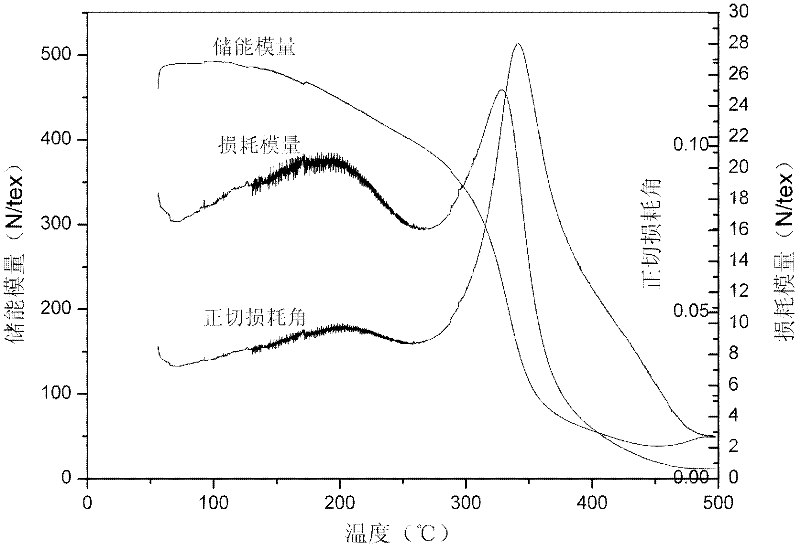
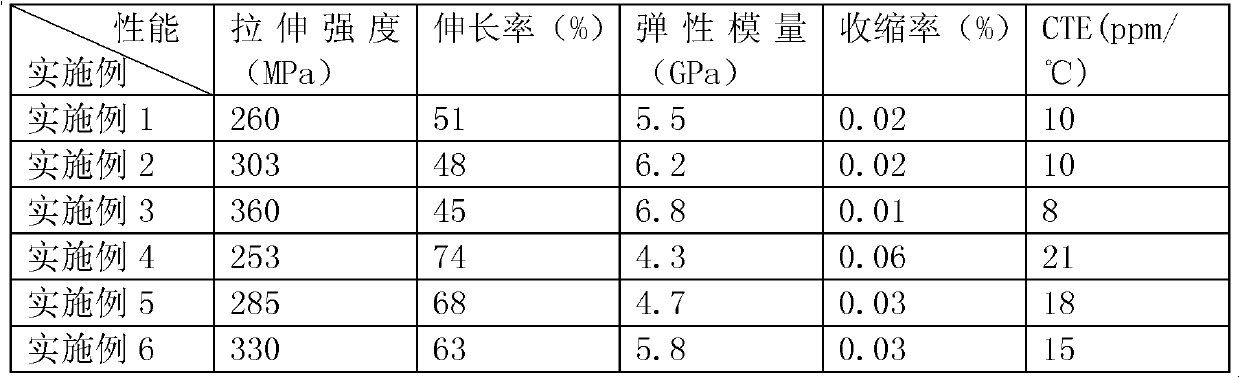
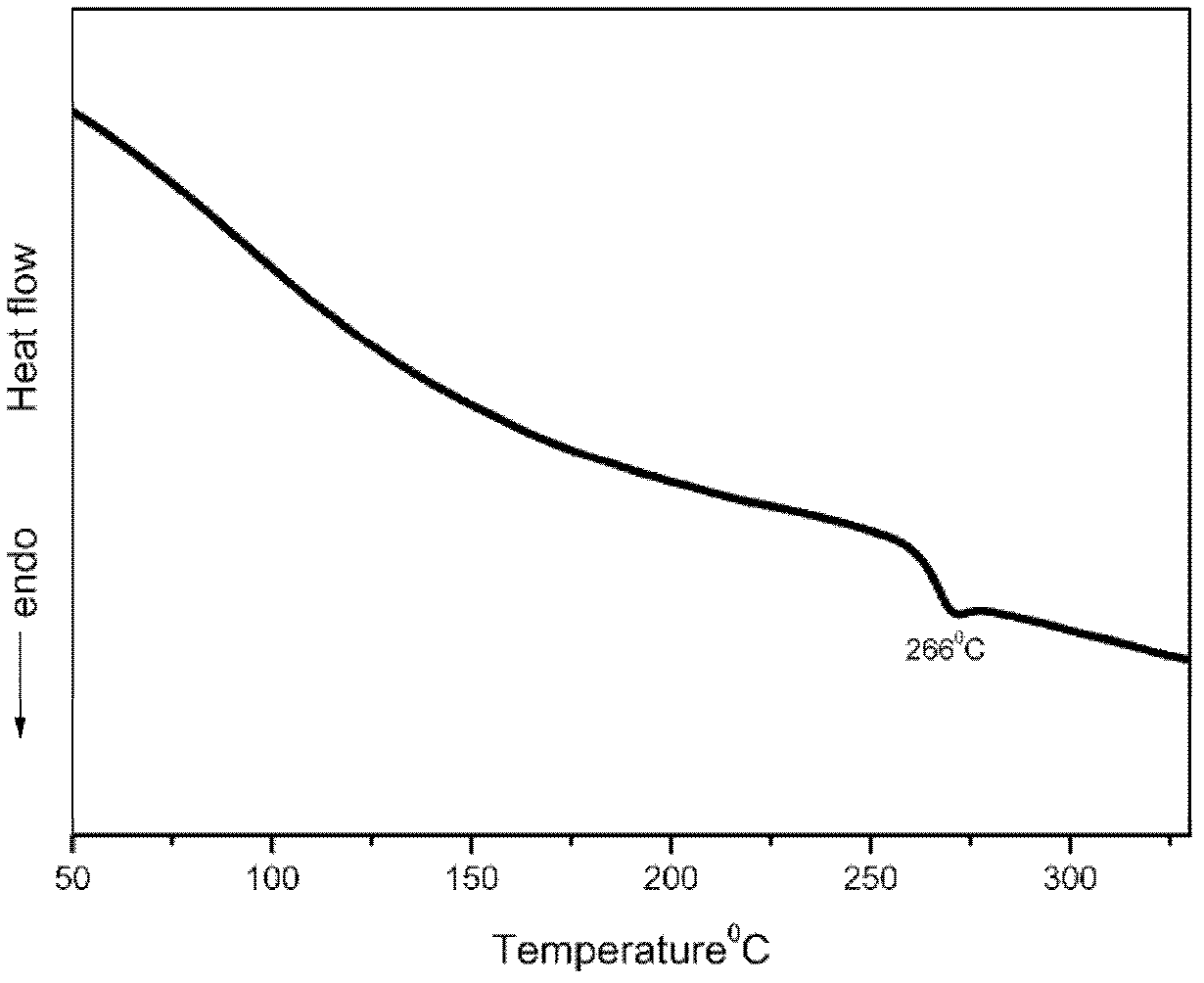
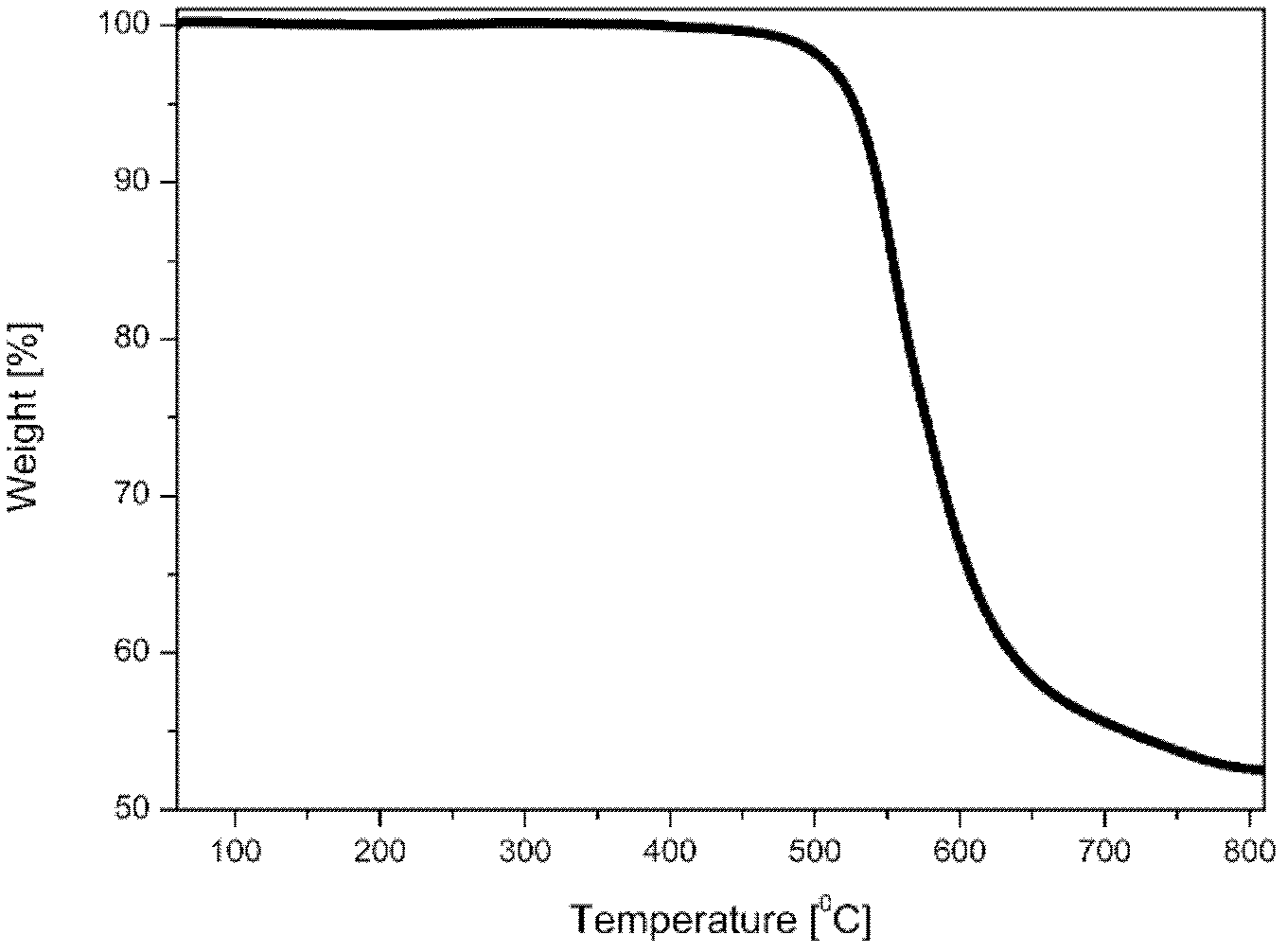
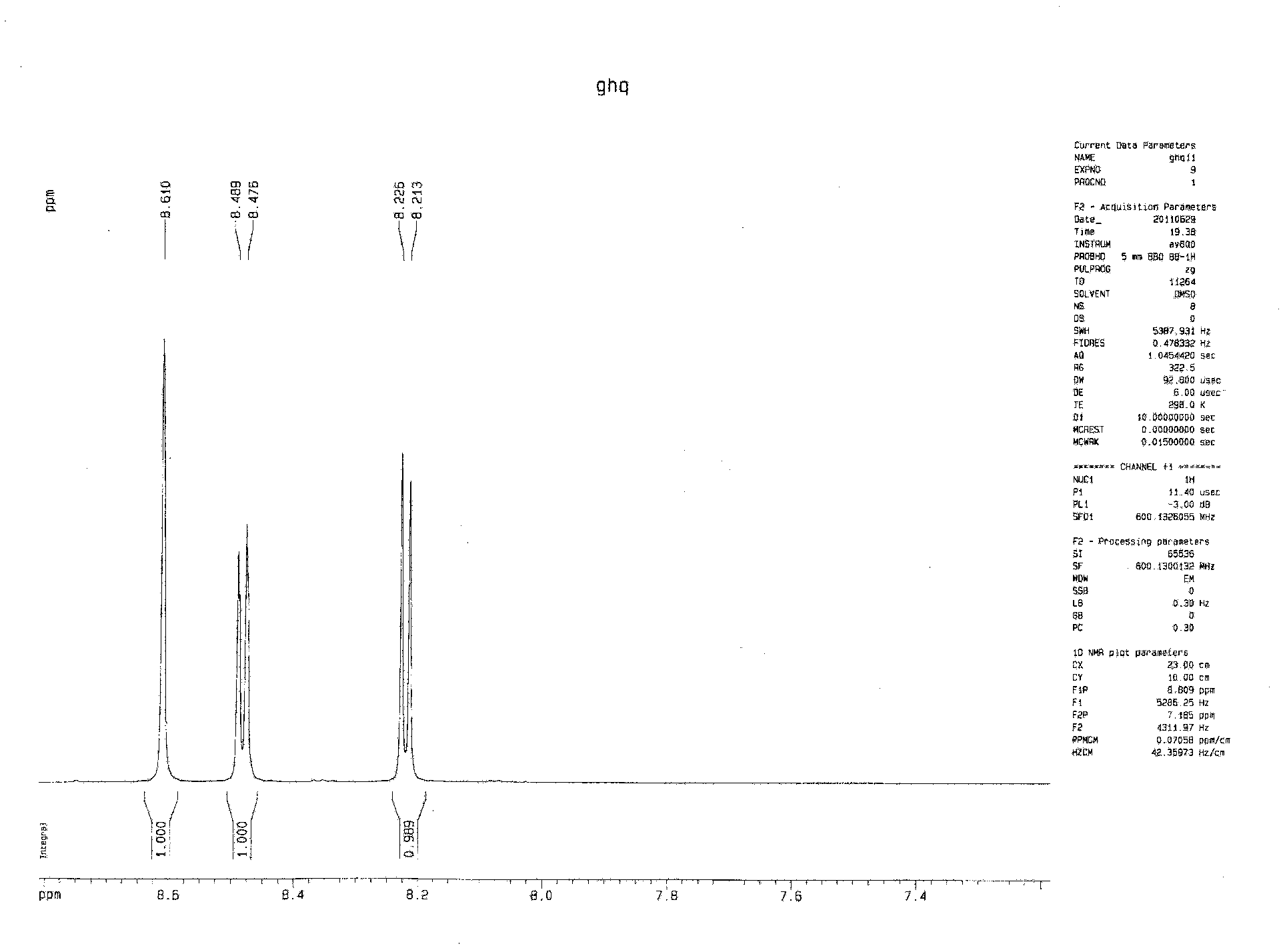
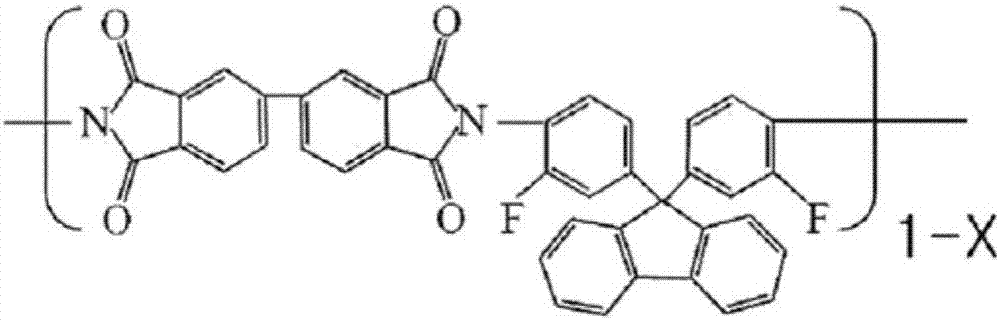
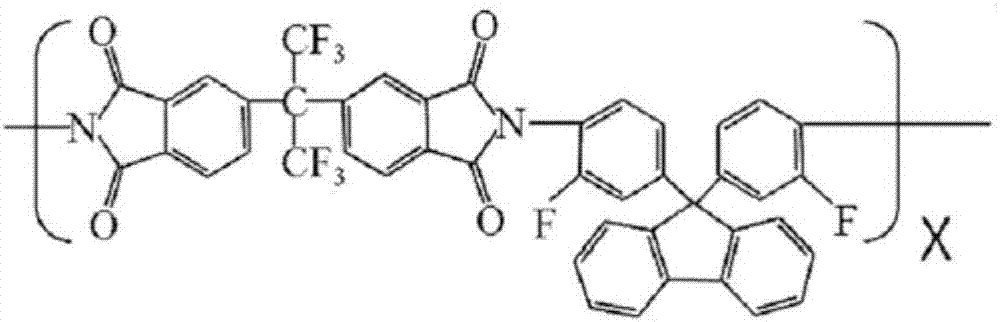
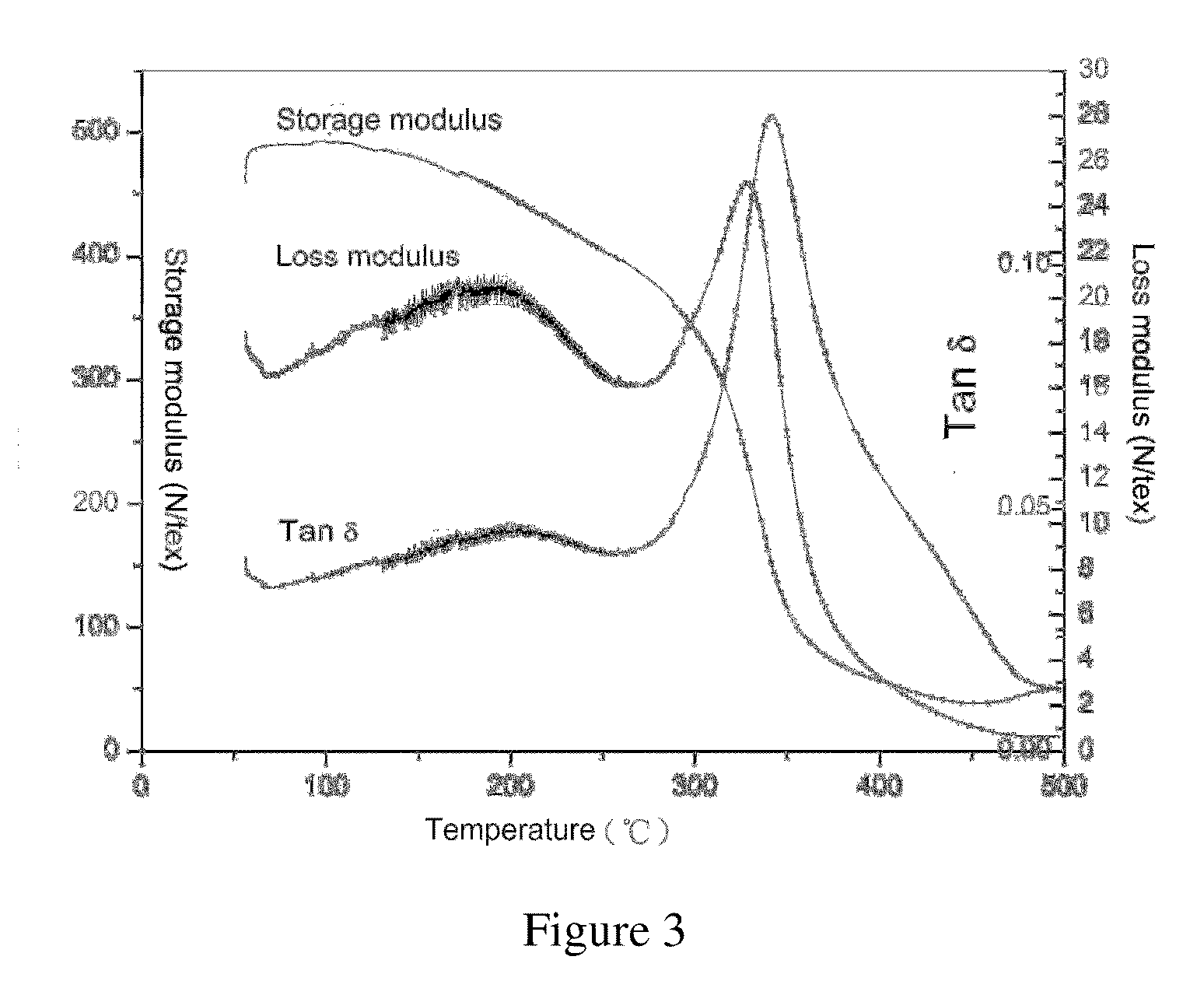
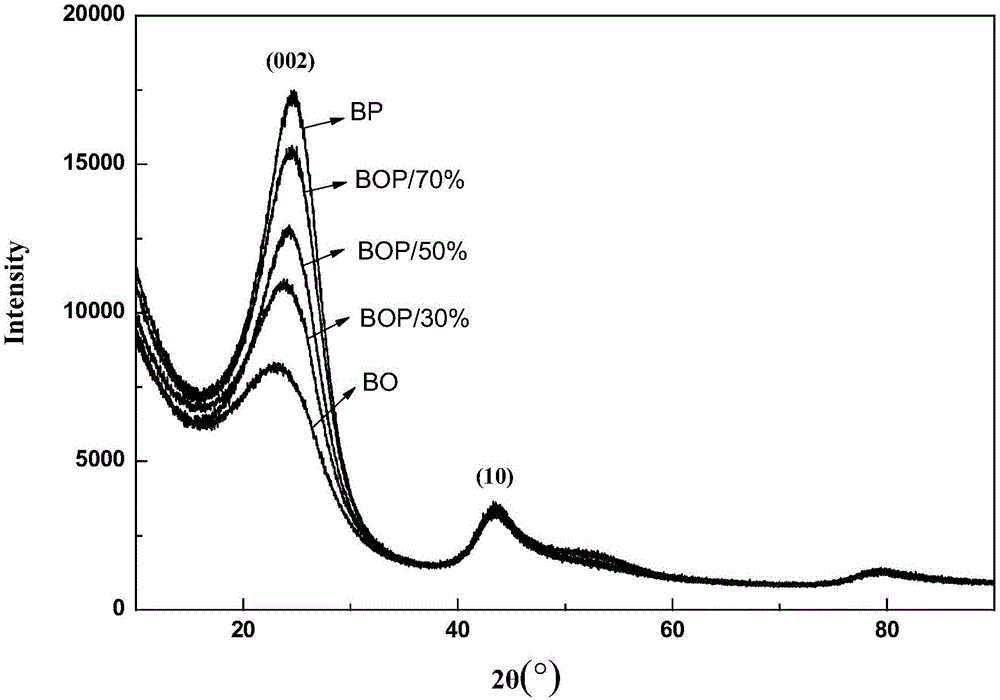
