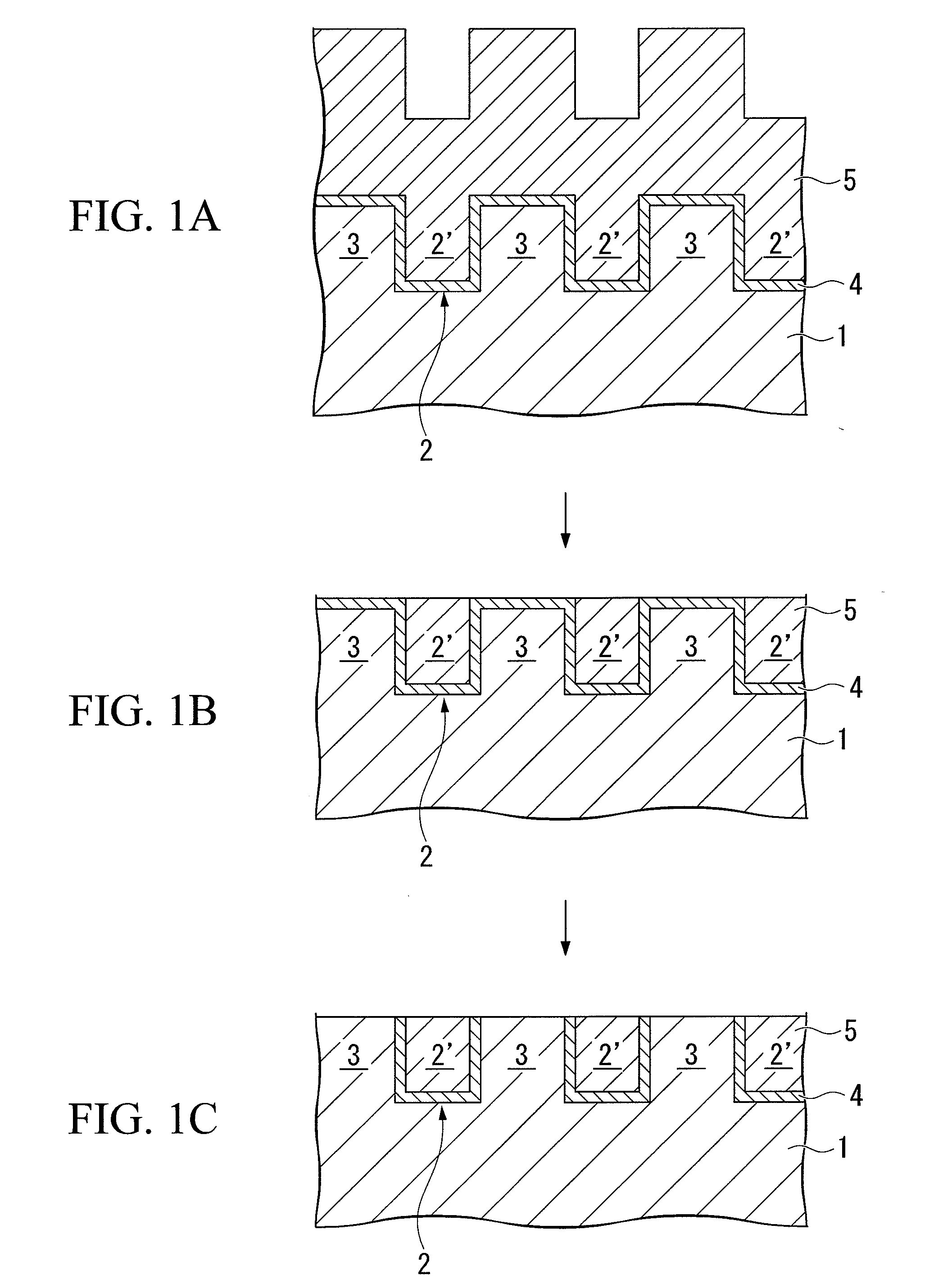
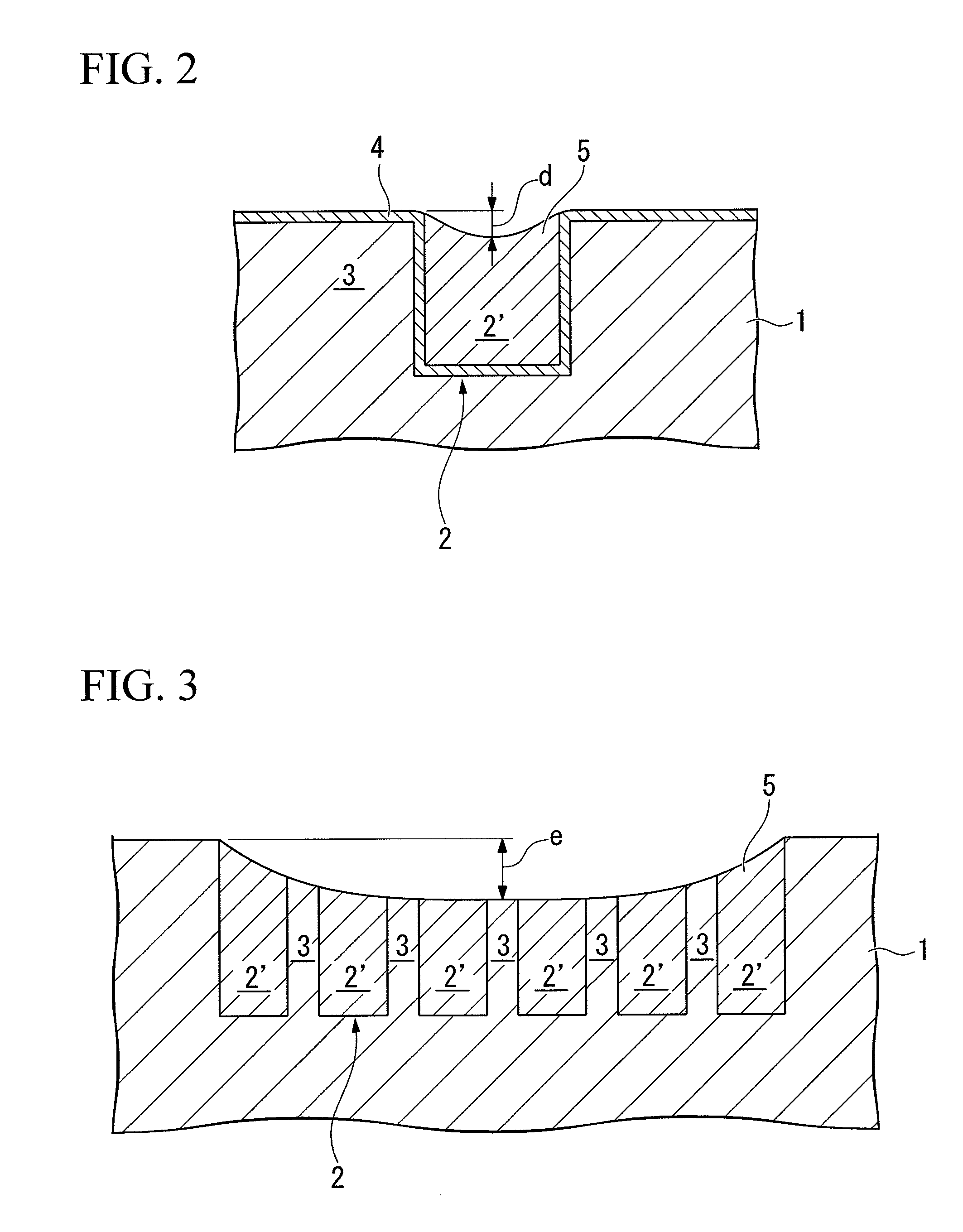
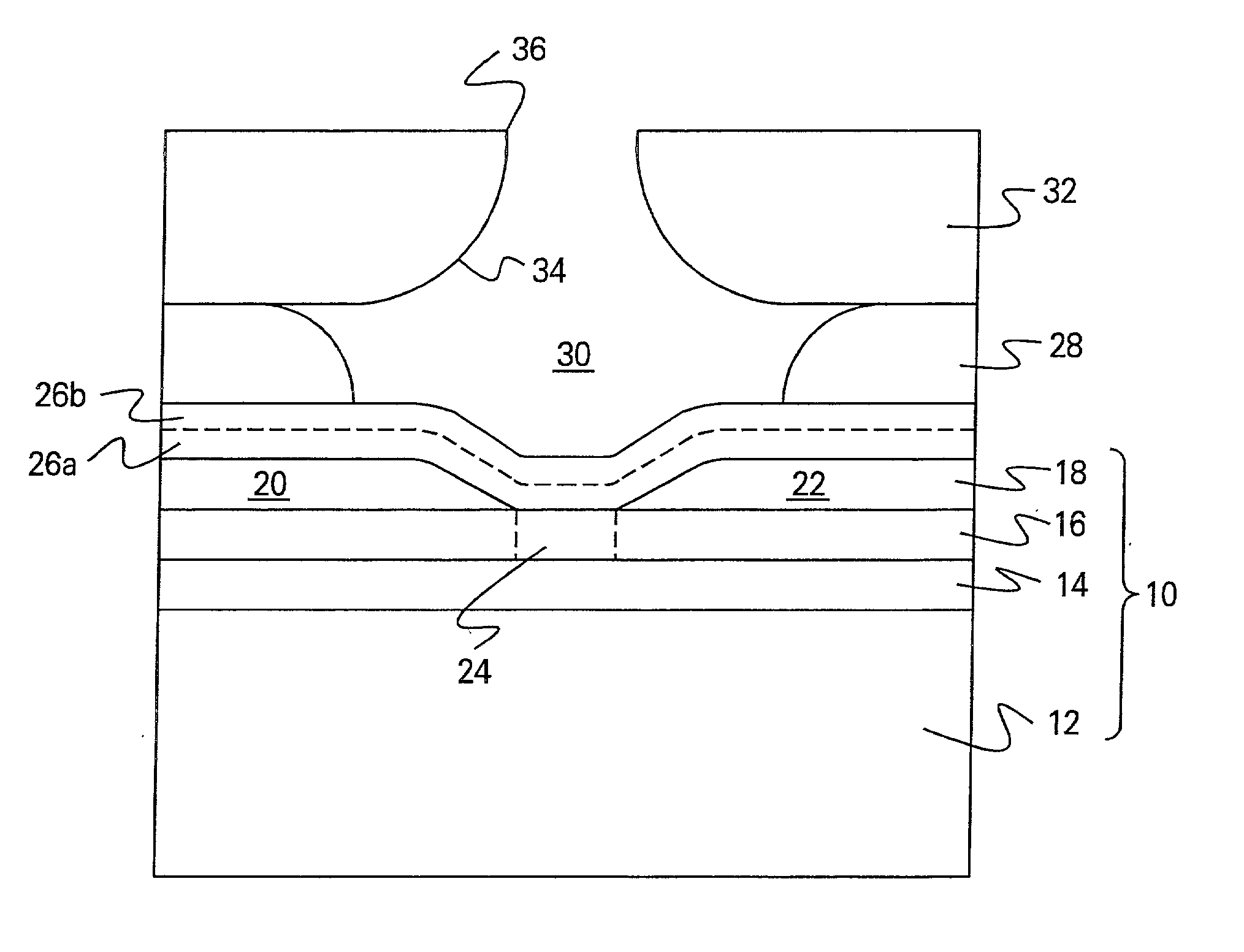
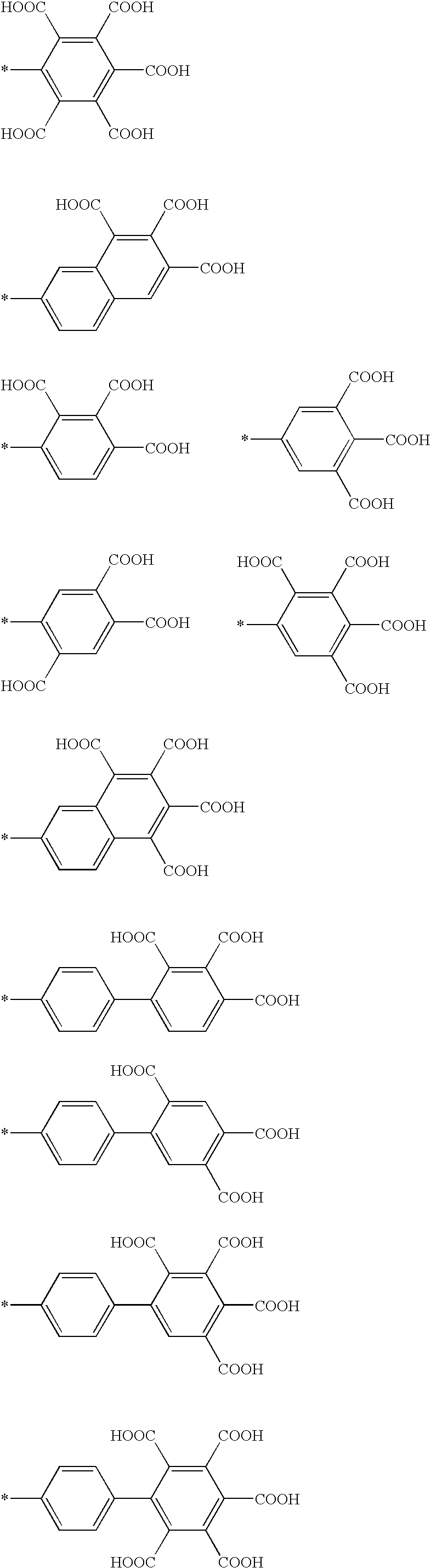
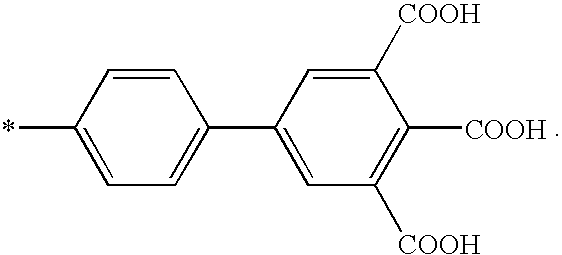
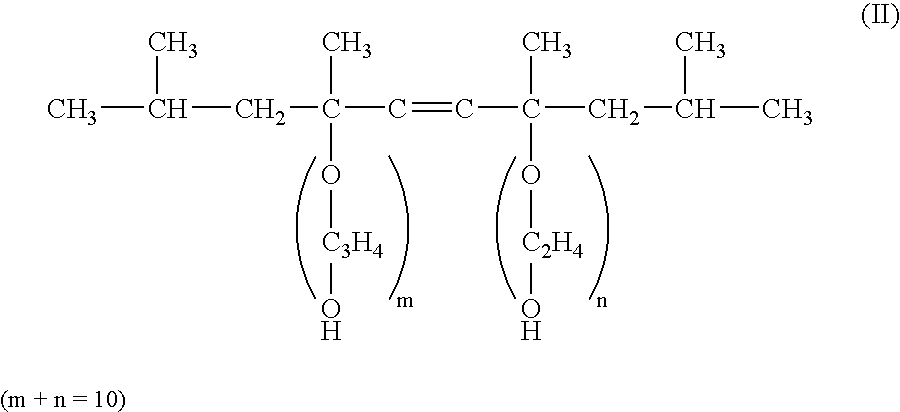
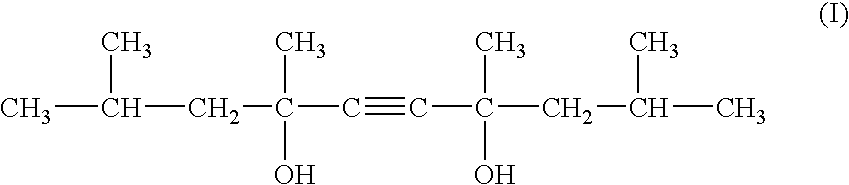
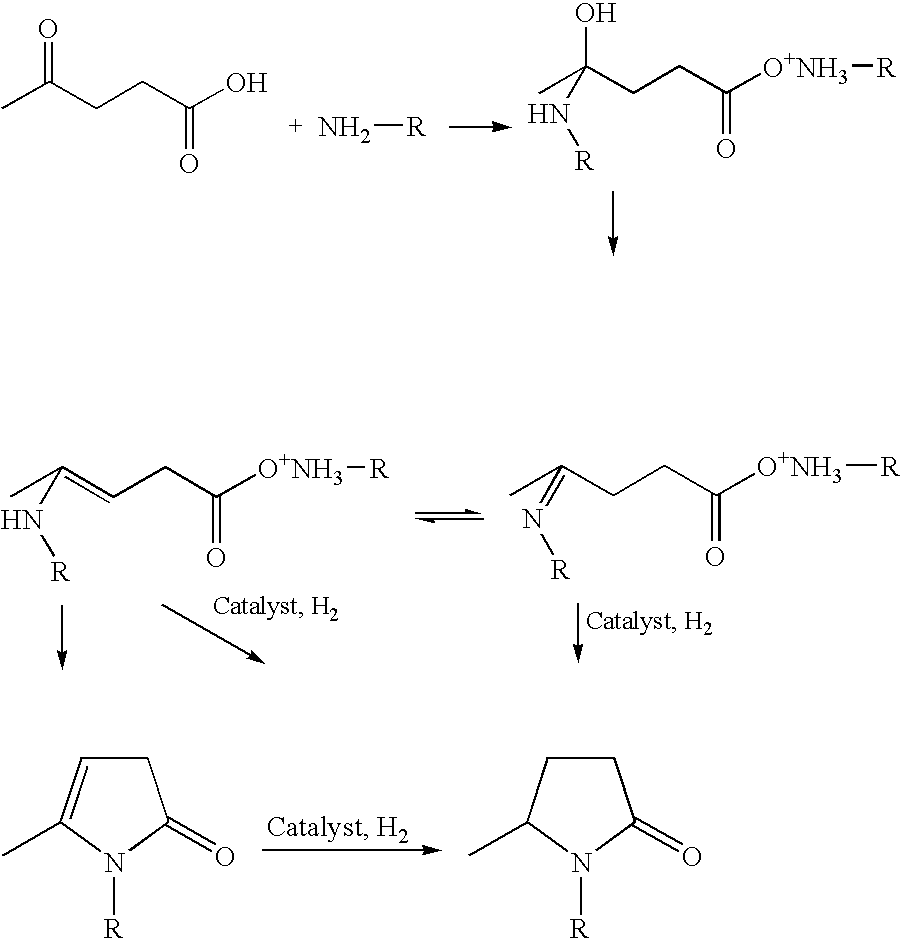
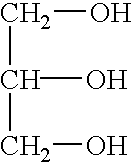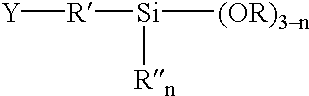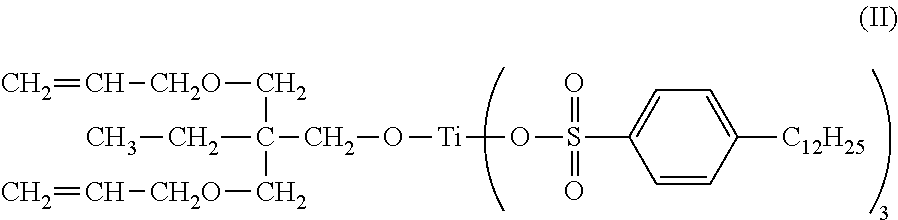Patents
Literature
629 results about "2-Pyrrolidone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
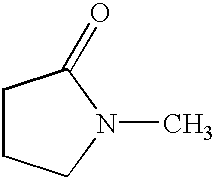
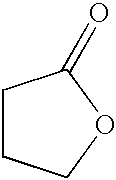
2-Pyrrolidone is an organic compound consisting of a 5-membered lactam, making it the simplest γ-lactam. It is a colorless liquid that is miscible with water and most common organic solvents. It is produced industrially by treating butyrolactone with ammonia. Alternative routes include the partial hydrogenation of succinimide and the carbonylation of allylamine with methyl amine. 2-Pyrrolidone is an intermediate in the production of vinylpyrrolidone and the drug piracetam.
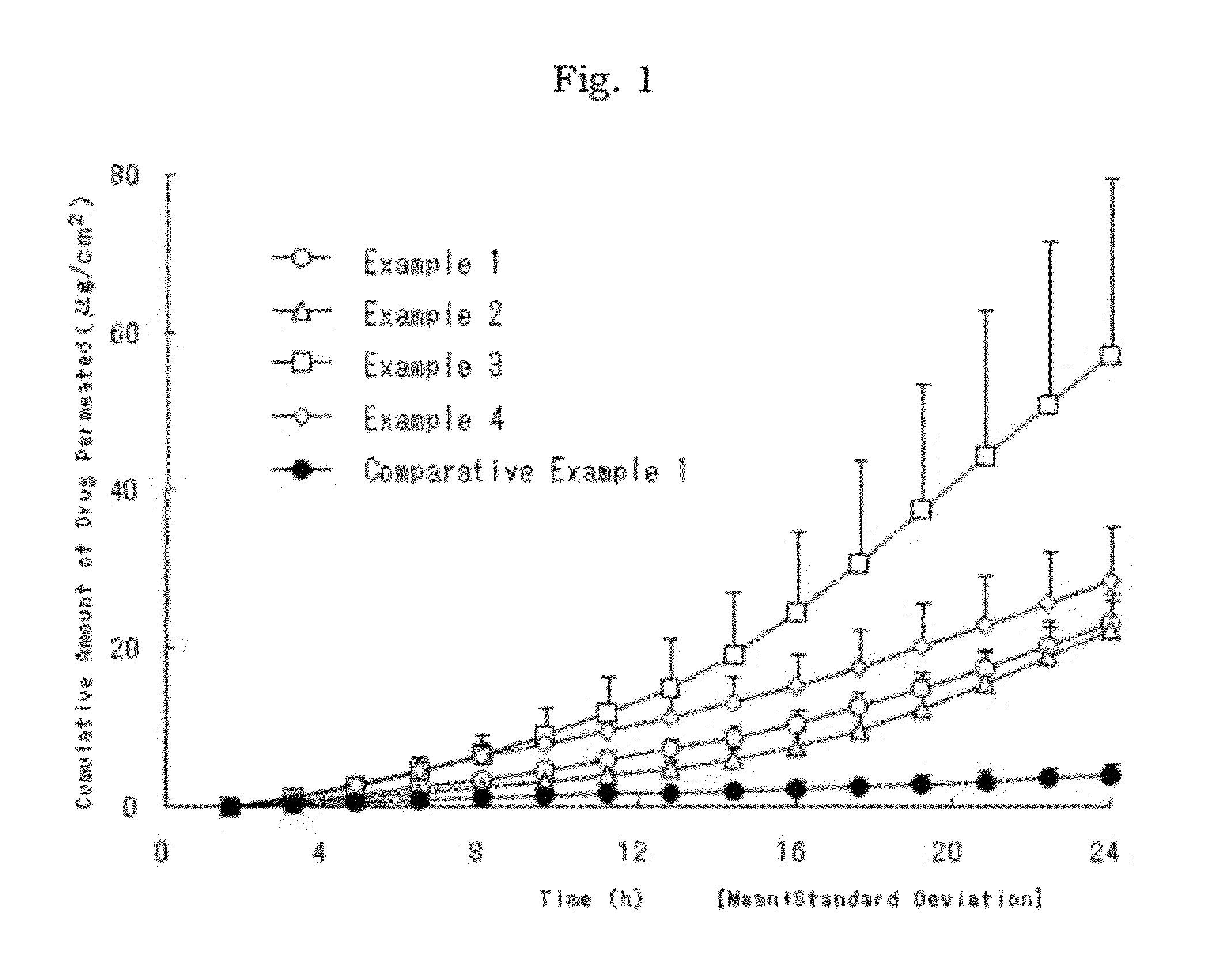
Oral capsule formulation with increased physical stability
InactiveUS7011846B2Improve capsule stabilityImprove stabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCapsule deliveryMonoglycerideOral medication
A formulation for a stabilized capsule for oral administration of a hydrophobic pharmaceutically active agent; comprising a non-aqueous solubilizer selected from 2-pyrrolidone, N-alkylpyrrolidones and combinations thereof; and a capsule stabilizing agent selected from mono-, di- and triglycerides, mono- and di-fatty esters of polyethylene glycol, fatty acids and combinations thereof wherein capsule integrity is maintained for at least 24 hours is disclosed.
