Patents
Literature
81 results about "Conceptus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
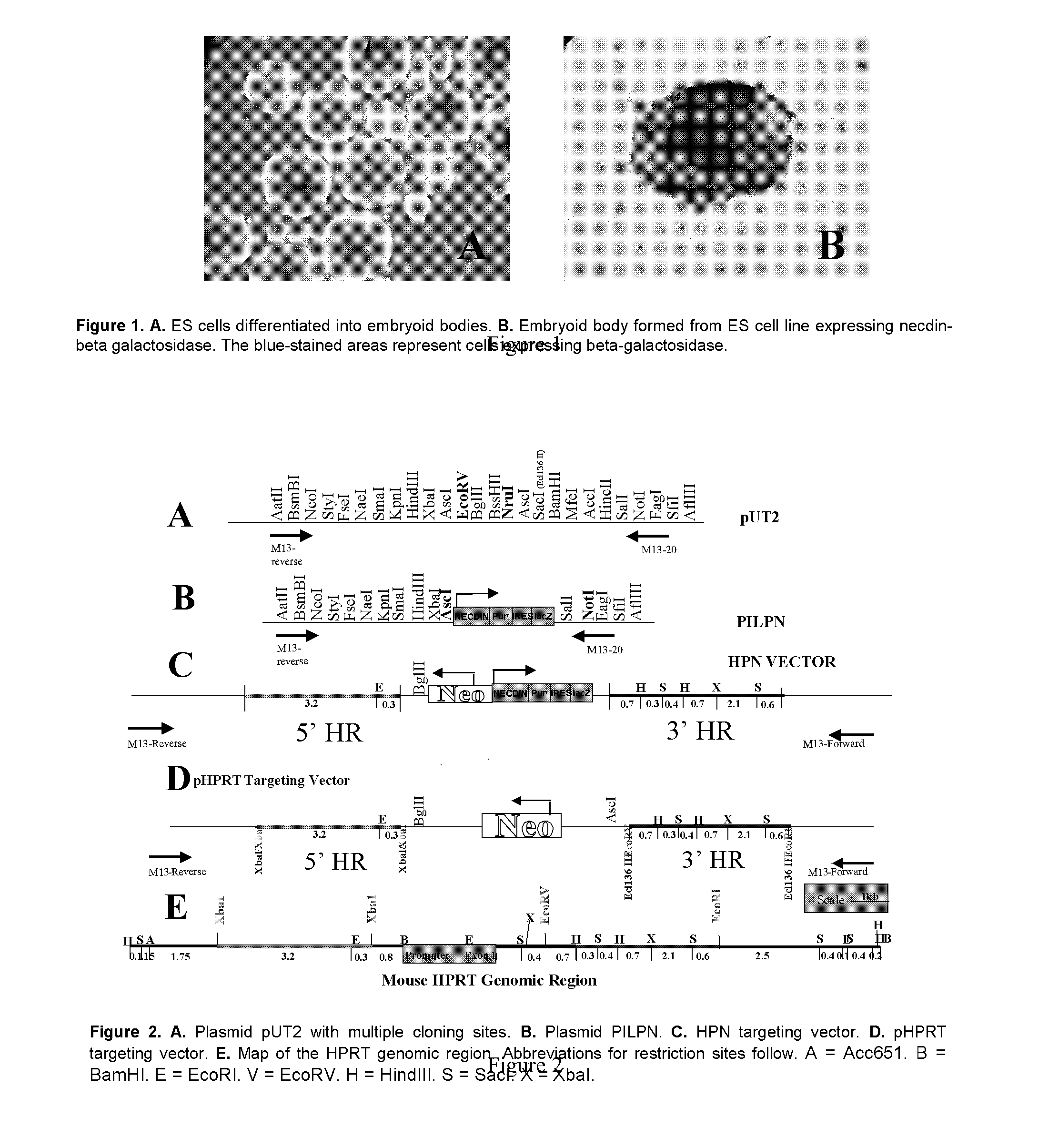
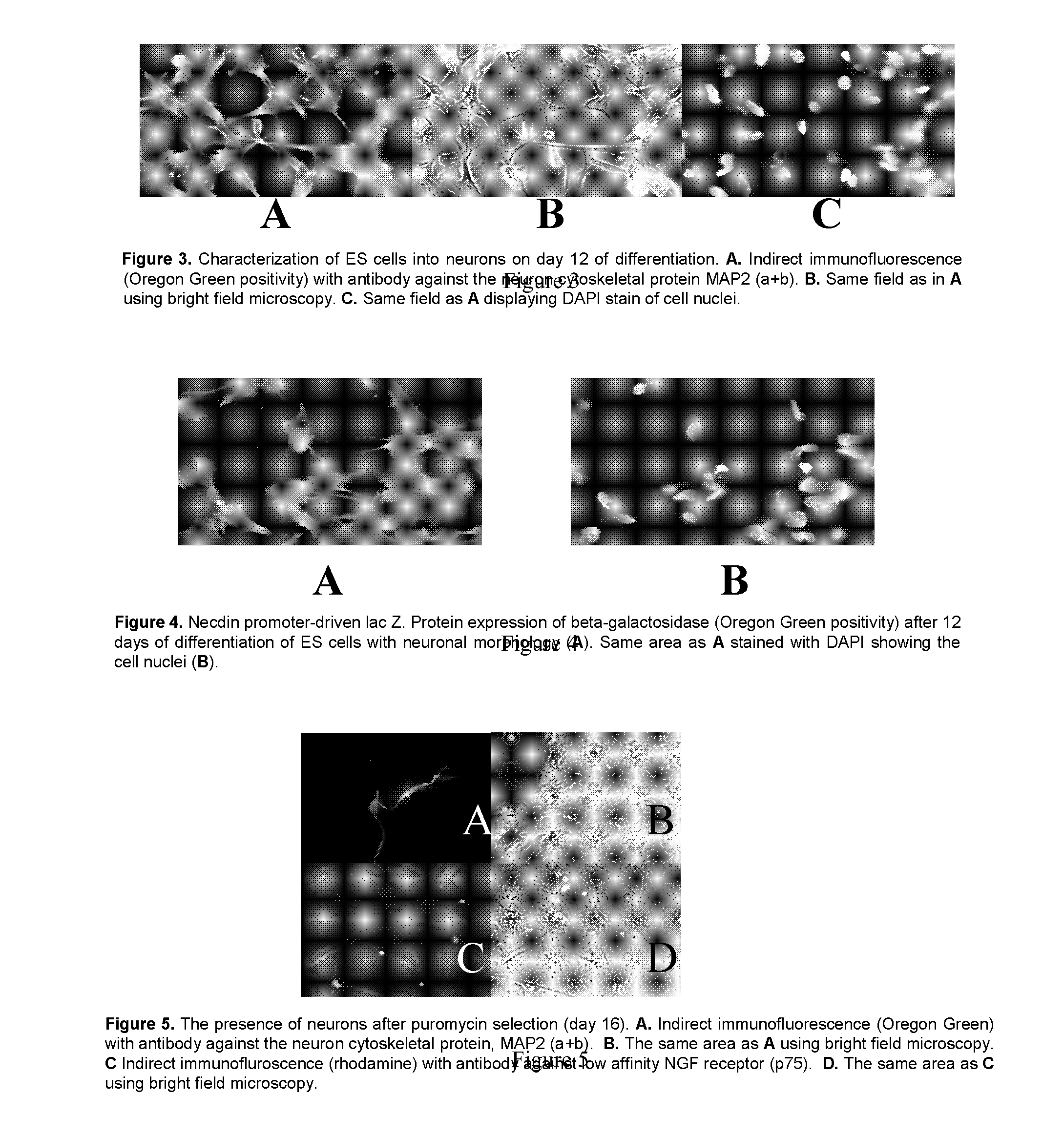
Conceptus (Latin: conceptio, meaning derivatives of zygote) denotes the embryo and its adnexa (appendages or adjunct parts) or associated membranes (i.e. the products of conception). The conceptus includes all structures that develop from the zygote, both embryonic and extraembryonic. It includes the embryo as well as the embryonic part of the placenta and its associated membranes - amnion, chorion (gestational sac), and yolk sac.
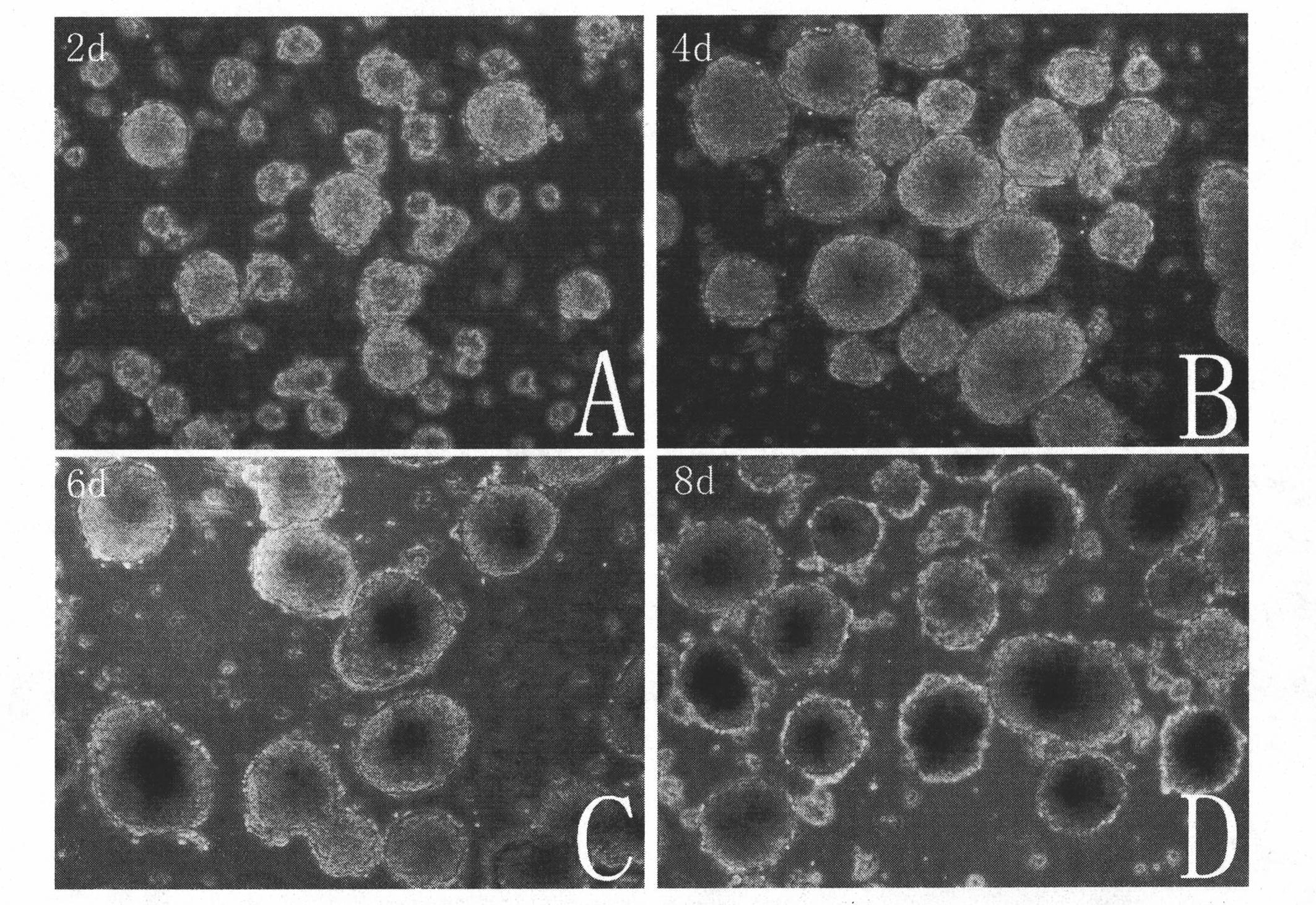
Embryoid Body - Based Screen
InactiveUS20070015210A1Uniform sizeEasy to produceGenetically modified cellsLibrary screeningTest agentConceptus
Disclosed are embryoid bodies having a uniform size of approximately 415 nm and comprising genetically modified embryonic stem cells, and methods of making same. The genetically uniform embryoid bodies can be multiplexed as one embryoid body per well in a multiwell format, and used as a high to medium throughput screen for test agents that affect the development and homeostasis of animals, including humans. The genetic modification of the embryonic stem cells is a promoter-report-selection construct that enables the selection and detection of cells of a particular lineage in the EB, to determine the effects of a test agent.
Owner:GENEPROTECH
Methods and compositions for vaccination of poultry
The present invention provides methods of inducing an immune response against Clostridium species in birds, for protecting birds from Clostridium infection, and / or for protecting birds from related disorders such as necrotic enteritis. The methods can be practiced in ovo and / or post-hatch. The invention further provides compositions and methods for delivery of a composition of this invention in ovo directly to the embryo body.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Methods and compositions for vaccination of poultry
The present invention provides methods of inducing an immune response against Clostridium species in birds, for protecting birds from Clostridium infection, and / or for protecting birds from related disorders such as necrotic enteritis. The methods can be practiced in ovo and / or post-hatch. The invention further provides compositions and methods for delivery of a composition of this invention in ovo directly to the embryo body.
