Method for non-invasive preimplantation hereditary detection of embryos
A pre-implantation, genetic technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of large volume range changes, low free DNA concentration, and complex culture medium components, etc., to achieve improvement The effects of data quality, good amplification uniformity, and avoiding sampling risks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] A kit for noninvasive preimplantation genetic testing consisting of the following reagents:
[0039] Pre-amplification mixture: 0.7mM dNTP, 40mM Tris-HCl (pH=7.5), 10mM MgCl 2 , 10% DMSO, 6uM primers, 1 μL high-fidelity DNA polymerase (1U / μL) (TAKARA);
[0040] Amplification mixture: 0.6mM dNTP, 40mM Tris-HCl (pH=7.5), 5mM MgCl 2 , 8% DMSO, 2.5uM primers, 5U high-fidelity DNA polymerase (1U / μL) (TAKARA);
[0041] Lysis solution: 25mM Tris-HCl (pH=8.3), 0.05% Triton X-100, 1.5mM EDTA;
[0042] Lyase: 2mg / mL proteinase K;
[0043] End repair reaction solution; end repair enzyme; DNA ligation buffer; DNA ligase; adapter; PCR amplification reaction solution; universal primers; index primers; deionized water.
experiment example 1
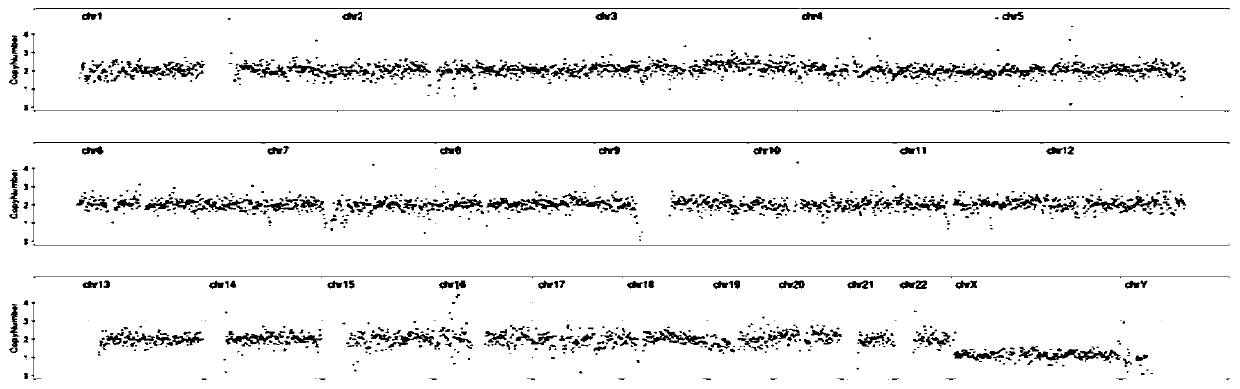
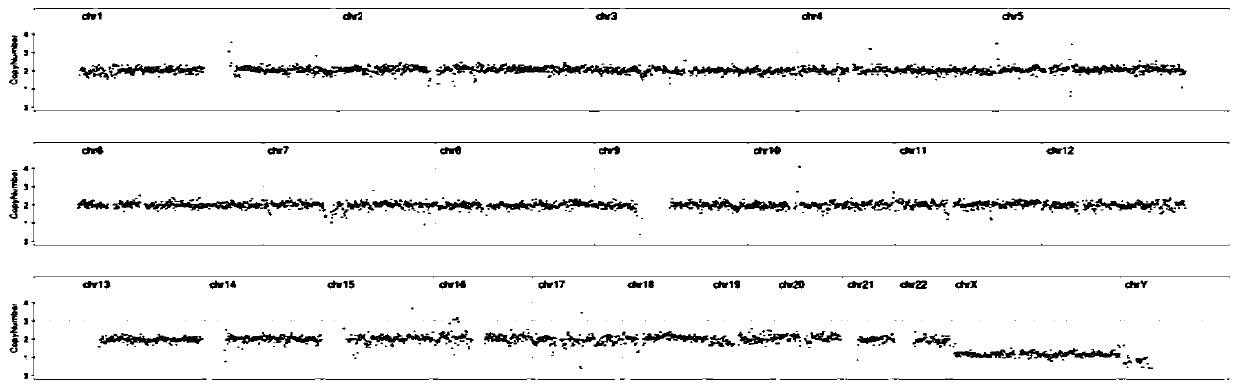
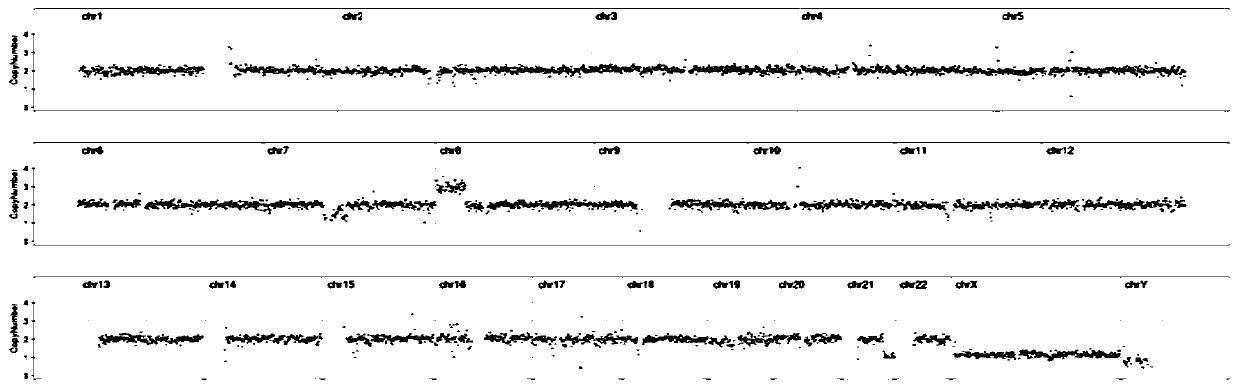
[0052] The two kits of Comparative Example 1 and Comparative Example 1 performed whole genome amplification, library preparation and on-machine sequencing on the same sample respectively. The amplification effects were compared, and the results are shown in Table 1. figure 1 and figure 2 shown.
[0053] Table 1
[0054] sample WGA concentration value (ng / ul) Comparative example 1 28.5 Example 1 46.7
[0055] Through the optimization of the kit in this application, it can be seen that the WGA concentration of the optimized kit in this application is significantly higher than that before optimization, and the CNV result dispersion of sequencing results after optimization is significantly better than that after optimization.
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embryo samples fertilized by intracytoplasmic sperm injection were cultured to the blastocyst stage, and conventional PGT-A blastocyst trophoblast cell biopsy and blastocyst culture fluid were used to detect chromosomal aneuploidy to evaluate whether the embryos were chromosomally normal.
[0058] Specific steps are as follows:
[0059] 1. Obtain samples of blastocyst culture fluid
[0060] After ICSI insemination, the fertilized eggs were cultured to the blastocyst stage, the blastocyst culture fluid was aspirated with a clean pipette, and 5-20 μL of the culture fluid was used as a sample for chromosomal aneuploidy detection. After aspirating the culture medium, the embryos were biopsied, and blastocyst trophoblast cells were taken for PGT-A detection.
[0061] 2. Whole genome amplification in blastocyst culture medium
[0062] 2.1 Lysis of blastocyst culture fluid samples
[0063] Add 10-20 μL of lysate and 0.6-1.2 μL of lyase to the culture solution sample tube co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com