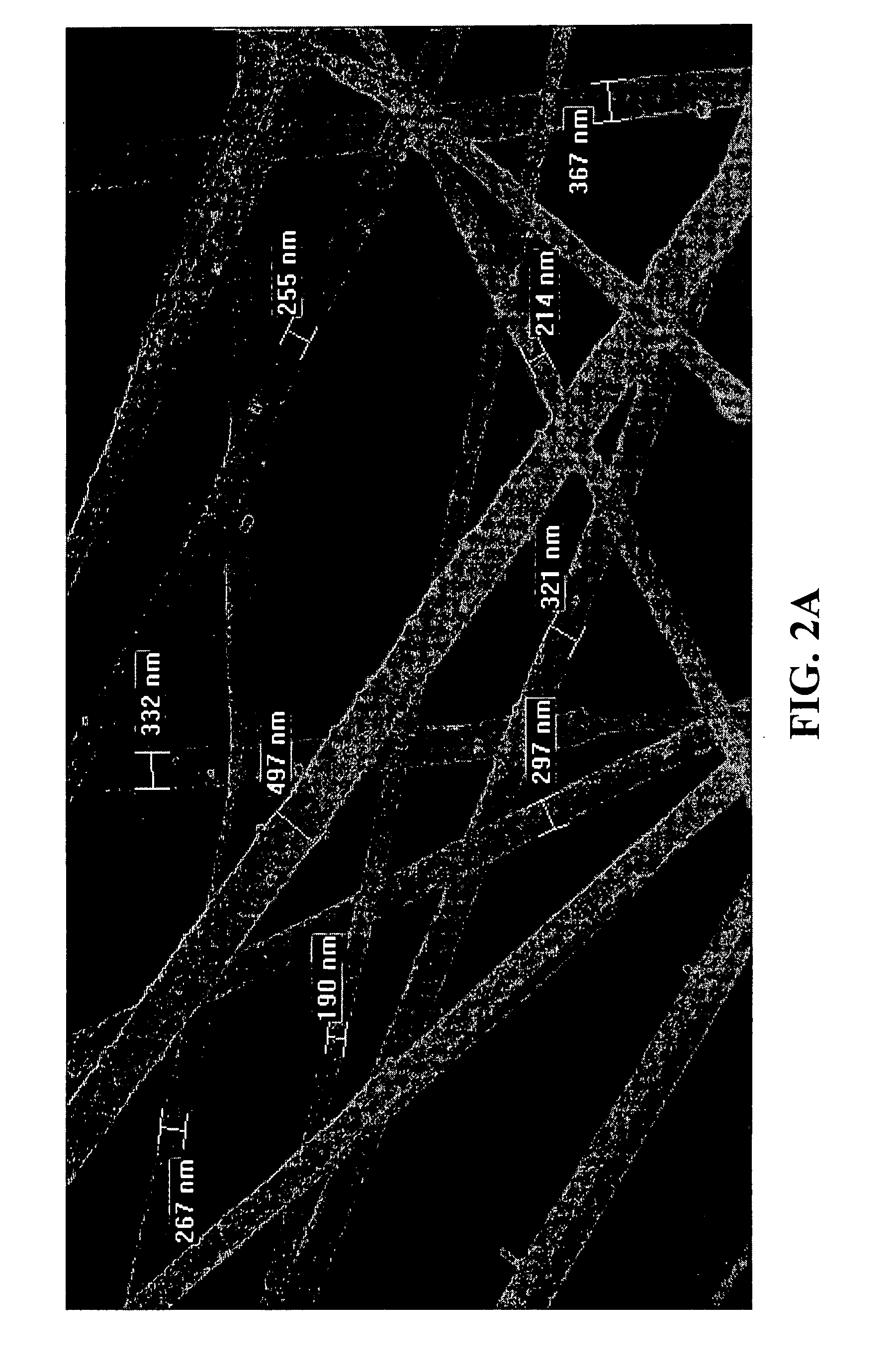
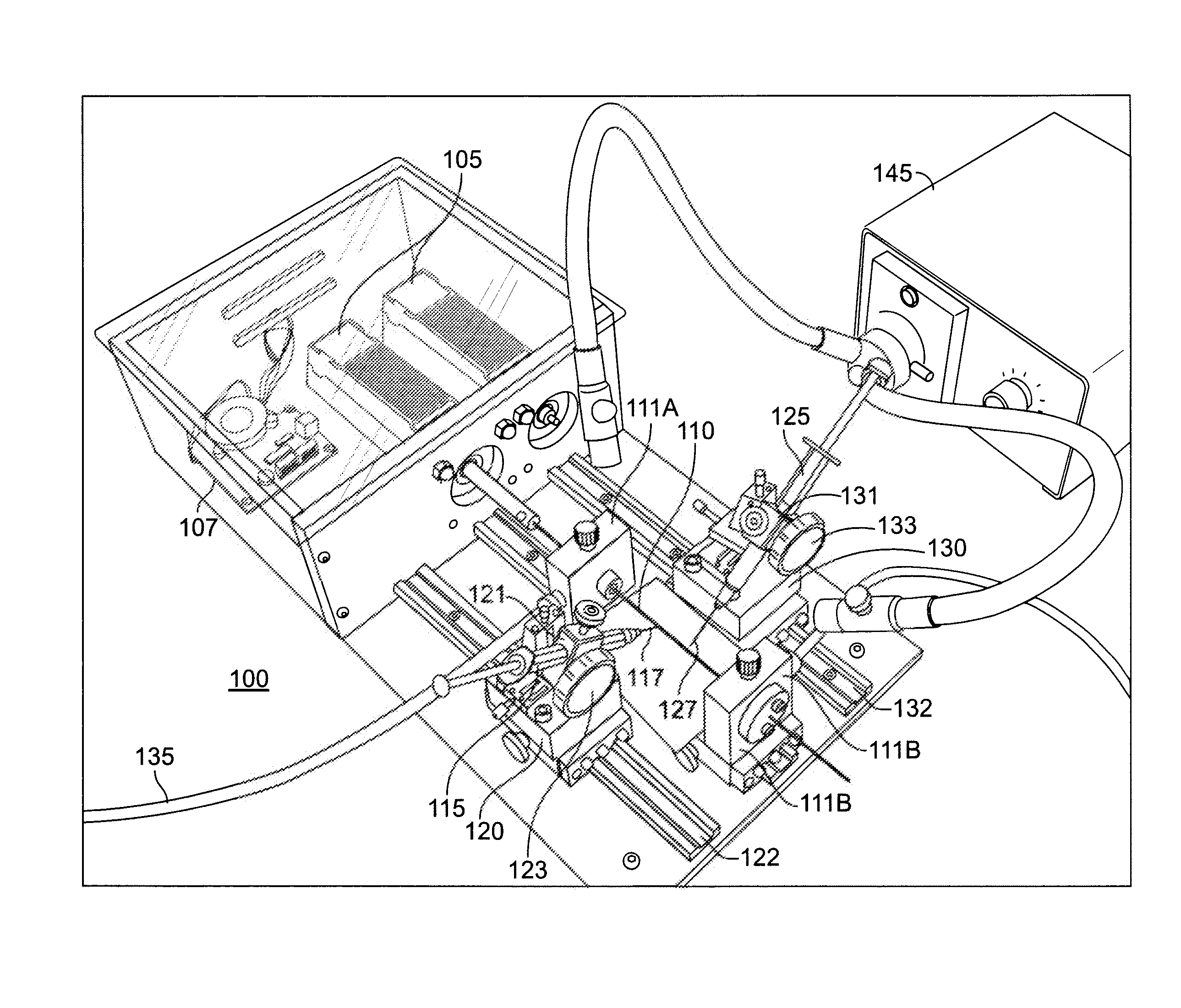
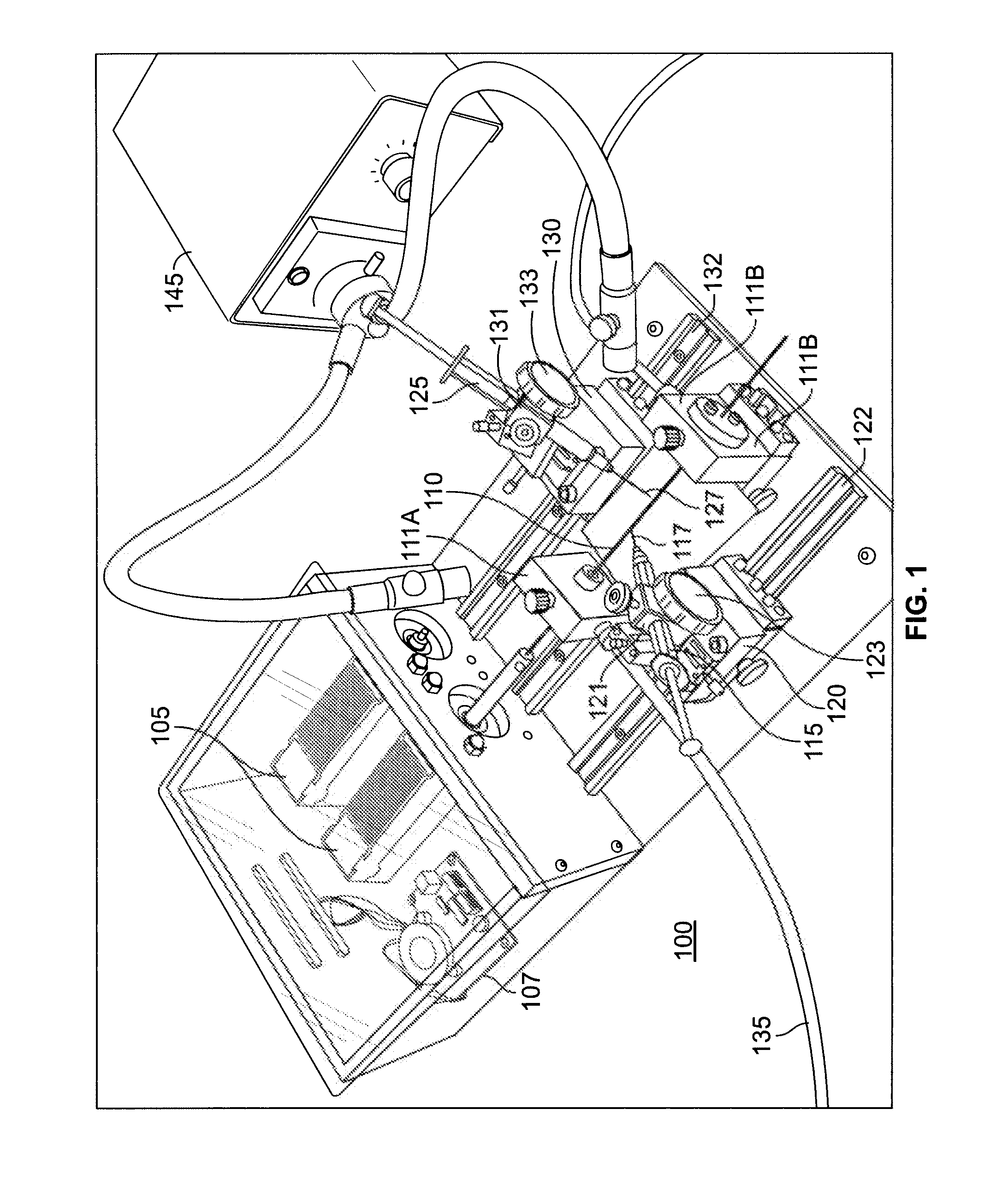
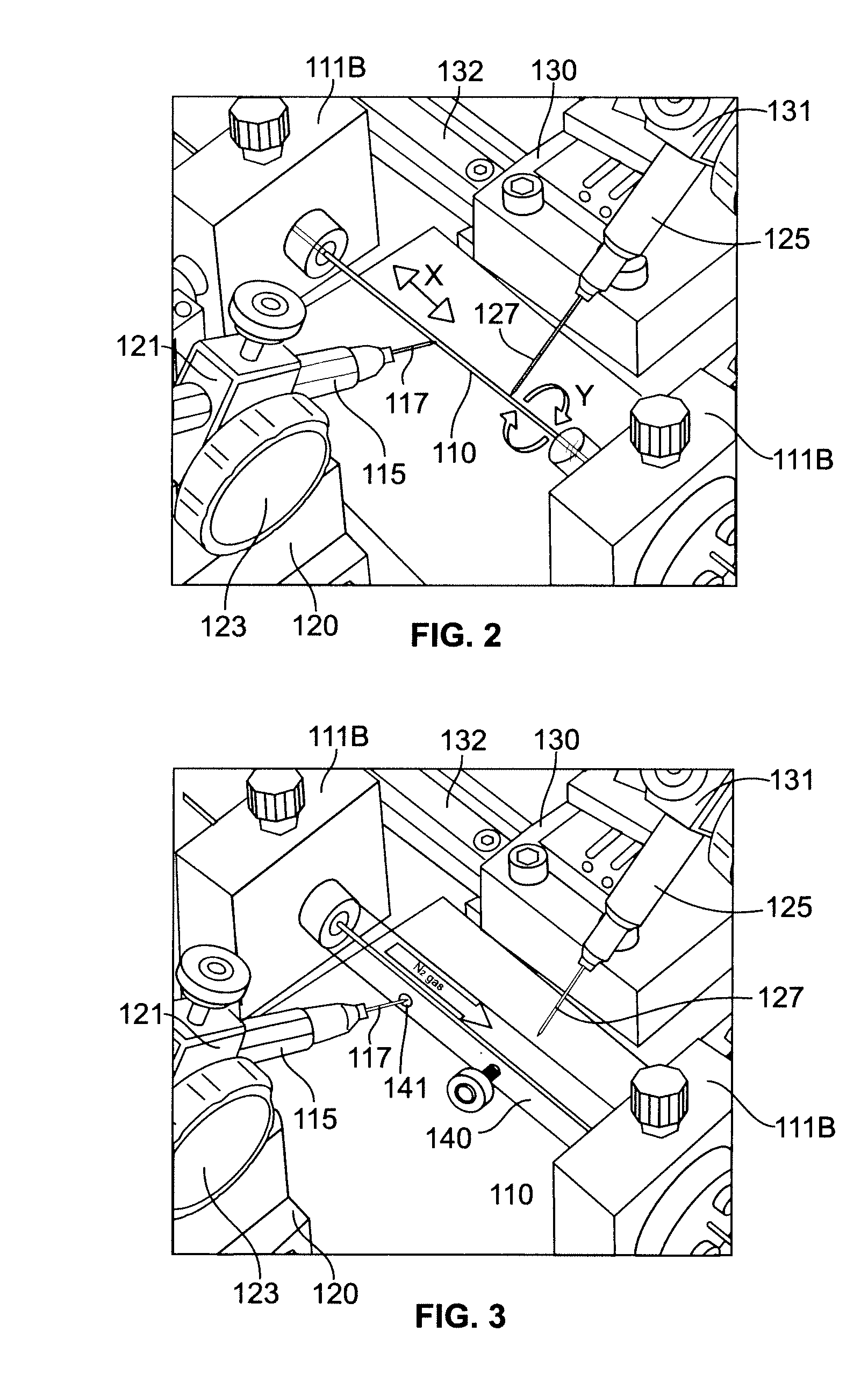
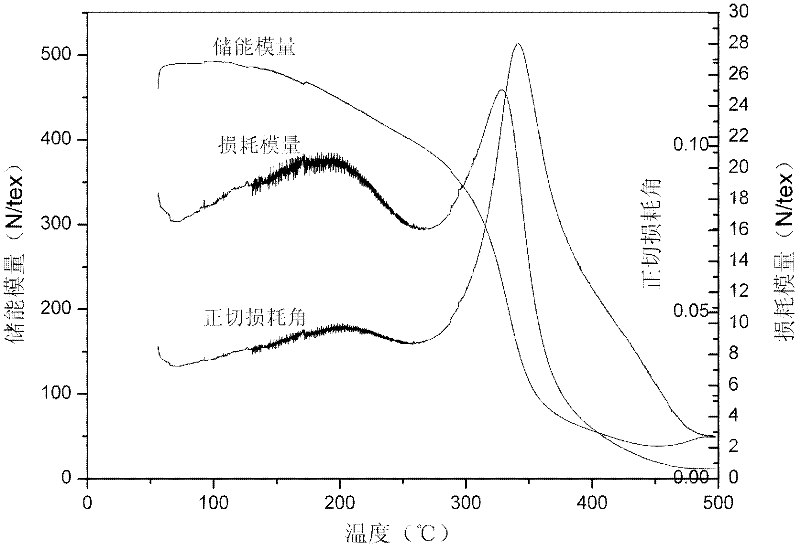
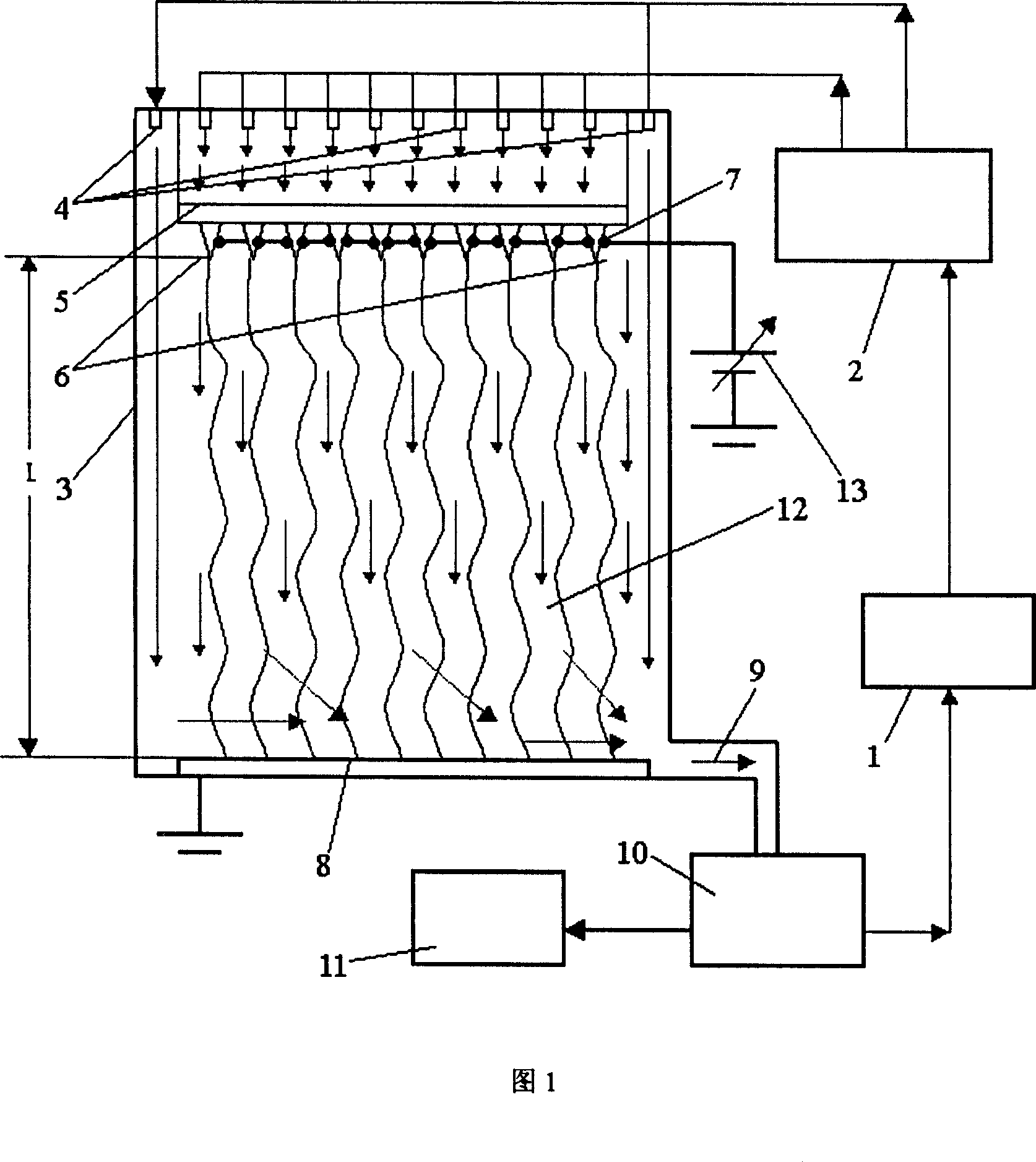
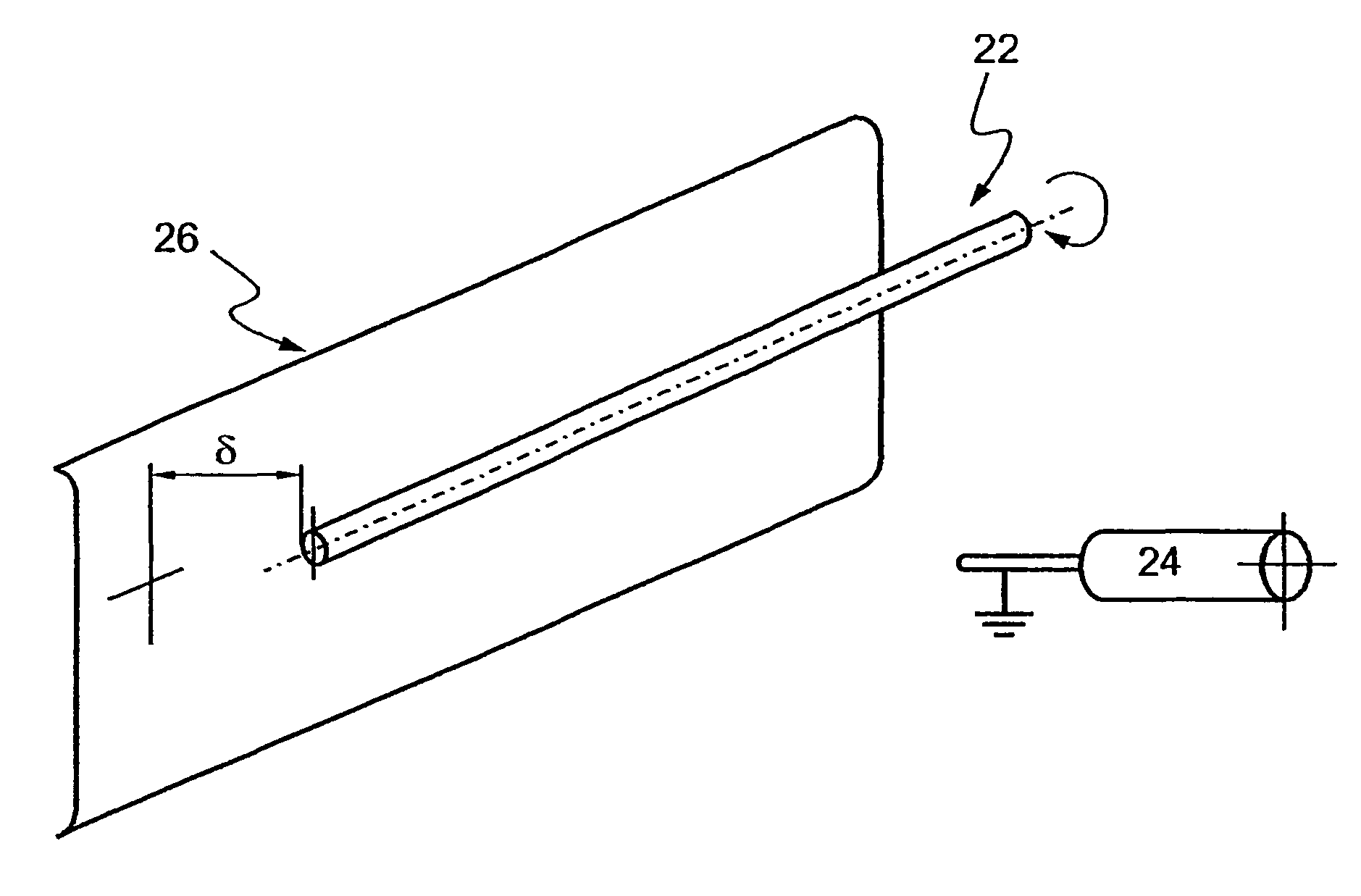
Patents
Literature
776results about "Dry spinning methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods for the manufacture of sheets having a highly inorganically filled organic polymer matrix
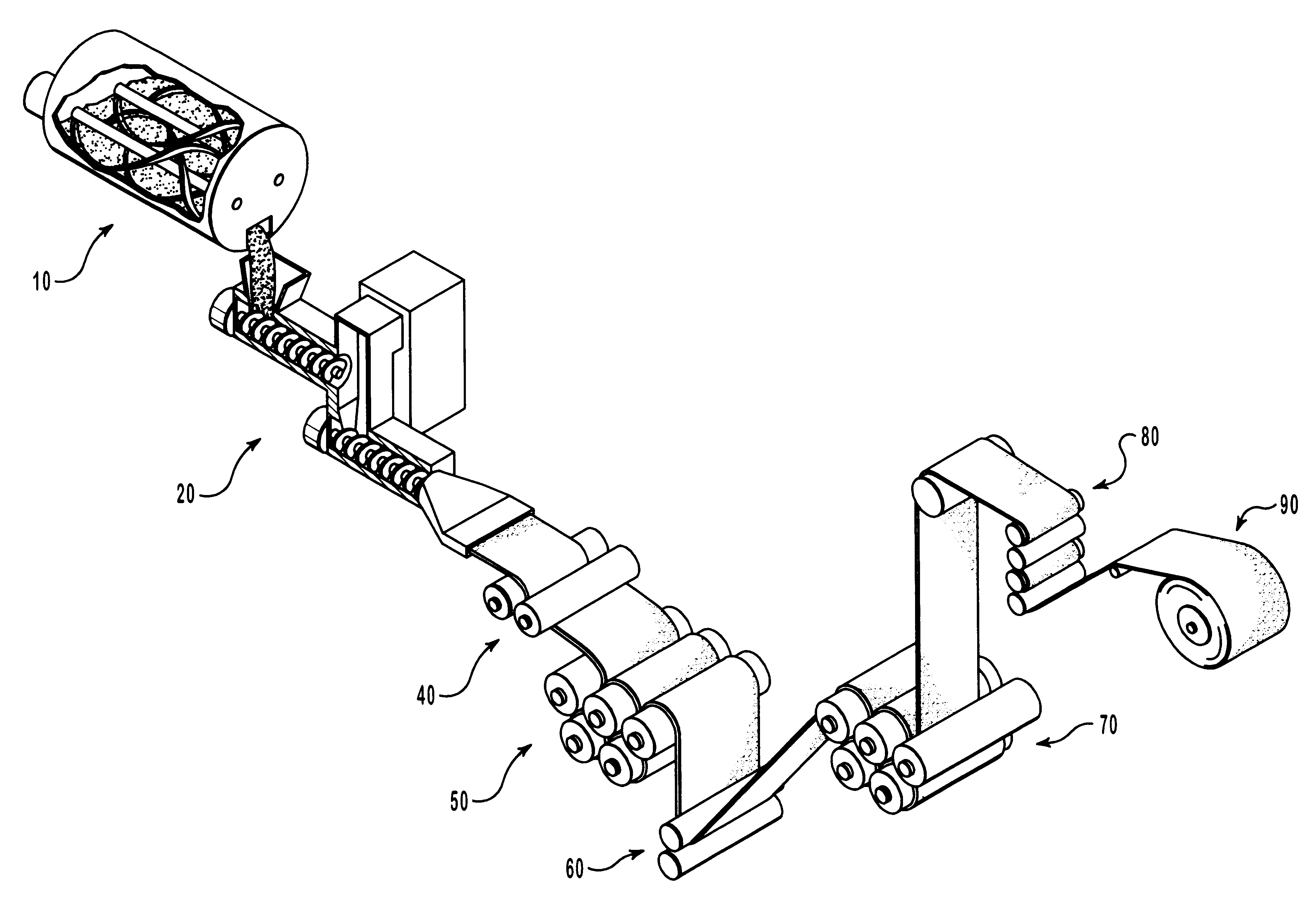
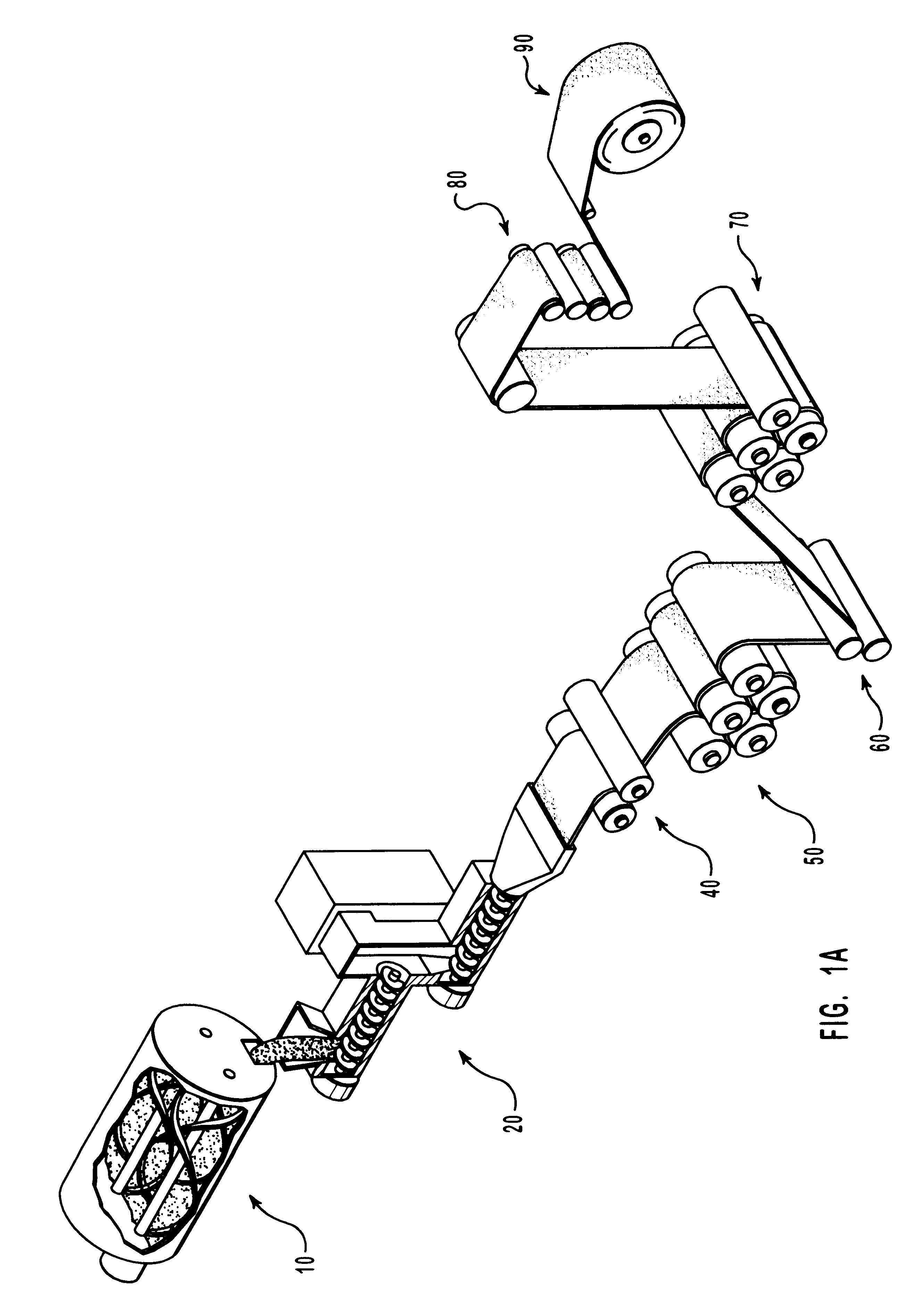
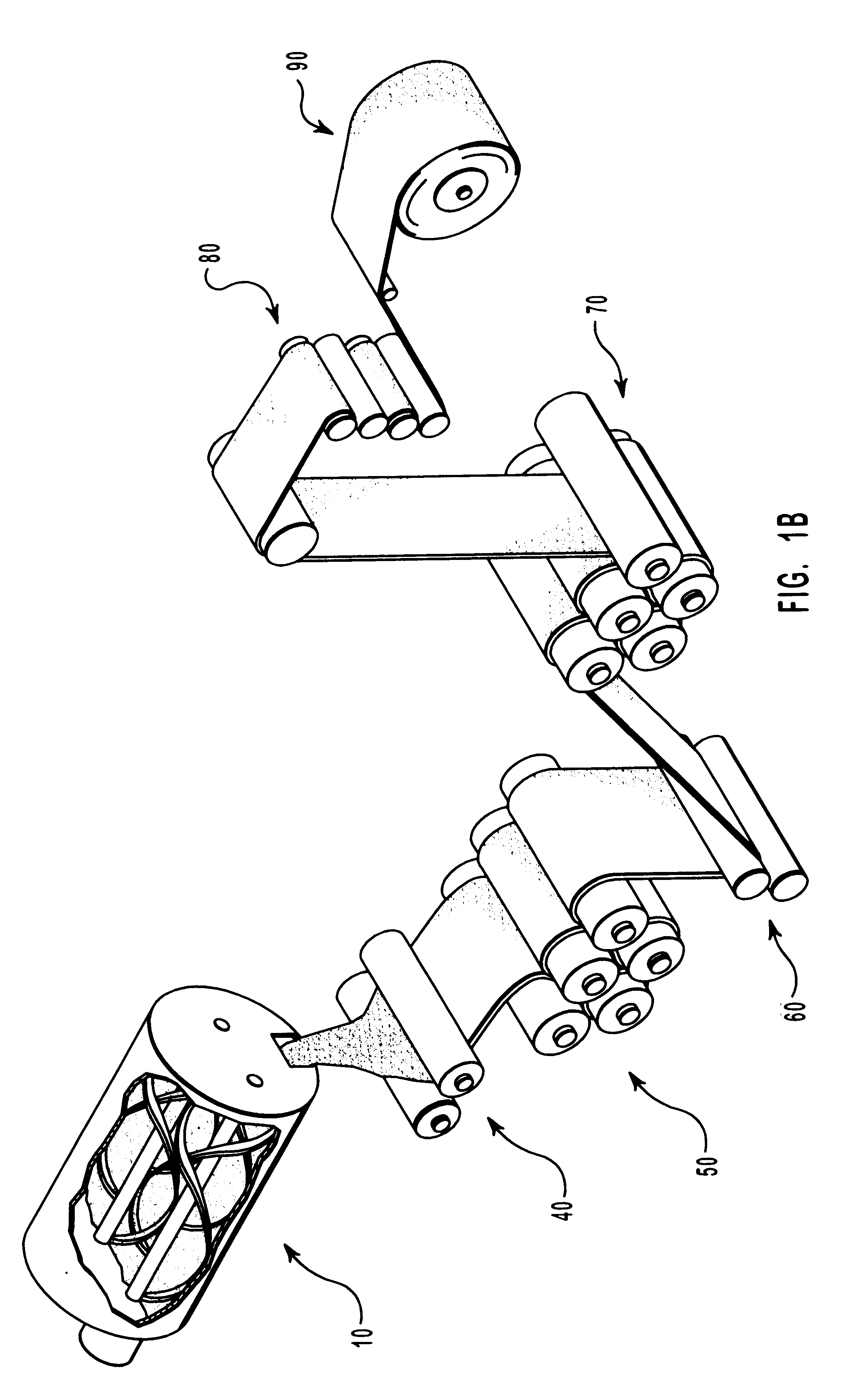
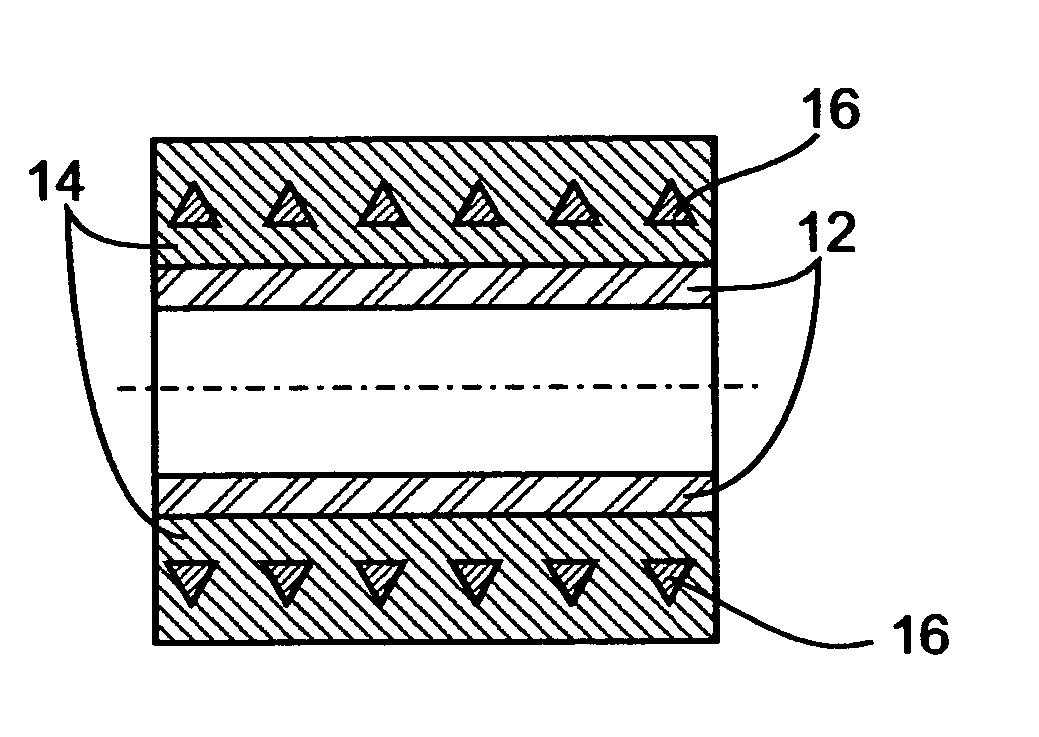
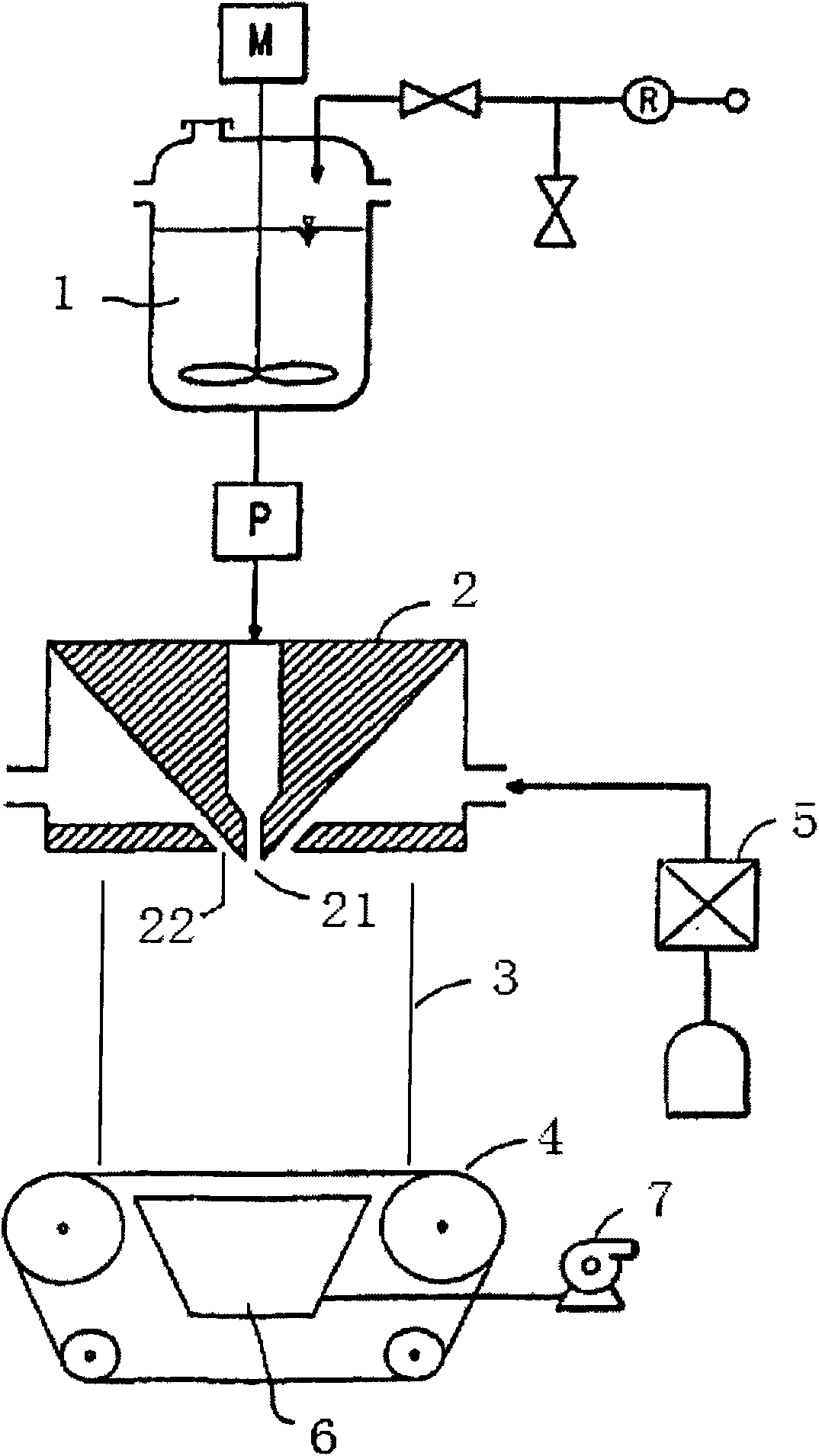
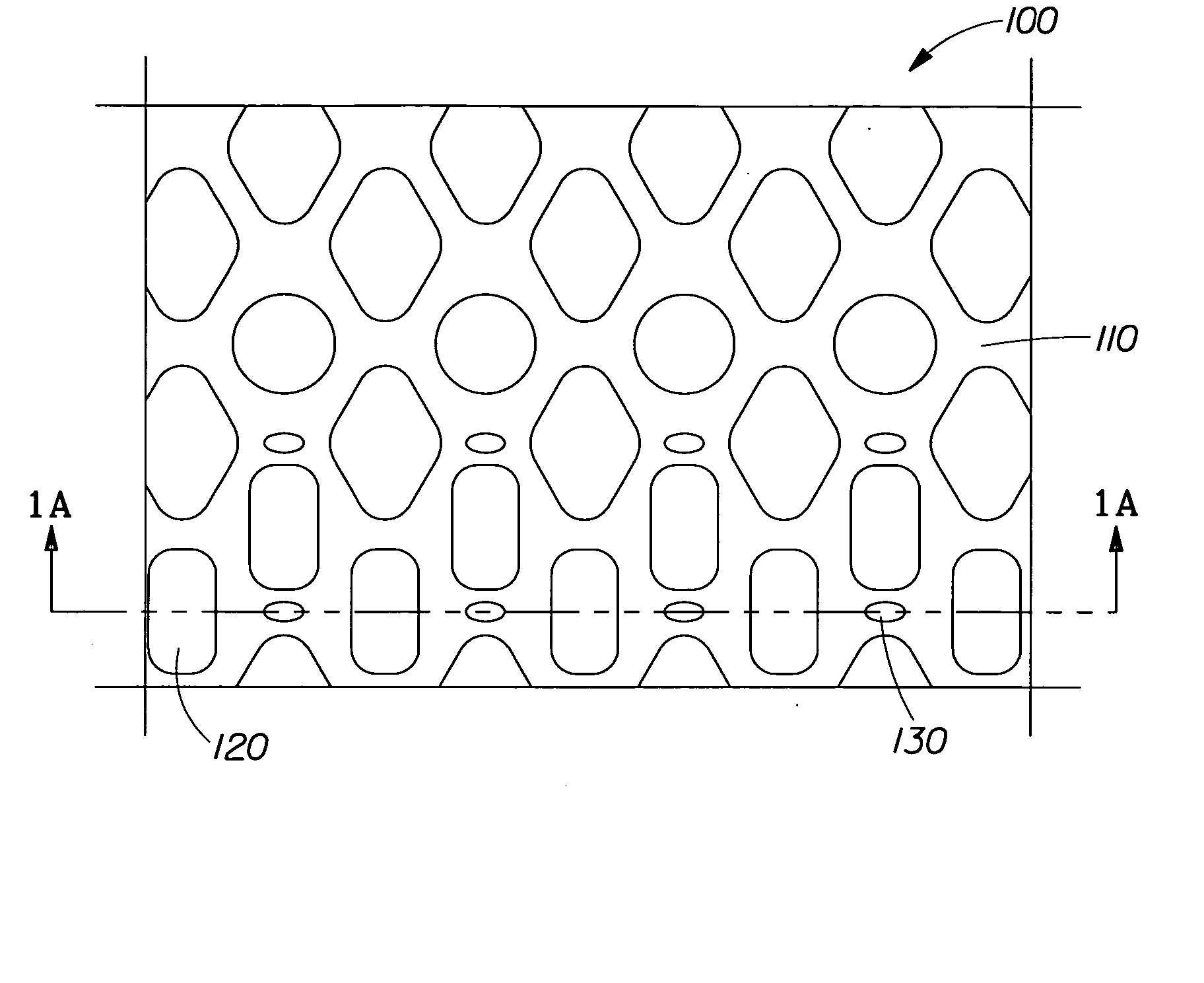
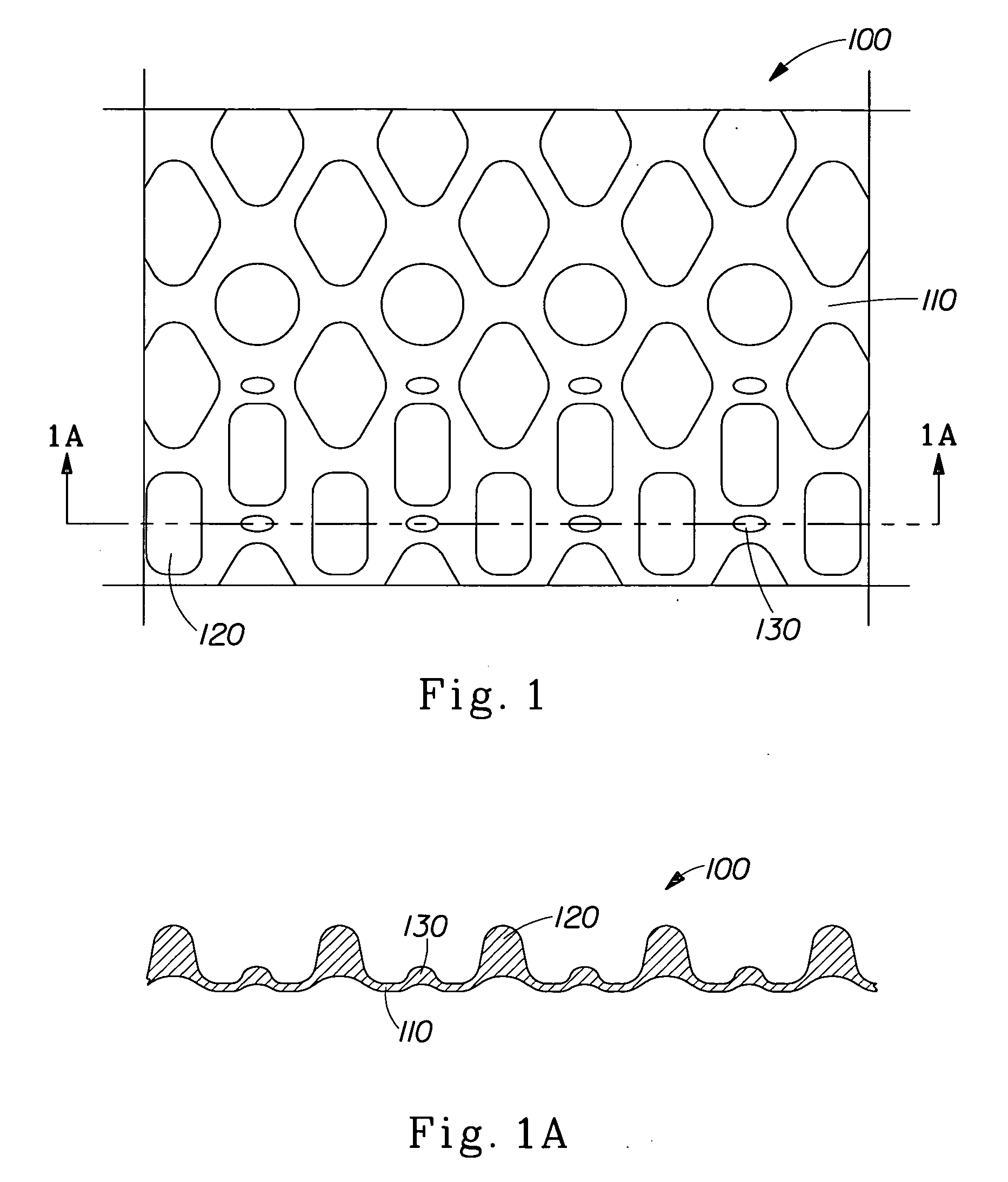
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a highly inorganically filled matrix. Suitable inorganically filled mixtures are prepared by mixing together an organic polymer binder, water, one or more inorganic aggregate materials, fibers, and optional admixtures in the correct proportions in order to form a sheet which has the desired performance criteria. The inorganically filled mixtures are formed into sheets by first extruding the mixtures and the passing the extruded materials between a set of rollers. The rolled sheets are dried in an accelerated manner to form a substantially hardened sheet, such as by heated rollers and / or a drying chamber. The inorganically filled sheets may have properties substantially similar to sheets presently made from traditional materials like paper, cardboard, polystyrene, plastic, or metal. Such sheets can be rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued. They have especial utility in the mass production of containers, particularly food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
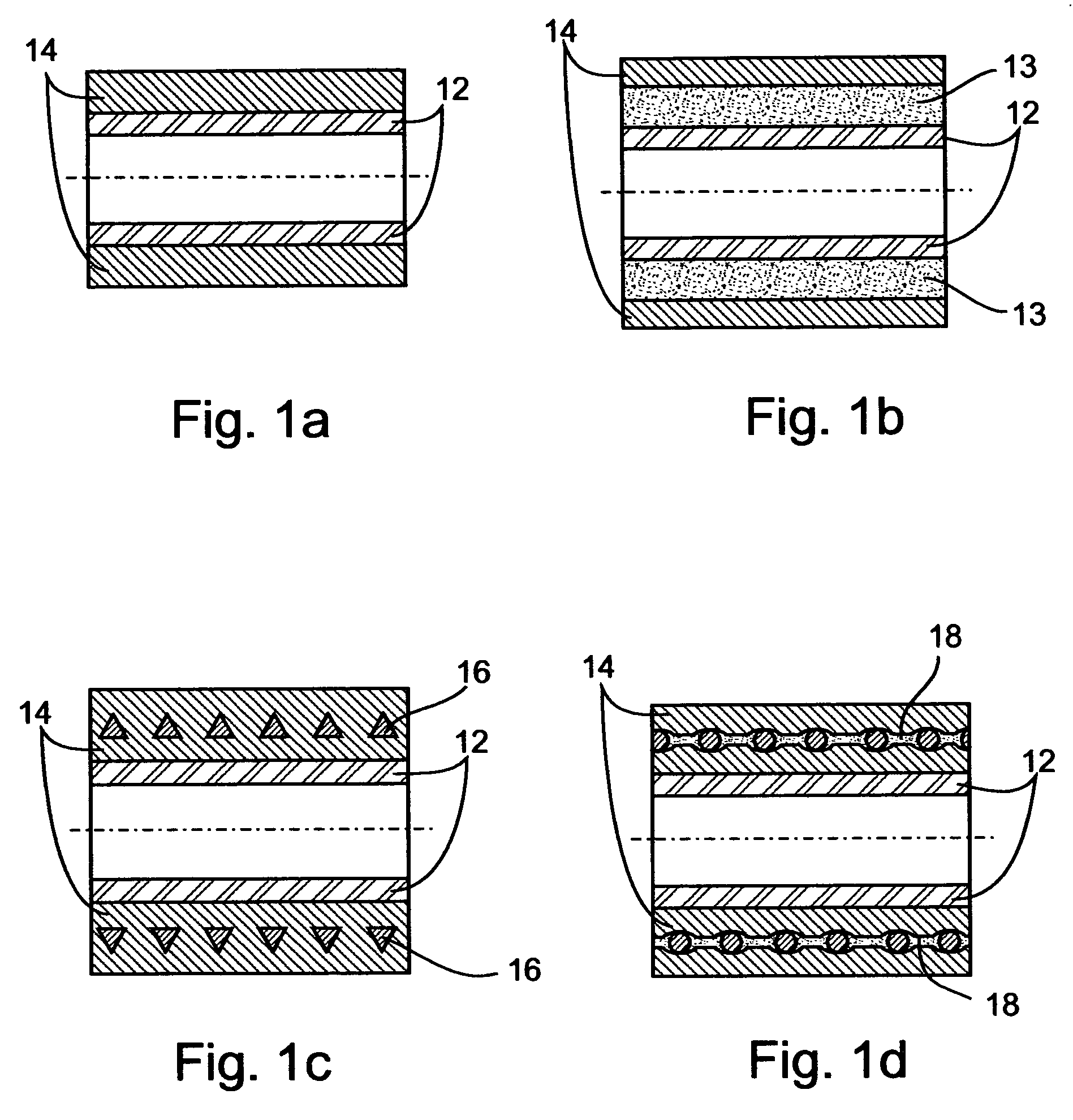
Vascular prosthesis and method for production thereof
A vascular prosthesis comprising a first layer having a predetermined first porosity and a second layer having a predetermined second porosity, wherein the first layer and the second layer are each made of first and second electrospun polymer fibers.
Owner:NICAST LTD
Process for drawing gel-spun polyethylene yarns
A process for drawing essentially diluent-free gel-spun polyethylene multi-filament yarns in a forced convection air oven and the drawn yarns produced thereby, The process conditions of draw ratio, stretch rate, residence time, oven length and feed speed are selected in specific relation to one another so as to achieve enhanced efficiency and productivity. The drawn yarns are useful in armor, composites, fishing line, ropes, sutures, fabrics and other applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Composite fiber filter comprising nan0-materials, and manufacturing method and apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20080217807A1Improve efficiencyPronounced antibacterial activityLayered productsWood working apparatusYarnElectrospinning