Owner:EMBREX INC
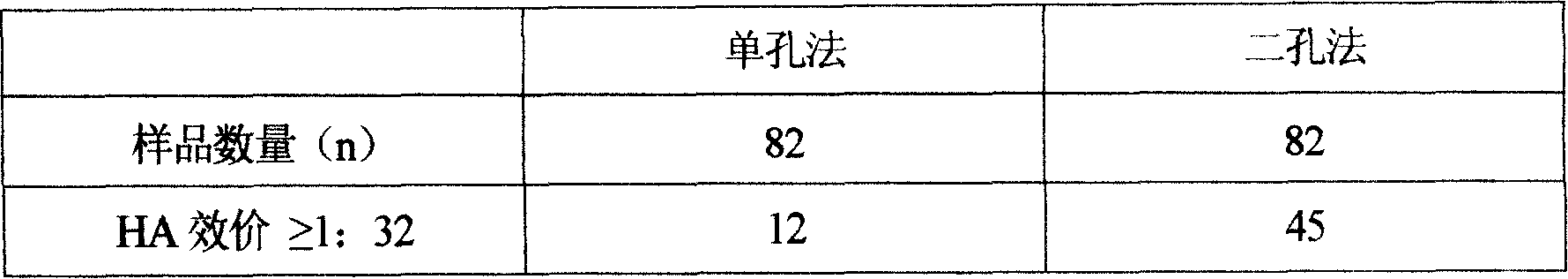
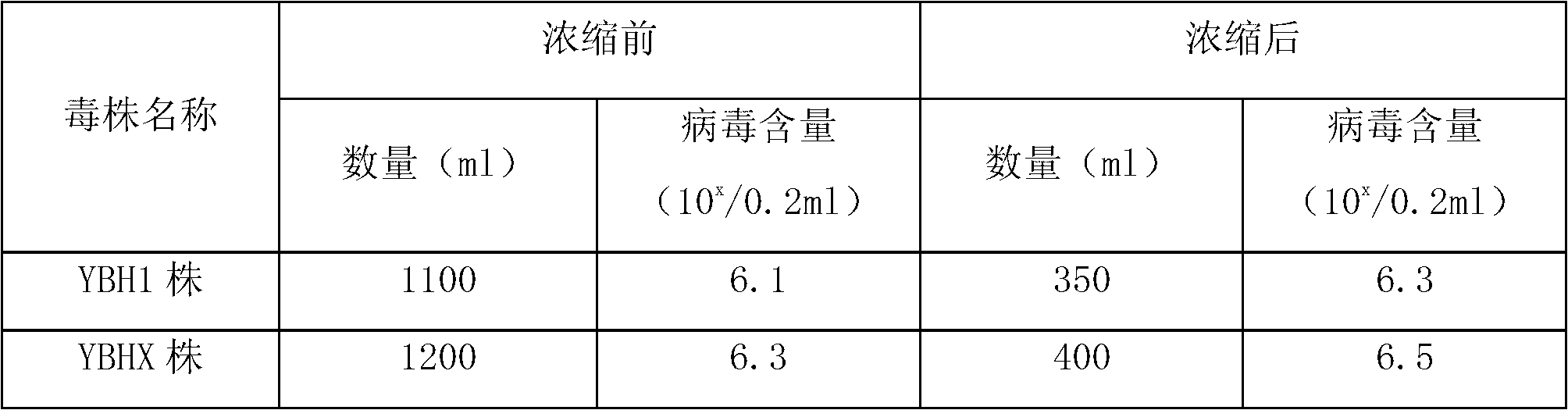
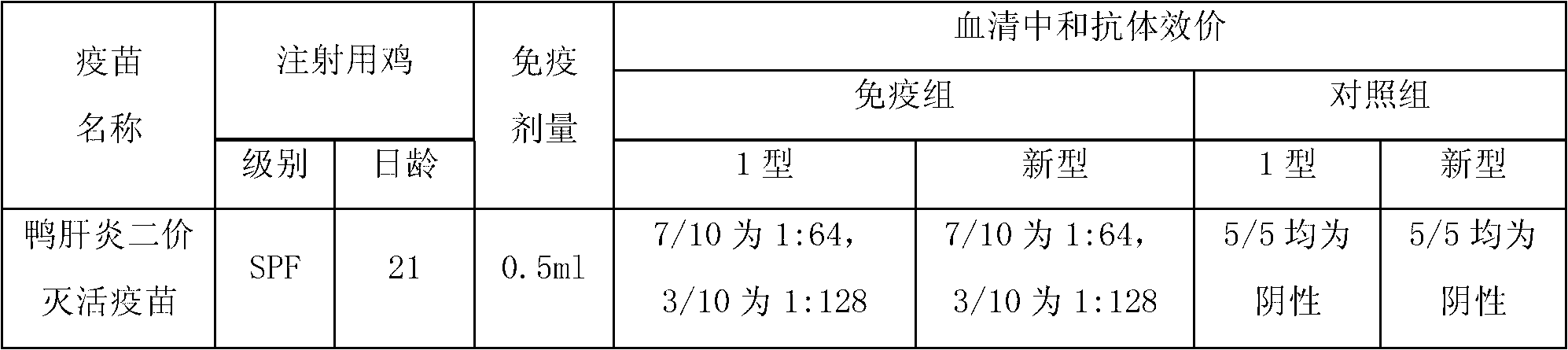
Method for preparing duck virus hepatitis divalent refined egg yolk antibody
ActiveCN102827275AImprove securityHigh protection rateEgg immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against virusesDuck hepatitis A virusFreeze thawing
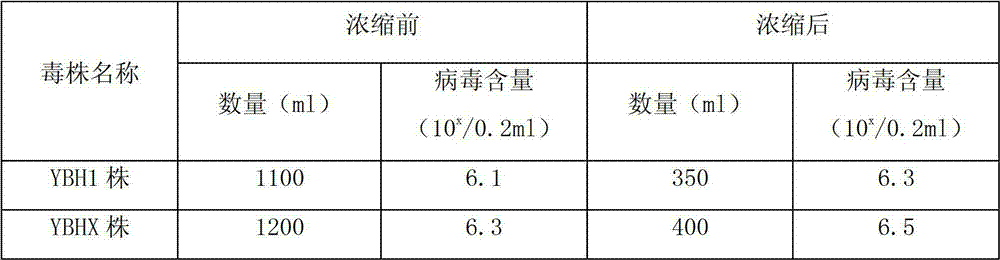
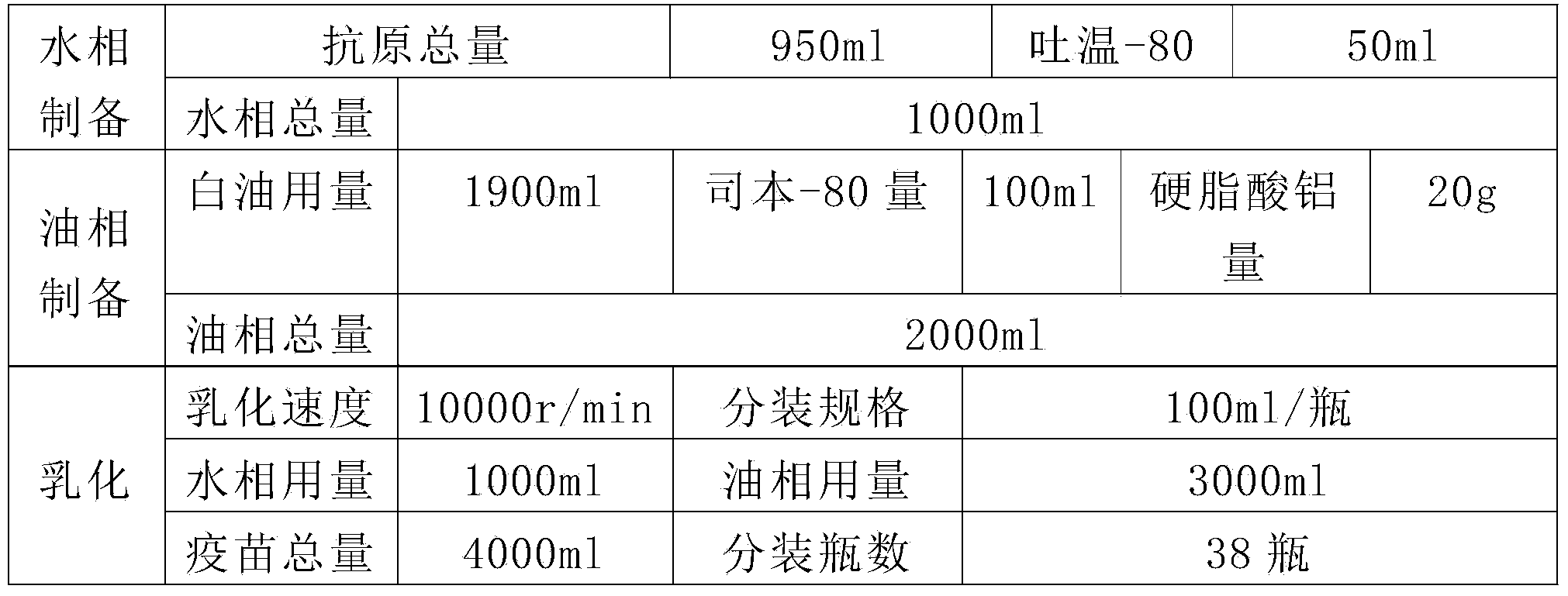
The invention relates to a method for preparing a duck virus hepatitis divalent refined egg yolk antibody. The method is that vaccines of a duck virus hepatitis virus 1 type YBH1 strain and novel YBHX strain with good immunogenicity are selected from duck virus hepatitis superior prevalent strains to prepare strains, the strains are respectively inoculated to a chicken embryo and a duck embryo, a dead embryo body and the embryo juice are respectively obtained, the virus liquid is collected after grinding and freeze thawing, ultrafiltration concentration and inactivation with formaldehyde solution are carried out, and oil adjuvant is added to mix and emulsify to produce the vaccine. The vaccine is inoculated to a laying hen, the egg with high immunity is obtained, the yolk is separated, inactivated, extracted and refined to produce the duck virus hepatitis divalent refined egg yolk antibody which can prevent the duck virus hepatitis which is caused by the 1 type and novel duck hepatitis viruses, so the egg yolk has the advantages of high efficiency, good safety, high protection ratio and the like.
