Patents
Literature
70 results about "Vacuum assisted resin transfer molding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
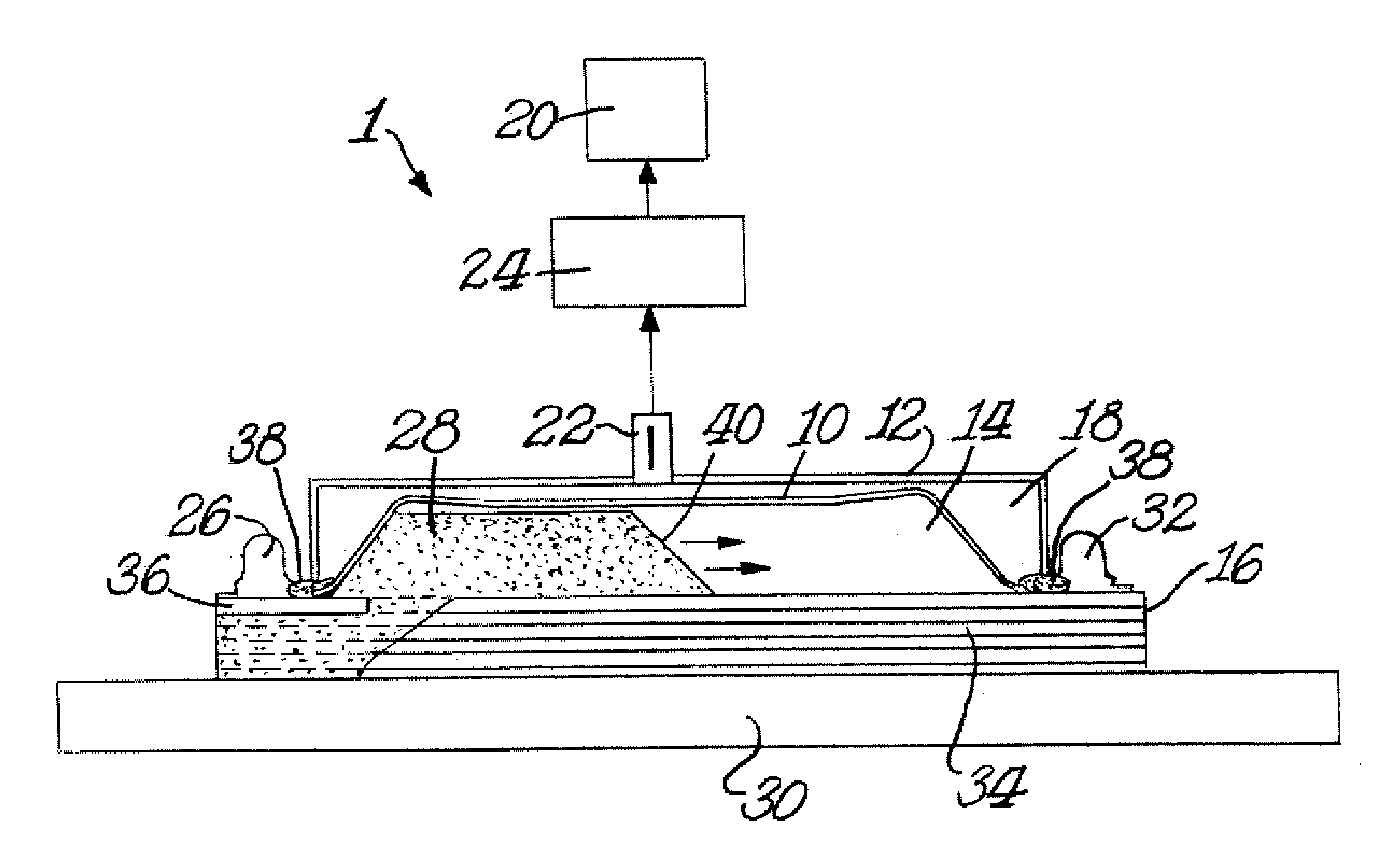
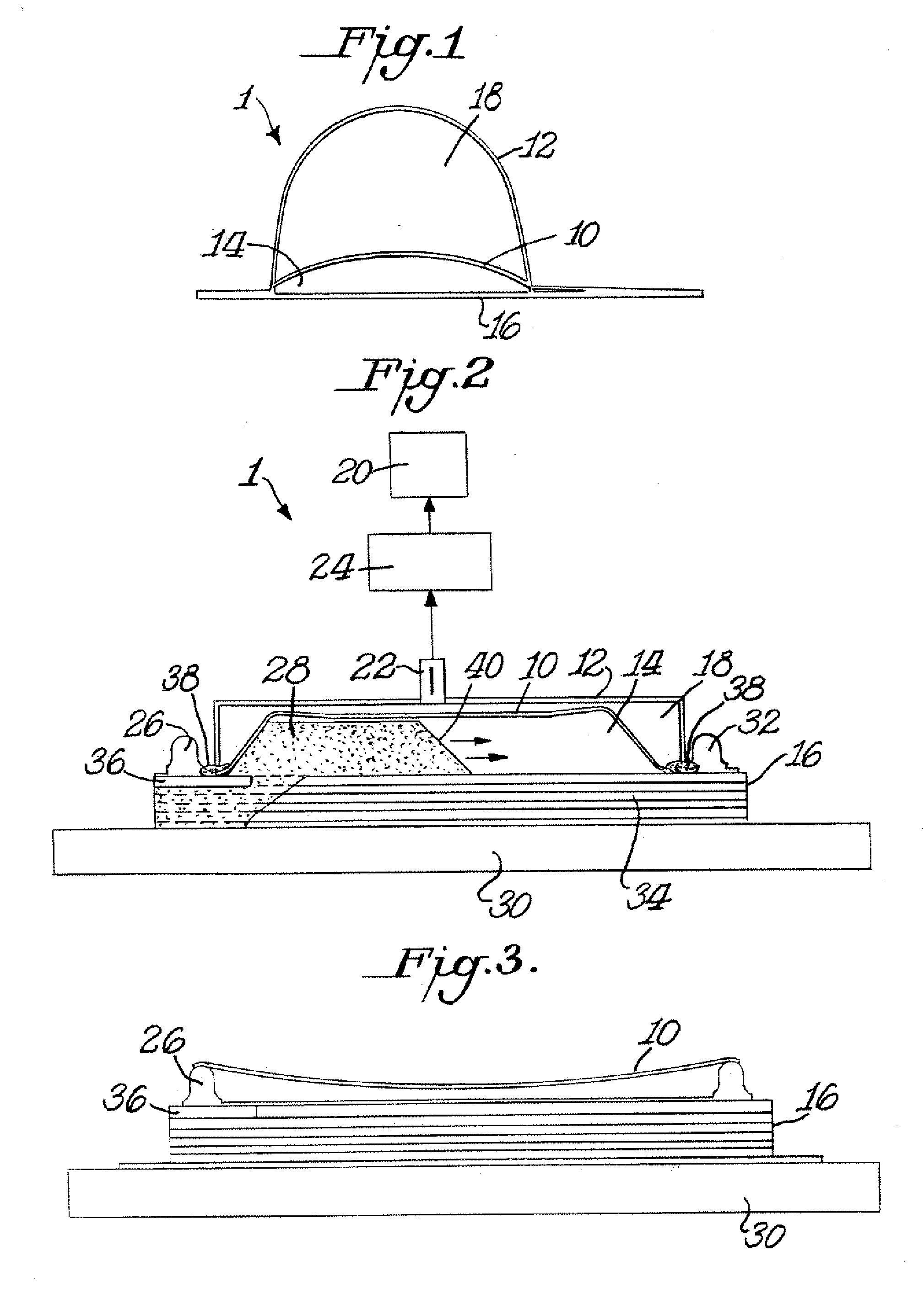
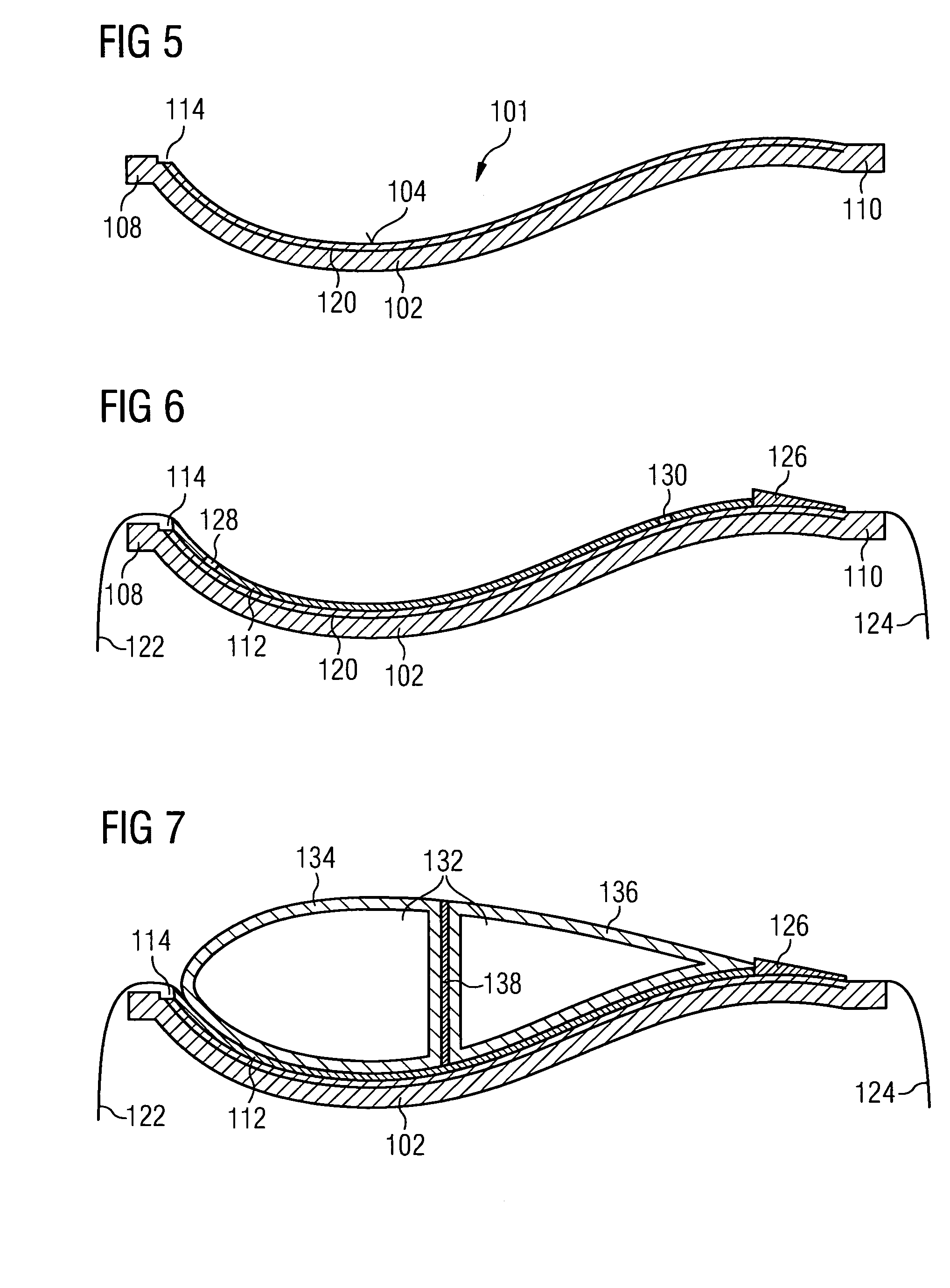
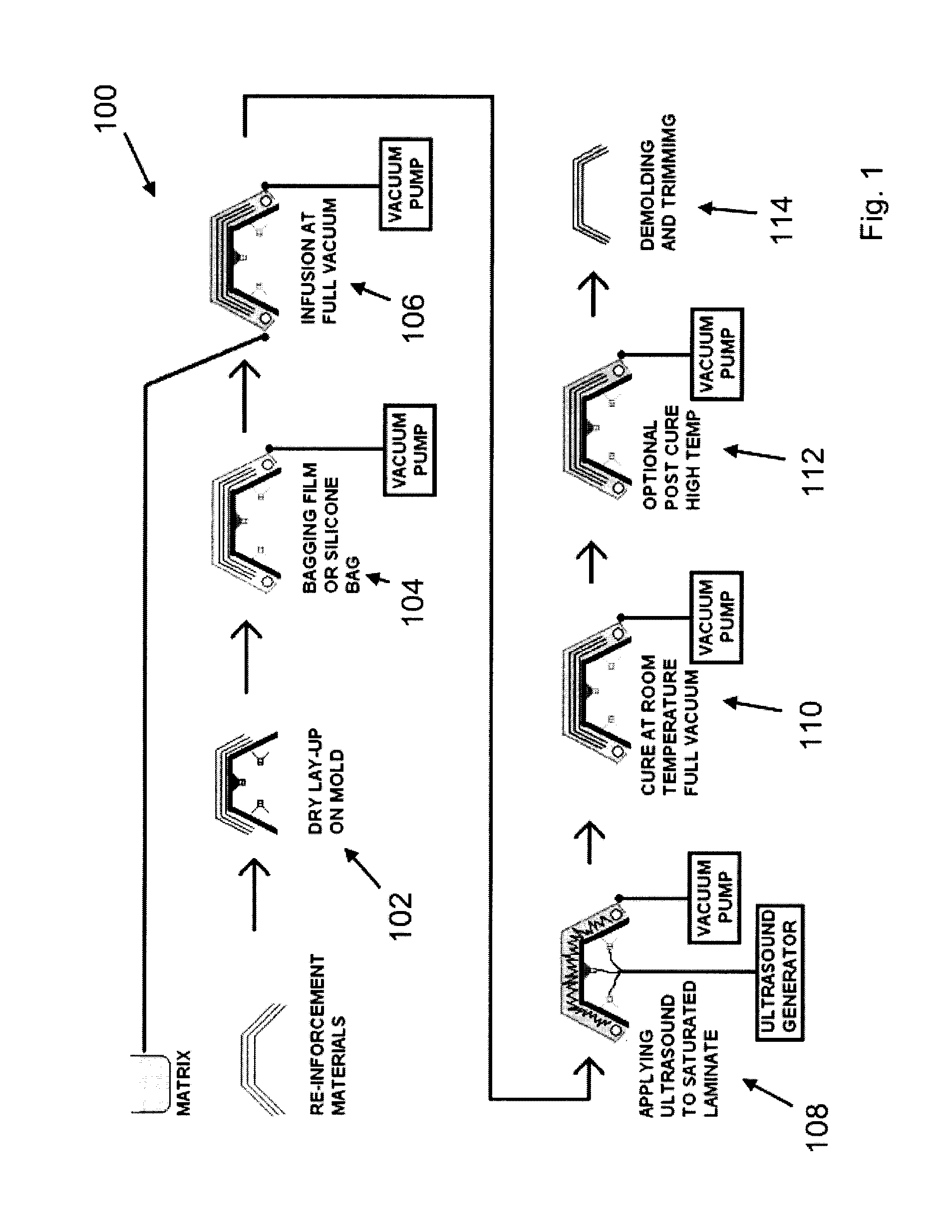
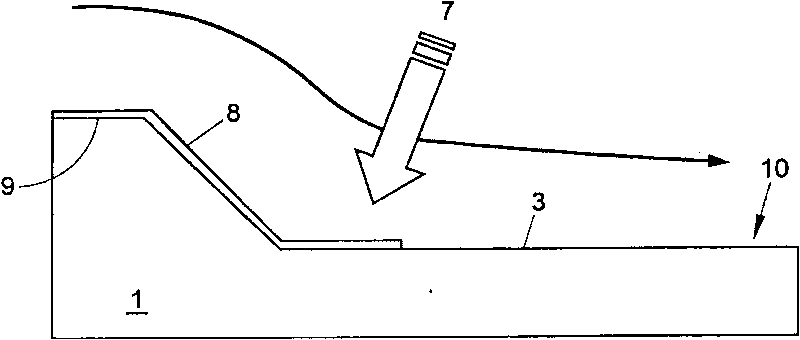
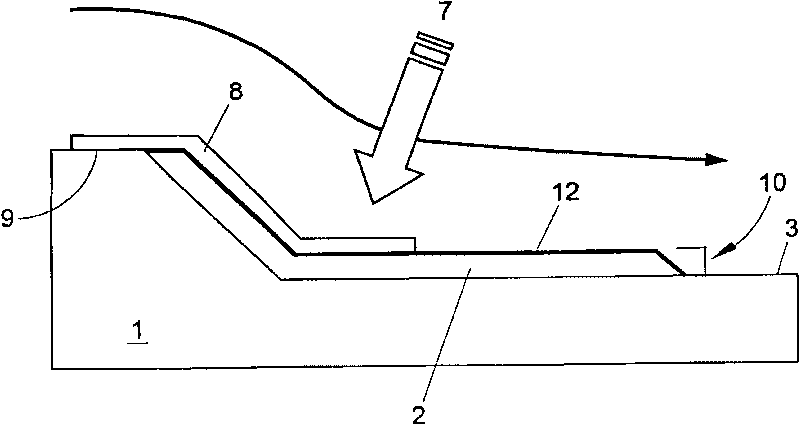
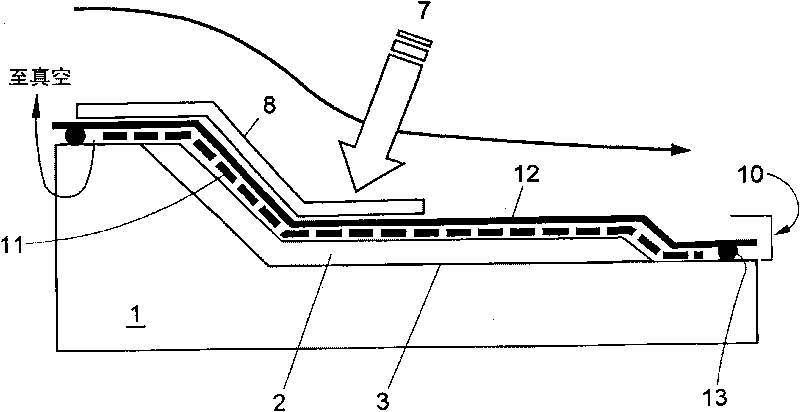
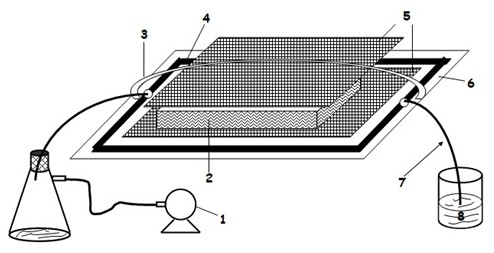
Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding (VARTM) or Vacuum Injected Molding (VIM) is a closed mold, out of autoclave (OOA) composite manufacturing process. VARTM is a variation of Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) with its distinguishing characteristic being the replacement of the top portion of a mold tool with a vacuum bag and the use of a vacuum to assist in resin flow. The process involves the use of a vacuum to facilitate resin flow into a fiber layup contained within a mold tool covered by a vacuum bag. After the impregnation occurs the composite part is allowed to cure at room temperature with an optional post cure sometimes carried out.