Disclosed herein is a method for manufacturing a composite fiber filter having high efficiency and high functionality, the method comprising: melt-spinning microfiber yarns on a forming rod, which is made of a conductive material, grounded at one end thereof and rotatably driven, using a melt-spinning device, to form on the forming layer a microfiber layer consisting of the microfiber yarns; and electrospinning on the microfiber layer an electrospinnable polymer solution having a given dielectric constant, using an electrospinning device, so as to form on the microfiber layer a nanofiber layers consisting of nanofiber yarns, wherein the microfiber yarns of the microfiber layer and the nanofiber yarns of the nanofiber layer contain silver nanoparticles so as to have an antibacterial function.
Owner:LEE BONG DAE +2
High molecular weight poly(alpha-olefin) solutions and articles made therefrom
ActiveUS20070231572A1Improve productivityDry spinning methodsMonocomponent polyolefin artificial filamentPolymer scienceHigh molecular mass
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Process for making cellulose acetate tow
A process for making a cigarette tow comprising: spinning a dope; taking-up the as-spun cellulose acetate filaments; lubricating the filaments; forming a tow from the filaments; crimping the tow with a stuffer box crimper; drying the crimped tow; and baling the dried crimped tow. The process further comprises at least two of the following:A. crimping further comprising one roller of the pair of nip rollers being adapted to induce crimp into the tow;B. crimping further comprising one roller of the pair of nip rollers being made of a solid ceramic material;C. crimping further comprising a pair of tow edge lubricators;D. crimping further comprising a steam injector;E. further comprising plasticizing the tow;F. lubricating the filaments further comprises a finish consisting of a water emulsion.
Owner:DEUT BANK AG NEW YORK BRANCH AS COLLATERAL AGENT +1
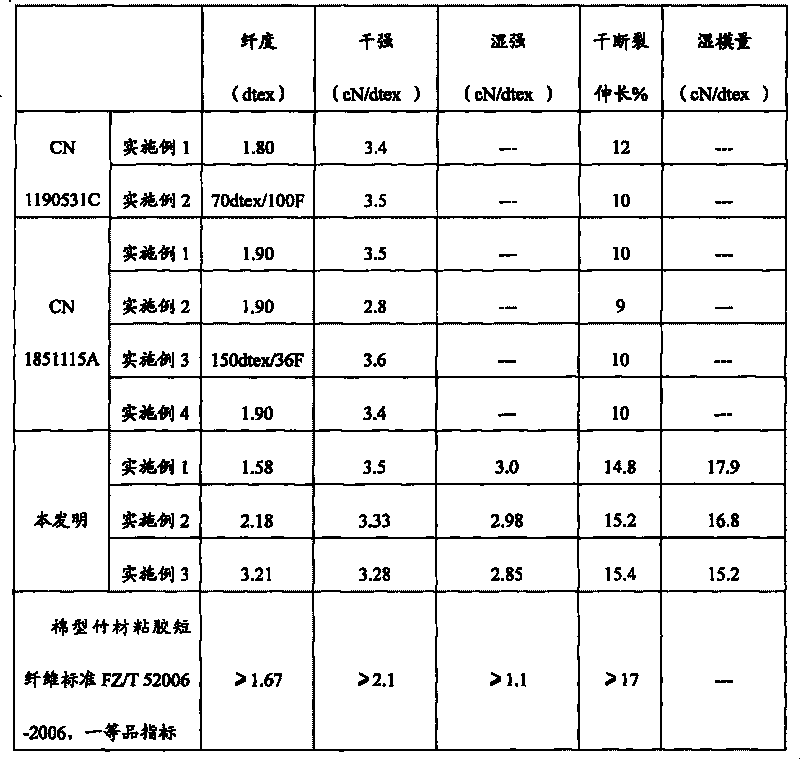
Solvent method high-wet-modulus bamboo fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101694019AEasy to operateReduce energy consumptionMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentVegetable materialFiberCellulose
The invention discloses a solvent method high-wet-modulus bamboo fiber and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the bamboo fiber comprises the following steps: activation, adding bamboo pulp into deionized water, adjusting the pH value, adding cellulase for activation, and then adding alkali to adjust the pH value; squeezing, vacuum dewatering and squeezing; pre-dissolving, adding water solution containing 50-88% of N-methyl morpholine-N-oxide; dissolving, entering a dissolving machine, heating, vacuumizing, dehydrating, dissolving, homogenizing and defoaming; spinning, spraying through a spinneret plate, and molding by adopting a dry wet spinning; washing; whitening; oiling; and drying. The preparation method has simple operation, no industrial pollution, low energy consumption and high safety performance, and is applicable to manufacturing the solvent method bamboo fiber by large-scale industrialized continuous production; furthermore, the bamboo fiber prepared by the method not only maintains the natural physical and chemical properties of the bamboo fiber, but also generates no harmful chemical residue and has higher wet modulus.
