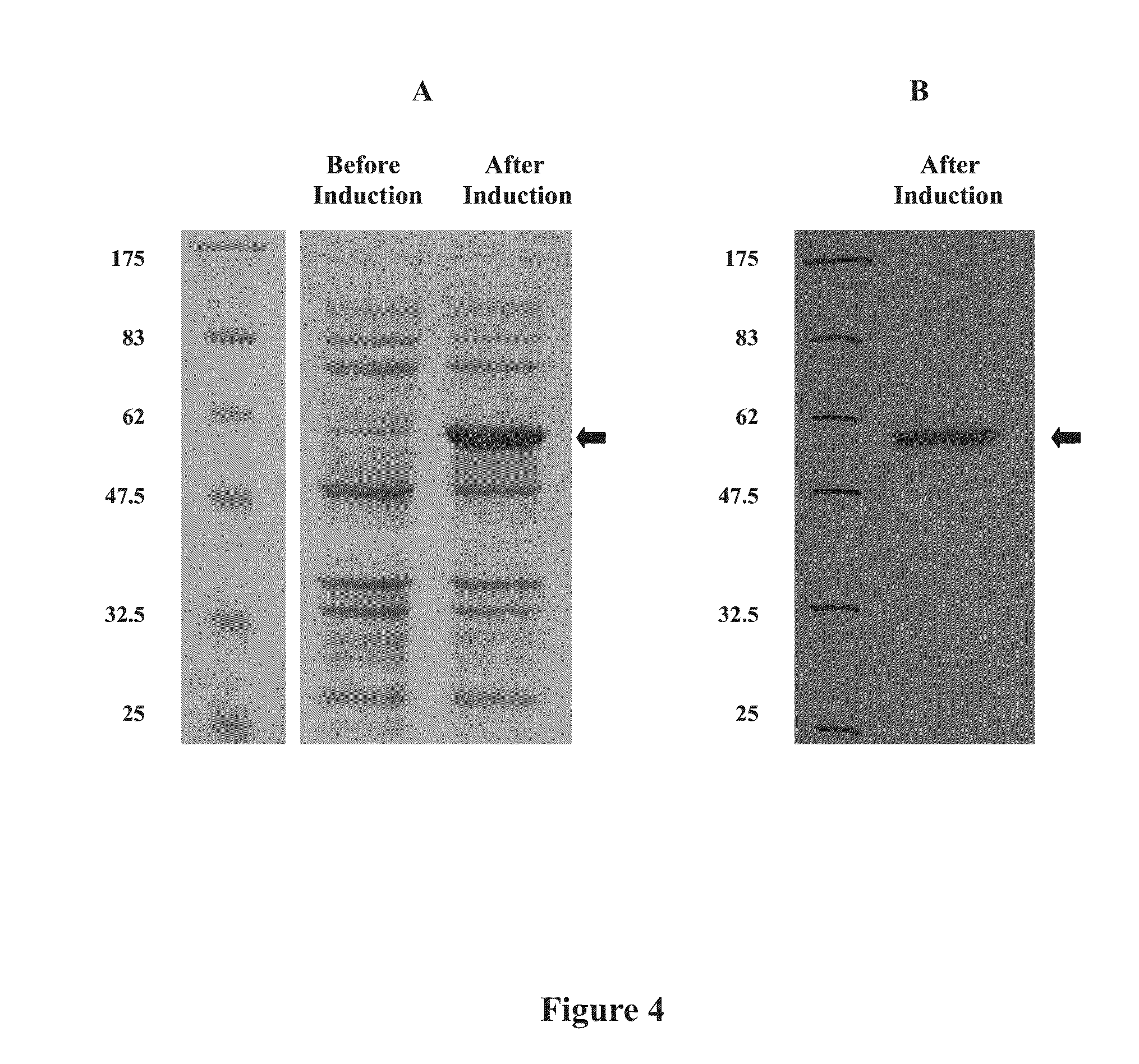
Patents
Literature
140 results about "Tandem Repeat Sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
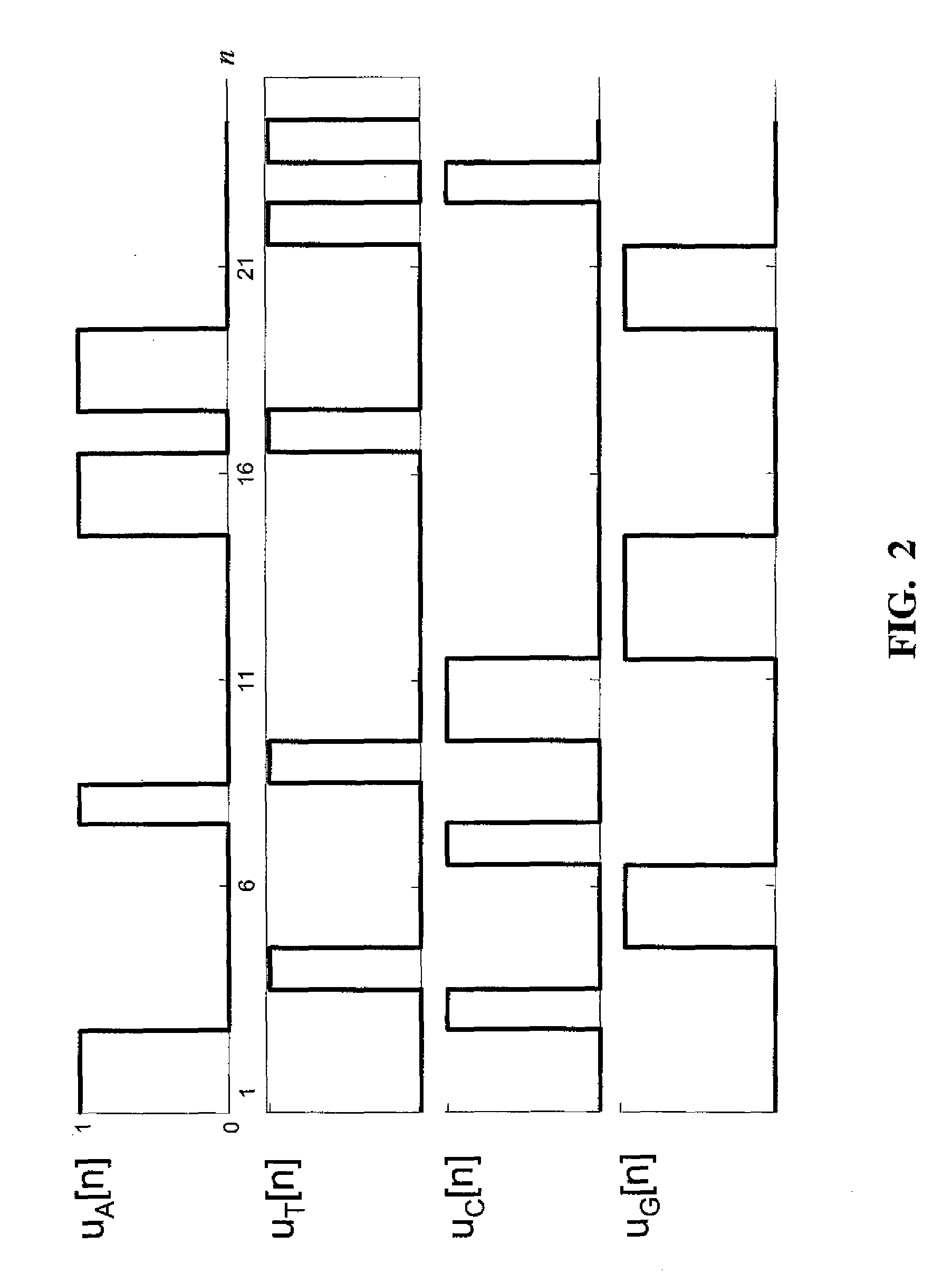
Tandem repeat sequences: Multiple copies of the same DNA base sequence on a chromosome; used as a marker in physical mapping of the chromosome.
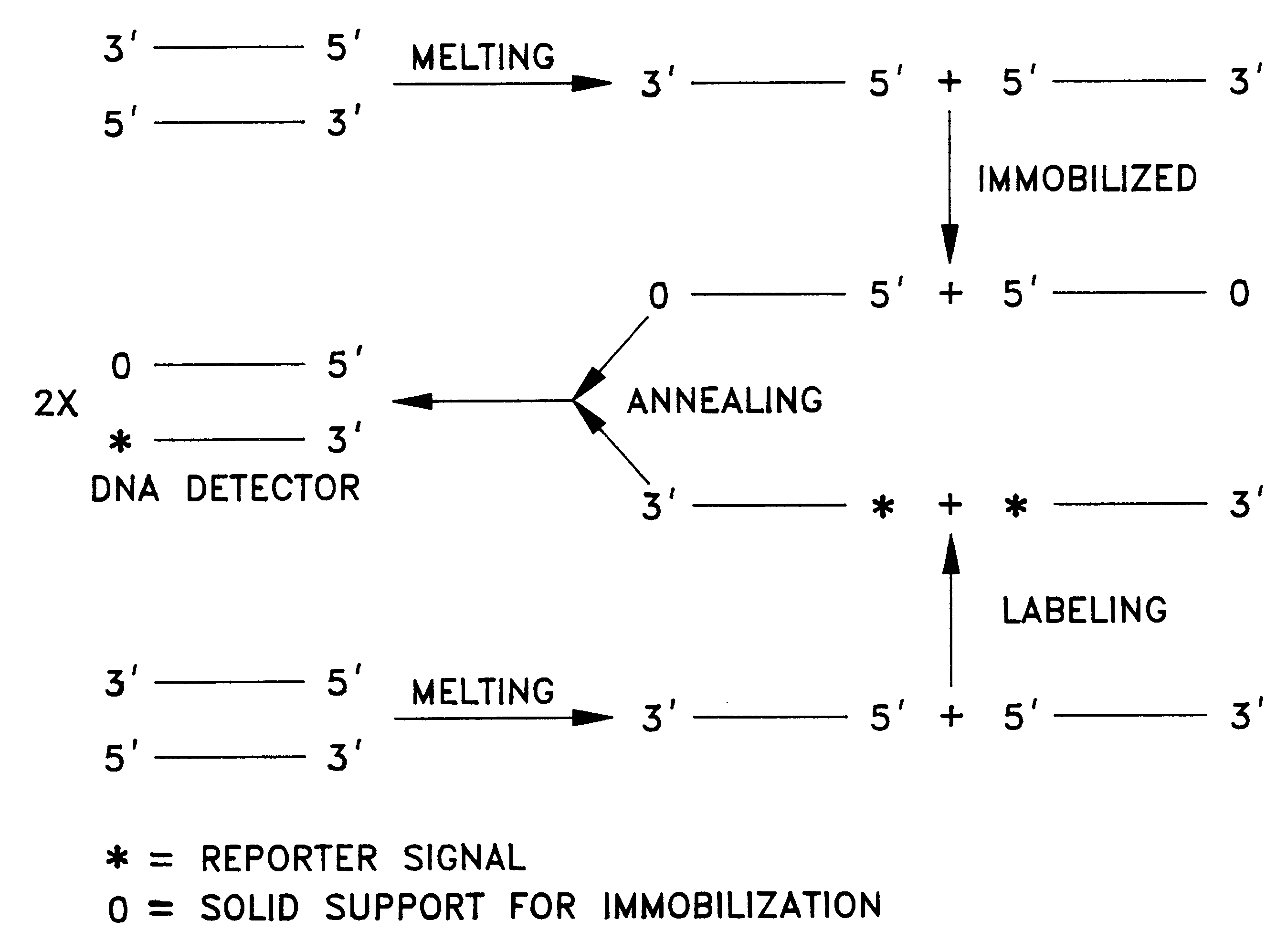
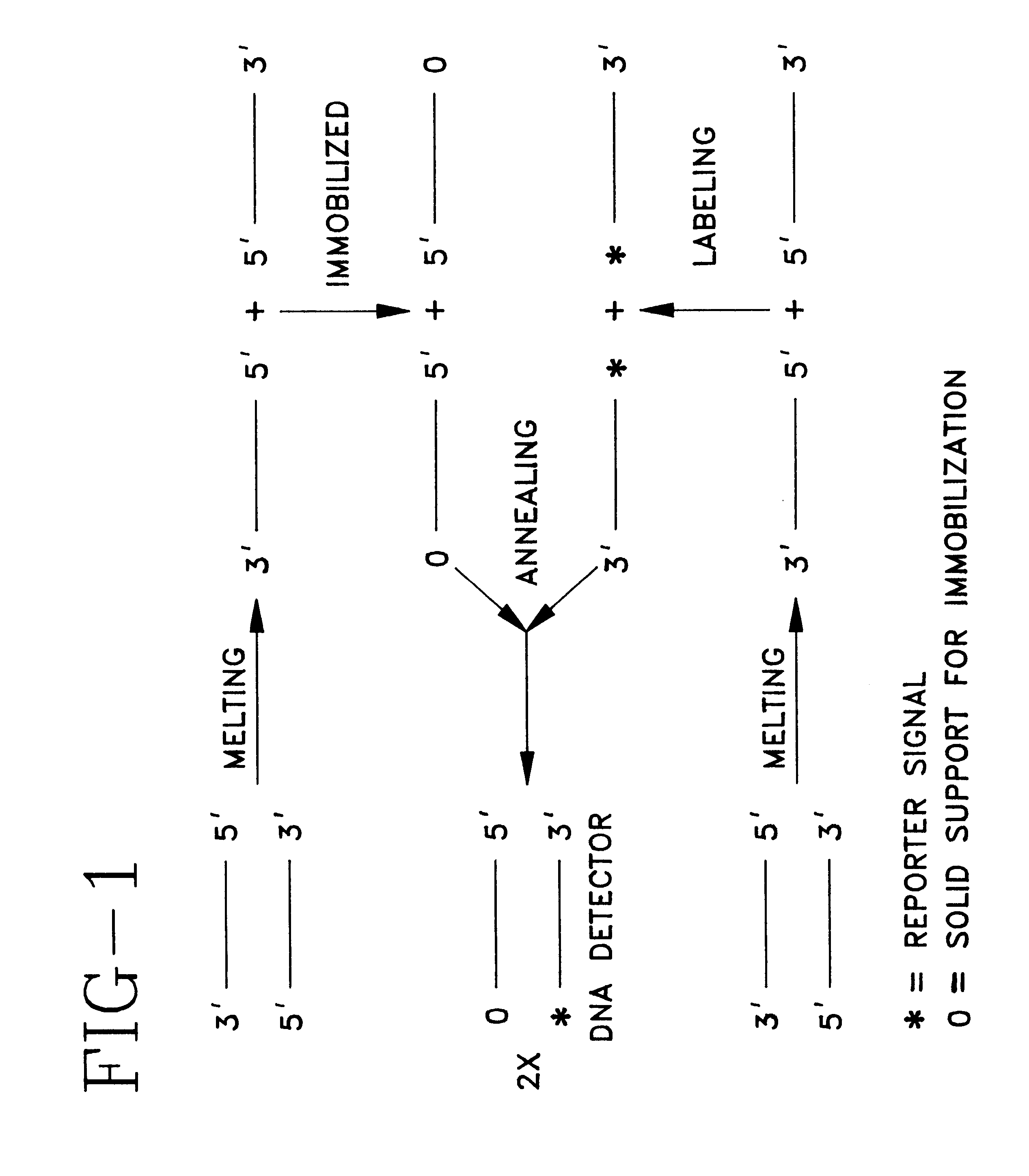
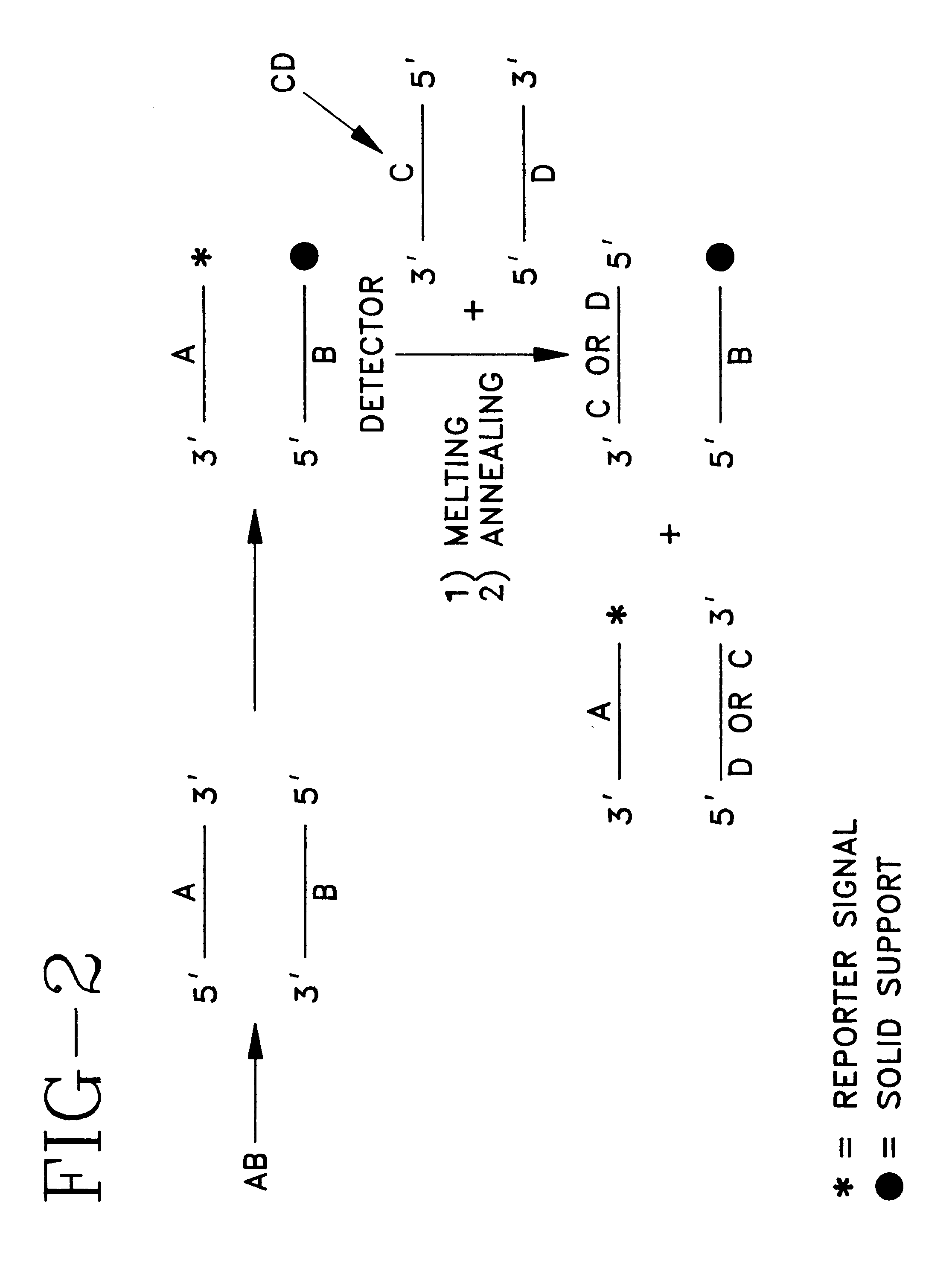
Detector for nucleic acid typing and methods of using the same
InactiveUS6238866B1Easy constructionSimple designSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteTyping
The present invention provides devices and methods for detecting or characterizing a nucleic acid analyte without requiring electrophoresis or the direct sequencing of analyte samples or analyte fragments. The device includes a panel or array of double stranded oligonucleotide probes immobilized on a solid support. each probe comprising a nucleotide sequence having a hypervariable number of tandem repeat sequences. Desirably, the specificity of the probes is varied with the location on the panel or array. One strand of each probe is preferably anchored at one terminus to a solid support and the opposite terminus of a second strand is not so anchored. The probes and / or the analyte are labeled by one or more reporter moieties, designed, for example, to allow for visual or instrument based detection of hybridization events.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
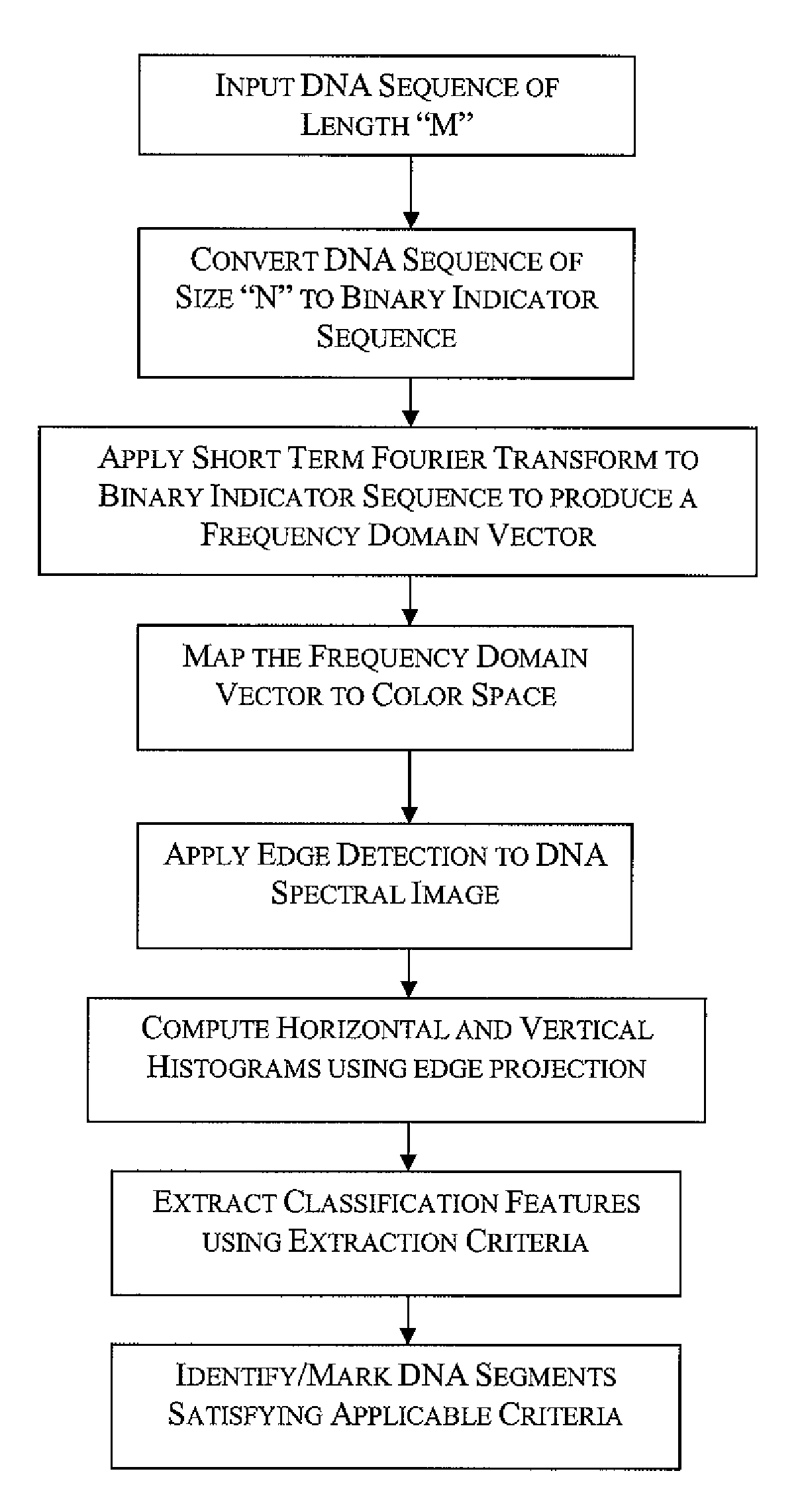
Methods and systems for identification of DNA patterns through spectral analysis
InactiveUS20090129647A1Improve visualizationHigh resolutionData visualisationBiostatisticsDNA PatternsCo-occurrence
