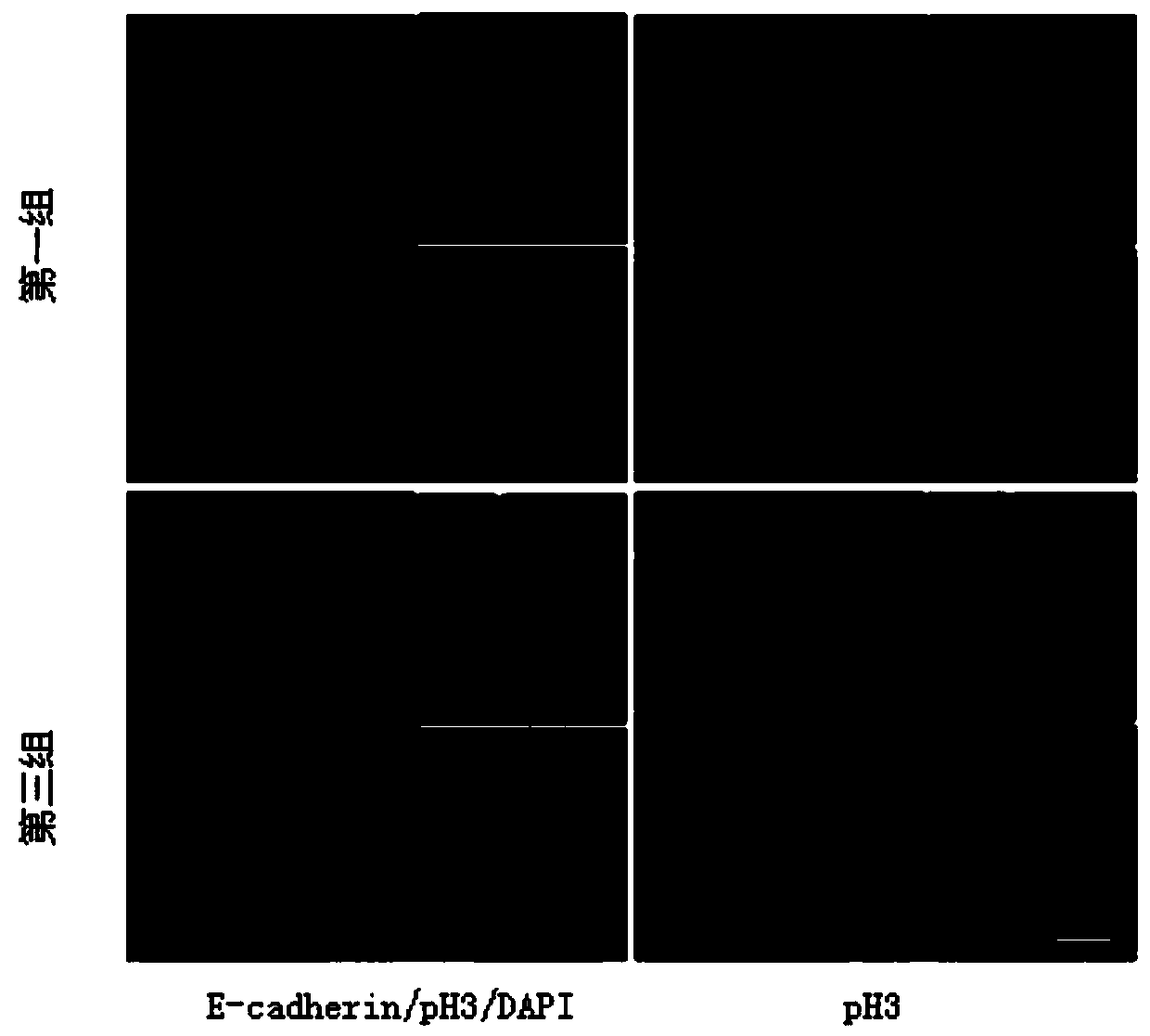
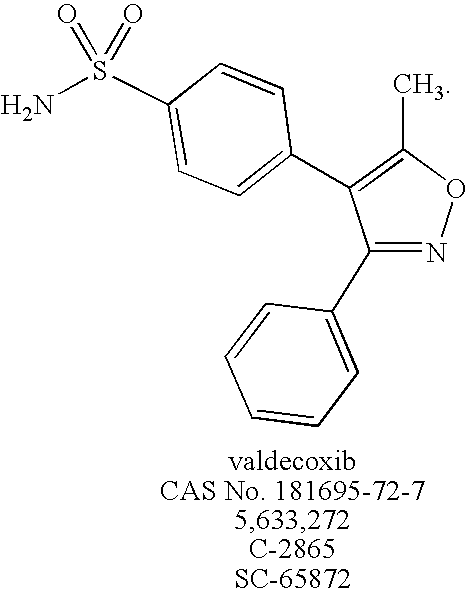
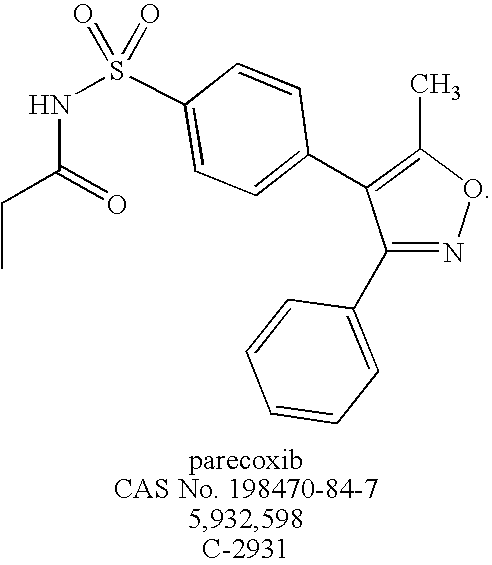
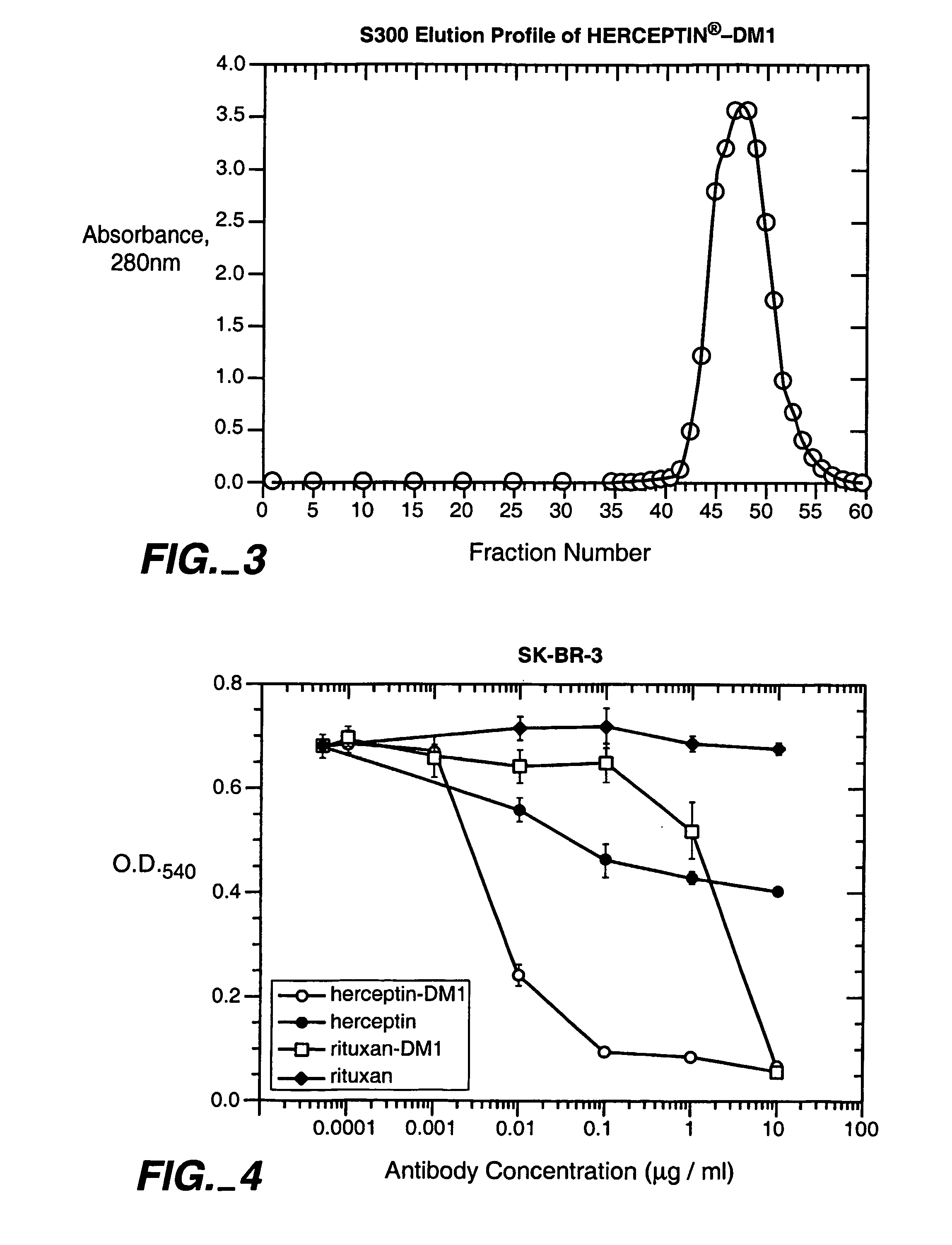
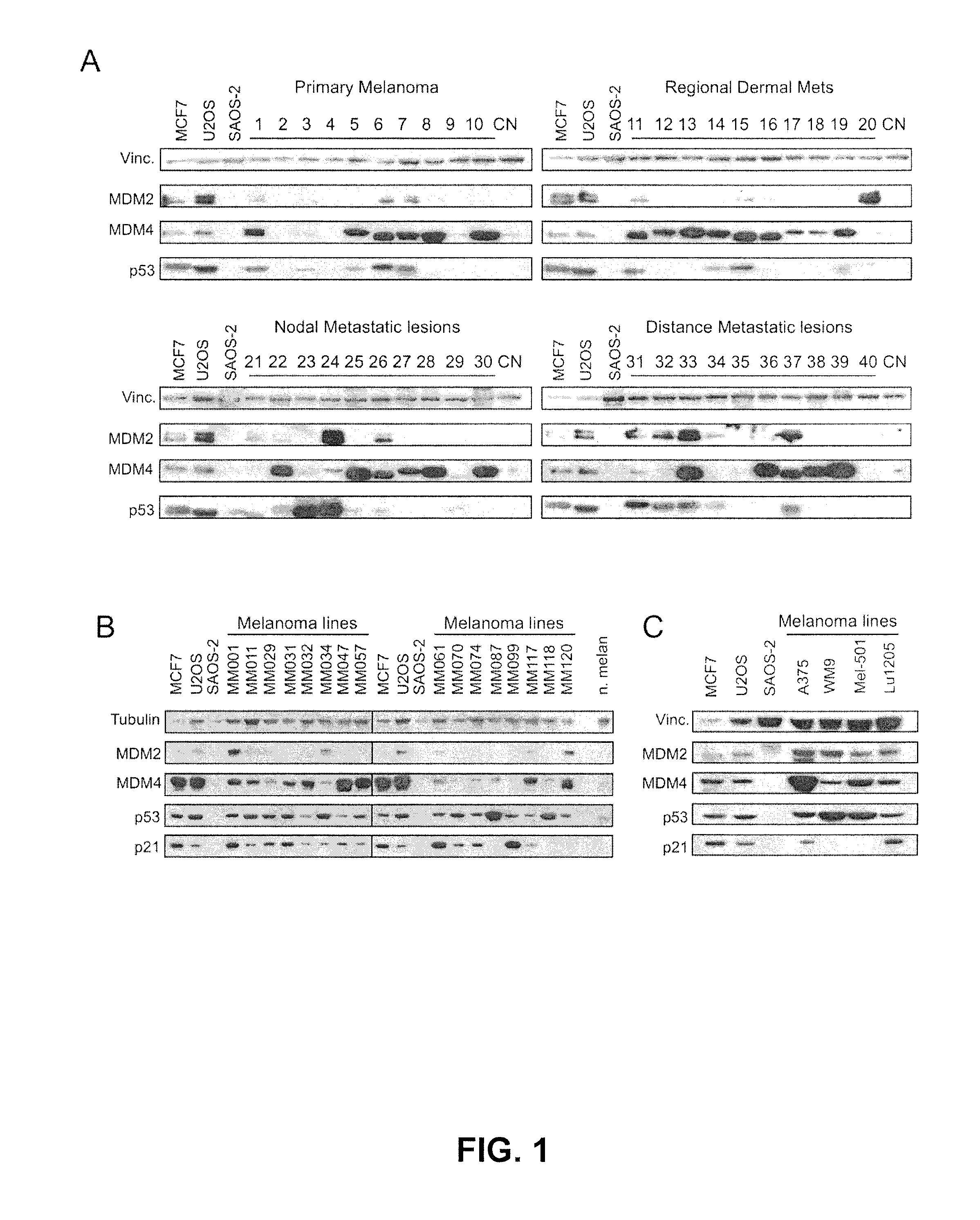
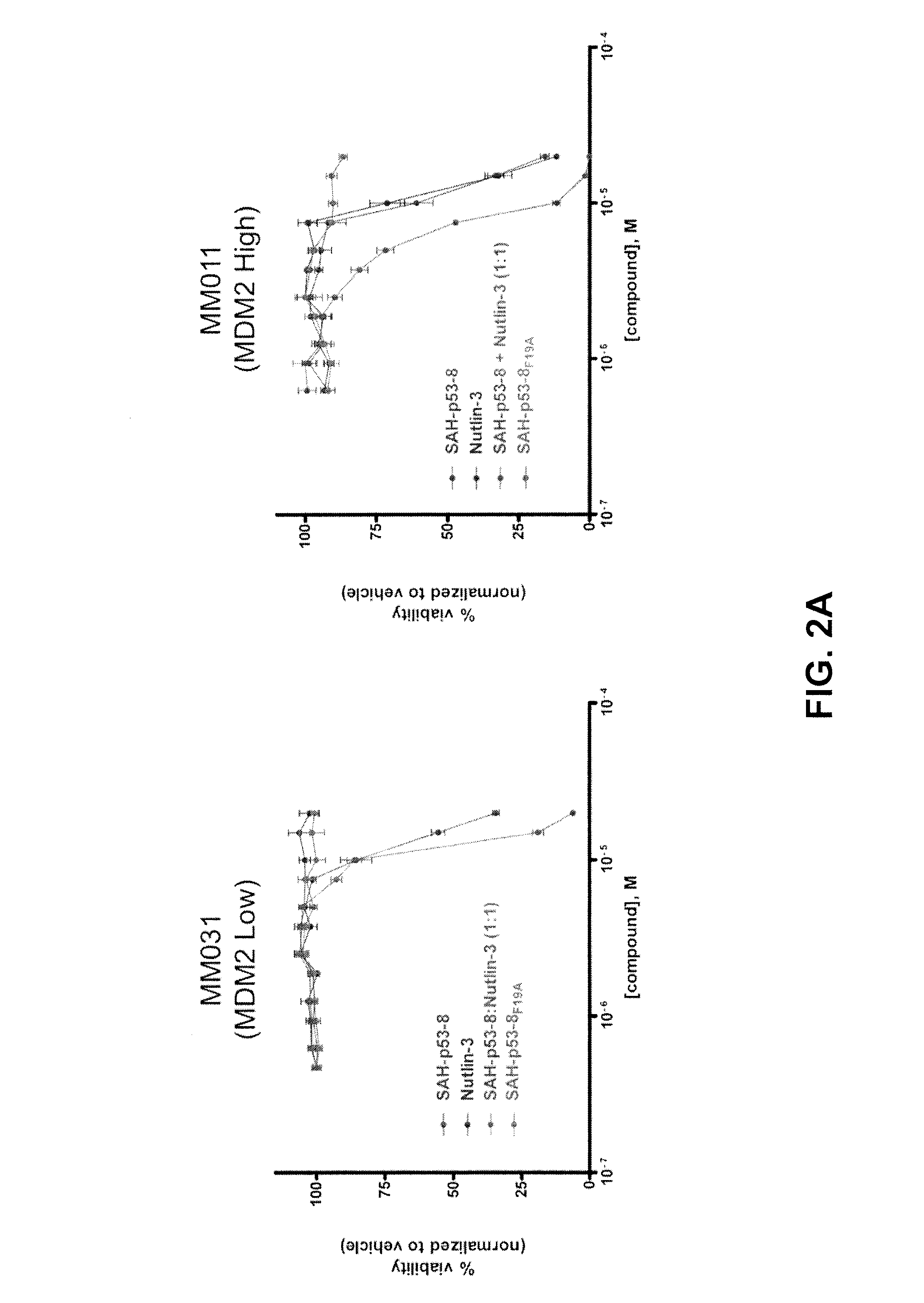
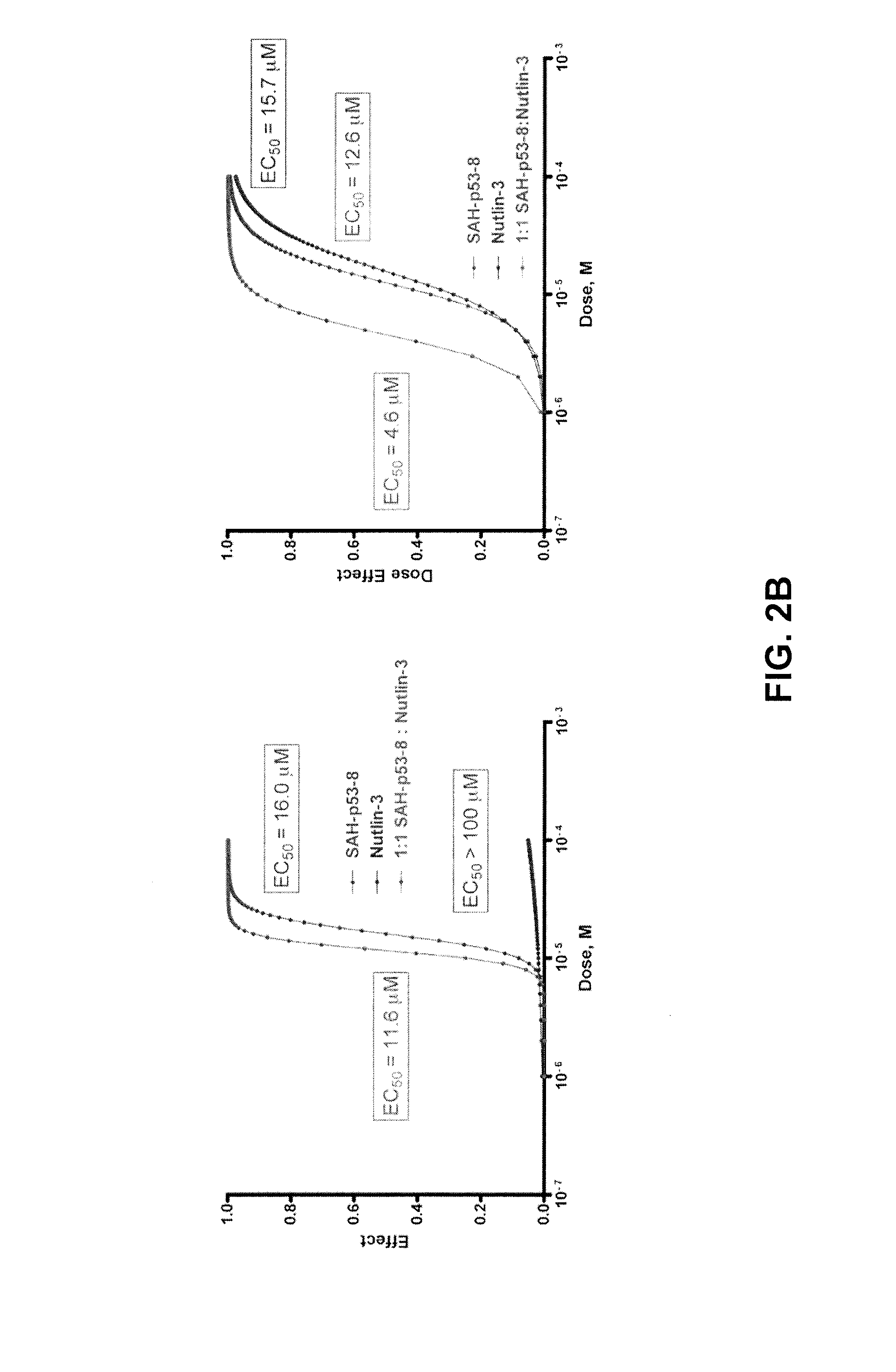
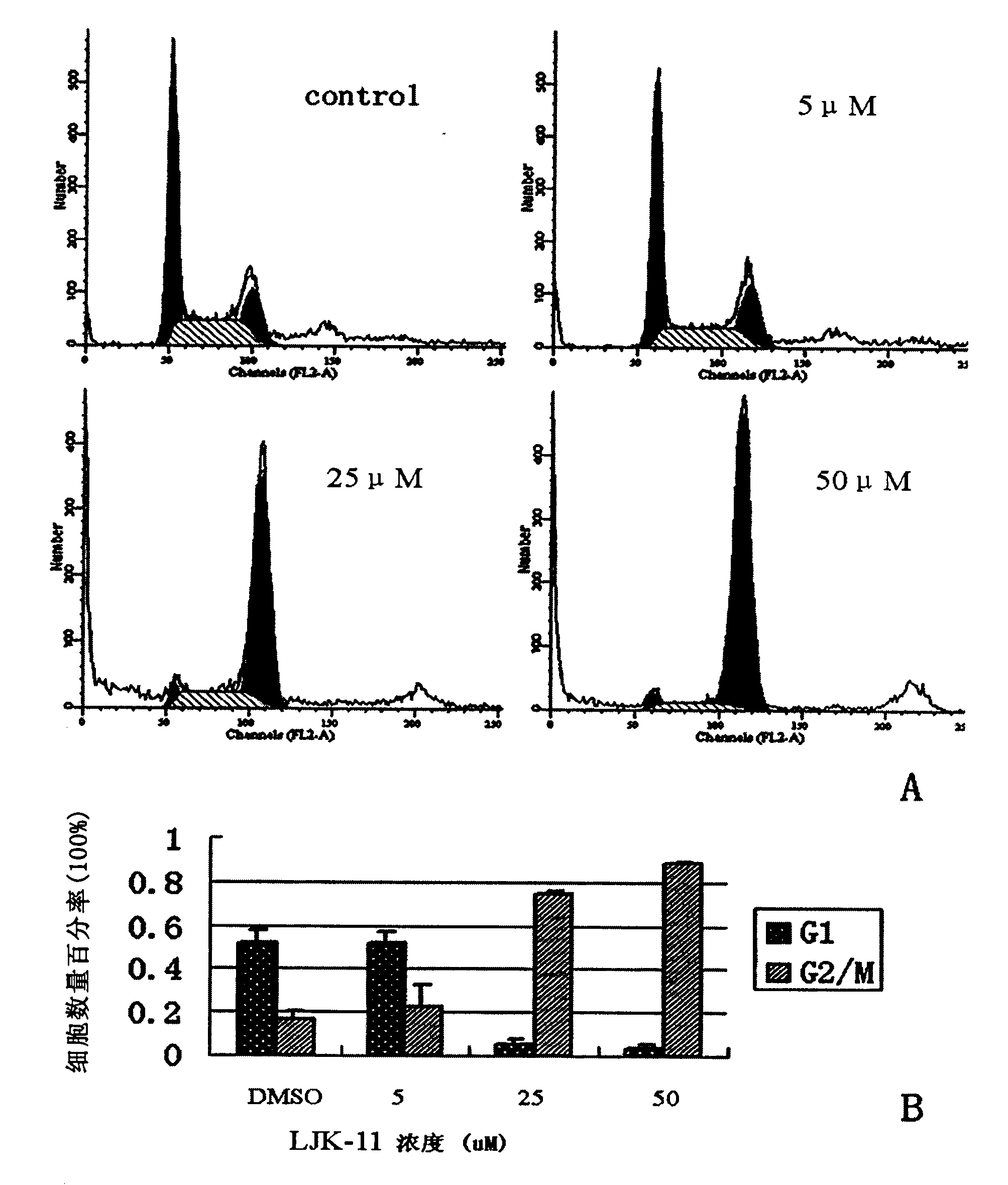
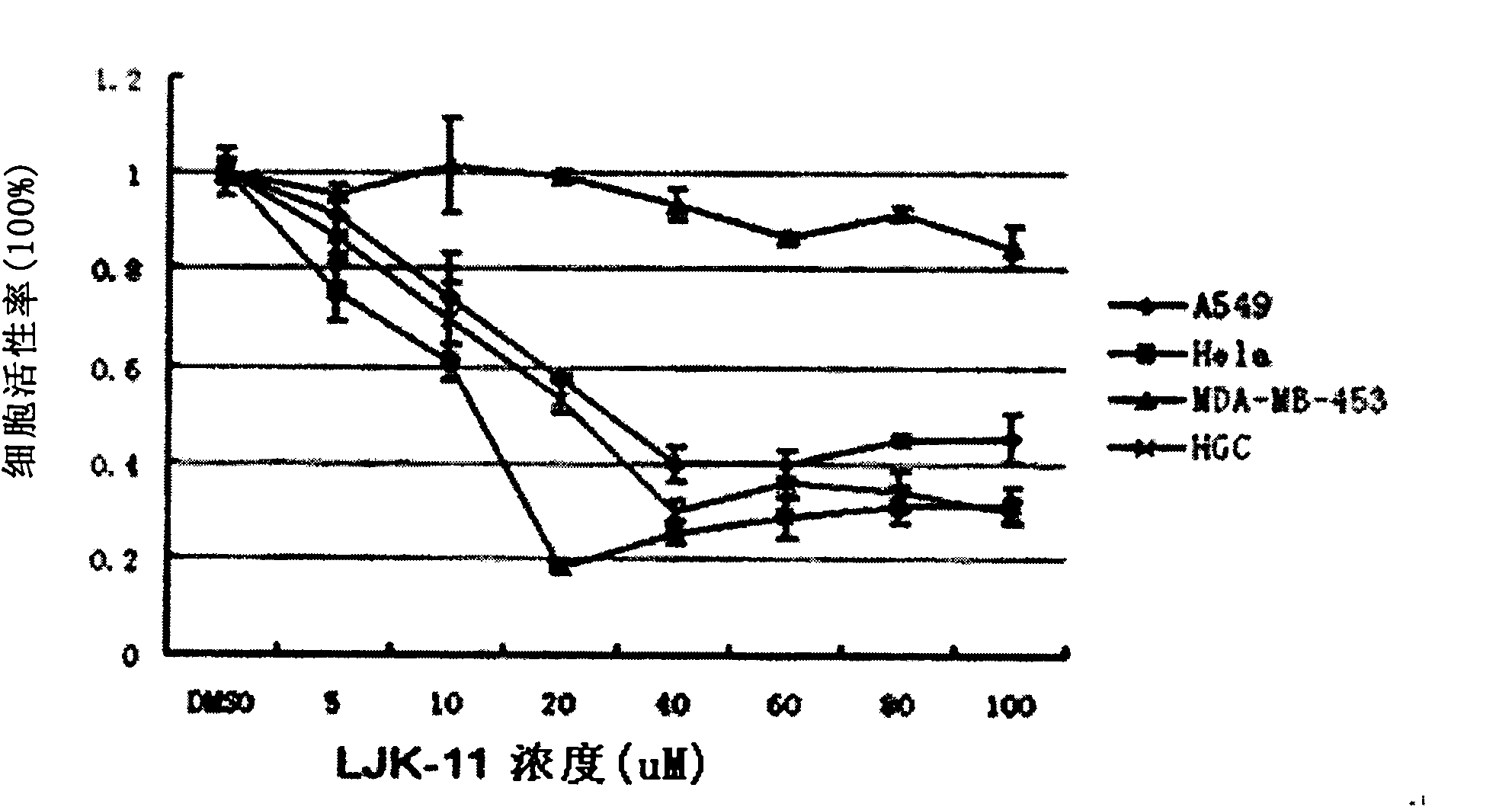
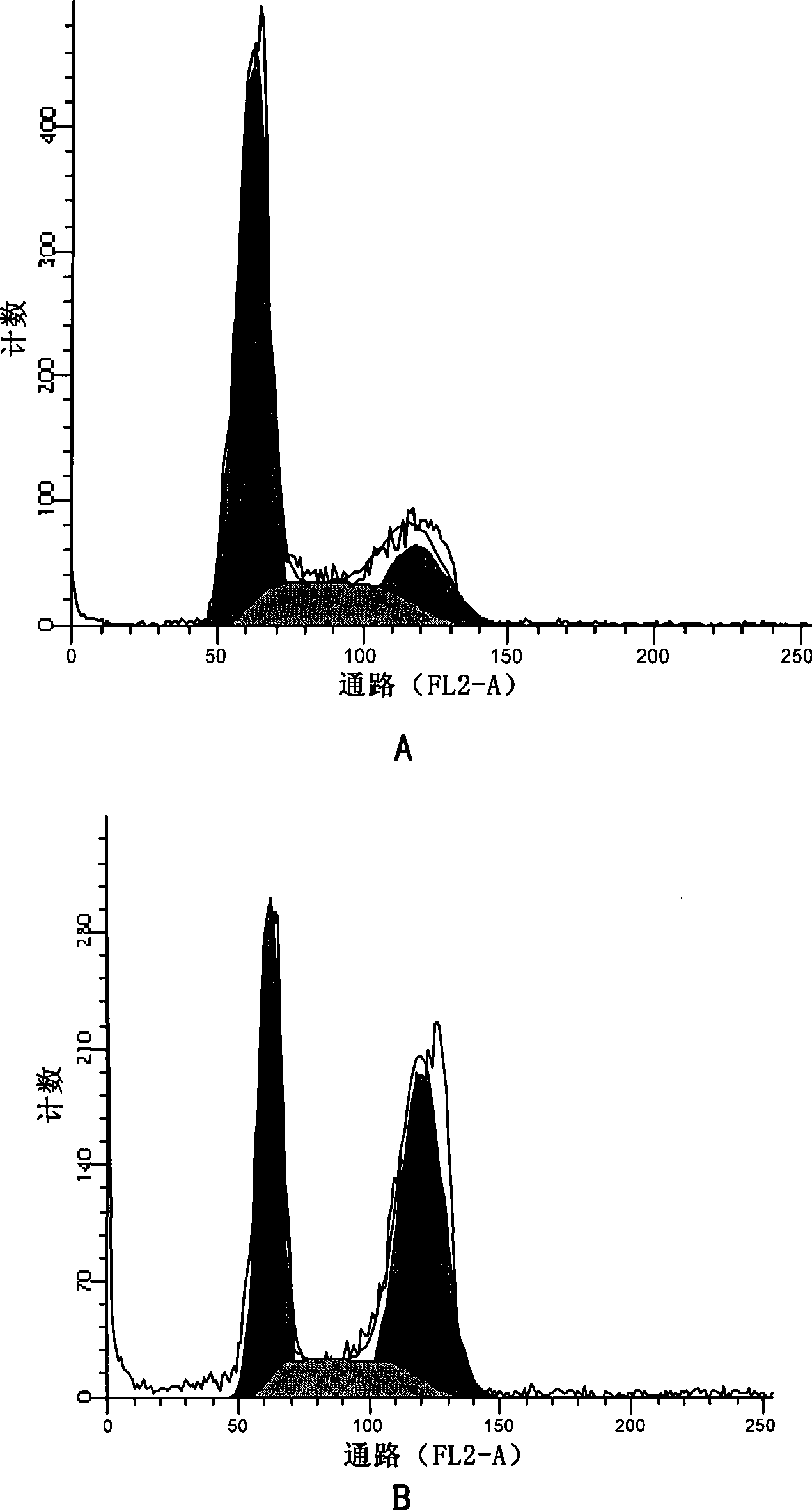
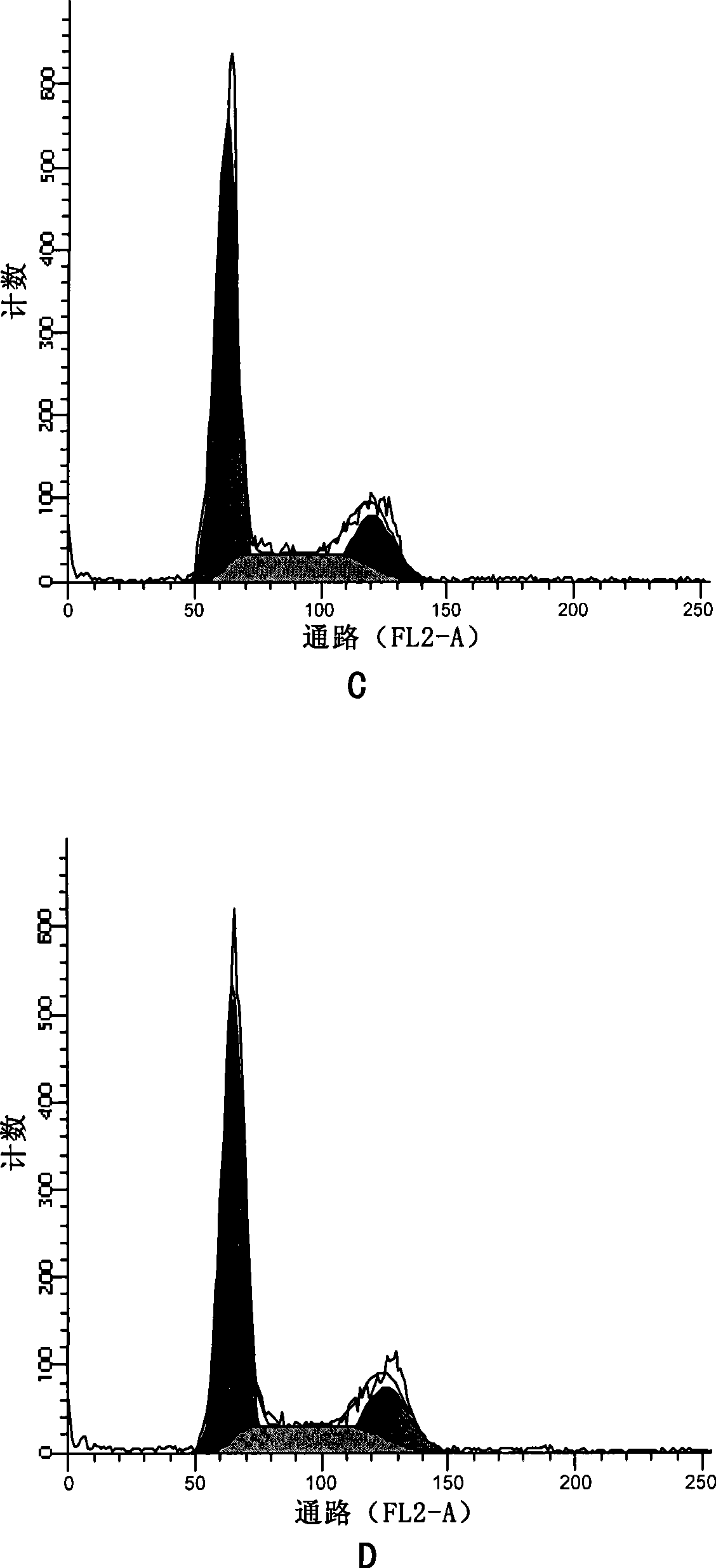
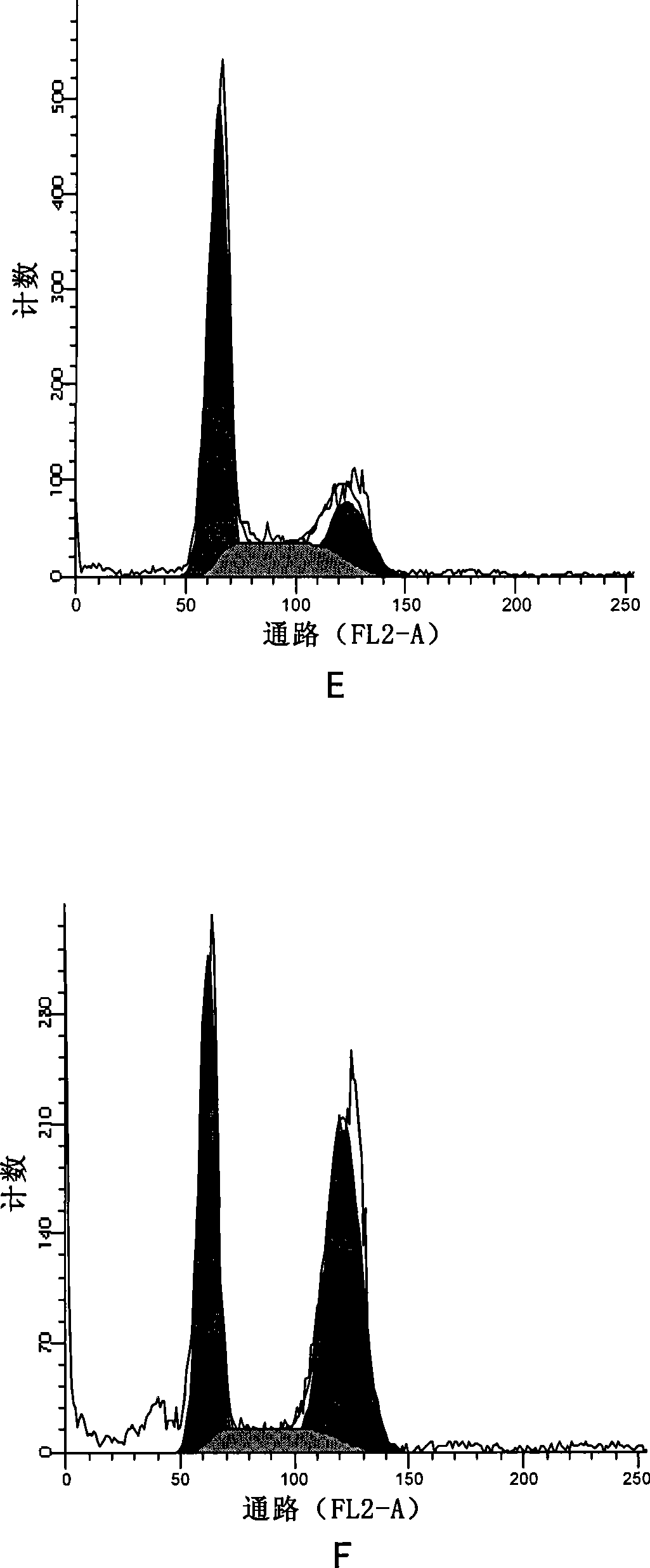
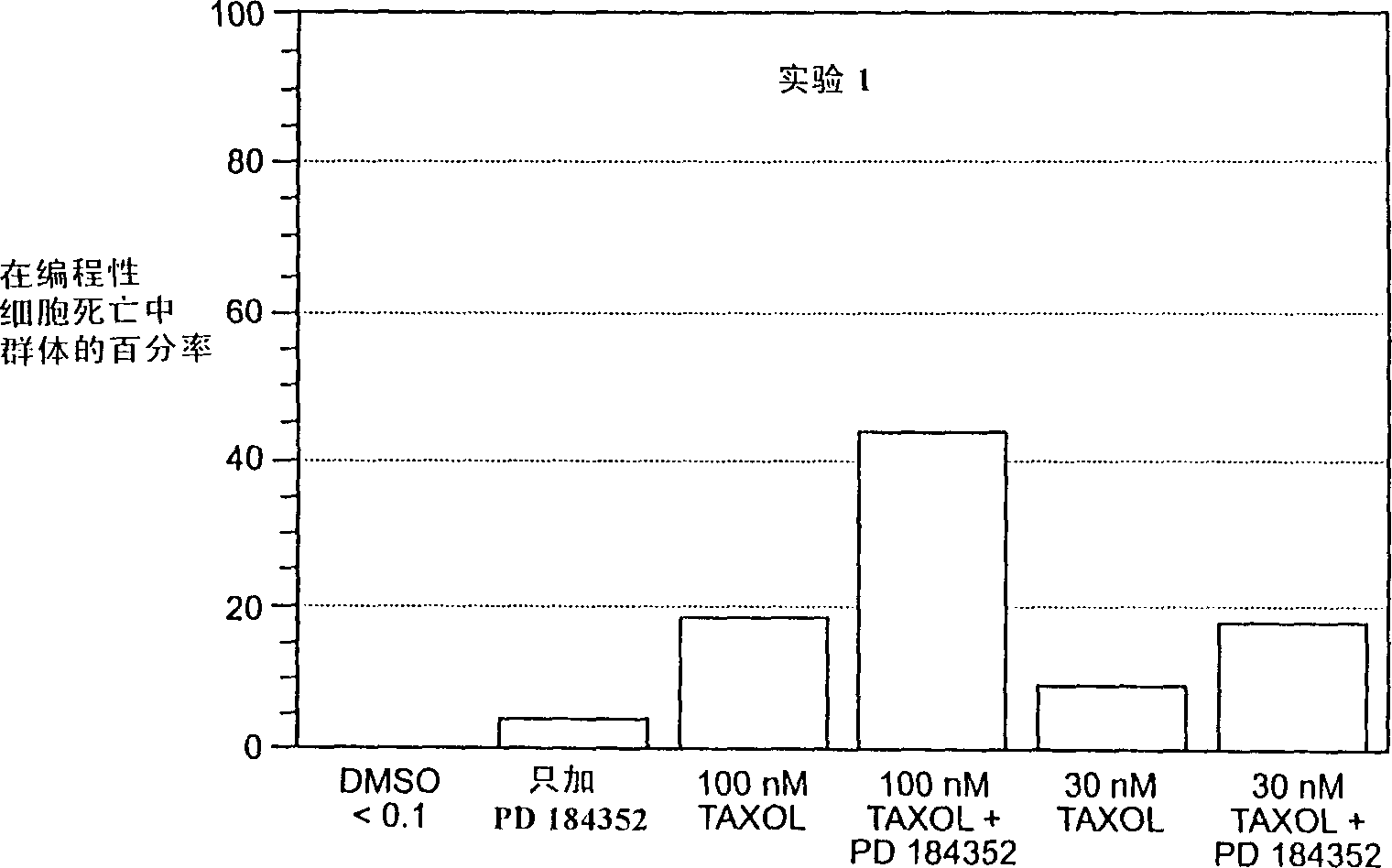
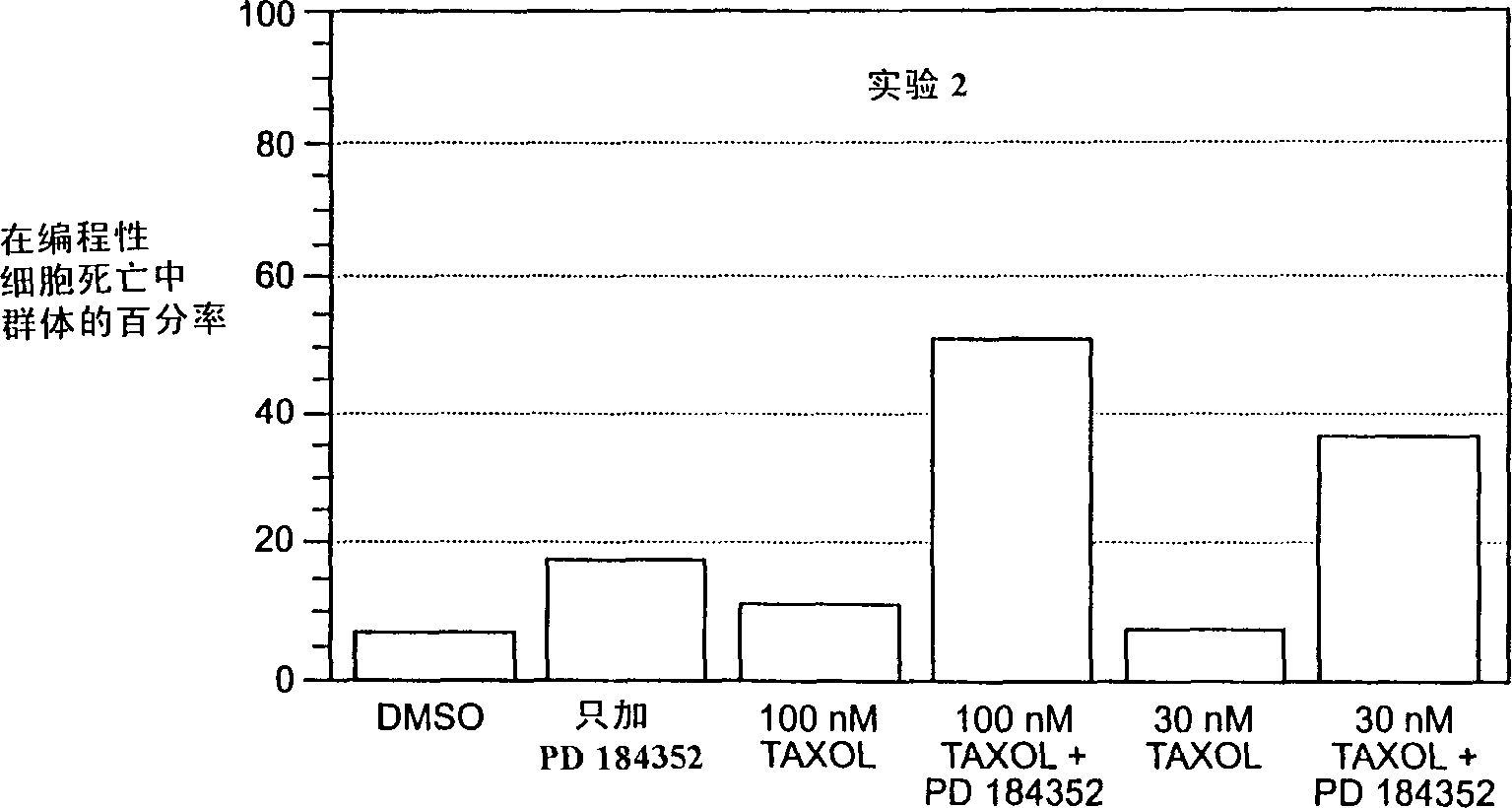