Owner:YEBIO BIOENG OF QINGDAO
Method of dynamically culturing embryonic stem cells
he present invention is of a method of dynamically generating human embryoid bodies which can be used for generating lineage specific cells and cell lines. Specifically, the present invention can be used to generate ESC-differentiated cells for cell-replacement therapy.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Extracellular matrix gel model used for researching development and differentiation of embryonic stem cells
The invention relates to an extracellular matrix gel model used for researching development and differentiation of embryonic stem cells, belonging to the research field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, and mainly solving the problem that no ideal model exists for the research of differentiation and development of embryonic stem cells in vitro. We the extracellular matrix gel adopt as the in vitro three dimensional model of the differentiation and development of embryonic stem cells, inoculate the embryonic stem cells to the three dimensional model in different cell densities, and observe the phenomena of the forming of embryoid body by self-differentiation of the embryonic stem cells and the law of the embryoid body being differentiated into cells of different ancestries; and the microenvironment in which the embryonic stem cells grow is regulated, the extracellular matrix gel is taken as the main body to carry out the directional differentiation and development research of the embryonic stem cells, thus disclosing the inherent law and mechanism of the in vitro differentiation and development of the embryonic stem cells, and searching for new methods for directional differentiation of embryonic stem cells to the functional cells of important vital organs at the terminal differentiation period; and the invention will provide a new technical method for exploring the development mechanism of the embryonic stem cells.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Method of forming multicellular spheroids from the cultured cells
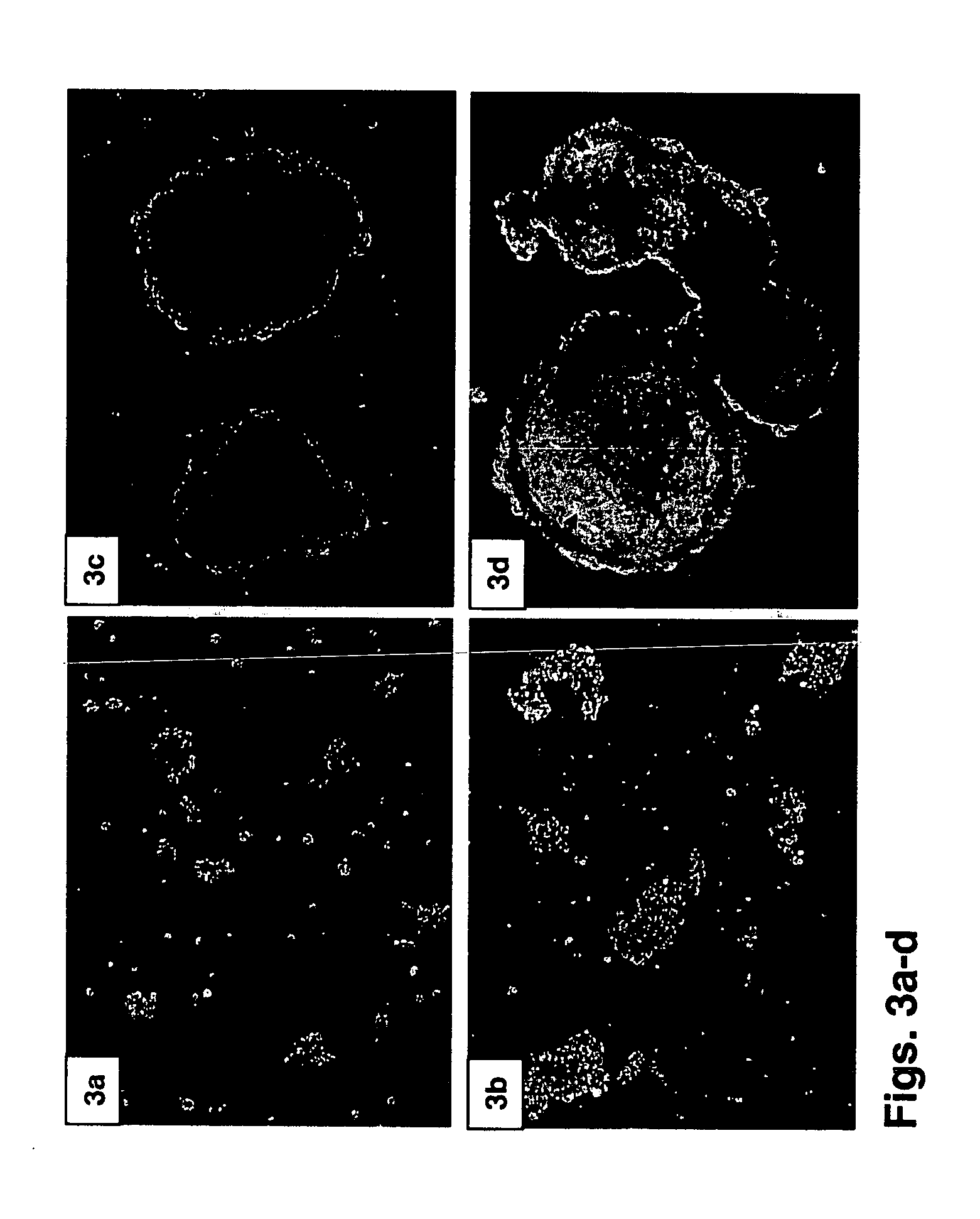
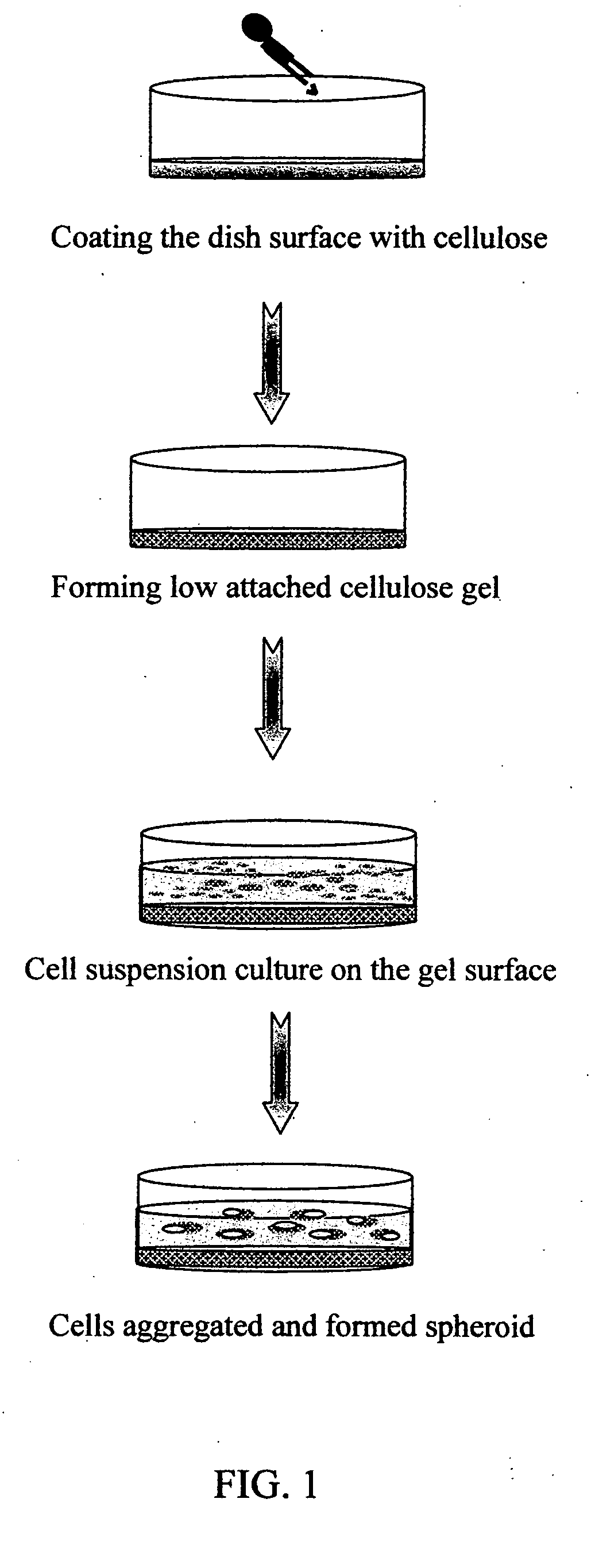
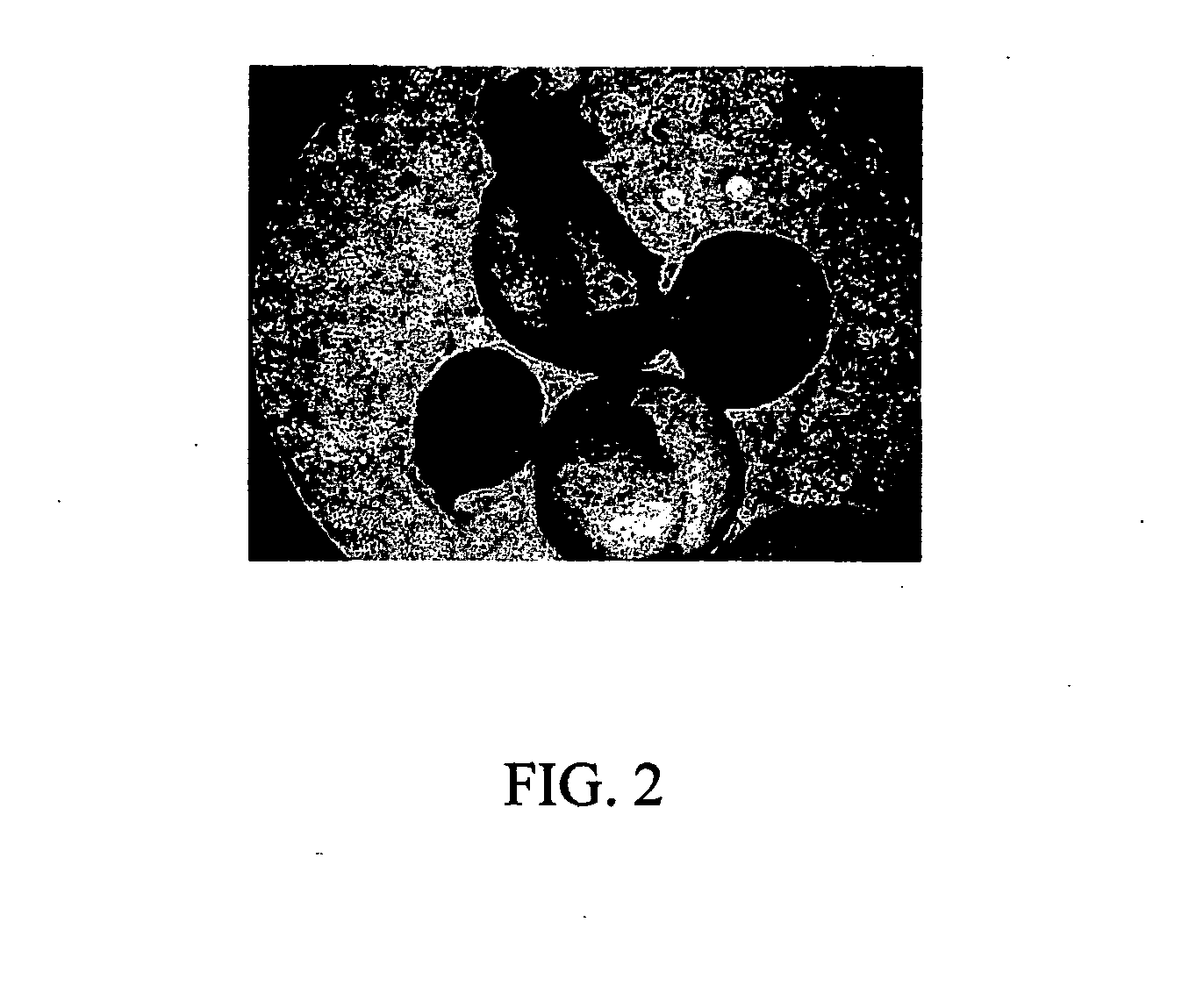
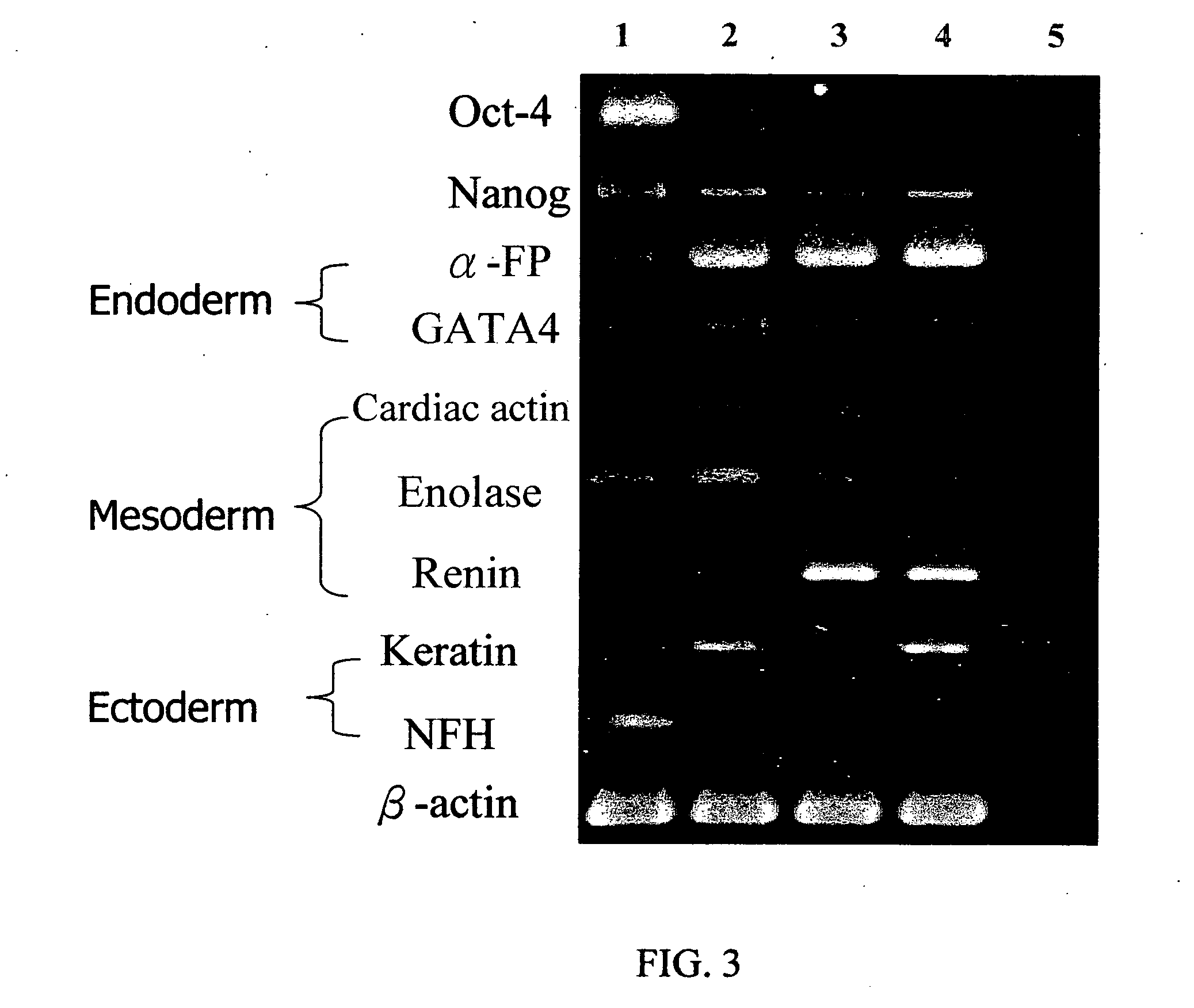
InactiveUS20070148767A1Generate efficientlyArtificial cell constructsCell culture supports/coatingCelluloseConceptus
Provided herein are methods for producing multicellular spheroids or embryoid bodies suitable for providing cells in large scale for various medical applications. In one embodiment, a method of forming embryoid bodies is provided, which comprises culturing undifferentiated HES cells in a culture vessel pre-coated with cellulose and / or its derivatives. In another embodiment, a method of forming hepatic spheroids is provided, which comprises culturing hepatocytes in a culture vessel pre-coated with cellulose and / or its derivatives.