Spectrogram extraction from DNA sequence has been known since 2001. A DNA spectrogram is generated by applying Fourier transform to convert a symbolic DNA sequence consisting of letters A, T, C, G into a visual representation that highlights periodicities of co-occurrence of DNA patterns. Given a DNA sequence or whole genomes, with this method it is easy to generate a large number of spectrogram images. However, the difficult part is to elucidate where are the repetitive patterns and to associate a biological and clinical meaning to them. The present disclosure provides systems and methods that facilitate the location and / or identification of repetitive DNA patterns, such as CpG islands, Alu repeats, tandem repeats and various types of satellite repeats. These repetitive elements can be found within a chromosome, within a genome or across genomes of various species. The disclosed systems and methods apply image processing operators to find prominent features in the vertical and horizontal direction of the DNA spectrograms. Systems and methods for fast, full scale analysis of the derived images using supervised machine learning methods are also disclosed. The disclosed systems and methods for detecting and / or classifying repetitive DNA patterns include: (a) comparative histogram method, (b) feature selection and classification using support vector machines and genetic algorithms, and (c) generation of spectrovideo from a plurality of spectral images.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Nucleic acid size detection method
InactiveUS20080124709A1Finer of numberSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFragile X chromosomeFractionation
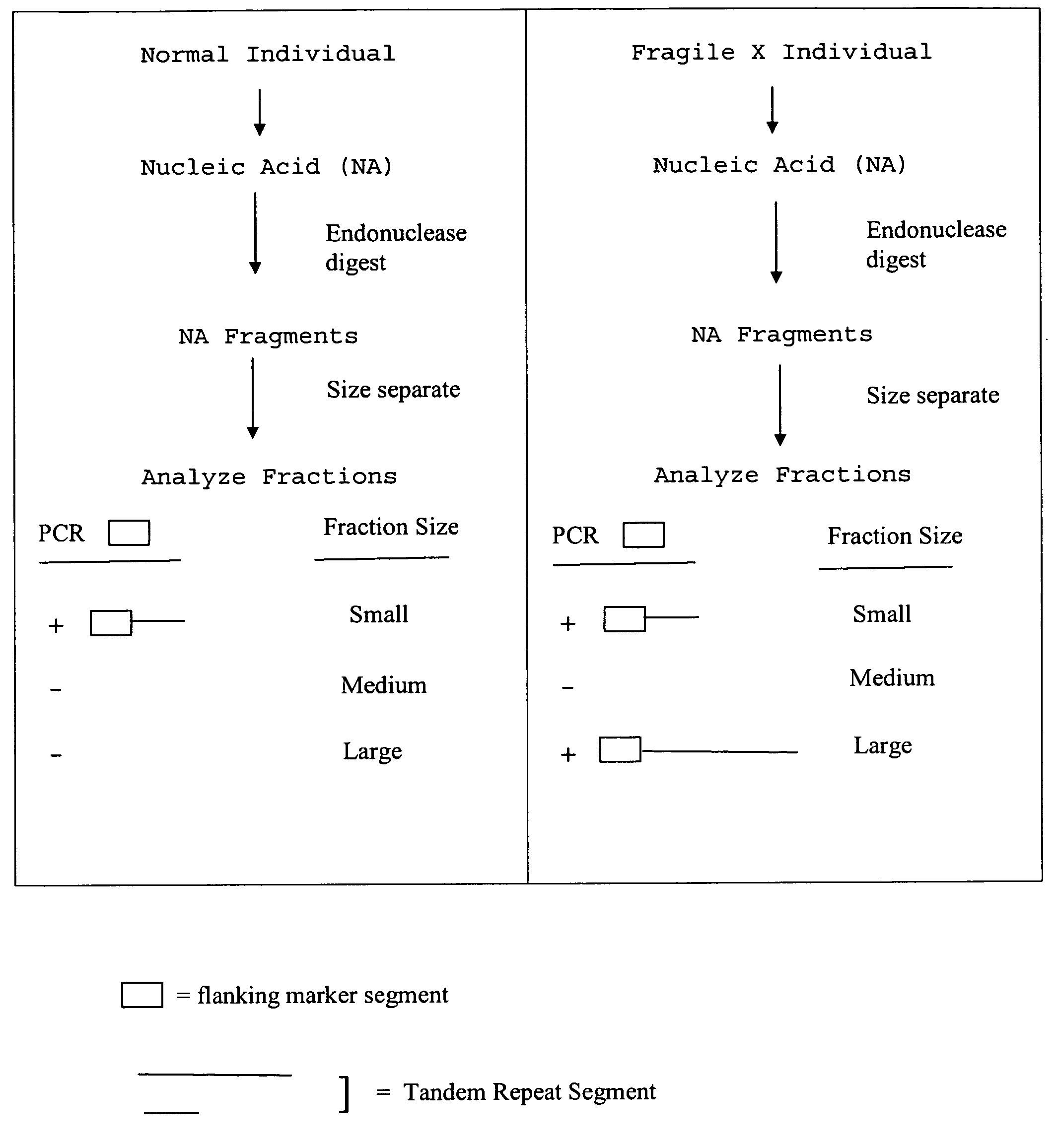
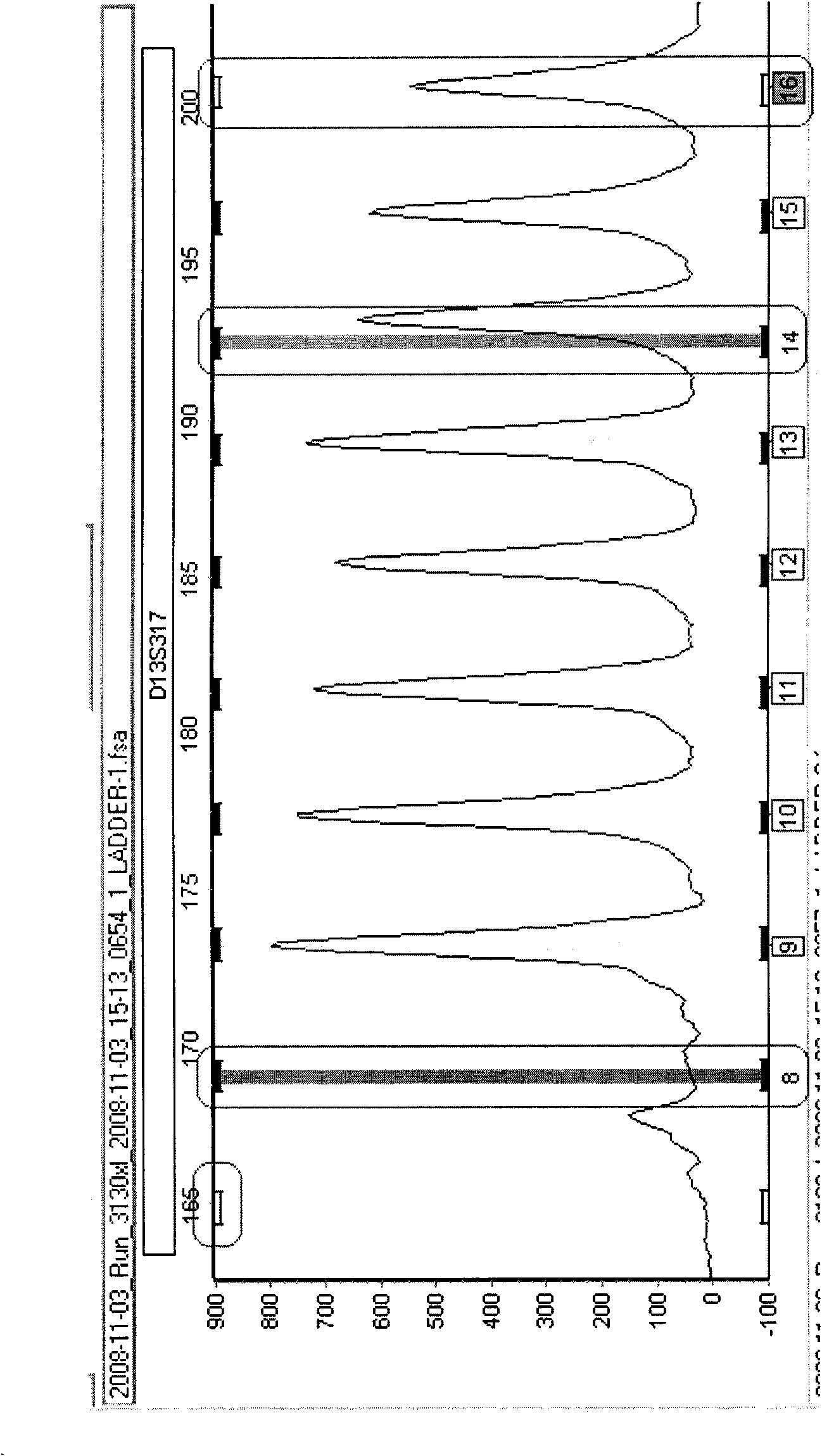
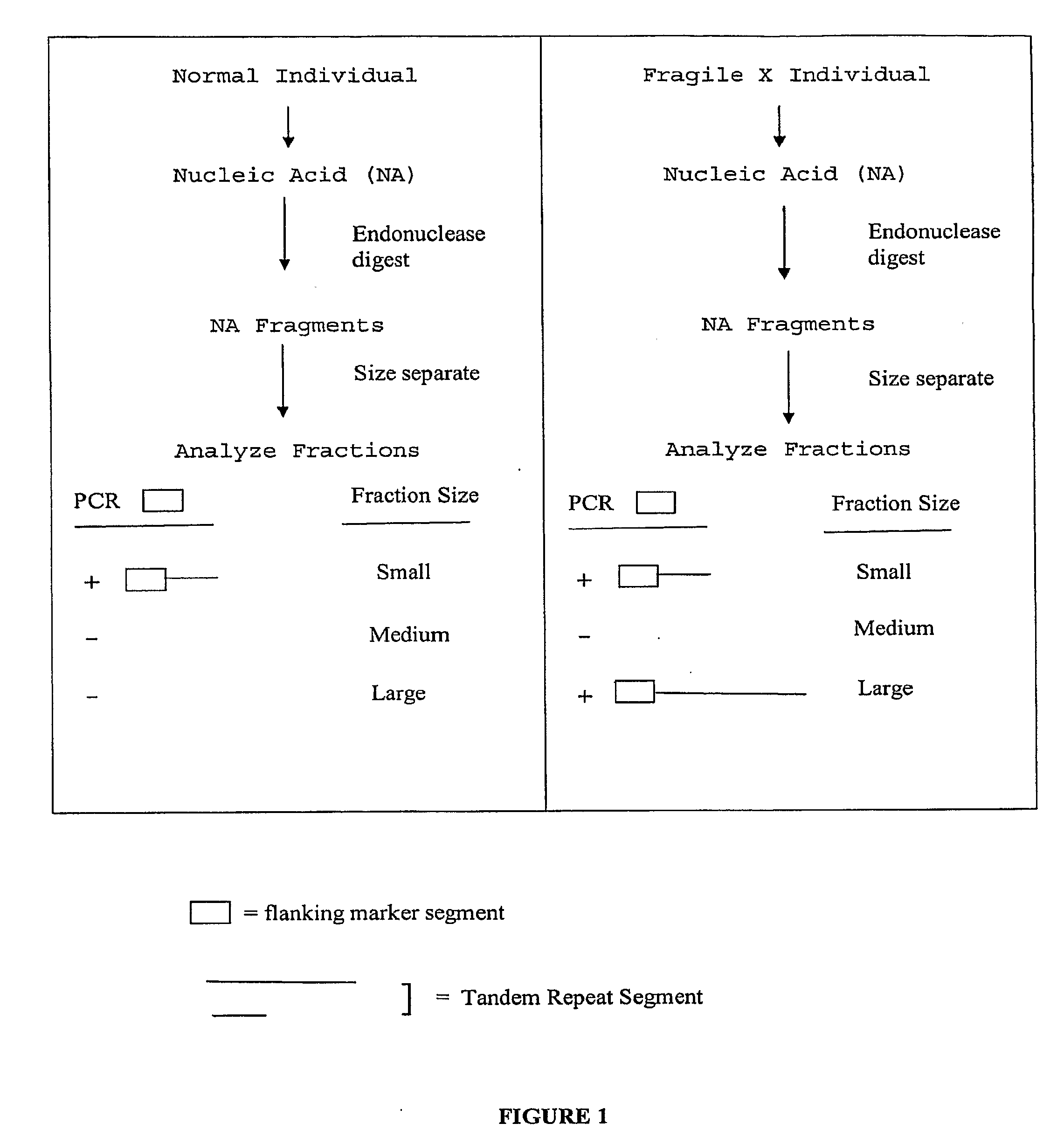
The present invention provides methods of determining the size of a particular nucleic acid segment of interest in a sample of nucleic acids through fragmentation of DNA, size fractionation, an optional second fragmentation, and identification using a marker sequence. In particular aspects, an expansion or reduction of tandem repeat sequences can be detected. In further aspects, carriers and individuals afflicted with fragile X syndrome or other diseases associated with tandem repeats can be distinguished from normal individuals.