Owner:SUPERNUS PHARM INC
Ectoparasite control compositions
Provided are ectoparasite control compositions, a method of controlling an ectoparasite and uses of a composition for controlling an ectoparasite. The ectoparasite control compositions comprise a solvent and 1-methyl-2-nitro-3-[(3-tetrahydrofuryl)methyl]guanidine, wherein said solvent contains mainly N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone. The methods of controlling an ectoparasite, comprise applying to a host animal, an ectoparasite control composition which comprises a solvent and 1-methyl-2-nitro-3-[(3-tetrahydrofuryl)methyl]guanidine, wherein said solvent contains mainly N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Anti-inflammatory analgesic adhesive patch for external use
ActiveUS20120283671A1Promote absorptionLess irritatingAntipyreticAnalgesicsAdditive ingredientTackifier
An external patch containing diclofenac hydroxyethylpyrrolidine prepared by laminating an adhesive layer on a backing, wherein said adhesive layer is characterized by comprising 5-50% by weight of styrene•isoprene•styrene block copolymer, 20-50% by weight of a tackifier resin, 5-70% by weight of a softening agent, and 0.5-20% by weight of one or more solubilizers selected from N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, propylene glycol and dimethyl sulfoxide as essential ingredients, and 0.5-20% by weight of diclofenac hydroxyethylpyrrolidine as an active ingredient. The patch has excellent transdermal absorption, less skin-irritation and excellent stability of the drug.