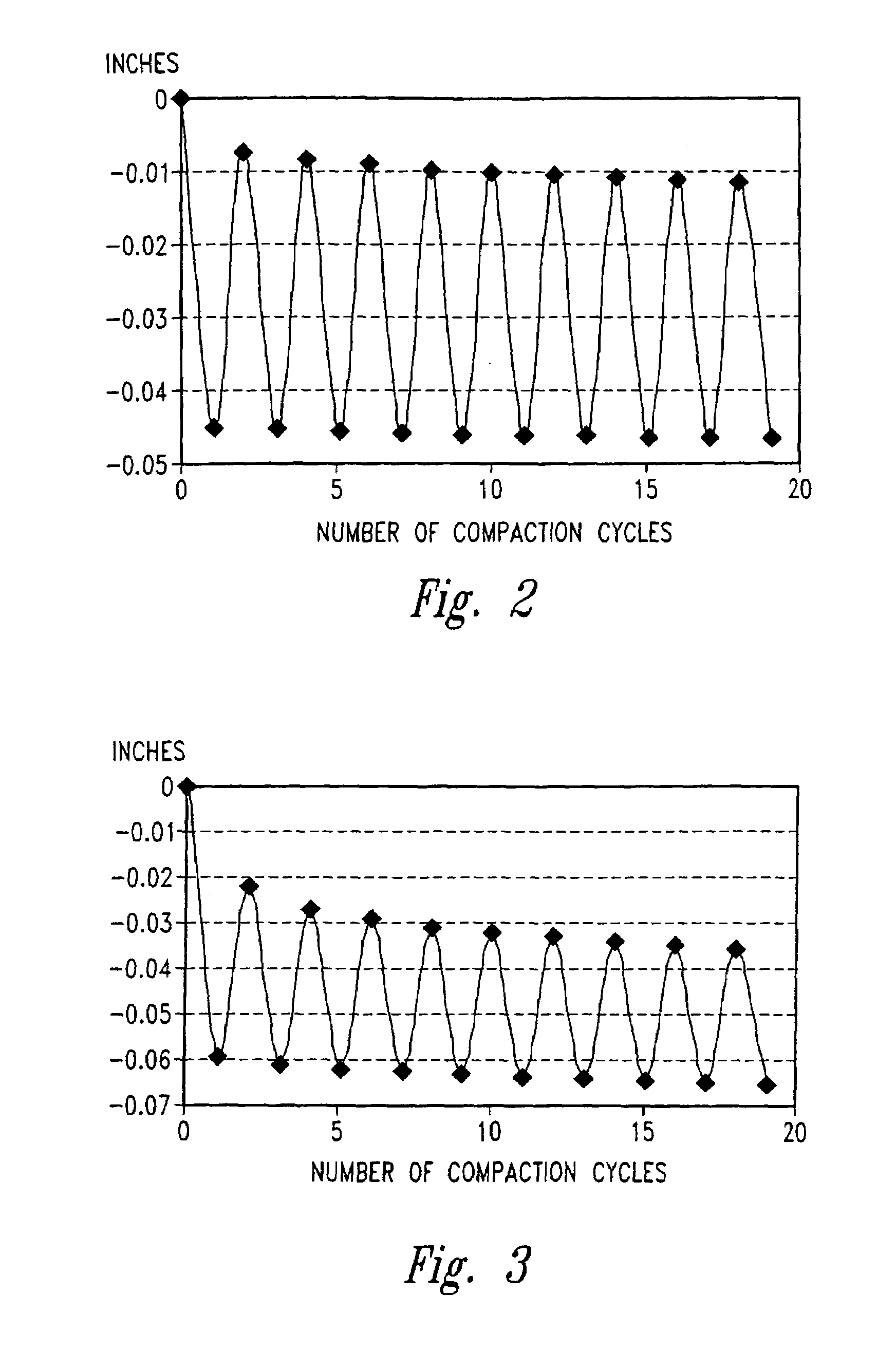
Controlled atmospheric pressure resin infusion process
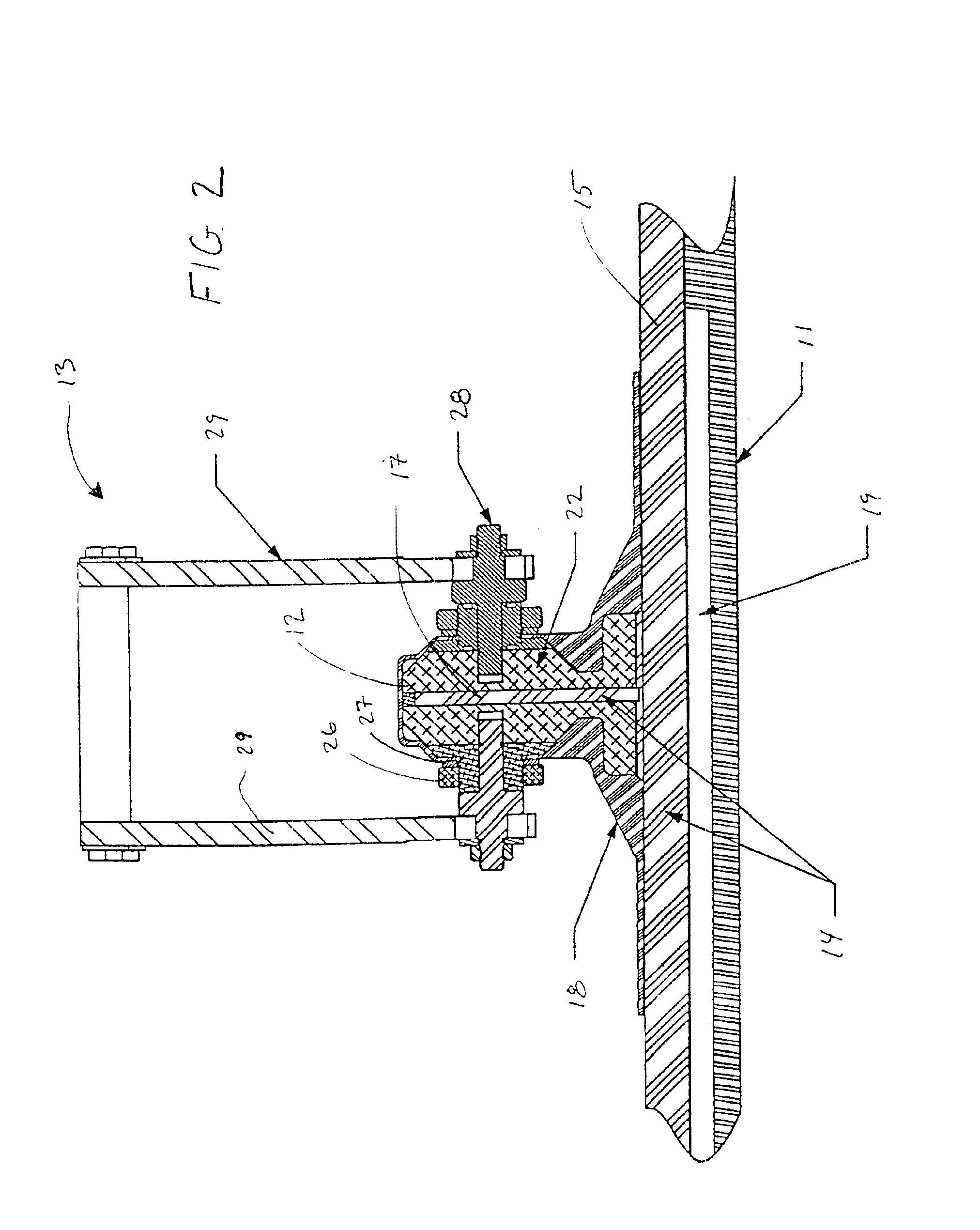
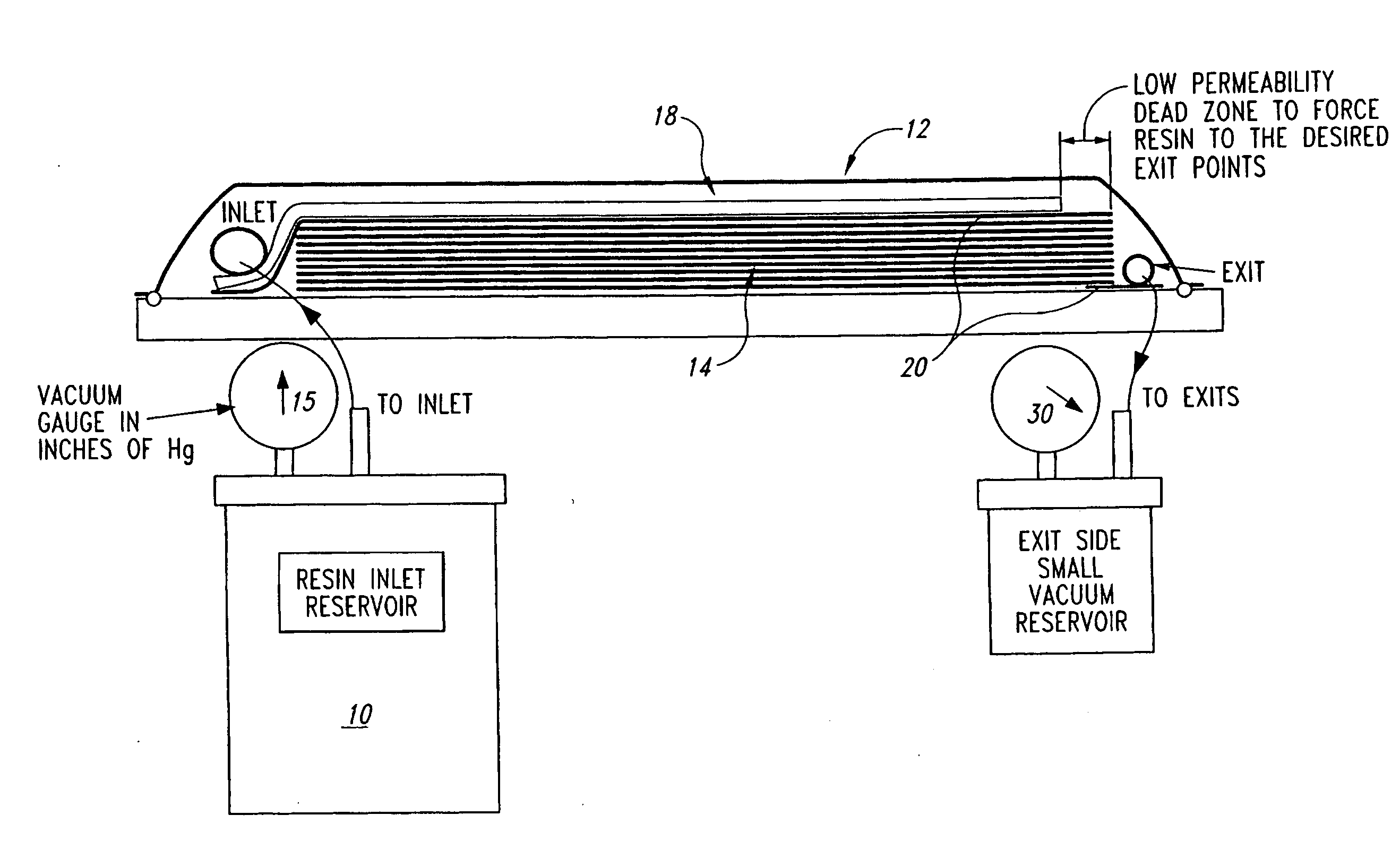
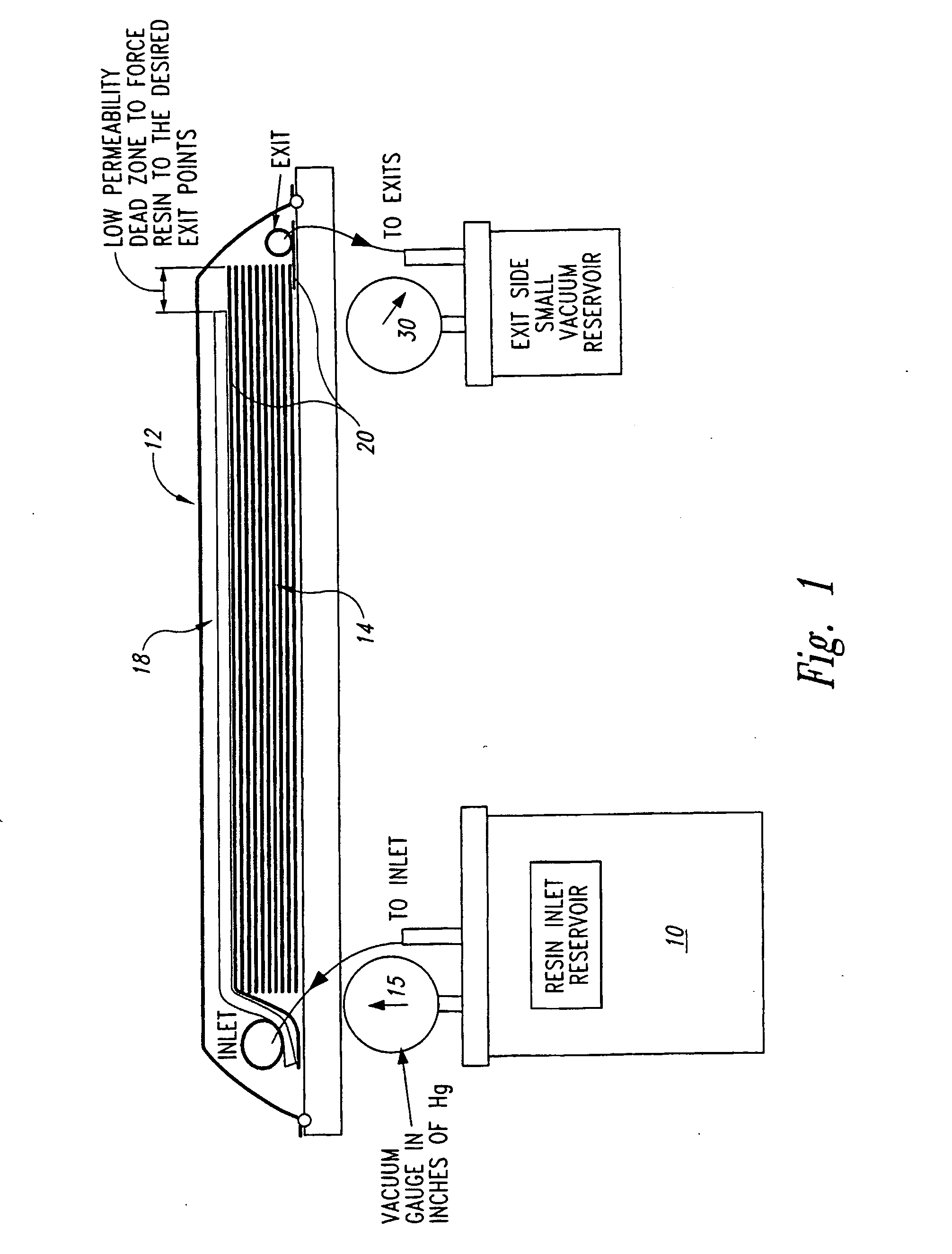
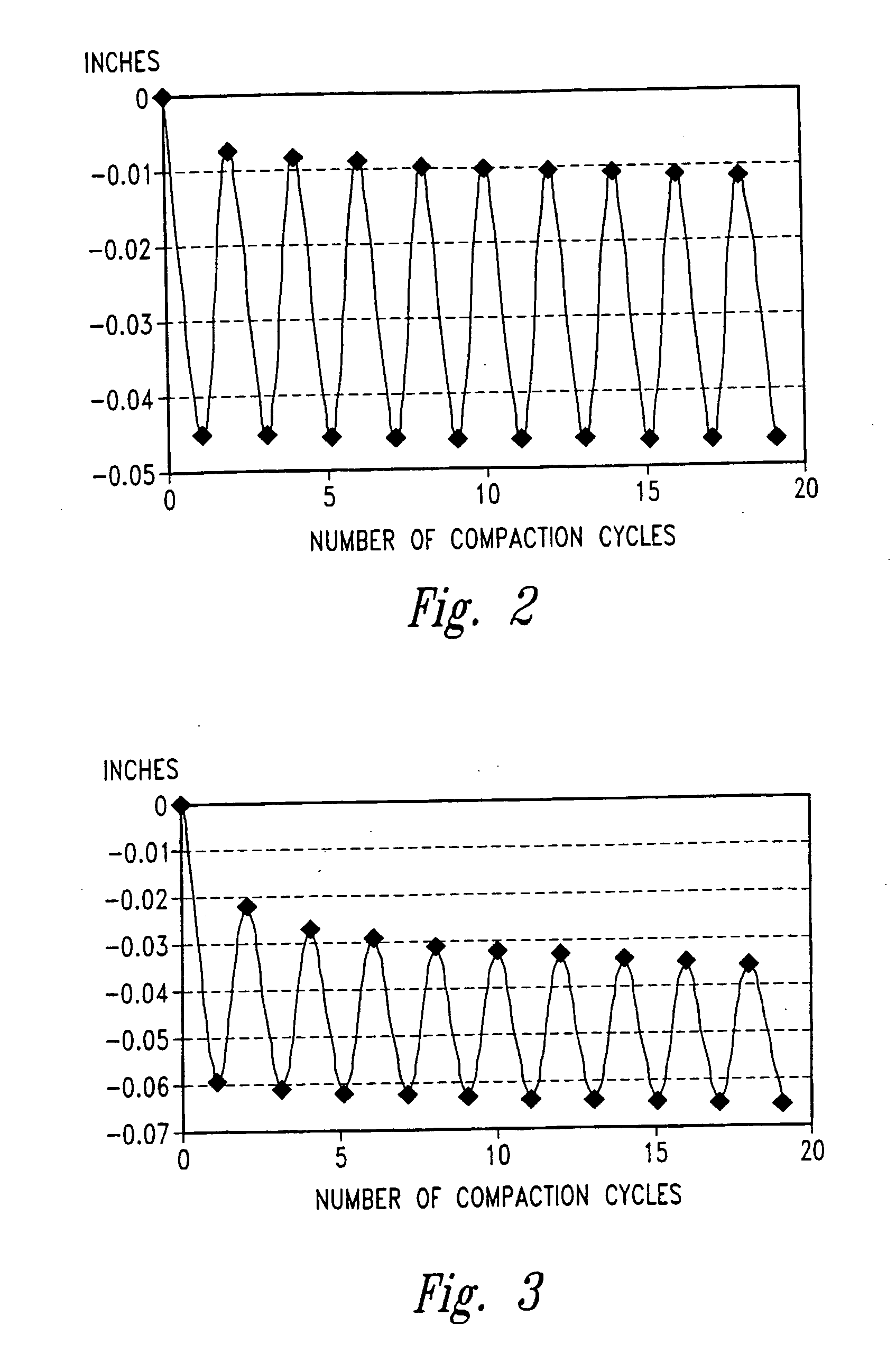
By evacuating the resin feed tank to a pressure below atmospheric pressure, employing cyclic compaction, and controlling the net compaction pressure, we are better able to control a resin infusion process, particularly a vacuum assisted resin transfer molding process, and produce aerospace-grade fiber-reinforced resin composite having fiber volume fractions and tool-side surface finishes comparable to or exceeding those made using an autoclave.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
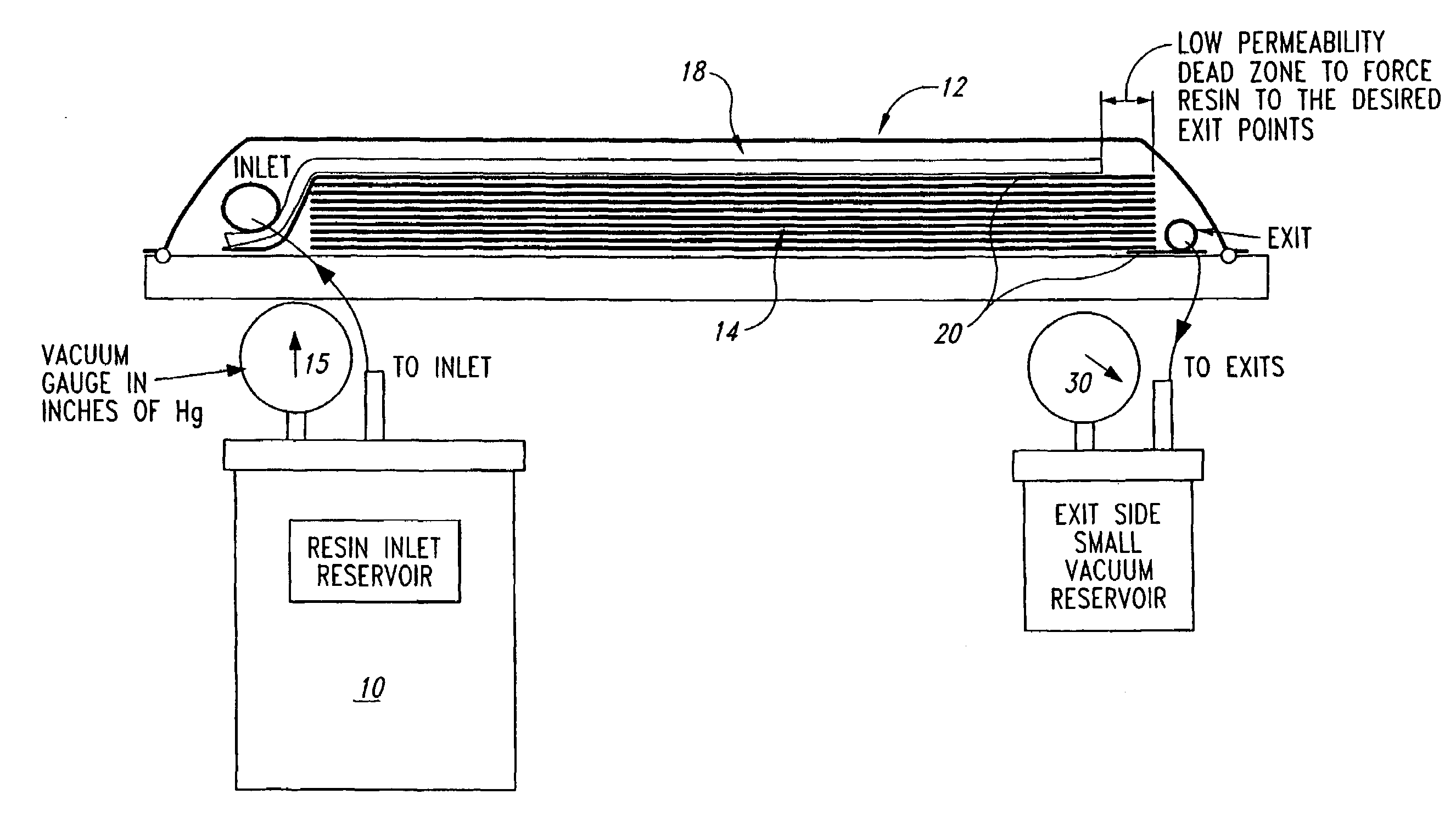
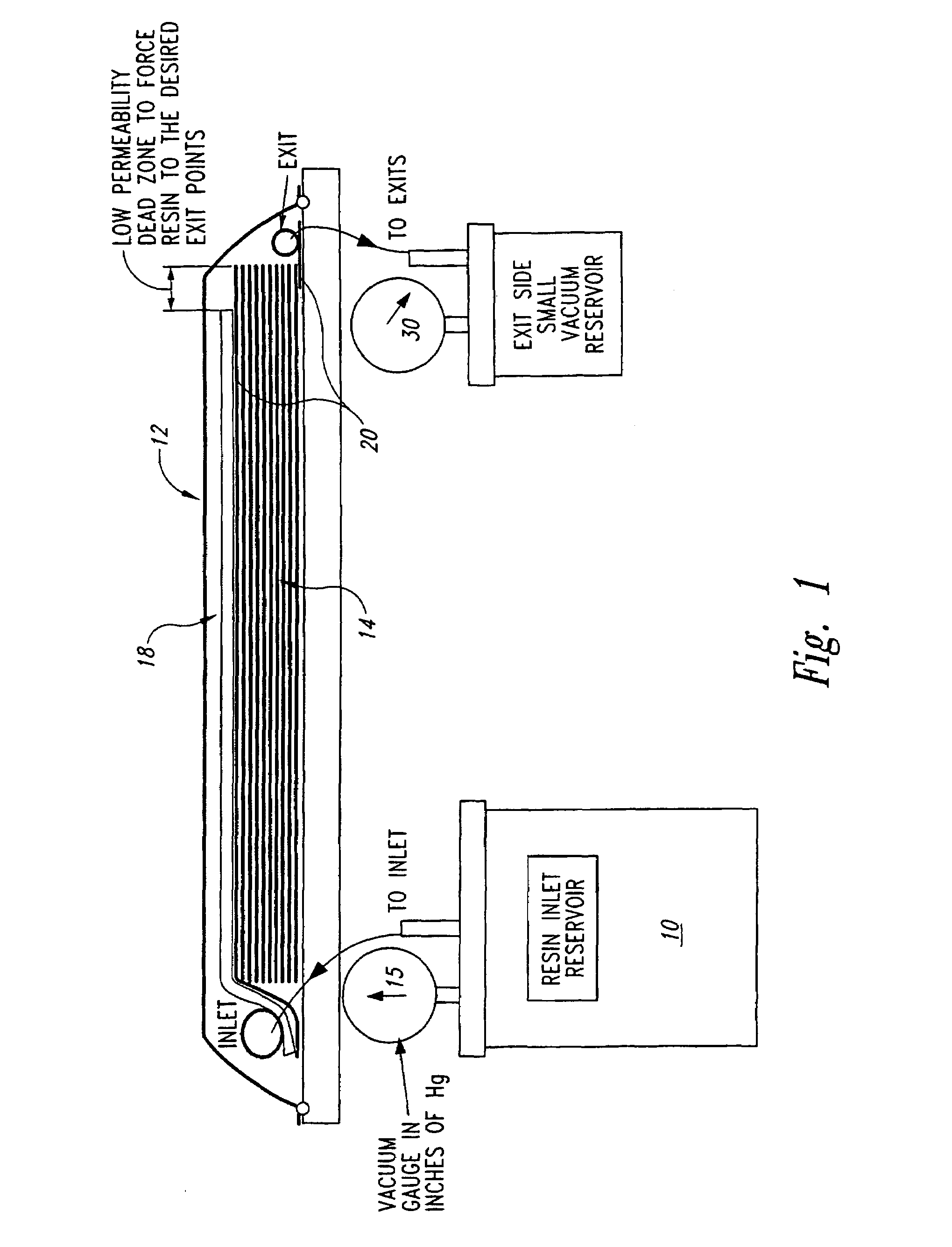
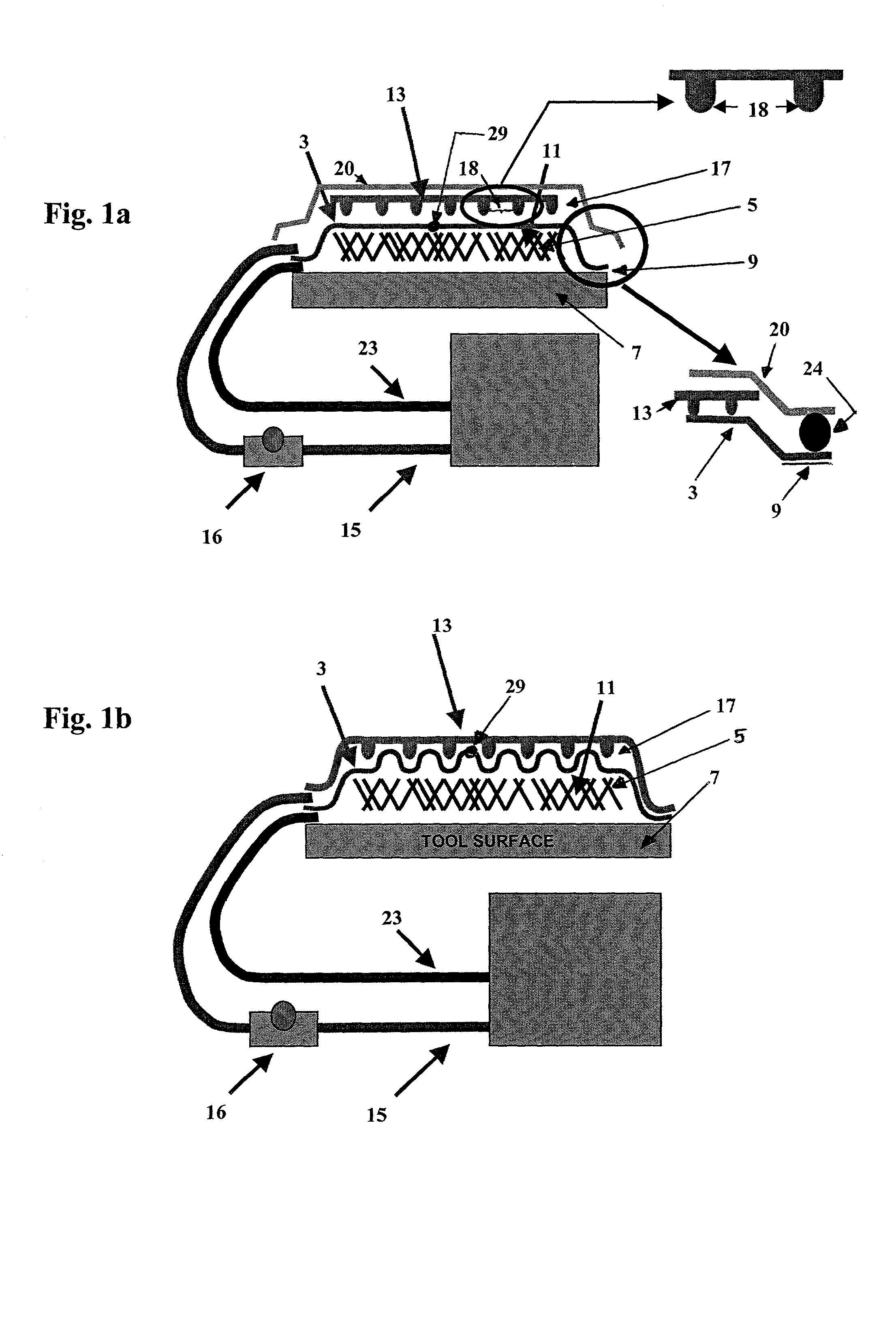
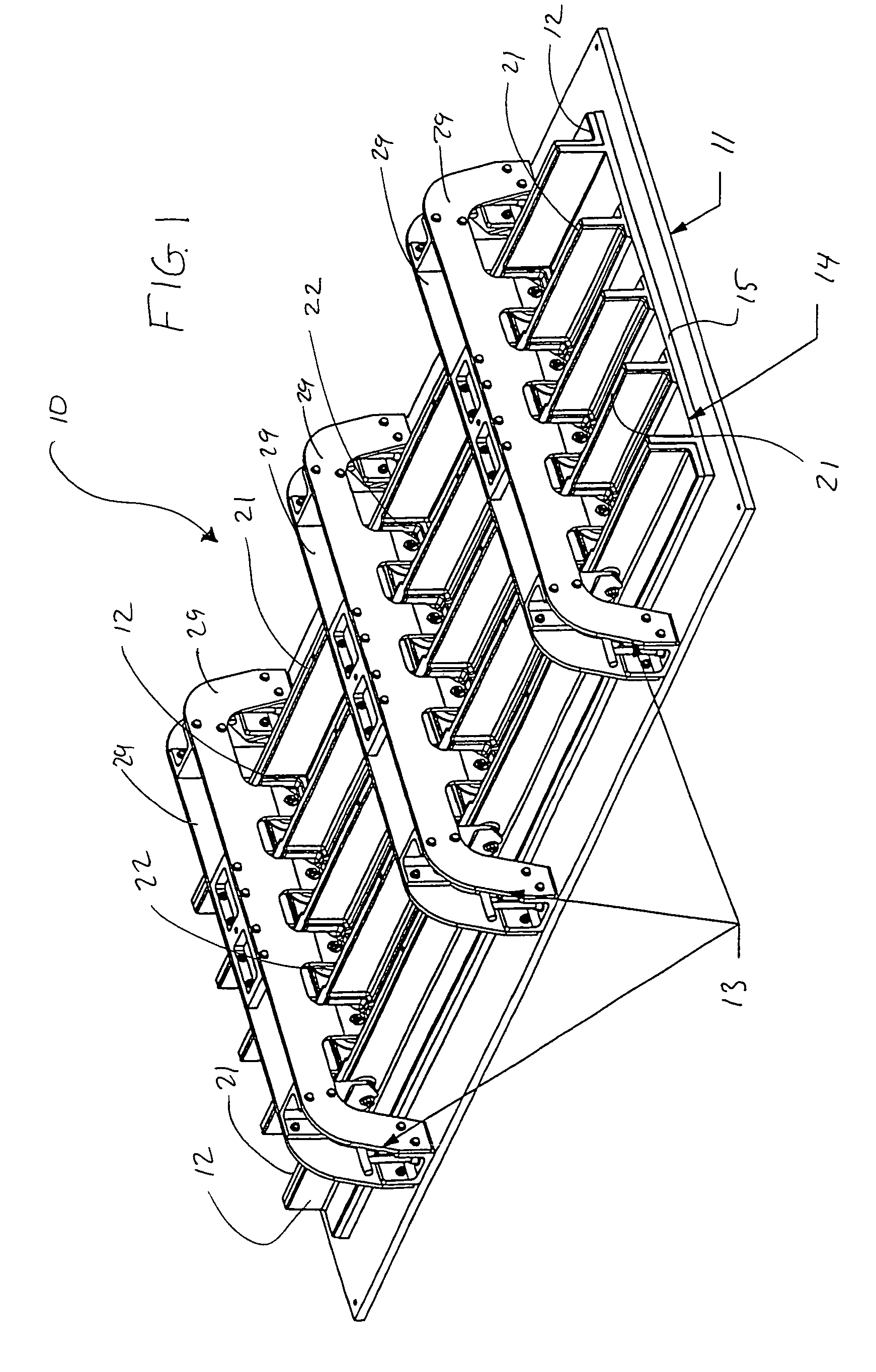
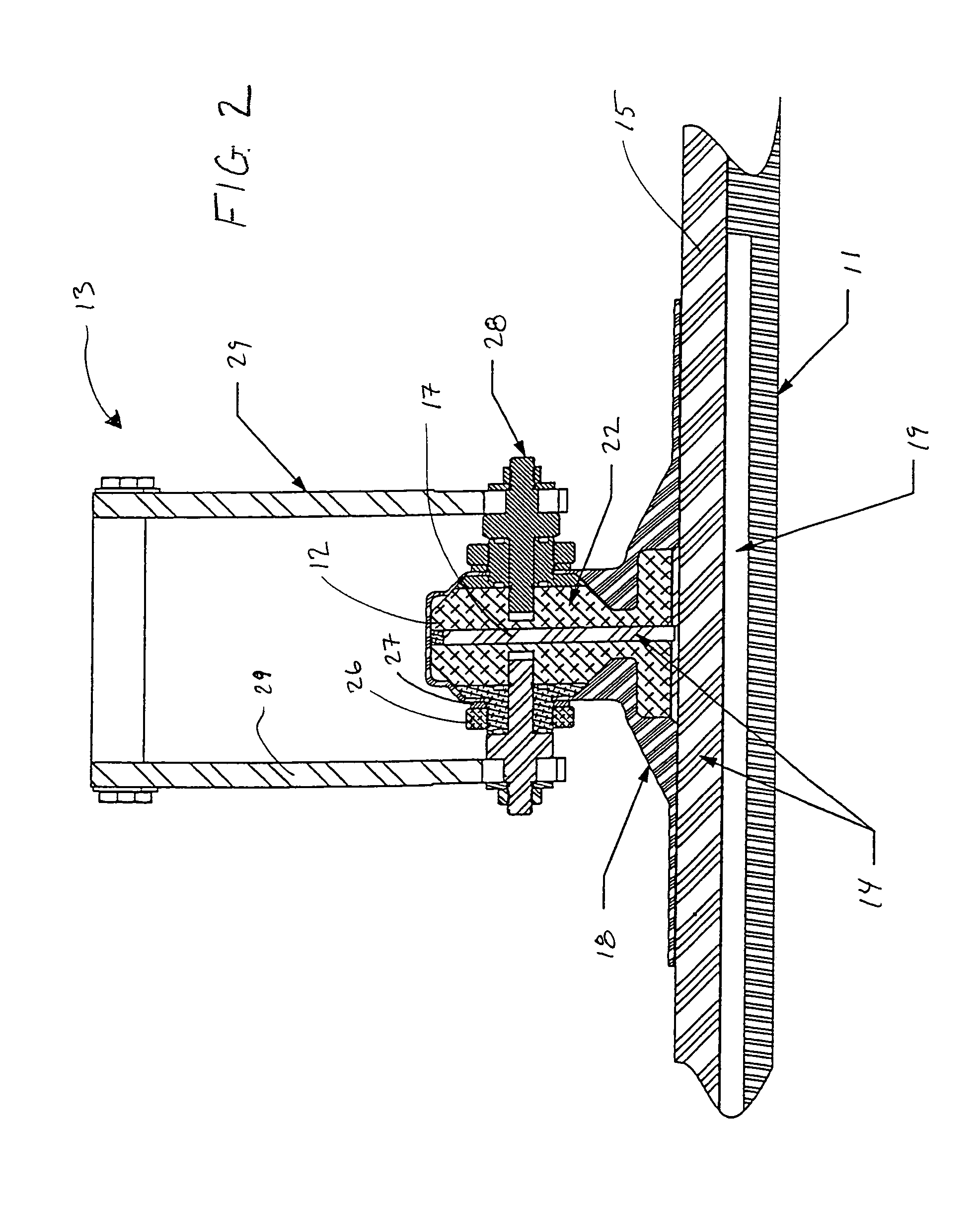
Apparatus and method for selectively distributing and controlling a means for impregnation of fibrous articles
InactiveUS20020155186A1Quick configurationMinimize and eliminate wasteTailstocks/centresConfectioneryFiberLine tubing
A process and apparatus for producing fiber reinforced resin structures using vacuum assisted resin transfer molding technology, wherein the apparatus and process employ a first fluid impervious flexible sheet containing therein a resin port; a fiber containing preform; a primary vacuum line; a resin channeling means; and a secondary vacuum line. The fluid impervious flexible sheet is placed over or around the fiber containing preform to form a chamber to which the primary vacuum line is connected. The resin channeling means is positioned on top of the fluid impervious flexible sheet, exterior to the chamber containing the preform in a fashion so as to form a pocket between or around the resin channeling means and said fluid impervious flexible sheet to which the secondary vacuum is applied. Activation of the secondary vacuum causes formation of channels in the fluid impervious flexible sheet. These channels increase the speed and efficiency of resin impregnation of the fiber containing preform.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF THE ARMY AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE
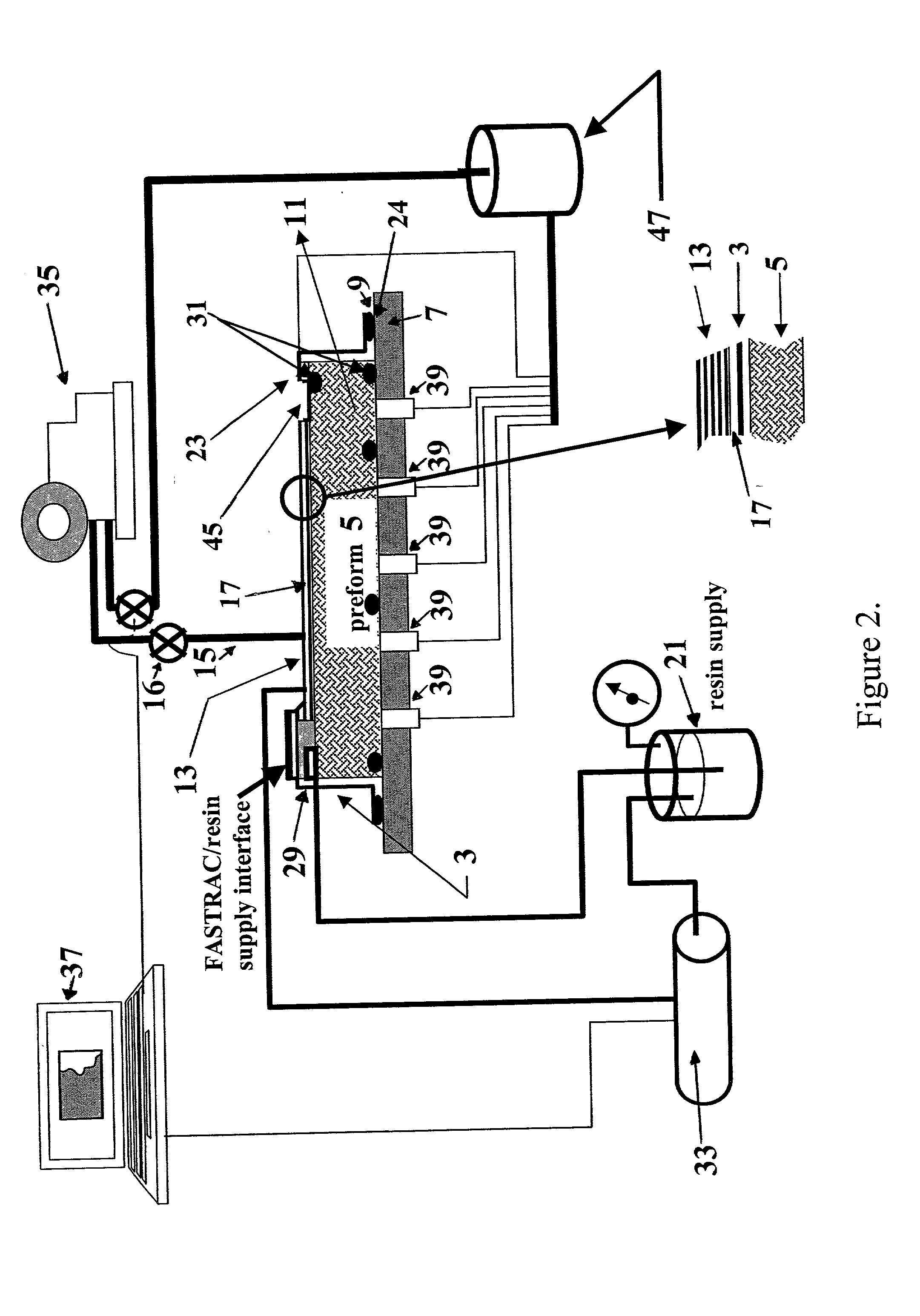
Resin infusion mold tool system and vacuum assisted resin transfer molding with subsequent pressure bleed
InactiveUS6840750B2Highly structuredHigh fiber volume fractionConfectioneryLaminationFiberLine tubing
A resin infusion mold tool system for use in a vacuum assisted resin transfer molding process with a subsequent pressure bleed step. The mold tool system includes a mold assembly having an outer mold line tool connected to resin supply lines and supplying resin to the preform. A plurality of inner mold line tools form a hard interface with the inner mold line of the fiber preform and are held to within tight tolerances by an external locating fixture. Excess resin is drawn out of the fiber preform using a vacuum bag connected to vacuum lines and disposed over the inner mold line tools but not between the tools and the fiber preform. The mold assembly is placed in an autoclave, the resin supply lines are detached and the autoclave pressurized to bleed additional resin out of the preform to raise the fiber volume of the composite structure.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Controlled atmospheric pressure resin infusion process