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC +1
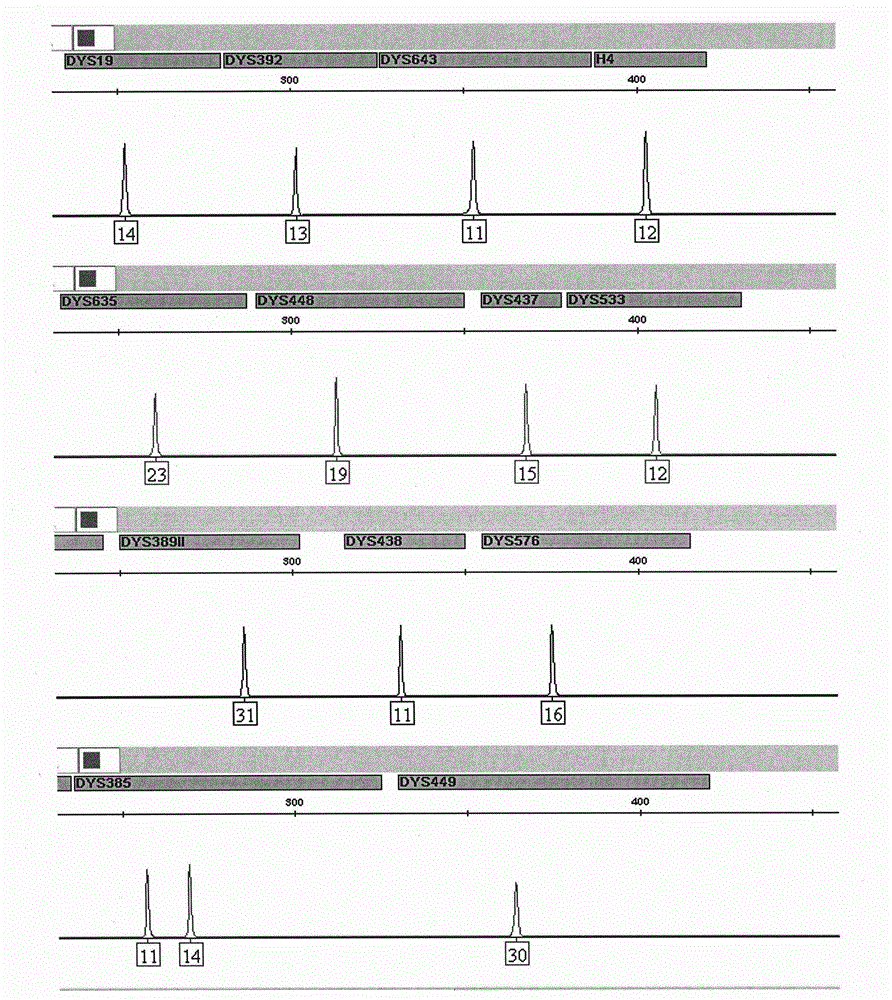
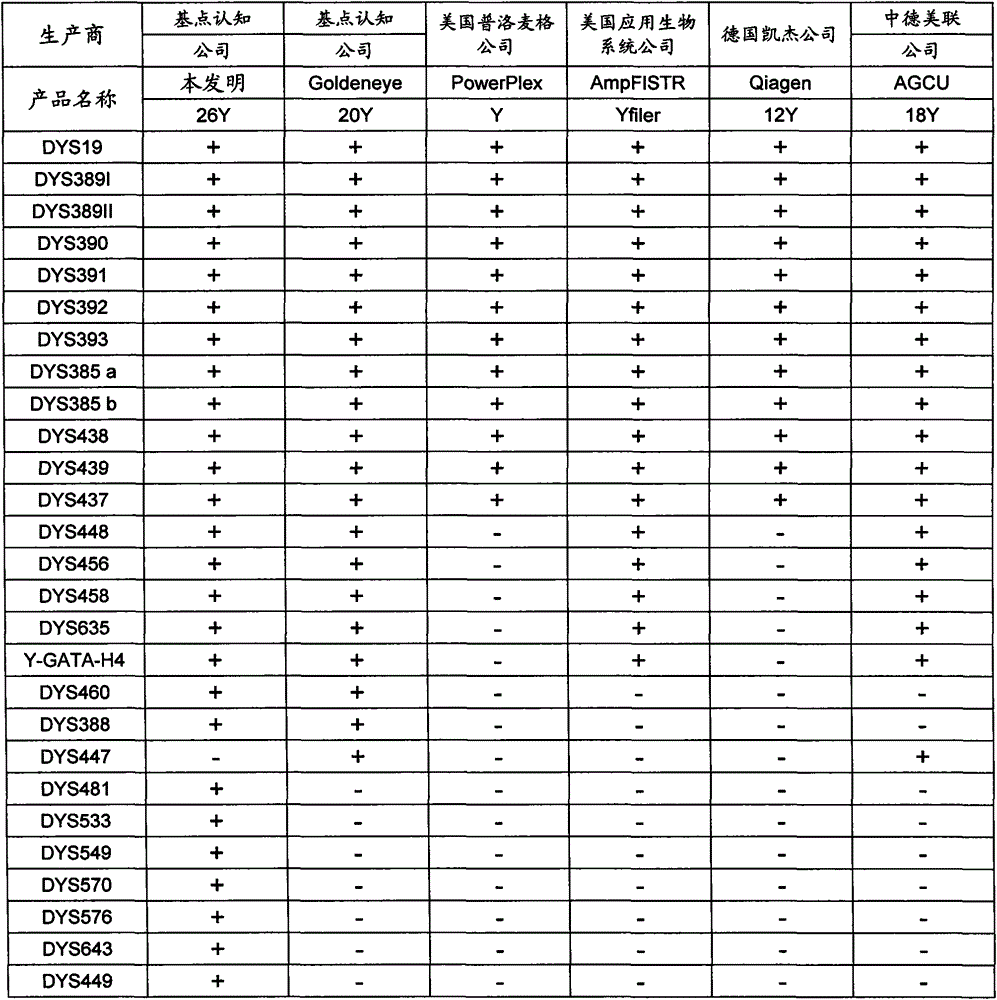
Composite amplification kit for 26 Y chromosome short tandem repeats
ActiveCN104017895AHigh individual recognition rateImprove compatibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAnalysis dnaTandem repeat
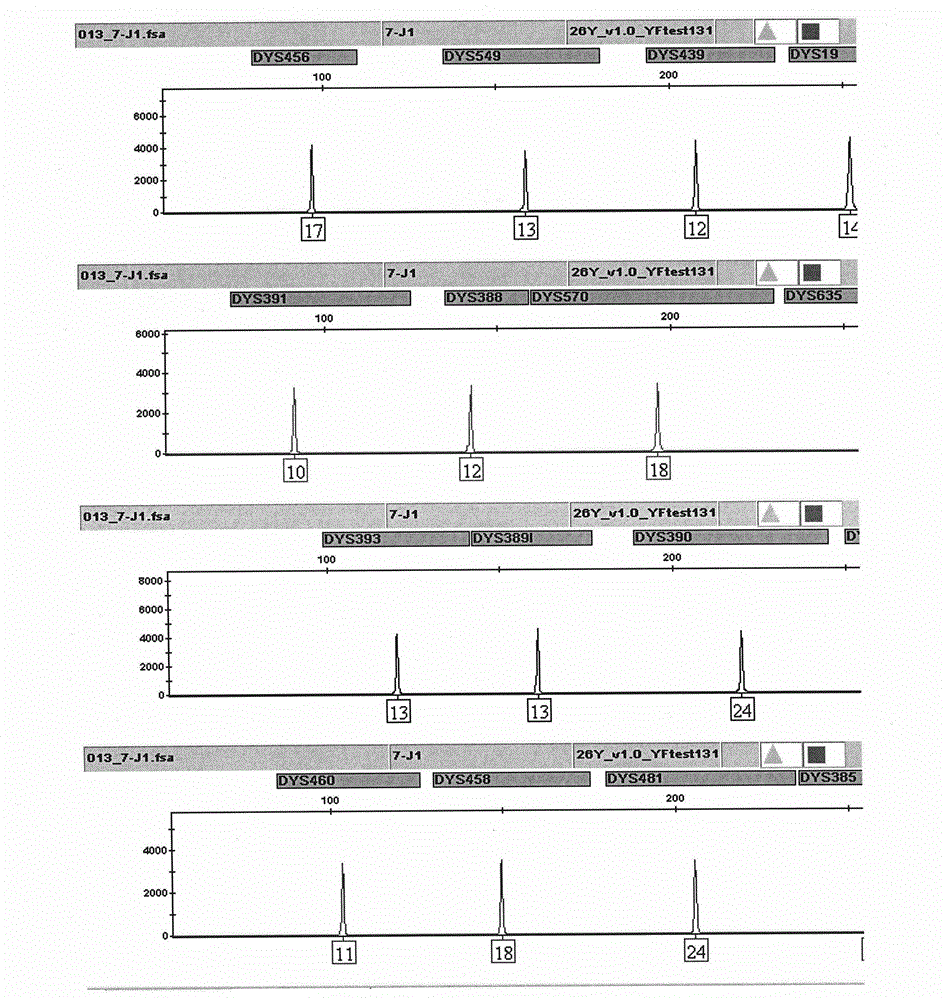
The invention relates to a composite amplification system for simultaneously analyzing multiple Y-STR loci. The composite amplification kit is characterized by compositely amplifying the following 26 Y chromosome loci: DYS19, DYS388, DYS389I, DYS389II, DYS390, DYS391, DYS392, DYS393, DYS385a, DYS385b, DYS437, DYS438, DYS439, DYS448, DYS456, DYS458, DYS635, DYS460, DYS481, DYS533, DYS549, DYS570, DYS576, DYS643, DYS449 and Y-GATA-H4. The invention also relates to a method and a kit for simultaneously analyzing DNA samples, and applications thereof.
Owner:BEIJING PEOPLESPOT TECH
Composite amplification system of 23 short tandem repeat sequences and a kit
ActiveCN103834732AImprove performanceIncrease independenceMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyDNA paternity testing
The invention relates to a composite amplification system of 23 short tandem repeat sequences and a kit, is used for detecting heredity mark gene of polymorphism in a mankind genome, and belongs to the biology technical field. The invention relates to a scheme that a plurality of short tandem repeat sequences are simultaneously amplified in a PCR system; a specific gene locus comprises 22 short tandem repeat sequences with high level heredity polymorphism and 1 gender determination locus; primers are respectively designed and a fluorophore is marked; the system has very high individual recognition rate and non-father elimination rate; the system and kit can be used for legal medical individual recognition, paternity tests, and colony genetics analysis, is high in accuracy, and good in sensitivity.
Owner:SUZHOU MICROREAD GENETICS
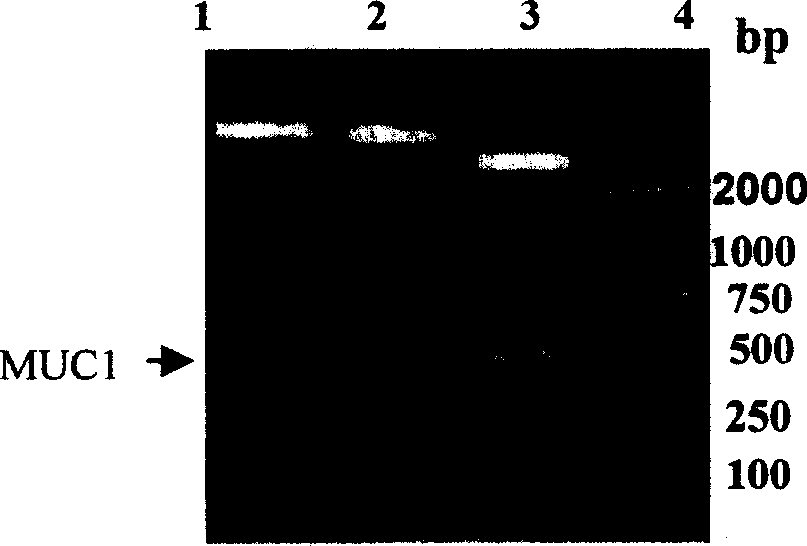
Recombination human Mucl-MBP fusion protein antitumour vaccine and production technology
InactiveCN1513556ATo achieve the purpose of anti-tumorLow costPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsEscherichia coliChemical synthesis
An anticancer vaccine of recombinant human MOC1-MBP fusion protein is disclosed, in which MBP is used as its adjuvant. The MBP gene and MUC1 gene are fused together. The MBP substituted for other fusion protein to induce CTL reaction. The pMAL-P2 is the carrier for effectively expressing maltose fusion protein. The serial repetitive sequence of MUC1 is inserted to downstream of malE gene.
Owner:台桂香
Human cytotoxic T-lymphoctye epitope and its agonist eptiope from the non-variable number of tandem repeat sequence of MUC-1
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Human Cytotoxic T-Lymphoctye Epitope and Its Agonist Eptiope From the Non-Variable Number of Tandem Repeat Sequence of Muc-1
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
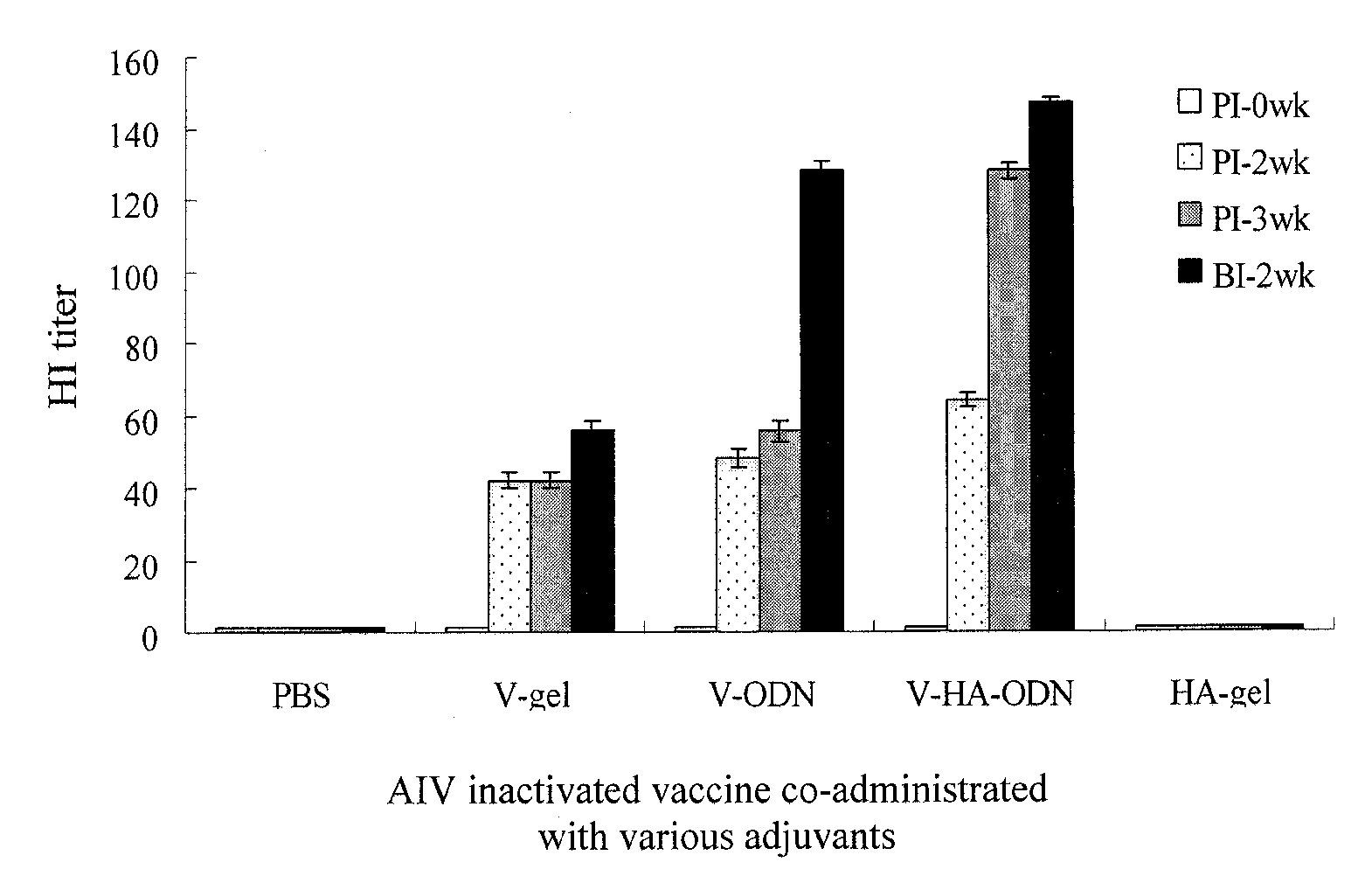
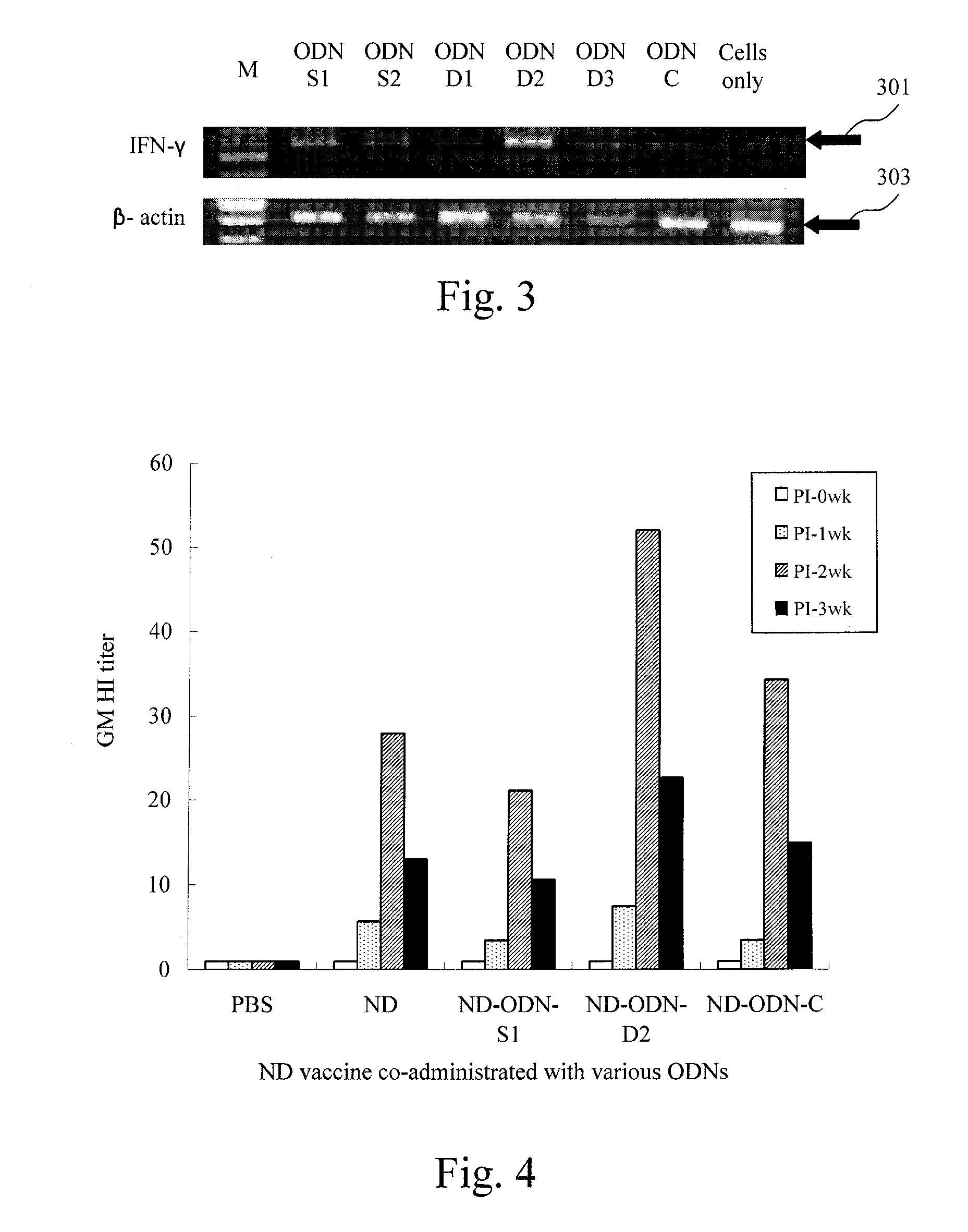
CpG DNA Adjuvant in Avian Vaccines
ActiveUS20100003288A1Enhance innateEnhance adaptive immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsAdjuvantMethylation
A CpG DNA adjuvant in avian vaccines is disclosed, which includes an immunostimulatory oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) having a plurality of TCG tandem repeats at a 5′end, a poly-G structure at a 3′ end, and at least one unmethylated CpG motif with avian specific flanking sequences at two ends thereof between the 5′ end and the 3′ end. The CpG DNA adjuvant in avian vaccines is advantageous to carry out large-scale production, specifically enhance avian innate and adaptive immune responses, and the CpG DNA adjuvant is hardly to be digested by DNase due to its particular structures.