Owner:TEIKOKU SEIYAKU KK TEIKOKU SEIYAKU CO LTD +1
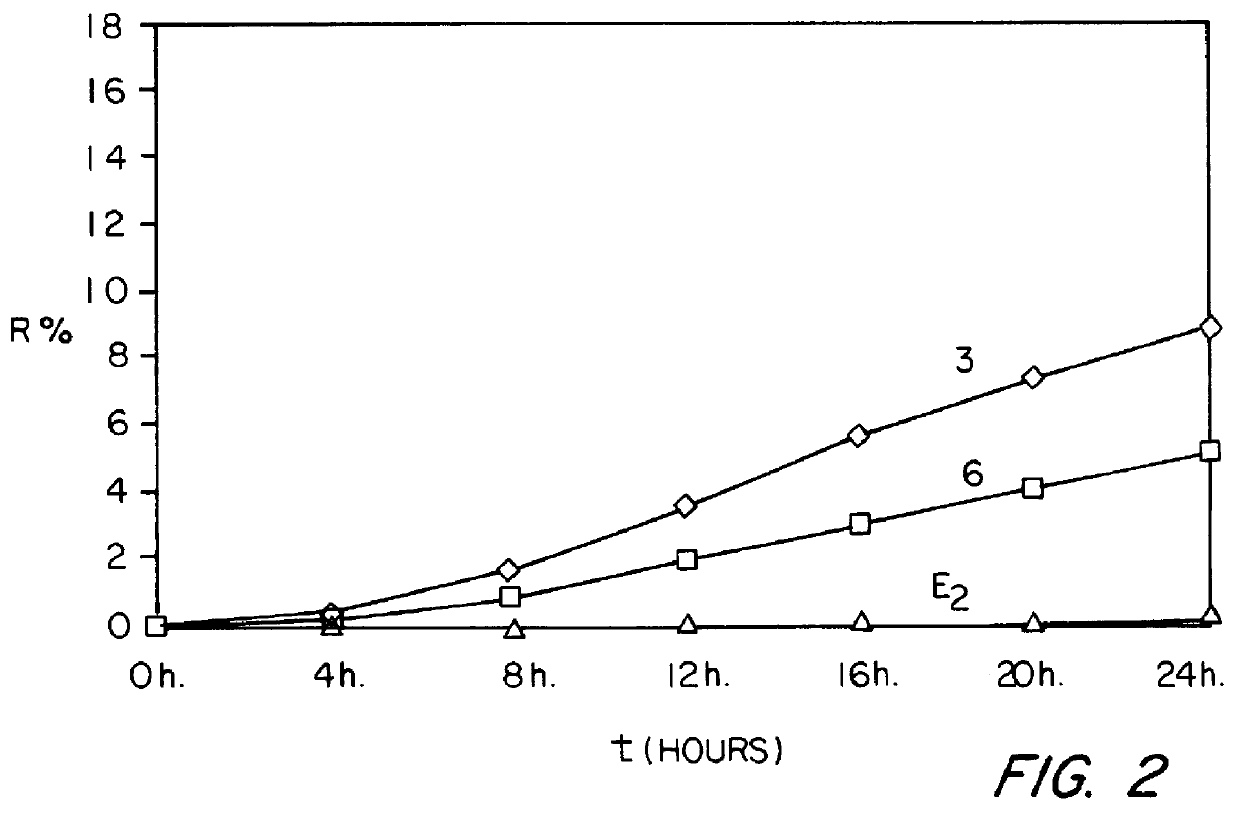
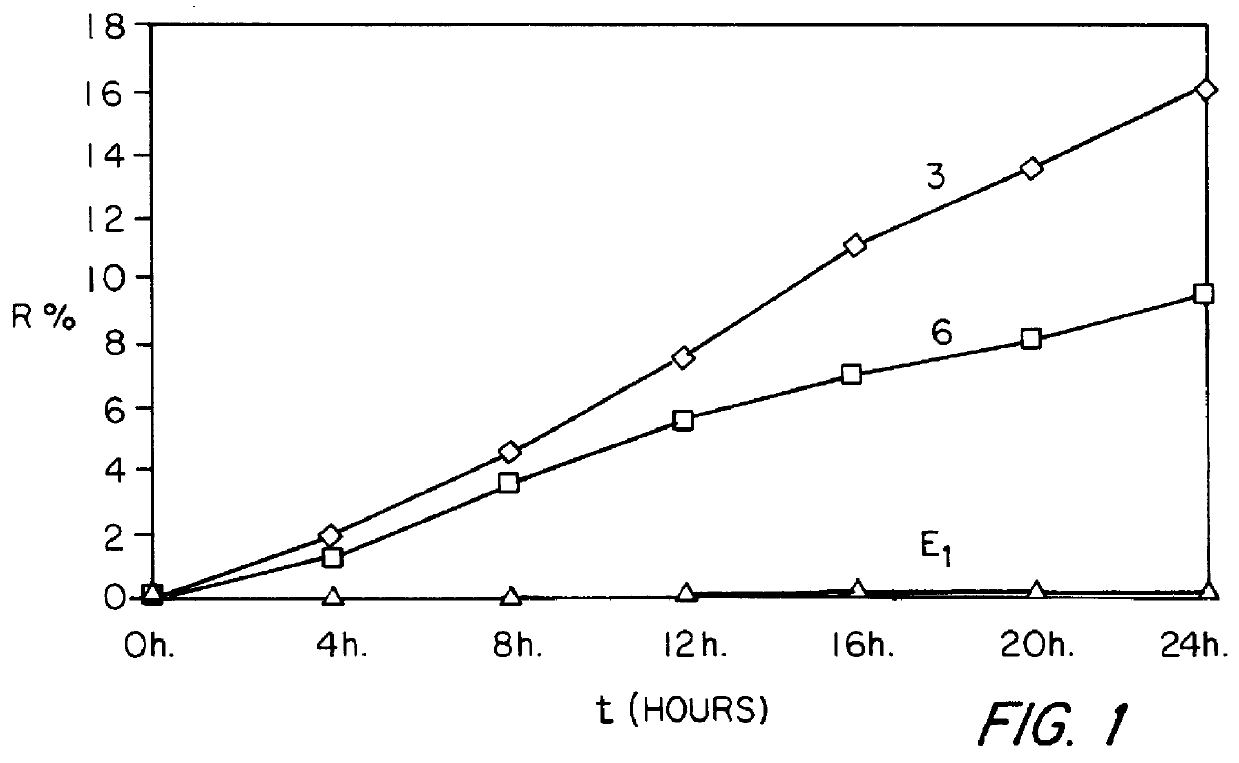
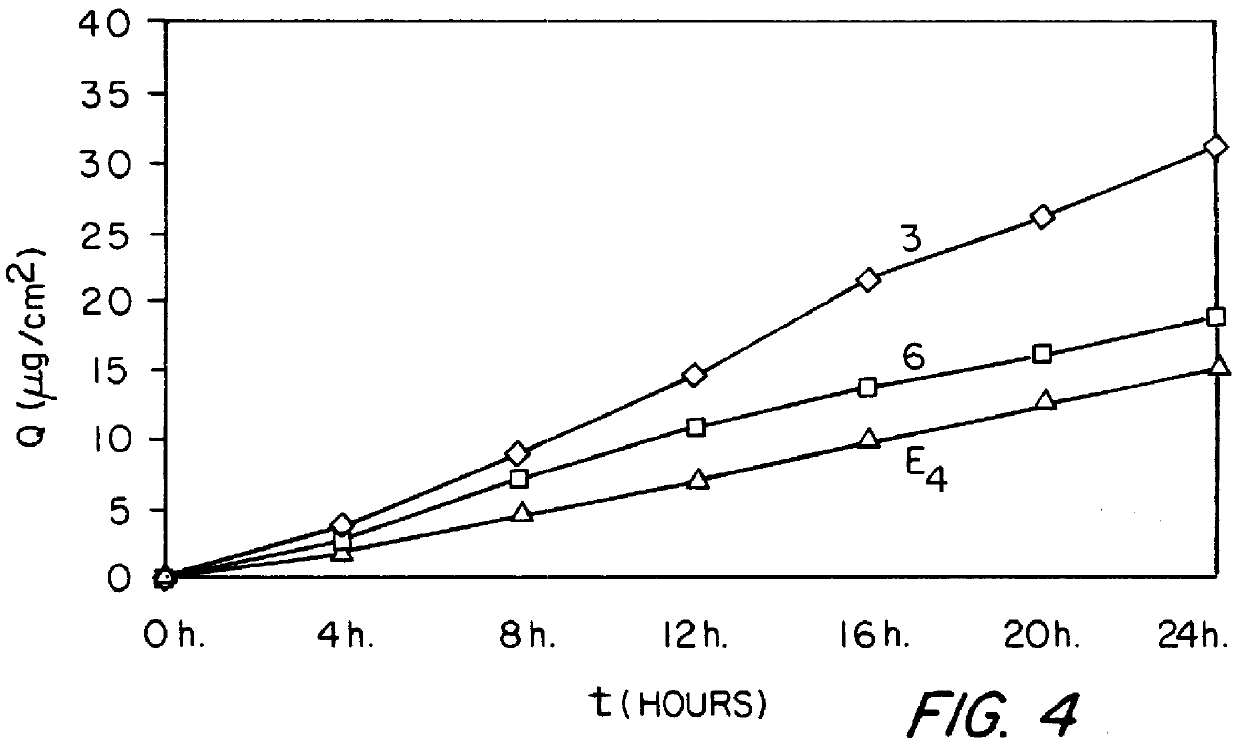
Transdermal matrix system
PCT No. PCT / FR96 / 01494 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 26, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 26, 1998 PCT Filed Sep. 25, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 11687 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 3, 1997A novel transdermal matrix system for the percutaneous delivery of a hormone, including a carrier and an adhesive matrix, is disclosed. The matrix includes (a) 39-61 parts by weight of an ethylene / vinyl acetate copolymer, (b) 12-17 parts by weight of 2-octyldodecyl myristate, (c) 5-17 parts by weight of diethyl phthalate, (d) 10-16 parts by weight of a compound selected from N-alkyl-2-pyrrolidones, wherein the alkyl group is a C4-15 group, and (e) 1-12 parts by weight of at least one hormone selected from the group consisting of oestrogenic and progestogenic components. A method for preparing said transdermal matrix system and the therapeutical use of said system are also disclosed.
Owner:LABES DHYGIENE & DE DIETETIQUE L H D
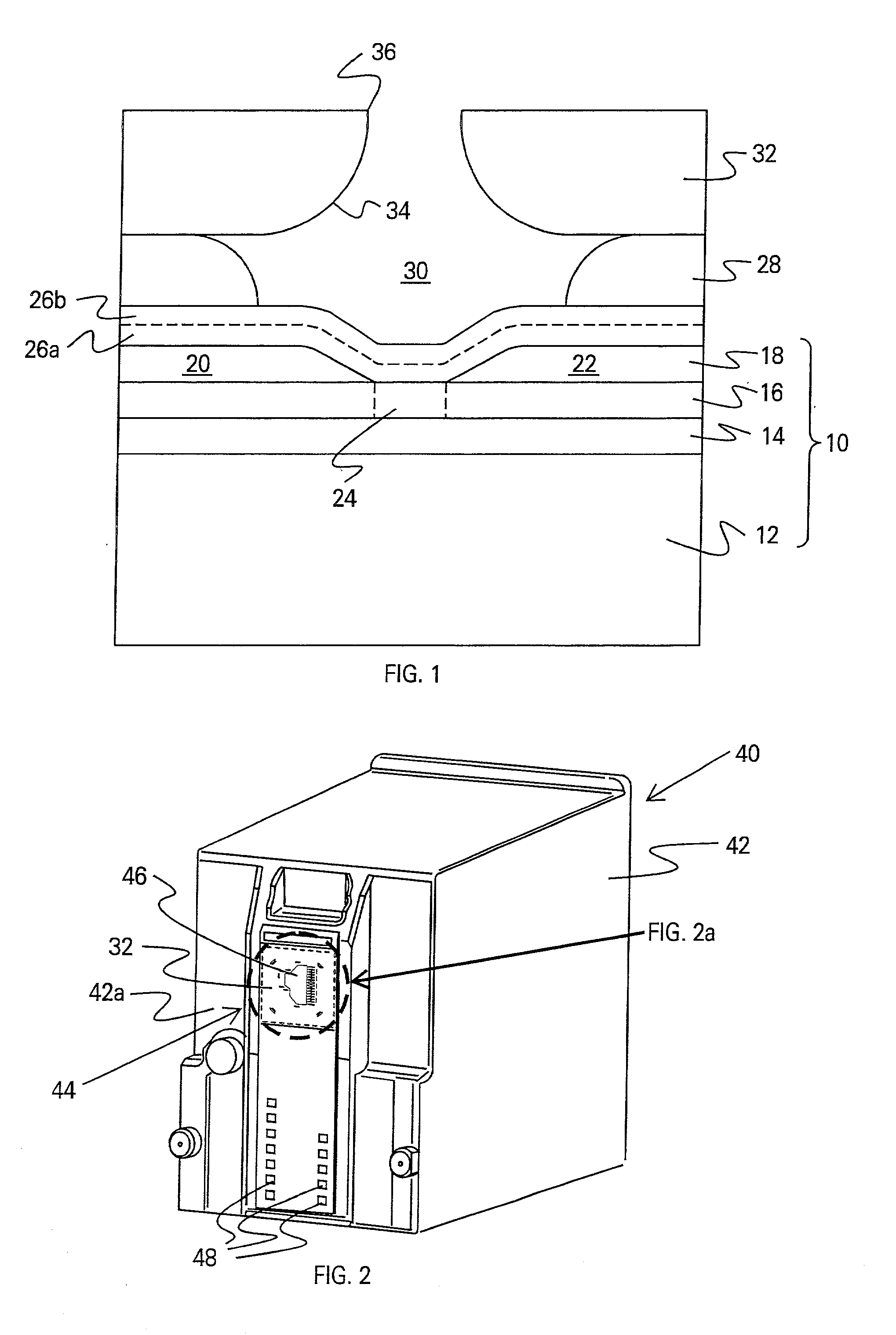
Manufacturing method of liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS6806925B2High affinityAvoid distractionStatic indicating devicesOptical filtersLiquid-crystal display2-Pyrrolidone
The irregularities of coloring concentration which is generated between dyed media when a color filter substrate which is prepared in a manufacturing method of a liquid crystal display device is manufactured by supplying ink to dyed media formed on a main surface of the color filter substrate using an ink jet method. In the present invention, as color filter ink which is supplied to the dyed media formed on the color filter substrate using the inkjet method, liquid which contains dye which colors the dyed media, solvent (for example, water) which has an affinity for the dye, a volatility-adjusting agent (for example, glycerin) which lowers the volatility of the ink to a level below the volatility of the solvent, and a dyeing-promoter agent (for example, N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone) which exhibits a higher affinity for the dye and the dyed media than the volatility adjusting agent. Then, the dyed media is colored with this ink.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Polymeric wood preservative compositions
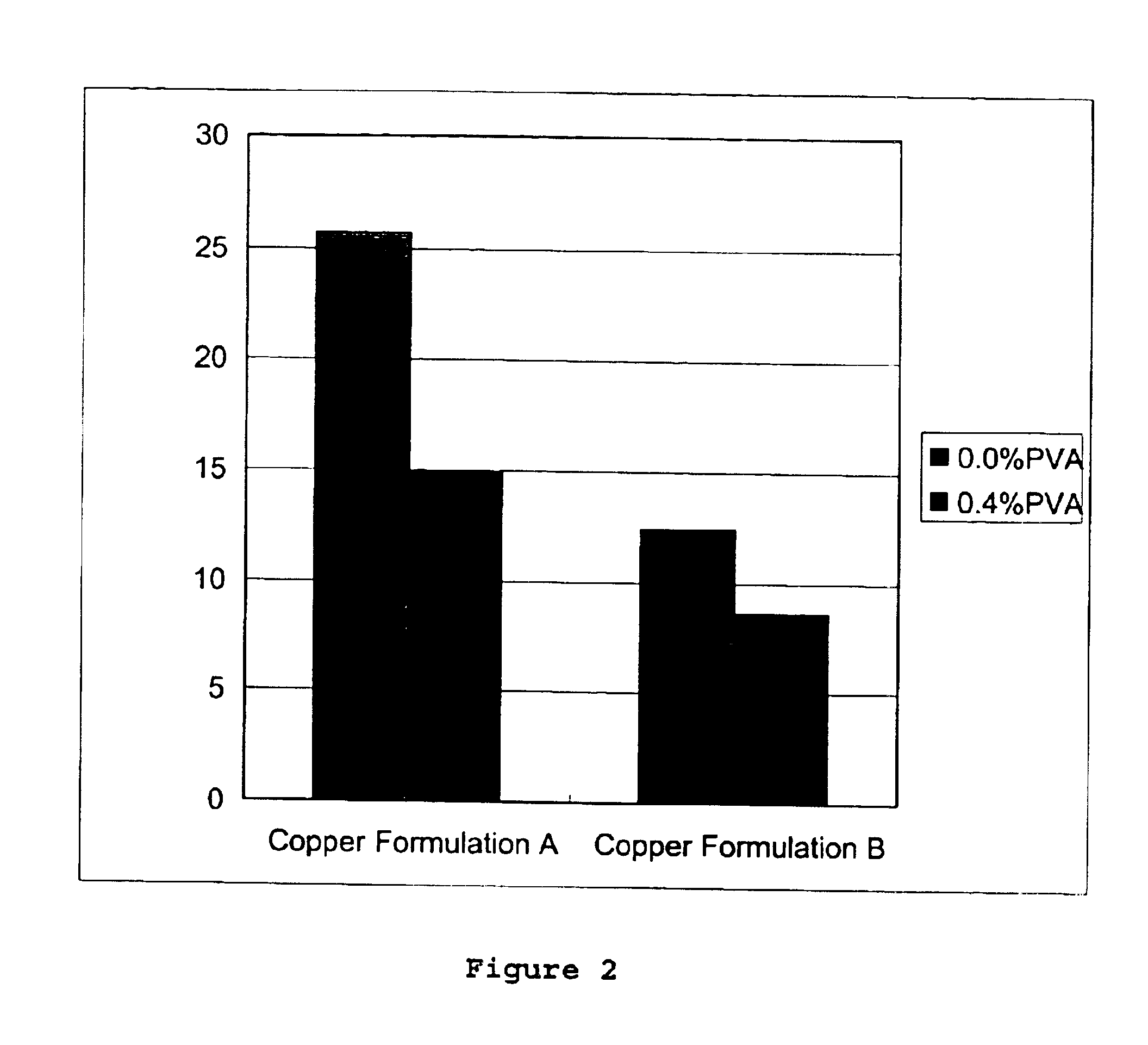
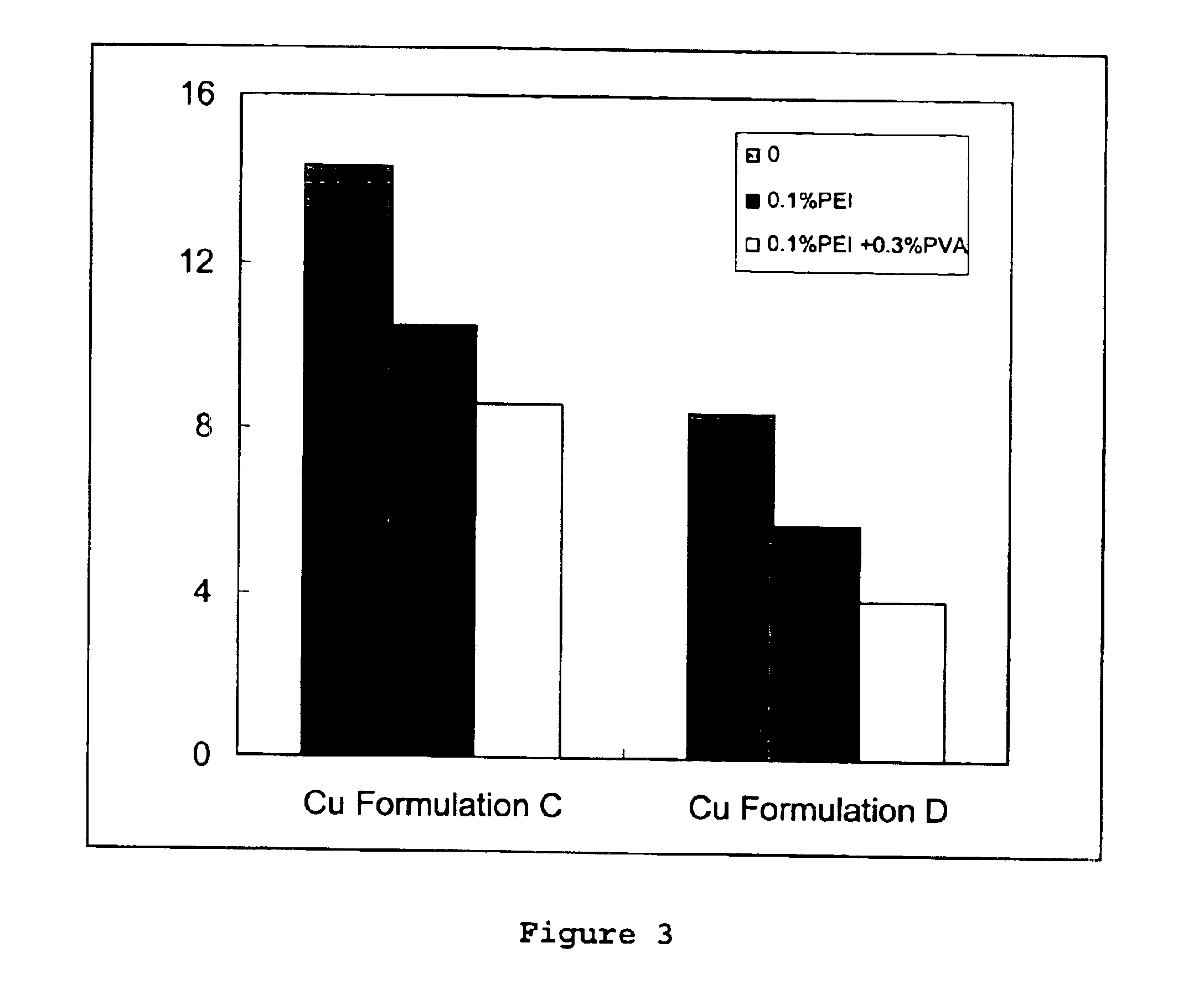
The present invention relates to a method and a wood preserving composition which comprises mixtures of a metal compound, complexing agents selected from ethanolamines, polyethylenimine, ammonia or a mixture of these compounds, and a vinyl based polymer selected from poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), poly(acrylamide) (PA), poly(N-vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP) and poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) (PNIPAM). The resulting metal amine solution can then be used to formulate a variety of metal-based cellulosic material preserving products.