ActiveUS20050073076A1Specific strength of partLow costLaminationLamination apparatusSurface finishEngineering
By evacuating the resin feed tank to a pressure below atmospheric pressure, employing cyclic compaction, and controlling the net compaction pressure, we are better able to control a resin infusion process, particularly a vacuum assisted resin transfer molding process, and produce aerospace-grade fiber-reinforced resin composite having fiber volume fractions and tool-side surface finishes comparable to or exceeding those made using an autoclave.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Vacuum assisted resin transfer molding techniques with flow flooding chamber
InactiveUS20070063393A1Short injection timeLabor savingLaminationLamination apparatusMechanical engineeringVacuum assisted resin transfer molding
Vacuum assisted resin transfer molding techniques are improved by mounting a rigid external shell on top of a vacuum bag. The shell is sealed around the vacuum bag so that a vacuum is created between the shell and the vacuum bag, the vacuum causes the vacuum bag to be freely stretched and lifted away from the preform to create a flow flooding chamber which provides a flow channel on the top face of the preform to accelerate the resin flow and reduce the injection time.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Solvent free low-melt viscosity imide oligomers and thermosetting polyimide composites
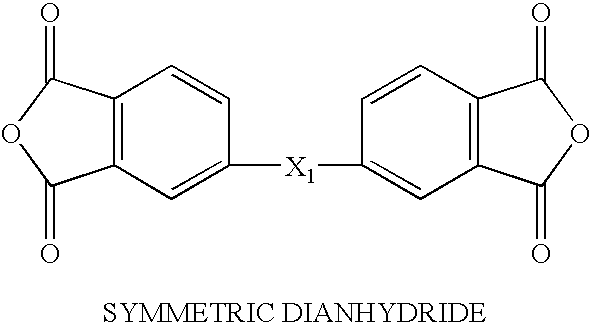
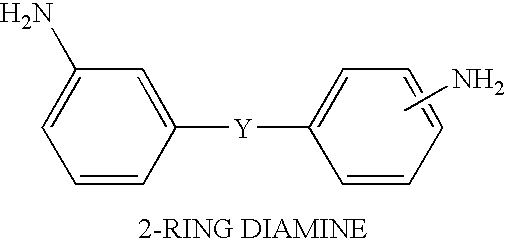
This invention relates to the composition and a solvent-free process for preparing novel imide oligomers and polymers specifically formulated with effective amounts of a dianhydride such as 2,3,3′,4-biphenyltetra carboxylic dianydride (a-BPDA), at least one aromatic diamine and an endcapped of 4-phenylethynylphthalic anhydride (PEPA) or nadic anhydride to produce imide oligomers that possess a low-melt viscosity of 1–60 poise at 260–280° C. When the imide oligomer melt is cured at about 371° C. in a press or autoclave under 100–500 psi, the melt resulted in a thermoset polyimide having a glass transition temperature (Tg) equal to and above 310° C. A novel feature of this process is that the monomers; namely the dianhydrides, diamines and the endcaps, are melt processable to form imide oligomers at temperatures ranging between 232–280° C. (450–535° F.) without any solvent. These low-melt imide oligomers can be easily processed by resin transfer molding (RTM), vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding (VARTM) or the resin infusion process with fiber preforms e.g. carbon, glass or quartz preforms to produce polyimide matrix composites with 288–343° C. (550–650° F.) high temperature performance capability.