Owner:NAT PINGTUNG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Oligonucleotide probe and acquisition method thereof
ActiveCN106566876ASimple designLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationRepetitive SequencesIn situ hybridisation
The invention relates to a method for acquisition of an oligonucleotide probe. The method comprises the following steps: downloading genomic sequence of crop species from a public database, filtering and finding out tandem repeat sequences, screening preliminarily found repetitive sequences, comparing residual tandem repeat sequence and known probe sequence, removing already used probe sequence, comparing residual screened tandem repeat sequences, carrying out probe design and synthesizing and verifying the designed probe sequence so as to obtain effective oligonucleotide sequence. According to the invention, cost is low and efficiency is high. The probe can be used for non-degenerated fluorescence in situ hybridization (ND-FISH) analysis of crop chromosome, determination of distribution of tandem repeat sequences represented by the probe on chromosome, understanding of the structure characteristics of chromosome and establishment of specific landmark of chromosome. Thus, specific chromosome or chromosome region of crops is identified, and the developed new oligonucleotide probe has specificity of chromosome or chromosome region.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
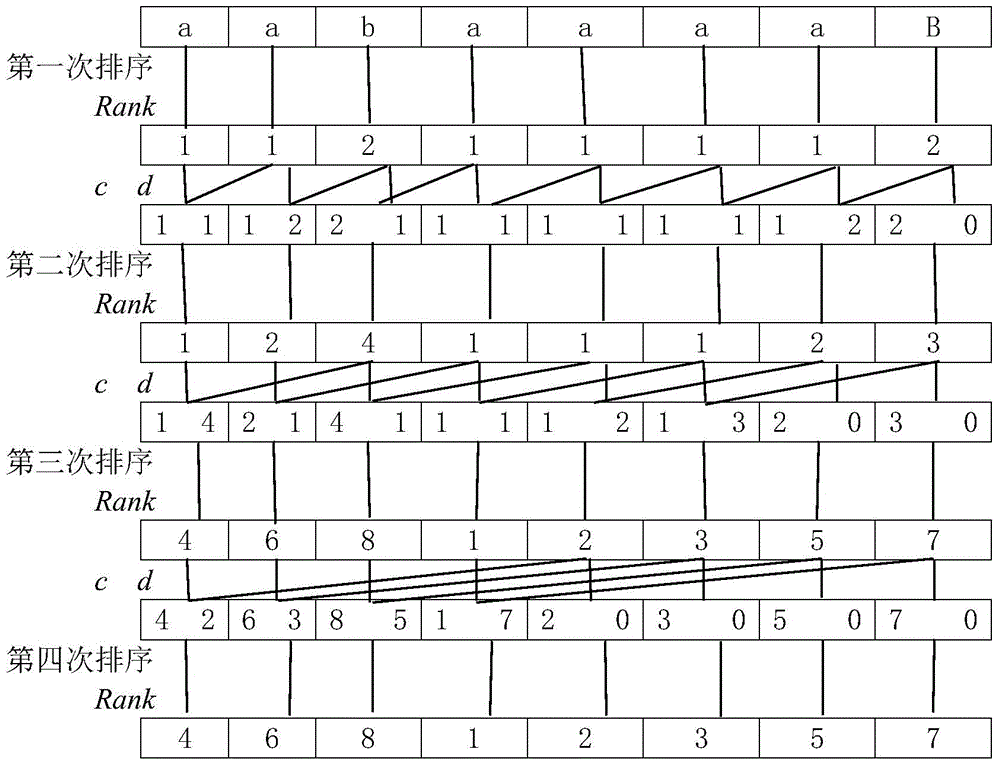
Suffix array based fuzzy tandem repeat recognition method
InactiveCN104156636AQuick analysisAccurate analysisSpecial data processing applicationsFast Fourier transformArray data structure
The invention discloses a suffix array based fuzzy tandem repeat recognition method. The suffix array based fuzzy tandem repeat recognition method includes: imputing acquired DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) alkali-based sequences into a computer in the form of character strings; processing genomic sequences on the basis of the dictionary sorting algorithm to generate corresponding suffix arrays; acquiring the largest public prefix sequences on the basis of the suffix arrays; acquiring the largest tandem repeats on the basis of the accurate tandem repeat recognition algorithm; acquiring the optimal offset on the basis of improved FFT (fast fourier transform) transform; comparing the sequences on the basis of the dynamic programming algorithm; acquiring the fuzzy tandem repeats on the basis of the fuzzy tandem repeat recognition method. By the method, the repetitive sequences in the genomic sequences can be rapidly recognized and accurately analyzed, and the fuzzy tandem repeats of the sequences can be found out.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
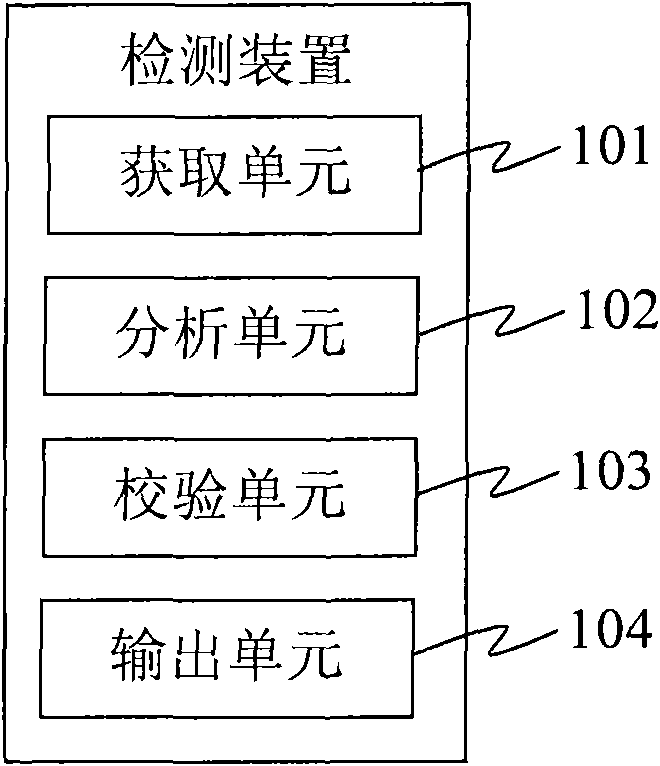
Detection device and detection system
InactiveCN101560564AAccurate identification of inspection workLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsProgramming languageDNA sequencer
The invention provides a detection device and a detection system. The detection device comprises an acquisition unit, an analysis unit, a check unit and an output unit, wherein the acquisition unit is used for acquiring DNA sample data which is generated by sampling through a DNA sequencer; the analysis unit is used for performing short tandem repeat sequence analysis on the DNA sample data and generating analysis result data; the check unit is used for checking the DNA sample data, verifying whether the DNA sample data has errors, and generating check result data; and the output unit is used for outputting the analysis result data and corresponding check result data. The detection device replaces the manual check process so as to efficiently and accurately finish the identification check work for the identification result and omit the process for analyzing and outputting the short tandem repeat sequence for the DNA sample data with poor check result, and reduces the cost.
Owner:北京华生恒业科技有限公司 +1
Nucleic acid size detection method
ActiveUS20100167284A1Finer of numberElectrolysis componentsMicrobiological testing/measurementFragile X chromosomeFractionation
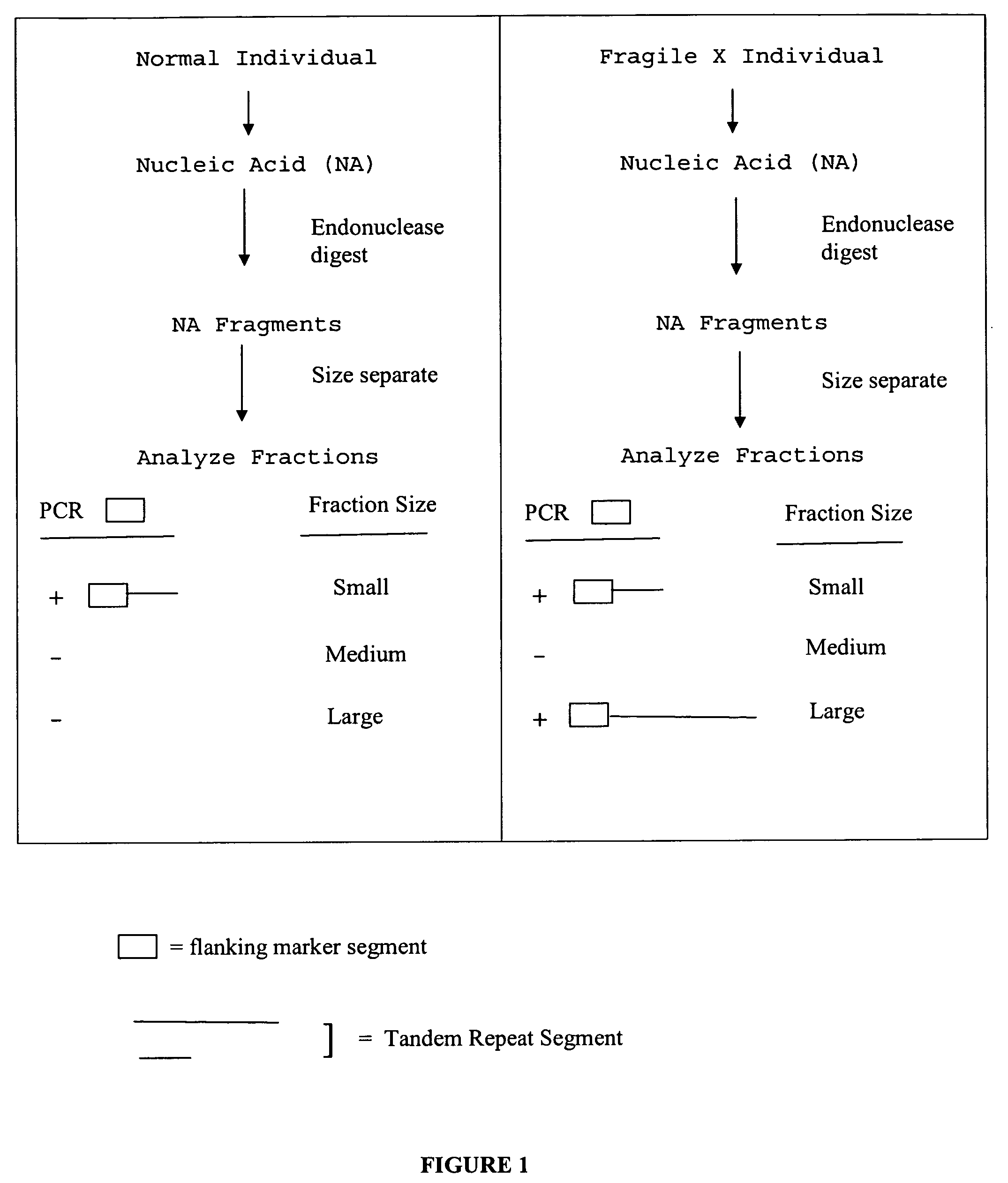
The present invention provides methods of determining the size of a particular nucleic acid segment of interest in a sample of nucleic acids through fragmentation of DNA, size fractionation, an optional second fragmentation, and identification using a marker sequence. In particular aspects, an expansion or reduction of tandem repeat sequences can be detected. In further aspects, carriers and individuals afflicted with fragile X syndrome or other diseases associated with tandem repeats can be distinguished from normal individuals.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC +1
Rapid generation of long synthetic centromeric tandem repeats for mammalian artificial chromosome formation
ActiveUS20090136924A1Fast constructionMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorLigationMammalian artificial chromosomes
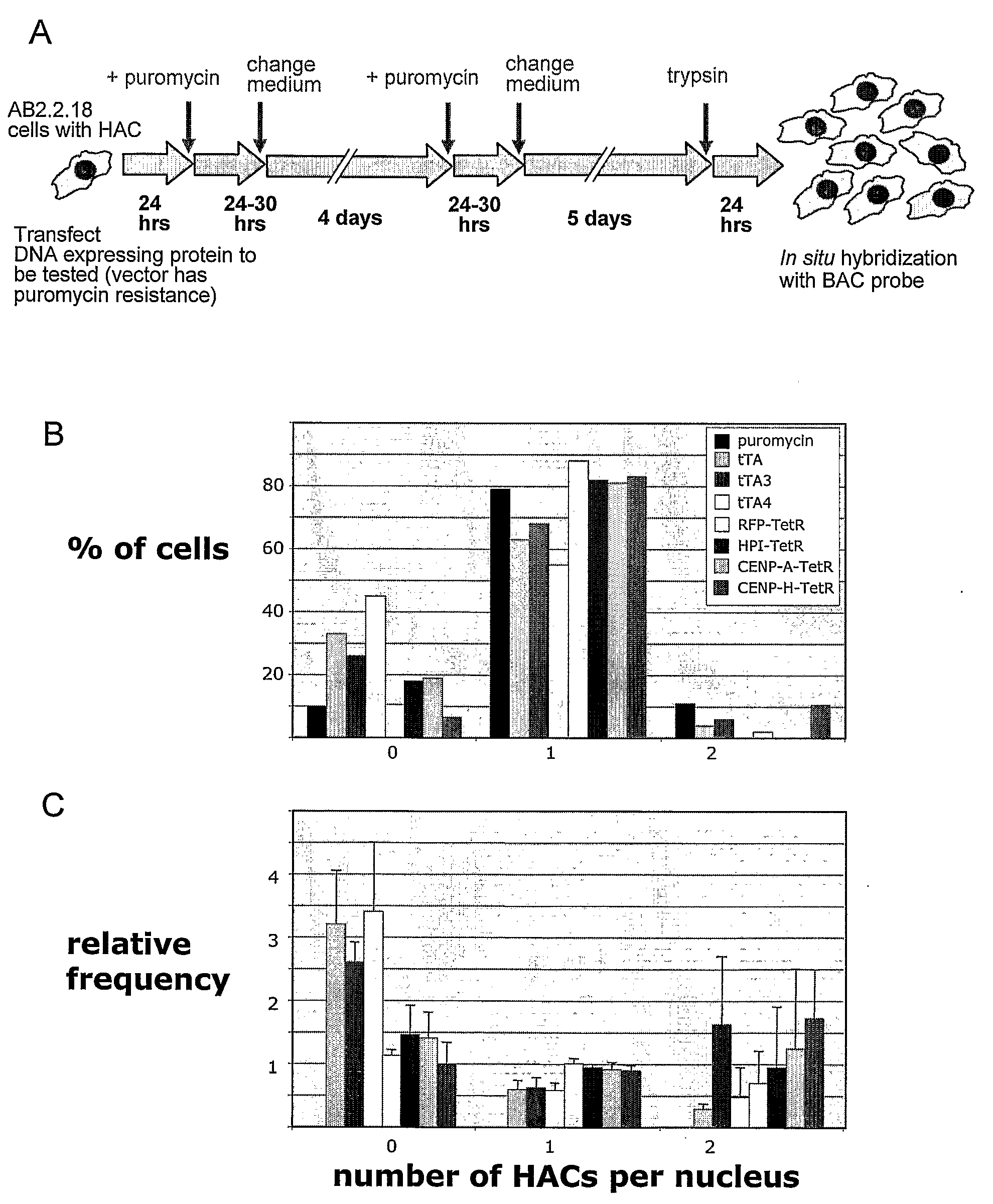
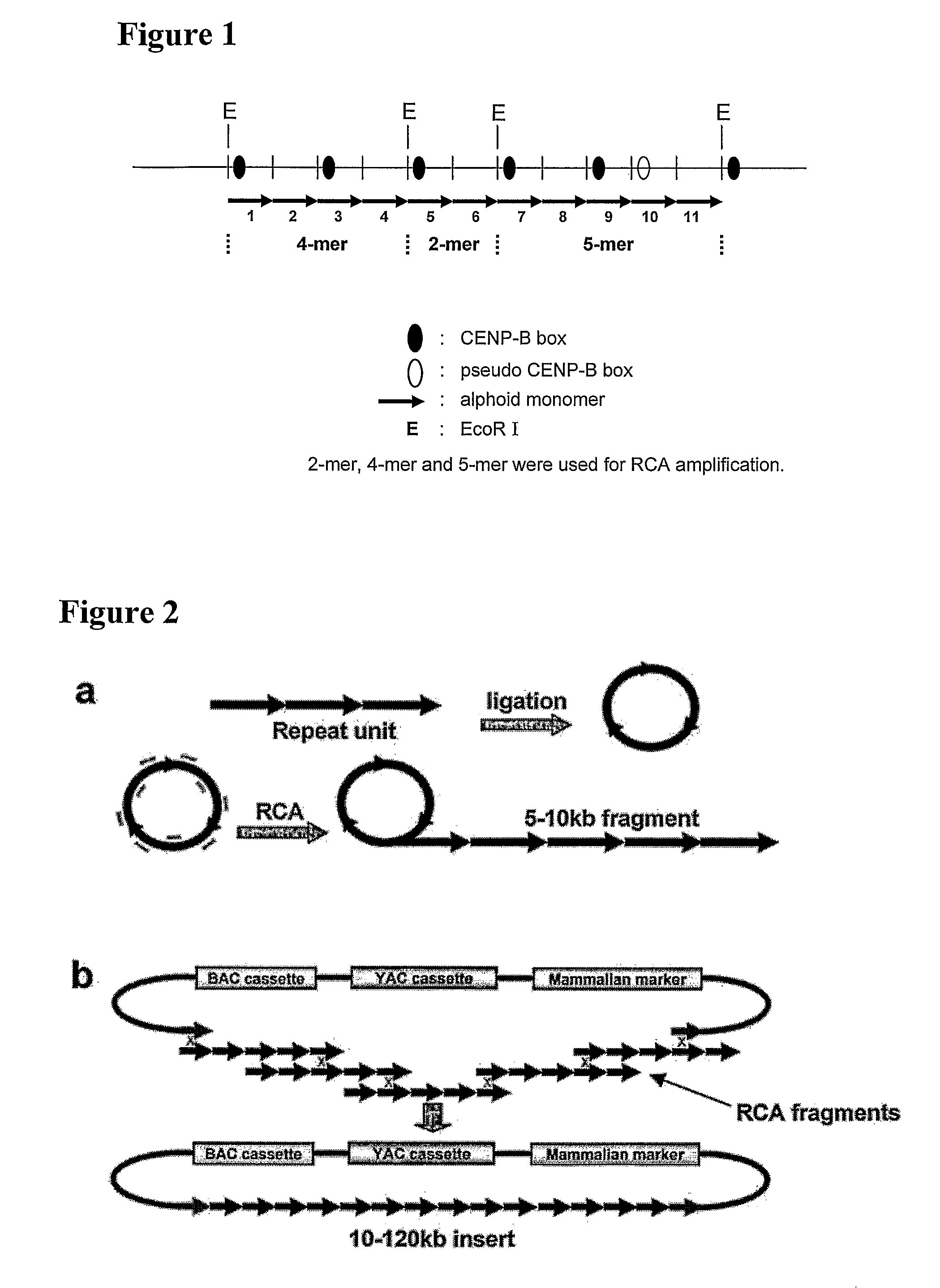
Methods are described for construction of long synthetic arrays of DNA repeats, such as alphoid repeats or other repeat sequences. The methods include concatamerization of DNA into short repeats (for instance using rolling circle amplification or directional in vitro ligation), followed by assembling the short repeats into long arrays by homologous recombination during transformation into microbe cells. These methods can be described generally as Recombinational Amplification of Repeats (RAR). The long arrays are engineered centromere-like regions that allow one to construct mammalian artificial chromosomes with a predefined centromeric region structure. Artificial chromosomes, including human artificial chromosomes with a regulated centromere, and methods of their use are also provided
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF EDINBURGH +1
Complex aplification detecting system of fluorescent marker short tandem repetitive sequence gene locus
InactiveCN1724688AHigh sensitivityHigh polymorphismMicrobiological testing/measurementRepetitive SequencesFluorescence
The invention supplies a fluorescence labeling verification system by compounding and expanding 14 short series repeating sequence locus to take personal identification and paternity test. The specific compounding method controls the expanding product in the range of 400 basic groups, and only labeling three fluorescence of the compounding expanding of the 14 locus would be realized. The invention takes a deep research to the gene characteristic of the 14 locus and the allele in five minorities in China, and supplies the compounding expanding verification system. The agent box suited for Chinese throng is researched.