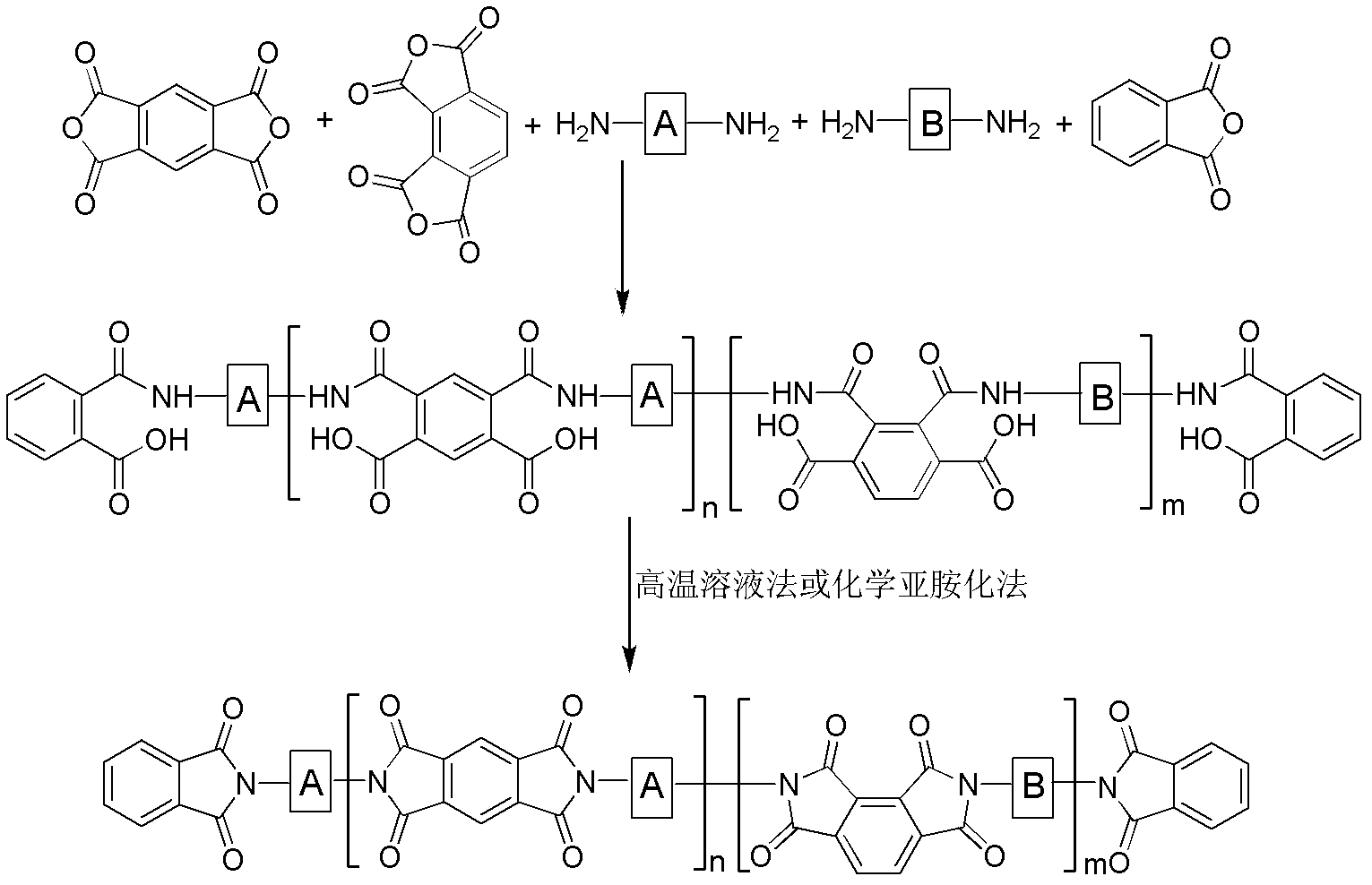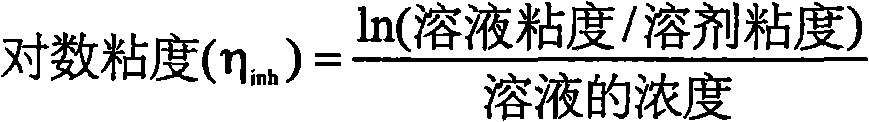Patents
Literature
86 results about "BPDA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
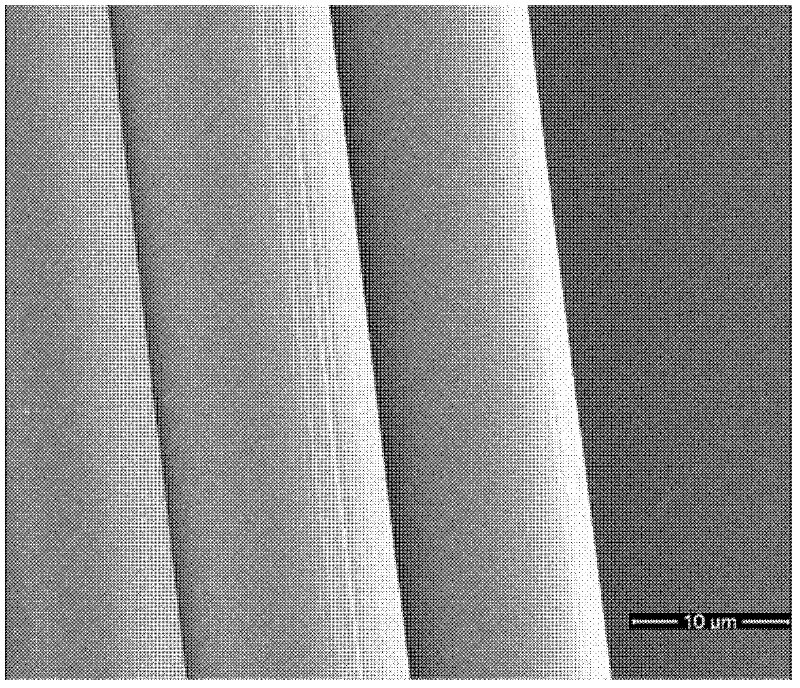
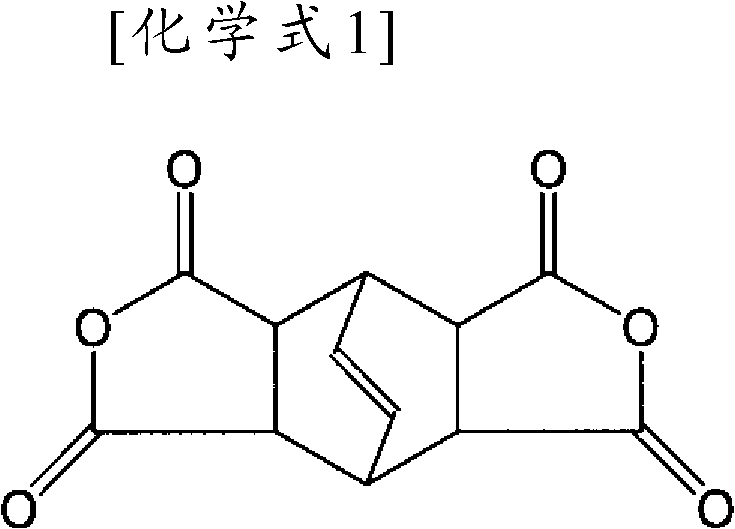
BPDA or biphenyl-tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride is a monomer used in the production of some polyimides.