Owner:OSMOSE
Ink jet ink, ink set, ink jet recording method, ink cartridge, recording unit, and ink jet recording apparatus
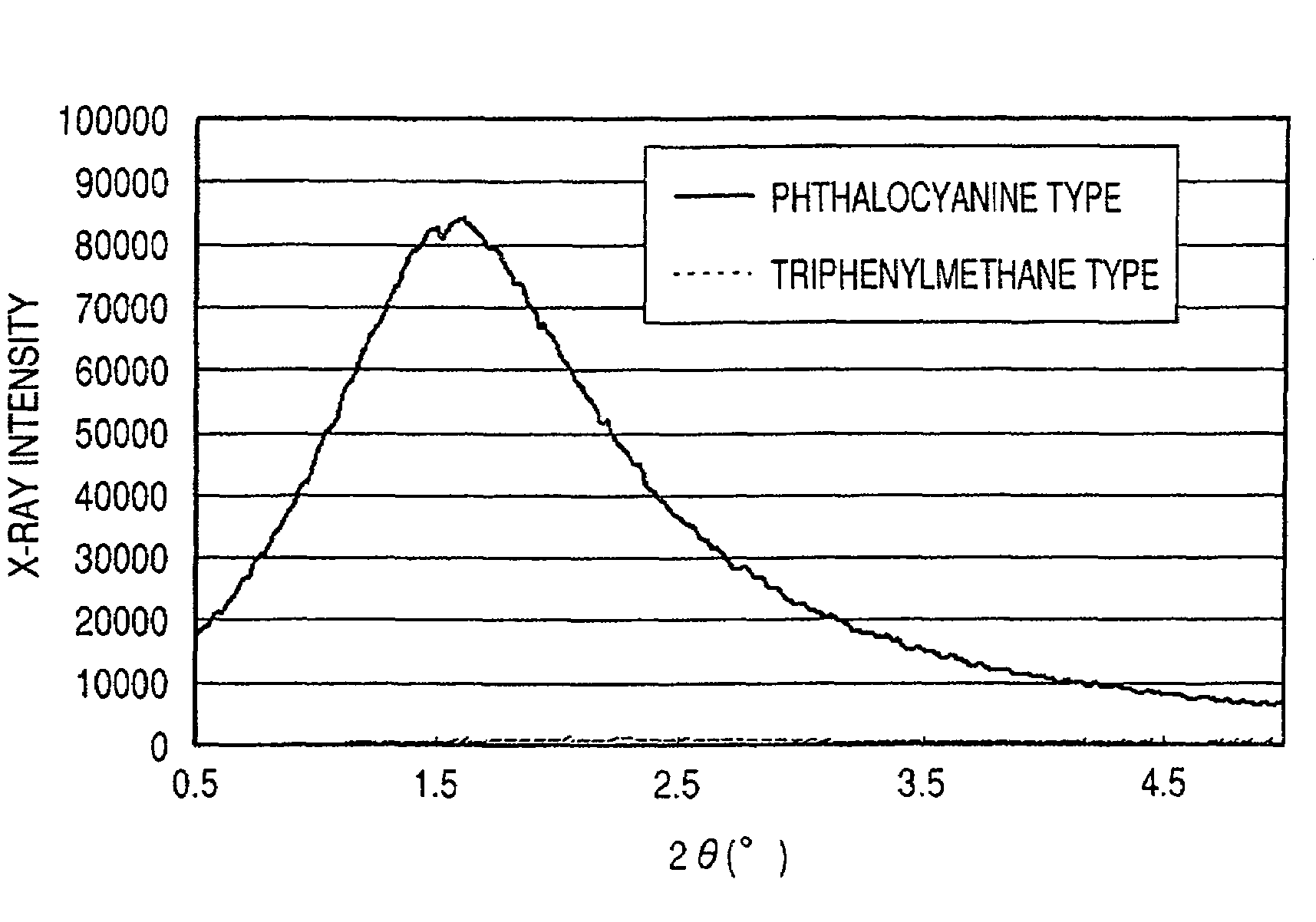
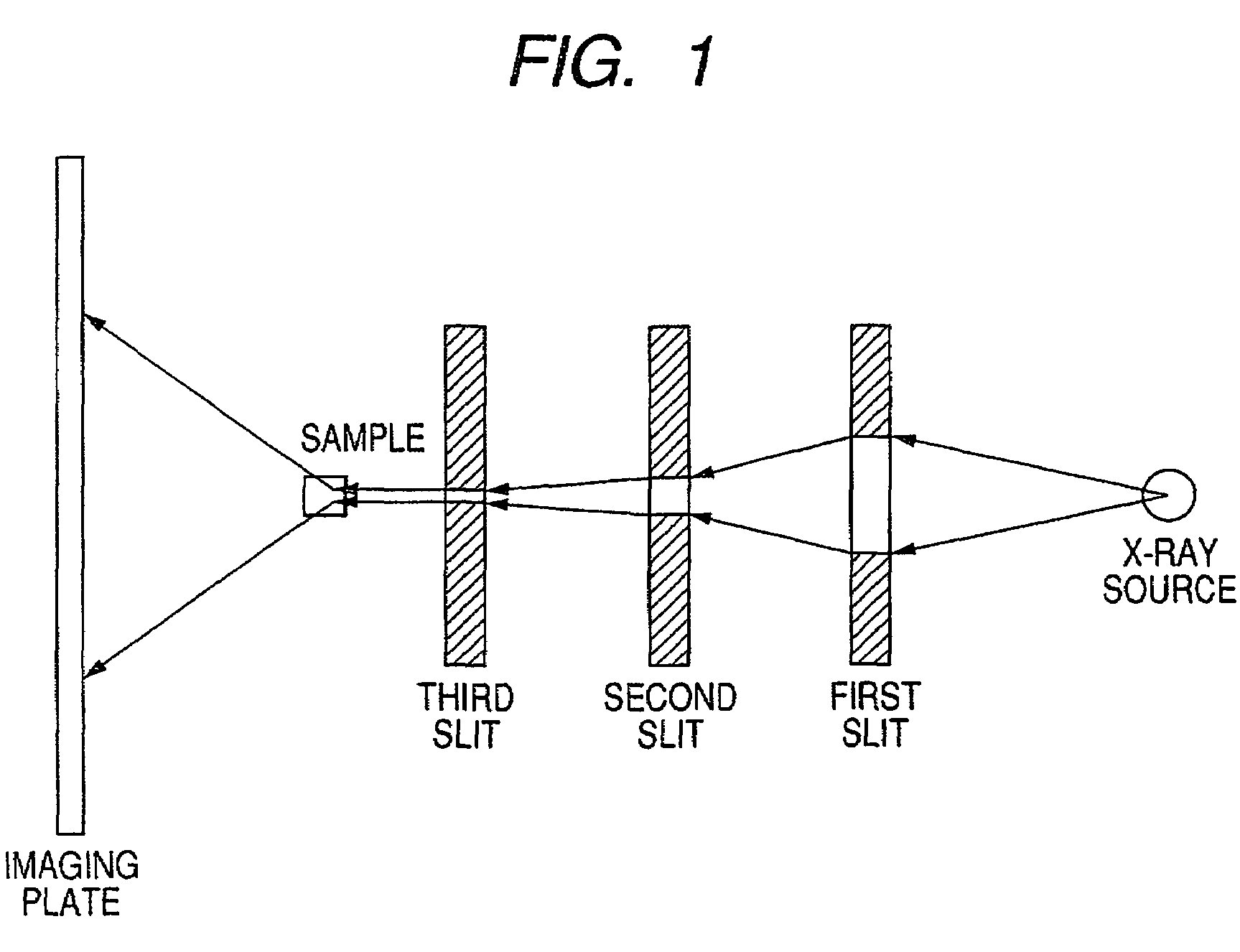
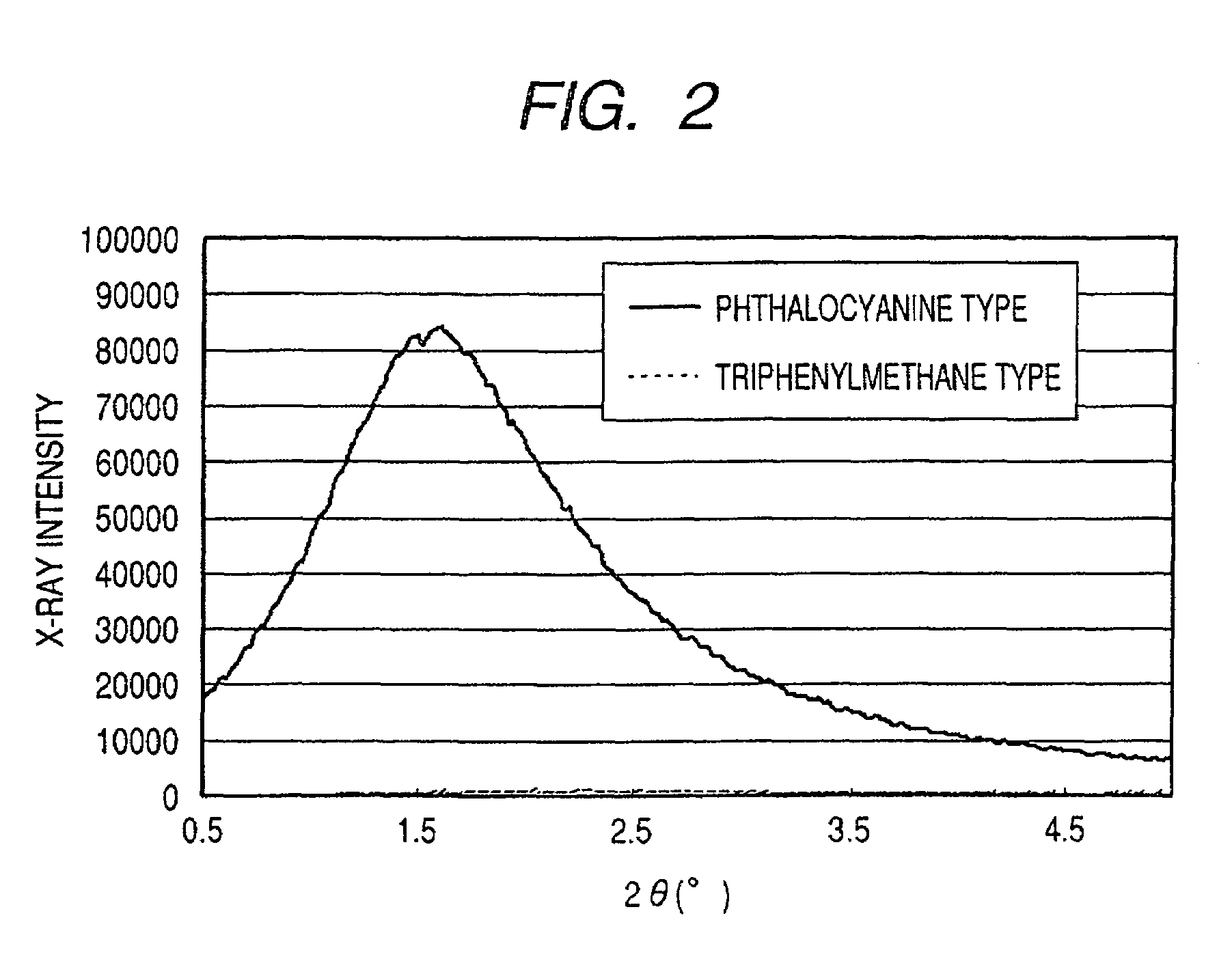
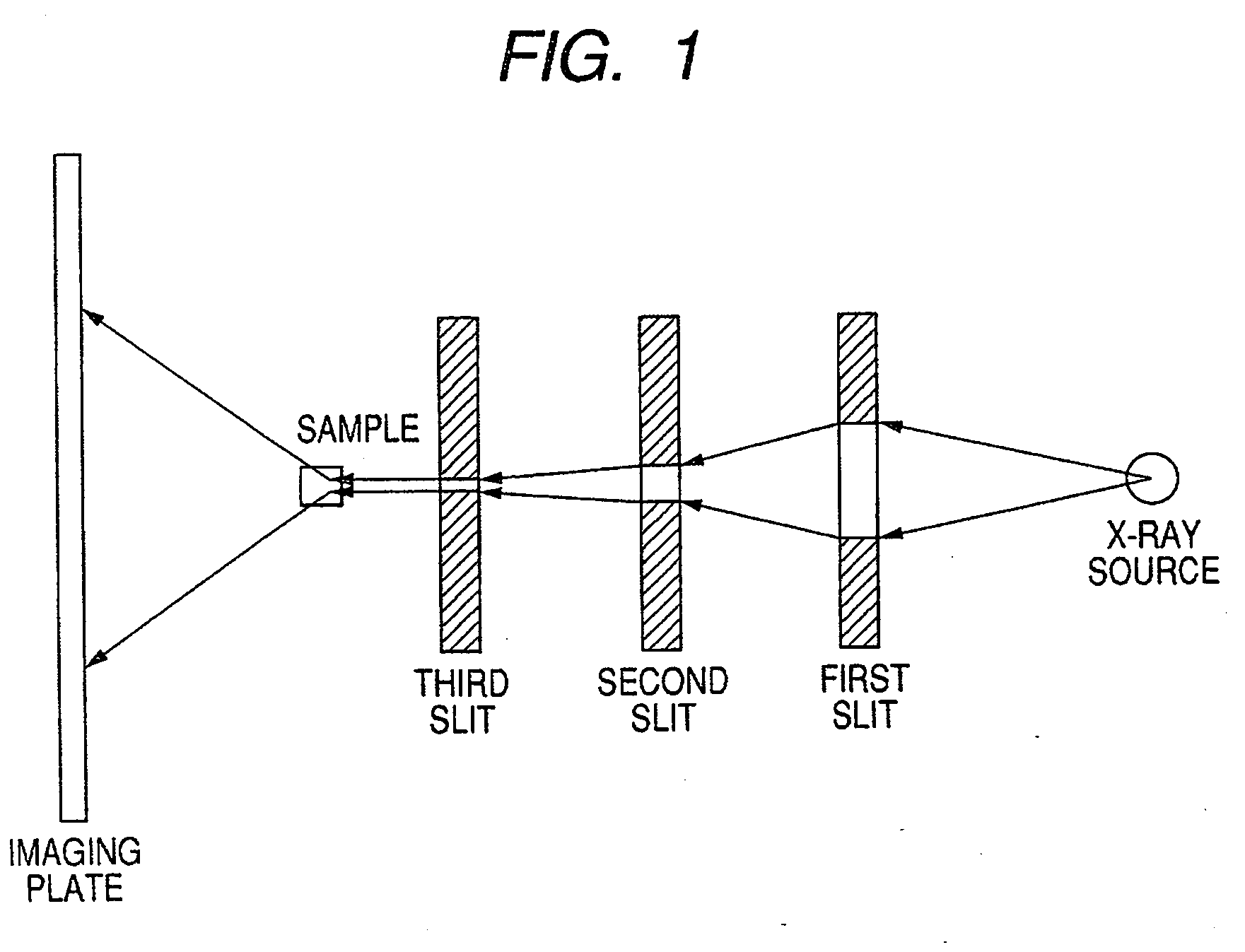
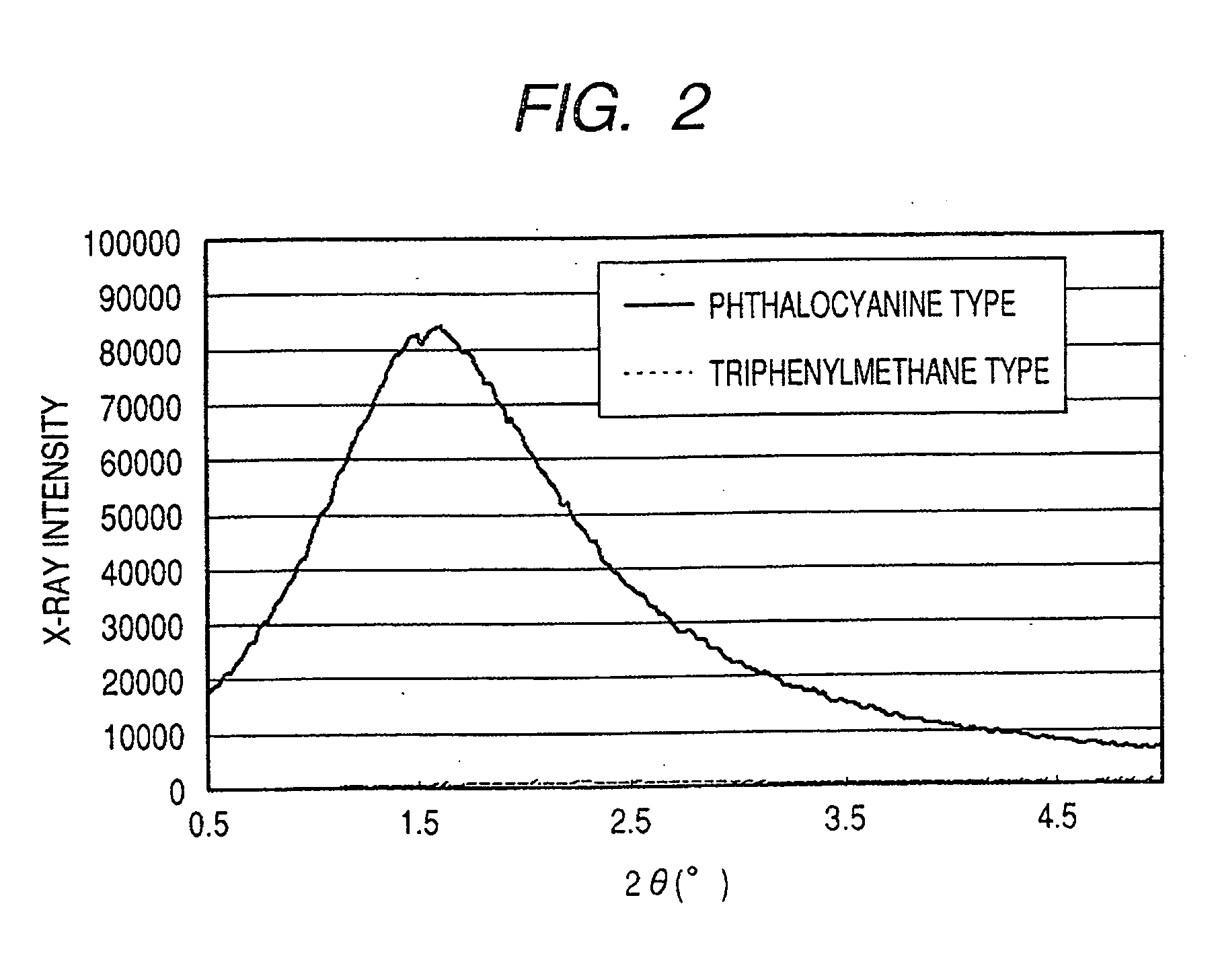
ActiveUS7247194B2Good colorIncrease resistanceMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsOrganic solventSmall-angle X-ray scattering
An ink jet ink is disclosed which includes water, a water-soluble organic solvent and a coloring material and has excellent properties. The coloring material is a specific phthalocyanine derivative and is contained in a specific amount in the ink. The water-soluble organic solvent includes a specific amount of 2-pyrrolidone. In addition, a d75 value is in a specific range where the d75 value corresponds to 75% of a dispersion distance distribution, measured by a small angle X-ray scattering method, of molecular aggregates in the ink jet ink whose coloring material concentration is adjusted to 0.5 mass %.
Owner:CANON KK
Manufacturing method of liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20020054252A1High affinityAvoid distractionStatic indicating devicesOptical filtersLiquid-crystal display2-Pyrrolidone
The irregularities of coloring concentration which is generated between dyed media when a color filter substrate which is prepared in a manufacturing method of a liquid crystal display device is manufactured by supplying ink to dyed media formed on a main surface of the color filter substrate using an ink jet method. In the present invention, as color filter ink which is supplied to the dyed media formed on the color filter substrate using the inkjet method, liquid which contains dye which colors the dyed media, solvent (for example, water) which has an affinity for the dye, a volatility-adjusting agent (for example, glycerin) which lowers the volatility of the ink to a level below the volatility of the solvent, and a dyeing-promoter agent (for example, N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone) which exhibits a higher affinity for the dye and the dyed media than the volatility adjusting agent. Then, the dyed media is colored with this ink.