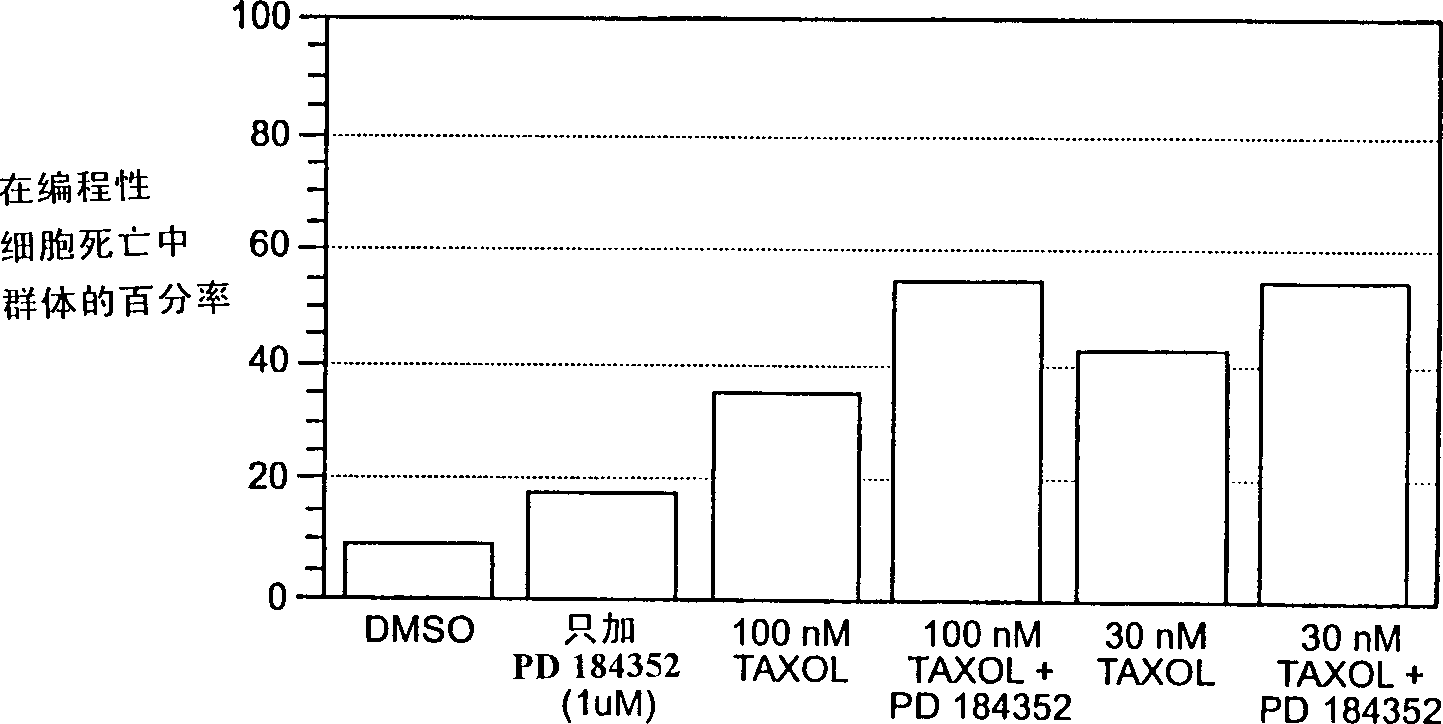
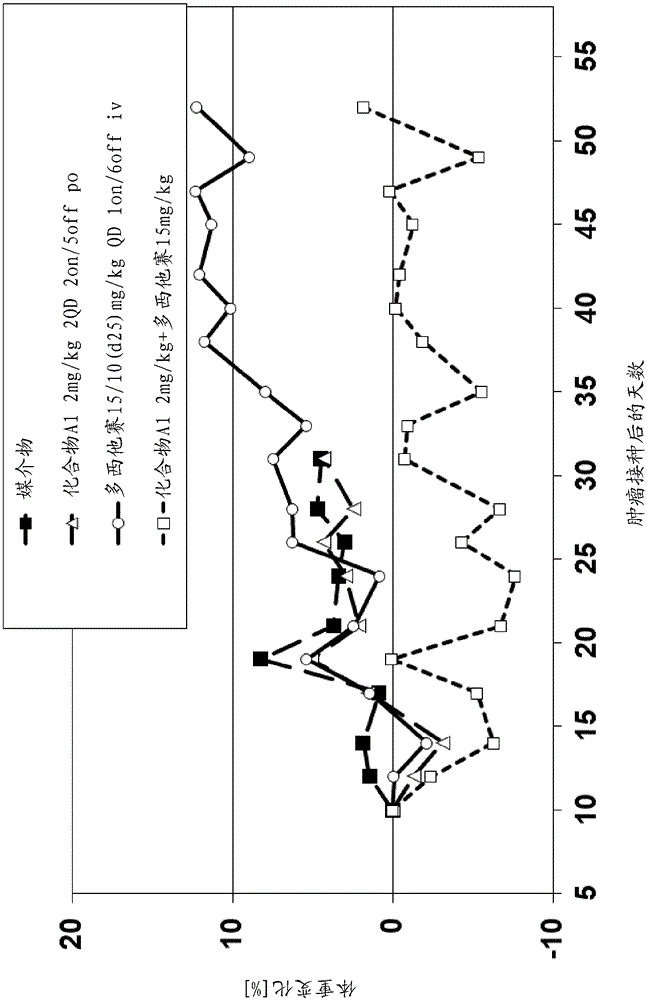
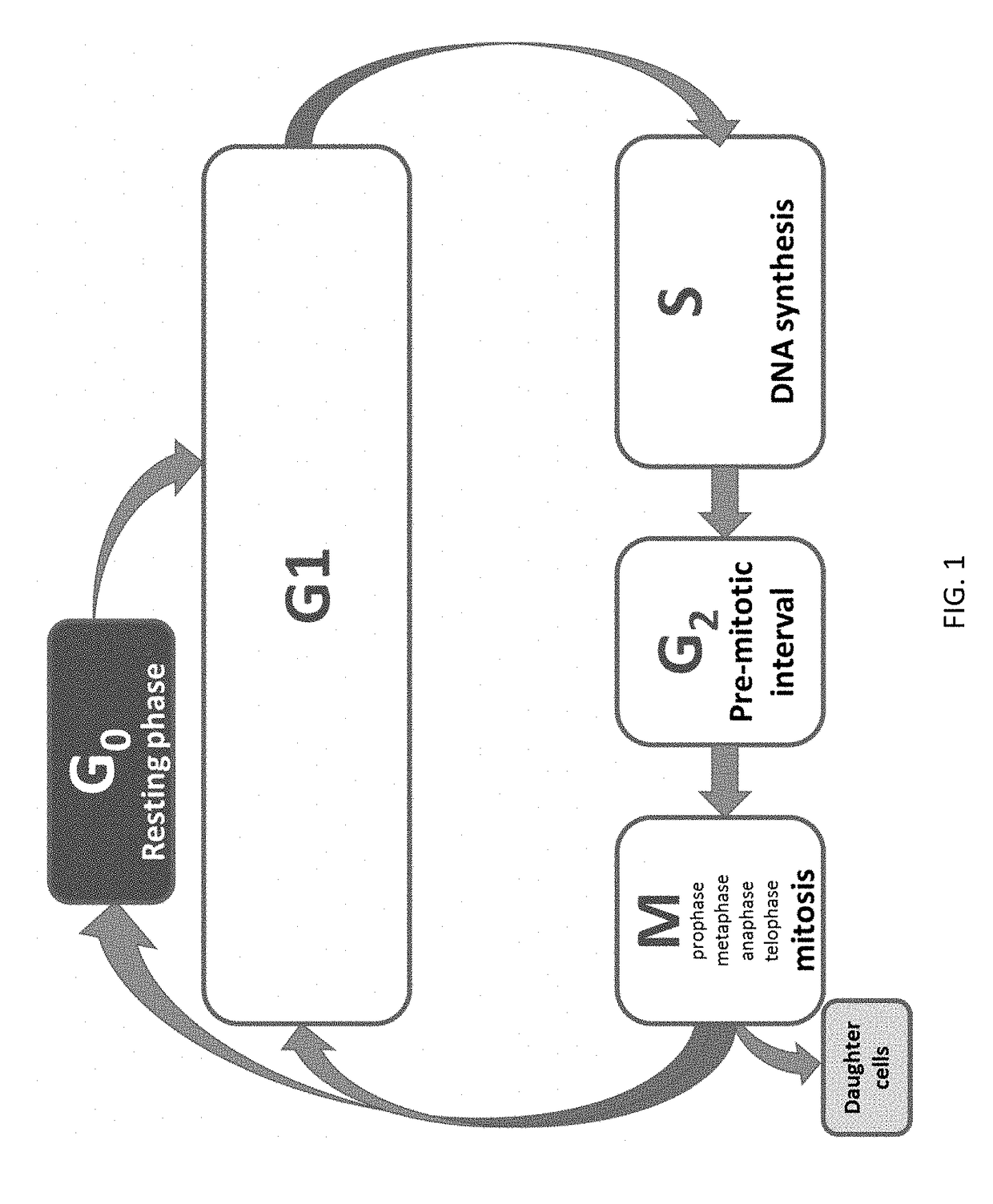
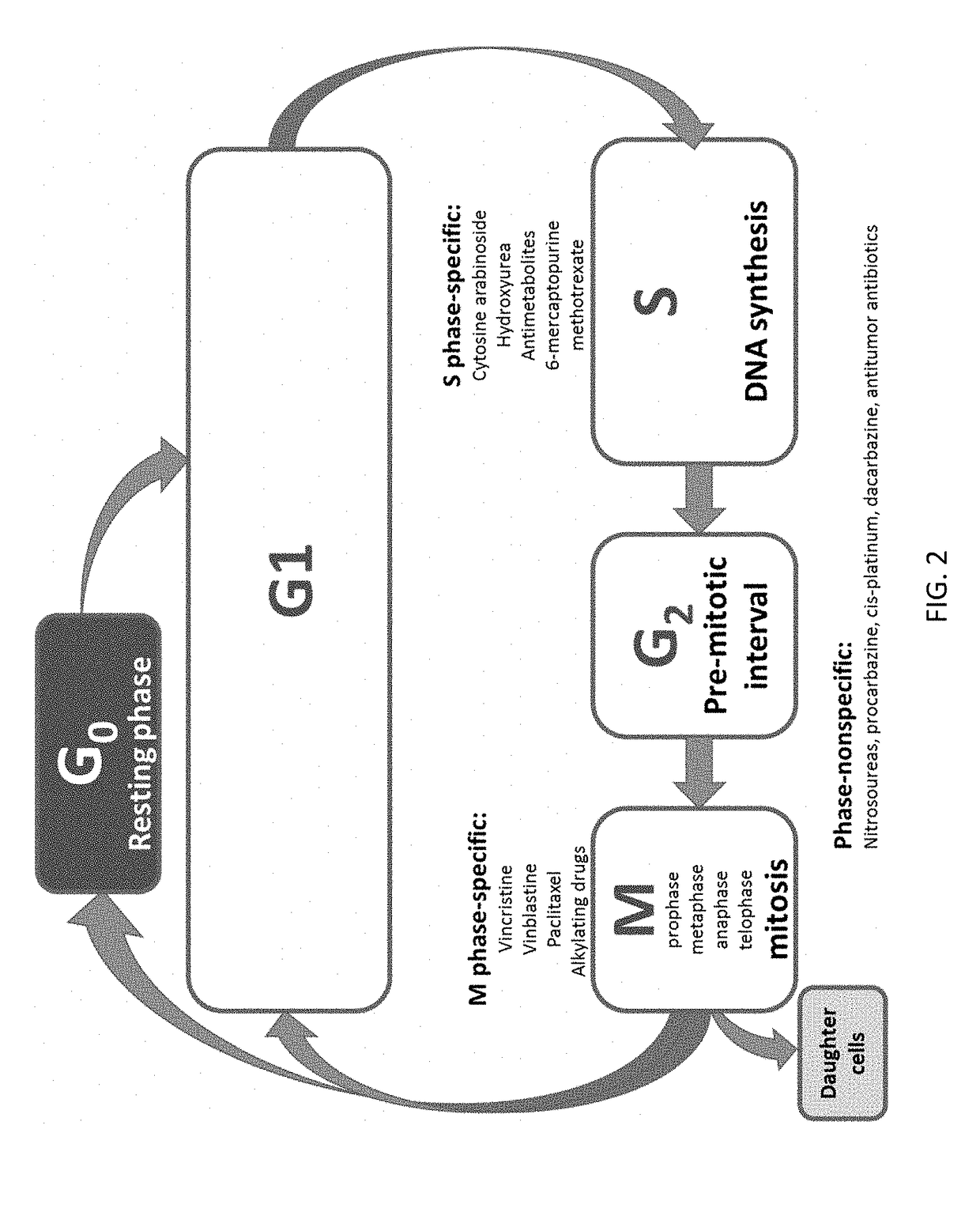
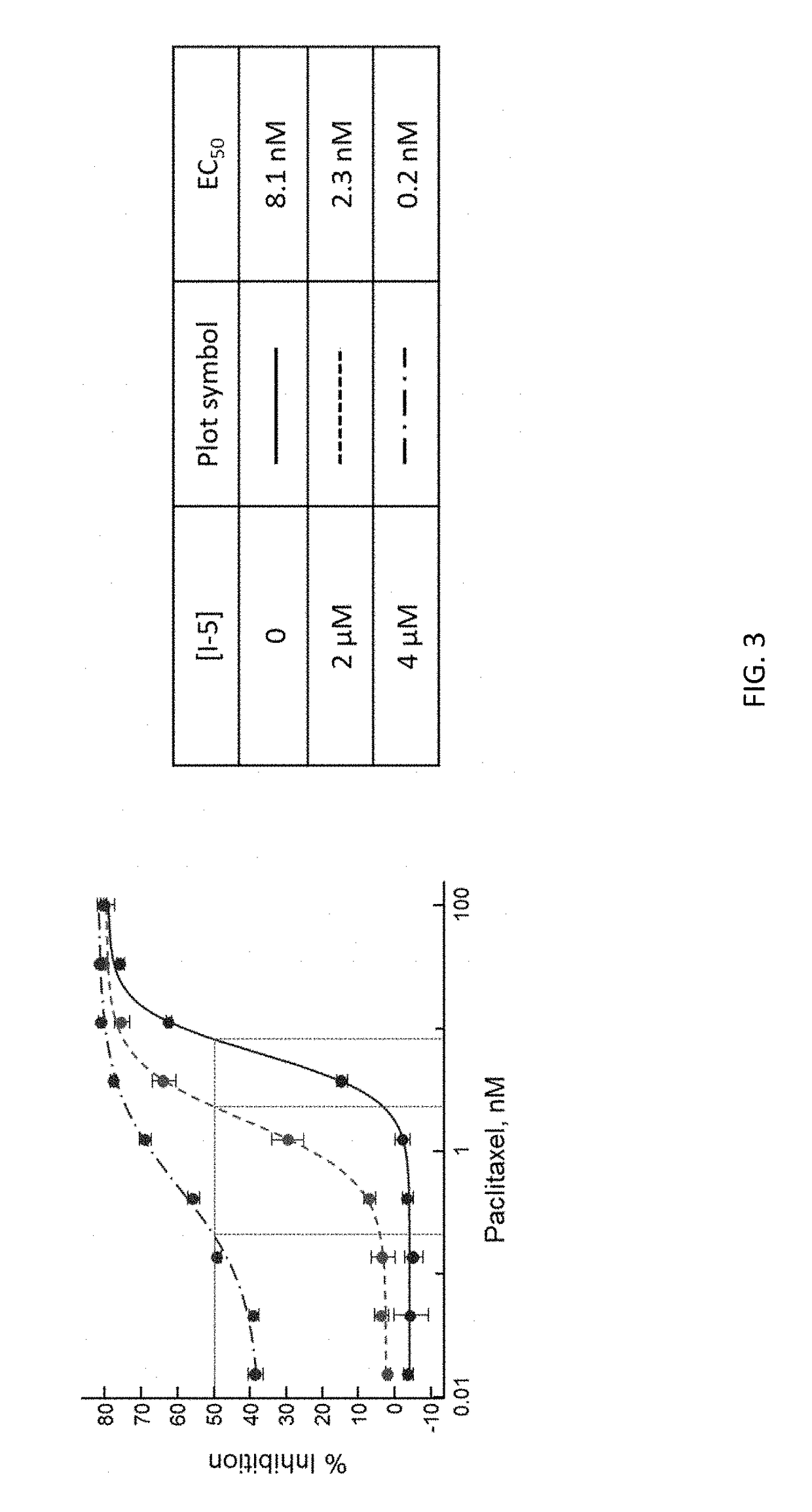
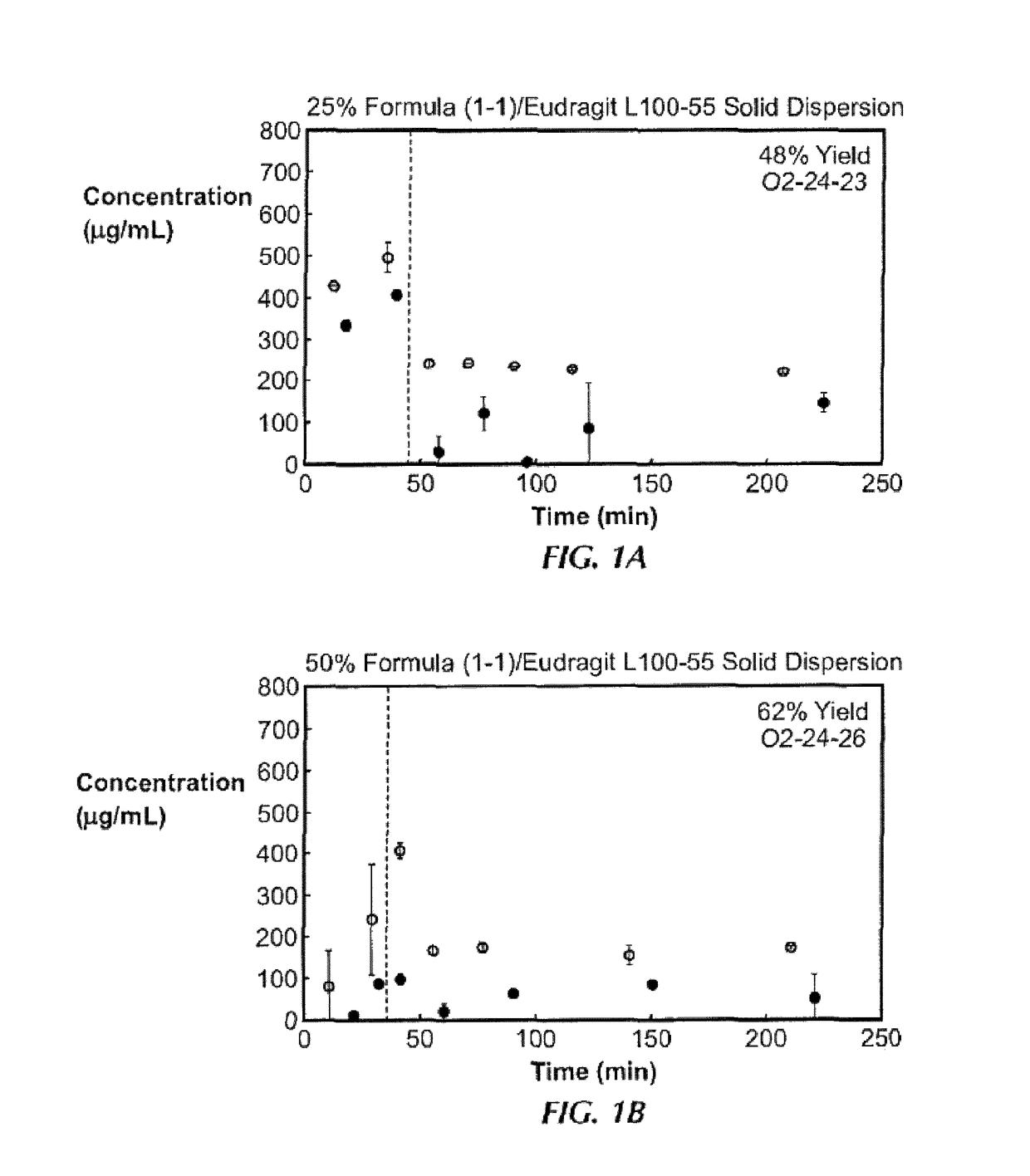
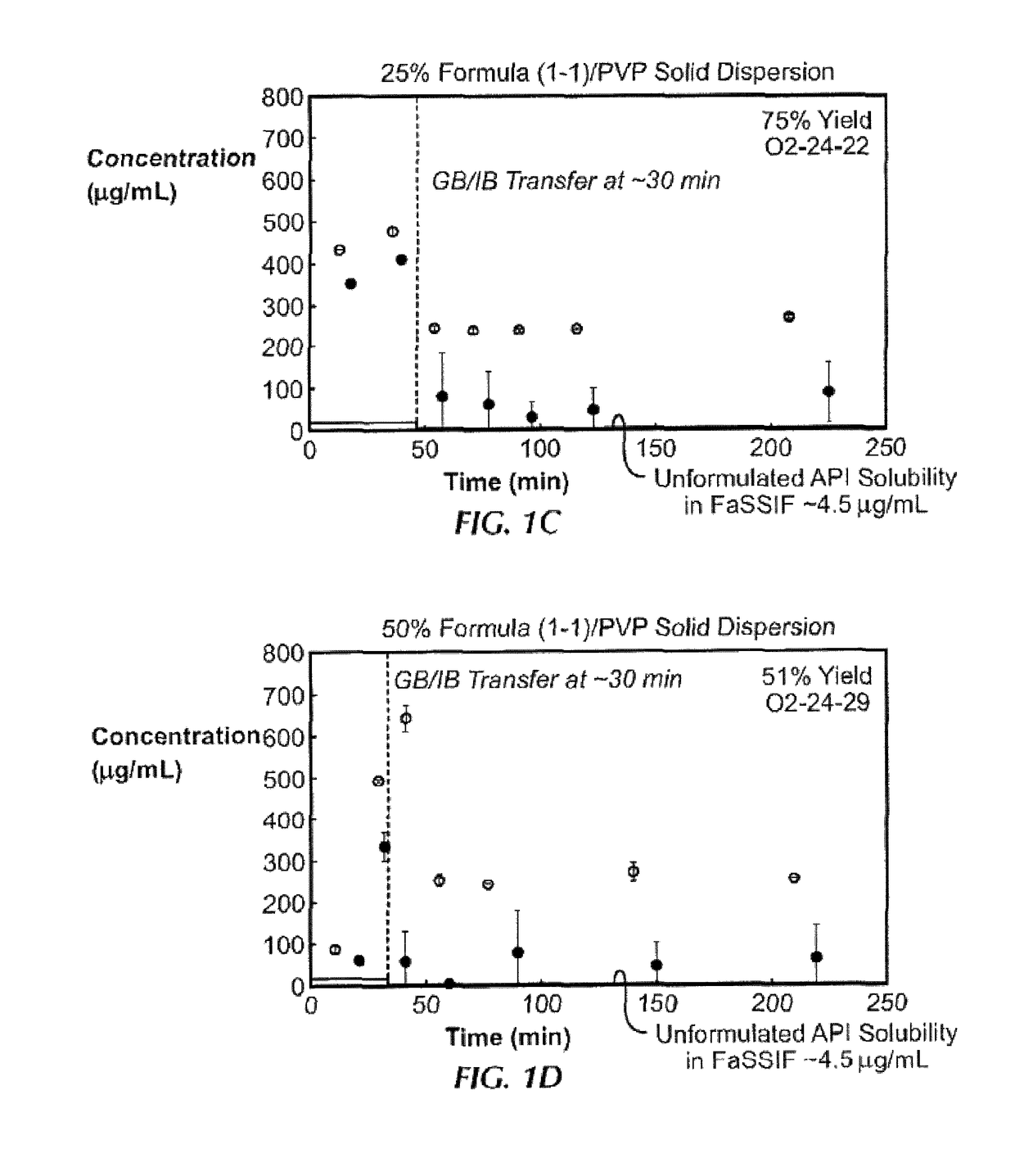
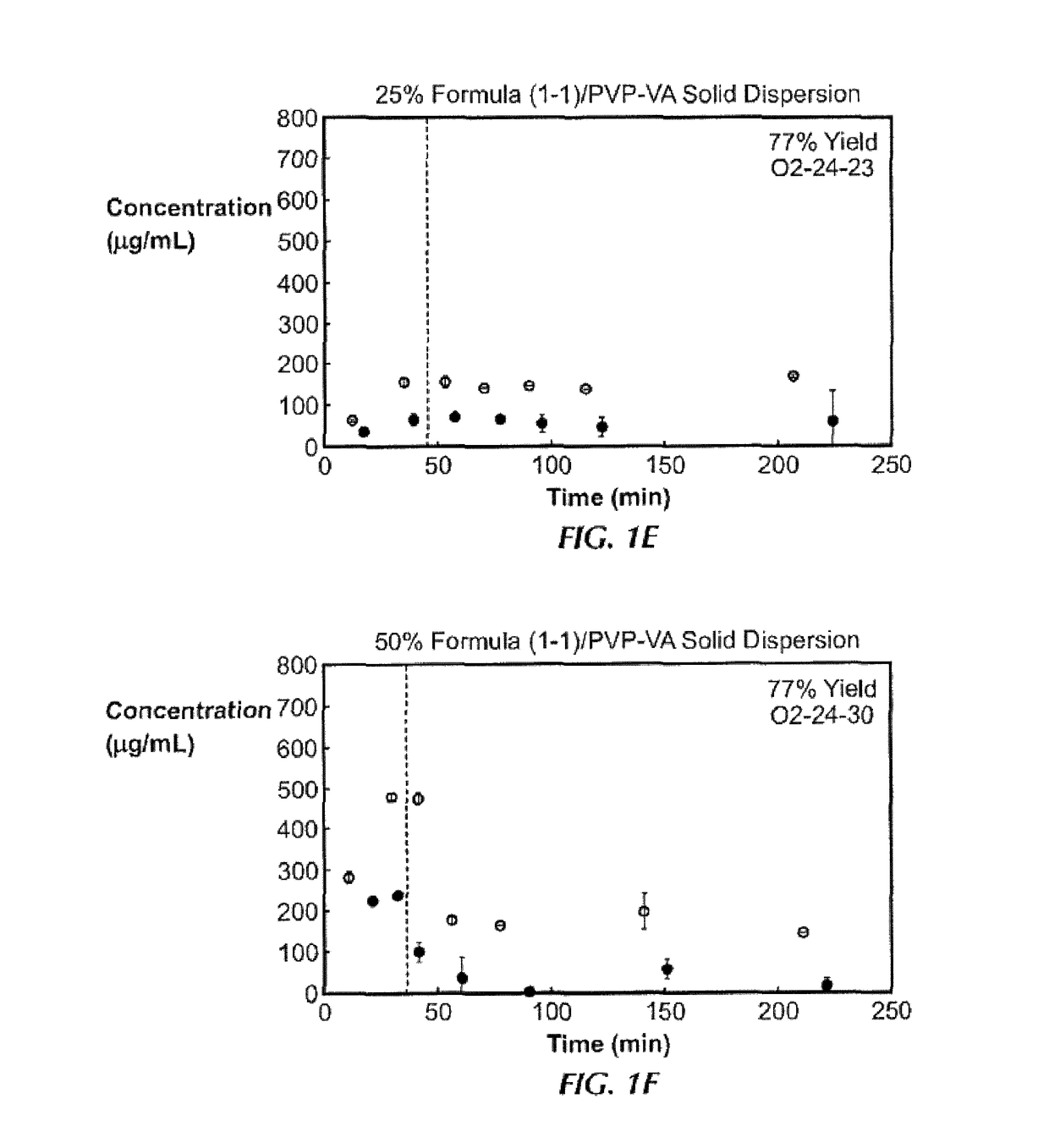
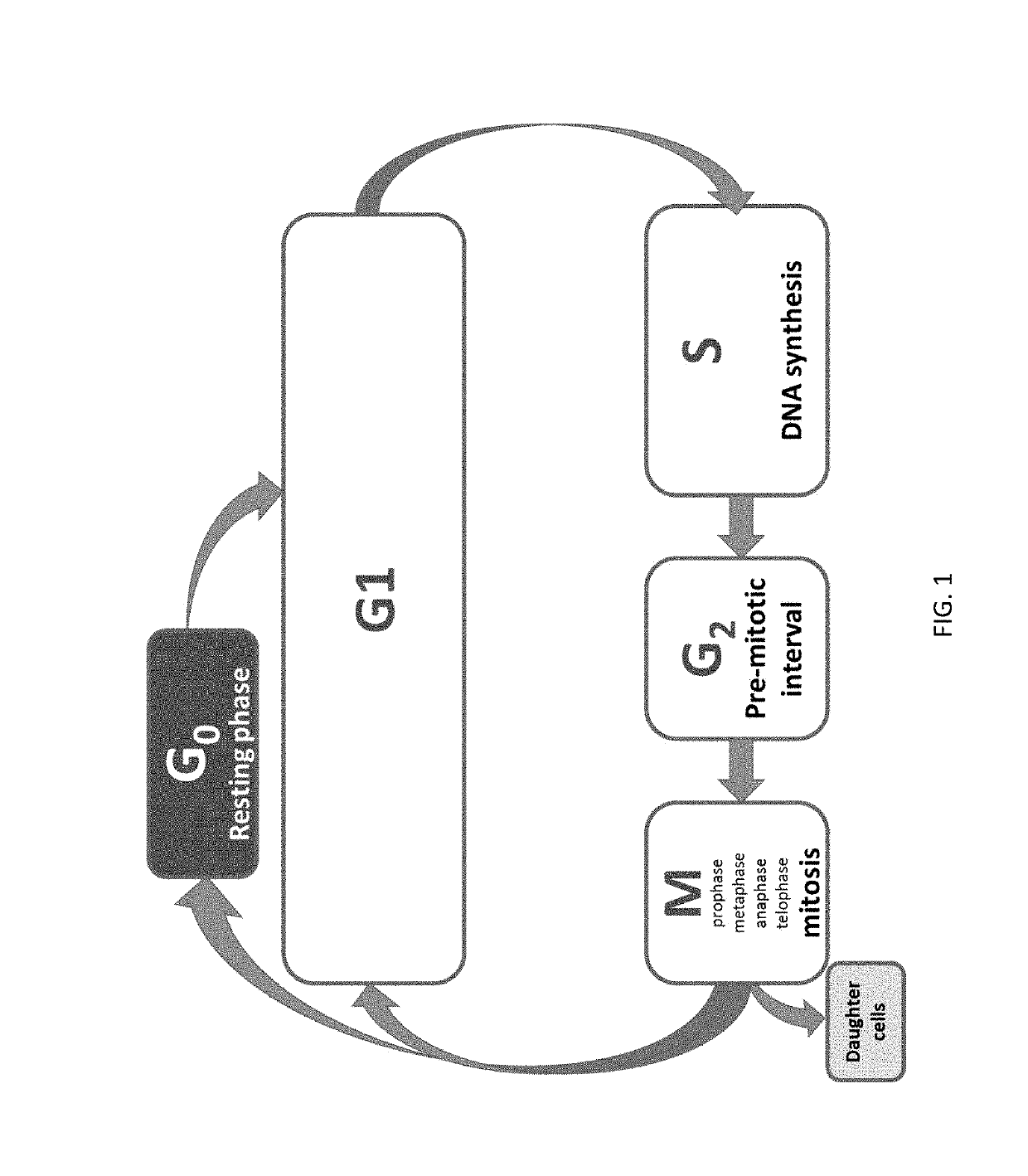
Patents
Literature
39 results about "Mitotic inhibitor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
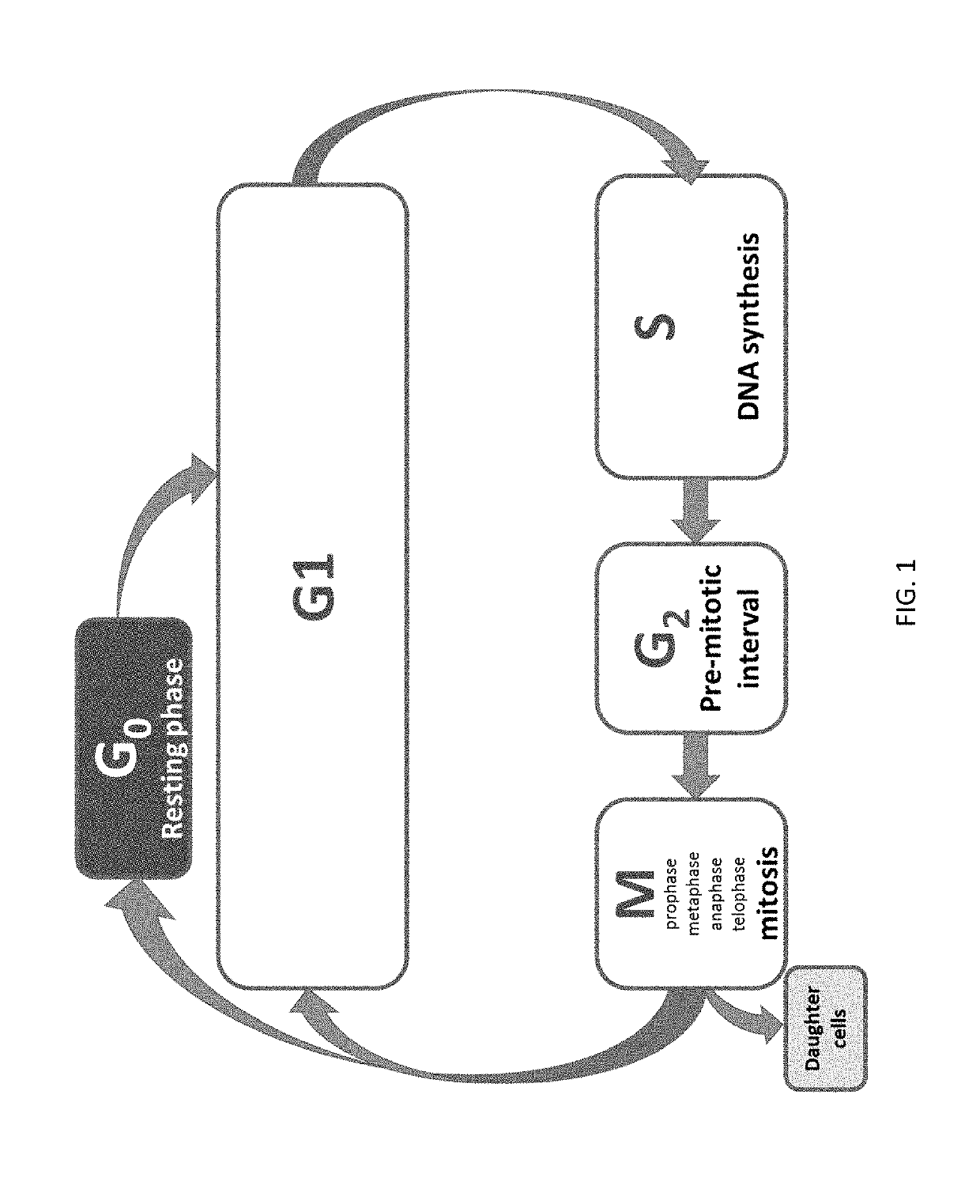
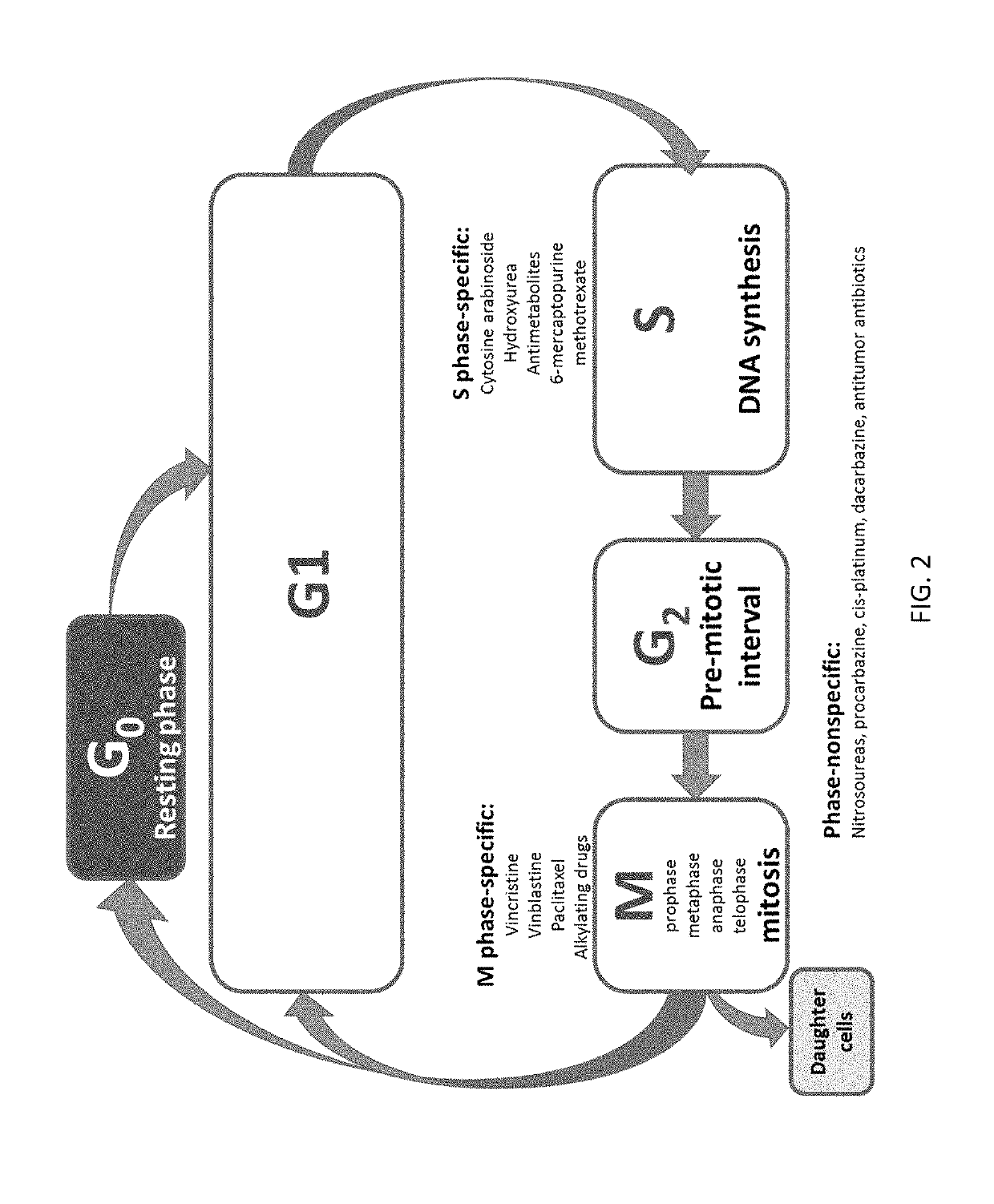
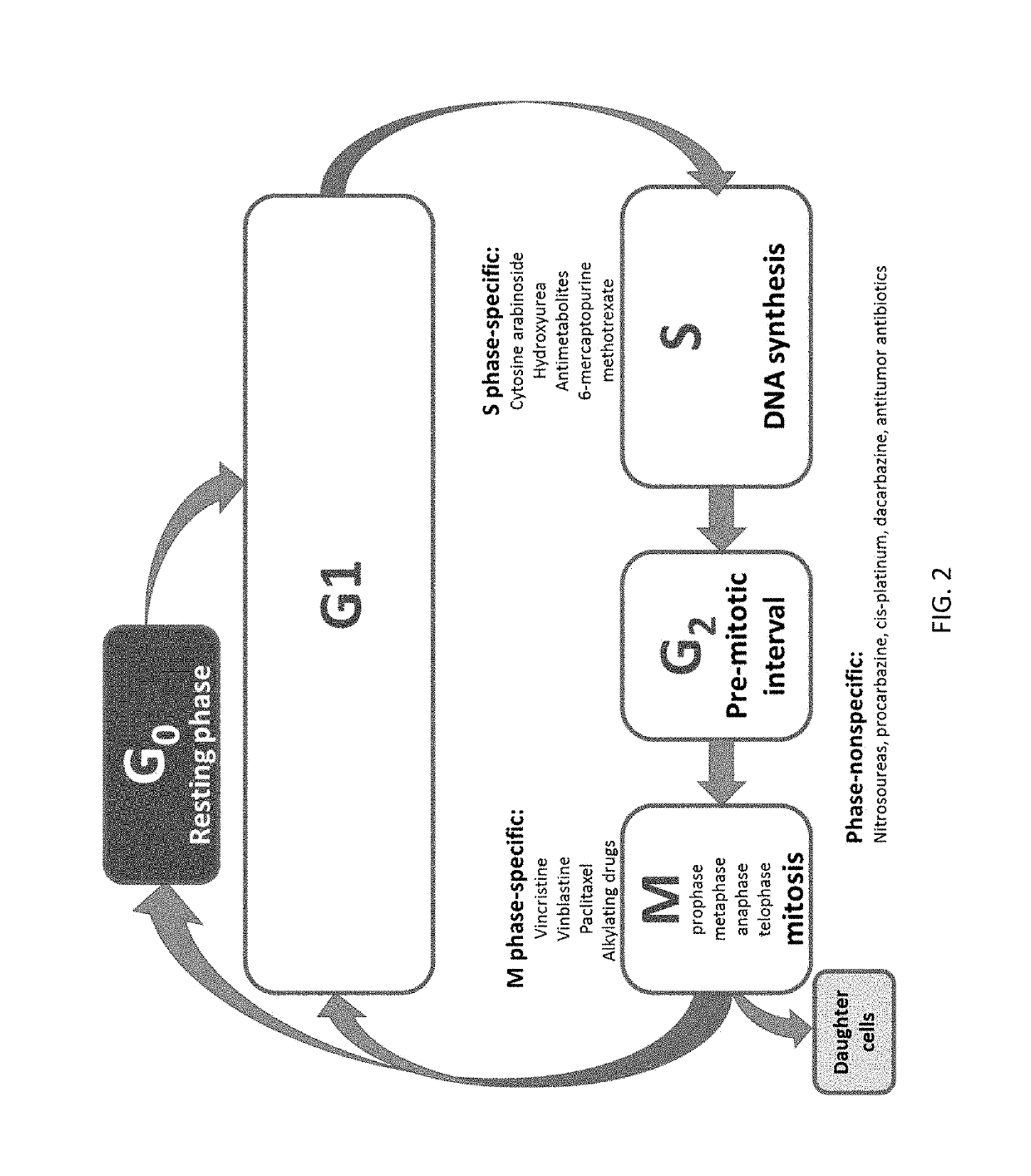
A mitotic inhibitor is a drug that inhibits mitosis, or cell division. These drugs disrupt microtubules, which are structures that pull the chromosomes apart when a cell divides. Mitotic inhibitors are used in cancer treatment, because cancer cells are able to grow and eventually spread through the body (metastasize) through continuous mitotic division. Thus, cancer cells are more sensitive to inhibition of mitosis than normal cells. Mitotic inhibitors are also used in cytogenetics (the study of chromosomes), where they stop cell division at a stage where chromosomes can be easily examined.