Owner:公安部第二研究所
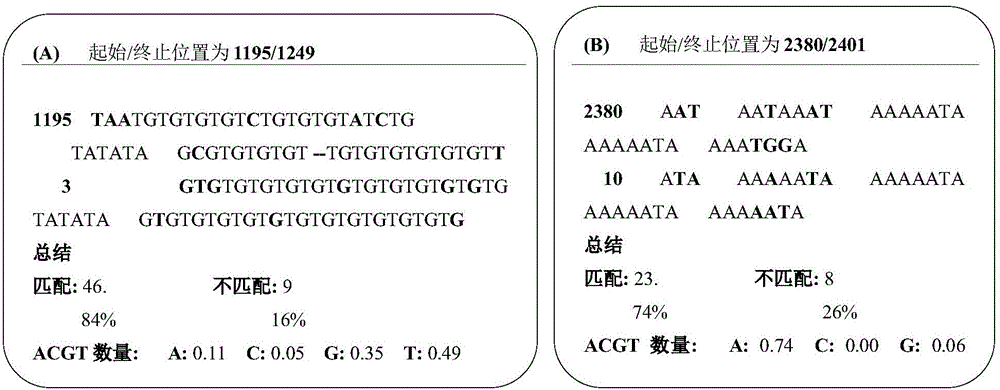
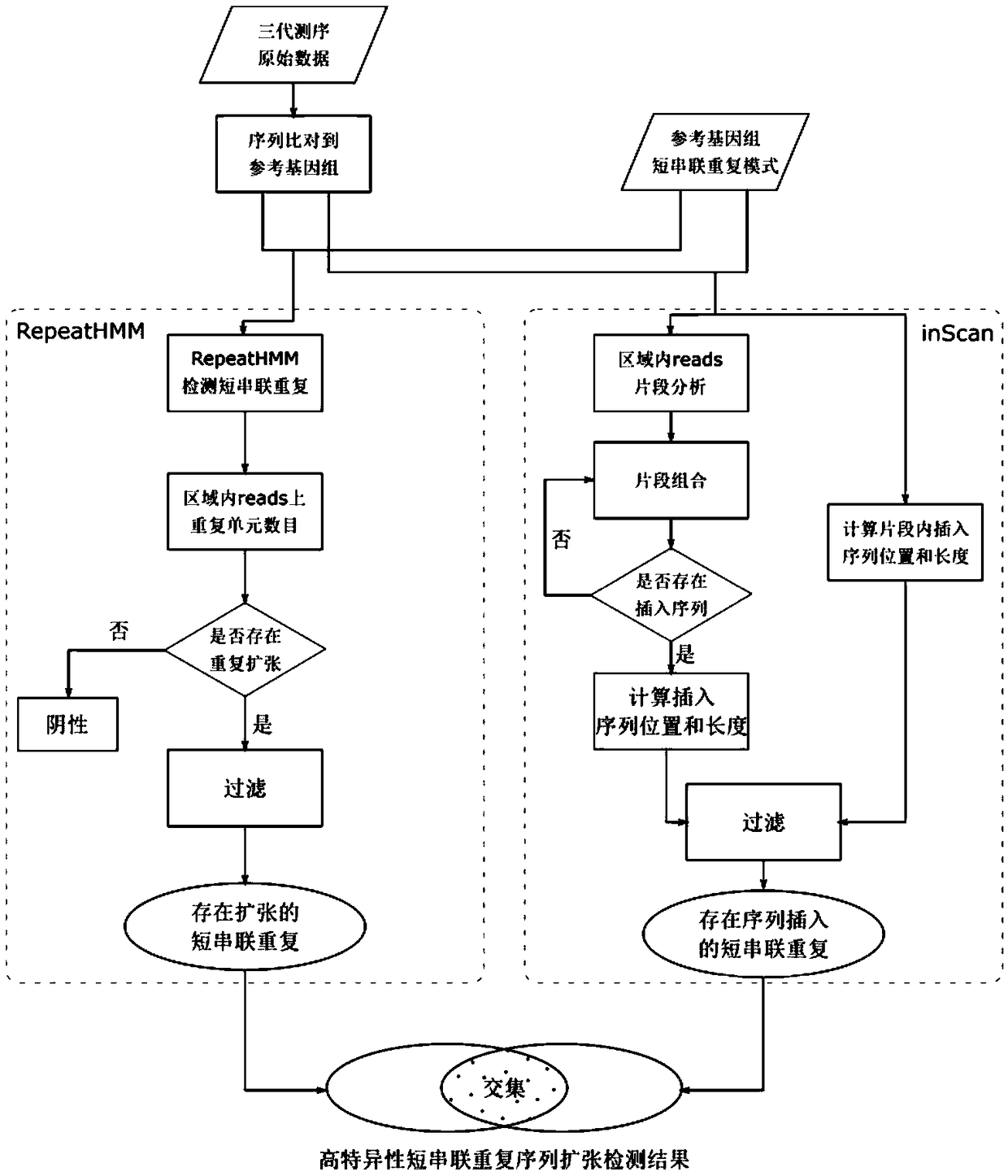
Method for detecting expansion of short tandem repeat
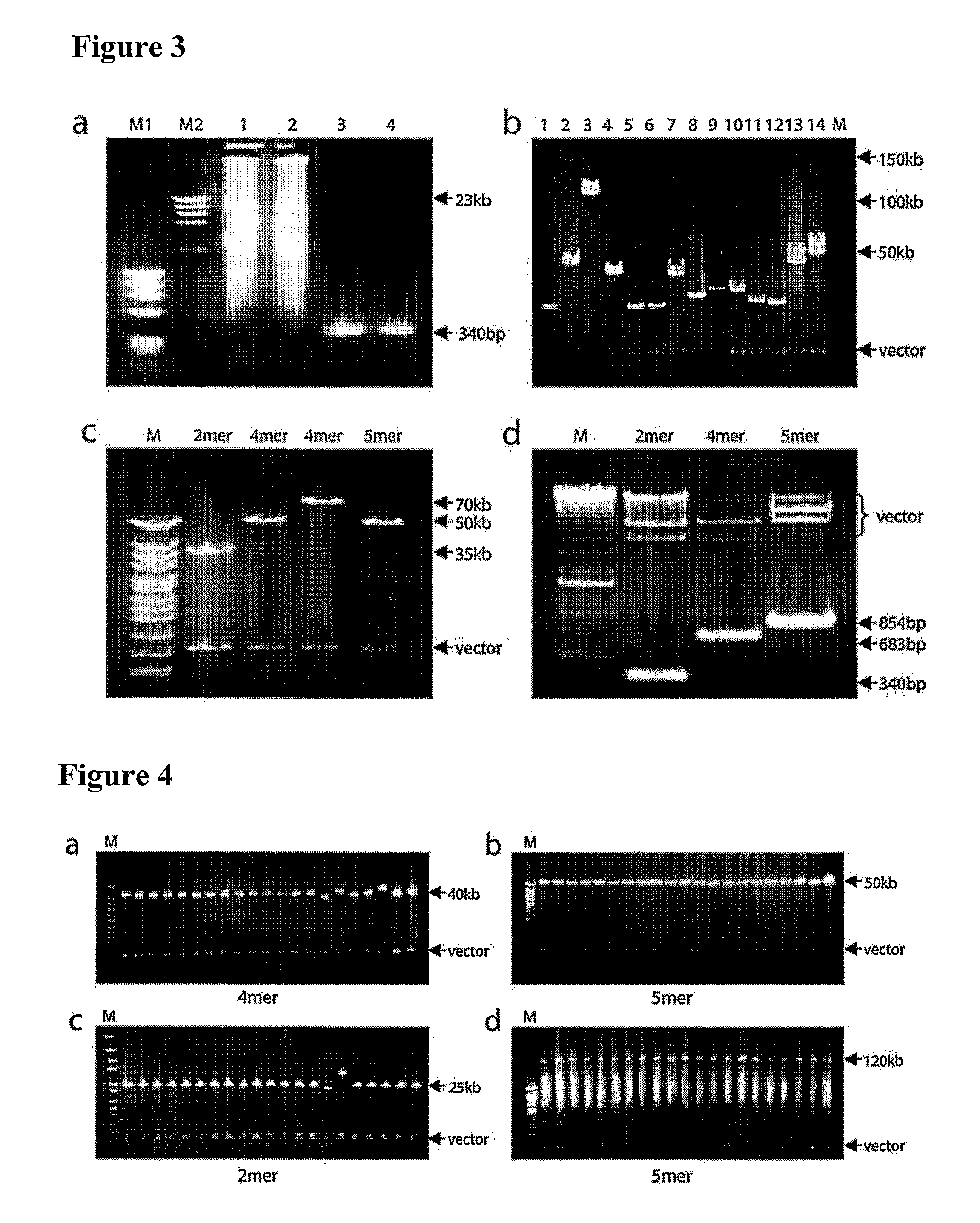
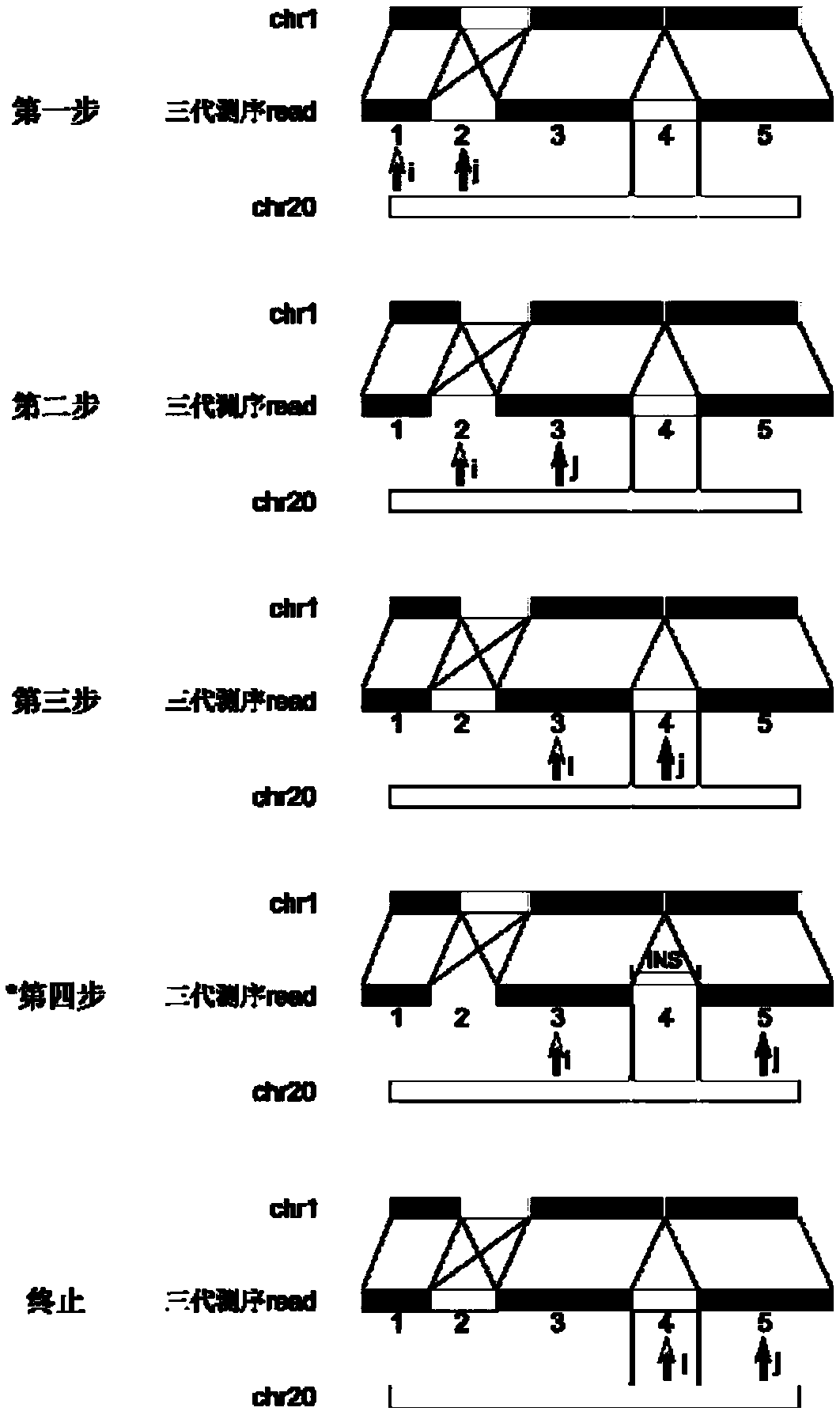
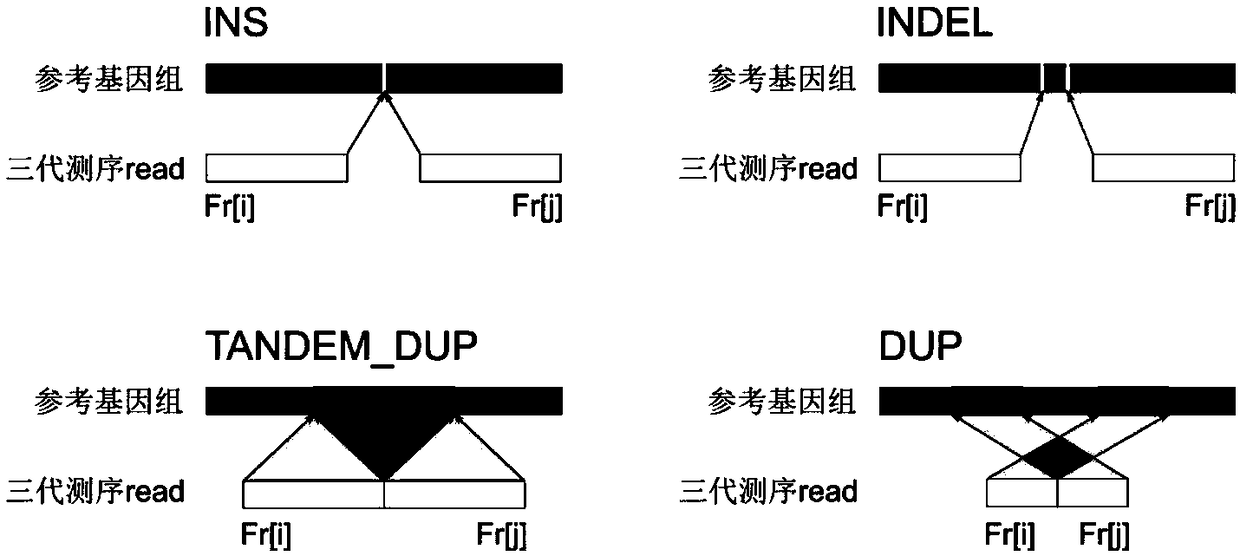
ActiveCN108660200AStrong specificityReduce false positivesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence InsertionsThird generation sequencing
The invention provides a method for detecting expansion of a short tandem repeat. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out sequence alignment; secondly, detecting short tandem repeat of third-generation sequencing data by RepeatHMM; thirdly, detecting sequence insertion of a short tandem repeat area by inScan; fourthly, calculating an intersection of RepeatHMM detection results and sequence insertion detection results of the short tandem repeat area. According to the method provided by the invention, the results of the sequence insertion and RepeatHMM short tandem repeatdetection are combined, so that the specificity of detecting the expansion of the short tandem repeat is improved.
