample respectively belongs to the first isotope class and the second isotope class are calculated. Based on the first and second probabilities, the unknown sample is classified as either the first radioactive isotope, the second radioactive isotope, or a mixture of the first and second radioactive isotopes.
Owner:SMITHS DETECTION
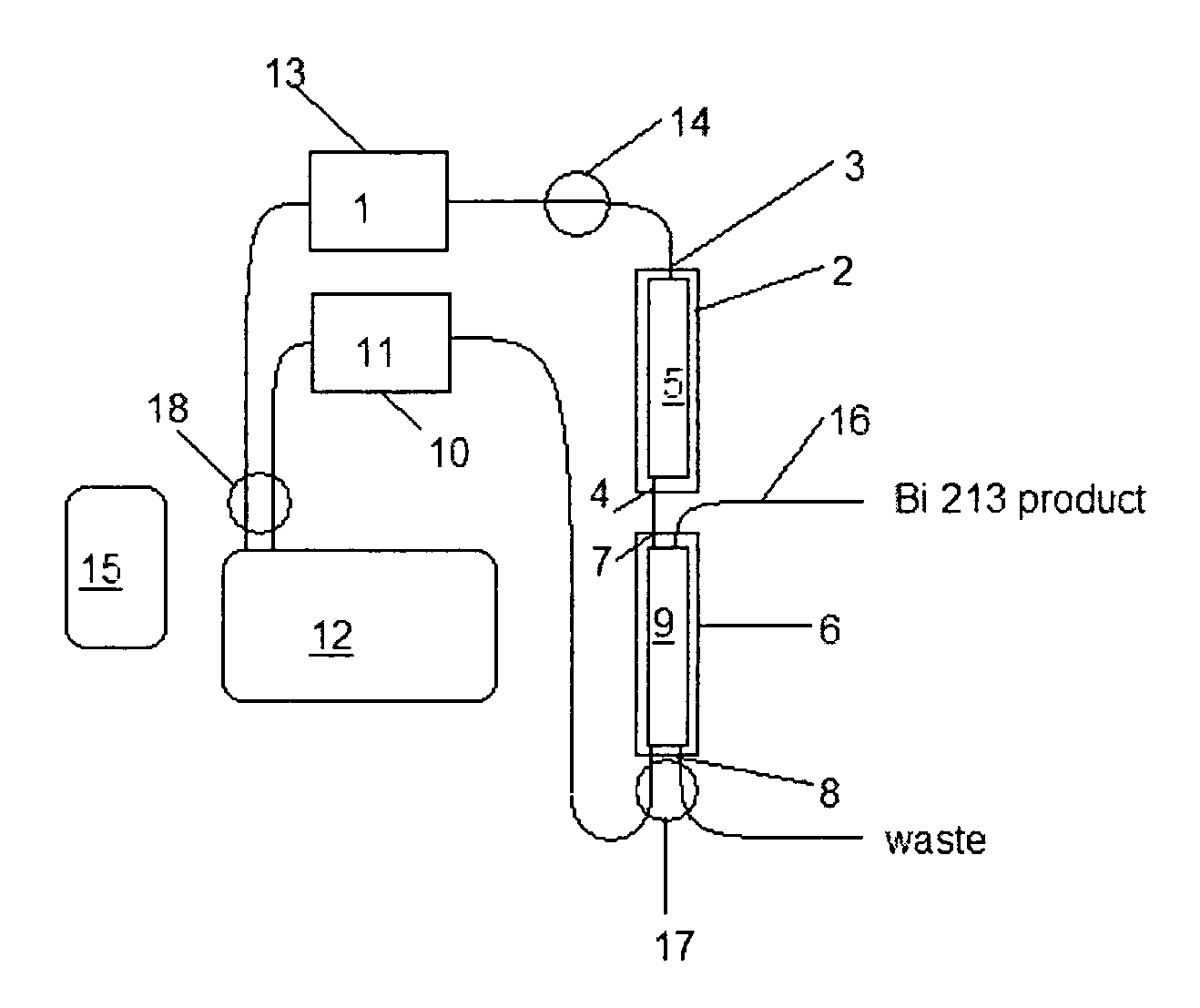
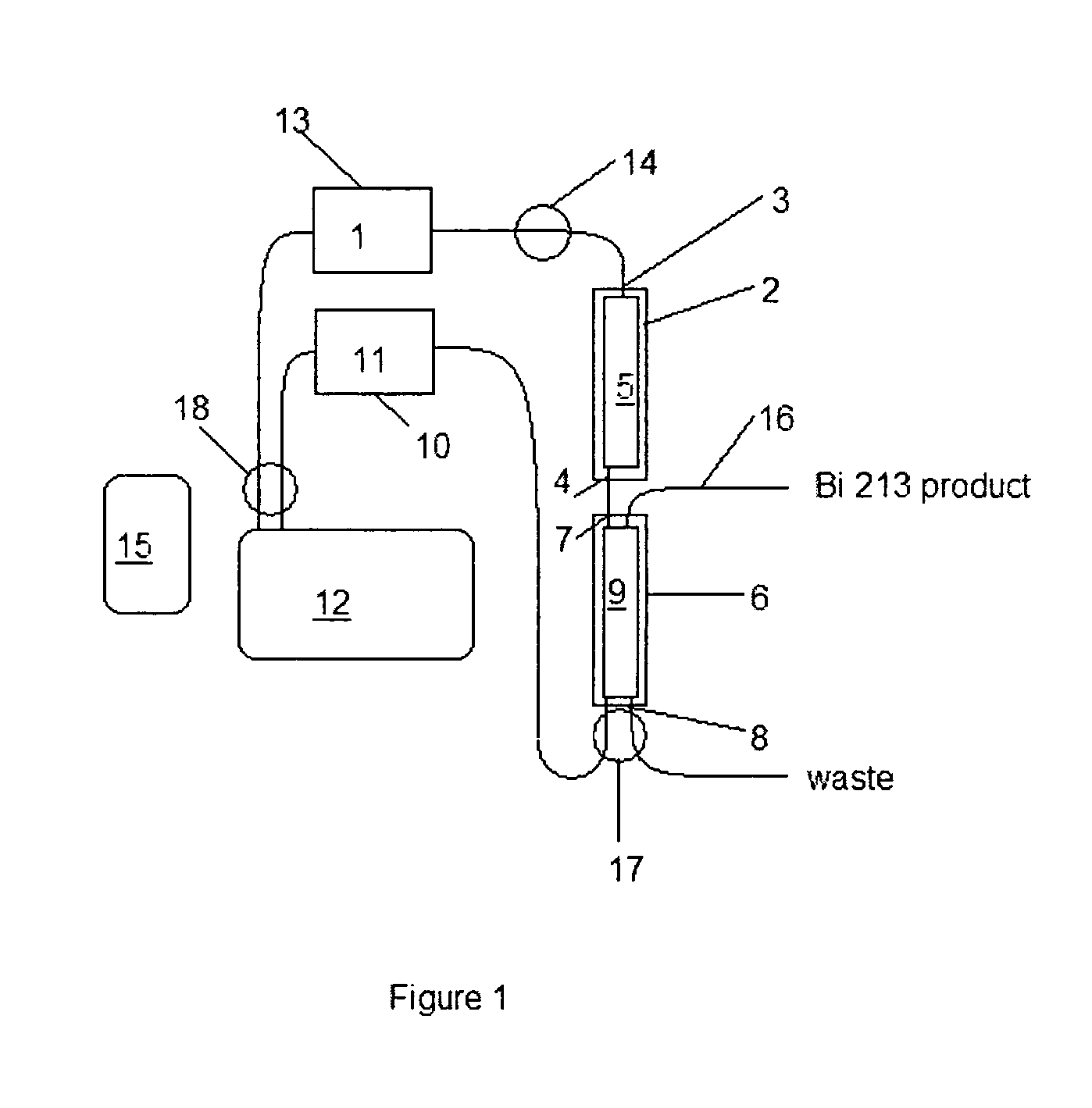
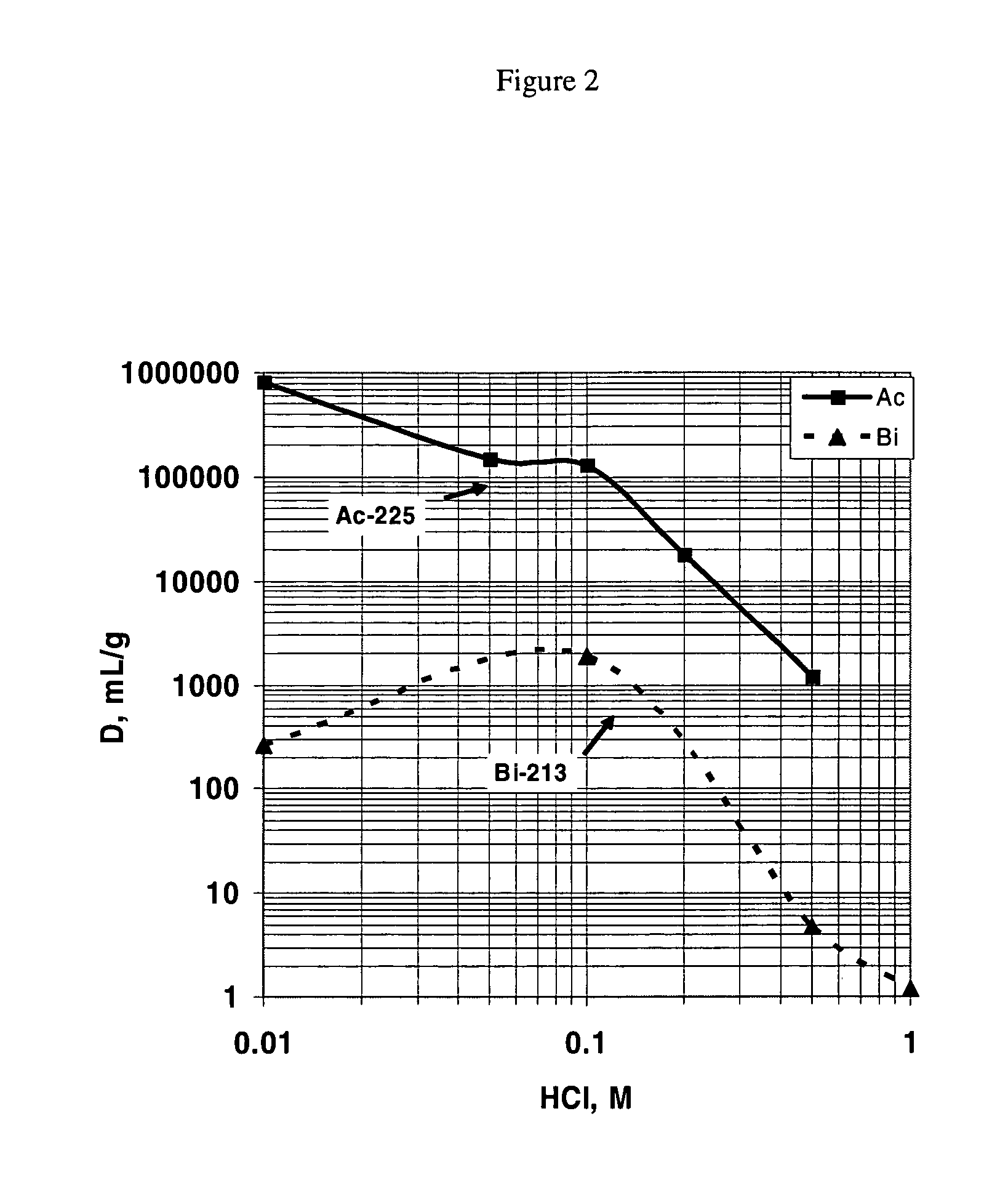
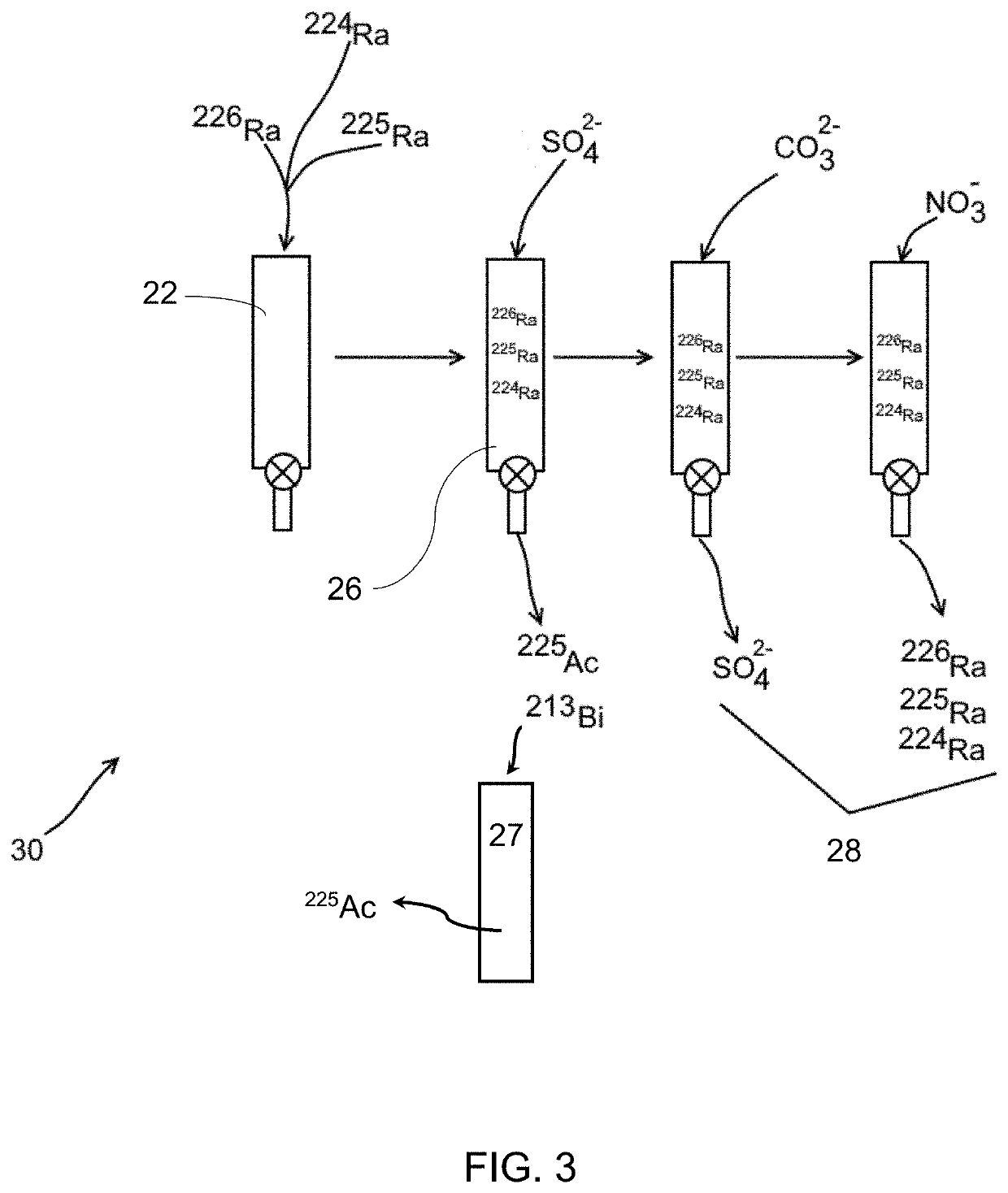
Method and apparatus for production of 213Bi from a high activity 225Ac source
A method and apparatus for isolating and purifying a 213Bi radioactive isotope from an 225Ac source using a primary column and a primary sorbent which preferentially retains 225Ac over 213Bi when exposed to a compatible solvent in combination with a secondary column having a secondary sorbent which retains 213Bi when exposed to a mixture of the compatible solvent and 213Bi. A “compatible solvent” is a solvent which will preferentially remove 213Bi radioactive isotopes from a primary sorbent without removing 225Ac radioactive isotopes, and then allow 213Bi radioactive isotopes removed from the primary sorbent to be retained on a secondary sorbent, without having to dilute or otherwise chemically or physically modify the compatible solvent in between exposure to the primary and secondary sorbents.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