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Polishing composition
InactiveUS20090289217A1Satisfactory polishing rateEasy to manufactureOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEthylenediamineCarboxylic acid
A polishing composition which achieves surfaces with high planarity and the reduction of corrosions in the wiring metal surface at the same time is provided.Such compositions include(A) an oxidizing agent;(B) at least one acid selected from an amino acid, a carboxylic acid of no more than 8 carbon atoms, and an inorganic acid;(C) a sulfonic acid having a concentration of 0.01% by mass or more and having an alkyl group of 8 or more carbon atoms;(D) a fatty acid having a concentration of 0.001% by mass or more and having an alkyl group of 8 or more carbon atoms; and(E) at least one compound selected from a pyridine carbonyl compound, a nonionic water-soluble polymer, 2-pyrrolidone, N-methylpyrrolidone, 1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone, gramine, adenine, N,N′-diisopropylethylenediamine, N,N′-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ethylenediamine, N,N′-dibenzylethylenediamine, and N,N′-diphenylethylenediamine.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
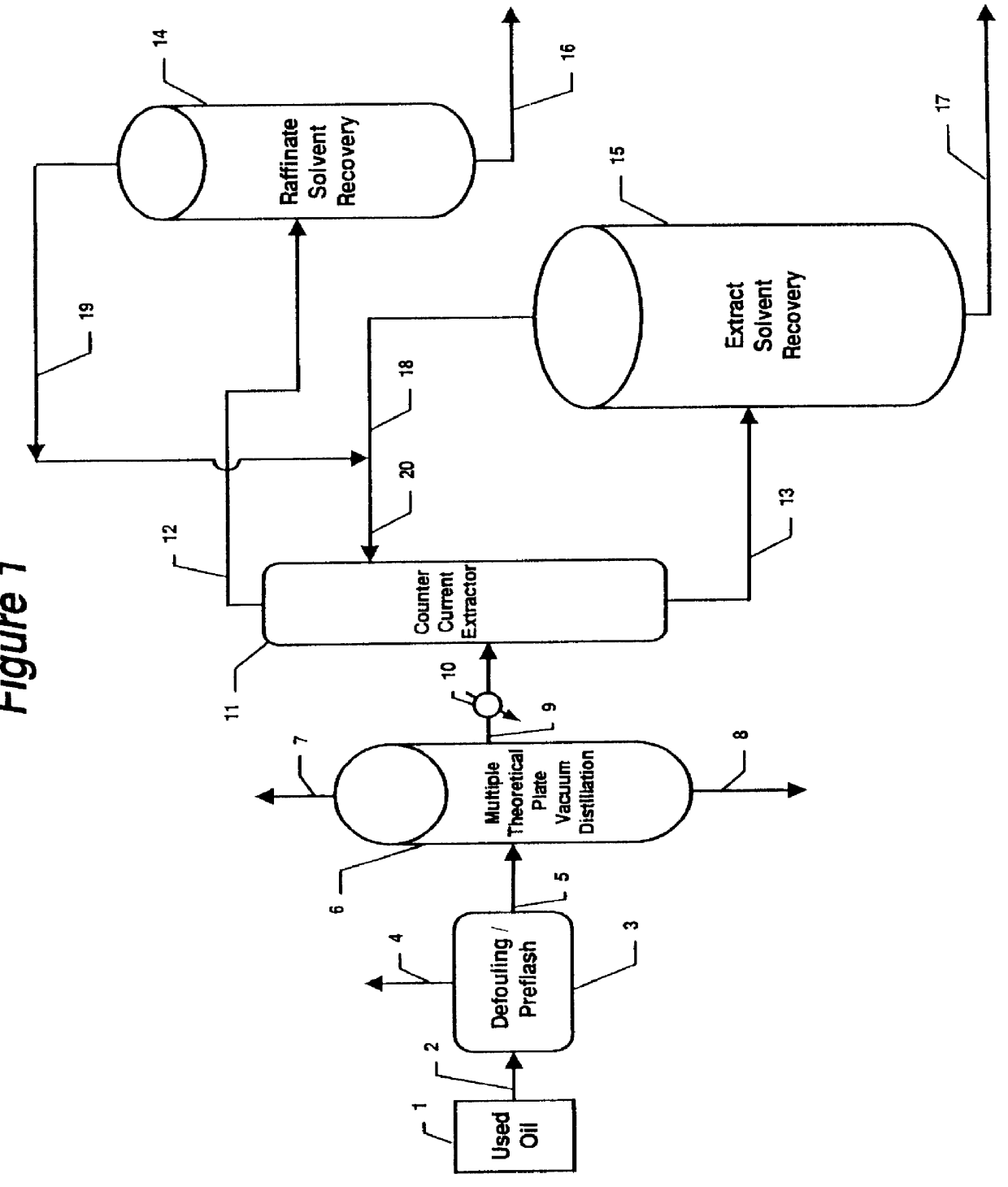
Method of rerefining waste oil by distillation and extraction
InactiveUS6117309AHigh yieldLower the volumeRefining with acid-containing liquidsLubricant compositionTheoretical plateDistillation
Owner:SARP
Environmentally friendly, reliable, fast drying ink for point-of-sale thermal ink jet application
InactiveUS20020112643A1Improve printing qualityDecrease puddlingInksPrintingSurface-active agentsPolymer