Owner:NASA
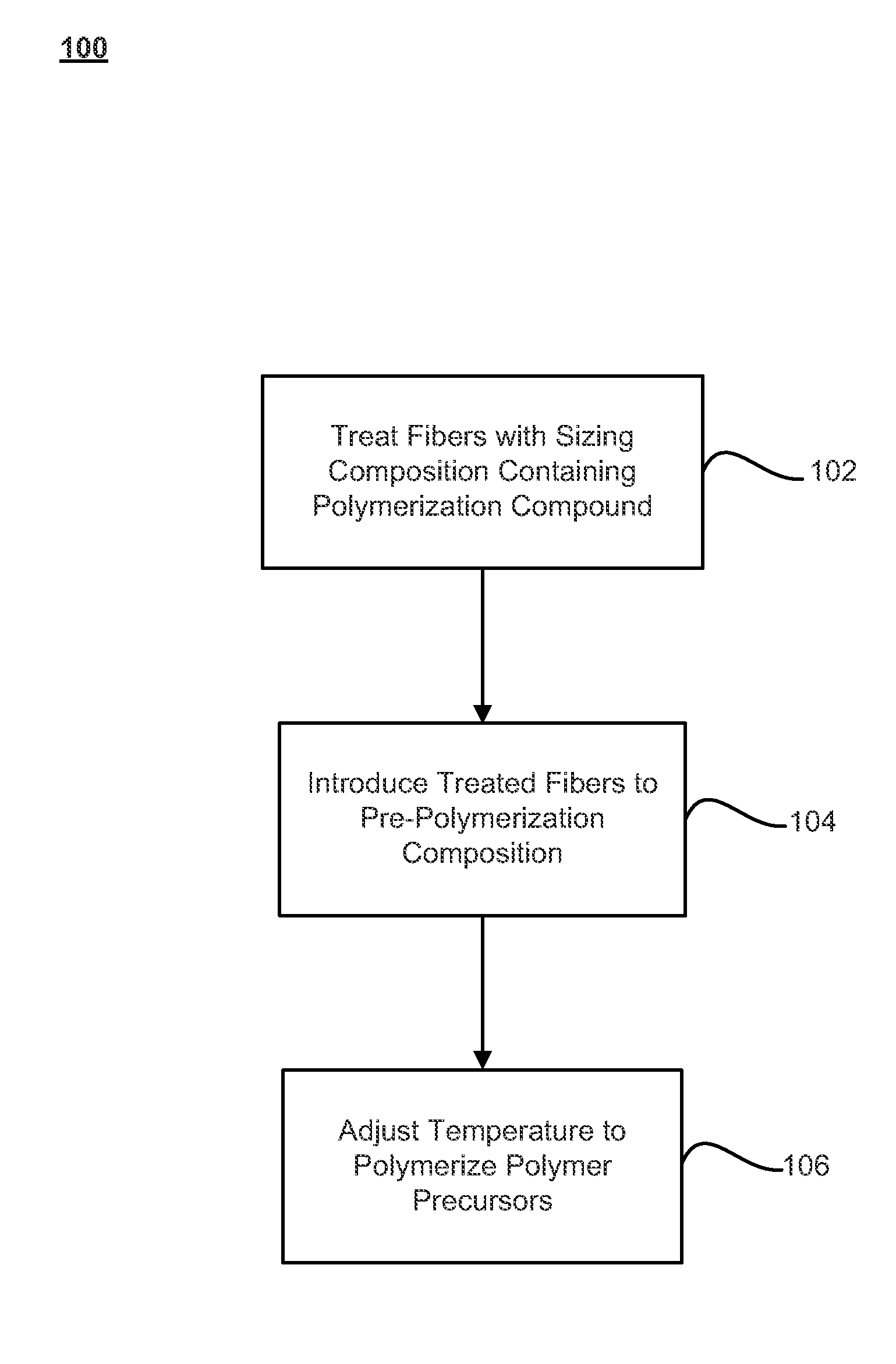
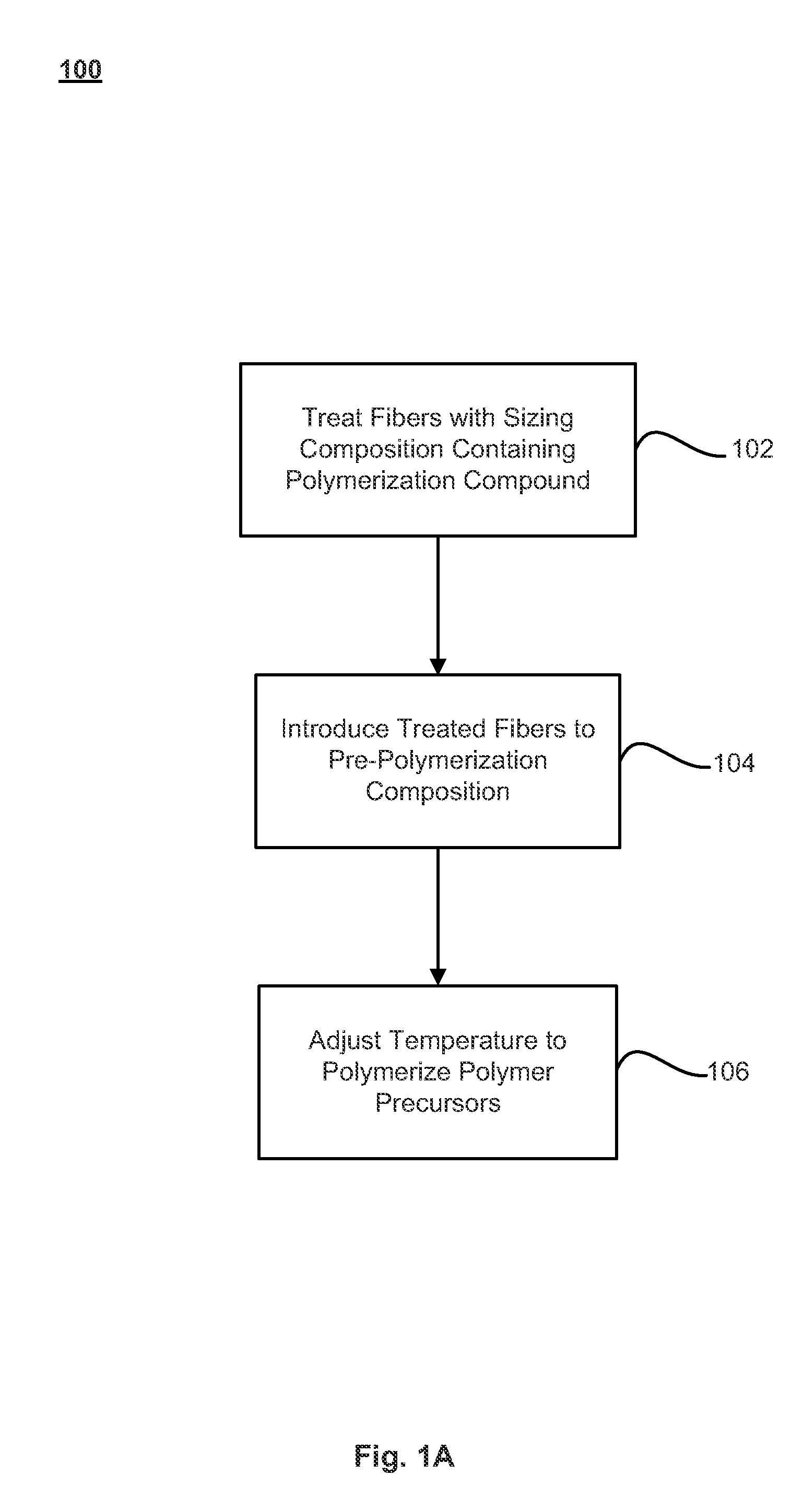
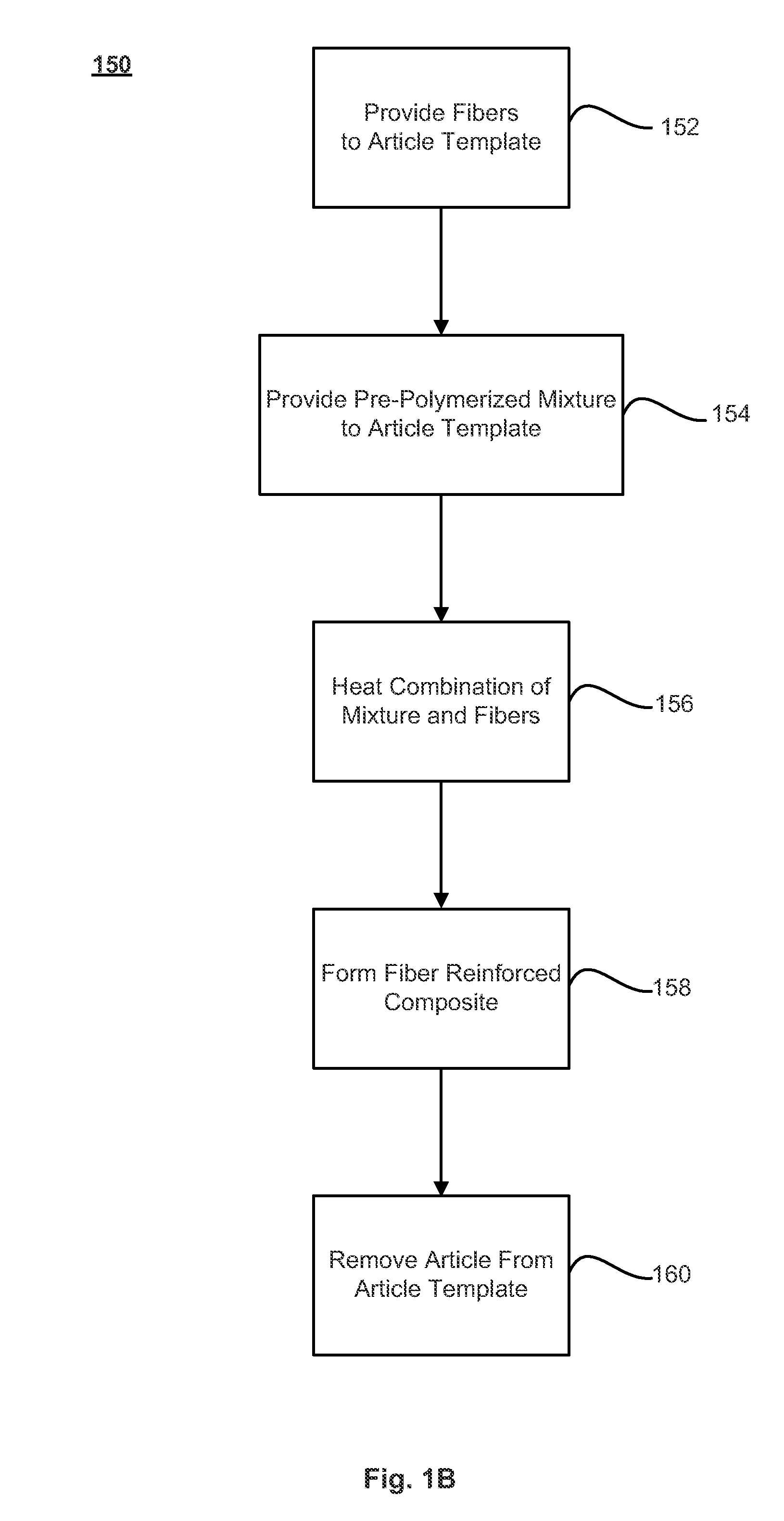
Fibers treated with polymerization compounds and fiber reinforced composites made therefrom
InactiveUS20110045275A1Group 4/14 element organic compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsFiber-reinforced compositePolymer chemistry
Methods of making fiber reinforced composite articles are described. The methods may include treating fibers with a sizing composition that includes a polymerization compound, and introducing the treated fibers to a pre-polymerized composition. The combination of the treated fibers and pre-polymerized composition may then undergo a temperature adjustment to a polymerization temperature at which the pre-polymerized composition polymerizes into a plastic around the fibers to form the fiber-reinforced composite article. Techniques for introducing the treated fibers to the pre-polymerized composition may include pultrusion, filament winding, reactive injection molding (RIM), structural reactive injection molding (SRIM), resin transfer molding (RTM), vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding (VARTM), long fiber injection (LFI), sheet molding compound (SMC) molding, bulk molding compound (BMC) molding, a spray-up application, and / or a hand lay-up application, among other techniques.
Owner:TADEPALLI RAJAPPA +3
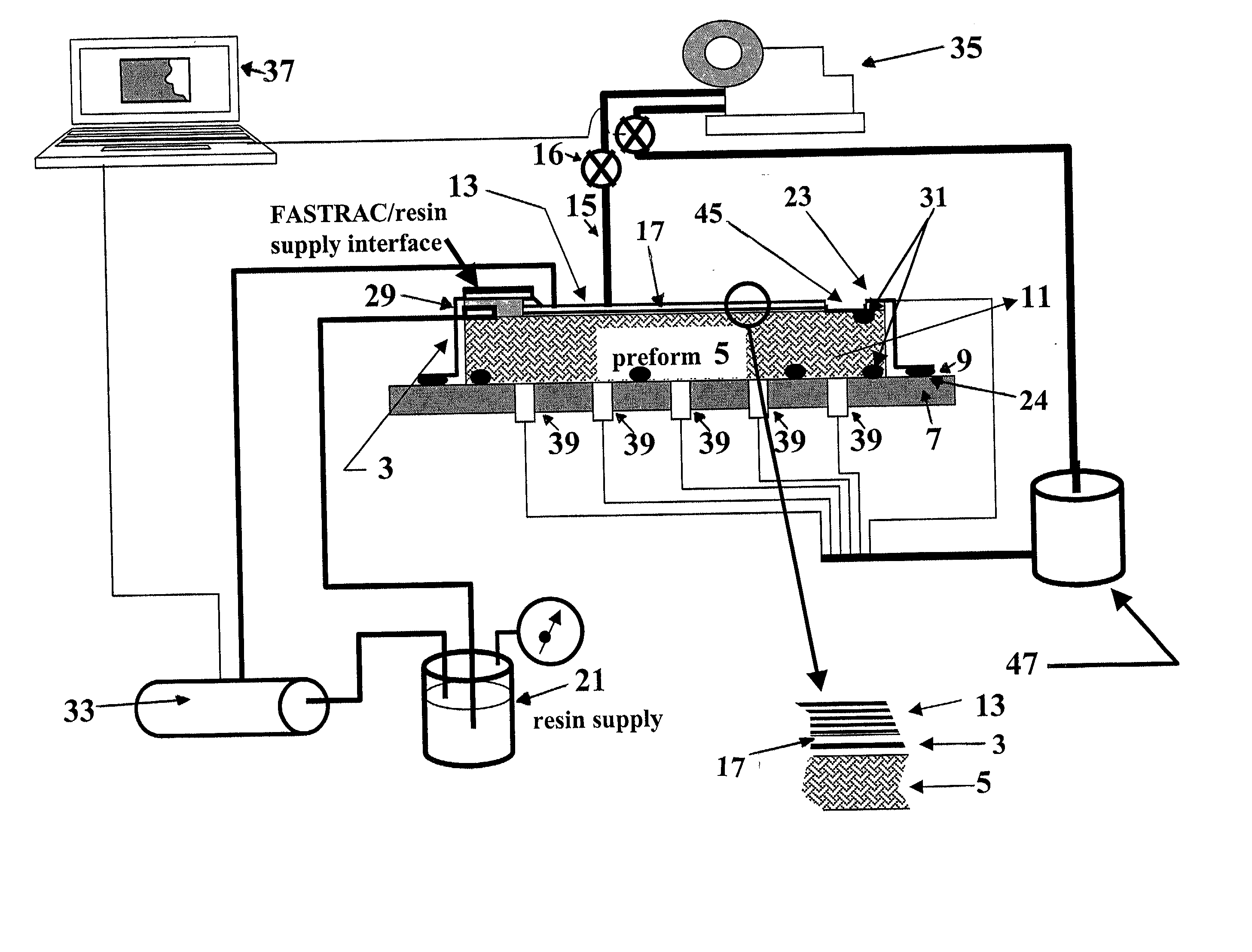
Co-cured vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding manufacturing method
ActiveUS7419627B2Substantial eliminationGood size controlLaminationWood working apparatusShell moldingEngineering
According to one embodiment of the invention, a co-cured vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding manufacturing method includes providing a tool base, disposing a prepreg skin panel outwardly from the tool base, disposing one or more tooling details outwardly from the prepreg skin panel, and disposing one or more preforms proximate the one or more tooling details. The one or more preforms are either dry or binderized. The method further includes disposing a high permeability medium between the one or more tooling details and the one or more preforms, enclosing the prepreg skin panel, the one or more tooling details, the one or more preforms, and the high permeability medium with at least one vacuum bag, pulling a vacuum on the vacuum bag, infusing the one or more preforms with a resin, and curing the one or more preforms and the prepreg skin panel.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
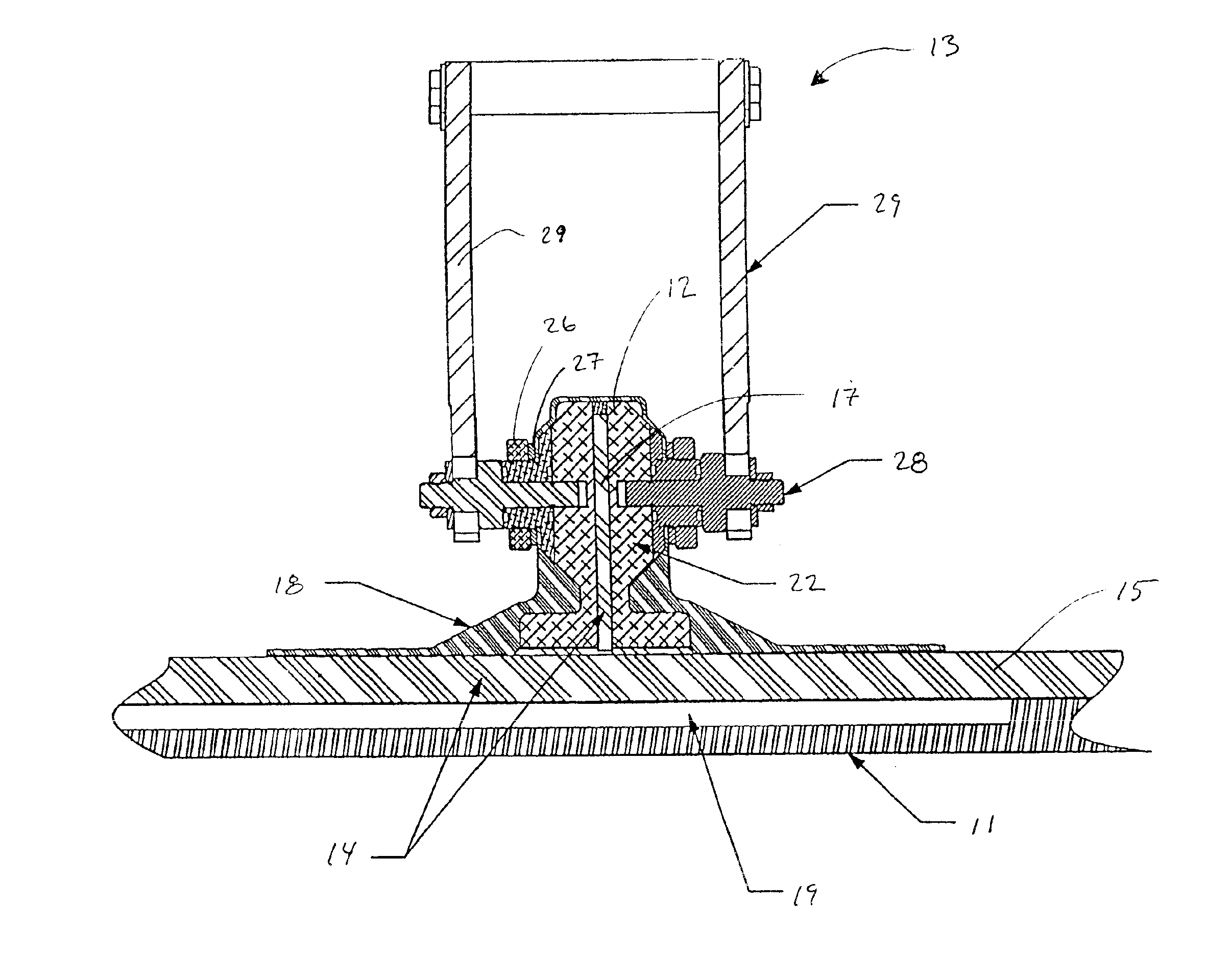
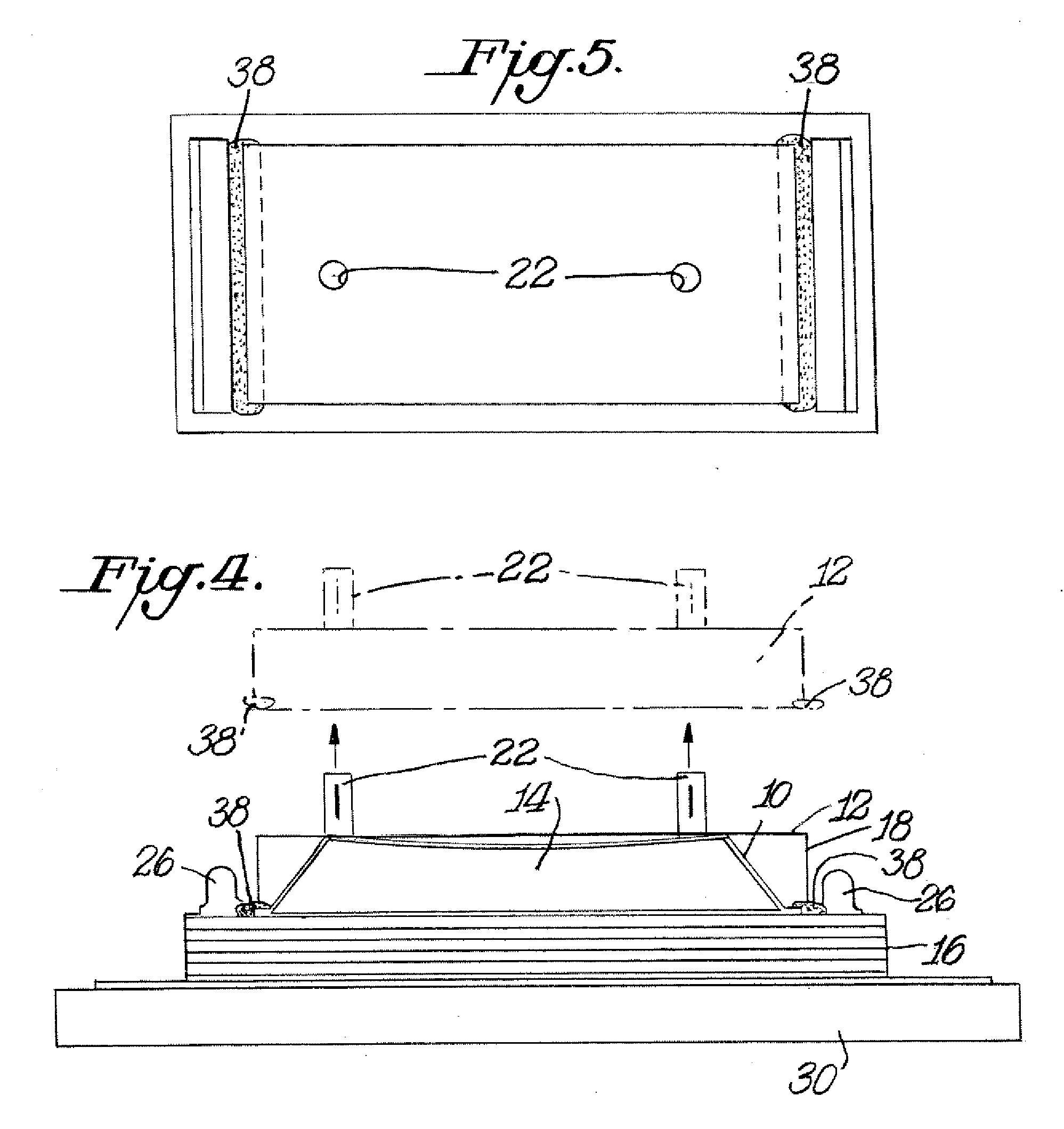
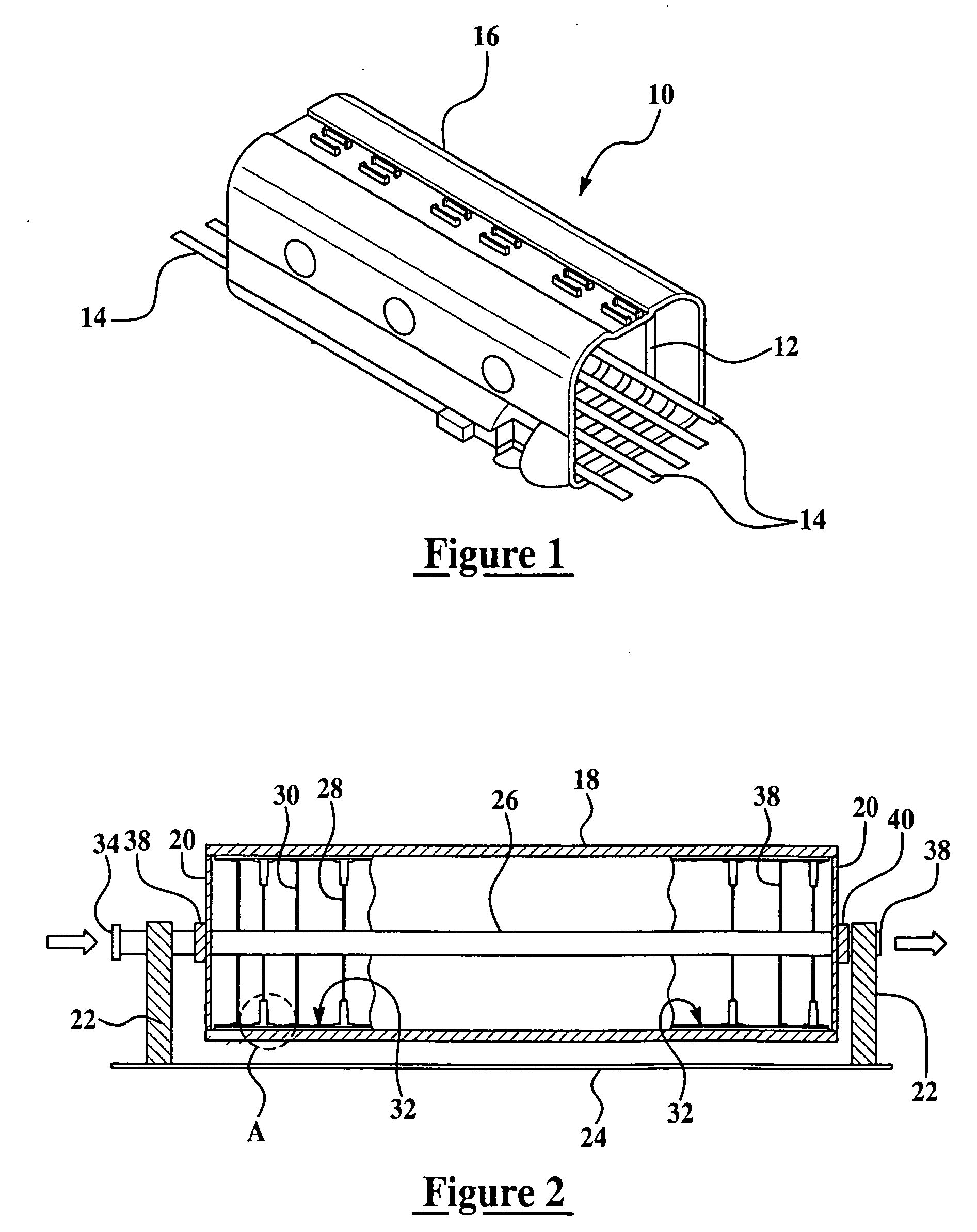
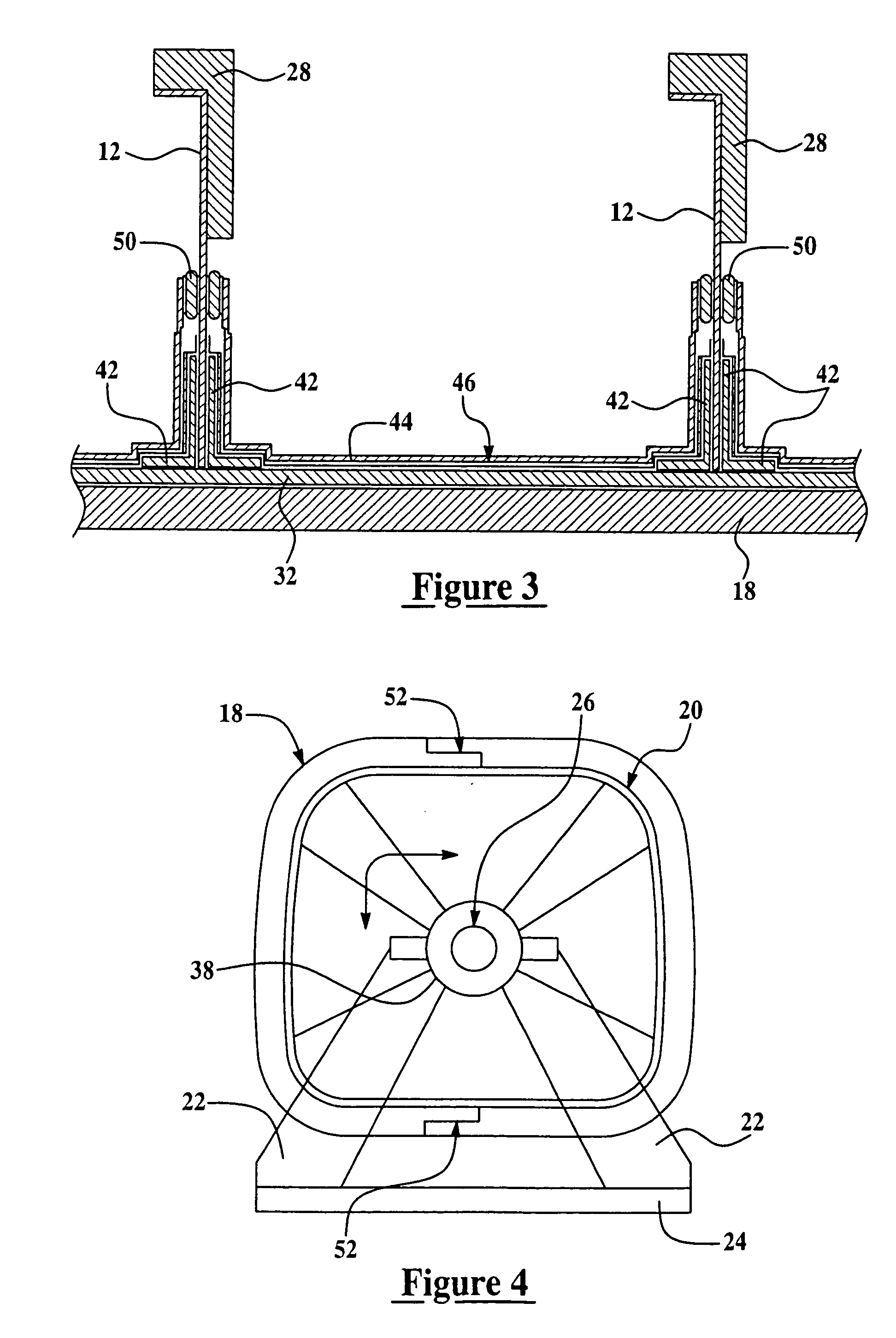
Method and apparatus for vacuum assisted resin transfer molding
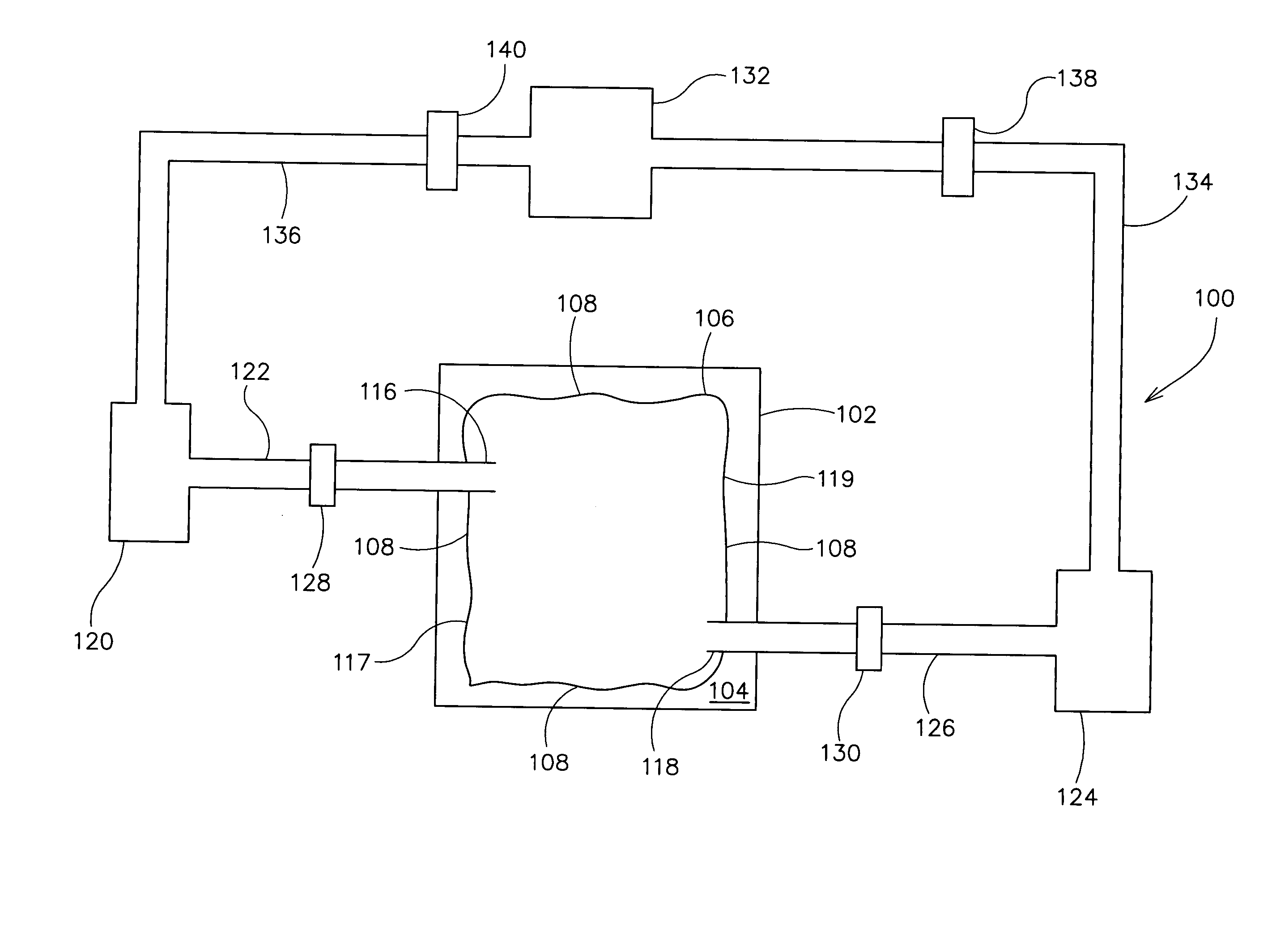
A method for vacuum assisted resin transfer molding a composite structure including fibers at least partially surrounded by resin using a mold including a tool having a surface shaped to correspond to the composite structure and an inflatable bladder for forcing the composite structure against the tool. A resin inlet is connected to a resin source for introducing resin into a mold cavity at least partially defined by the tool surface and the bladder and a vacuum port spaced from the resin inlet. The method includes the steps of opening the mold cavity, loading fibers into the open mold cavity, closing the loaded mold cavity, introducing resin through the resin inlet into the closed mold cavity loaded with fibers, and pulling a vacuum at the resin inlet and the vacuum port to draw excess resin from the structure prior to curing thereof.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
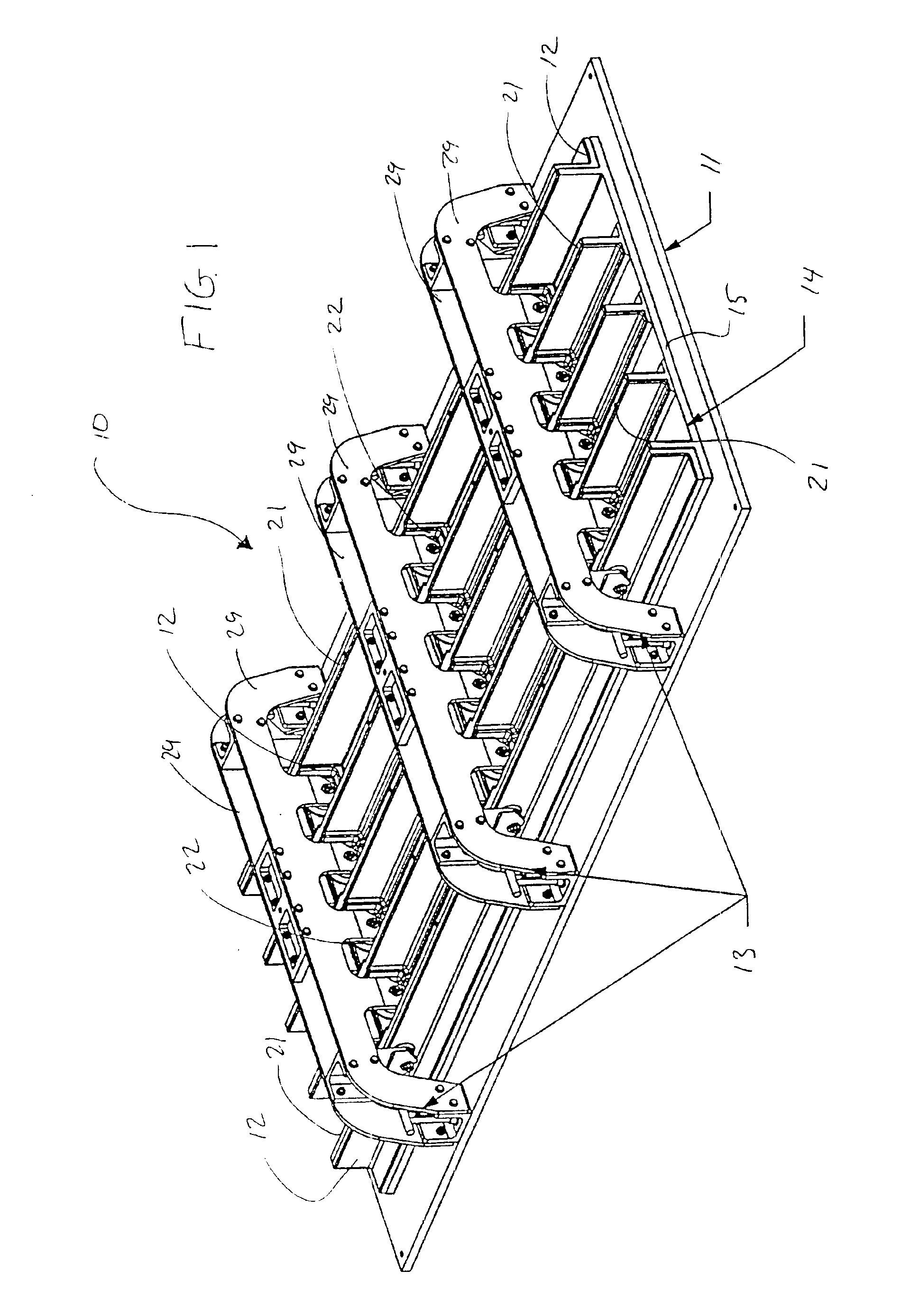
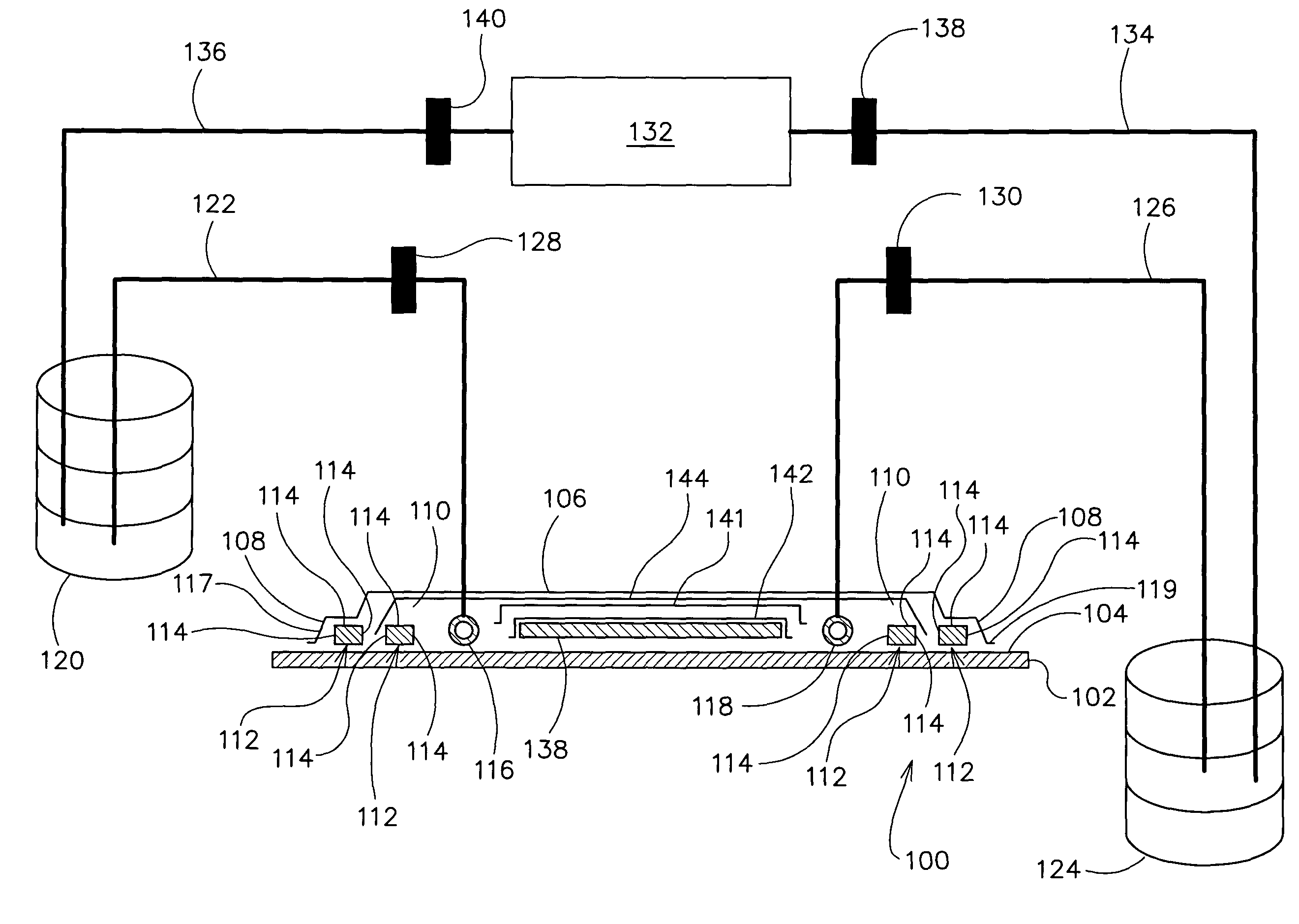
Vacuum-Assisted Resin Transfer Molding Process with Reusable Resin Distribution Line
ActiveUS20110169190A1Reduce deliveryConfectioneryWood working apparatusResin dispensingShell molding
A method and apparatus for a reusable resin distribution line for use in conjunction with a resin transfer molding apparatus is disclosed. The apparatus includes a soft tool and a hard tool (i.e., mold). In the illustrative embodiment, two inflatable bladders are disposed on a side of the soft tool, wherein a bridge spans the bladders. The soft tool is coupled to the bridge. When the bladders are inflated, the bridge moves away from the hard tool, drawing the soft tool away from the hard tool in the region between the bladders. This creates a temporary passage or reusable resin distribution line for distributing resin to a reinforcement constituent disposed between the soft tool and the hard tool.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Mould and method for vacuum assisted resin transfer moulding
ActiveUS7980840B2Reduce complexityLow costFinal product manufactureConfectioneryVacuum assistedShell molding
A mold and method for vacuum assisted resin transfer molding of a fiber reinforced laminated structure are provided. The mold includes a first mold part and a second mold part. The first mold part defines a negative impression of the laminated structure, being structurally stable and forming a support for fiber reinforcement layers of the laminated structure. The second mold part connectable to the first mold part for closing the mold and defines together with the first mold part an enclosed space which can be evacuated. The mold further includes a flow duct for guiding a liquid polymer which is formed as a recess in the first mold part and / or a recess in the second mold part that is open towards the enclosed space and extends along a section of the periphery of the first mold part and / or the second mold part.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