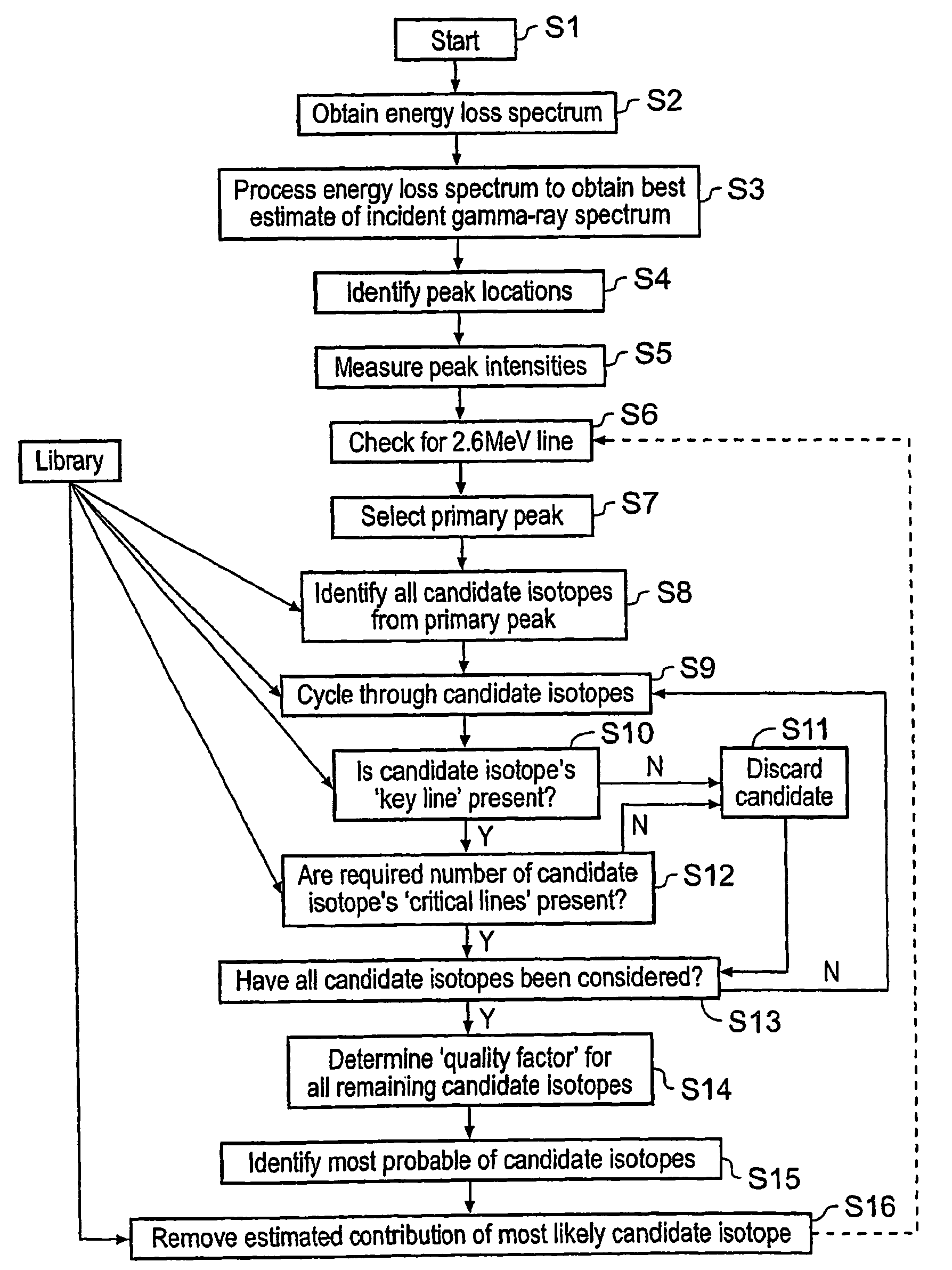
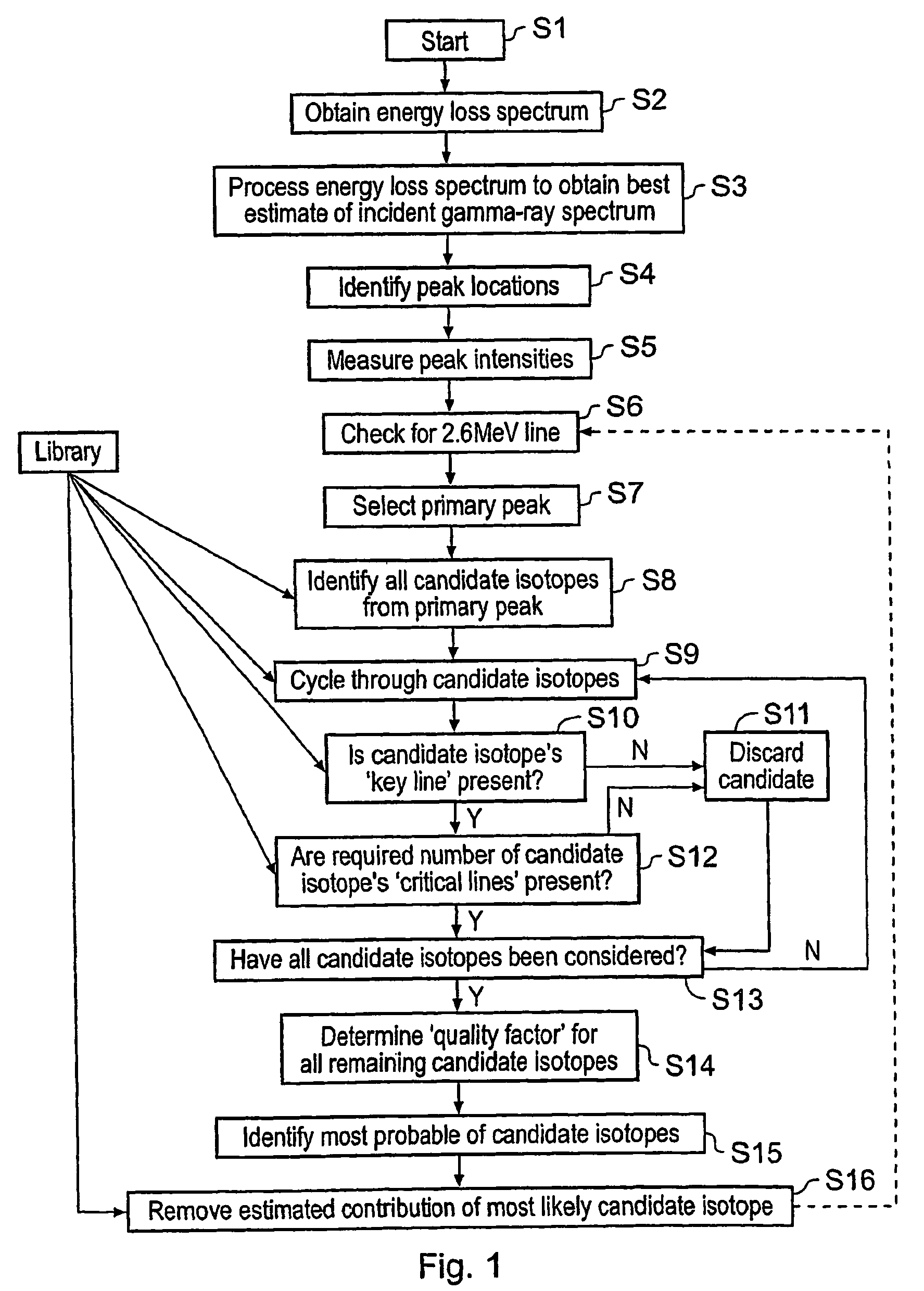
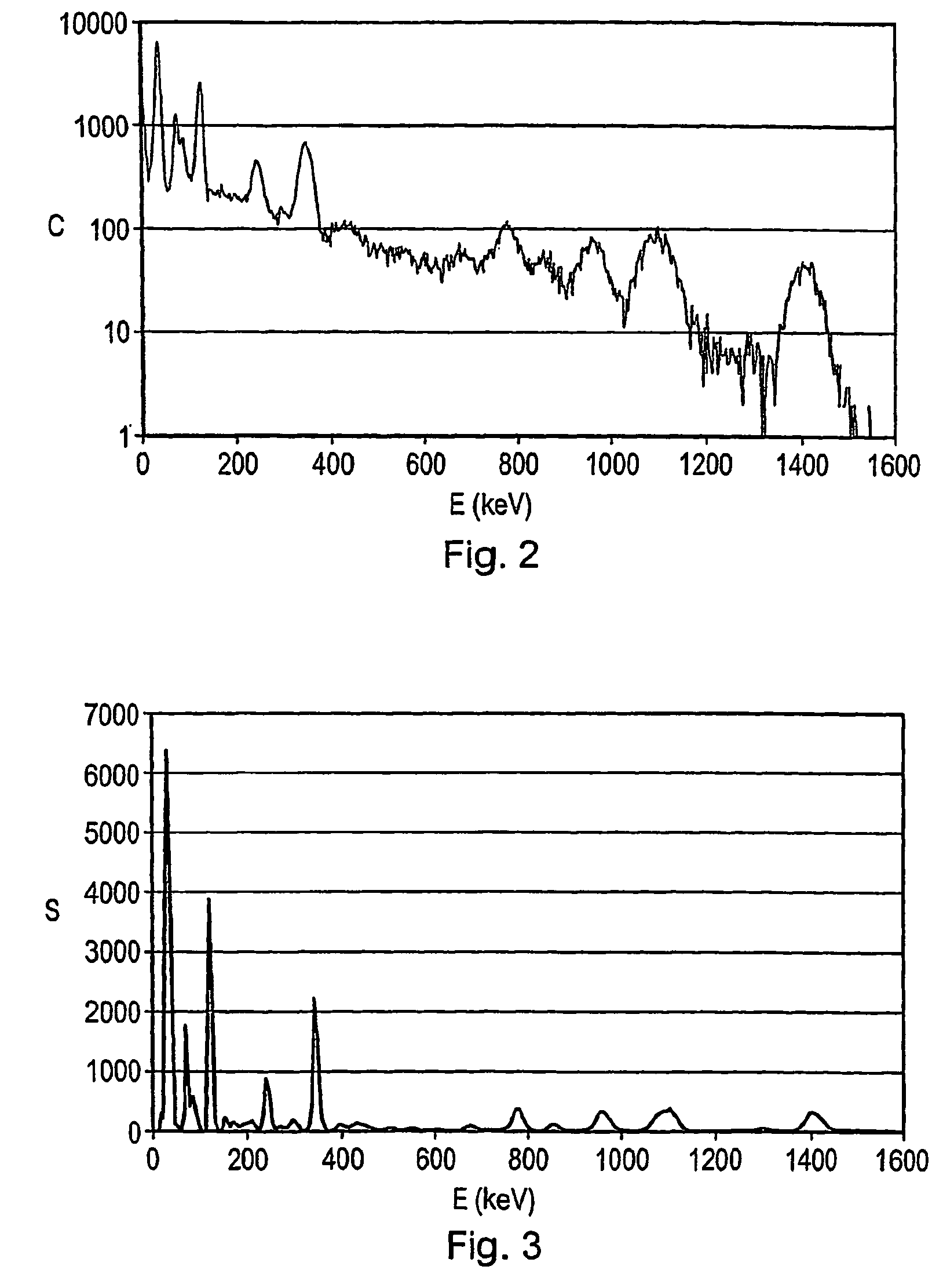
Radioactive isotope identification
ActiveUS8374993B2Reduce calculationReliable choiceX-ray spectral distribution measurementDigital computer detailsGamma rayPeak intensity
A method of identifying radioactive components in a source comprising (a) obtaining a gamma-ray spectrum from the source; (b) identifying peaks in the gamma-ray spectrum; (c) determining an array of peak energies and peak intensities from the identified peaks; (d) identifying an initial source component based on a comparison of the peak energies with a database of spectral data for radioactive isotopes of interest; (e) estimating a contribution of the initial source component to the peak intensities; (f) modifying the array of peak energies and peak intensities by subtracting the estimated contribution of the initial source component; and (g) identifying a further source component based on a comparison of the modified array of peak energies with the database of spectral data. Thus a method for identifying radioactive components in a source is provided which does not rely on comparing template spectra with an observed spectrum.
