Patents
Literature
268 results about "Hyperthermia Treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A type of treatment in which body tissue is exposed to high temperatures to damage and kill cancer cells or to make cancer cells more sensitive to the effects of radiation and certain anticancer drugs.
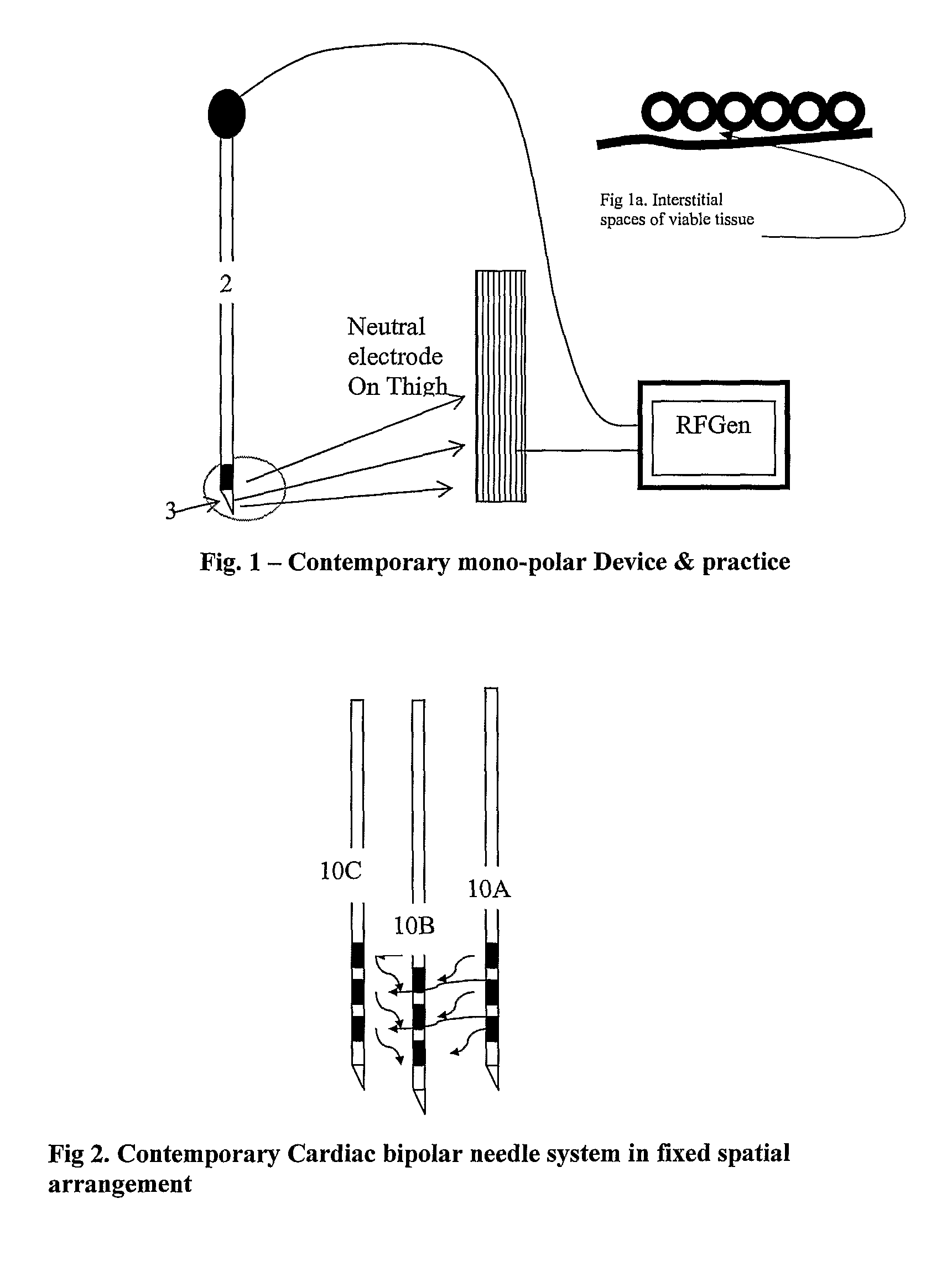
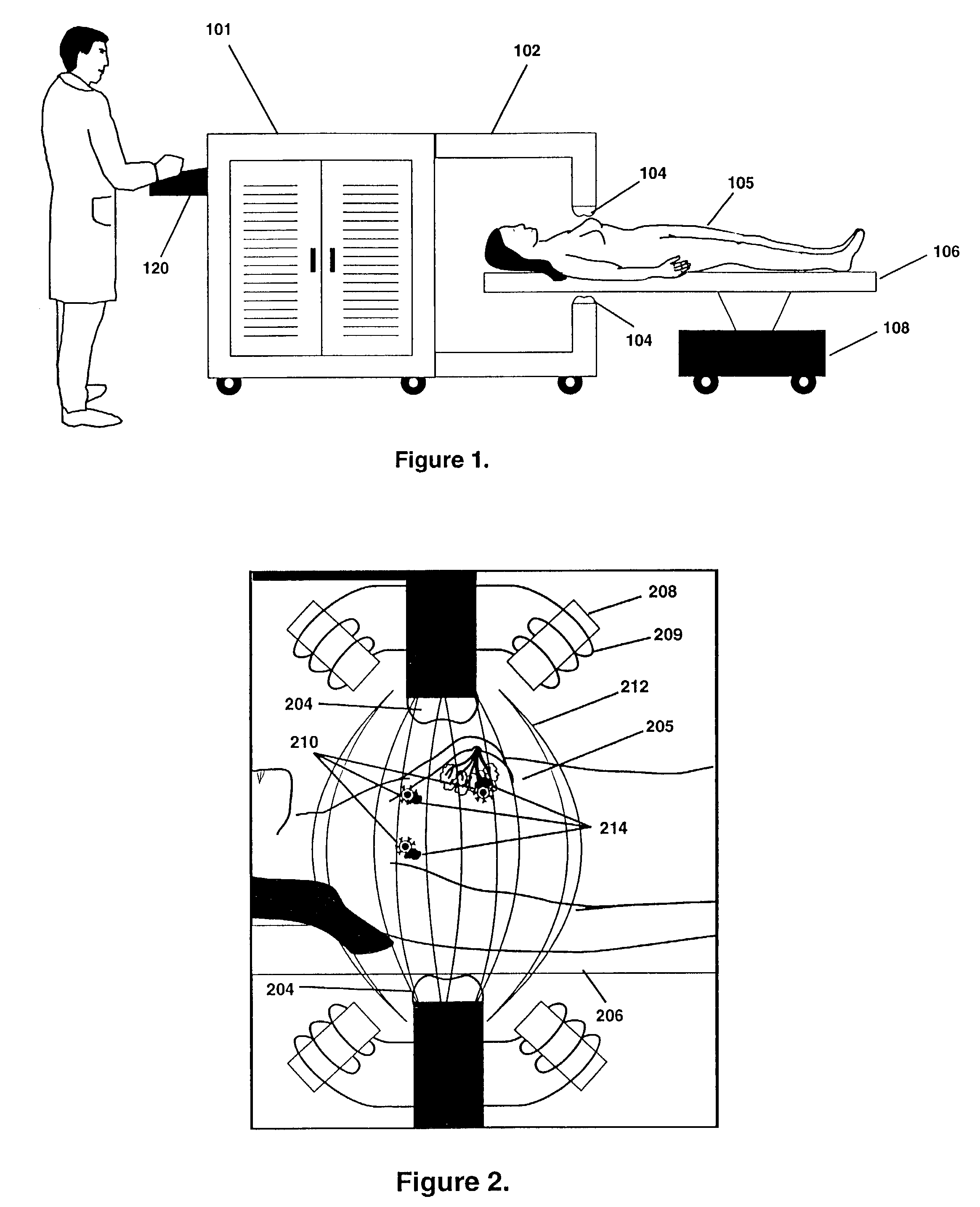
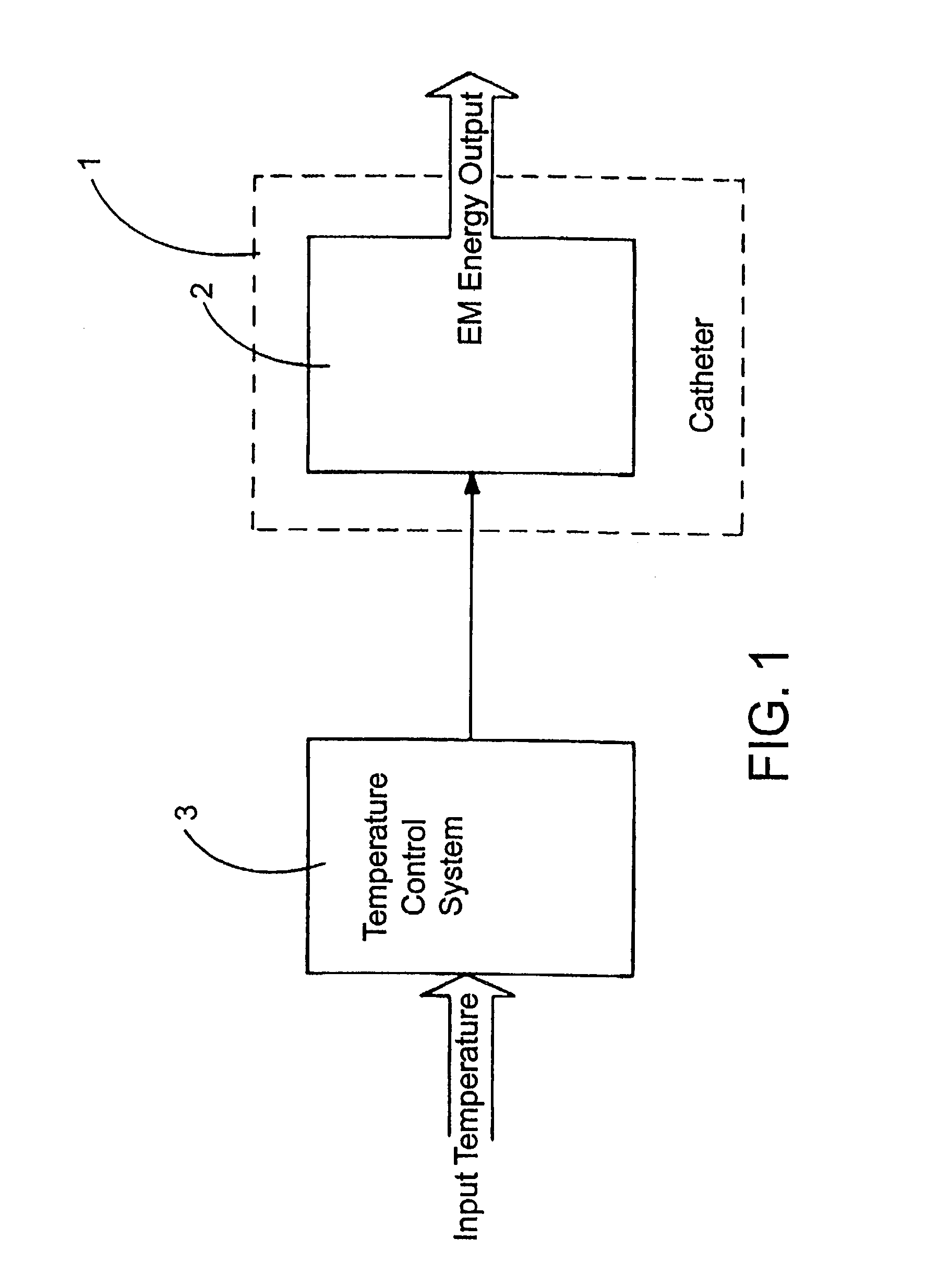
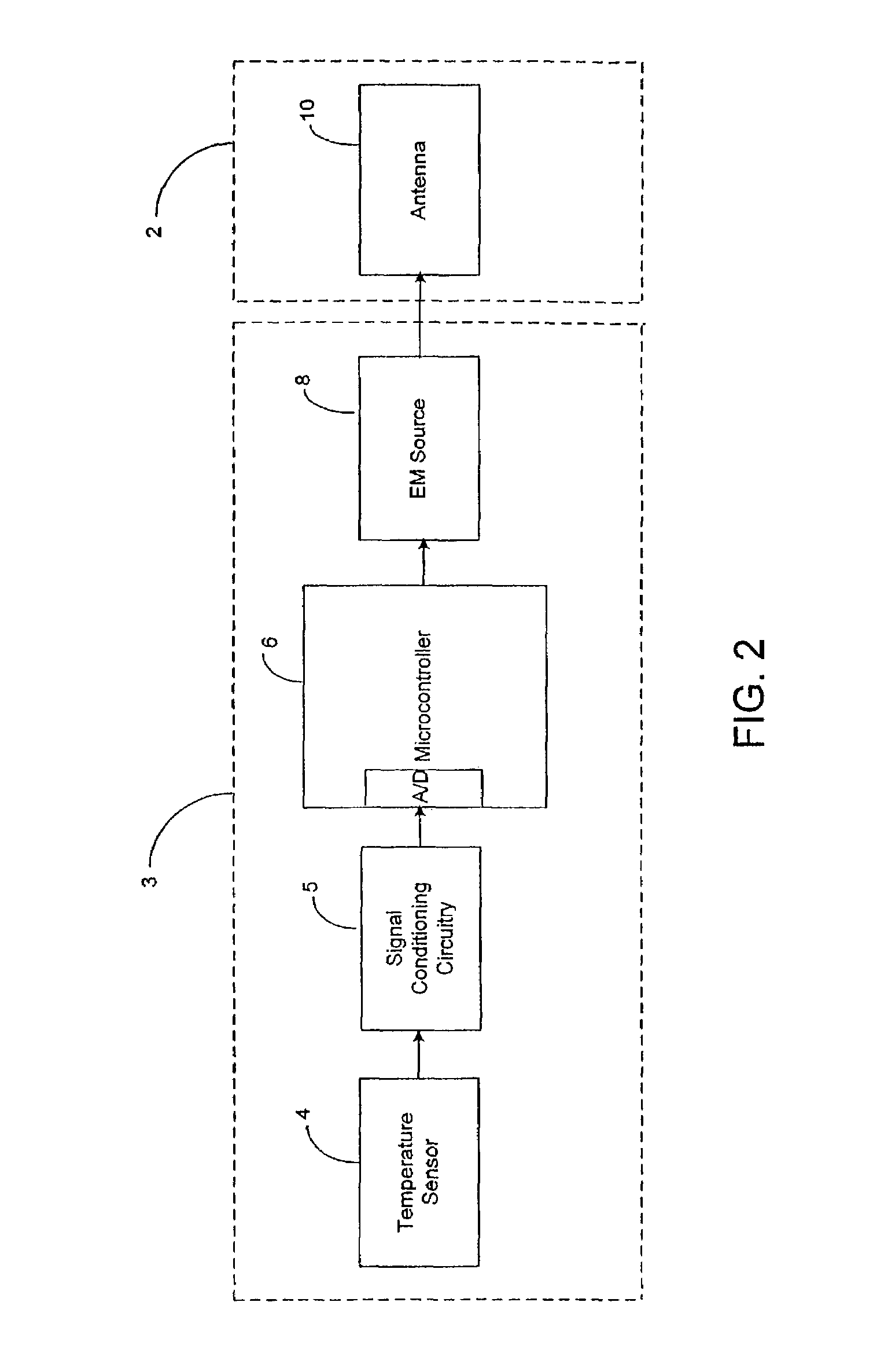
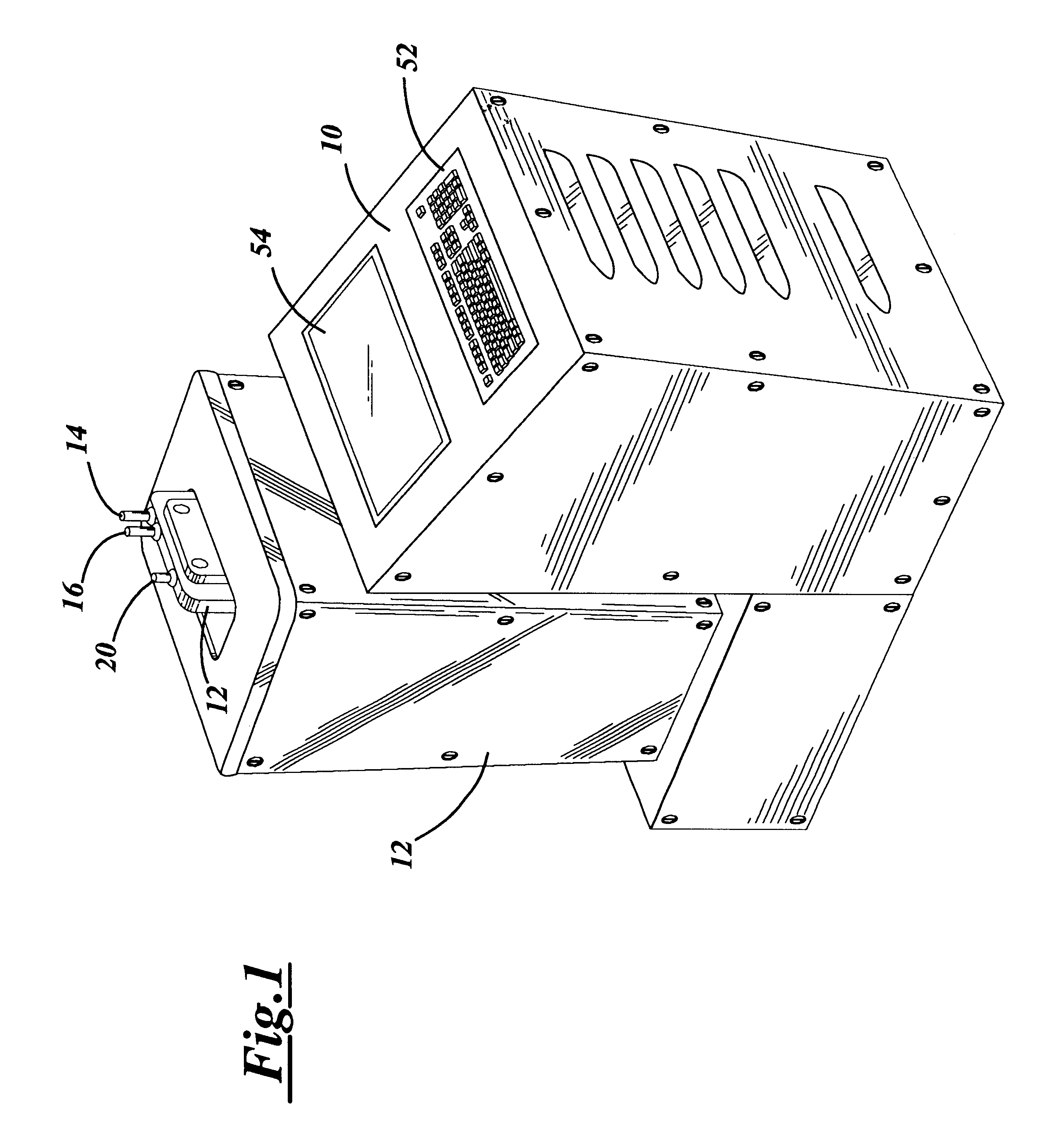
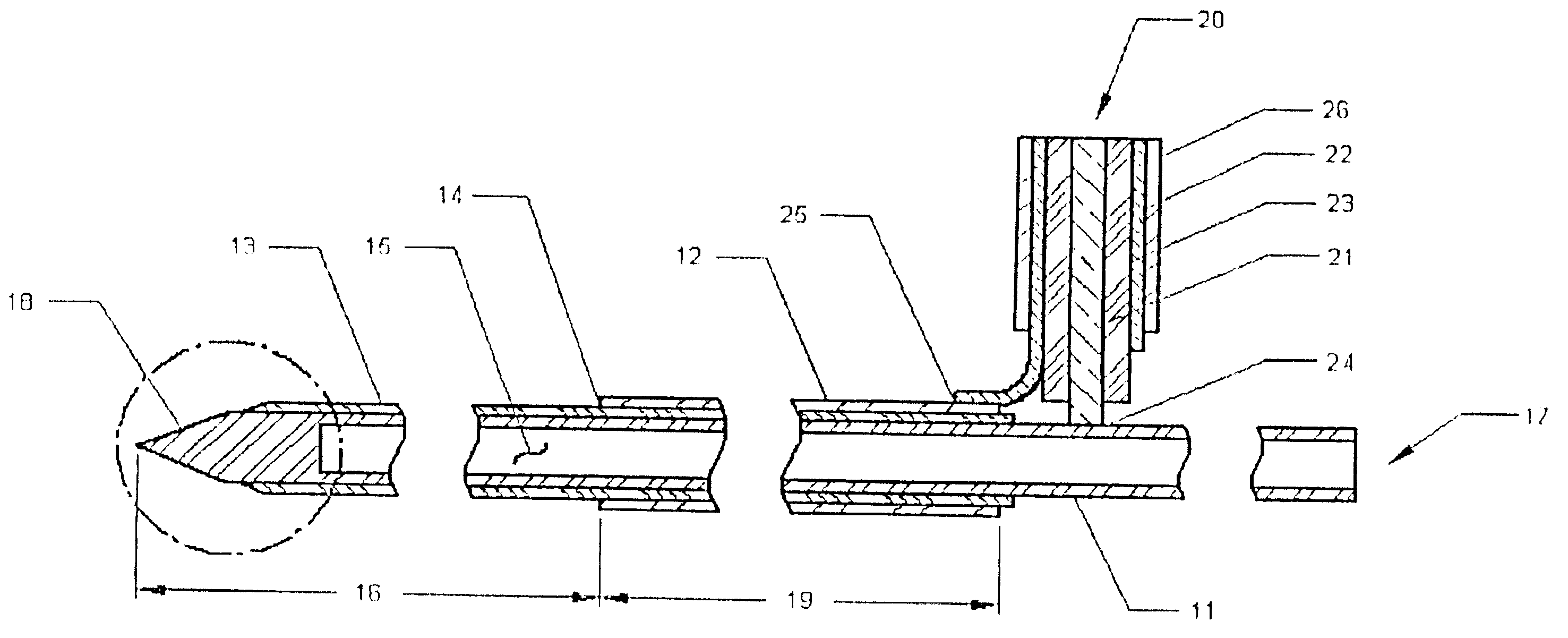
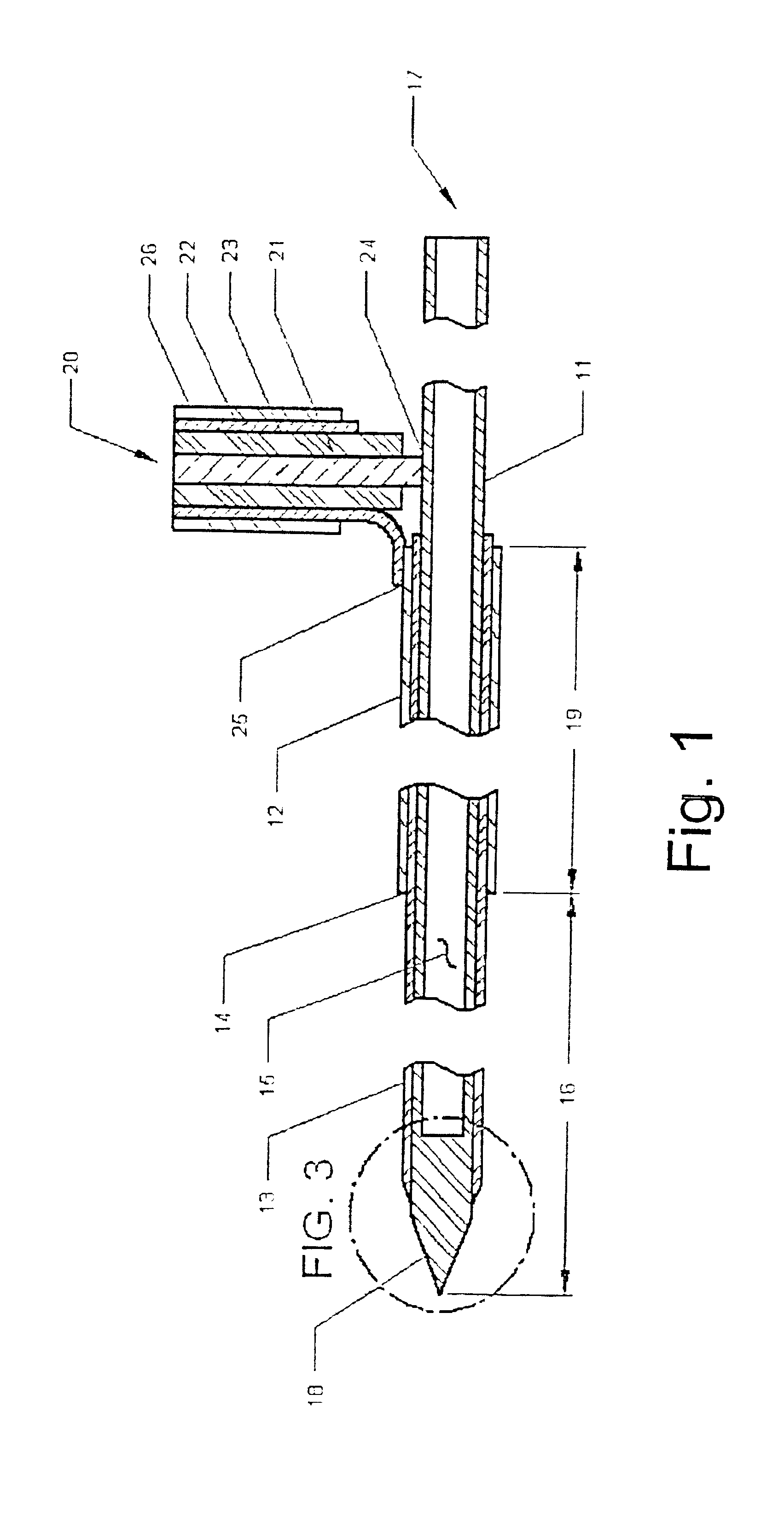
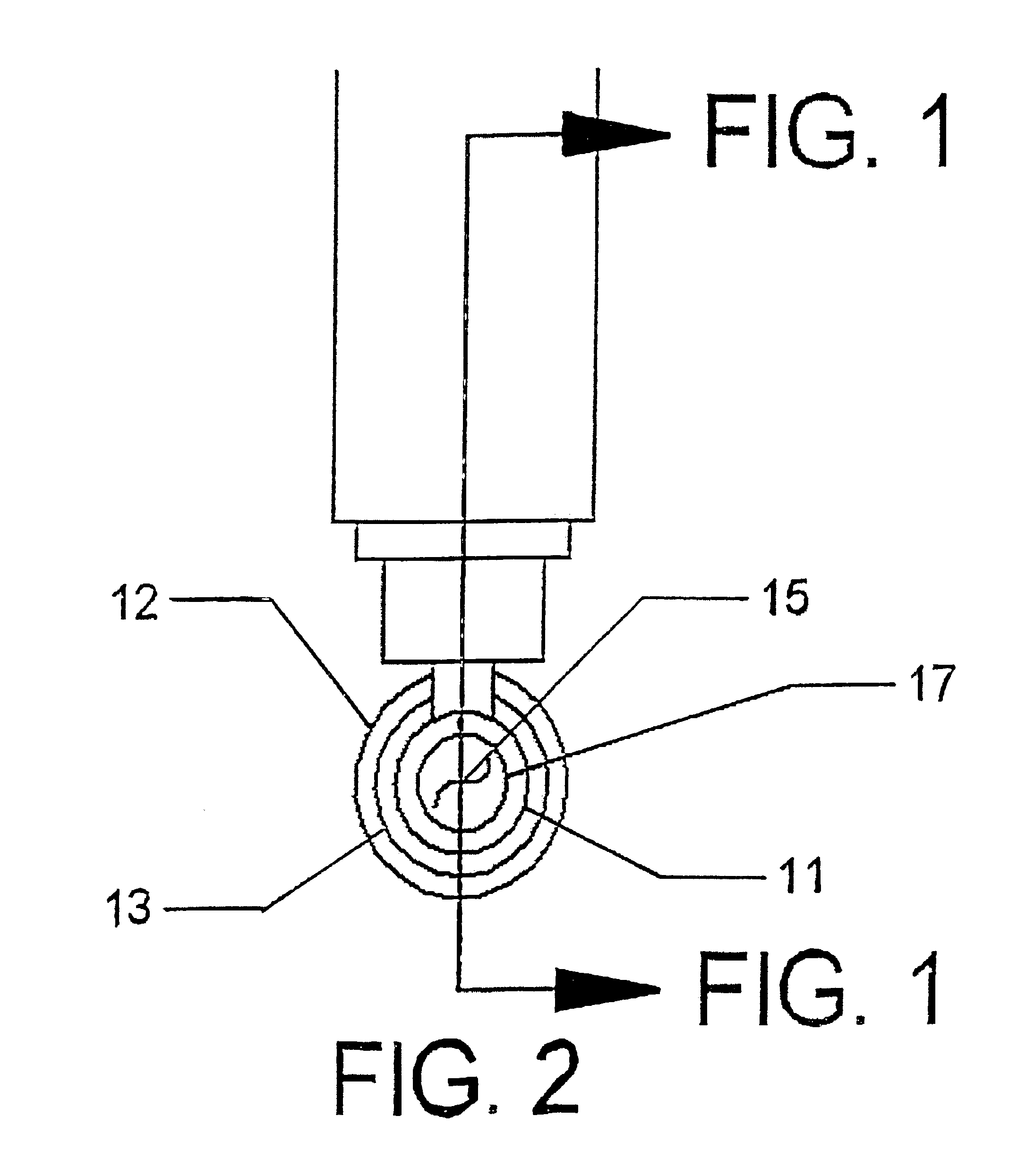
Medical system and method of use
ActiveUS20090149846A1Simple methodPrevent drynessBalloon catheterDiagnosticsThermal energyLiquid medium
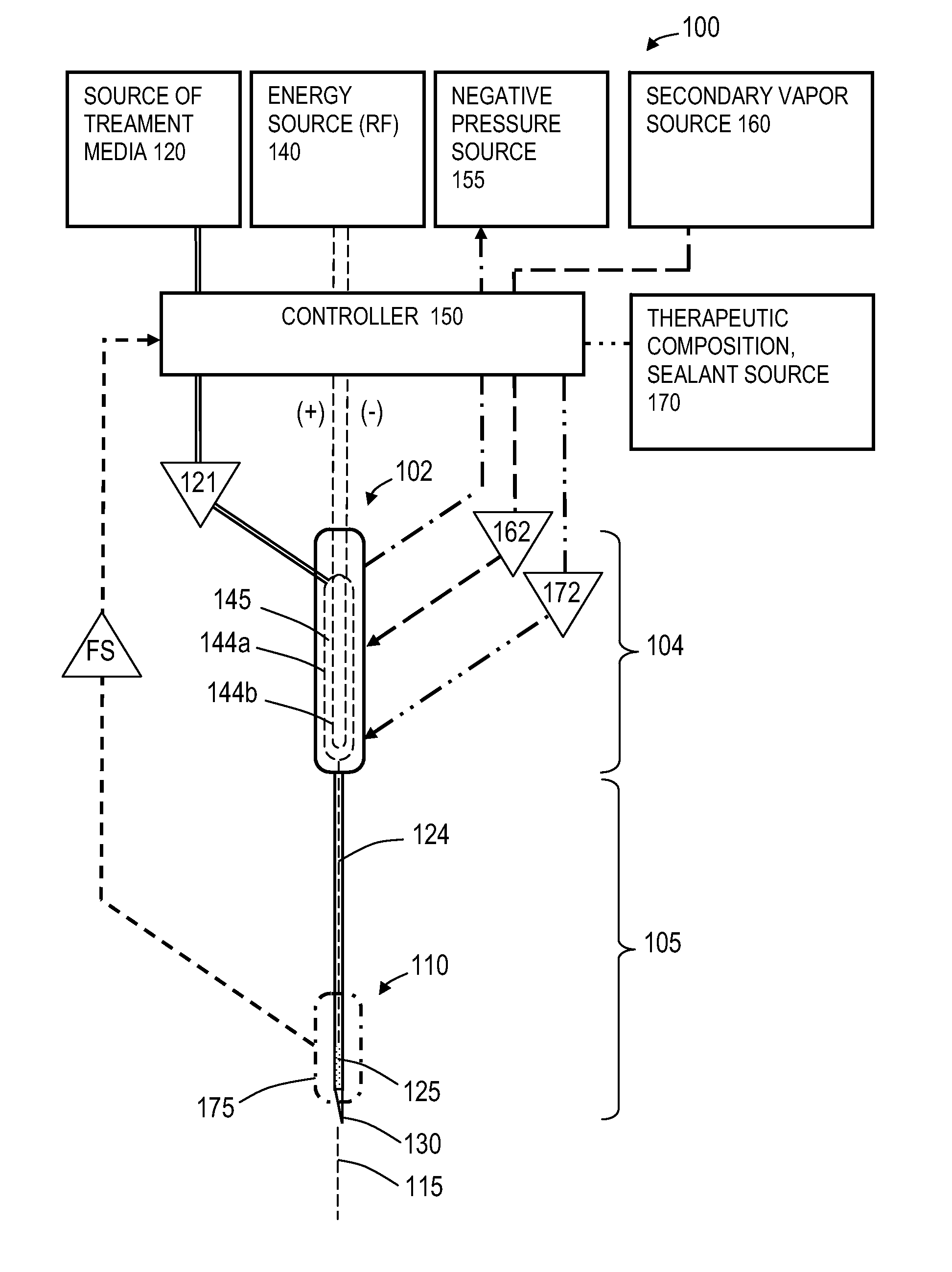
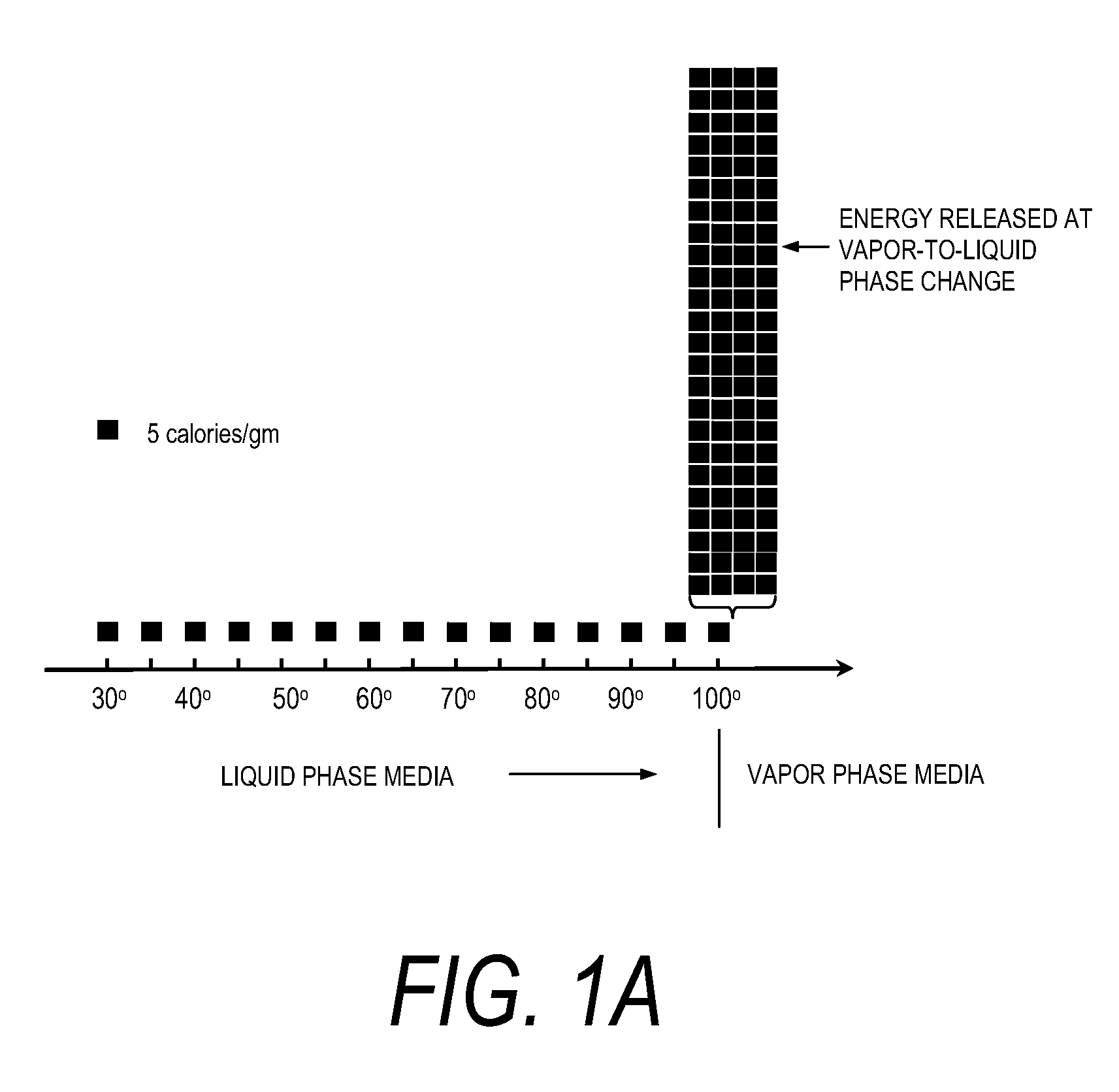
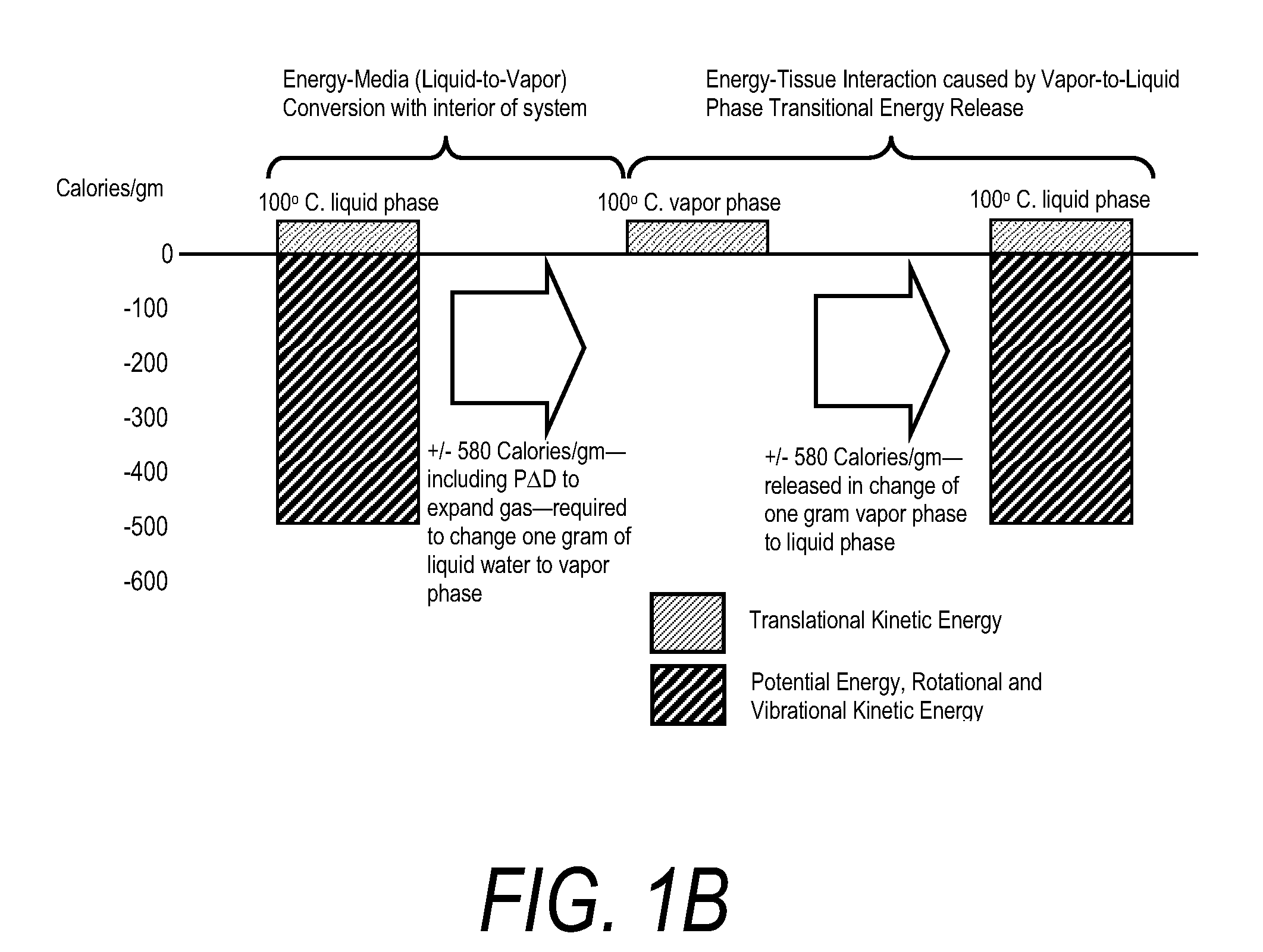
An instrument and method for applying thermal energy to targeted tissue. An instrument and method for tissue thermotherapy. In one embodiment, a method includes providing a vapor source comprising a pump configured for providing a flow of liquid media from a liquid media source into a vaporization chamber having a heating mechanism, actuating the pump to provide the liquid into the vaporization chamber, applying energy from the heating mechanism to convert a substantially water liquid media into a minimum water vapor level for causing an intended effect in tissue. For examples such levels can comprise at least 60% water vapor, at least 70% water vapor, at least 80% water vapor or at least 90% water vapor for causing an intended effect in tissue.
Owner:TSUNAMI MEDTECH
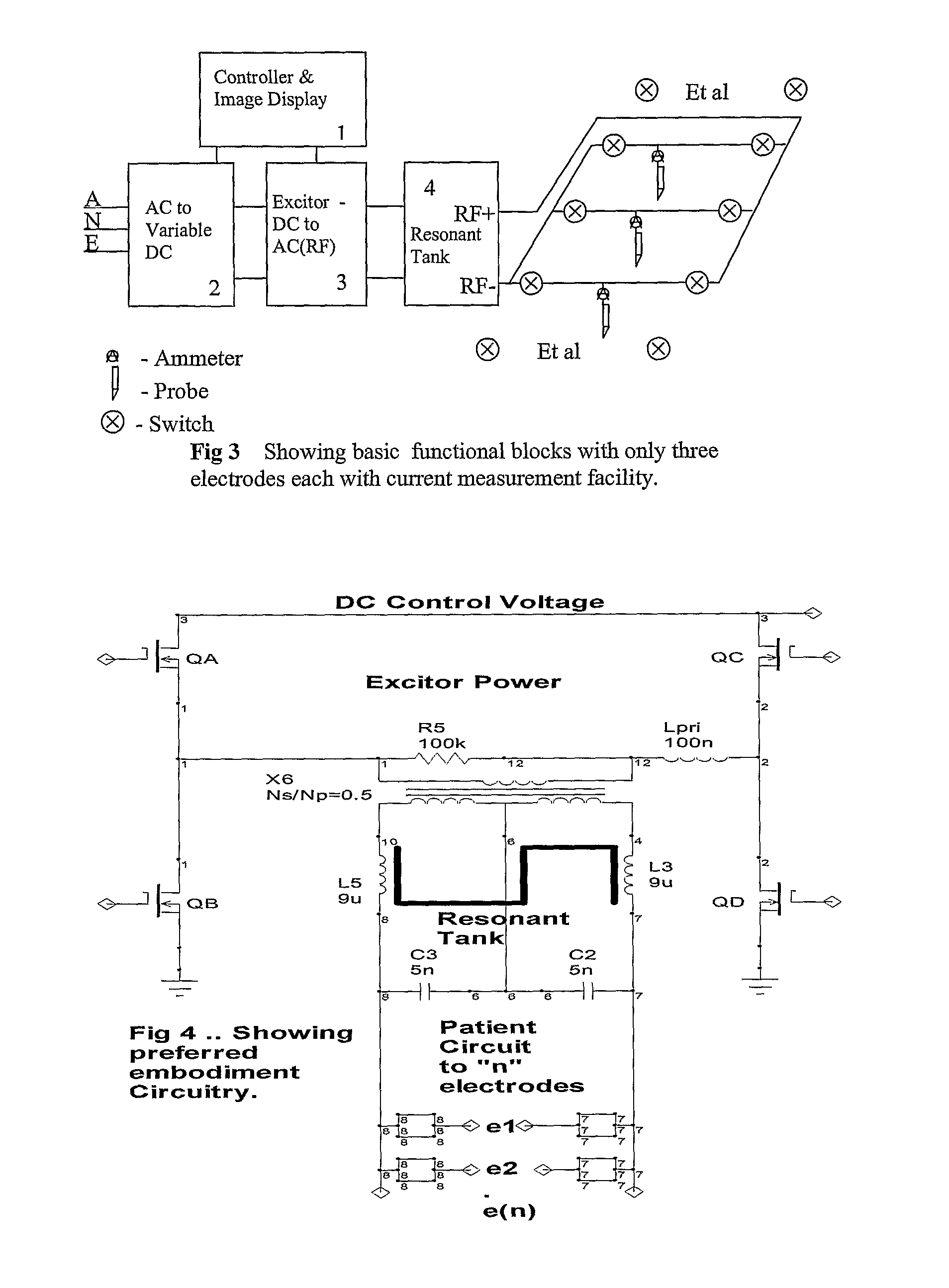