Owner:BEIJING GRANDOMICS BIOTECH +1
Method for non-invasive preimplantation hereditary detection of embryos
ActiveCN111440857AHigh amplification yieldThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementGranular leucocyteLibrary preparation
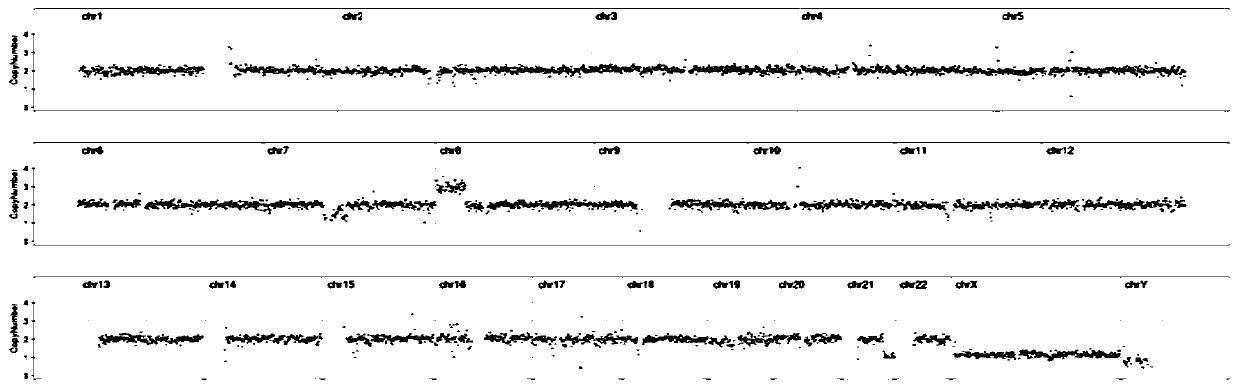
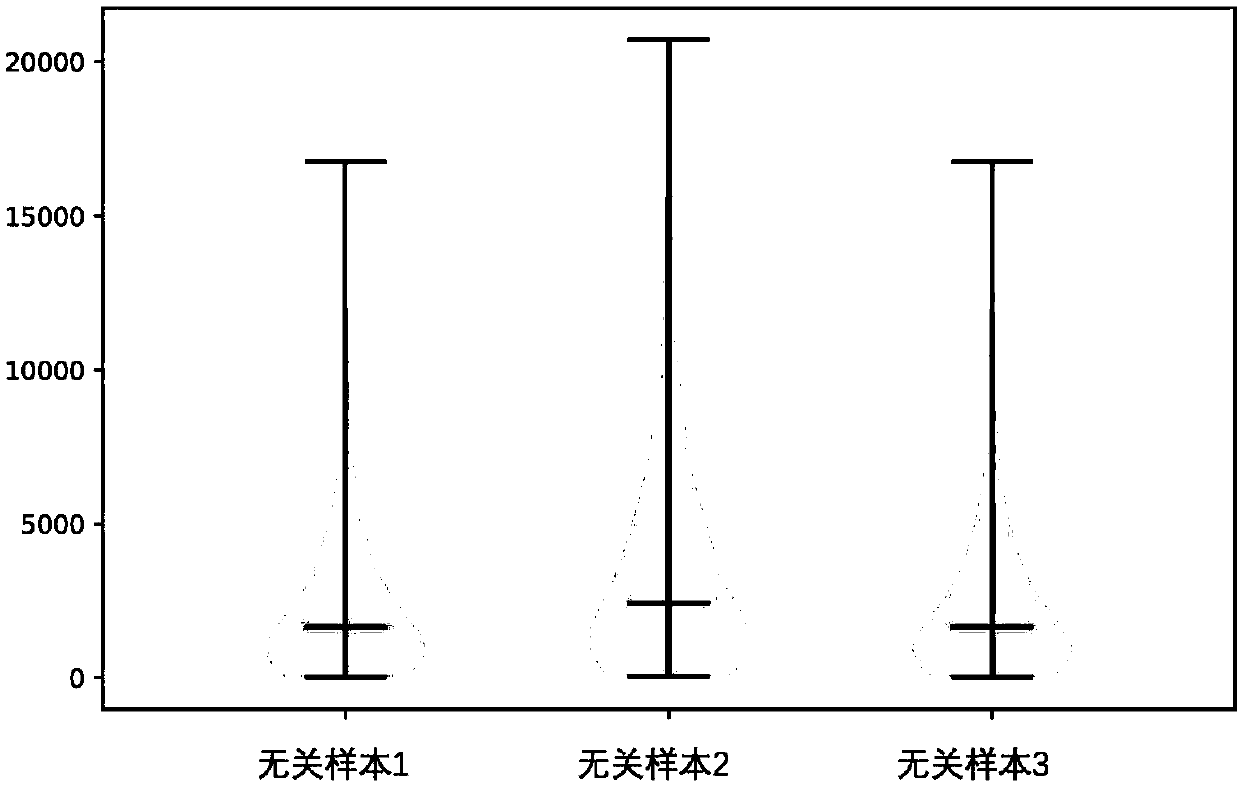
The invention discloses a method for non-invasive preimplantation hereditary detection of embryos, and belongs to the technical field of biological detection. The method comprises the following steps:carrying out whole genome amplification on a blastocyst culture solution sample by using a kit, carrying out short tandem repeat sequence analysis on an amplification product and DNA samples of parents to detect maternal pollution, carrying out library preparation and next-generation sequencing detection on the amplification product to determine whether the number of chromosomes is abnormal or not; and optimizing a pre-amplification mixed solution and an amplification mixed solution by the provided kit. According to the method provided by the invention, the blastocyst culture solution can besubjected to parent source pollution detection, so that whether the chromosome aneuploidy detection result of the culture solution is accurate and reliable or not is judged. The invention provides a detection method for judging whether granular cells are completely removed or not, and the inhibition effect of components in the culture solution on amplification is effectively avoided through optimization of the kit, so that amplification uniformity is good, and the single cell amplification yield is high. The detection method is simple, the result is accurate, and data quality is improved.
Owner:阿吉安(福州)基因医学检验实验室有限公司
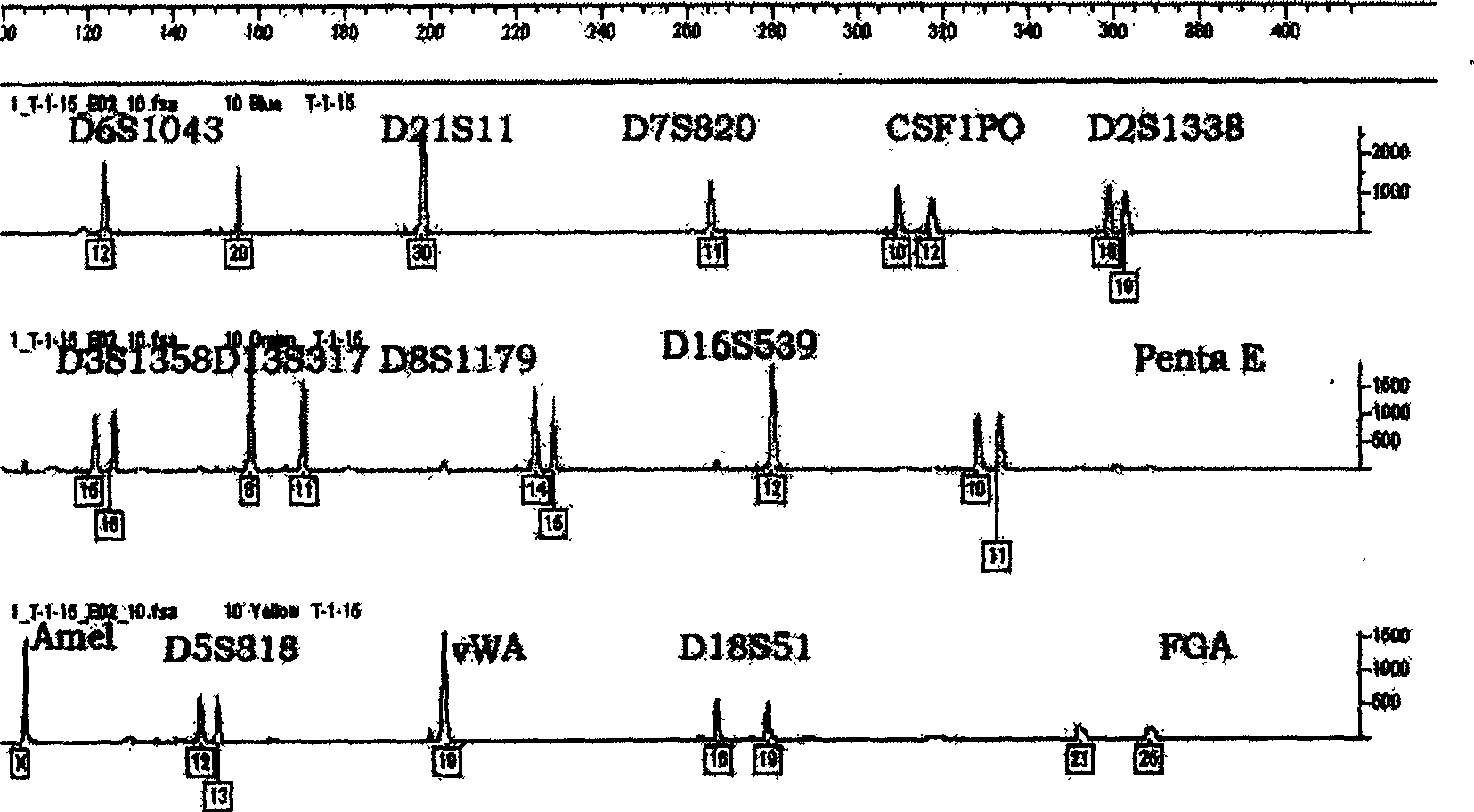
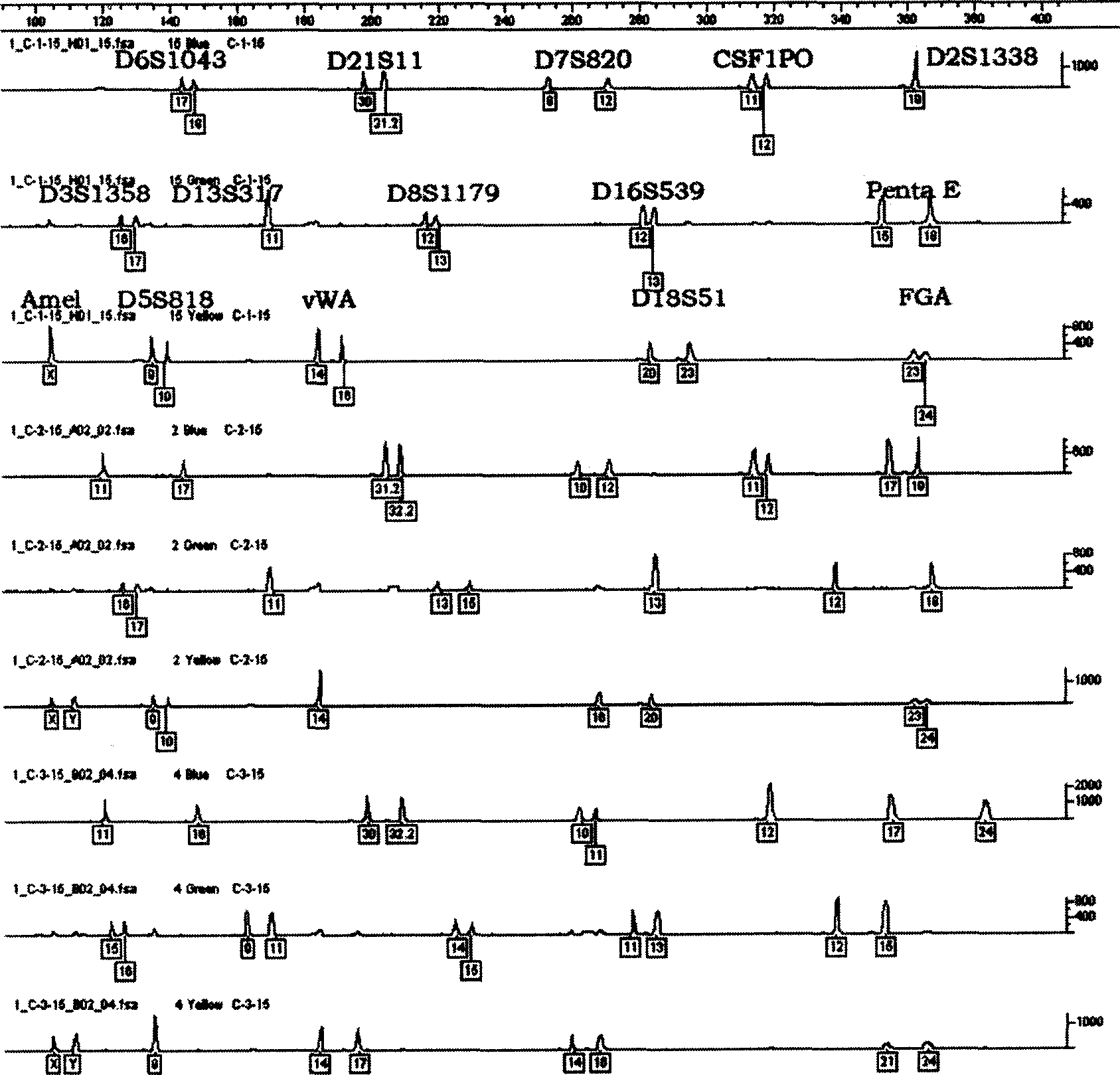
Accurate human DNA typing method, reagent and application
PendingCN110863056AHigh resolutionImprove individual recognitionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHuman DNA sequencingGenomic data
The application discloses an accurate human DNA typing method, a reagent and application. According to the accurate human DNA typing method, a short tandem repeat sequence, polynucleotide polymorphicsites covering a whole genome, a mitochondrial DNA hypervariable region I, a mitochondrial DNA hypervariable region II and an Amel enamel gene are detected simultaneously to obtain accurate typing andbase sequences of all the sites, thereby realizing accurate typing of human DNAs. The disclosed method having high resolution ratio is capable of carrying out efficient and accurate individual recognition and has the extremely high individual recognition capacity for difficult detection materials and highly-degraded detection materials; the non-parent exclusion rate is larger than 99.999999% in paternity identification and the accuracy is high; the compatibility is high, the existing individual recognition detection kit can be covered, and the method can be used for analyzing race groups in different regions or countries by combining human genome data. Besides, the method disclosed by the invention is relatively high in adaptability of detection materials and the human DNA extracted by various experimental methods can be detected.