Owner:SYMETRICA
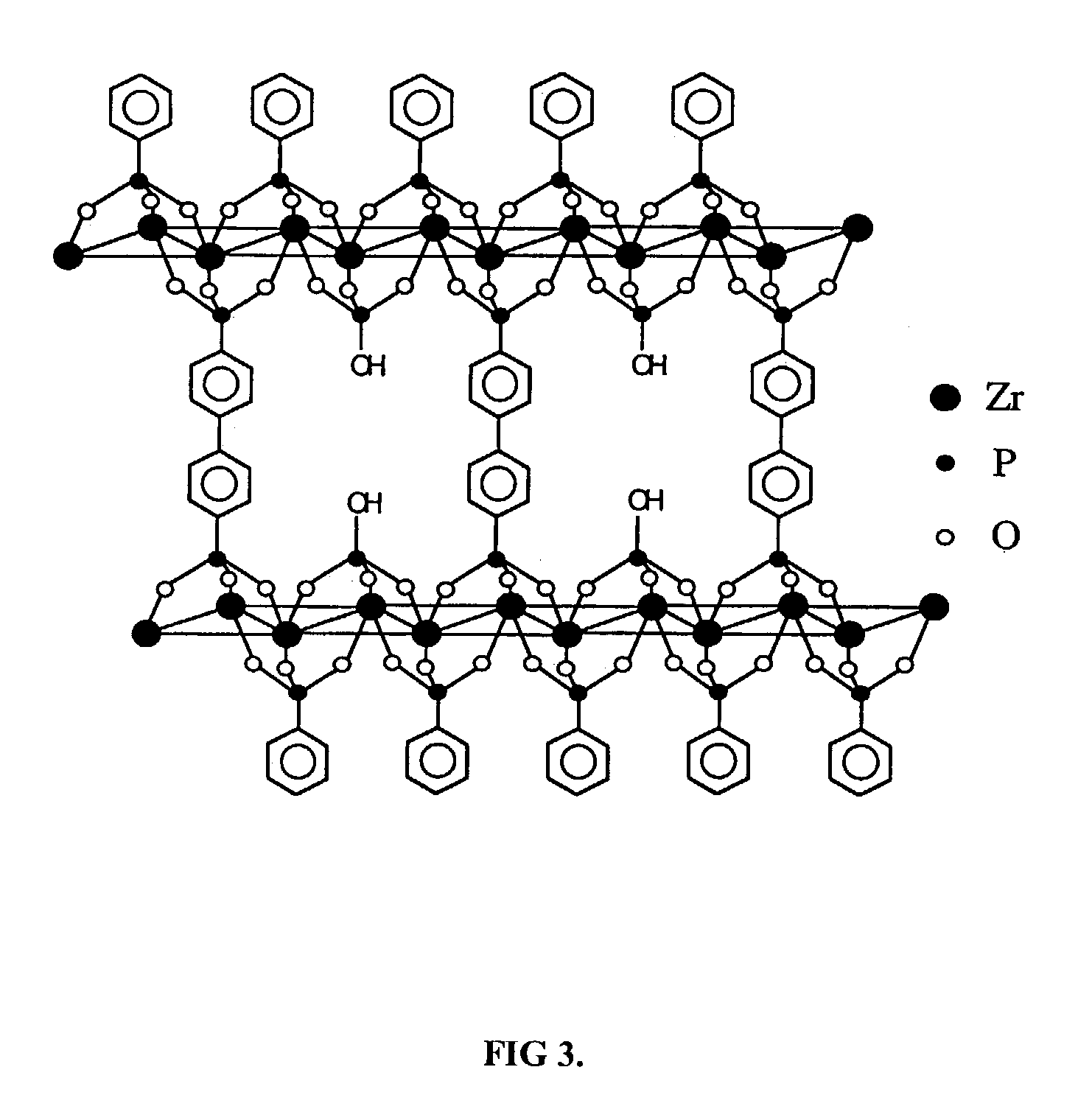
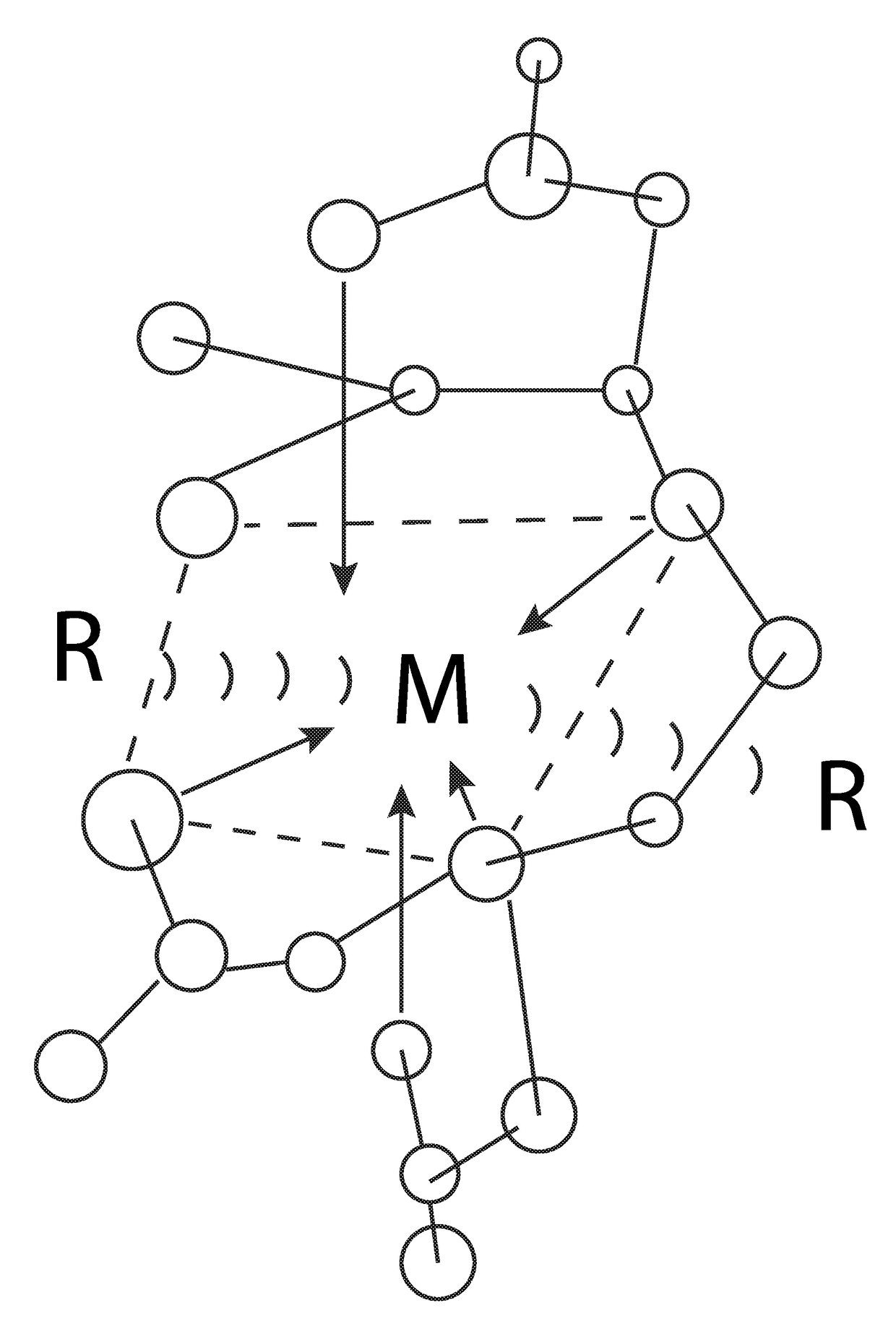
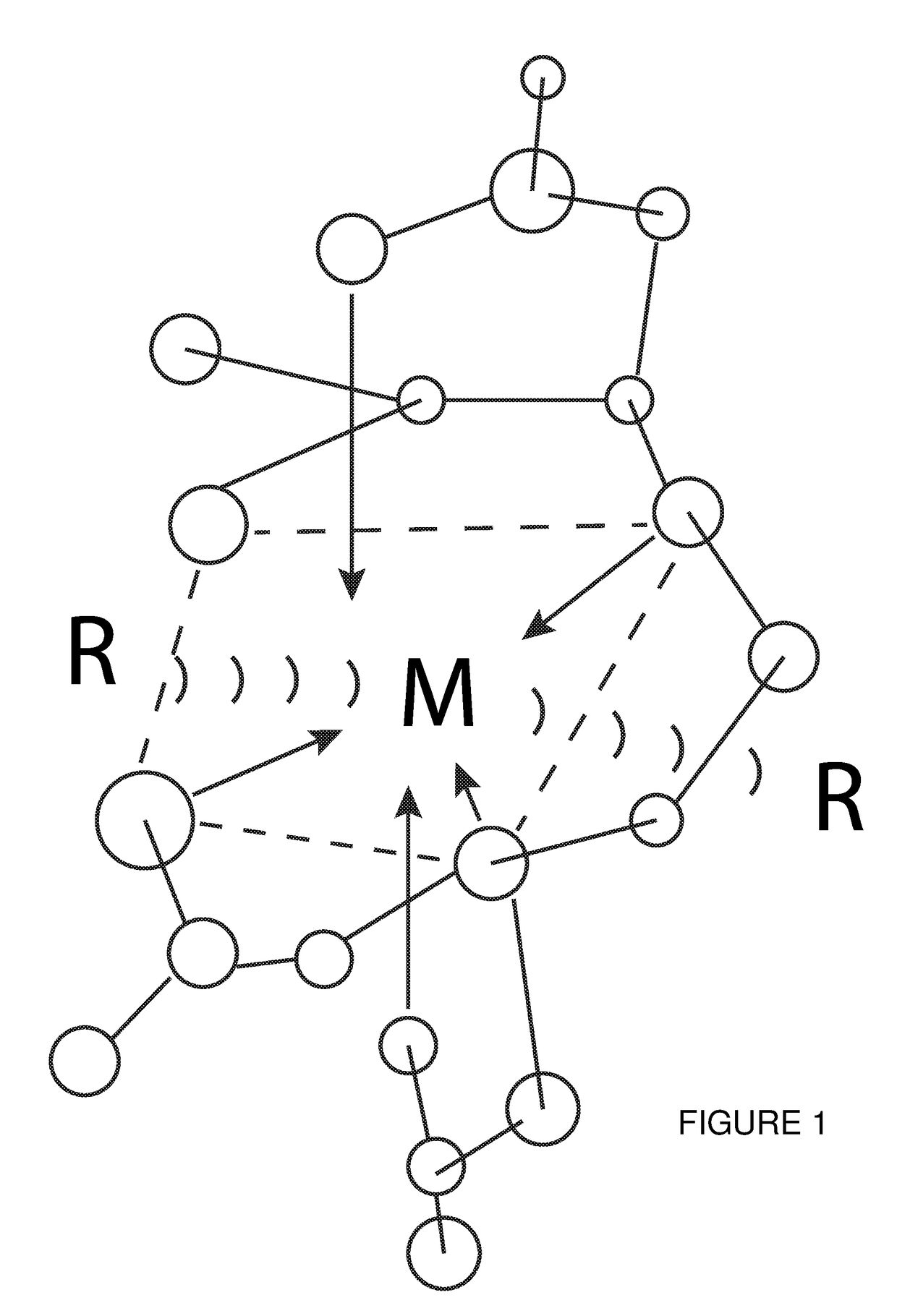
Ion exchange materials for use in a 213Bi generator
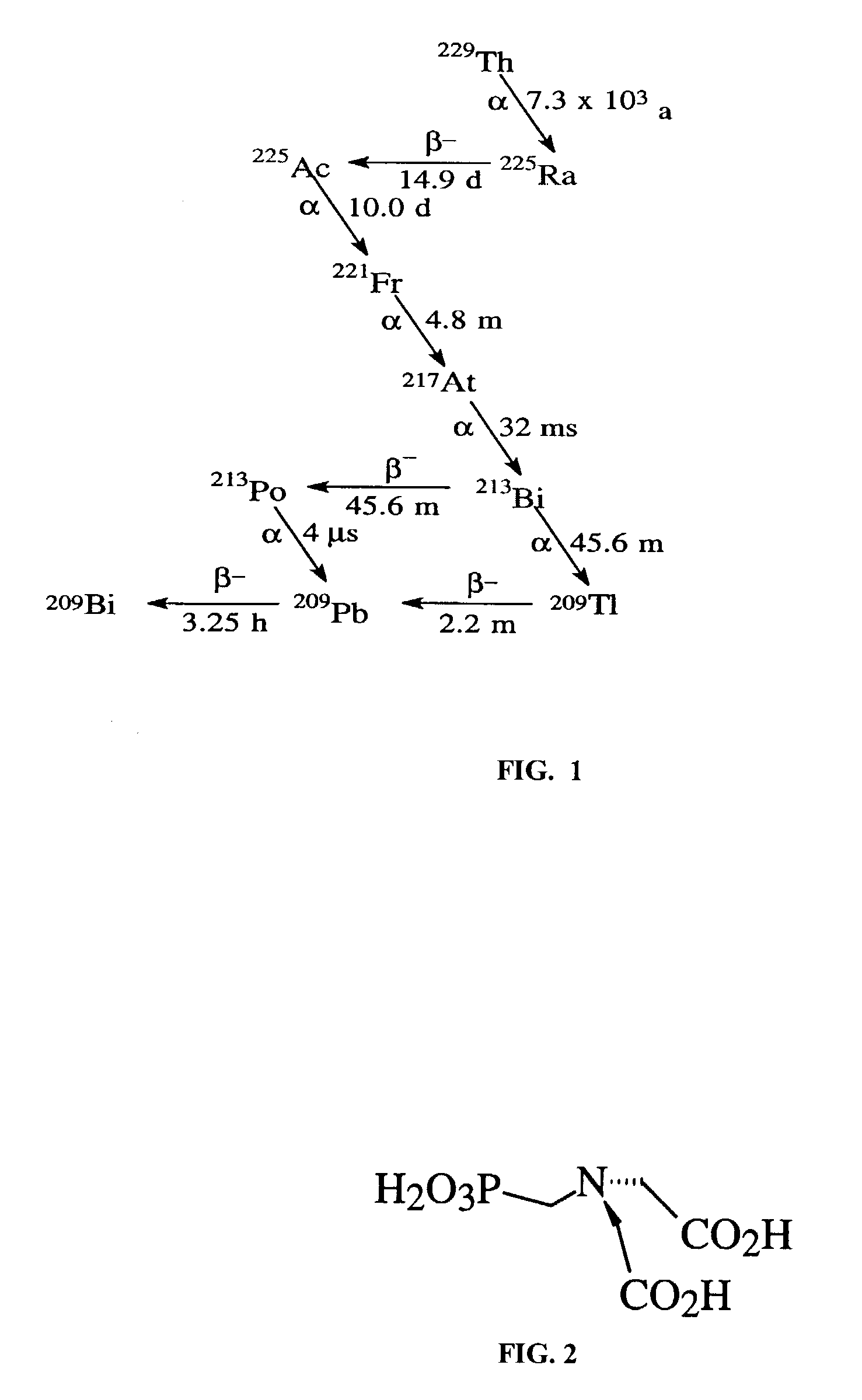
A bismuth-213 generator comprising an insoluble composition having the general formula Zr(Phosponate)x(HPO4)2−x.nH2O, wherein x is between 0 and 2; and n is the number of waters of hydration; and wherein cations of radioactive isotopes selected from radium, actinium and combinations thereof are immobilized on the composition. The value of x may be between about 0.2 and about 1. The phosphonate may be n-phosphonomethyl-miniodiacetic acid (PMIDA), wherein x may be between about 0.1 and about 1.9. The phosphonate may be one or more phosphonate having the formula:H2O3P—(CH2)a—N—((CH2)bCO2H)—((CH2)cCO2H),wherein a, b, and c are numbers from 1 to 3 that may or may not be equal. The value of x may also be between about 0.1 and 1.9.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +2
Pressure testing method for radioactive isotope carrier
ActiveCN102445389ALow costEasy to operateMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesCotton gauzeChemical reaction
The invention discloses a pressure testing method for a radioactive isotope carrier. The method comprises the following steps of: coating a certain quantity of radioactive isotope carriers with cotton gauze, and putting into a high-pressure reaction kettle which is resistant to the pressure of 10-40 MPa; putting chemical reagents which can produce gases through chemical reactions into the high-pressure reaction kettle in an isolating way; sealing the high-pressure reaction kettle, mixing the at least two types of chemical reagents, and raising the pressure of a system to a target pressure; when the pressure is constant, preserving pressure for 3-5 hours; and safely deflating to the normal pressure in a ventilation kitchen, opening the high-pressure reaction kettle, taking the radioactive isotope carriers out, and measuring the breakage rate, density and granularity by experimenting. The pressure testing method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of low equipment cost and easiness, convenience and practicability for operating.