Methods and compositions for modulating cell proliferation and cell death
InactiveUS6599912B1Enhance in vitroImprove in vivo activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAnticarcinogenTopoisomerase-II Inhibitor
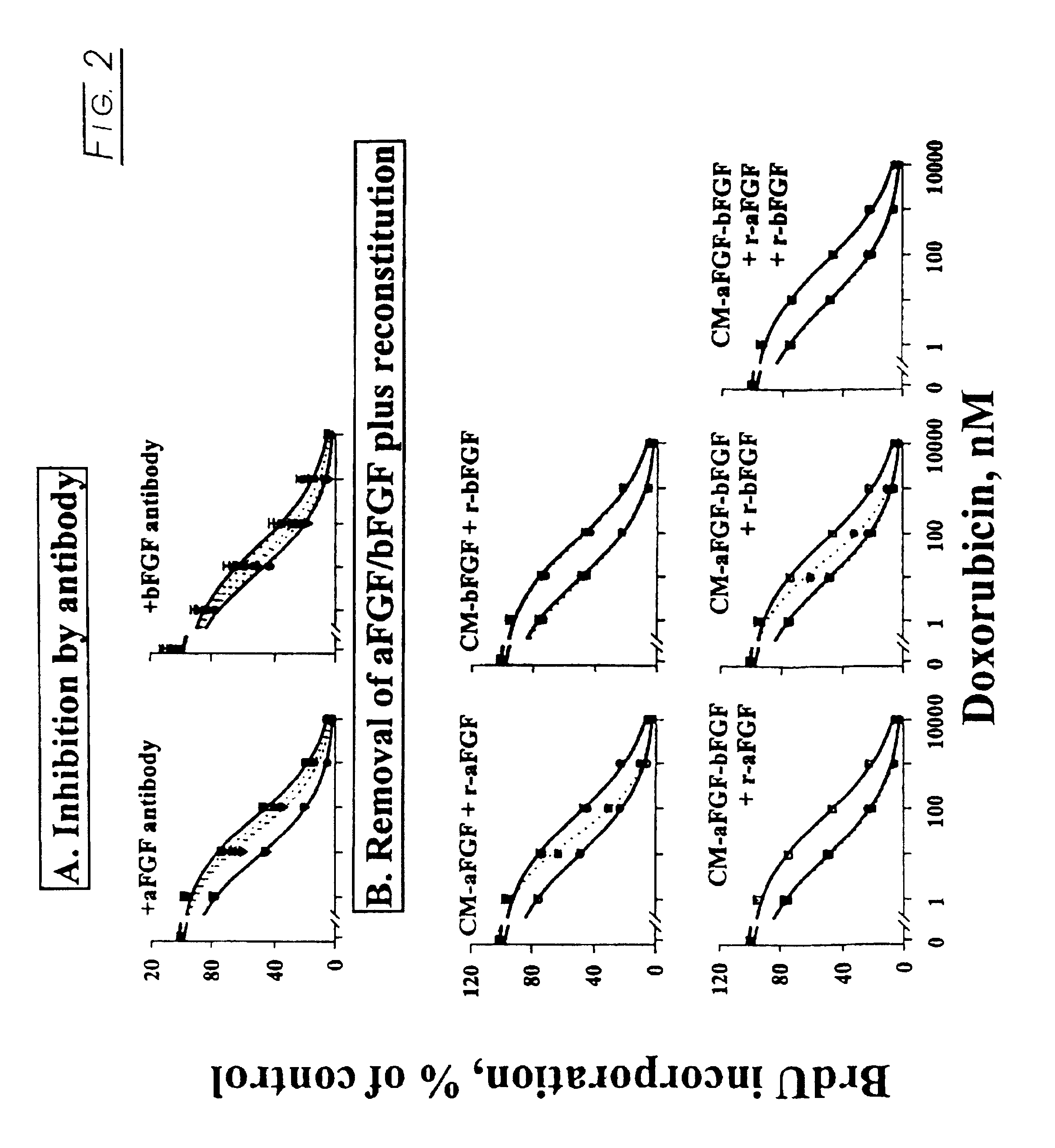
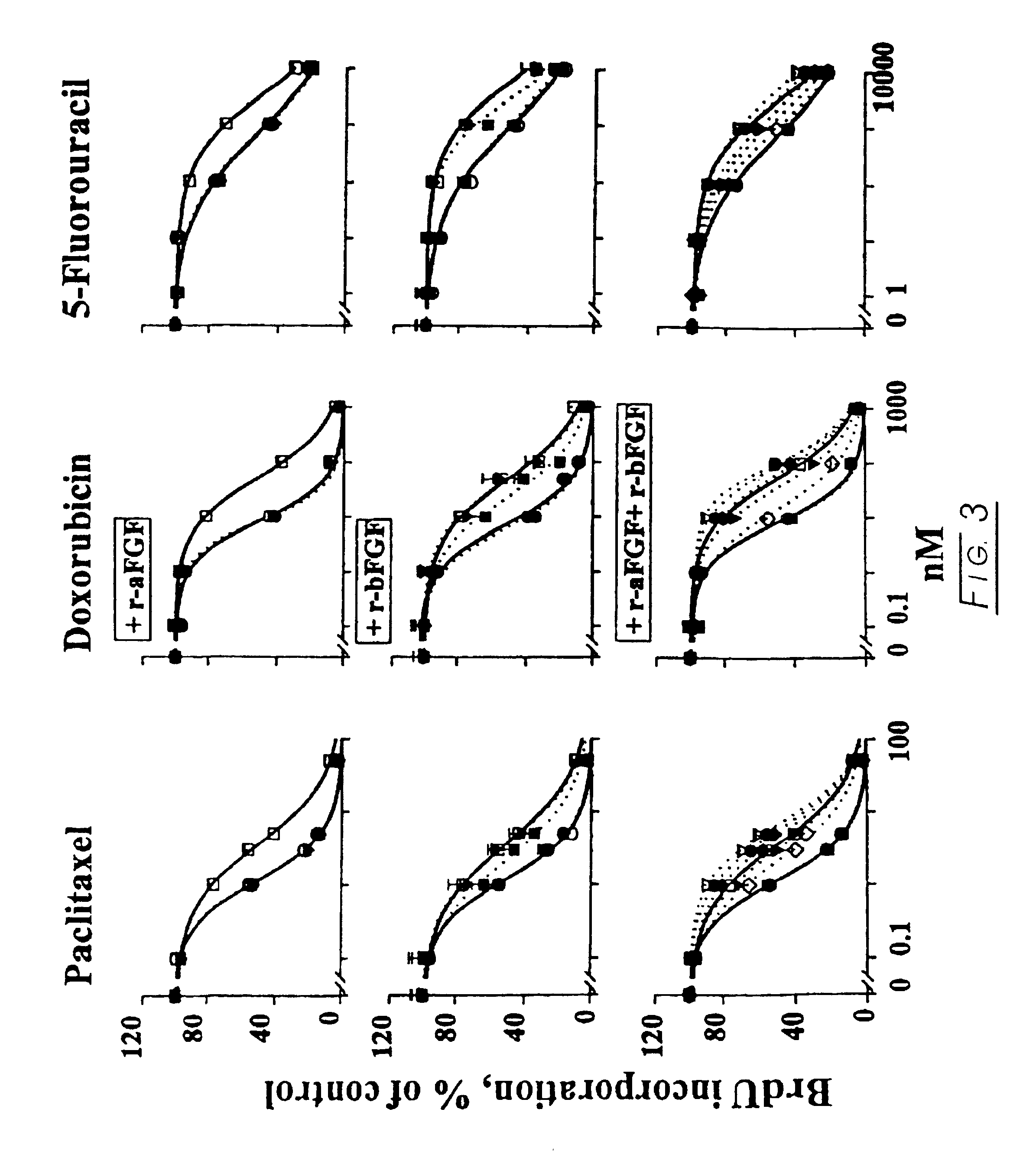
Methods and compositions for modulating the FGF effect on the sensitivity of malignant and normal cells to anticancer agents are provided. In particular, methods and compositions for inhibiting FGF-induced resistance to a broad spectrum of anticancer agents in solid and soft-tissue tumors, metastatic lesions, leukemia and lymphoma are provided. Preferably, the compositions include at least one FGF inhibitor in combination with a cytotoxic agents, e.g., antimicrotubule agents, topoisomerase I inhibitors, topoisomerase II inhibitors, antimetabolites, mitotic inhibitors, alkylating agents, intercalating agents, agents capable of interfering with a signal transduction pathway (e.g., g., a protein kinase C inhibitor, e.g., an anti-hormone, e.g., an antibody against growth factor receptors), an agent that promotes apoptosis and / or necrosis, and interferon, an interleukin, a tumor necrosis factor, and radiation. In other embodiments, methods and composition for protecting a cell in a subject, from one or more of killing, inhibition of growth or division or other damage caused, e.g., by a cytotoxic agent, are provided. Preferably, the method includes: administering, to the subject, an effective amount of at least one FGF agonist, thereby treating the cell, e.g., protecting or reducing the damage to the dividing cell from said cytotoxic agent.
Owner:AU JESSIE L S +1
Method for treating abnormal cell growth
InactiveUS20050272755A1Ease of detectabilityEasy to prepareBiocideAnimal repellantsAbnormal tissue growthMetabolite
The present Invention relates to a method of treating abnormal cell growth in a subject, comprising administering to said subject having abnormal cell growth: (a) a compound selected from the group consisting of a camptothecin, a camptothecin derivative, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate or prodrug of said compounds; (b) a pyrimidine derivative or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate or prodrug of said pyrimidine derivative; and (c) an anti-tumor agent selected from the group consisting of antiproliferative agents, kinase inhibitors, angiogenesis inhibitors, growth factor inhibitors, cox-I inhibitors, cox-II inhibitors, mitotic inhibitors, alkylating agents, anti-metabolites, intercalating antibiotics, growth factor inhibitors, radiation, cell cycle inhibitors, enzymes, topoisomerase inhibitors, biological response modifiers, antibodies, cytotoxics, anti-hormones, anti-androgens and combinations thereof.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Methods for the identification of polypeptide antigens associated with disorders involving aberrant cell proliferation and compositions useful for the treatment of such disorders
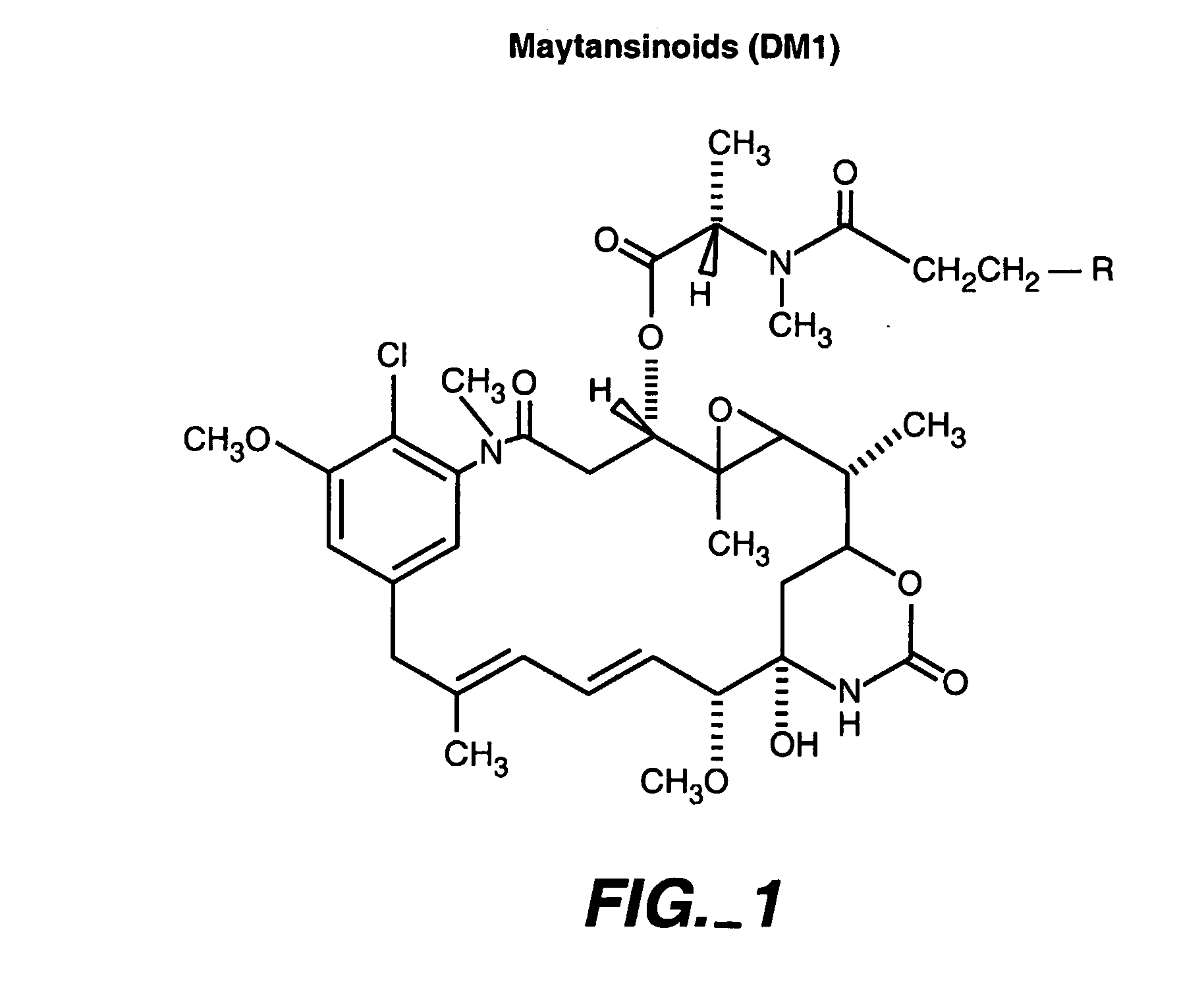
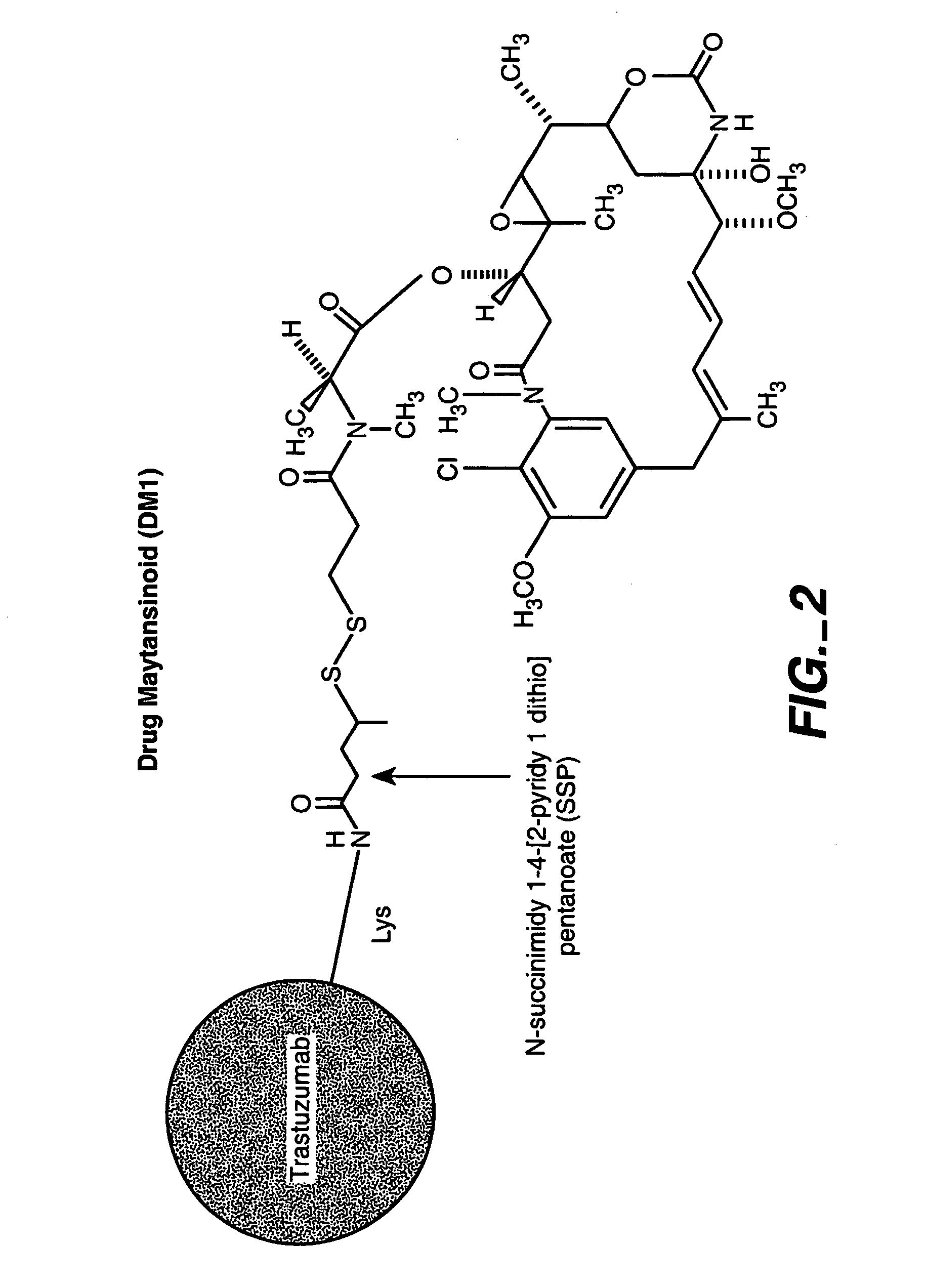
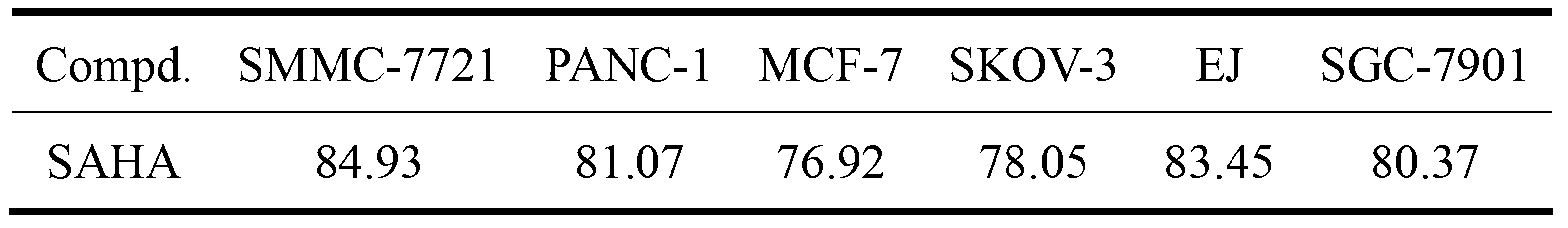
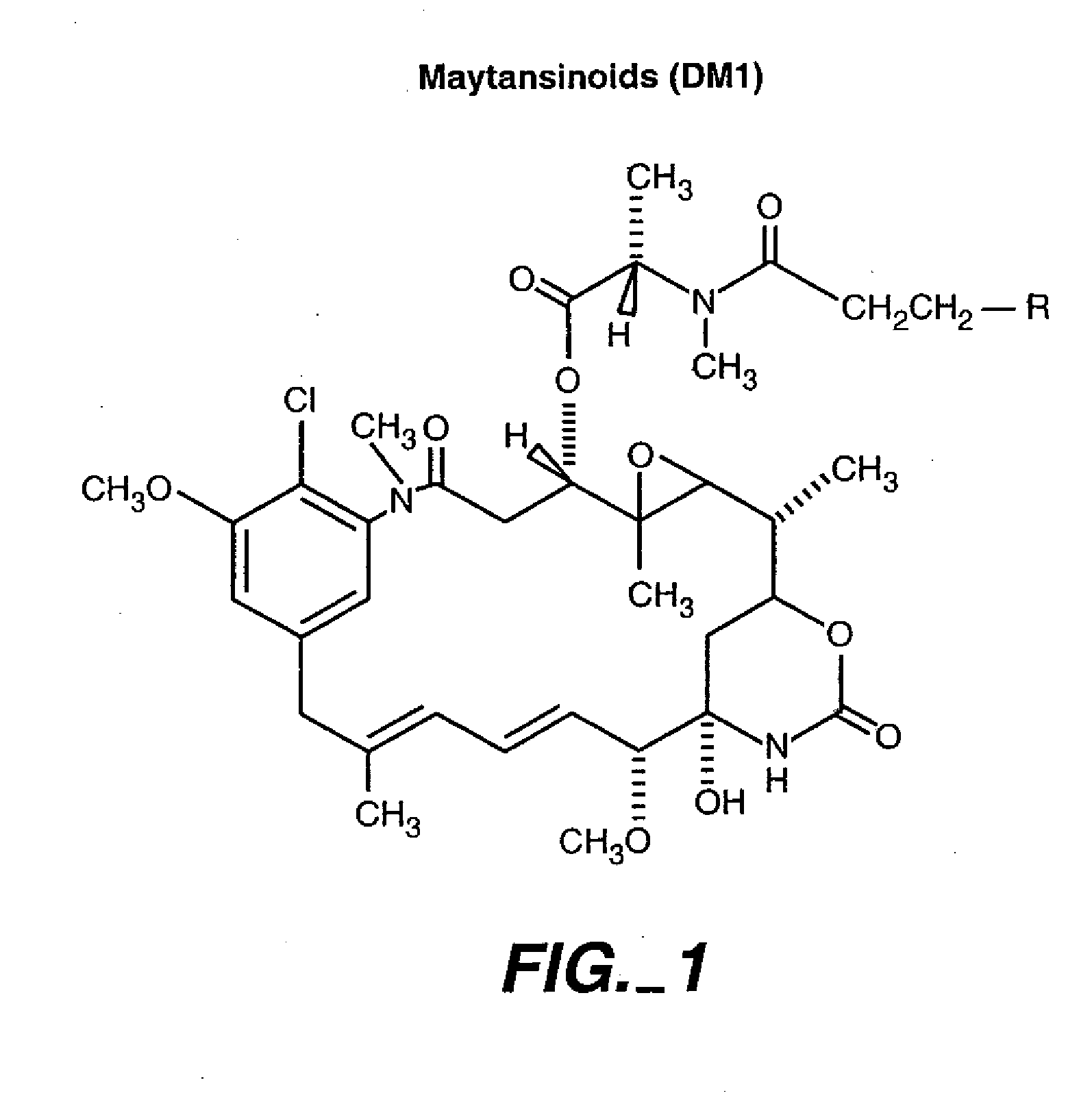
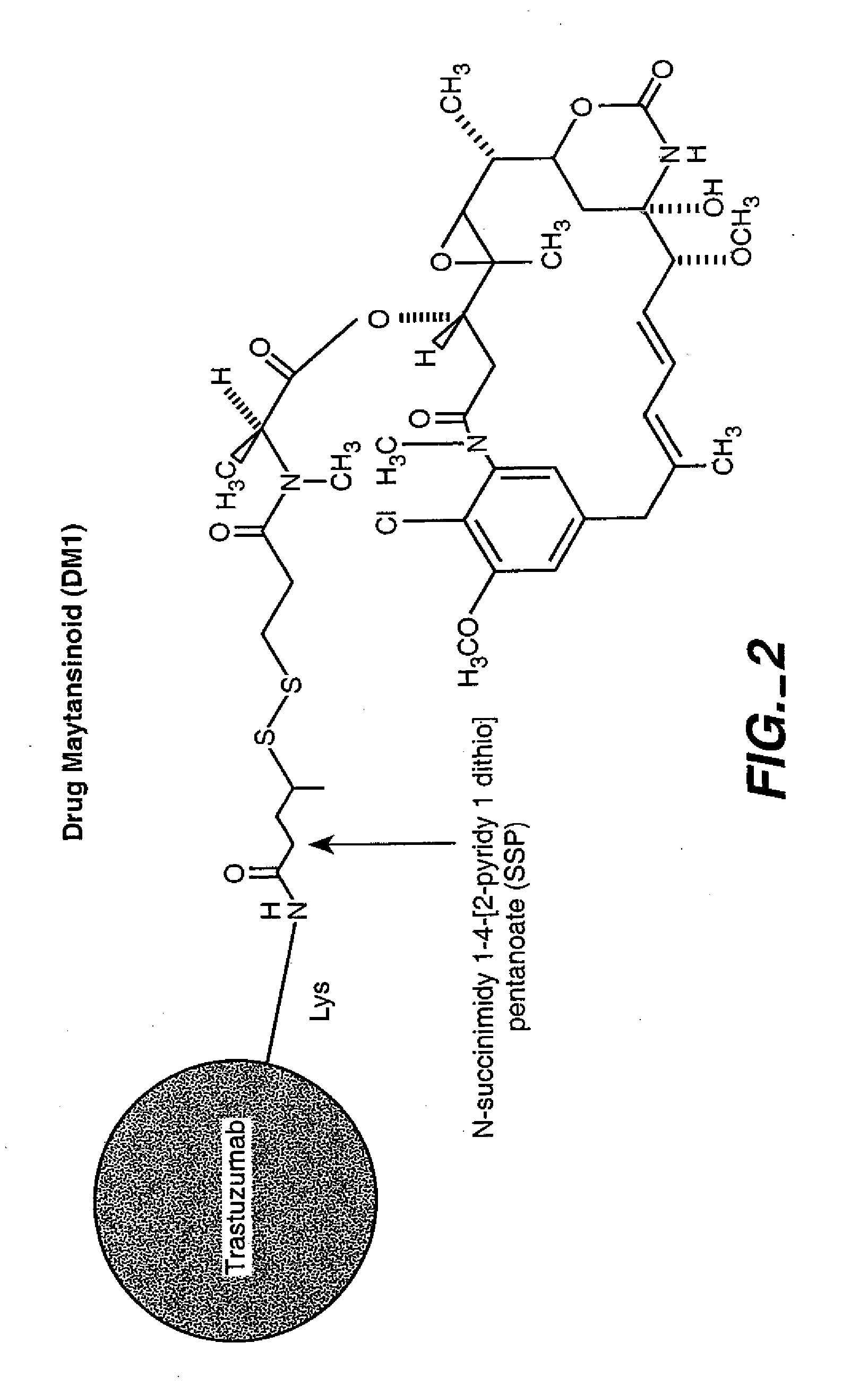
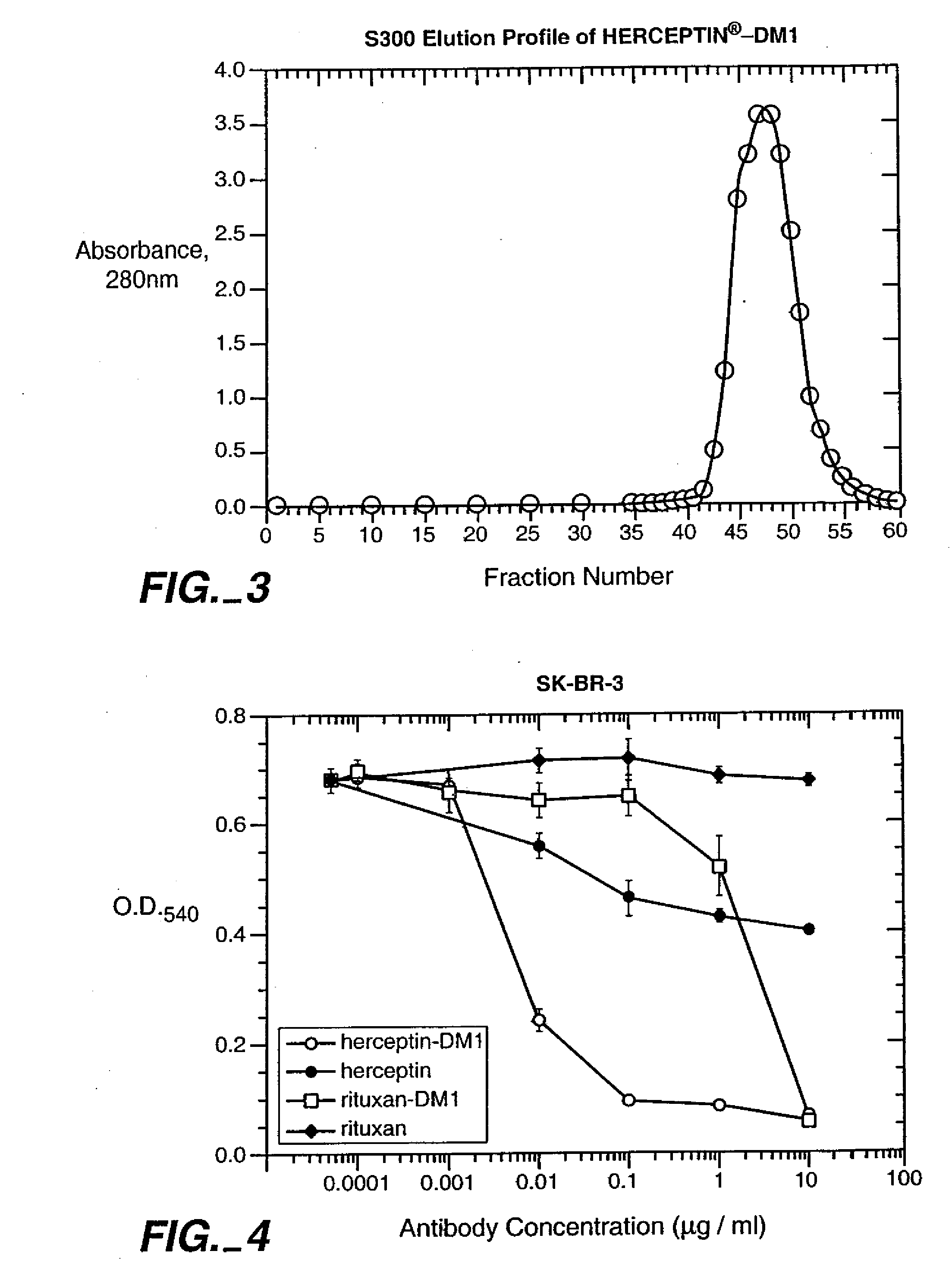
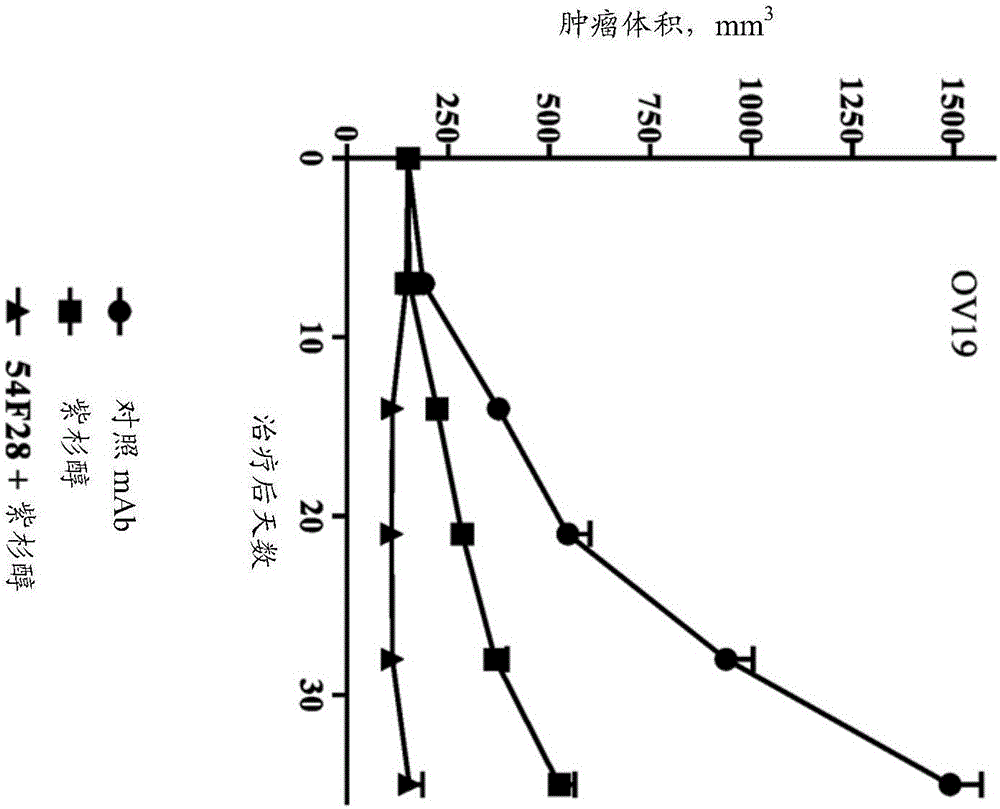
Methods and compositions for the development of effective cancer therapies using mitotic inhibitors which have limited general toxicity to normal, non-cancerous cells and tissues are provided. The methods and compositions utilize cytotoxic compounds comprised of a cell-binding agent (e.g., antibodies) conjugated to an anti-mitotic compound (e.g., maytansinoids). The invention further provides antibodies which are substantially incapable of inducing antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), thereby ensuring that the therapeutic effect is mediated primarily by the anti-mitotic component of the cytotoxic compound, rather than by indirect cell killing via ADCC and / or CDC. The antibodies of the invention further are capable of differentiating between polypeptide antigens which are more highly expressed on proliferating cancer cells as compared to proliferating non-cancer cells.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Anticarcinogenic internal implant agent
InactiveCN1679950APharmaceutical delivery mechanismAmide active ingredientsTreatment effectWhole body
An anticancer in vivo implant applied locally is prepared from the anticancer nitrosourea-type medicine, the anticancer synergist chosen from nitrogen mustard compound, mitotic inhibitor and antimetabolic anticancer medicine, and the biocompatible and biodegradable high-molecular polymer as medicinal additive.