Minimal device and method for effecting hyperthermia derived anesthesia
InactiveUS9031667B2Improve comfortLess chance of physical damageElectrotherapySurgical needlesFiberMammal
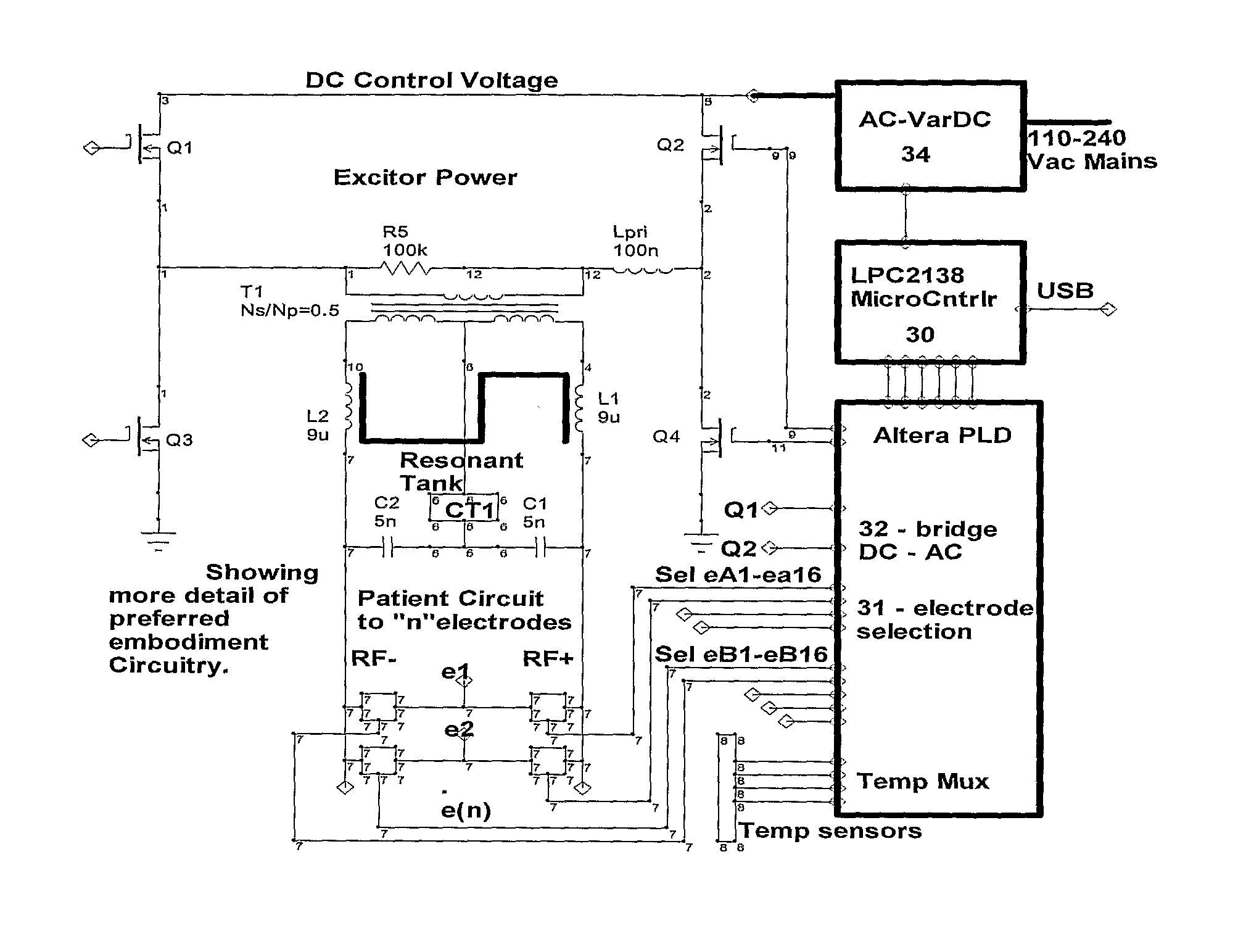
A method and device for inducing anaesthesia in mammals by the application of RF energy to create hyperthermia derived neural anaesthesia. An RF generator drives a plurality of electrodes placed in tissue surrounding the target nerve fiber to desiccate the desired length of nerve fiber to be desiccated in a single deployment. The device allows high-speed selection / de-selection of bipolar electrode pairs or sets under continuous RF excitation. Activation of electrode pairs is adapted in response to sensed current density and temperature (by electrodes not in the current discharge activation phase) in order to create lesions of complex and well defined shape necessary for the production of hyperthermia derived neural anaesthesia.
Owner:INTERVENTION TECH
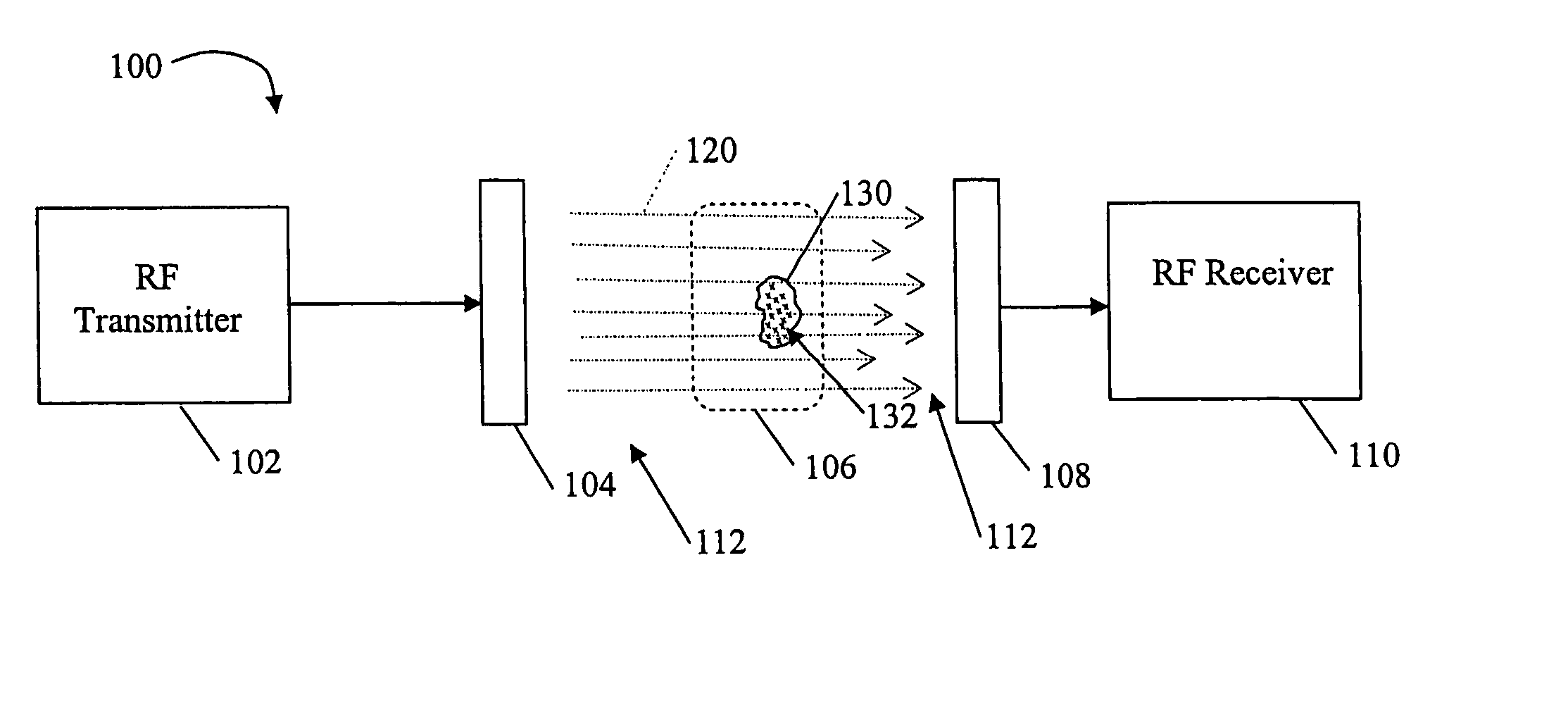
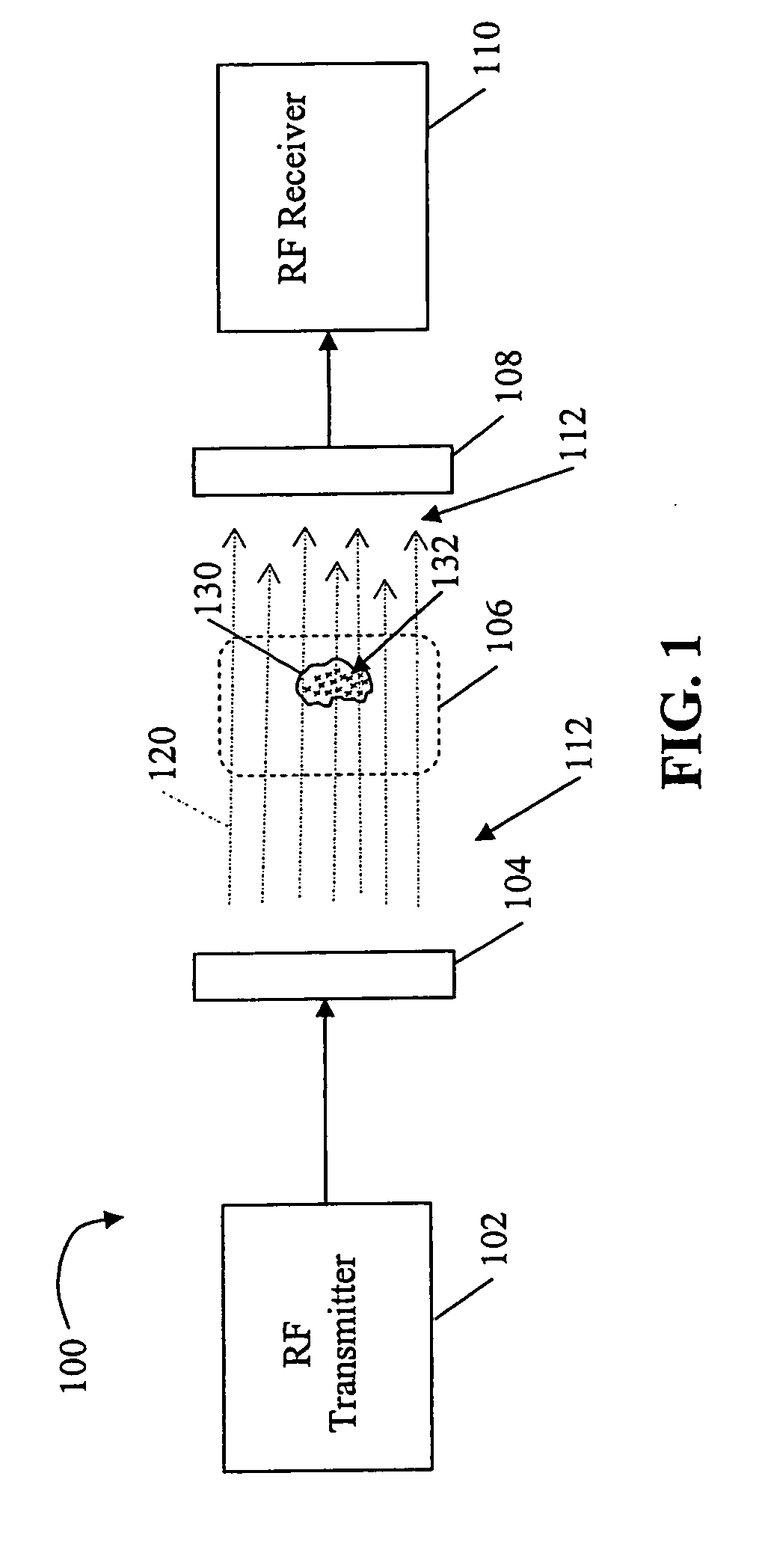
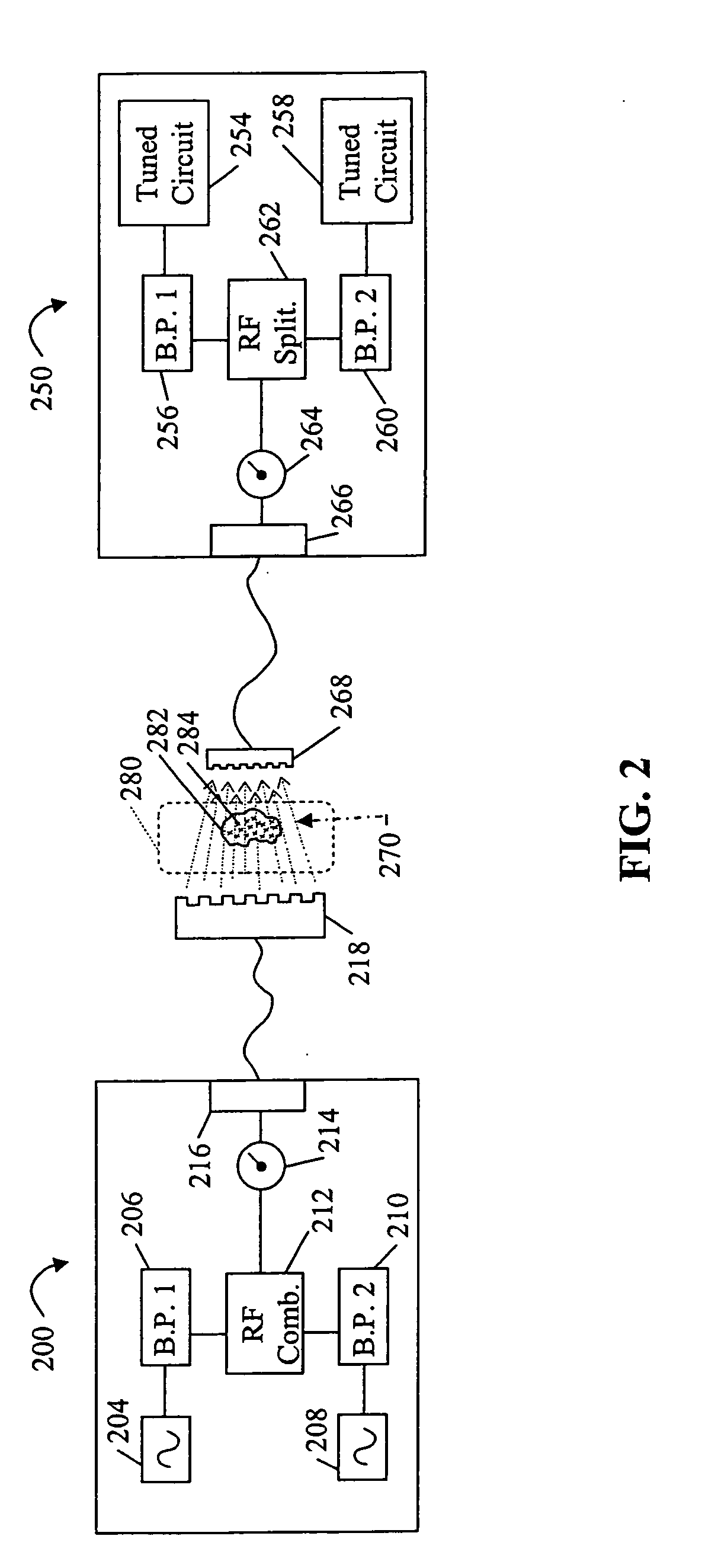
System and method for RF-induced hyperthermia
An embodiment of a non-invasive RF system for inducing hyperthermia in a target area, and a corresponding non-invasive RF method for inducing hyperthermia in a target area are provided. The system includes an RF transmitter and transmission head, and RF receiver and reception head wherein the transmission and reception heads are arranged proximate a target area so that an RF signal between the heads induces hyperthermia in the target area. The method includes arranging the transmission head and reception head proximate and on either side of a target area and transmitting an RF signal through the target area.