Owner:河南省同新科技有限责任公司
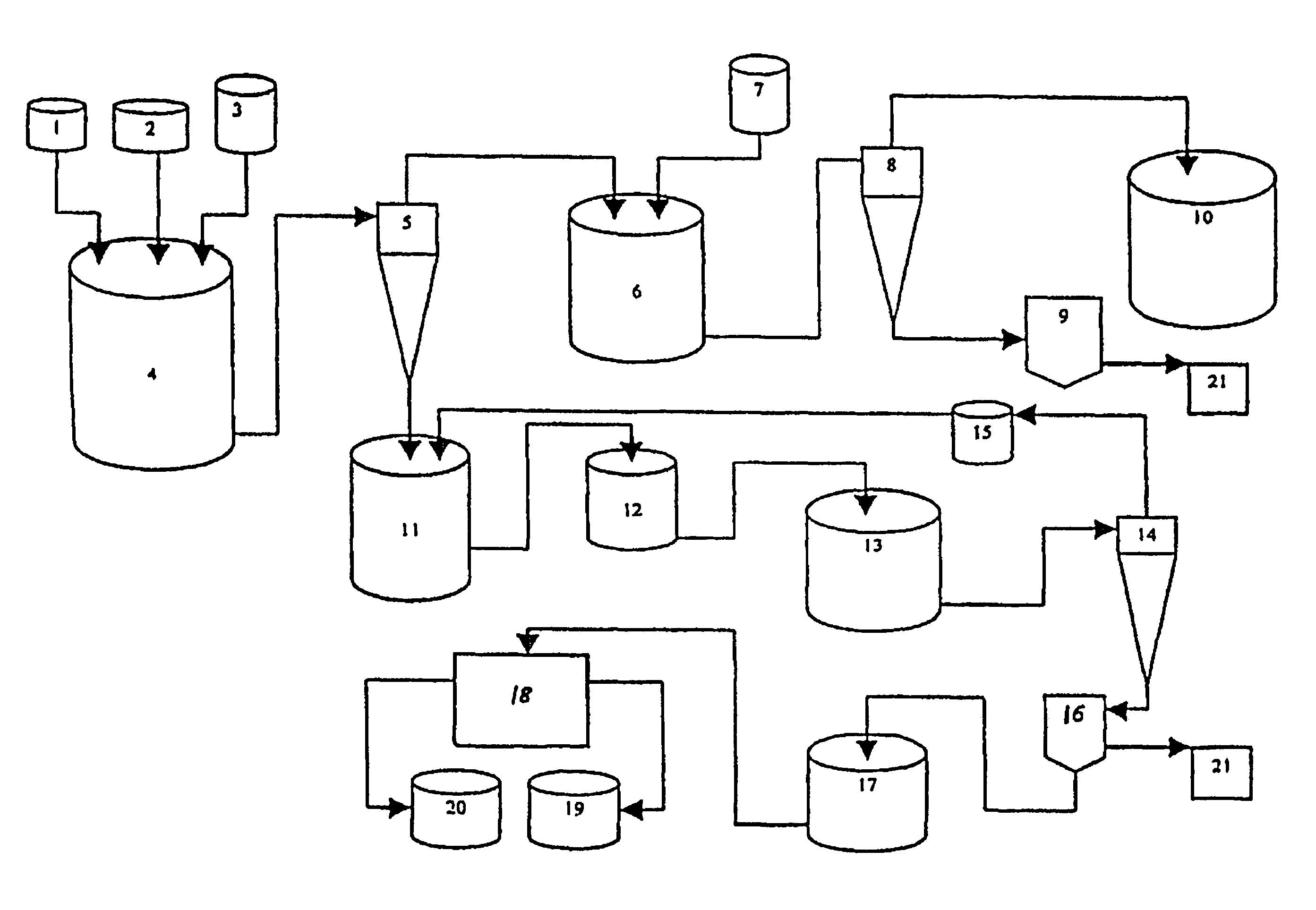
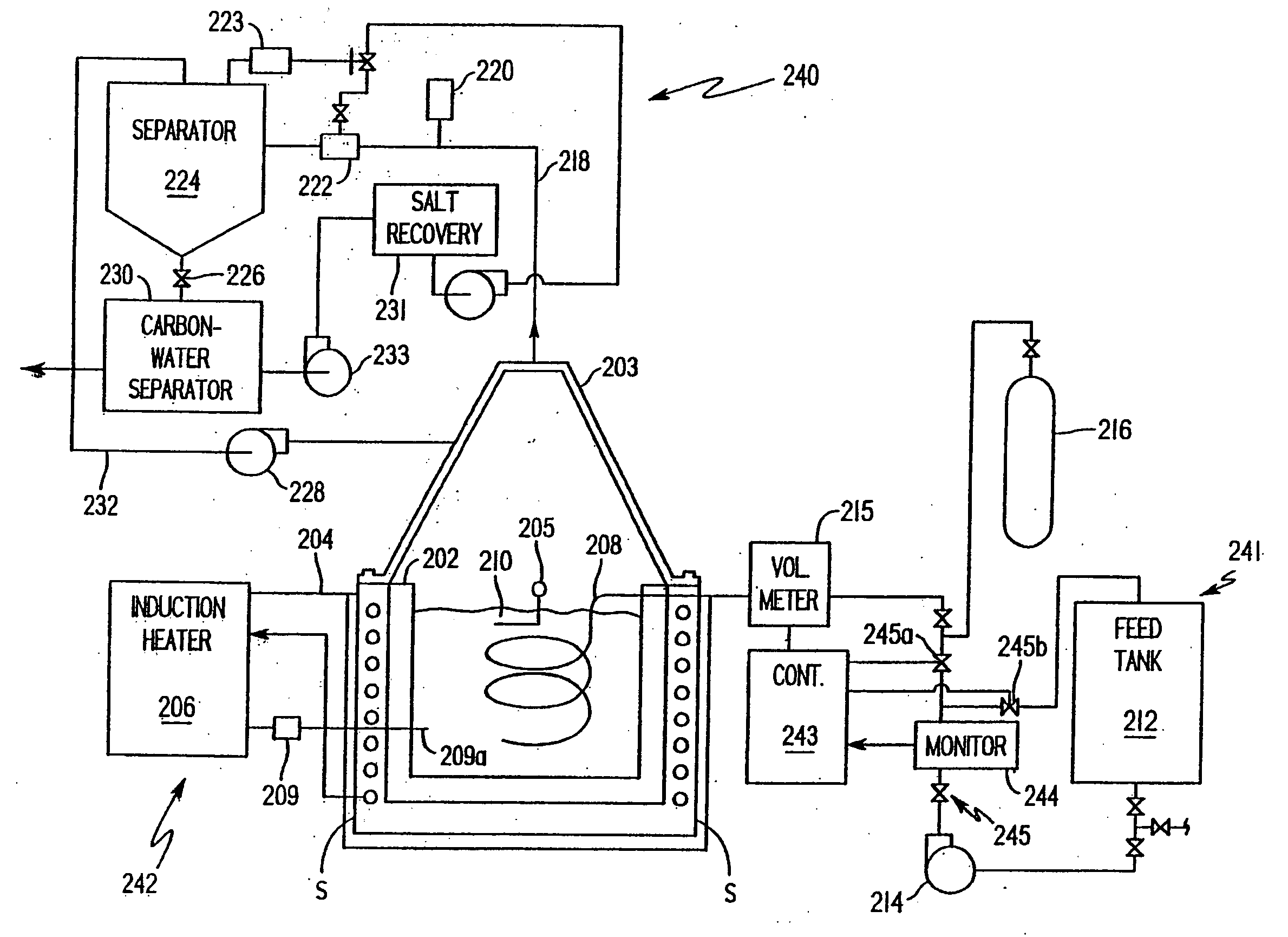
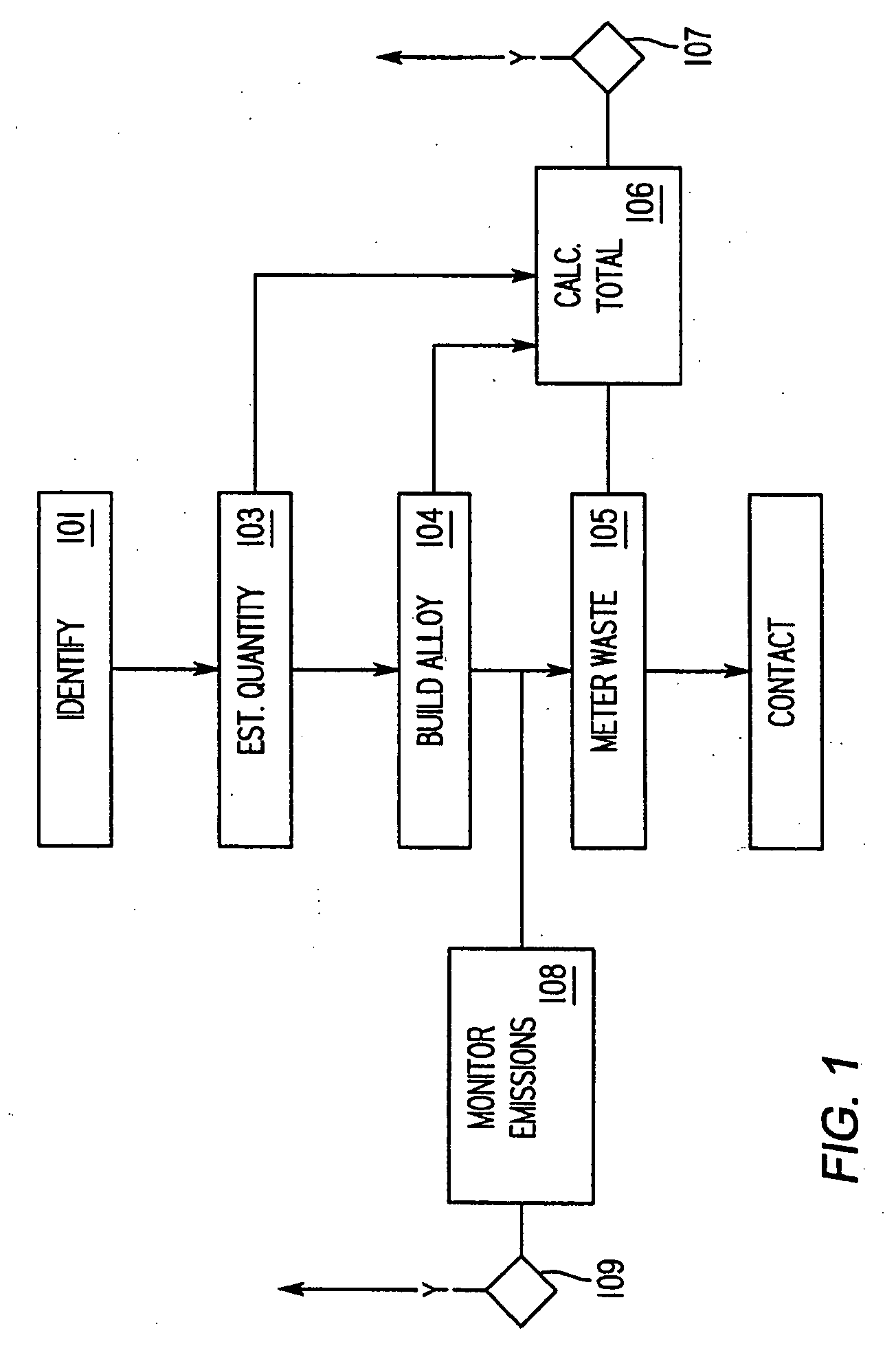
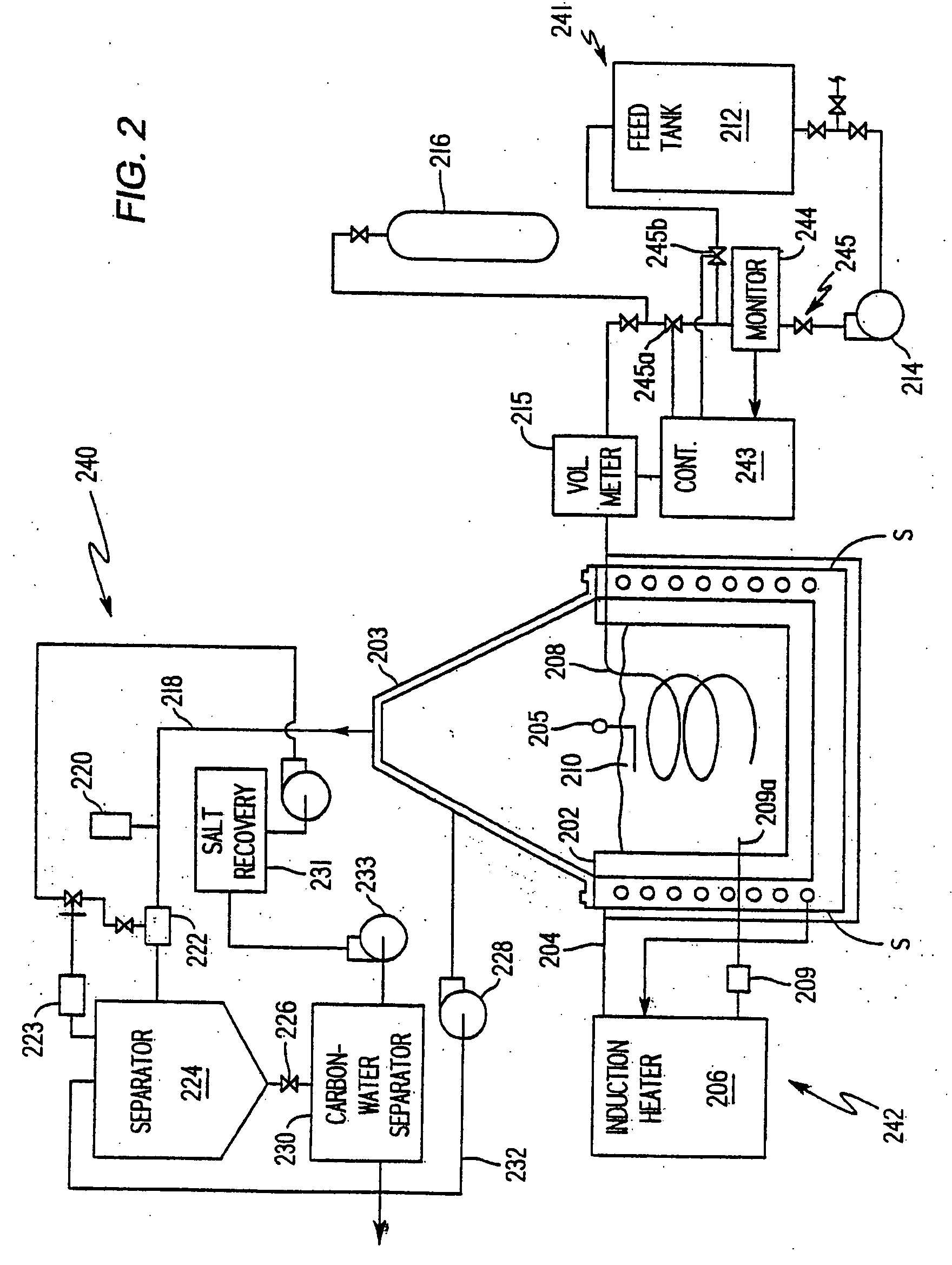
Method and installation for the treatment of radioactive wastes
InactiveUS7323613B2Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementCesium IsotopesPressurized water reactor
The invention relates to a method and system for the treatment of radioactive wastes produced as a consequence of the operation of nuclear power plants with pressurized water reactors and boron reactivity regulation accompanied by the simultaneous production of environmentally acceptable substances of, for example, borax, calcium-magnesium borates, boron acid and sodium hydroxide solutions.As a result of the radioactive waste treatment method and system according to the invention, the following products are obtained: borax with an environmentally acceptable content of radioactive isotopes that contain only the cesium isotopes with a maximum total concentration of 800 Bq in one kilogram of borax; calcium, magnesium and / or calcium-magnesium borates with an environmentally acceptable content of radioactive isotopes; boron acid solution with an environmentally acceptable content of radioactive isotopes; sodium hydroxide solution containing only the cesium isotopes with a maximum total concentration of 800 Bq in one kilogram of sodium hydroxide; and radioactive waste containing under 5 g / l of boron acid.