Owner:YANG MEI JU +4
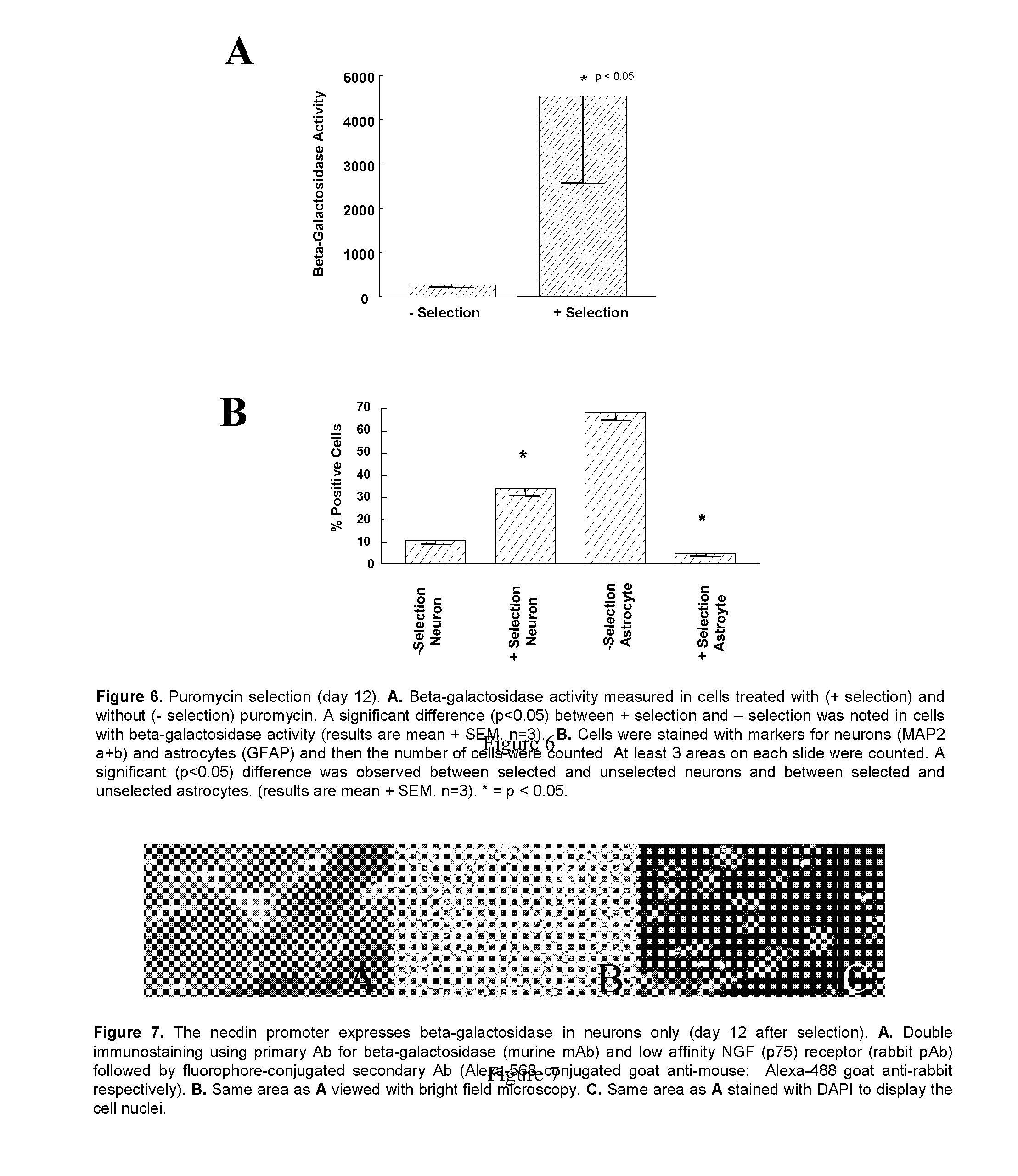
Method for differentiation of embryonic stem cells into nerve cells through in vitro induction
InactiveCN102899285APromote partial recoveryPromote regenerationNervous disorderMammal material medical ingredientsOLIG2Conceptus
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine, and relates to a method for differentiation of embryonic stem cells into nerve cells through in vitro induction, especially to a method for induction of Olig2<+>-GFP<+>-mES nerve cell differentiation through a purine derivative Purmorphamine, and uses thereof. According to the present invention, an embryoid body mediated nerve induction method is adopted, Olig2-GFP<+>-mES is adopted as a cell model, a purine derivative Purmorphamine and all-trans retinoic acid are combined to carry out directed induction on the Olig2-GFP<+>-mES cells to obtain spinal motor neurons and oligodendrocyte progenitor cells through differentiation; experiment results show that the Purmorphamine can be used as a substitute of SHH, can effectively induce Olig2<+>-GFP<+>-mES differentiation to obtain high purity and function spinal motor neurons and oligodendroglial cells, and can cause expression changes of related genes; and transplant experiment results show that the induced nerve cells can promote partial function and morphology restoration after rat spinal cord injury, and have effects of spinal cord injury regeneration promotion and function reconstruction.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for creating hepatocyte by human embryo stem cell external evoked differentiation
InactiveCN101117626AFully contactedEasy to observeArtificial cell constructsEmbryonic cellsDiseaseArtificial liver
The present invention provides a method that embryo of human embryonic stem cells (HES) is directionally induced and divided into liver cells. First, the biological property of high degree of self-regeneration multiplication of HES cell is made use of, the collagenase IV digestion is adopted for transfer of culture and augmentation, thereby obtaining a plurality of stem cells; second, the HES cell is inoculated into a cell utensil with lower adsorbability to form a mature imitated embryonic plant (EB); third, the mature cystic EB is digested with 0.25 tryptic enzyme to 0.02 percent EDTA to a single cell, and then is inoculated to a tissue culture dish which is packed with I-shaped collagen in advance, solution culture is induced under the condition of dexamethasone and human trypsin, and the differentiation towards the liver cell direction is observed and judged. The prevent invention provides the method that the HES is efficiently divided into liver cells, at the same time, the method makes the follow-up judging work more simply and more efficient, and lay a foundation for the stem cellular transplantation or biologic artificial liver curing the disease such as serious hepatitis, hepatic failure and so on.
Owner:FIELD OPERATION BLOOD TRANSFUSION INST OF PLA SCI ACAD OF MILITARY
Muscovy duck parvovirus and application thereof
ActiveCN103820397AEnhanced antibodyLow toxicityMicroorganism based processesImmunoglobulins against virusesFreeze thawingAdjuvant
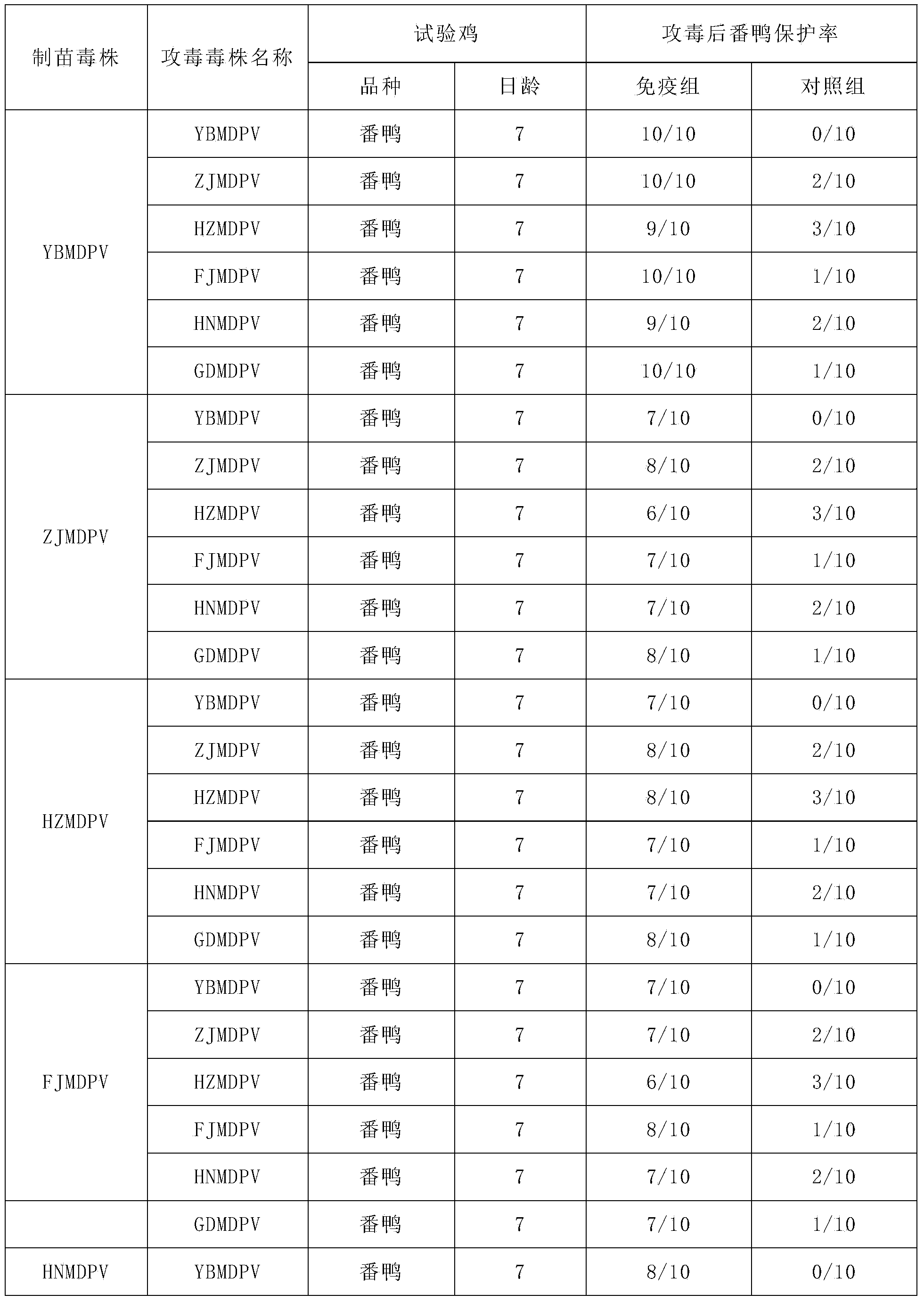
The invention aims to provide a Muscovy duck parvovirus. The Muscovy duck parvovirus is a YBMDV strain, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of the China Committee Of Culture Collection For Microorganisms in the Institute of Microbiology Chinese Academy of Science at the address of No. 3, No. 1 yard, Beichen west road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, on November 11th, 2013; the preservation number is CGMCC No. 8504. The Muscovy duck parvovirus screened by the invention has the characteristics of low toxicity and high immunogenicity; dead embryo and embryo liquid can be obtained by vaccinating the Muscovy duck parvovirus to a Muscovy duck embryo; virus liquid can be collected after grinding and freeze thawing; a vaccine is prepared by ultrafiltration concentration, formalin inactivation, the addition of an adjuvant, and mixing and emulsification; the Muscovy duck parvovirus can improve antibody of the Muscovy duck, ensure parent source antibody level of an offspring, and prevent green duck parvovirus infection caused by Muscovy duck parvovirus; the vaccine has the advantages of high efficiency and good safety.