Solvent free low-melt viscosity imide oligomers and thermosetting polyimide composites
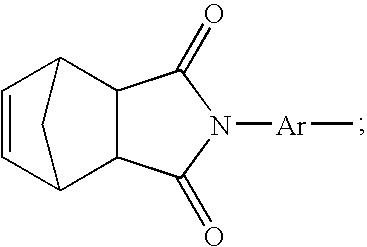
This invention relates to the composition and a solvent-free process for preparing novel imide oligomers and polymers specifically formulated with effective amounts of a dianhydride such as 2,3,3′,4-biphenyltetra carboxylic dianydride (a-BPDA), at least one aromatic diamine and an endcapped of 4-phenylethynylphthalic anhydride (PEPA) or nadic anhydride to produce imide oligomers that possess a low-melt viscosity of 1–60 poise at 260–280° C. When the imide oligomer melt is cured at about 371° C. in a press or autoclave under 100–500 psi, the melt resulted in a thermoset polyimide having a glass transition temperature (Tg) equal to and above 310° C. A novel feature of this process is that the monomers; namely the dianhydrides, diamines and the endcaps, are melt processable to form imide oligomers at temperatures ranging between 232–280° C. (450–535° F.) without any solvent. These low-melt imide oligomers can be easily processed by resin transfer molding (RTM), vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding (VARTM) or the resin infusion process with fiber preforms e.g. carbon, glass or quartz preforms to produce polyimide matrix composites with 288–343° C. (550–650° F.) high temperature performance capability.
Owner:NASA
High-strength high modulus polyimide fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102345177AImprove performanceReasonable molecular structureArtificial filament heat treatmentMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentFiberPolymer science
The invention relates to high-strength high modulus polyimide fiber and a preparation method thereof, which belongs to the high performance organic fiber technical field. The fiber comprises the polyimide fiber which is prepared by biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (BPDA), para-phenylene diamine (pPDA) and 2-(4-aminophenyl)-5-aminobenzimidazoles (BIA), wherein the mol ratio of pPDA to BIA is 1:10-3:1, other di-amine and di-anhydride monomers are added in the synthesis process, a gradient temperature reaction method and a one step continuous preparation method are used in the preparation process, so that the difficulties for synthesizing and processing due to the content increase of 2-(4-aminophenyl)-5-aminobenzimidazoles are solved, the problems of poor homogeneity and stability of thefiber performance can be solved, and the high-strength high modulus polyimide fiber can be obtained, the strength can reach 4.5GPa, the modulus can reach 201GPa, and the raw material source is wide, the spinning process can be continuously performed, the method has low cost and high efficiency which is capable of realizing the industrial production.
Owner:JIANGSU XIANNUO NEW MATERIAL TECH
Dimensionally-stable polyimide film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102558860ALow heat shrinkageSmall coefficient of thermal expansionDiaminodiphenyl etherPolymer science
The invention discloses a dimensionally-stable polyimide film and a preparation method thereof. According to the weight percentage, the polyimide film is manufactured by evenly mixing 40 to 80 percent of component A, 0 to 60 percent of component B and 0 to 60 percent of component C and then conducting slobbering and imidization according to a conventional process, wherein the component A is polyamide acid resin solutions obtained after 2-(4-aminophenyl)-5-amido-benzimidazole reacts with pyromellitic dianhydride (PMDA) or biphenyltetracarboxylic acid dianhydride (BPDA); the component B is polyamide acid resin solutions obtained after p-phenylenediamine (PDA) reacts with the PMDA; and the component C is polyamide acid resin solutions obtained after 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether (ODA) reacts with the BPDA and the PMDA. The polyimide film provided by the invention has the advantages of lower thermal shrinkage rate, lower thermal expansion coefficient, higher elastic modulus and higher tensile strength and reflects better dimensional stability. The whole preparation method is simple and is easy to operate.