Owner:VLADIMIROV
Inorganic cellular monobloc cation-exchange materials, the preparation method thereof, and separation method using same
ActiveUS20160318012A1Maintain good propertiesImprove exchange effectIon-exchange process apparatusCation exchanger materialsNanoparticleIon exchange
A material in the form of an alveolar monolith consisting of a matrix of an inorganic oxide with a hierarchical and opened porosity comprising macropores, mesopores and micropores, said macropores, mesopores and micropores being interconnected, and nanoparticles of at least one metal cation exchange inorganic solid material being distributed in said porosity.A method for preparing this material and a method for separating a metal cation notably a cation of a radioactive isotope of a metal such as cesium using this material.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Radioactive isotope wastewater treatment system
InactiveCN110787531AAvoid accumulationAvoid wastingWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationTransportation and packagingWater treatment systemTreatment system
The invention discloses a radioactive isotope wastewater treatment system, and belongs to the technical field of radioactive isotope wastewater treatment. Key points of the technical scheme are as follows: the system comprises a separation tank for separating solid wastes in wastewater, a plurality of radioactive isotope wastewater attenuation tanks, a plurality of waste storage chambers, a stirring device and a collecting device; the stirring device is arranged in the separation tank; an inclined plane sedimentation structure is arranged in the separation tank and is used for settling solid wastes crushed by the stirring device, so that the crushed solid wastes can enter into the collecting device; the radioactive isotope wastewater attenuation tanks are all provided with drainage pipes for drainage, the radioactive isotope wastewater attenuation tanks are connected with the separation tank through water inlet pipes; and after processed wastewater is detected to be qualified, the drainage pipes are opened to discharge wastewater in the radioactive isotope wastewater attenuation tanks. The radioactive isotope wastewater treatment system can achieve the purpose of synchronously treating radioactive wastewater and solid wastes, is suitable for treating radioactive isotope wastewater, and can effectively reduce the pollution of solid waste and wastewater to the environment.
Owner:南宁卫康医疗器械有限公司
Metal alloy and metal alloy storage product for storing fast neutron emitters
InactiveUS20050254988A1Prevent significant mechanical degradationEmission reductionFurnaces without endless coreSolid waste disposalNeutron emissionMixed waste
A liquid reactant metal alloy includes at least one chemically active metal for reacting with non-radioactive material in a mixed waste stream being treated. The reactant alloy also includes at least one radiation absorbing metal. Radioactive isotopes in the waste stream, including any fast neutron emitting isotopes alloy with, or disperse in, the chemically active metal and the radiation absorbing metals are able to absorb a significant portion of the radioactive emissions associated with the isotopes. A transmutation target fraction is included for absorbing fast neutrons and a transmutation emission absorbing fraction is provided for absorbing emissions that result from the absorption of a fast neutron by the transmutation target fraction. Non-radioactive constituents in the waste material are broken down into harmless and useful constituents, leaving the alloyed radioactive isotopes in the liquid reactant alloy. The reactant alloy may then be cooled to form one or more ingots in which the radioactive isotopes are effectively isolated and surrounded by the radiation absorbing metals. These ingots comprise the storage products for the radioactive isotopes.
Owner:CLEAN TECH INT
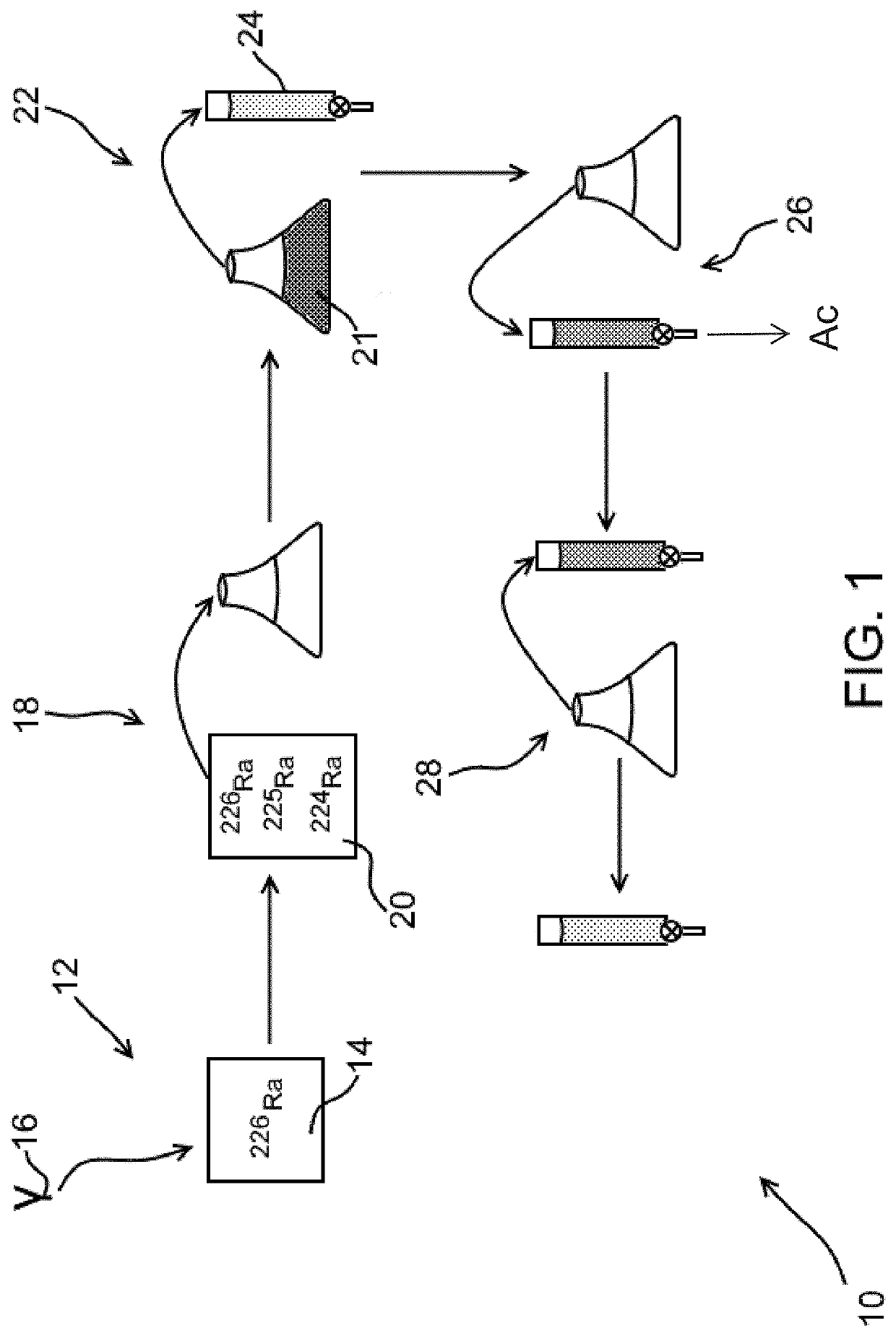
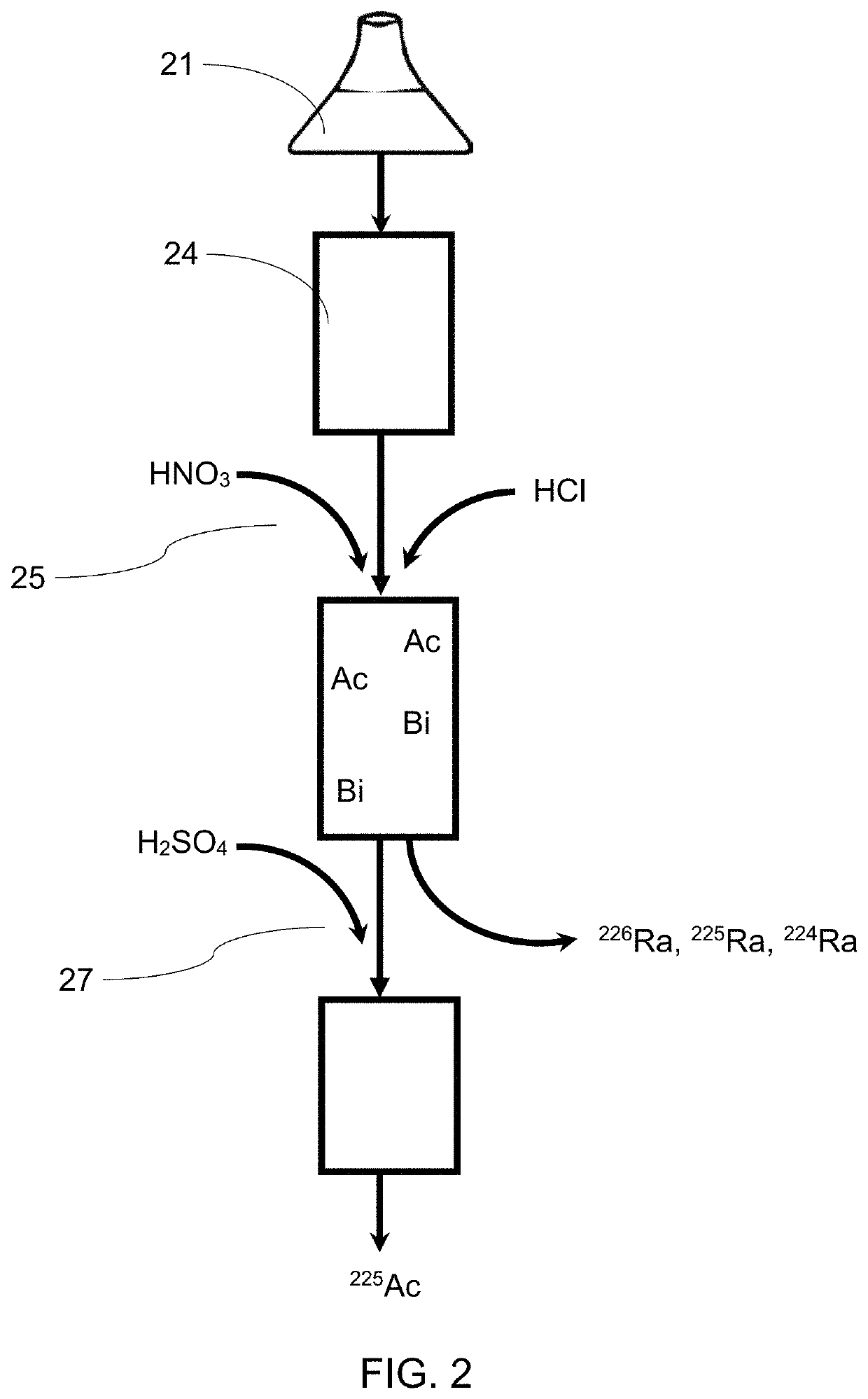
Sytem and method for collecting and isolating radiosotopes