Owner:DASEN BIOLOGICAL PHARMA CO LTD
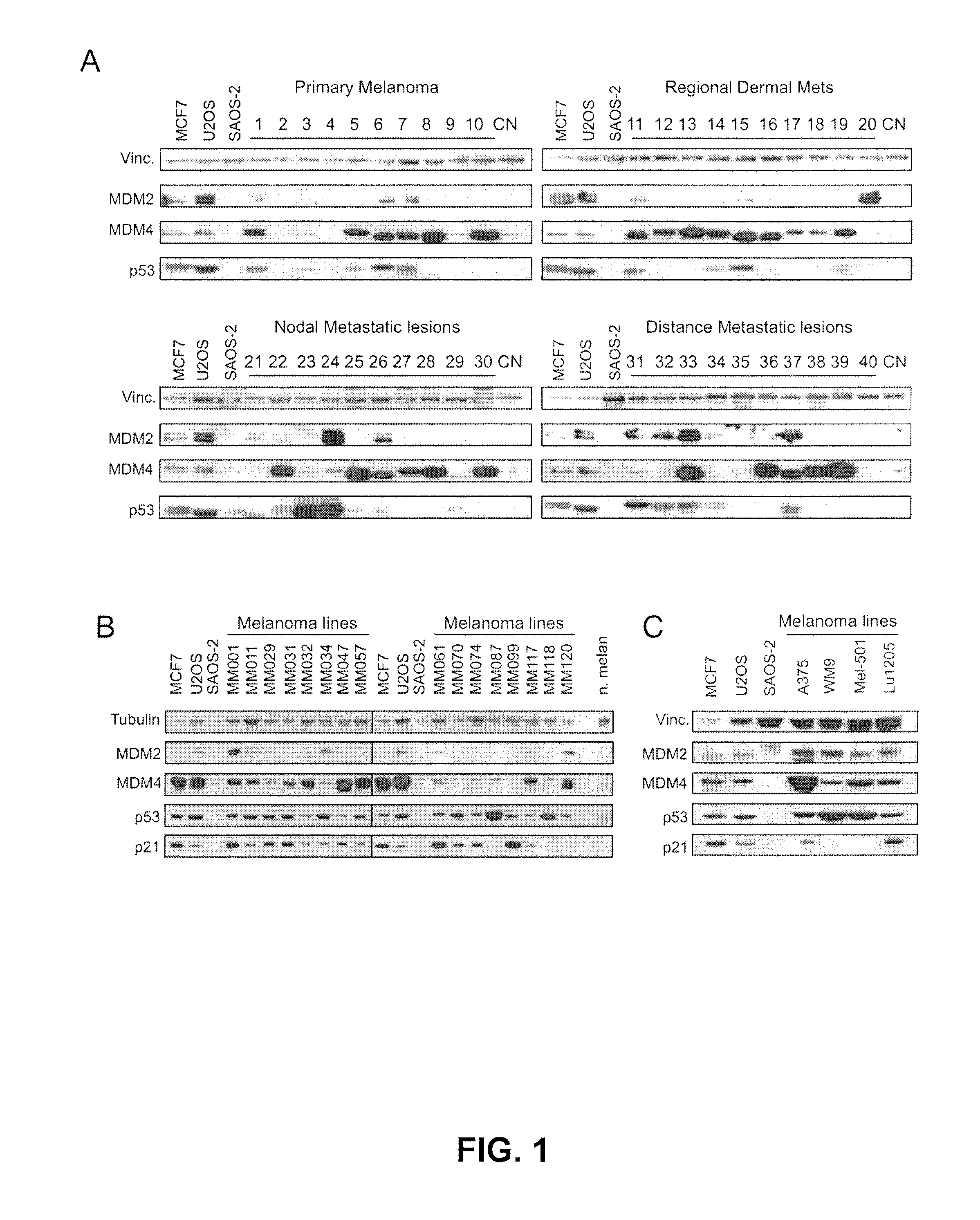
Combinations of therapeutic agents for treating melanoma
ActiveUS20130330421A1Less side effectsRemarkable effectHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsCarboplatinDocetaxel
The present disclosure relates to the field of oncology, more particularly to the field of melanoma. Provided are methods of treating melanoma, particularly advanced cutaneous melanoma, with a combination of pharmaceutical agents comprising MDM4-specific antagonists (such as an inhibitor of the MDM4-p53 interaction or a molecule that decreases MDM4 protein stability) or MDM4-MDM2 dual inhibitors (i.e., molecules that disrupt the interactions between p53 and MDM2 and p53 and MDM4) and one or more chemotherapeutic agents such as for example alkylating agents (i.e., Dacarbazine (DITC) or melphalan), alkylating-like agents (i.e., cisplatin or carboplatin) or mitotic inhibitors (taxanes docetaxel or paclitaxel) and PI3K-AKT, B-RAF and MEK inhibitors. Further provided are pharmaceutical formulations of MDM4-specific antagonists (be it an inhibitor of the MDM4-p53 interaction or a molecule that decreases MDM4 protein stability) or MDM4-MDM2 dual inhibitors (i.e., molecules that disrupt the interactions between p53 and MDM2 and p53 and MDM4) and a pharmaceutical formulation of one or more chemotherapeutic agents such as for example alkylating agents (i.e., Dacarbazine (DITC) or melphalan), alkylating-like agents (i.e., cisplatin or carboplatin) or mitotic inhibitors (taxanes docetaxel or paclitaxel) and B-RAF and MEK inhibitors.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Methods and Devices for Preventing or Delaying Posterior Capsule Opacification
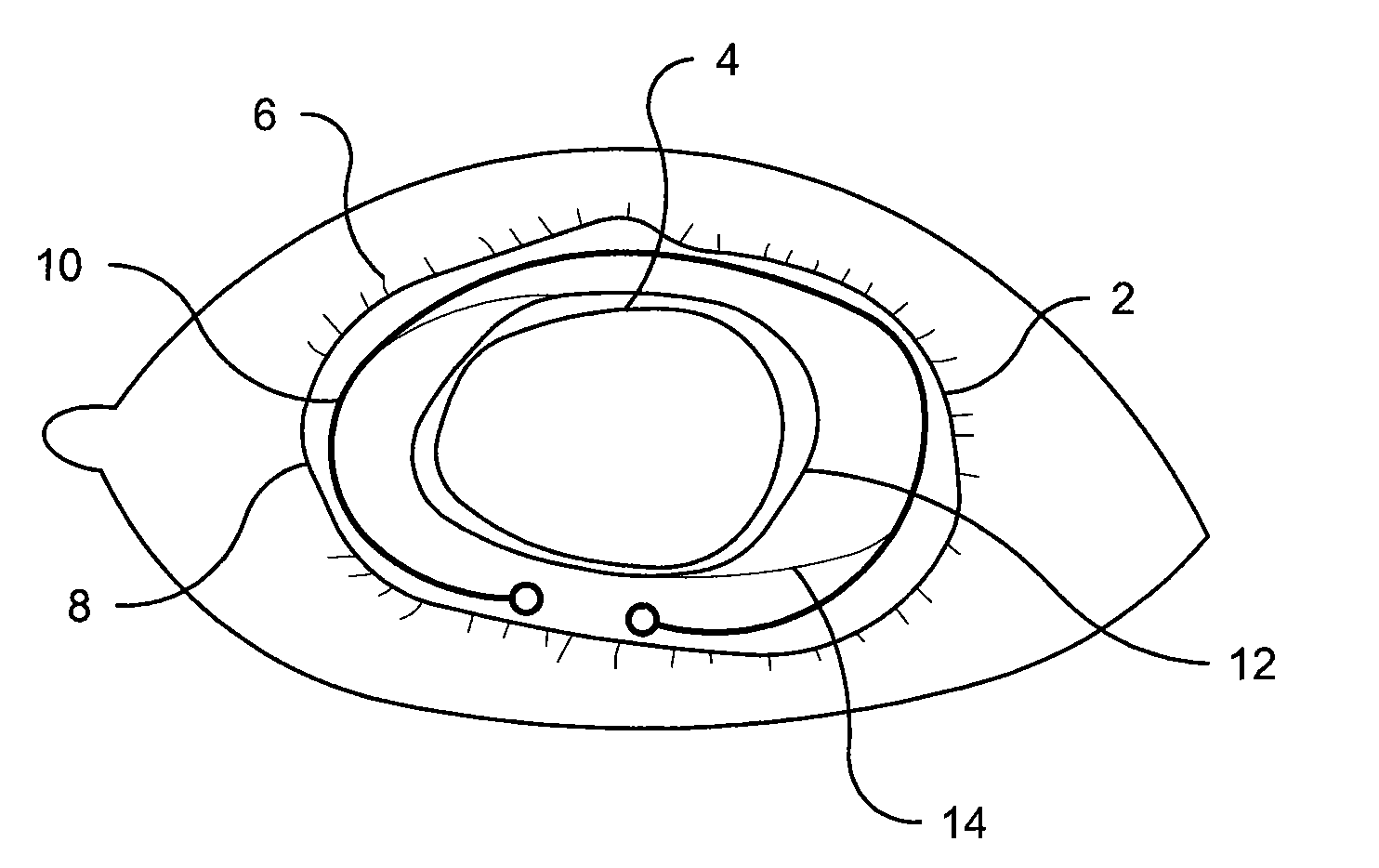
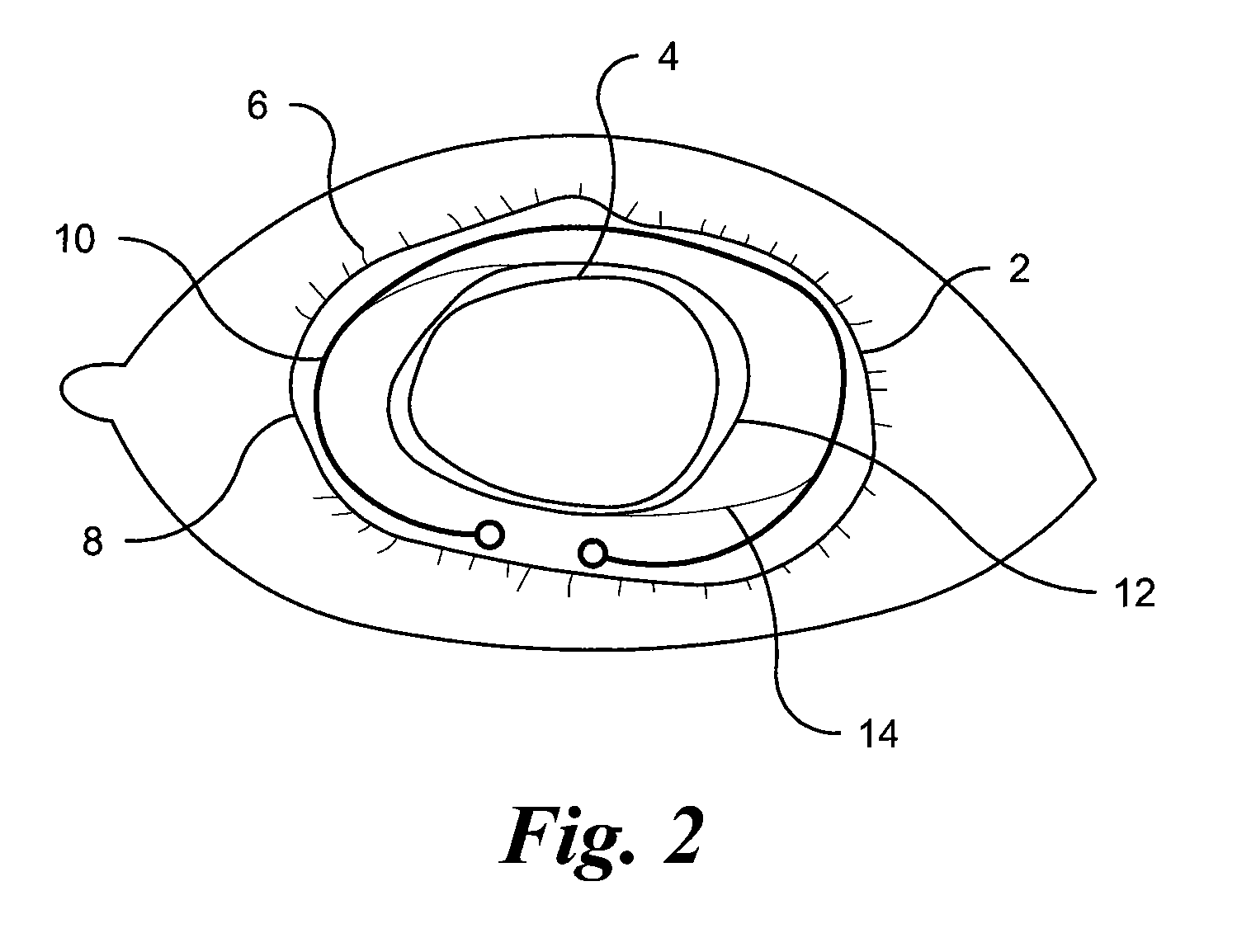
InactiveUS20110082543A1Prevents and minimizes and delays formationMinimize formationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismEye treatmentChemical MoietyBovine serum albumin
Several methods for preventing, minimizing, or delaying the incidence of posterior capsule opacification are provided. A first method involves chemically activating the surface of an implantable ocular device, such as an intraocular lens or a capsular tension ring, by grafting a chemical moiety onto the surface of the device, covalently attaching a non-cytotoxic inhibitor compound to the chemical moiety to produce an inhibitor implantable ocular device, and implanting this inhibitor implantable ocular device into the capsular bag of an eye of a patient during extracapsular cataract surgery. Appropriate inhibitor compounds include RGD mimetics, RGD peptides, and flavonoids. A second method involves surface modifying the exterior surface of a capsular tension ring by covalently attaching a mitotic inhibitor, preferably a conjugate of methotrexate and a bovine serum albumin, and implanting this inhibitor tension ring into the capsular bag of an eye of a patient during extracapsular cataract surgery. A third method involves surface modifying the exterior surface of a capsular tension ring by coating or grafting the exterior surface with a charged polyethylamine and implanting this inhibitor tension ring into the capsular bag of an eye of a patient during extracapsular cataract surgery. An implantable ocular device according to the invention, such as an intraocular lens or a capsular tension ring, contains a substrate with a chemical moiety grafted thereon and a non-cytotoxic inhibitor compound covalently bonded to the chemical moiety or contains a substrate modified with a mitotic inhibitor or charged polyethylamine. The inhibitor devices inhibits proliferation and migration of lens epithelial cells on the posterior capsule of the eye of the patient, thereby preventing, minimizing, or delaying the onset of posterior capsule opacification.
Owner:CLEO COSMETIC & PHARMA
Combinations of therapeutic agents for treating melanoma
ActiveUS9408885B2Less side effectsRemarkable effectHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsCarboplatinDocetaxel
The present disclosure relates to the field of oncology, more particularly to the field of melanoma. Provided are methods of treating melanoma, particularly advanced cutaneous melanoma, with a combination of pharmaceutical agents comprising MDM4-specific antagonists (such as an inhibitor of the MDM4-p53 interaction or a molecule that decreases MDM4 protein stability) or MDM4-MDM2 dual inhibitors (i.e., molecules that disrupt the interactions between p53 and MDM2 and p53 and MDM4) and one or more chemotherapeutic agents such as for example alkylating agents (i.e., Dacarbazine (DITC) or melphalan), alkylating-like agents (i.e., cisplatin or carboplatin) or mitotic inhibitors (taxanes docetaxel or paclitaxel) and PI3K-AKT, B-RAF and MEK inhibitors. Further provided are pharmaceutical formulations of MDM4-specific antagonists (be it an inhibitor of the MDM4-p53 interaction or a molecule that decreases MDM4 protein stability) or MDM4-MDM2 dual inhibitors (i.e., molecules that disrupt the interactions between p53 and MDM2 and p53 and MDM4) and a pharmaceutical formulation of one or more chemotherapeutic agents such as for example alkylating agents (i.e., Dacarbazine (DITC) or melphalan), alkylating-like agents (i.e., cisplatin or carboplatin) or mitotic inhibitors (taxanes docetaxel or paclitaxel) and B-RAF and MEK inhibitors.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
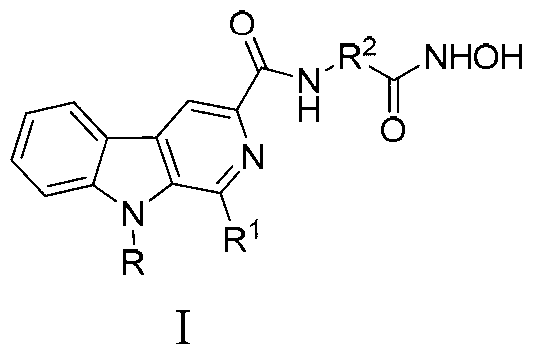
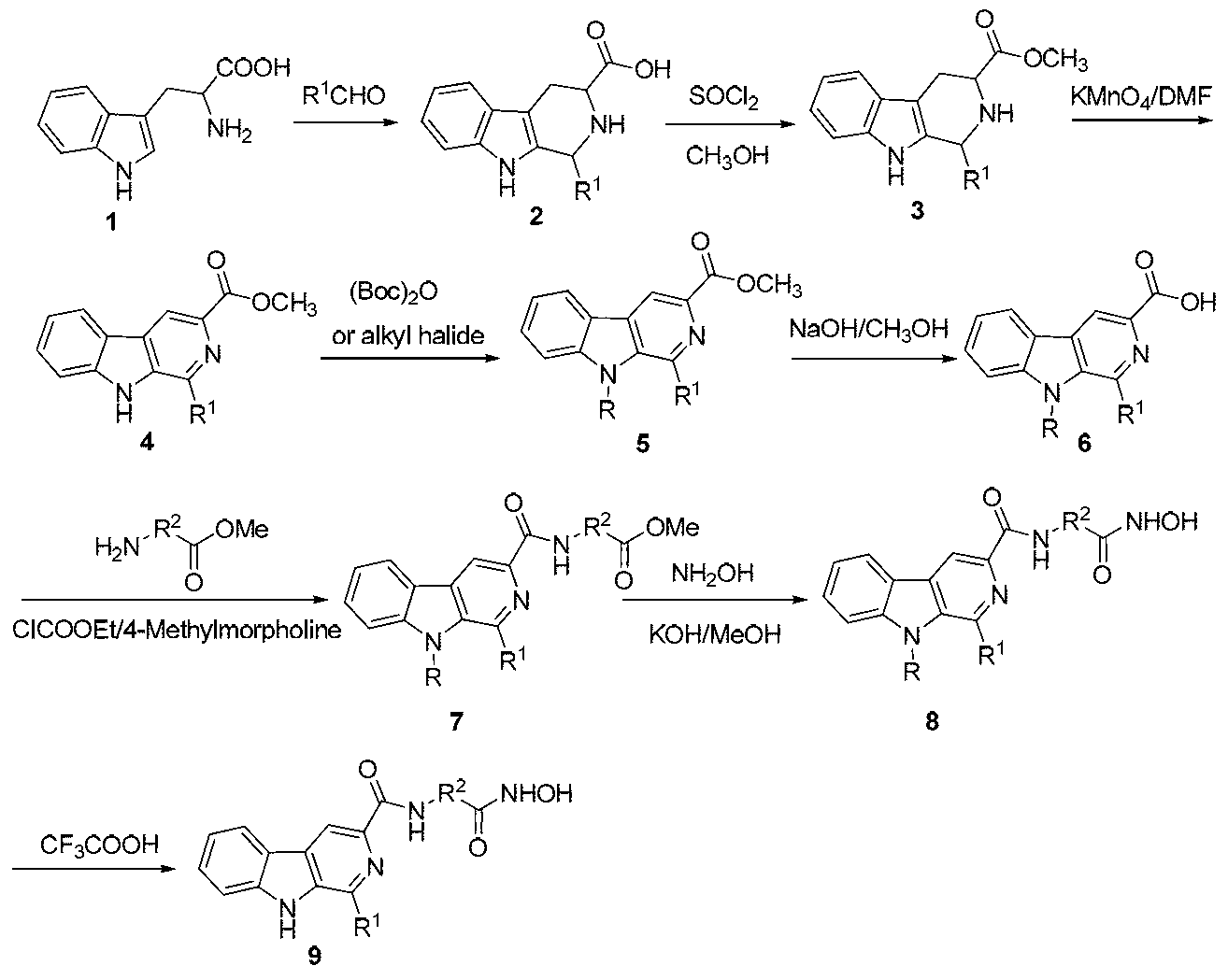
Beta-carboline derivative containing hydroximic acid as well as preparation method and medical application thereof
ActiveCN103304564APromote apoptosisApoptotic promotionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseTreatment effect
The invention discloses a beta-carboline derivative containing hydroximic acid as well as a preparation method and a medical application thereof. The product has the structure as shown in the general formula I. The compound can be combined with other antitumor drugs such as alkylating agents, antimetabolites, topoisomerase inhibitors, mitotic inhibitors and DNA intercalating agents and additionally can be combined with radiotherapy. The invention also discloses a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound with the general formula I as well as medical application thereof, particularly application of preparation of antitumor medicines, Alzheimer disease medicines and Parkinson disease medicines. The other antitumor medicines or radiotherapy can be administrated with the compound at the same time or in different times. The combination therapy can generate the synergistic effect, so that the treatment effect is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU FANGSHIYUANLVE SCI & TECH CONSULTING CO LTD +1
Methods for the identification of polypeptide antigens associated with disorders involving aberrant cell proliferation and compositions useful for the treatment of such disorders
Methods and compositions for the development of effective cancer therapies using mitotic inhibitors which have limited general toxicity to normal, non-cancerous cells and tissues are provided. The methods and compositions utilize cytotoxic compounds comprised of a cell-binding agent (e.g., antibodies) conjugated to an anti-mitotic compound (e.g., maytansinoids). The invention further provides antibodies which are substantially incapable of inducing antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), thereby ensuring that the therapeutic effect is mediated primarily by the anti-mitotic component of the cytotoxic compound, rather than by indirect cell killing via ADCC and / or CDC. The antibodies of the invention further are capable of differentiating between polypeptide antigens which are more highly expressed on proliferating cancer cells as compared to proliferating non-cancer cells.