Owner:GUILIN ELECTRICAL EQUIP SCI RES INST
Processable thermally stable addition polyimide for composite applications
A novel polyimide resin consisting essentially of 3,3′,4,4′-benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride (BTDA), 3,4,3′,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (BPDA), 2,2 bis (3′,4′-dicarboxy phenyl) hexafluoro propane dianhydride (6FDA), 2-(3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)-1-phenylacetylene anhydride (4-PEPA) and an aromatic diamine.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
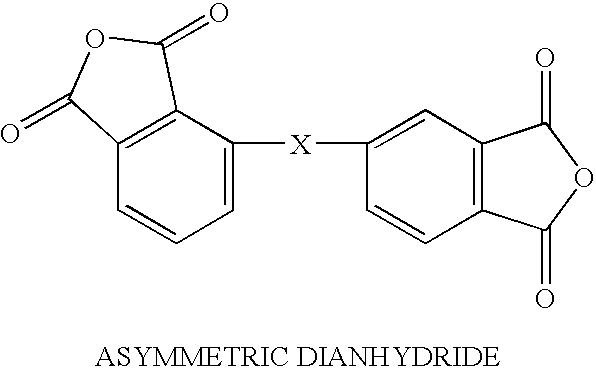
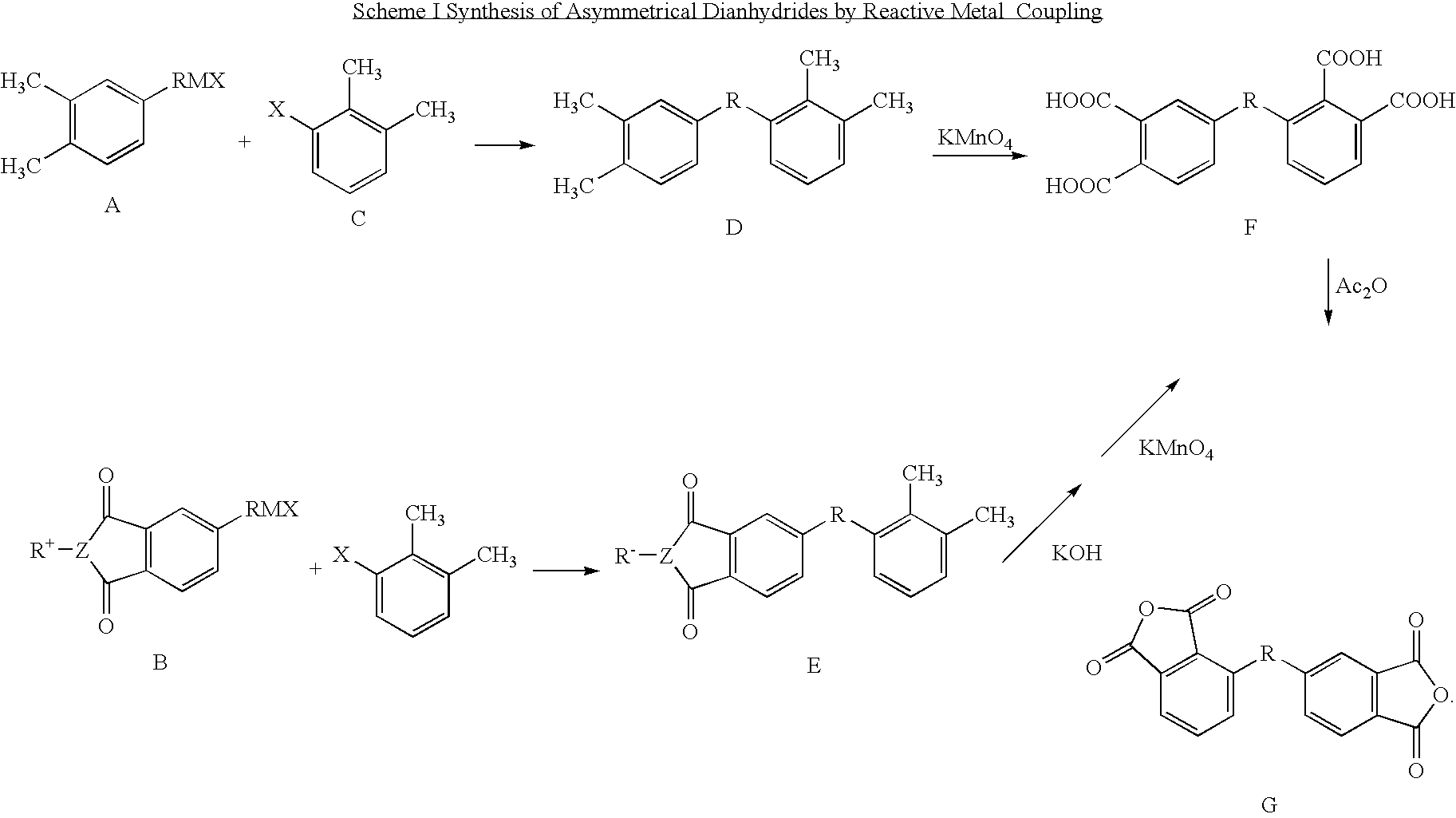
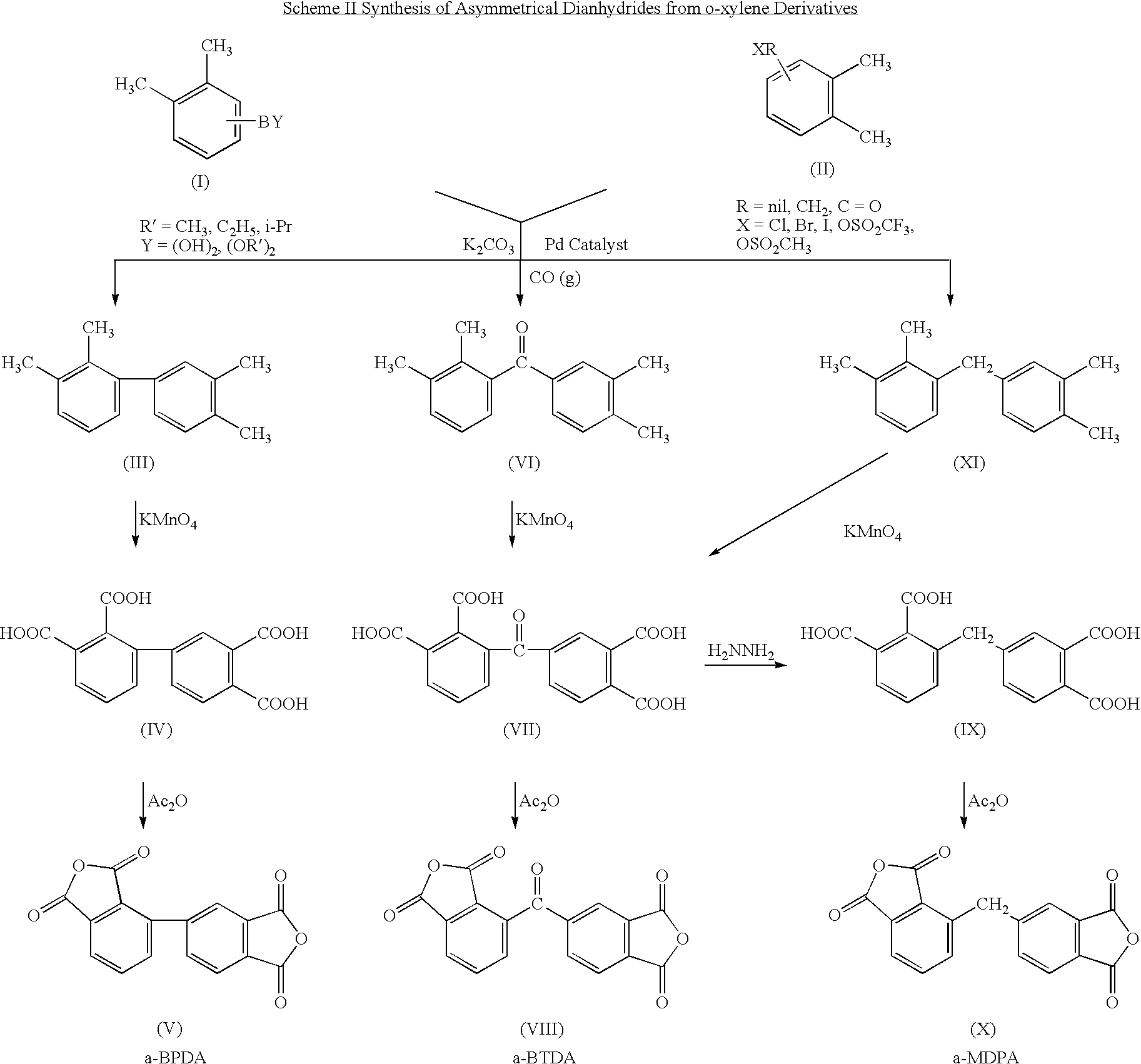
Synthesis of asymmetric tetracarboxylic acids and corresponding dianhydrides
ActiveUS7425650B1High yieldOrganic compound preparationPreparation from carboxylic acid amidesO-XyleneBPDA
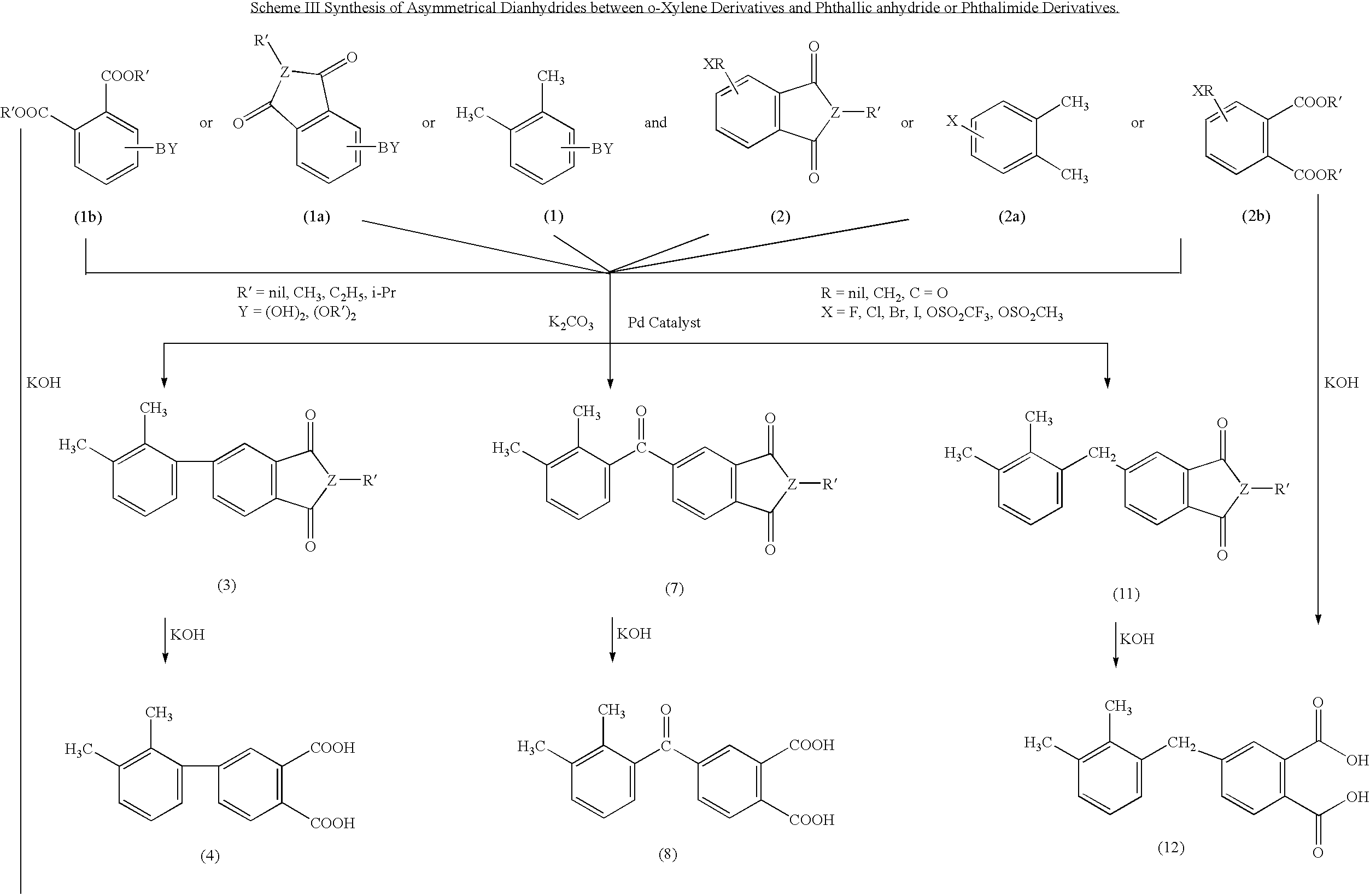
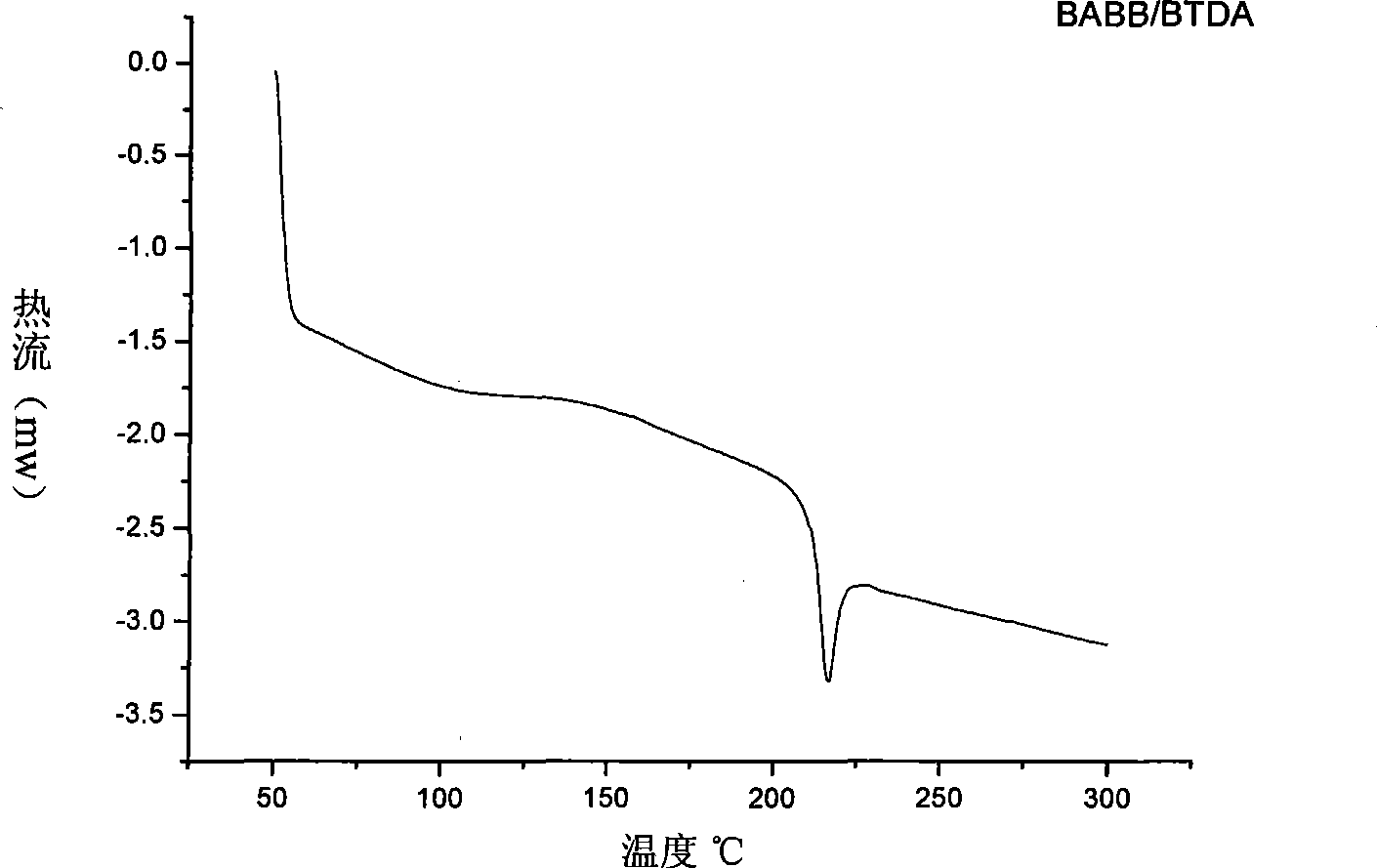
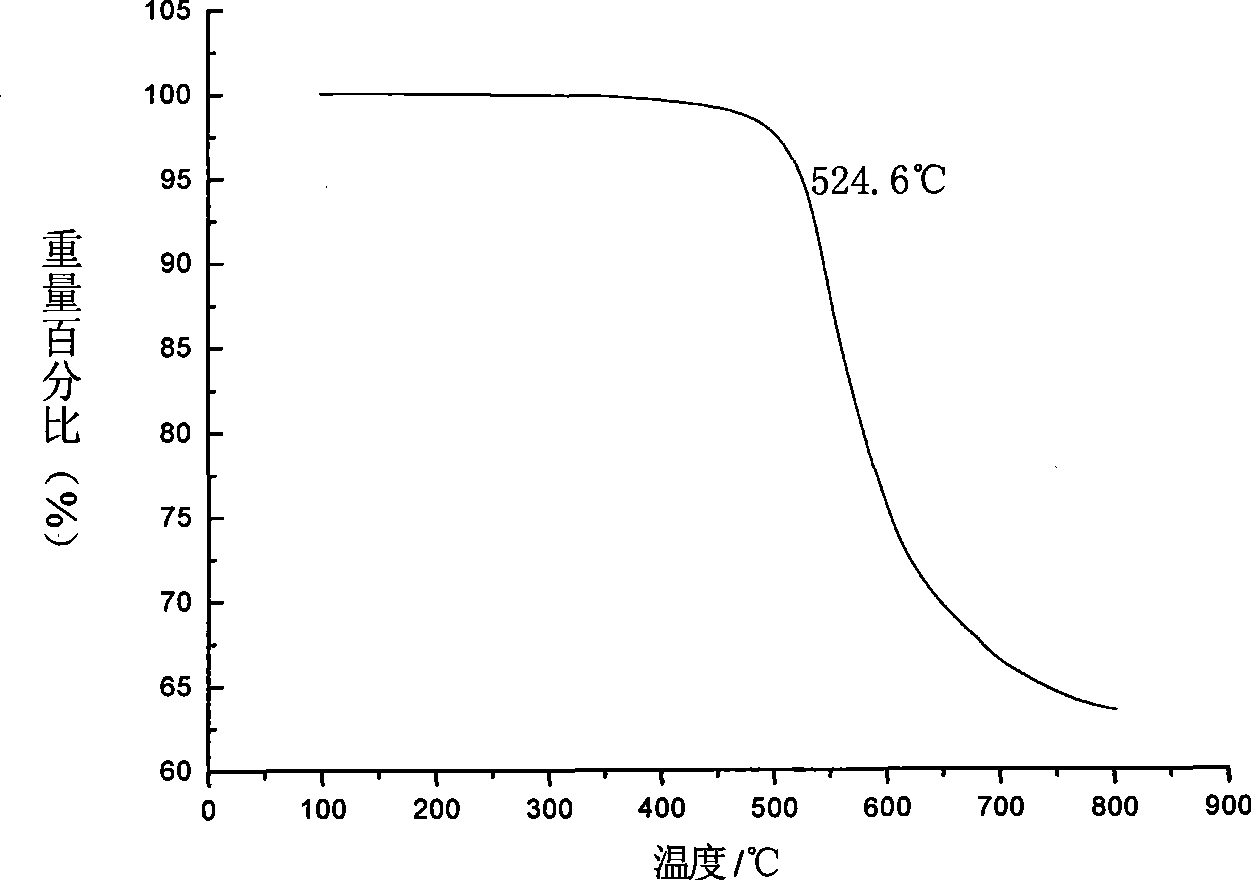
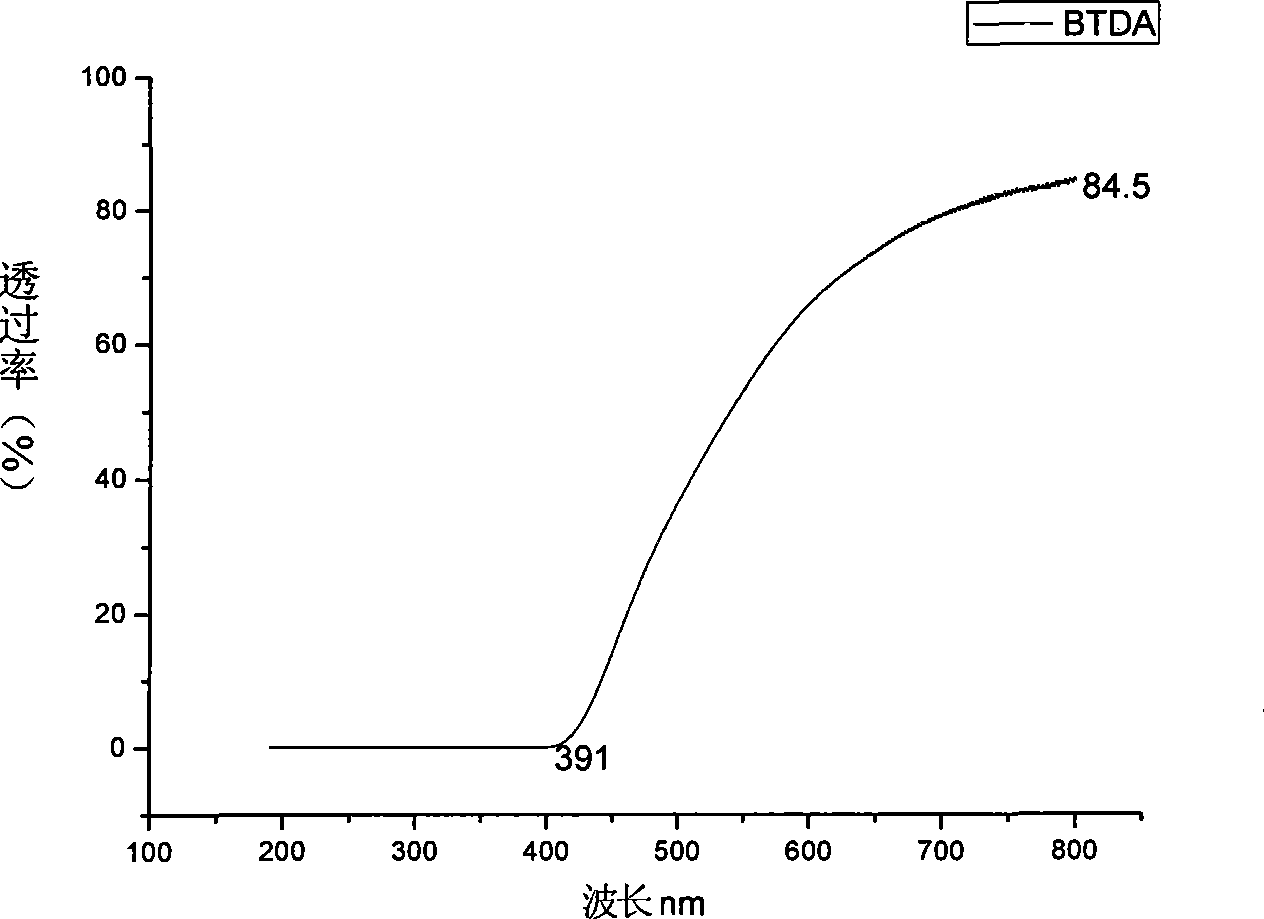
This invention relates to processes for preparing asymmetrical biphenyl tetracarboxylic acids and the corresponding asymmetrical dianhydrides, namely 2,3,3′,4′-biphenyl dianhydride (a-BPDA), 2,3,3′,4′-benzophenone dianhydride (a-BTDA) and 3,4′-methylenediphthalic anhydride (-MDPA). By cross-coupling reactions of reactive metal substituted o-xylenes or by cross-coupling o-xylene derivatives in the presence of catalysts, this invention specifically produces asymmetrical biphenyl intermediates that are subsequently oxidized or hydrolyzed and oxidized to provide asymmetric biphenyl tetracarboxylic acids in comparatively high yields. These asymmetrical biphenyl tetracarboxylic acids are subsequently converted to the corresponding asymmetrical dianhydrides without contamination by symmetrical biphenyl dianhydrides.
Owner:UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT ADMINSRATOR OF NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE
Thermoplastic poly(ether-ether-ketone) type polyimide and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of high polymer material, and in particular relates to a few kinds of polyimide with lower glass transition temperature as well as good mechanical properties, thermal stability and high UV transmittance and a method for preparing the same. The method comprises the steps of adding diamine 1,3-bis (3-amino phenoxy-4'-benzoyl) benzene, dianhydride (s-BPDA, a-BPDA, i-BPDA, BTDA, PMDA, ODPA, BPADA or 6FDA) into an organic solvent (DMF, DMAc or NMP ) to react for 2 to 24 hours in an ice-water bath at room temperature under nitrogen protection, or adding end-capping agent aniline or phthalic anhydride so as to obtain polyamic acid solution; then pouring the polyamic acid solution onto a clean glass sheet to remove the organic solvent in an oven after even scrapping; and then performing imidization on the polyamic acid solution in a vacuum oven to obtain a polyimide polymer film of no-sealed end, aniline sealed end, phthalic anhydride sealed end or dianhydride sealed end.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Thermoplastic polyimide resin powder and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses thermoplastic polyimide resin powder and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that a low-temperature polymerization reaction is performed by adopting s-BPDA, BAPP and 2-(4-aminophenyl)-5-aminobenzimidazole as raw materials under protection of nitrogen in non-proton organic solvent to prepare a polyamic acid solution; organic solvent capable of co-boiling with water and the non-proton organic solvent are added, and a high-temperature polymerization dehydration reaction is performed under the refluxing temperature condition to prepare a polyamide acid-polyimide mixed solution; imidization is performed to obtain the thermoplastic polyimide resin powder. The glass-transition temperature of the finally obtained thermoplastic polyimide resin powder can reach about 330 DEG C and can reach about 280 DEG C if the thermoplastic polyimide resin powder is used for a long term.