A method for obtaining 225AC from 225Ra having the steps of assembling a column having an inorganic stationary phase; priming the column to immobilize 226Ra 225Ra and natural decay products therefrom; immobilizing the 226Ra, 225Ra, 224Ra, and natural decay products therefrom onto a stationary phase within the column; and eluting the column containing the 225Ra with an aqueous sulfate solution to obtain a milking effluent that contains 225AC. Also provided is a method for obtaining pure 225AC from its isotope parents, the method comprising assembling a column having a stationary phase comprising an inorganic material; priming the column with the isotope parents to immobilize 225Ac, and natural decay products of 225AC; immobilizing the 225Ac, and natural decay products therefrom onto the stationary phase within the column 226Ra, 225Ra, 224Ra; and eluting the column containing the 225AC to obtain an effluent that contains the isotope parents.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Composition for removing naturally occurring radioactive material (NORM) scale
ActiveUS20170313927A1Improve stabilityDetergent mixture composition preparationDrilling compositionAlkaline earth metalRadioactive agent
Owner:FQE CHEM INC
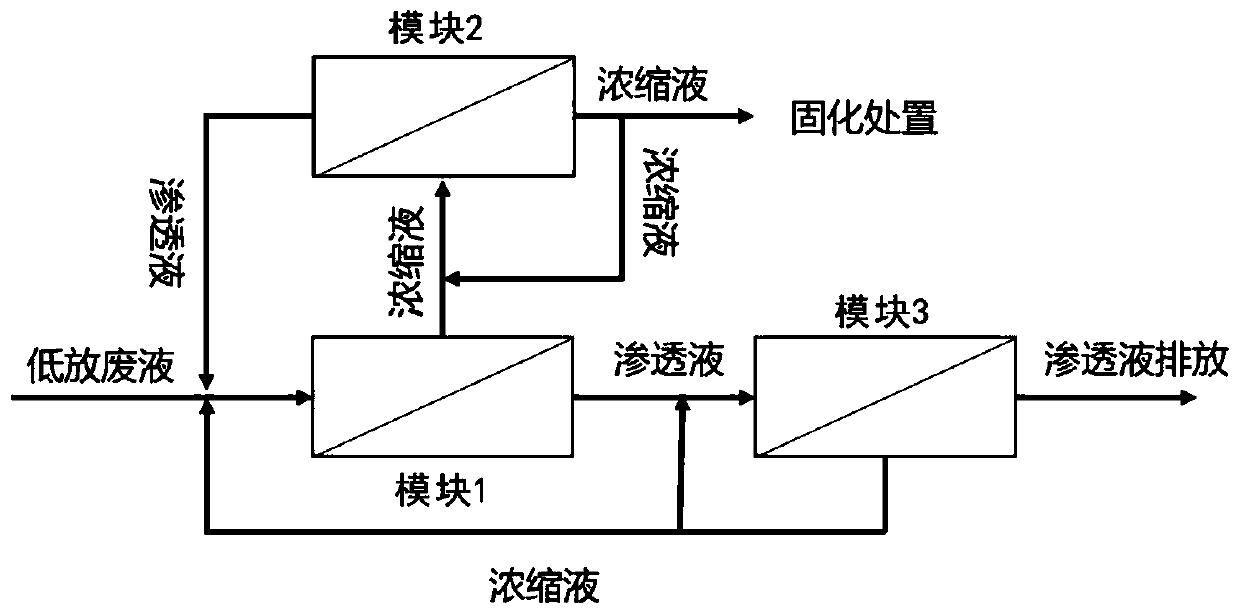
Method and system for separating and concentrating radionuclides in radioactive waste liquid by utilizing reverse osmosis membrane
ActiveCN111434373ALess secondary wasteImprove securityReverse osmosisRadioactive decontaminationReverse osmosisRadioactive waste
The invention relates to a method and a system for separating and concentrating radionuclides in radioactive waste liquid by utilizing a reverse osmosis membrane. In the method and system of the present invention, a specific membrane material having a high decontamination factor for radionuclides in the context of higher non-radioactive ion concentrations is employed. The method comprises the following steps: 1) providing the specific membrane material with a high decontamination factor for radionuclides under the background of higher non-radioactive ion concentration; and 2) enabling radioactive waste liquid to flow through the surface of the membrane material so as to separate and concentrate radionuclides. The method and the system can effectively separate and concentrate radionuclidesin the radioactive waste liquid and solidify the radionuclides, particularly have an excellent removal effect on radioactive isotopes Cs and Co, greatly reduce the amount of secondary wastes, simplifythe process and improve the safety.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
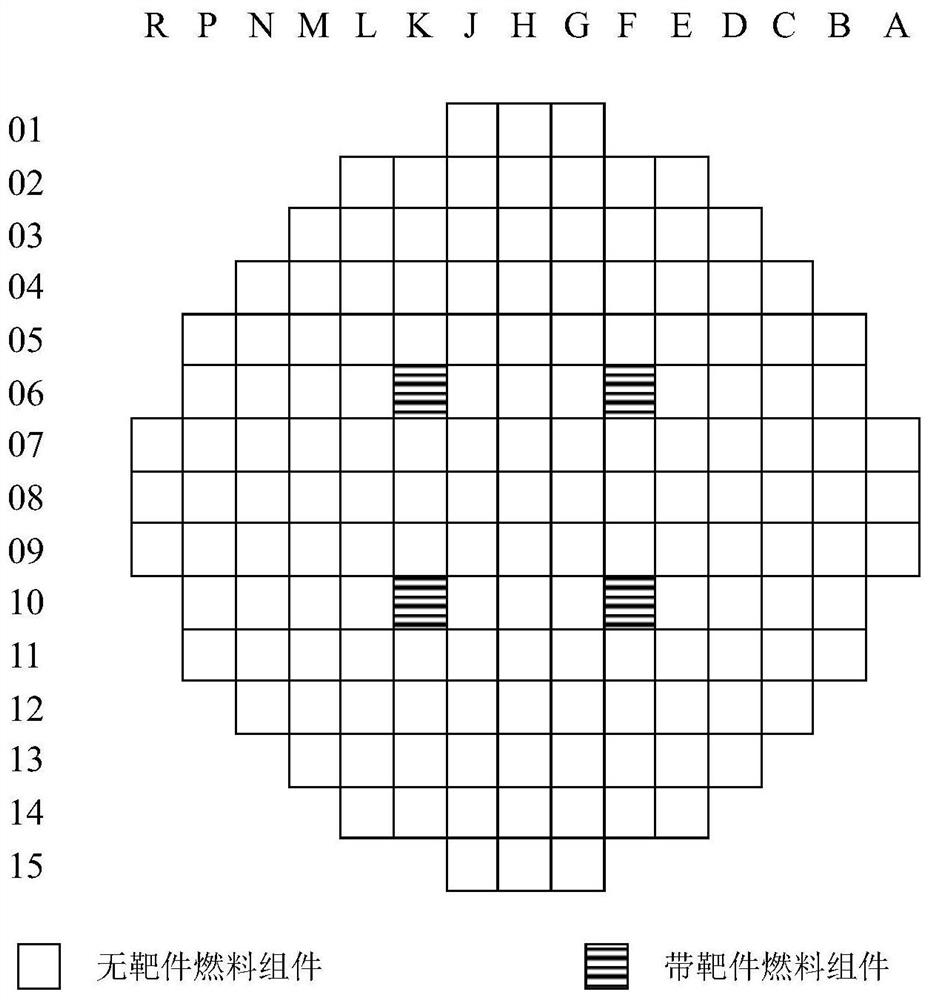
Method for producing radioactive isotopes based on commercial pressurized water reactor irradiation target
InactiveCN111899906AFlexible layoutEfficient use ofConversion in nuclear reactorPressurized water reactorEngineering
The invention discloses a method for producing radioactive isotopes based on a commercial pressurized water reactor irradiation target. The radioactive isotopes are produced by using the commercial pressurized water reactor irradiation target; specifically, the operation of producing the radioactive isotopes by using the commercial pressurized water reactor irradiation target comprises the following steps of: S1, during shutdown of a commercial pressurized water reactor, mounting the irradiation target in a guide pipe of a fuel assembly; S2, enabling the irradiation target to enter a reactor core along with the fuel assembly for irradiation, and carrying out reaction in a neutron field environment in the reactor to generate target radioactive isotopes; and S3, after the reactor is shut down again, taking out the irradiation target, and extracting the target radioactive isotopes. Due to the application of the technology, a new method is provided for the production of radioactive isotopes, the neutron field environment in the pressurized water reactor can be more fully utilized, and the economic performance of the pressurized water reactor is improved.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
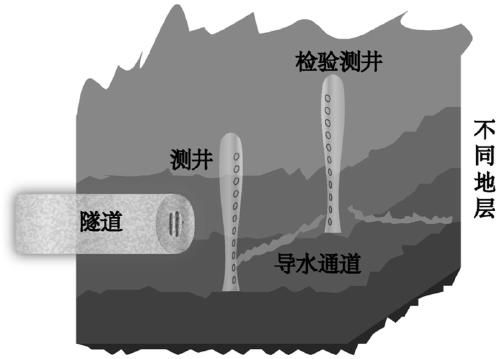
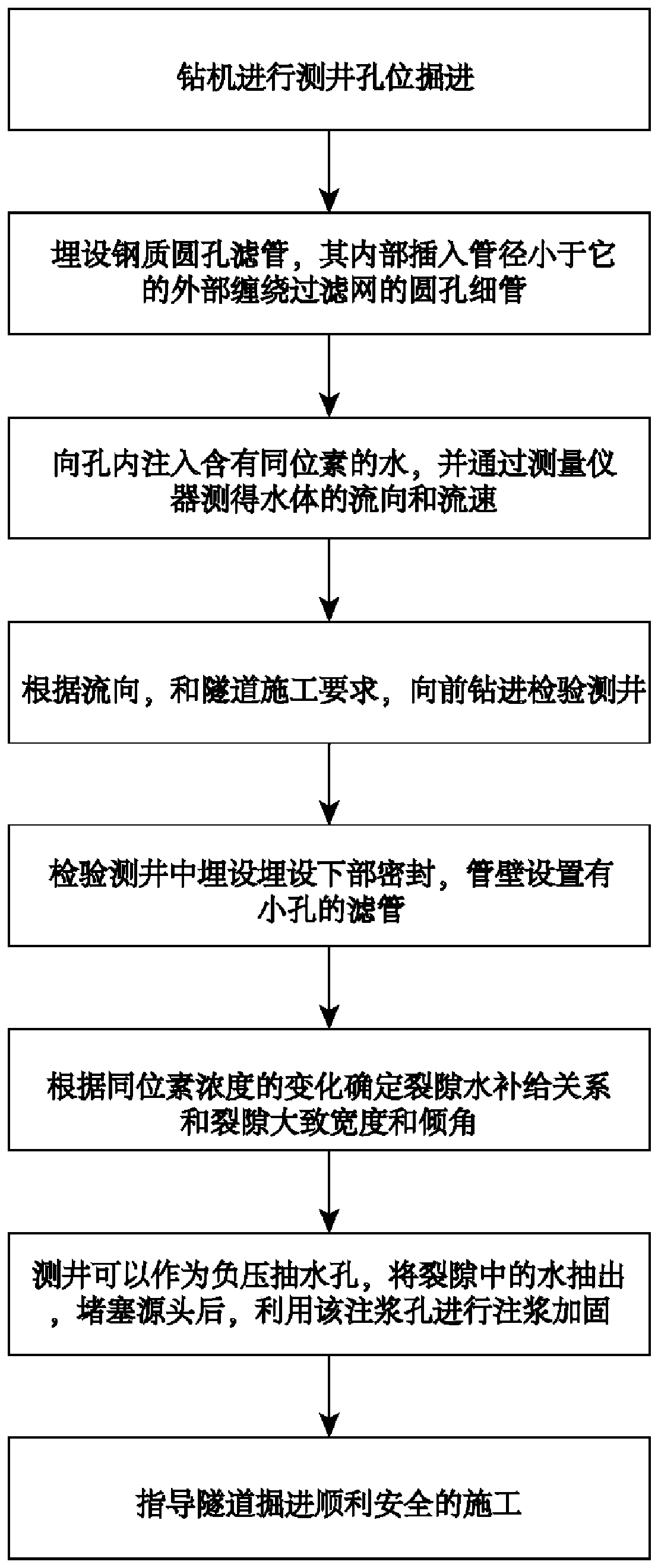
Advanced dynamic forecasting method applying isotope to tracing rock mass water flowing channel
ActiveCN111236927AImprove visibilityFind the locationMining devicesConstructionsSoil scienceWater volume
