Animal model for toxicology and dose prediction
An animal, vertebrate technology, applied in the field of cell biology, can solve different problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] The generation of embodiment 1 non-human animal model
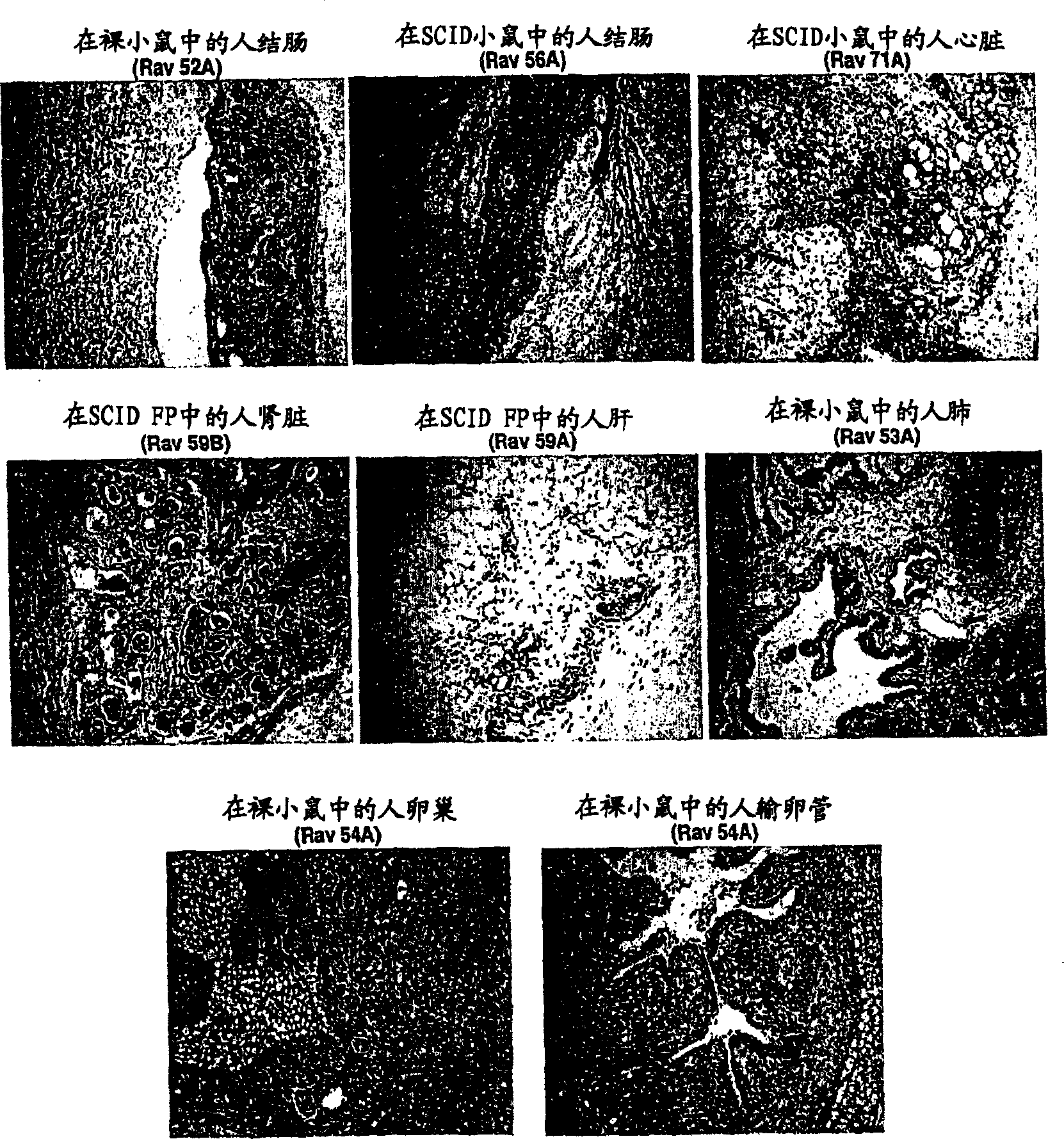
[0084] Tissues from normal embryonic organs (colon, heart, kidney, liver, lung, ovary, and fallopian tube) were cut into 1 mm cubed pieces and placed in the kidneys of nude mice (nu / nu) or SCID immunocompromised mice. in the bursa or fat pad. These tissues are left in the animals for 6-40 weeks to allow time to develop into mature tissues. Animals were euthanized and tissues were removed and sectioned for H&E staining and immunohistochemical evaluation.