Heat vacuum assisted resin transfer molding processes for manufacturing composite materials
ActiveUS20090189320A1Improving fiber volume fractionIncreasing the thicknessLaminationLamination apparatusFiberMaterials science
The present invention provides a process for forming a composite material. The present invention further provides methods of improving the fiber volume fraction and / or the dimensional thickness of a composite panel.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA AGRICULTURAL AND TECHNICAL STATE UNIVERSITY
Resin infusion mold tool system and vacuum assisted resin transfer molding with subsequent pressure bleed
A resin infusion mold tool system for use in a vacuum assisted resin transfer molding process with a subsequent pressure bleed step. The mold tool system includes a mold assembly having an outer mold line tool connected to resin supply lines and supplying resin to the preform. A plurality of inner mold line tools form a hard interface with the inner mold line of the fiber preform and are held to within tight tolerances by an external locating fixture. Excess resin is drawn out of the fiber preform using a vacuum bag connected to vacuum lines and disposed over the inner mold line tools but not between the tools and the fiber preform. The mold assembly is placed in an autoclave, the resin supply lines are detached and the autoclave pressurized to bleed additional resin out of the preform to raise the fiber volume of the composite structure.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
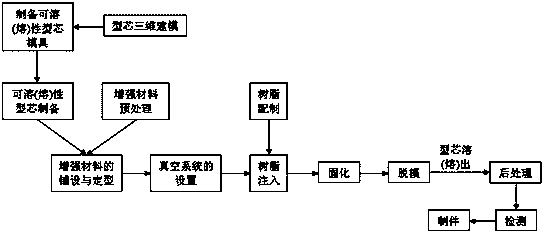
Vacuum assisted resin transfer molding integral-forming technology of composite material fuel-tank
The invention discloses a vacuum assisted resin transfer molding integral-forming technology of a composite material fuel-tank. A novel structural material fuel-tank is provided. Structural weight of a present fuel tank and vehicle noise level can be reduced effectively, and the novel structural material fuel-tank has characteristics of impact damage resistance, corrosion resistance and the like. Meanwhile, forming process cycle of the fuel tank can be greatly shortened, and production efficiency of the fuel tank can be raised. The technology is realized by the following technical scheme: core three-dimensional modeling; core forming-die manufacturing; soluble (fusible) core manufacturing; die preparation; laying and shaping of a reinforcing material; die locking; making of a resin solution; resin injection; resin curing; demoulding; core dissolution (fusing); and composite material product finishing. By the technology, production efficiency is high; demoulding is convenient; and cost is low.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
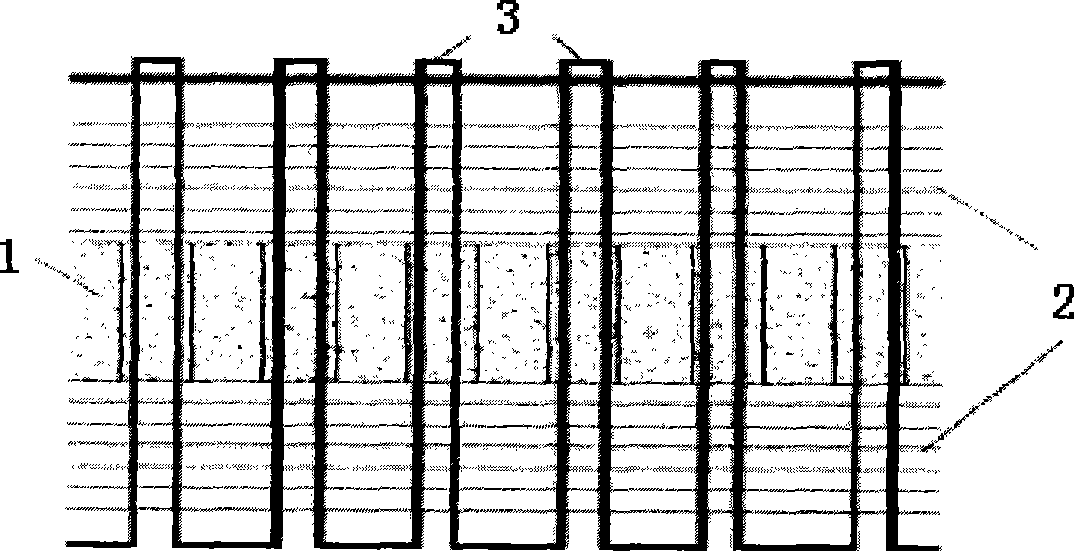
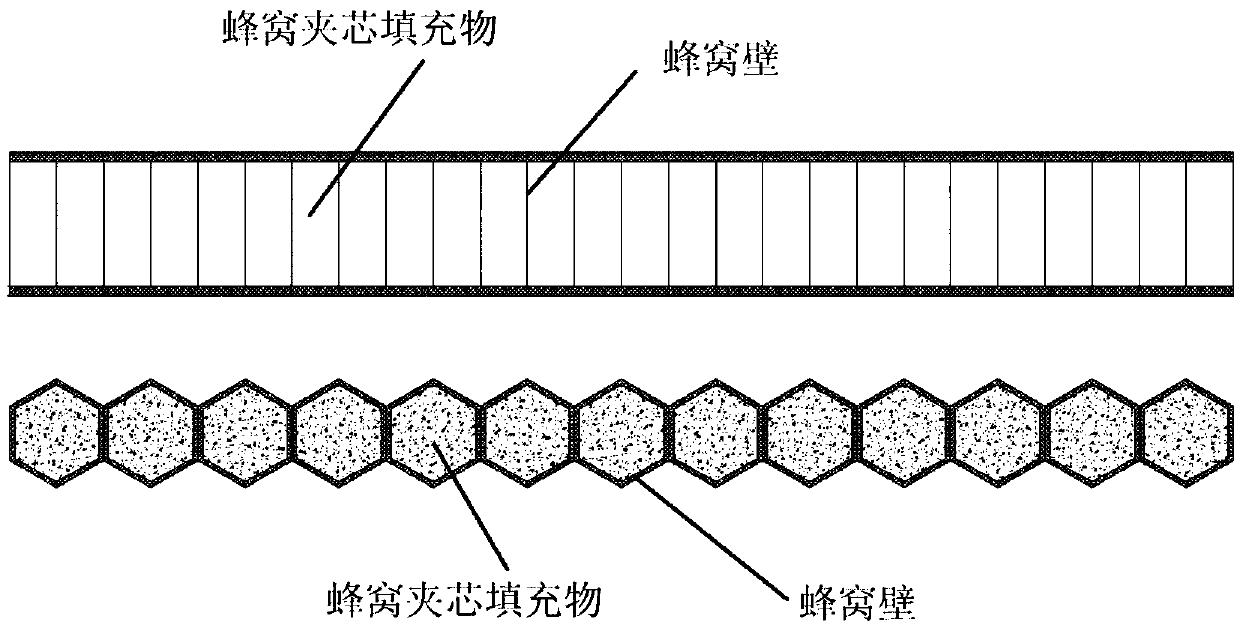
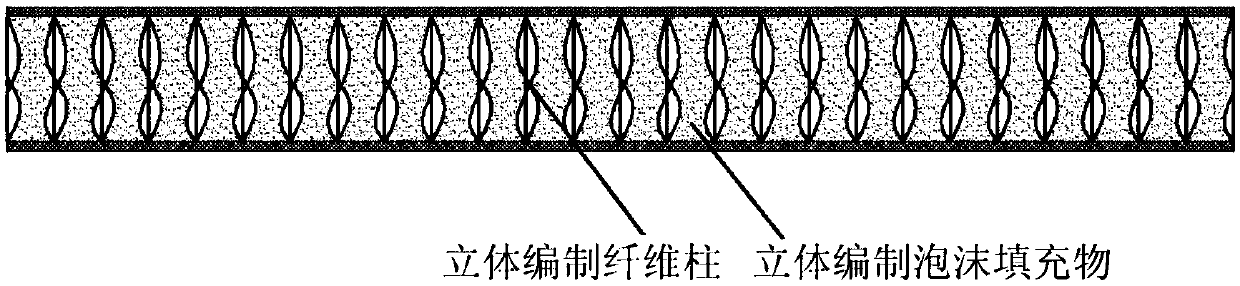
Sandwich structure composite material with elastic core material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a composite material of sandwich structure with an elastic core material. The composite material consists of upper and lower composite material panels and a porous elastic core material (1) positioned between the upper and lower composite material panels, which are stitched by fiber yarns (3) passing through holes of the elastic core material, wherein the composite material panels are made of fiber cloths (2) and matrix resins of the composite material. The method for preparing the composite material comprises the following steps: drilling holes on the elastic core material (1) at intervals, laying the fiber cloths (2) on the upper surface and the lower surface of the elastic core material, and making the fiber yarns (3) pass through the holes of the core material by a straight stitching lock type stitching method, to make the core material and the fabric cloths into a whole; making the resin soak the fabric cloths and the holes of the core material by the vacuum assisted resin transfer molding; and finally, solidifying and molding the whole by solidification technology, to obtain the composite material. The material has excellent performance, novel structure and simple preparation technology, is easy to operate, and is applicable to the industrialized production.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Process for Preparing Composites Using Epoxy Resin Formulations
InactiveUS20080308972A1High distinctness of imageImprove surface qualityCeramic shaping apparatusCoatingsEpoxyAlkane
The invention is a process for making reinforced composites using an epoxy resin composition. The epoxy resin compositions are hardened using a gem-di(cyclohexylamine)-substituted alkane as a hardener and a tertiary amine compound, a heat-activated catalyst, or a mixture thereof as an accelerator. This epoxy resin composition has a long open time, and then cures rapidly in a mold in the presence of a reinforcement. These cure characteristics make the composition well suited for use in manufacturing processes such as resin transfer molding (RTM), vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding (VARTM), Seeman Composites Resin Infusion Molding Process (SCRIMP) and reaction injection molding (RIM).