The invention provides an advanced dynamic forecasting method applying an isotope to tracing a rock mass water flowing channel. The advanced dynamic forecasting method comprises the following steps that pilot drilling is carried out in front of tunneling to form a logging well, and a filter tube is arranged in the logging well; a radioactive isotope tracer is put into the filter tube, a seepage principle is used for permeating water flows, and the flow velocity and the flow rate of water are measured; and an inspection logging well is drilled in front of the water flows, the distribution condition of the water flowing channel is reversely obtained through the determination of the isotope concentration and recording of the water quantity in the inspection logging well, and the feed relationof water of the water flowing channel is determined through the change of the isotope concentration of water flowing into the logging well.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Automatic identification and segmentation of target regions in pet imaging using dynamic protocol and modeling
InactiveUS20200261032A1Improve performanceReduce image noiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsComputerised tomographsRadioactive tracerDigital data
A continuous dynamic positron emission tomography (PET) assembly for imaging a target region of a subject. The assembly includes a radioactive tracer isotope injector configured to administer a radioactive isotope into the subject and a scintillator crystal configured to absorb ionizing radiation from the subject and emit scintillator light. The scintillator crystal undertakes the absorption substantially at the same time of the start of administering the radioactive isotope. The assembly also includes a photo detector in communication with the scintillator crystal, wherein the photodetector is configured to detect the emitted scintillation light as input and provide electrical signals as output. The assembly further includes a signal digitizing circuitry converting the output electrical signals into digital data. Moreover, the assembly includes a processor configured to receive the digital data and implement a model to convert the digital data into a three dimensional, tomographic image reconstruction.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Continuous sampling, detection and sample returning device of on-line ash tester
PendingCN112834289AWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationThermodynamicsAdhesive belt
The invention relates to the field of continuous sampling, detection and sample returning of an online ash meter for a coal preparation plant, and discloses a continuous sampling, detection and sample returning device of an online ash meter. The device is composed of a chute, a sampling port, an upper screw conveyer, an upper screw conveying channel, a lower screw conveying channel, a wear-resistant polyethylene measuring tube, a radioactive isotope online ash content meter, a lower screw conveyer, a return baffle and the like. Coal flow enters the upper spiral conveyor through the sampling port and is conveyed to the discharging end of the upper spiral conveyor, the coal flow falls into the lower spiral conveyor under the gravity action of a coal flow coal sample and is conveyed into the wear-resistant polyethylene measuring pipe, and a detector and a radioactive source of the ash content meter are located at the upper end and the lower end of the wear-resistant polyethylene measuring pipe respectively, and the measured coal flow returns to the chute through the chute discharge hole and the return baffle. The device can eliminate the influence of external factors such as steel wires in the adhesive tape, the compaction degree and the thickness of a coal seam and the like on ash content measurement, and can remarkably improve the measurement precision and the accuracy of an online ash meter.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
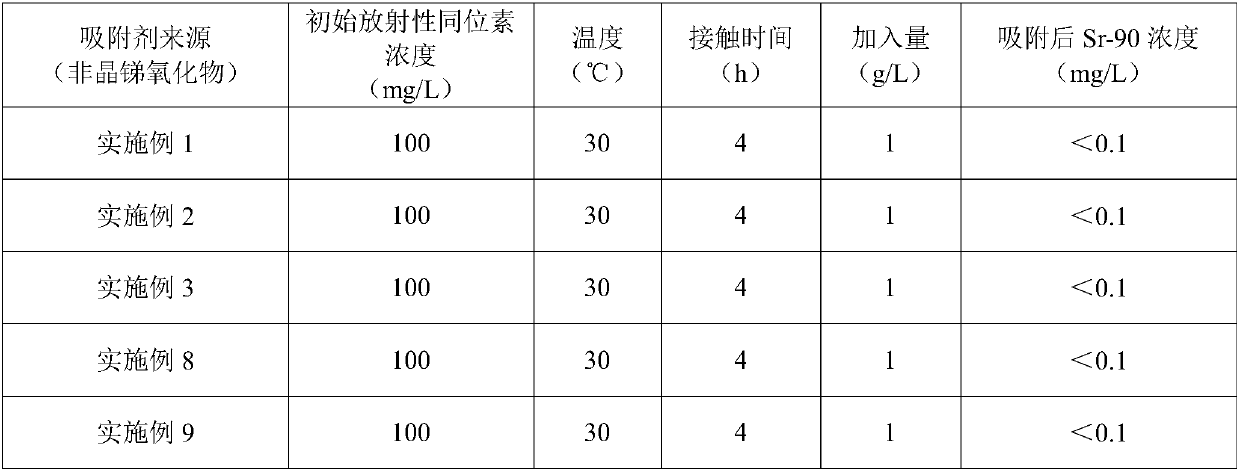
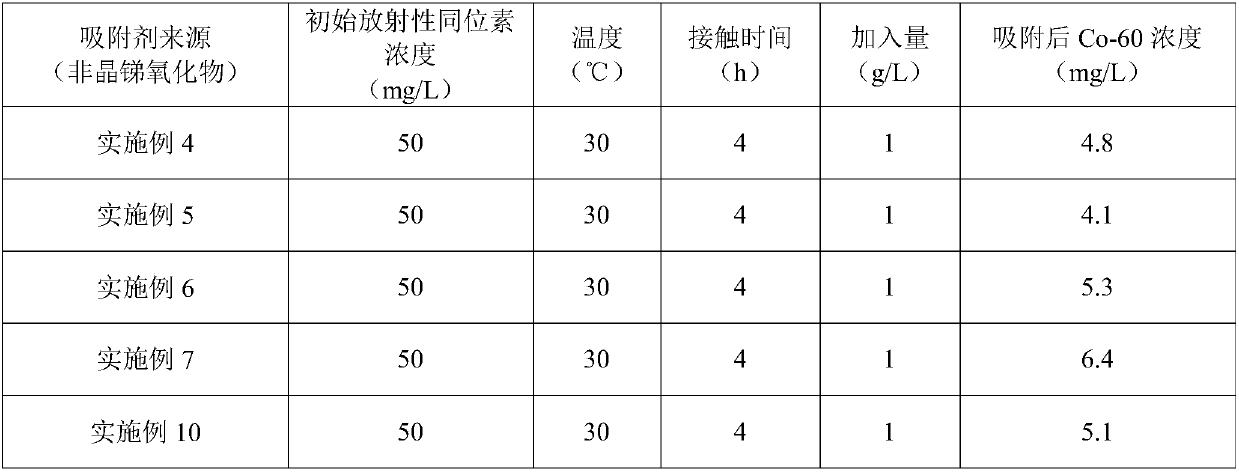
Amorphous antimony oxide for adsorbing radioactive strontium-90 and cobalt-60 and preparation method of amorphous antimony oxide
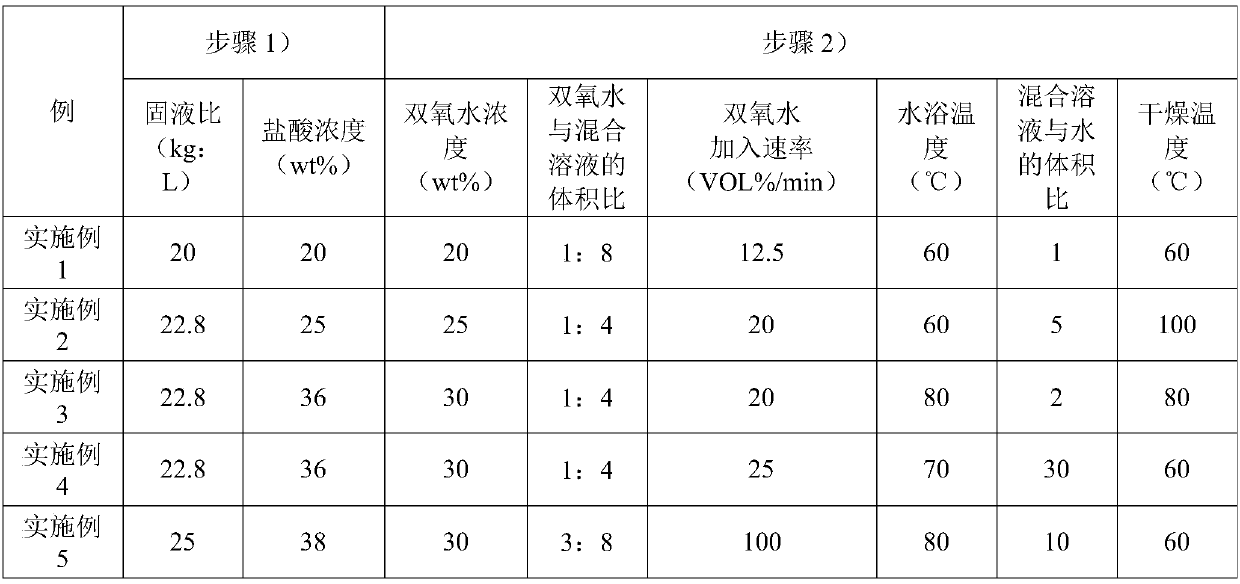
PendingCN109621884ALarge specific surface areaViolent explosive hydrolysis reactionOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesWater bathsSorbent