Owner:CHANGZHOU SUNCHEM HIGH FORMANCE POLYMER
Thermoplastic polyimide resin and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102634021AImprove thermal stabilityGood thermoplastic processabilityAdhesivesEngineering plasticBPDA
The invention discloses thermoplastic polyimide resin and a preparation method thereof. According to the thermoplastic polyimide resin, 1, 2, 3, 4--biphenyl-tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride (BPDA) is reacted with other mixed dianhydride formed by common tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride, diamine and phthalic anhydride or aniline to polymerize the mixed dianhydride with the diamine, and the phthalic anhydride or the aniline serves as a blocking agent to control molecular weight, thus obtaining the polyimide resin with good thermal stability and excellent thermoplastic processability. The inherent viscosity of the polyimide resin can reach 0.22dL / g to 0.90dL / g, and the glass-transition temperature of the polyimide resin ranges from 220 DEG C to 420 DEG C, therefore, the polyimide resin has wide application in the preparation of materials such as thermostability engineering plastics, thin films, adhesives and the like.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for preparing biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (BPDA)
The invention discloses a method for preparing biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (BPDA). The method comprises the following steps: carrying out a reaction on tetramethyl biphenyls and gases containing molecular oxygen to obtain biphenyltetracarboxylic acid by taking acetic acid as a solvent, cobalt source compounds as catalysts and a bromine source compound as a promoter; and then carrying out dehydration on biphenyltetracarboxylic acid to obtain BPDA. Under the catalytic actions of the cobalt source compounds and the bromine source compound, the gases containing molecular oxygen are used as oxidants, tetramethyl biphenyls and the gases containing molecular oxygen are subjected to an oxidation reaction and BPDA is obtained after dehydration. Compared with the prior art, the method has the following beneficial effects: the gases containing molecular oxygen are used as oxidants; the oxidants have low cost and are environmentally-friendly; therefore the environment is protected while the cost is lowered; and the experimental results show that BPDA is obtained by the preparation method.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Europium-terbium co-doped luminescent material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106497549AAvoid errorsImprove anti-interference abilityFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsIon exchangeRare earth
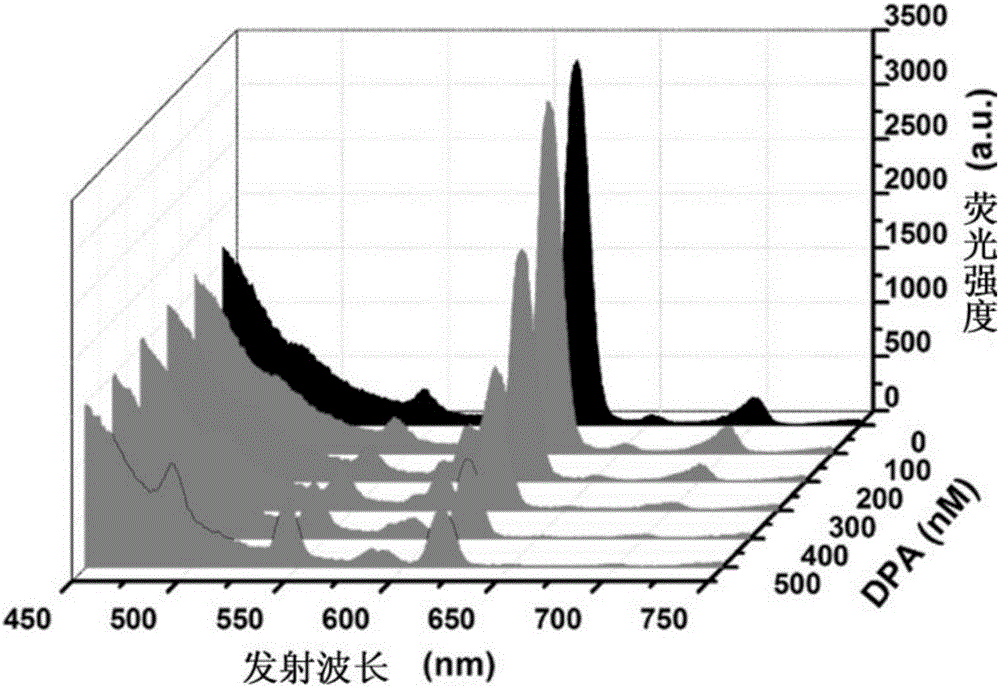
The invention provides a europium-terbium co-doped luminescent material. The material comprises one or more of the chemical compound as shown in the formula I, hydrates of the chemical compound as shown in the formula I and solvated compounds of the chemical compound as shown in the formula I, and the formula I is shown as Zn8 (Adenine)4(BPDA)6O EuxTb1-x I, wherein x is greater than 0.1 and less than 0.25, Adenine refers to adenine, and BPDA refers to 4,4'-biphenyldicarboxylic acid. Metal-organic frameworks with a porous structure serve as carriers, and the europium-terbium co-doped luminescent porous material is obtained through ion exchange with europium terbium rare earth. The co-doped luminescent porous material can efficiently transfer energy from terbium to europium, so that the material has changes of ratio fluorescence to a bacillus anthraci biomarker, and reduces possible measuring errors caused by changes of single fluorescence intensity. Moreover, the co-doped luminescent porous material can further concentrate molecules of the bacillus anthraci biomarker in the environment, and improve the detection limit of the bacillus anthraci biomarker.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of superhydrophobic super-lipophilic nanofiber membrane based on layer-by-layer self-assembly technology for oil-water mixture separation
InactiveCN108771977AHas superhydrophobic wettabilityEasy to separateMembranesSemi-permeable membranesPhytic acidSynthetic Polymeric Macromolecules
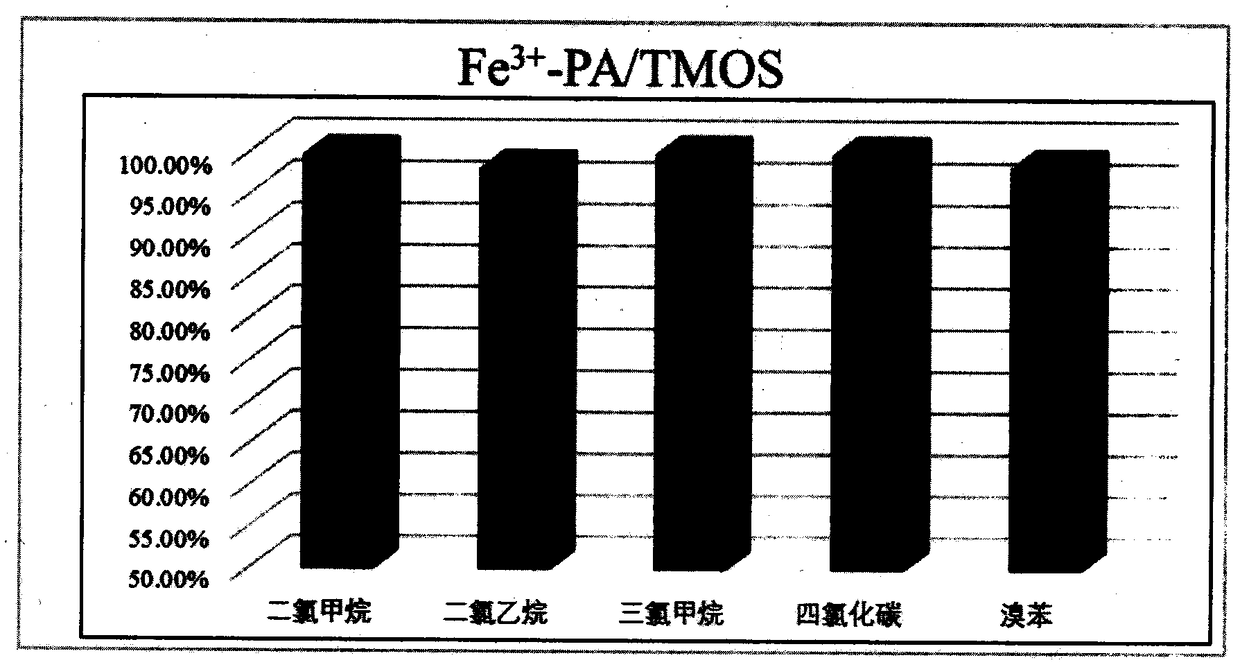
The invention discloses a preparation method of superhydrophobic oil-water separation membrane. The membrane has excellent oil-water separation effect, and can quickly separate oil-water mixture, andhas no pollution to the environment and good tolerance, and can be recycled. Polydiformyl biphthalate p-phenylenediamine (BPPAA) can be obtained by reacting biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (BPDA)and p-phenylenediamine (PDA) as monomers at -5 DEG C for 12 hours. The polymer is a precursor for synthesizing high molecular weight polyimide (PI), and a PAA nanofiber membrane is prepared by an electrospinning technique and imidized at 300 DEG C to form a PI membrane. The layer-by-layer self-assembly of the PI membrane is performed by using ferric chloride (FeCI3) and phytic acid (PA) for initially modifying the PI membrane, and then trimethoxyoctadecylsilane (TMOS) is used for the modification of the membrane to obtain the core material. Various analytical testing methods are used for characterizing the material, and the efficacy of the super-hydrophobic oil-water separation membrane can be verified.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Preparation method of thin electronic polyimide film
The invention discloses a preparation method of a thin electronic polyimide film. The method comprises the following specific steps of 1) performing methyl esterification on 3,4'-BPDA and 4-PEPA to prepare white and yellowish esterification powder (PDE and PEPE), adding BPDE, PEPE and diamine to a solvent at a certain ratio, and performing heating and reflux stirring for 2h to obtain a red-brown synthetic polyamide acid solution, 2) performing filtration, vacuum defoamation, cast film forming, two-way stretch, high-temperature thermoforming treatment, corona treatment and reeling on the synthetic polyamide acid solution to prepare the electronic polyimide film with excellent physical and mechanical properties, and 3) allowing a surface organification modified superfine inorganic crystal whisker and / or a nano particle material and multi-polyamide acid to form in-situ micro-nano compounding to imidize the polyimide film by virtue of crushing and cavitation of high-energy density ultrasonic.
Owner:刘庆祝
Preparation method of polyimide aerogel adsorption material
InactiveCN109867785ALarge specific surface areaHigh porosityProductsReagentsSupercritical dryingCross-link
The invention belongs to a preparation method of a polyimide aerogel adsorption material. A sol-gel method is adopted, and a mixed diamine component of conventional polyimide aerogel is changed. Aromatic oxydianiline (ODA) and aliphatic 1,3-propane diamine are used as mixed diamine, 3,3',4,4'-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (BPDA) is used as a dianhydride, 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenoxy)benzene (TAB) is used as a cross-linking agent, acetic anhydride and pyridine are used as imidization reagents, and polyimide hydrogel is synthesized at normal temperature; replacing and aging is carried out onthe solution, and then CO2 supercritical drying is carried out to obtain the complete block-shaped polyimide aerogel. The polyimide aerogel prepared by the method has relatively low heat conductivityand good mechanical properties, and meanwhile, a flexible structure is obtained. Experiments prove that the polyimide aerogel can be used for adsorbing CO2. The density of the polyimide aerogel adsorption material is 0.08-0.11 g / cm<3>, the compression modulus is 2.03-3.26 MPa, and the CO2 adsorption amount is 8.2-11.5 cm<3> / g.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
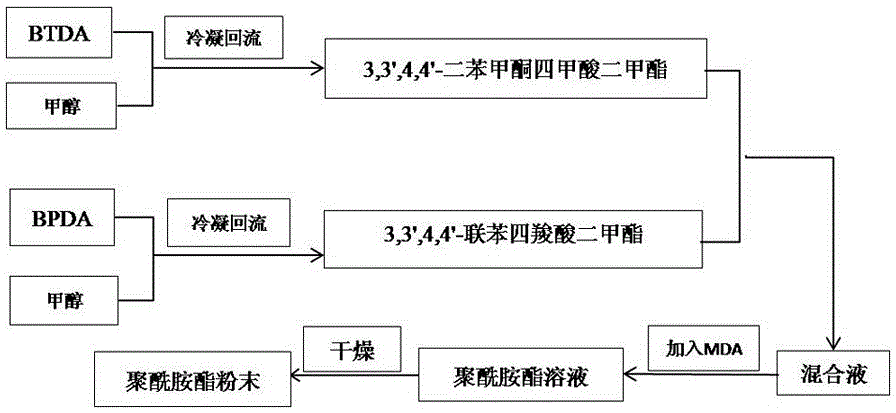
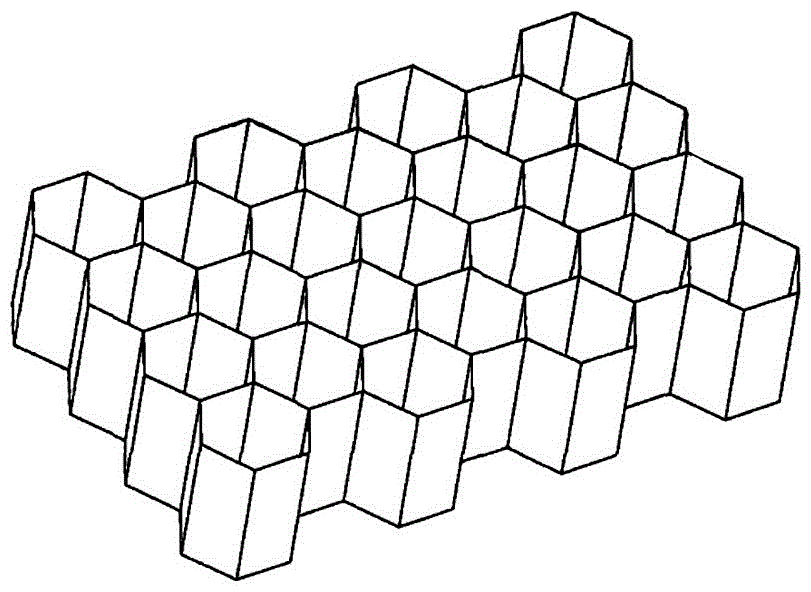
Carbon fiber honeycomb reinforced polyimide foam material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a carbon fiber honeycomb reinforced polyimide foam material and a preparation method thereof. The foam material is obtained through a reaction of polyimide prepolymer powder and a carbon fiber honeycomb material. A preparation method of the polyimide prepolymer powder comprises the steps that BTDA and methyl alcohol are reacted for 1.5-2.5 h in a backflow state to prepare a 3,3',4,4'-benzophenone tetramethyl acid dimethyl ester solution, BPDA and methyl alcohol are reacted for 10-11 h in a backflow state to obtain a 3,3',4,4'-biphenyl tetracarboxylic acid dimethyl ester solution, the obtained 3,3',4,4'-benzophenone tetramethyl acid dimethyl ester solution and the obtained 3,3',4,4'-biphenyl tetracarboxylic acid dimethyl ester solution are mixed, MDA is added into the mixture, stirring is performed at room temperature for 0.5-1 h, a foam stabilizer is added, stirring continues to be performed for 0.5-3 h, a polyimide prepolymer solution is prepared, and the polyimide prepolymer solution is dried to obtain the polyimide prepolymer powder, wherein the mole ratio of the BTDA to the BPDA is (6-8):(2-4). The carbon fiber honeycomb reinforced polyimide foam material has uniform foam holes and quite high mechanical property and is low in production cost.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
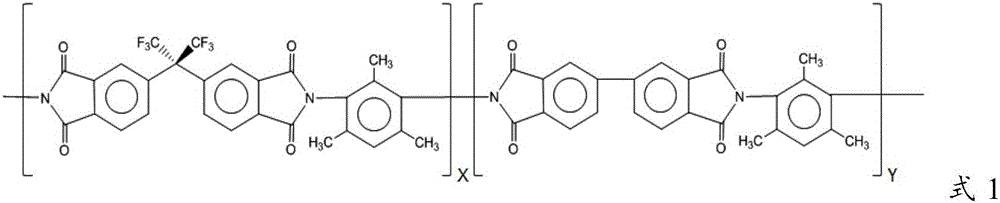
Polyamic acid, polyimide resin and polyimide film
The present invention relates to a poliamic acid which is a polymerization reaction product of diamine and dianhydride, wherein the diamine comprises 9,9-bis(3-fluoro-4-aminophenyl)fluororene (FFDA), and the dianhydride comprises 2-bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)hexafluoropropane dianhydride (6FDA) and 3,3',4,4'-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (BPDA) and, more particularly, to a polyamide resin which is an imide thereof, and a polyamide film.
