Separation method of buffering stem cell in human placenta
A technology of mesenchymal stem cells and human placenta, applied in the field of separation of human placental mesenchymal stem cells, can solve the problems of cumbersome separation methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1 Placental MSC isolation and culture method
[0039] According to the anatomical structure of the placenta, under sterile conditions, a polyethylene catheter was inserted from the umbilical vessels (two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein) to form a circulating fluid perfusion system, and heparin-containing DMEM or IMDM medium was used as the perfusion fluid. First use perfusate to wash out the residual blood within 0.5-2.5 hours postpartum through arteriovenous circulation, and then incubate with 100-250ml perfusate at 20-25°C for 12-24 hours. Mononuclear cells were isolated from the perfusate by density gradient centrifugation, and the cells were suspended in MSC medium after washing, at 37°C, 5% CO 2 After culturing for 24-48 hours under full-humidity conditions, the medium was changed to remove unattached suspended cells, and the culture was continued, changing the medium every 3-4 days. After the early scattered cells form clones, pi...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2 Identification of biological characteristics of placental MSCs
[0041] 1. Cell growth characteristics and morphological characteristics
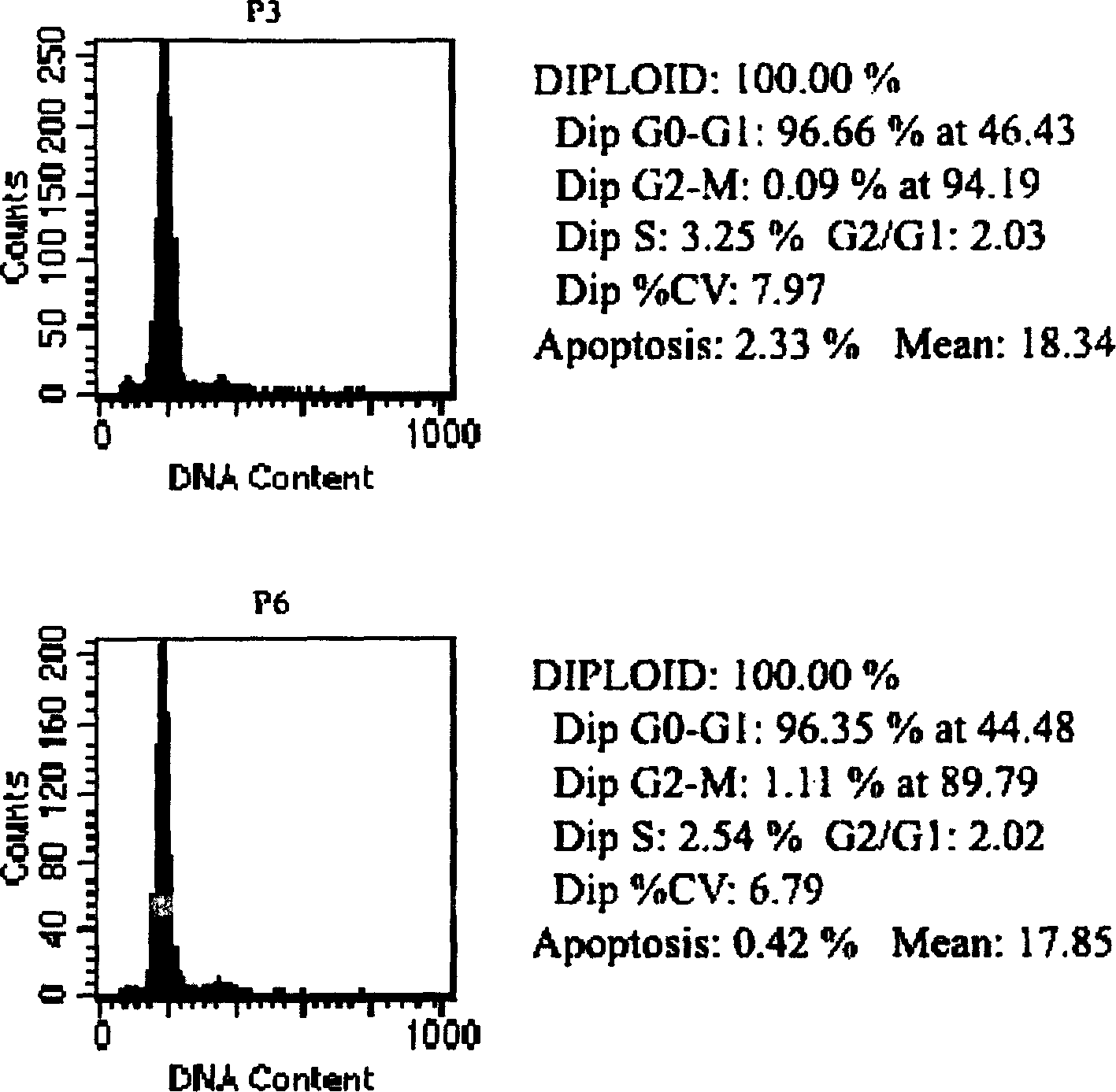
[0042] It takes about 3 days to cultivate by the method of Example 1. Scattered spindle-shaped adherent cells can be seen under the microscope, and radial clones are formed in about 7-10 days. Each clone is picked out and cultured separately in a 24-well plate. After the cells were purified to passage 3, they were used for the detection of cell biological characteristics. During the culture process, it was found that the cell shape was relatively uniform, the growth rate was fast, the adherence speed was fast, and it was easily digested by trypsin. After passage to more than 15 generations, its shape and growth characteristics did not change significantly. See figure 1 .