Owner:SHANGHAI LYOCELL FIBER DEV
System and method for making biomaterial structures
ActiveUS20110076384A1Unique and robust mechanical propertyProperty is limitedNew-spun product collectionMonocomponent fibroin artificial filamentFiberMaterials processing
A system and method for making a biomaterial device includes a support structure providing a shape for a biomaterial device. At least one applicator has a supply of biomaterial solution and is positioned along the support structure. The at least one applicator forms a biomaterial fiber by applying shear force to the biomaterial solution and delivering the biomaterial fiber to the support structure. A controller causes relative movement between the support structure and the at least one applicator, and the biomaterial fiber is arranged on the support structure according to the relative movement to form the biomaterial device. The biomaterial may be silk fibroin which may be wound onto a reciprocating and rotating mandrel. Control over the properties of the biomaterial device is achieved through appropriate selection of material processing, winding strategy, and post-winding processing.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE +1
Method for preparing polymeric nano-micro fiber non-woven fabric
ActiveCN102071542AOvercoming demandsUniversally applicableNon-woven fabricsDry spinning methodsFiberPolymer dissolution
The invention discloses a method for preparing a polymeric nano-micro fiber non-woven fabric. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, dissolving at least one polymer in at least one solvent to prepare spinning solution; then supplying the spinning solution to a spinneret plate with a series of spinneret orifices so as to make the spinning solution extruded from the spinneret orifices of the spinneret plate to form a trickle of the spinning solution; secondly, stretching and refining the trickle of the spinning solution by utilizing at least one high-speed jet airflow, and accelerating the volatilization of the solvent to form nano-micro fiber; and finally, collecting the nano-micro fiber on a web curtain by utilizing high-speed airflow and suction airflow. The polymer is a fiber-forming polymer; the solvent can dissolve the fiber-forming polymer and has the volatility; a jet angle of the high-speed airflow is between 15 and 60 degrees, and the jet velocity is at least 50 times higher than extrusion speed of the trickle of the spinning solution; the mass concentration of the polymer in the spinning solution is between 2 and 50 percent; and the viscosity of the spinning solution at a spinning temperature is between 10 and 100, 000mP.s.