Owner:AKESOGENX
Hyperthermia Treatment Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20090118802A1Surgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingTemperature differenceHyperthermia Treatment
Owner:THERMOSURGERY TECH
Apparatus and method for treatment of malignant tumors
InactiveUS6866624B2Increase powerIncrease temperatureElectrotherapyMicrowave therapyAbnormal tissue growthBrachytherapy
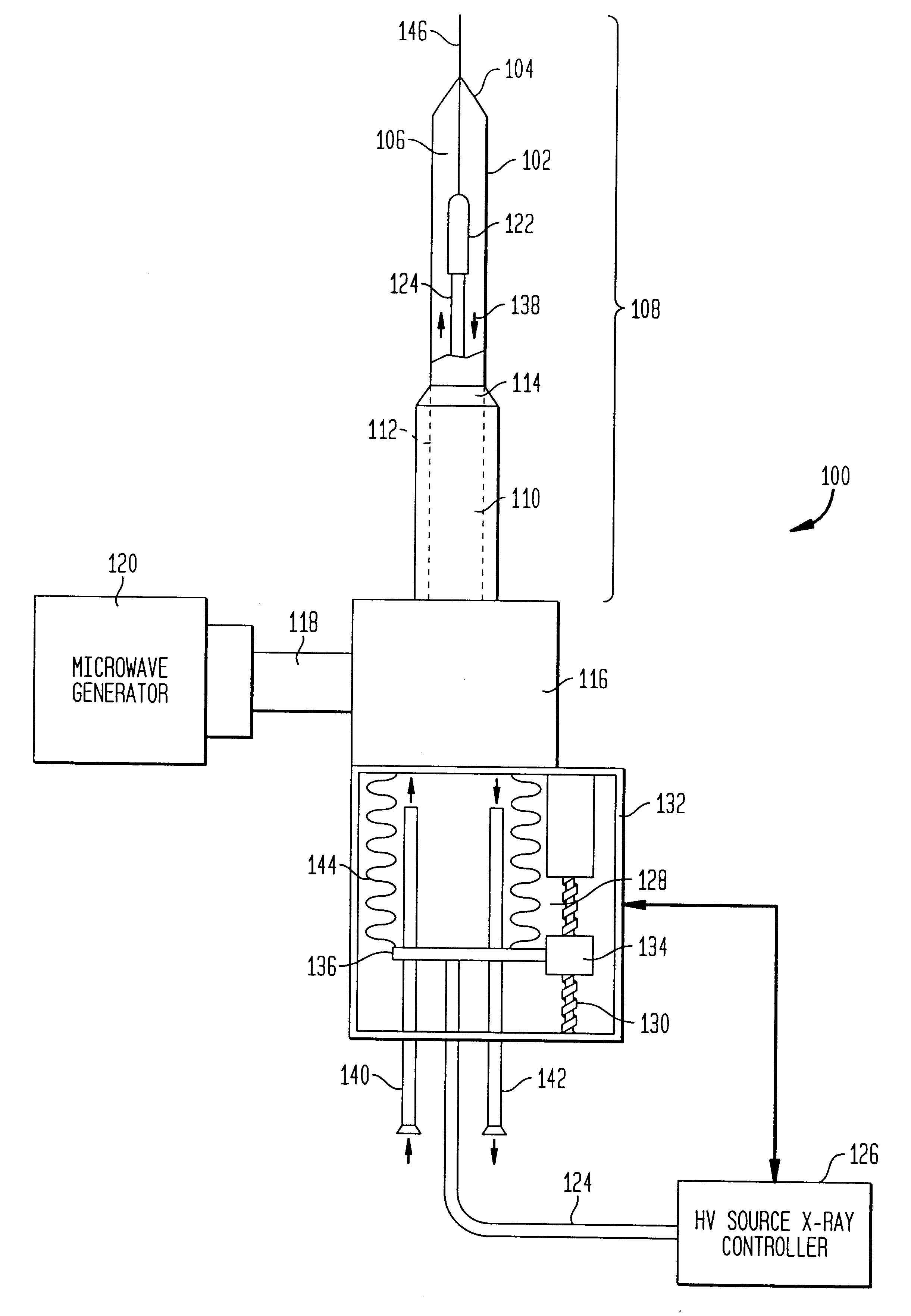
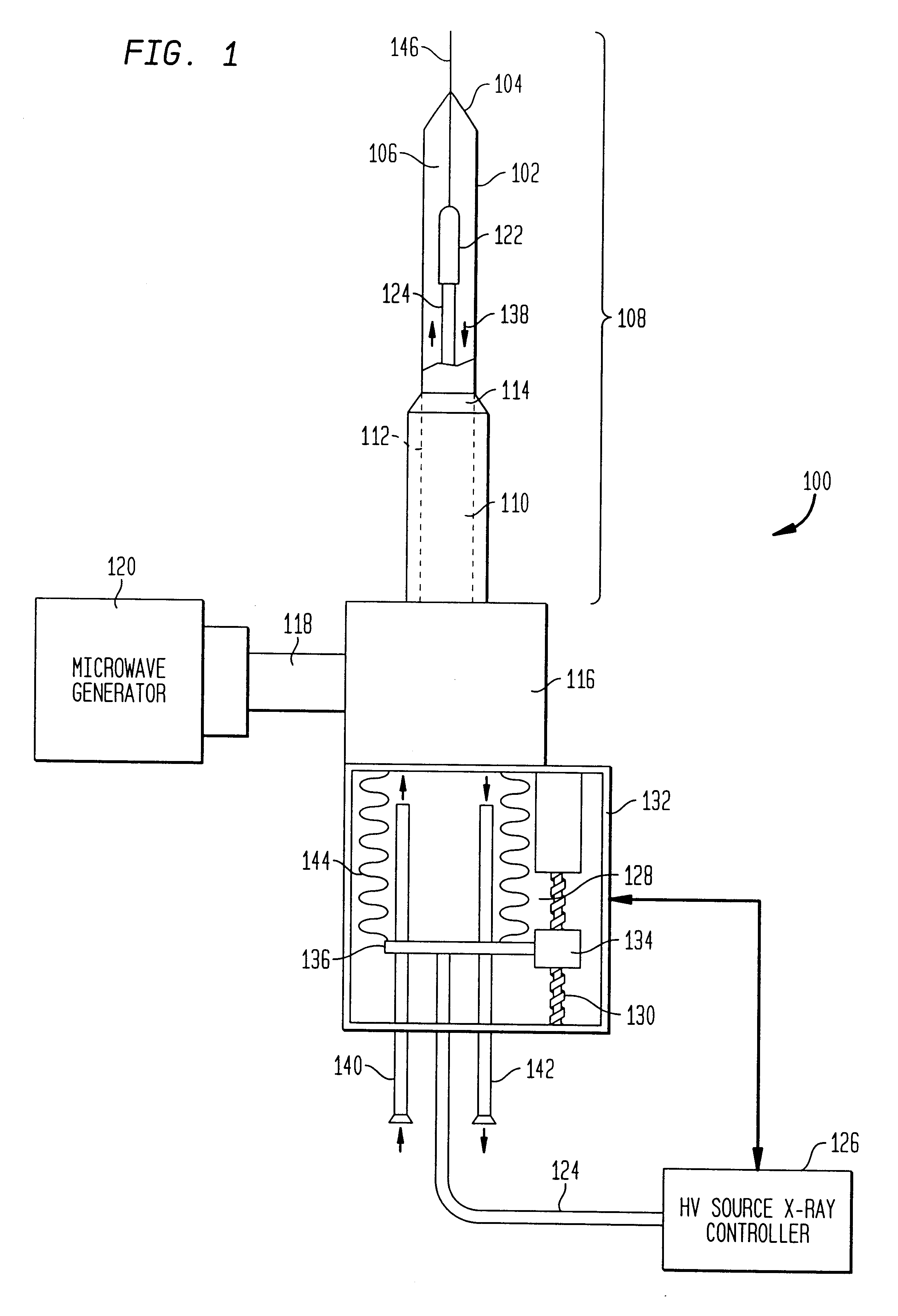
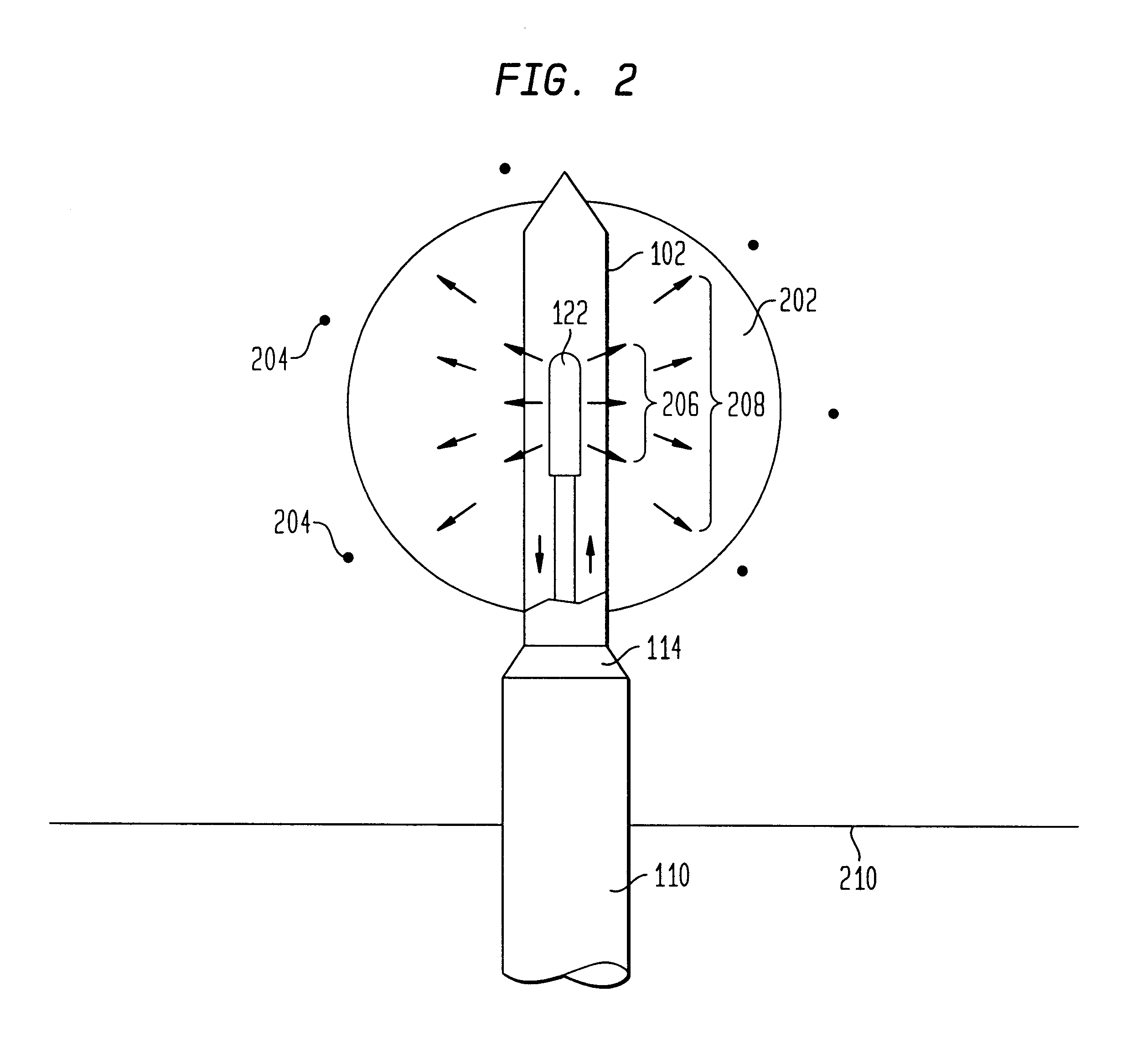
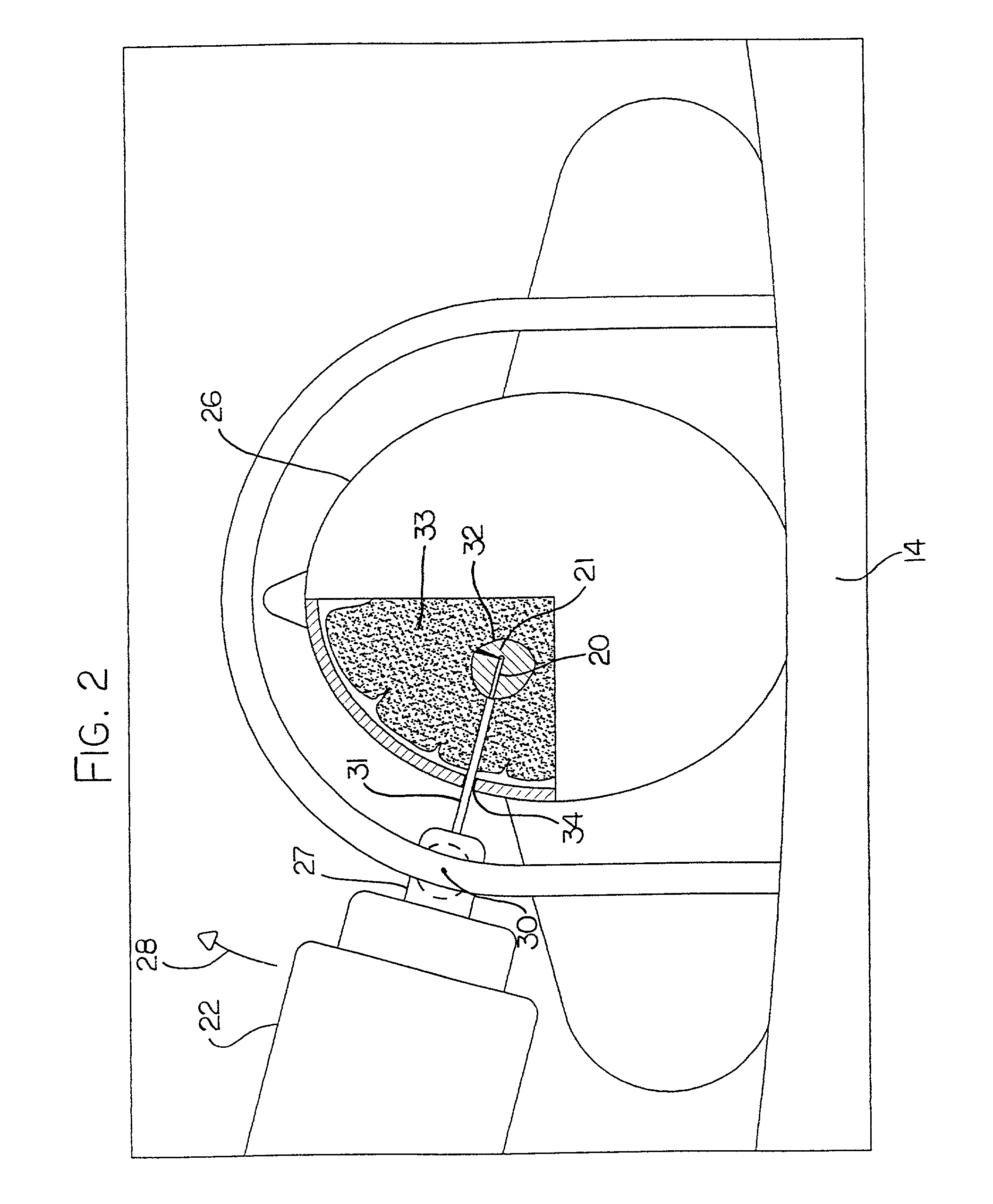
The present invention relates to a device for simultaneously treating a tumor or cancerous growth with both hyperthermia and X-ray radiation using brachytherapy. The device includes a needle-like introducer serving as a microwave antenna. Microwaves are emitted from the introducer to increase the temperature of cancerous body tissue. The introducer is an inner conductor of a coaxial cable. The introducer contains a hollow core which houses an X-ray emitter. The X-ray emitter is connected to a high voltage miniature cable which extends from the X-ray emitter to a high voltage power source. The X-ray emitter emits ionizing radiation to irradiate cancerous tissue. A cooling system is included to control the temperature of the introducer. Temperature sensors placed around the periphery of the tumor monitor the temperature of the treated tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC AVE
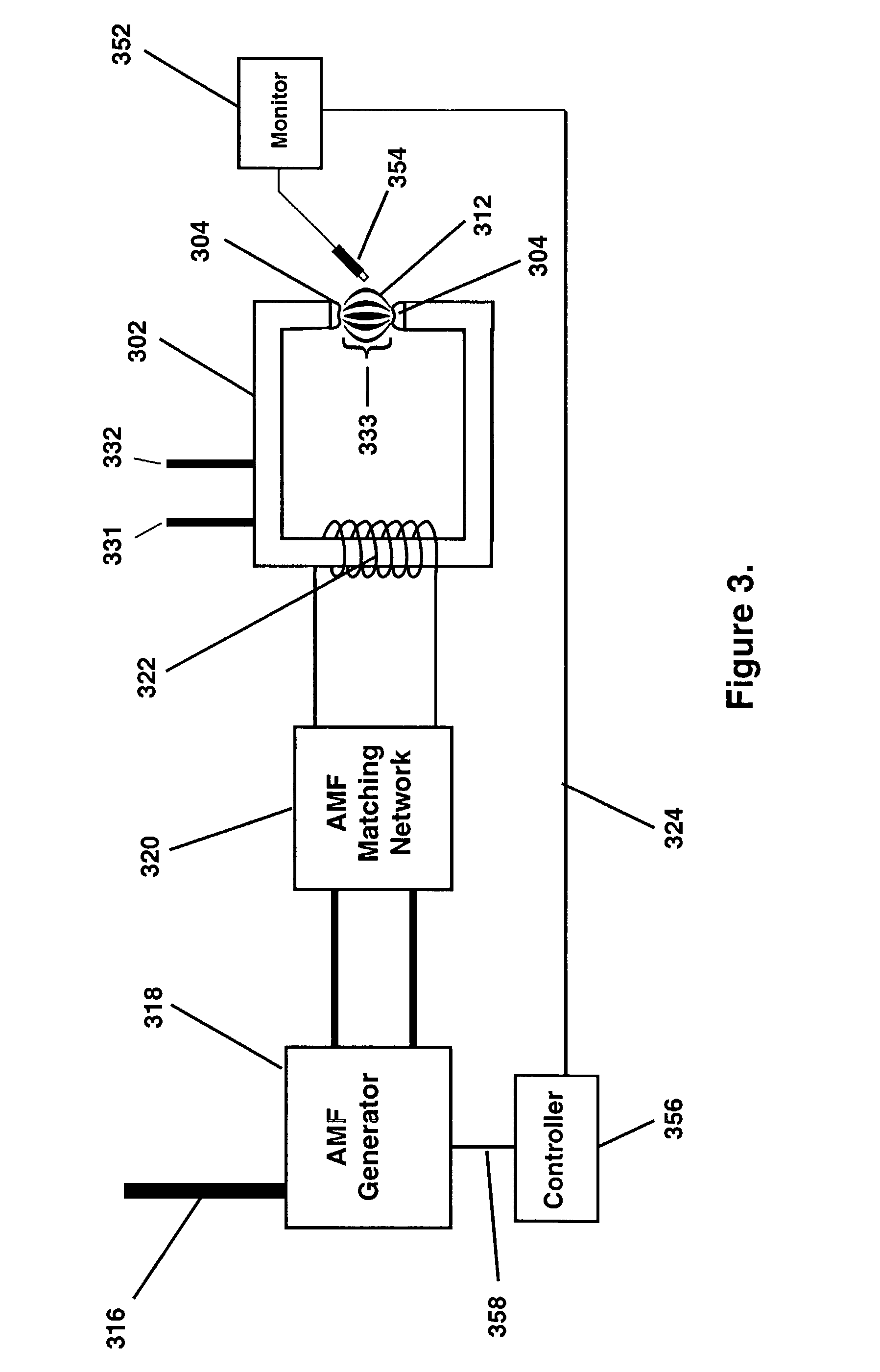
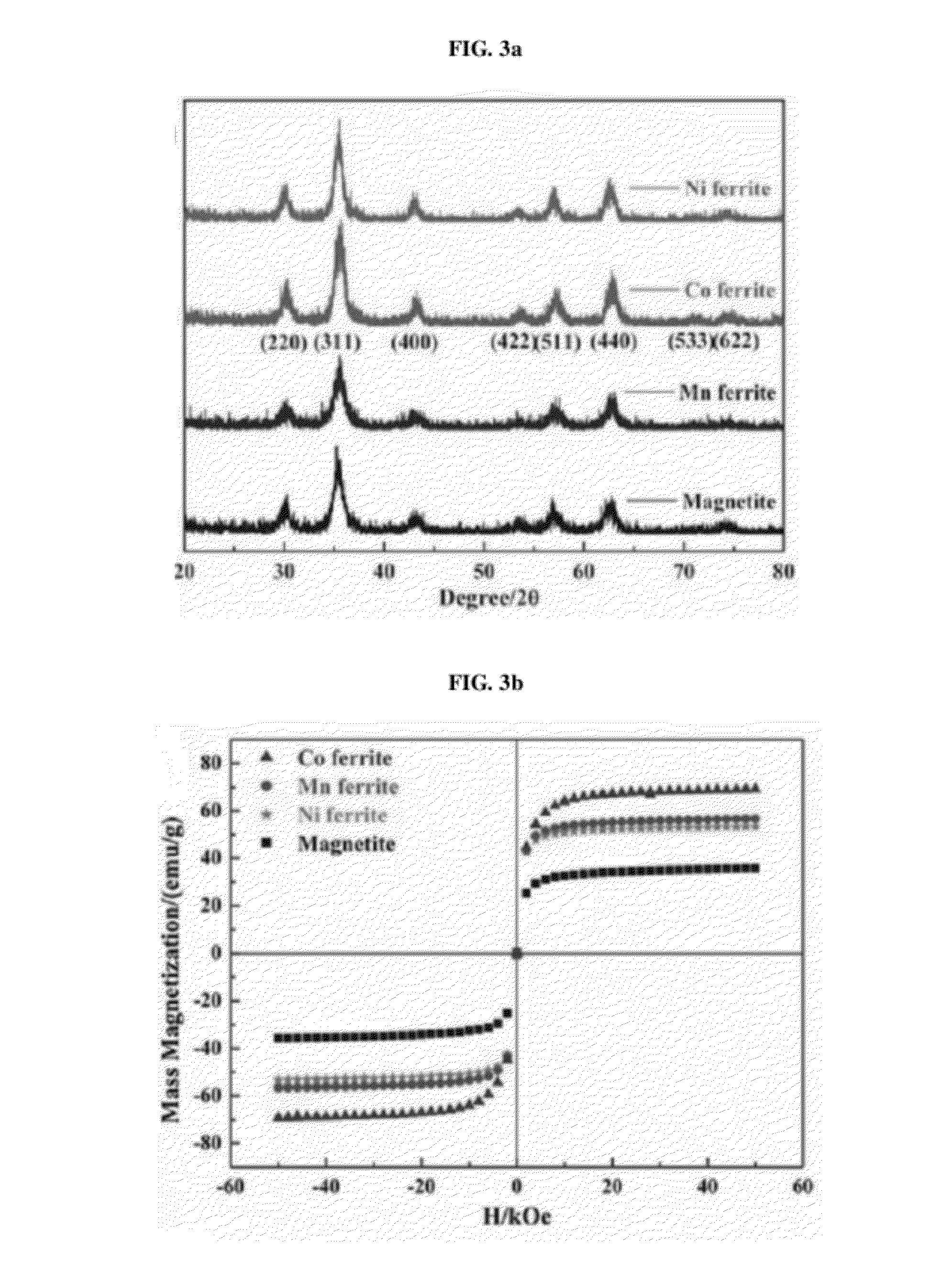
Thermotherapy via targeted delivery of nanoscale magnetic particles
Disclosed are therapeutic methods for the treatment of disease material involving administration of a thermotherapeutic magnetic composition, which contains single-domain magnetic particles attached to a target-specific ligand, to a patient and application of an alternating magnetic field to inductively heat the thermotherapeutic magnetic composition. Also disclosed are methods of administering the thermotherapeutic magnetic material composition. The thermotherapeutic methods may be used where the predetermined target is associated with diseases, such as cancer, diseases of the immune system, and pathogen-borne diseases, and undesirable targets, such as toxins, reactions associated with organ transplants, hormone-related diseases, and non-cancerous diseased cells or tissue.
