Process and apparatus for producing nanofiber and polymer web
A nanofiber and manufacturing method technology, which is applied in the field of manufacturing and device of nanofibers and polymer meshes, can solve the problems of complex device structure, inability to stack and distribute to give full play to effects, and rising equipment costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
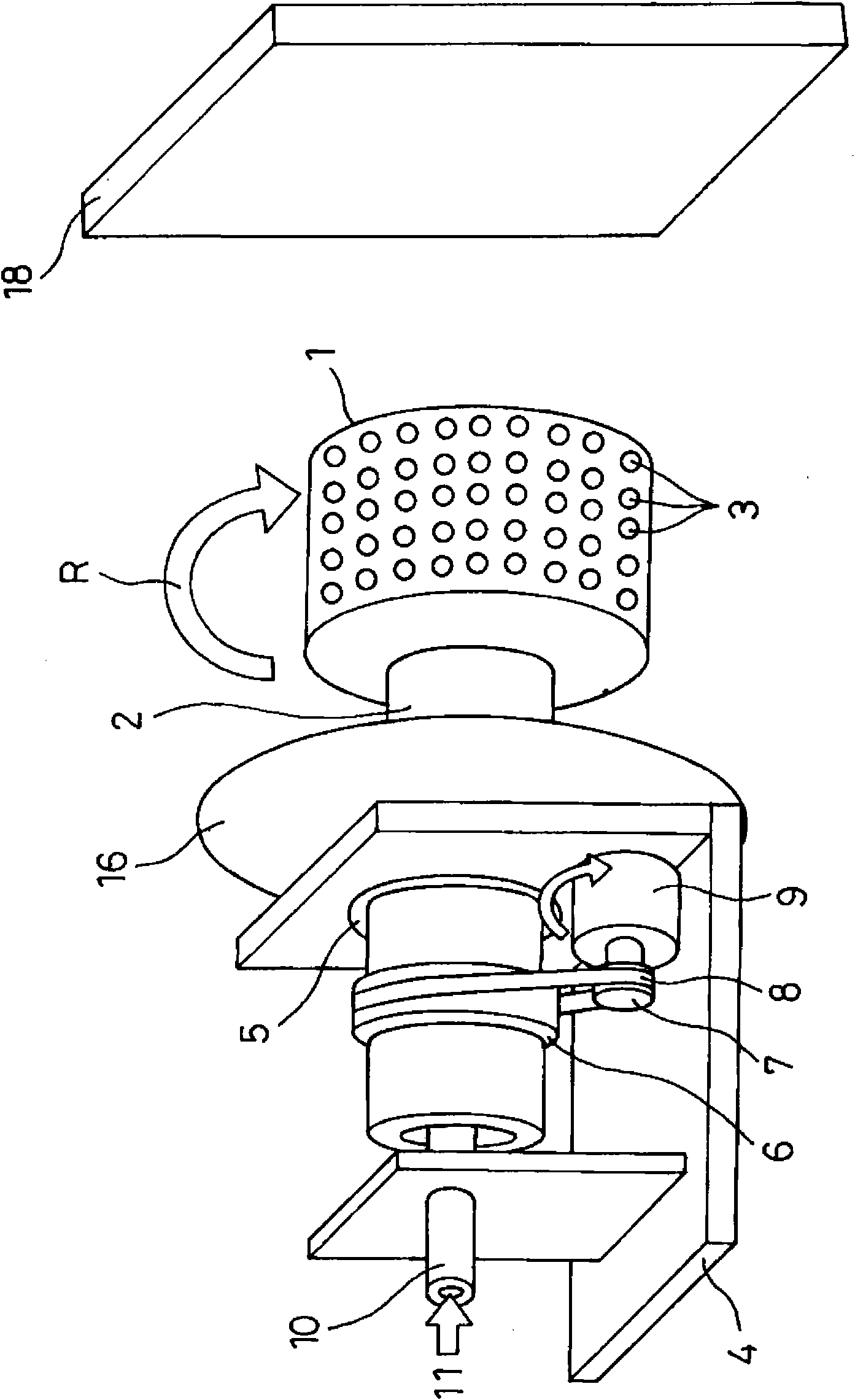
[0062] First, refer to Figure 1 ~ Figure 6C Embodiment 1 of the manufacturing apparatus of the polymer network of this invention is demonstrated.
[0063] exist Figure 1 ~ Figure 3 Among them, symbol 1 is a cylindrical container with a diameter of 20 to 500 mm as a rotating container. The axial center part of one end is penetrated by the end of the rotating cylinder 2 and fixed integrally with the rotating cylinder 2 so that it can rotate around the axis. The form rotating like the arrow R is supported by the rotating cylinder 2 . The rotating cylinder 2 is made of a material with better insulation. The other end of the cylindrical container 1 is closed, and many small holes 3 with a diameter of about 0.01 to 2 mm are formed on the peripheral surface at intervals of several mm. In addition, the small hole 3 may be formed by a hole directly opened on the peripheral wall of the cylindrical container 1, or may be constituted by a short nozzle member attached to the periphera...