Owner:上海榕融新材料技术有限公司
Process of preparing continuous filament composed of nanofibers
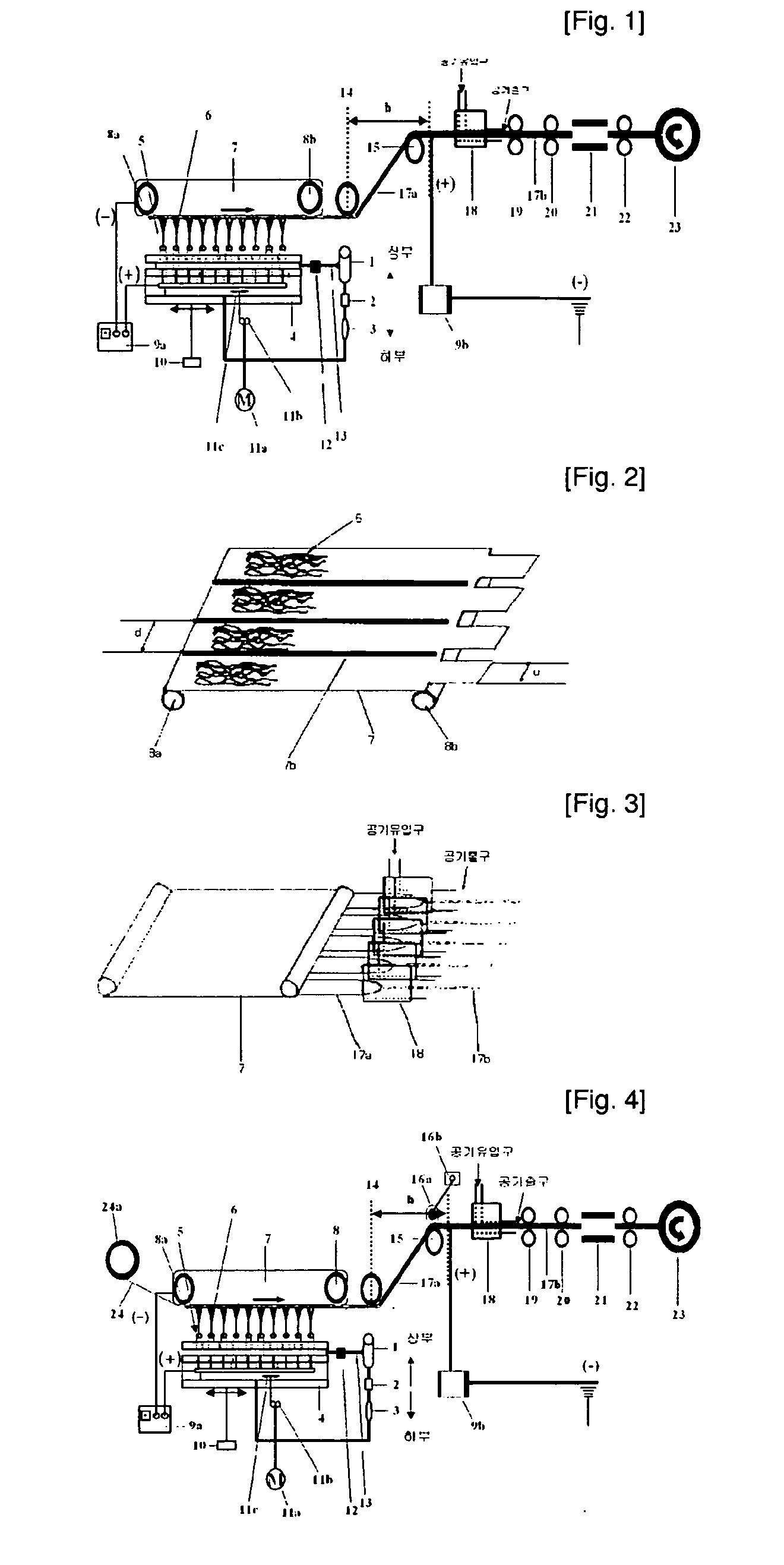
InactiveUS20090189319A1Good physical propertiesElectric discharge heatingNon-woven fabricsFiberElectrospinning
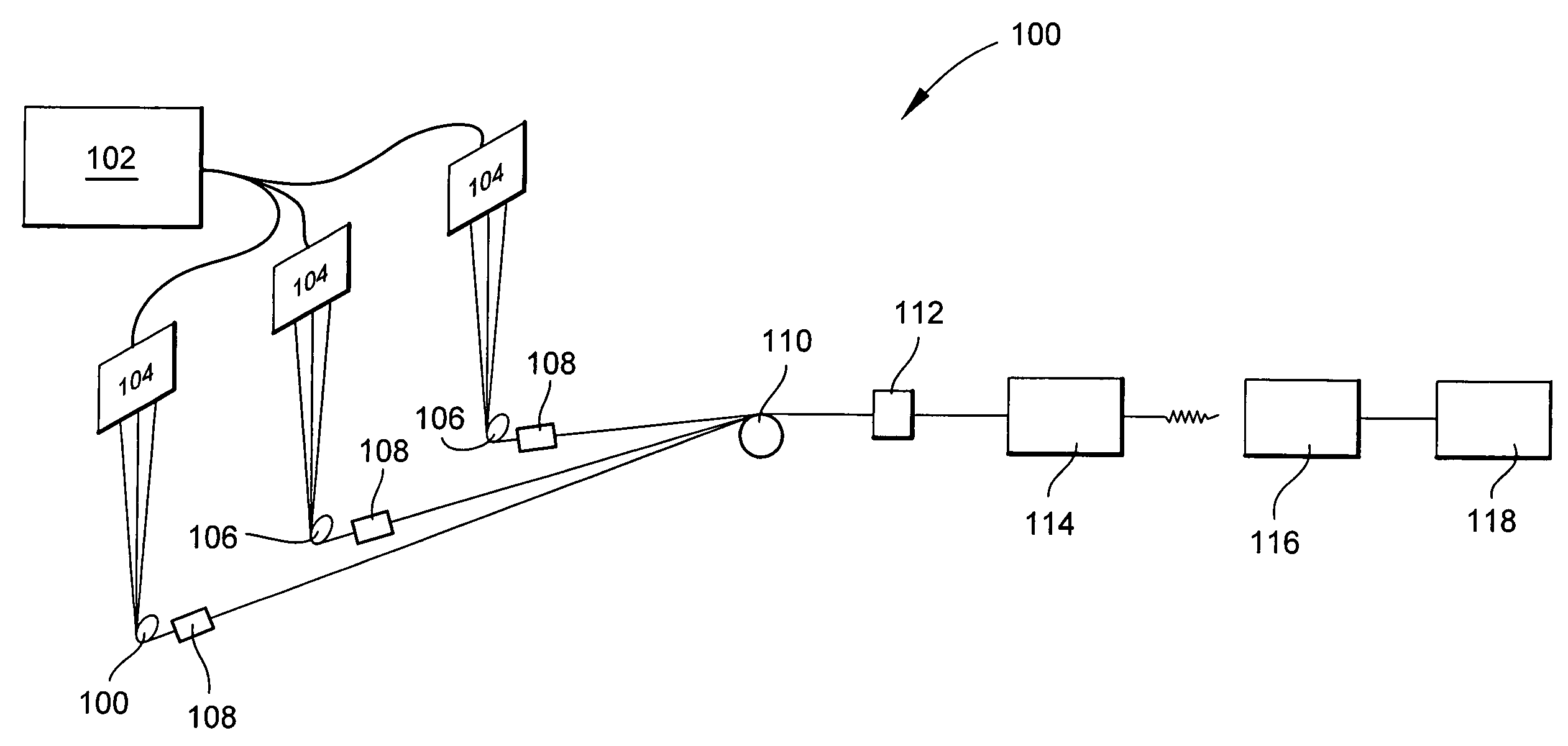
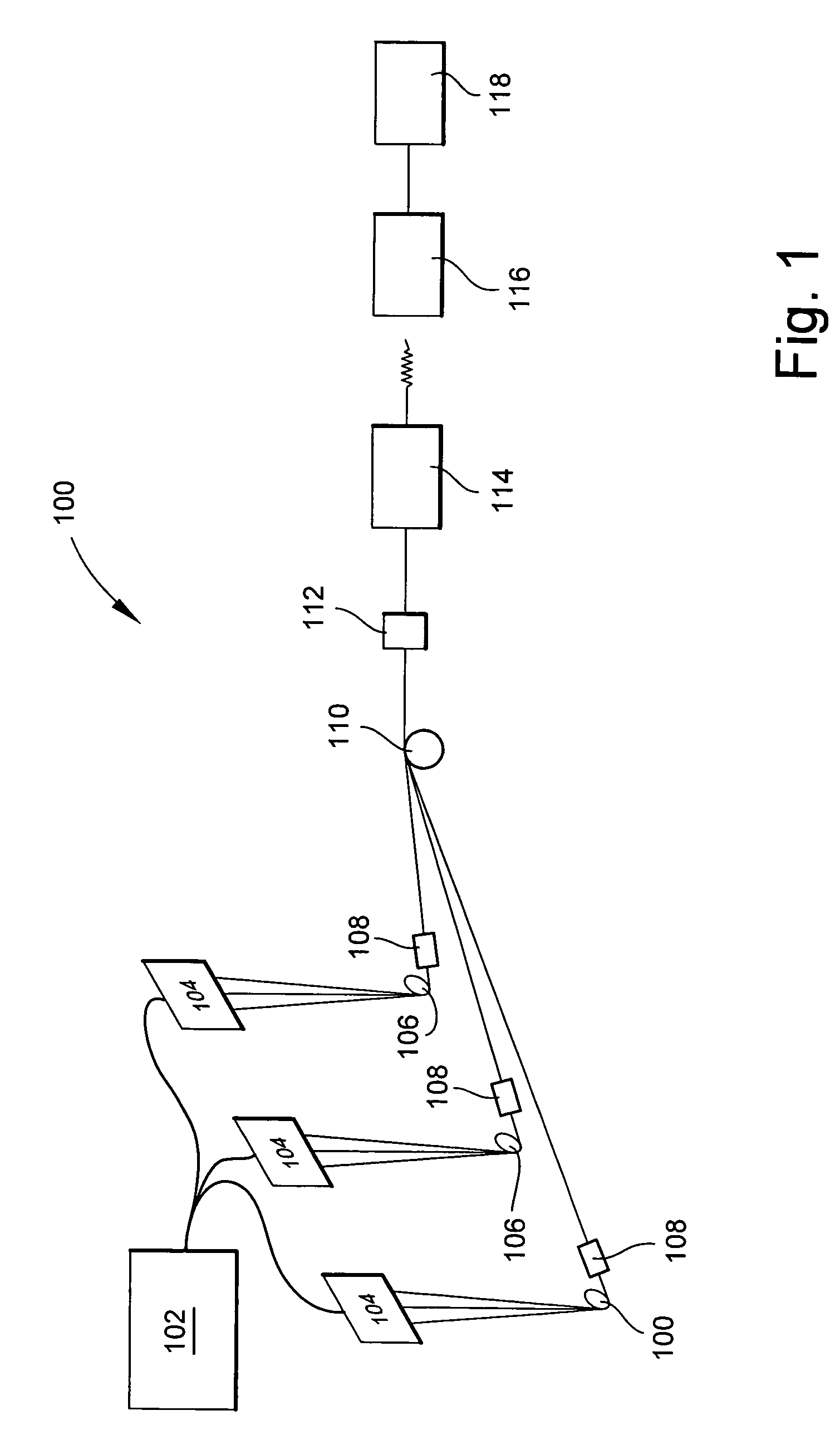
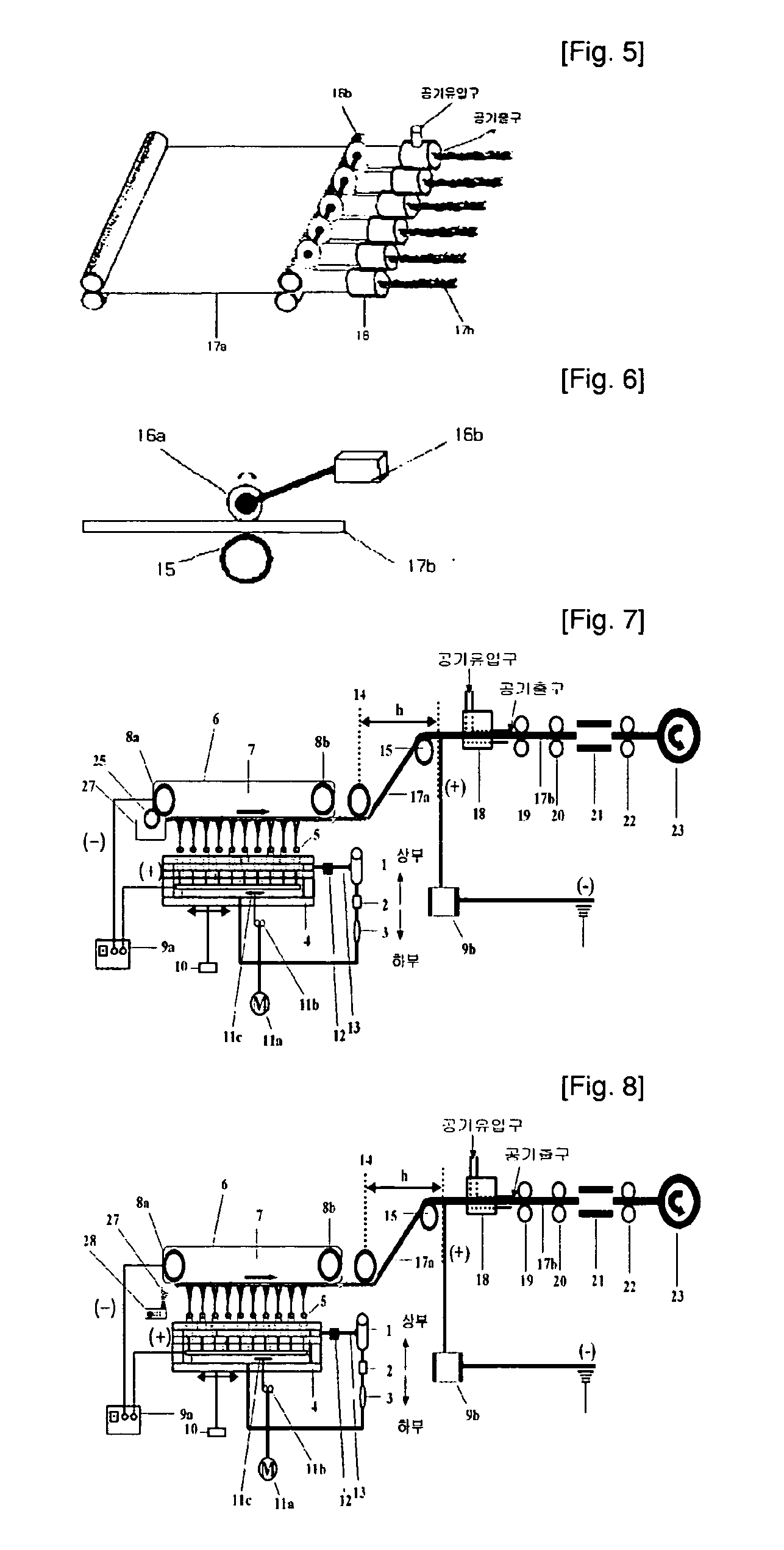
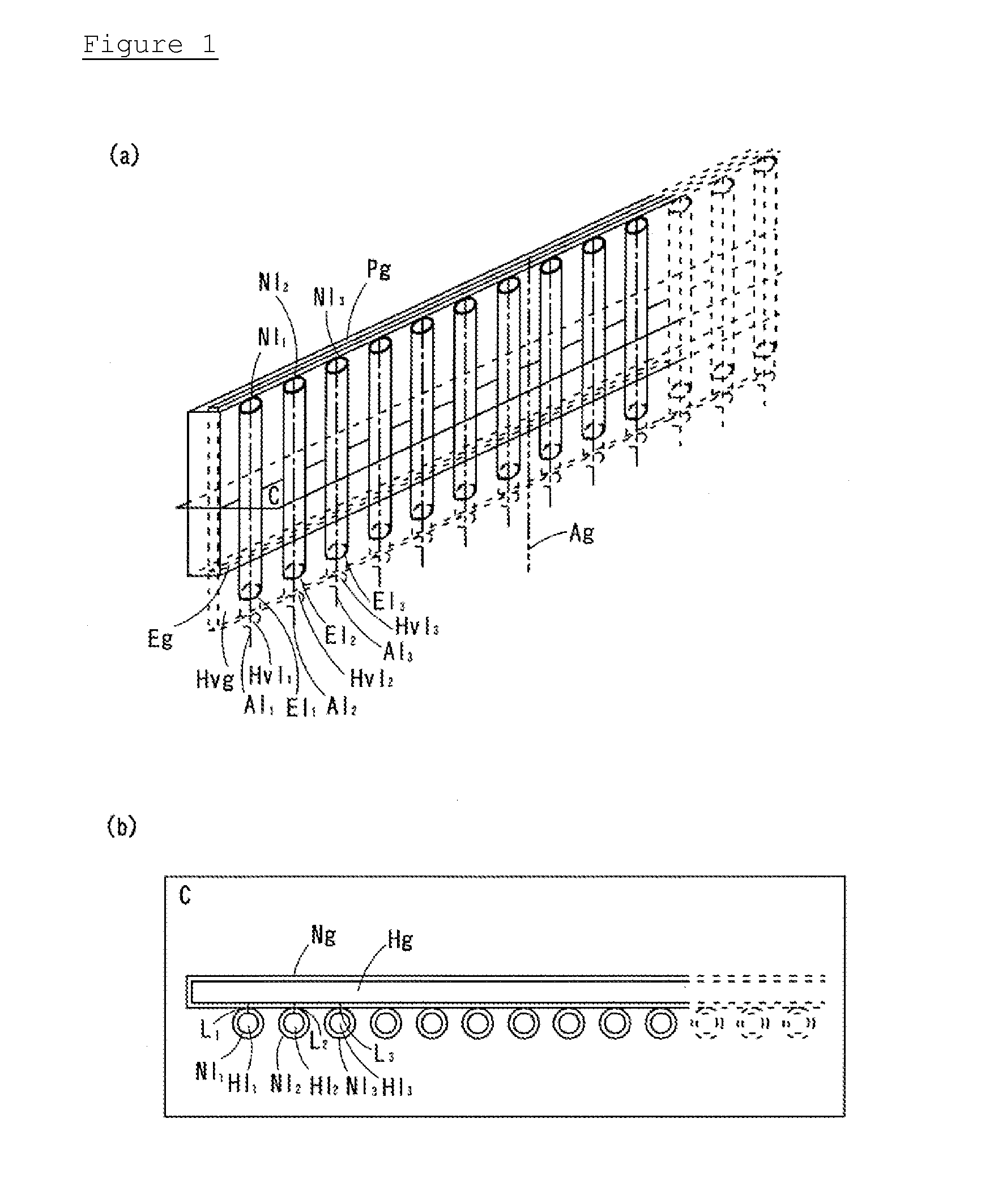
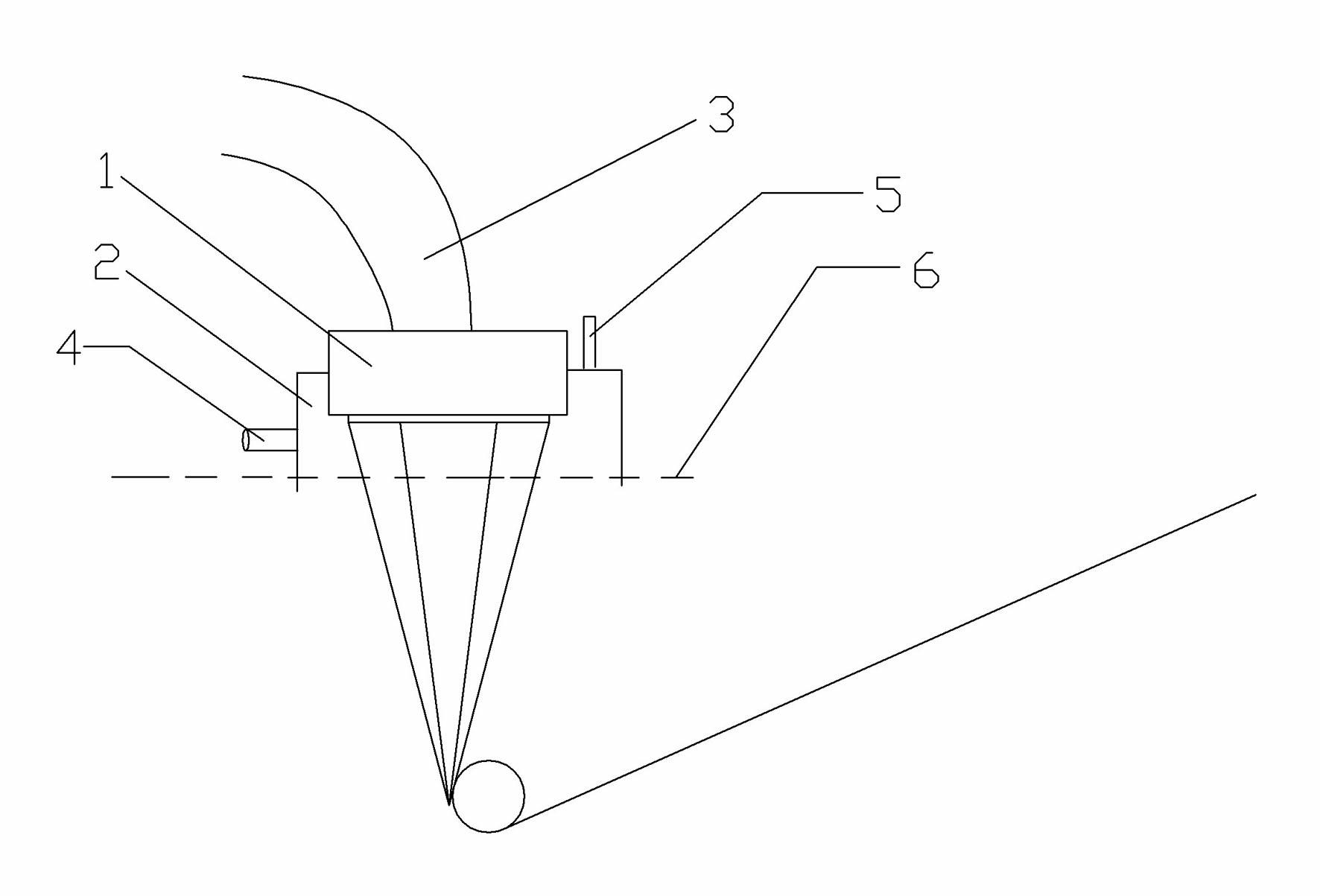
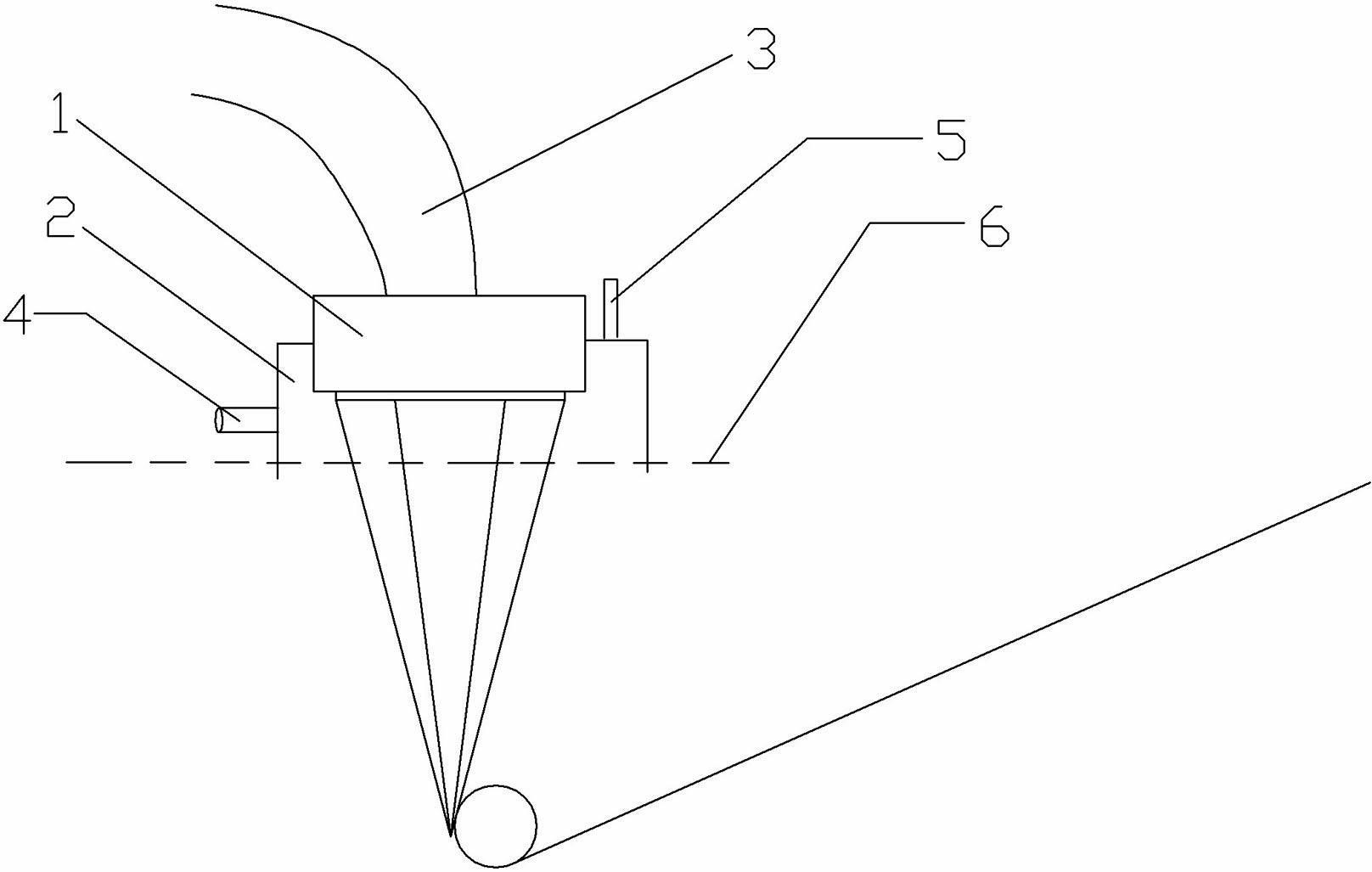
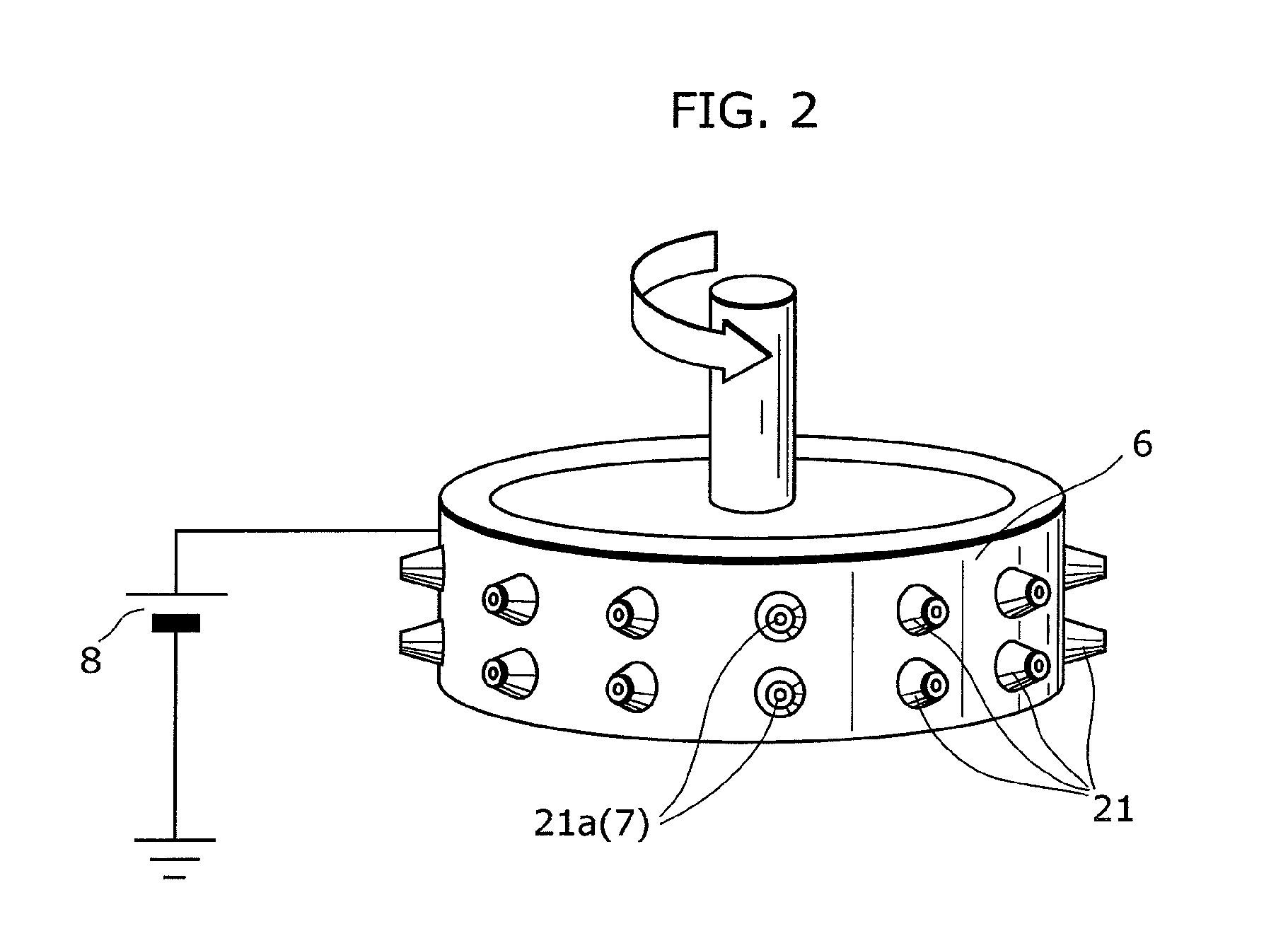
Conventional electrospinning was problematic in that it is incapable of making a continuous filament (yarn) by a simple and continuous process. To solve the above problem, there is provided a method for making a continuous filament consisting of nanofibers according to the present invention, wherein a polymer spinning liquid is electrostatically spun to a collector 7 through nozzles 5 to obtain a nanofiber web 17a of ribbon form, then the nanofiber web 17a is passed through an air twister 18 and twisted to obtain a nanofiber filament 17b of a continuous filament form, and then the nanofiber filament 17b is drawn.
Owner:FINETEX TECH GLOBAL +1
Spinning apparatus, apparatus and process for manufacturing nonwoven fabric, and nonwoven fabric
InactiveUS20110130063A1Smooth rotationImprove productivitySpinnerette packsCeramic shaping apparatusProduction rateManufactured apparatus
Provided are a spinning apparatus capable of stably spinning fibers having a small fiber diameter with a high productivity, an apparatus comprising the same for manufacturing a nonwoven fabric, a process for manufacturing a nonwoven fabric using the nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus, and a nonwoven fabric produced by the process.The spinning apparatus of the present invention comprises one or more exits for extruding liquid, which are capable of extruding a spinning liquid, and one or more exits for ejecting gas, which extend linearly and are located upstream of each of the exits for extruding liquid and which are capable of ejecting a gas, wherein a shearing force by the gas and its accompanying airstream can be single-linearly exerted on the spinning liquid extruded. The apparatus of the present invention for manufacturing a nonwoven fabric comprises a fibers collection means as well as the spinning apparatus. The process of the present invention for manufacturing a nonwoven fabric is a process using the apparatus for manufacturing a nonwoven fabric. The nonwoven fabric of the present invention is a nonwoven fabric produced by the process.
Owner:NIPPON BAIRIIN
Compostable container for storing fluids
ActiveUS20100044267A1Low production costFully biodegradableWrappersBio-packagingFiberNatural environment
A fully compostable container is provided having an enclosed body with an opening through an interior surface and an exterior surface. The enclosed body having a plant fiber structural layer configured to biodegrade in ambient conditions into nontoxic residue and a fluid barrier layer formed on a first side of the structural layer to form the interior surface of the enclosed body, the fluid barrier layer configured to biodegrade in ambient conditions into nontoxic residue. The container is gradually biodegradable when exposed to a set of factors in a natural environment and has a shelf life of six months when stored under standard commercial conditions.
Owner:SACRED GREEN
Method and apparatus of improving mechanical characteristics of nonwoven materials
An apparatus for forming a nonwoven material from a liquefied polymer, the apparatus comprising: (a) a precipitation electrode; (b) a dispenser spaced apart from the precipitation electrode, and defining a first axis therebetween, the dispenser being at a first potential relative to the precipitation electrode; and (c) a system of electrodes being laterally displaced from the dispenser, being at a second potential relative to the precipitation electrode and capable of providing an electric field having at least one rotating component about the first axis; the dispenser and the system of electrodes being designed and constructed such that the liquefied polymer is dispensed from the dispenser and forms a plurality of entangled fibers moving in a direction of the precipitation electrode, hence forming the nonwoven material thereupon.
Owner:NICAST LTD
A method for preparing polyacrylonitrile carbon fiber precursors by dry jet wet spinning
ActiveCN102277629AFull and even contactInhibition formationArtificial filament heat treatmentMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentYarnGas liquid reaction
The invention relates to a method for preparing a polyacrylonitrile carbon fiber precursor. The method comprises the following steps of: copolymerizing acrylonitrile and copolymerization components in multicomponent solution so as to form polymer spinning stock solution which has a relatively uniform and controllable molecular structure, performing demonomerization on the spinning stock solution,defoaming, filtering, and preparing the polyacrylonitrile carbon fiber precursor by a dry-jet wet-spinning process. The key technology of the method is that: a gas storage box is arranged on a dry wet spinning pack, the gas storage box and the liquid level of coagulating bath fluid form a dry-jet wet-spinning air layer into a confined space, and ammonia is persistently aerated into the space to carry out gas-liquid reaction with spinning solution trickle in the air layer. The polyacrylonitrile precursor prepared by the method has regular sections and few defects, the density is not less than 1.187g / cm<3>, the density after carbonization is not less than 1.79g / cm<3>, the strength is not less than 5.1GPa, and the modulus of elasticity is 280 to 300GPa.
Owner:KINGFA SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
Polymer fiber tubular structure having kinking resistance