An ink jet ink for thermal ink jet point-of-sale printers is provided, comprising: (a) a vehicle comprising (i) 5 to 10 wt % of a drying agent selected from the group consisting of 1,2-hexanediol and 1,2-pentanediol, (ii) 15 to 32 wt % 2-pyrrolidone, (iii) 15 to 37 wt % of at least one humectant, and (iv) the balance water; (b) 0.5 to 10 wt % of a water-soluble dye; and (c) 0 to 3 wt % comprising buffers, corrosion inhibitors, surfactants, biocides, polymers, pigments, and binders, with the proviso that the total amount of surfactants is 0.1 wt % or less, based on the total ink composition. In particular, the ink jet ink is employed in combination with a printhead having a nickel orifice plate through which droplets of the ink are expelled onto a print medium. The ink jet ink composition is environmentally friendly, reliable, and fast drying, on the order of 300 msec and less. Further, the ink composition exhibits minimal puddling on the nickel orifice plate, leading to improved print quality.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Ink for use in ink jet recording and ink jet recording method utilizing the same
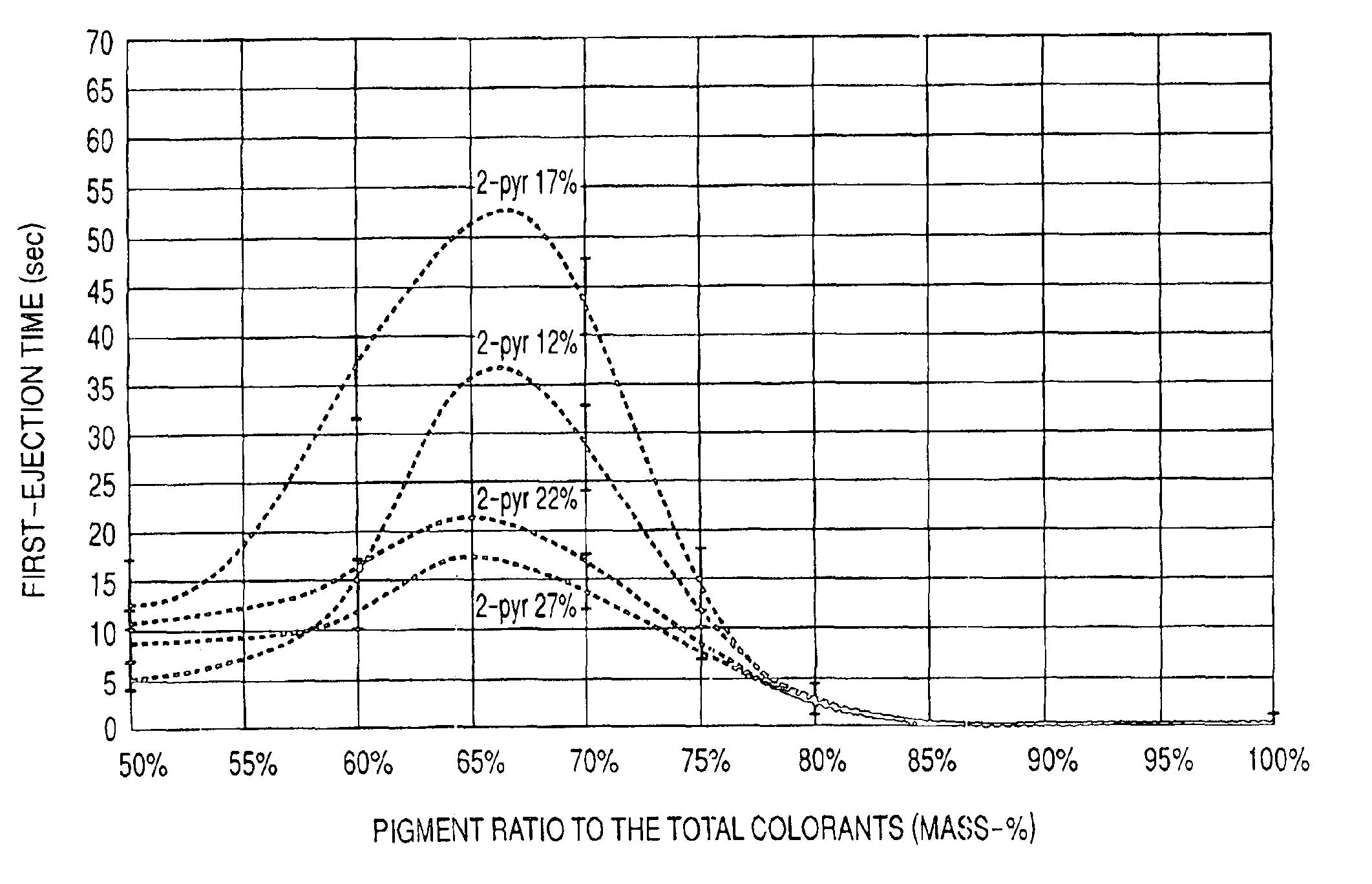
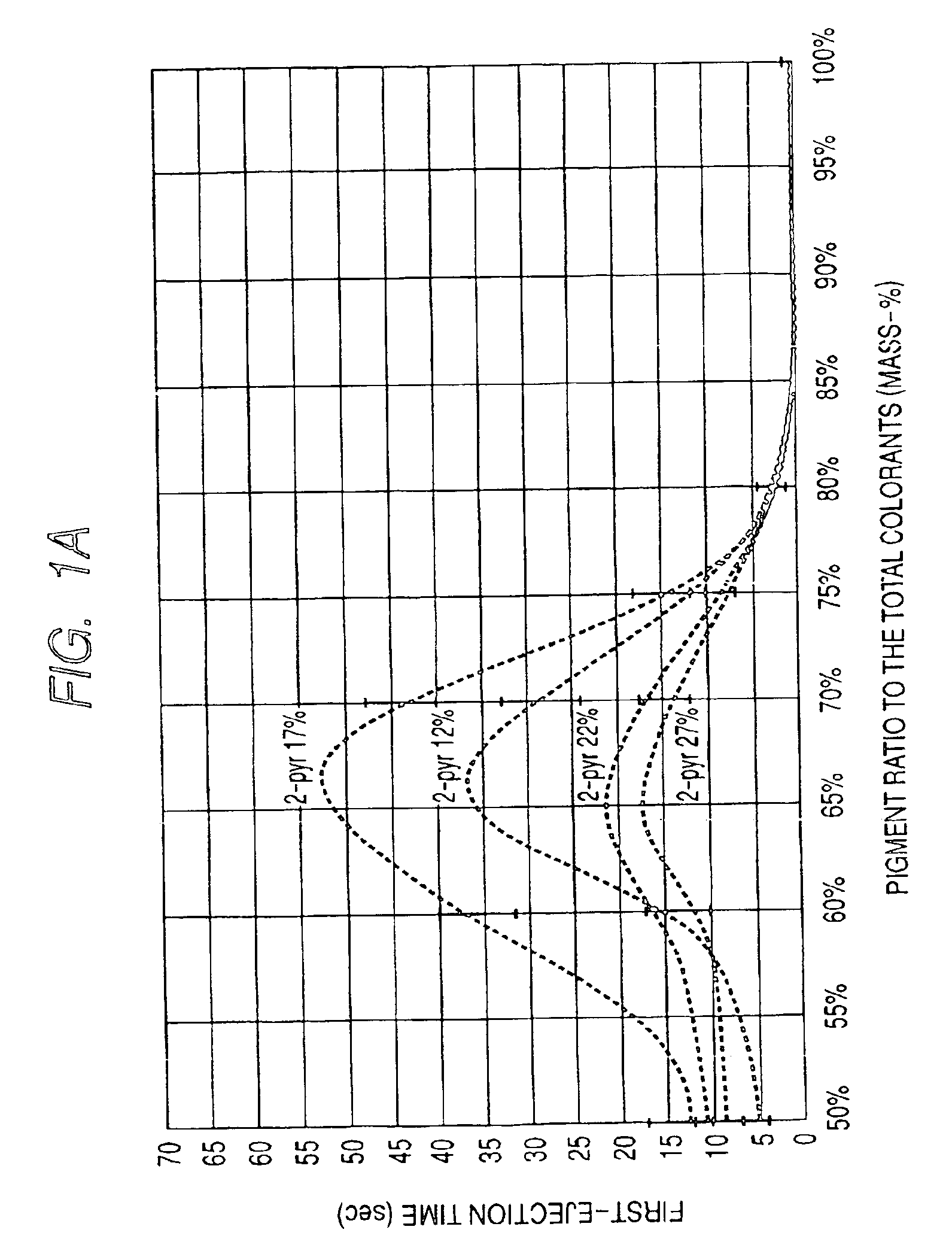
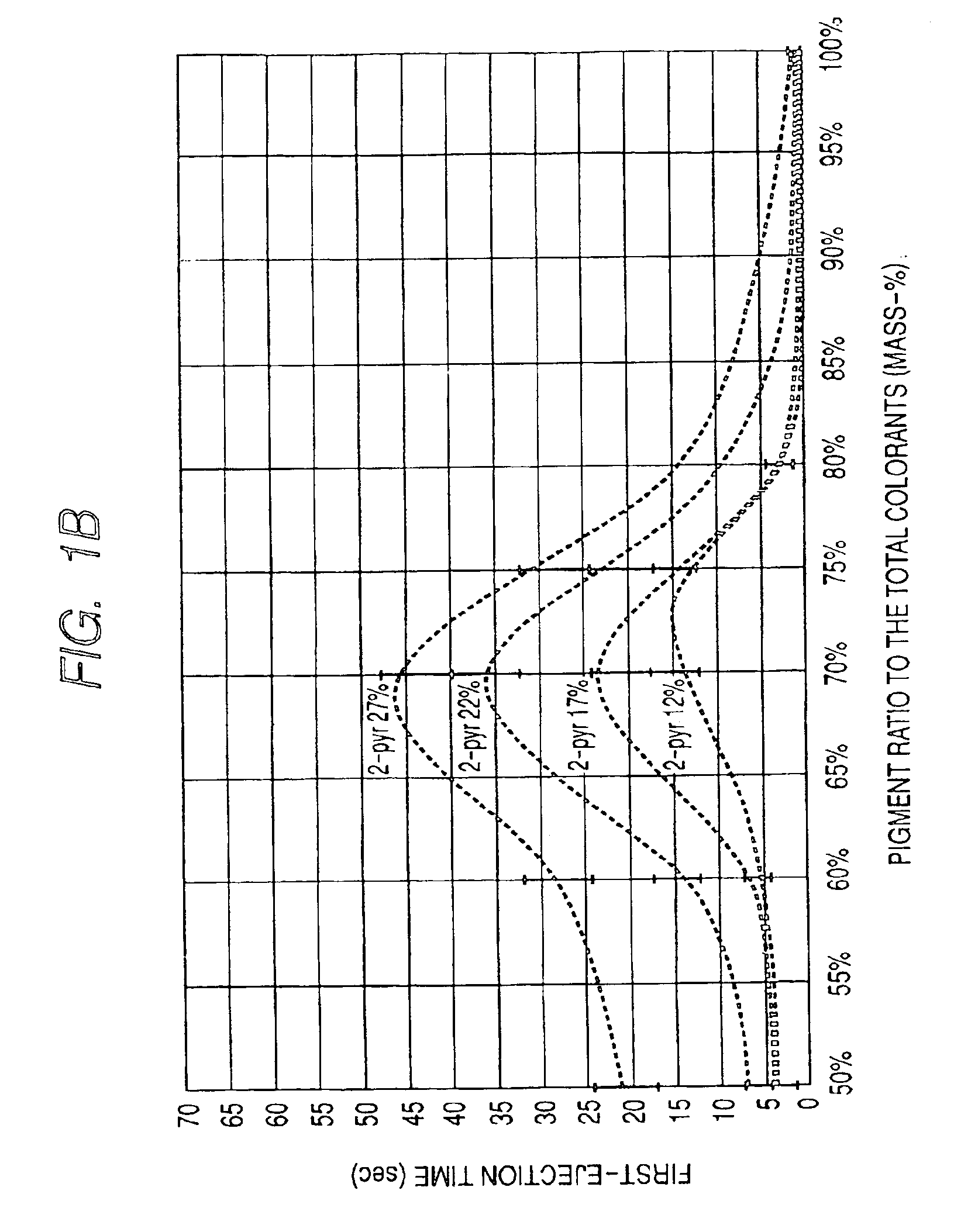
InactiveUS6964700B2High image densityImproving first-ejection timeMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsAtomic group2-Pyrrolidone
An ink for use in ink jet recording which contains a dye and a pigment as colorants. The pigment is a self-dispersible pigment in which at least one anionic group is bonded directly or through another atomic group to a surface of the pigment, the dye is an anionic dye, 2-pyrrolidone is further contained in the ink as a solvent, and the mass-based content X of 2-pyrrolidone in the ink and the ratio Y of the pigment to the sum of the dye and the pigment satisfy the following formulas 1 to 3 at the same time:12≦X<30 formula 150≦Y≦75 formula 2Y≧−2X+84 formula 3.