Owner:BGI FORENSIC TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Method for genetic detection using interspersed genetic elements: a multiplexed DNA analysis system
ActiveUS20160108462A1Easy to produceSize andNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingPaternity analysis
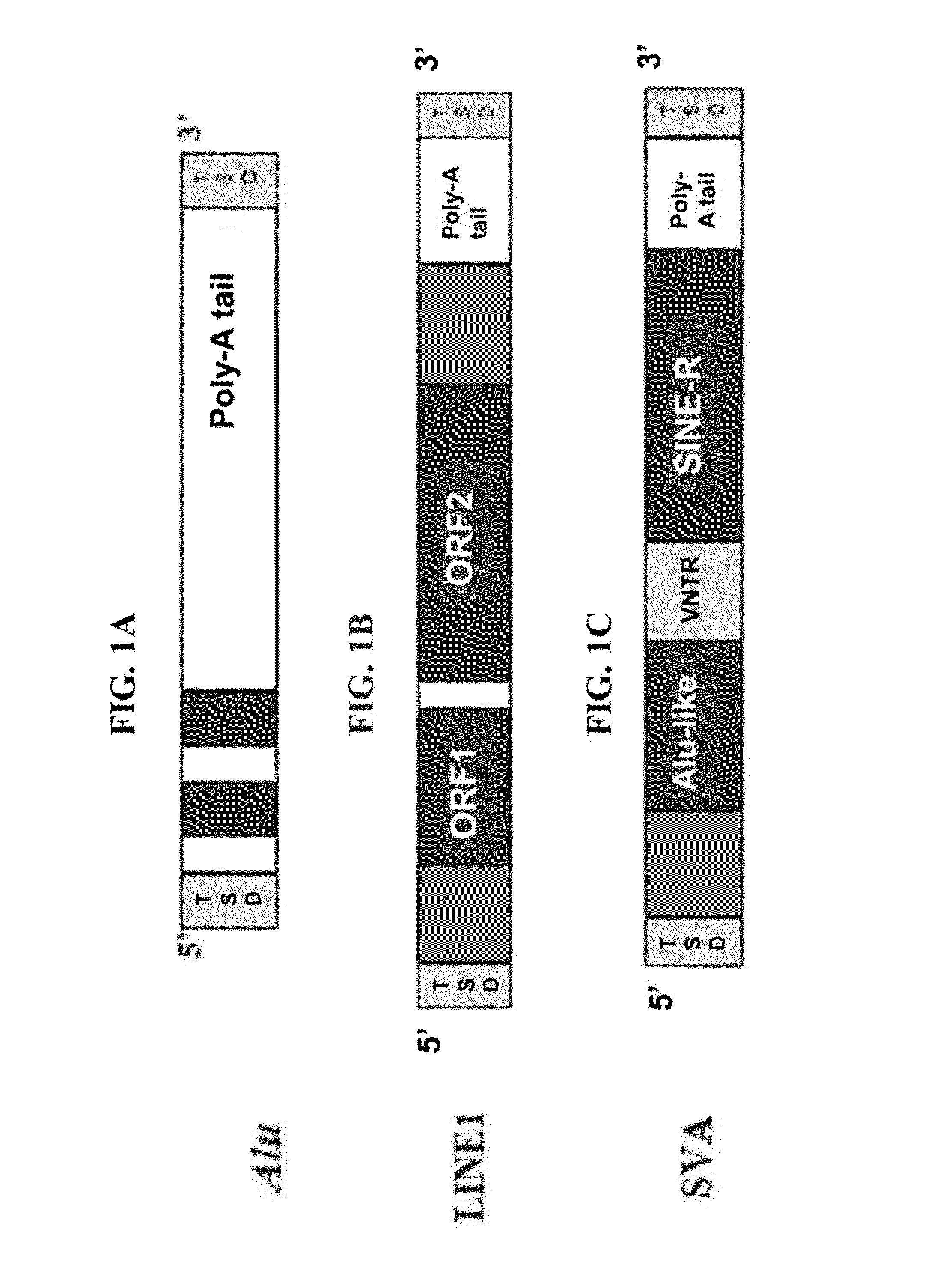
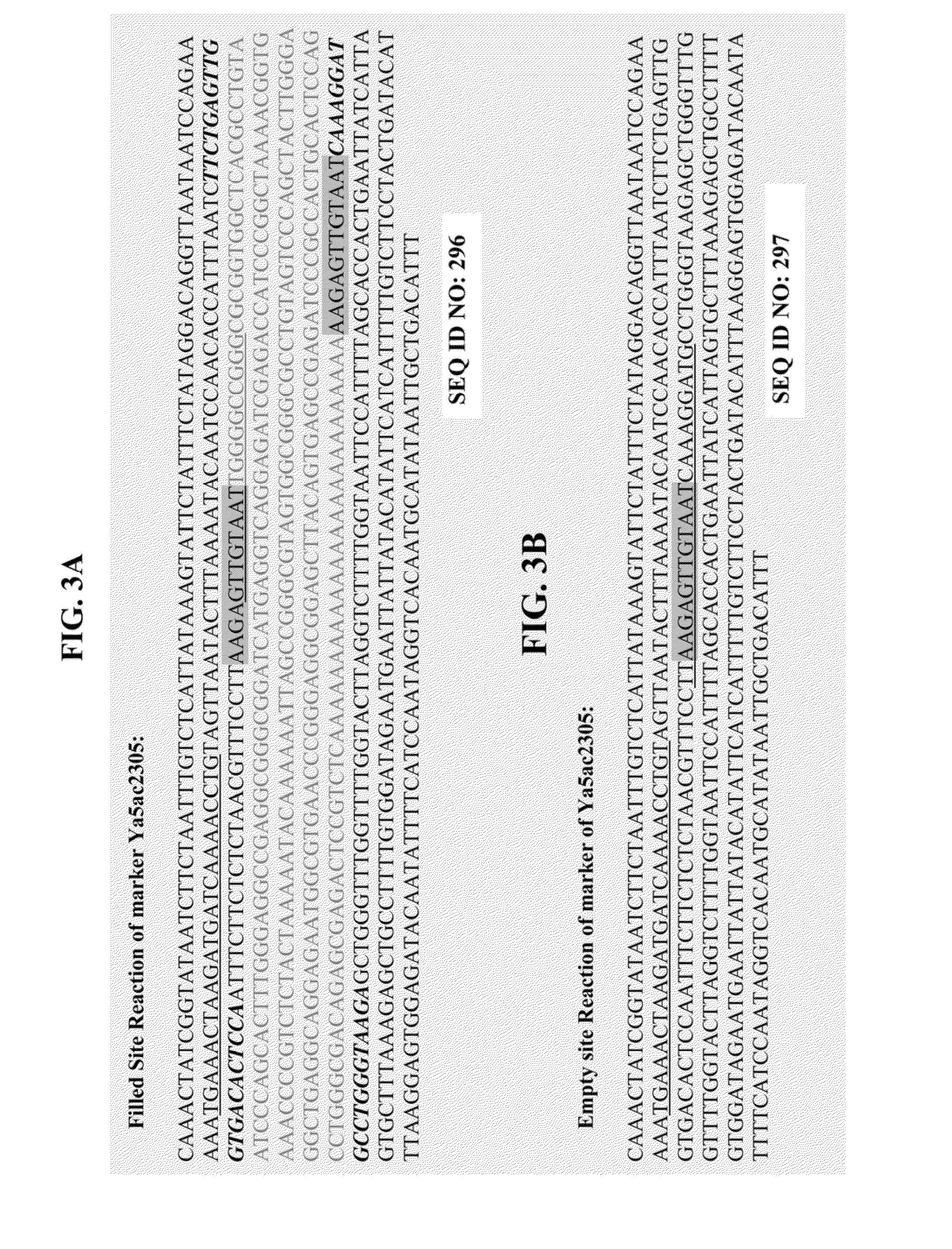
By utilizing a Mini-Primer strategy targeting the target site duplication (TSD) sequence of retrotransposons, insertion and null allele (INNUL) markers, which include short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs), long interspersed nuclear elements (LINEs), and composite SVA retrotransposons (SINE / VNTR / Alu, where VNTR represents “variable number of tandem repeats” and Alu represents a type of primate specific SINE that has reached a copy number in excess of one million in the human genome), can be effectively used as markers for human identification and bio-ancestry studies regardless of the size of the inserted element. The size of the amplicons for INNULs and the difference between allelic states can be reduced substantially such that these markers have utility for analyzing high and low quality human DNA samples. Multiplexes including either 15 or 20 retrotransposable element (RE) markers plus Amelogenin for single tube amplification of DNA in four color detection were successfully designed. The multiplexes provided power of discrimination suitable for forensic and paternity analyses.
Owner:LIFE GENETICS LAB
Preparation method of placenta source matrix mesenchymal stem cell
ActiveCN103451150AAvoid damageThe method is simple and fastMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSerum free mediaVirus type
The invention provides a preparation method of a placenta source matrix mesenchymal stem cell. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) separating the placenta source matrix mesenchymal stem cell; (2) cultivating the placenta source matrix mesenchymal stem cell, wherein a trypLE<TM> enzyme solution is utilized to process a placenta tissue in two steps in the step (1), and a serum-free medium is utilized in the step (2). By adopting the method provided by the invention, the placenta source matrix mesenchymal stem cell is a complete matrix source by short tandem repeat sequence (STR) atlas analysis, and is qualified by chromosome karyotype examination, pathogenic microorganism examination of bacteria, funguses and viruses, cell purity identification and cell biology function identification. Therefore, the placenta source matrix mesenchymal stem cell obtained by the method provided by the invention does not contain foreign protein, can meet the requirements of clinical use, is especially suitable for use by mothers, and also provides a technical support for building an excellent placenta source matrix mesenchymal stem cell bank.
Owner:BEIJING HEALTH & BIOTECH (H&B) CO LTD
New 10 Y-chromosome short tandem repeat locus parting method therefor
InactiveCN101225386AOvercome the defect of not being able to reflect the genetic characteristics of China's multi-ethnic groupsSimple instrumentMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationTyping methodsForensic science
The invention discloses a new kind of ten STR gene loci for Y chromosome and the typing method, which is characterized in that polyacrylamide gel is utilized for electrophoresis typing; the ten STR gene loci for Y chromosome, which can be applied in forensic medicine field, are screened out with silver staining coloration method; furthermore, the allelic ladder of each locus is prepared; a PCR primer and the expansion condition of the Y chromosome STR locus are optimized; wherein the optimization to the PCR primer and the expansion condition and the preparation of allelic ladder can be standardized and simplified, which is suitable for popularization of base unit. The ten STR gene loci for Y chromosome can be applied for individual identification, paternity testing and gene diagnosis in forensic medicine, anthropology, genetics, disease and other field. The new kind of ten STR gene loci for Y chromosome and the typing method has the advantages of wide application prospect, which is particularly suitable for paternity testing in the condition of patrilateral loss such as death or missing in forensic medicine practice and individual identification of mixed stain in rape and gang-rape cases, in particular to the identification to suspect having azoospermia or oligospermia disease.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for efficiently expressing multi-copy human epidermal growth factor
ActiveCN105385693AOvercome the problem of small molecular weight and insufficient expressionMaintain spatial conformationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBase JProtein target
The invention provides a method for efficiently expressing a multi-copy human epidermal growth factor. The method comprises the steps that restriction enzyme cutting sites are introduced to the upstream and downstream of a gene fragment, a tandem repeat sequence of a mature peptide gene of the human epidermal growth factor is obtained after enzyme cutting and connection are conducted, and the problems that the human epidermal growth factor is low in molecular weight and insufficient in expression quantity are solved; meanwhile, an kex2 enzyme cutting site is introduced to the upstream of the gene fragment of the human epidermal growth factor, part of nucleotide bases are modified at downstream, a carboxyl terminal ELR of an original amino acid sequence is changed into a saccharomycete kex2 enzyme cutting site, it is guaranteed that recombinant expressed target protein is cut into monomers through kex2 enzyme inherent to saccharomycetes, the expression quantity is obviously increased, a natural N-terminal is achieved, the difference that only one amino acid residue exists at the C-terminal is achieved, redundant amino acids do not exist, and the activity is not changed; due to the fact that the human epidermal growth factor is naturally synthesized in pichia pastoris, original native state spatial conformation of the protein can be maintained, and therefore efficient large-scale preparation of the human epidermal growth factor is achieved.
Owner:ANYANG INST OF TECH
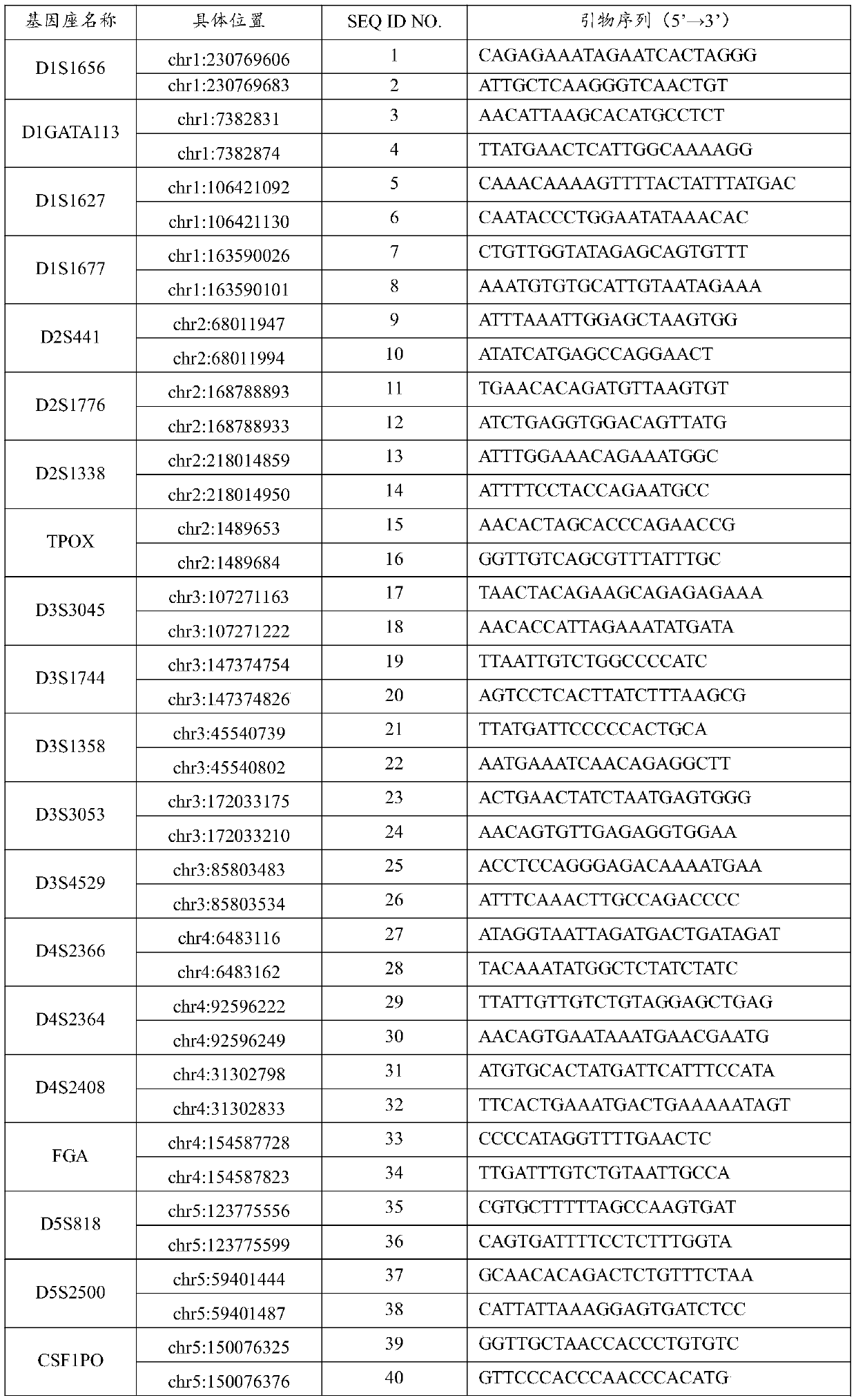
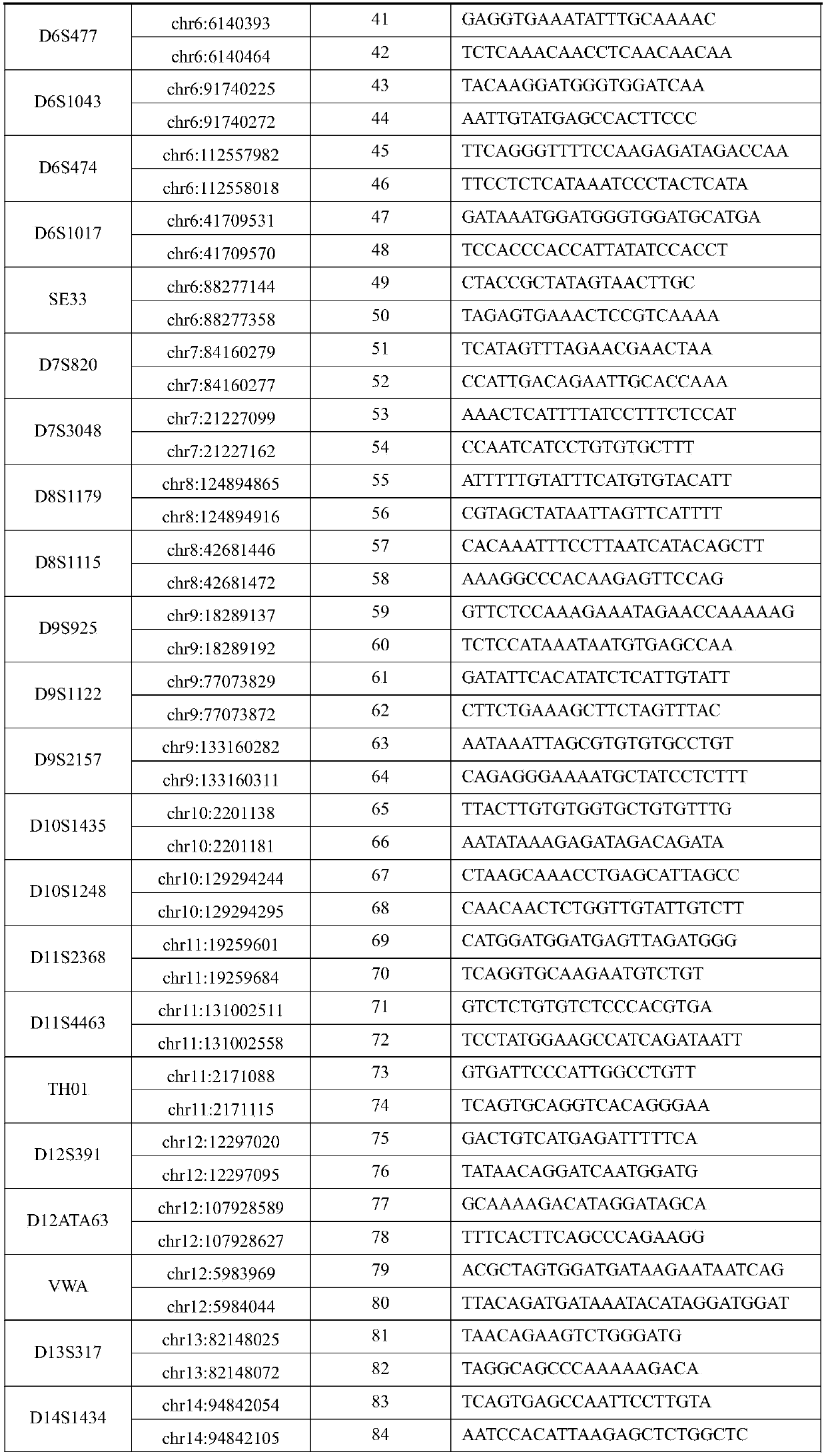
High-throughput multi-site human short fragment tandem repeat sequence detection kit as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN106834428ATest stableImprove individual recognitionMicrobiological testing/measurementMulti siteMagnetic bead
The invention relates to the fields of medical jurisprudence, criminal investigation, evidence identification and the like, and specifically relates to a high-throughput multi-site human short fragment tandem repeat sequence detection kit as well as preparation and application thereof. The detection kit comprises a multiplex-PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer pool, with human short fragment tandem repeat sequence specificity, labeled by different sample labels, a PCR amplification enzyme free of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) extraction, a PCR reaction buffer fluid and optional reference DNA and DNA purified magnetic beads. The detection kit has the characteristics of high resolution, high accuracy and high throughput.