Owner:YEBIO BIOENG OF QINGDAO
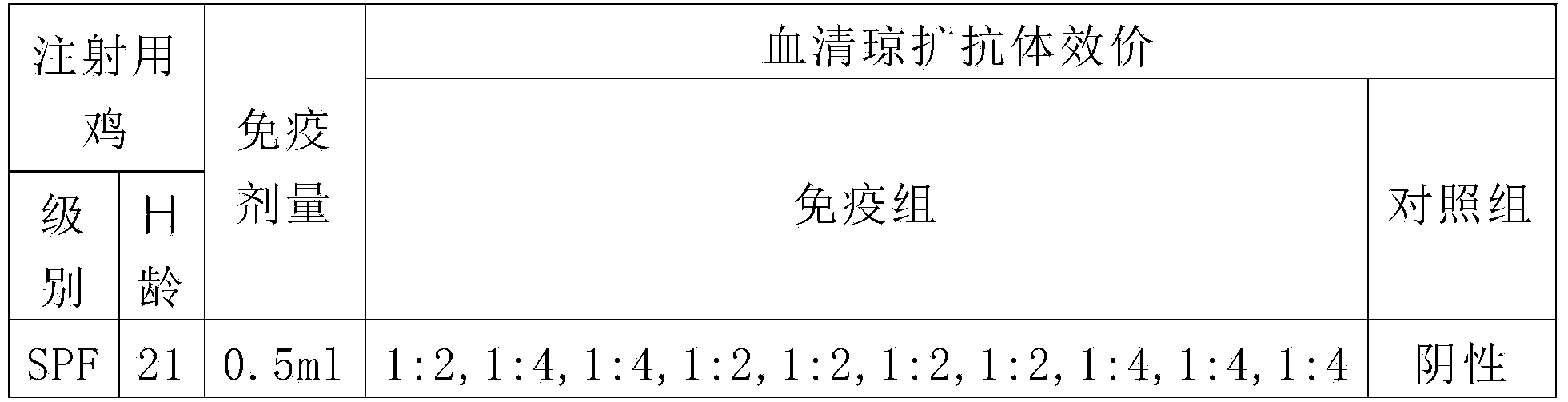
Method for preparing infectious chicken Fabricius bursa refined yolk cryodesiccation antibody
InactiveCN101113176AEmergency prevention is goodGood treatment effectEgg immunoglobulinsAntiviralsAntigenYolk
A preparation method of a purified vitelline freezing antibody for chickens infectious bursal disease is characterized in that: high purity antigens are adopted to vaccinate IBDV B87 to SPF chickens, then velvet urine, idiosome, velvet urine membrence are acquired, grinded, filtered and inactivated to antigens, and the steps are: producing immune eggs, collecting high immune egg, separating vitelline, diluting with distilled water, inactivating, extraction, decentering, inactivating, freezing and checking; the eggs is radiated by Co60 to kill viruses and bacterium, and finally froze by novel immuno-enhancer - Astragali Polysaccharoses and preserved under a temperature of 2-8 DEG C. Composite drugs for prevention and therapy are prepared by adopting the vitelline antibody for chickens infectious bursal disease as major components and cooperating with a novel immuno-enhancer, to decrease the jeopardy of the chicken breeding industry, and improve the living level of people and benefit mankind.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Inducing medium and inducing method for inducing multipotential stem cells to form mesoblastic cells
InactiveCN106867961AReduce riskImprove securityCulture processArtificial cell constructsGerm layerPenicillin
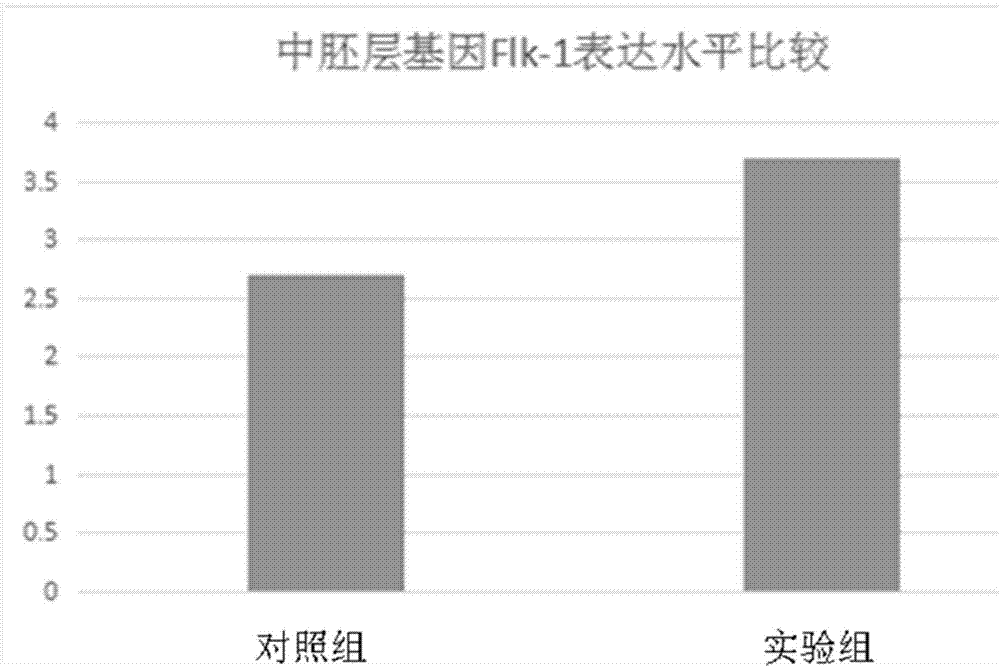
The invention provides an inducing medium for inducing multipotential stem cells to form mesoblastic cells. The inducing medium is prepared from the following components with the corresponding concentrations: 5-15 mM of LiCl, 0.5-2 % of glutamine, 0.5-2 % of non-essential amino acid, 5-15 [mu] M of CHIR99021, 8-15 ng / ml of bFGF, 0.05-0.2 mmol / l of beta mercaptoethanol, 0.2-0.6 [mu] g / ml of hydrocortisone, 4-10 [mu] g / ml of insulin, 80-120 [mu] g / ml of transferrin, 8-12 ng / ml of sodium selenite, 0.05-0.2 mg / ml of penicillin, and 0.05-0.2 mg / ml of streptomycin. For the inducing medium, on the basis of the DMEM / F12 culture medium, some specific cytokines and supplements are added, and thus the probability of inducing the multipotential stem cells to differentiate towards the mesoblastic cells is improved. In addition, the invention provides an inducing method for inducing the multipotential stem cells to form the mesoblastic cells, according to the method, the simple embryoid body for inducing the multipotential stem cells is inoculated to the inducing medium for induced culture, and thus the multipotential stem cells efficiently differentiate to form the mesoblastic cells.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RAINHOME PHARM&TECH CO LTD
Induction factor for inducing differentiation of iPS (induced pluripotent stem) cells into cardiac muscle cells and application thereof
InactiveCN102093977APromote differentiationNo side effectsVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsCardiac muscle tissue regenerationSide effect
The invention belongs to the field of regenerative medicine of cardiac muscle tissues, and discloses application of ascorbic acid as an induction factor in inducting differentiation of iPS (induced pluripotent stem) cells into cardiac muscle cells and a differentiation-inducing culture medium containing ascorbic acid. The invention also discloses a method for inducing differentiation of iPS cells into cardiac muscle cells by using the differentiation-inducing culture medium, which comprises the following step: inducing an iPS cell derived embryoid body, which has grown in a suspension mode for 5-7 days, to differentiate by utilizing the differentiation-inducing culture medium, thereby obtaining cardiac muscle cells. By using ascorbic acid as the induction factor, the invention obviously enhances the differentiation efficiency of the iPS cells into the cardiac muscle cells, and the differentiation percentage can reach 50-60%; the differentiation-inducing culture medium does not have toxic or side effect on the cells; and in addition, the method provided by the invention is simple, has the advantage of low cost, can be operated in common laboratories, and is suitable for large-scale proceeding.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Egg yolk antibody for preventing and curing muscovy duck parvovirus diseases
ActiveCN103833848AHigh potencyHigh protection rateEgg immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against virusesAntigenDisease
The invention aims to provide an egg yolk antibody for preventing and curing muscovy duck parvovirus diseases, and the egg yolk antibody is prepared by using muscovy duck parvoviruses the preserving number of which is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.8504 as an antigen. The egg yolk antibody is characterized in that a muscovy duck parvoviruse YBMDP plant is inoculated with a muscovy duck embryo, a die embryo body and embryo liquid are respectively obtained and are grinded and are subjected to freeze thawing so as to obtain a virus solution, and the oil adjuvant mixing emulsification is added in the virus solution after ultrafiltration concentration and formaldehyde solution inactivation so as to obtain a vaccine. The vaccine is utilized to inoculate a laying hen, eggs are obtained, yolks are separated, and the antibody is obtained after inactivation and extraction and rectification. The prepared antibody can prevent ducklings from the parvovirus infection because of muscovy duck parvoviruses, and the egg yolk antibody has the advantages of high efficiency, good safety, high protection rate and the like.
Owner:YEBIO BIOENG OF QINGDAO
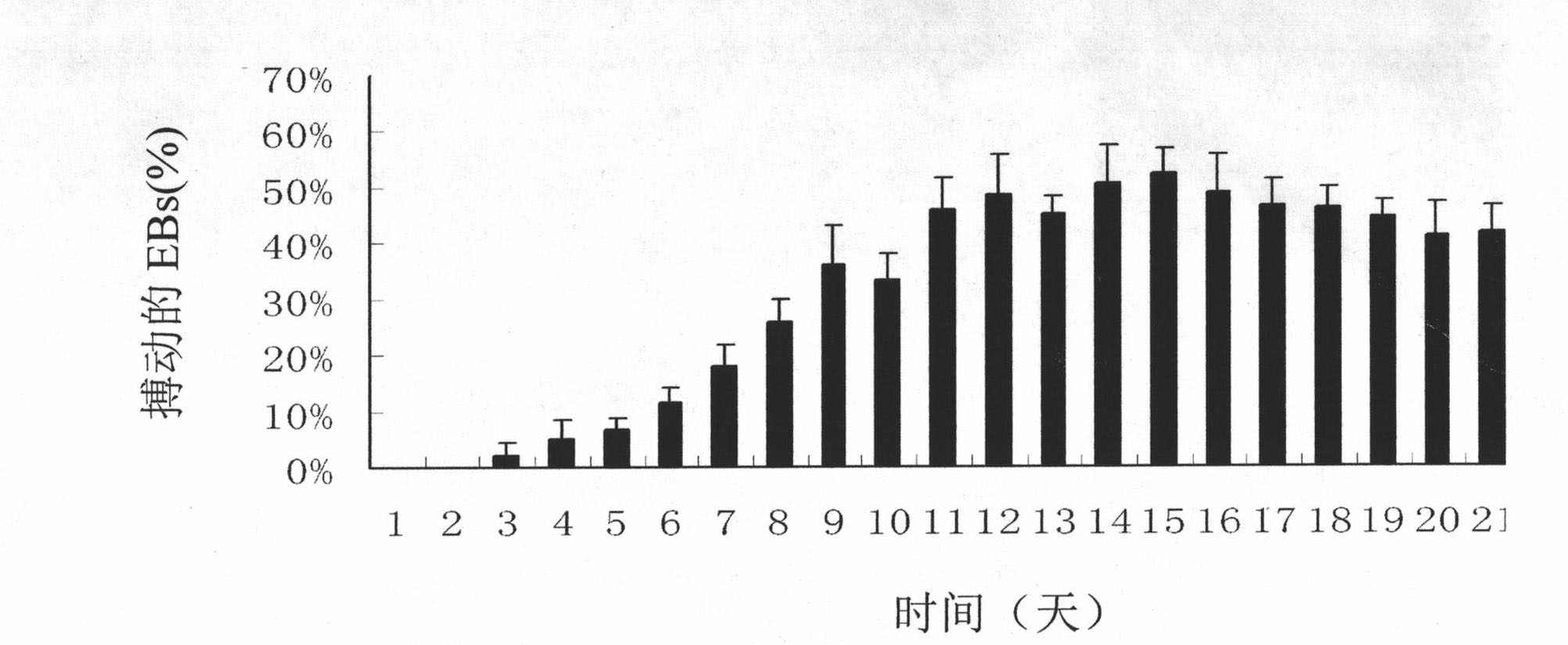
Novel culture method for in vitro differentiation from human embryonic stem cells to functional myocardial cells
InactiveCN104164402ANot easy to addFully absorbedSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSerum freeCardiac muscle
The invention discloses a novel culture method for in vitro differentiation from human embryonic stem cells to functional myocardial cells. The novel culture method is different from a conventional typical hanging-drop culture method. According to the novel culture method, an embryoid body is formed by adopting a simplified suspension differentiation culture method, serum-free culture liquid is adopted for improvement, and various inducing and nutrition-enriching substances are added into the culture liquid to increase the differentiation rate of the myocardial cells and prolong the survival time of the myocardial cells; a method for differentiation from embryonic stem cells to myocardial cells is further effectively updated and perfected, the proportion of the myocardial cells differentiated by the embryoid body is greatly increased, and a large quantity of myocardial cell sources with powerful functions can be provided for stem cell clinical transplantation treatment technology, drug screening and the like; the method is simple and feasible to carry out, the culture time is shortened, the functions for in vitro differentiation from the embryonic stem cells to the myocardial cells are improved and include pulsation time as well as autorhythmicity and rhythmicity of myocardial cell beating, and the method is good in repeatability.
Owner:奥思达干细胞有限公司
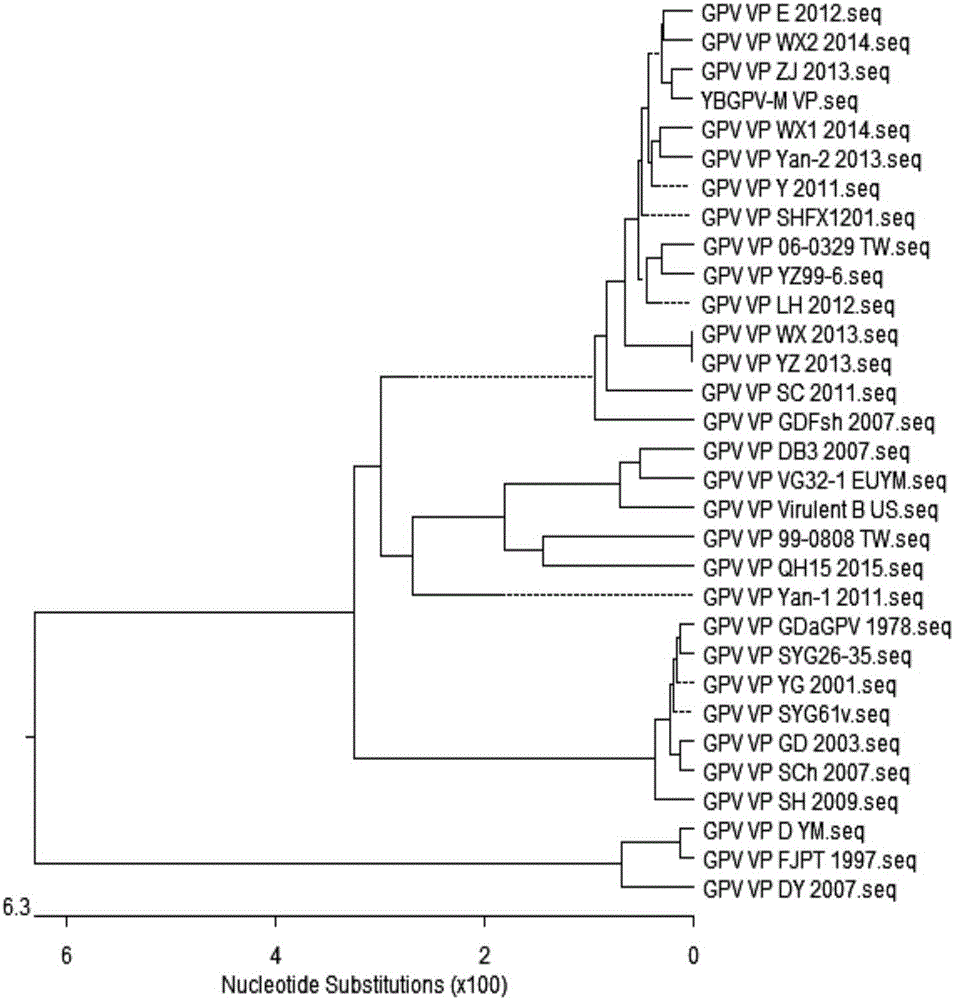
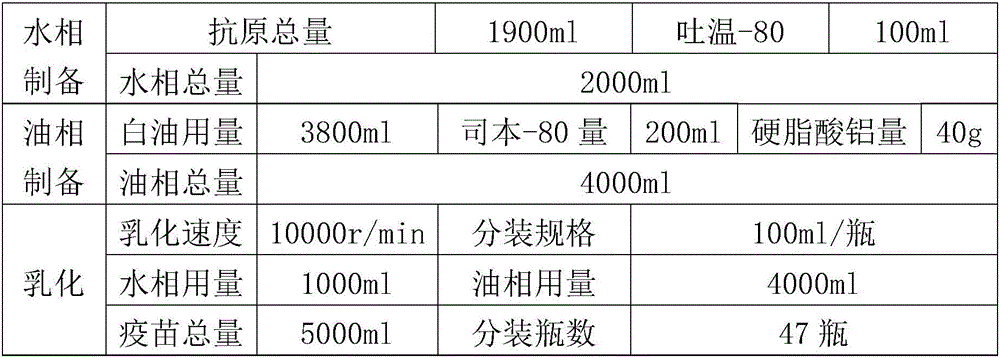
Egg yolk antibody used for preventing and treating Muscovy duck source gosling plague
ActiveCN105949307AHigh potencyHigh protection rateEgg immunoglobulinsMicroorganism based processesYolkFreeze thawing
The invention provides an egg yolk antibody used for preventing and treating Muscovy duck source gosling plague. The egg yolk antibody is prepared with a Muscovy duck source gosling plague virus with the preservation serial number of CCTCC NO: V201620 as an antigen. Muscovy duck embryos are inoculated with the Muscovy duck source gosling plague virus strain YBGPV-M, idiosome and blastochyle of dead embryos are obtained respectively, virus liquid is obtained after grinding and freeze thawing, an oil adjuvant is added for mixing emulsification after ultrafiltration concentration and formaldehyde solution inactivation, and a vaccine is obtained; laying hens are inoculated with the vaccine, eggs are obtained, yolks are separated, inactivation, extraction and refining are carried out, and the antibody is obtained. The prepared antibody can prevent young Muscovy duck gosling plague virus infection caused by the gosling plague virus; the egg yolk antibody has the advantages of being efficient, good in safety, high in protection rate and the like.