Owner:ASPEN MEDISYS +1
Magnetic nanoscale particle compositions, and therapeutic methods related thereto
InactiveUS20060142749A1Minimal invasionShort course of treatmentAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryDiseaseMagnetite Nanoparticles
Disclosed are thermotherapeutic compositions for treating disease material, and methods of targeted therapy utilizing such compositions. These compositions comprise a) stable single domain magnetic particles; b) magnetic nanoparticles comprising aggregates of superparamagnetic grains; or c) magnetic nanoparticles comprising aggregates of stable single magnetic domain crystals and superparamagnetic grains. These compositions may also comprise a radio isotope, potential radioactive isotope, chemotherapeutic agent. These methods comprise the administration to a patient's body, body part, body fluid, or tissue of bioprobes (energy susceptive materials attached to a target-specific ligand), and the application of energy to the bioprobes so as to destroy, rupture, or inactivate the target in the patient. Energy forms, such as AMF, are utilized to provide the energy. The disclosed methods may be useful in the treatment of a variety of indications, including cancers, diseases of the immune system, central nervous system and vascular system, and pathogen-borne diseases.
Owner:ASPEN MEDISYS +1
Few seconds beam on time, breathing synchronized image guided all fields simultaneous radiation therapy combined with hyperthermia
This invention relates to single session image guided all field simultaneous radiation therapy combined with hyperthermia. Hyperthermia renders the radiation resistant cells as more radiation sensitive cells. The high and super-high dose rate radiation greatly improves the RBE of the photon radiation. It also minimizes photon radiation therapy's OER and cell cycle dependent tumor cell kill by minimizing the repair capacity of cell after photon radiation. Single session hyperthermia and radiation therapy overcomes the thermotolerance-associated inefficiency of hyperthermia treatment as it is when hyperthermia is combined with fractionated, lower dose rate radiation. The synergetic effects of sublethal damage repair inhibiting single session hyperthermia-combined with high dose and dose rate single session radiation therapy, and combined chemotherapy brings the photon radiation therapy's tumor cure and control capabilities closer to high LET radiation therapy.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
Magnetic particle composition for therapeutic hyperthermia
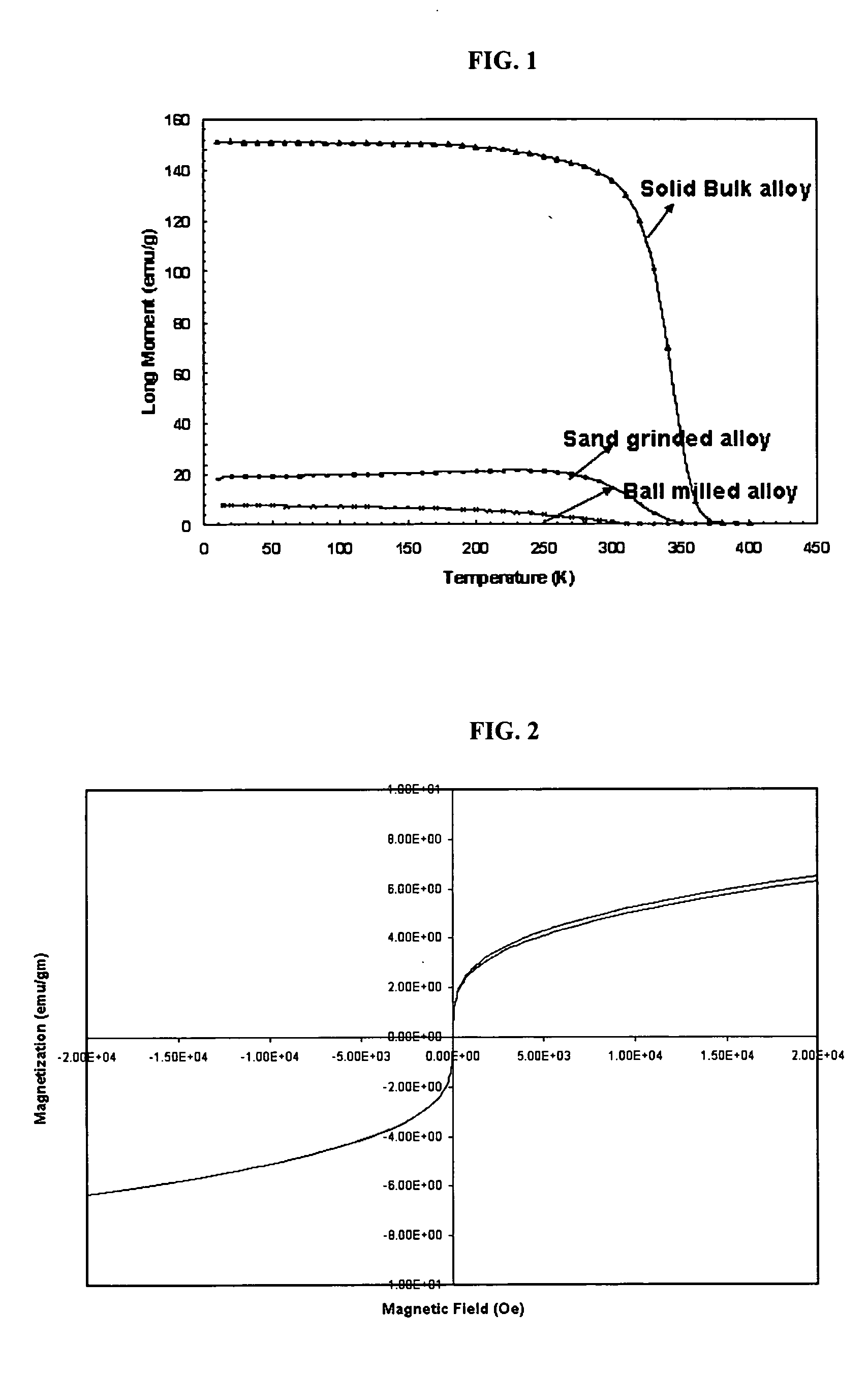
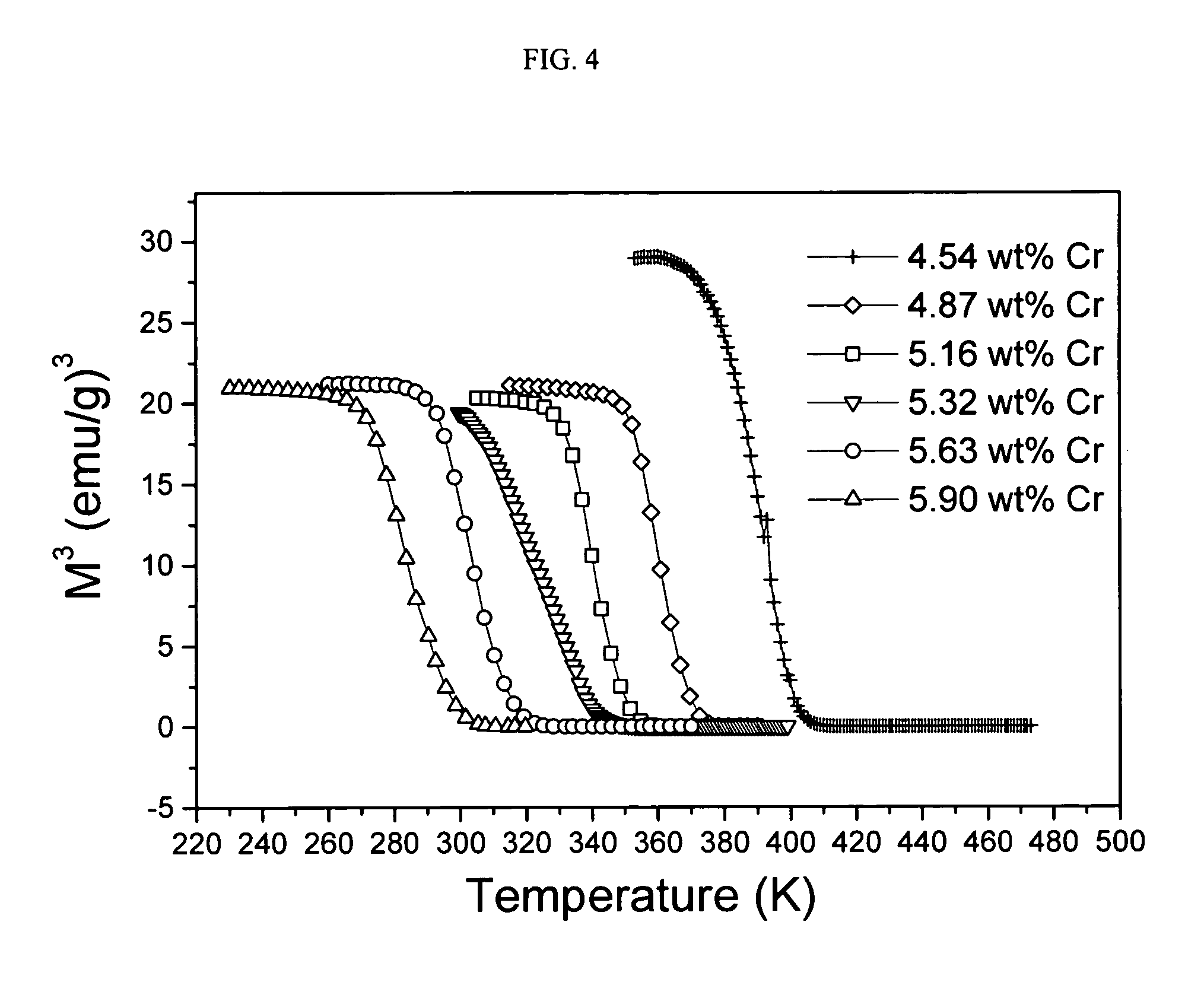
InactiveUS20050249817A1Heat generationHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideHysteresisMagnetite Nanoparticles
Magnetic nanoparticle compositions are provided which provide an inherent temperature regulator for use in magnetic heating, particularly for use in magnetic hyperthermia medical treatments. The composition includes magnetic nanoparticles having a Curie temperature of between 40 and 46° C., preferably about 42° C., and may further include a polymeric material and optionally a drug or radiosensitizing agent. Methods of hyperthermia treatment of a patient in need thereof are provided which include the steps of administering to the patient a composition comprising magnetic nanoparticles having a Curie temperature of between 40 and 46° C.; and exposing the magnetic nanoparticles in the patient to an alternating magnetic field effective to generate hysteresis heat in the nanoparticles.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Therapeutic prostatic thermotherapy
The present invention provides a method of treating a prostate in a patient in need thereof and a heating catheter, or an electromagnetic radiation applicator, system suitable for effecting the present inventive method. The present inventive method provides for substantial unexpected improvement in patient outcome by providing, inter alia, a preferred therapeutic temperature for thermotherapy of the prostate and a method of decreasing a patient's intolerance due to pain. The present inventive system provides for, inter alia, automatic implementation of the present inventive method.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