Owner:CANON KK
Composite construction containing barrier layer
This invention relates to a composite construction for use as a label or a tape to be adhered to a second substrate comprising a rubber-based material (e.g., vehicular tire), said composite construction comprising: a first substrate (e.g., paper, polymer film or combination thereof), said first substrate having a face side and an underside opposite said face side; an adhesive layer; and a barrier layer adhered to the underside of said first substrate and positioned between said first substrate and said adhesive layer, said barrier layer comprising a radiation cured acrylated epoxy derived from at least one acrylated epoxy oligomer and at least one reactive diluent selected from N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone and N-vinylcaprolactam, said barrier layer being substantially impervious to migratory components in said adhesive layer and said second substrate. In one embodiment, a release liner is adhered to the adhesive layer. In one embodiment, the composite construction is adhered to the second substrate.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
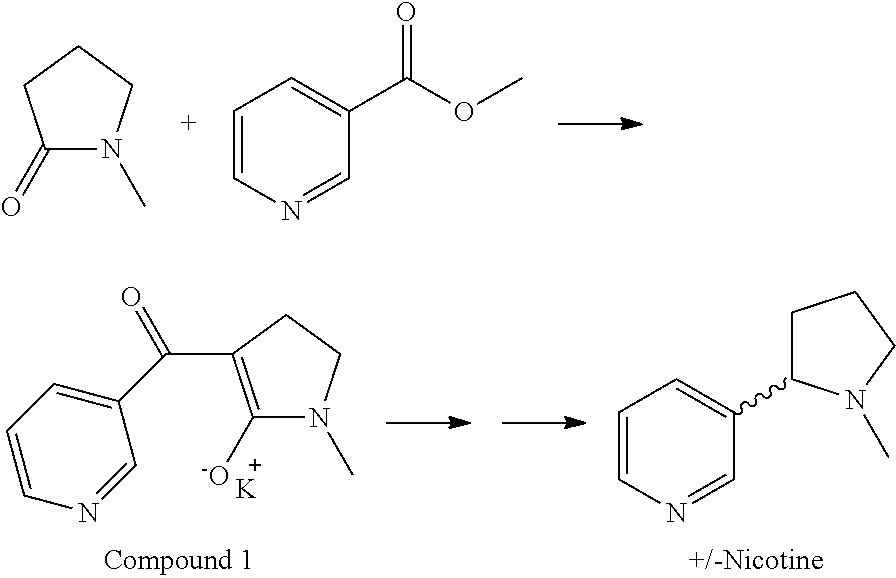
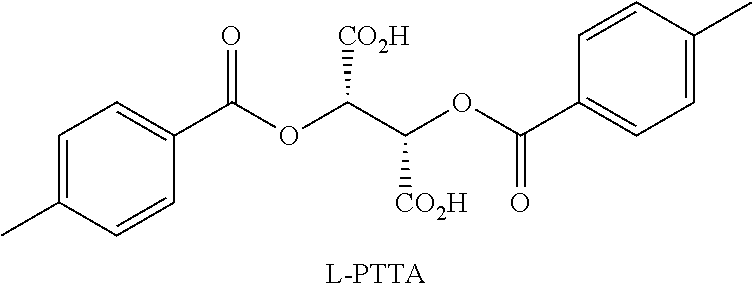
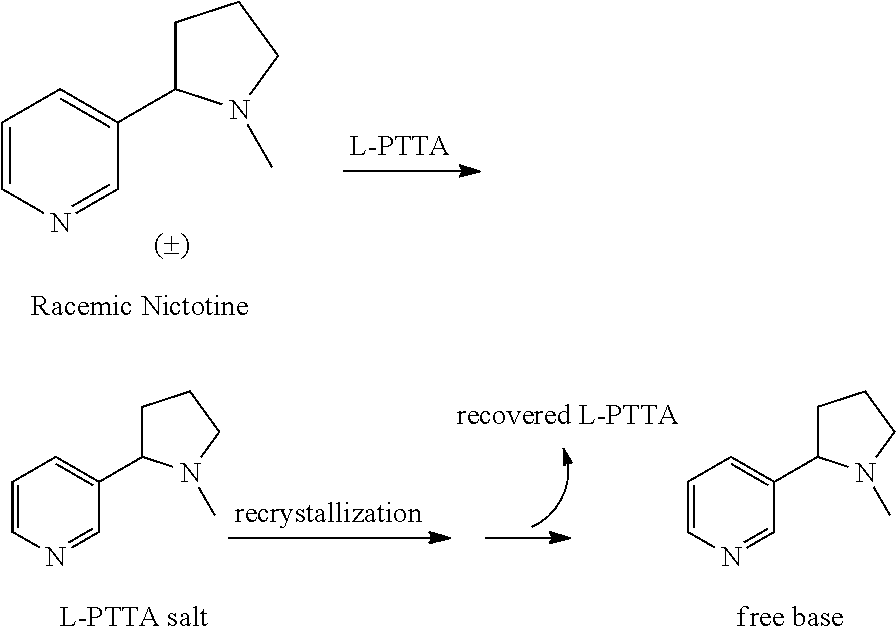
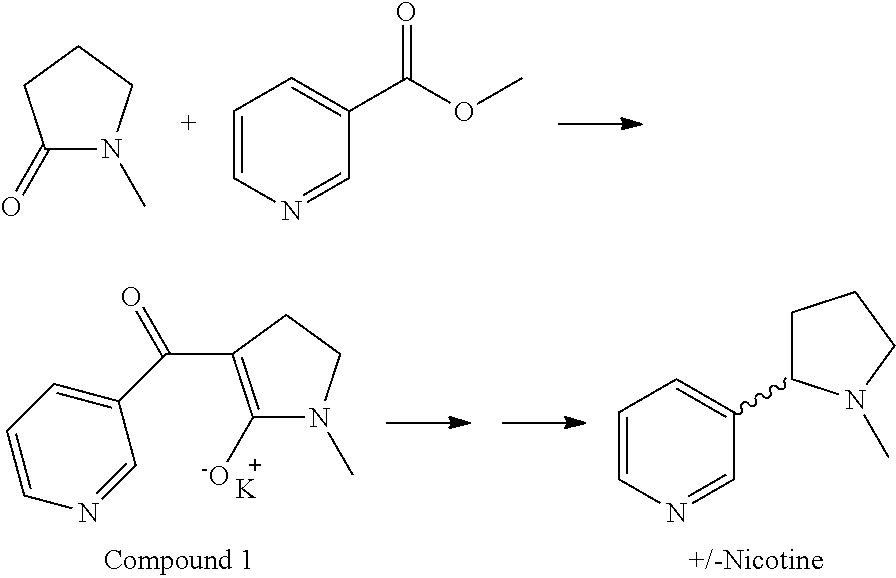
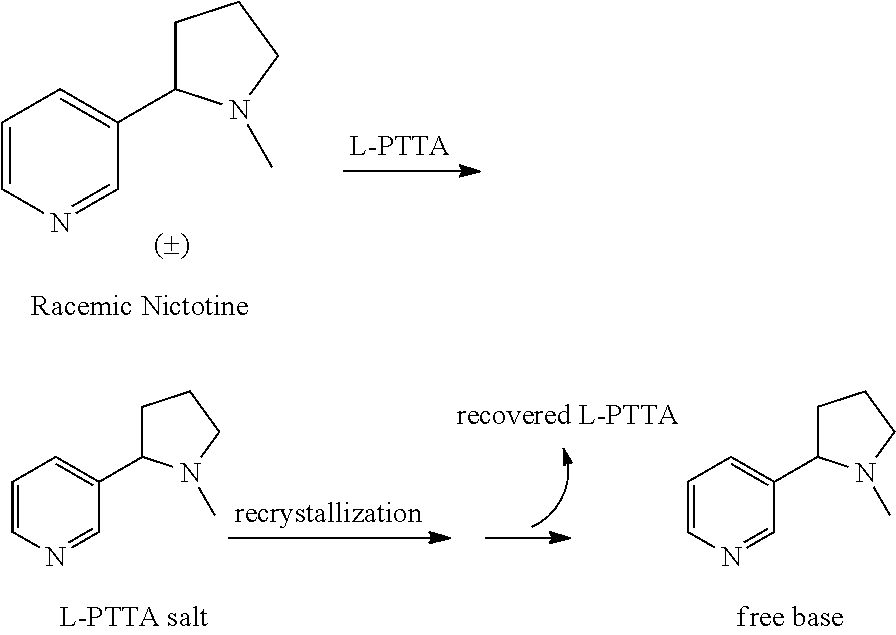
Synthesis and resolution of nicotine
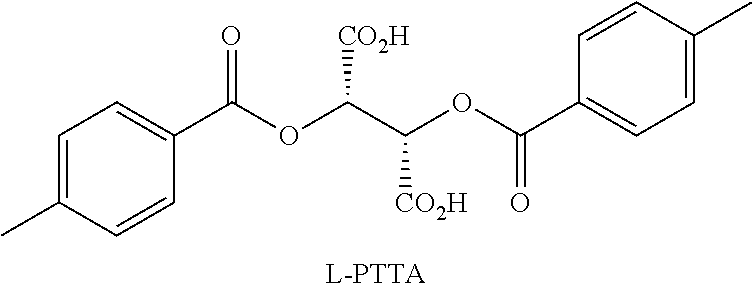
The present disclosure generally relates to methods of preparing nicotine and resolving R,S nicotine to enrich the (S)(−) enantiomer. The method may comprise combining N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone or a salt thereof with a nicotinate compound in the presence of a solvent and a strong base to form 1-methyl-3-nicotinoyl-2-pyrrolidone or a salt thereof; and reducing the 1-methyl-3-nicotinoyl-2-pyrrolidone or salt thereof in solution with Na2S2O4 to produce racemic nicotine or salt thereof. Resolving the racemic nicotine (or other enantiomeric mixture) may comprise combining the nicotine with (−)-O,O′-di-p-toluoyl-L-tartaric acid (L-PTTA).
Owner:NJOY LLC
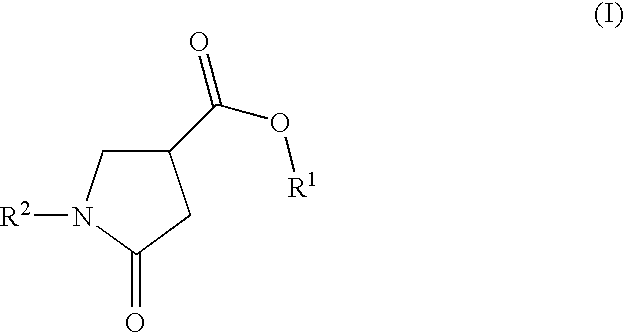
Cosmetic compositions comprising photostabilized dibenzoylmethane compounds and 2-pyrrolidinone-4- carboxy esters
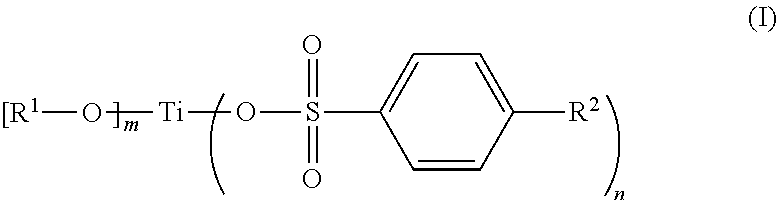
InactiveUS20100183529A1Good chemical stabilityHigh photochemical stabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparations2-PyrrolidonePyrrolidinones
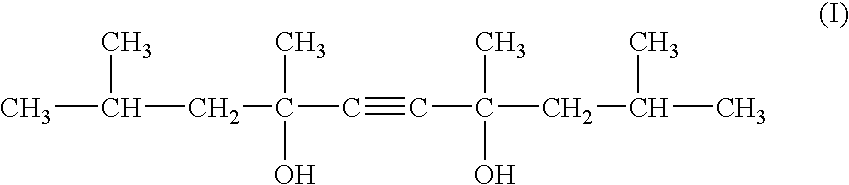
Photostable cosmetic compositions contain, formulated into a cosmetically acceptable vehicle, at least one UV-screening system that includes:(a) at least one dibenzoylmethane compound, and(b) at least one 2-pyrrolidinone-4-carboxy ester compound having the following formula (I):in which:R1 is a linear or branched C1-C20 alkyl radical, andR2 is a linear or branched C1-C20 alkyl radical which optionally includes a C5-C6 ring member, the phenyl radical, the benzyl radical or the phenethyl radical.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Synthesis and resolution of nicotine
The present disclosure generally relates to methods of preparing nicotine and resolving R,S nicotine to enrich the (S)(−) enantiomer. The method may comprise combining N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone or a salt thereof with a nicotinate compound in the presence of a solvent and a strong base to form 1-methyl-3-nicotinoyl-2-pyrrolidone or a salt thereof; and reducing the 1-methyl-3-nicotinoyl-2-pyrrolidone or salt thereof in solution with Na2S2O4 to produce racemic nicotine or salt thereof. Resolving the racemic nicotine (or other enantiomeric mixture) may comprise combining the nicotine with (−)-O,O′-di-p-toluoyl-L-tartaric acid (L-PTTA).
Owner:NJOY LLC
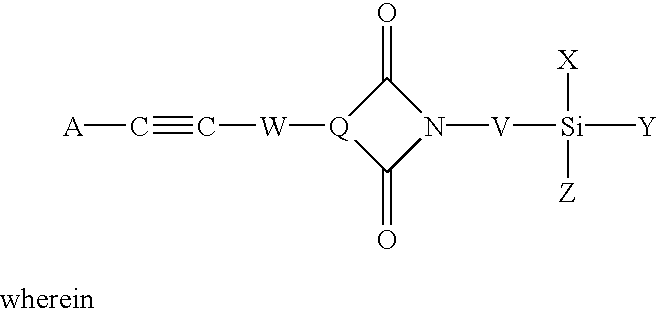
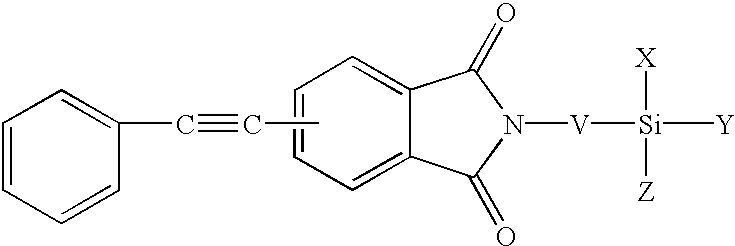
Phenylethynyl-containing imide silanes
Phenylethynyl containing imide-silanes were prepared from aminoalkyl and aminoaryl alkoxy silanes and 4-phenyletbynylphthalic anhydride in toluene to form the imide in one step or in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone (NMP) to form the amide acid intermediate. Controlled molecular weight pendent phenylethynyl amide acid oligomers terminated with aminoaryl alkoxy silanes were prepared in NMP from aromatic dianhydrides, aromatic diamines, diamines containing pendent phenylethynyl groups and aminoaryl alkoxy silanes. The phenylethynyl containing imide-silanes and controlled molecular weight pendent phenylethynyl amide acid oligomers terminated with aminoaryl alkoxy silanes were used to improve the adhesion between phenylethynyl containing imide adhesives and inorganic substrates (i.e. metal). Hydrolysis of the alkoxy silane moiety formed a silanol functionality which reacted with the metal surface to form a metal-oxygen-silicon (oxane) bond under the appropriate reaction conditions. Upon thermal cure, the phenylethynyl group of the coupling agent reacts with the phenylethynyl functionality of phenylethynyl containing imide adhesives and becomes chemically bonded to the matrix. The resultant adhesive bond is more durable (i.e. hot-wet environmental resistance) than adhesive bonds made without the use of the coupling agent due to covalent bond formation between the phenylethynyl containing imide-silane coupling agent or the controlled molecular weight pendent phenylethynyl amide acid oligomers terminated with aminoaryl alkoxy silanes and both the metal substrate and phenylethynyl containing imide adhesives.
Owner:SMITH JOSEPH G JR +4
Ink jet ink, ink set, ink jet recording method, ink cartridge, recording unit, and ink jet recording apparatus
ActiveUS20060102046A1Good colorHigh environmental gas resistanceMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsOrganic solventSmall-angle X-ray scattering
An ink jet ink is disclosed which includes water, a water-soluble organic solvent and a coloring material and has excellent properties. The coloring material is a specific phthalocyanine derivative and is contained in a specific amount in the ink. The water-soluble organic solvent includes a specific amount of 2-pyrrolidone. In addition, a d75 value is in a specific range where the d75 value corresponds to 75% of a dispersion distance distribution, measured by a small angle X-ray scattering method, of molecular aggregates in the ink jet ink whose coloring material concentration is adjusted to 0.5 mass %.