An apparatus for forming a tubular structure from a liquefied polymer, the apparatus comprising: (a) a dispenser for dispensing the liquefied polymer; (b) a precipitation electrode being at a first potential relative to the dispenser, the precipitation electrode being designed and constructed for generating a polymeric shell thereupon; and (c) a mechanism for increasing a local density of the polymeric shell in a plurality of predetermined sub-regions of the polymeric shell, thereby to provide a tubular structure having an alternating density in a longitudinal direction.
Owner:NICAST LTD
High-strength high modulus polyimide fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102345177AImprove performanceReasonable molecular structureArtificial filament heat treatmentMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentFiberPolymer science
The invention relates to high-strength high modulus polyimide fiber and a preparation method thereof, which belongs to the high performance organic fiber technical field. The fiber comprises the polyimide fiber which is prepared by biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (BPDA), para-phenylene diamine (pPDA) and 2-(4-aminophenyl)-5-aminobenzimidazoles (BIA), wherein the mol ratio of pPDA to BIA is 1:10-3:1, other di-amine and di-anhydride monomers are added in the synthesis process, a gradient temperature reaction method and a one step continuous preparation method are used in the preparation process, so that the difficulties for synthesizing and processing due to the content increase of 2-(4-aminophenyl)-5-aminobenzimidazoles are solved, the problems of poor homogeneity and stability of thefiber performance can be solved, and the high-strength high modulus polyimide fiber can be obtained, the strength can reach 4.5GPa, the modulus can reach 201GPa, and the raw material source is wide, the spinning process can be continuously performed, the method has low cost and high efficiency which is capable of realizing the industrial production.
Owner:JIANGSU XIANNUO NEW MATERIAL TECH
Titanium white for dry acrylic spinning delustering its preparing method
InactiveCN1858309ADry spinning methodsPigment treatment with organosilicon compoundsWeather resistanceWhite powder
The present invention discloses a kind of titanium white powder for extinction in dry spinning acrylic fiber and its preparation process. The titanium white powder is prepared with anatase type titanium white as material and through pulping, sanding milling, grading, purifying and other steps to eliminate coarse grains and impurity ions, coating with compact Al2O3 to obtain high weather resistance, water washing and coating with organic material. It has excellent dispersivity in spinning solution for dry spinning acrylic fiber and is used for extinction. It can result in excellent filtering performance and spinnability, low end breakage, high tow strength, high whiteness and high dyeability.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Gas layer propulsion electrostatic spinning apparatus and industrial application thereof
InactiveCN101033559AIncrease temperatureLow viscosityArtificial filaments from cellulose derivativesDry spinning methodsElectrospinningAirflow
This invention relates to a static filature device pushed by a gas layer and its industrial application, in which, the device includes: a gas circulation push device, a gas drying and heating device, a sealed filaturing room, and air inlet at the top of the sealed room, a material room at the upper part of the sealed room, a spinneret at the lower part of the material room, electrode connected on the spinneret, a material receiving device at the lower part of the sealed room, an air outlet at the lower-right part of the room, a cooling device cooling gas flow with solvent and a solvent recovering device, which can make static filature to molding to polymers, increases spinning efficiency greatly by applying multiple sprayers, controls the temperature and humid of the entry flows to alter the temperature and humid of filature raw liquid, and further more, the pushed gas flow can drive the volatiled solvent in the process to flow out to be recovered.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method and apparatus for manufacturing polymer fiber shells via electrospinning
InactiveUS7112293B2Minimize volume chargeReduce unevennessSuture equipmentsElectro-spinningFiberPolymer science
An apparatus for manufacturing a polymer fiber shell from liquefied polymer is provided. The apparatus includes: (a) a precipitation electrode being for generating the polymer fiber shell thereupon; (b) a dispenser, being at a first potential relative to the precipitation electrode so as to generate an electric field between the precipitation electrode and the dispenser, the dispenser being for: (i) charging the liquefied polymer thereby providing a charged liquefied polymer; and (ii) dispensing the charged liquefied polymer in a direction of the precipitation electrode; and (c) a subsidiary electrode being at a second potential relative to the precipitation electrode, the subsidiary electrode being for modifying the electric field between the precipitation electrode and the dispenser.
Owner:NICAST LTD
Process of making asymmetric polybenzoxazole membranes
InactiveUS20110316181A1High selectivityImprove permeabilitySemi-permeable membranesDispersed particle separationMolecular sieveBenzoxazole
The present invention provides a process for making an integrally skinned asymmetric polybenzoxazole hollow fiber membrane comprising spinning a dope solution via a dry-wet phase inversion technique to form a porous integrally skinned asymmetric o-hydroxy substituted polyimide or an o-hydroxy substituted polyamide hollow fiber membrane comprising microporous inorganic molecular sieve followed by thermal rearrangement at a temperature from about 250° to 500° C. to convert the polyimide or polyamide membrane into a polybenzoxazole membrane. These membranes contain microporous inorganic molecular sieve materials that can have a particle size from about 20 nm to 10 μm.