Owner:YEBIO BIOENG OF QINGDAO
Method for obtaining analogous retinal tissues rich in cone and rod cells by using human induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveCN108795864AShort digestion timeHigh activityNervous system cellsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsMatrigelOptic tectum
The invention discloses a mmethod for obtaining analogous retinal tissues rich in cone and rod cells by using human induced pluripotent stem cells. The method comprises the following steps: digestinghiPSCs to obtain cell pellets, and then carrying out suspension cultivation on the cell pellets to obtain an embryoid body; reinoculating the embryoid body into a culture dish enveloped by Matrigel, and carrying out induced differentiation inside an induced cultivation solution to obtain nerve retina (NR) and RPE; stirring up the NR and the RPE, carrying out suspension cultivation to obtain 3D analogous retina comprising NR tissues, then carrying out continuous suspension cultivation inside an optimized culture solution without retinoic acid, carrying out NR differentiation on all retinal cells, comprising highly matured photoreceptor cells, Rhodopsin positive rod cells, L / M OPSIN positive red and green cone cells and S-OPSIN positive blue cone cells, and thus particularly obtaining the analogous retinal tissues rich in red and green cone and rod cells.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN OPHTHALMIC CENT SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
Method for differentiating human multipotential stem cells into hematopoietic stem cells and culture additive
ActiveCN108300695AHigh differentiation efficiencyReduce the cost of differentiationGenetically modified cellsCulture processCulture fluidConceptus
The invention discloses a method for differentiating human multipotential stem cells into hematopoietic stem cells and a culture additive. The invention develops a culture solution capable of greatlyimproving the efficiency of differentiating human multipotential stem cells into hematopoietic stem cells. The invention also provides a novel method for differentiating human multipotential stem cells into hematopoietic stem cells. The hematopoietic stem cells can be obtained by adopting the preparation method provided by the invention, and compared with traditional matrix cell co-culture methodand embryoid body culture method, the doubly positive hematopoietic stem cells capable of expressing CD34 and CD343 can be efficiently obtained through the method, and the chemical components are definite and free of animal-derived components, so that the safety of cell preparation is greatly improved, and the method has the characteristics of low time consumption, high differentiation efficiency,relatively low cost and the like. The artificial hematopoietic stem cells can be produced in large scale by adopting the preparation method provided by the invention, the method is stable in qualityand high in safety, and a large number of cell sources are provided for tissue engineering, research and development of drugs and cell therapy.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Pluripotent stem cells directional differentiation method
InactiveCN107488629AIncrease productionQuality improvementCulture processCell culture supports/coatingGerm layerProcess mechanism
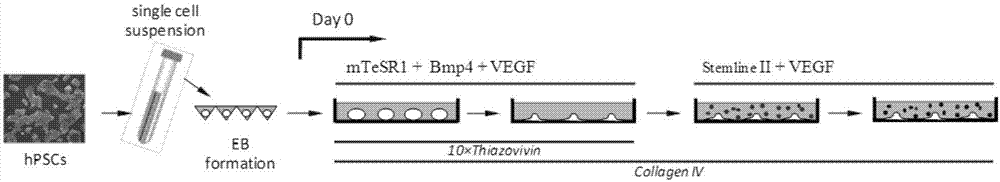
The invention discloses a pluripotent stem cells directional differentiation method. The method is characterized in that pluripotent stem cells are cultured under cell culture environment of non exogenous hematopoietic cytokines, non serum, non matrix cells and clear component, after embryoid is formed, a vascular endothelial growth factor and bone morphogenetic protein 4 are added, the embryoid is attached on the surface spread with collagen IV, mesoderm differentiation is induced, and hemopoietic progenitor cells and blood corpuscles are generated. The cell culture system with determined component enables directional differentiation on the pluripotent stem cells, has the advantages of low cost, simple operation, high repeatability and ordered differentiation process, can massively generate hemopoietic progenitor cells and blood corpuscles, and has important meaning for researching a blood growth process mechanism.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
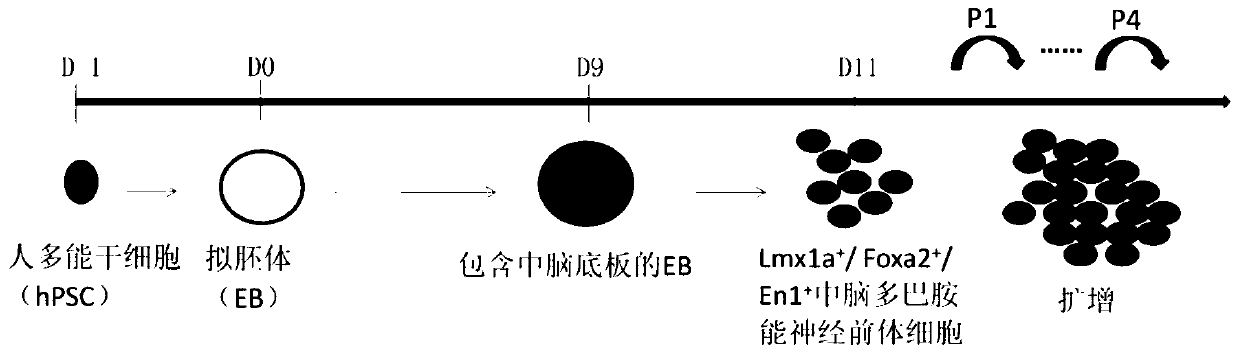
Midbrain dopaminergic nerve precursor cells and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109880800AFunctionalClinical majorNervous disorderNervous system cellsClinical gradeMidbrain
The invention relates to the field of stem cell biology, in particular to midbrain dopaminergic neural precursor cells and a preparation method and application thereof. The midbrain dopaminergic neural precursor cell expresses Lmx1a+, Foxa2+, En1+ and Otx2+, wherein the midbrain dopaminergic neural precursor cell does not express one or more of Nkx2.1, DBX1 and GBX2. The method for preparing the mesencephalic dopaminergic neural precursor cell comprises the following steps: embryoid bodies are formed, midbrain floor cells are obtained, and midbrain dopaminergic neural precursor cells are obtained. By adopting the preparation method, the mesencephalic dopaminergic nerve cells can be rapidly and efficiently differentiated from the human pluripotent stem cells, and the problems are solved that an existing differentiation method is long in time, unstable in effect and low in efficiency, the culture system containing serum or the trophoblast cells are not conducive to the production of subsequent clinical-grade cell preparations and the like.
Owner:安徽中盛溯源生物科技有限公司
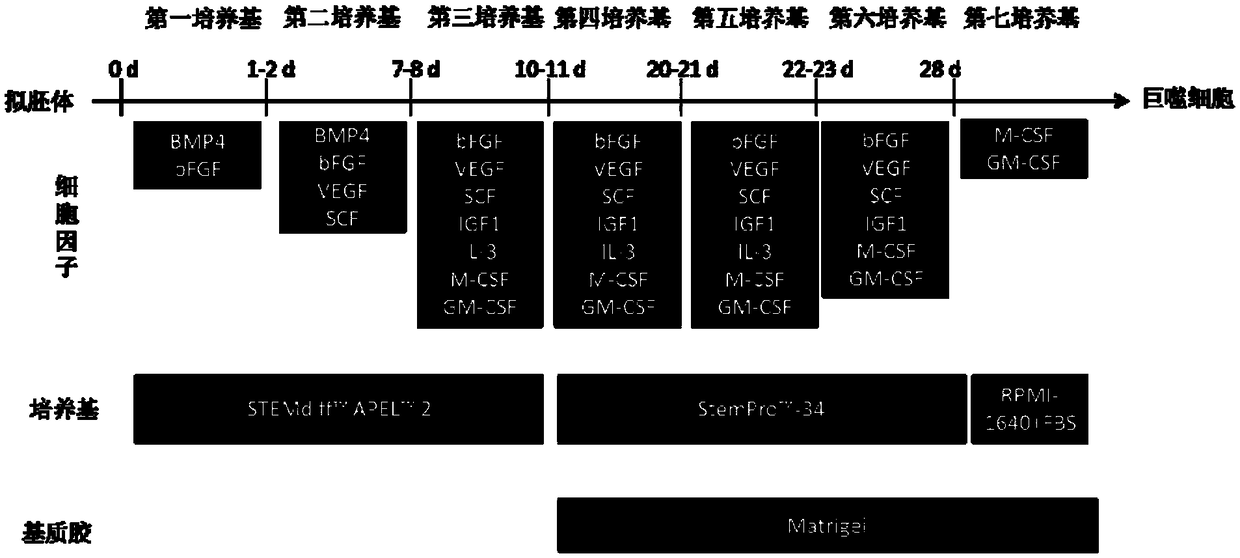
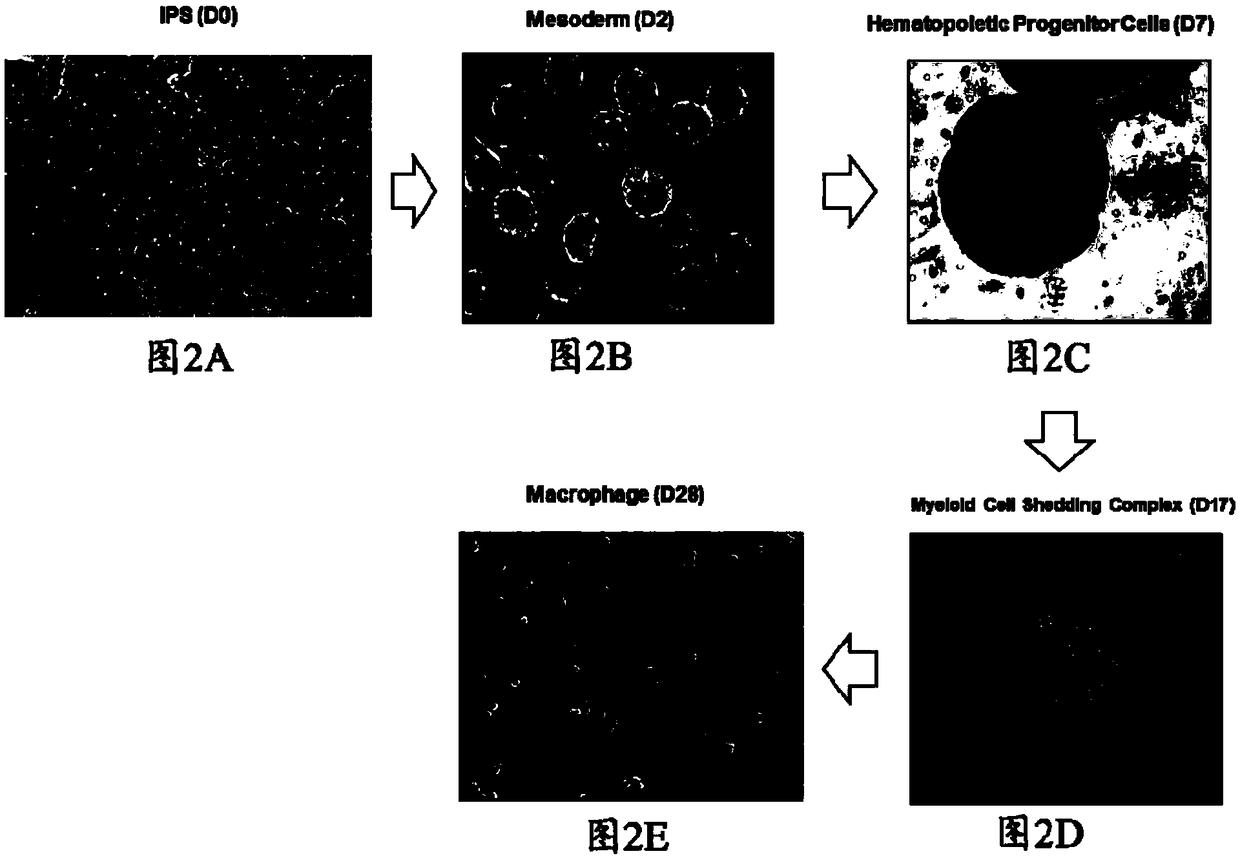
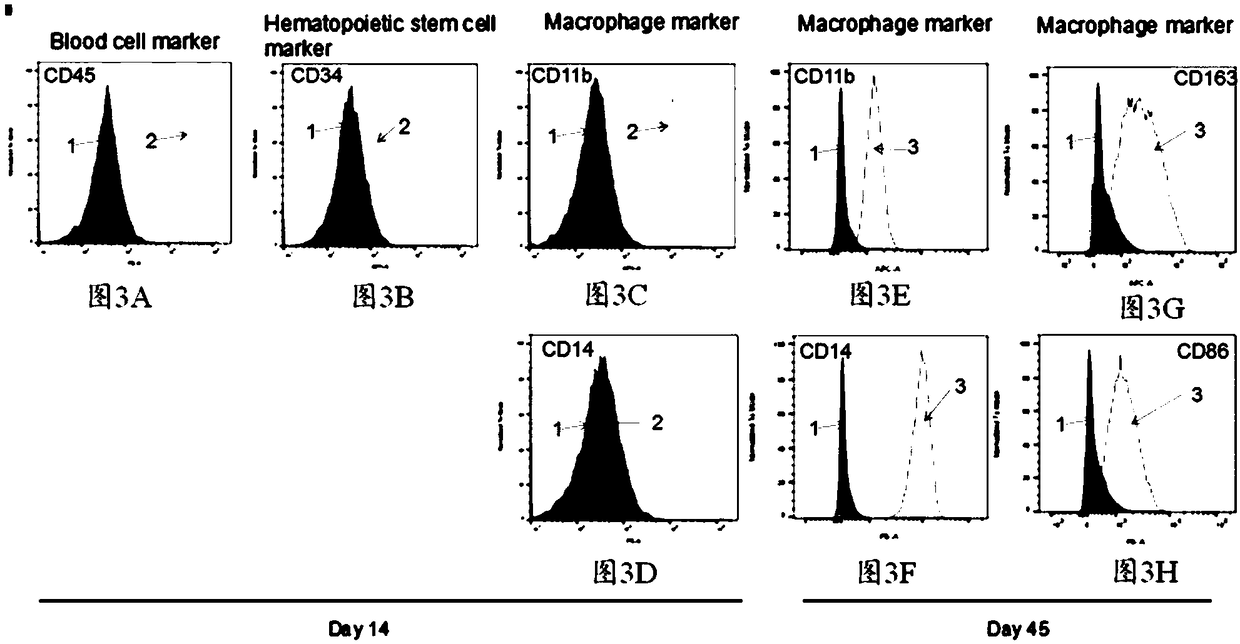
Method for acquiring macrophages with phagocytic functions by means of pluripotent stem cell differentiation
ActiveCN109082411AGuaranteed normal growthPromote directed differentiationCulture processBlood/immune system cellsPluripotential stem cellConceptus
The invention relates to the technical field of cell culture, and particularly provides a method for acquiring macrophages with phagocytic functions by means of pluripotent stem cell differentiation.Induced differentiation can be quickly and substantially carried out on cells of embryoid bodies by the aid of cell induced culture media to obtain the macrophages. First six culture media include serum-free culture media, basic nutrient substances which are required by growth, proliferation and differentiation of cells in various phases can be provided by the serum-free culture media, exogenous substances can be prevented, and accordingly pollution risks can be reduced. A seventh culture medium contains serum, FBS (fetal bovine serum) is additionally added into the seventh culture medium, andaccordingly growth of the macrophages can be effectively maintained. Each culture medium further contains diversified cell factors, and accordingly directional differentiation of the cells can be promoted. The method has the advantages that the method for carrying out induced culture on the cells is simple, is high in efficiency and low in cost and has important significance in clinical treatmentand research, and the high-quality and high-purity macrophages can be obtained in short periods by means of substantial amplification.
Owner:赛元生物科技(杭州)有限公司
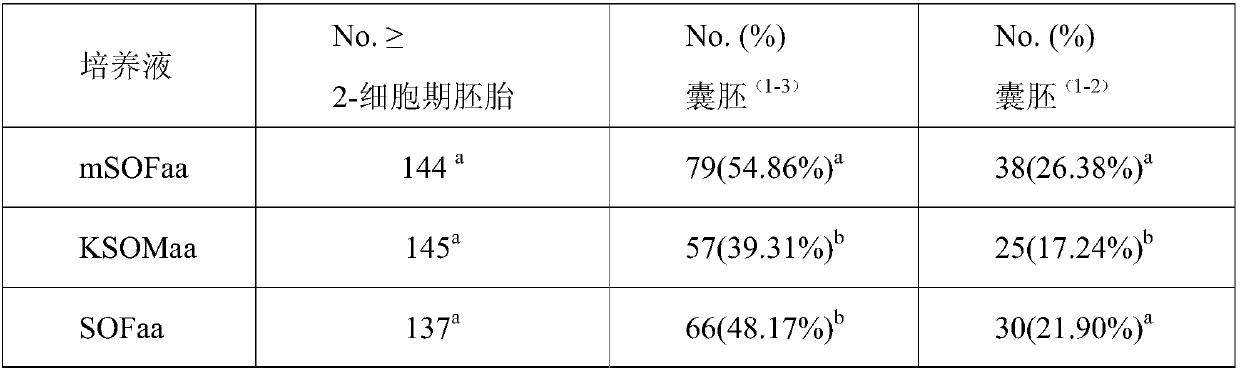
Mice somatic cell nuclear transplantation method
InactiveCN107099553AIncrease success rateIncrease cleavage rateAnimal reproductionFermentationConceptusBiological activation