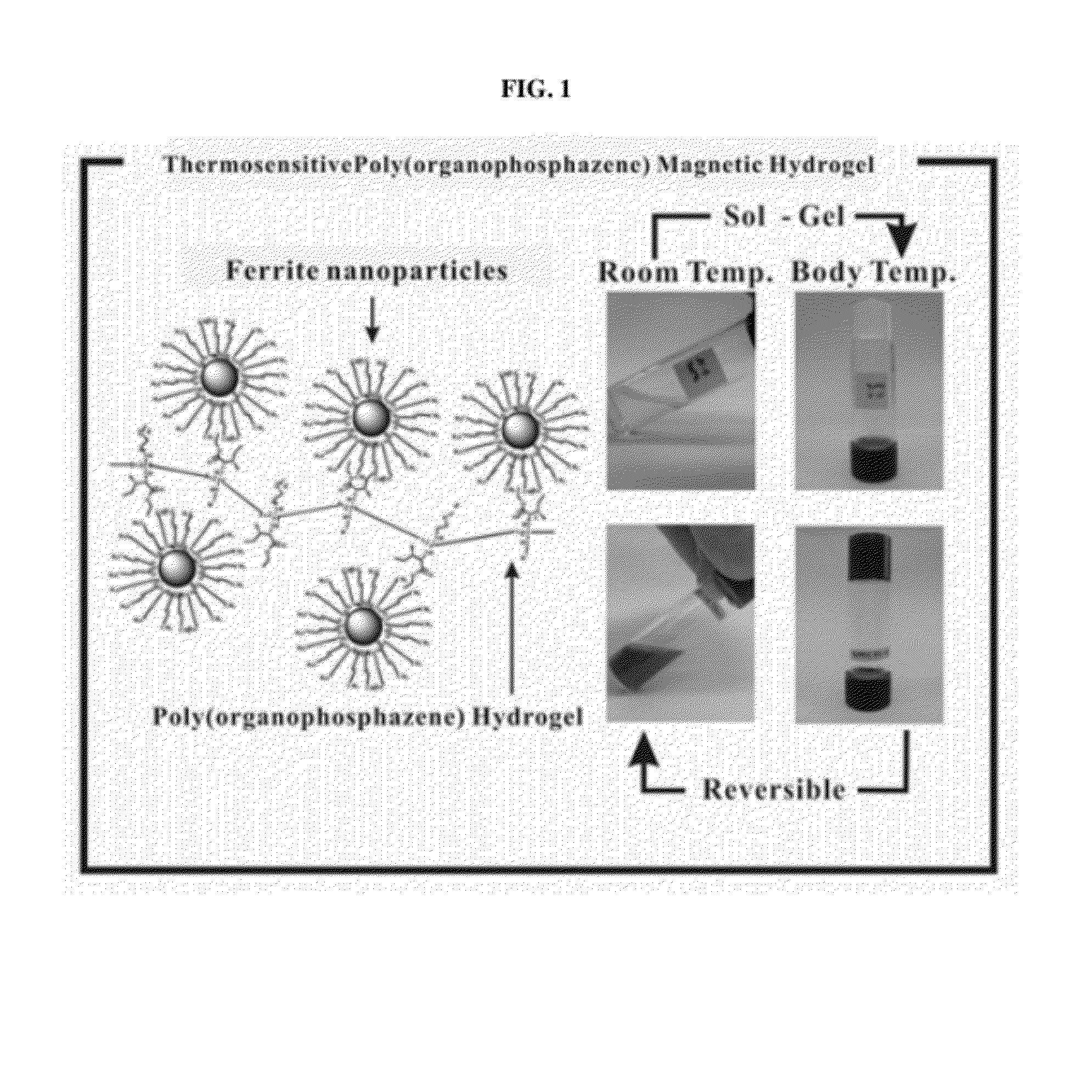
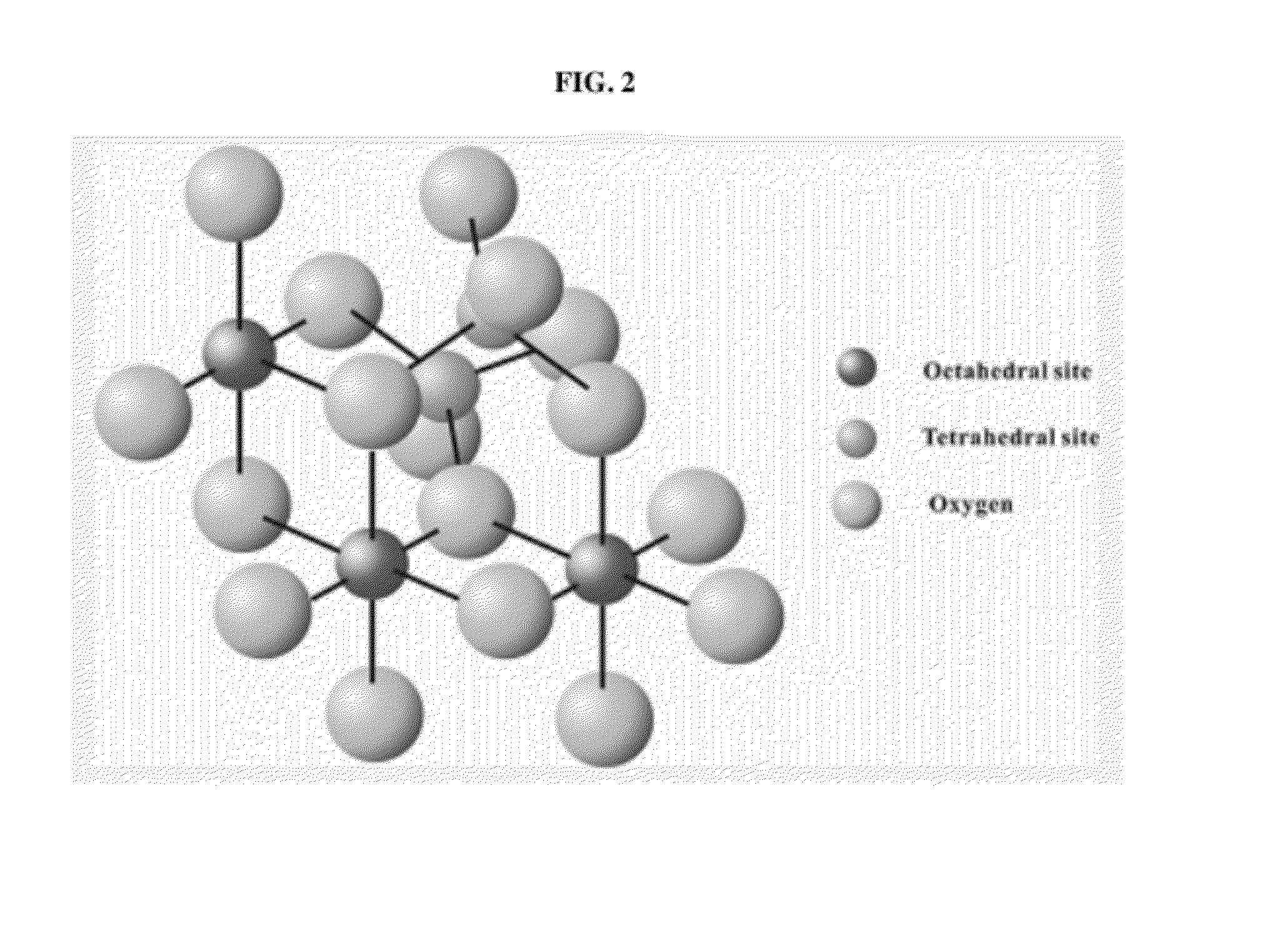
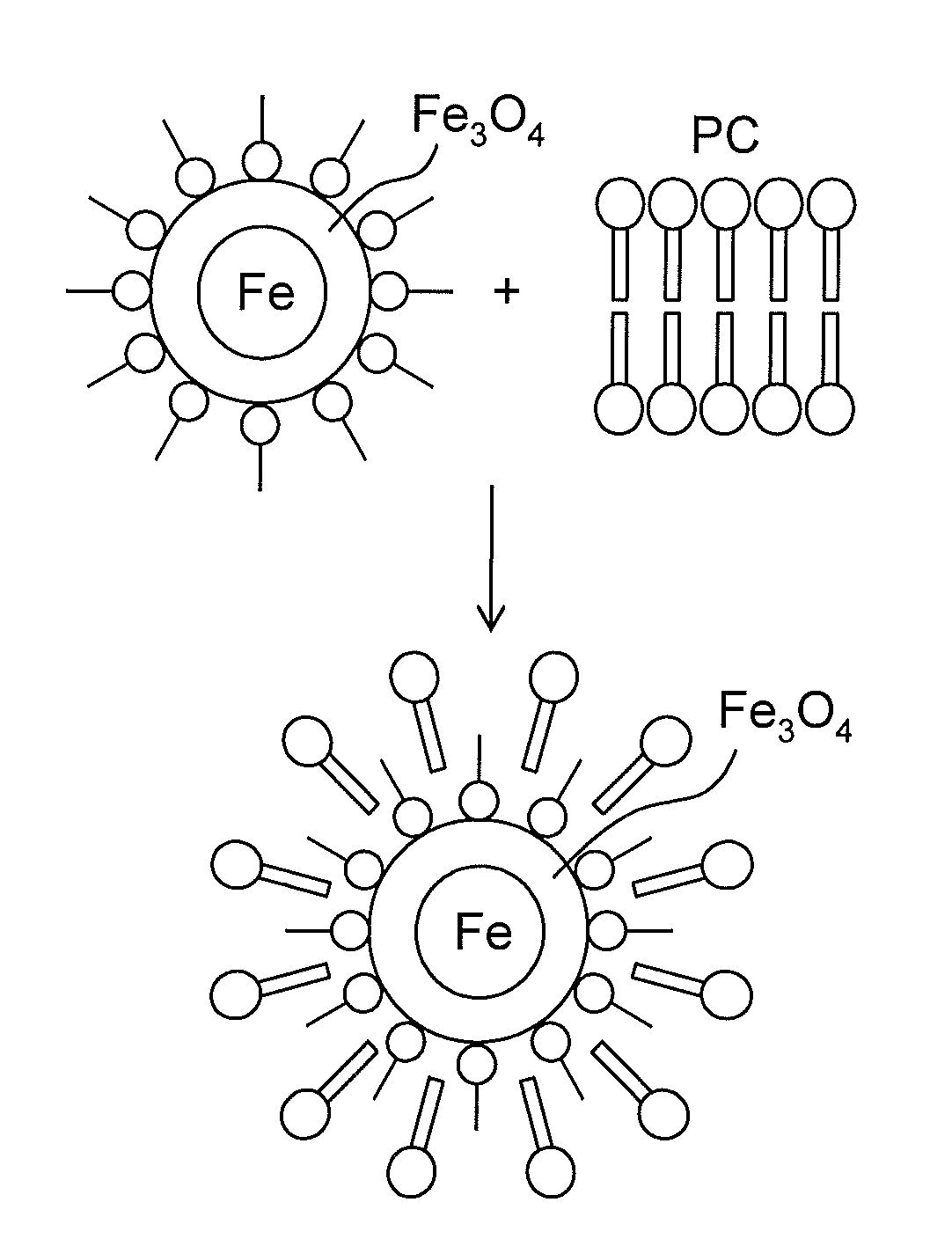
Biodegradable and thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene)-superparamagnetic nanoparticle complex, preparation method and use thereof
ActiveUS20120121517A1Facilitated releaseImprove load effectMaterial nanotechnologyBiocideMRI contrast agentFerrite nanoparticles
The present invention relates to a poly(organophosphazene)-superparamagnetic nanoparticle complex including a biodegradable and thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene) and a iron oxide (Fe3O4, Magnetite)-series ferrite superparamagnetic nanoparticle, a preparation method, and uses of carrying a physiologically-active material, a bio-material and a biomaterial for cancer hyperthermia. The iron oxide is used as a MRI contrast agent for T-2 and T2* weighted image, and the poly(organophosphazene) shows a sol-to-gel behavior depending upon the temperature change. The complex is a bound-type where the superparamagnetic ferrite nanoparticle is bonded to phosphazene-based polymer via hydrophobic binding, and a mixed-type where the superparamagnetic ferrite nanoparticle is physically mixed with the phosphazene-based polymer.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
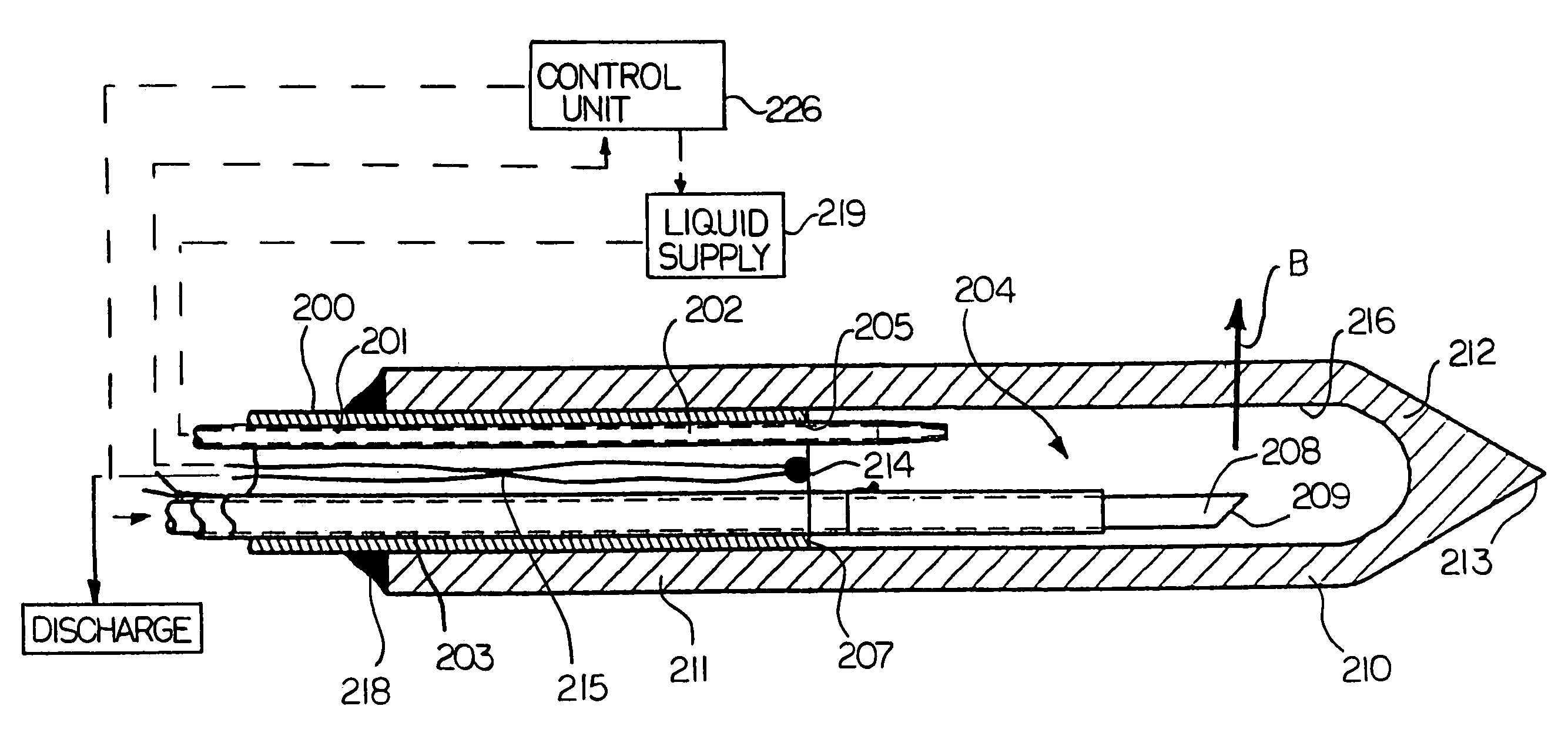
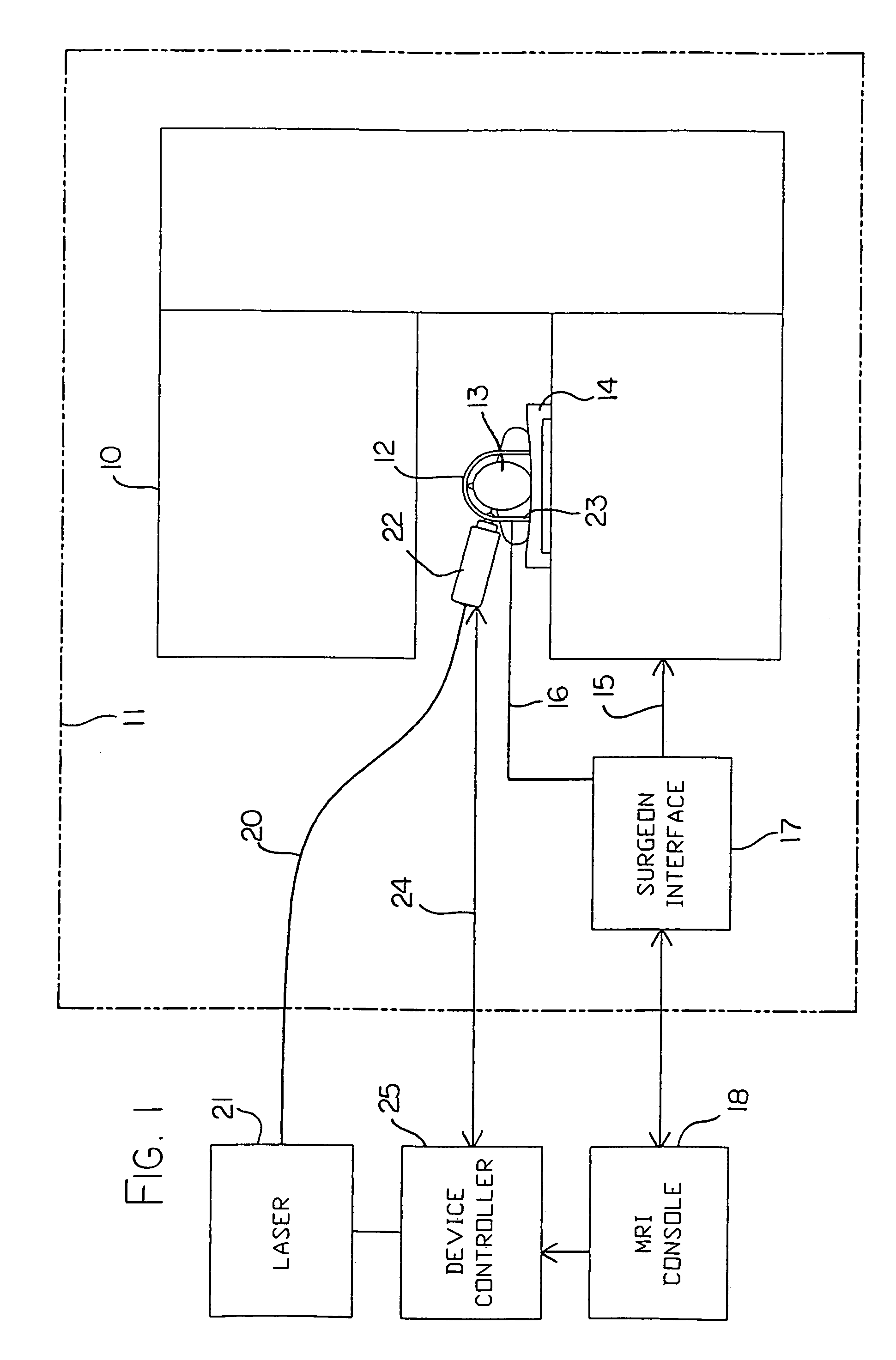
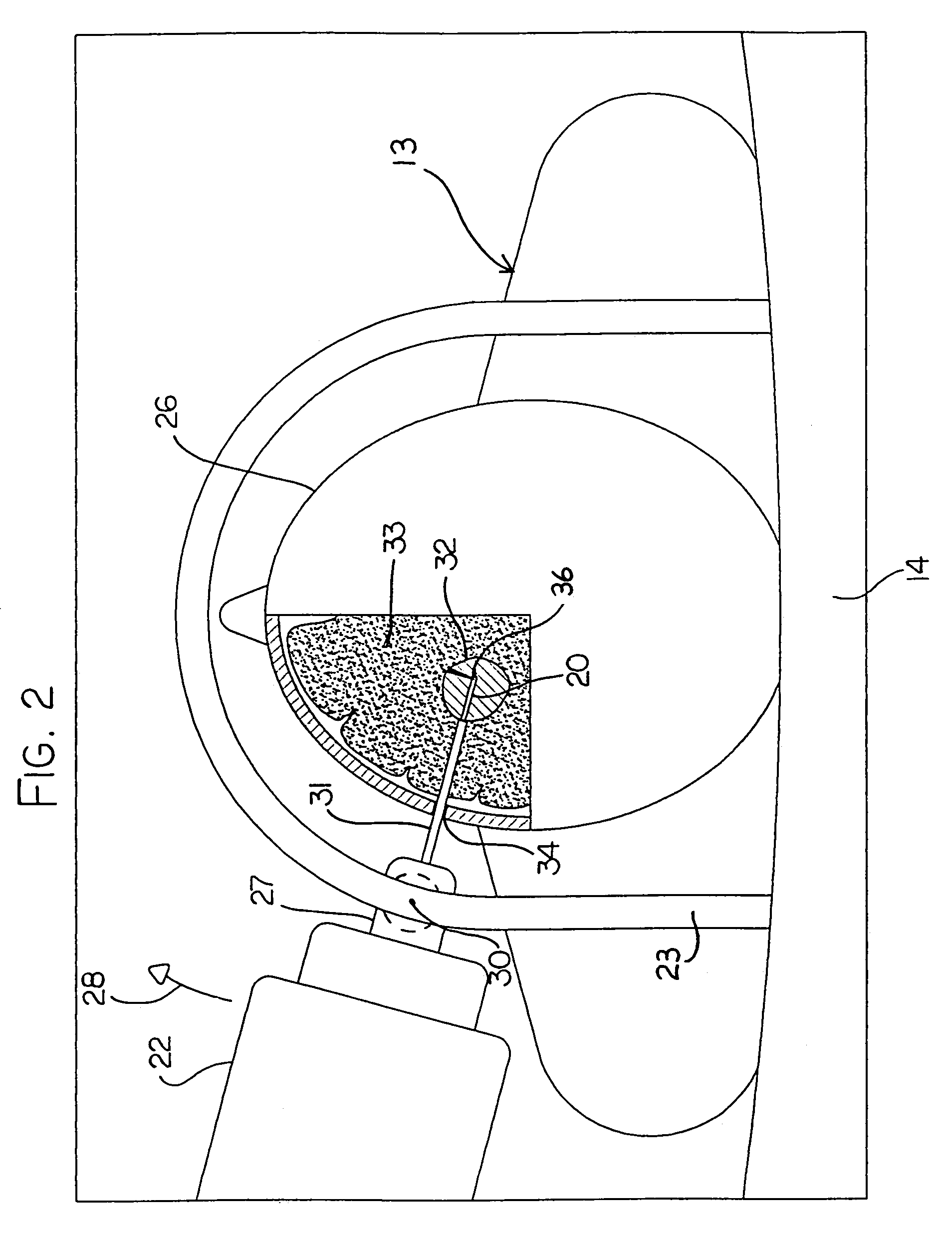
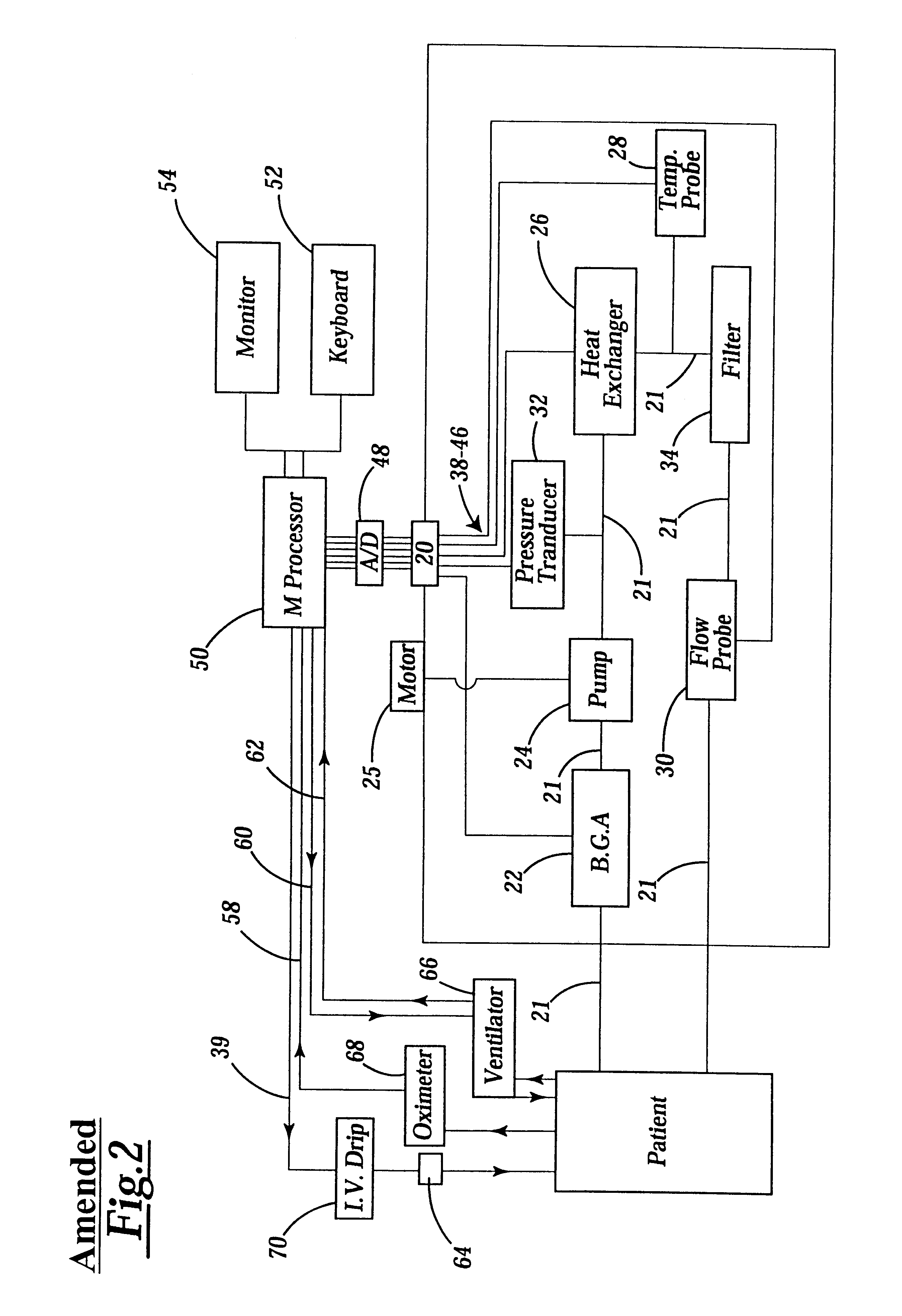
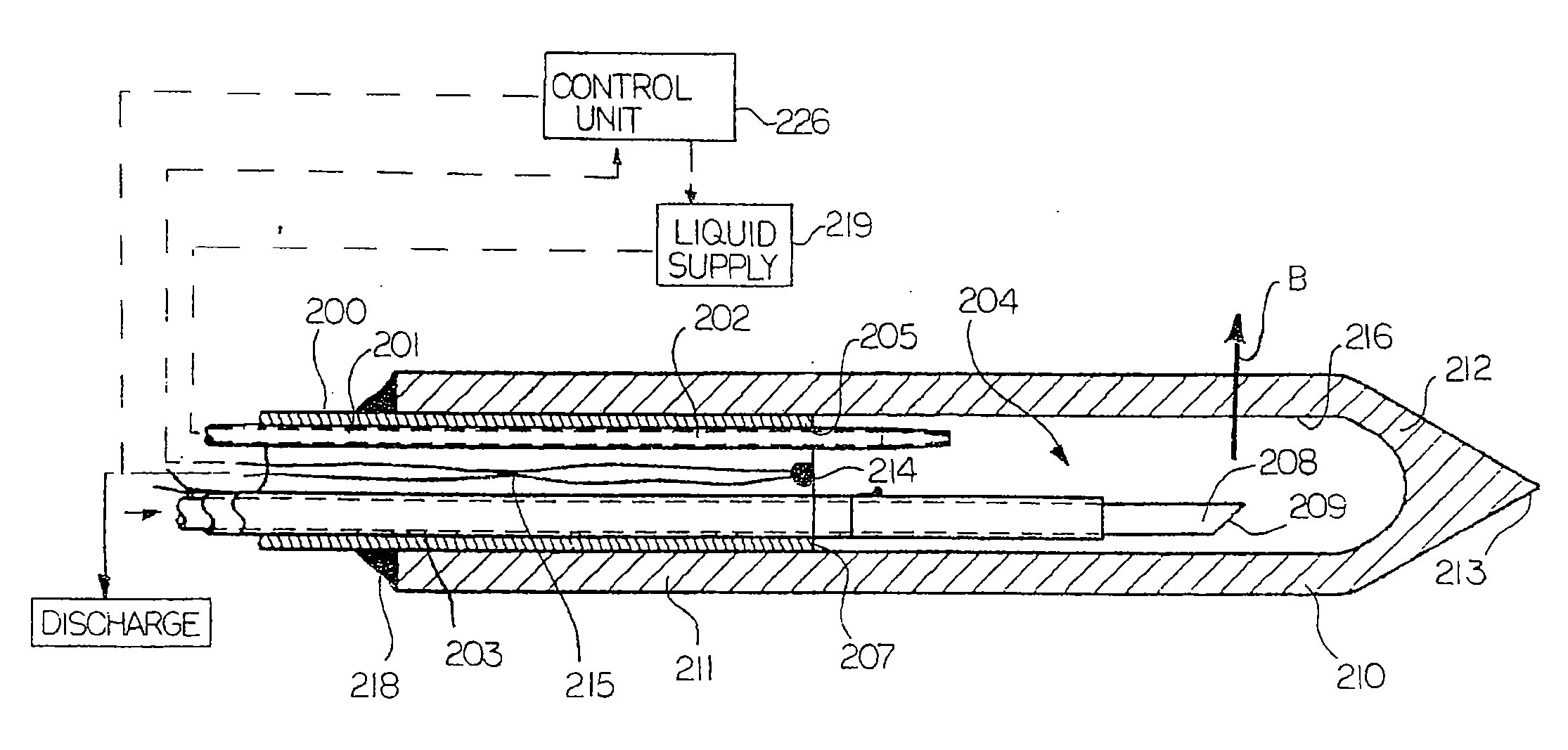
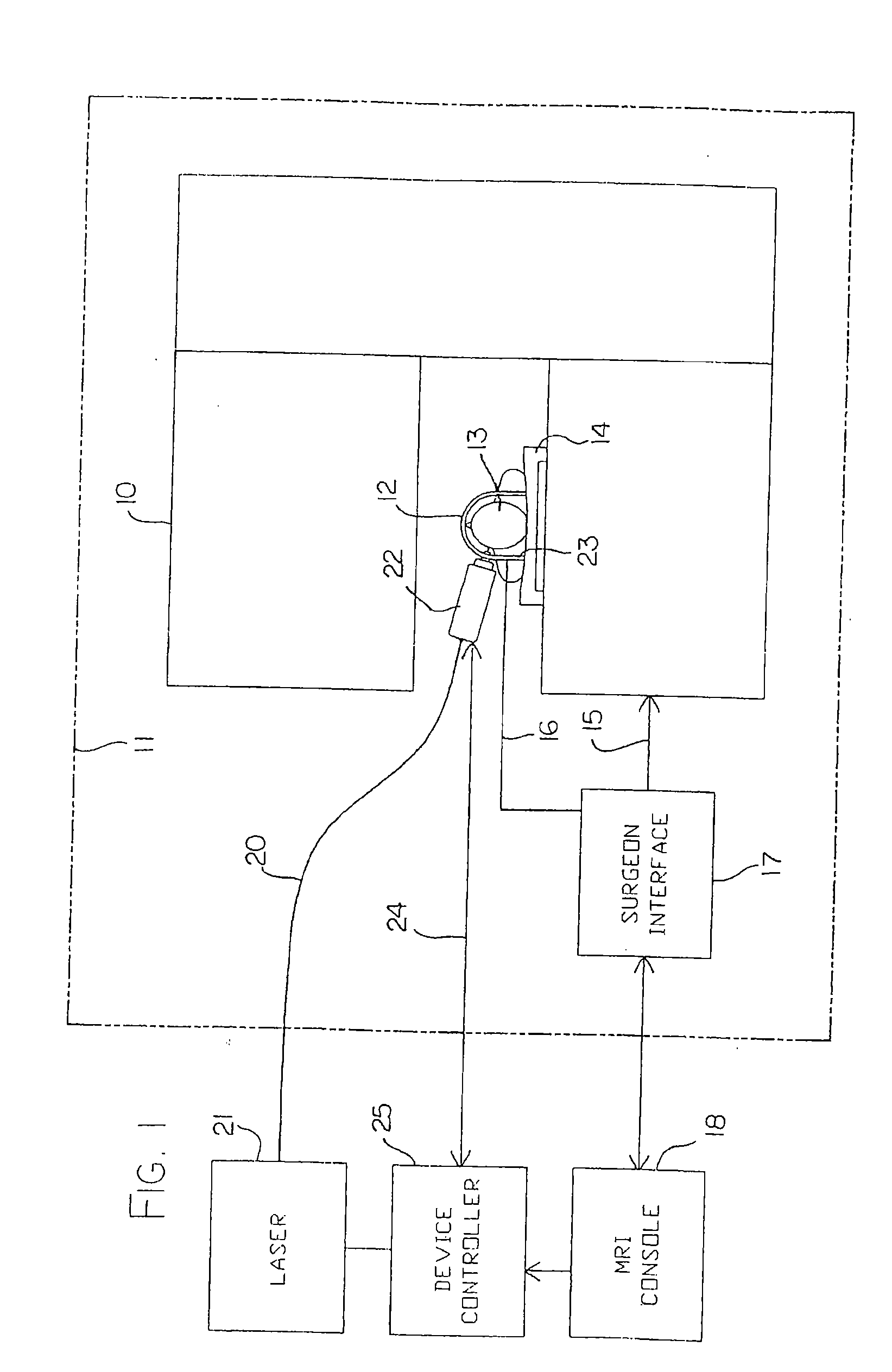
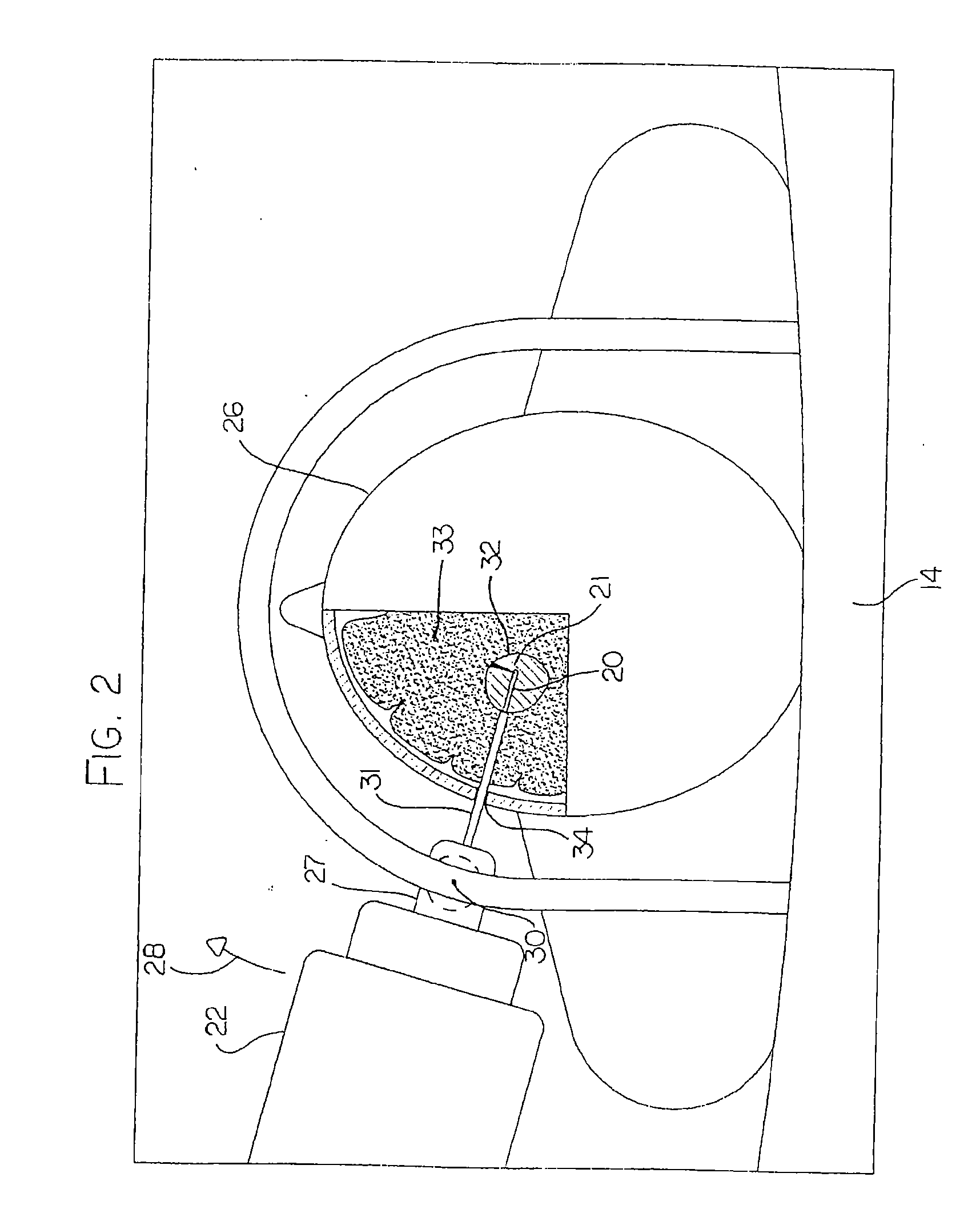
Hyperthermia treatment and probe therefor
InactiveUS7344529B2Prevent overheating cellsCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringLight beamPiezo electric
A method of using a probe that emits energy to coagulate lesions is disclosed. The probe is constructed and arranged to emit light from its distal end, either at an angle to its longitudinal axis, or along its longitudinal axis. Optionally, an end reflector may be used to direct the energy in a beam to one side of the fiber end. A reinforcing sleeve for the fiber is mounted to a shielded, Piezo-electric motor constructed and arranged to move the fiber both longitudinally and rotationally within an optional elongate cannula. An MRI system is arranged to generate a series of output signals indicative of temperature in the targeted area. The application of energy is stopped when the temperature at the boundary of the lesion reaches the required hyperthermic temperature. Cooling of the tip portion of the probe is effected by expansion of a supplied cooling fluid through a restrictive orifice into an expansion zone at the probe end. The fiber is encased in a stiff tubular titanium probe with a relatively small fluid supply duct inside the probe with the interior of the probe acting as a return duct for the expanded liquid. The temperature of the probe end is monitored by a sensor in the probe end and controlled by controlling the pressure in the supplied cooling fluid.
Owner:MONTERIS MEDICAL CORP
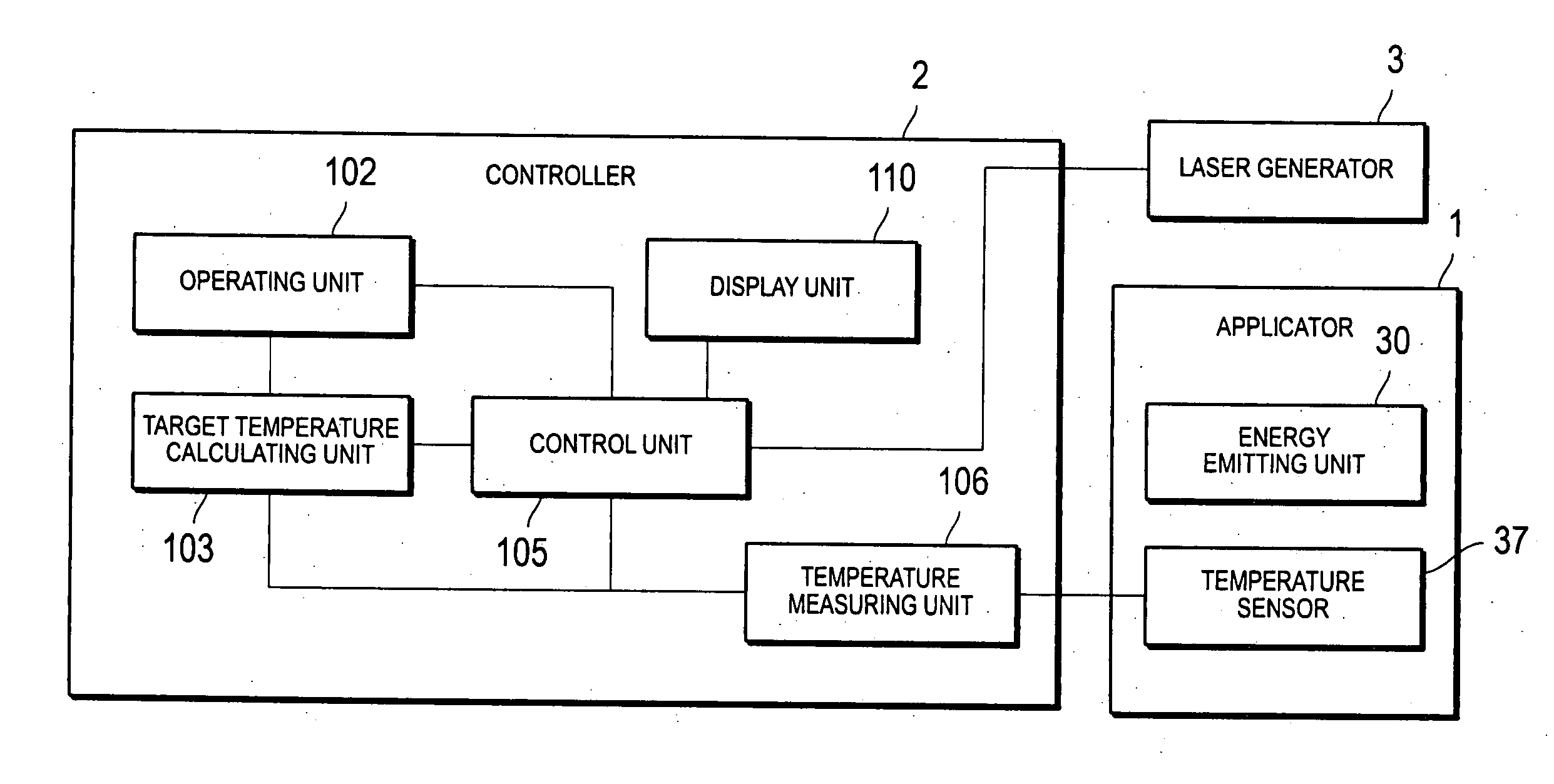
Apparatus and method for hyperthermia treatment
InactiveUS20050222556A1Way stableControlling energy of instrumentLight therapyEngineeringChange patterns
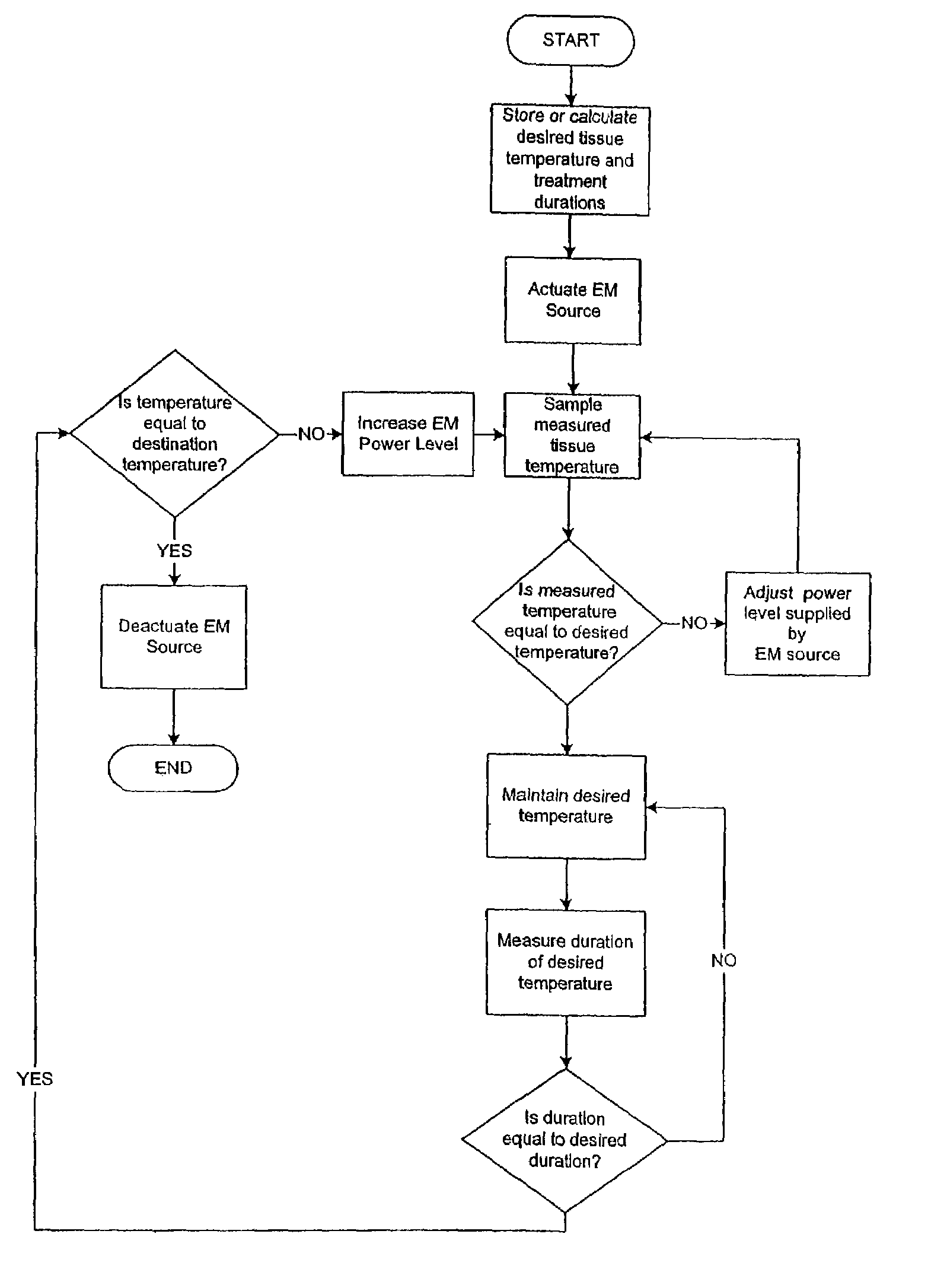
The apparatus and method of the invention is equipped with an applicator for heating a target are of body tissue by a heating unit, a temperature sensor for measuring the body tissue's temperature, a target temperature calculating unit for calculating target temperatures based on temperature change pattern set up from an operating unit, and a control unit for controlling the laser power from the heating unit so that the temperature measured by the temperature sensor follow the calculated temperature change pattern.