Owner:UOP LLC
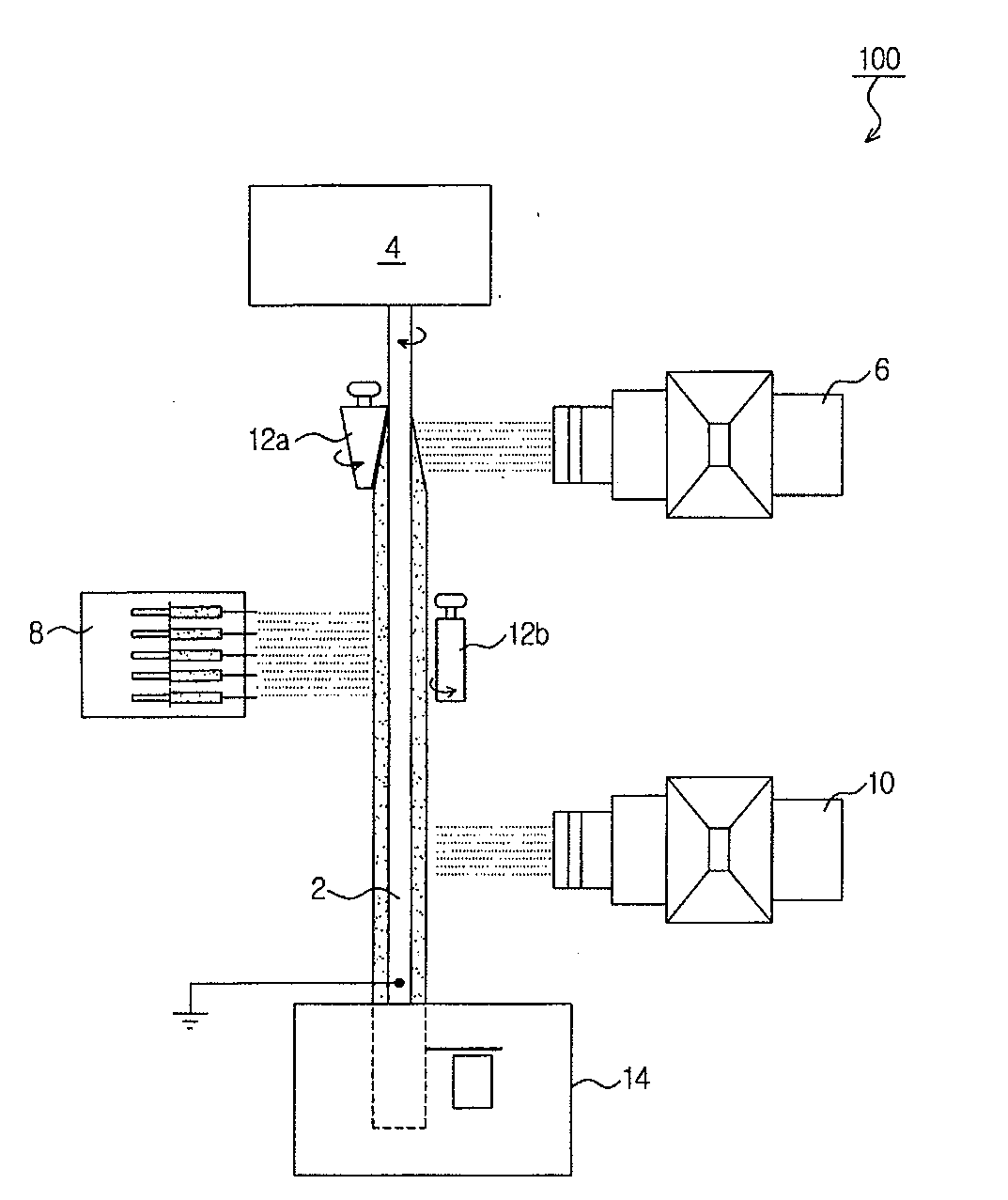
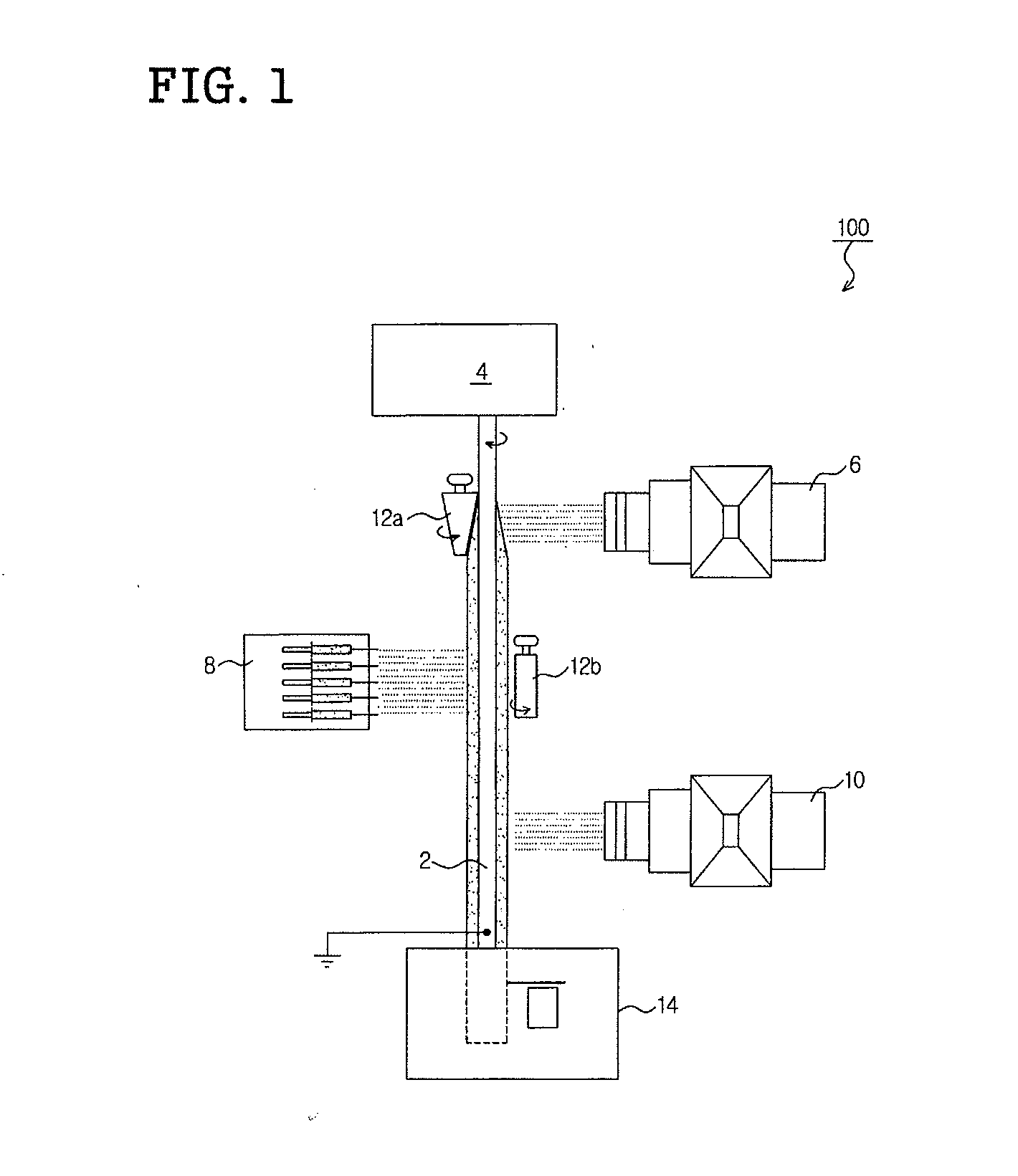
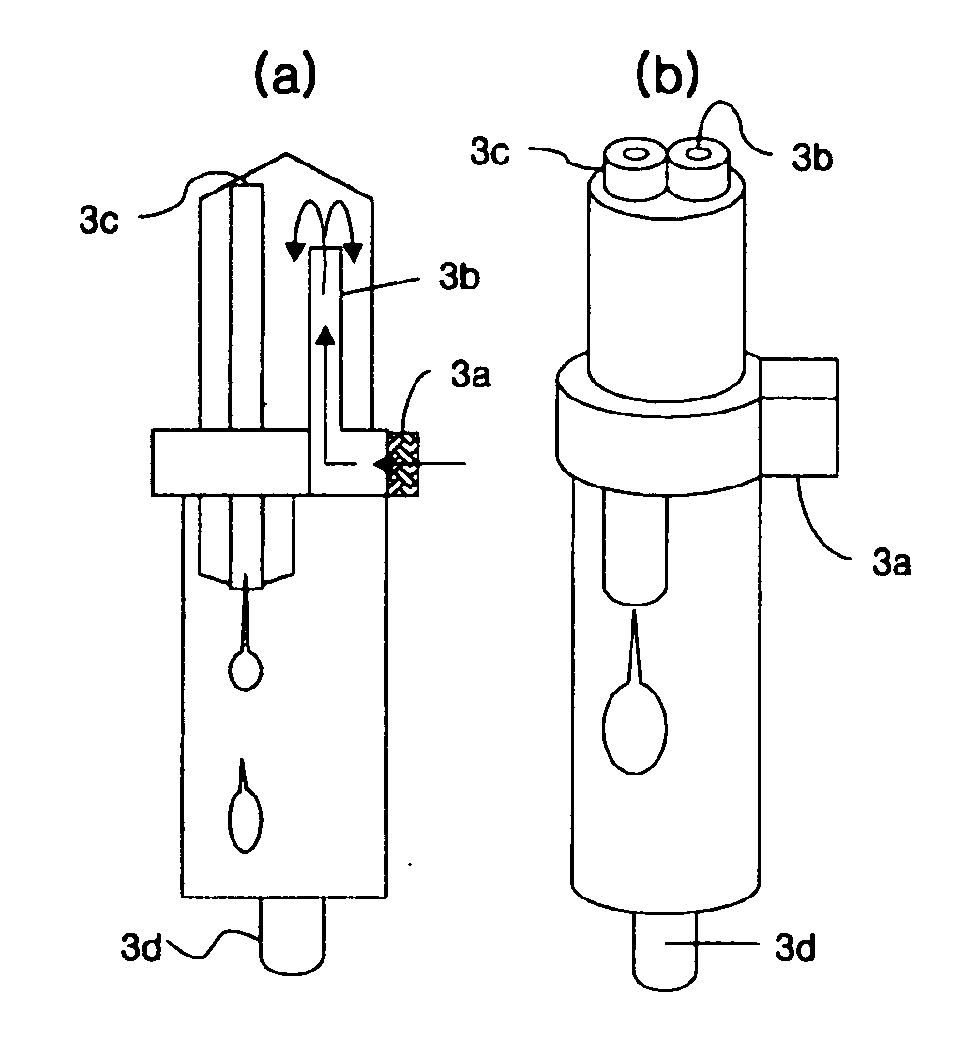
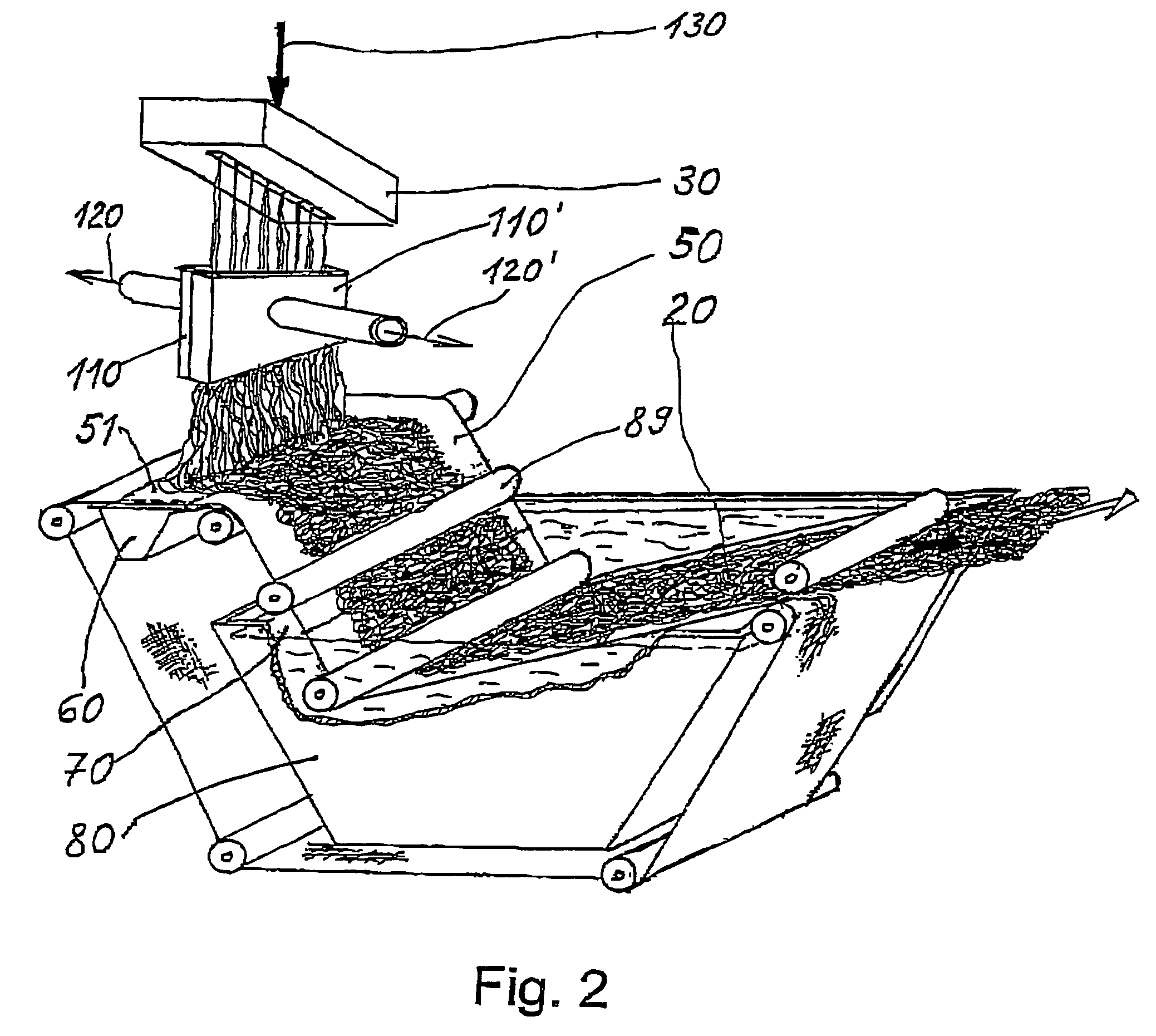
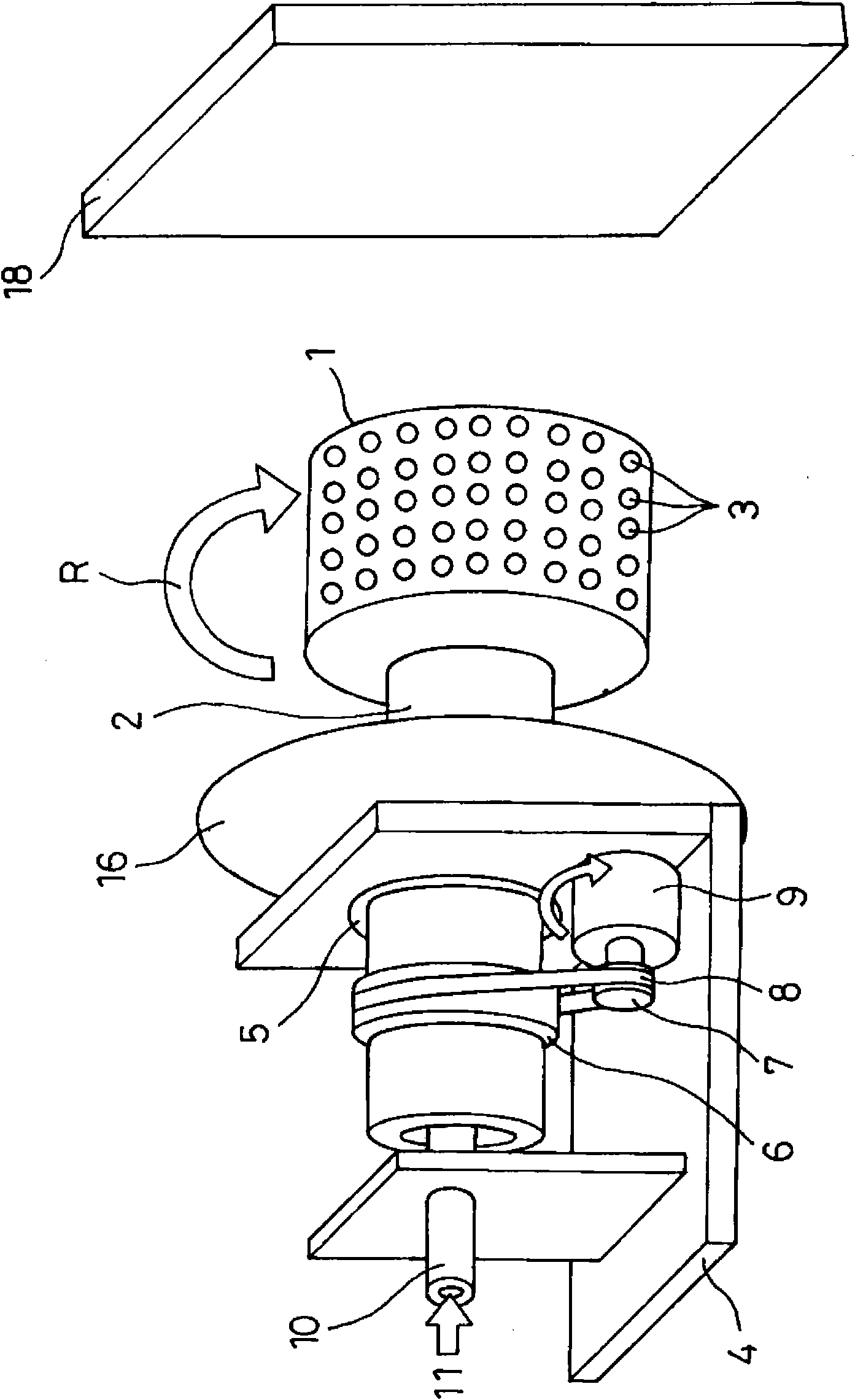
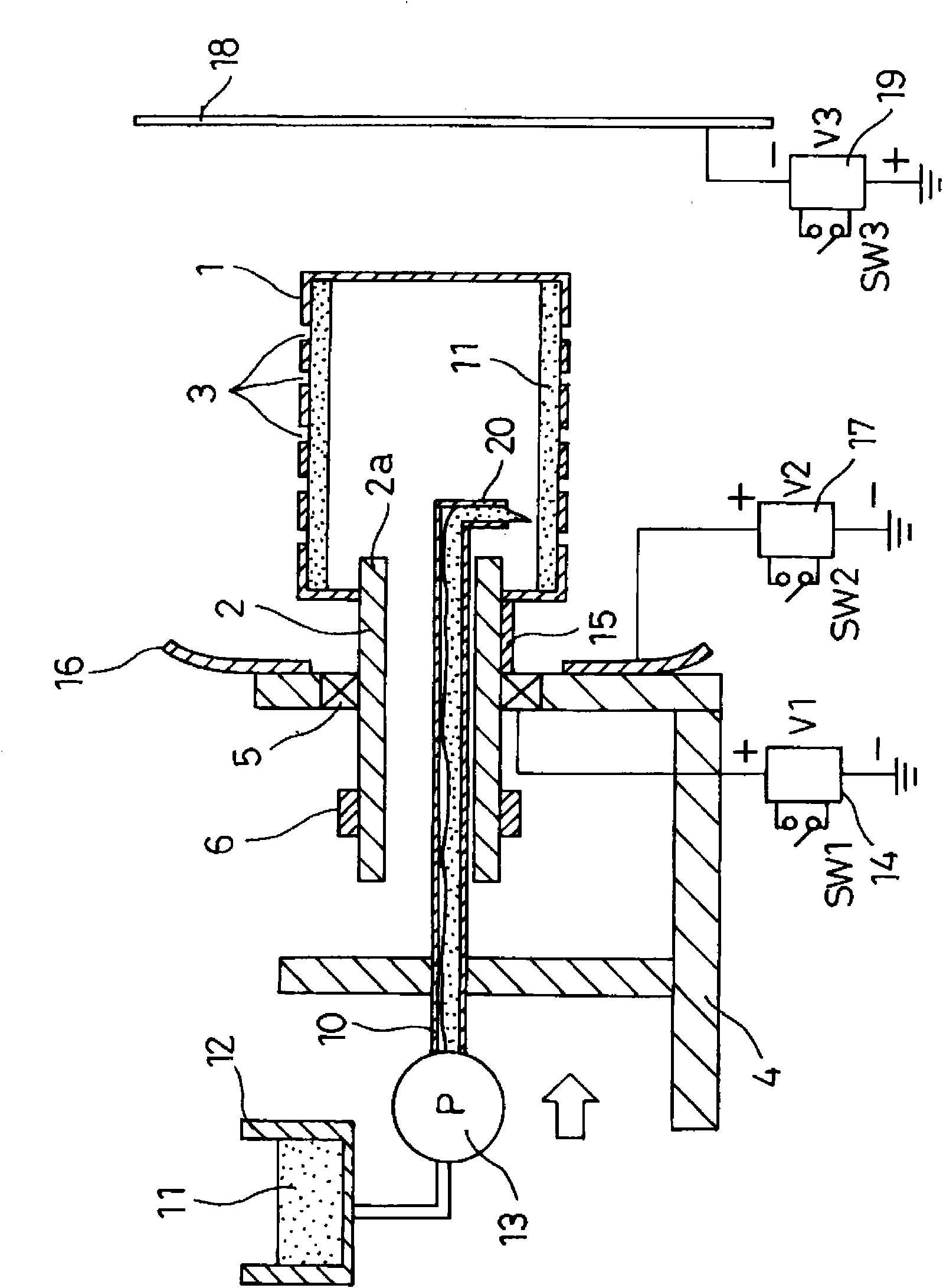
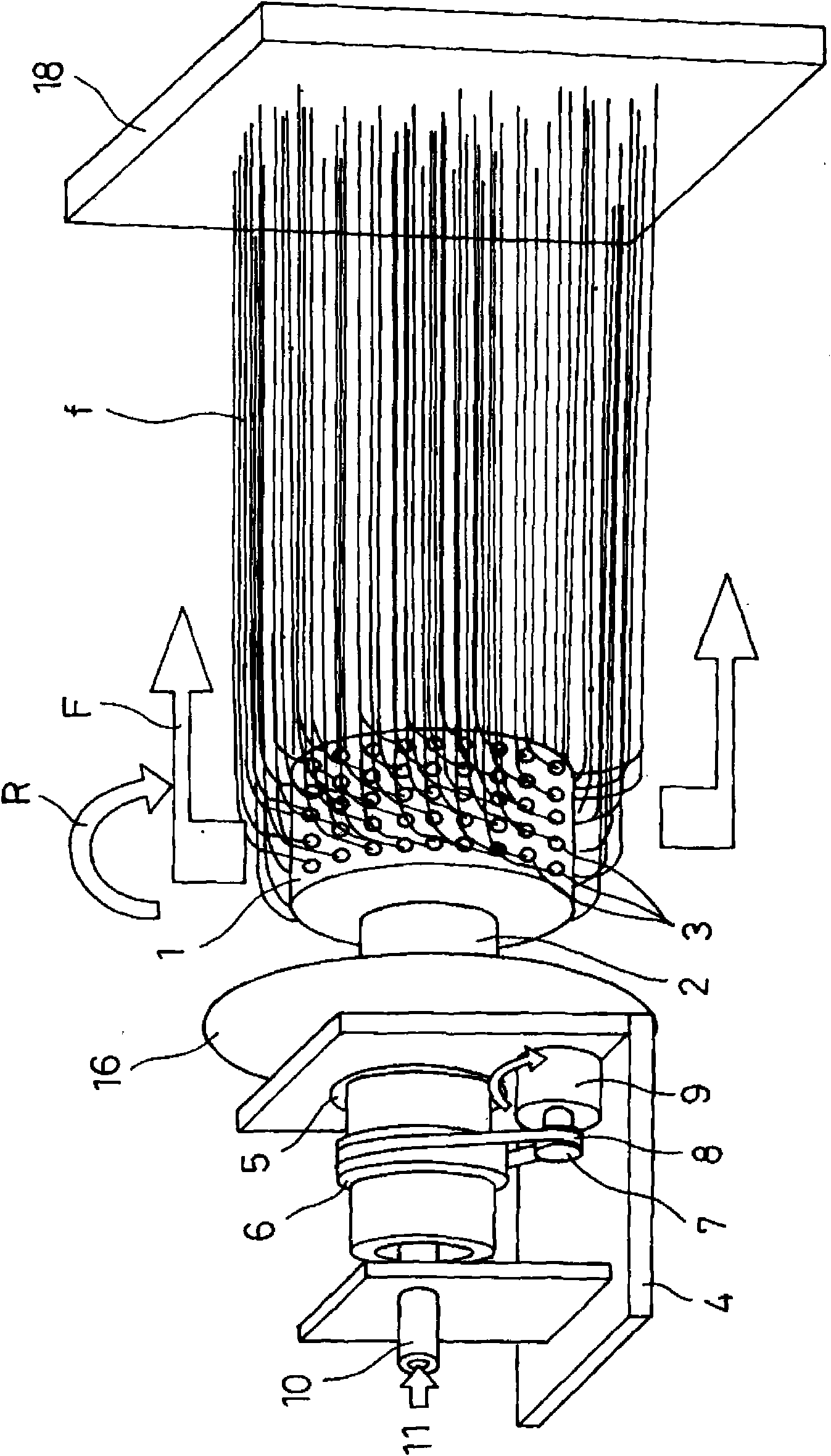
Nanofiber spinning method and device
Provided is a nanofiber spinning method and device for producing a high strength and uniform yarn made of nanofibers with high productivity and at a low cost.The device includes: a nanofiber producing unit (2) which produces nanofibers (11) by extruding polymer solution, prepared by dissolving polymeric substances in a solvent, through small holes (7) and charging the polymer solution, and by allowing the polymer solution to be stretched by an electrostatic explosion, and which allows the nanofibers to travel in a single direction; a collecting electrode unit (3) to which an electric potential different from that of the charged polymer solution is applied, and which attracts the produced nanofibers (11) while simultaneously rotating and twisting the nanofibers, and gathers them for forming a yarn (20) made of the nanofibers (11); and a collecting unit (5) which collects the yarn (20) passed through the center of the collecting electrode unit (3).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Polyurethane Elastic Fiber And Process For Producing Same
ActiveUS20070196650A1Improve stabilityReduce yarn breakageMonocomponent polyurethanes artificial filamentOther chemical processesFiberInorganic compound
A polyurethane elastic fiber, containing inorganic compound particles that have an average particle size of 0.5 to 5 mm and that show a refractive index of 1.4 to 1.6, having at least one protruded portion that has a maximum width of 0.5 to 5 μm, in the fiber surface, per 120-μm length in the fiber axis direction.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI FIBERS CORPORATION
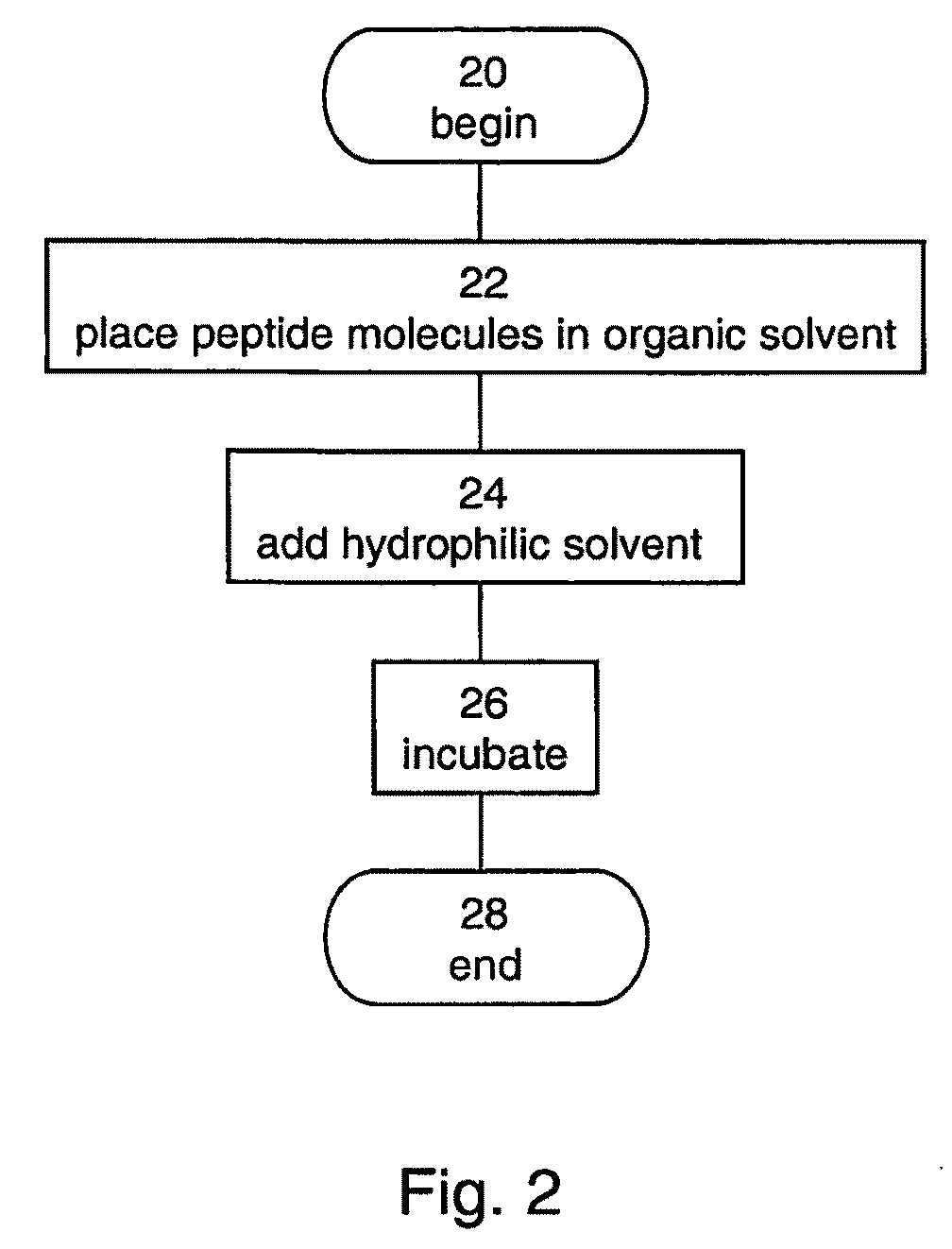
Articles of peptide nanostructures and method of forming the same
InactiveUS20090061190A1Monocomponent protein artificial filamentElectric discharge heatingFiberNanostructure
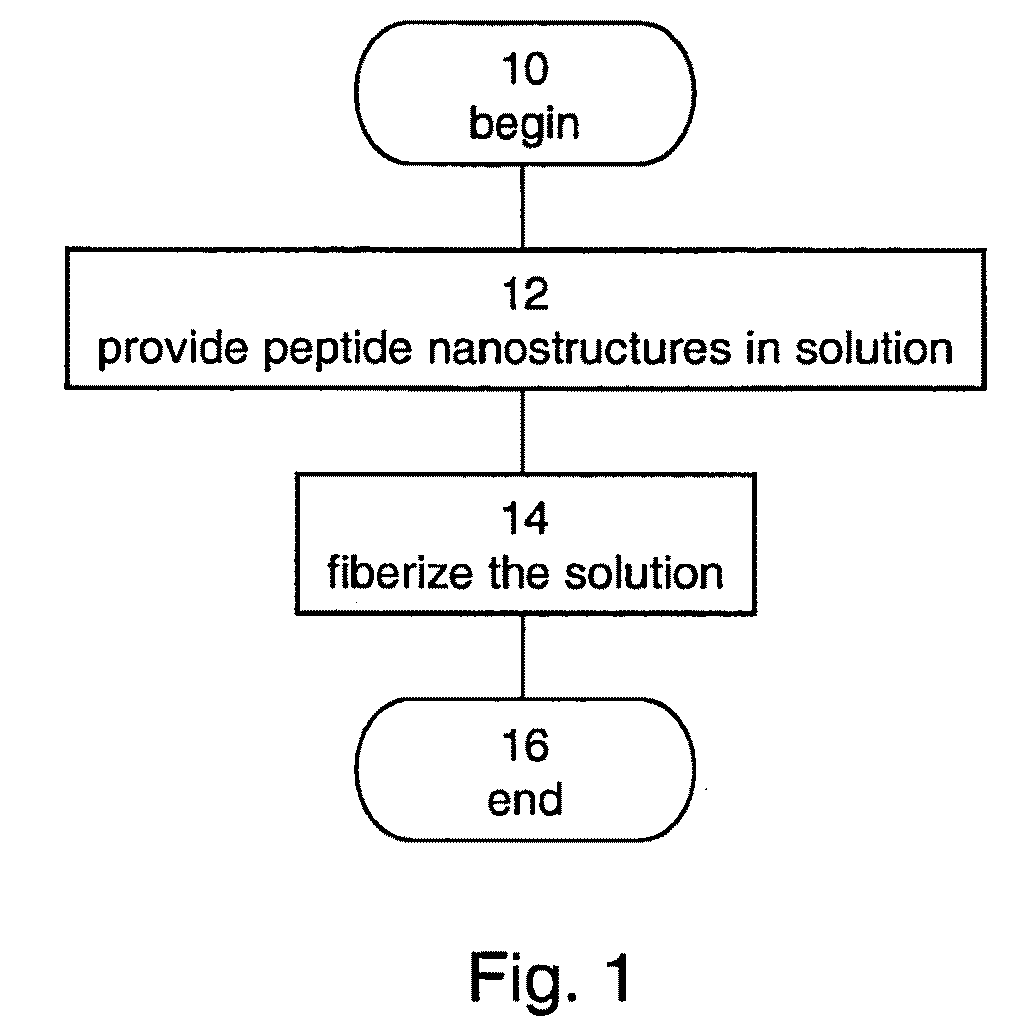
A method of forming a fiber made of peptide nanostructures is disclosed. The method comprises: providing peptide nanostructures in solution, and fiberizing the solution thereby forming at least one fiber of the peptide nanostructures. Also disclosed are methods of forming films and other articles using the peptide nanostructures.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
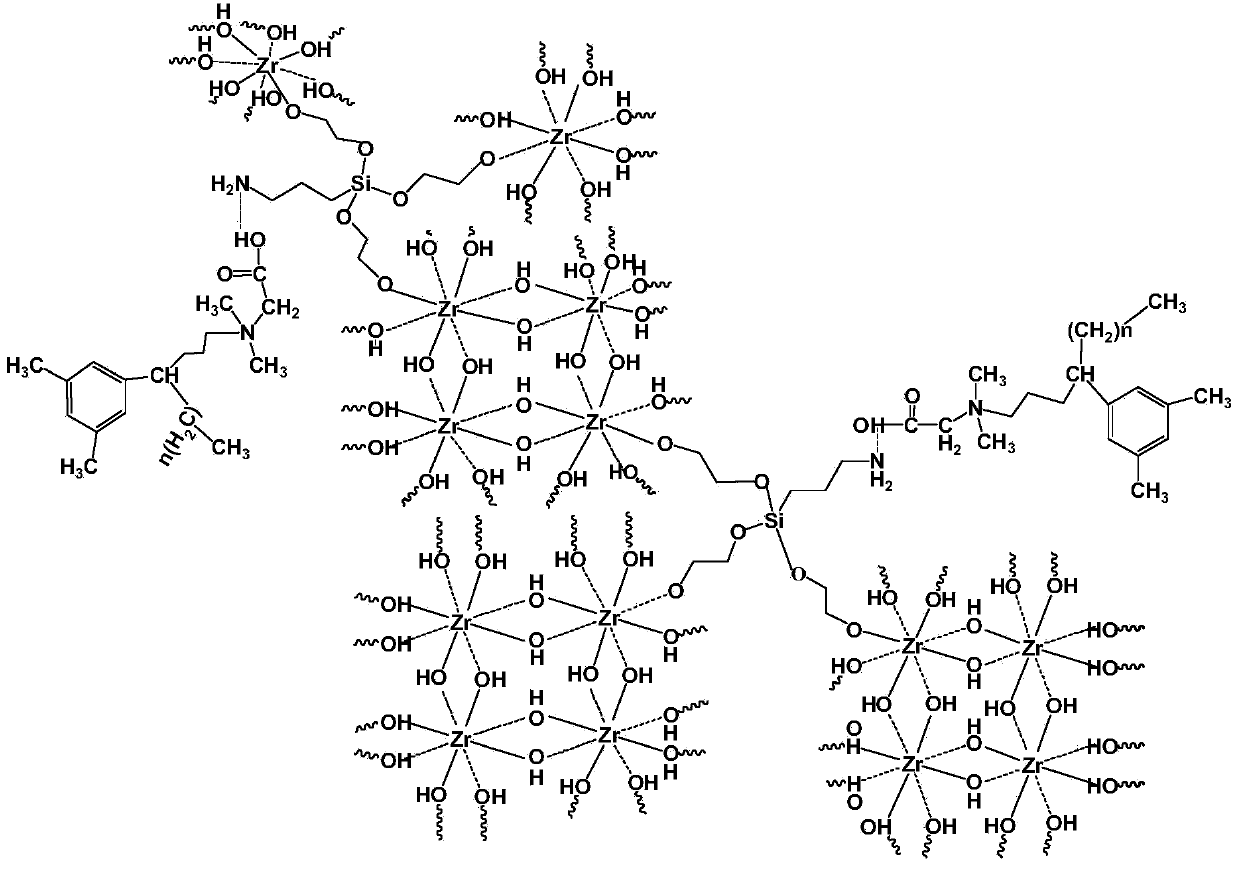
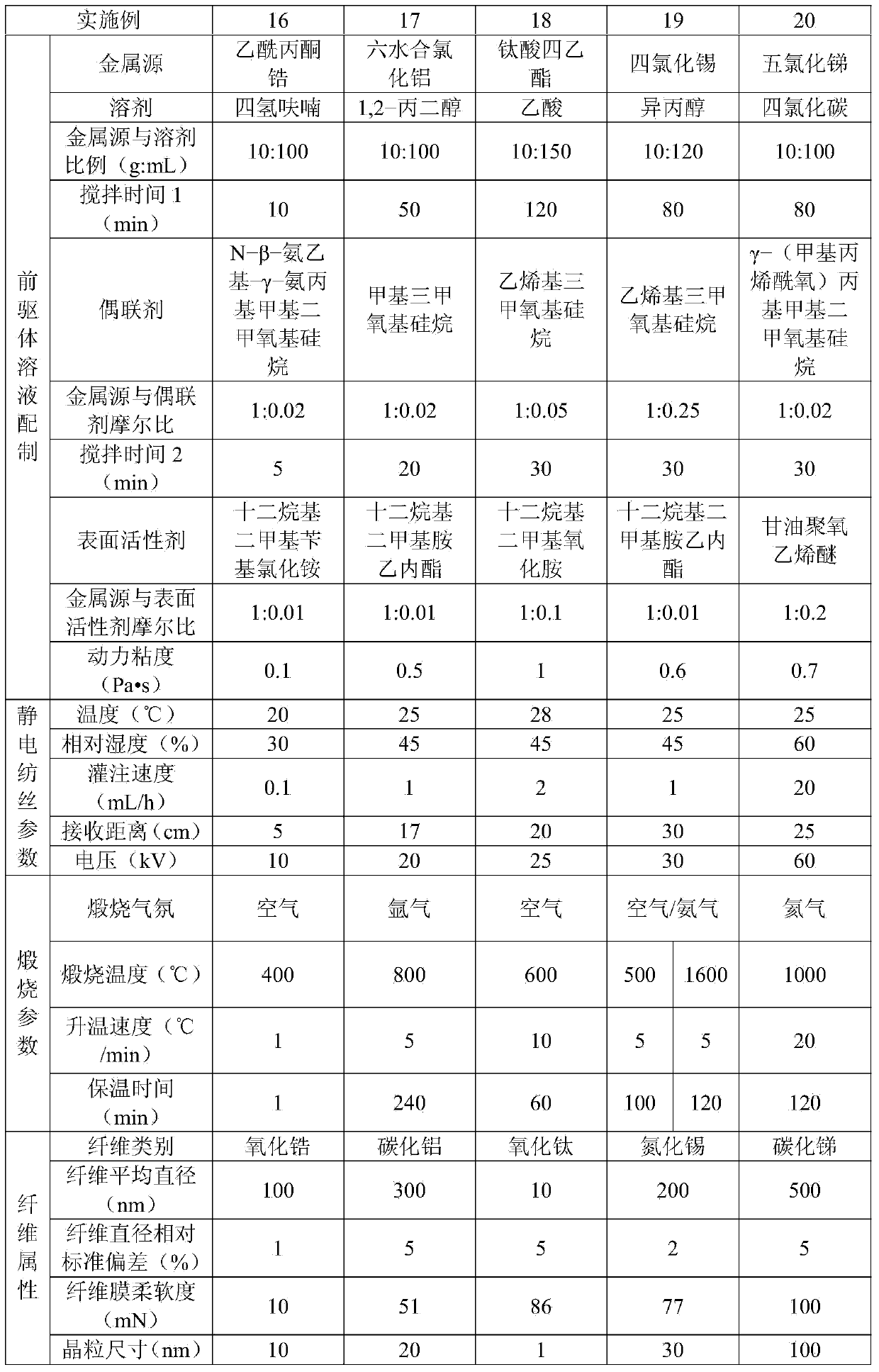
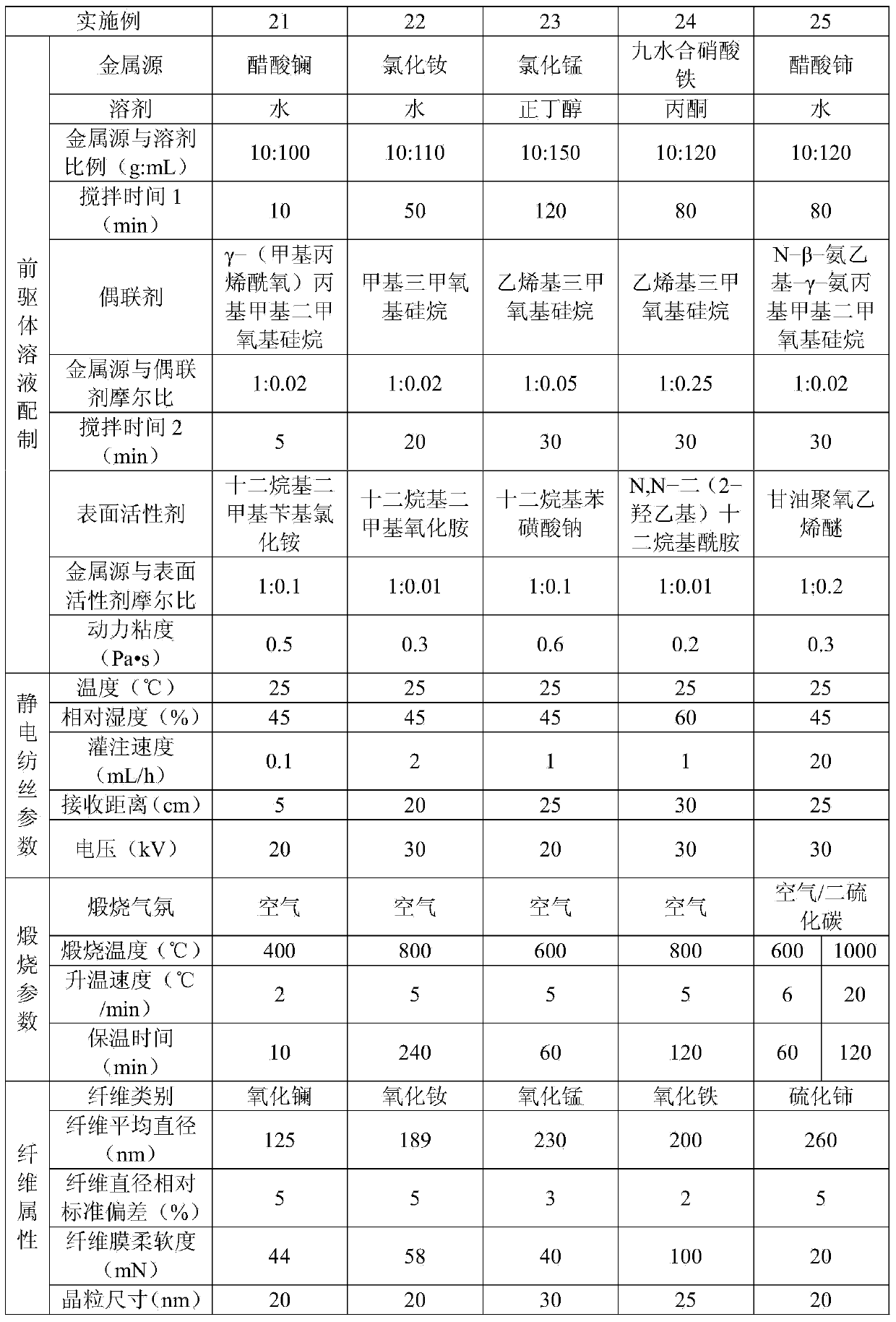