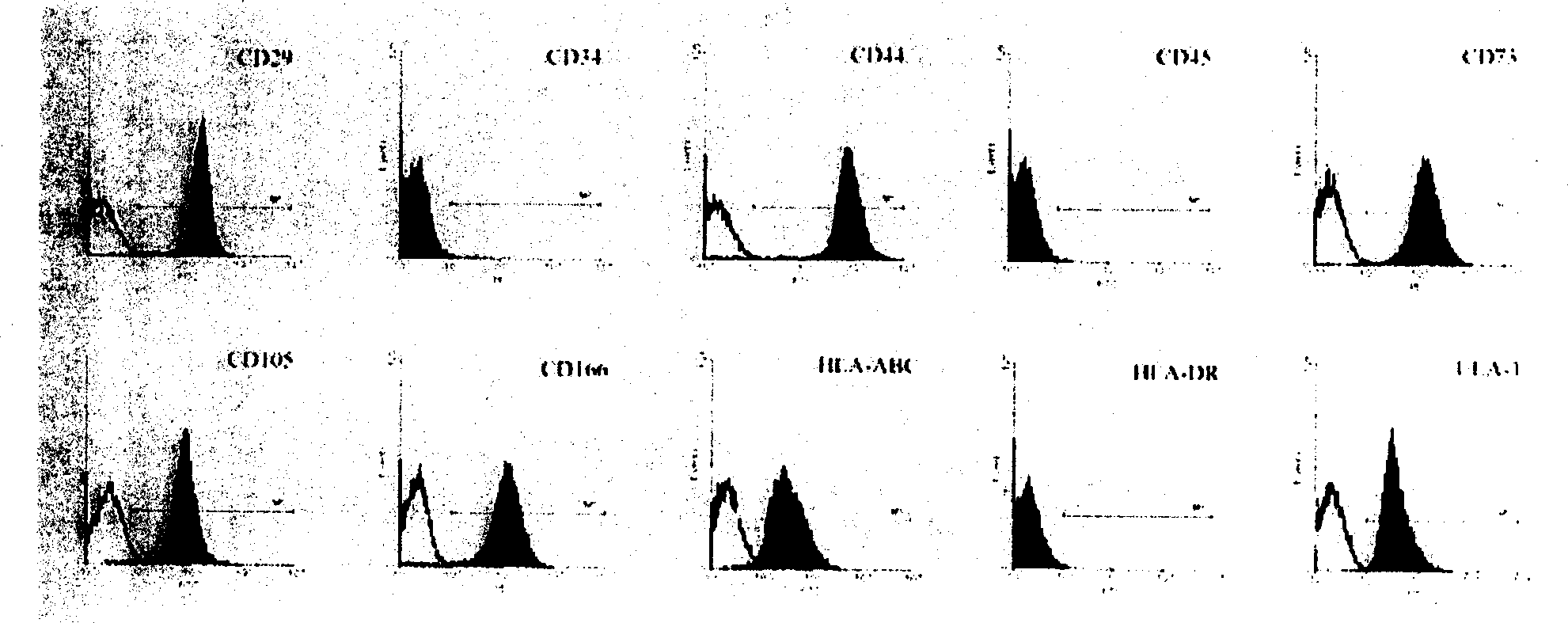
[0043] 2. Identification of MSC surface markers by flow cytometry
[0044] The 3rd, 6th, 9th, 12th, and 15th passage cells were collec...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3 Identification of multilineage differentiation potential of placental MSCs
[0053] 1. Adipogenic induction
[0054] More than 3 generations of MSC, press 1×10 5 Inoculate each well in a six-well plate, and after culturing the standard medium for 24 hours, replace it with high-sugar DMEM containing 10% screened FBS, and add 1 μM of dexamethasone, 200 μM of indomethacin, 0.5 mM of IBMX, and 10 μg / ml of insulin, half the amount every 3 days The medium was changed, induced for 2w, and oil red staining was used to identify lipid droplet formation.
[0055] In DMEM-HG containing 10% filtered FBS, add dexamethasone 1μM, indomethacin 200μM, IBMX 0.5mM, insulin 10μg / ml and culture for 3 days, the cells will undergo morphological changes, gradually shrinking from spindle-shaped fibroblasts to Short, more than 90% of the cells become cubic or polygonal; continuous culture for 7 days, microscopic lipid droplets appear in the cells, as the culture time prolon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com