Owner:KOLON IND INC
Polyamic acid solution, polyimide resin and flexible metal clad laminate using the same
ActiveUS20120085570A1High bonding strengthPrinted circuit aspectsSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceBPDA
Disclosed are a polyamic acid solution, a polyimide resin prepared by imidization of the polyamic acid solution, a flexible metal clad laminate using the polyimide resin, and a printed circuit board including the flexible metal clad laminate, wherein the polyamic acid solution includes (a) 3,3′,4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic acid dianhydride (BPDA), and pyromellitic dianhydride (PMDA) as aromatic tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride; (b) at least one aromatic diamine; (c) an organic solvent; and (d) an inorganic filler.
Owner:DOOSAN CORP
Organic-solvent-soluble polyimide comprising PMDA, DADE, BPDA, and BCD
Disclosed is an organic-solvent-soluble, heat-resistant polyimide that comprises (a) a pyromellitic dianhydride (PMDA), (b) a biphenyl tetracarboxylic dianhydride (BPDA), (c) a bicyclooctene tetracarboxylic dianhydride (BCD), and (d) a diaminodiphenyl ether (DADE) as components. The organic-solvent-soluble, heat-resistant polyimide has a thermal decomposition initiation temperature in the range of 530 DEG C to 570 DEG C and is synthesized by means of a three-step hydrogenation reaction: in the first step, a low molecular weight imide compound is generated by the reaction of an acid dianhydride and an aromatic diamine; in the second step, a low molecular weight imide compound is generated by further reacting an acid dianhydride and an aromatic diamine with the low molecular weight imide compound generated in the first step; and in the third step, a polycondensation reaction is performed.
Owner:SOLPIT IND
Polyamide-imide precursor, polyamide-imide film and display device comprising same
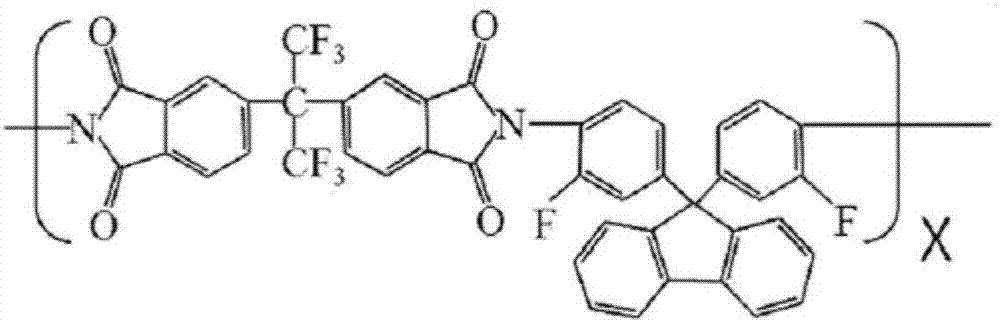
This invention relates to a polyamide-imide precursor, a polyamide-imide obtained by imidizing the same, a polyamide-imide film, and an image display device including the film. The polyamide-imide precursor includes, in a molecular structure thereof, a first block, obtained by copolymerizing monomers including dianhydride and diamine, and a second block, obtained by copolymerizing monomers including an aromatic dicarbonyl compound and aromatic diamine. The dianhydride includes biphenyltetracarboxylic acid dianhydride (BPDA) and 2-bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)hexafluoropropane dianhydride (6FDA), and the diamine includes bistrifluoromethylbenzidine (TFDB).
Owner:KOLON IND INC
Polyimide film, copper-clad laminate, and circuit substrate
PendingCN109789689ALow moisture absorptionLow Dielectric TangentSynthetic resin layered productsElectrical equipmentPolymer scienceBPDA
Provided is a polyimide film having a non-thermoplastic polyimide layer, wherein: the non-thermoplastic polyimide constituting the non-thermoplastic polyimide layer preferably contains at least one ofa biphenyl-tetracarboxylic dianhydride (BPDA) residue derived from 3,3',4,4'-BPDA and a phenylenebis(trimellitic monoester) dianhydride (TAHQ) residue derived from 1,4-TAHQ, as well as at least one of a pyromellitic dianhydride (PMDA) residue derived from PMDA and a napthalenetetracarboxylic dianhydride (NTCDA) residue derived from 2,3,6,7-NTCDA, the total amount of these residues being at least80 mol parts with respect to 100 mol parts of a tetracarboxylic acid residue; and the dielectric loss tangent (Df) is preferably 0.004 or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CHEMICALL &MATERIAL CO LTD
Sulfonate functionalized covalent organic polymer solid-phase extraction column
InactiveCN110302560AIncreased extraction mode of actionGood choiceSolid sorbent liquid separationSulfanilic acidSulfonate
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Thermoplastic PI (polyimide) hot melt adhesive film and preparation method thereof