[0085] figure 1 Results are shown for a series of implants in which tissues were allowed to mature for 4 months. In this example, for all references to "pictures" see figure 1 . Pictures 1, 2, 3, 6, 7 and 8 show implantation under the renal capsule and pictures 4 and 5 show implantation under the fat pad. Pictures 1, 6, 7 and 8 show the implantation of normal embryonic organs in nude (nu / nu) mice, while pictures 2, 3, 4 and 5 show the implantation of normal ...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Example 2 Mature Tissues for Safety / Efficacy Models
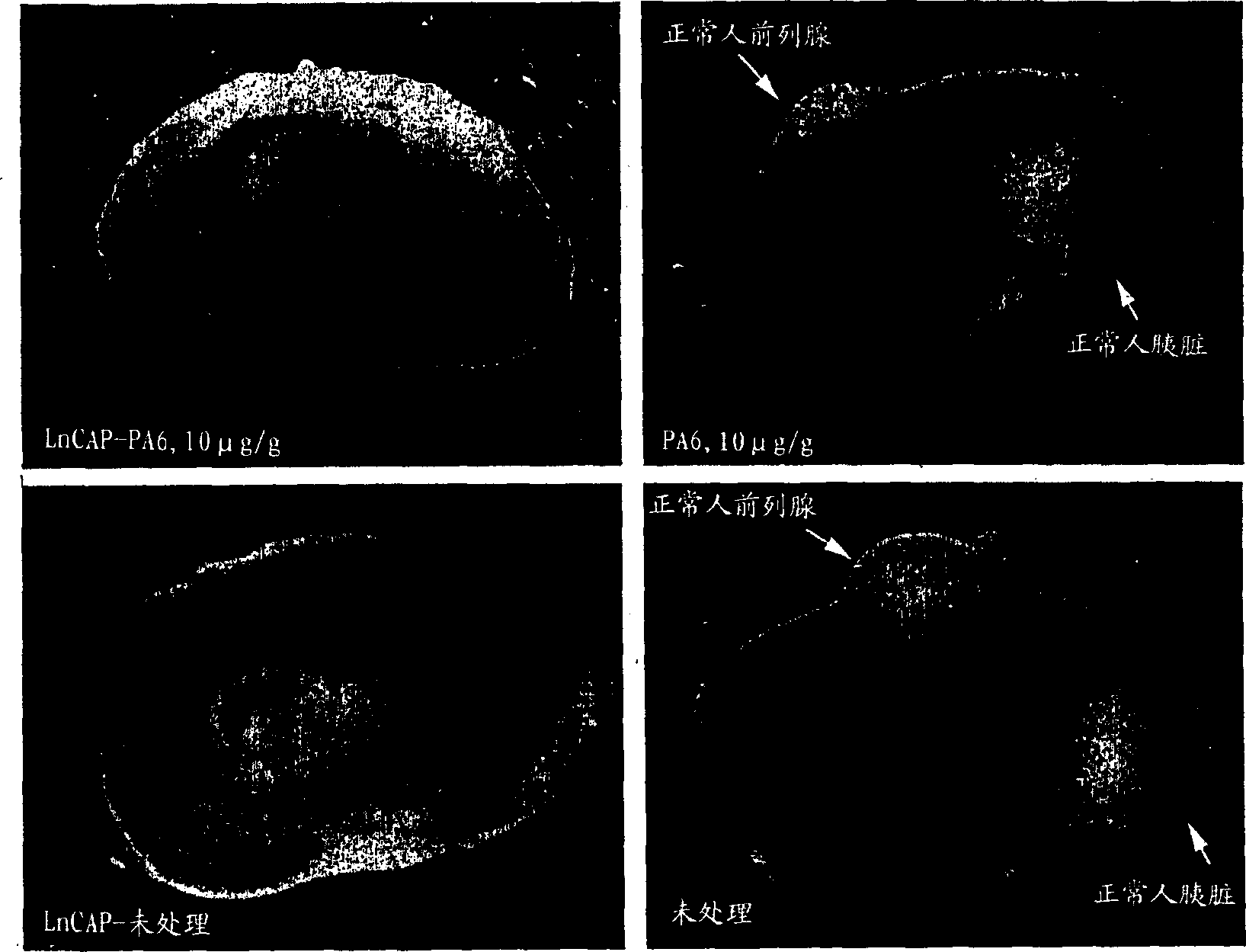
[0087] Small pieces of normal human prostate and pancreas were placed under the renal capsule and allowed to mature for 6 weeks. At this point, human prostate cancer cells (LnCAP) were placed under the contralateral renal capsule of the same animals and allowed to grow for an additional week. On day 7 after LnCAP tumor implantation, one animal was treated with 10 μg / g PA6 antibody (anti-human EpCAM) by intraperitoneal injection. Control animals were treated with saline injections. 4 injections in two weeks. At the end of this time, animals were euthanized and examined for tumor and normal tissue xenografts. animal kidneys figure 2 displayed in . figure 2 The left side shows LpCAP tumors and the right side shows normal tissue (a total of 9 weeks of development in this animal). The upper pictures are from treated animals and the lower pictures are from control animals. Other treated animals contained normal co...