Owner:LEVINSON ARTHUR D
Combination Therapy with an Antitumor Alkaloid
InactiveUS20130266666A1Improve anti-tumor activitySuccessful useHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideAntineoplastic alkaloidDepressant
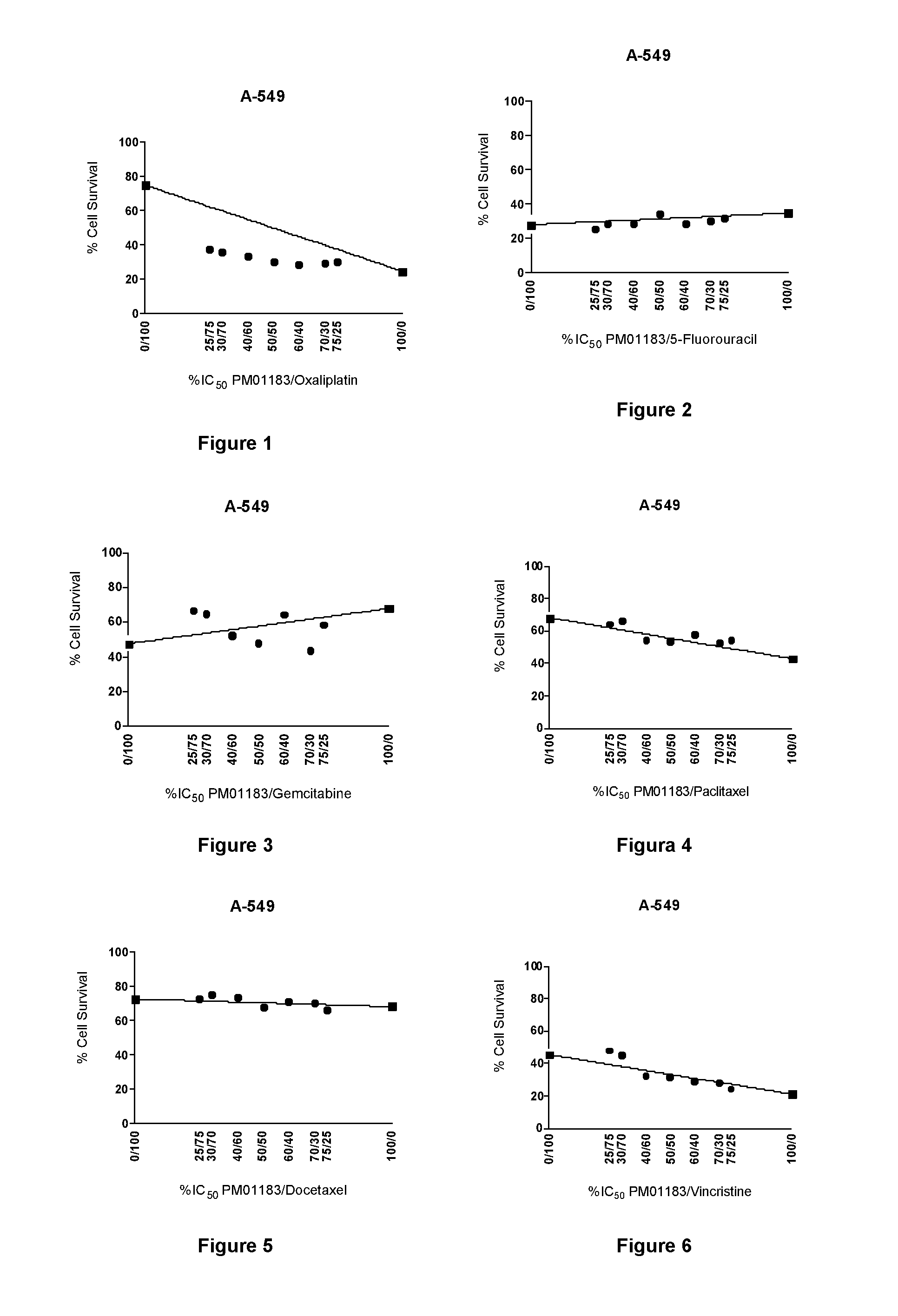
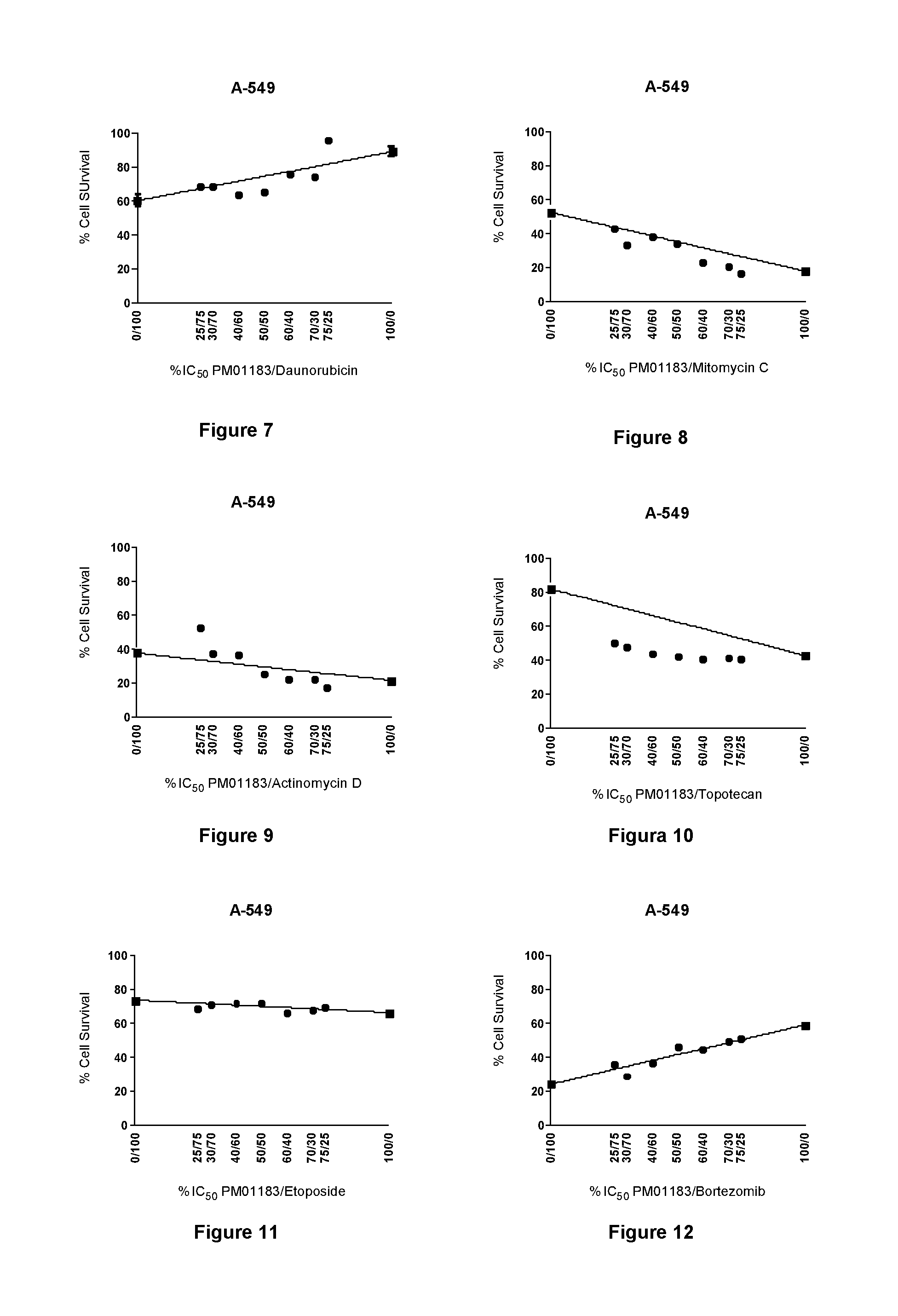
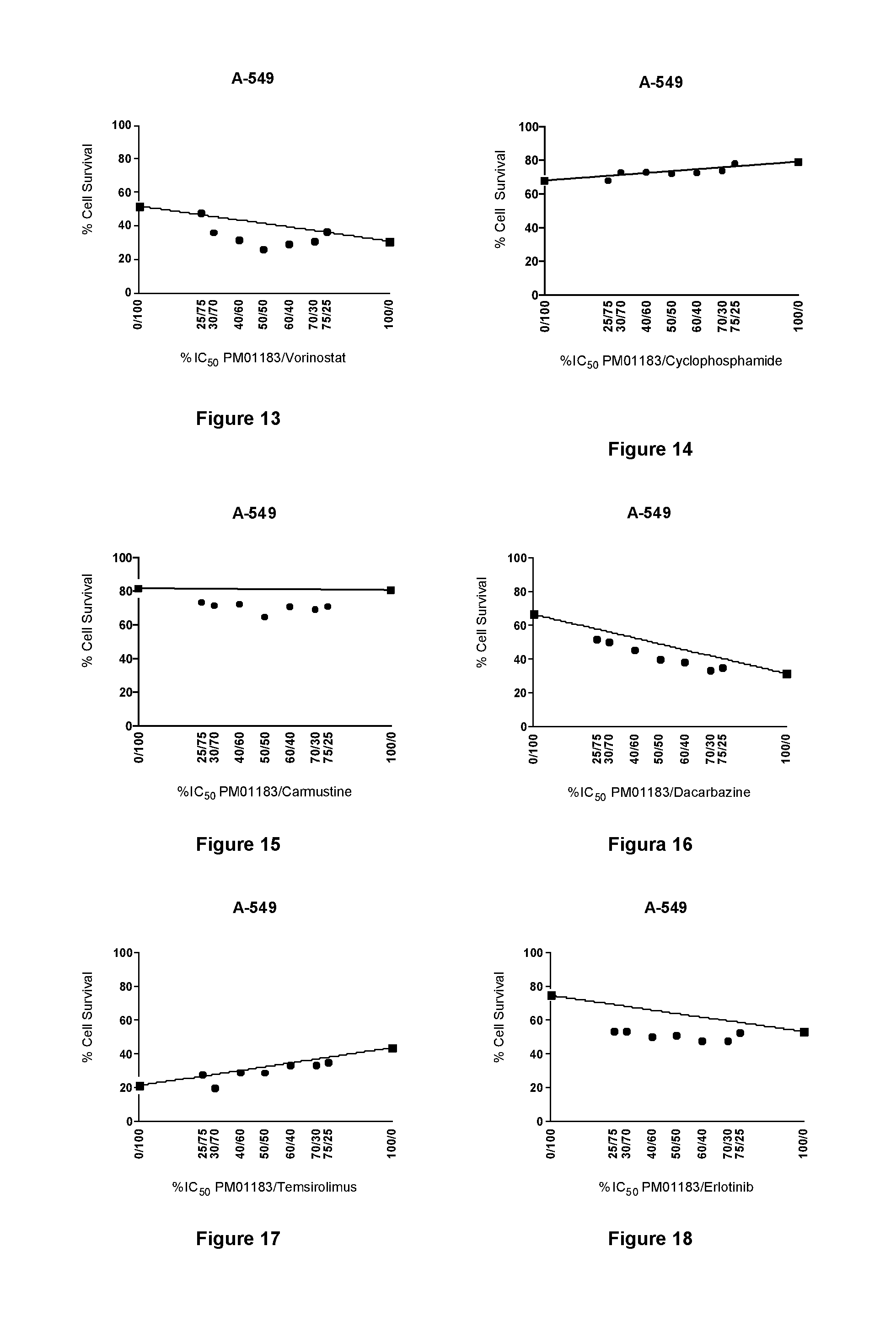
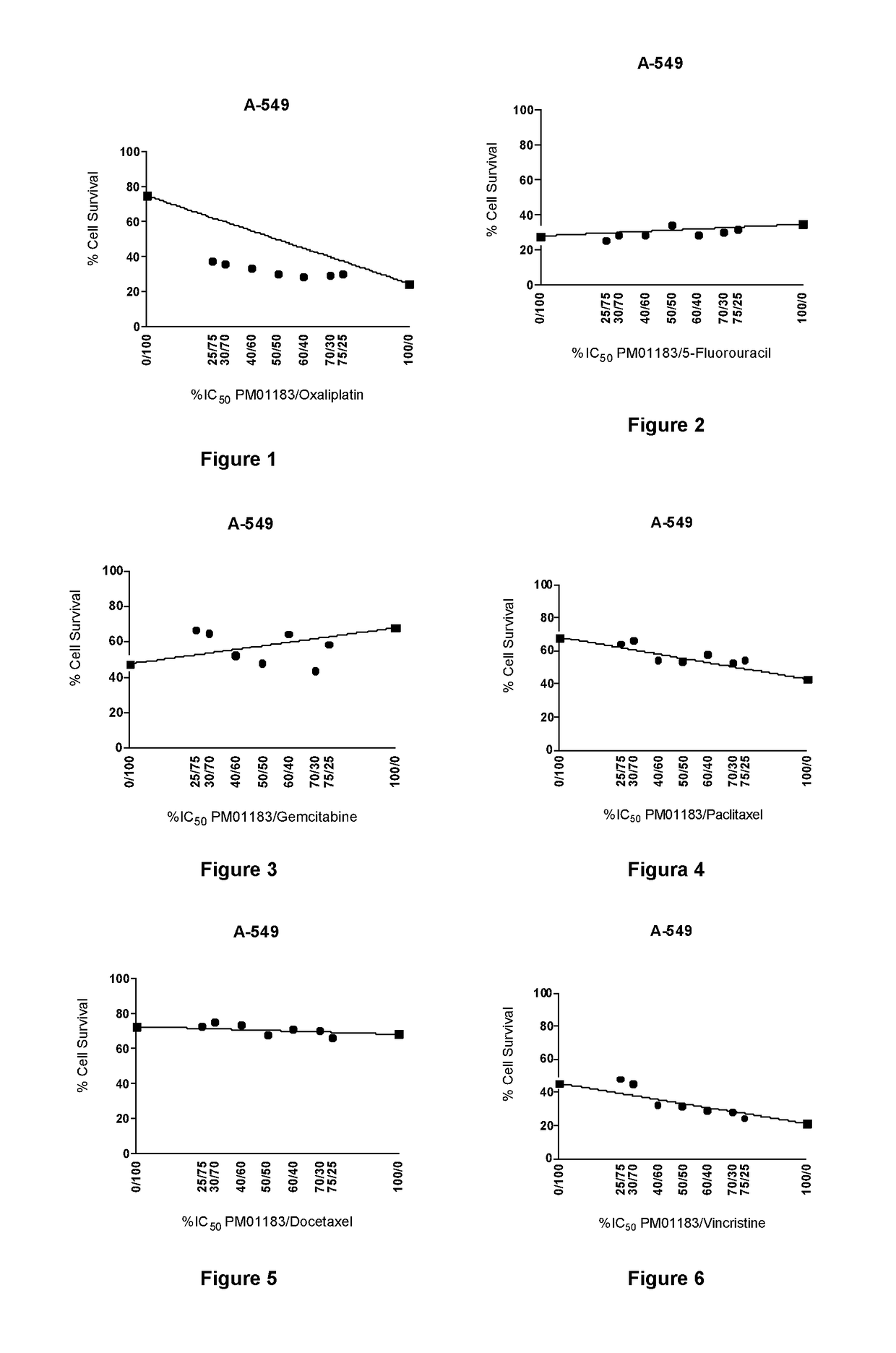
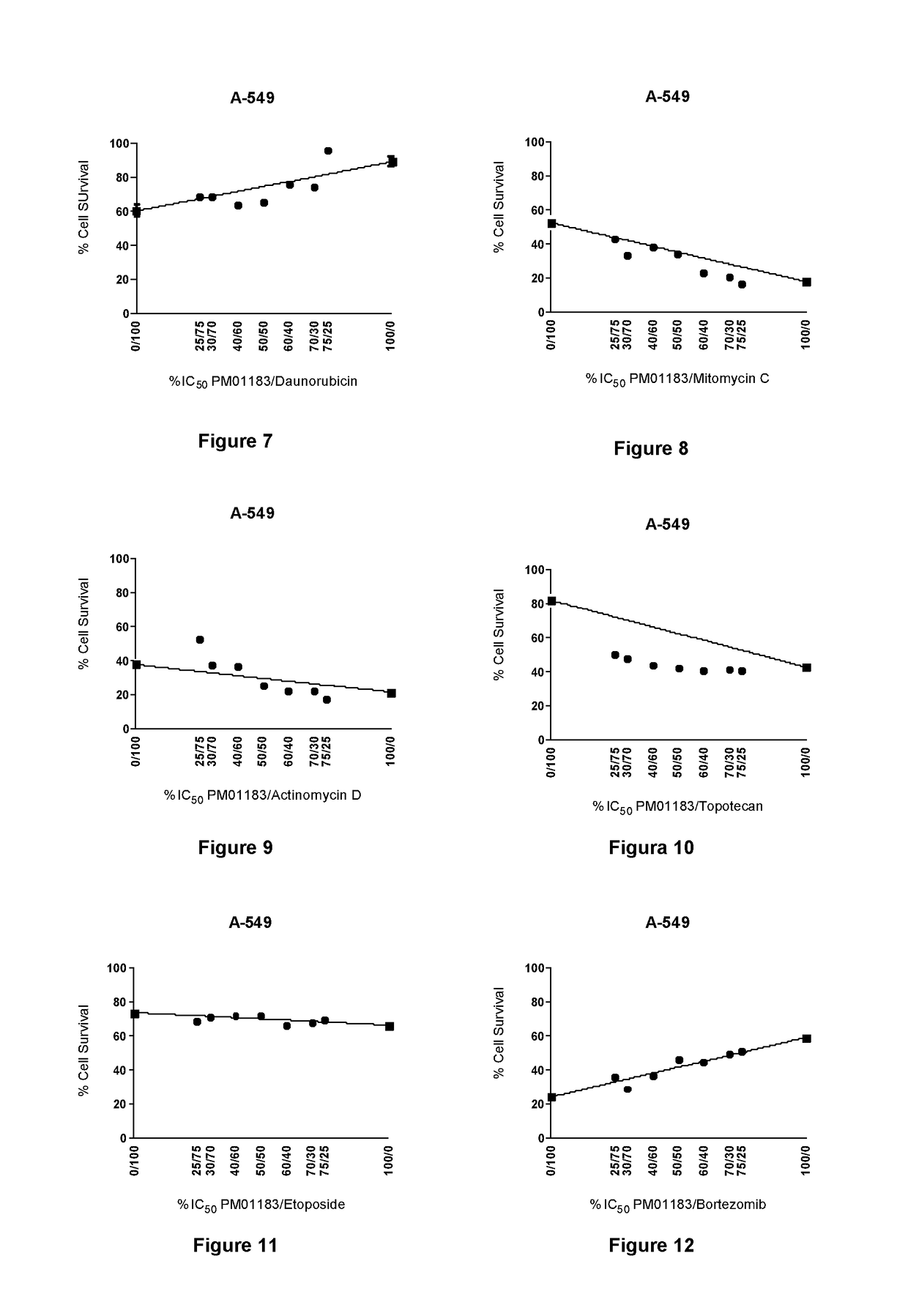
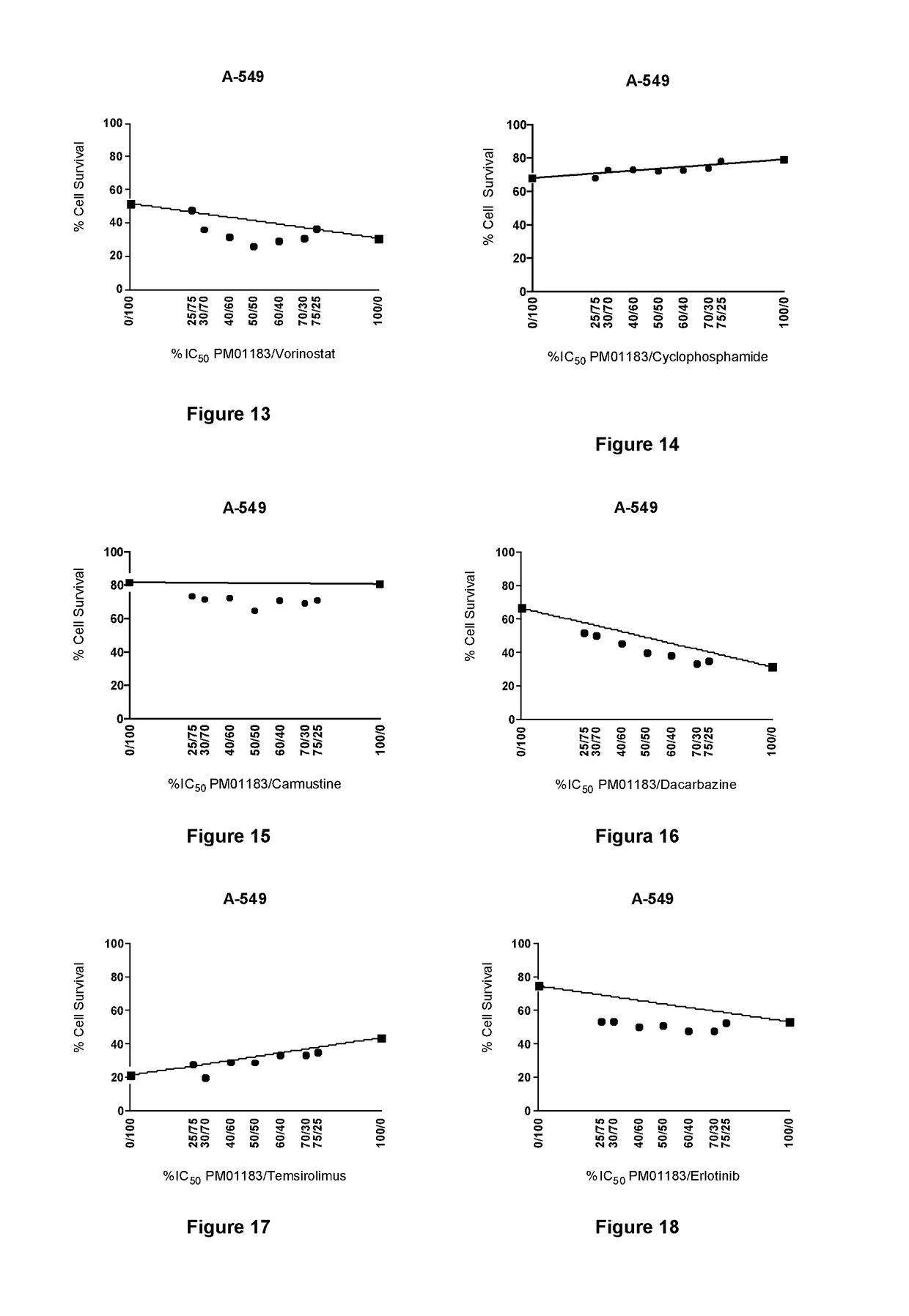
The present invention relates to the combination of PM01183 with several anticancer drugs, in particular other anticancer drugs selected from antitumor platinum coordination complexes, antimetabolites, mitotic inhibitors, anticancer antibiotics, topoisomerase I and / or II inhibitors, proteasome inhibitors, histone deacetylase inhibitors, nitrogen mustard alkylating agents, nitrosourea alkylating agents, nonclassical alkylating agents, estrogen antagonists, androgen antagonists, mTOR inhibitors, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and other agents selected from aplidine, ET-743, PM02734 and PM00104, and the use of these combinations in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:PHARMA MAR U
Application of quinazoline compounds
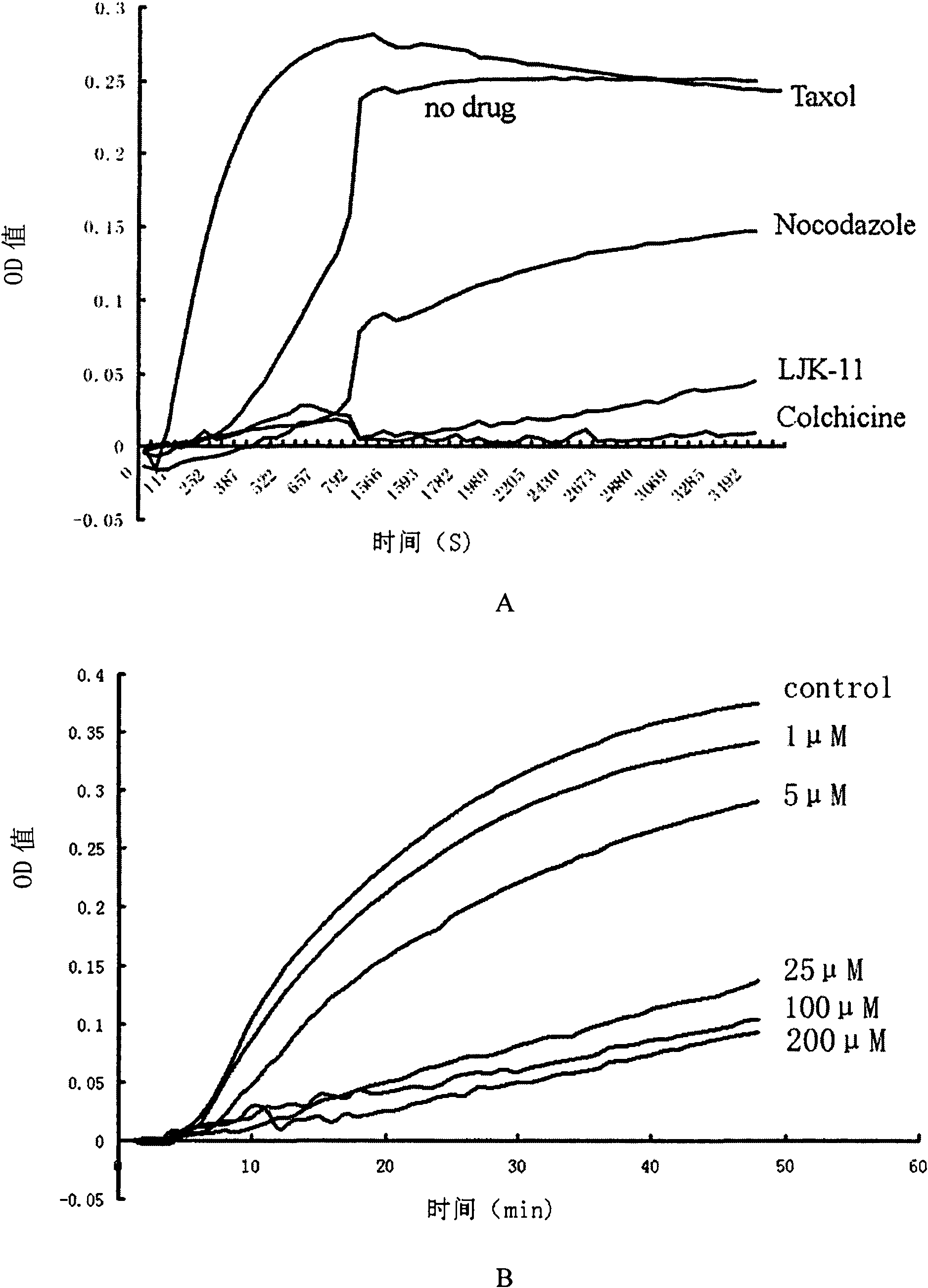
InactiveCN101926802AInhibits mitosisInhibit abnormal proliferationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMitotic ProcessQuinazoline
The invention relates to the technical field of drugs, in particular to application of quinazoline compounds. The invention discloses application of the quinazoline compounds shown in the general formula I or pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrugs or isomers thereof in preparing mitotic inhibitors. The quinazoline compounds shown in the general formula I or pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrugs or isomers have the effect of inhibiting tubulin polymerization and can effectively inhibit mitosis.
Owner:XIANGBEI WELMAN PHARMA CO LTD +1
Anti-tumor pharmaceutical composition
ActiveCN101480394AStrong synergyReduce dosageOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAbnormal tissue growthHydrogen
The invention discloses a composition which contains aporphine alkaloid shown in a formula I, mitotic inhibitors of cells and receivable carriers on pharmaco; in the formula I, R1 represents hydrogen, a hydroxyl group, a methyl group, an aldehyde group or an acetyl group, R2 represents hydrogen (having two different spatial configurations of R or S), R3 represents hydrogen, a hydroxyl group or a methyl group, R11 represents hydrogen, a hydroxyl group or a methyl group, R12 represents hydrogen or an aldehyde group, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9 and R10 are respectively selected from hydrogen, a hydroxyl group or a methoxyl group, or R8 and R9 form an alcoxyl ring. The invention also discloses an application of the composition for treating tumors.
Owner:XIANGBEI WELMAN PHARMA CO LTD
Combination chemotherapy
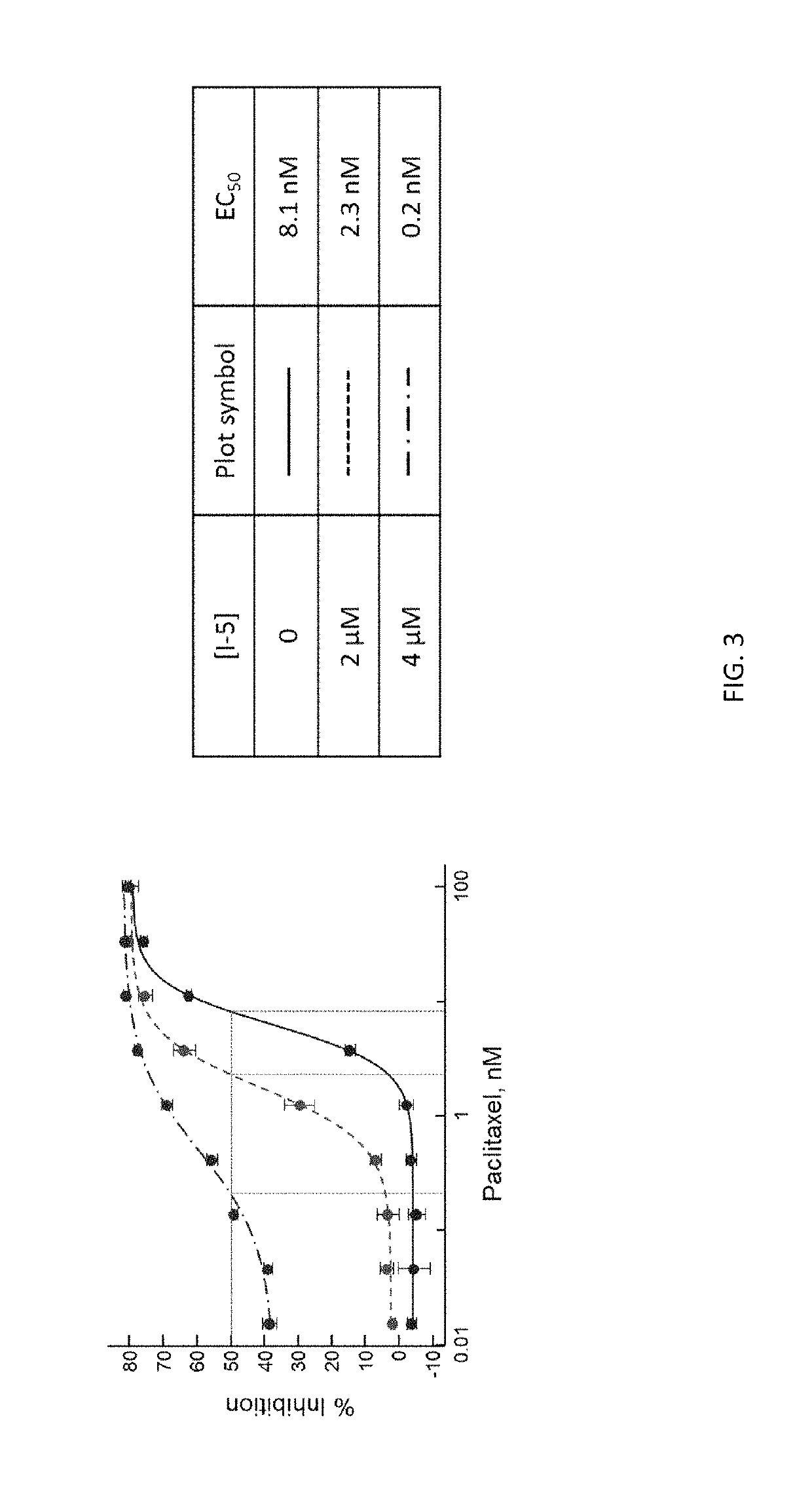
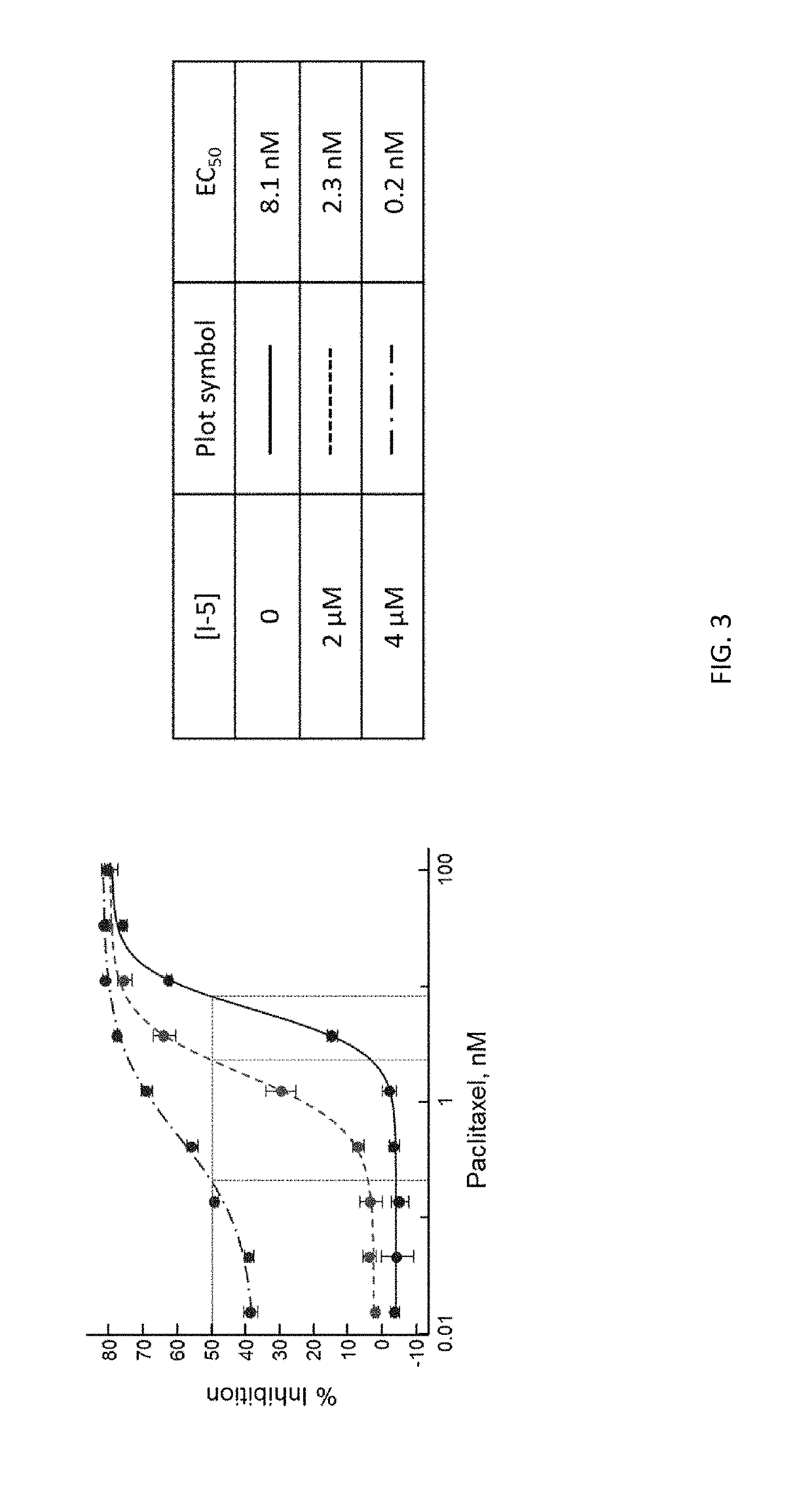
Mitotic inhibitors such as paclitaxel have improved antitumor activity when used in combination with a selective MEK inhibitor, especially a phenyl amine compound of Formula (I) and (II).