The invention relates to the field of radioactive element wastewater treatment, and provides an amorphous antimony oxide for adsorbing radioactive Sr-90 and Co-60 and a preparation method of the amorphous antimony oxide in order to solve the problems that an existing organic ion exchange agent has a poor effect and shorter service life when being used for treating low-concentration nuclear radioactive wastewater, and an antimony pentoxide adsorbent prepared in the prior art has the smaller adsorption capacity for Sr-90. The preparation method comprises the following steps that 1) antimony butter and hydrochloric acid are taken as raw materials, weighed and mixed to obtain a mixed solution; 2) the mixed solution is oxidized in a water bath condition and then is mixed and hydrolyzed with a large amount of water, filtering separation is carried out to obtain a hydrolysis product, and the amorphous antimony oxide for adsorbing the radioactive Sr-90 and Co-60 is obtained after drying. The amorphous antimony oxide for adsorbing the radioactive Sr-90 and Co-60 and the preparation method of the amorphous antimony oxide have the advantages that the preparation method is concise and efficient, and a part of raw materials can be recycled; the prepared amorphous antimony oxide has huge specific surface area and a disordered structure, and has a very strong adsorbing effect on Sr-90, Co-60and other radioactive isotopes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Engine internal flow field measuring system and measuring method thereof
ActiveCN112067308ADynamic characteristics truly reflect theDynamic characteristic reflectionX-ray spectral distribution measurementGas-turbine engine testingParticle flowNuclear engineering
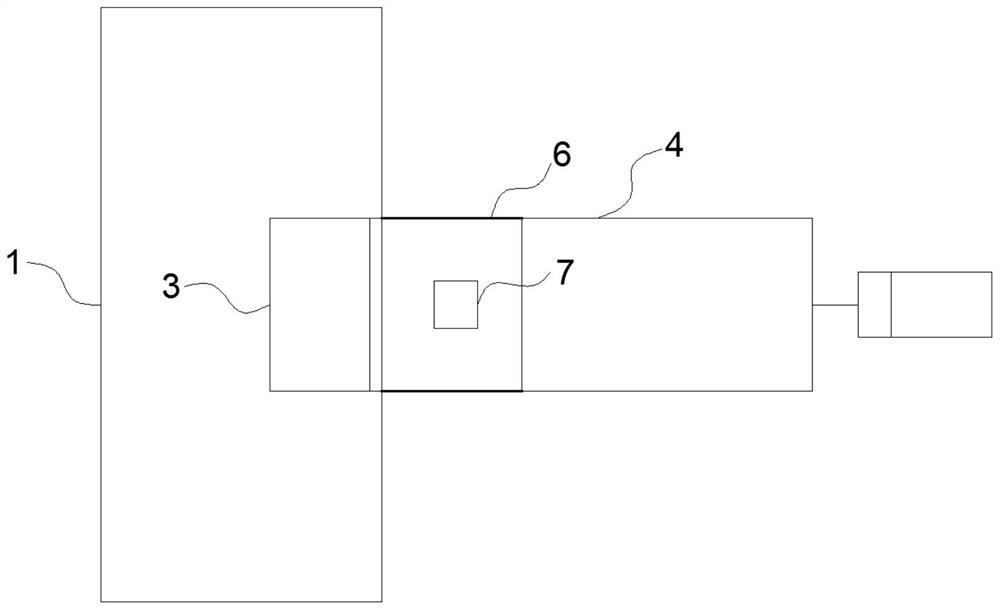
The invention discloses an engine internal flow field measuring system and a measuring method thereof. The method comprises the steps of preparing a grain of a solid rocket engine through employing aradioactive isotope raw material, generating a large amount of high-speed high-temperature fuel gas after the grain is ignited to form a flow field, generating plume through the spraying of a sprayingpipe, and enabling radioactive isotope particles to release gamma rays when the radioactive isotope particles flow along with the flow field, and using the gamma ray dynamic collector for collectingreleased gamma rays to measure the dynamic characteristics of the internal flow field of the solid rocket engine. The measuring system uses radioactive isotopes as tracer particles to achieve non-contact measurement of the internal flow field of the solid rocket engine, and compared with a traditional measuring method, the original structure of the solid rocket engine does not need to be damaged,the problem that a traditional measuring method disturbs an internal flow field can be avoided, and compared with an existing numerical calculation method, the defect that the numerical calculation result is insufficient in accuracy can be overcome.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
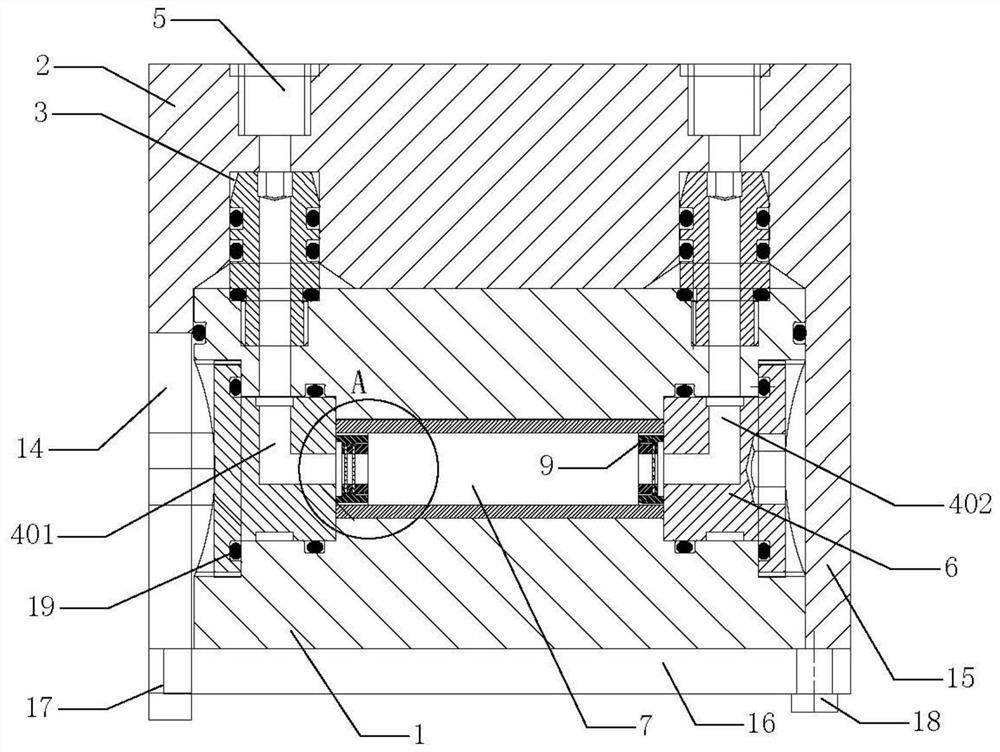
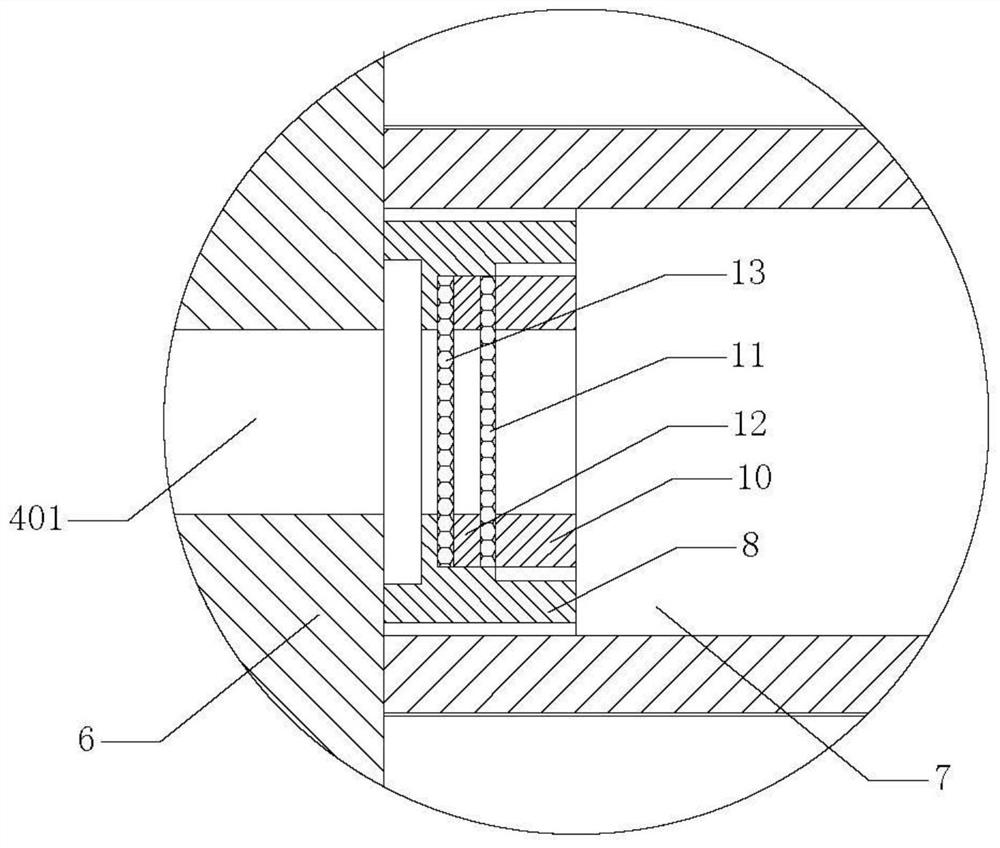
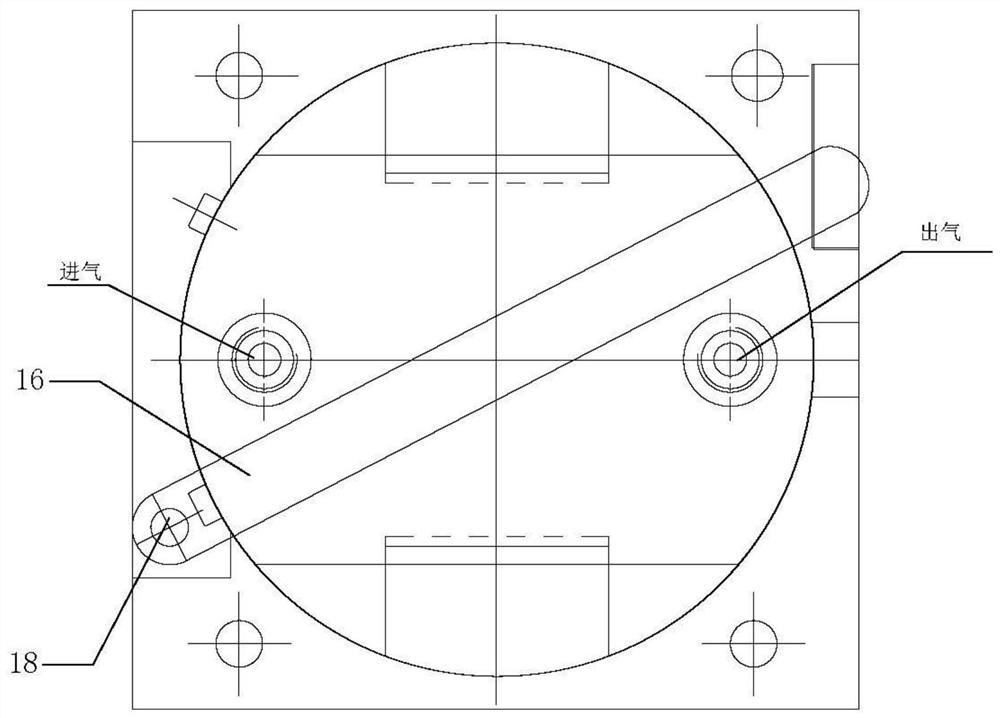
Device for extracting gaseous iodine in loop for producing iodine-125
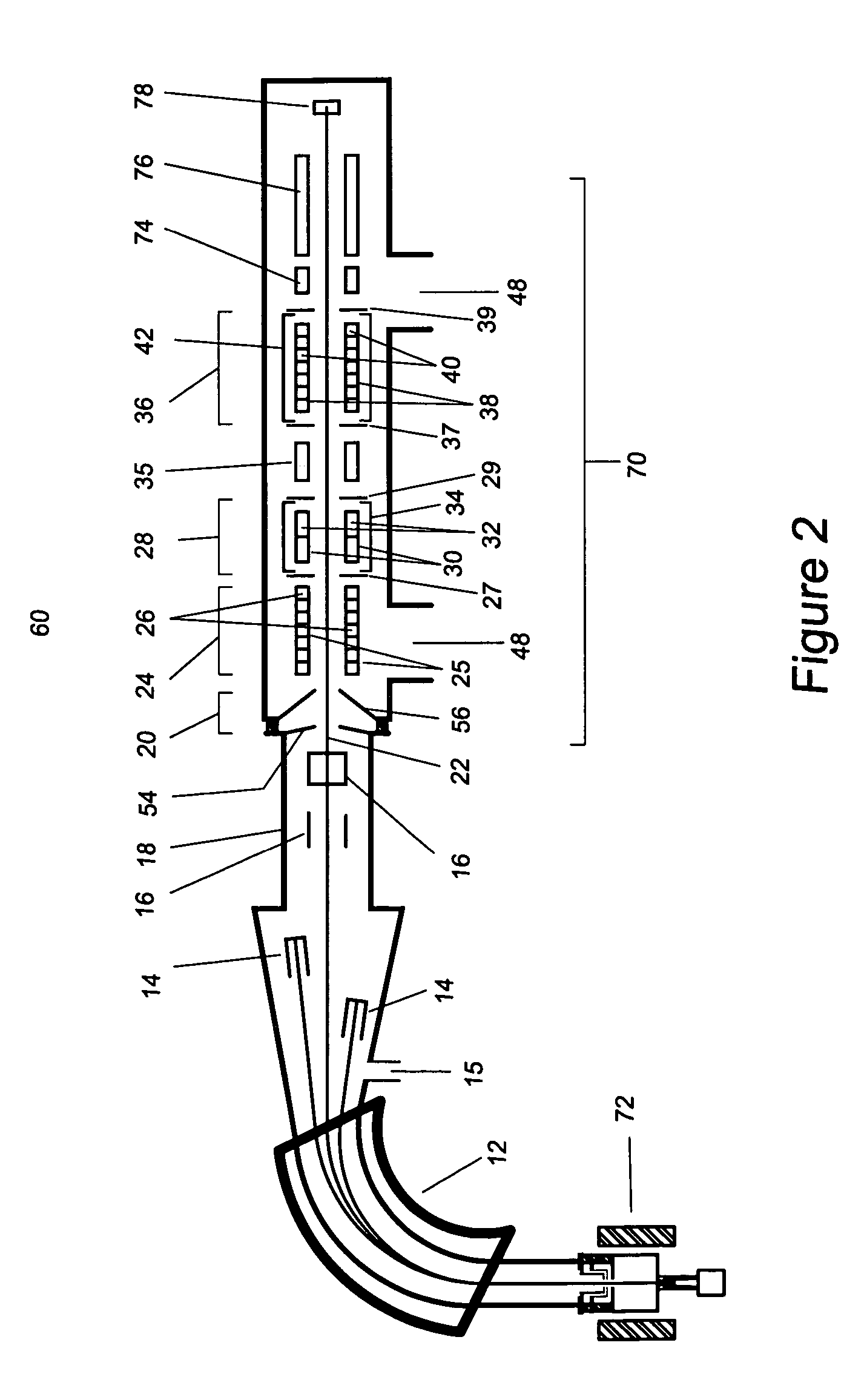
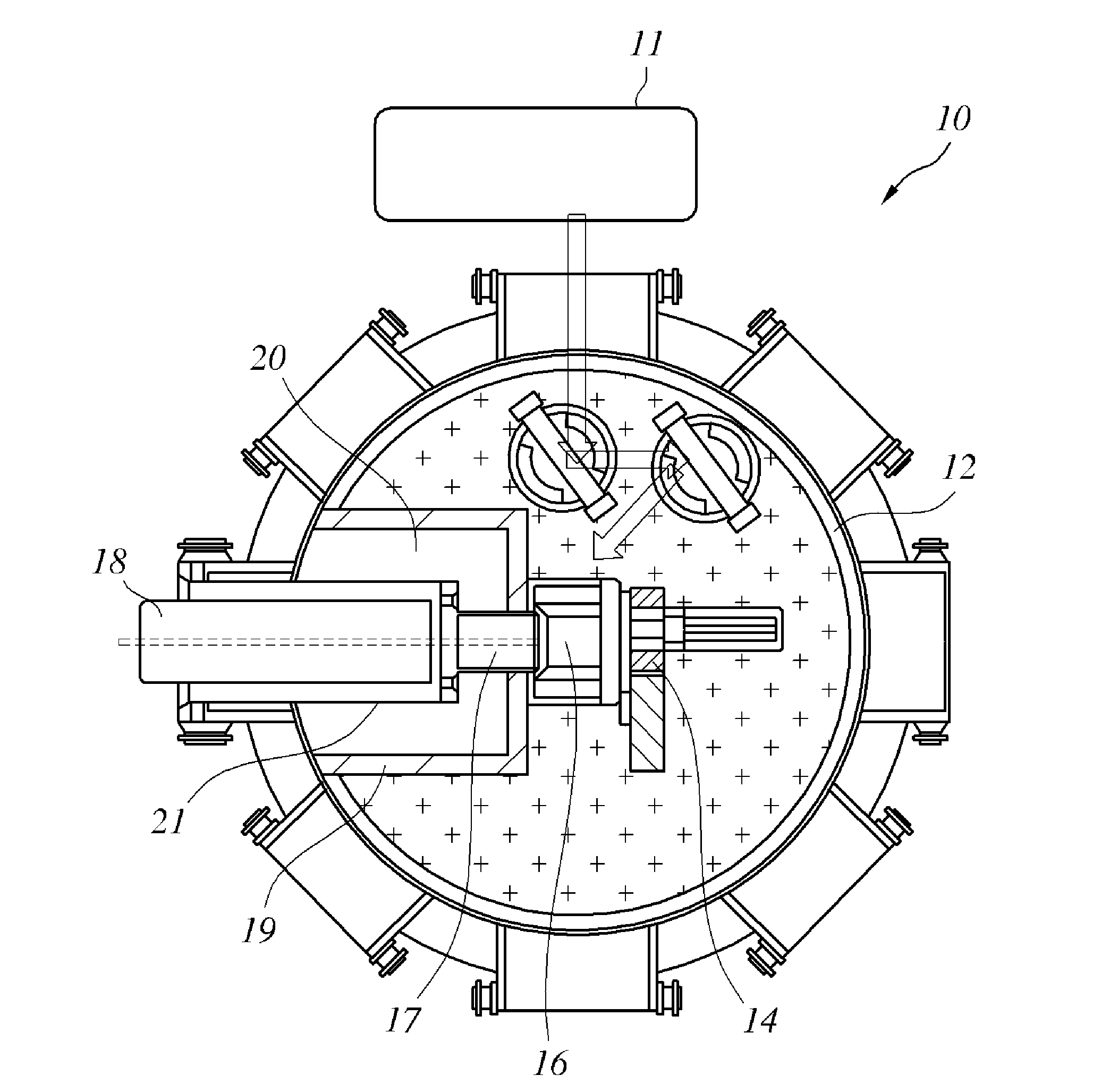
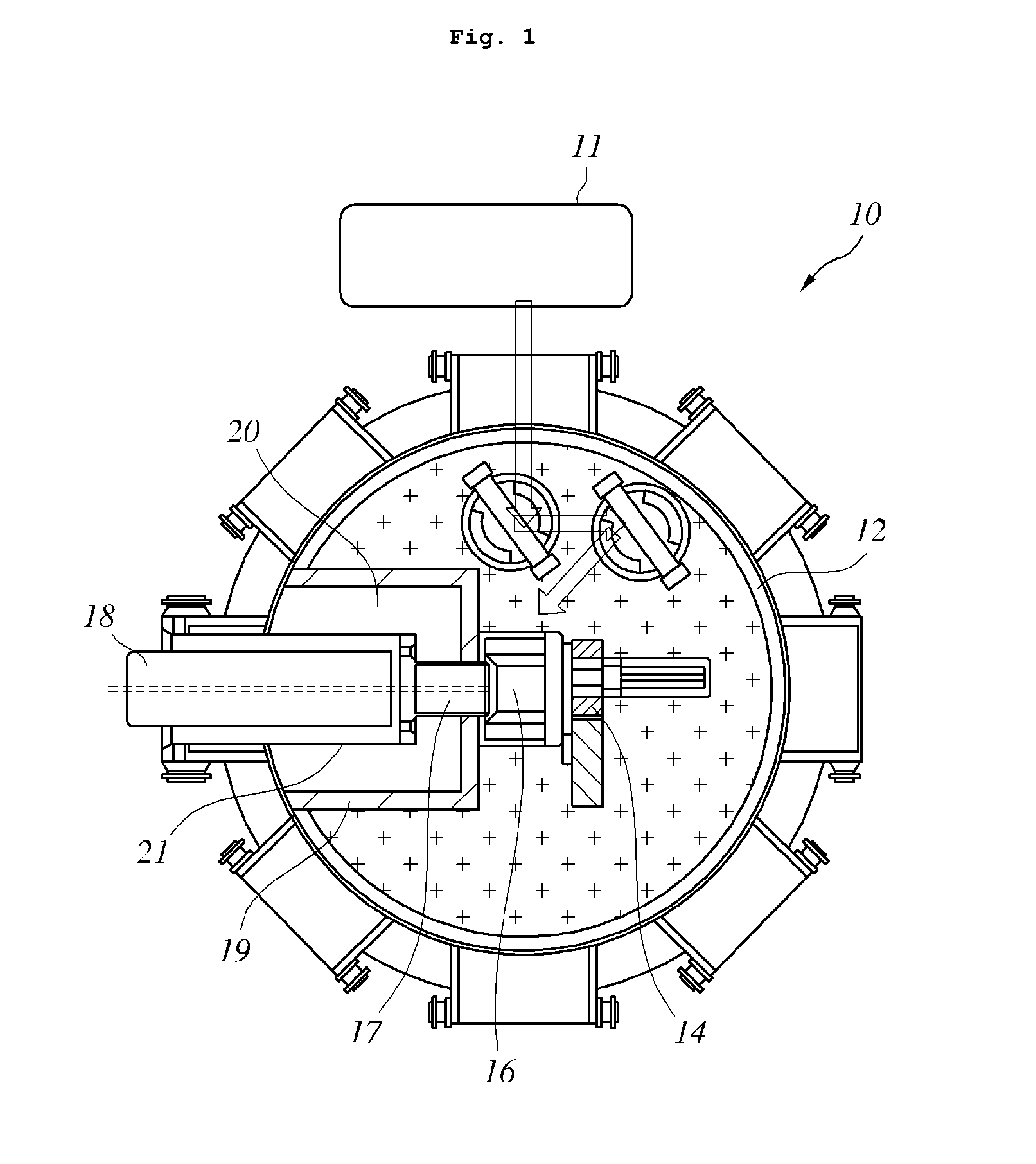
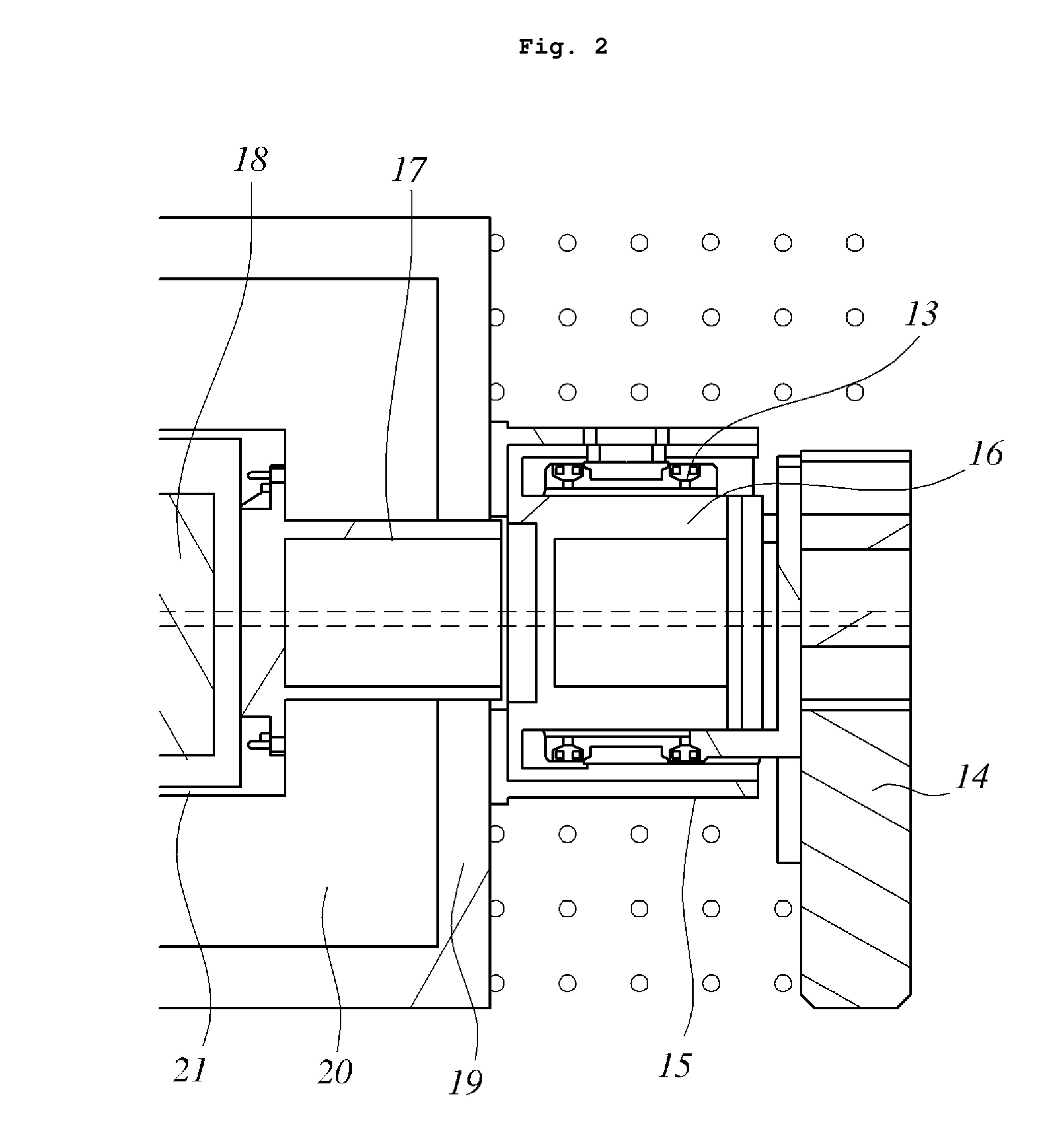
The invention belongs to the field of radioactive isotope preparation, and relates to a device for extracting gaseous iodine in a loop for producing iodine-125. The device comprises a turntable, an extraction mechanism and a fixed seat; the extraction mechanism is mounted in the turntable, one ends of two symmetrically arranged gas nozzles are fixedly connected with the turntable and are butted and communicated with a first gas channel in the extraction mechanism, the other ends of the gas nozzles are inserted into the fixed seat and are respectively butted and communicated with two second gas channels in the fixed seat; and the two second gas channels, the two gas nozzles and the first gas channel form a closed circulating gas loop for gas to enter and exit, and an iodine separation material is arranged in the first gas channel. The extraction mechanism can be plugged on the loop device as an independent structure. The extraction mechanism can prevent iodine-125 generated in the loop from participating in circulation loop irradiation. During recovery, only the extraction mechanism needs to be leached, so that the processes of xenon-125 gas transfer, liquid nitrogen freezing, target cylinder cutting and the like are reduced, the operation process is simplified, the device can be repeatedly used, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:四川海同同位素科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com