Embodiment 3
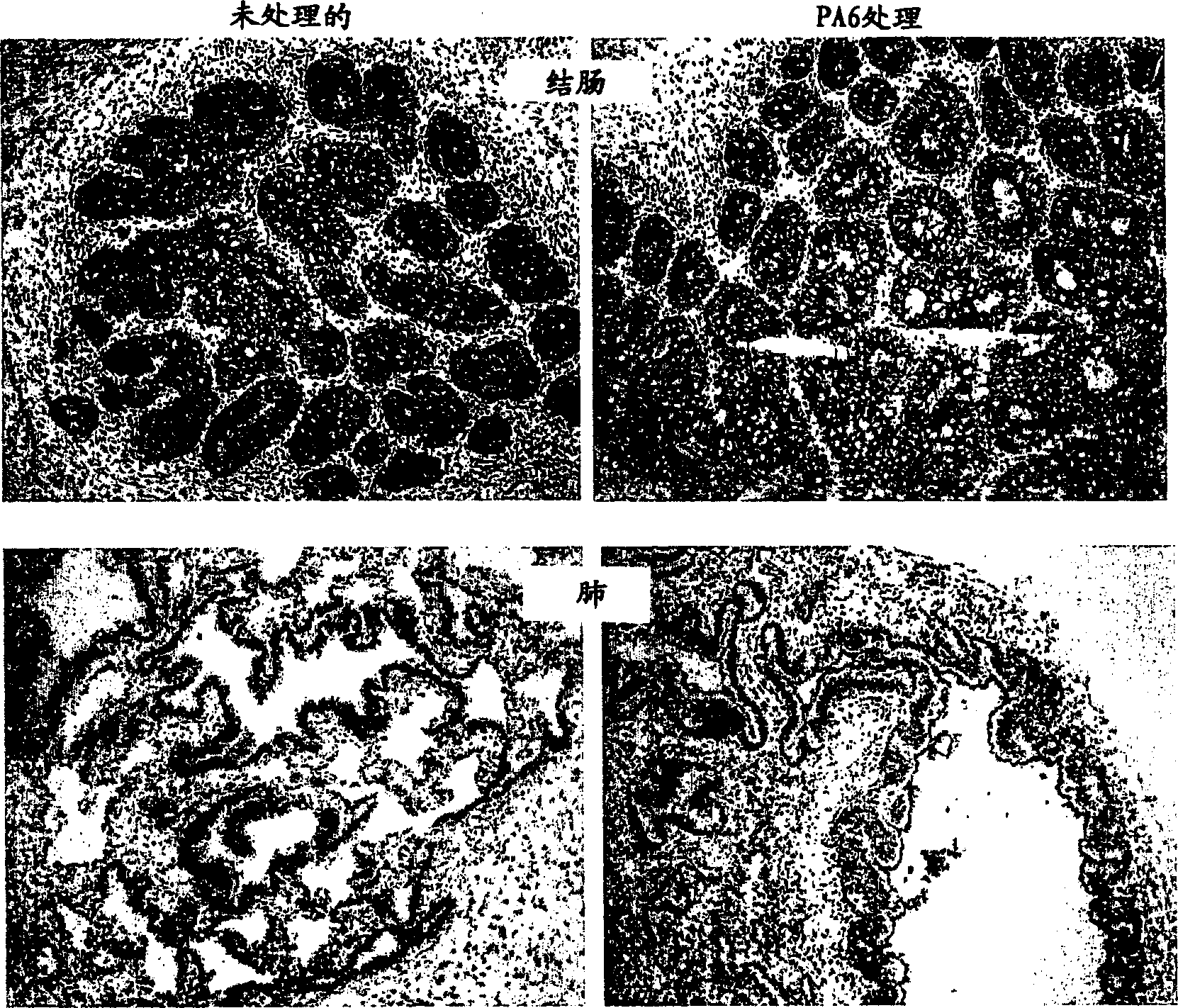
[0088] Example 3 Immunohistochemistry of Human Prostate and Human Colon Mature Tissues
[0089] Immunohistochemistry of human prostate and human colon mature tissues from experiments in figure 2 described in. While tumors were affected by antibody treatment leading to cell death and hemorrhage, normal tissues were not (A-D). To determine whether the tissue contained the antibody target (EpCAM), the tissue was stained with a directly labeled PA6 (anti-human EpCAM) antibody. Both treated and untreated tissues showed antibody binding. Mature human prostate tissue also stains strongly for prostate-specific antigen (PSA), a marker of prostate cells.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com