Embodiment approach 2
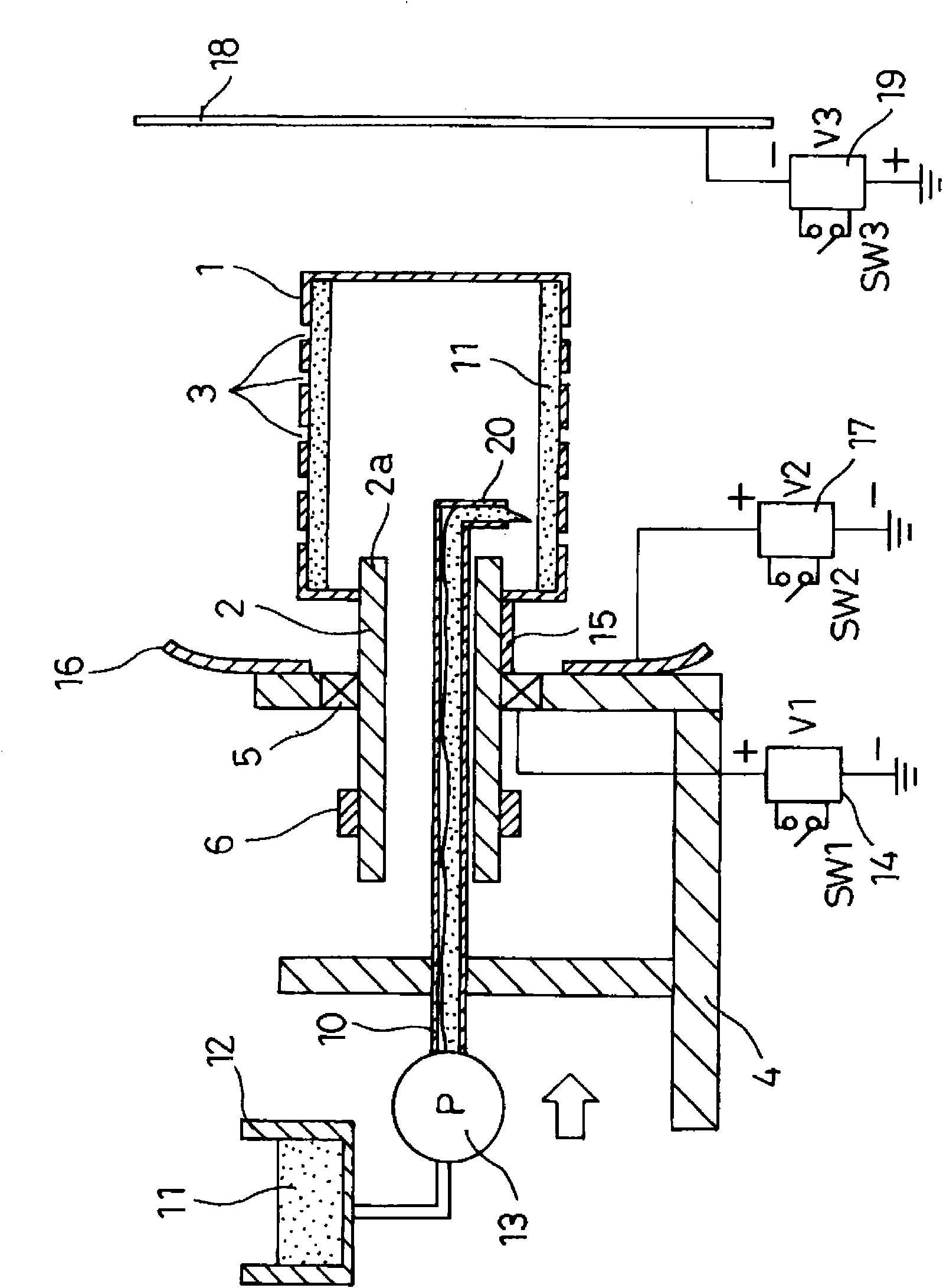
[0080] Next, refer to Figure 7 ~ Figure 10 Embodiment 2 of the manufacturing apparatus of the polymer network of this invention is demonstrated. In addition, in the description of the following embodiments, the same reference numerals are assigned to the same components as those in the above-mentioned embodiment, and description thereof will be omitted, and only main differences will be described.
[0081] In the above-mentioned embodiments, an example in which a predetermined amount of polymer solution 11 is supplied into the cylindrical container 1 according to the production amount of the polymer network has been described. The amount of the polymer solution 11 is detected, and the operation control of the supply pump 13 is performed based on the detection result so that the cylindrical container 1 contains a substantially constant amount of the polymer solution 11 .