Owner:IPE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
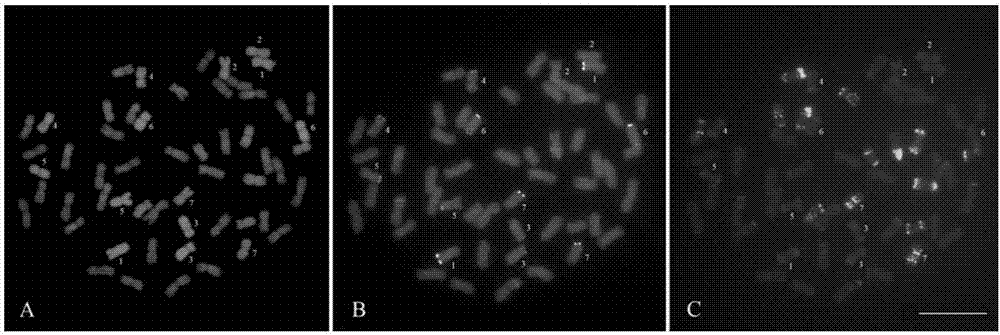
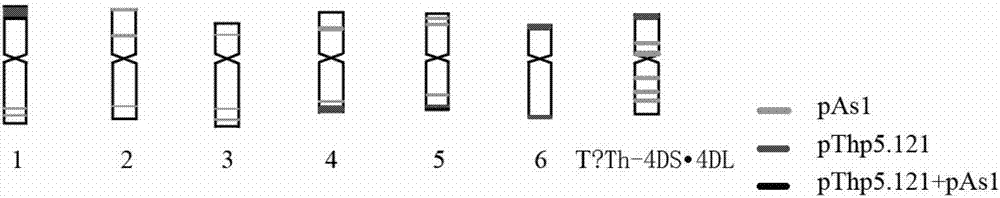
Method for quickly establishing metaphase chromosome karyotype of cucumber through genomic in-situ hybridization
InactiveCN104004849AImprove test efficiencyProbe signal is clearMicrobiological testing/measurementDispersityMetaphase chromosome
The invention discloses a method for quickly establishing a metaphase chromosome karyotype of a cucumber through a genomic in-situ hybridization technology. The method includes the steps that genome DNA of the cucumber is extracted and marked as a probe; enzymolysis is conducted on an extracted root tip of the cucumber, a sheet is prepared through a flame drying method, and then a metaphase chromosome sheet with the good dispersity is acquired; the genome DNA serving as the probe is degenerated and then hybridized to the degenerated metaphase chromosome sheet, under the hybridization condition with the high preciseness, clear and differentiable fluorescence signals are produced through a chromosome tandem repeated sequences, and then the metaphase chromosome karyotype of the cucumber is established. The genome DNA of the cucumber serves as the probe, the metaphase chromosome karyotype of the cucumber is quickly established through one-time GISH, and then testing efficiency is improved. Through the method, based on the different signal distribution modes of the genome DNA probe of the cucumber on chromosomes, the metaphase chromosome karyotype of the cucumber can be quickly established, and a novel method and reference are provided for analytical investigation of karyotypes of species.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
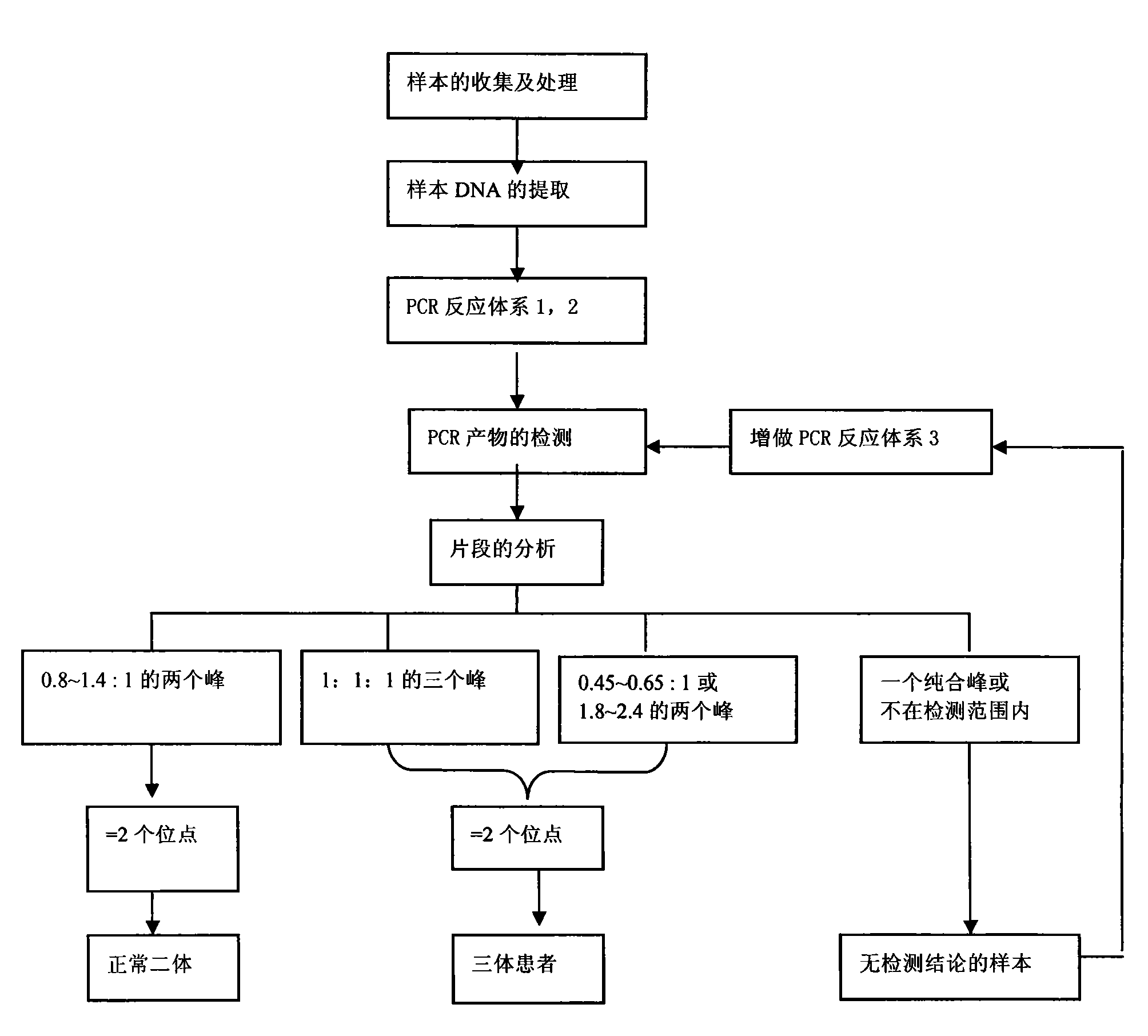
Reagent kit for fast detecting common chromosome trisome by quantitative fluorescence PCRs
InactiveCN101550439AWidely distributedEvenly distributedMicrobiological testing/measurementCord blood stem cellAmniotic fluid
The invention relates to a method for fast detecting common chromosome trisome by quantitative fluorescence PCR, which comprises the following steps: sample collection and processing, DNA extraction, primer design and synthesis, PCR amplified reaction of a first system and a second system, PCR product detection, PCR amplified reaction of a third system and PCR product detection. The invention also provides an accurate and reliable reagent kit for fast detecting the common chromosome trisome by the quantitative fluorescence PCR. The invention is integrated with the sensitivity and the accuracy of the quantitative fluorescence PCR and the extensive and uniform distribution, the polymorphism and the high heterozygosity of a tandem repeat sequence and can be used for detecting the number of common chromosomal disorders of prenatal samples, such as peripheral blood, amniotic fluids, cord blood, tomenta, and the like.
Owner:广州医学院
Anti-fmd vaccine composition and preparation and use thereof
ActiveUS20110206718A1Safe and effectiveHybrid immunoglobulinsSsRNA viruses positive-senseImmunoglobulin heavy chainRecombinant vaccines
The present invention pertains to the field of immunology and genetic engineering. In particular, the present invention relates to the construction, preparation and use of a recombinant vaccine against foot-and-mouth disease virus. The vaccine comprises a tandem repeat of an antigenic epitope of FMDV VP1 protein, the constant region of the immunoglobulin heavy chain or a functional fragment thereof, and the FMDV 3D protein or an immunogenic fragment thereof. The vaccine can induce protective immune response against FMDV in an animal.
Owner:PHAROS VACCINE
Processing method for high-throughput sequencing information of human short tandem repeat
The invention discloses a processing method for high-throughput sequencing information of human short tandem repeat and belongs to the field of biological detection. The method comprises the steps that sequences with a preset sequencing length in STR high-throughput sequencing information of a single chip are reserved, and first sequences are formed; the first sequences are classified into different sample folders according to sample label information, the first sequences are reclassified into different STR locus folders according to STR target fragment specific primer information, and second sequences are formed; stepped reference sequences for different STR loci are established, the second sequences are compared with sequences of corresponding STR loci in the second sequences, and third sequences with the sequence similarity greater than or equal to 90% are reserved; and the threshold value of the number of sample sequencing entries is set to be 1,000, the threshold value of the number of locus sequencing entries is set to be 50, the threshold value of the number of typing sequencing entries in the loci is set to be 5, the threshold value of the number of the typing sequencing entries in the loci and the number of the locus sequencing entries is set to be 40%, and sequences with threshold values greater than or equal to the threshold values in the third sequences are screened to obtain an STR typing result.
Owner:IPE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Application of tandem repeat sequence capable of improving expression activity of plant gene
InactiveCN102604955AAngiosperms/flowering plantsDNA/RNA fragmentationSocial benefitsPromoter activity
The invention relates to application of a tandem repeat sequence capable of improving expression activity of a plant gene, namely application of a fragment containing five tandem repeat TTTACAC sequences on a zinc finger transcription factor At5g15840 gene promoter of Arabidopsis thaliana in improving expression of a target gene in a transgenic plant. When the tandem repeat sequence is deleted, the activity of the promoter is sharply lowered, and therefore, the tandem repeat sequence has the characteristic of enhancing gene expression. By use of the tandem repeat sequence provided by the invention, the transgene development of a plant is performed, so that the expression of the target gene is improved, and the important economic and social benefits are achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Development and application of decaploid agropyron elongatum tandem repeat sequence specific probe
ActiveCN107475390AImproved genetic traitsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgropyron elongatumAgricultural science
The invention discloses development and application of a decaploid agropyron elongatum tandem repeat sequence specific probe. According to the development and the application, a specific length amplified fragment sequencing technology (SLAF-seq) is utilized to perform sequencing on common wheat, a common wheat-decaploid agropyron elongatum translocation line and decaploid agropyron elongatum, a decaploid agropyron elongatum specific sequence is acquired through sequence data comparative analysis, and the tandem repeat sequence specific probe is developed based on the decaploid agropyron elongatum specific sequence. The tandem repeat sequence specific probe provided by the invention can be used for rapidly identifying decaploid agropyron elongatum chromosomes and identifying a translocation line in a process that chromosome fragments of agropyron elongatum are transferred into the wheat, providing an important way of molecular marker-assisted selection to improve the wheat hereditary property and also providing an important application basis for wheat molecular breeding, phyletic evolution and germplasm resource identification.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
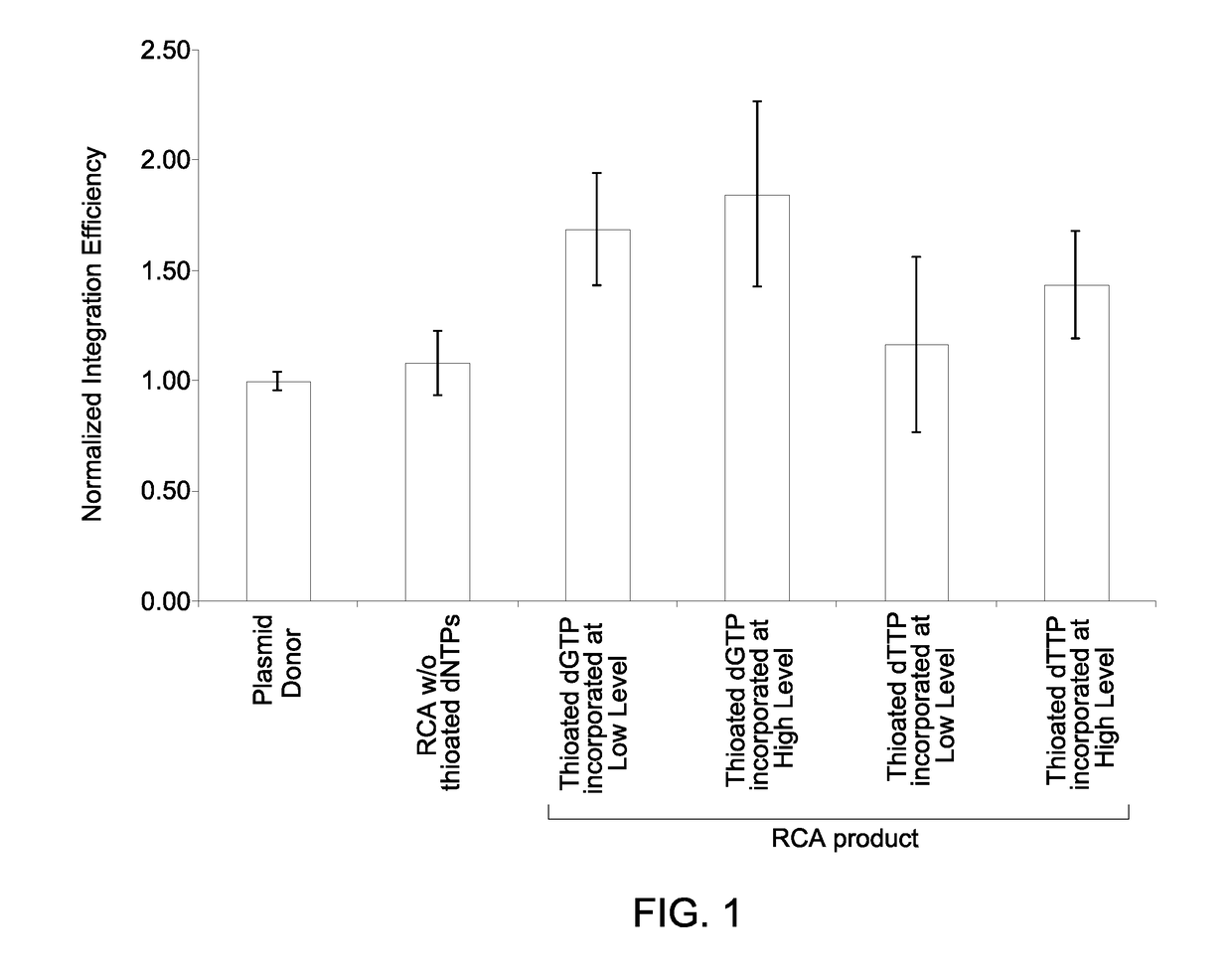
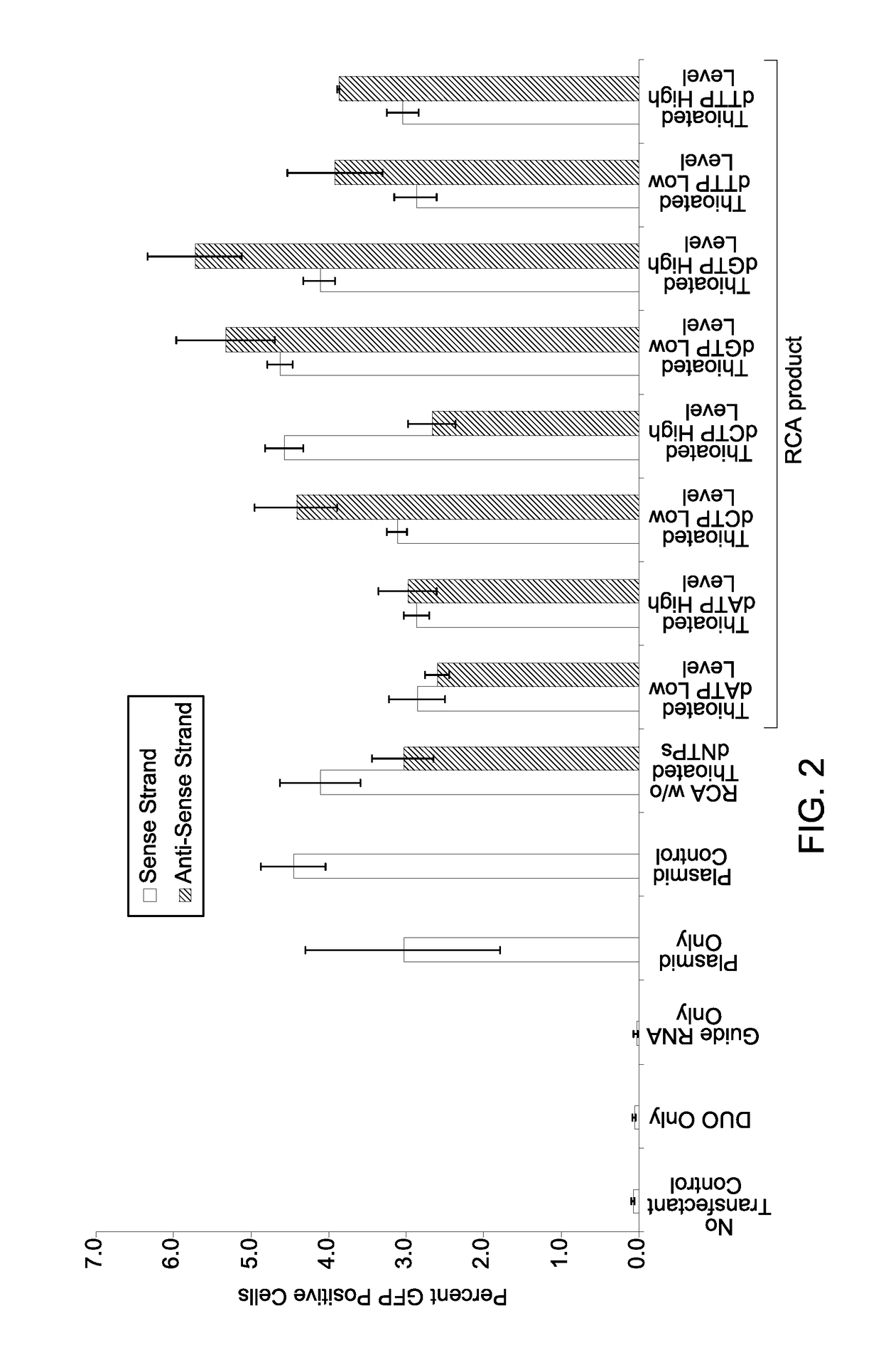
Site-specific DNA modification using a donor DNA repair template having tandem repeat sequences
A method of site-specific modification of an endogenous target DNA of a eukaryotic cell is provided. The method includes contacting the endogenous target DNA having an intended modification site with (i) a gene editing system configured to introduce a double strand break in the endogenous target DNA at or near the intended modification site, and (ii) a donor DNA repair template comprising a plurality of tandem repeat sequences. In the method, each of the plurality of tandem repeat sequences comprises an exogenous donor DNA sequence flanked by a donor 5′ flanking sequence and a donor 3′ flanking sequence. The donor 5′ flanking sequence and the donor 3′ flanking sequence are homologous to a continuous DNA sequence on either side of the intended modification site in the endogenous target DNA.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com