The invention discloses an optimized mice somatic cell nuclear transplantation method. According to the mice somatic cell nuclear transplantation method, three kinds of cells, including cumulus cell, fetal fibroblasts, and embryonic stem cell, are adopted to construct reconstructed embryos; the activation efficiencies of three reconstructed embryos in different activation mediums are compared, development efficiencies in different solutions are compared, and pregnancy efficiencies of different embryo transplantation methods are compared; it is concluded that calcium-free KSOM activation medium is a universal high efficiency activation medium, and the activation efficiency is about 93.5%; KSOM-AA culture medium is suitable for in vitro culture of the reconstructed embryos of cumulus cells and embryonic stem cells, and the best culture medium for fetal fibroblasts is alpha MEM culture medium; when the reconstructed embryos are at 2-cell period, nuclear transplanted animals can be obtained via transplantation of embryos through bilateral fallopian tubes, wherein for each fallopian tube, transplantation of 15 embryos is carried out. The optimized mice somatic cell nuclear transplantation method is capable of increasing reconstructed embryo cleavage rate, blastula development rate, cloning animal birth rate, and survival rate, so that the success rate of obtaining embryonic stem cells from the reconstructed embryos is increased.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Neural crest spectrum mesenchymal cell derived from pluripotent stem cells and induced differentiation method thereof
InactiveCN107858328AEnhanced CytologyIncreased therapeutic functionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsCell phenotypeCulture fluid
The invention discloses a neural crest spectrum mesenchymal stem cell derived from pluripotent stem cells and an induced differentiation method thereof. The induced differentiation method of the neural crest spectrum mesenchymal stem cell comprises the following steps: dissociating the pluripotent stem cells to obtain cell aggregates, carrying out suspension culture to form embryoid bodies, replacing a culture solution with a neural crest cell culture solution, carrying out suspension culture of the embryoid bodies, collecting the embryoid bodies and replacing the culture solution every day; enabling the embryoid bodies to grow for a certain time by adhering to the wall after culturing for a certain time; digesting and collecting cells; culturing the collected cells by enabling the cells to adhere to the wall, replacing the culture solution with a mesenchymal stem cell culture solution, carrying out passage culture, then detecting the mesenchymal cell phenotype to obtain the neural crest spectrum mesenchymal cell. Through the method, the defects of heterogeneity and hybridity between adult-derived mesenchymal stem cells and other mesenchymal stem cells derived from the pluripotentstem cells of non-finite induction pathways can be solved; the prepared neural crest spectrum mesenchymal stem cell has higher immunoregulation and osteogenic differentiation capabilities; the standardized induced differentiation process is capable of ensuring that cell populations prepared between different batches have good consistency.
Owner:广州赛隽生物科技有限公司
Real-time fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR kit for detection of chicken astrovirus and application thereof
InactiveCN108251558AEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEmbryoConceptus
The invention discloses a real-time fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR kit for detection of chicken astrovirus and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The kit can achieve accurate quantitative detection of amount of mRNA expression of CAstV in a sample by reverse transcription (RT) of the mRNA sample to obtain cDNA and combination of real-time quantitative PCR detection technology. The kit can be used for the expression analysis of the CAstV in chicken embryos, and can also be used for detecting the nucleic acid level of gene of the CAstV virus in clinical cases. A rapid, accurate and reproducible detection method for detecting the level of CAstV virus infection in clinical samples is provided.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for differentiation of embryonic stem cells (ESC) into mesenchymal stem cells (MSC)
InactiveCN105154393AImprove induction efficiencyTake advantage ofSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMesenchymal stem cellEmbryo
The invention discloses a method for differentiation of embryonic stem cells (ESC) into mesenchymal stem cells (MSC). The method comprises the following steps of 1, culturing ESC until a part of ESC trends a differentiation state so that fibrous cells are obtained, 2, digesting ESC obtained by the step 1 so that the adhesive fibrous cells are retained, 3, carrying out multiplication culture on the retained fibrous cells obtained by the step 2, and 4, digesting the fibrous cells obtained by the step 3, transferring the digested fibrous cells into an adhesive cell culture bottle and carrying out culture to obtain MSC. The method is free of embryo (EB) culture, realizes direct conversion of ESC into MSC and is simple. Compared with the method comprising direct digestion of ESC by pancreatin, then inoculation and MSC culture, the method provided by the invention has high MSC induction efficiency and short successful induction time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Chick embryo allantoic cavity inoculation method for increasing avian influenza virus separation rate
InactiveCN101191125AImprove separation rateIncreased viral loadViruses/bacteriophagesBird fluAvian influenza virus
The invention relates to a chick embryo allantoic cavity inoculation method for improving separation rate of bird flu viruses. The invention is characterized in that: a pinhole is arranged on the side of an air chamber of a chick embryo and taken as a pressure-relief vent; a pinhole is arranged on an embryo body of the chick embryo close to an allantoic cavity and taken as a needle insertion hole; a needle is directly inserted into the allantoic cavity for inoculation of sample by 0.5 to 1.0 milliliter per embryo. The invention reaches the goal of increasing viral load by increasing inoculum concentration, thereby the separation rate of viruses is improved.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
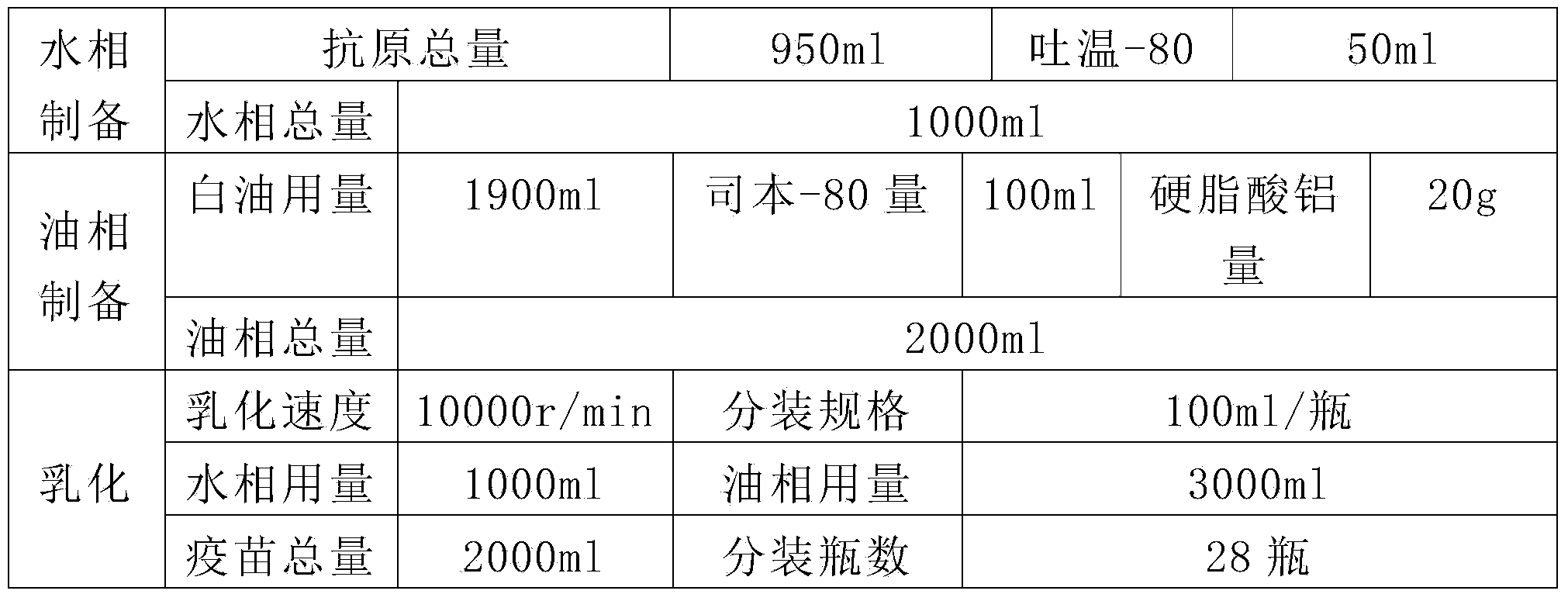
Preparation method of divalent inactivated vaccines for duck virus hepatitis
ActiveCN102908618APrevention of Duck Viral HepatitisAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsFreeze thawingDuck hepatitis A virus
The invention relates to a preparation method of divalent inactivated vaccines for duck virus hepatitis. According to the invention, the preparation method comprises the following steps of: screening duck virus hepatitis type I YBH1 strains and novel YBHX strain vaccines with good immunogenicity from preponderant popular strains so as to prepare strains, respectively inoculating the vaccines on a chicken embryo and a duck embryo, respectively harvesting embryoid bodies and embryoid fluid of dead embryos, collecting a viral solution after the embryoid bodies and the embryoid fluid are ground and frozen-thawed, and adding an oil adjuvant for mixing and emulsifying to obtain the vaccines after the viral solution is carried out ultrafiltration and concentration and is inactivated through a formaldehyde solution. The vaccines can carry out immunization for animals and can simultaneously prevent the duck virus hepatitis caused by type I duck virus hepatitis and novel duck virus hepatitis, and the divalent inactivated vaccines for the duck virus hepatitis have the advantages of high efficiency, good safety and high protective ratio and the like.