[0082] exist Figure 7 Among them, a storage capacity detection device 25 is provided. The storage capa...
Embodiment approach 3
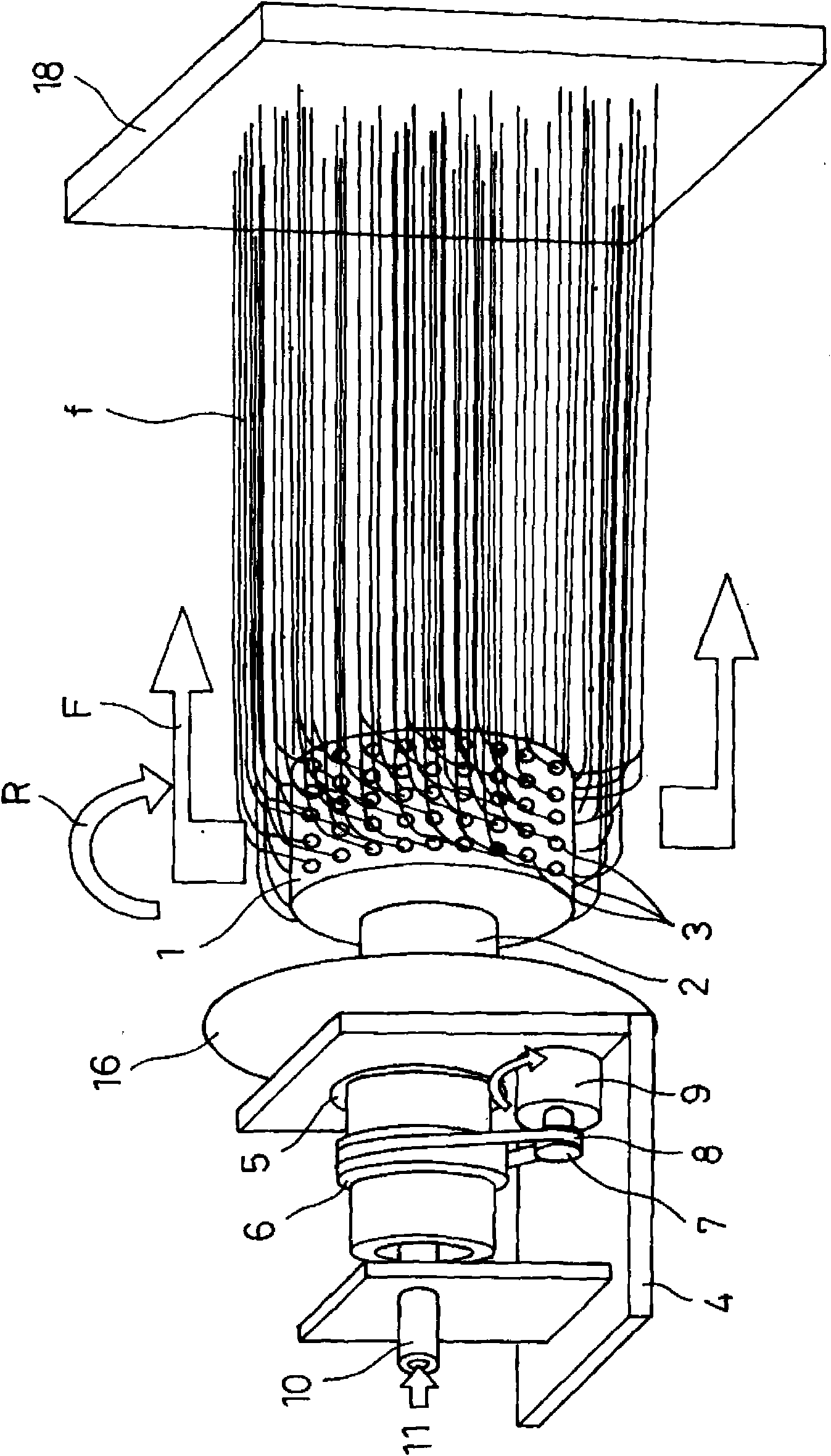
[0088] Next, refer to Figure 11 Embodiment 3 of the manufacturing apparatus of the polymer network of this invention is demonstrated.
[0089] In this embodiment, if Figure 11 As shown, an air blower 34 is arranged between the cylindrical container 1 and the reflective electrode 16 on one side thereof. Specifically, air blowing blades 35 are installed on the rotating cylinder 2 at a position between the reflective electrode 16 and the cylindrical container 1, and as the rotating cylinder 2 rotates, the wind blows toward the direction of the cylindrical container 1 as indicated by arrow D. Air on the other side.
[0090] According to this structure, the solvent evaporated by the air blowing of the air blowing device 34 is quickly discharged, and the concentration of the solvent in the surrounding environment will not increase. to generate the desired nanofiber f. In addition, it is also possible to more effectively deflect the flow direction of the nanofiber f in the prod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com