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Rotational vacuum assisted resin transfer molding
ActiveUS20070141334A1Reduces gravity induced settlingDomestic articlesCoatingsVacuum pressureEngineering
Thickness gradients in large, cobonded composite structures resulting from gravity-induced resin migration during curing is substantially reduced by rotating the structure during the resin infusion and curing stages. The layup for the structure is placed on a rotatable tool fixture and vacuum bagged. The tool fixture is mounted on a central support tube provided with motors for rotating the tool fixture about the axis of the tube. The tube has internal passageways that deliver resin to the bagged layup and carry away excess resin from the layup using vacuum pressure. The resulting composite structures exhibit thickness gradients less than 10%.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method for vacuum assisted resin transfer molding
A method for vacuum assisted resin transfer molding a composite structure including fibers at least partially surrounded by resin using a mold including a tool having a surface shaped to correspond to the composite structure and an inflatable bladder for forcing the composite structure against the tool. A resin inlet is connected to a resin source for introducing resin into a mold cavity at least partially defined by the tool surface and the bladder and a vacuum port spaced from the resin inlet. The method includes the steps of opening the mold cavity, loading fibers into the open mold cavity, closing the loaded mold cavity, introducing resin through the resin inlet into the closed mold cavity loaded with fibers, and pulling a vacuum at the resin inlet and the vacuum port to draw excess resin from the structure prior to curing thereof.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Reusable infusion bag
A reusable apparatus and method for forming a composite part through vacuum assisted resin transfer molding (VARTM). The reusable apparatus may be configured to vacuum seal a curable material, such as composite material, against a tool and disperse a permeating substance such as liquid resin through the curable material. The reusable apparatus may comprise a sheet of material such as rubber having a plurality of surface deviations facing the curable material and the tool. The surface deviations may provide paths for evenly distributed air flow as air is evacuated from between the sheet of material and the tool. Additionally, the surface deviations may allow the permeating substance to be evenly dispersed throughout the curable material. A vacuum outlet of the tool may be positioned between two sealing apparatuses to provide continuous vacuum suction proximate a perimeter of the sheet of material to prevent air from leaking in.
Owner:SPIRIT AEROSYSTEMS
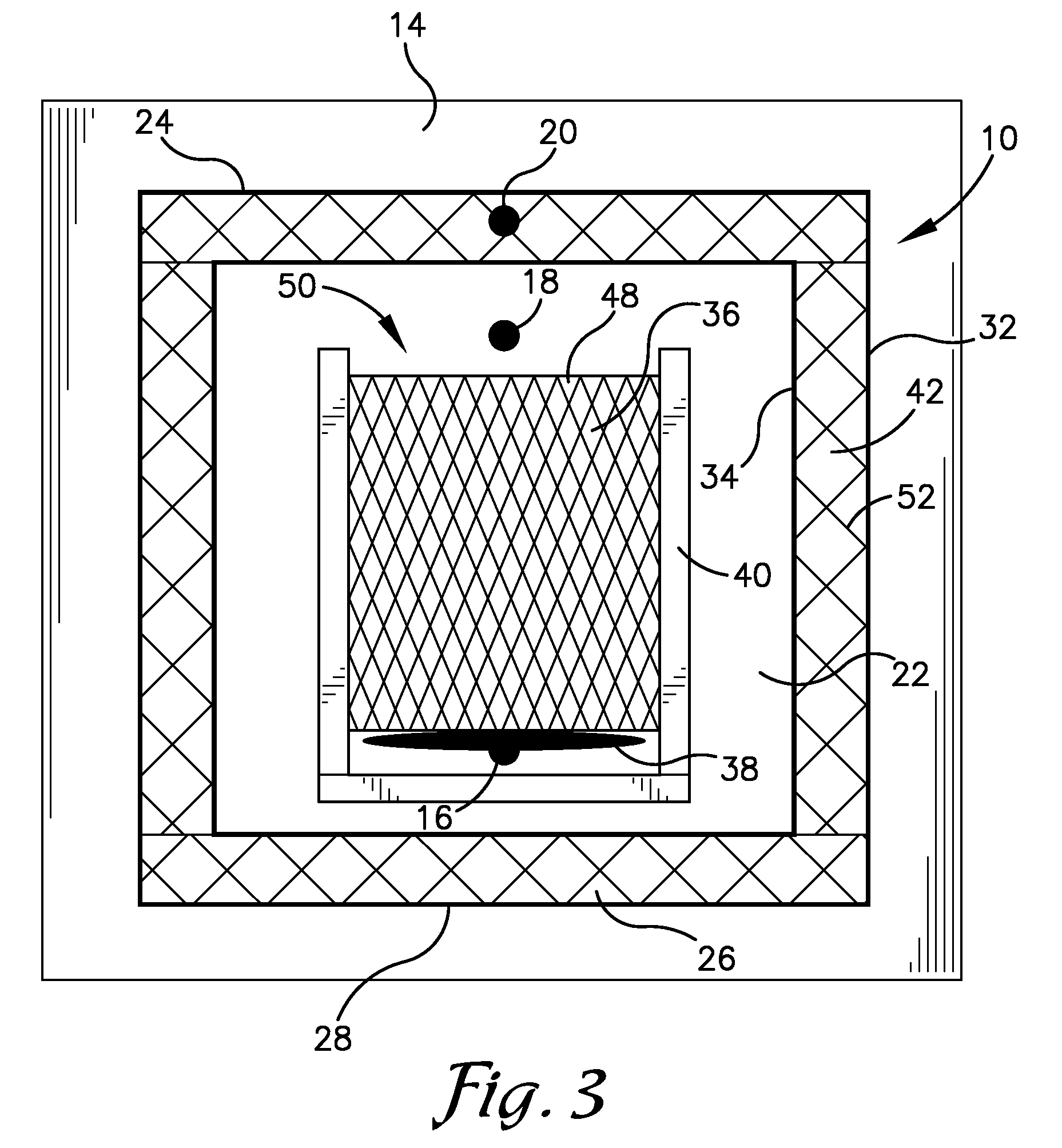
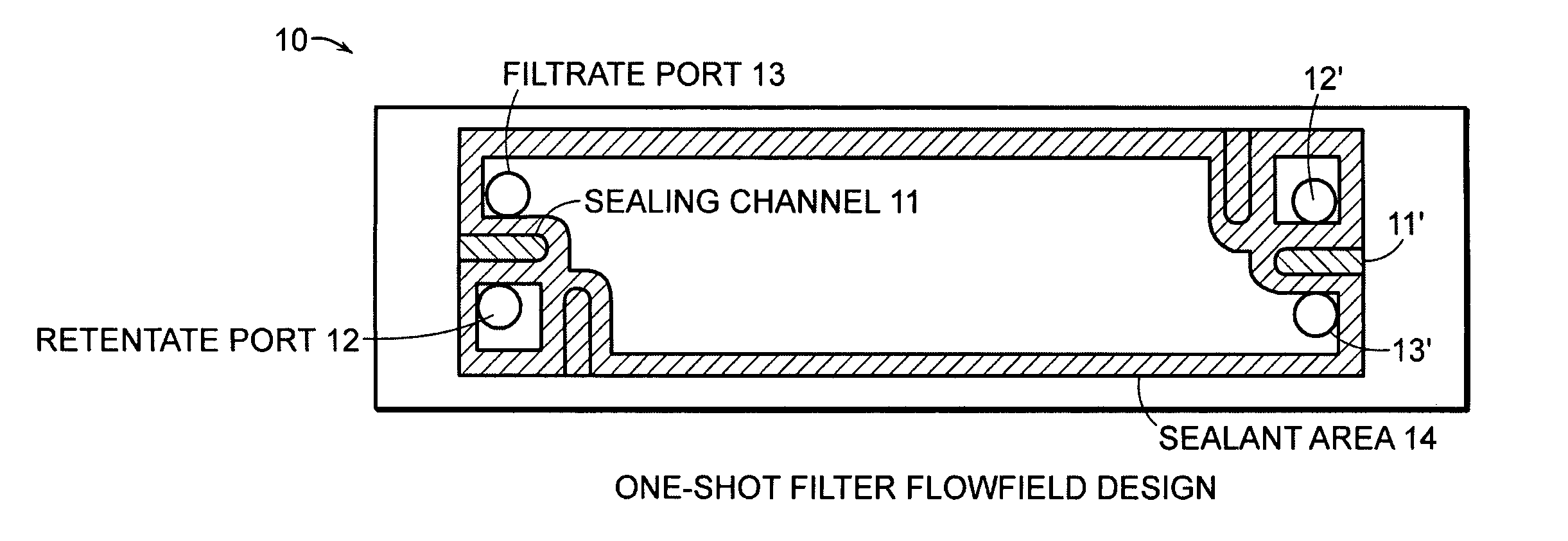
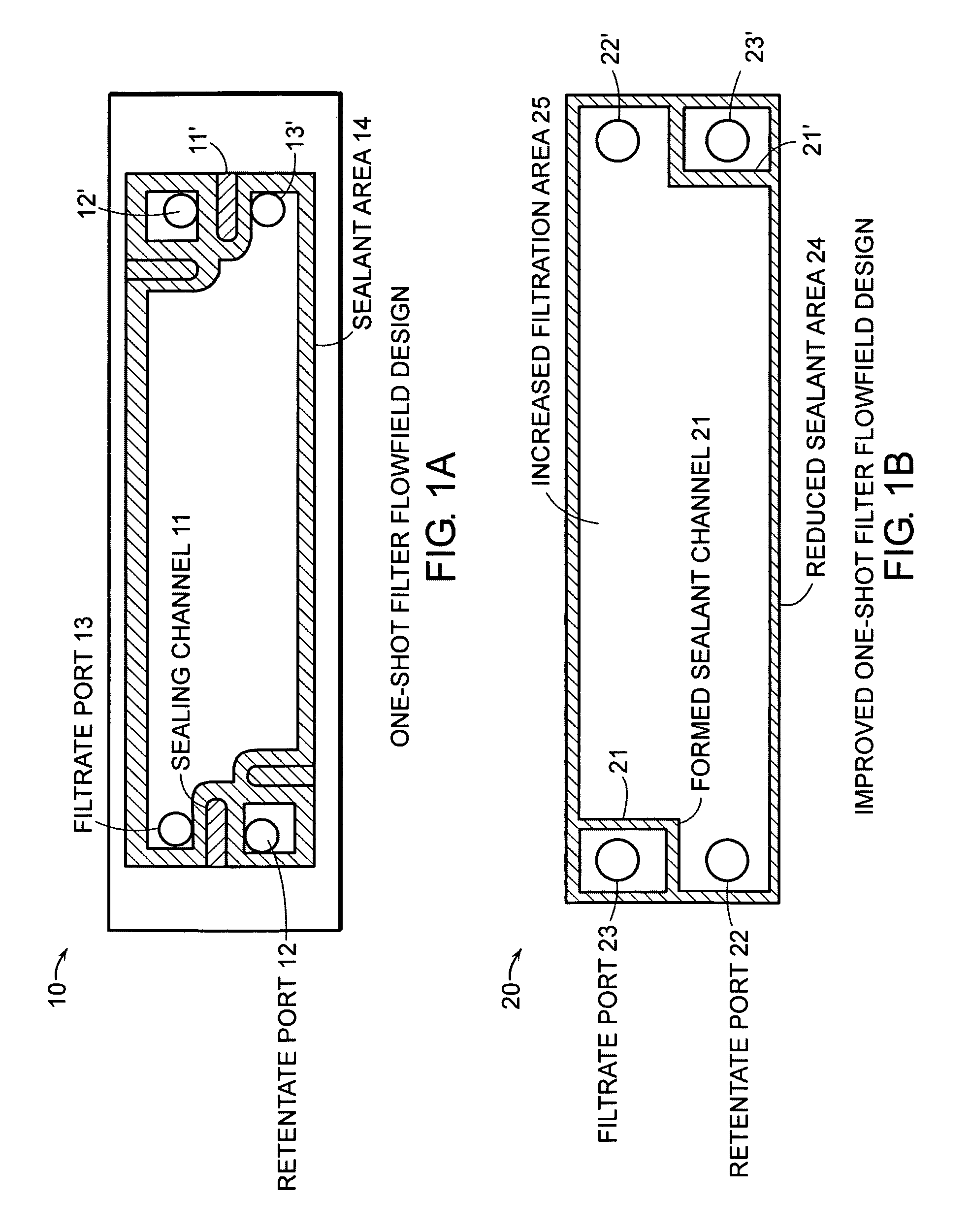
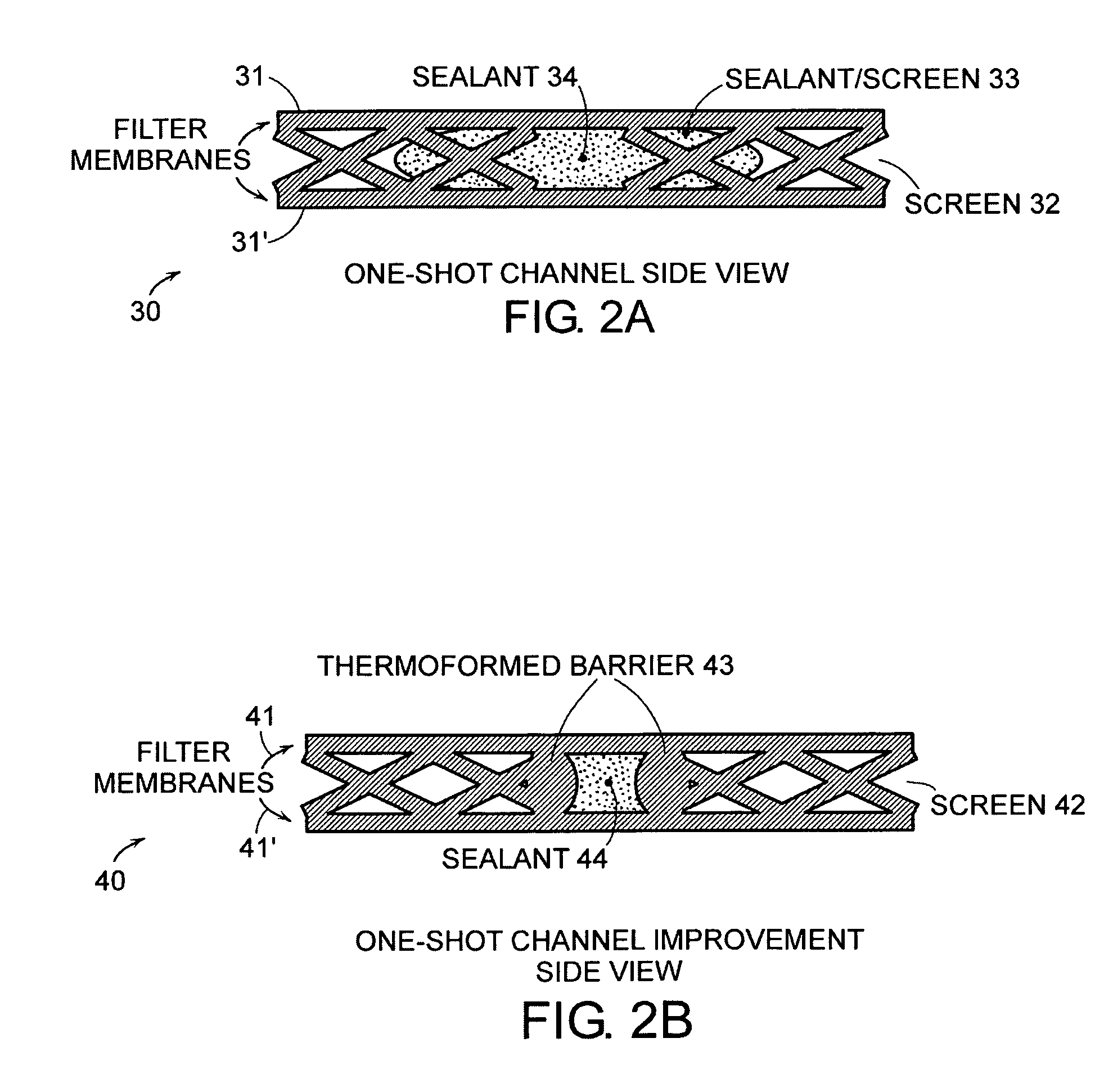
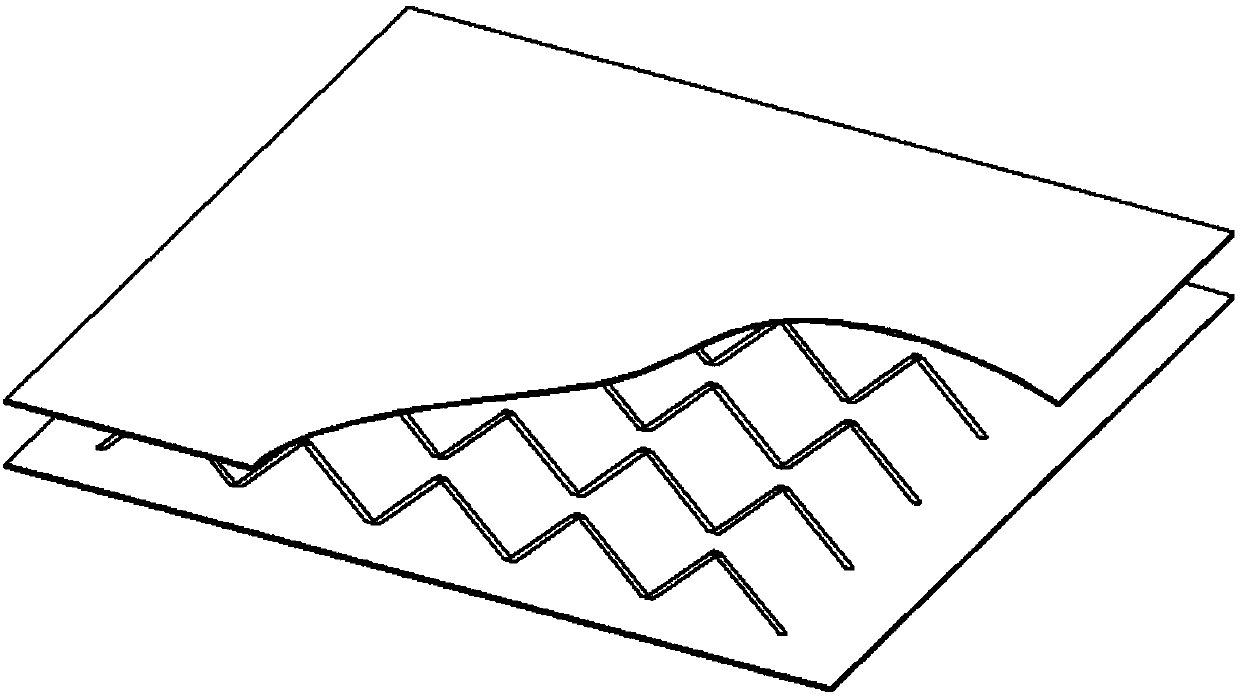
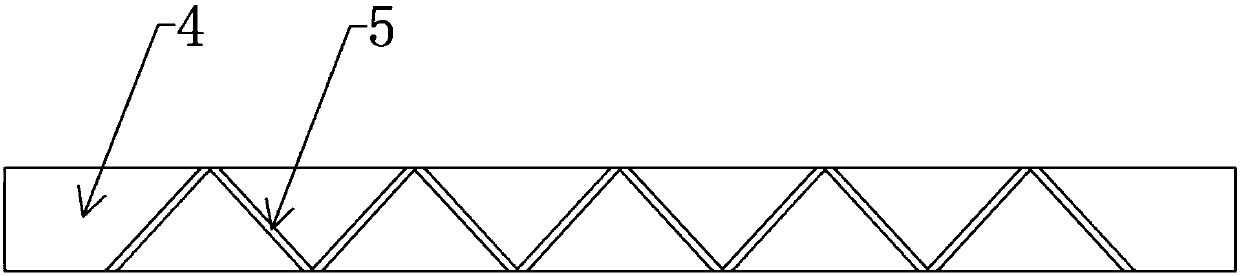
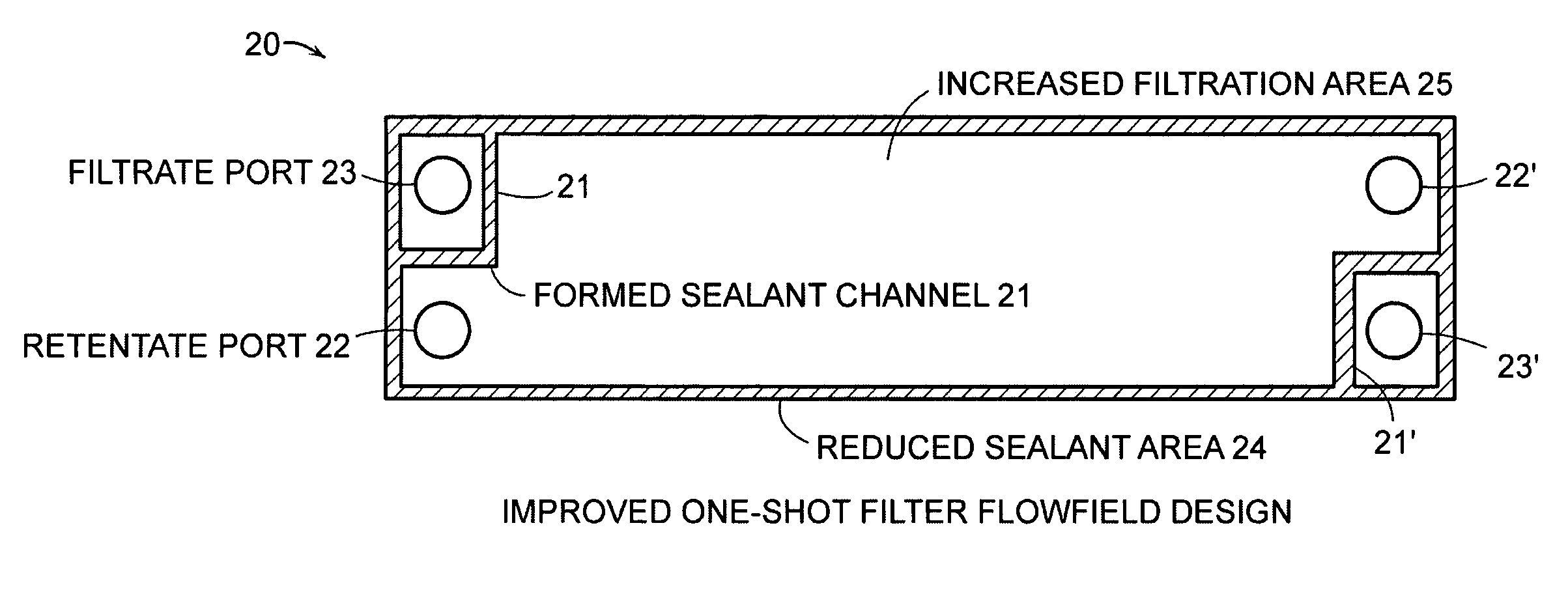
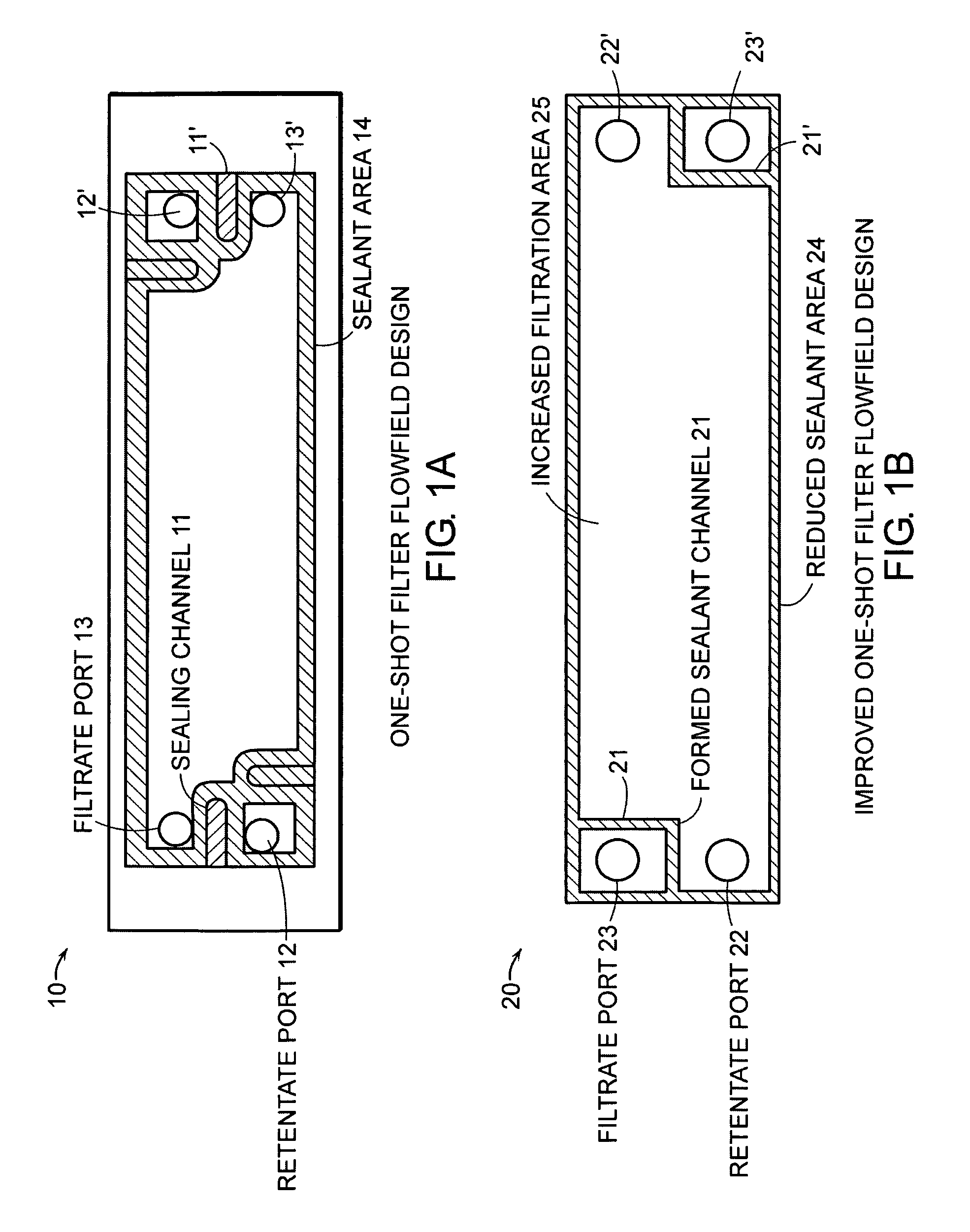
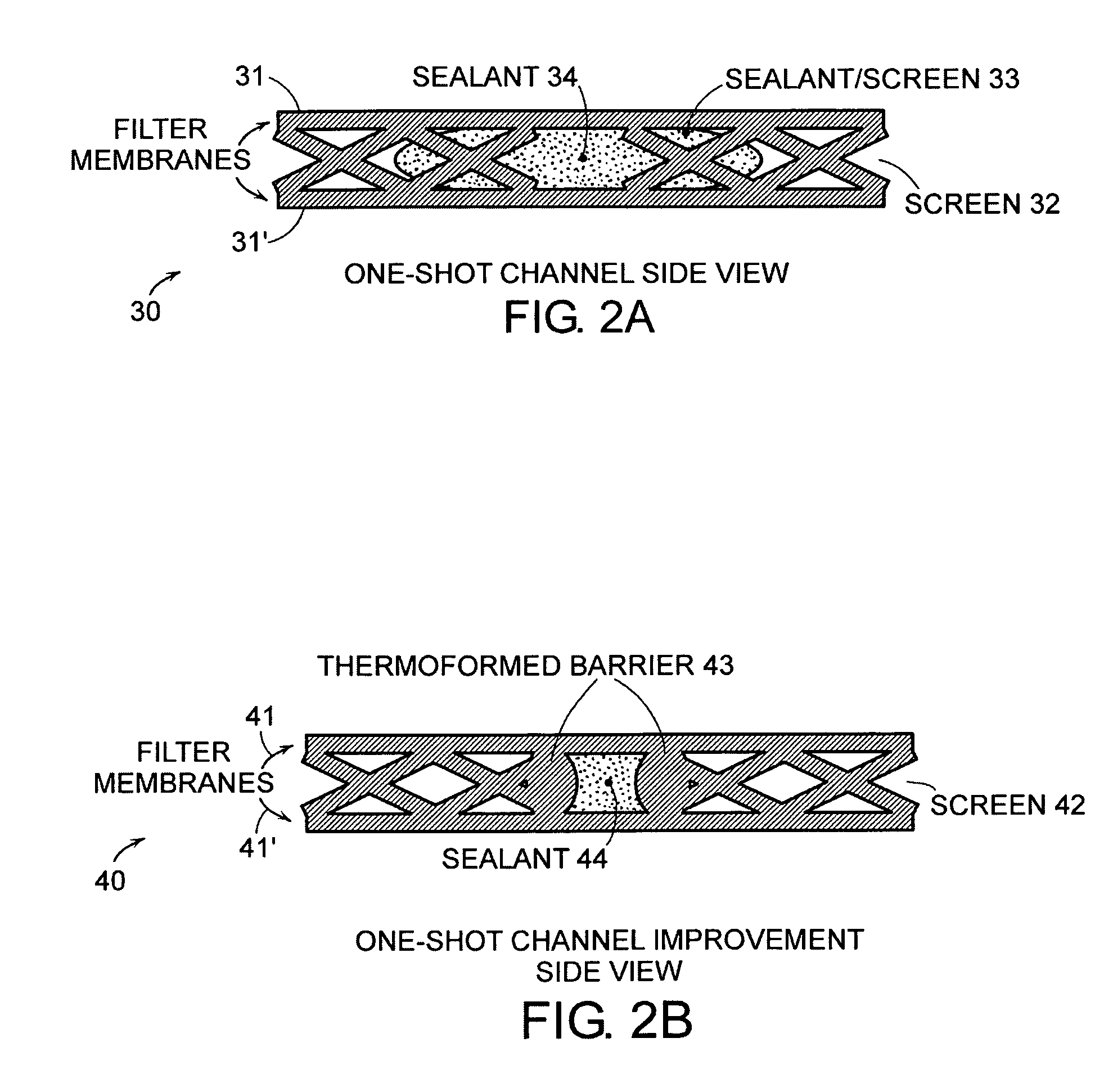
Cross-flow filtration cassettes and methods for fabrication of same