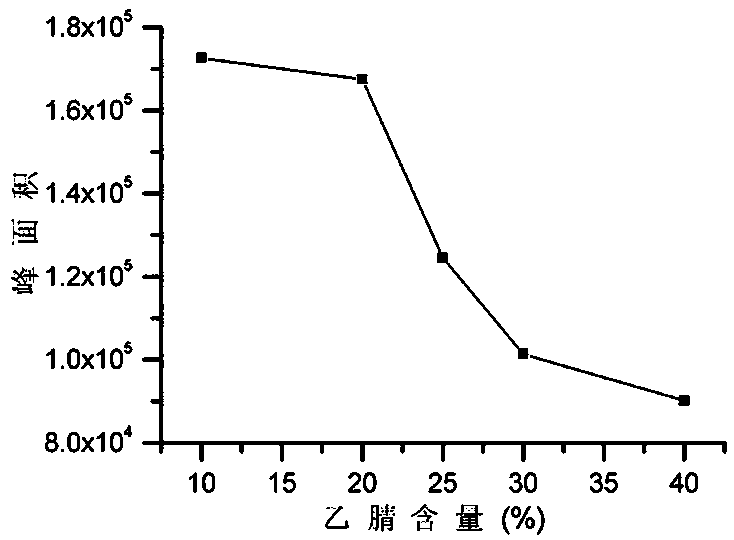
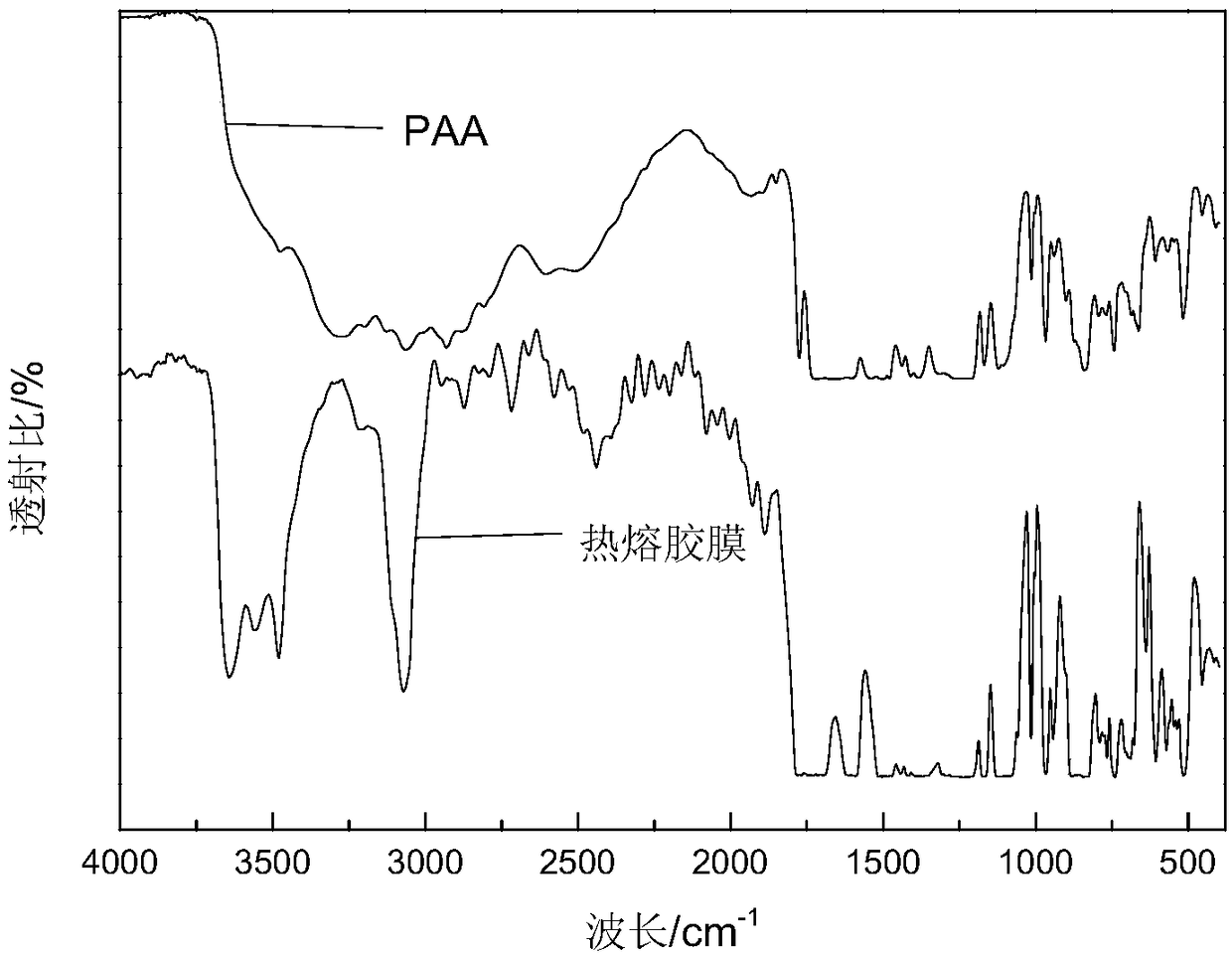
The invention discloses a thermoplastic PI (polyimide) hot melt adhesive film and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises following steps: ODA (4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether), TPER(1,3-Bis(4-aminophenoxyl)benzene), alpha-BPDA (2,3,3',4'-biphenyl tetracarboxylic dianhydride) and BPDA (3,3',4,4'-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride) are taken as raw materials, and a PAA (polyamide acid) solution is prepared from the raw materials through a low-temperature polymerization reaction in a non-protic organic solvent under protection of N2; a dry and clean glass board is smeared with the prepared PAA solution, and after solvent evaporation and thermal imidization, the thermoplastic PI hot melt adhesive film is obtained. The water absorption rate of the film is lower than 1%, thefilm has excellent high-temperature resistance and can be bonded with copper foil effectively without glue, peel strength is as high as 1.3 N / mm, and accordingly, the film can be applied to fields ofa high-temperature binder, a high-temperature resistant material and a multi-layer copper-clad plate.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
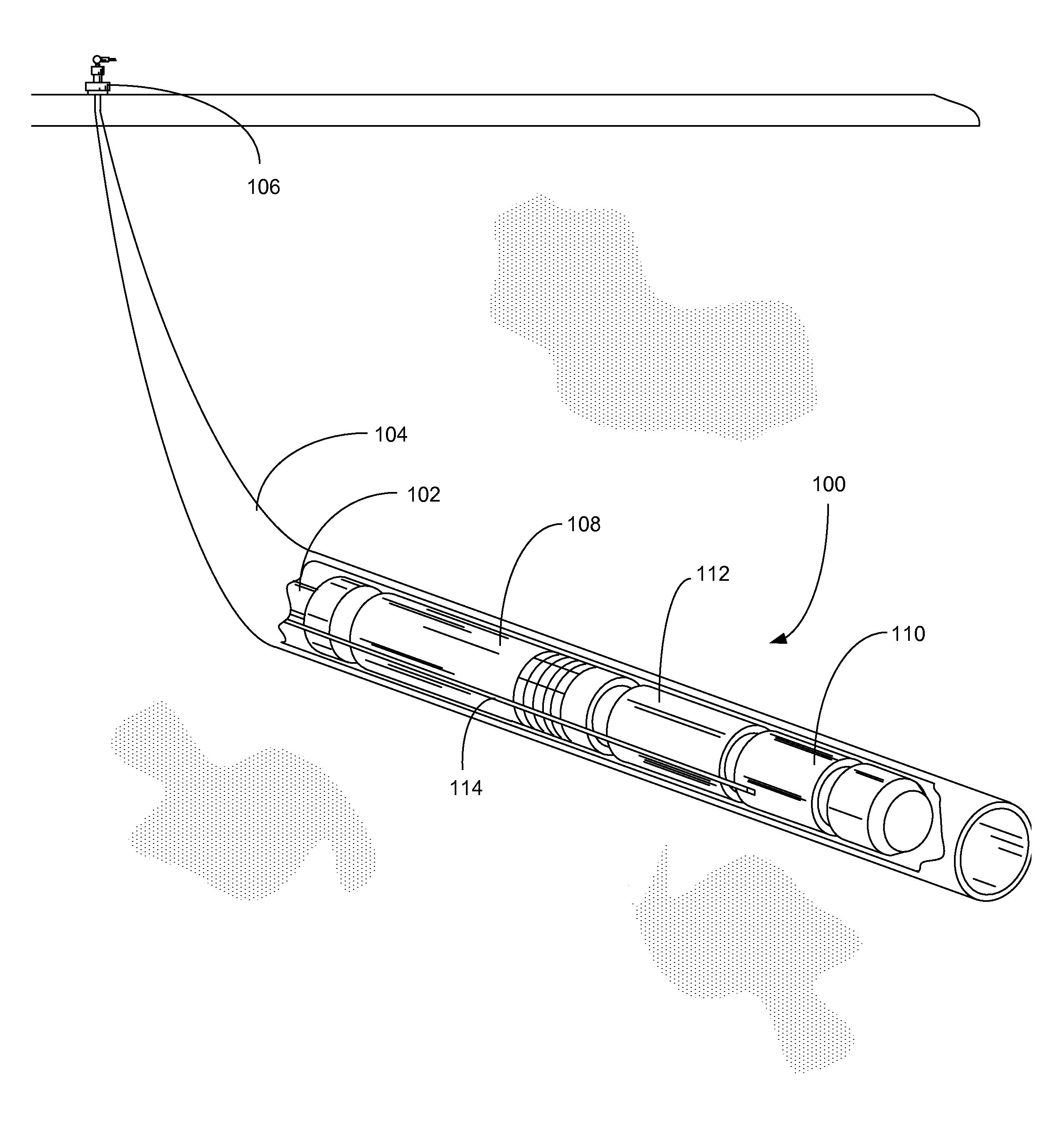
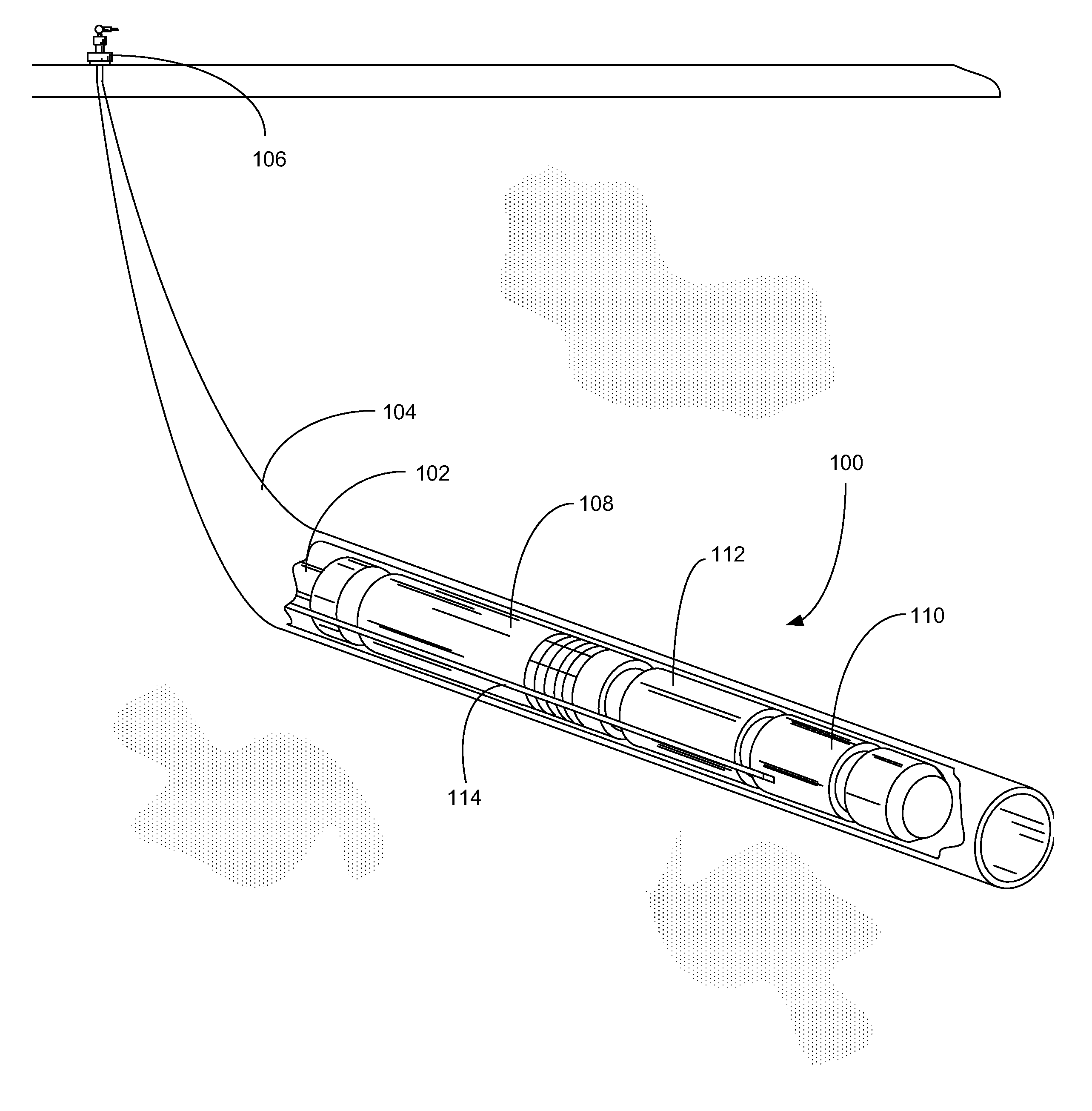
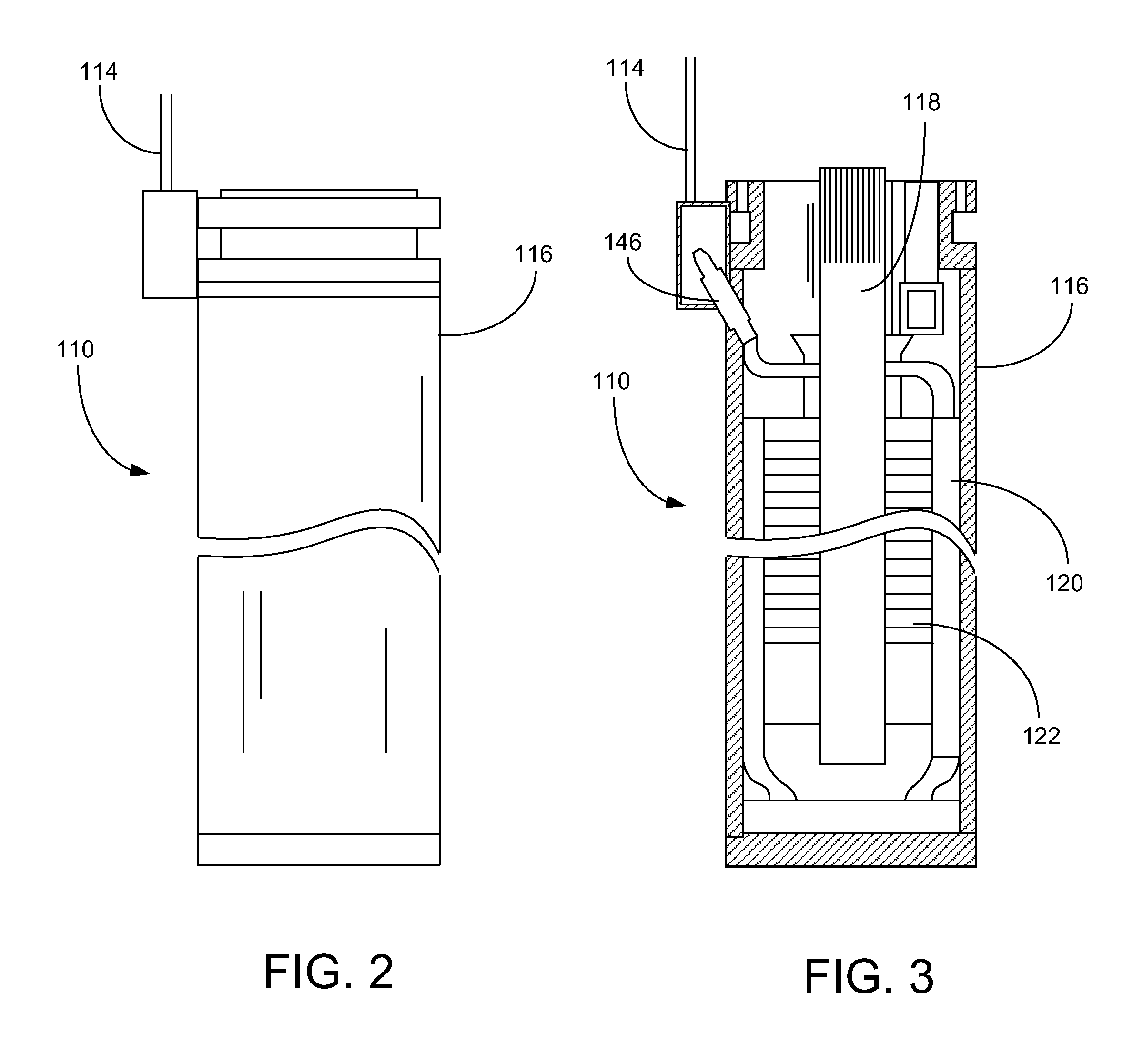
High temperature downhole motors with advanced polyimide insulation materials
InactiveUS20140152155A1Windings insulation materialWindings insulation shape/form/constructionBPDAStator coil
An electric motor assembly configured for use in a downhole pumping system includes a number of electrically conductive components that are insulated from fluids, mechanical abrasion, electrical current and electrical grounds using an advanced polyimide film. Preferred polyimide films include poly(4,4′-oxydiphenylene-pyromellitimide) and biphenyl-tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride (BPDA) type polyimide films. Magnet wire, stator laminates, stator coil end turns, motor leads and power cables can all be insulated with the selected polyimide film.
Owner:GE OIL & GAS ESP
Biphenyltetracarboxylic acid dianhydride, method for producing the same, polyimide using the same and method for producing the same
A process for producing BPDA by which high productivity is attained while maintaining a high purity. The process for biphenyltetracarboxylic acid dianhydride production comprises heating biphenyltetracarboxylic acid to produce biphenyltetracarboxylic acid dianhydride, wherein the heat treatment is conducted at a pressure of 1*102-1.1*105 Pa to a maximum temperature in the range of 210-250 DEG C in such a manner that at least 1 / 4 the period used for heating from 60 DEG C to 210 DEG C has a heating rate of 50 DEG C / Hr or higher and that the acid is held at 150-250 DEG C for 0.5-10 hours.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Process for production of polyimide film, and polyamic acid solution composition
ActiveCN101802059AHigh tensile strengthIncrease elasticityCoatingsN-ethyl-2-pyrrolidone2-Pyrrolidone
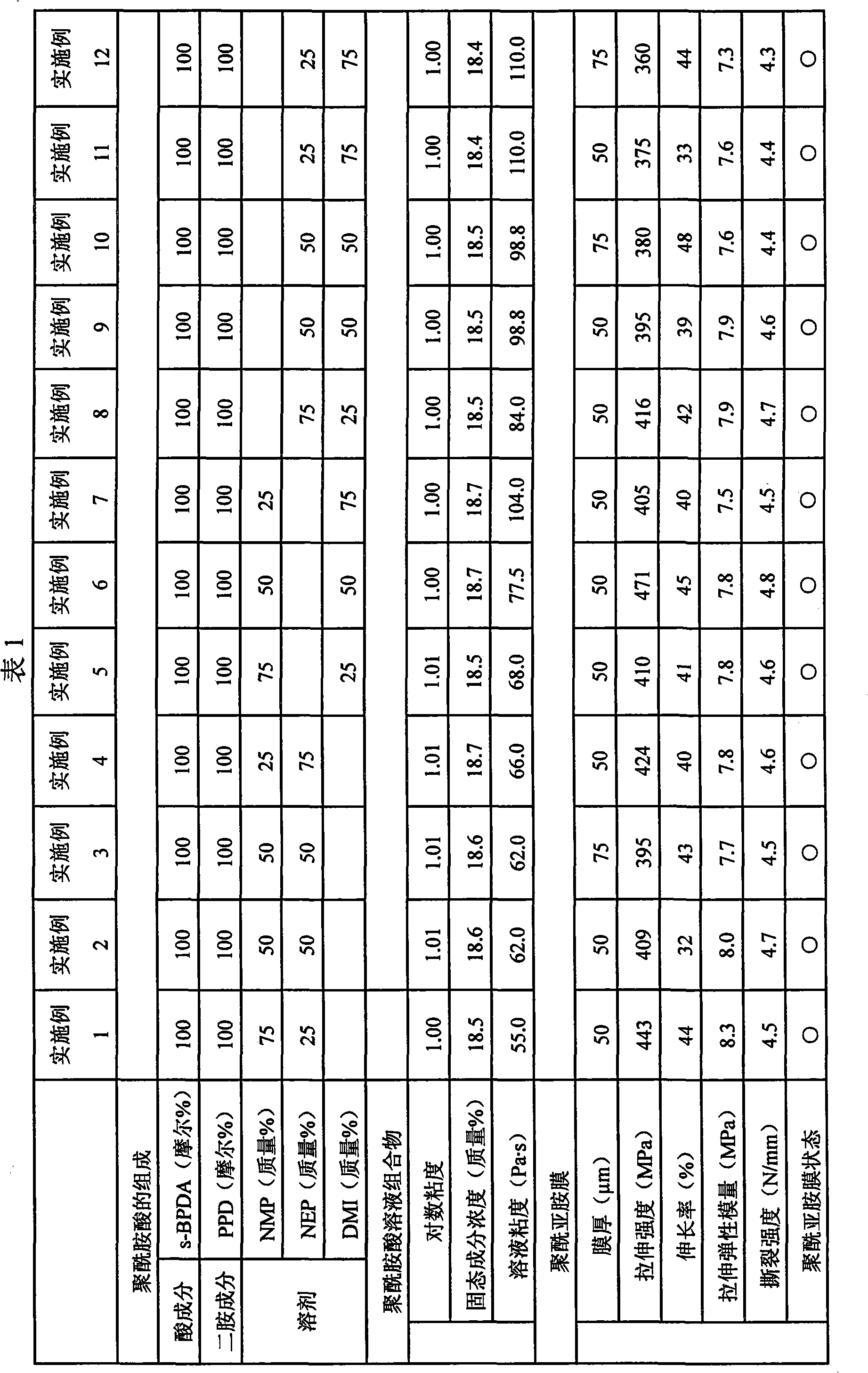
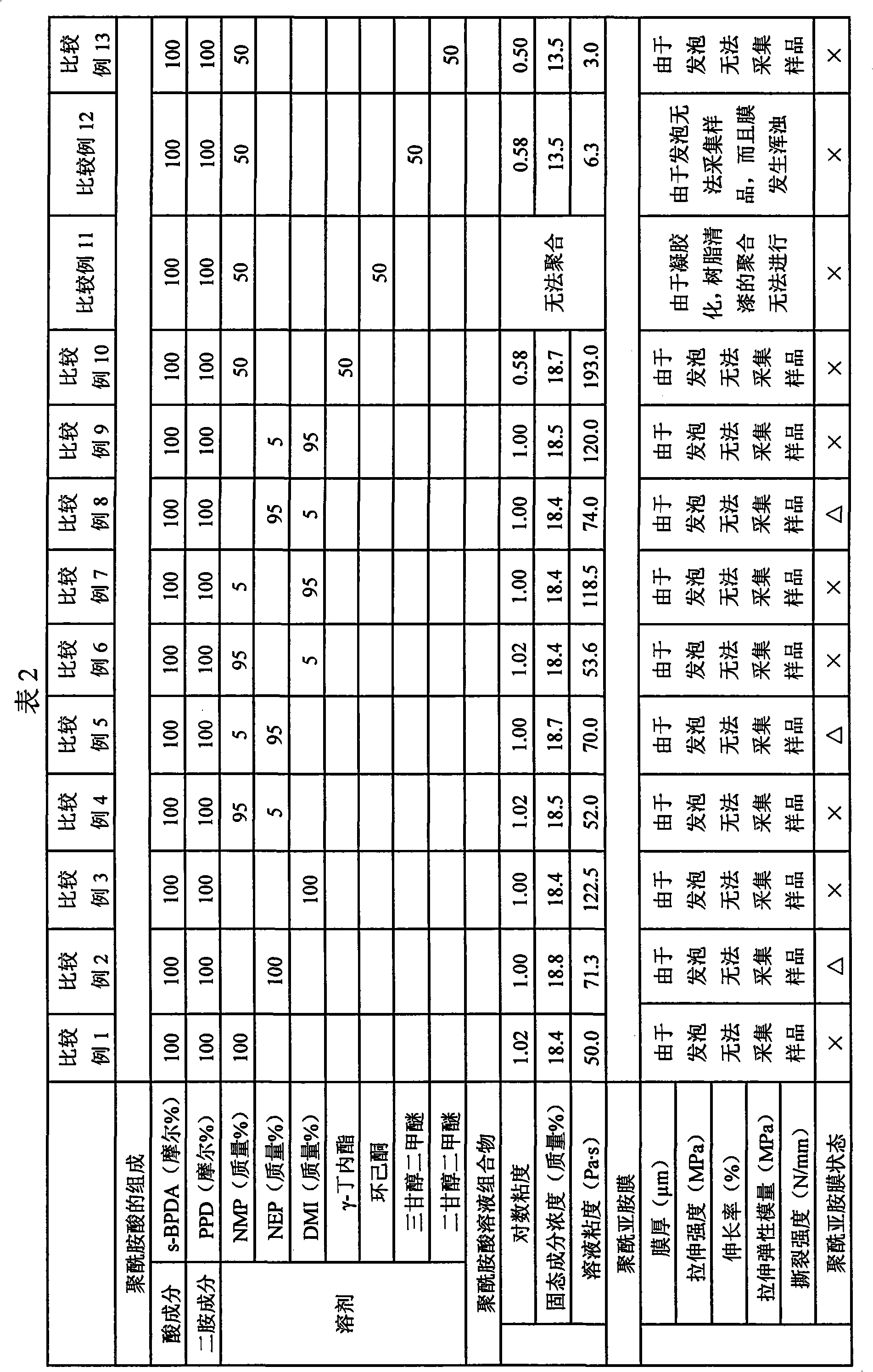
Disclosed is a process for producing a polyimide film, which comprises applying a polyamic acid solution composition to a base material to form a coating film, and subsequently heating the coating film, wherein the polyamic acid solution composition comprises a mixed solvent of two or more solvents selected from N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, N-ethyl-2-pyrrolidone and 1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone (wherein each of the solvents is contained in an amount of 7 to 93 mass% relative to 100 mass% of the total amount of the solvents) and a polyamic acid mainly composed of s-BPDA and PPD. The process enables to produce a polyimide film having a film thickness of more than 40 [mu]m without the need of expanding the film.