Owner:CANON KK
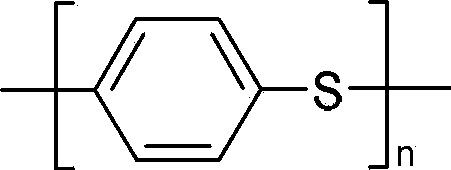
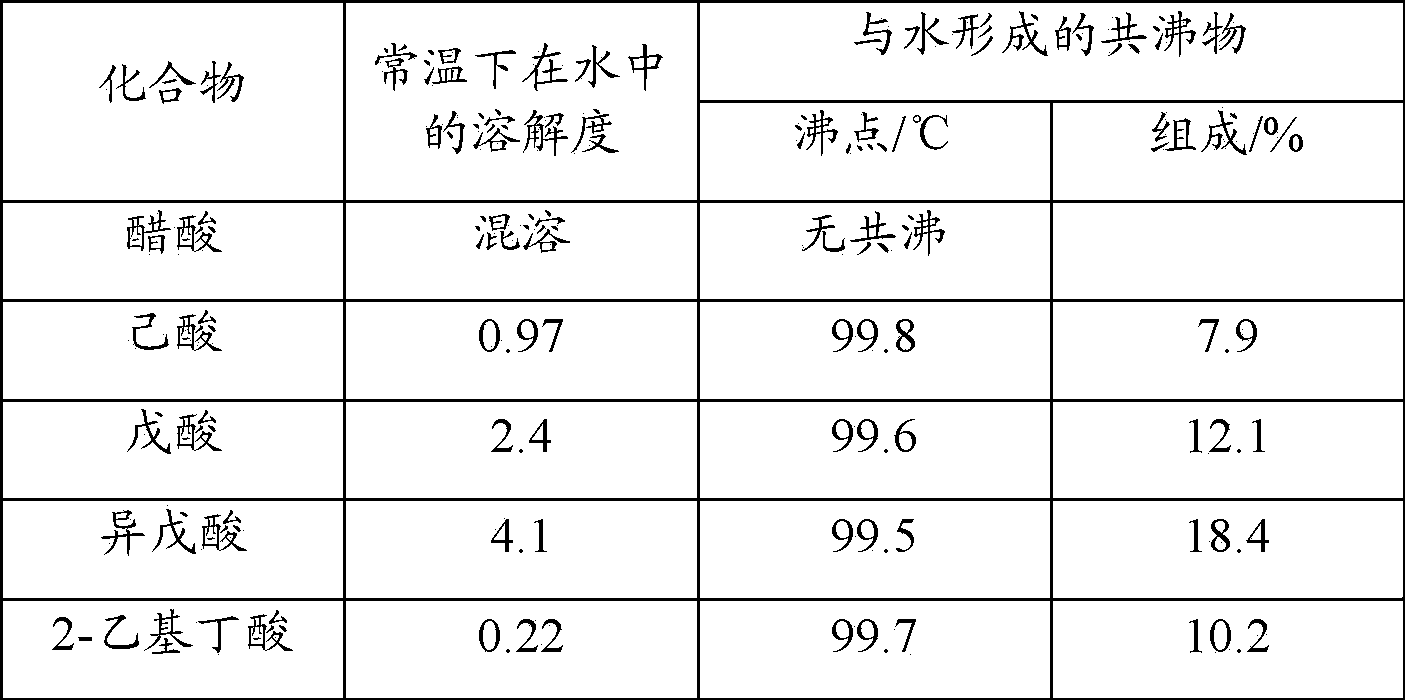
Synthesis method of fiber-grade polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) resin
Disclosed is a method for synthesizing a fibre-grade polyphenylene sulphide resin, comprising synthesizing via a polycondensation reaction by using a sodium hydrosulphide solution and p-dichlorobenzene as raw materials, N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone as a solvent, and a C5-C6 fatty acid salt formed by dehydration of a C5-C6 fatty acid and sodium hydroxide as an auxiliary for the polycondensation reaction. The reaction liquid is subjected to acidification and washing to obtain a white polyphenylene sulphide resin, the melt flow rate of the product is less than 125 g / 10 min, the weight-average molecular weight measured by GPC is greater than 4.2 × 104, and the whiteness is higher than 90, meeting the requirements of the fibre-grade polyphenylene sulphide resin. In the method of the present invention, the C5-C6 fatty acid salt used has good solubility in NMP and can better promote the polycondensation reaction, all of it enters a filtrate after reaction and filtration, and it is again converted into a free fatty acid through acidification with hydrochloric acid; and the C5-C6 fatty acid can co-boil with water, has low solubility in water, and can be recovered from the filtrate by the method of co-boiling with water, thereby avoiding the problem that both the auxiliary and sodium chloride are dissolved in water and cannot be separated and recovered.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NHU SPECIAL MATERIALS +3
Pesticidal emulsifiable concentrate composition
InactiveUS6878674B2Improve emulsion stabilityGood low temperature stabilityBiocideDead animal preservationPolyoxyethylene castor oilPhenyl Ethers
There is provided a novel pesticidal emulsifiable concentrate composition that contains a phenoxypropionate herbicide (e.g., quizalofop-p-ethyl), a polar solvent (e.g., N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone), non-polar solvent (e.g., aromatic or aliphatic hydrocarbon) and a surfactant (e.g., polyoxyethylene castor oil ether, polyoxyethylene styryl phenyl ether), and that is improved in low-temperature stability and emulsion stability.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
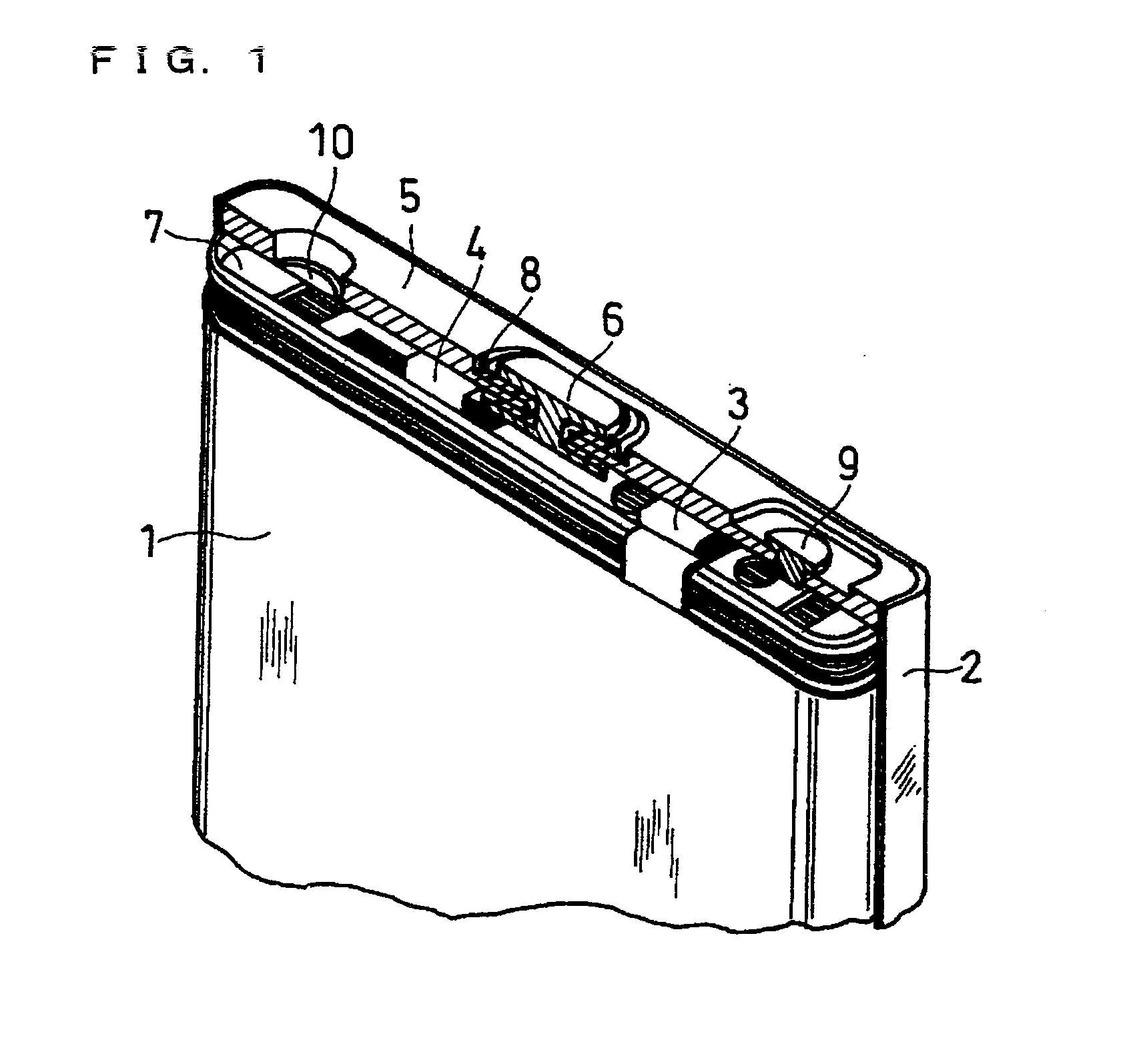
Lithium Ion Secondary Battery And Method For Producing Negative Electrode Therefor
InactiveUS20070292765A1Improve securityEasy to separateElectrode thermal treatmentFinal product manufacture2-PyrrolidoneInorganic compound
The present invention relates to an improvement in a lithium ion secondary battery including a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a separator, a non-aqueous electrolyte, and a porous film formed on at least one electrode surface. The porous film includes inorganic compound particles and polyvinylidene fluoride. The viscosity of the N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone solution dissolving 8 wt % polyvinylidene fluoride is 600 to 2400 mPa·s at 25° C., and the amount of the polyvinylidene fluoride in the porous film is 1 to 10 parts by weight per 100 parts by weight of the inorganic compound particles.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Mixtures and Emulsions for Use in Providing Strength to Gypsum Compositions
Settable gypsum compositions are described herein which include a gypsum slurry, comprising water; and a first additive comprising a vinyl acetate / ethylene copolymer in latex or emulsion form and a second additive which is at least one of (i) a wetting agent and / or a surfactant; (ii) a titanium coupling agent, (iii) a zirconium coupling agent, and (iv) mixtures thereof. The compositions demonstrate improved strength and gypsum core adhesion. Such compositions may also include at least one dispersant and / or a wetting agent and / or a surfactant. Such dispersants may be lignosulfonic acid, naphthalene sulfonic acid, and combinations and salts thereof and the wetting agent and / or surfactant may be N-dodecyl 2-pyrrolidone, ethoxylated alcohol, and combinations thereof. The dispersant and / or wetting agents and / or surfactants can further enhance rheological properties to benefit the enhanced strength gypsum compositions.
Owner:OU HENRY
High-temperature-resistant salt-resistant fluid loss agent and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-temperature-resistant salt-resistant fluid loss agent which is prepared by polymerizing the following components in parts by weight: 40-60 parts of 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid, 10-40 parts of acrylamide, 10-40 parts of alkyl substituted acrylamide or N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone, 5-30 parts of unsaturated carboxylic acid and 5-20 parts of sodium p-styrenesulfonate, and an initiator which accounts for 0.1-1.0 wt% of the five components above. The invention also provides a preparation method of the fluid loss agent. The fluid loss agent has better high temperature resistance, and the maximum normal use temperature can reach 200 DEG C. The fluid loss agent has higher salt resistance, and can resist a saturated NaCl solution. The cement mortar with the fluid loss agent has the advantages of high system stability and high compression strength, and does not have the phenomenon of longer thickening time along with the temperature increase.
Owner:CNPC BOHAI DRILLING ENG
Aryltricarboxyl-attached pigment-based inks with improved slewing decap
ActiveUS20070076068A1Measurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methods2-PyrrolidonePigment
Compositions, systems, and methods for ink-jet printing having improved slewing decap time can comprise a pigment having an aryltricarboxyl group covalently attached thereto; at least 12 wt % of an anti-slewing decap cosolvent selected from the group consisting of 2-pyrrolidone, derivatized 2-pyrrolidone, and mixtures thereof; and a liquid vehicle.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Ink jet recording process
ActiveUS20110234728A1Quick drying effect is goodHigh-quality and abrasion resistanceMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methods2-PyrrolidoneSolvent
Recording onto a non-ink-absorbing recording medium is performed using an aqueous ink composition containing a first solvent composed of at least one selected from 2-pyrrolidone, 1,3-dimethyl-imidazolidinone, and N,N′-dimethylpropylene urea, a second solvent composed of at least one selected from 1,2-hexanediol and 1,2-pentanediol, and a third solvent composed of at least one selected from glycol diethers and heating the non-ink-absorbing recording medium at 40 to 60° C.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Polishing composition
InactiveCN101496143AFull grinding speedImprove flatnessOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEthylenediamineEthyl group
Disclosed is a polishing composition which realizes both high planarity and reduction of corrosion in the surface of a wiring metal. Specifically disclosed is a polishing composition containing an oxidizing agent (A), at least one or more acids (B) selected from amino acids, carboxylic acids having 8 or less carbon atoms and inorganic acids, a sulfonic acid (C) having a concentration of not less than 0.01% by mass and an alkyl group having 8 or more carbon atoms, a fatty acid (D) having a concentration of not less than 0.001% by mass and an alkyl group having 8 or more carbon atoms, and at least one or more compounds (E) selected from pyridinecarbonyl compounds, nonionic water-soluble polymers, 2-pyrrolidone, N-methylpyrrolidone, 1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone, gramine, adenine, N,N'-diisopropylethylenediamine, N,N'-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ethylenediamine, N,N'-dibenzylethylenediamine and N,N'-diphenylethylenediamine.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Ink composition and method of recording a recording medium using this
This consists in an ink composition containing: a coloring agent, 2-pyrrolidone, a specific surfactant, a butyl ether-based solvent, water, and a water-soluble organic solvent. With the present invention, it is possible to provide an ink composition with which clogging cannot occur, which is of excellent discharge stability, and which affords excellent printing quality by preventing blurring.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Process for making 5-methyl-N-alkyl-2-pyrrolidone from alkyl amine(s) and levulinic acid
This invention relates to a process for producing a reaction product comprising 5-methyl-N-alkyl-2-pyrrolidone by (a) reacting levulinic acid with alkyl amine(s) and (b) hydrogenating the products of step (a) in the presence of a metal catalyst, which is optionally supported.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for producing lithium-containing composite oxide and non-aqueous secondary battery
InactiveUS20100136412A1Suppress inclusionExcellent battery characteristicsConductive materialAlkali metal oxides2-PyrrolidoneWater soluble
A method for producing a lithium-containing composite oxide represented by General Formula (1):LixMyMe1−yO2+δ (1)where M represents at least one element selected from the group consisting of Ni, Co and Mn, Me represents a metal element that is different from M, 0.95≦x≦1.10 and 0.1≦y≦1. A lithium compound and a compound that contains M and Me are baked. The thus-obtained baked product is washed with a washing solution that contains one or more water-soluble polar aprotic solvents such as N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP), N,N′-dimethylimidazolidinone (DMI) and dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Ink Composition for Inkjet Printing
The invention provides an ink composition for ink-jet printing which does not cause clogging of nozzles of an ink-jet printer during printing, to thereby provide a print of desired printing quality; which ensures an appropriate drying rate of printed images; and which attains excellent color development. The ink composition for ink-jet printing, containing a pigment, a binder resin, a pigment dispersant, and a solvent, wherein the solvent is formed of (1) at least one glycol ether and at least one of a lactone compound and 2-pyrrolidone, or (2) at least one glycol ether acetate and at least one of cyclohexane and isophorone.
Owner:DAI NIPPON TORYO CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com