Owner:TERUMO KK +1
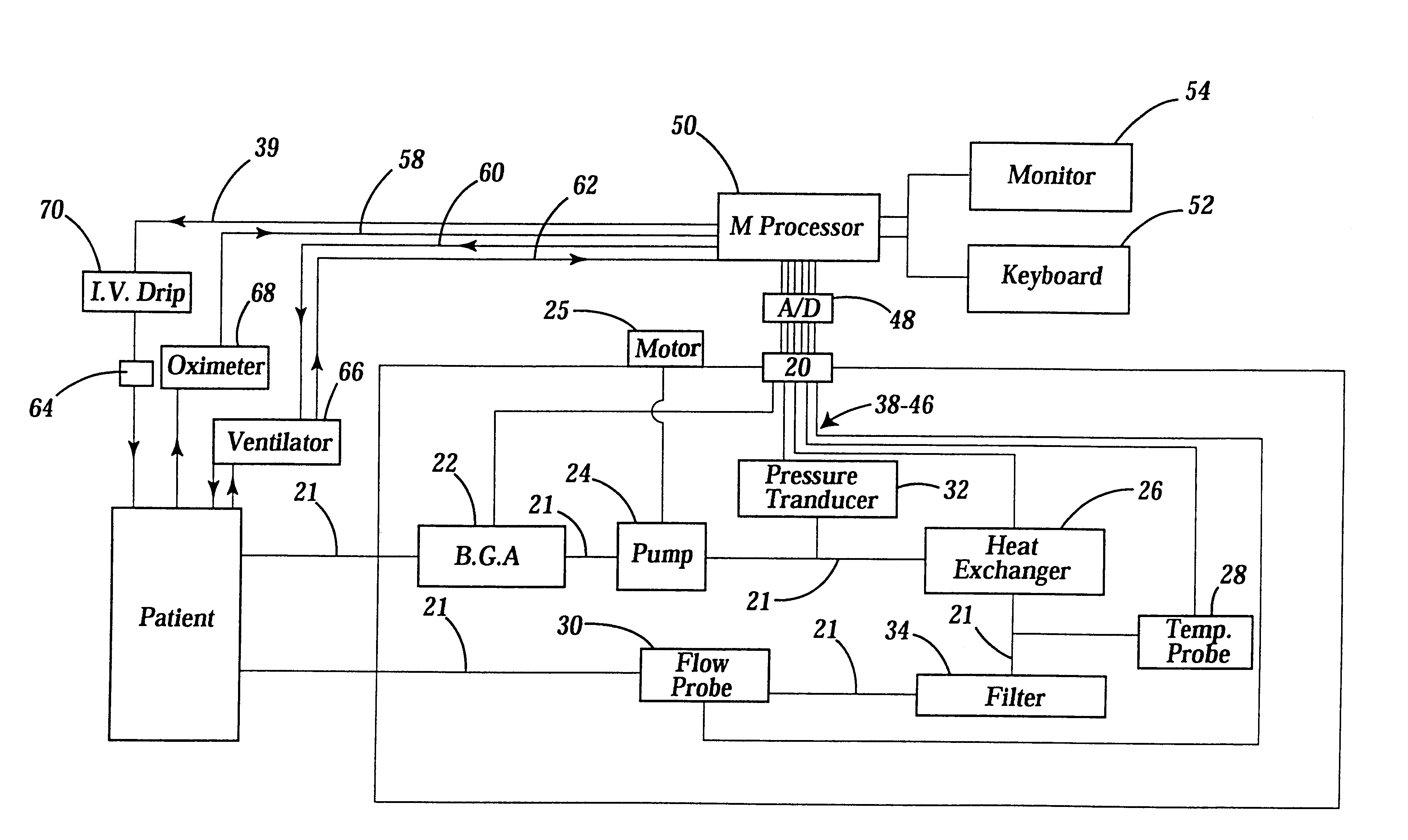
Extracorporeal whole body hyperthermia using alpha-stat regulation of blood pH and pCO2
InactiveUSRE38203E1Stabilizing biochemical reactionRespiratorsOther blood circulation devicesBiological bodyWhole body
A device and method for extracorporeal whole body hyperthermia treatment of a patient's blood using alpha-stat regulation of blood pH and pCO2 is described. The respiratory rate of a patient is either increased or decreased in accordance with the changes in pH, pCO2, and base excess. The regulation of blood during the hyperthermic treatment of the patient's blood stabilizes the biochemical reactions fundamental to the metabolic welfare of the organisms within the patient's blood while the viruses within the patient's blood are eliminated.
Owner:FIRST CIRCLE MEDICAL
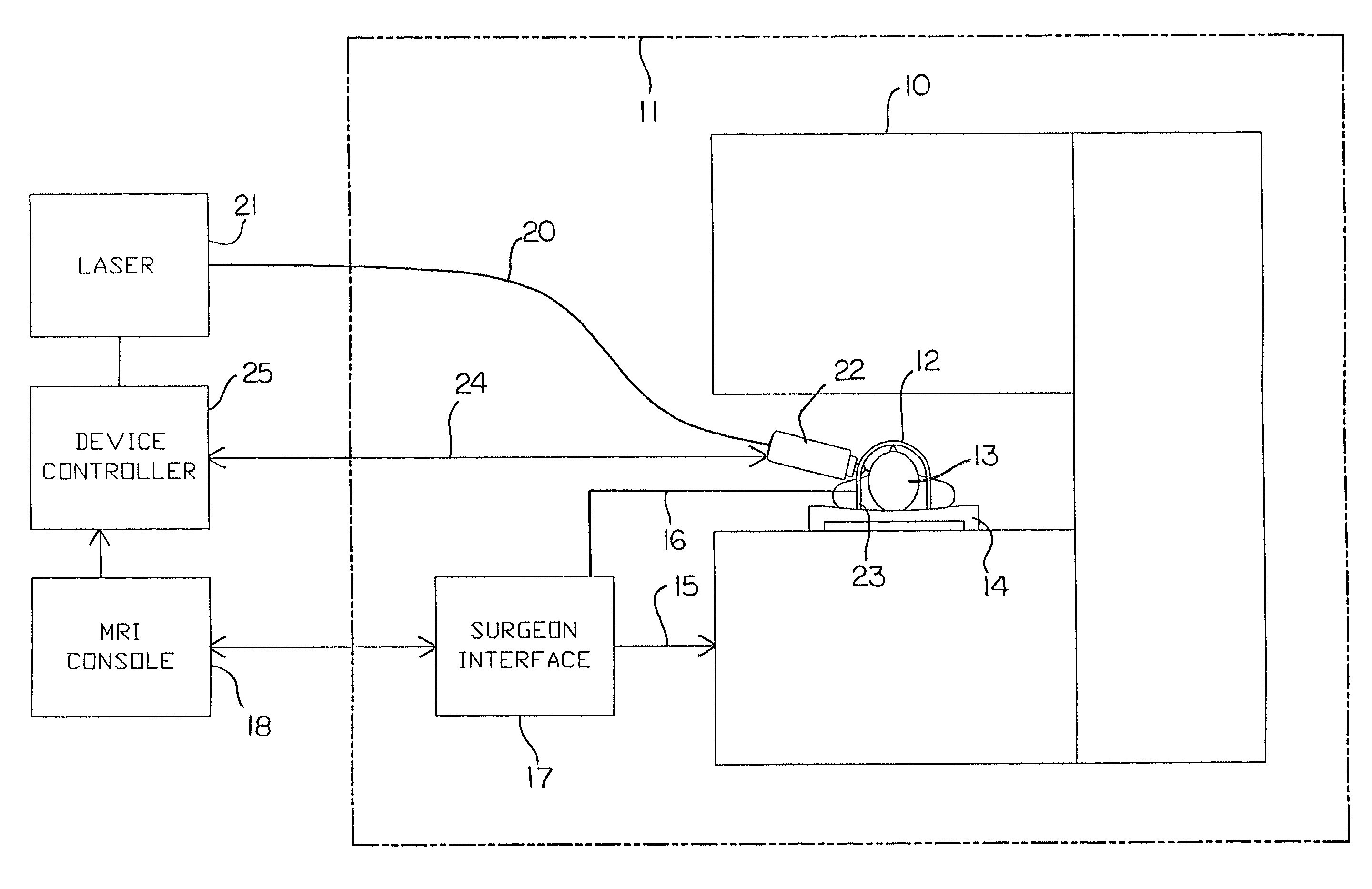
Hyperthermia treatment and probe therefor
InactiveUS7167741B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyHyperthermia TreatmentCooling fluid
This surgical device uses a laser beam to coagulate tissue. The elongate device carries the beam through an optical fiber that has a chamfered end for deflecting the beam out of a distal end of the device at an angle. Tissue coagulation is monitored using a magnetic resonance imaging system that provides periodic tissue temperature data. A small fluid supply duct provides cooling fluid that expands to a gas near the distal end of the device, thereby cooling the tip.
Owner:MONTERIS MEDICAL
Deep heating hyperthermia using phased arrays and patient positioning
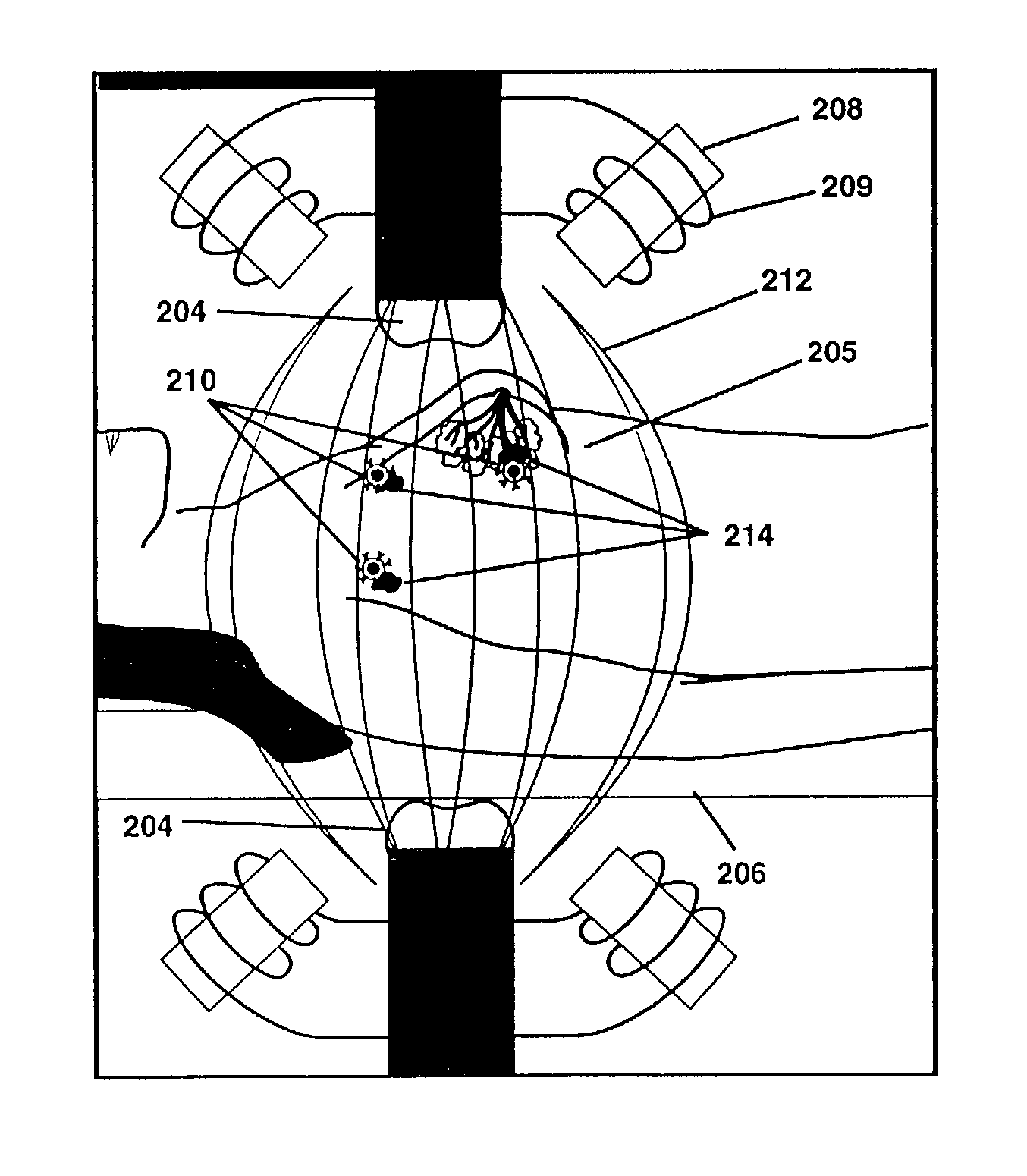
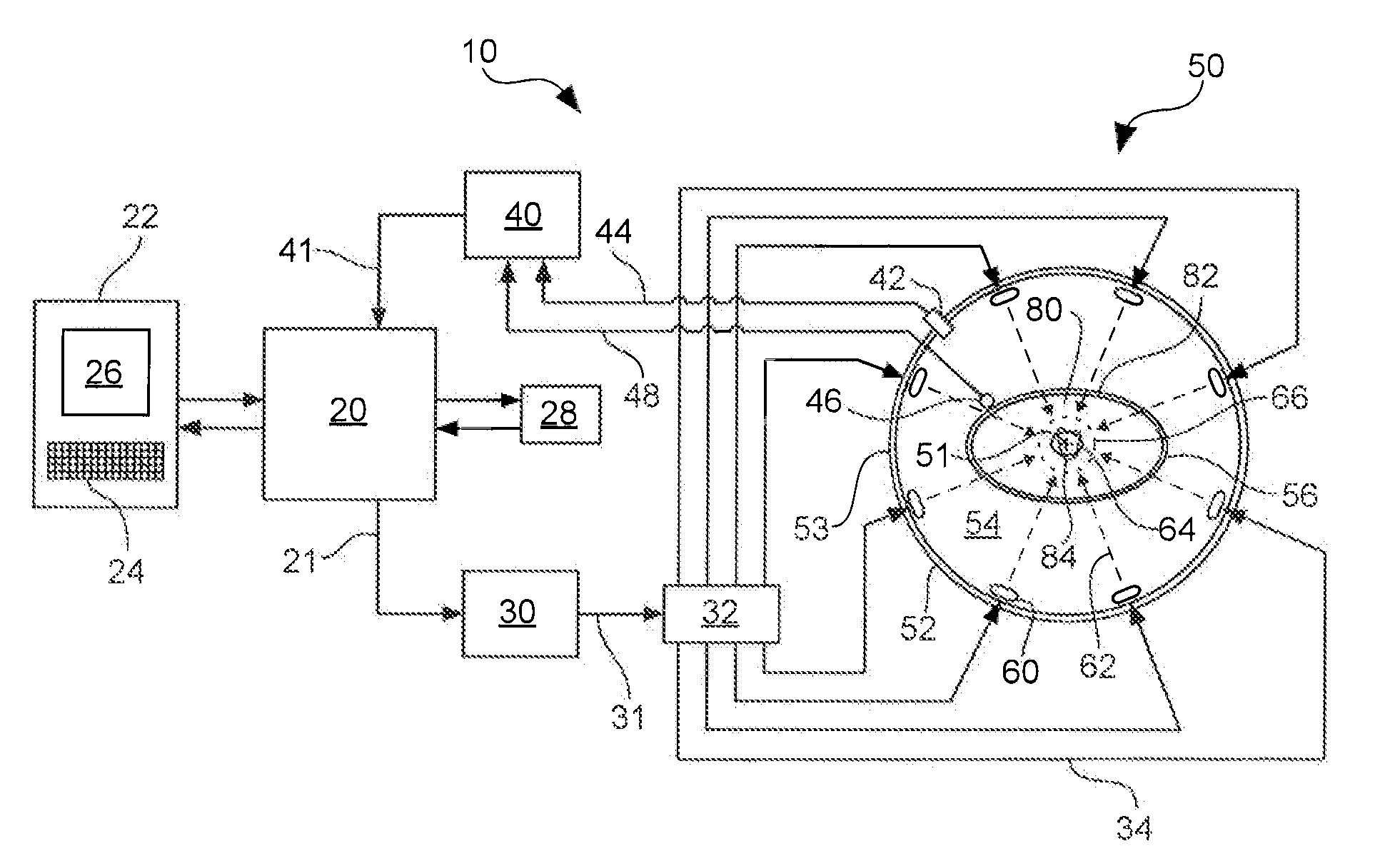
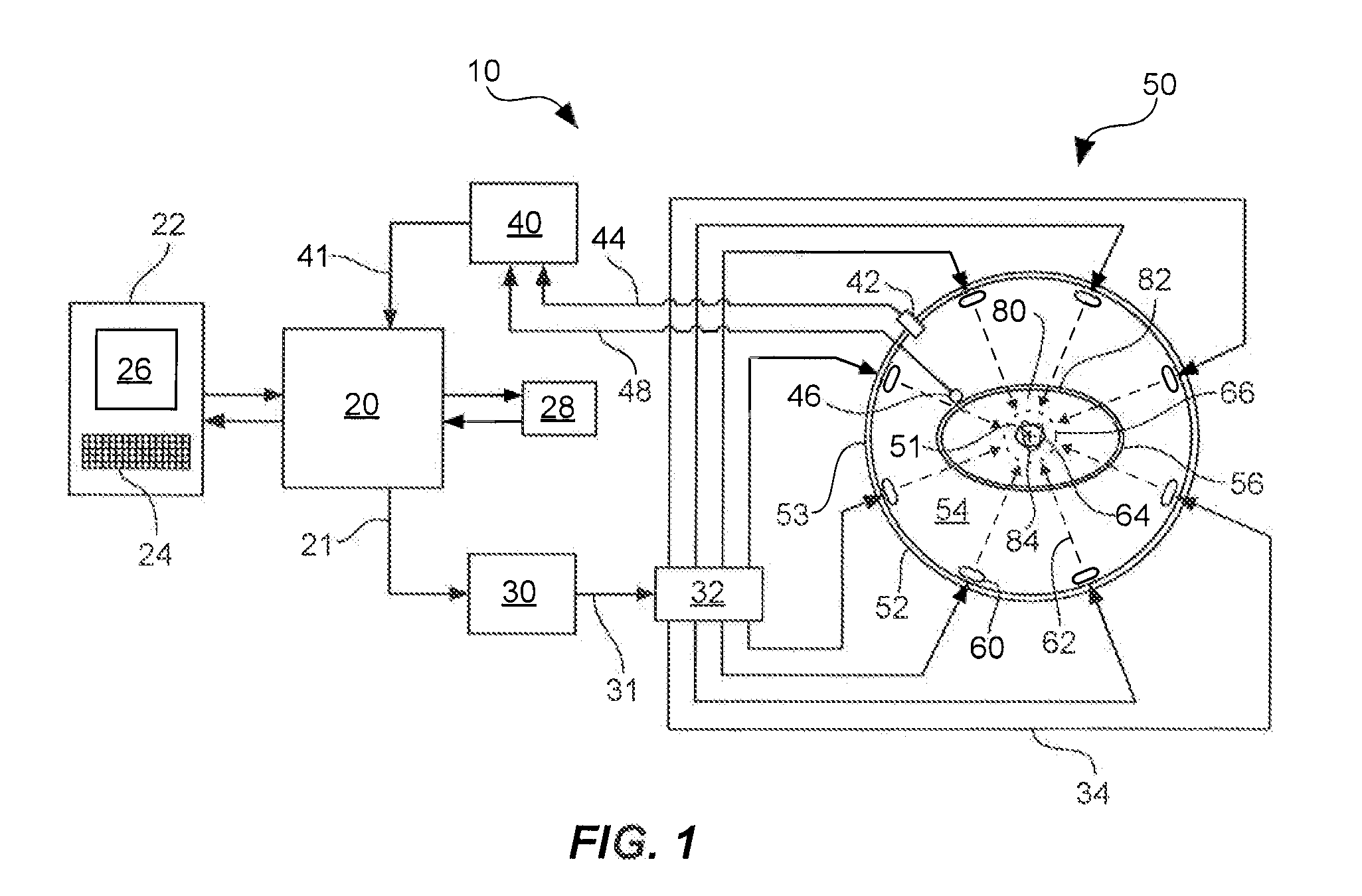
A hyperthermia treatment system for heating a selected region within a target body that includes a power source and a plurality of electromagnetic applicators that are in electrical communication with the power source and arranged in a surrounding array around a focal region to concentrate their combined radiation output onto the focal region. The treatment system also includes a support mechanism that is adapted to support a target body within the surrounding array of applicators, and a positioning mechanism adapted to move the support mechanism and align the selected region within the target body with the focal region. Furthermore, the positioning mechanism is adapted to compensate for movement of the focal region in response to an interaction between the combined radiation output and the target body.
Owner:PYREXAR MEDICAL
Invasive microwave antenna array for hyperthermia and brachytherapy
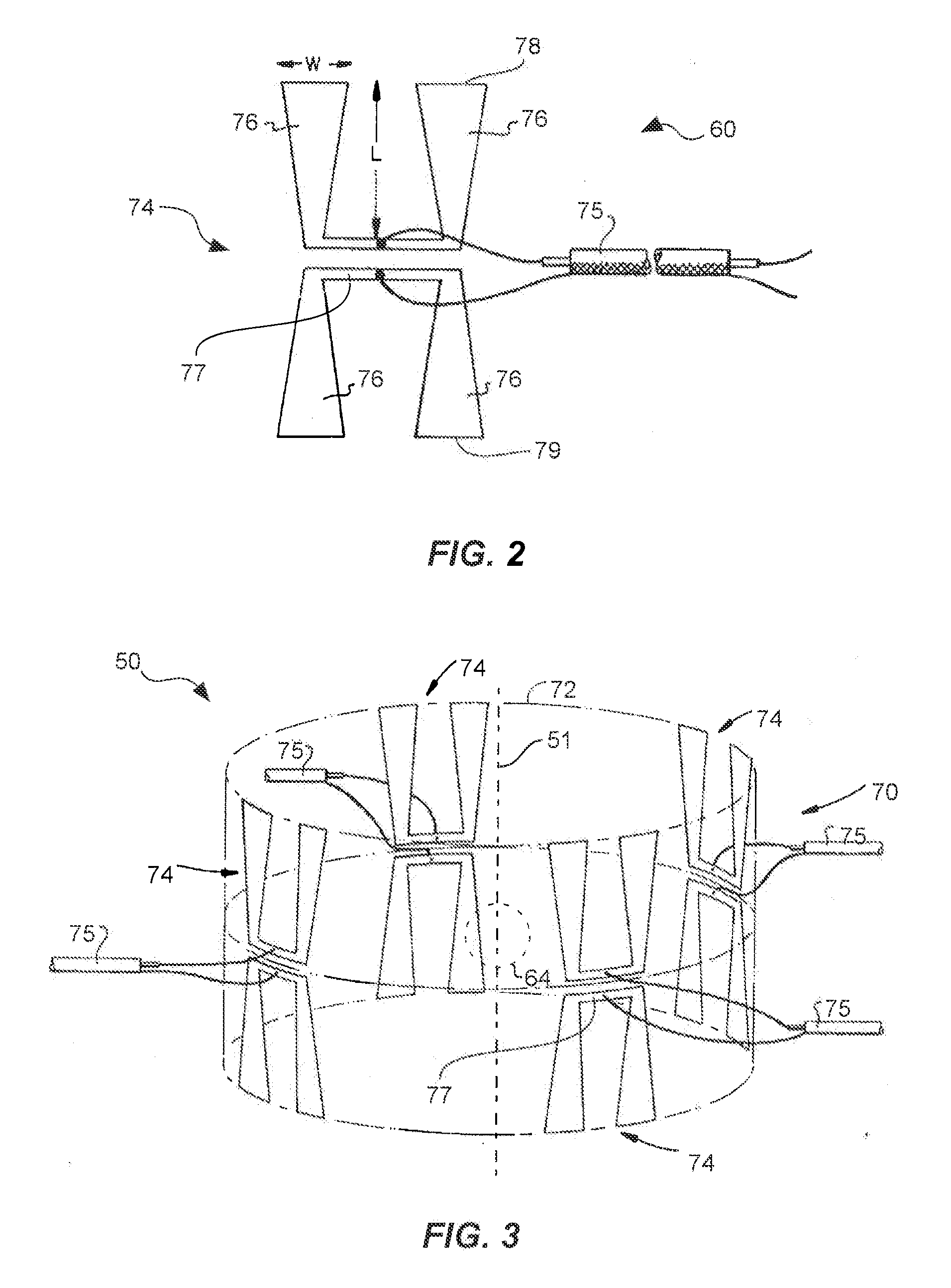
InactiveUS6957108B2Increase oxygenationSpeed up the flowMicrowave therapySurgical instruments using microwavesElectrical conductorEngineering
Owner:PYREXAR MEDICAL
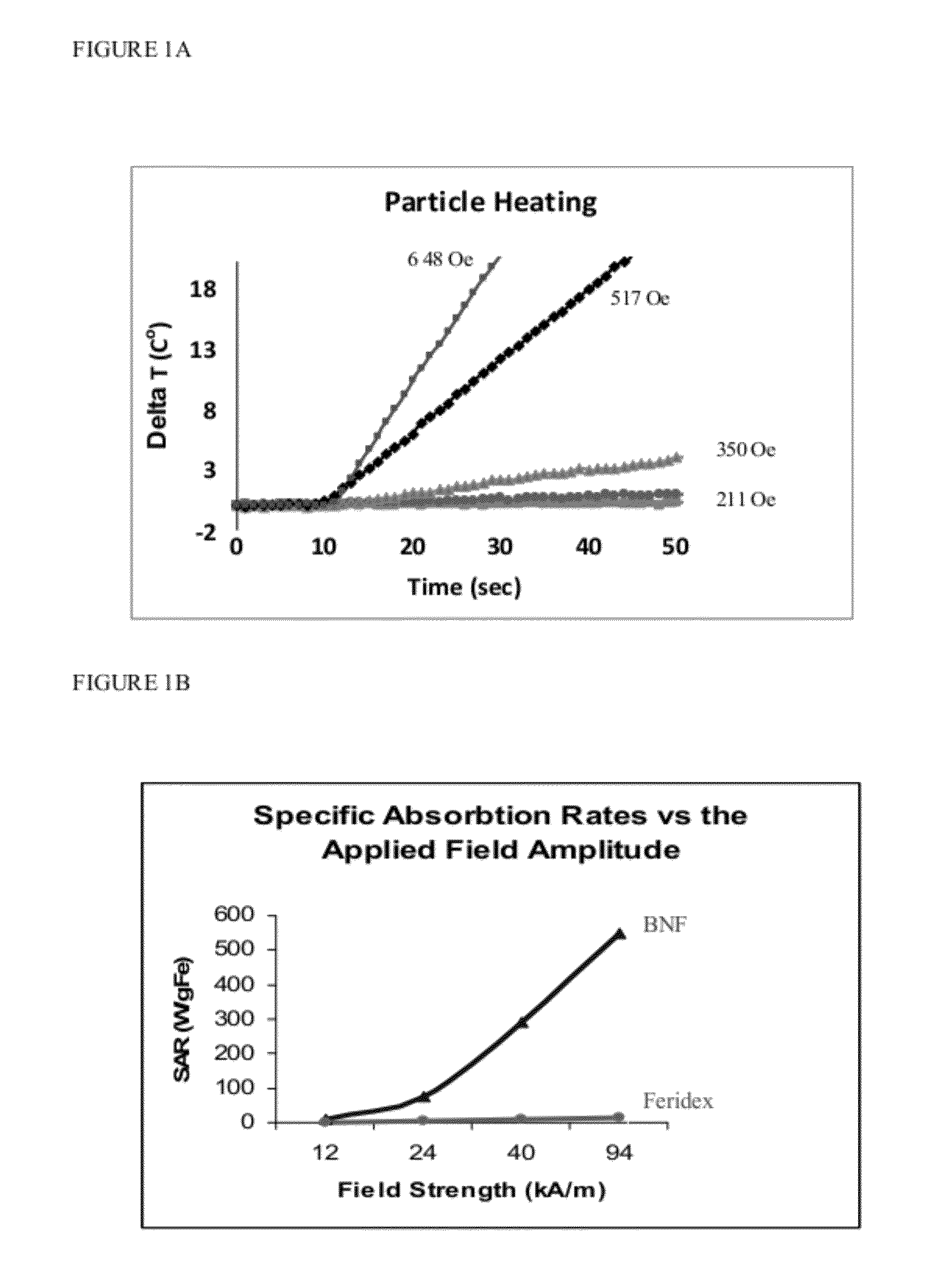
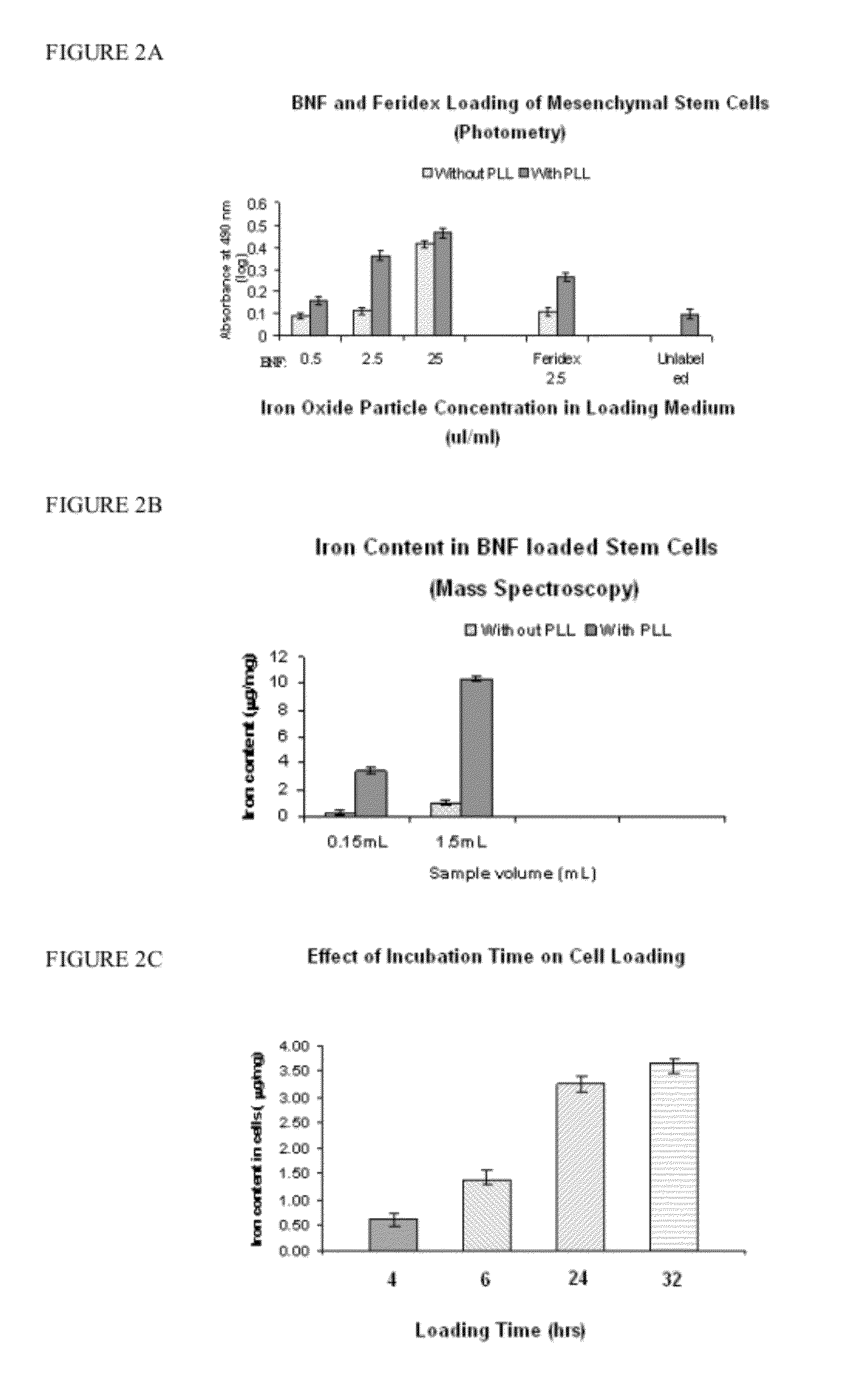
Nanoparticle loaded stem cells and their use in MRI guided hyperthermia
InactiveUS20120283503A1Enhanced MR propertyEnough timeElectrotherapyMedical devicesMri guidedMagnetite Nanoparticles
The present invention provides stem cells loaded with bi-functional magnetic nanoparticles (nanoparticle-loaded stem cells (NLSC)) that both: a) heat in an alternating magnetic field (AMF); and b) provide MRI contrast enhancement for MR-guided hyperthermia. The nanoparticles in the NLSC are non-toxic, and do not alter stem cell proliferation and differentiation, the nanoparticles do however, become heated in an alternating magnetic field, enabling therapeutic applications for cancer treatment. NLSC can deliver hyperthermia to hypoxic areas in tumors for sensitization of those areas to subsequent treatment, thus delivering therapy to the most treatment-resistant tumor regions. The heating of diseased tissue either results in direct cell killing or makes the tumor more susceptible to radio- and / or chemotherapy. The NLSC of the present invention can be used for MR image-guided hyperthermia in oncology, in stem cell research for cell tracking and heating, and for elimination of mis-injected stem cells.