InactiveUS20050173330A1Increase filter surface areaEffective spaceLiquid surface applicatorsLaboratory glasswaresCross-flow filtrationEngineering
This invention relates generally to filtration cassettes, and, more particularly to methods of fabricating cross-flow filtration cassettes. Cassettes of the invention are characterized, in part, by a series of sealing channels which selectively seal the filtrate and retentate ports to prevent undesired flow. The sealing channels have formed barriers on either side thereof which create side-walls for precisely controlling the flow of the sealant during the cassette formation. Filtration cassettes of the present invention can be manufactured from conventional membrane and flow screen components and can utilize both injection molding and vacuum assisted resin transfer molding fabrication processes.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
Fiber-enhanced light interlayer composite material and subway cockpit body prepared from same
PendingCN109514951AImprove impact resistanceLight in massRailway roofsLamination ancillary operationsShock resistanceResin-Based Composite
The invention belongs to the technical field of machining of railway traffic equipment, particularly relates to a fiber-enhanced light interlayer composite material and further discloses a subway cockpit body prepared from the same. The fiber-enhanced light interlayer composite material is of an integral structure integrally formed by taking a fiber-enhanced resin composite material as a skin material and foam with a three-dimensional net as an interlayer material through a vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding process, has the advantages of light weight, high structural strength, good shockresistance and environment friendliness and can be used for processing and preparing large-scale complex components such as the subway cockpit body. The subway cockpit body is prepared by taking the fiber-enhanced light interlayer composite material as a main body material and has the performance advantages of light weight, high structural strength and good shock resistance.
Owner:JINAN NORTH TAIHE NEW MATERIAL +1
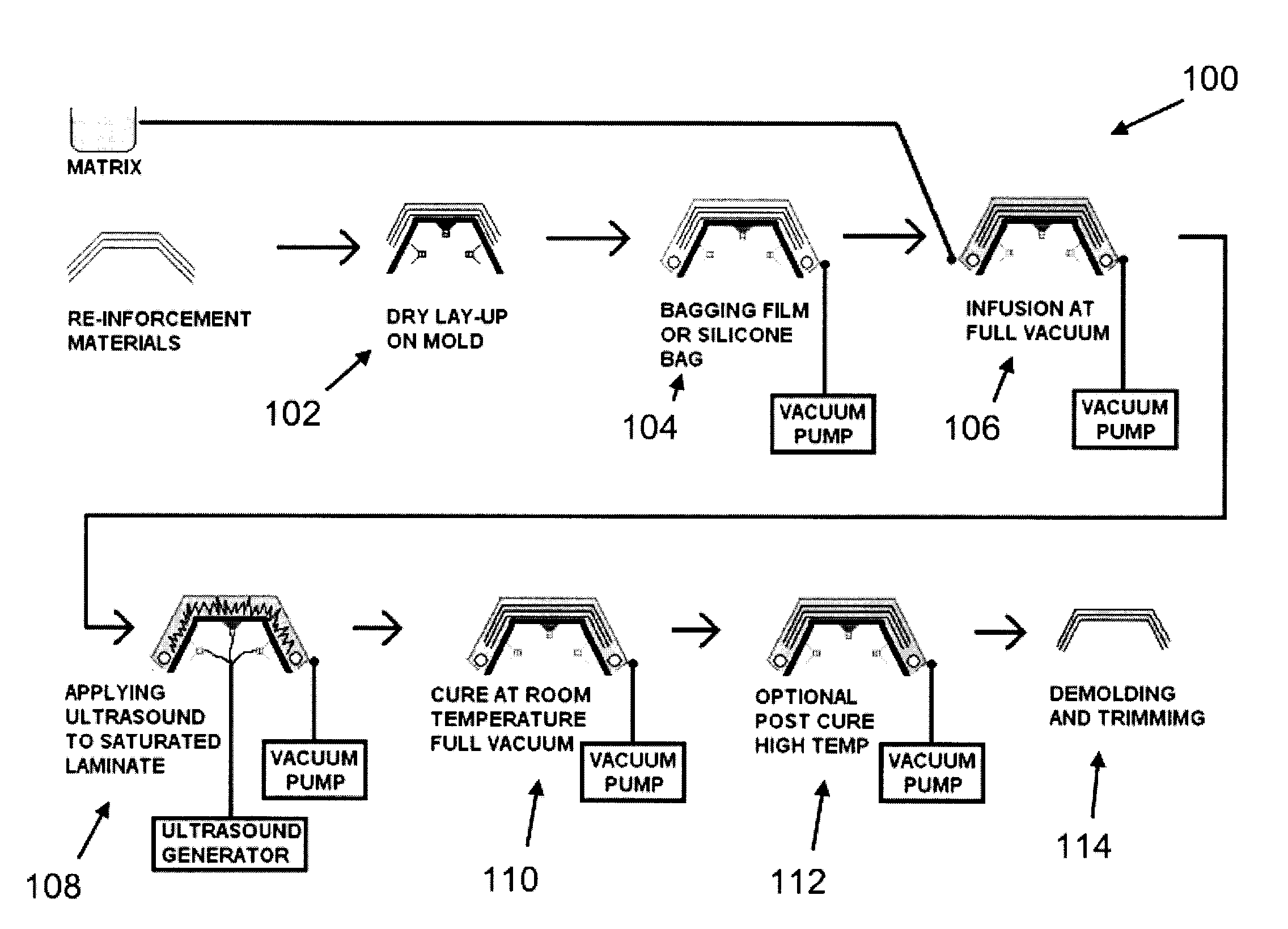
Process and Apparatus for Molding Composite Articles
ActiveUS20140327187A1Reduce disadvantagesAdvantageously compactTailstocks/centresConfectioneryGlass fiberPolyester
A method and an apparatus for molding composite articles are disclosed. The method generally involves the saturation of reinforcing fibers (e.g. glass fibers, carbon fibers, etc.) with a matrix (e.g. resin, epoxy, cyanate ester, vinyl ester, polyester, etc.) in / on a mold using a conventional resin transfer molding (“RTM”) process (e.g. “RTM-light”) or a vacuum assisted resin transfer molding (“VARTM”) process (e.g. advanced VARTM or “A-VARTM”), and, once saturation is completed, the vibration of the matrix-infused fibers using controlled ultrasonic sound waves transmitted through the mold. By vibrating the matrix-infused fibers with the ultrasonic sound waves, the method and apparatus allow voids present between fibers to be closed and localized pockets of gases to be dislodged and degassed, and also allow the fibers to compact, thereby producing composite articles with reduced porosity and higher compaction.