Flexible inorganic fiber material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104178822AHigh content of inorganic componentsHigh yieldInorganic material artificial filamentsFilament-forming treatmentFiberThermal insulation
The invention relates to a flexible inorganic fiber material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the flexible inorganic fiber material comprises the steps as follows: firstly, at least one metal source is dissolved in a solvent, a coupling agent and a surfactant are added sequentially and uniformly mixed to prepare a homogeneous and stable precursor solution which contains interpenetrating molecular chains adopting a three-dimensional network structure, and then a precursor fiber material is prepared by the precursor solution through a spinning forming process; and the precursor fiber material is calcined in an appropriate atmosphere to obtain the flexible inorganic fiber material. According to the invention, various inorganic fiber materials can be prepared through different spinning processes, the preparation process is simple and high in yield, and the prepared inorganic fiber material has good flexibility and has broad application prospect in the fields of catalysis, energy, electronics, filtration, thermal insulation and the like.
Owner:嘉兴富瑞邦新材料科技有限公司
Rotary disc spinning process and apparatus
A rotating-disk spinning method features that the polymer solution is applied onto high-speed rotating disk at constant speed, under the action of centrifugal force the solution flys toward all around to become high stretched fibres, and after the solvent is evaporated, the non-woven fabric of superfine fibres is collected. Its spinning apparatus is composed of a rotating disk fixed to shaft driven by power mechanism, a container of polymer solution, and a fibre collector. Its advantages are simple technology, low cost, high-strength fine fibres, and high productivity.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for producing substantially endless fine threads
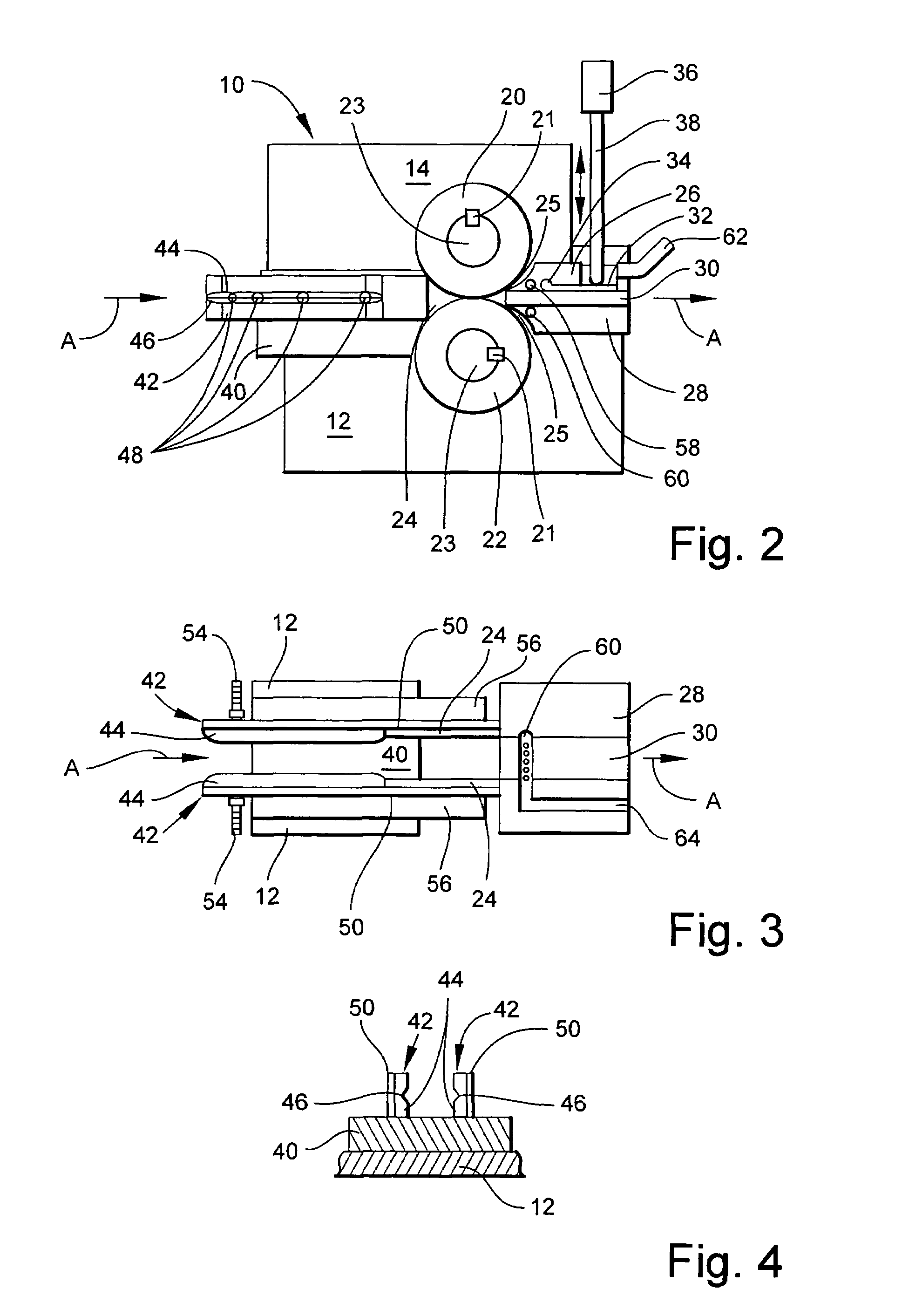
InactiveUS7922943B2Reduced strengthMore energySpinnerette packsMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentYarnPolymer solution
The invention relates to a method and a device for producing substantially endless fine threads from polymer solutions, especially spinning material for lyocell, wherein the spinning material is spun from at least one spinning hole or a spinning slot. The spun thread or film is drawn by high-speed accelerated gas flows using a Laval nozzle whose narrowest cross-section is located beneath the point where the spinning material exists. The threads are arranged on a strip in the form of a non-woven or are taken up in the form of a yarn and are subsequently separated in spinning baths by means of solvents.
Owner:GERKING LUDER
Process and apparatus for producing nanofiber and polymer web