Owner:UBE IND LTD
Tailorable polyimide prepolymer blends, crosslinked, polyimides, and articles formed therefrom
A tailorable polyimide prepolymer blend including a diamine component including 1,3-phenylenediamine (mPDA), Bisaniline M, and 1,4-phenylenediamine (pPDA), a dianhydride component including 3,4,3′,4′-benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride (BTDA) and 3,4,3′,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (BPDA), and an end group component. The components may be provided as a monomeric mixture. The prepolymer blend, prior to cure, may provide at least one predetermined prepolymer blend property; and the cured prepolymer blend may provide a crosslinked polyimide matrix having at least one predetermined crosslinked matrix property. Articles formed from the tailorable polyimide prepolymer blend may include powders, neat resins, coating materials, films, adhesives, fibers, composites, laminates, prepregs and parts.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
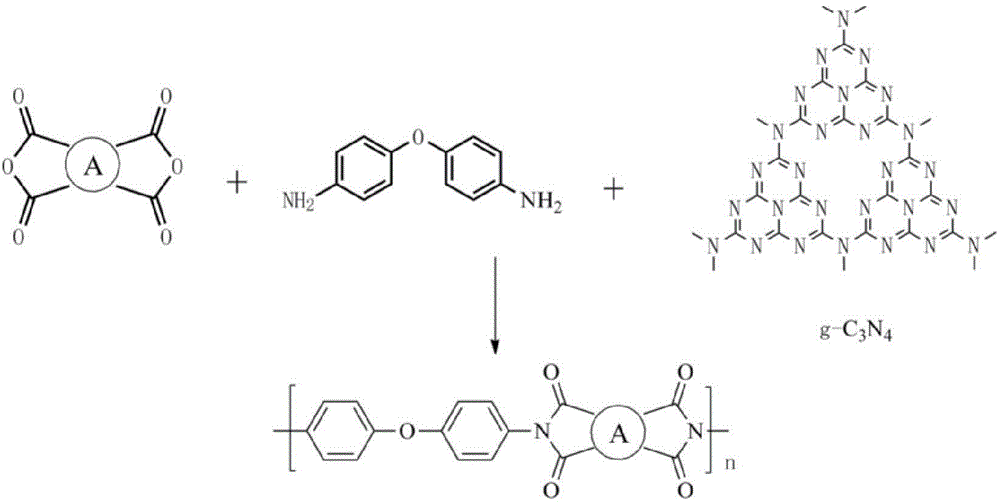
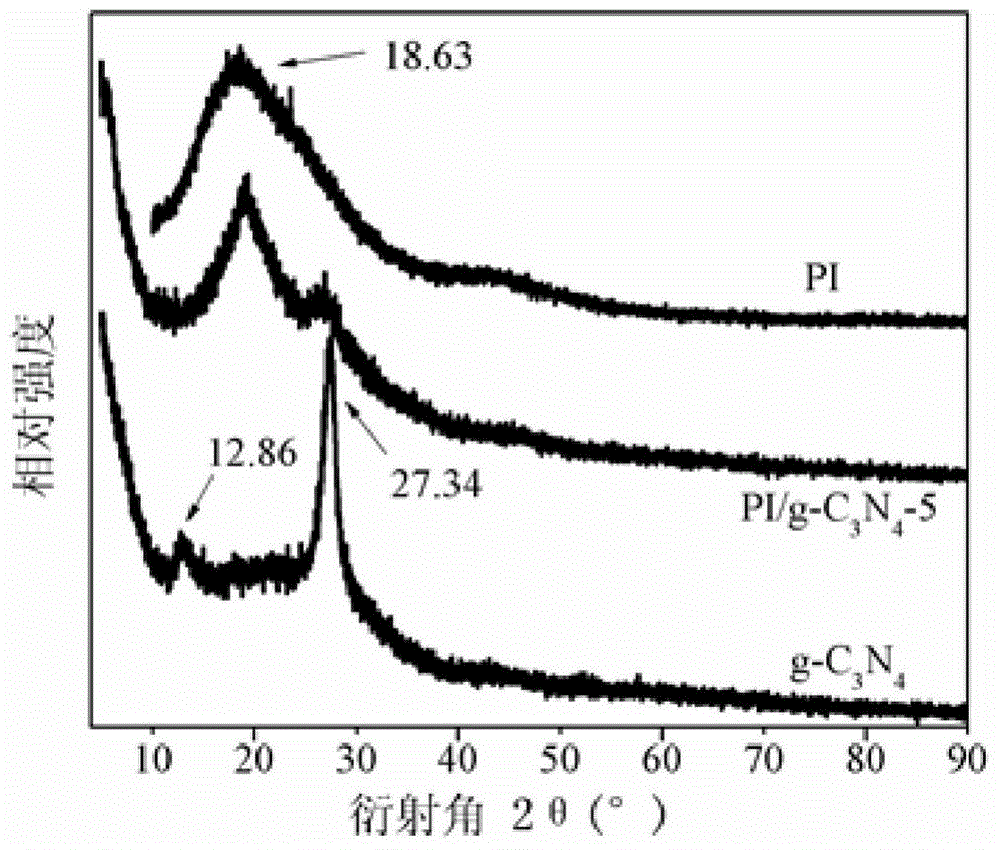
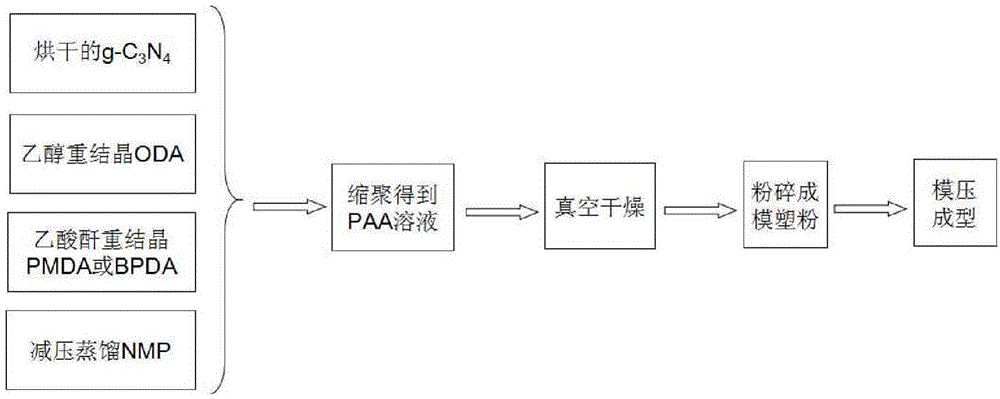
g-c3n4-doped polyimide composite material, and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN104910381AOvercome mechanical propertiesOvercoming adaptabilityGraphite carbonDiaminodiphenyl ether
The invention discloses a g-C3N4-doped polyimide composite material which is prepared by the following steps: polymerizing a diamine monomer ODA (diaminodiphenyl ether) and another dianhydride monomer PMDA (pyromellitic dianhydride) or BPDA (3,3',4,4'-biphenyl dianhydride) to form polyamic acid, wherein graphite carbon nitride (g-C3N4) is added before the polyamic acid solution formation process; and after the system is imidized, carrying out hot pressing to form the g-C3N4-doped polyimide composite material. The g-C3N4 is doped into the polyimide system under the physical action. The g-C3N4-containing polyimide film material obtained by the method has favorable thermal neutron shielding property. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the g-C3N4-doped polyimide material and application of the g-C3N4-doped polyimide material in neutron radiation shielding.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Carbon molecular sieve (cms) hollow fiber membranes and preparation thereof from pre-oxidized polyimides
Prepare a carbon molecular sieve membrane from a polyimide (e.g., a 6FDA / BPDA-DAM polyimide) that has a glass transition temperature of at least 400 DEG C and includes a bridged phenyl compound for separation of hydrogen and ethylene from one another whether present as a pure mixture of hydrogen and ethylene or as components of a cracked gas. Preparation comprises two sequential steps a) and b). In step a), place a membrane fabricated from defect-free fibers of the polyimide in contact with an oxygen-containing atmosphere under conditions of time and temperature sufficient to produce a pre-oxidized and pre-carbonized polymeric membrane that is insoluble in hot (110 DEG C) n-methylpyrolidone and at least substantially free of substructure collapse. In step b) pyrolyze the pre-oxidized and pre-carbonized membrane in the presence of a purge gas under conditions of time and temperature sufficient to yield a carbon molecular sieve membrane that has at least one of a hydrogen permeance and a hydrogen / ethylene selectivity greater than that of a carbon molecular sieve membrane prepared from the same membrane using only pyrolysis as in step b).
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
High temperature downhole motors with advanced polyimide insulation materials
InactiveUS20140154113A1Windings insulation materialWindings insulation shape/form/constructionPower cableBPDA
An electric motor assembly configured for use in a downhole pumping system includes a number of electrically conductive components that are insulated from fluids, mechanical abrasion, electrical current and electrical grounds using an advanced polyimide film. Preferred polyimide films include poly(4,4′-oxydiphenylene-pyromellitimide) and biphenyl-tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride (BPDA) type polyimide films. Magnet wire, stator laminates, stator coil end turns, motor leads and power cables can all be insulated with the selected polyimide film.
Owner:GE OIL & GAS ESP
Polyimide fiber with high strength and high modulus and its preparation method
ActiveUS20130137846A1Improve mechanical propertiesPerformance requirementArtificial filament heat treatmentMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentFiberBPDA
A high-strength high-modulus polyimide fiber and its preparation method pertain to the technical field of high-performance organic fiber. This fiber includes the polyimide (PI) fiber made from 3,3′,4,4′-biphenyl tetracarboxylic diandhydride (BPDA), p-phenylenediamine (pPDA) and 2-(4-aminophenyl)-1H-benzimidazol-5-amine (BIA), wherein the molar ratio between PPDA and BIA is 1:10˜3:1. During the synthesis, other diamine and diandhydride monomers may also be added. In the preparation process, the gradient temperature reaction method and one-step continuous preparation method are adopted, the synthesis and processing difficulty caused by the increase of the content of BIA is overcome, the problem of poor uniformity and stability of fiber is solved and PI fiber with high strength and high modulus is obtained. Its strength may reach 4.5 GPa and modulus may reach 201 GPa. Moreover, the sources of the raw materials are extensive, the spinning process is continuous, the cost is low, the efficiency is high and industrial production may be realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for improving polyimide-based carbon fiber microstructure
ActiveCN105256410AGood effectHigh carbon contentWet spinning methodsMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentChemical structurePolymer science
The invention discloses a method for improving a polyimide-based carbon fiber microstructure and belongs to the technical field of carbon fibers. The method comprises that BPDA, p-PDA and ODA monomers are synthesized into polyamic acid solutions with different molecular chain plane regularities, through a wet spinning technology and gradient heating heat amidation, polyimide fibers are prepared from the polyamic acid solutions, the polyimide fibers are fixed into a vacuum tube furnace and are heated for carbonization to a temperature of 1500 DEG C in a N2 protective atmosphere, and then the carbonization product is naturally cooled so that the polyimide-based carbon fibers are obtained. The polyimide fiber chemical structure has high plane regularity. The polyimide-based carbon fiber has a perfect microstructure. The invention provides the method for improving a polyimide-based carbon fiber structure. The prepared polyimide-based carbon fiber retains polyimide base fiber morphology characteristics, and has good compactness, less defects, high carbon content and conductive characteristics.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com