Owner:HURDLE ERIC
On-site Fabricated Fiber-Composite Floating Platforms for Offshore Applications
ActiveUS20120155967A1Increase the number ofNon-magnetic metal hullsWind motor supports/mountsFiberFloating platform
A spar platform comprises one or more continuous-fiber composite tubes fabricated at or near the intended site use of the platform. In some embodiments, the spar platform includes a relatively longer central tube and relatively shorter peripheral tubes. In some other embodiments, the spar platform is a single long tube. In some embodiments, the spar platform supports a wind turbine assembly. The continuous-fiber composite tubes are formed, in either a vertical or horizontal orientation, using a modified vacuum assisted resin transfer molding process.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
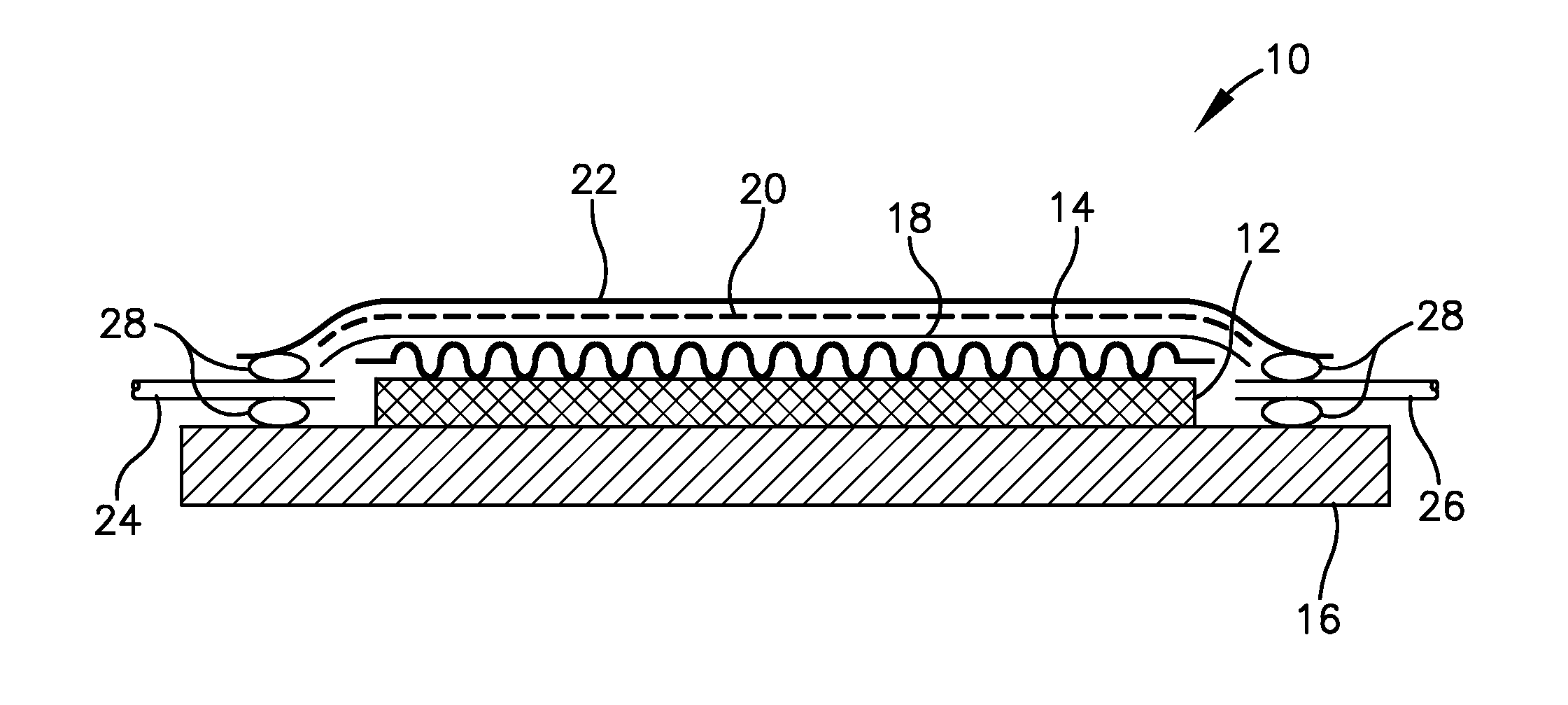
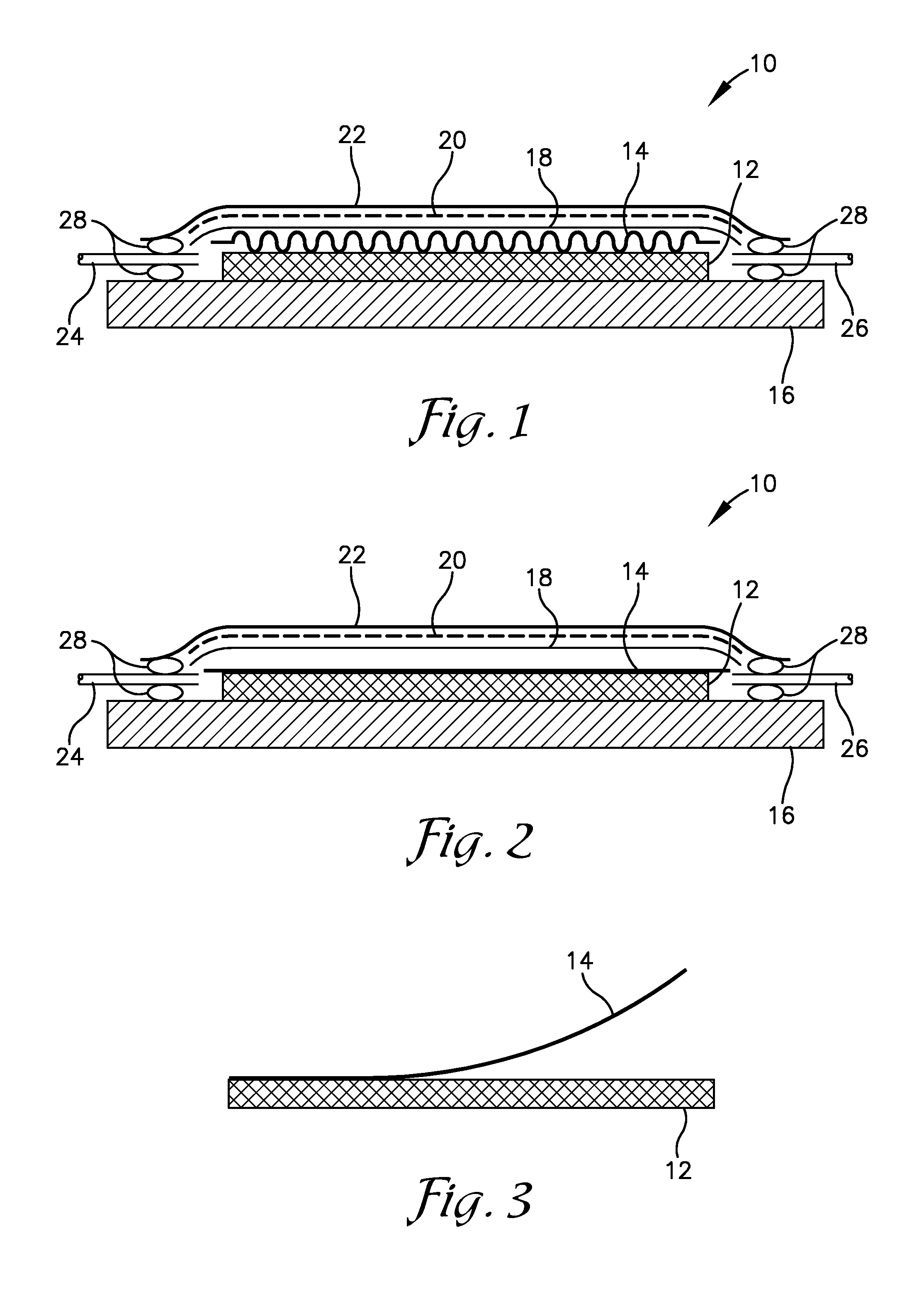
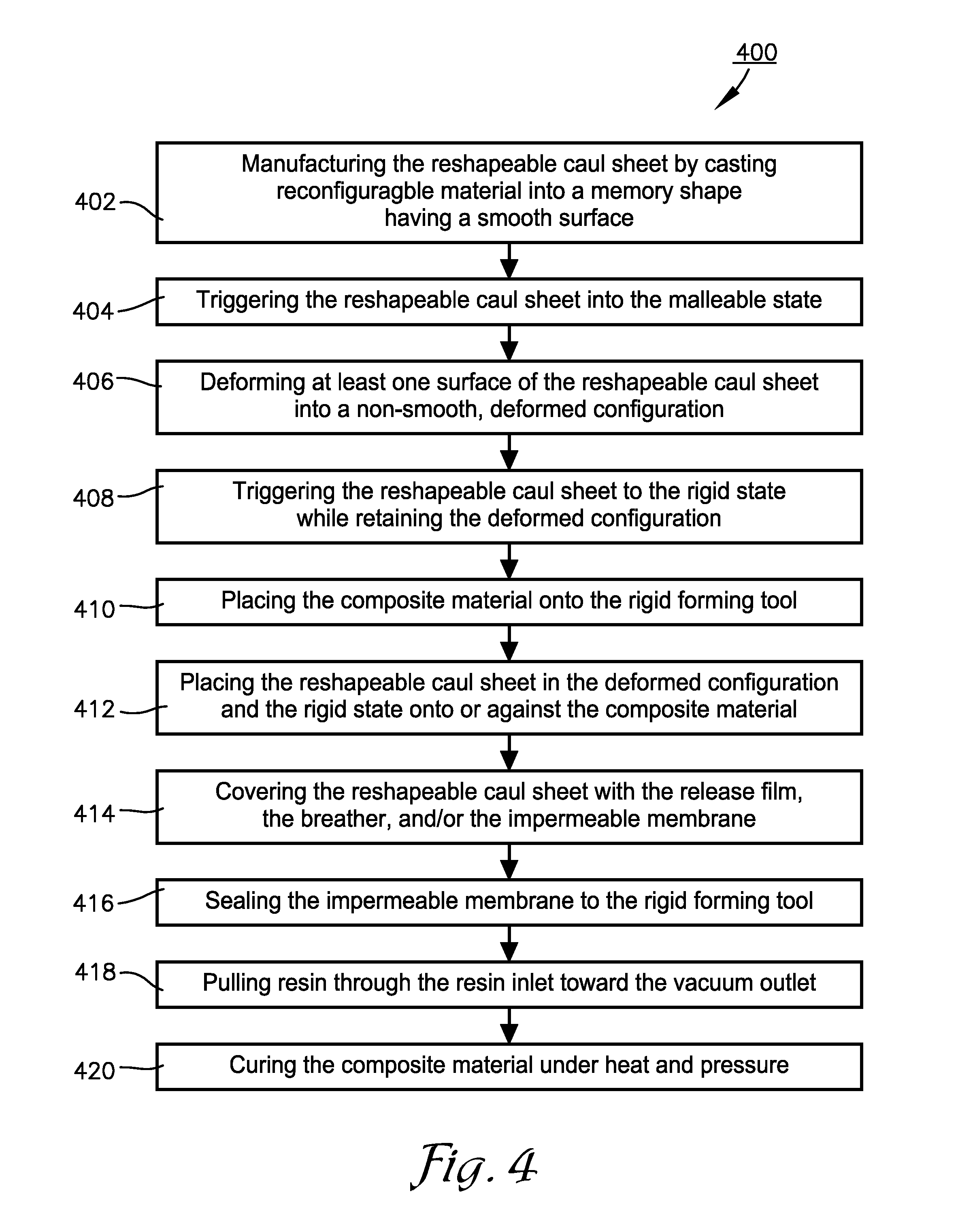
Shape memory polymer (SMP) flow media for resin infusion
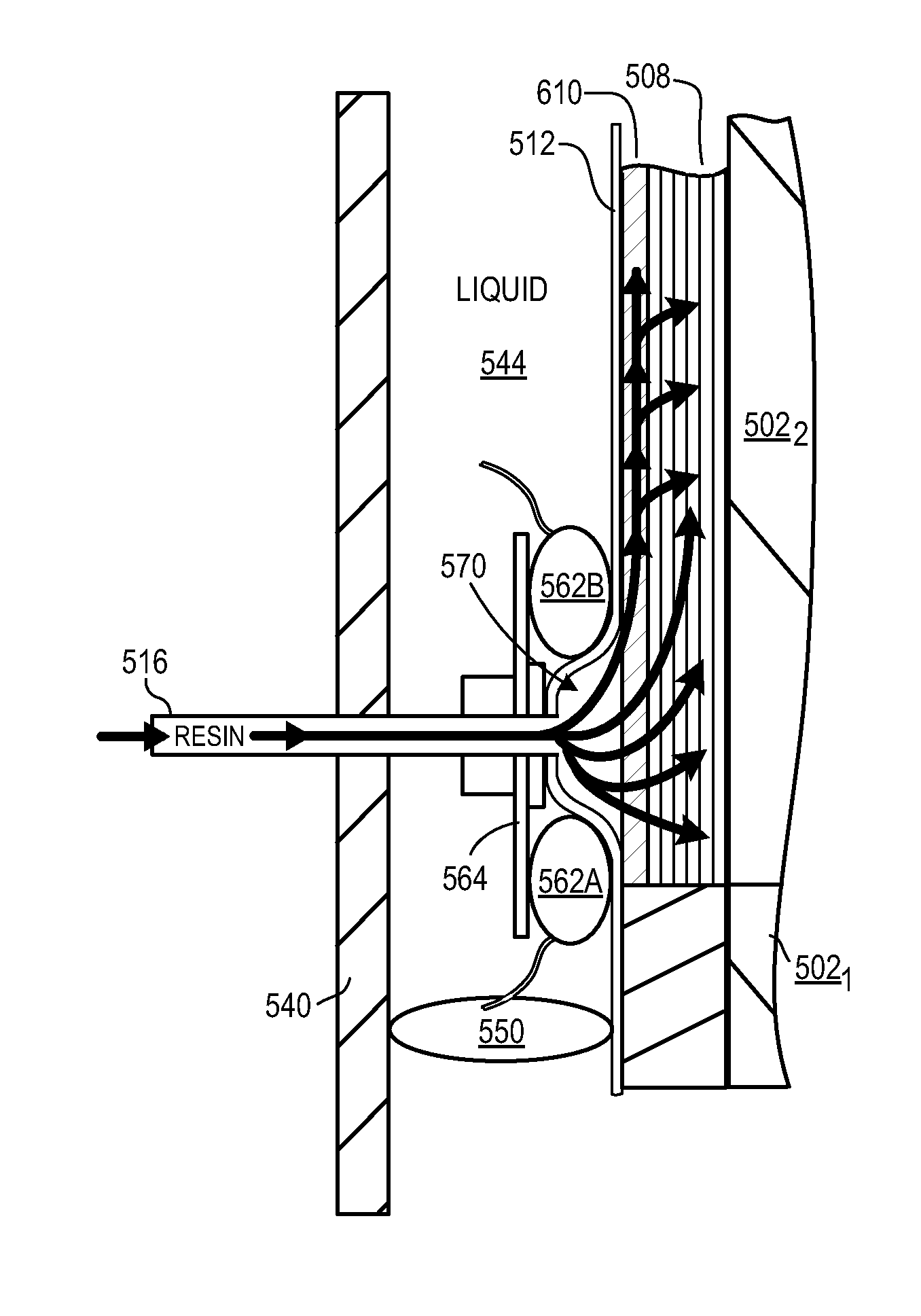
A system and method of vacuum assisted resin transfer molding (VARTM) using a reconfigurable material, such as shape memory polymer (SMP), for a caul sheet or a forming tool. The reconfigurable material may have a rough or non-smooth, deformed configuration to serve as a flow media during resin transfer, but may be triggered to return to a smooth memory shape at composite cure temperatures at least high enough to place the reconfigurable material into a malleable state. Thus, a surface of the composite material facing the reconfigurable material will have a substantially smooth finish following curing thereof. The rough or non-smooth deformed configuration may be created by embossing or otherwise forming various patterns into the reconfigurable material in the malleable state, and holding this pattern while triggering the reconfigurable material back to a rigid state for use during resin transfer.
Owner:SPIRIT AEROSYSTEMS
Method of making a natural rubber vacuum bag by spray processes natural rubber vacuum bag made using spray process, and method for usingnatural rubber bag made using spray process
The invention discloses a method for making a membrane for use as a vacuum bag, a natural rubber vacuum bag made using such methods, and methods for using such a natural rubber bag to form a composite article. One method can include providing a substantially non-porous working surface having a desired shape for forming a vacuum bag, spraying at least one layer of a natural rubber liquid over at least a portion of working surface, and solidifying the natural rubber liquid to form a membrane having a shape substantially corresponding to that of the working surface. The membrane formed being elastically deformable and substantially impermeable for functioning as a vacuum bag in Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding, debulking, compaction, or similar processes.
Owner:R·W.·吕丁 +1
Method of preparing a mould for vacuum resin transfer moulding
InactiveUS20150321385A1Easy to moveSmall roughnessFinal product manufactureDomestic articlesShell moldingTurbine blade
A method of preparing a mould having a moulding cavity surface with vacuum flow topology for vacuum resin transfer moulding is provided. This method includes: pressing a number of peel ply layers into an uncured resin layer for building up the moulding cavity surface, curing the resin of the resin layer, and detaching the peel ply layers to generate the vacuum flow topology in the moulding cavity surface. A mould for wind turbine blades having a vacuum flow topology prepared by such a method is also provided.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Preparation method of epoxy resin composite material strengthened by in situ growth of CNT (carbon nano tube) on surface of quartz fibre
InactiveCN102329431AIncreased interlaminar shear strengthImprove interface strengthInterlaminar shearCarbon nanotube
The invention discloses a preparation of an epoxy resin composite material strengthened by in situ growth of CNT (carbon nano tube) on the surface of quartz fiber. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: arranging a layer of catalyst particles on the surface of quartz fiber, and decomposing a carbon source under the catalysis of the catalyst by using a CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) method to obtain the quartz fiber with a CNT array evenly growing on the surface; completely mixing epoxy resin and a curing agent under the conditions of ultrasonic oscillation and high-speed stirring; and compounding the quartz fiber with a CNT array evenly growing on the surface and the epoxy resin through VARTM (Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding). The interface adhesive strength of epoxy resin with the quartz fiber is improved, and the interlaminar shear strength property of the quartz fiber-CNT / epoxy resin composite material can be enhanced further.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
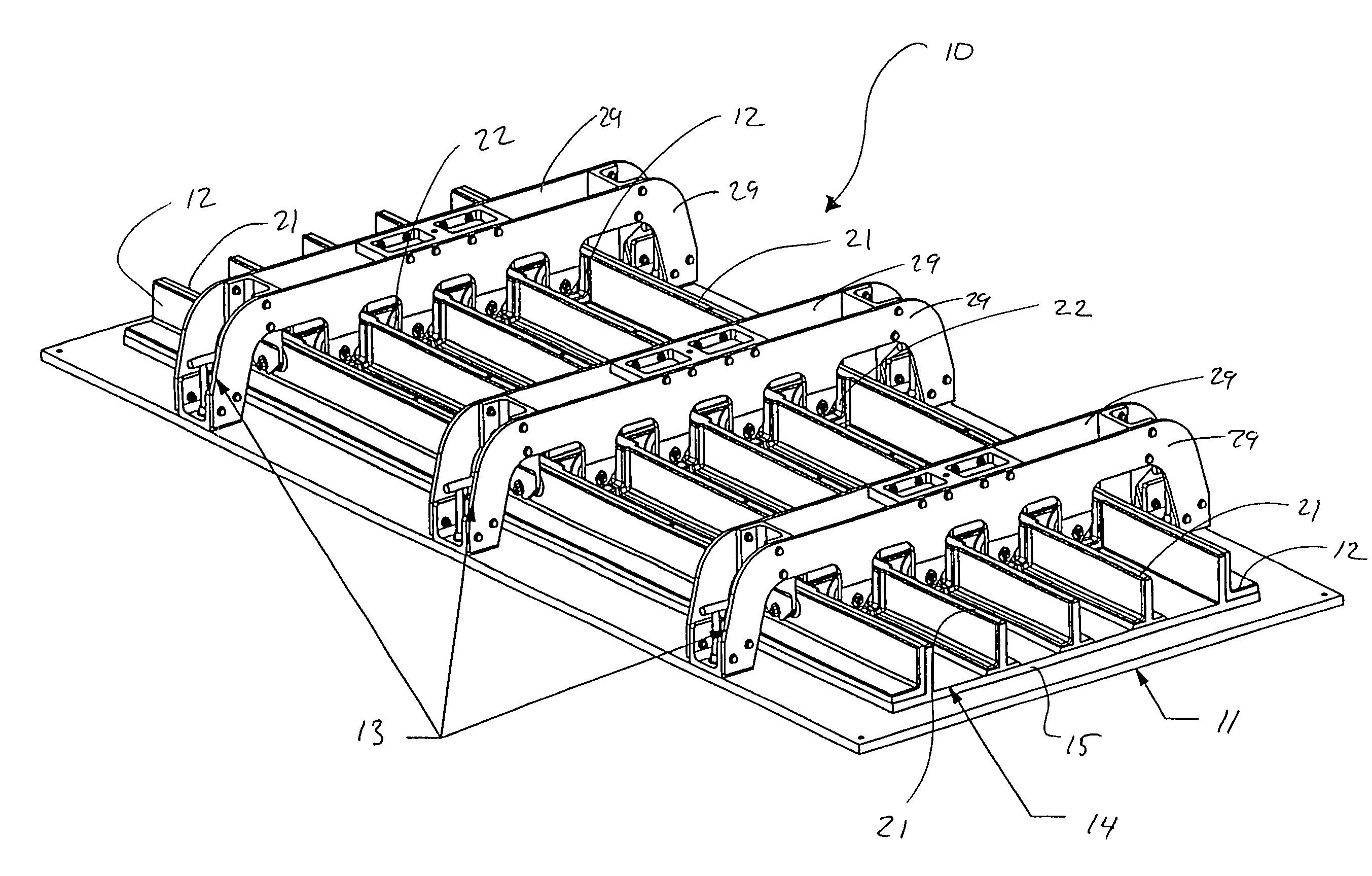
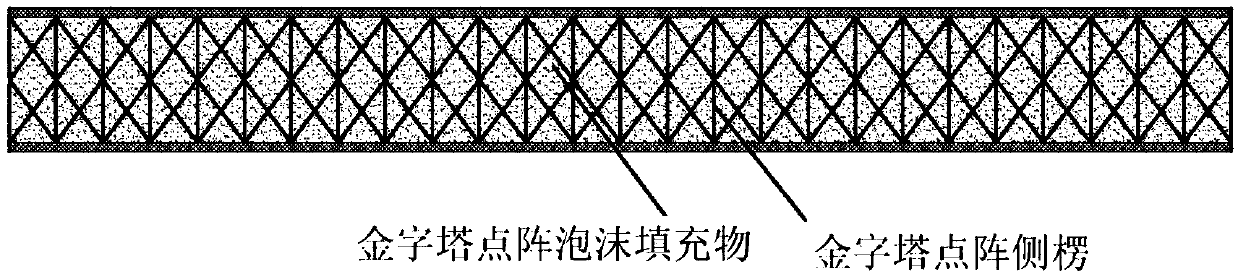
Composite lattice structure and preparation method
ActiveCN107599445AIncrease productivitySuitable for large-scale production of composite lattice structuresLayered productsFiberShell molding
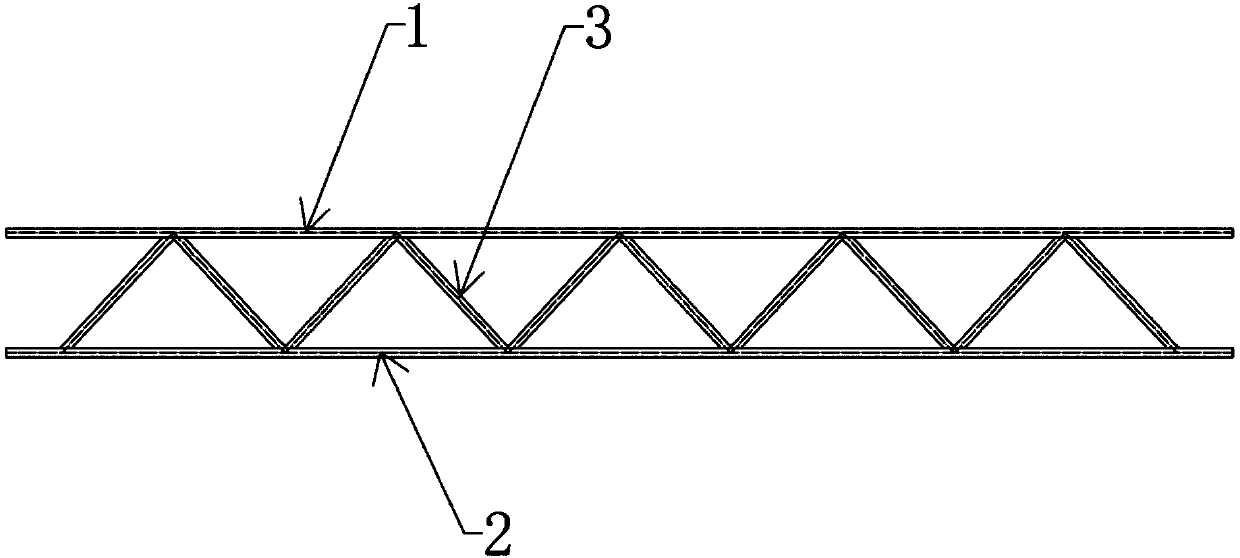
The invention provides a composite lattice structure and a preparation method. The composite lattice structure is composed of an upper face plate, a lower face plate and a lattice core arranged between the upper face plate and the lower face plate. The lattice core is formed in the manner that lattice core triangular fibers and trapezoidal fibers are interlaced. Foam interlayers are arranged in the upper face plate and the lower face plate. A specific injection manner is applied to the composite lattice structure for VARTM formation. The preparation method of the composite lattice structure comprises the seven steps of (1) preparing a fusible alloy mold core; (2) inserting the triangular fibers; (3) laying fibers on the bottom layers of the upper face plate and the lower face plate; (4) inserting the trapezoidal fibers; (5) arranging the face plate interlayers and laying surface fibers of the face plates; (6) conducting VARTM (vacuum assisted resin transfer molding) formation; (7) heating and melting the fusible alloy mold core. The composite lattice structure and the preparation method effectively solve the connection problem between a composite lattice core and the face plates, integrated formation is achieved, the quality is reliable, the technology is simple, and the node strength is high.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Cross-flow filtration cassettes and methods for fabrication of same
InactiveUS7297269B2Increase filter surface areaEffective spaceMembranesSemi-permeable membranesShell moldingCross-flow filtration
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
Manufacturing method of three-dimensional woven composite material hollow spiral spring
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a three-dimensional woven composite material hollow spiral spring. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: first, using spinnable and weavable fiber to weave a three-dimensional braidd tube on the outer surface of a bent strip-type core model through the three-dimensional weaving technology so as to obtain a strip-type fabric preform; then, placing the strip-type fabric preform in a spiral space formed between an internal model and an external model; next, injecting basis material in the spiral space by adopting the vacuum assisted resin transfer molding process (VARTM), and adopting warming and pressurization to solidify the basis material and the three-dimensional braidd tube into the composite material spiral spring; and finally, removing the core model in the spiral spring to obtain the three-dimensional woven composite material hollow spiral spring. The three-dimensional woven composite material hollow spiral springmanufactured through the manufacturing method has the advantages of light weight, antifatigue, corrosion resistance and impact resistance of the composite material spiral spring to further improve theperformance including light weight and spring rigidity.
Owner:刘念
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com