Owner:WARNER-LAMBERT CO
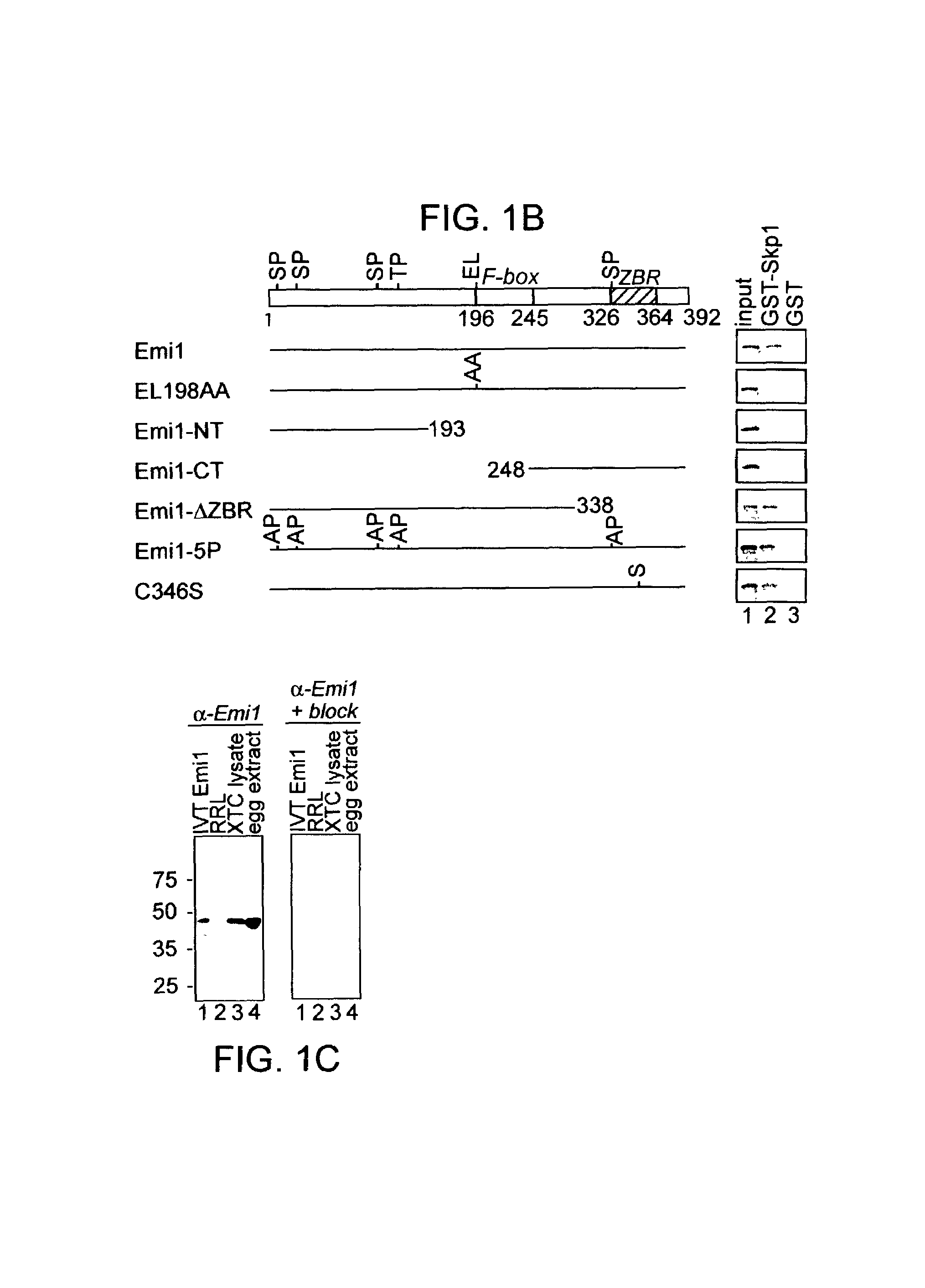
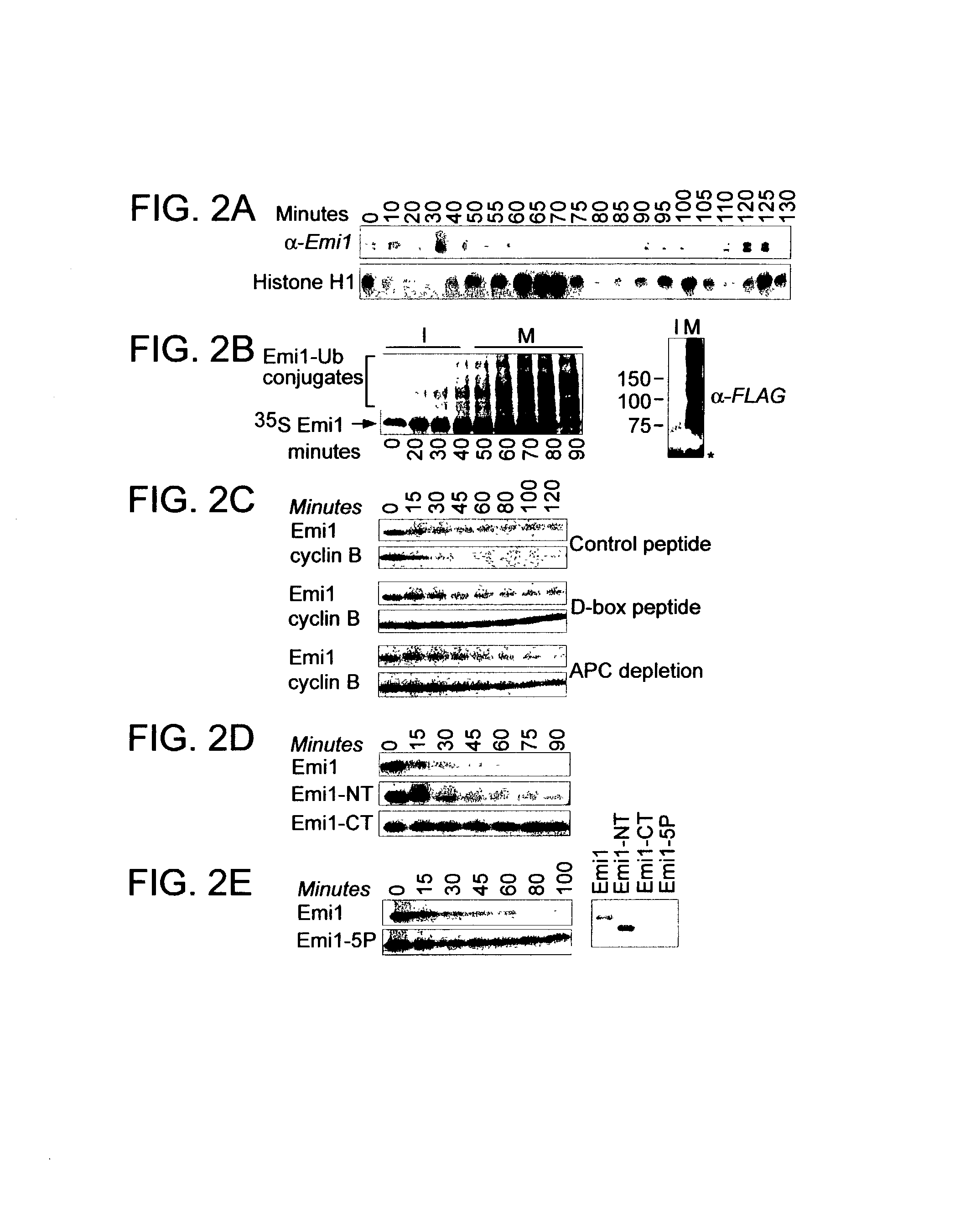
Modulation of cell division by an early mitotic inhibitor protein
Emi1 regulates progression through early mitosis by preventing premature APC activation. Depleting Emi1 from cycling cells strongly delays cyclin B accumulation and mitotic entry, while expression of a stabilized form of Emi1 stabilizes APC substrates and causes a mitotic block. Emi1 binds the APC activators Cdc2O and Cdh1 and inhibits APC activation by Cdc20 or Cdh1. Hence, products that modulate the expression and / or activity of Emi1 have a therapeutic effect in the treatment of cancer, leukemia, solid tumors, chronic or acute inflammatory disease, restenosis, diabetes, neurological disorders, arthritis and osteoporosis, among other indications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Combinations for the treatment of cancer comprising an MPS-1 kinase inhibitor and a mitotic inhibitor
InactiveCN105283178AOrganic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsGlioblastomaGastric carcinoma
The present invention relates to a combination comprising an Mps-1 kinase inhibitor and a mitotic inhibitor. The present invention also relates to the use of said combination for the treatment of cancer, in particular of pancreatic cancer, glioblastoma, ovarian cancer, non-small cell lung carcinoma, breast cancer and / or gastric cancer.
Owner:BAYER PHARMA AG
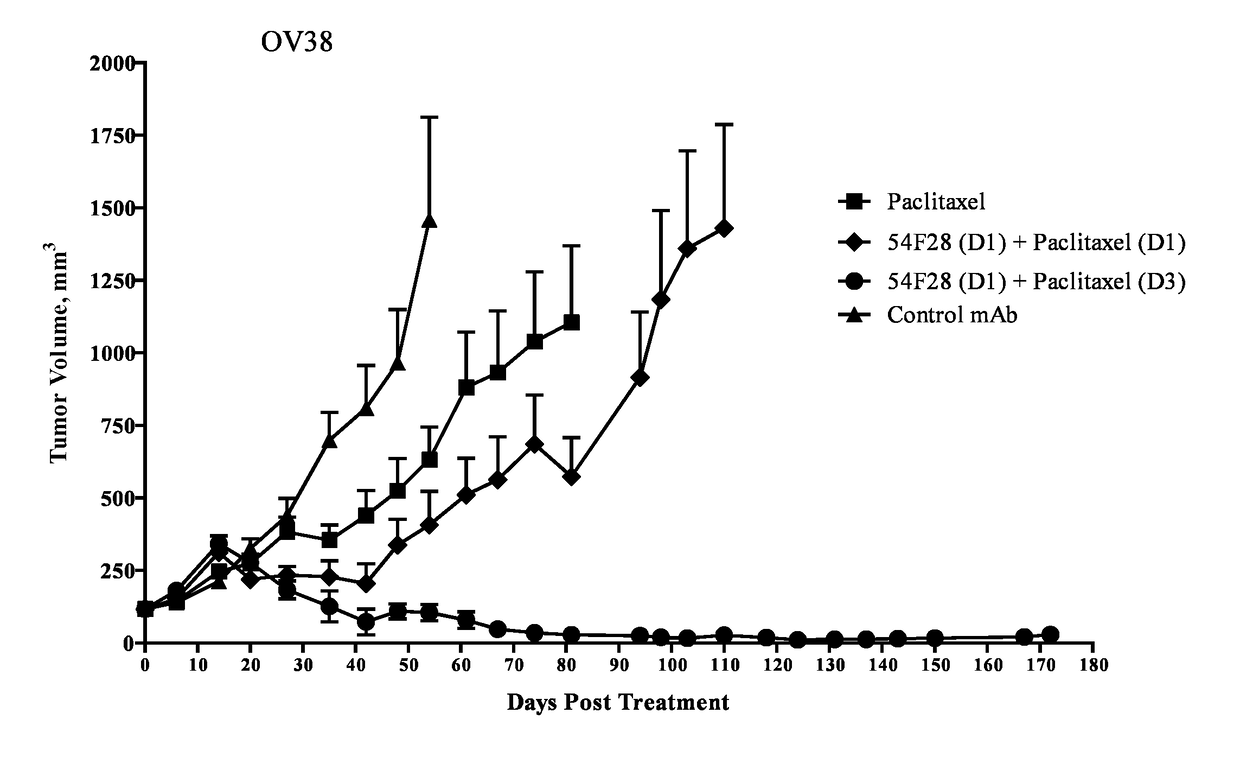
Combinations for the treatment of neoplasms using quiescent cell targeting and inhibitors of mitosis
ActiveUS20170296542A1Promote resultsImprove survivalOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCancer cellNeoplasm
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the treatment of neoplasms, in particular, by targeting of quiescent cancer cells with therapeutic agents in combination with other treatments effective against certain neoplastic conditions, in particular, anti-cancer treatment with therapeutic agents that are inhibitors of mitosis (a mitotic inhibitor).
Owner:FELICITEX THERAPEUTICS
Combinations for the treatment of cancer comprising a mps-1 kinase inhibitor and a mitotic inhibitor
The present invention relates to a combination comprising an Mps-1 kinase inhibitor and a mitotic inhibitor. The present invention also relates to the use of said combination for the treatment of cancer, in particular of pancreatic cancer, glioblastoma, ovarian cancer, non-small cell lung carcinoma, breast cancer and / or gastric cancer.
Owner:BAYER PHARMA AG
Methods and compositions for modulating cell proliferation and cell death
InactiveUS7625860B2Enhance in vitro and in vivo activityLow cytotoxicityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAnticarcinogenTopoisomerase-II Inhibitor
Methods and compositions for modulating the FGF effect on the sensitivity of malignant and normal cells to anticancer agents are provided. In particular, methods and compositions for inhibiting FGF-induced resistance to a broad spectrum of anticancer agents in solid and soft-tissue tumors, metastatic lesions, leukemia and lymphoma are provided. Preferably, the compositions include at least one FGF inhibitor in combination with a cytotoxic agents, e.g., antimicrotubule agents, topoisomerase I inhibitors, topoisomerase II inhibitors, antimetabolites, mitotic inhibitors, alkylating agents, intercalating agents, agents capable of interfering with a signal transduction pathway (e.g., g., a protein kinase C inhibitor, e.g., an anti-hormone, e.g., an antibody against growth factor receptors), an agent that promotes apoptosis and / or necrosis, an interferon, an interleukin, a tumor necrosis factor, and radiation.In other embodiments, methods and composition for protecting a cell in a subject, from one or more of killing, inhibition of growth or division or other damage caused, e.g., by a cytotoxic agent, are provided. Preferably, the method includes: administering, to the subject, an effective amount of at least one FGF agonist, thereby treating the cell, e.g., protecting or reducing the damage to the dividing cell from said cytotoxic agent.
Owner:AU JESSIE L S +1
Methods and compositions for cryopreservation of dissociated primary animal cells
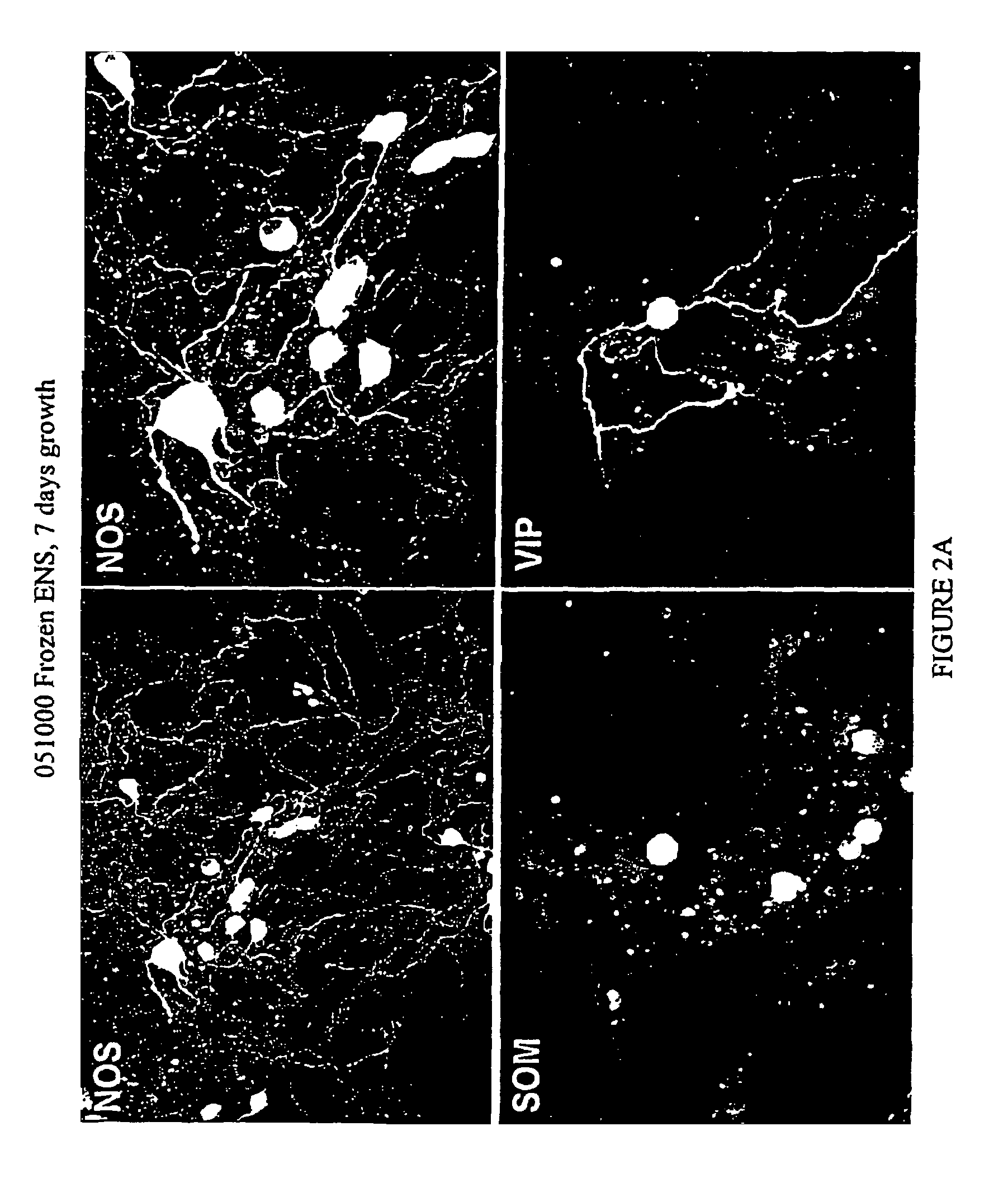
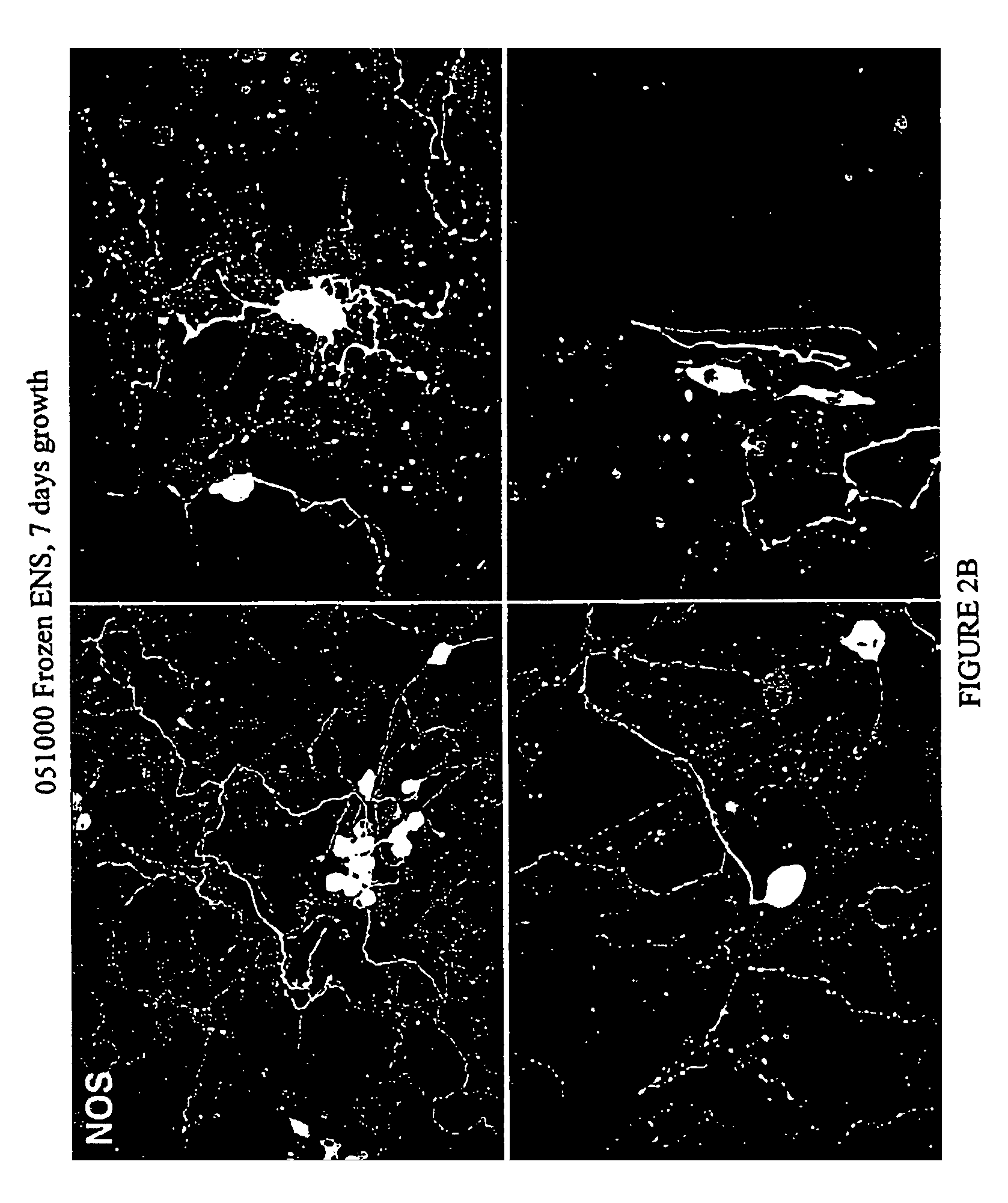
The invention can be summarized as follows. The present invention provides cell culture compositions and cell cryopreservation compositions for culturing and cryopreserving enteric system (ENS) neurons and central nervous system (CNS) neurons. The present invention also provides a method of culturing and cryopreserving ENS and CNS cells. The compositions of the present invention comprise nutrient medium, serum, glutamine, glucose an antibiotic and one or more of the following components: one or more mitotic inhibitors, one or more antioxidants, and a cryopreservative.
Owner:OTTAWA UNIV OF
Combination therapy with an antitumor alkaloid
InactiveUS20180008602A1Heavy metal active ingredientsNervous disorderAntineoplastic alkaloidDepressant
The present invention relates to the combination of PM01183 with several anticancer drugs, in particular other anticancer drugs selected from antitumor platinum coordination complexes, antimetabolites, mitotic inhibitors, anticancer antibiotics, topoisomerase I and / or II inhibitors, proteasome inhibitors, histone deacetylase inhibitors, nitrogen mustard alkylating agents, nitrosourea alkylating agents, nonclassical alkylating agents, estrogen antagonists, androgen antagonists, mTOR inhibitors, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and other agents selected from aplidine, ET-743, PM02734 and PM00104, and the use of these combinations in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:PHARMA MAR U
Combination therapy for treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20170247465A1Eliminate side effectsImprove therapeutic indexOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCombined Modality Therapy
The present invention provides methods comprising combination therapy for treating cancer. Wnt pathway inhibitors in combination with mitotic inhibitors administered in a staggered or sequential dosing manner for the treatment of cancer and other diseases.