InactiveCN101542025ACompact structureImprove productivityNon-woven fabricsDry spinning methodsFiberEvaporation
A process and apparatus for producing nanofiber and polymer web, the electroconductive rotary vessel (1, 36) having a plurality of small holes (3) is rotated while supplying a polymer solution (11), prepared by dissolving a polymer material in a solvent, into the rotary vessel (1, 36). Electric charges are applied by electrifying means (14, 19) to the polymer solution (11) which flows from the small holes (3) in the rotary vessel (1, 36). The flowout linear polymer solution (11) is stretched by electrostatic explosion induced by centrifugal force and the evaporation of the solvent to produce nanofibers (f) formed of a polymer material. The nanofibers (f) in the course of the production thereof are allowed to flow so as to be deflected from one side to the other side in a shaft center direction of the rotary vessel (1, 36) by a reflection electron (16) and / or air blow means (34, 46, 59) and to be deposited to produce a polymer web, whereby nanofibers and a polymer web using the nanofibers can be produced with good productivity uniformly and in a simple construction.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for preparing aramid IIII fiber
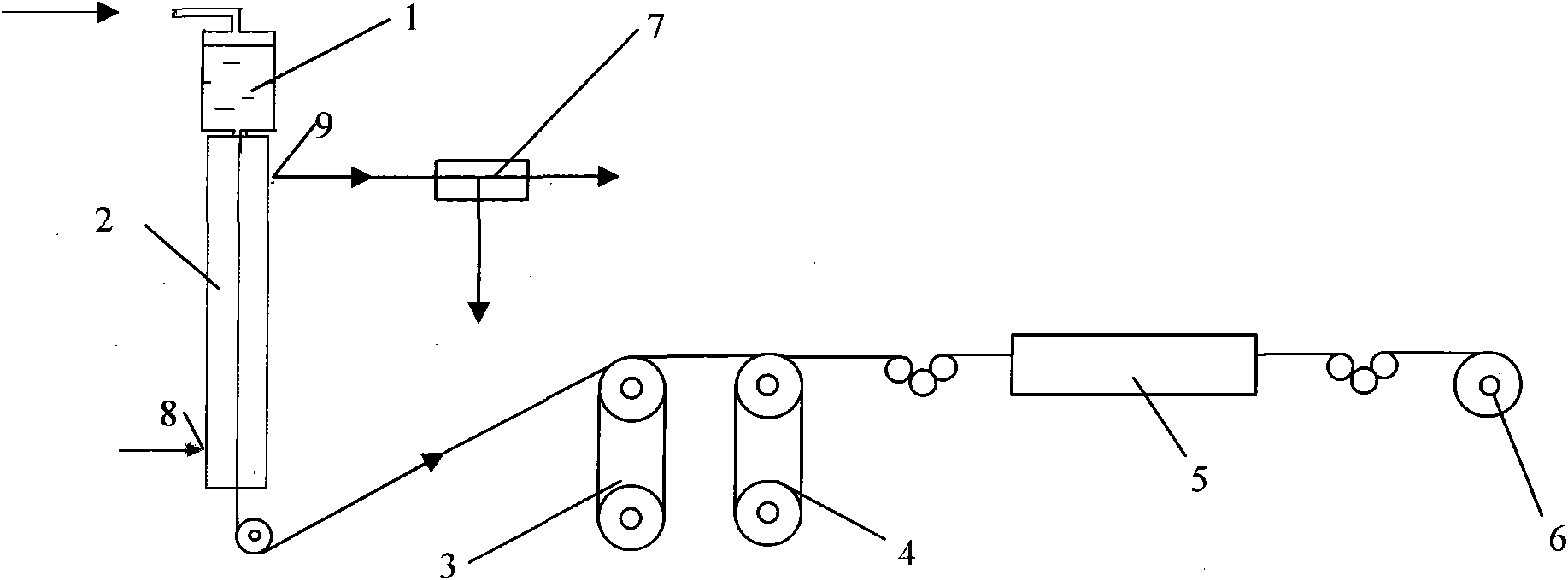
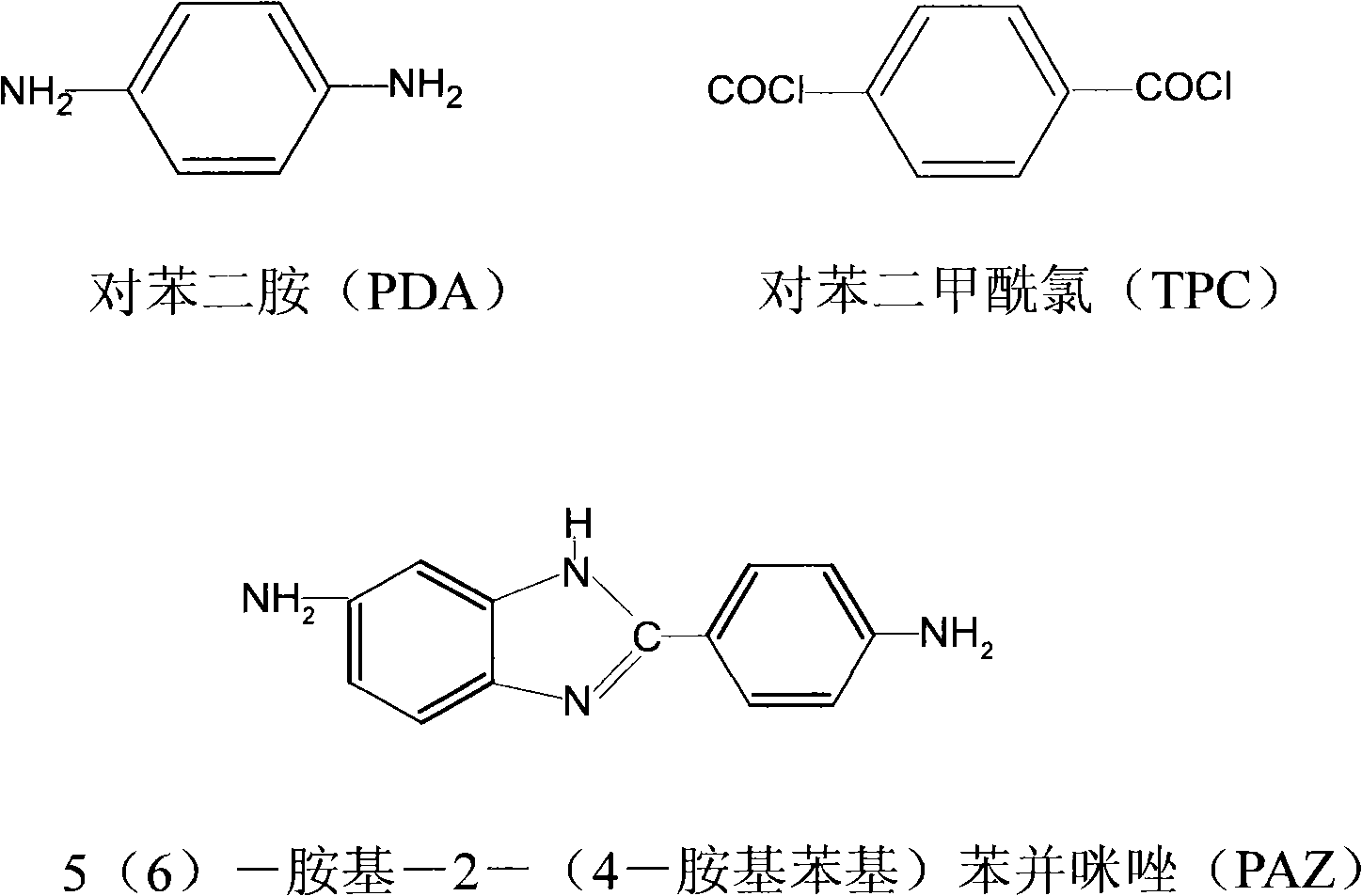
InactiveCN101851809AImprove spinning efficiencyLow investment costMonocomponent copolyamides artificial filamentDry spinning methodsYarnLithium chloride
The invention relates to a method for preparing an aramid IIII fiber, which comprises the following steps of: (1) synthesizing a spinning stock solution, carrying out low-temperature copolymerization by adopting three monomers of p-phenylenediamine, paraphthaloyl chloride and 5(6)-amido-2-(4-amidophenyl)benzimidazole as raw materials and adopting dimethylacetylamide / lithium chloride as a solvent; (2) spinning by adopting a dry method spinning process, i.e. leading the spinning stock solution obtained in the previous step to pass through a spinneret and directly enter a hot inert gas channel and evaporating and removing the solvent in the spinning stock solution by utilizing a hot inert gas to obtain cured raw yarn; and (3) carrying out water washing and heat treatment on the raw yarn and winding to obtain the aramid IIII fiber. The method has high solid content of the spinning stock solution, high spinning speed, great improvement of spinning efficiency, obvious reduction of fiber manufacturing cost, improved mechanical performance of the manufactured aramid IIII fiber and wide application prospect.
Owner:SINOSELEN HI TECH
Process for making a flexible structure comprising starch filaments
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com