Owner:OSTROVSKA LYUBOV PHD
System and Method For Magnetic-Nanoparticle, Hyperthermia Cancer Therapy
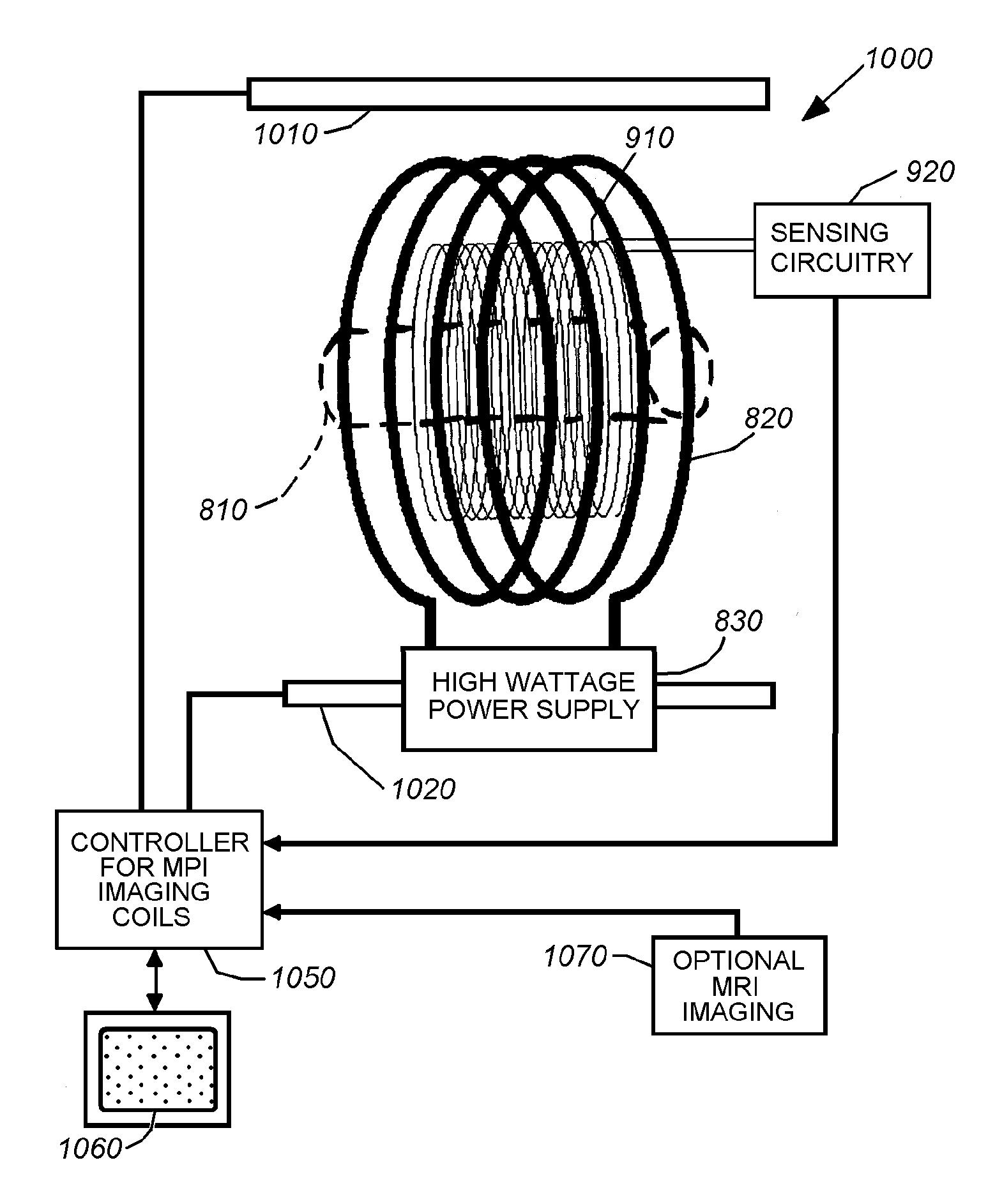
InactiveUS20100292564A1Overcomes drawbackElectrotherapyMagnetic measurementsMedical imaging dataMagnetite Nanoparticles
A system and method is provided for performing and monitoring a magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia process on a subject having received a dose of a magnetic nanoparticle configured to bind to tissue within a target area of the subject. A low-field MRI system is utilized having a static magnetic field and a radio frequency (RF) system configured to receive MRI data from the target area. A hyperthermia system is coupled to the low-field MRI system and configured to generate a hyperthermia excitation field configured to cause the magnetic nanoparticle to rotate at a lag with respect to a magnetic field experienced by the magnetic nanoparticle to cause a temperature increase in the target area. The MRI system is configured to acquire medical imaging data from the target area and reconstruct images therefrom indicating at least one of a spatial distribution of the nanoparticle in and a temperature of the target area.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Core-Excited Nanoparticles and Methods of Their Use in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Disease
InactiveUS20130195979A1Cost-effectiveEffective and practicalPowder deliveryNanotechDiseaseExternal energy
Owner:TERSIGNI SAMUEL HARRY
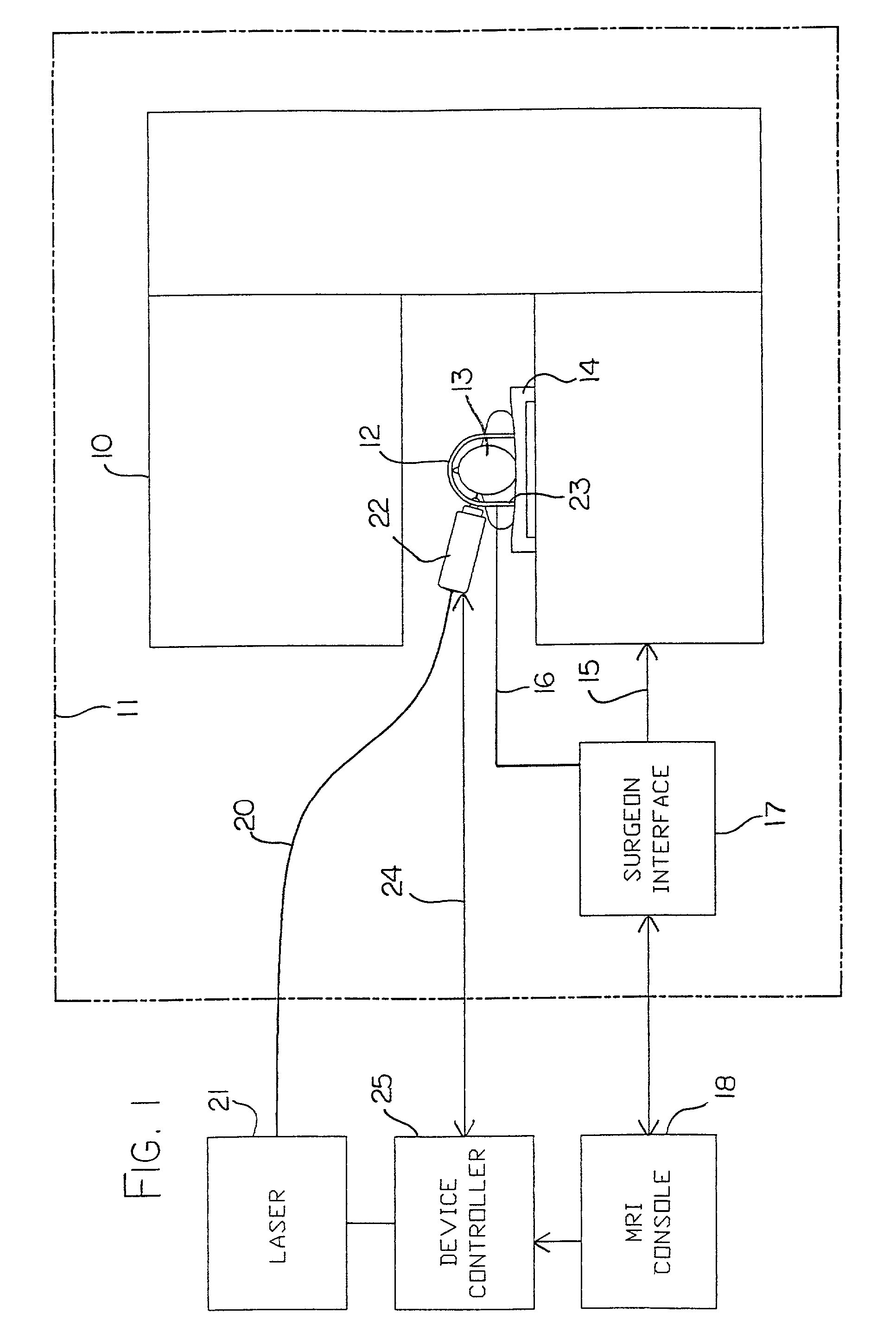
Hyperthermia treatment and probe therefor
An MRI guided surgical apparatus includes a heat source formed by a laser and an optical fiber carrying the heat energy into a part to be coagulated by hyperthermia with an end reflector to direct the energy in a beam to one side of the fiber end. A reinforcing sleeve for the fiber is mounted in a shielded, Piezo-electric motor which causes movement of the fiber longitudinally and angularly within a rigid elongate cannula. A magnetic resonance imaging system is arranged to generate a series of output signals over a period of time representative of temperature in the part as the temperature of the part changes during that time. The heat source is controlled in heat energy applied and location and orientation of the beam to stop heating when the temperature at the boundary of a tumor reaches the required hyperthermic temperature. Cooling of the tip portion of the probe is effected by expansion of a supplied cooling fluid in gaseous form through a restrictive orifice into an expansion zone at the probe end. The fiber is thus encased in a stiff tubular titanium probe with a relatively small fluid supply duct along the inside of the probe with the interior of the probe acting as a return duct for the expanded gas. Thus the fiber end is contained in gas rather than liquid and the temperature of the probe end can be monitored by a sensor in the probe end and controlled by controlling the pressure in the supplied cooling fluid. The probe is driven in the longitudinal and rotational directions to move the fiber tip.
Owner:MONTERIS MEDICAL
Iron/Iron Oxide Nanoparticle and Use Thereof
The present invention is a nanoparticle composition composed of an iron core with an iron oxide shell which is optionally coated with a micro-emulsion. The disclosed nanoparticle compositions are disclosed for use in hyperthermia treatment and imaging of cancer.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Core-excited nanoparticles and methods of their use in the diagnosis and treatment of disease
InactiveUS8197471B1Minimal side-effectsEffective and practicalPowder deliveryNanotechDiseaseCore shell nanoparticles
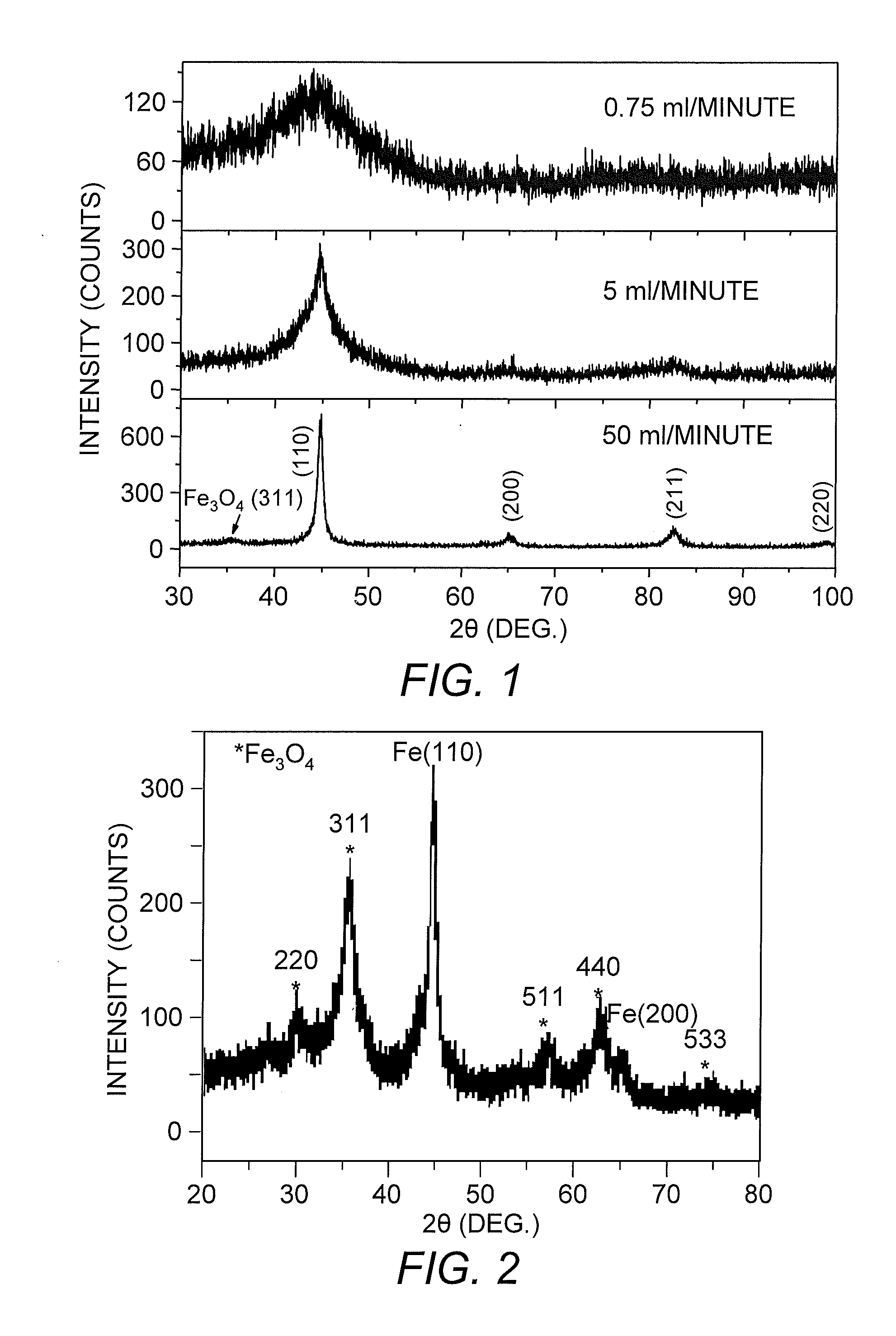
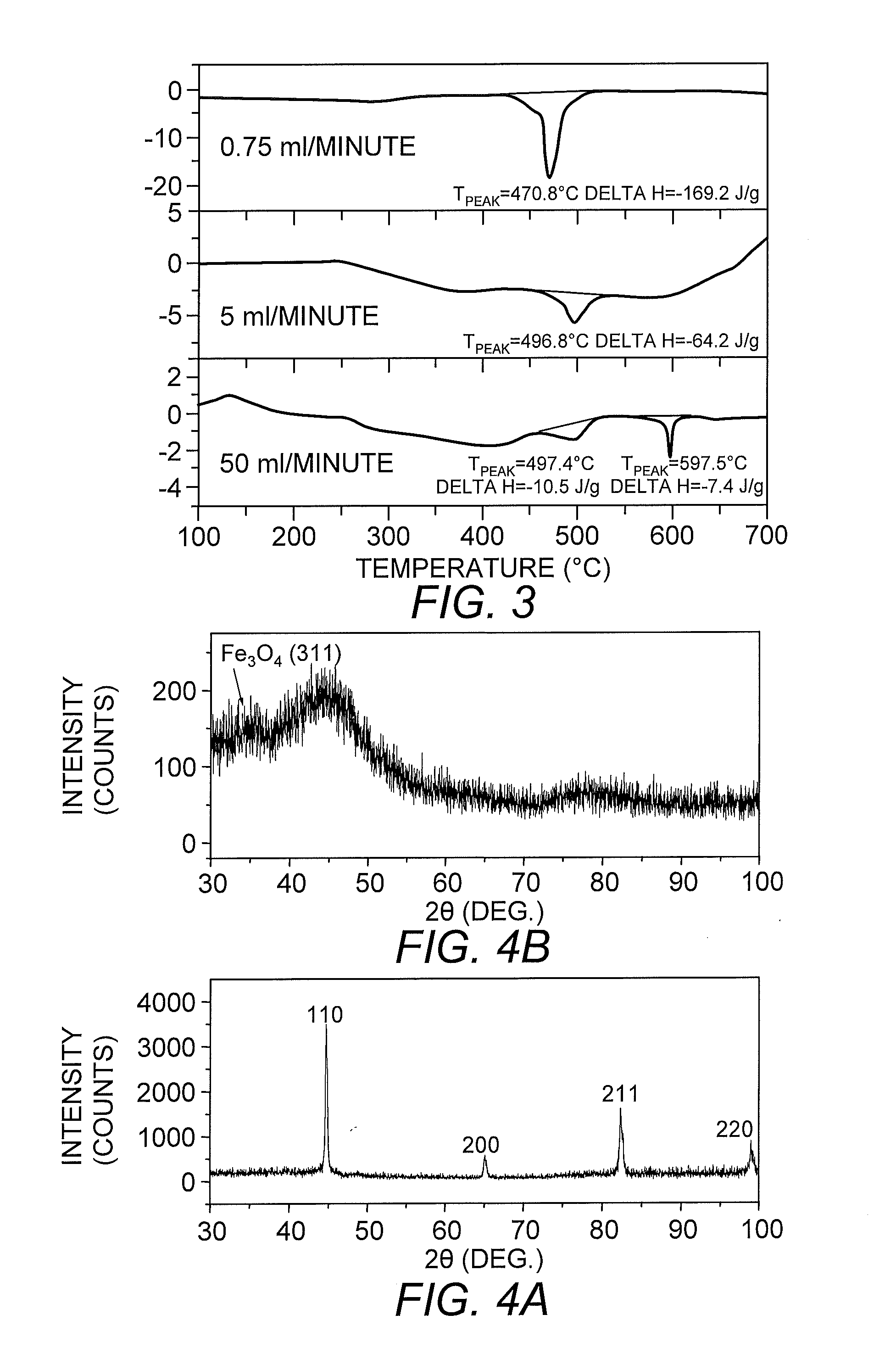
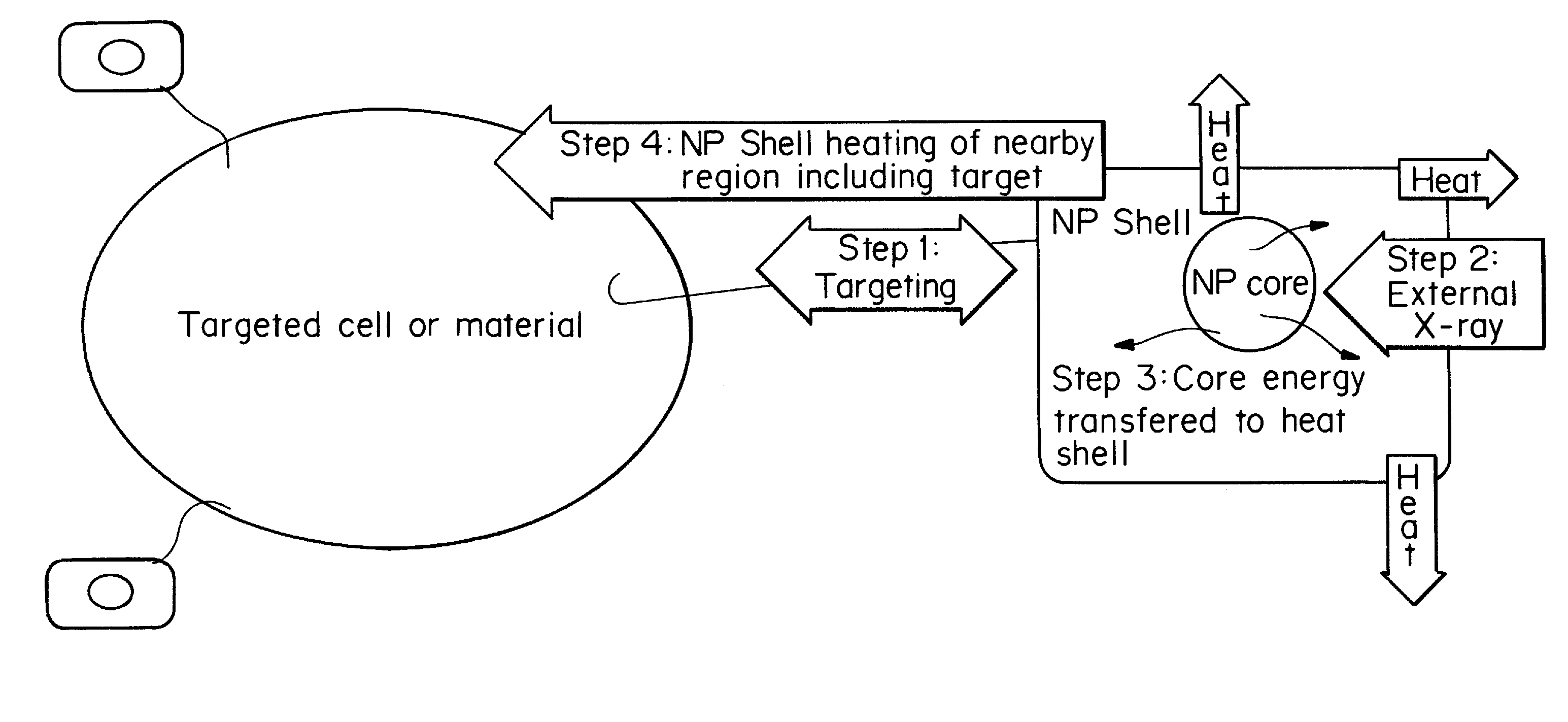
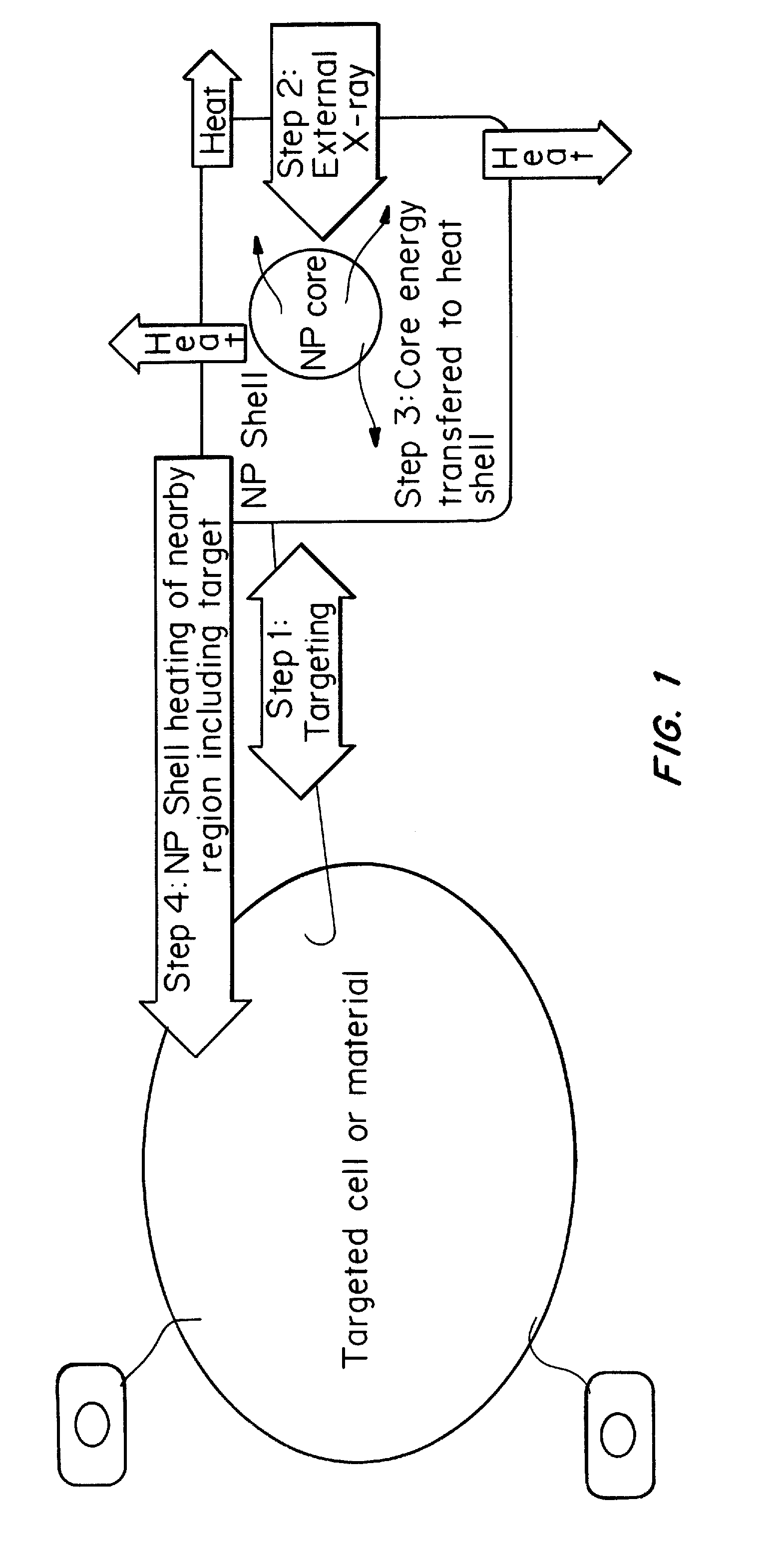
Core-excited nanoparticle thermotherapy (CENT), is an improved material for use in thermotherapy. The CENT method uses both core-exciting energy (including x-rays) and core-shell nanoparticles, specifically designed to absorb radiation in their core structure, then transfer energy from the core to the shell, to heat the outer shell of the nanoparticle. The heated nanoparticle then heats the surrounding region to a temperature sufficient to detect, affect, damage and / or destroy the targeted cell or material. CENT nanoparticles can be bound to targeting agents that deliver them to the region of the diseased cell.