Owner:YEBIO BIOENG OF QINGDAO
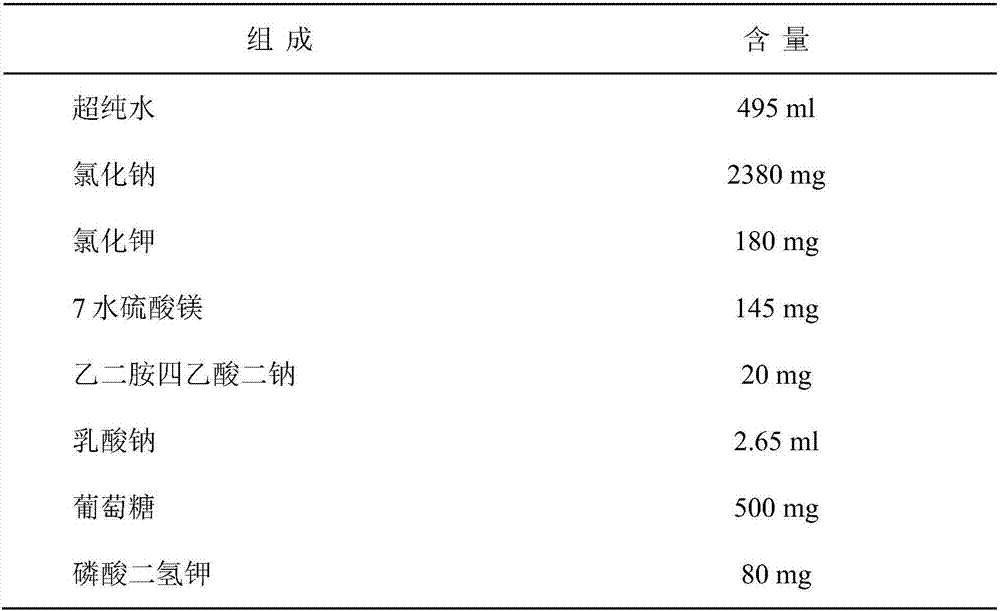
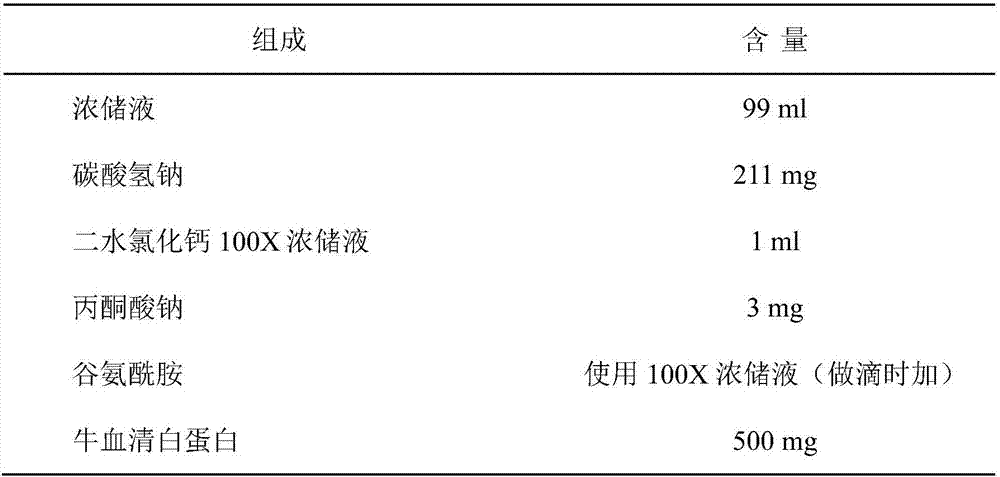
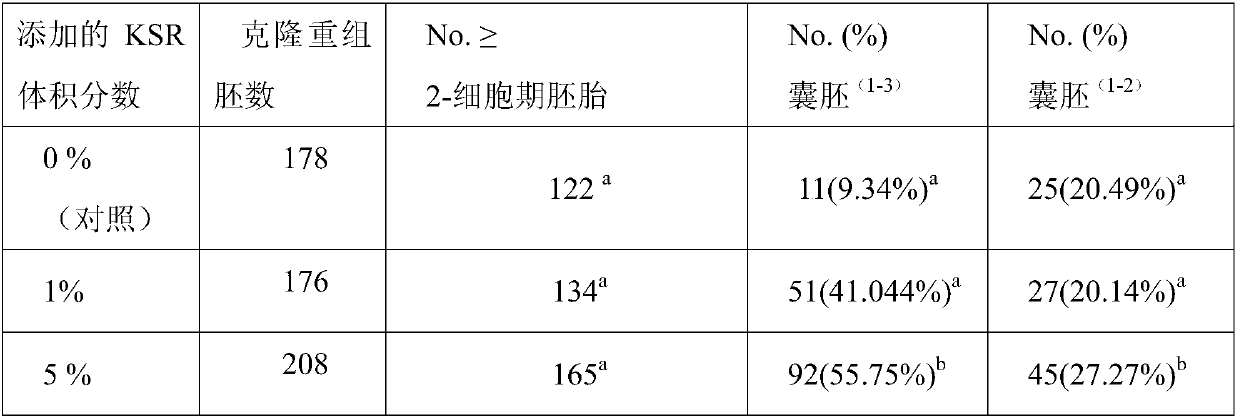
Culture solution for improving development quality of cell cloning embryos and in-vitro fertilized embryos of cow body and culture method
InactiveCN107916249AImprove in vitro growth rateQuality improvementCulture processCell culture active agentsBovine serum albuminConceptus
The invention provides a culture solution for improving the development quality of cell cloning embryos and in-vitro fertilized embryos of a cow body and a culture method. The culture solution comprises the following components: BME (Basal Eagle Medium) with the volume fraction being 2%, MEM (Minimum Essential Medium) with the volume fraction being 1%, 1mmol / L of glutamine, 8mg / mL of BSA (Bovine Serum Albumin), 50mu g / mL of gentamicin and 50mu g / mL of cephalosporin. After the cow embryo is cultured to the 96th hour, KSR (Knockout Serum Replacement) with the volume fraction being 5% is added. The culture solution and the culture method provided by the invention have the beneficial effects that the culture solution is utilized for in-vitro culture of the cell cloning embryos and the in-vitrofertilized embryos of the cow body, a result shows that the development rate and the quality of the blastosphere are respectively higher than those of a control group; by application of the culture solution and the culture method, the cell cloning embryos or the in-vitro fertilized embryos of the cow body can be obtained with high efficiency.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for preparing macrophage by iPS cell differentiation
InactiveCN109971709AWith phagocytosisMaintain propertiesBlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsConceptusHemocyte differentiation
The invention aims to provide a method for preparing mature macrophages by effectively differentiating and inducing iPS cells in vitro. The invention provides a method system for suspending and culturing iPS into embryoid-like EBs and differentiating the embryoid-like EBs into macrophages through an EB induction way so as to obtain a large number of macrophages with an immune function from iPS. Inaddition, the method for inducing differentiation of EB is provided to further culture under conditions suitable for induction of differentiation of blood cells, and is capable of producing various blood cells.
Owner:杭州荣泽生物科技集团有限公司
Method and culture media for inducing osteogenic differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cell of mouse
InactiveCN103710310AShort cycleHigh differentiation rateSkeletal/connective tissue cellsForeign genetic material cellsOsteoblastOsseous Cell
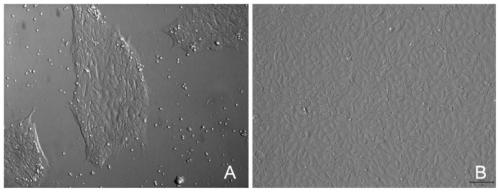
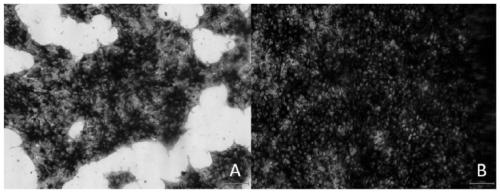
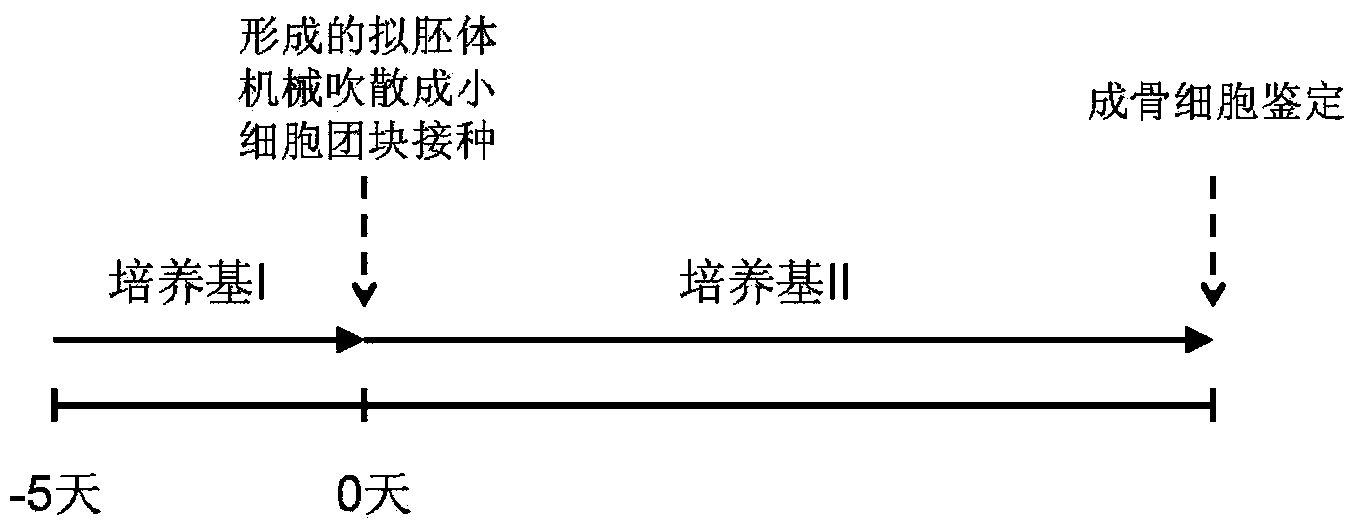
The invention discloses a method and culture media for inducing osteogenic differentiation of an induced pluripotent stem cell of a mouse. The method provided by the invention comprises the steps of inoculating the pluripotent stem cell of the mouse into a differentiation culture medium I to form an embryoid body with enriched mesenchymal cells, then separating the embryoid body and culturing in a differentiation culture medium II to obtain an osteoblast, wherein the differentiation culture medium I disclosed by the invention is formed by adding all-transretinoic acid and basic fibroblast growth factor on the basis of a fibroblast culture medium, and the differentiation culture medium II is formed by reducing the D-glucose content and adding BMP4 or BMP7 on the basis of an osteoblast culture medium. The method and the culture media provided by the invention can significantly promote the osteogenic differentiation of the pluripotent stem cell of the mouse, have the characteristics of short cycle, high differentiation rate, stable effect and the like, and have broad application prospect and practical value.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com