Owner:ONCOMED PHARMA
Identification of inhibitors of mitosis
Methods and compositions are described for using NIMA-like kinases to identify anti-mitotic compounds and to diagnose cancer.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
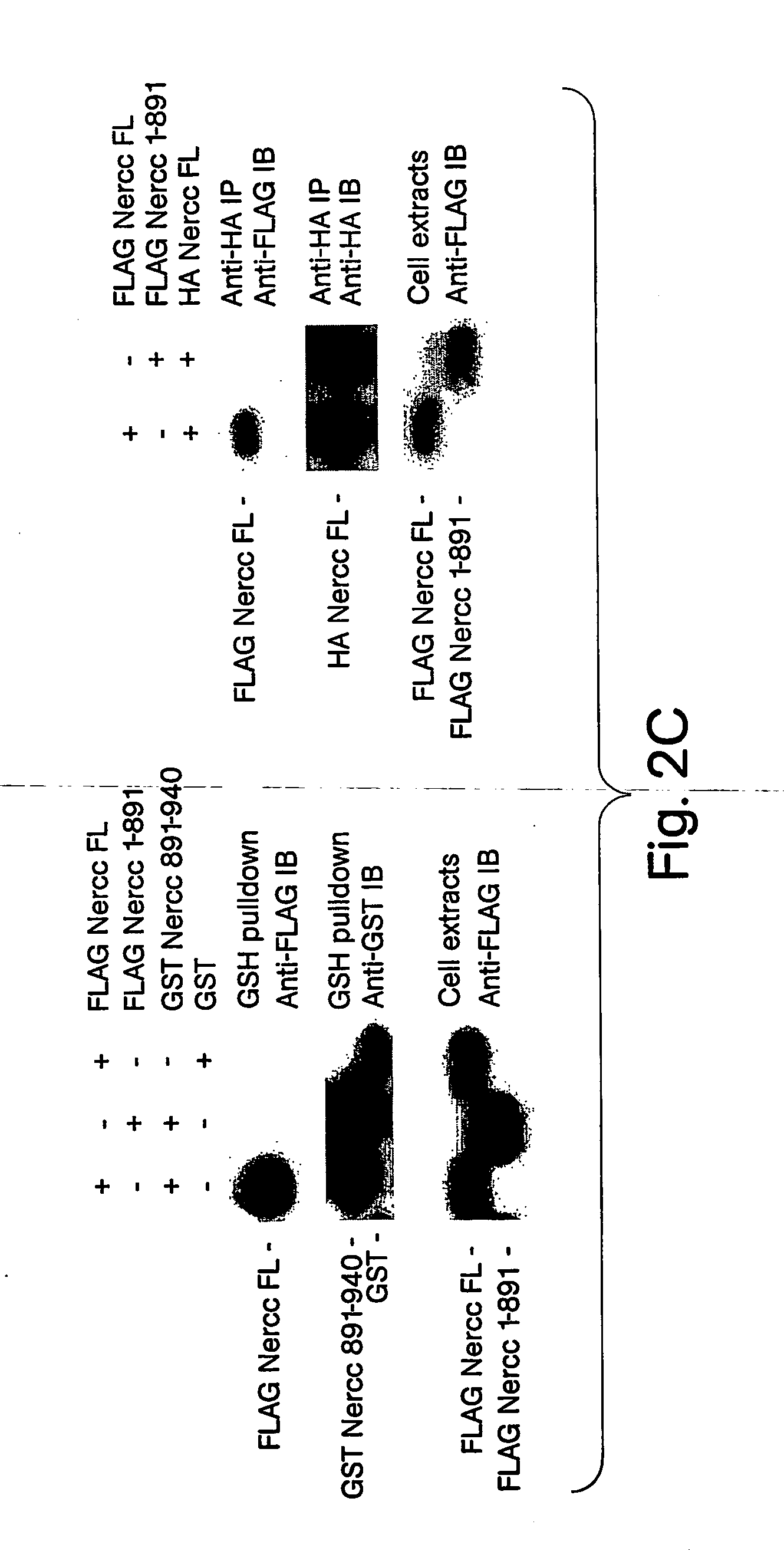
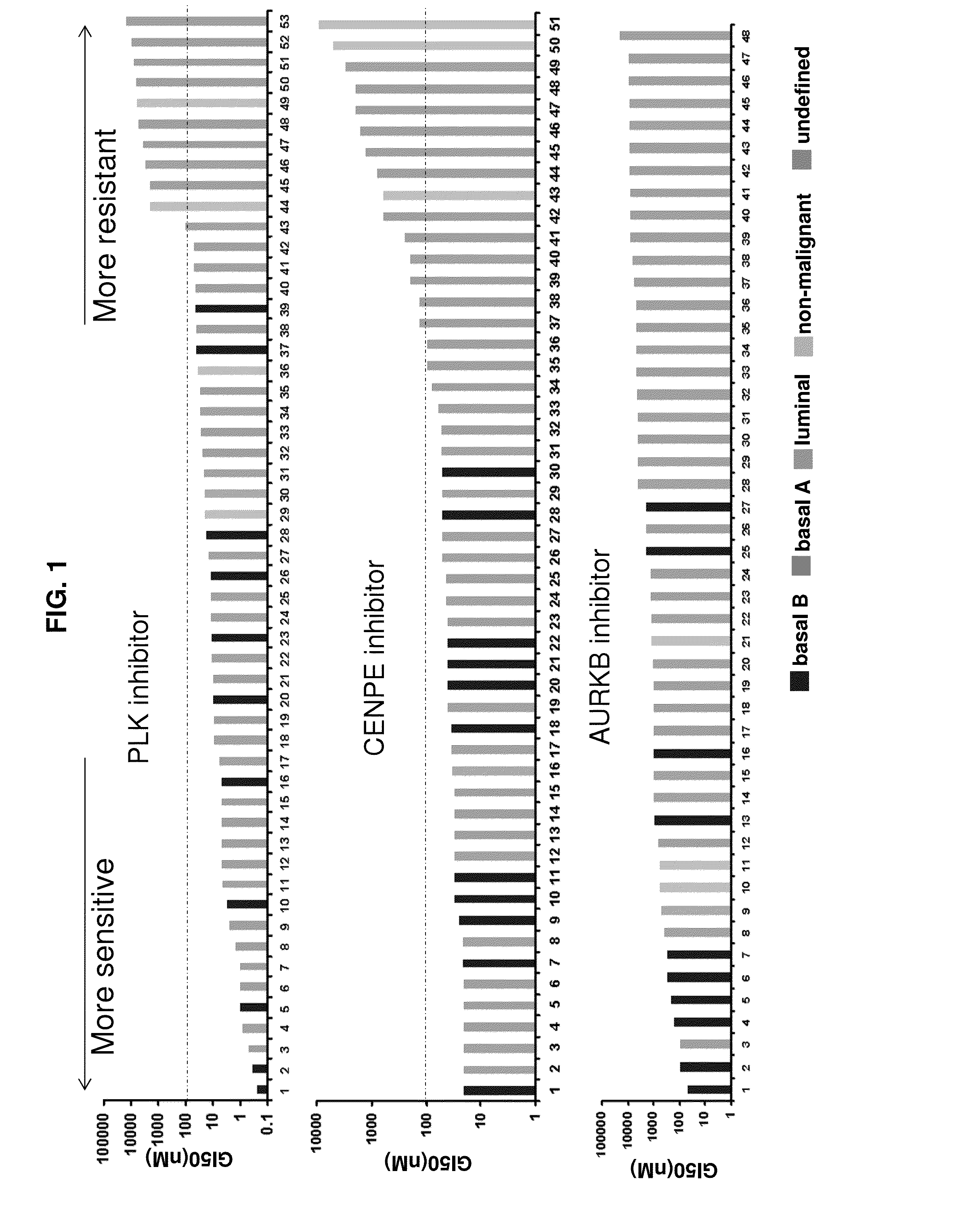
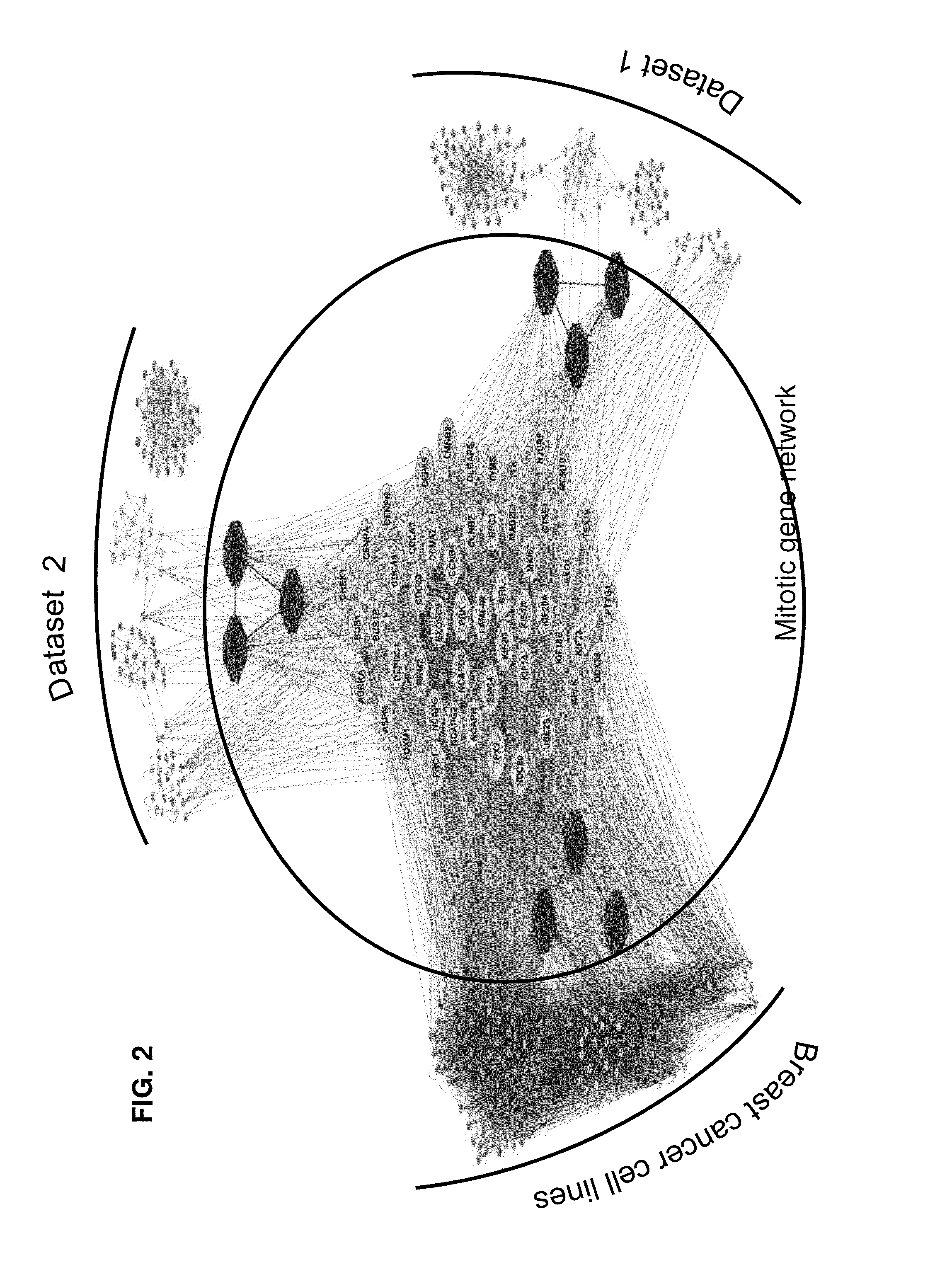
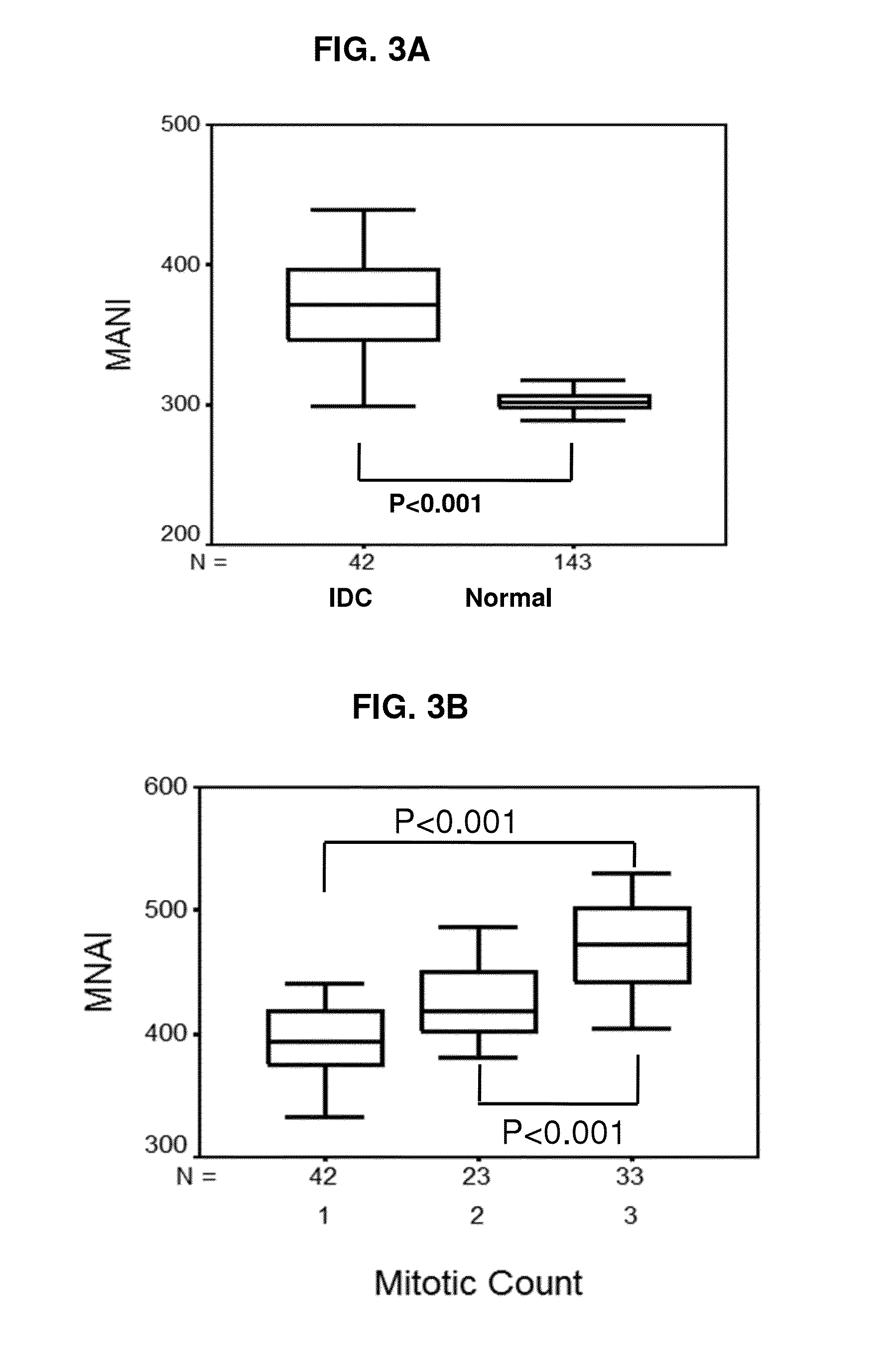
Cancer Specific Mitotic Network
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Combinations for the treatment of neoplasms using quiescent cell targeting and inhibitors of mitosis
ActiveUS10314843B2Reduce doseIncrease fraction of apoptotic cellOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCancer cellNeoplasm
Owner:FELICITEX THERAPEUTICS
Combination therapy for treatment of cancer
The present invention provides methods comprising combination therapy for treating cancer. Wnt pathway inhibitors in combination with mitotic inhibitors administered in a staggered or sequential dosing manner for the treatment of cancer and other diseases.
Owner:ONCOMED PHARMA INC
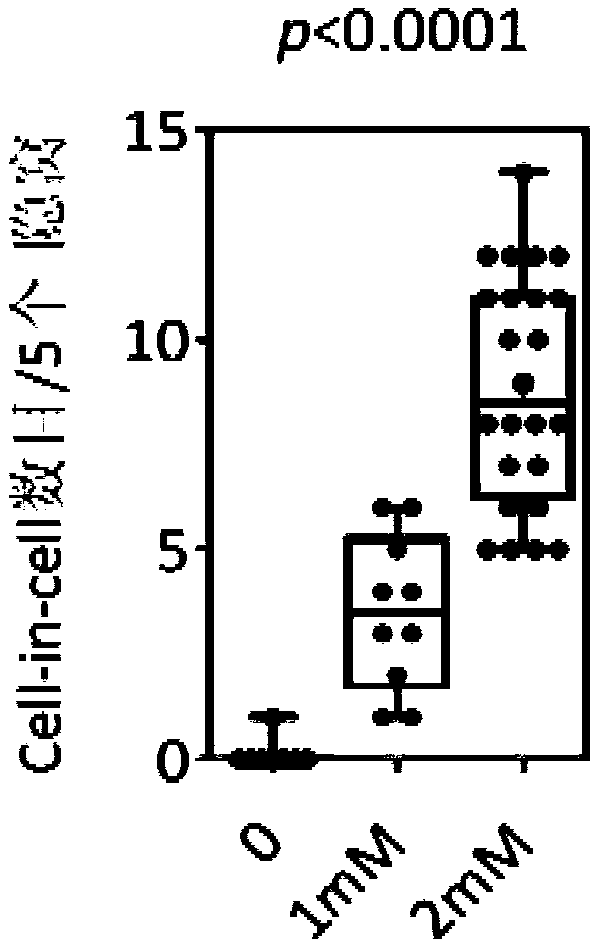
Animal model with cell-in-cell (CIC) structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110732025ACompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsAnimal bodyPathology diagnosis
The invention discloses an animal model with a cell-in-cell (CIC) structure and a preparation method thereof. The invention protects application of a mitotic inhibitor in preparation of a kit; and thefunction of the kit is to prepare the animal model with the CIC structure. The invention also protects application of the mitotic inhibitor in preparation of the animal model with the CIC structure.The invention further protects a method for preparing an animal model. The method for preparing the animal model comprises the following step of administrating an animal with a mitotic inhibitor, thereby obtaining the animal model with the CIC structure. The invention still further protects application of an animal model prepared by any of the above methods, including: application of the animal model in CIC structure research, application of the animal model in screening of substances with tumor therapeutic functions, and application of the animal model in toxicological analysis of substancesto be tested to evaluate biosafety of the substance to be tested. For the first time, the invention discloses a preparation method by which the CIC structure is successfully induced in an animal body;and therefore, a favorable experimental basis is provided for further exploring of physiological and pathological significance of CIC.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Method of treating triple-negative breast cancer using thienotriazolodiazepine compounds
A method of treating triple-negative breast cancer in a mammal comprising the step of: administering to a patient a pharmaceutical acceptable amount of a compound being a thienotriazolodiazepine compound of the Formula (1) wherein R1 is alkyl having a carbon number of 1-4, R2 is a hydrogen atom; a halogen atom; or alkyl having a carbon number of 1-4 optionally substituted by a halogen atom or a hydroxyl group, R3 is a halogen atom; phenyl optionally substituted by a halogen atom, alkyl having a carbon number of 1-4, alkoxy having a carbon number of 1-4 or cyano; —NR5—(CH2)m—R6 wherein R5 is a hydrogen atom or alkyl having a carbon number of 1-4, m is an integer of 0-4, and R6 is phenyl or pyridyl optionally substituted by a halogen atom; or —NR7—CO—(CH2)n—R8 wherein R7 is a hydrogen atom or alkyl having a carbon number of 1-4, n is an integer of 0-2, and R8 is phenyl or pyridyl optionally substituted by a halogen atom, and R4 is —(CH2)n—CO—NH—R9 wherein a is an integer of 1-4, and R9 is alkyl having a carbon number of 1-4; hydroxyalkyl having a carbon number of 1-4; alkoxy having a carbon number of 1-4; or phenyl or pyridyl optionally substituted by alkyl having a carbon number of 1-4, alkoxy having a carbon number of 1-4, amino or a hydroxyl group or —(CH2)b—COOR10 wherein b is an integer of 1-4, and R10 is alkyl having a carbon number of 1-4, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or a hydrate or solvate thereof, in combination with one or more chemotherapy drugs selected from the group consisting of m-TOR inhibitors and mitotic inhibitors.
Owner:ONCOETHIX
Combinations for the treatment of neoplasms using quiescent cell targeting and inhibitors of mitosis
InactiveUS20190290651A1Reduce doseIncrease fraction of apoptotic cellOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCancer cellNeoplasm
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the treatment of neoplasms, in particular, by targeting of quiescent cancer cells with therapeutic agents in combination with other treatments effective against certain neoplastic conditions, in particular, anti-cancer treatment with therapeutic agents that are inhibitors of mitosis (a mitotic inhibitor).
Owner:FELICITEX THERAPEUTICS
Herbicide composition for cotton field, preparation thereof, application and application method of composition and preparation
ActiveCN113100243AImprove securityImprove efficiencyBiocideAnimal repellantsFatty Acid Synthesis InhibitorsLong-chain fatty acid synthesis
Owner:MAXUNITECH INC
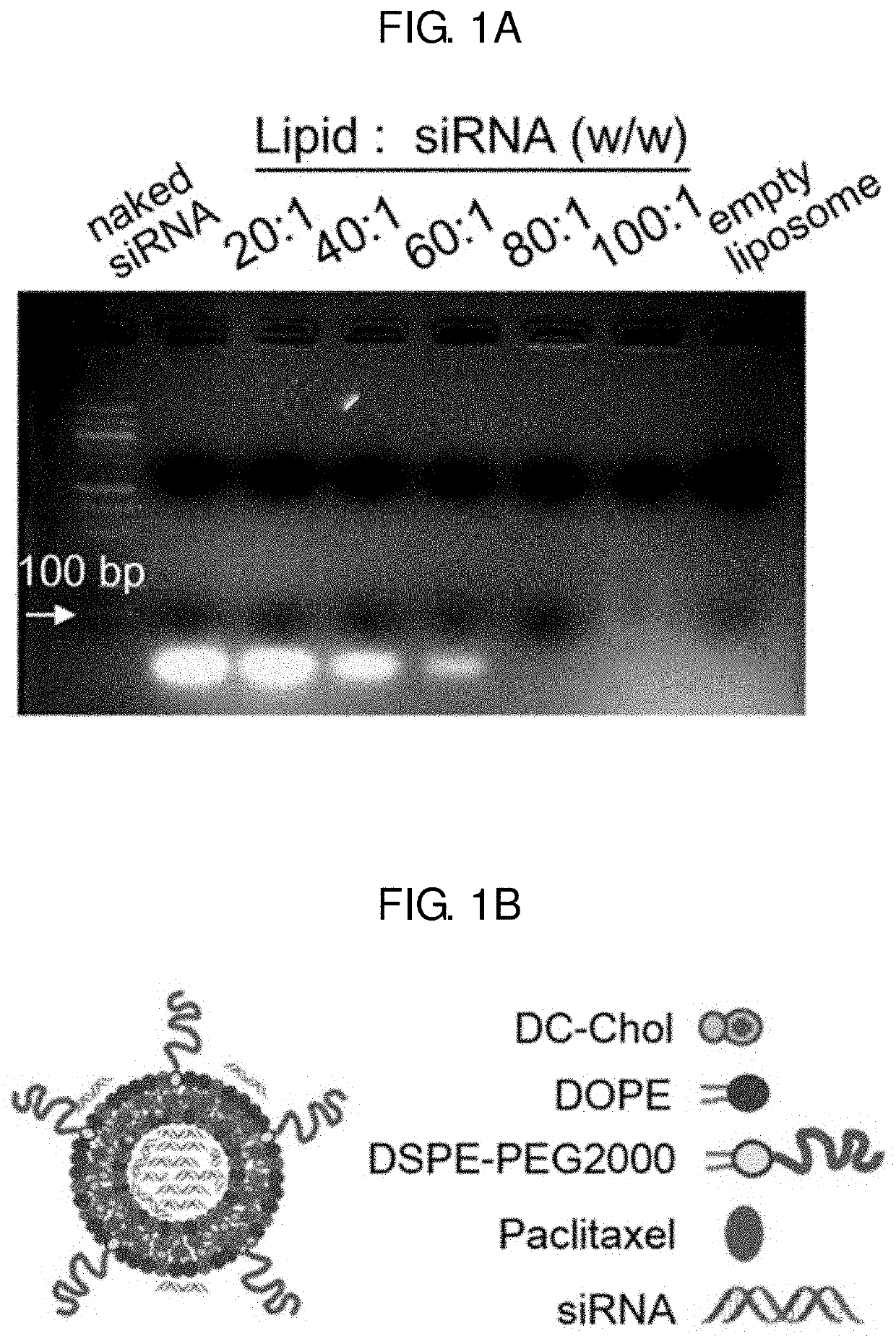
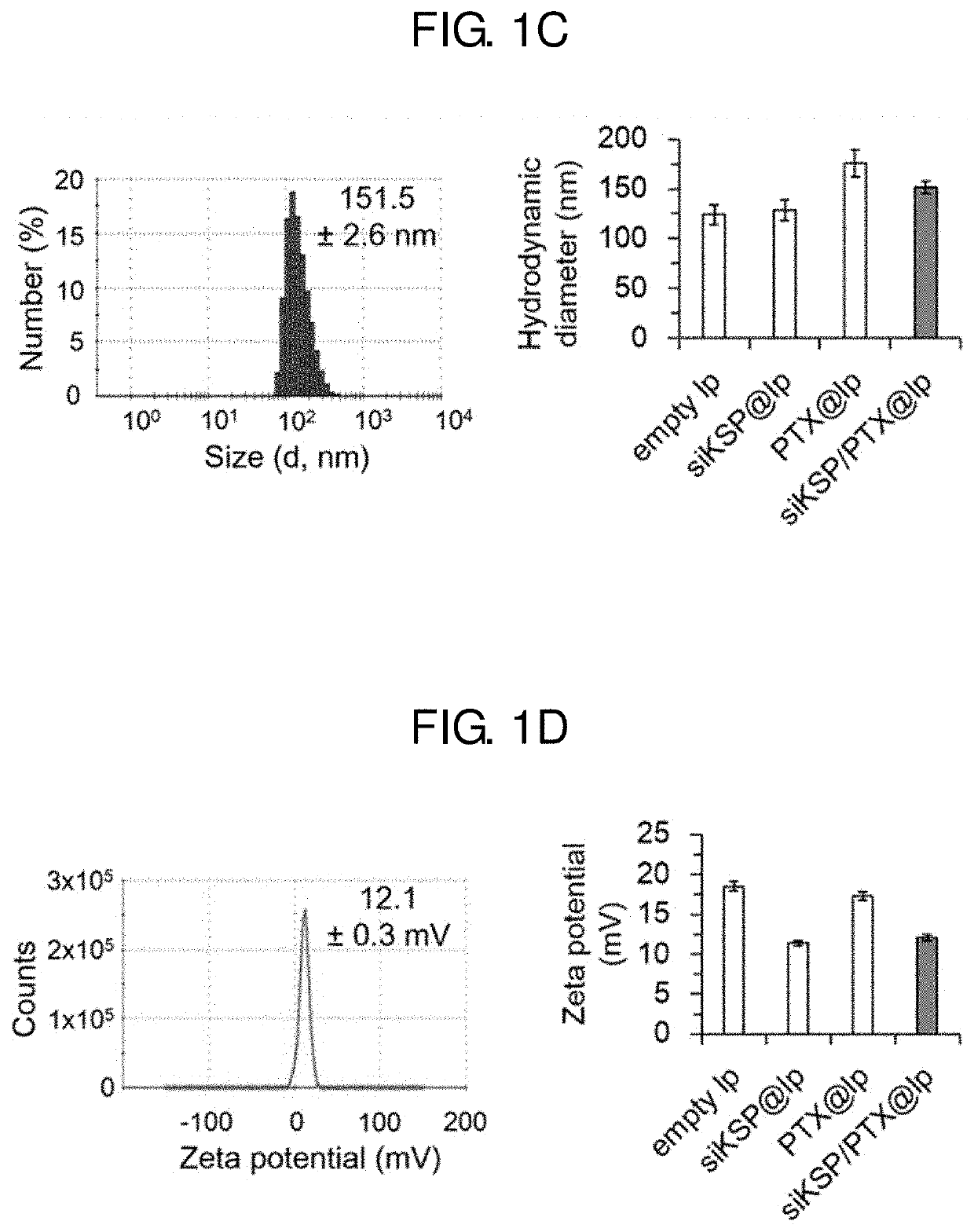
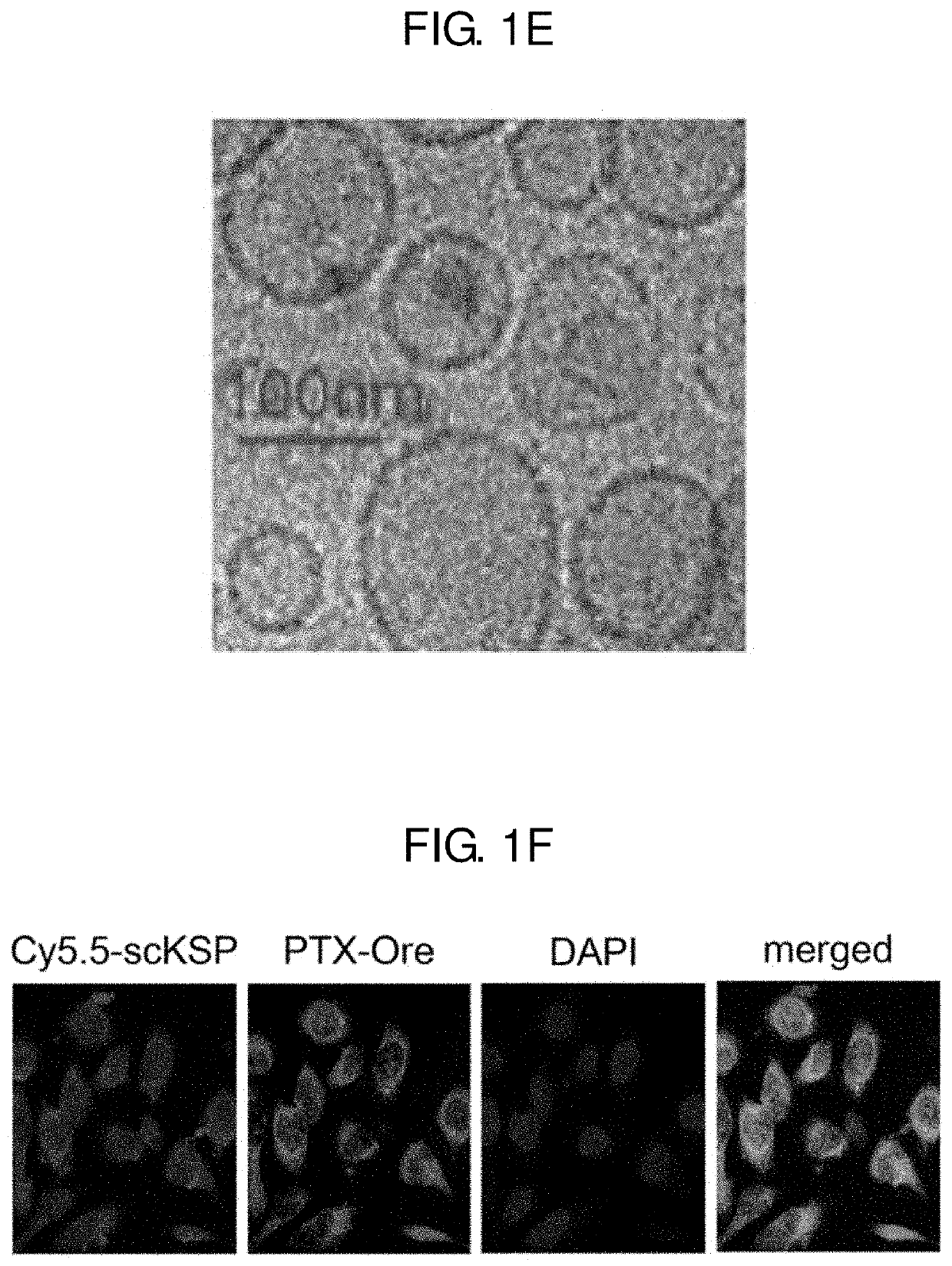
Pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating cancer comprising ksp inhibitor and mitosis inhibitor
PendingUS20210260063A1Induce synergistic effectEasy to useOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsKinesinPharmaceutical drug
The present invention relates to a method of treating a cancer including administering a pharmaceutical composition to an individual suspected to have the cancer excluding humans in a pharmaceutically effective amount, where the pharmaceutical composition comprises an agent capable of inhibiting expression of kinesin spindle protein (KSP) and a mitosis inhibitor.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com