Owner:TERSIGNI SAMUEL HARRY
Iron/Iron Oxide Nanoparticle and Use Thereof
The present invention is a nanoparticle composition composed of an iron core with an iron oxide shell which is optionally coated with a micro-emulsion. The disclosed nanoparticle compositions are disclosed for use in hyperthermia treatment and imaging of cancer.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Devices for targeted delivery of thermotherapy, and methods related thereto
InactiveUS7951061B2Minimal invasionShort maintenance periodElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsDiseaseHyperthermia Treatment
Disclosed are devices for targeted delivery of thermotherapy. These devices are useful in the treatment of diseased tissue in conjunction with magnetic compositions. Further disclosed are methods for treating diseased tissue, which involve the administration of a thermotherapeutic magnetic composition to a patient or a portion of a patient, and the application of an alternating magnetic field to inductively heat the thermotherapeutic magnetic composition. The devices and the methods disclosed herein are useful for the treatment of a variety of indications, such as cancer, diseases of the immune system, pathogen-borne diseases, hormone-related diseases, non-cancerous diseased cells or tissue, and undesirable matter, such as toxins and reaction-by-products associated with organ transplants.
Owner:ASPEN MEDISYS +1
Enhanced ultrasound detection with temperature-dependent contrast agents
InactiveUS7179449B2Enhancing acoustic reflectivityLittle and no detectable change in acoustic reflectivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImaging modalities
Methods and devices for enhanced ultrasound detection based upon changing temperature and ultrasound reflectivity of a temperature-dependent contrast agent bound to an ultrasound target are disclosed. The methods and devices can be used for enhanced imaging alone or in conjunction with drug delivery, with therapeutic approaches such as hyperthermia or cryotherapy or with other imaging modalities.
Owner:BARNES JEWISH HOSPITAL
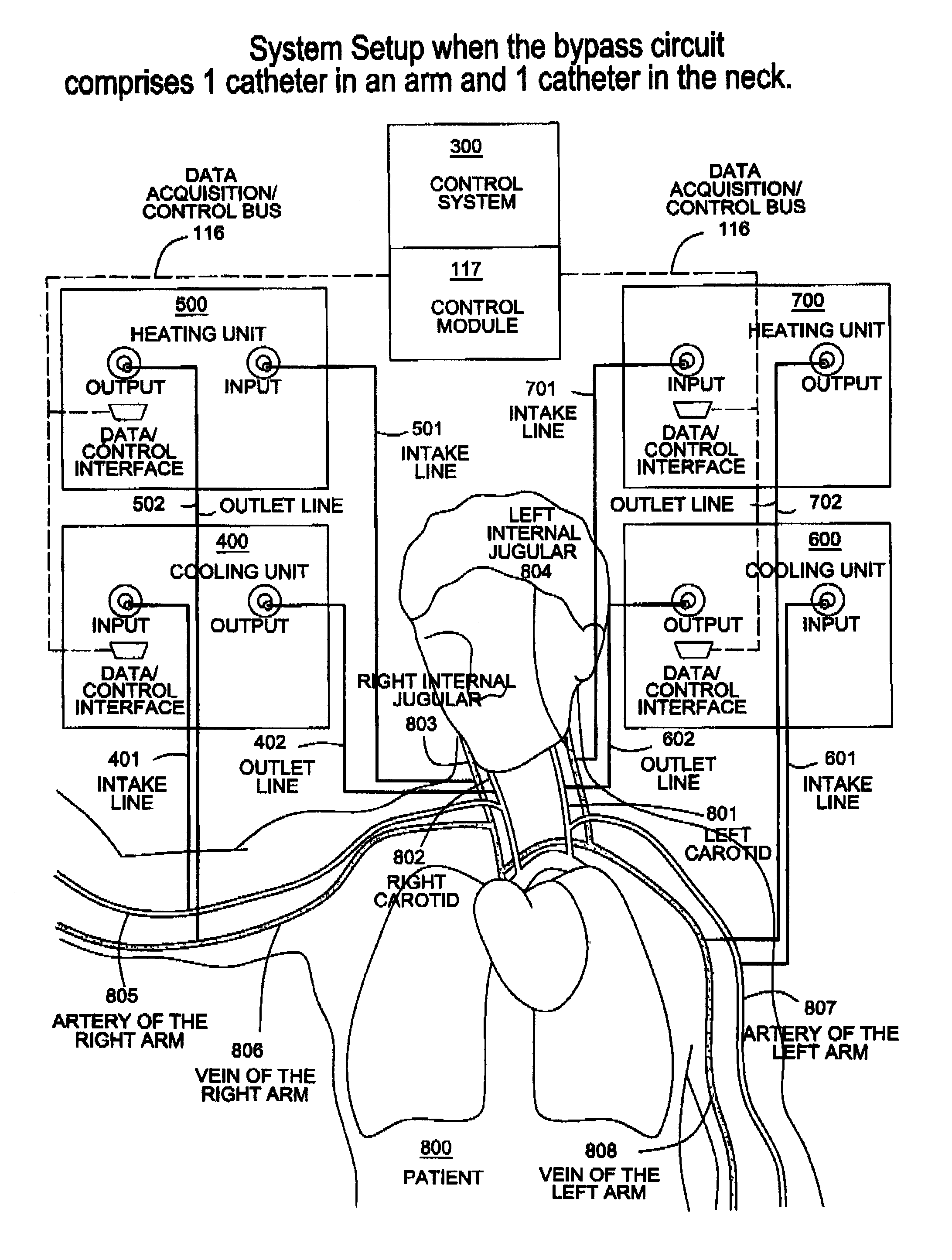
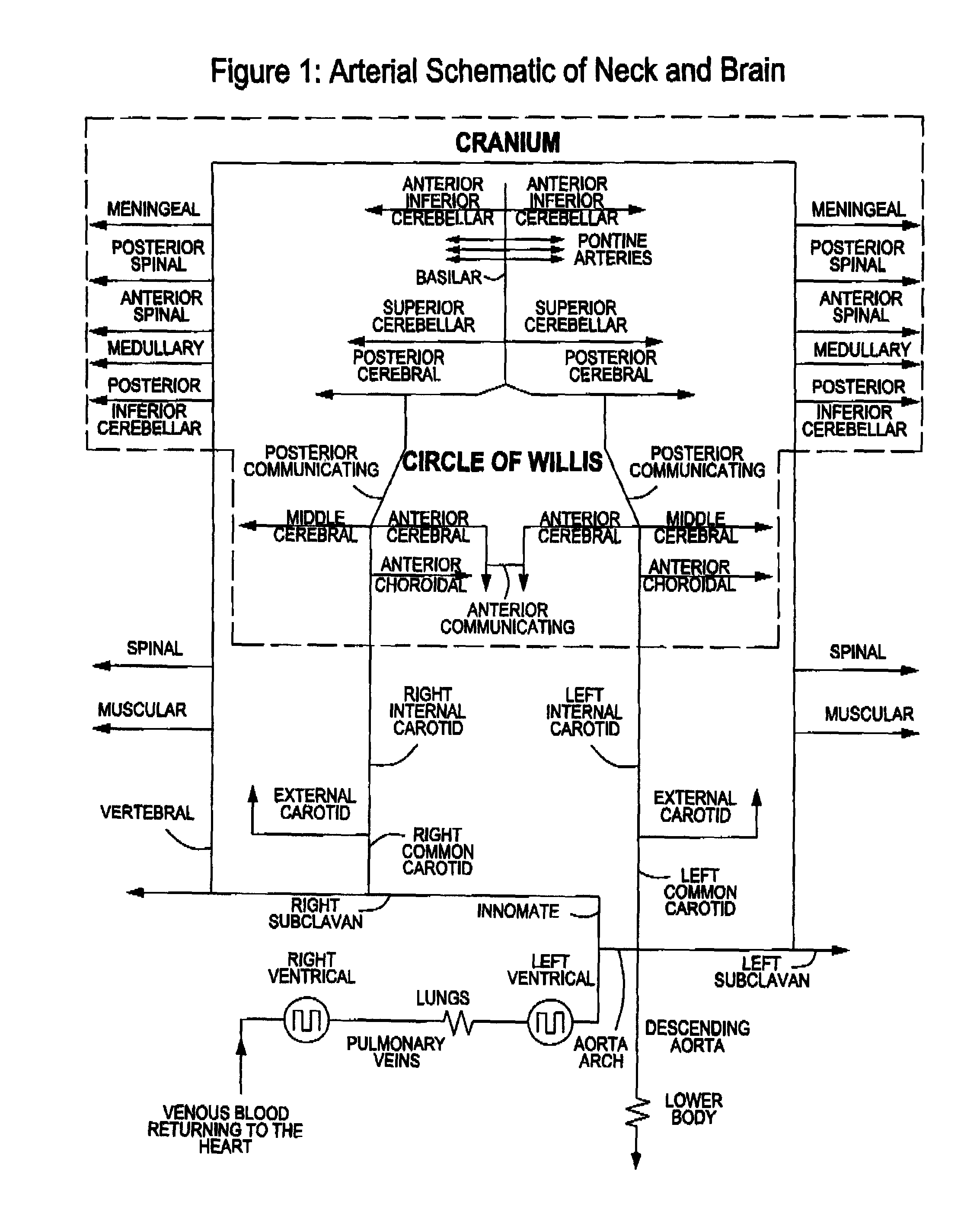
Apparatus, system and methods for extracorporeal blood processing for selectively cooling the brain relative to the body during hyperthermic treatment or to induce hypothermia of the brain
InactiveUS8834404B2Reduce adverse reactionsReduce riskOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesTherapeutic treatmentBlood processing
Owner:BEAUDIN STEVE ANDRE
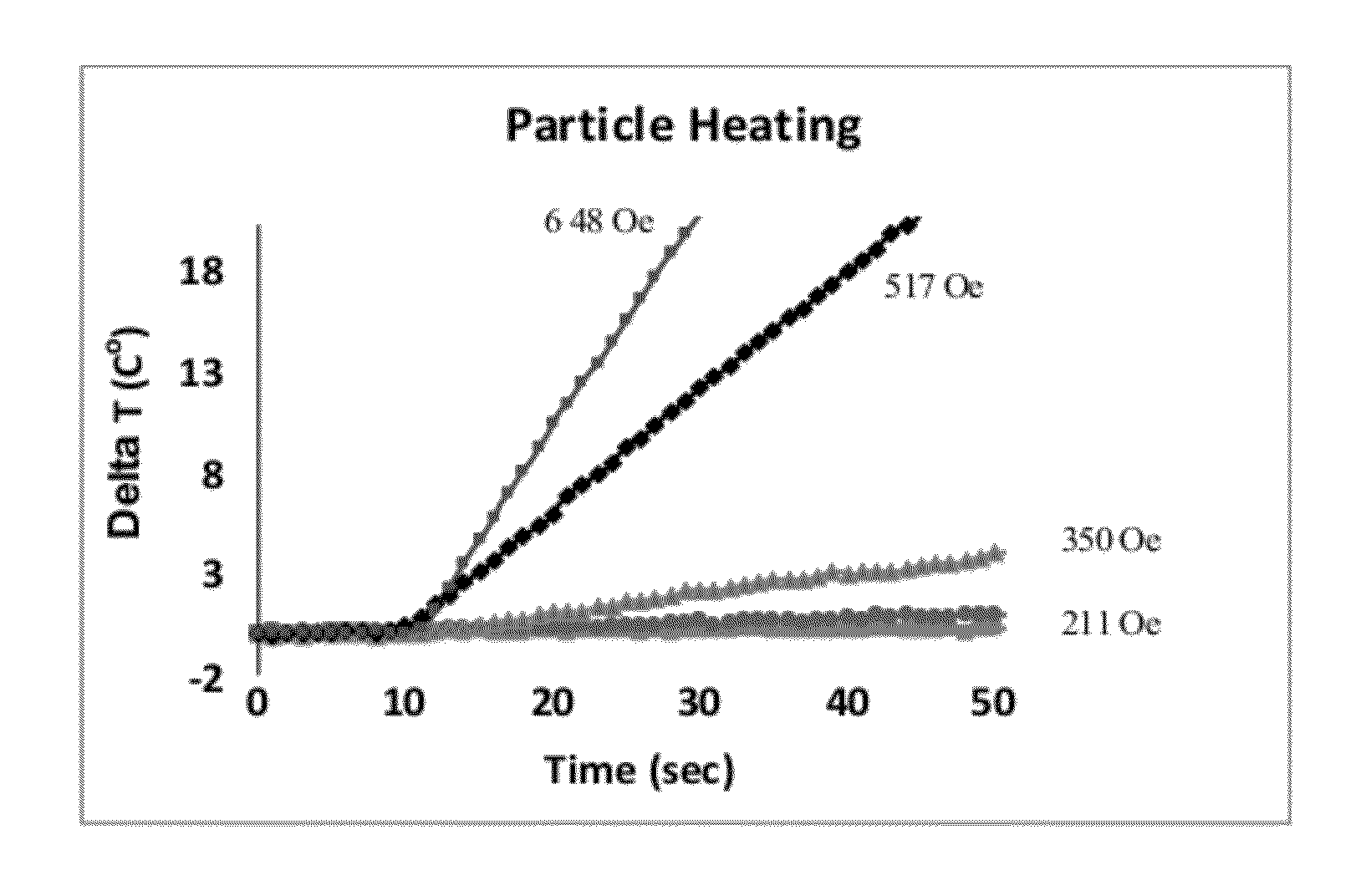
Nanoparticle heating and applications thereof
This invention provides magnetic nanoparticles, which when placed in a magnetic field are selectively heated at a certain frequency of the magnetic field, as a function of their size, composition, or both. The invention also provides for use of such nanoparticles, in applications including, inter alia, selective nanoparticle heating and applications thereof, hyperthermia induction in cells or tissue, remote alteration of protein structure and / or drug delivery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Hyperthermia, system, method and components
ActiveUS20090043256A1Effective and safe for patientInfusion devicesMedical devicesIntensive care medicineHigh body temperature
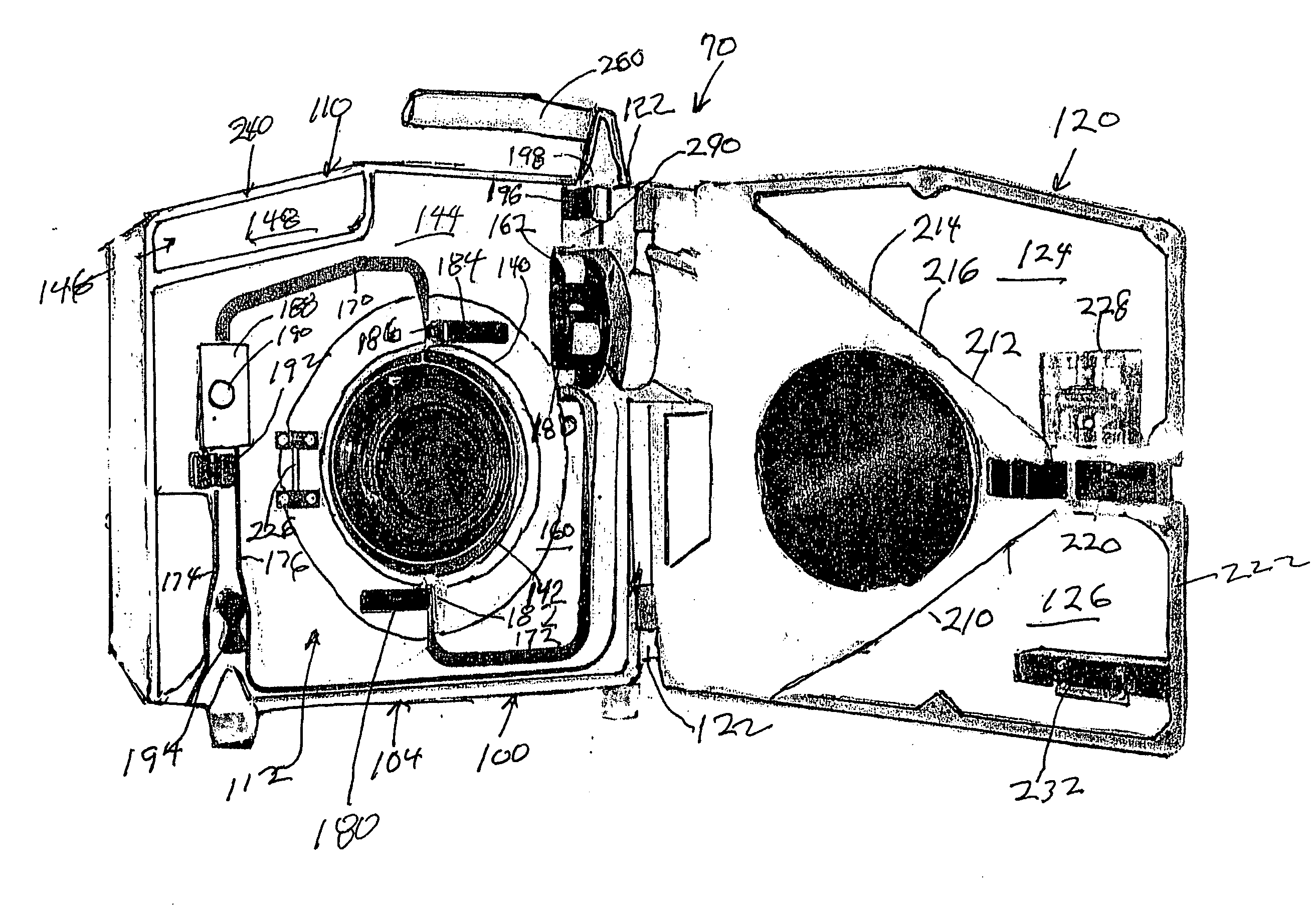
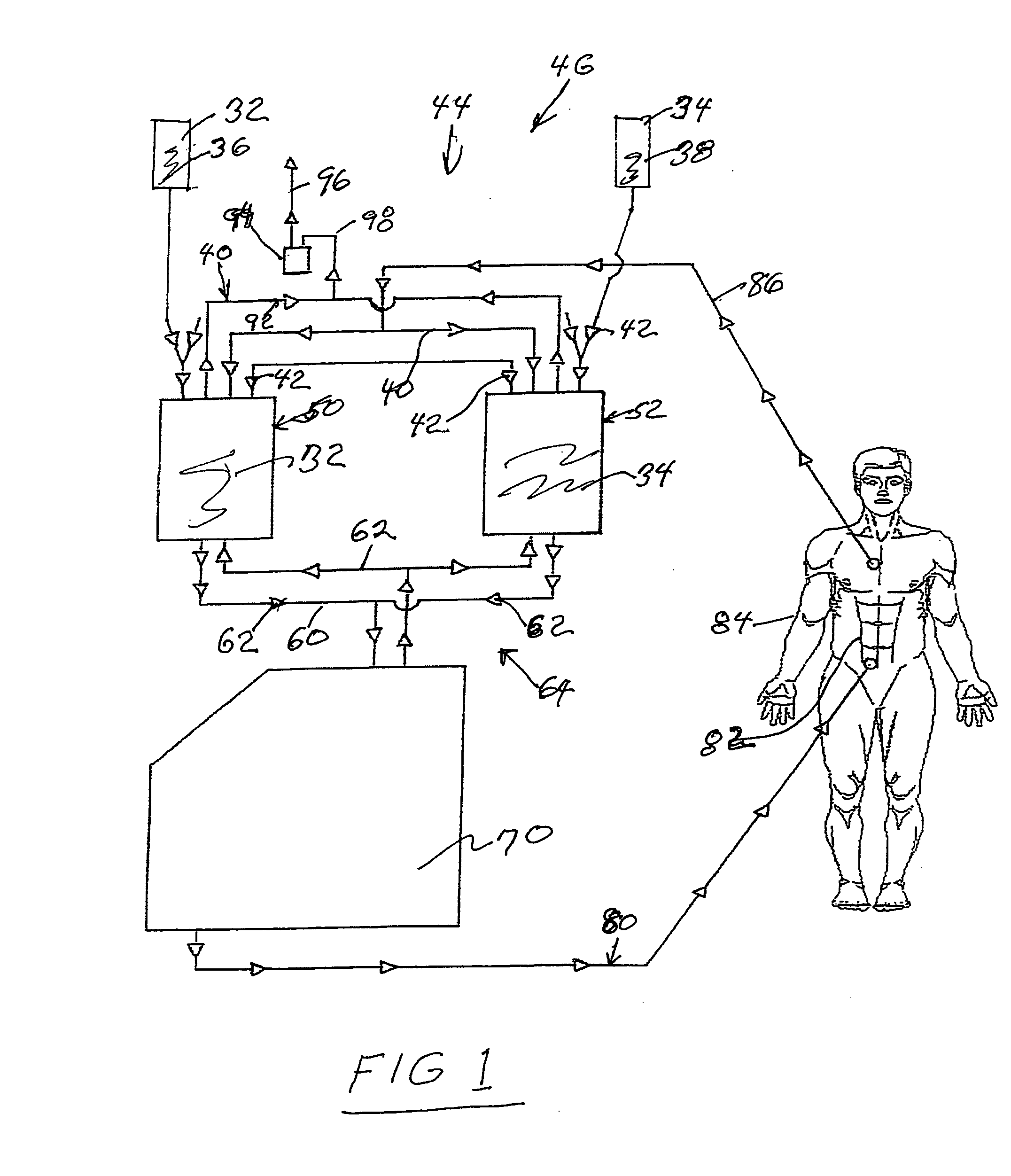
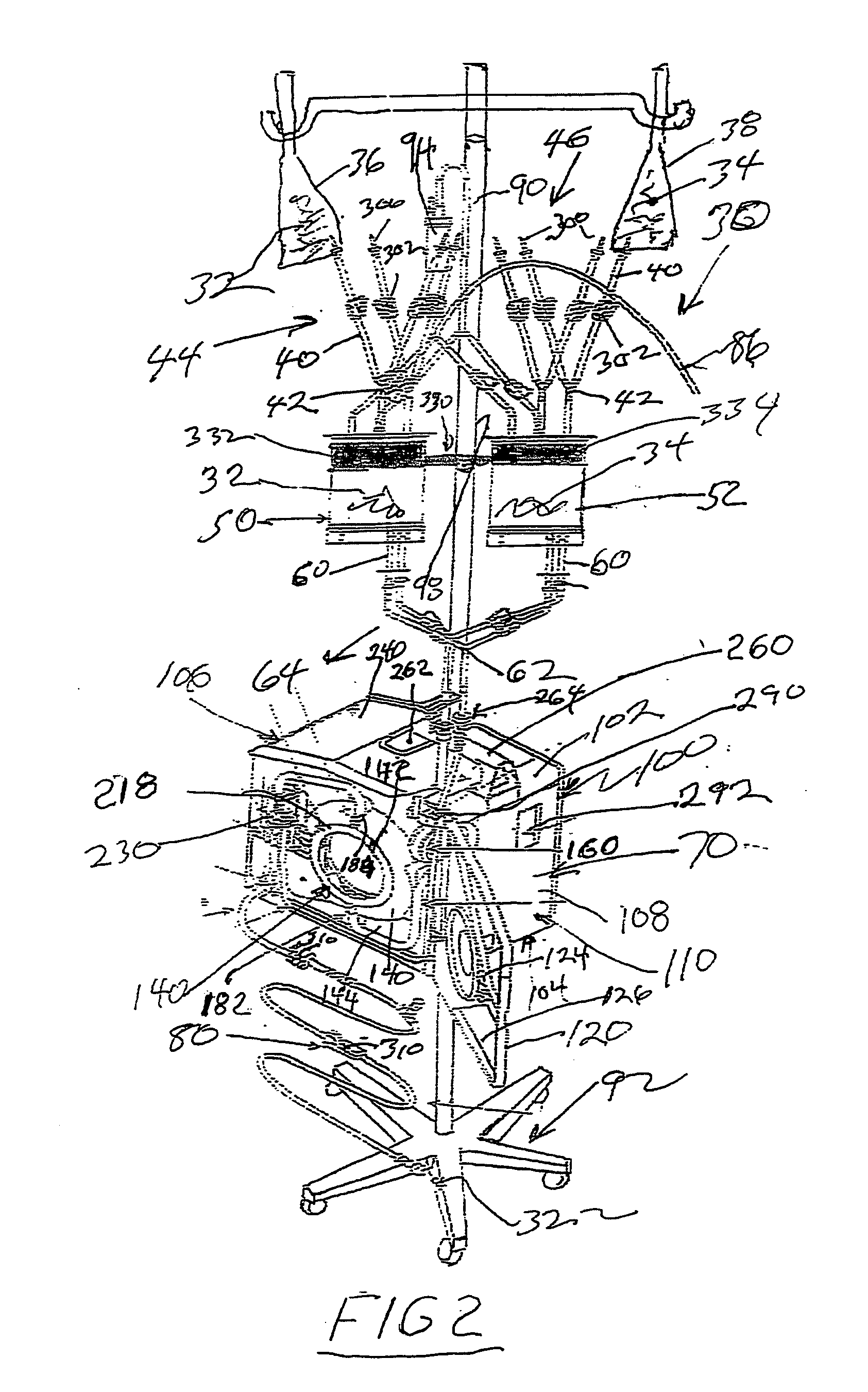
An IV pole mountable, therapeutic infusate processing device is incorporated into a hypothermia system to receive therapeutic fluid(s), such as normal saline, peritioneal dialysis solution, or other crystalloid solution, to heat such therapeutic fluid(s) a few degrees centigrade above normal body temperature and to direct the resulting heated infusate to and through a selected anatomical portion of a patients body to raise the temperature of that body portion so as to affect any cancerous or other tumors that may be located therein. The processing device is provided with touch screen controls and visual indicators to facilitate its proper use; while the system further includes temperature and pressure sensors to monitor the hyperthermia processing to insure patient safety.
Owner:BELMONT INSTR LLC
System and method for use of nanoparticles in imaging and diagnosis
ActiveUS20110098558A1High sensitivityImprove signal-to-noise ratioNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsCancer cellNanoparticle
A method for diagnosing certain types of cancers provides a nanoparticle agent to be uptaken by cancer cells for diagnosis and treatment of certain cancers. A compound containing nanoparticles is directed toward a tumor site, and then a predetermined time period passes to allow the nanoparticles to be uptaken by the cancer cells. Imaging is then performed on the nanoparticles by an appropriate imaging device to determine the concentration of nanoparticles uptaken by the cancer cells. Finally, image data provided by the imaging device is analyzed to determine the concentration of nanoparticles and thereby determine whether a tumor is present. The nanoparticle agent can further be employed as a treatment of certain cancers. After the uptake of nanoparticles into the cells, a predetermined field applied to the nanoparticles for a sufficient period of time activates the magnetic cores of the nanoparticles to include hyperthermia-mediated destruction of the cancer cells.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com